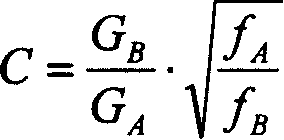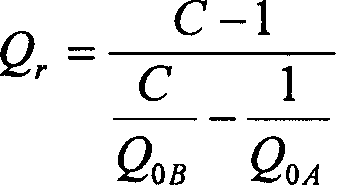Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
970 results about "Superconducting material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
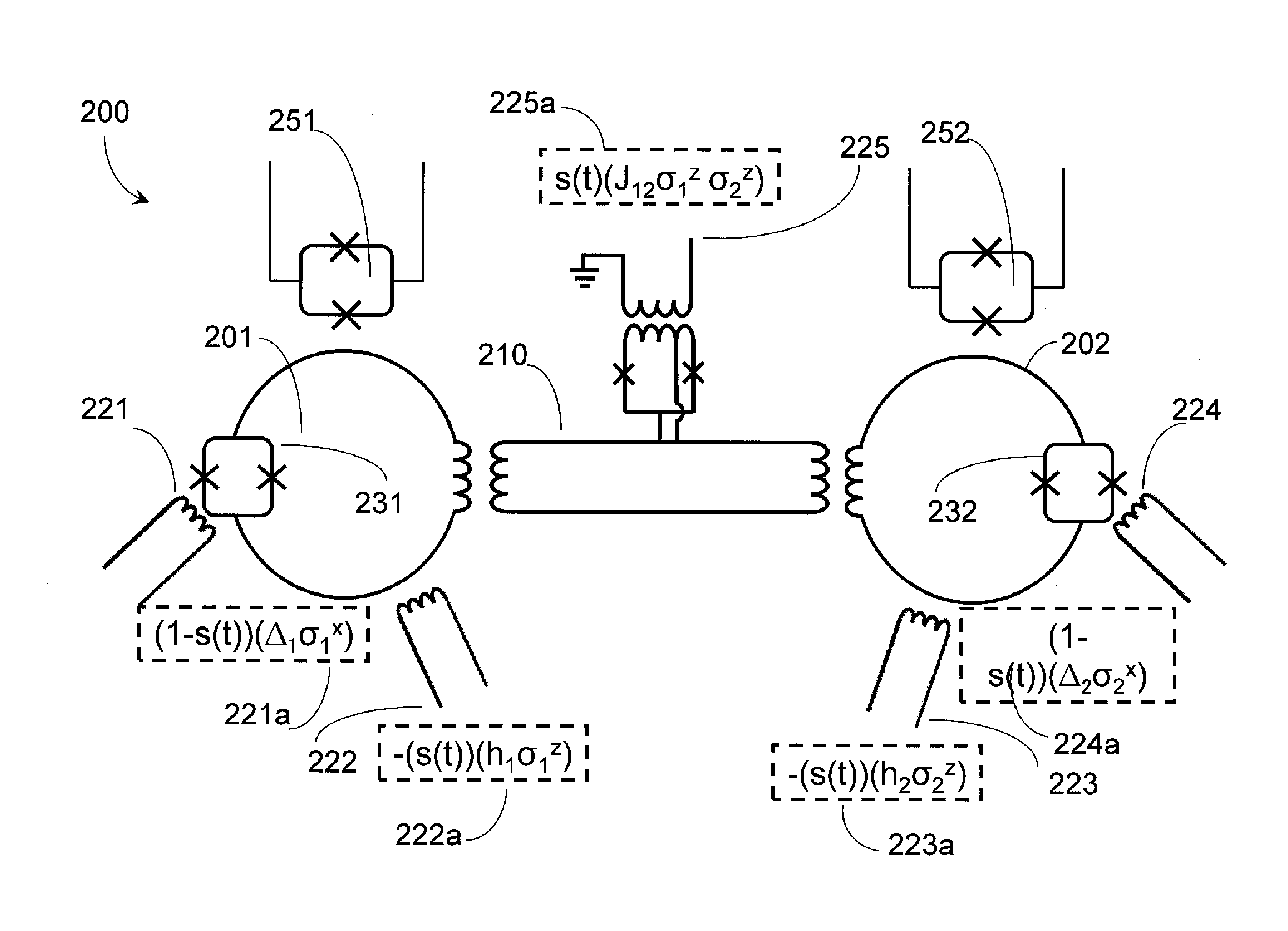
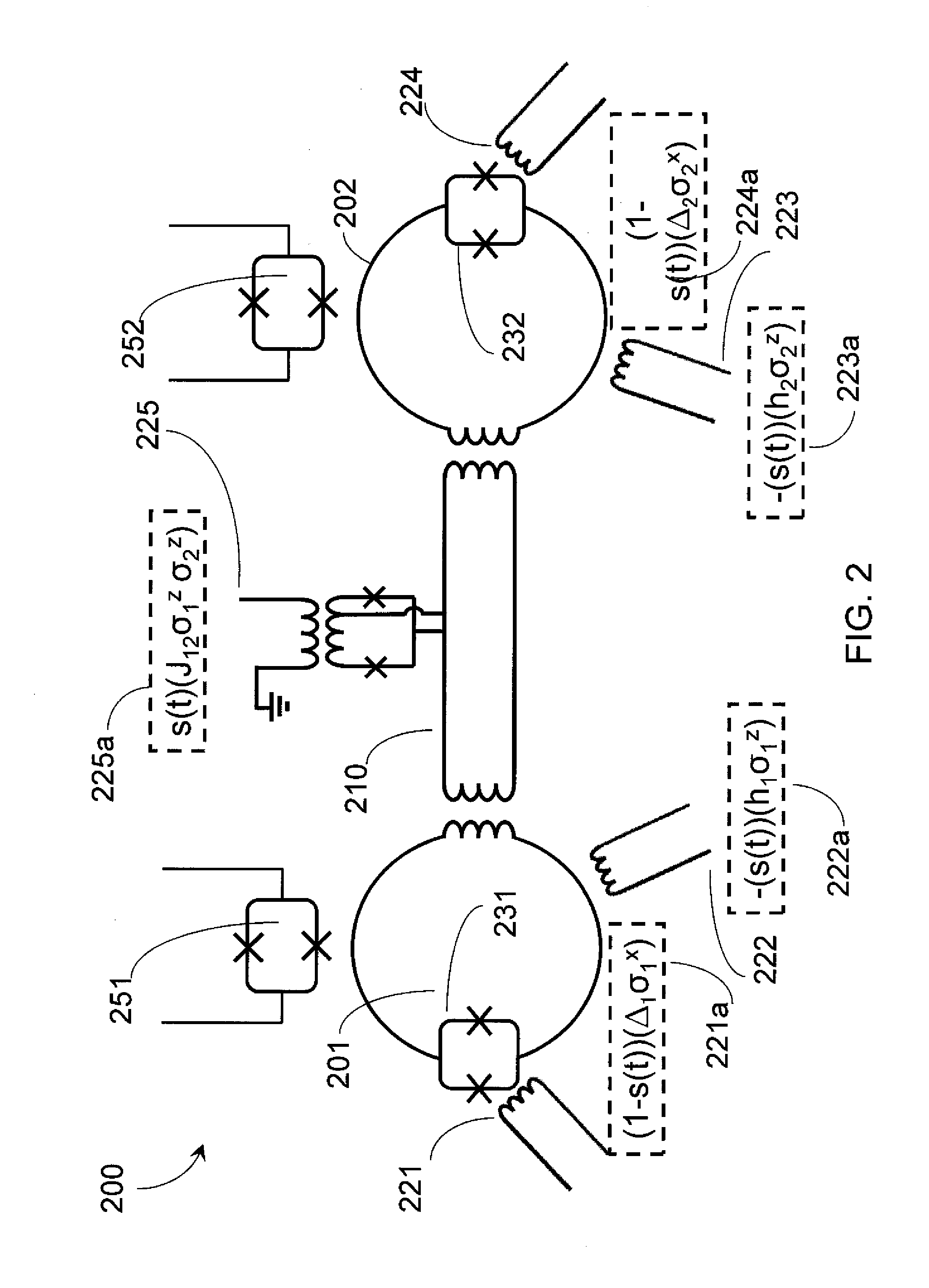
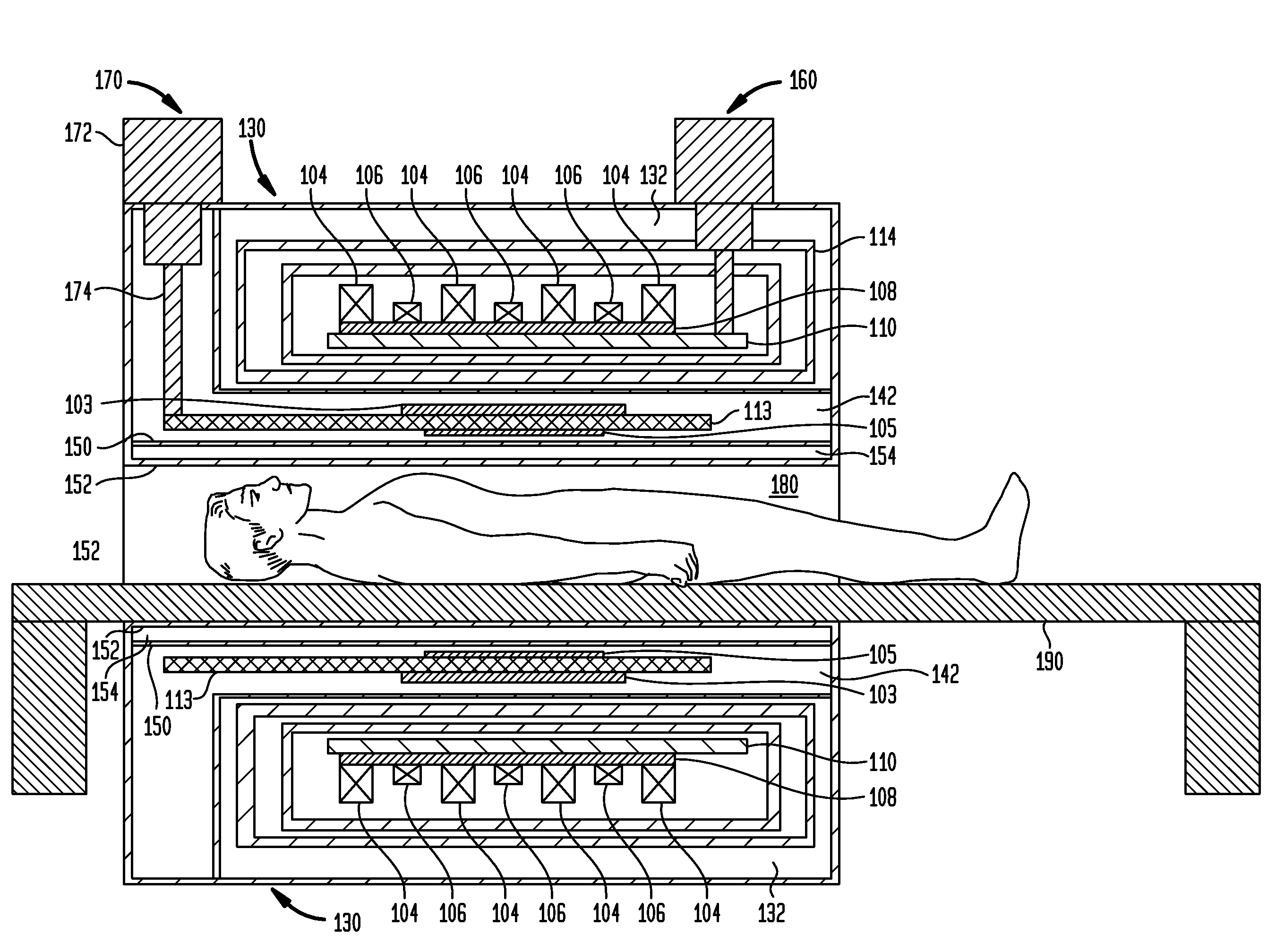
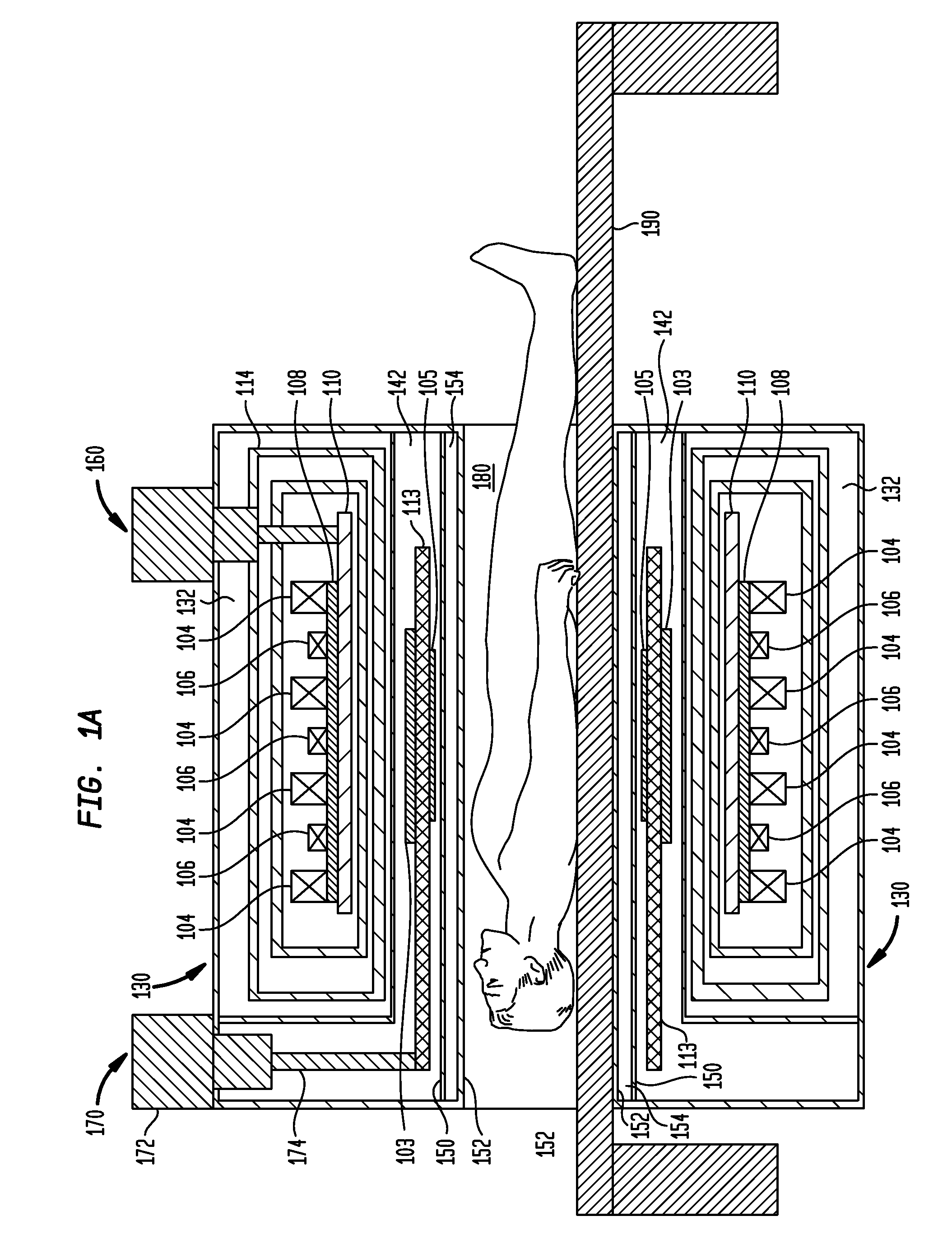
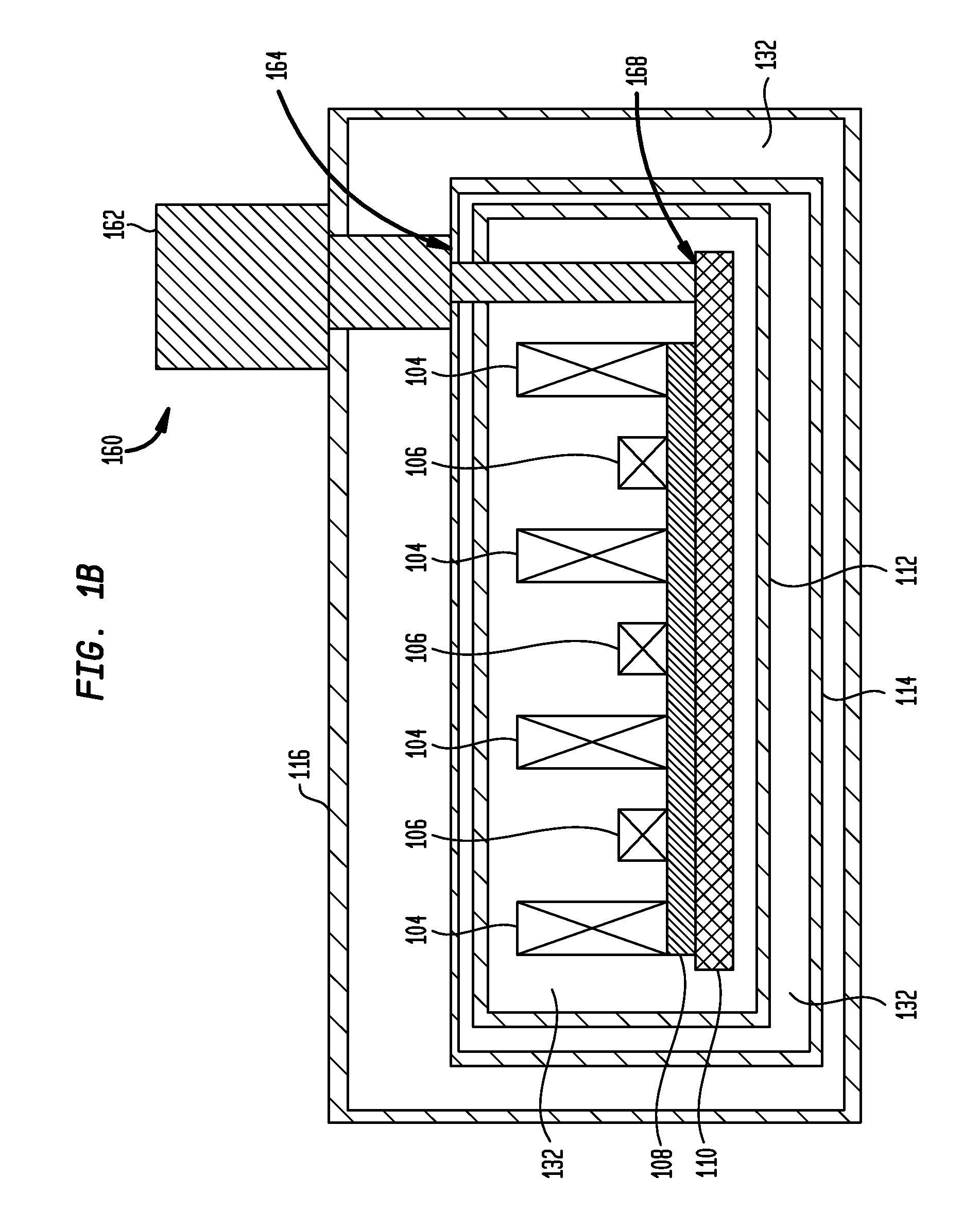
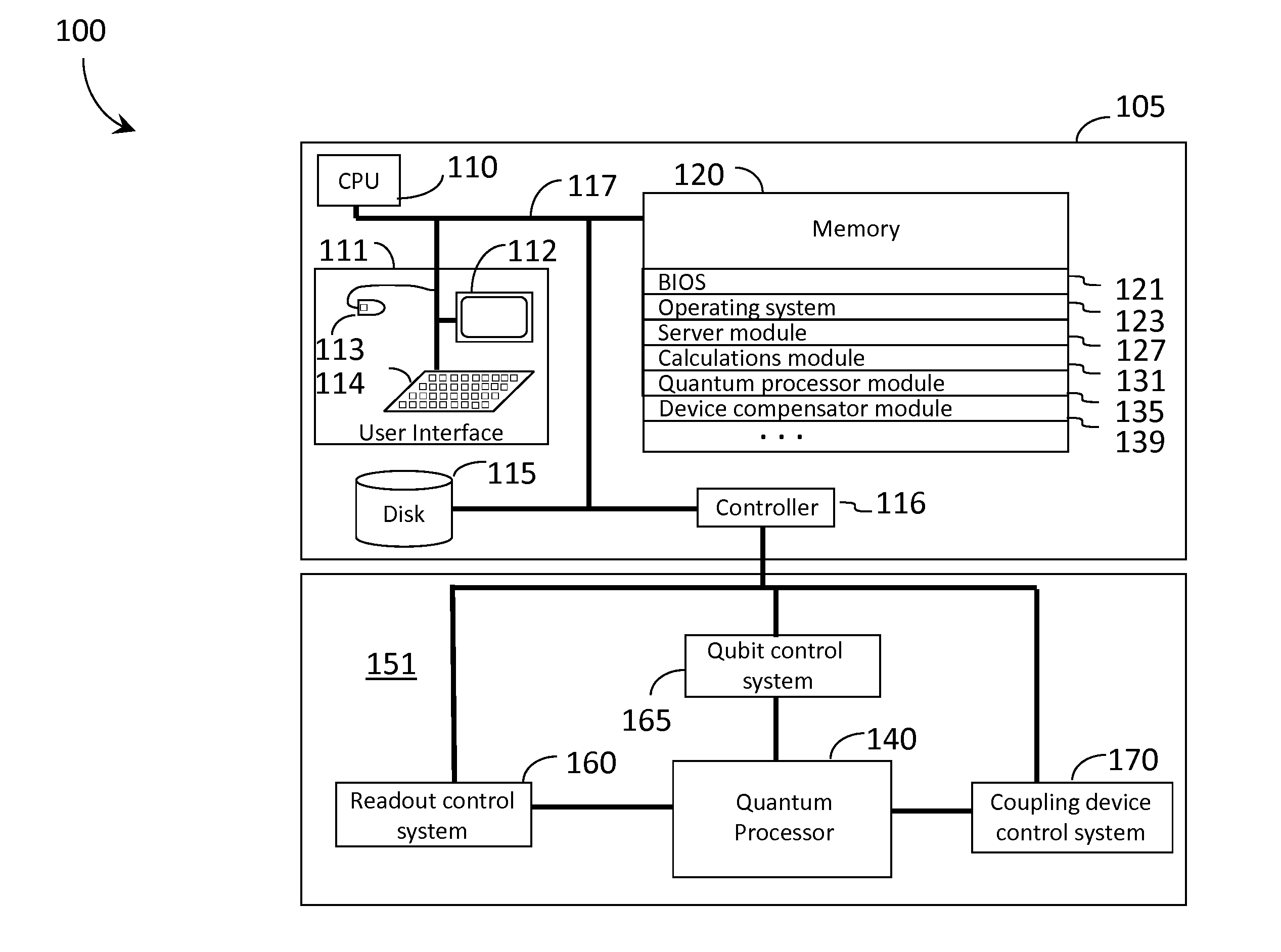
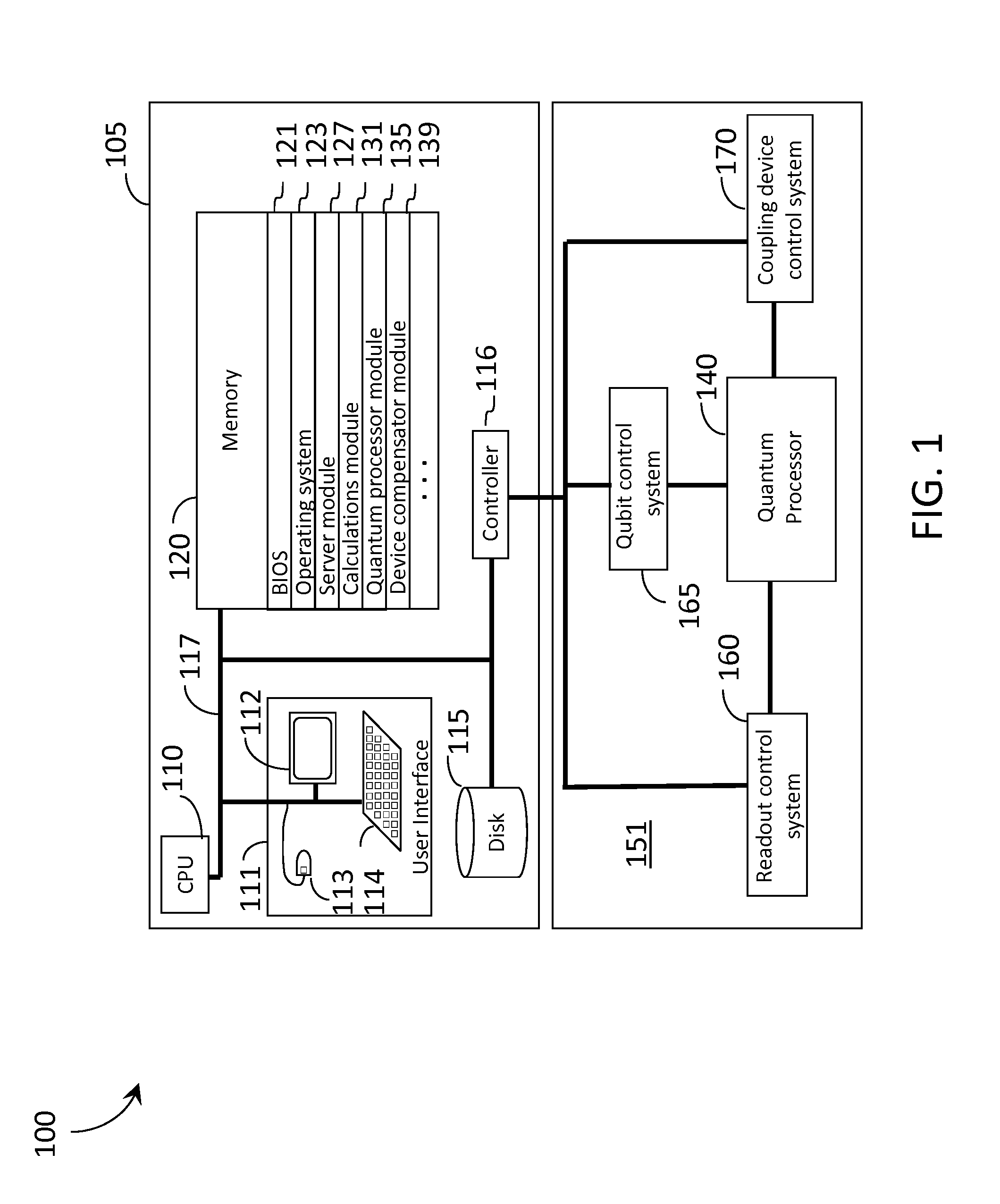
Systems, devices, and methods for controllably coupling qubits
InactiveUS20080238531A1Improve drawing legibilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCoupling systemInductor
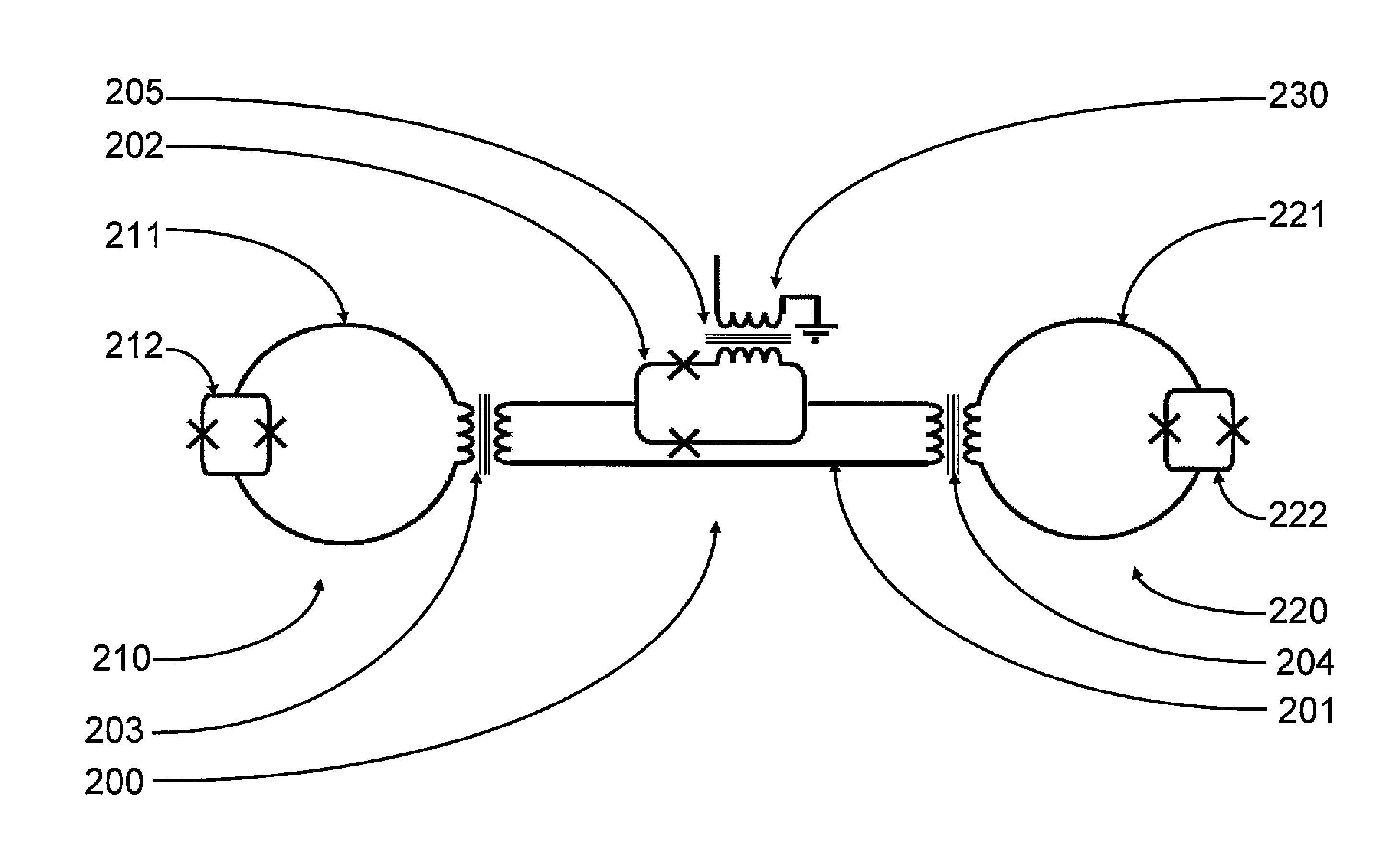
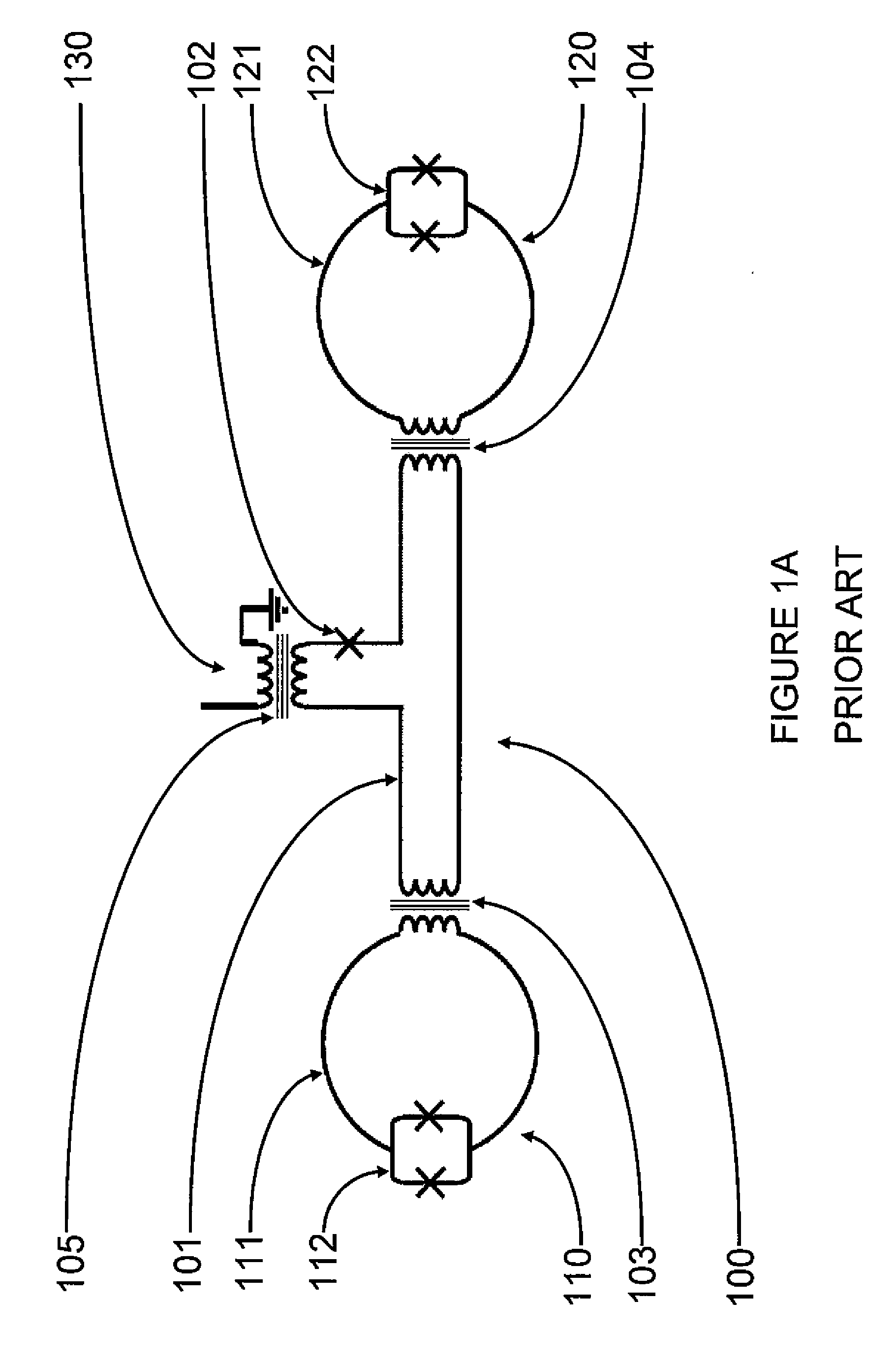
A coupling system may include an rf-SQUID having a loop of superconducting material interrupted by a compound Josephson junction; and a first magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a mutual inductance coupling the first magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction, wherein the loop of superconducting material positioned with respect to a first and second qubits to provide respective mutual inductance coupling therebetween. The coupling system may further include a second magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a second magnetic flux inductor mutual inductance coupling the second magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction. A superconducting processor may include the coupling system and two or more qubits. A method may include providing the first, the second and the third mutual inductances.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Sub-flux quantum generator
InactiveUS6885325B2Reliable and reliableUse is biasedAnalogue/digital conversionQuantum computersLondon penetration depthMagnetic flux
A sub-flux quantum generator includes an N-turn ring having a plurality of connected turns about a common aperture. The width of each respective turn in the N-turn ring exceeds the London penetration depth of a superconducting material used to make the respective turn. The generator includes a switching device configured to introduce a reversible localized break in the superconductivity of at least one turn in the N-turn ring. The generator includes a magnetism device configured to generate a magnetic field within the aperture of the N-turn ring. A method for biasing a superconducting structure that encompasses all or a portion of an N-turn ring. While a supercurrent is flowing through the N-turn ring, a quantized magnetic flux is introduced into the aperture of the N-turn ring using a reversible localized break in a turn in the ring. The quantized magnetic flux is trapped in the ring by removal of the localized break. The trapped flux biases the superconducting structure.
Owner:D-WAVE SYSTEMS
Superconducting low inductance qubit
A superconducting structure that can operate, for example, as a qubit or a superconducting switch is presented. The structure includes a loop formed from two parts. A first part includes two superconducting materials separated by a junction. The junction can, for example, be a 45° grain boundary junction. The second part can couple the two superconducting materials across the junction. The second part includes a superconducting material coupled to each of the two superconducting materials of the first part through c-axis junctions. Further embodiments of the invention can be as a coherent unconventional superconducting switch, or a variable phase shift unconventional superconductor junction device.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method and system for long range wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20120010079A1Improve power transfer efficiencyReduce eliminateDc network circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemLow dissipationCapacitance
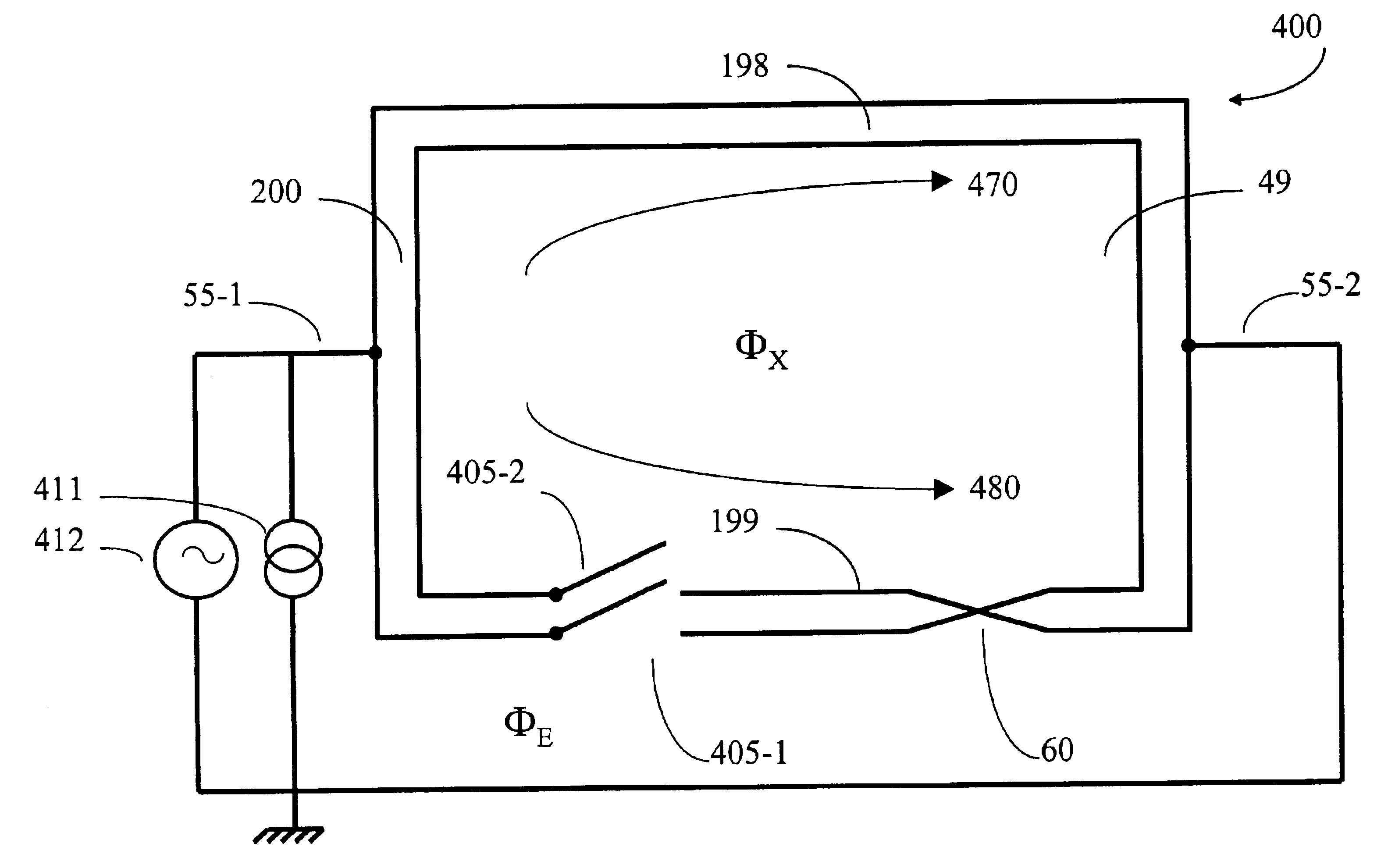
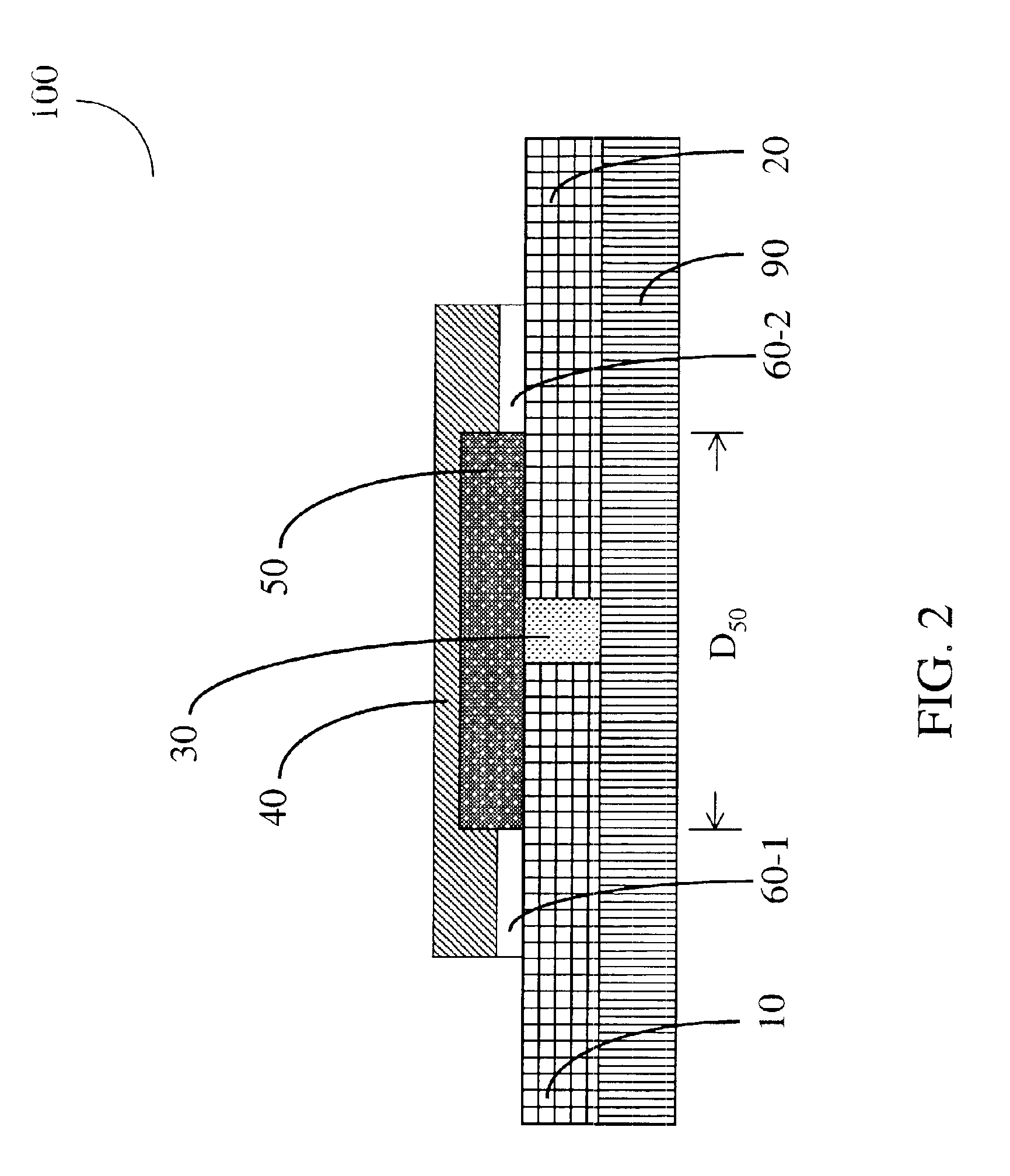
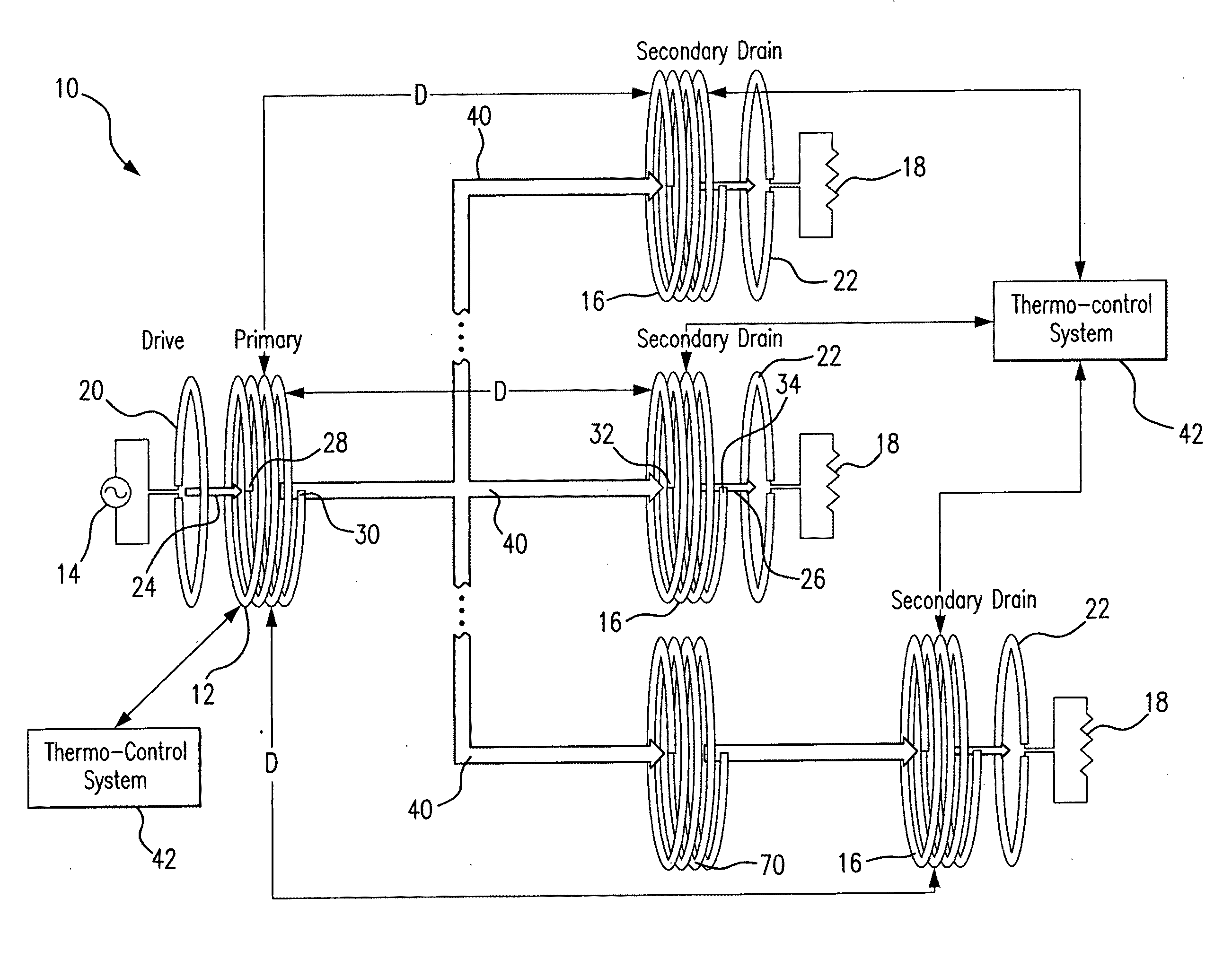
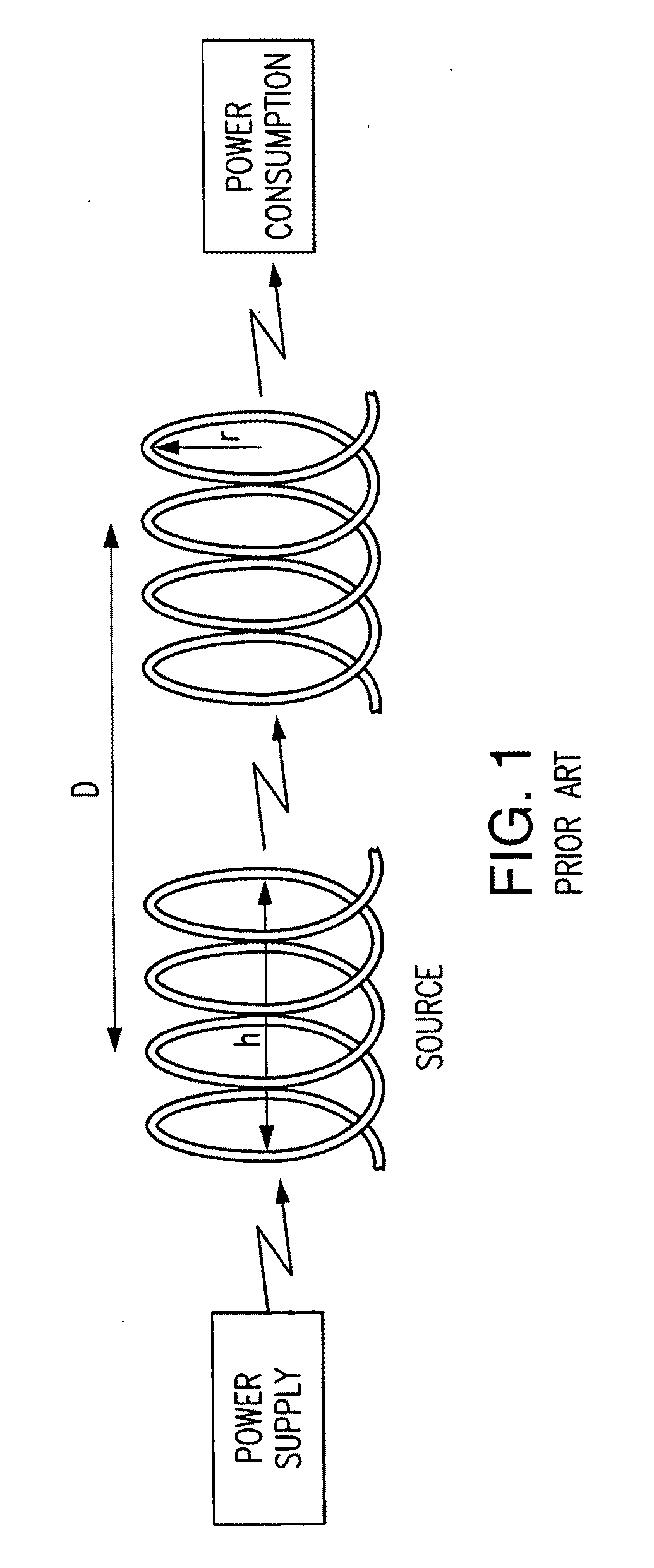
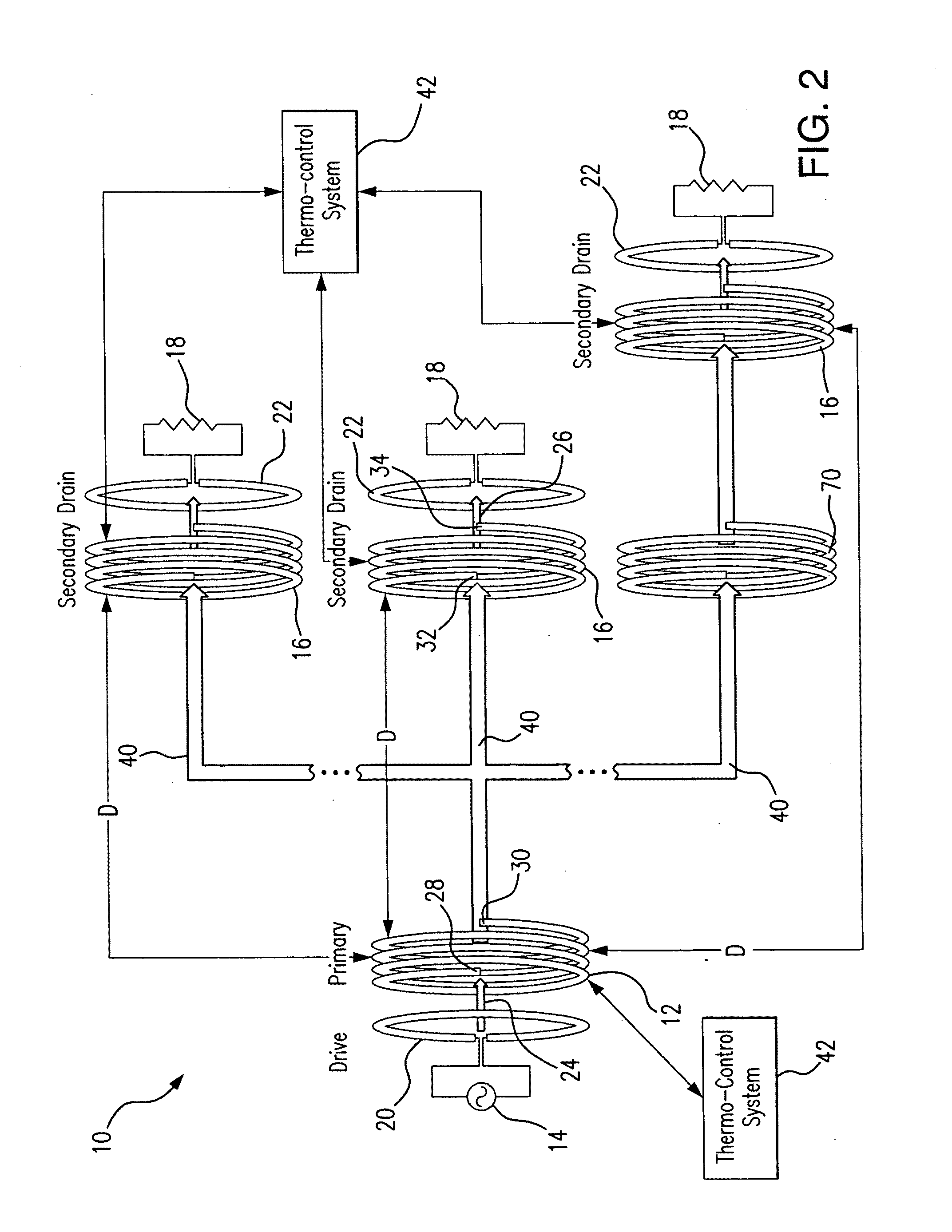
A wireless energy transfer system includes a primary and one (or more) secondary oscillators for transferring energy therebetween when resonating at the same frequency. The long range (up to and beyond 100 m) efficient (as high as and above 50%) energy transfer is achieved due to minimizing (or eliminating) losses in the system. Superconducting materials are used for all current carrying elements, dielectrics are either avoided altogether, or those are used with a low dissipation factor, and the system is operated at reduced frequencies (below 1 MHz). The oscillators are contoured as a compact flat coil formed from a superconducting wire material. The energy wavelengths exceed the coils diameter by several orders of magnitude. The reduction in radiative losses is enhanced by adding external dielectric-less electrical capacitance to each oscillator coil to reduce the operating frequency. The dielectric strength of the capacitor is increased by applying a magnetic cross-field to the capacitor to impede the electrons motion across an air gap defined between coaxial cylindrical electrodes.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
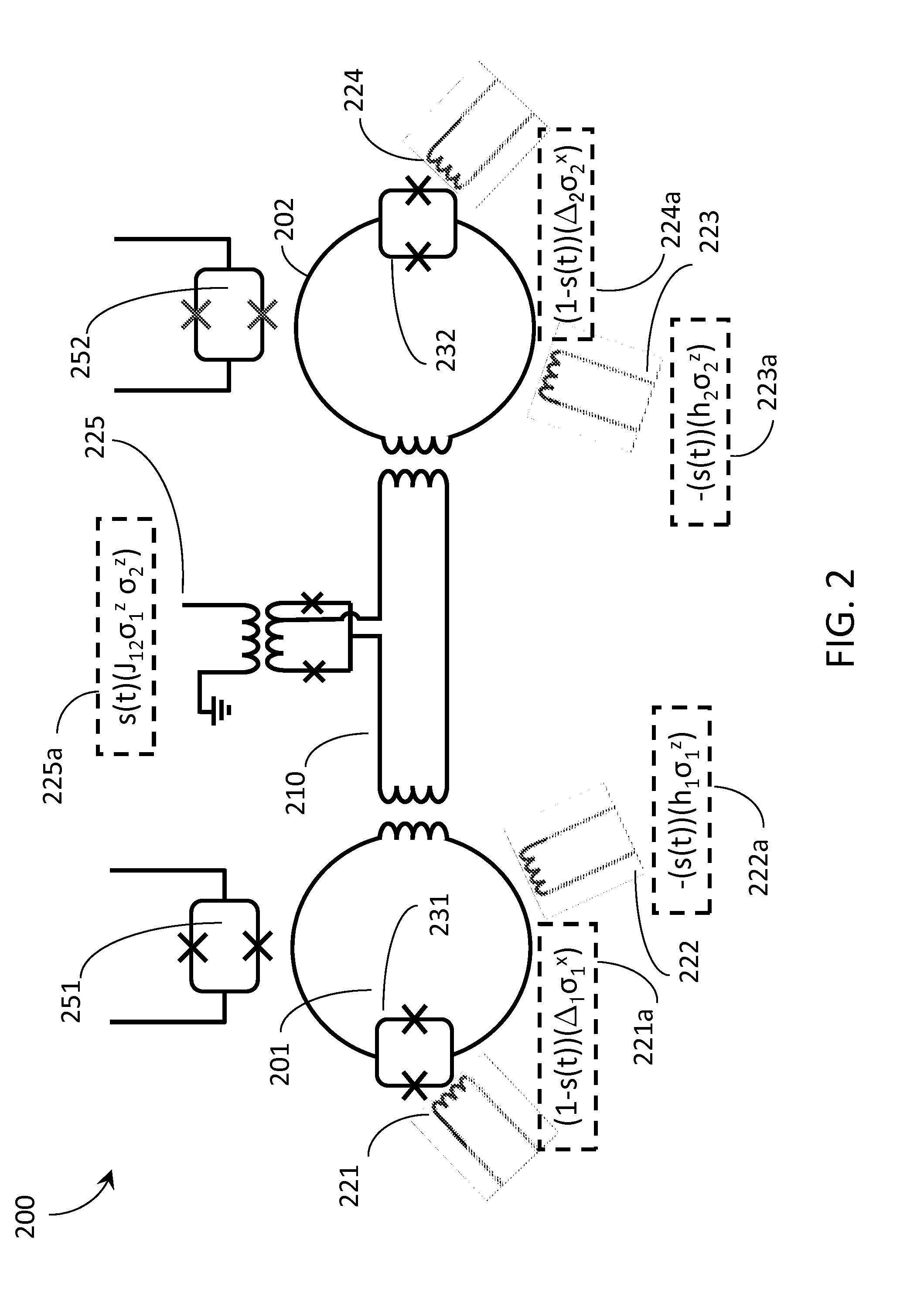
Universal adiabatic quantum computing with superconducting qubits
A quantum processor is operable as a universal adiabatic quantum computing system. The quantum processor includes physical qubits, with at least a first and second communicative coupling available between pairs of qubits via an in-situ tunable superconducting capacitive coupler and an in-situ tunable superconducting inductive coupler, respectively. Tunable couplers provide diagonal and off-diagonal coupling. Compound Josephson junctions (CJJs) of the tunable couplers are responsive to a flux bias to tune a sign and magnitude of a sum of a capacitance of a fixed capacitor and a tunable capacitance which is mediated across a pair of coupling capacitors. The qubits may be hybrid qubits, operable in a flux regime or a charge regime. Qubits may include a pair of CJJs that interrupt a loop of material and which are separated by an island of superconducting material which is voltage biased with respect to a qubit body.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
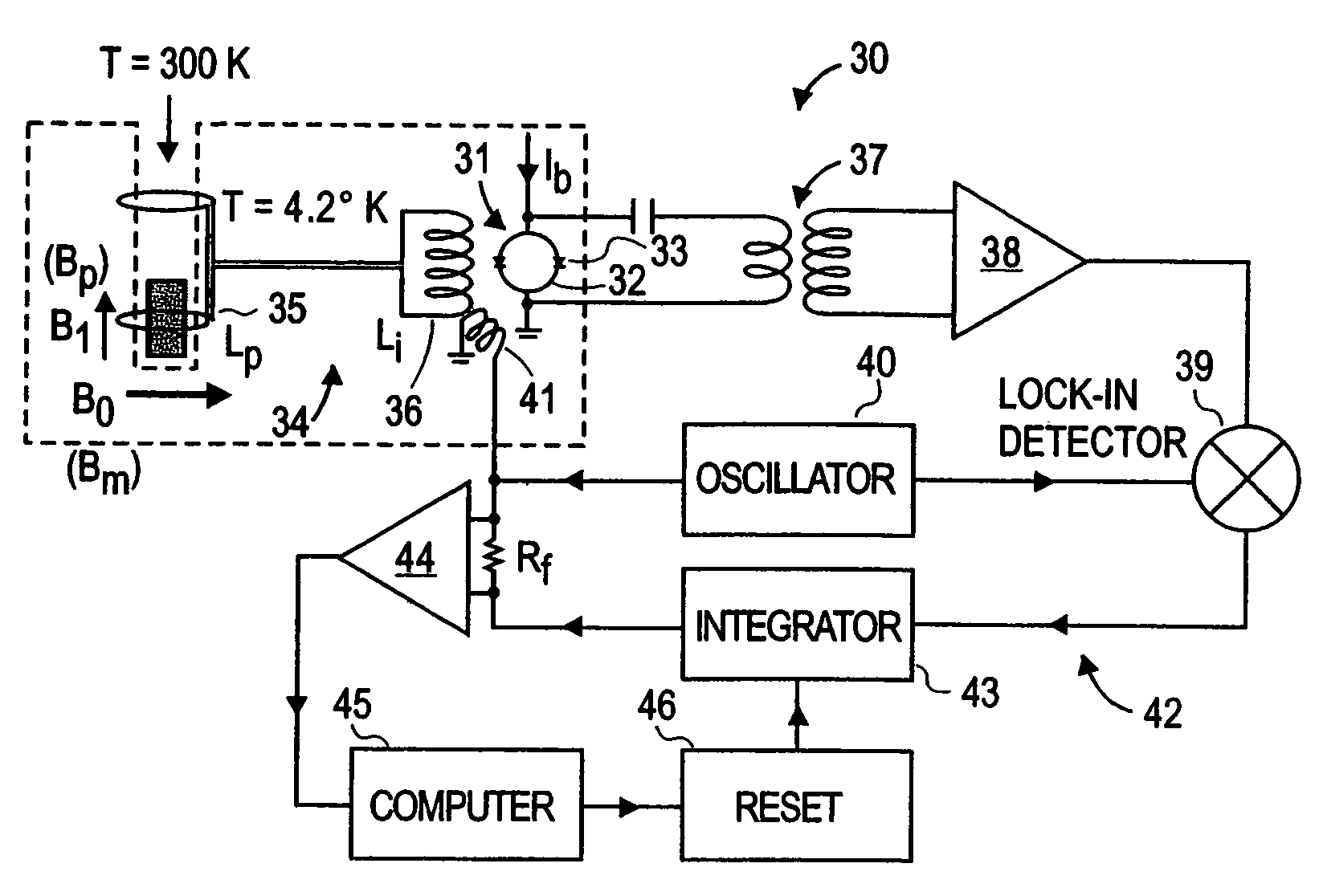
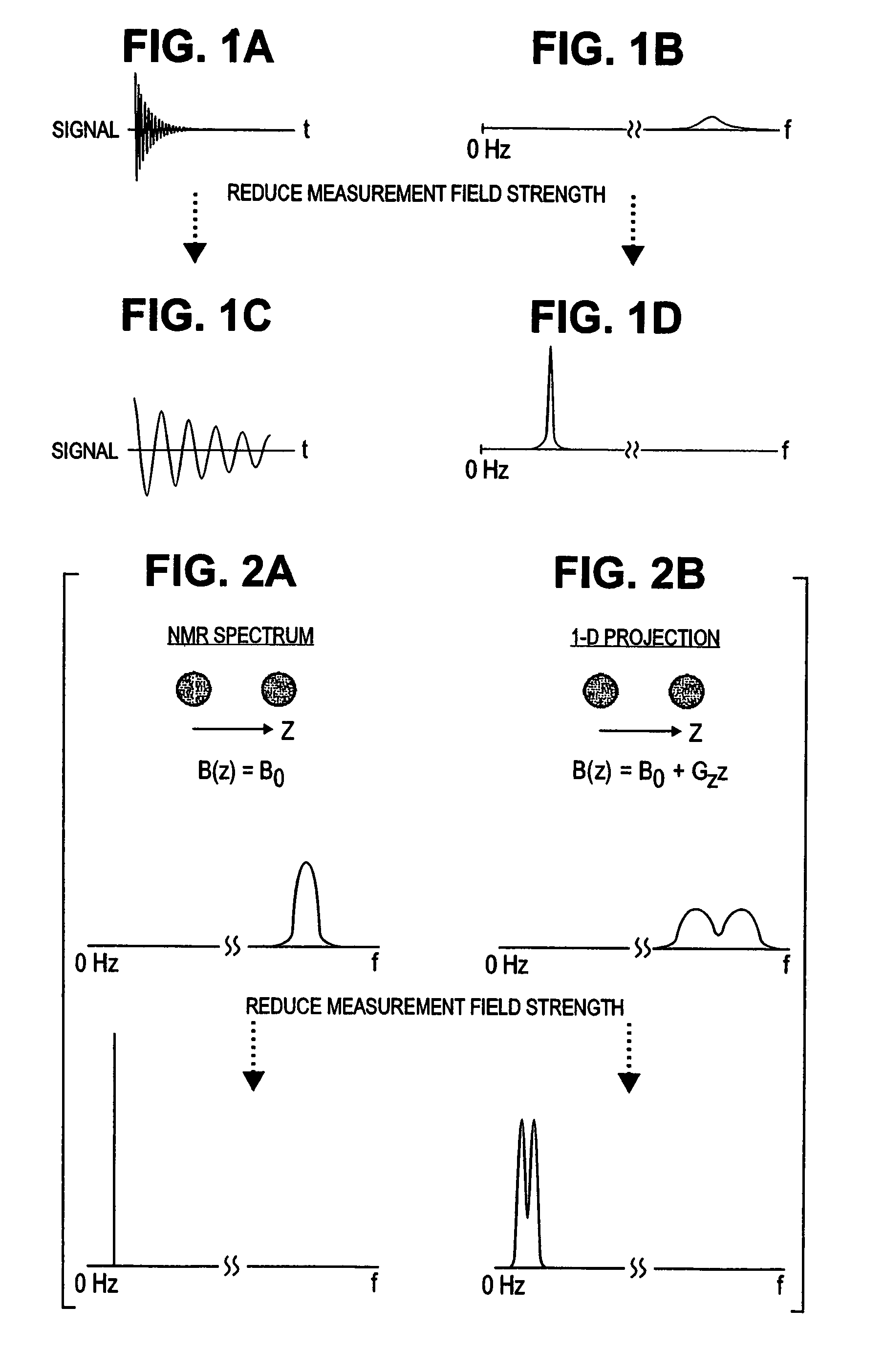
NMR and MRI apparatus and method
InactiveUS7187169B2Avoid interferenceRaise the ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionLow noiseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
NMR and MRI apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060091881A1Avoid interferenceRaise the ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionLow noiseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
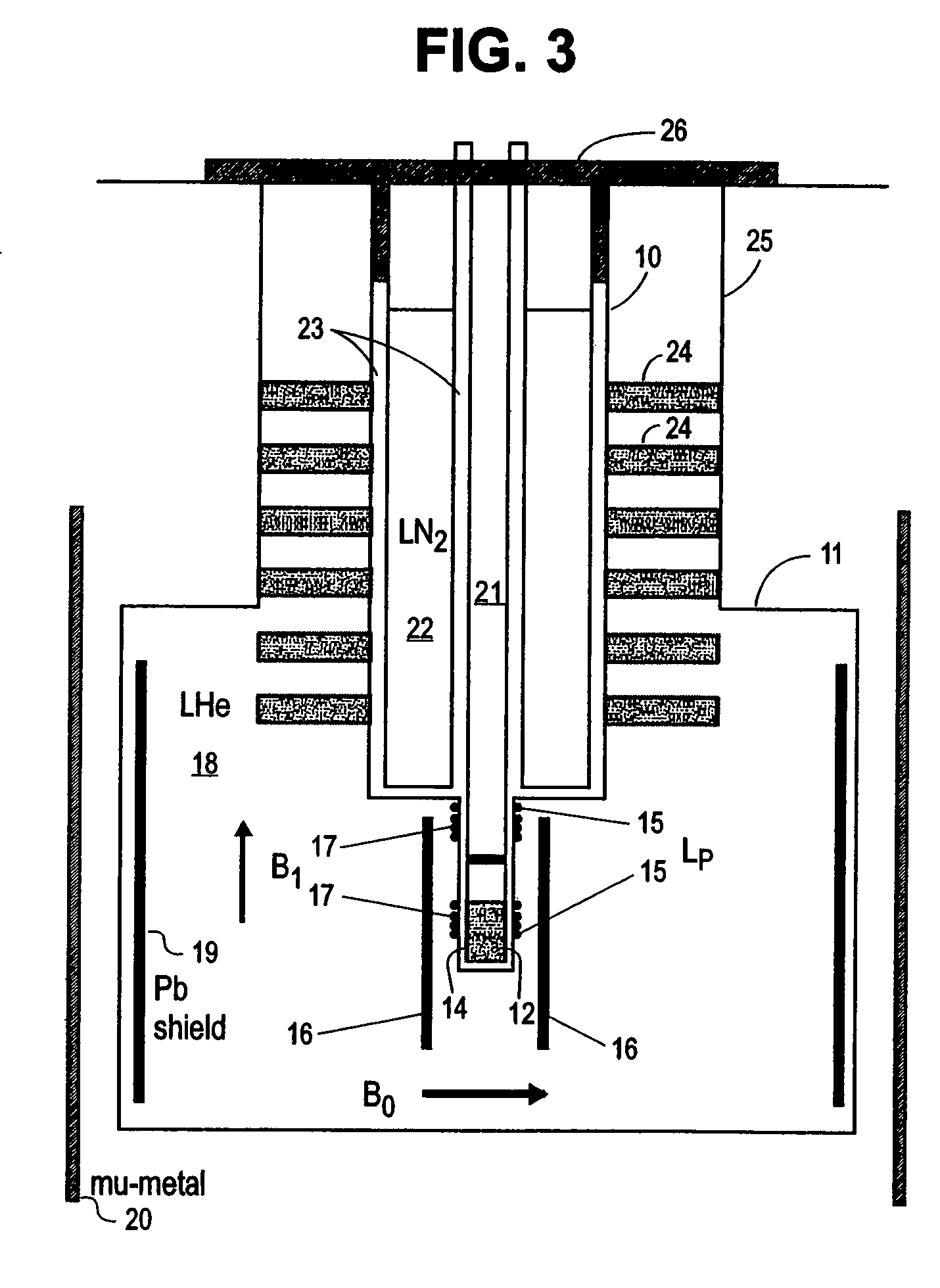
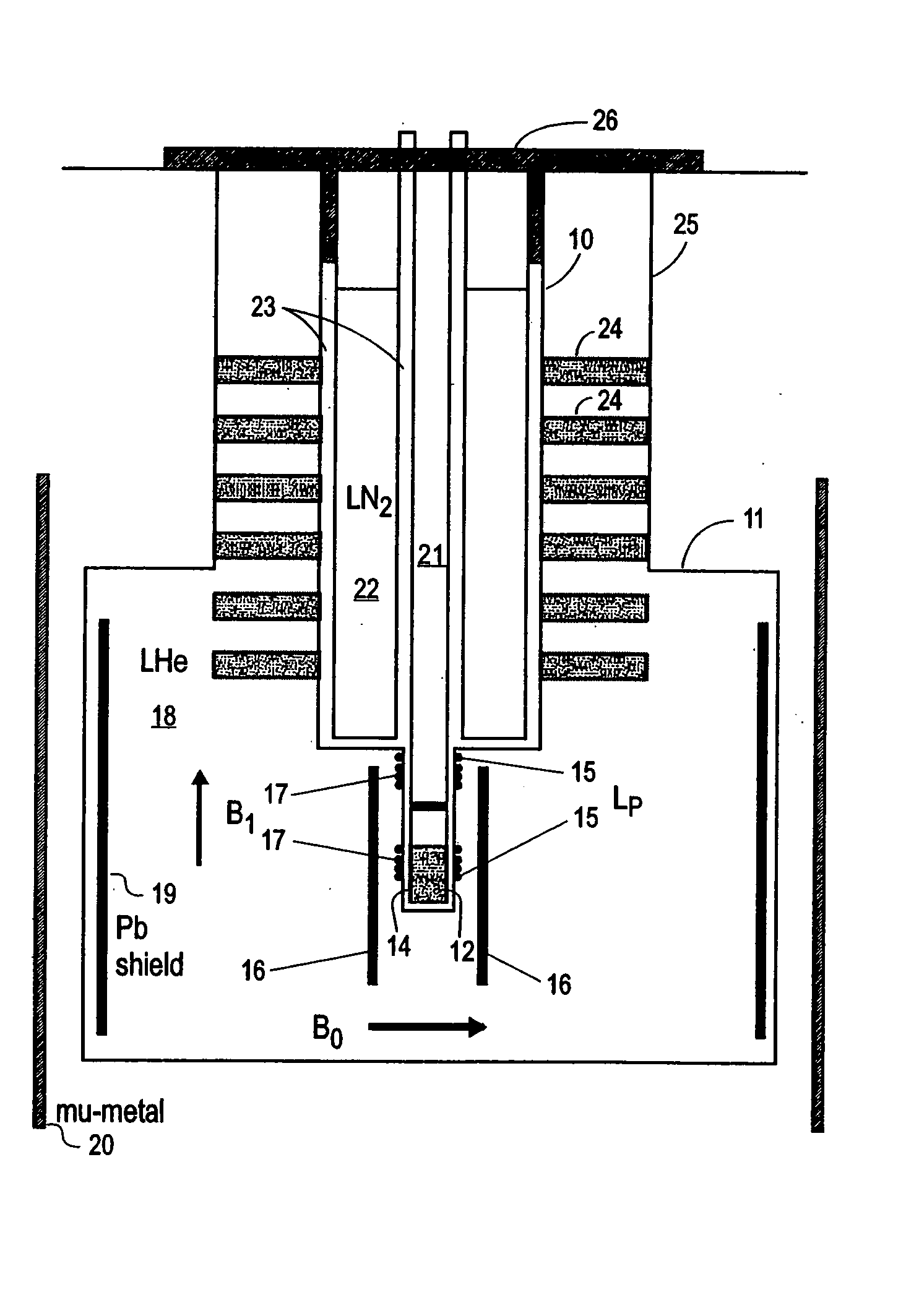
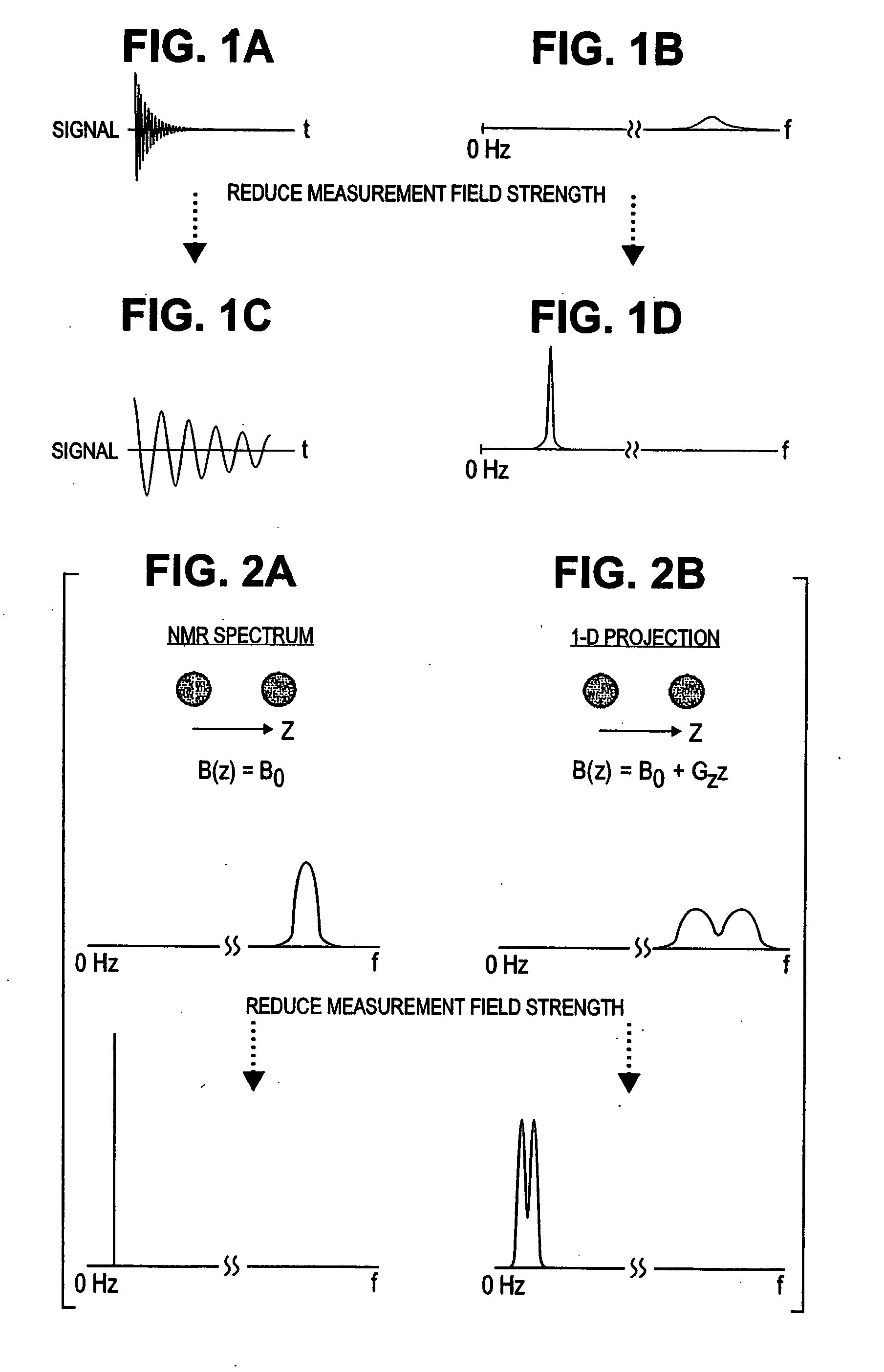
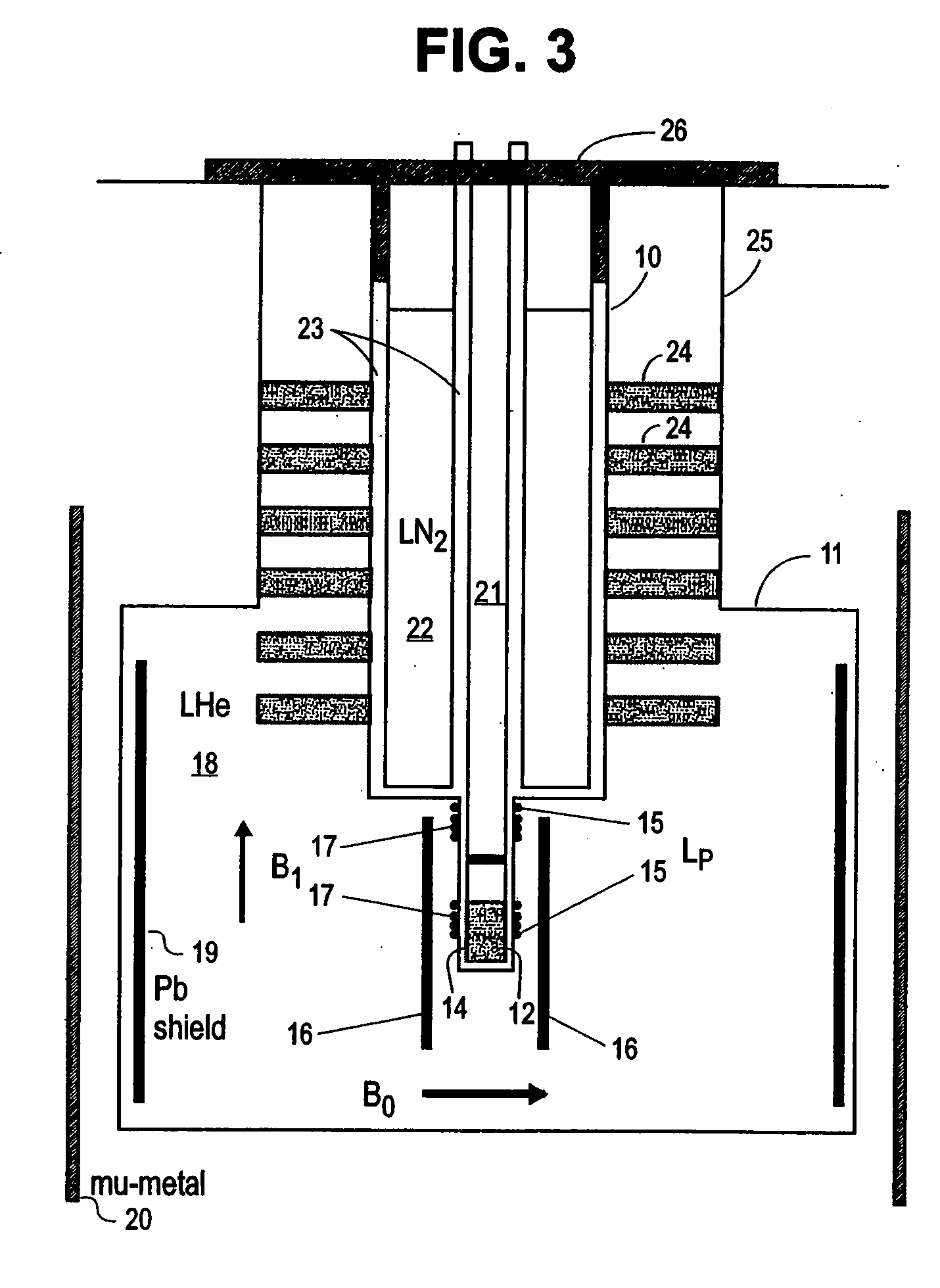
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signals are detected in microtesla fields. Prepolarization in millitesla fields is followed by detection with an untuned dc superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer. Because the sensitivity of the SQUID is frequency independent, both signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and spectral resolution are enhanced by detecting the NMR signal in extremely low magnetic fields, where the NMR lines become very narrow even for grossly inhomogeneous measurement fields. Additional signal to noise benefits are obtained by use of a low noise polarization coil, comprising litz wire or superconducting materials. MRI in ultralow magnetic field is based on the NMR at ultralow fields. Gradient magnetic fields are applied, and images are constructed from the detected NMR signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Superconducting quantum antenna
ActiveUS7369093B2Increase sensitivity-orPointing stableSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsThermal insulationElectromagnetic electron wave
An antenna for electromagnetic waves including a quantum interference filter, at least one low-temperature transistor and primary antenna structures, means for deriving an electromagnetic wave from the circuit, cooling elements and insulating means. The interference filter and the transistor act as active components, the primary antenna structure is connected up to at least one of the active components in such a way that upon incidence of an electromagnetic wave on the primary antenna structure there is present at the output of the at least one active component a conducted electromagnetic wave, and wherein at least one part of the circuit and at least one part of the primary antenna structure are thermally insulated, the thermal insulation is frequency transparent to electromagnetic waves, and the cooling elements are designed to cool down at least one part of the circuit below the transition temperature of at least one of the superconducting materials.
Owner:QEST QUANTENELEKTRONISCHE SYST TUBINGEN GMBH
Multifilament Superconductor Having Reduced AC Losses and Method for Forming the Same
ActiveUS20110319271A1CoatingsCable/conductor manufactureHigh-temperature superconductivityMaterials science
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC +1
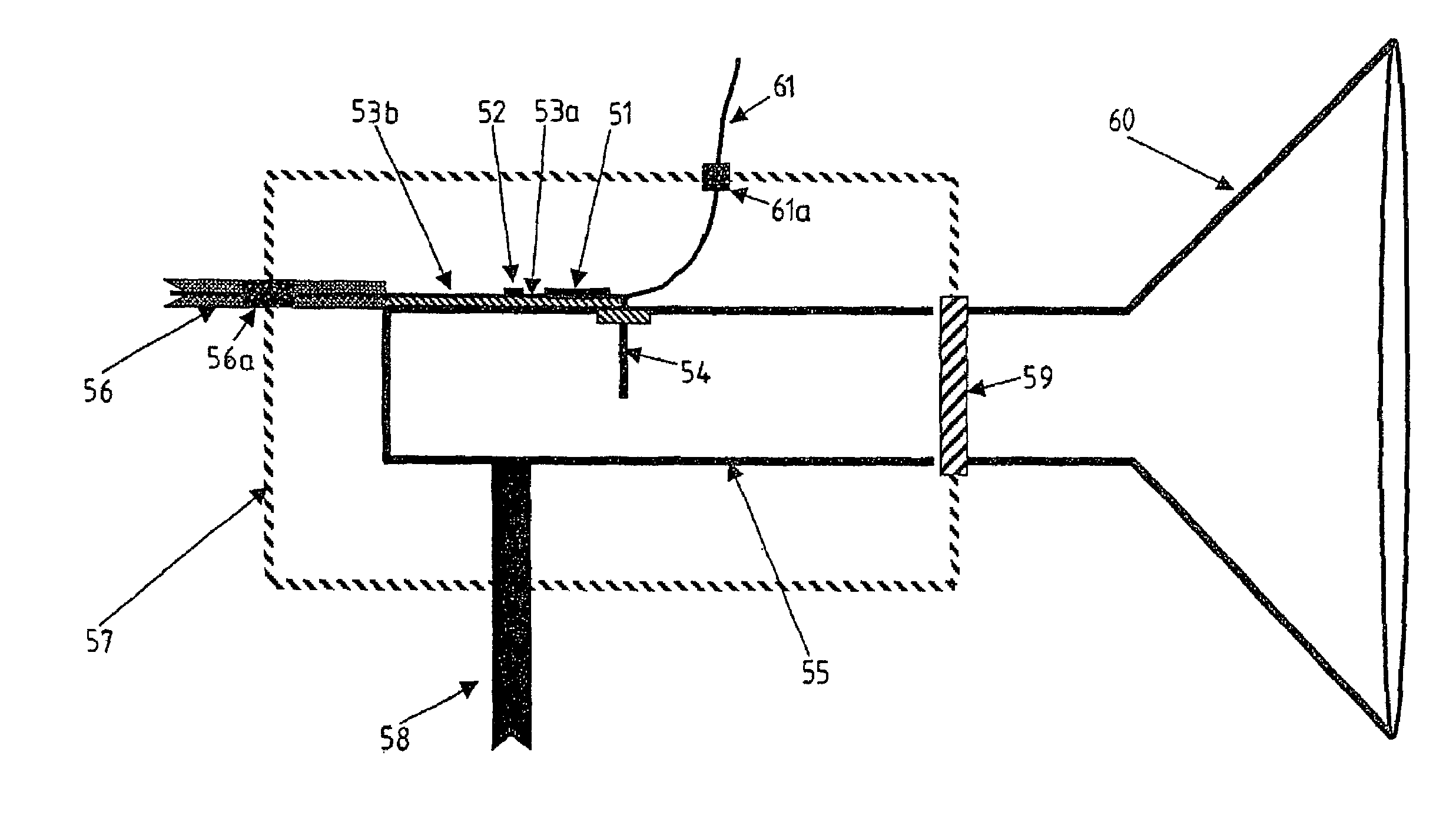
NMR probe having an inner quadrature detection coil combined with a spiral wound outer coil for irradiation
InactiveUS6876200B2Minimal mutual inductanceImprove reliability and power efficiency and sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceClose couplingSaddle coil
A high resolution NMR probe having two or more resonators, an inner resonator which is closely coupled to a sample and is used to stimulate and receive a response from one nuclear species, and an outer resonator to induce transitions in another nuclear species, wherein the resonators may be provided with cooling capability and may be made of superconducting material, and wherein the inner resonator may be a saddle coil or a birdcage coil with capability of being tuned, and wherein the outer resonator may be one or more spiral wound saddle coil.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
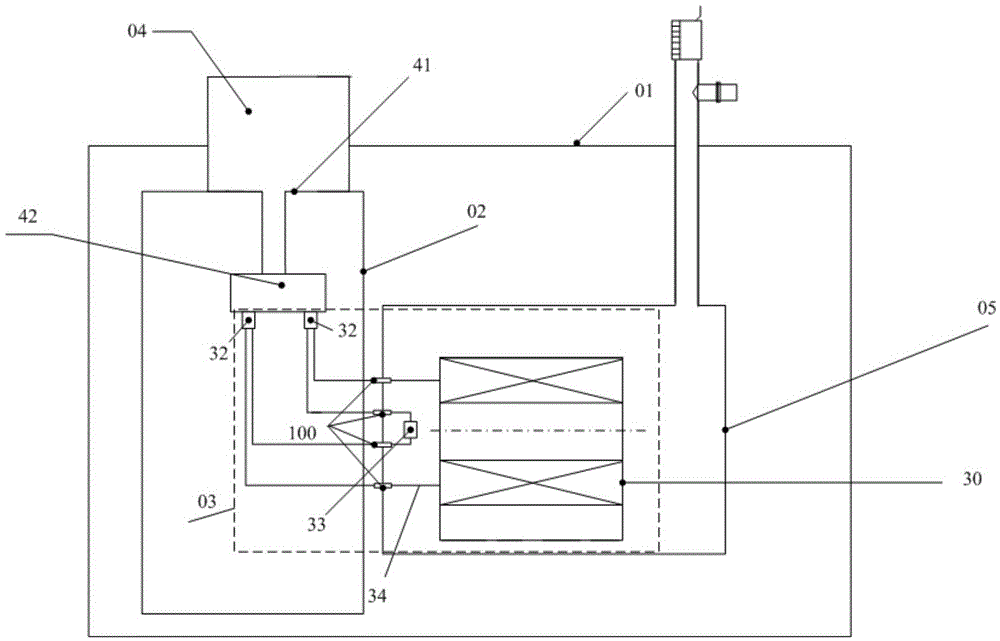
Multi-field coupling test system for superconducting material at temperature of between 373 and 4.2K
InactiveCN102323160AEasy to replaceImprove performanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMulti fieldTest sample
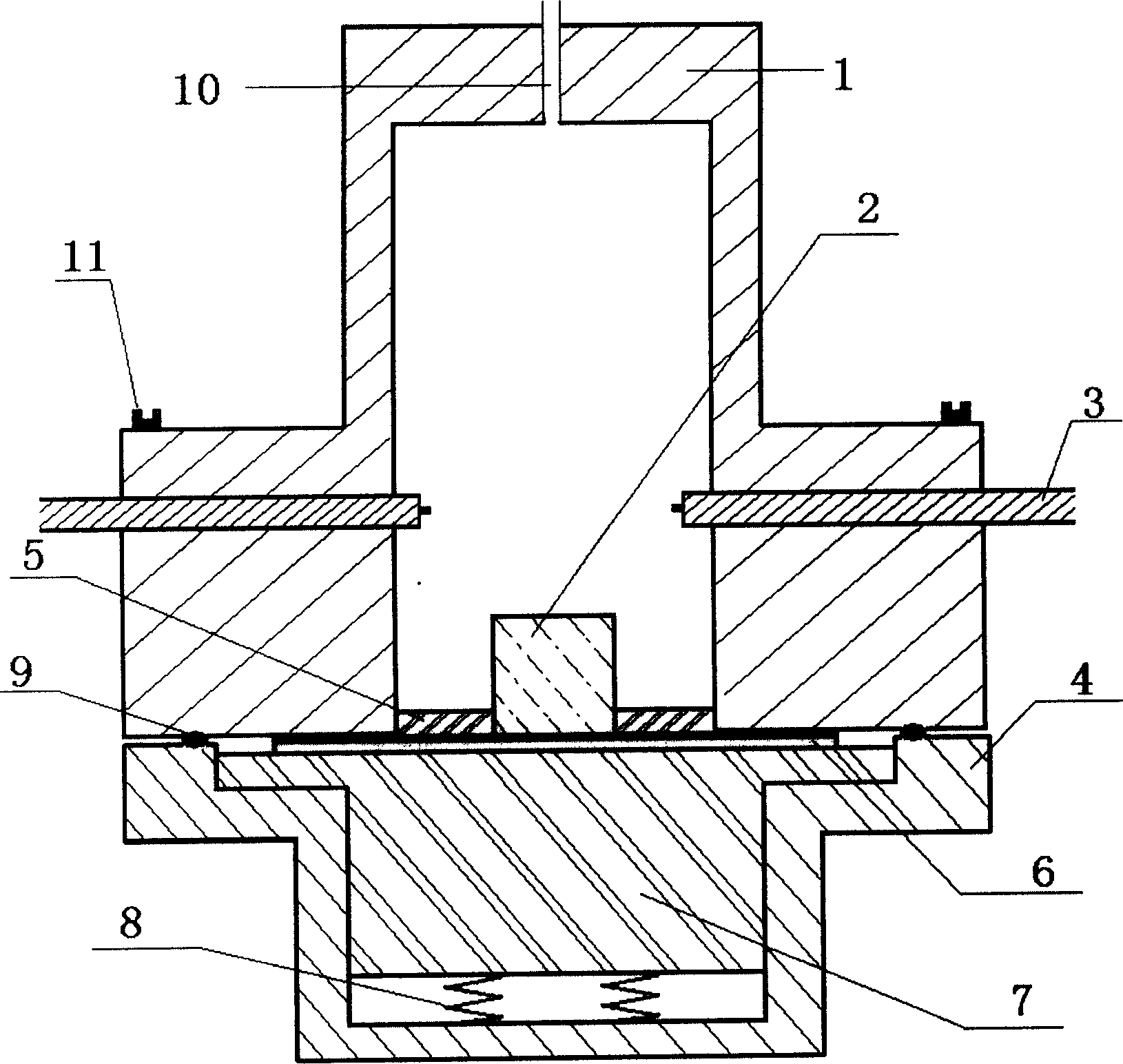
The invention discloses a multi-field coupling test system for a superconducting material at the temperature of between 373 and 4.2K. The system comprises a large-sized temperature alternating experiment box, a liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask, a Dewar flask bracket, a mechanical test experiment device, a liquid helium injection pipe, a plurality of heating bodies, an air circulating device and an air circulating fan, wherein the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask is sleeved inside the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the Dewar flask bracket is arranged at the bottom of a box body at the bottom of the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask; the mechanical test experiment device and the liquid helium injection pipe are arranged in coordination with the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask and the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the plurality of heating bodies are arranged inside the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the air circulating device is arranged behind the box body of the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; and the air circulating fan is connected with the air circulating device through a bearing. By the multi-field coupling test system for the superconducting material at the temperature of between 373 and 4.2K, the defects of poor functions, small application ranges, long test time, high cost and the like in the prior art can be overcome, so that the system has the advantages of making a test sample conveniently replaced and saving test time, along with a powerful function, a wide application range and low cost.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for producing boride thin films
InactiveUS6797341B2High purityReduce roughnessElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseBoron containing
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
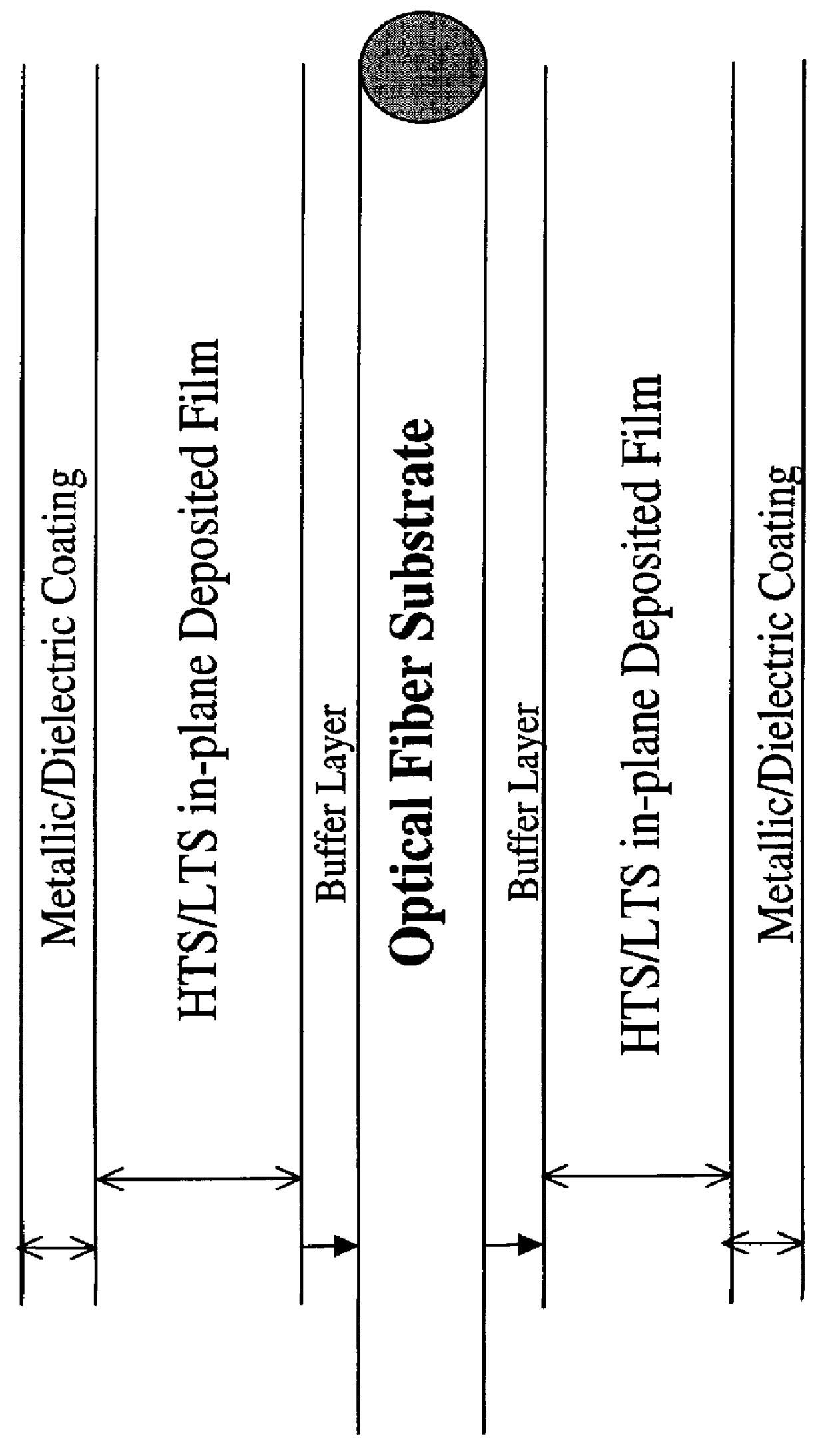
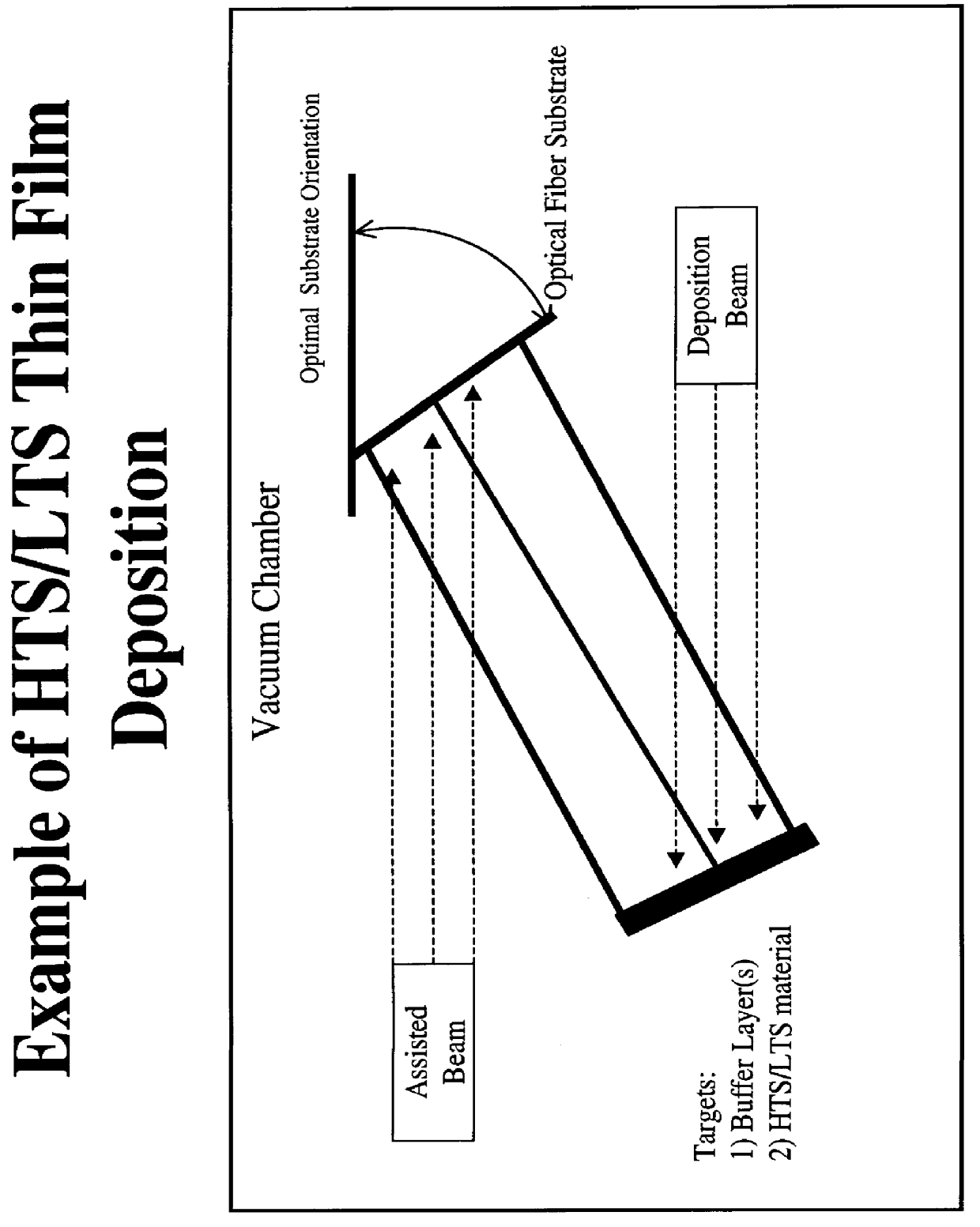
Superconducting wires fabricated using thin optical fibers
This patent application relates to the use of thin high temperature fibers, specifically optical fibers, for use as a substrate material in the fabrication of long-length low temperature superconducting and high temperature superconducting wire. The superconducting material is deposited on the fiber using either a thin or thick film deposition technique. The fiber can have a dual use in the transmission of data using either traditional optical means or the transmission of electrical current via the deposited superconductor. A buffer layer or layers is used between the high temperature fiber and the superconductor to promote grain alignment and enhance the current carrying capacity of the wire.
Owner:REY CHRISTOPHER M
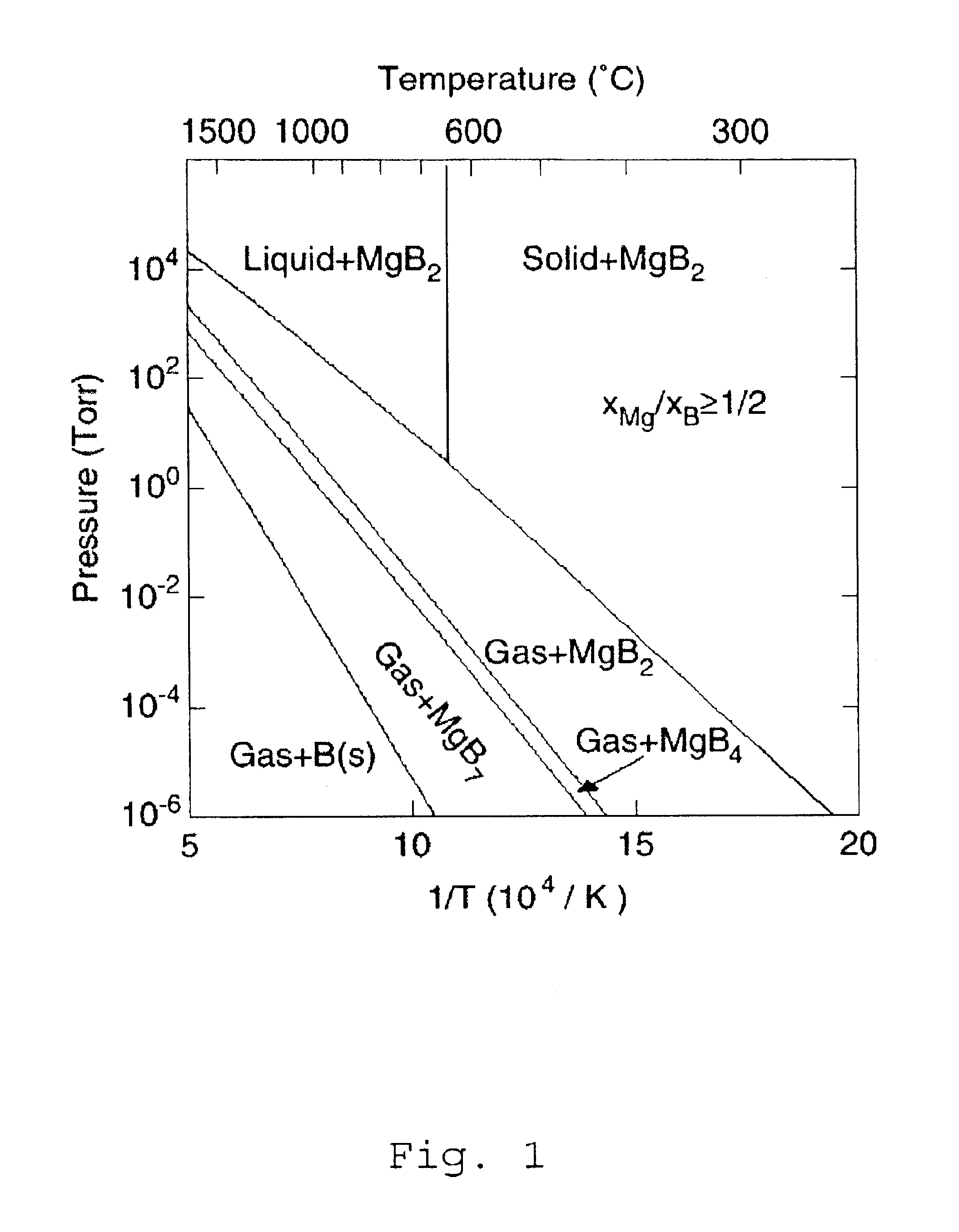
MgB2 superconducting material and its preparation method
InactiveCN1329370AEnhanced pinningGrain refinementSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsArgon atmosphereMetal
The present invention relates to a novel MgB2 superconductivity material with high critical current density and its preparation method. It is characterized by that in the MgB2 superconductivity material, one method element Me selected from Ti, Zr, Mo, Nb, W or Hf is doped, and the mole ratio of its composition is Mg:Me:B=(0.8-0.9):(0.1-0.2):2. Its preparation method includes the steps of proportioning Mg powder, Me powder and B material component, mixing them uniformly and sintering at normal pressure in argon atmosphere. This invented MgB2 superconductivity material possesses high critical curcent density at above 10K temp., and its performance also is excellent under the magnetic field.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Systems and methods for removing unwanted interactions in quantum devices
ActiveUS20150262073A1Quantum computersGeneral purpose stored program computerMagnetic susceptibilityQuantum devices
Systems, devices, articles, methods, and techniques for advancing quantum computing by removing unwanted interactions in one or more quantum processor. One approach includes creating an updated plurality of programmable parameters based at least in part on a received value for the characteristic magnetic susceptibility of the qubit in the at least one quantum processor, and returning the updated plurality of programmable parameters. Examples programmable parameters include local biases, and coupling values characterizing the problem Hamilton. Also, for example, a quantum processor may be summarized as including a first loop of superconducting material, a first compound Josephson junction interrupting the first loop of superconducting material, a first coupler inductively coupled to the first loop of superconducting material, a second coupler inductively coupled to the first loop of superconducting material, and a second loop of superconducting material proximally placed to the first loop of superconducting material inductively coupled to the first coupler and the second coupler.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
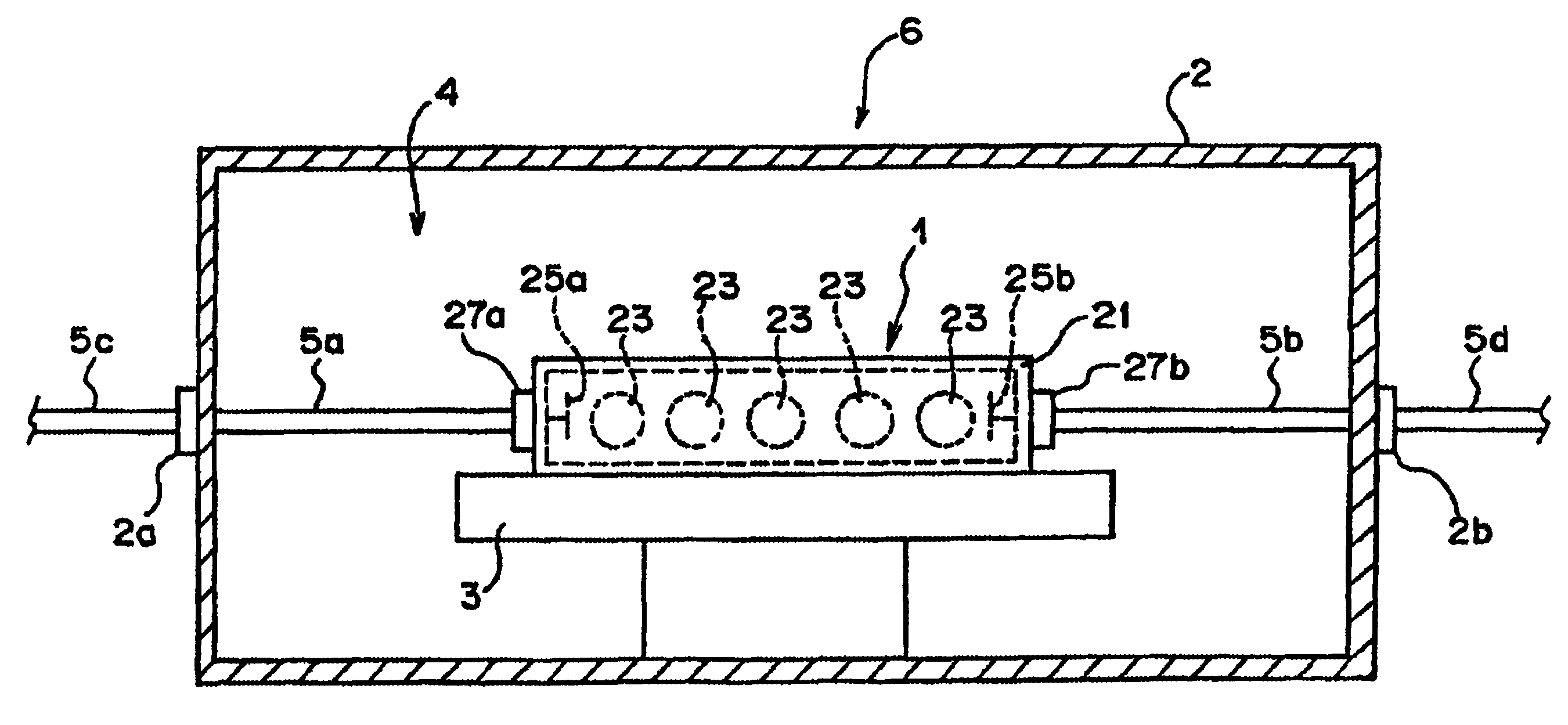
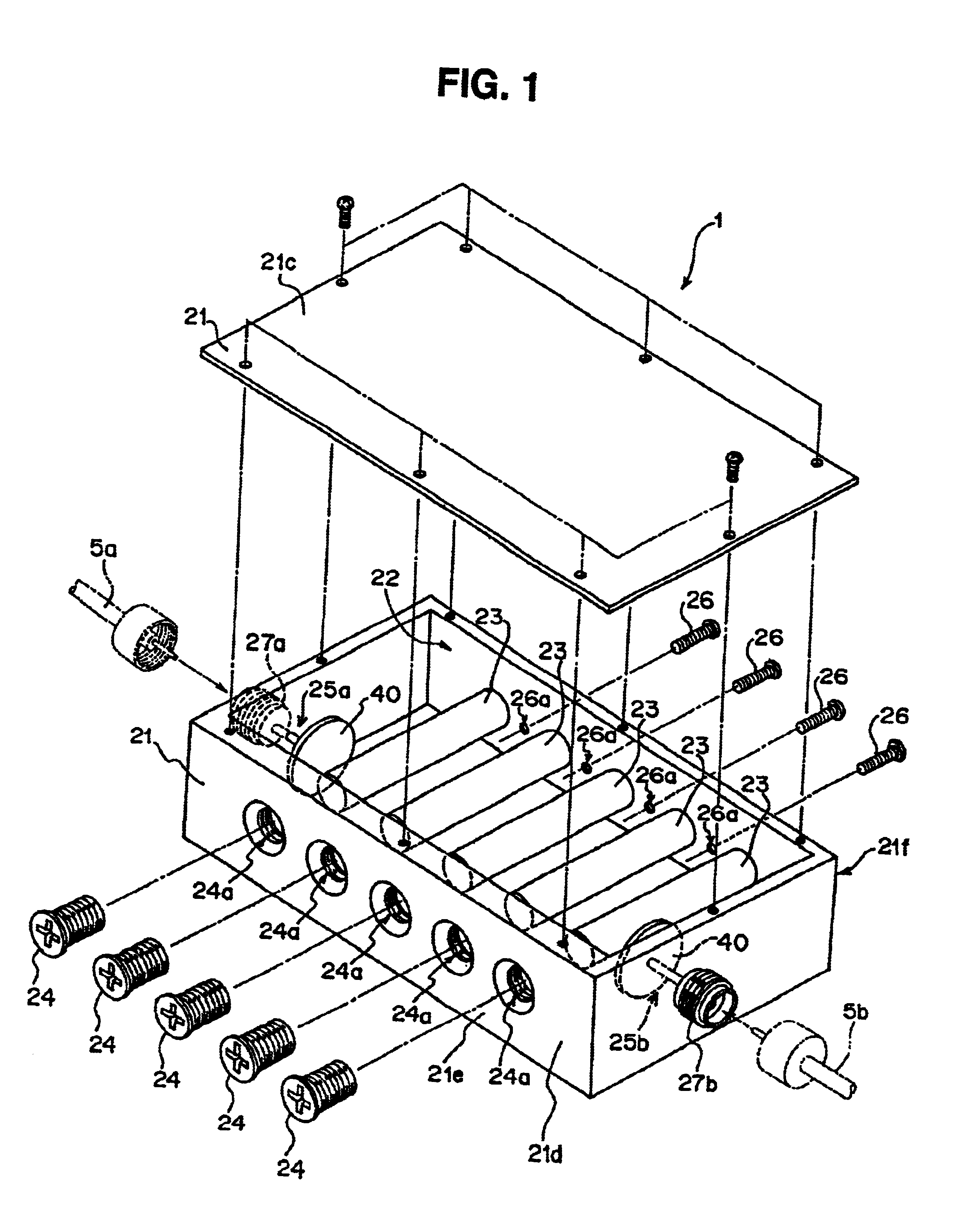
Superconductive filter module, superconductive filter assembly and heat insulating type coaxial cable
InactiveUS6873864B2Reduce lossStable and satisfactory characteristicMultiple-port networksSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCoaxial cableElectrical and Electronics engineering
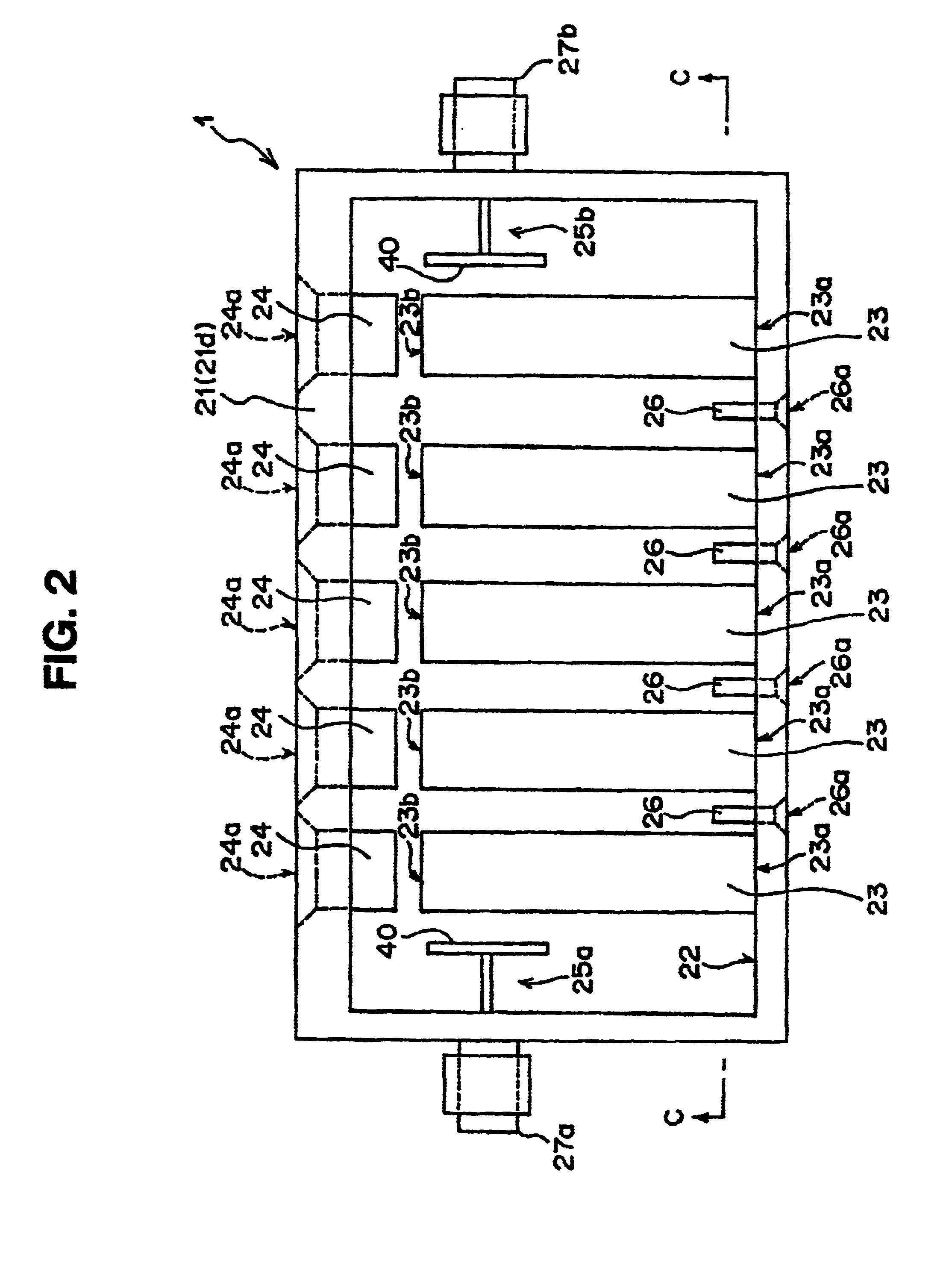
The present invention relates to superconductive filter technology. According to the arrangement of the superconductive filter (1), a columnar resonating member (23) having a superconductive material formed on the surface thereof is attached at one of its ends thereof to an inner wall (22) of a filter housing (21) so that a space is interposed between the columnar resonating member and each of connectors (27a, 27b) which are connectable to a signal input / output cables (5a, 5b), respectively. According to this arrangement, heat conduction from the outside can be suppressed as far as possible, and the superconductive condition can be created with stability, with the result that a stable filtering characteristic can be created. Further, the superconductive filter according to the present invention will become excellent in power withstand performance, and hence even if the number of stages of filters is increased for attaining a steep cutoff characteristic, the loss deriving from the increased number of stages can be suppressed to the minimum level.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Superconducting strand based on ReBCO high-temperature superconducting tape
InactiveCN102779581AImprove engineering current densityImprove toughness and strengthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesHigh temperature superconductingSeam welding
The invention belongs to the field of superconducting material and relates to a superconducting strand based on a ReBCO high-temperature superconducting tape. The superconducting strand comprises a superconducting strand core and a coating layer. The ReBCO high-temperature superconducting tape is cut into tapes which are arranged and stacked to be the superconducting strand core with circular, square or rectangular cross section; the coating layer is made of copper tapes, aluminum tapes, aluminum alloy tapes, stainless steel tapes or ReBCO coating superconducting tapes; the coating layer is rolled and coated on the superconducting strand core. A laser Ag welding technology is used for carrying out butt-seam welding on the coating tapes. The superconducting strand provided by the invention expands the application range of the coating superconductor, improves engineering current density, flexibility and mechanical strength of the superconducting wire, and is applicable to a superconducting cable, a current guide wire, and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +2
Method and device for measuring super conducting film surface resistance
InactiveCN1580792AAchieving Absolute MeasurementsHigh precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceMeasurement deviceFilm material
The present invention relates to a method for measuring surface resistance and its device, which is used for detecting metal material and superconducting material, in particular, it is a method and measuring device for detecting surface resistance of high-temperature superconducting film material. It adopts a medium-loaded resonator whose one end is short-circuited and another end is in opened state. It can respectively measure two microwave media loaded resonant cavities in which the decribed microwave media are respectively formed from two medium columns which are identical in material and length and different in diameter, so that it can define the system quality factor value Qr correspondent to other loss except tested sample, and further can meausre tested sample so as to obtain the surface resistance R of tested sample.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Superconducting magnet
ActiveCN105655084AEasy to replaceImprove stabilitySuperconducting magnets/coilsClosed loopSuperconducting Coils
The invention provides a superconducting magnet which comprises a vacuum container and a refrigerator. A cold screen and a superconducting coil are arranged in the vacuum container; superconducting wires are wound on a coil framework to form the superconducting coil, and two free ends of the superconducting coil are connected with a superconducting switch by superconducting connectors to form a closed superconducting circuit; the refrigerator is arranged on the vacuum container and comprises a primary cold head and a secondary cold head, and the primary cold head is thermally connected with the cold screen; the superconducting wires are made of superconducting materials with critical superconducting transit temperatures higher than 35 K; the superconducting connectors are made of superconducting welding flux with a low melting point, can be cooled by the aid of the secondary cold head or cooling media and accordingly can be assuredly in superconducting states. Compared with low-temperature closed-loop superconducting magnets in the prior art, the superconducting magnet has the advantage of high superconducting stability.
Owner:NINGBO JANSEN SUPERCONDUCTING TECH CO LTD
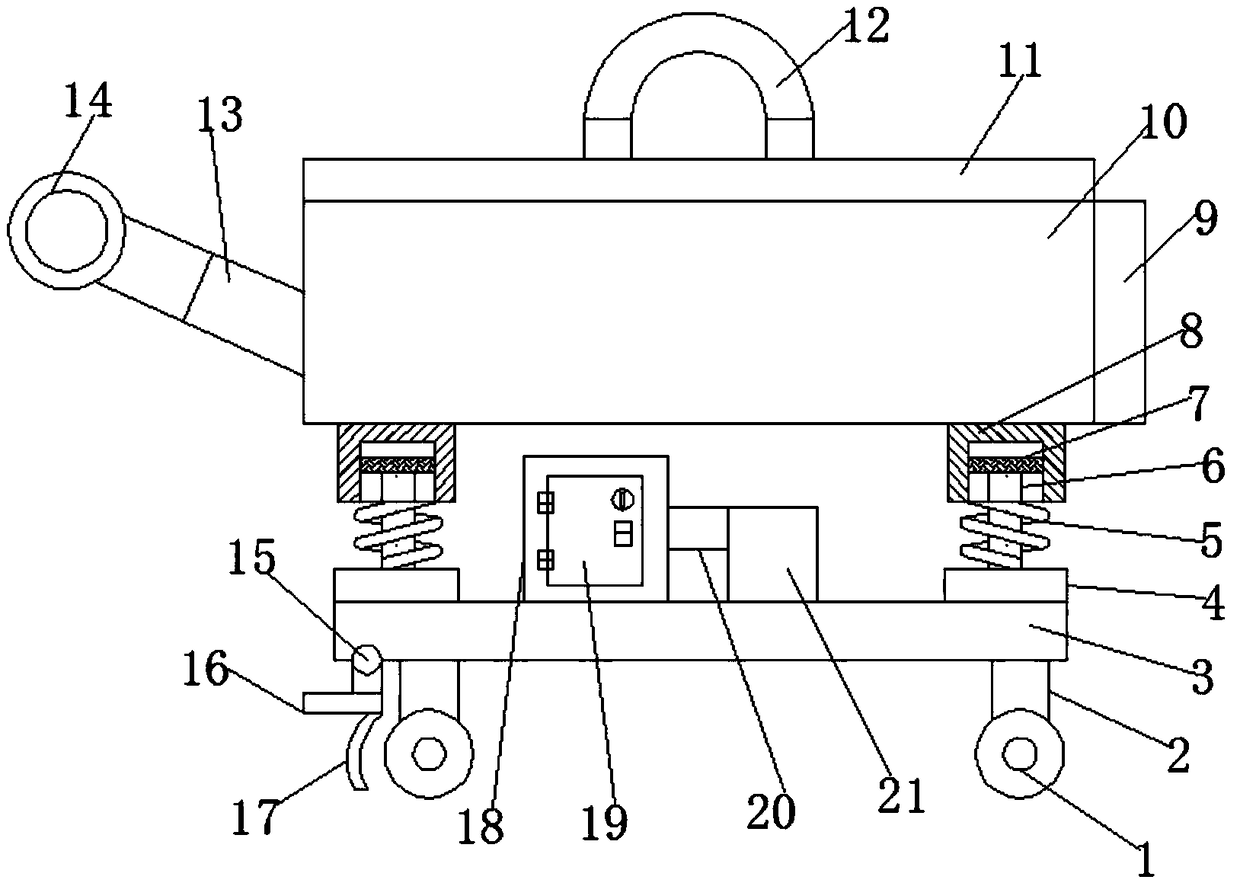
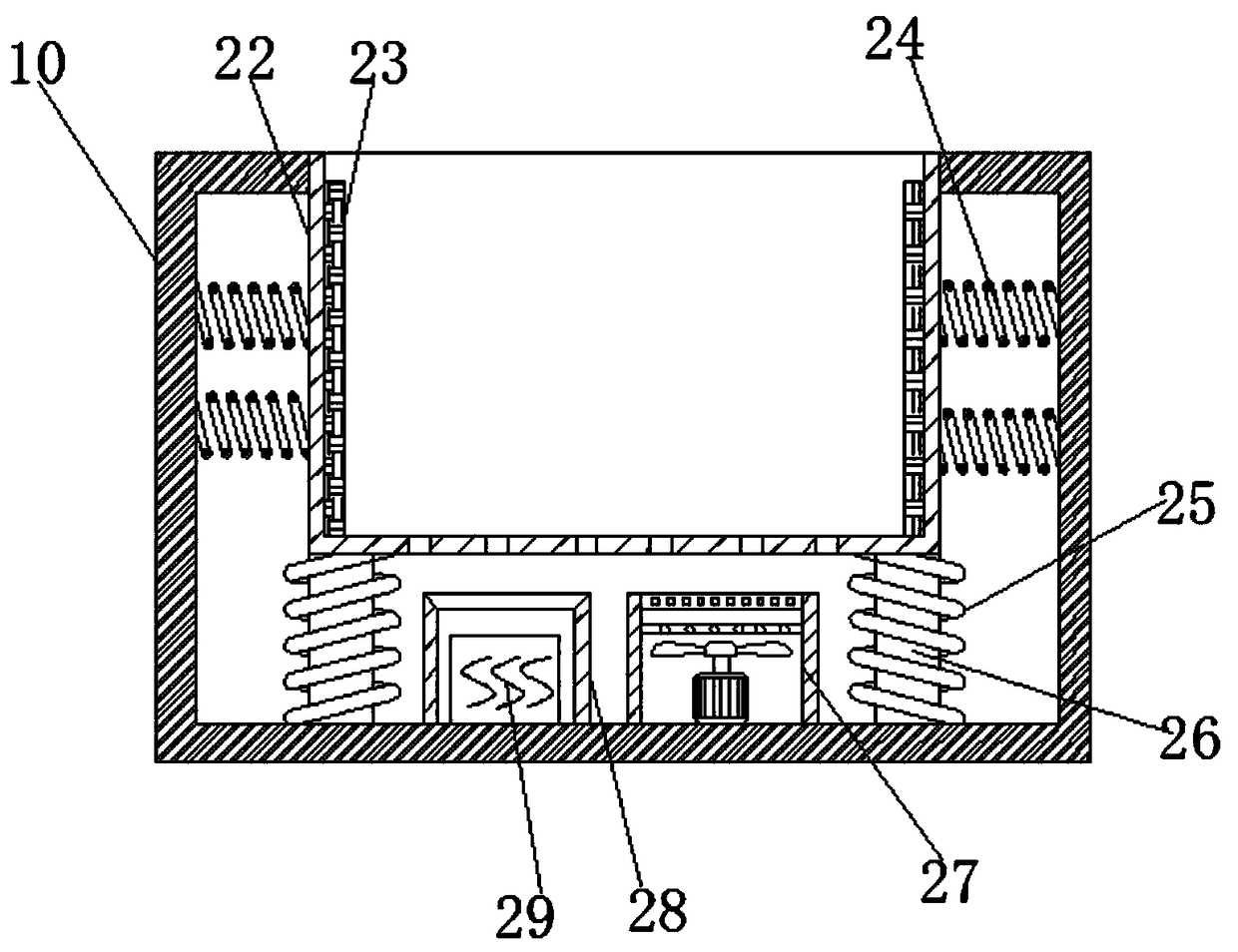
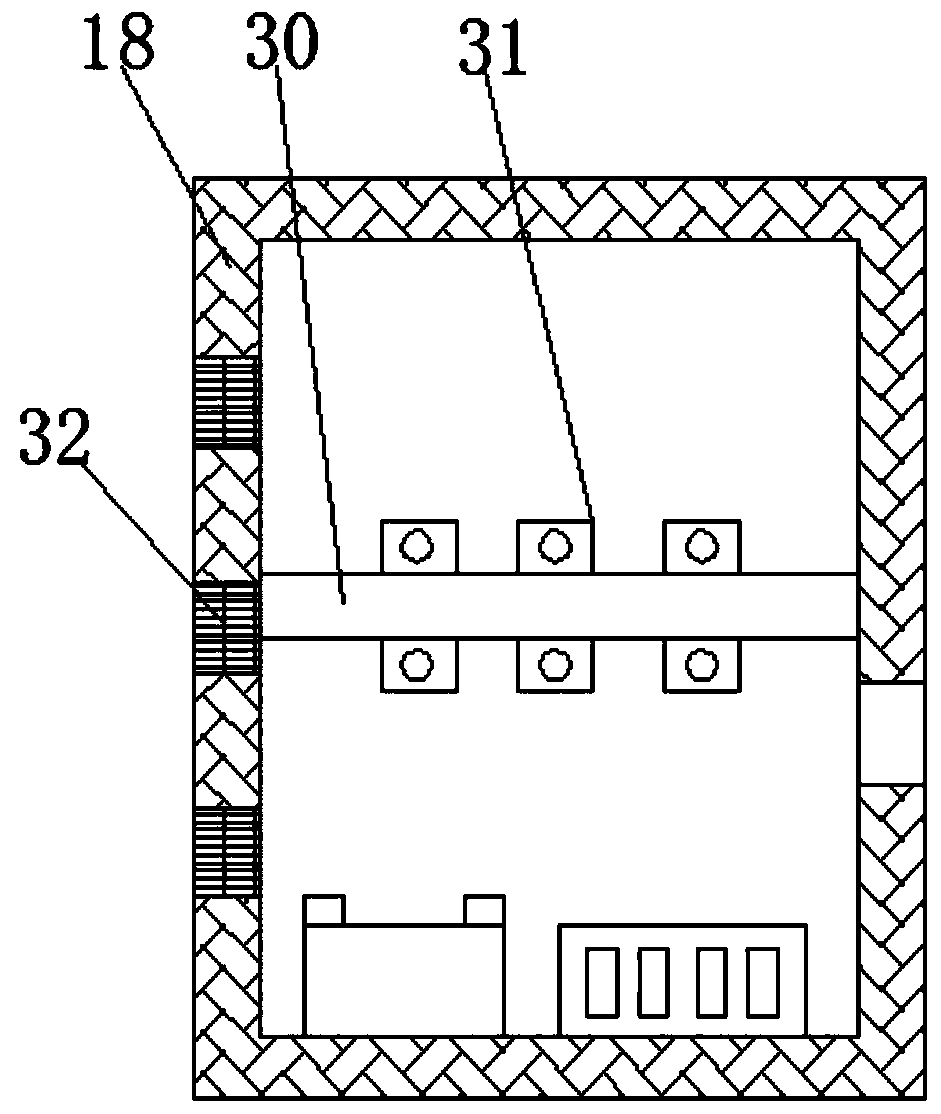
New material technological development superconducting material transporting device with good stability
ActiveCN108928370AAvoid damageImprove shock absorptionShock-sensitive articlesHand carts with multiple axesMechanical engineeringNew materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of transporting devices and in particular relates to a new material technological development superconducting material transporting device with good stability. In order to solve the technical problem that a superconducting material is easy to vibrate and collide during transportation to be damaged, the following scheme is provided. The new material technological development superconducting material transporting device with the good stability comprises a bottom plate, an internal box body and a transporting box body; a placing opening is formed in the external wall of the top of the transporting box body; a box cover is hinged to the internal wall of the placing opening through a hinge; two fixing blocks are welded on the external wall of the topof the box cover; the same pull handle is fixed on the external walls of the tops of the two fixing blocks through bolts; an internal box body is arranged in the transporting box body; and vent holeswhich are distributed in an equally spaced manner are formed in the external wall of the bottom of the internal box body. According to the new material technological development superconducting material transporting device with the good stability, as a second shock absorbing spring, a third shock absorbing spring and a shock absorbing rubber pad, a very good shock absorbing effect is realized toprevent the superconducting material from being damaged due to bumping and shaking during transportation; and a dehumidifier has a very good dehumidifying effect to prevent the superconducting material from being affected with damp to affect the quality of the superconducting material.
Owner:阜阳佰恩得新材料技术有限公司
Superconducting integrated circuit technology using iron-arsenic compounds
A new family of superconducting materials with critical temperature up to 55 K have recently been discovered, comprising a crystal structure with atomic layers of iron and arsenic alternating with atomic layers of rare-earth oxide or alkaline earth. The present invention identifies structures for integrated circuit elements (including Josephson junctions) in these and related materials. These superconducting circuit elements will operate at a higher temperature than low-temperature superconductors such as niobium, and may be easier to manufacture than prior-art high-temperature superconductors based on copper-oxides.
Owner:HYPRES
Dispersion-engineered traveling wave kinetic inductance parametric amplifier
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
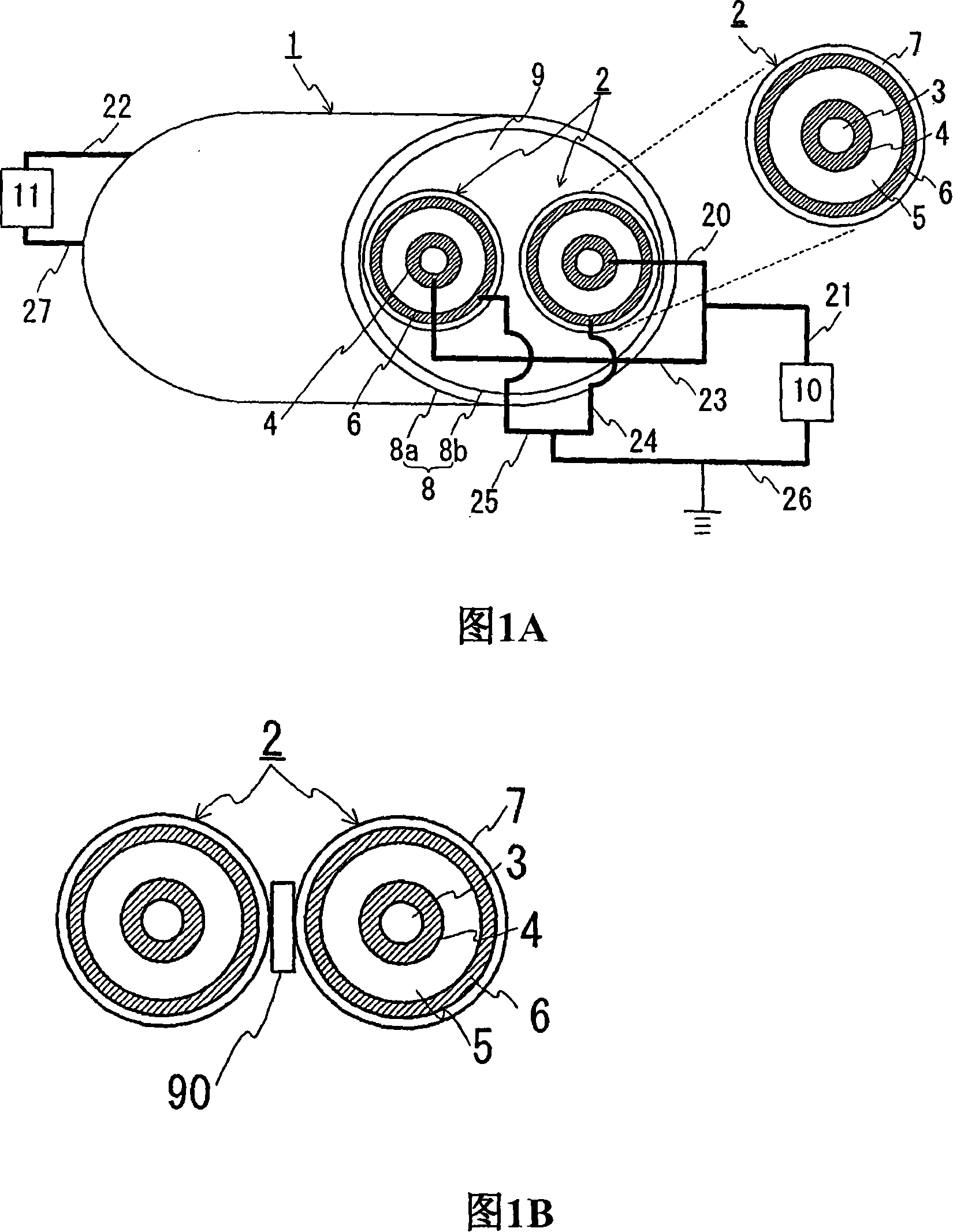
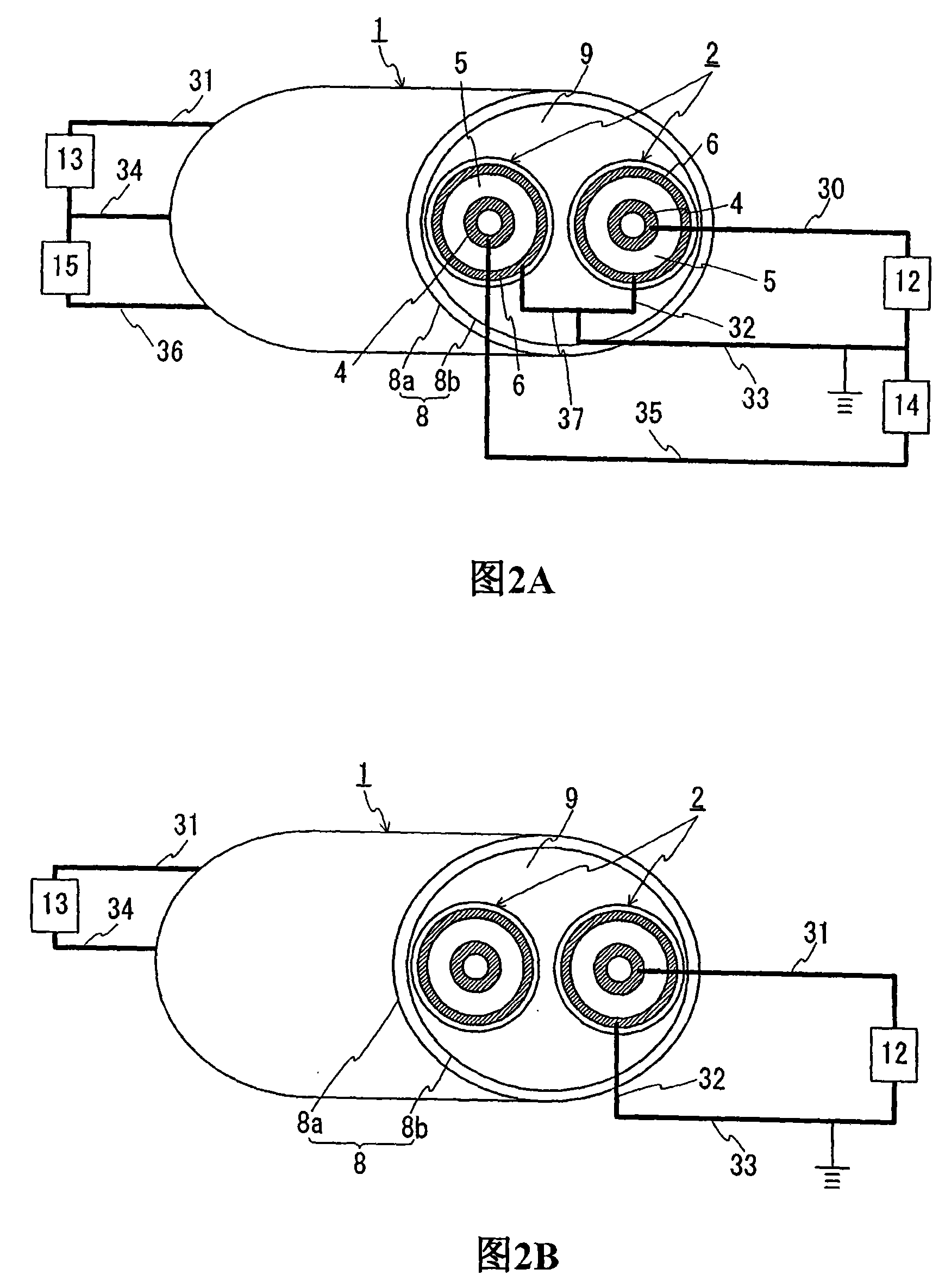
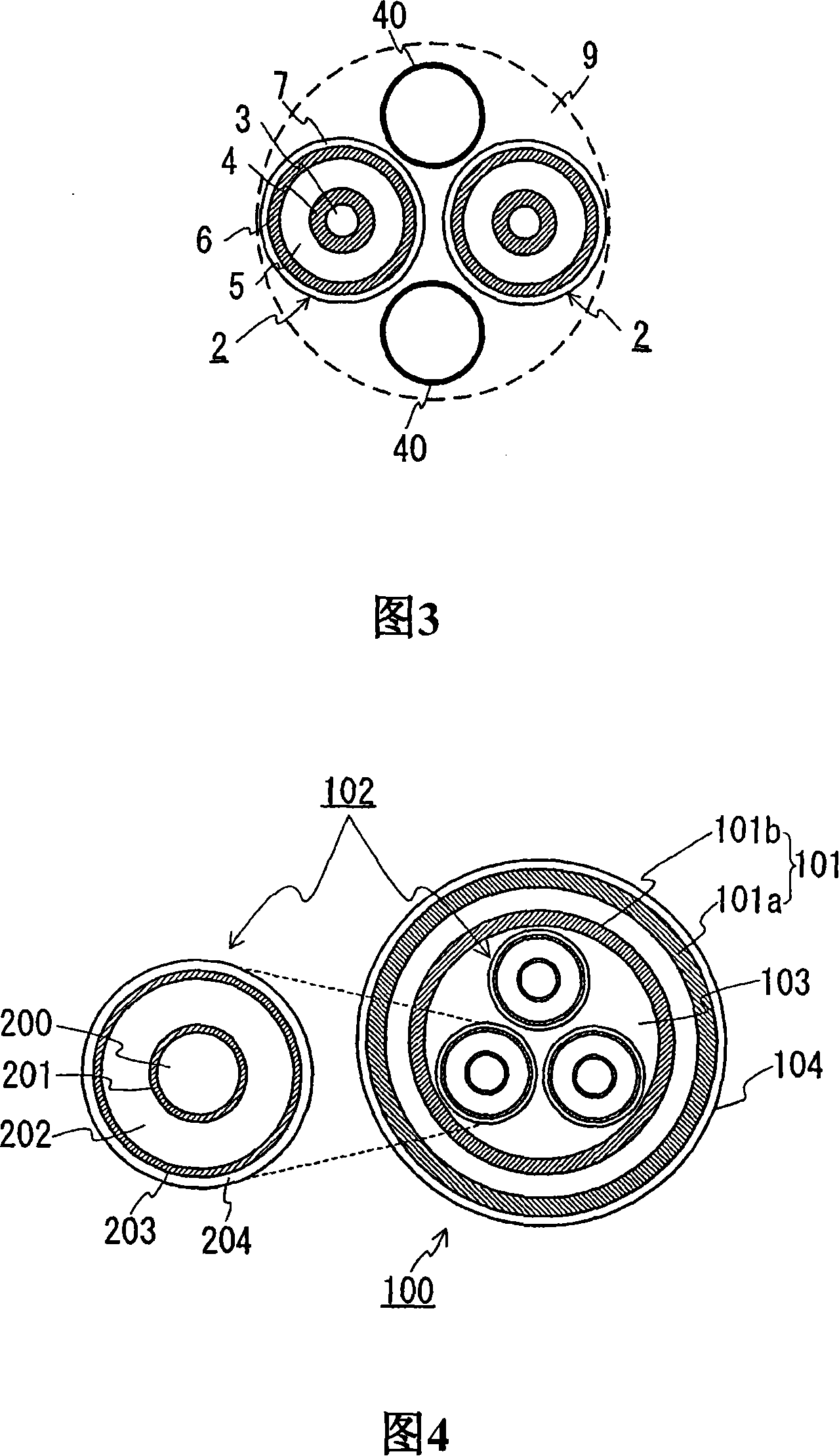
Superconductive cable
InactiveCN101142637ASmall diameterNo increase in diameterSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorReturn current
A superconducting cable having a smaller outside diameter and a DC power transmission method utilizing this superconducting cable. The superconducting cable (1) comprises two stranded cable cores (2) each having a superconductor layer (4) of a superconducting material and an external superconducting layer (6) and contained in a heat insulating pipe (8). Each cable core (2) consists of a former (3), the superconductor layer (4), an insulating layer (5), the external superconducting layer (6), and a protective layer (7) arranged sequentially from the center. In the case of unipolar transmission, the superconductor layers (4) provided to both cores (2) are fed with an unipolar current and used as a supply line and the external superconducting layers (6) provided to both cores (2) are fed with a return current and used as a return line. In the case of bipolar transmission, the superconductor layer (4) provided to one core (2) is used for positive pole transmission, the superconductor layer (4) provided to the other core (3) is used for negative pole transmission, and the external superconducting layers (6) of both cores (2) are used as a neutral line layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
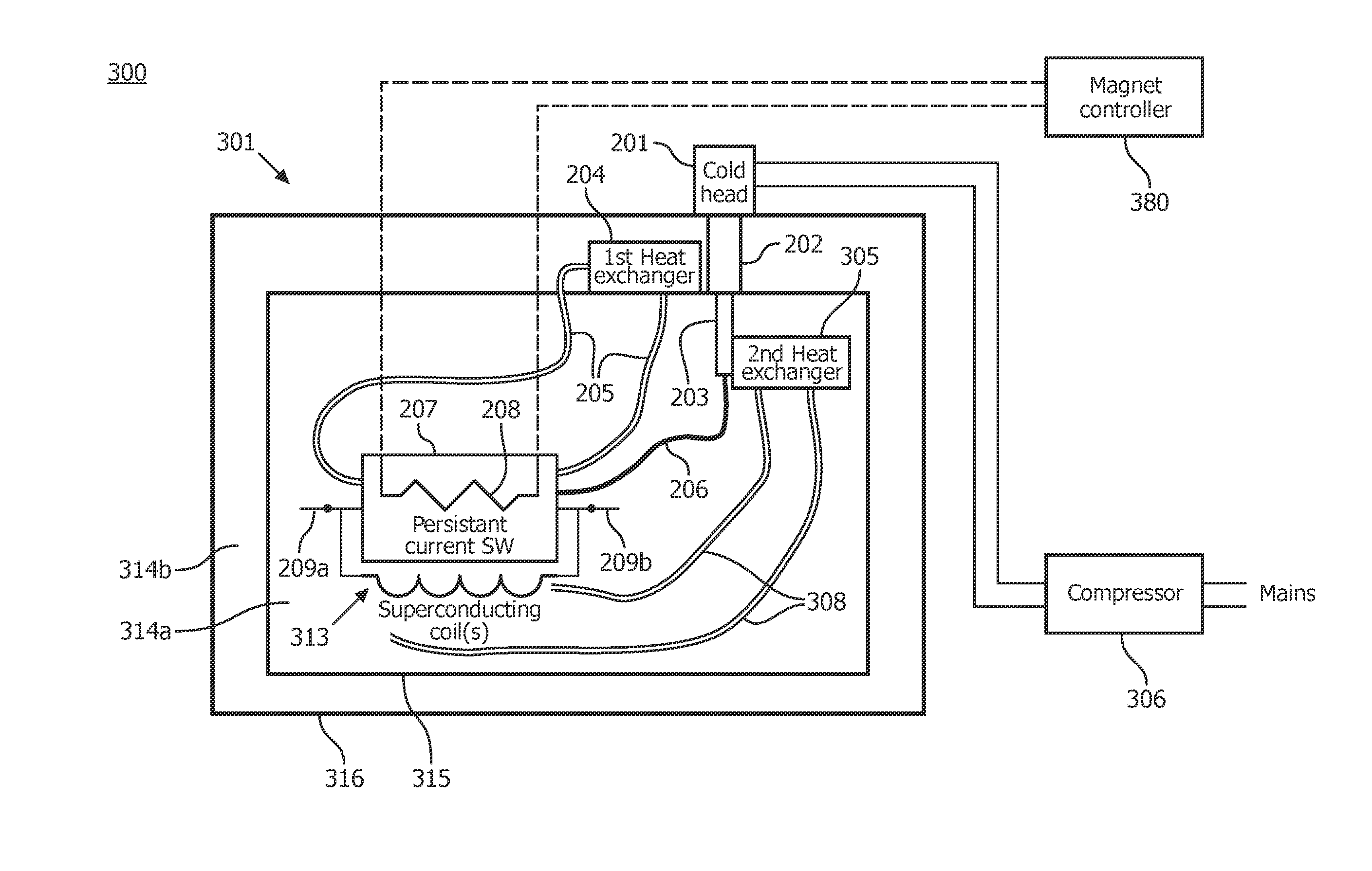
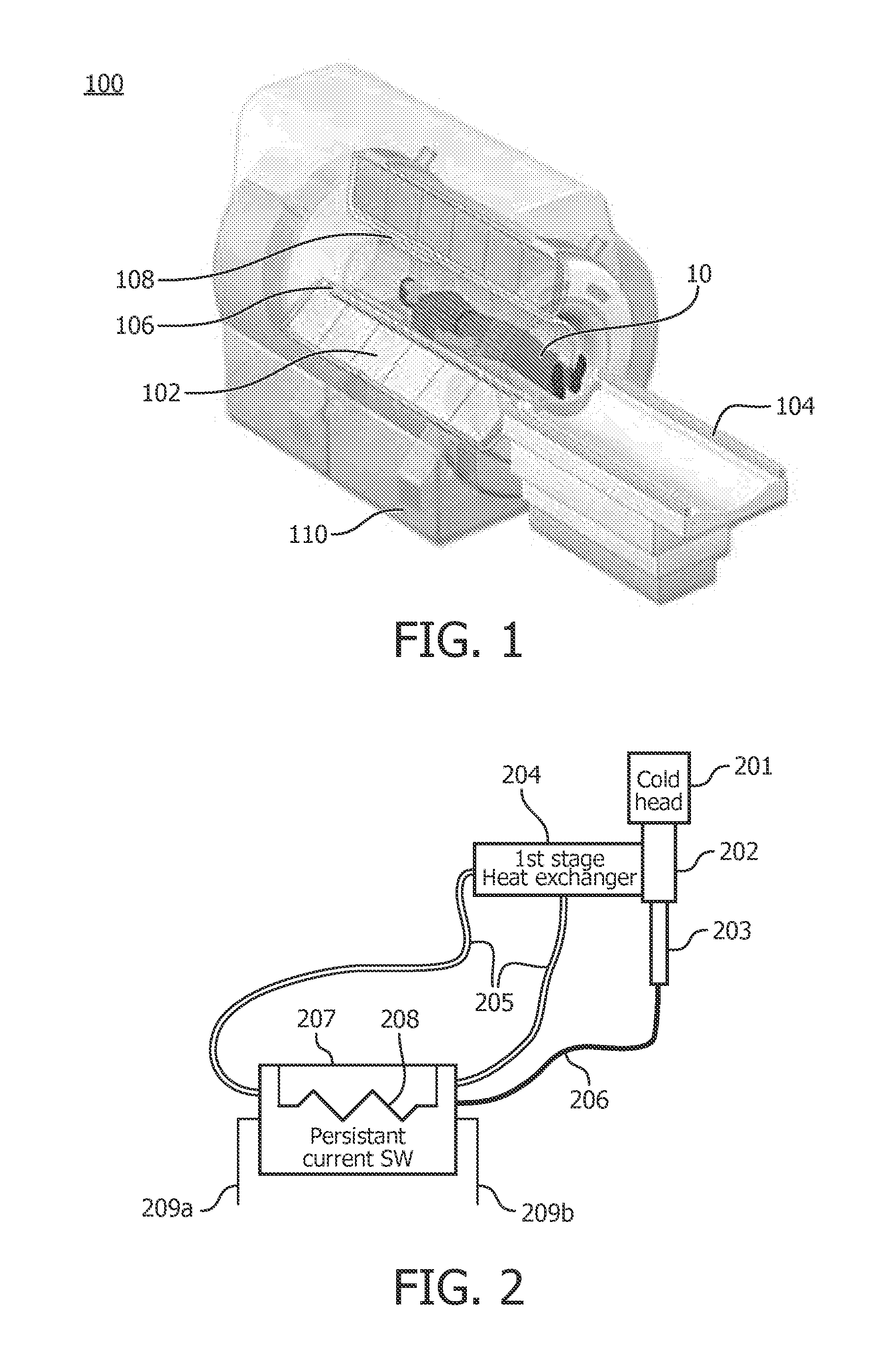
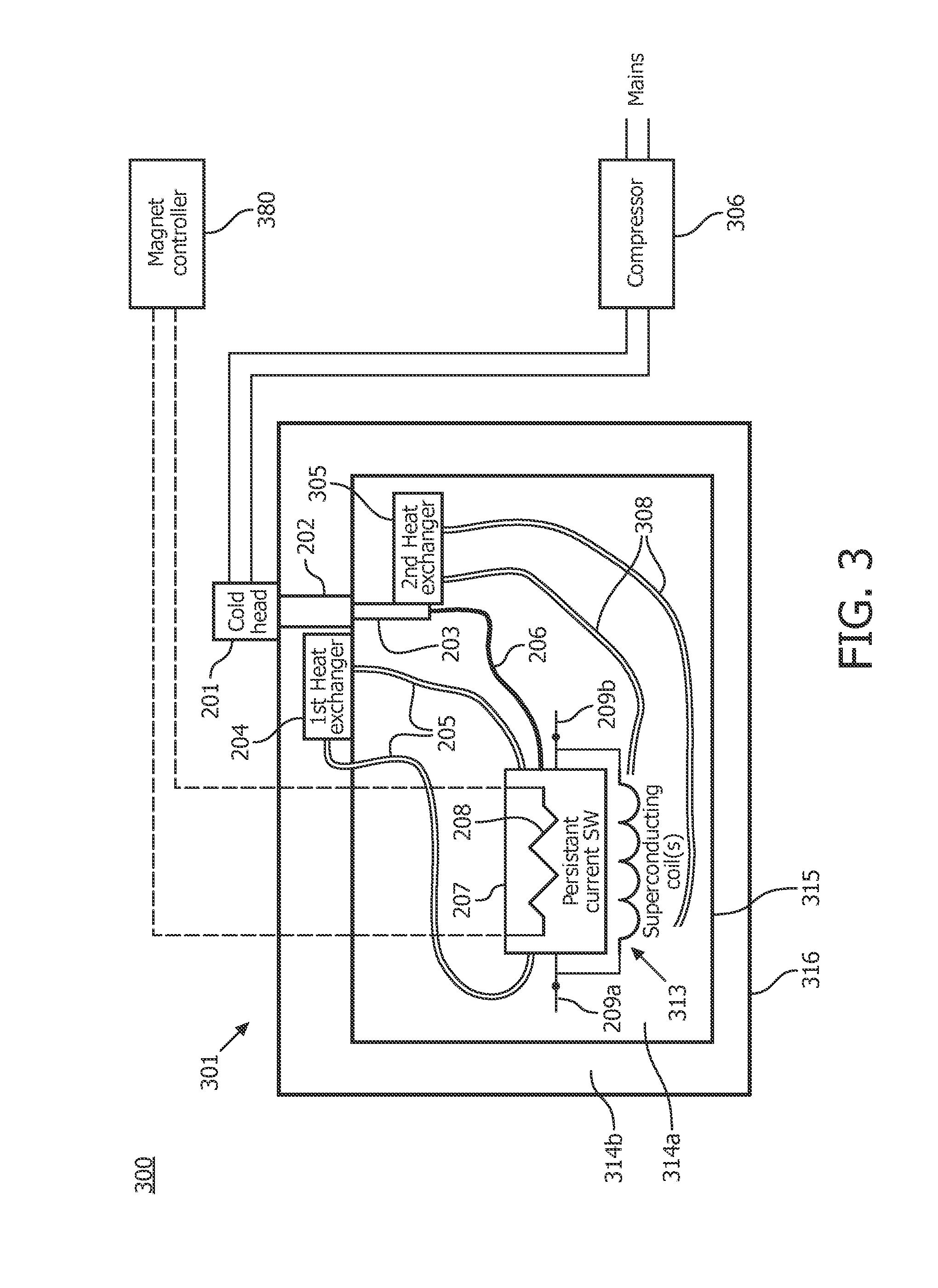
Low-loss persistent current switch with heat transfer arrangement
ActiveUS20150323626A1Superconducting magnets/coilsElectric/magnetic detectionEngineeringElectric current flow
An apparatus including a persistent current switch of a superconducting material which is electrically superconducting at a superconducting temperature and electrically resistive at a resistive mode temperature which is greater than the superconducting temperature. The apparatus further includes a first heat exchange element; a convective heat dissipation loop thermally coupling the persistent current switch to the first heat exchange element; a second heat exchange element spaced apart from the first heat exchange element; and a thermally conductive link thermally coupling the persistent current switch to the second heat exchange element. The first heat exchange element is disposed above the persistent current switch. The thermally conductive link may have a greater thermal conductivity at the superconducting temperature than at a second temperature which is greater than the superconducting temperature.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
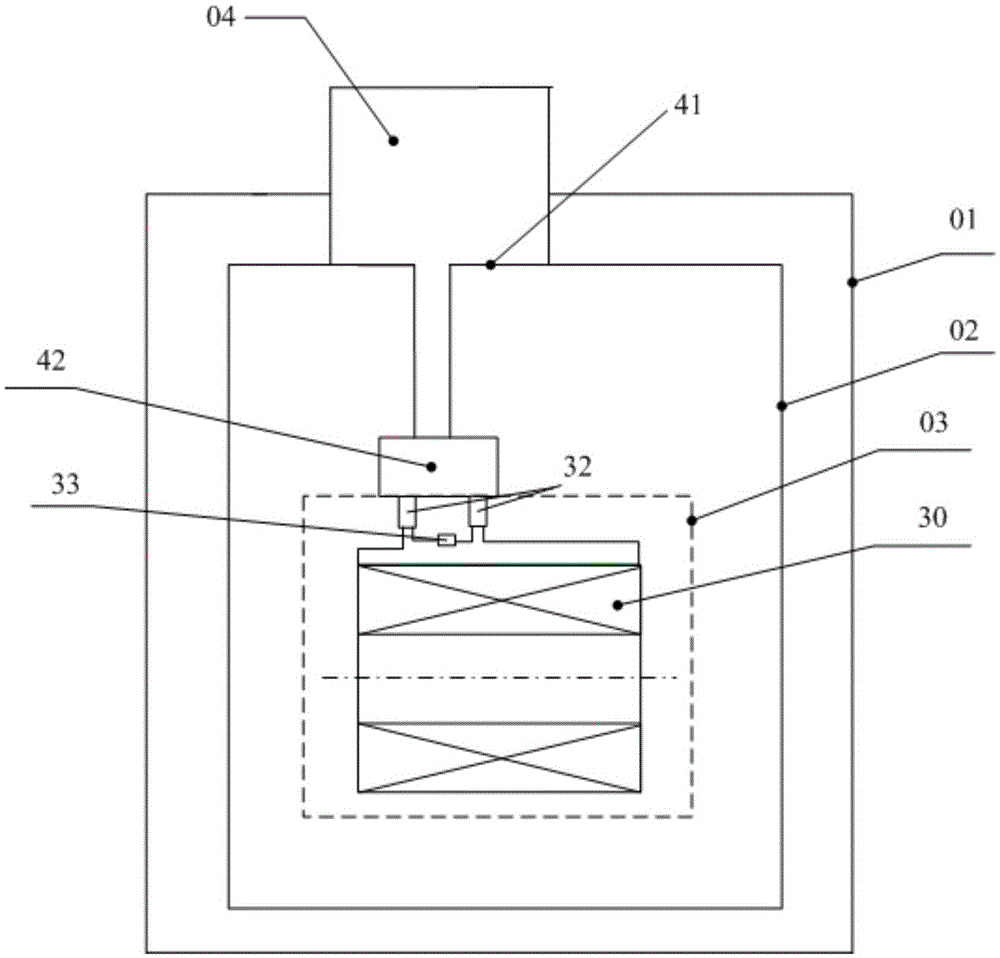
Measuring device and measuring method of superconductive AC magnetic susceptibility
ActiveCN102507725AAvoid missingReduce temperature hysteresis effectSusceptibility measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic susceptibilityAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method of superconductive AC magnetic susceptibility, belonging to the field of superconducting electronics. The measuring method comprises the steps of: positioning a measured superconducting material between a primary coil and a secondary coil, and fixing the elements in a sealed vacuum chamber, refrigerating the measured superconducting material via a compression refrigeration machine, extracting a voltage signal induced by the secondary coil through a phase-locking amplifier, and simultaneously providing AC voltage excitation to the primary coil through the phase-locking amplifier, measuring the temperature of the measured superconducting material through a temperature controller, storing the voltage signal measured by the phase-locking amplifier and a temperature signal measured by the temperature controller in a computer, and displaying the temperatiredependent curve of the voltage signal measured by the phase-locking amplifier in real time. The measuring method of the invention has the advantages of performing a nondestructive measurement on the conversion temperature of the superconducting material to conveniently master the measurement condition in time, and the measuring method is an efficient, accurate and reliable measurement manner, so that the measuring method has certain practical value for detecting the performance of the superconducting material.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
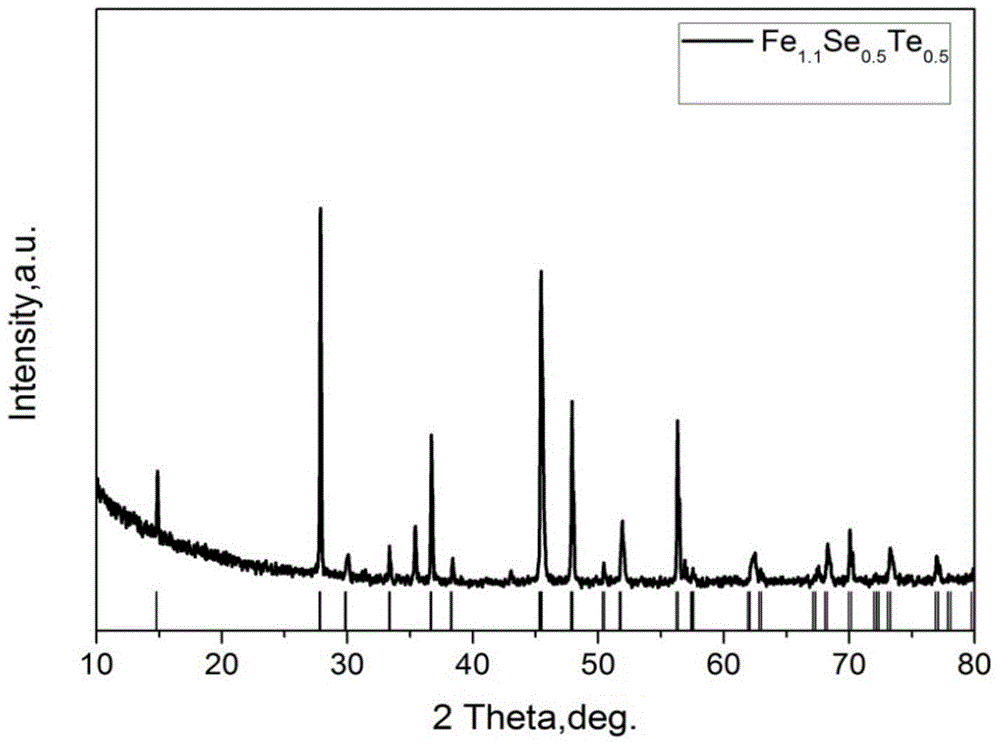
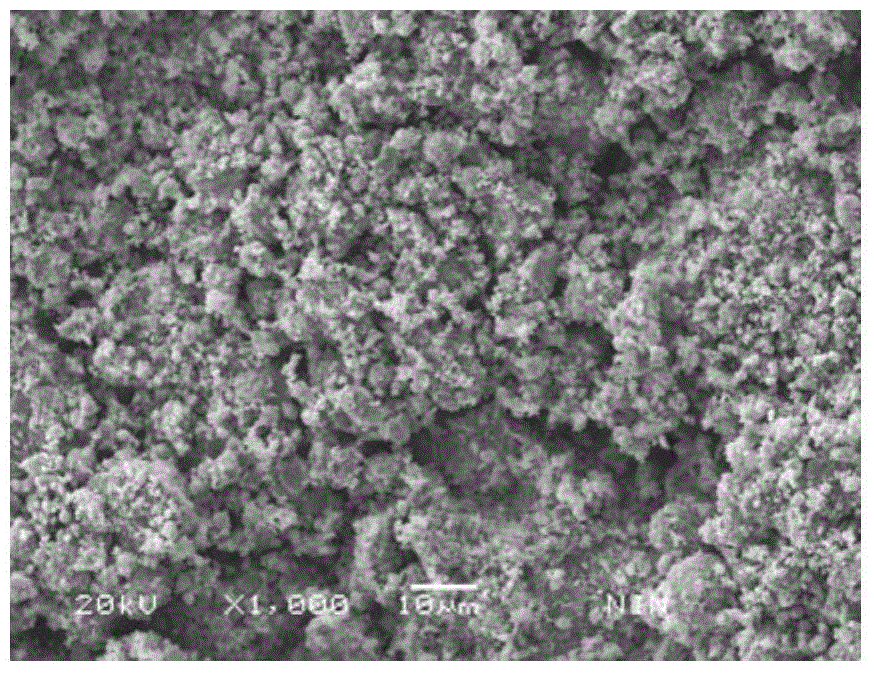
Preparation method of high-density Fe(Se,Te) superconducting material
InactiveCN104953023AShort energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionSuperconductor detailsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentReaction rateHigh energy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-density Fe(Se,Te) superconducting material. The method comprises steps as follows: step one, ferrous powder, selenium powder and tellurium powder are mixed to form mixed powder, and the mixed powder is placed in a vacuum ball milling tank; step two, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling; step three, the mixed powder is pressed, and a Fe(Se,Te) green body is obtained; step four, the Fe(Se,Te) green body is sintered, and the Fe(Se,Te) superconducting material is obtained. The mole ratio of the ferrous powder to the selenium powder to the tellurium powder in the mixed powder is adjusted and controlled, the Fe content in the generated tetragonal phase Fe(Se, Te) is optimized, the mixed powder is subjected to high-energy ball milling in shorter time by means of a high-energy ball mill, limit to the reaction rate in the diffusion process during sintering is eliminated, holes formed after melting of the selenium powder are avoided, and the high-density Fe(Se,Te) superconducting material with high superconducting phase content is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Fluorine Passivation of Dielectric for Superconducting Electronics
InactiveUS20150179913A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterface layerAmorphous silicon
An amorphous silicon (a-Si) dielectric for superconducting electronics is fabricated with reduced loss tangent by fluorine passivation throughout the bulk of the layer. Complete layers or thinner sub-layers of a-Si are formed by physical vapor deposition at low temperatures (<350 C, e.g. ˜200 C) to prevent reaction with superconducting materials, then exposed to fluorine. The fluorine may be a component of a gas or plasma, or it may be a component of an interface layer. The fluorine is driven into the a-Si by heat (e.g., <350 C) or impact to passivate defects such as dangling bonds.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Superconducting cable
InactiveUS6759593B2Avoid mechanical damageStress minimizationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentSuperconducting magnetEngineering
A superconducting cable includes at least one layer of tapes of superconducting material circumferentially wound side by side on a support at a prefixed distance forming gaps circumferentially among adjacent tapes. Within the superconducting cable, a non-superconducting material is interposed between adjacent tapes to partially fill the gaps.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA +1
Method for preparing FeSe-based superconducting material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a FeSe-based superconducting material. The method comprises the following steps: 1, putting mixed powder of iron powder and selenium powder into a vacuum ball-milling tank; 2, performing high energy ball-milling treatment on the mixed powder; 3, pressing the mixed powder to obtain a FeSe-base blank; and 4, sintering the FeSe-base blank, thereby obtaining the FeSe-based superconducting material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a high energy ball-milling machine is adopted to perform high energy ball-milling treatment on the mixed powder within a relatively short time firstly, after the sizes of original grains of the mixed powder are reduced, a Fe-Se solid solution is obtained, Fe and Se in the mixed powder reach atom-grade mixing, the limit on reaction rate in the dispersion process in the sintering treatment is eliminated, the mixed powder is laminated and is subsequently sintered, thereby obtaining the FeSe-based superconducting material with high superconducting phase content and advantages of small energy consumption, short process, high repeatability and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com