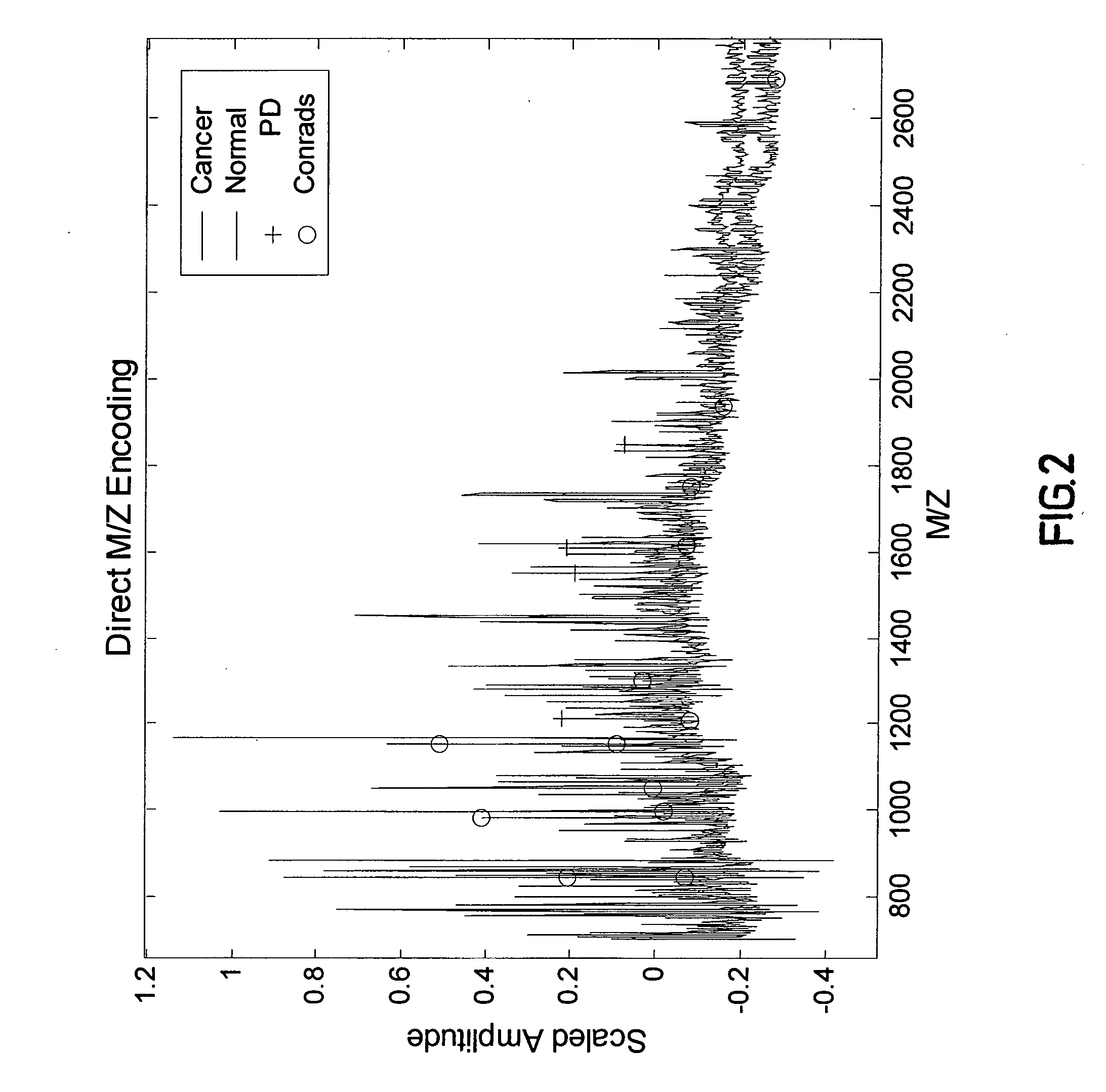
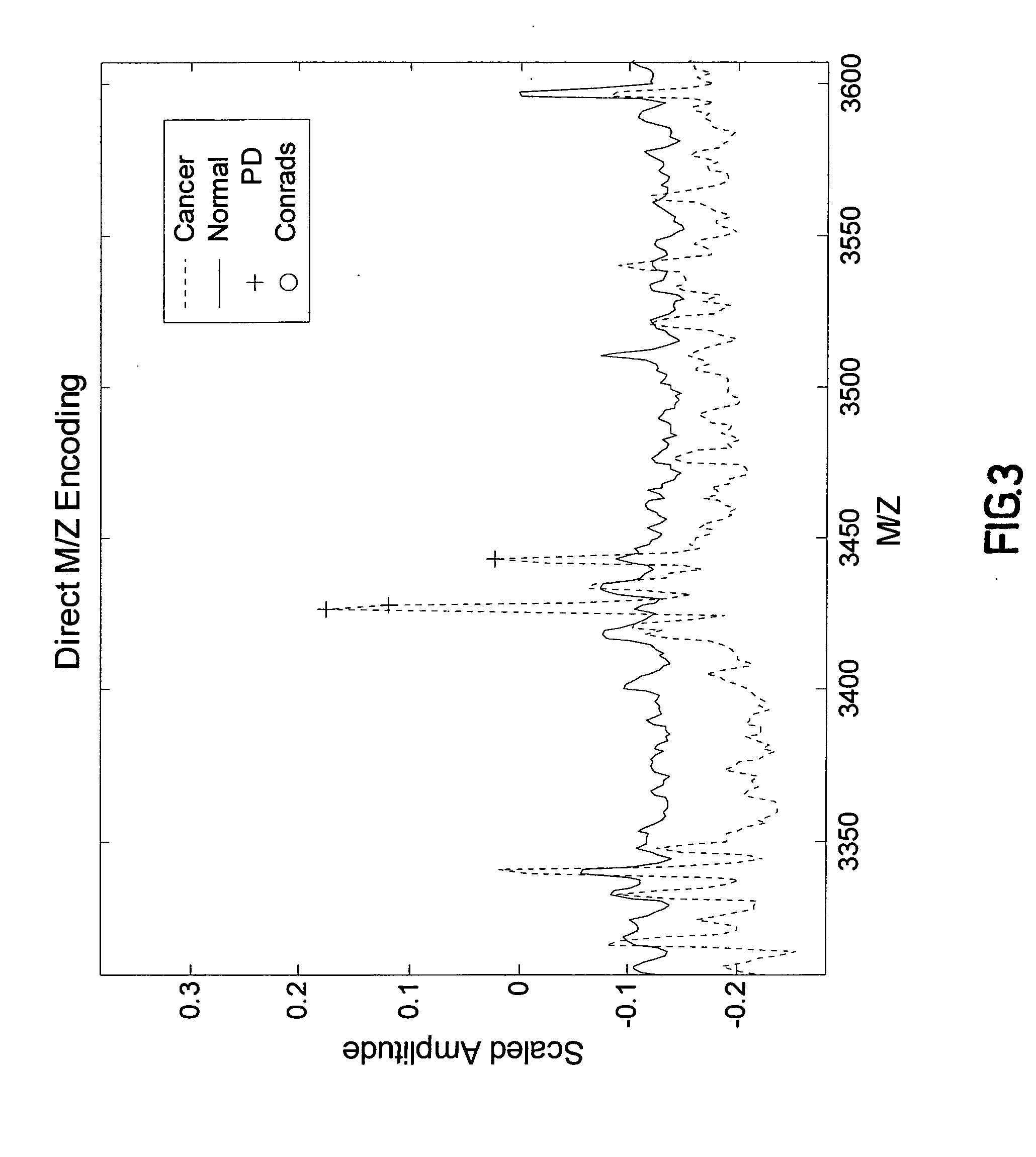
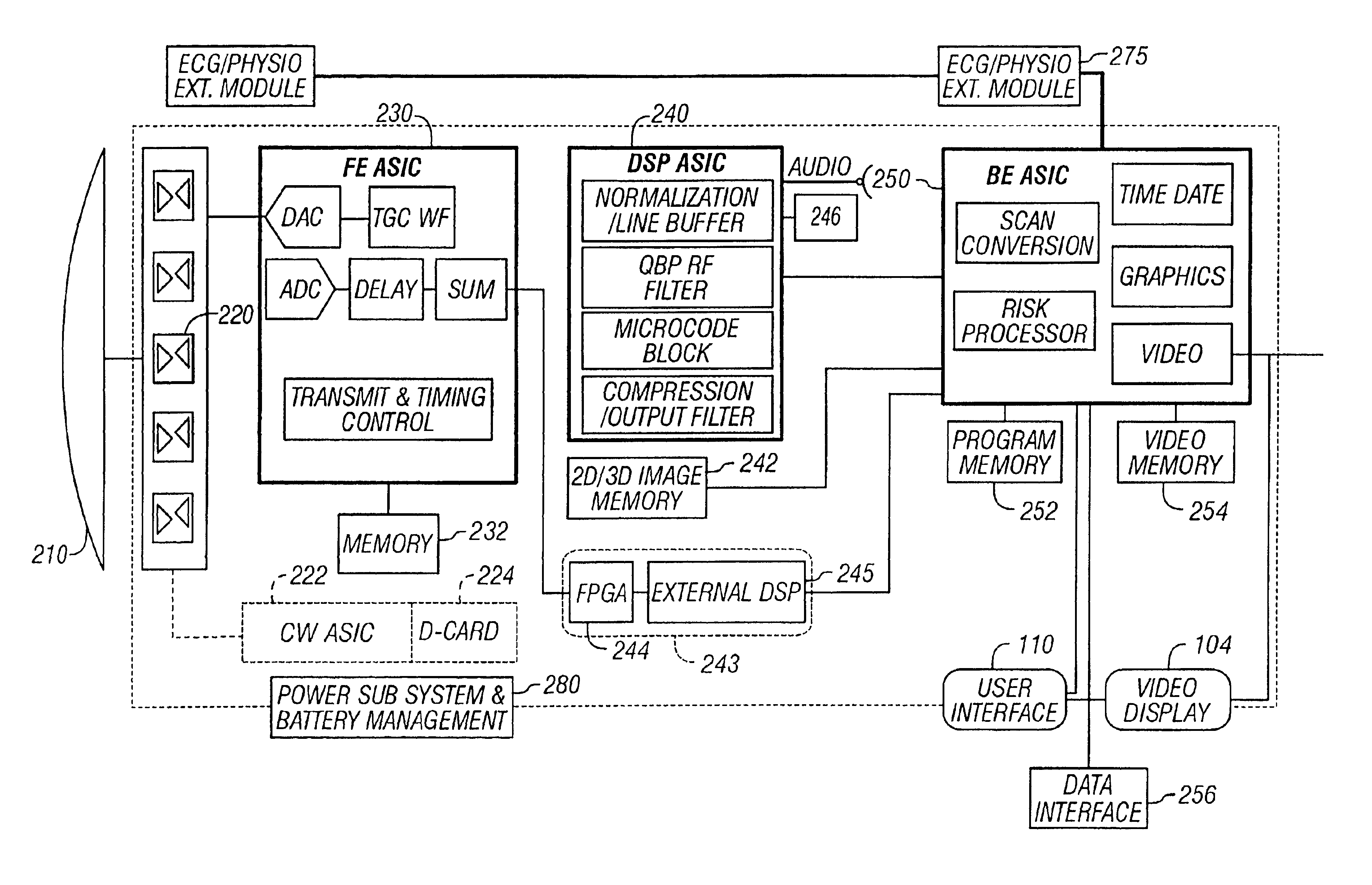
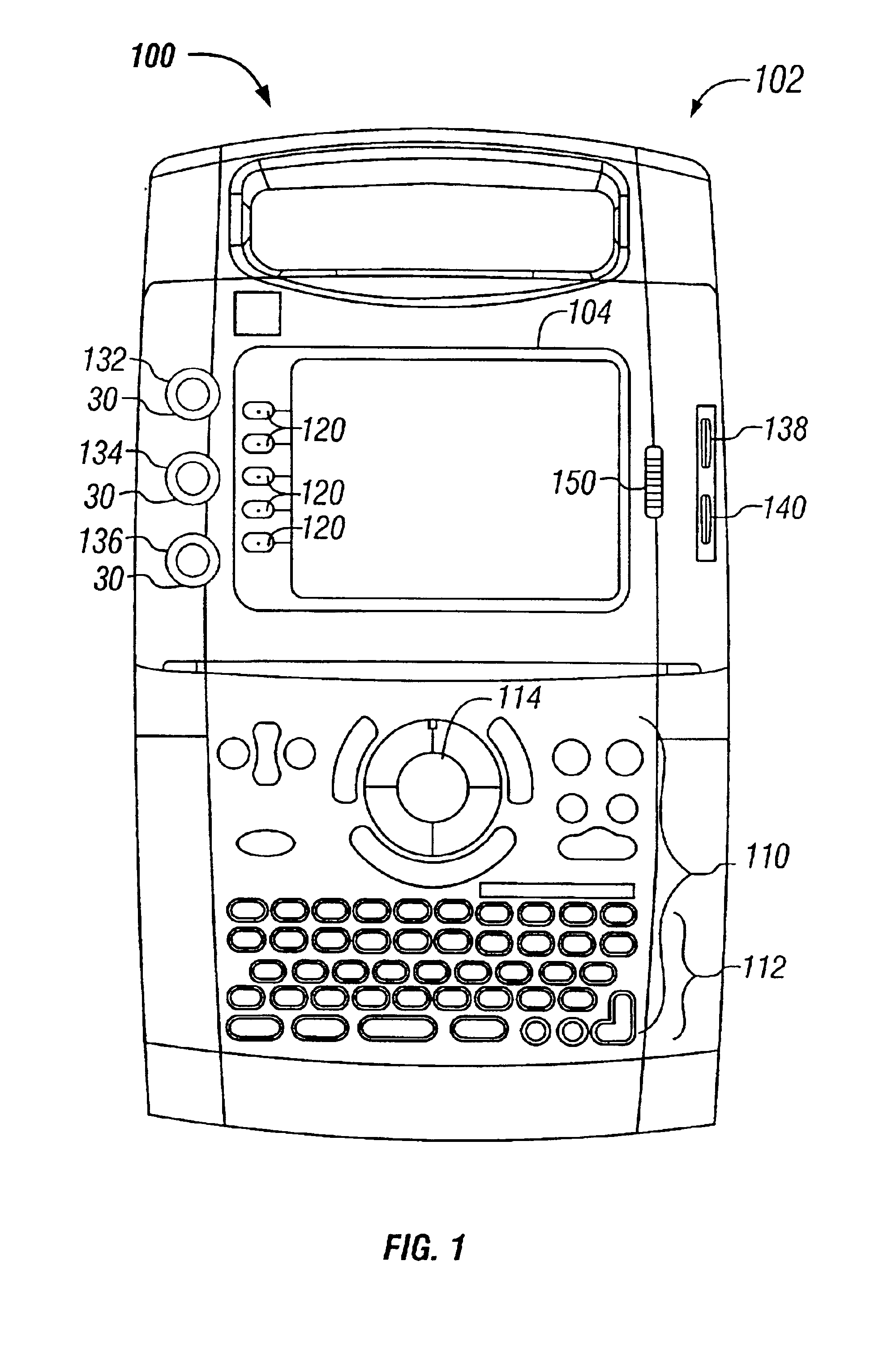
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1358 results about "Medical diagnostic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
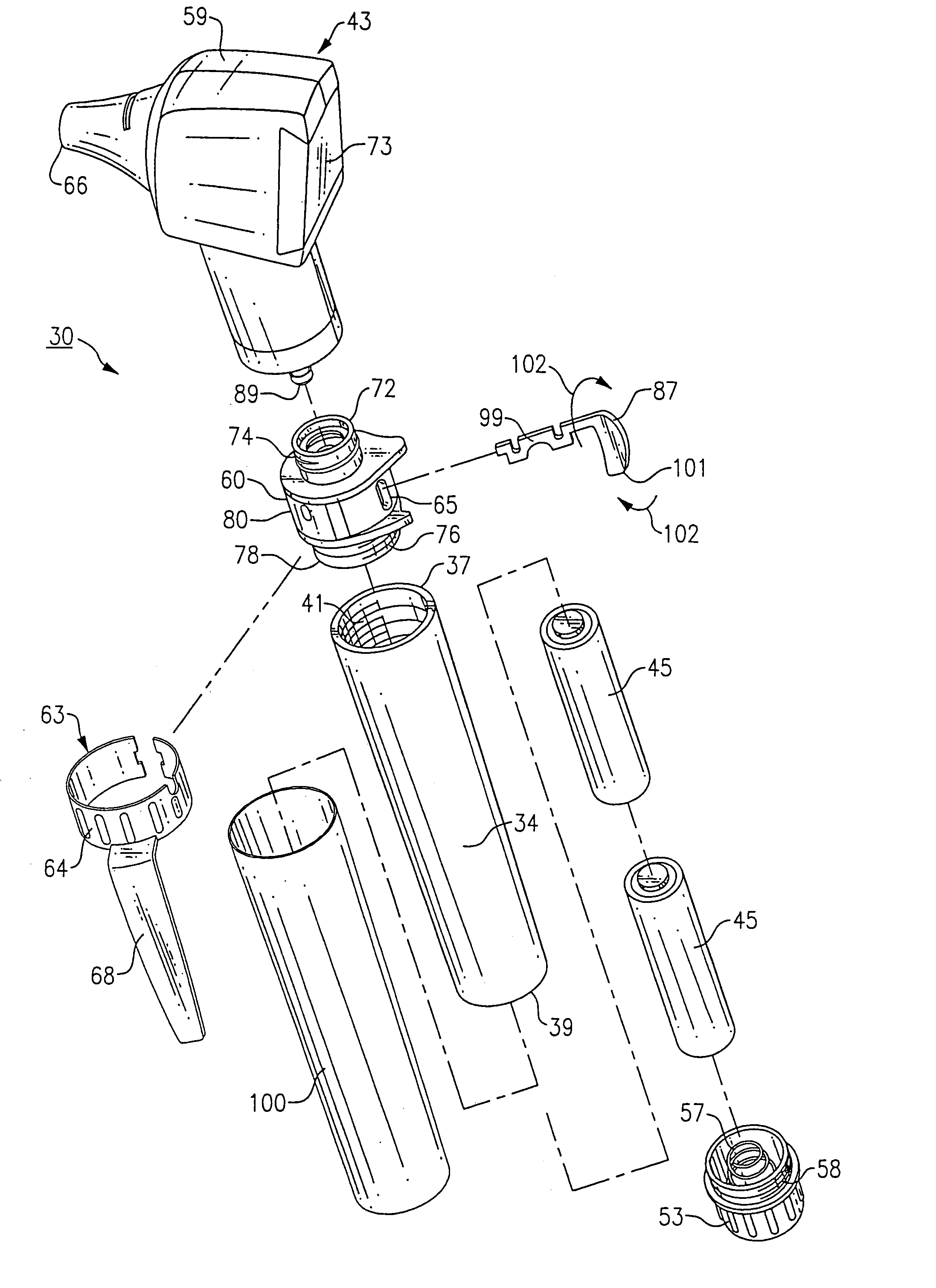
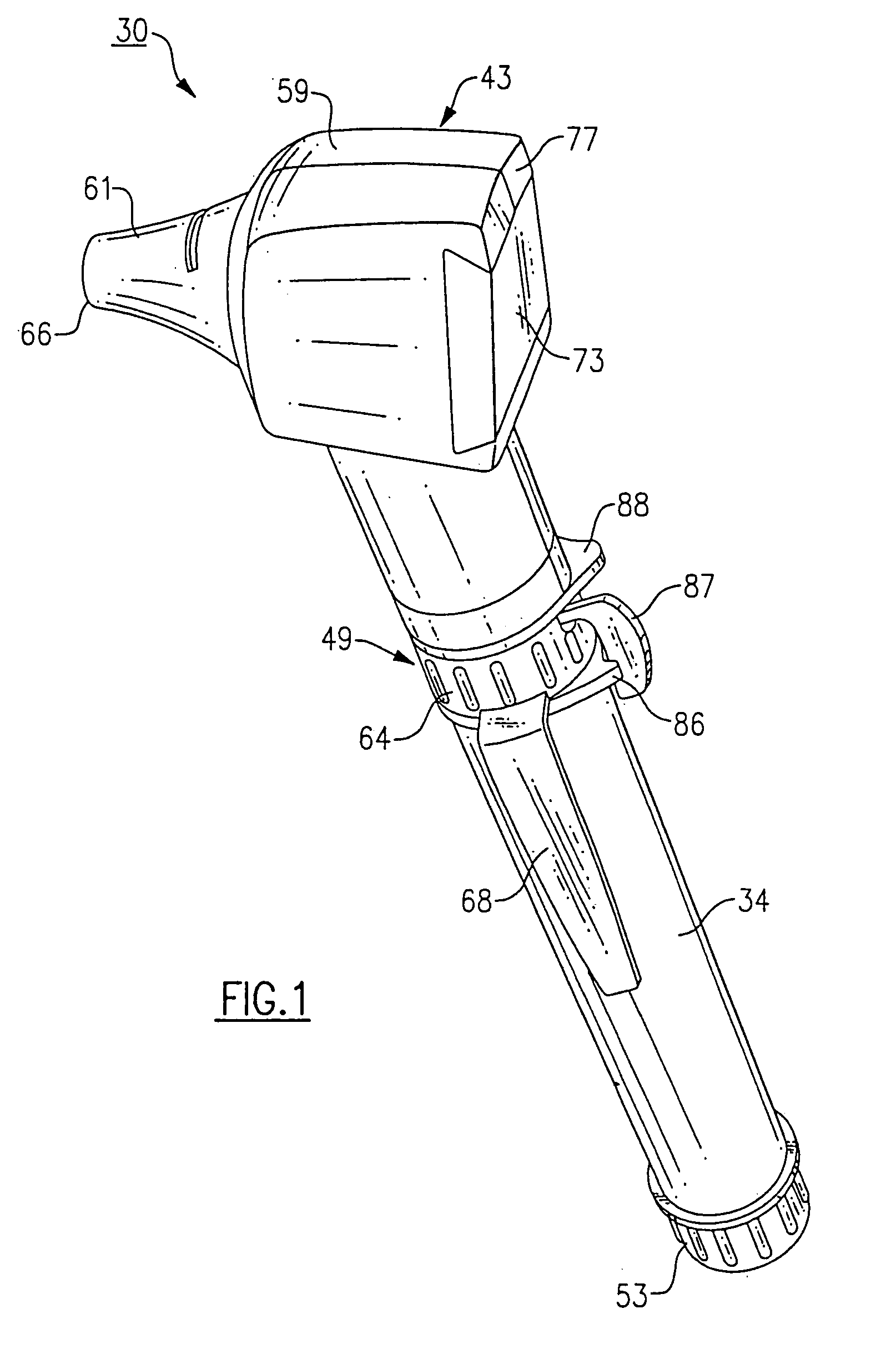
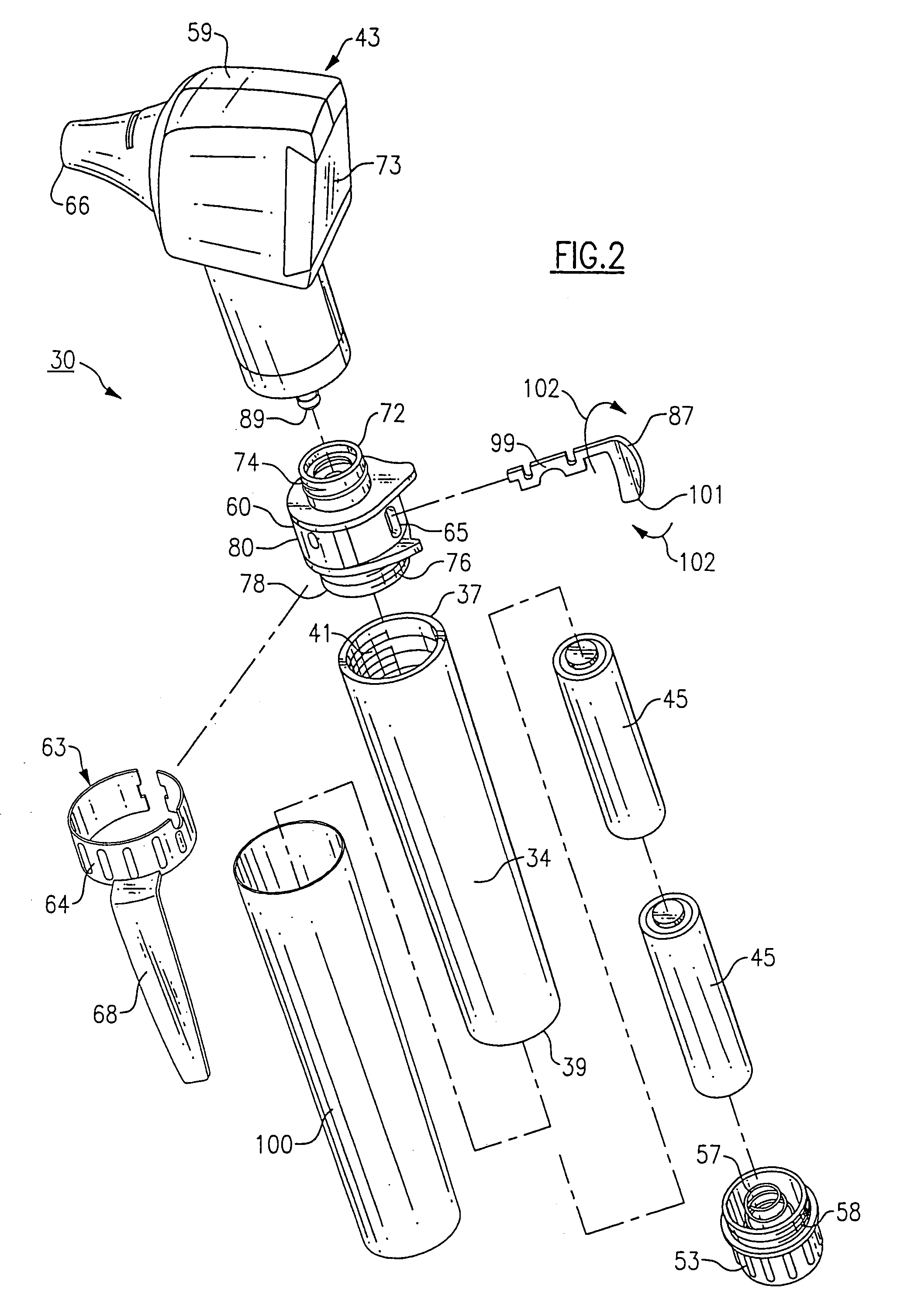
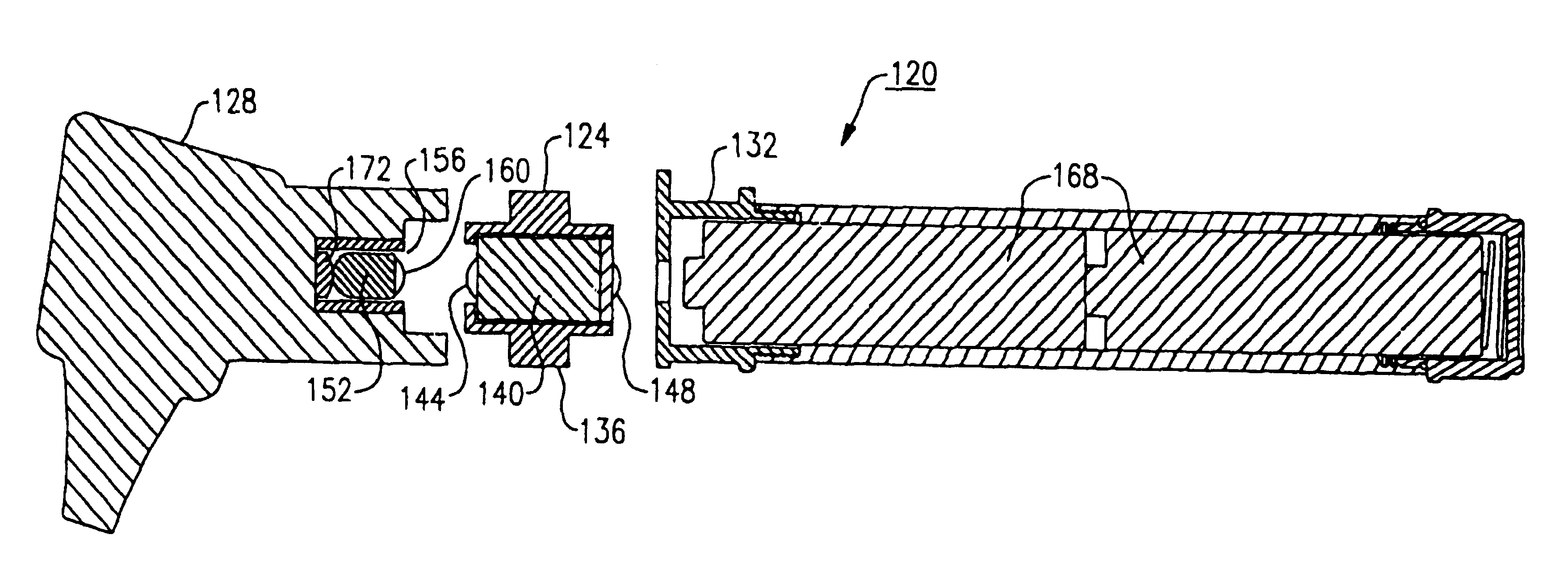
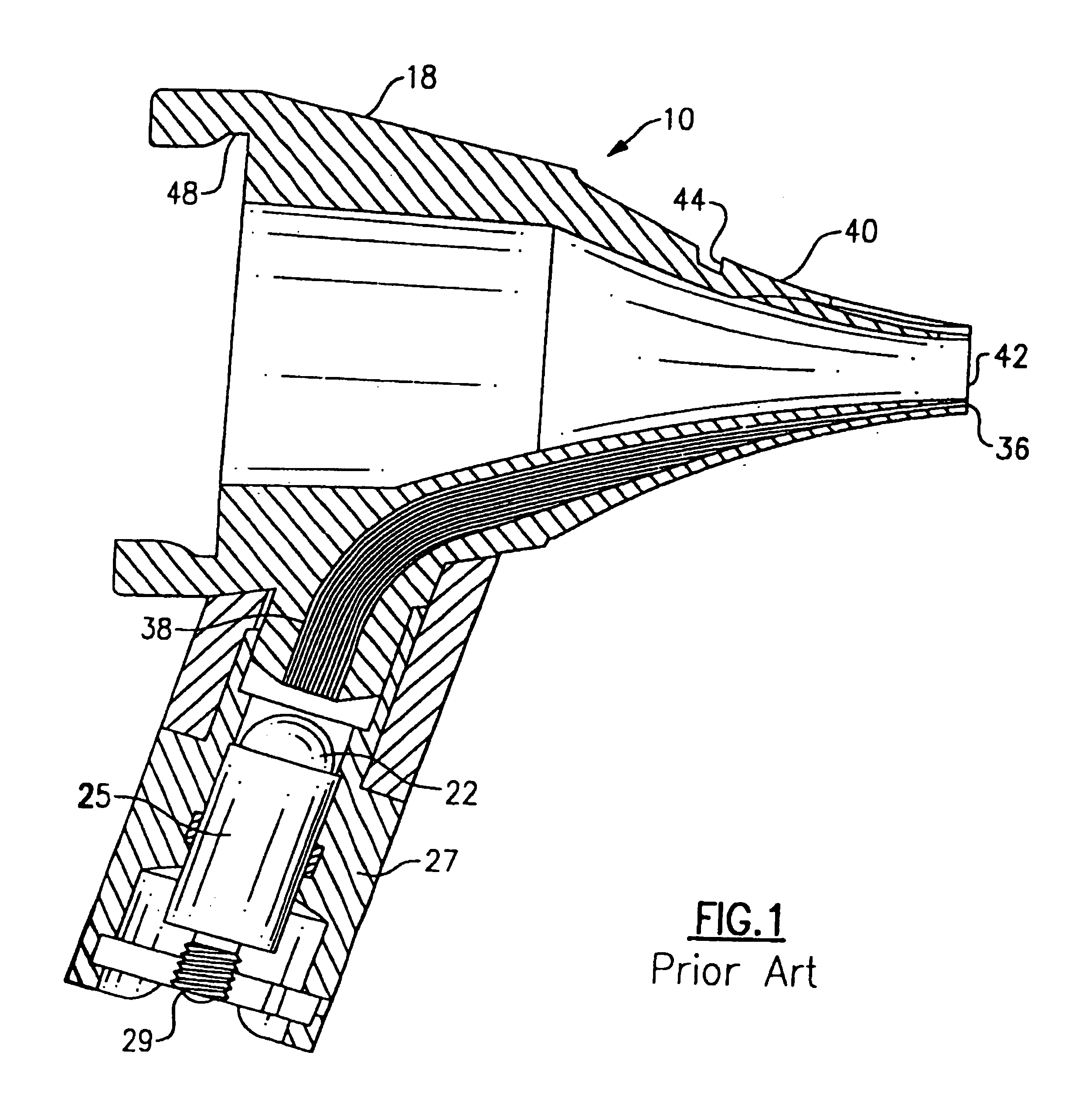
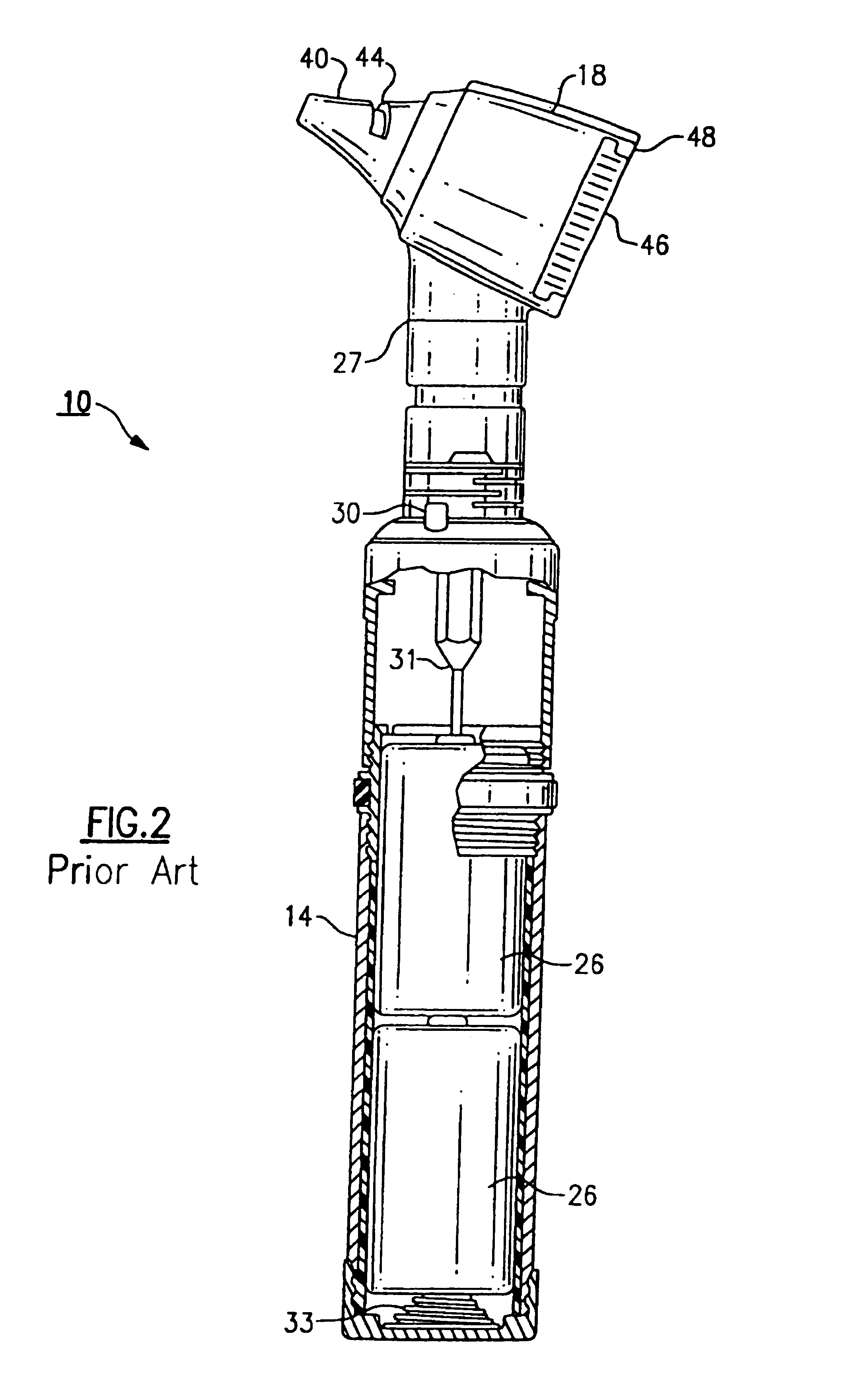
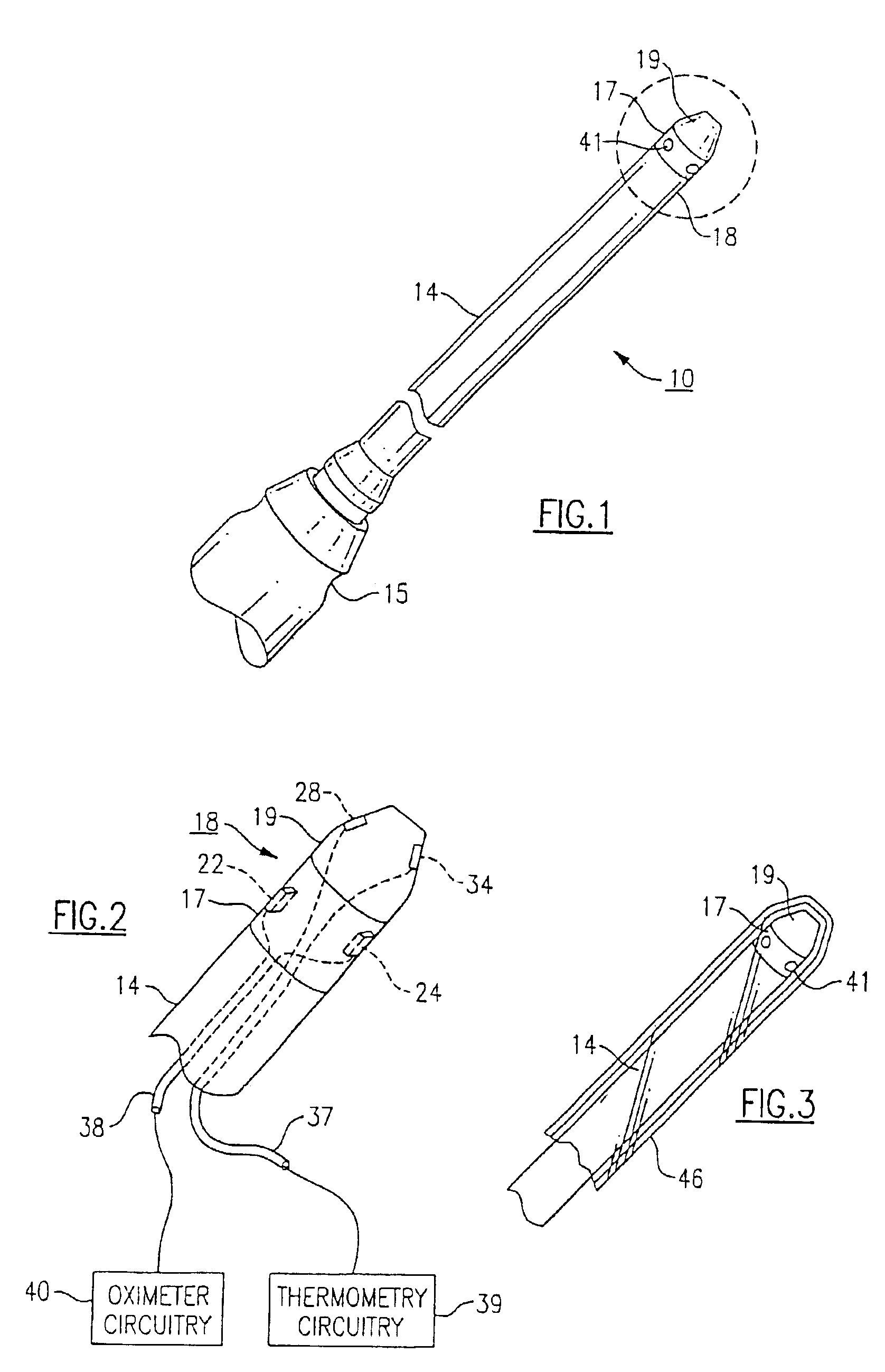
Medical diagnostic instrument
InactiveUS7029439B2Easy to manufactureImprove versatilityBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesElectricityElectrical connection
A medical diagnostic instrument includes a housing containing at least one battery and a light source, such as a lamp, for illuminating a medical target. A switch includes a movable member that selectively moves at least one of the battery and the lamp into and out of electrical connection with the other. The instrument is preferably fabricated from a diecast or an extrusion process wherein a thin plastic sleeve member having text and / or graphic materials can be shrink fitted onto an extruded handle.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Medical Diagnostic and Treatment Platform Using Near-Field Wireless Communication of Information Within a Patient's Body
ActiveUS20080306359A1Efficient communicationSmall sizeElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit arrangementsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides implantable systems that communicate wirelessly with each other using a unique format that enables devices configurations and applications heretofore not possible. Embodiments of the present invention provide communication apparatuses and methods for exchanging information with implantable medical devices. In some embodiments, two implantable devices communicate with each other using quasi-electrostatic signal transmission in a long wavelength / low frequency electromagnetic band, with the patient's body acting as a conductive medium.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
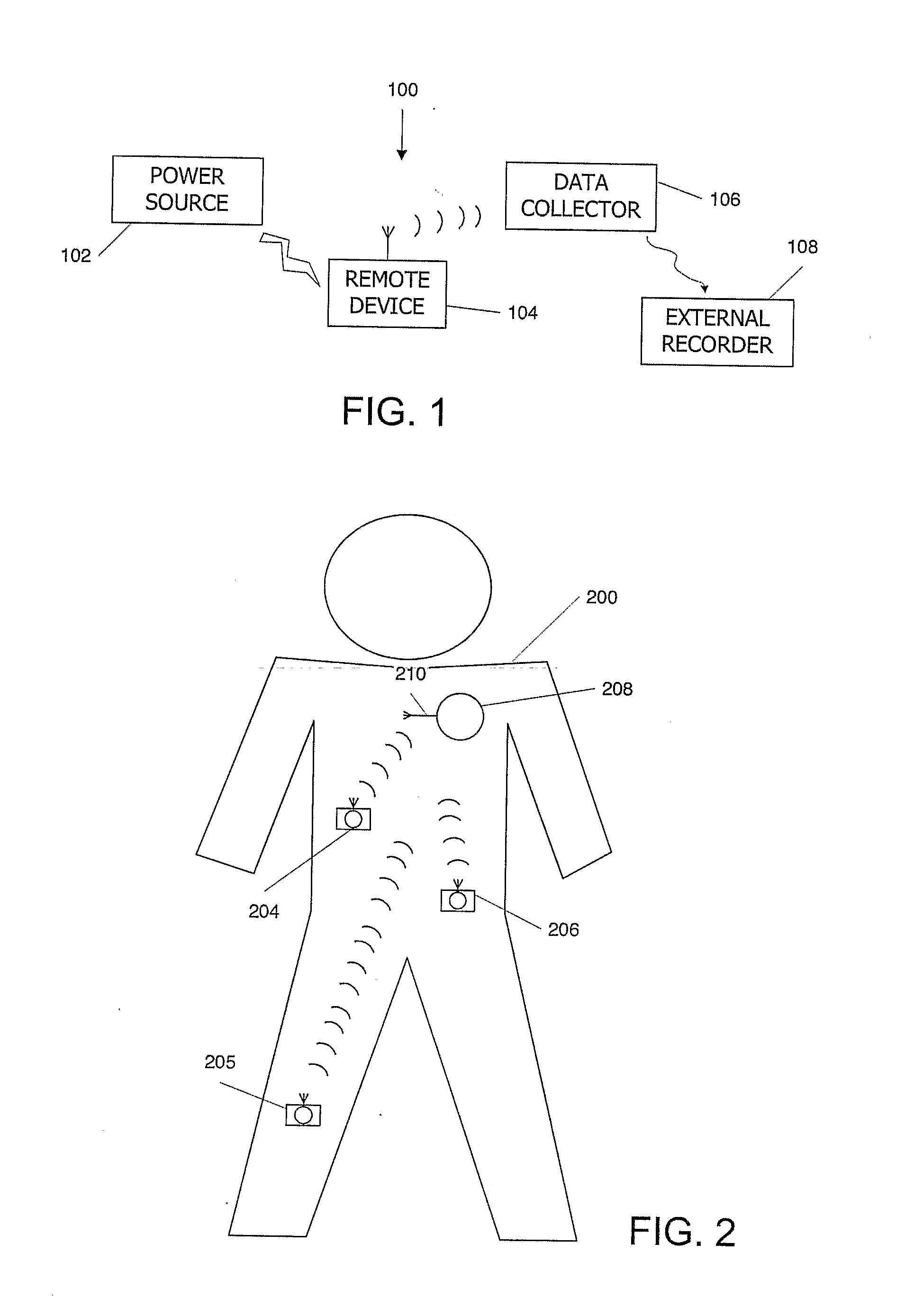
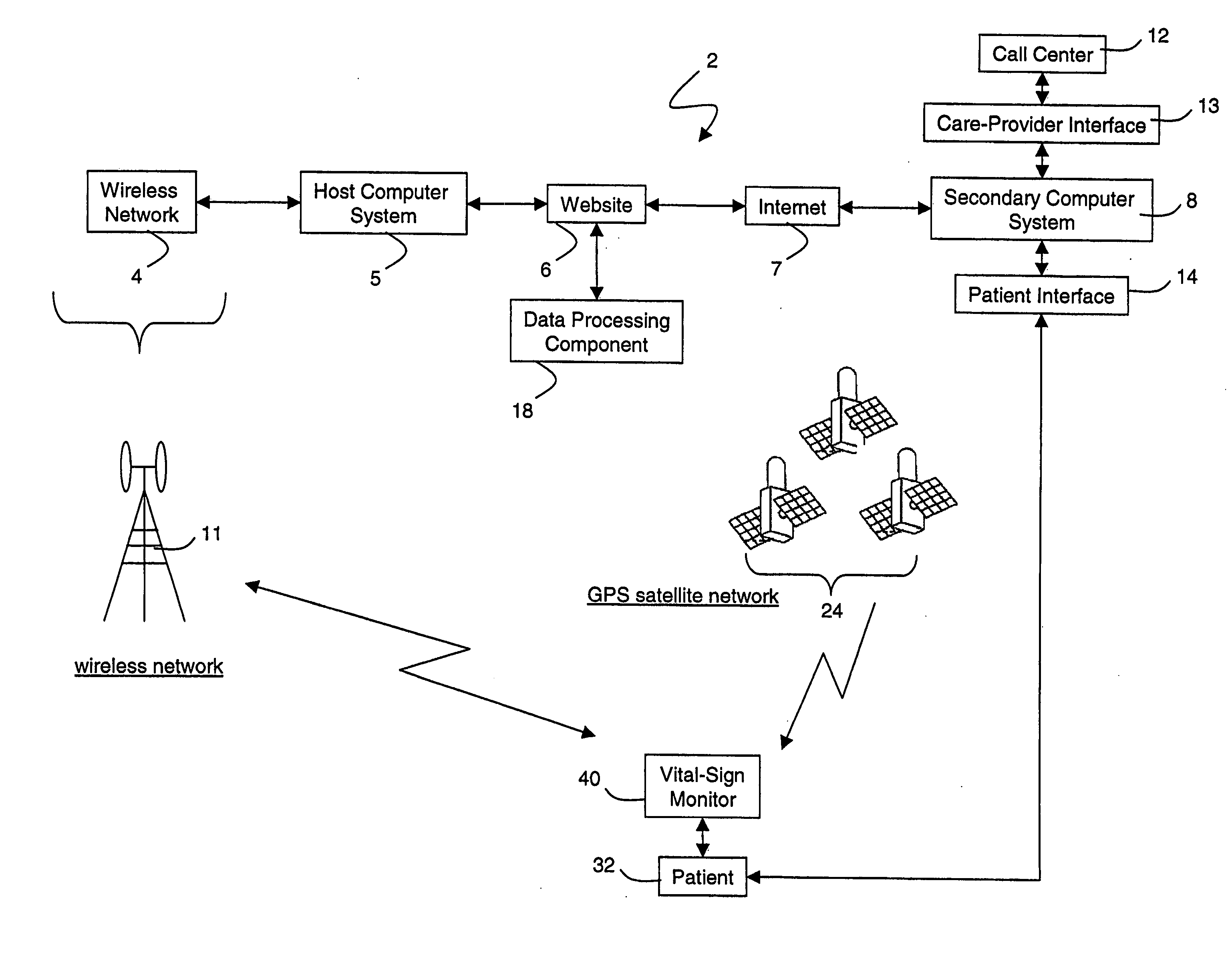
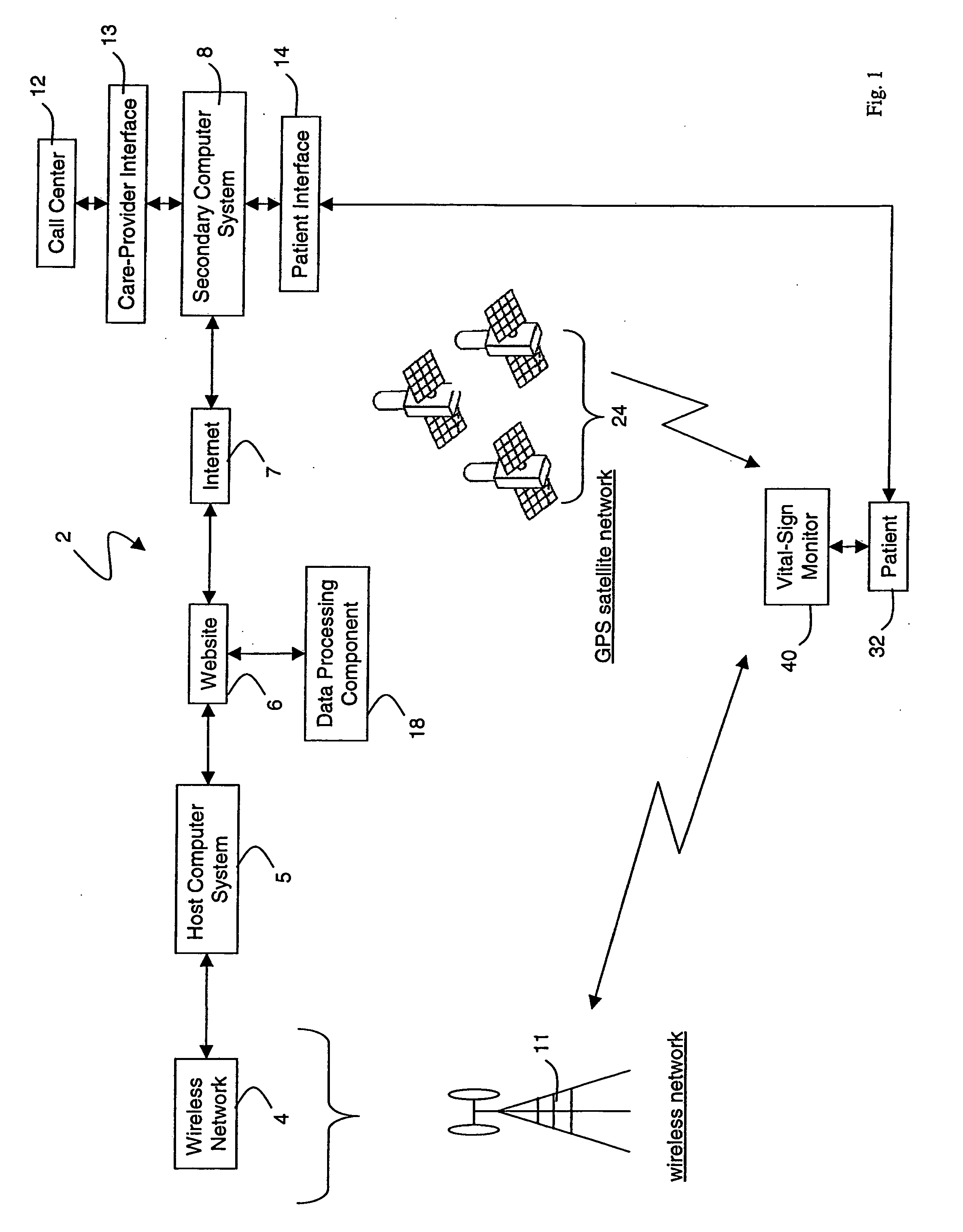
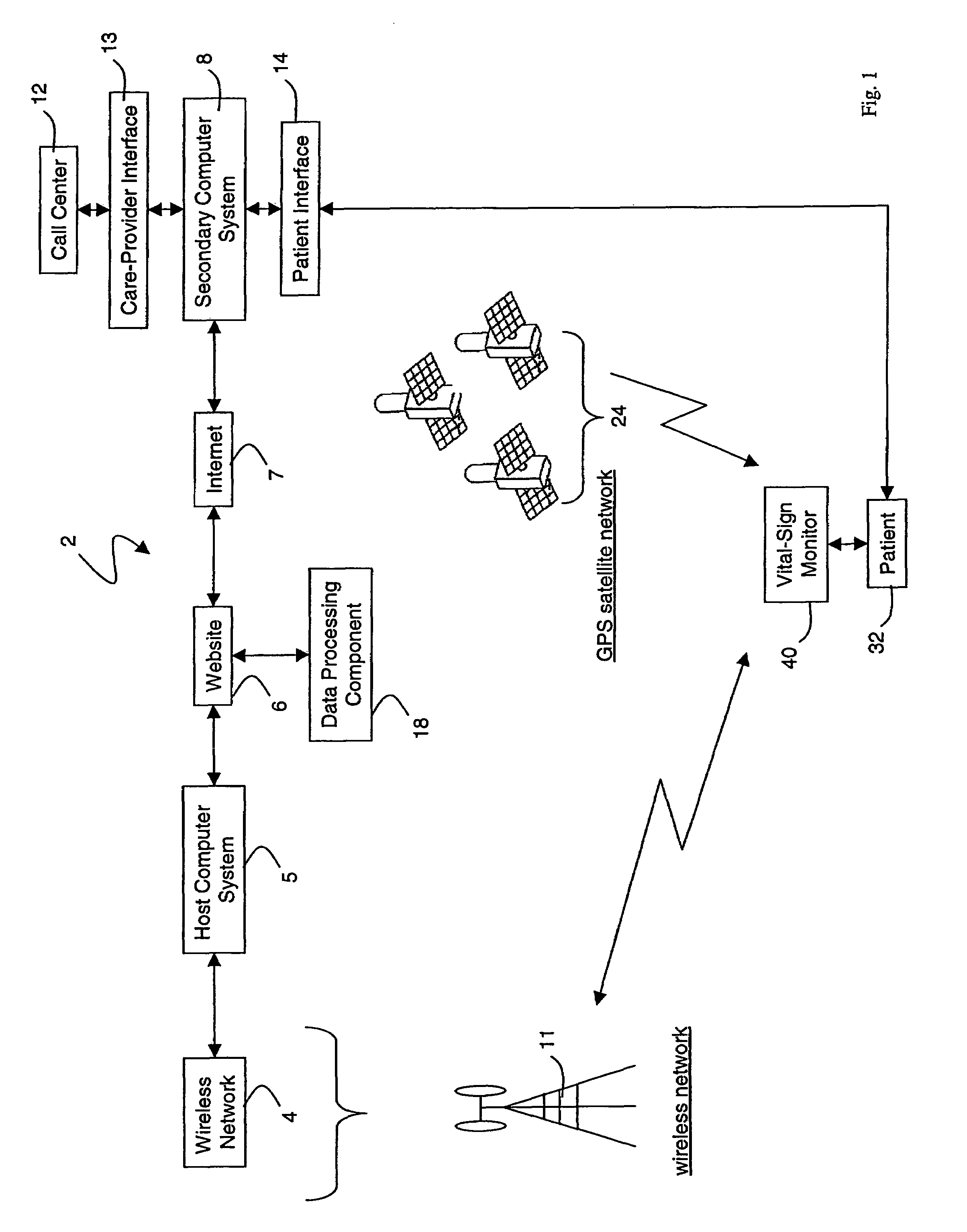
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
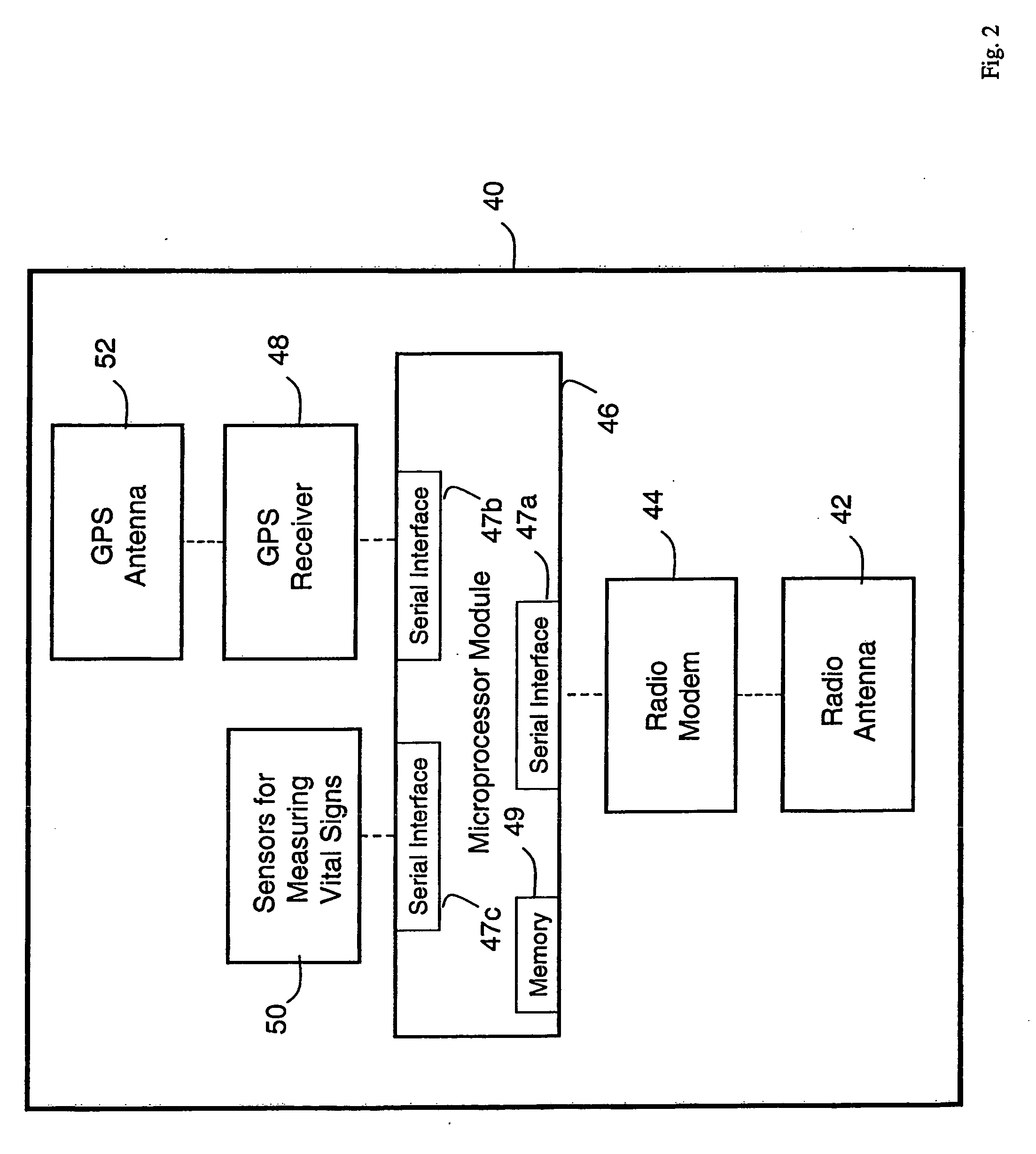
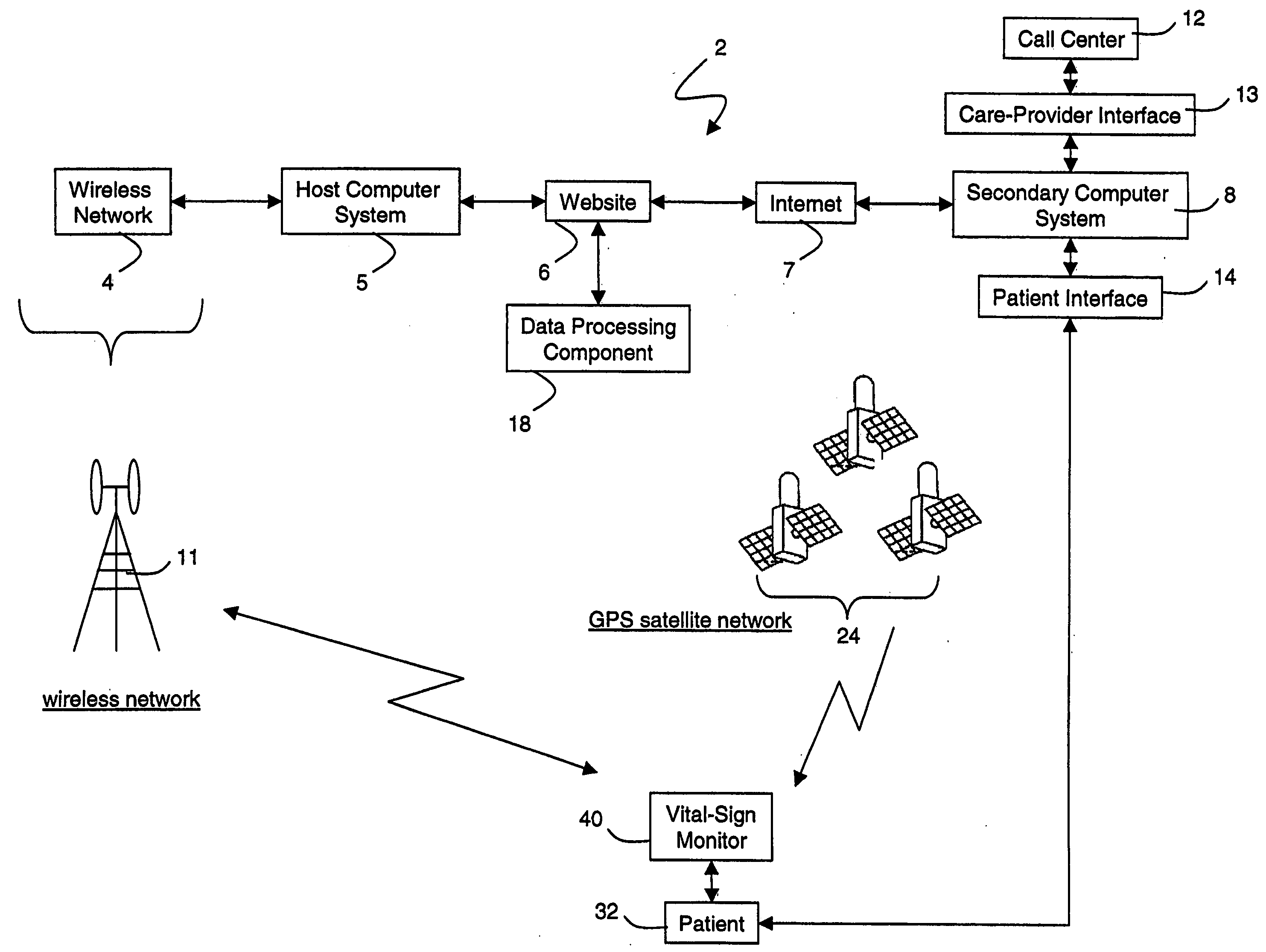
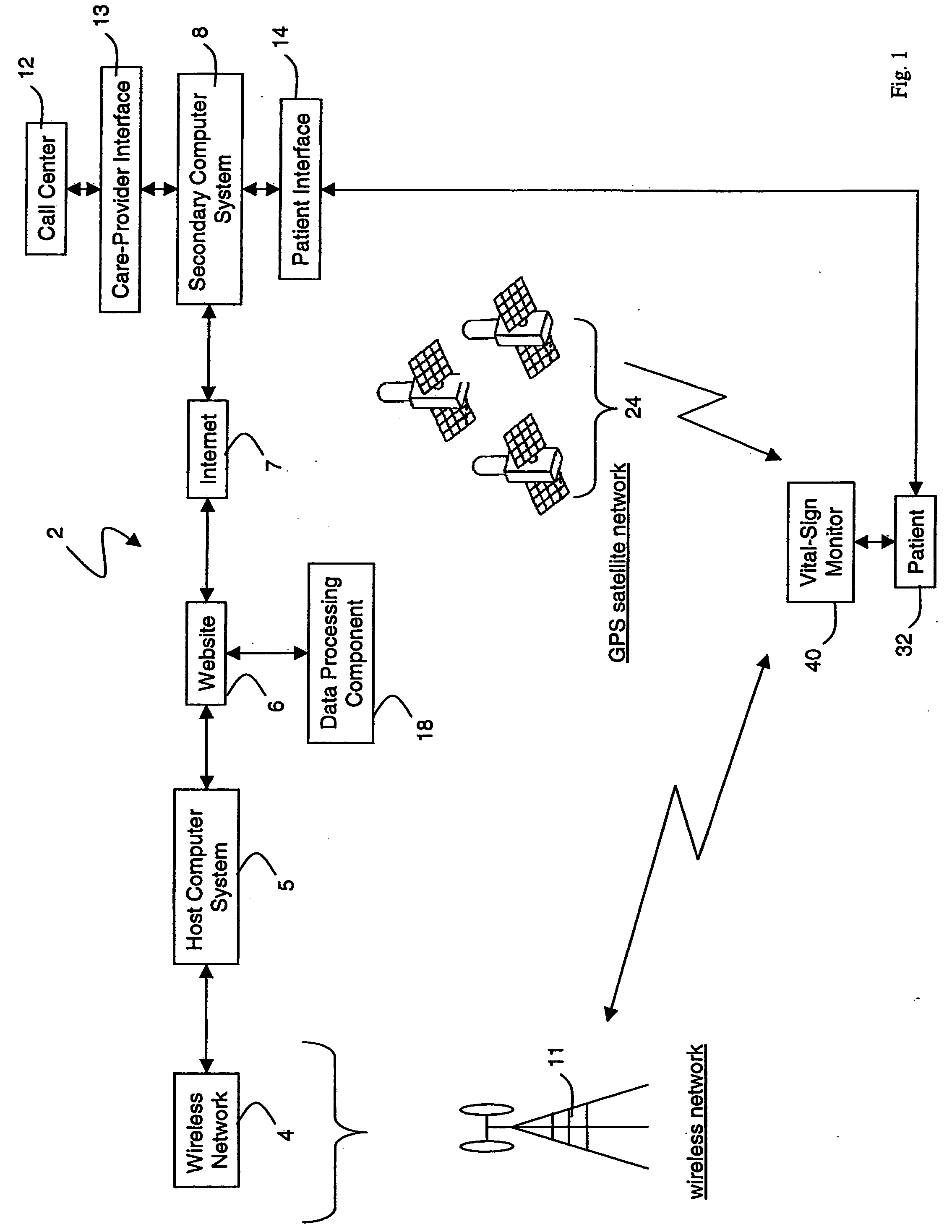
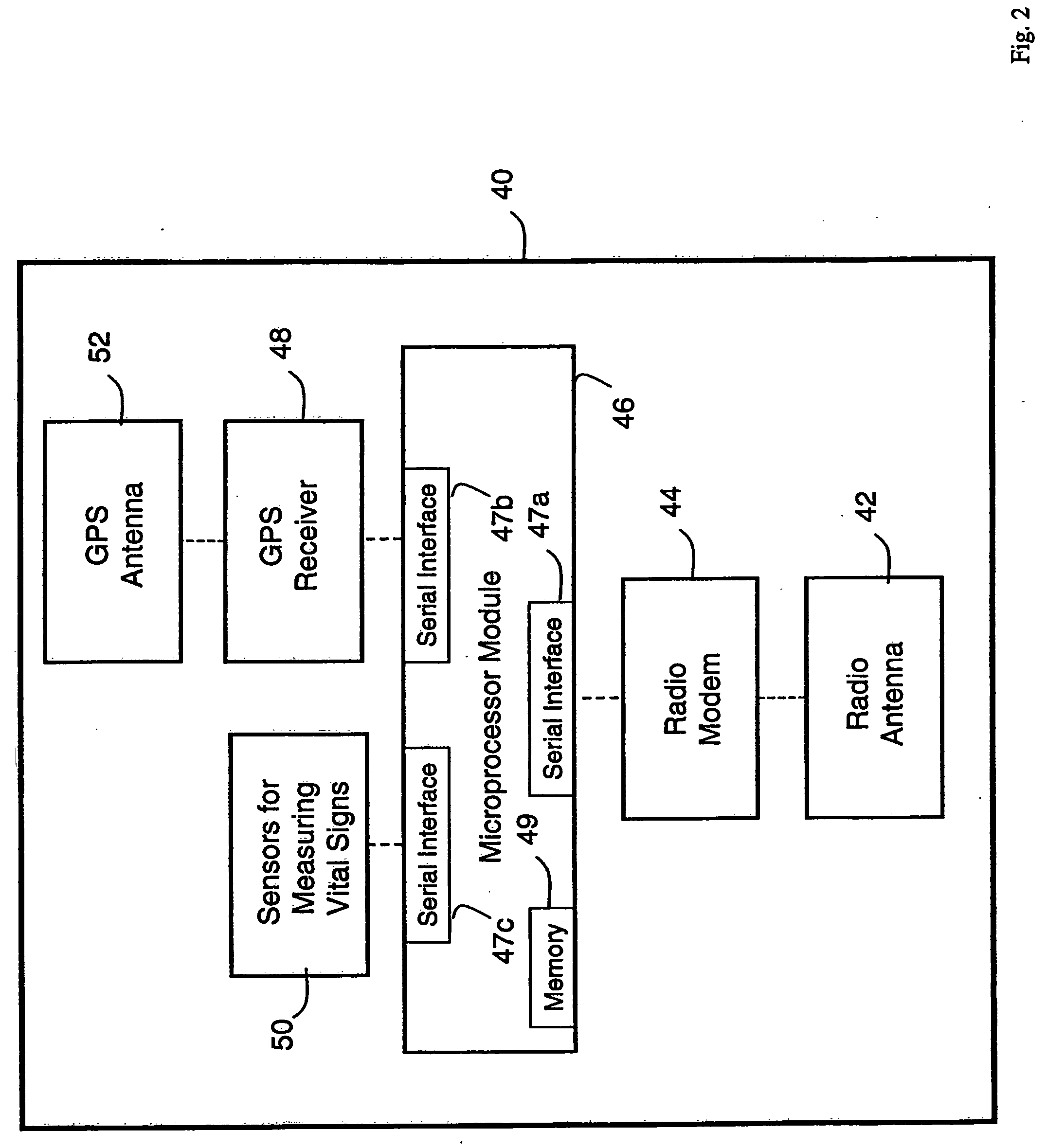
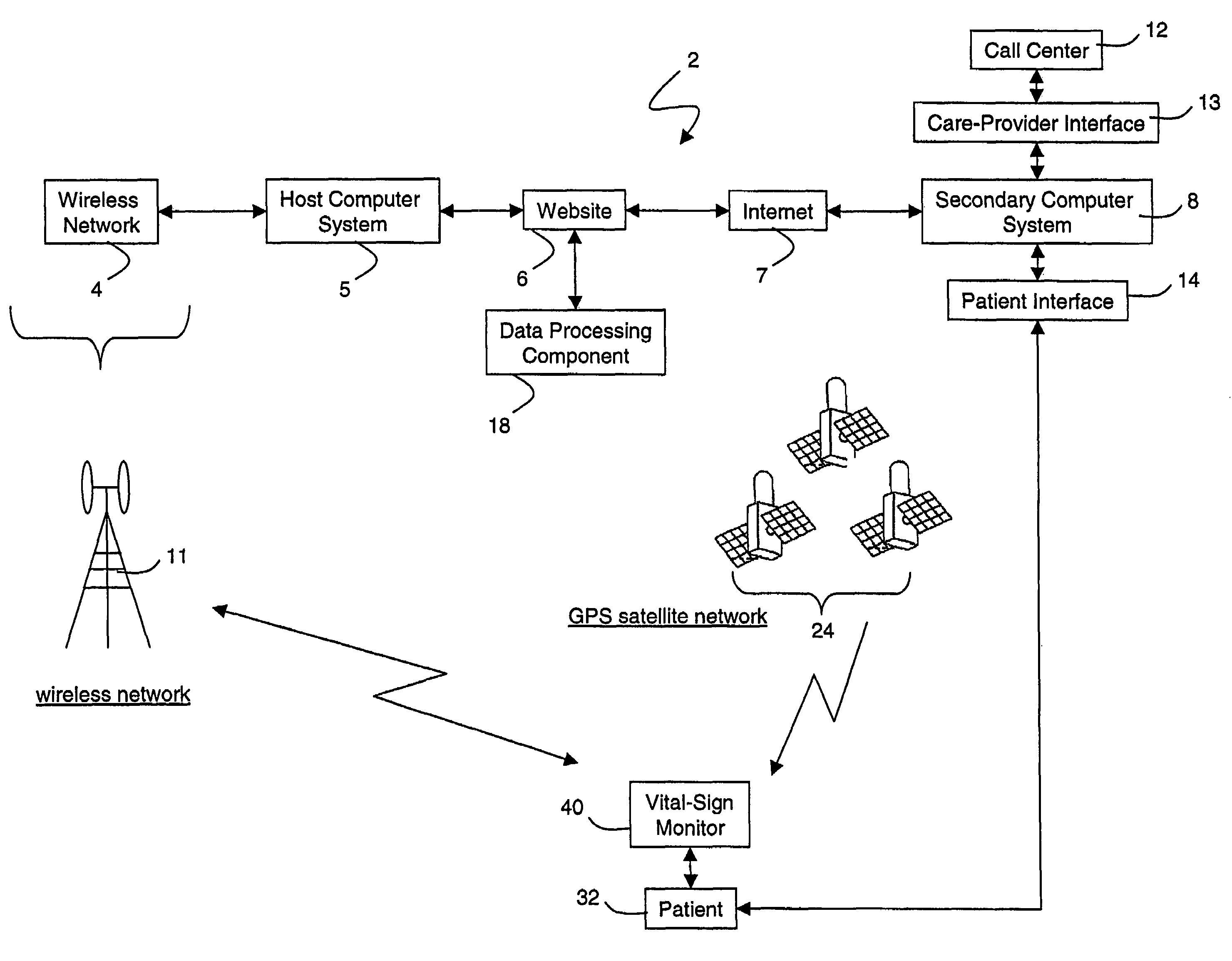
ActiveUS20050010087A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
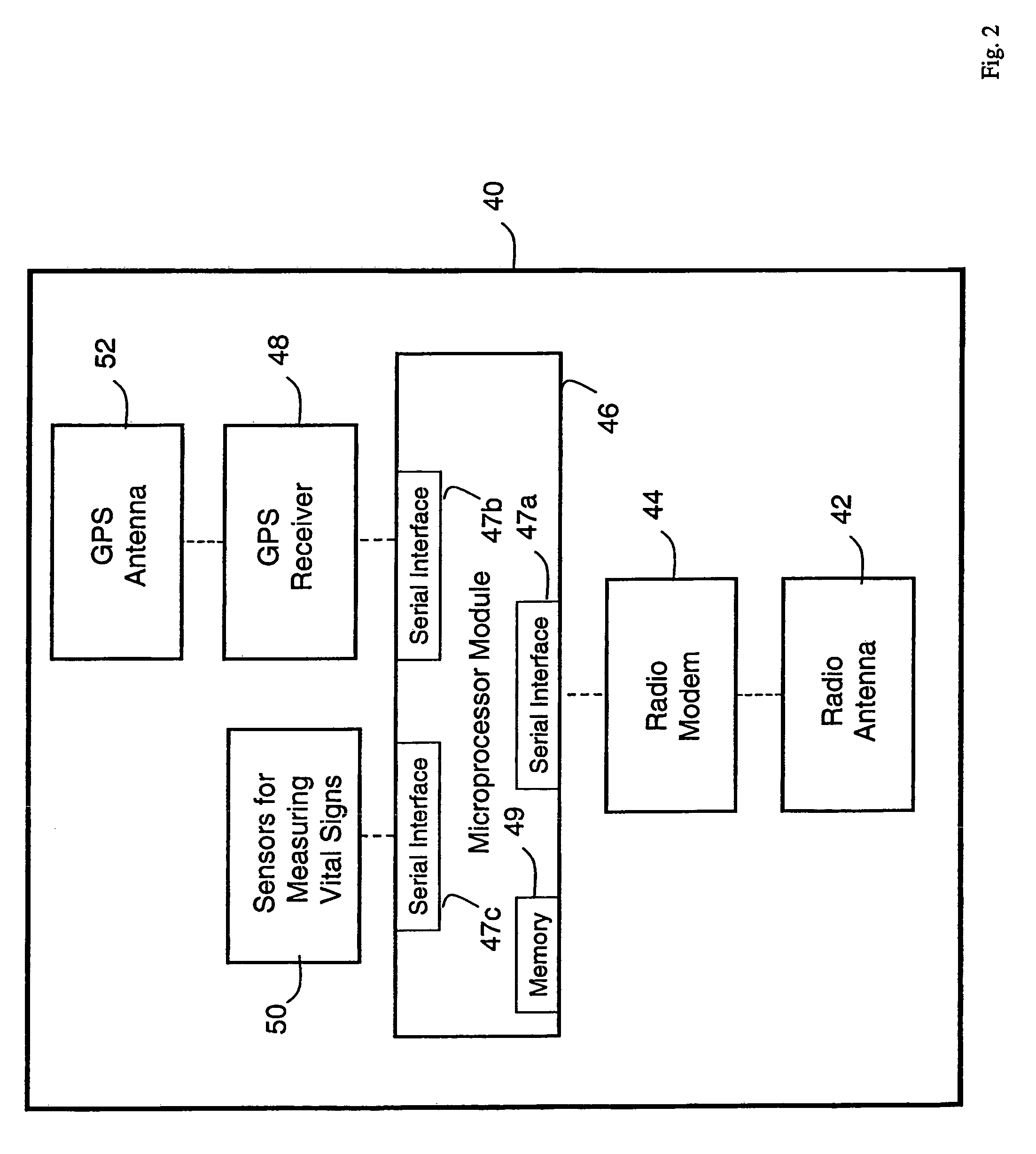
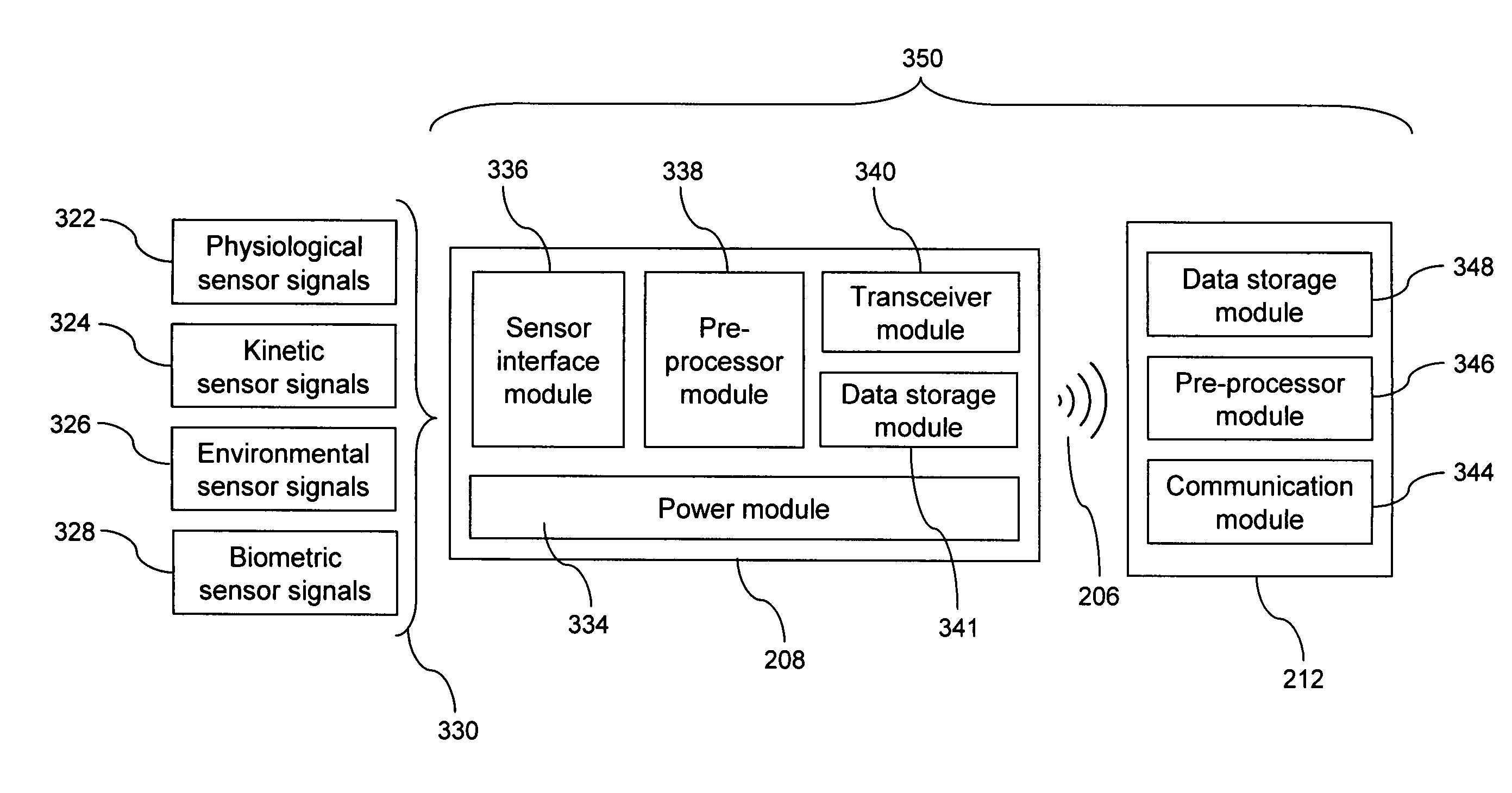
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
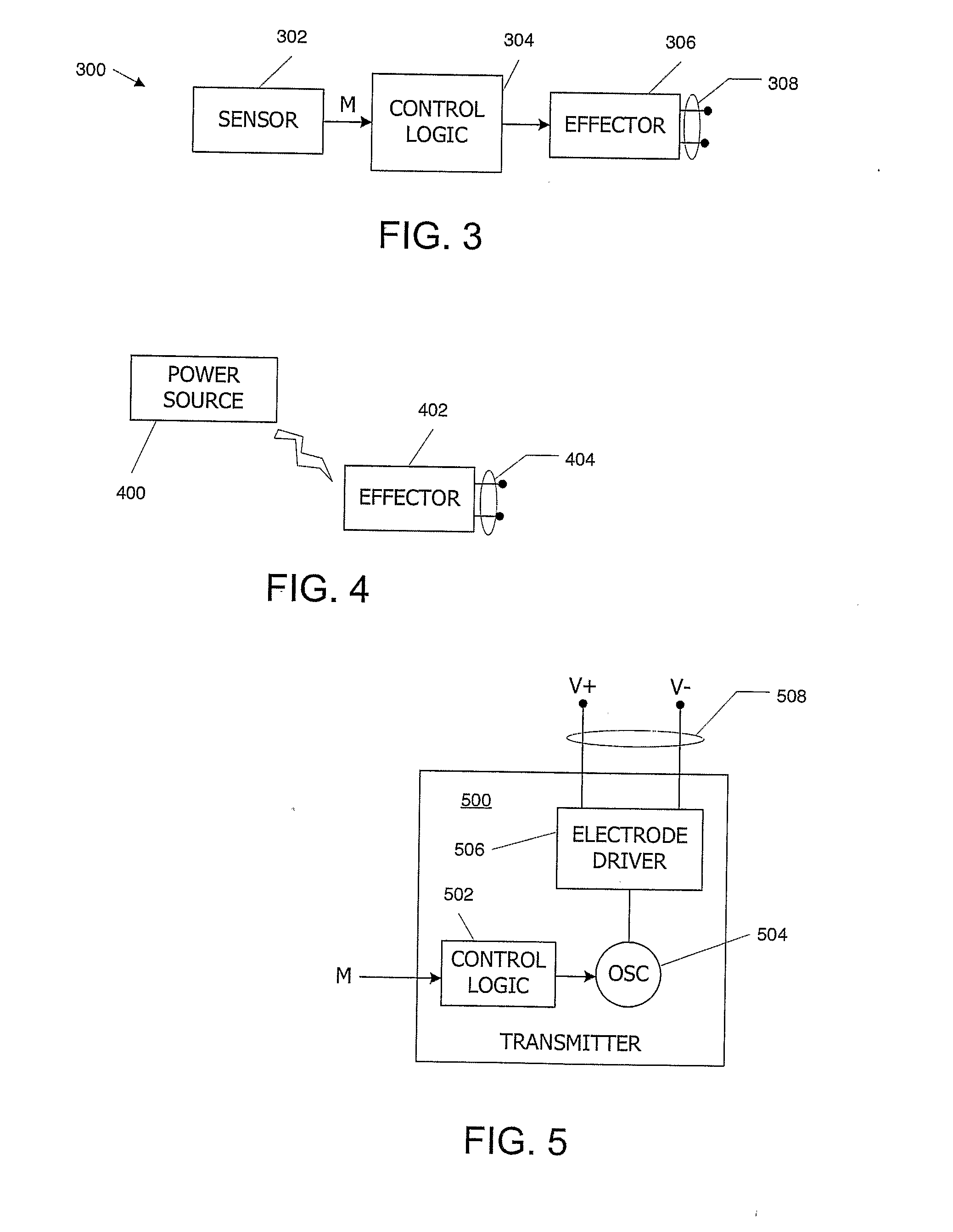
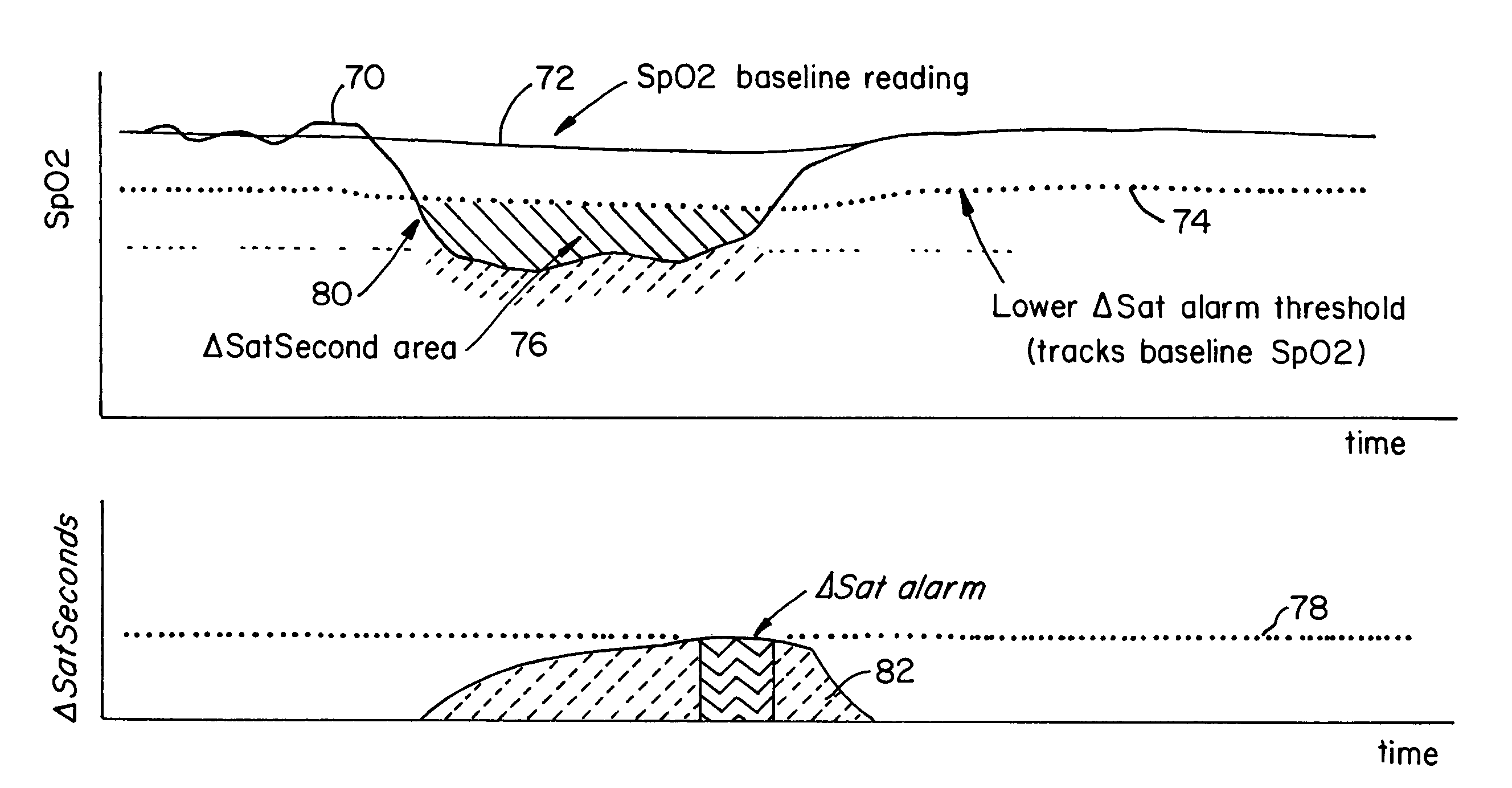
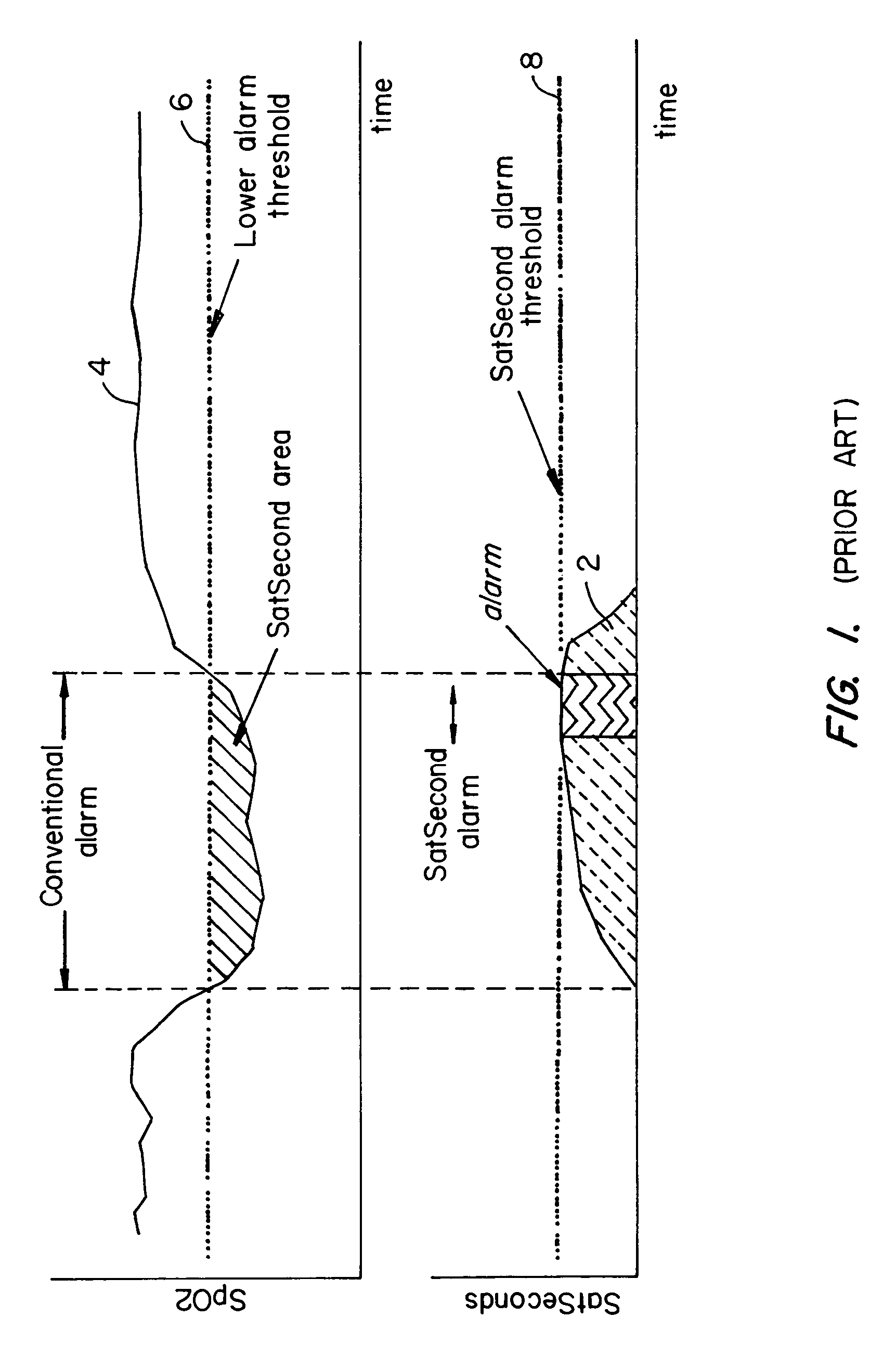
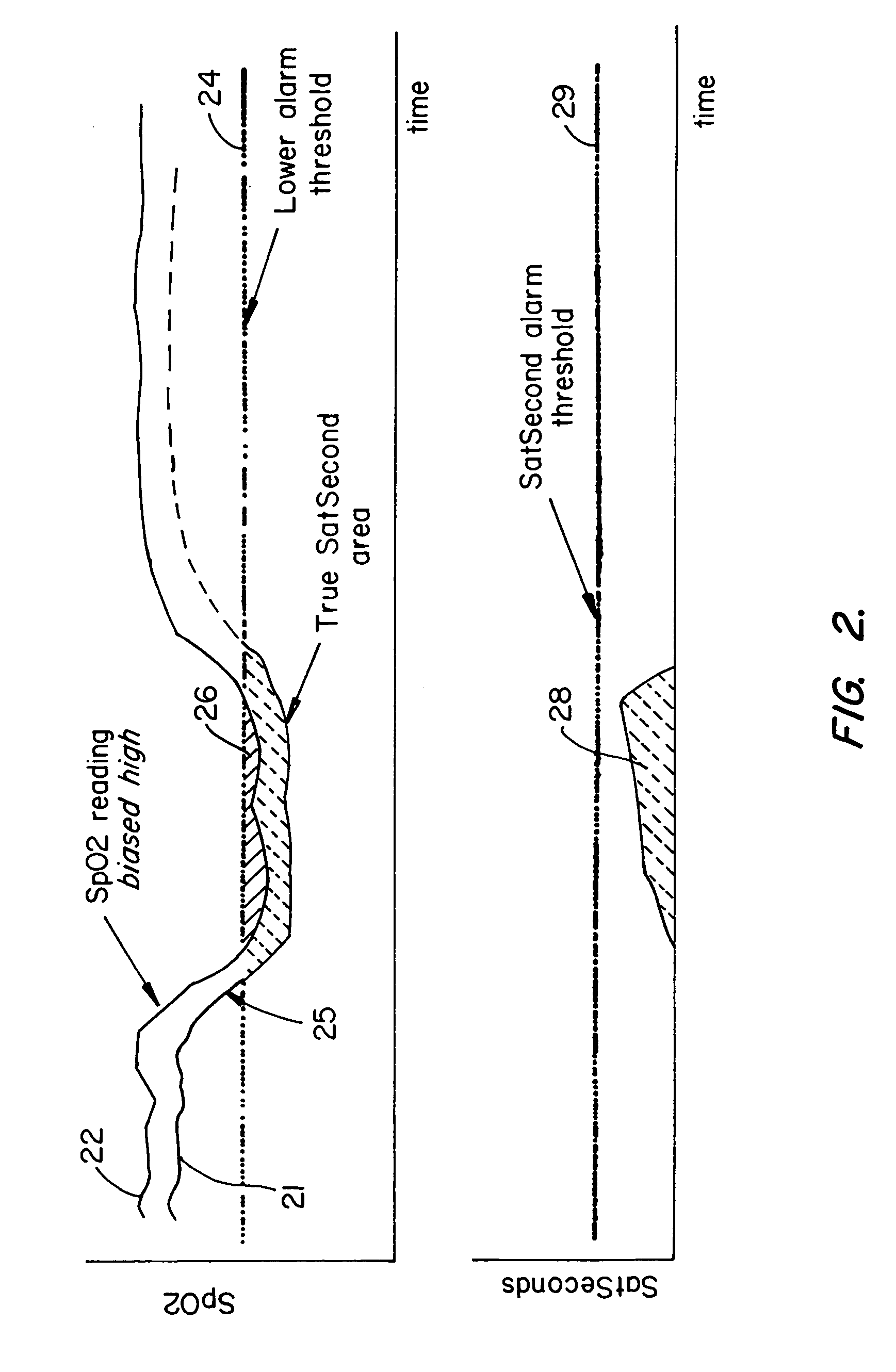
Nuisance alarm reductions in a physiological monitor
A method and apparatus for controlling alarms in a medical diagnostic apparatus where an alarm is generated when a measured value for a physiological parameter is outside a specified range. The method continuously calculates a baseline value, and establishes dynamic thresholds that are related to and continuously track the baseline value. The method determines the amount of time the measured value is past the dynamic threshold, and the amount by which the threshold is passed. Alarms are triggered based upon a combination of the amount of time and the amount by which the threshold is passed. Preferably, the combination is an integral or some function of an integral.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Wireless, internet-based, medical diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060142648A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmergency medicineGlobal Positioning System
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:TRIAGE DATA NETWORKS
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS7396330B2Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
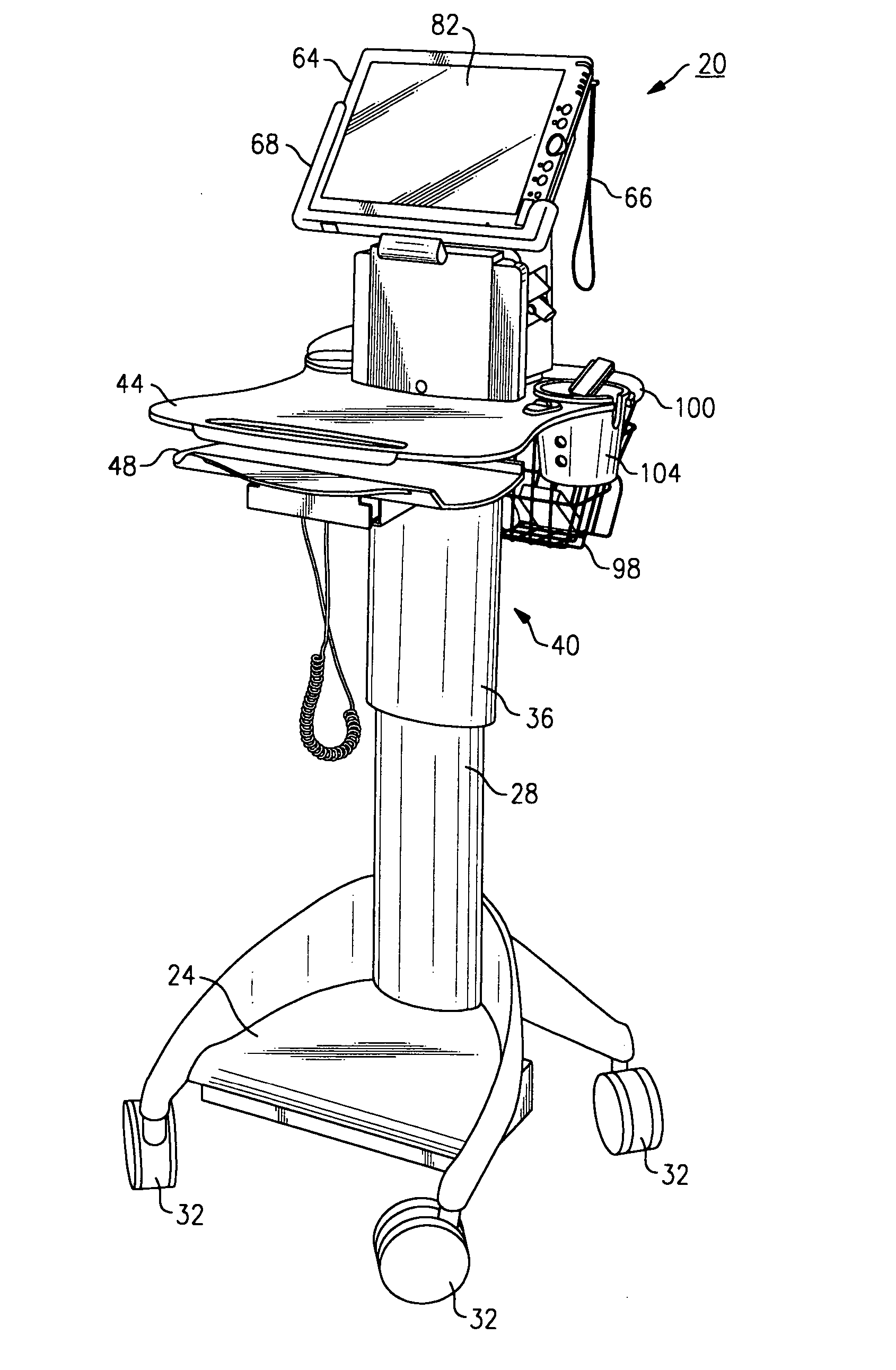
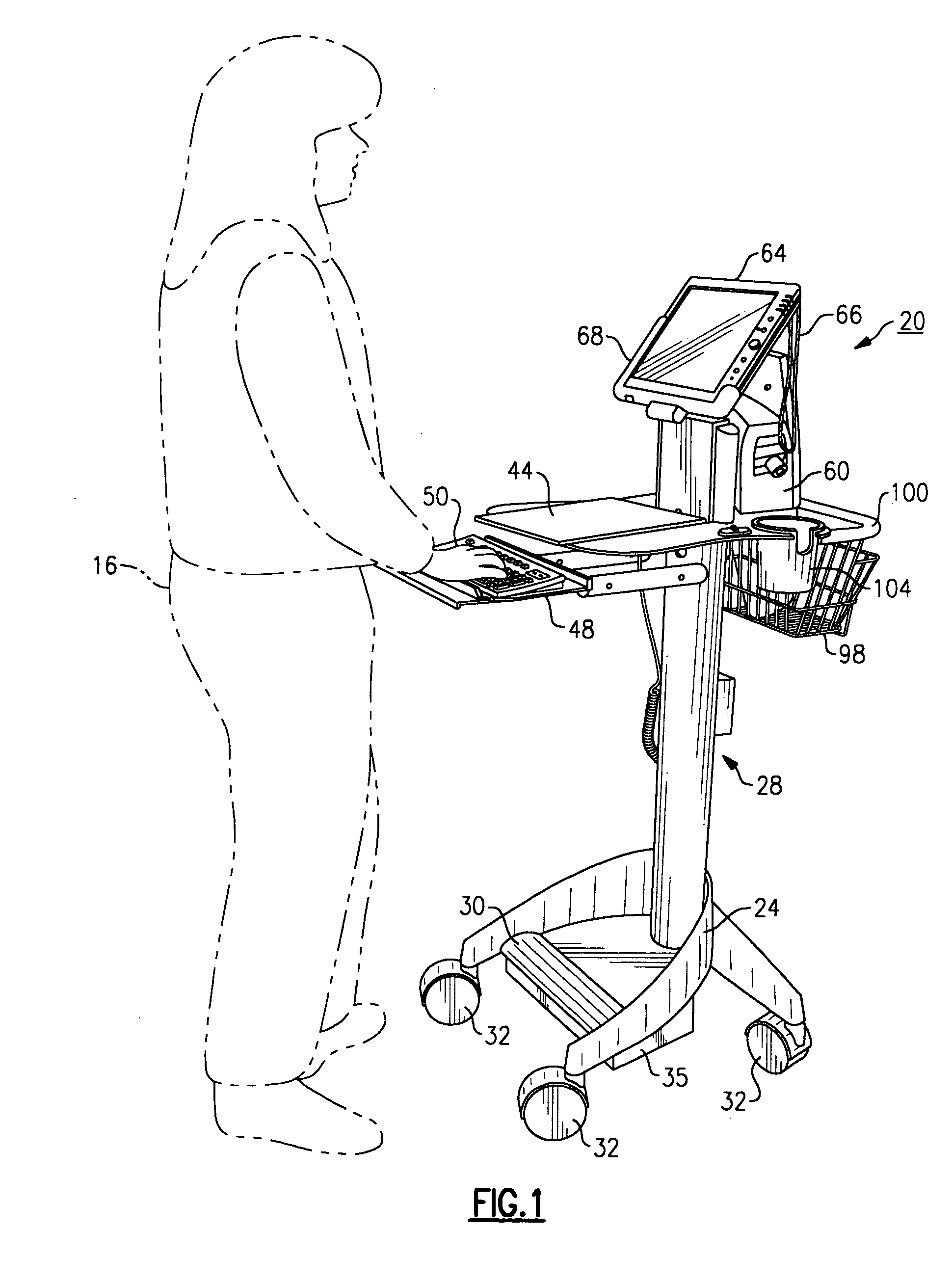
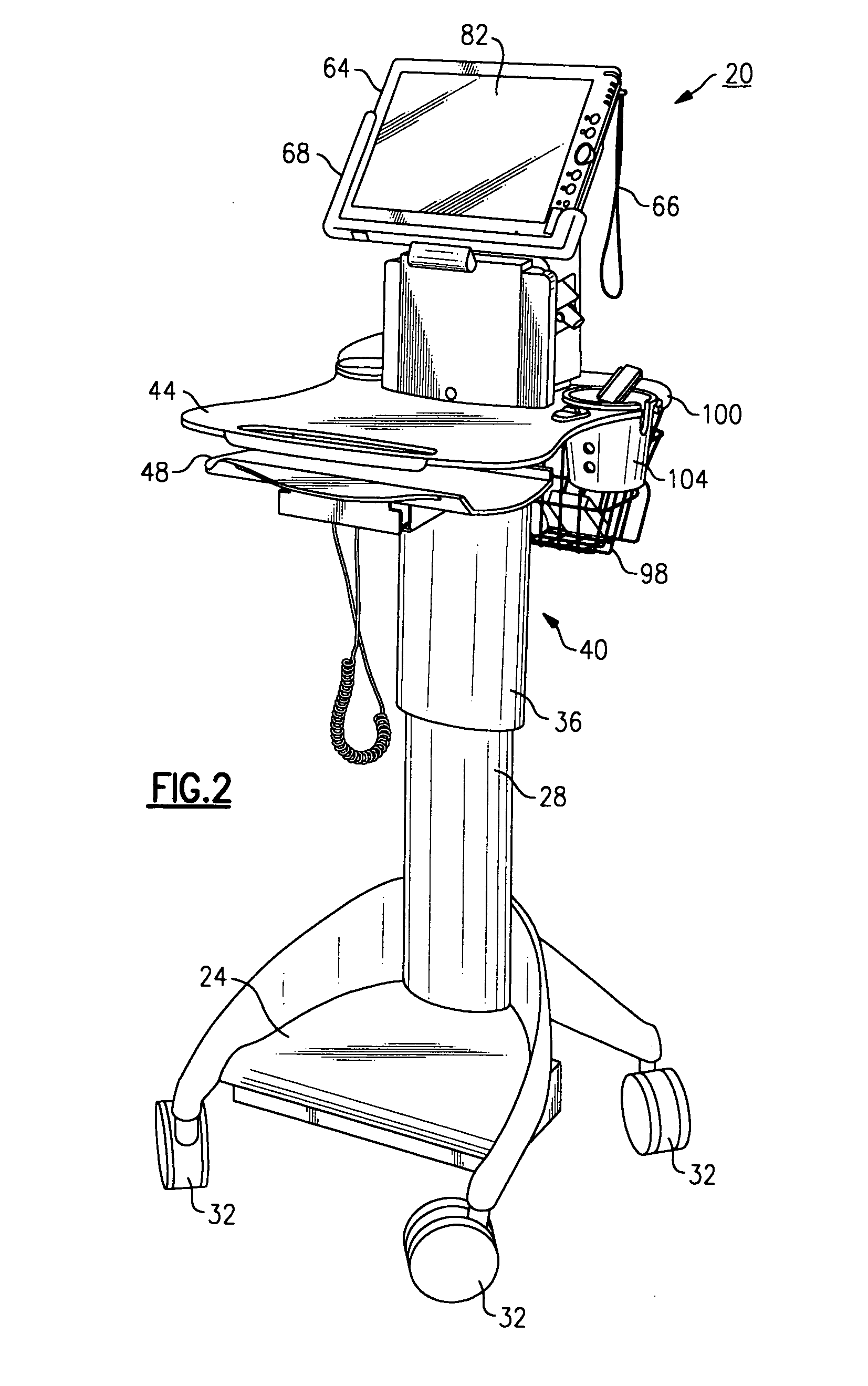
Mobile medical workstation
InactiveUS20050288571A1Short response timeReduce usageElectrocardiographySurgical furnitureDisplay deviceEngineering
A medical workstation is defined by a supporting structure having at least one medical diagnostic instrument disposed thereupon. A first display is further disposed on a first side of the supporting structure and a second display is disposed on a second side of the supporting structure in a manner substantially opposite from the first display. Each of the first and second displays are interconnected to the at least one medical diagnostic instrument to permit at least one of the displays in order to display diagnostic results and are tandemly or independently controllable.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Transformable pressure sensitive adhesive tape and use thereof in display screens
InactiveUS20060100299A1Easy and safe applicationLow level of VOC 'sNanostructure manufactureGas-filled discharge tubesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
A transformable pressure sensitive adhesive composition comprised of from about 15 to about 80% by weight of a polymer having a softening point greater than 60° C.; from about 20 to about 85% by weight of a polymerizable resin having a softening point less than 30° C.; a latent initiator in an amount sufficient to cause a reaction between said polymer and said resin; and optionally, a crosslinking agent. The transformable pressure sensitive adhesive has particular applicability in connection with organic light emitting diode display devices, light emitting diode display devices, medical diagnostic testing devices, flexible or rigid LCD display devices, plasma display devices, and electrochromic devices.
Owner:ADHESIVES RES
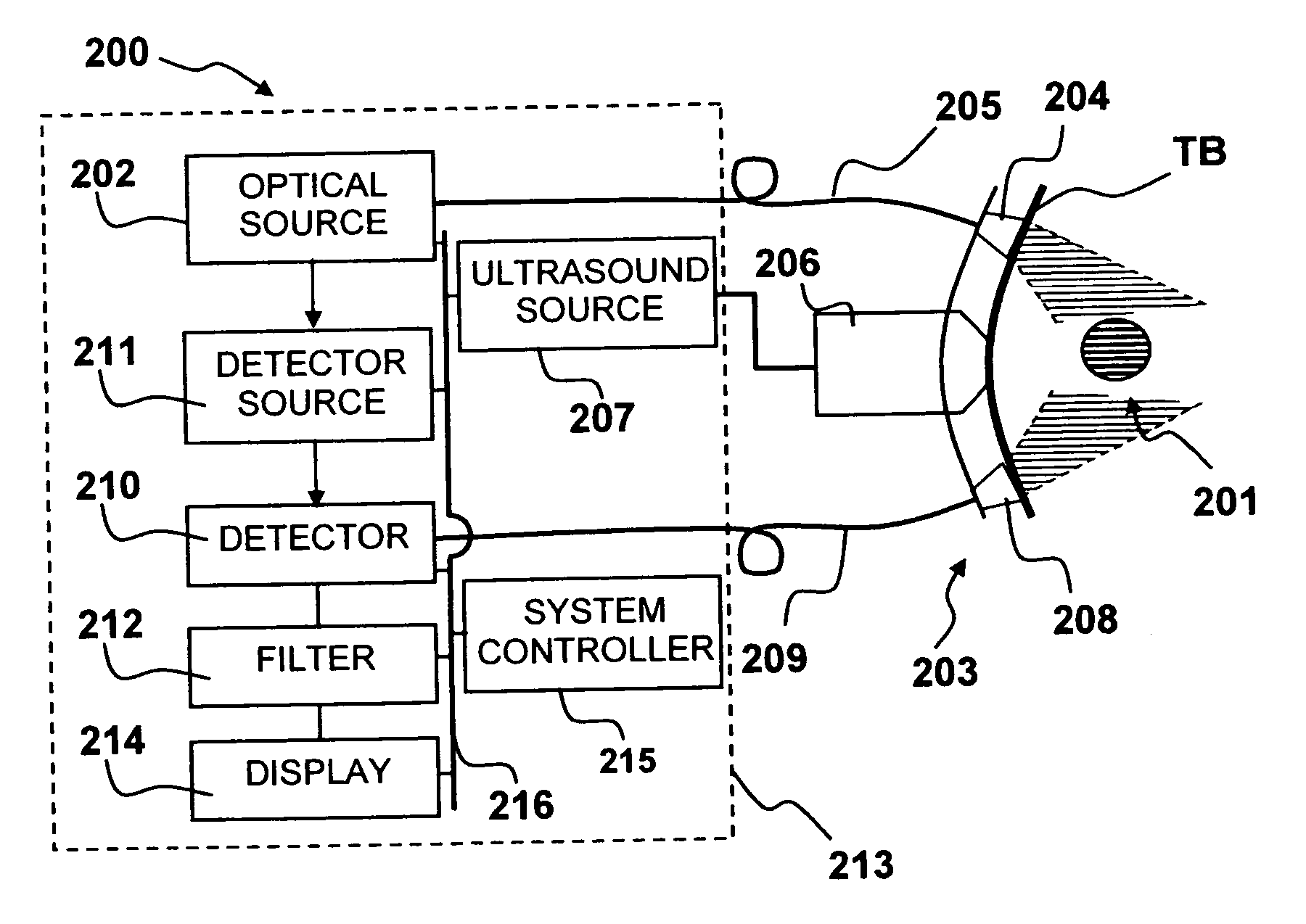
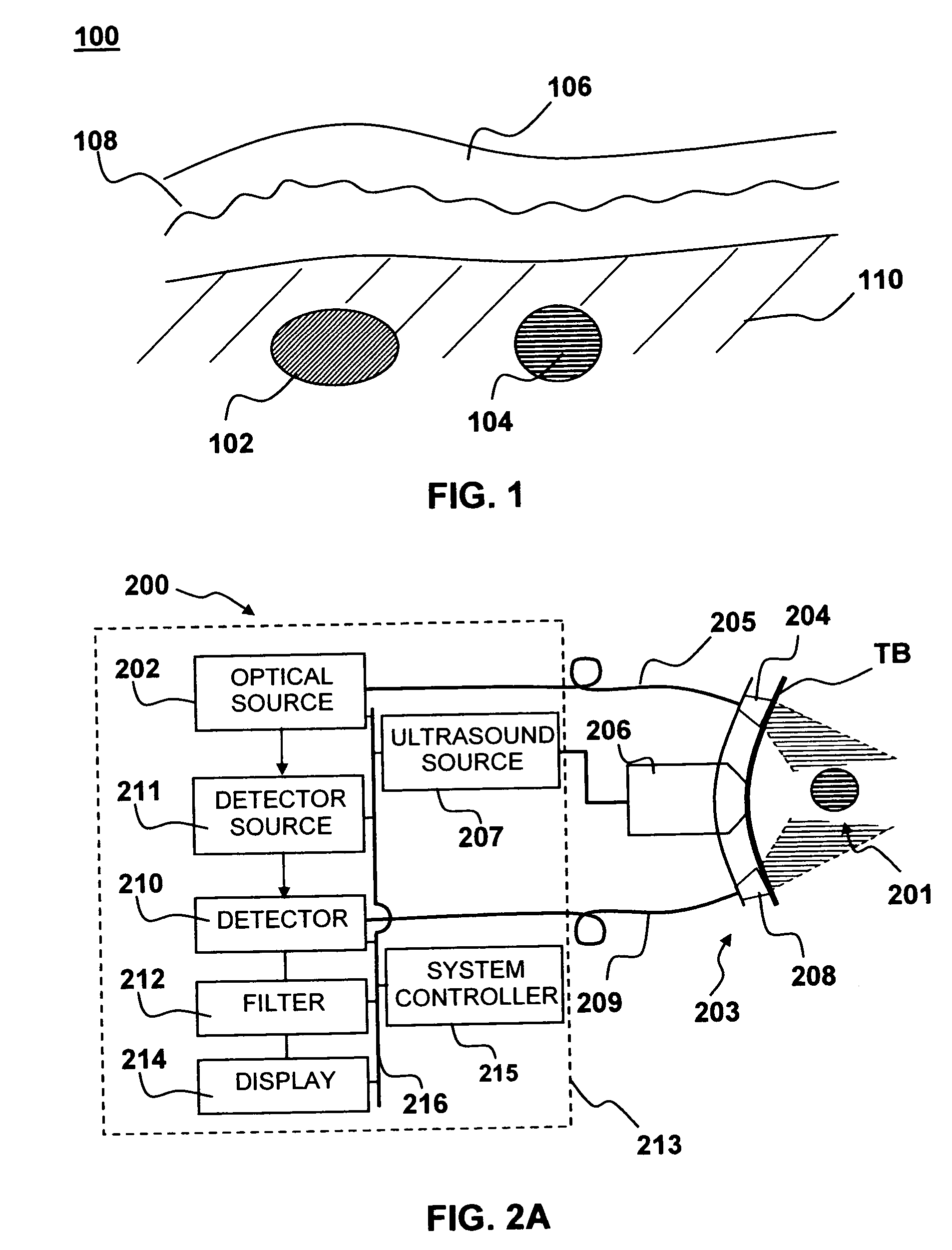
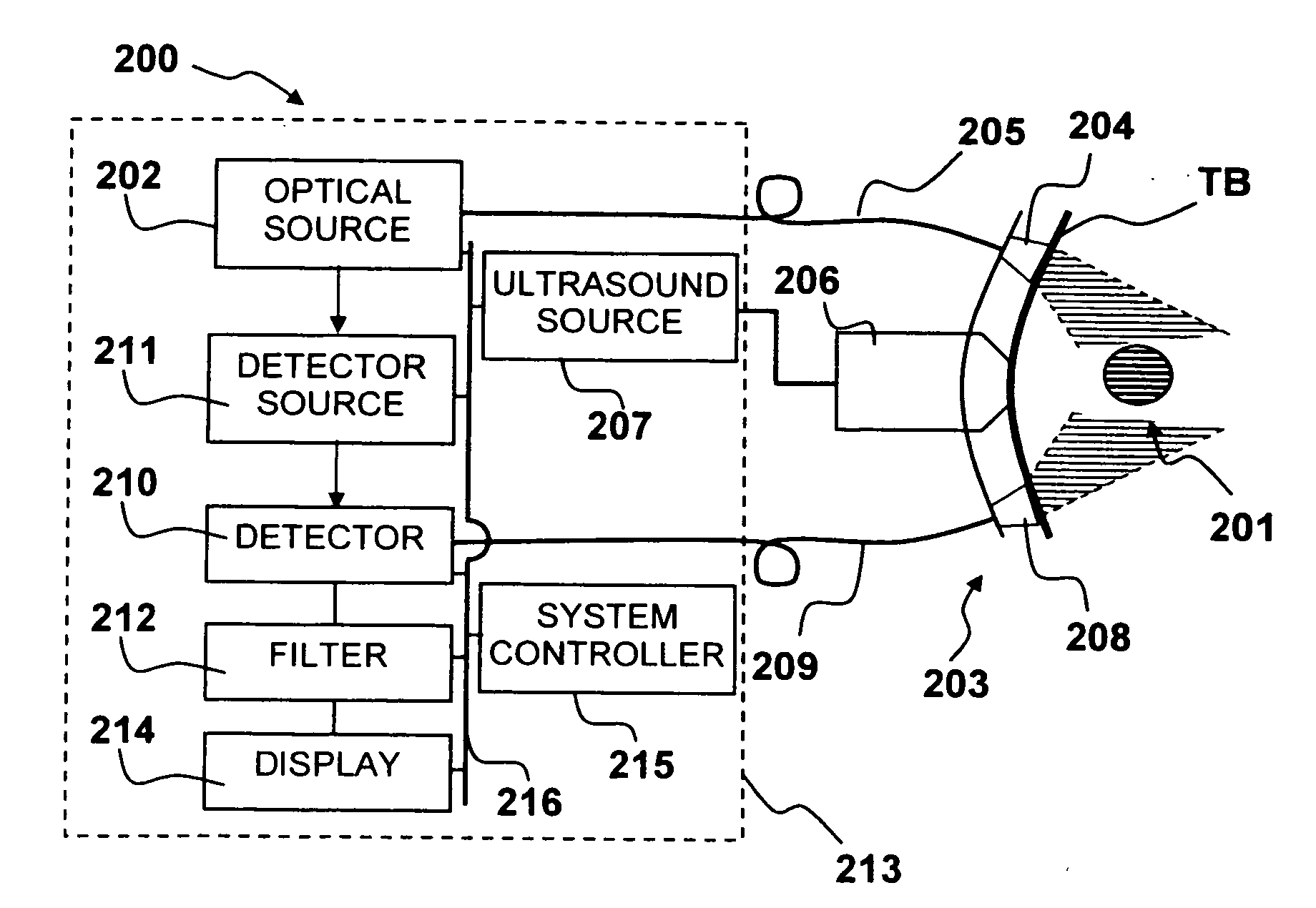
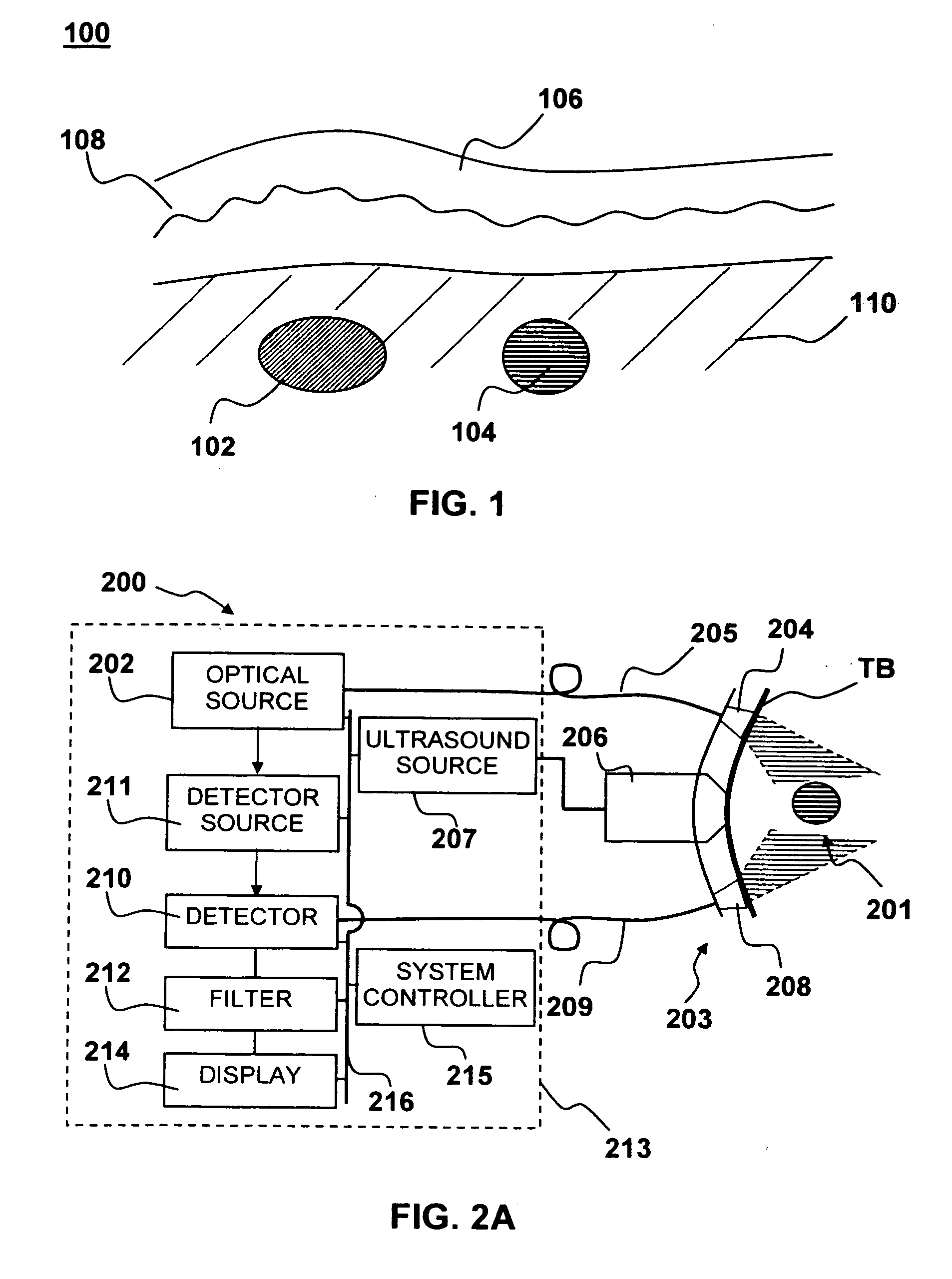
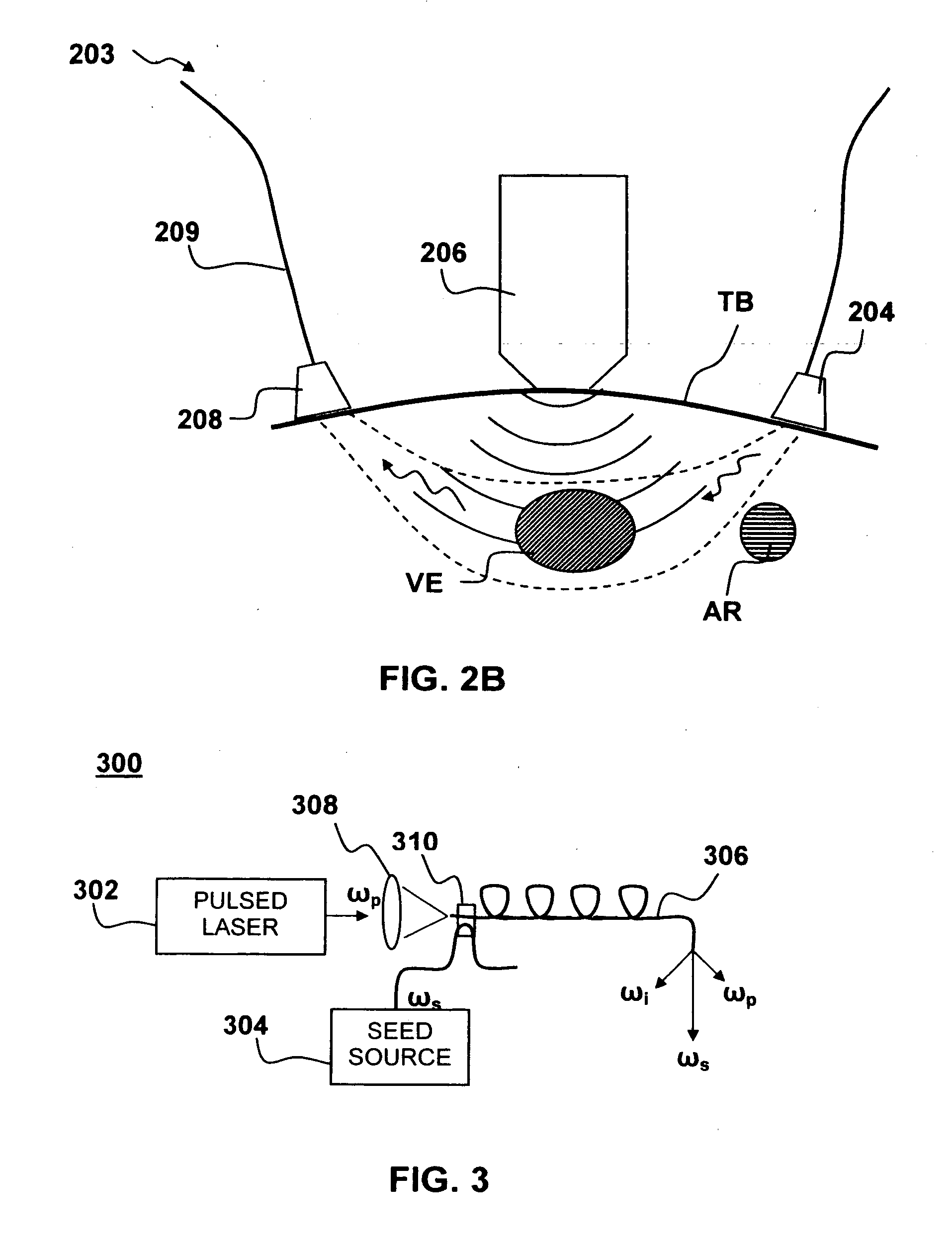
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of venous oxygen saturation and pH levels
InactiveUS20060224053A1Easy to useCost effectiveOrgan movement/changes detectionSensorsSonificationScattering cross-section
Medical diagnostic apparatus and methods are disclosed. Ultrasound radiation pressure selectively modulates a target area within a body. One or more pulses of radiation containing temporally correlated groups of photons are generated. The photons are characterized by two or more different wavelengths that are selected to have specific interaction with a target chromophore. The two or more different wavelengths are also selected to have substantially similar scattering cross-sections and anisotropy parameters in the target and its surroundings. The pulses of radiation are injected into the body proximate the target area being modulated by the radiation pressure field. Photon groups at each of the different wavelengths that are backscattered from the target area are detected in temporal coincidence. Time-gated background-free amplification of the return signal is used to exclude photons which could not by virtue of their arrival time have interacted with the radiation-pressure-modulated target. Photon groups are selected with a modulation component at the modulation frequency of the radiation pressure modulation field, or at a harmonic of the modulation frequency. From the arrival rate of the detected temporally correlated photon pairs or multiplets, chemical information about the target area, such as an oxygenation or pH level can be inferred. Cardiac output may be computed from measurements of venous and / or arterial oxygenation using this technique.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
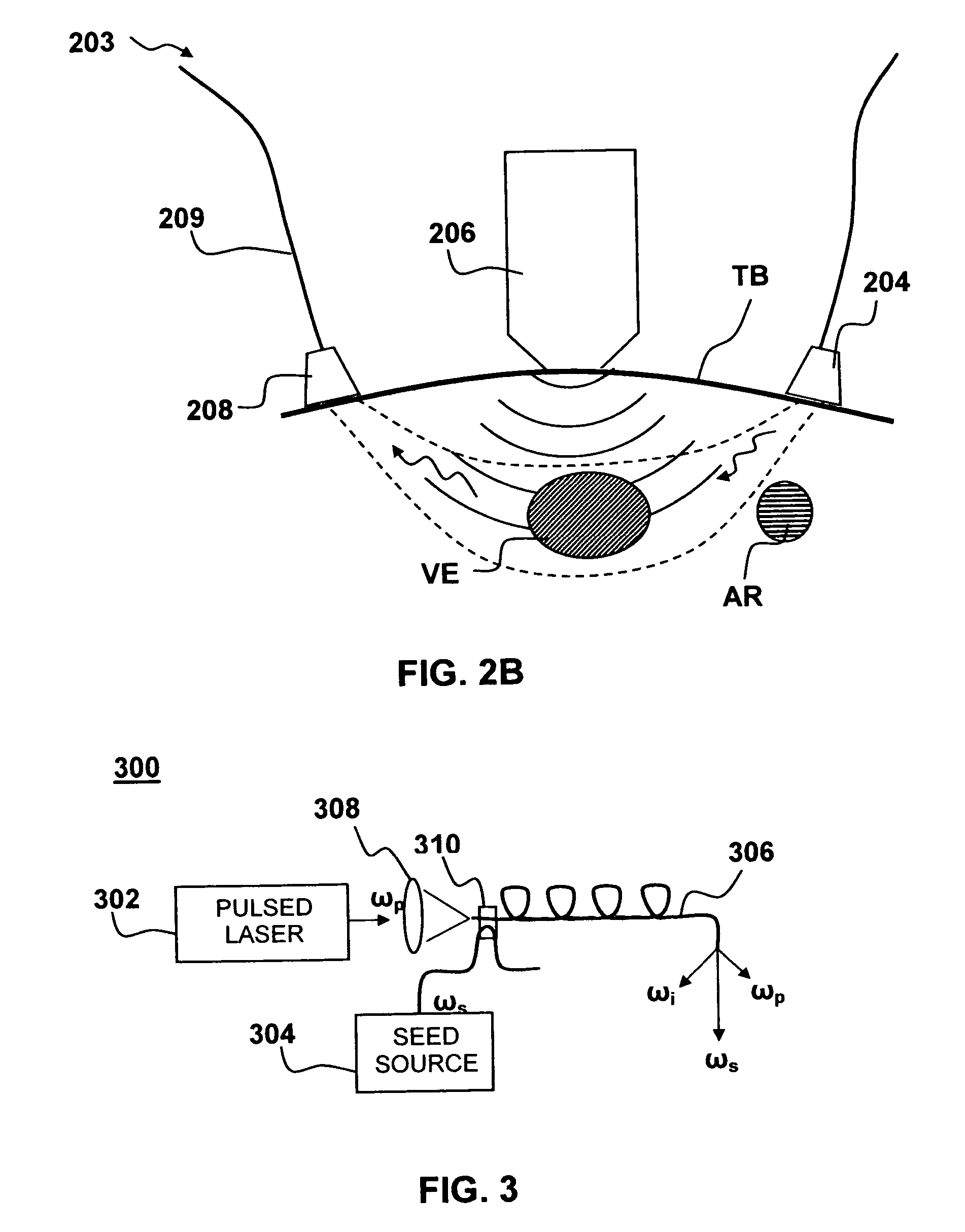
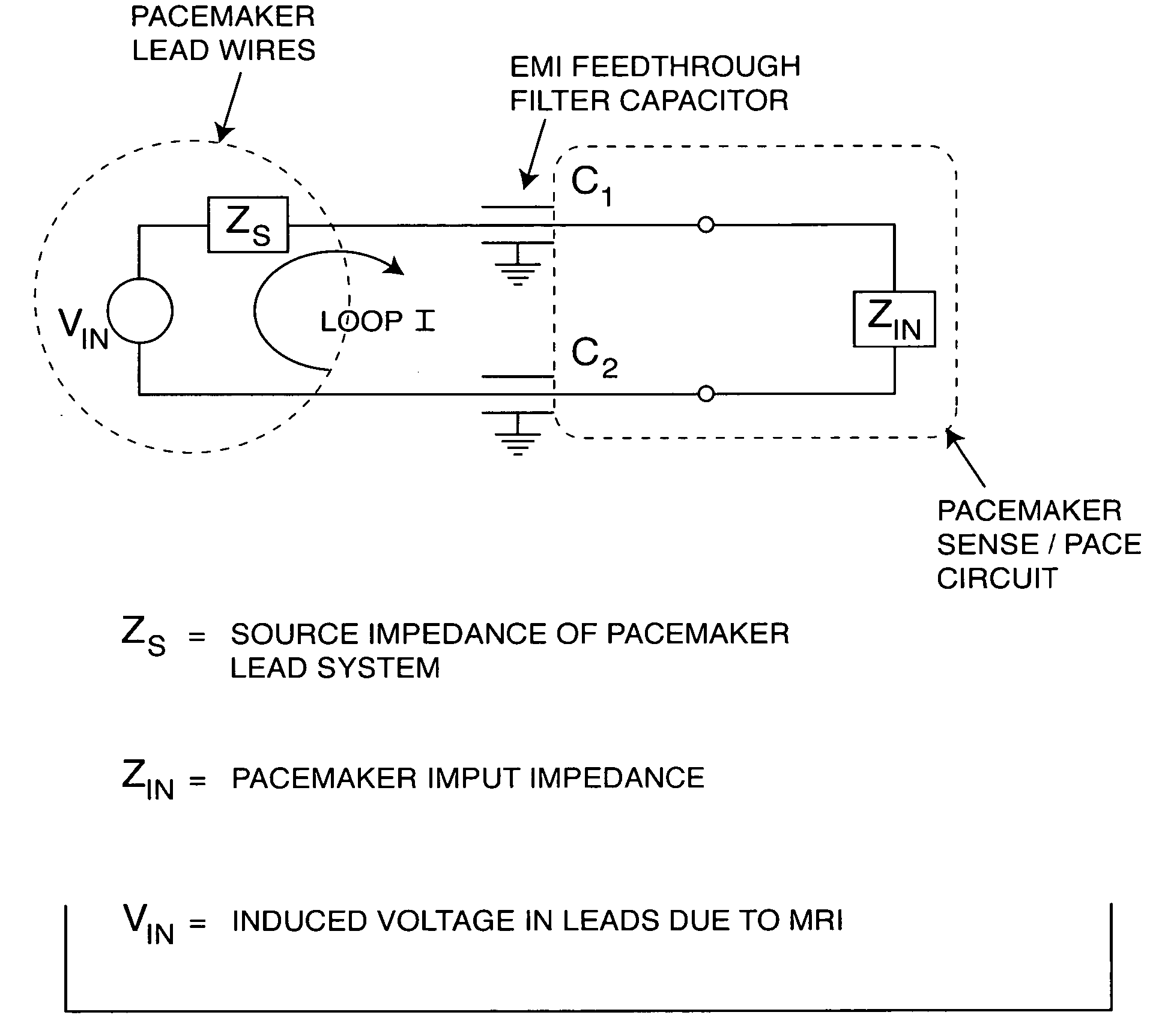
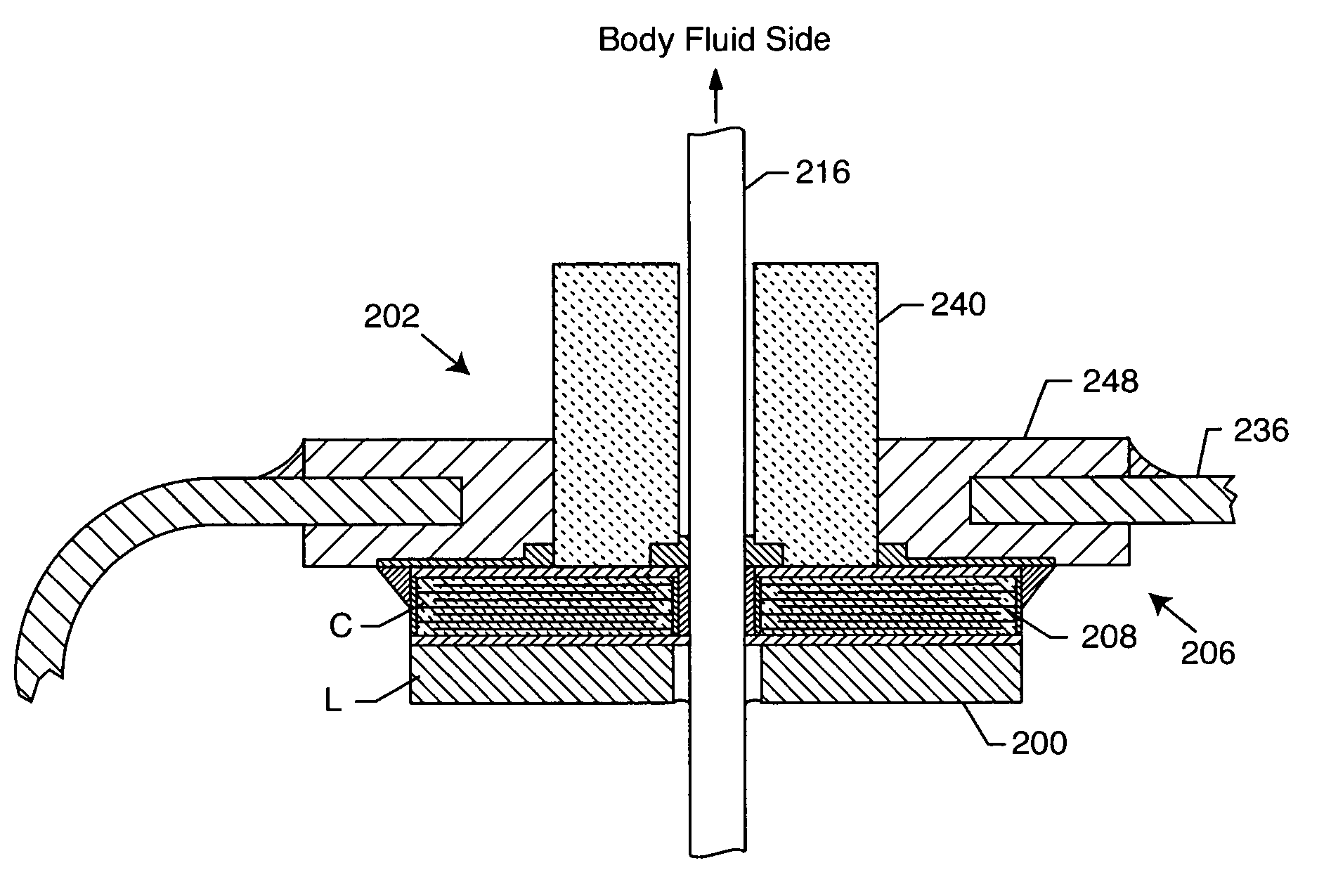
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20050197677A1Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic field
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
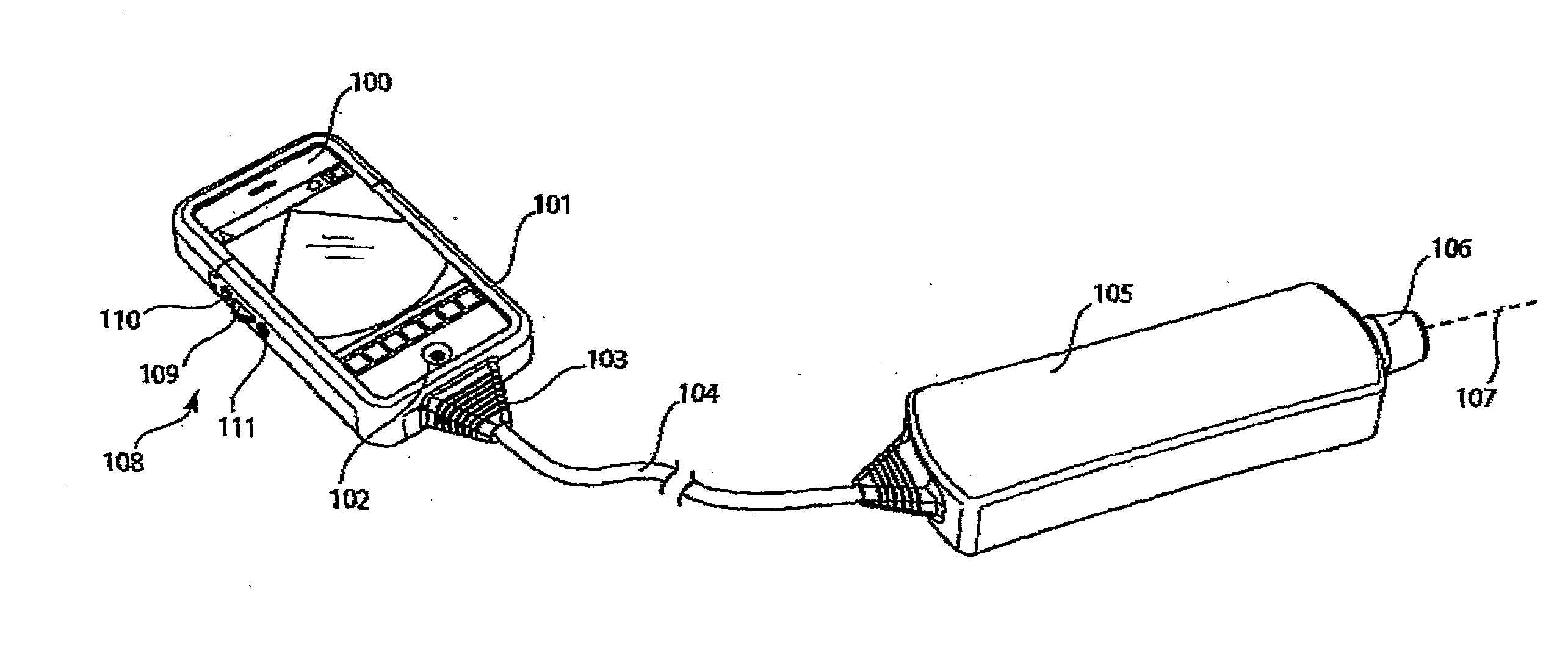
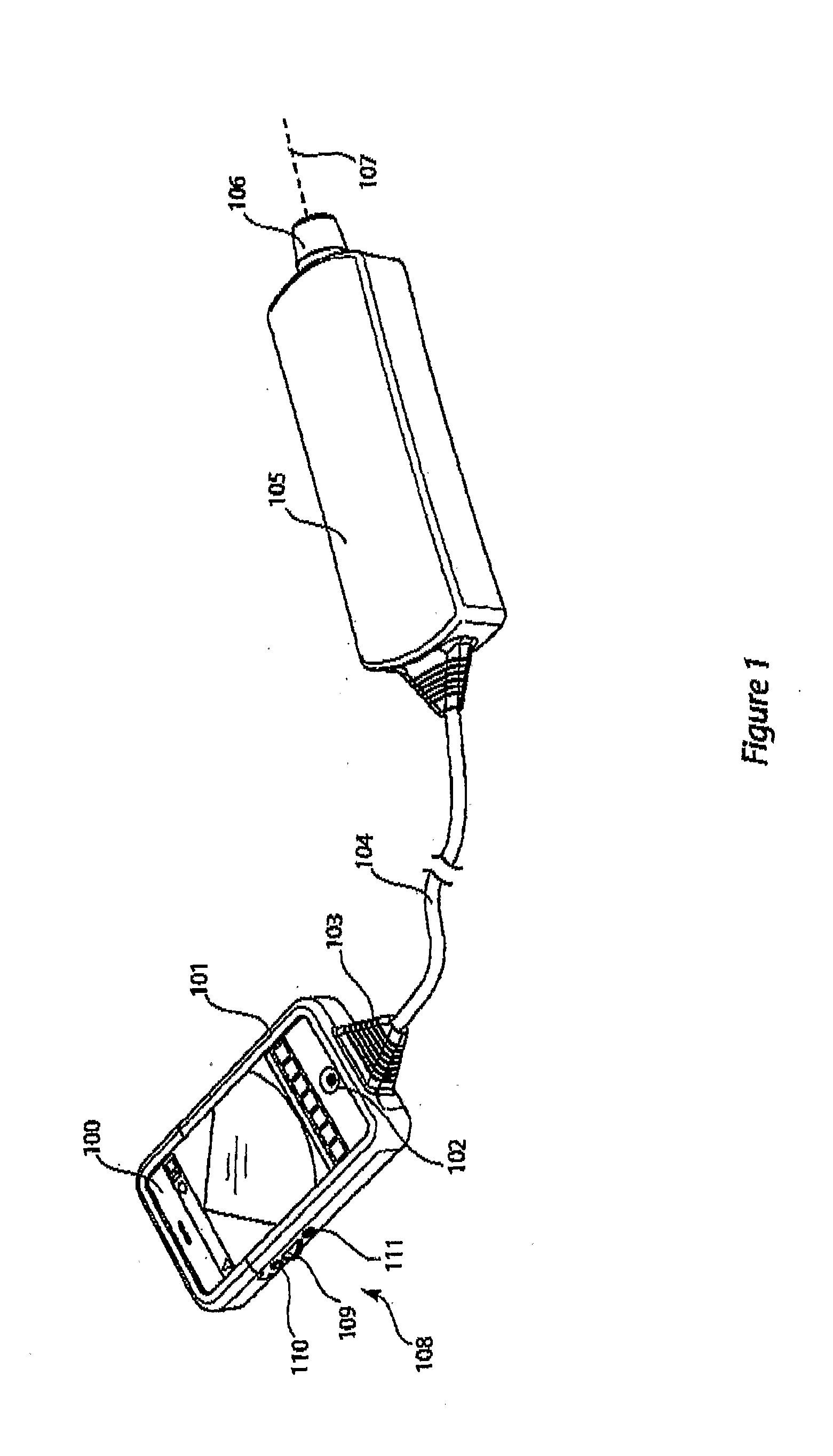
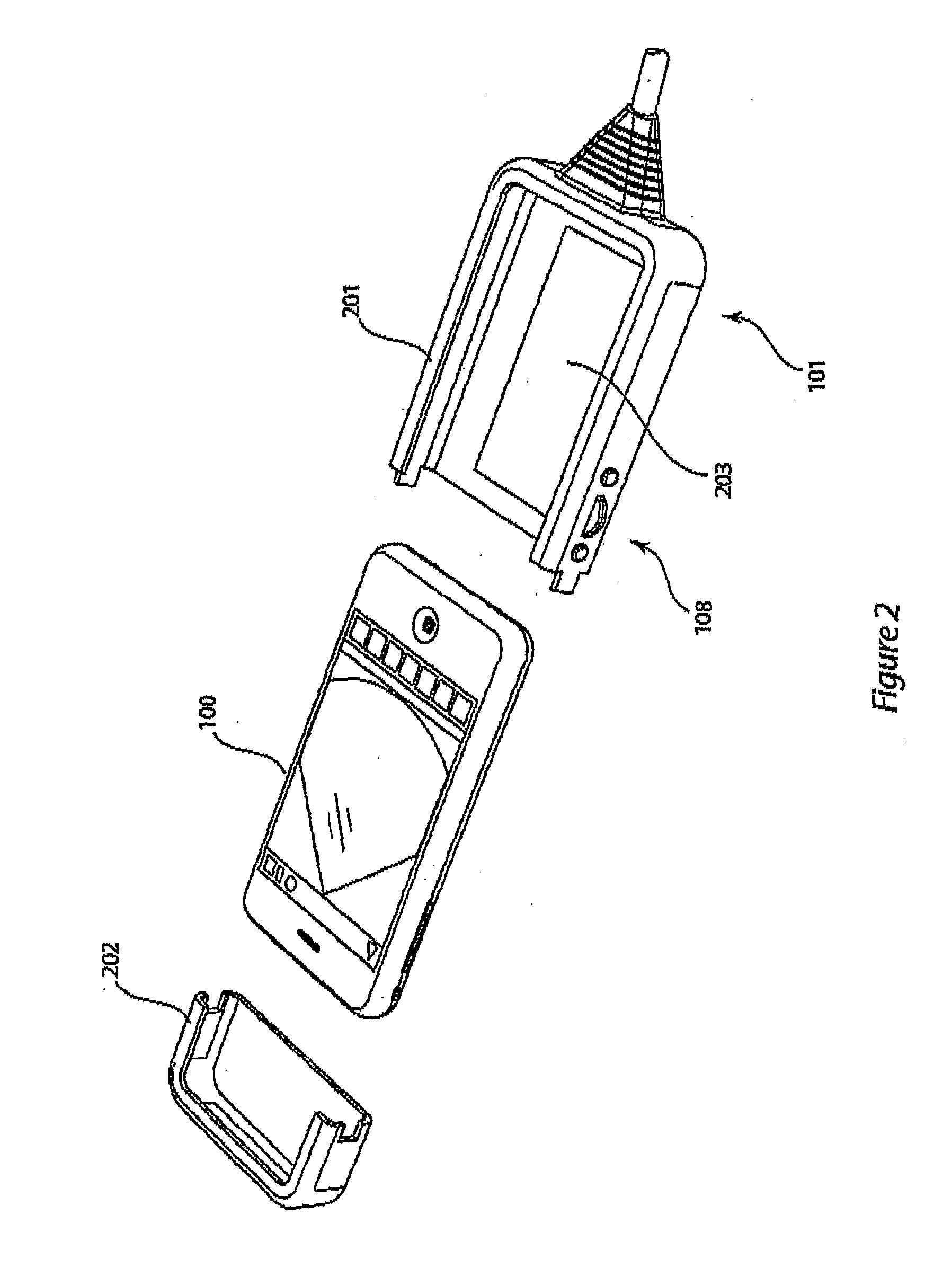
Docking system for medical diagnostic scanning using a handheld device
InactiveUS20110055447A1Low costMore weatherproofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDigital data processing detailsData acquisitionHandheld equipment
A docking system Including a clocking assembly which is able to surround and at least partially protect a handheld device such as a PDA or a smartphone, on In particular an IPhoπe, as made by Apple Inq, whilst providing means for connection of a probe unit to the handheld device. The probe unit has a data acquisition function.
Owner:SIGNOSTICS LTD
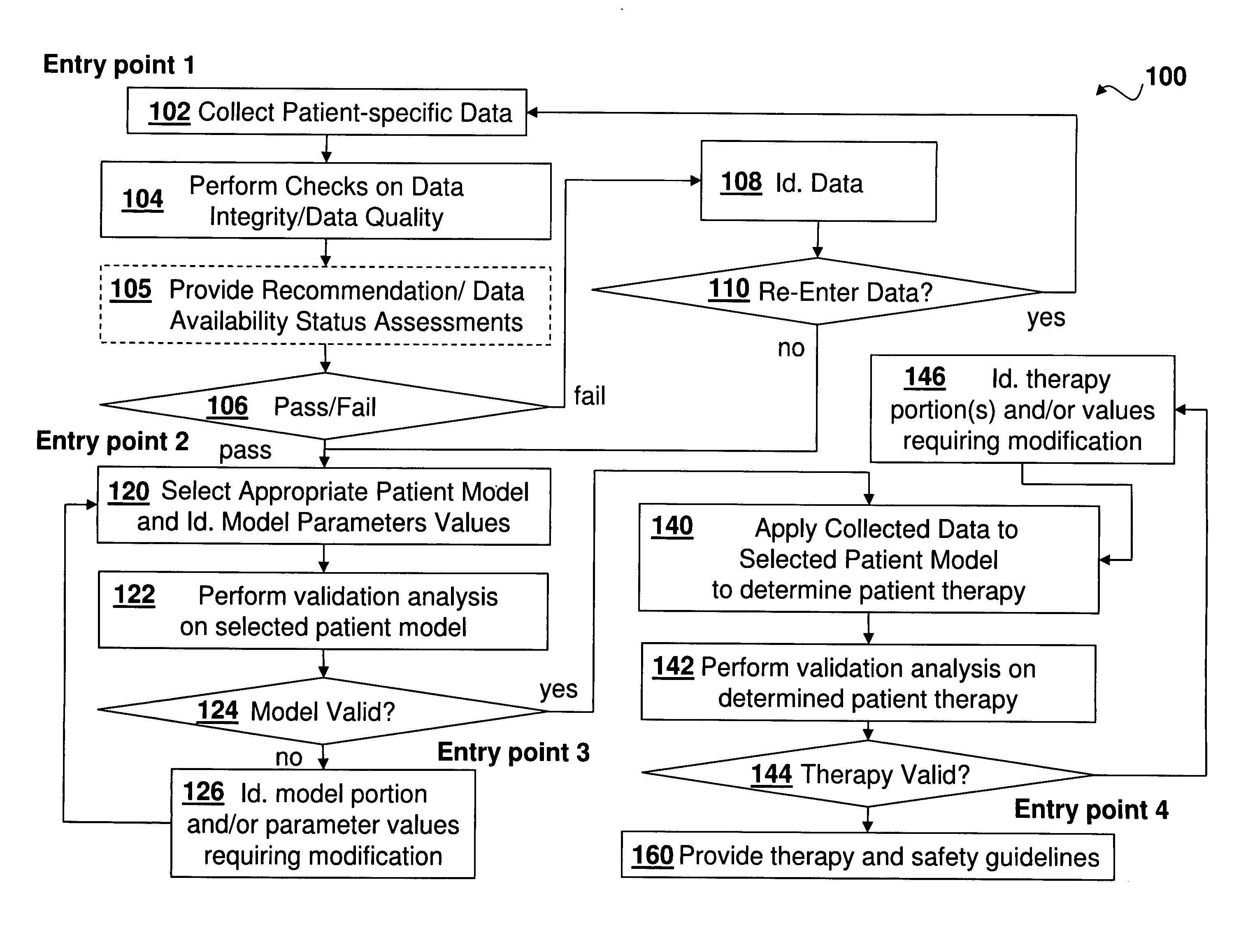
Medical Diagnosis, Therapy, And Prognosis System For Invoked Events And Methods Thereof
A diagnosis, therapy and prognosis system (DTPS) and method thereof to help either the healthcare provider or the patient in diagnosing, treating and interpreting data are disclosed. The apparatus provides data collection based on protocols, and mechanism for testing data integrity and accuracy. The data is then driven through an analysis engine to characterize in a quantitative sense the metabolic state of the patient's body. The characterization is then used in diagnosing the patient, determining therapy, evaluating algorithm strategies and offering prognosis of potential use case scenarios.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
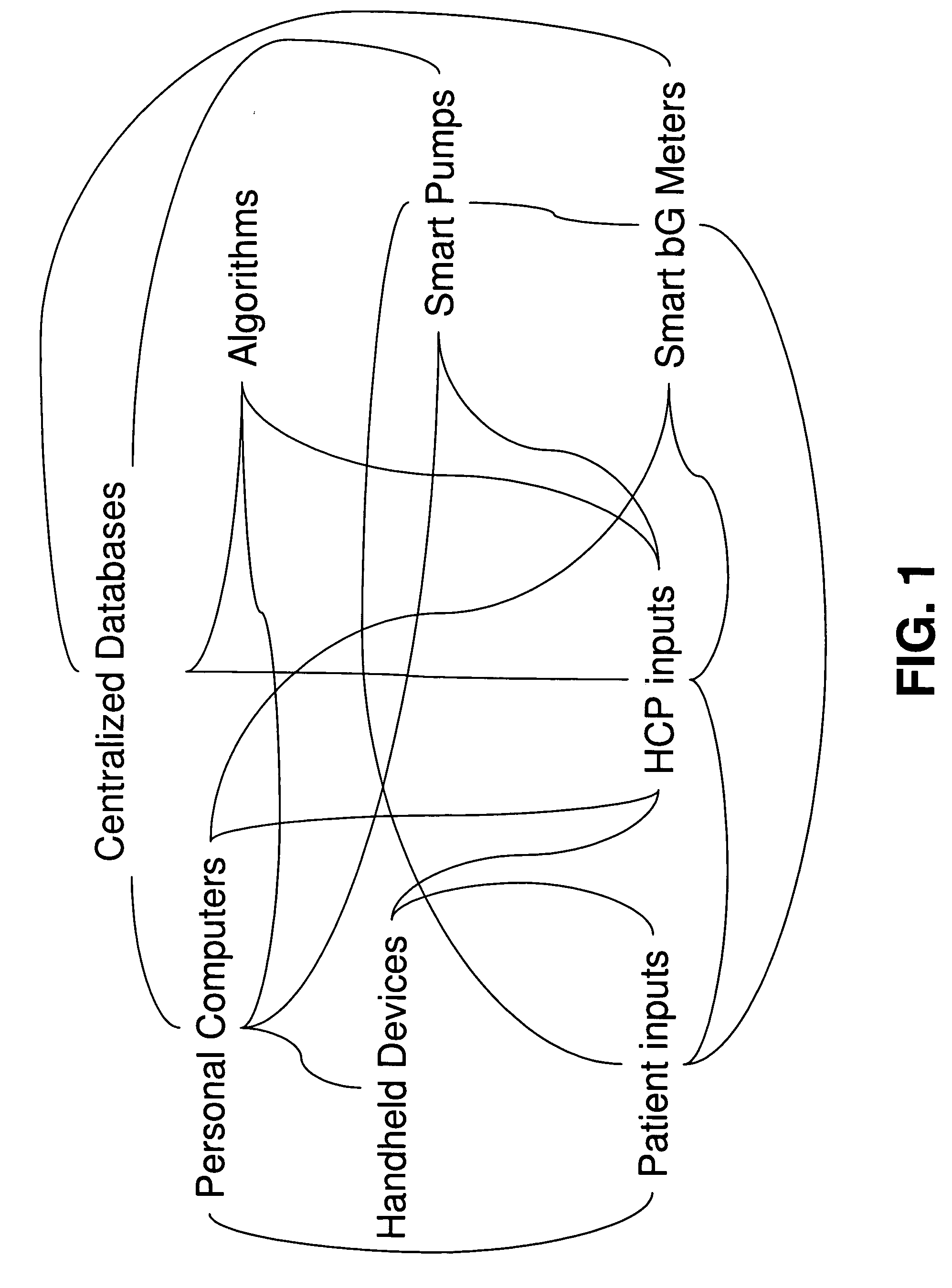
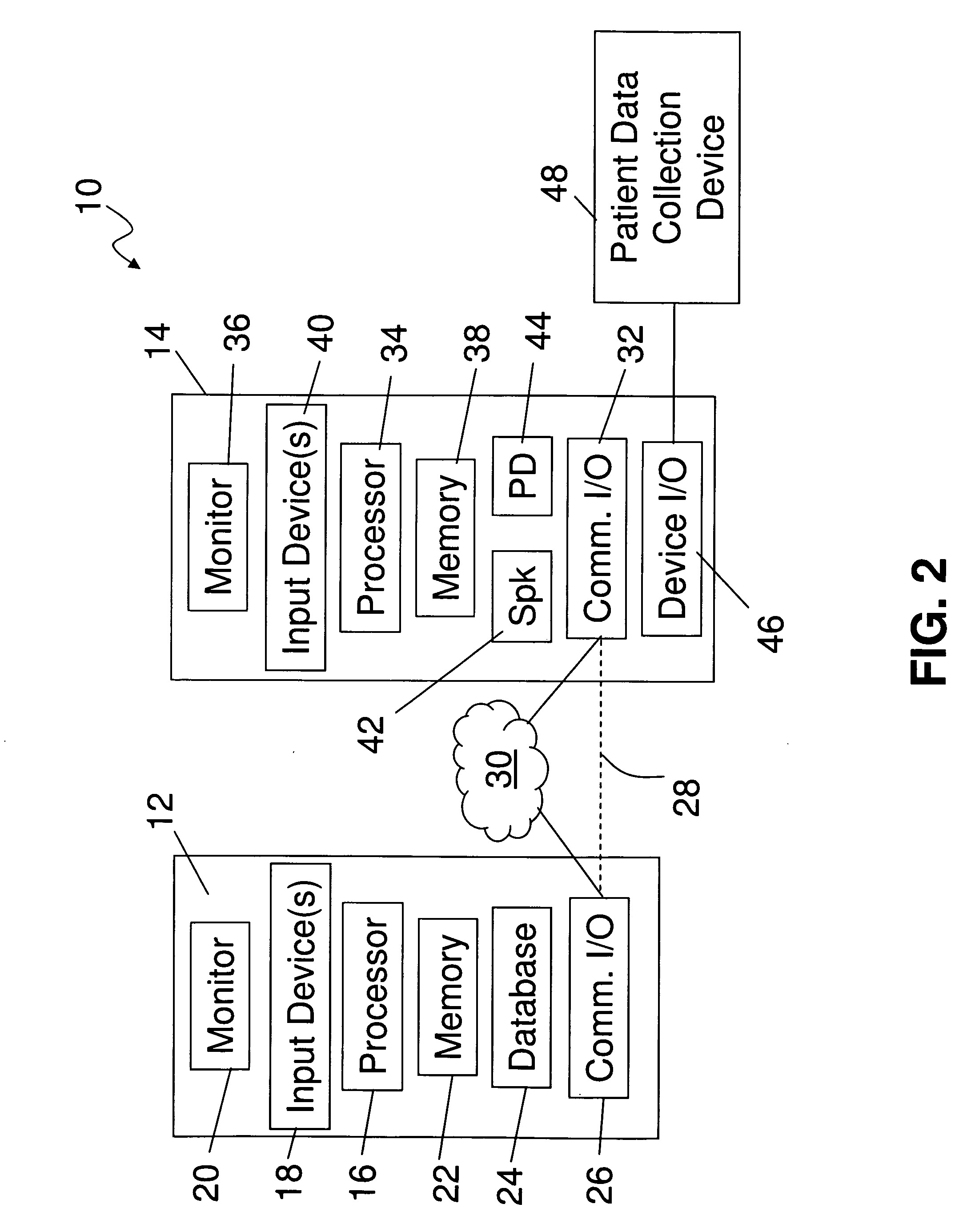
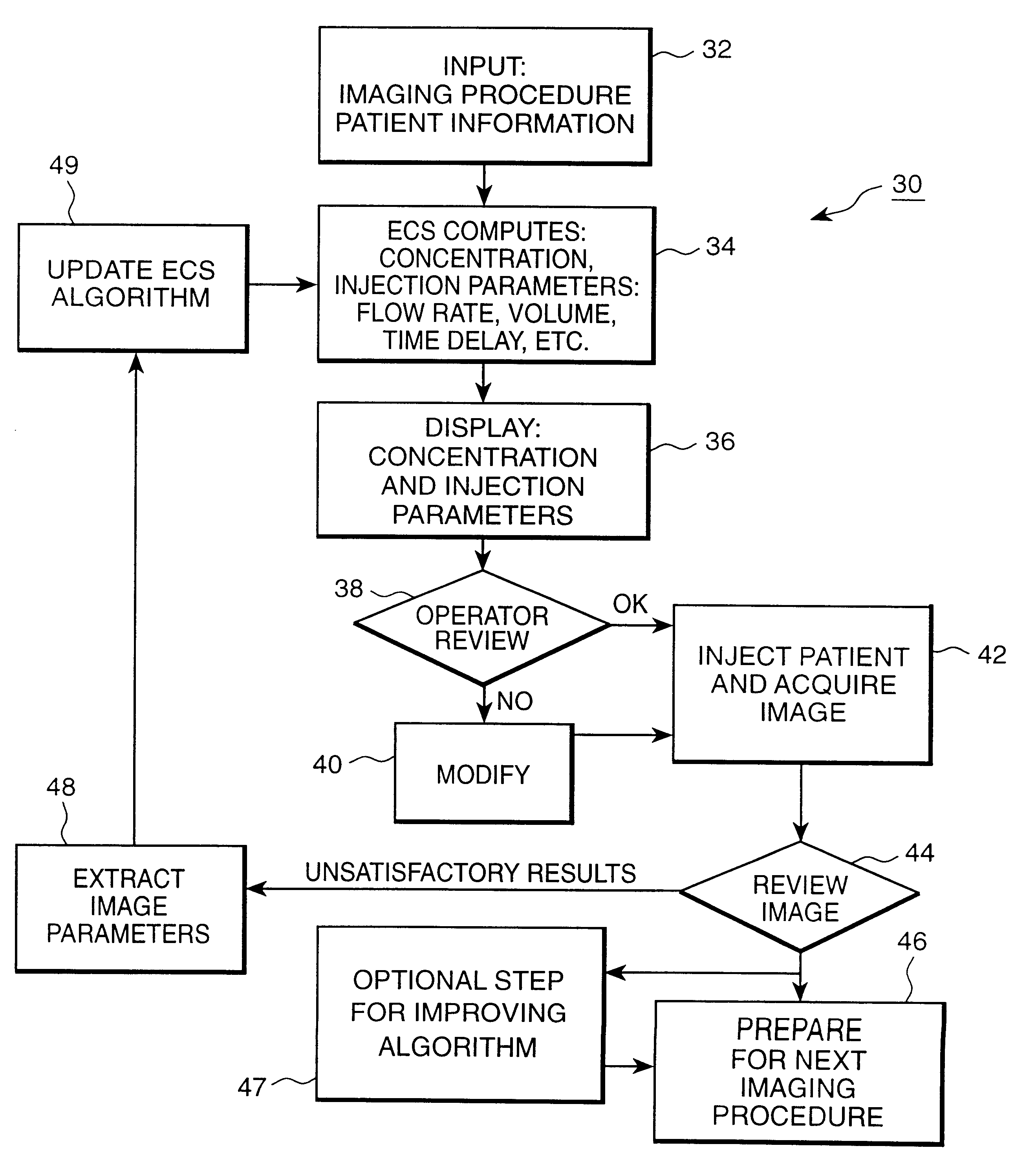
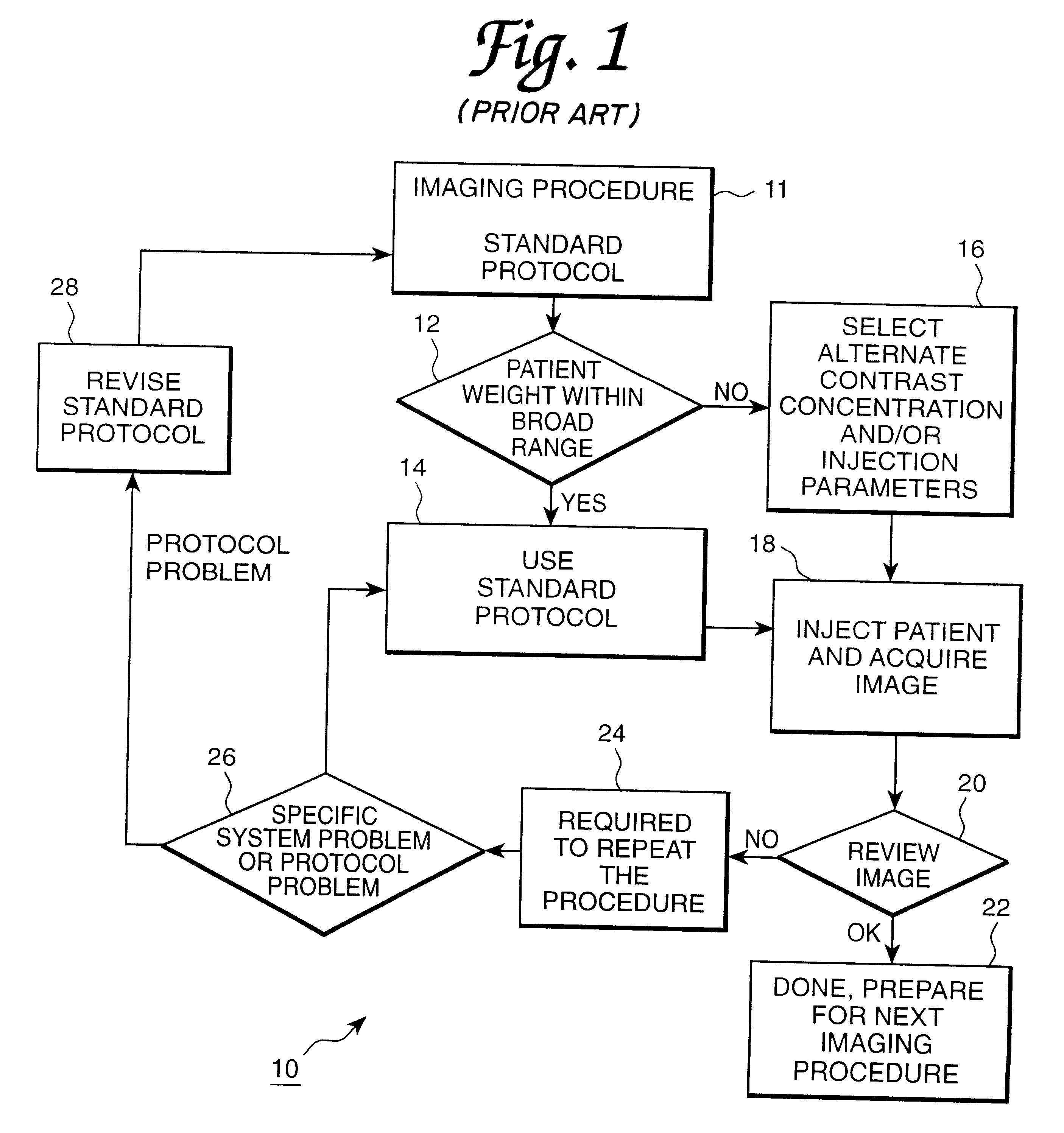
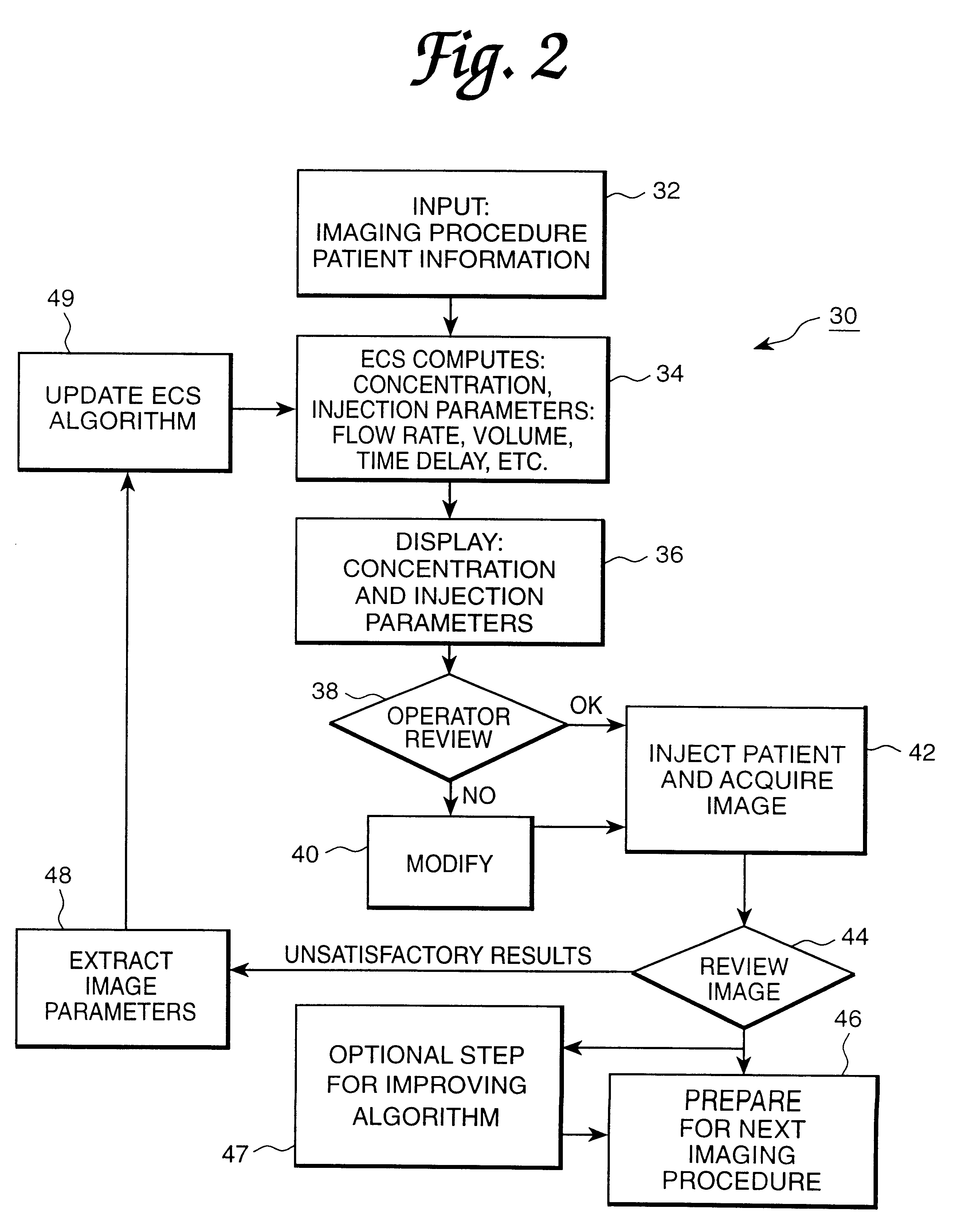
Patient specific dosing contrast delivery systems and methods
InactiveUS6385483B1Improve image qualityMinimum risk and costDrug and medicationsSurgeryMedicineMedical device
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
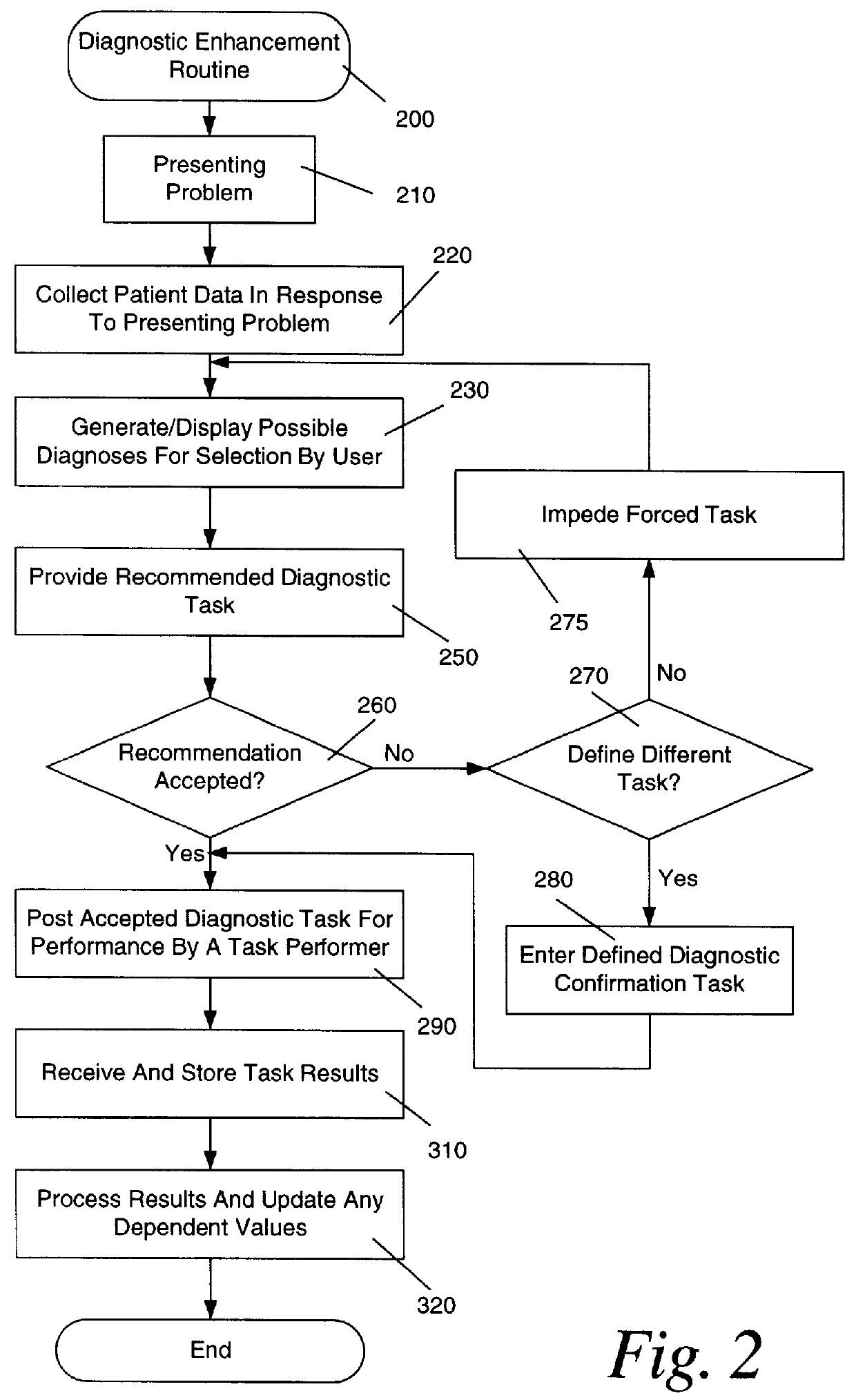
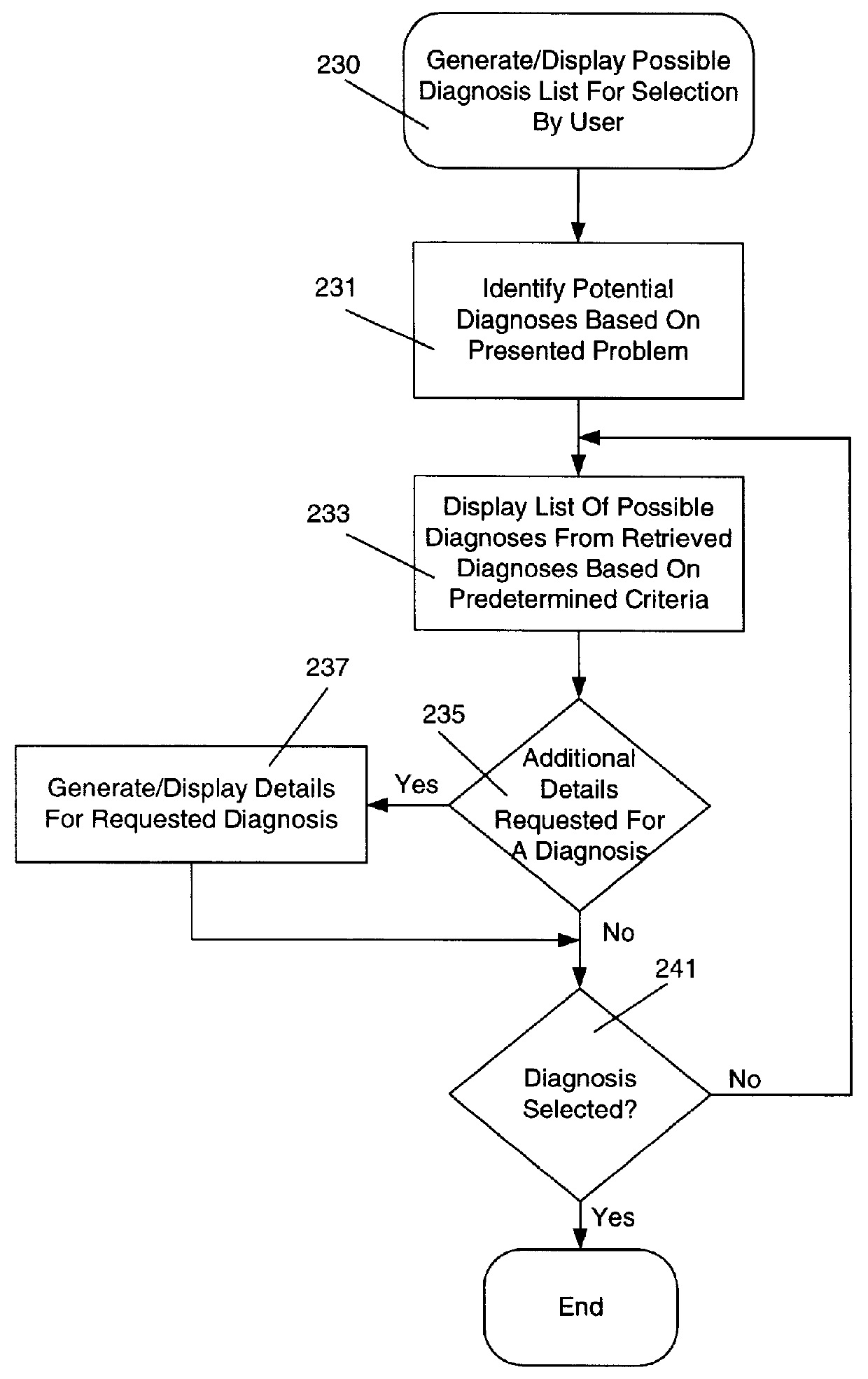
Diagnostic enhancement method and apparatus
A medical diagnostic enhancement method and system for determining diagnostic tasks to fine-tune a patient diagnosis based upon a possible diagnosis and acquired data for the patient. With this method, a presenting problem is received. Responsive to the presenting problem, particular patient data is then collected. Next, based on predetermined criteria, a plurality of possible diagnoses are presented for selection by a user. The user is then provided with a recommended diagnostic task based on the selected possible diagnosis. The system is a repository of the results of the diagnostic task or it can continue to process the patient data for other suspected diagnoses.
Owner:SAGE HEALTH MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
System and method for efficient diagnostic analysis of ophthalmic examinations
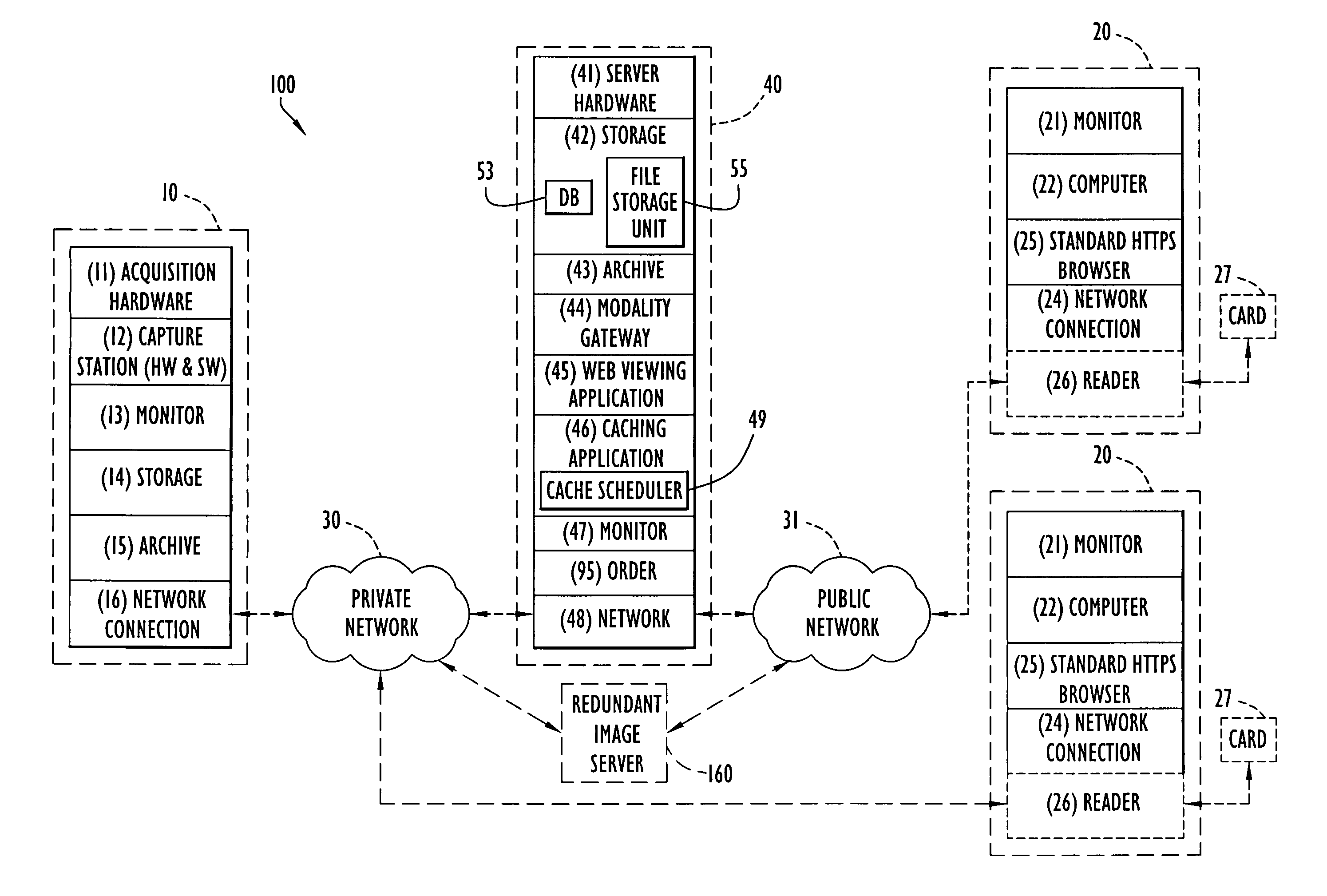
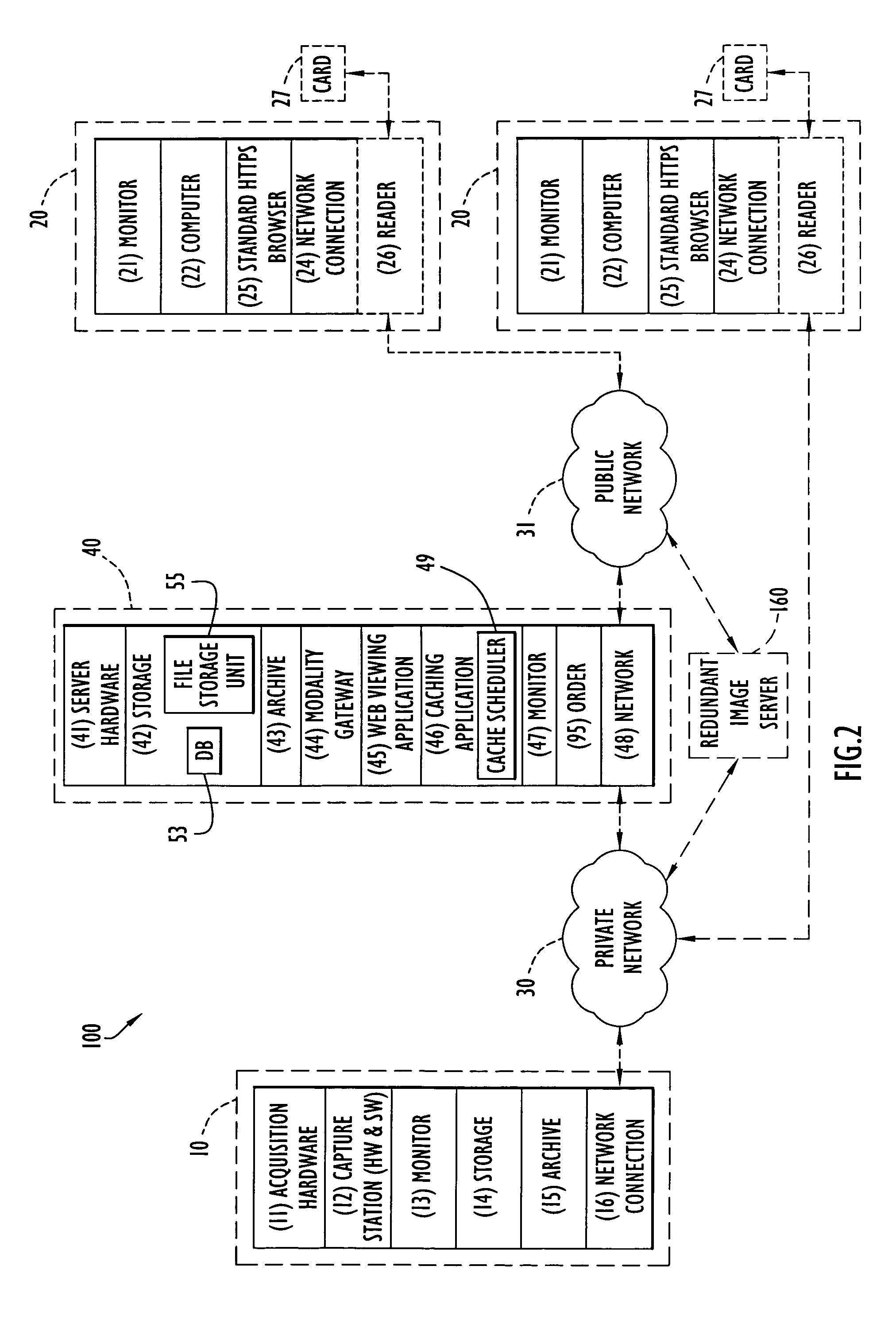
ActiveUS7818041B2Easy diagnosisSimplifies and optimizes wayMedical communicationInfrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImage server
A digital medical diagnostic system according to the present invention enables ophthalmologists to view patient and other images remotely to diagnose various conditions. The system includes at least one modality, one or more viewing stations, and an image server. The modality generates patient images associated with examinations, while the image server retrieves and processes information from the modalities. The image server may accommodate modalities utilizing different interfaces and / or formats. The viewing stations enable remote access to the images via a network (e.g., Internet), where the image server provides the interface for a user in the form of screens or web pages for security and viewing of information. The system enables an ophthalmologist or other medical personnel to view and / or manipulate one or more images to enhance diagnosis of patient examinations.
Owner:ANKA SYST INC
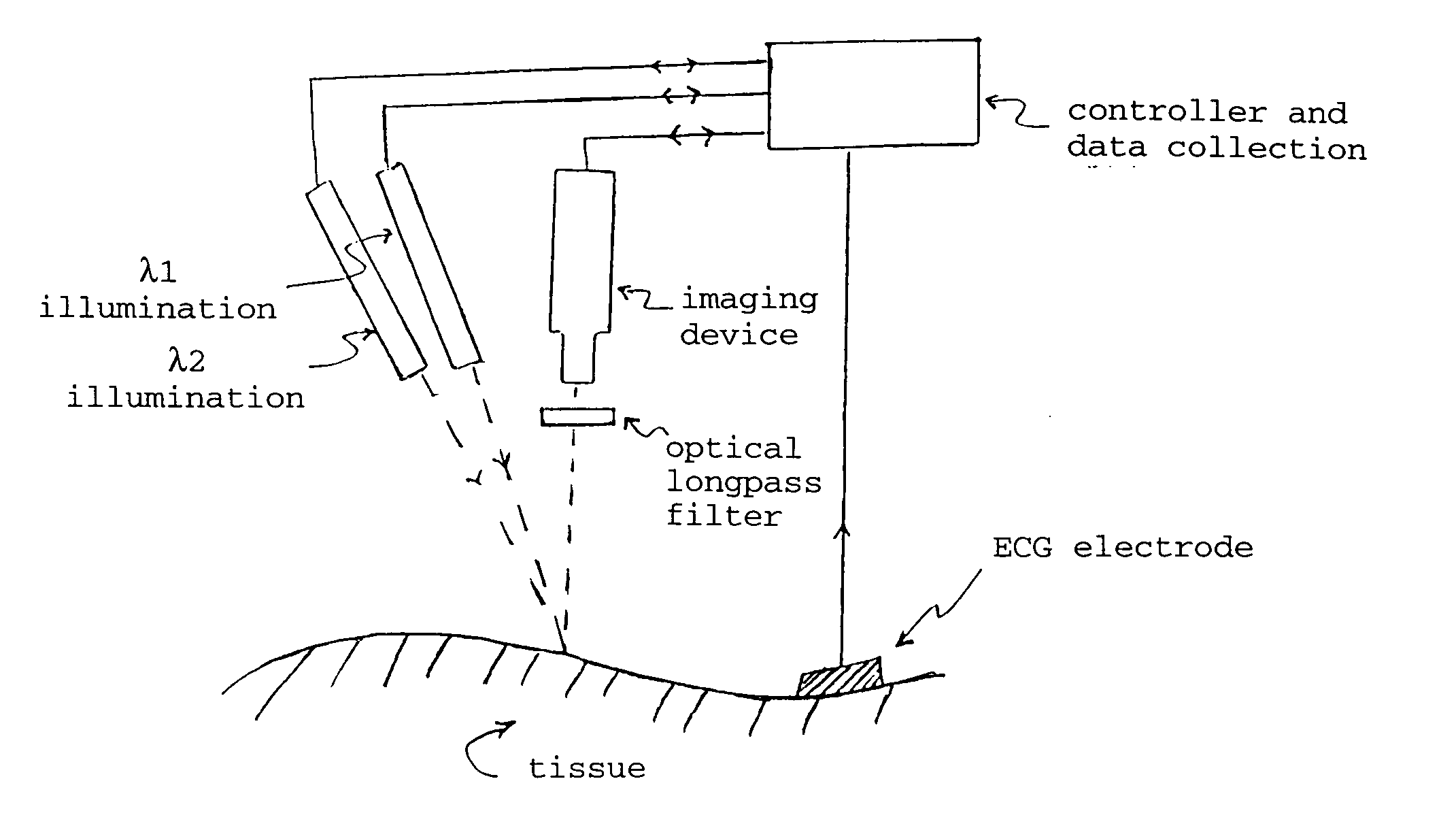
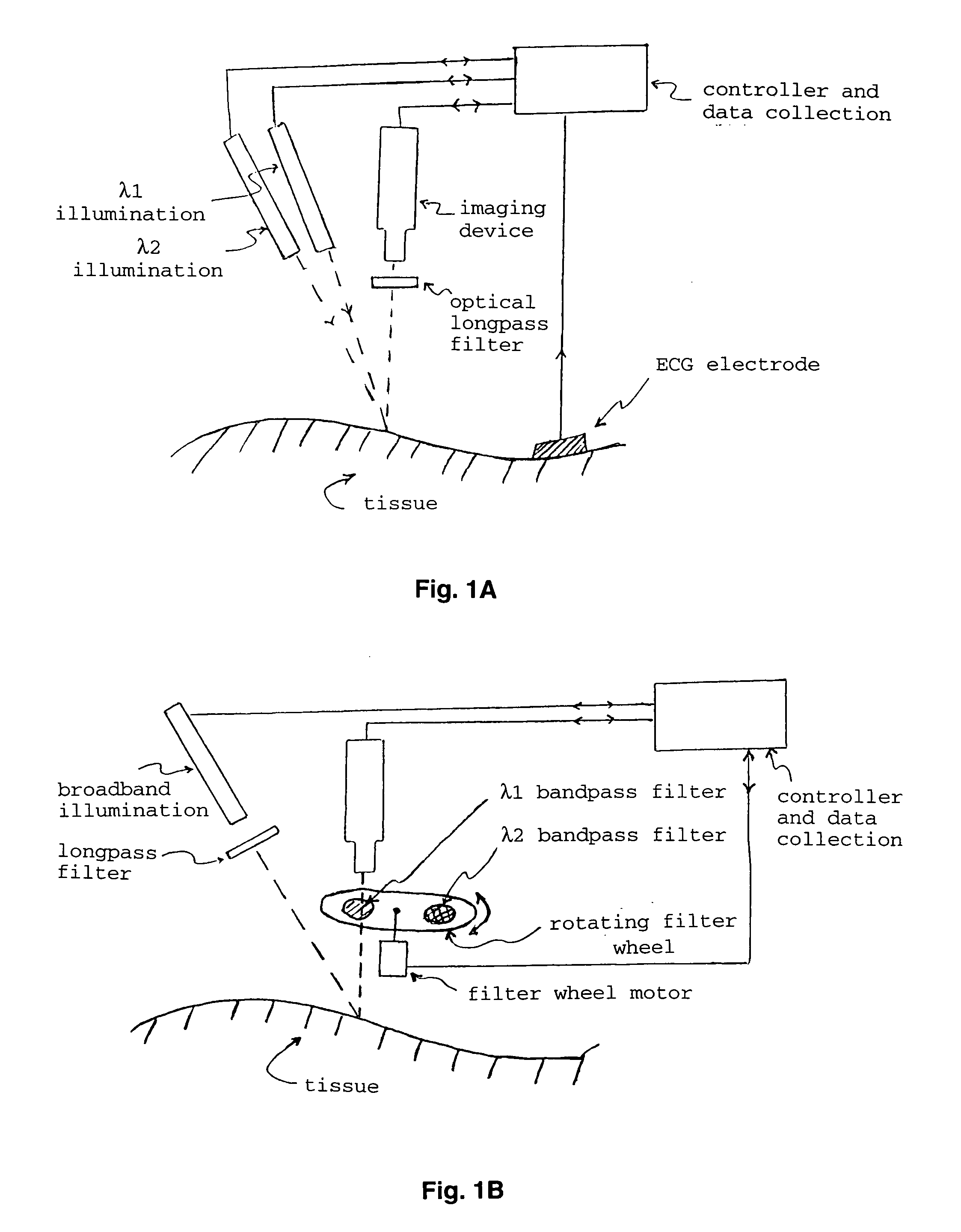
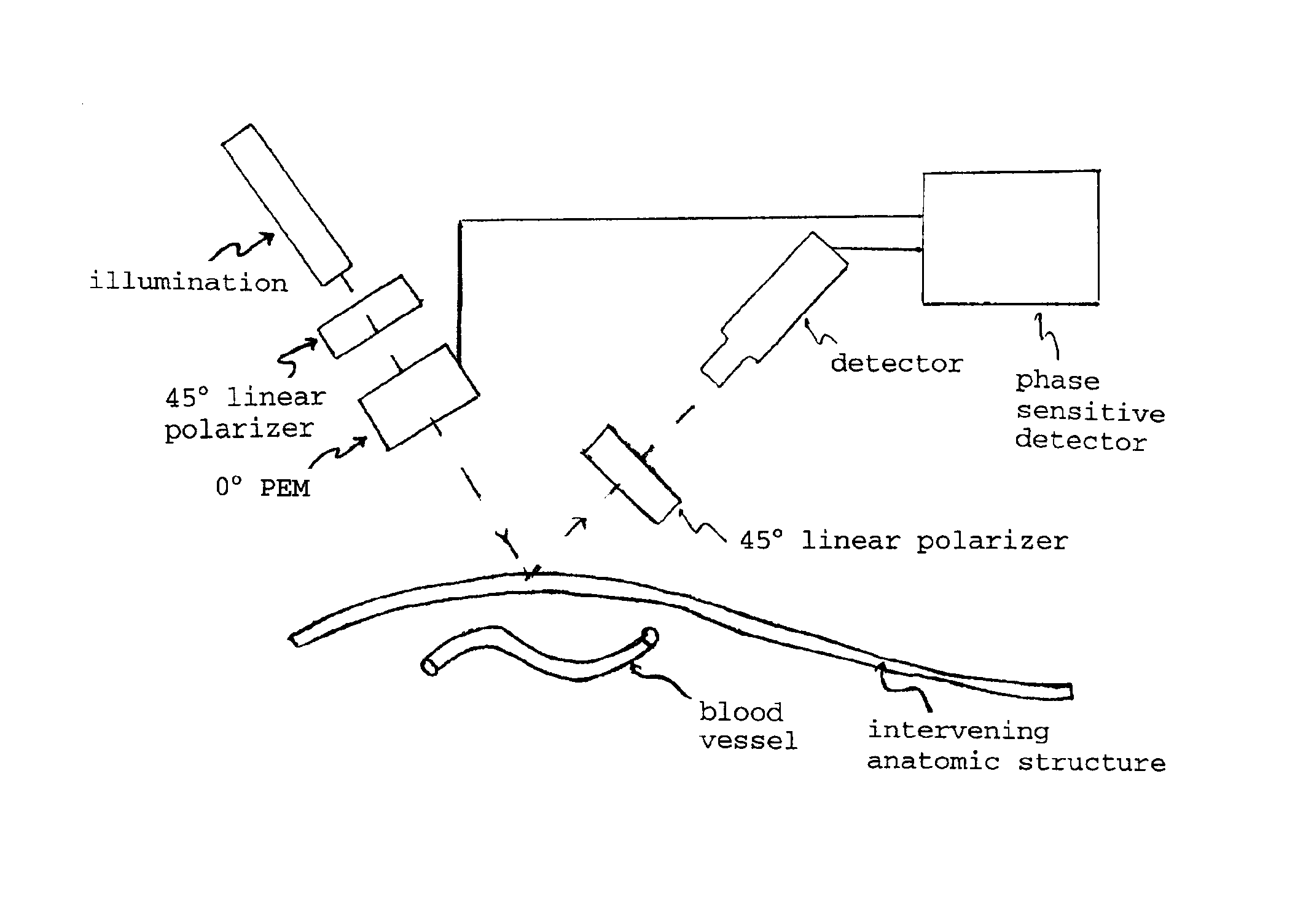
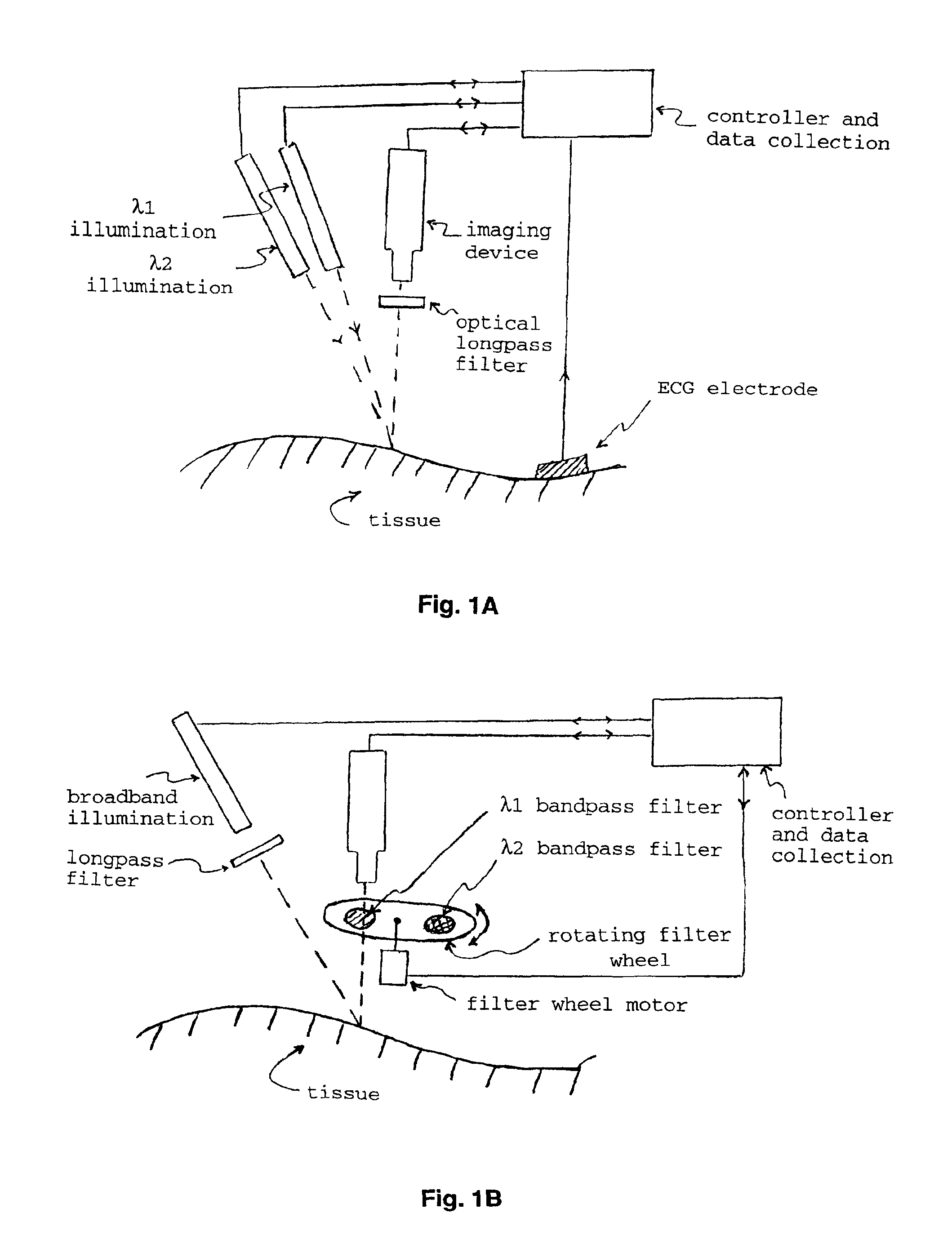
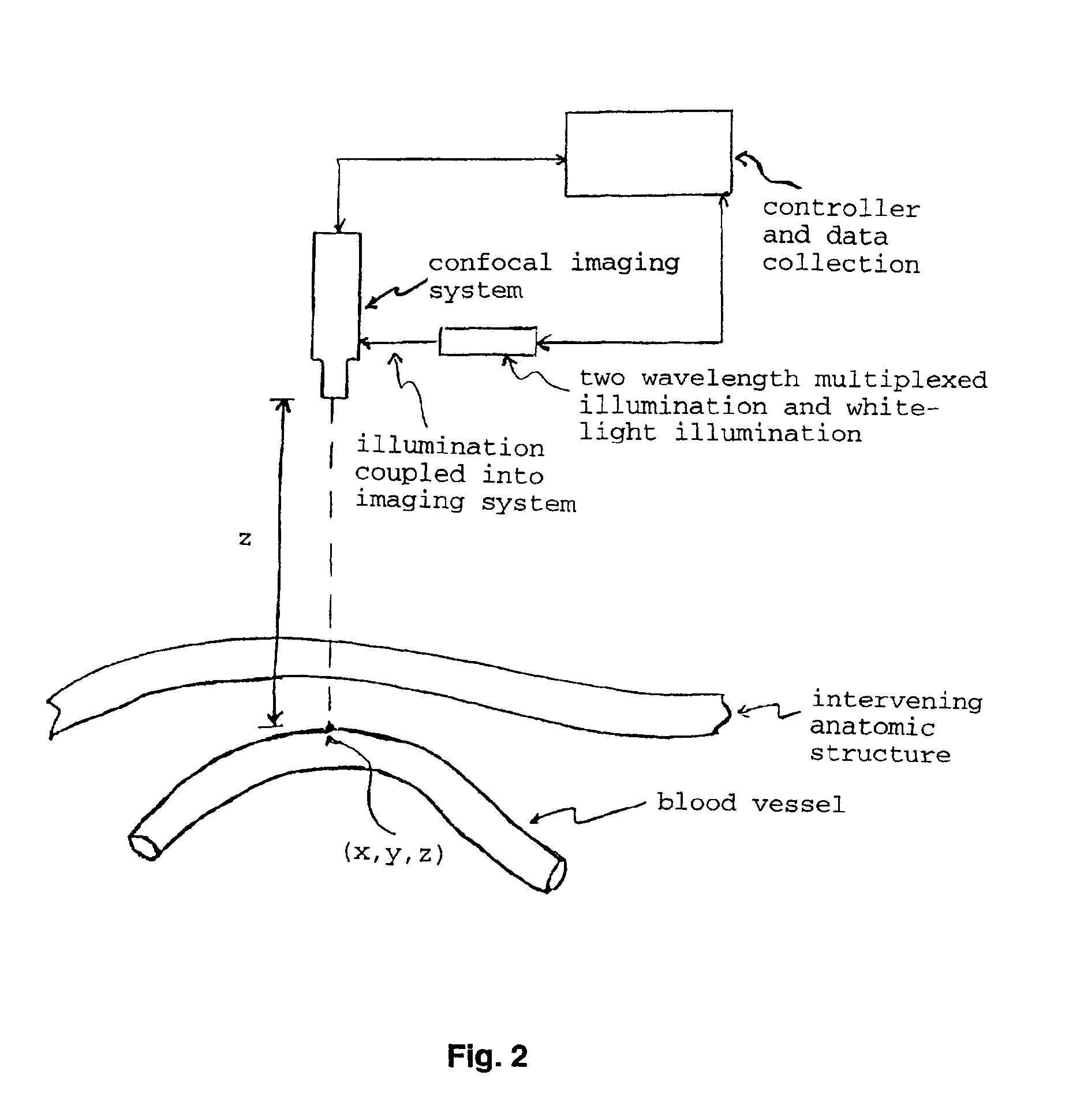
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS20050143662A1Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographySurgeryAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
Portable medical diagnostic systems and methods using a mobile device
ActiveUS20140072189A1High resultControl moreMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAmbient lightingColor correction
A system and method for analysis of colorimetric test strip strips and disease management. The system can include an accessory that is operably coupled to a mobile device, the mobile device acquiring and / or analyzing images of the colorimetric test strips. The light box accessory can be detachably attached to the mobile device, or made to remain attached to the mobile device, but with the capability of having the light box accessory removed from the field of view of the camera for general photography purposes. In other embodiments, an image containing known calibration color(s) and reagent area(s) is obtained sans the light box for comparison with a previous calibration image to model changes in ambient lighting conditions and determine a color correction function. The correction can be applied to the detected reagent area color(s) for matching between the detected reagent area color(s) and reference color(s) on the reference chart. Optionally, the information can be processed and displayed to provide feedback, as well as transmitted to a health provider for analysis.
Owner:JANA CARE
Optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules
InactiveUS6889075B2Increase contrastLow costElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMedical diagnosis
The present invention provides various methods / systems of optical imaging of subsurface anatomical structures and biomolecules utilizing red and infrared radiant energy. Also provided are various applications of such methods / systems in medical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:ROCKY MOUNTAIN BIOSYST
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7765005B2Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic interference
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
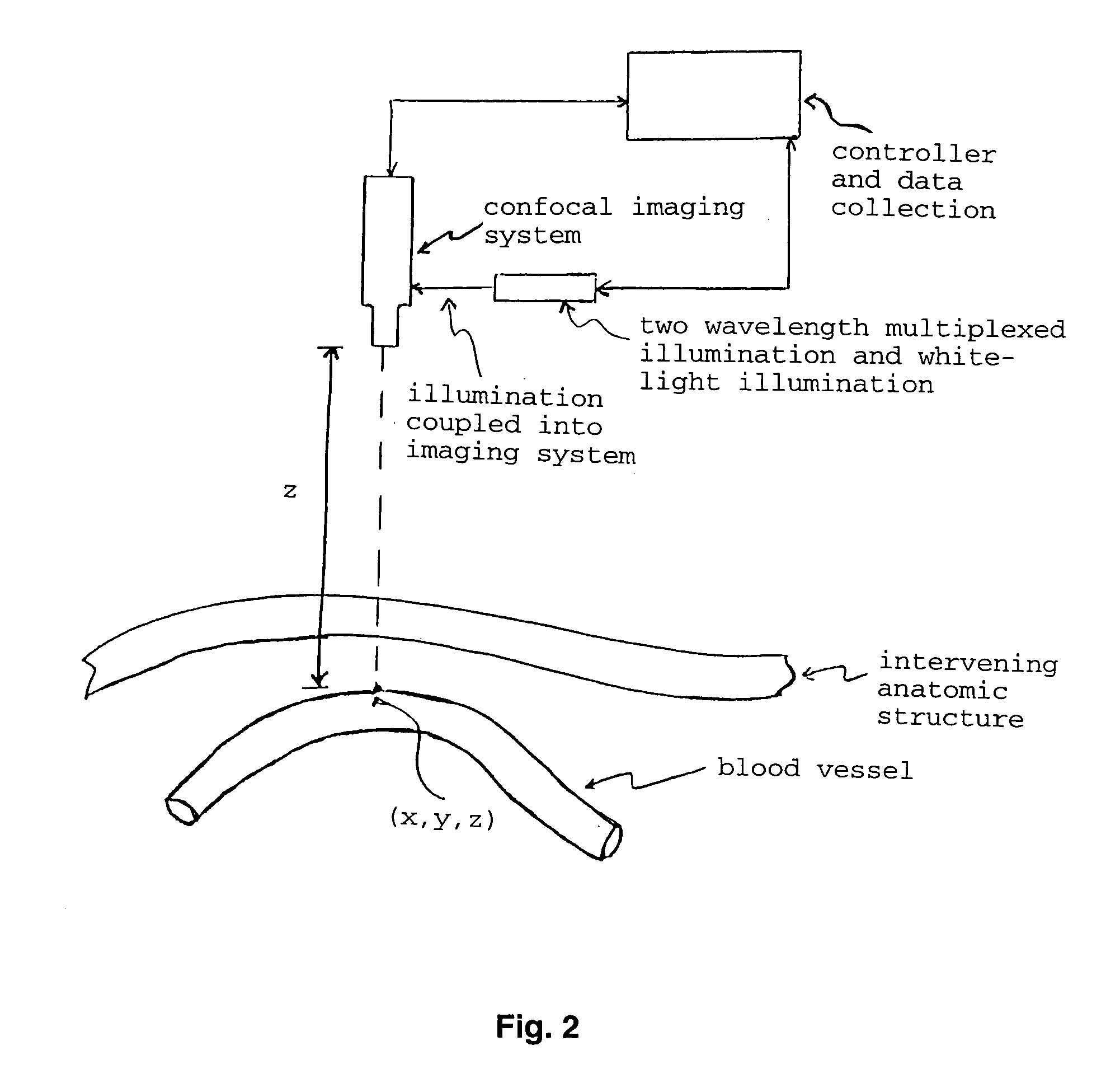
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20060253007A1Reduce disadvantagesImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionNon invasiveThree vessels
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
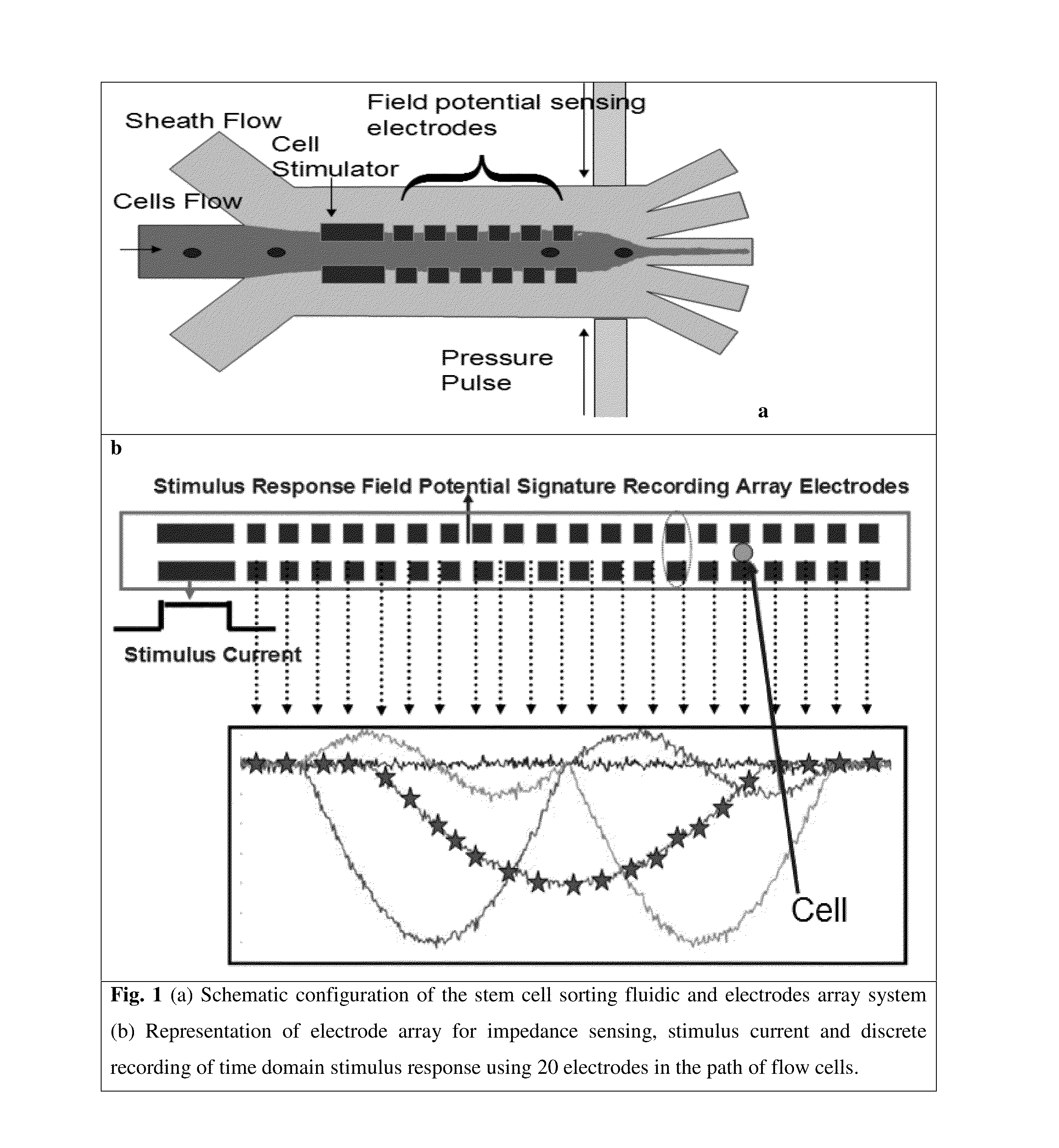
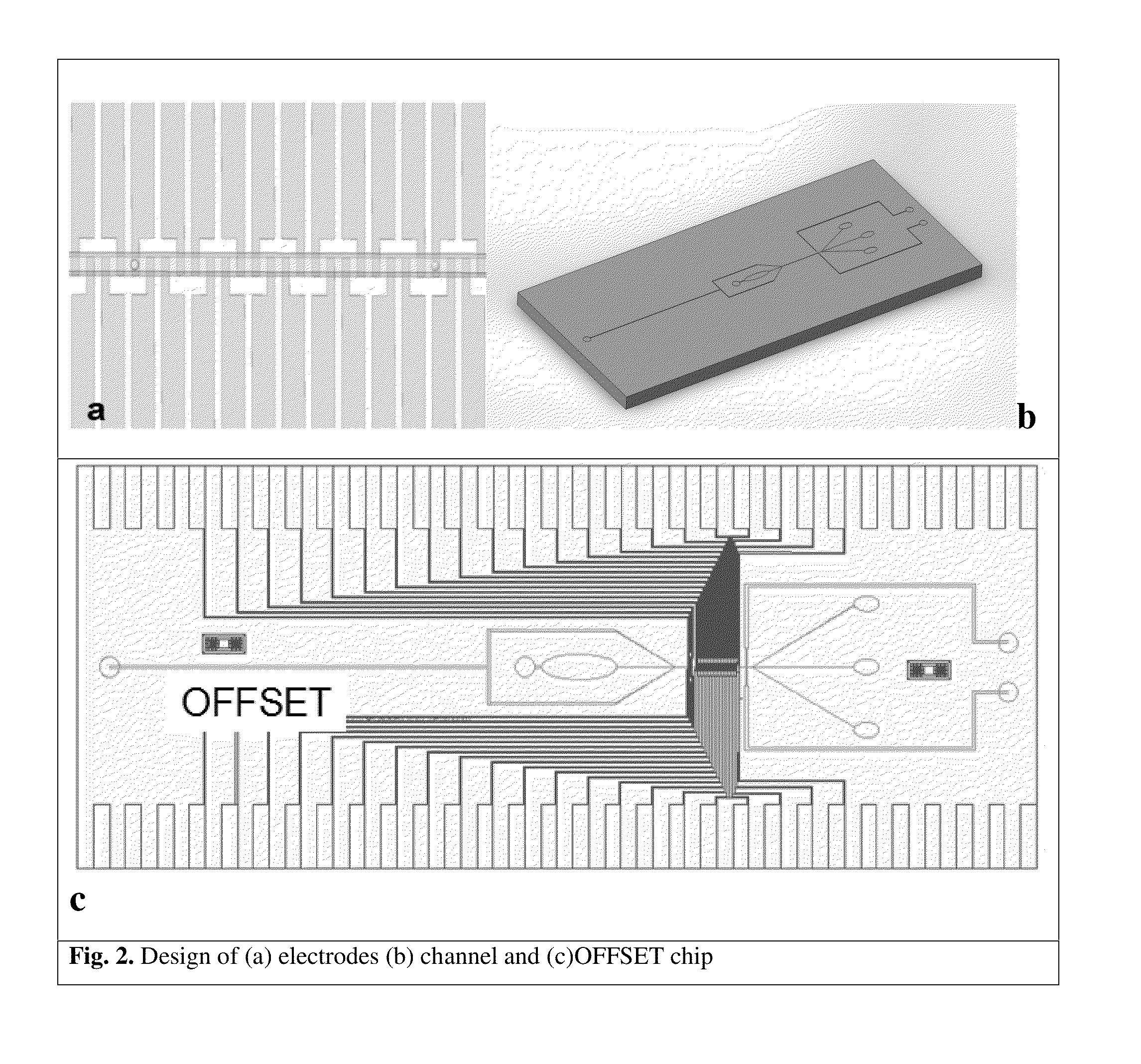
Microfluidic devices and methods for cell sorting, cell culture and cells based diagnostics and therapeutics
ActiveUS20140248621A1Uniform pressure distributionReduce widthHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurement3D cell cultureTumor cells
Microfluidic devices and methods that use cells such as cancer cells, stem cells, blood cells for preprocessing, sorting for various biodiagnostics or therapeutical applications are described. Microfluidics electrical sensing such as measurement of field potential or current and phenomena such as immiscible fluidics, inertial fluidics are used as the basis for cell and molecular processing (e.g., characterizing, sorting, isolation, processing, amplification) of different particles, chemical compositions or biospecies (e.g., different cells, cells containing different substances, different particles, different biochemical compositions, proteins, enzymes etc.). Specifically this invention discloses a few sorting schemes for stem cells, whole blood and circulating tumor cells and also extracting serum from whole blood. Further medical diagnostics technology utilizing high throughput single cell PCR is described using immiscible fluidics couple with single or multi cells trapping technology.
Owner:BIOPICO SYST
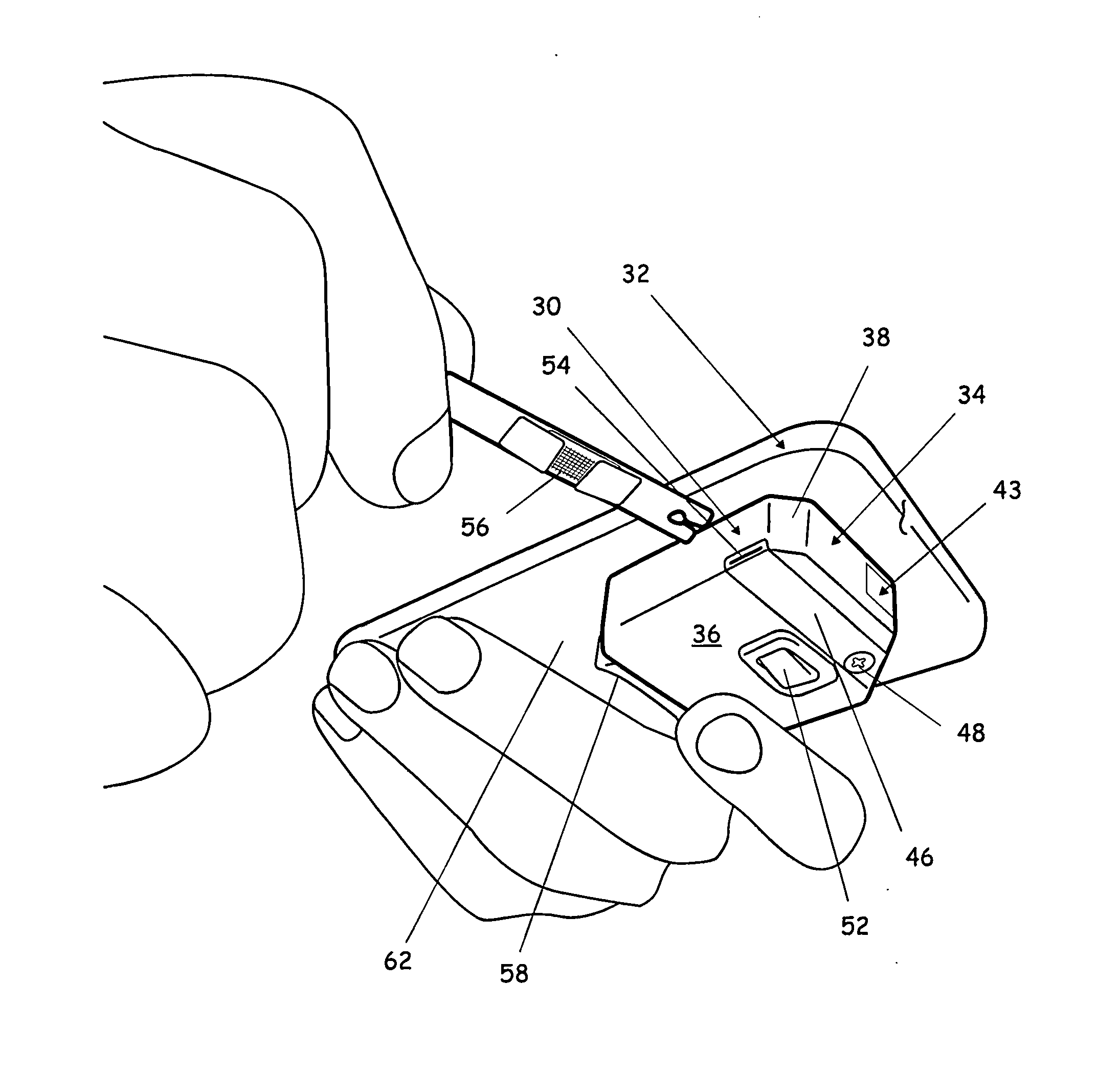
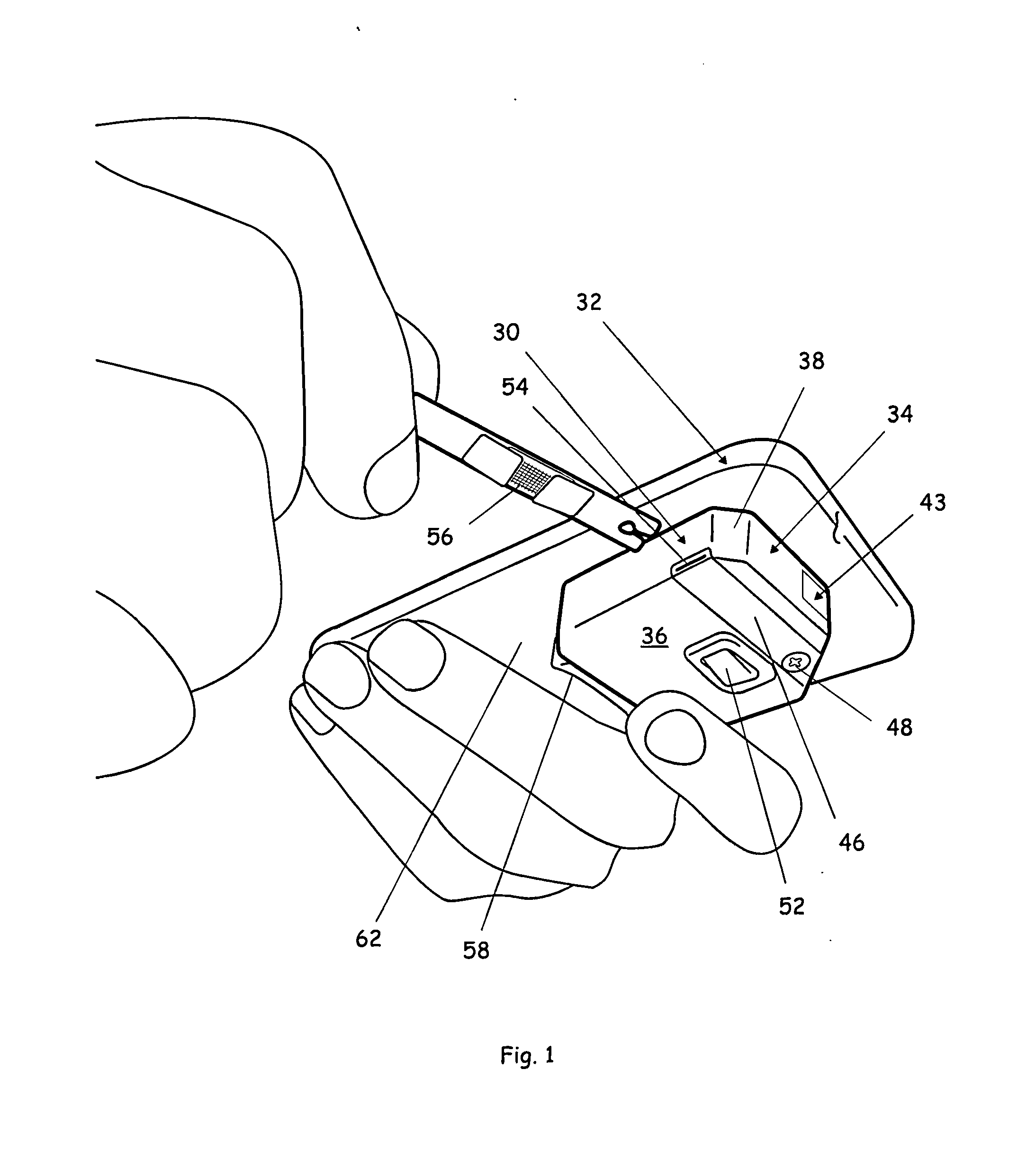
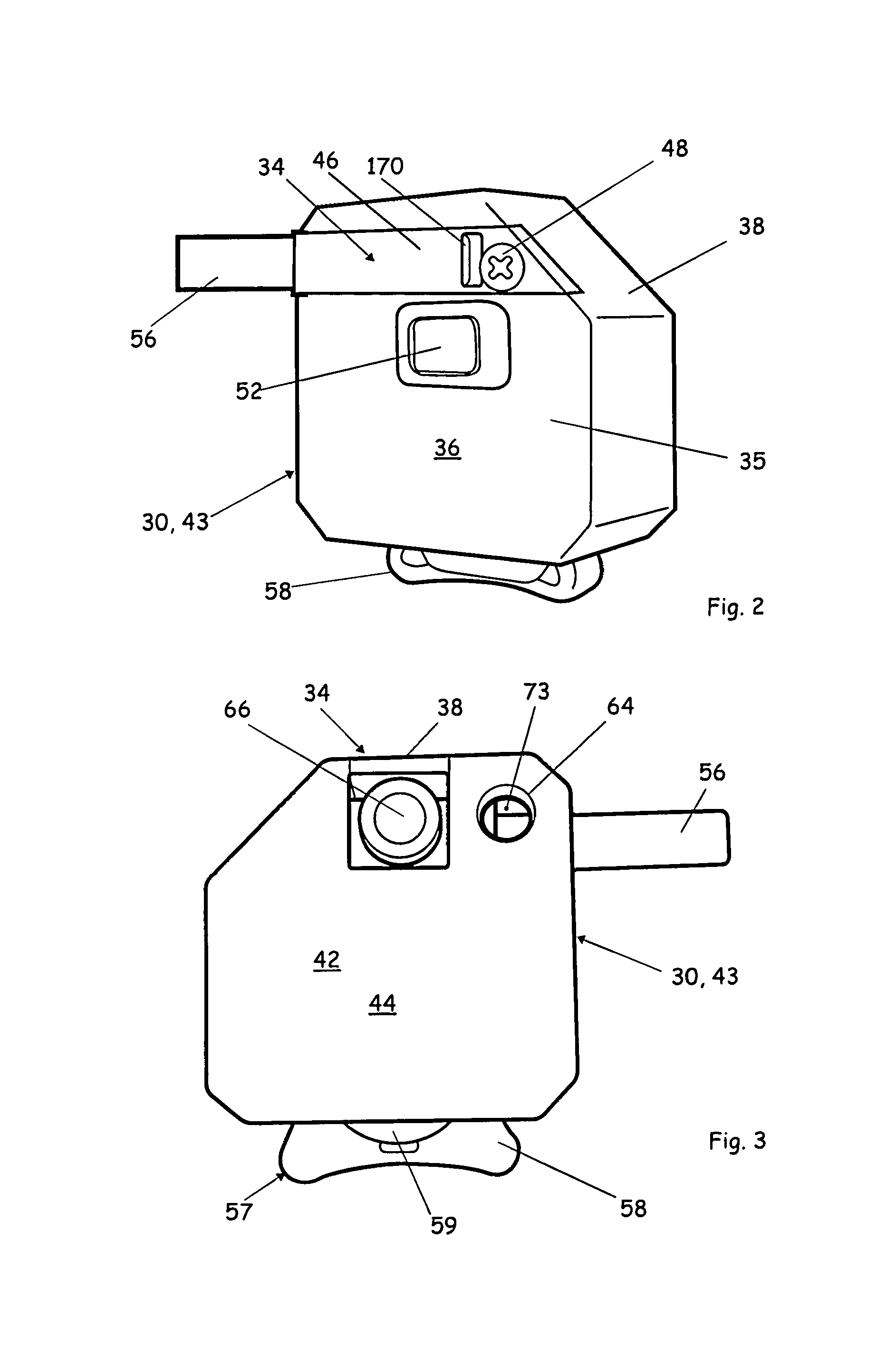
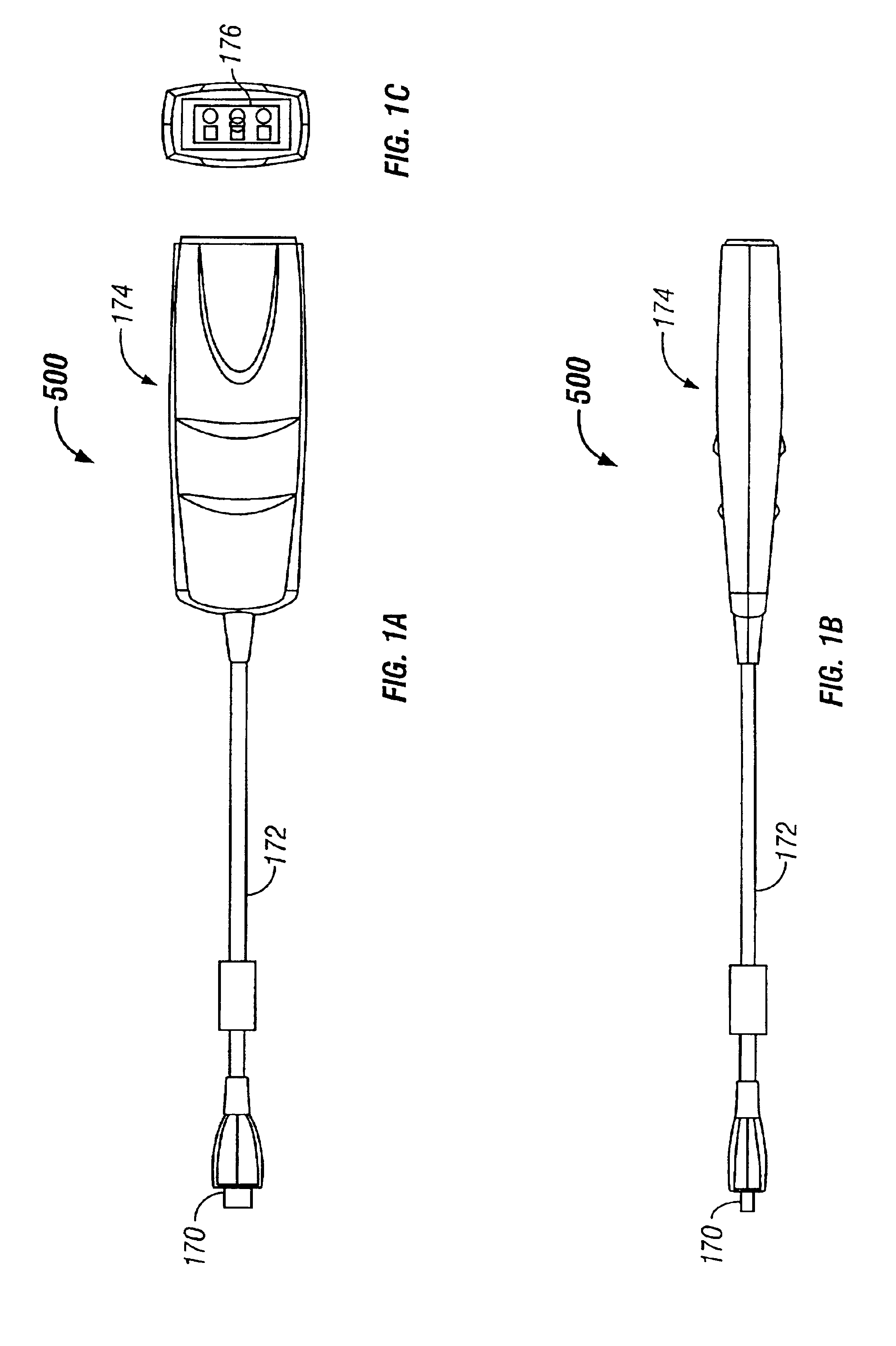
Medical diagnostic instrument having portable illuminator
ActiveUS20090287192A1Great degreeExcellent ease of useBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A portable medical diagnostic instrument includes an instrument head and a handle portion having an open-ended receiving cavity. A compact illuminator defined by a housing retaining a miniature light source and a power supply is releasably fitted within the open-ended receiving cavity of the handle portion wherein the light source of the illuminator is optically coupled with the instrument on assembly therewith. The handle portion can be integral with the instrument or releasably attached. The handle portion according to at least one version is made from a plastic or other suitable material, permitting disposability and / or single patient use. In one version, the handle portion is flexibly deformable, at least partially, to facilitate release of the portable illuminator.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
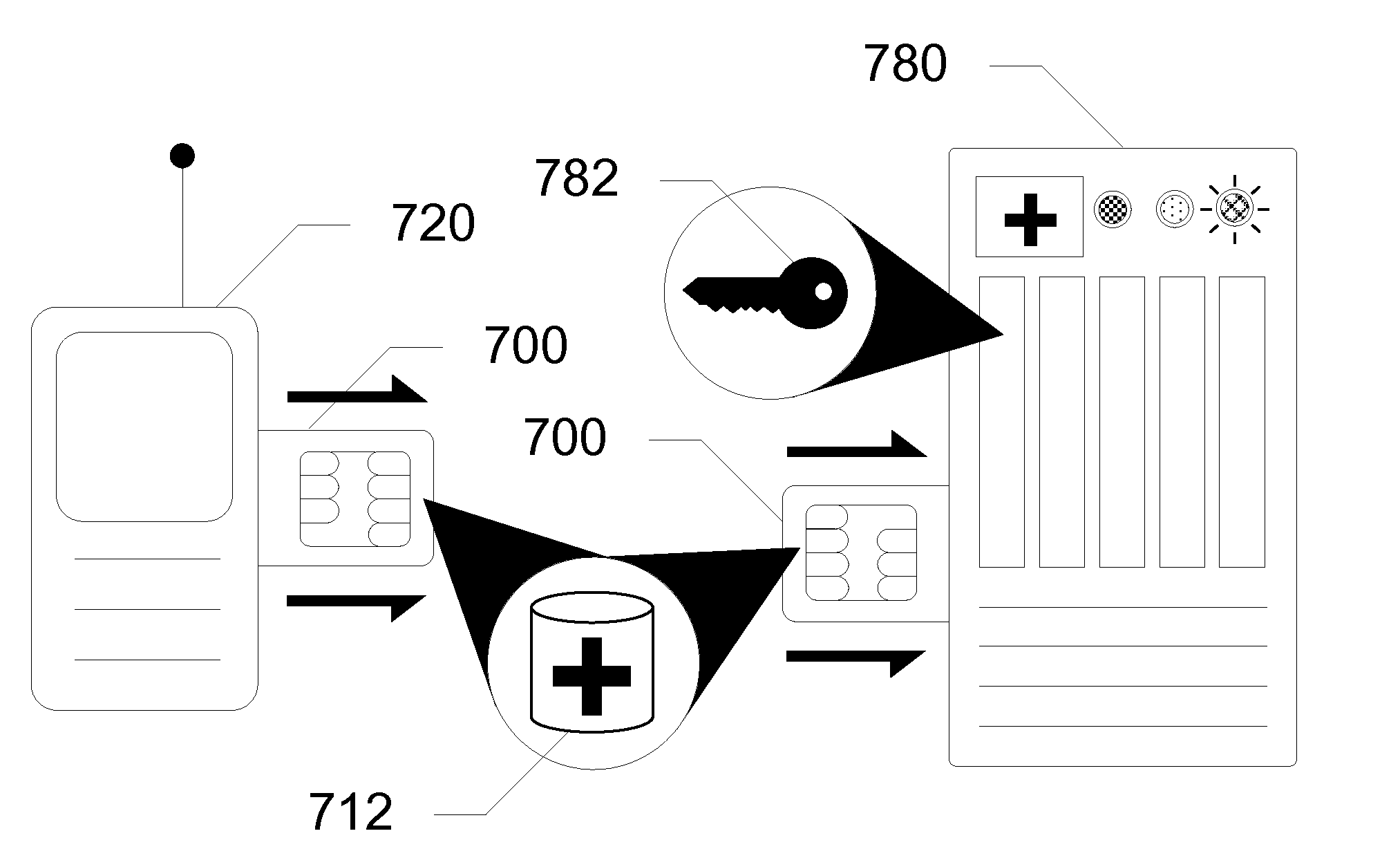
Devices, Systems and Methods for Secure Remote Medical Diagnostics
InactiveUS20110084132A1Secure transmissionData processing applicationsTelemedicineSmart cardData store
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed which relate to collecting and distributing medical diagnostics using a smart card. A smart card with secure medical diagnostics logic on the memory is disclosed. When the smart card is inserted into a wireless communications device, the smart card receives data from a wireless medical diagnostic device. The wireless medical diagnostic device can be wearable by a user. The smart card stores the data in a medical diagnostics database on the smart card memory. A doctor or other medical professional may access the data in the medical diagnostics database after providing authentication.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method and apparatus for discovering patterns in binary or categorical data
InactiveUS20050143928A1Save time and costGood sensitivityBiostatisticsProteomicsMedical diagnosisBinary trait
The present invention relates to a computationally efficient method of finding patterns in any data that can be expressed in the form of arrays of binary features or arrays of categorical features. This includes data represented by continuous-valued attributes that can be transformed to a categorical representation, such as the discovery of patterns of genetic variability that may be causally related to diseases or traits, as well as the discovery of patterns of protein biomarkers that may be used for medical diagnostics, prognostics, and therapeutics. The invention further relates to a program storage device having instructions for controlling a computer system to perform the methods, and to a program storage device containing data structures used in the practice of the methods.
Owner:MOSER ALLAN ROBERT
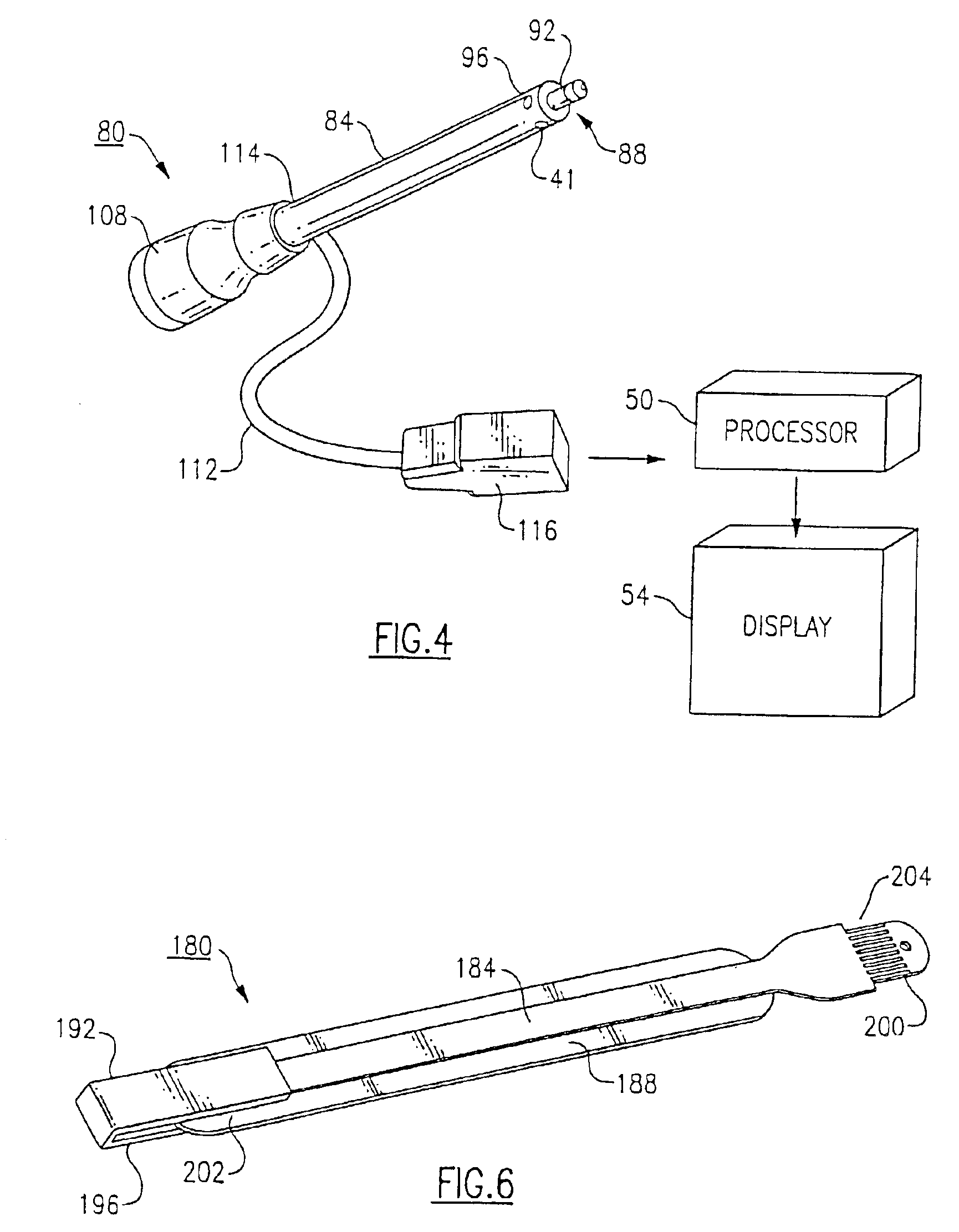
Medical diagnostic ultrasound instrument with ECG module, authorization mechanism and methods of use
InactiveUS6962566B2Restricts modificationImprove distributionElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic modalitiesColor doppler
A handheld ultrasound instrument is disclosed having enhanced diagnostic modes including pulse / continuous wave Doppler, time-motion analysis, spectral analysis and tissue harmonic imaging. An external electrocardiograph (ECG) recording unit is also disclosed. The ECG unit is adaptable to be used with the handheld ultrasound instrument to provide for ECG monitoring while performing an ultrasound scan in B-mode, Doppler, color Doppler, M-mode, and CW / PW mode. The enhanced handheld ultrasound instrument further includes a security mechanism allowing any combination of the diagnostic modes to be enabled by the manufacturer, and later to enable or disable any one or group of the diagnostic modes. The invention also discloses a method for a manufacturer to maintain a database of handheld ultrasound instrument capabilities after the instruments enter the stream of commerce.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Electrical adapter for medical diagnostic instruments using LEDs as illumination sources
ActiveUS7276025B2Impacting costProlong lifeBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEngineeringDiagnostic instrument
An adapter for permitting a medical diagnostic instrument having an illumination source including at least one LED (light emitting diode) to be used with a power supply normally configured for use with a diagnostic instrument having at least one incandescent lamp as an illumination source. The adapter includes circuitry for compensating LED specific characteristics for permitting the power supply to be used with the LED.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Medical device and method with improved biometric verification
ActiveUS8679012B1Prevents misuse and fraudPrevent fraudSensorsBiometric pattern recognitionComputer scienceMedical device
The present invention is both a device and a method for verifying a subject's identity while using a medical device or undergoing a medical diagnostic or therapeutic procedure, particularly at home or at a remote location. The method and device can be used for inpatient and remote sleep and signal analysis with biometric identification. The present invention is further related to the devices and sensors used in executing the method, and includes various embodiments of a method of inpatient and remote sleep analysis.
Owner:CLEVELAND MEDICAL DEVICES
Combination SPO2/temperature measuring apparatus
InactiveUS6850789B2Hasten overall measurement timeAvoid thermal effectsRadiation pyrometryThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsMedicineAxilla
A medical diagnostic instrument includes at least one blood oxygen saturation sensor and at least one temperature sensor. The sensors are being capable of measuring blood oxygen saturation and temperature simultaneously after insertion of a probe portion of the instrument relative to a defined body site, such as the axilla, rectum, or sublingual pocket of a patient. At least a portion of the probe portion of the instrument is disposable.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
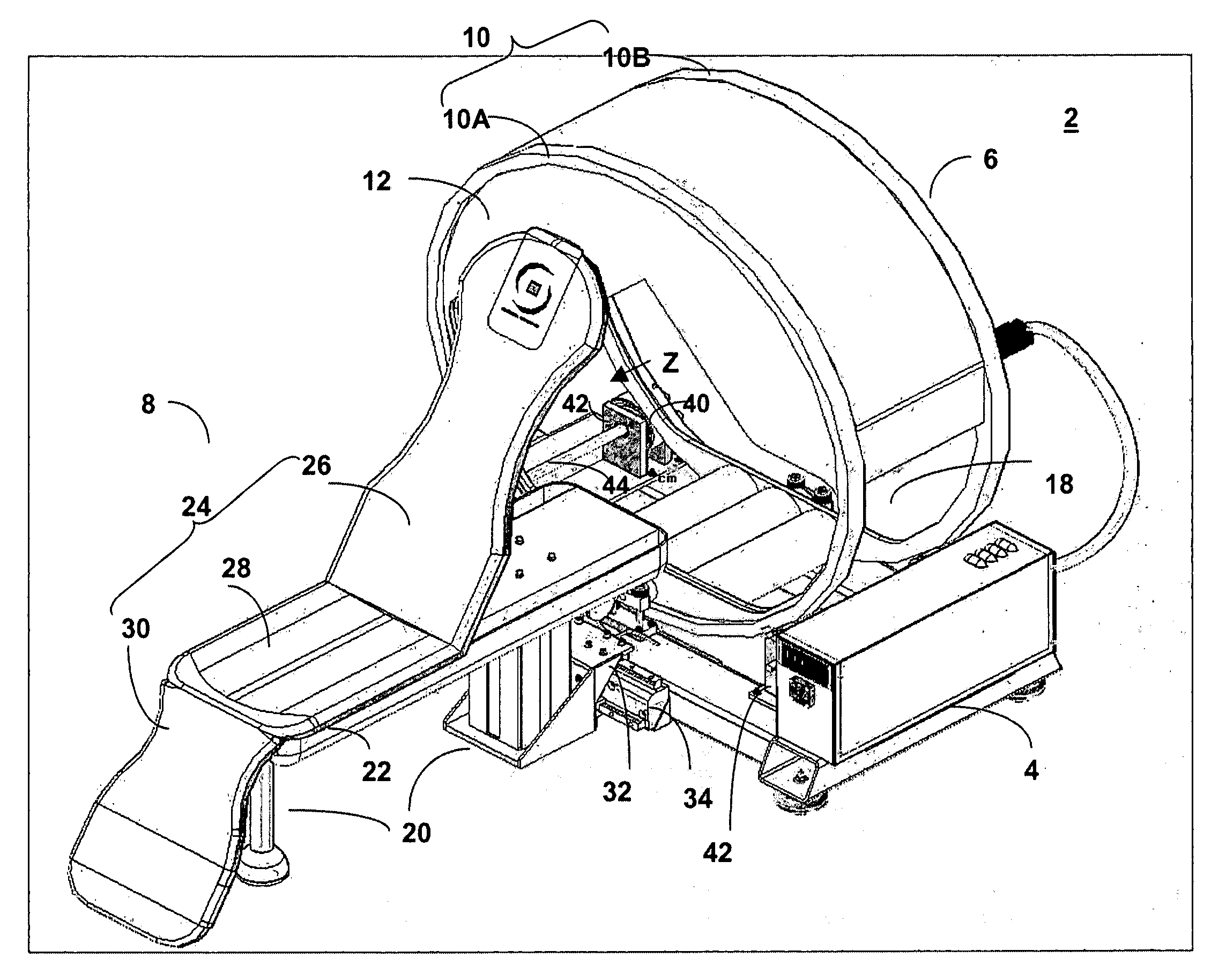
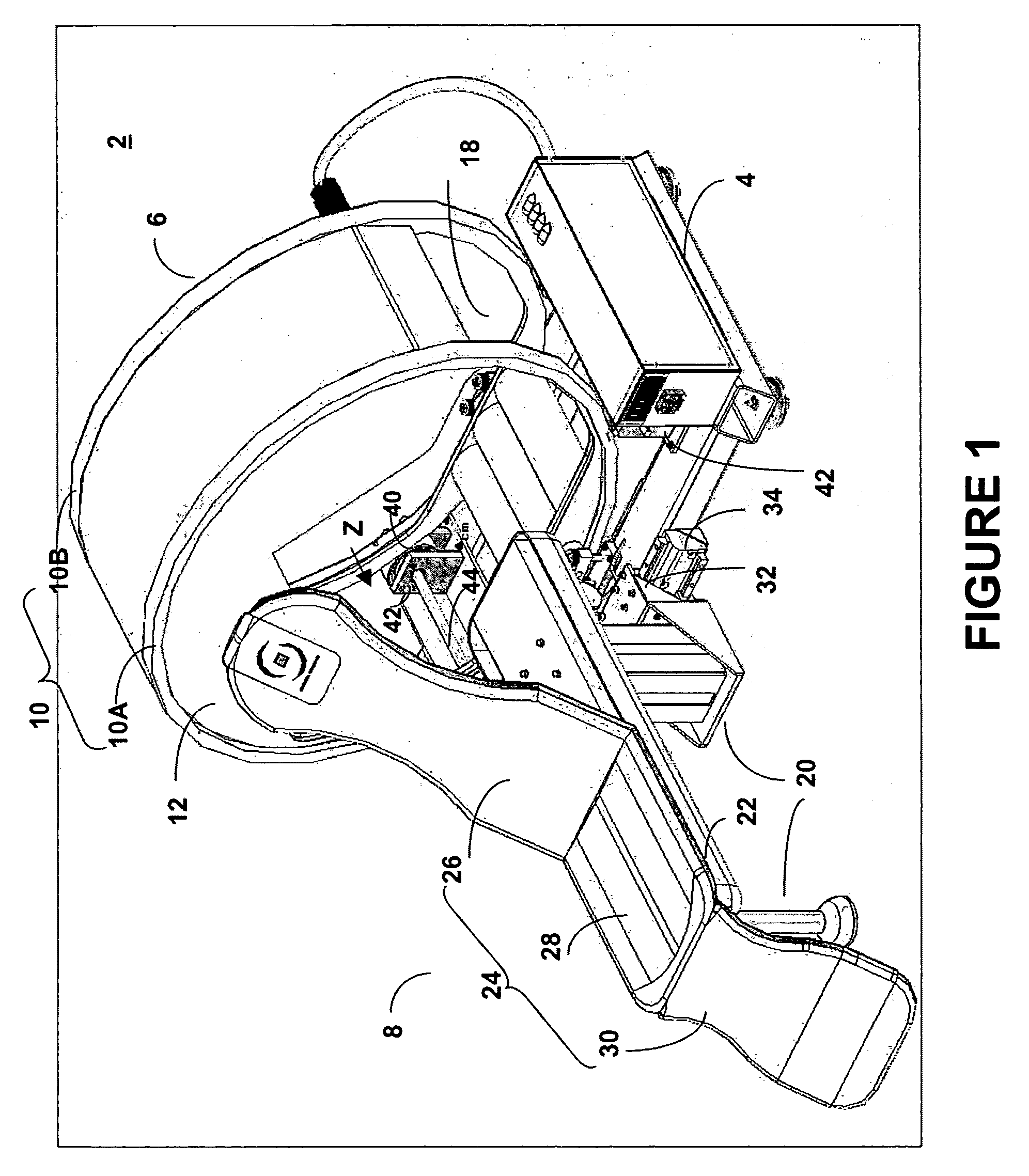
System for medical imaging and a patient support system for medical diagnosis
InactiveUS20050211905A1Preventing horizontal and vertical and angular movementPatient positioning for diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansMedical imagingEngineering
A system for medical imaging and a patient support system for medical diagnosis are provided. The system includes a gantry mounted on the base. The gantry has an annular support. A detector head is fixed to the inner surface of the annular support. The annular support rotates along an axis of the inner space, and is prevented from moving in horizontal and vertical direction and moving angularly. The patient support system has a patient bed system having a plurality of configurations. The contact surface of the patient has a couch back support, a thigh support and a leg support. A controller is provided for angular movements of the supports, and for vertical / horizontal movements of the supports.
Owner:IS2 MEDICAL SYST
System and method of performing medical diagnosis in real time
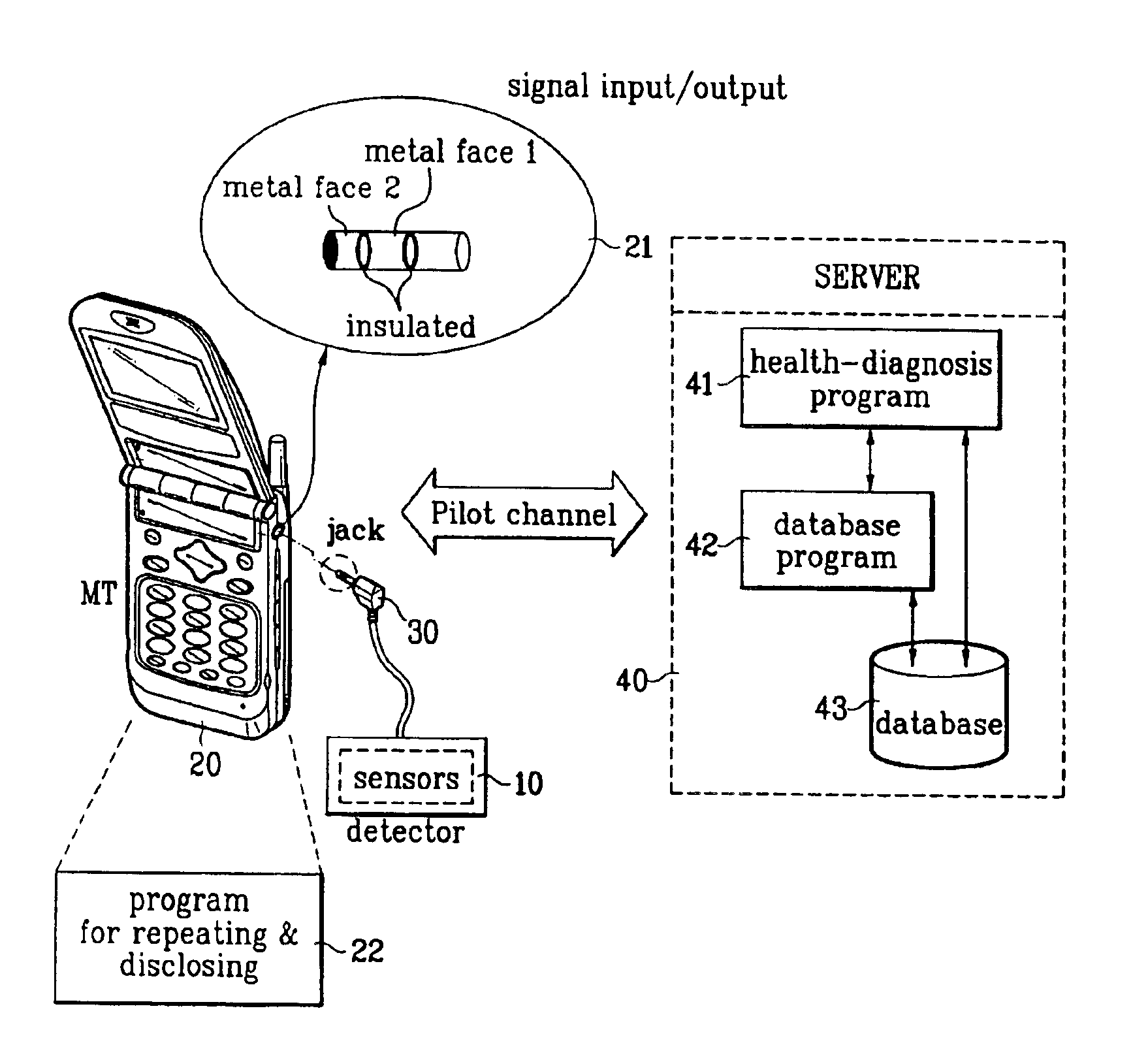
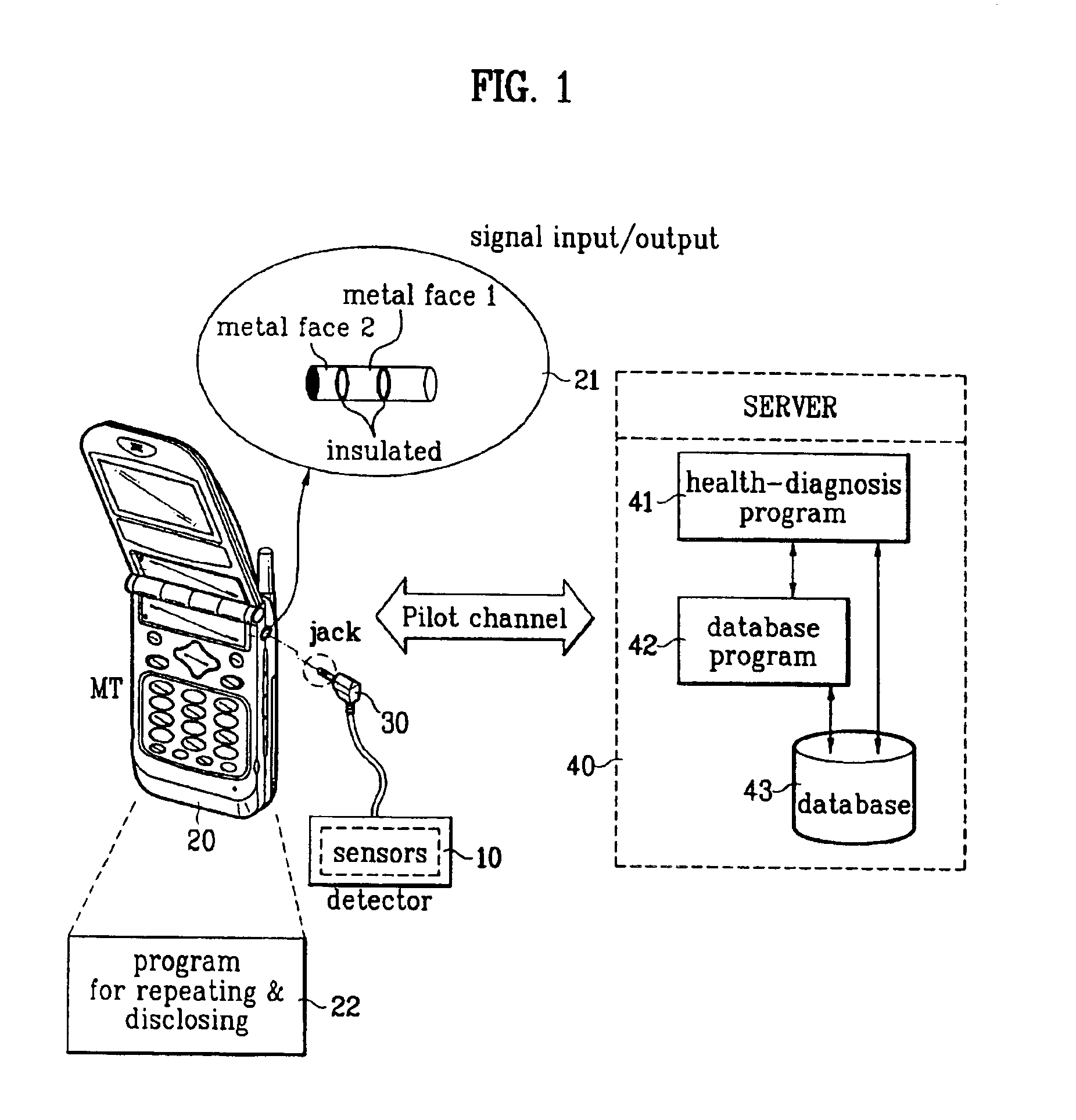
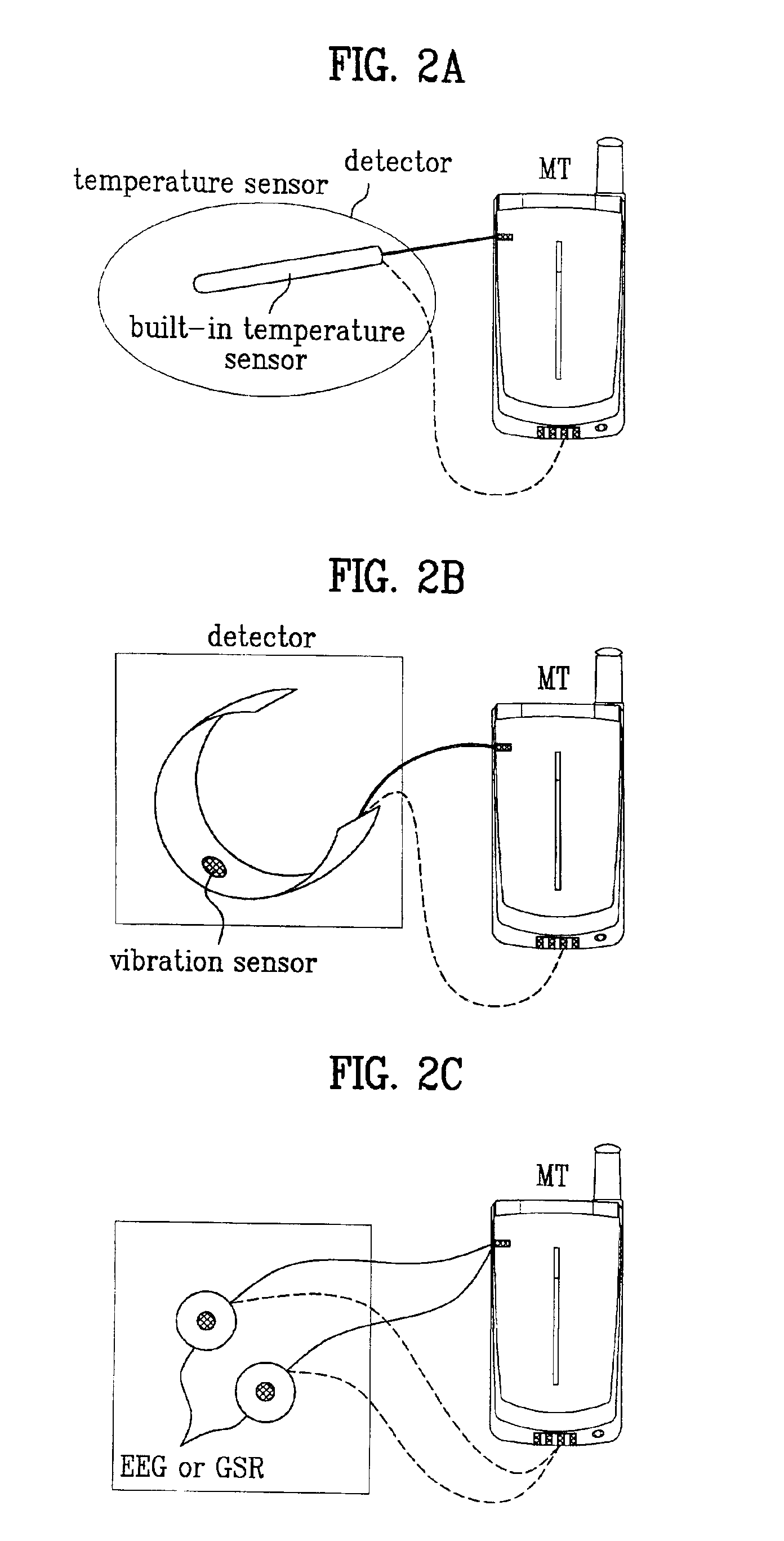
InactiveUS6903657B2Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsMedical diagnosisComputer terminal
A system and method of performing a medical diagnosis in real time that can diagnose a health condition of a mobile terminal user in real time is disclosed. Various sensors provided in the mobile terminal sense a body condition, and a server diagnoses the health condition of the user from the sensed condition information, and informs the user of the corresponding health keeping plan and medical treatment as well. Thus, the user can conveniently check his / her health condition any time and anywhere.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com