Superconductive cable
一种超导电缆、电缆的技术,应用在超导电缆,DC传输系统领域,能够解决电流大、温度过度上升、AC损耗大等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
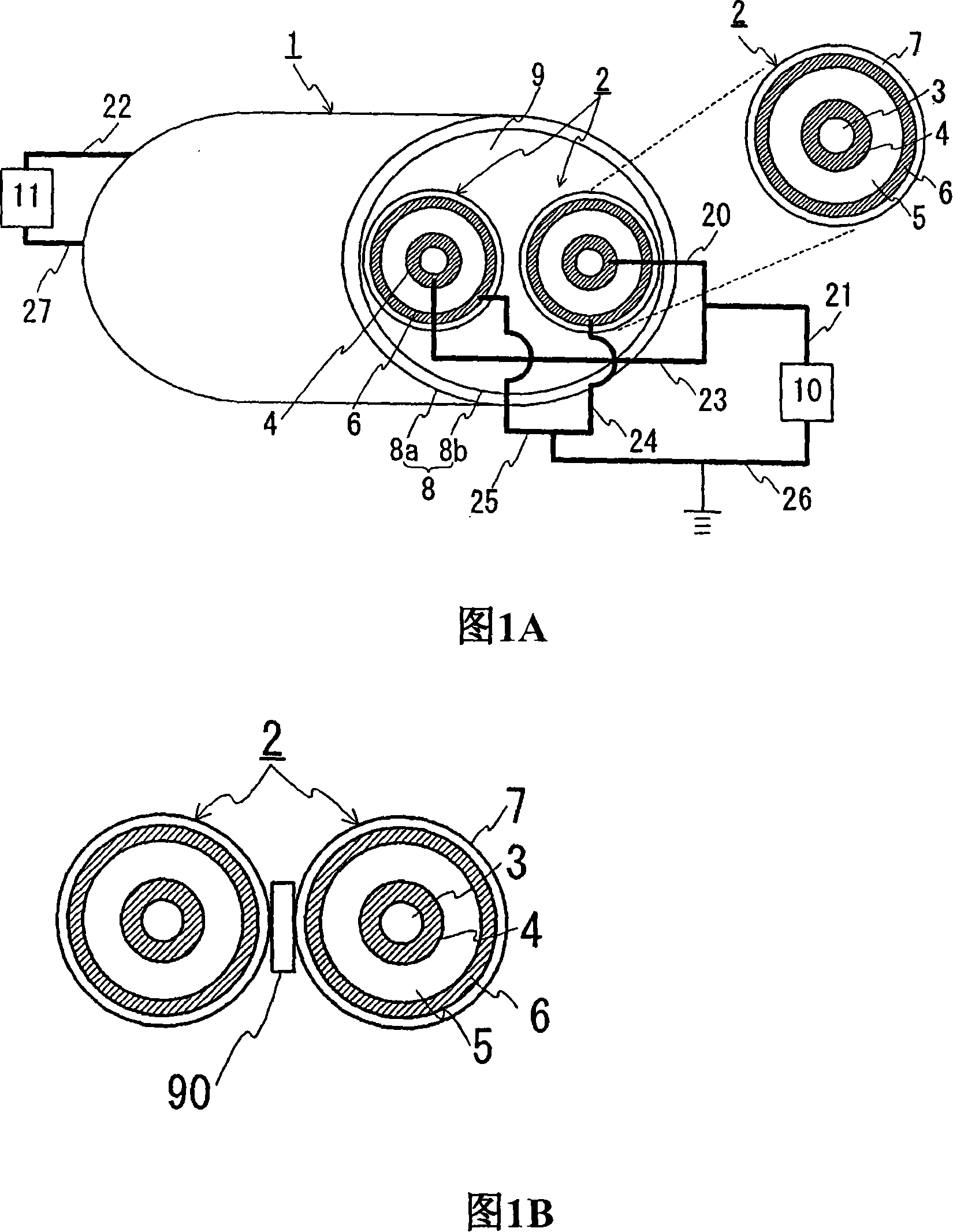
[0063]FIG. 1(A) is a schematic structural view showing a state in which a DC transmission line for unipolar transmission is constructed by using the superconducting cable of the present invention. FIG. 1(B) is a schematic cross-sectional view showing a state where spacers are provided between cable cores in a superconducting cable. In the following drawings, the same reference numerals denote the same elements. The superconducting cable 1 has a structure in which two cable cores 2 each having a superconducting conductor layer 4 and an outer layer made of a superconducting material are twisted together and housed in a heat insulating tube 8. superconducting layer6. Each cable core 2 has a shaper 3 , a superconducting conductor layer 4 , an insulating layer 5 , an outer superconducting layer 6 and a protective layer 7 in order from the center.
[0064] In this example, the superconducting conductor layer 4 and the outer superconducting layer 6 were formed by using a Bi-2223-ba...
example 2
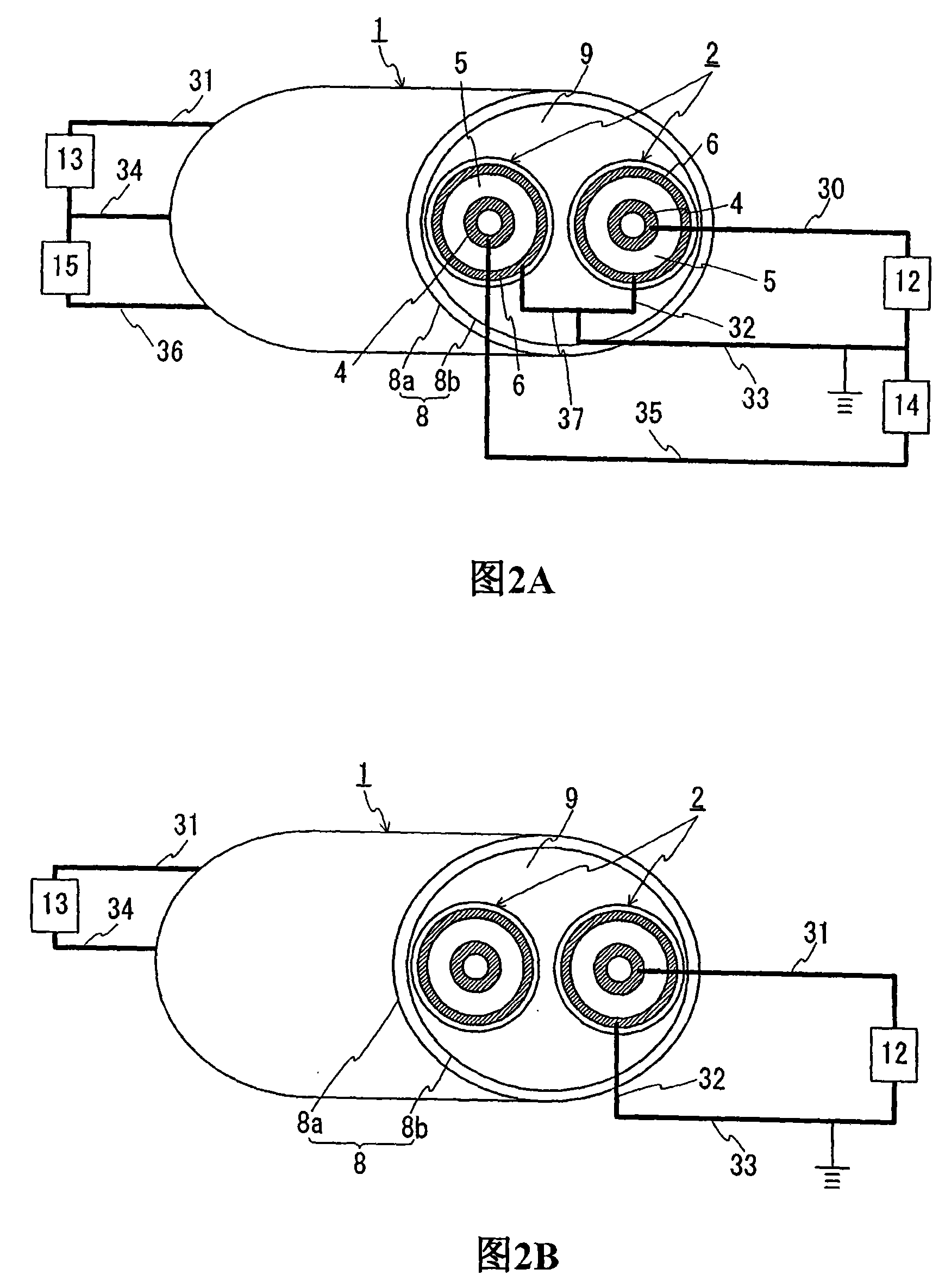
[0069] Next, the case where bipolar transmission is performed is explained. FIG. 2(A) is a schematic structural view showing the state of constructing a DC transmission line for bipolar transmission by using the superconducting cable of the present invention. (B) is a structural schematic diagram showing a state in which a DC transmission line for unipolar transmission is constructed by using a superconducting cable layer of one of the cores and an outer superconducting layer. The superconducting cable 1 used in Example 1 can also be used for bipolar transmission. For bipolar transmission, it is recommended to construct the transmission line as shown in Fig. 2(A). More specifically, one end of the superconducting conductor layer 4 provided in one of the cores 2 (the right core 2 in FIG. to the AC system (not shown). The other end of the same superconducting conductor layer 4 is connected via a lead wire 31 to a DC-AC converter 13, which is connected to an AC system (not sho...
example 3
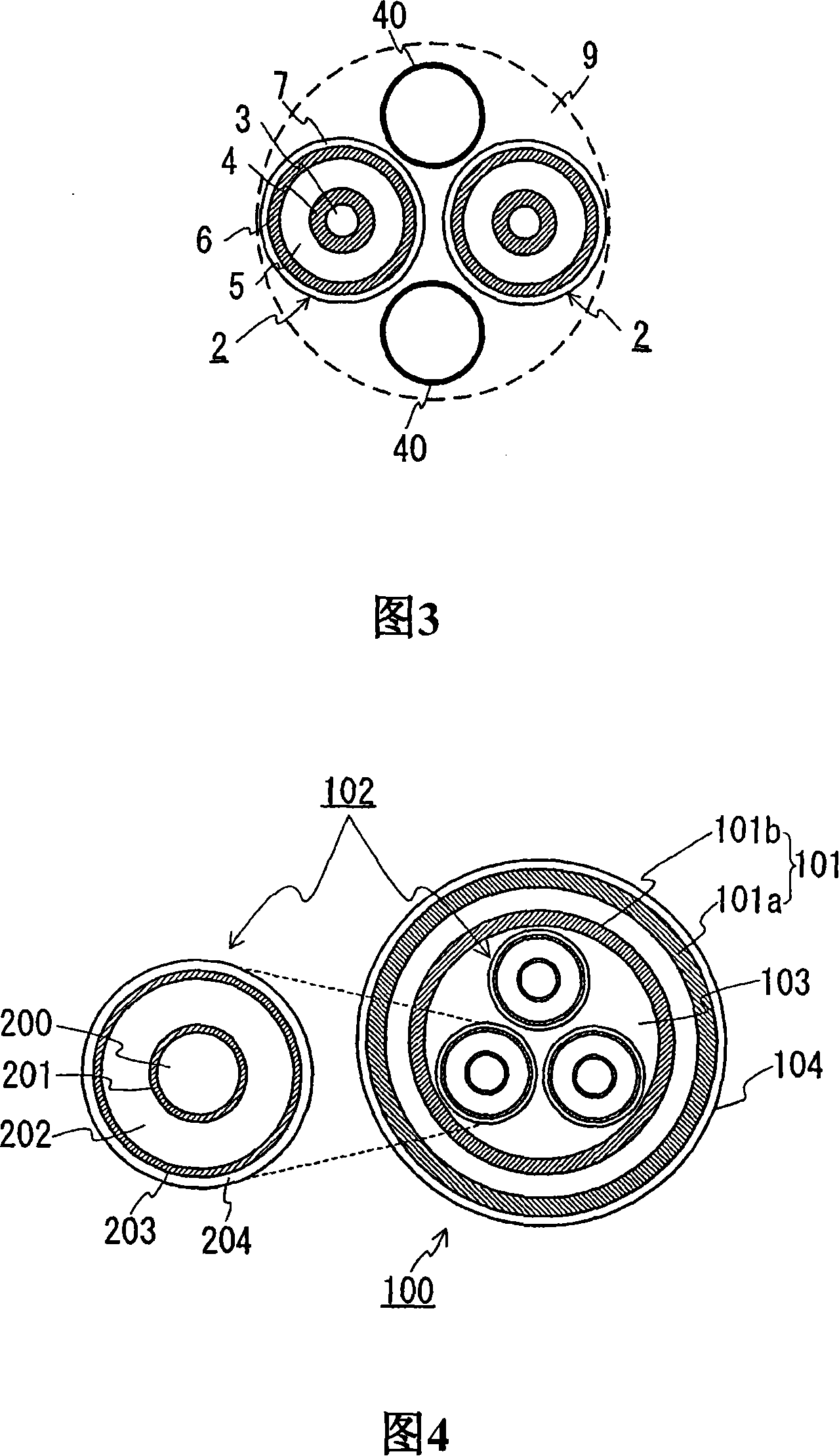
[0080] Next, an explanation is given of a structure provided with both the coolant external passage and the coolant return passage. Fig. 3 shows a schematic cross-sectional view of a superconducting cable of the present invention, which is formed by twisting two cable cores and a coolant circulation tube together. In the above-mentioned Examples 1 and 2, an explanation was given of the structure in which the inner side of the inner pipe of the heat insulating pipe is used as the coolant passage. However, as shown in FIG. 3, the coolant circulation pipe 40 may be provided separately so that the void 9 in the inner pipe can be used as an external passage of the coolant so that the inside of the coolant circulation pipe 40 can be used as a return flow of the coolant. aisle. When the external passage and the return passage of the coolant are provided as described above, the intrusion of heat can be reduced.
[0081] In this example, two coolant circulation pipes 40 are prepared ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com