Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50results about How to "Absorbs stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
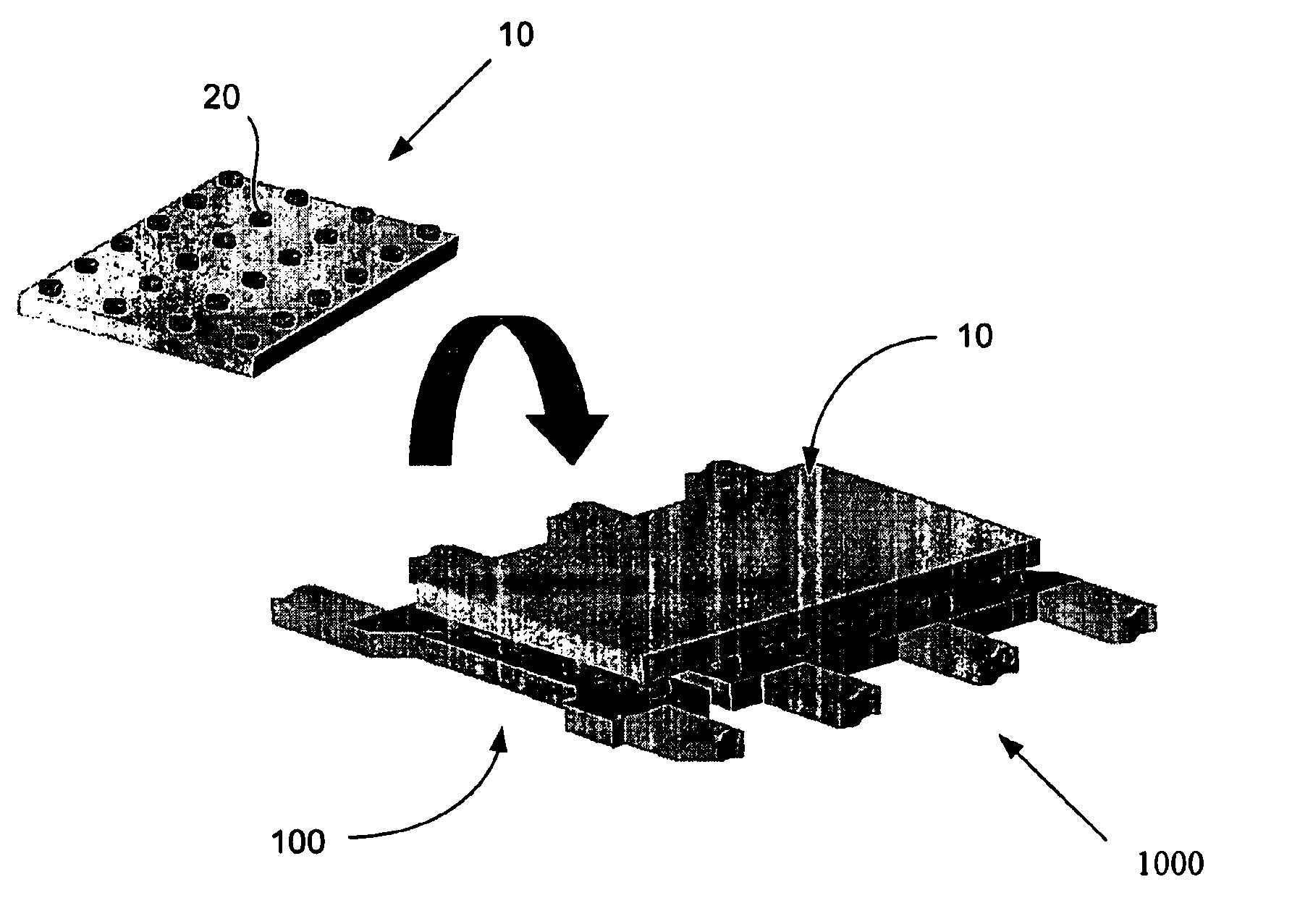
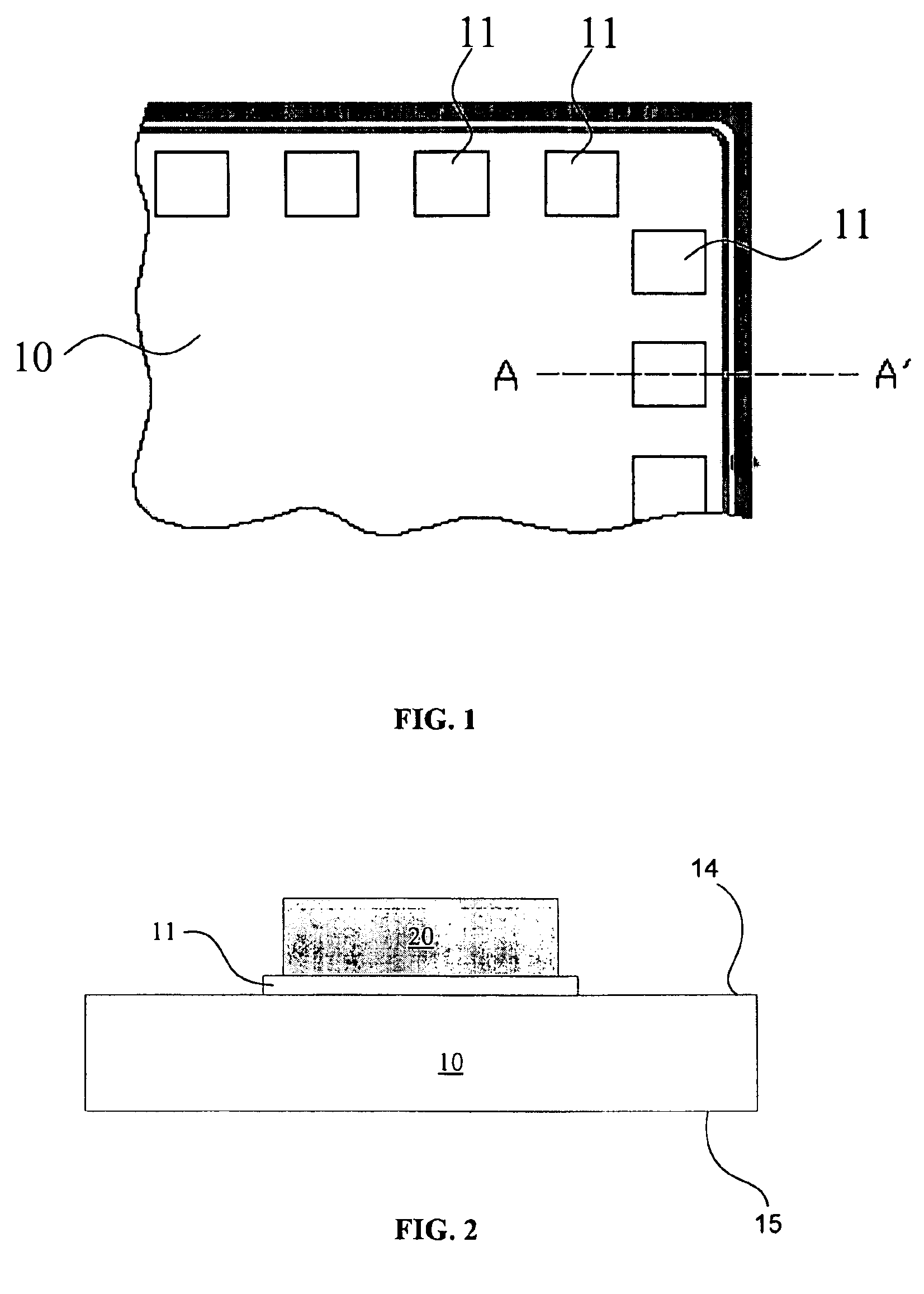
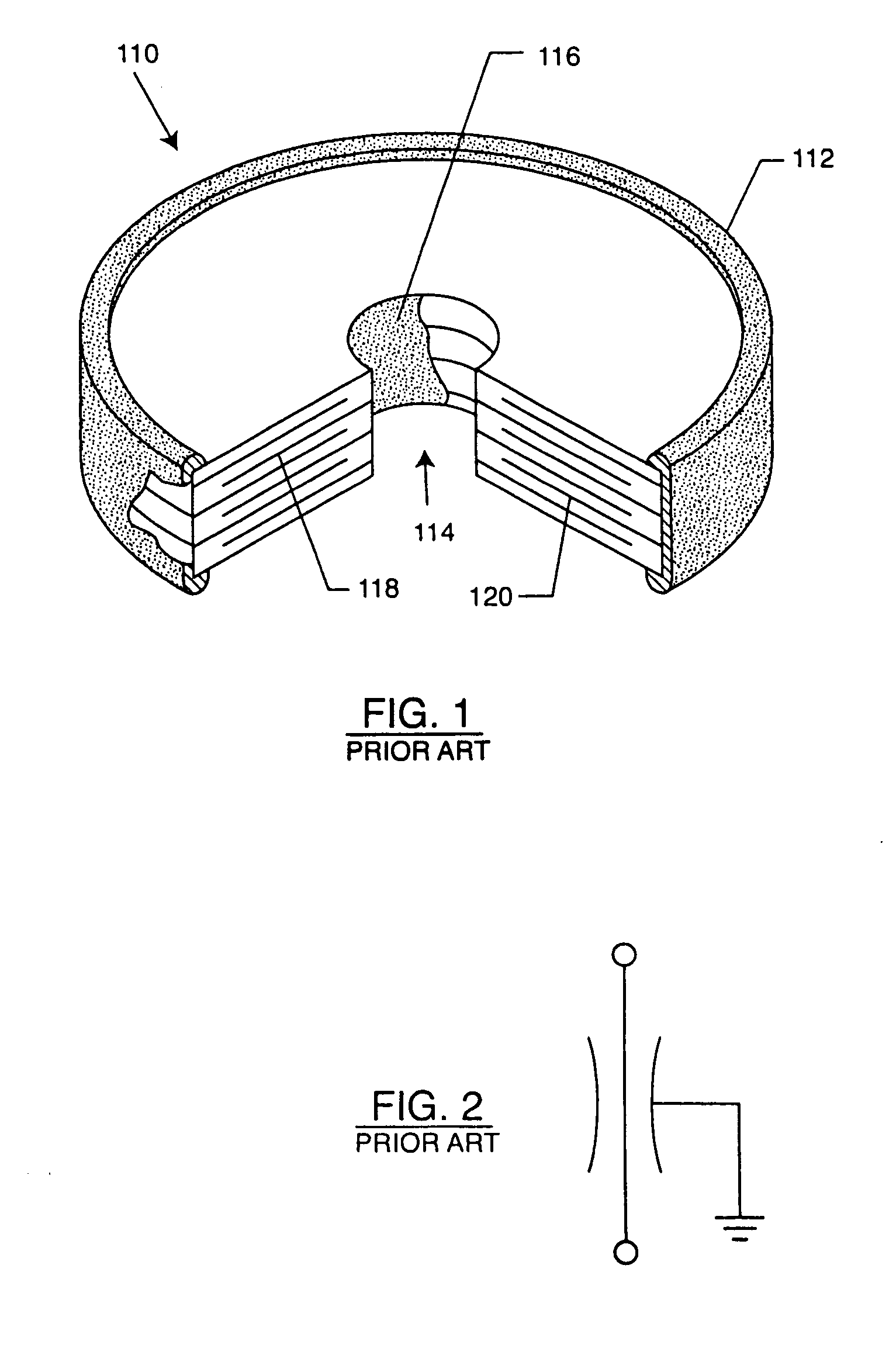
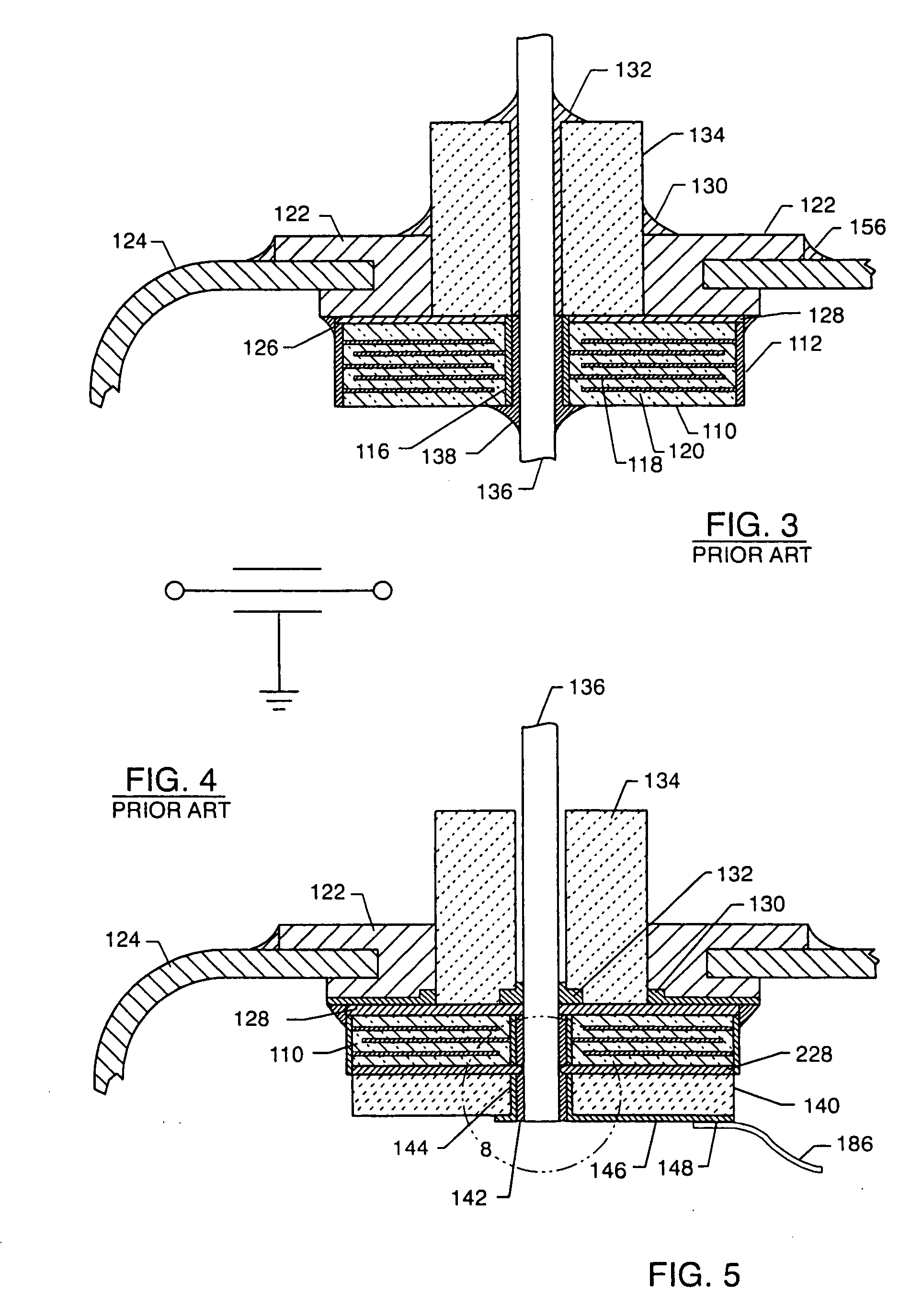
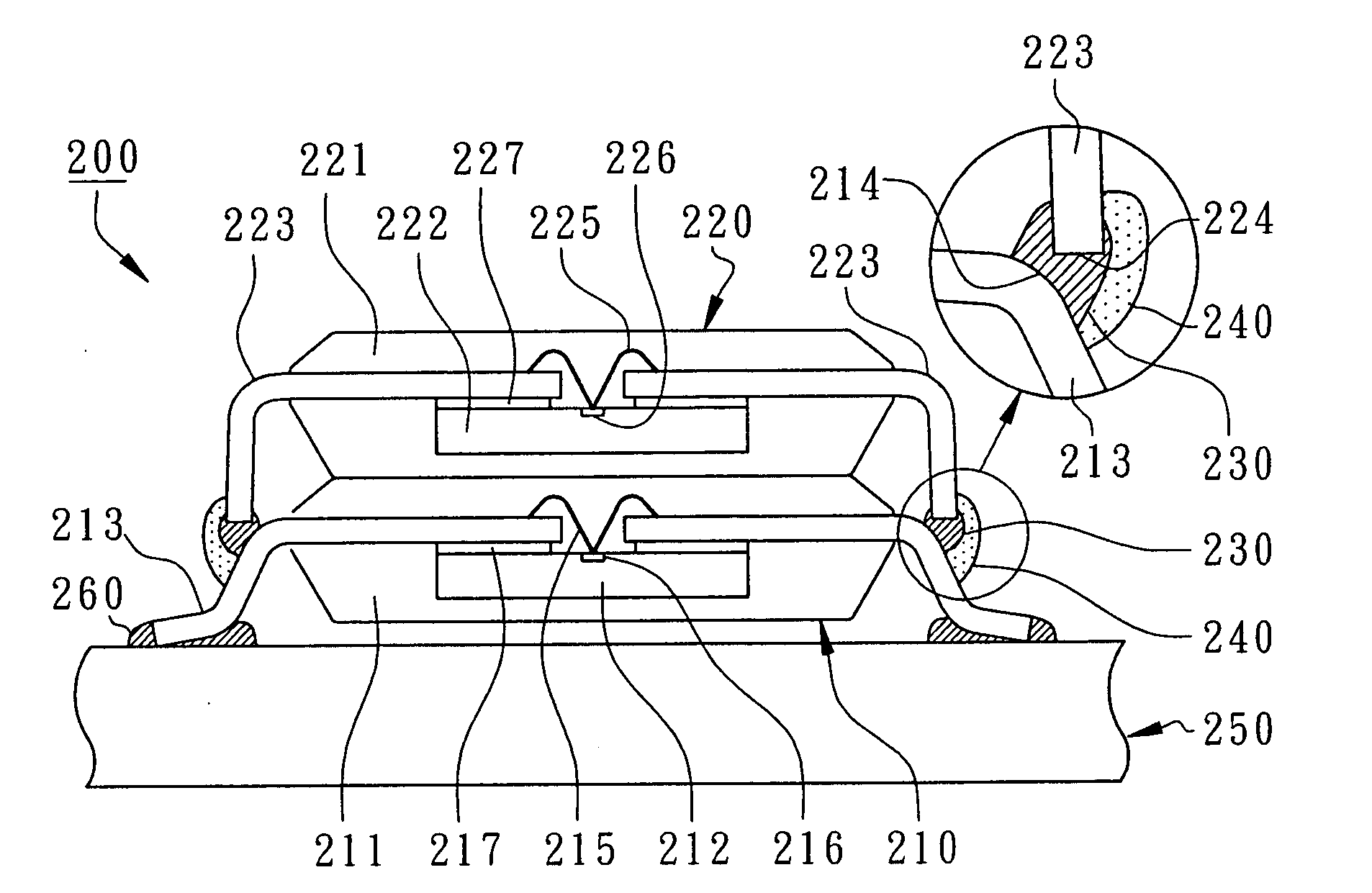
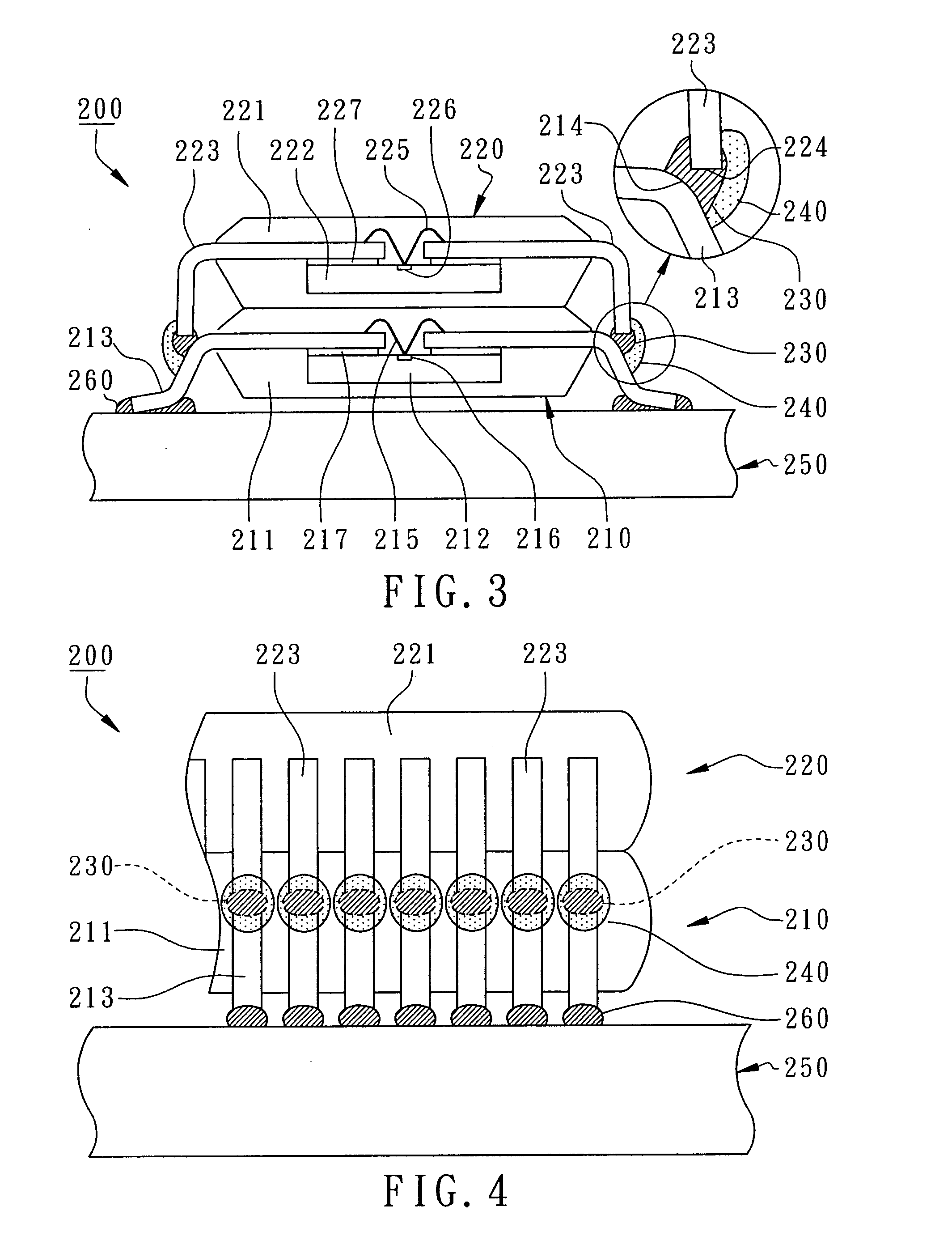
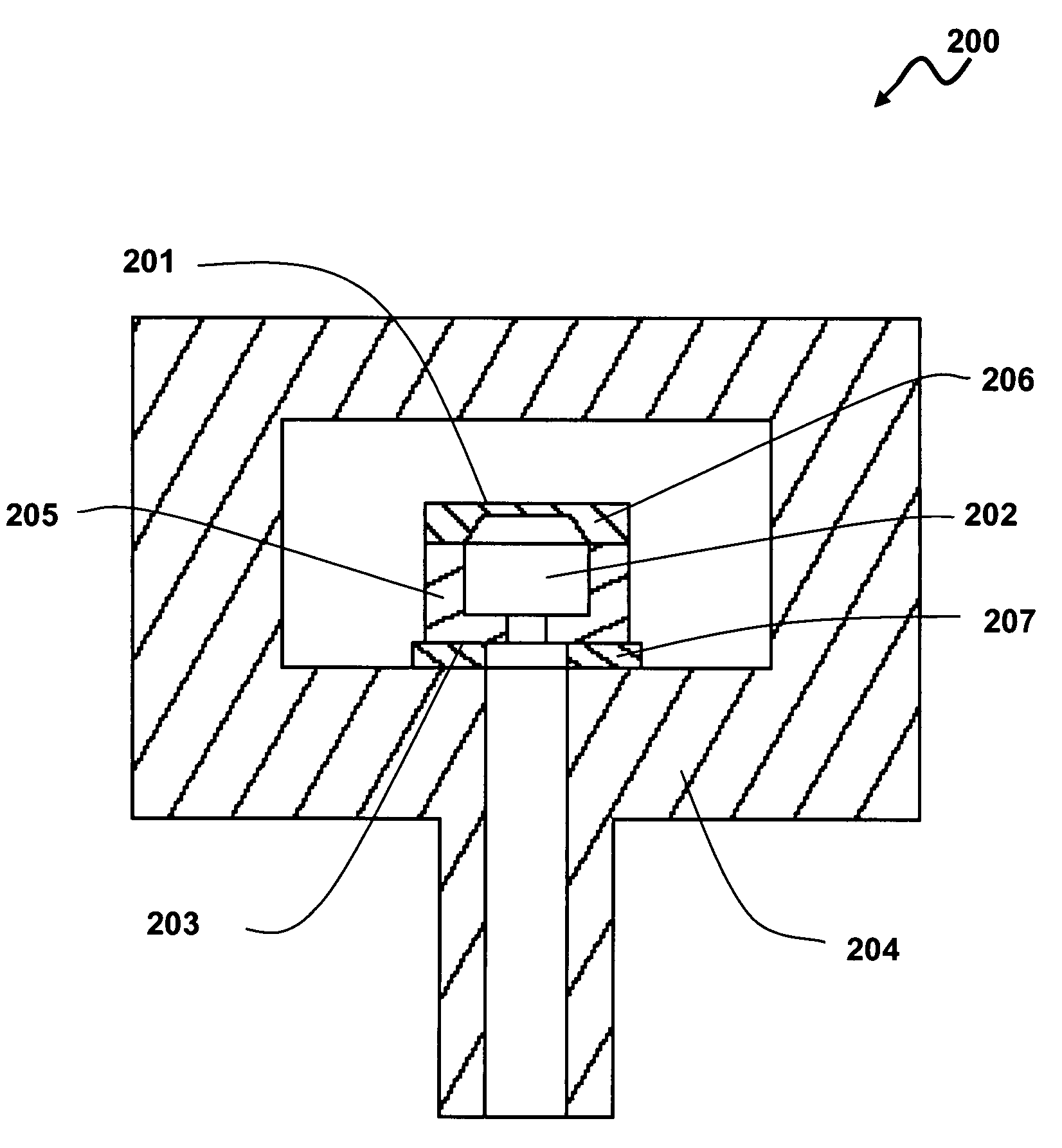
Method for maintaining solder thickness in flipchip attach packaging processes
ActiveUS6943434B2Absorbs stressDesirable thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballEngineering
A packaging assembly for semiconductor devices and a method for making such packaging is described. The invention provides a non-Pb bump design during a new flip-chip method of packaging. The design uses special conductive materials in a stud form, rather than a solder ball containing Pb. This configuration maintains a desirable solder thickness between the die and the leadframe and forms a high standoff by restricting solder wettabilty on the leadframe side. This configuration also absorbs any stress and protects the die from cracking. The invention also provides methods for making such semiconductor packages.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
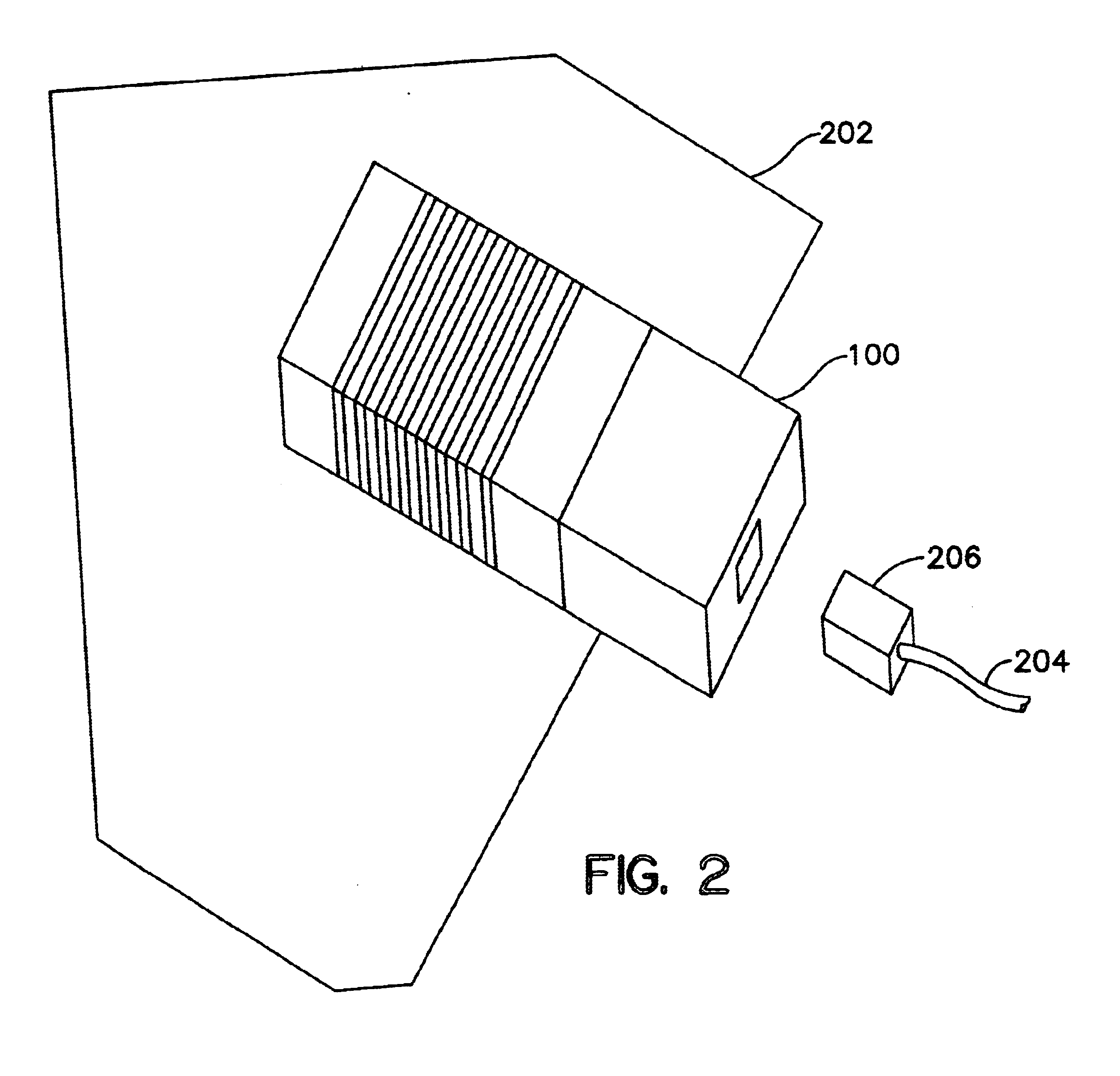
EMI filter terminal assembly with wire bond pads for human implant applications
ActiveUS20050248907A1More stressImprove featuresAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyElectromagnetic interferenceSoldering
An electromagnetic interference filter terminal assembly for active implantable medical devices includes a structural pad in the form of a substrate or attached wire bond pad, for convenient attachment of wires from the circuitry inside the implantable medical device to the capacitor structure via thermal or ultrasonic bonding, soldering or the like while shielding the capacitor from forces applied to the assembly during attachment of the wires.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Phototherapy bandage
InactiveUS20080058689A1Promote wound healingAbsorbs stressLight therapySheet deliveryPhotodynamic therapyLight treatment
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Thin-film capacitor
ActiveUS20080186654A1Easily adjustAbsorbs stressThin/thick film capacitorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFilm capacitorEngineering
A thin-film capacitor and a method for making the thin-film capacitor having a structure that can prevent vertical stress acting on outer connecting terminals, such as bumps, from concentrating on electrode layers, and capable of easily increasing the equivalent series resistance to a desired value. The thin-film capacitor includes a substrate, a capacitor unit disposed above the substrate and composed of at least one dielectric thin film and two electrode layers, a protective layer covering at least part of the capacitor unit, a lead conductor electrically connected to one of the electrode layers of the capacitor unit, and a bump disposed above the lead conductor. The lead conductor includes a connecting part disposed in an opening in the protective layer and electrically connected to one of the electrode layers of the capacitor unit, and a wiring part extending over the protective layer. The bump is disposed above the wiring part.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20080121326A1Improve wear resistanceImprove the immunityTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesEngineeringTread
A pneumatic tire of the invention includes: a stepped-shaped raised area provided in the main groove positioned at a center area of the tire so as to be continued circumferentially of the tire, connected to either the main groove walls, and raised from the groove bottom; and a ridge lower than a tread surface of the tire in each of the main grooves on both outsides of the main groove at the center area of the tire so as to be raised from the center of the groove bottom continuously along the length thereof without being joined with the groove walls, and the angle of inclination of the main groove walls with respect to the normal line of the tangential line on the tread surface of the main groove portion is parallel to each other or is 5° or smaller.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
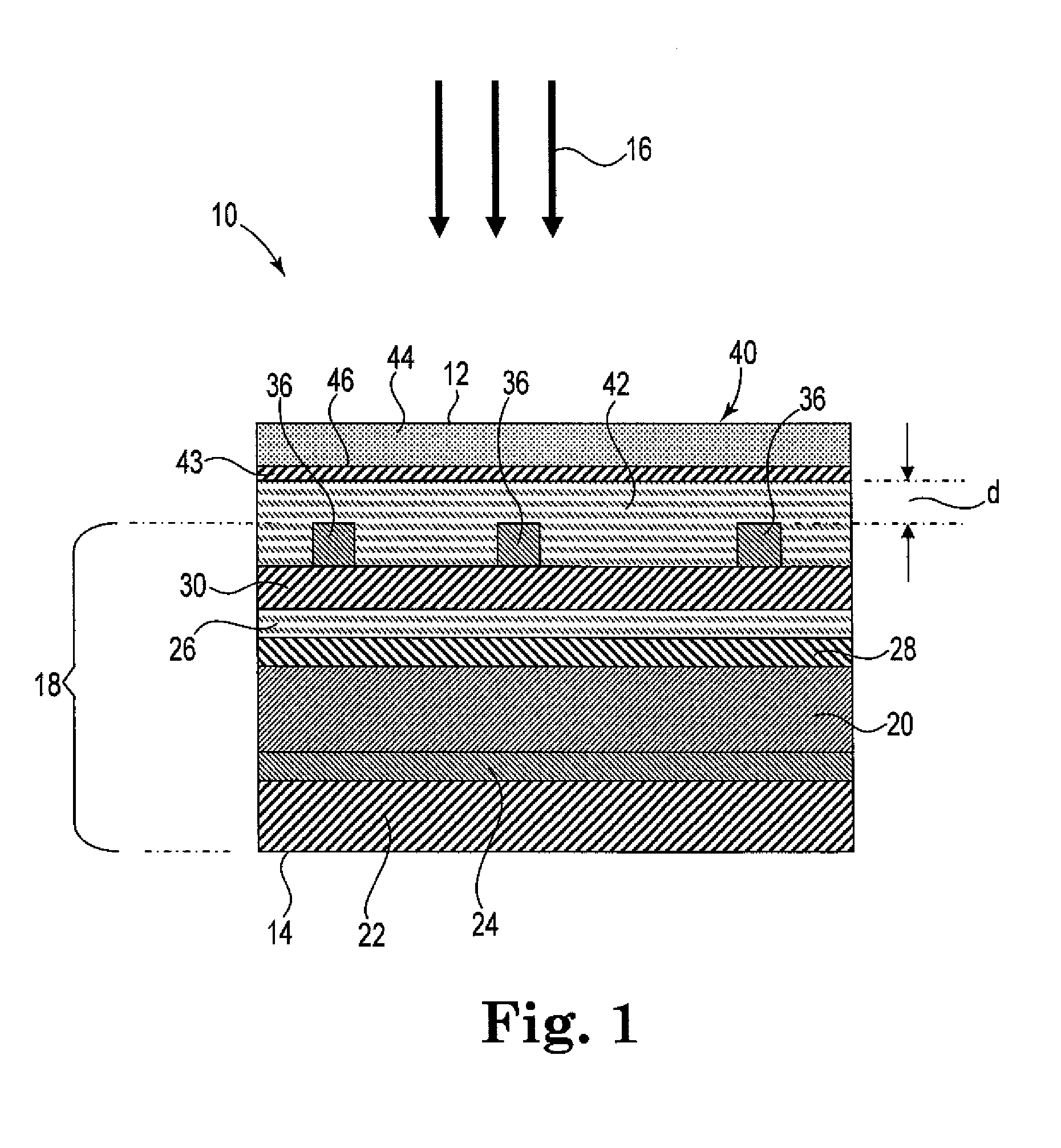
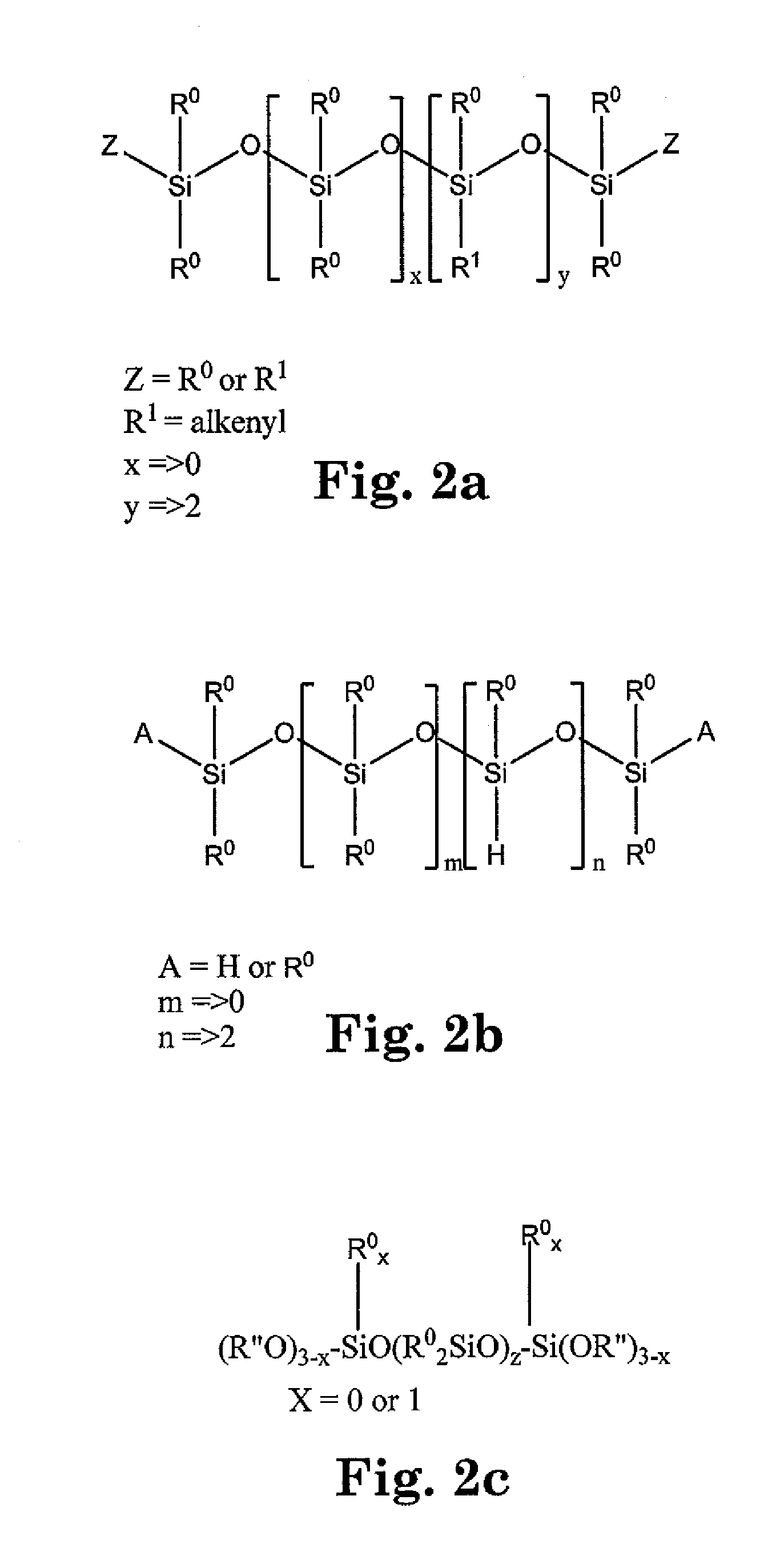
Moisture resistant photovoltaic devices with elastomeric, polysiloxane protection layer
InactiveUS20110162705A1Improves waterproof protectionImprove protectionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElastomerElectrical conductor
Improved protection systems for CIGS-based microelectronic devices of the type incorporating electric conductor(s) such as an electronic collection grid. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a photovoltaic device having a light incident surface and a backside surface. The device includes a chalcogenide-containing photovoltaic layer comprising at least one of copper, indium and / or gallium. A transparent conductive layer is interposed between the photovoltaic layer and the light incident surface, wherein the transparent conductive layer is electrically coupled to the photovoltaic layer. An electronic collection grid is electrically coupled to the transparent conductive layer and overlying at least a portion of the transparent conductive layer. An elastomeric structure having a light incident surface, said structure overlying at least portions of the electronic collection grid and the transparent conductive layer in a manner such that the light incident surface of the elastomeric structure is spaced apart from a major portion of the conductor, and wherein the elastomeric structure comprises an elastomeric siloxane polymer having a WVTR of at least 0.1 g / m2-day. An optional protective barrier overlies the elastomeric structure. The protection systems of the invention incorporate elastomers with water vapor transmission rates that are atypically high in the context of CIGS-based devices.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
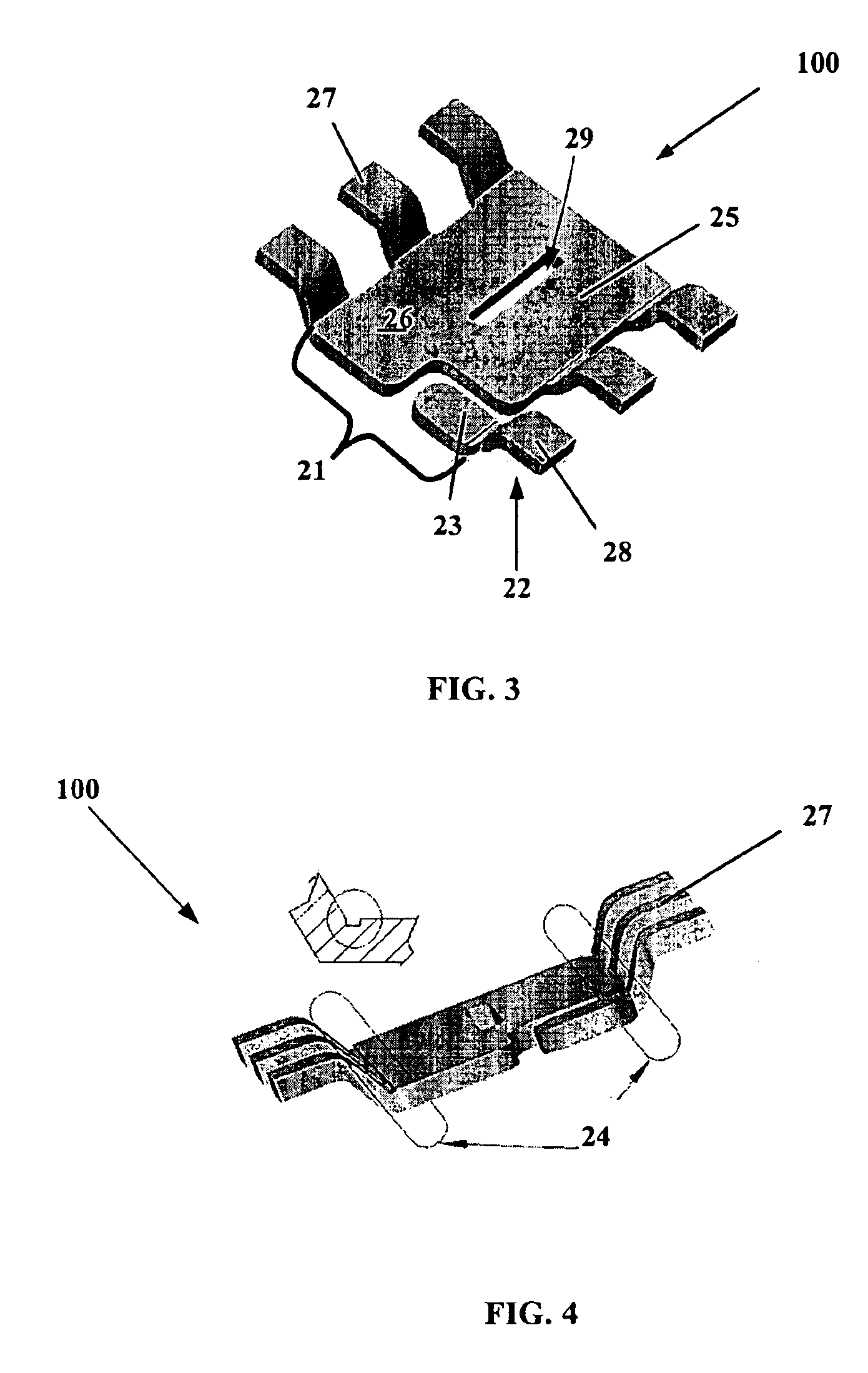
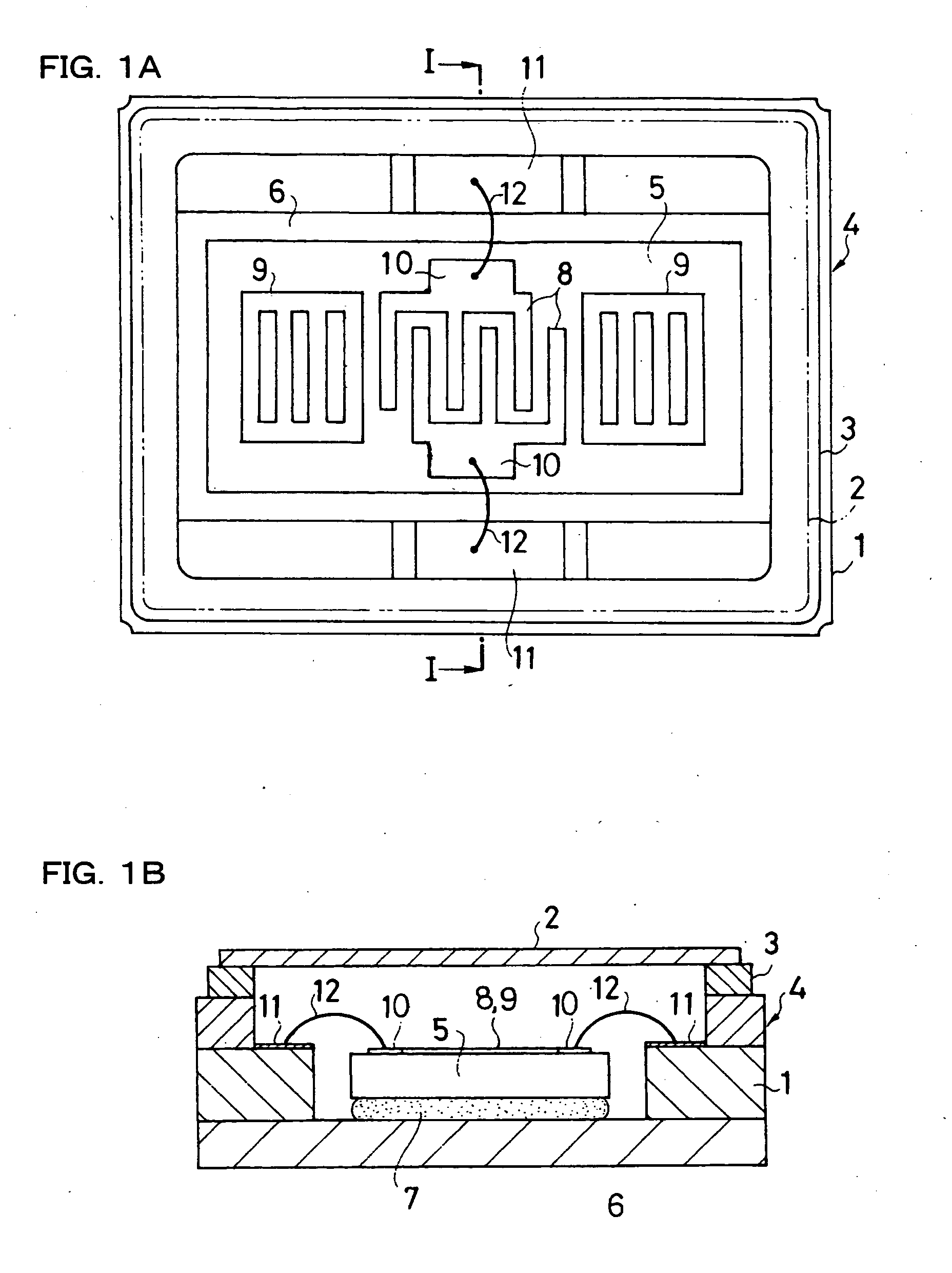
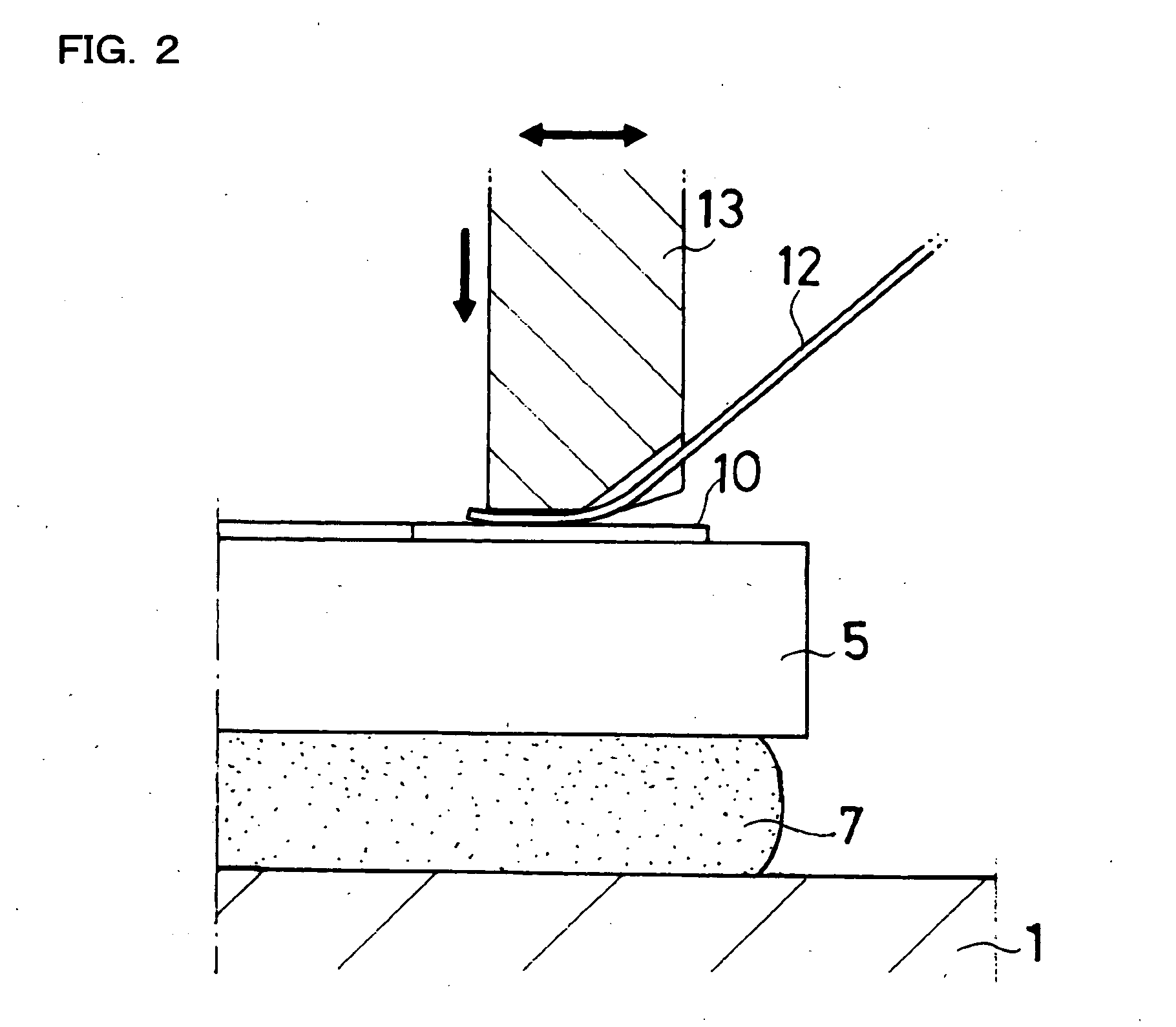
Conductive adhesive and piezo-electric device having piezo-electric element mounted thereon using such adhesive
InactiveUS20050085578A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesParticulatesAdhesive
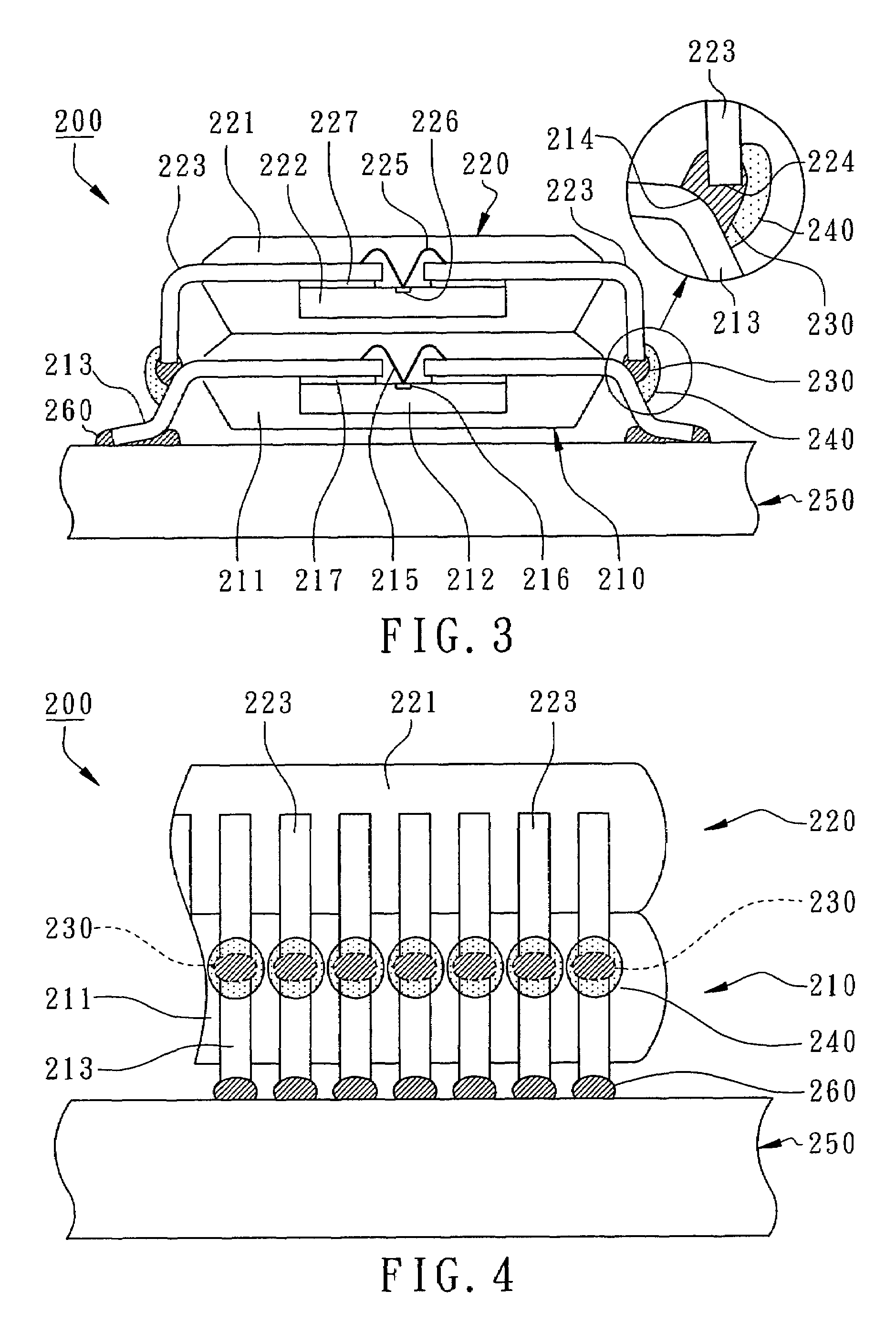
A piezo electric device in which a SAW element 5 is mounted on a base 1 of a package 4 having bonding pads 10,10 connected through bonding wires to corresponding connection terminals 11,11 in the package and having a lid 2 being joined to the base by seam welding and hermetically sealed thereto. The SAW element 5 is bonded and affixed to a mounting surface 6 in the base 1 using a conductive adhesive 7 which contains 80 to 85% resin material by weight and a 20 to 15% flaky conductive filler by weight, or using a conductive adhesive which contains 82.5 to 85% resin material by weight and a 17.5 to 15% conductive filler by weight, wherein the conductive filler comprises a 30% small particulate conductive filler 21 by weight and a 70% large particulate conductive filler 22 by weight.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Hybrid substrate, production method therefor, and semiconductor integrated circuit package
ActiveUS20130200516A1Suitable for treatmentCrack and breakSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCeramic sinteringGlass-ceramic
A hybrid substrate according to the present invention comprises a core layer composed of a glass woven cloth as a reinforcing material, and a glass-ceramic sintered body which at least comprises a glass component and a metal oxide component. The glass woven cloth and the glass-ceramic sintered body formed by an impregnation with respect to the glass woven cloth are in a form of sintering integration with each other.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
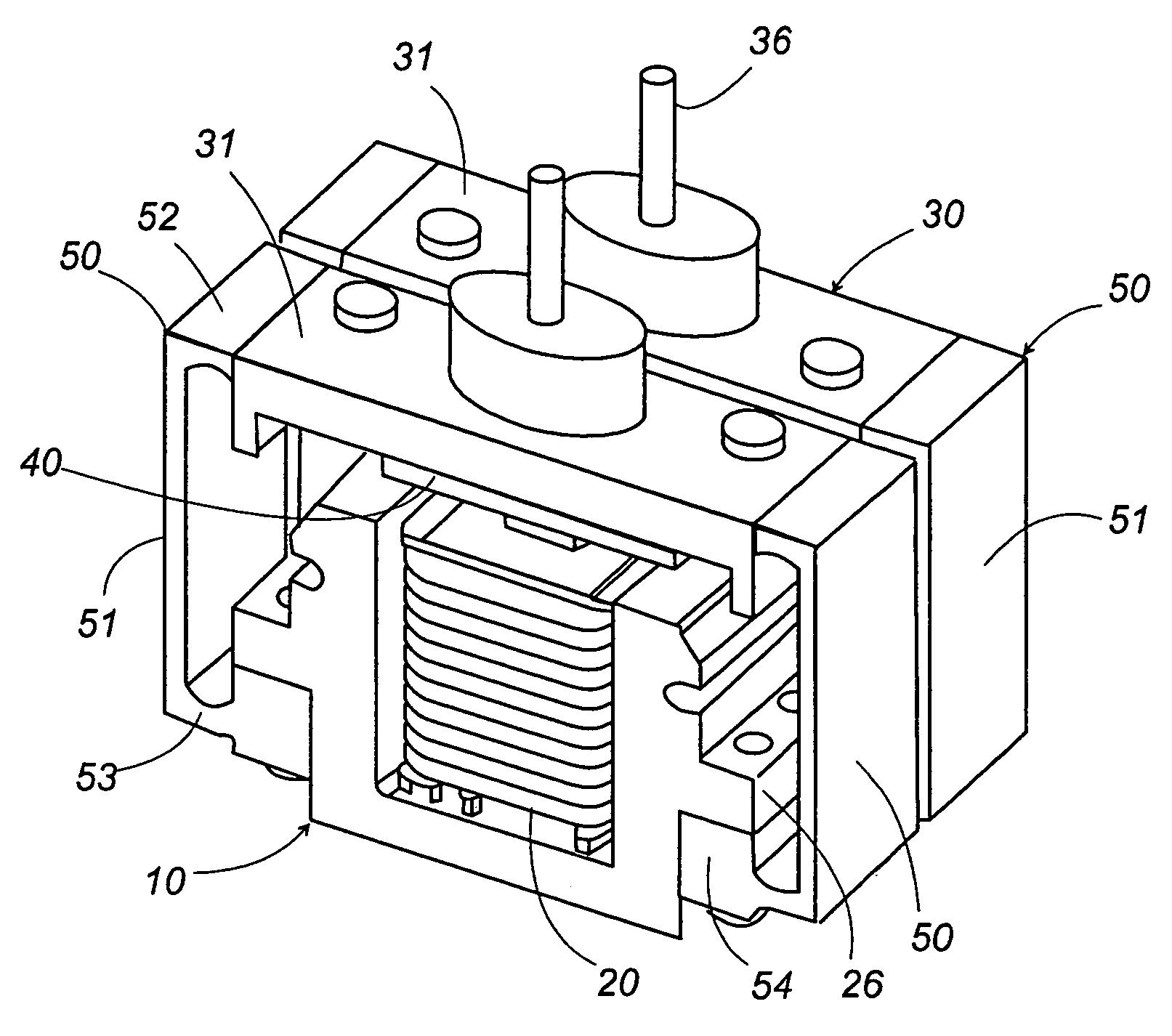
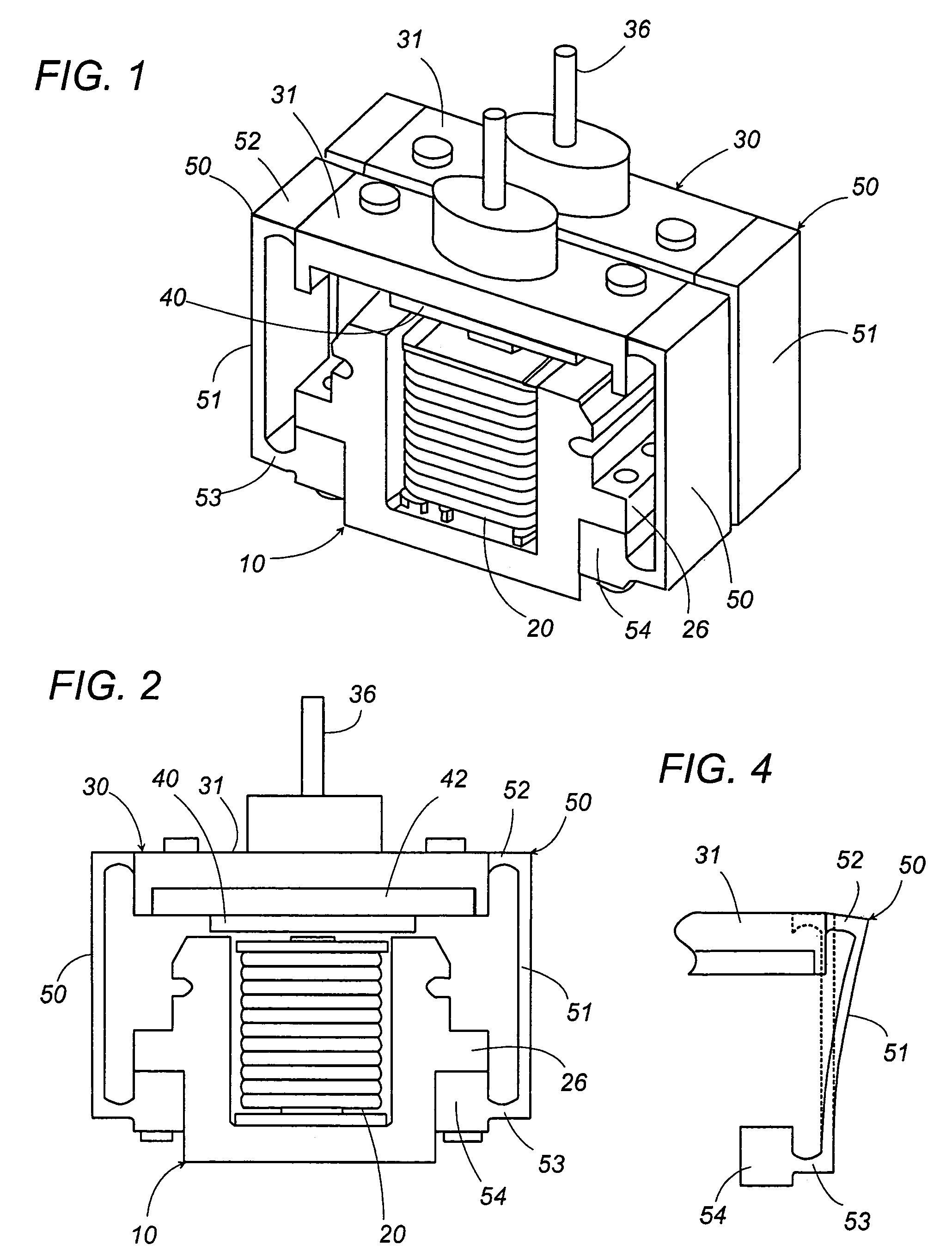
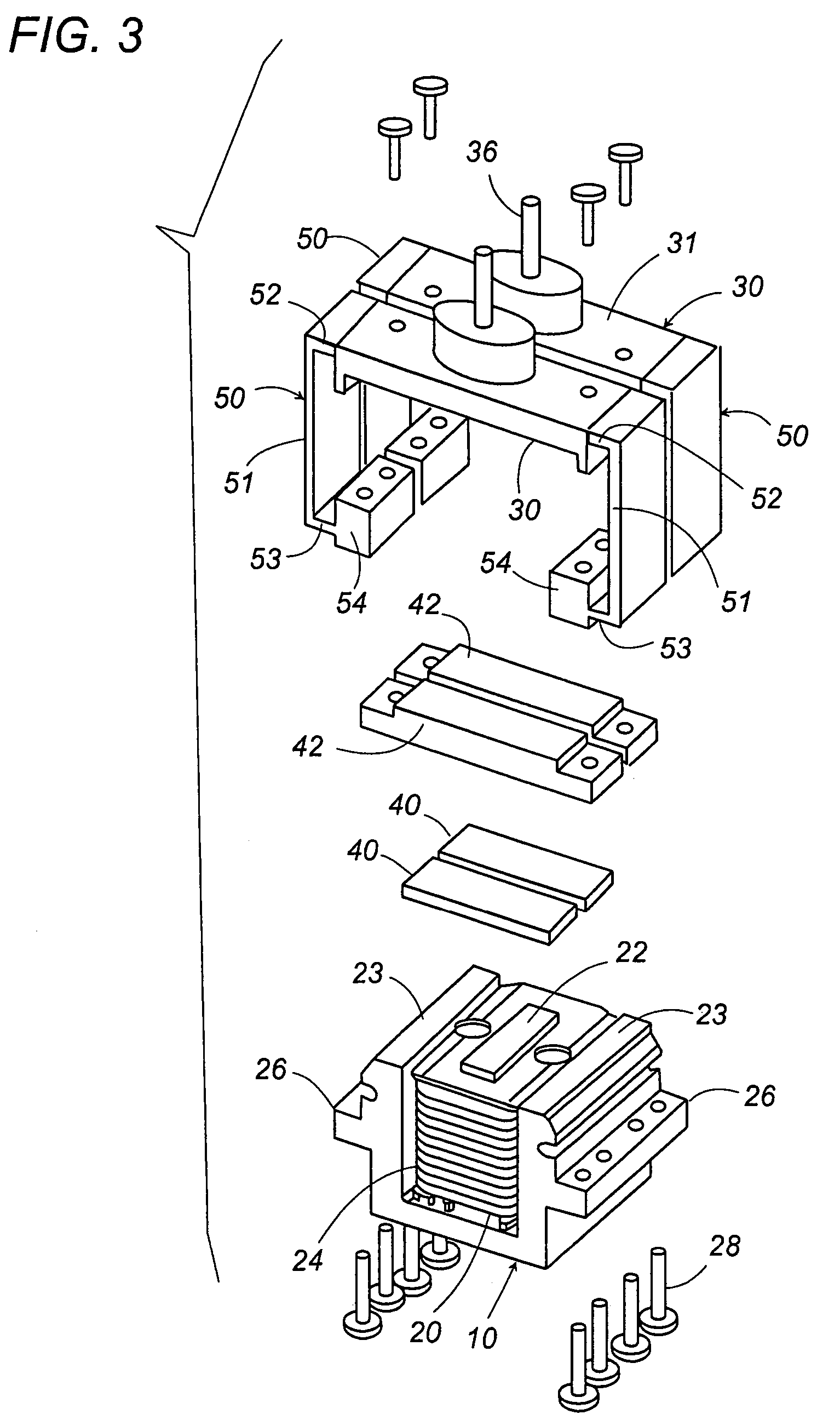
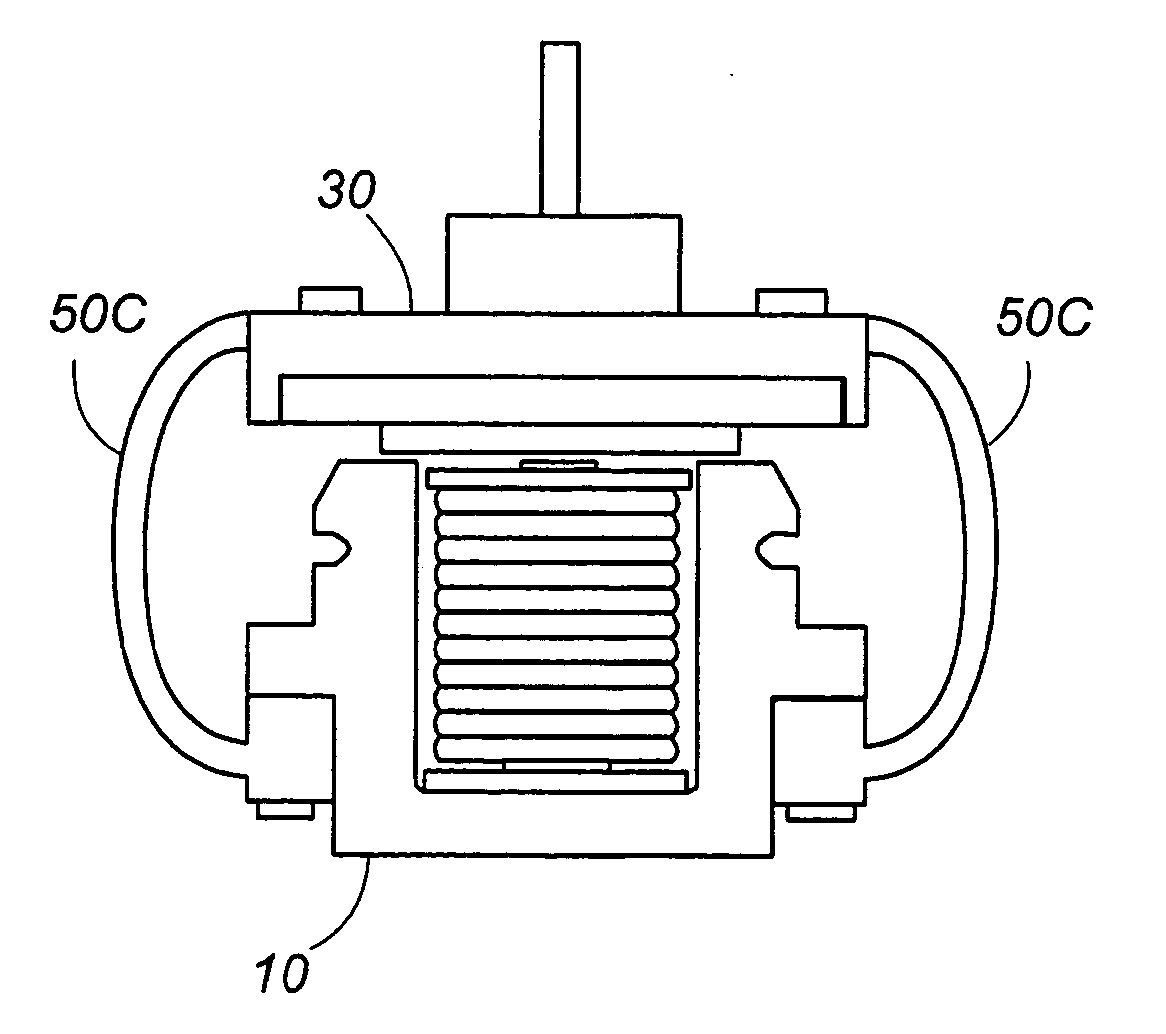
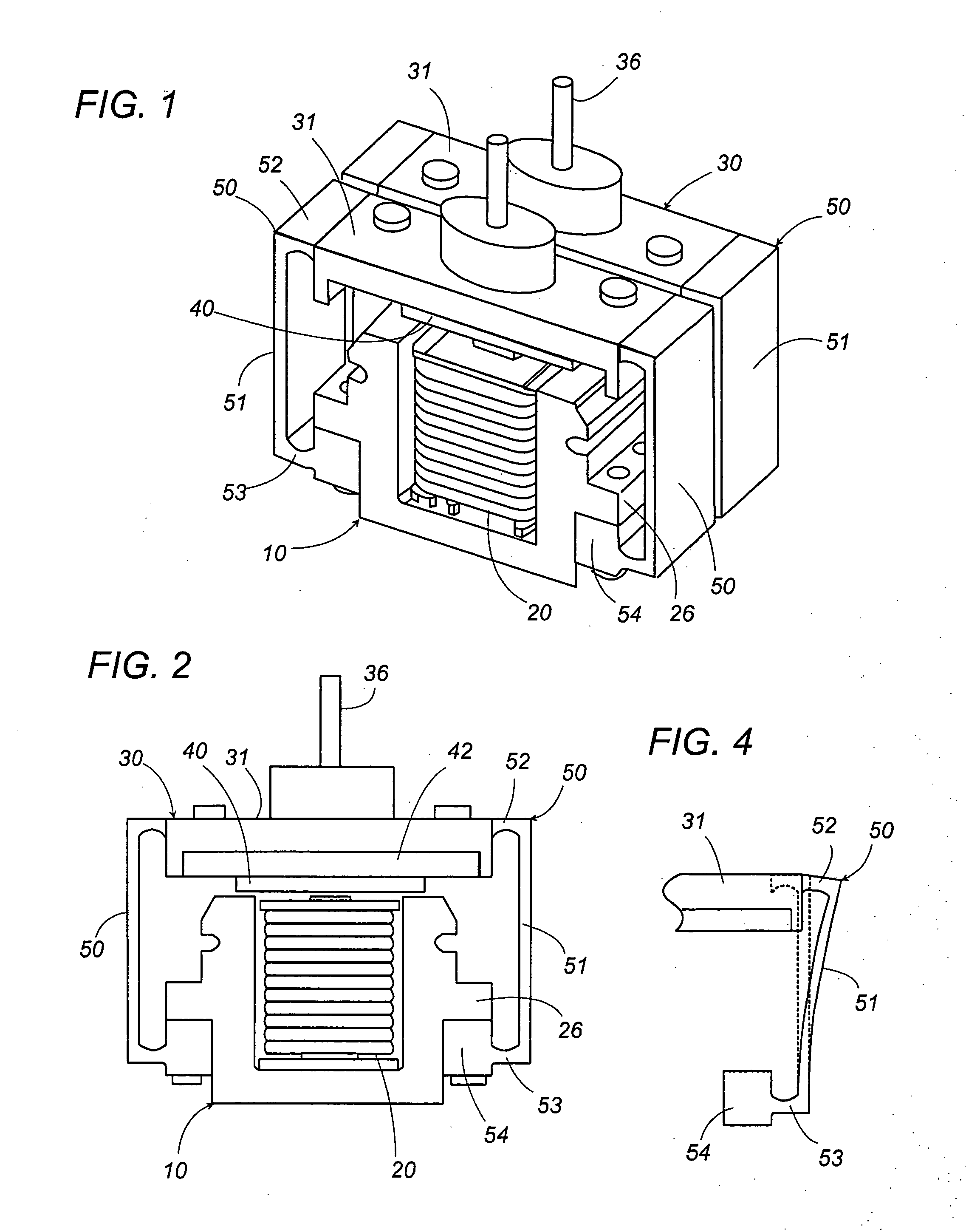
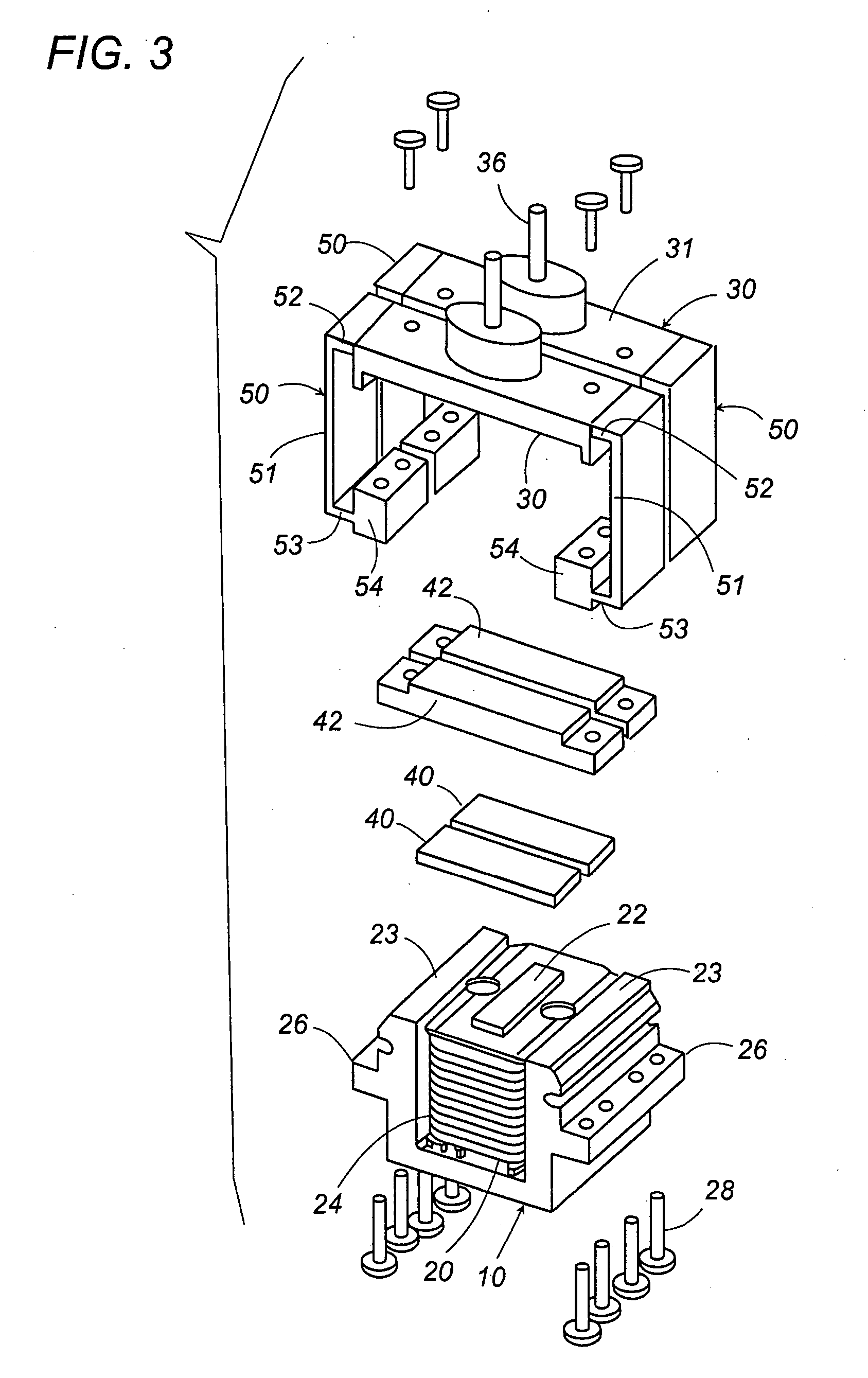
Linear oscillating actuator
ActiveUS7304407B2Minimum of stressMinimum of vibrationWindingsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesReciprocating motionEngineering
A linear oscillating actuator gives a smooth reciprocatory movement with a minimum of incidental vibrations or stresses. The actuator includes an oscillator carrying a permanent magnet as well as an output shaft which is adapted to be connected to drive a load, and a stator assembly carrying an electromagnet. The electromagnet generates a magnetic field which interacts with the permanent magnet to reciprocate the oscillator relative to the stator assembly in a linear path. A spring link is provided to resiliently support the oscillator to the stator assembly with a gap distance left therebetween for allowing the oscillator to reciprocate in the linear path. The spring link is configured to deform resiliently also in a direction other than along the linear path so as to allow the oscillator to move to and away from the stator assembly or to twist relative to the stator assembly. Thus, the spring link can absorb incidental stresses or displacements from which the oscillator may suffer in the directions other than along the linear path, assuring to give a smooth reciprocatory movement to the oscillator with a minimum of fatigue accumulated in the spring link.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Linear oscillating actuator
ActiveUS20050140219A1Minimum of incidental vibrationMinimum of stressWindingsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesReciprocating motionEngineering
A linear oscillating actuator gives a smooth reciprocatory movement with a minimum of incidental vibrations or stresses. The actuator includes an oscillator carrying a permanent magnet as well as an output shaft which is adapted to be connected to drive a load, and a stator assembly carrying an electromagnet. The electromagnet generates a magnetic field which interacts with the permanent magnet to reciprocate the oscillator relative to the stator assembly in a linear path. A spring link is provided to resiliently support the oscillator to the stator assembly with a gap distance left therebetween for allowing the oscillator to reciprocate in the linear path. The spring link is configured to deform resiliently also in a direction other than along the linear path so as to allow the oscillator to move to and away from the stator assembly or to twist relative to the stator assembly. Thus, the spring link can absorb incidental stresses or displacements from which the oscillator may suffer in the directions other than along the linear path, assuring to give a smooth reciprocatory movement to the oscillator with a minimum of fatigue accumulated in the spring link.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Electro-optical module and electronic device
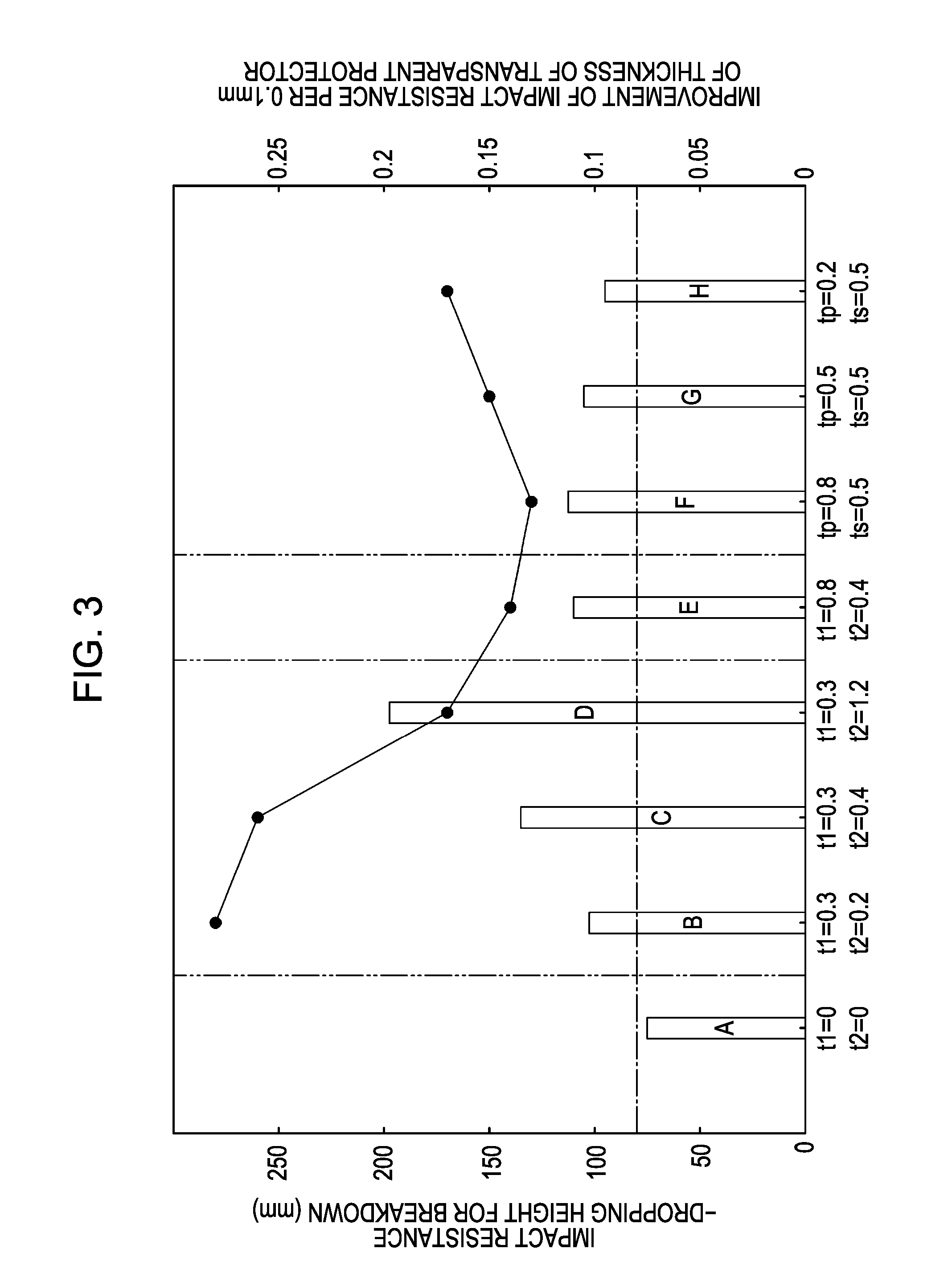
ActiveUS20070046873A1Improve impact resistanceThin thicknessLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingOptical ModuleEngineering
An electro-optical module includes: an electro-optical panel; and a transparent protector disposed on a viewer-side surface of the electro-optical panel, wherein transparent protector has a stack structure including a first transparent protection layer that faces the electro-optical panel and is formed of an elastic material and a second transparent protection layer that has a higher dynamic elasticity value than that of the first transparent protection layer within a frequency range of 1 to 10 Hz.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Plug-socket connector apparatus for optical fiber termination
InactiveUS20080260334A1Connection working is improvedAdd dimensionElectric connection structural associationsCoupling light guidesMechanical engineeringMolded interconnect device
Plug-socket connector apparatus for optical fiber termination comprises first and second plugs and a socket. The first and second plugs are both single ferrule plugs. The socket is a molded interconnect device and a plug holder, and includes terminals located on the bottom face of the socket, first and second bores located at one side of the socket, and first and second retainers. The retainers retain latches formed in the plugs so as to prevent the plugs from falling out of the bores and to restrict rotation angles of the plugs around the axes within predetermined rotation angle ranges, when the plugs is plugged in the bores.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
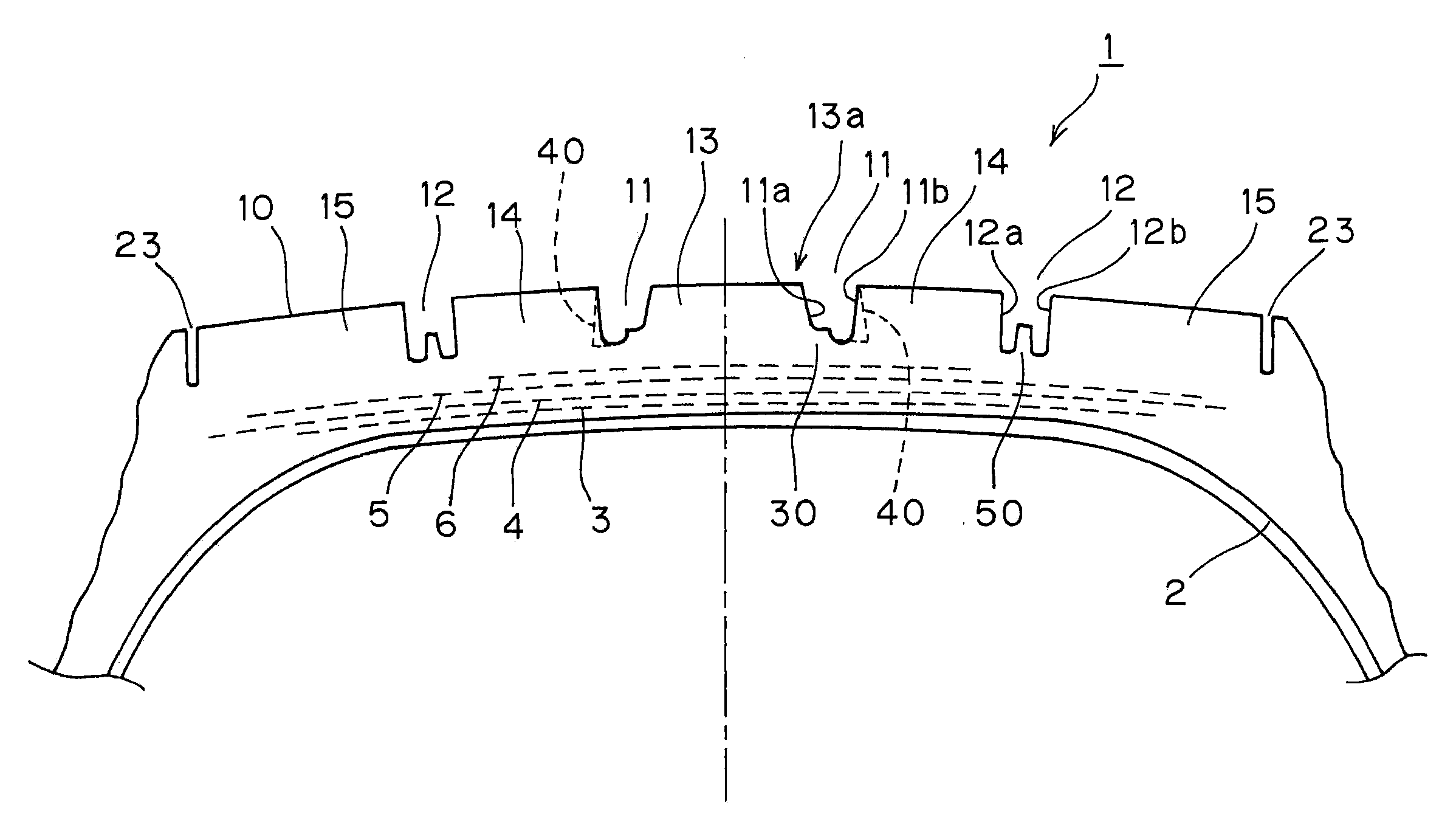
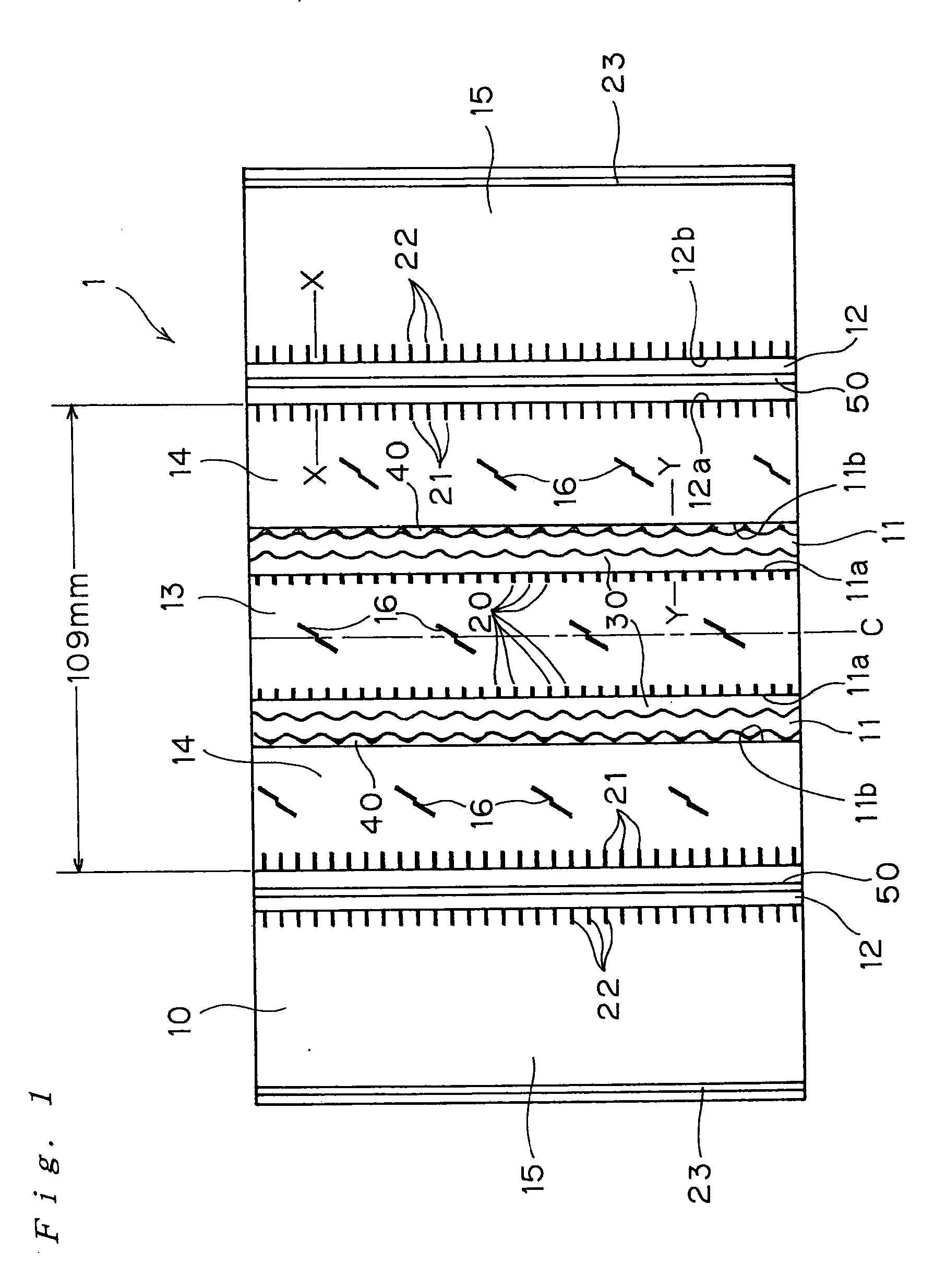
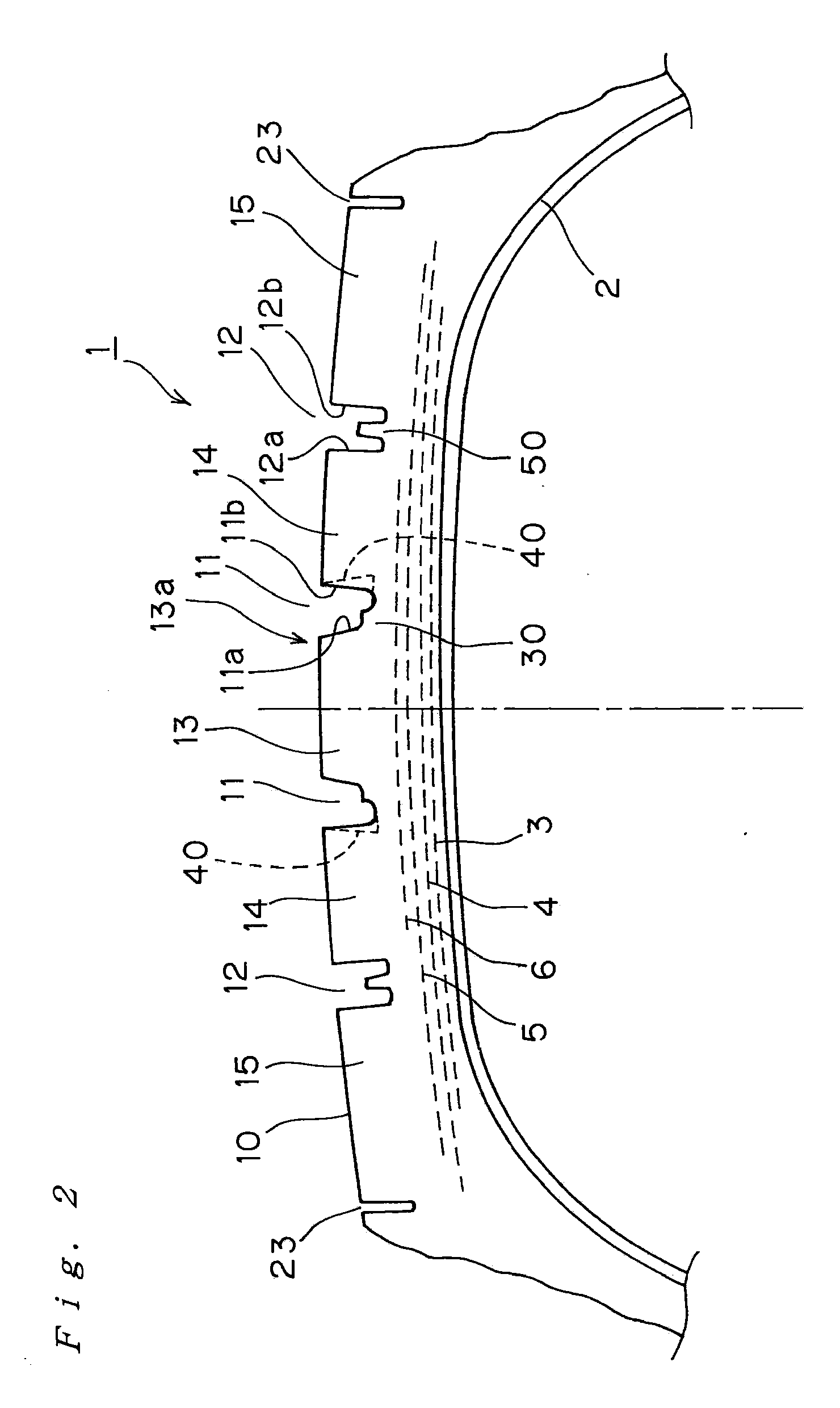
Pneumatic tire with tread having circumferential main grooves
InactiveUS8006730B2Improve uneven wear resistanceInhibit the generation of cracksTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesEngineeringTread
A pneumatic tire of the invention includes: a stepped-shaped raised area provided in the main groove positioned at a center area of the tire so as to be continued circumferentially of the tire, connected to either the main groove walls, and raised from the groove bottom; and a ridge lower than a tread surface of the tire in each of the main grooves on both outsides of the main groove at the center area of the tire so as to be raised from the center of the groove bottom continuously along the length thereof without being joined with the groove walls, and the angle of inclination of the main groove walls with respect to the normal line of the tangential line on the tread surface of the main groove portion is parallel to each other or is 5° or smaller.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
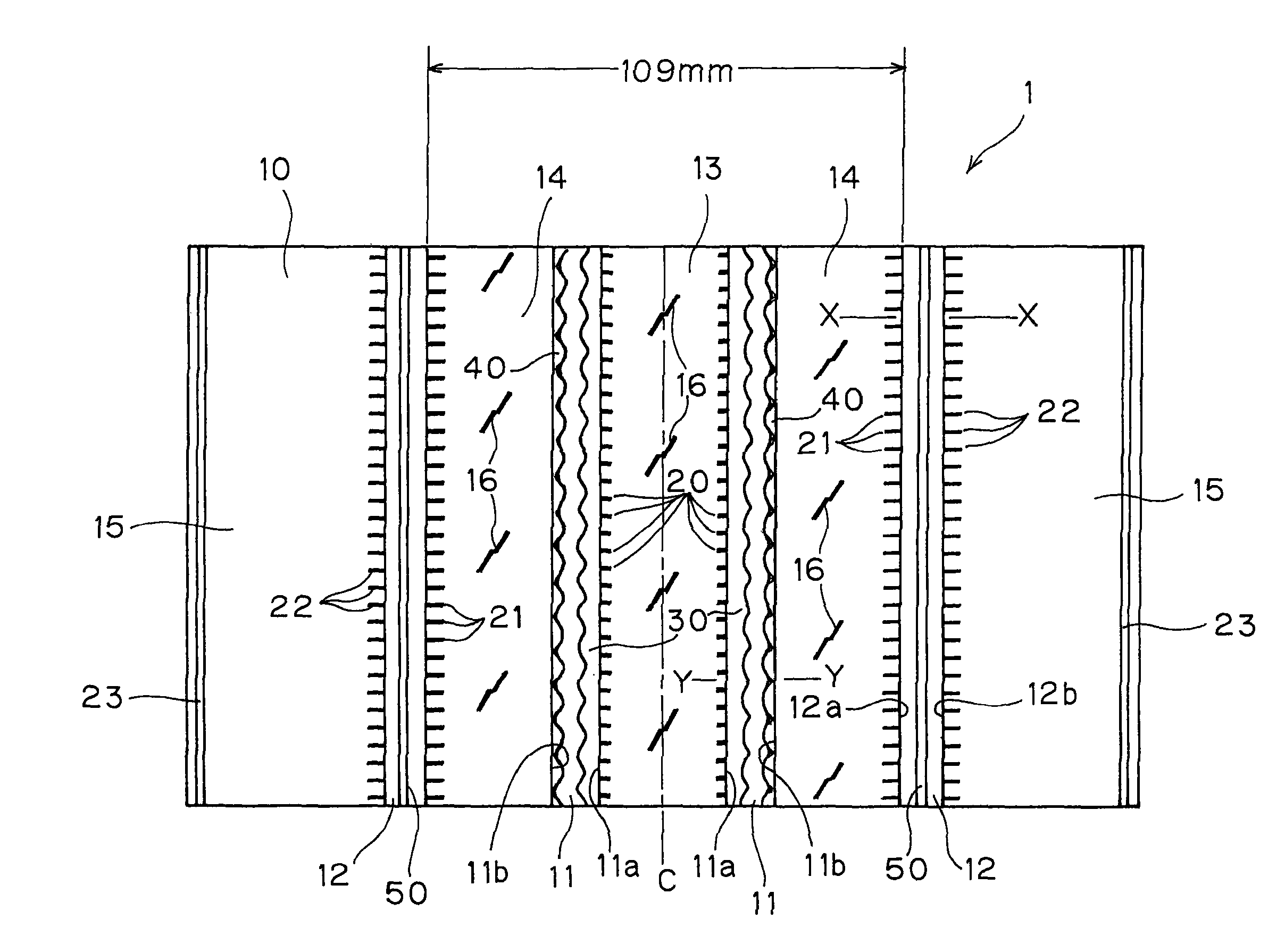
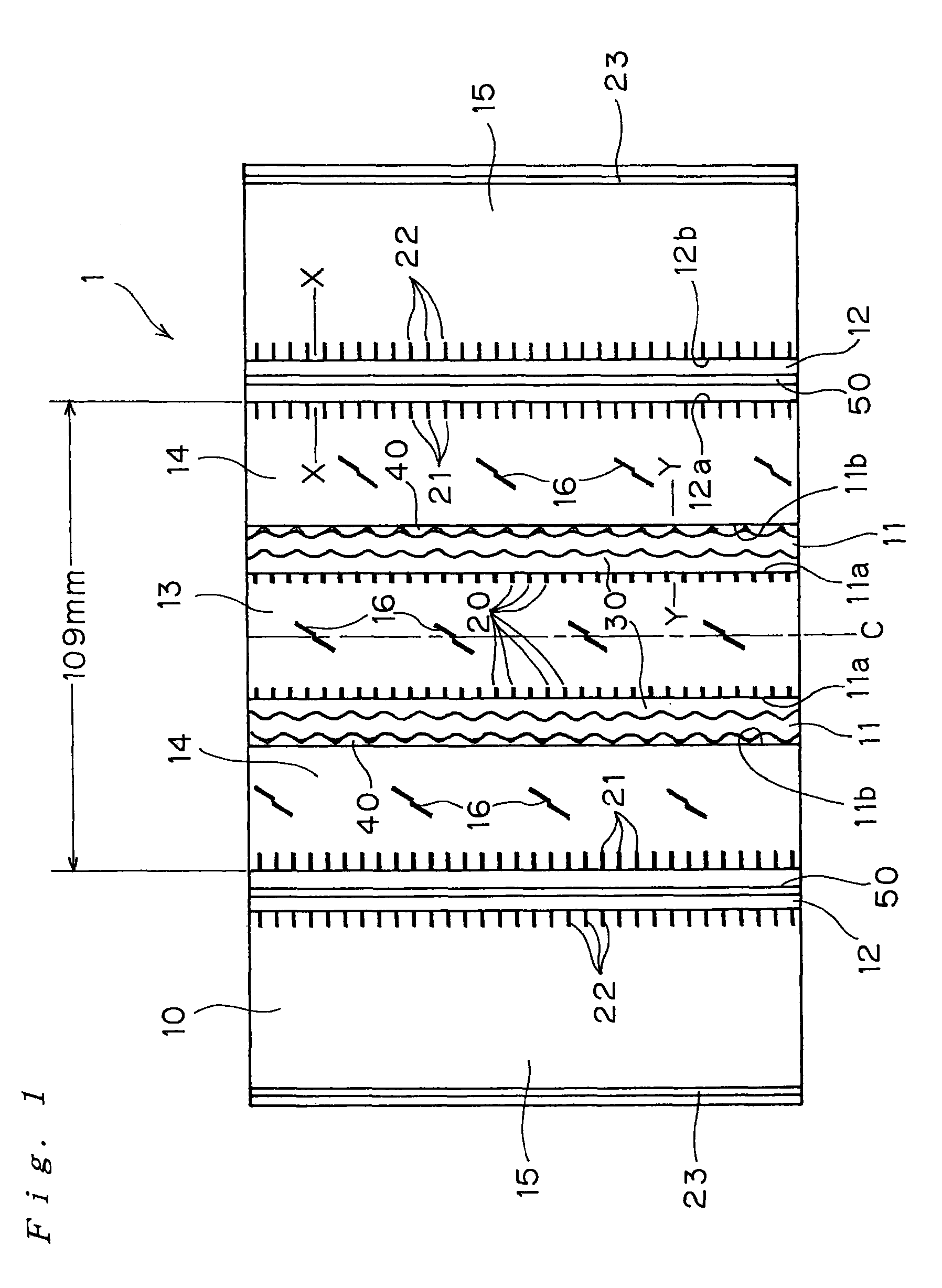
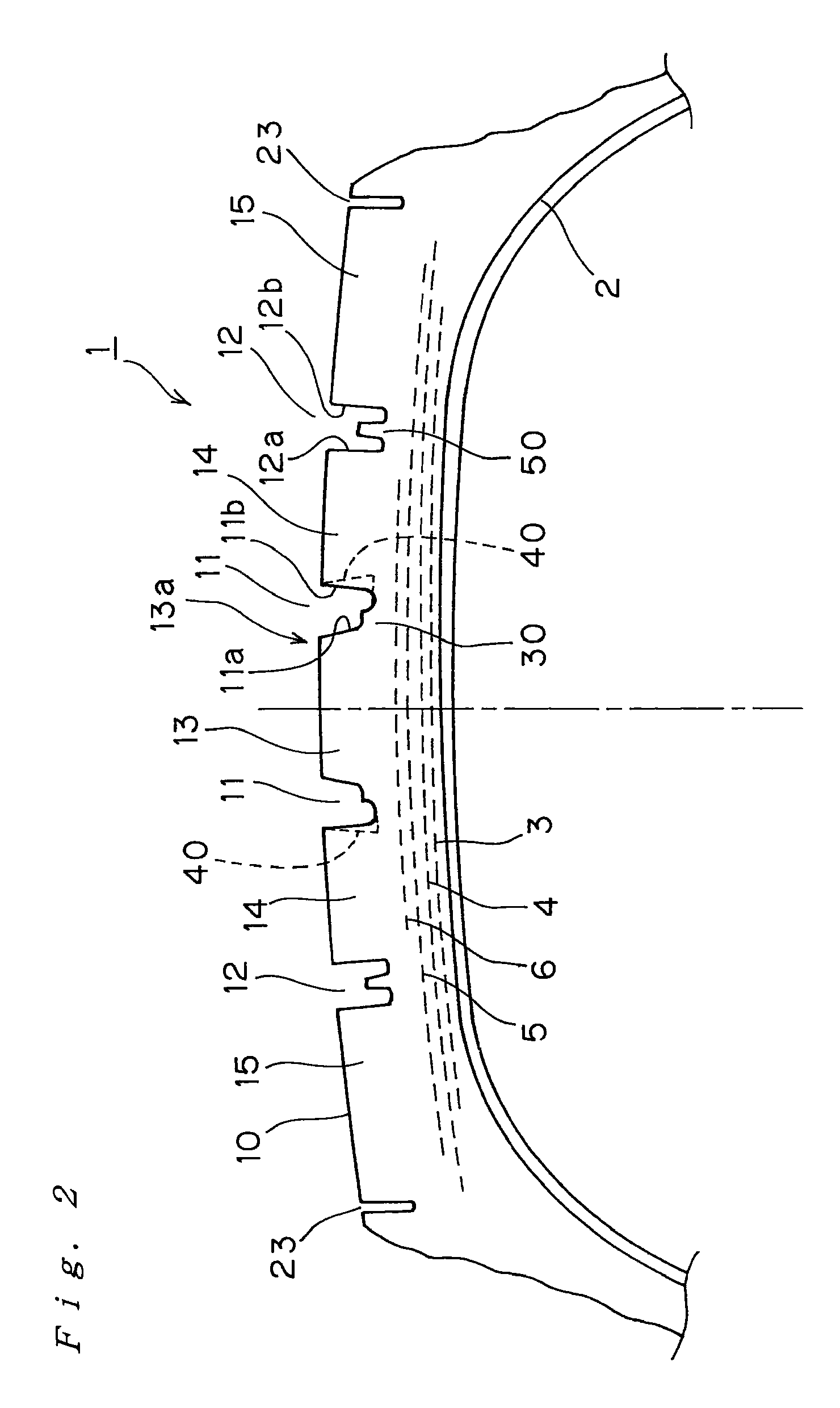
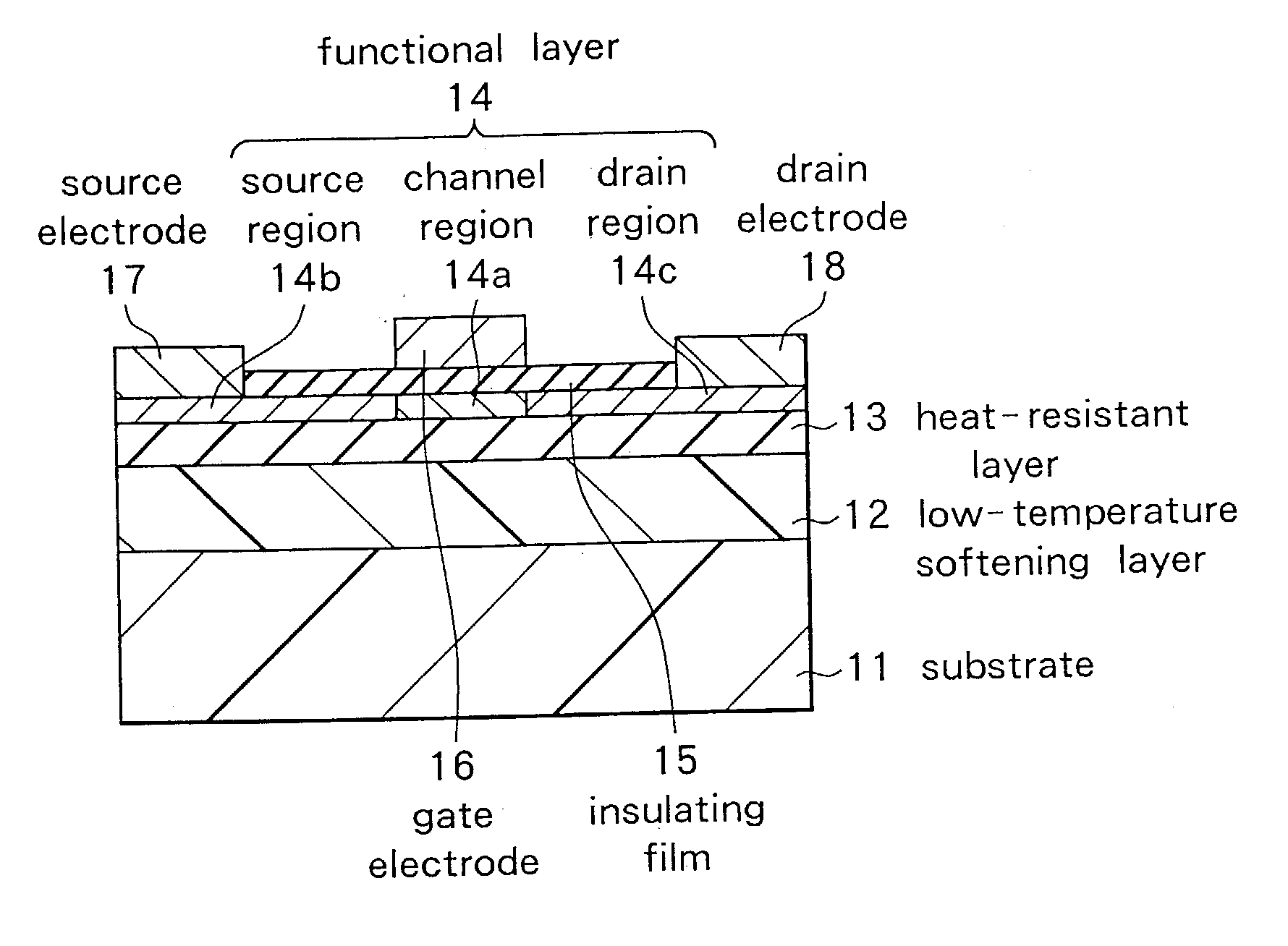
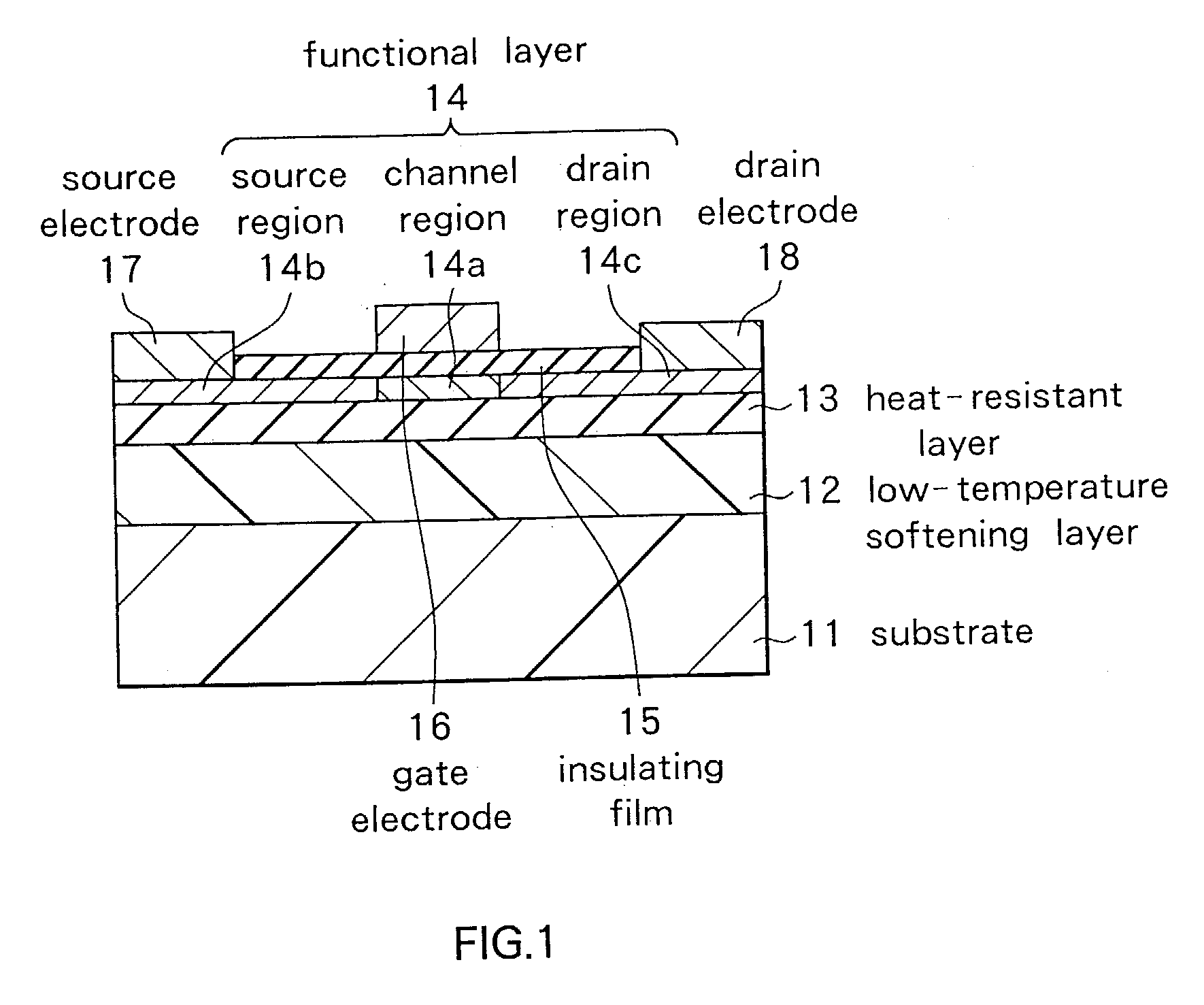
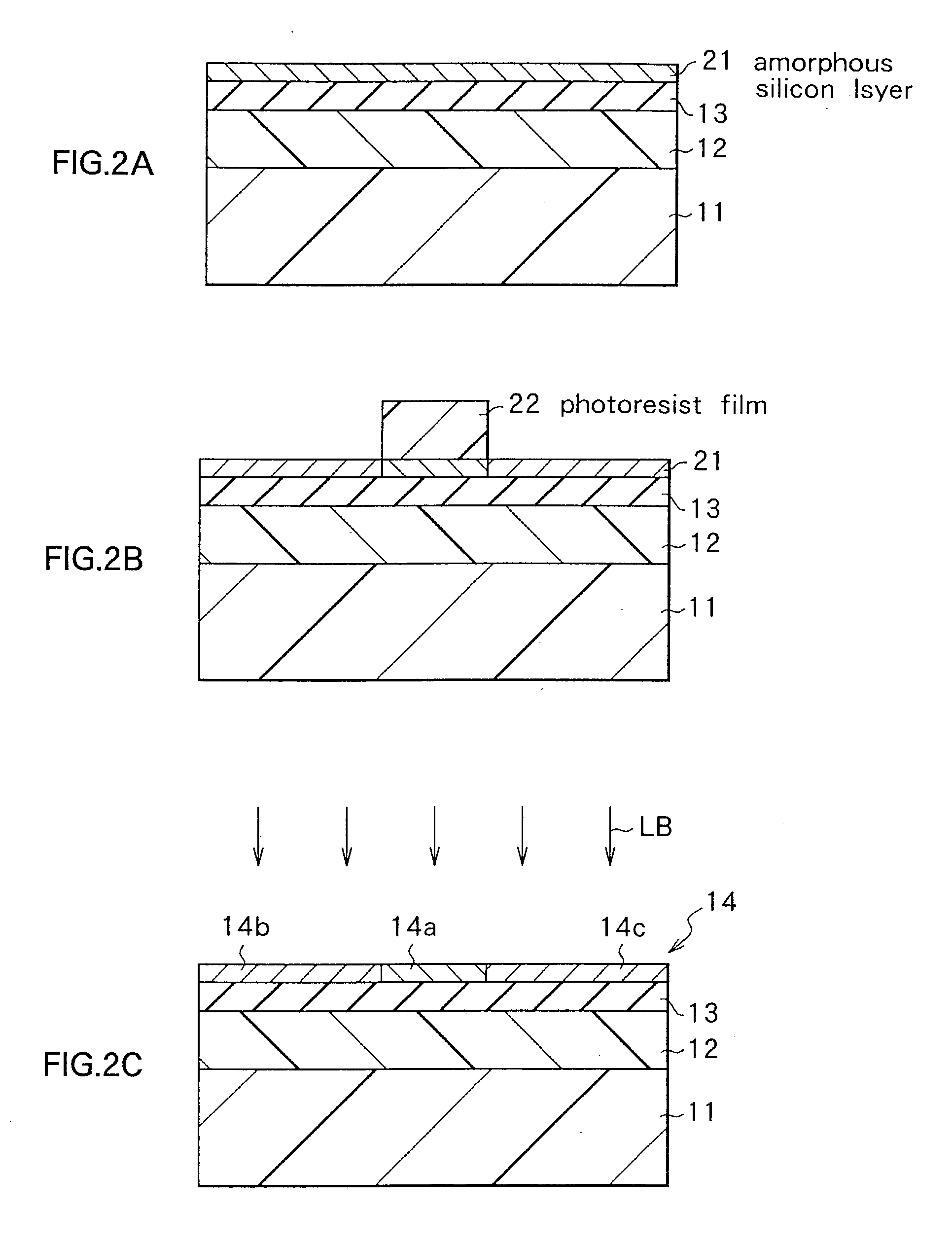
Functional device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030173601A1Inhibit the occurrence of cracksAvoid layeringTransistorSolid-state devicesAcrylic resinThermal expansion
A functional device free from cracking and having excellent functional characteristics, and a method of manufacturing the same are disclosed. A low-temperature softening layer (12) and a heat-resistant layer (13) are formed in this order on a substrate (11) made of an organic material such as polyethylene terephthalate, and a functional layer (14) made of polysilicon is formed thereon. The functional layer (14) is formed by crystallizing an amorphous silicon layer, which is a precursor layer, with laser beam irradiation. When a laser beam is applied, heat is transmitted to the substrate (11) and the substrate (11) tends to expand. However, a stress caused by a difference in a thermal expansion coefficient between the substrate (11) and the functional layer (14) is absorbed by the low-temperature softening layer (12), so that no cracks and peeling occurs in the functional layer (14). The low-temperature softening layer (12) is preferably made of a polymeric material containing an acrylic resin. By properly interposing a metal layer and a heat-resistant layer between the substrate (11) and the functional layer (14), a laser beam of higher intensity can be irradiated.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for coupling optical elements to optoelectronic devices for manufacturing optical transceiver modules
InactiveUS6905260B2Absorbs stressHighly precise machinery and adhesiveCoupling light guidesVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserTransceiver
A process is provided for aligning and connecting at least one optical fiber to at least one optoelectronic device so as to couple light between at least one optical fiber and at least one optoelectronic device. One embodiment of this process comprises the following steps: (1) holding at least one optical element close to at least one optoelectronic device, at least one optical element having at least a first end; (2) aligning at least one optical element with at least one optoelectronic device; (3) depositing a first non-opaque material on a first end of at least one optoelectronic device; and (4) bringing the first end of at least one optical element proximate to the first end of at least one optoelectronic device in such a manner that the first non-opaque material contacts the first end of at least one optoelectronic device and the first end of at least one optical element. The optical element may be an optical fiber, and the optoelectronic device may be a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The first non-opaque material may be a UV optical adhesive that provides an optical path and mechanical stability. In another embodiment of the alignment process, the first end of at least one optical element is brought proximate to the first end of at least one optoelectronic device in such a manner that an interstitial space exists between the first end of at least one optoelectronic device and the first end of at least one optical element.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC DEVICE INNOVATIONS U S A
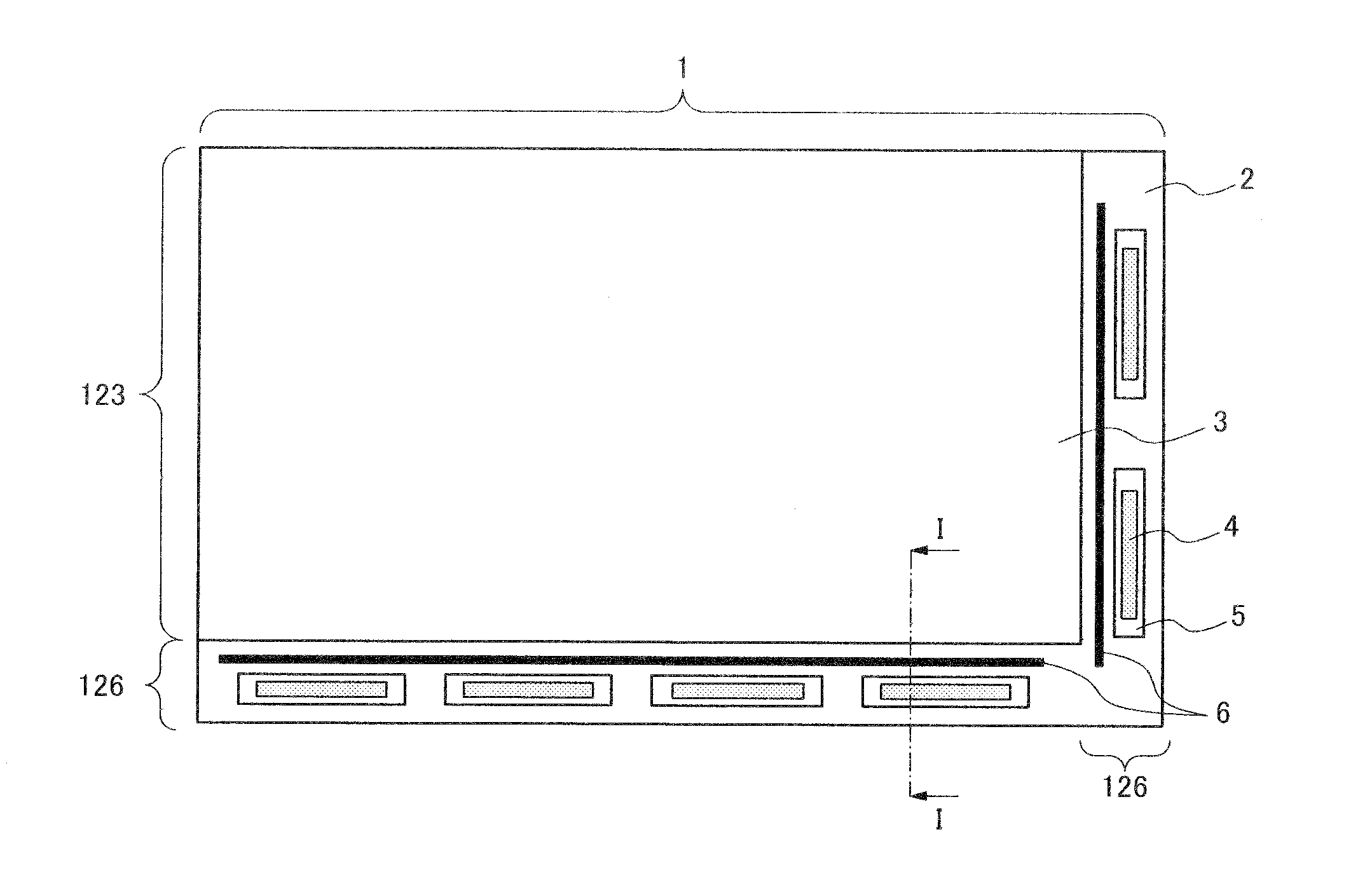
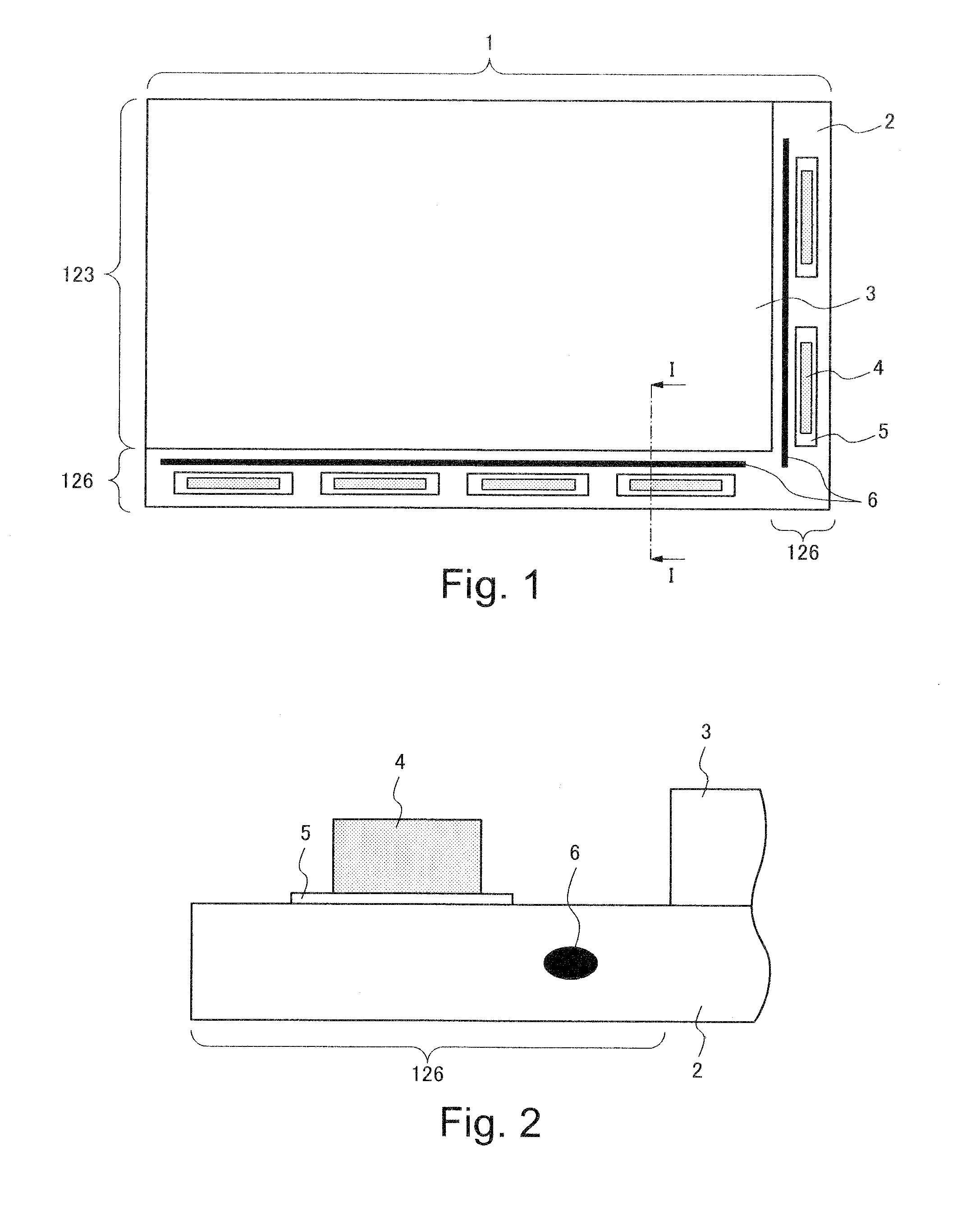
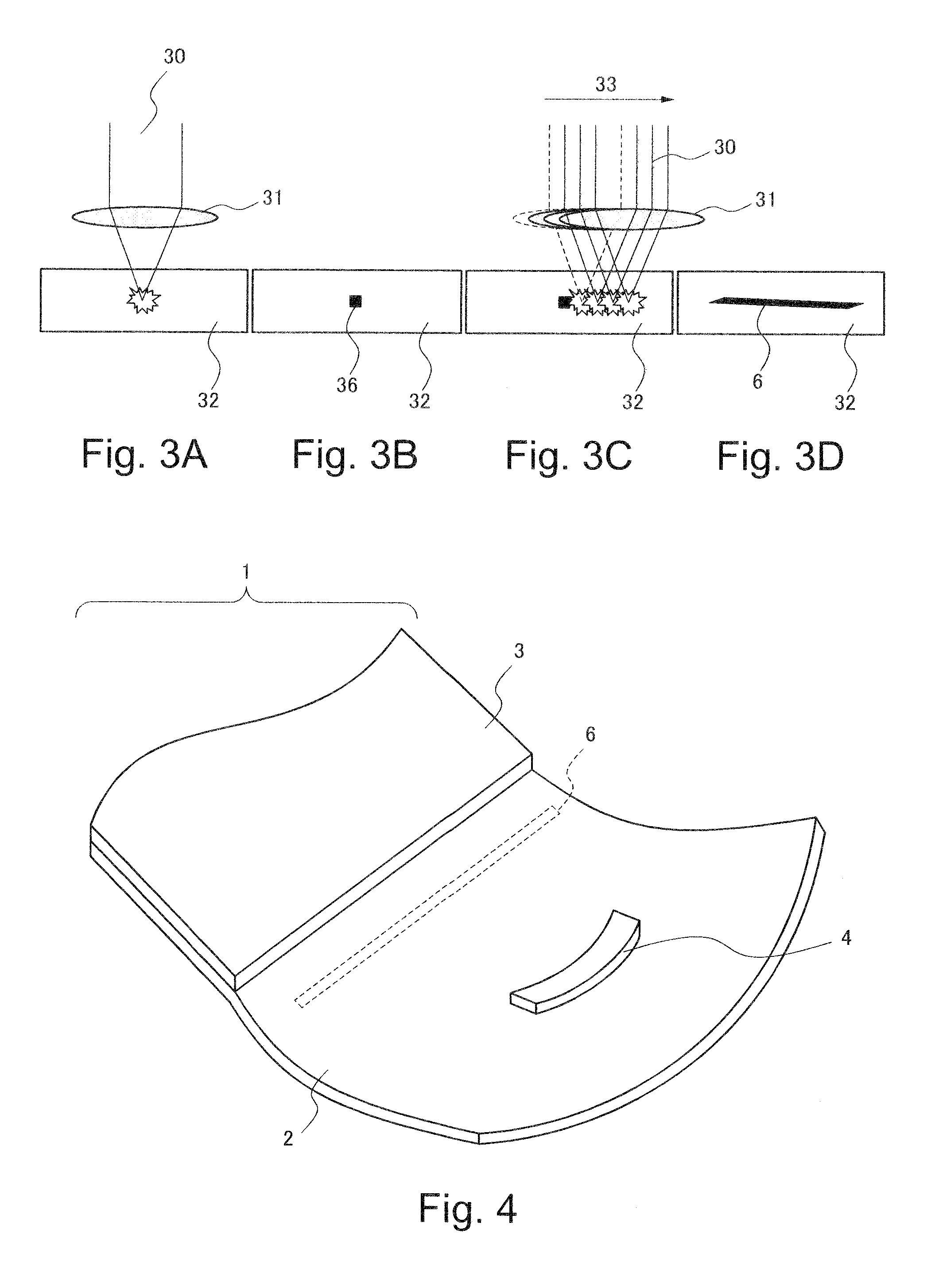
Display device and method of manufacturing the same
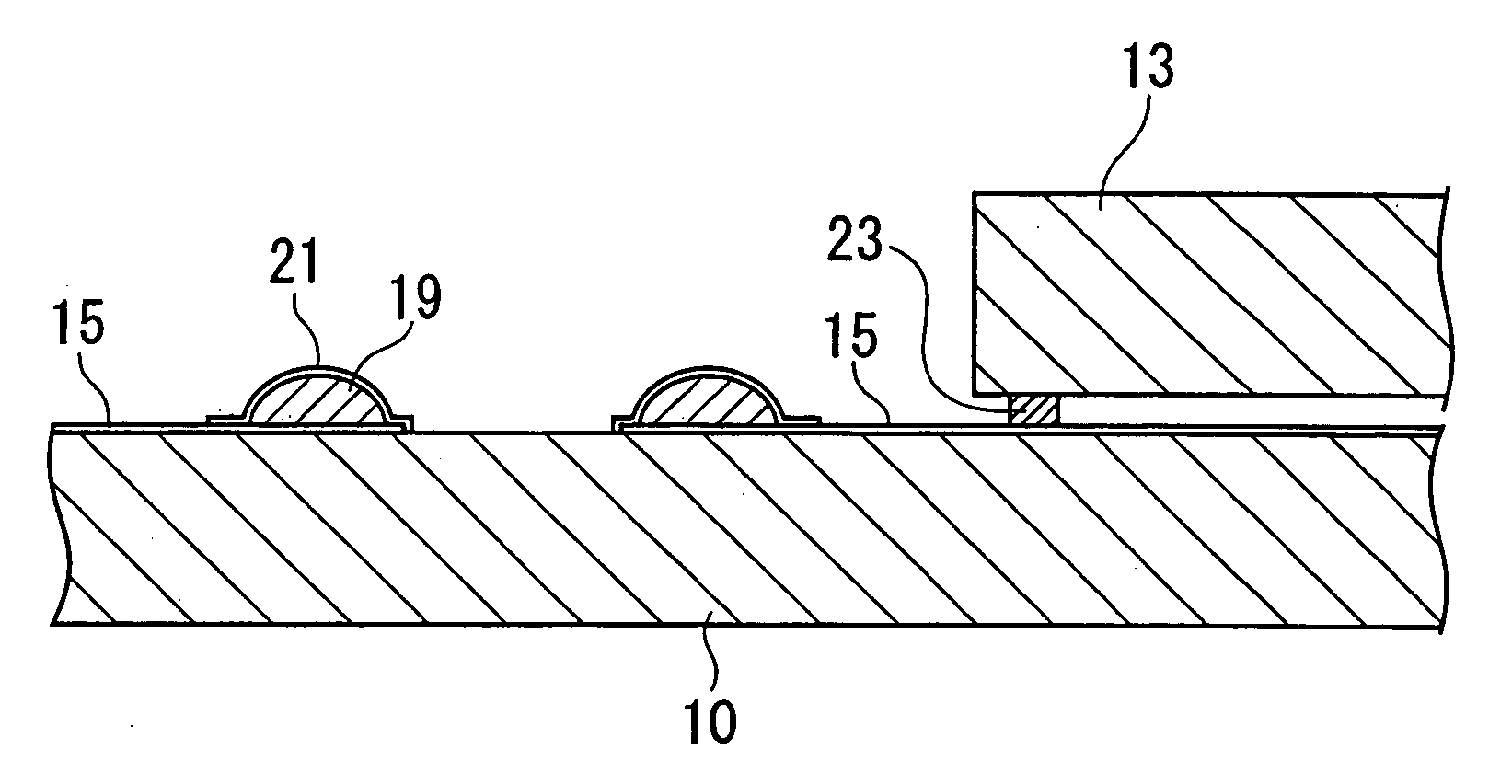
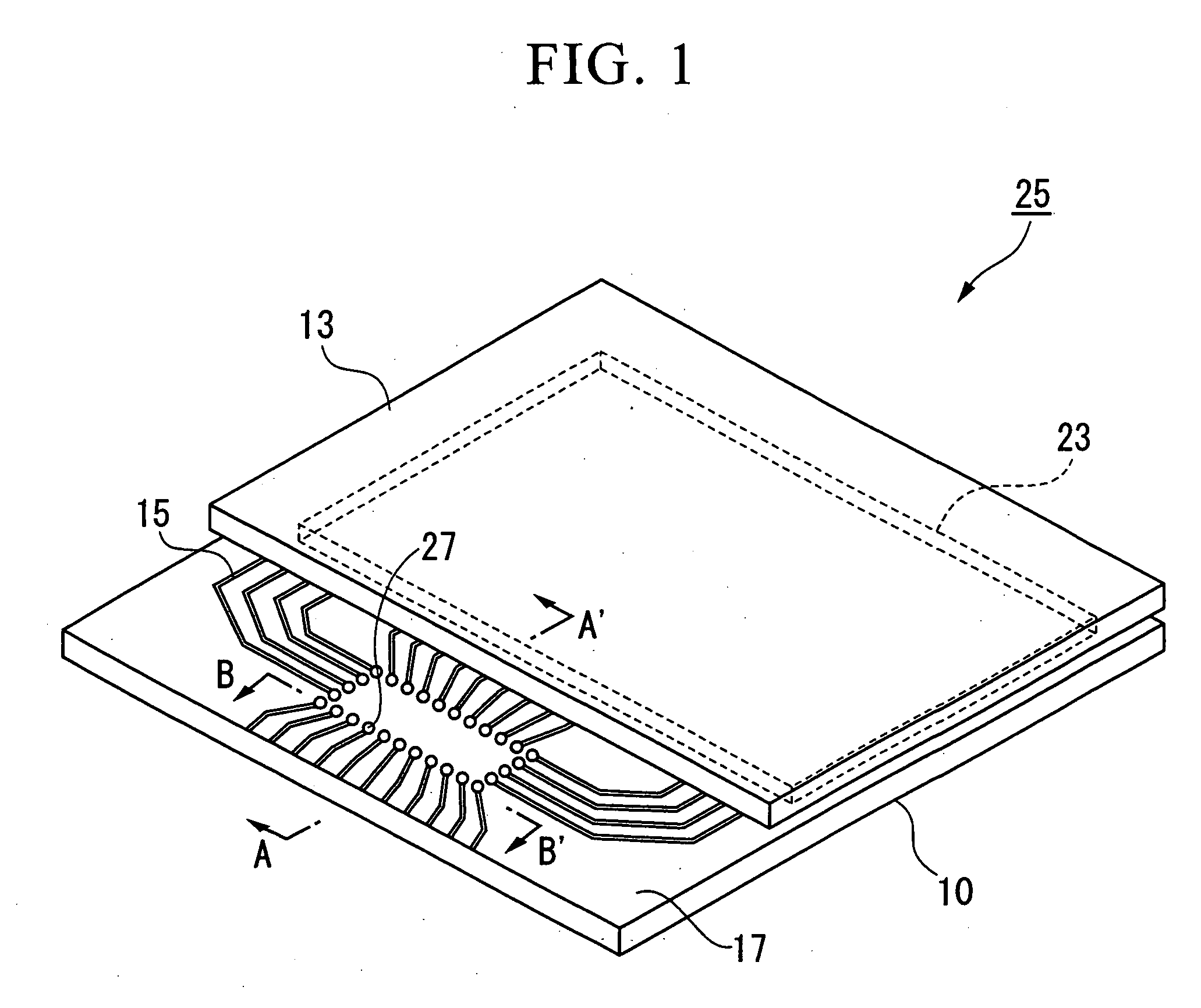
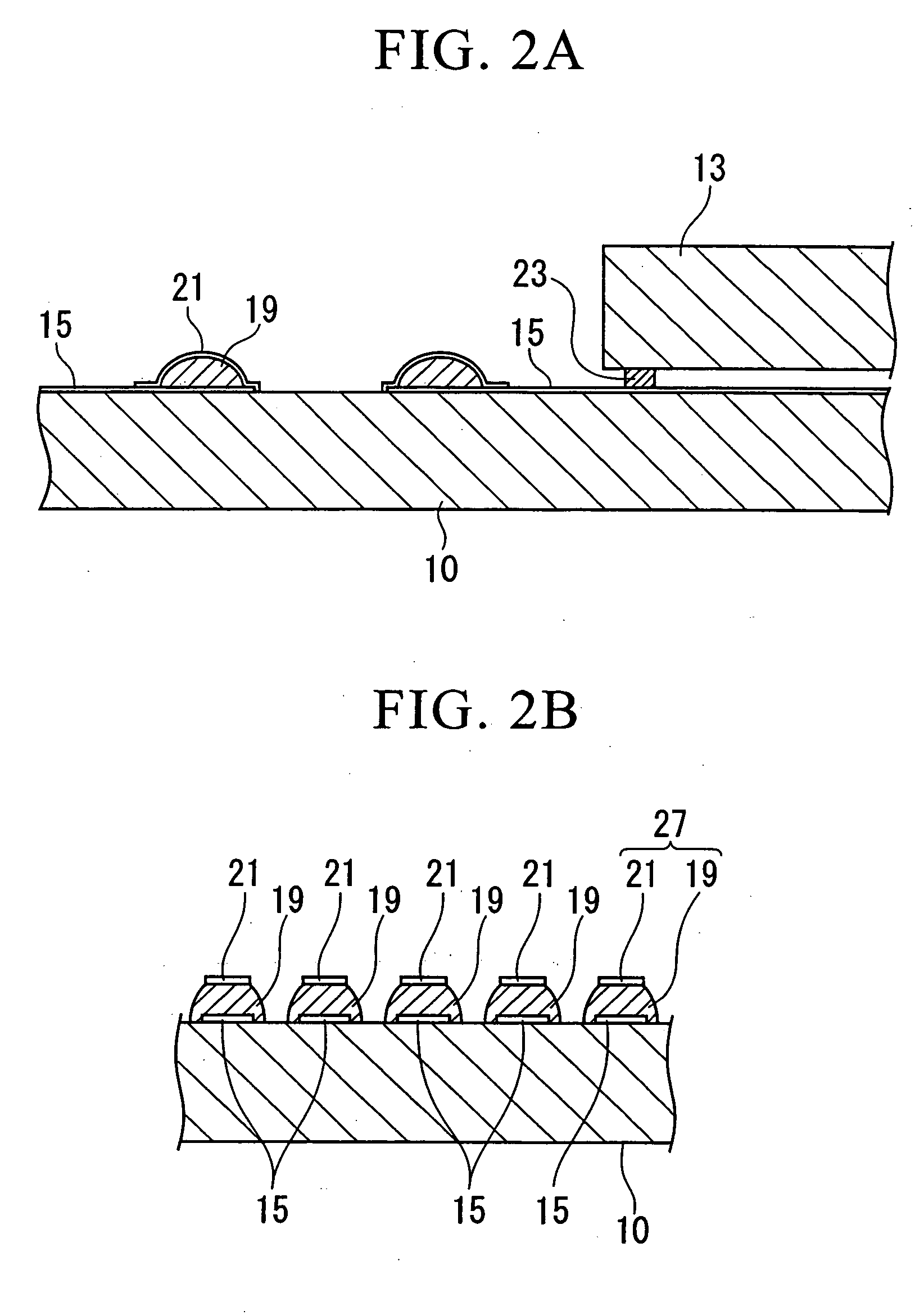
InactiveUS20100002404A1Absorbs stressReduce the numberPrinted circuits stress/warp reductionCircuit fluid transportThermal deformationDisplay device
A display device includes a glass substrate having a display area and a peripheral area. A drive circuit component is mounted on the glass substrate by thermocompression bonding on the peripheral area, and a stress absorption region is provided within the glass substrate close to the circuit component so as to absorb stress produced by thermal deformation of the circuit component. A method of manufacturing the display device of the present invention includes a step of forming stress absorption region into the glass substrate so as to absorb the stress caused by thermocompression bonding of the the circuit component.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Apparatus, systems and methods for packaging electronic products
Owner:NEW CONCEPTS DEV
Flexing chip heatsink
InactiveUS20070133177A1High heat conductivitySmall footprintSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
A method, apparatus and system are disclosed for using a flexible radiating heatsink for cooling electronic components on integrated circuit chips. The heatsink elastically deforms without breaking or disconnecting in response to an external contact and then returns to its original size, shape and position, without transmitting the external force to the electronic component(s) it is cooling.
Owner:IBM CORP
POP (package-on-package) device encapsulating soldered joints between external leads
InactiveUS7692311B2Avoid the breaks of the soldering jointsAvoid electrical openSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageLead frame
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY INC
Apparatus, Systems and Methods for Packaging Electronic Products
ActiveUS20140027337A1Absorbs stressEasily and cost-effectively constructedBio-packagingSolid materialEngineering
Owner:NEW CONCEPTS DEV
Plug-socket connector apparatus for optical fiber termination
InactiveUS7510336B2Add dimensionAvoid problemsElectric connection structural associationsCoupling light guidesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Plug-socket connector apparatus for optical fiber termination comprises first and second plugs and a socket. The first and second plugs are both single ferrule plugs. The socket is a molded interconnect device and a plug holder, and includes terminals located on the bottom face of the socket, first and second bores located at one side of the socket, and first and second retainers. The retainers retain latches formed in the plugs so as to prevent the plugs from falling out of the bores and to restrict rotation angles of the plugs around the axes within predetermined rotation angle ranges, when the plugs is plugged in the bores.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
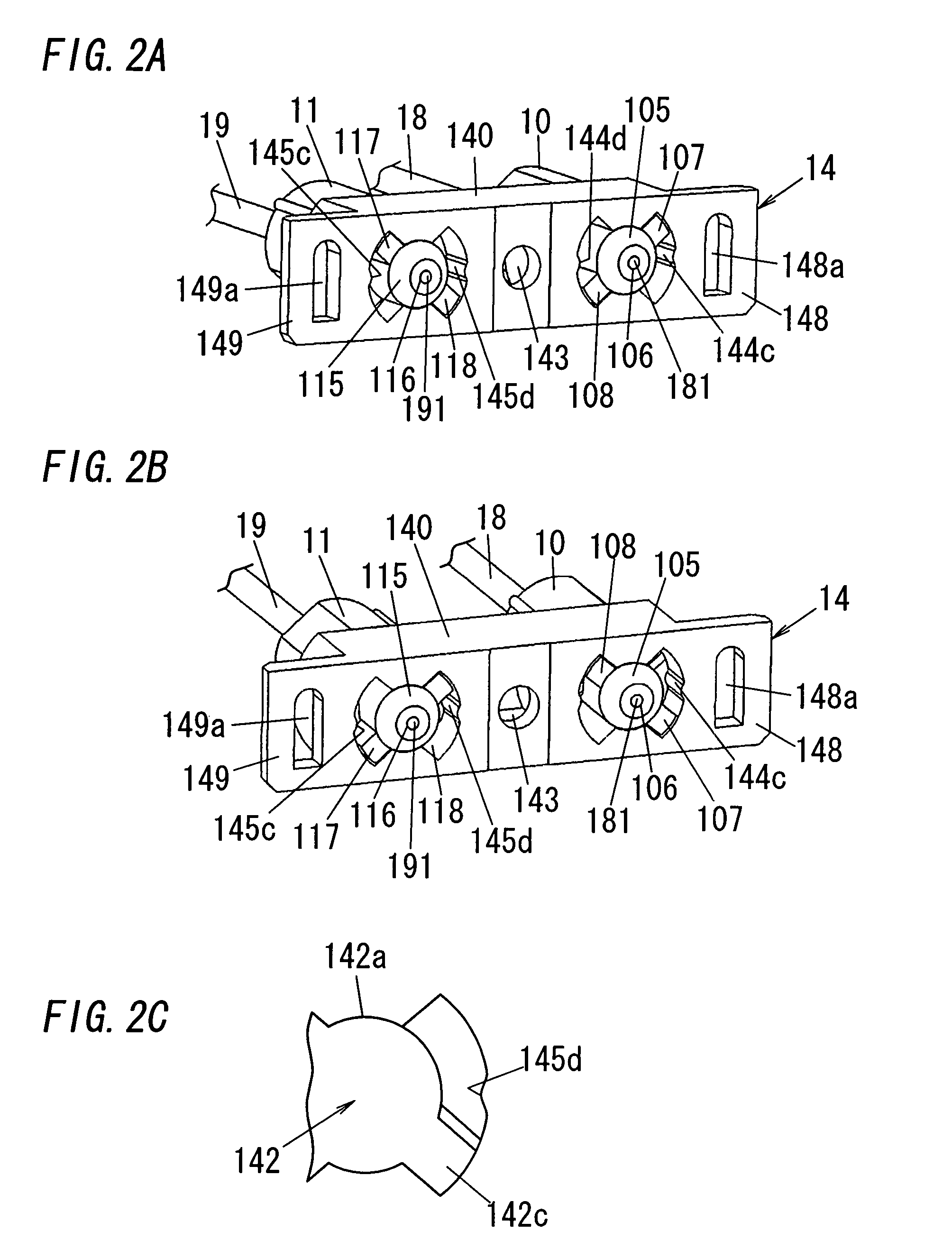
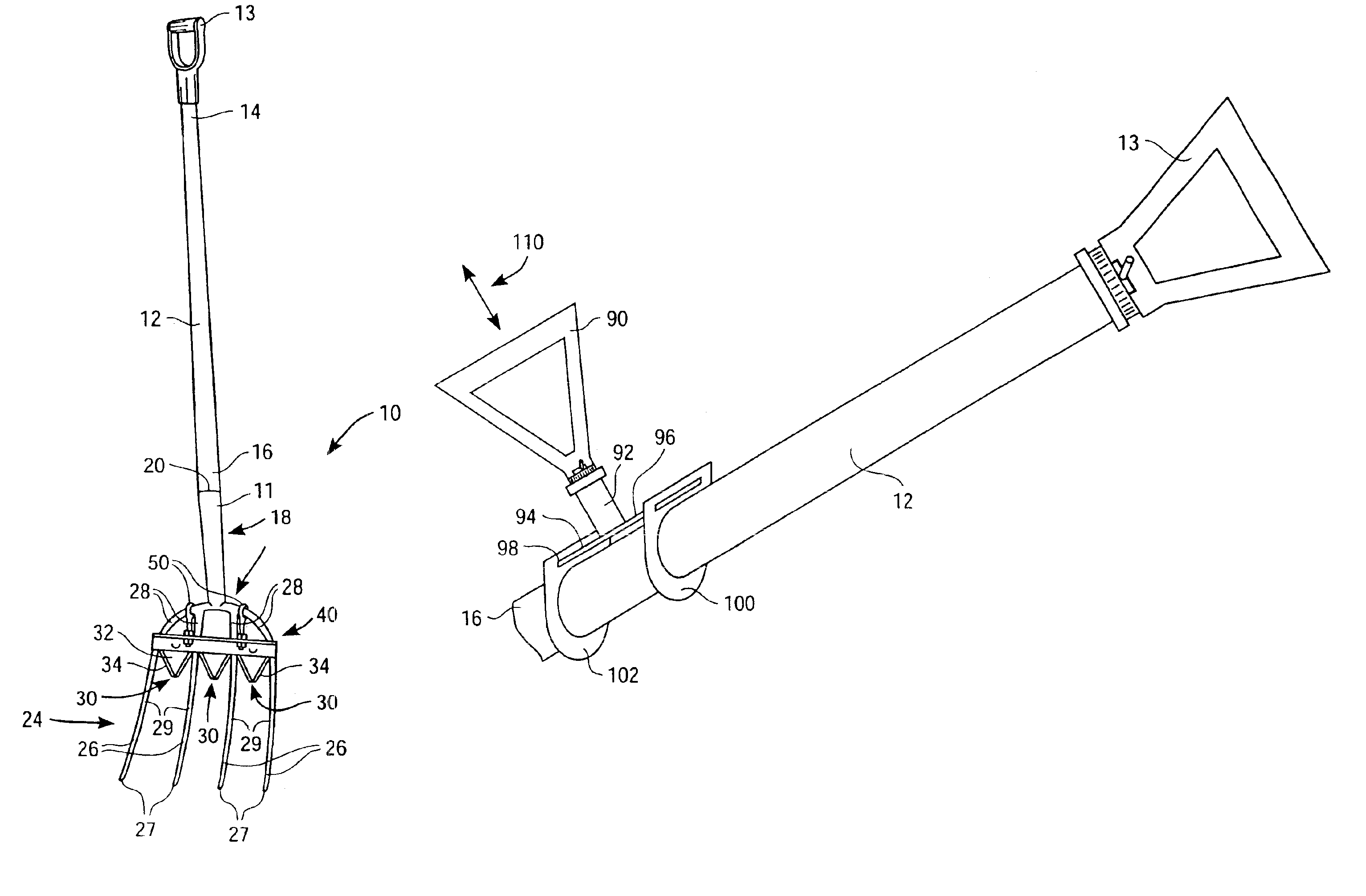
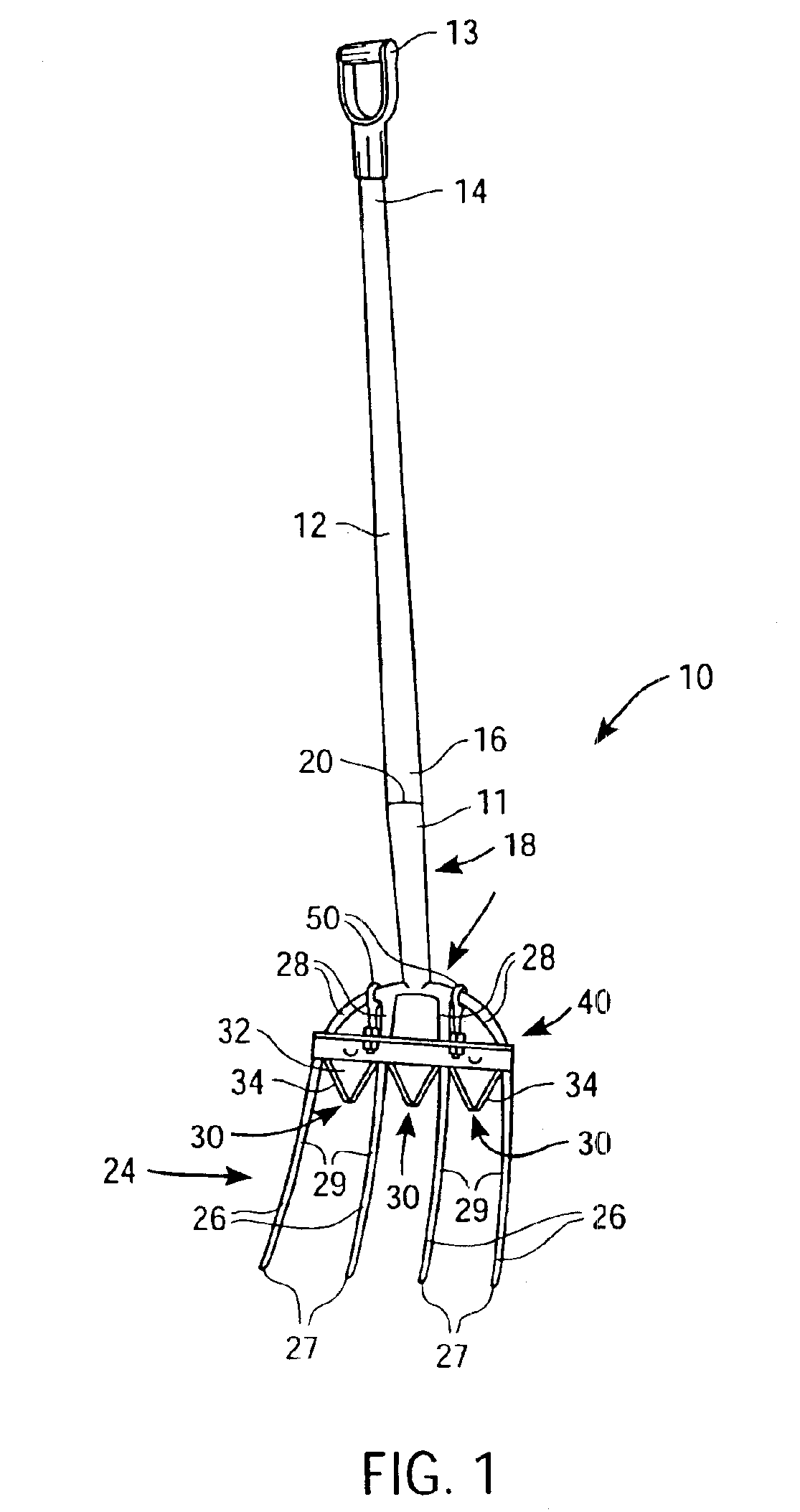
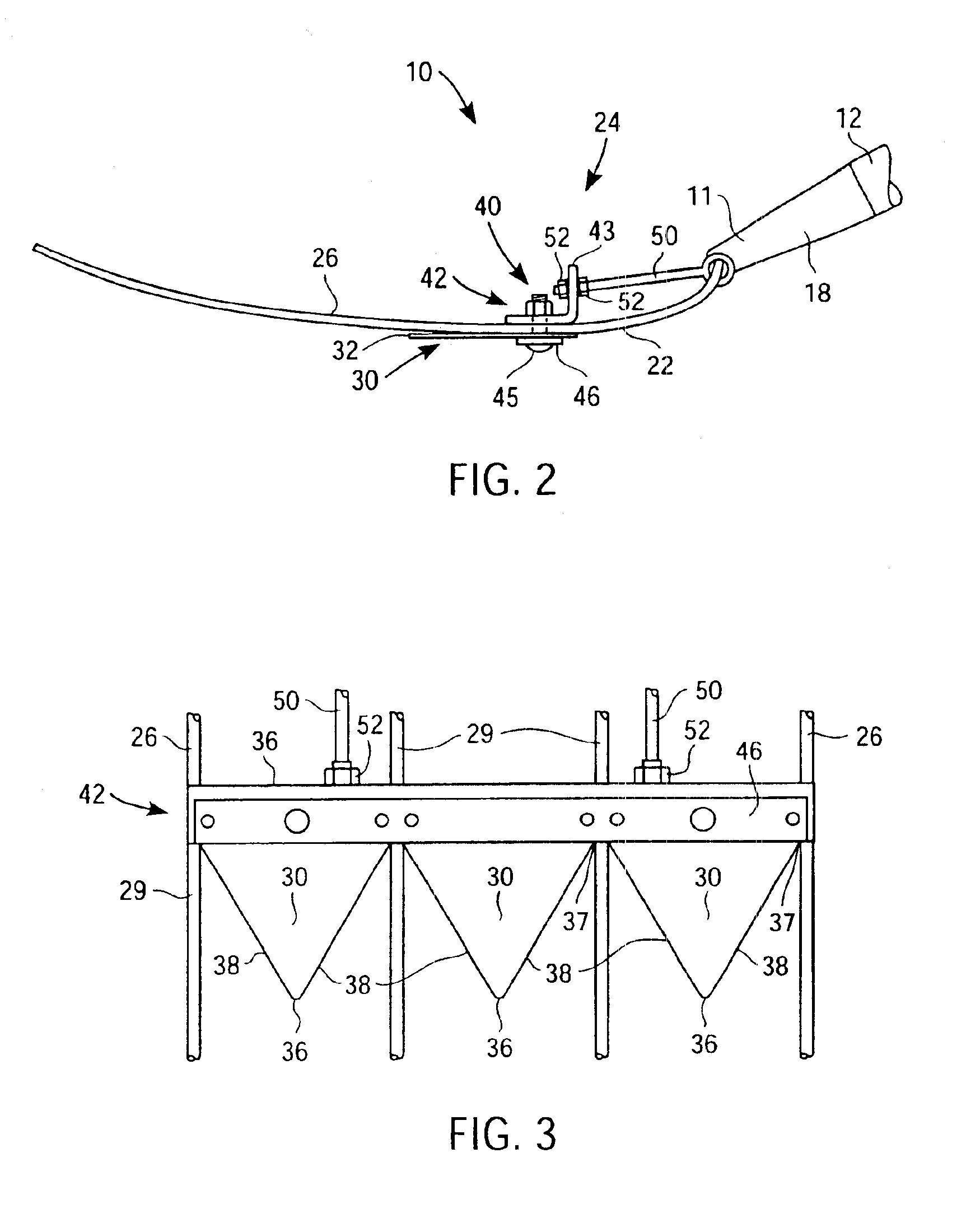
Tool with rotatable handle grip
A tool having a rotatable handle grip includes an elongated handle having a first end and second end, wherein a handle grip is rotatably coupled with the first end, and a working end is coupled with the second end. The working end may include a plurality of spaced tines with the prongs having points, wherein at least one cutting blade is coupled to the device between adjacent tines allowing a user to slide the tines of the fork along the ground surface, thereby using the blade to harvest vegetation. Additionally, the working end allows a stack of cut vegetation to accumulate on the device to be carried and placed in a preferred location or container.
Owner:HIXON WILLIAM K
Flexible and foldable electromagnetic shielding
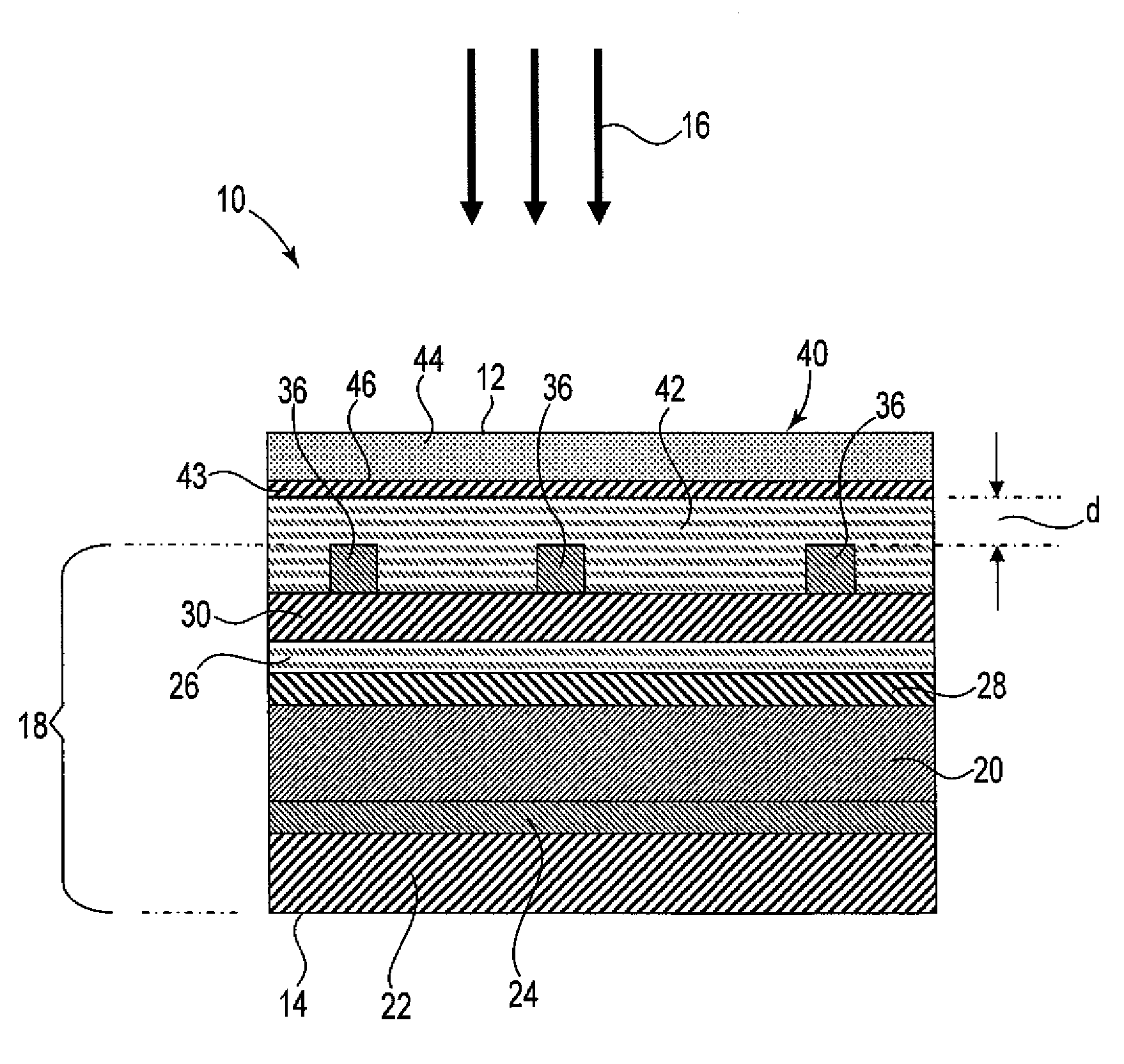
ActiveUS20200315072A1Avoid emissionsHighly effectiveShielding materialsProtective equipmentElastomerThermal insulation
A flexible, foldable EM barrier attenuates electromagnetic radiation by at least 20 dB from 1 GHz to 30 GHz. The barrier comprises an LF layer that blocks EM radiation at least at low frequencies, laminated to a textile support layer that reduces stress cracking of the LF layer and prevents widening of any cracks that do form. Embodiments further comprise an HF layer that blocks EM radiation at high frequencies, such as a metallized polymer film and / or an elastomer layer filled with conductive particles. The LF layer can be foil, mesh, or electroless metallization of the support textile or of another textile. A thermal insulation layer can be included. A topcoat can block UV, and primer layers can resist moisture. Barriers can be joined to each other and / or to adjacent structures by lanyards, webbing, sewing, soft connections, and / or flex joints formed by adhesively attached metallized textiles or films.
Owner:WARWICK MILLS INC
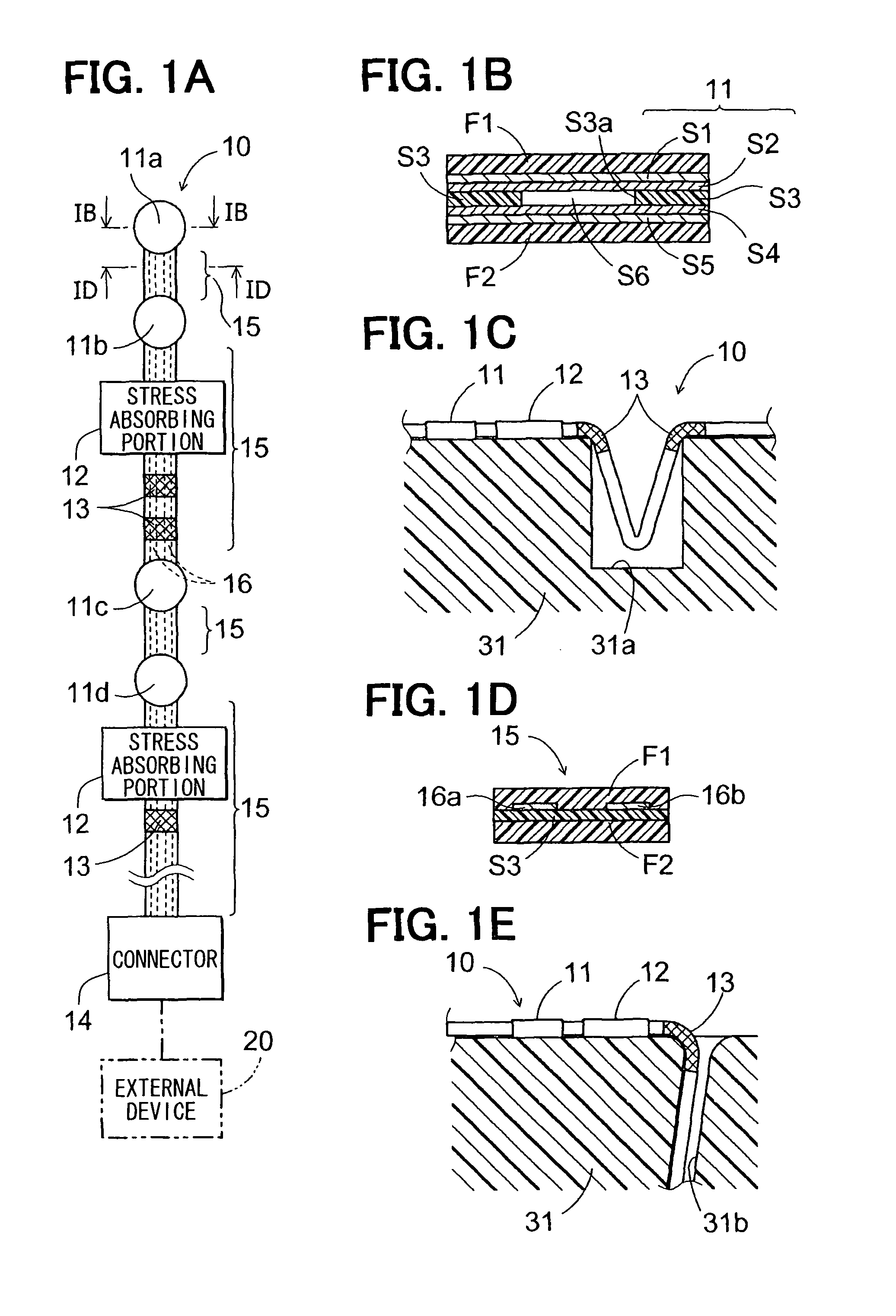
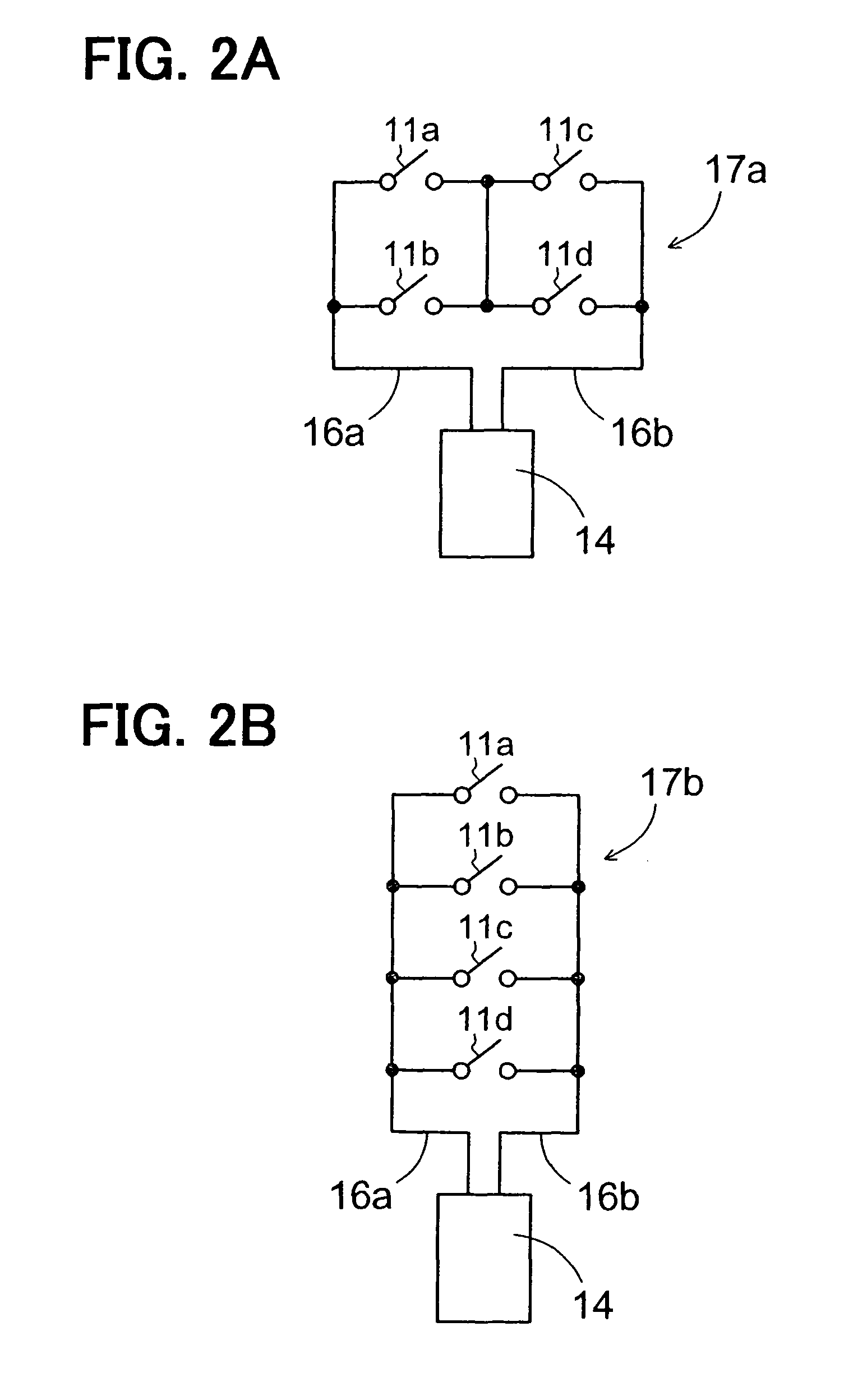
Occupant detection sensor including a bent portion and a stress absorbing portion and method of manufacturing the same
An occupant detection sensor includes a sensor member disposed on a surface of a vehicle seat and detecting sitting of an occupant, a wiring member electrically coupling the sensor member with an external device, and a covering member covering the sensor member and the wiring member. The wiring member and the covering member are included in a coupling section that is disposed along the surface of the vehicle seat. The coupling section includes a bent portion and a stress absorbing portion that absorbs stress generated at the bent portion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
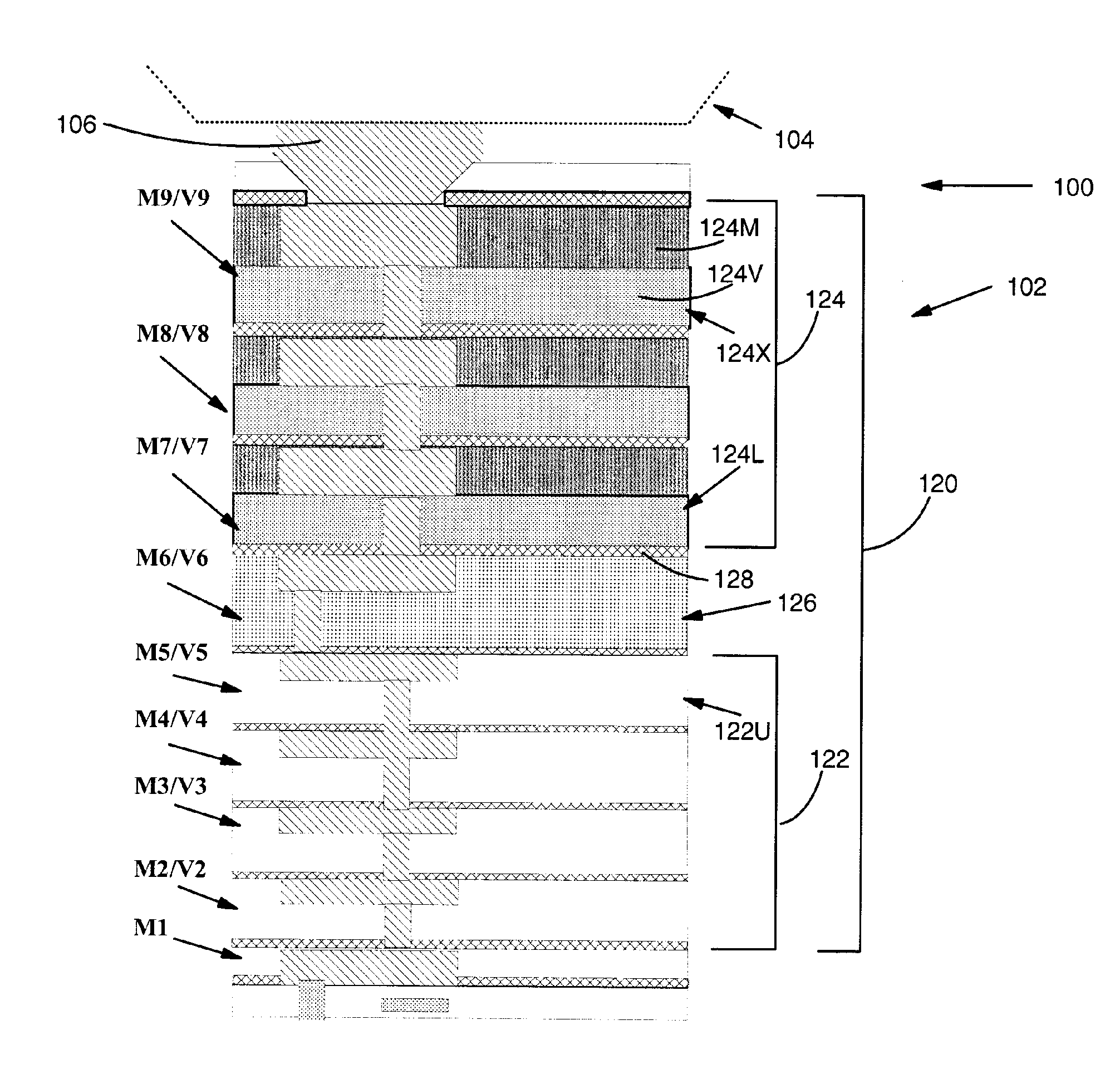
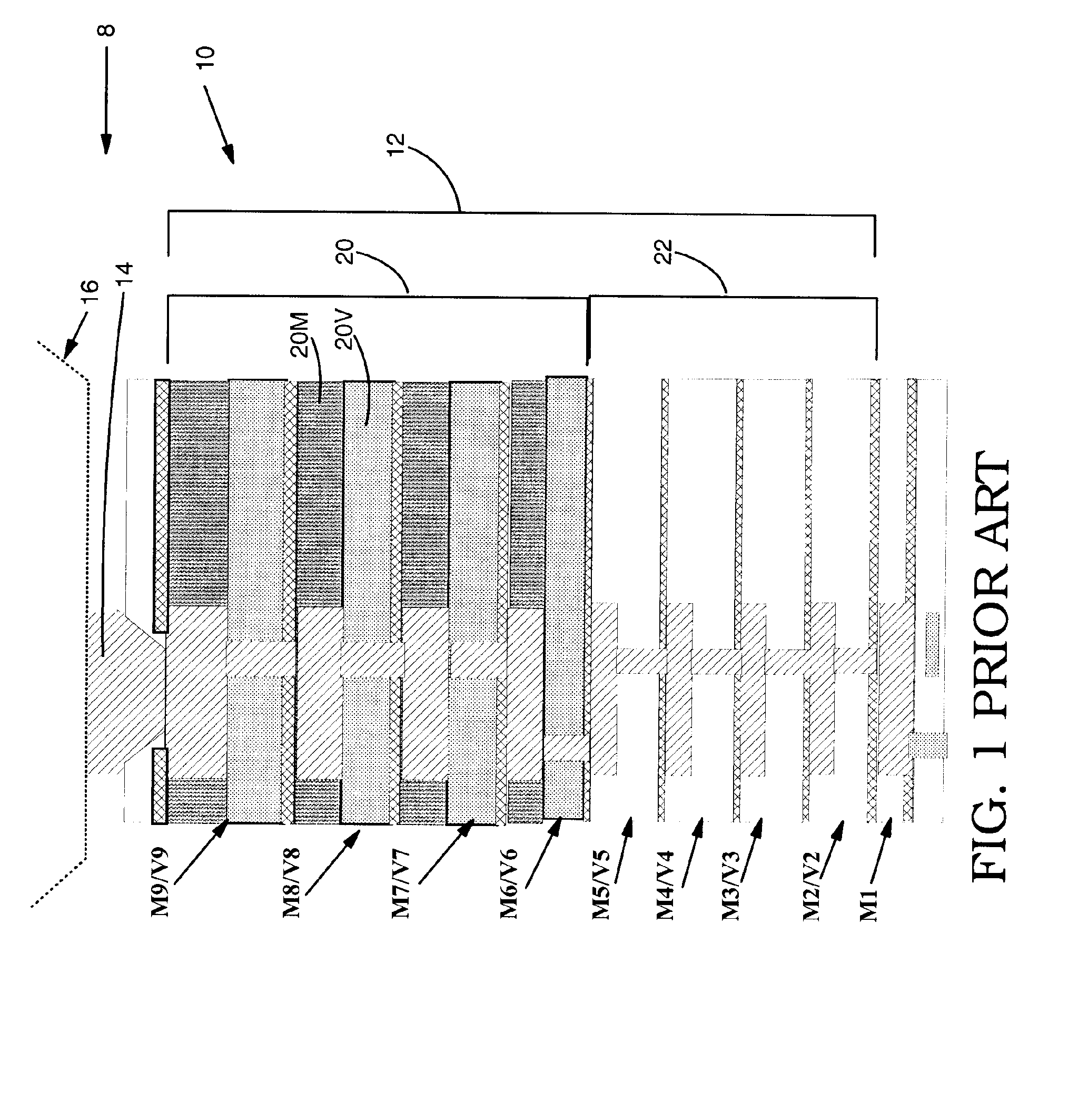
Ild layer with intermediate dielectric constant material immediately below silicon dioxide based ild layer
InactiveUS20070187828A1Sufficient electrical propertyReduce the likelihood of failureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIsolation layerSilicon dioxide
An integrated circuit (IC) chip and related package are disclosed including a first interlevel dielectric (ILD) layer(s) including an ultra low dielectric constant (ULK) material, a second ILD layer(s) including a silicon dioxide (SiO2) based dielectric material above the first ILD layer(s), and a transitional ILD layer including an intermediate dielectric constant material. The transitional ILD layer is positioned directly below a lowermost one of the second ILD layer(s), excepting any isolation layer, which represents the layer most susceptible to failure. The intermediate dielectric constant material can have a dielectric constant and an elastic modulus greater than that of the ULK material and less than that of the SiO2 based dielectric material. Hence, the intermediate dielectric constant provides adequate electrical properties, but also absorbs more of the stress than the typical ULK material, which reduces the likelihood of failure. A method of forming the IC chip is also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
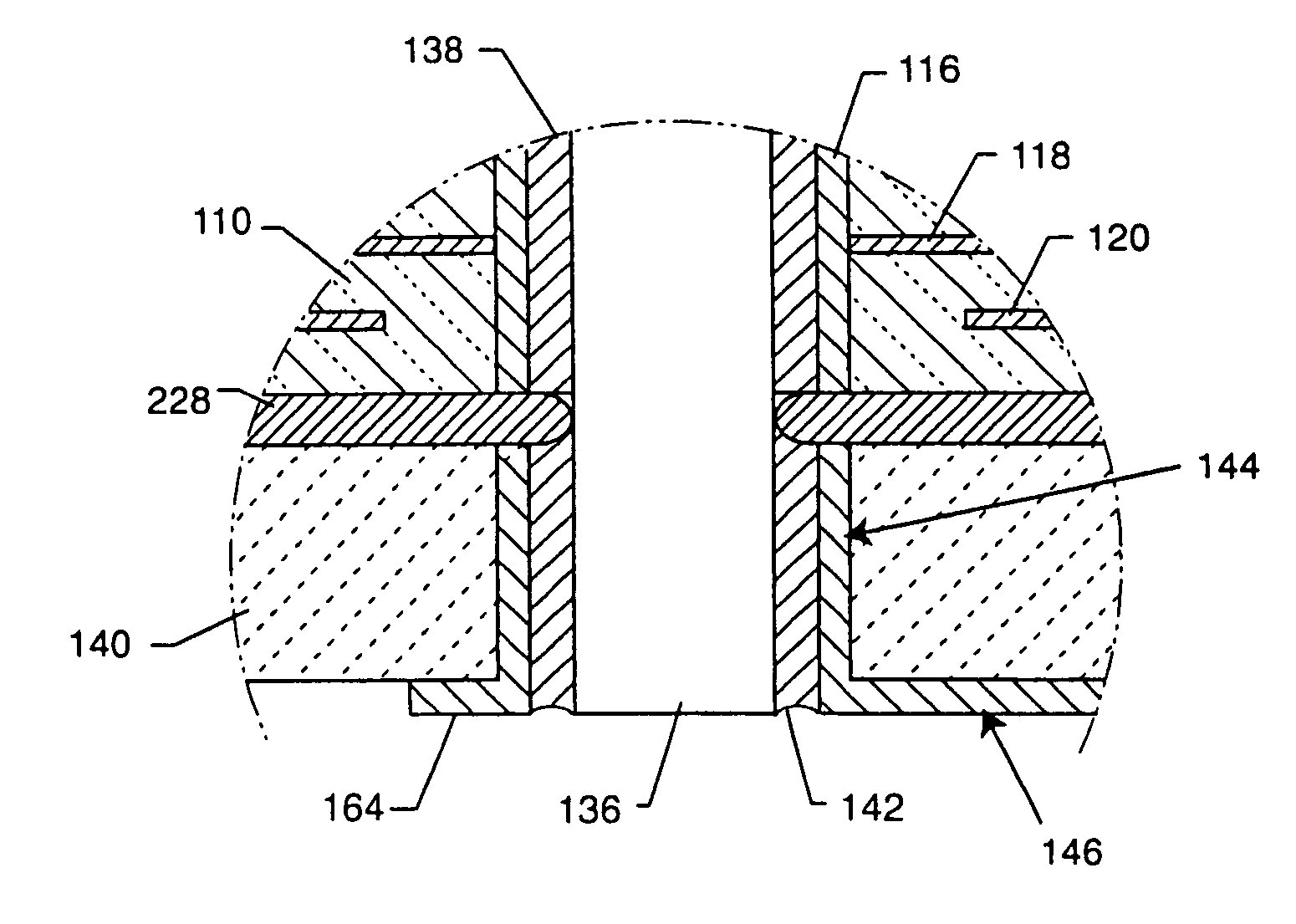
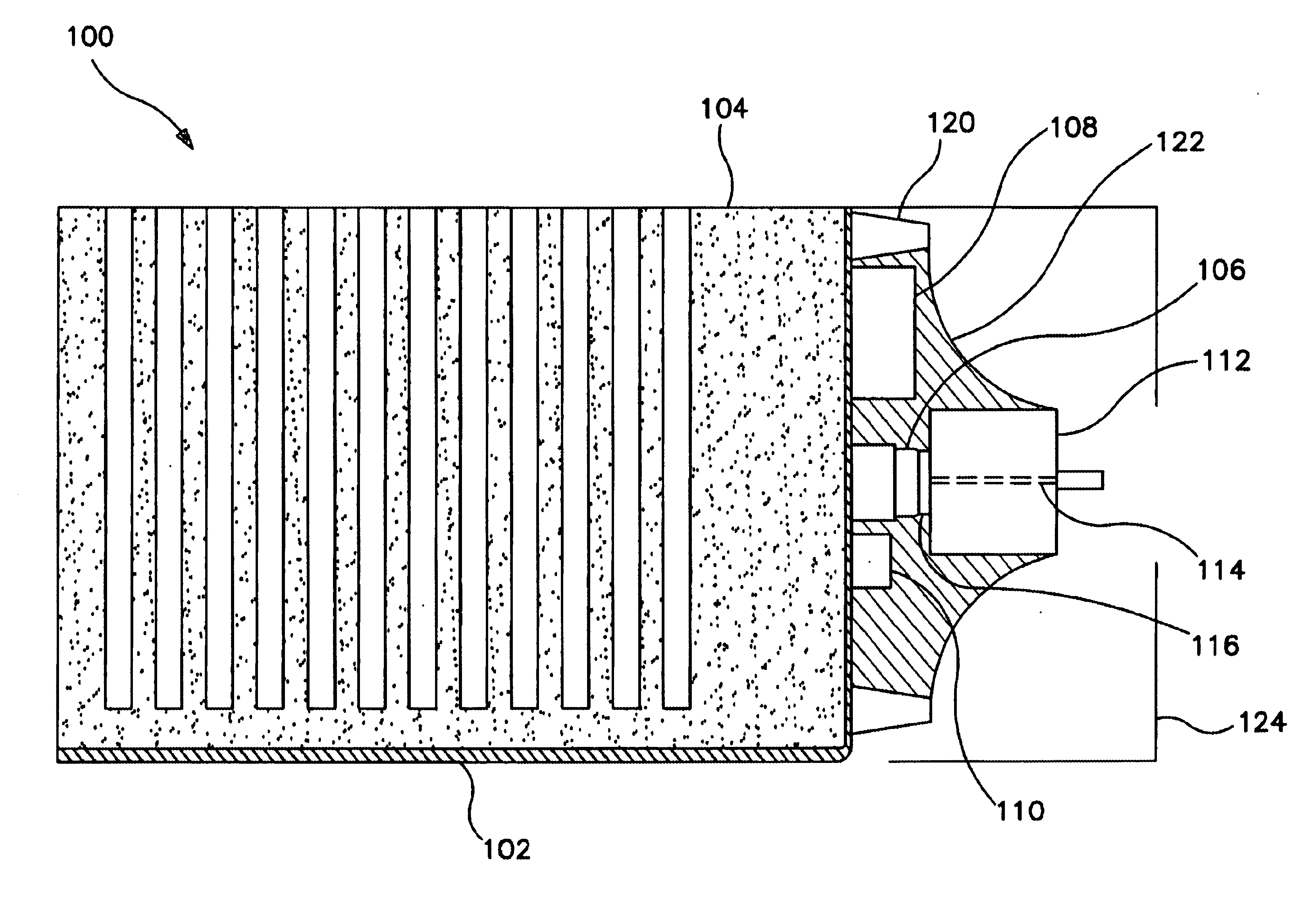
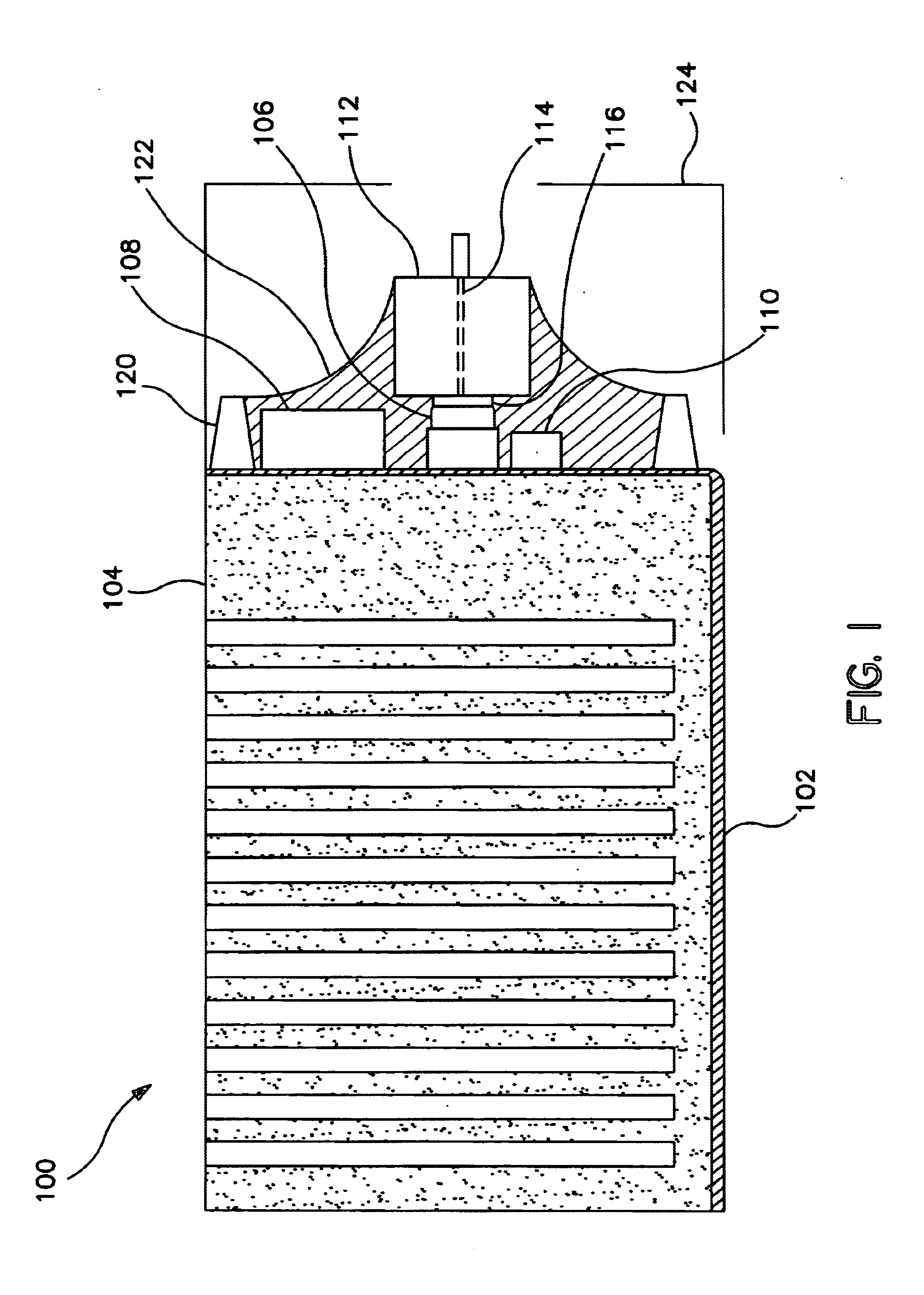
X-ray radiation generator
ActiveUS20170338076A1Improve breakdown resistanceIncrease surface areaX-ray tube electrodesElectricityX-ray
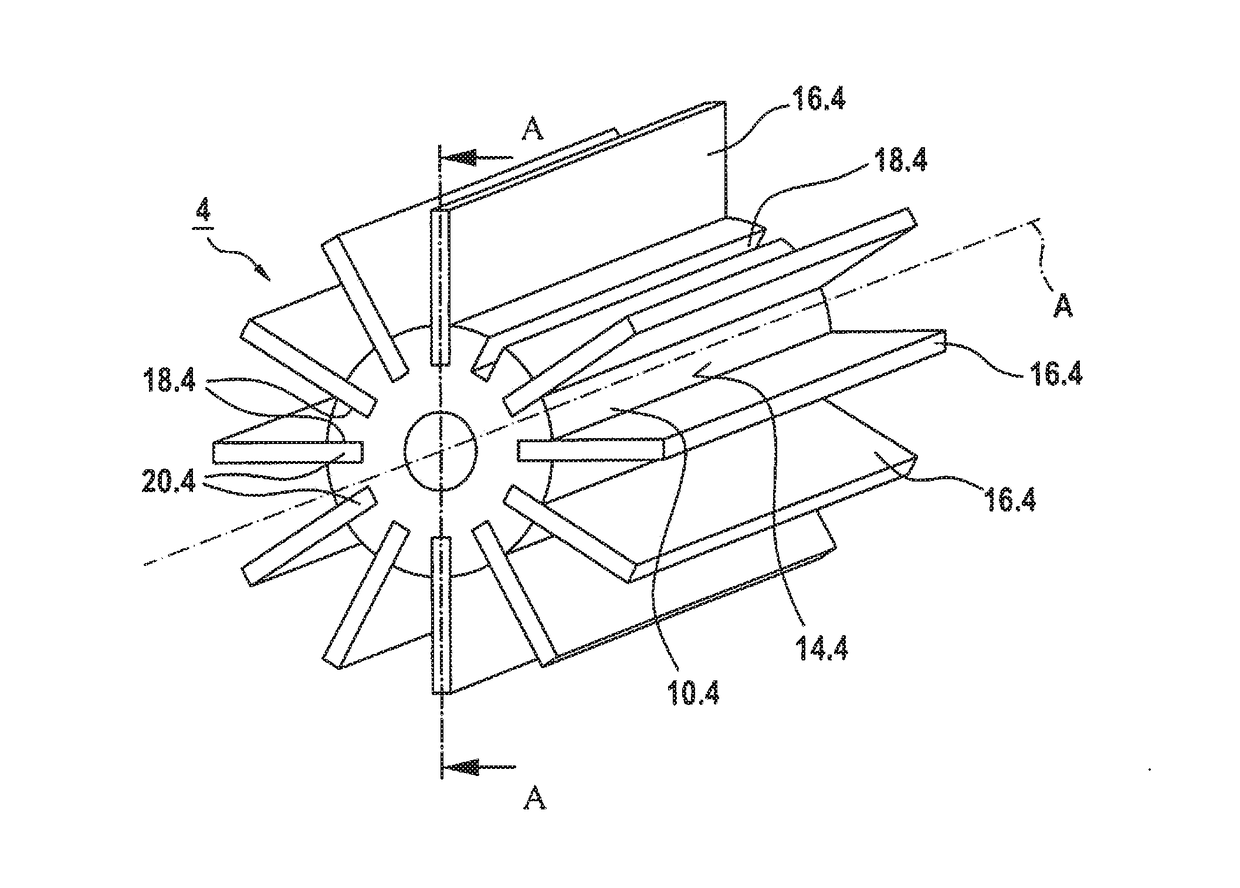
The present invention relates to an X-ray tube (30) with an anode (36) that conducts a high voltage, preferably greater than 120 kV, particularly preferably greater than 300 kV, and heats up during operation, wherein the anode is connected in a thermally conductive way to a heat sink (4), which has a base body (10.4) composed of a metal with a heat absorbing surface (12.4) for coupling to the anode (36) as a heat source (36) and a heat dissipating surface (14.4) that is enlarged by means of heat dissipating elements (16.4) that are connected to the base body (10.4), wherein the heat dissipating elements (16.4) are composed of an electrically insulating material having a thermal conductivity on the same order of magnitude as that of the metal of the base body (10.4), and wherein the heat dissipating elements (16.4) have a height (H) starting from the base body (10.4) of the heat sink (4) so that taking into account the high voltage and an insulating medium surrounding the heat dissipating elements (16.4), there is a sufficient insulation breakdown resistance relative to the surroundings of the X-ray tube (30).
Owner:SMITHS HEIMANN
POP (Package-On-Package) device encapsulating soldered joints between externals leads
InactiveUS20090127679A1Distribute pressureAvoid the breaks of the soldering jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering
A POP (Package-On-Package) semiconductor device with encapsulating protection of soldered joints between the external leads, primarily comprises a plurality of stacked semiconductor packages and dielectric coating. Each semiconductor package includes at least a chip, a plurality of external leads of leadframe, and an encapsulant where the external leads are exposed and extended from a plurality of sides of the encapsulant. Terminals of a plurality external leads of a top semiconductor package are soldered to the soldered regions of the corresponding external leads of a bottom semiconductor package. The dielectric coating is disposed along the sides of the encapsulant of the bottom semiconductor package to connect the soldered points between the external leads and to partially or completely encapsulate the soldering materials so that the stresses between the soldered joints can be dispersed and no electrical shorts happen.
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY
Sensor geometry for improved package stress isolation
ActiveUS7798010B2Improve stress conditionReduce stiffnessForce measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringCounterbore
The sensor geometry for improved package stress isolation is disclosed. A counterbore on the backing plate improves stress isolation properties of the sensor. The counterbore thins the wall of the backing plate maintaining the contact area with the package. The depth and diameter of the counterbore can be adjusted to find geometry for allowing the backing plate to absorb more package stresses. Thinning the wall of the backing plate make it less rigid and allows the backing plate to absorb more of the stresses produced at the interface with the package. The counterbore also keeps a large surface area at the bottom of the backing plate creating a strong bond with the package.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Safety sheath for hypodermic syringe needle
InactiveUS20120022463A1Facilitate subsequent sleeving processImprove tightnessMedical devicesInfusion needlesHypodermic needleEngineering
The present invention provides a safety sheath for hypodermic syringe needle comprising a proximal mounting ring, a distal mounting ring and a shielding sheath. The shielding sheath includes two symmetrical slits, two symmetrical semicircular aprons and an inward annular fillet, which is bisected into two symmetrical curved segments with crescent thickness, namely marginal thickness is less than central thickness. During sleeving the shielding sheath over the distal mounting ring and proximal mounting ring, both symmetrical semicircular aprons are outwardly hauled by outwards forces such that the bore profile of the inward annular fillet is dilated into circular shape, which will not only facilitate subsequent sleeving process without difficulty but also enhance the tightness for the latch of the shielding sheath with the distal mounting ring in locked manner without any possibility of mutually slipping displacement so that medical personnel in handling can prevent from accidental pricks by hypodermic needle.
Owner:WU KUO CHENG
Panel for electro-optical apparatus, method of manufacture thereof, electro-optical apparatus and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050205296A1Avoid failureAbsorbs stressPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted electric component incorporationElectricityEngineering
A panel for an electro-optical apparatus, includes a substrate, a plurality of wires formed on the substrate, convex portions formed from resin and provided either on the plurality of wires or on the substrate, conductive layers provided so as to cover at least a portion of the surfaces of the convex portions, and that are electrically connected to the respective wires, and a plurality of external connection terminals for electrically connecting electronic components, formed by the convex portions and the conductive layers.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com