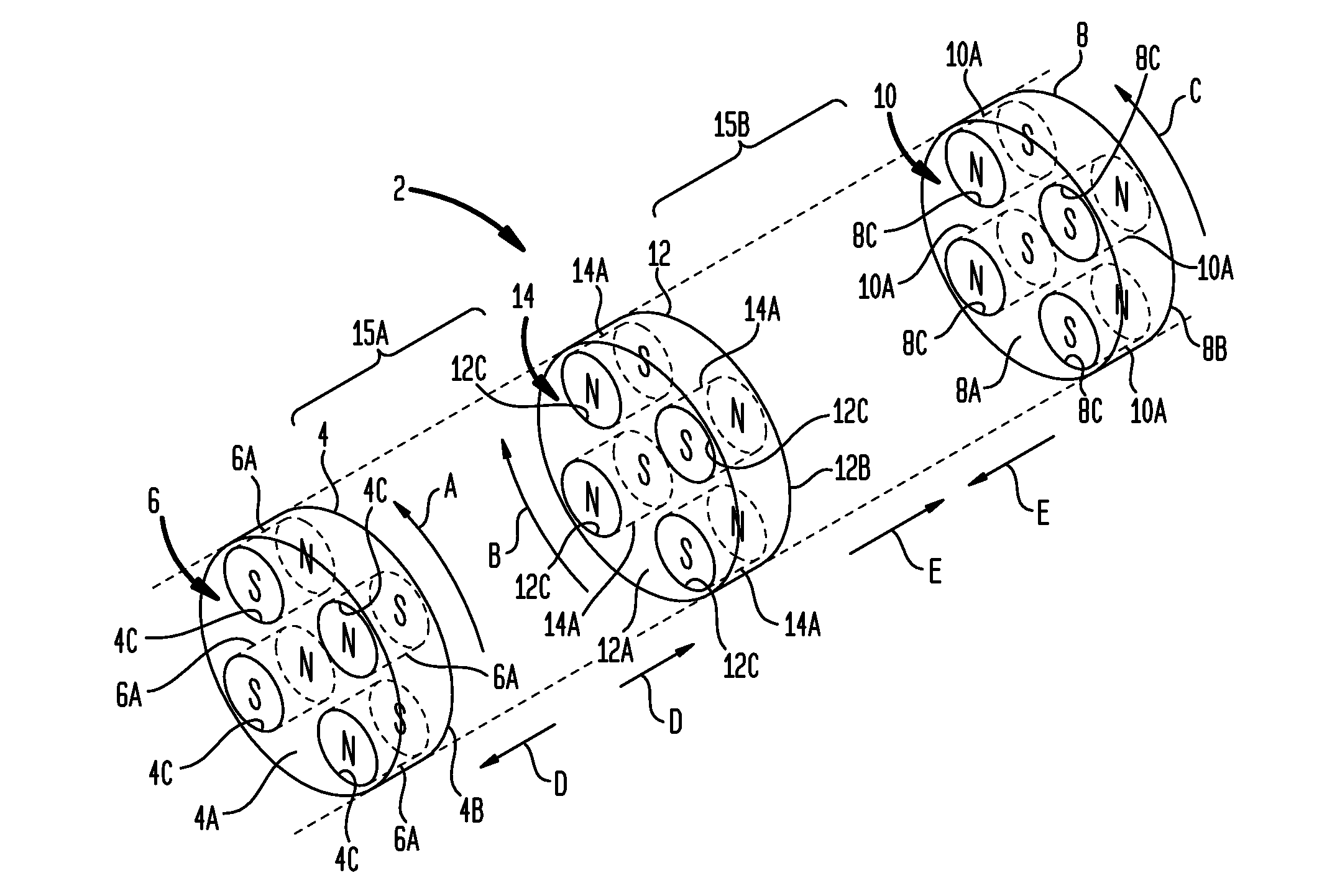
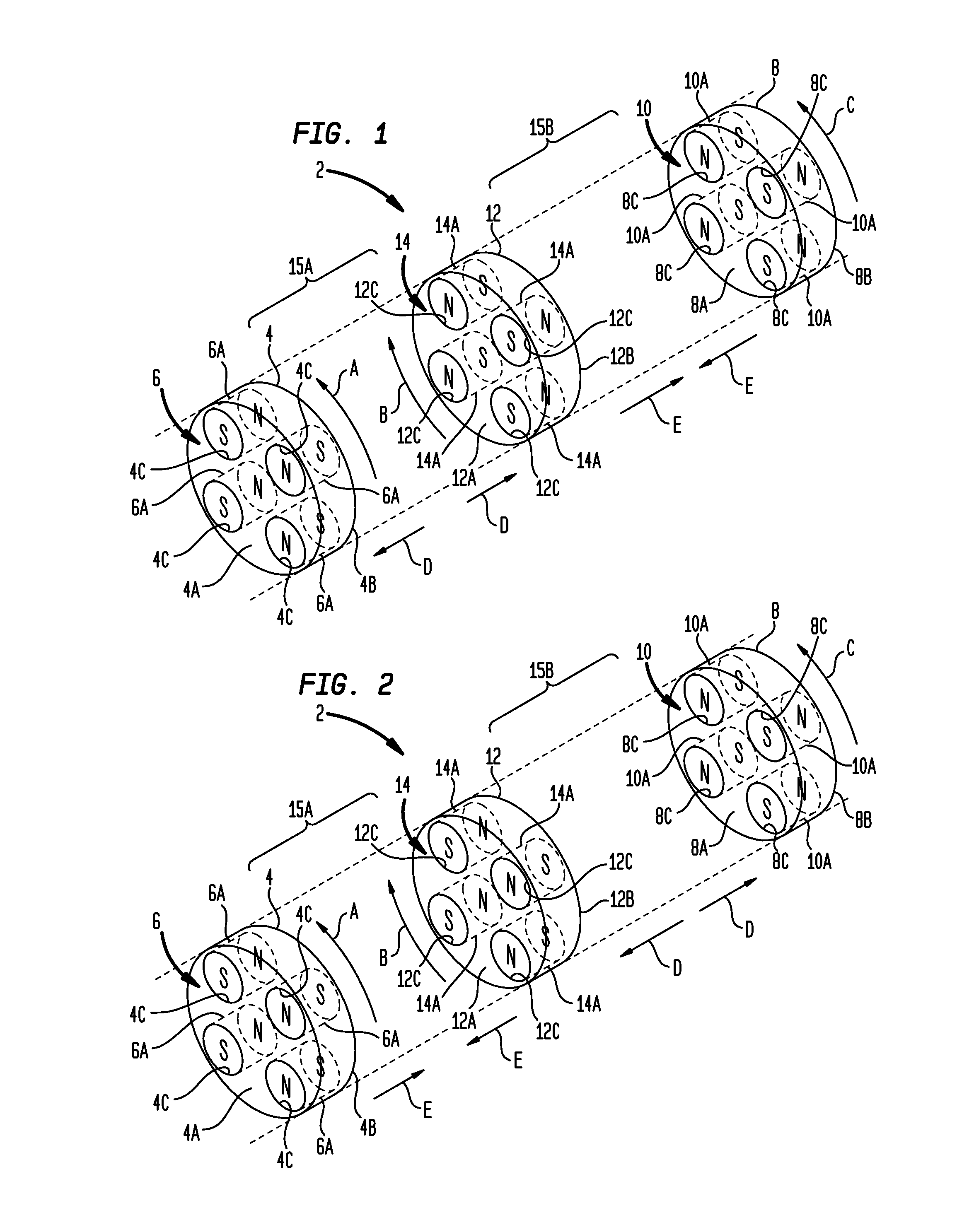
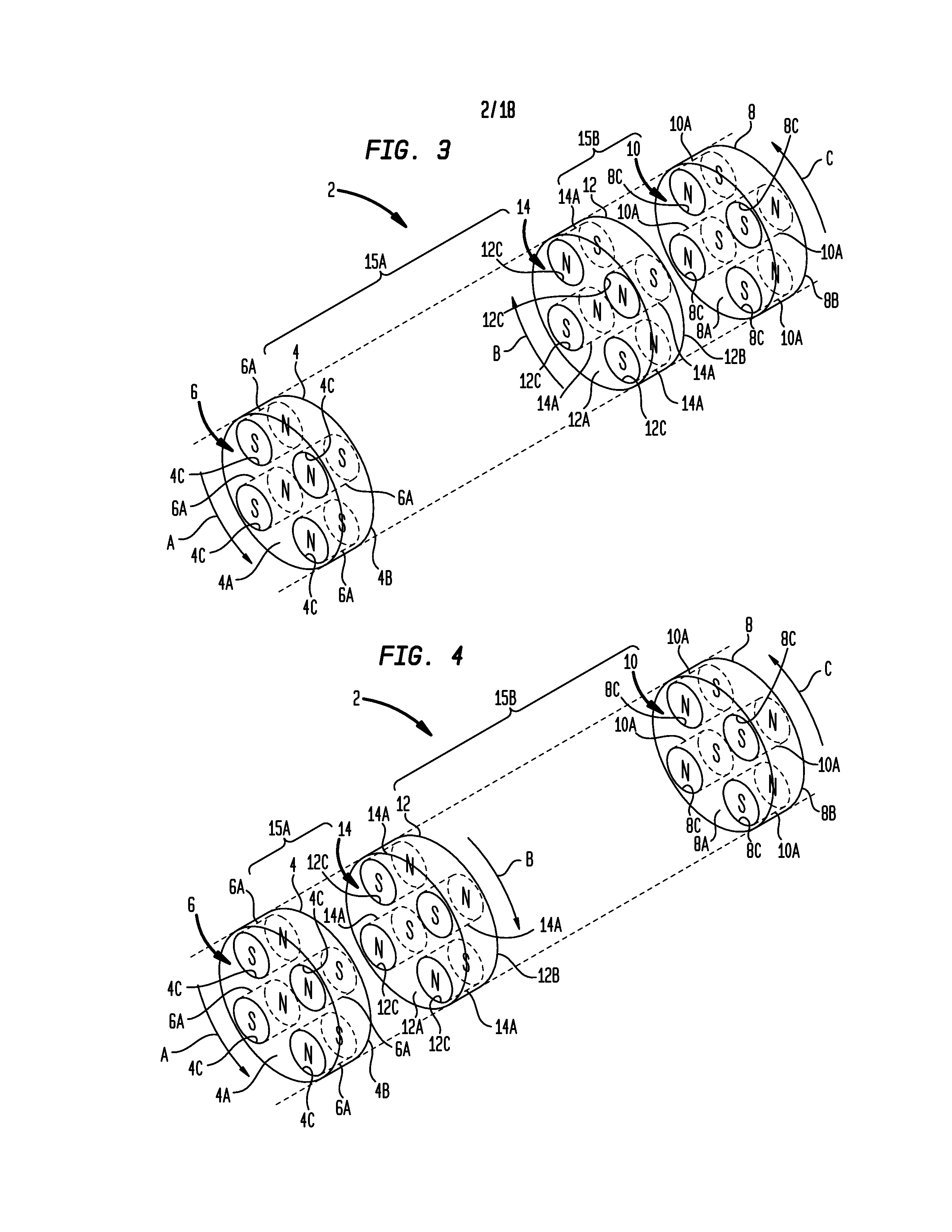
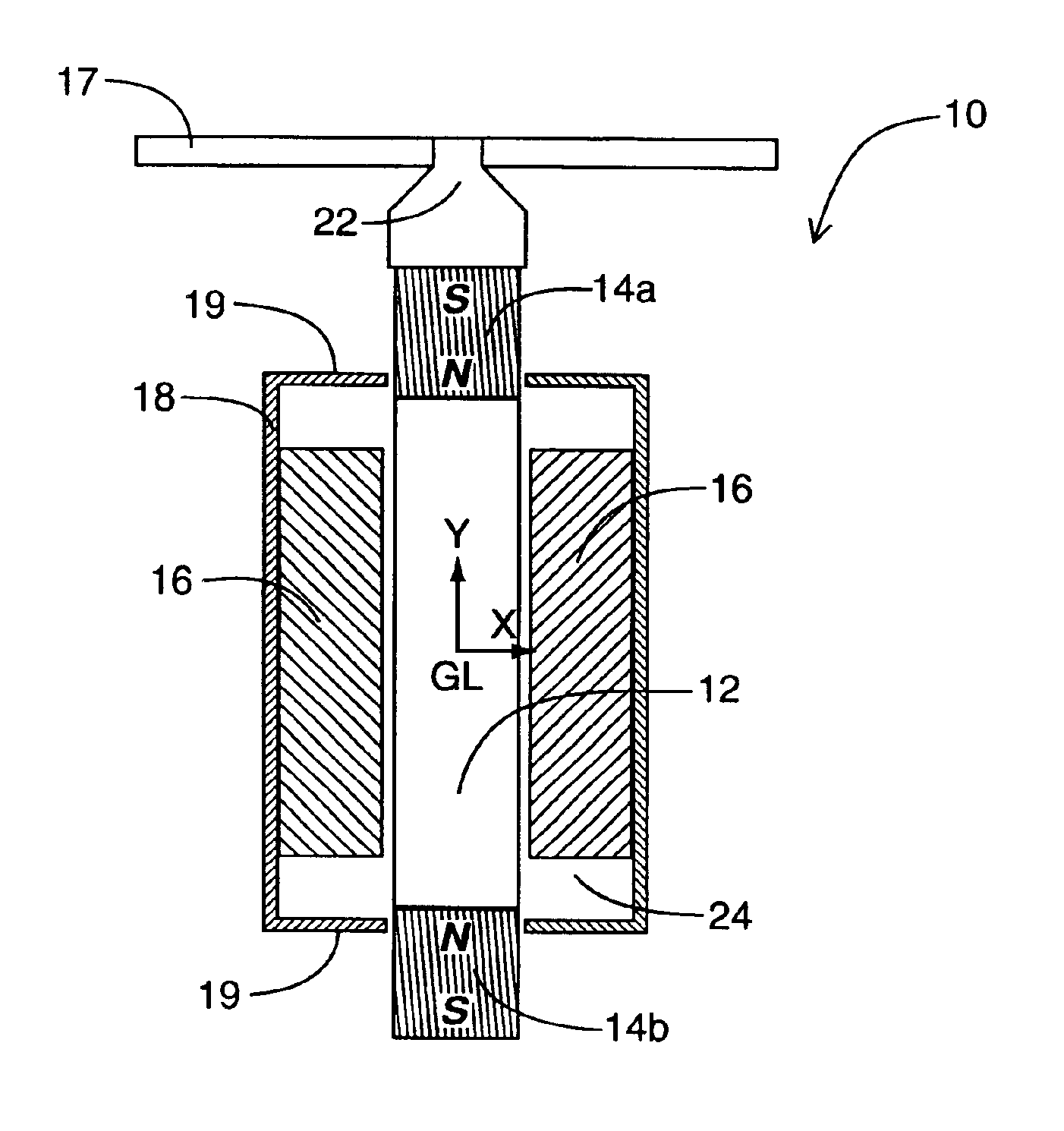
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
337 results about "Magnetic interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A magnetic interaction hypothesis (MIH) is suggested which leads to a re-interpretation of the interaction mechanism for the magnetic force. This MIH is used to explain energization of charged particles on micro scale. Further considerations including the nuclear force, inter-atomic stability, and the reproduction of spectral lines, are reported.
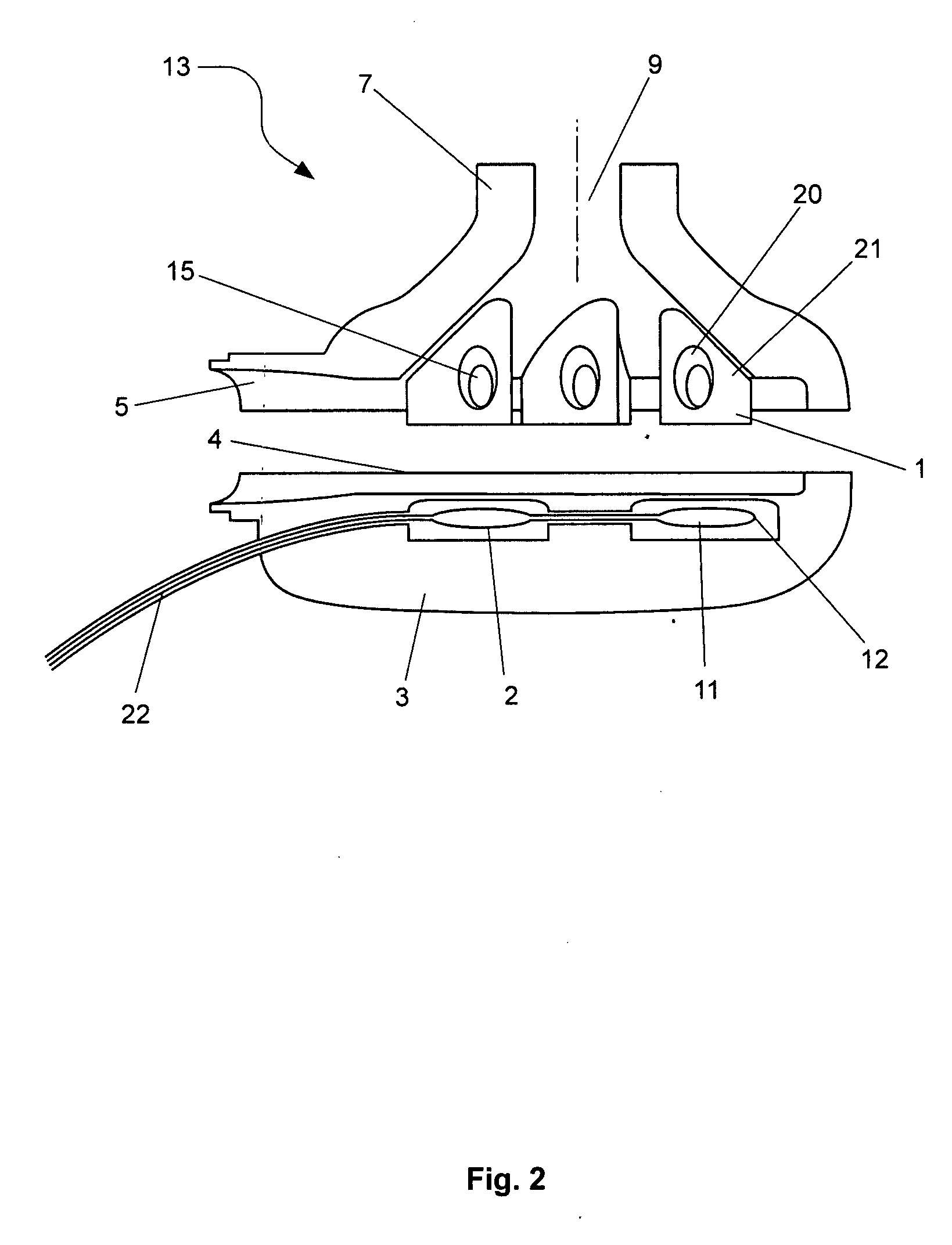
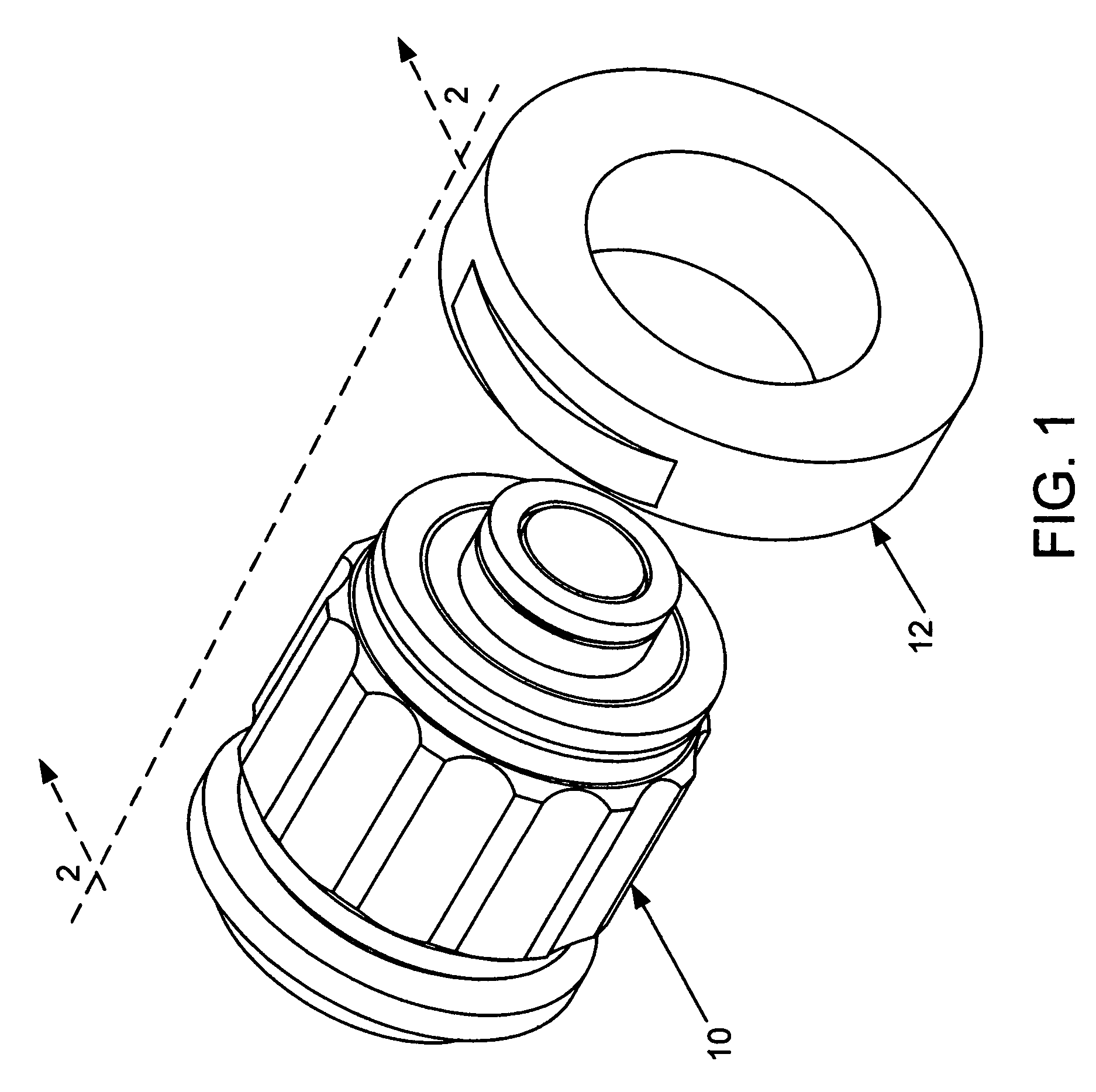
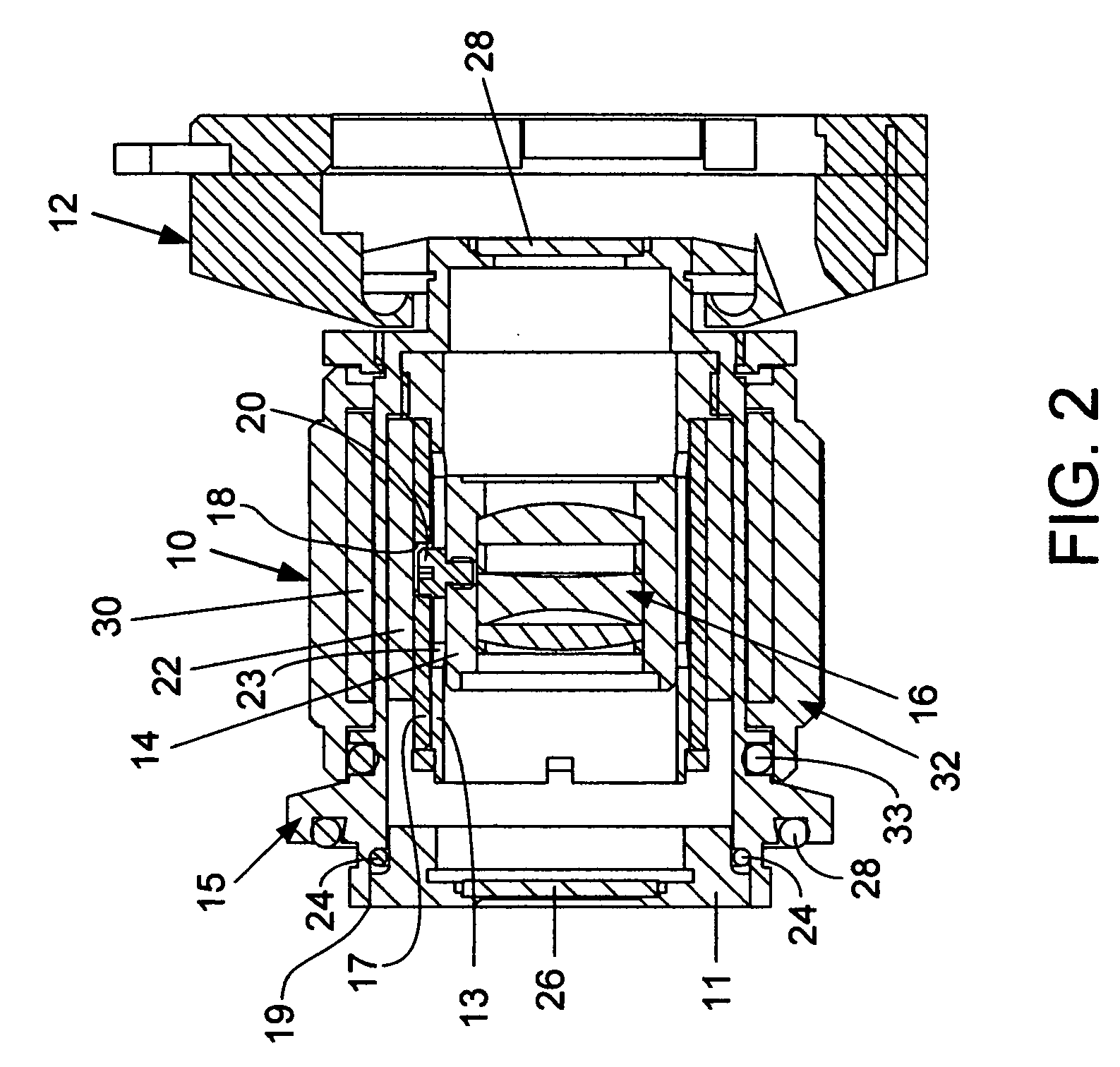
Method and device for measuring density of a liquid
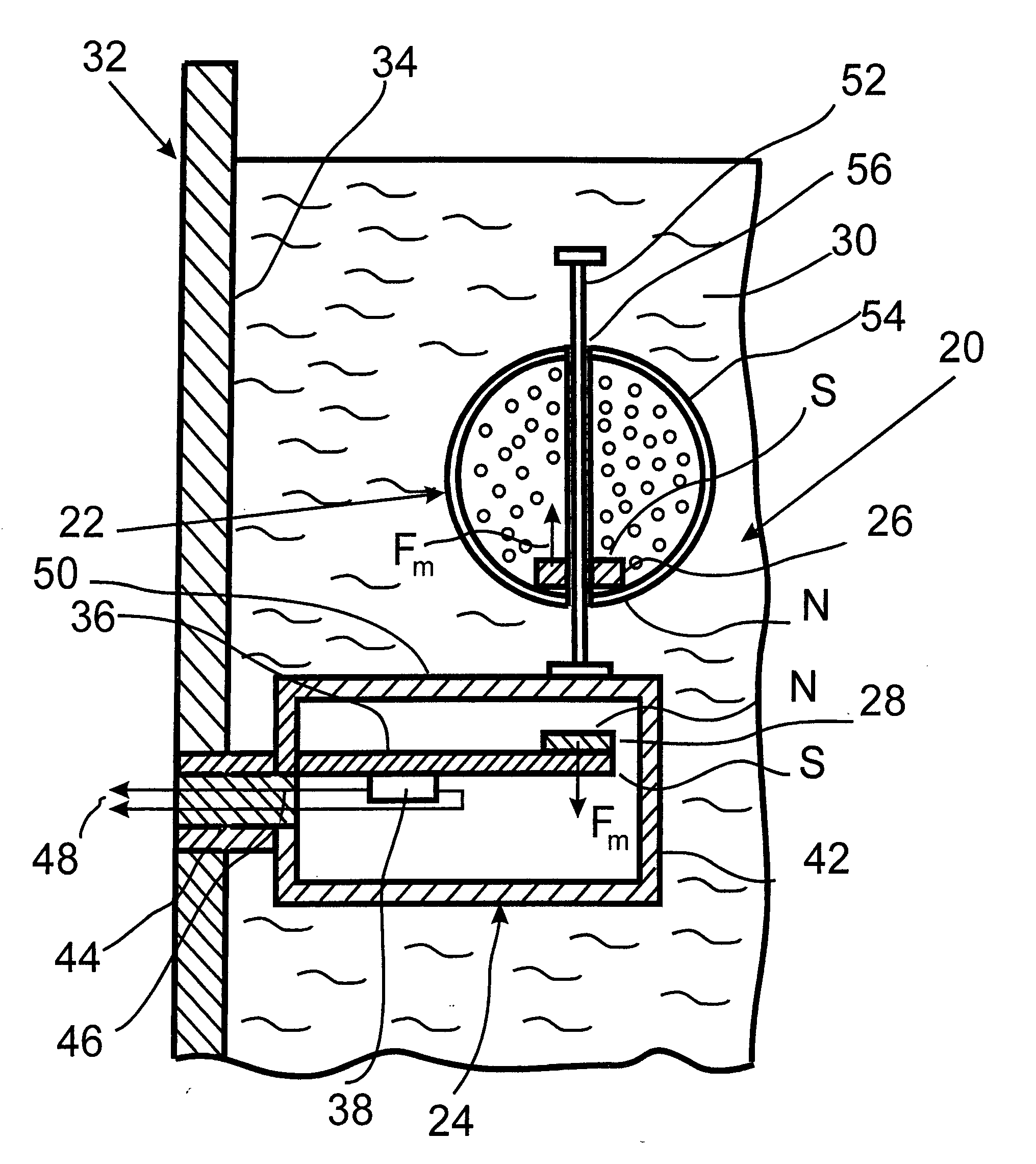
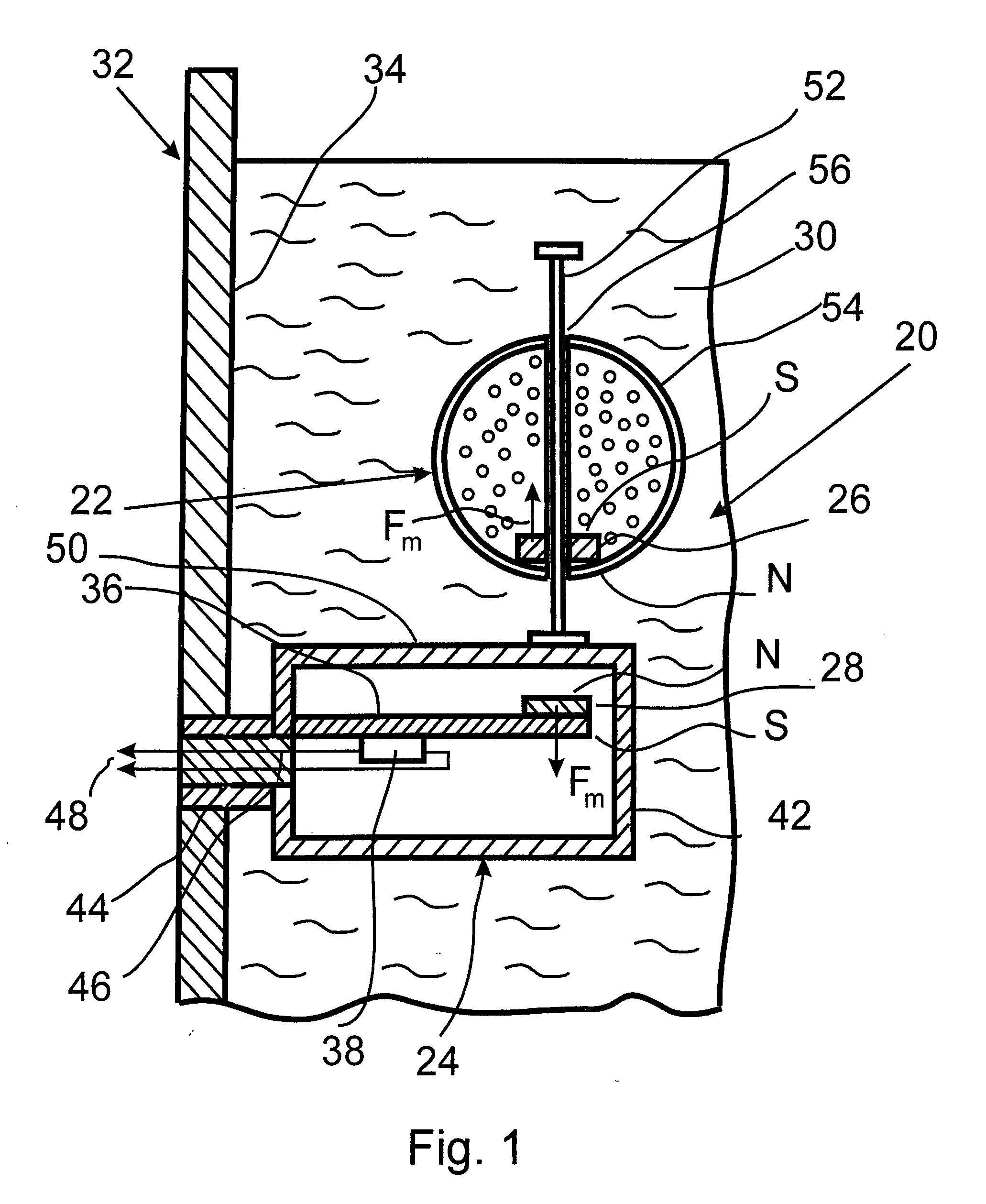
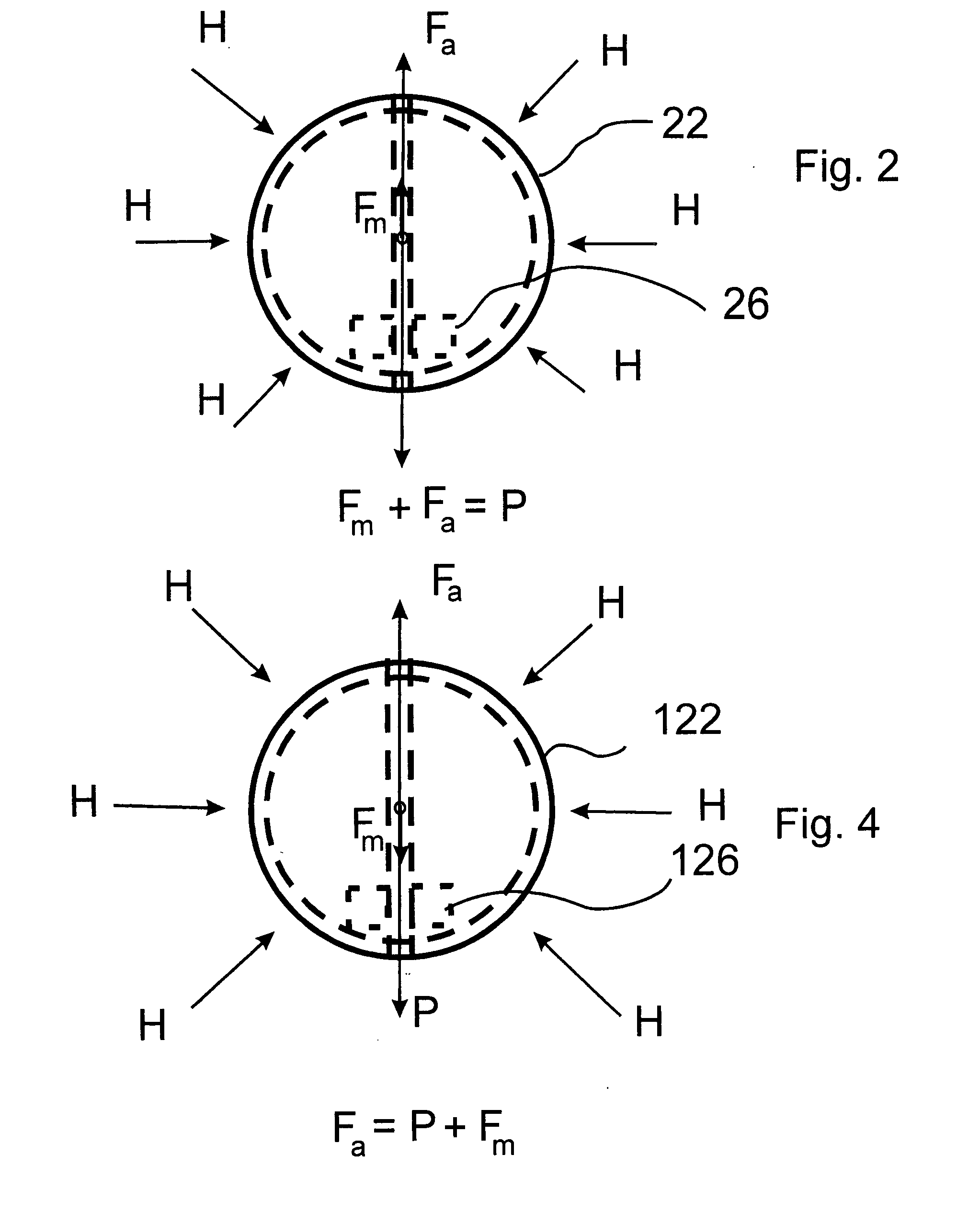
InactiveUS20080223130A1Improve accuracyMinimal roughnessMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesSpecific gravity using centrifugal effectsLiquid densityEngineering
A sensor for measuring density of a liquid that comprises a float unit having a sealed hollow casing that contains a first magnet and a strain-gauge unit having a sealed hollow casing that contains a strain gauge and a second magnet arranged coaxially to the first magnet. Coaxiality of the magnets is provided by means of a guide rod installed on the casing of the strain-gauge unit and used to guide the float unit by inserting the guide rod into the central opening of the float unit casing. A characteristic feature of the sensor is that changes in the density of the liquid that cause displacement of the float cause detectable deformations of the strain gauge via forces of magnetic interaction between the first and second magnets without physical contact between the magnets. Since the elements of the sensor are located in sealed casings, they are not subject to damage and do not require maintenance.
Owner:PROVINA
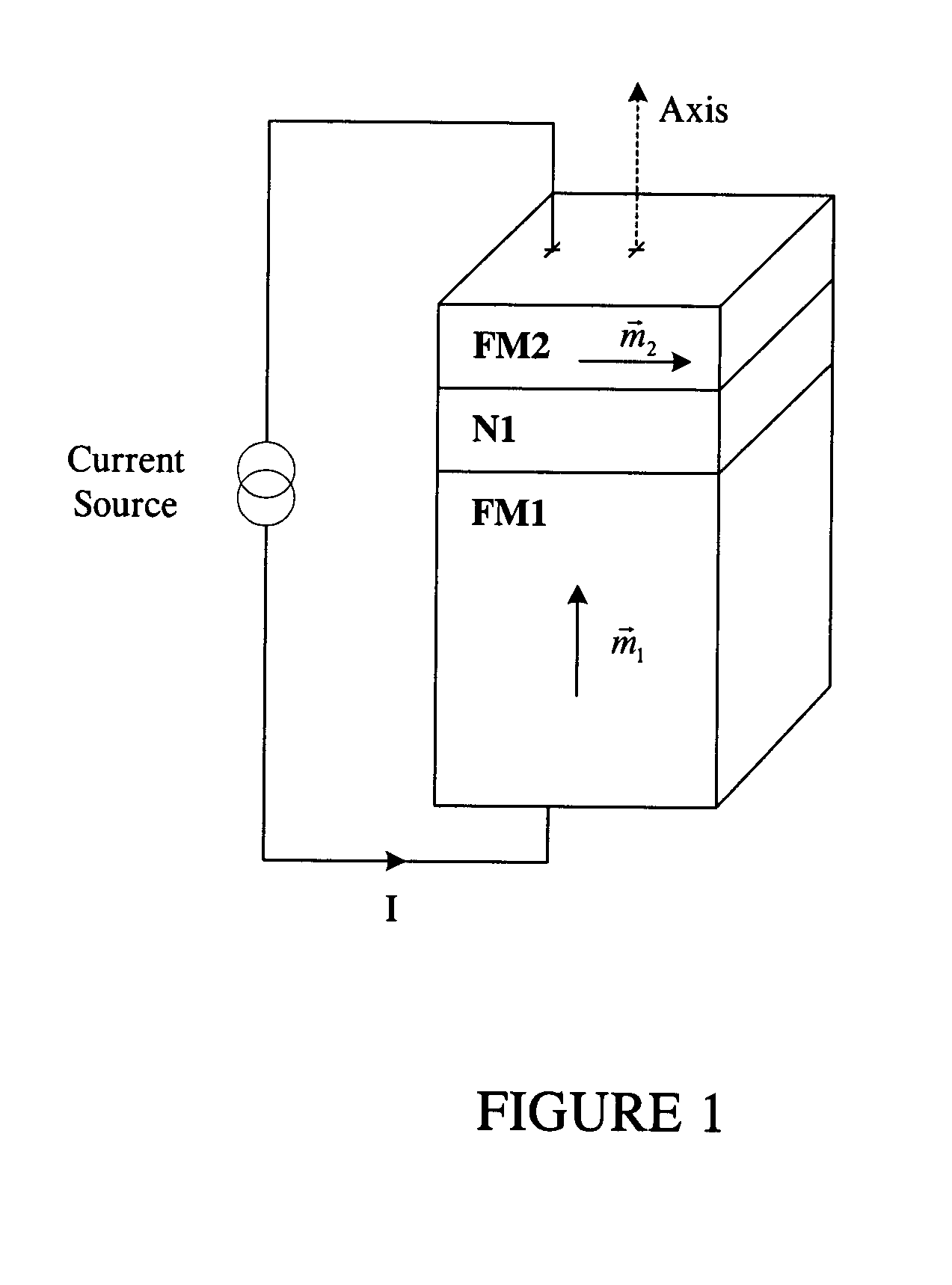
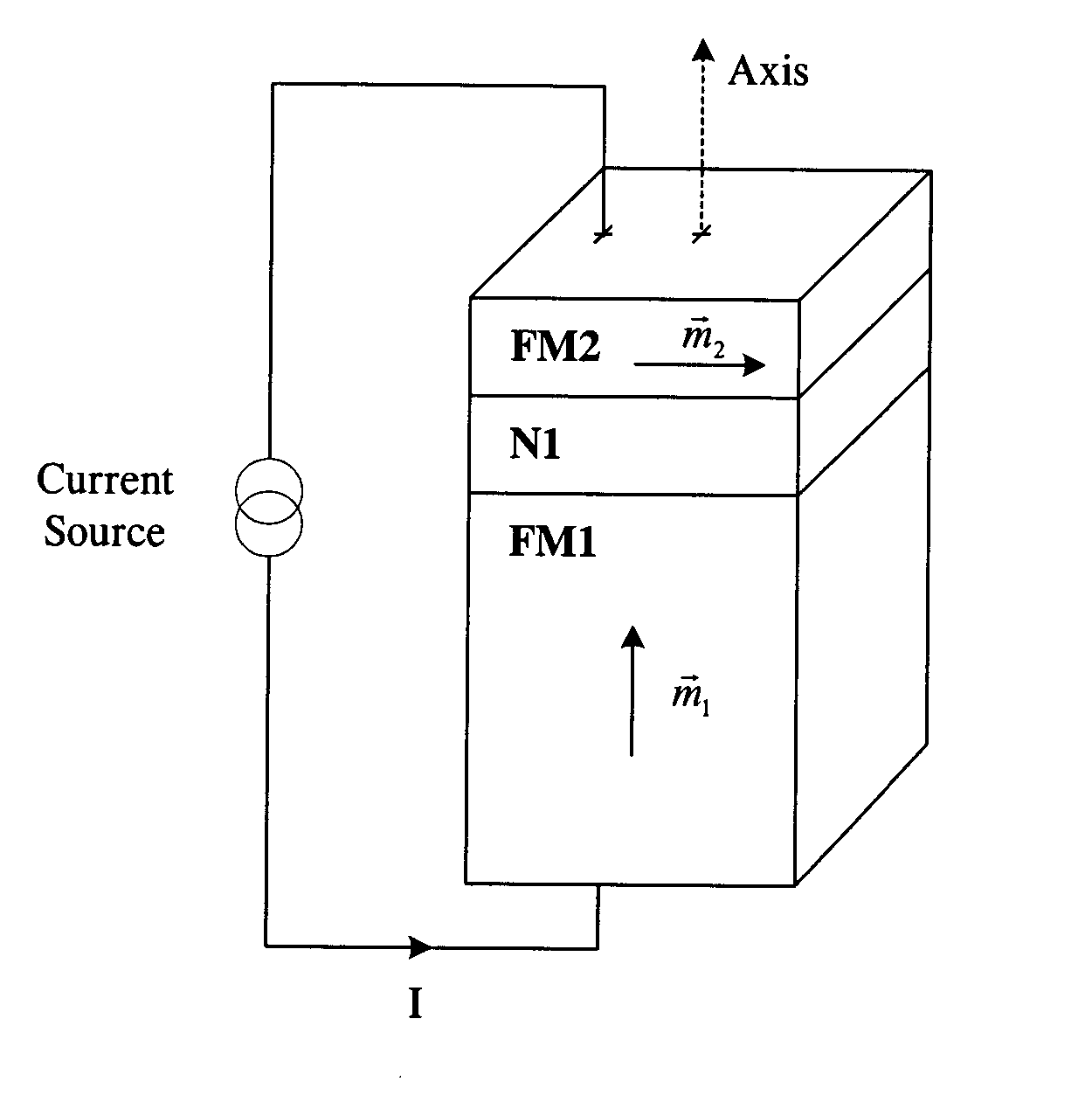
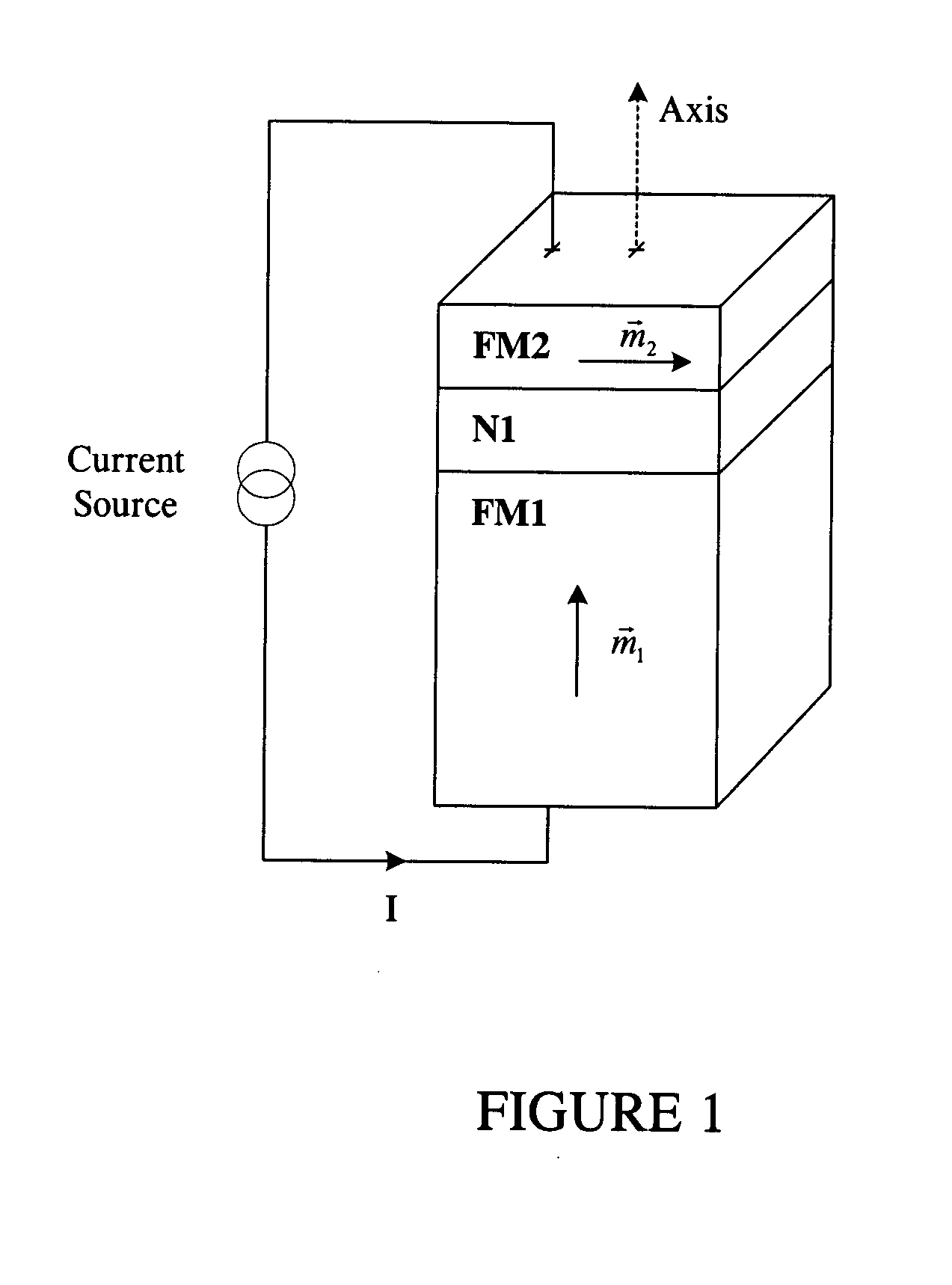
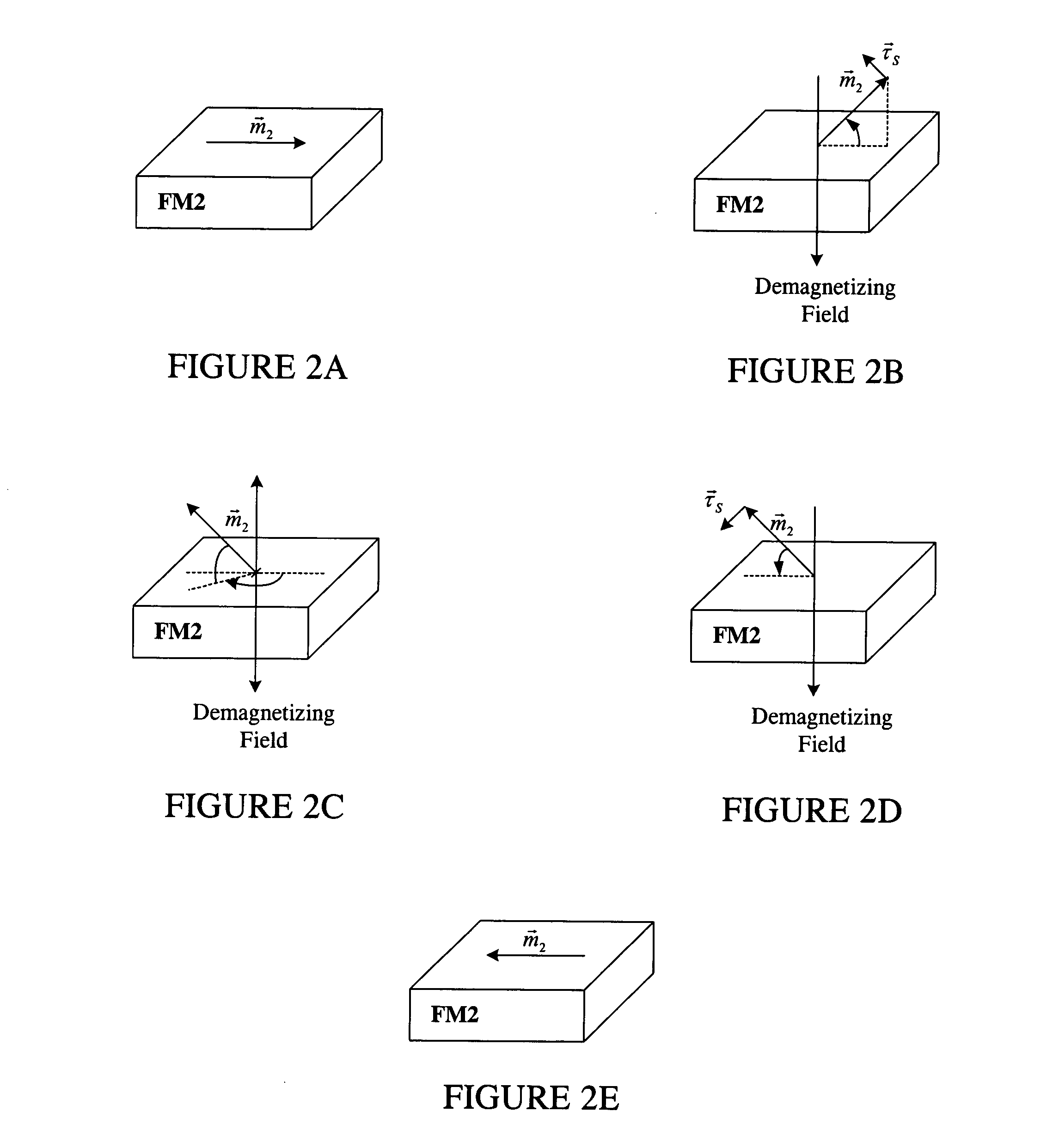
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
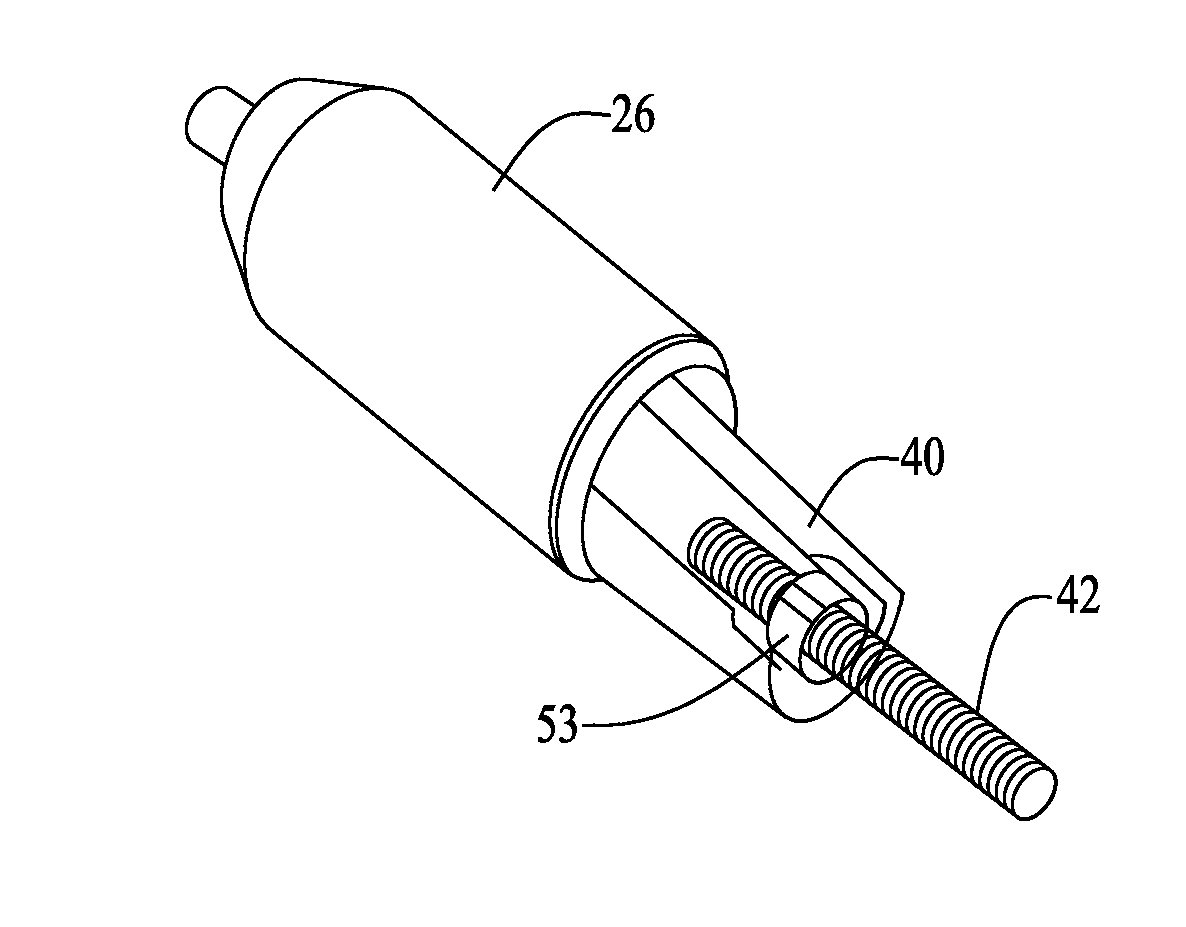
Infusion medium delivery device and method with drive device for driving plunger in reservoir
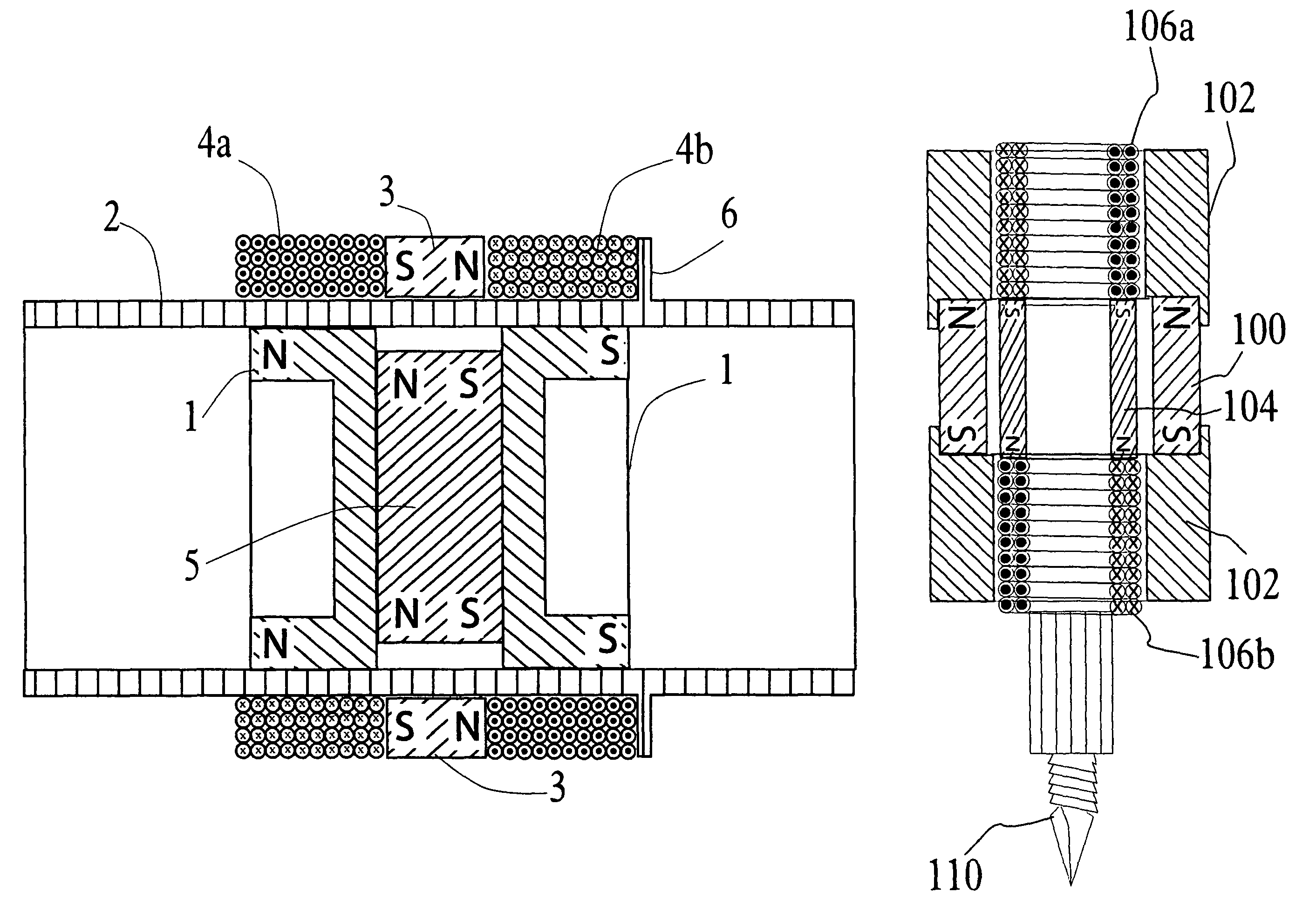
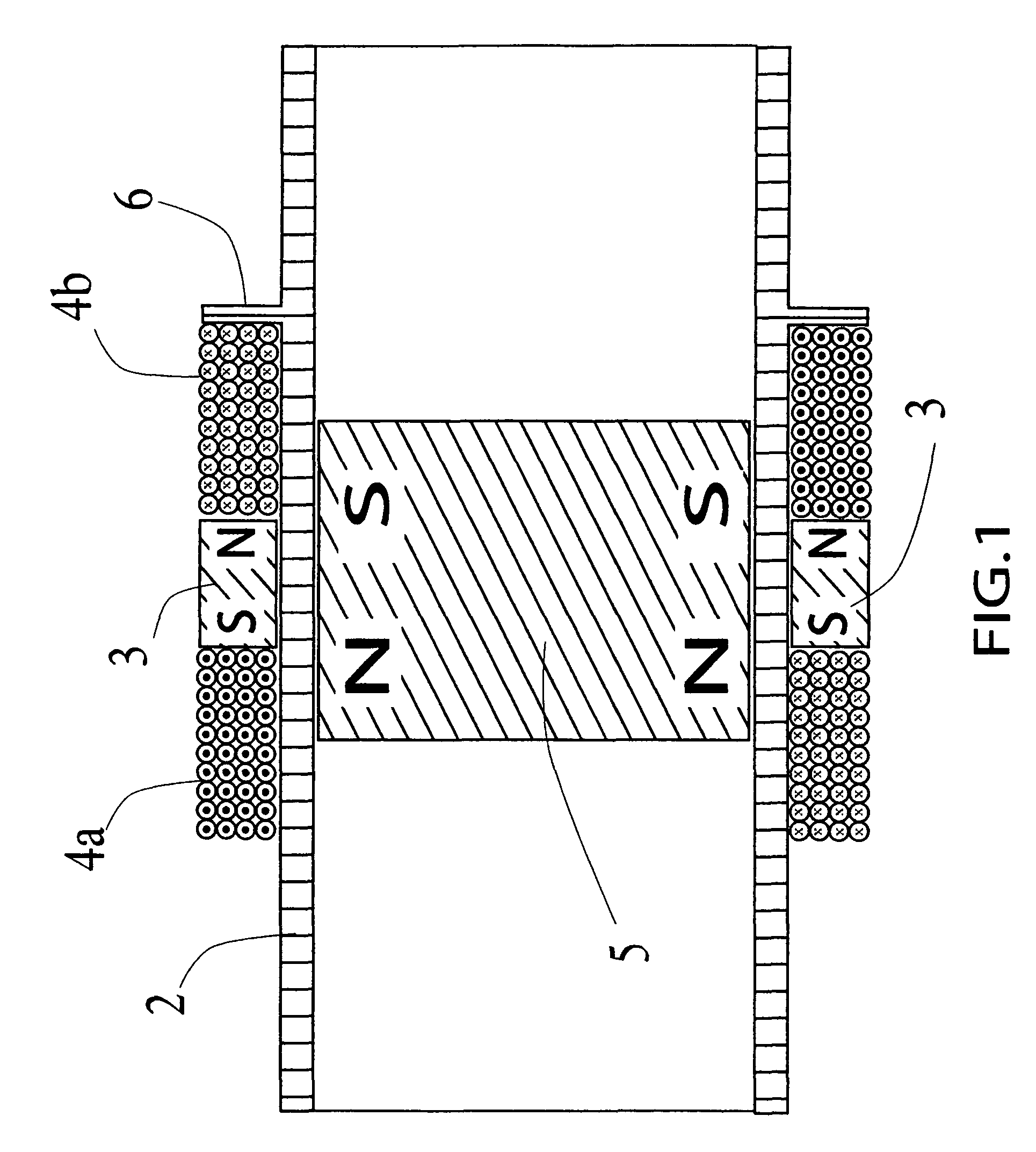
A delivery device includes first and second housing portions that selectively engage and disengage. A reservoir on one housing portion operatively engages a drive device and / or a needle inserting device on the other housing portion. Upon proper engagement of the housing portions, the reservoir operatively couples to the drive device and / or the needle inserting device. A first magnet on the first housing portion and a second magnet (or a magnetically-attractive material) on the second housing portion are positioned to magnetically interact with each other, upon operative engagement of the housing portions. A third magnet on the second housing portion may be opposed to the first magnet to help align the housing portions for connection. A magnet-responsive device may be on one or both housing portions to detect alignment and / or connection of the housing portions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Use of magnetic implants to treat body tissue structures
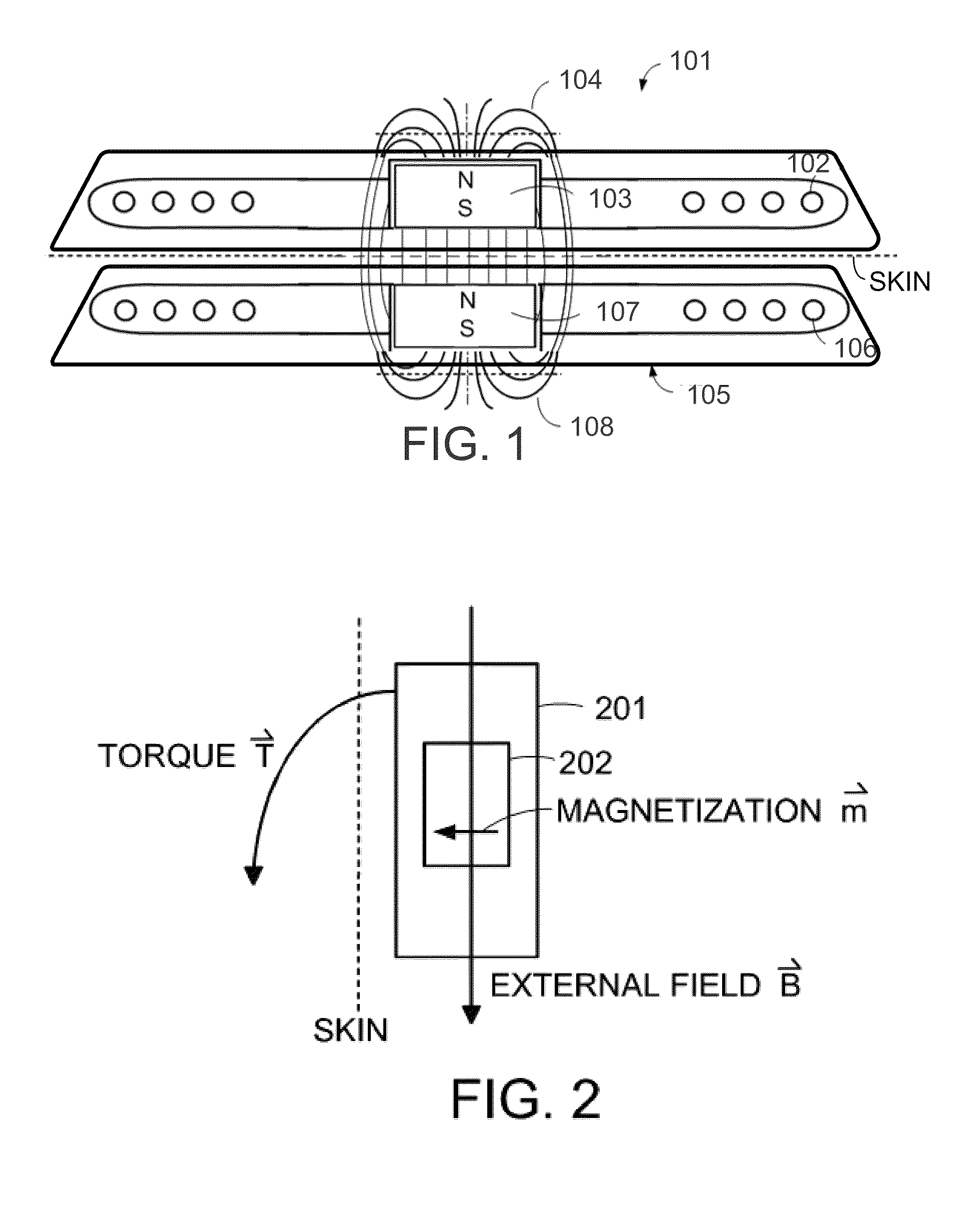
Plural (at least two) magnetic devices are implanted in a patient so that magnetic interaction between those devices modifies the patient's body in one or more respects (e.g., by modifying the shape and / or performance of some part of the body) Prior to implantation, a location in the body may be marked for later reference during the implantation. The magnetism of one or more of the magnetic devices may be changed in vivo after implantation. One or more of the implanted devices may be subsequently removed from the patient if desired. Use of the magnetic devices inside tissue conduits (e.g., as a treatment for GERD) is especially considered by way of illustration.
Owner:TORAX MEDICAL
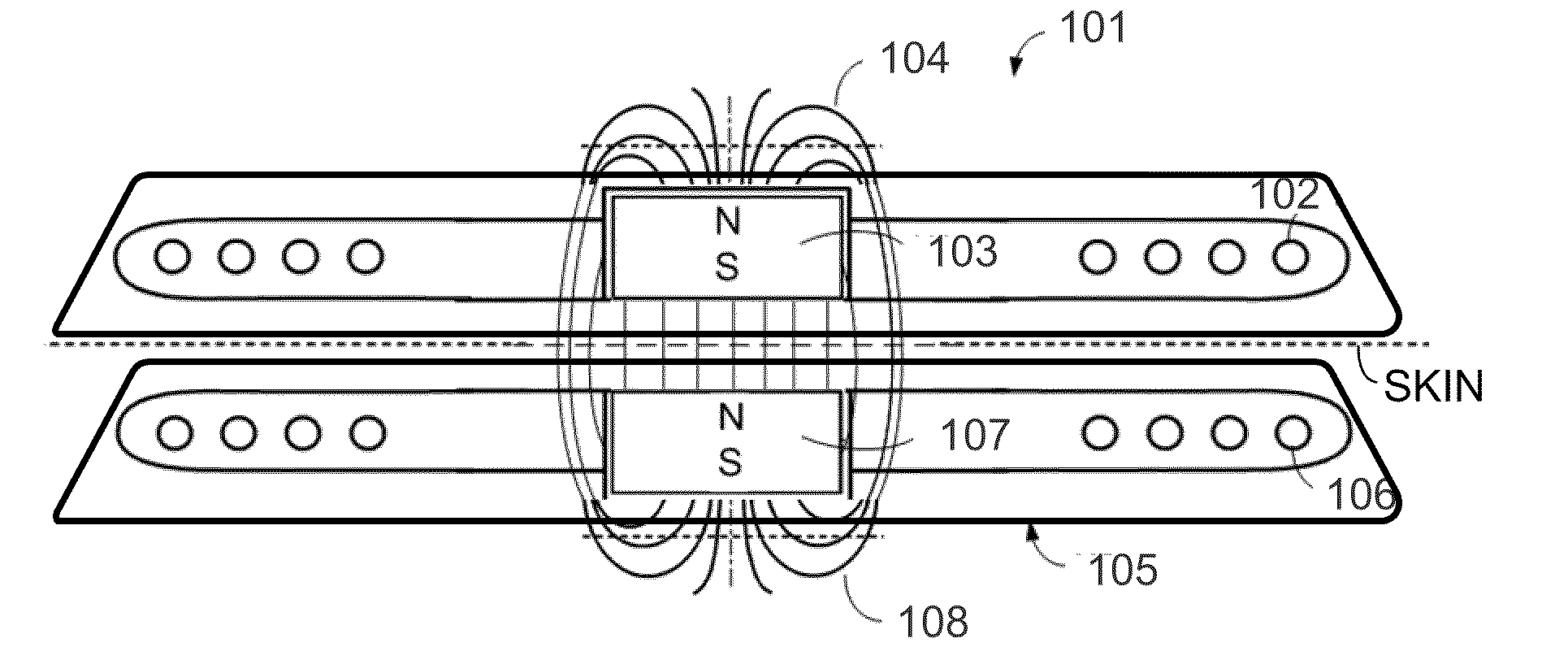
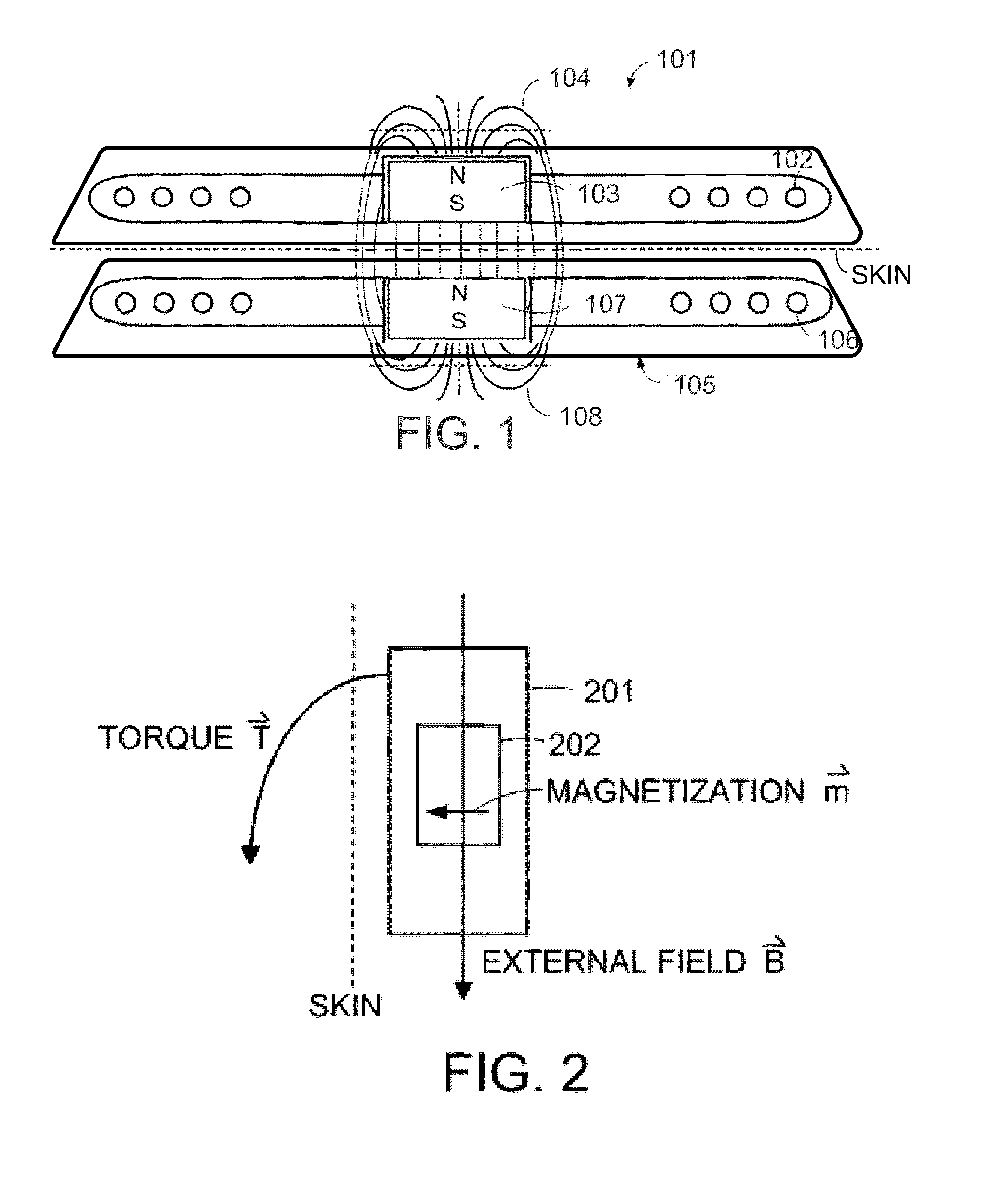
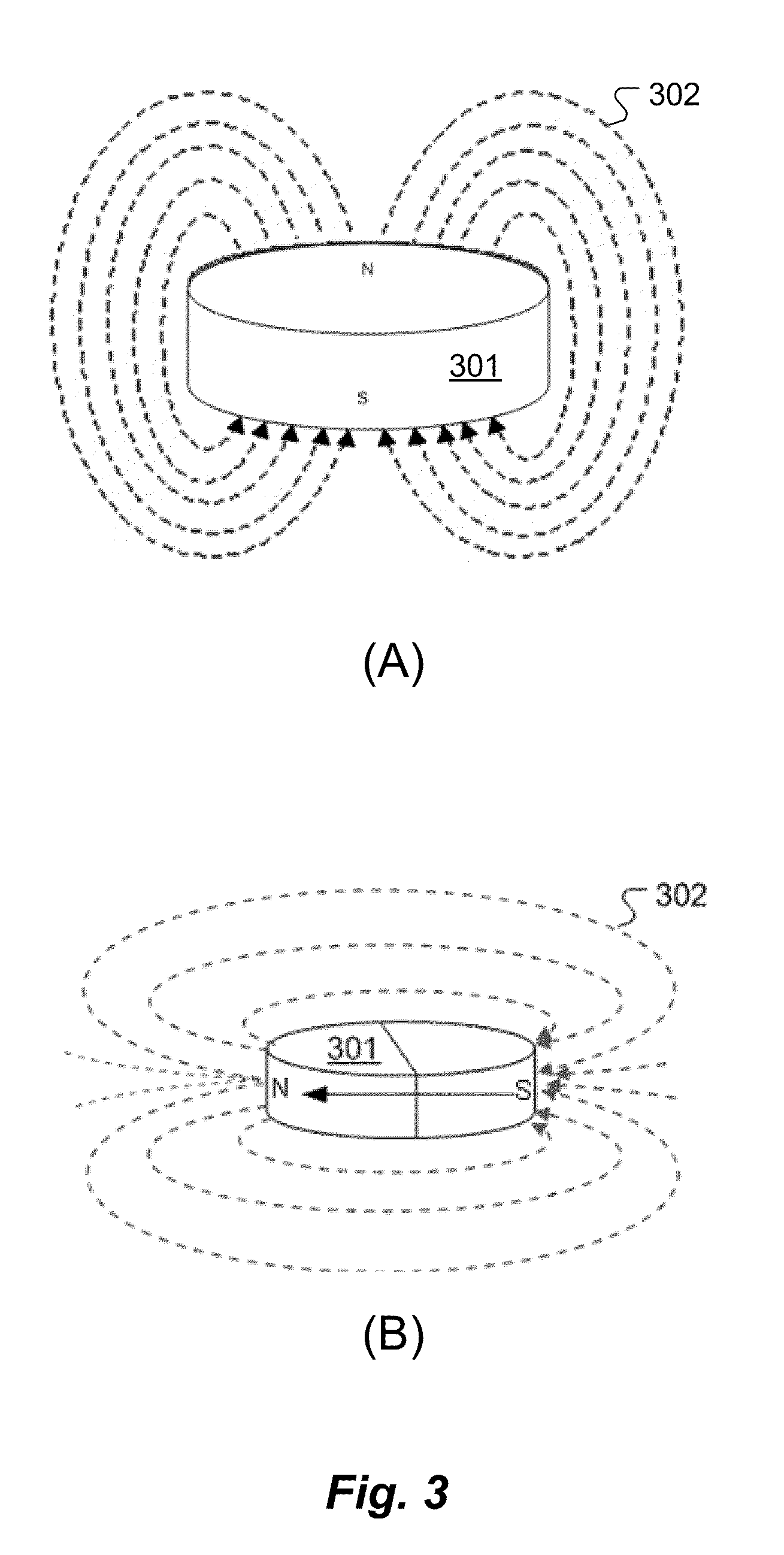
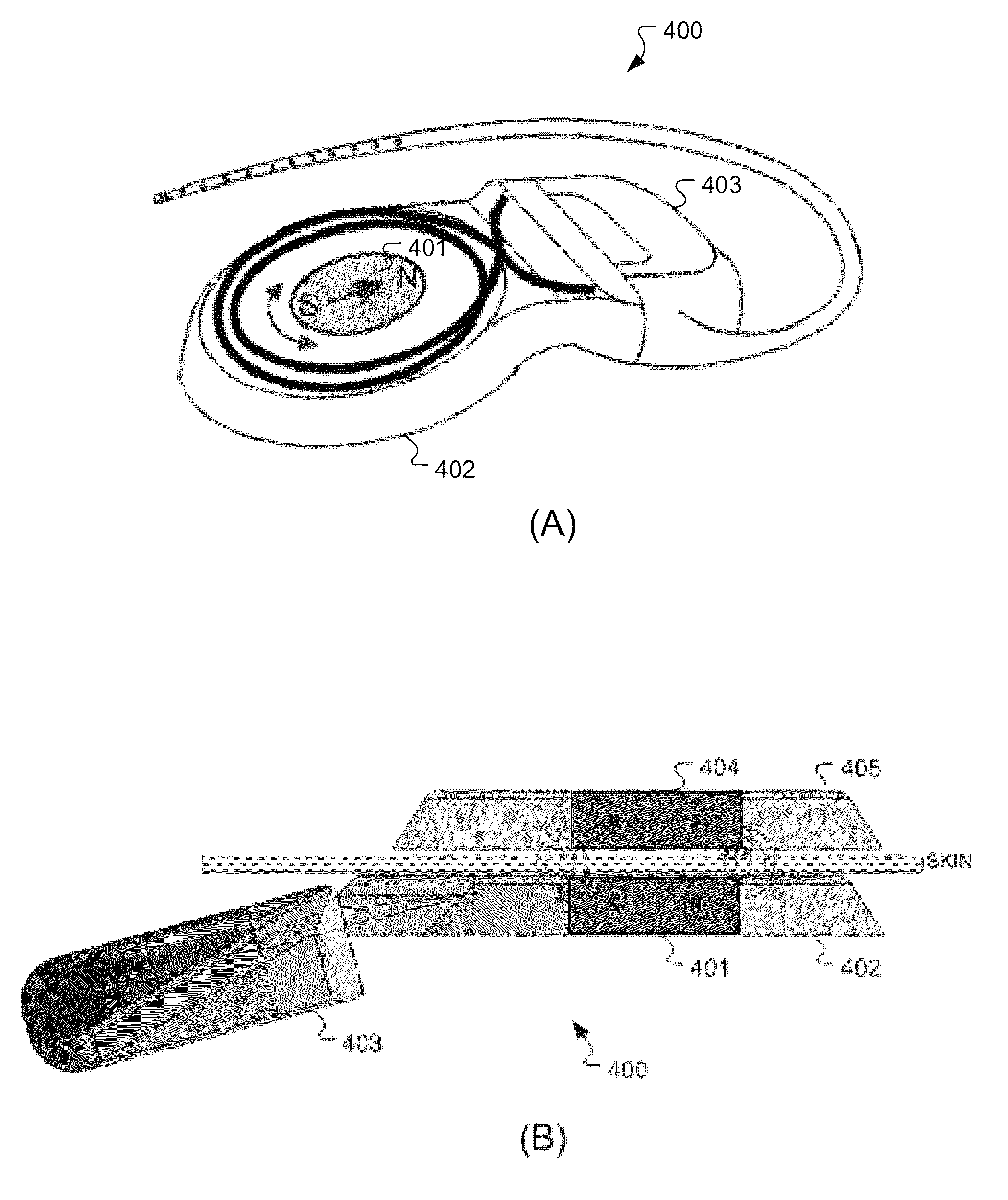
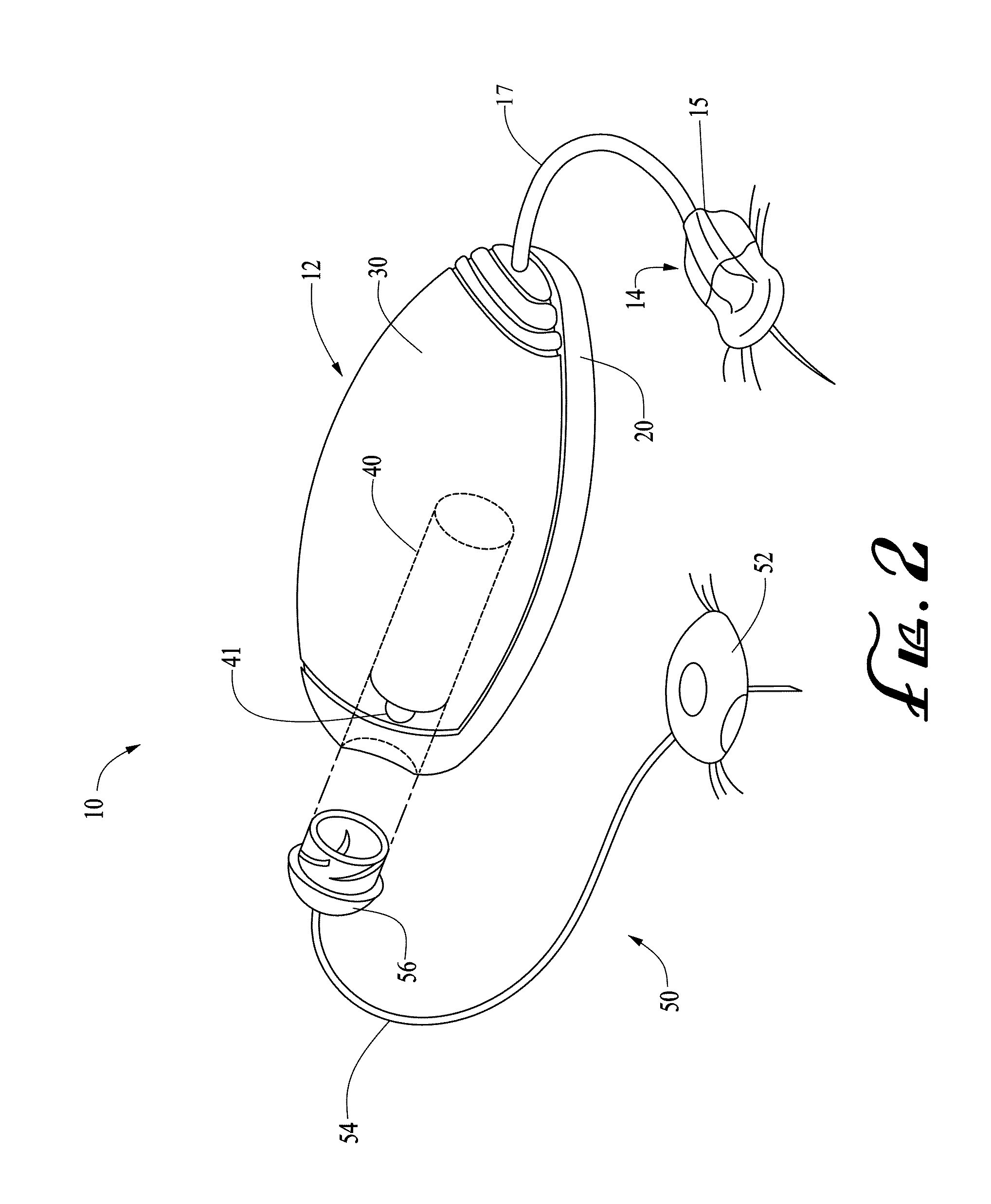
MRI-Safe Disc Magnet for Implants
ActiveUS20110264172A1Smooth rotationReduce frictionElectrotherapyTracheaeMagnetic interactionMagnetic dipole
A magnetic arrangement is described for an implantable system for a recipient patient. A planar coil housing contains a signal coil for transcutaneous communication of an implant communication signal. A first attachment magnet is located within the plane of the coil housing and rotatable therein, and has a magnetic dipole parallel to the plane of the coil housing for transcutaneous magnetic interaction with a corresponding second attachment magnet.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
MRI-safe disc magnet for implants
A magnetic arrangement is described for an implantable system for a recipient patient. A planar coil housing contains a signal coil for transcutaneous communication of an implant communication signal. A first attachment magnet is located within the plane of the coil housing and rotatable therein, and has a magnetic dipole parallel to the plane of the coil housing for transcutaneous magnetic interaction with a corresponding second attachment magnet.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Low frequency electromagnetic motor to create or cancel a low frequency vibration
Electromagnetic motor with a piston that moves linearly with respect to the stator in either direction. Embodiments include a piston internal or external the stator. The piston includes one or more magnetic flux producing elements in all embodiments, with some embodiments having a ferro-magnetic plate on either side of the flux producing element. Further, in all embodiments the stator includes three magnetic flux producing elements with either two coils with one or more magnets therebetween or with the two coils and a coil magnet substitute therebetween. All embodiments provide positive piston return to a center at rest position. In all embodiments the piston is centered with respect to the stator resulting from either magnetic interaction between the piston and stator magnets, or between the piston magnet and the stator magnet substitute coil.
Owner:EARTHQUAKE SOUND
Touch detection method and system for a touch sensor
InactiveUS20080018604A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingCapacitanceControl signal
A a touch sensor including a keyboard having a key defining a touch sensing location, wherein the key is responsive to at least one of capacitive and electro-magnetic interactions with a user during a touch event includes control circuitry associated with the key, wherein the control circuitry outputs a control signal, and wherein an amplitude of the control signal is representative of an amount of interaction between the user and the key during a touch event. A controller is connected to the control circuitry and analyzes a variation in the amplitude of the control signal over a time period to identify the touch event.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS CANADA
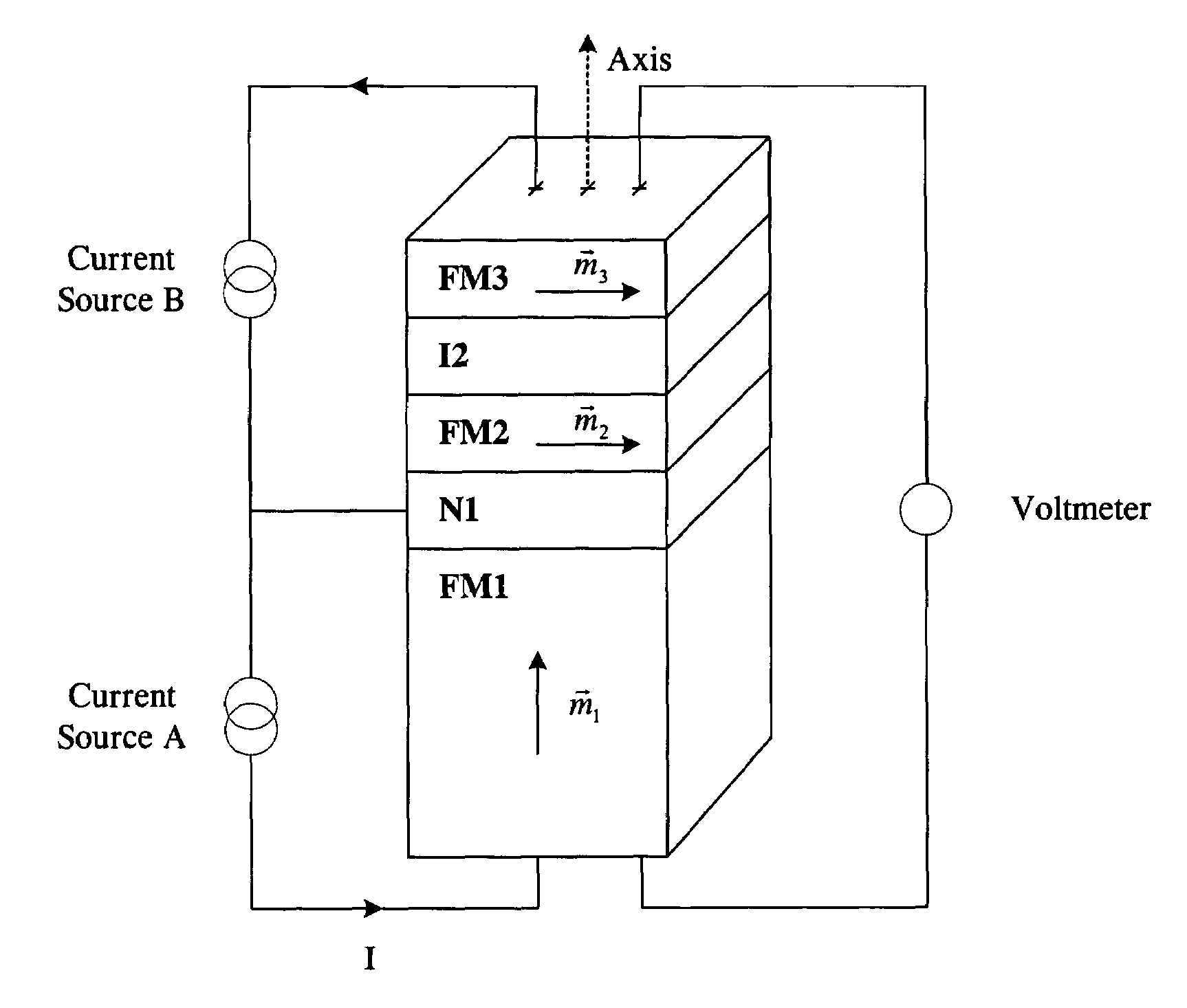
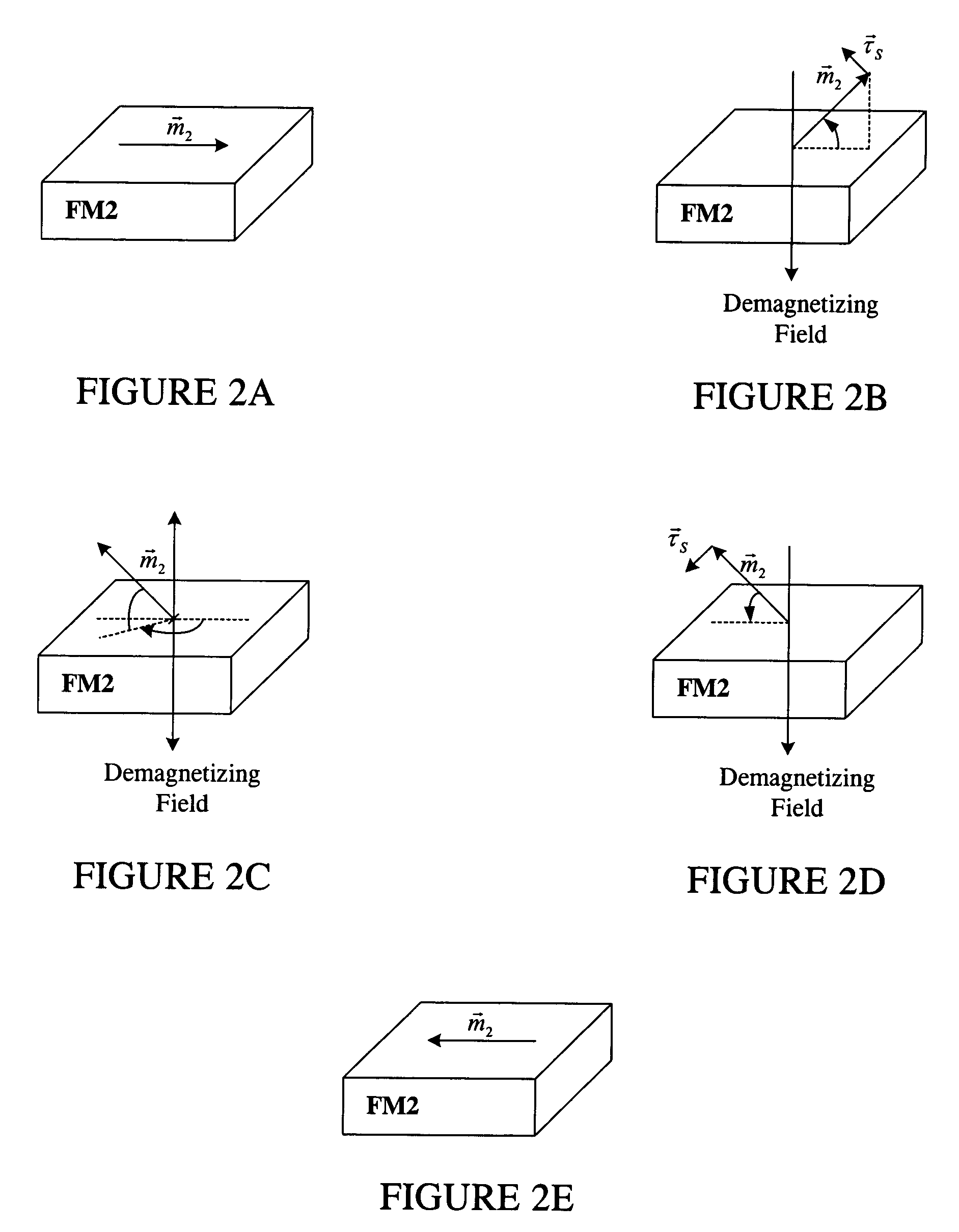
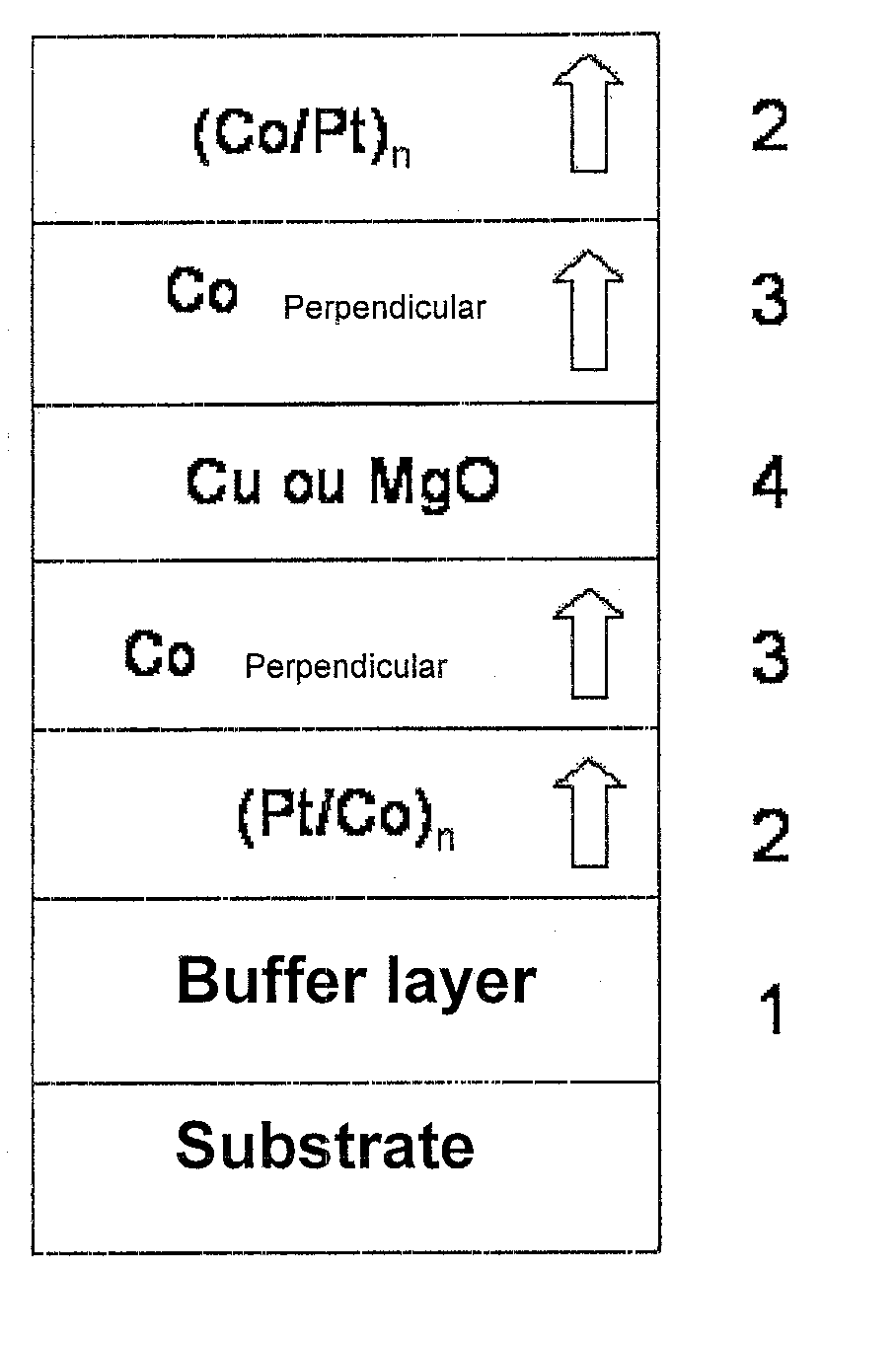
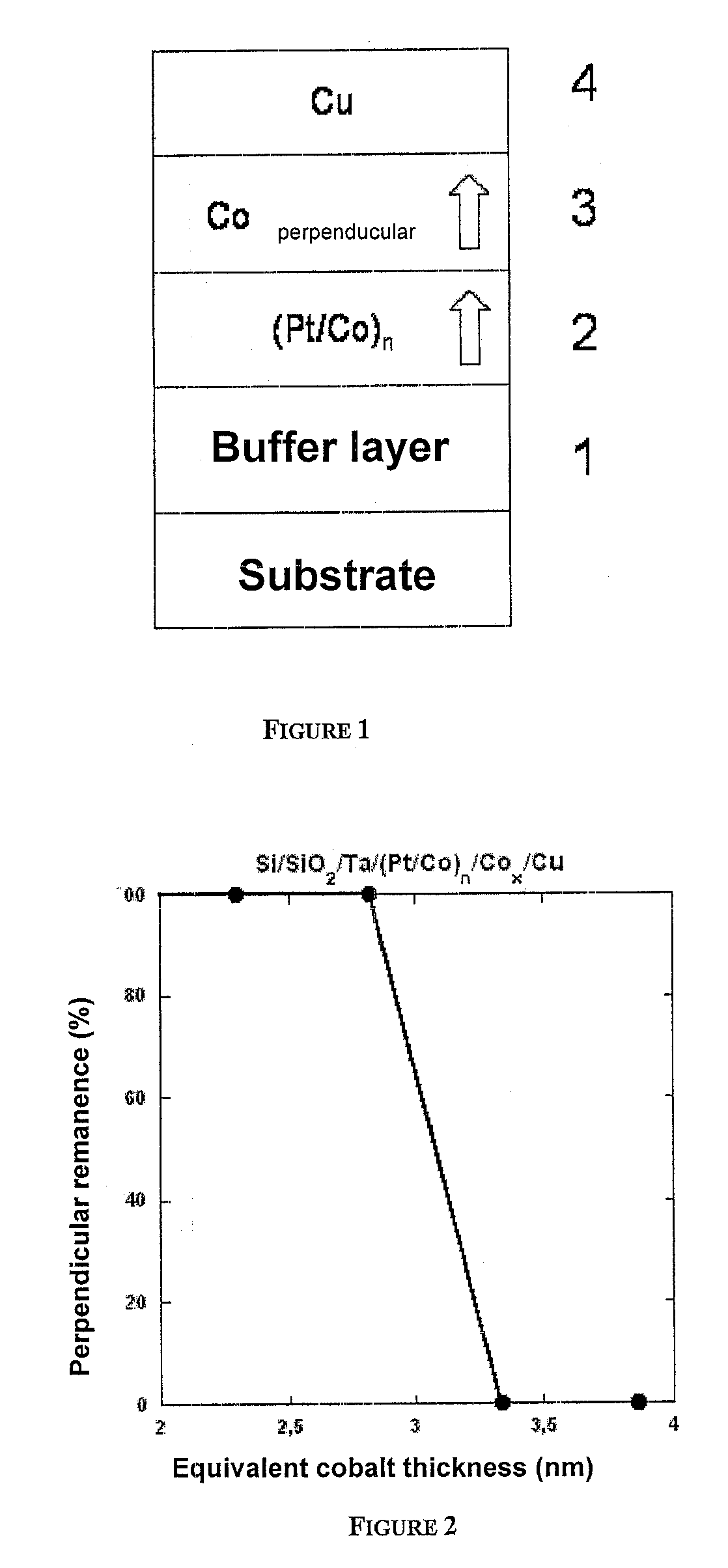
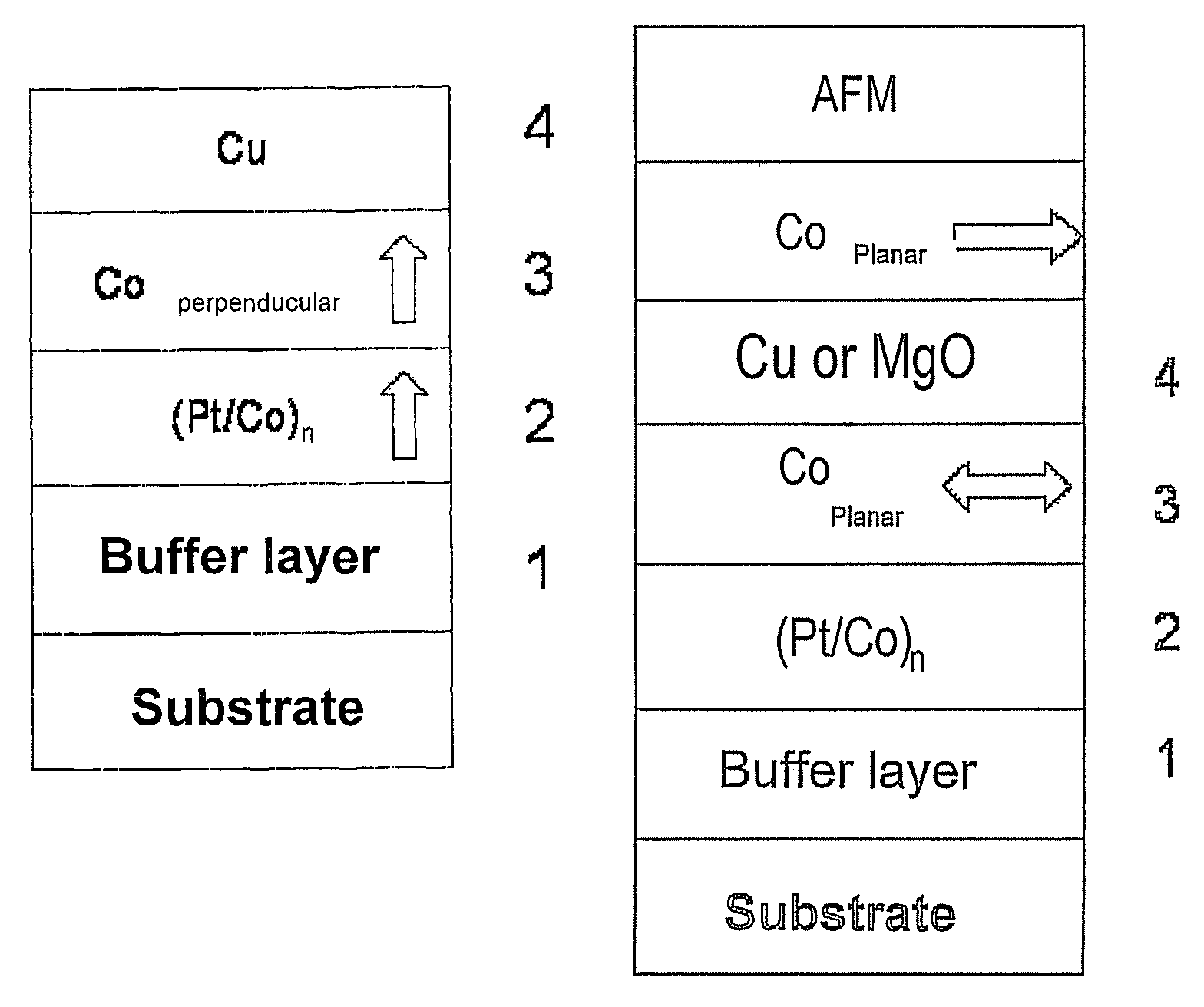
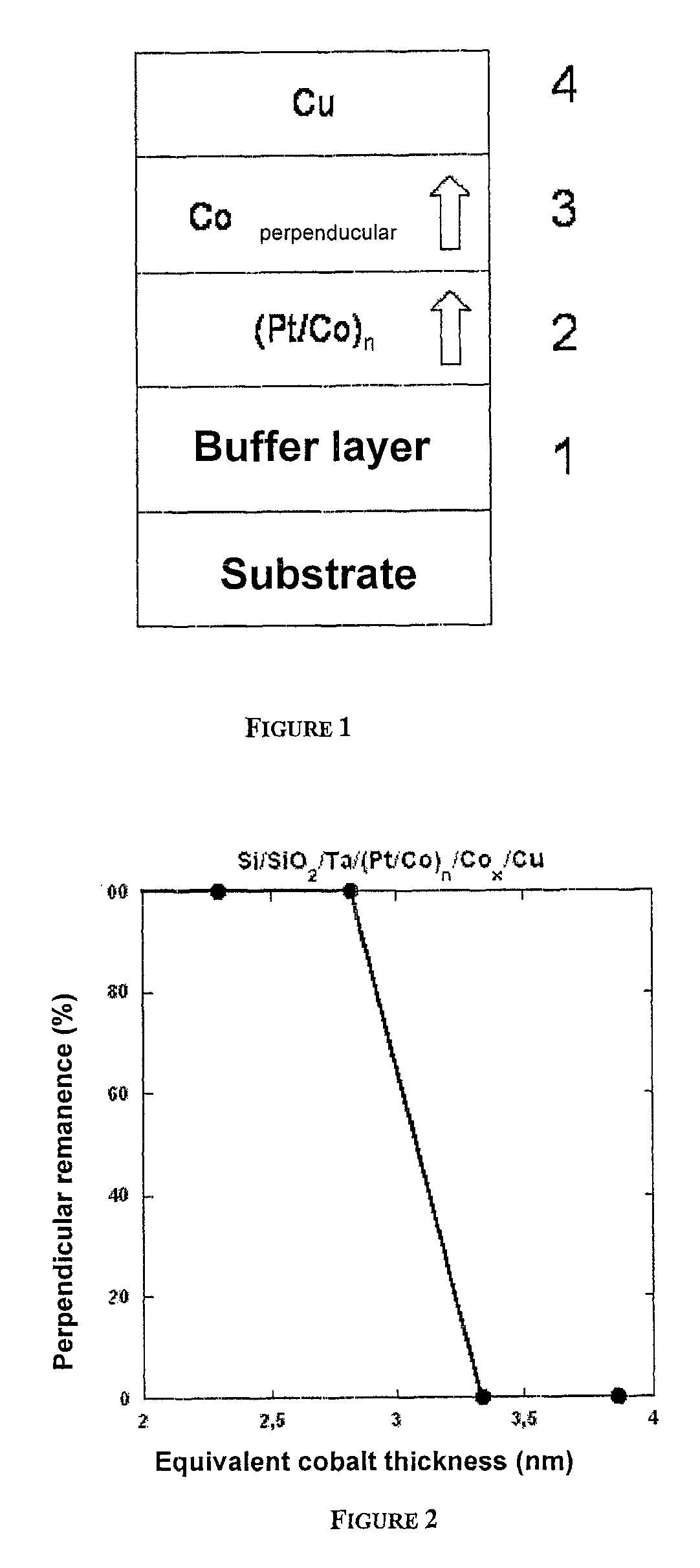
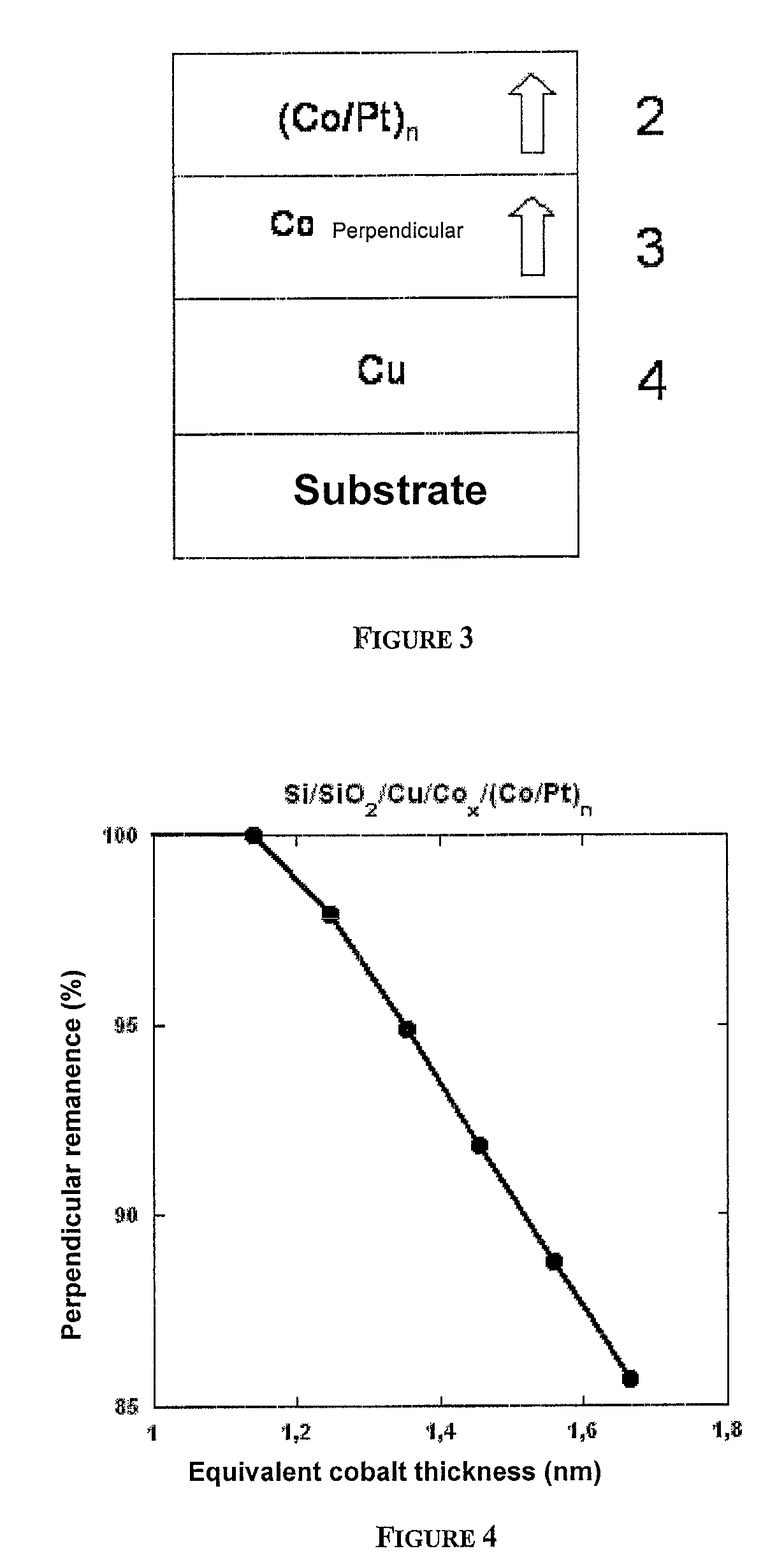
Thin-film magnetic device with strong spin polarisation perpendicular to the plane of the layers, magnetic tunnel junction and spin valve using such a device
ActiveUS20080031035A1Improve scalabilityImprove adhesionNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeHigh rate
A thin-film magnetic device comprises, on a substrate, a composite assembly deposited by cathode sputtering and consists of a first layer made of a ferromagnetic material with a high rate of spin polarisation, the magnetisation of which is in plane in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, a second layer made of a magnetic material with high perpendicular anisotropy, the magnetisation of which is outside the plane of said layer in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, and coupling of which with said first layer induces a decrease in the effective demagnetising field of the entire device, a third layer that is in contact with the first layer via its interface opposite to that which is common to the second layer and made of a material that is not magnetic and not polarising for electrons passing through the device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
ActiveUS20050041462A1High precession rateQuick switchNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetizationMagnetic memory
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Diagnostic and therapeutic magnetic propulsion capsule and method for using the same
InactiveUS20110301497A1Reduced field generator powerImprove art of robotic guidanceVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEndoscopesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
A guided medical propulsion capsule driven by strong electro-magnetic interaction between an external AC / DC magnetic gradient-lobe generator and a set of uniquely magnetized ferrous-conductive elements contained within the capsule. The capsule is navigated through the lumens and cavities of the human body wirelessly and without any physical contact for medical diagnostic, drug delivery, or other procedures with the magnetically guiding field generator external to the human body. The capsule is equipped with at least two sets of magnetic rings, disks and / or plates each possessing anisotropic magnetic properties. The external magnetic gradient fields provide the gradient forces and rotational torques on the internal conductive and magnetic elements needed to make the capsule move, tilt, and rotate in the body lumens and cavities according to the commands of an operator.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP +1
Homopolar machine with shaft axial thrust compensation for reduced thrust bearing wear and noise
InactiveUS6856062B2Reduce induced magnetic forceConstant contact pressureRotary current collectorMagnetic bodiesFiberContact pressure
A homopolar machine produces an axial counter force on the rotating shaft to compensate for the load on the shaft's thrust bearing to reduce wear and noise and prolong bearing life. The counter force is produced through magnetic interaction between the shaft and the machine's field coils and is created by changing the current excitation of the field coils, which results in a magnetic flux asymmetry in an inner flux return coupled to the shaft. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration that uses current collectors that maintain substantially constant contact pressure in the presence of high magnetic fields to improve current collector performance. The current collectors are flexible and may be made from either electrically conductive fibers or stacked strips such that they bear up against the armature so that the pressure is maintained by the spring constant of the current collector material. The homopolar machine may also have a configuration where the brushes are oriented so that the current is aligned as much as is practical with the local magnetic field lines so as to reduce the lateral electromagnetic forces on the brushes.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Magnetic lock device
InactiveUS6215381B1Coupled more securely and moreIncreasing magnetic interactionSnap fastenersNon-mechanical controlsForeign matterMagnetic tension force
A magnetic lock device includes a first element and a second element that are capable of being detachably coupled together by attracting each other magnetically under the magnetic interaction of permanent magnets, wherein each of the first and second elements includes an annular permanent magnet having a center bore through it, a ferromagnetic disk-like plate disposed to make contact with the permanent magnet, and a ferromagnetic projecting member extending from the disk-like plate and through the center bore of the permanent magnet. All of the component parts for the first and second elements are covered with any suitable synthetic resin film, sheet or the like and shielded from the outside, so that any foreign matter such as dust, particularly ferromagnetic particles like iron, cannot enter the gap or space that is present between the outer peripheral wall of the projecting member and the inner peripheral wall of the center bore through the annular permanent magnet. In one specific form of the magnetic lock device, each of the first and second elements is entirely covered with any suitable non-magnetic, synthetic resin film, sheet, covering or casing, or is entirely covered with a coating of any suitable non-magnetic, synthetic resin layer. In another specific form, each of the first and second elements is covered with any suitable non-magnetic, synthetic resin film, sheet, covering or casing, or is covered with a coating of any suitable non-magnetic, synthetic resin layer, except for the ends of the ferromagnetic projecting members in the first and second elements engaging each other that remain uncovered or exposed. In both forms, each of the first and second elements includes an annular permanent magnet, wherein one annular permanent magnet has a given polarity (S or N) opposed to the polarity (N or S) of the other annular permanent magnet on the side on which the first and second elements are to engage each other.
Owner:APPL ART LAB
Self-anchoring magnetic force implant devices, systems, and methods
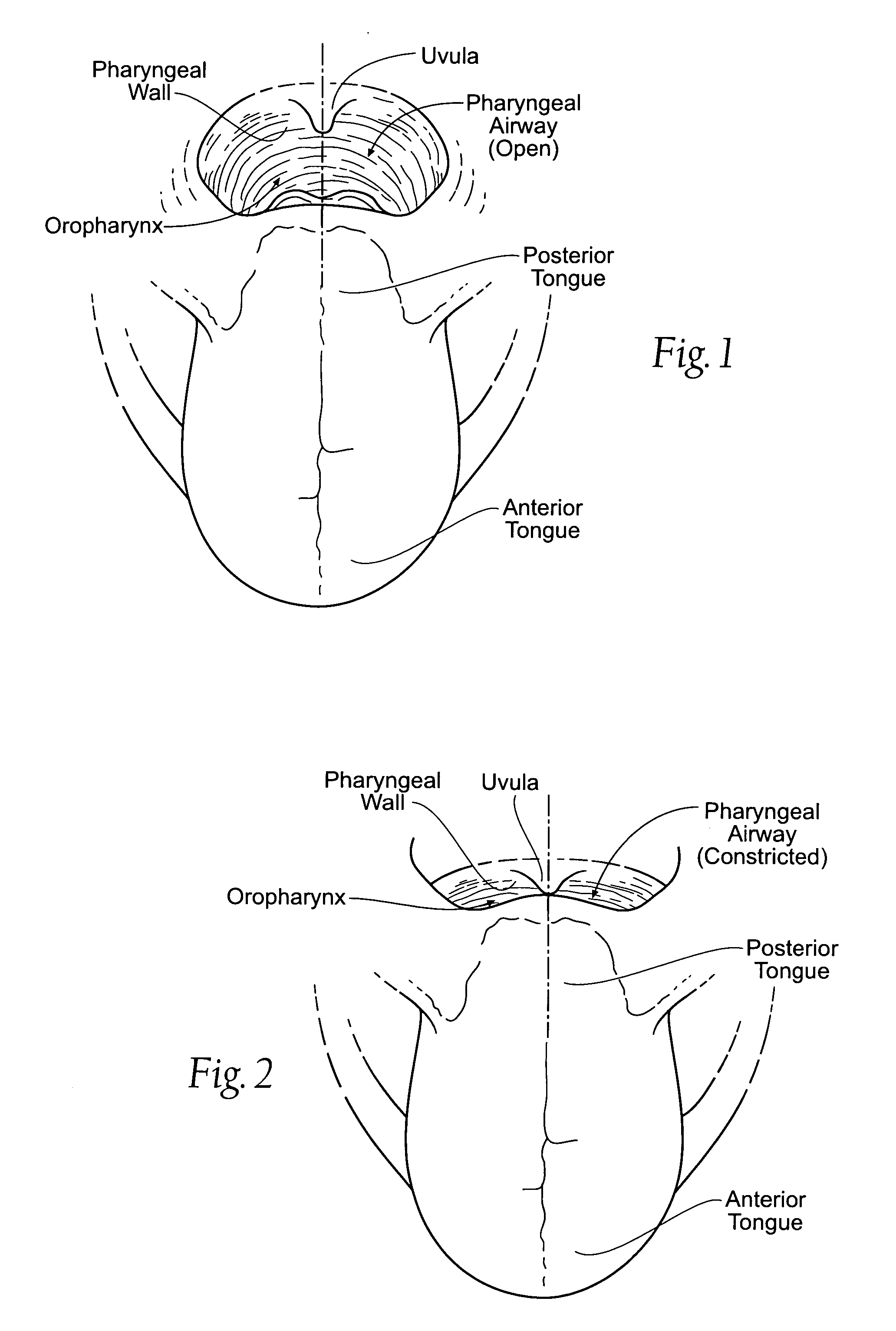
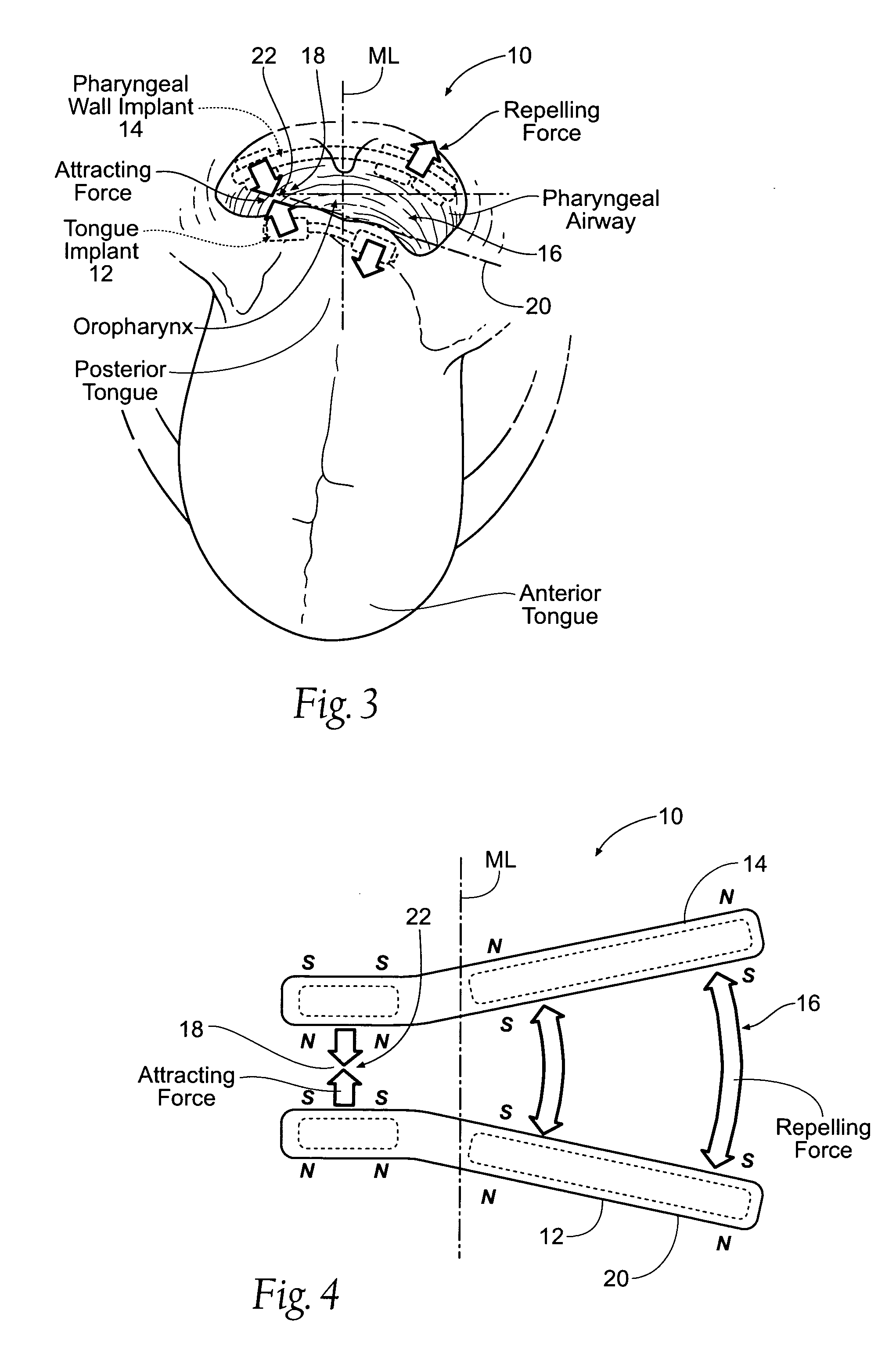
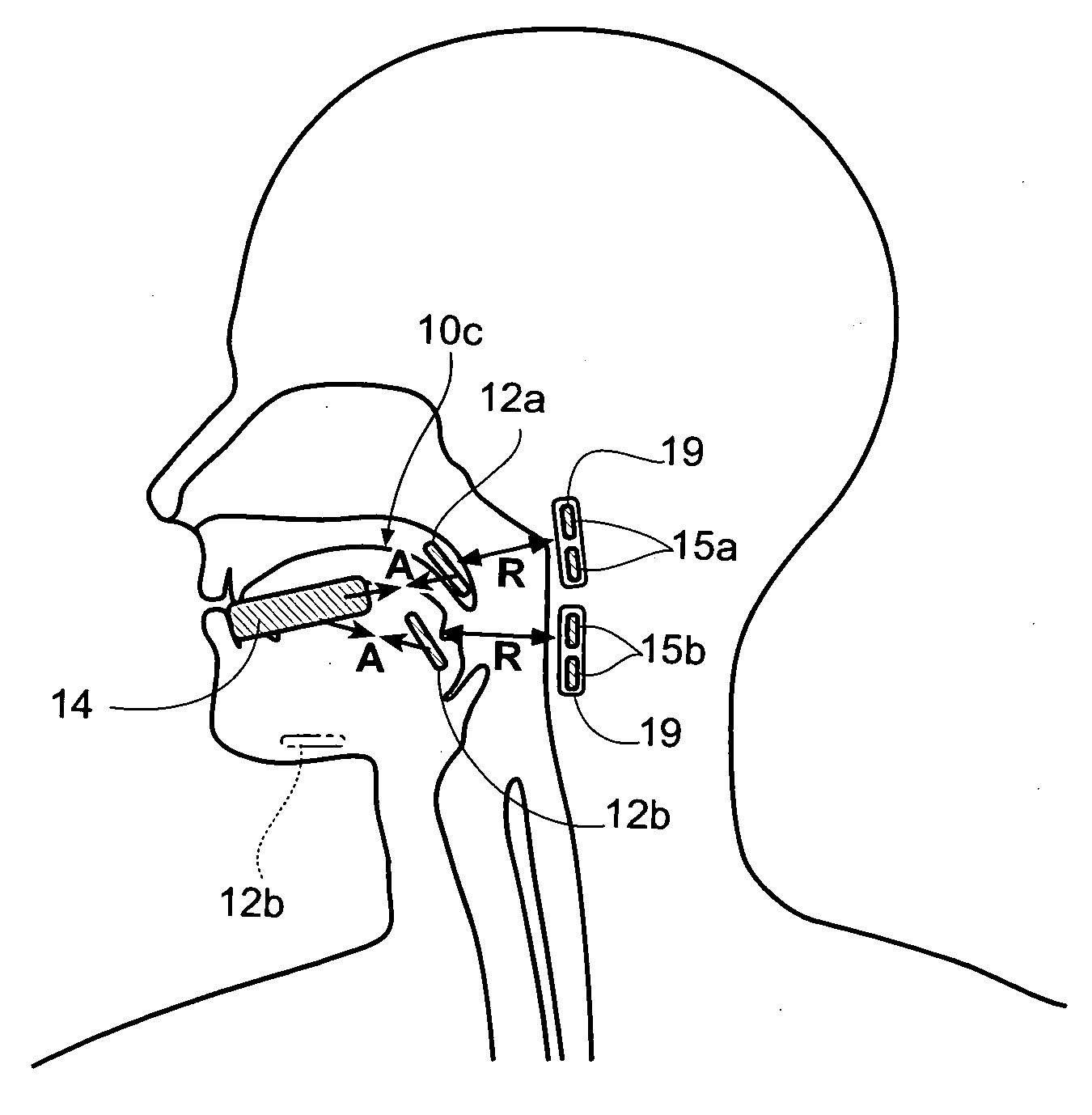
InactiveUS20070209665A1“hinge” structureSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesMagnetic tension forcePharynx
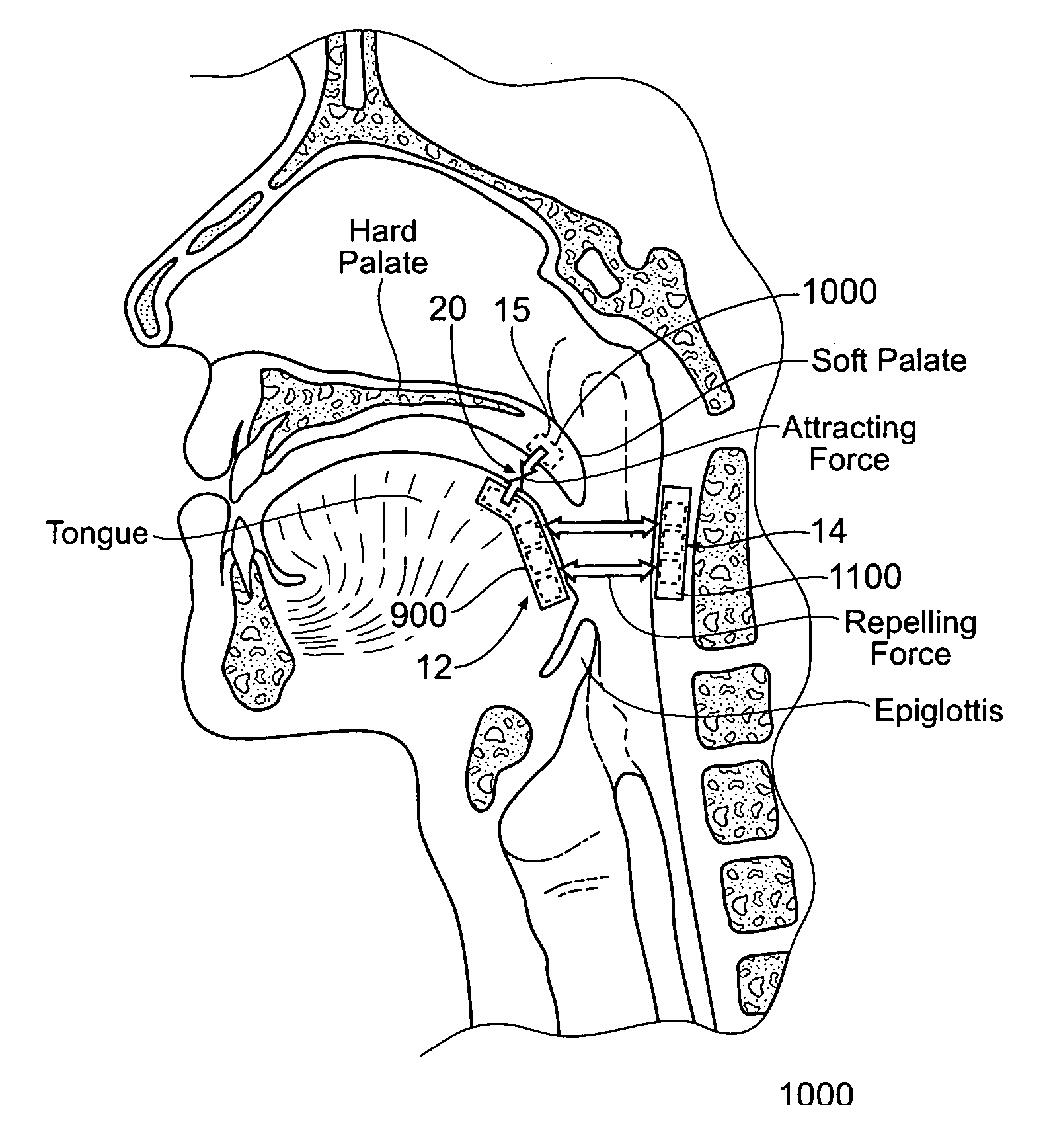
A magnetic force system uses a magnetic implant sized and configured to be inserted in the pharynx and another magnetic implant sized and configured to be inserted in the tongue, palate, or pharynx. The system establishes different regions of magnetic interaction between the two implants across the airway, attracting and repelling, such that attractive interaction in one region of the implants combines with repelling interaction in another region of the implants, to provide a “hinge” structure. Alternatively, a magnetic force system that uses three magnetic implants sized and configured to be inserted in the tongue, pharynx, and palate, respectively. The tongue implant is attracted to the palatal implant, and repels the pharyngeal implant, forming a modified “hinge” structure. Forces of magnetic attracting bring tissue together to form a magnetic hinge joint, providing an anchor to stabilize the regions where repelling forces work to separate tissue to keep the airway open.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Polymer encapsulation for medical device
InactiveUS20080200750A1Prevent component leakagePrevent leakageBlood pumpsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImpellerBlood pump
A rotary blood pump comprising an impeller suspended hydrodynamically within pump housing by thrust forces generated by said impeller during movement in use of said impeller as it rotates about an impeller axis, and the driving torque of said impeller is derived from the magnetic interaction between permanent magnets within the blades of said impeller and windings within said housing, and wherein said windings are encapsulated by a first fluid resistant polymer material, and said housing is at least partially made of a second polymer material that encapsulates said first polymer material.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
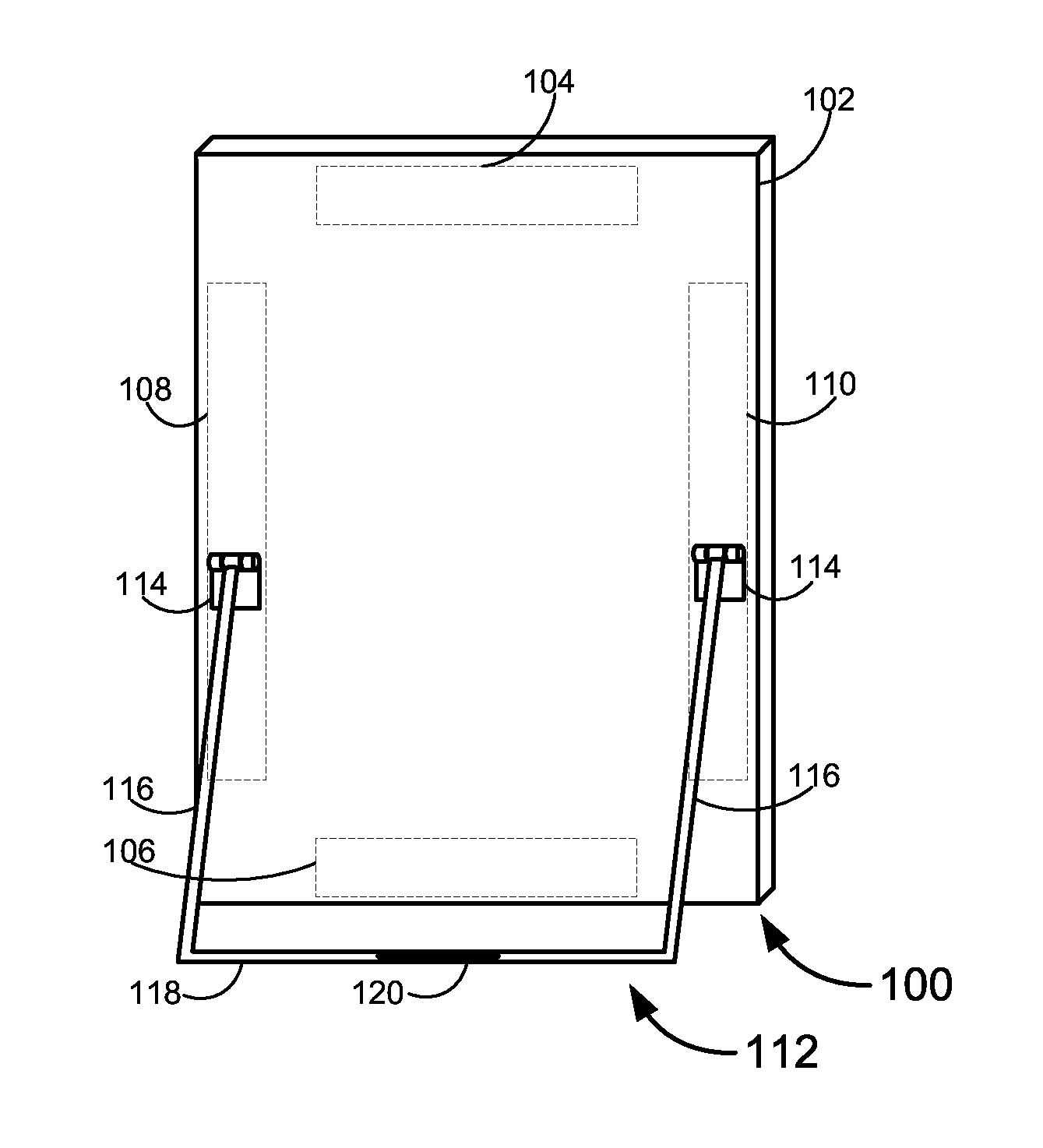
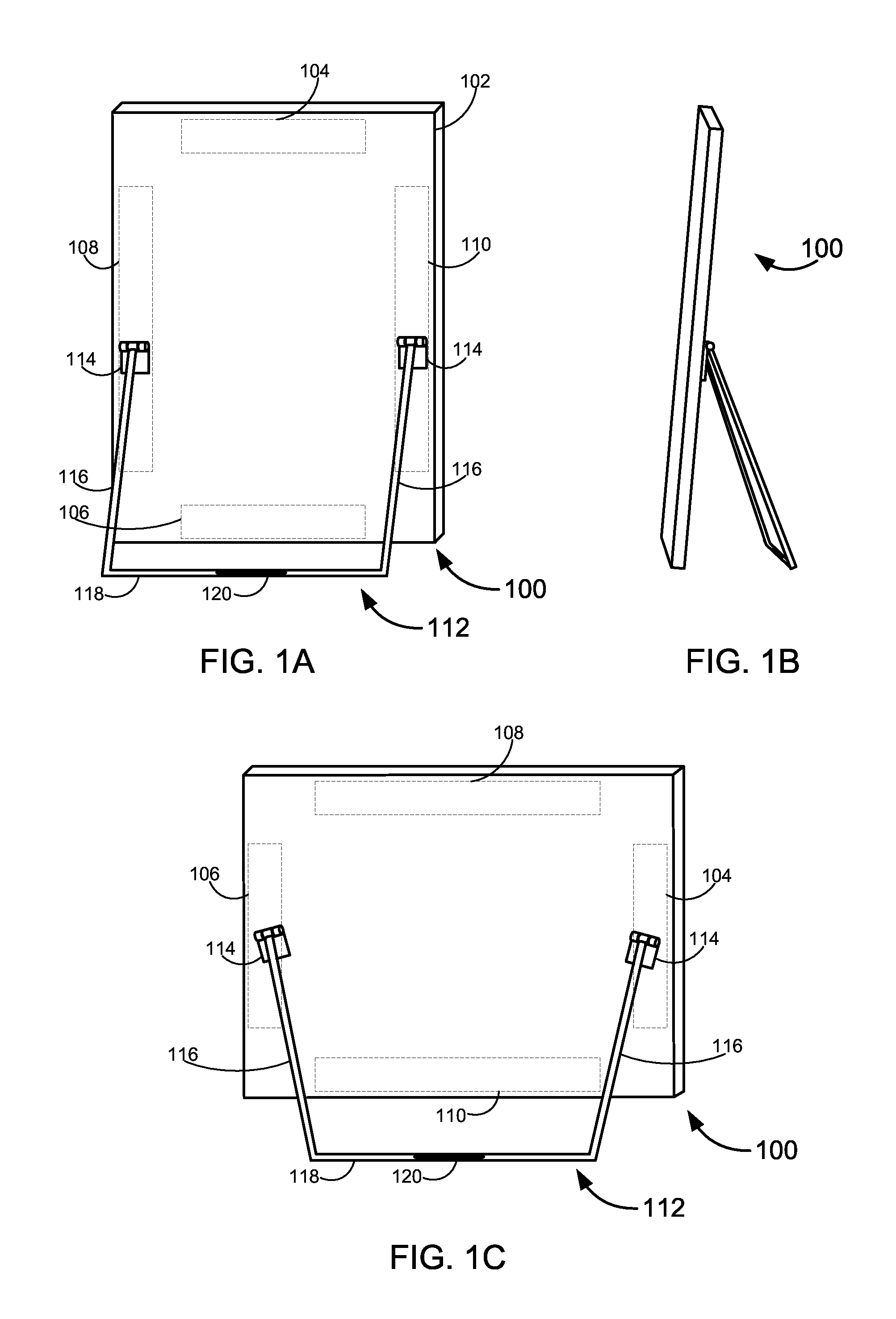
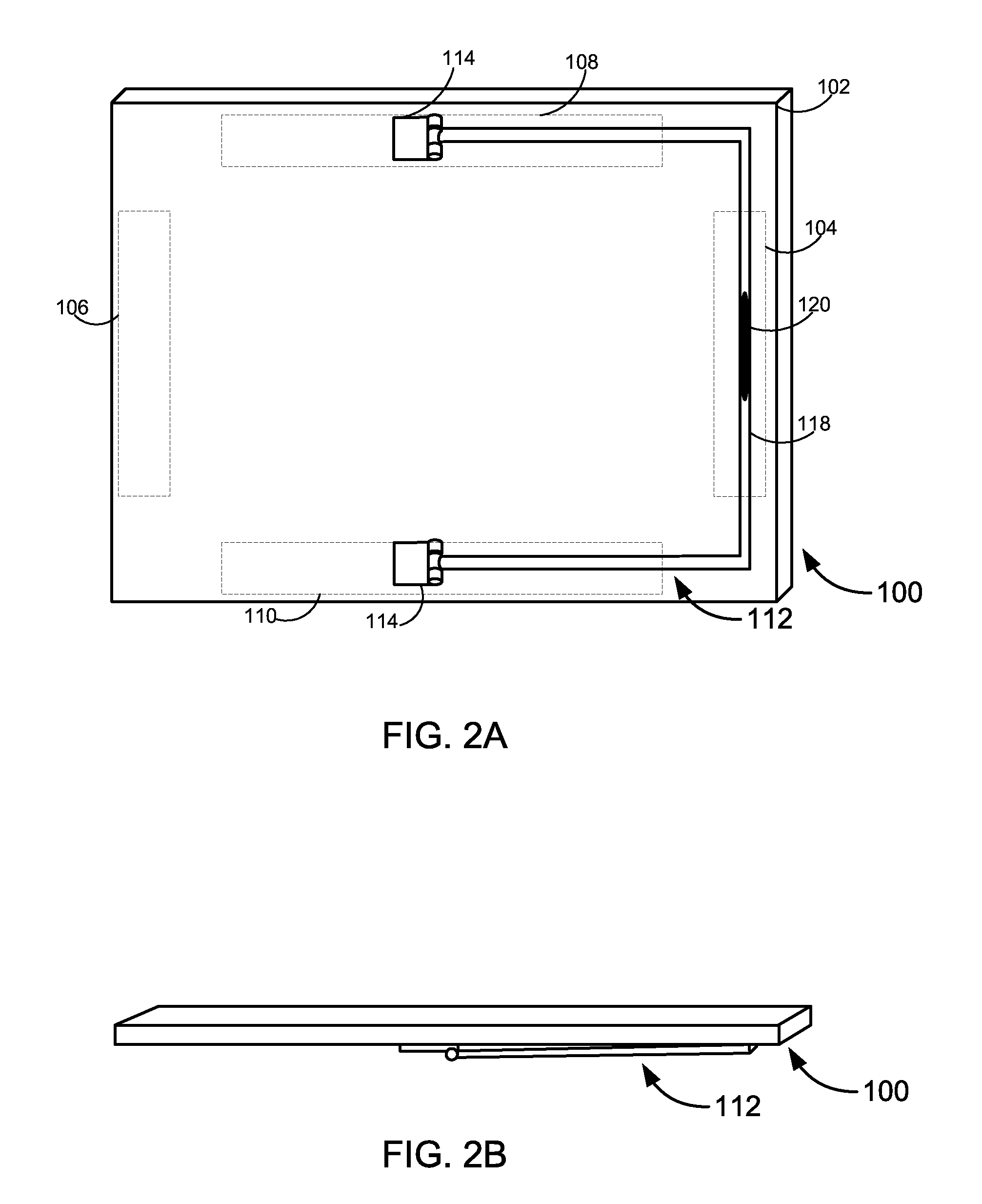
Integrated Magnetic Tablet Stand
Novel stands for tablet computers and other electronic devices. A stand for a tablet may comprise a body having one or more attachment mechanisms at one location and a crossbar at a second location. The crossbar may comprise a portion of a first material disposed to magnetically interact with a portion of a second material that is provided by the tablet. The magnetic interaction may cause the crossbar to serve as one or more detents that movably affixes the stand in a desired position relative to the tablet.
Owner:QWEST
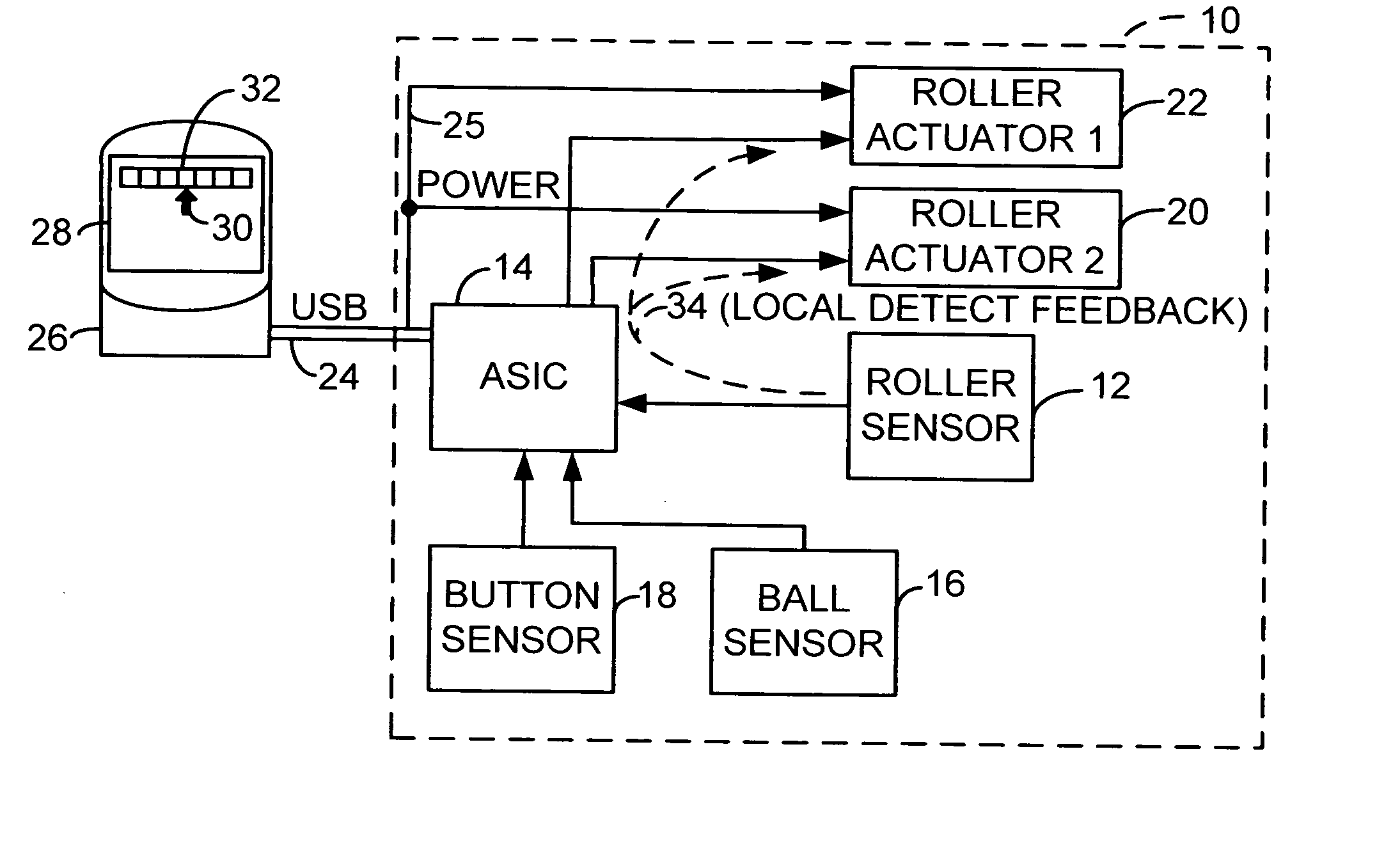
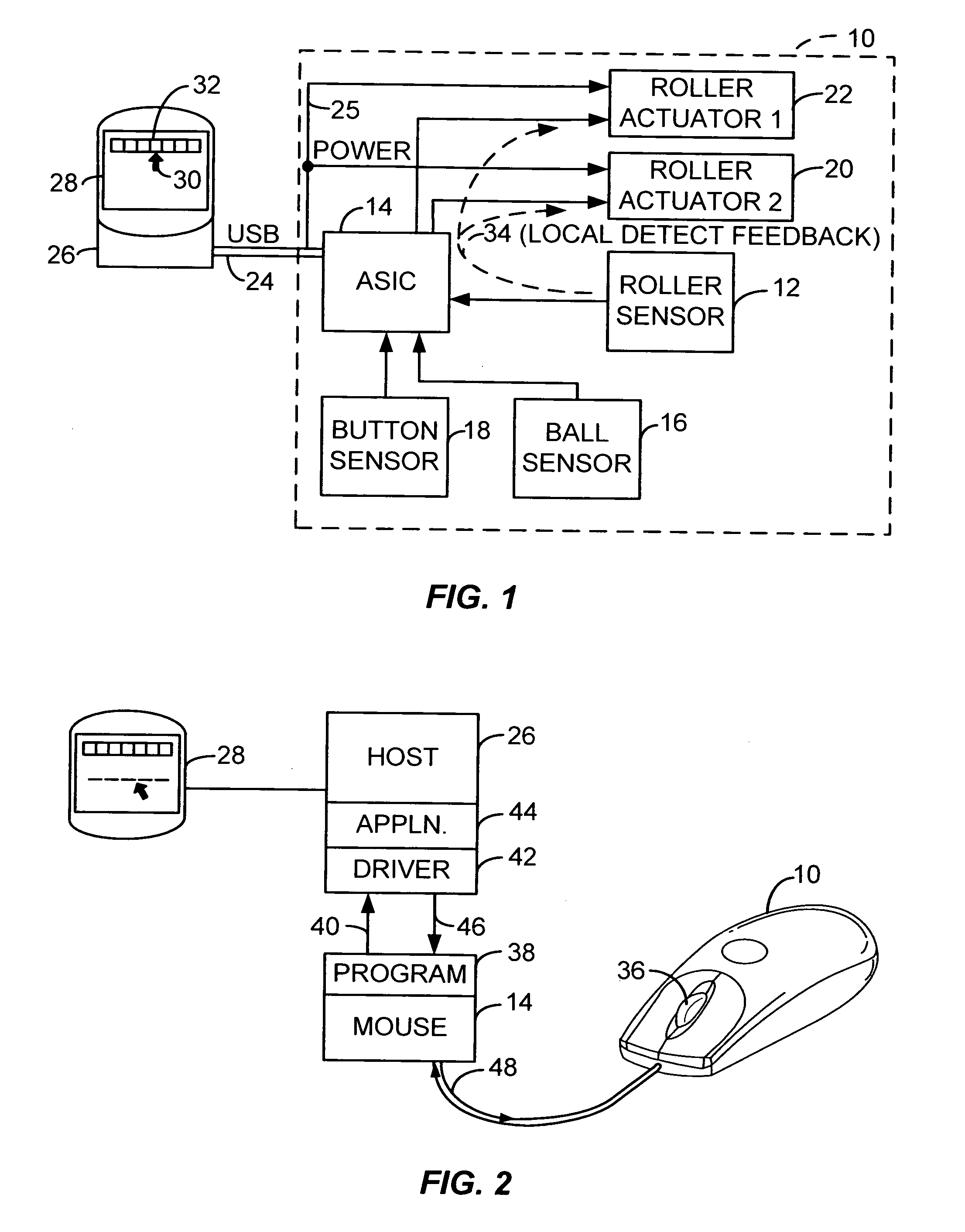
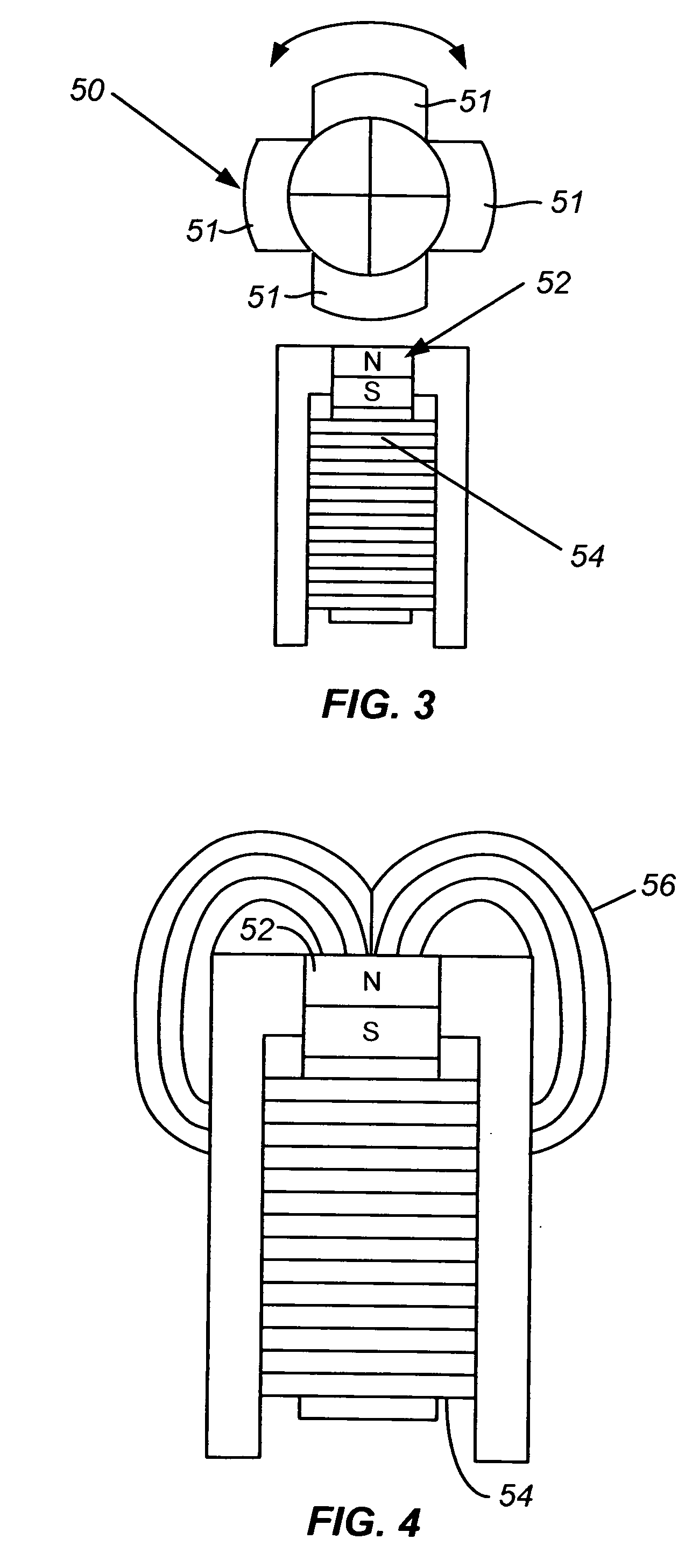
Input device roller with hybrid magnetic ratchet system
InactiveUS20070188453A1Easy scrollingStrength of spring can be adjustedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingMagnetic tension forceFreewheel
A rotatable wheel for an input device which interfaces with a computer. The input device includes both a permanent magnet and an electromagnet. A rotor of material which will magnetically interact with the permanent magnet and electromagnet is coupled to the rotatable wheel. The permanent magnet and electromagnet can be used to control a ratchet force applied to the rotatable wheel. In an alternate embodiment, a rotatable wheel with a flywheel is engaged with a roller. A ratchet wheel can be intermittently engaged with the flywheel to provide a ratchet force. By disengaging the ratchet wheel, the flywheel can be allowed to spin, providing momentum to allow for easier scrolling in certain conditions, such as for scrolling through a long document.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Magnetically actuated endoscope coupler
An endoscopic coupler by which the rotary and / or linear motion of an external ring is transferred via magnetic interaction of specially configured continuous plastic magnets to a lens resident in a hermetically sealed housing to effect focusing and / or zooming action of the lens without mechanically breaching the integrity of the hermetic seal thereby making the coupler particularly suitable for withstanding the rigors of autoclaving.
Owner:LIGHTHOUSE IMAGING
Eliminating mechanical spring with magnetic forces
InactiveUS20060267933A1Feel smoothImprove abilitiesCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingMagnetic tension forceCircular disc
Magnetic force is used to re-center a puck in a pointing device or similar transducer-based device. A user can apply finger pressure to move the puck laterally away from the central position. The puck has a first magnet system, and the base of the device has a second magnet system. The magnetic repulsion or other magnetic interaction returns the puck to a central position when the user removes the finger pressure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Device, systems and methods having mobile ferromagnetic structures
InactiveUS20070144531A1Prevent tissue collapseSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCombined useEngineering
A carrier is sized and configured for placement in or on a tissue region. The carrier includes at least one interior compartment. At least one ferromagnetic material is carried within the compartment. The compartment and the ferromagnetic material are mutually sized and configured to allow movement of the ferromagnetic material within the compartment in response to magnetic interaction with a magnetic material located outside the carrier. The magnetic interaction can include either a magnetic attracting force or a magnetic repelling force. The carrier can be used in association with a source of magnetism sized and configured for placement in or on a tissue region outside the carrier for magnetic interaction with the ferromagnetic material carried within the compartment, e.g., to stabilize the orientation of a tissue region within an airway.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
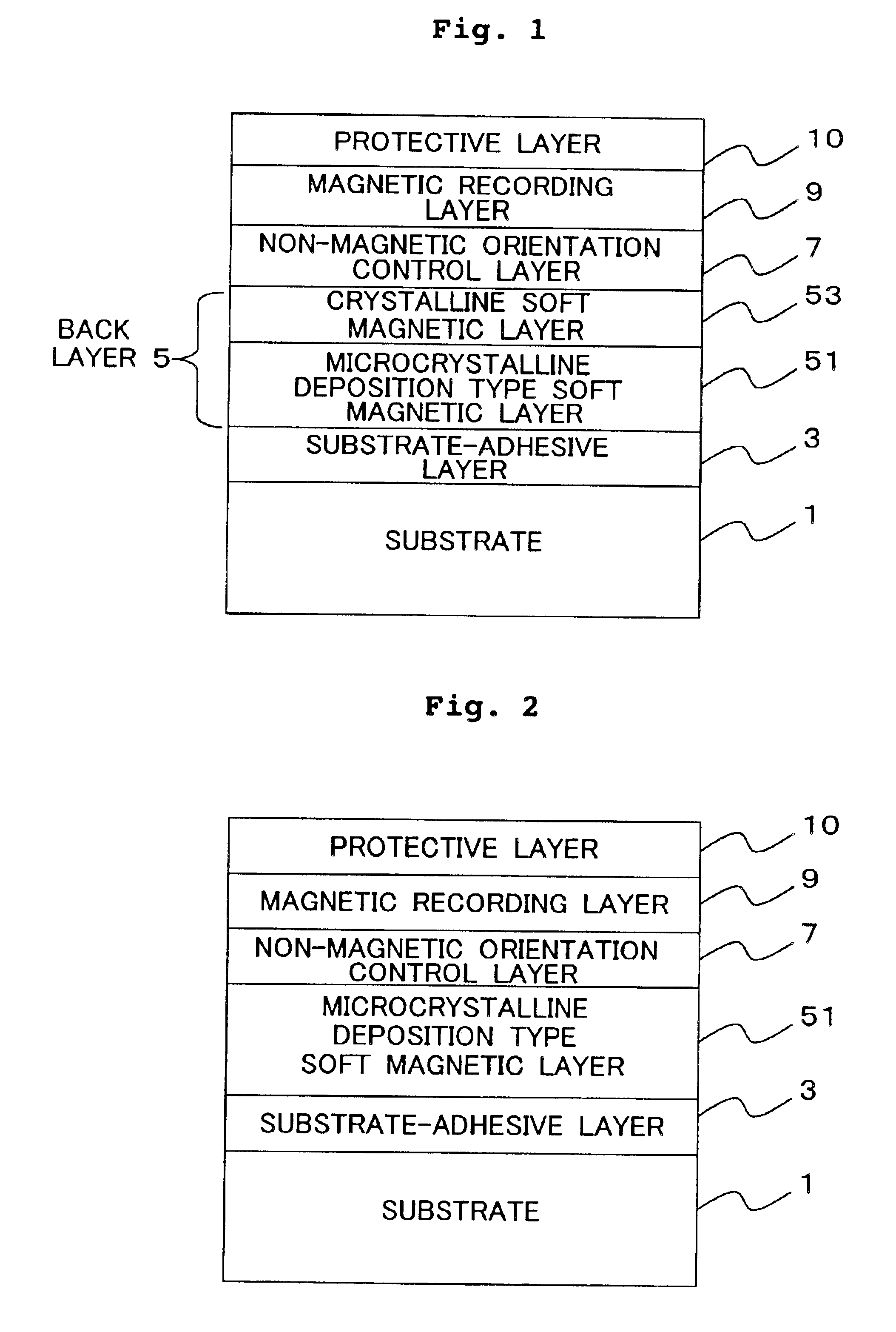
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording apparatus
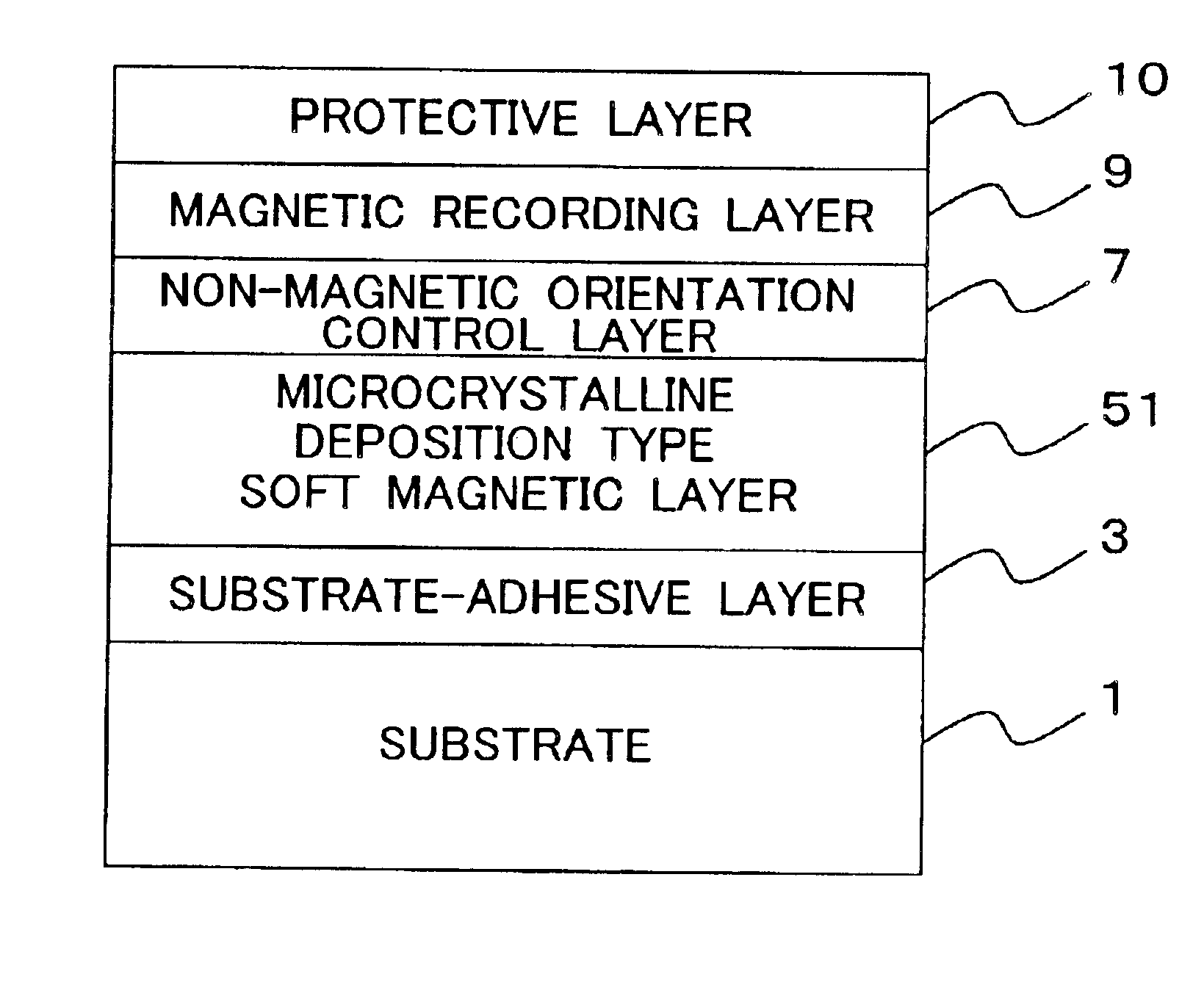
InactiveUS6846583B2Improve thermal stabilityResistant to thermal thermal demagnetizationBase layers for recording layersCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsAlloyRecording layer
A magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic recording layer 63 which is formed by using an ordered alloy containing B on a substrate 1 containing an amorphous component. A part of B in the ordered alloy is segregated in a grain boundary, and thus the magnetic interaction, which acts between magnetic grains, can be reduced. Accordingly, it is possible to form fine and minute magnetic domains in the magnetic recording layer 63, and it is possible to reduce the medium noise as well. The temperature, at which the substrate is heated during the film formation of the magnetic recording layer 63, can be suppressed to be low, because the ordering temperature for the ordered alloy containing B is lower than those of ordered alloys not containing B. Therefore, it is possible to use a substrate made of glass which is suitable for the mass production. The magnetic recording layer 63 is also excellent in thermal stability because of the use of the ordered alloy having high magnetic anisotropy. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide the magnetic recording medium for high density recording which is excellent in thermal stability and which involves low medium noise.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Method of molding a multi-pole magnetized beverage container holder
InactiveUS7897088B2Decrease magnetic force of attractionPicture framesWash-standsEngineeringMagnetic interaction
A beverage container holder is disclosed which includes a magnet within the sleeve of a beverage container holder. The beverage container holder, along with any beverage container placed in the beverage container holder, may be mounted on any mounting surface having an associated ferrous material. The beverage container holder is held in place due to the force of the magnetic interaction between the magnet and the mounting surface.
Owner:ELWARD LOUIS JOINT VENTURE
Apparatus for securing ornamentation to personal items
Owner:MODERN MUSE
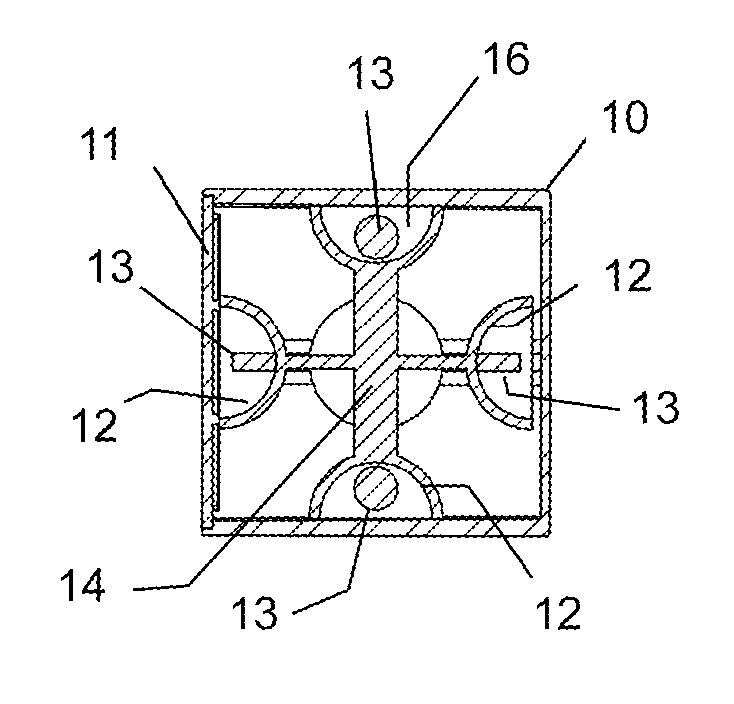
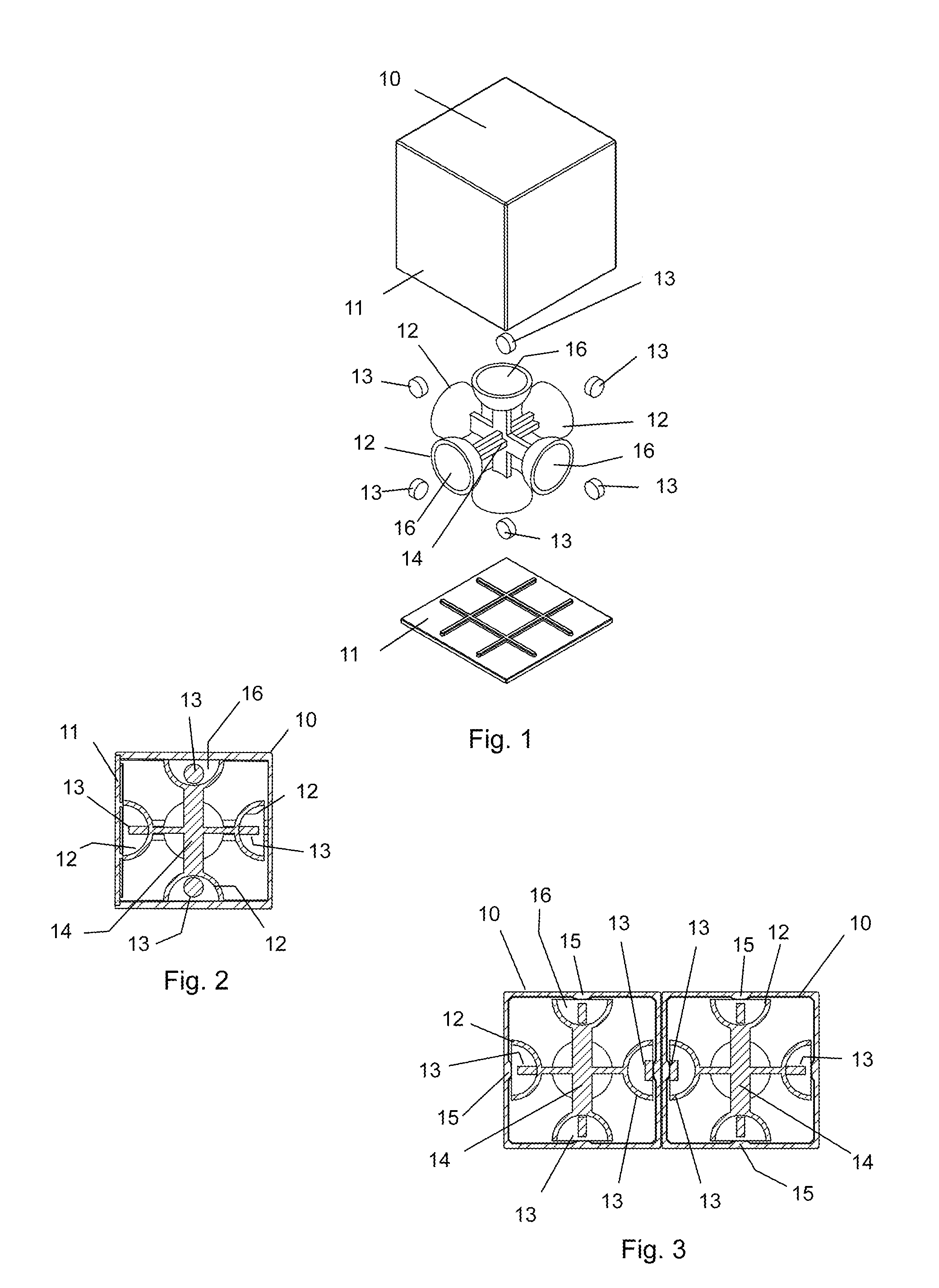
Magnetic Toy Block
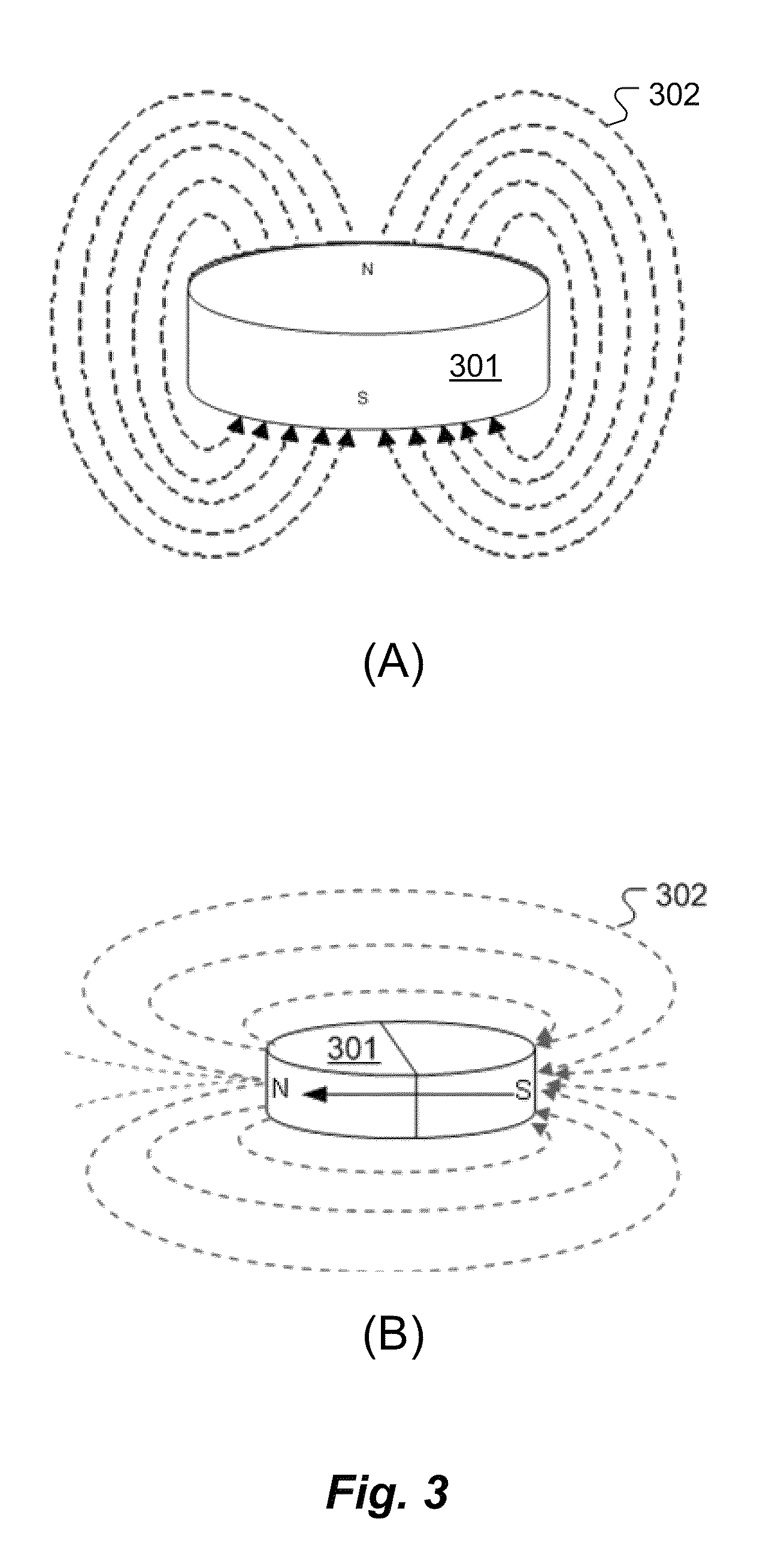
A toy block includes a body having external faces. A compartment is located behind each of the external faces and houses a magnet located freely within the compartment and adapted to turn upon magnetic interaction with another magnet external of the body so as to align attractively therewith. Two such toy blocks can be brought together face-to-face in any orientation and the magnet of one block will turn automatically into N-S alignment with a magnet of the other block so that the blocks attract and connect.
Owner:HOP LEE CHEONG INDAL
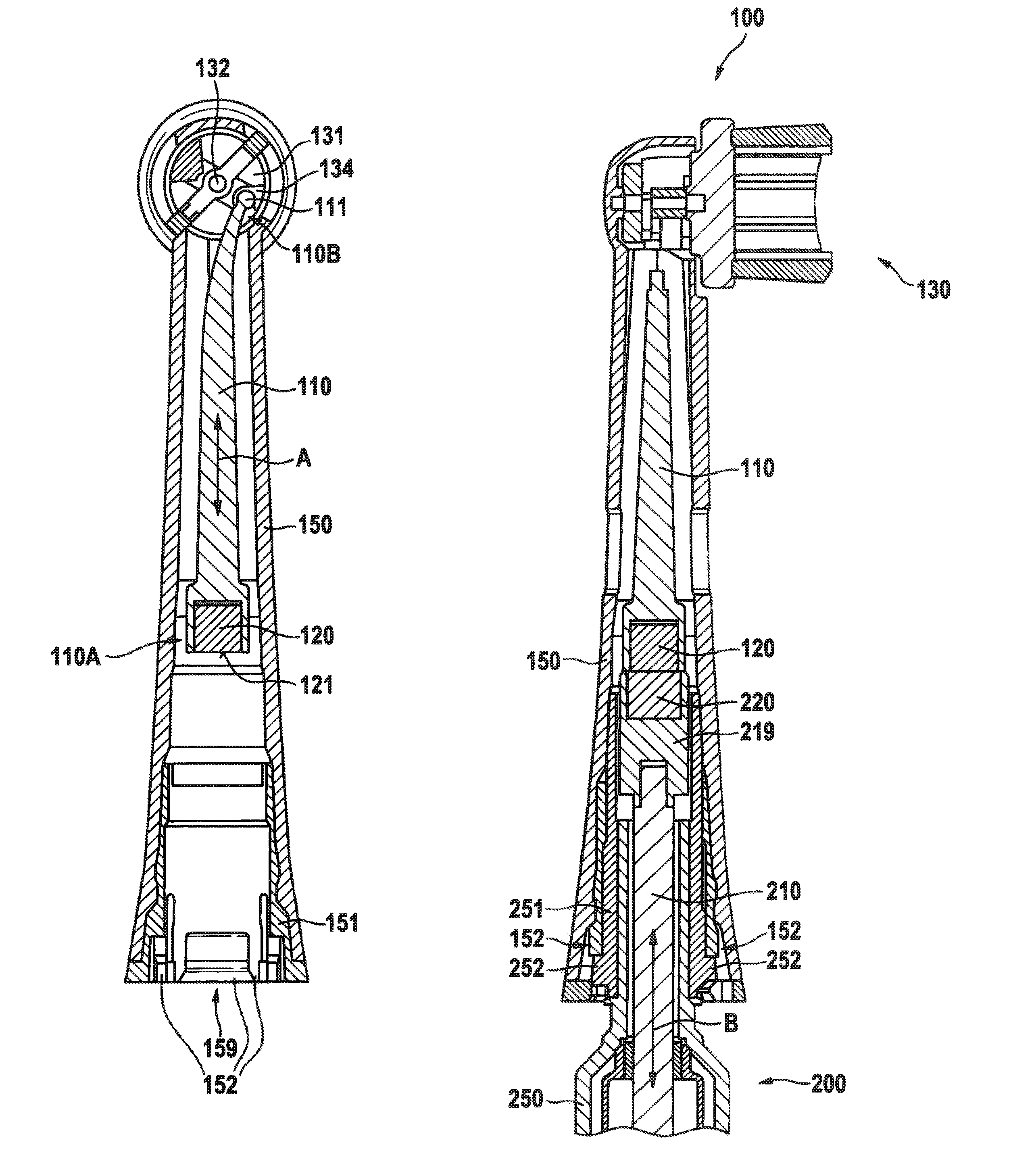
Connection and alignment detection systems and methods
A medical device includes a first housing portion (FHP) and a second housing portion (SHP) configured to be to be movable relative to each other from a first position to operatively engage at a second position to couple at least one of a drive device and a needle-inserting device supported by one of the FHP and the SHP to a reservoir supported by the other of the FHP and the SHP. Electronic circuitry configured to detect at least one of a first magnetic interaction between a magnet and at least one of a first magnetically attractive material and a first magnet-responsive device and a second magnetic interaction between the magnet and at least one of a second magnetically attractive material and a second magnet-responsive device, and to provide a signal or a change in state in response to detecting at least one of the interactions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
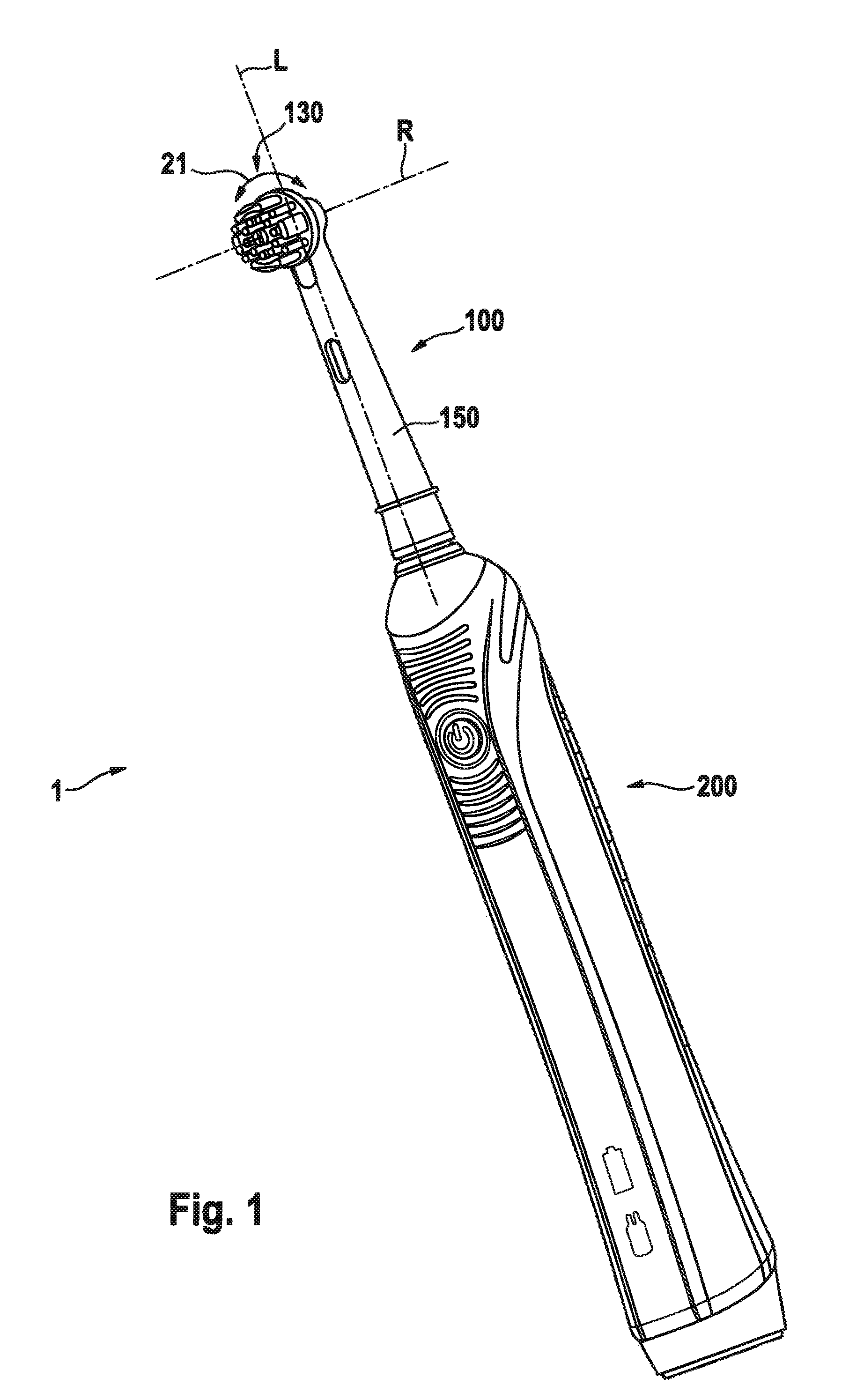
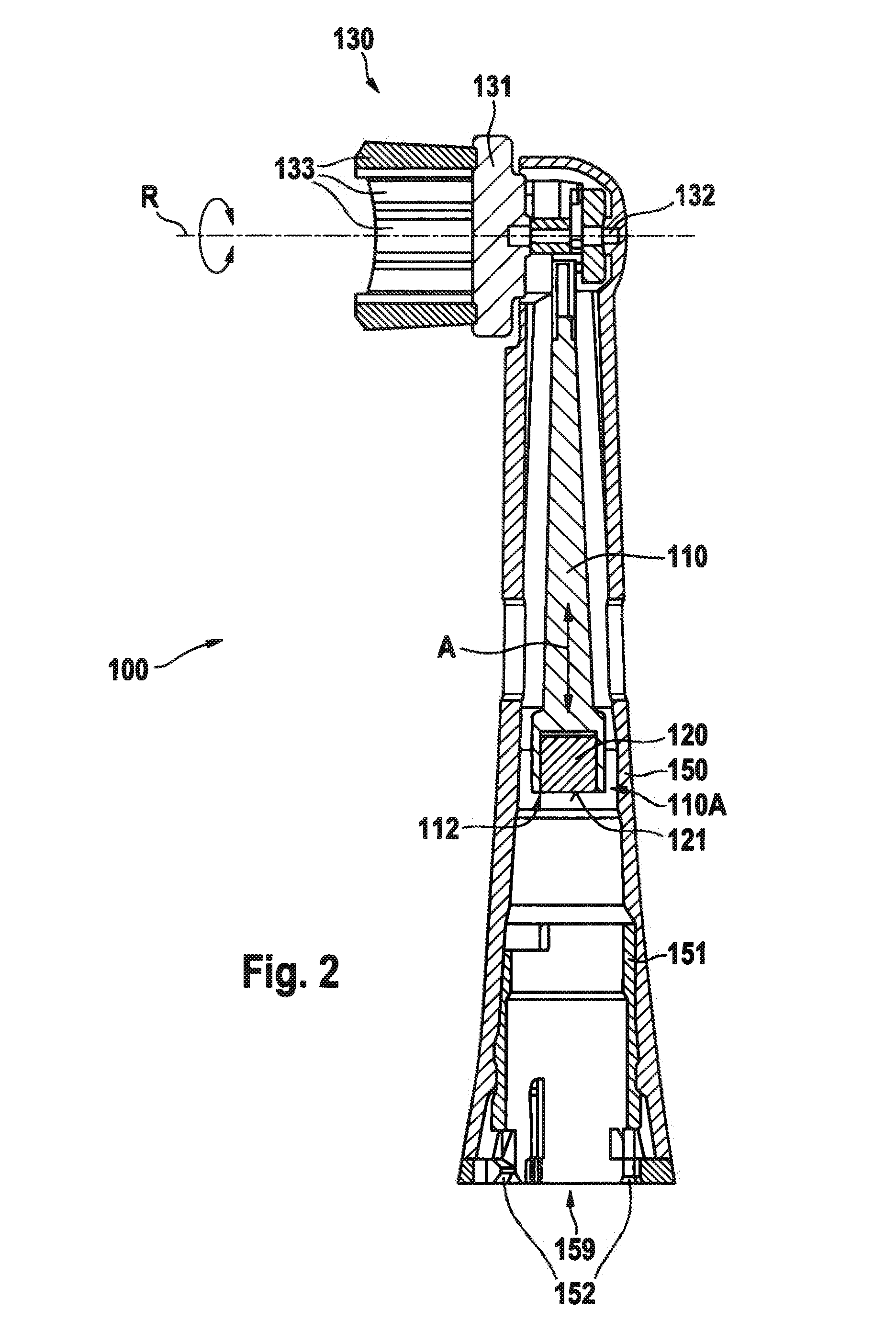
Oral hygiene device
An oral cleaning tool for an electric oral hygiene device is disclosed. The oral cleaning tool includes a housing having a head section with a head cavity for accommodating a movable oral cleaning head and a neck section with a neck cavity and a handle coupling section; a first magnetic coupling element including at least a permanent magnet or a magnetizable element being provided in the neck section for mechanical handle drive shaft connection by magnetic interaction. The first magnetic coupling element is mounted at a motion transmitter, the motion transmitter extending inside the neck cavity to the head cavity, the motion transmitter arranged so as to be movable in a linear or longitudinal direction. The motion transmitter is coupled with the oral cleaning head, the oral cleaning head arranged so as to oscillate in a rotational direction.
Owner:BRAUN GMBH
Permanent magnet drive apparatus and operational method
InactiveUS8487484B1Magnetic circuitPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesMagnetic tension forcePush and pull
A magnetic drive apparatus includes first and second magnet carriers carrying first and second permanent magnet arrangements. An intermediate magnet carrier disposed between the first and second magnet carriers carries a third permanent magnet arrangement. The magnet carriers are arranged for rotation relative to each other such that the magnet arrangements produce magnetic interactions that result in power stroke forces causing the magnet carriers to undergo relative reciprocation in first and second stroke directions during power zone portions of the relative rotation. The magnetic interactions impart substantially no power stroke forces during dead zone portions of the relative rotation. The dead zones include magnet carrier relative rotation positions wherein opposing magnetic poles are mutually coaxially aligned but produce a substantially equal balance of push and pull magnetic forces. The apparatus may be synchronized so that the dead zones coincide with top dead center and bottom dead center relative reciprocation positions.
Owner:COLSON ANDREW E JR MR
Linear switch actuator
A linear switch actuator for actuating a movable element within a microwave switch includes a ferromagnetic shield, a coil positioned within, and a movable armature assembly positioned within the coil. The armature assembly is coupled to the movable element and includes a ferromagnetic rod and first and second permanent magnets. The permanent magnets are coupled on either end of the rod and have opposite pole orientations. The armature assembly moves between first and second stroke end positions. When one of the permanent magnets is positioned substantially outside the shield, the magnetic permeance of the armature assembly is maximized, and the armature assembly experiences bi-stable latching between the two stroke end positions. When the coil is energized, the armature assembly moves between these positions due to magnetic interaction between the energized coil and the field associated with the permanent magnets and the solenoid magnetic field associated with the coil which reduces the magnetic permeance associated with said armature assembly.
Owner:HONEYWELL LIMITED HONEYWELL LIMITÉE
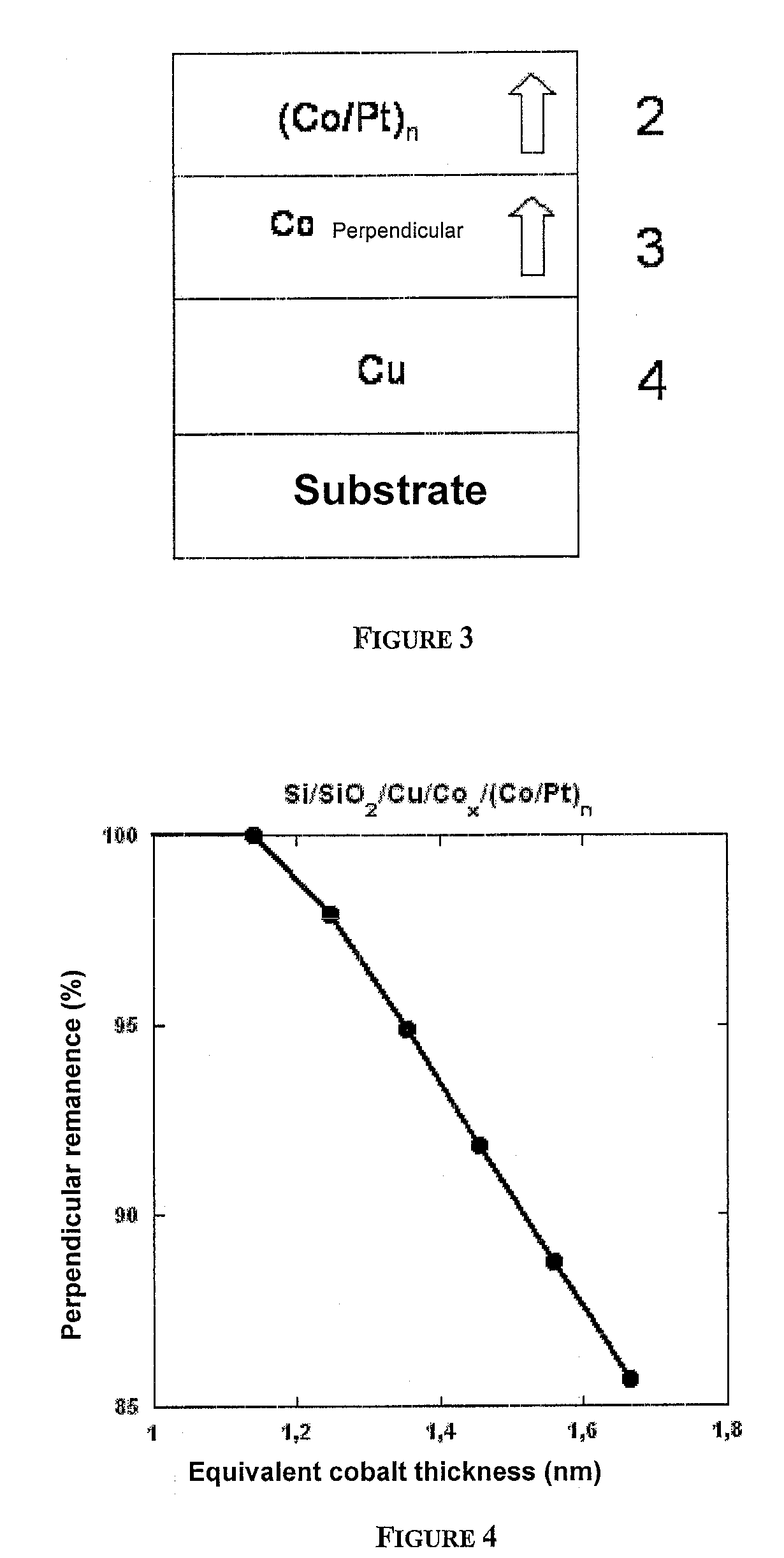
Thin-film magnetic device with strong spin polarization perpendicular to the plane of the layers, magnetic tunnel junction and spin valve using such a device
ActiveUS7813202B2Optimize spin polarizationImprove polarizationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeHigh rate
A thin-film magnetic device comprises, on a substrate, a composite assembly deposited by cathode sputtering and consists of a first layer made of a ferromagnetic material with a high rate of spin polarization, the magnetization of which is in plane in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, a second layer made of a magnetic material with high perpendicular anisotropy, the magnetization of which is outside the plane of said layer in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, and coupling of which with said first layer induces a decrease in the effective demagnetizing field of the entire device, a third layer that is in contact with the first layer via its interface opposite to that which is common to the second layer and made of a material that is not magnetic and not polarizing for electrons passing through the device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
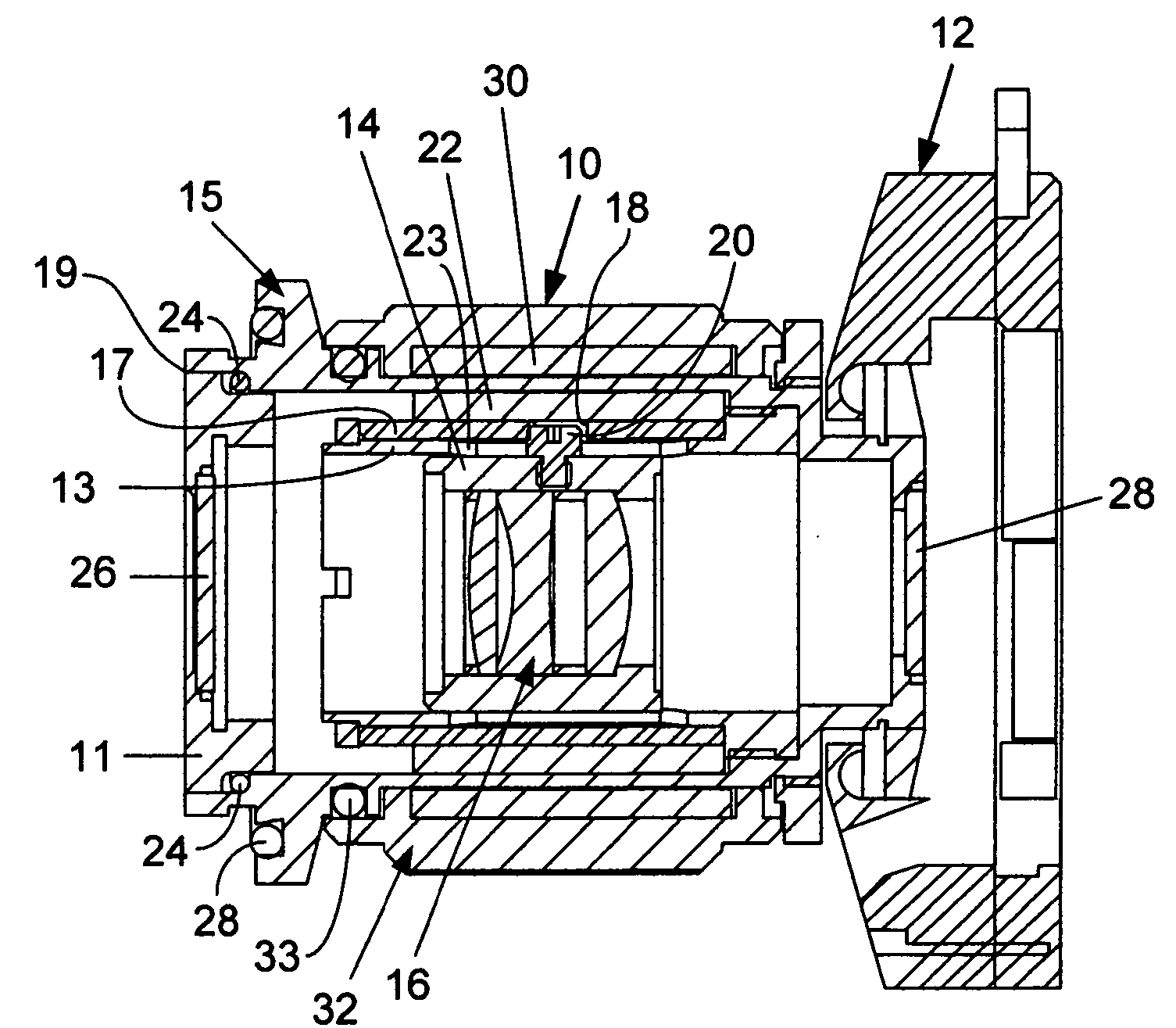
Gripping device for containers
ActiveUS7784603B2Reduce forceReduce percentageCharge manipulationLiquid bottlingBottleMagnetic interaction
Owner:KRONES AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com