Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3283results about "Superconductor elements usage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
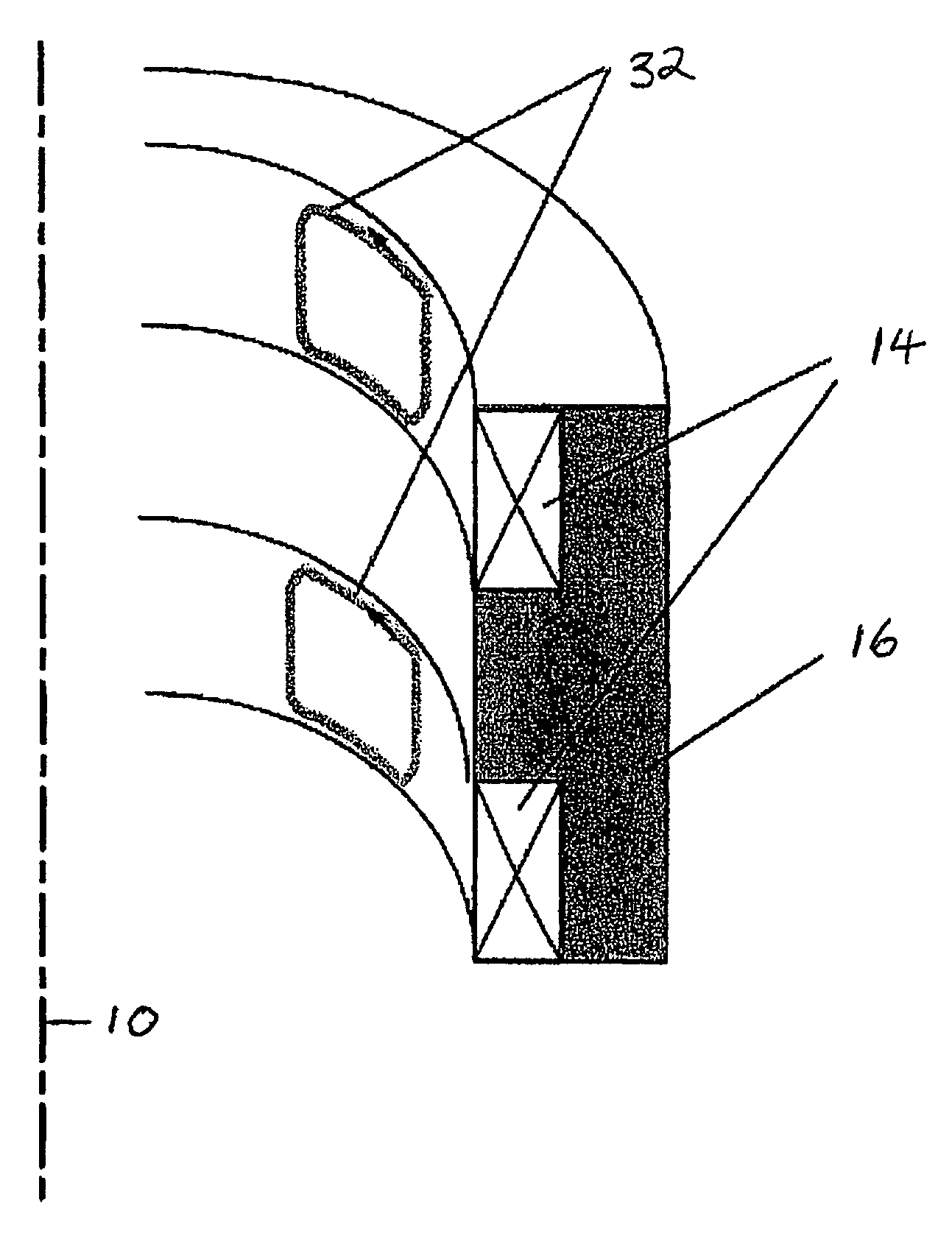
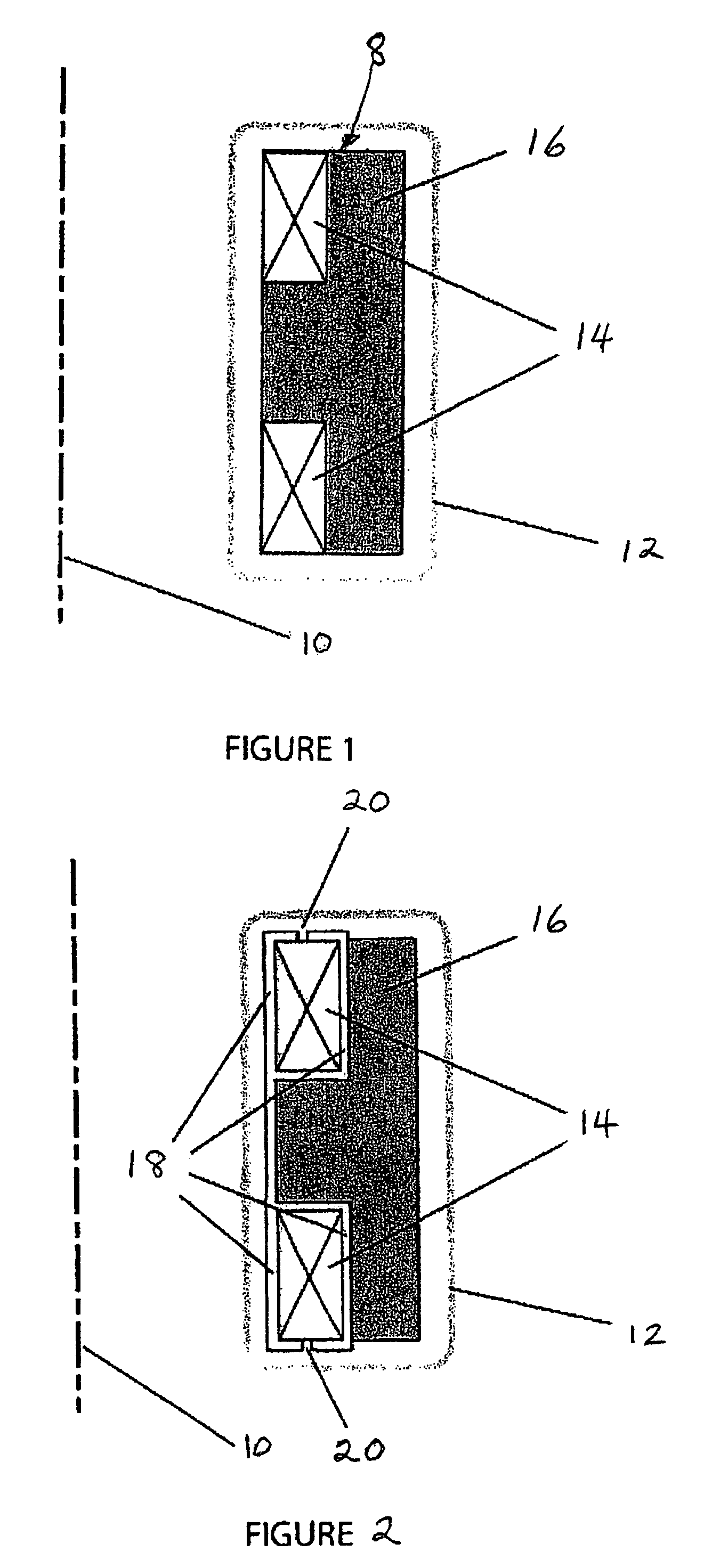
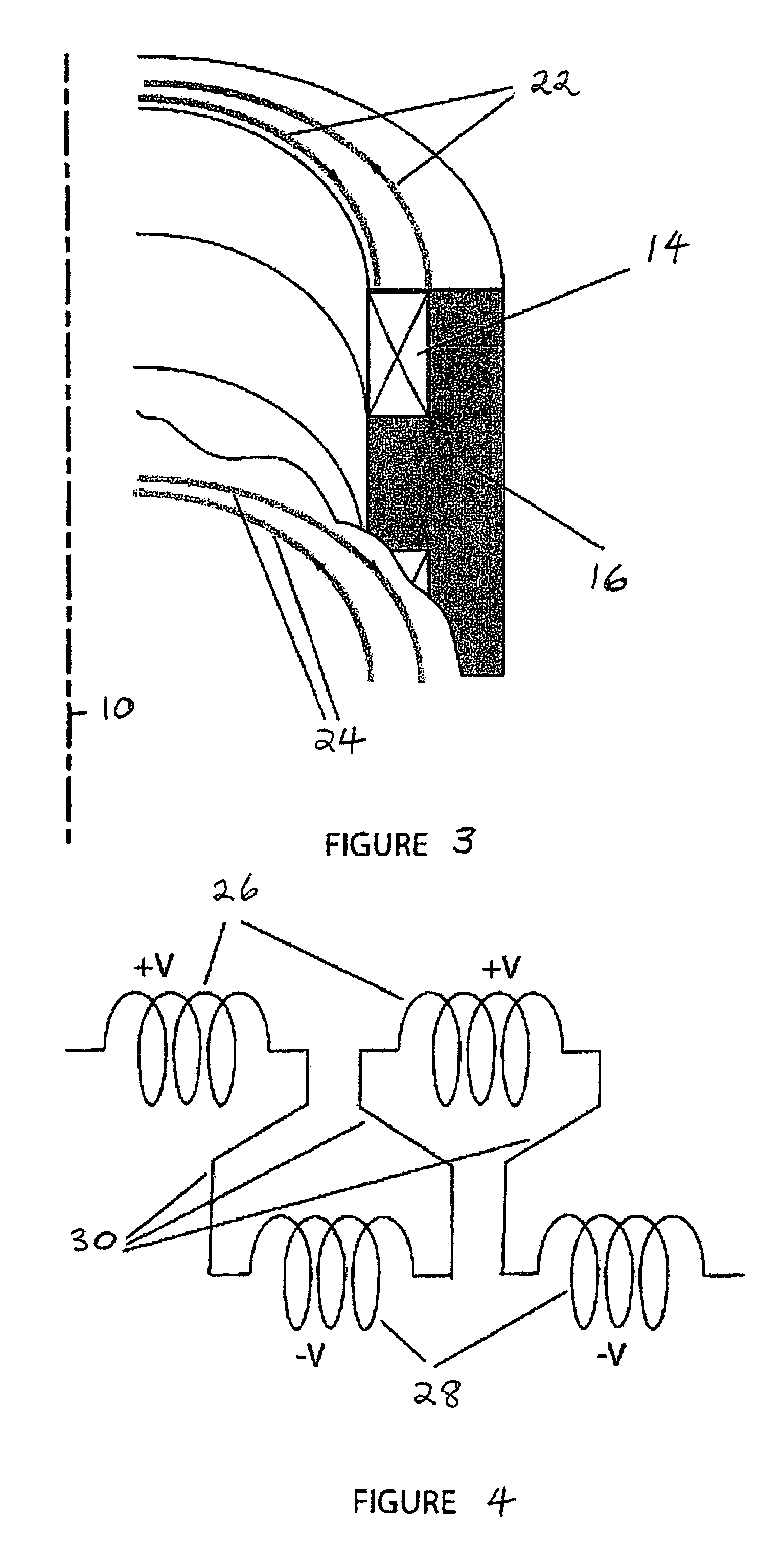
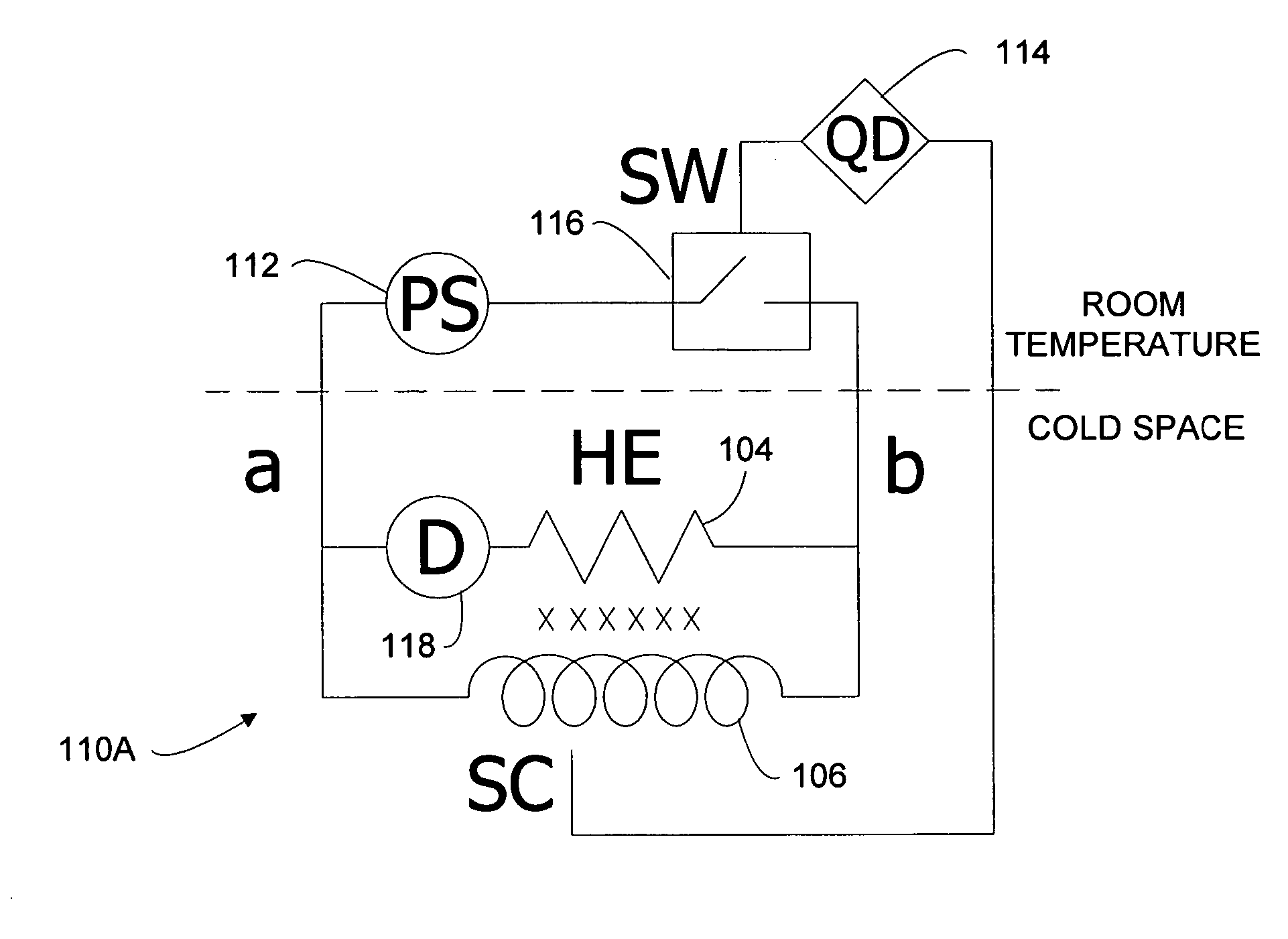
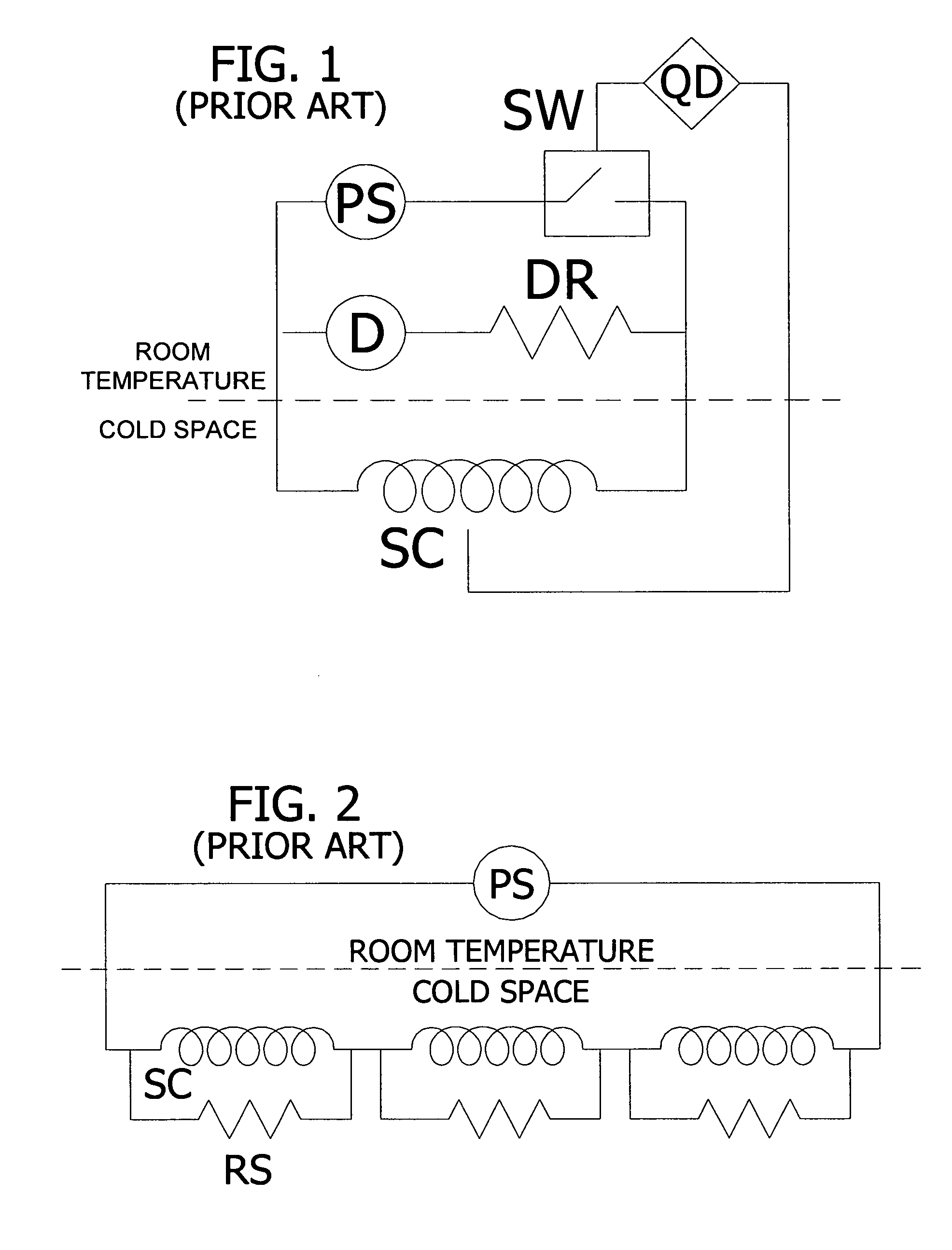
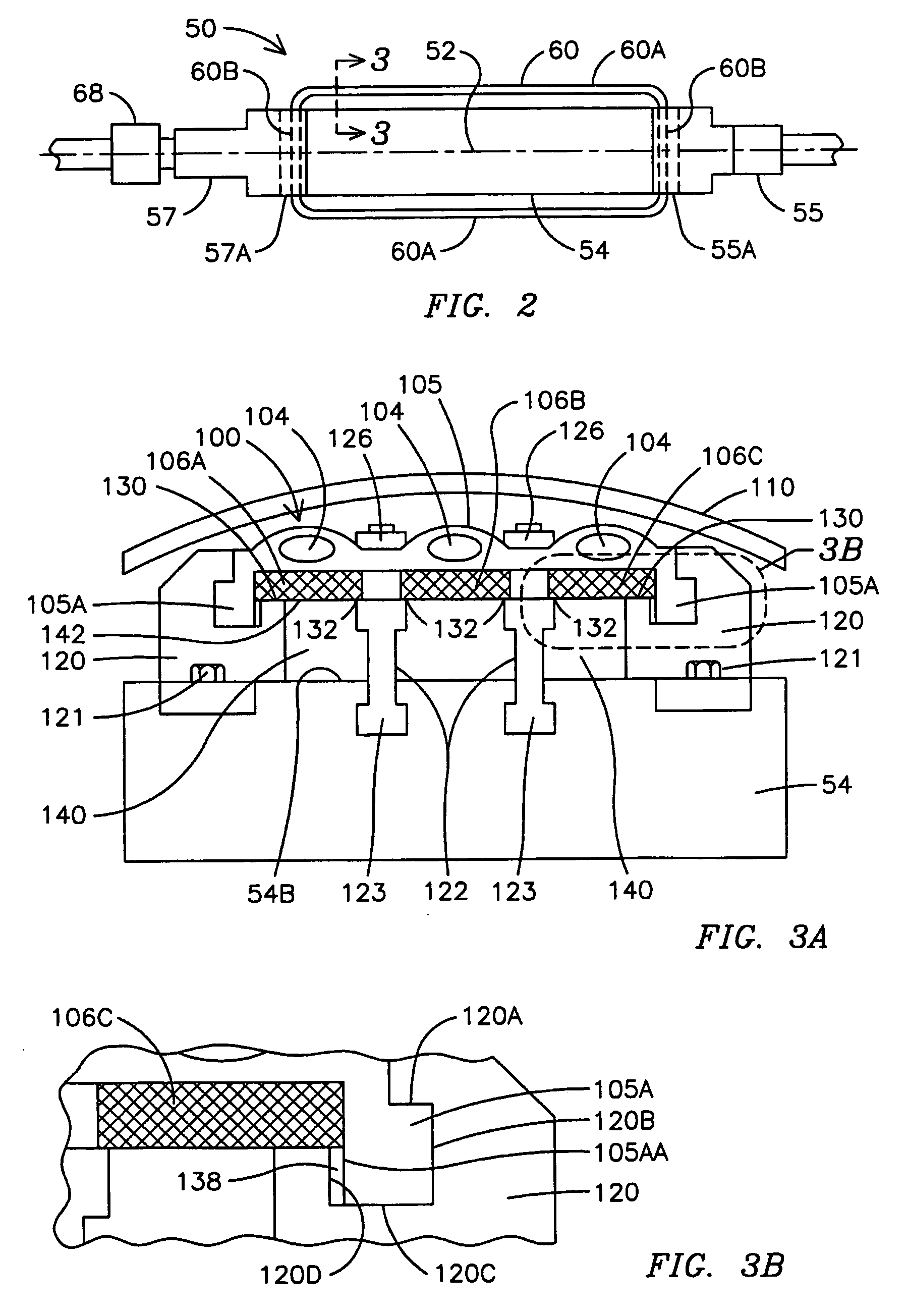
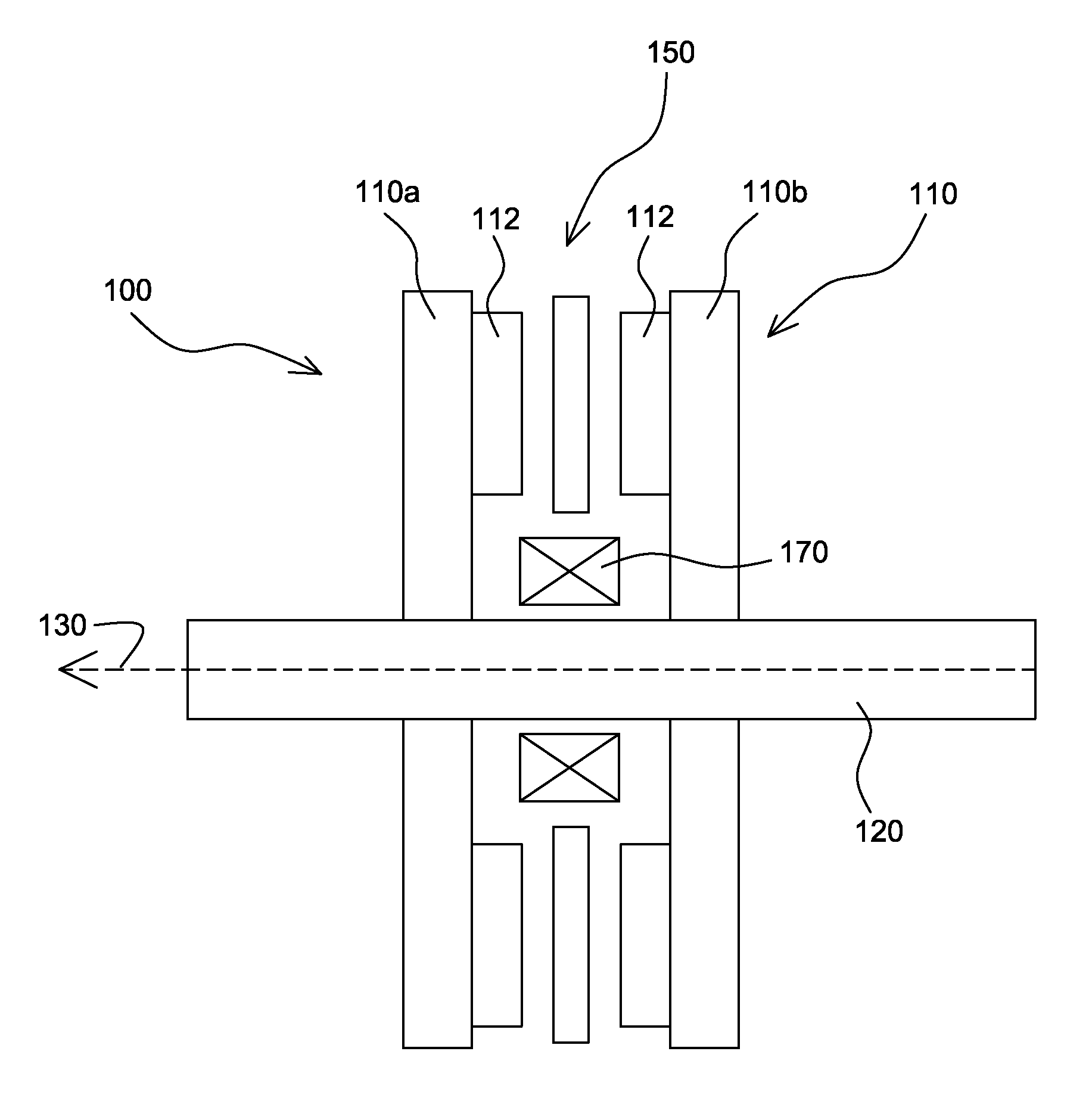
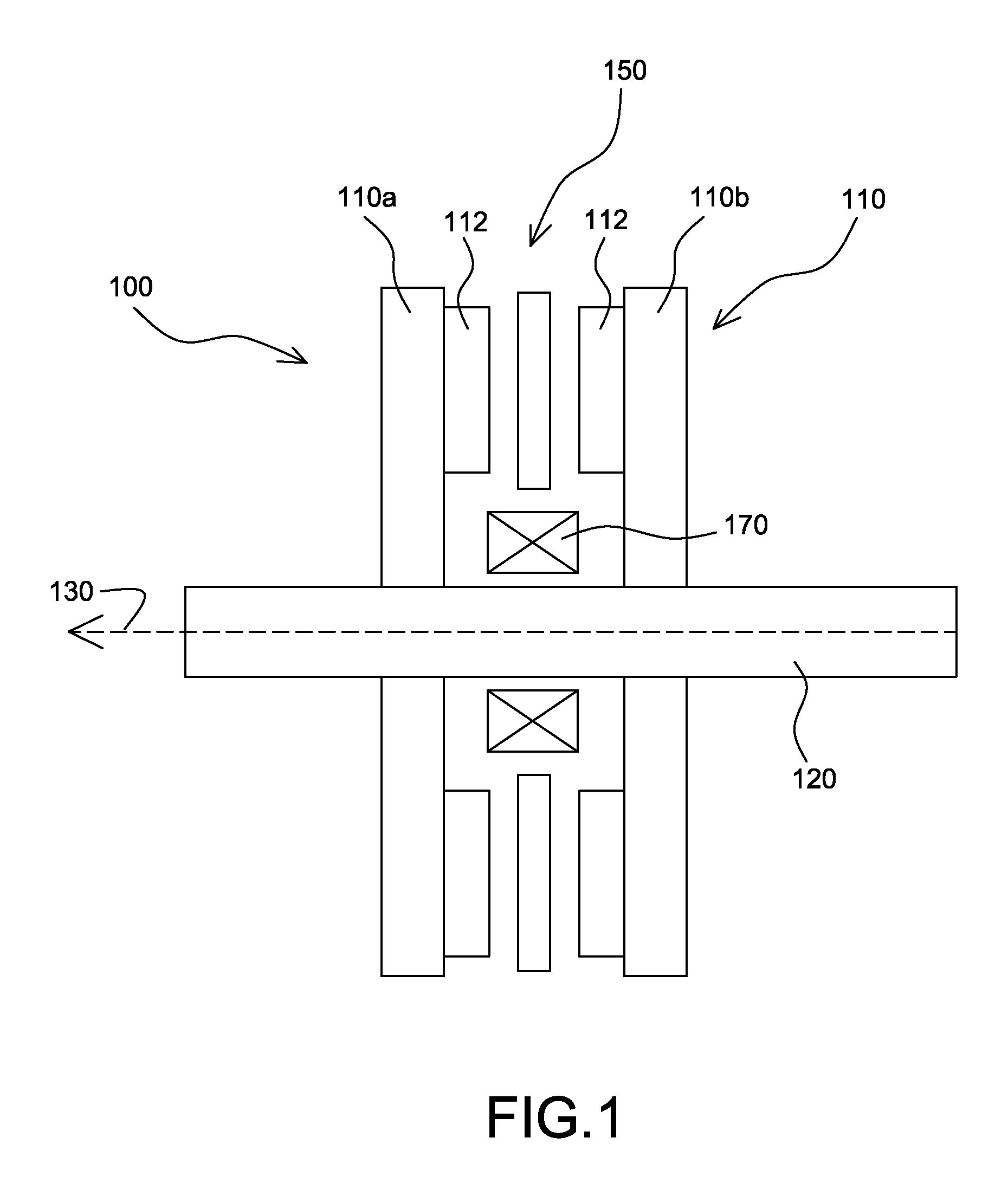
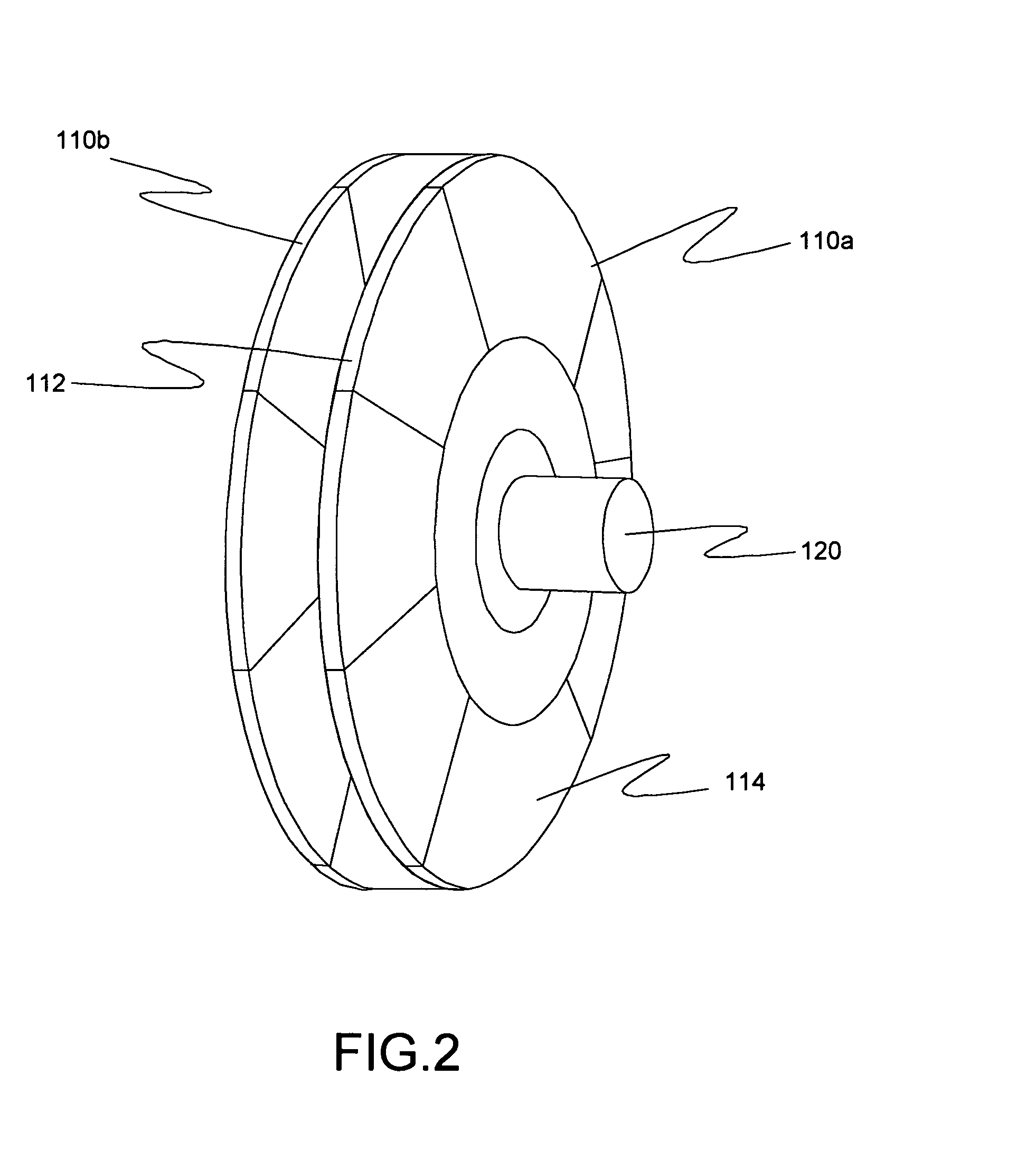
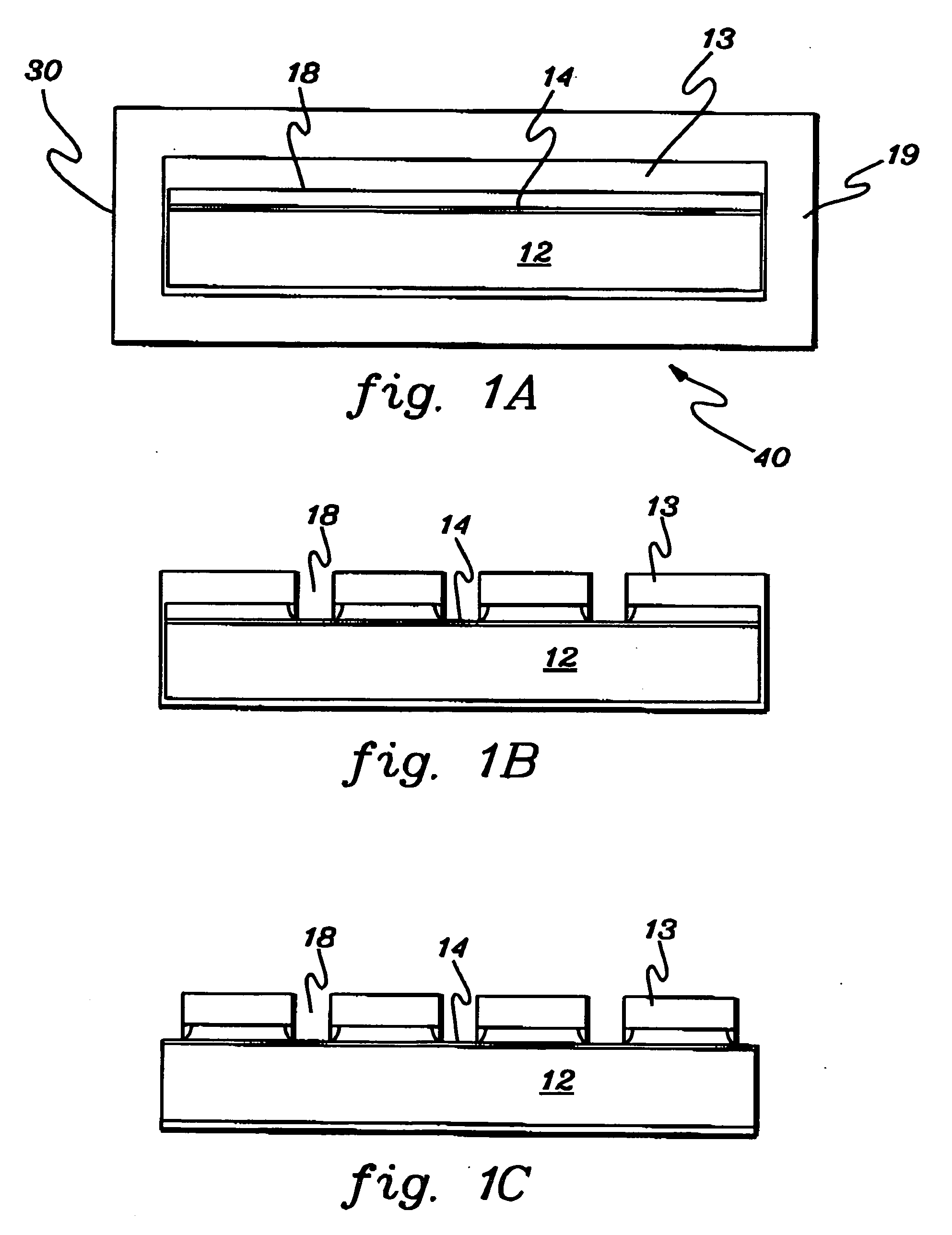
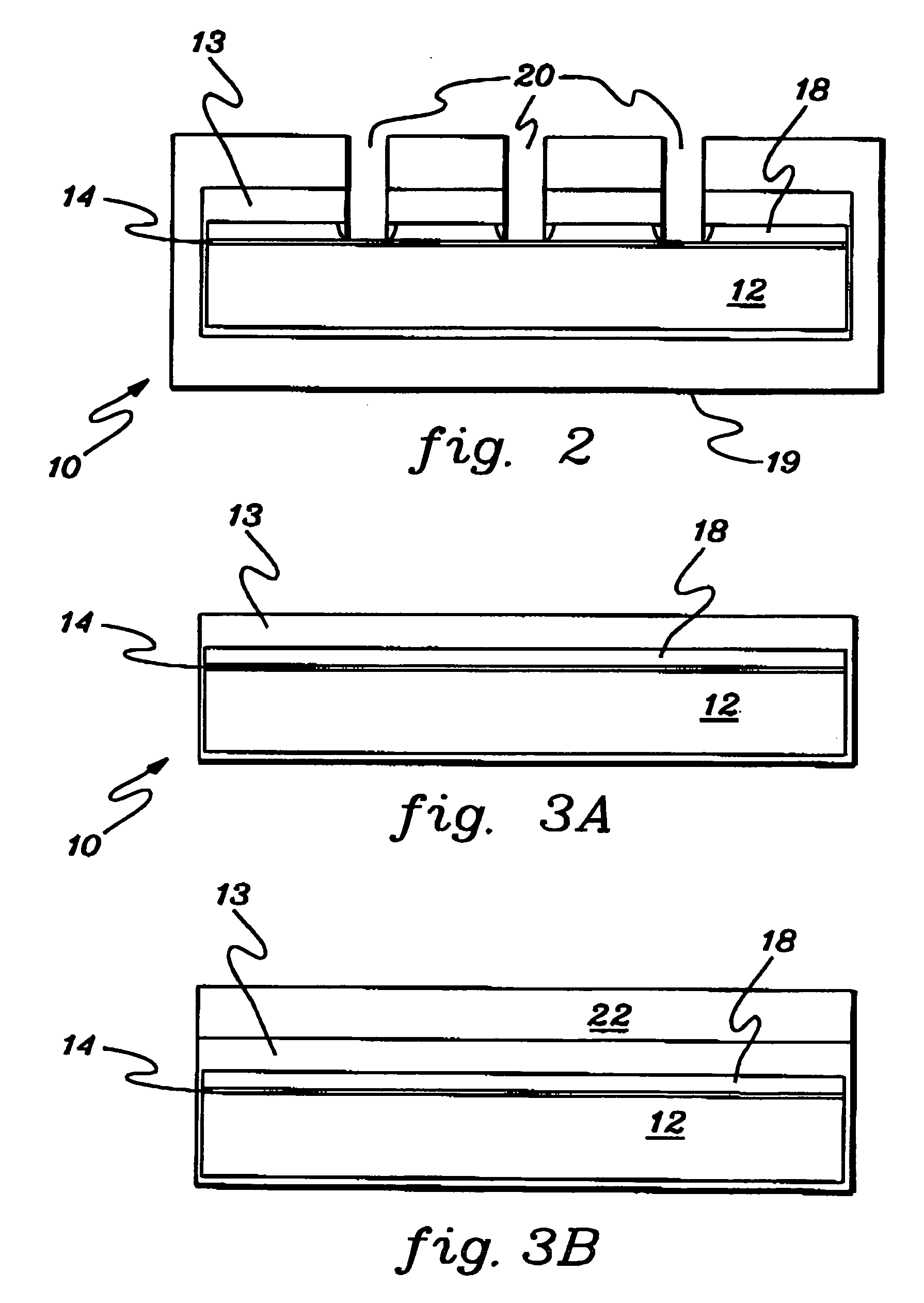
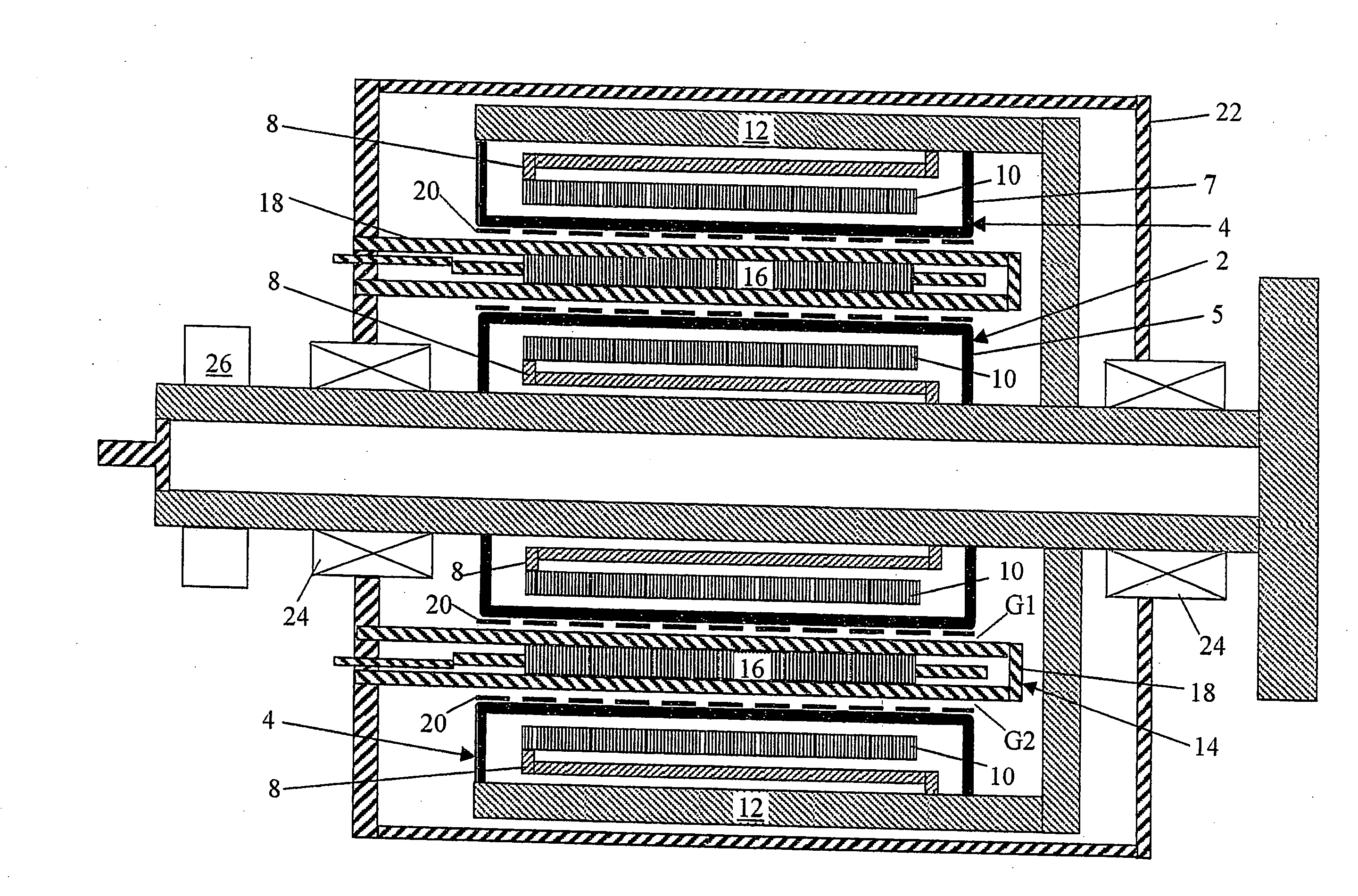
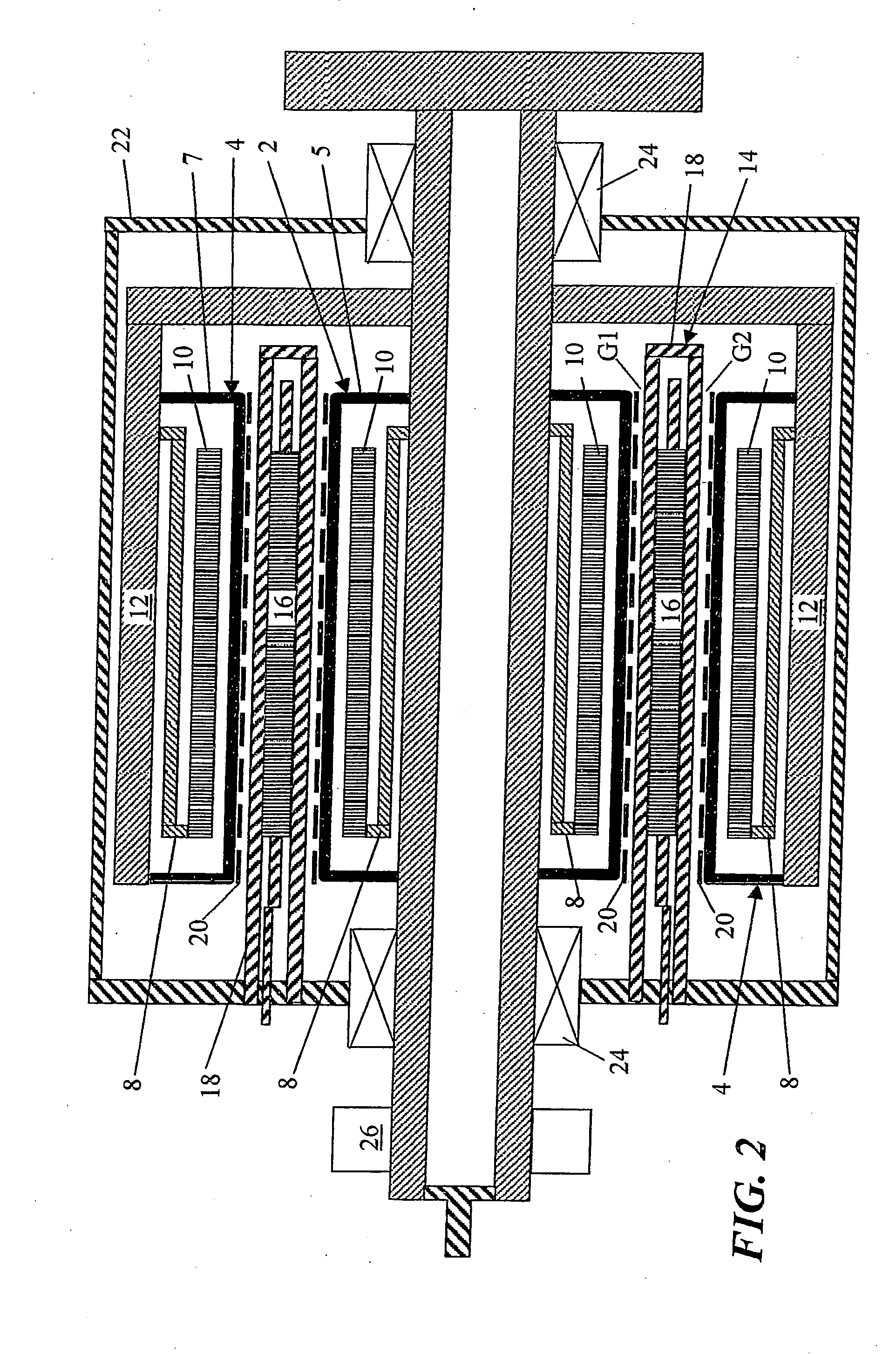
Inductive quench for magnet protection
ActiveUS7701677B2Effective heat conductionMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsInternal energy
A coil system for inductively heating a superconducting magnet in order to provide an internal energy dump by uniformly quenching a high performance superconducting magnet. The quench-inducing system uses AC magnetic fields that require negligible reactive power. The system is especially suited for inducing a relatively uniform quench in dry superconducting magnets.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
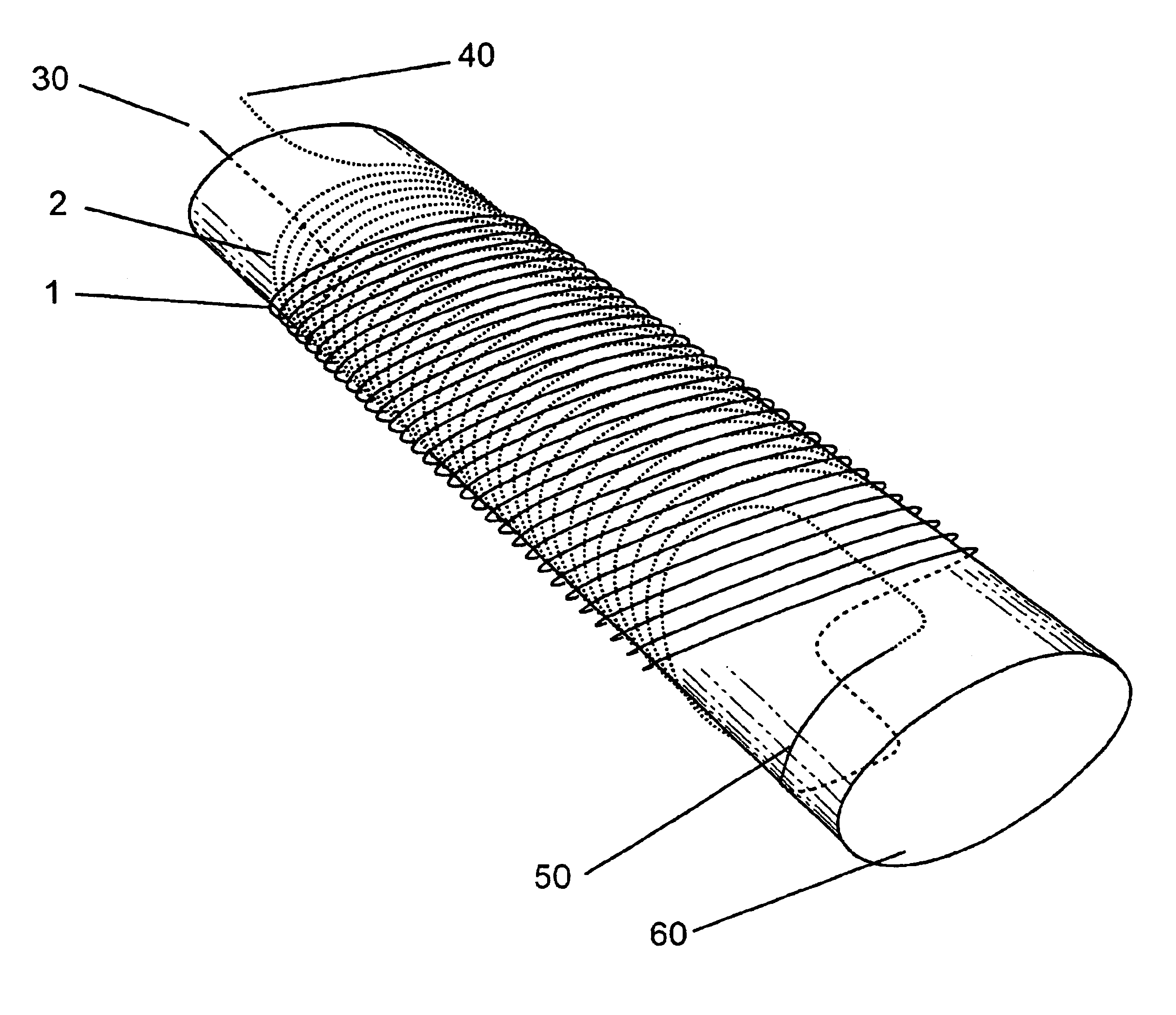
Concentric tilted double-helix dipoles and higher-order multipole magnets
InactiveUS6921042B1Simple processLess costlyElectromagnets without armaturesFilament handlingElectric machineryMagneto hydrodynamic
Concentric tilted double-helix magnets, which embody a simplified design and construction method for production of magnets with very pure field content, are disclosed. The disclosed embodiment of the concentric tilted double-helix dipole magnet has the field quality required for use in accelerator beam steering applications, i.e., higher-order multipoles are reduced to a negligibly small level. Magnets with higher multipole fields can be obtained by using a simple modification of the coil winding procedure. The double-helix coil design is well-suited for winding with superconducting cable or cable-in-conduit conductors and thus is useful for applications that require fields in excess of 2 T. The coil configuration has significant advantages over conventional racetrack coils for accelerators, electrical machinery, and magneto-hydrodynamic thrusting devices.
Owner:GOODZEIT CARL L +2
Low resistance conductors, processes of production thereof, and electrical members using same
InactiveUS20030213611A1Low resistivityEconomical priceNon-insulated conductorsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A conductor obtained by connecting a plurality of superconductors by normal conductivity or a conductor comprised of superconductors and normal conductors, said low resistance conductor using superconductors characterized in that an apparent specific resistance of said conductor at below a superconducting transition temperature of said superconductors is lower than the specific resistance of copper at that superconducting transition temperature.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
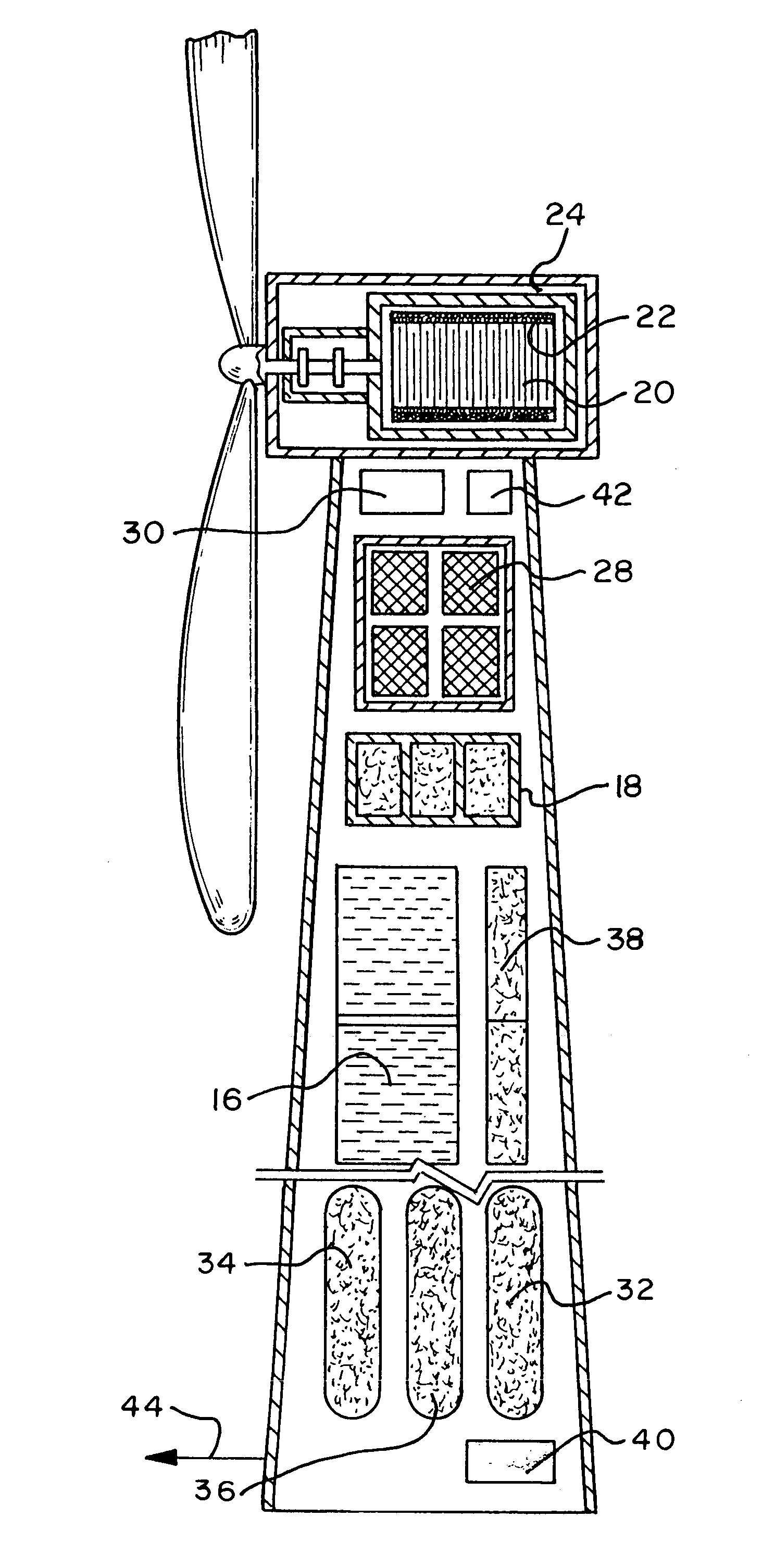
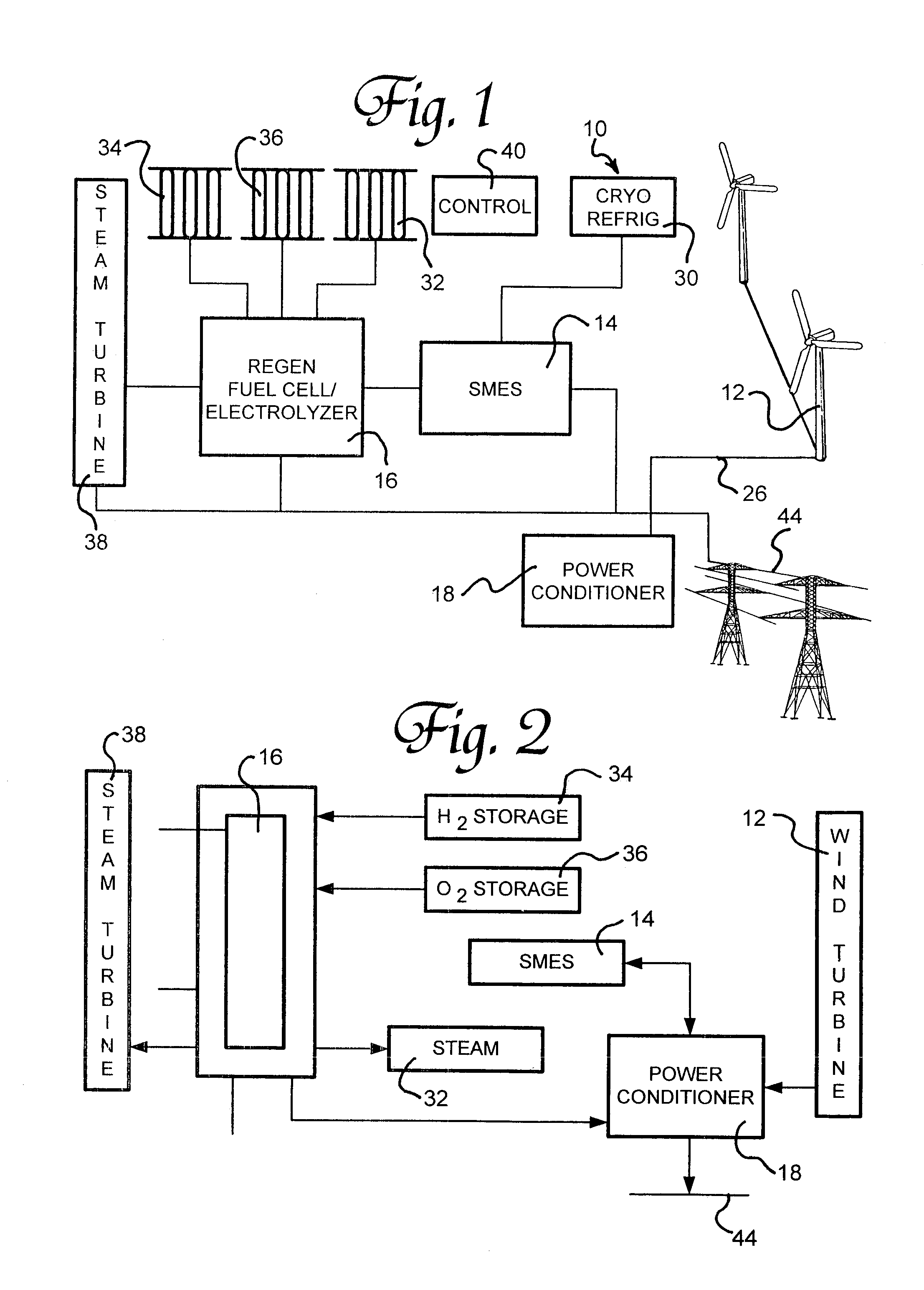
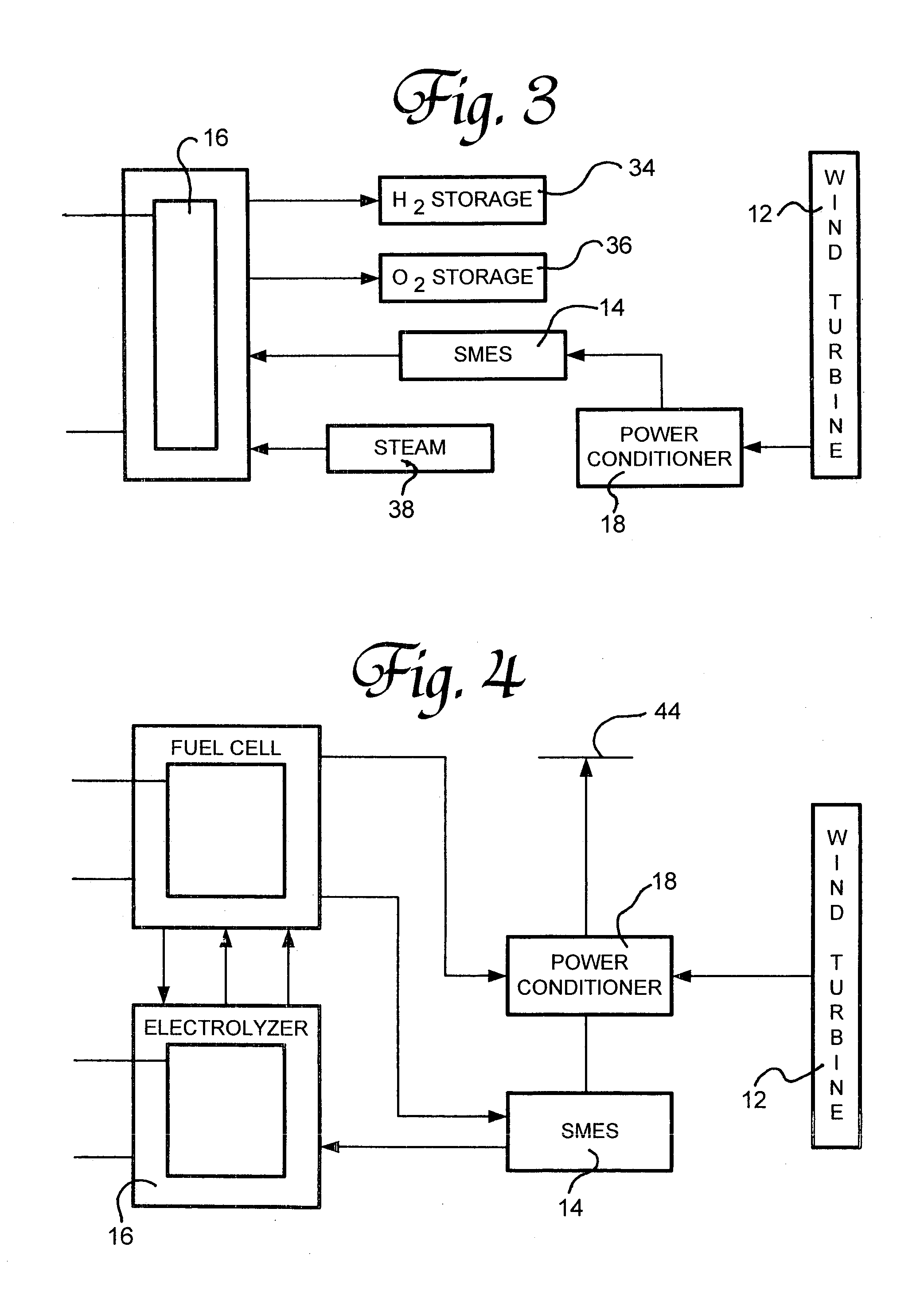
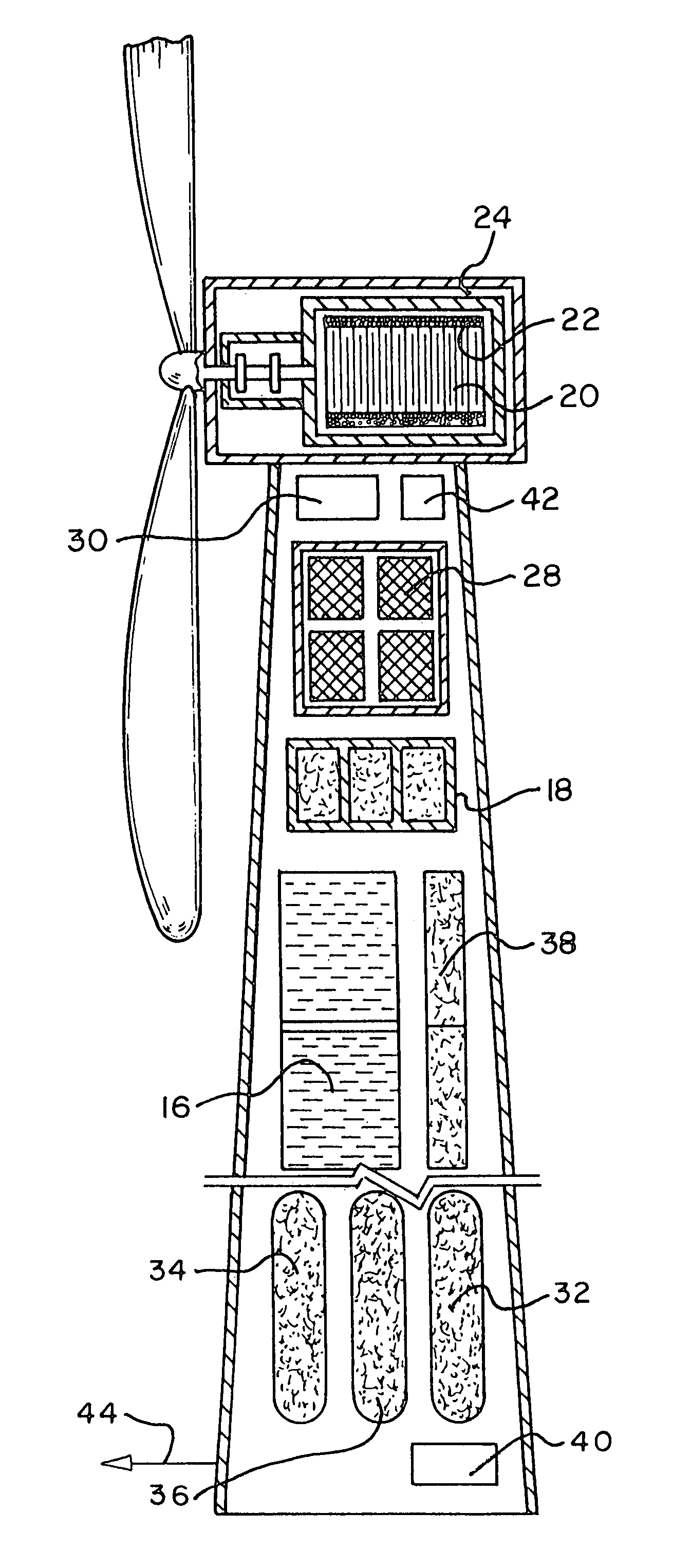
Renewable energy electric power generating system
InactiveUS7233079B1Large capacityEasy to useMachines/enginesWind energy generationElectrolysisMagnetic storage
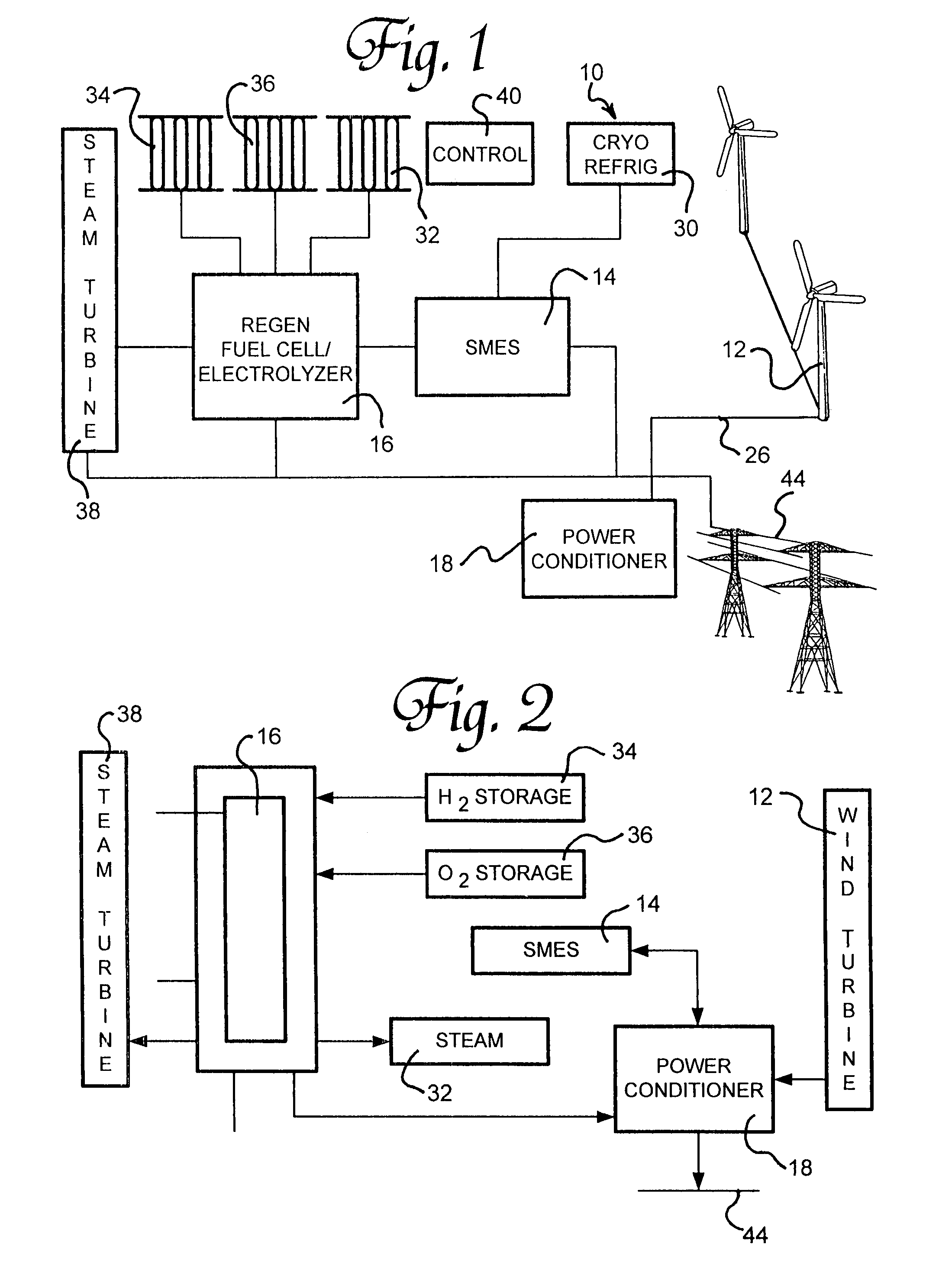
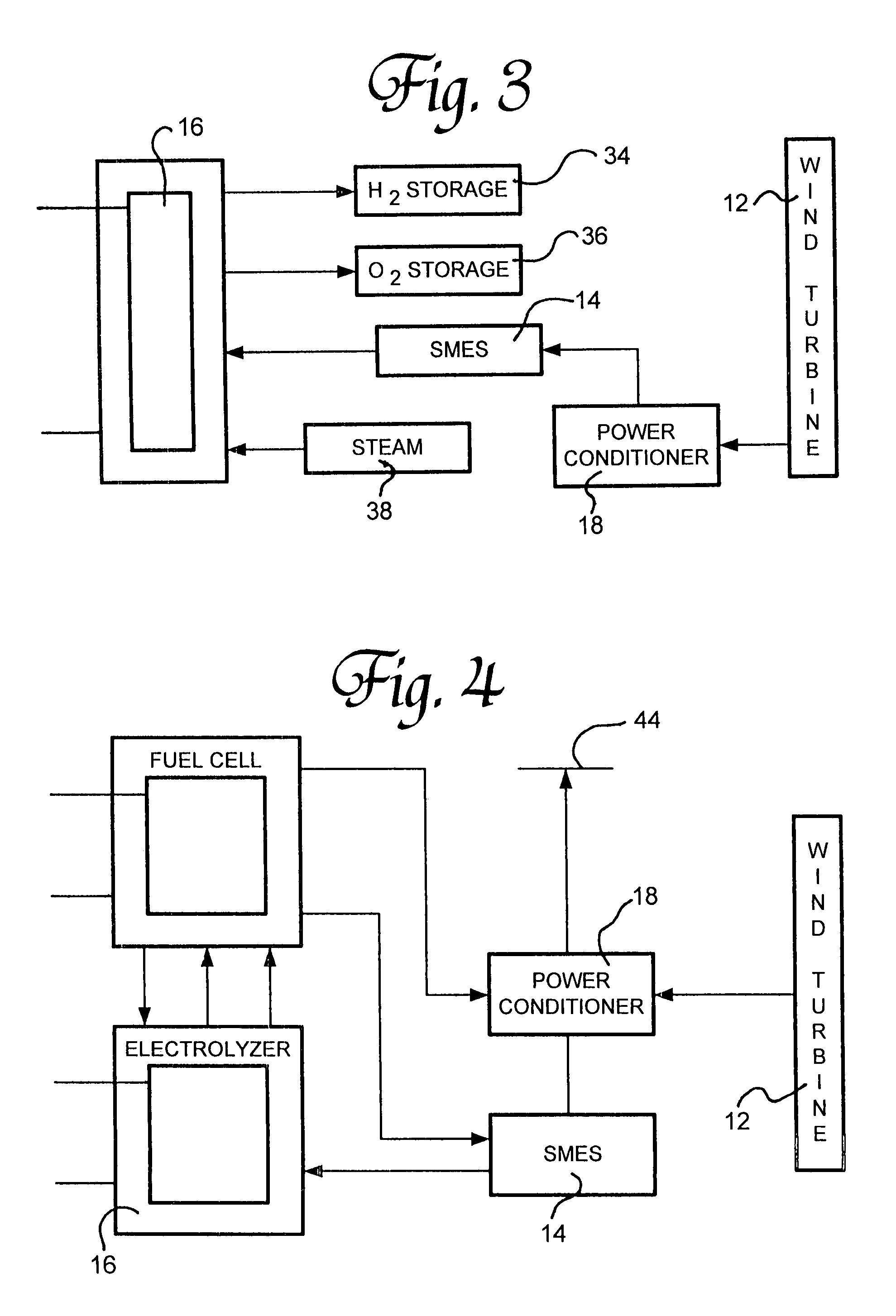
A renewable electric power system includes a high temperature superconducting wind turbine using high temperature superconducting yttrium-barium-copper oxide for the rotor and stator windings as well as a superconducting bearing. Power from the turbine is stored in a high temperature superconducting magnetic storage system that also uses HTS YBCO. Also included is a regenerative solid oxide fuel cell / electrolyzer with steam turbine cogeneration. The system operates on a managed day / night cycle. During daytime, the energy produced by the wind turbines and fuel cells is transmitted to the grid. During nocturnal hours, the wind turbine is used to provide low cost electricity to the reversible fuel cells operating in the electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen that is stored for later use. Alternatively, the fuel cells can remain in electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen for the market. A modified interactive system generates power on a continuous twenty-four hour cycle.
Owner:COOPER WILLARD
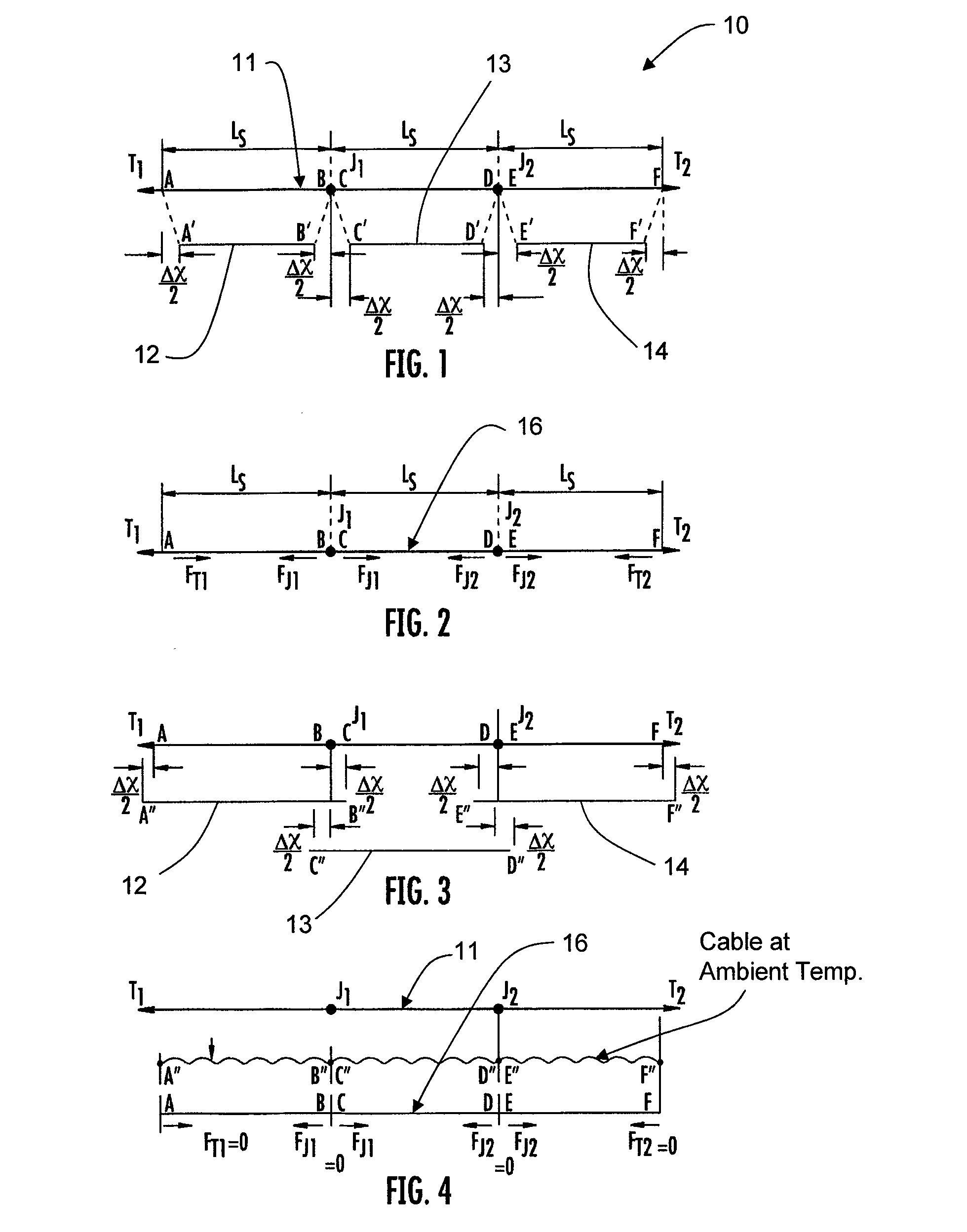
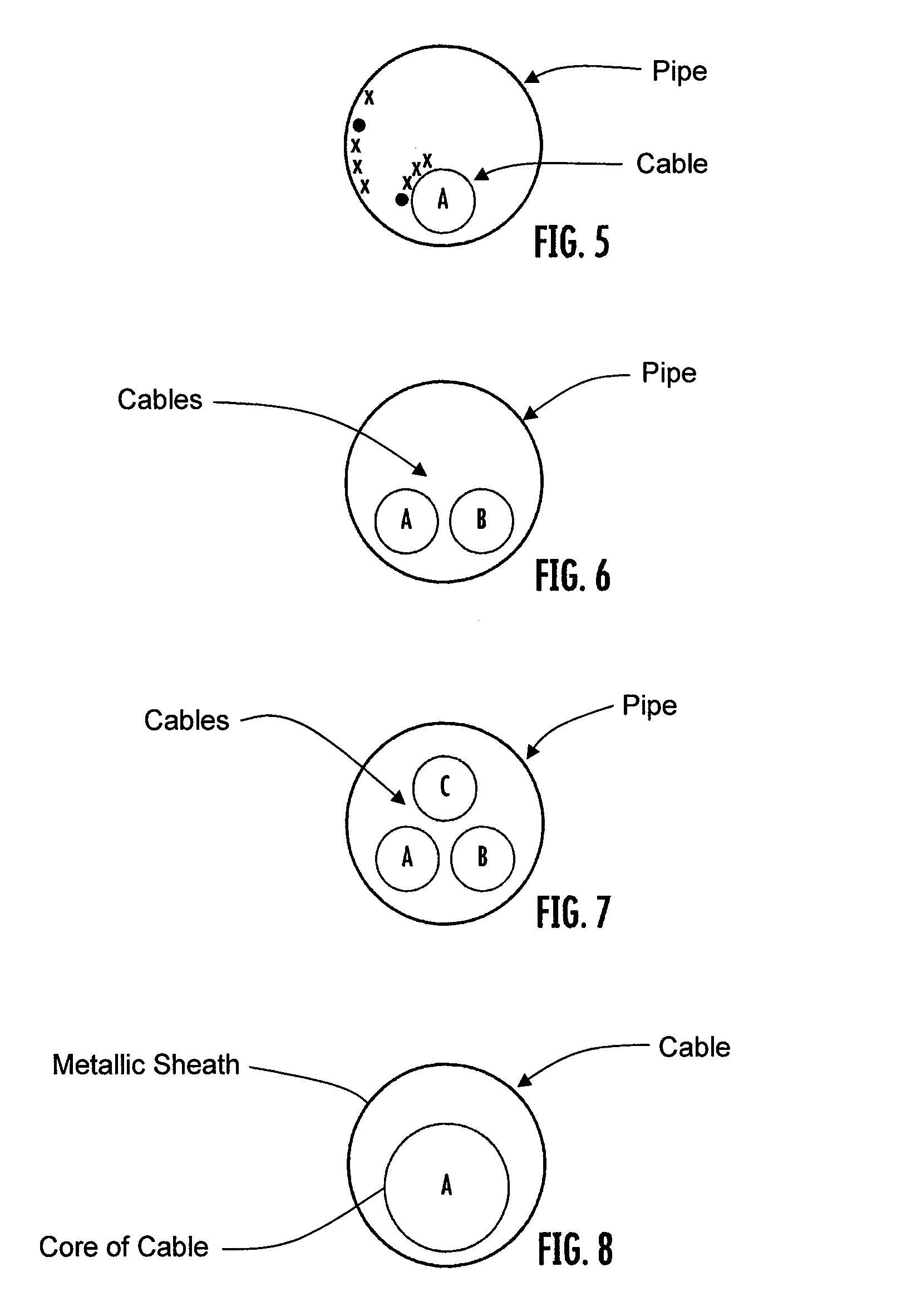
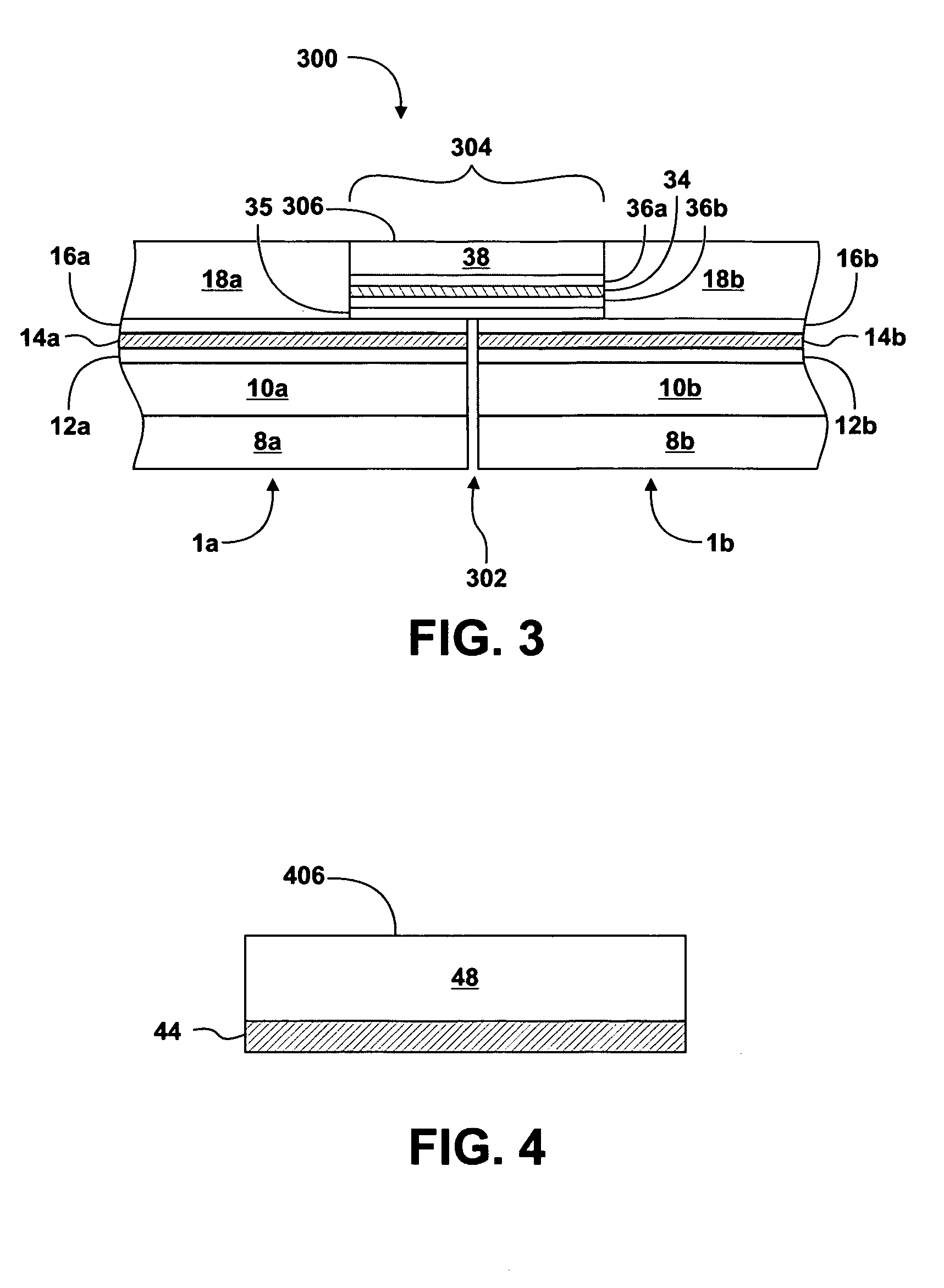
Thermal contraction compensation for superconducting and cryo-resistive cables
InactiveUS20100285968A1Eliminate and reduce magnitude of thermomechanicalSuperconductors/hyperconductorsApparatus for feeding conductors/cablesEngineeringThermal contraction
A method of compensating for thermal contraction of superconducting and cryo-resistive cables. The method includes the steps of determining a compensation length for a cable such that when the cable is subjected to an operating temperature, the cable is in or near a stress-free state, and installing the cable into a pipe such that portions of the cable extend outwardly past ends of the pipe. The method further includes the steps of marking each end of the cable such that the determined compensation length is visibly shown, forcing the cable into the pipe at an ambient installation temperature such that a cable pattern is formed therein, and maintaining the cable in the pipe to prevent the cable from being pushed out of the pipe.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
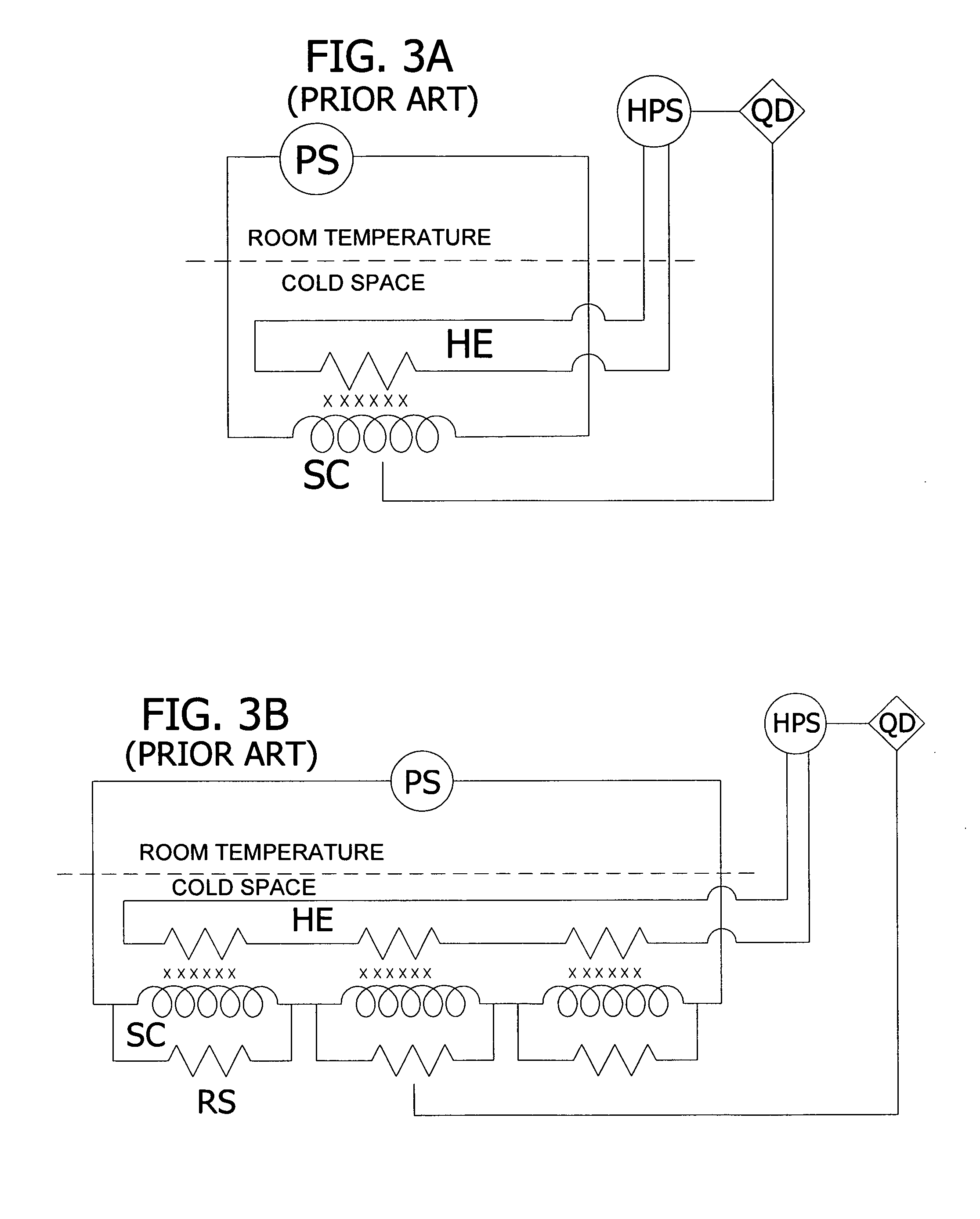
Quench protection of HTS superconducting magnets
InactiveUS20060291112A1Improved active protectionEffective quench protectionTransformers/inductances coolingSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh-temperature superconductivitySuperconducting Coils
A method of constructing a superconducting coil. The method includes embedding a plurality of heater elements throughout a superconducting coil. The heater elements are positioned according to a predetermined distribution and substantially in thermal contact with the coil for heating the coil in response to a quench condition. Other aspects of the invention involve an active protection circuit and a high temperature superconductor magnet that includes such an active protection circuit for internally dissipating stored magnetic energy in the event of a quench.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Joined superconductive articles
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
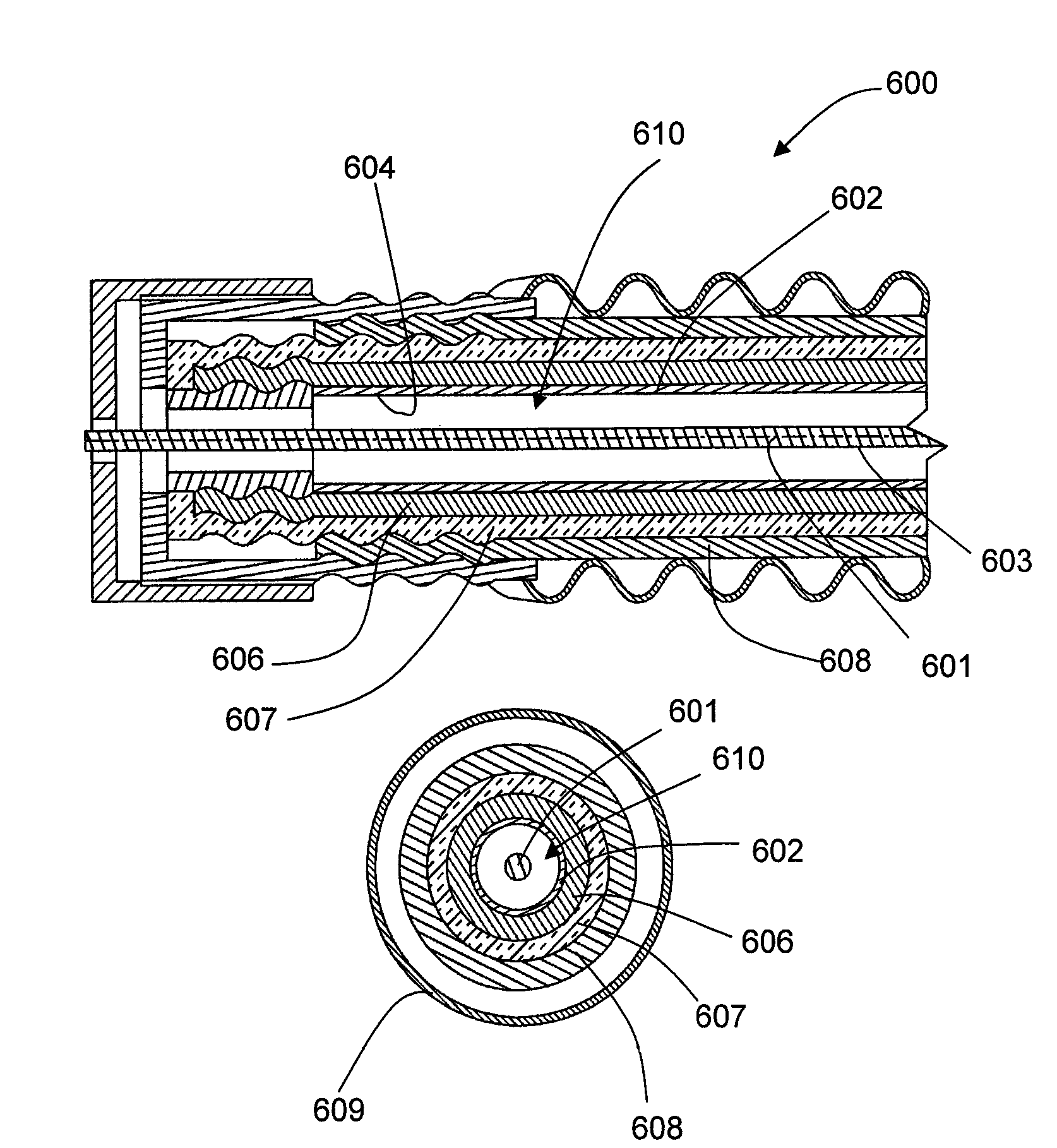
Terminal for connecting a superconducting multiphase cable to a room temperature electrical equipment
InactiveUS6049036ALine/current collector detailsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectrical conductorRoom temperature
A terminal for connecting a superconducting multiphase cable, a superconducting three-phase cable for example, to a room temperature electrical equipment is described. The terminal includes a casing with cooling fluid, inside which the three cable superconductors are each connected with a resistive conductor the end of which is connected to the room temperature equipment phases at the outside of the casing. The terminal includes superconducting connectors between the three neutral superconductors and a single resistive conductor the end of which is externally associated with the room temperature equipment. The neutral superconducting connectors and the junction area of the connector of the single conductor are disposed inside the cold area of the casing.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA
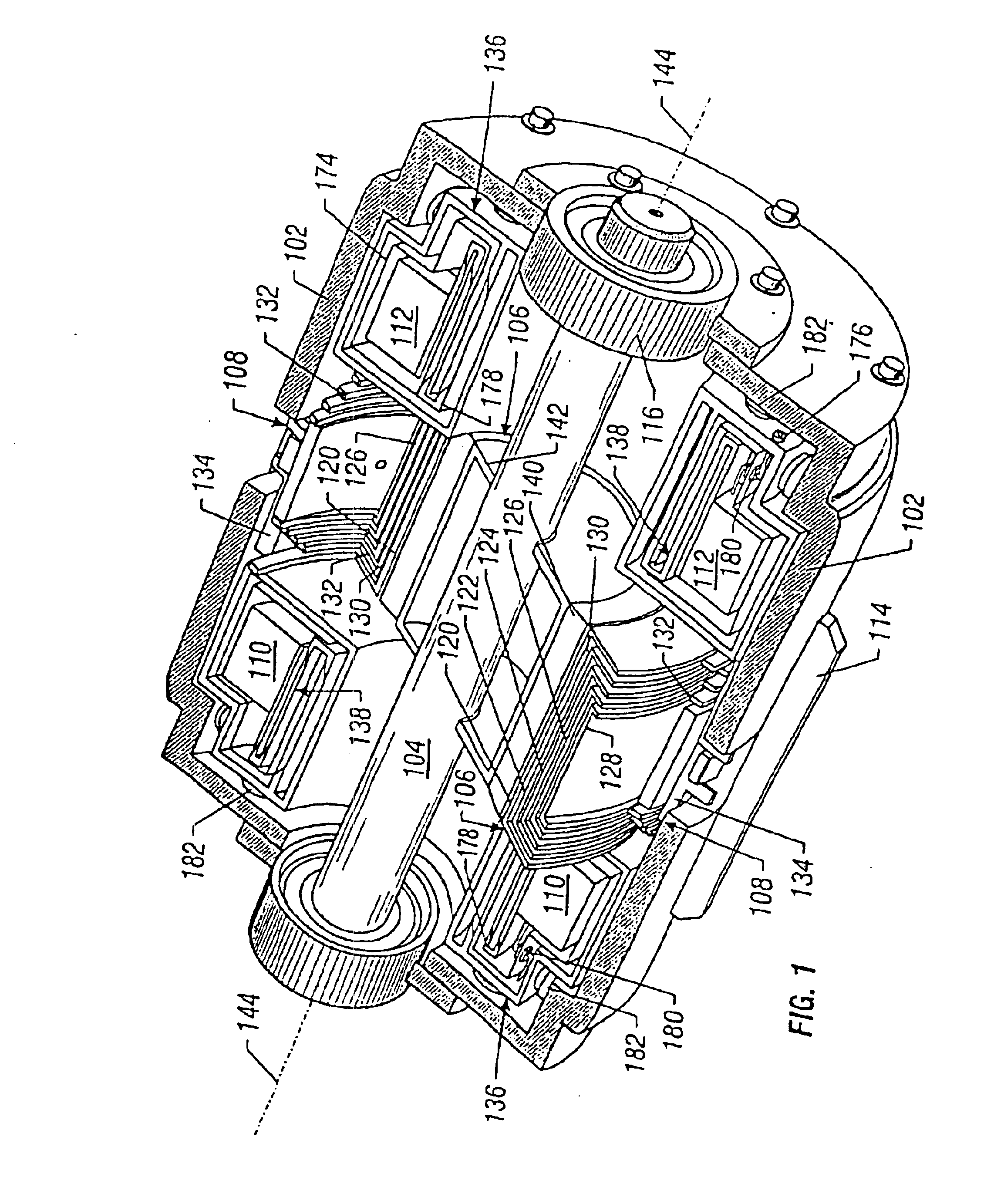
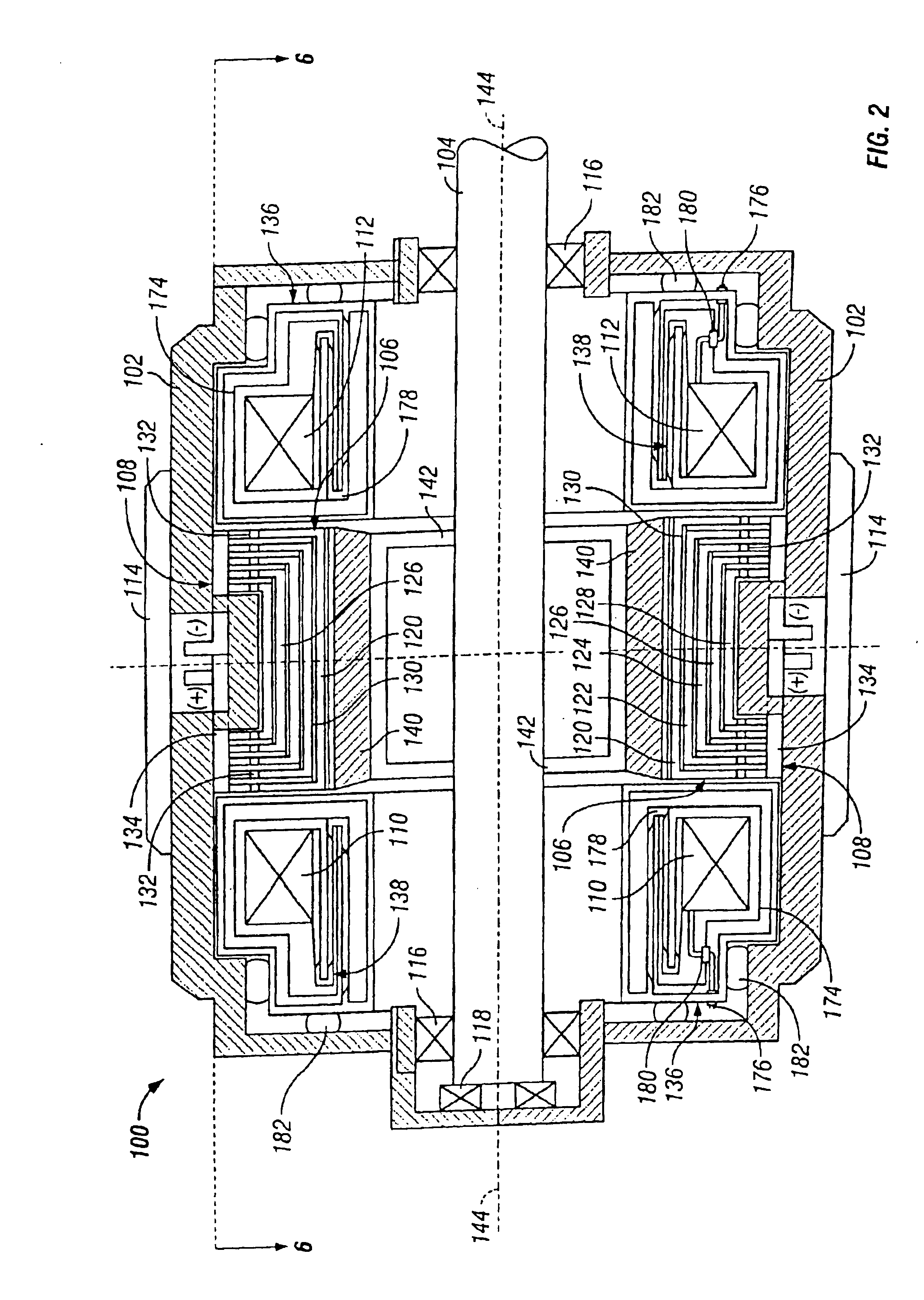
Homopolar machine with shaft axial thrust compensation for reduced thrust bearing wear and noise
InactiveUS6856062B2Reduce induced magnetic forceConstant contact pressureRotary current collectorMagnetic bodiesFiberContact pressure
A homopolar machine produces an axial counter force on the rotating shaft to compensate for the load on the shaft's thrust bearing to reduce wear and noise and prolong bearing life. The counter force is produced through magnetic interaction between the shaft and the machine's field coils and is created by changing the current excitation of the field coils, which results in a magnetic flux asymmetry in an inner flux return coupled to the shaft. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration that uses current collectors that maintain substantially constant contact pressure in the presence of high magnetic fields to improve current collector performance. The current collectors are flexible and may be made from either electrically conductive fibers or stacked strips such that they bear up against the armature so that the pressure is maintained by the spring constant of the current collector material. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration where the brushes are oriented so that the current is aligned as much as is practical with the local magnetic field lines so as to reduce the lateral electromagnetic forces on the brushes.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
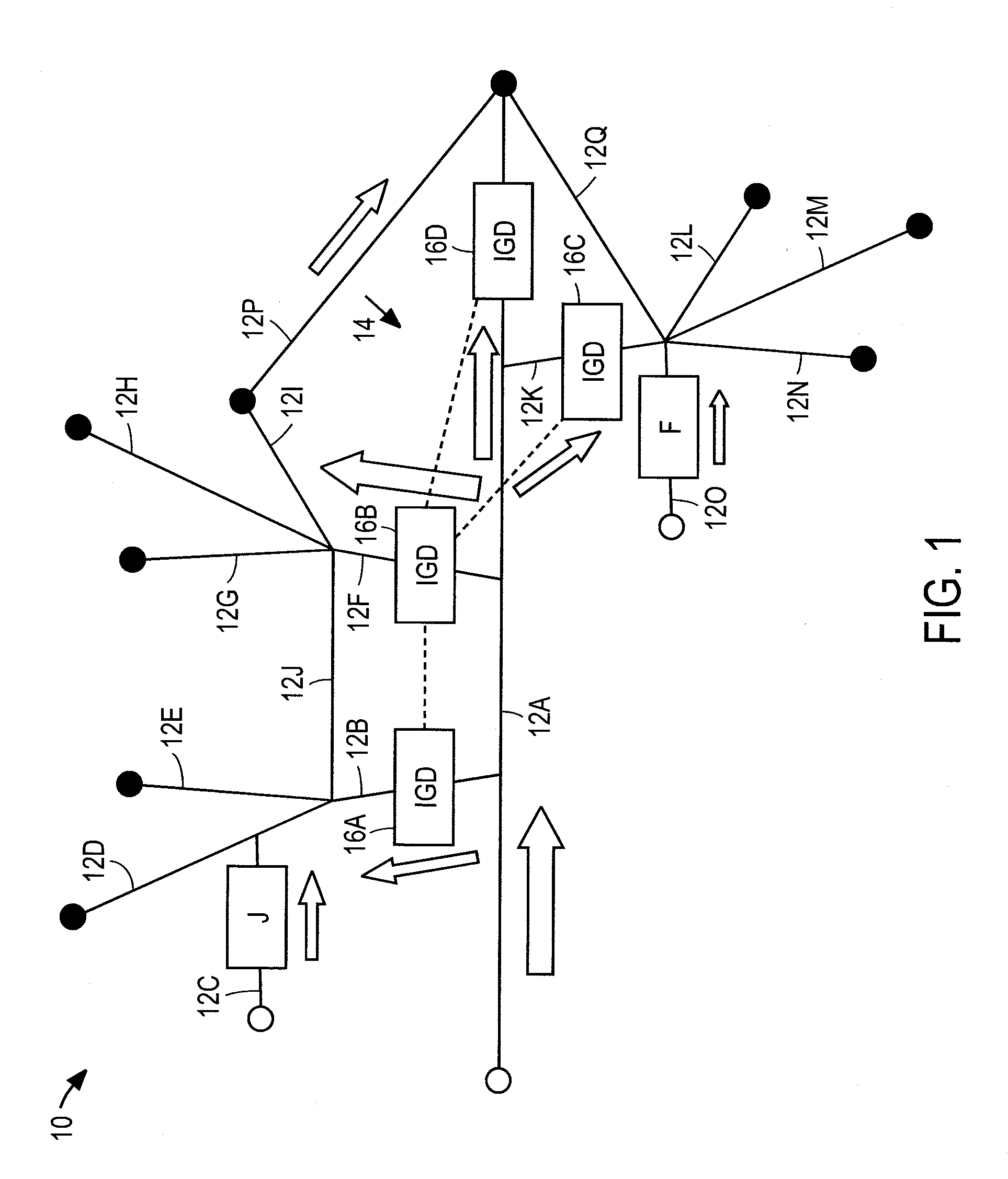
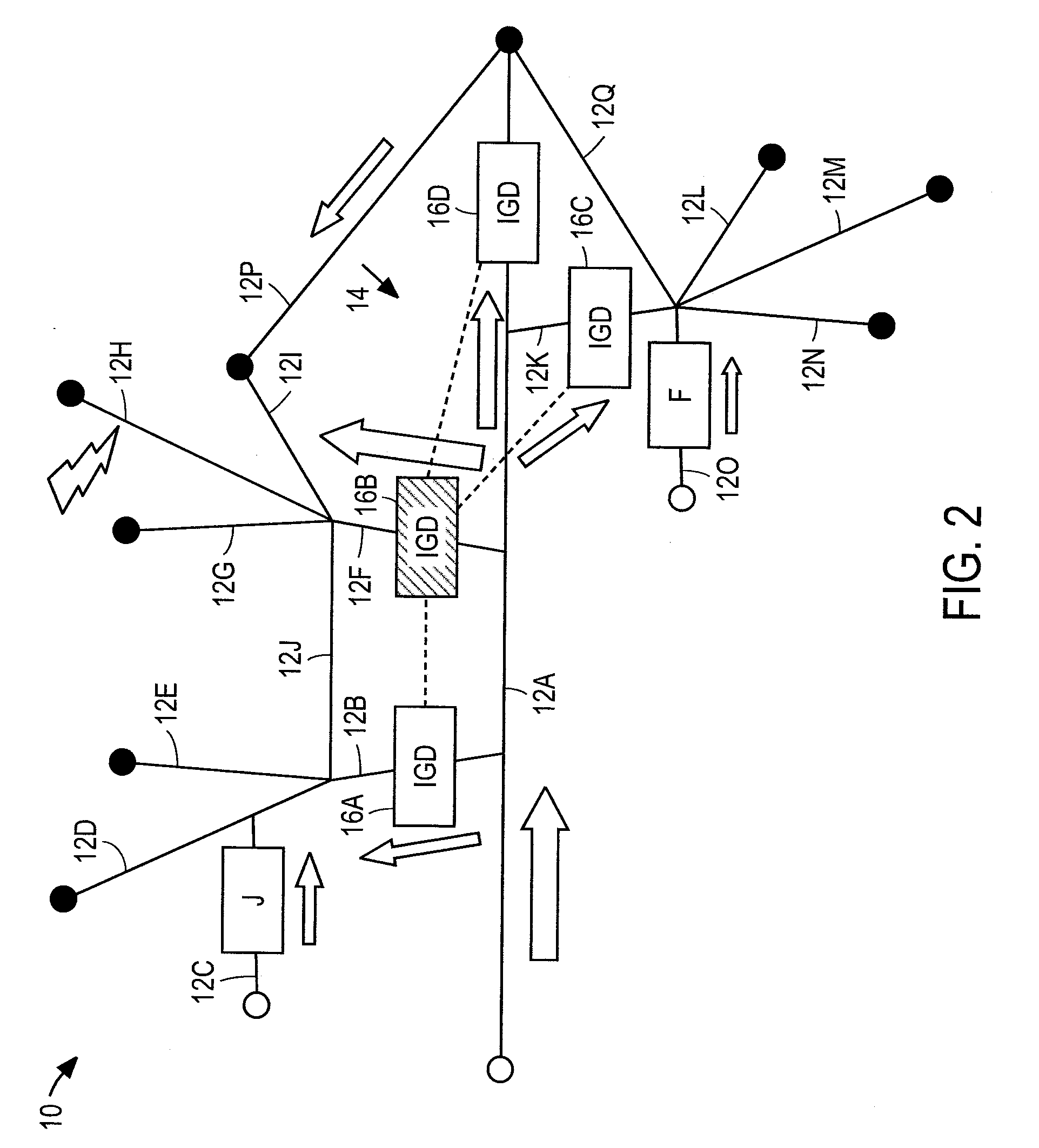
Method and devices for stabilizing electric grid power
InactiveUS20100177450A1Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSuperconductor elements usageCommunications systemCurrent limiting
The invention provides an electric grid stabilization metadevice including a plurality of interactive grid devices each forming part of a respective electrical path of an electric grid and each including, a variable impedance device that inserts a current limiting impedance in the respective path when a fault occurs, a state detection transducer connected to the variable impedance device to change a detection state when the fault occurs and an integral communications system having transmission and reception capabilities and being connected to the state detection transducer and variable impedance device, wherein a fault detected by each of the interactive grid devices automatically causes transmission of a signal to another integrated grid device, reception of the signal by the other integrated grid device and an insertion of a current limiting impedance by the other integrated grid device.
Owner:GRID LOGIC
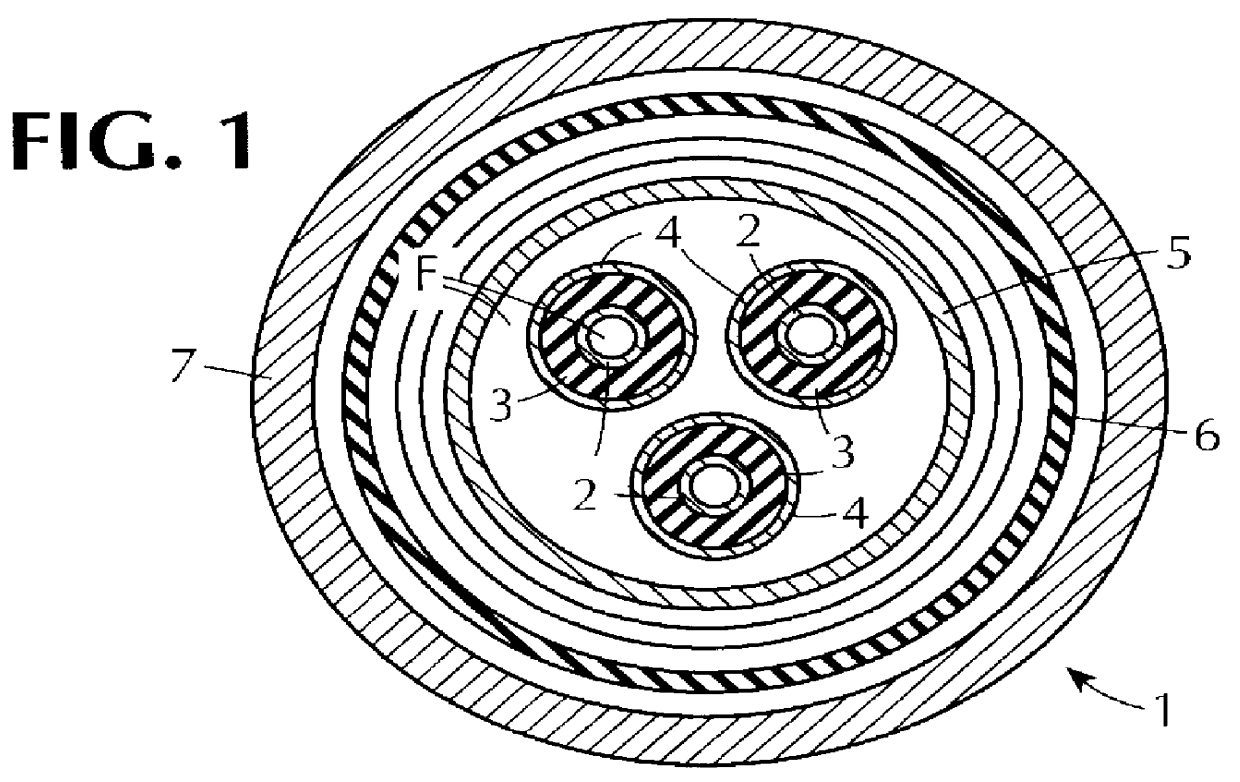
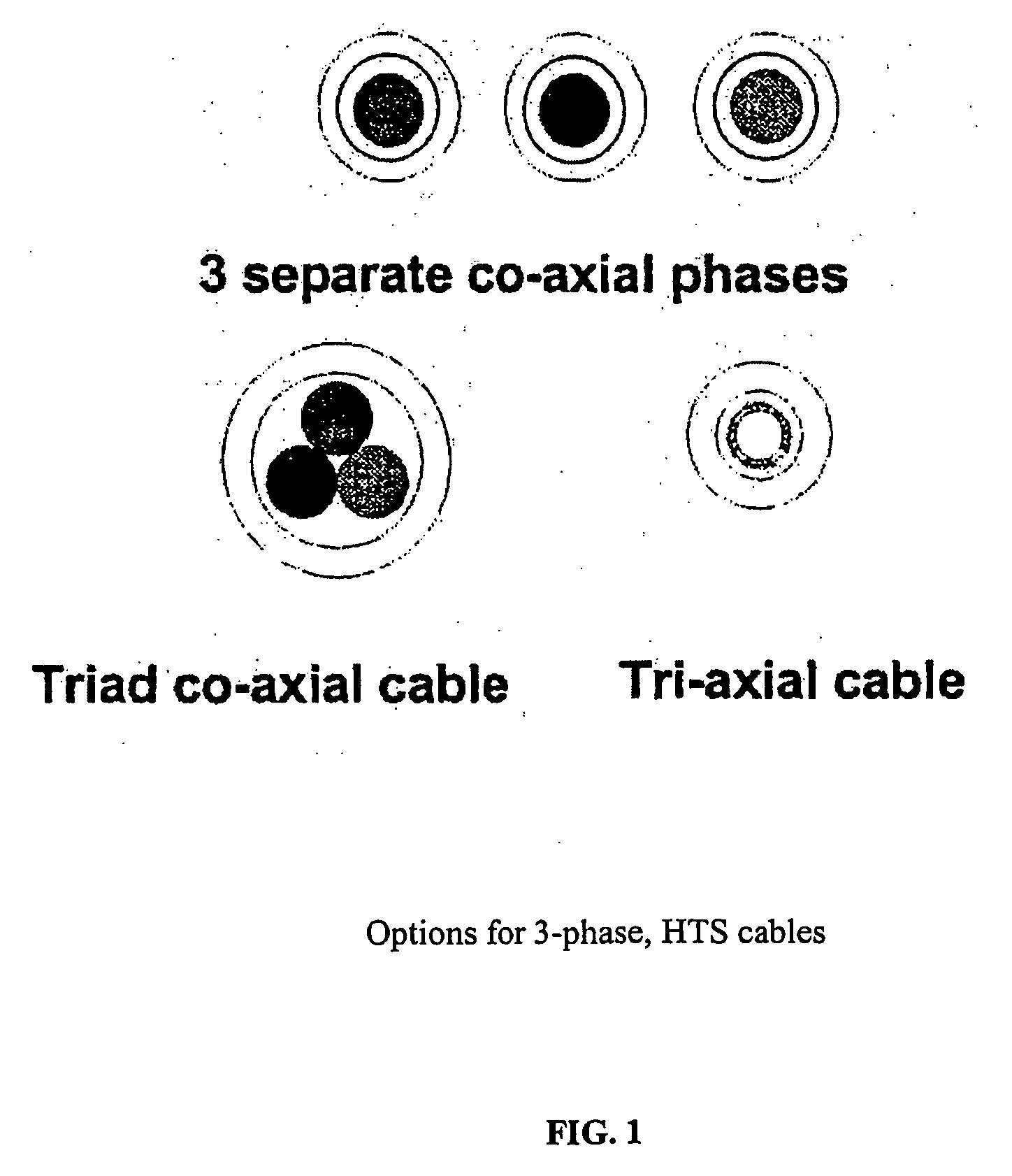
Triaxial superconducting cable and termination therefor
InactiveUS20050173149A1Improve superconductivityIncrease the critical currentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCable fittings for cryogenic cablesBand shapeBending strain
In order to provide a flexible oxide superconducting cable which is reduced in AC loss, tape-shaped superconducting wires covered with a stabilizing metal are wound on a flexible former. The superconducting wires are preferably laid on the former at a bending strain of not more than 0.2%. In laying on the former, a number of tape-shaped superconducting wires are laid on a core member in a side-by-side manner, to form a first layer. A prescribed number of tape-shaped superconducting wires are laid on top of the first layer in a side-by-side manner, to form a second layer. The former may be made of a metal, plastic, reinforced plastic, polymer, or a composite and provides flexibility to the superconducting wires and the cable formed therewith. Methods of forming and terminating a triaxial superconductor are disclosed.
Owner:SOUTHWIRE CO LLC
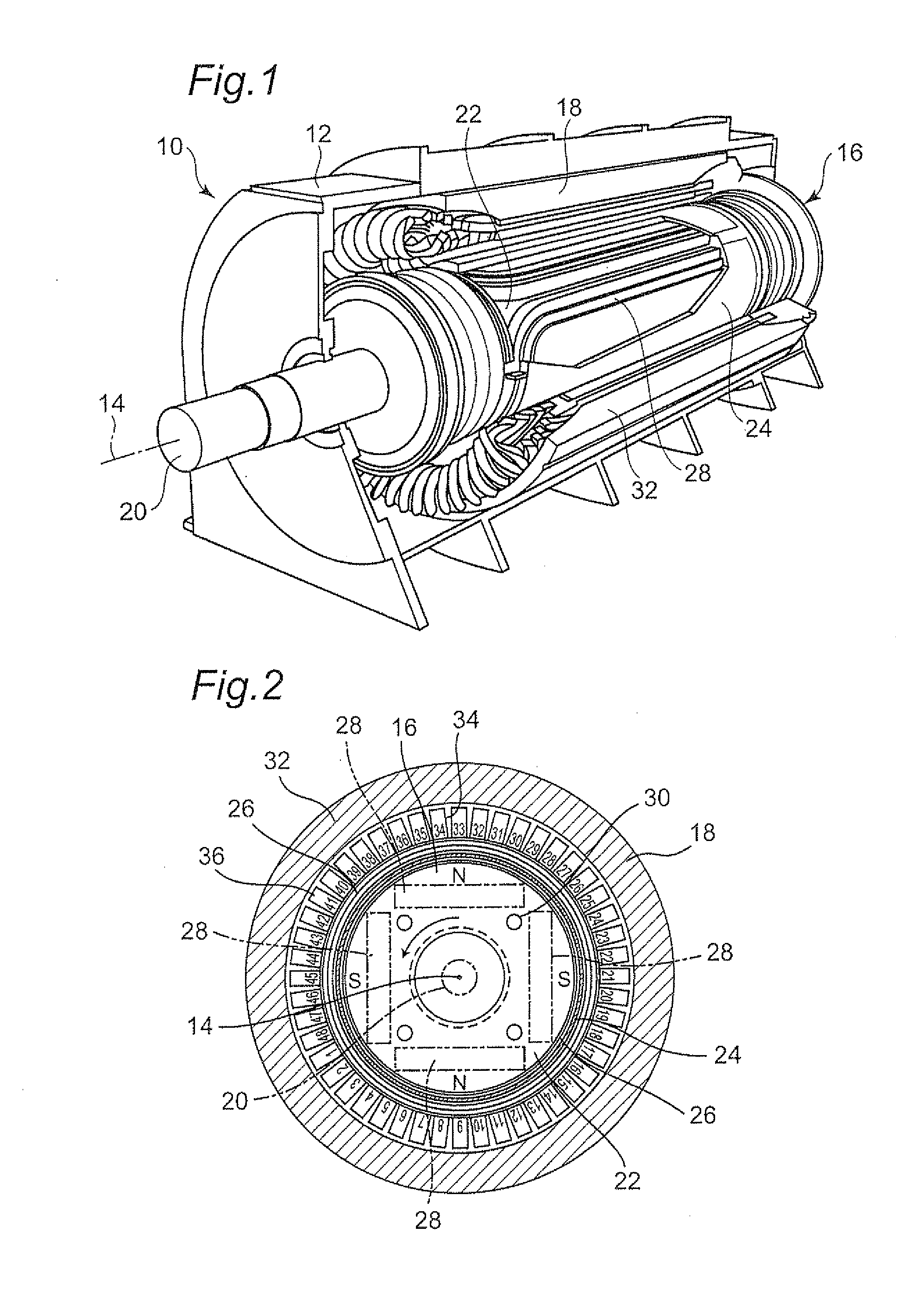
Method and apparatus for a superconducting generator driven by wind turbine
A generator including: an annular armature connectable to rotate with blades of a wind turbine; an annular stationary field winding assembly coaxial with the armature and separated by a gap from an inside surface of the armature, wherein the field winding include superconducting coils, and support structure connectable to an upper region of a tower of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting coil support structures
Support structures (100) for attaching superconducting conductors (106) to a rotor (50) of an electrical machine (10). The support structures (100) are mechanically configured to transfer loads exerted on the superconducting conductors (106) during both normal and transient operation of the rotor (50). The mechanical configuration and material of the support structures (100) further present a thermal path that is longer than the physical distance between the superconducting conductors (106) and the rotor (50) thereby minimizing heat flow from the warm rotor (50) to the cold superconducting conductors (106).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC +4
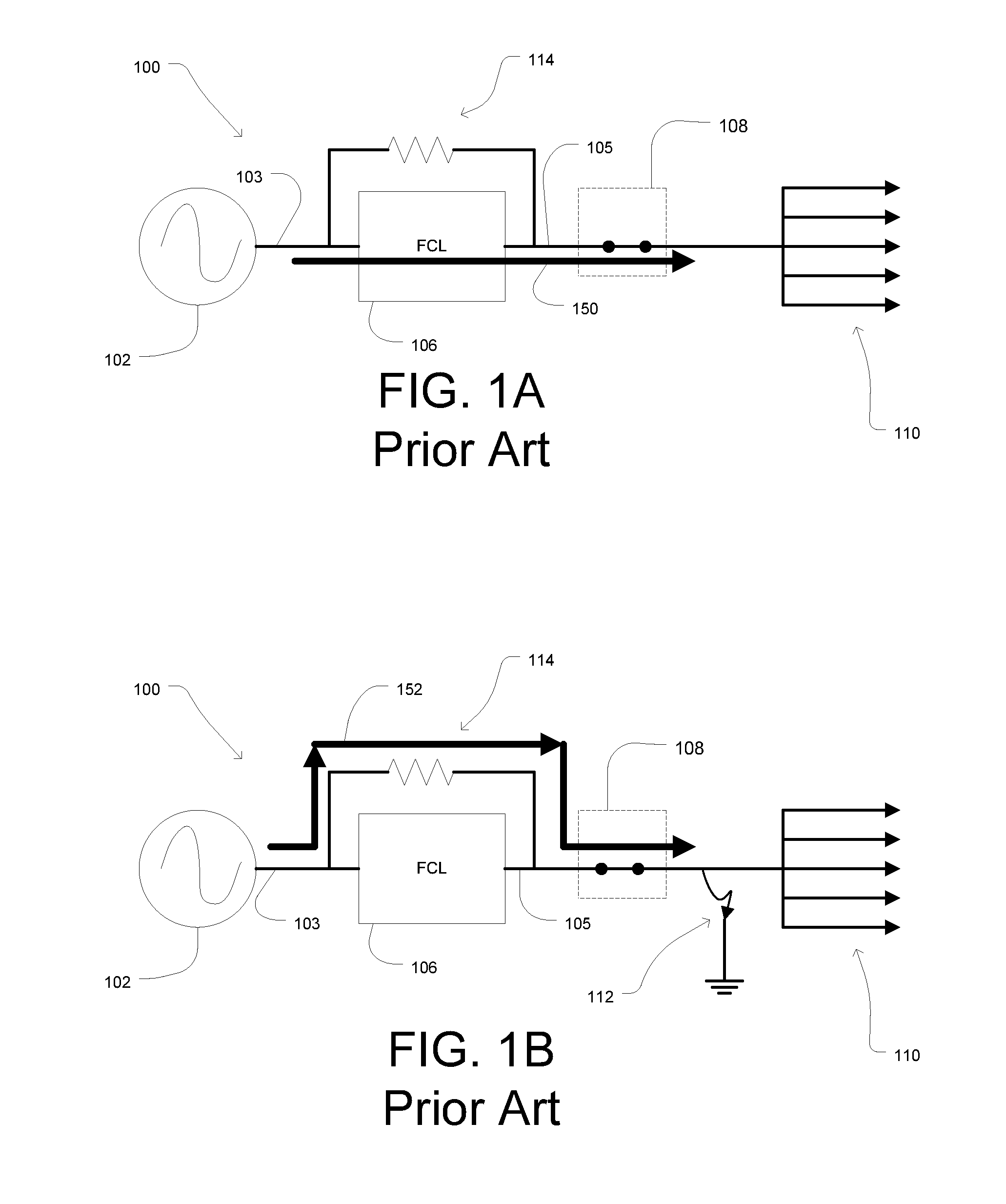
Superconducting fault current limiter
InactiveUS7193825B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsTransformersCurrent limitingSuperconducting fault current limiters
Owner:ZENERGY POWER
Complex superconducting fault current limiter
InactiveUS20080043382A1Large currentEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSuperconducting fault current limitersCurrent limiting reactor
The present invention relates to a complex superconducting fault current limiter which adds a current limiting reactor to a superconductor to protect the power line from a fault current, and more particularly, to a complex superconducting fault current limiter using a minimum number of superconducting fault current limiters, while avoiding series and parallel connections of a plurality of superconductors and coils, in order to economically manufacture the fault current limiter in a small size. A superconductor, a high speed switch, and a circuit breaker are connected in series to each other, and a first reactor with a low impedance and a second reactor with a high impedance are connected in parallel to the power line so as to provide a branch circuit for the current to the series circuit. A semiconductor switch is connected in parallel to the second reactor with a high impedance in accordance with the opening high speed switch. A circuit is breaker trip drive controller is configured so as to be connected to the superconductor and the branch circuit, and when a fault current occurs, the fault current is branched into the branch circuit, so that the second reactor limits the fault current. When a fault current occurs, the circuit breaker trip drive controller provides a trip drive signal to the circuit breaker for tripping in accordance with the voltage of the superconductor or the current of the branch circuit.
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
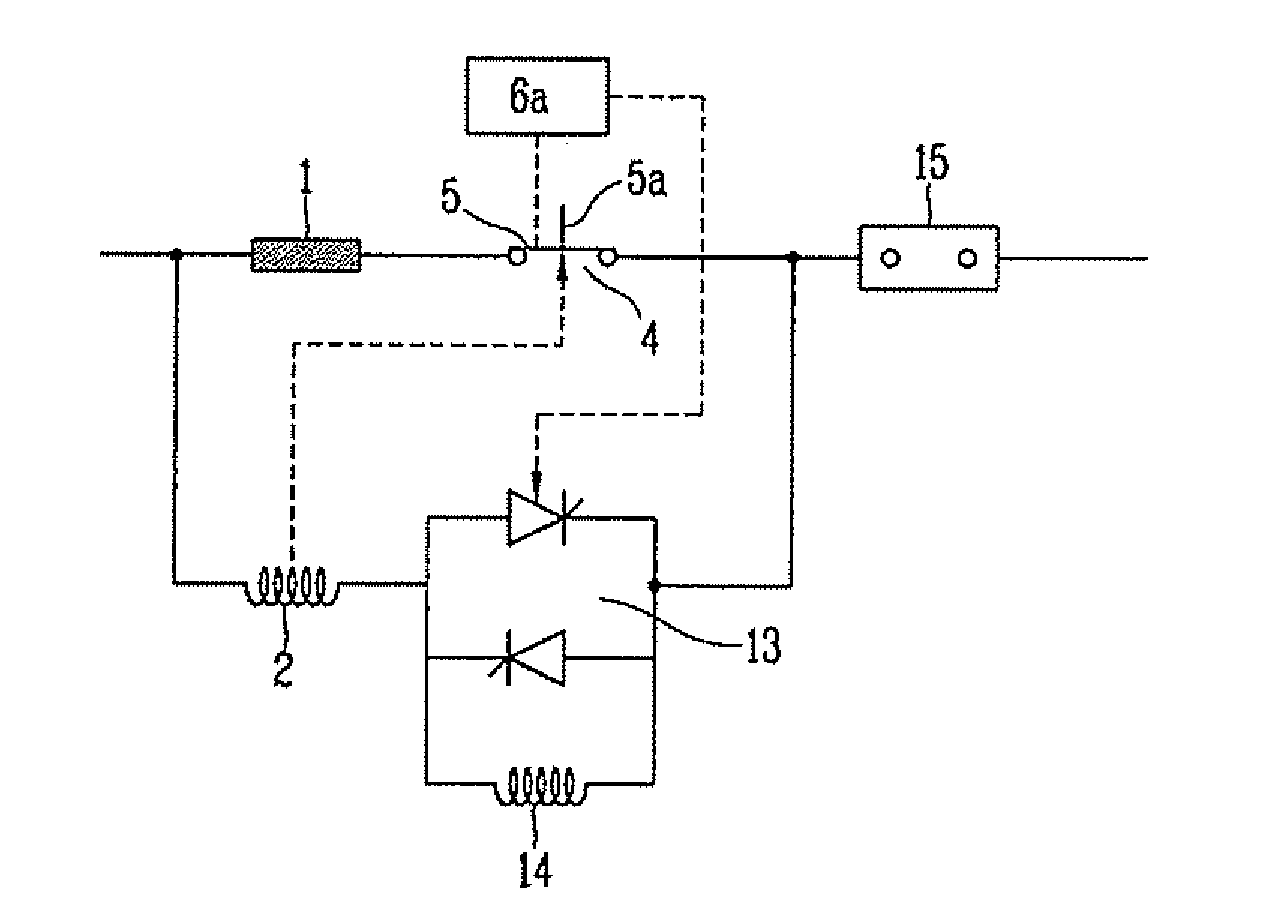
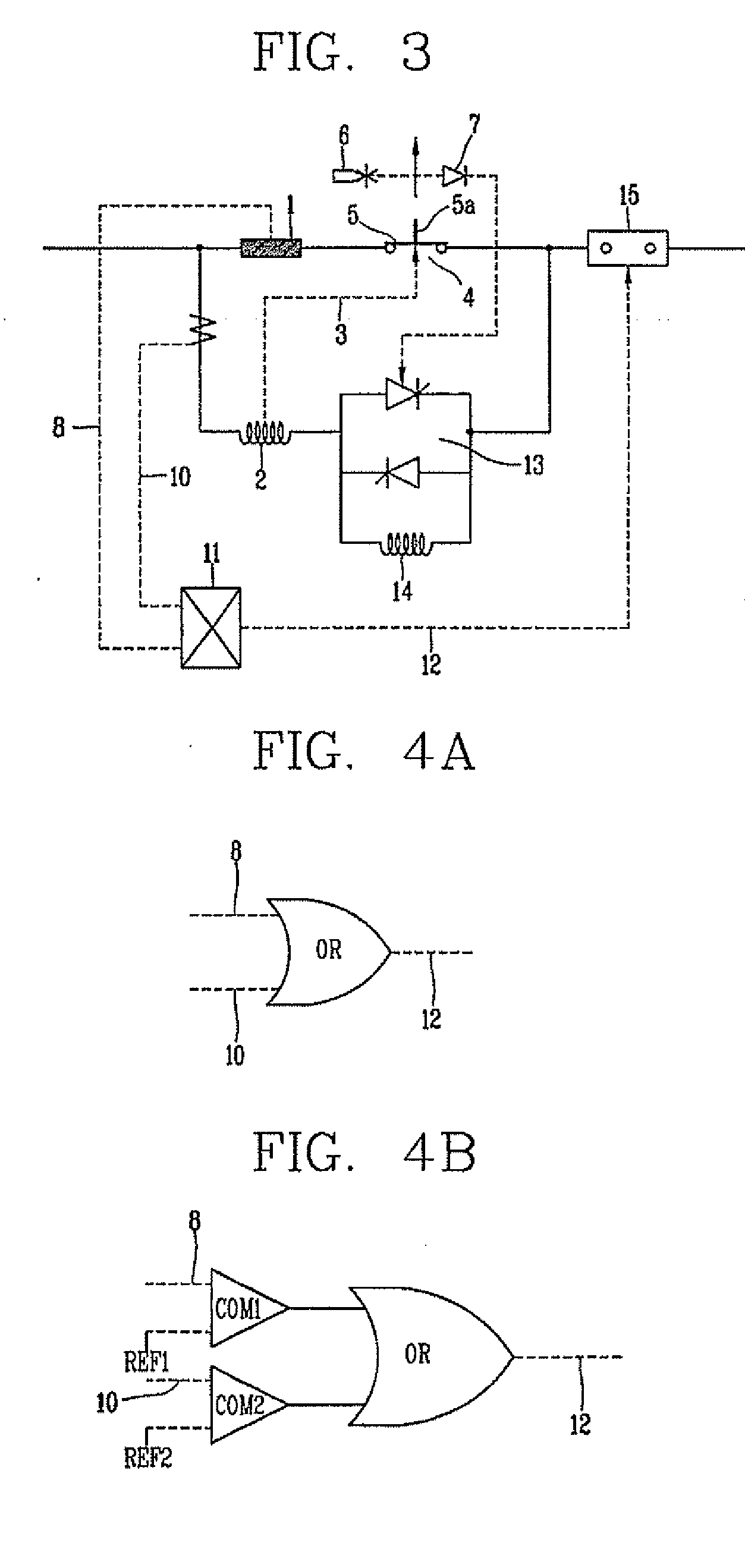
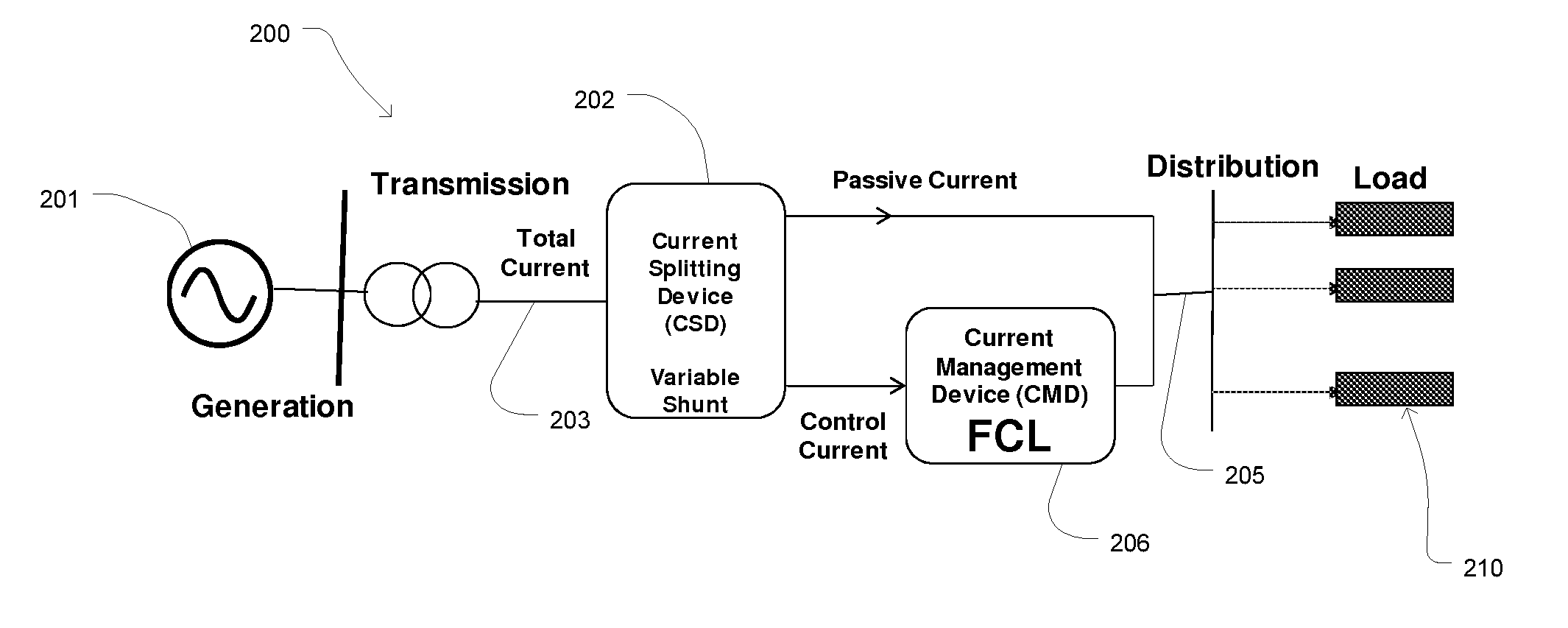
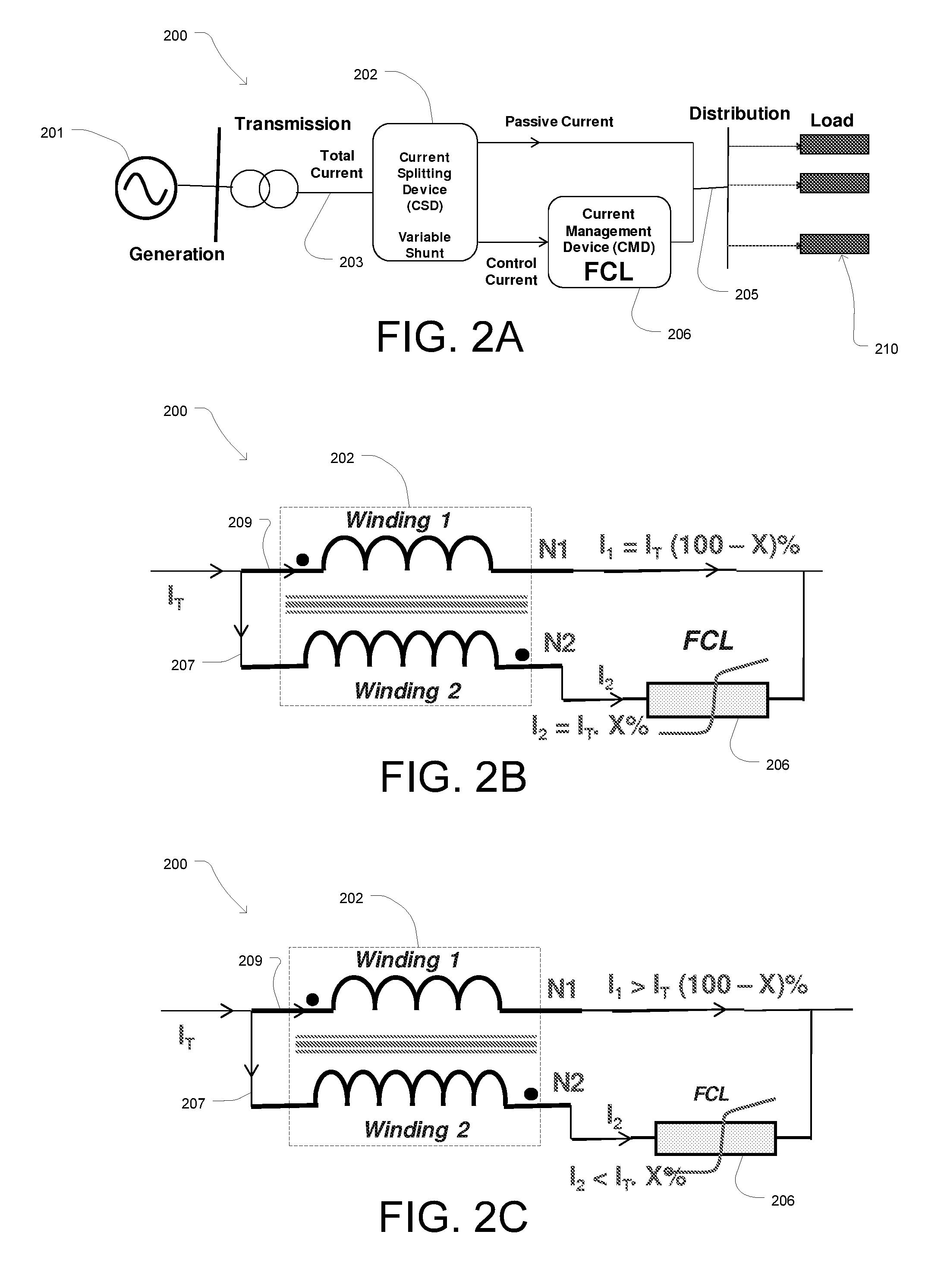
Fault Current Limited System with Current Splitting Device
InactiveUS20120264613A1Cost size be reducedReduce physical sizeSuperconductor detailsEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectricityCurrent load
A fault current limiter system including a fault current limiter and a variable shunt current splitting device. The current splitting device includes first and second conductive windings, wherein the first conductive winding is connected in parallel with the fault current limiter and is configured to carry current in a first direction. The second conductive winding is electrically connected in series with the fault current limiter and is configured to carry current in a second direction opposite to the first direction so that the reactance of the first winding is negated by the reactance of the second winding during steady state operation of the fault current limiter system. Thus, a first portion of a steady state current is conveyed through the fault current limiter and a second portion of the current is conveyed through the current splitting device. The steady state current load, on the fault current limiter is thereby reduced.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
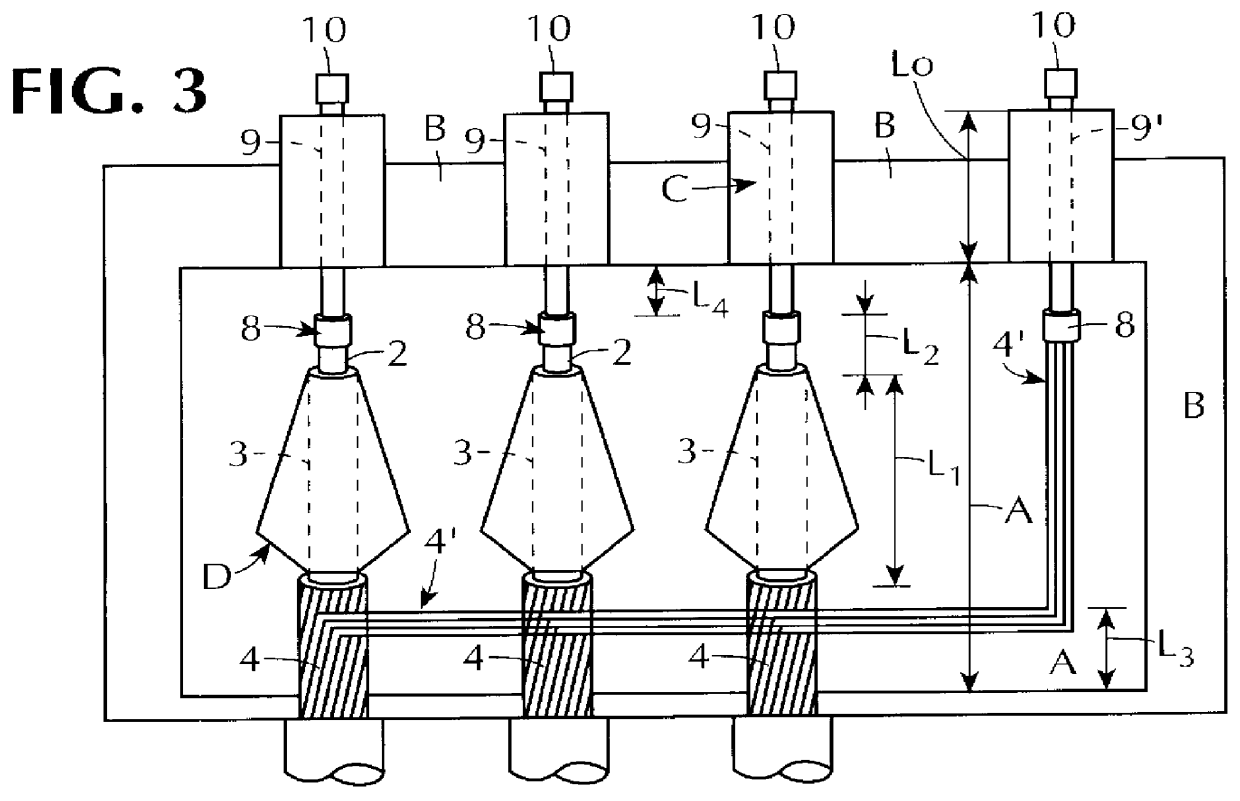
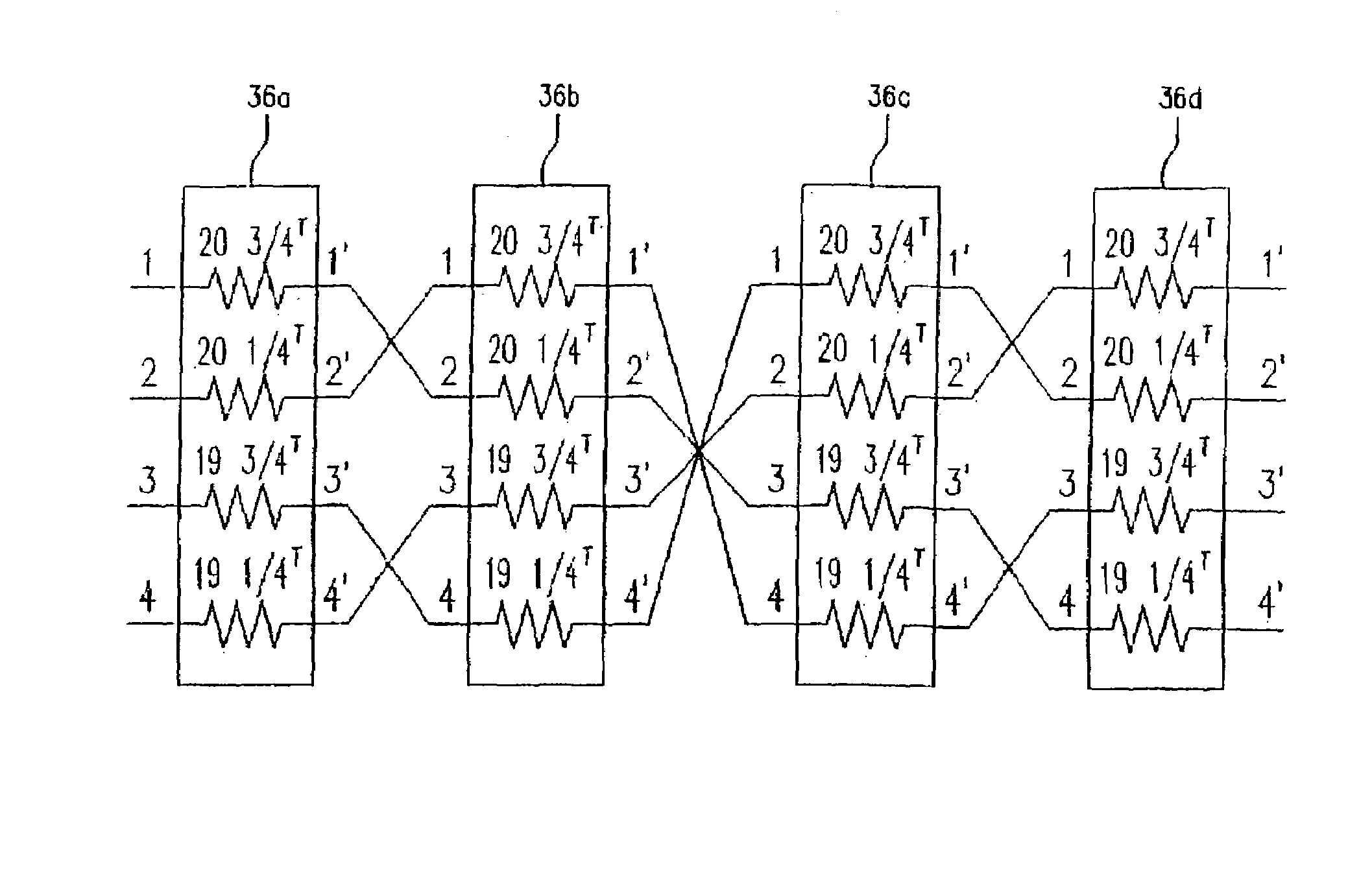
Superconducting wire transposition method and superconducting transformer using the same
InactiveUS7227438B2TransformersTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical conductorTransformer
The present invention discloses a superconducting wire transposition method and superconducting transformer whose winding is formed of superconducting wire to enable the formation of transpositions. The superconducting wire transposition method characterized of different winding start positions of at least two disks wound with a plurality of parallel superconductive wires, and usage of different superconducting wires for conductors to be connected between the disks, thereby forming transpositions outside of the disks. Preferably, part of the plurality of disks are rotatably assembled in pairs so as to form transpositions while maintaining a total number of windings equally. Therefore, according to the present invention, transpositions can be formed without bending or welding superconducting wires and thus, deteriorations in superconductivity can be prevented.
Owner:HYOSUNG CORP
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
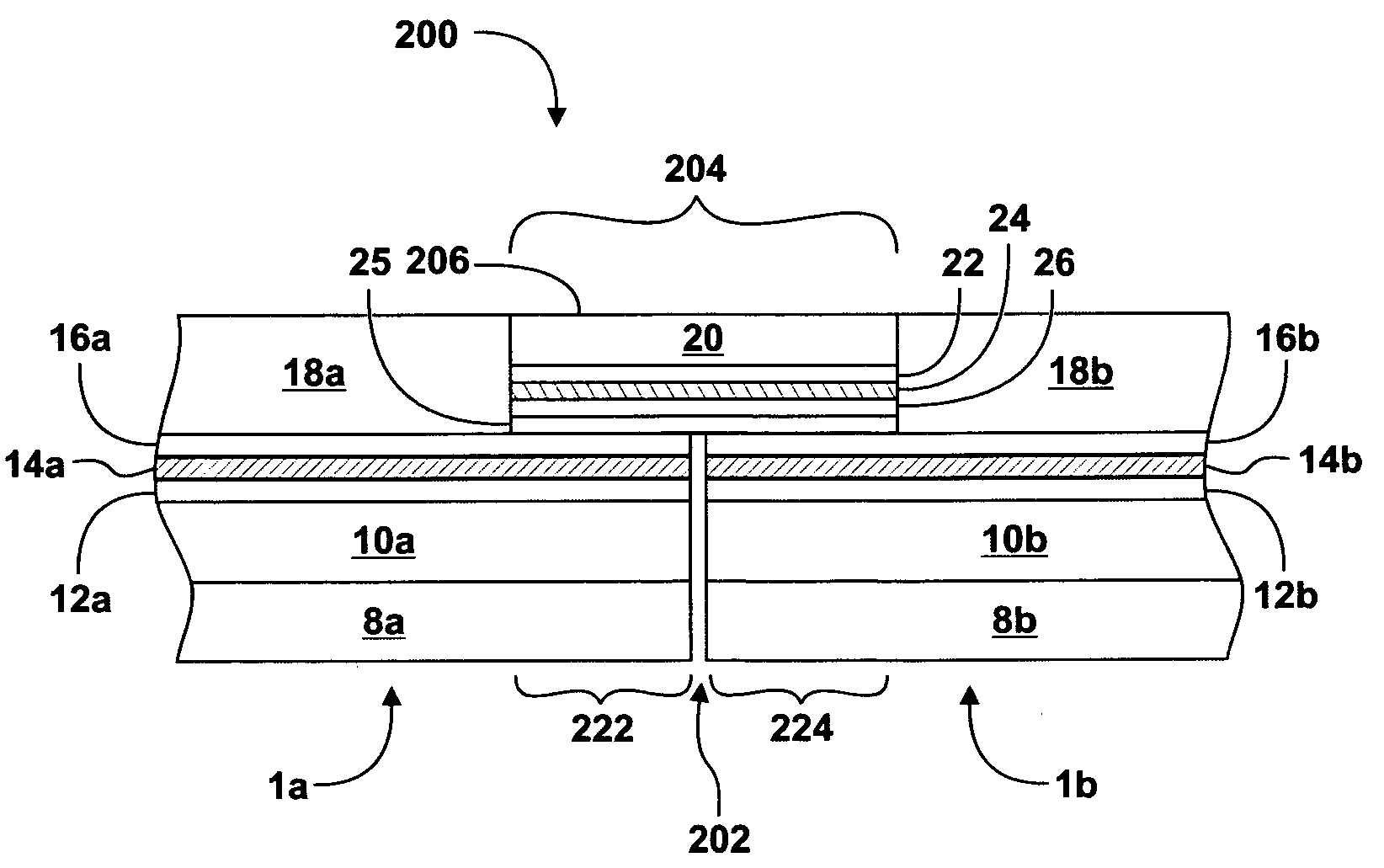
Biaxially-textured film deposition for superconductor coated tapes
ActiveUS20050239659A1Fast in-plane growth rateHigh speedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingIn planeIon beam
Methods for depositing, at a very high deposition rate, a biaxially-textured film on a continuously moving metal tape substrate are disclosed. These methods comprise: depositing a film on the substrate with a deposition flux having an oblique incident angle of about 5° to about 80° from the substrate normal, while simultaneously bombarding the deposited film using an ion beam at an ion beam incident angle arranged along either a best ion texture direction of the film or along a second best ion texture direction of the film, thereby forming the biaxially-textured film, wherein a deposition flux incident plane is arranged parallel to a direction along which the biaxially-textured film has a fast in-plane growth rate. Superconducting articles comprising a substrate, a biaxially-textured film deposited on said substrate by said methods above; and a superconducting layer disposed on the biaxially-textured film are also disclosed.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
High-temperature superconducting magnetic levitation motor
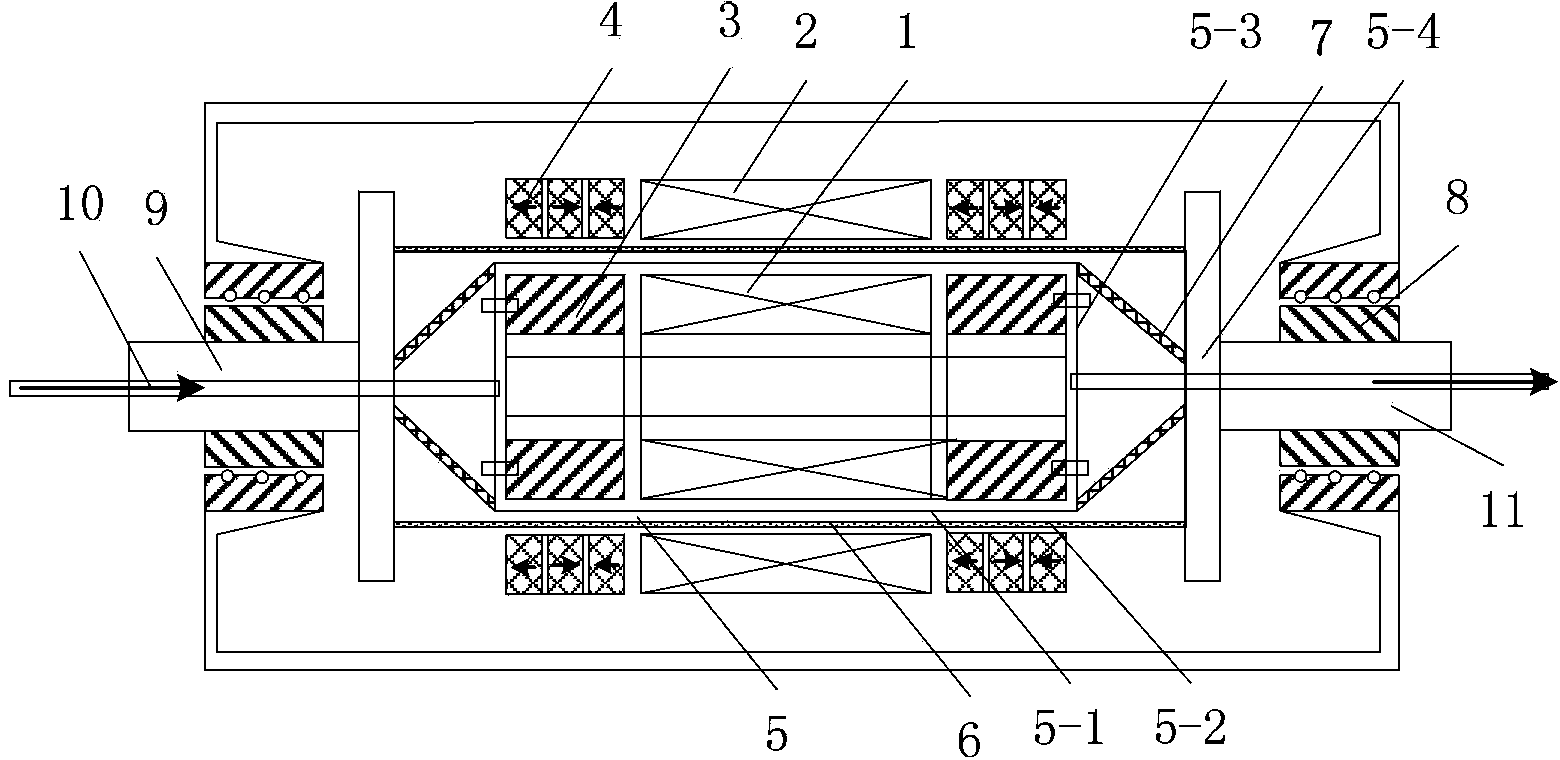
InactiveCN103441648AReduce weightIncrease speedDynamo-electric machinesMagnetic holding devicesMagnetic bearingSuperconducting electric machine
A high-temperature superconducting magnetic levitation motor is formed by a superconducting motor rotor (1), a motor stator (2), superconducting bearing rotors (3), permanent magnetic bearing stators (4), a rotary dewar (5), an electromagnetic screen (6), torque tubes (7), mechanical protection bearings (8), a main shaft (9), a low-temperature liquid (gas) inlet pipeline (10) and a low-temperature liquid (gas) outlet pipeline (11). The superconducting motor rotor (1) and the superconducting bearing rotors (3) are arranged in the rotary dewar (5) and are cooled by liquid nitrogen or liquid neon or liquid helium or cold helium, the motor stator (2) and the permanent magnetic bearing stators (4) are arranged outside the rotary dewar (5) and are coaxial with the rotary dewar (5), and the two mechanical protection bearings (8) are used in a left and right mode in the radial direction for protecting against the influence brought by the failure of superconducting bearings.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of forming a multifilament ac tolerant conductor with striated stabilizer, articles related to the same, and devices incorporating the same
ActiveUS20090131262A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
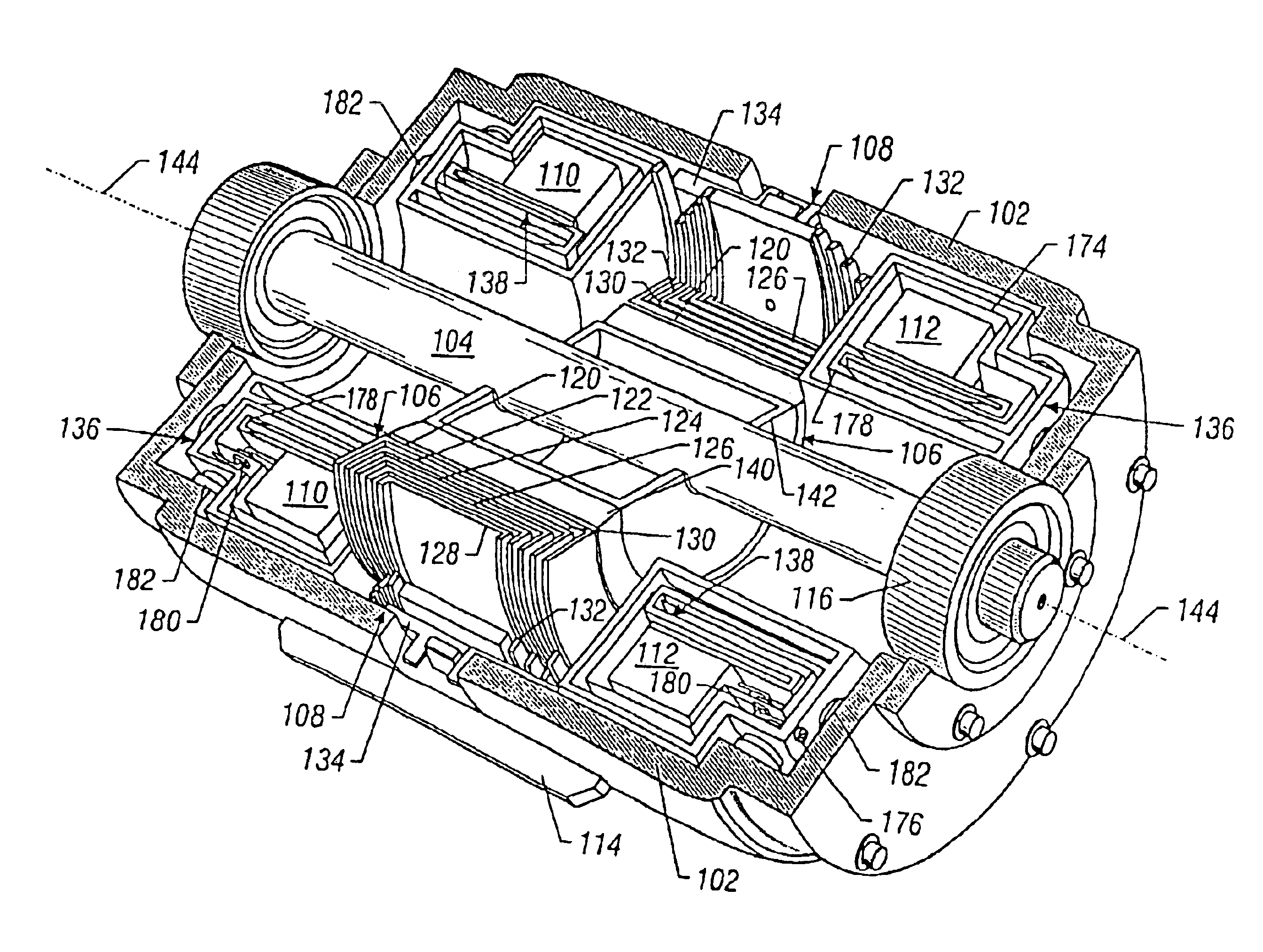
Superconducting rotating electrical machine and stator for use with superconducting rotating electrical machine
ActiveUS20120161568A1Improve conversion efficiencyMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesRotational axisEngineering
A superconducting rotating electrical machine has a rotor with superconducting windings and a stator disposed around the rotor. The stator has a number of teeth disposed at a regular interval about a rotational axis of the rotor to define slots each between adjacent teeth and a plurality of windings, each winding having a strip-like wire member, the wire member having a plurality of rectangular cross-section wires in which said rectangular wires are arranged in parallel to each other and electrically insulated away from each other, the winding being constructed by winding the strip-like wire member a plurality of times to have first and second winding portions having a cross section in which the rectangular wires are positioned in matrix.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
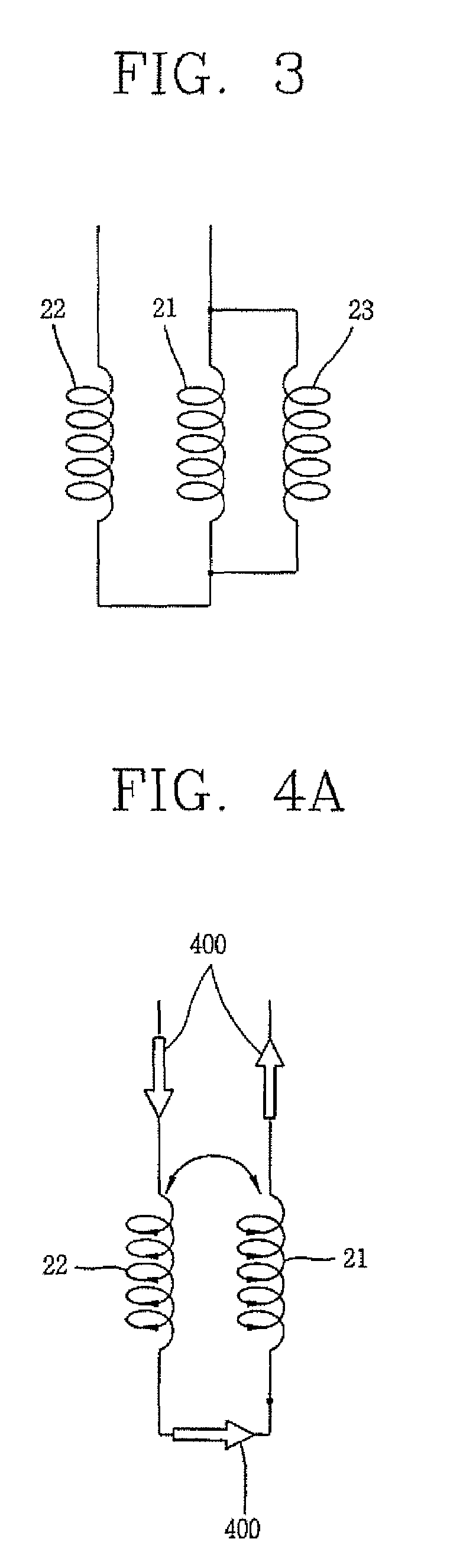
Resistive superconducting fault current limiter
ActiveUS7558030B2Total current dropImprove toleranceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A resistive superconducting fault current limiter comprises: a superconducting limiter element which is in a superconductive state in the event of a normal current occurrence, and which is in a normal conductive state having a predetermined resistance when a fault current larger than a predetermined threshold current value flows; a superconducting serial coil serially connected to the superconducting limiter element so as to face each other so that a current loss can be minimized accordingly as currents flow in opposite directions thus to cancel magnetic fields, and having a threshold current value greater than the threshold current value of the superconducting limiter element by a predetermined ratio; and a normal conductor parallel coil connected to the superconducting limiter element in parallel and having a predetermined resistance smaller than the resistance of the superconducting limiter element when a fault current occurs, for preventing the superconducting limiter element from being overheated by dividing a current flowing through the superconducting limiter element and for uniformly quenching the superconducting limiter element by generating a magnetic field when a fault current occurs
Owner:LS IND SYETEMS CO LTD
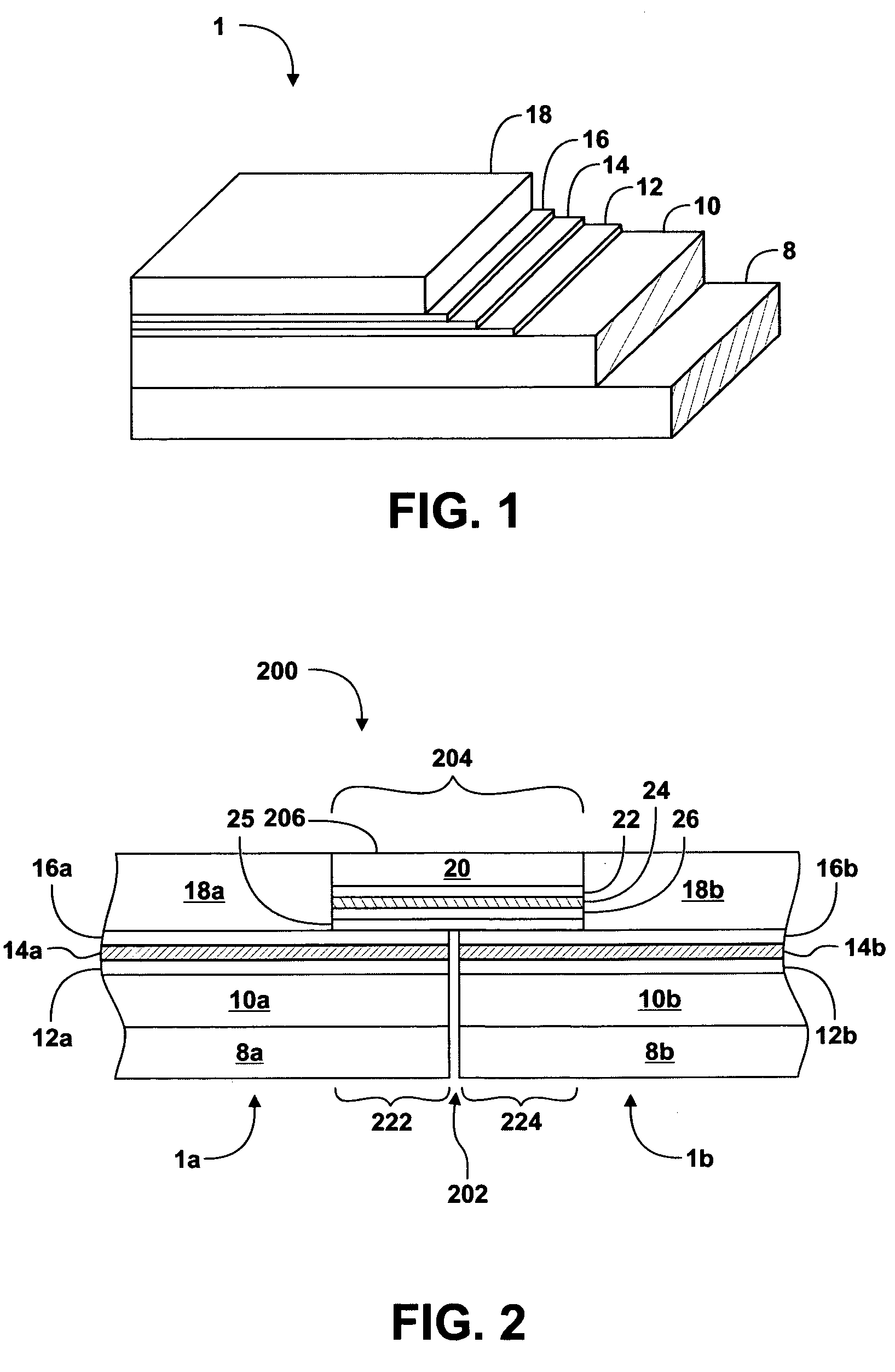
Method of producing biaxially textured buffer layers and related articles, devices and systems
ActiveUS6849580B2Polycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsIon beam-assisted depositionOut of plane
A superconductor article includes a substrate and a first buffer film disposed on the substrate. The first buffer film has a uniaxial crystal texture characterized (i) texture in a first crystallographic direction that extends out-of-plane of the first buffer film with no significant texture in a second direction that extends in-plane of the first buffer film, or (ii) texture in a first crystallographic direction that extends in-plane of the first buffer film with no significant texture in a second direction that extends out-of-plane of the first buffer film. A second buffer film is disposed on the first buffer film, the second buffer film having a biaxial crystal texture. A superconductor layer can be disposed on the second buffer film. Ion-beam assisted deposition (IBAD) can be used to deposit the second buffer film.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
Electric utility system with superconducting magnetic energy storage
InactiveUS6906434B1Stabilizing voltageReduce transmission lossElectrical storage systemFlexible AC transmissionMagnetic storageElectric power system
a voltage recovery device is configured to provide real and reactive power to a utility power network at a sufficient level and for a sufficient duration to recover the voltage on the utility power network within a predetermined proportion of the nominal voltage, following a fault condition detected on the utility power network. Moreover, the voltage recovery device reduces the overall transmission losses in a utility power system.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
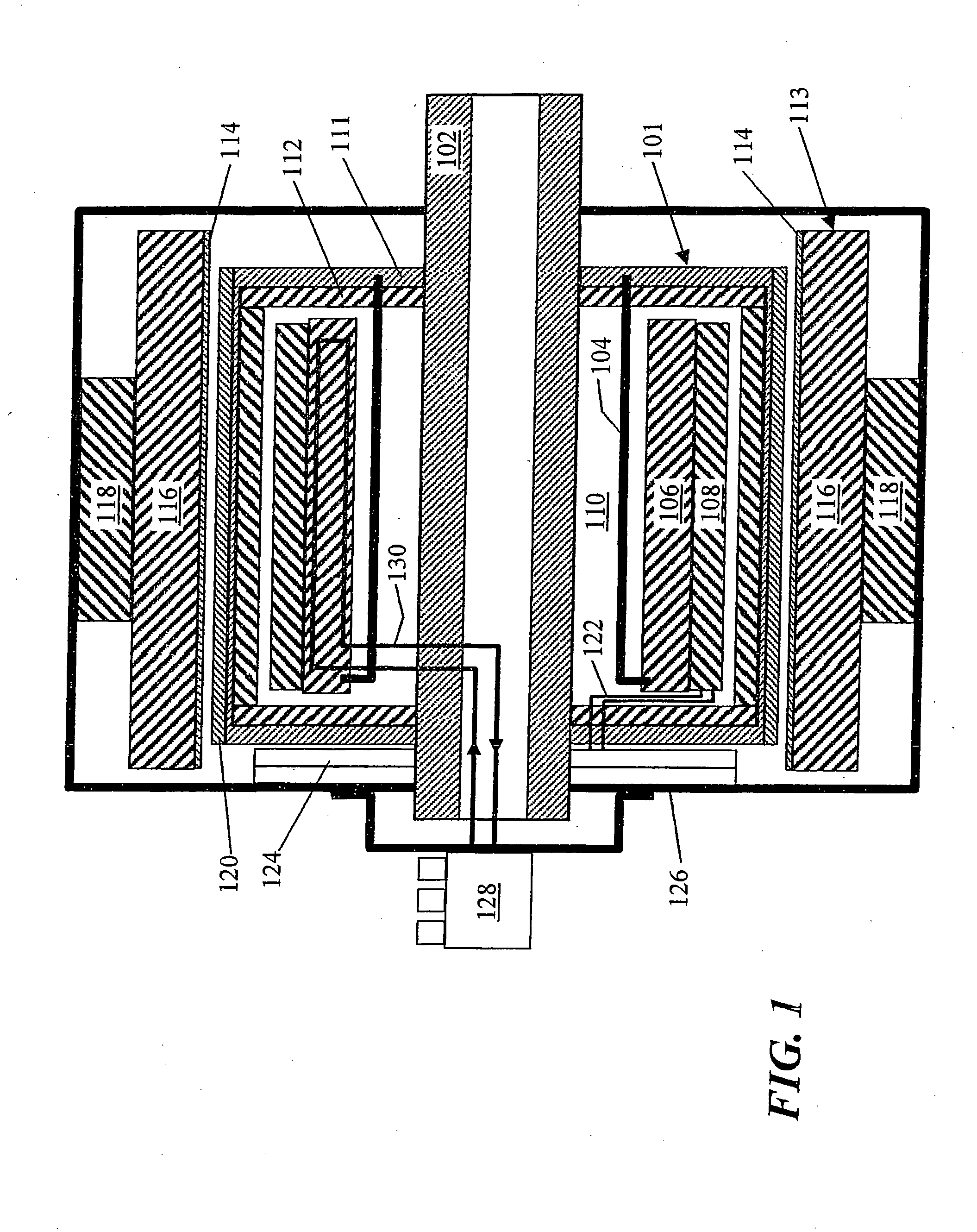
Superconducting Electrical Machines
InactiveUS20080161189A1Eliminate any stray magnetic fluxCreates lossSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentWind energy generationSuperconducting electric machineExternal rotation
A superconducting electrical machine has rotor and stator assemblies. A first rotor assembly is located to rotate within a stator assembly and is spaced from the stator assembly by an air gap. A second rotor assembly is located to rotate outside the stator assembly and is also spaced from the stator assembly by an air gap. The first and second rotor assemblies have at least one superconducting field winding. The superconducting field windings are formed from a High Temperature Superconducting (HTS) material such as BSCCO-2223 or YBCO, for example. The double rotor assembly configuration provides a new technical effect over conventional rotating superconducting machines having a single rotor assembly.
Owner:LEWIS CLIVE +1
Renewable energy electric power generating system
A renewable electric power system includes a high temperature superconducting wind turbine using high temperature superconducting yttrium-barium-copper oxide for the rotor and stator windings as well as a superconducting bearing. Power from the turbine is stored in a high temperature superconducting magnetic storage system that also uses HTS YBCO. Also included is a regenerative solid oxide fuel cell / electrolyzer with steam turbine cogeneration. The system operates on a managed day / night cycle. During daytime, the energy produced by the wind turbines and fuel cells is transmitted to the grid. During nocturnal hours, the wind turbine is used to provide low cost electricity to the reversible fuel cells operating in the electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen that is stored for later use. Alternatively, the fuel cells can remain in electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen for the market. A modified interactive system generates power on a continuous twenty-four hour cycle.
Owner:COOPER WILLARD
High temperature superconducting wires and coils
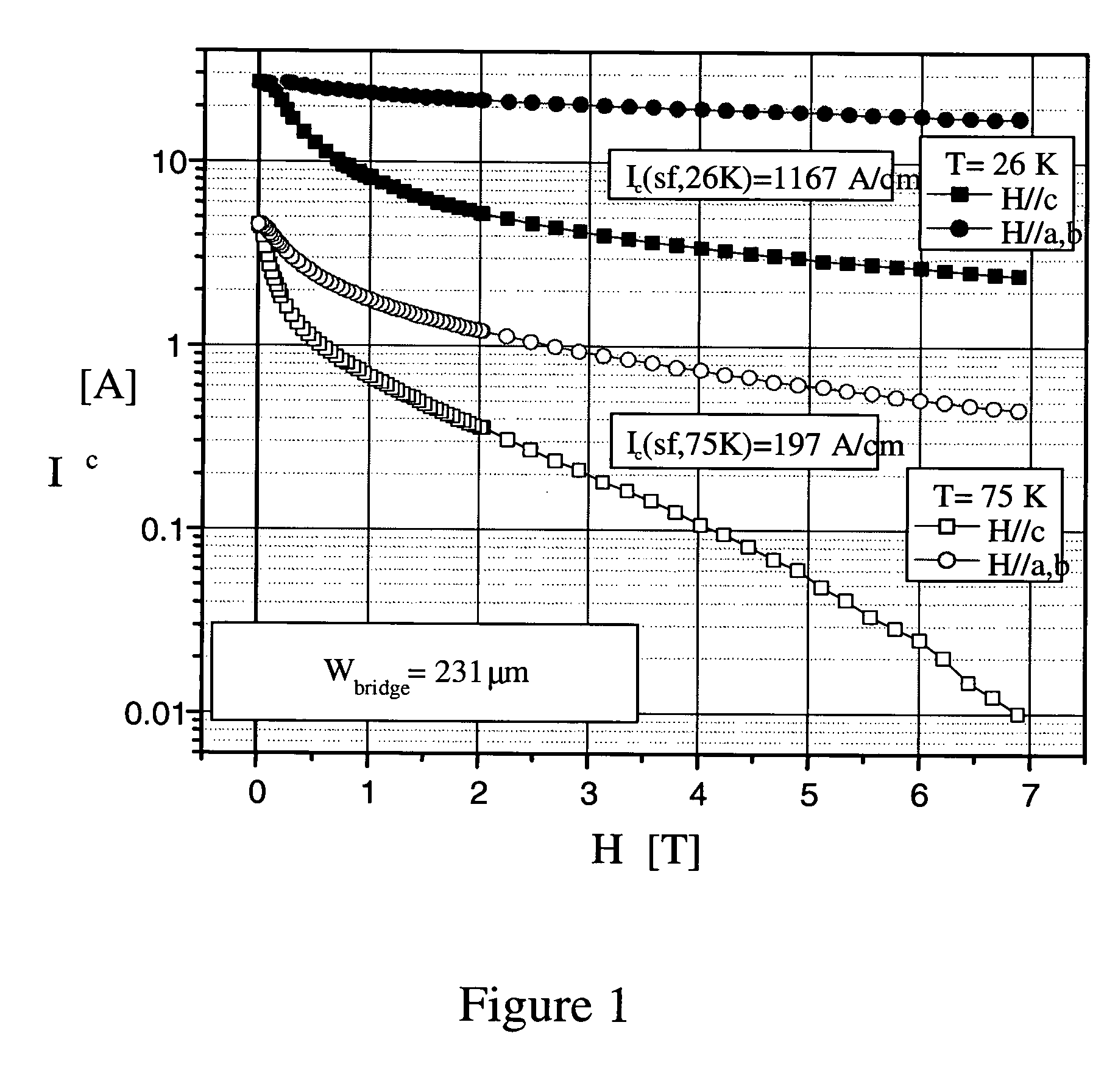
ActiveUS20070111893A1Enhance critical current densityHigh densitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetsElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
A superconducting wire includes first and second superconducting layers disposed on one or more substrates in stacked relationship, the first superconducting layer comprising a high temperature superconducting oxide of a first composition and the second superconducting layer comprising a high temperature superconducting layer of a second composition, wherein the first and second compositions are different. The first superconductor layer optionally includes a high temperature superconductor composition selected to provide enhanced critical current (Ic(c)) in the presence of magnetic fields perpendicular to surface of the superconducting layer (H / / c). The second superconductor layer optionally includes a high temperature superconductor composition selected to provide enhanced critical current (Ic) in the presence of magnetic fields parallel to surface of the superconducting layer (H / / ab).
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Preparation method for NbTi/Cu multi-core composite superconducting wire with rectangular section
InactiveCN101728029AThe process steps are simpleShort processSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesConductor CoilMaterials science
The invention discloses a preparation method for an NbTi / Cu multi-core composite superconducting wire with a rectangular section, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, assembling an NbTi bar, a pure Nb inner pipe and an oxygen-free copper sheath in turn to form an NbTi / Cu composite sheath, sealing an upper end cap and a lower end cap of the NbTi / Cu composite sheath through vacuum welding, and then performing primary extrusion to obtain an NbTi / Cu composite bar; secondly, drawing and scaling the composite bar, and keeping on drawing the composite bar to obtain a hexagonal core rod, and performing assembling for the second time; and thirdly, performing vacuum solder sealing, hot isostatic pressing, secondary extrusion, bar drawing and scaling on the sheath which is assembled in the second time to finally obtain the NbTi / Cu multi-core composite superconducting wire with the rectangular section. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process flow, low preparation cost and good preparation effect, improves the fill factor among windings in the process of coiling a superconducting magnet but simultaneously keeps high critical current density for the wire, and overcomes the defects that the conventional four-high mill or forming roll mill is unevenly stressed, is difficult to process and the like in the rolling process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Cable cooling system
InactiveUS20060150639A1Increase pressureCable fittings for cryogenic cablesPressure vesselsEngineeringCryocooler
A system for providing cooling to cable such as superconducting cable which employs at least one cryocooling station or consolidated cryocooler / pumping station which processes coolant involving multiple cable lengths.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com