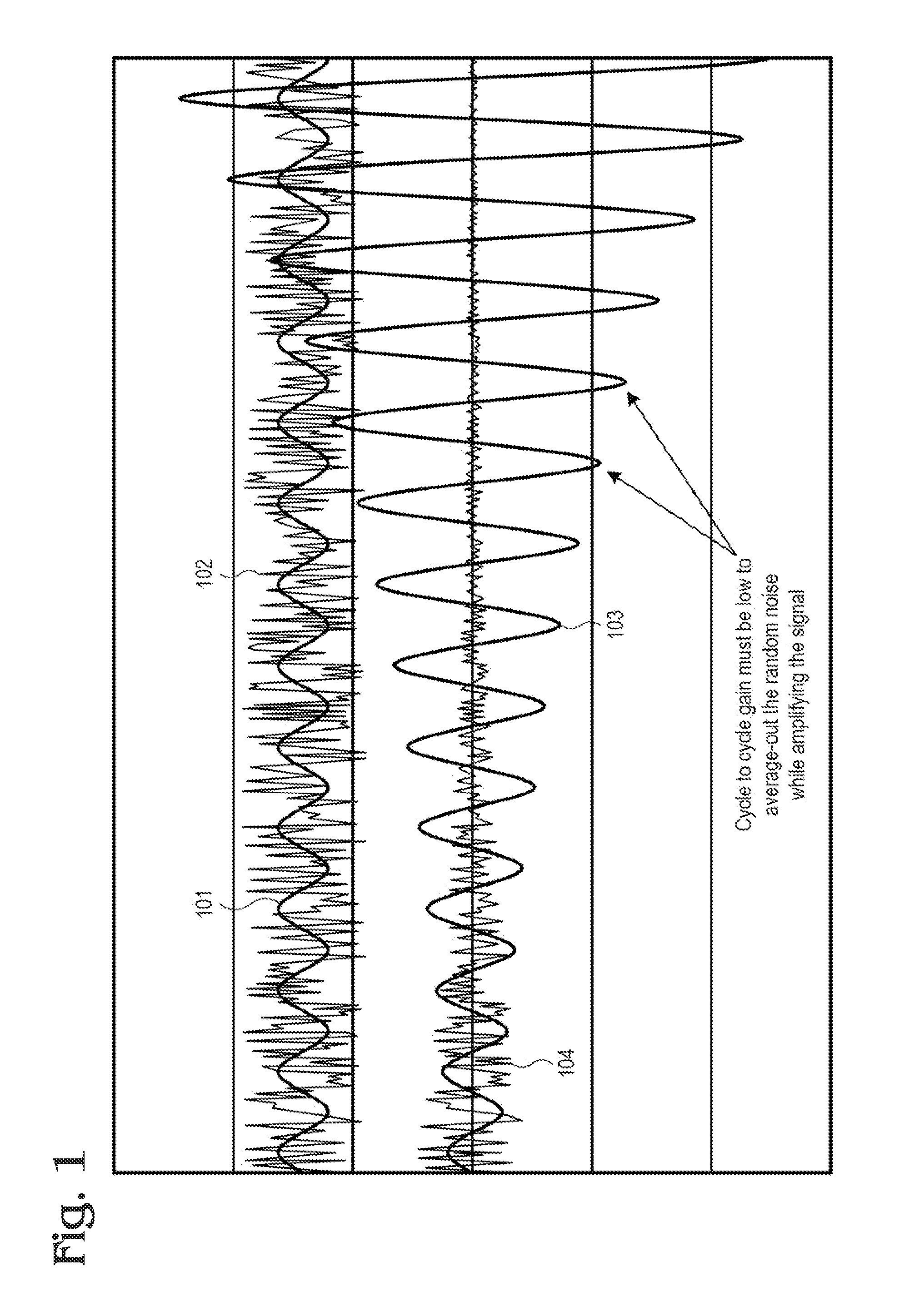
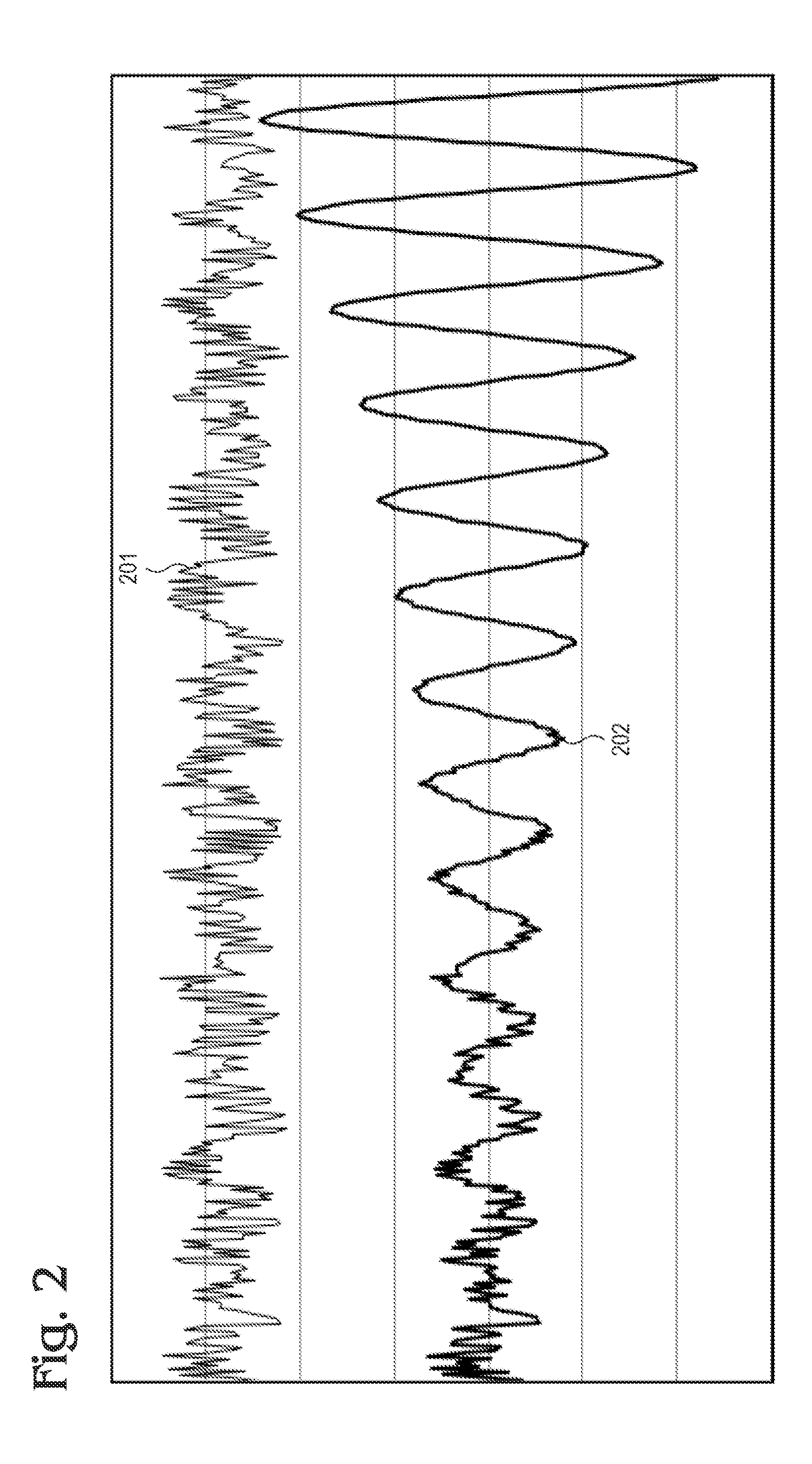
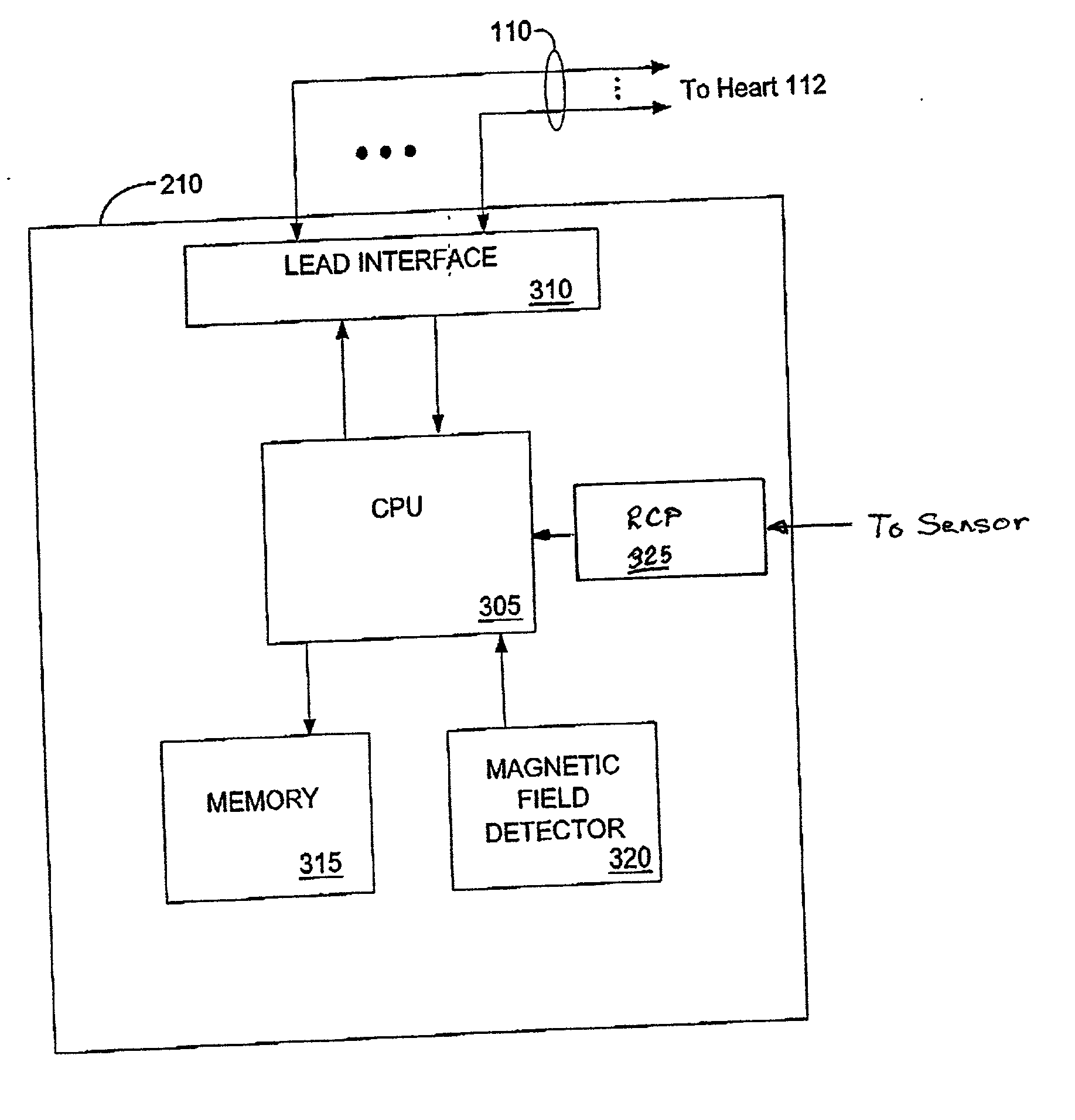
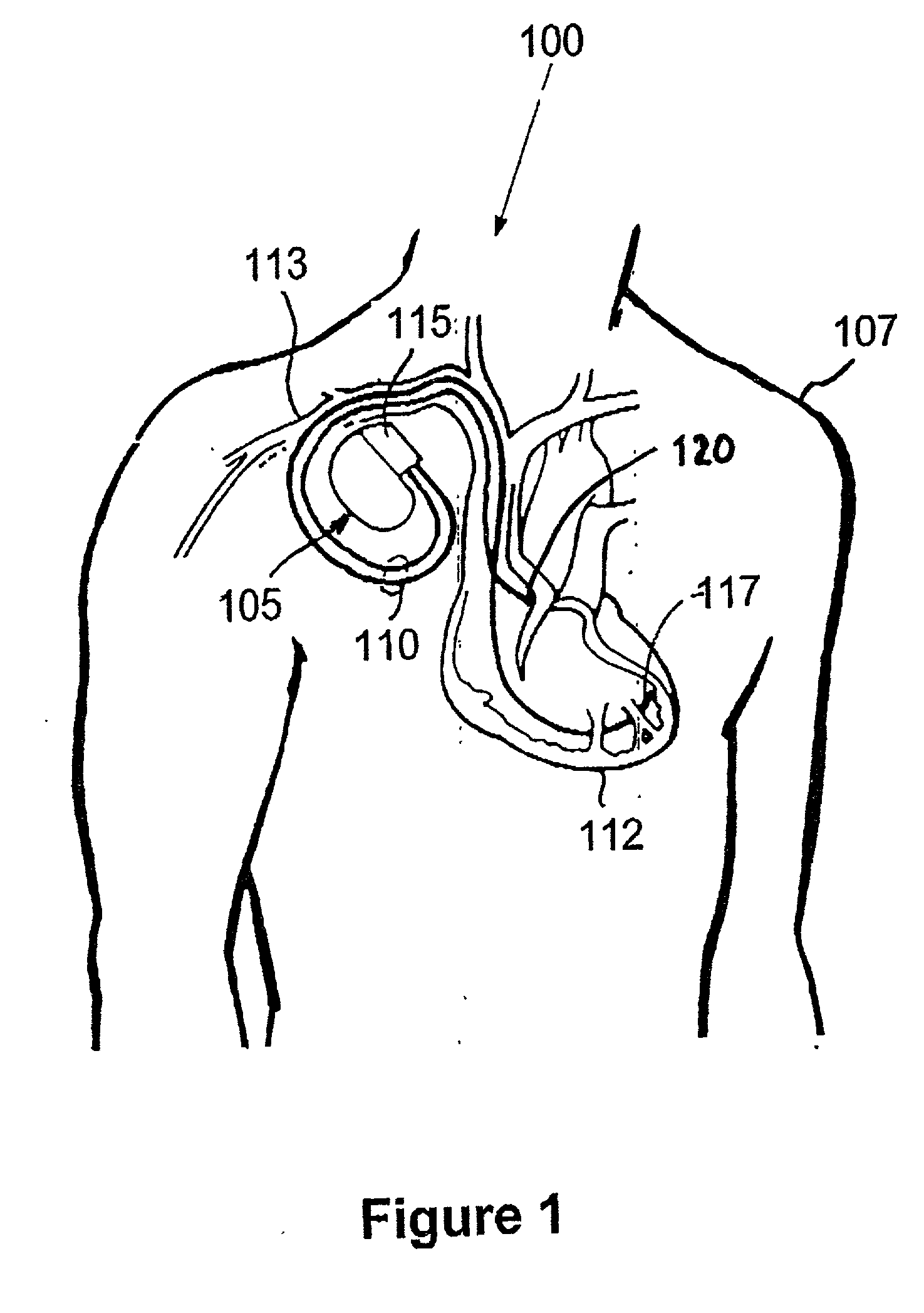
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14081 results about "Electromagnetic interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrostatic coupling, or conduction. The disturbance may degrade the performance of the circuit or even stop it from functioning. In the case of a data path, these effects can range from an increase in error rate to a total loss of the data. Both man-made and natural sources generate changing electrical currents and voltages that can cause EMI: ignition systems, cellular network of mobile phones, lightning, solar flares, and auroras (northern/southern lights). EMI frequently affects AM radios. It can also affect mobile phones, FM radios, and televisions, as well as observations for radio astronomy and atmospheric science.
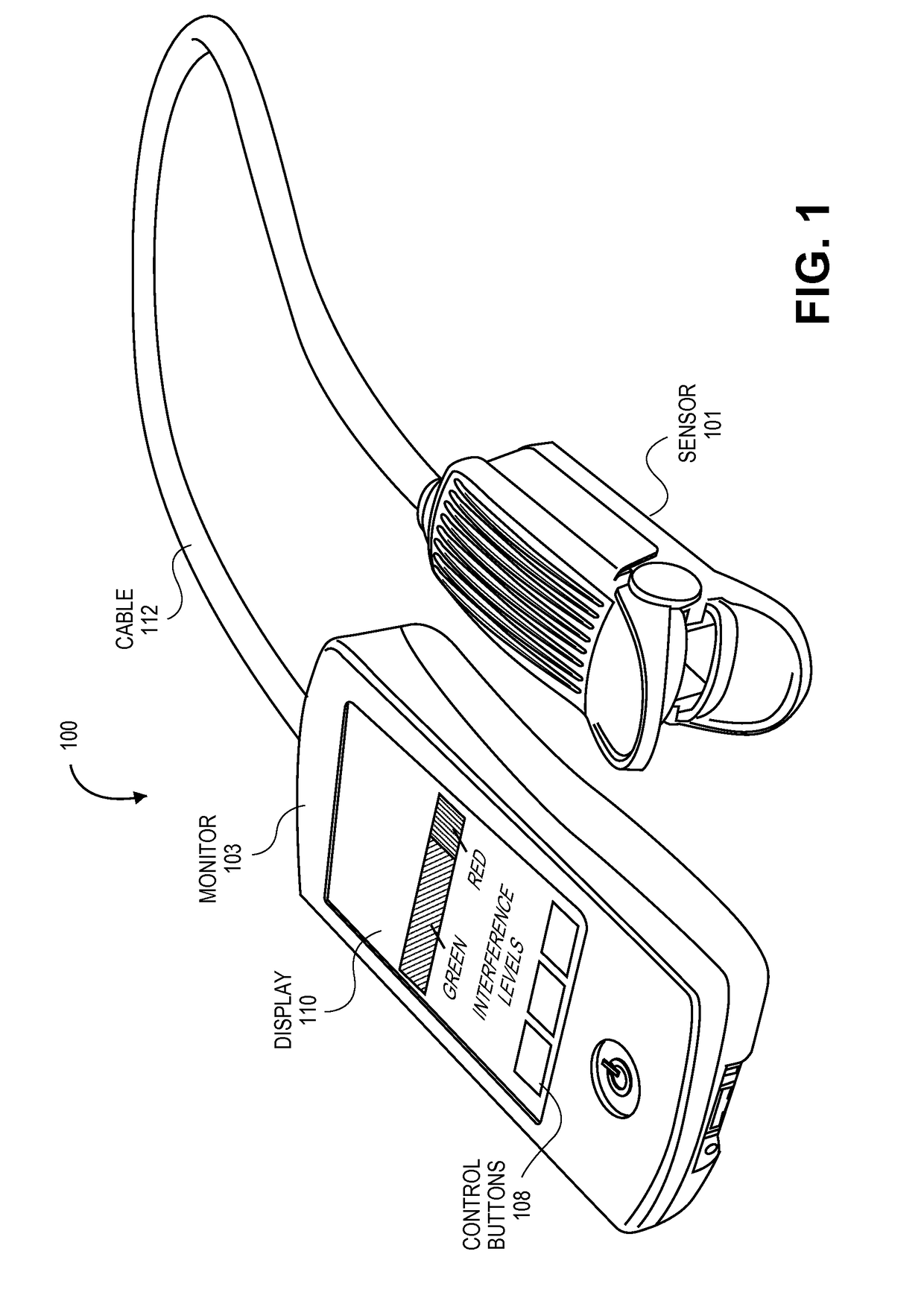
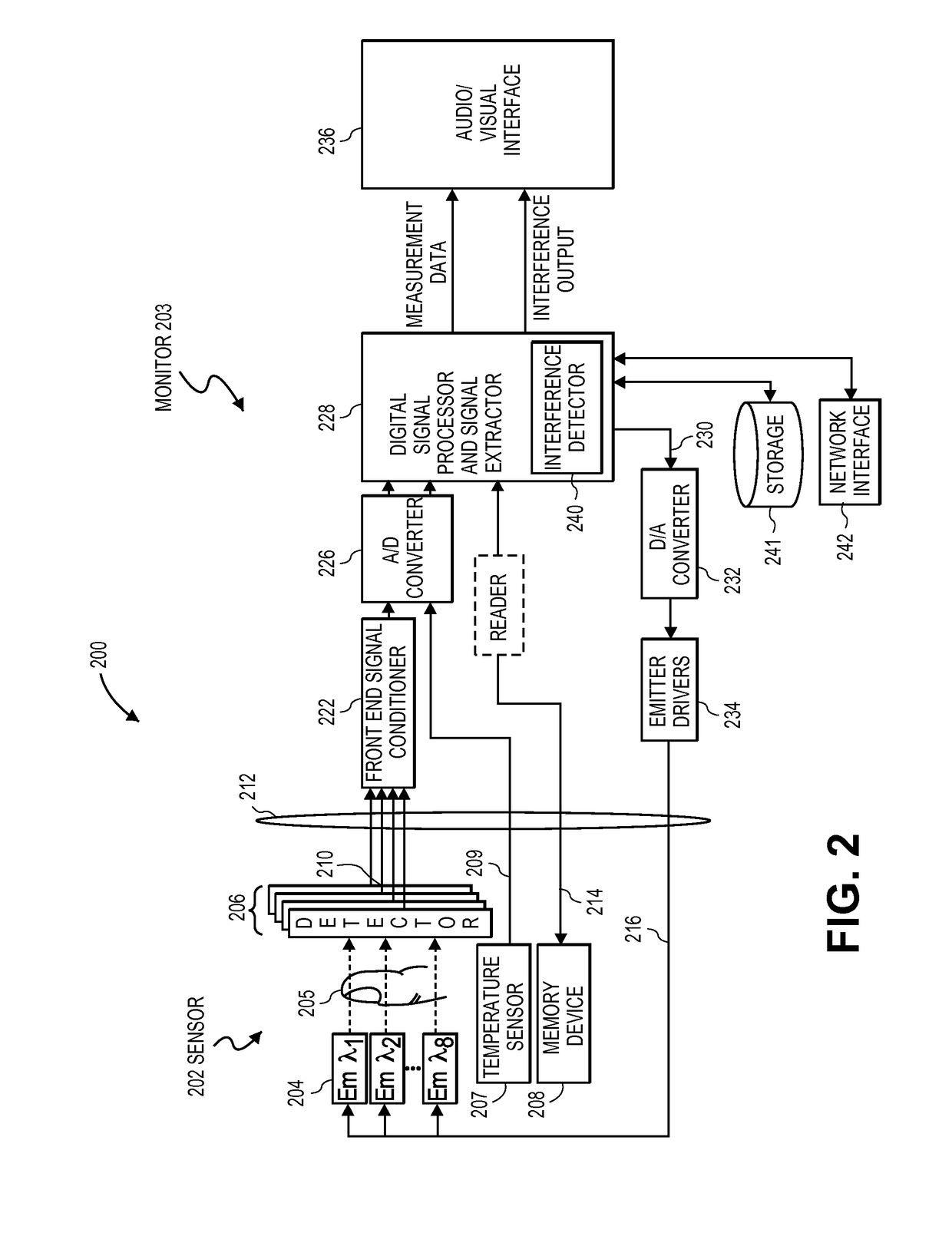
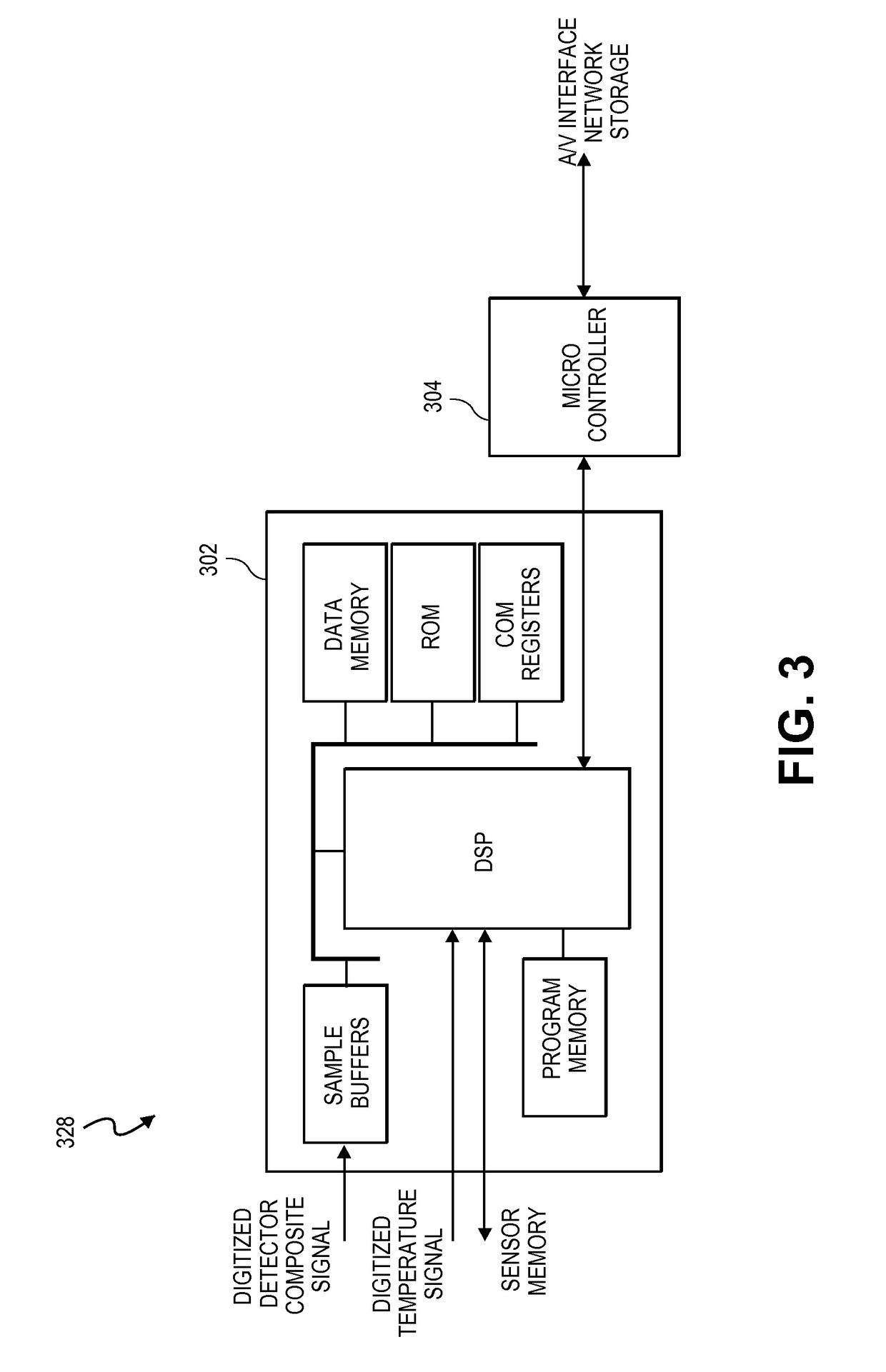
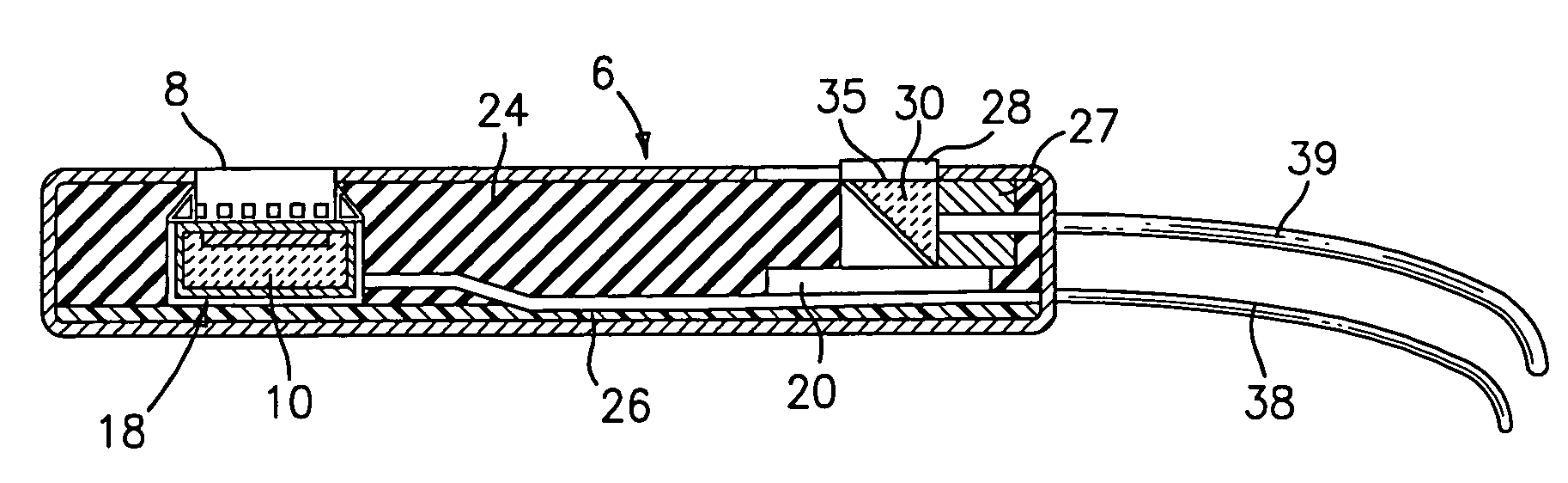
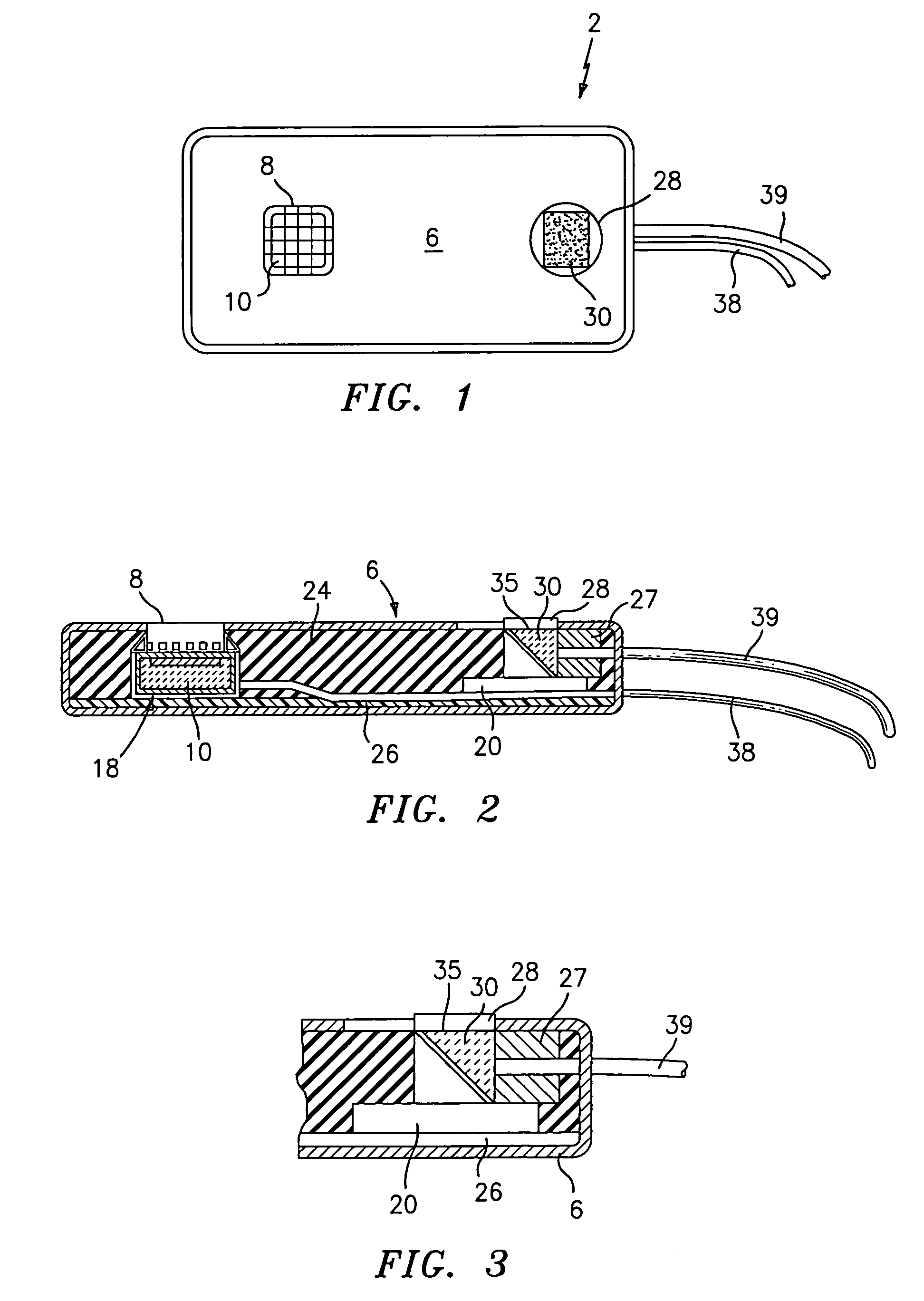
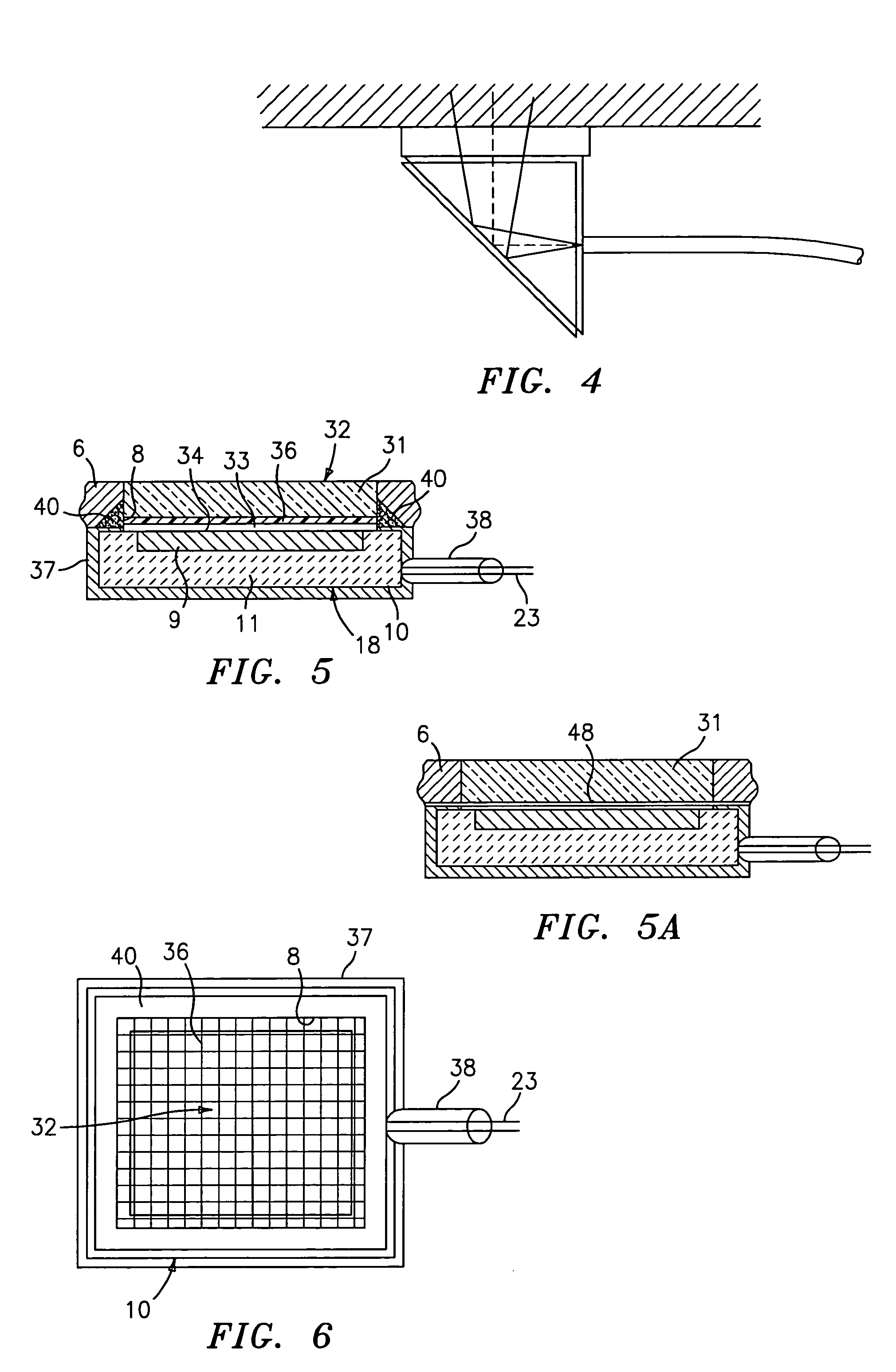
Interference detector for patient monitor
ActiveUS8471713B2Quickly informedQuickly alertedNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectric testing/monitoringEnvironmental noiseMedical equipment
A system is disclosed for detecting and calculating the level of ambient and / or environmental noise, such as electromagnetic interference generated by electric power lines, ambient lights, light dimmers, television or computer displays, power supplies or transformers, and medical equipment. In some embodiments, the system performs frequency analysis on the interference signal detected by light photodetectors and determines the power of the interference signal concentrated in the analyzed frequency bands. The worst-case interference level can be determined by selecting the maximum from the computed power values. In some embodiments, the determined interference signal power can be compared with the noise tolerance of a patient monitoring system configured to reliably and non-invasively detect physiological parameters of a user. The results of the comparison can be presented to the user audio-visually. In some embodiments, the system can be used to perform spot check measurements of electromagnetic interference.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
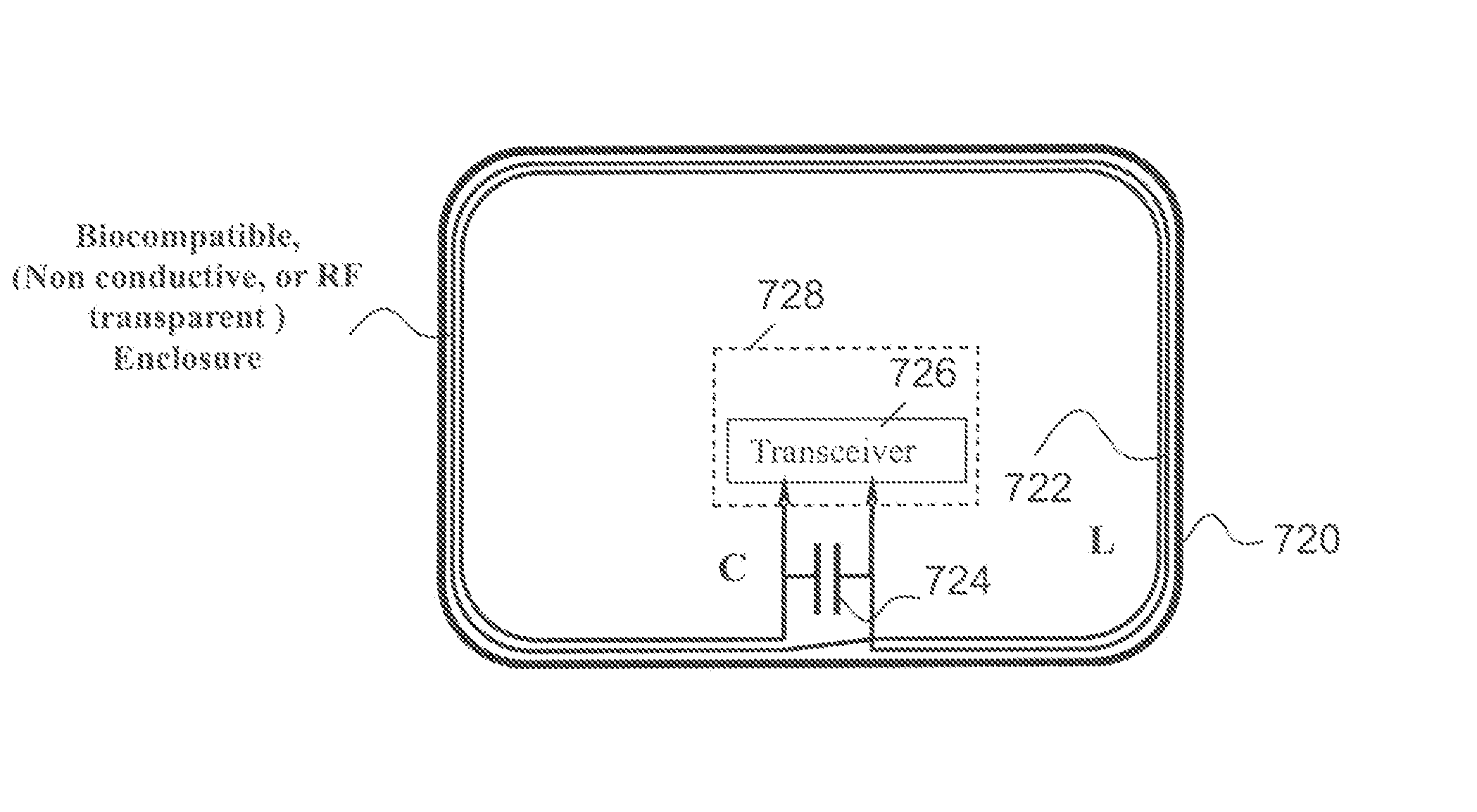
MRI compatible implanted electronic medical device with power and data communication capability
InactiveUS20080051854A1Minimizing electromagnetic interferenceInterference minimizationElectrotherapyElectromagnetic interferenceMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
An antenna module, that is compatible with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner for the purpose of diagnostic quality imaging, is adapted to be implanted inside an animal. The antenna module comprises an electrically non-conducting, biocompatible, and electromagnetically transparent enclosure with inductive antenna wires looping around an inside surface. An electronic module is enclosed in an electromagnetic shield inside the enclosure to minimize the electromagnetic interference from the magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
Owner:KENERGY INC
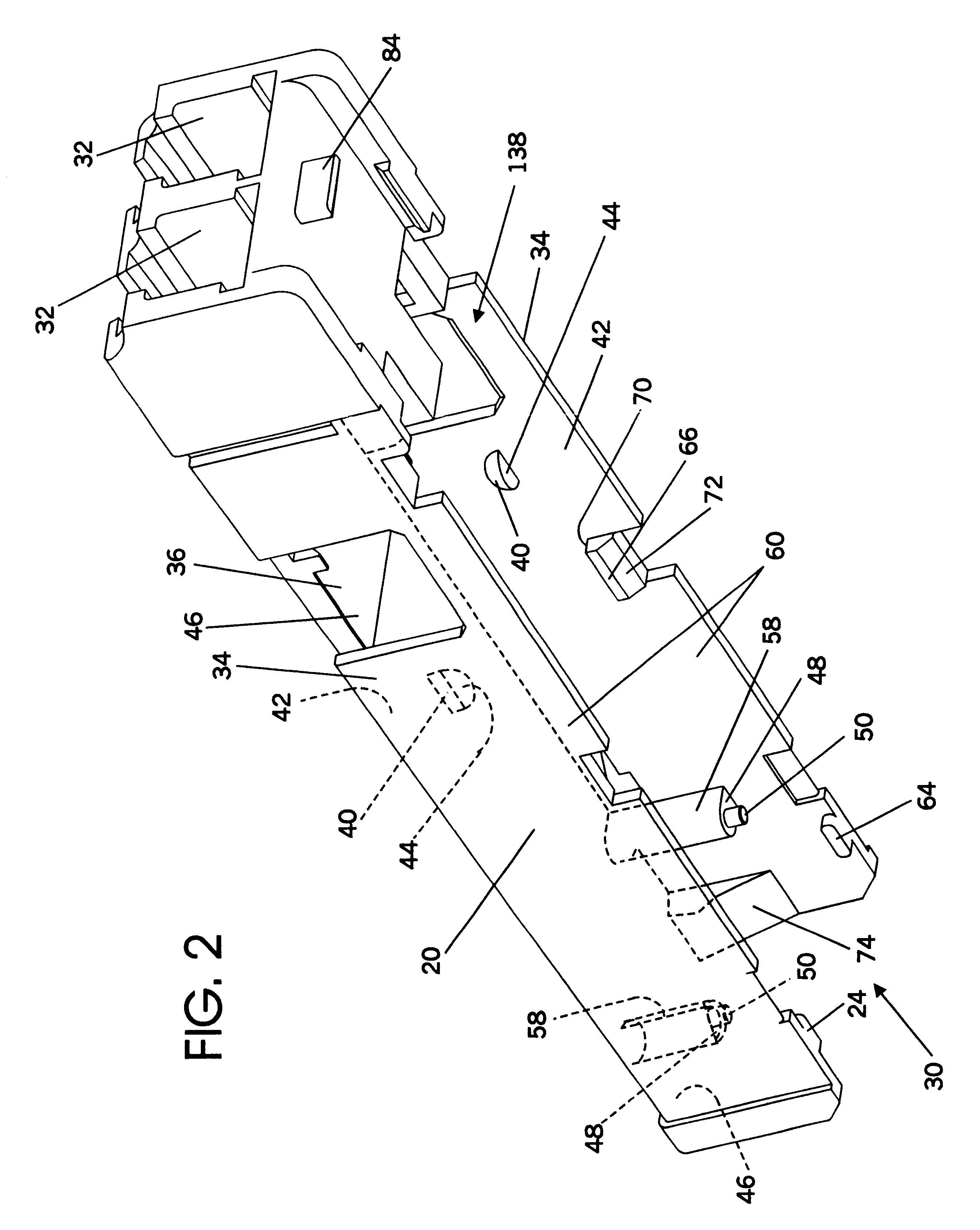
Method and apparatus for grounding a heat sink in thermal contact with an electronic component using a grounding spring having multiple-jointed spring fingers
InactiveUS20070097653A1Not easy to slipRestrict movementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectromagnetic interference
A grounding spring for electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression is interposed between a heat sink and a printed circuit board (PCB). The grounding spring comprises a conductive material having an opening formed at its base through which the heat sink makes thermal contact with an electronic module mounted on the PCB. The base makes electrical contact with a peripheral surface of the heat sink, and multiple-jointed spring fingers extend from the base to make electrical contact with conductive pads on the PCB. During compression, the movement of each spring finger's tip is substantially limited to the z-axis. Accordingly, the final installed location of the tip can be precisely controlled even when the grounding spring must accommodate a wide variety of installed heights of the heat sink relative to the PCB. Preferably, the spring fingers terminate with a concave tip that is less susceptible to sliding off the conductive pads.
Owner:IBM CORP
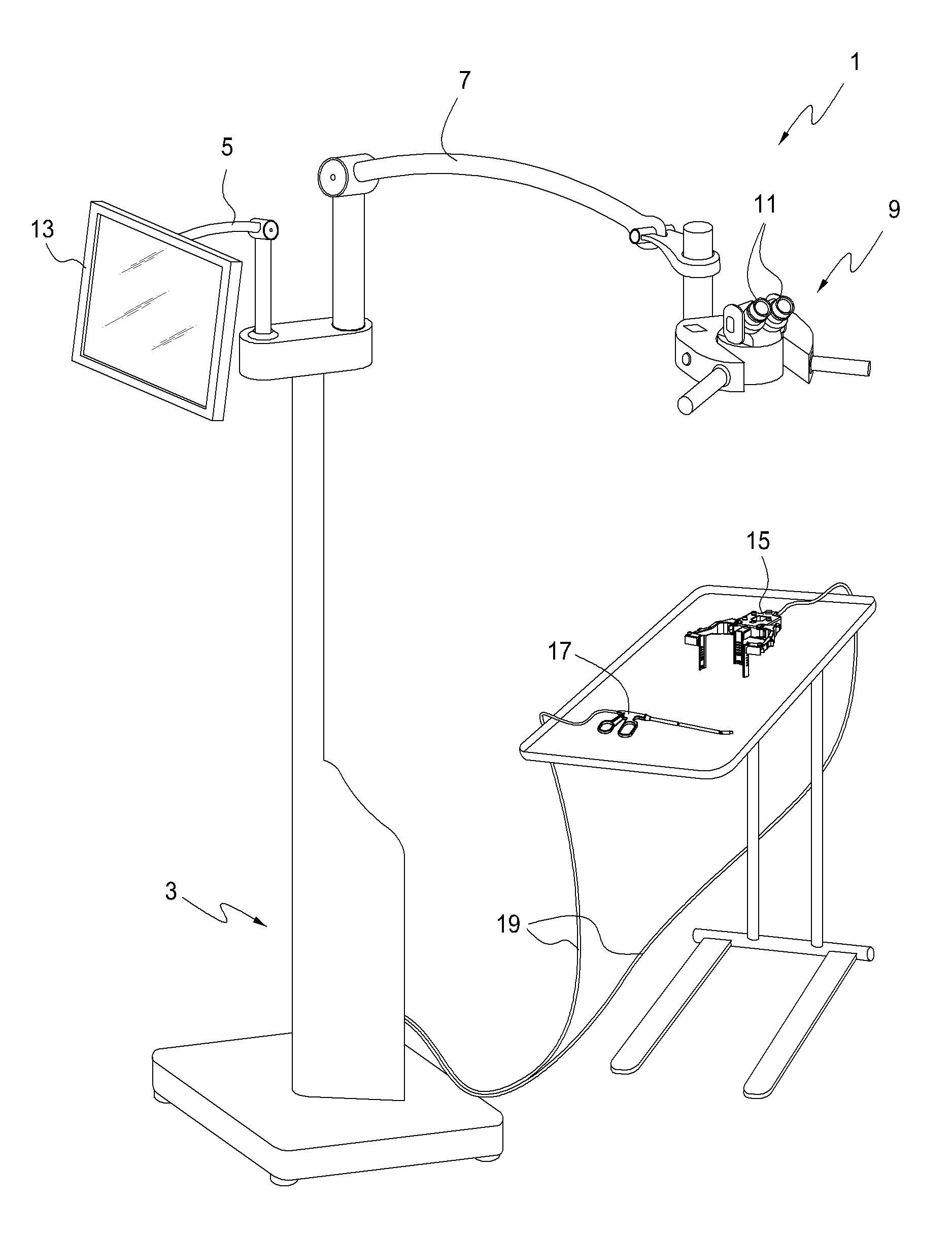
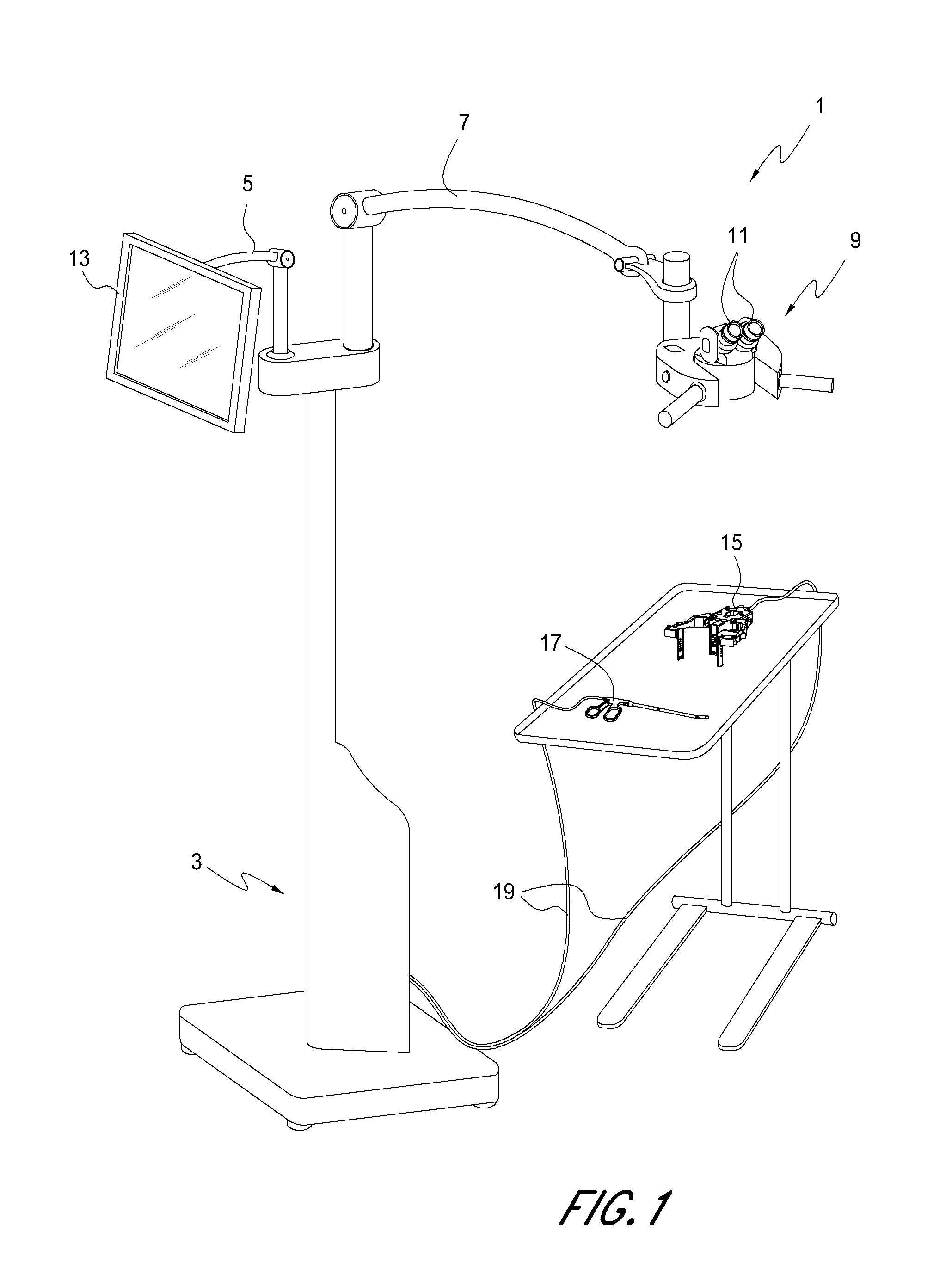
Interface for viewing video from cameras on a surgical visualization system
ActiveUS8882662B2Medical imagingIncision instrumentsComputer graphics (images)Electromagnetic interference
A surgical device includes a plurality of cameras integrated therein. The view of each of the plurality of cameras can be integrated together to provide a composite image. A surgical tool that includes an integrated camera may be used in conjunction with the surgical device. The image produced by the camera integrated with the surgical tool may be associated with the composite image generated by the plurality of cameras integrated in the surgical device. The position and orientation of the cameras and / or the surgical tool can be tracked, and the surgical tool can be rendered as transparent on the composite image. A surgical device may be powered by a hydraulic system, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference with tracking devices.
Owner:CAMPLEX
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20050197677A1Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic field
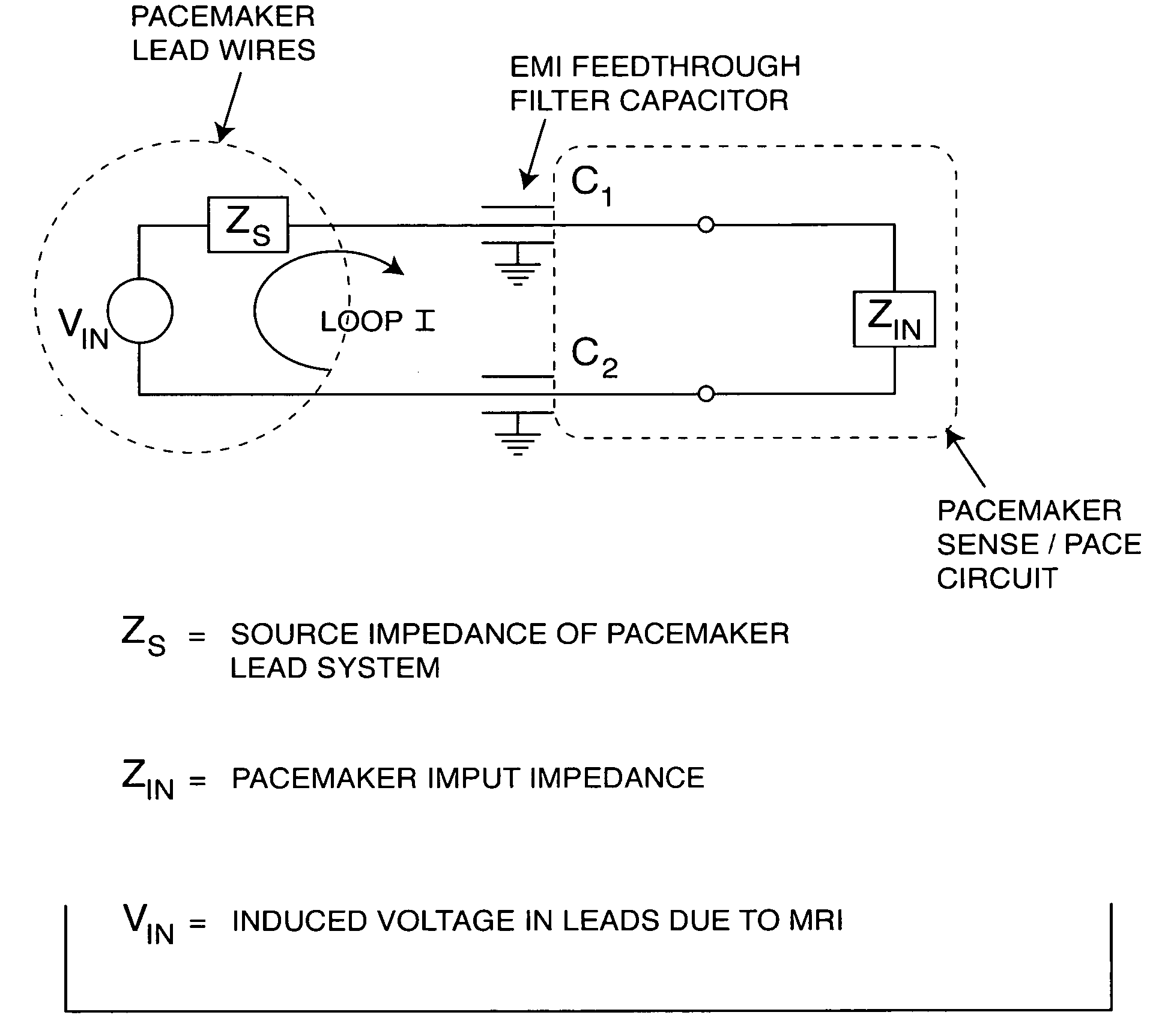
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Low-Power, Noise Insensitive Communication Channel using Logarithmic Detector Amplifier (LDA) Demodulator
ActiveUS20140269972A1Reduce generationMinimize power consumptionFrequency demodulator arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringFrequency modulation
A method is provided for communicating signals at a low power level in an electromagnetic interference (EMI) environment. A first device transmits a modulated signal having a first carrier frequency, including the encoded information via a hardwire transmission medium. In one aspect, the power level of the modulated signal can be adjusted to minimize power consumption or reduce the generation of EMI. The modulated signal may be in one of the following formats: frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) to name a few examples. A second device including a logarithmic detector amplifier (LDA) demodulator circuit receives the signal, which may be mixed with EMI. The LDA demodulator circuit amplifies the modulated signal, without amplifying the EMI, to supply a demodulated baseband signal, which may be an n-ary digital signal, or an audio signal. A low-power, noise insensitive communication channel is also provided.
Owner:DOCKON
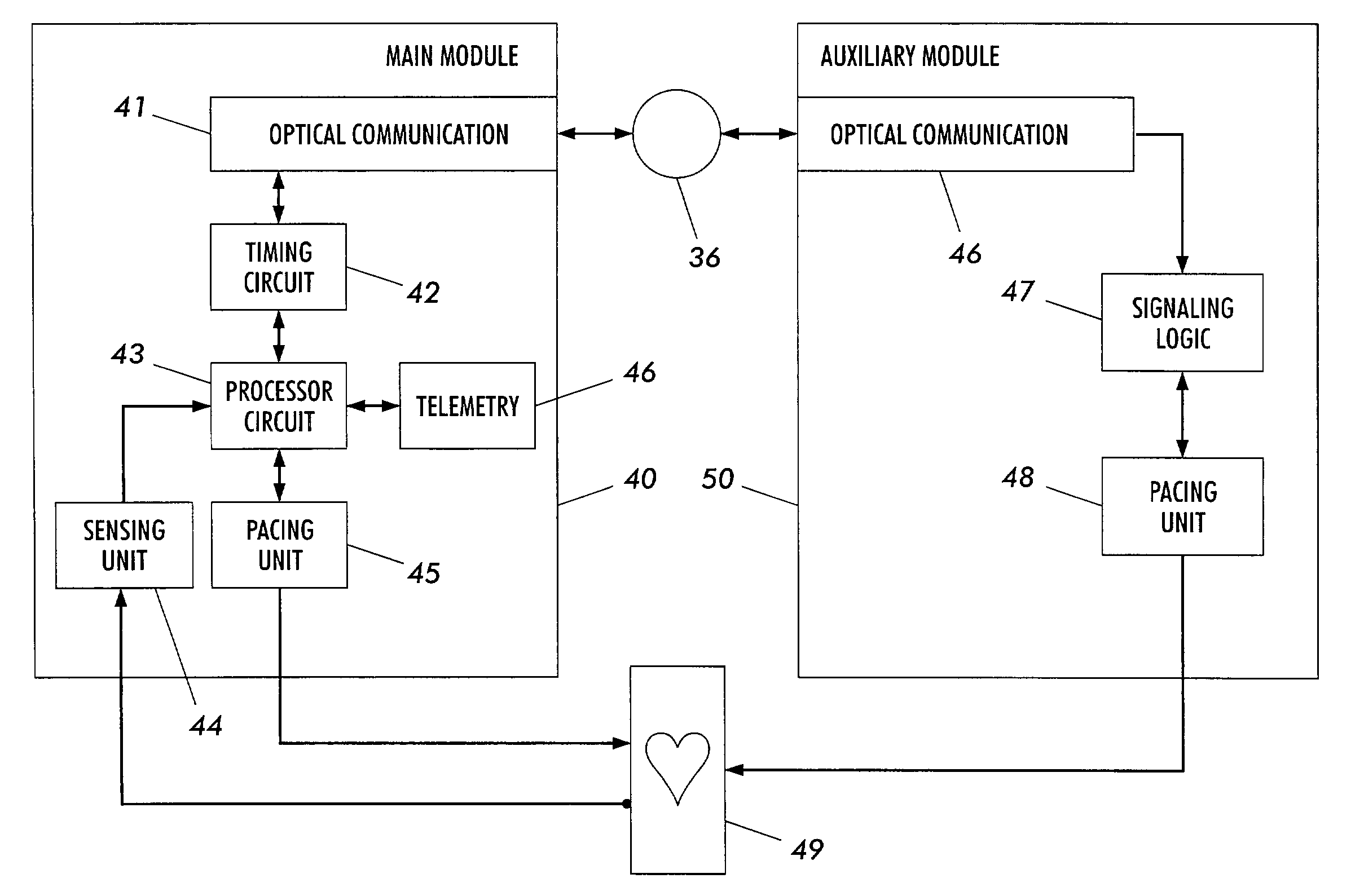
Methods and apparatus for controlling a pacing system in the presence of EMI
ActiveUS20030144705A1Generate accuratelyHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac pacemaker electrodeElectromagnetic interference
Pacing systems are disclosed including detectors for detecting the presence of electromagnetic interference and setting an interference state pacing mode and pacing rate. The interference state pacing mode and pacing rate are altered as a function of patient pacemaker dependency and the prevailing mean heart rate. When pacemaker dependency exists, the pacing rate is maintained and even increased from the prevailing mean heart for the duration of the interference state. When the patient is determined to not be pacemaker dependent, pacing is inhibited or suspended for the duration of the interference state.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wireless energy transfer modeling tool
ActiveUS20130159956A1Tune performanceCircuit arrangementsDesign optimisation/simulationEnergy transferElectromagnetic interference
A method includes defining and storing one or more attributes of a source resonator and a device resonator forming a system, defining and storing the interaction between the source resonator and the device resonator, modeling the electromagnetic performance of the system to derive one or more modeled values and utilizing the derived one or more modeled values to design an impedance matching network.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Electrically optimized hybird "last mile" telecommunications cable system
InactiveUS6091025AEqual performanceEquivalent signal performanceCoaxial cables/analogue cablesQuad constructionsElectrical conductorTelecommunications cable
A cable system is provided which can accomodate electrical and optical cabling. The conductors of the system employ a layer which is impedance-matched to space, decreasing their cross-section to electromagnetic interference. The conductors of the system also employ a layer which symmetrizes electromagnetic interference signals, reducing the effect of interference and crosstalk on the signals carried by the conductors. The system also includes a node interface device for connection to a global electrical and fiber network. The node interface device connects to a user interface device through the cable.
Owner:KHAMSIN TECH LLC
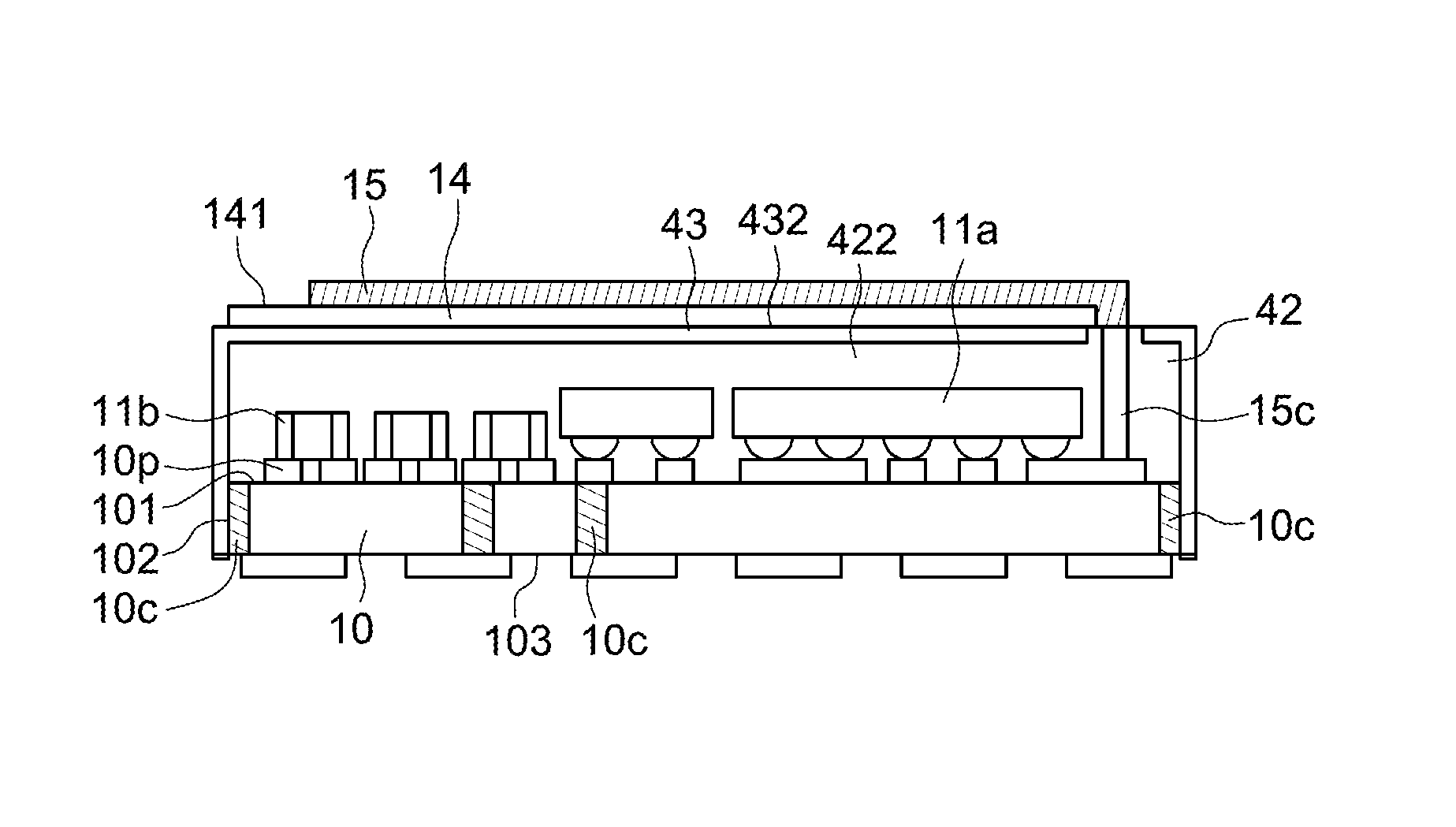
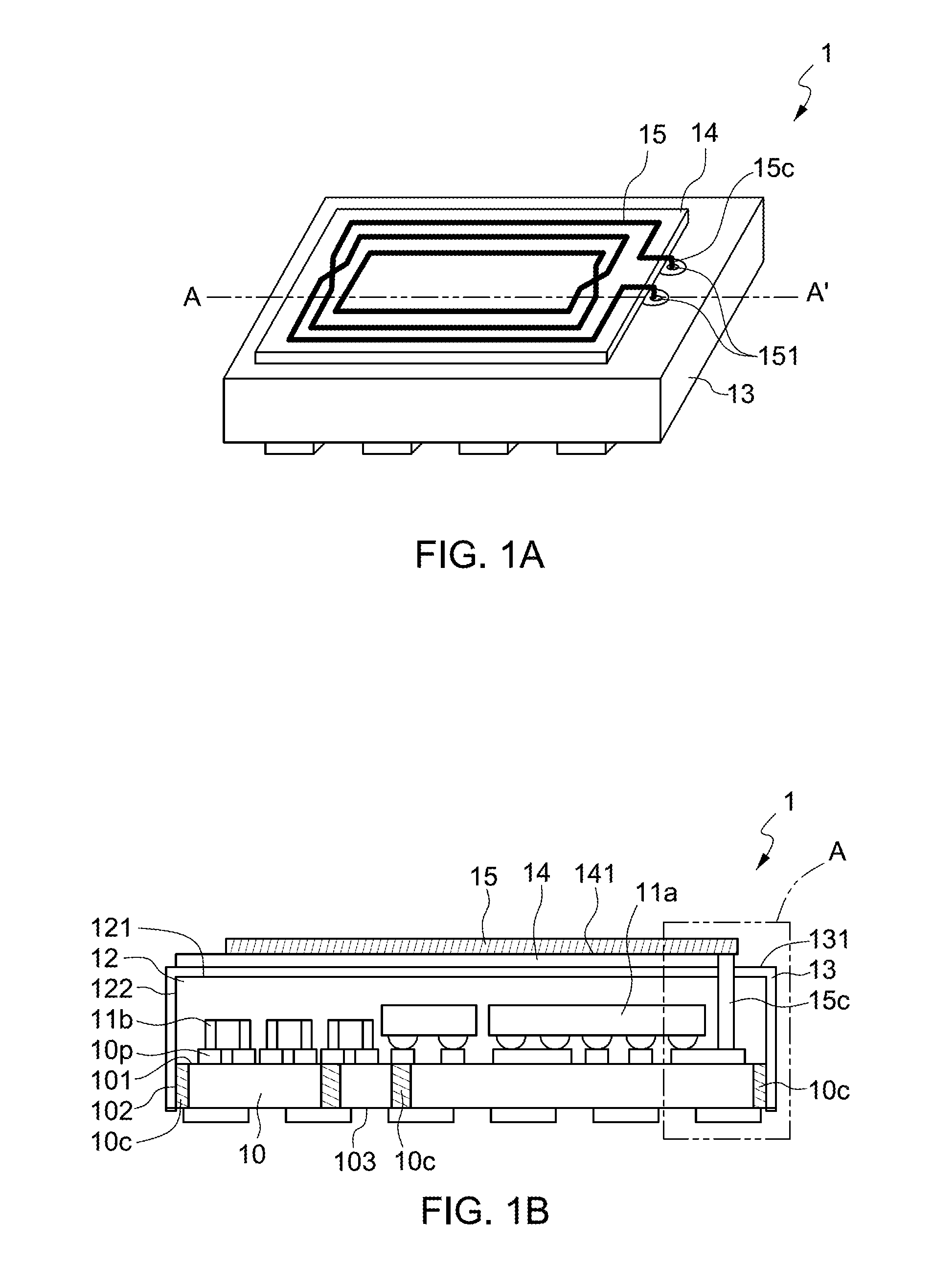
Semiconductor device package integrated with coil for wireless charging and electromagnetic interference shielding, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9461001B1Batteries circuit arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityElectromagnetic interference
The present disclosure relates to a semiconductor device package which includes a carrier, an electronic component, conductive elements, a package body, a shield, a magnetic insulating layer, and a patterned conductive layer. The carrier has a top surface on which the electronic component is disposed. The conductive elements are disposed on the top surface of the carrier. The package body is disposed on the top surface of the carrier and encapsulates the electronic component and a portion of each of the conductive elements. The shield is disposed on the package body and covers an exterior of the package body. The magnetic insulating layer is disposed on a top surface of the shield. The patterned conductive layer is disposed on the magnetic insulating layer. Each of the conductive elements electrically connects the patterned conductive layer to the electronic component.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
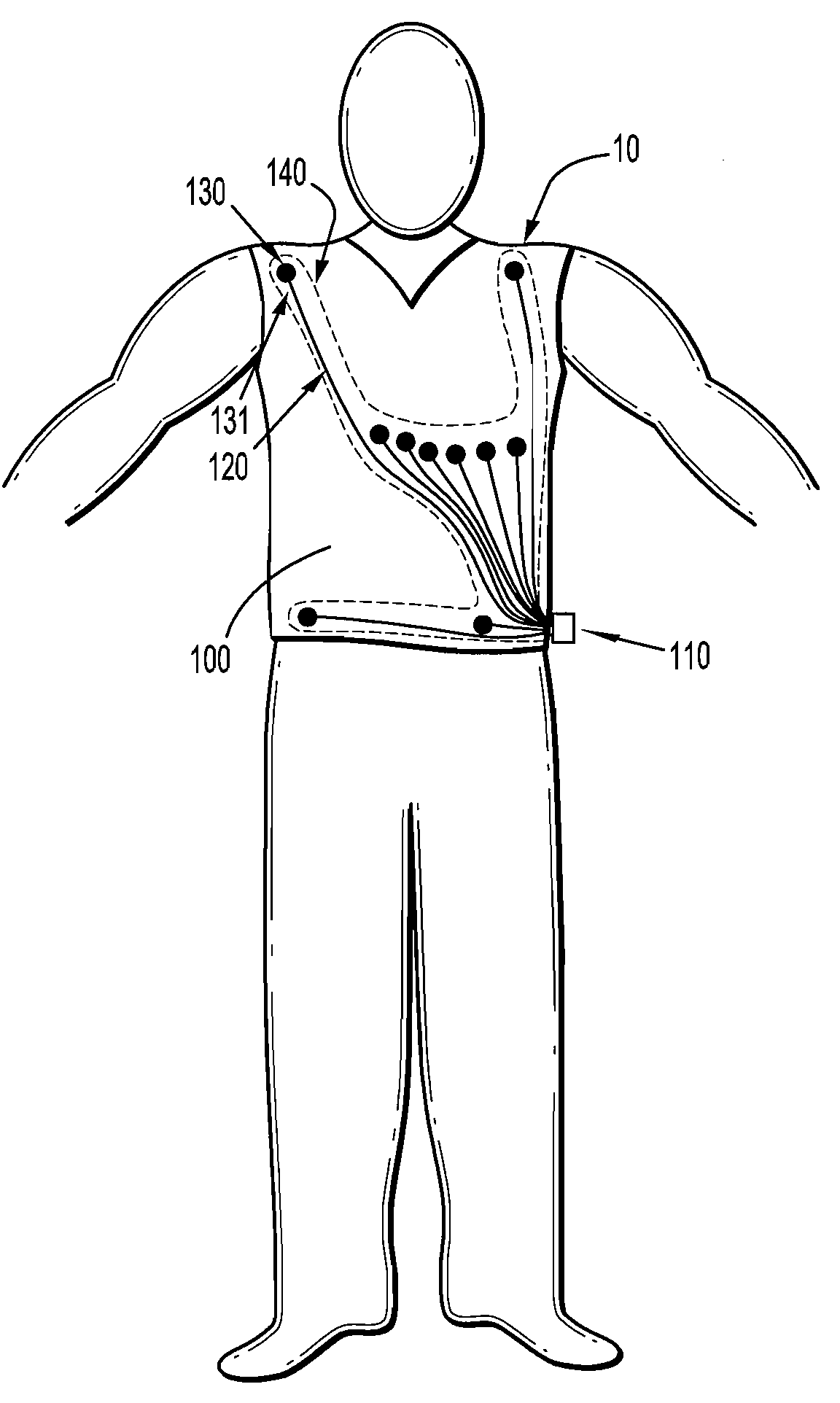
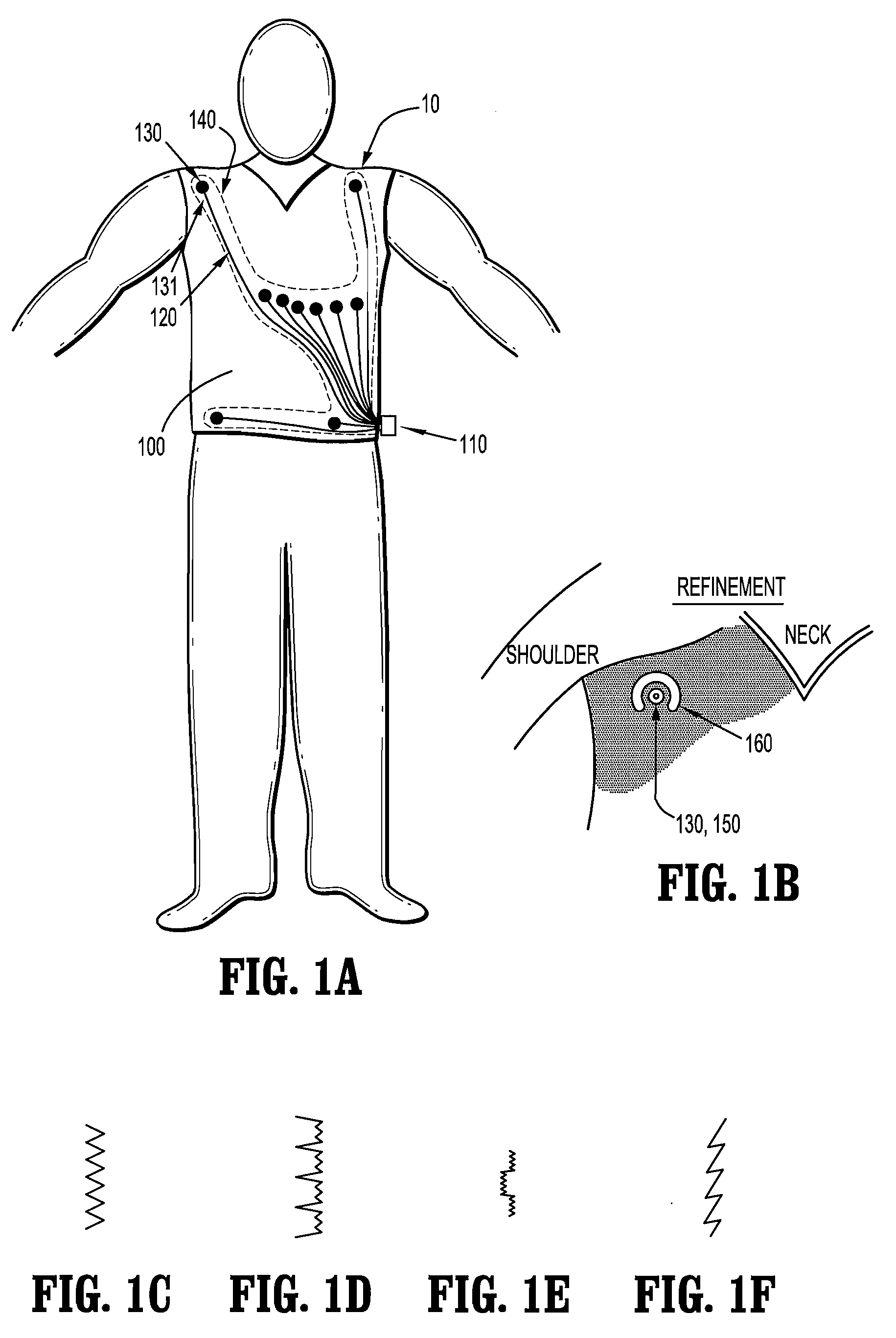
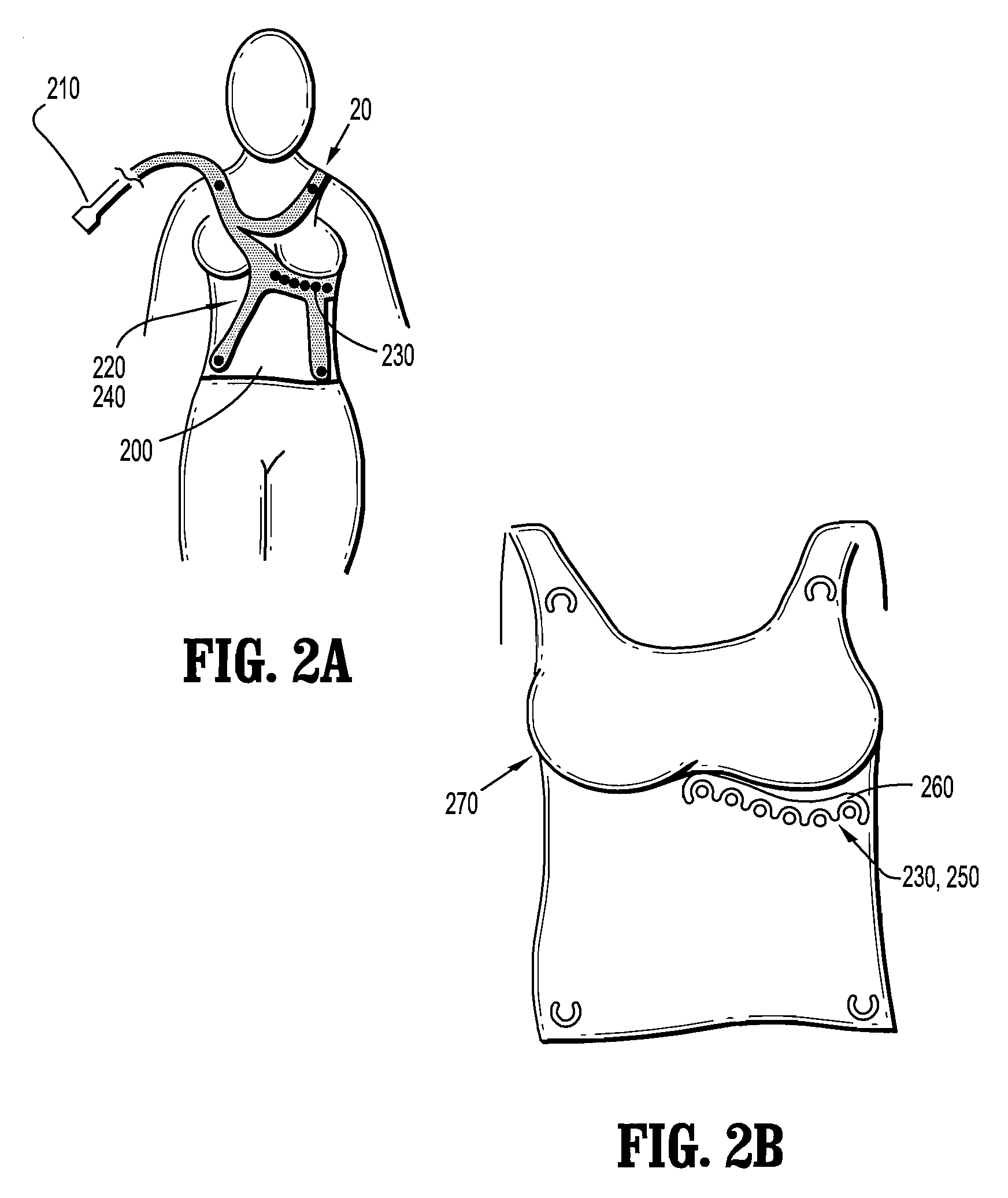
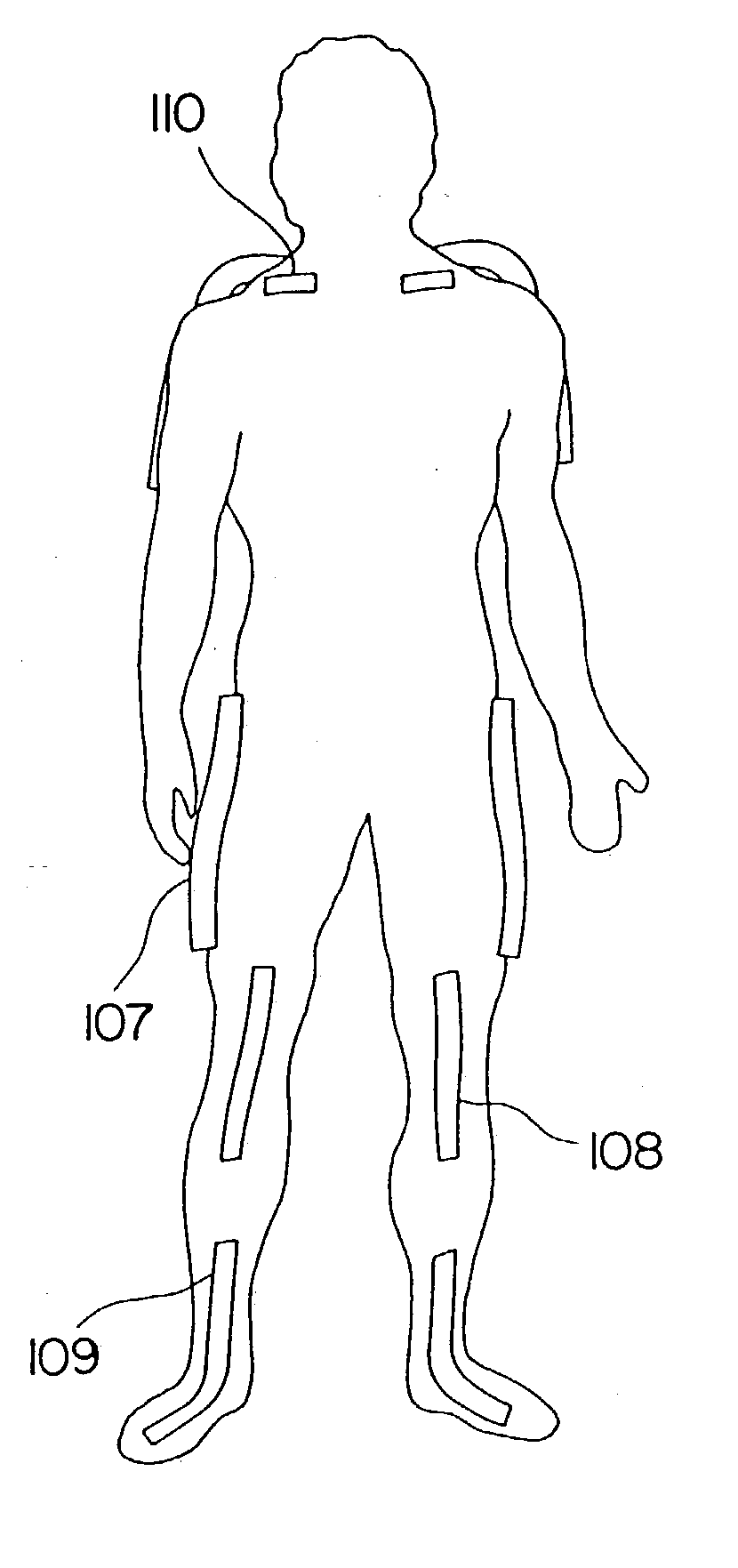
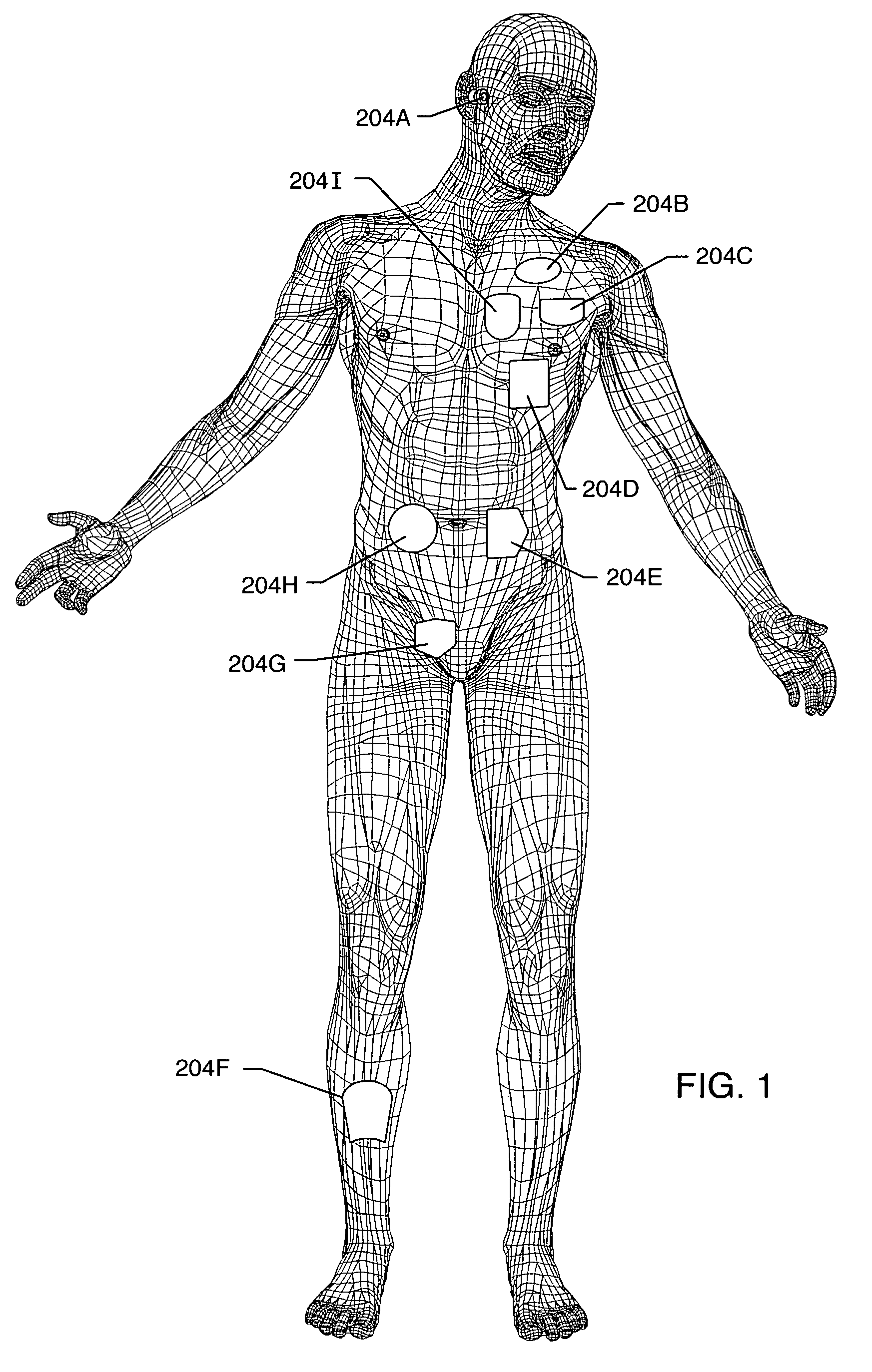
Physiological sensor placement and signal transmission device
InactiveUS20090088652A1Firmly connectedAvoid interferenceElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyElectrode placementBiomedical sensors
A garment is used to facilitate the placement of biomedical sensors or other electrodes on the body. The garment is comfortable and allows freedom of movement much like typical clothing. Textile based electrical components are included in the garment which are capable of transmitting an electrical signal to and from various external electrodes placed on the body. A textile based EMI shield protects the signals from electromagnetic interference. The garment may take any form such as a vest, sports bra, long sleeve shirt, bonnet, or other form and may provide access to an electrode placement site without requiring removal of the garment.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
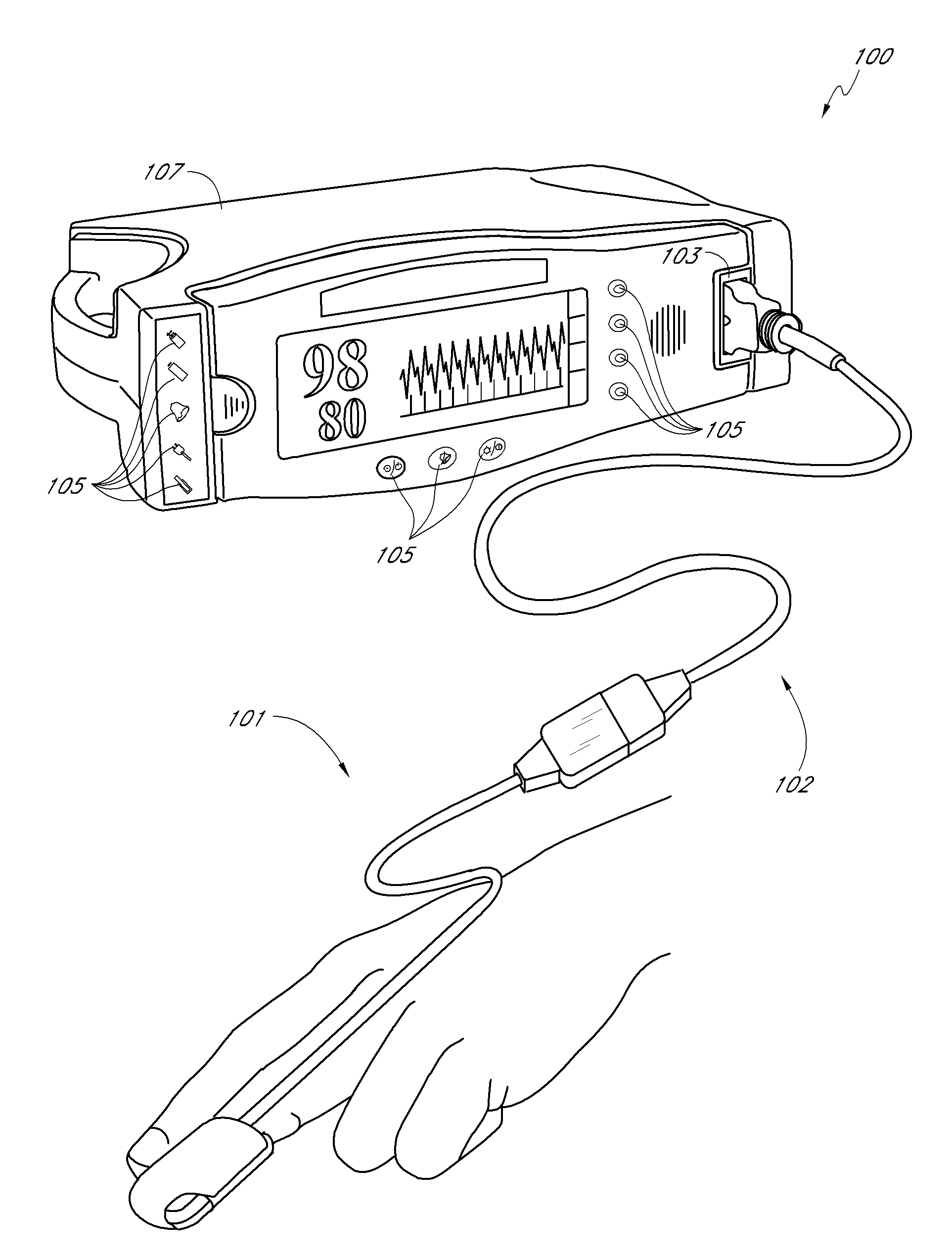
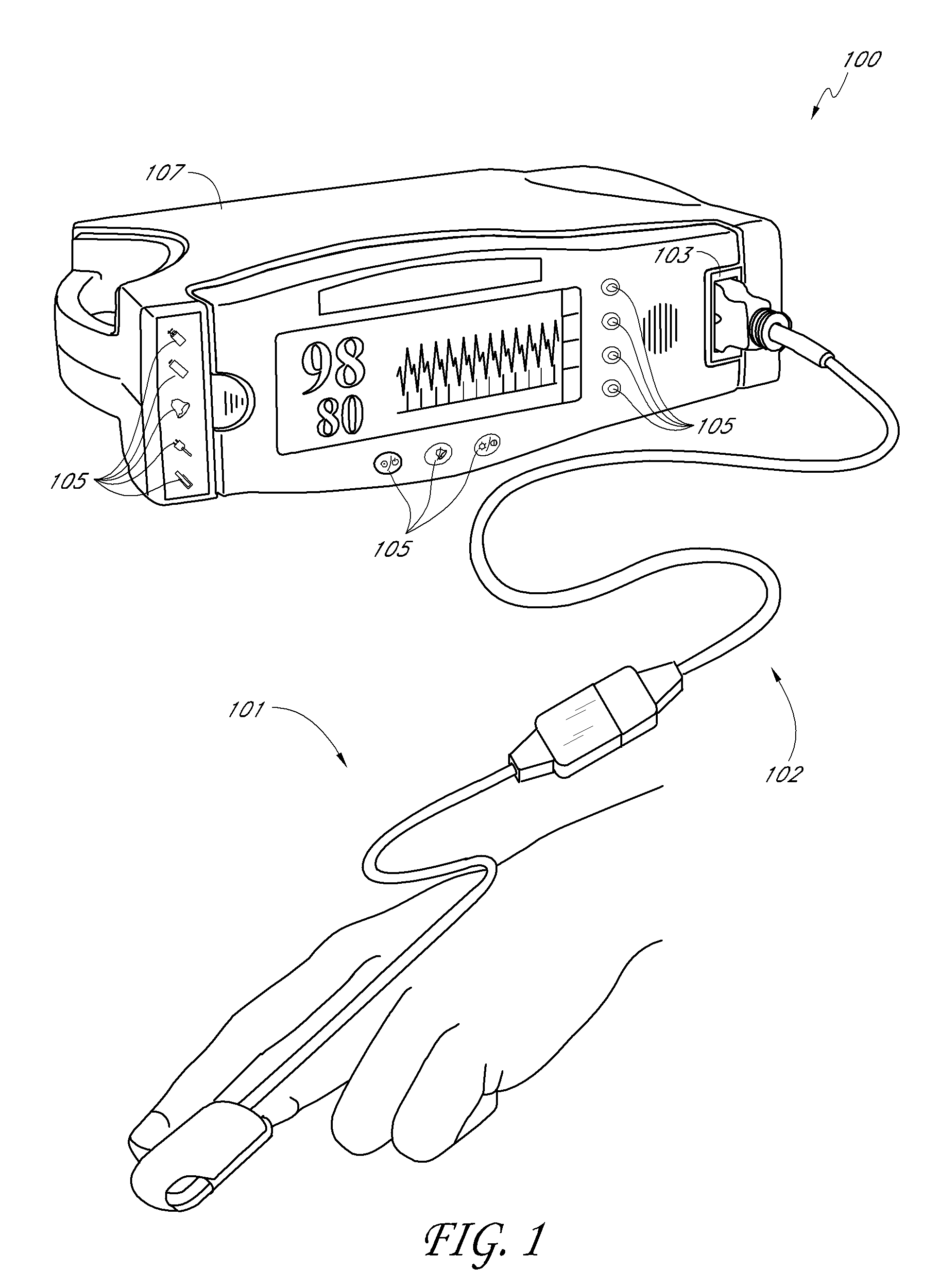
Physiological parameter detector
InactiveUS20090095926A1Improving electromagnetic noise immunityImprove electromagnetic immunityRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsOptical radiationElectromagnetic interference
A pulse oximetry sensor has an emitter adapted to transmit optical radiation into a tissue site and a ceramic detector adapted to receive optical radiation from the emitter after tissue site absorption. The detector is surrounded by shielding material to reduce undesirable electromagnetic interference.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
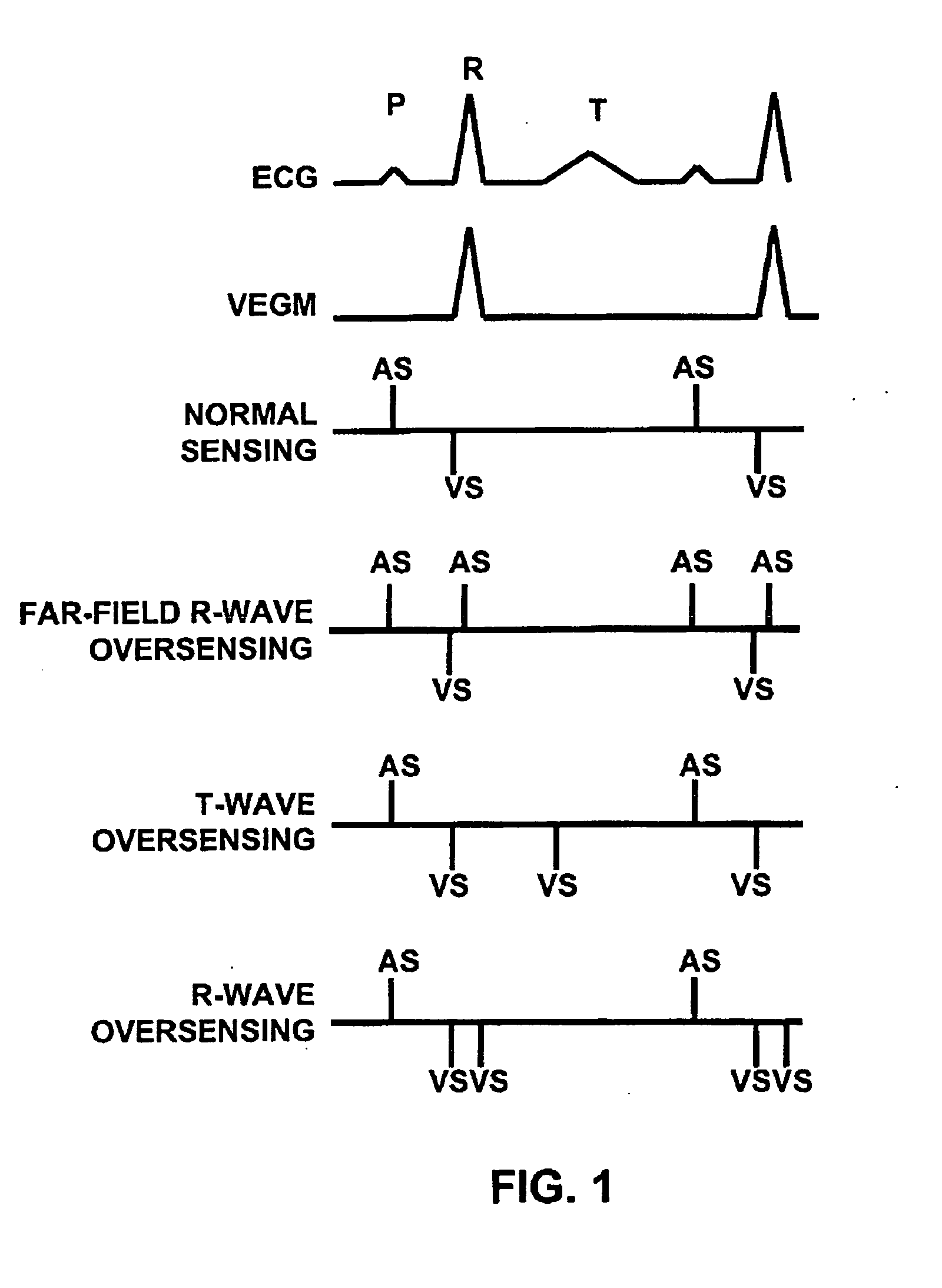
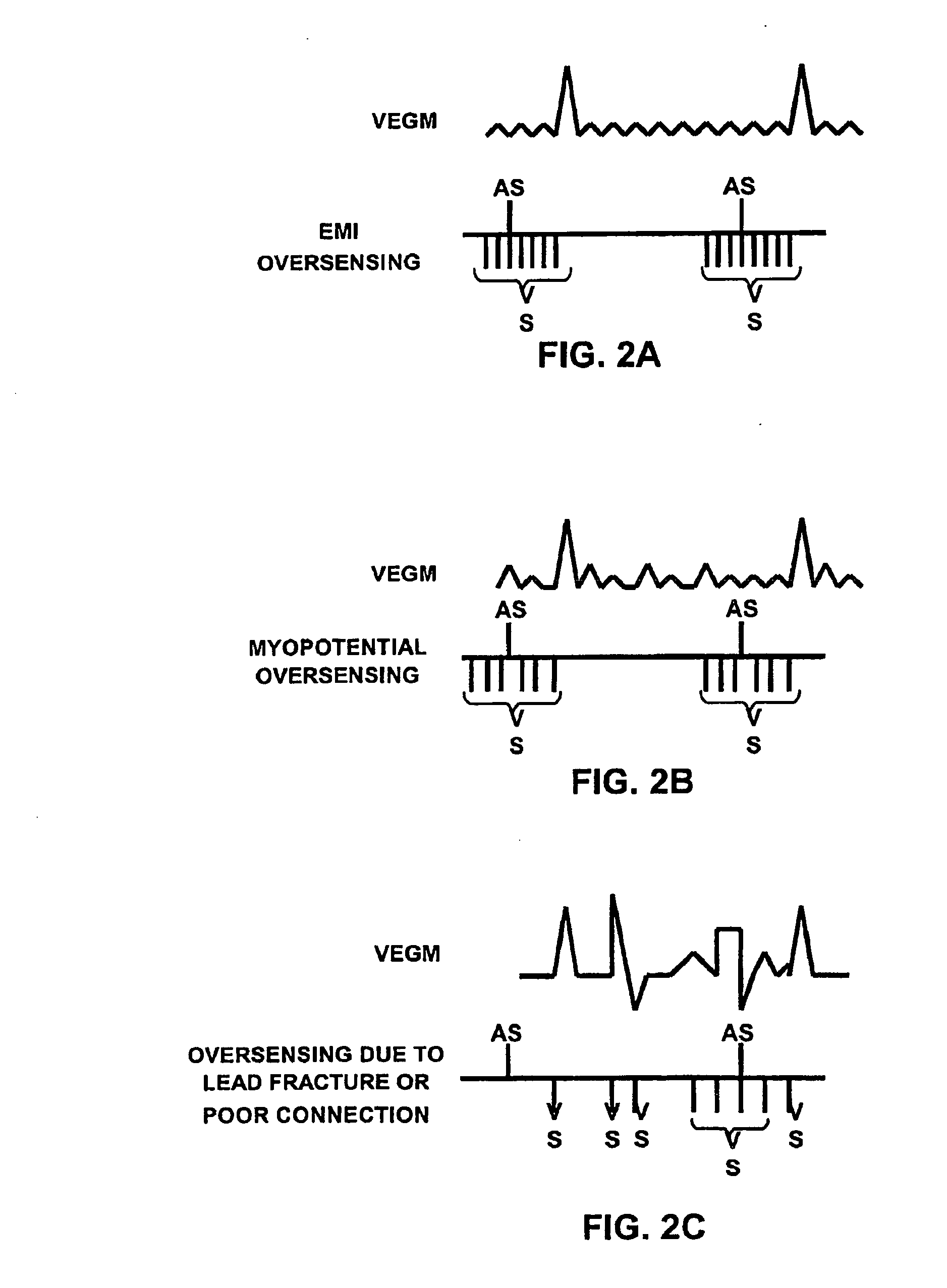
Method and apparatus for identifying oversensing using far-field intracardiac electrograms and marker channels
A method for identifying and classifying various types of oversensing in implantable medical devices (IMDs), such as implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), to assist a physician in choosing corrective action to reduce the likelihood of oversensing and inappropriate therapy delivery. Far-field electrogram (EGM) signals are analyzed to detect the occurrence of R-waves, and the result is compared to the number and pattern of R-waves sensed by the IMD and indicated on the marker channel. A marker channel with more sensed R-waves than indicated by analysis of the far-field EGM indicates the presence of oversensing, including double-counting of R-waves, T-wave oversensing, lead malfunction or failure, poor lead connections, noise associated with electromagnetic interference, non-cardiac myopotentials, etc. Identification of the type of oversensing may be determined by analysis of the number and pattern of marker channel sensed R-waves with respect to the timing of the R-waves detected from the far-field EGM.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Removable small form factor fiber optic transceiver module and electromagnetic radiation shield
InactiveUS6335869B1Small apertureControl speedElectrically conductive connectionsMagnetic/electric field screeningFiberTransceiver
An easily removable modular optical signal transceiver unit for conversion between modulated light signal transmission and electronic data signals and which conforms to the Small Form Factor standard for transceiver interfaces is disclosed. The structural details of its chassis include aspects which insure the proper positioning of electronic circuit boards of a transmitter optical subassembly and a receiver optical subassembly as well as the positioning of electromagnetic radiation shielding on the chassis. In conjunction with an interface device on an electronic circuit board of a host device, the chassis supports electromagnetic radiation shielding which substantially encloses the sources of electromagnetic radiation within the module and suppresses the escape of electromagnetic radiation, thereby preventing electromagnetic interference with sensitive components and devices in proximity to the module.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
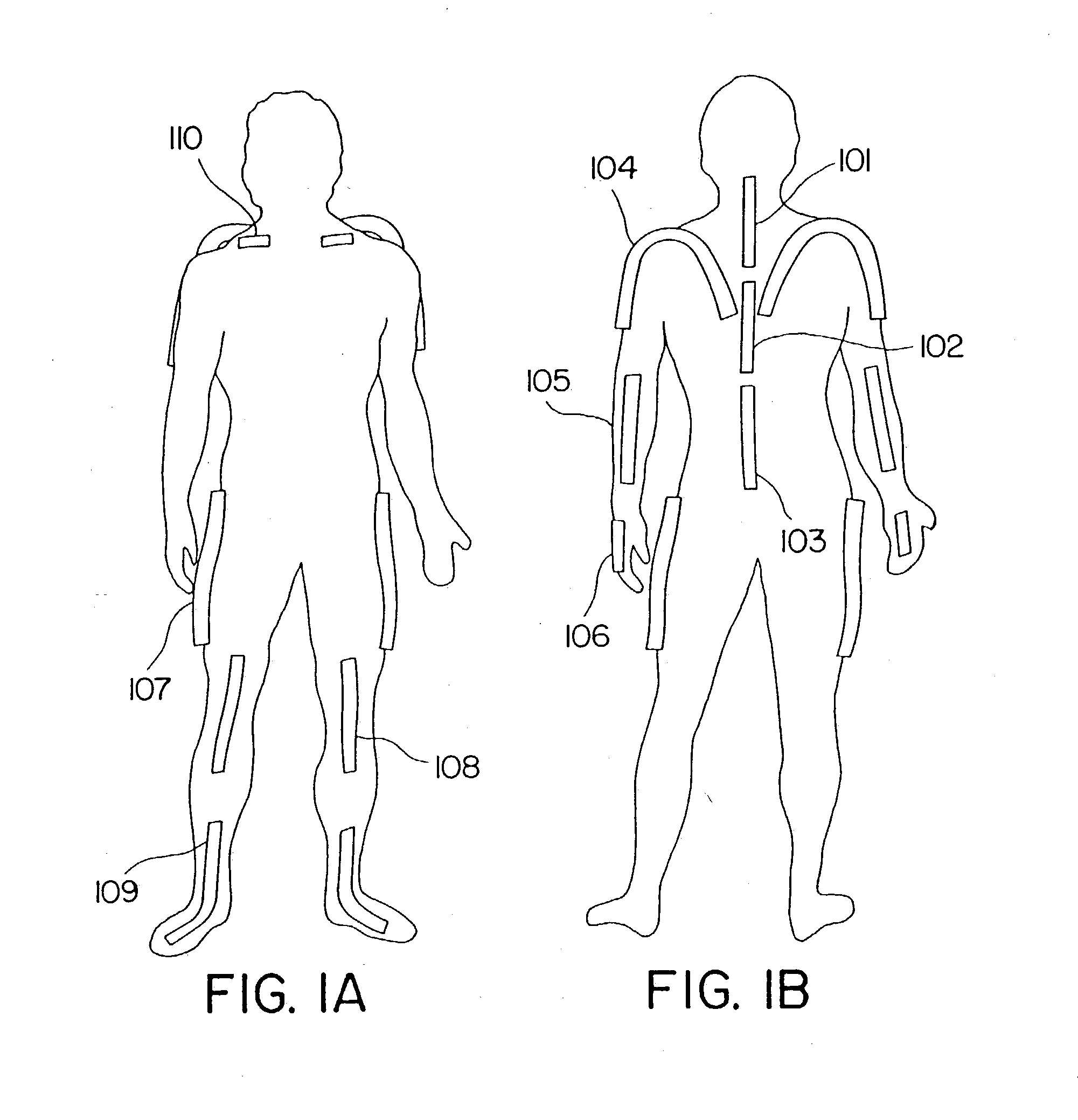
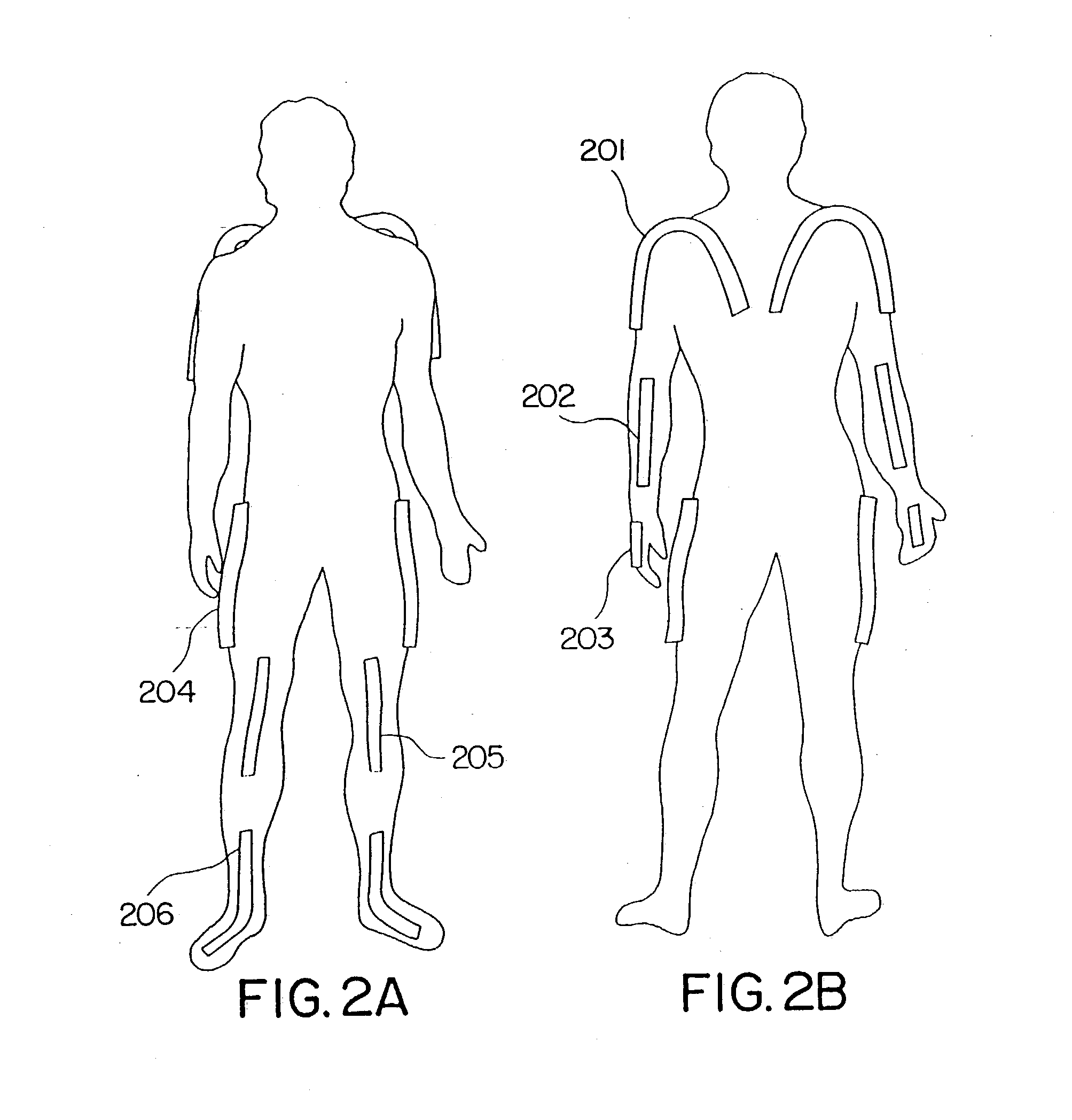
Goniometer-based body-tracking device and method
A sensing system is provided for measuring various joints of a human body for applications for performance animation, biomechanical studies and general motion capture. One sensing device of the system is a linkage-based sensing structure comprising rigid links interconnected by revolute joints, where each joint angle is measured by a resistive bend sensor or other convenient goniometer. Such a linkage-based sensing structure is typically used for measuring joints of the body, such as the shoulders, hips, neck, back and forearm, which have more than a single rotary degree of freedom of movement. In one embodiment of the linkage-based sensing structure, a single long resistive bend sensor measures the angle of more that one revolute joint. The terminal ends of the linkage-based sensing structure are secured to the body such that movement of the joint is measured by the device. A second sensing device of the sensing system comprises a flat, flexible resistive bend sensor guided by a channel on an elastic garment. Such a flat sensing device is typically used to measure various other joints of the body which have primarily one degree of freedom of movement, such as the elbows, knees and ankles. Combining the two sensing devices as described, the sensing system has low sensor bulk at body extremities, yet accurately measures the multi-degree-of-freedom joints nearer the torso. Such a system can operate totally untethered, in real time, and without concern for electromagnetic interference or sensor occlusion.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
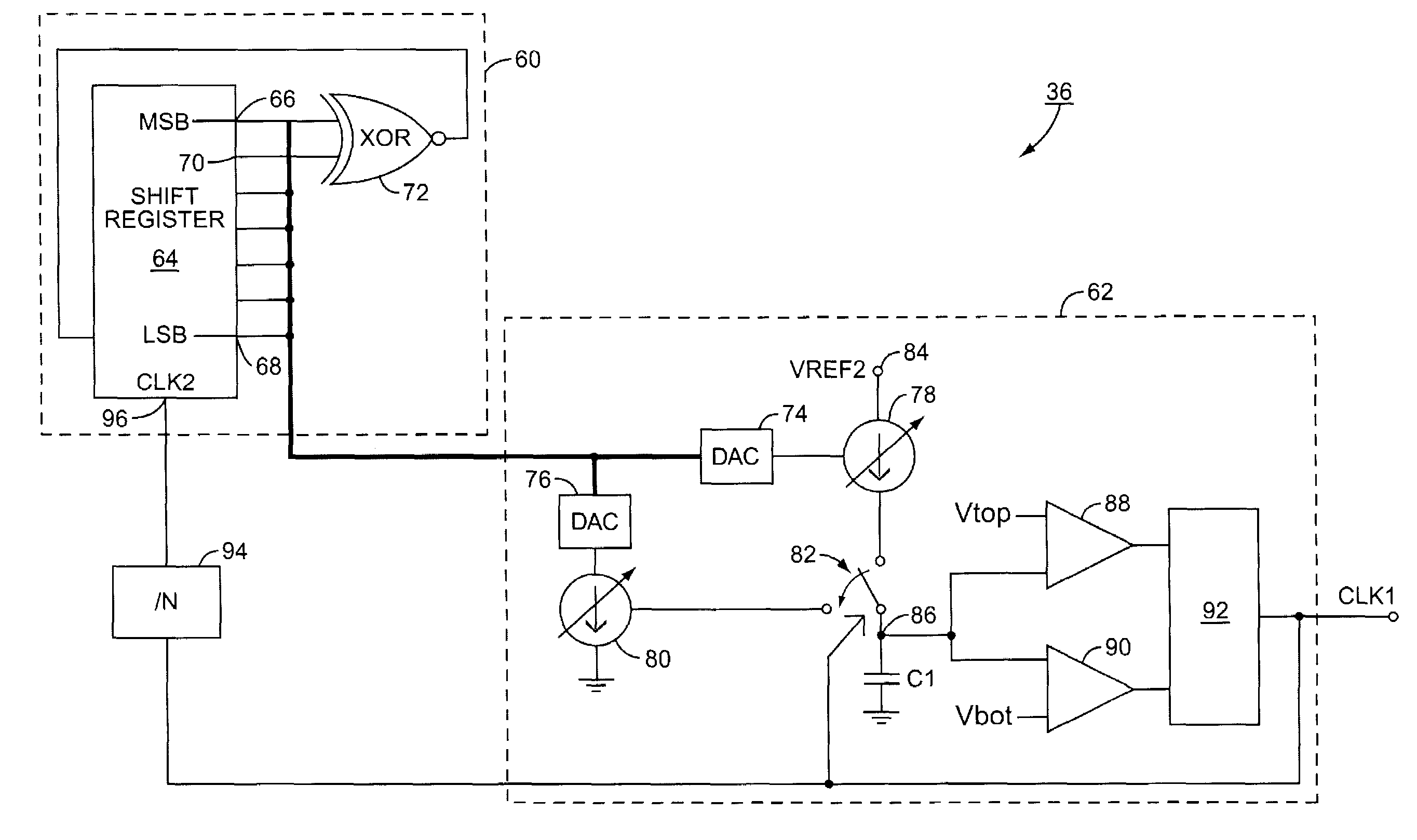
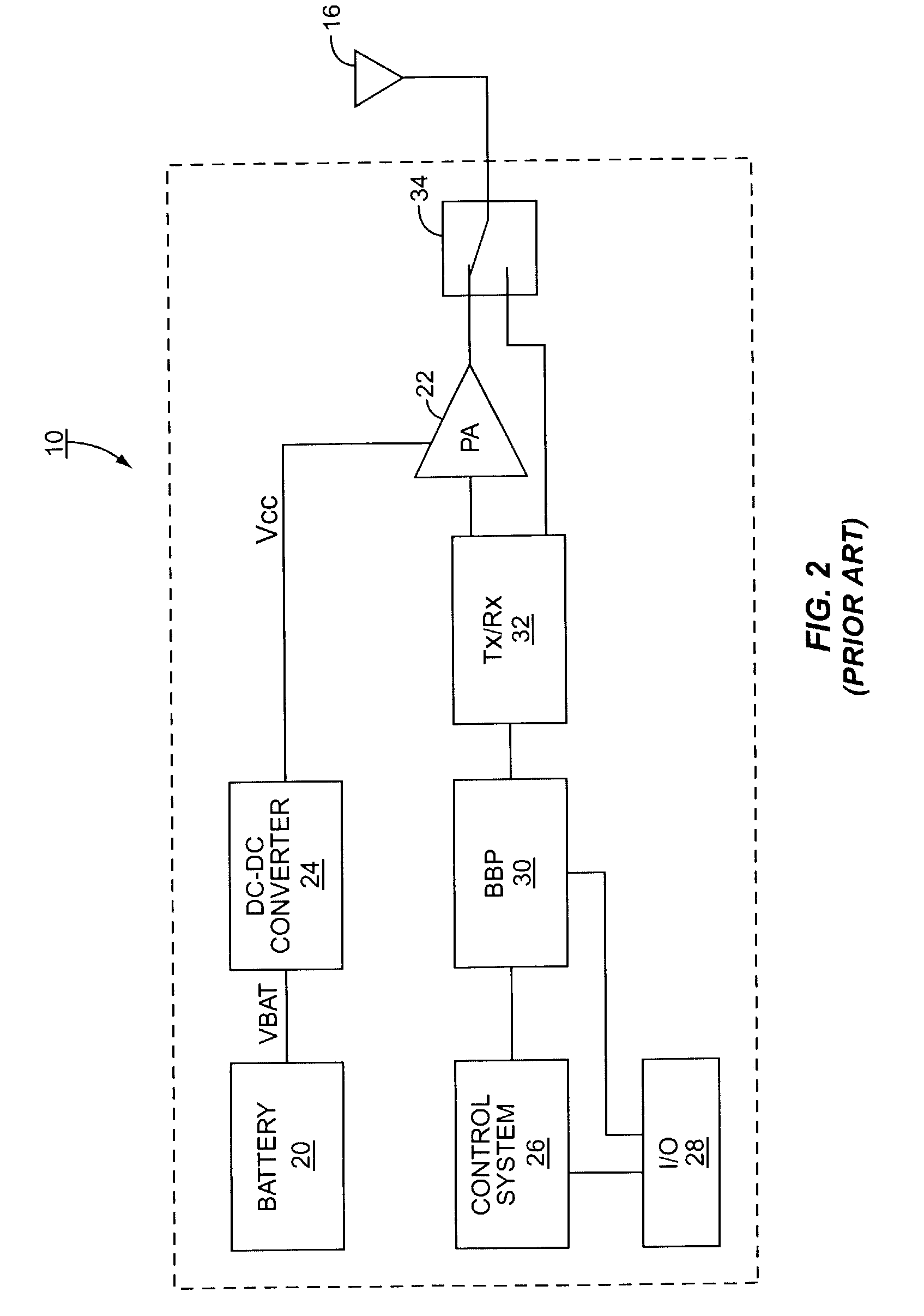
DC-DC converter with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS6969978B2Emission reductionLess spaceDc-dc conversionPulse duration/width modulationDc dc converterControl system
A DC-DC converter includes a variable frequency oscillator, a control system and a power train. The DC-DC converter is well suited for use in a cell phone. The control system uses the output of the oscillator to control the power train. The oscillator varies its frequency as a function of a pseudo random number generator, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference caused by ripple in the output of the DC-DC converter.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Conformal coatings comprising carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7118693B2Material nanotechnologyMagnetic/electric field screeningModified carbonElectromagnetic interference
Owner:EIKOS
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7765005B2Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic interference
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Laser diode optical transducer assembly for non-invasive spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
InactiveUS7047054B2Easily and securely attachedLight couplingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCapacitanceFiber
A non-invasive near infrared spectrophotometric monitoring transducer assembly includes a housing member, which is adhered directly on a patient's skin. The housing member contains a prism coupled to a flexible and lightweight single core optical light guide, which provides a means of transferring narrow spectral bandwidth light from multiple distant laser diodes of different wavelengths by use of a multi-fiber optic light combining assembly. Different wavelengths are needed to monitor the level of blood oxygenation in the patient. The assembly also contains a planar light guide mounted on the prism located in the housing member, which light guide contacts the patient's skin when the housing member is adhered to the patient's skin. The light guide controls the spacing between the prism and the patient's skin, and therefore controls the intensity of the area on the patient's skin which is illuminated by the laser light. The housing member contains a photodiode assembly, which detects the infrared light at a second location on the skin to determine light absorption. The photodiode assembly is preferably shielded from ambient electromagnetic interference (EMI) by an optically transparent EMI attenuating window. This rigid window placed over the photodiode also provides a planar interface between the assembly and the skin, improving optical coupling and stability as well as reducing the capacitive coupling between skin and the photodiode resulting in further EMI attenuation. The housing may be associated with a disposable sterile hydrogel coated adhesive envelope, or pad, which when applied to the patient's skin will adhere the housing to the patient's skin. The transducer assembly will thus be reusable, and skin-contacting part of the device, i.e., the envelope or pad can be discarded after a single use. The assembly also includes a laser safety interlock means, which is operable to turn off the laser light output in the event that the assembly accidentally becomes detached from the patient's skin.
Owner:CAS MEDICAL SYST
Surgical visualization systems
ActiveUS20150018622A1Different stiffnessReduce condensationSurgical furnitureSurgical scissorsDisplay deviceCombined use
A surgical device includes one or more cameras integrated therein. The view of each of the one or more cameras can be integrated together and provided to a surgeon display and / or an assistant display. A surgical tool that includes an integrated camera may be used in conjunction with the surgical device. The image produced by the camera integrated with the surgical tool may be associated with the images generated by the one or more cameras integrated in the surgical device. The position and orientation of the cameras and / or the surgical tool can be tracked, and the surgical tool can be rendered as at least partially transparent. A surgical device may be powered by a hydraulic system, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference with tracking devices.
Owner:CAMPLEX
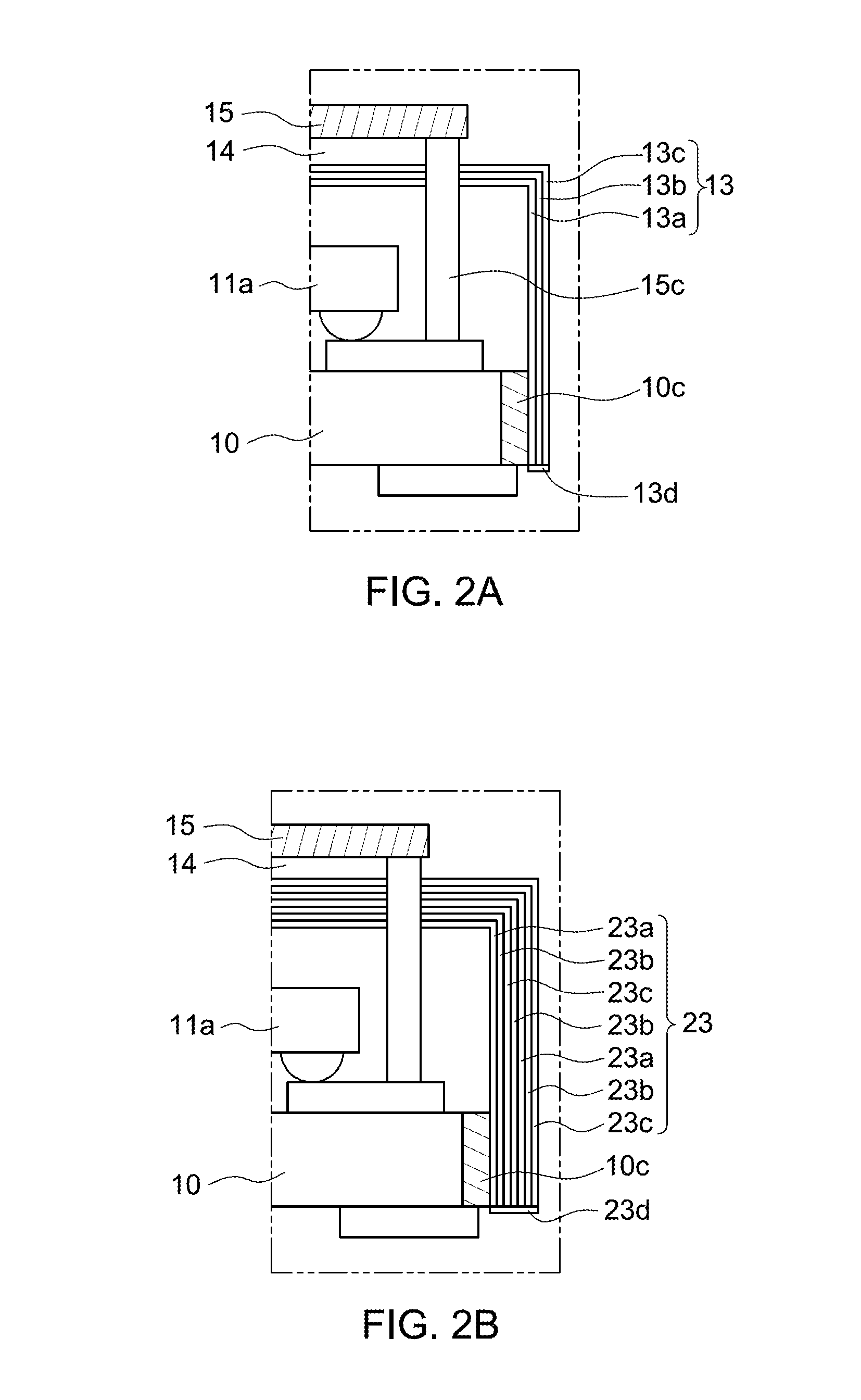
Semiconductor package integrated with conformal shield and antenna
ActiveUS20130292808A1High dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageElectromagnetic interference
A semiconductor package includes a substrate, a semiconductor die, a package body, an electromagnetic interference shield, a dielectric structure and an antenna element. The substrate comprises a grounding segment and a feeding point. The semiconductor die is disposed on the substrate. The package body encapsulates the semiconductor die. The electromagnetic interference shield is formed on the package body. The dielectric structure encapsulates the electromagnetic interference shield. The antenna element is formed on the dielectric structure and electrically connecting the grounding segment of the substrate and the feeding point.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Electromagnetic shielding using through-silicon vias
ActiveUS20080073747A1Good electromagnetic isolationImprove isolationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectromagnetic interferenceDirect path
An isolation structure for electromagnetic interference includes a semiconductor substrate, a first integrated circuit in the semiconductor substrate, a second integrated circuit in the semiconductor substrate, and an isolation structure in a direct path between the first and the second integrated circuits, wherein the isolation structure comprises a through-silicon via.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
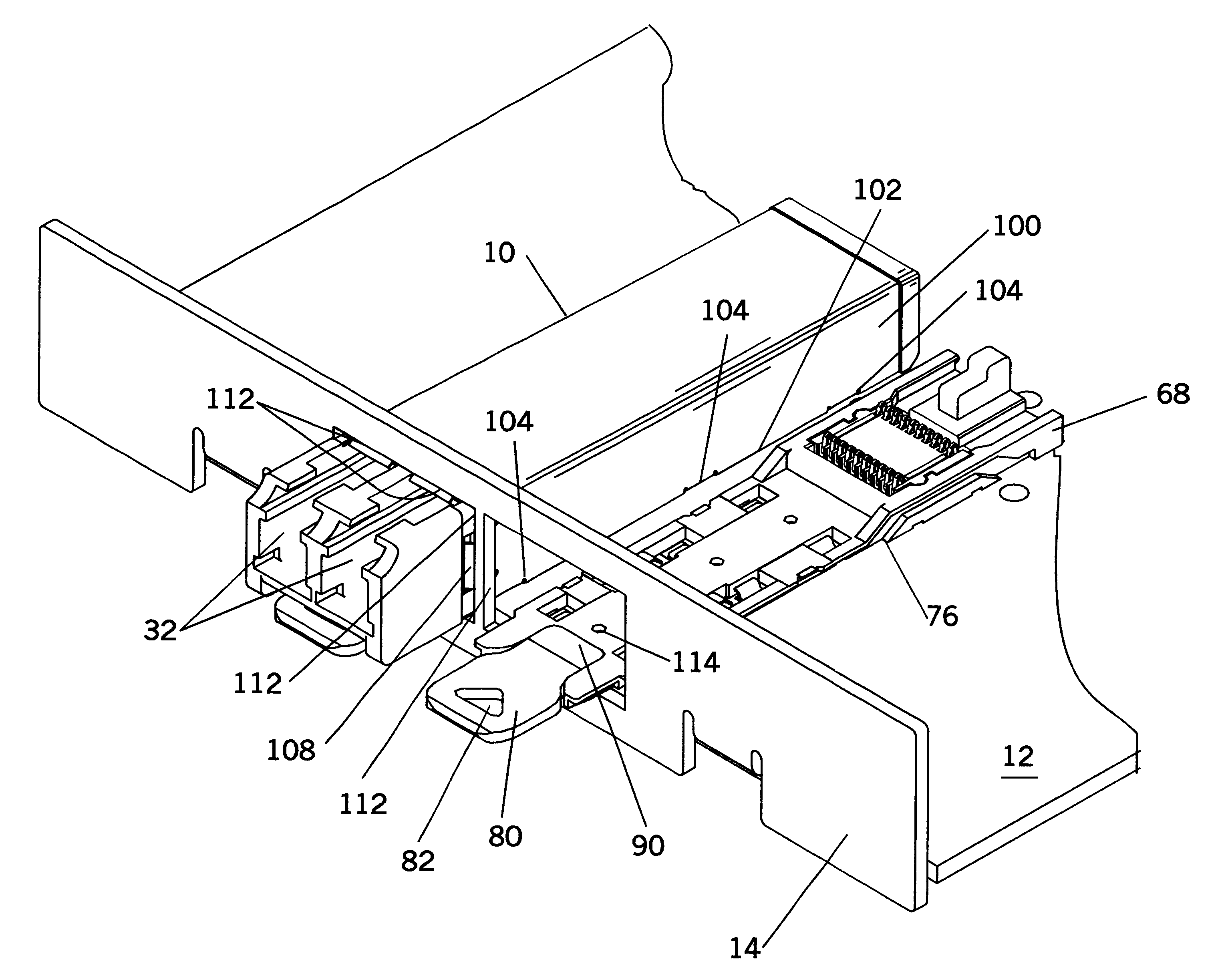
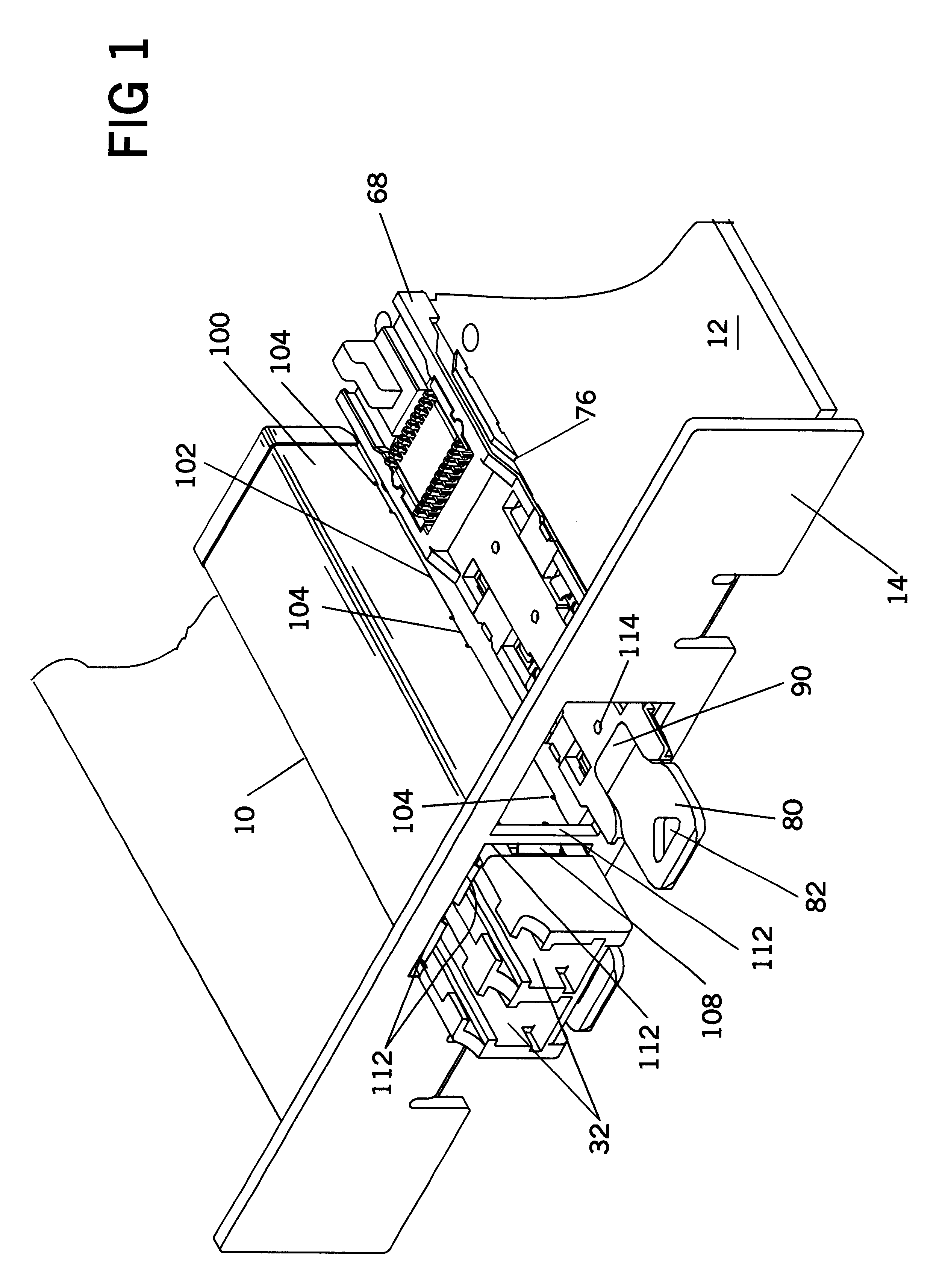
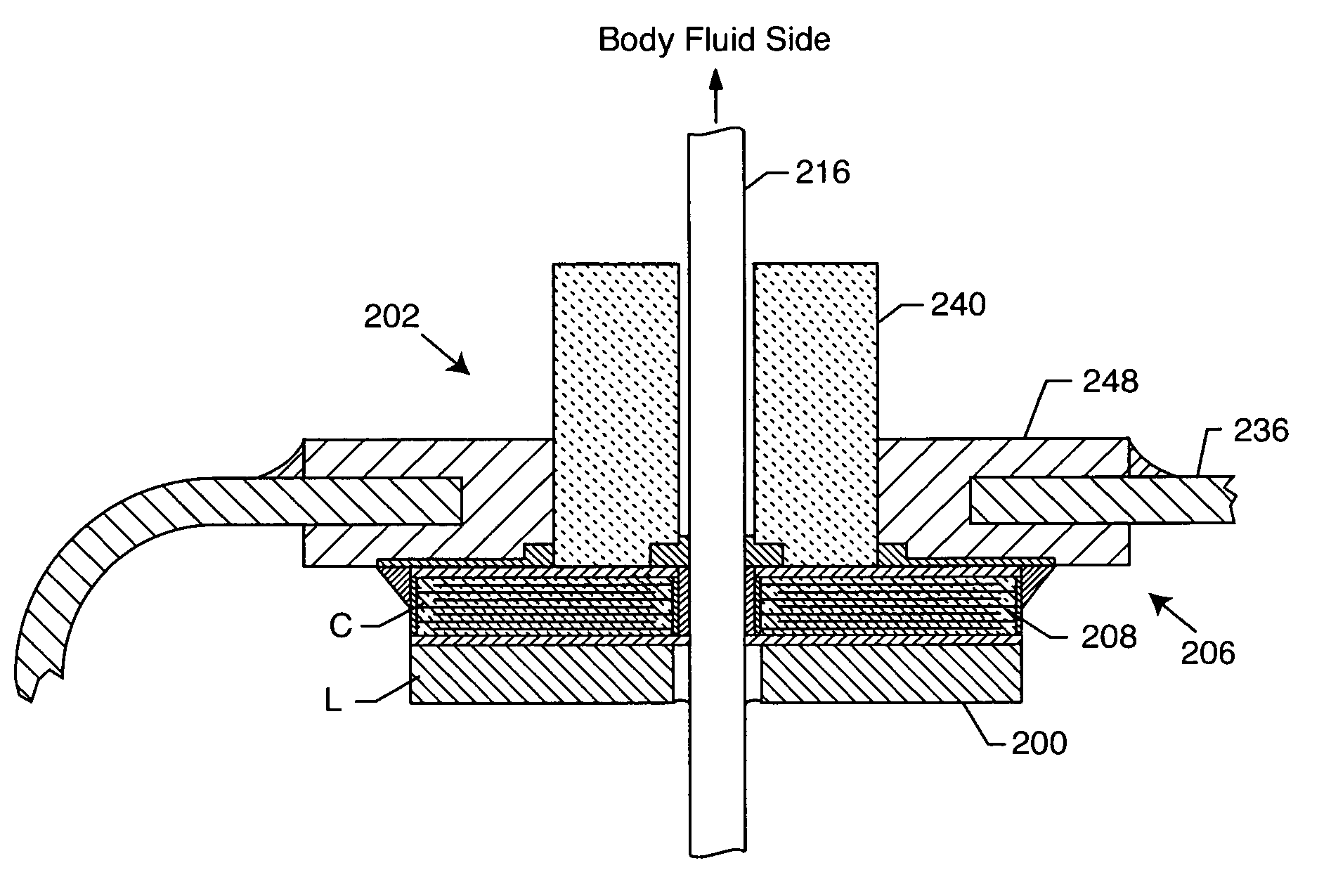
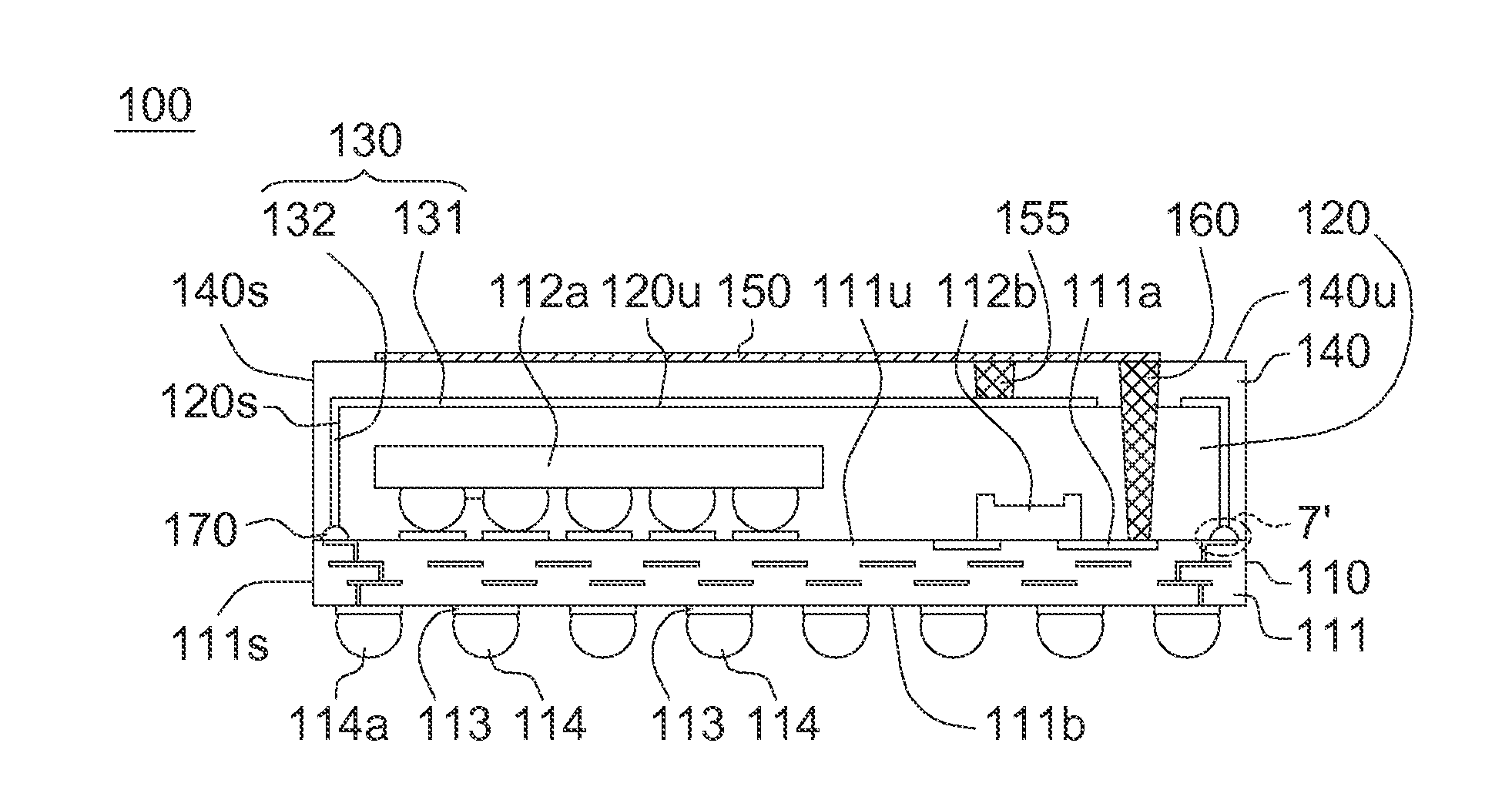
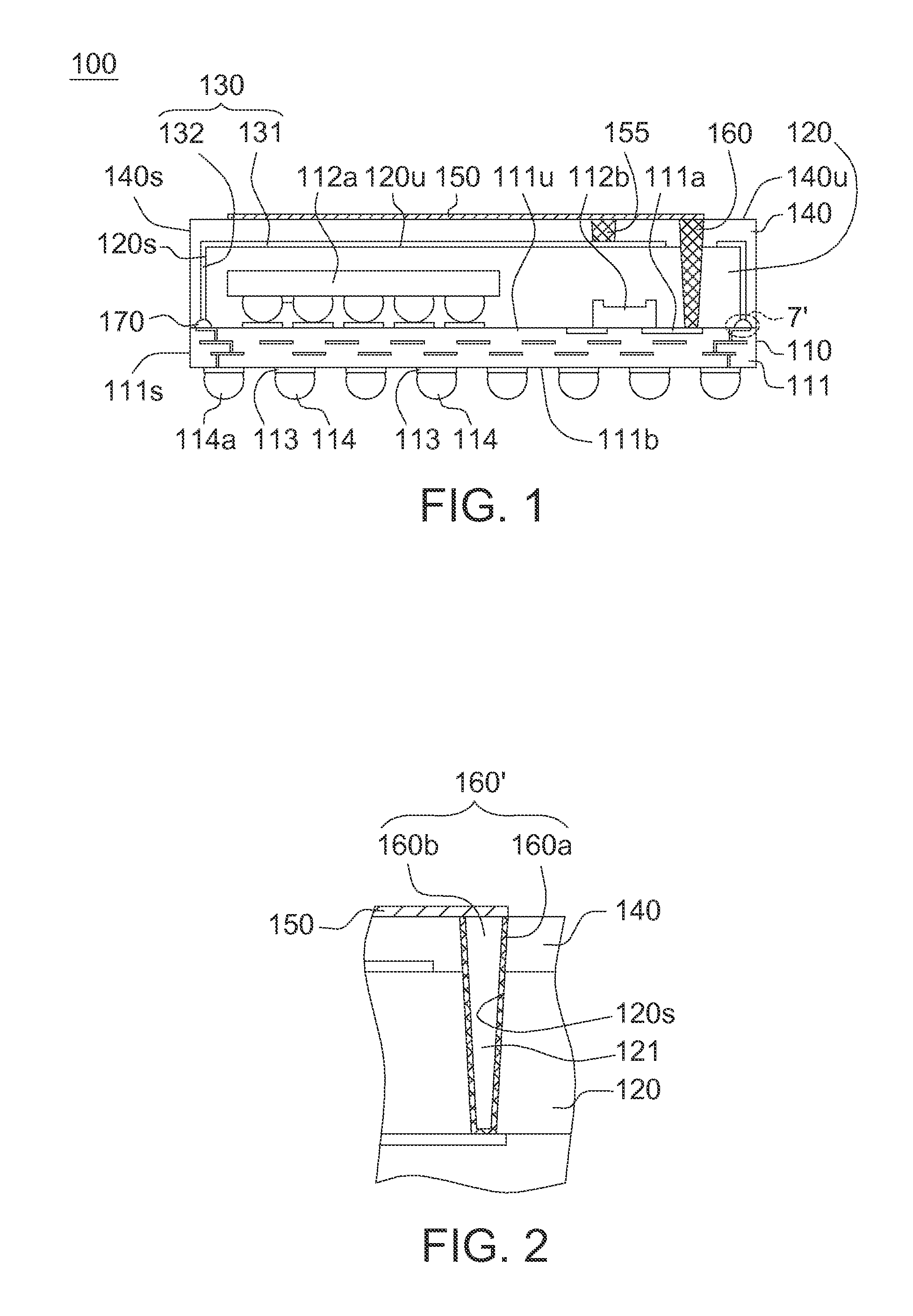
EMI filter terminal assembly with wire bond pads for human implant applications
ActiveUS20050007718A1Avoid crackingAbsorbs stressMultiple-port networksElectrotherapyElectromagnetic interferenceSoldering
An electromagnetic interference filter terminal assembly for active implantable medical devices includes a structural pad in the form of a substrate or attached wire bond pad, for convenient attachment of wires from the circuitry inside the implantable medical device to the capacitor structure via thermal or ultrasonic bonding, soldering or the like while shielding the capacitor from forces applied to the assembly during attachment of the wires.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Top-emitting OLED display having transparent touch panel
InactiveUS20070242055A1High light transmittanceHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingDisplay deviceElectromagnetic interference
A top-emitting OLED display having a transparent touch panel includes a substrate, an upper cover plate, an OLED display device, a capacitive touch device and a sealant layer. The OLED device is stacked on the substrate, the capacitive touch device is stacked on the upper cover plate, and the sealant layer combines the substrate and the upper cover plate such that the OLED device and the capacitive touch device are enclosed between the substrate and the upper cover plate. The capacitive touch device includes a first transparent conductive layer, an isolating layer, a second transparent conductive layer and an electromagnetic shielding layer sequentially formed on the upper cover plate. The electromagnetic shielding layer can effectively reduce the electromagnetic interfering between the OLED device and the capacitive touch device.
Owner:RITDISPLAY
Conformal electromagnetic interference shield
An electromagnetic shield for an electronic module includes a surface finish that is applied to the surface of an electronic module so as to minimize the size of the shield. Once the shield is in place, the shield acts to address electromagnetic interference (EMI) concerns associated with the electronic module. An electronic module having a ring of conductive material embedded about its peripheral edge is formed. The electronic module is then sub-diced so as to expose the ring of conductive material. After sub-dicing, a conductive material may be applied through an electroless plating process followed by an electrolytic plating process. Alternatively, a conductive epoxy may be sprayed or painted onto the surface of the electronic module.
Owner:QORVO US INC
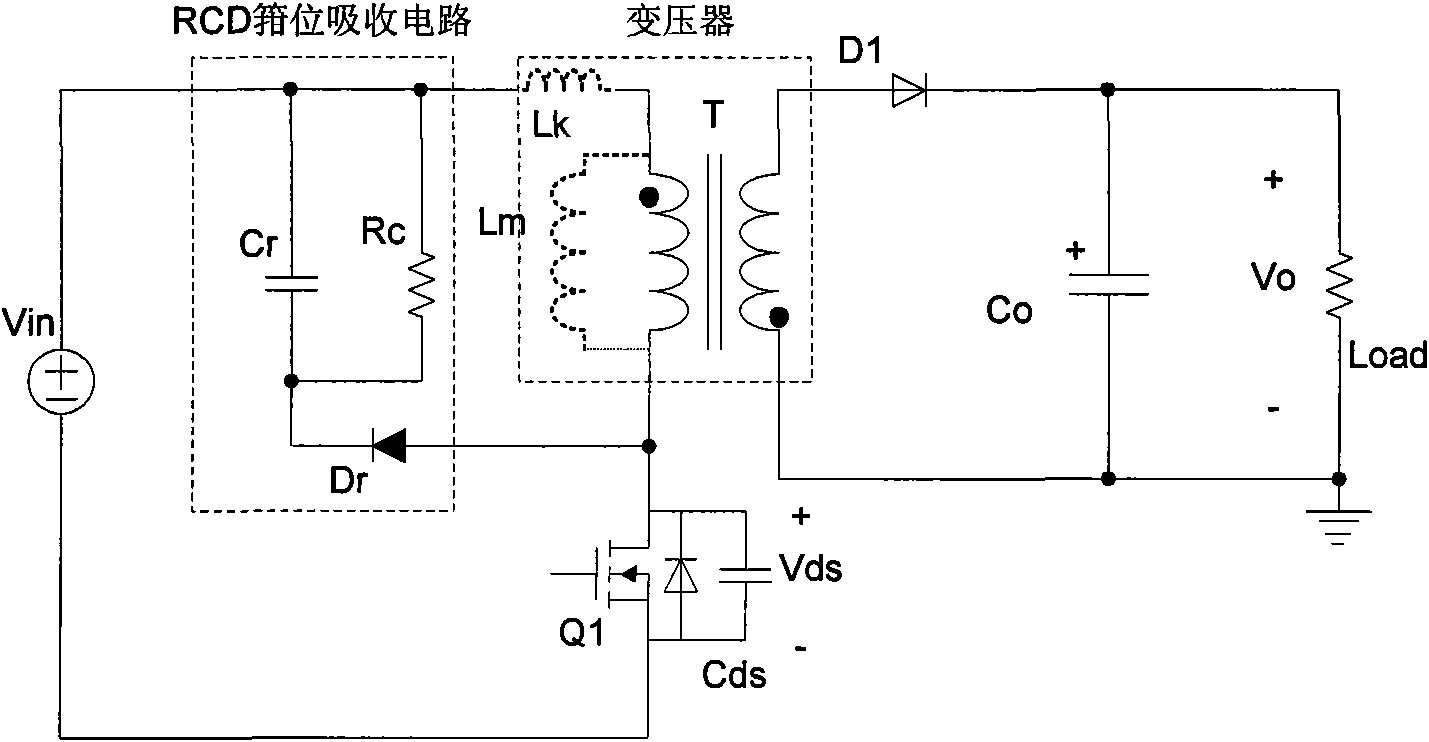
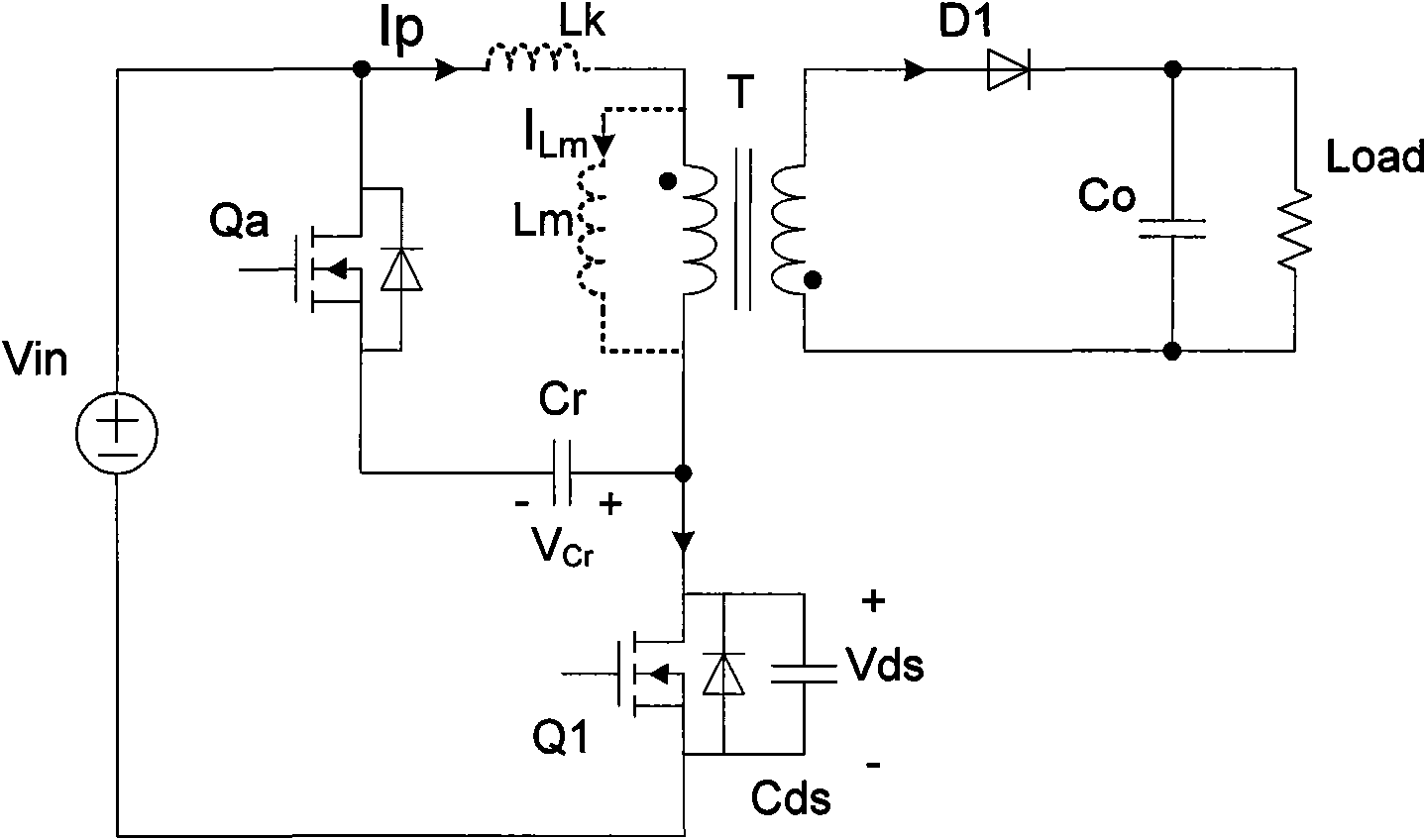
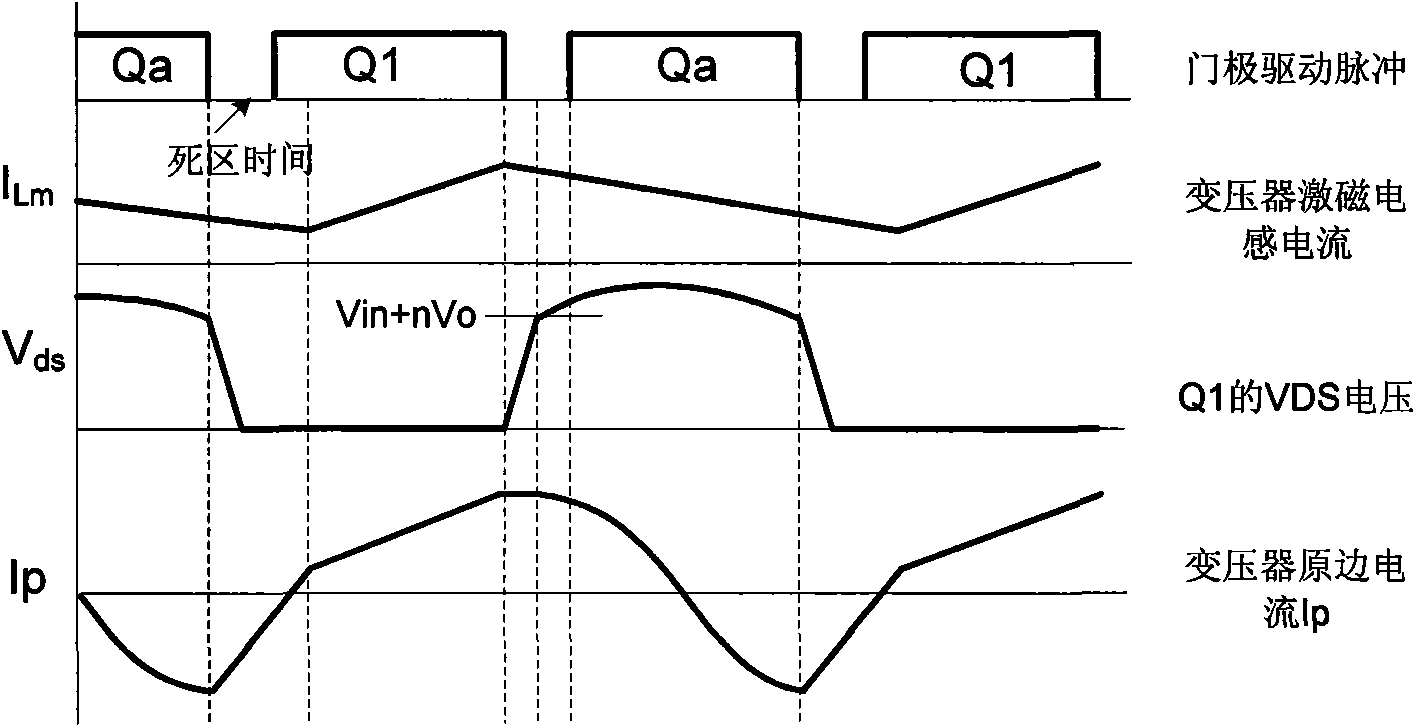
Zero-voltage switch flyback-type DC-DC power supply conversion device
ActiveCN101572490AEasy to controlImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceTransformer
The invention relates to a DC-DC power supply conversion device, in particular to a zero-voltage switch (ZVS) flyback-type DC-DC power supply conversion device with efficient conversion, efficient light-load conversion and low standby power consumption. An auxiliary switch and an absorption capacitor are additionally arranged on the flyback circuit; the auxiliary switch and the absorption capacitor are connected in series so as to form an auxiliary branch circuit; the auxiliary branch circuit can be connected in parallel to the two ends of the primary winding of a transformer or alternatively connected in parallel to the two ends of a primary-side switch; and the auxiliary switch is conductive for a determined period of time before the primary-side switch is conductive. Compared with the prior art, the energy of the circuit leakage inductor can be absorbed and transferred to the output terminal and a soft switch for realizing the primary-side switch, so that the invention can greatly improve the circuit efficiency; the parasitic oscillation caused by the leakage inductor can be suppressed, so that the EMI (electromagnetic interference) characteristics of the circuit can be improved; and the circuit can be controlled more easily, thereby improving the light-load circuit efficiency and reducing the idle-load energy loss.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
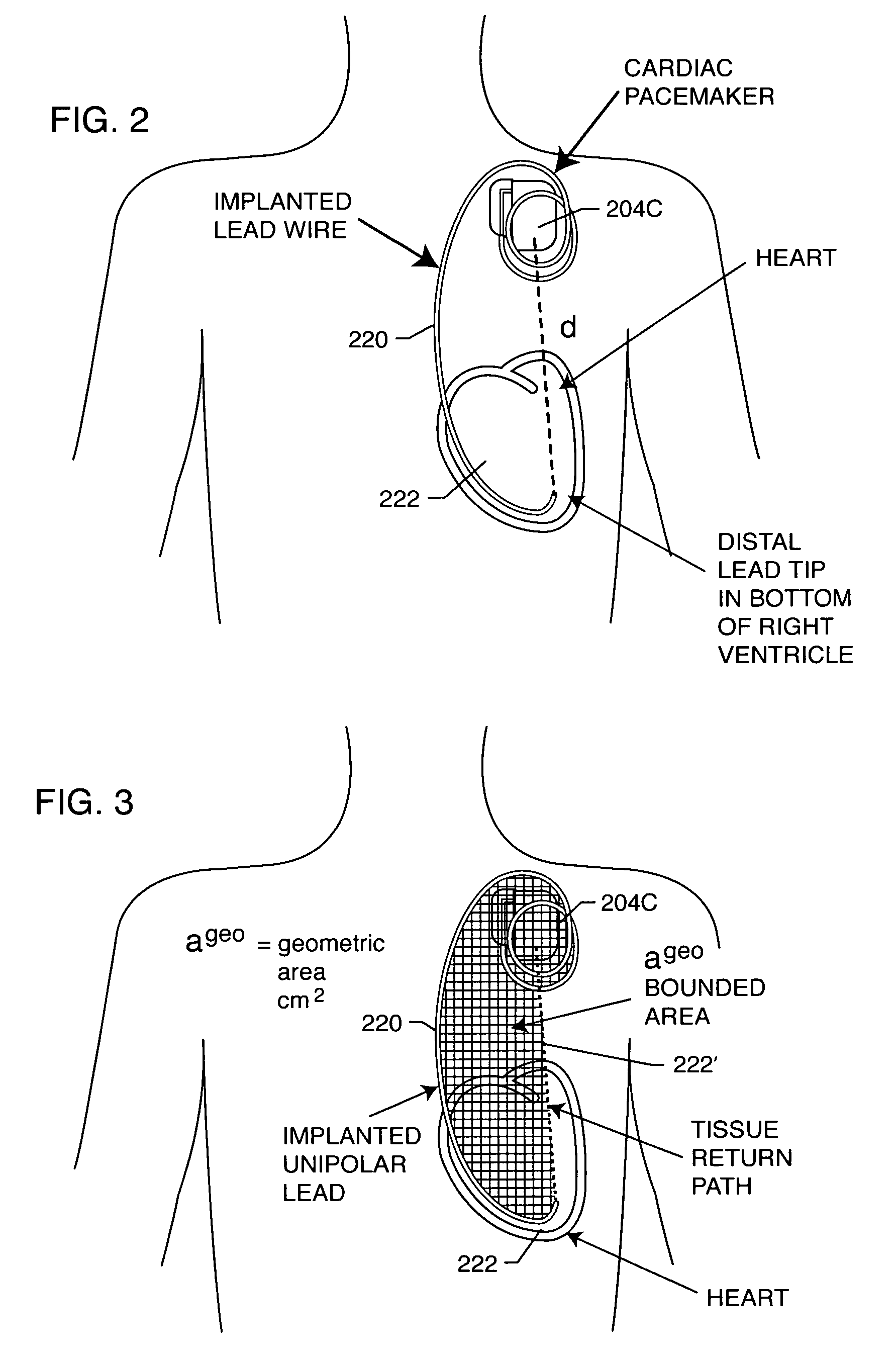
Electromagnetic interference immune tissue invasive system
InactiveUS20020128689A1Avoid failureAvoid interferenceMagnetic measurementsTransvascular endocardial electrodesFiberElectricity
An electromagnetic immune tissue invasive system includes a primary device housing. The primary device housing having a control circuit therein. A shielding is formed around the primary device housing to shield the primary device housing and any circuits therein from electromagnetic interference. A lead system transmits and receives signals between the primary device housing. The lead system is either a fiber optic system or an electrically shielded electrical lead system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
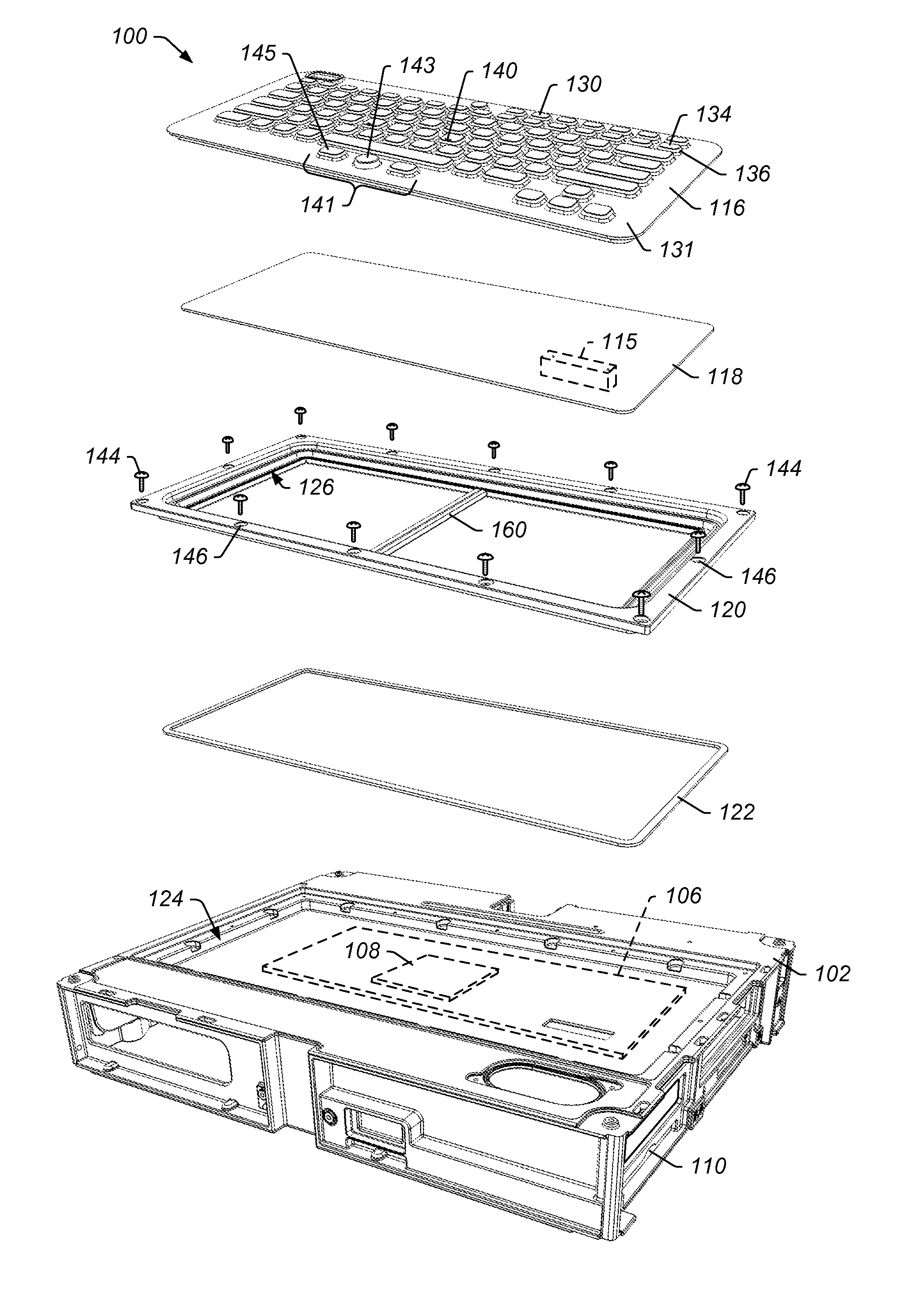
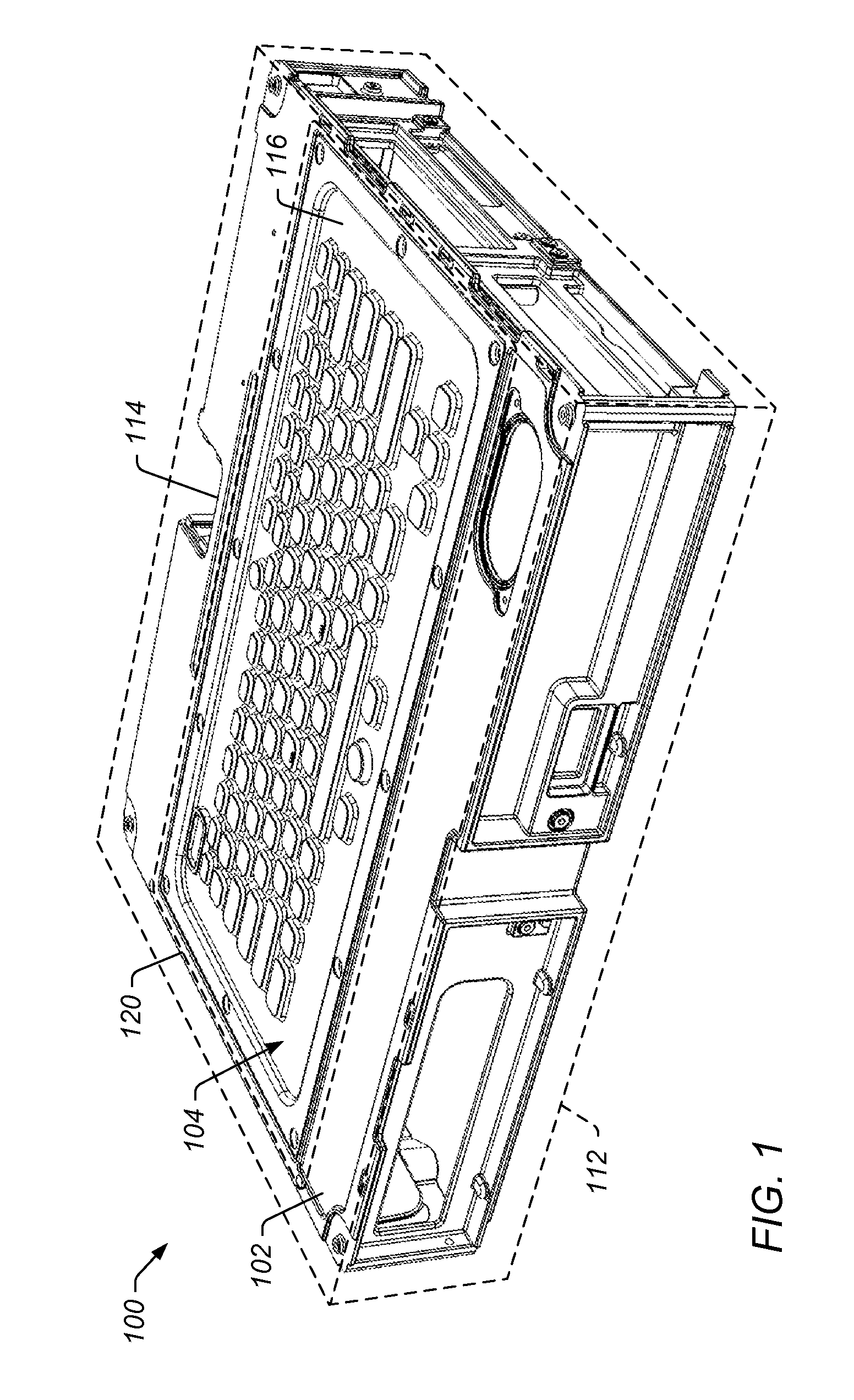
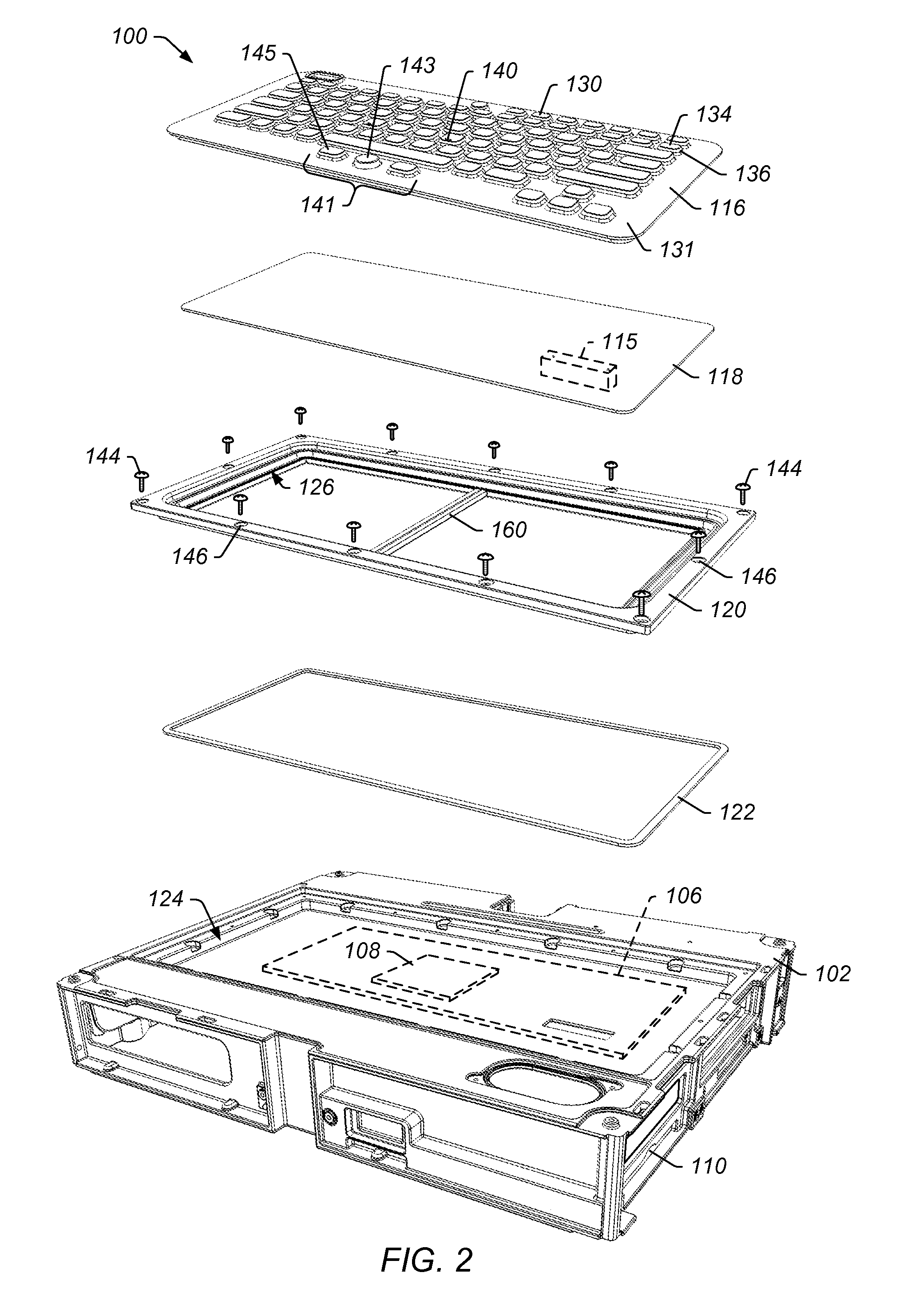
Panel Mount Keyboard System
InactiveUS20110267272A1Improve protectionInput/output for user-computer interactionOperation facilitationElectromagnetic interferencePrinted circuit board
A keyboard system having improved protection from electromagnetic interference includes a keypad and a printed circuit board assembly. The keypad includes one or more keys and one or more keypad conductive elements for at least one of the keys. The printed circuit board assembly is coupled to the keypad. The printed circuit board assembly includes a printed circuit board having at least one switch contact area for each of one or more keys on the keypad. The printed circuit board also includes, for at least one of the keys of the keypad, one or more first side vias in a switch contact area and one or more second side vias in the switch contact area. The first side vias are electrically coupled on a first side of a switch for the key. The second side vias are electrically coupled on a second side of the switch for the key.
Owner:IKEY
Method for shielding an electronic component
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com