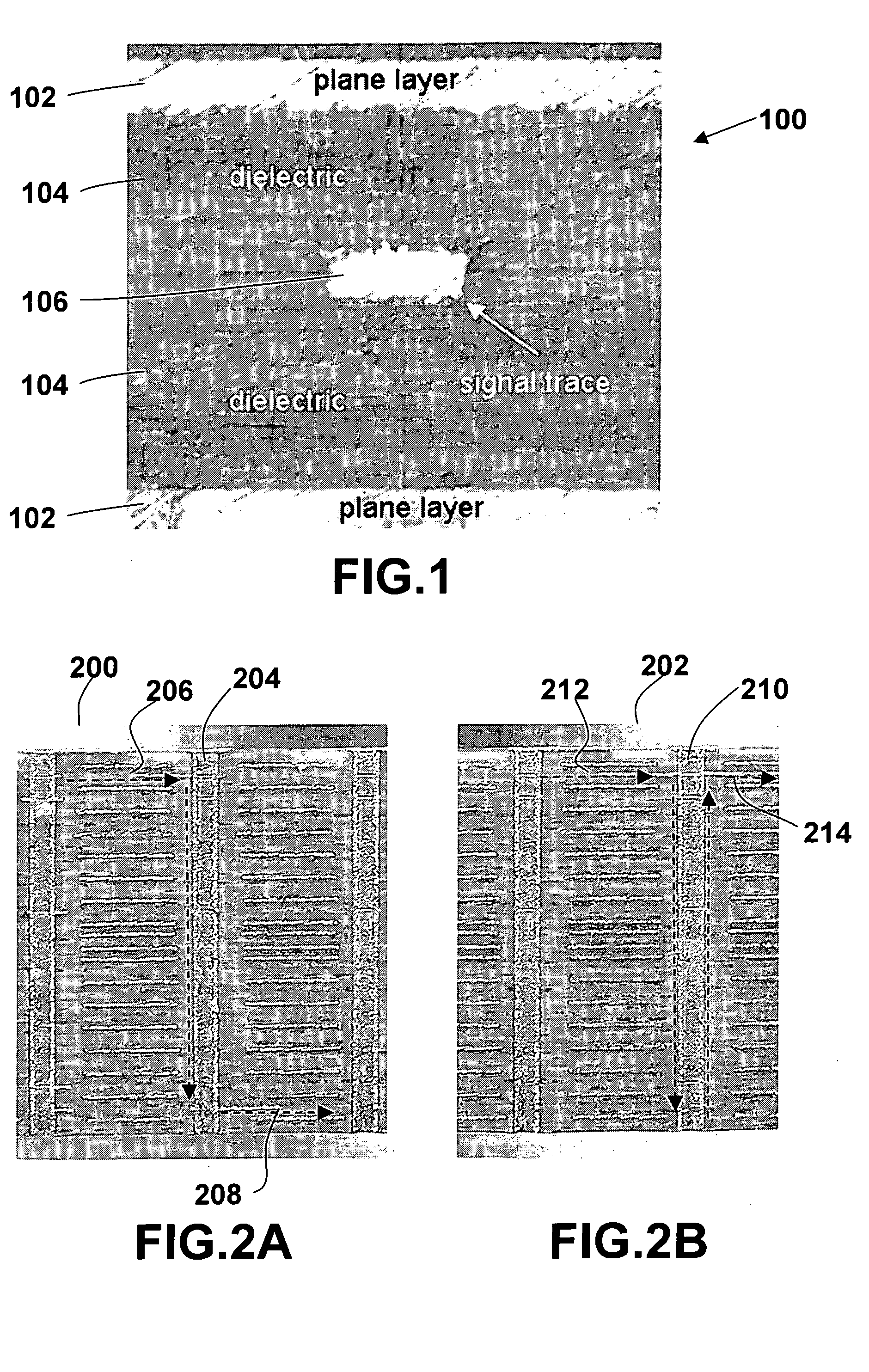
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36results about How to "Impacting cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
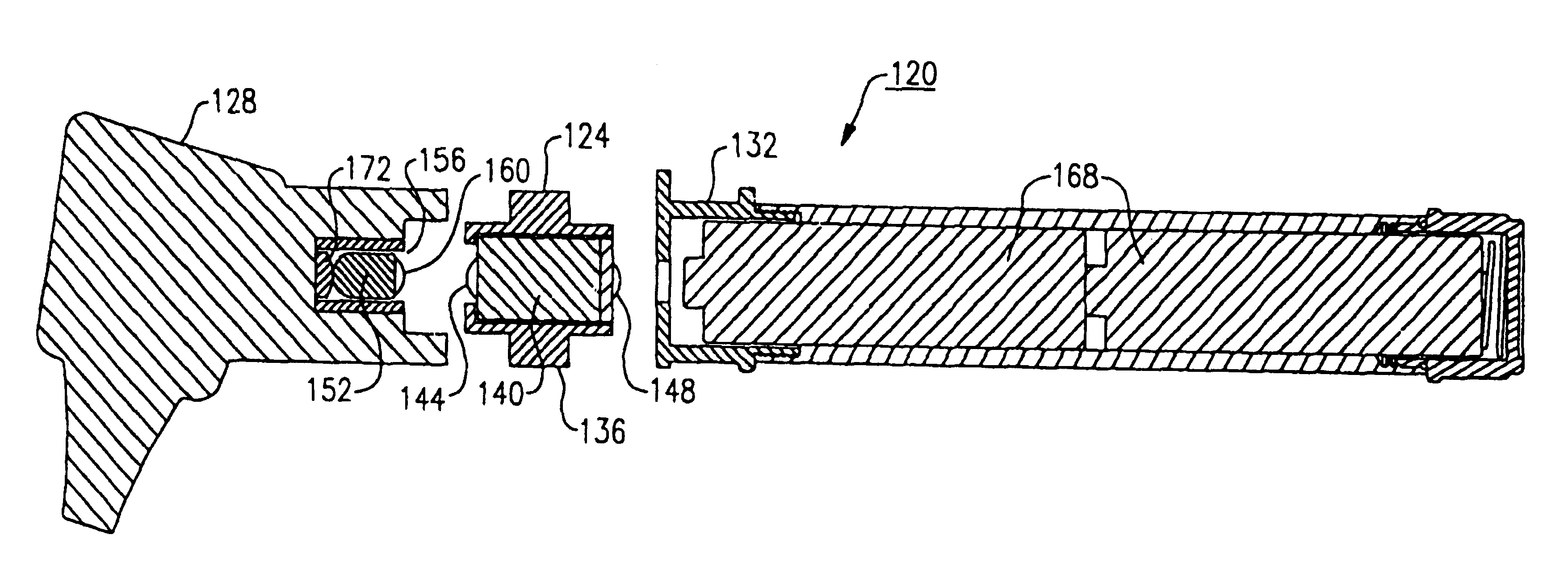
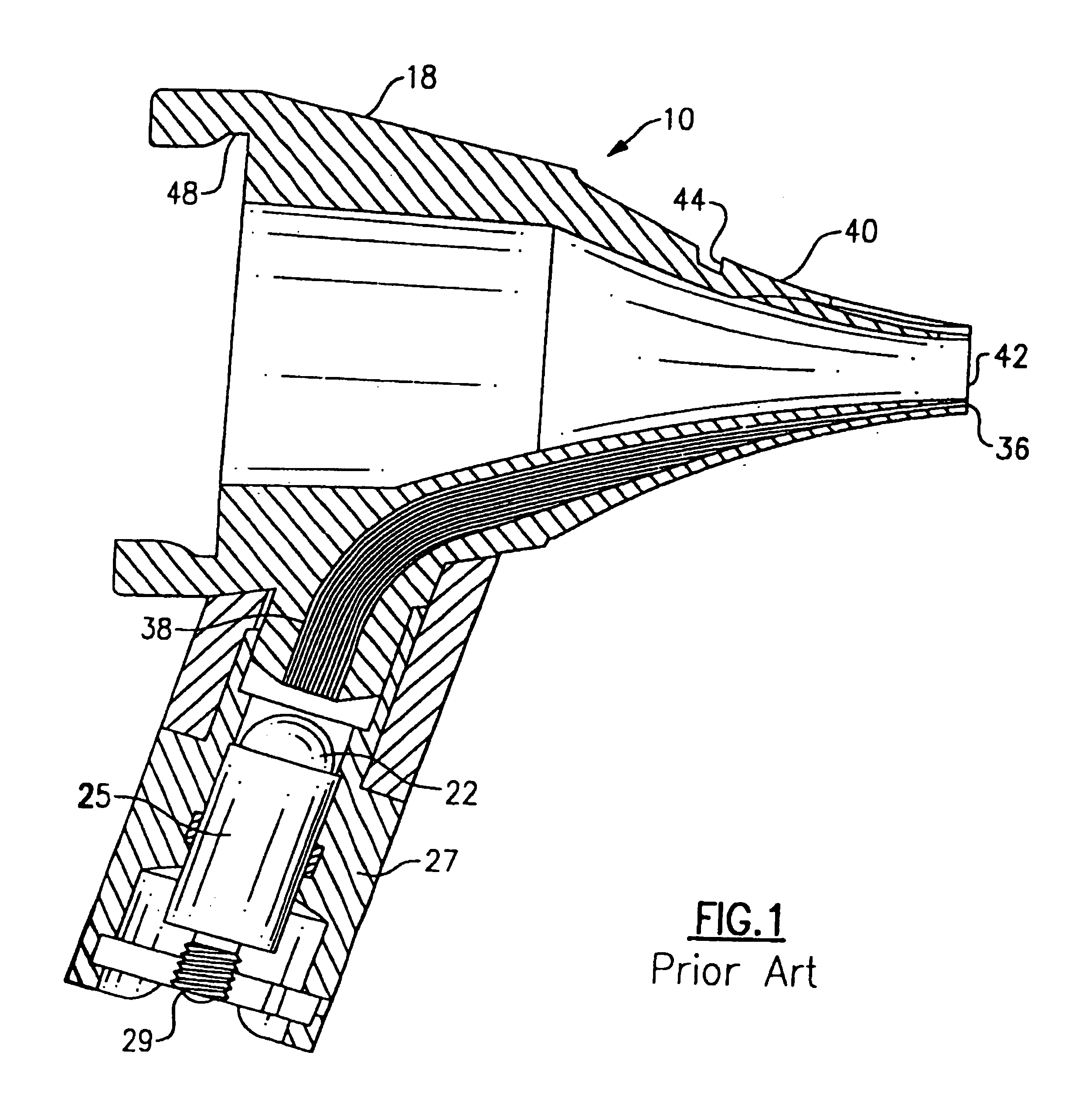
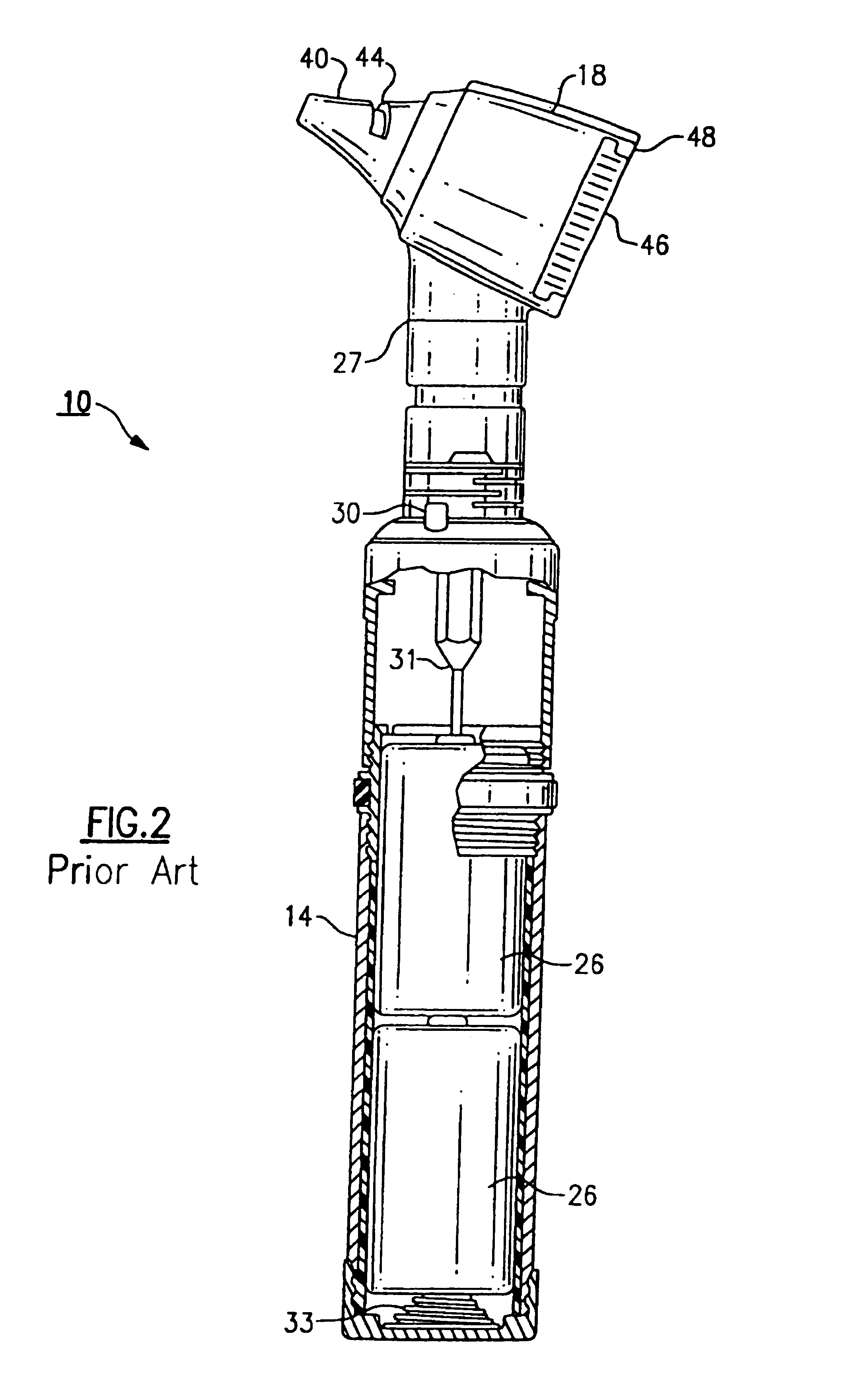
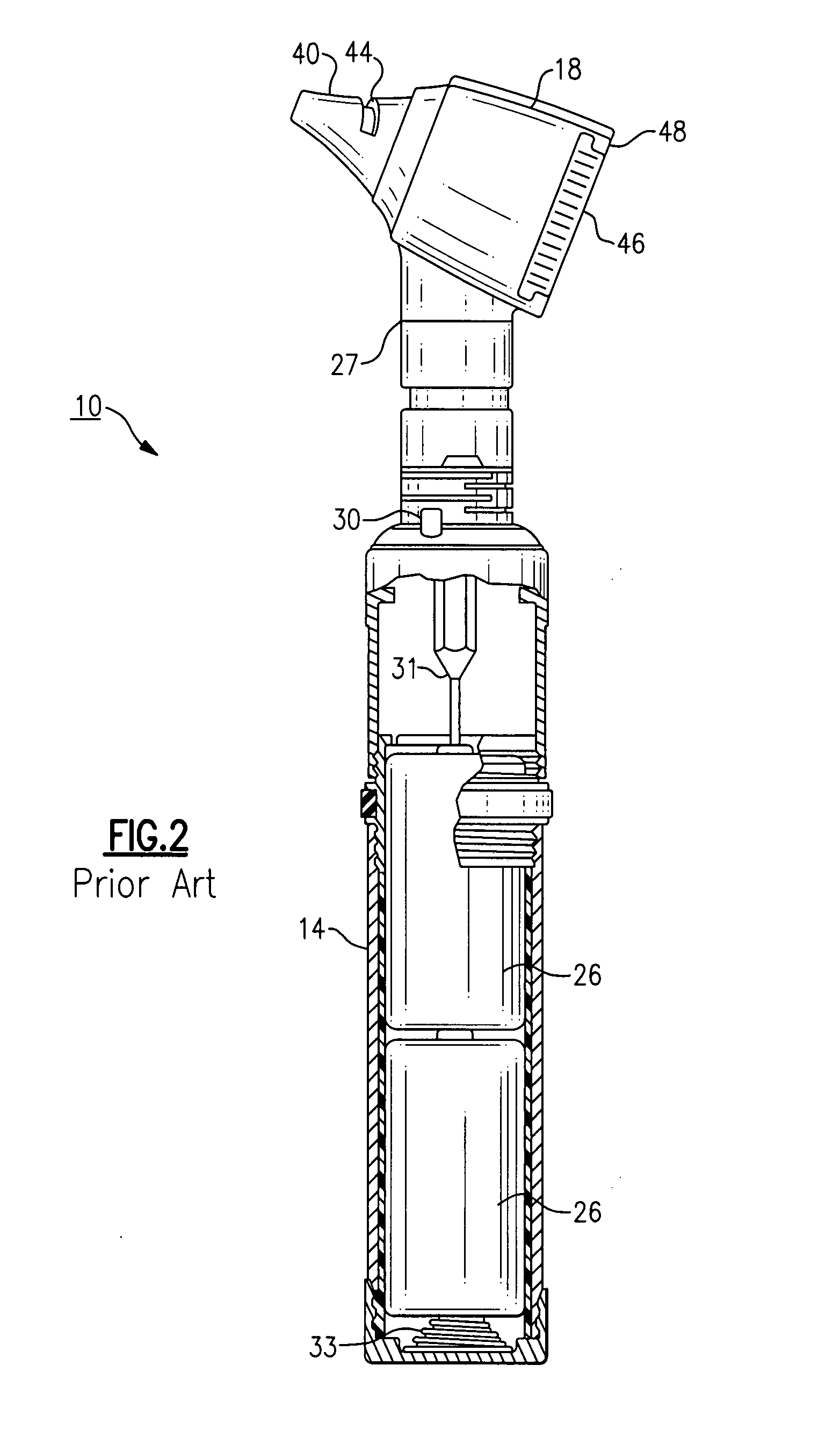
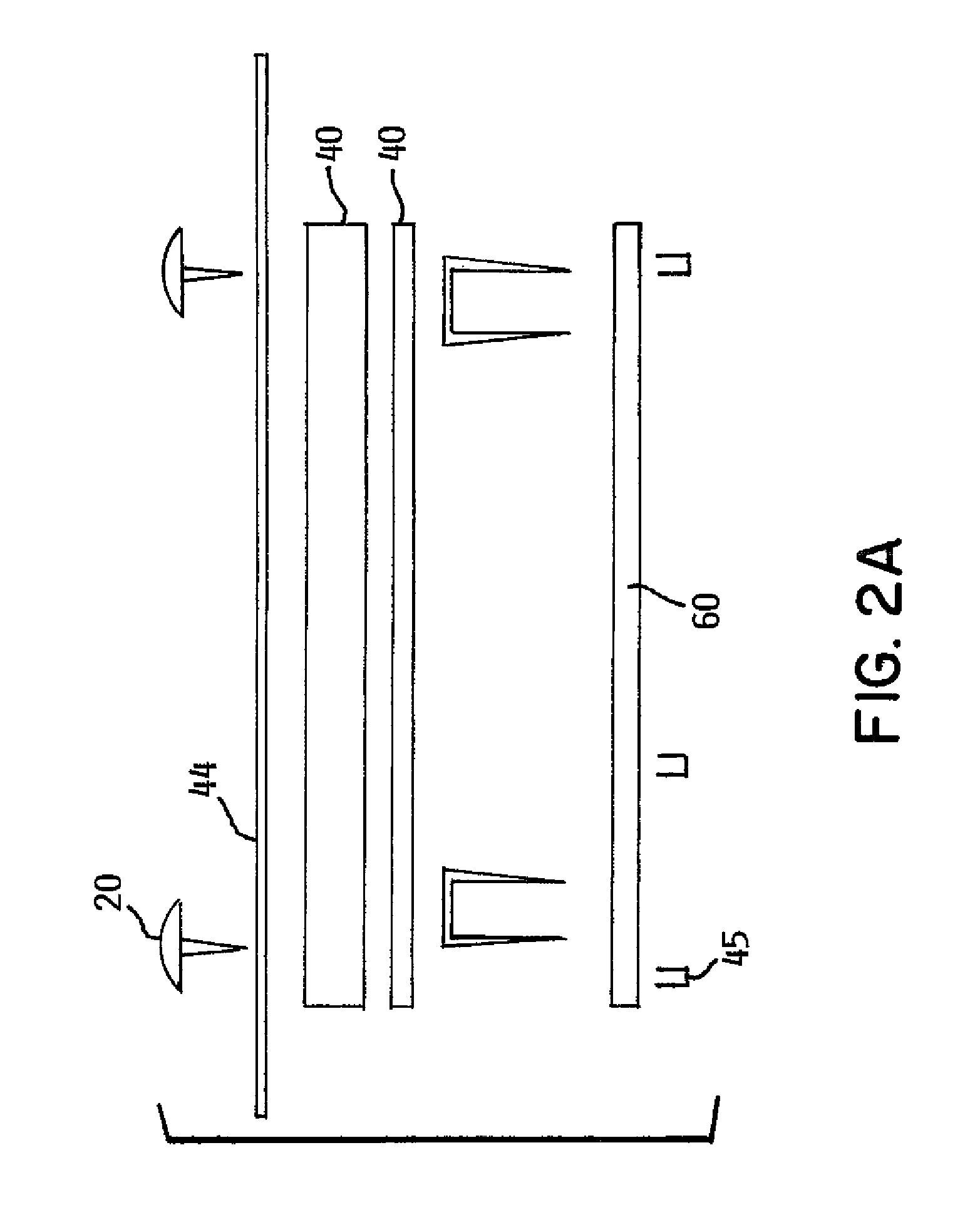
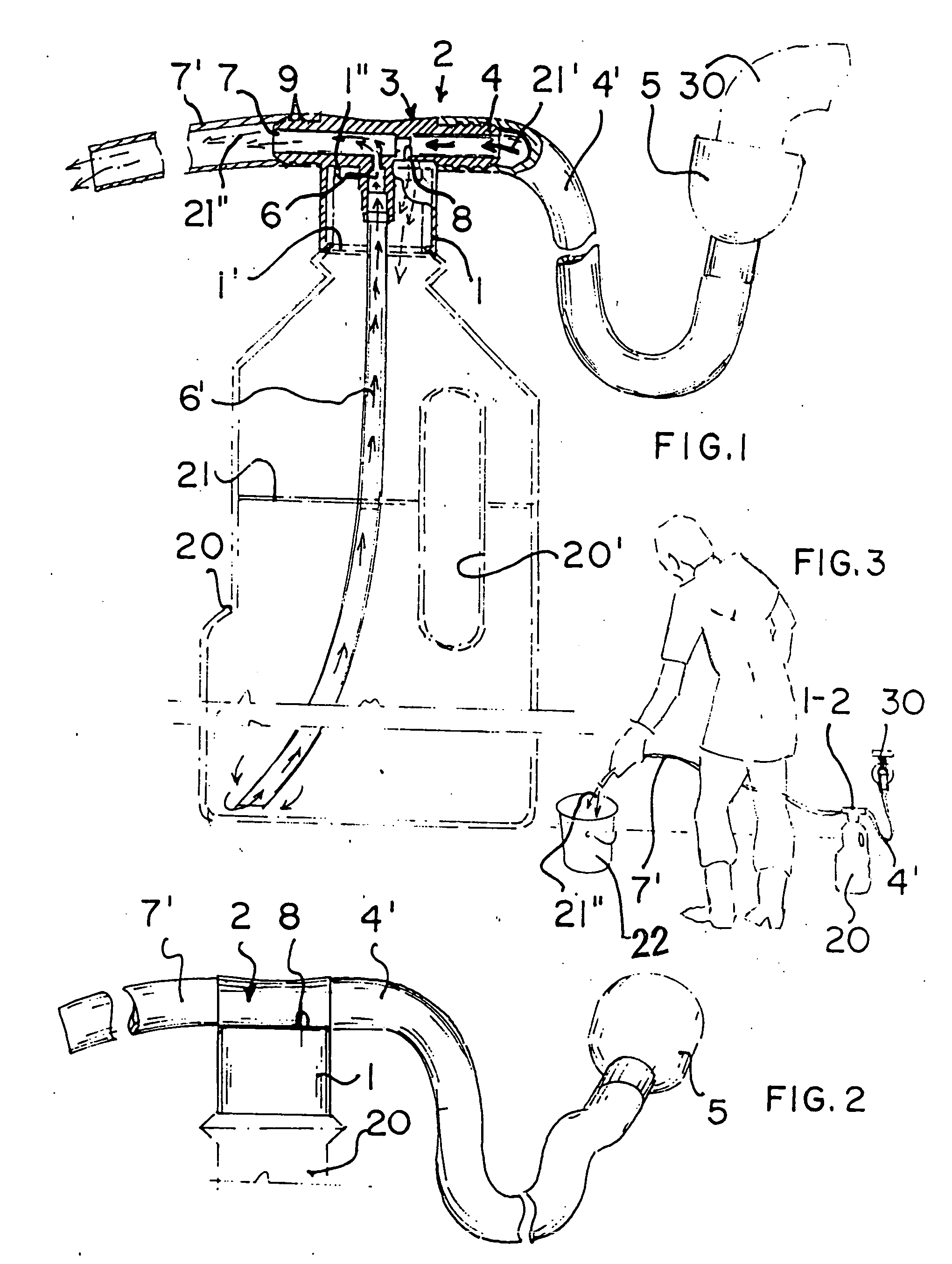
Electrical adapter for medical diagnostic instruments using LEDs as illumination sources
ActiveUS7276025B2Impacting costProlong lifeBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEngineeringDiagnostic instrument
An adapter for permitting a medical diagnostic instrument having an illumination source including at least one LED (light emitting diode) to be used with a power supply normally configured for use with a diagnostic instrument having at least one incandescent lamp as an illumination source. The adapter includes circuitry for compensating LED specific characteristics for permitting the power supply to be used with the LED.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
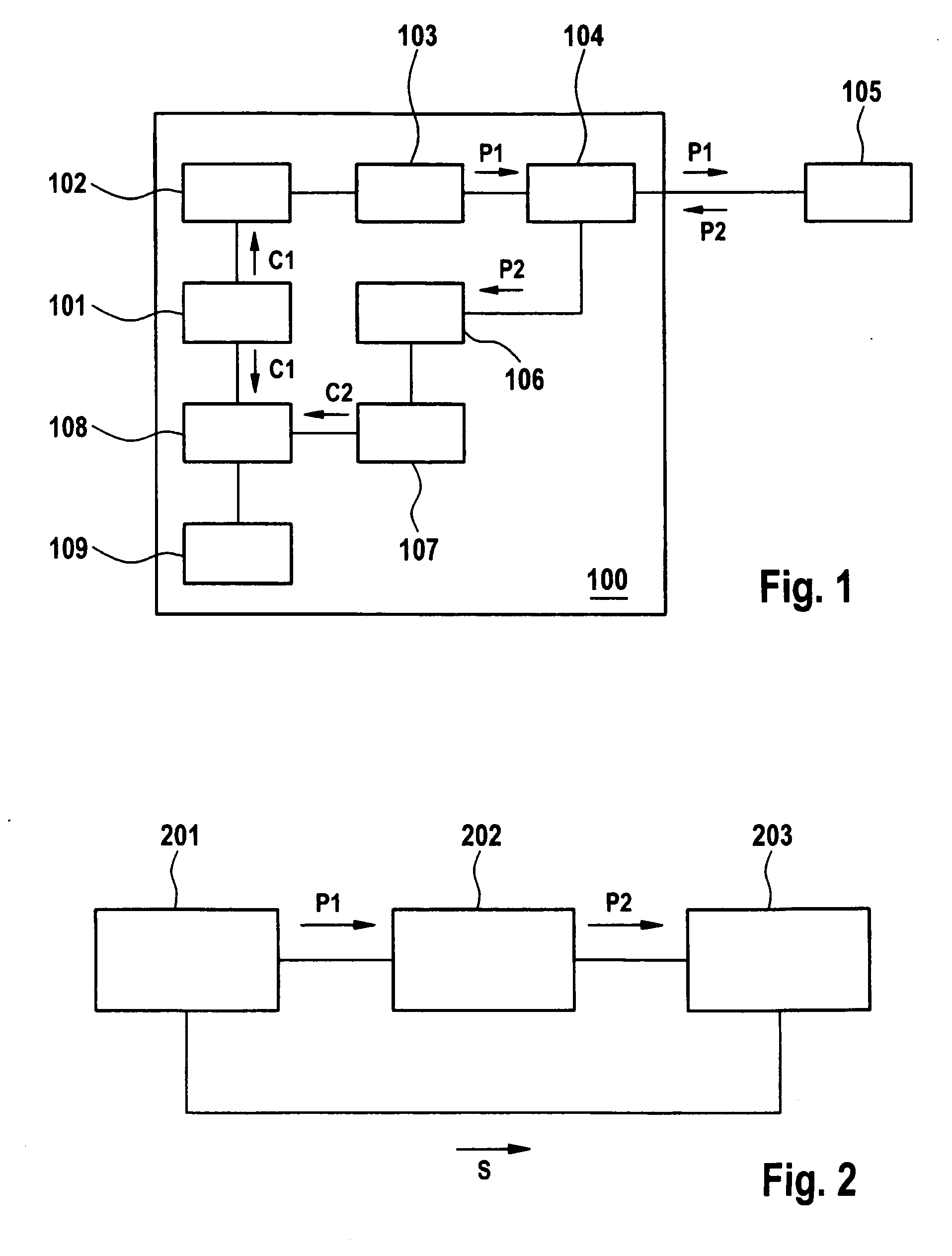
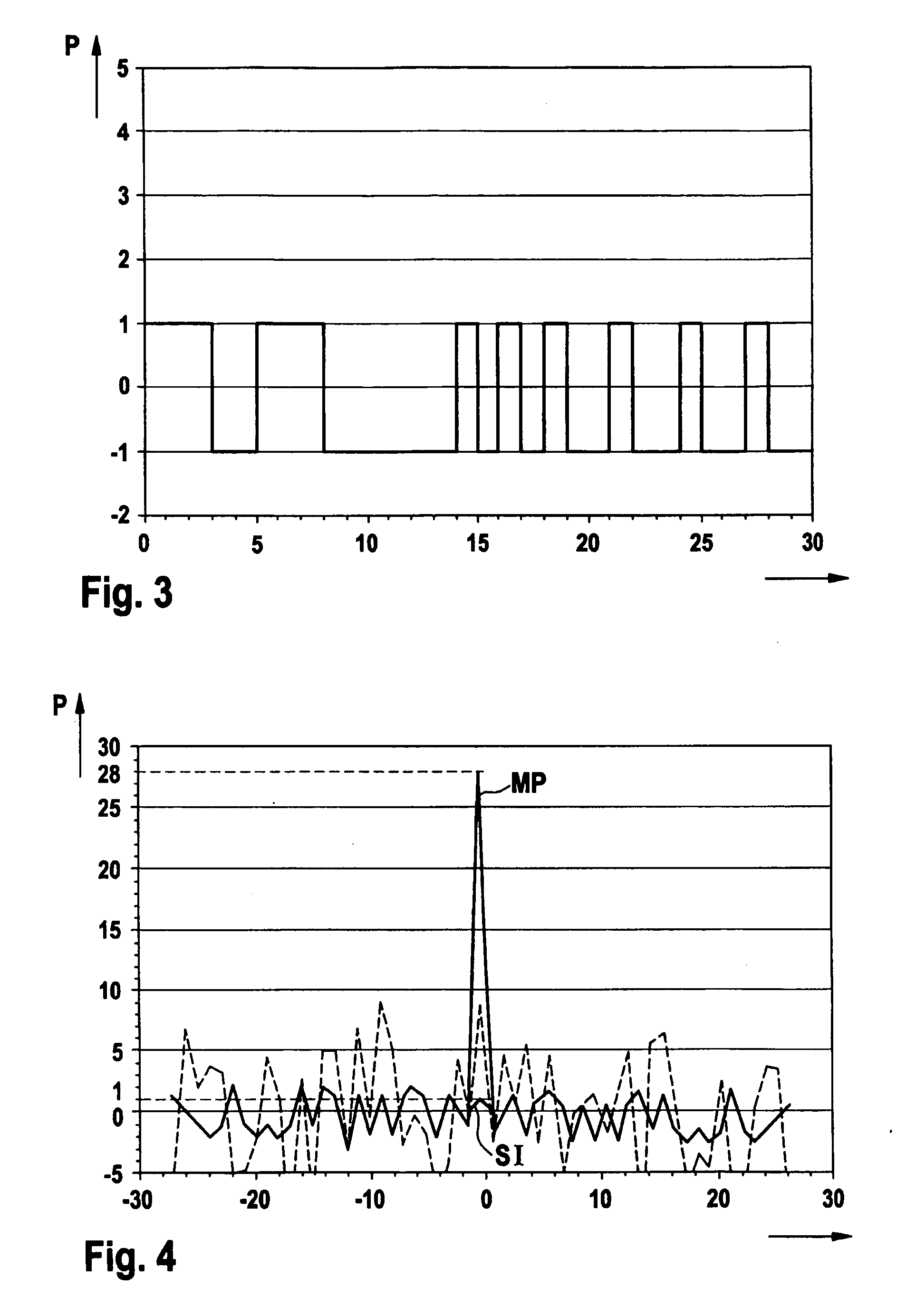
Time-of-flight measurement using pulse sequences
InactiveUS20060227315A1Accurate identificationEasy to processOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementCorrelation functionPulse sequence
A method for determining the time-of-flight of a device under test, wherein a return signal returning from the device under test in response to the probing signal comprising a sequence of pulses according to a first code sequence is detected and a second code sequence from the detected return signal is derived, and a correlation function is determined by correlating the first code sequence and the second code sequence, a main peak is identified, a time position of the main peak is determined and the time-of-flight is derived from the time position.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Electrical adapter for medical diagnostic instruments using replaceable LEDs as illumination sources
InactiveUS20070219417A1Extend lamp lifeReduce maintenanceBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesMedical treatmentInstrumentation
An LED for use with a medical diagnostic instrument having an adapter disposed between an instrument head and a hand-grippable handle, the LED being removably attachable in relation to the adapter in order to permit selective replacement of the LED, as needed. The LED is situated in order to provide mechanical and electrical interface with at least one of the adapter and the instrument, thereby enabling the adapter and the LED to convert the illumination source of the instrument selectively between an incandescent light source and the LED. The adapter matches a polarity between the LED and a power supply that is specifically intended for powering an incandescent light source.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
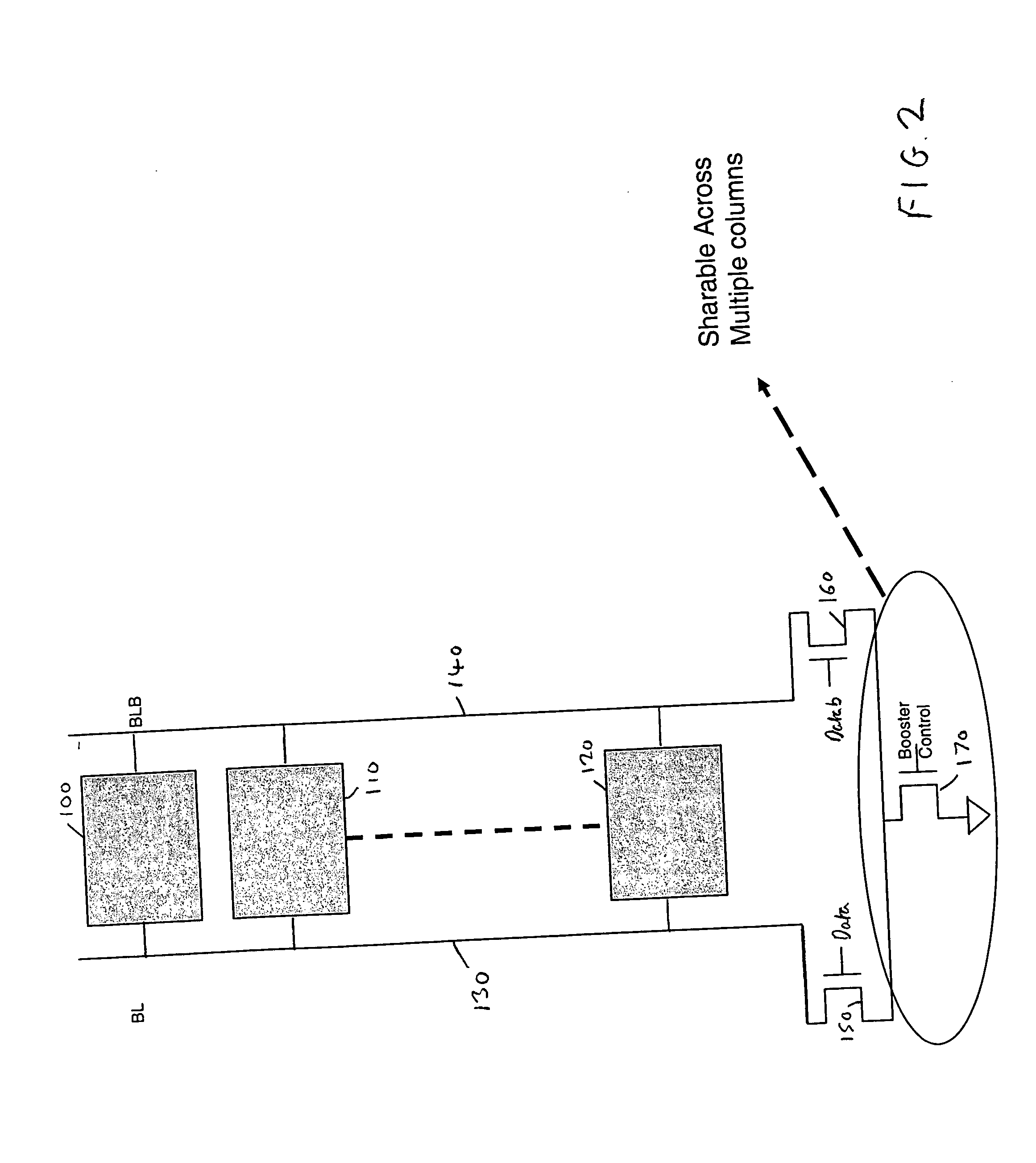
Memory device and method for performing write operations in such a memory device
A memory device and method of performing a write operation in such a memory device are provided. The memory device comprises a memory array having a plurality of memory cells, and a plurality of word lines and a plurality of bit lines via which the plurality of memory cells are accessed. Write driver circuitry is responsive to a write request to write data into at least one memory cell during a programming interval by altering voltage on at least one of the bit lines connected to that at least one memory cell whilst one of the word lines connected to the at least one memory cell is selected, to cause a value indicative of the data to be stored in the at least one memory cell. At a start of the programming interval the at least one bit line is at a first voltage, and the write driver circuitry comprises first coupling circuitry responsive to the write request to couple the at least one bit line to a second voltage to cause the voltage on that at least one bit line to transition towards the second voltage. The first and second voltages represent the operating voltages of the memory cells. Further, additional coupling circuitry is provided which is triggered at a predetermined time during the programming interval to cause the at least one bit line to transition beyond the second voltage towards a third voltage. It has been found that such an approach significantly improves the writeability of memory cells within a memory device arranged to operate at low supply voltages.
Owner:ARM LTD
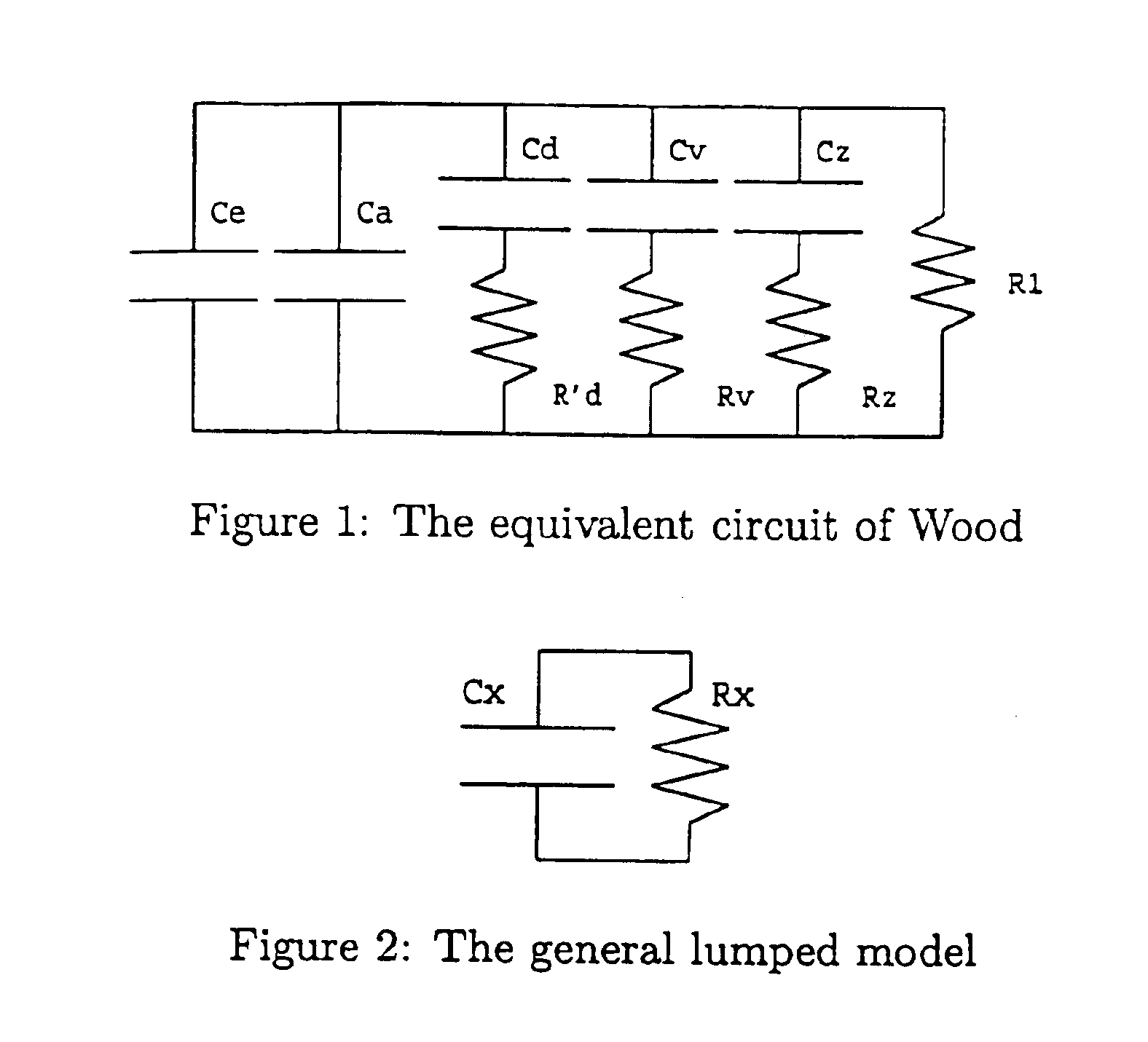
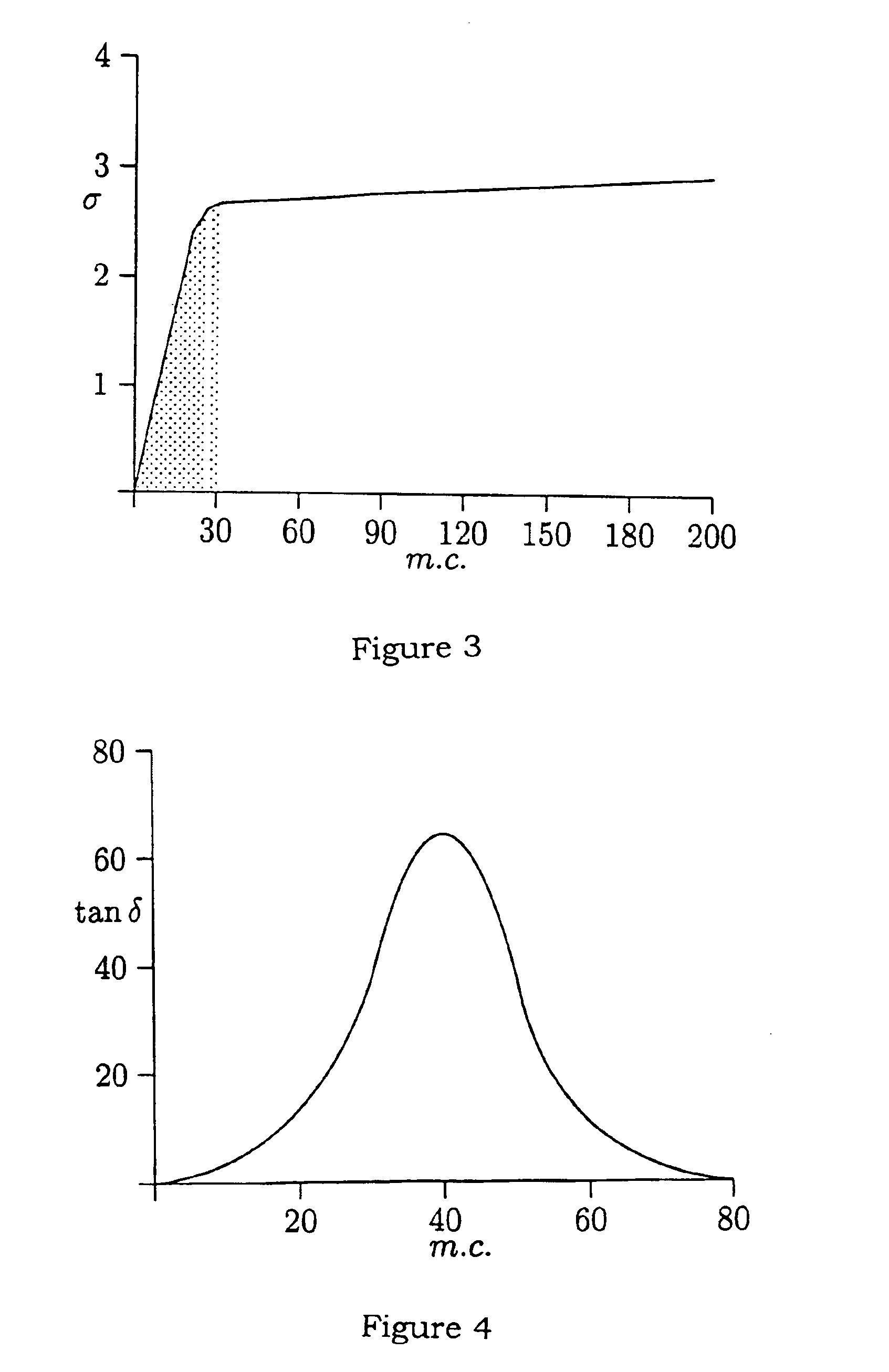
Determining the dielectric properties of wood
InactiveUS6989678B2Dependent on conductivityReduce conductivityResistance/reactance/impedenceWood testingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A wood drying installation for a wood drying kiln including a pair of electrodes adapted to be inserted into a wood stack contained in the kiln, a resistance connected in a series circuit with the electrodes, an AC voltage source connected to apply an AC voltage across the series circuit, a phase detecting circuit connected to the series circuit operable to generate a signal representing the phase angle between AC voltages applied to different parts of the series circuit, and a processor to receive the signal. The system is operable to determine a moisture value corresponding to a capacitive component of the reactive impedance between the electrodes in accordance with a predetermined arithmetic algorithm relating the value to the phase angle.
Owner:VENTER LIEBRECHT +1
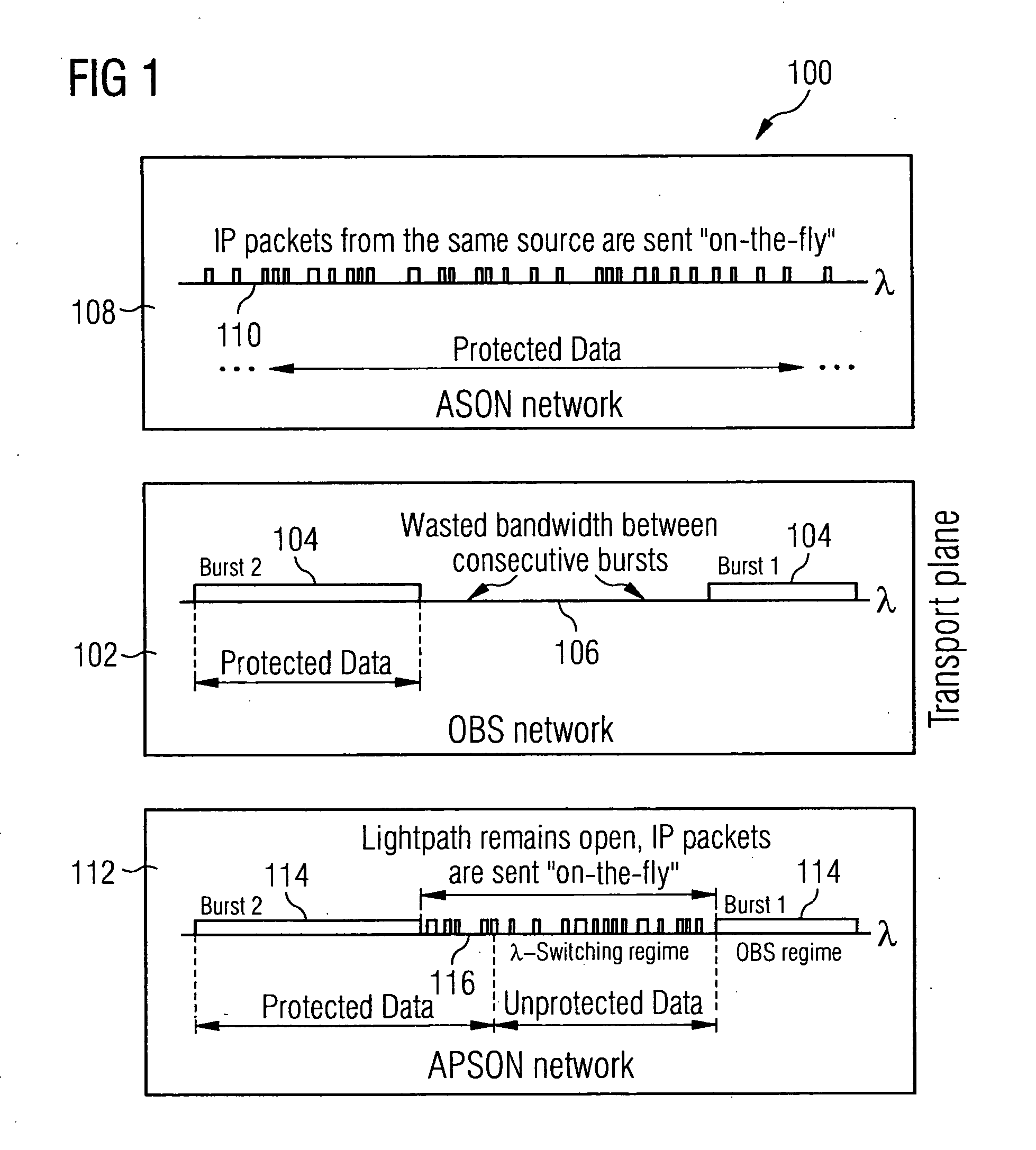
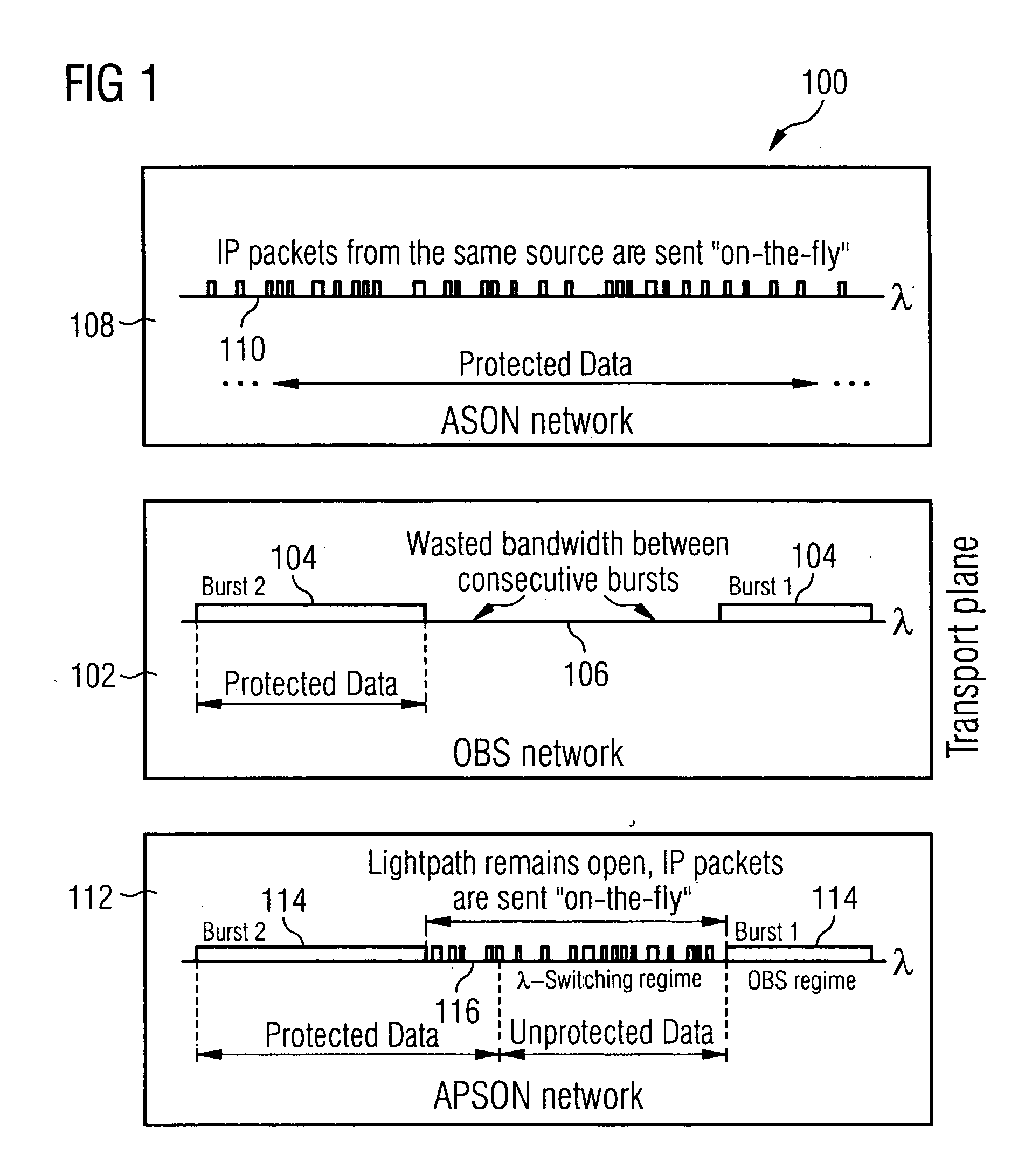
Ring network for a burst switching network with distributed management
InactiveUS20060104296A1Reduce in quantityImpacting costMultiplex system selection arrangementsLoop networksNetwork packetRing network
Transmitting data in a ring network that transmits bursts and data packets. A path setup message is sent to request a data transmission between a source node and a destination node j through intermediate nodes connecting the source node and the destination node j. Each intermediate node determines that a connection to a next node along the path is available when the connection to the next node, that normally transmits bursts and data packets, transmits data packets. A current data transmission of data packets on the path is stopped when the entire path is determined to be available.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
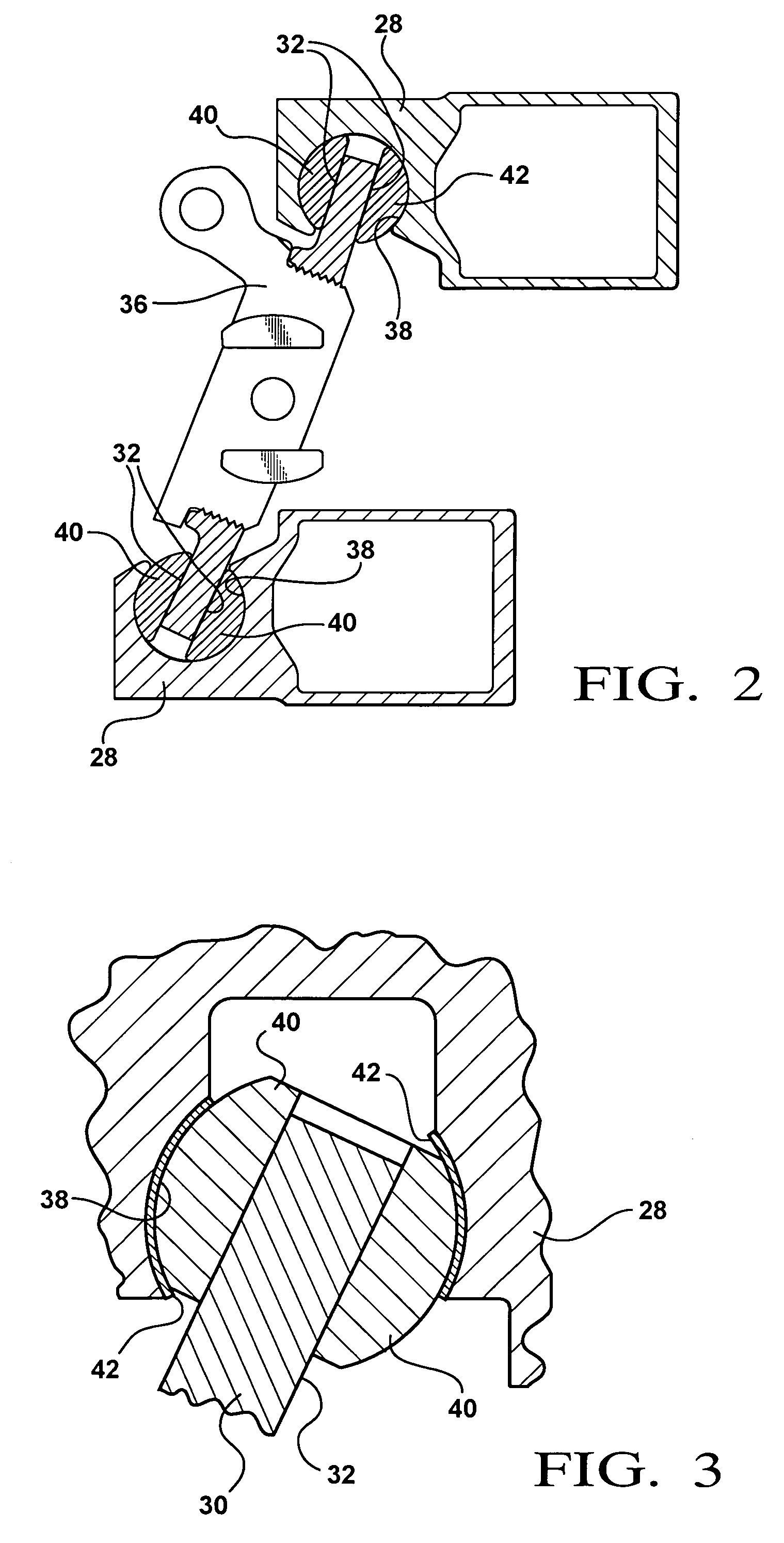
Bone Compression and Distraction System
ActiveUS20110172662A1Improve impactEasy to processInternal osteosythesisInvalid friendly devicesDistractionIliac screw
A bone compression and distraction system which has an apparatus and a plurality of pins. The apparatus includes a body, a worm screw and a pair of pin attachment members. The worm screw is placed in the body and the pin attachment members are coupled to the worm screw, and constrained from rotation relative to the worm screw, wherein the worm screw has opposing threads extending away from a central region. Upon rotation of the worm screw, the pin attachment members travel in opposite directions, either toward each other or away from each other to either decrease or increase the spacing therebetween. A pin may be coupled to each of the pin attachment members.
Owner:LITHOS SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Memory device and method for performing write operations in such a memory device
A memory device and method of performing a write operation in such a memory device are provided. The memory device comprises a memory array having a plurality of memory cells, and a plurality of word lines and a plurality of bit lines via which the plurality of memory cells are accessed. Write driver circuitry is responsive to a write request to write data into at least one memory cell during a programming interval by altering voltage on at least one of the bit lines connected to that at least one memory cell while one of the word lines connected to the at least one memory cell is selected, to cause a value indicative of the data to be stored in the at least one memory cell. At a start of the programming interval the at least one bit line is at a first voltage, and the write driver circuitry comprises first coupling circuitry responsive to the write request to couple the at least one bit line to a second voltage to cause the voltage on that at least one bit line to transition towards the second voltage. The first and second voltages represent the operating voltages of the memory cells. Further, additional coupling circuitry is provided which is triggered at a predetermined time during the programming interval to cause the at least one bit line to transition beyond the second voltage towards a third voltage. It has been found that such an approach significantly improves the writeability of memory cells within a memory device arranged to operate at low supply voltages.
Owner:ARM LTD
Compressor piston ball pocket coating
ActiveUS20070157799A1High degreeMinimum VOC emissionPretreated surfacesEngine componentsCross-linkEpoxy
The invention is applied to a compressor assembly wherein a coating is applied to the pocket in the piston for sliding engagement with a shoe for reciprocating the piston. The coating is a composite of solid particles of a lubricant, suspended in an adhesive, bonded to the to the aluminum alloy defining the pocket. More specifically, the coating comprises particles of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) suspended in an epoxy resin having a low cross-linking characteristic. The particles of PTFE are sub-micron in size and the ratio of PTFE to epoxy resin is optimally one to one. The thickness of the coating is between two and ten microns and preferably substantially four microns.
Owner:MAHLE INT GMBH
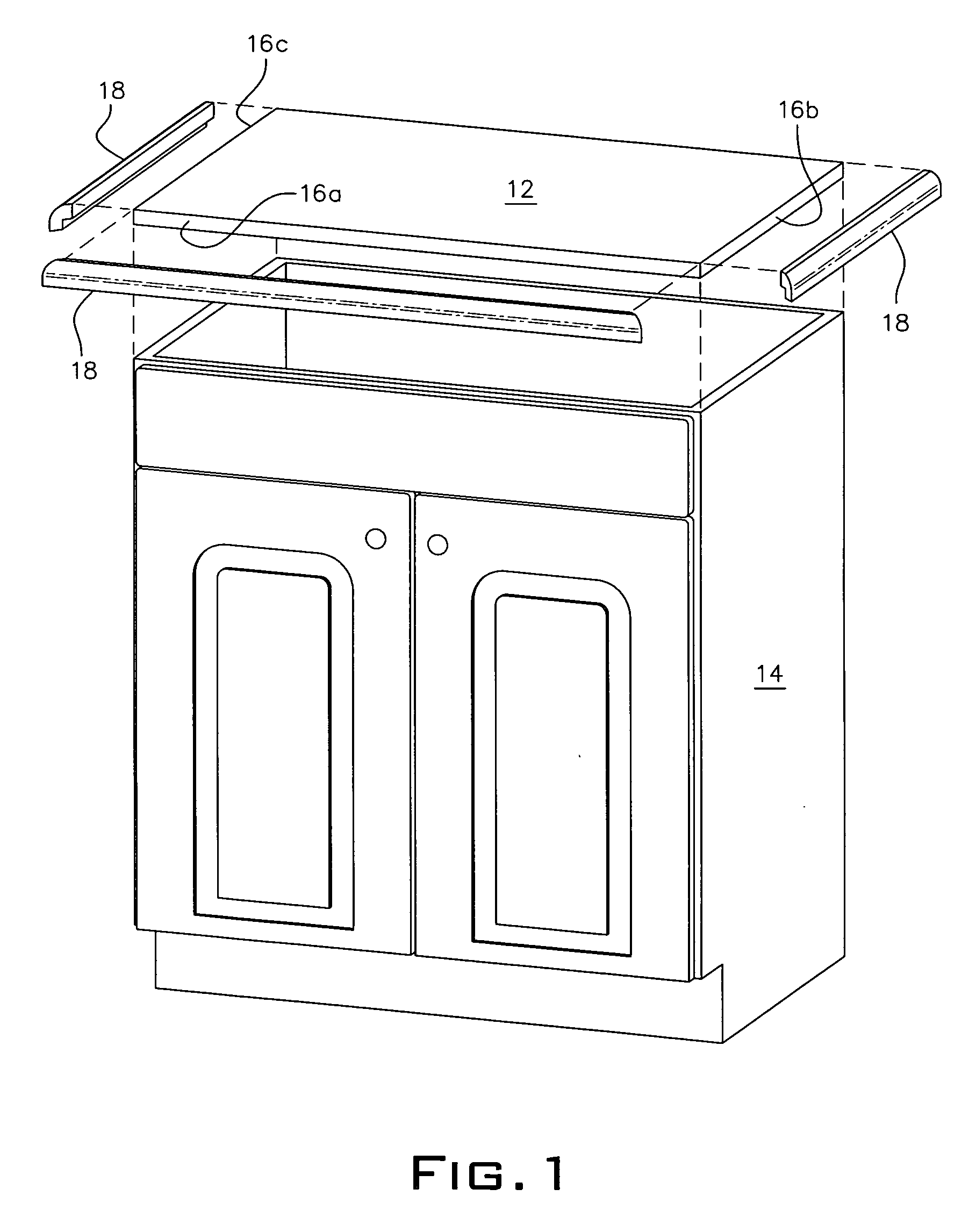
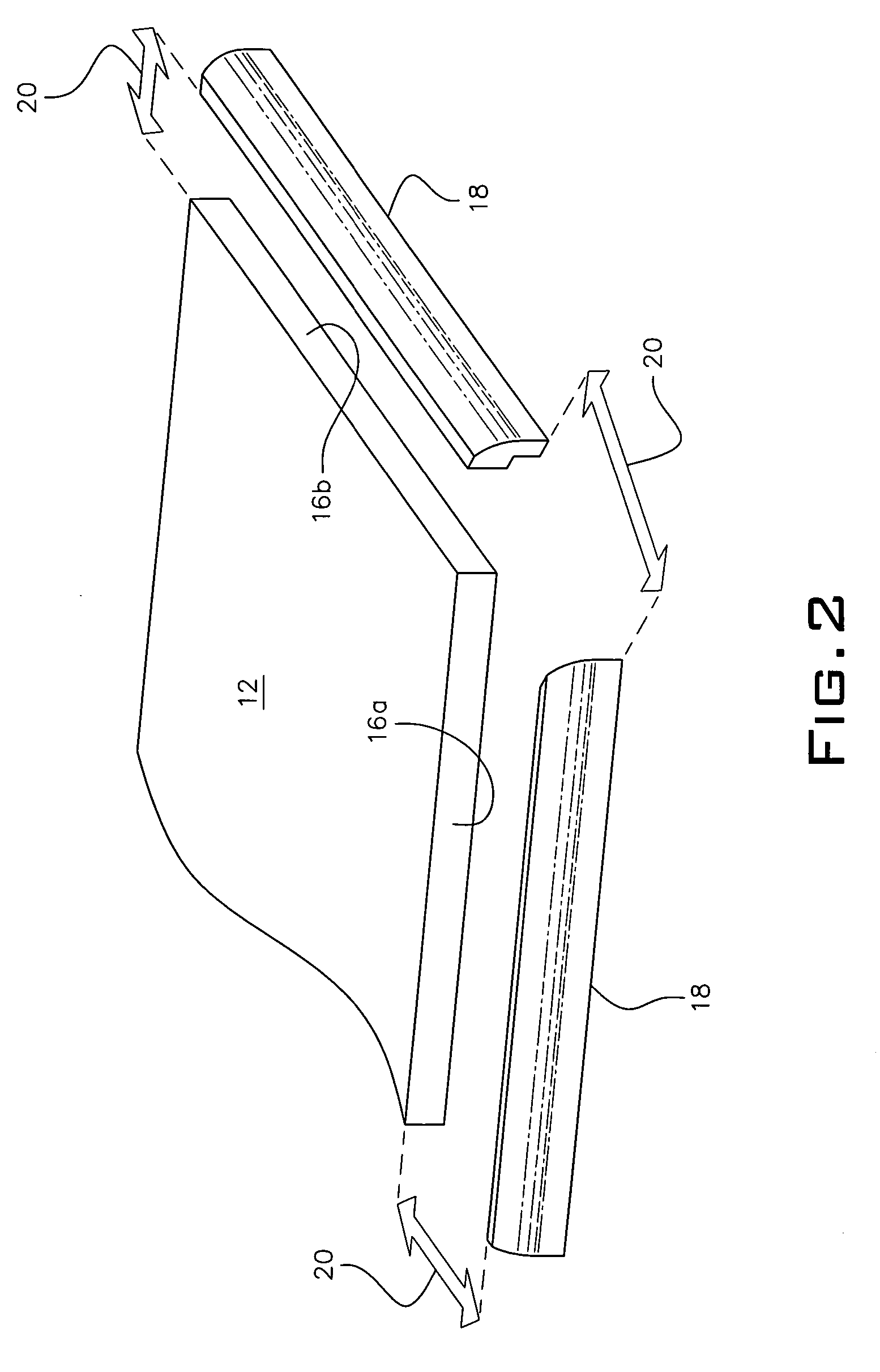
Furniture with decorative fasteners
ActiveUS8764115B2Efficiently and safely shippedEfficient and cost-effectiveUpholstery manufactureUpholstered panelsEngineeringUpholstered furniture
A method of assembling an upholstered furniture piece comprising decorative fasteners comprising providing an underlayment material layer, a foam material layer and a covering material layer. The foam material layer is positioned between the underlayment material layer and the covering material layer. The covering material layer extends beyond the underlayment material layer and the foam material layer. Fasteners are used to fasten the underlayment material layer, the foam material layer and the covering material layer together forming a layered component. A template may be used to guide positioning of the fasteners. The fasteners are decorative fasteners. Excess covering material that extends beyond the fasteners is stretched around the edges of the layered component and is affixed to a bottom surface of the layered component, thereby forming a layered assembly. The layered assembly is affixed to an upholstered furniture piece.
Owner:ASHLEY FURNITURE IND INC
Method for installation of natural stone surfaces
InactiveUS20070246145A1Cost reductionEasy to convertCovering/liningsLamination ancillary operationsStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
A method for installing natural stone surfaces is disclosed wherein the natural stone is provided with a thickness cut from its quarried block, which is between about ⅜ inch to about ⅝ inch thick. It is sized so that an installer can handle and install the natural stone surface on the job site without the use of an off-site fabrication shop. When the natural stone surface needs to be cut on the job site, the thickness allows an installer to make the cuts using a wet or dry rotary saw, as appropriate. Desired cut edges are then polished to a desired finish. Where desired, a natural stone prefabricated edge is installed against edges of the natural stone surface. The prefabricated edge is adhesively applied to the natural stone surface edge using a resinous material. The seam is then polished as needed.
Owner:FEIERTAG DAVID
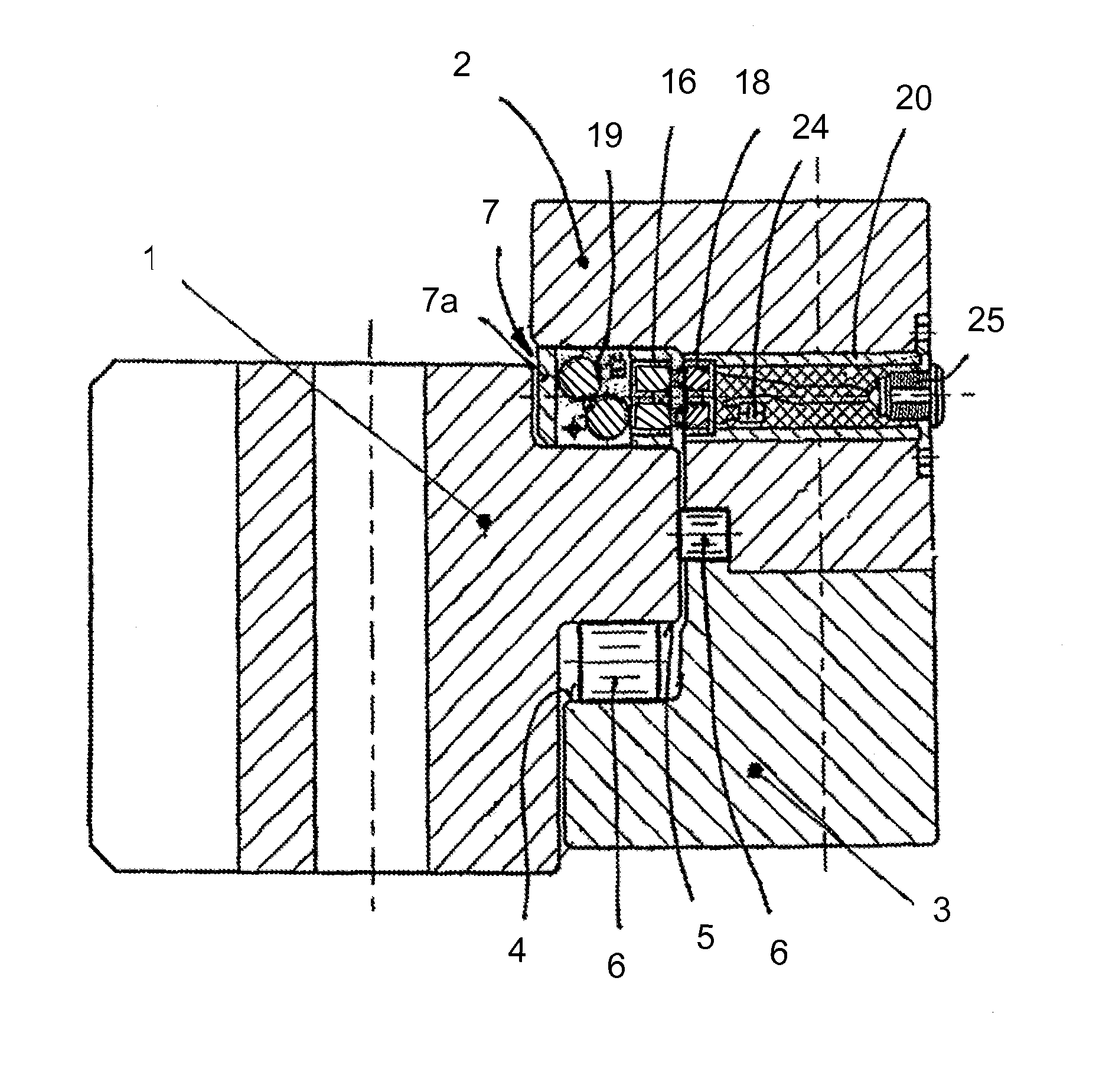
Device for detecting and monitoring damage to Anti-friction bearings
ActiveUS20100058868A1Reduce spendingLess costlyVibration measurement in solidsBatteries circuit arrangementsInductive transferEnergy source
The invention relates to a device for detecting and monitoring damage to races or adjacent regions of bearing rings (1, 2, 3) of anti-friction bearings. The device includes a measuring device, disposed in the anti-friction bearing chamber, having a sensor and structure for supplying sensor measurement data to the outside. The device has an energy source, which is also disposed in the anti-friction roller bearing chamber and which comprises a first coil (16) for the measuring device and a second coil (18) disposed outside the anti-friction bearing chamber and destined for inductive transfer of electrical energy to the first coil (16). The second coil (18) extends only over a part of the bearing circumference and the energy source comprises an energy accumulator (19) connected to the first coil (16).
Owner:ROTHE ERDE GMBH
Container for hot-filling
InactiveUS20100300043A1High crystallinitySlow downPackage sterilisationLarge containersBlow moldingEngineering
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing and hot-filling a PET container comprising the following steps:a) providing a PET preform capable of being blow molded;b) blow molding the preform in the cavity of a mold so as to form a container;c) removing the container from the mold cavity;d) filling the container with a liquid, the temperature of which is above 80° C.;e) sealing the container in a leaktight fashion;f) sterilizing and cooling the container; andg) shrinking the container,characterized in that:in step a) a PET preform composed of a copolymer based on terephthalic acid is used;in step a), at least one part of the preform is at a temperature greater than or equal to 110° C.;the temperature of the mold used in step b) is less than or equal to 65° C.; andduring step g) the container is heated for a duration between 1 and 5 seconds at a temperature between 600 and 1000° C. in at least one part of the container so as to create a shrinkage and a reduction in the volume of the container.The invention also relates to a container obtained using the process described above.
Owner:AISAPACK HLDG SA
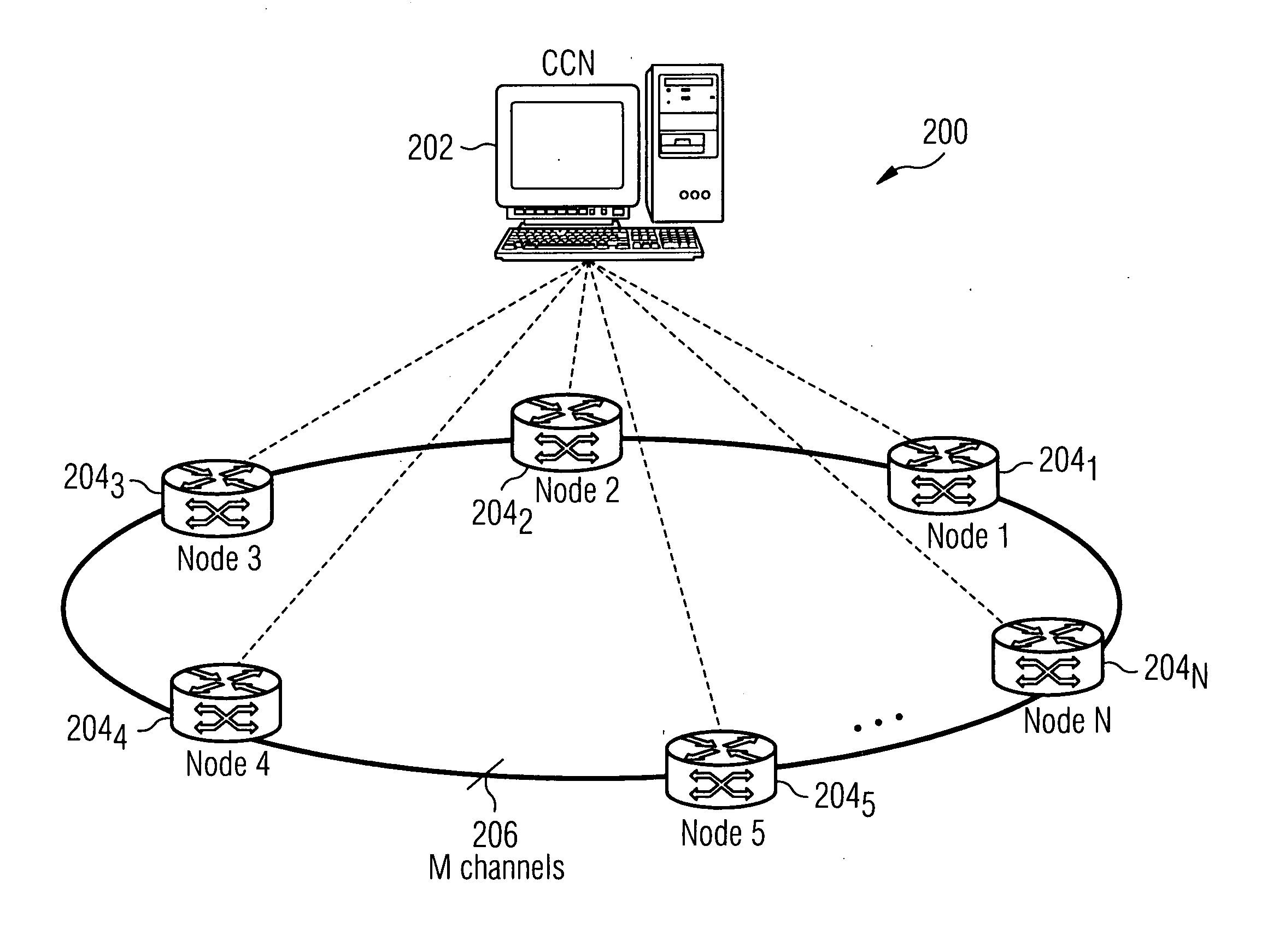
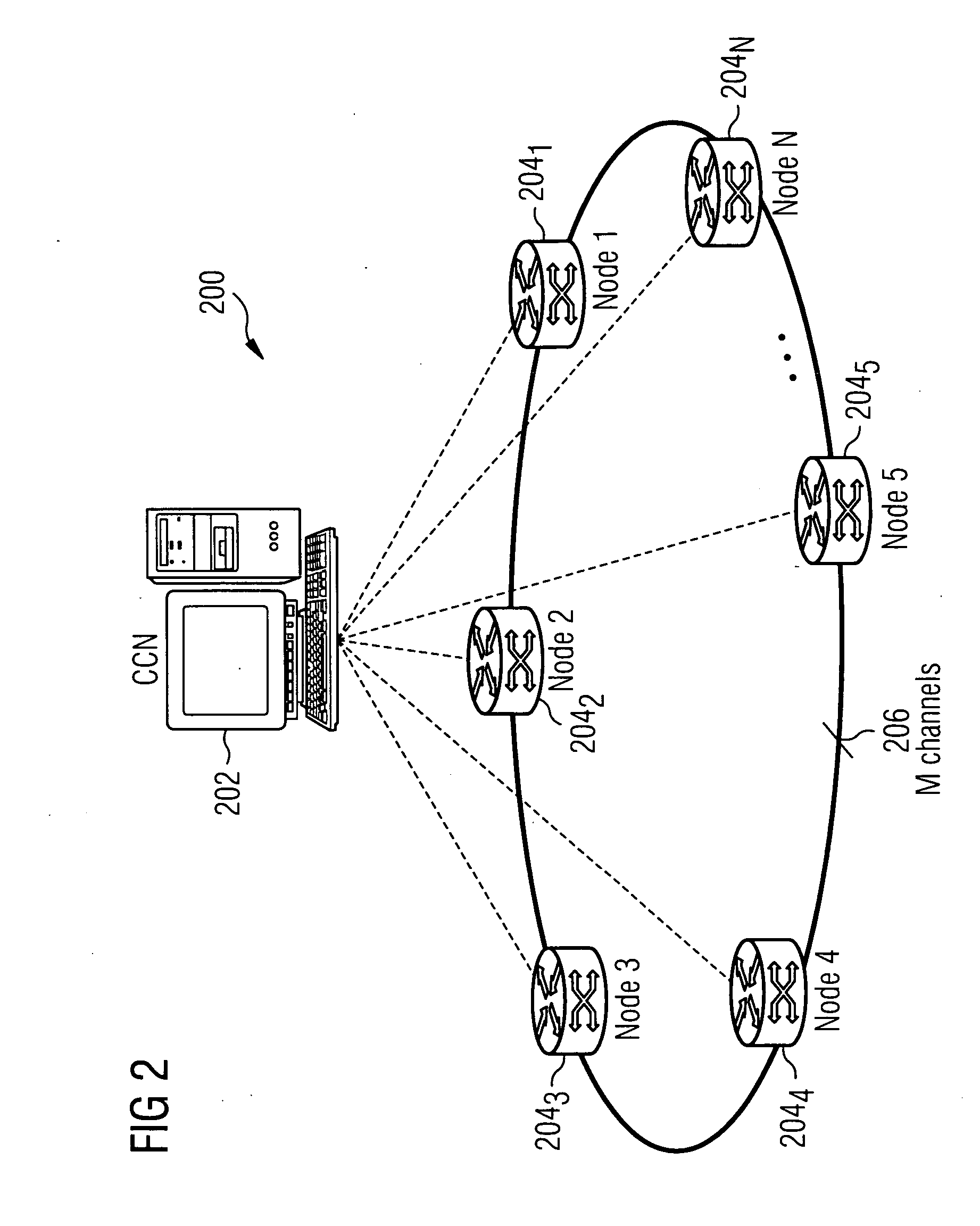
Ring network for a burst switching network with centralized management
InactiveUS20060109855A1Quick and easy deploymentAvoid excessive delayData switching by path configurationRing networkCentralized management
A ring network that transmits bursts and data packets is provided. In one embodiment, setup message is sent from a node i to a central node to set up communication between the node i and a node j. The central node stops a current transmission on a path between the node i and a node j that transmits bursts and data packets when the current transmission of the path transmits data packets. The central node ( establishes the communication between the node i and the node j along the path.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
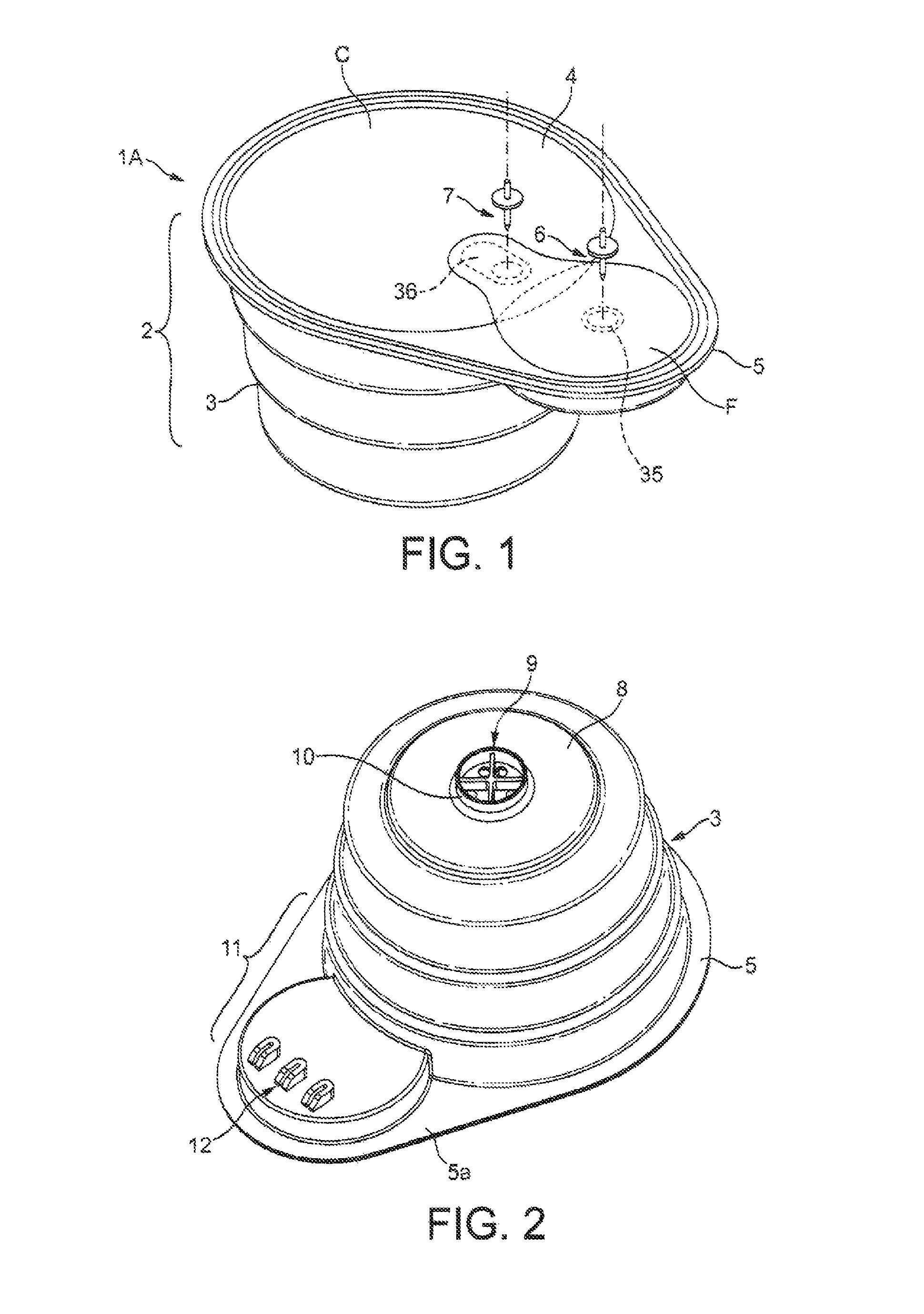
Capsule for preparing a nutritional product including a filter
InactiveUS8703219B2Impacting costHigh priceReady-for-oven doughsMembranesAdditive ingredientNutritional products
Capsule for the preparation of a nutritional product in a device adapted to supply liquid in the capsule, said capsule comprising: at least one compartment (13) containing nutritional ingredients for the preparation of the nutritional product in combination with the supplied liquid, a filter (18) adapted for removing contaminants contained in the liquid, wherein the filter (18, 20) has a filtering surface (F) smaller than the cross section (C) of the compartment and at least a part of its filtering surface (F) is preferably offset relative to the cross section (C) of the compartment when viewed in the axial projection of the capsule.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Device for detecting and monitoring damage to anti-friction bearings
ActiveUS8376622B2Reduce spendingLess costlyBatteries circuit arrangementsRolling contact bearingsMeasurement deviceInductive transfer
The invention relates to a device for detecting and monitoring damage to races or adjacent regions of bearing rings (1, 2, 3) of anti-friction bearings. The device includes a measuring device, disposed in the anti-friction bearing chamber, having a sensor and structure for supplying sensor measurement data to the outside. The device has an energy source, which is also disposed in the anti-friction roller bearing chamber and which comprises a first coil (16) for the measuring device and a second coil (18) disposed outside the anti-friction bearing chamber and destined for inductive transfer of electrical energy to the first coil (16). The second coil (18) extends only over a part of the bearing circumference and the energy source comprises an energy accumulator (19) connected to the first coil (16).
Owner:ROTHE ERDE GMBH
Device for mixing-dosing liquid cleaning product
InactiveUS20060109736A1Easily disposableThe material is lowFlow mixersRotary stirring mixersCouplingWater flow
A device for mixing-dosing liquid cleaning products with water or other carriers is disclosed. The device comprises a body with a cover, which is fixed and hermetically sealed to a flask containing a series of doses of liquid concentrated cleaning products diluted in the water in the act of use. A venturi is incorporated into the body with a cover and includes a water entry that receives a hose with the opposed end having easy coupling to a tap. An orthogonal hole is formed in the entry, with the hole opening in the interior of the flask and gauged to join the water flow with the appropriate quantity of the cleaning product. An exit is aligned to the entry and receives a dispenser hose of the cleaning solution already mixed
Owner:NETO CECILIO ANTONIO
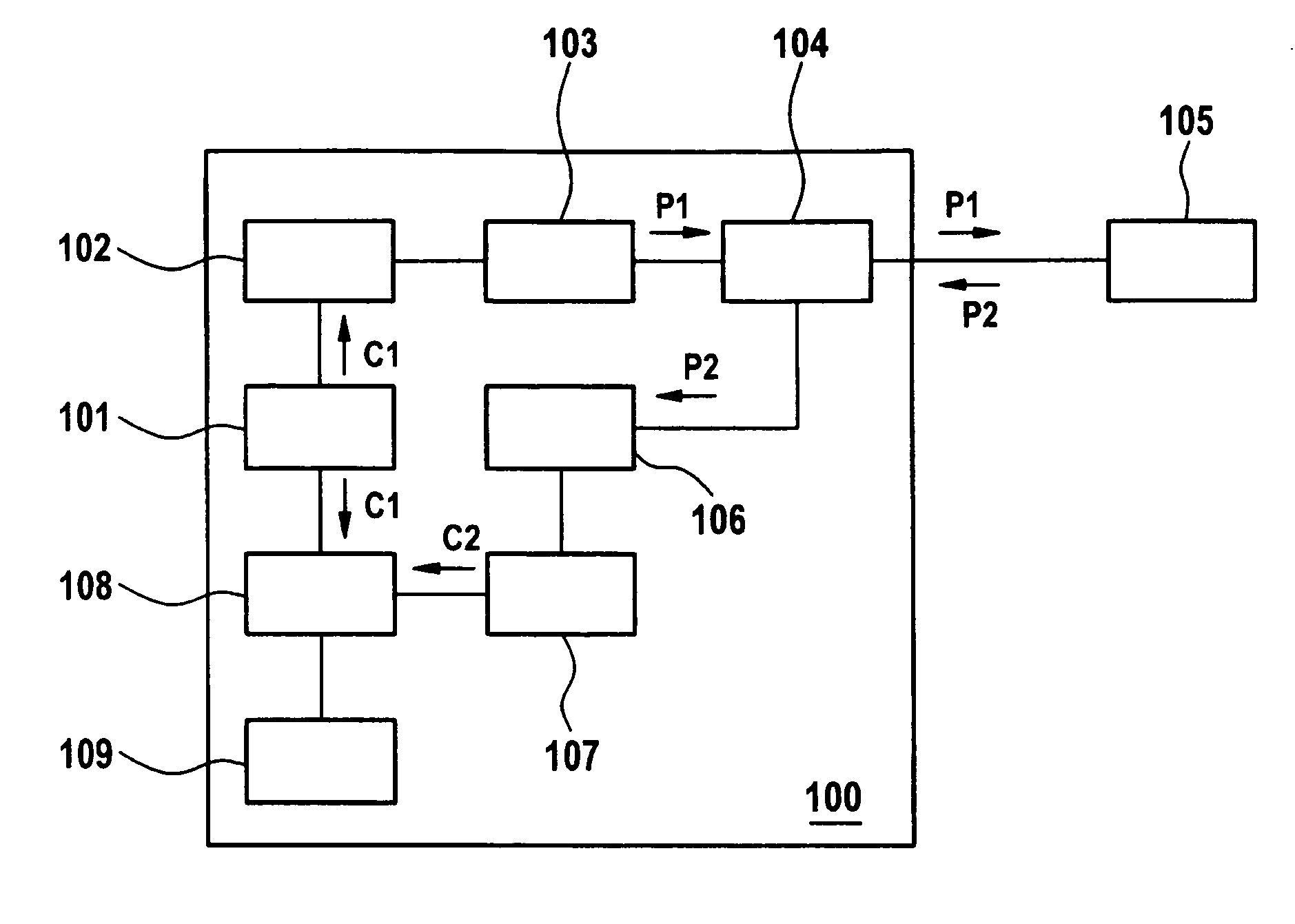
System and method for scheduling background synchronization of application data
InactiveUS20170188177A1Low costTime neededTelephonic communicationMobile application execution environmentsComputer moduleApplication software
A system (1) for scheduling background synchronization of application data (2) between a mobile communication device (3) and a cloud storage (4), comprising: a collecting unit (100) estimating the size of application data (2); a prediction unit (101) adapted to predict future locations (300) of the mobile communication device (3) at future times(301); a cost module (102) adapted to calculate a cost of transfer (5) at future times (301) and future locations(300); and a scheduler (103) adapted to schedule the background synchronization at a future time (311) based on cost of transfer (511).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Bone compression and distraction system
A bone compression and distraction system which has an apparatus and a plurality of pins. The apparatus includes a body, a worm screw and a pair of pin attachment members. The worm screw is placed in the body and the pin attachment members are coupled to the worm screw, and constrained from rotation relative to the worm screw, wherein the worm screw has opposing threads extending away from a central region. Upon rotation of the worm screw, the pin attachment members travel in opposite directions, either toward each other or away from each other to either decrease or increase the spacing therebetween. A pin may be coupled to each of the pin attachment members.
Owner:LITHOS SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Furniture with decorative fasteners
ActiveUS20080309145A1Efficiently and safely shippedEfficient and cost-effectiveUpholstery manufactureUpholstered panelsEngineeringUpholstered furniture
A method of assembling an upholstered furniture piece comprising decorative fasteners comprising providing an underlayment material layer, a foam material layer and a covering material layer. The foam material layer is positioned between the underlayment material layer and the covering material layer. The covering material layer extends beyond the underlayment material layer and the foam material layer. Fasteners are used to fasten the underlayment material layer, the foam material layer and the covering material layer together forming a layered component. A template may be used to guide positioning of the fasteners. The fasteners are decorative fasteners. Excess covering material that extends beyond the fasteners is stretched around the edges of the layered component and is affixed to a bottom surface of the layered component, thereby forming a layered assembly. The layered assembly is affixed to an upholstered furniture piece.
Owner:ASHLEY FURNITURE IND INC
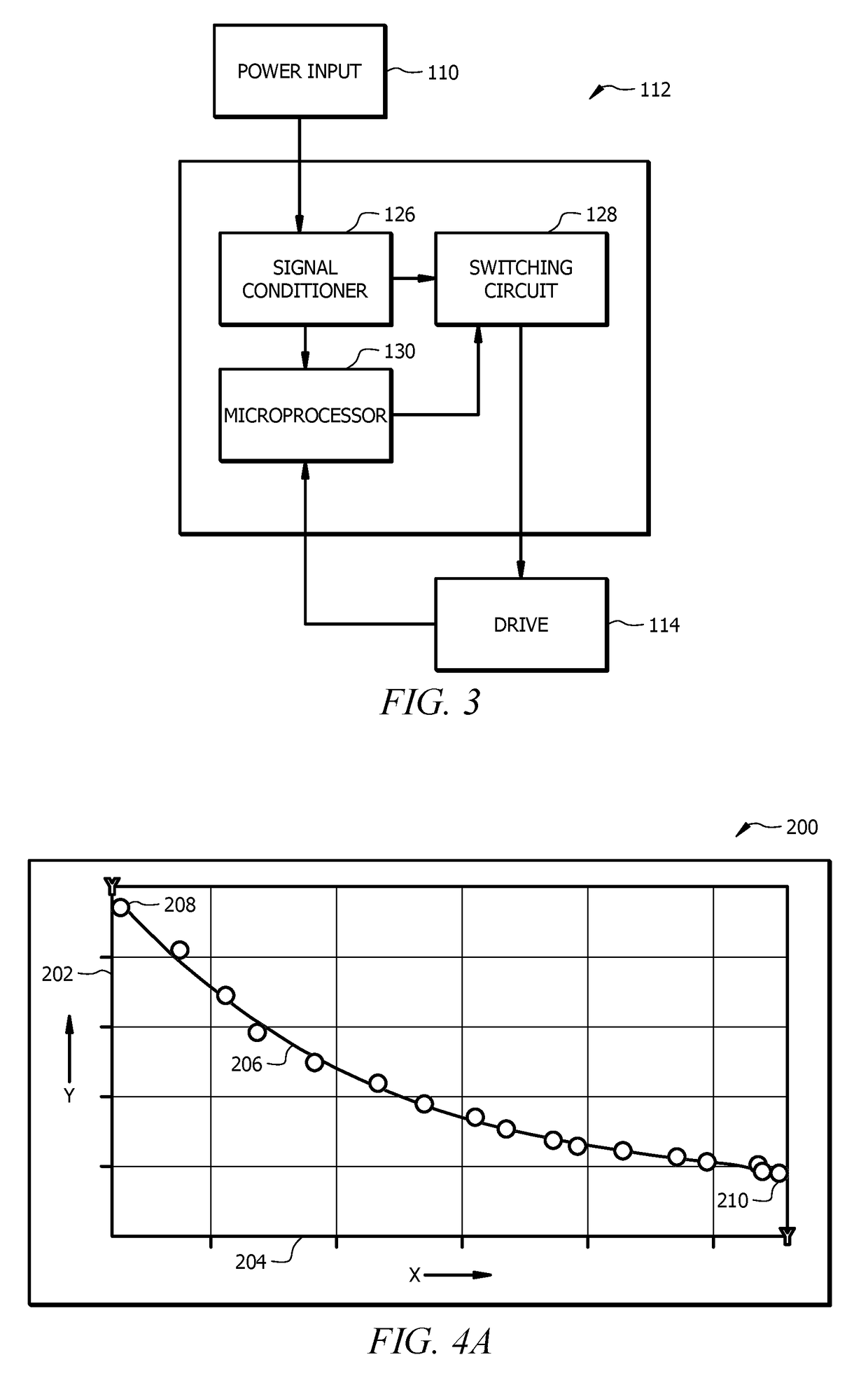
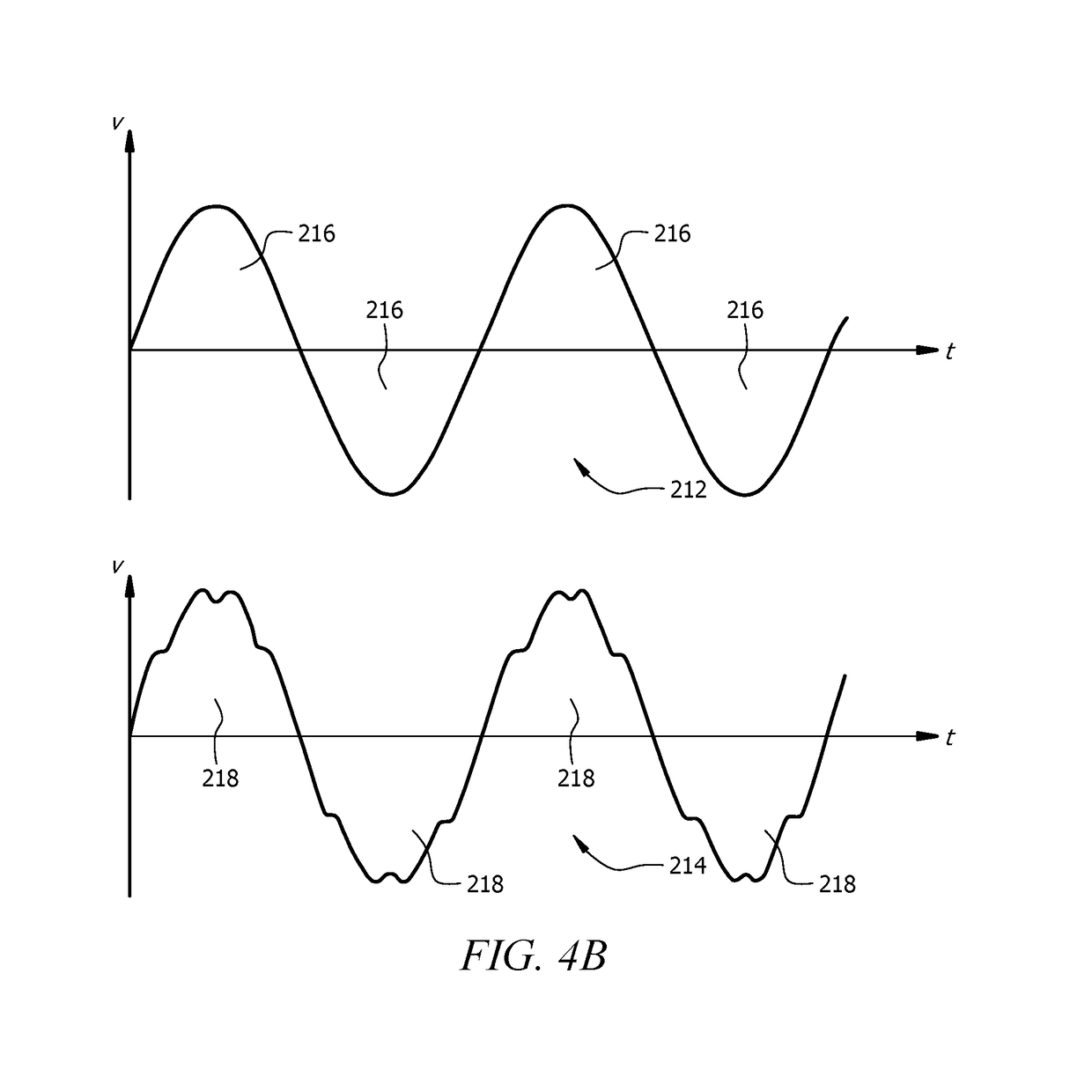
Dynamic Solenoid Drive Duty Cycle Adjustment
ActiveUS20190078565A1Minimize impactImprove efficiencyFluid parameterFlexible member pumpsComputer moduleEngineering
The performance of a solenoid drive liquid pump can be very dependent on the magnitude and stability of an input voltage, with non-ideal input power resulting in loss of efficiency and potential damage to the pump. Pulse width of drive signals provided to the pump, which cause solenoids to alternately energize to move liquid through the pump, may be adjusted in duration in order to compensate for non-ideal input voltage. A drive control module of the pump gathers voltage information, determines an improved pulse width based upon that voltage information, and then provides drive signals based upon the improved pulse width. Operating in this manner, a pump can operate at or near peak efficiency despite both significant variances in input voltage and non-sinusoidal input voltage, and without customized components or adapters.
Owner:MILTON ROY
Method and apparatus to supply water to a tank of an exhaust system provided with exhaust gas after-treatment for a combustion engine
ActiveUS20180258812A1Small impactEasy to implementInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustionWater volume
An exhaust system provided with exhaust gas after-treatment for a combustion engine comprising an exhaust pipe and a pumping device, which is buried inside the tank, from which it draws so as to feed a water solution of urea under pressure to an electromagnetic injector; the tank is supplied with urea powder and water, which are mixed on the inside so as to obtain a water solution of urea with a variable concentration; and a water supply circuit to supply water to the tank, which is provided with a first pipe, which draws the water from a basin and is regulated by a first valve, which allows water to be introduced into the tank, if necessary, or to be drained to the surrounding environment when the water quantity already contained in the tank is sufficient.
Owner:MARELLI EURO SPA
Burner for dryers and process of manufacturing said burner
InactiveUS20110179666A1Reducing and facilitating assembling operationManufactureMetal-working apparatusDrying chambers/containersFuel gasNozzle
A burner for dryers that includes a tubular element having at least a funnel-shaped region tapering toward an inlet end for fuel gas and combustion air to form a gas / air mixing venturi tube, and an opposite having an outlet nozzle for said mixture. According to the invention, the burner body is made of two half shells tightly joined together along corresponding mutually coupling longitudinal flanges, which, once coupled together, form two opposite perimetrical longitudinal edges The burner body has a substantially rectangular plan shape with two longitudinal edges that are parallel substantially for the entire length of the burner body. The invention relates also to a process for manufacturing said burner.
Owner:CASTFUTURA
Compressor piston ball pocket coating
Owner:MAHLE INT GMBH
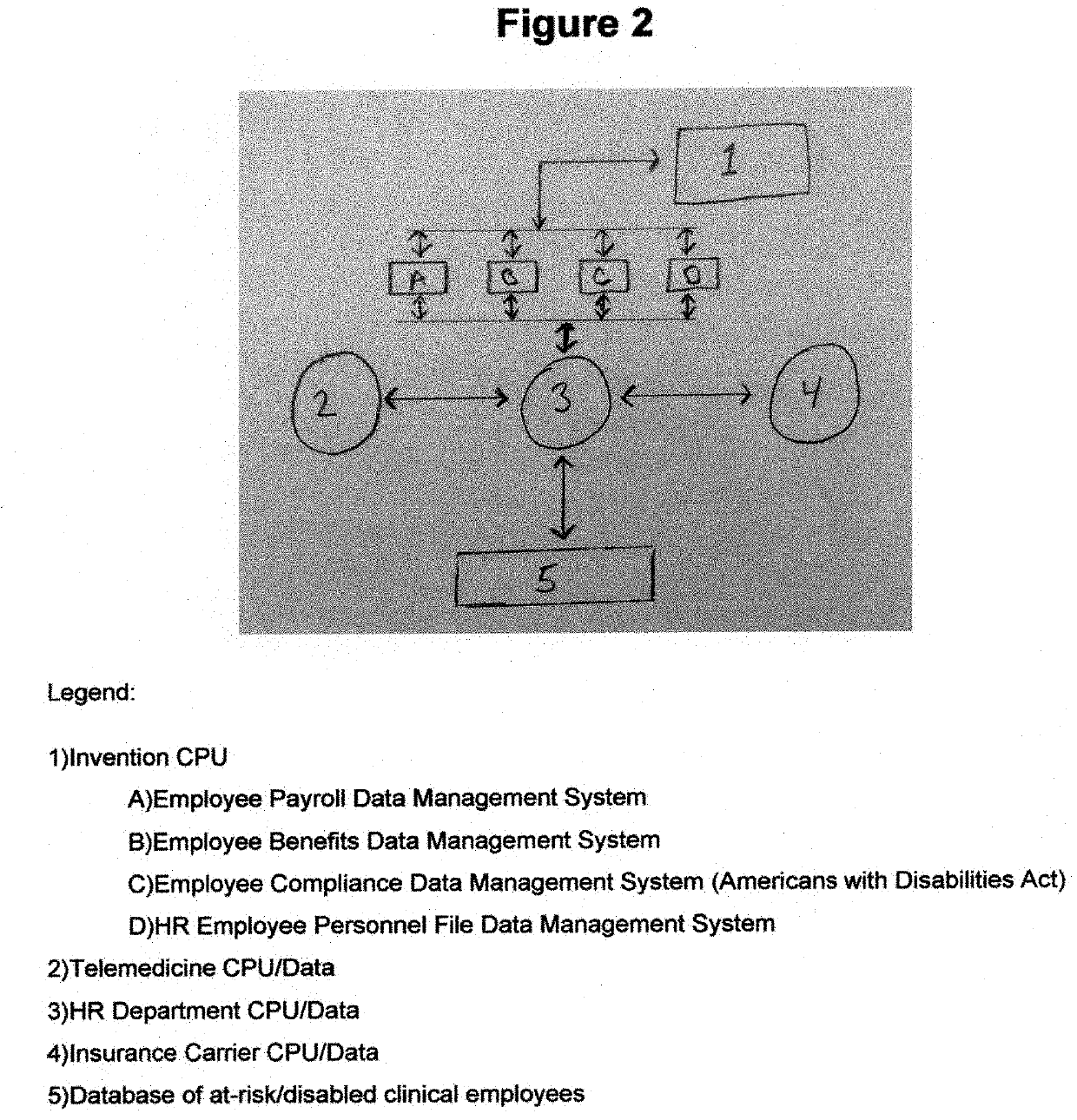
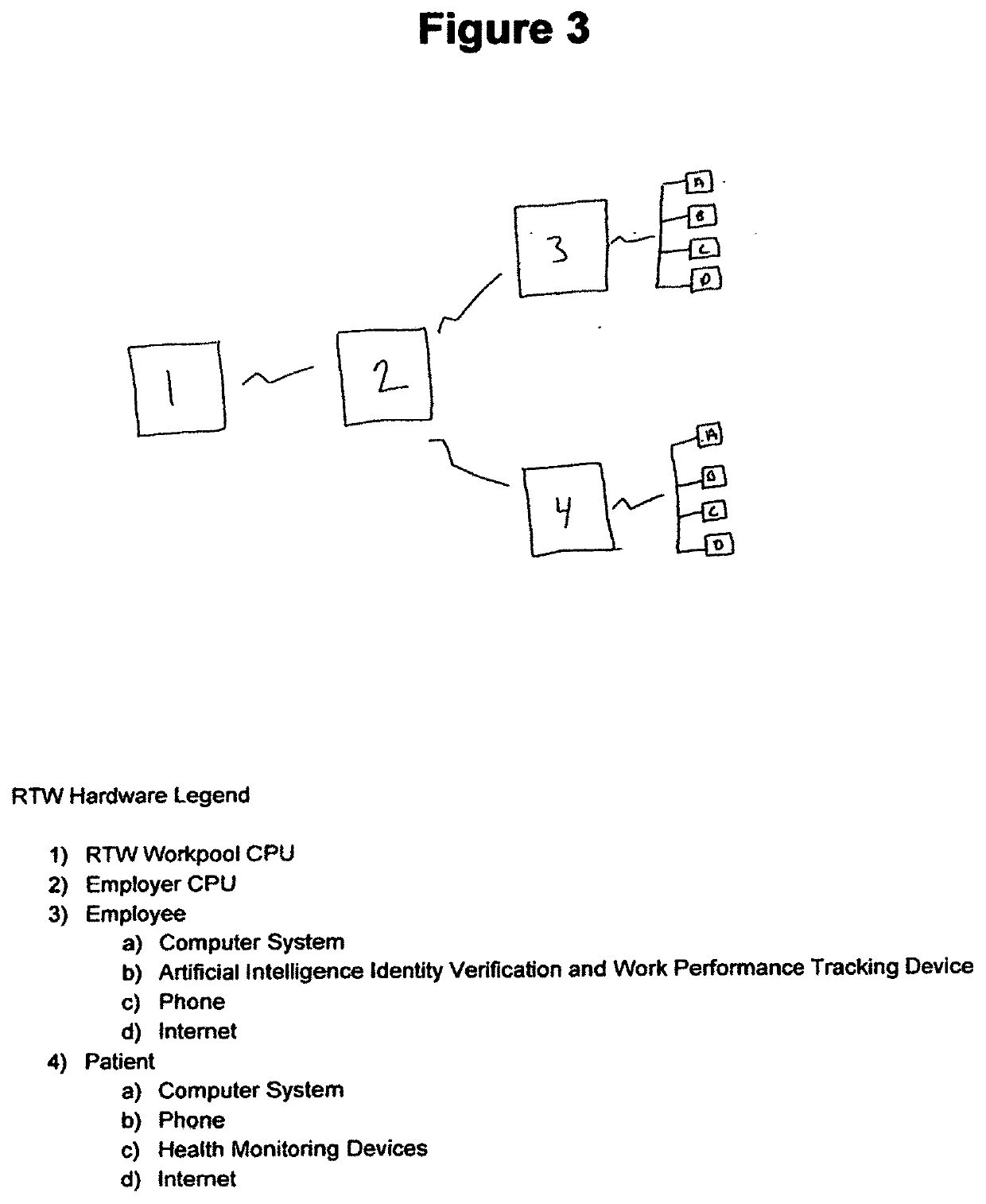
Hospital clinical workforce redeployment system and method of use
A status and workflow management system, analytic tools, artificial intelligence, and monitoring indexes along with a status and workflow management system, including an intake mechanism and computer systems for use by responsible persons responsible for respective parts of the processing of individual telehealth workforce redeployment opportunities for the at-risk clinical employee populations at a hospital, interests in monitoring hospital telehealth initiatives, and or evaluating the utilization of at-risk clinical employees within telehealth initiatives. A system comprising at least two computers, a telemetric data collection system, and artificial intelligence providing a mechanism that generates for each responsible person a workflow status screen and monitoring dashboards comprising of information pertaining to the given responsible person's perspective of involvement. A task generator element capable of displaying to the given responsible person on his or her screen tasks to which he or she has been assigned and or self-elected to do so. A task update mechanism updates tasks on the screen of the given responsible person in accordance with a sequence of workflow steps. An automatic mechanism for displaying monitoring indexes relative to fluctuations in data. An automatic mechanism for updating reporting and decision making tools via evolving artificial intelligence applied predictive modeling.
Owner:PIERONI ALEXANDER
Scanning mirror based display system and method
ActiveUS8493289B2Improve certaintySimple hardwarePhotometry using reference valueProjectorsOptoelectronicsScanning mirror
Scanning mirror based display system and method. A method comprises sampling a scanned light provided by a scanning mirror, converting the sampled scanned light into an electrical signal, analyzing the electrical signal to determine a position of the scanned light, and controlling the light source or the scanning mirror based on the analyzed electrical signal. The electrical signal based on the sampled scanned light may be used to ensure proper operation of the scanning mirror display system, such as determining failure of the scanning mirror, proper rendering of colors, determining whether the scanned light is following a desired scan path at a desired scan rate, and so forth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Radar System For Detecting Profiles Of Objects, Particularly In A Vicinity Of A Machine Work Tool
ActiveUS20190129001A1Low bandwidthReduce the sampling frequencyMechanical machines/dredgersGain controlFrequency changerData stream
A radar system is disclosed for detecting profiles of objects, particularly in a vicinity of a machine work tool. The radar system uses a direct digital synthesiser to generate an intermediate frequency off-set frequency. It also uses an up-converter comprising a quadrature mixer, single-side mixer or complex mixer to add the off-set frequency to the transmitted frequency. It further uses a down-converter in the receive path driven by the off-set frequency as a local oscillator. The radar system enables received information to be transferred to the intermediate frequency. This in turn can be sampled synchronously in such a way as to provide a complex data stream carrying amplitude and phase information. The radar system is implementable with a single transmit channel and a single receive channel.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
High performance resonant element
InactiveUS20070286293A1High performance resonantIncrease the number ofTransmission control/equlisationCurrent interference reductionSignal lines
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
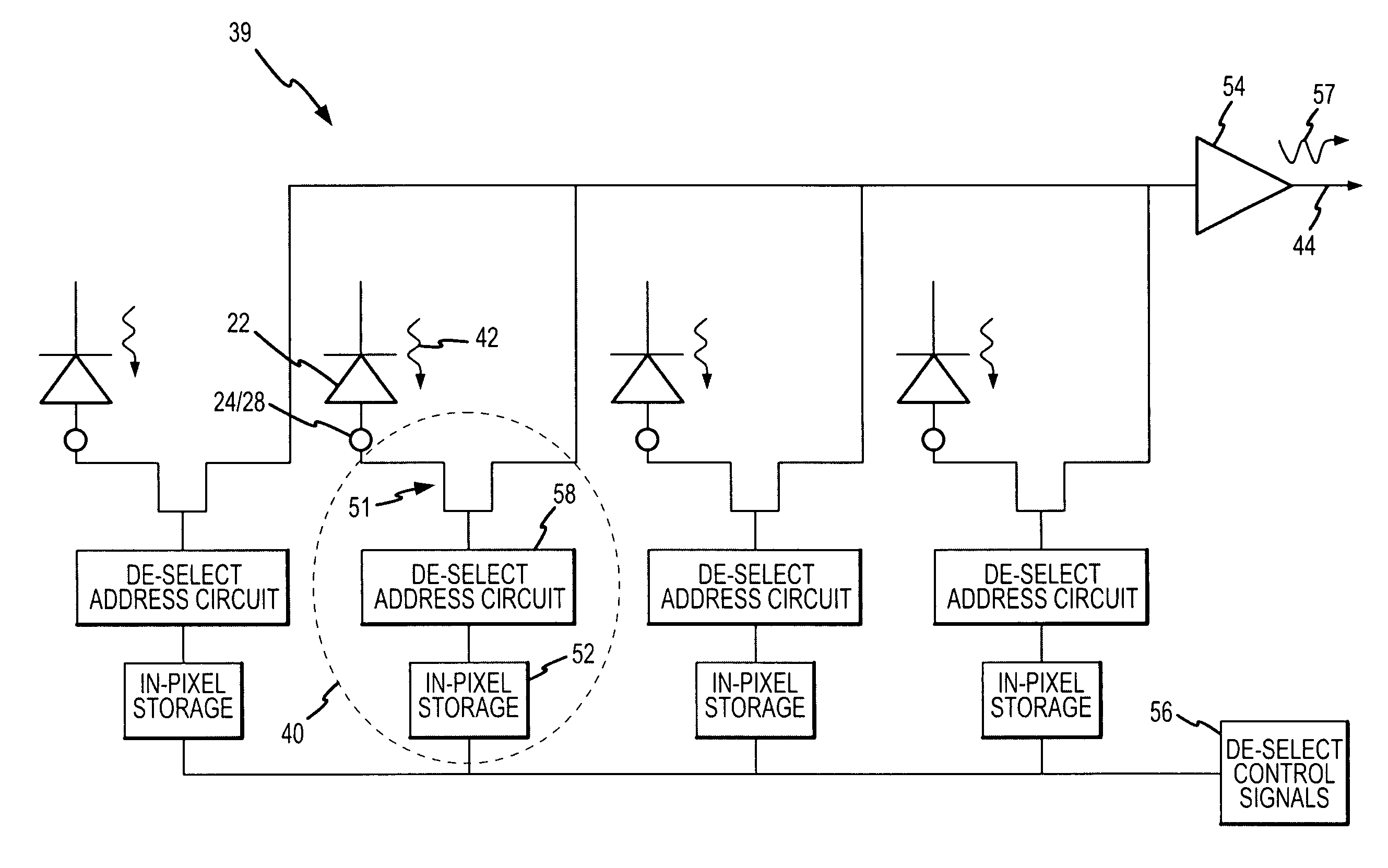
Microlensed focal plane array (FPA) using sub-pixel de-selection for improved operability
ActiveUS7491920B2Cost-effective and robust and flexibleImprove collection efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsOperabilityMicro lens array
A cost-effective FPA includes a plurality of detectors per pixel, wherein radiation is directed by a microlens array into respective focal regions that are covered by the union of the detectors' collections regions within each pixel and any defective detectors are de-selected in the ROIC. The operability of each pixel is evaluated, and a map generated specifying detector de-selection for each pixel. This map is read into memory in the ROIC to de-select bad detectors. Bad detectors are preferably allowed to float to a photovoltage and re-emit some of their accumulated photo charge to neighboring detectors to improve collection efficiency. The radiation levels are preferably read out on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Accordingly, the signals from the selected detectors are combined within each pixel.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Pump drive that minimizes a pulse width based on voltage data to improve intake and discharge strokes
ActiveUS10920768B2Improve efficiencyIncreased longevityFluid parameterFlexible member pumpsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The performance of a solenoid drive liquid pump can be very dependent on the magnitude and stability of an input voltage, with non-ideal input power resulting in loss of efficiency and potential damage to the pump. Pulse width of drive signals provided to the pump, which cause solenoids to alternately energize to move liquid through the pump, may be adjusted in duration in order to compensate for non-ideal input voltage. A drive control module of the pump gathers voltage information, determines an improved pulse width based upon that voltage information, and then provides drive signals based upon the improved pulse width. Operating in this manner, a pump can operate at or near peak efficiency despite both significant variances in input voltage and non-sinusoidal input voltage, and without customized components or adapters.
Owner:MILTON ROY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com