Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Superconducting magnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire has no electrical resistance and therefore can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest non-superconducting electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers, fusion reactors and particle accelerators. They are also used for levitation, guidance and propulsion in a magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system being constructed in Japan.
Superconductive magnet
ActiveUS20100295640A1Reduce the amount requiredLow costMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting magnetBobbin
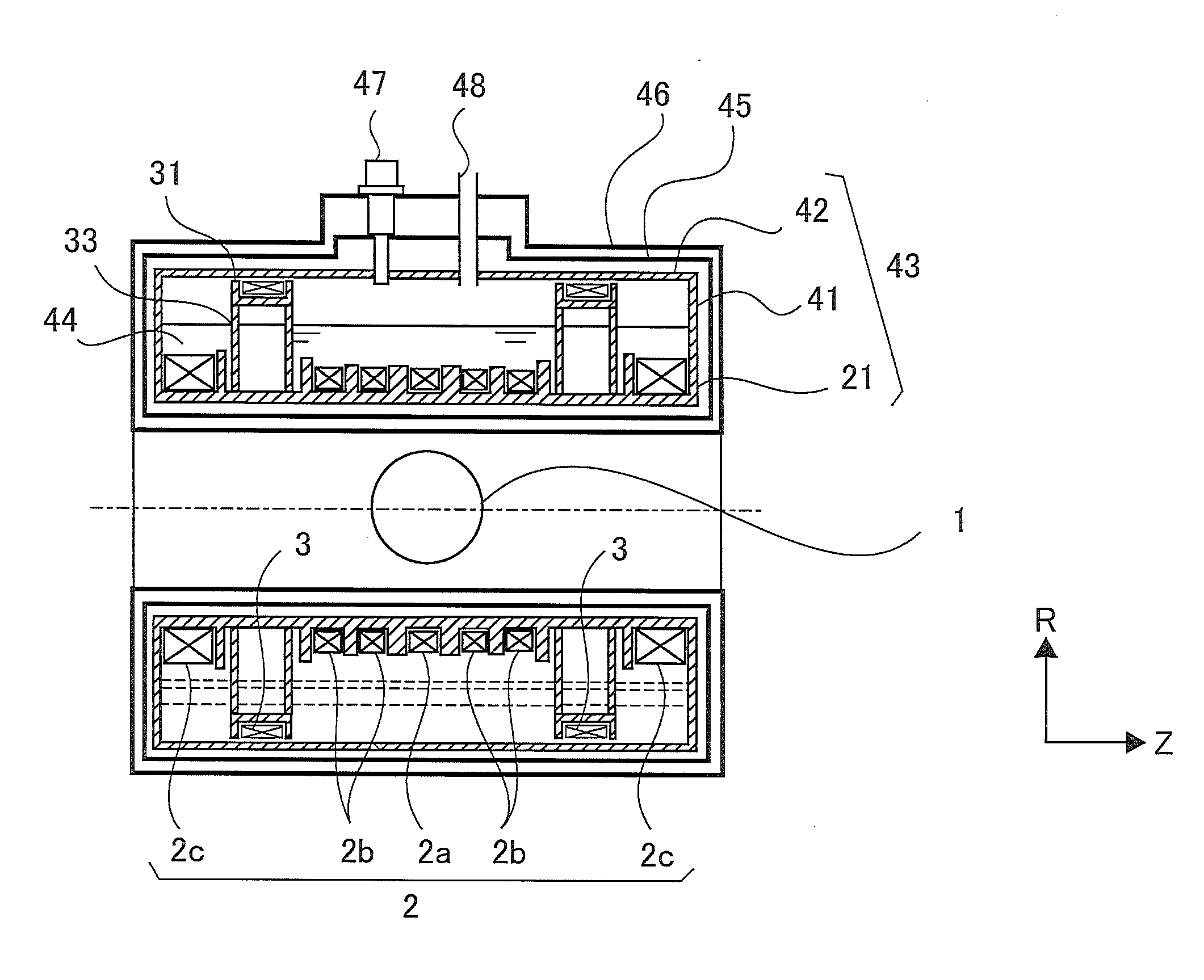
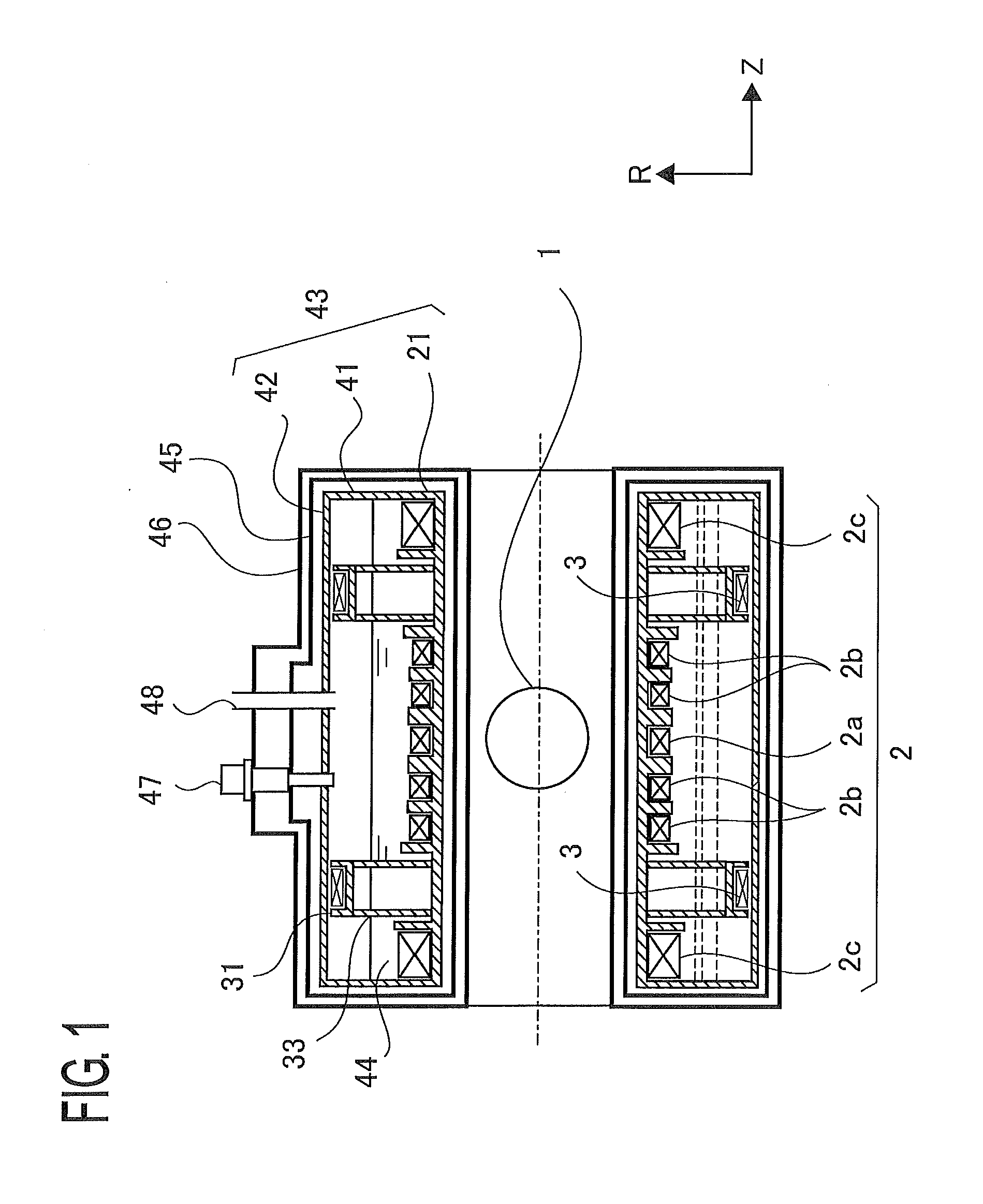
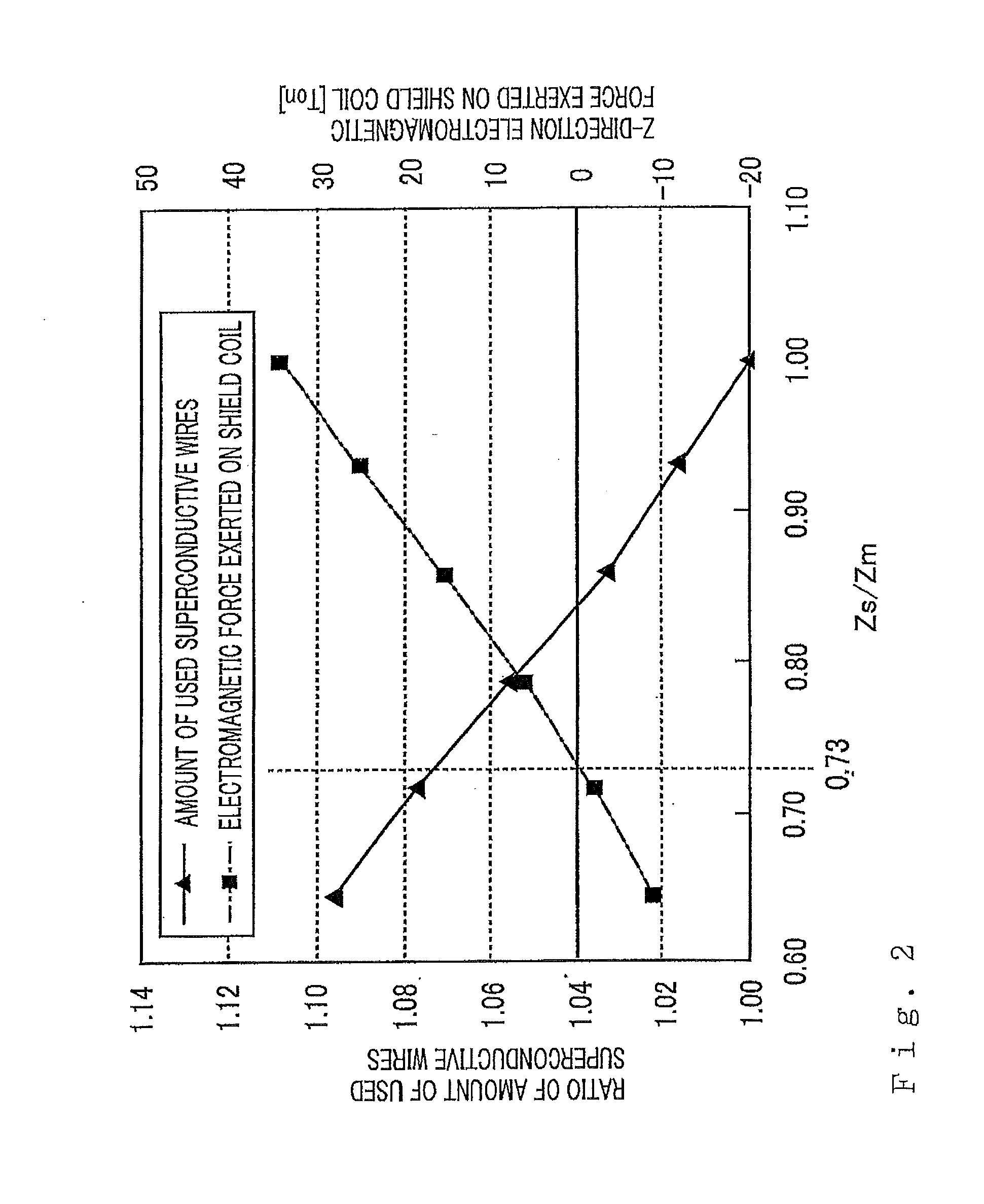
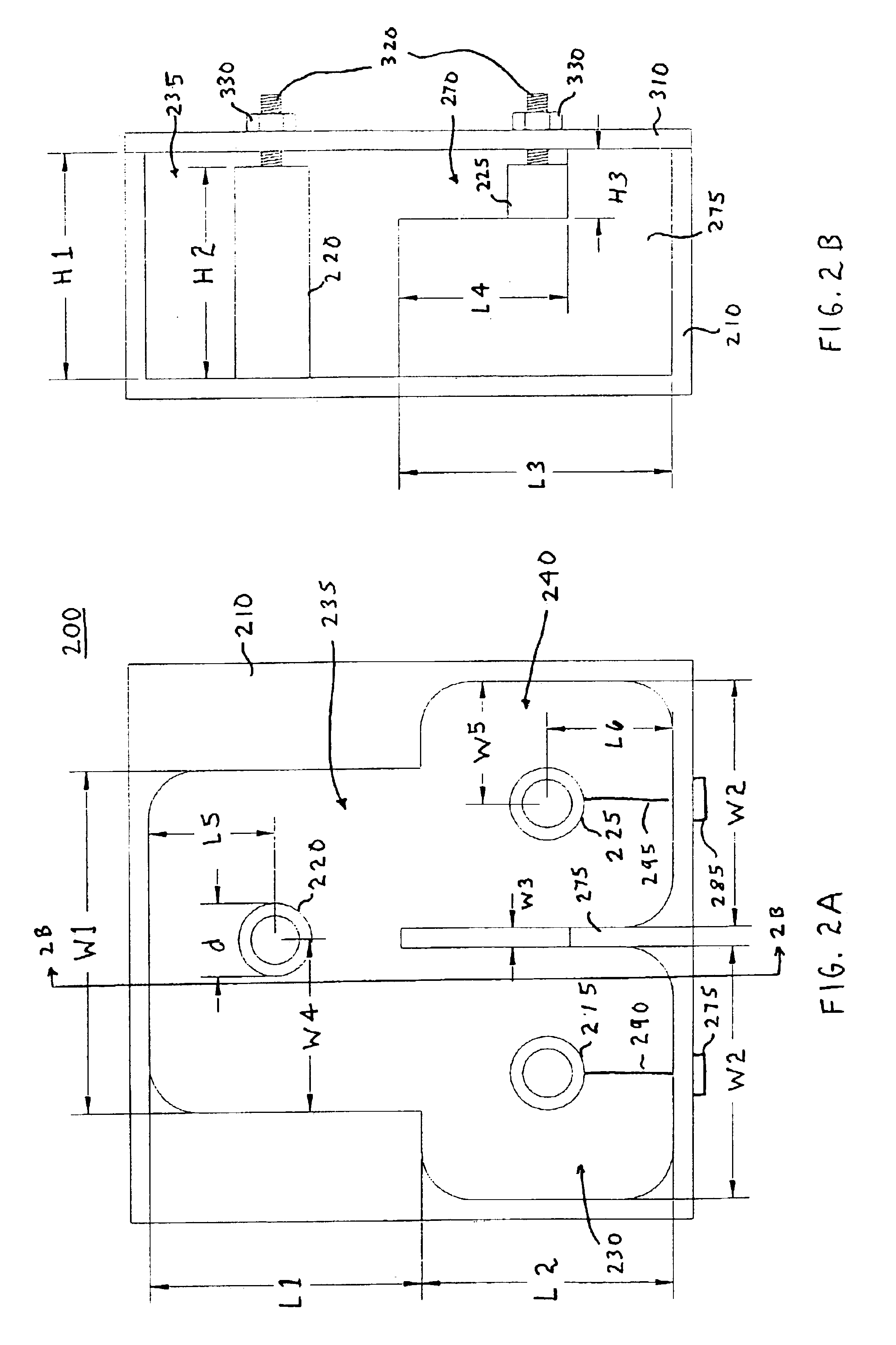
There is obtained a superconductive magnet in which there are reduced the machining costs and the amount of materials for bobbins and supporting members that support coils. In a superconductive magnet provided with a first group of coils serving as main coils for generating a magnetic field and a second group of coils serving as shield coils that are arranged coaxially with the first group of coils and generate a magnetic field whose direction is opposite the direction of a magnetic field generated by the first group of coils so that a magnetic field that leaks outside is cancelled, the second group of coils are arranged at axis-direction positions where axis-direction electromagnetic force generated by the first group of coils and exerted on the second group of coils and axis-direction electromagnetic force generated by the second group of coils balance with each other and cancel out each other.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
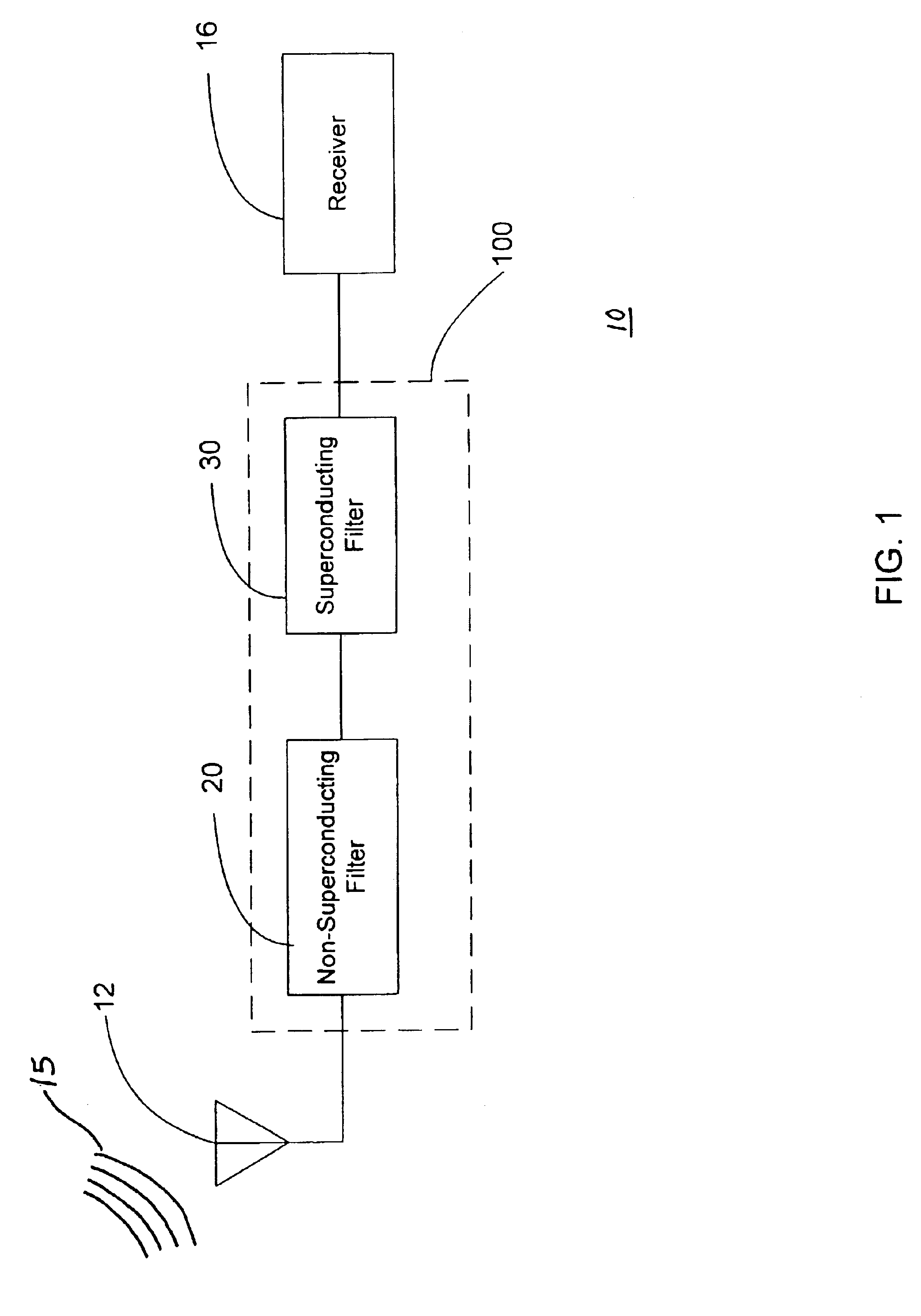
Filter network combining non-superconducting and superconducting filters
InactiveUS6933748B2Improve frequency selectivityHigh frequencyExclusive-OR circuitsComputation using non-contact making devicesElectronicsPhysics
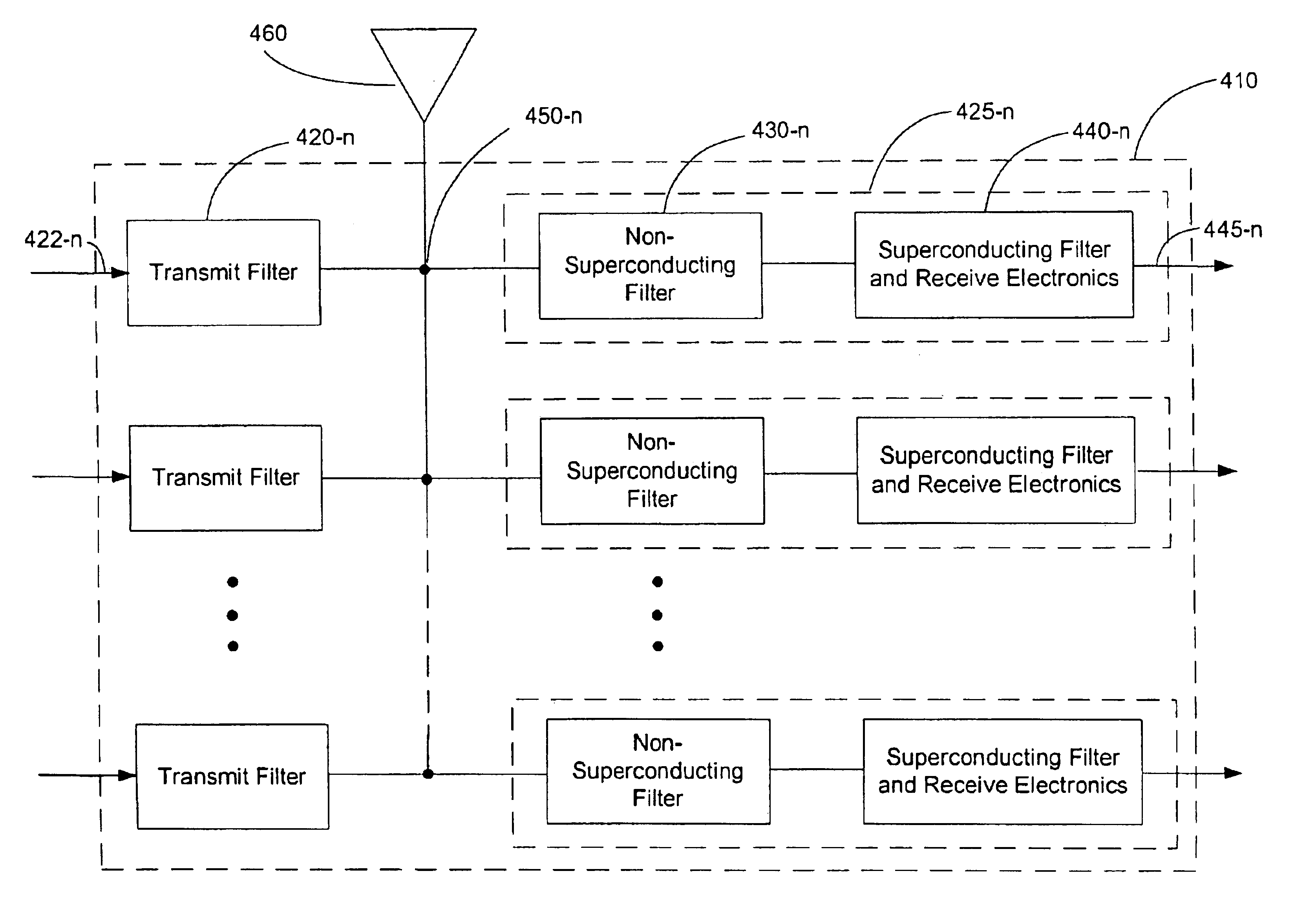
A filter network designed for providing high frequency selectivity with a high degree of reliability and availability. The filter network comprises a superconducting filter and a non-superconducting filter, or a combination thereof to form multiplexers. A receive side of the non-superconducting filter pre-filters received RF signals before inputting them to the superconducting filter. The non-superconducting filter is constructed and arranged to pass RF signals having a frequency within a first pass band to the superconducting filter. The superconducting device is constructed and arranged to exhibit a high-degree of frequency selectivity in further narrowing the received RF signals. Other aspects are directed to the arrangement, construction, and uses of the same structures to accomplish different but similar goals. In a multiplexed configuration, various combinations of transmit filters are used to enable the use of a common antenna with the receive side electronics, which may be located at the top of the antenna tower or in the base station.
Owner:SUPERCONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGIES INC
Superconductivity magnet apparatus
InactiveUS20050134414A1Uniform magnetic fieldErroneous generation can be suppressedMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting magnetBobbin
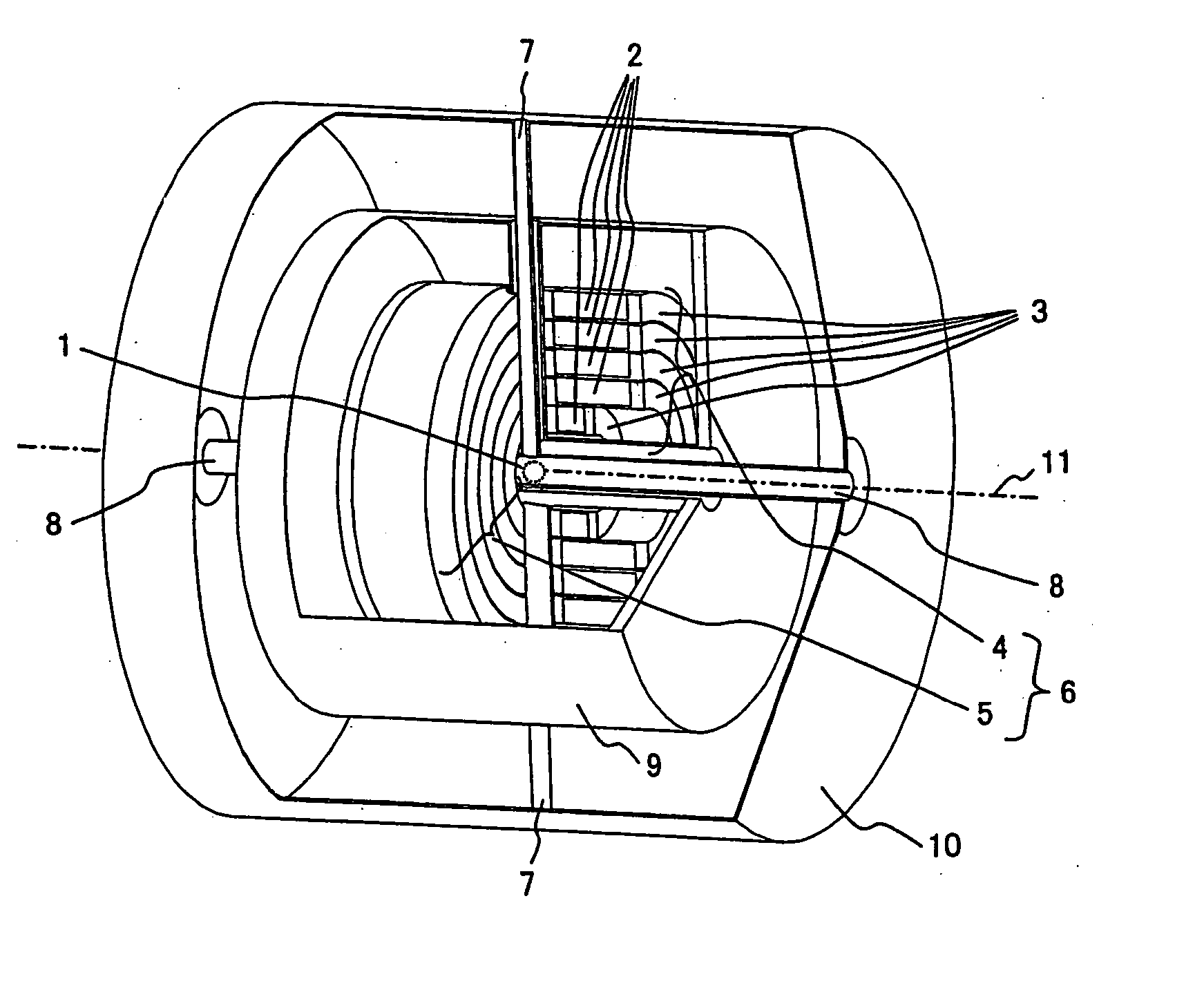
The present invention provides a superconductivity magnet apparatus for generating a uniform magnetic field suitable for NMR applications. The superconductivity magnet apparatus has an access port for allowing an access to the center of the magnetic field from an external position separated away from the center in a direction other than the axial direction of a split-type superconductivity electromagnet employed in the magnet apparatus. In the superconductivity magnet apparatus, a gap exists between first and second superconductivity coil blocks facing each other to form the split-type superconductivity electromagnet. To put it in detail, the access port allows an access to a measurement space at the center of the magnet by way of the gap. A configuration element of the magnet such as a coil bobbin is cut out for providing the access port. An area including a deficiency portion caused by the cutout portion or the like is filled up with a material having a relative magnetic permeability in the range 1.000 to 1.002 as an axis-symmetrical area. By using the material with a relative magnetic permeability in the range 1.000 to 1.002, the strength of an erroneously generated magnetic field can be reduced so that a magnet producing a uniform magnetic field can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Superconducting cable
InactiveUS6759593B2Avoid mechanical damageStress minimizationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentSuperconducting magnetEngineering
A superconducting cable includes at least one layer of tapes of superconducting material circumferentially wound side by side on a support at a prefixed distance forming gaps circumferentially among adjacent tapes. Within the superconducting cable, a non-superconducting material is interposed between adjacent tapes to partially fill the gaps.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA +1
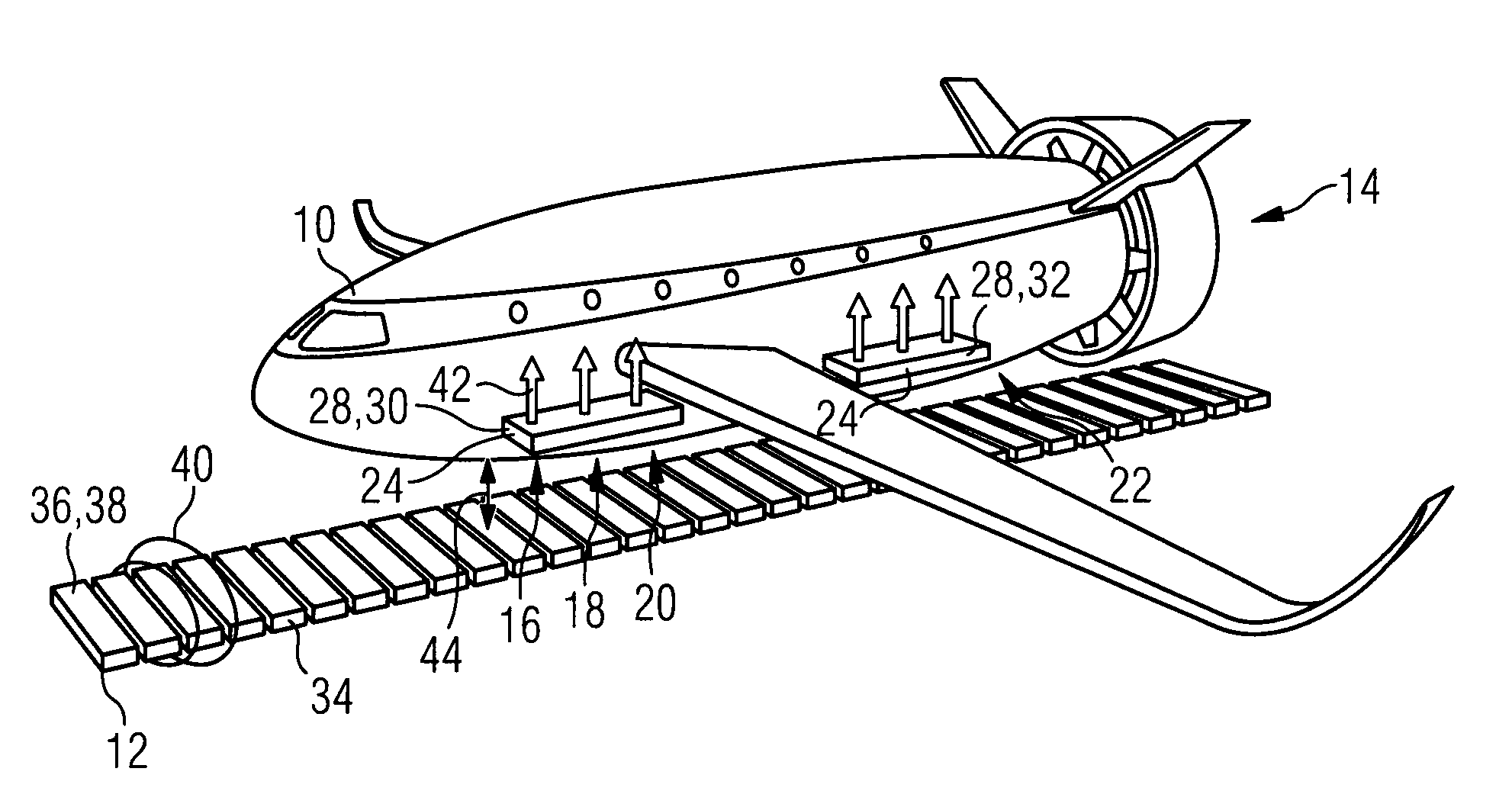
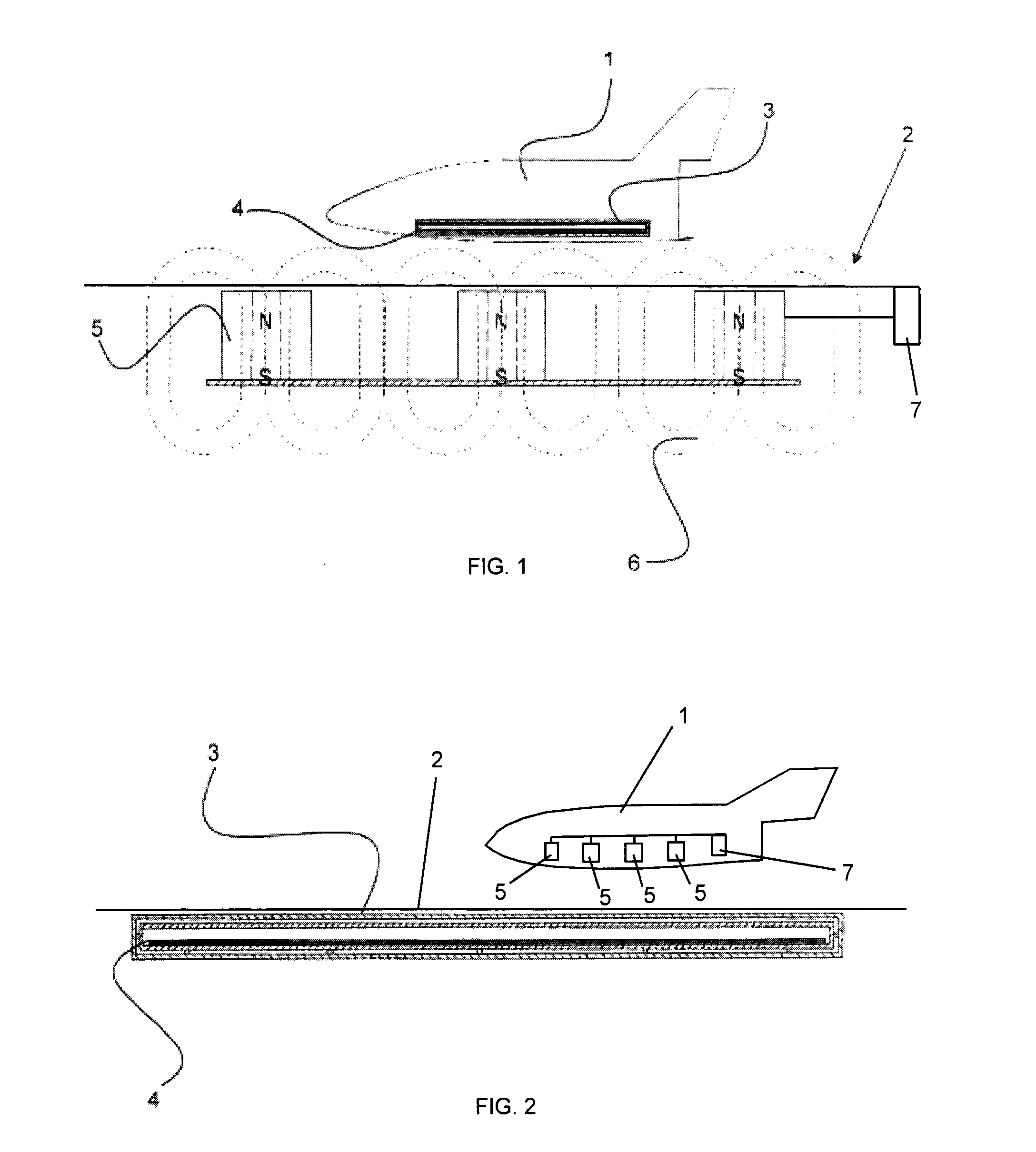
Air Vehicle and Levitation System for Air Vehicle
InactiveUS20150251561A1Minimum energy consumptionPower plant cooling arrangmentsEnergy efficient operational measuresContact freeSuperconducting magnet
Magnetically active elements, namely magnets or superconducting elements respectively, are incorporated respectively in an air vehicle and in a guide path on which the air vehicle is to land, take-off and / or taxi. A cooling apparatus may be provided to cool the superconducting elements. The magnets may be electromagnets, and an electrical energy source and a controller are provided to energize the electromagnets in an independently controlled manner. The magnets produce a magnetic field, and the superconducting elements expel the magnetic field and cause a quantum levitation effect, by which the air vehicle is supported in a contact-free manner above the guide path. Thus, the air vehicle may omit mechanical landing gear.
Owner:AIRBUS DS
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS20110068789A1Energy consumption is minimizedHigher prepolarization magnetic fieldDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSuperconducting magnetNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
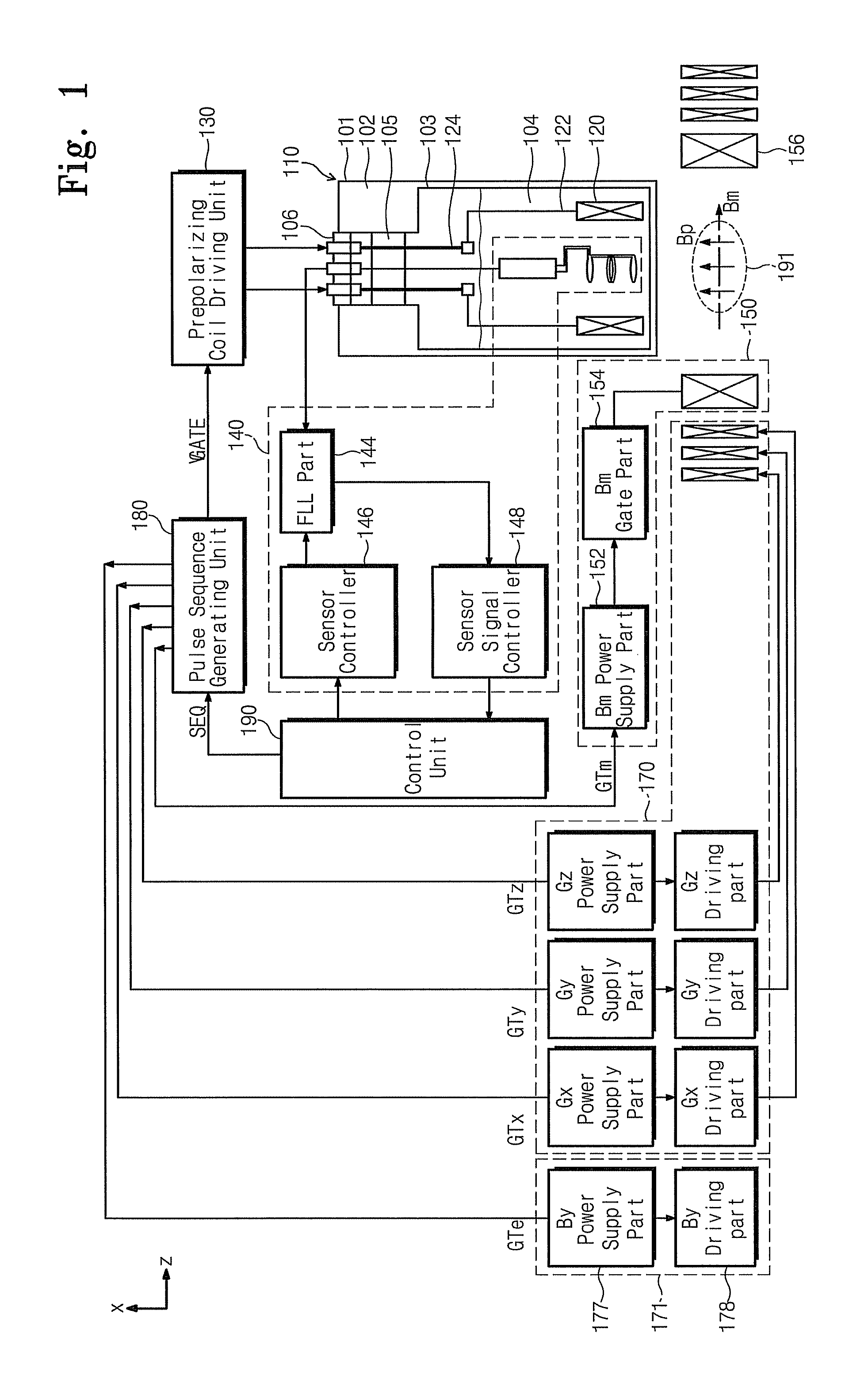
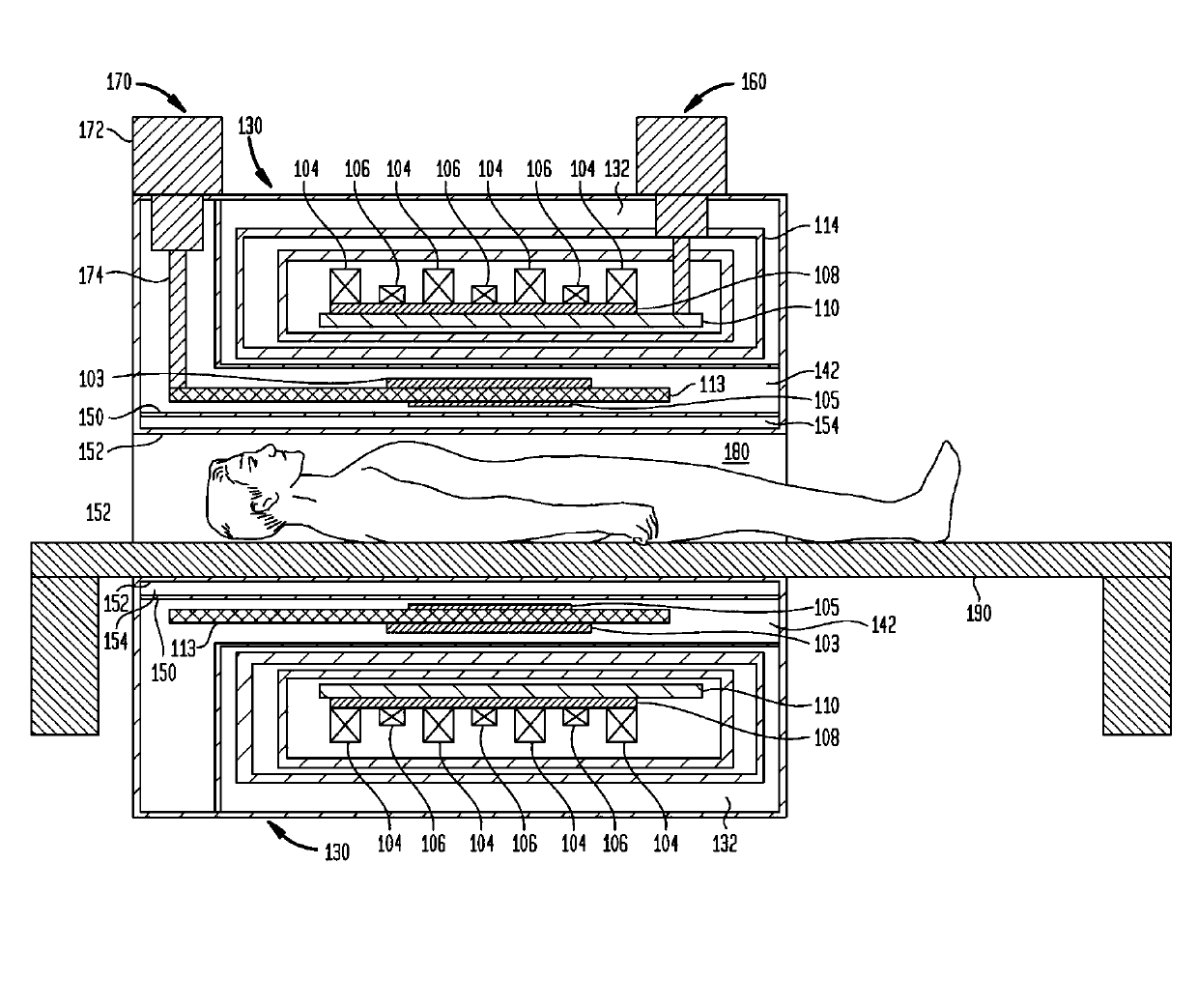
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus includes a dewar containing a low-temperature liquid refrigerant, a prepolarization coil disposed inside the dewar and including a superconducting wire, a prepolarization coil driving unit for intermittent application of current to the prepolarization coil in a capacitor charge / discharge method to generate a prepolarization magnetic field, a sensor unit for measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal from a sample to which a prepolarization magnetic field is applied with the prepolarization coil, and a readout magnetic field generation unit for applying a readout magnetic field to the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Method for preparing iron-based superconducting wire
ActiveCN103354130AReduce crackingReduce voidsCable/conductor manufactureSuperconducting magnetMetal substrate
The invention relates to a method for preparing an iron-based superconducting wire. The method comprises the steps of: (1) putting iron-based superconducting precursor powder into a metal tube under an inert atmosphere, and processing the iron-based superconducting precursor powder into an iron-based wire or strip through rotary forging, drawing and rolling; (2) carrying out sheathing and sealing processing on the iron-based wire or strip prepared in the step (1), that is, two ends of the iron-based wire or strip are sealed by silver foil pressing or argon arc welding; (3) carrying out heat treatment on the sealed iron-based wire or strip acquired in the step (2) so as to acquire the iron-based superconducting wire, wherein the temperature of the heat treatment is 500-950 DEG C, the pressure is 1-300MPa, and the time of the heat treatment is 1min-200hr; and (4) feeding a gas medium in the heat treatment process of the step (3), wherein the gas medium is argon. The prepared iron-based superconducting wire comprises at least one superconducting core with superconducting performance and at least one kind of metal substrate coated around the superconducting core, wherein the principal phase of the superconducting core is 1111 or 122 or 111 or 11.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Triaxial Superconducting Cable and Termination Therefor
InactiveUS20080179070A1Improve superconductivityHigh currentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCable fittings for cryogenic cablesSuperconducting magnetBand shape
In order to provide a flexible oxide superconducting cable which is reduced in AC loss, tape-shaped superconducting wires covered with a stabilizing metal are wound on a flexible former. The superconducting wires are preferably laid on the former at a bending strain of not more than 0.2%. In laying on the former, a number of tape-shaped superconducting wires are laid on a core member in a side-by-side manner, to form a first layer. A prescribed number of tape-shaped superconducting wires are laid on top of the first layer in a side-by-side manner, to form a second layer. The former may be made of a metal, plastic, reinforced plastic, polymer, or a composite and provides flexibility to the superconducting wires and the cable formed therewith. Methods of forming and terminating a triaxial superconductor are disclosed.
Owner:GOUGE MICHAEL J +4
Superconducting cable
ActiveCN106716558AImprove physical strengthDiversified shunt pathsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsConductive materialSuperconducting magnetEngineering
The present invention relates to a superconducting cable for reinforcing the physical rigidity of a superconducting wire and, furthermore, for diversifying a distribution path of a fault current so as to reduce the diameter (cross-sectional area) or weight of a former.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
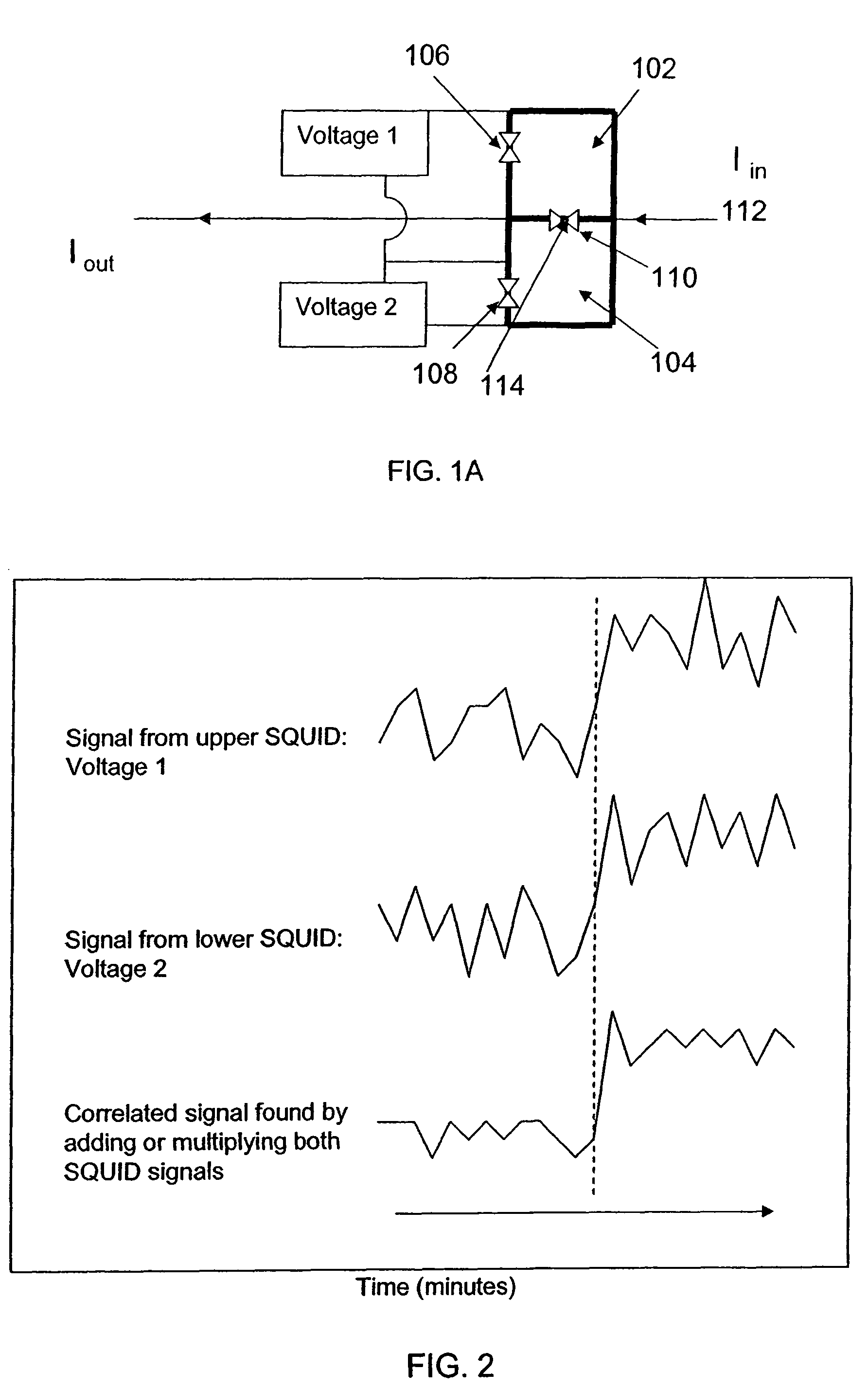
Multiple SQUID magnetometer
InactiveUS7863892B2Avoid complicationsHigh sensitivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesSuperconducting magnetPi Josephson junction
Multiple SQUID magnetometers that include at least two SQUID loops, each of which is composed of at least two Josephson Junctions connected in parallel with superconducting wires, are provided. The SQUID loops are fabricated such that they share a common Josephson Junction. Devices and application that employ the multiple SQUID magnetometers are also provided.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
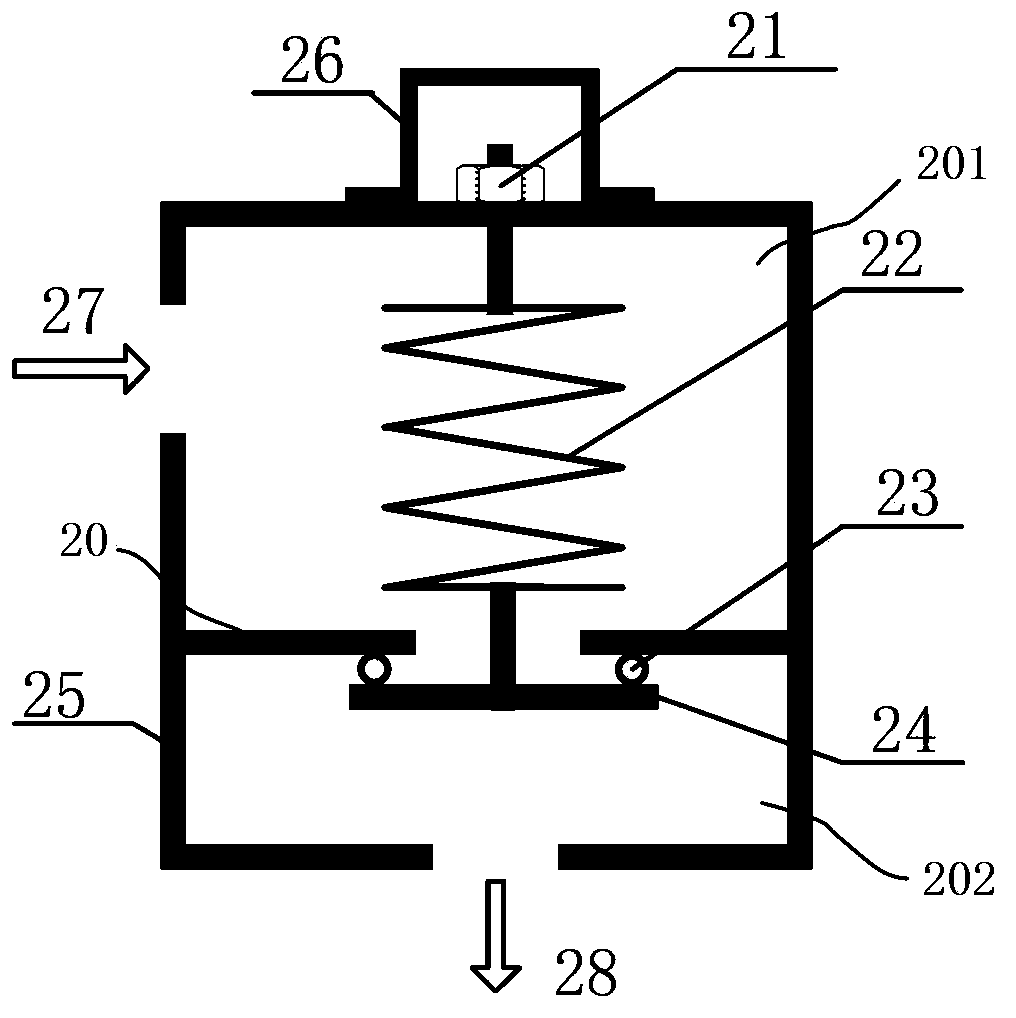
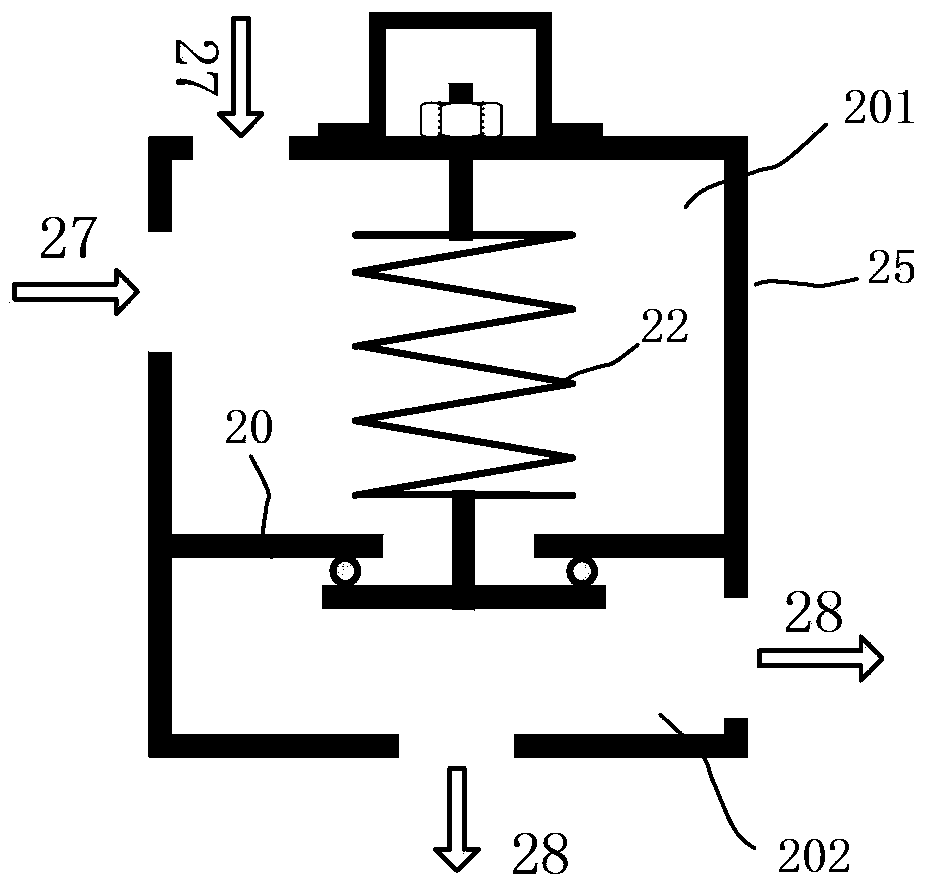
Superconducting magnet pressure release valve and pressure release system
ActiveCN103775699ASolve problems that cannot be effectively closedCompensate for the lack of rebound caused by the problem of not being able to sealEqualizing valvesSafety valvesSuperconducting magnetCheck valve
The invention discloses a superconducting magnet pressure release valve and a pressure release system. The pressure release valve comprises a valve body. An elastic part with a tensioning function and a partition plate with the middle open are arranged in the valve body. The valve body is divided into an upper cavity and a lower cavity through the partition plate. An air inlet is formed in the upper cavity. An exhaust opening is formed in the lower cavity. An opening sealing plate is arranged in the lower cavity. The opening sealing plate and the elastic part are connected and then attached to the partition plate so as to completely cover the opening portion in the partition plate. According to the superconducting magnet pressure release valve and the pressure release system, a compression resistance spring is replaced by a tension spring for conducting sealing, and therefore the problem of poor sealing performance caused when the rebound amount of the spring is not enough can be effectively solved, and the problem that the release system can not be effectively closed after releasing is completed is solved. In addition, a first check valve and a bypass loop are added to the air inlet of the pressure release valve, and therefore less ultralow temperature media can pass through the pressure release valve, the service life can be prolonged, and reliability can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Preparation method iron based SmFeAsO1-xFx superconducting wire
InactiveCN101345103AEvenly distributedIncrease the critical current densitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesCritical magnetic fieldSuperconducting transition temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of an iron-based SmFeAsO<1-x>Fx superconducting wire, comprising the steps as follows: a: material preparation: the material is prepared according to the stoichiometry of the iron-based superconducting material SmFeAsO<1-x>Fx (wherein, x is not more than 0.35 and not less than 0.15, the raw materials such as SmAs, Fe, Fe2O3 and FeF3 are weighed, grinded, uniformly mixed, arranged into a Tantalum pipe, fully fixed and compacted; the two ends of the Tantalum pipe are sealed; b: wire preparation: the Tantalum pipe is sheathed into a copper pipe and rotatablely forged; subsequently, the wire with the diameter of 1.8-2.2mm is formed by pulling and drawing; c: burning: the wire is arranged in a quartz pipe and sealed in vacuum and then put into a sintering furnace; under the protection of inert gas, the temperature of the wire is increased to 1150-1170 DEG C at the speed of 100-150 DEG C / hour, the temperature is kept for 36-50 hours and the wire is cooled with the furnace. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple technology and facilitating industrial production, and the compactness, high purification, stable superconducting performance, high superconducting conversion temperature and high critical magnetic field of the prepared iron-based SmFeAsO<1-x>Fx superconducting wire.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Iron-based superconducting material, iron-based superconducting layer, iron-based superconducting tape wire material, and iron-based superconducting wire material
InactiveUS20140349854A1Little dependencySuppress a decrease in JSuperconductors/hyperconductorsConductive materialWire rodSuperconducting magnet
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and static magnetic field generating apparats used therefor
InactiveCN1496237AMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSuperconducting magnetResonance
An MRI apparatus having an open structure includes a static magnetic field generating magnet including magnetic field generating sources arranged above and below an imaging space and magnetic field fluctuation reducing plates arranged inside the magnet. Gradient magnetic field coils are fixed to the static magnetic field generating magnet so as to not be in contact with the magnetic field fluctuation reducing plates. When the strength of the magnetic field generated by the static magnetic field generating magnet fluctuates due to vibration of the gradient magnetic field coils or other devices during an imaging operation of the MRI apparatus, an eddy current is generated on the magnetic field fluctuation reducing plates in response to the magnetic field fluctuation components. Magnetic flux which cancels the static magnetic field fluctuation components is generated due to this eddy current, and consequently, a time-sequentially stable static magnetic field can be obtained.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Superconducting wire connection structure, superconducting wire connection method, and superconducting wire for connecting
ActiveCN103688316AFirmly connectedStable superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSuperconducting magnetPhysics
A superconducting wire connection structure is adopted in which, in a section where the ends of a first superconducting wire (11) and a second superconducting wire (12) are spaced apart from and arranged across from each other, the third superconducting wire (13), which is narrower in at least one portion than the first superconducting wire (11) and the second superconducting wire (12), spans and connects the first superconducting wire (11) and the second superconducting wire (12) along the longitudinal direction of the first superconducting wire (11) and second superconducting wire (12). Thereby, it is possible to reduce degradation of the superconducting layer (3) by suppressing generation of heat caused by current flow concentration at the section where the third superconducting wire (13) is connected, and stable superconducting performance can be achieved.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Cooling system and method for a magnetic resonance imaging device
InactiveUS20160187435A1Machines using refrigerant evaporationSuperconducting magnets/coilsSuperconducting magnetNuclear engineering
A cooling system includes a first cooling loop having a first cooling fluid configured for circulation therethrough and a second cooling loop having a second cooling fluid configured for circulation therethrough. The first cooling loop is in thermal communication with the superconducting magnet and is configured to provide primary cooling for the magnet, and the second cooling loop is in thermal communication with the superconducting magnet and is configured to provide secondary cooling for the magnet.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Semifinished wire with PIT elements for a superconducting wire containing Nb3Sn and method of producing the semifinished wire
ActiveUS20160247606A1Good deformation behaviorAvoid soilSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesSuperconducting magnetWire rod
A semifinished wire (1) for a superconducting wire containing Nb3Sn has a Cu stabilization cladding tube (2), a ring-shaped closed diffusion barrier (3) in the inside of the Cu stabilization cladding tube (2) and a plurality of PIT elements (6) in the inside of the diffusion barrier (3), each having a cladding (8) containing Cu, a small tube (9), and a powder core (10) containing Sn. The small tube (9) consists of Nb or an alloy containing Nb and the diffusion barrier (3) has a percentage of area ADF in cross-section of the semifinished wire (1) of 3% ADF 9% and a wall thickness WDF with 8 μm≦WDF≦25 μm. A plurality of filler elements (5) are arranged inside the diffusion barrier (3), with the inner sides of the filler elements (5) abutting the PIT elements (6).
Owner:BRUKER EAS
Superconductive magnet
ActiveUS8305173B2Reduce the amount requiredLow costMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting magnetBobbin
There is obtained a superconductive magnet in which there are reduced the machining costs and the amount of materials for bobbins and supporting members that support coils. In a superconductive magnet provided with a first group of coils serving as main coils for generating a magnetic field and a second group of coils serving as shield coils that are arranged coaxially with the first group of coils and generate a magnetic field whose direction is opposite the direction of a magnetic field generated by the first group of coils so that a magnetic field that leaks outside is cancelled, the second group of coils are arranged at axis-direction positions where axis-direction electromagnetic force generated by the first group of coils and exerted on the second group of coils and axis-direction electromagnetic force generated by the second group of coils balance with each other and cancel out each other.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
Precise robot radiotherapy system under guidance of MRI
InactiveCN105251135AIncreased therapeutic functionStrong therapeutic functionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSuperconducting magnetMedicine
The invention relates to a precise robot radiotherapy system under guidance of MRI. The system comprises an x / gamma-ray source and on-line magnetic resonance imaging equipment. The on-line magnetic resonance imaging equipment is provided with a split type / cylindrical superconducting magnet for generating a magnetic field. The x / gamma-ray source is installed on a mechanical arm of a robot and is driven by the robot to move, so that a radiotherapy beam emitted by the x / gamma-ray source can enter a focus imaging region between two magnetic poles of the split type superconducting magnet or inside the cylindrical superconducting magnet through the gap between the magnetic poles and / or holes in the magnetic poles. According to the invention, under guidance of the open type magnetic resonance imaging equipment, a mechanical arm or mechanical arms of one or more robots is / are used for operating one or a plurality of treatment heads to irradiate x / gamma rays on tumor focuses, so that the x / gamma ray therapeutic machine can have more treatment functions for patients, a fast treatment speed, a better treatment capacity, and a good treatment effect.
Owner:BEIJING JIANLIAN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS8350568B2Energy consumption is minimizedHigher prepolarization magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSuperconducting magnetNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus includes a dewar containing a low-temperature liquid refrigerant, a prepolarization coil disposed inside the dewar and including a superconducting wire, a prepolarization coil driving unit for intermittent application of current to the prepolarization coil in a capacitor charge / discharge method to generate a prepolarization magnetic field, a sensor unit for measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal from a sample to which a prepolarization magnetic field is applied with the prepolarization coil, and a readout magnetic field generation unit for applying a readout magnetic field to the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Superconducting Wire
ActiveCN107710345AImprove physical strengthAvoid breakingNon-metal conductorsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconducting magnetCondensed matter physics
The present invention relates to a superconducting wire having improved electrical and physical properties.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
Liquid nitrogen refrigeration magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveCN103105595AReduce power consumptionReduce weightDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHigh current densityNuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a liquid nitrogen refrigeration magnetic resonance imaging system. The system comprises a high-temperature superconductor main magnet capable of generating even magnetic fields in an imaging area, at least one low-temperature gradient coils capable of generating magnetic filed gradients in the imaging area, and at least one low-temperature radio frequency coil capable of receiving and transmitting radio frequency signals in the imaging area. The system comprises at least one of the following materials: non-superconducting materials and superconducting materials, wherein the non-superconducting materials and the superconducting materials have higher electrical conductivity than copper when cooled to the temperature of 77K. The main magnet, the gradient coils and the radio frequency coils of a preset system adopt low-temperature conducting materials, and the low-temperature conducting materials comprise high-temperature conducting materials, the high-temperature conducting materials are used for manufacturing coils of the main magnet, and therefore high current density can be produced in the coils, and power consumption can be saved; the high-temperature conducting main magnet is small and light and capable of operating under the temperature of 77K, and therefore refrigeration efficiency is improved greatly; and the gradients and the radio frequency coils are made of low-temperature conducting materials, resistance of the coils can be reduced, and coil efficiency can be improved.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL JIANGSU
Thermal radiation shield for superconducting magnet, superconducting magnet and magnetic resonance imaging device
ActiveUS20160202332A1Reduce processing costsReduce time costSuperconducting magnets/coilsElectric/magnetic detectionSuperconducting magnetPunching
A thermal radiation shield for a superconducting magnet has an inner tube, an outer tube arranged around the periphery of the inner tube, and an annular end cap disposed therebetween, and connected in a fixed manner to an edge of the inner tube by an inner edge of the annular end cap. A first toothed part is formed at an outer edge of the annular end cap, the first toothed part being connected by meshing with a second toothed part formed by an edge of the outer tube. The annular end cap with a toothed structure allows only a simple cutting process on raw material to be performed in order to obtain the annular end cap and the first toothed part formed at the outer edge thereof, thereby avoiding complex punching, spinning and similar processes, and saving production costs.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
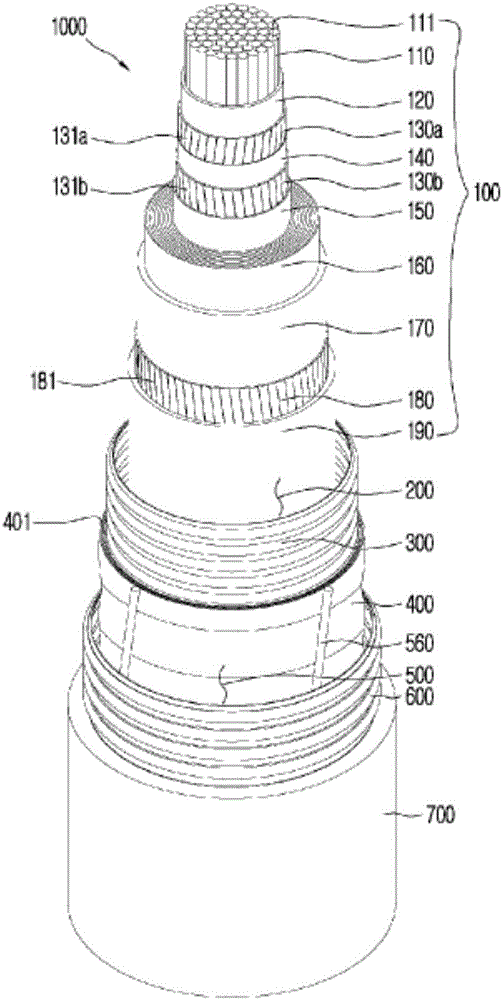
Superconducting magnet
There is provided a superconducting magnet including a superconducting coil, in which the superconducting coil includes: a bobbin; one or more superconducting wires wound around the bobbin in a plurality of turns, each superconducting wire being one or more superconducting filaments embedded in a matrix; and one or more metallic members, each metallic member being in electrical and thermal contact with a plurality of portions of the one or more superconducting wires.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Emergency run-down unit for superconducting magnets
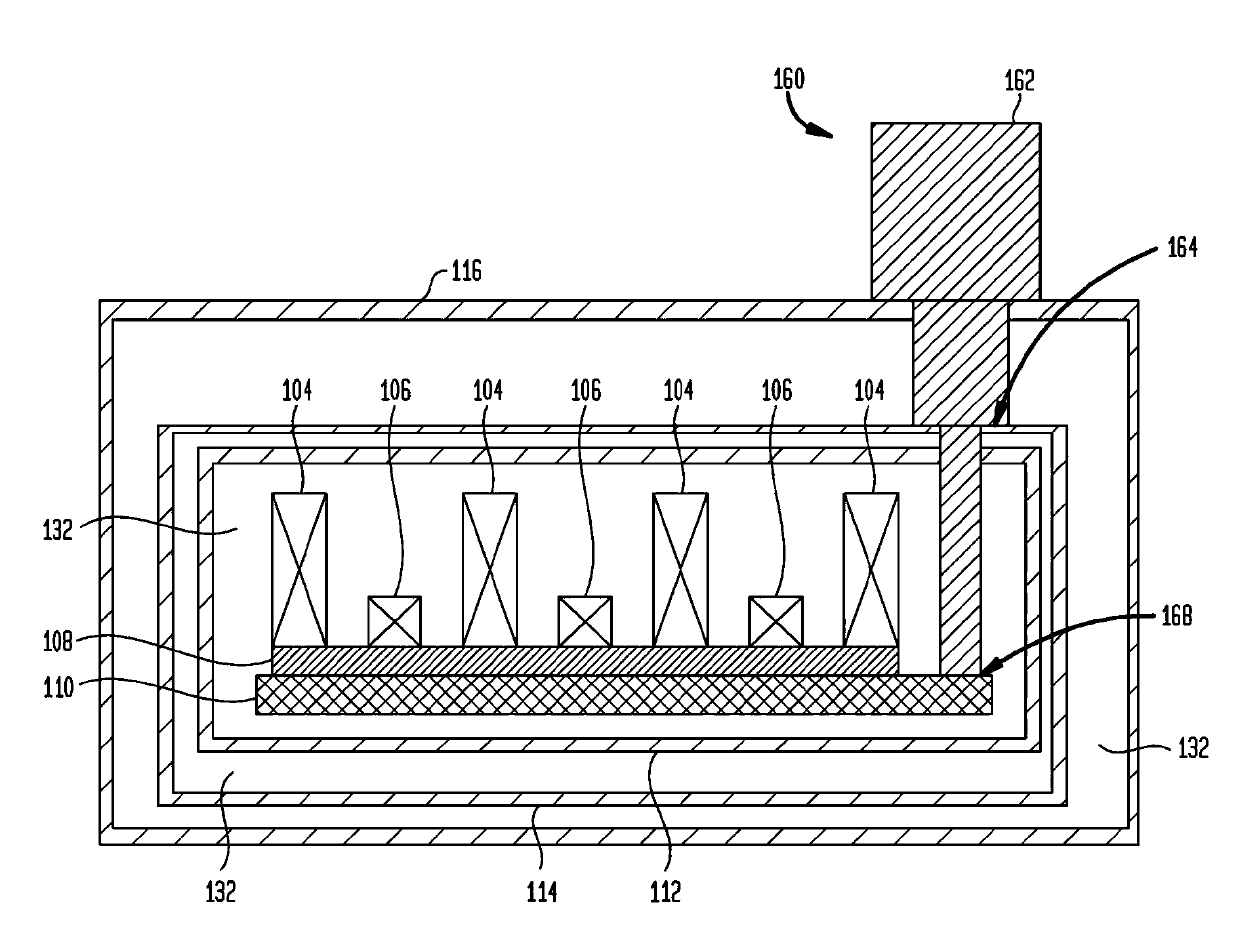
ActiveUS8385033B2MovementEasy to moveMagnetsMagnetic materialsSuperconducting magnetMechanical energy
In an emergency run down unit for a superconductive magnet assembly, a quench in the magnet is induced by the release of stored mechanical energy or by direct manual actuation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE LTD
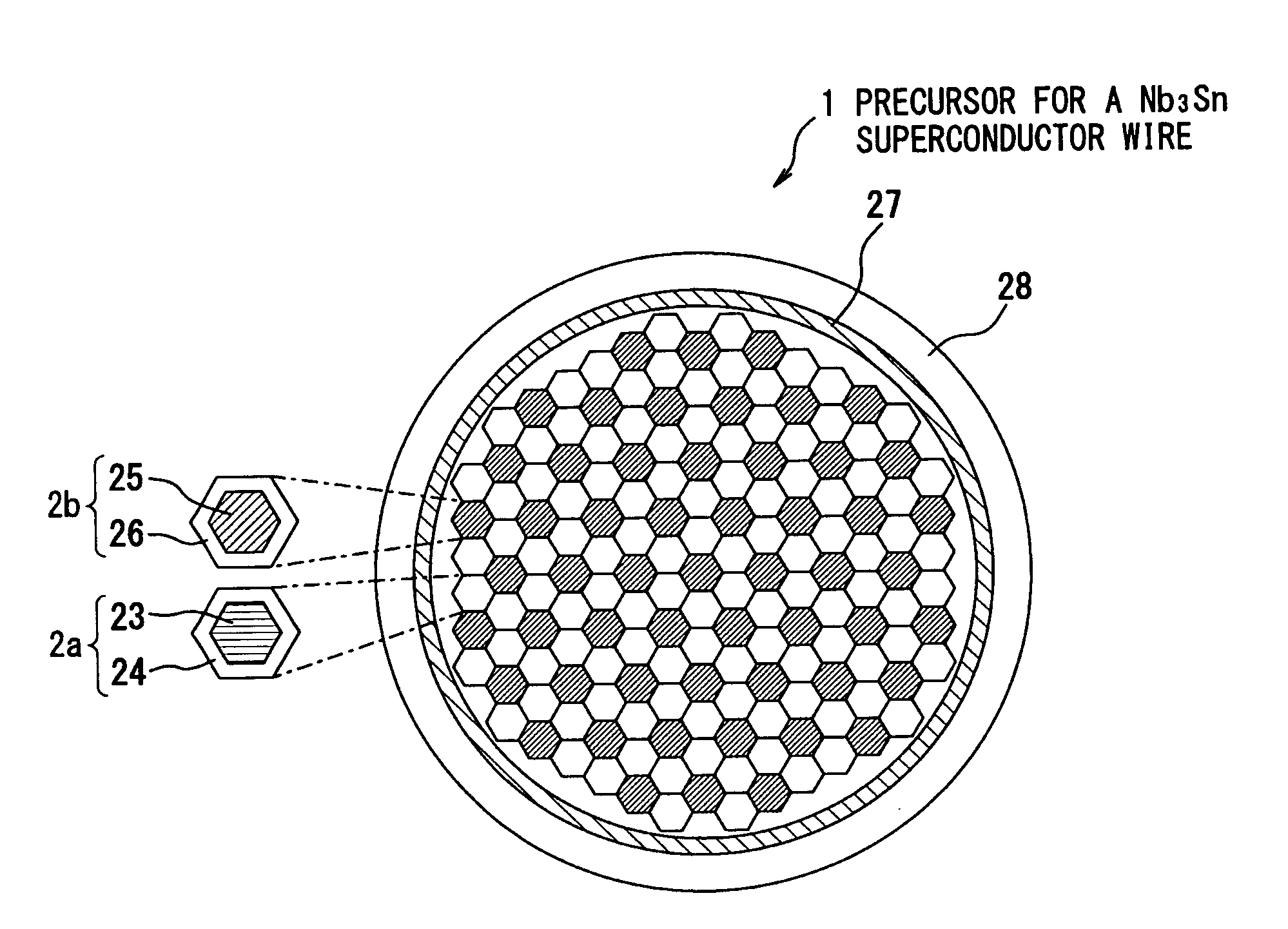
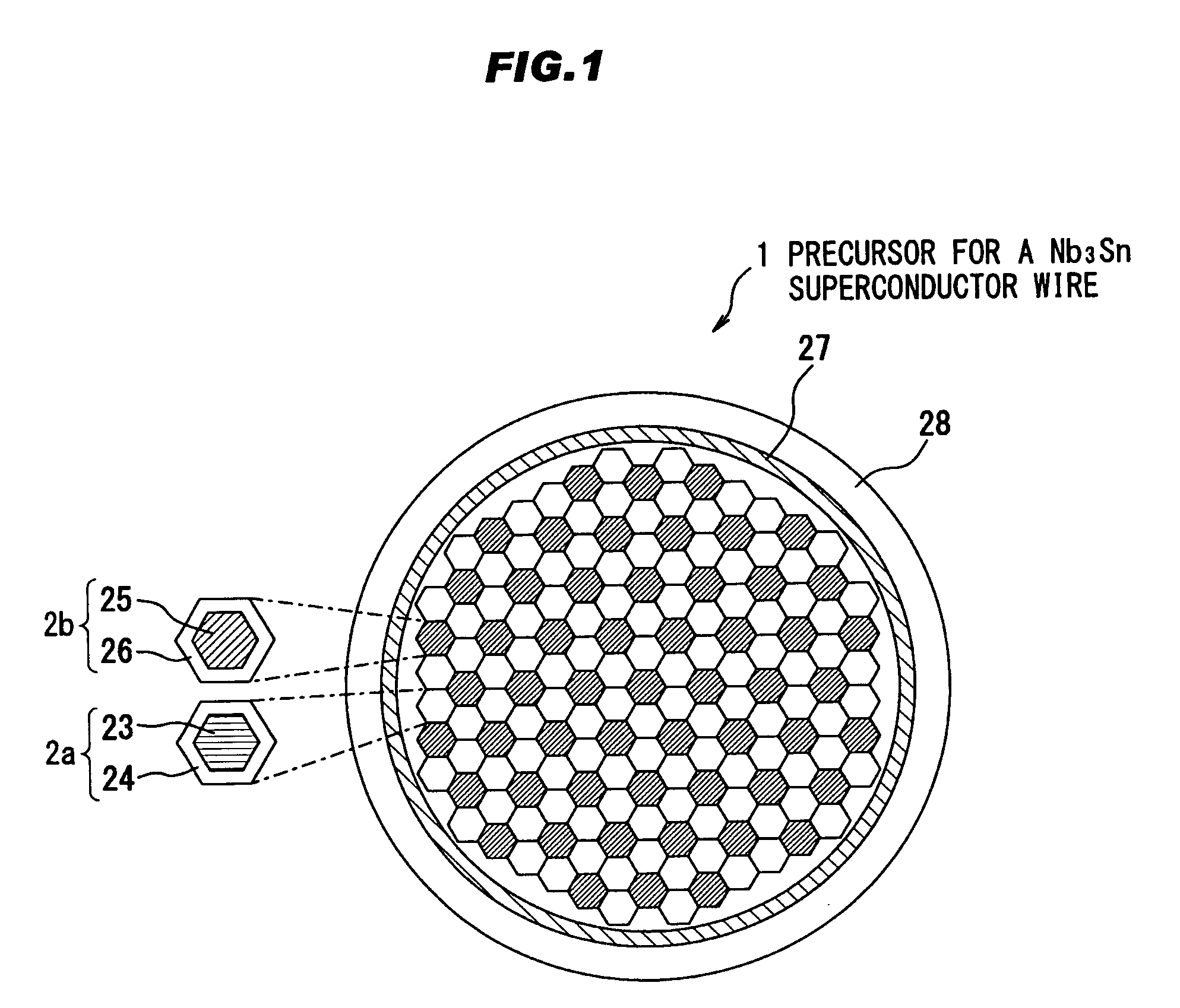
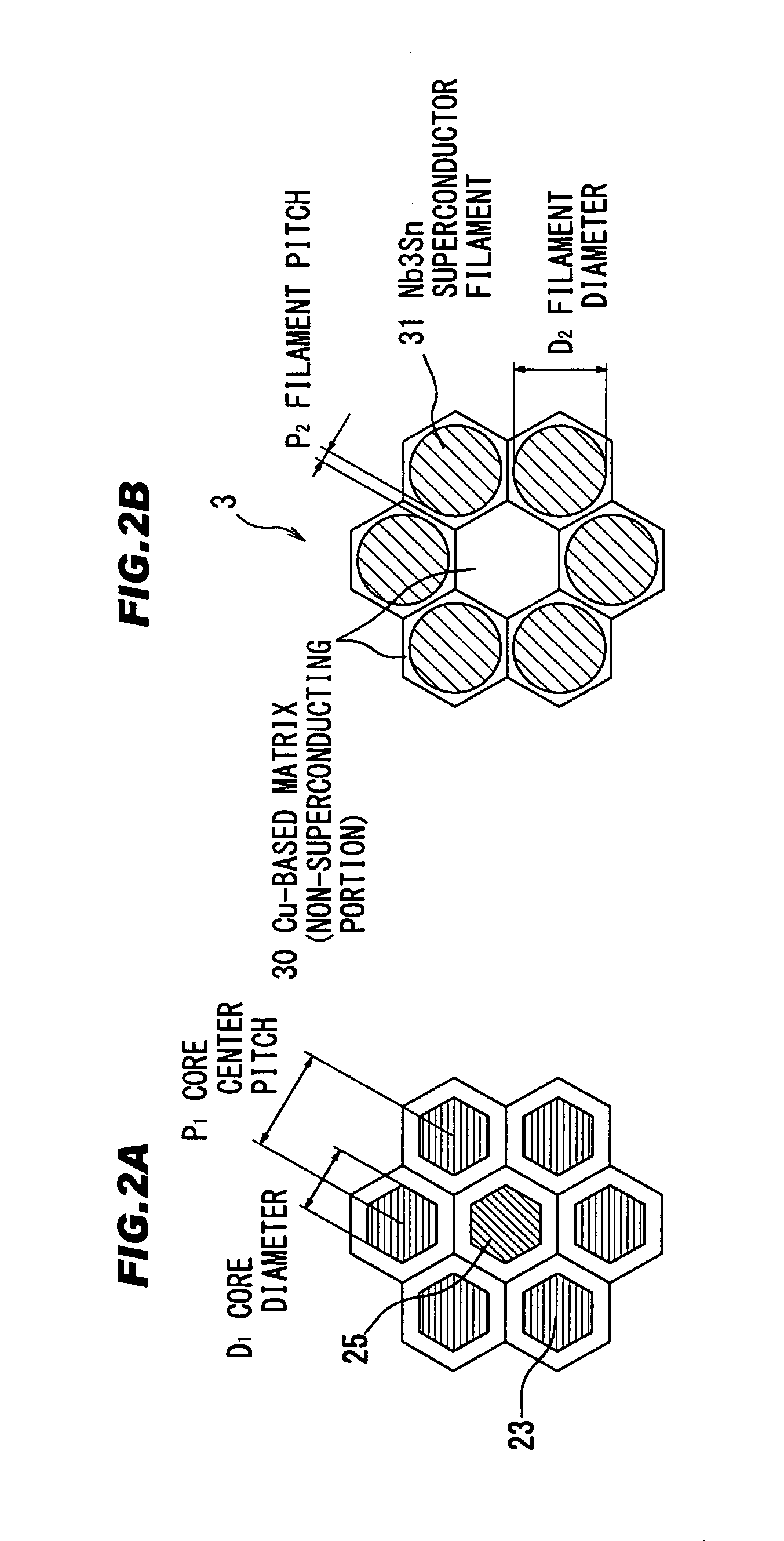
Precursor for a Nb3Sn superconductor wire, method for manufacturing the same, Nb3Sn superconductor wire, and superconducting magnet system
ActiveUS20120149579A1High currentGood magnetic stabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsSuperconducting magnetDiffusion barrier
Owner:SH COPPER PROD CO LTD
Fault current limiter having superconducting bypass reactor for simultaneous quenching
InactiveUS7589941B2Reduce the burden onShorten recovery timeSuperconducting magnets/coilsNormal-superconductive switchable devicesSuperconducting magnetBobbin
A fault current limiter comprises a pancake type current limiting module, comprising at least two pancake type bifilar winding modules stacked and connected to each other in series, each of the bifilar winding modules having a bobbin, a first superconducting wire wound around the bobbin in a bifilar manner, and at least one pair of first metal blocks installed and fixed to the bobbin and attached to the first superconducting wire; and a superconducting bypass reactor that has the current limiting module disposed therein, and is connected in parallel with the current limiting module.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Superconducting cable
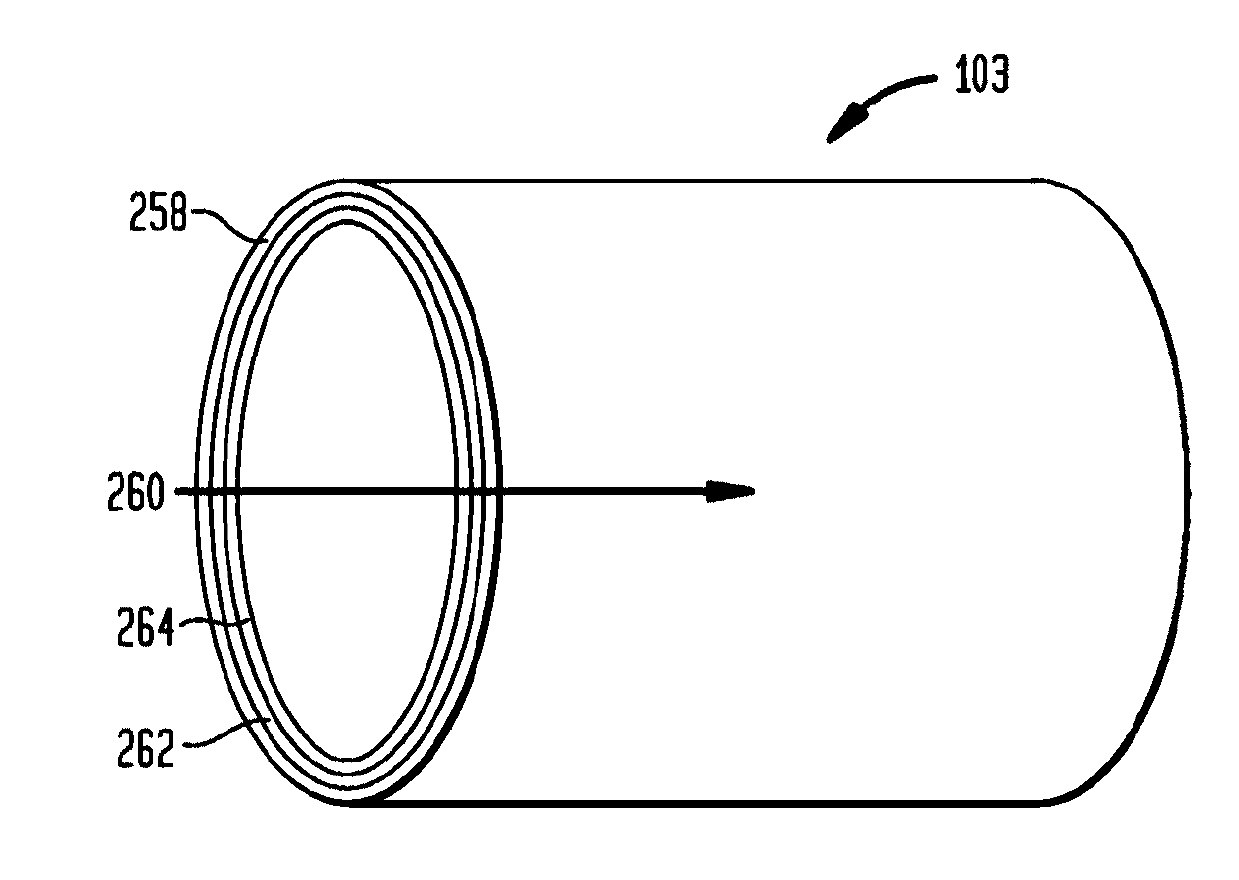
InactiveUS7091423B2Uniform impedanceUniform currentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsInsulated cablesSuperconducting magnetCondensed matter physics
A superconducting cable has a plurality of superconducting wires wound around a core material (former) in a multilayered manner. The superconducting wires employ a twisted filament type superconducting wire having spiral superconducting filaments and an untwisted filament type superconducting wire having straight superconducting filaments. The layer in which an applied magnetic field is large and of which the low loss effect is expected is formed of twisted filament type superconducting wires, and the other layers are formed using the untwisted filament type superconducting wires; thus the AC loss can be reduced effectively. Thus, in the superconducting cable, the AC loss can be effectively reduced while a degradation of the current characteristics and the increase of cost are suppressed.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for preparing superconducting film through bismuth-based superconducting material
InactiveCN105845270ALow costImprove uniformitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesVacuum pumpHeating temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing a superconducting film through bismuth-based superconducting material. The method comprises the following process steps that the technology of preparing bismuth-based superconducting powder suspension liquid is performed; a substrate is arranged on a spin coater tray, and a vacuum pump is started so that the substrate is enabled to be adsorbed on the tray; the bismuth-based superconducting powder suspension liquid is spin-coated on a spin coater so that a high temperature superconducting thick film is formed; after completion of film coating, the thermal decomposition process is started, and the thermal decomposition steps are listed as follows: the high temperature superconducting thick film of the required number of layers is heated, heating temperature rises to 480 DEG C from 60 DEG C, and heating time is 50min; heat is preserved for 5h at temperature of 480 DEG C; and the high temperature superconducting thick film of the required number of layer is cooled to normal temperature from temperature of 480 DEG C so that the superconducting film is obtained. The defects in the prior art that cost is high and practicability is not facilitated in preparing the bismuth-based superconducting film can be solved, the bismuth-based superconducting thick film preparation method which is simple and convenient in technology, low in cost and high in benefic is designed, and the large-area bismuth-based superconducting film can be prepared by adopting the method.
Owner:CHENGDU JUNHE TIANCHENG TECH
High-temperature superconducting non-insulation magnet
InactiveCN111863374AGuaranteed reliabilityReduce heat radiationSuperconducting magnets/coilsElectric machineSuperconducting Coils
The invention relates to the technical field of superconducting magnets, and discloses a high-temperature superconducting non-insulation magnet. The magnet comprises a vacuum protection shell and a plurality of superconducting coil groups arranged in the vacuum protection shell, wherein each superconducting coil group comprises a motor, a first switching device, a second switching device, a heat anchor, a refrigerating machine, a cold storage tank, a plurality of flux pumps, a plurality of non-insulation superconducting coils connected in series, a constant-current switch and a cold shield. Therefore, the heat radiation of the magnet can be reduced through the vacuum layer and the cold shield, the stability and robustness of a magnet system can be improved by adopting the non-insulation superconducting coils, and the reliability of refrigeration can be ensured through a mixed refrigeration mode that the refrigerator refrigerates the cold shield, the plurality of non-insulation superconducting coils and the refrigeration medium.
Owner:HIWING TECH ACAD OF CASIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com