Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114results about "Measurements using double resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
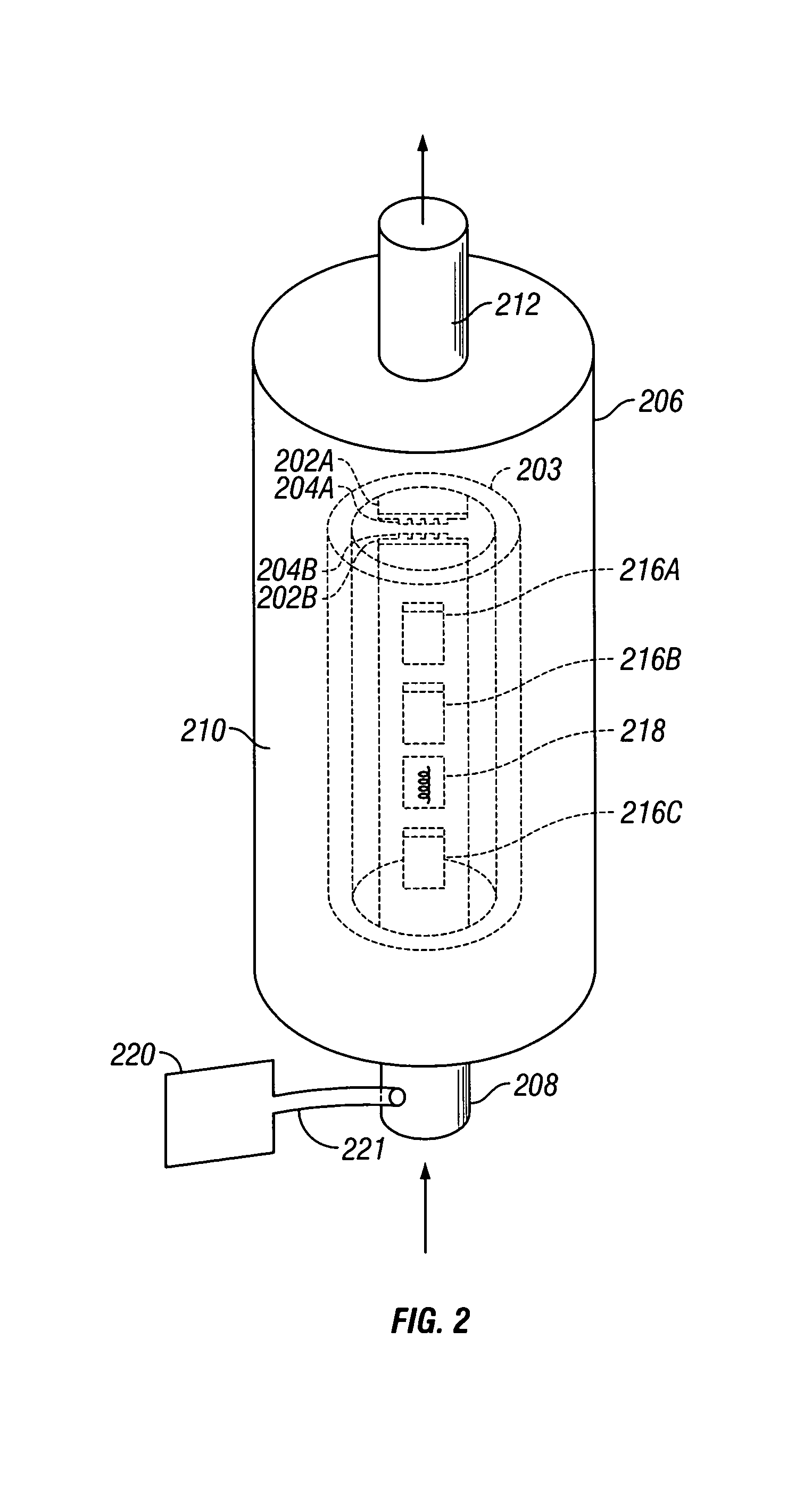
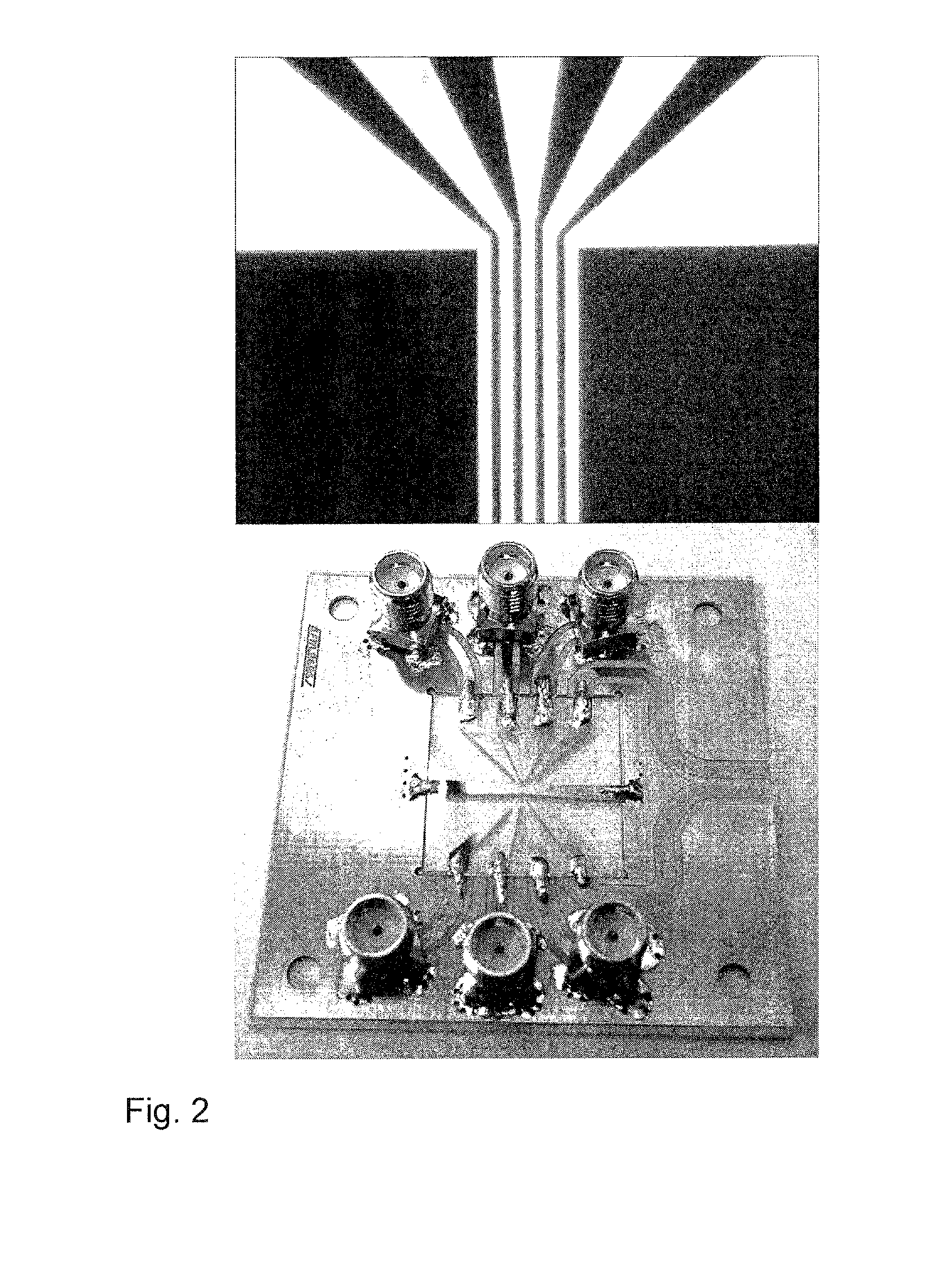
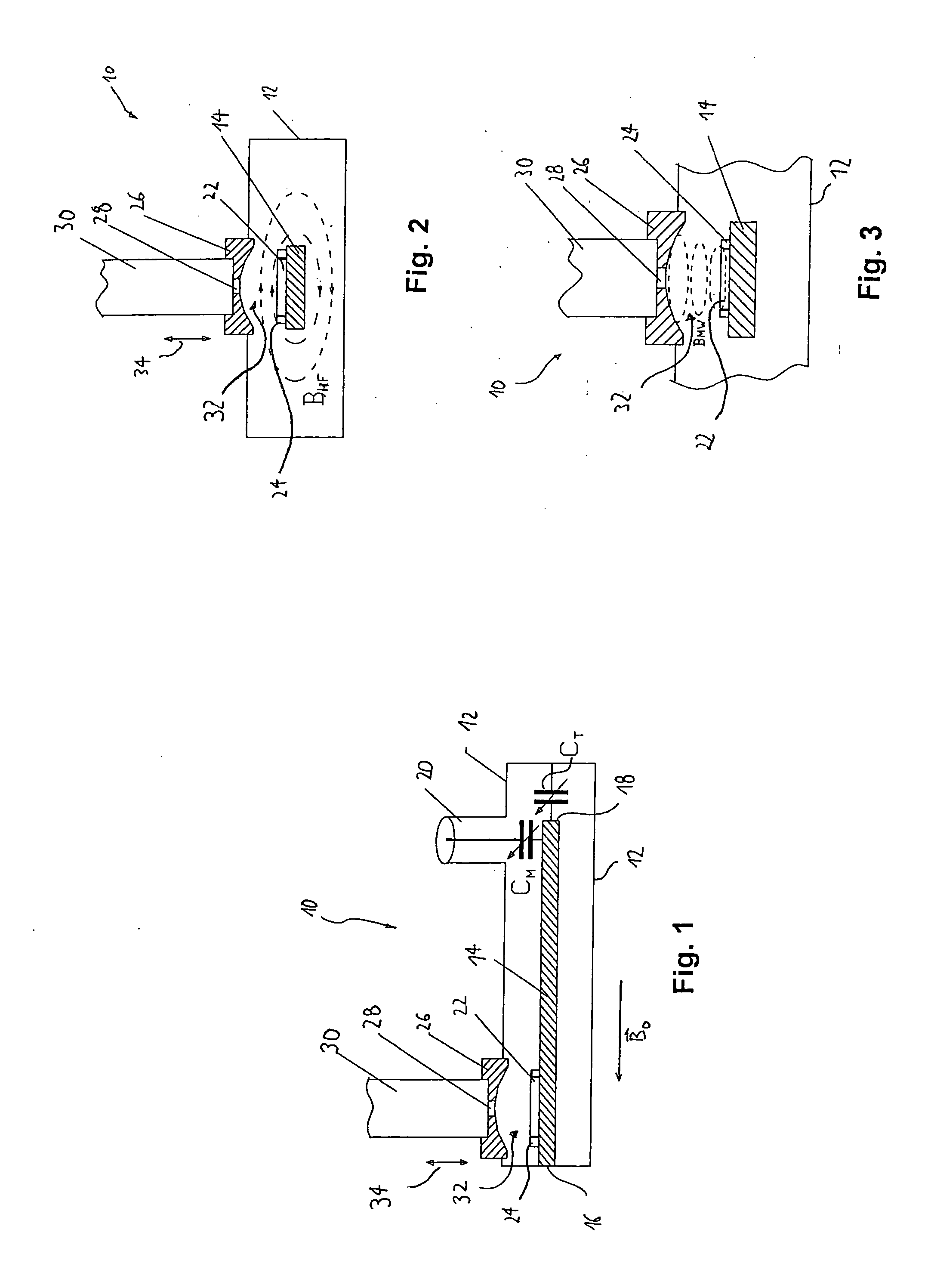
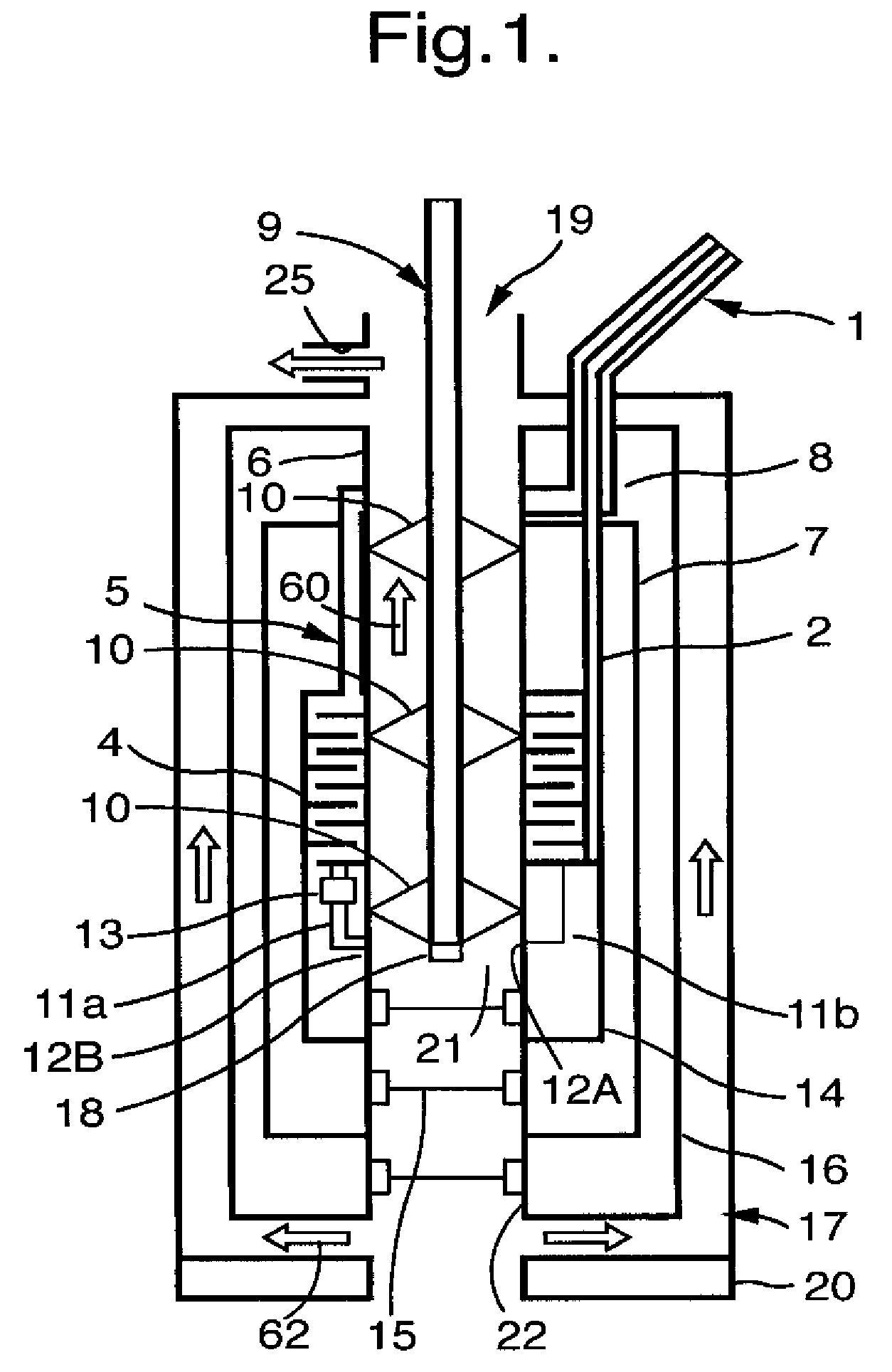
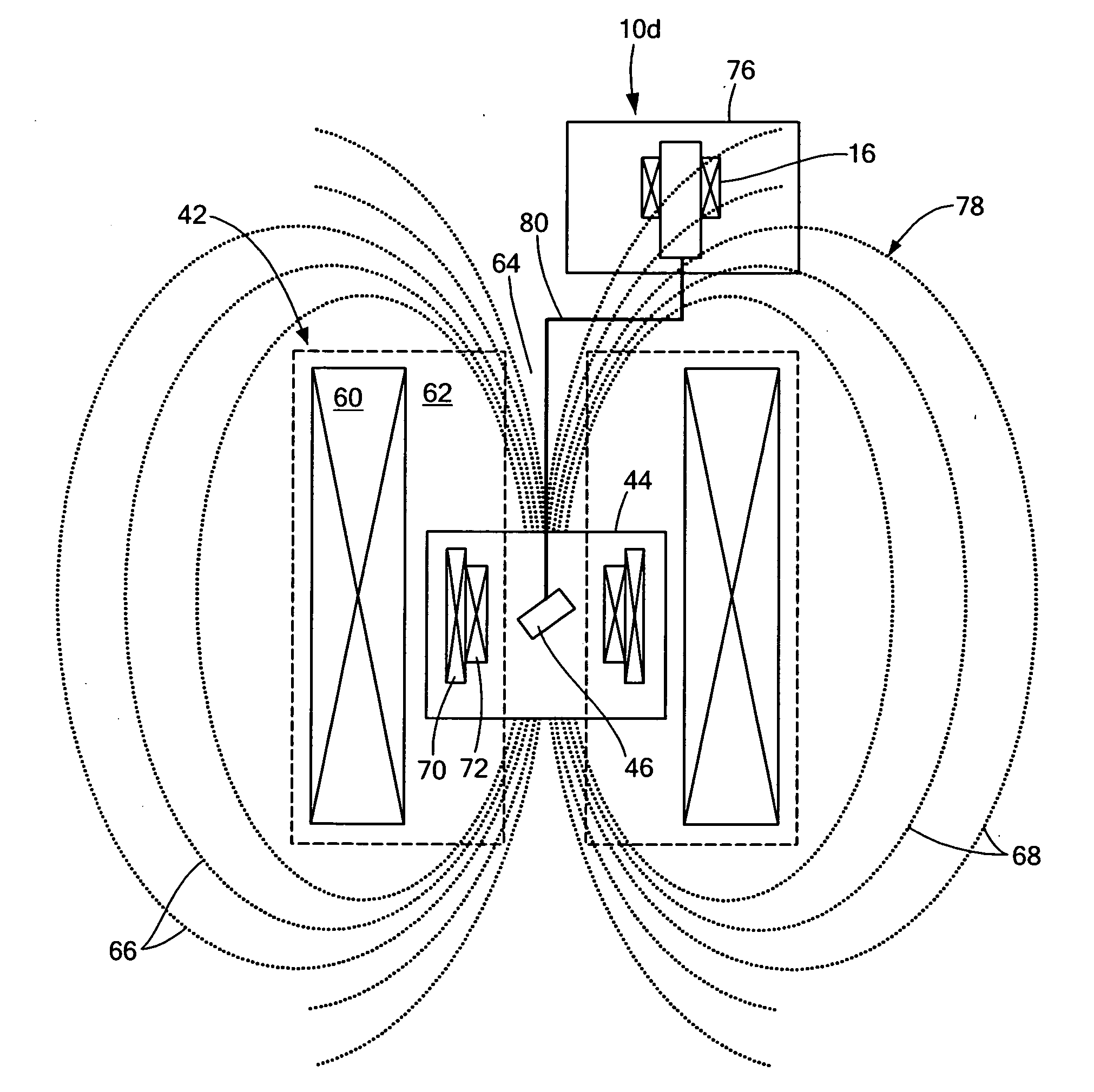
Integrated high-frequency generator system utilizing the magnetic field of the target application
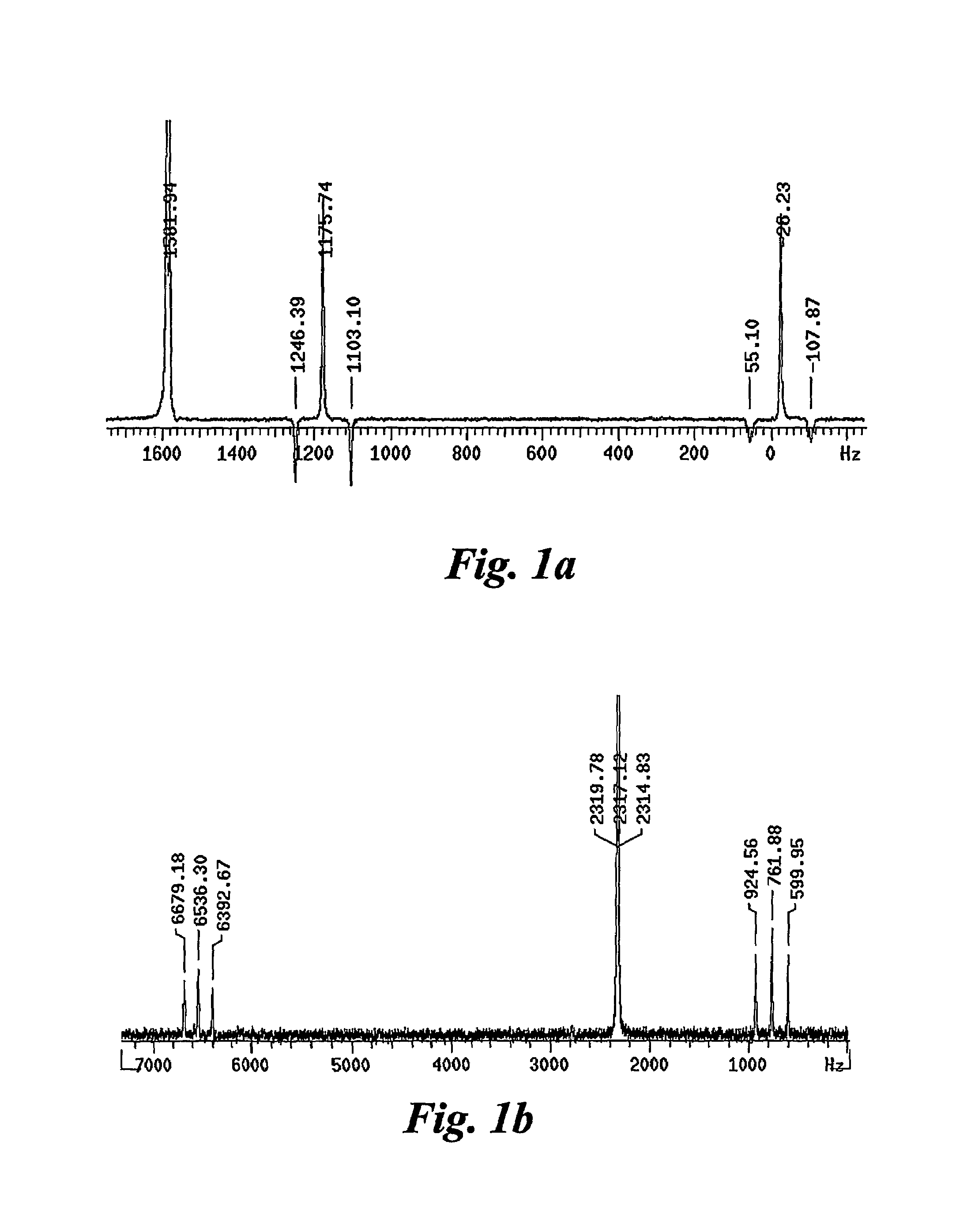
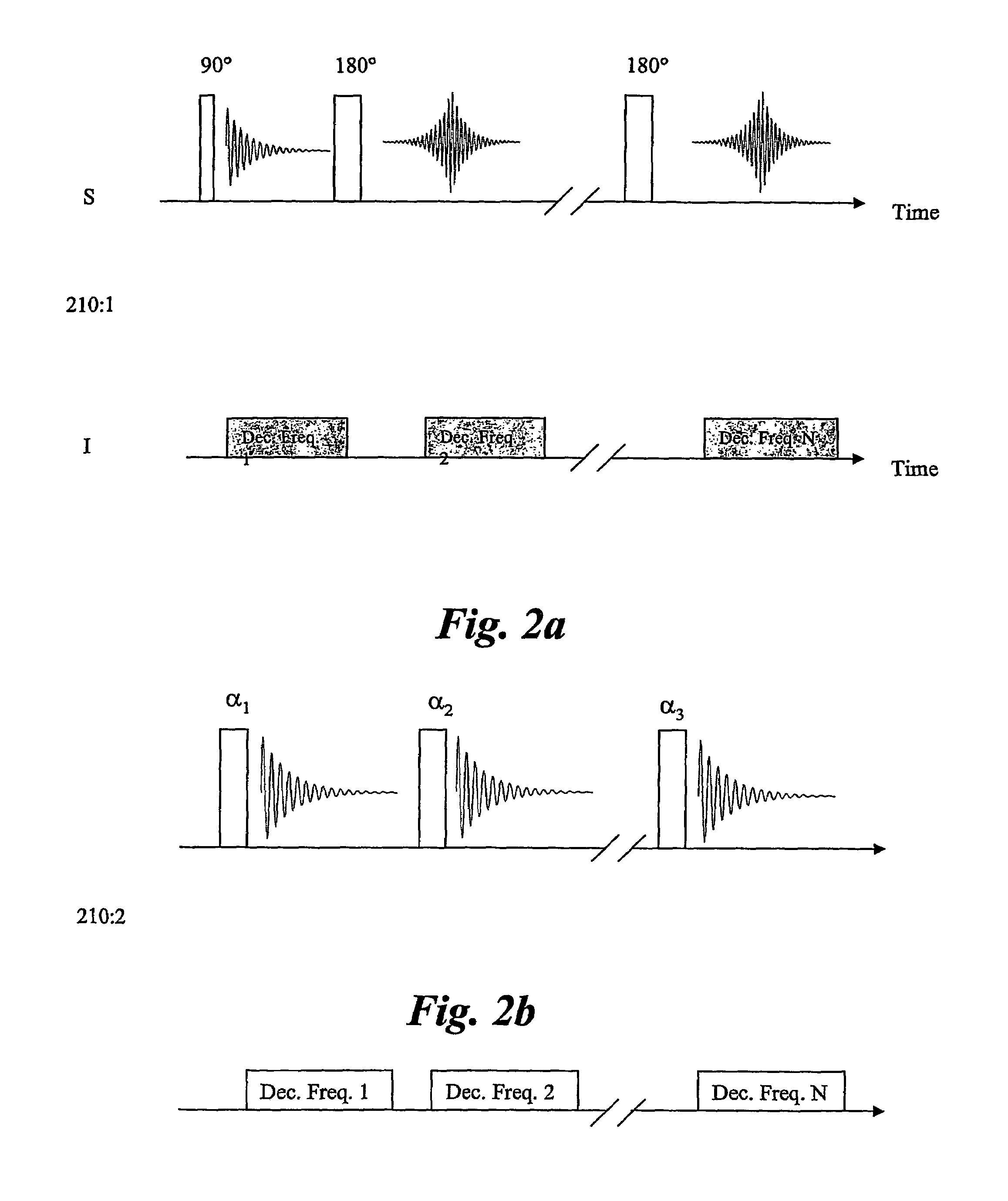
ActiveUS8786284B2Easily and simply adapted for DNP operationSmall and compactMeasurements using double resonanceTubes with helical electron streamInternal modeMicrowave
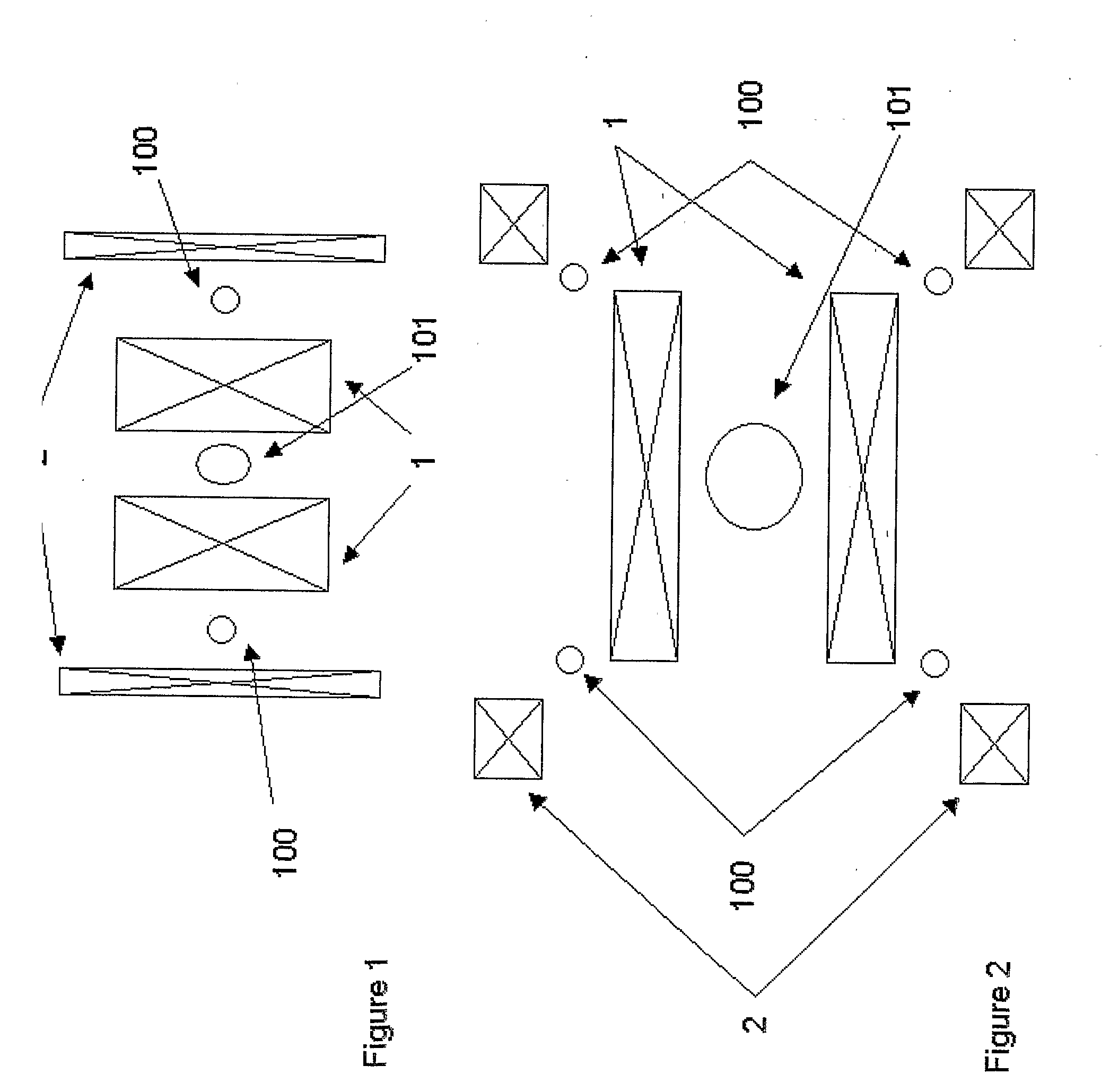
An integrated high-frequency generator system utilizing the magnetic field of the target application including a magnetic resonance magnet having an application zone and a high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance magnet; and a high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator disposed in the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone and utilizing the magnet field of the magnetic resonance magnet to generate the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation. The magnetic resonance magnet may have an auxiliary magnetic field source for modifying the magnetic field profile in the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone. The high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator may include an electron gun for generating an electron beam adapted to be focused by a magnetic field source having a spatially rising region, a homogenous region and a decaying region, an interaction structure for generating high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation, an internal mode converter in the homogenous region for extracting the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation through a window, and a reduced collector disposed substantially in the homogenous region before the electron beam spreads in the decaying region.
Owner:BRIDGE 12 TECH
Method of magnetic resonance imaging of a sample with ex vivo polarization of an MR imaging agent
The present invention provides a method of magnetic resonance investigation of a sample, preferably of a human or non-human animal body, said method comprising the step of ex vivo polarisation of a high T1 agent and wherein the polarising agent is optionally seperated from the high T1 agent before the high T1 agent is administered to the sample.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
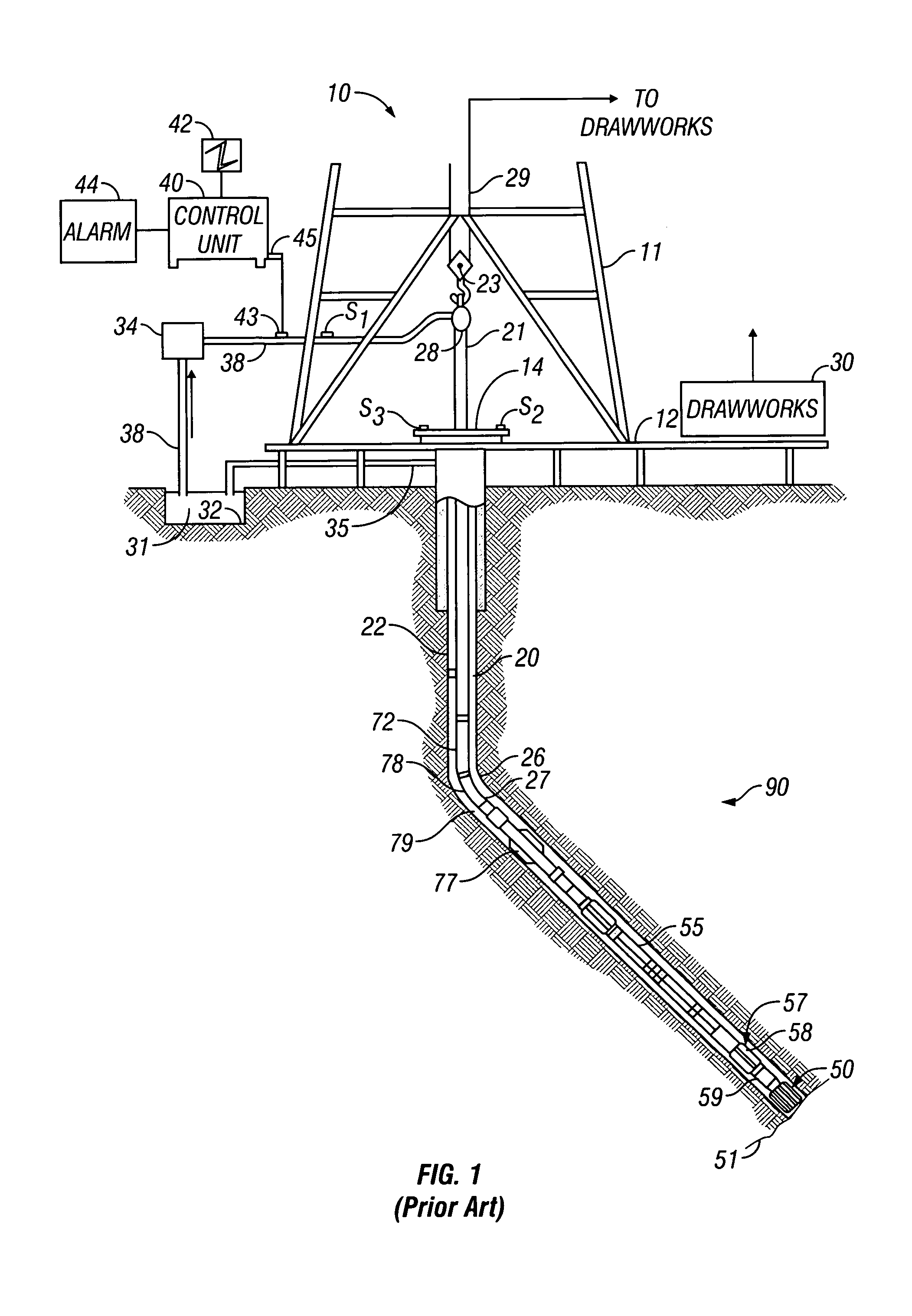
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for polarizing nuclear and electronic spins
ActiveUS20160054402A1Great degreeHigh sensitivityMeasurements using double resonanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceAnalyteElectronic spin
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods and devices for dissolving hyperpolarised solid material for nmr analyses
ActiveUS20040066193A1Raise the ratioImprove resolutionElectrical measurement instrument detailsPreparing sample for investigationSolid massEngineering
The present invention relates to devices and method for dissolving solid polarised material while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a material is polarised in a strong magnetic field in a cryostat 2 and then brought into solution while still inside the cryostat 2.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
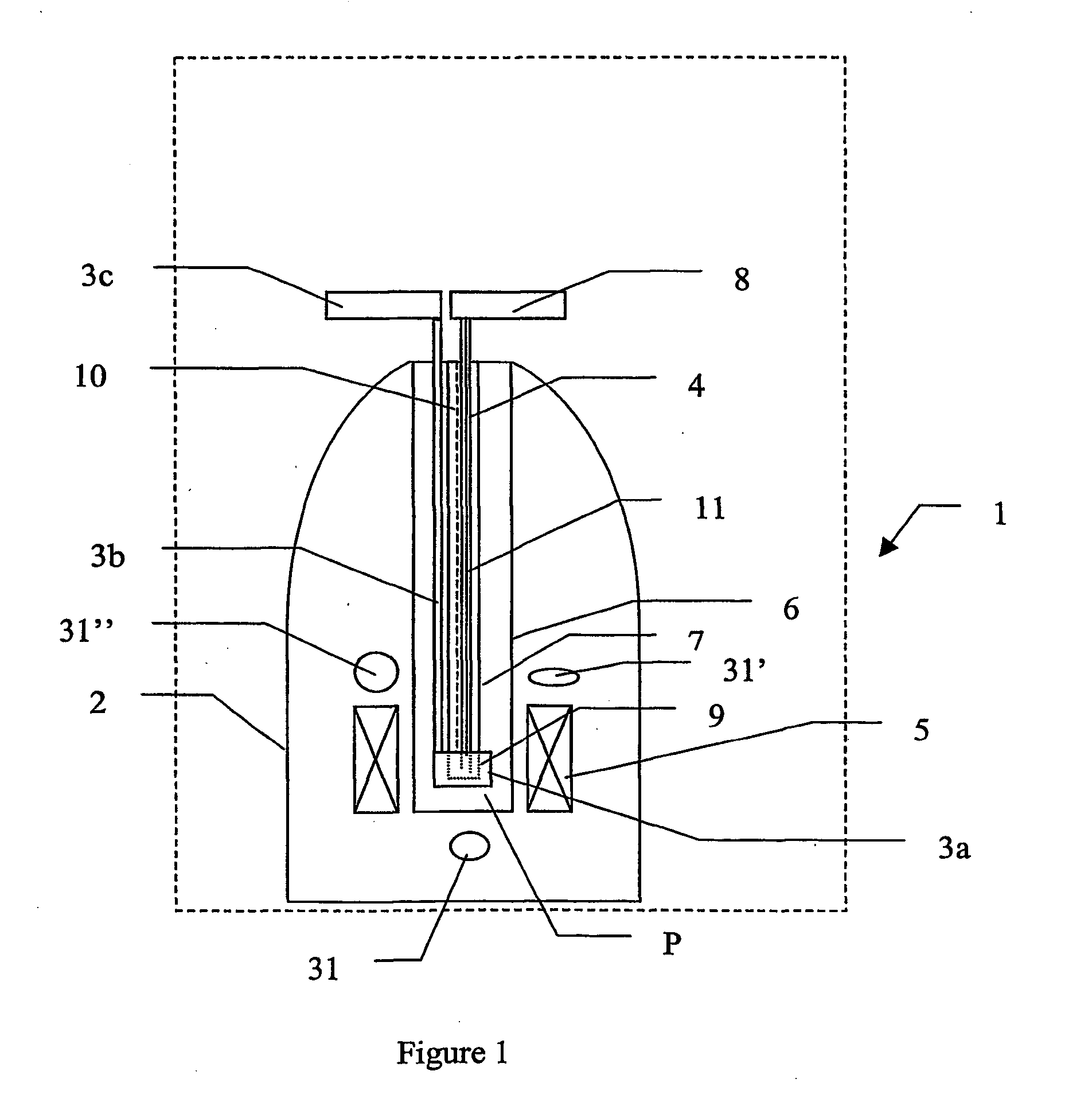
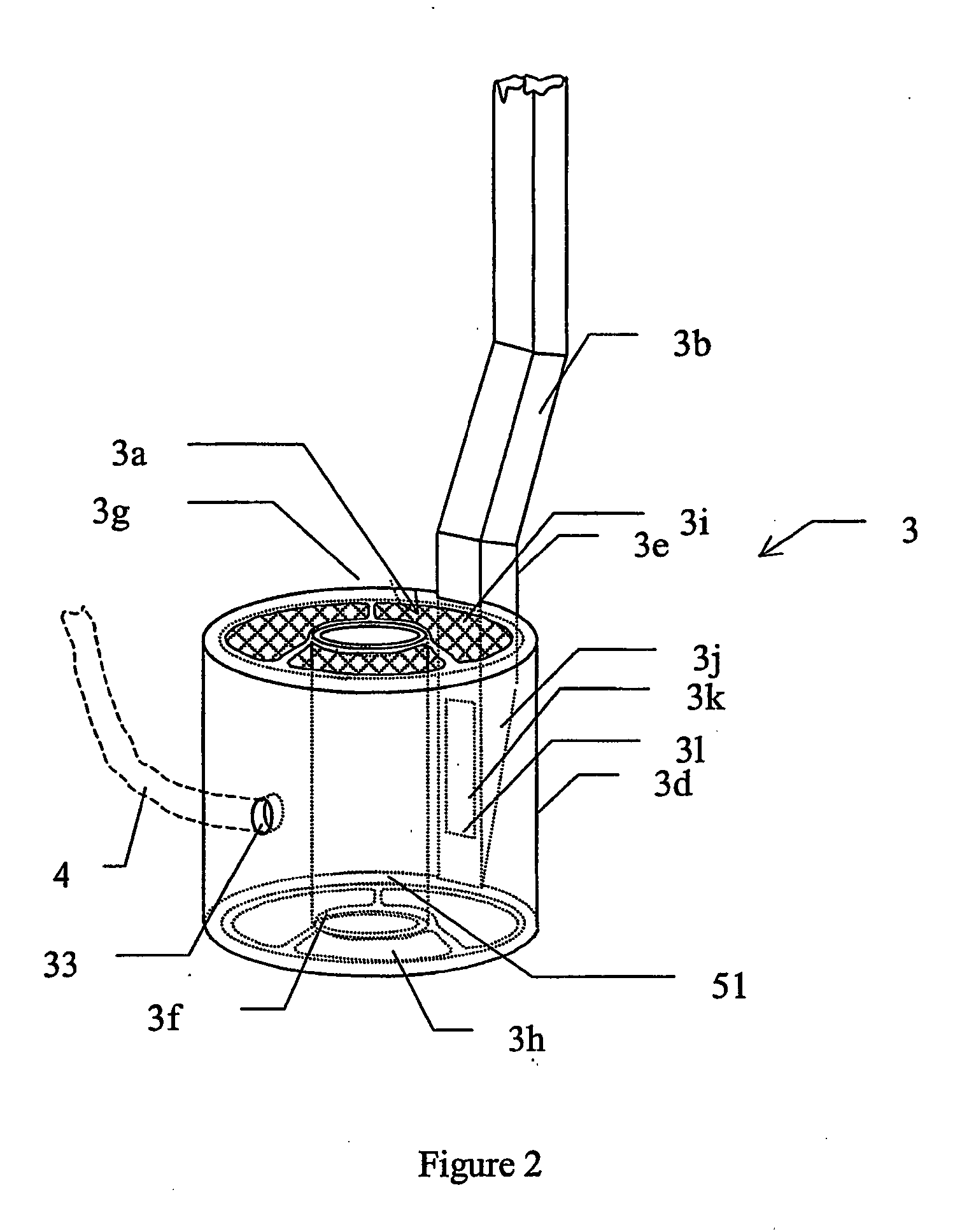
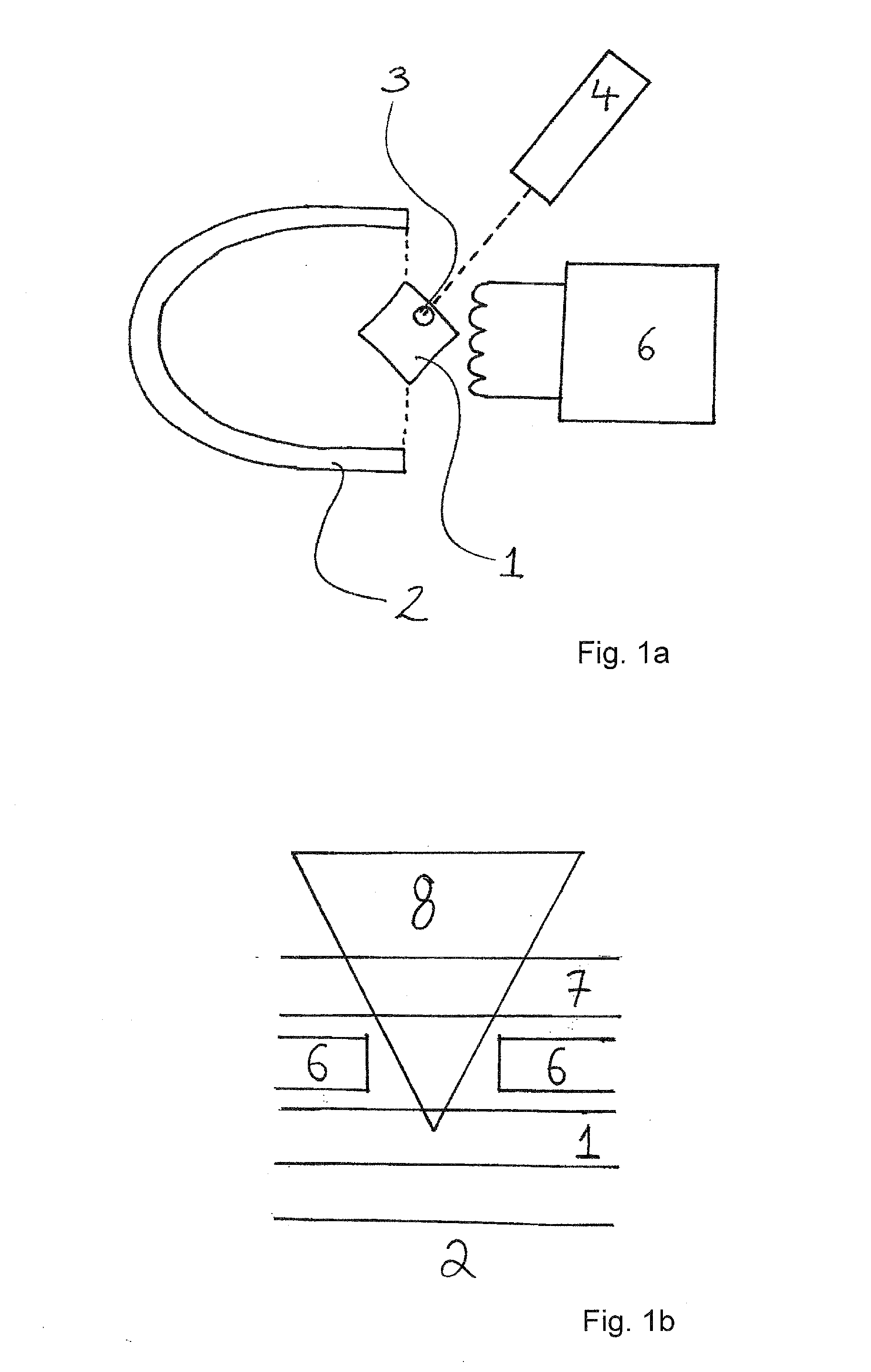
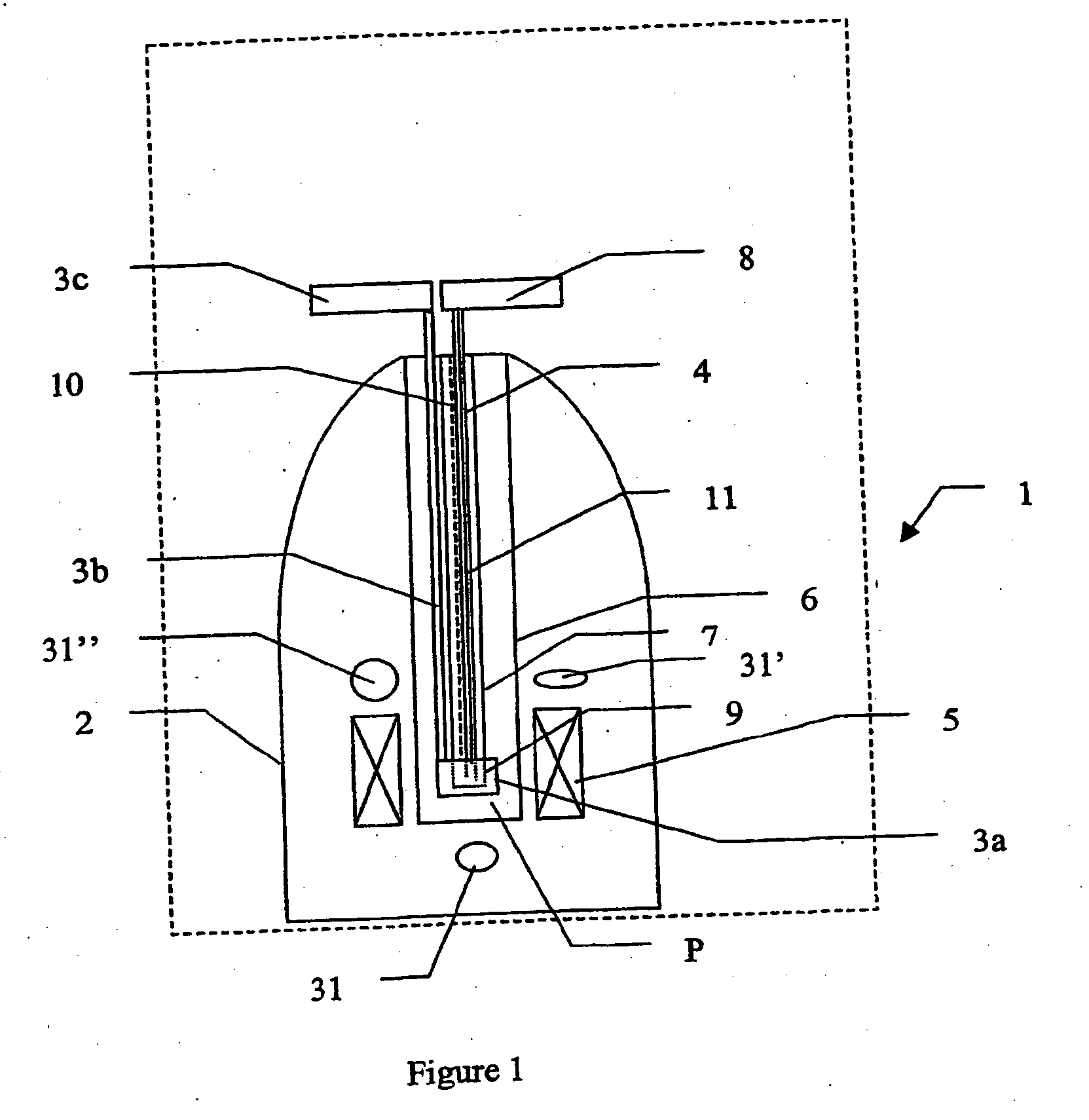
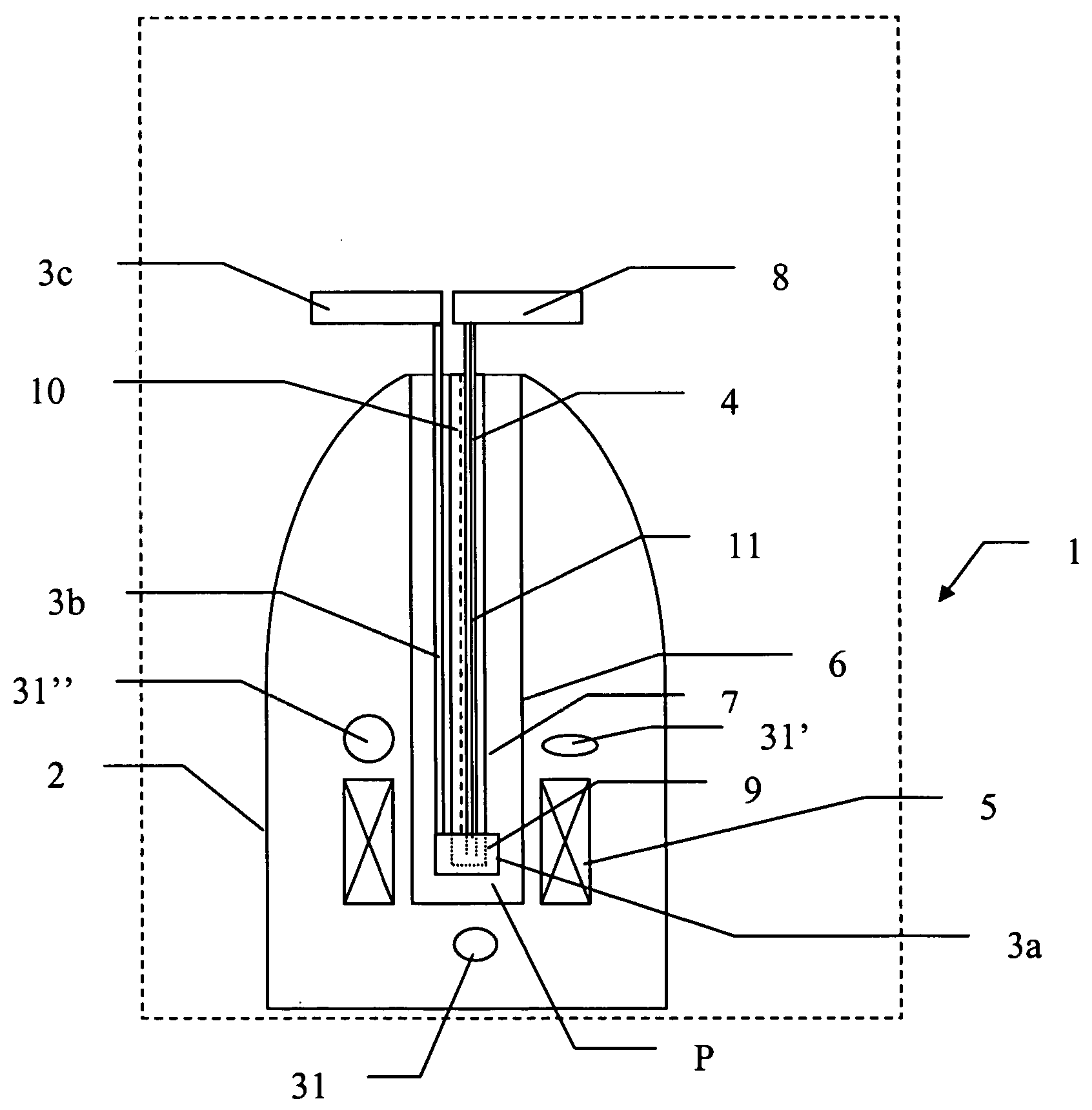
Methods and devices for polarised nmr samples
InactiveUS20040049108A1Raise the ratioImprove resolutionMeasurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSolid massLaser
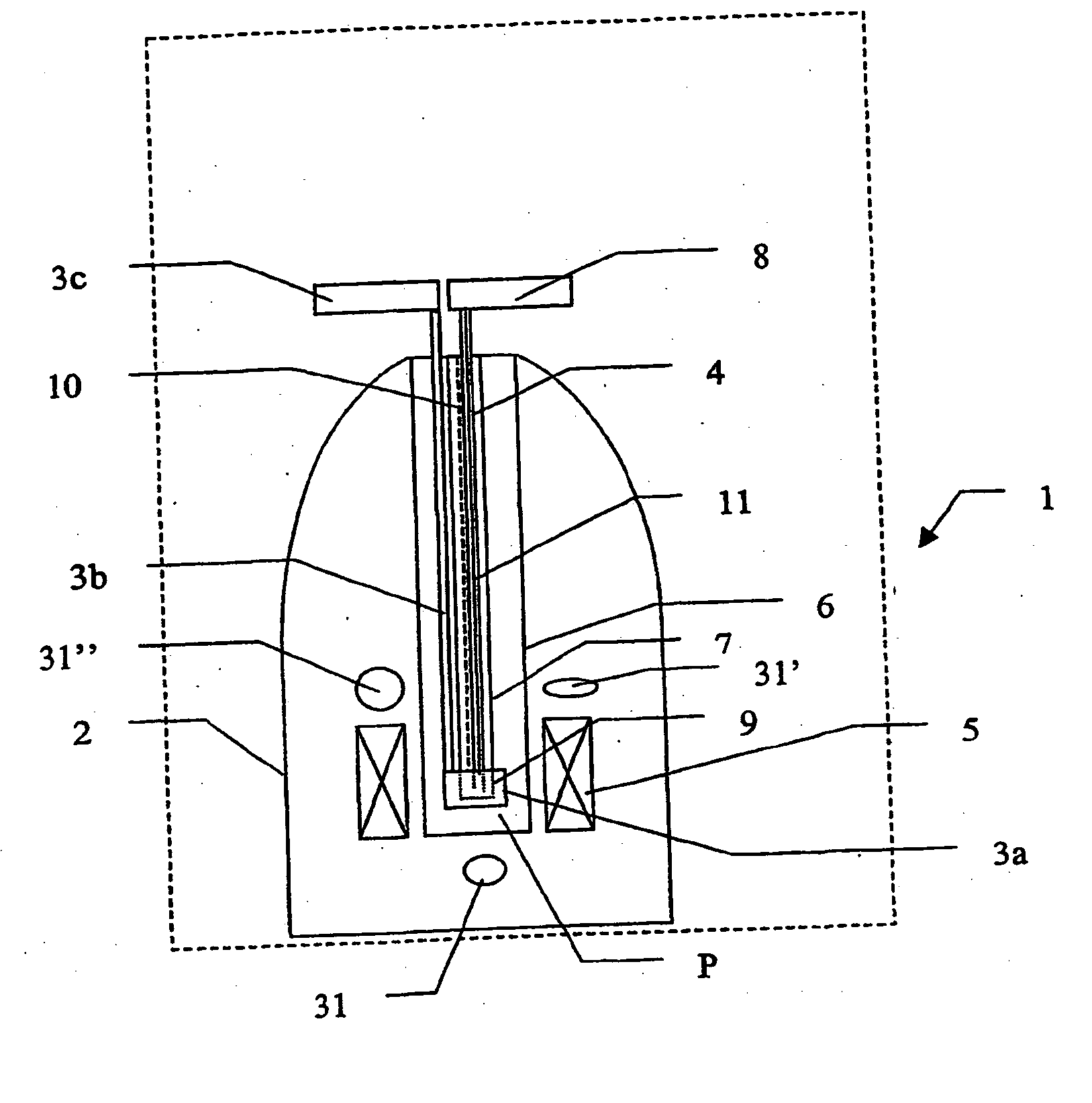
The present invention relates to devices and method for melting solid polarised sample while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a sample is polarised in a sample-retaining cup (9) in a strong magnetic field in a polarising means (3a, 3b, 3c) in a cryostat (2) and then melted inside the cryostat (2) by melting means such as a laser (8) connected by an optical fibre (4) to the interior of the cryostat.
Owner:AMERSHAM HEALTH
Method for the hyperpolarisation of nuclear spin in a diamond via a long-range interaction
ActiveUS20160061914A1Narrow line widthEfficient transferQuantum computersNanoinformaticsColour centreOptical pumping
The invention concerns a method for the hyperpolarisation of 13C nuclear spin in a diamond, comprising an optical pumping step, in which colour centre electron spins in the diamond are optically pumped. The method further comprises a transfer step in which the polarisation of a long-lived state of the colour centre electron spins is transferred to 13C nuclear spins in the diamond via a long-range interaction.
Owner:UNIV ULM
Methods and devices configured for dissolving hyperpolarised solid material with a solvent within a cryostat for NMR analyses
ActiveUS7372274B2Polarisation is minimisedLoss of polarisationElectrical measurement instrument detailsPreparing sample for investigationSolid massEngineering
The present invention relates to devices and method for dissolving solid polarised material while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a material is polarised in a strong magnetic field in a cryostat 2 and then brought into solution while still inside the cryostat 2.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
Method And System For Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers
InactiveUS20170038411A1Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientElectronic spin
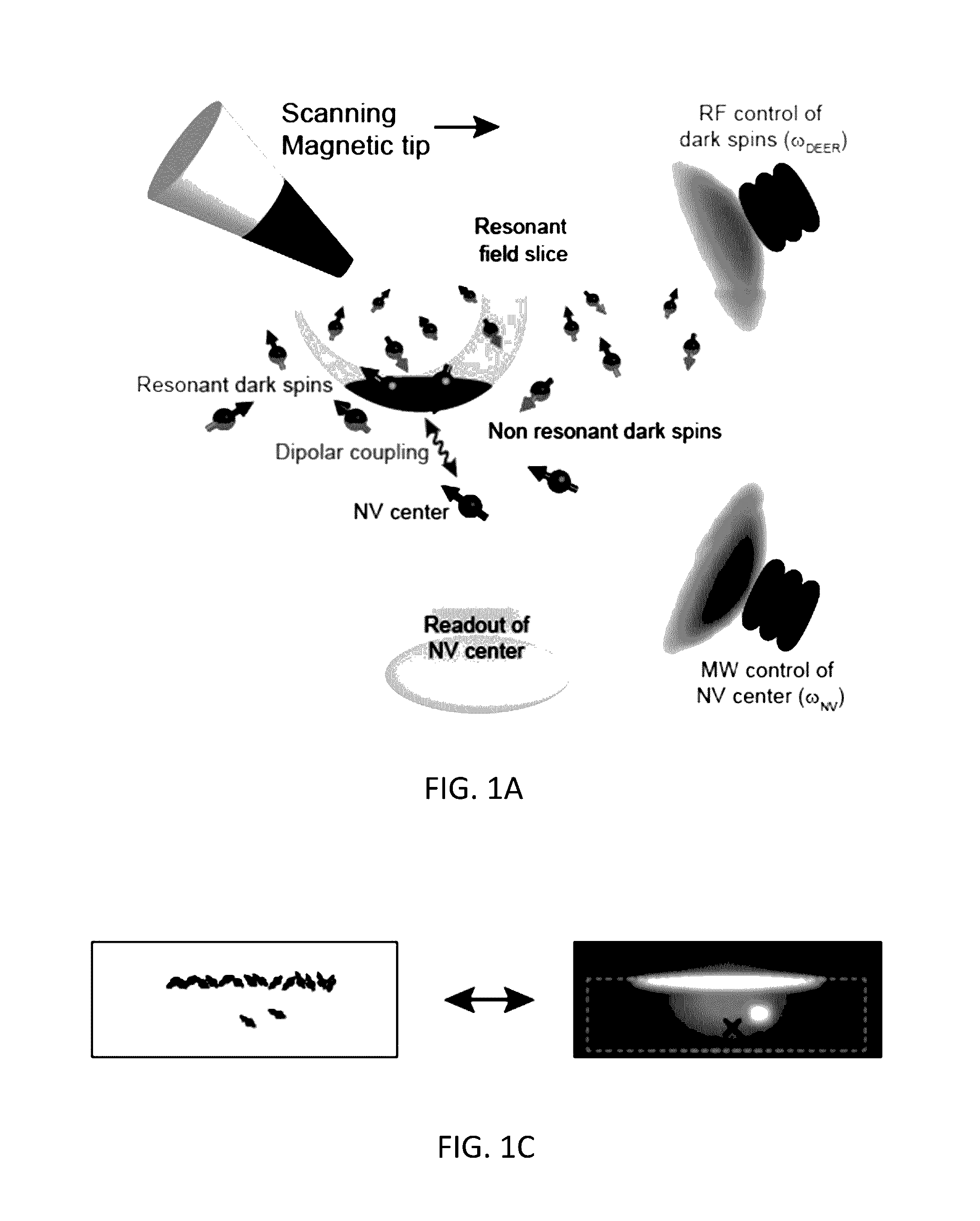
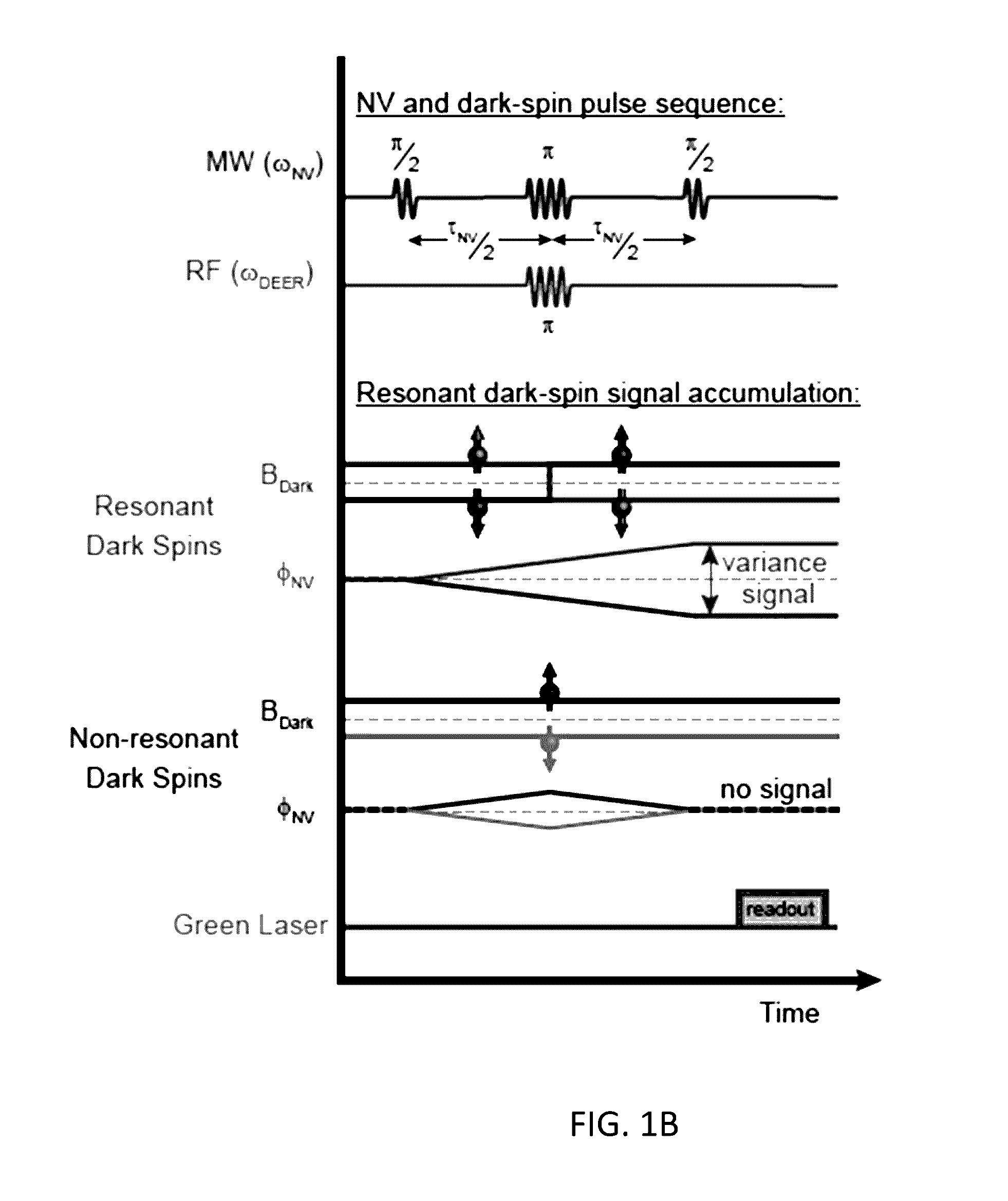
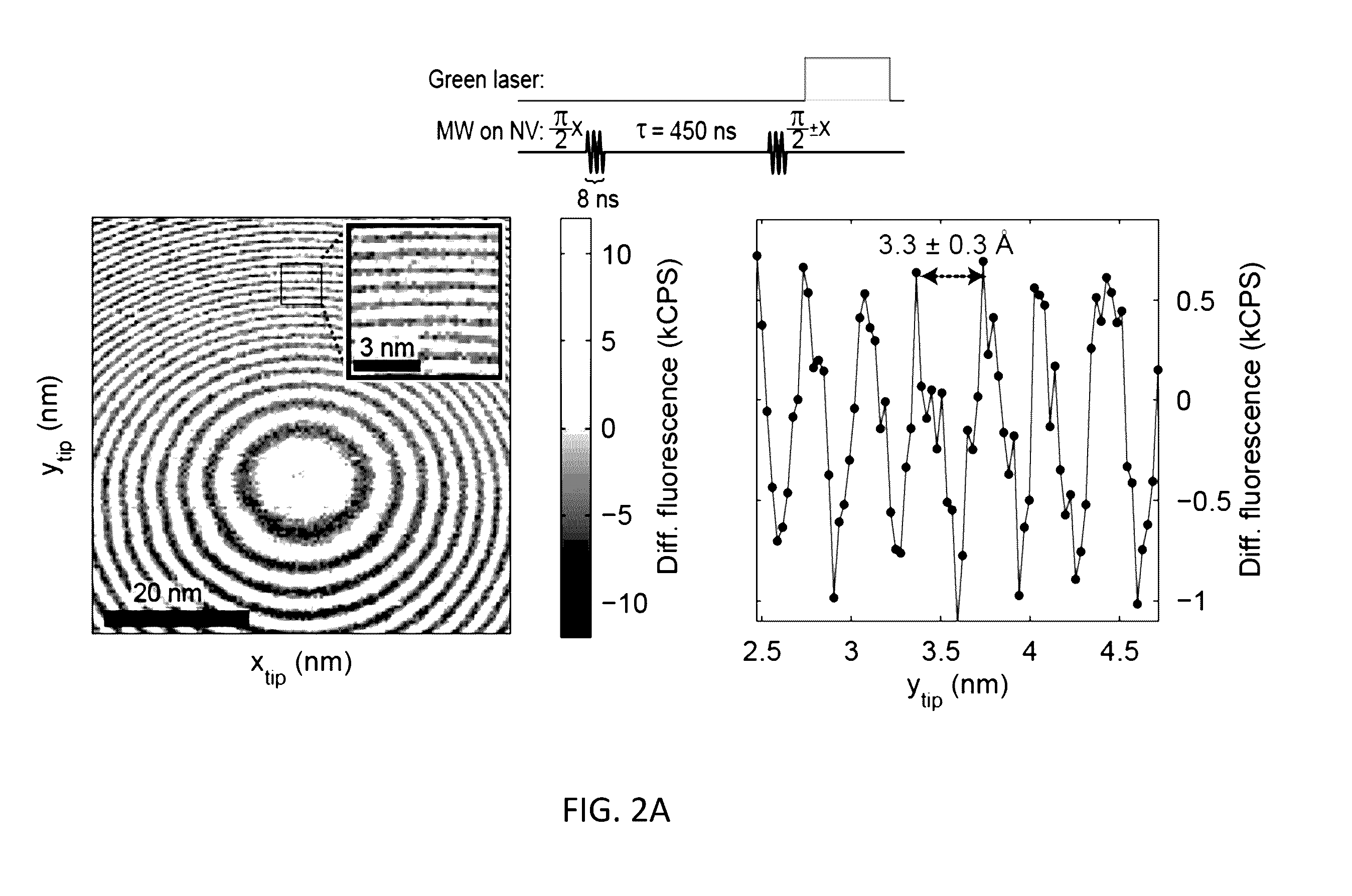
A method for performing sub-nanometer three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of a sample under ambient conditions using a diamond having at least one shallowly planted nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center. A driving radio-frequency (RF) signal and a microwave signal are applied to provide independent control of the NV spin and the target dark spins. A magnetic-field gradient is applied to the sample with a scanning magnetic tip to provide a narrow spatial volume in which the target dark electronic spins are on resonance with the driving RF field. The sample is controllably scanned by moving the magnetic tip to systematically bring non-resonant target dark spins into resonance with RF signal. The dark spins are measured and mapped by detecting magnetic resonance of said nitrogen-vacancy center at each of said different magnetic tip positions. The dark-spin point-spread-function for imaging the dark spins is directly measured by the NV center.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
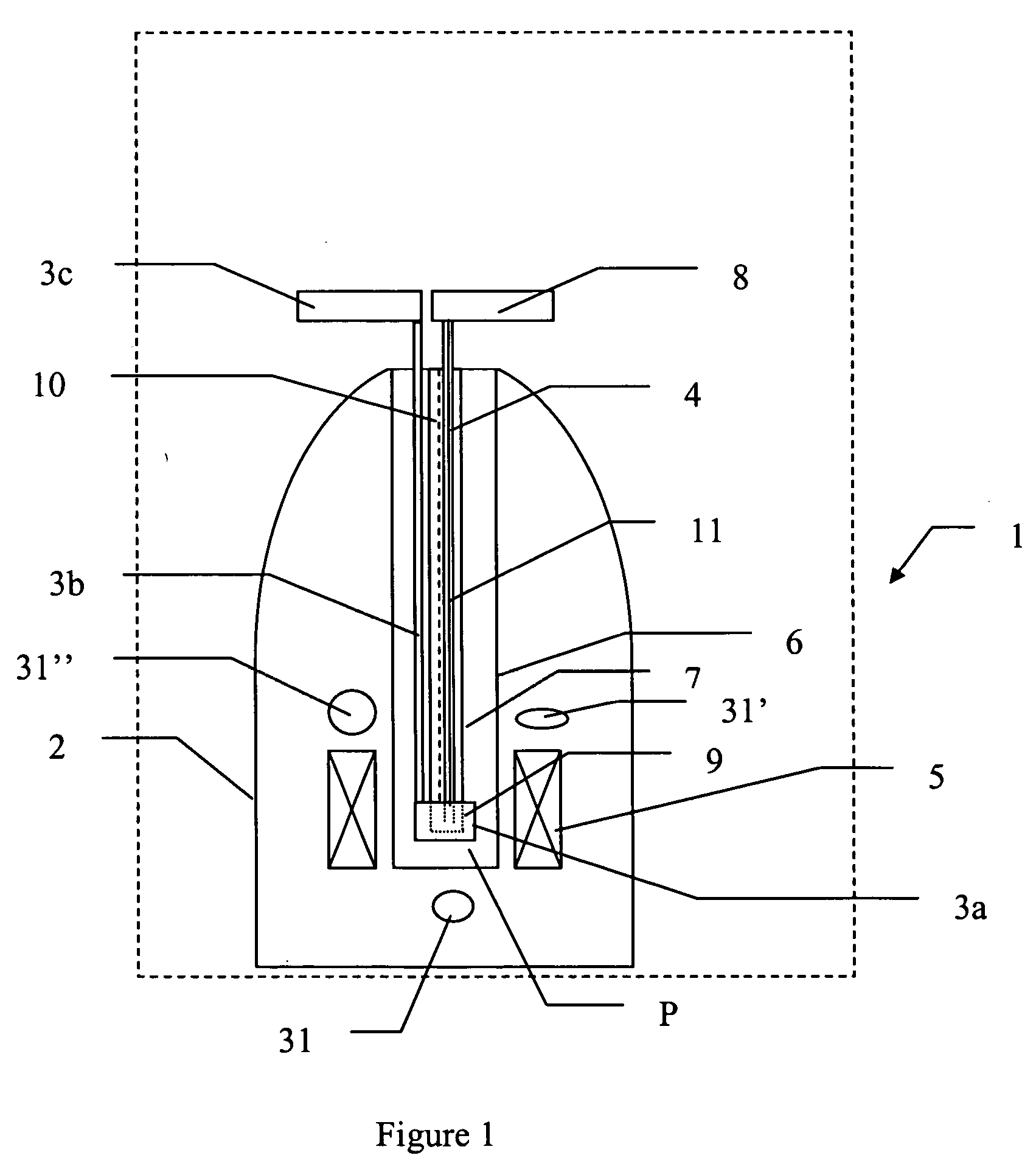
Methods and devices for polarized NMR samples
InactiveUS20060192559A1Preparing sample for investigationMeasurements using double resonanceLaserMagnetic field
The present invention relates to devices and methods for melting a solid polarised sample while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a sample is polarised in a sample-retaining cup in a strong magnetic field in a polarising means in a cryostat and then melted inside the cryostat by melting means such as a laser connected by an optical fibre to the interior of the cryostat.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
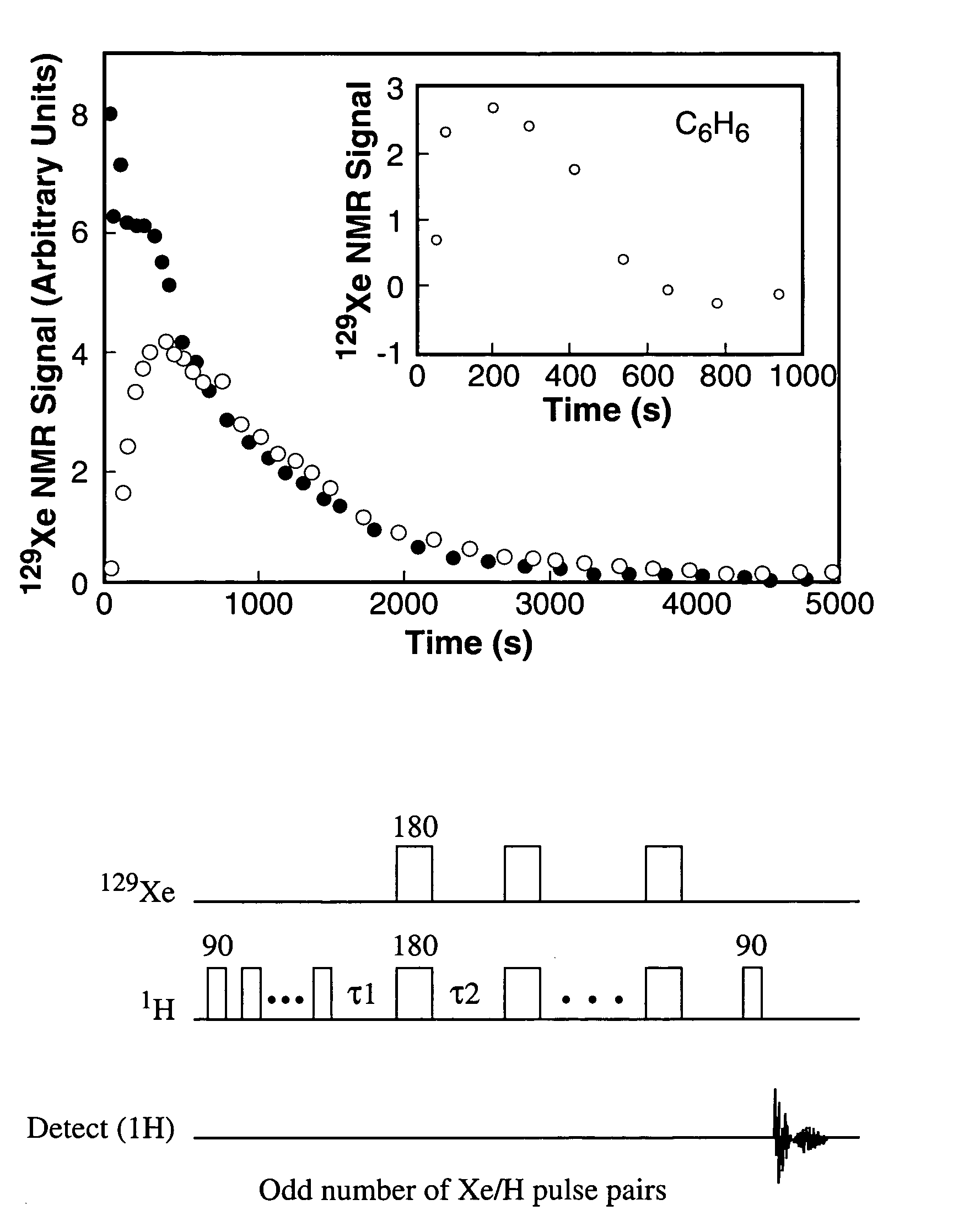
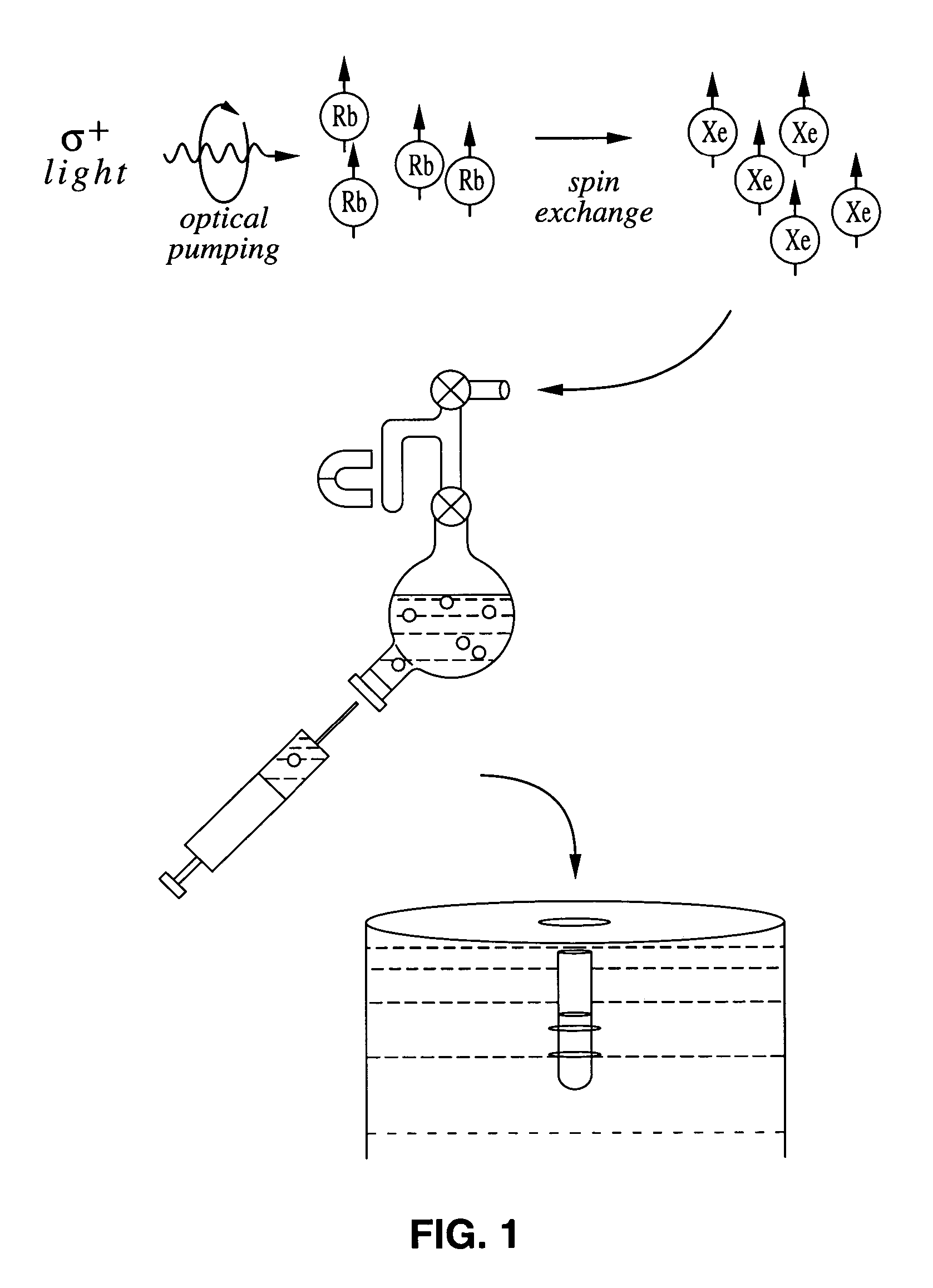
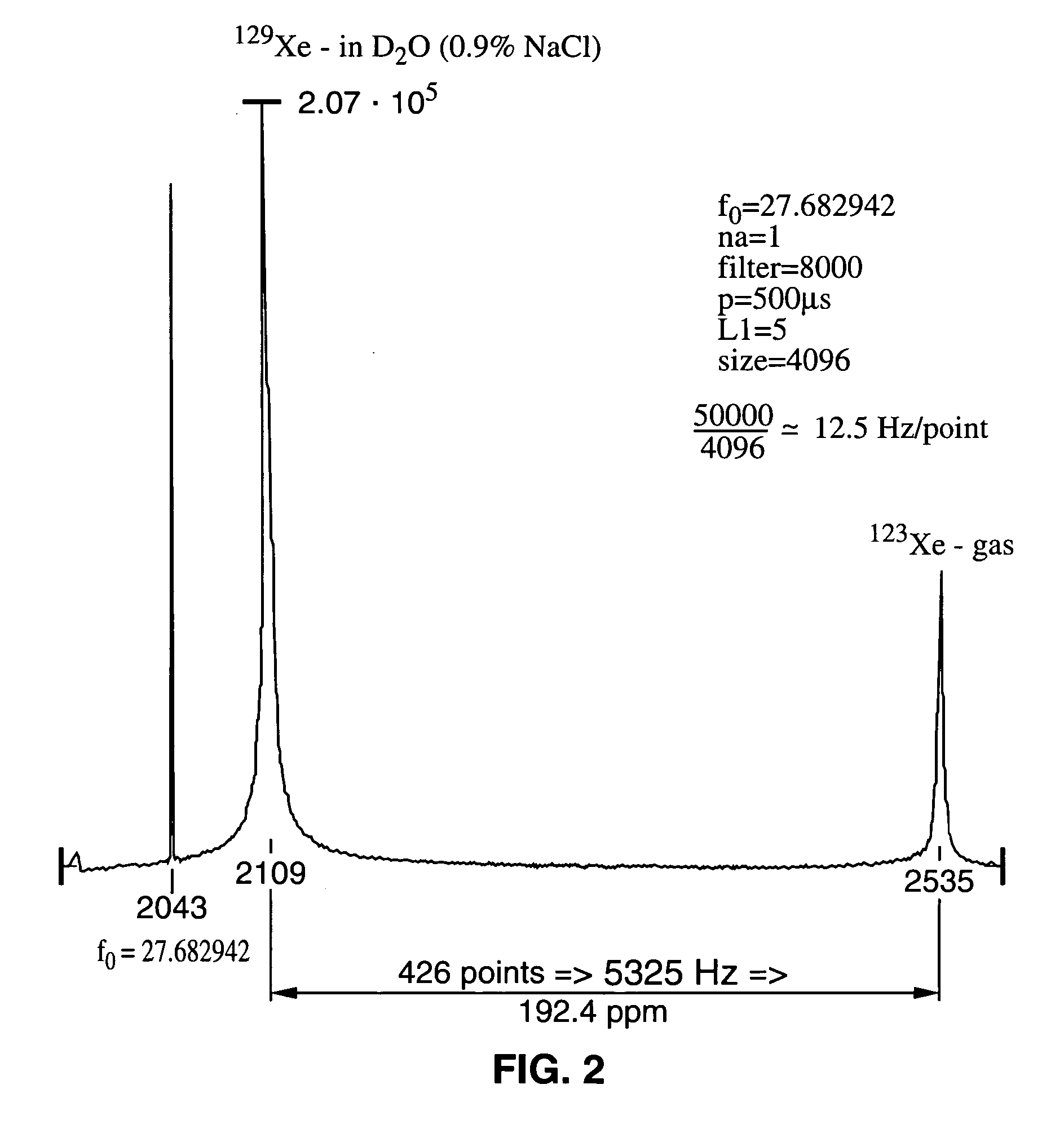
Enhancement of NMR and MRI in the presence of hyperpolarized noble gases
InactiveUS20050030026A1Increase relaxation timeDispersion deliveryMeasurements using double resonanceNoble gasNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention relates generally to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques for both spectroscopy and imaging. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods in which hyperpolarized noble gases (e.g., Xe and He) are used to enhance and improve NMR and MRI. Additionally, the hyperpolarized gas solutions of the invention are useful both in vitro and in vivo to study the dynamics or structure of a system. When used with biological systems, either in vivo or in vitro, it is within the scope of the invention to target the hyperpolarized gas and deliver it to specific regions within the system.
Owner:LAWRENCE BERKELEY NAT LAB
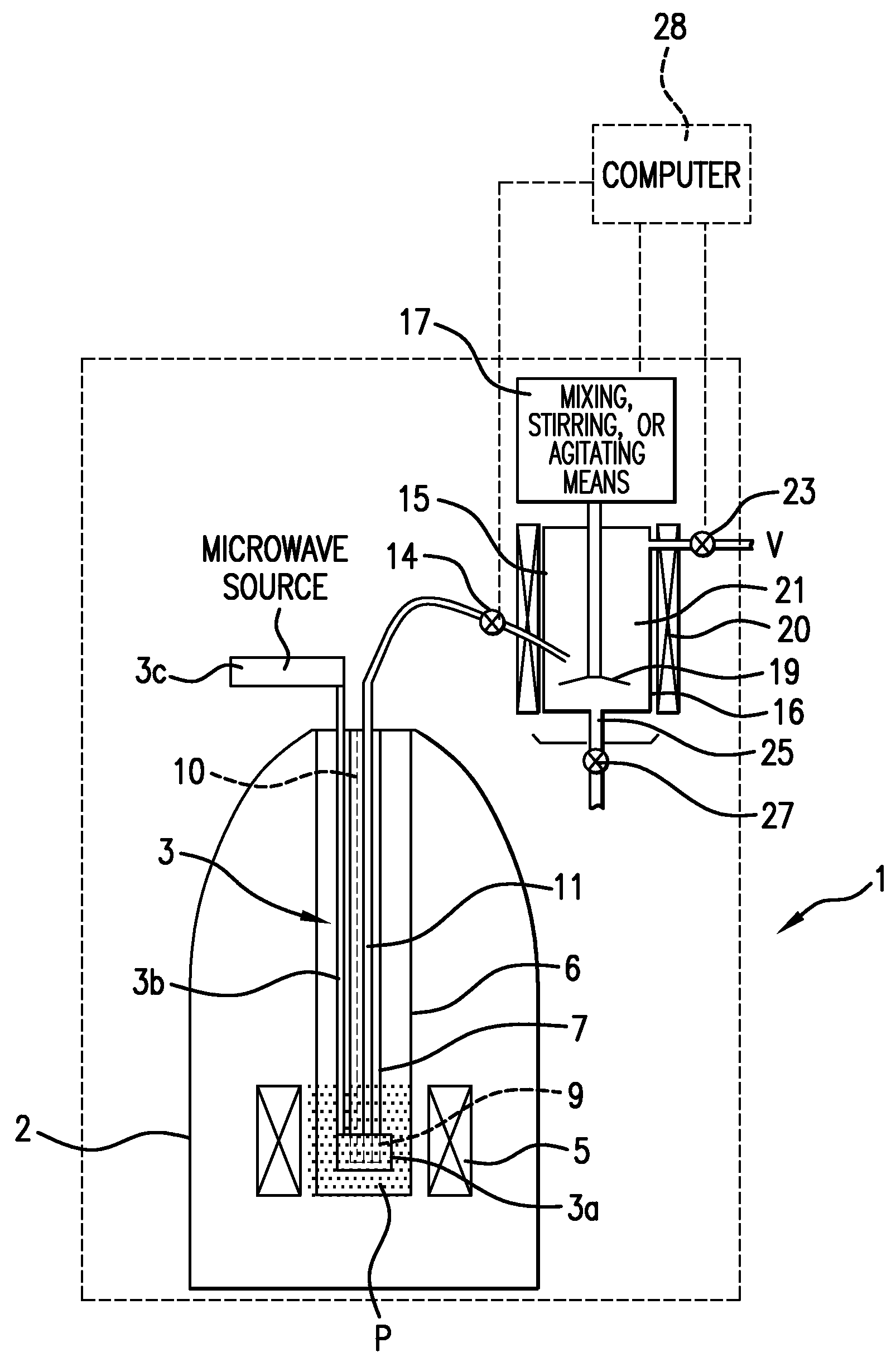
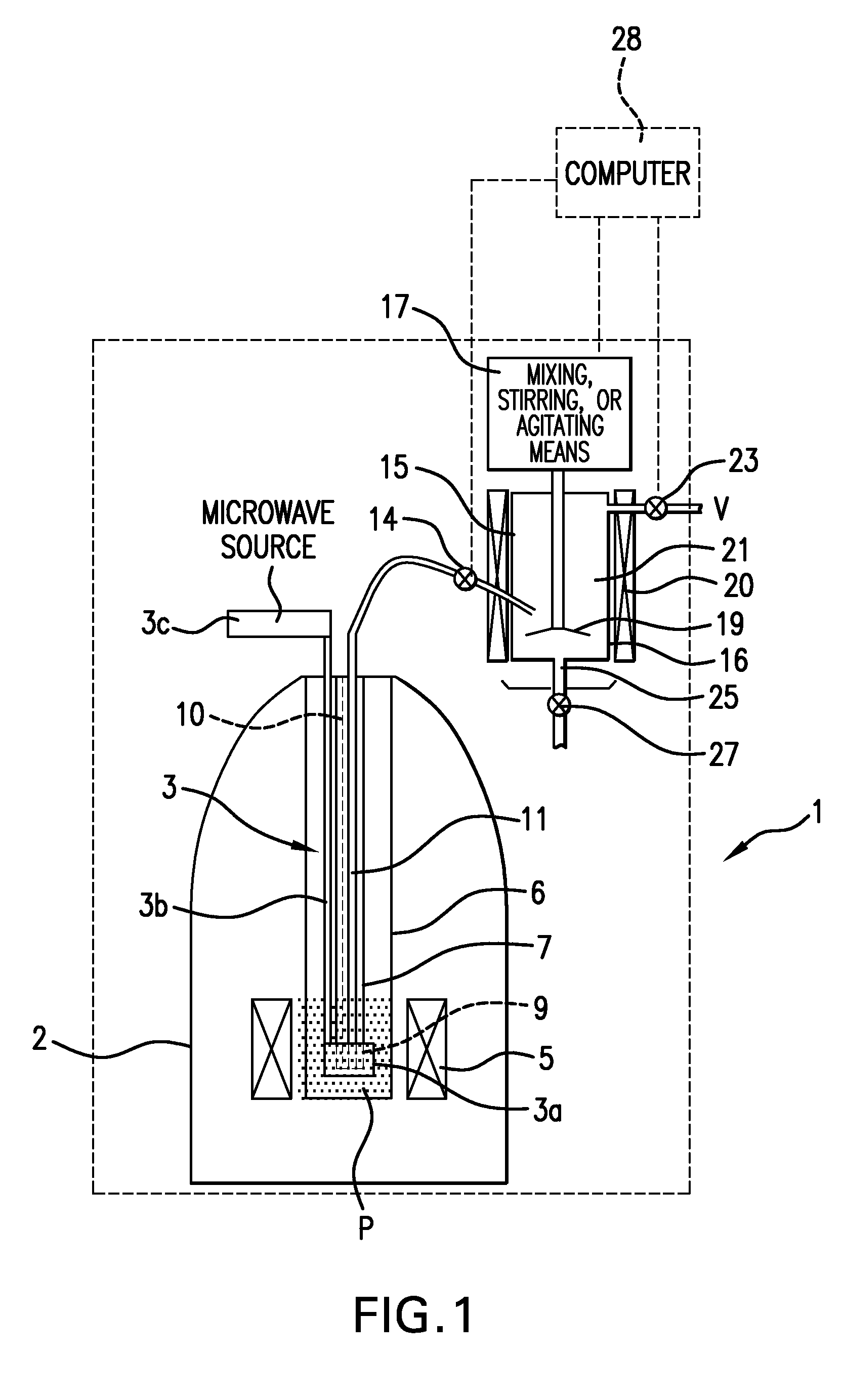
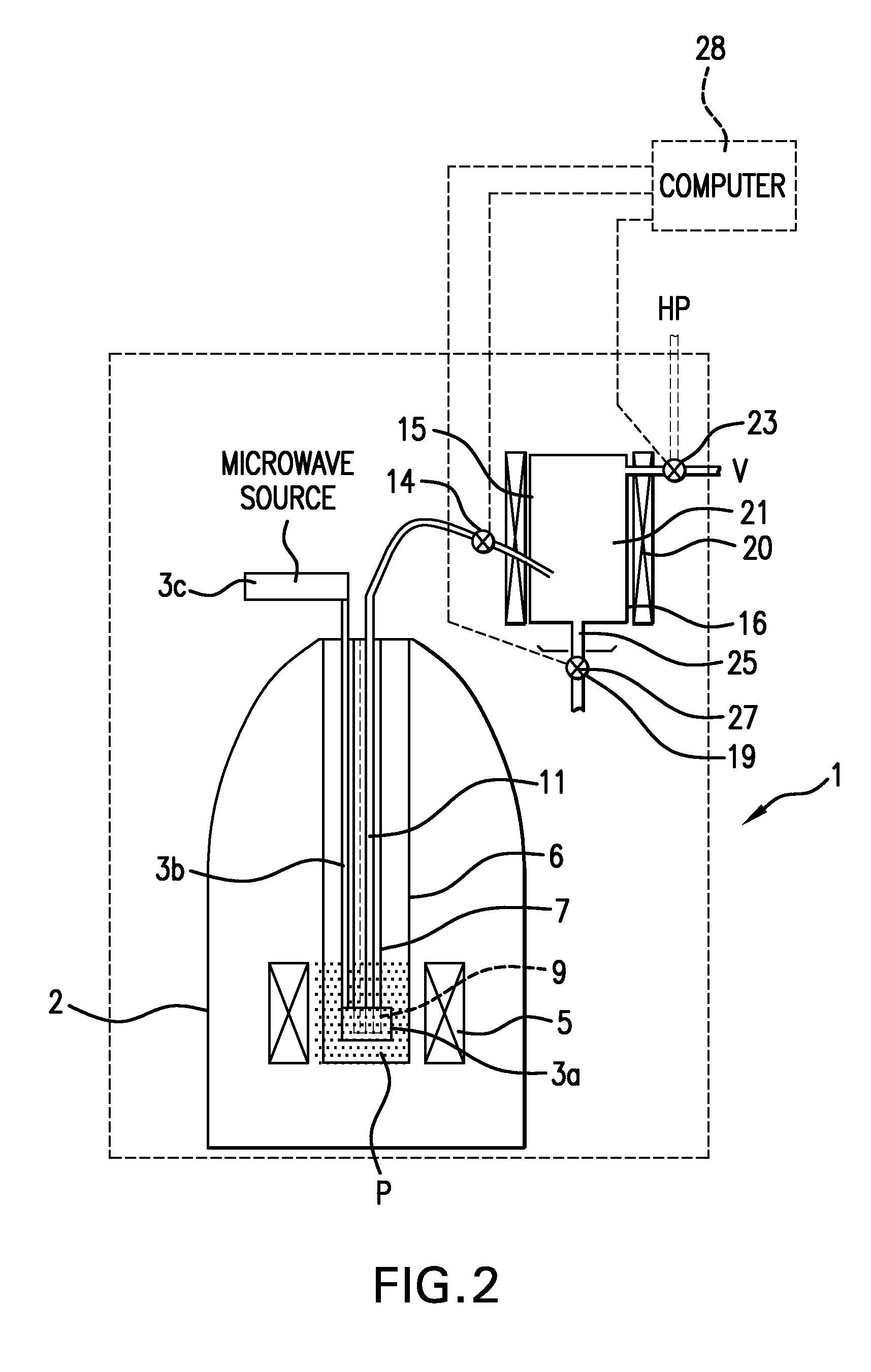
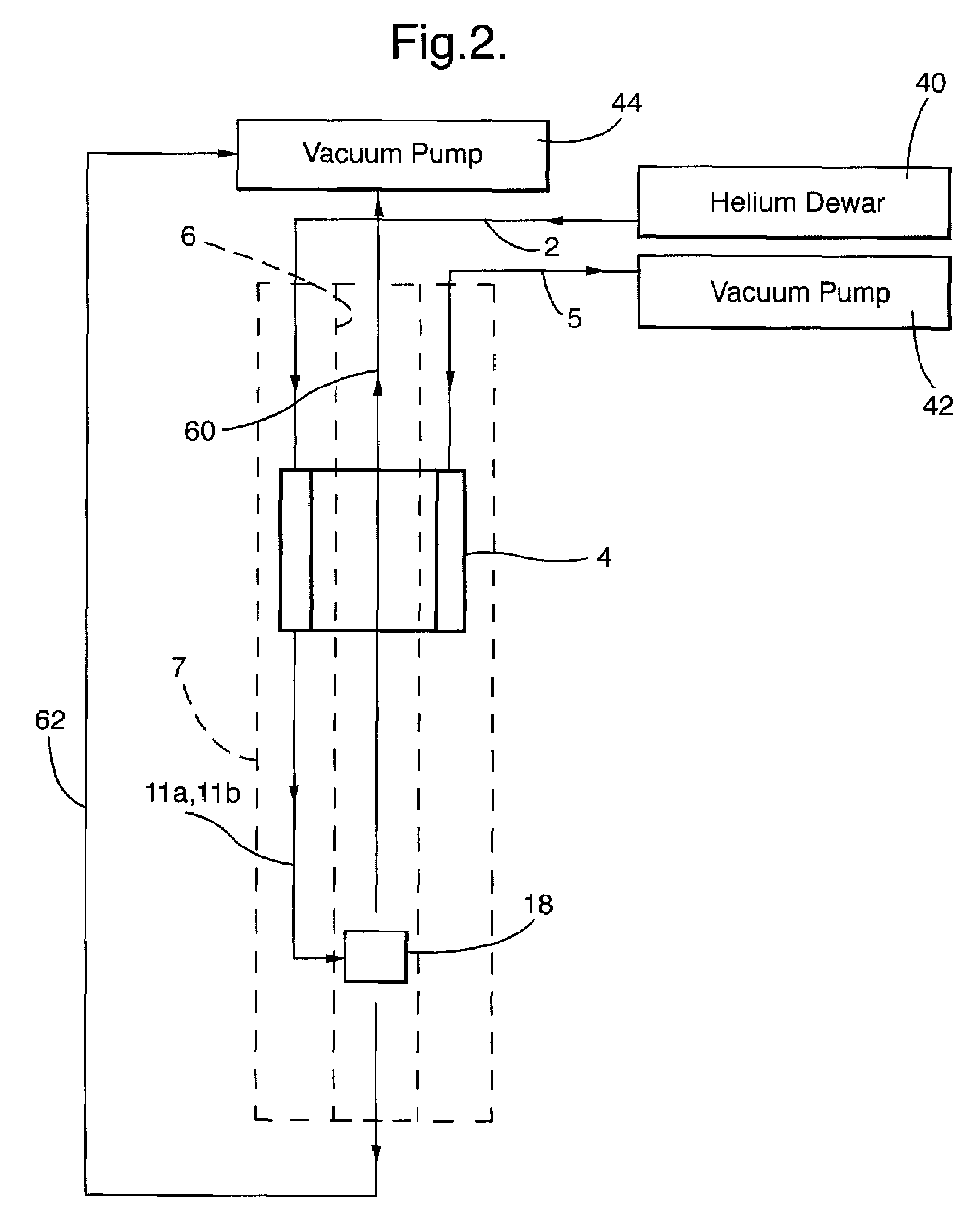
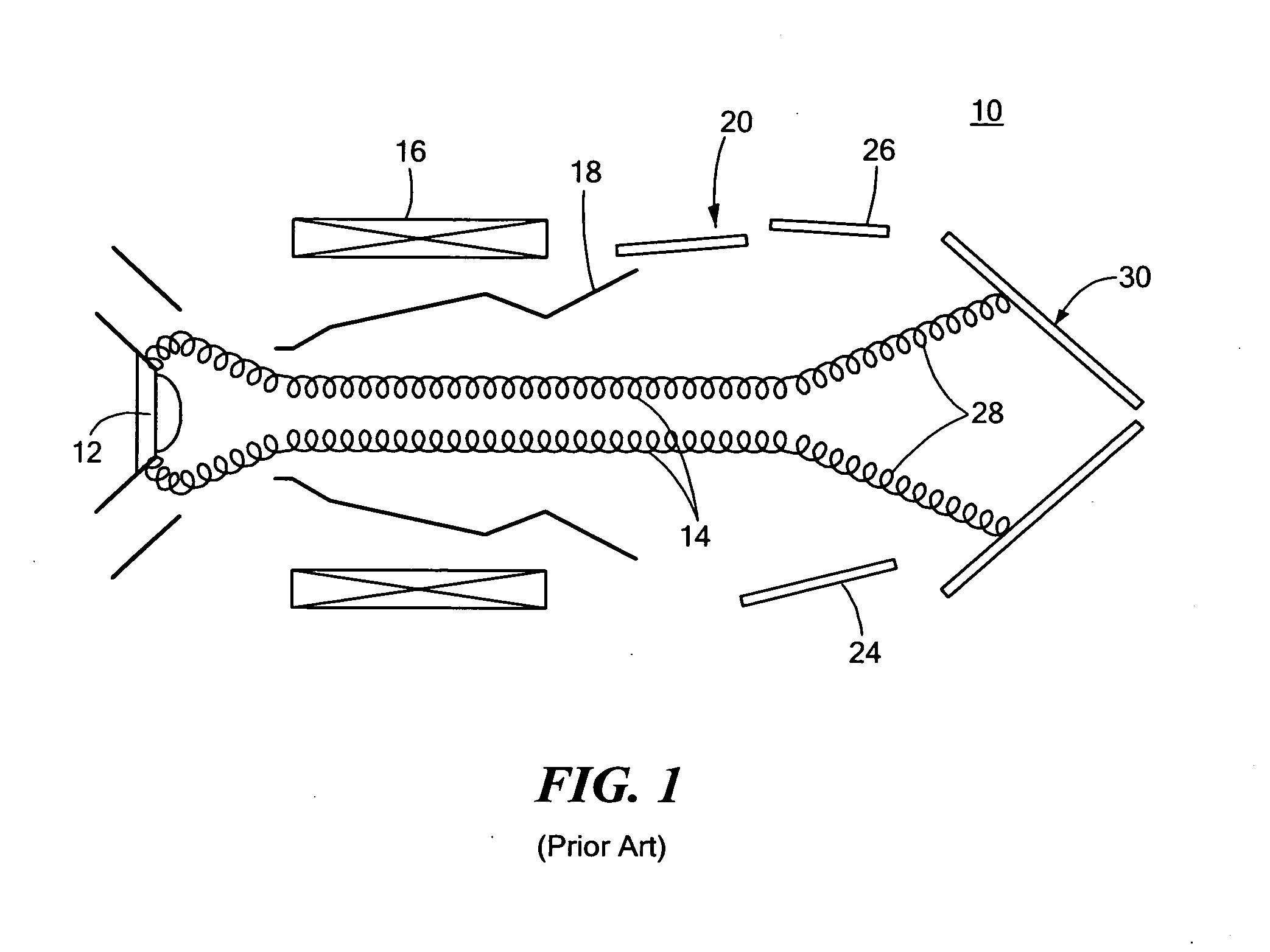
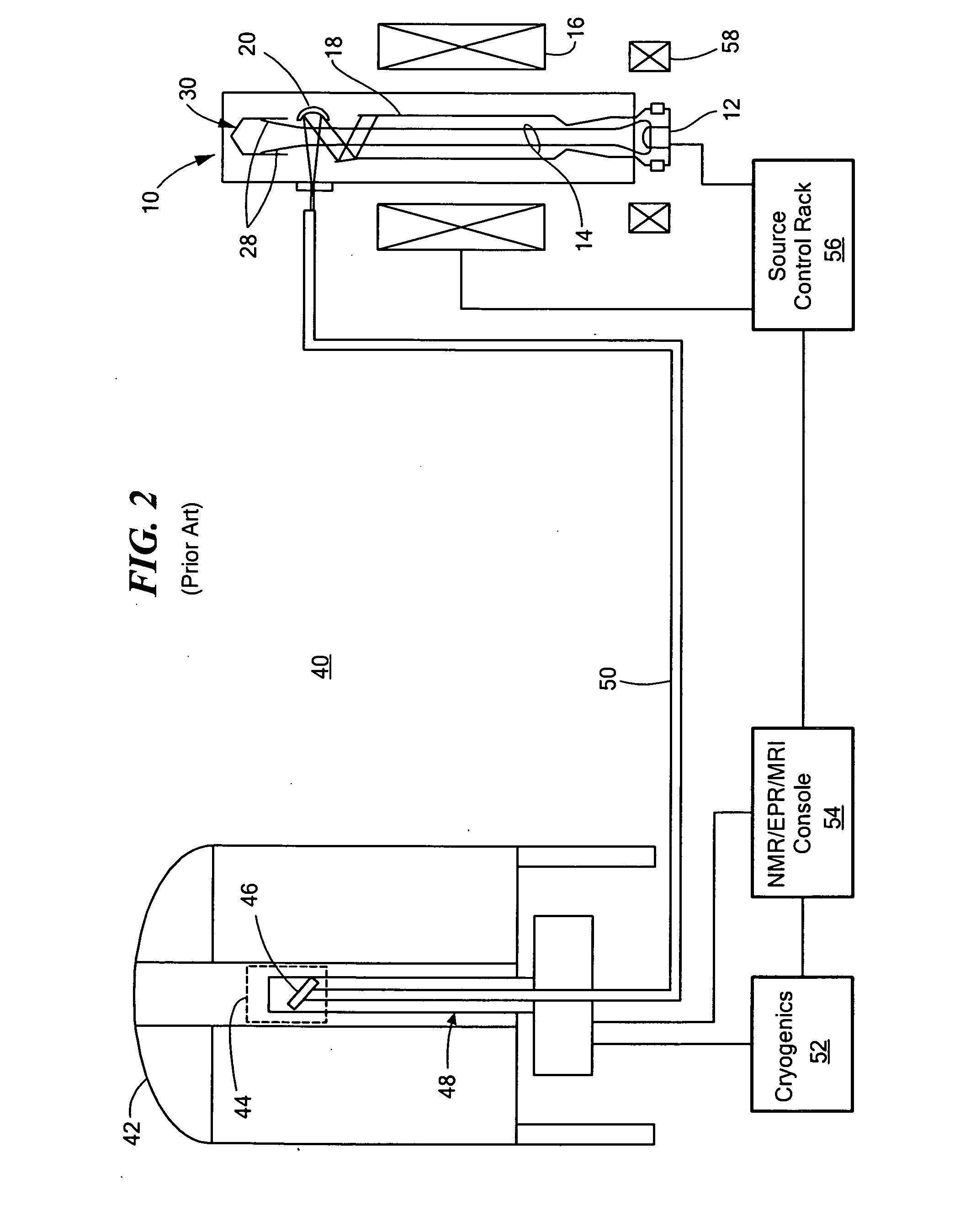
Apparatus and method for performing in-vitro DNP-NMR measurements
InactiveUS7639007B2Reduce lossesMinimizing reaction forceMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyCryostatMagnetic field
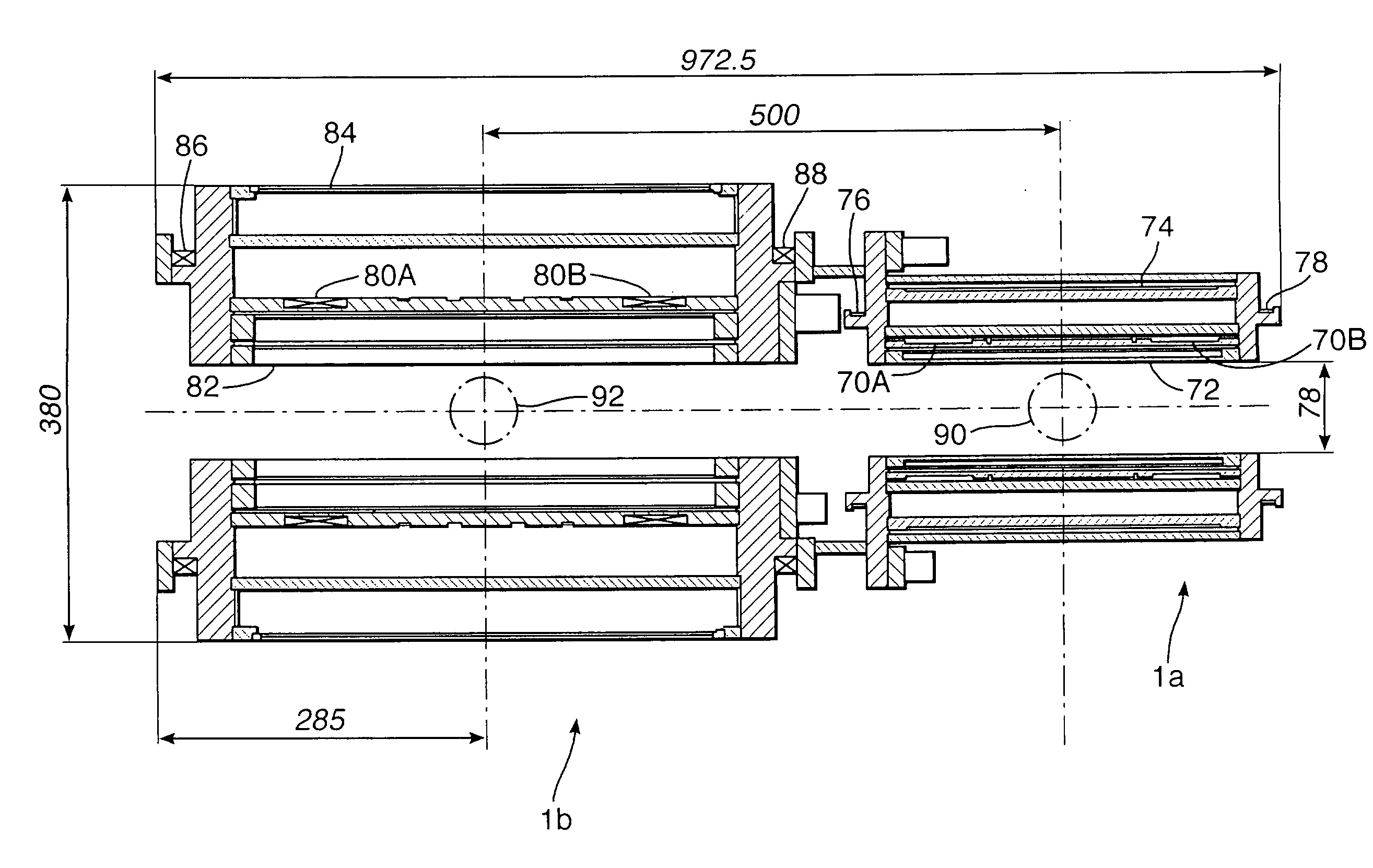
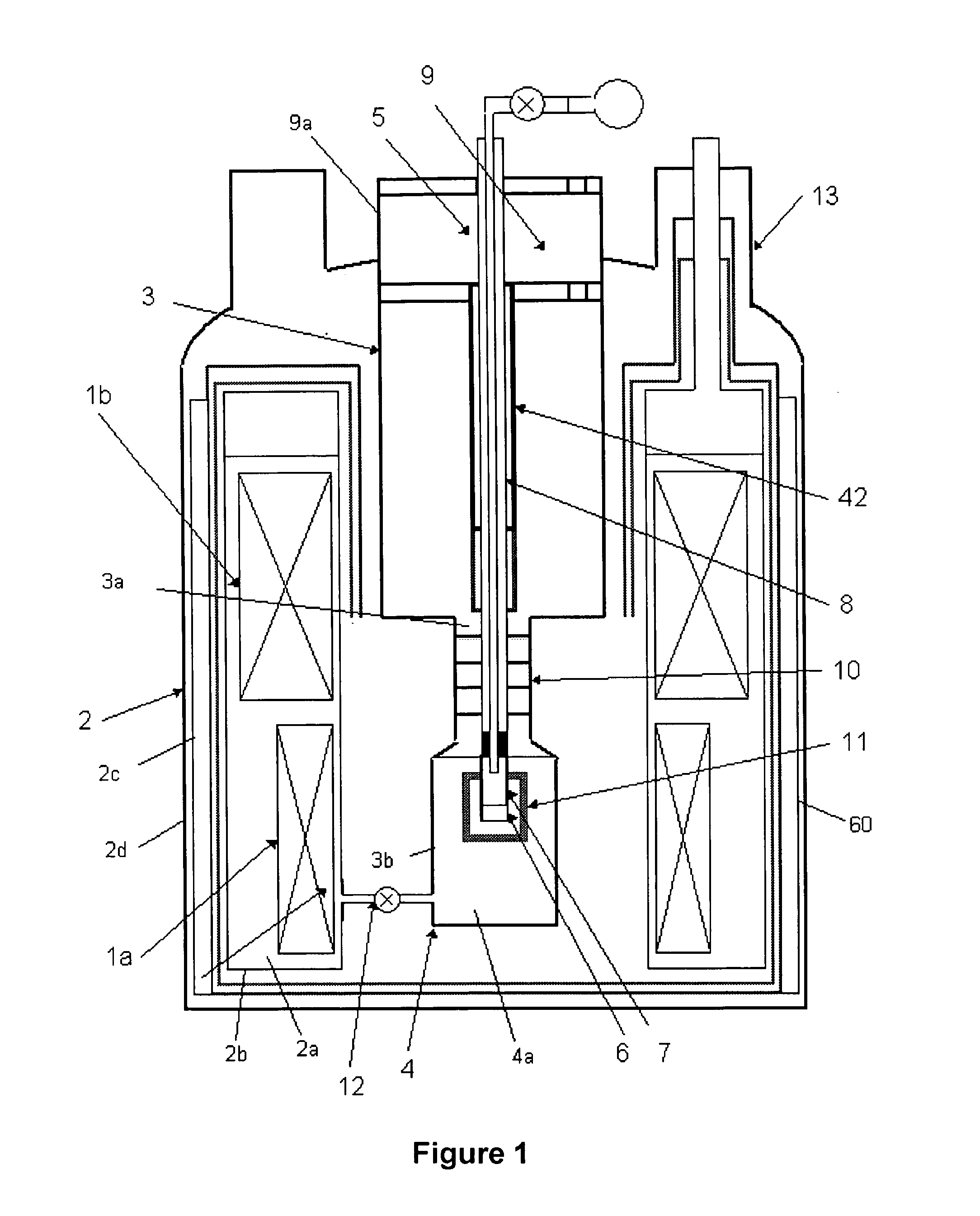
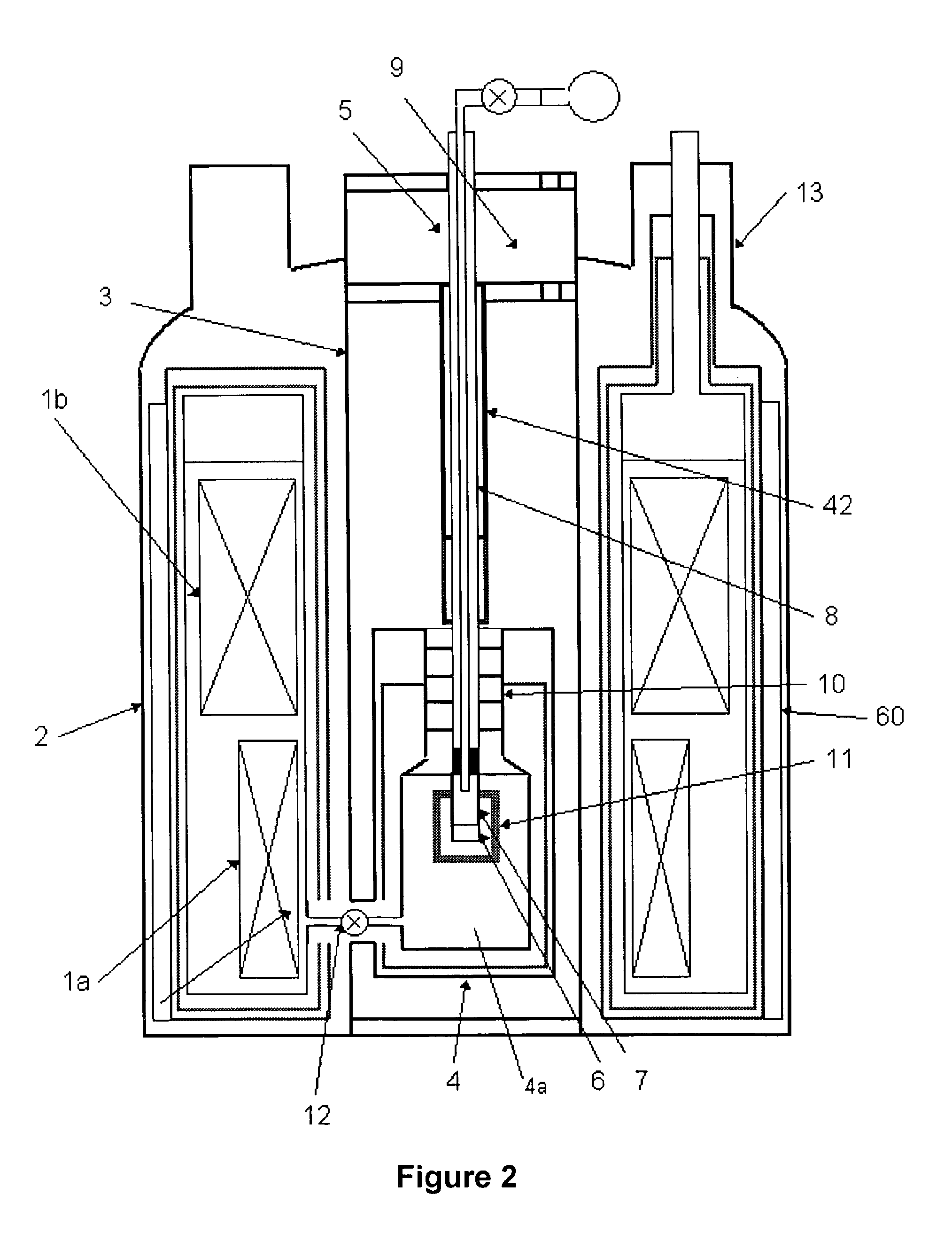
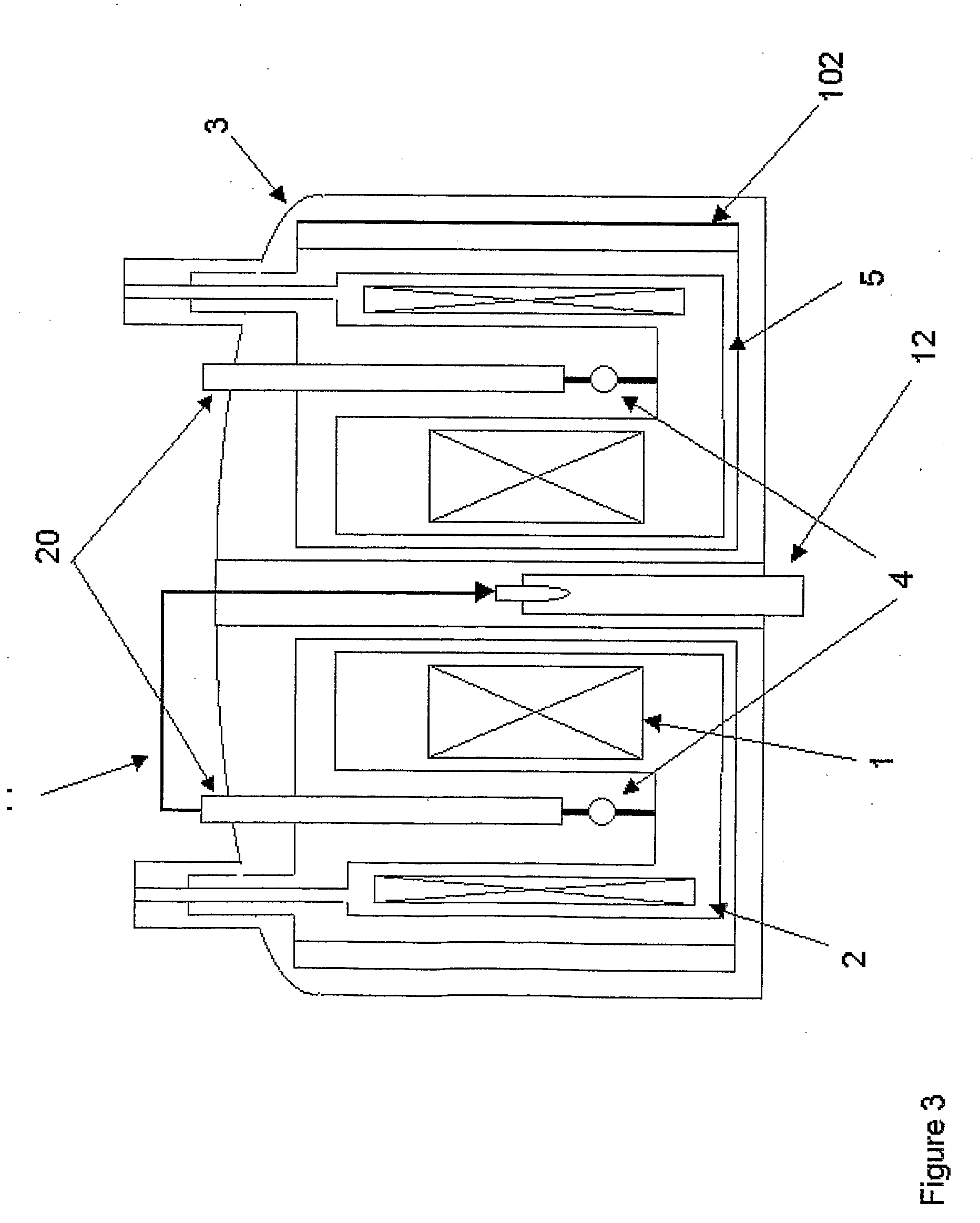
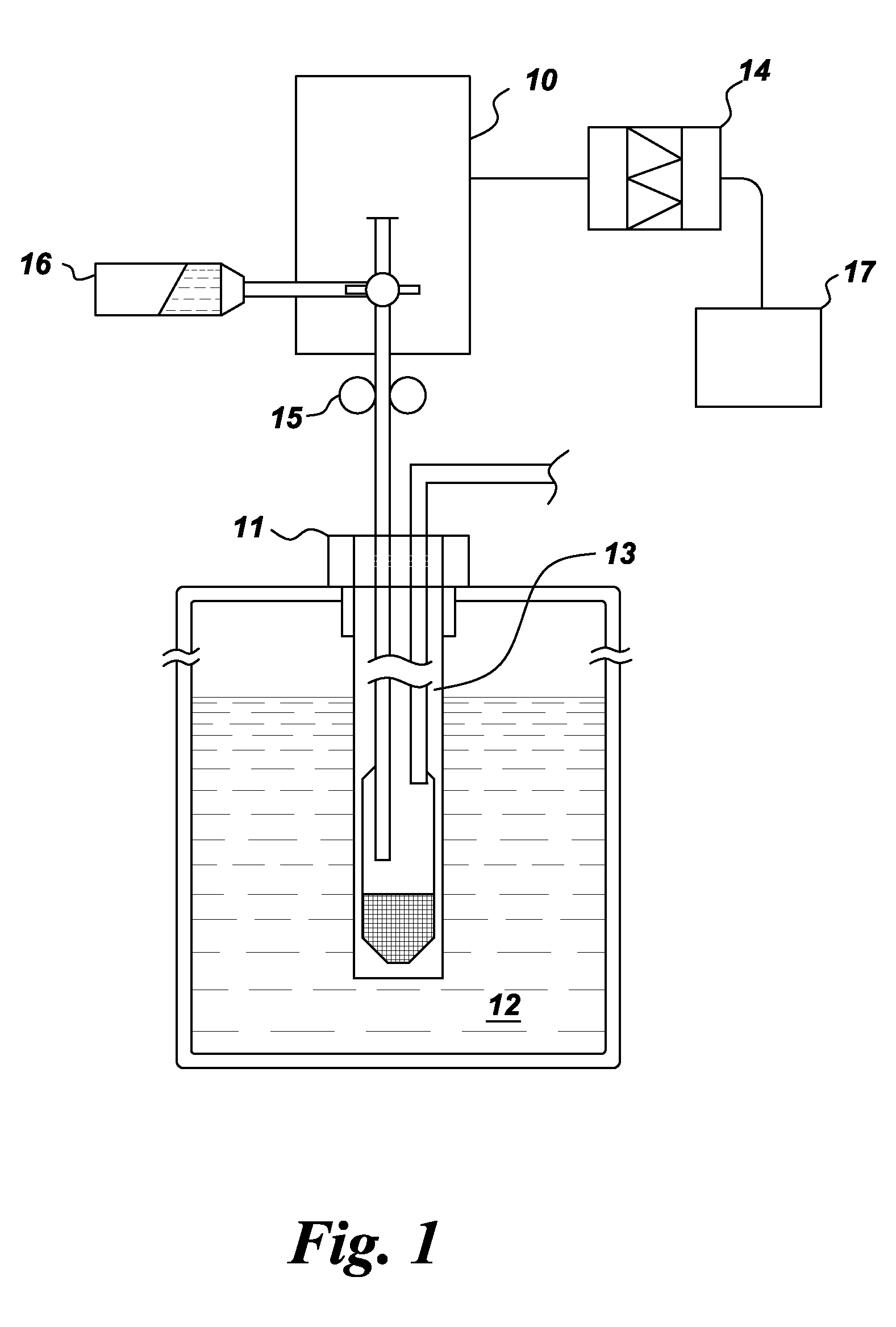
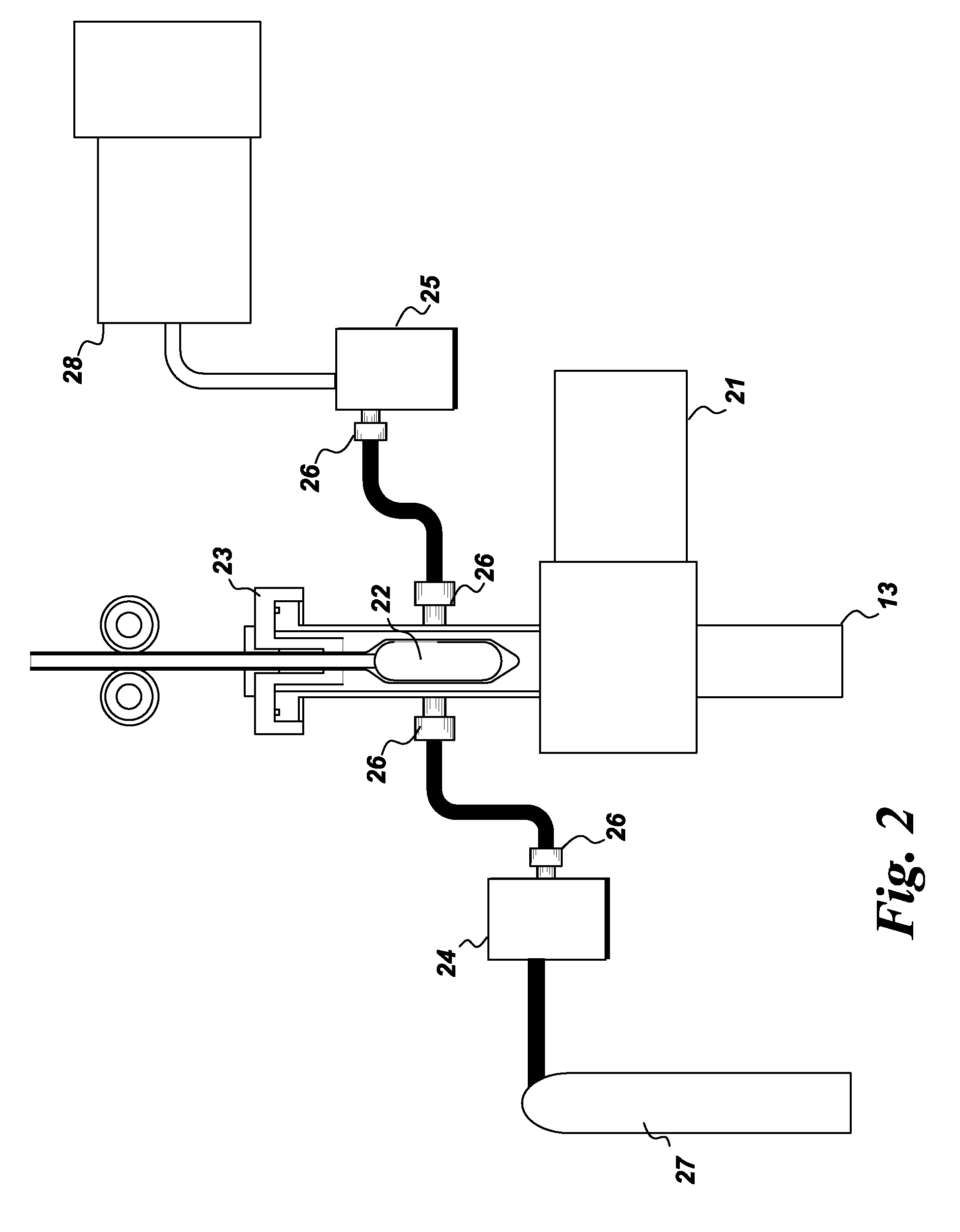
Apparatus for performing in-vitro DNP-NMR measurements on a sample comprises magnetic field generating apparatus (1a, 1b) located in a cryostat (2) and surrounding a bore defining respective NMR and DNP working regions (90, 92). A system for performing DNP on a suitably prepared sample in the DNP working region. A system for performing a NMR process on a sample in the NMR working region. A sample positioning mechanism (5) which can be inserted in the bore (3) to bring a sample in turn into each of the working regions. The magnetic field generating apparatus is suitably structured so that the magnetic field in the DNP working region has a homogeneity or profile suitable for performing DNP on the sample and the magnetic field in the NMR working region has a homogeneity or profile suitable for performing a NMR process on the sample.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR NANOTECH TOOLS
Double-resonance structure and method for investigating samples by DNP and/or ENDOR
InactiveUS20110050225A1Increased NMR sensitivitySolve the lack of spaceMeasurements using double resonanceAnalysis using double resonanceResonanceElectromagnetic field
A double-resonance structure for DNP-NMR experiments and / or ENDOR experiments and methods using such a double-resonance structure. The double-resonance structure comprises a microwave resonator for generating electromagnetic fields suitable for EPR and an HF resonator for generating electromagnetic fields suitable for NMR. The HF resonator is formed by a strip resonator, a section of the strip resonator at the same time forming a portion of the microwave resonator.
Owner:JOHANN WOLFGANG GOETHE UNIV FRANKFURT AM MAIN
Methods and devices for polarised NMR samples
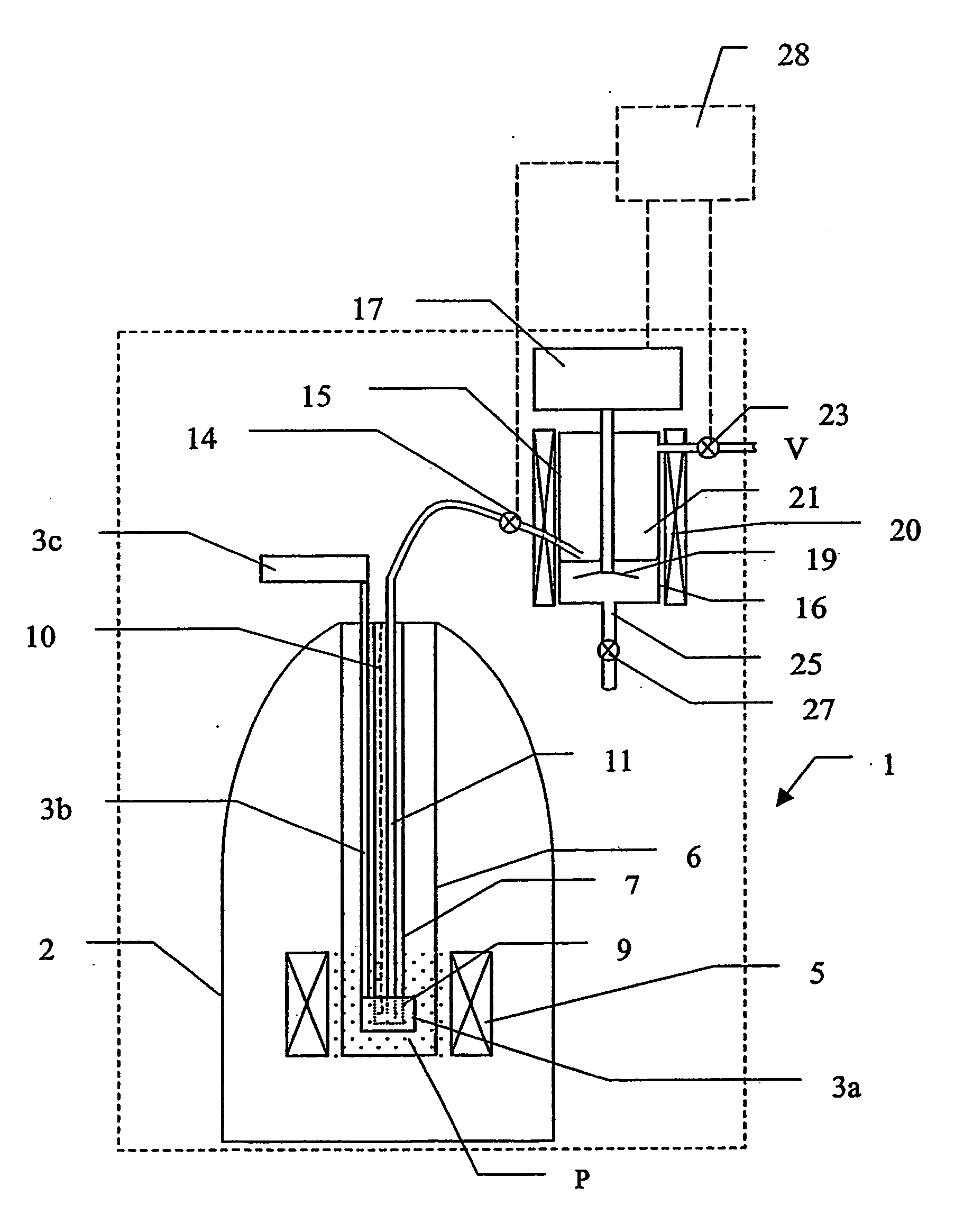
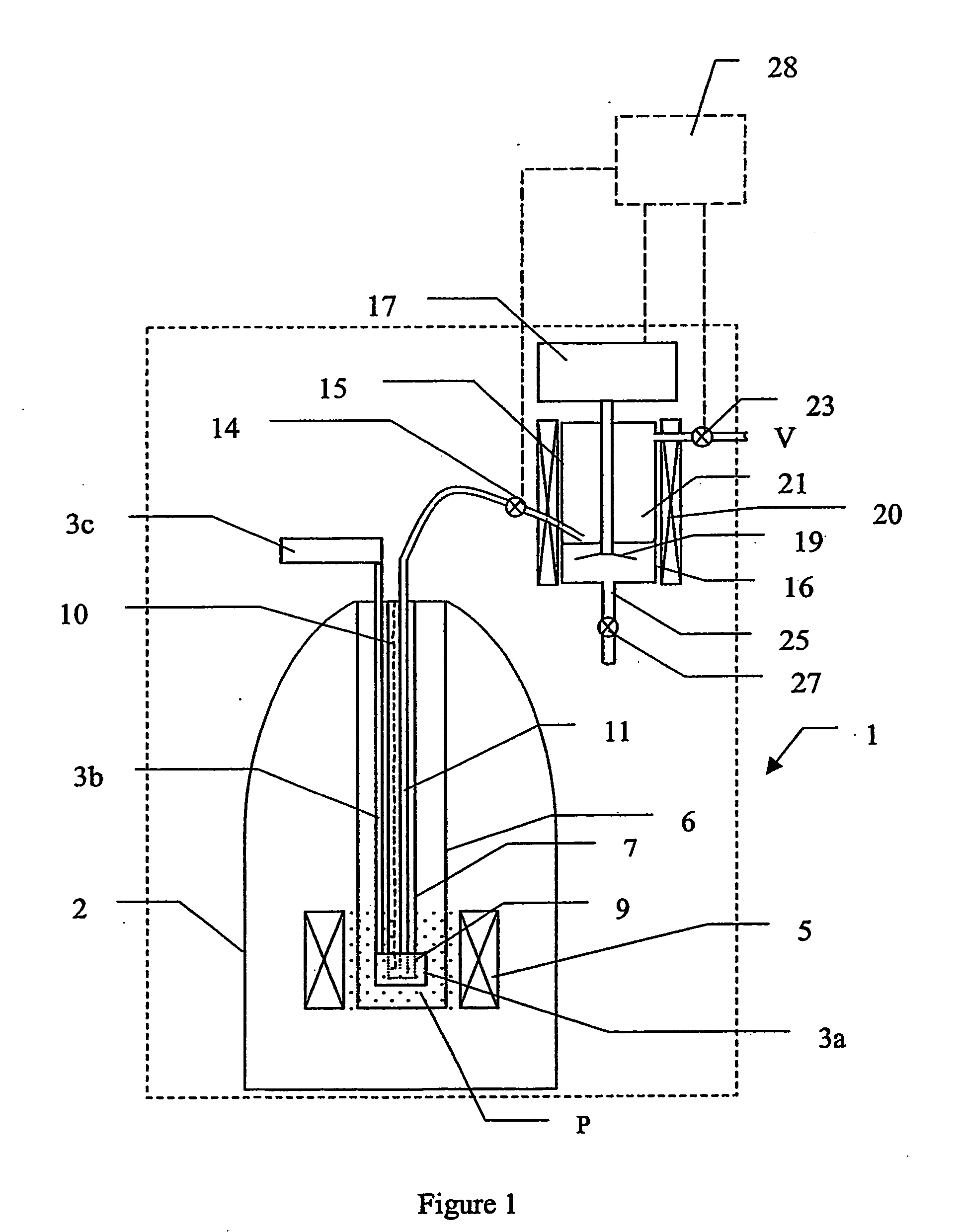
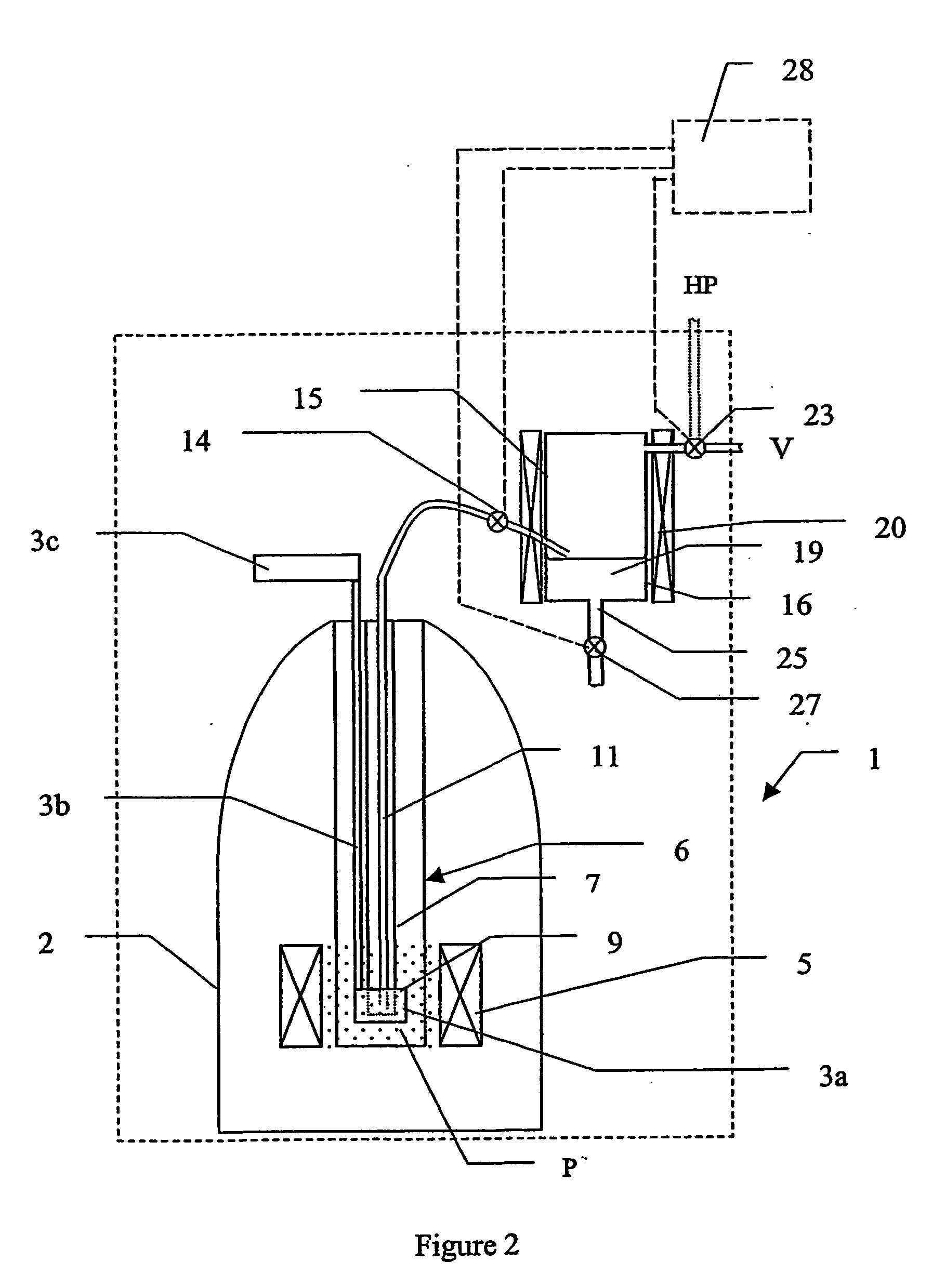
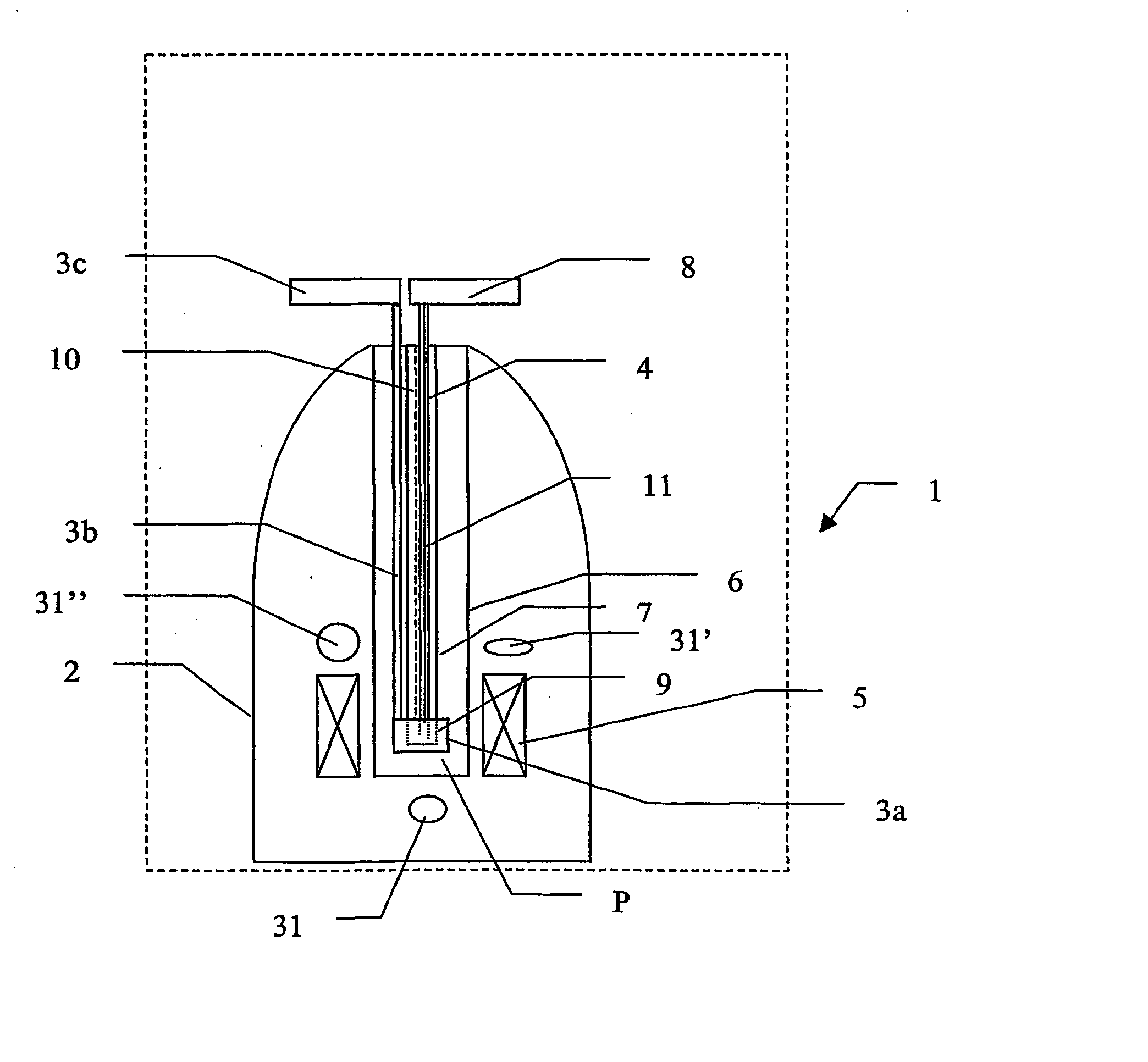
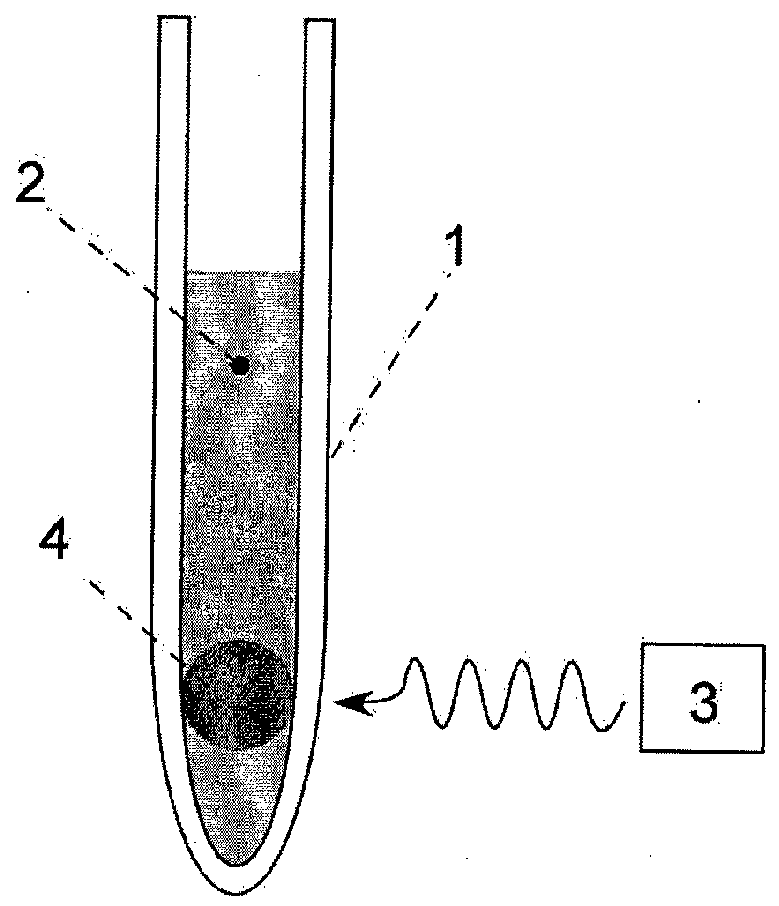
The present invention relates to devices and method for melting solid polarised sample while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a sample is polarised in a sample-retaining cup 9 in a strong magnetic field in a polarising means 3a, 3b, 3c in a cryostat 2 and then melted inside the cryostat 2 by melting means such as a laser 8 connected by an optical fibre 4 to the interior of the cryostat.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
Enhancement of NMR and MRI in the presence of hyperpolarized noble gases
InactiveUS20030017110A1Reduce the overall heightHigh saturationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDispersion deliveryNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceNoble gas
The present invention relates generally to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques for both spectroscopy and imaging. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods in which hyperpolarized noble gases (e.g., Xe and He) are used to enhance and improve NMR and MRI. Additionally, the hyperpolarized gas solutions of the invention are useful both in vitro and in vivo to study the dynamics or structure of a system. When used with biological systems, either in vivo or in vitro, it is within the scope of the invention to target the hyperpolarized gas and deliver it to specific regions within the system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
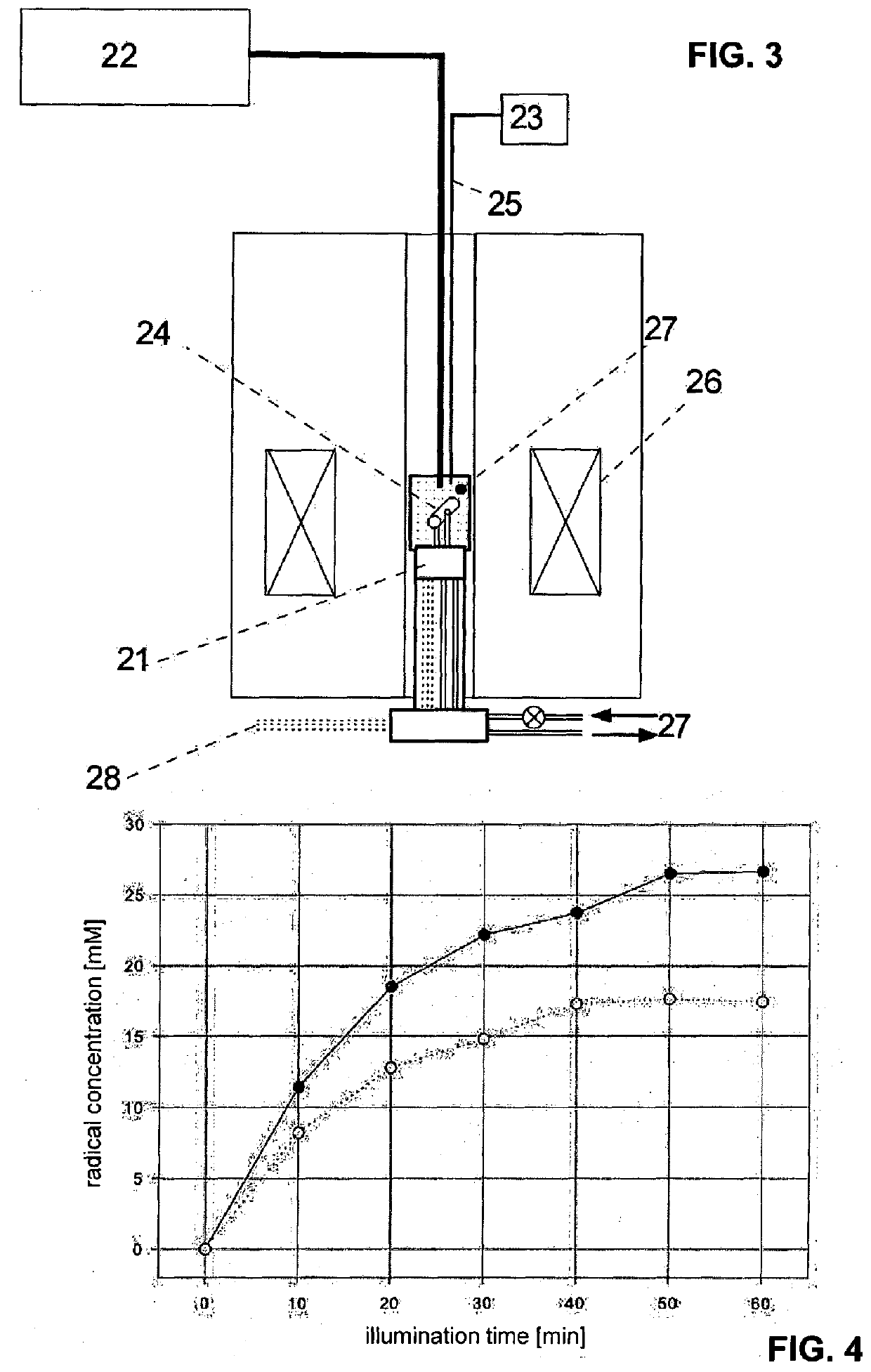
Method for the generation of radicals for dynamic nuclear polarization and uses thereof for nmr, mrs and MRI
ActiveUS20160033590A1Increased polarizationImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUltravioletElectromagnetic radiation
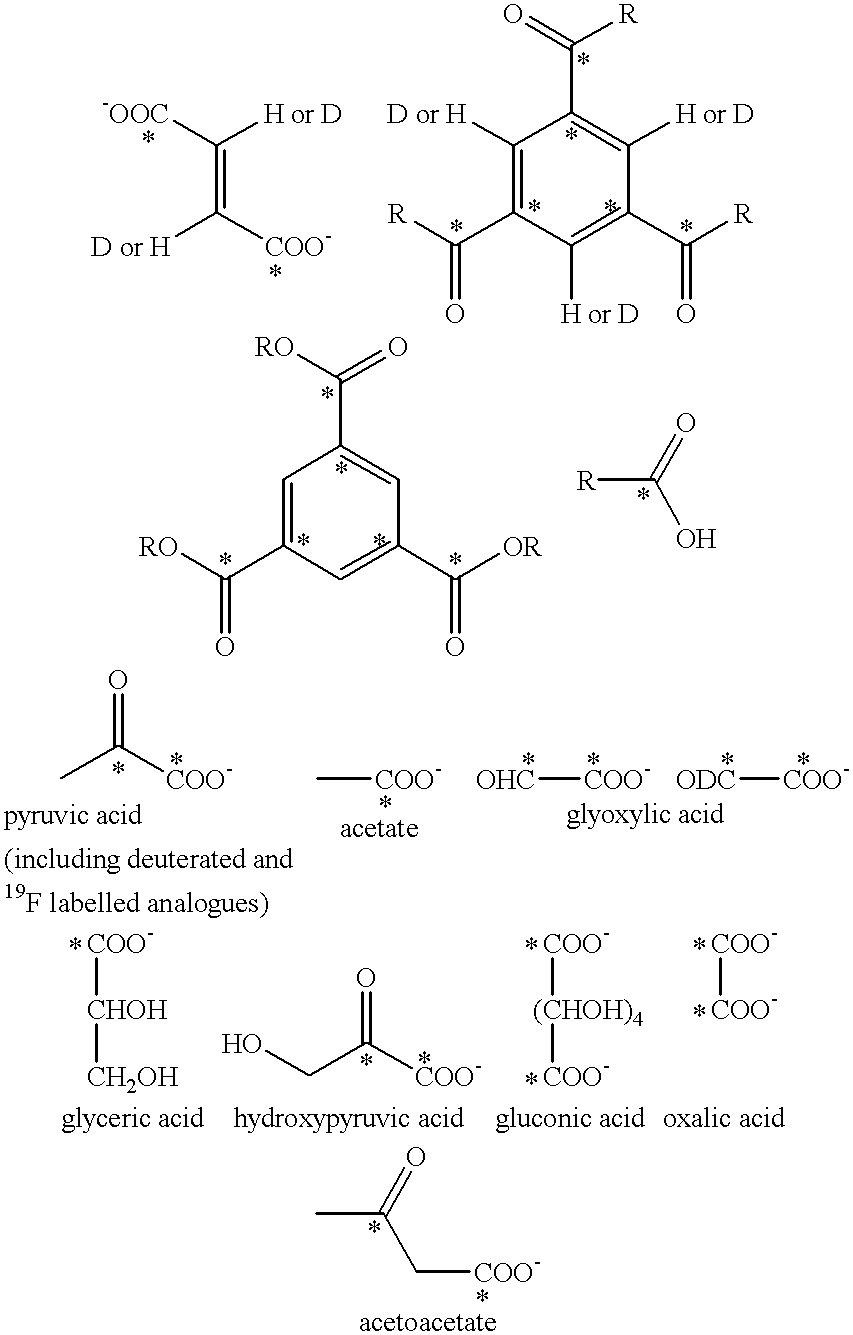
A method for the preparation of a sample comprising highly polarized nuclear spins is proposed, comprising at least the following steps:a) provision of molecules with 1,2-dione structural units and / or molecules with 2,5-diene-1,4-dione structural units in the solid state;b) generation of radicals from these molecules by photo induced electron transfer by a first electromagnetic irradiation in the visible or ultraviolet frequency range in the solid state;c) dynamic nuclear polarization in the presence of a magnetic field in the solid state by applying a second electromagnetic irradiation with a frequency adapted to transfer spin polarization from the electrons to the nuclear spins leading to a highly polarized state thereof. Furthermore uses of correspondingly prepared samples for NMR, MRS and MRI experiments are proposed.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
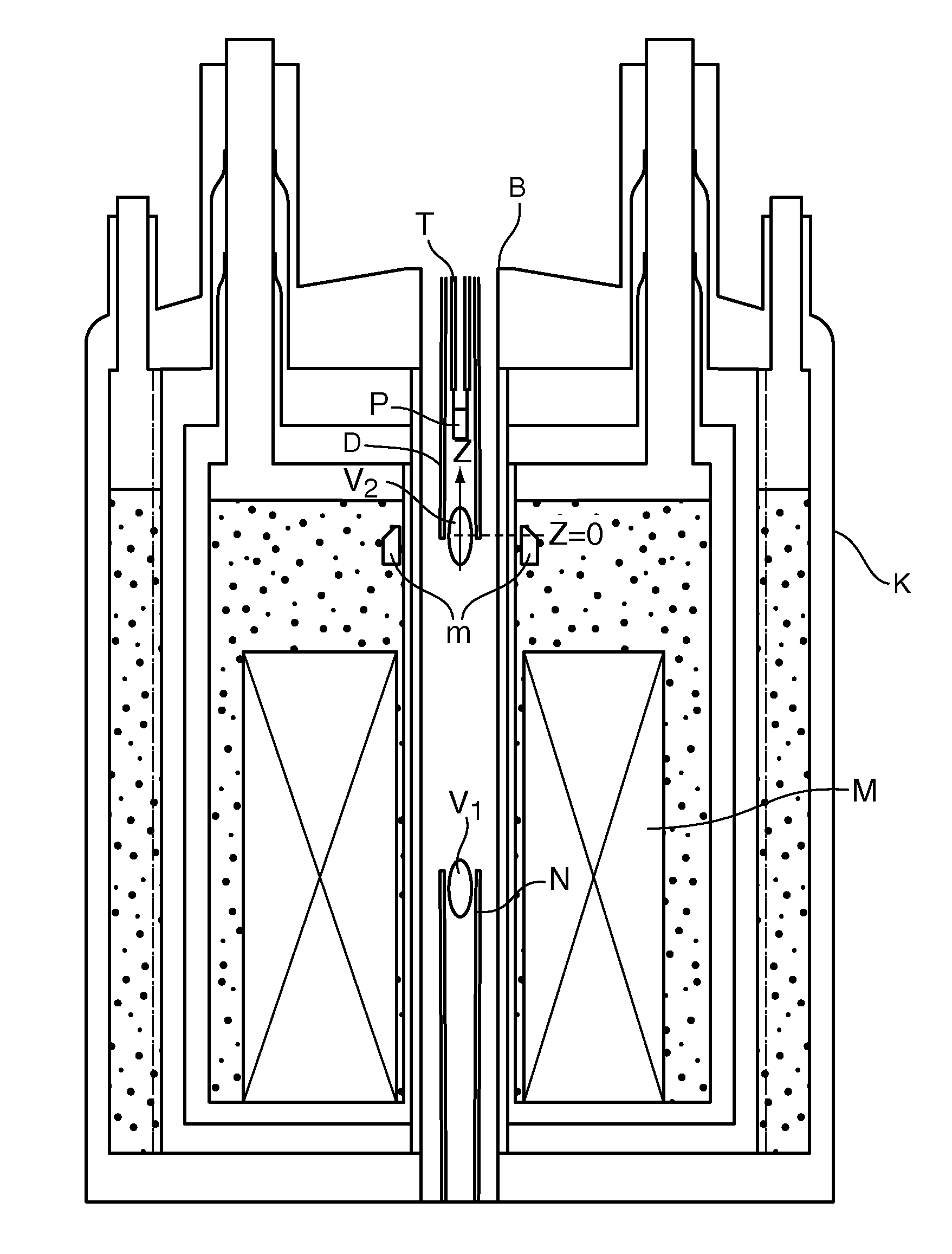
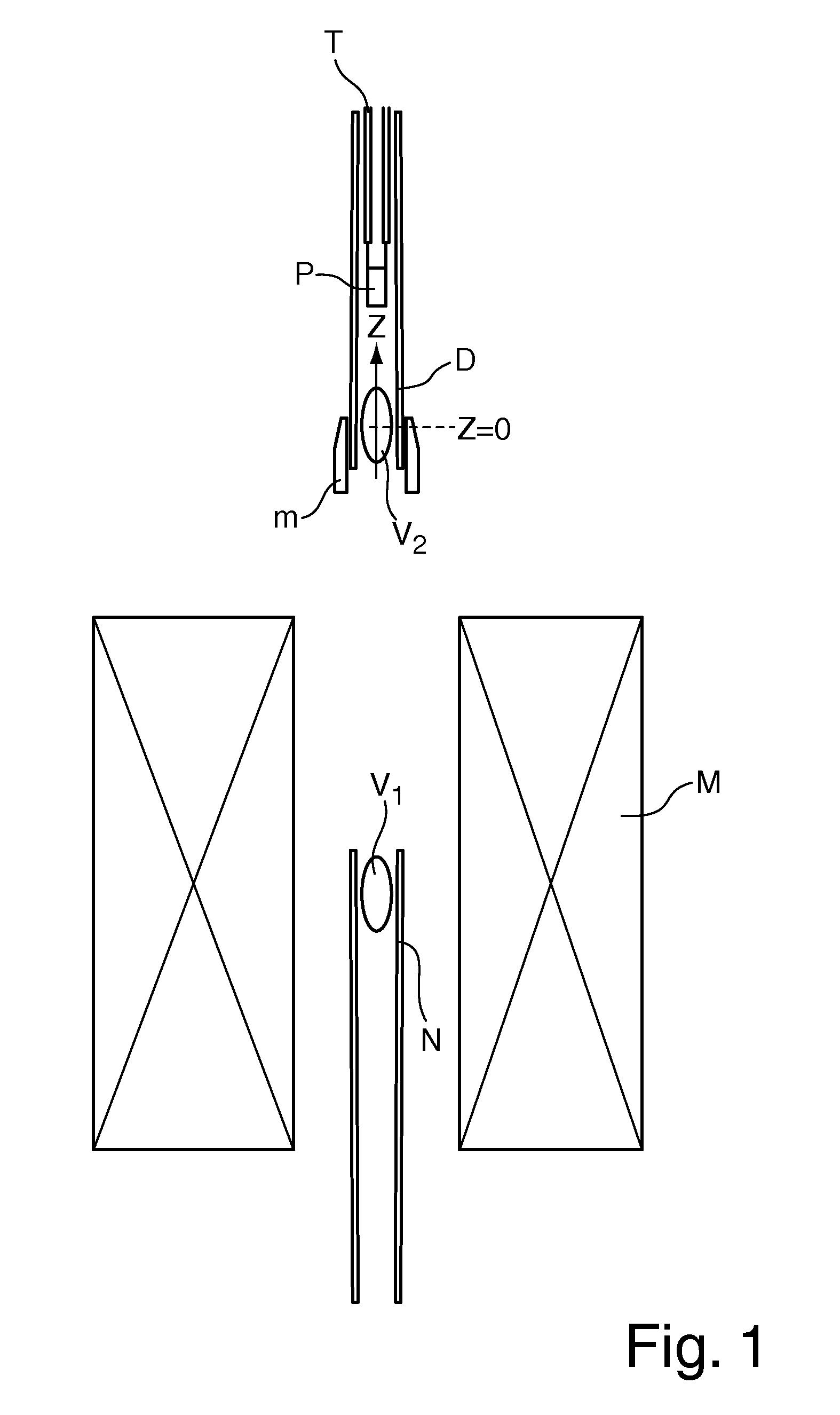
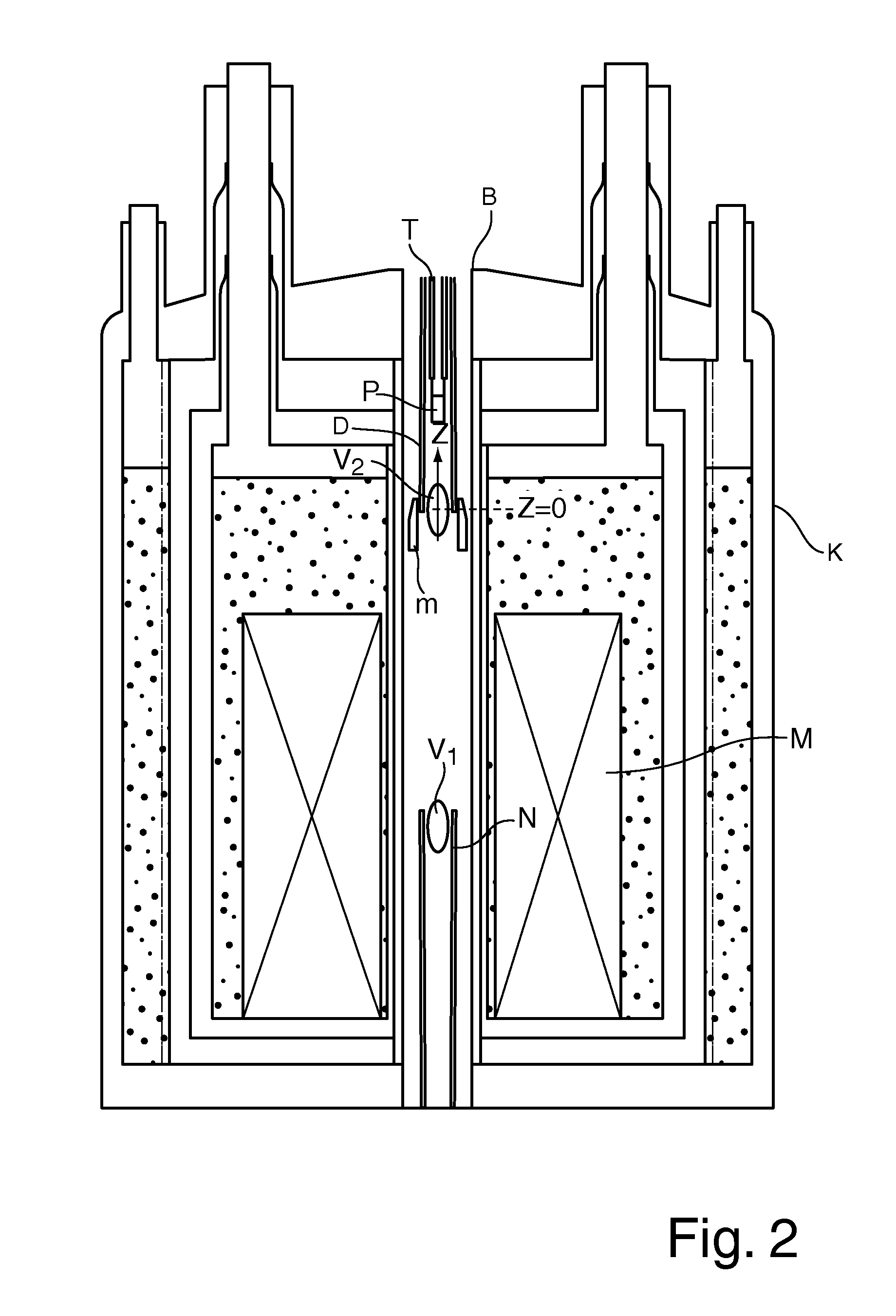
Apparatus for carrying out DNP-NMR measurements with a compensation configuration and method for designing the compensation configuration
ActiveUS20100171495A1Short transfer timeReduce lossesMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientMagnet
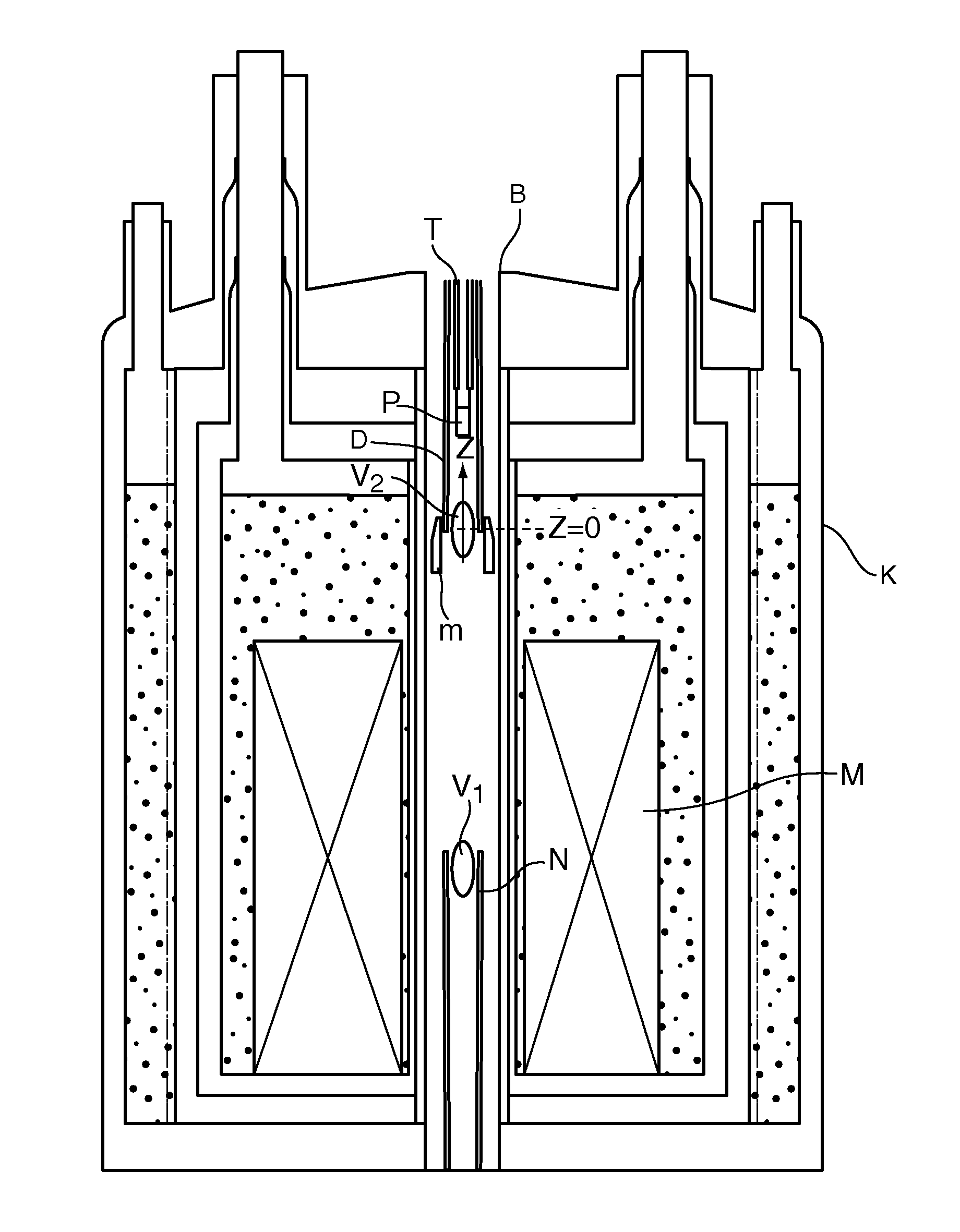
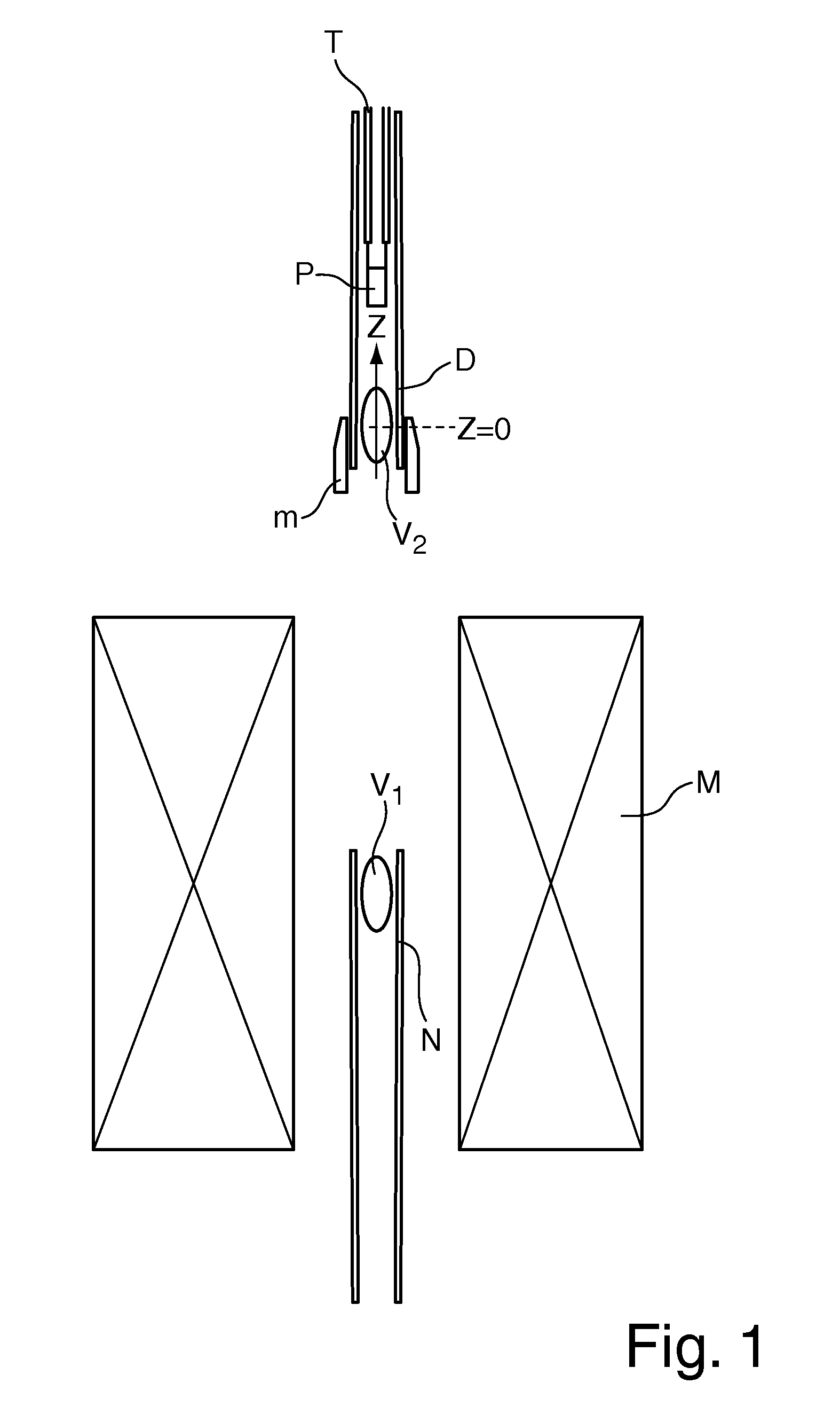
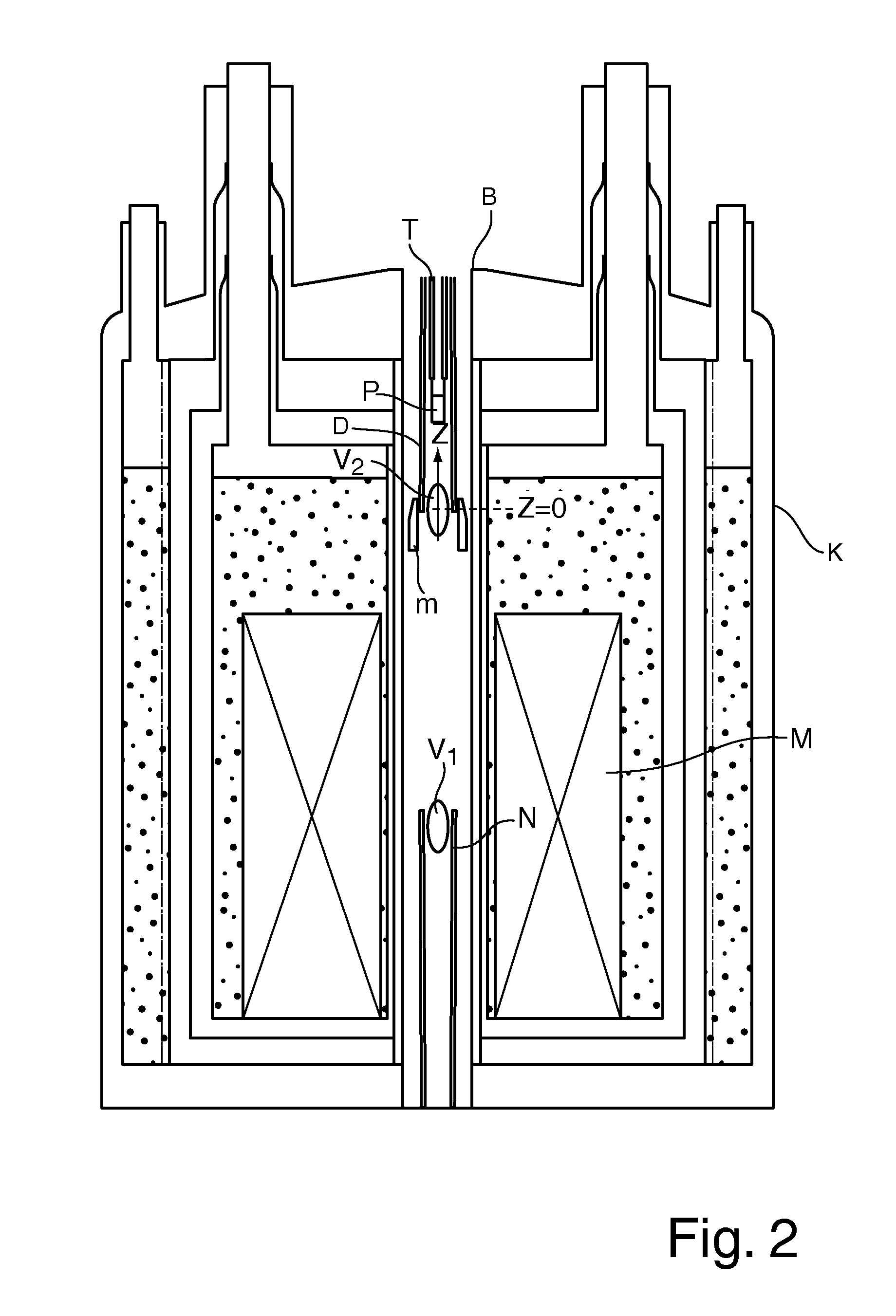
An apparatus for DNP-NMR measurement on a sample (P), with a magnet configuration (M) for producing a magnetic field in a first working volume (V1), wherein the magnet configuration (M) produces a stray field in a second working volume (V2) in the direction of an axis (z) with a magnetic field gradient (H1M, H2M, HnM) in the direction of the axis (z), wherein the axis (z) extends through the second working volume (V2), with a device (N) for measuring MR signals, with a DNP excitation device (D), and with a positioning mechanism (T) for transferring the sample (P), is characterized in that, near the second working volume (V2), a compensation configuration (m) made of magnetic material is mounted that, in the operating condition of the magnet configuration (M), produces a magnetic field gradient (H1m, H2m, Hnm) in the direction of the axis (z) in the second working volume (V2) that is between −90% and −110% of the magnetic field gradient of the same order (H1M, H2M, . . . ; HnM) of the stray field of the magnet configuration (M) in the direction of the axis (z) in the second working volume (V2). Thus, homogenization of the magnetic field in the second working volume can be achieved by technically simple means.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
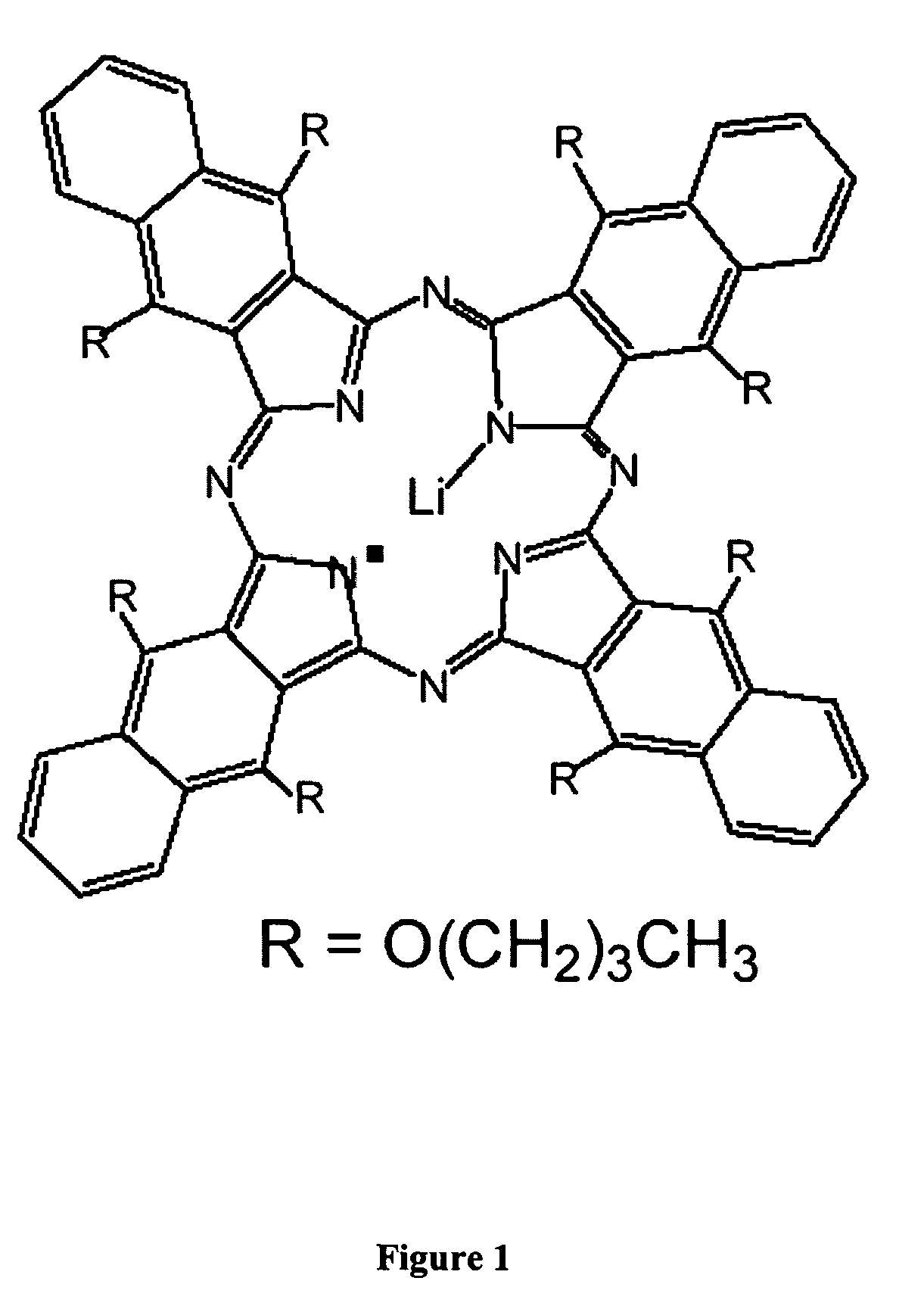
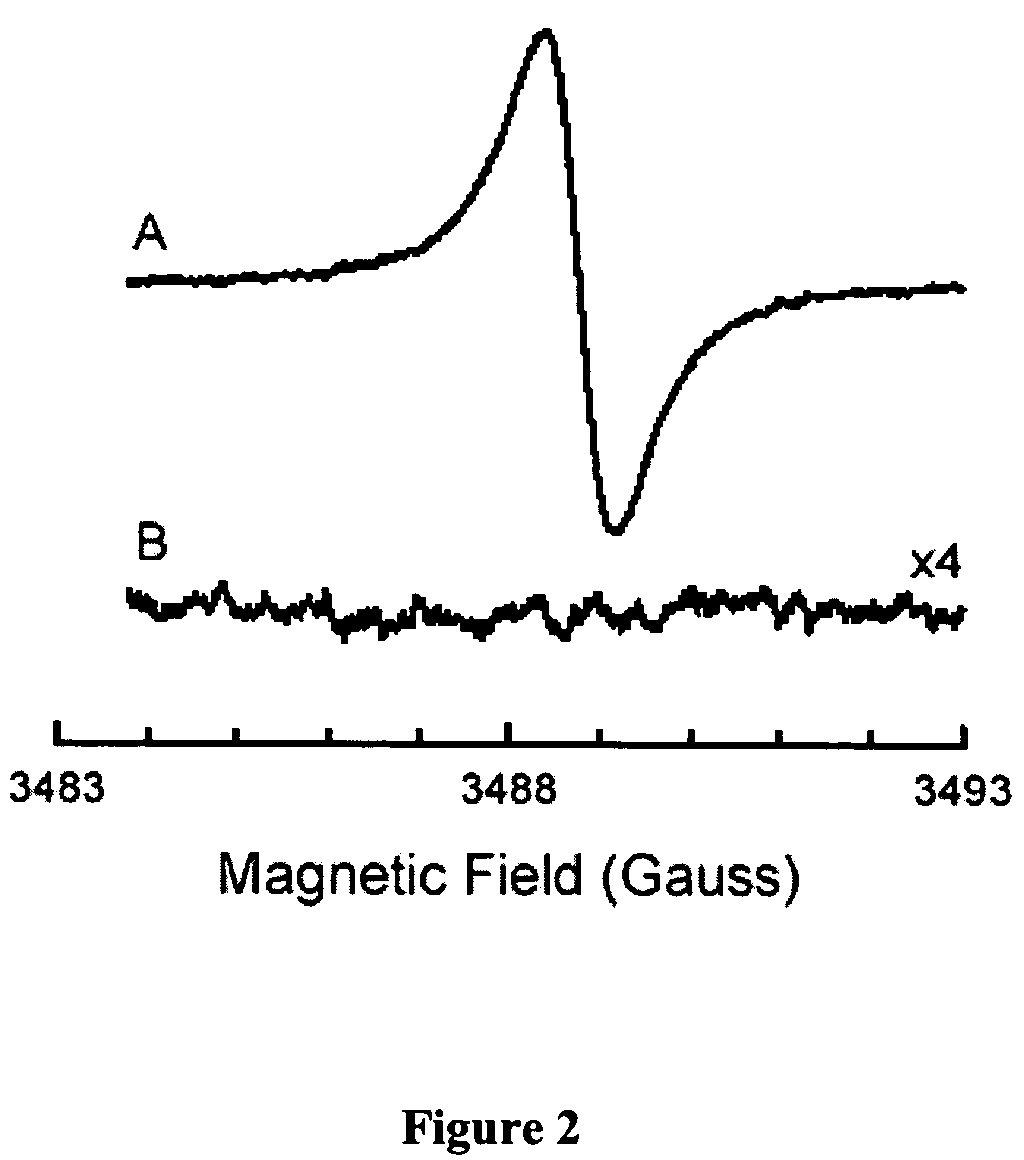
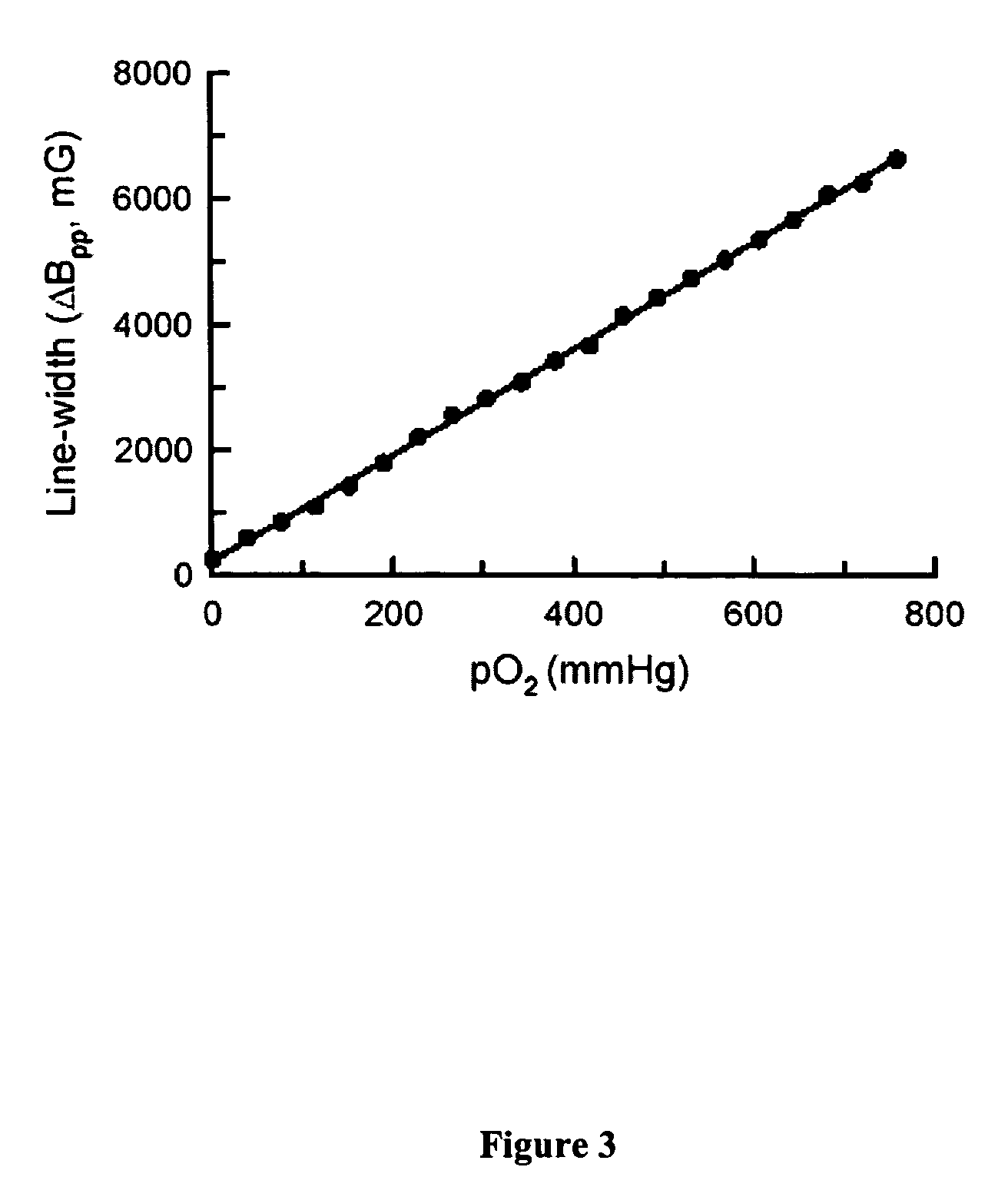
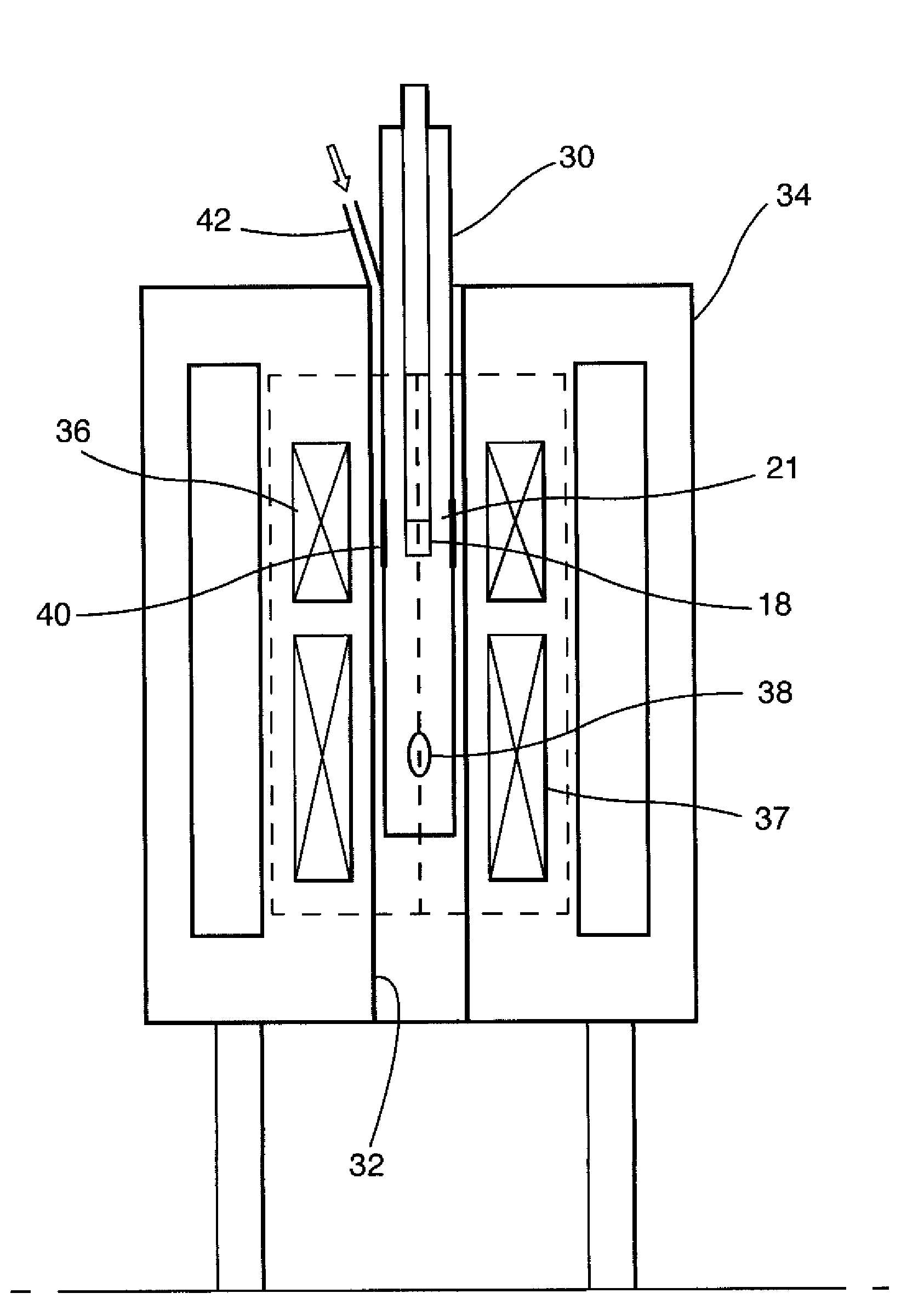
Nanoparticulate probe for in vivo monitoring of tissue oxygenation
A new class of micro- and nano-particulate paramagnetic spin probes especially useful for magnetic resonance imaging techniques, including electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The probes are lithium phthalocyanine derivative compounds. Also provided are suspensions and emulsions comprising lithium phthalocyanine derivative probes. Also provided are noninvasive methods for measuring noninvasive methods of measuring oxygen concentration, oxygen partial pressure, oxygen metabolism, and nitric oxide concentration in a specific tissue, organ, or cell in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
DNP apparatus
InactiveUS7646200B2Fast transferFurther limitedMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionHeat flowEngineering
A coolant sub-assembly is provided for use in a DNP apparatus. The sub-assembly comprises a plurality of concentric jackets surrounding an inner bore tube having first and second opposed ends. The jackets are adapted to inhibit heat flow to the inner bore tube, a DNP working region being defined within the inner bore tube where a DNP process will be performed on a sample in the DNP working region. A coolant supply path extends adjacent an outer surface of the inner bore tube at the DNP working region in order to cool said outer surface, whereby a sample holder assembly can be inserted through the first end of the inner bore tube to bring a sample holder into the DNP working region and can be moved through the second end of the inner bore tube. An auxiliary coolant supply path supplies coolant to a sample, located in use in the sample holder at the DNP working region, through at least one aperture in the inner bore tube wall at the DNP working region. One or both ends of the inner bore tube opens into a coolant waste path for conveying coolant away from the inner bore tube, and wherein the coolant, auxiliary coolant, and waste paths are coupled to pumping means in use to cause coolant to pass along the coolant, auxiliary coolant and waste paths.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND PROD +1
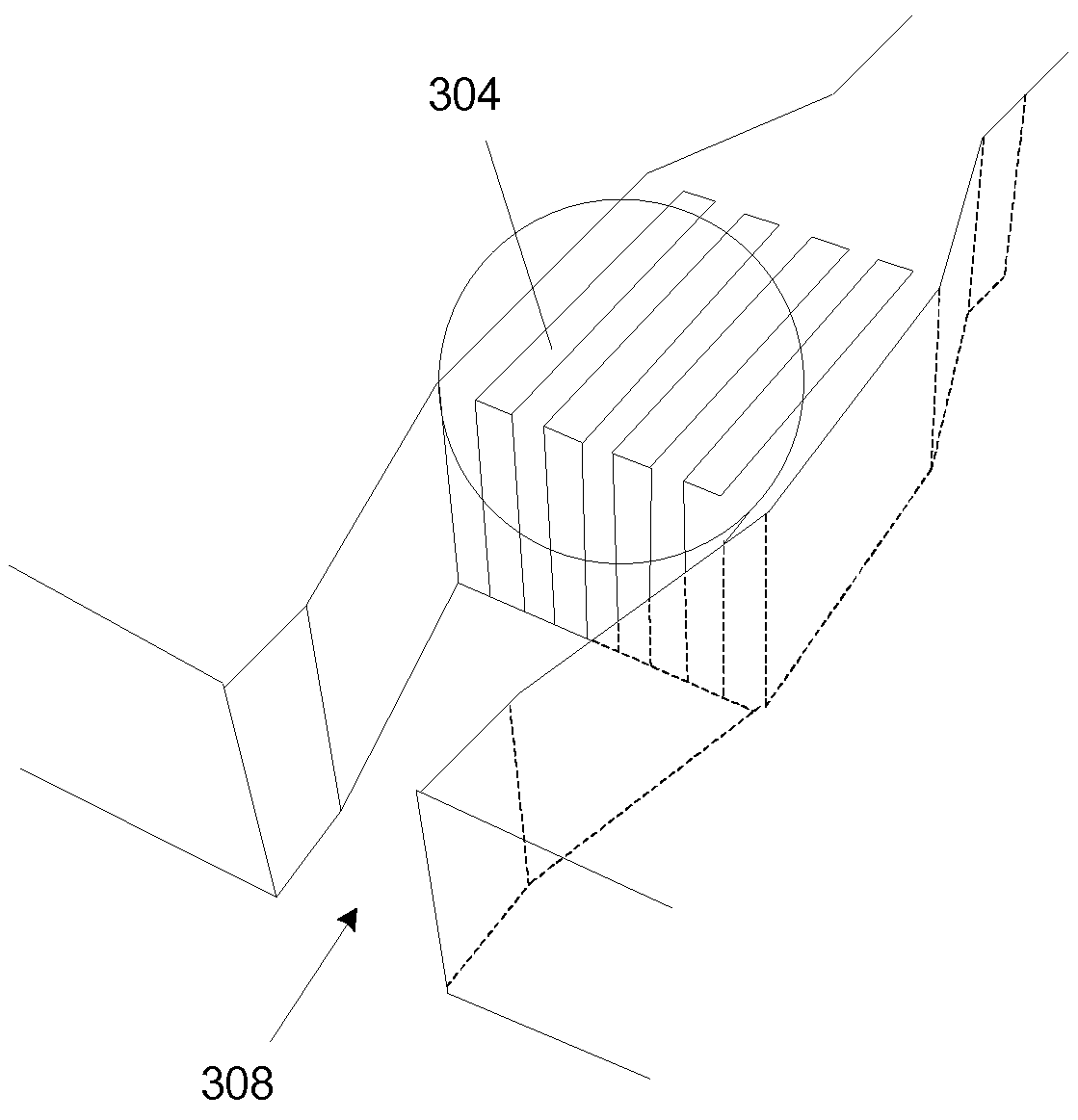
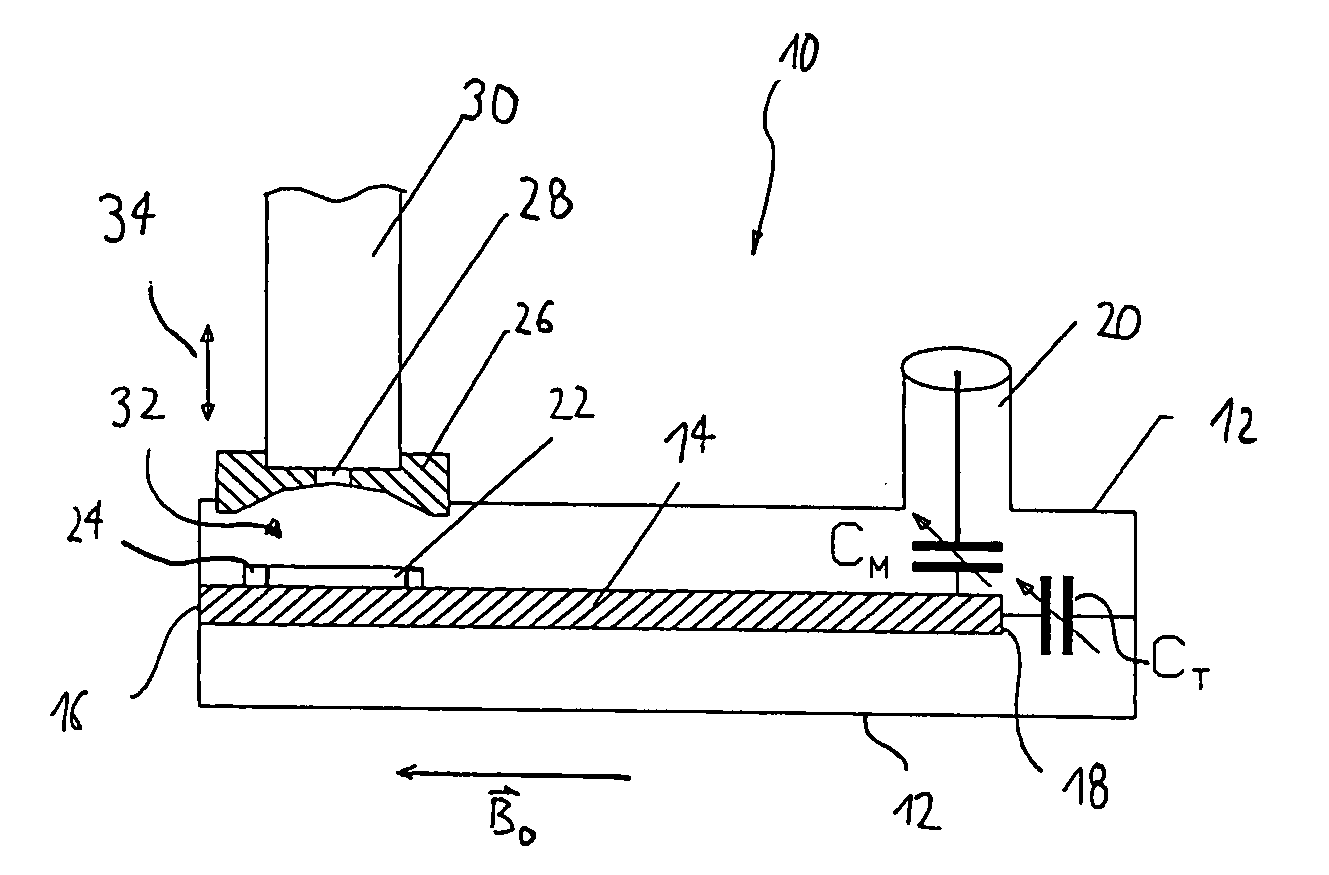
NMR RF probe coil exhibiting double resonance
ActiveUS8779768B2Improve homogeneityMinimize interactionMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionRF probeResonance
NMR probe coils designed to operate at two different frequencies, producing a strong and homogenous magnetic field at both the frequencies. This single coil, placed close to the sample, provides a method to optimize the NMR detection sensitivity of two different channels. In addition, the present invention describes a coil that generates a magnetic field that is parallel to the substrate of the coil as opposed to perpendicular as seen in the prior art. The present invention isolates coils from each other even when placed in close proximity to each other. A method to reduce the presence of electric field within the sample region is also considered. Further, the invention describes a method to adjust the radio-frequency tuning and coupling of the MAR probe coils.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
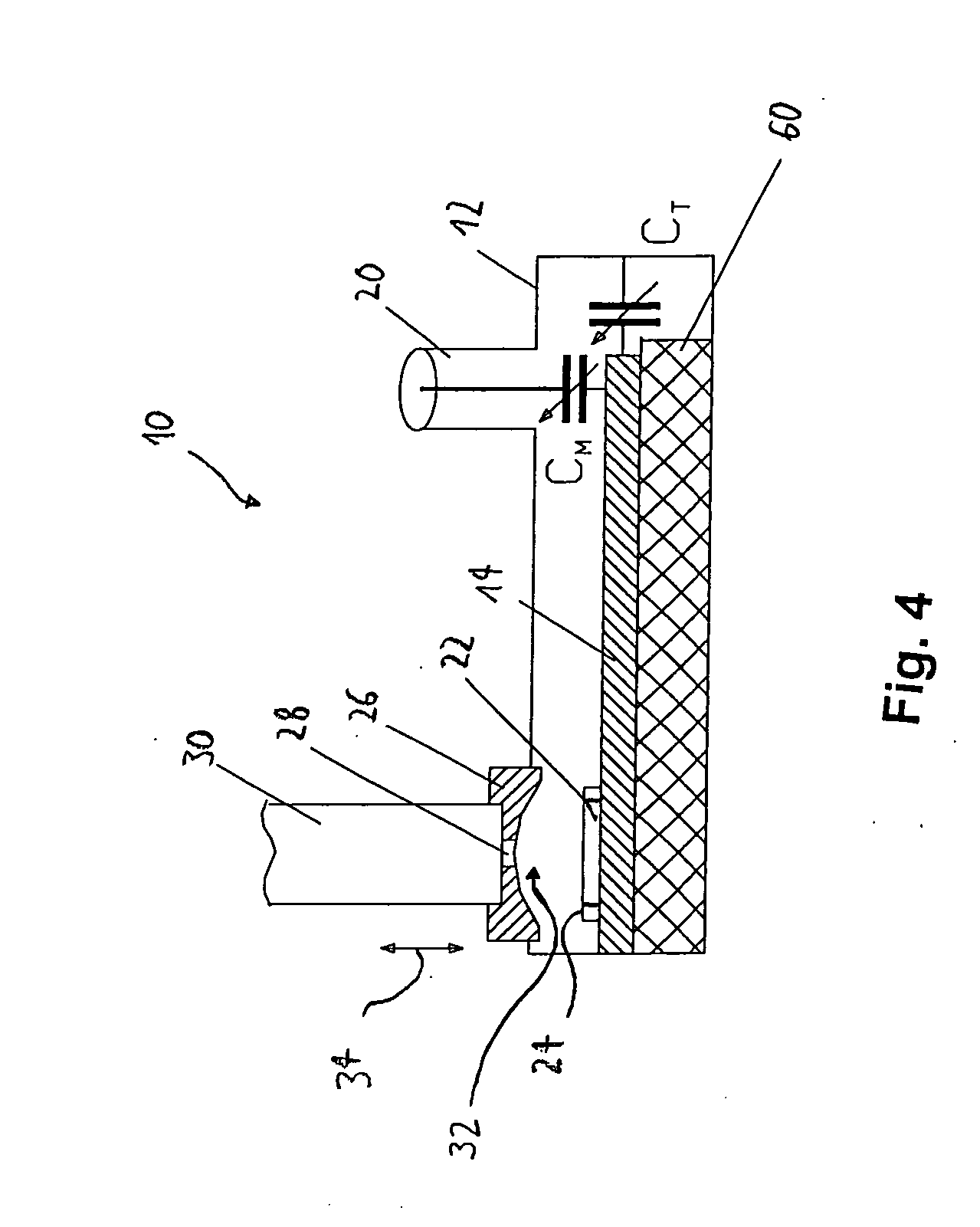
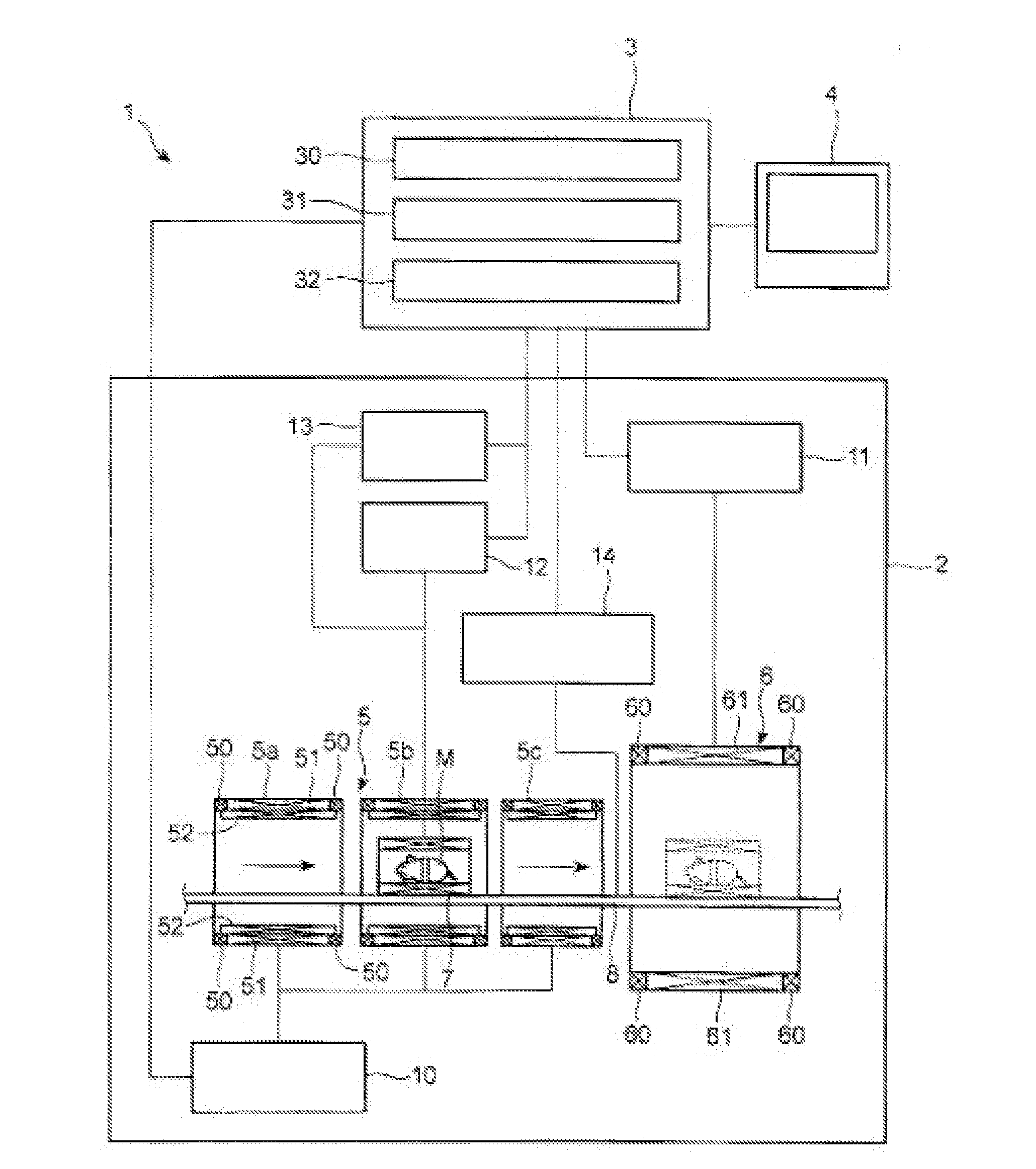
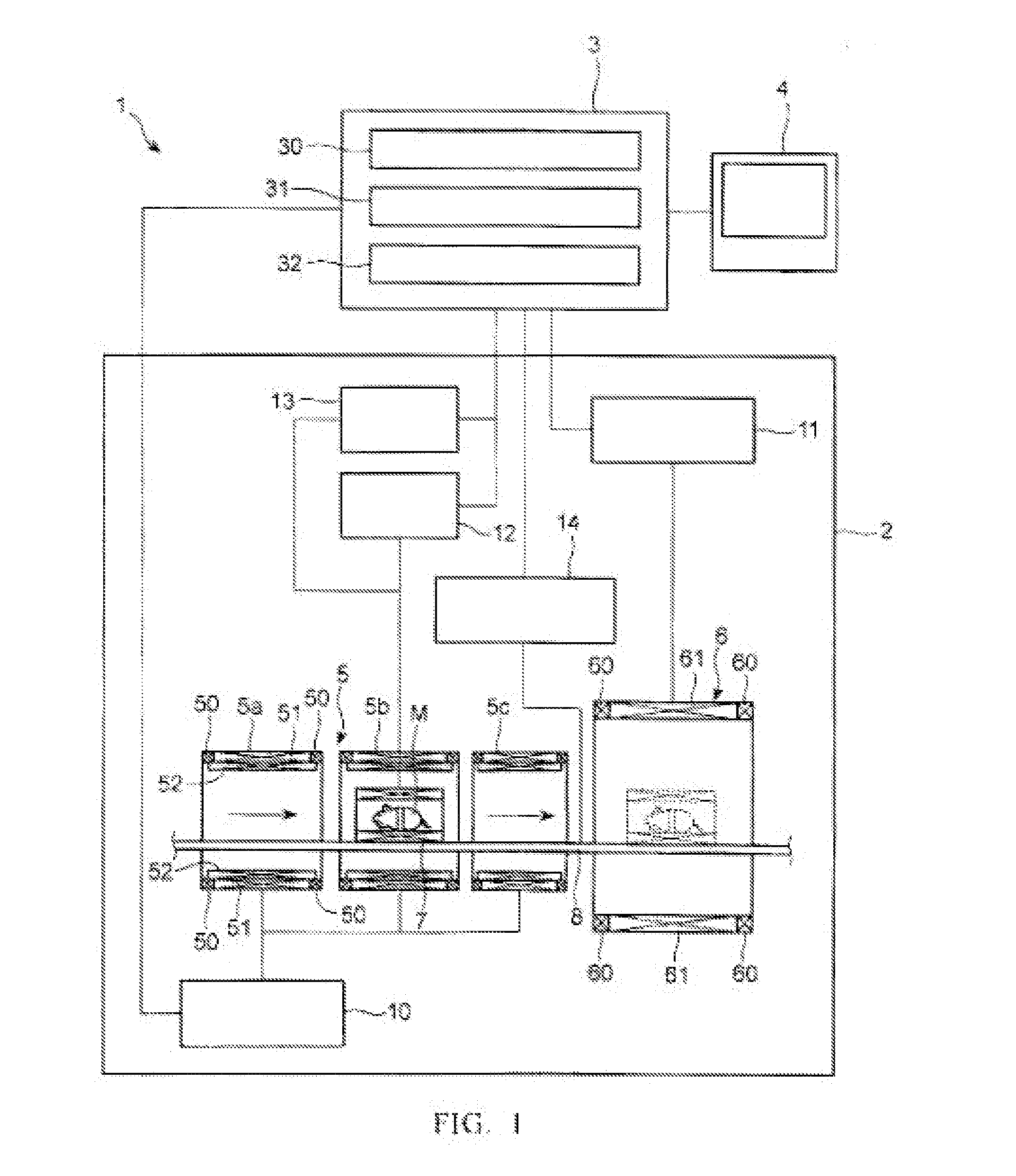
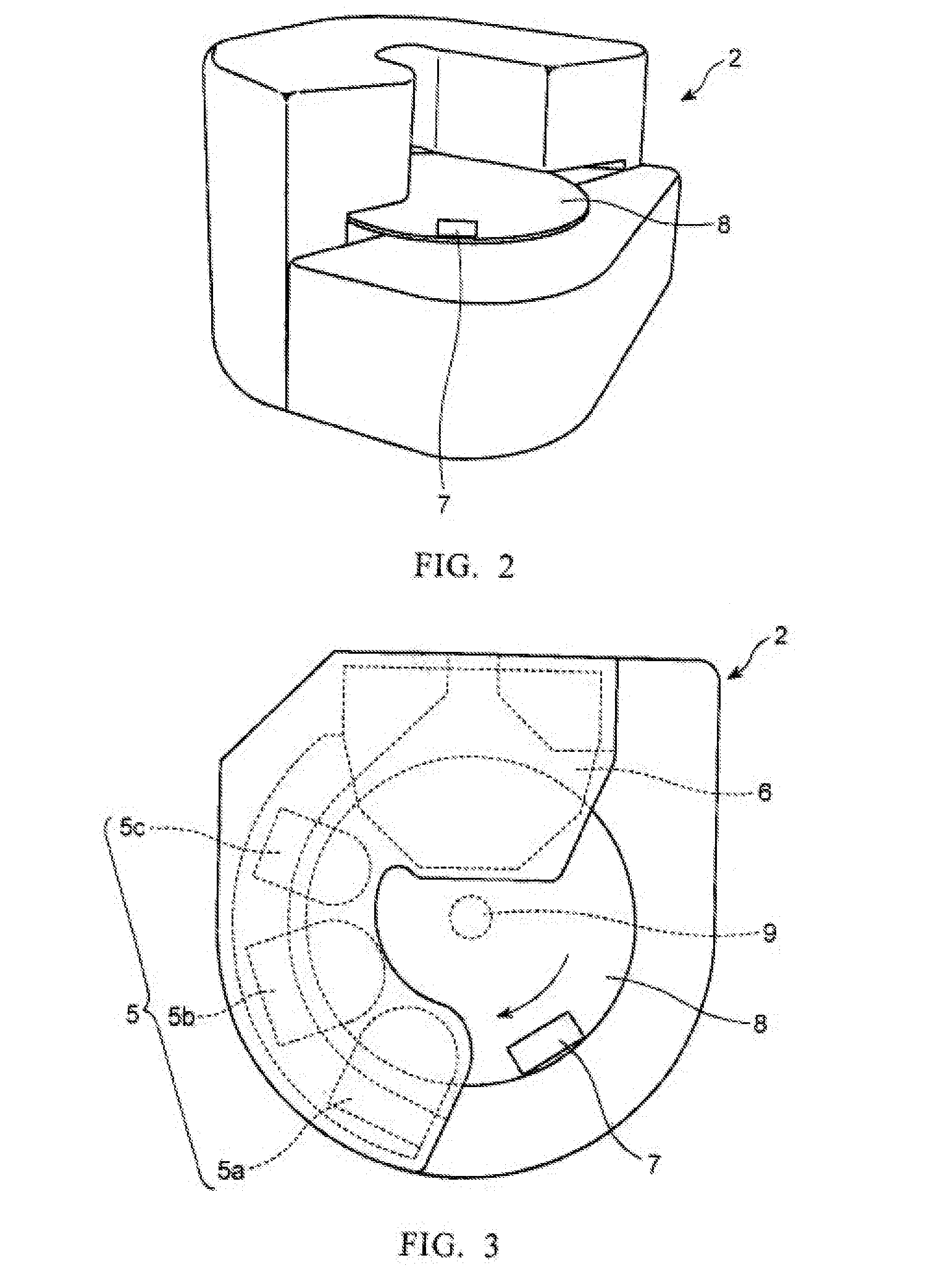
Integrated high-frequency generator system utilizing the magnetic field of the target application
ActiveUS20120176133A1Easily and simply adapted for DNP operationLow costMeasurements using double resonanceTubes with helical electron streamInternal modeMicrowave
An integrated high-frequency generator system utilizing the magnetic field of the target application including a magnetic resonance magnet having an application zone and a high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance magnet; and a high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator disposed in the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone and utilizing the magnet field of the magnetic resonance magnet to generate the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation. The magnetic resonance magnet may have an auxiliary magnetic field source for modifying the magnetic field profile in the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator zone. The high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) generator may include an electron gun for generating an electron beam adapted to be focused by a magnetic field source having a spatially rising region, a homogenous region and a decaying region, an interaction structure for generating high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation, an internal mode converter in the homogenous region for extracting the high-frequency (microwave / terahertz) radiation through a window, and a reduced collector disposed substantially in the homogenous region before the electron beam spreads in the decaying region.
Owner:BRIDGE 12 TECH
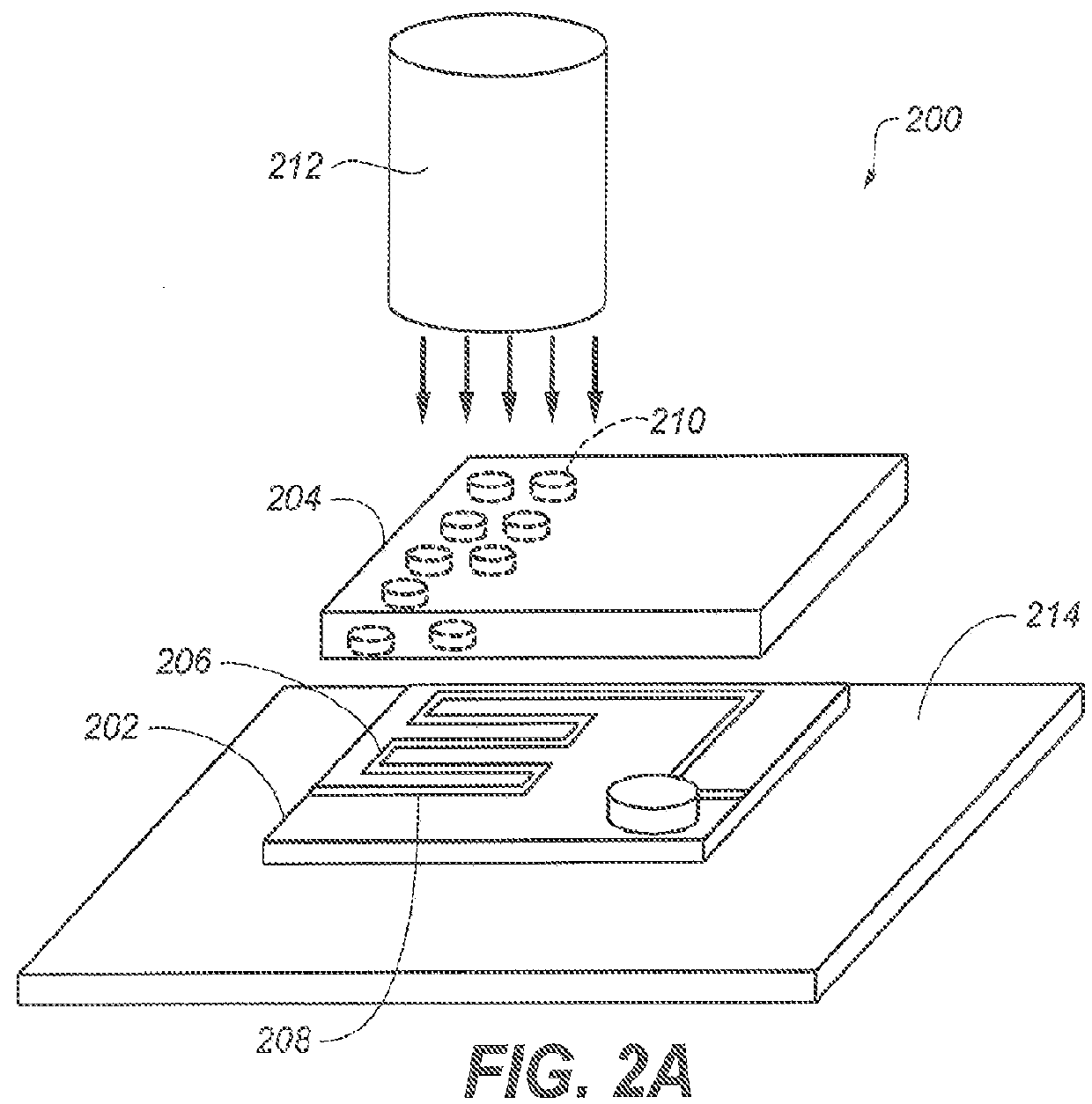
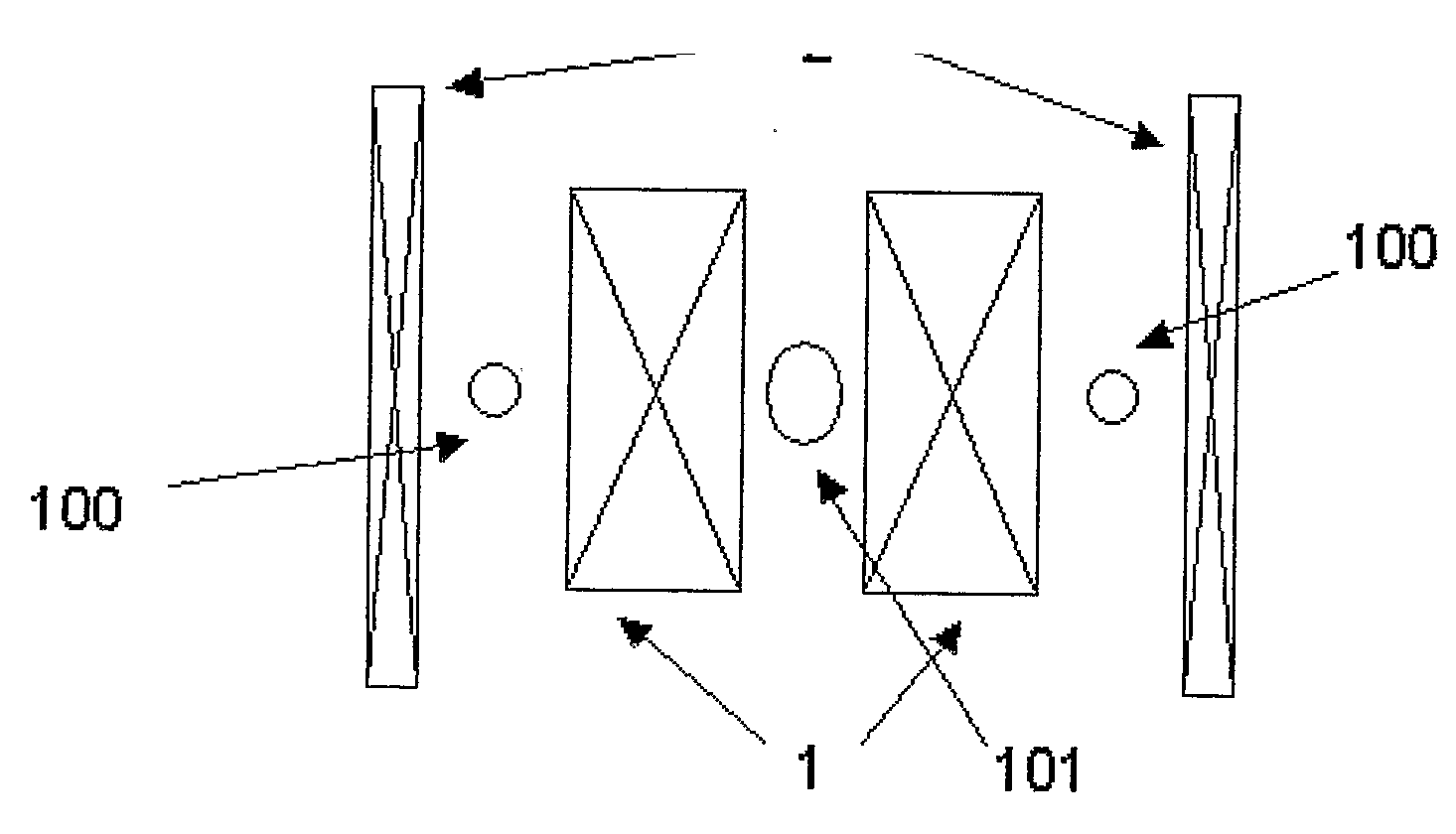
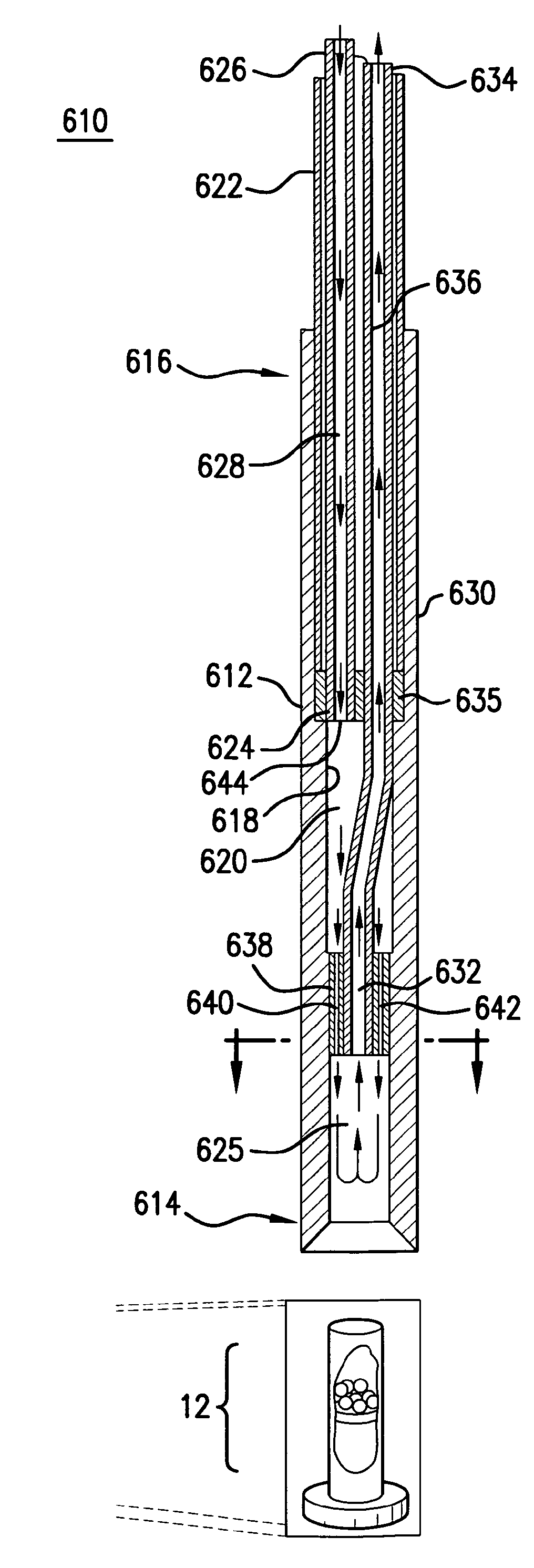
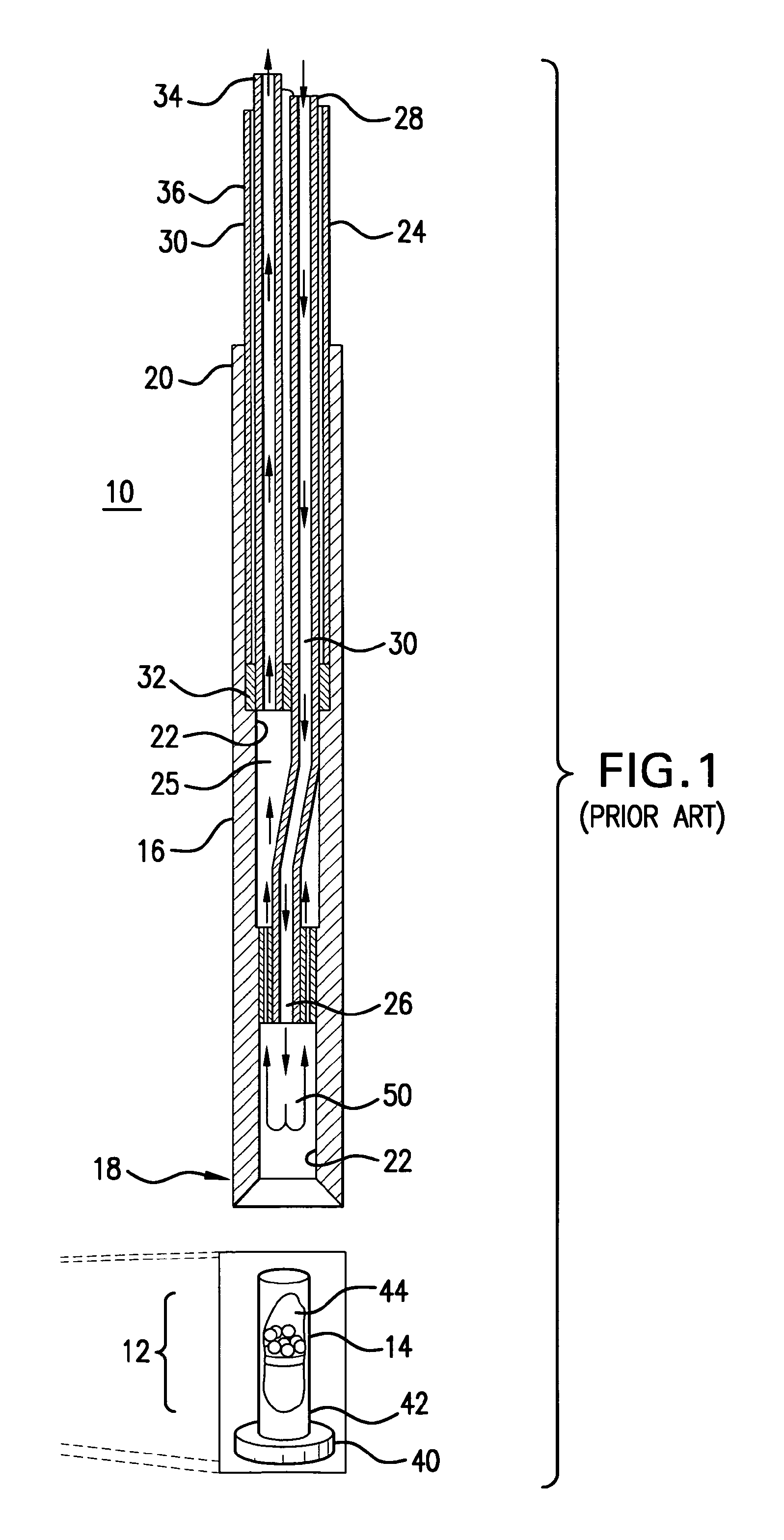
Magnet assembly
InactiveUS20090134868A1Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSuperconducting Coils
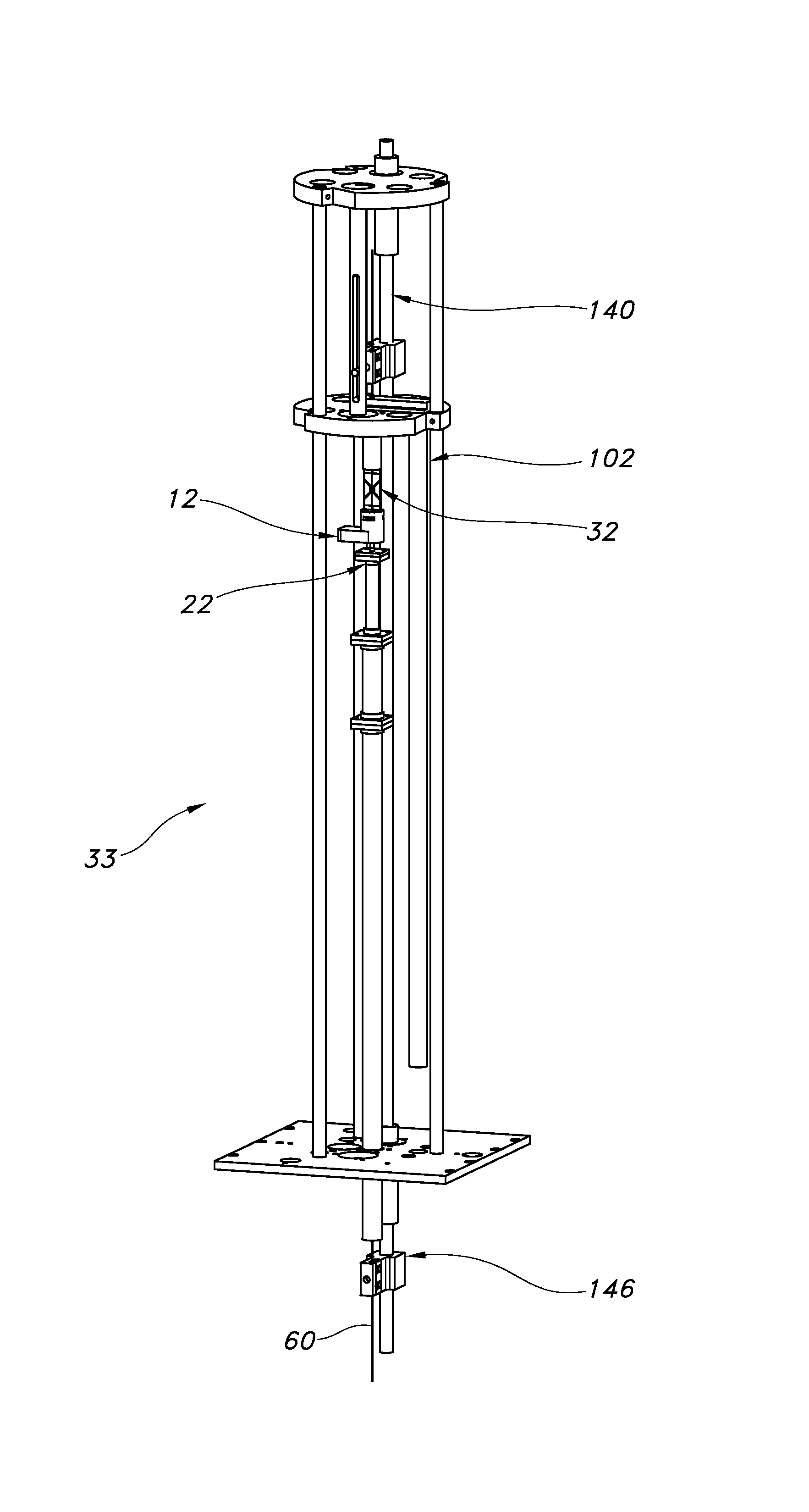
A magnet assembly for use in carrying out nuclear magnetic resonance experiments on a body or sample. The assembly comprises a set of superconducting coils (12) within a cryostat, located about a bore, and arranged to generate a substantially uniform magnetic field in a primary working volume (101) within the bore, and to generate a substantially uniform magnetic field in a secondary working volume (100) within the coil structure and separate from the bore. At least part of a hyperpolarisation system intersects the at least one secondary working volume (101) so as to hold a sample to be hyperpolarised in the secondary working volume.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND PROD
Nmr RF probe coil exhibiting double resonance
ActiveUS20140057792A1Minimize interactionImprove homogeneityPrinted circuit assemblingMeasurements using double resonanceRF probeResonance
NMR probe coils designed to operate at two different frequencies, producing a strong and homogenous magnetic field at both the frequencies. This single coil, placed close to the sample, provides a method to optimize the NMR detection sensitivity of two different channels. In addition, the present invention describes a coil that generates a magnetic field that is parallel to the substrate of the coil as opposed to perpendicular as seen in the prior art. The present invention isolates coils from each other even when placed in close proximity to each other. A method to reduce the presence of electric field within the sample region is also considered. Further, the invention describes a method to adjust the radio-frequency tuning and coupling of the MAR probe coils.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
Apparatus and method for a fully automated preparation of a hyperpolarizing imaging agent
ActiveUS7633290B1Measurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionImaging agentDissolution
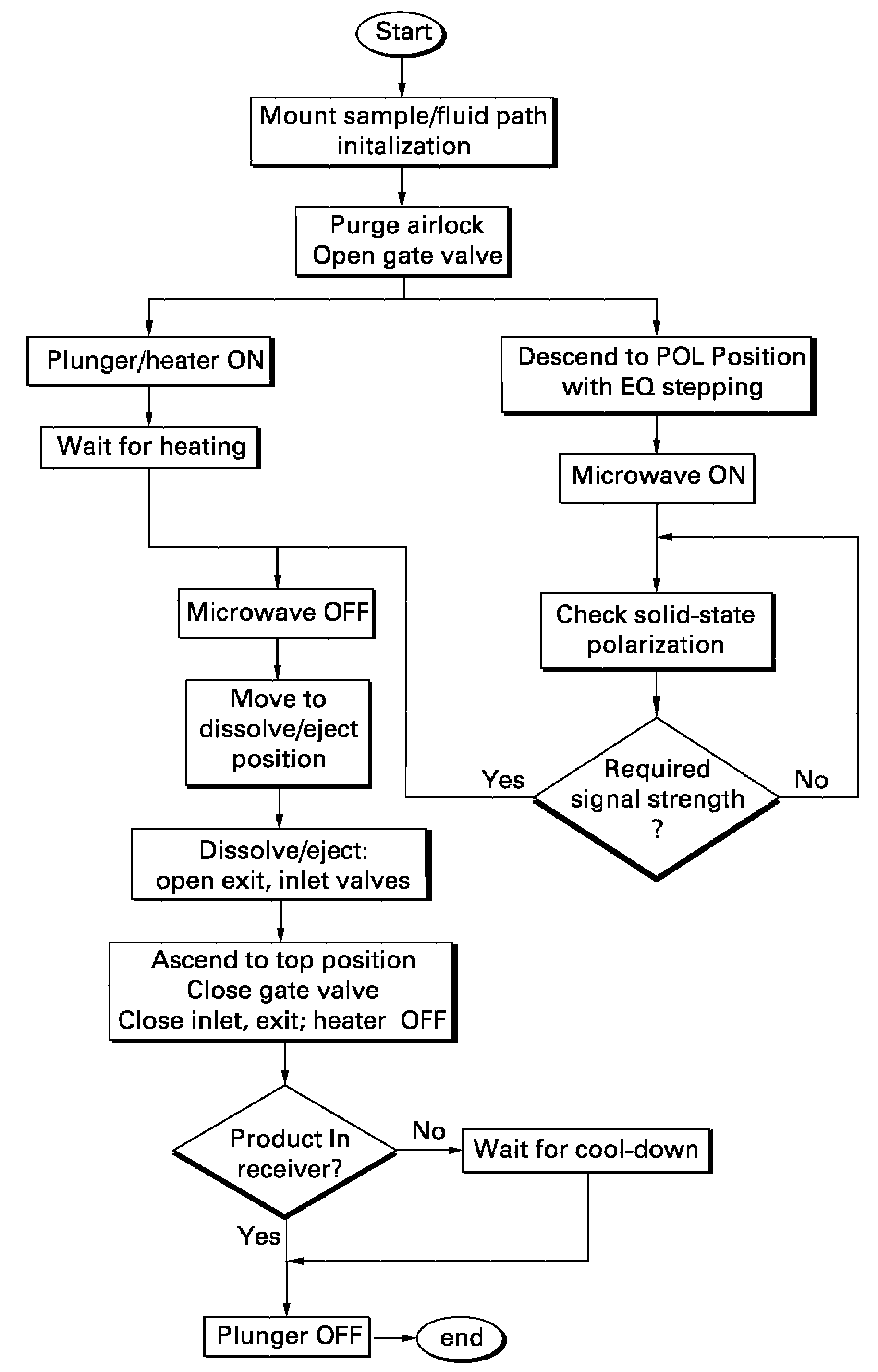
Provided is an apparatus and method for automated hyperpolarization of samples for use as an imaging agent comprising a sample box, an airlock chamber configured to receive a sample from the sample box, a cryogenic chamber, a guide channel to transport samples from the airlock chamber to the cryogenic chamber, a heater and pressure module coupled to the sample box, an insertion and retraction device to transport samples through the guide channel to and from the cryogenic chamber, a dissolution module coupled to the sample box, and a controller to regulate hyperpolarization of the samples by controlling one or more of position, sequencing, temperature, pressure, and dissolution of the samples within the apparatus. Also provided is a machine-readable medium comprising instruction which, when executed by a controller, causes a hyperpolarization apparatus to perform the steps of hyperpolarization of a sample.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
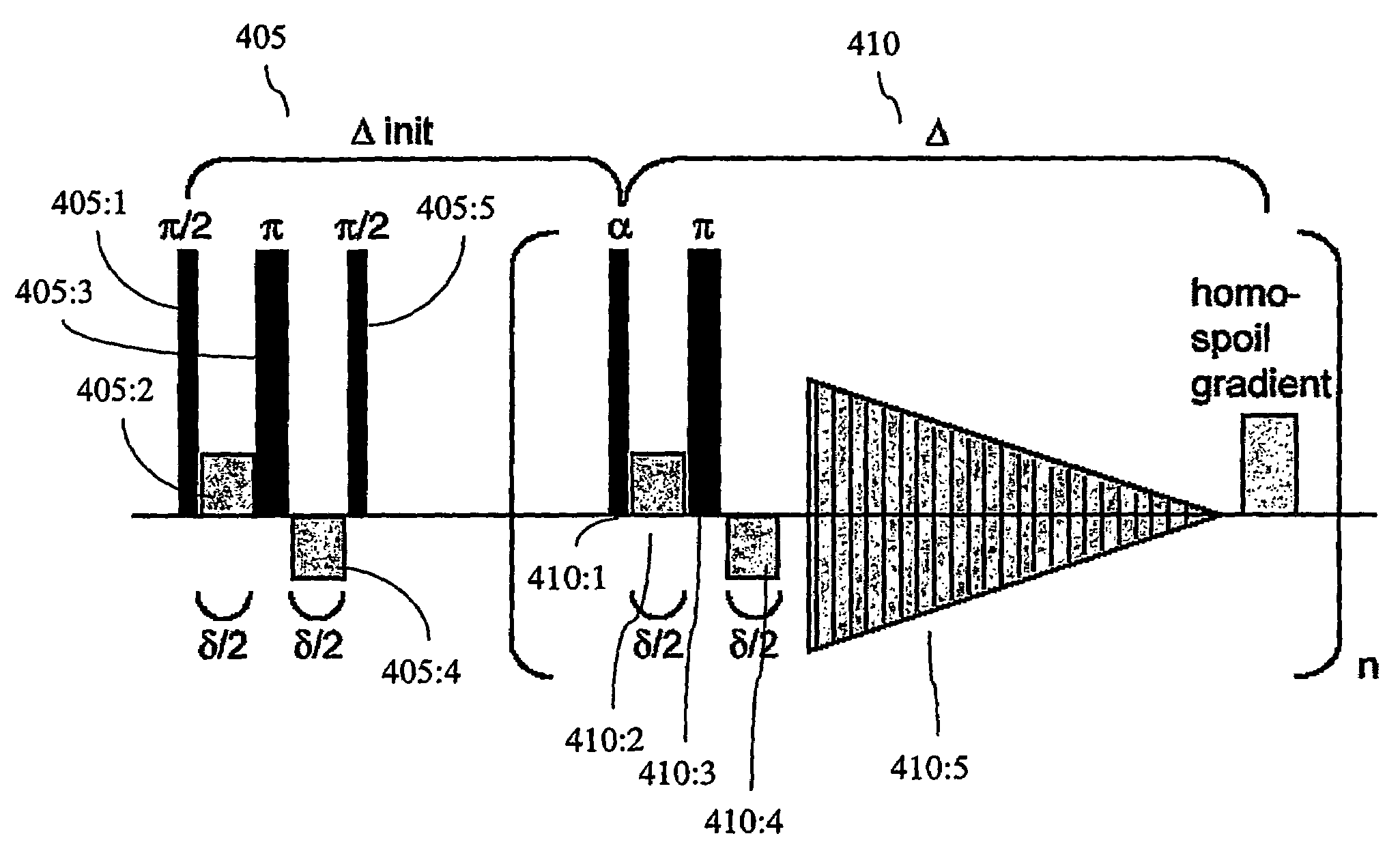
Rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS20150008917A1Low costReduce complexityMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceDynamic nuclear polarisation
A rapid cycle dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) NMR apparatus comprises (i) a cooling unit, configured to cool a sample in a capillary, (b) a DNP polarization unit configured to polarize the sample in the capillary, (c) a stripline-based NMR detector comprising a stripline for NMR analysis of the sample in the capillary, (d) a transport unit configured to guide the capillary from the DNP polarization unit to the stripline of stripline-based NMR detector; and (e) a heating unit configured to heat the sample in the capillary before analysis of the sample by the stripline-based NMR detector. Fast (1D-3D) NMR measurements with high resolution may be obtained.
Owner:STICHTING KATHOLIEKE UNIV
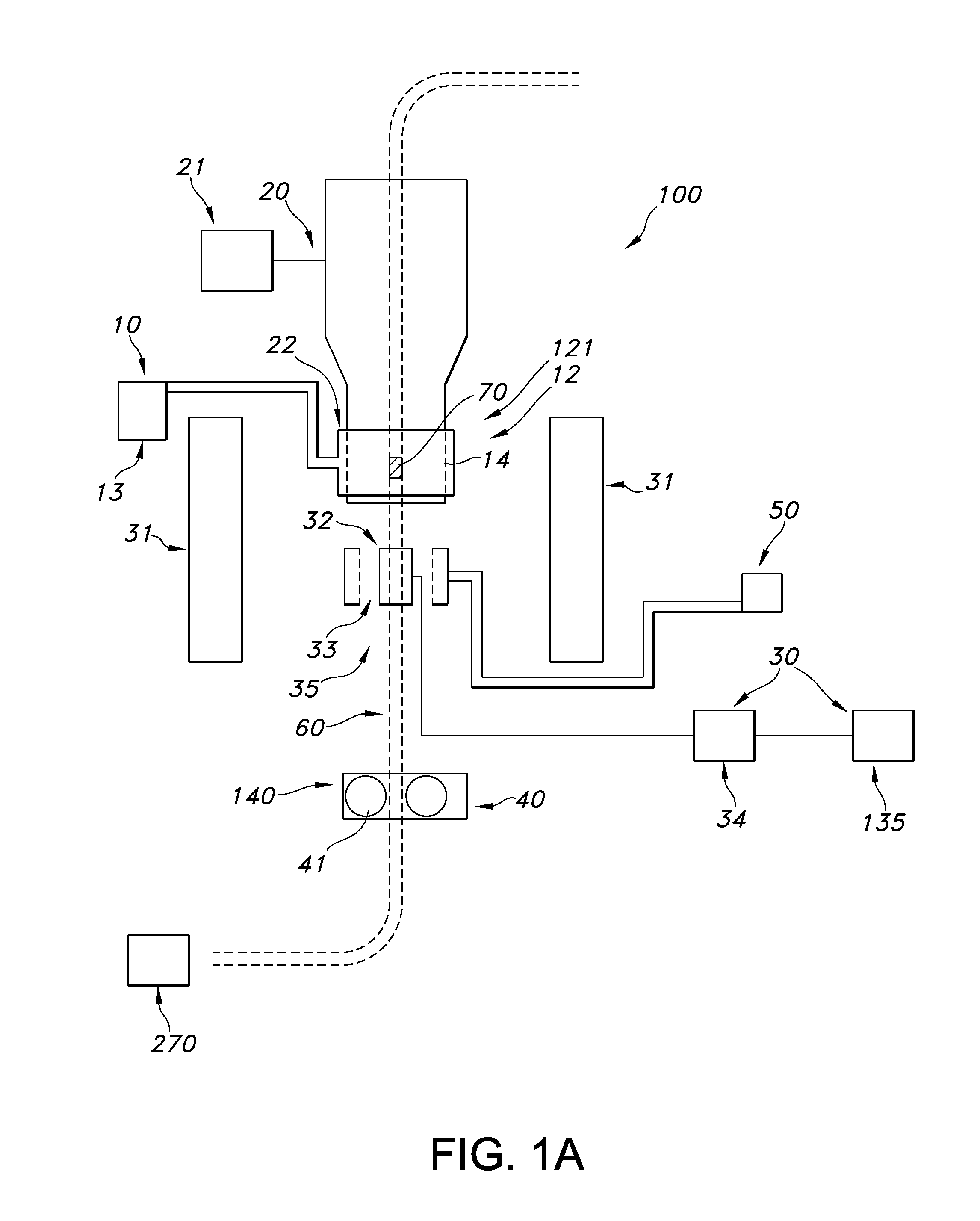
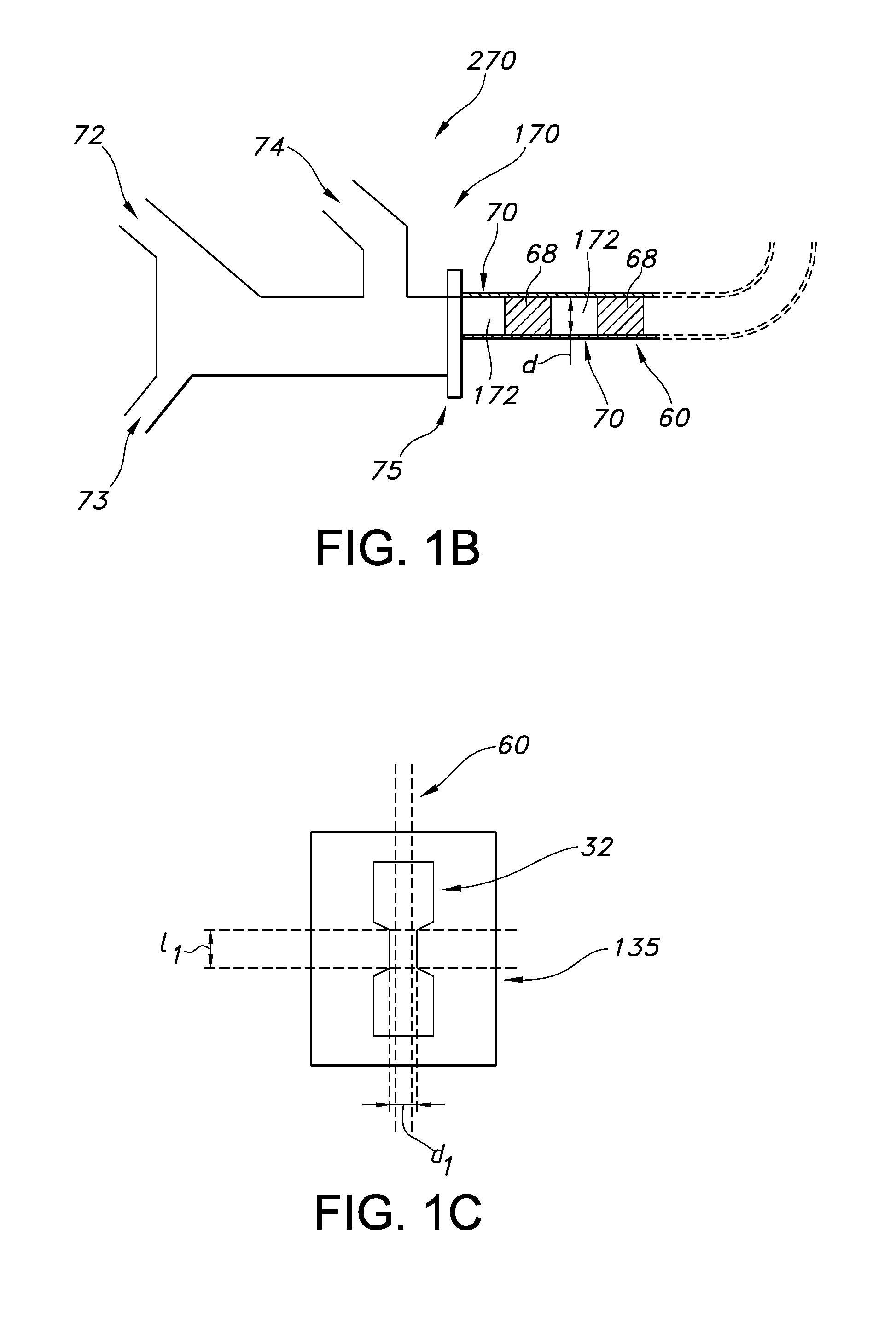
Nozzle for dnp polarizer
DNP polarizer comprising a housing receiving a free end of a tubular fluid conduit positioned in fluid communication with a nozzle supported by said housing, said nozzle including an input port, a dispense port and a tapering inner surface or a stepped inner surface defining a nozzle flowpath extending in fluid communication between said input port and said dispense port.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Apparatus for carrying out DNP-NMR measurements with a compensation configuration and method for designing the compensation configuration
ActiveUS8154292B2Improve homogeneityCompact dimensionsMeasurements using double resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientMagnet
An apparatus for DNP-NMR measurement on a sample, with a magnet configuration for producing a magnetic field in a first working volume and in, a second working volume with a magnetic field gradient in the direction of an axis (z) which extends through the second working volume, with a device for measuring MR signals, with a DNP excitation device, and with a positioning mechanism for transferring the sample, is characterized in that, near the second working volume, a compensation configuration made of magnetic material is mounted that, in the operating condition of the magnet configuration, produces a magnetic field gradient in the direction of the axis (z) in the second working volume that is between −90% and −110% of the magnetic field gradient of the same order of the stray field of the magnet configuration.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Downhole high resolution NMR sprectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS20060192554A1Increased polarizationIncrease amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onNuclear Overhauser effect
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
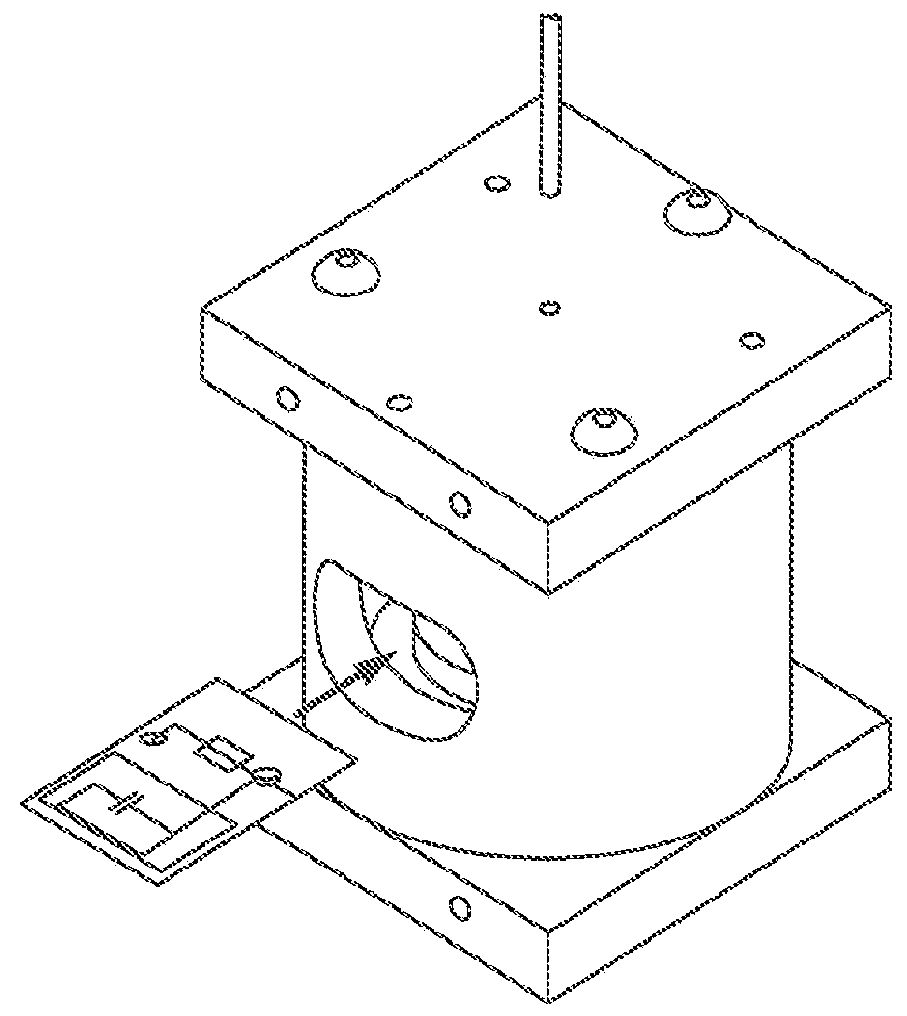
Measurement device and measurement method
InactiveUS20110112395A1Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMeasurement deviceFunctional image
A measurement device and measurement method make it possible to eliminate the load generated by stopping on a measurement subject that is moved among multiple magnetic field generating devices. The measurement device includes a first external magnetic field generating device that generates a magnetic field of a set size, a second external magnetic field generating device that generates a magnetic field of a size that differs from that of the magnetic field of the first external magnetic field generating device, a rotating table that causes the subject of measurement to pass in sequence through the magnetic fields of the first and second external magnetic field generating devices by causing the subject of measurement to move rotationally, and an OMRI measurement processing part and MRI measurement processing part that measures images such as functional images or structural images of the subject of measurement while it is being moved rotationally by the rotating table.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Multidimensional NMR spectroscopy of a hyperpolarized sample
InactiveUS7550970B2Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSpectroscopy
The present invention relates to methods of performing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy adapted for a hyperpolarized sample. The methods comprise the steps of hyperpolarizing a sample using DNP, wherein at least a portion of the NMR active nuclei receives hyperpolarization; performing NMR spectroscopy on the sample with the use of sequences of rf-pulses, wherein the pulse sequences comprises at least two rf-pulses, either on the same nuclei or on different nuclei, and wherein the pulse sequence is adapted for a hyperpolarized sample; and analyzing at least two of the NMR spectra to obtain a characterization of the sample, or to obtain an interim result to be used in the NMR spectroscopy step.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com