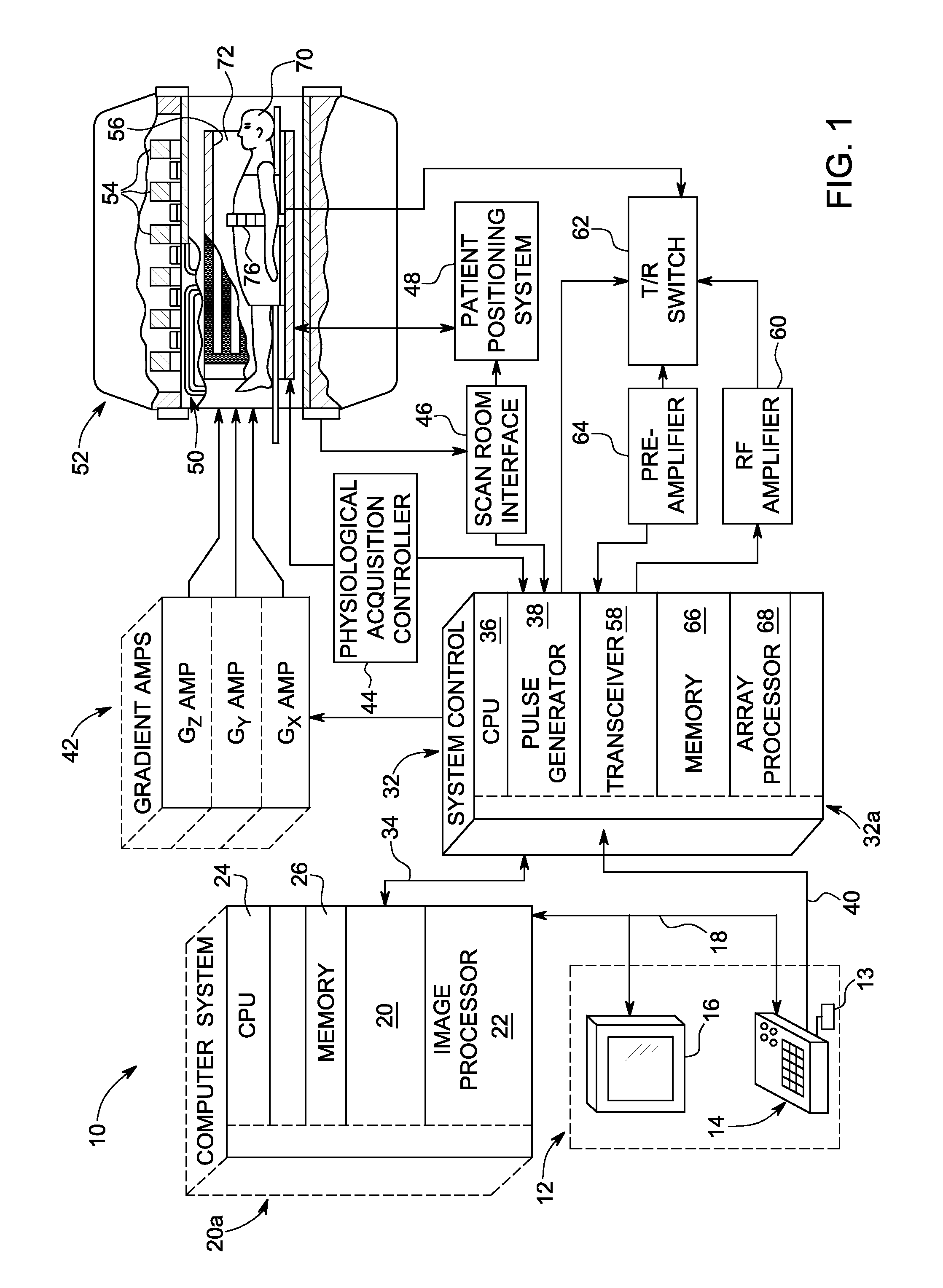
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
661 results about "Cryostat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
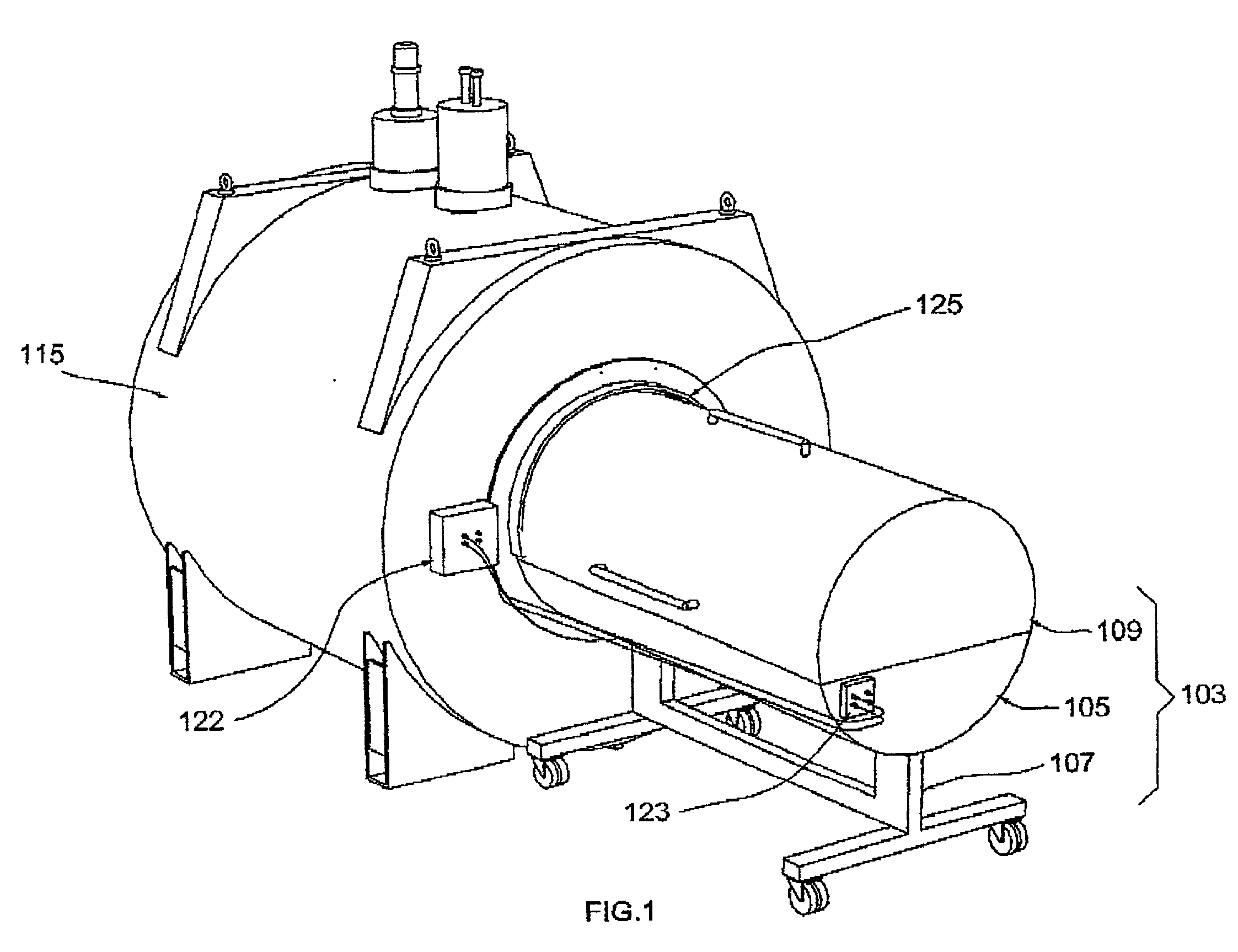
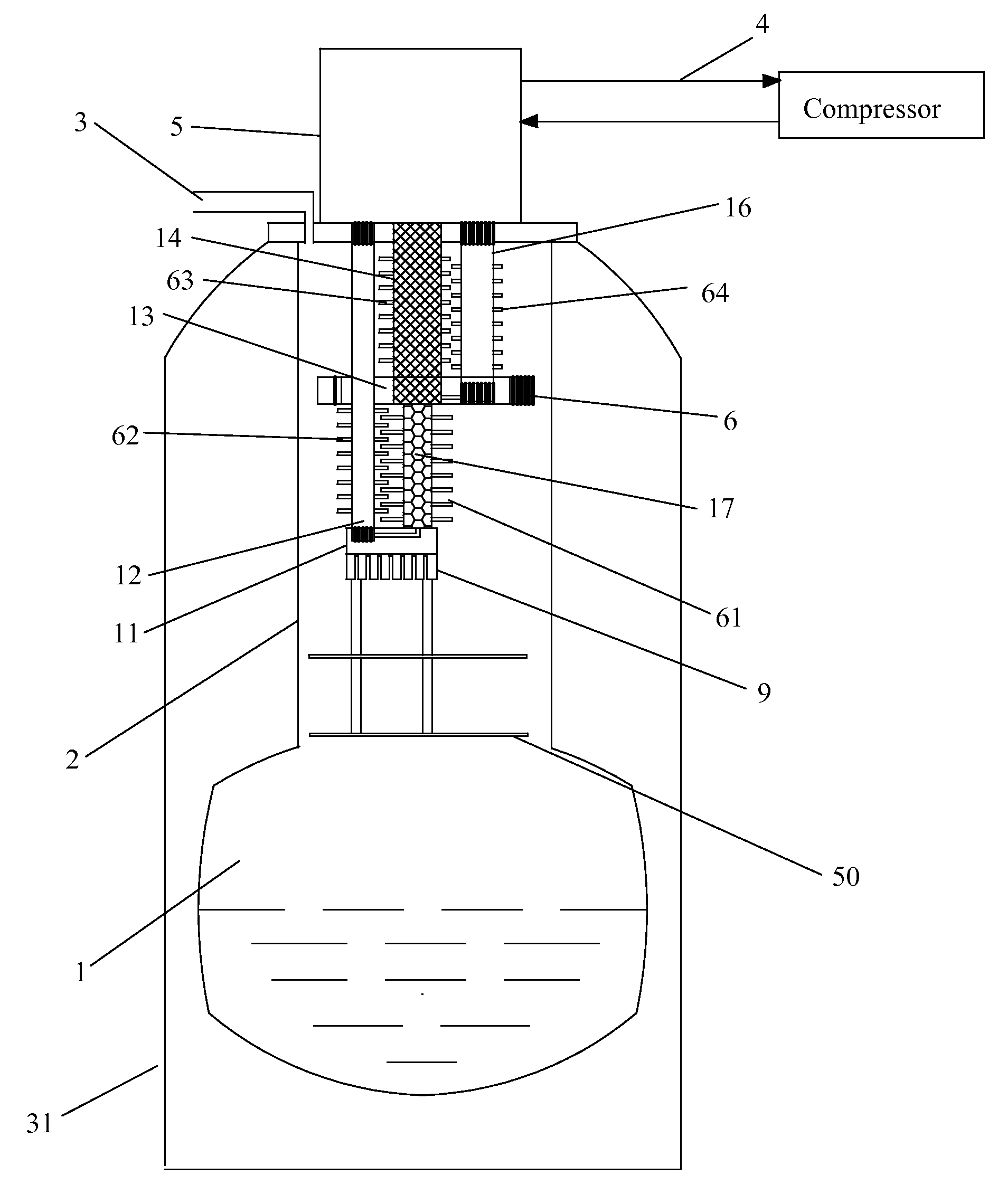
A cryostat (from cryo meaning cold and stat meaning stable) is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium. Hence it is usually assembled into a vessel, similar in construction to a vacuum flask or Dewar. Cryostats have numerous applications within science, engineering, and medicine.
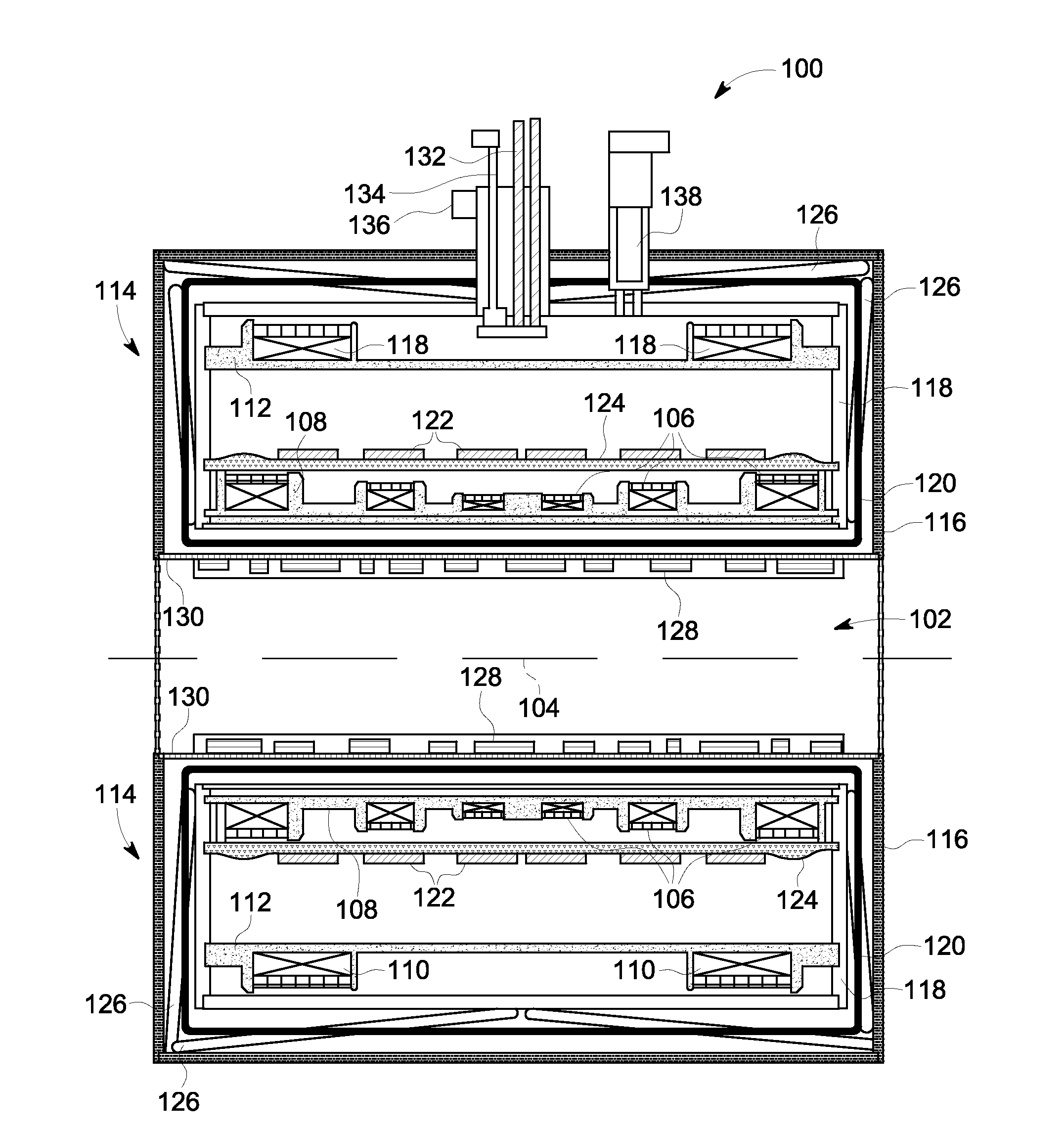
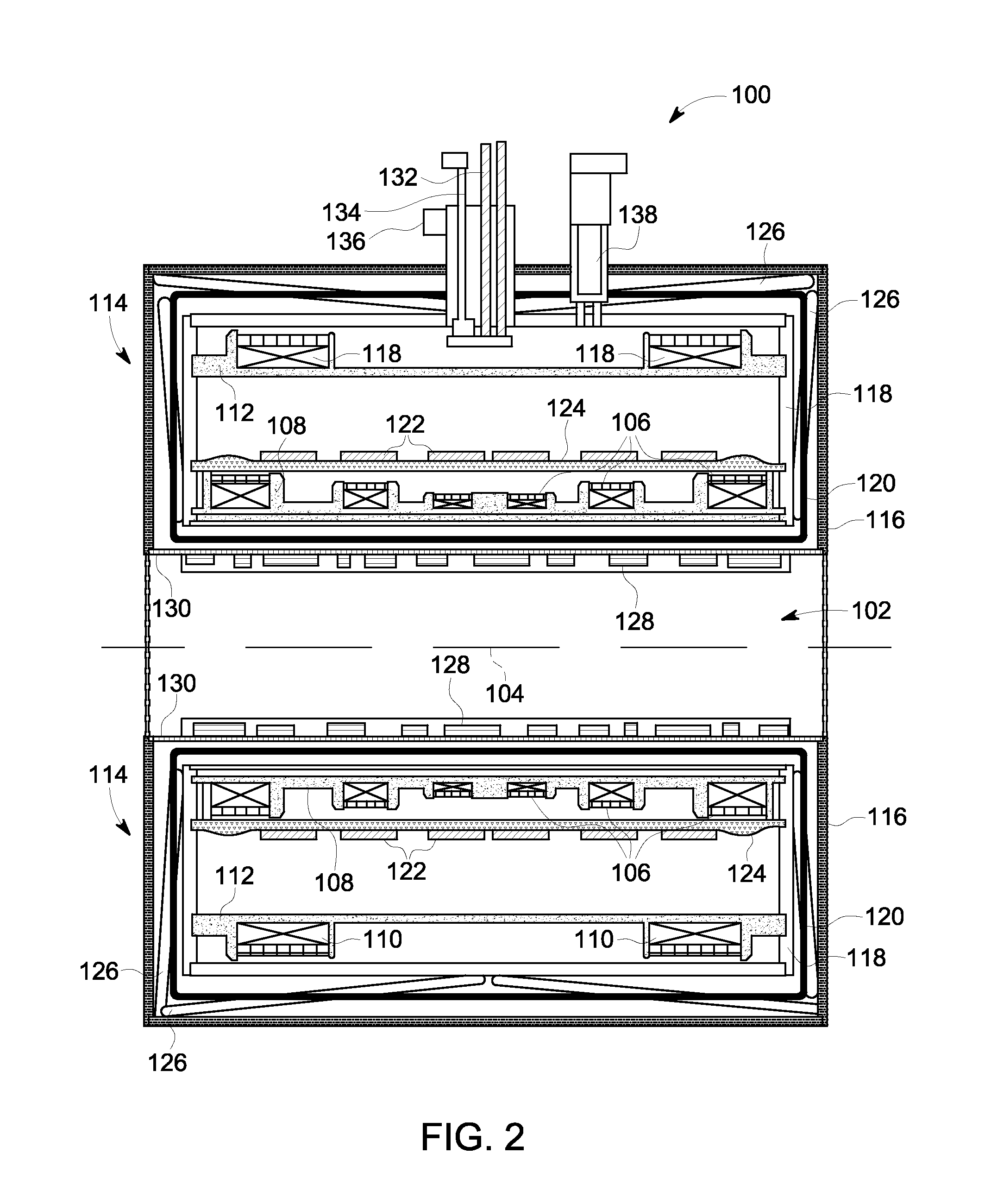
Radio frequency shield for nuclear magnetic resonance procedures
InactiveUS20030088175A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
An apparatus and method for providing RF shielding for performing nuclear magnetic resonance ("NMR") procedures, comprising a radio-opaque holder in combination with radio-opaque magnet components to form an RF shield around a patient undergoing an NMR procedure. In embodiments, a radio-opaque holder having a radio-opaque bottom portion and a radio-opaque canopy is adjoined to an NMR magnet having a radio-opaque cryostat and a radio-opaque service end cap to form an RF shield. A patient is placed on a patient support unit located in the holder bottom portion. The patient support unit, including the patient, is then inserted into the cavity of the NMR magnet and a canopy is placed on top of the bottom portion of the holder. An RF shield is thus created comprising the canopy, the bottom portion, the cryostat of the magnet, and an end cap on the service end of the magnet.
Owner:ADVANCED VETERINARY TECH
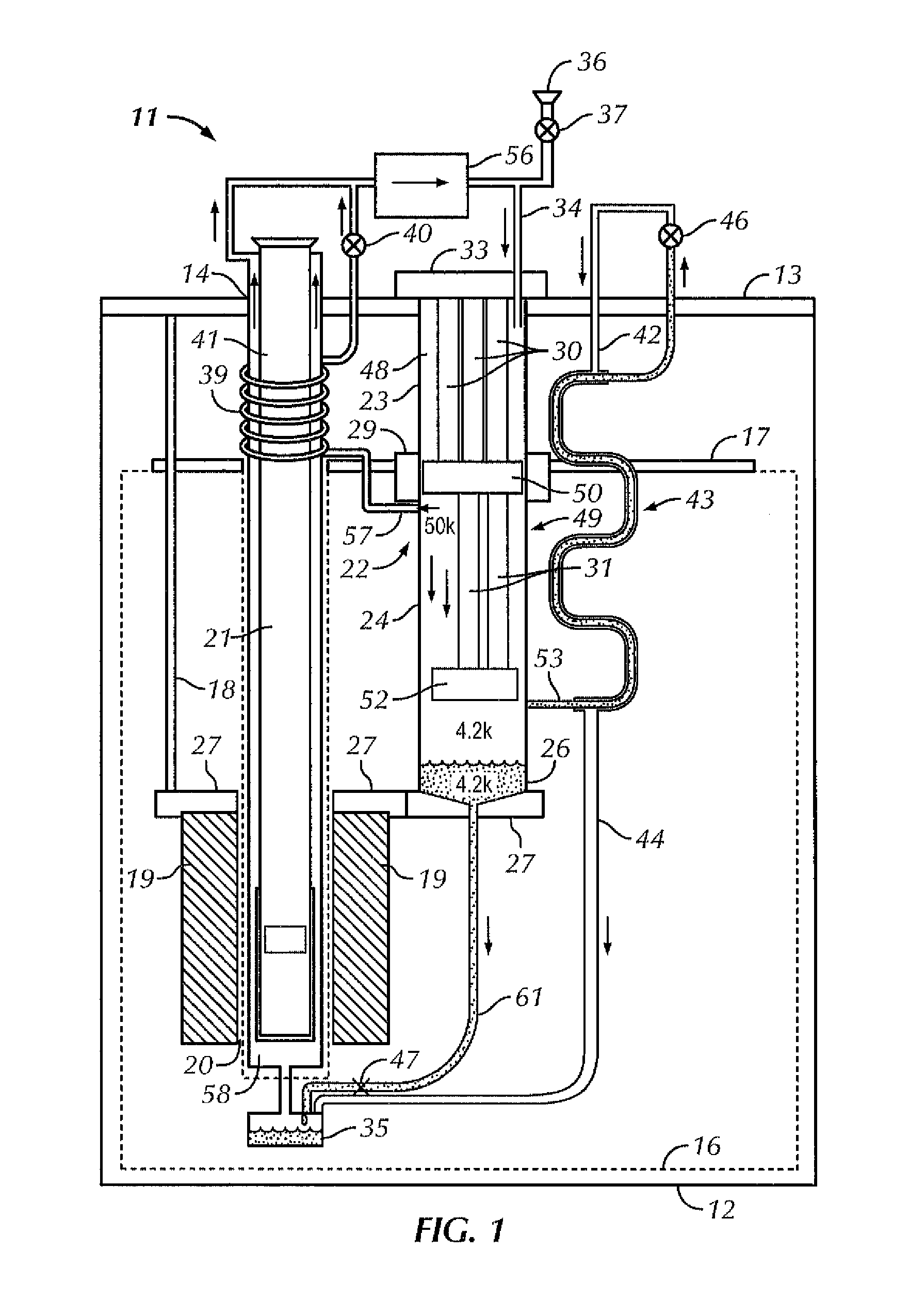
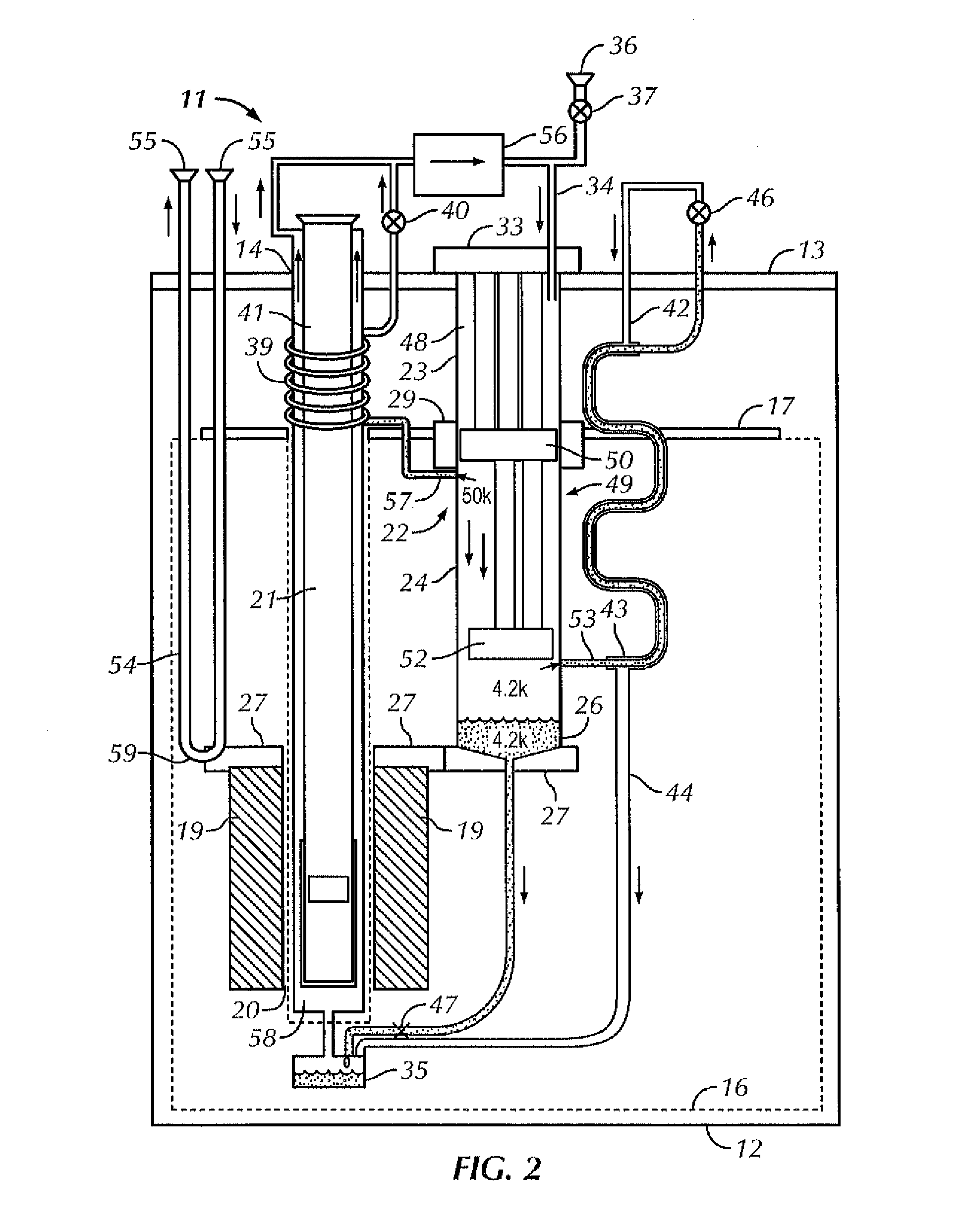
Cryostat configuration with cryocooler
InactiveUS20070089432A1Low heat inputIncrease expensesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic measurementsContact freeEngineering
A cryostat configuration for keeping cryogenic fluids in at least one cryocontainer, comprising an outer shell and a neck tube containing a cold head of a cryocooler, wherein the coldest cold stage of the cold head is disposed in a contact-free manner relative to the neck tube and the cryocontainer, and wherein a cryogenic fluid is located in the neck tube, is characterized in that the neck tube is disposed between the outer shell and a cryocontainer and / or the radiation shield, the neck tube is closed in a gas-tight manner at the end facing the cryocontainer and / or the radiation shield, the neck tube is coupled to the cryocontainer and / or a radiation shield disposed between the cryocontainers or a cryocontainer and the outer shell, via a connection having a good thermal conductivity, the neck tube comprising a fill-in device at an end located at ambient temperature. This permits efficient heat transfer between the cryocooler and the cryocontainer with little vibration, while simultaneously ensuring great safety during maintenance work without discharging the magnet.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Evacuated tube transport system with interchange capability
ActiveUS20140261054A1Reduces magnetic drag forceLightning protection is goodRailway tunnelsRailway componentsLevitationTransport system
A High Temperature Superconductor Maglev (HTSM) for Evacuated Tube Transport (ETT) with a magnetic levitation structure for ETT capsule vehicles traveling in an evacuated tube. At least one ETT capsule travels within an evacuated tube, an upper and a lower cryostat respectively mount at the top and bottom of said ETT capsule along the length thereof, at least a plurality of superconductor levitation force elements divided between said upper and lower cryostats. The levitation force being spread over the length of capsule, however substantially concentrated in a compact cross-sectional area. At least a pair of permanent magnetic elements mounted at the top and bottom of the evacuated tube to levitate the capsule. At least a pair of capsule based switchable diverge force elements cooperate with at least a pair of tube based diverge force elements to steer the capsule while in an interchange.
Owner:OSTER DARYL
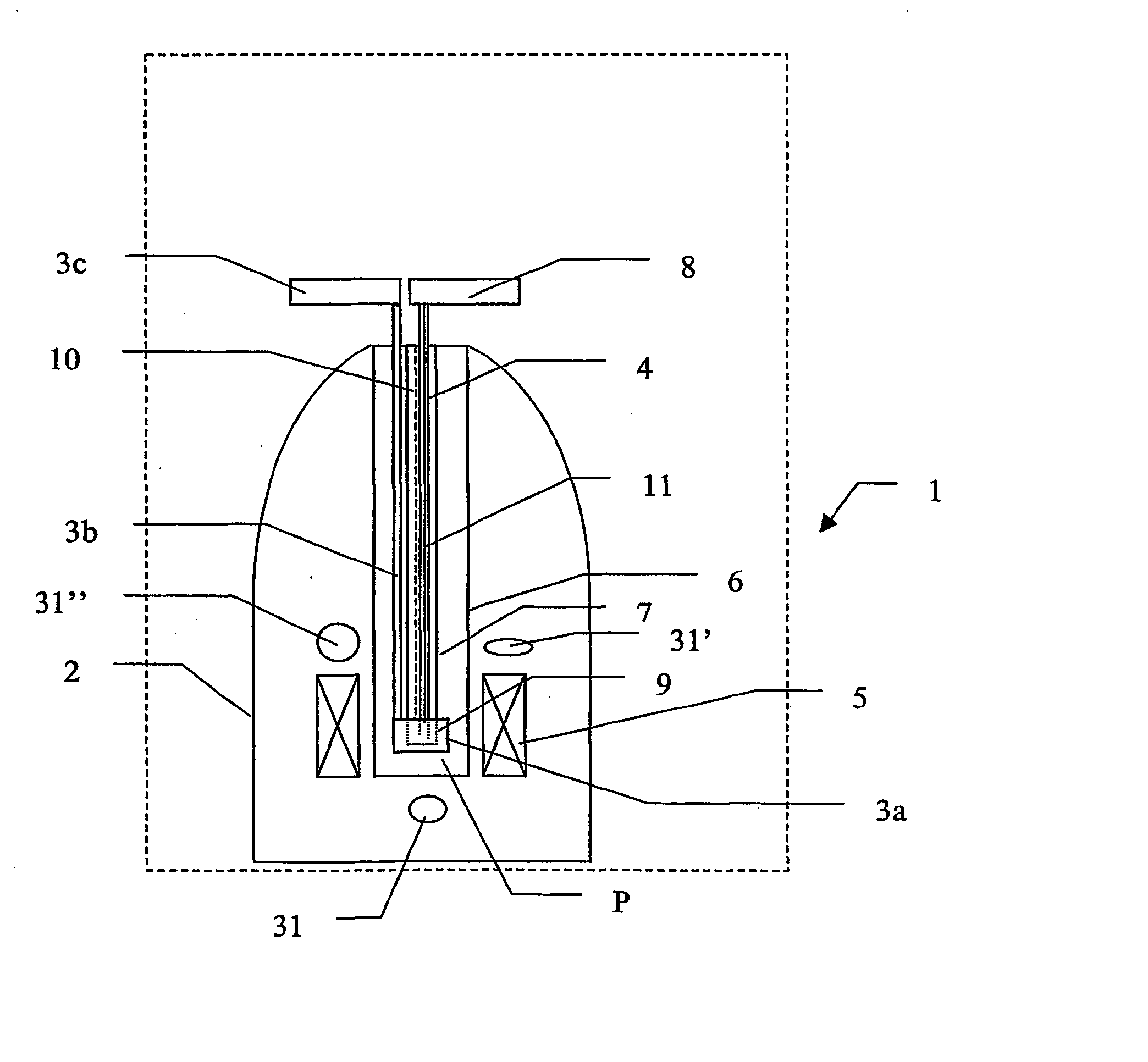
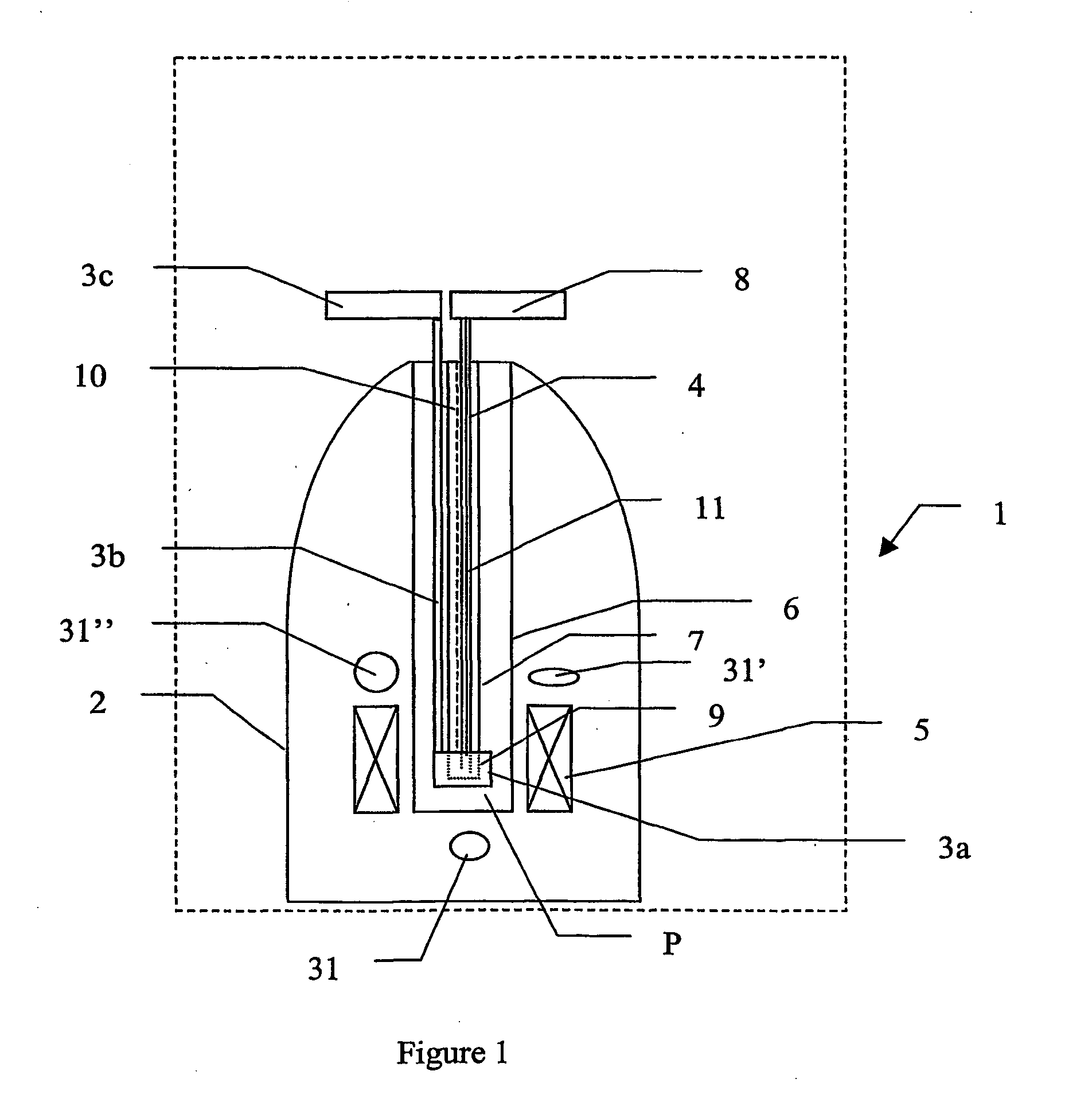
Methods and devices for dissolving hyperpolarised solid material for nmr analyses
ActiveUS20040066193A1Raise the ratioImprove resolutionElectrical measurement instrument detailsPreparing sample for investigationSolid massEngineering
The present invention relates to devices and method for dissolving solid polarised material while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a material is polarised in a strong magnetic field in a cryostat 2 and then brought into solution while still inside the cryostat 2.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
NMR spectrometer with common refrigerator for cooling an NMR probe head and cryostat
ActiveUS20060130493A1Optimum adjustment of performanceUtilization capacitySolidificationLiquefactionCryocoolerRefrigerated temperature
An NMR apparatus comprising a superconducting magnet coil system, in particular, an NMR spectrometer, with a cryostat which comprises an outer shell and a helium tank which contains the magnet coil system, and with an NMR probe head which is disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat and which contains a cooled RF resonator for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be examined and is cooled, together with the NMR probe head, by a cold head of a common, multi-stage, compressor-operated refrigerator, is characterized in that the cold head of the refrigerator is disposed in a neck tube, the upper end of which is connected to the outer shell of the cryostat and the lower end of which is connected to the helium tank in such a manner that the neck tube and the helium tank delimit a helium space, with at least one cooling circuit with thermally insulated transfer lines being provided between the helium space and the NMR probe head, wherein the cryogenic helium in the helium space is used as coolant for the cooling circuit. This produces an NMR apparatus which cools a plurality of elements at different temperature levels using only one single cryocooler to optimally utilize the cooling resources of the refrigerator.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
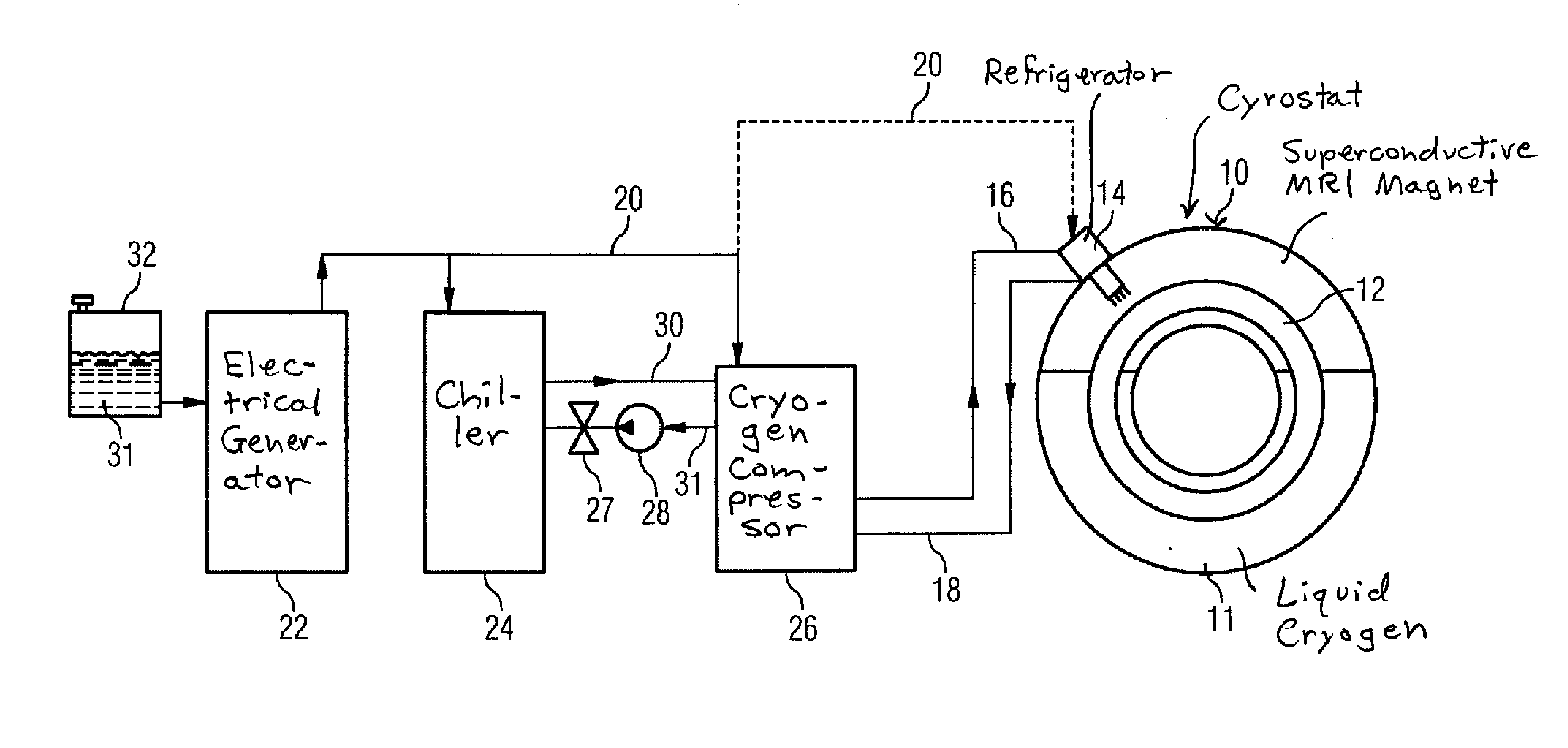
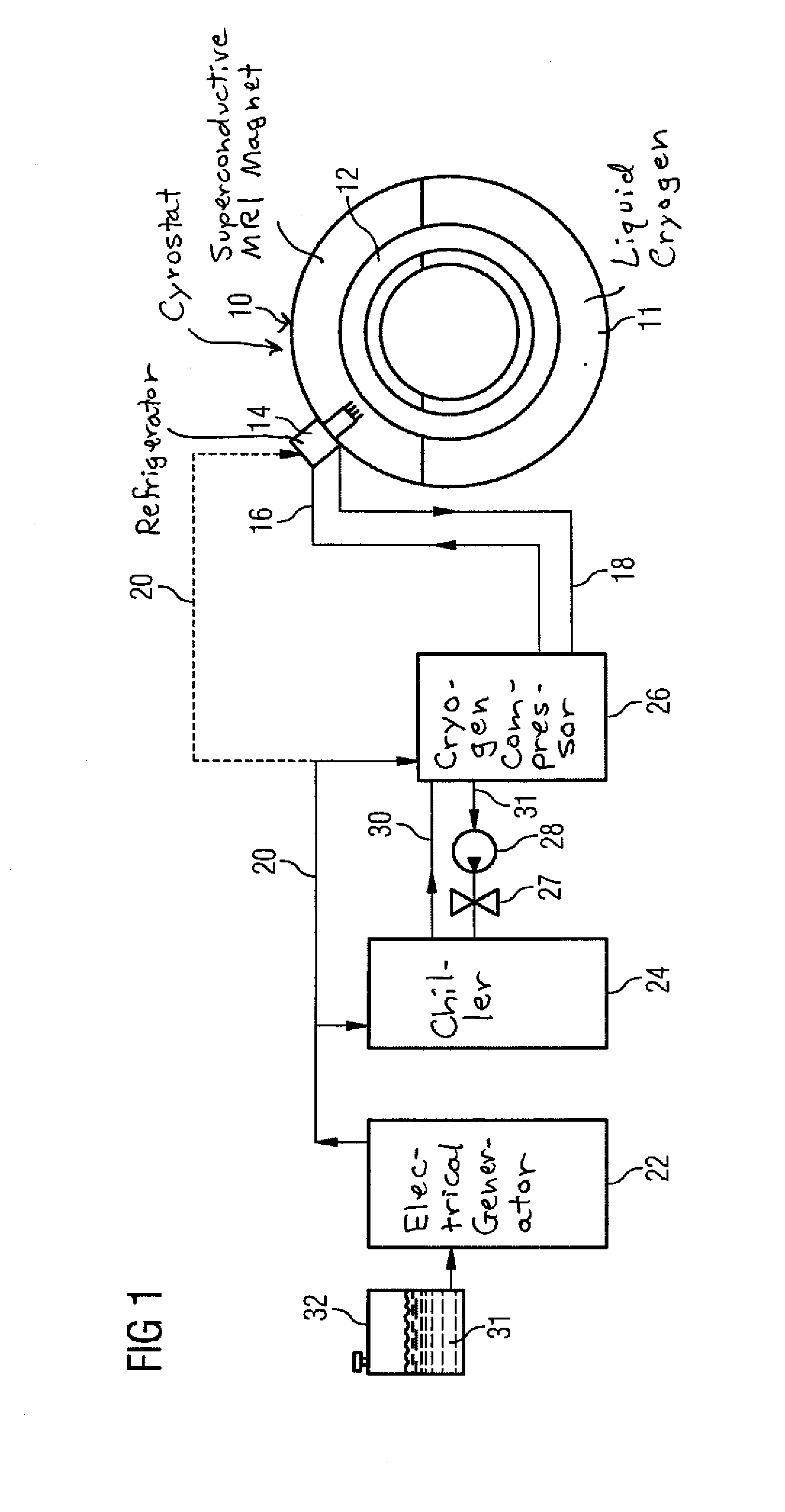
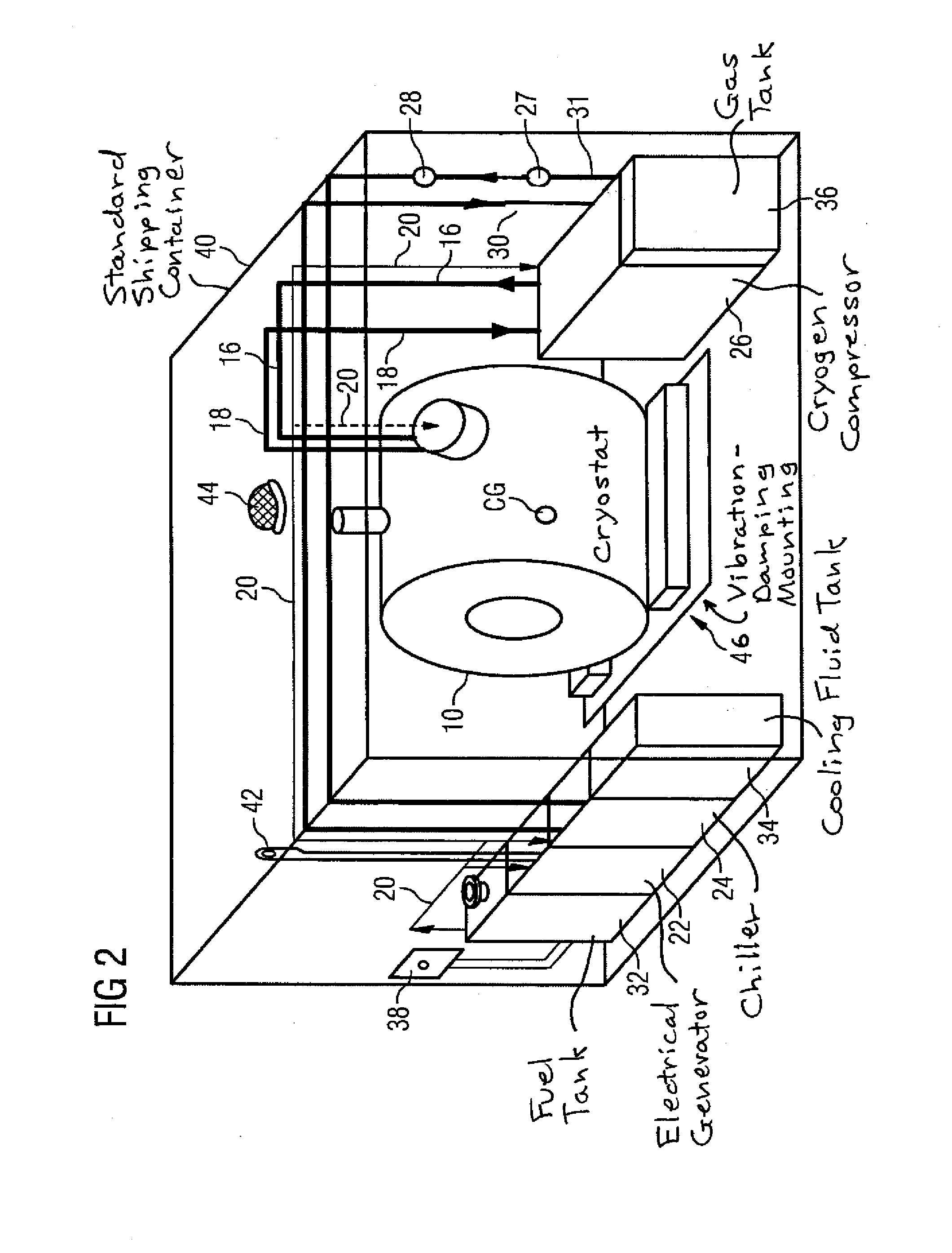
Apparatus and method for transporting cryogenically cooled goods or equipment
InactiveUS20100016168A1Lower the volumeAvoid lostContainer filling methodsSuperconductor detailsActive coolingProcess engineering
In an apparatus and method for transporting cryogenically cooled goods or equipment, a cryostat containing the cryogenically cooled goods or equipment and partially filled with liquid cryogen is provided with a cryogenic refrigerator for active cooling; and auxiliary equipment sufficient to maintain the cryogenic refrigerator in operation, are all mounted on a transportable carrier such that the transportable carrier may be transported with the cryogenic refrigerator in operation without connection of any of the cryostat, refrigerator and auxiliary equipment to any supplies located off of the transportable carrier.
Owner:SIEMENS PLC
Method and apparatus for controlling temperature in a cryocooled cryostat using static and moving gas
ActiveUS20110219785A1Rapid initial cool-downMinimal, if any, helium replenishmentSolidificationLiquefactionCounter flowTemperature conditioning
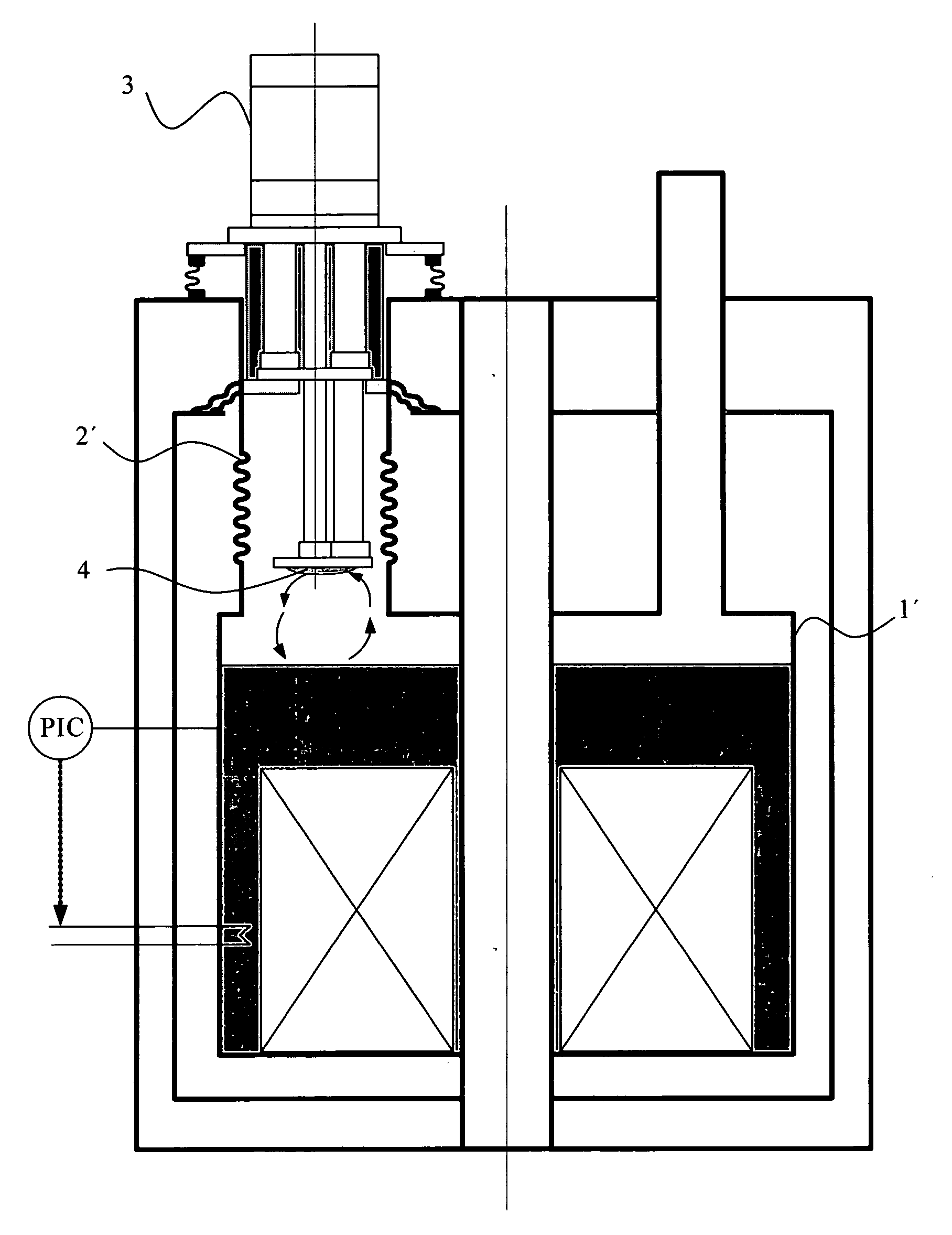
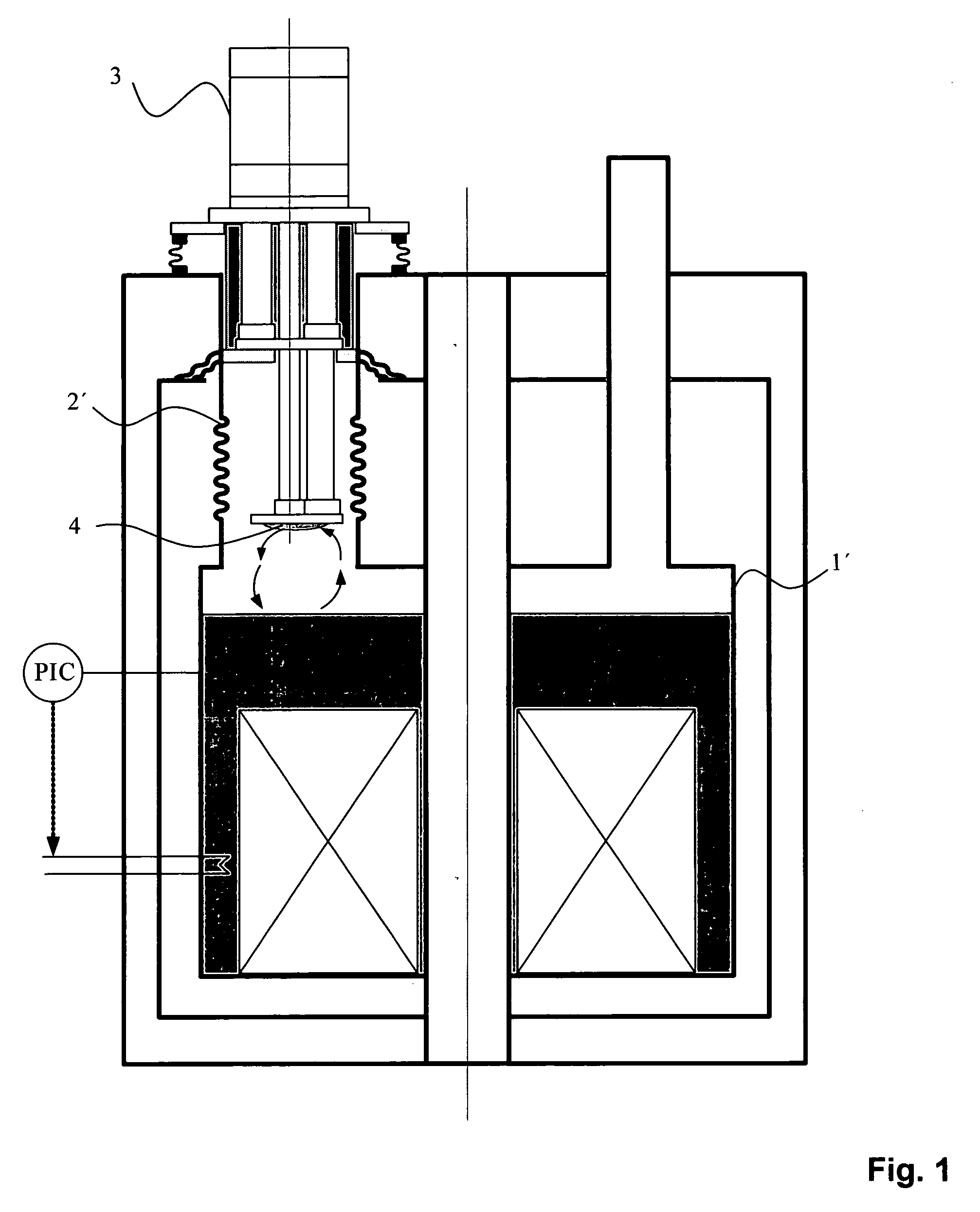
A cryostat for providing temperature regulation, one purpose being measuring physical properties of materials, the cryostat employing a superconducting magnet assembly for generating variable magnetic field in the sample space and a cryogenic cooler for cooling the sample space. The cryogenic cooler chamber configuration provides for efficient heat exchange between different stages of the cryogenic cooler without the need for physical heat links. This construction enables selective delivery of cooling power from the cryogenic cooler to the desired areas within the cryostat without using flexible physical thermal links. A counter flow exchanger and ambient temperature valves facilitate efficient use of the cryogenic cooler stages. The removal of large heat load generated by the superconducting magnet while operating in the sweeping mode is achieved, in part, by employing a solid plate thermal coupling element between the cryogenic cooler chamber and the magnet assembly.
Owner:QUANTUM DESIGN
Methods and devices for polarised nmr samples
InactiveUS20040049108A1Raise the ratioImprove resolutionMeasurements using double resonanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSolid massLaser
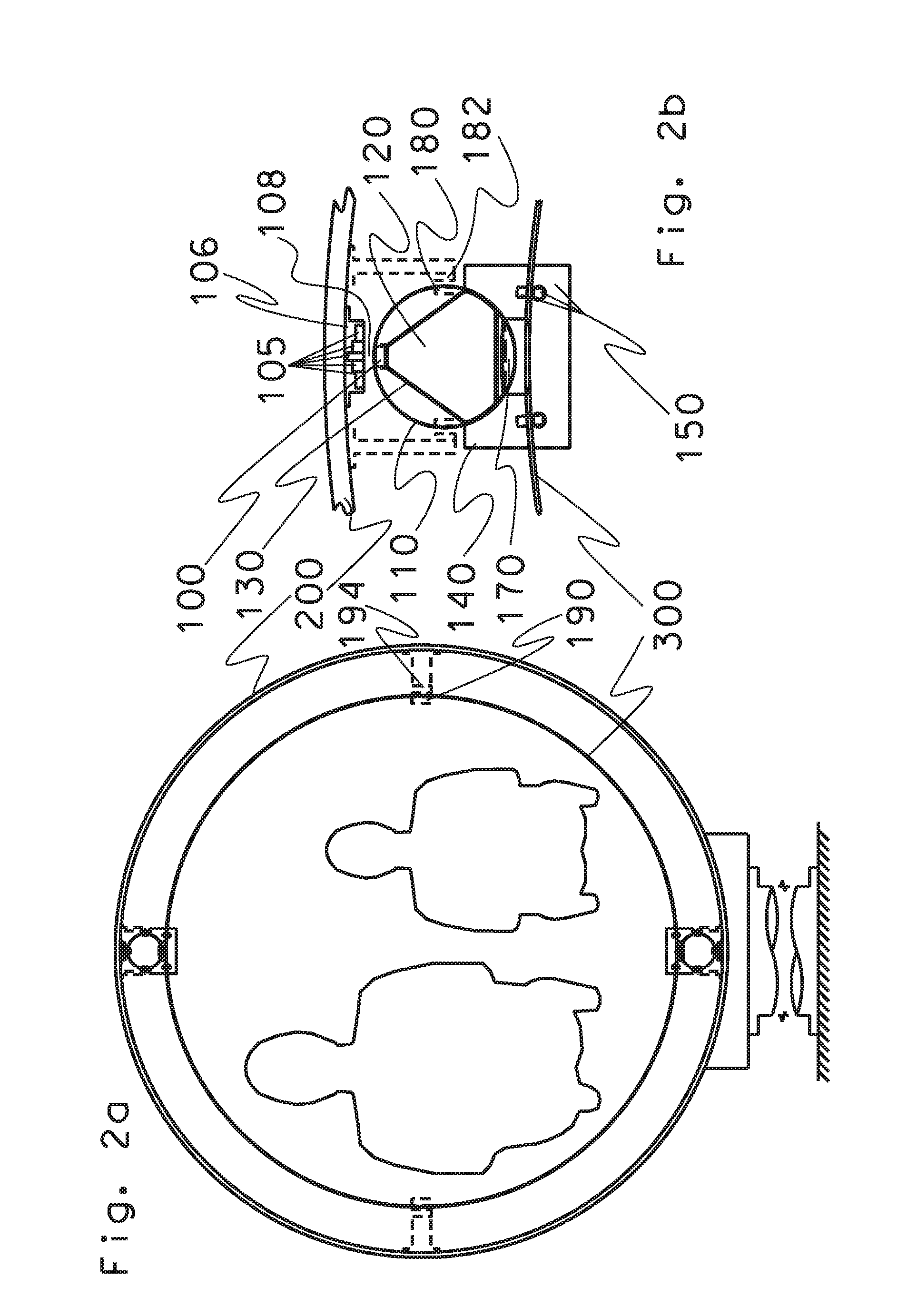
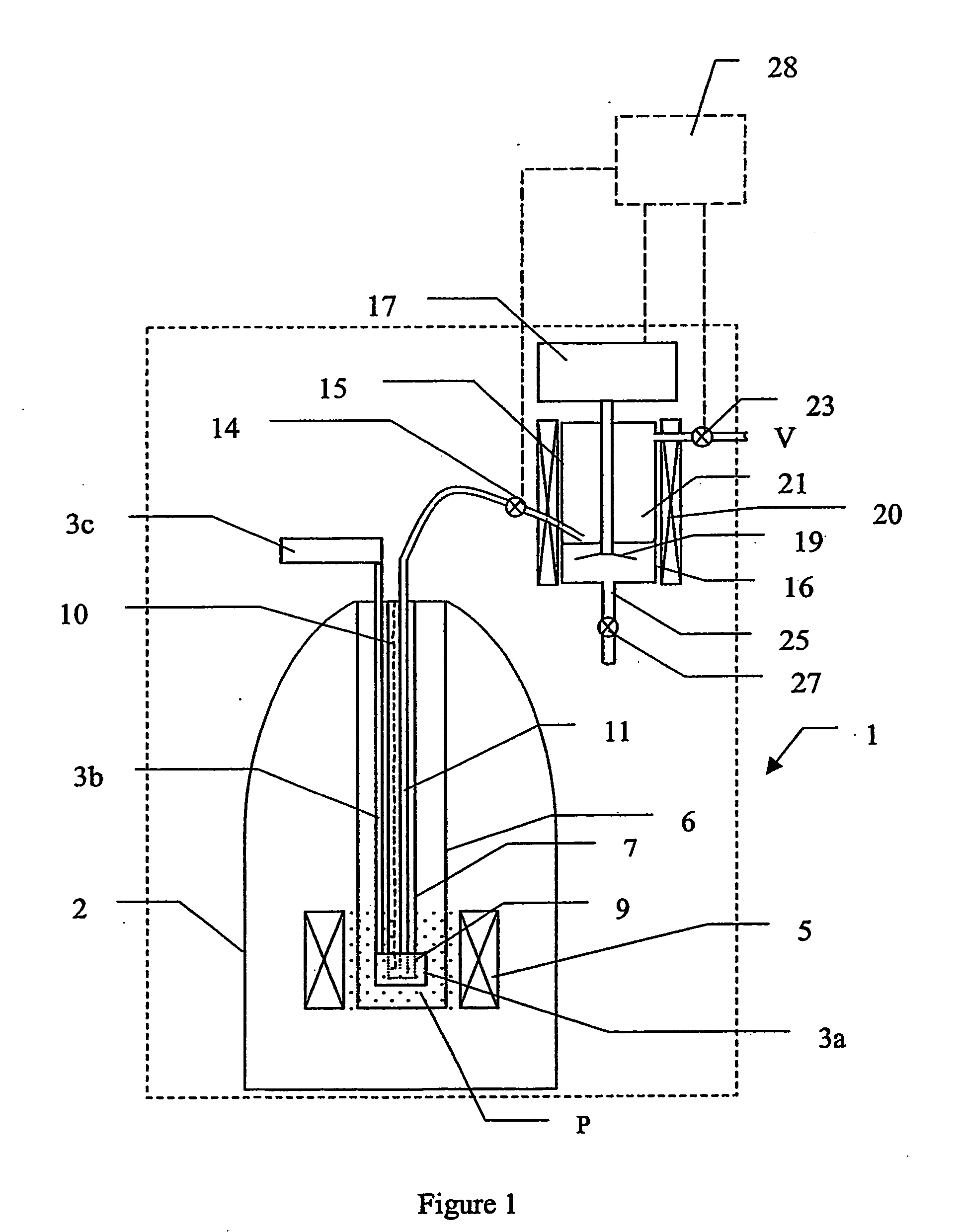
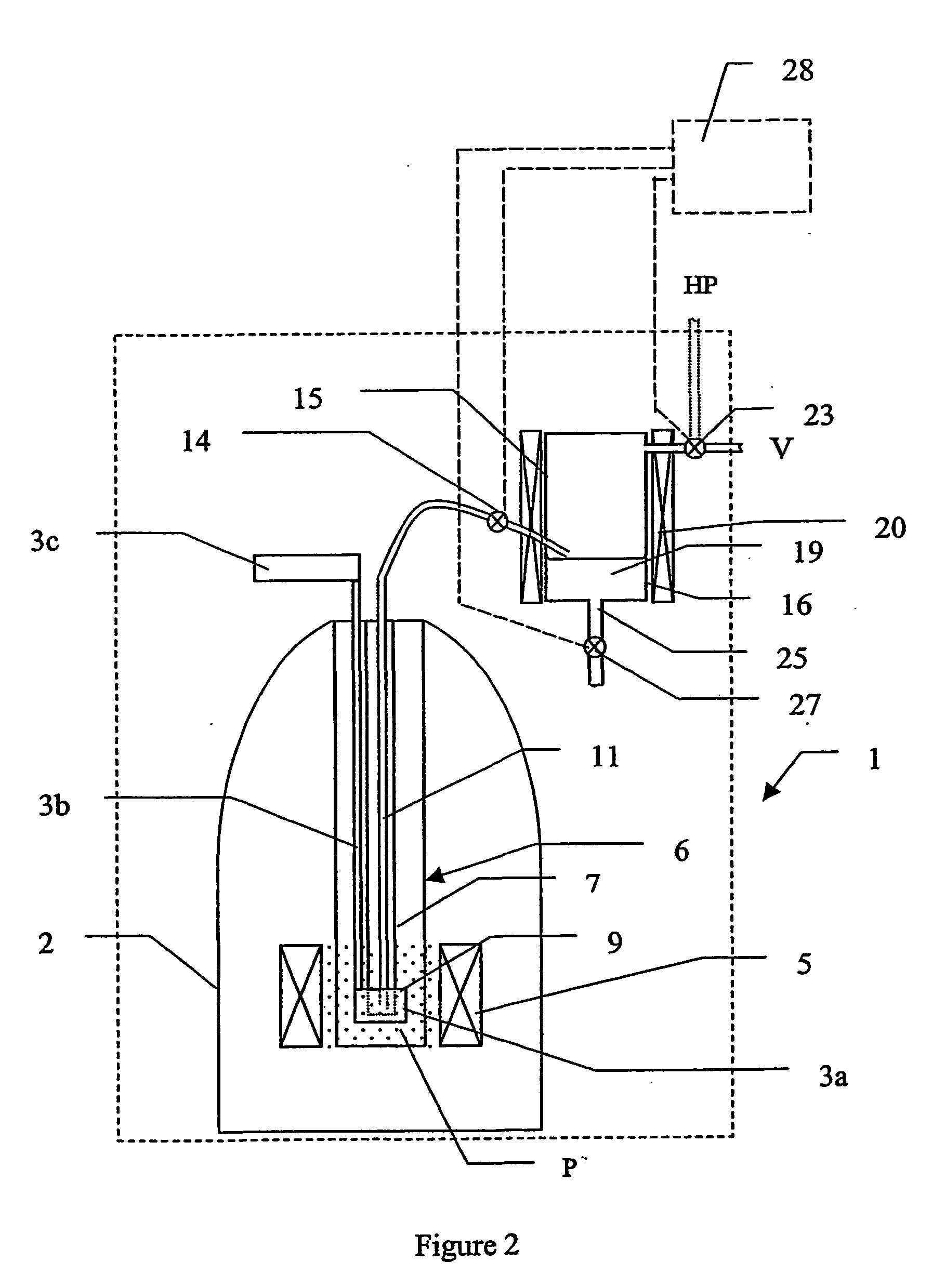
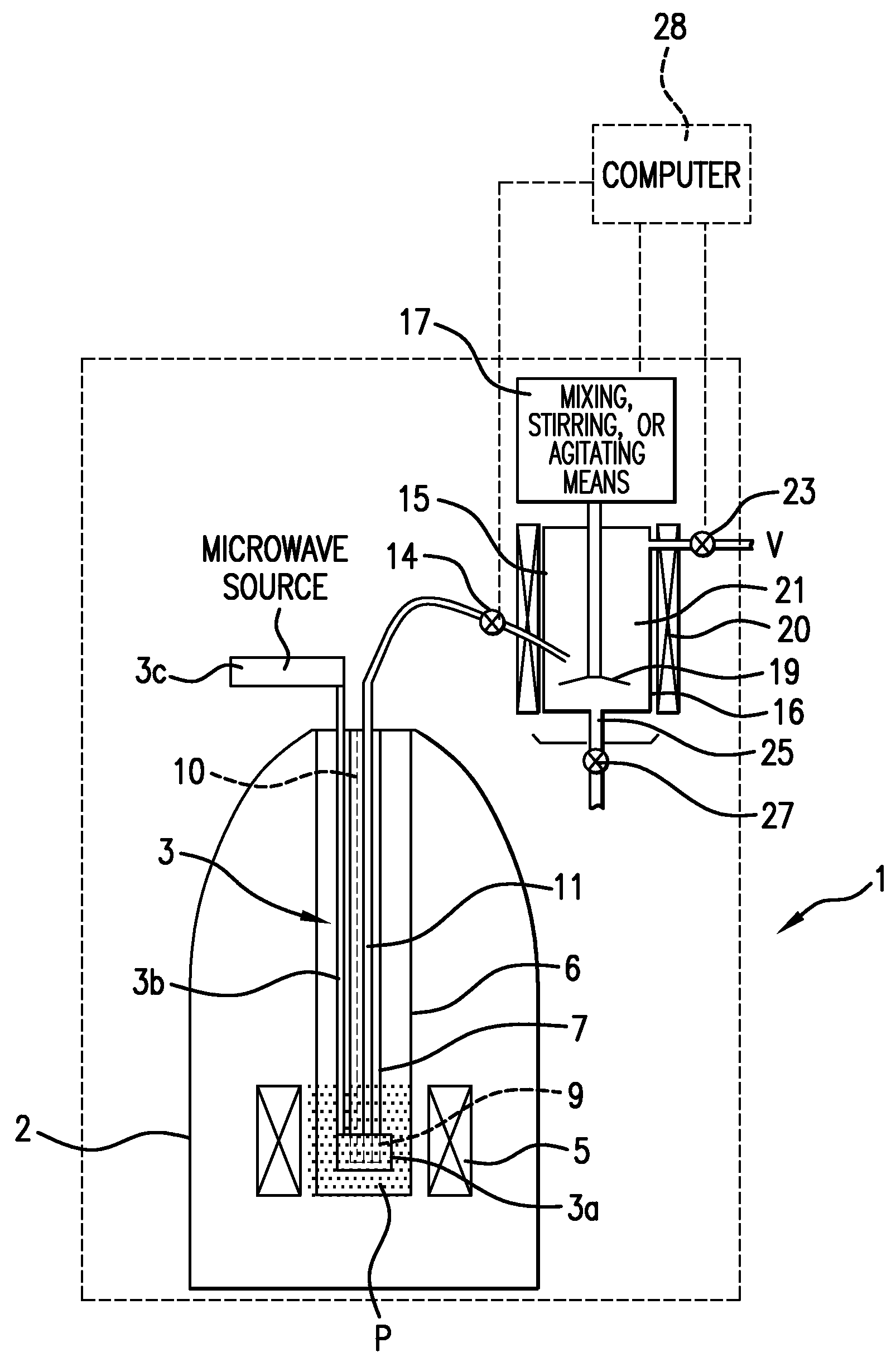
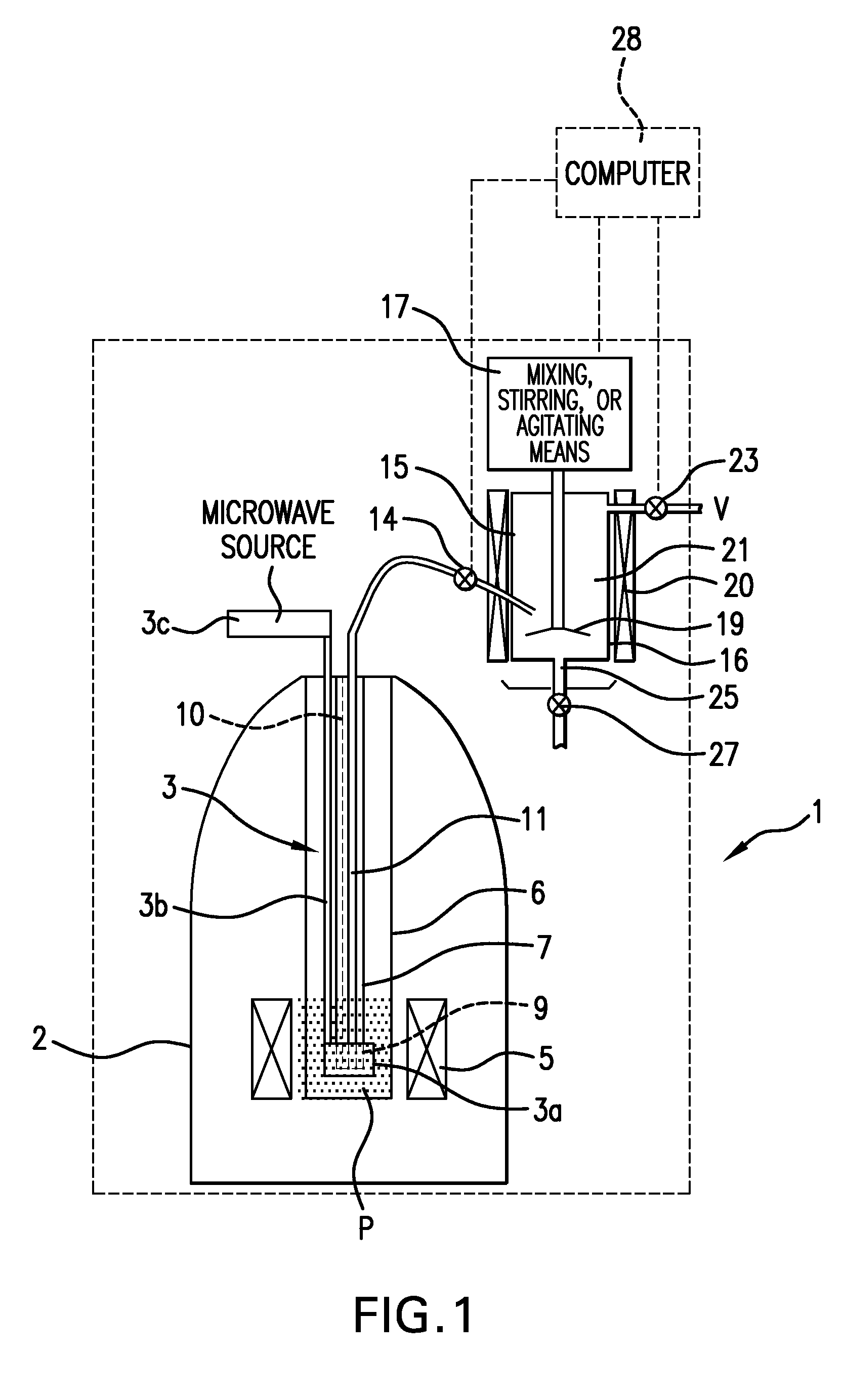
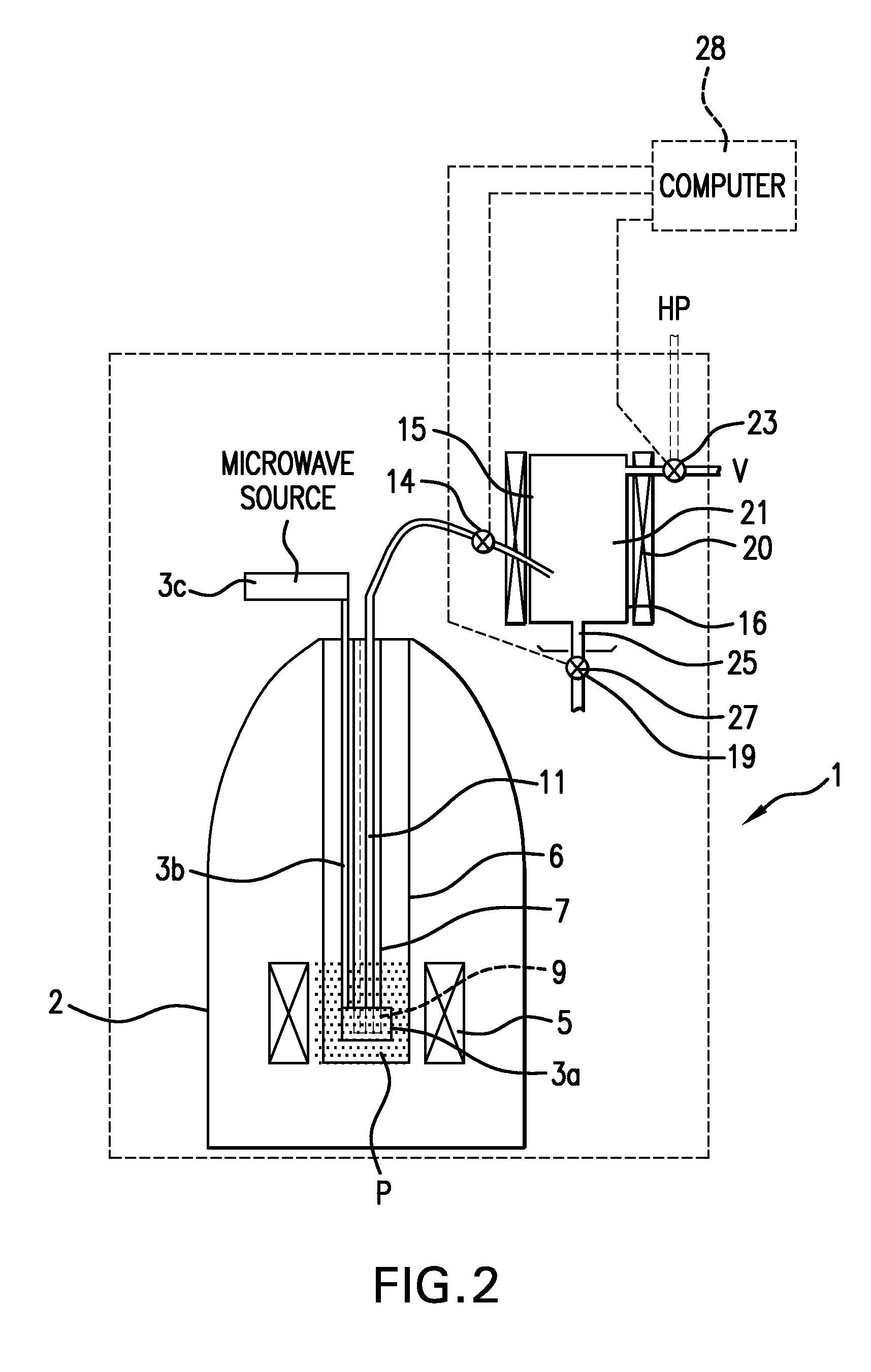
The present invention relates to devices and method for melting solid polarised sample while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a sample is polarised in a sample-retaining cup (9) in a strong magnetic field in a polarising means (3a, 3b, 3c) in a cryostat (2) and then melted inside the cryostat (2) by melting means such as a laser (8) connected by an optical fibre (4) to the interior of the cryostat.
Owner:AMERSHAM HEALTH
Cryogenic cooling apparatus
InactiveUS20050126187A1Avoid spreadingVessel mounting detailsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
A cold head of a refrigerator is secured to a support stage provided separately from a cryostat so that the support stage supports the load of the cold head. On the other hand, a low-vibration stage for supporting a load of an object to be cooled is secured to a top flange of the cryostat. Thus, vibration that occurs due to the refrigerator is prevented from being transmitted to the entire cryostat and the object to be cooled.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD +1
Low vibration liquid helium cryostat
An extra-low vibration cryostat, which incorporates a cryocooler and cryostat to cool and house a vibration-sensitive device, with the cryocooler and cryostat sealed gas-tight to each other, but mechanically isolated, so that vibration from the cryocooler does not affect the device.
Owner:CRYOMECH
Methods and devices configured for dissolving hyperpolarised solid material with a solvent within a cryostat for NMR analyses
ActiveUS7372274B2Polarisation is minimisedLoss of polarisationElectrical measurement instrument detailsPreparing sample for investigationSolid massEngineering
The present invention relates to devices and method for dissolving solid polarised material while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a material is polarised in a strong magnetic field in a cryostat 2 and then brought into solution while still inside the cryostat 2.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
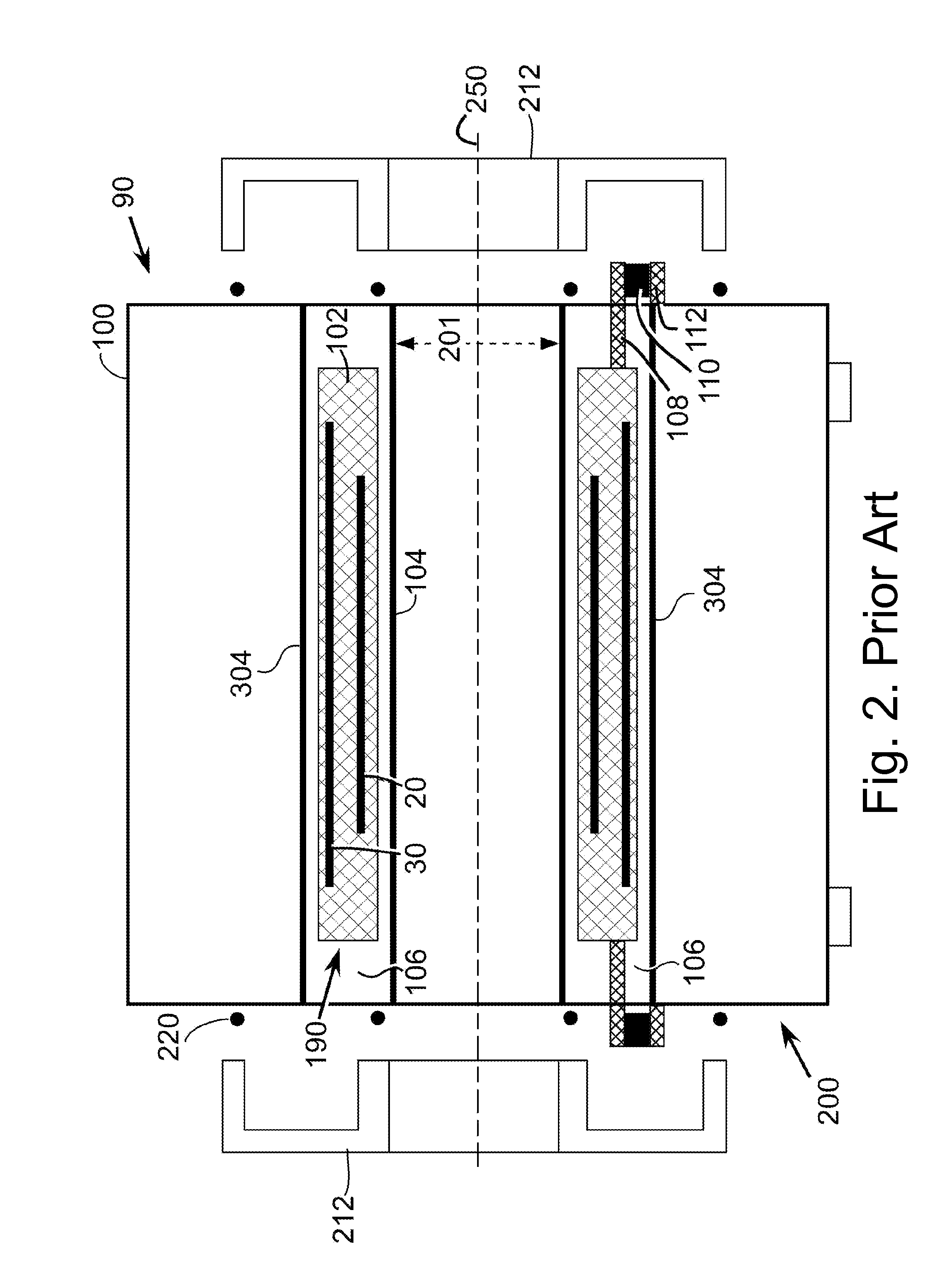
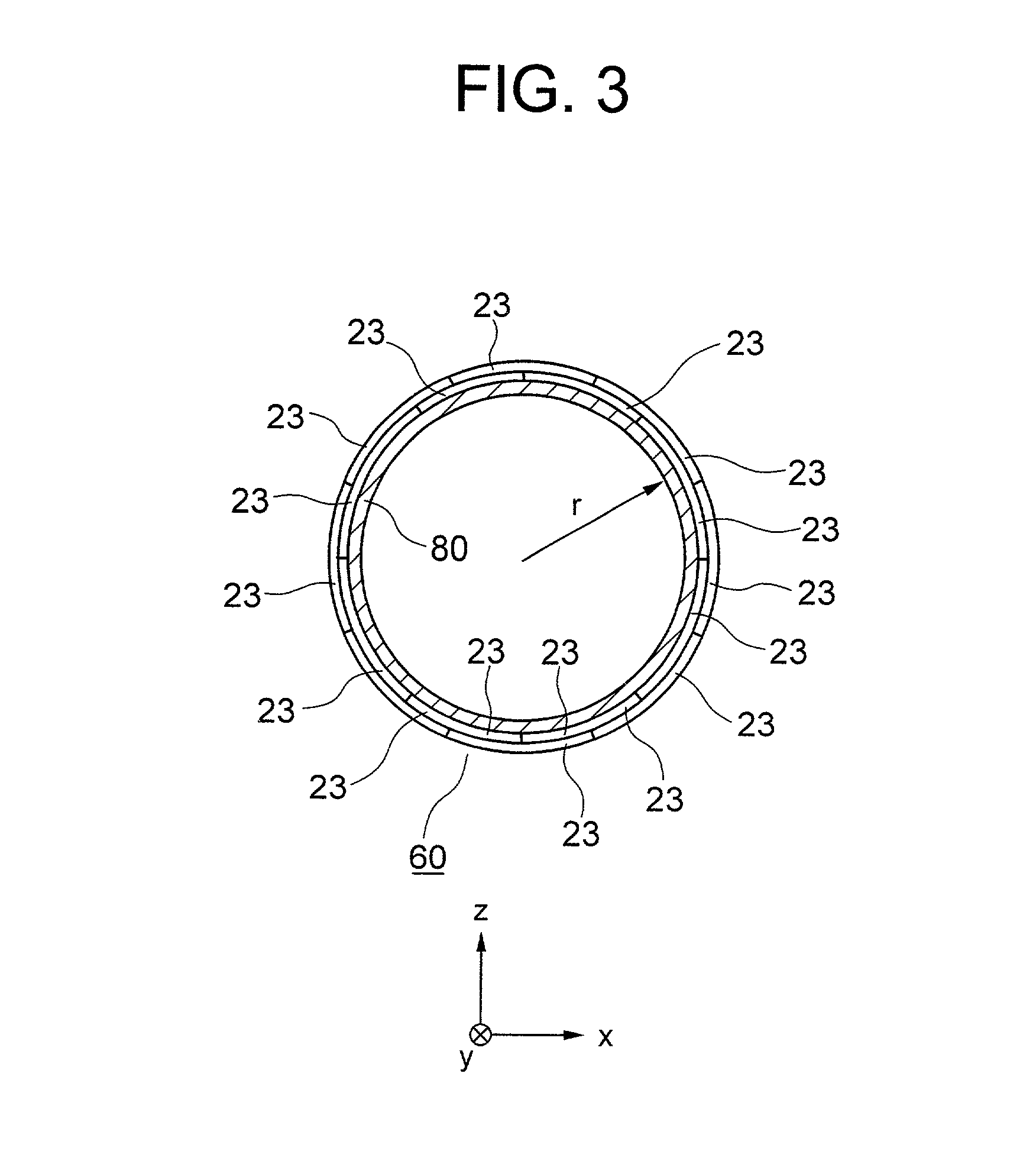
Superconducting magnet split cryostat interconnect assembly
InactiveUS6289681B1High strengthReduce thermal resistanceMagnetic measurementsGas handling applicationsElectricitySuperconducting Coils
A multi purpose interconnect assembly between upper and lower helium vessels in a recondensing superconducting magnet to provide isothermal connections to extend the ride-through period, and to provide for helium liquid and gas passage, electrical interconnections, and to accommodate differential thermal contraction and expansion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
NMR spectrometer with refrigerator cooling
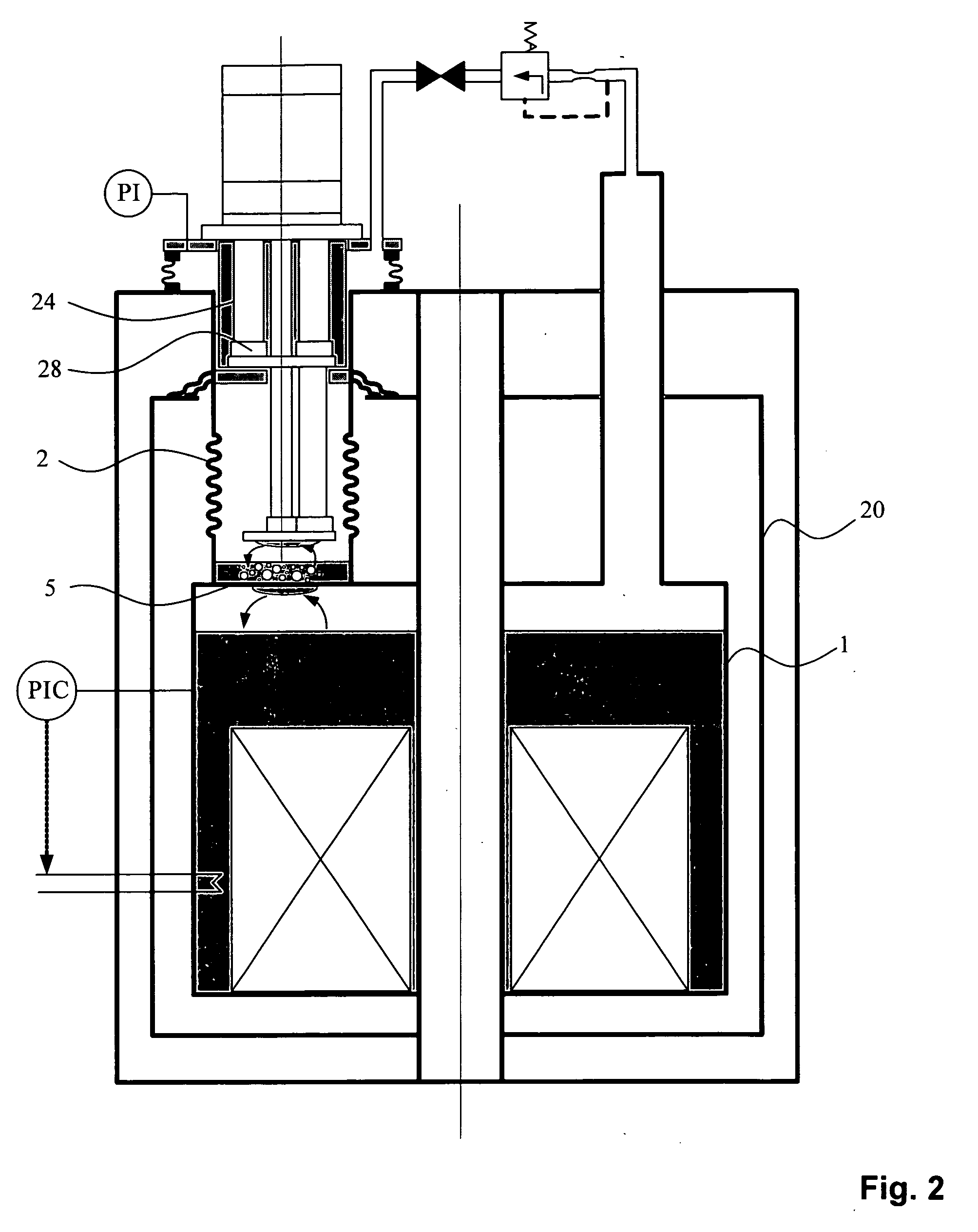
ActiveUS20060096301A1Reduce temperature lossReduce energy lossMagnetic measurementsCompression machinesEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
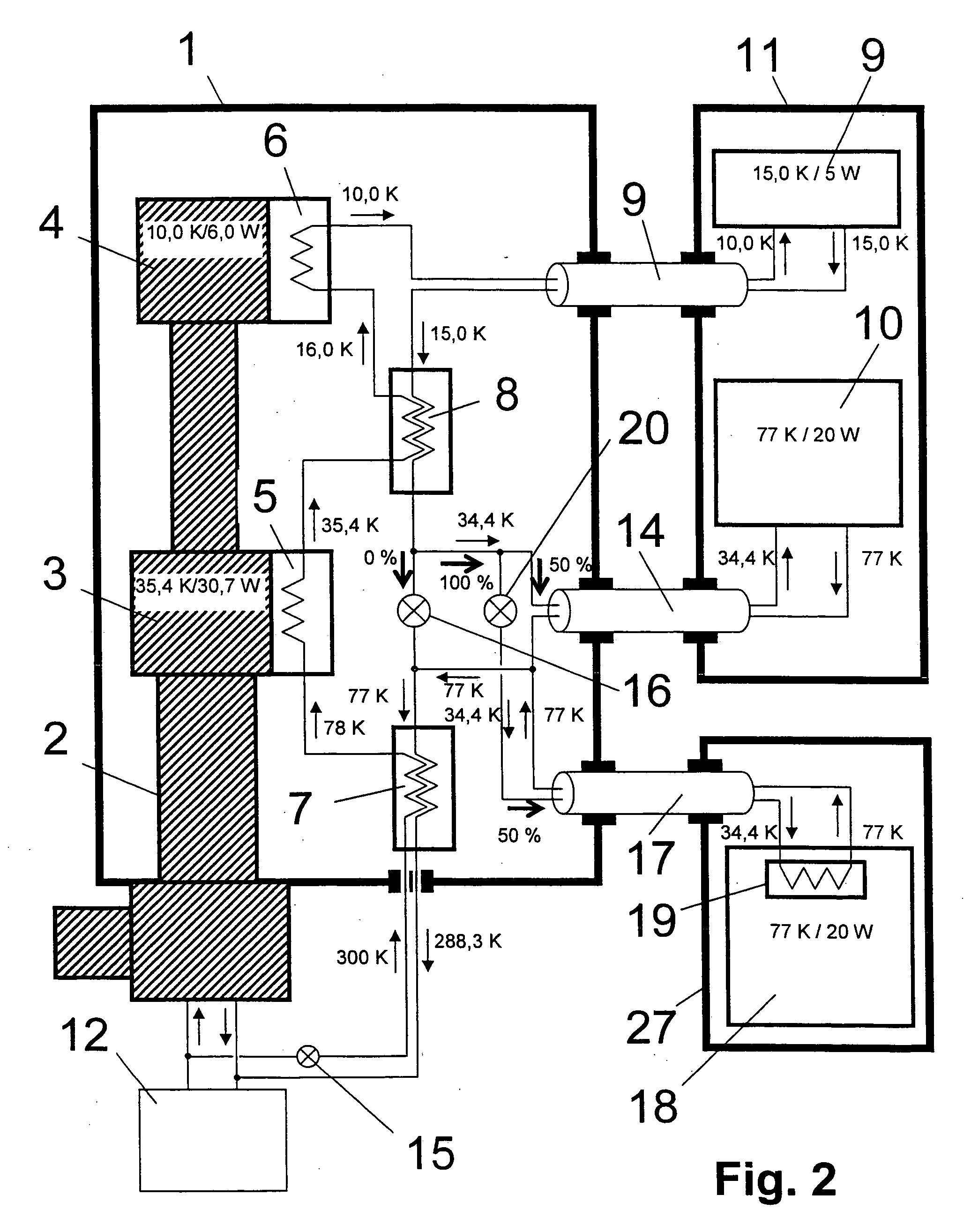
An NMR spectrometer comprising an NMR magnet system (27) disposed in a helium tank of a cryostat and an NMR probe head (11) disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat, which contains a cooled RF resonator (9) for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be investigated, and a cooled pre-amplifier (10), wherein the NMR probe head (11) is cooled by a common multi-stage compressor-operated refrigerator (2), wherein the refrigerator (2) comprises a cold head and several heat exchangers (5, 6) at different temperature levels, wherein the refrigerator (2) is disposed at a spatial separation from the cryostat in a separate, evacuated and thermally insulated housing (1) and wherein at least one cooling circuit with cooling lines, which are thermally insulated by a transfer line (13, 14) is disposed between the housing (1) containing the heat exchangers (5, 6) and the NMR probe head (11), is characterized in that additional cooling lines to an LN2 tank (18) or radiation shield (21) disposed in the cryostat and surrounding the helium tank are provided, and the refrigerator (2) also cools the LN2 tank (18) or the radiation shield (21). The inventive NMR spectrometer comprises a simple and inexpensive device for matching the holding time of LN2 to that of LHe through cooling the LN2 tank using the refrigerator provided for cooling the NMR probe head and without great expense.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus provided with means for preventing closed loop circuit formation across and between inside and outside of cryostat
InactiveUS7304478B2Guaranteed uptimeElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic measurementsClosed loopEXAMINATION ROOM
A MRI apparatus includes a super-conducting magnet including a superconducting coil circuit having a super-conducting coil and a permanent current switch for controlling permanent current flowing through the super-conducting coil; at least one electrical circuit which is electrically connected to at least one electrical element and disposed at the outside of the super-conducting magnet; a gradient magnetic filed generating means; a high frequency magnetic field generating means; and shielded examination room which accommodates the super-conducting magnet. The apparatus further comprises means for interrupting noise current generated based on tomographic image measurement of the subject. Said means is disposed outside the super-conducting magnet and inside the shielded examination room while being inserted between the electrical circuit and the super-conducting magnet.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
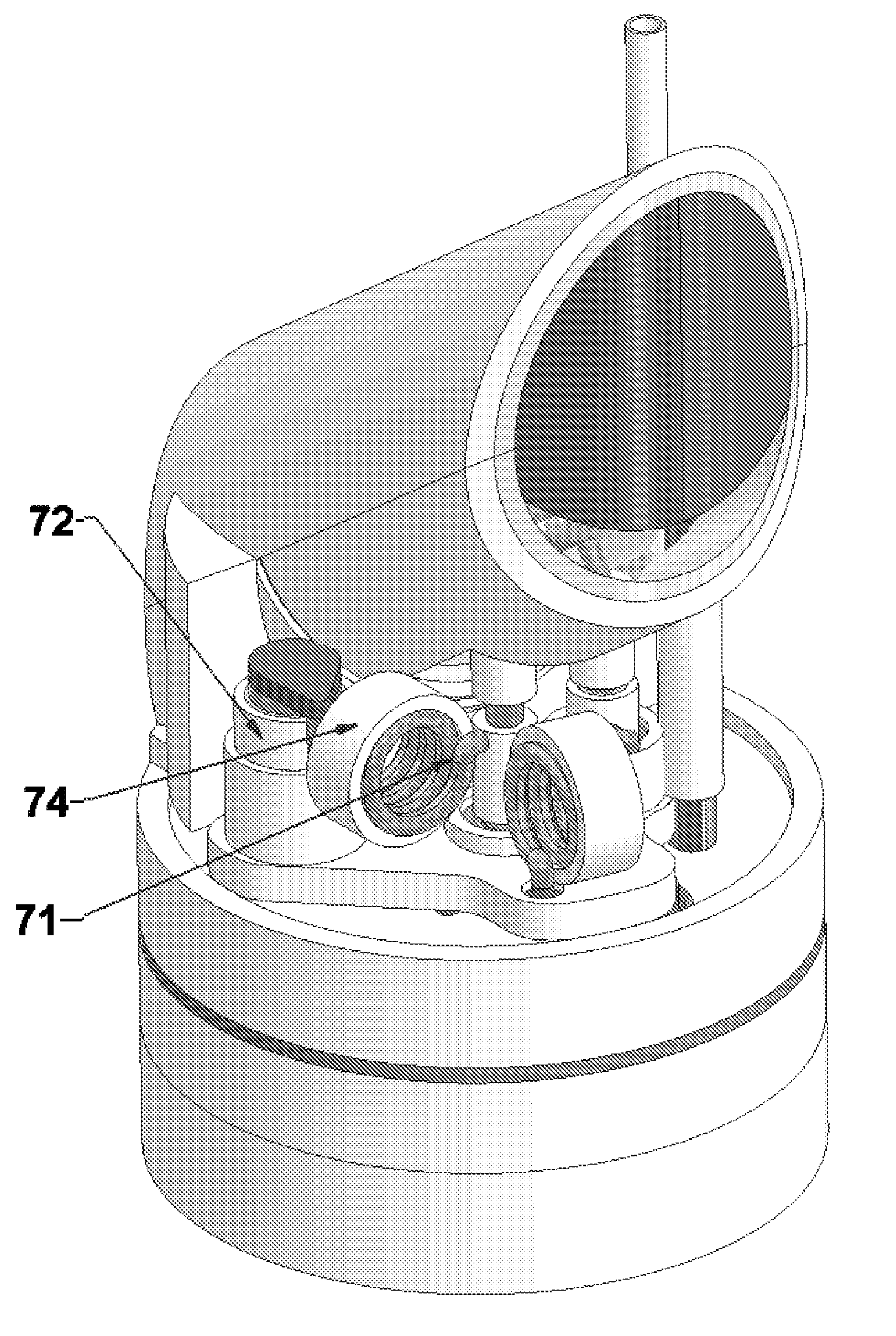
Gas liquifier
A cryocooler for liquefying gas in which the neck of the dewar or cryostat includes a cold end of a cryocooler with the first stage cooling station, the first stage regenerator, the second stage cooling station, the second stage regenerator, and a condenser thermally coupled to the second cooling station. Radiation baffles are also present within the neck portion of the dewar between the storage portion for the dewar and the condenser, such that when the cryocooler is turned off, the radiation baffles reduce heat radiation on the cryogen in the storage section of the dewar.
Owner:CRYOMECH
Active-passive electromagnetic shielding to reduce MRI acoustic noise
InactiveUS7375526B2Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
The present invention provides an apparatus for reducing acoustic noise in a magnetic resonance imaging device including passive shielding located outside the actively shielded gradient winding elements in order to reduce the magnitude of fields that spread outside the gradient coil assembly in unwanted directions and interact with the magnet cryostat or other metallic magnet parts, inducing eddy currents that cause consequent acoustic noise. The passive shielding elements are conducting layers located on the outer radius of the cylindrical gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, conducting layers located at the ends of the gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, and conducting layers located inside the actively shielded gradient winding inner elements in a cylindrical magnet system. The passive shielding could also be located on separate structures that are vibrationally isolated from the magnet cryostat. The actively shielded gradient winding can also be extended to portions at the ends of the actively shielded gradient winding and further to portions inside the inner radius of the inner portion of the actively shielded gradient winding. The actively shielded gradient windings and passive shielding should be designed concurrently in order to substantially optimize the gradient linearity and reduce the eddy currents generated in metallic parts of the magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHARKSTONE
Active-passive electromagnetic shielding to reduce MRI acoustic noise
InactiveUS7141974B2Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionEddy currentElectromagnetic shielding
The present invention provides an apparatus for reducing acoustic noise in a magnetic resonance imaging device including passive shielding located outside the actively shielded gradient winding elements in order to reduce the magnitude of fields that spread outside the gradient coil assembly in unwanted directions and interact with the magnet cryostat or other metallic magnet parts, inducing eddy currents that cause consequent acoustic noise. The passive shielding elements are conducting layers located on the outer radius of the cylindrical gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, conducting layers located at the ends of the gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, and conducting layers located inside the actively shielded gradient winding inner elements in a cylindrical magnet system. The passive shielding could also be located on separate structures that are vibrationally isolated from the magnet cryostat. The actively shielded gradient winding can also be extended to portions at the ends of the actively shielded gradient winding and further to portions inside the inner radius of the inner portion of the actively shielded gradient winding. The actively shielded gradient windings and passive shielding should be designed concurrently in order to substantially optimize the gradient linearity and reduce the eddy currents generated in metallic parts of the magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHARKSTONE
NMR apparatus with commonly cooled probe head and cryogenic container and method for the operation thereof
ActiveUS20070107445A1Improve thermodynamic efficiencyLow heat inputCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesEngineeringRadiation shield
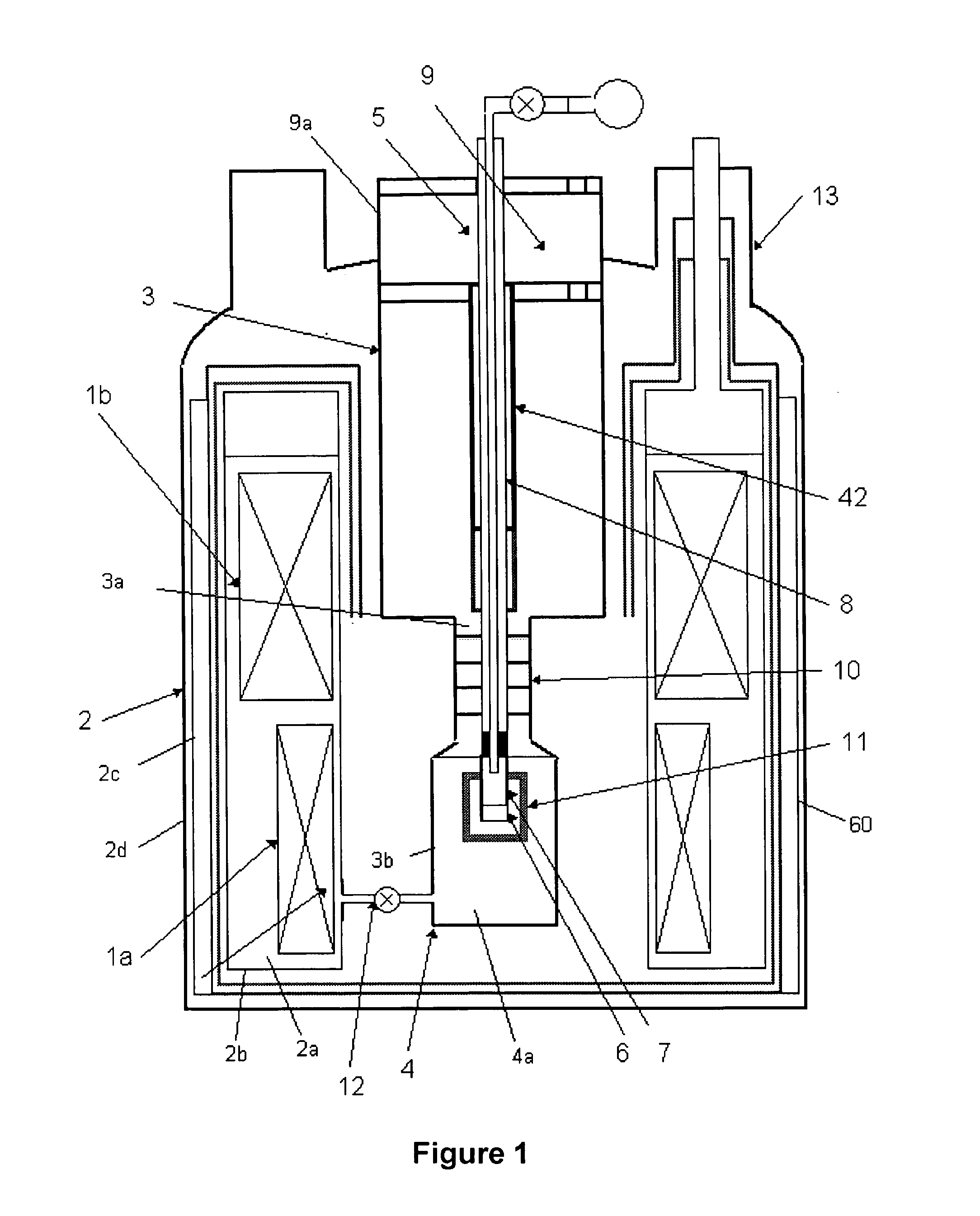
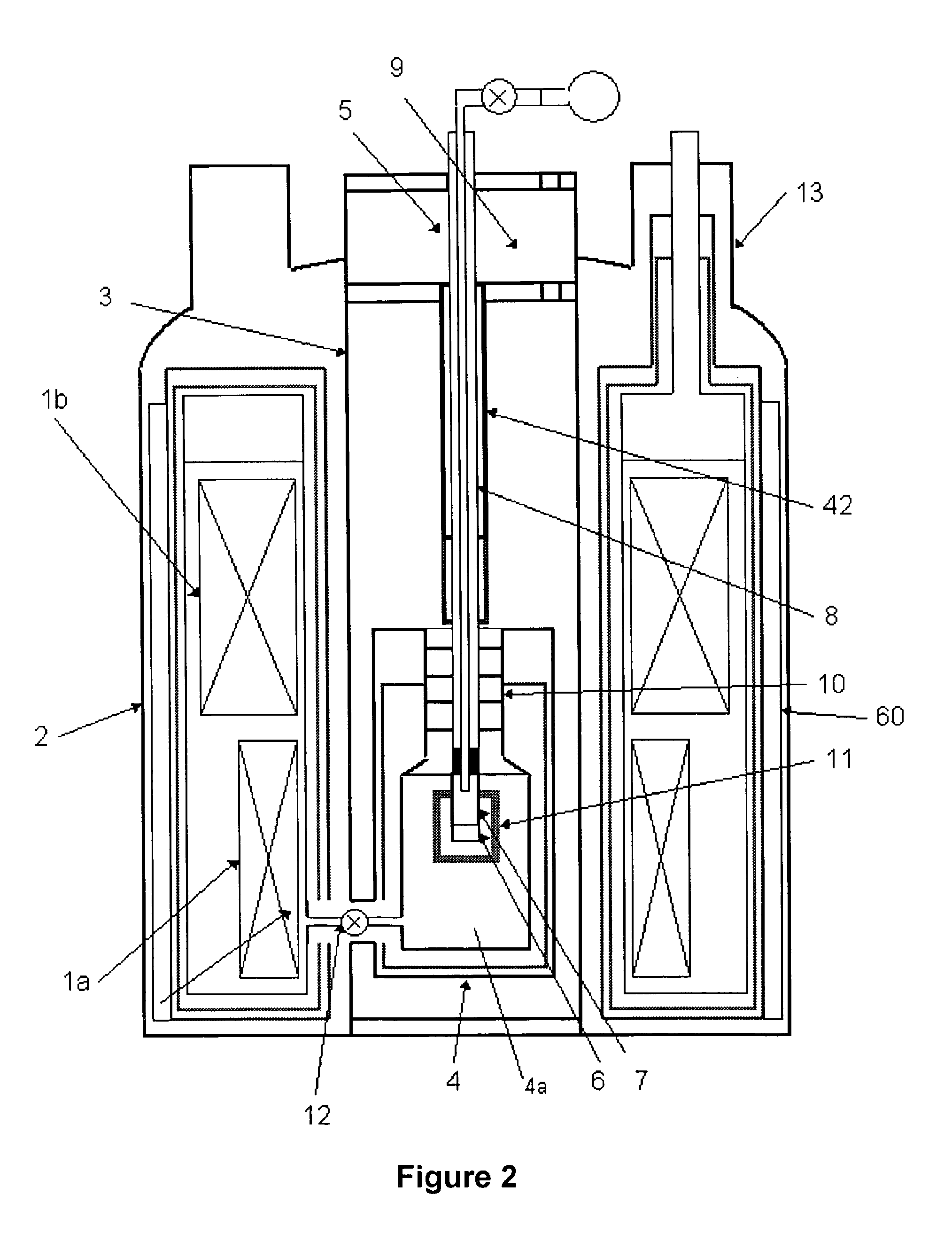
An NMR apparatus comprising an NMR magnet system disposed in a first cryocontainer (2) of a cryostat (9), and an NMR probe head (1), wherein the first cryocontainer (2) is installed in an evacuated outer jacket and is surrounded by a radiation shield (24) and / or a further cryocontainer (3), wherein a cooling device is provided for cooling the NMR probe head (1) and a cryocontainer (2, 3), which comprises a cold head (4, 4a, 4b, 4c) with several cold stages (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a), wherein one cold stage (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a) is connected to a heat-transferring device, and wherein a cooling circuit is provided between the cooling device and the NMR probe head (1), is characterized in that the cooling device is disposed in a separate, evacuated housing (6) which is positioned directly above the cryostat (9), wherein the heat-transferring device is inserted directly into suspension tubes (29a, 29c) of the cryocontainer (2, 3) and / or is in contact with the radiation shield (24). This effects a simple construction that is efficient for cooling an NMR apparatus.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Active-passive electromagnetic shielding to reduce MRI acoustic noise
InactiveUS20080094062A1Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
The present invention provides an apparatus for reducing acoustic noise in a magnetic resonance imaging device including passive shielding located outside the actively shielded gradient winding elements in order to reduce the magnitude of fields that spread outside the gradient coil assembly in unwanted directions and interact with the magnet cryostat or other metallic magnet parts, inducing eddy currents that cause consequent acoustic noise. The passive shielding elements are conducting layers located on the outer radius of the cylindrical gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, conducting layers located at the ends of the gradient coil assembly in a cylindrical magnet system, and conducting layers located inside the actively shielded gradient winding inner elements in a cylindrical magnet system. The passive shielding could also be located on separate structures that are vibrationally isolated from the magnet cryostat. The actively shielded gradient winding can also be extended to portions at the ends of the actively shielded gradient winding and further to portions inside the inner radius of the inner portion of the actively shielded gradient winding. The actively shielded gradient windings and passive shielding should be designed concurrently in order to substantially optimize the gradient linearity and reduce the eddy currents generated in metallic parts of the magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHARKSTONE
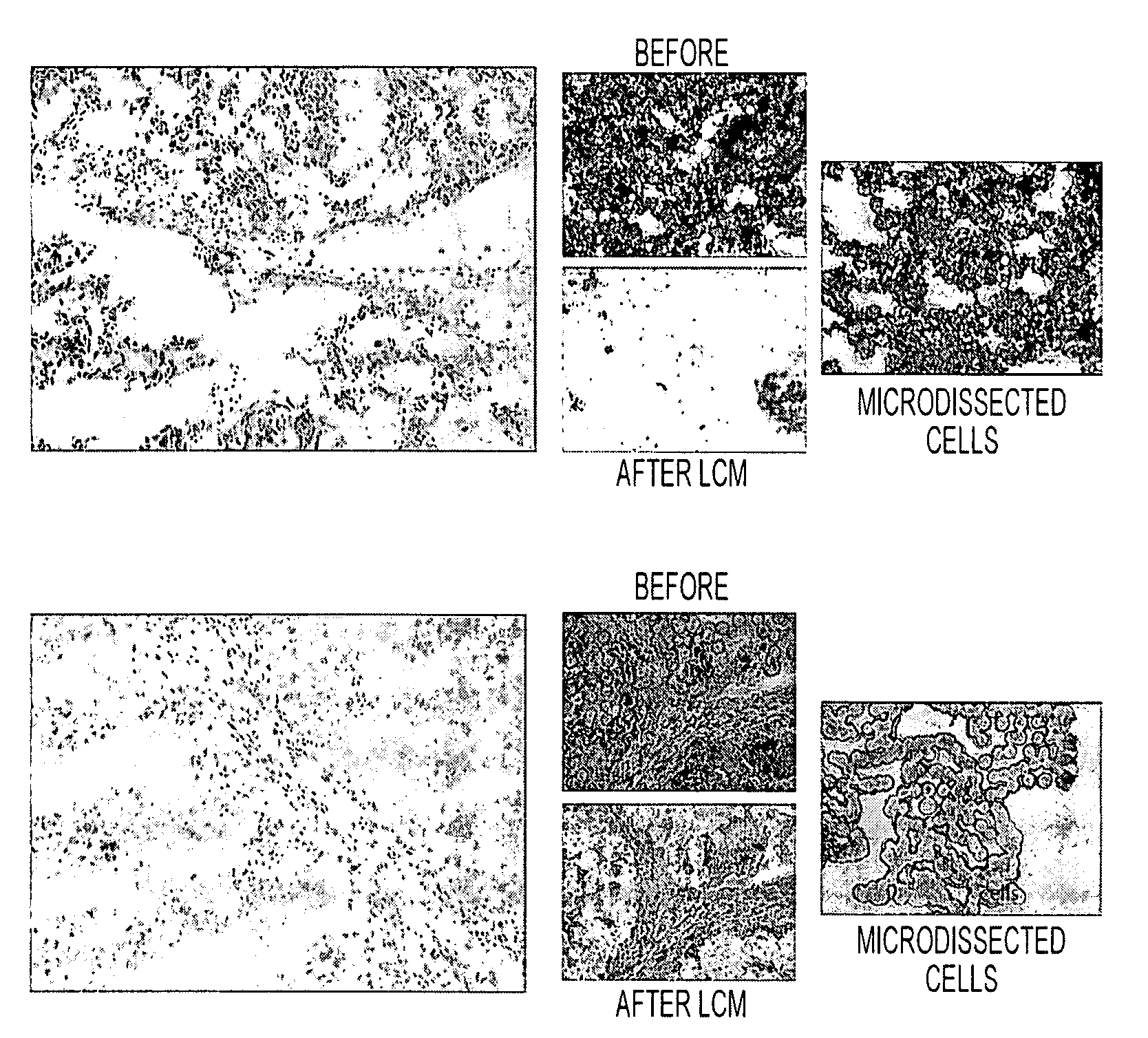
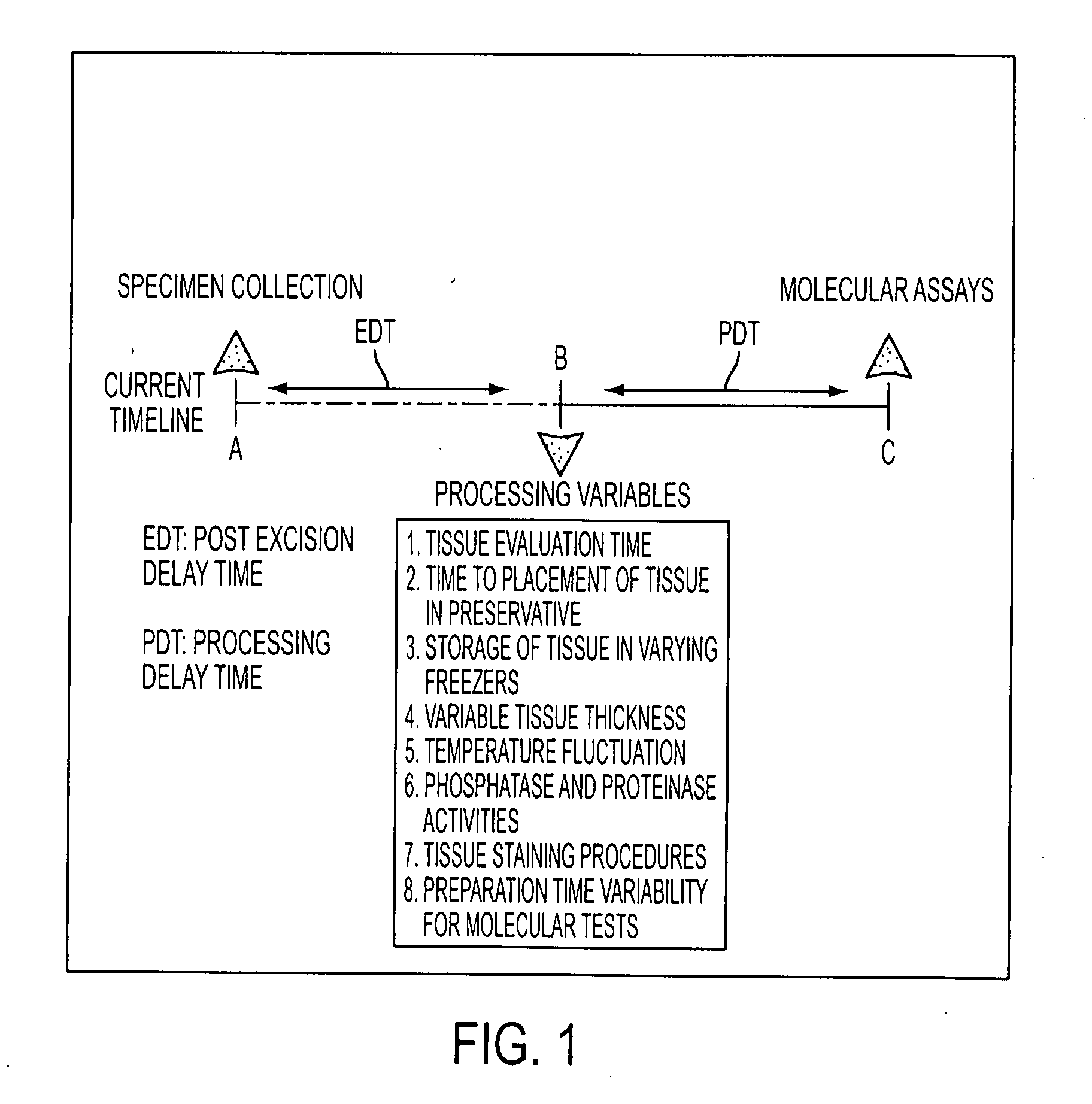
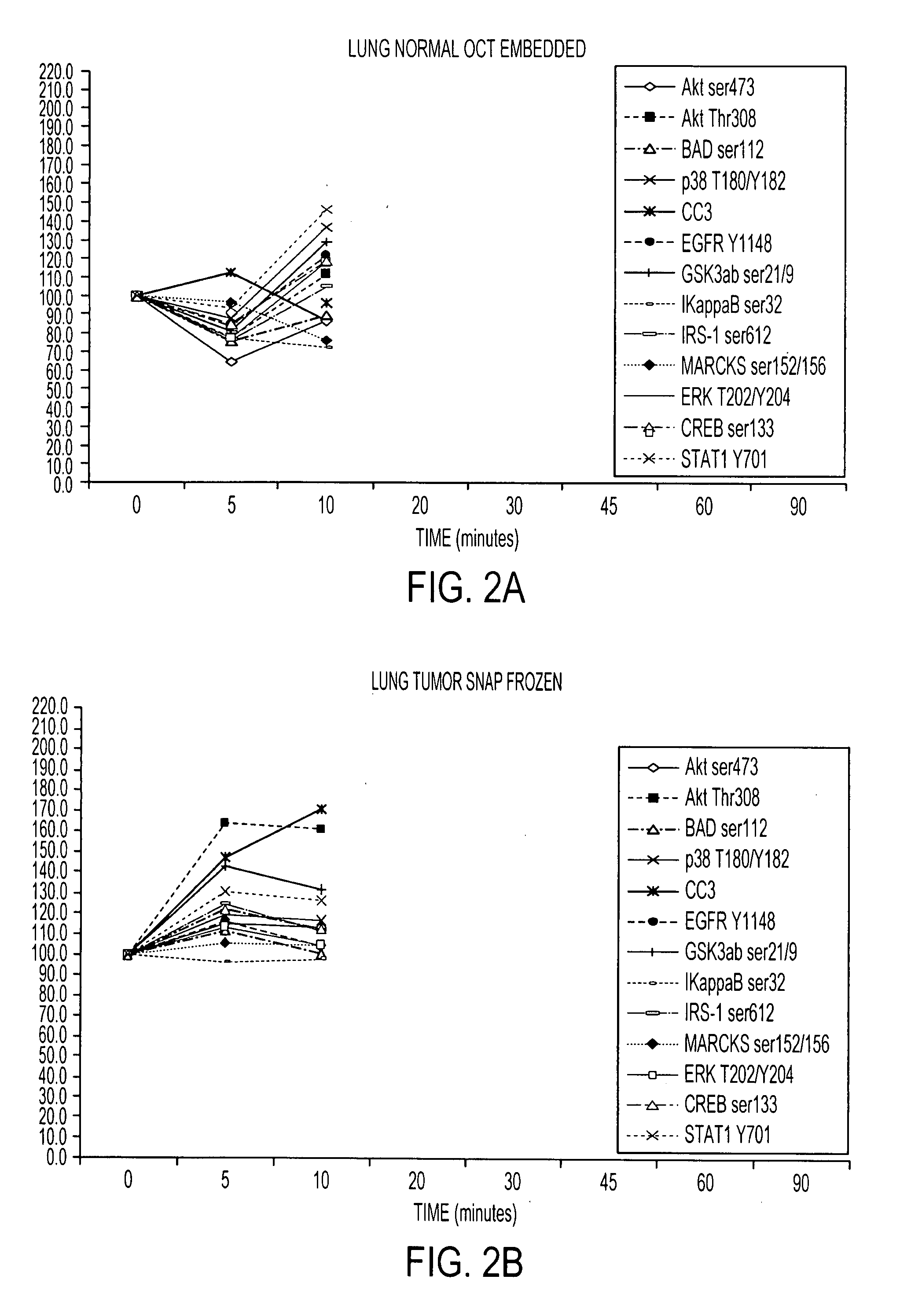
Tissue preservation and fixation method
ActiveUS20100068690A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyPopulation sampleMolecular analysis
This invention relates, e.g., to a composition that, at room temperature, when contacted with a sample comprising phosphoproteins, can fix and stabilize cellular phosphoproteins, preserve cellular morphology, and allow the sample to be frozen to generate a cryostat frozen section suitable for molecular analysis. The composition comprises (1) a fixative that is effective to fix the phosphoproteins, and that has a sufficient water content to be soluble for a stabilizer and / or a permeability enhancing agent); (2) a stabilizer, comprising (a) a kinase inhibitor and (b) a phosphatase inhibitor and, optionally, (c) a protease (e.g., proteinase) inhibitor; and (3) a permeability enhancing agent (e.g. PEG). Methods are described for preserving phosphoproteins, using such a composition. Also described are endogenous surrogate markers for monitoring protein degradation, including the loss of posttranslational modifications (such as phosphorylation), e.g. the following removal of a cell or tissue from a subject; and exogenous molecular sentinels (e.g. phosphoproteins attached to magnetic nanoparticles) that allow one to evaluate the processing history of a cellular or tissue population sample.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
Magnetic field measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20020050815A1Reduce weightLow priceMagnetic/electric field screeningSuperconductor detailsEngineeringNon magnetic
A magnetic field measuring apparatus has a magnetic field shielding apparatus including non-magnetic cylindrical members on which high-permeability sheets are located in a state of being partially overlapped with each other. The cylindrical members are located to surround an axis of a first direction concentrically and having a hollow portion, the cylindrical member located on an innermost-side having a first opening at one end of the first direction, a second opening at the other end of the first direction, and a third opening penetrating the cylindrical members in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the first direction. In addition, the magnetic field measuring apparatus has a living-body holder located in an inner-side space of the cylindrical member and a cryostat inserted into the third opening and maintaining SQUID magnetic-flux meters.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
NMR CryoMAS Probe for High-field Wide-bore Magnets
InactiveUS20060176056A1Reduce riskImprovement factorElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePartial solutionNitrogen gas
An MAS probe is disclosed for obtaining a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high-field magnets where the magnet's RT shim bore is greater than 60 mm. All critical circuit components, including the sample coils, are located along with the spinner assembly in a thermally insulated cold zone pressurized with helium gas. The spinner assembly attaches to a sealed, curved, rotor-loading tube to permit automatic sample change, and it is surrounded by a partially insulated jacket cooled with a cryogenic fluid, generally nitrogen gas. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, variable temperature operation, field locking, and commonly available closed-cycle cold fingers. One major challenge in implementing CryoMAS is solving the problem of gas leakage from the spinner bearing, drive, and exhaust nitrogen into the cold zone, as some components will necessarily be ceramic, some plastic, and some metal. It is not desirable to use helium for the spinner bearing and drive gases for cost reasons and to prevent risk of degradation of o-ring-sealed magnet cryostats. A pressurized helium atmosphere in the cold zone may be utilized to prevent nitrogen flow from the spinner exhaust streams or atmosphere into the cold zone. The drawback to a pressurized cold zone is that the heat transfer coefficient in dense helium at low temperatures is very high, making it challenging to cool the sample coils and all the large, critical, circuit components in a practical manner. Part of the solution here is to use a first-stage cooling-jacket around the major heat leaks near the spinner exhaust flows. The critical components may be insulated with fine glass wool or teflon foam and conduction cooled without cooling much of the cold zone below the temperature of the first-stage cooling. The use of coaxial sapphire capacitors allows the noise contributions from the most critical capacitors to be reduced to a minor fraction of the total.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Evacuated tube transport system with improved cooling for superconductive elements
InactiveUS20140261055A1Reduce constructionLow costRailway tunnelsRailway componentsHigh-temperature superconductivityTransport system
A High Temperature Superconductor Maglev (HTSM) for Evacuated Tube Transport (ETT) with a magnetic levitation structure for ETT capsule vehicles traveling in an evacuated tube. At least one ETT capsule travels within an evacuated tube, an upper and a lower cryostat respectively mount at the top and bottom of said ETT capsule along the length thereof, at least a plurality of superconductor levitation force elements divided between said upper and lower cryostats. The levitation force being spread over the length of capsule, however substantially concentrated in a compact cross-sectional area. At least a pair of permanent magnetic elements mounted at the top and bottom of the evacuated tube to cooperate with the superconductor elements to levitate the capsule.
Owner:OSTER DARYL
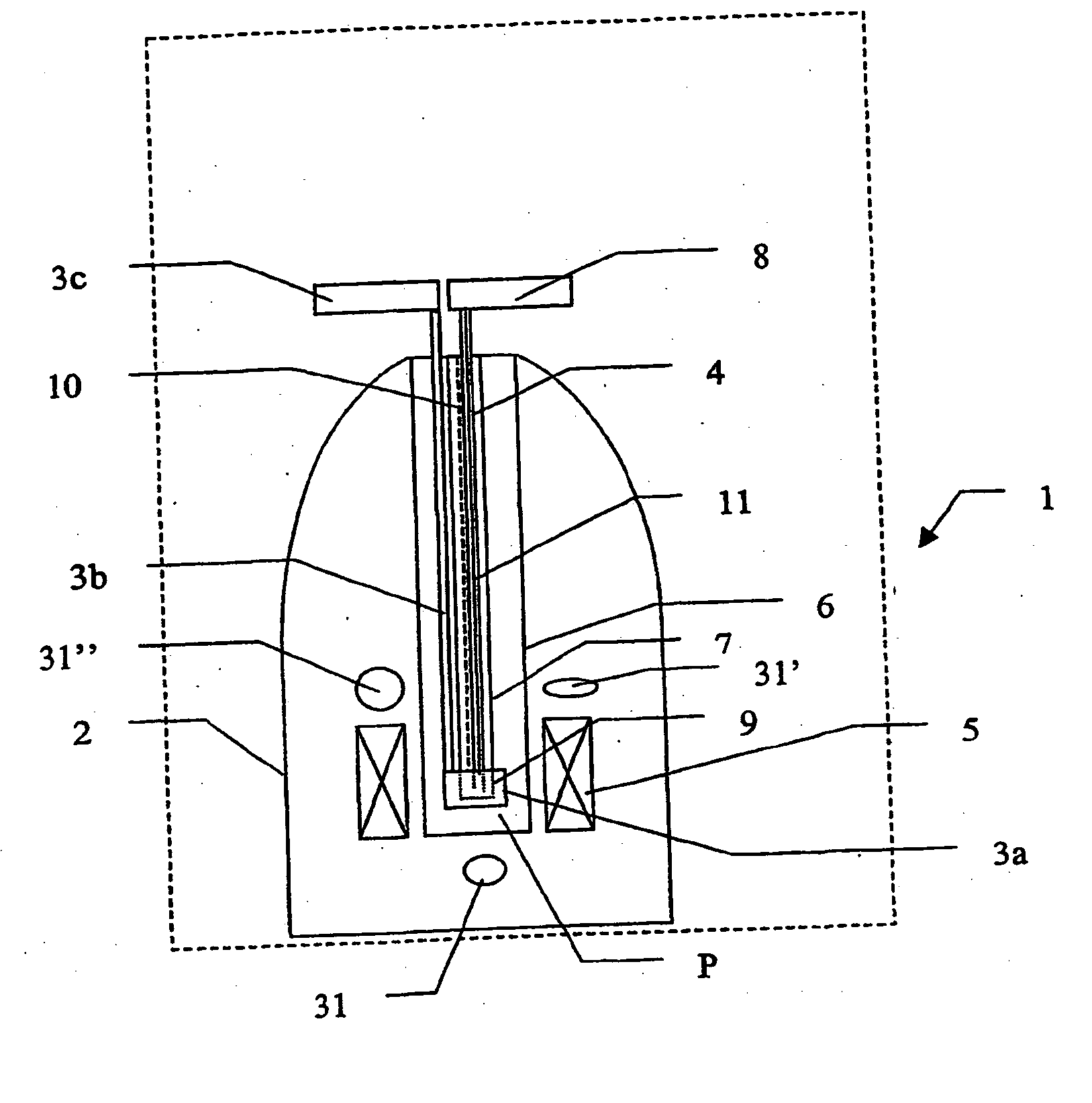
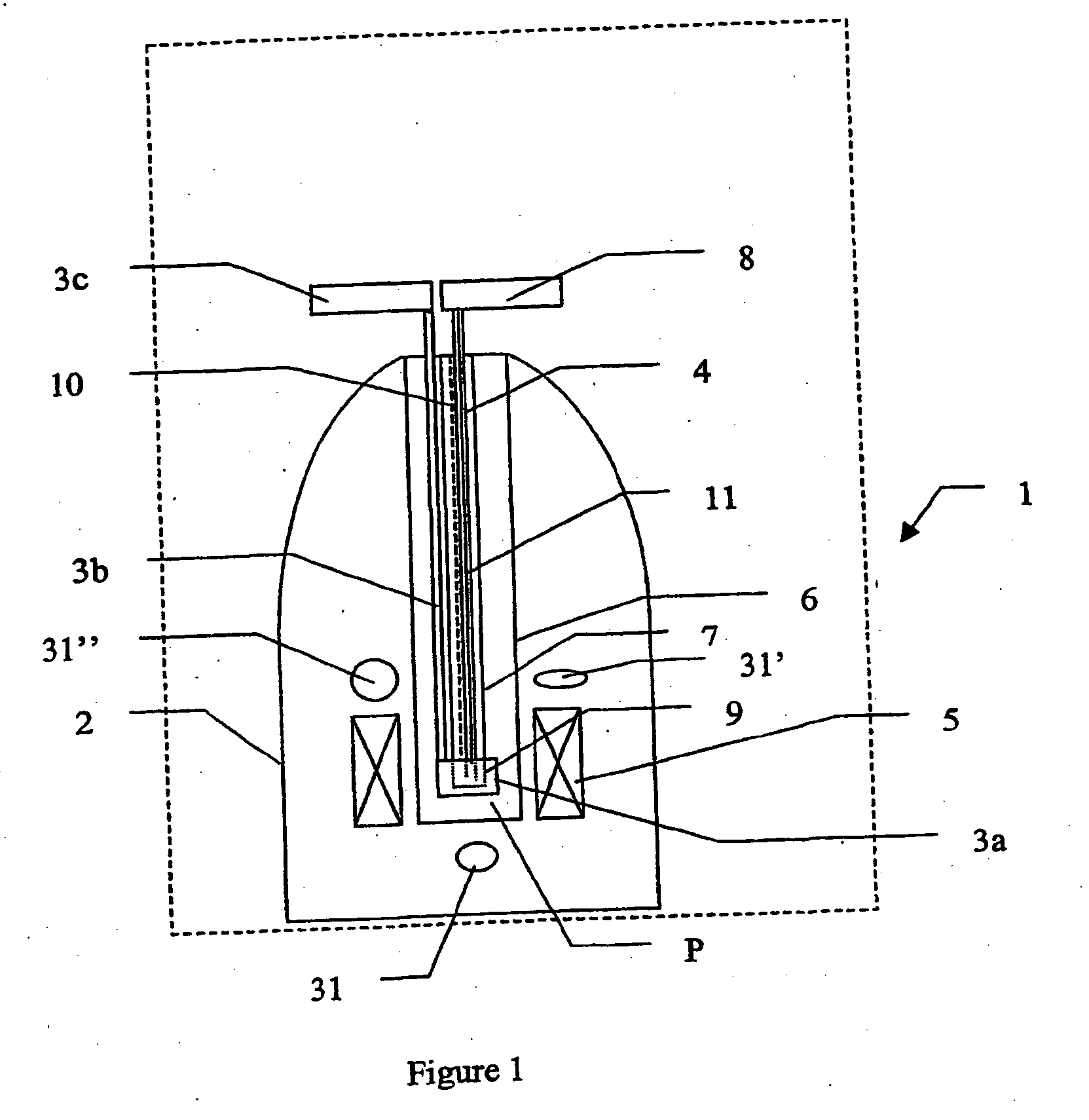
Methods and devices for polarized NMR samples
InactiveUS20060192559A1Preparing sample for investigationMeasurements using double resonanceLaserMagnetic field
The present invention relates to devices and methods for melting a solid polarised sample while retaining a high level of polarisation. In an embodiment of the present invention a sample is polarised in a sample-retaining cup in a strong magnetic field in a polarising means in a cryostat and then melted inside the cryostat by melting means such as a laser connected by an optical fibre to the interior of the cryostat.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR MOLECULAR BIOTOOLS
System for magnetic field distortion compensation and method of making same
ActiveUS20130157865A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentEngineeringEddy current
A system and method for magnetic field distortion compensation includes a cryostat for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. The cryostat includes a vacuum casing having a vacuum therein. A cryogen vessel is disposed within the casing, the vessel having a coolant therein. A thermal shield is disposed between the vacuum casing and the cryogen vessel. An eddy current compensation assembly is disposed within the casing. The eddy current compensation assembly includes a plurality of electrically conductive loops formed on one of the vacuum casing, the cryogen vessel, and the thermal shield and constructed to mitigate vibration-induced eddy currents in the MRI system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
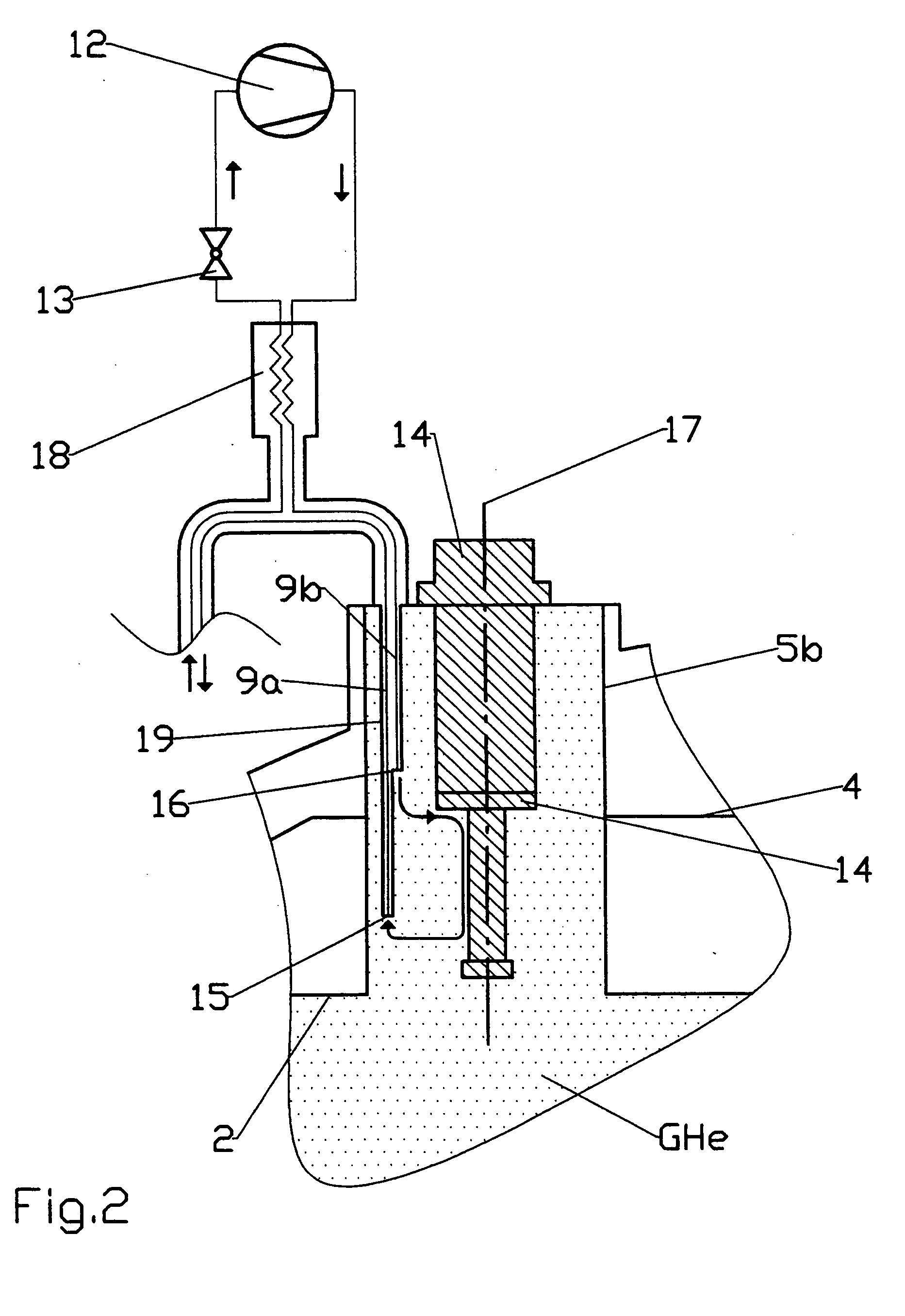
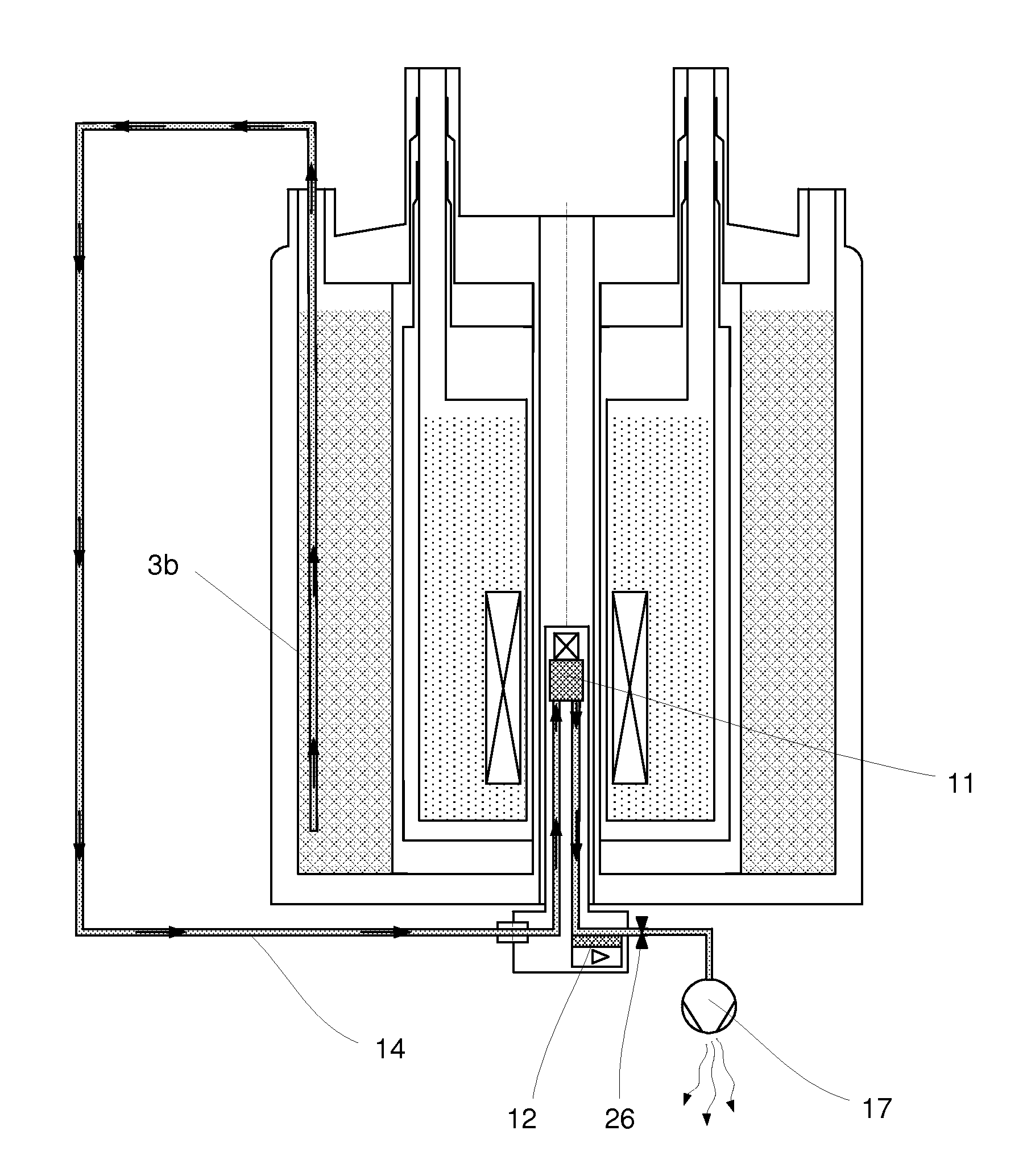
Cryogenic probehead cooler in a nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus
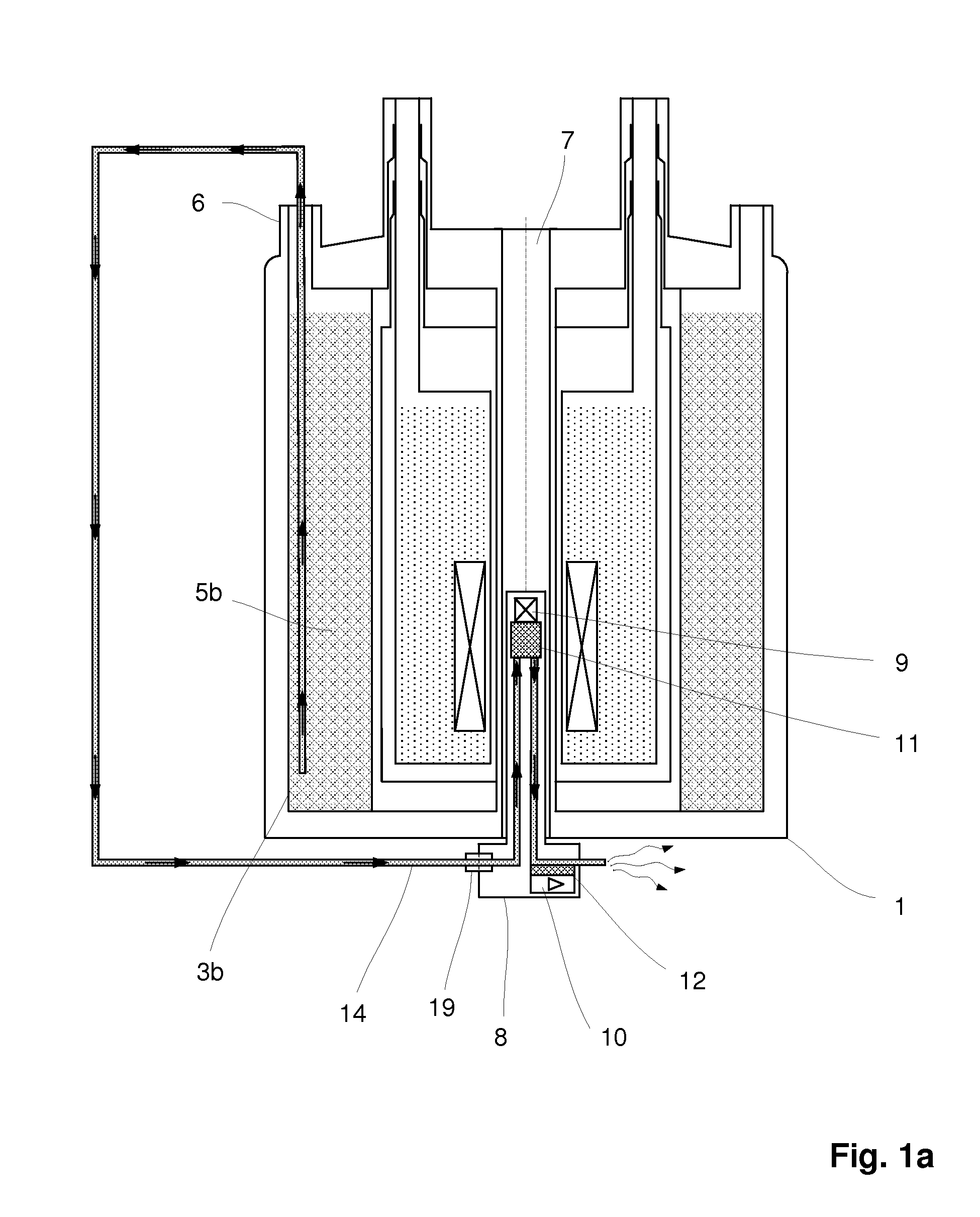
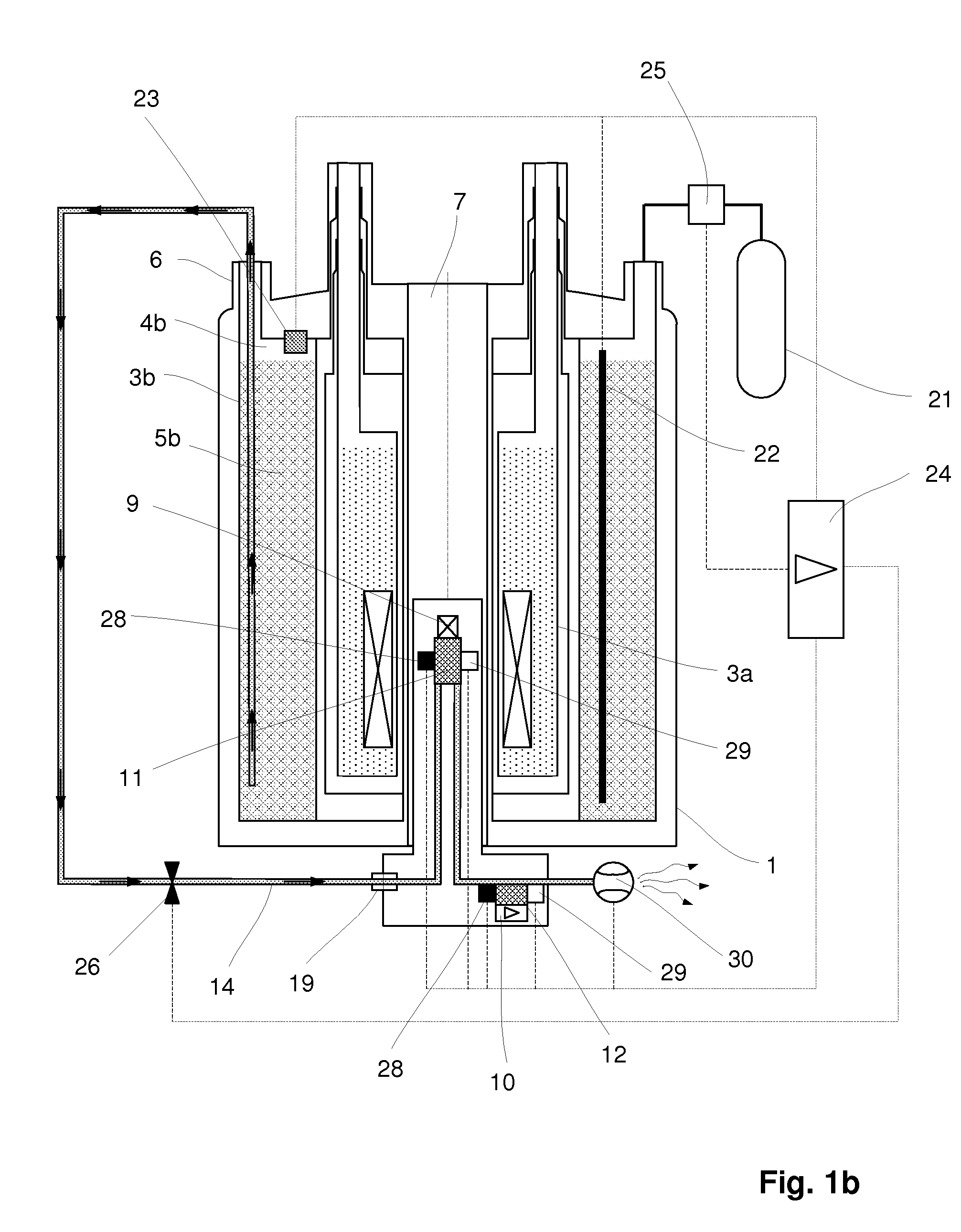
ActiveUS20120242335A1Lower energy requirementsLess cooling energyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceNuclear engineering
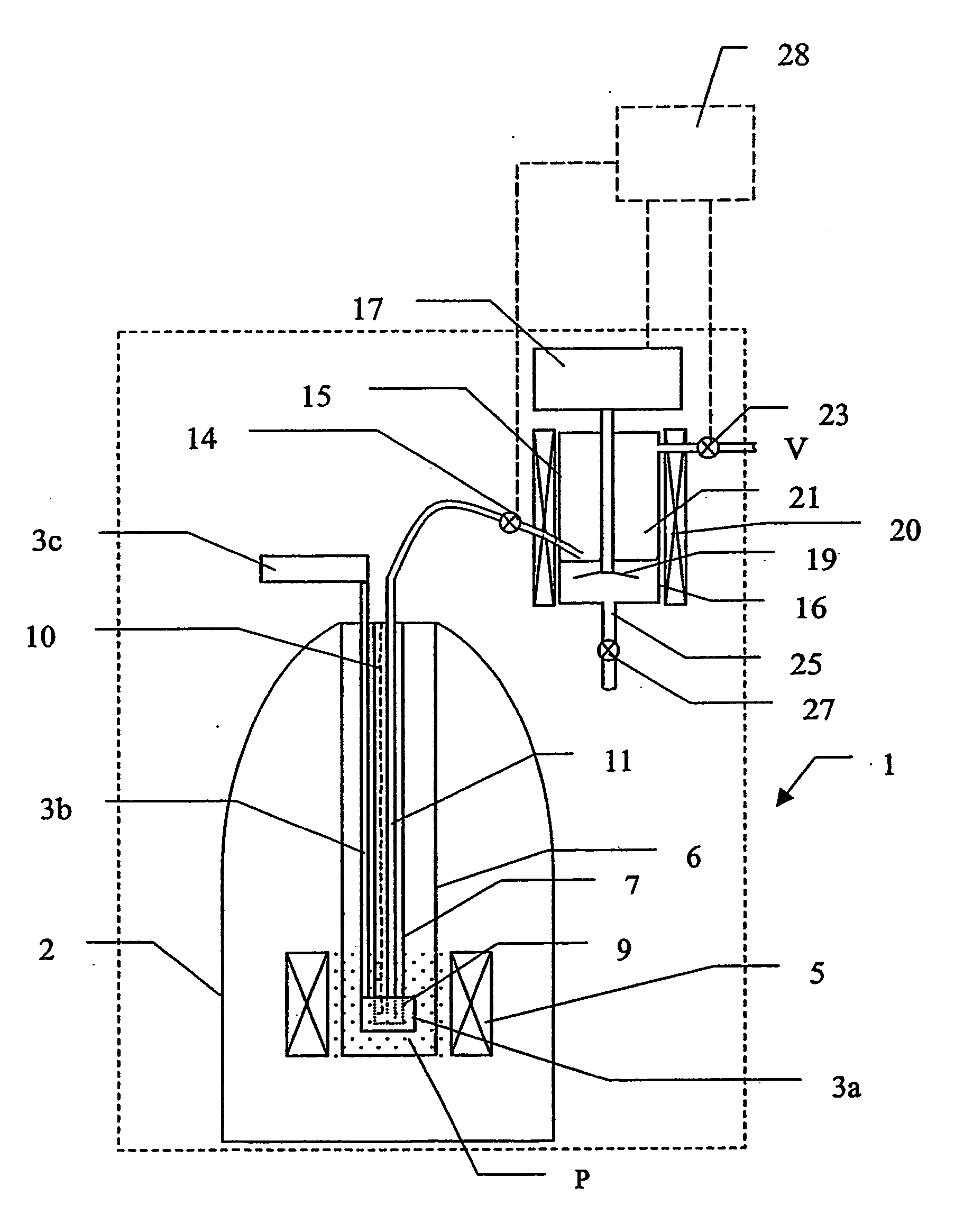
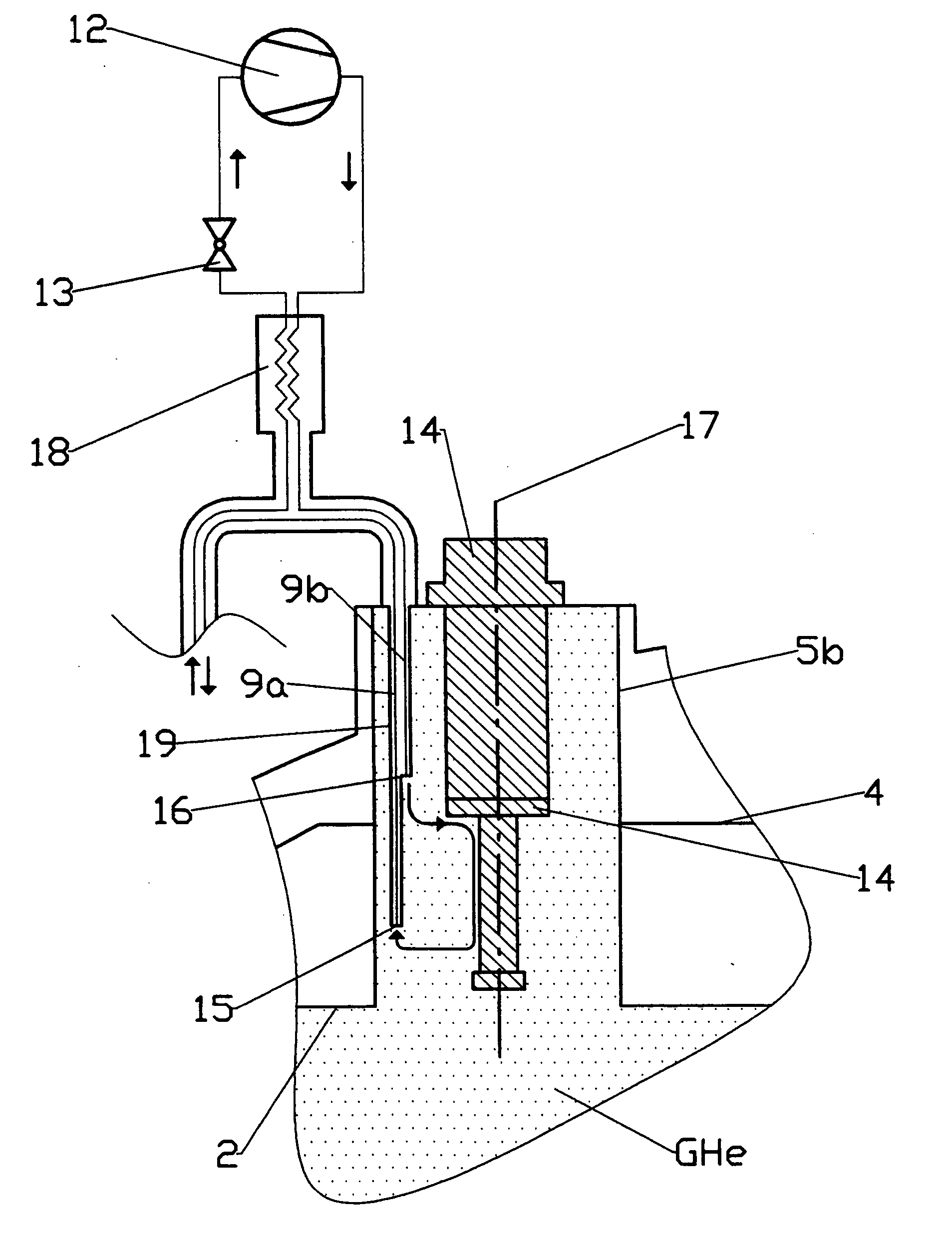
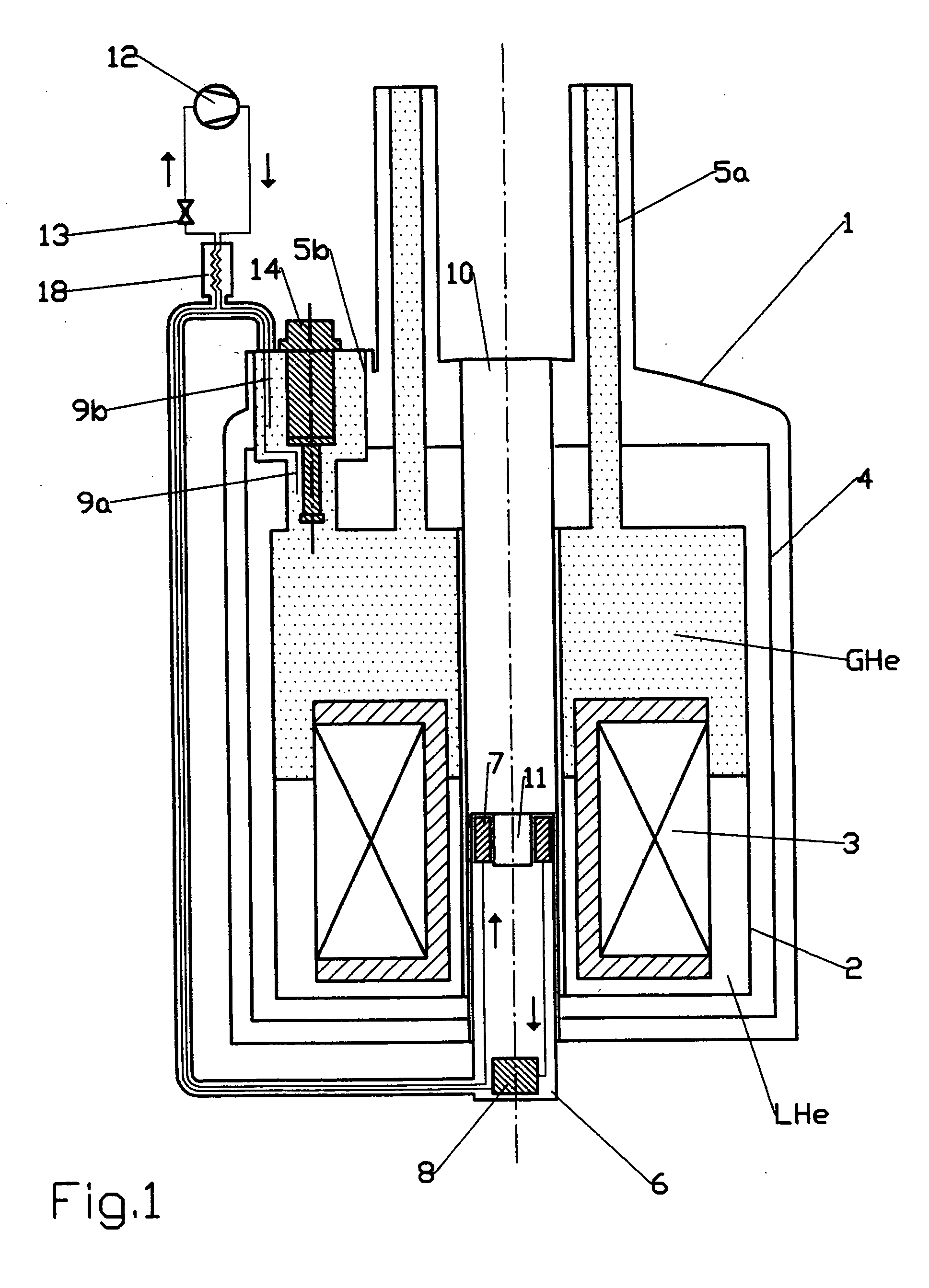
An NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) apparatus has a magnet system disposed in a cryostat (1), the cryostat having at least one nitrogen tank (3b) for receiving liquid nitrogen (5b) and a room temperature bore (7) for receiving an NMR probehead (8), wherein part(s) of the probehead or the overall probehead can be cooled to cryogenic temperatures by supplying liquid nitrogen (5b) via a supply line (14). The nitrogen tank (3b) of the cryostat (1) is connected to the NMR probehead (8) by means of a supply line (14) in such a fashion that liquid nitrogen (5b) is removed from the nitrogen tank (3b) and guided to the NMR probehead (8). The overall apparatus is therefore more compact, the operating comfort of the apparatus is increased, and the costs for acquisition, operation and maintenance are considerably reduced compared to previous comparable devices.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Transportation and/or storage device comprising a double-walled insulating bulb
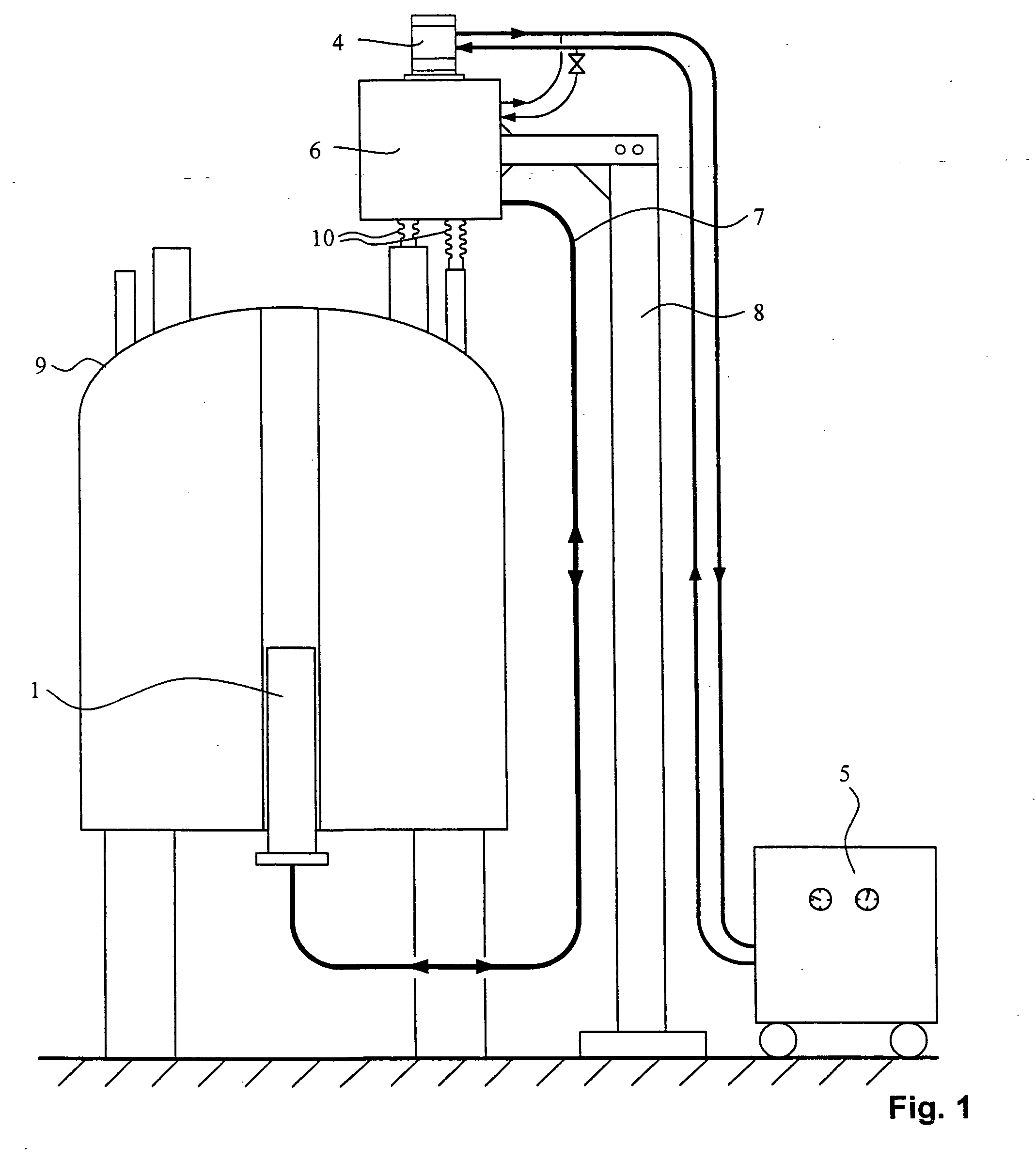
ActiveUS20110056902A1Good mechanical resistanceRisk of severeDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a device (10) for transporting and / or storing products, particularly of cryostat type, having an external packaging structure (14) comprising walls defining an internal volume (16) within which is a double-walled insulating bulb (12) whose body (32) is formed by an outer wall (34) and an inner wall (36) defining an internal volume (38), bulb (12) comprising an upper neck (40) defining an upper filling opening (42), and the device (10) comprising bulb (12) supporting means (46) that comprise attachment means (48) capable of engaging with the inner wall (36) only of bulb (12) in order to suspend the bulb (12) vertically by its neck (40) in such a way that the bulb (12) hangs freely in the empty space inside the internal volume (16) defined by the packaging structure (14, 18, 22), with no contact between the outer wall (34) of the bulb (12) and the walls (24, 22) of the packaging structure (14), said device being characterized in that the means (46) for the suspended support of the bulb (12) consist of at least one (20) of the walls of the packaging (14).
Owner:ST REPRODUCTIVE TECH LLC
Insulation Test Cryostat with Life Mechanism
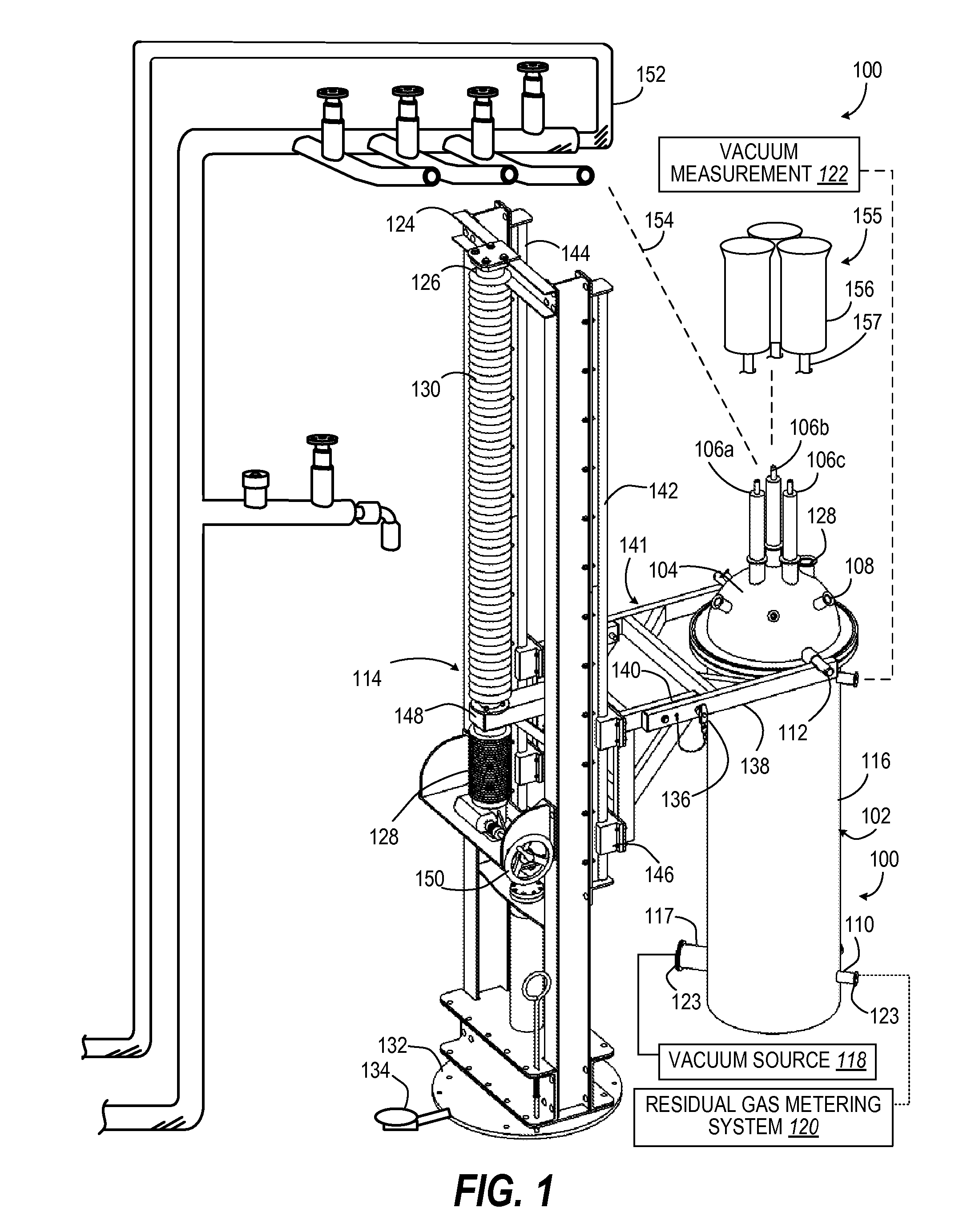
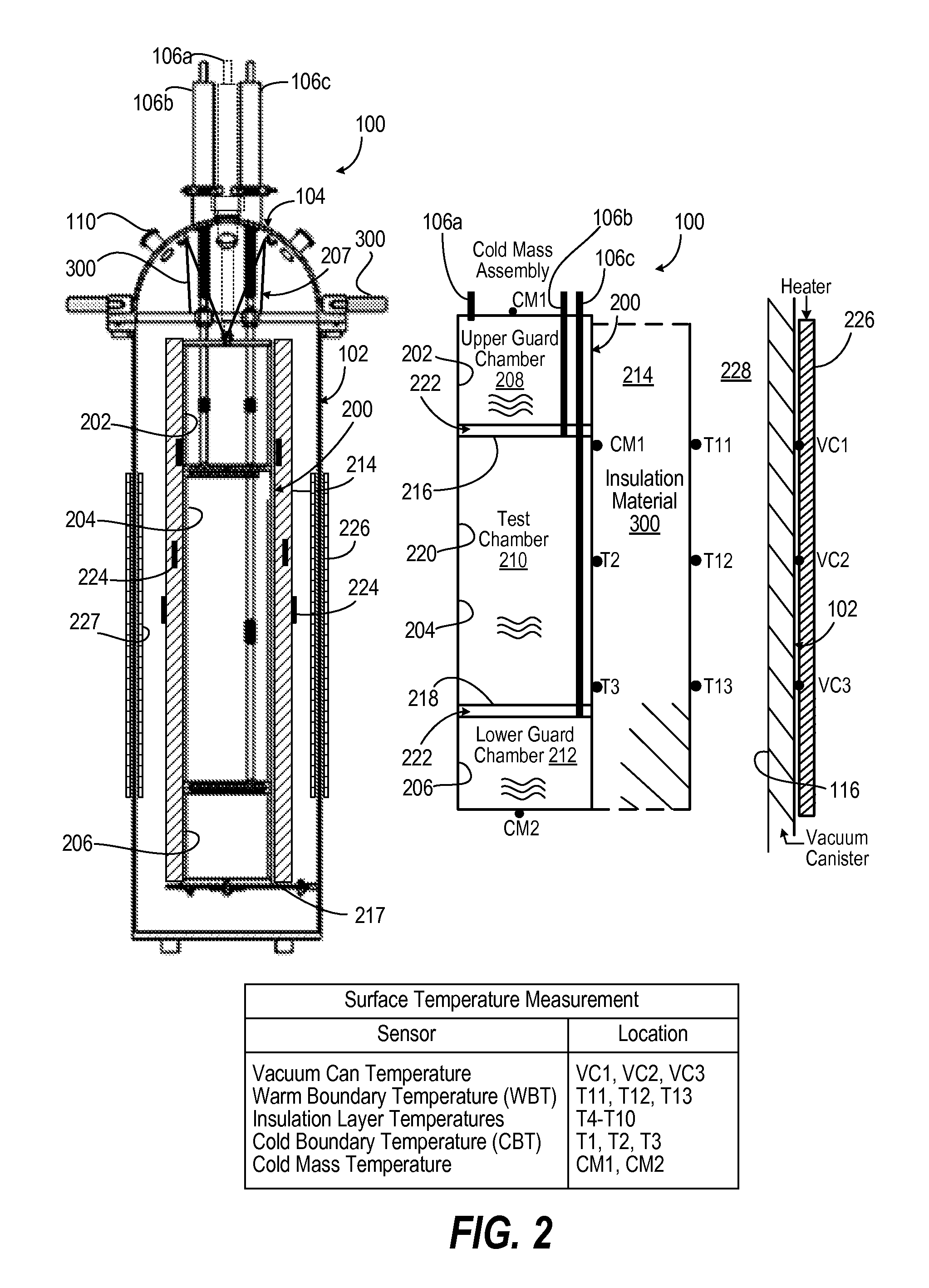
ActiveUS20100318316A1Material thermal conductivityDigital computer detailsHeat fluxThermal insulation
A multi-purpose, cylindrical thermal insulation test apparatus is used for testing insulation materials and systems of materials using a liquid boil-off calorimeter system for absolute measurement of the effective thermal conductivity (k-value) and heat flux of a specimen material at a fixed environmental condition (cold-side temperature, warm-side temperature, vacuum pressure level, and residual gas composition). The apparatus includes an inner vessel for receiving a liquid with a normal boiling point below ambient temperature, such as liquid nitrogen, enclosed within a vacuum chamber. A cold mass assembly, including the upper and lower guard chambers and a middle test vessel, is suspended from a lid of the vacuum canister. Each of the three chambers is filled and vented through a single feedthrough. All fluid and instrumentation feedthroughs are mounted and suspended from a top domed lid to allow easy removal of the cold mass. A lift mechanism allows manipulation of the cold mass assembly and insulation test article.
Owner:NASA
Direct-action superconducting synchronous generator for a wind turbine
InactiveUS20120306212A1Shorten the timeReduce frictionEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesThermal insulationEngineering
The invention refers to a direct drive electric generator for a wind turbine provided with rotor salient poles and a ladder-like cryostat for housing superconductive coils and keeping them at a cryogenic temperature while the interior of the cryostat is kept free of coolant.The invention achieves optimal thermal insulation of the coils without the need of a continuous re-filling of the cryostat and ensuring a good distribution of the magnetic field avoiding the use of expensive materials.
Owner:FUNDACION TECNALIA RES & INNOVATION
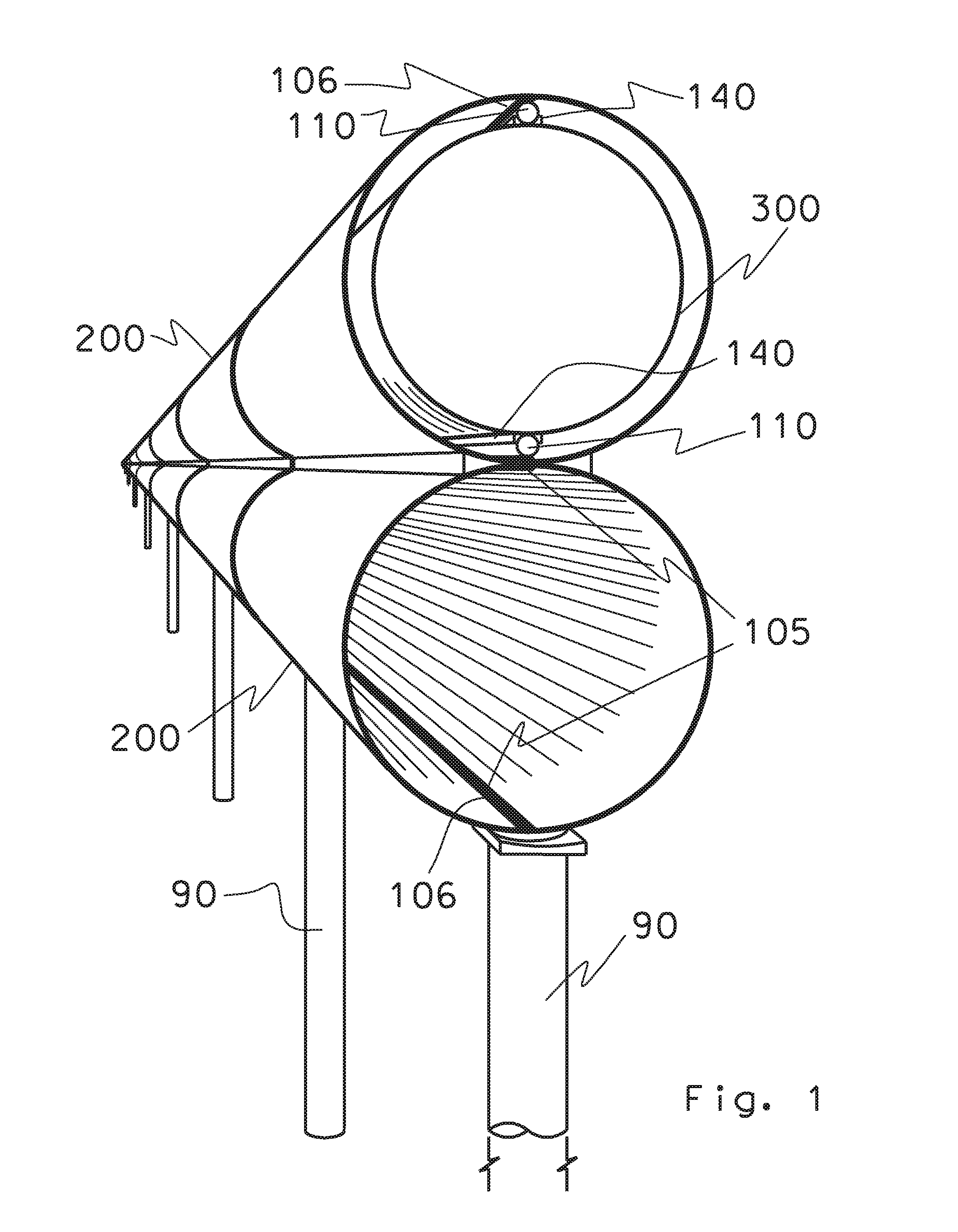
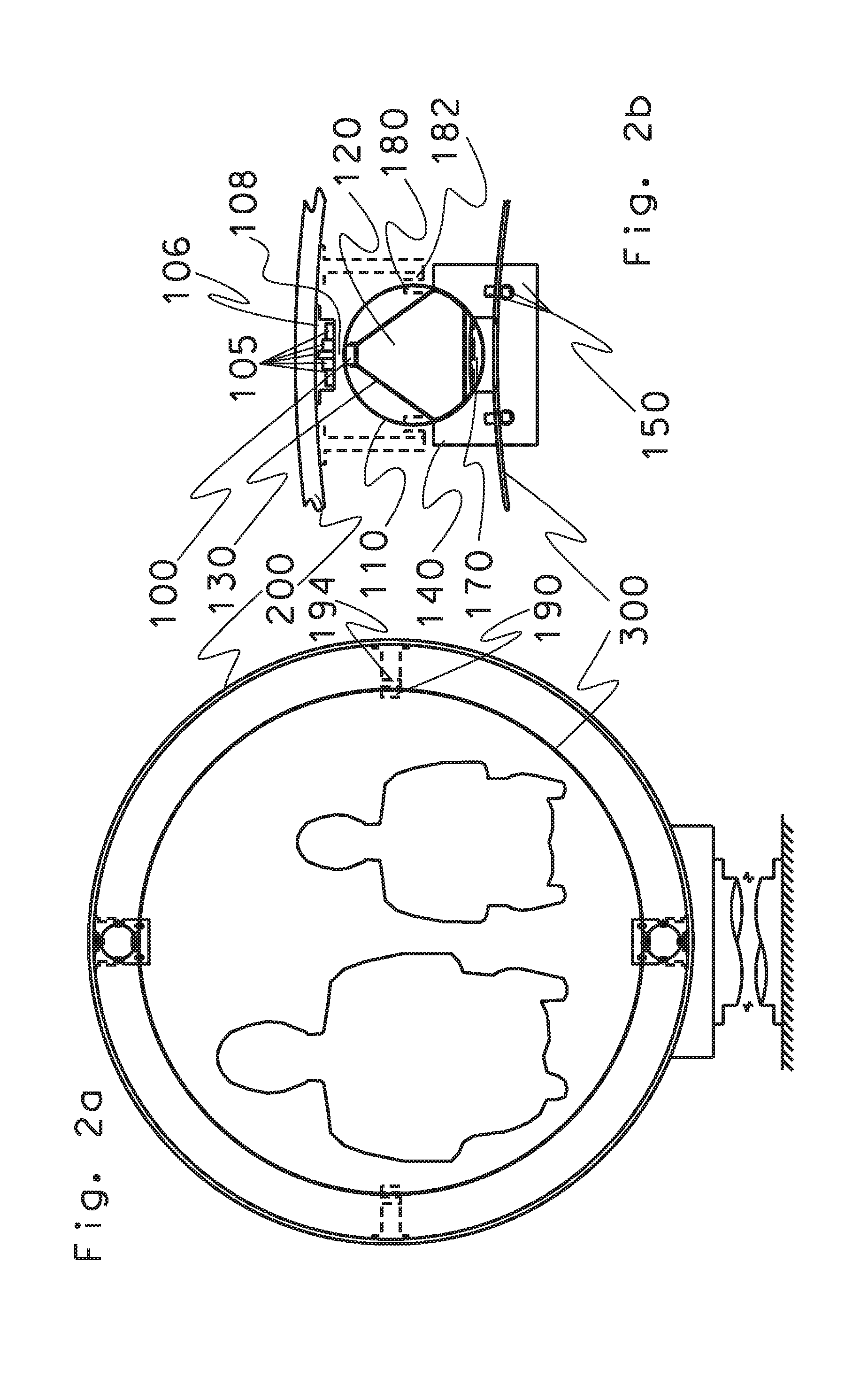
Apparatus and method for performing in-vitro DNP-NMR measurements
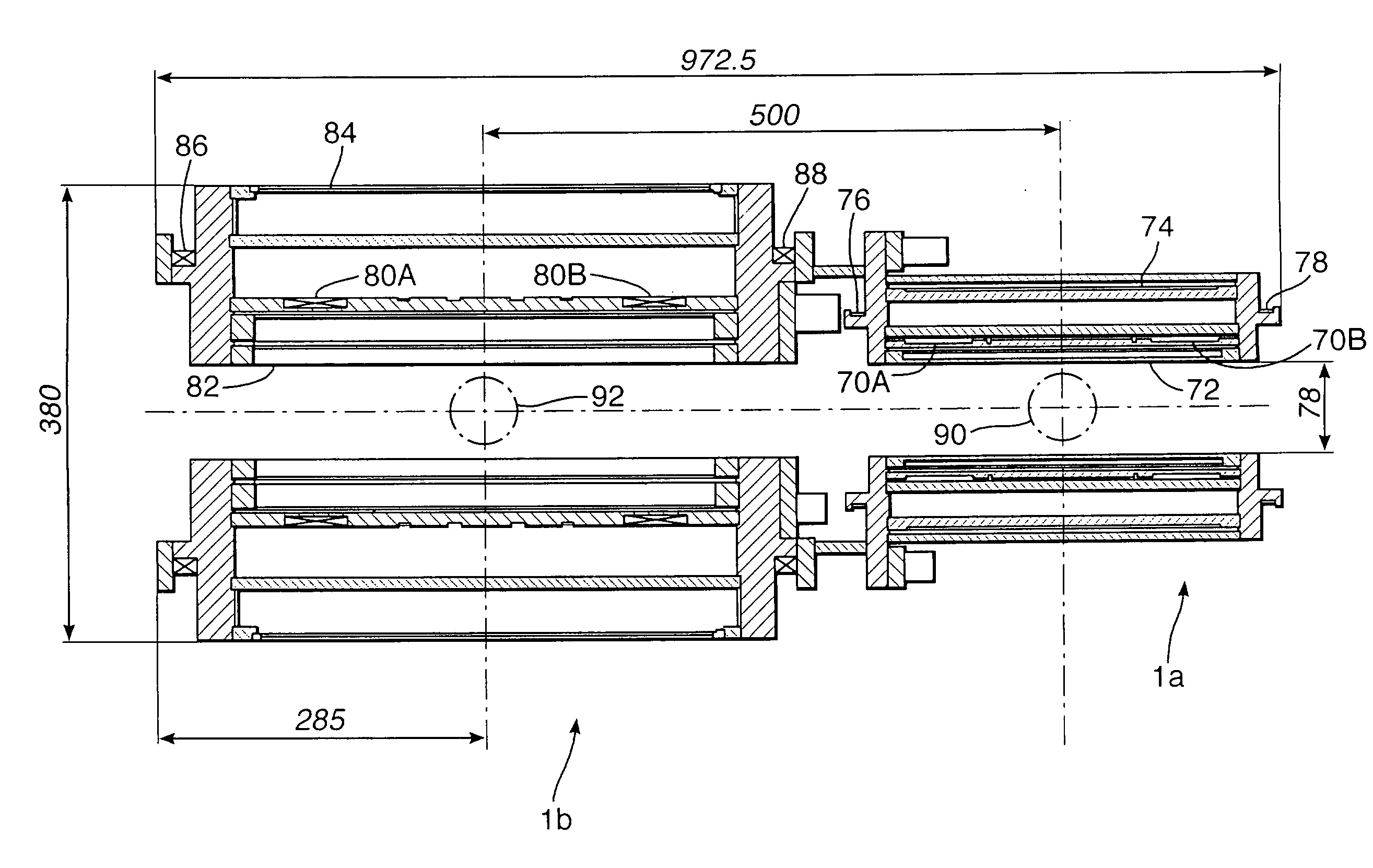
InactiveUS7639007B2Reduce lossesMinimizing reaction forceMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyCryostatMagnetic field
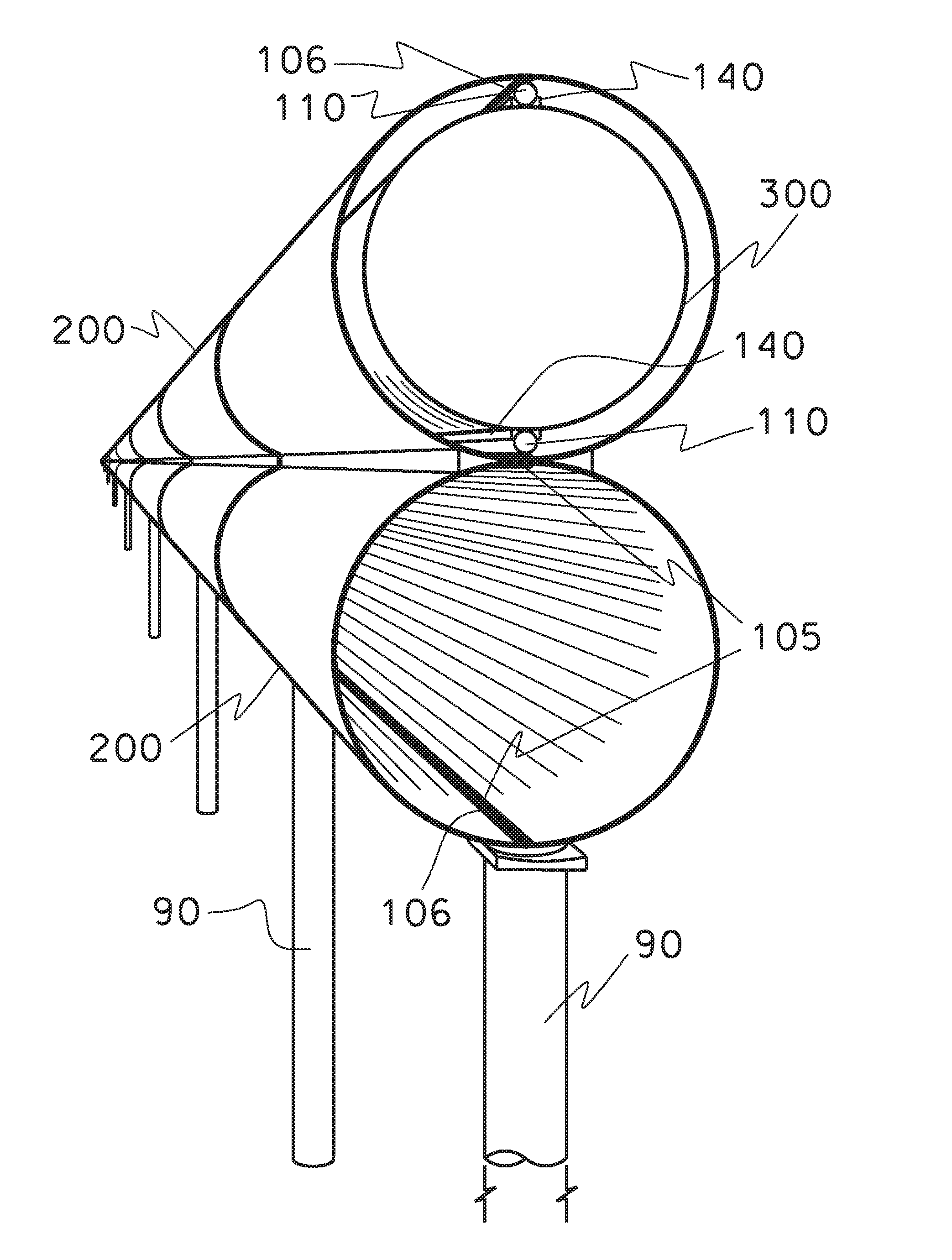
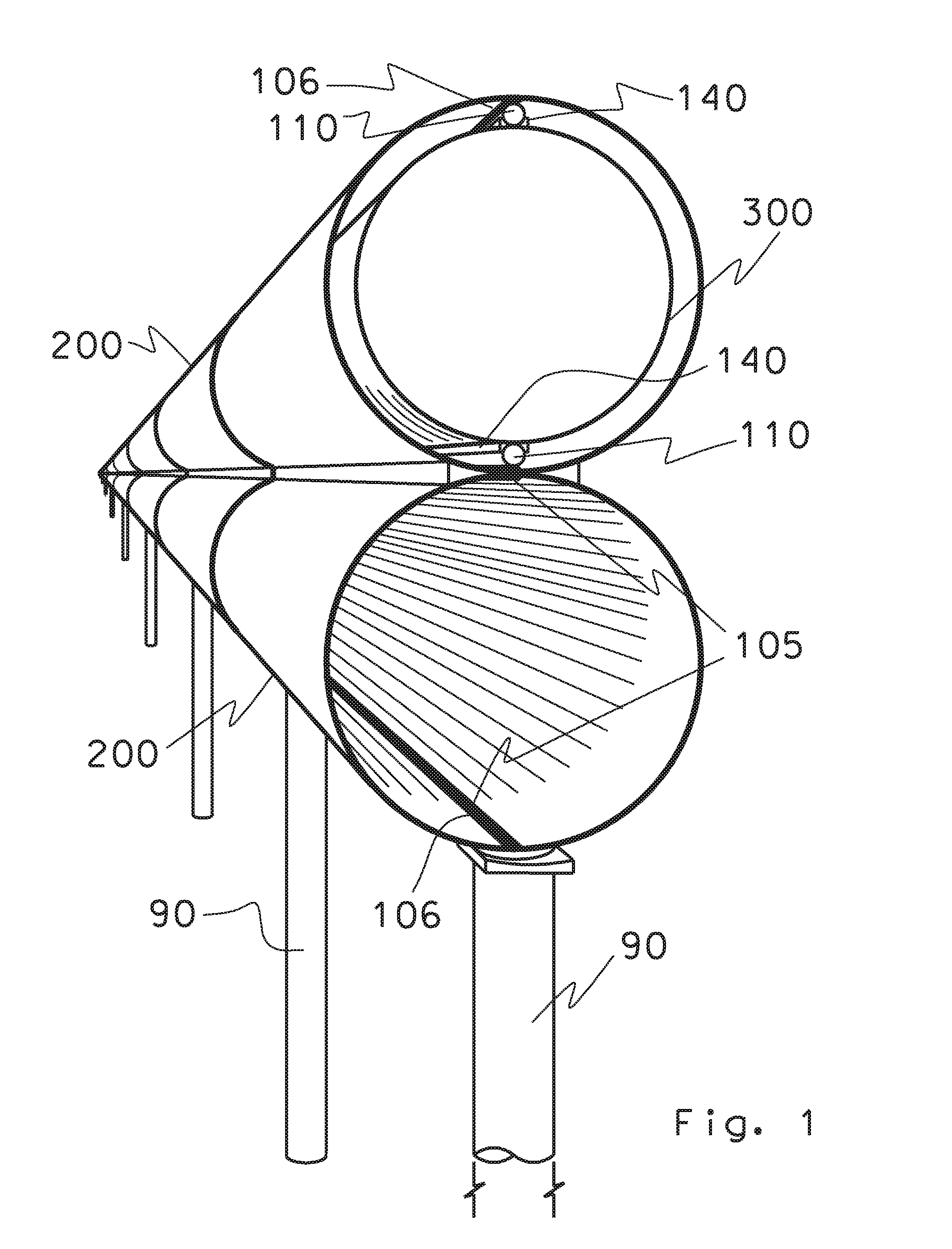
Apparatus for performing in-vitro DNP-NMR measurements on a sample comprises magnetic field generating apparatus (1a, 1b) located in a cryostat (2) and surrounding a bore defining respective NMR and DNP working regions (90, 92). A system for performing DNP on a suitably prepared sample in the DNP working region. A system for performing a NMR process on a sample in the NMR working region. A sample positioning mechanism (5) which can be inserted in the bore (3) to bring a sample in turn into each of the working regions. The magnetic field generating apparatus is suitably structured so that the magnetic field in the DNP working region has a homogeneity or profile suitable for performing DNP on the sample and the magnetic field in the NMR working region has a homogeneity or profile suitable for performing a NMR process on the sample.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR NANOTECH TOOLS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com