Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3232 results about "Micro lens array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
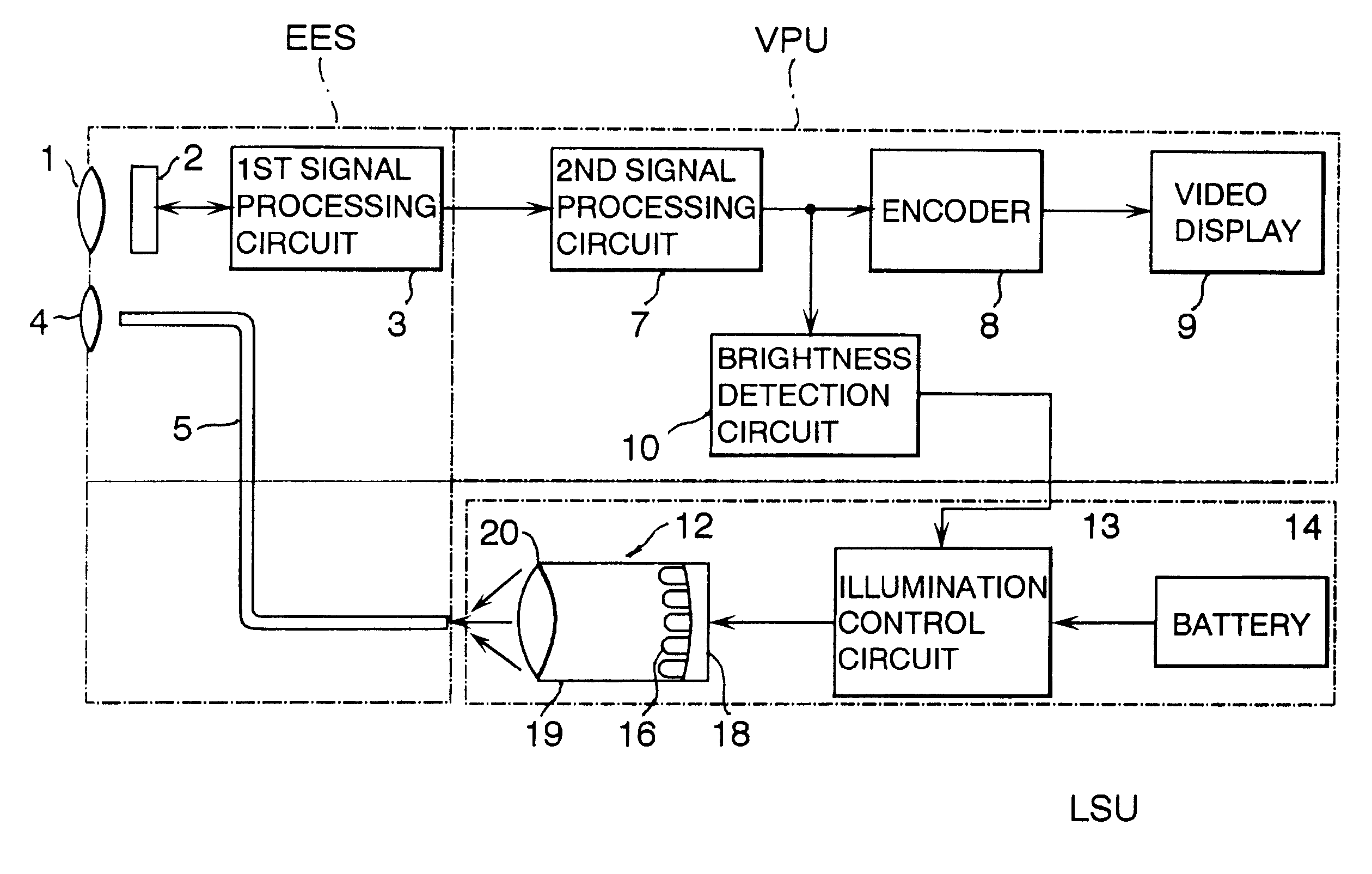
High-density illumination system
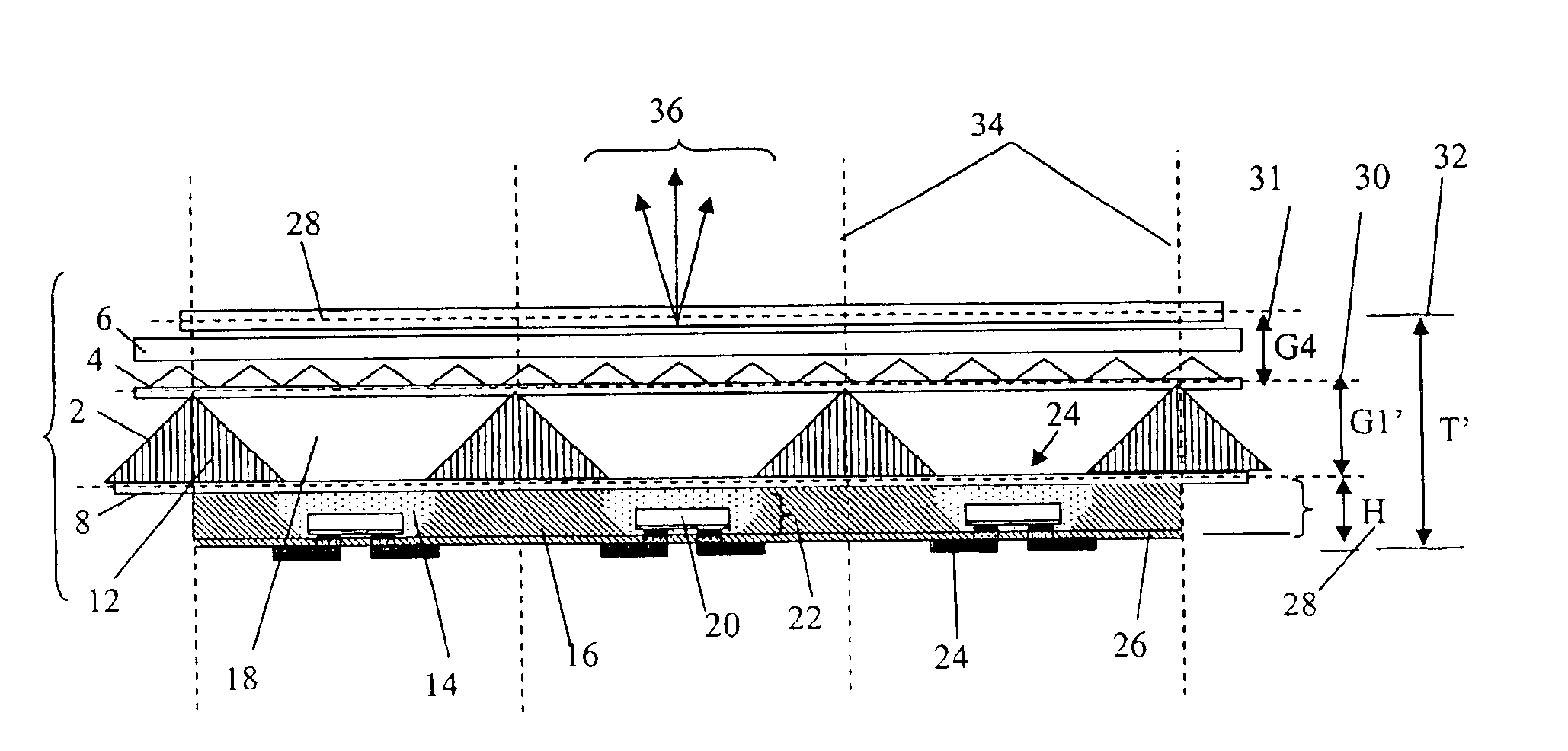
ActiveUS6871982B2Valid conversionIncrease Lumen DensityPrismsMechanical apparatusHigh densityLed array
A compact and efficient optical illumination system featuring planar multi-layered LED light source arrays concentrating their polarized or un-polarized output within a limited angular range. The optical system manipulates light emitted by a planar array of electrically-interconnected LED chips positioned within the input apertures of a corresponding array of shaped metallic reflecting bins using at least one of elevated prismatic films, polarization converting films, micro-lens arrays and external hemispherical or ellipsoidal reflecting elements. Practical applications of the LED array illumination systems include compact LCD or DMD video image projectors, as well as general lighting, automotive lighting, and LCD backlighting.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
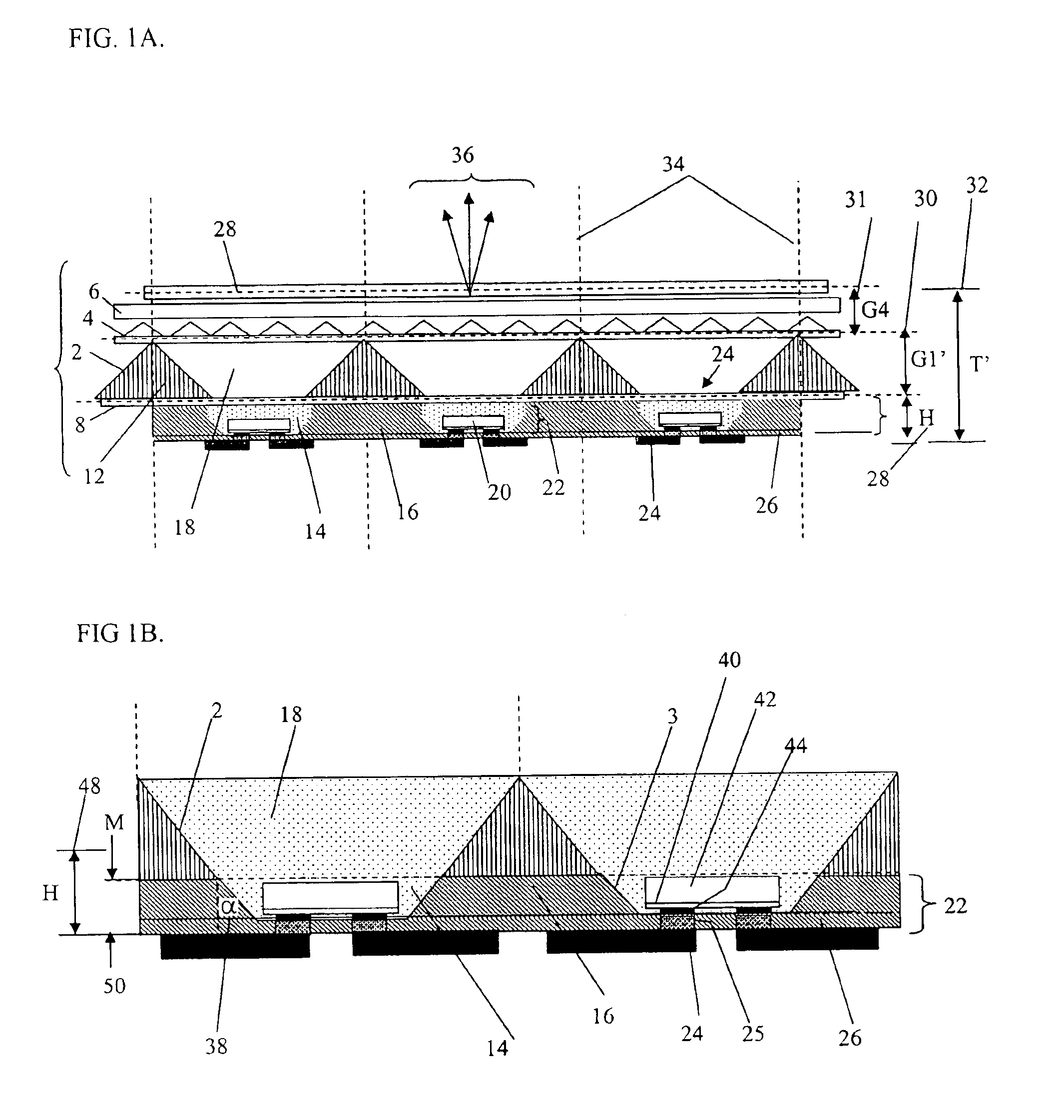
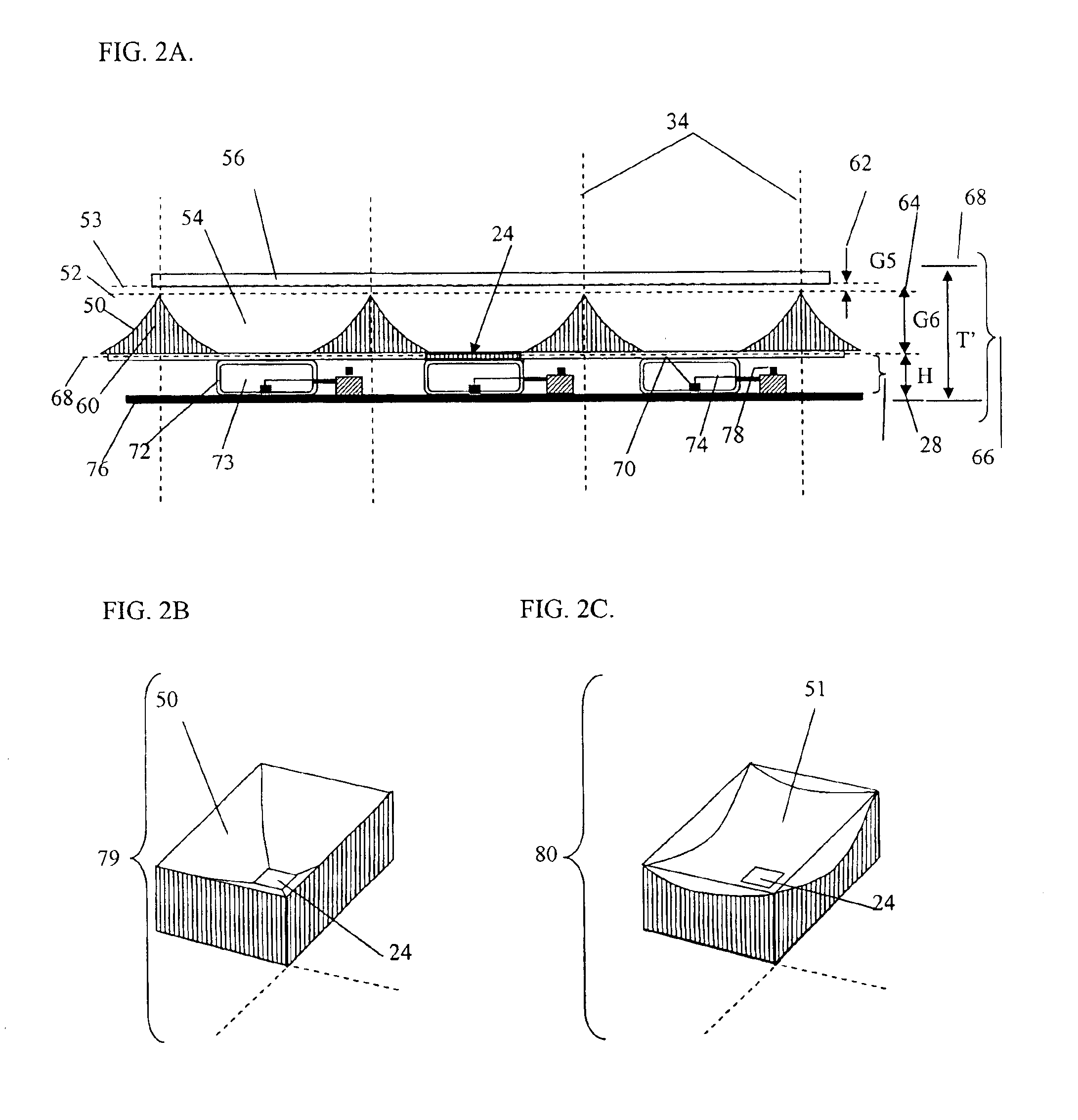
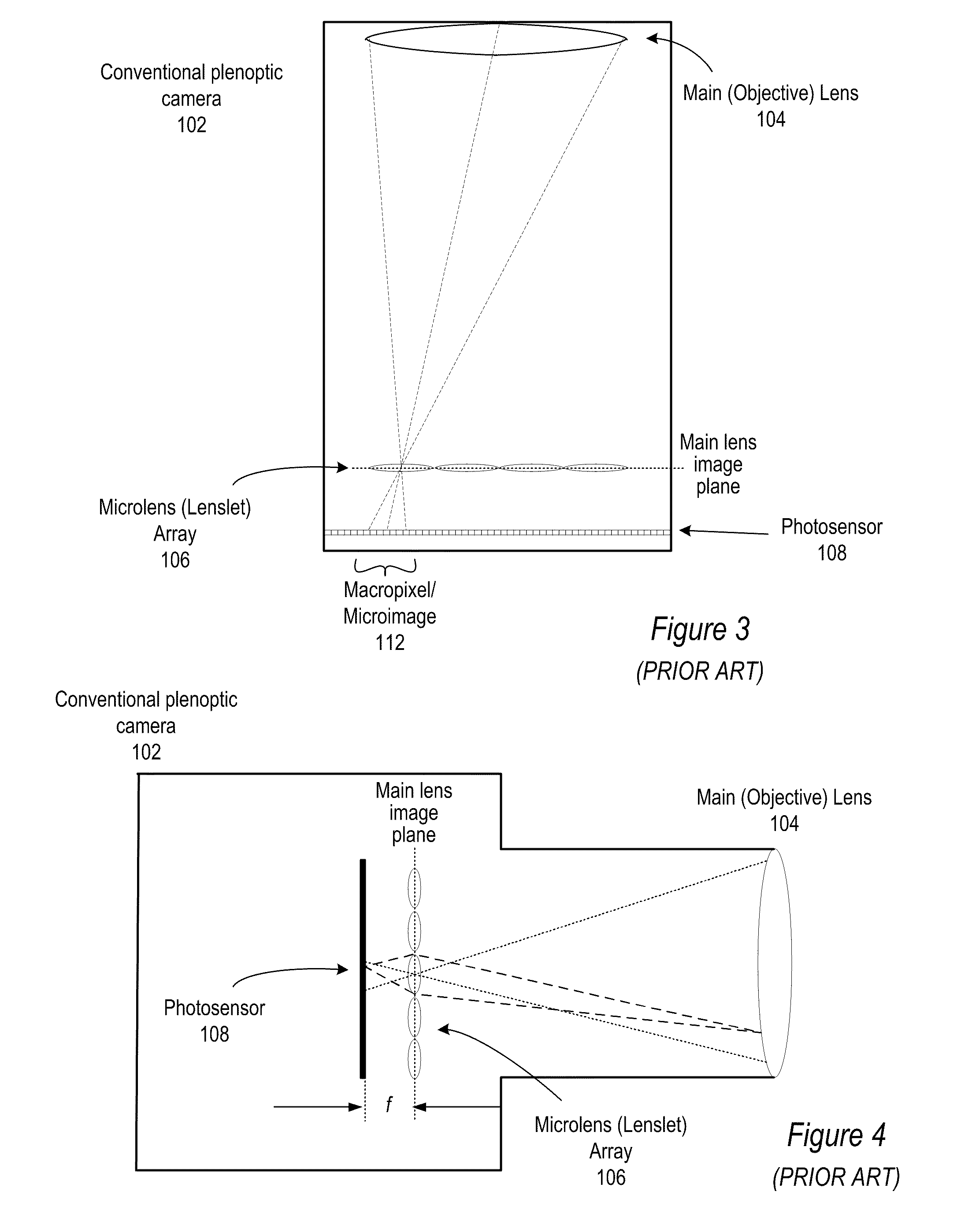
Focused plenoptic camera employing microlenses with different focal lengths
ActiveUS8400555B1Large apertureLow F-numberTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro lens arrayMultiple image
Methods and apparatus for capturing and rendering images with focused plenoptic cameras employing microlenses with different focal lengths. A focused plenoptic camera that includes an array of microlenses with at least two different focal lengths may be used to simultaneously capture microimages from at least two different planes at different distances from the microlens array. Image operations such as refocusing and focus bracketing may be performed on flats captured with the camera. Images may be constructed from subsets of the microimages captured using each type of microlens, thus creating multiple images each focused at a different depth. An array of stacked microlenses including stacks that provide different focal lengths may be used. The lens stacks may be provided by stacking two microlenses arrays on top of each other in the camera.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Near-eye microlens array displays
In embodiments of the invention, an apparatus may include a display comprising a plurality of pixels and a computer system coupled with the display and operable to instruct the display to display images. The apparatus may further include a microlens array located adjacent to the display and comprising a plurality of microlenses, wherein the microlens array is operable to produce a light field by altering light emitted by the display to simulate an object that is in focus to an observer while the display and the microlens array are located within a near-eye range of the observer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Spatially corrected full-cubed hyperspectral imager
ActiveUS7433042B1Accurate resolutionImprove fill factorSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsImage resolutionDetector array
A hyperspectral imager that achieves accurate spectral and spatial resolution by using a micro-lens array as a series of field lenses, with each lens distributing a point in the image scene received through an objective lens across an area of a detector array forming a hyperspectral detector super-pixel. Spectral filtering is performed by a spectral filter array positioned at the objective lens so that each sub-pixel within a super-pixel receives light that has been filtered by a bandpass or other type filter and is responsive to a different band of the image spectrum. The micro-lens spatially corrects the focused image point to project the same image scene point onto all sub-pixels within a super-pixel.
Owner:SURFACE OPTICS
Compact spectrometer device
InactiveUS6057925ARugged in constructionEasy to manufactureRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDetector arrayLight beam
A color measuring sensor assembly includes an optical filter such as a linear variable filter, and an optical detector array positioned directly opposite from the optical filter a predetermined distance. A plurality of lenses, such as gradient index rods or microlens arrays, are disposed between the optical filter and the detector array such that light beams propagating through the lenses from the optical filter to the detector array project an upright, noninverted image of the optical filter onto a photosensitive surface of the detector array. The color measuring sensor assembly can be incorporated with other standard components into a spectrometer device such as a portable calorimeter having a compact and rugged construction suitable for use in the field.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Controlling lens shape in a microlens array
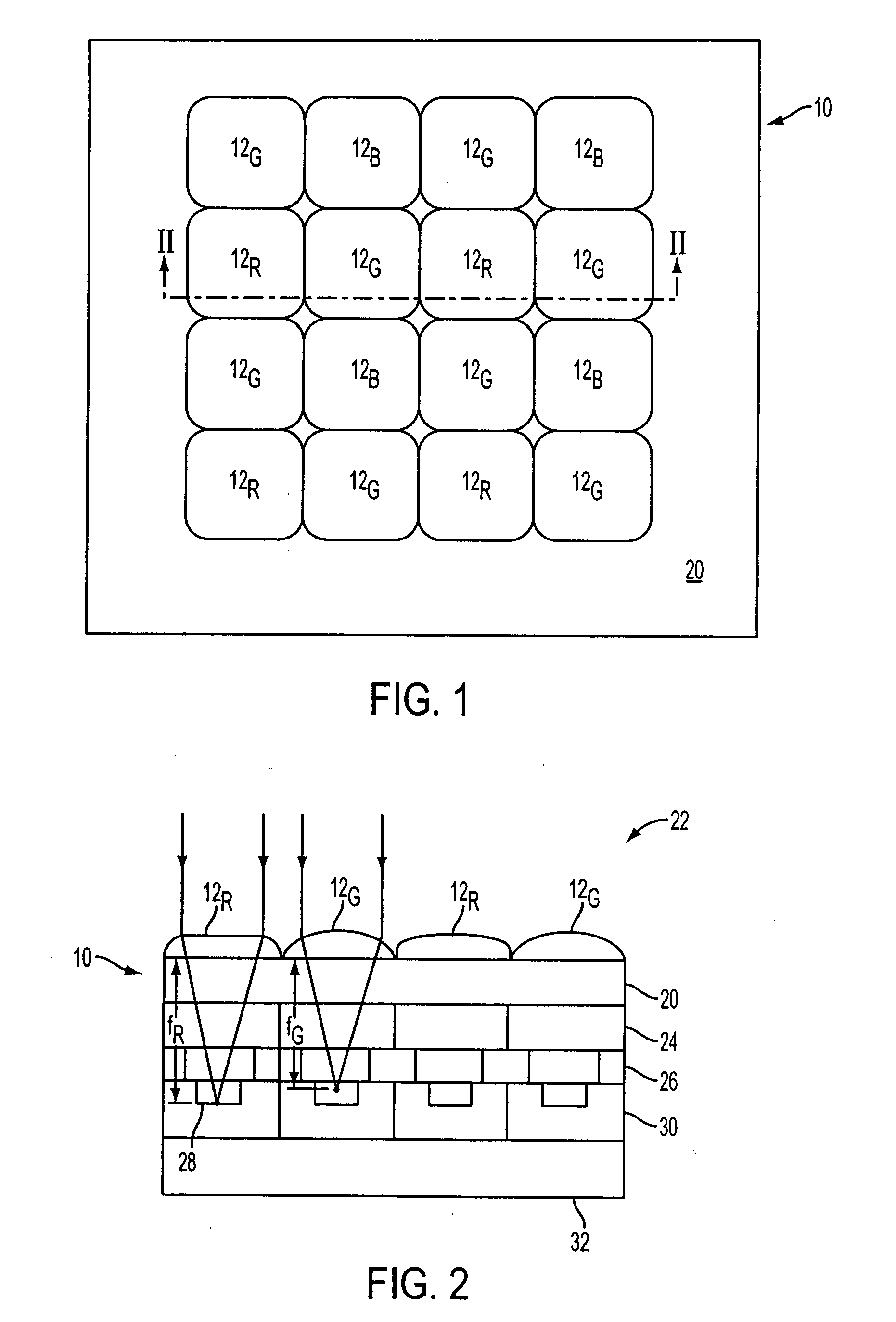
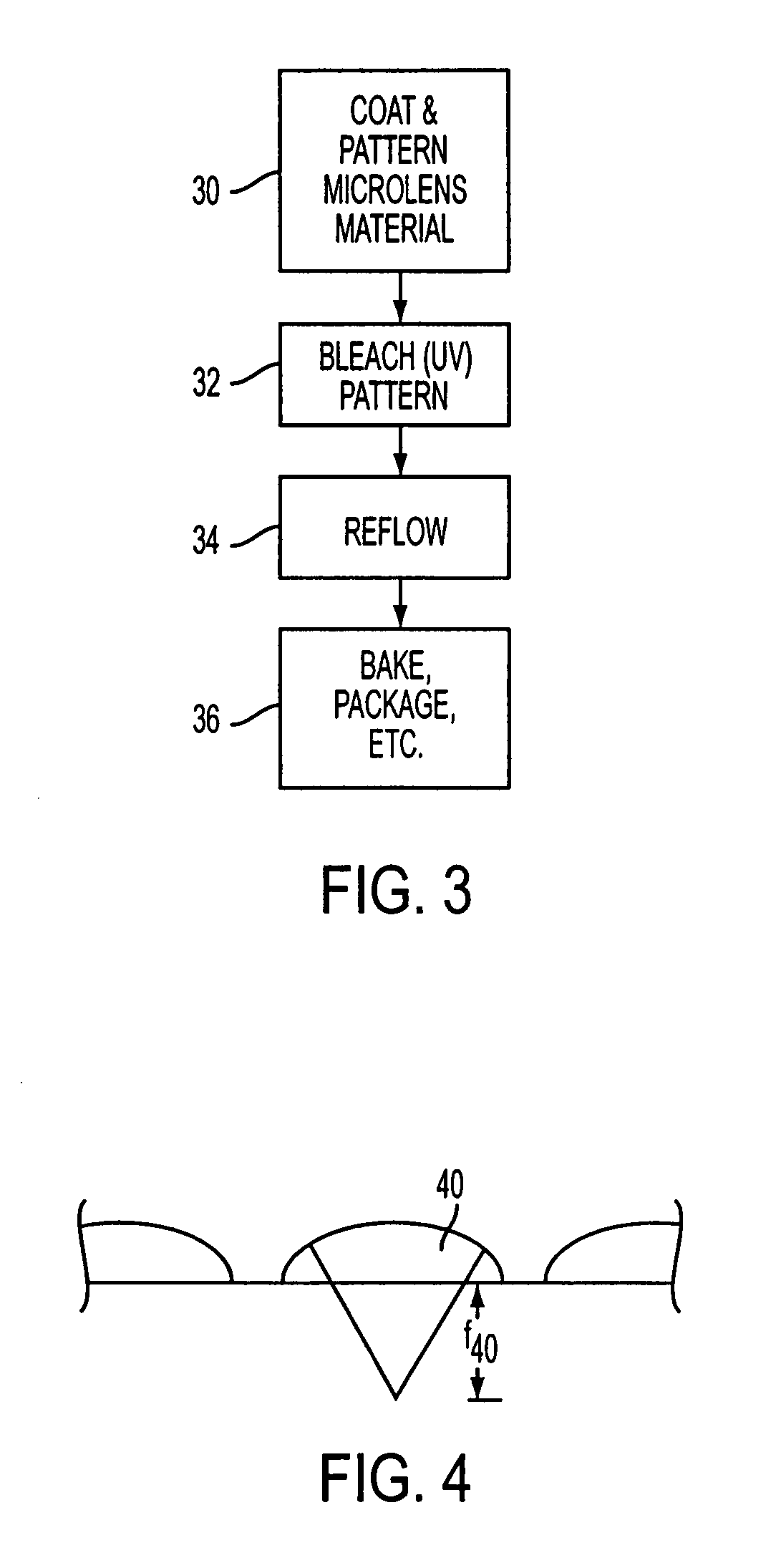
A semi-conductor based imager includes a microlens array having microlenses with modified focal characteristics. The microlenses are made of a microlens material, the melting properties of which are selectively modified to obtain different shapes after a reflow process. Selected microlenses, or portions of each microlens, are modified, by exposure to ultraviolet light, for example, to control the microlens shape produced by reflow melting. Controlling the microlens shape allows for modification of the focal characteristics of selected microlenses in the microlens array.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
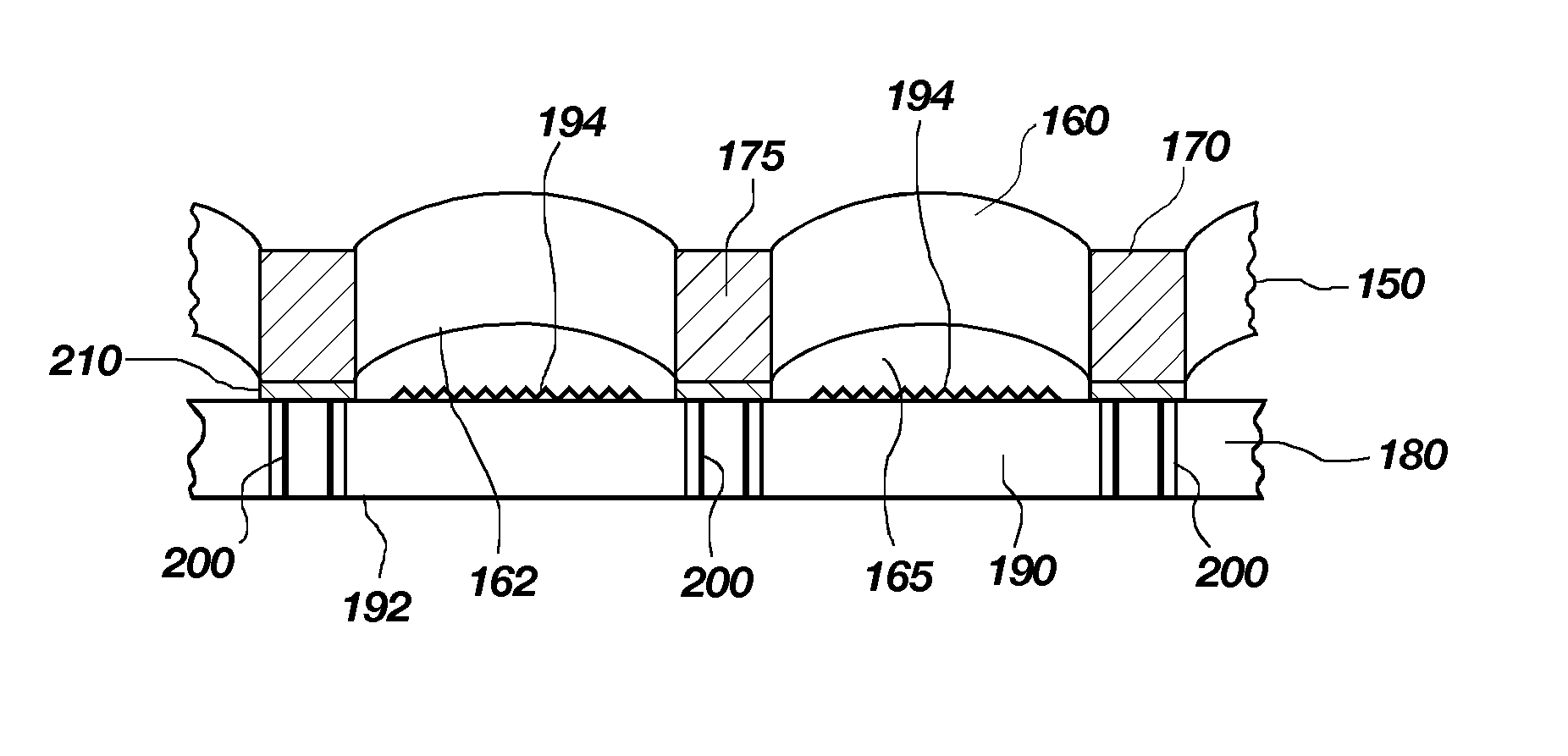
Wafer level lens arrays for image sensor packages and the like, image sensor packages, and related methods
Image sensor packages, lenses therefore, and methods for fabrication are disclosed. A substrate having through-hole vias may be provided, and an array of lenses may be formed in the vias. The lenses may be formed by molding or by tenting material over the vias. An array of lenses may provide a color filter array (CFA). Filters of the CFA may be formed in the vias, and lenses may be formed in or over the vias on either side of the filters. A substrate may include an array of microlenses, and each microlens of the array may correspond to a pixel of an associated image sensor. In other embodiments, each lens of the array may correspond to an imager array of an image sensor. A wafer having an array of lenses may be aligned with and attached to an imager wafer comprising a plurality of image sensor dice, then singulated to form a plurality of image sensor packages.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Image input device
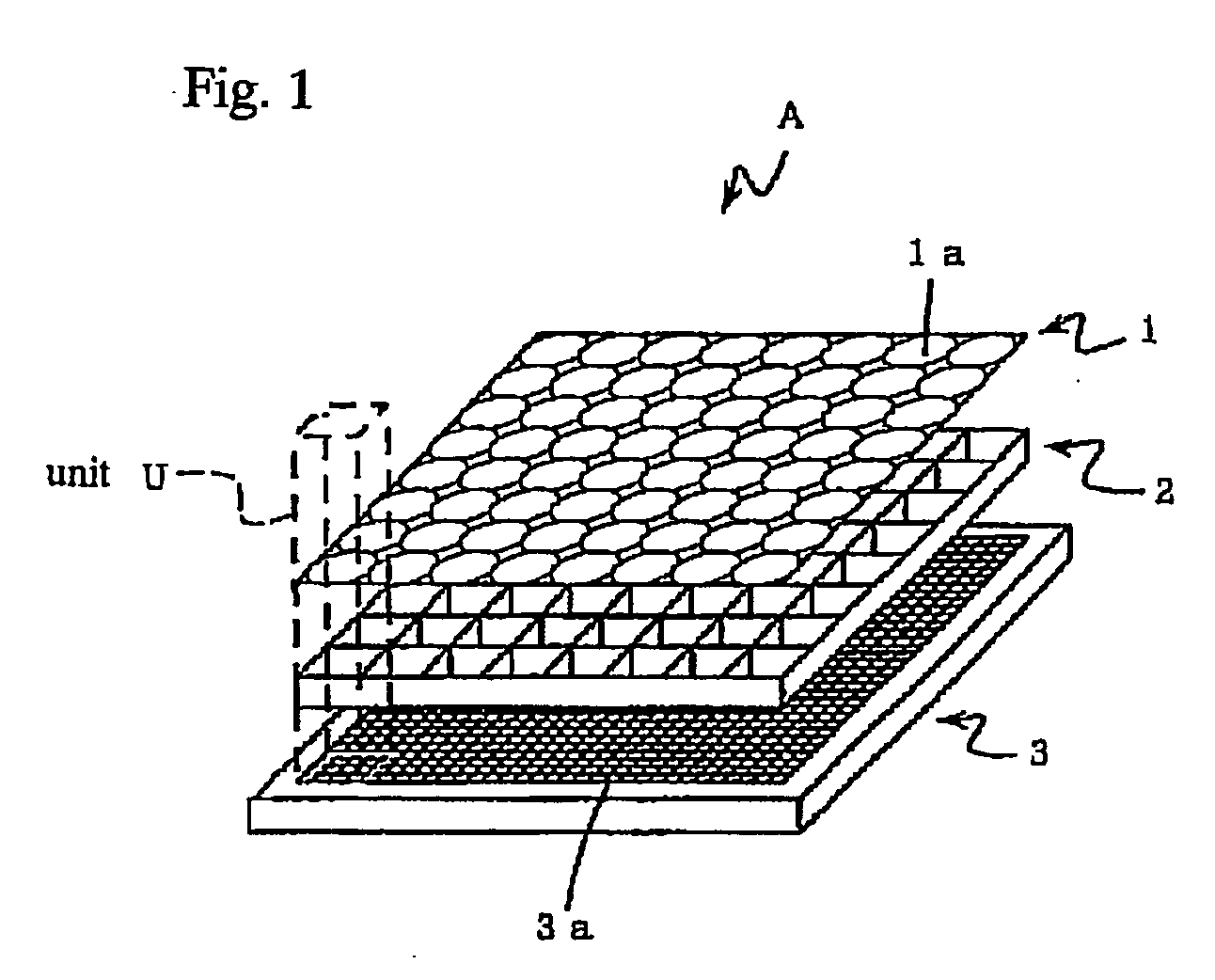
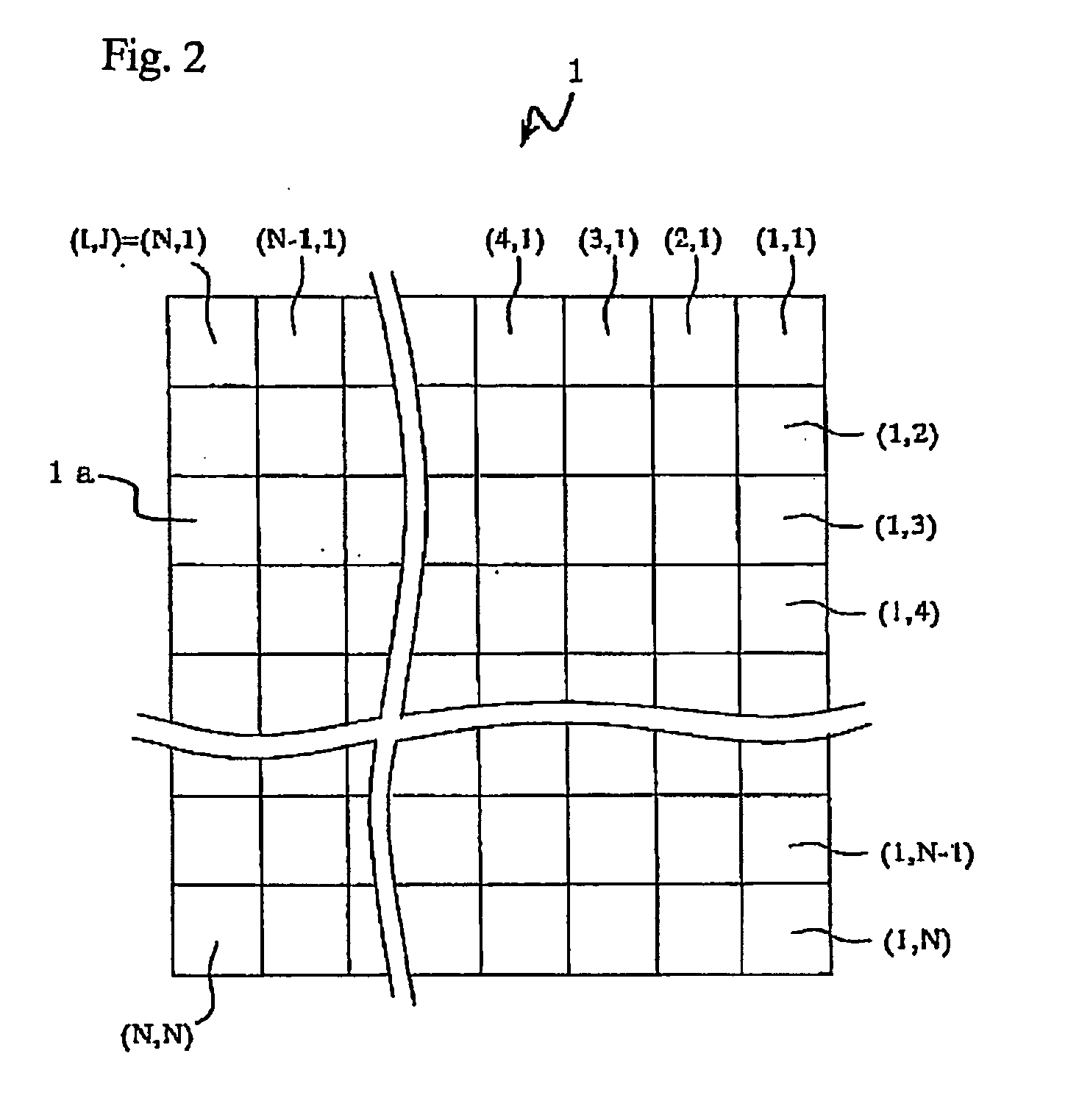
InactiveUS20060072029A1Quality improvementHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionComplementary colors
An image input apparatus which reconfigures a single reconfigured image from a plurality of low-resolution, object reduced images formed in a specified region on the light detecting element by the micro-lens array, wherein a high-resolution, single reconfigured image can be obtained even if the distance between the subject and the micro-lens array is long (infinitely long, for example), and further a reconfigured image can be realized in colors. The image input apparatus is characterized in that the relative distance between a micro-lens (1a) and light detecting cells (3a) in a specified region, where object reduced images corresponding to the micro-lens (1a) are formed, is different in each micro-lenses (1a). In addition, the light detecting cells (3a) are divided into a plurality of regions, and color filters (primary color filter, or complementary color filter, for example) are disposed in each of the divided regions.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
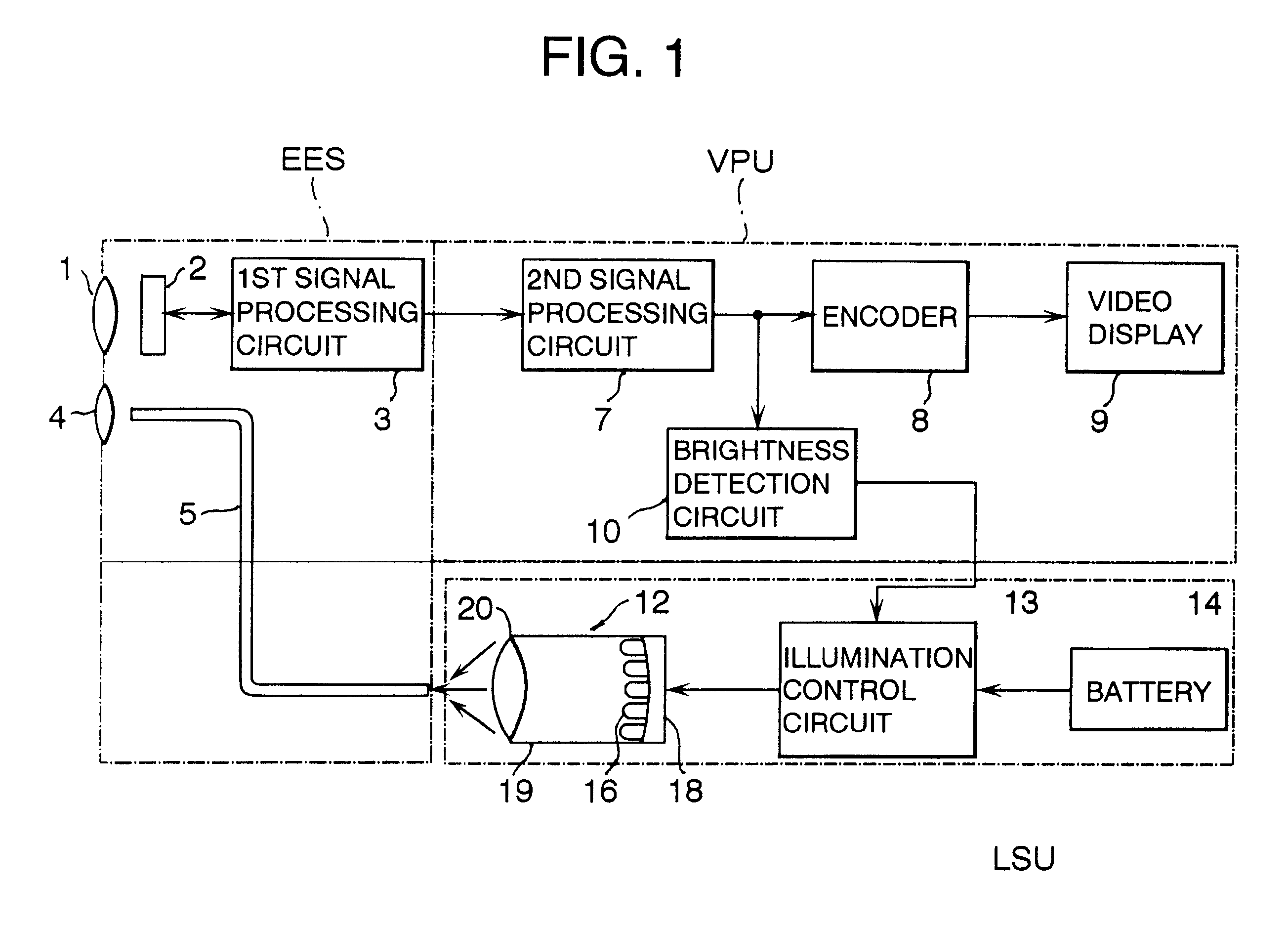
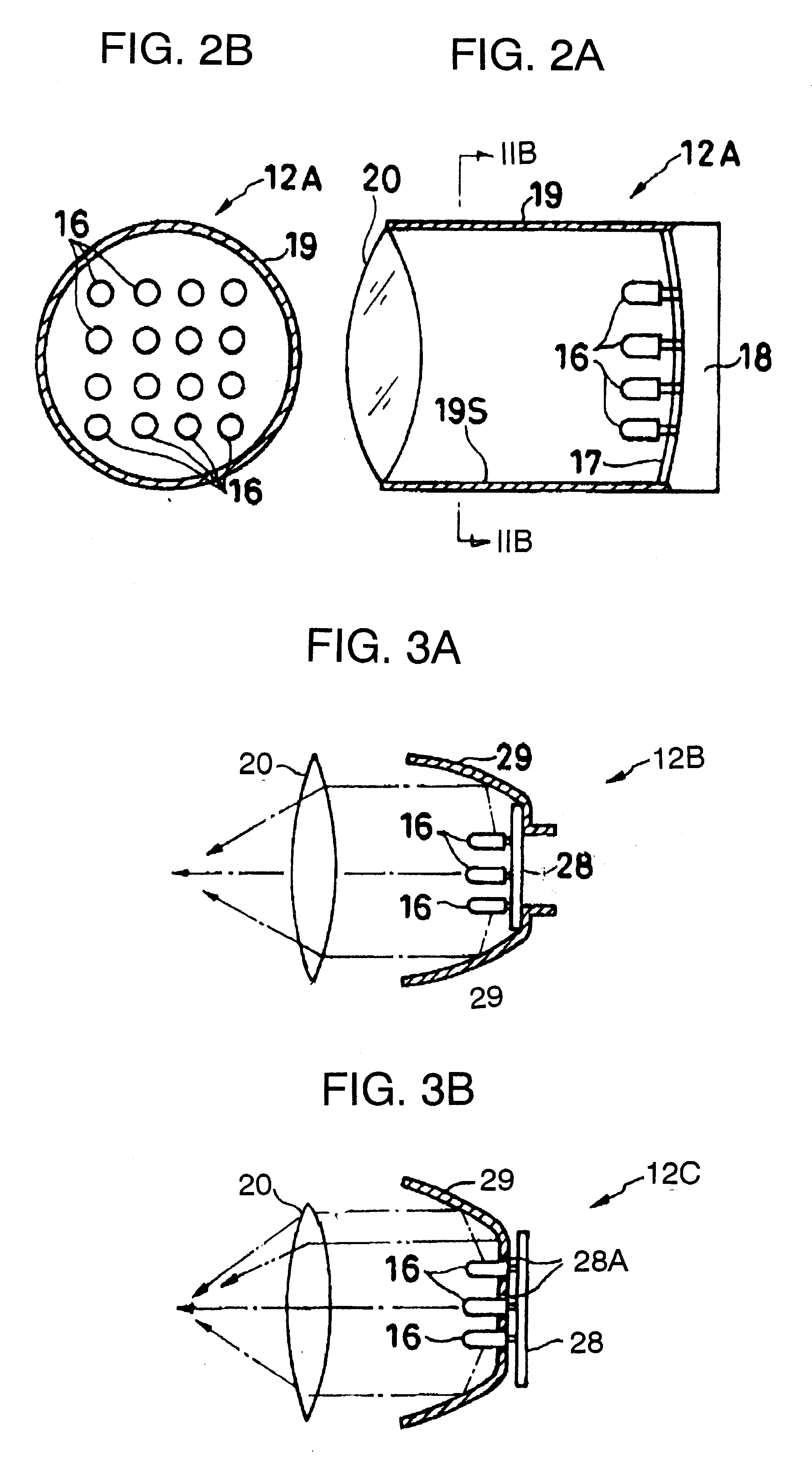
Battery-powered light source arrangement for endoscope
InactiveUS6260994B1Less overall consumptionLittle electrical powerMechanical apparatusPrintersElectrical batteryLight guide
A light source arrangement for a battery-powered light source unit of an endoscope comprises a cylindrical housing, a base disposed at one end of the housing, a plurality of LEDs connected to a flexible circuit board supported on the base and a focusing lens. A light guide for directing light emanating from the LEDs. The light guide comprises a reflective surface formed on an inner wall of the housing, a reflector having a concave reflective surface which is disposed at one end of the housing so as to surround the LEDs or a micro-lens array disposed in front of the LEDs with each micro lens aligned with the LED.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
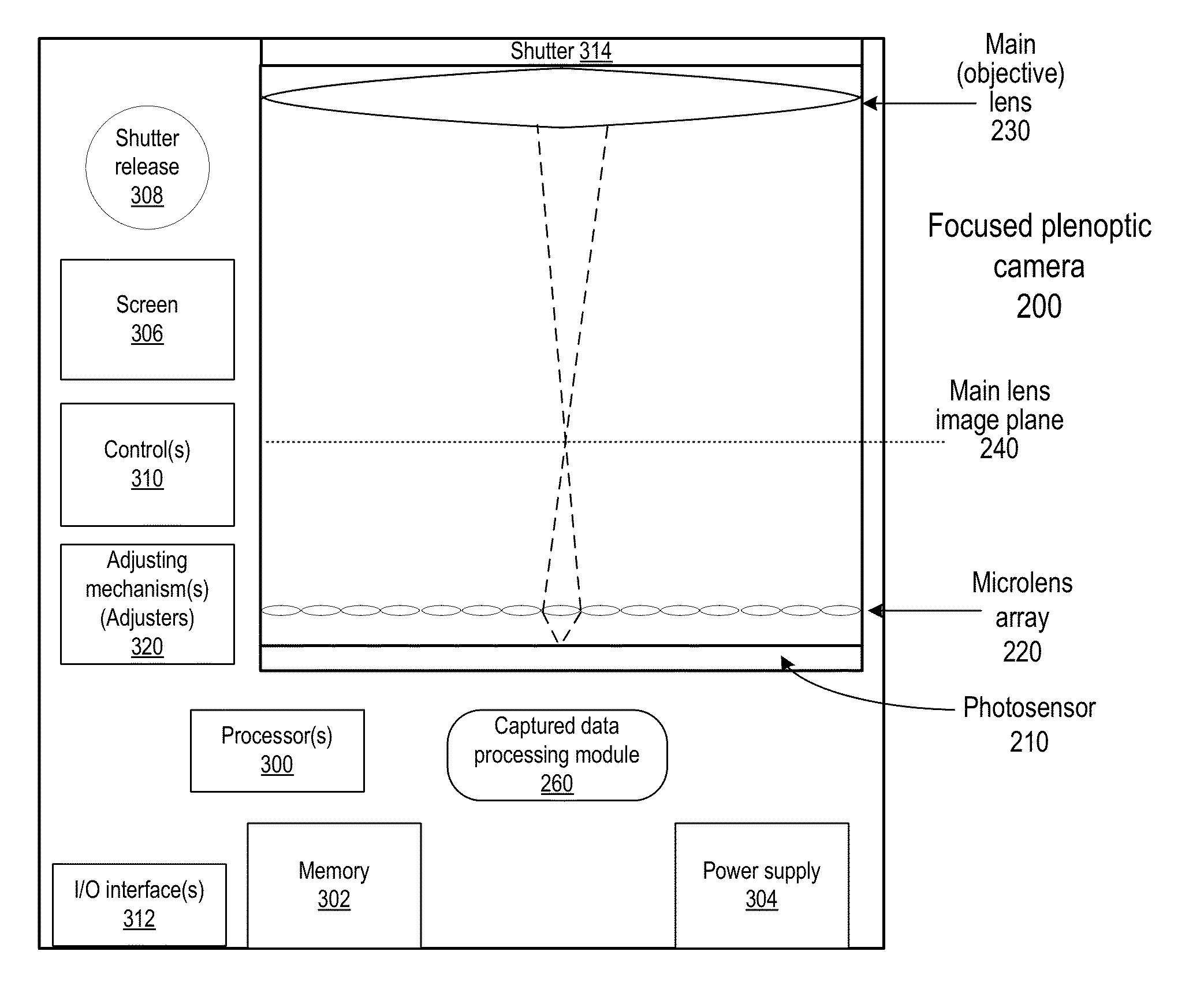
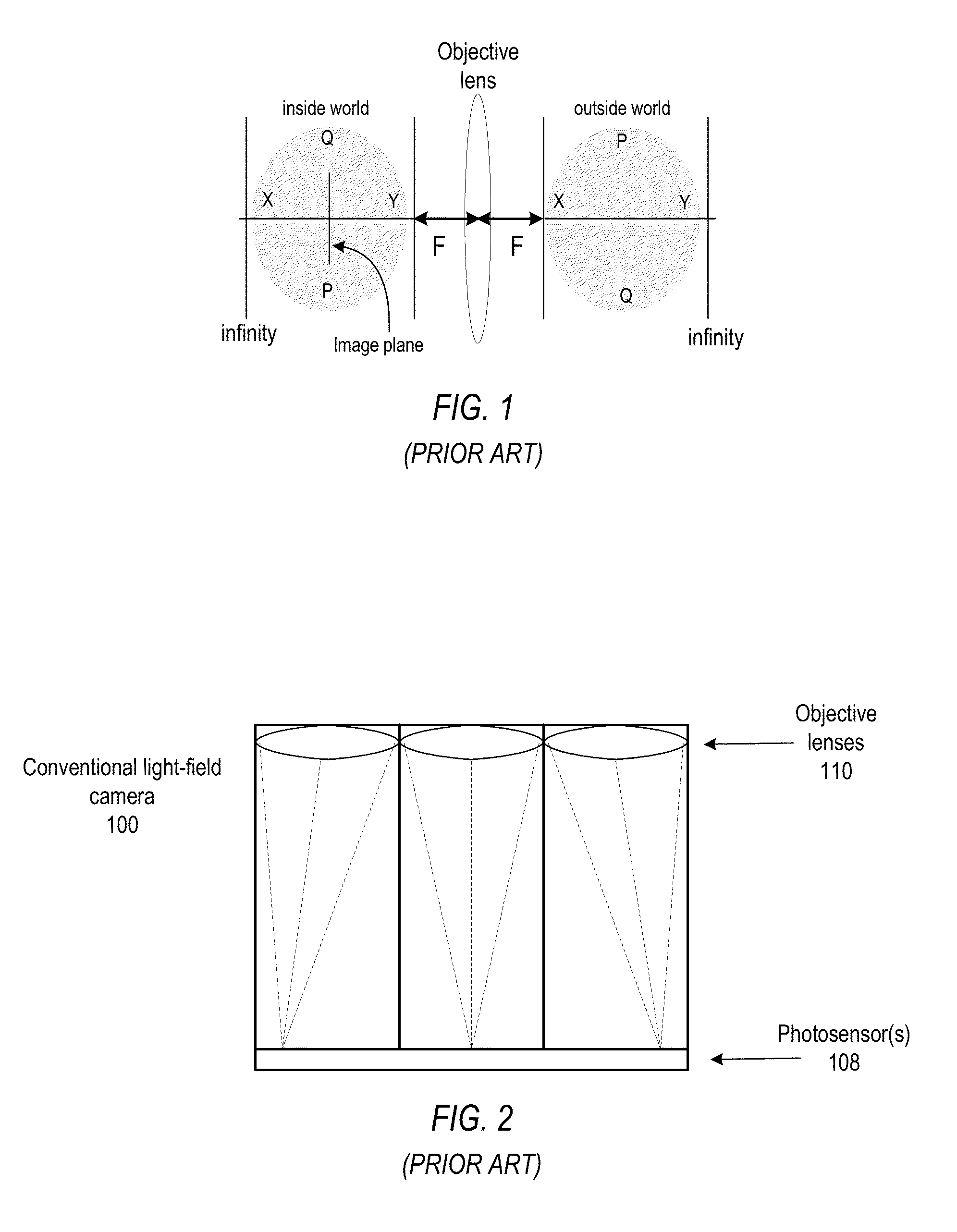
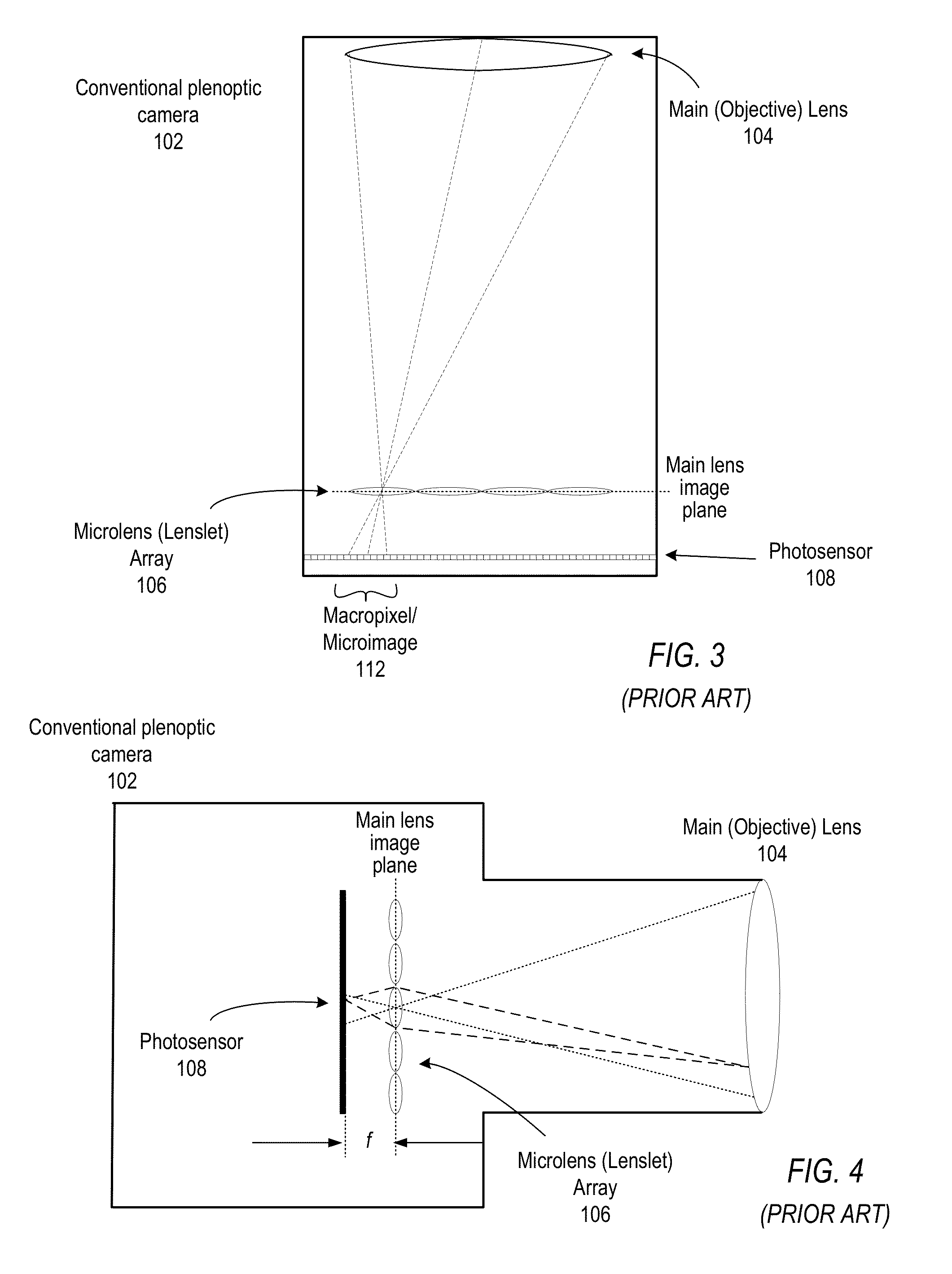
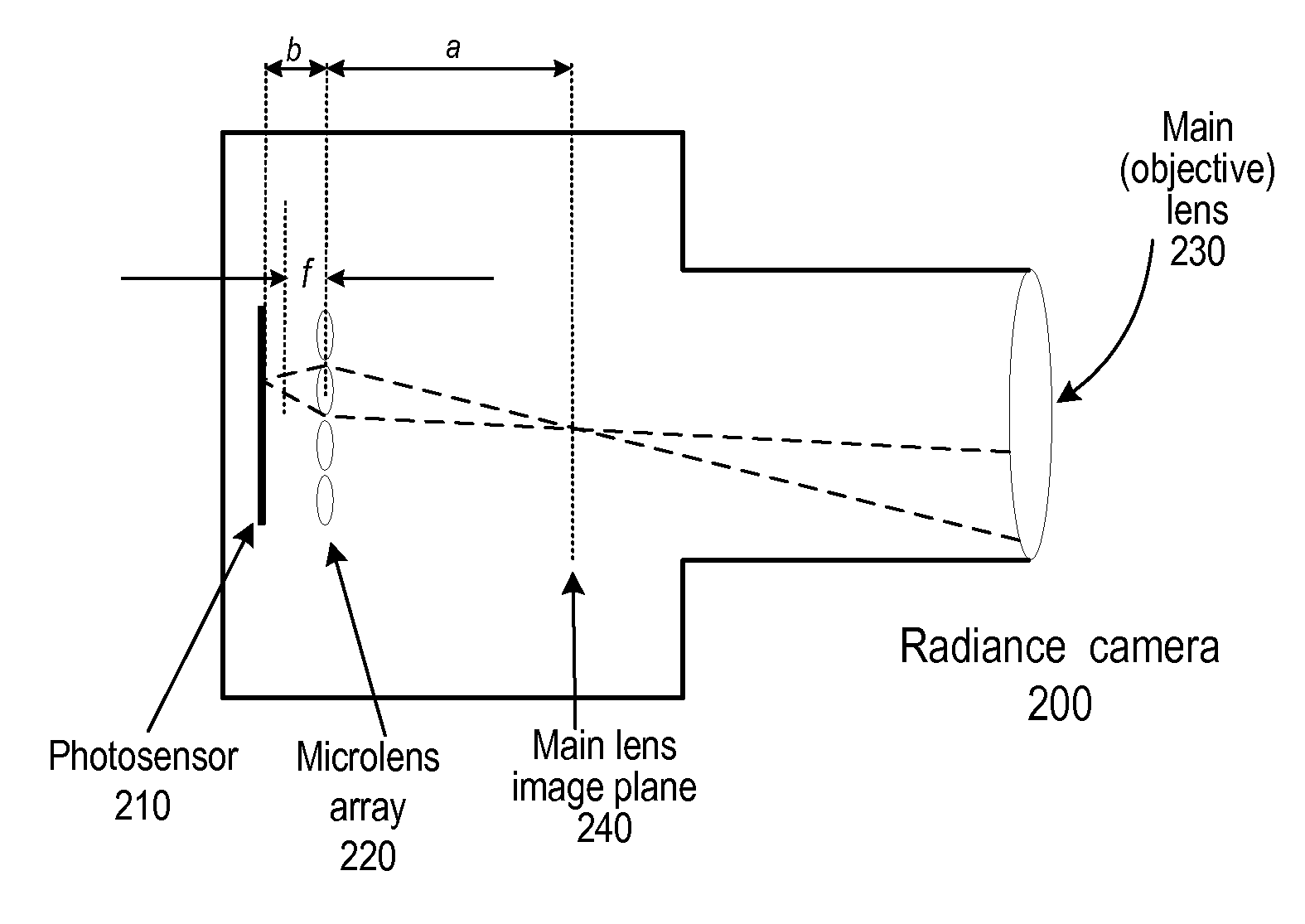
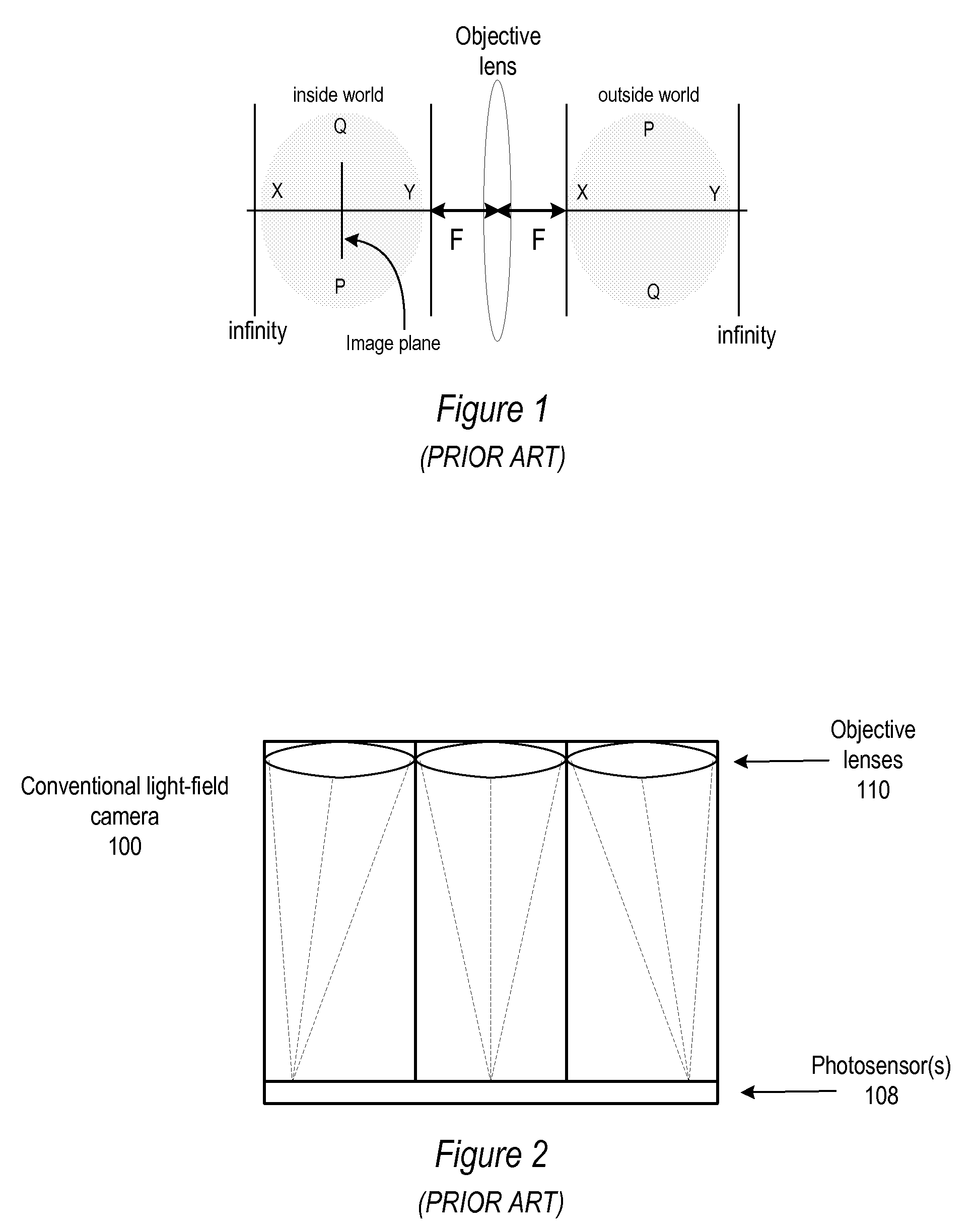
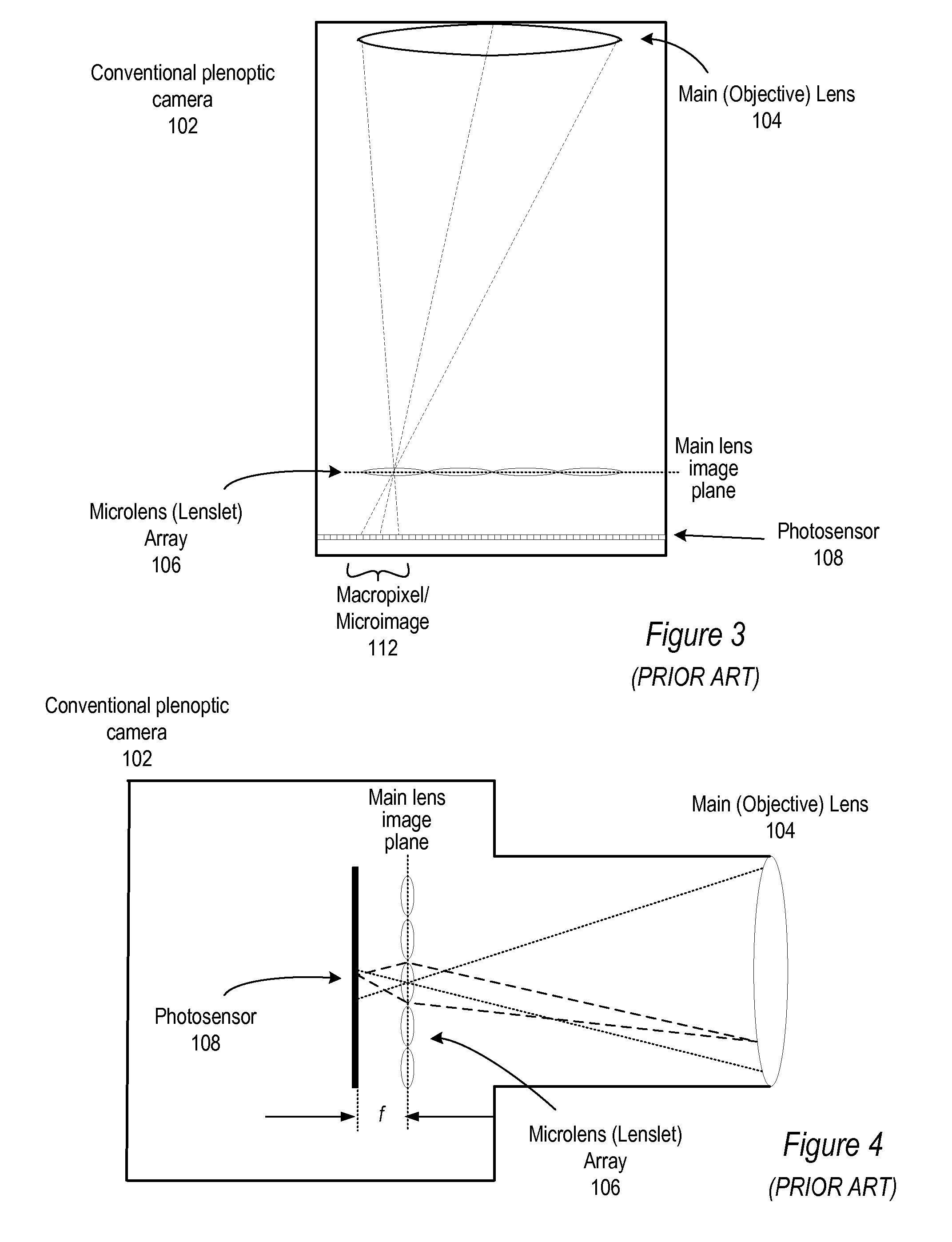
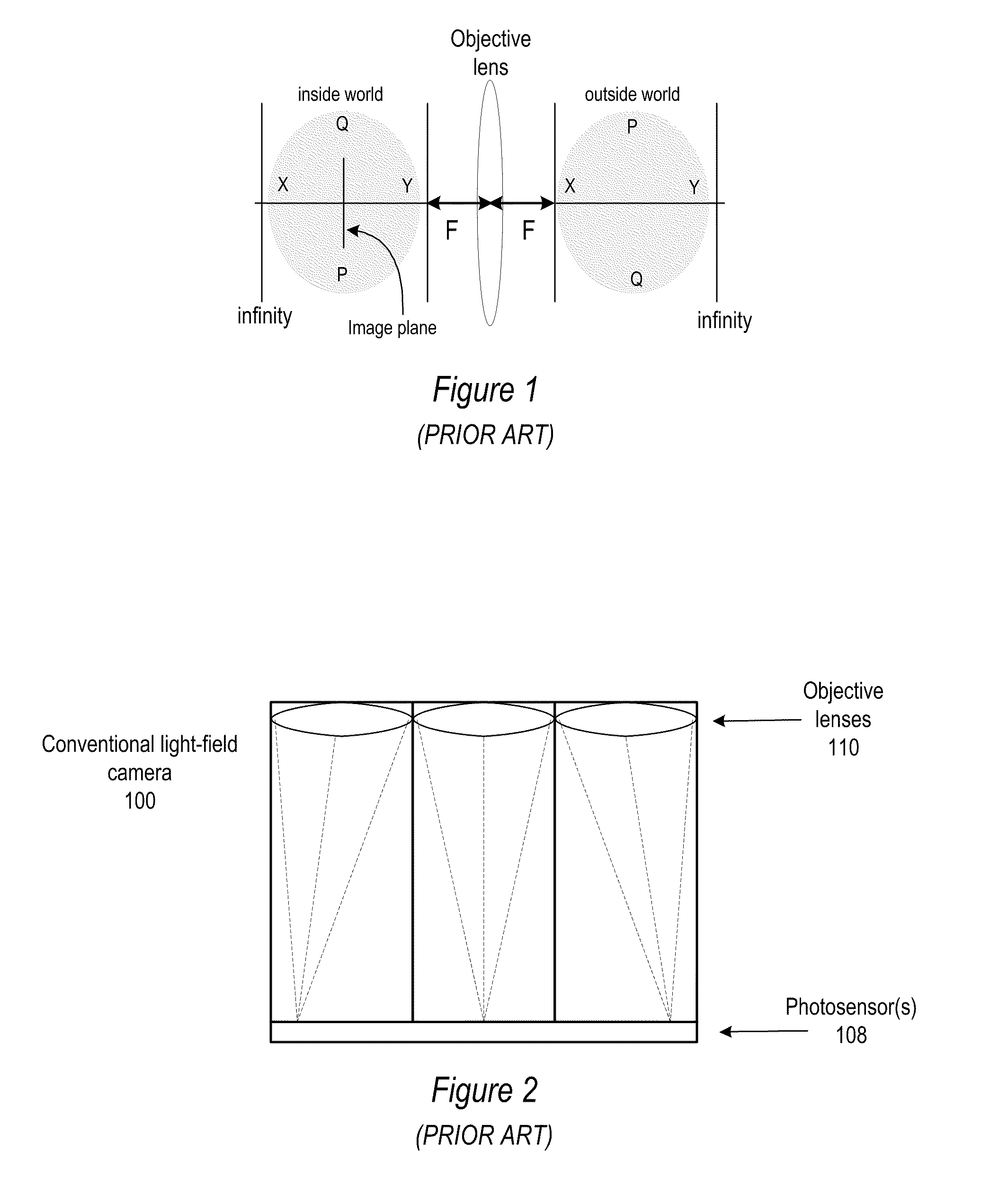
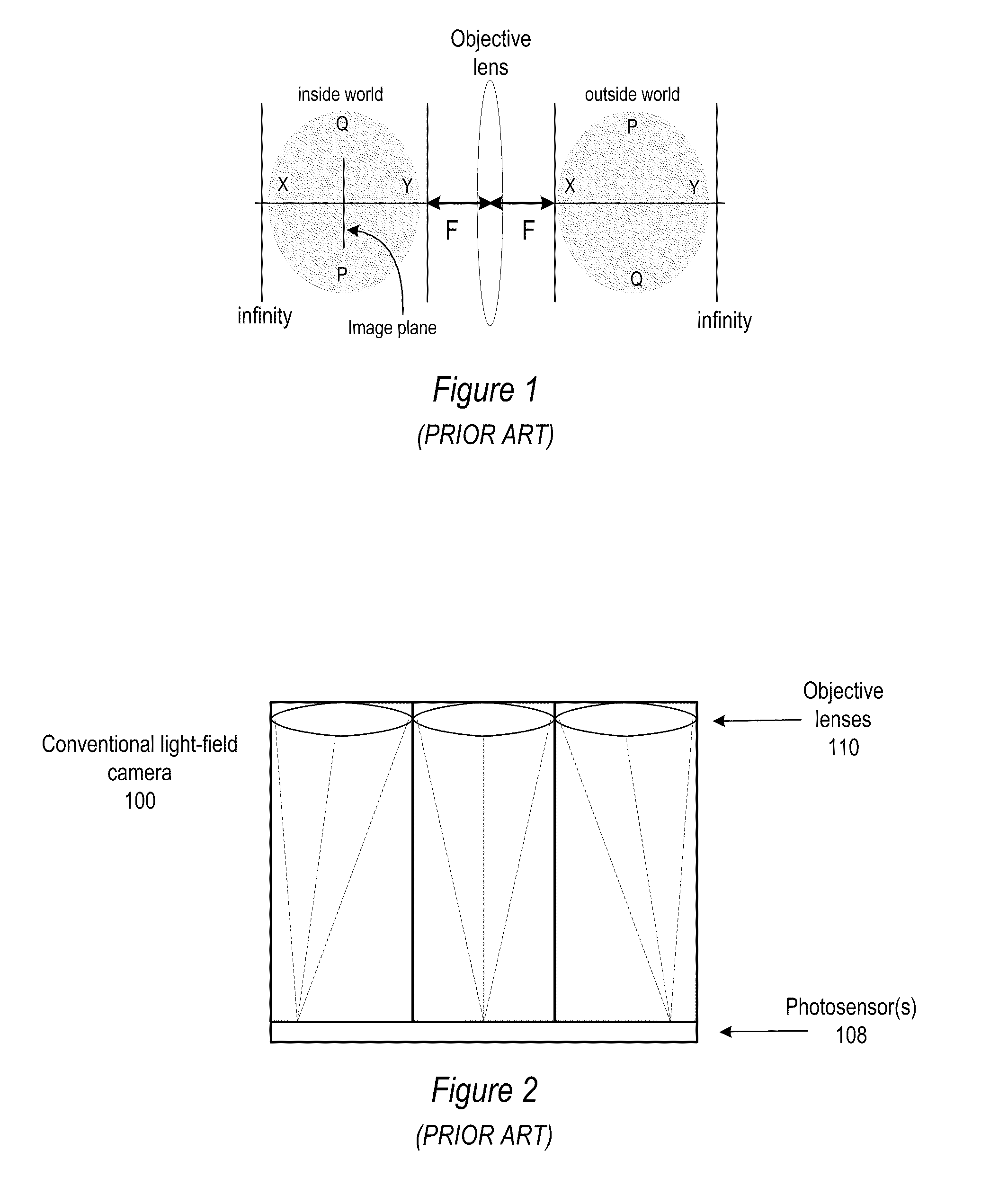
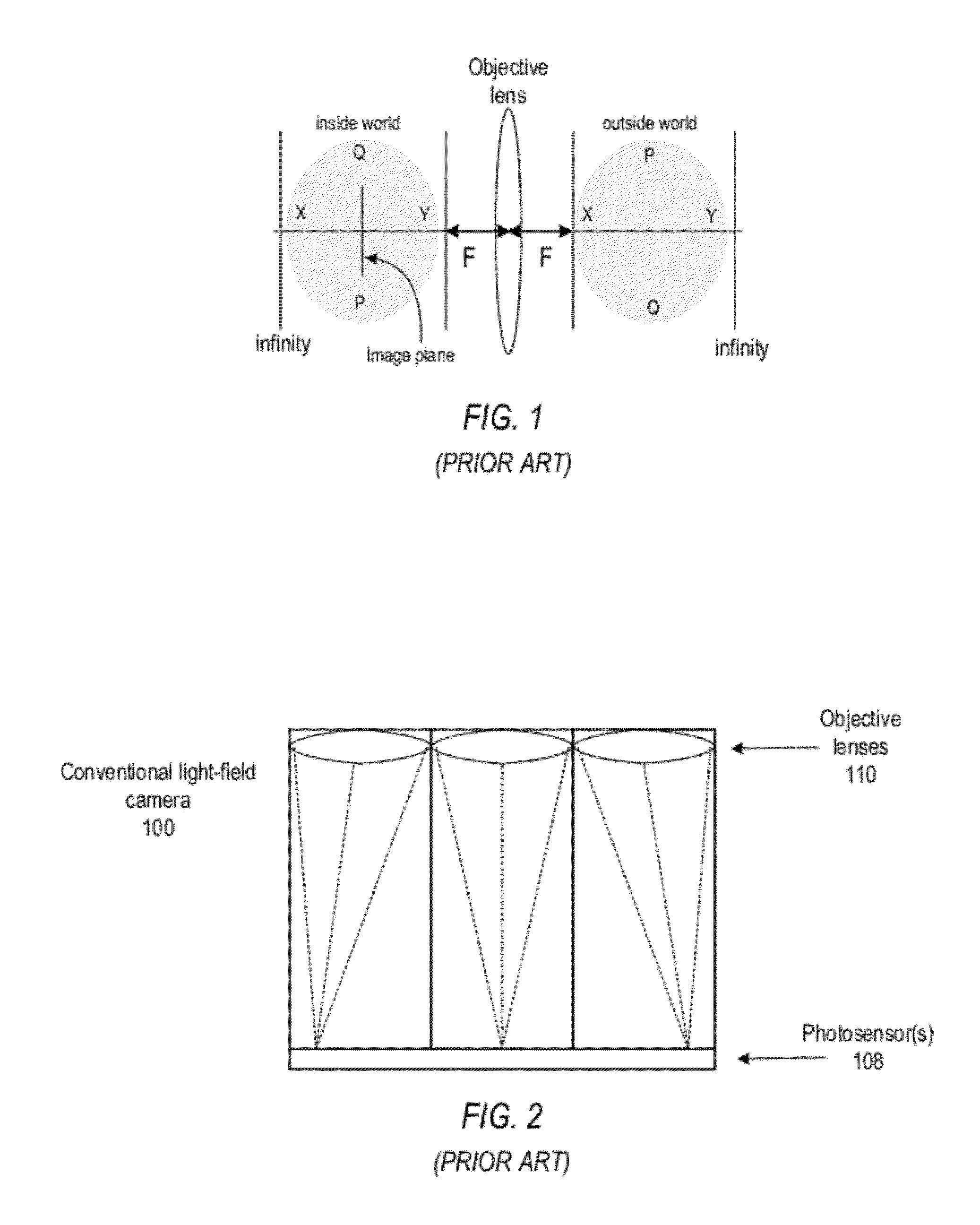
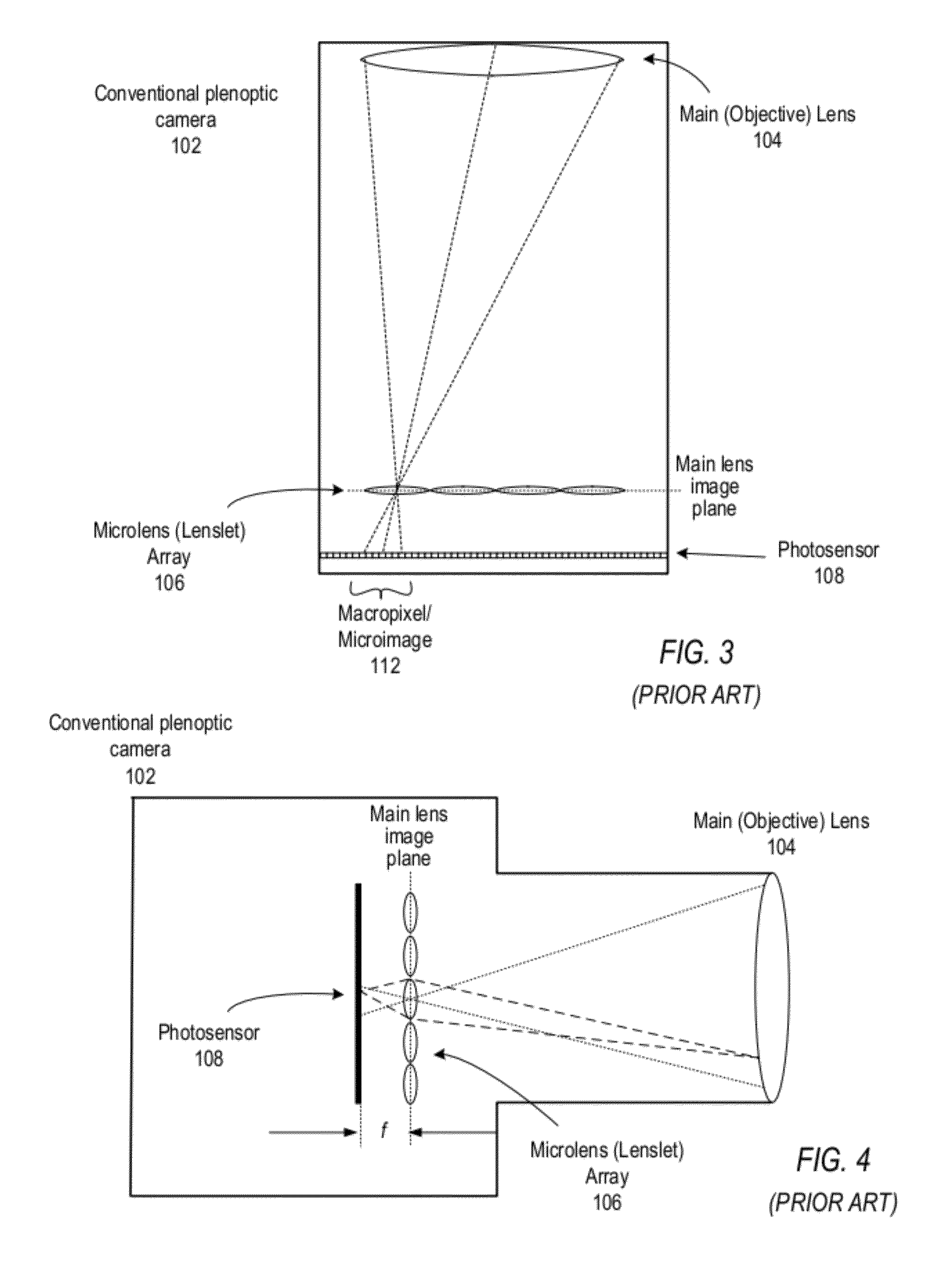
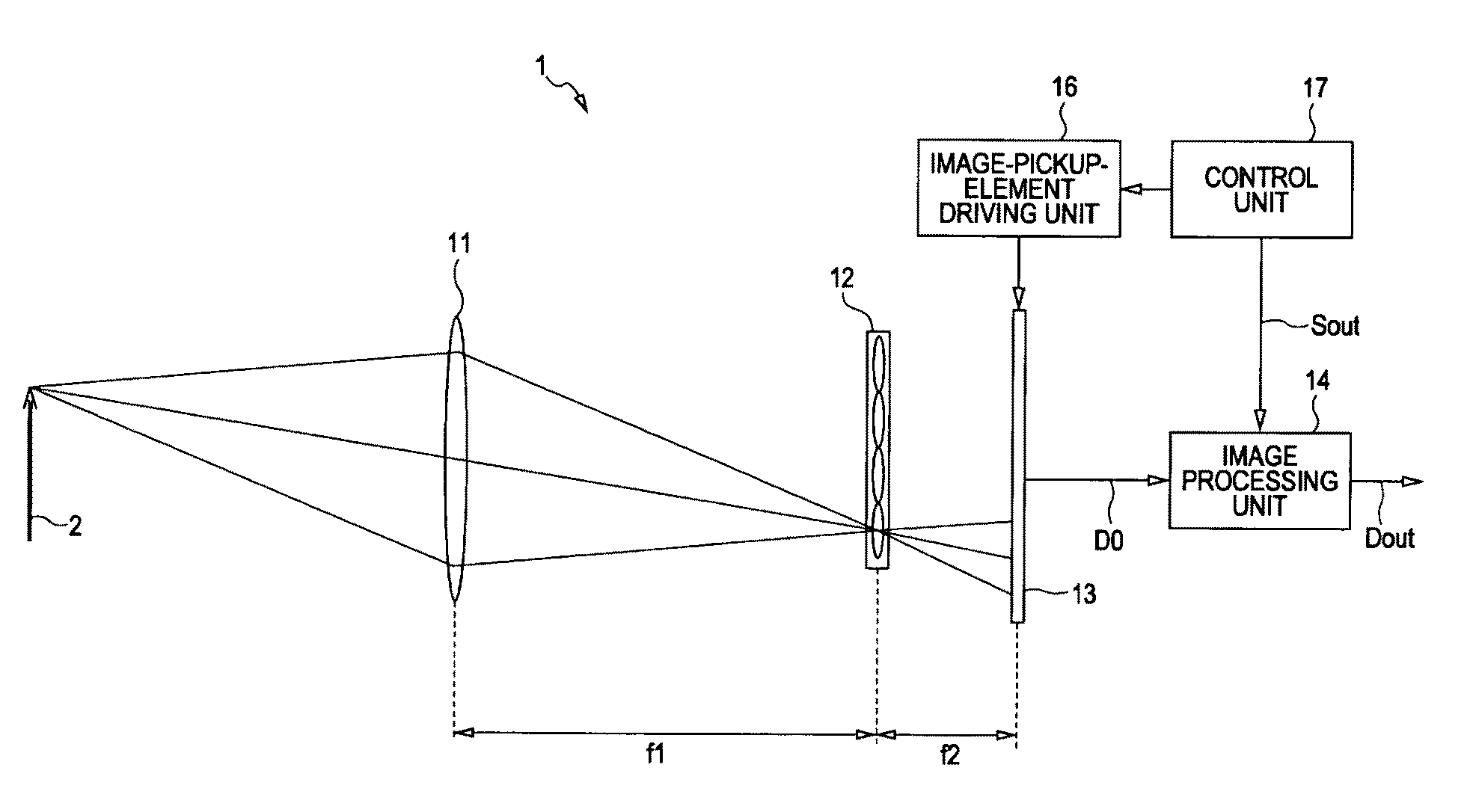
Methods and Apparatus for Full-Resolution Light-Field Capture and Rendering
ActiveUS20090185801A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionRadiance
Method and apparatus for full-resolution light-field capture and rendering. A radiance camera is described in which the microlenses in a microlens array are focused on the image plane of the main lens instead of on the main lens, as in conventional plenoptic cameras. The microlens array may be located at distances greater than f from the photosensor, where f is the focal length of the microlenses. Radiance cameras in which the distance of the microlens array from the photosensor is adjustable, and in which other characteristics of the camera are adjustable, are described. Digital and film embodiments of the radiance camera are described. A full-resolution light-field rendering method may be applied to light-fields captured by a radiance camera to render higher-resolution output images than are possible with conventional plenoptic cameras and rendering methods.
Owner:ADOBE INC
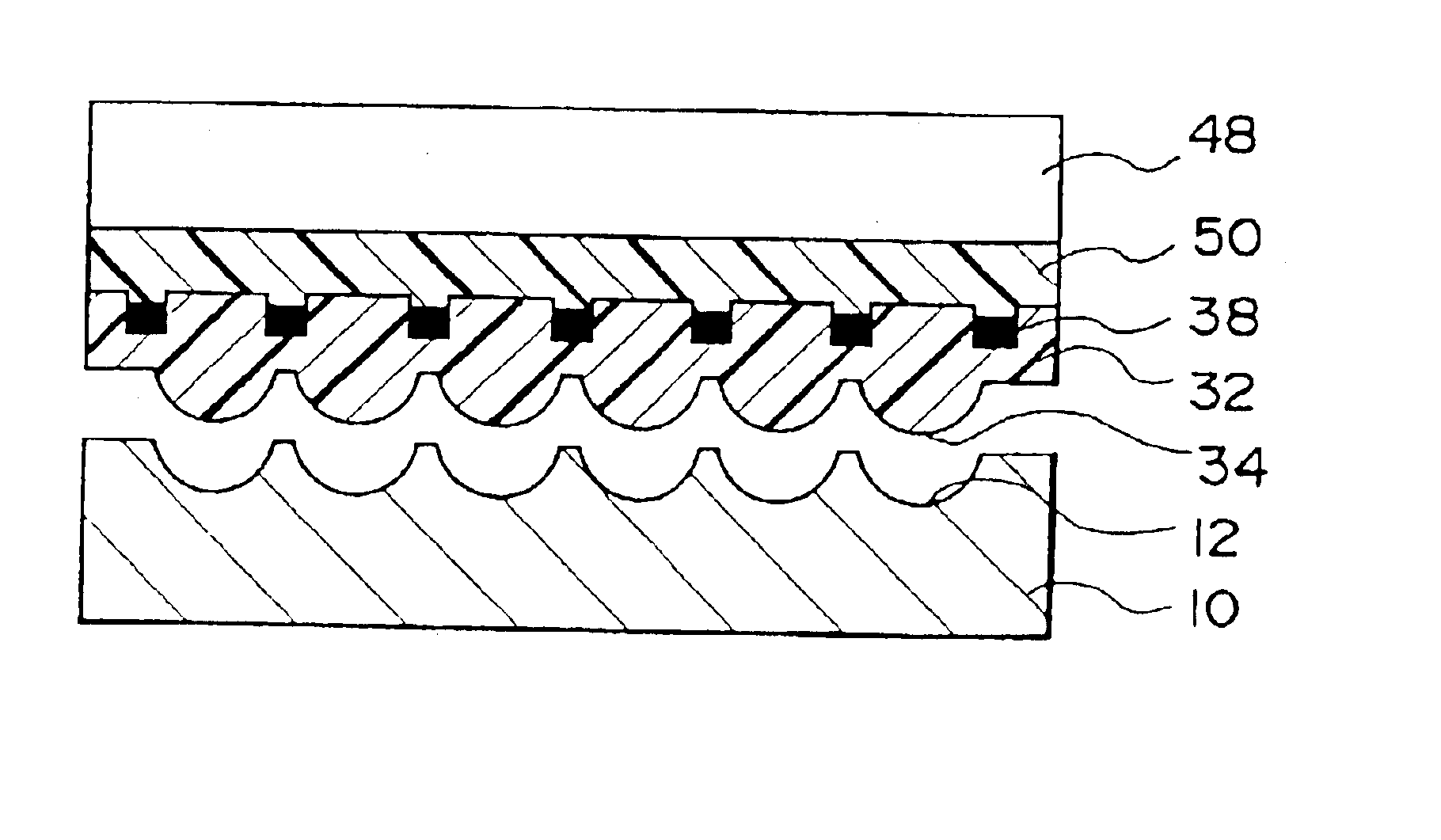
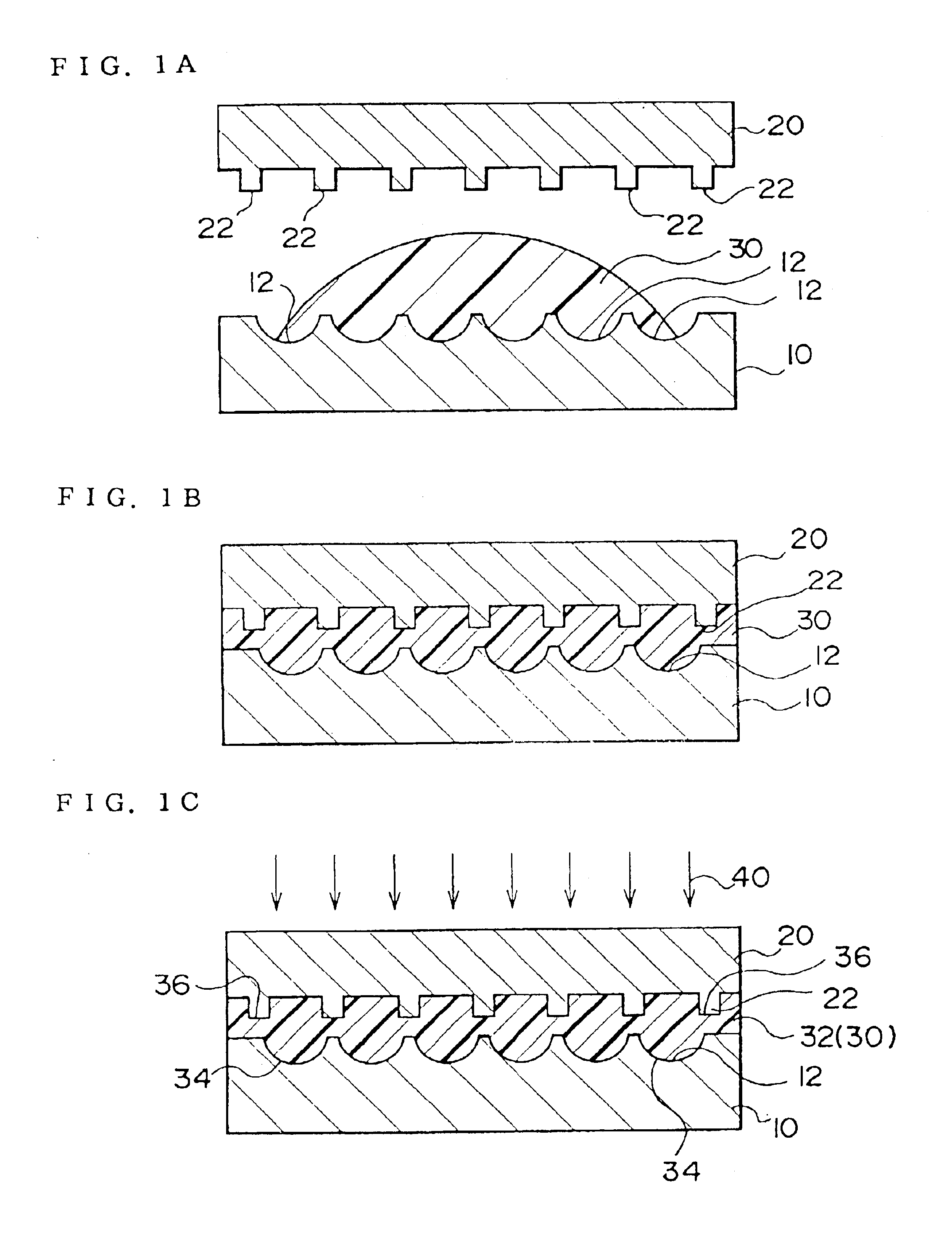
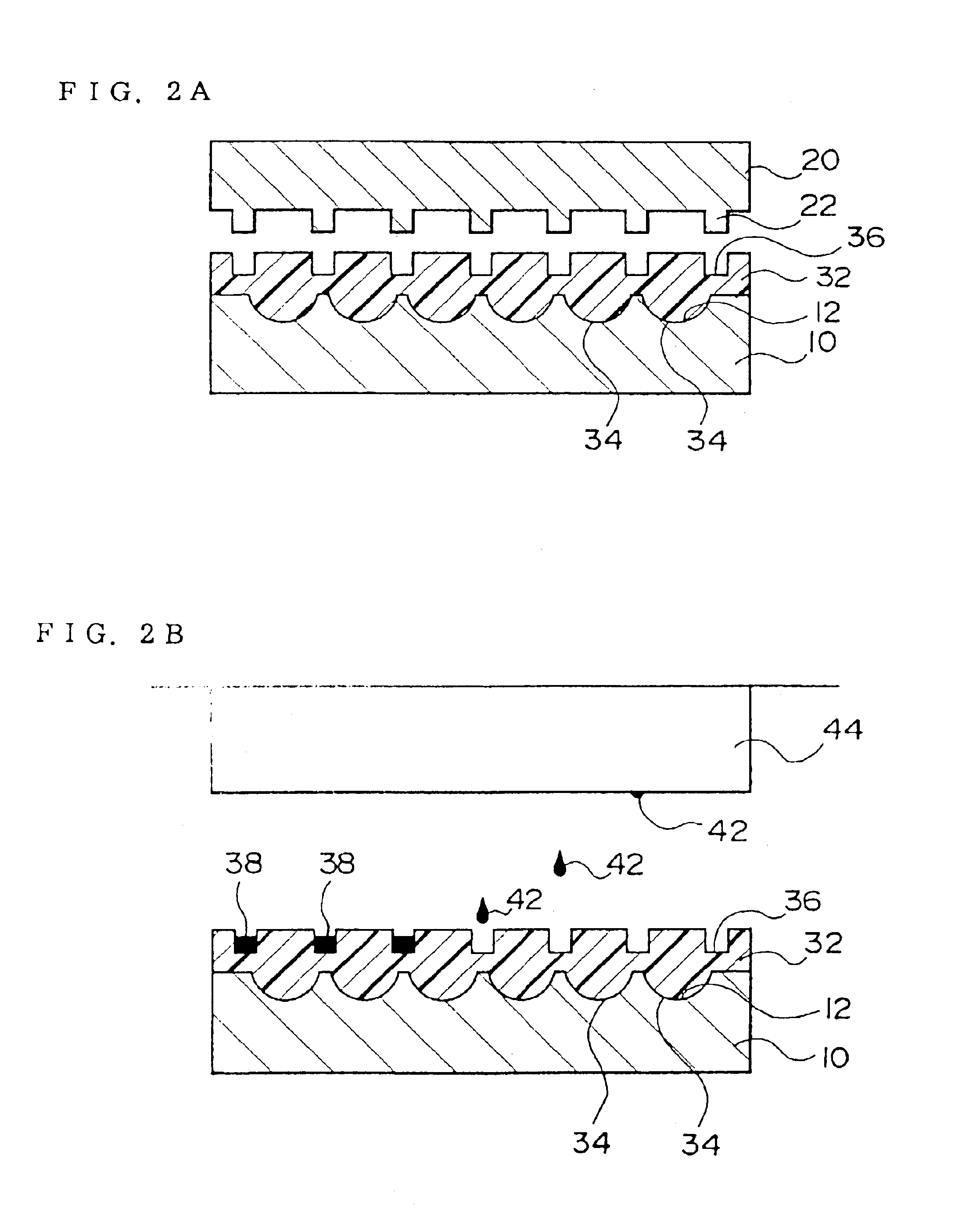
Microlens array substrate, method of manufacturing the same, and display device
InactiveUS6909121B2Well formedBrighter illuminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical articlesDisplay deviceEngineering
A method of manufacturing a microlens array substrate is provided comprising the steps of: closely providing a substrate precursor (30) between a first master mold (10) having a plurality of curved surfaces (12) and a second master mold (20) having a plurality of projections (22) to form a substrate (32) having a plurality of lenses (34) formed by the curved surfaces (12) and recesses (36) formed by the projections (22); removing the first and second master molds (10, 20) from the substrate (32); and filling the recesses (36) with a shading material (42) after the second master mold (20) is removed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Methods and apparatus for full-resolution light-field capture and rendering
ActiveUS8189065B2High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRadianceImage resolution
Method and apparatus for full-resolution light-field capture and rendering. A radiance camera is described in which the microlenses in a microlens array are focused on the image plane of the main lens instead of on the main lens, as in conventional plenoptic cameras. The microlens array may be located at distances greater than f from the photosensor, where f is the focal length of the microlenses. Radiance cameras in which the distance of the microlens array from the photosensor is adjustable, and in which other characteristics of the camera are adjustable, are described. Digital and film embodiments of the radiance camera are described. A full-resolution light-field rendering method may be applied to flats captured by a radiance camera to render higher-resolution output images than are possible with conventional plenoptic cameras and rendering methods.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
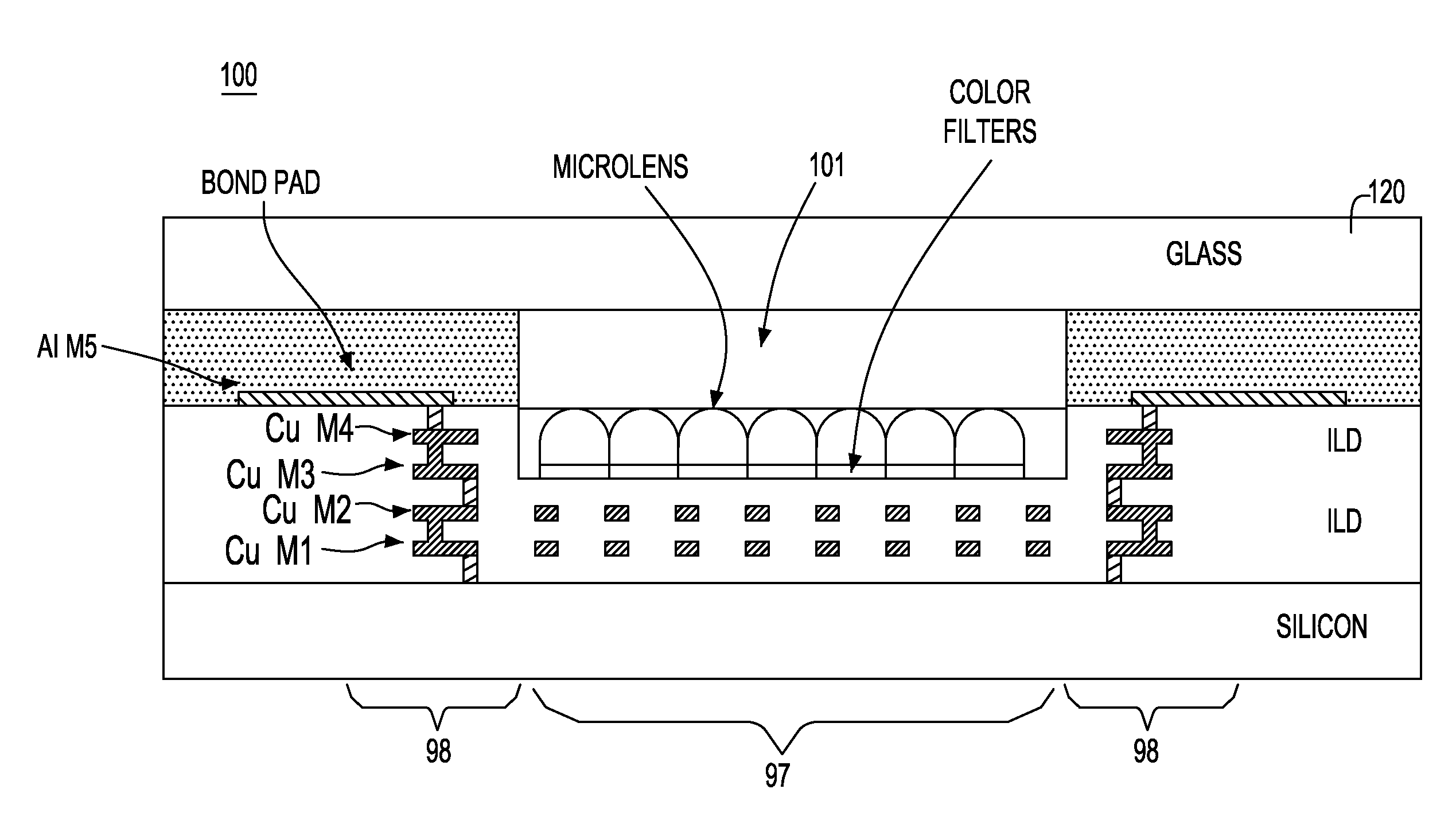
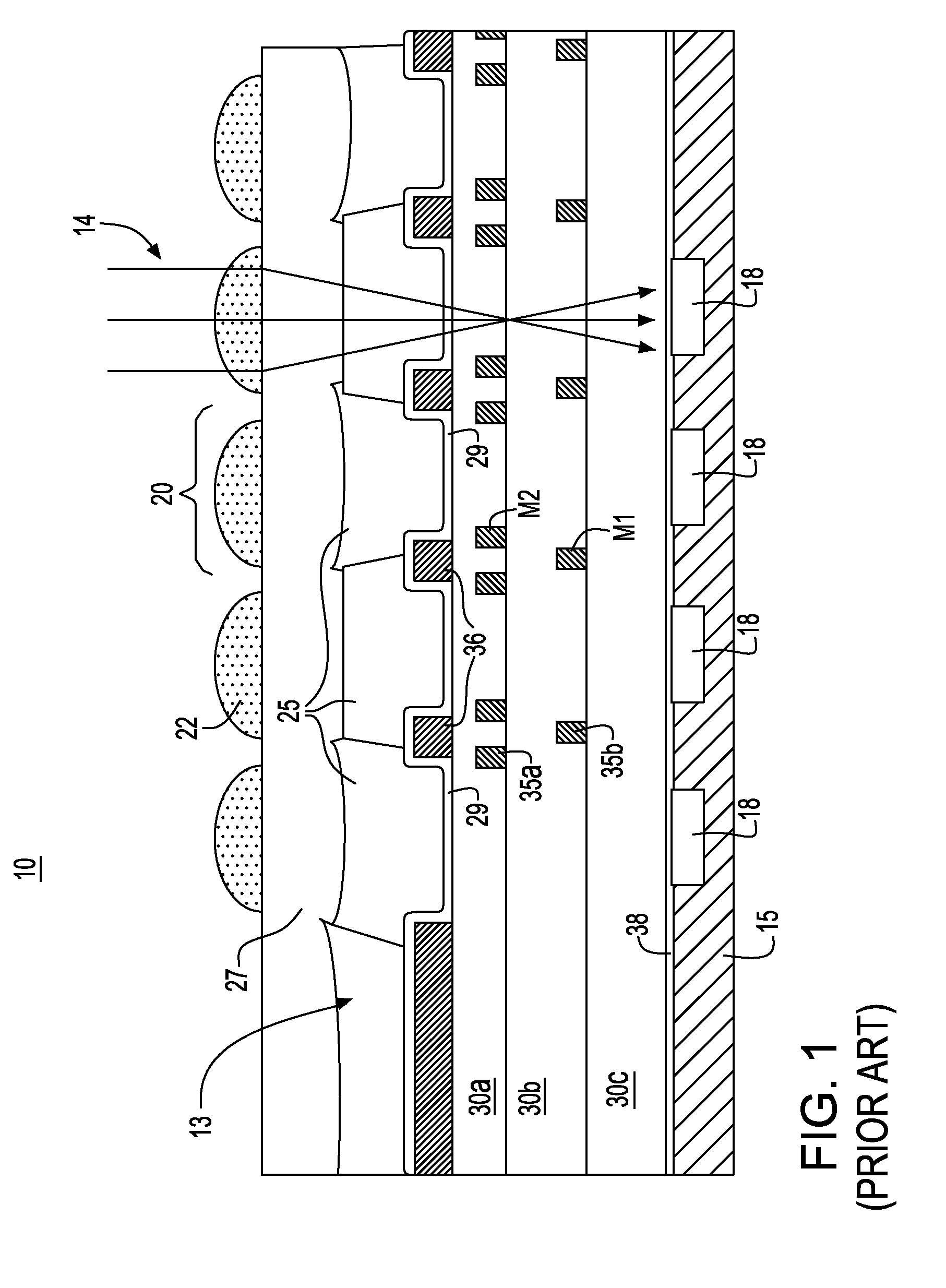
CMOS imager array with recessed dielectric
ActiveUS20080116537A1Thin dielectric stackHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSensor arrayCMOS
A CMOS image sensor array and method of fabrication. The CMOS imager sensor array comprises a substrate; an array of light receiving pixel structures formed above the substrate, the array having formed therein “m” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer; a dense logic wiring region formed adjacent to the array of light receiving pixel structures having “n” levels of conductive structures, each level formed in a corresponding interlevel dielectric material layer, where n>m. A microlens array having microlenses and color filters formed above the interlevel dielectric material layer, a microlens and respective color filter in alignment with a respective light receiving structure formed at a surface of the substrate. A top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layer beneath the microlens array is recessed from a top surface of the interlevel dielectric material layers of the dense logic wiring region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Spatially corrected full-cubed hyperspectral imager
ActiveUS7242478B1Accurate spectralAccurate resolutionSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsFrequency spectrumImage resolution
A hyperspectral imager that achieves accurate spectral and spatial resolution by using a micro-lens array as a series of field lenses, with each lens distributing a point in the image scene received through an objective lens across an area of a detector array forming a hyperspectral detector super-pixel. Each sub-pixel within a super-pixel has a bandpass or other type filter to pass a different band of the image spectrum. The micro-lens spatially corrects the focused image point to project the same image scene point onto all sub-pixels within a super-pixel. A color separator can be used to split the image into sub-bands, with each sub-band image projected onto a different spatially corrected detector array. A shaped limiting aperture can be used to isolate the image scene point within each super-pixels and minimize energy coupling to adjacent super-pixels.
Owner:SURFACE OPTICS
Methods and Apparatus for Full-Resolution Light-Field Capture and Rendering
ActiveUS20090295829A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRadianceComputer graphics (images)
Method and apparatus for full-resolution light-field capture and rendering. A radiance camera is described in which the microlenses in a microlens array are focused on the image plane of the main lens instead of on the main lens, as in conventional plenoptic cameras. The microlens array may be located at distances greater than f from the photosensor, where f is the focal length of the microlenses. Radiance cameras in which the distance of the microlens array from the photosensor is adjustable, and in which other characteristics of the camera are adjustable, are described. Digital and film embodiments of the radiance camera are described. A full-resolution light-field rendering method may be applied to flats captured by a radiance camera to render higher-resolution output images than are possible with conventional plenoptic cameras and rendering methods.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Focused plenoptic camera employing different apertures or filtering at different microlenses
ActiveUS8228417B1Increase and maximize spatial resolutionSharper and high spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensMicro lens array
Owner:ADOBE INC
Curved near-to-eye display
A display apparatus includes an array of microlenses disposed in or on a substrate. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes scattering centers disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The scattering centers are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that light incident upon a first side the substrate is scattered off of the scattering centers and collimated by corresponding ones of the microlenses before emission from the display apparatus. In another embodiment, the apparatus includes light emitting pixels disposed in or on the substrate and offset relative to the microlenses. The light emitting pixels are positioned substantially at focal points of the microlenses such that non-collimated light emitted from the light emitting pixels is collimated by the microlenses upon emission from the display apparatus.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Digital imaging system, plenoptic optical device and image data processing method
ActiveUS20120050562A1Avoid disadvantagesSimple methodTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceDigital imagingMicro lens array
A digital imaging system being configured for synthesizing an image of a plenoptic optical device, comprises a photosensor array comprising a plurality of photosensors arranged in a predetermined image plane, and a microlens array comprising a plurality of microlenses arranged for directing light from an object to the photosensor array, wherein the photosensor array and the microlens array are arranged with a predetermined distance, the microlenses have different focal lengths varying over the microlens array, and the image plane of the photosensor array is arranged such that the distance between the photosensor array and the microlens array does not equal the microlenses' focal lengths. Furthermore, a plenoptic optical device including the digital imaging system and a method for processing image data collected with the digital imaging system are described.
Owner:RAYTRIX
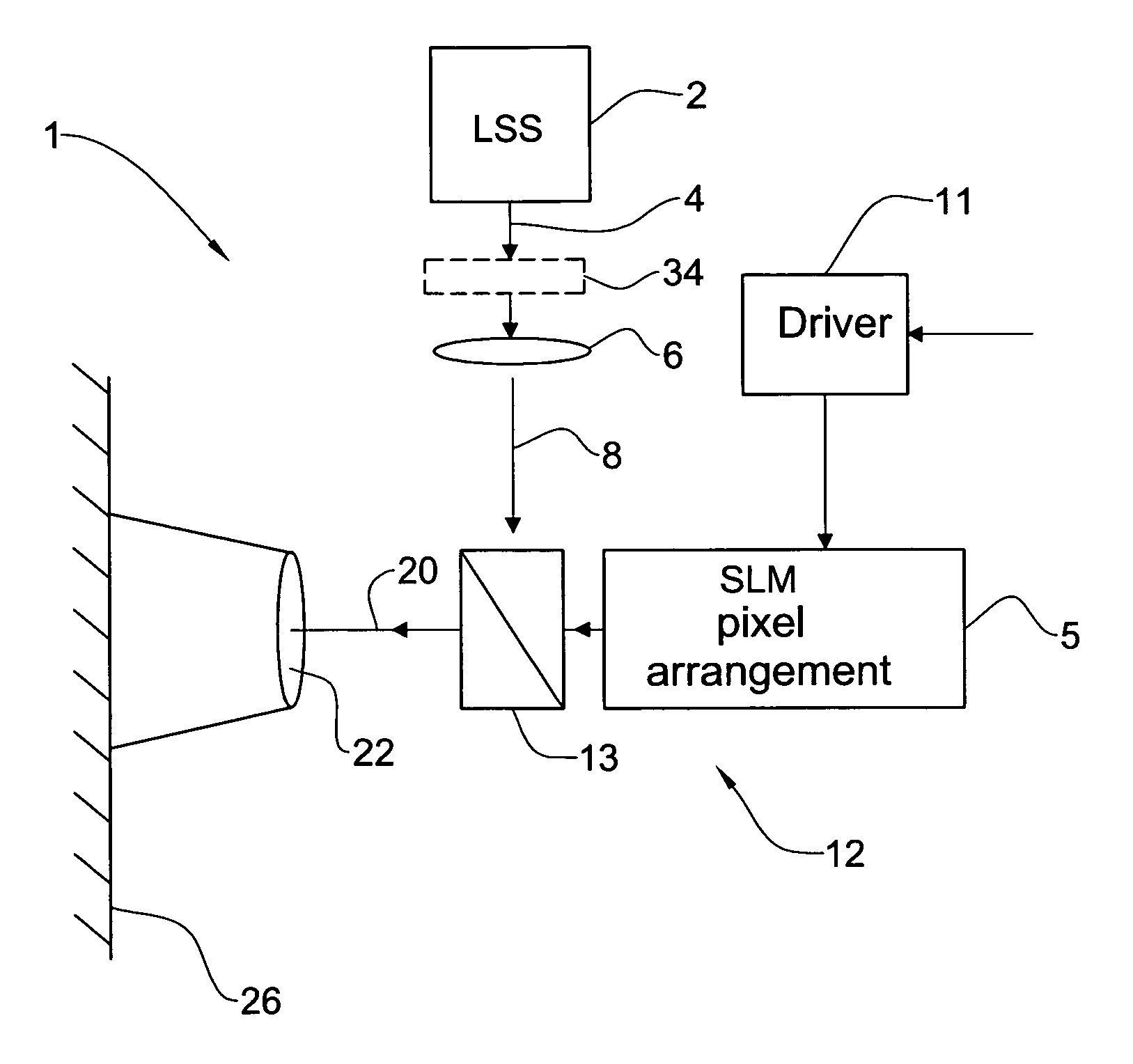
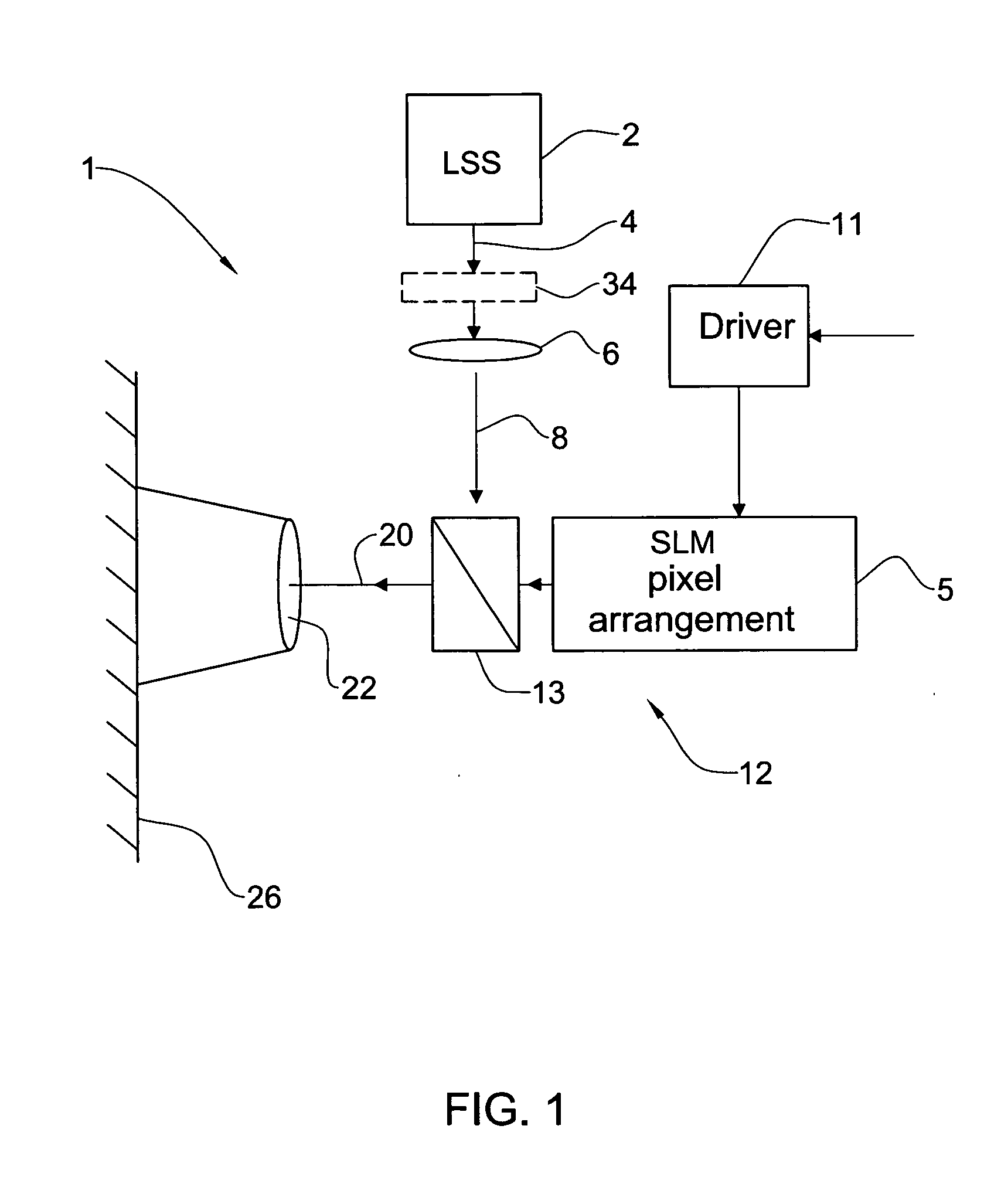
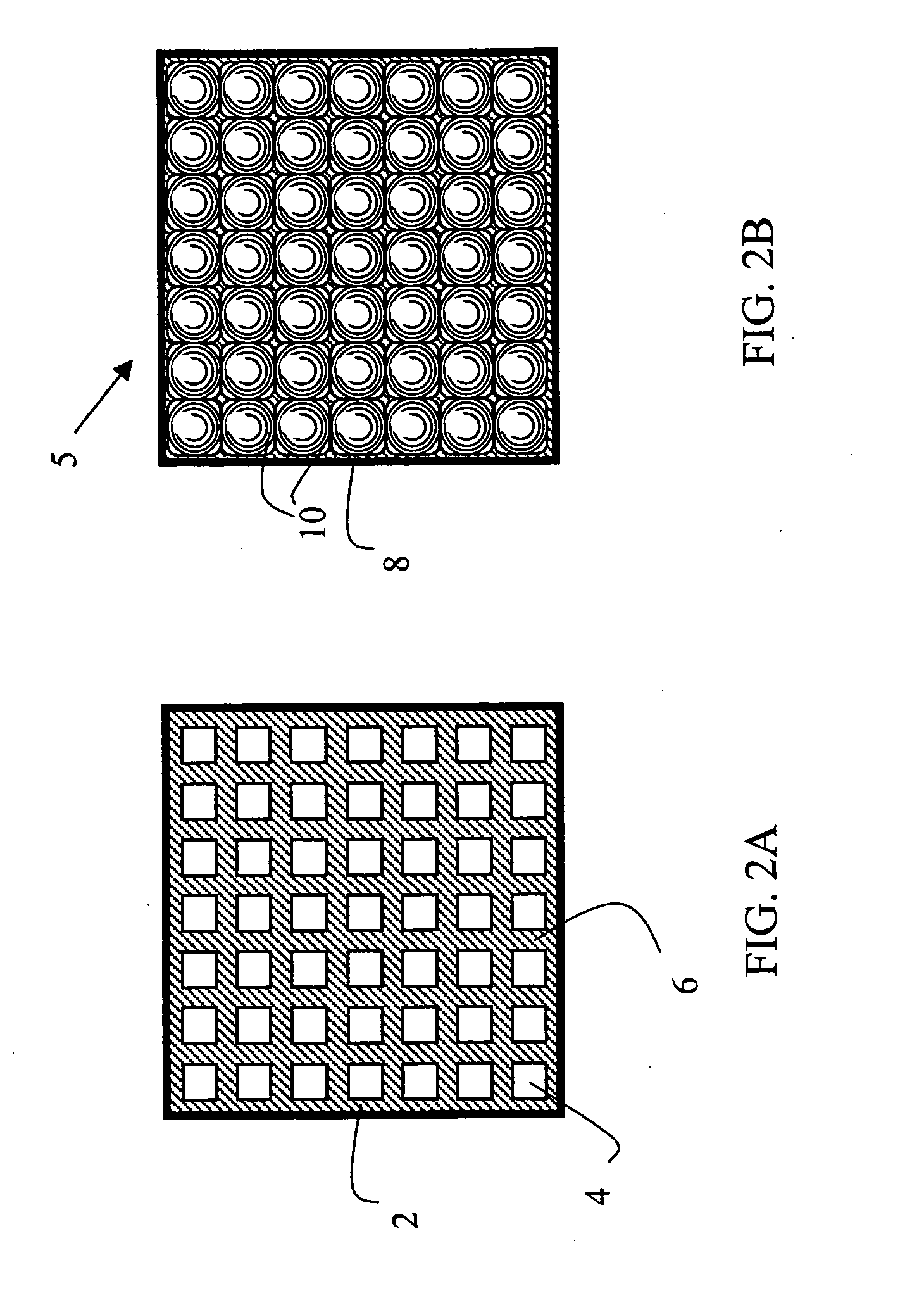
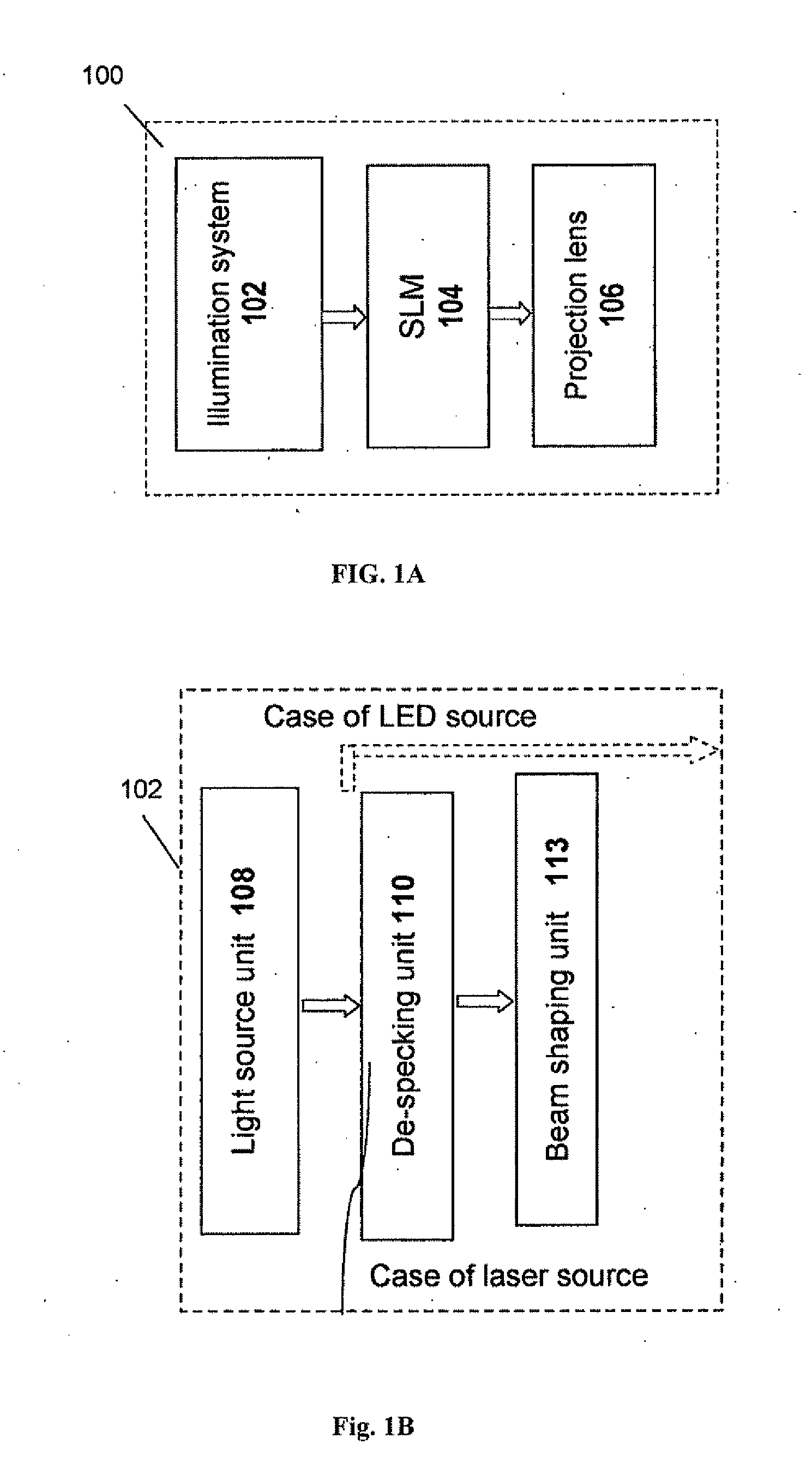
Image projecting device and method
InactiveUS20060018025A1Easy to castImprove efficiencyPicture reproducers using projection devicesOptical elementsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
An image projecting device and method are presented. The device comprises a light source system, a spatial light modulator (SLM) unit, and an image projection optics accommodated at the output side of the SLM unit. The SLM unit may be reflective or transmissive. The SLM unit comprises an SLM pixel arrangement enclosed between two glass substrates. The pixel array arrangement is formed by a pixel array assembly and at least one microlens assembly. The microlens assembly includes at least one microlens array accommodated proximate of the pixel array assembly. The light source system may comprise n light sources and a light converting means in optical path of light generated by the n light sources, to thereby produce m light beams of different wavelength ranges, wherein m>n. The light source system may comprise a multi-mode laser, thereby reducing a speckle effect in an integrated speckle pattern produced by the multiple modes, as compared to that of a single mode.
Owner:EXPLAY
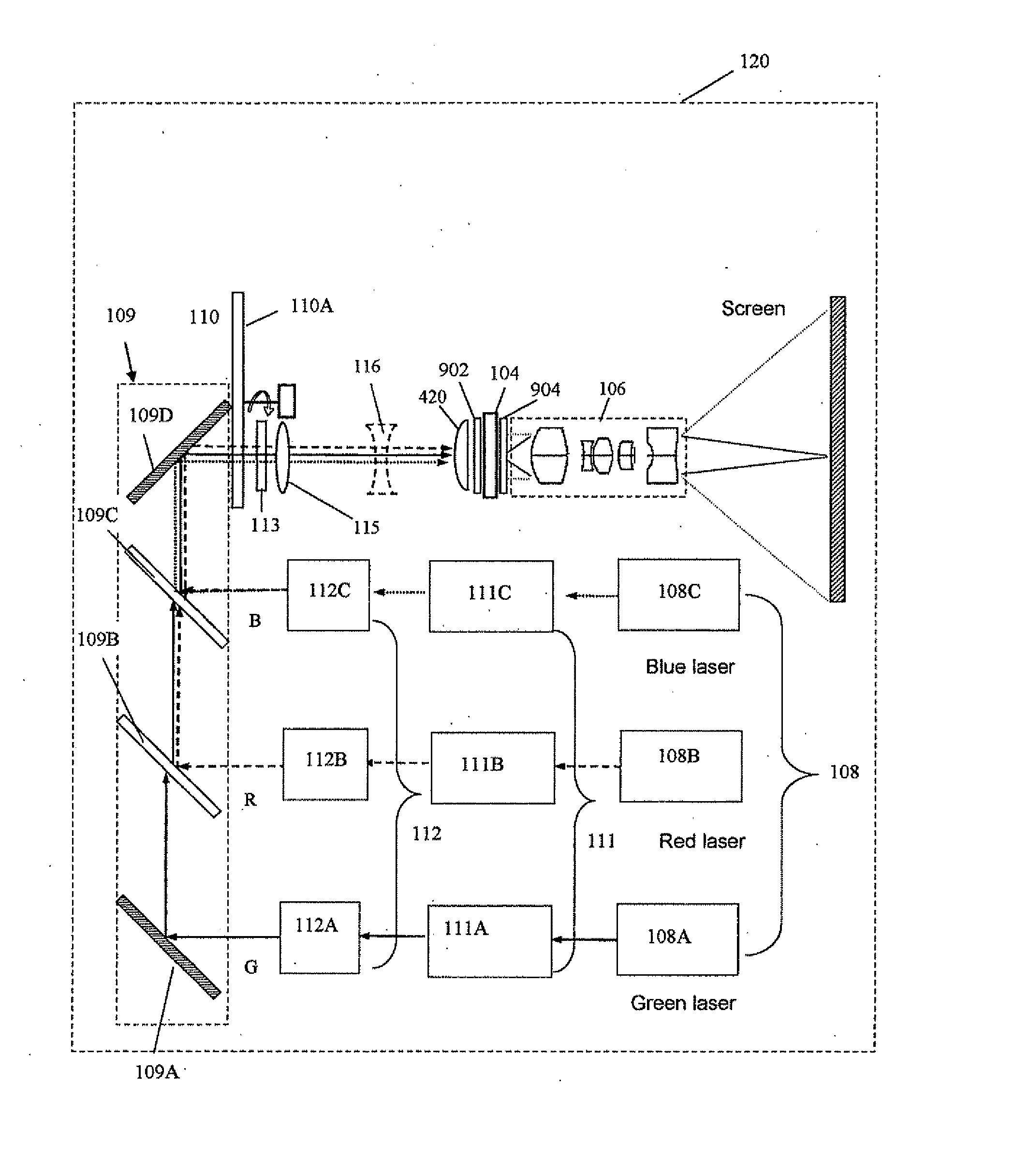
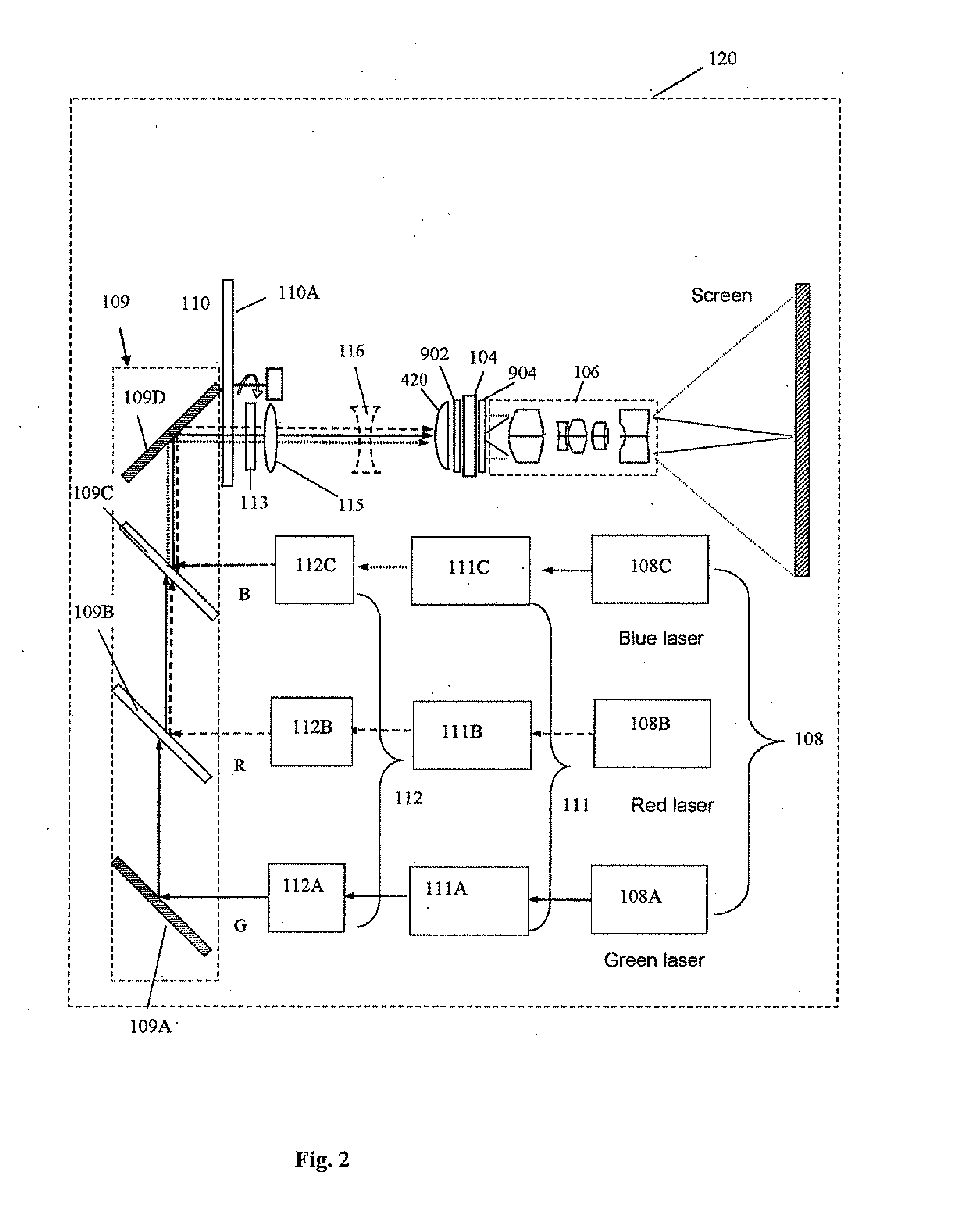
Micro-projector
InactiveUS20110037953A1Increase brightnessQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceLaser source
The present invention provides a projection display comprising an illumination system comprising at least one laser source unit and configured and operable for producing one or more light beams; a spatial light modulating (SLM) system accommodated at output of the illumination system and comprising one or more SLM units for modulating light incident thereon in accordance with image data; and a light projection optics for imaging modulated light onto a projection surface. The illumination system comprises at least one beam shaping unit comprising a Dual Micro-lens Array (DMLA) arrangement formed by front and rear micro-lens arrays (MLA) located in front and rear parallel planes spaced-apart along an optical path of light propagating towards the SLM unit, the DMLA arrangement being configured such that each lenslet of the DMLA directs light incident thereon onto the entire active surface of the SLM unit, each lenslet having a geometrical aspect ratio corresponding to an aspect ratio of said active surface of the SLM unit.
Owner:EXPLAY
Micro-lens arrays for display intensity enhancement
InactiveUS6984934B2Increased light coupling efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLength waveMicro lens array
A microlens array for a light emitting device is disclosed. The light emitting device includes a plurality of OLEDs, each OLED having a minimum planar dimension. The array includes a plurality of microlenses, each of which has a minimum planar dimension and a maximum planar dimension. The minimum planar dimensions of the microlenses are larger than the maximum wavelength of visible light emitted from the OLEDs. The maximum planar dimensions of the microlenses are smaller than the smallest minimum planar dimension of any of the OLEDs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Wearable display devices
A wearable display device is described that allows the image from a semi-transparent display screen placed close to the eye to be correctly focused onto the retina while simultaneously allowing the image from the external environment to pass through the device without significant aberration. Focus of the display screen image is achieved through use of a micro-lens array between the screen and the eye, and a separate set of micro-lens arrays on the distant side of the screen in conjunction with the micro-lens array on the near side of the screen allows the external environmental image to pass through. In this manner images from the display screens can overlay the eye's usual view of the external environment. Use of micro-lens arrays that have dynamically adjustable focus properties allow for simulated three-dimensional images and corrective optics for far- or near-sightedness.
Owner:BELL JONATHAN ARNOLD
Waveguide-Based Displays With Exit Pupil Expander
ActiveUS20170299860A1Good optical performanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesHead-up displayExit pupil
A near eye or heads up display system includes a scan beam projector engine, an optical waveguide, and an exit pupil expander (EPE) optically coupled between the scan beam projector engine and the optical waveguide. The EPE improves the optical performance of the display system. The EPE could include a diffusive optical element, diffractive optical element, micro-lens array (MLA), or relay of aspherical lenses. A dual MLA EPE may have cells that prevent cross-talk between adjacent pixels. A dual MLA EPE may have a non-periodic lens array. The optical power of one MLA may be different from the other MLA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Quantum dot near-to-eye display
A multi-layer optical structure includes a pixel array layer, an addressing matrix layer, and a micro lens array. The pixel array layer includes an array of quantum dot pixels for emitting an image from a first side of the multi-layer optical structure. The addressing matrix layer adjoins the pixel array layer and includes electrically conductive signal lines to individual address and activate the quantum dot pixels to generate the image. The micro lens array includes micro lenses optically aligned with the quantum dot pixels in an emission path of the image to focus the image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
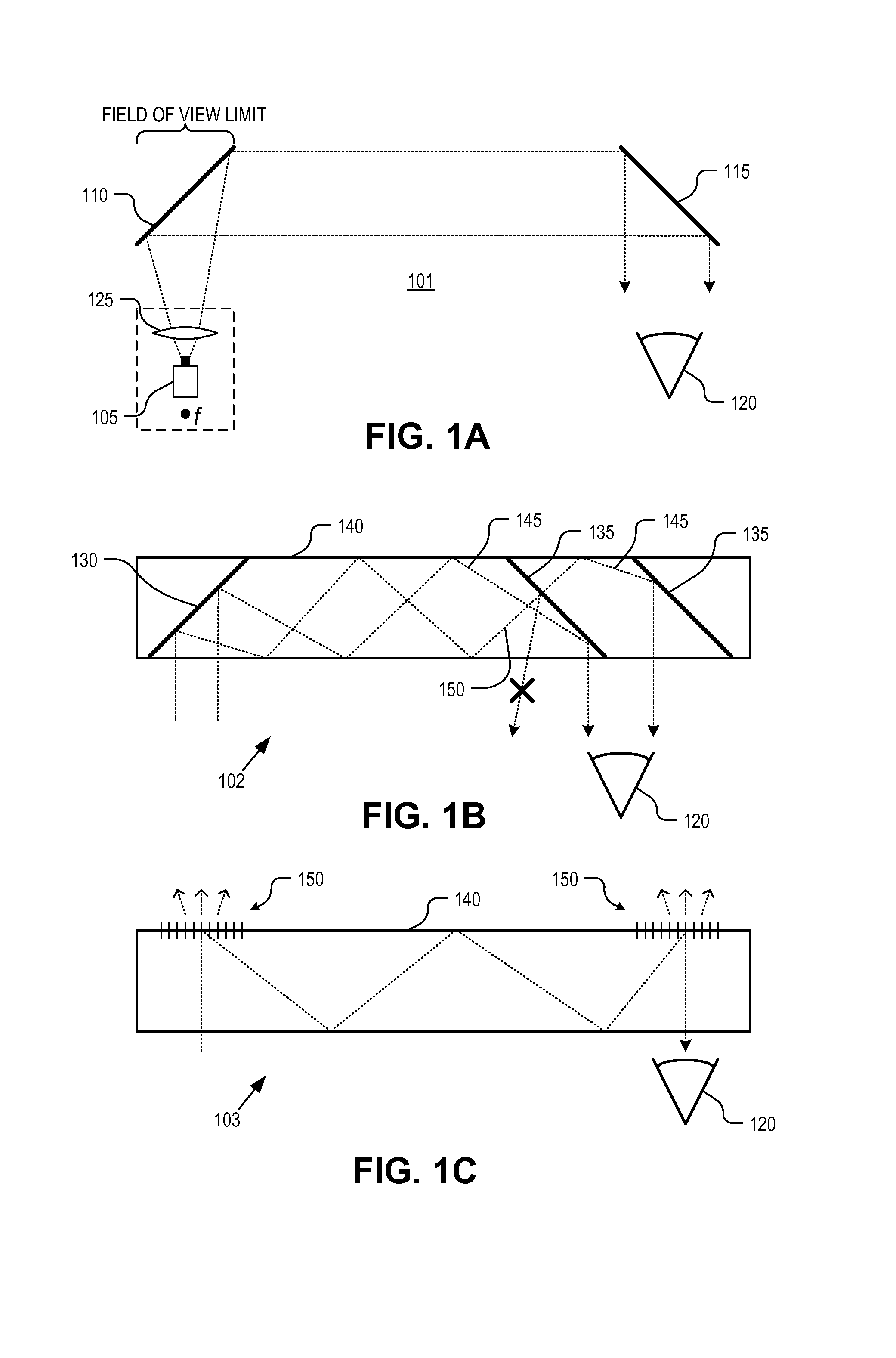
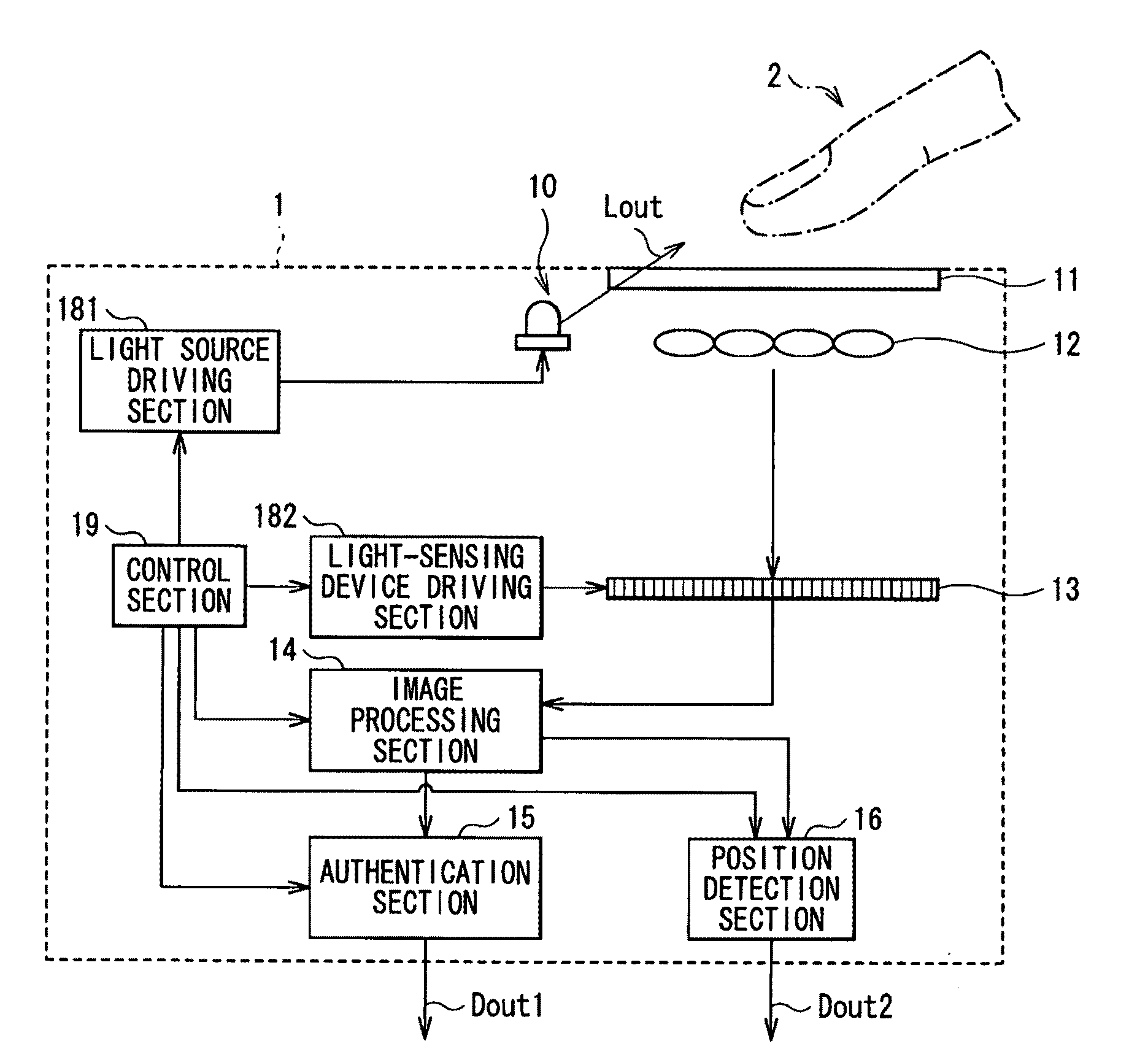
Biometrics authentication system
InactiveUS20100026453A1Small and simple configurationSimple configurationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisLight sensingLiving body
A biometrics authentication system having a small and simple configuration and being capable of implementing both of biometrics authentication and position detection is provided. A biometrics authentication system includes: a light source emitting light to an object; a microlens array section condensing light from the object; a light-sensing device obtaining light detection data of the object on the basis of the light condensed by the microlens array section; a position detection section detecting the position of the object on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device; and an authentication section, in the case where the object is a living body, performing authentication of the living body on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
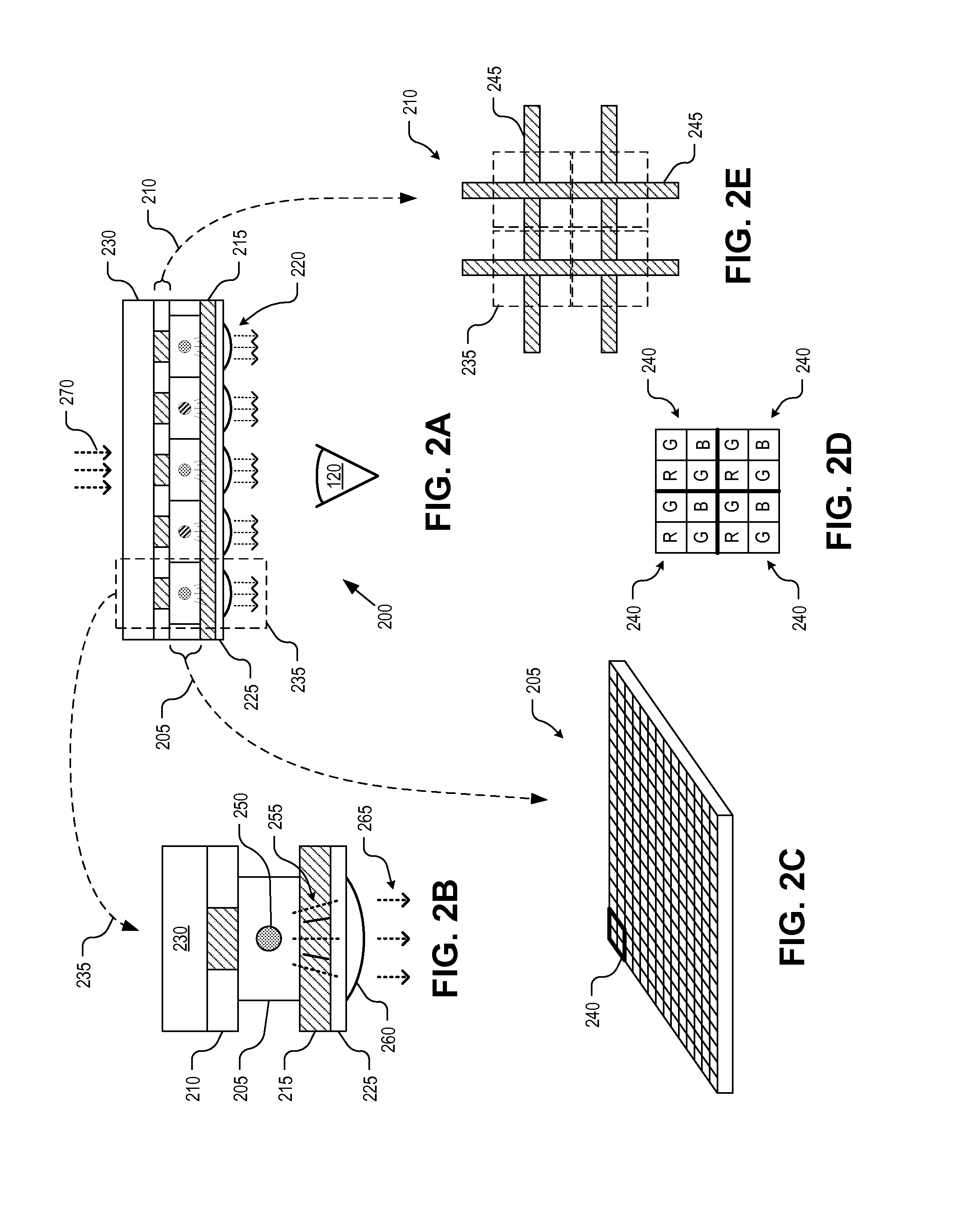
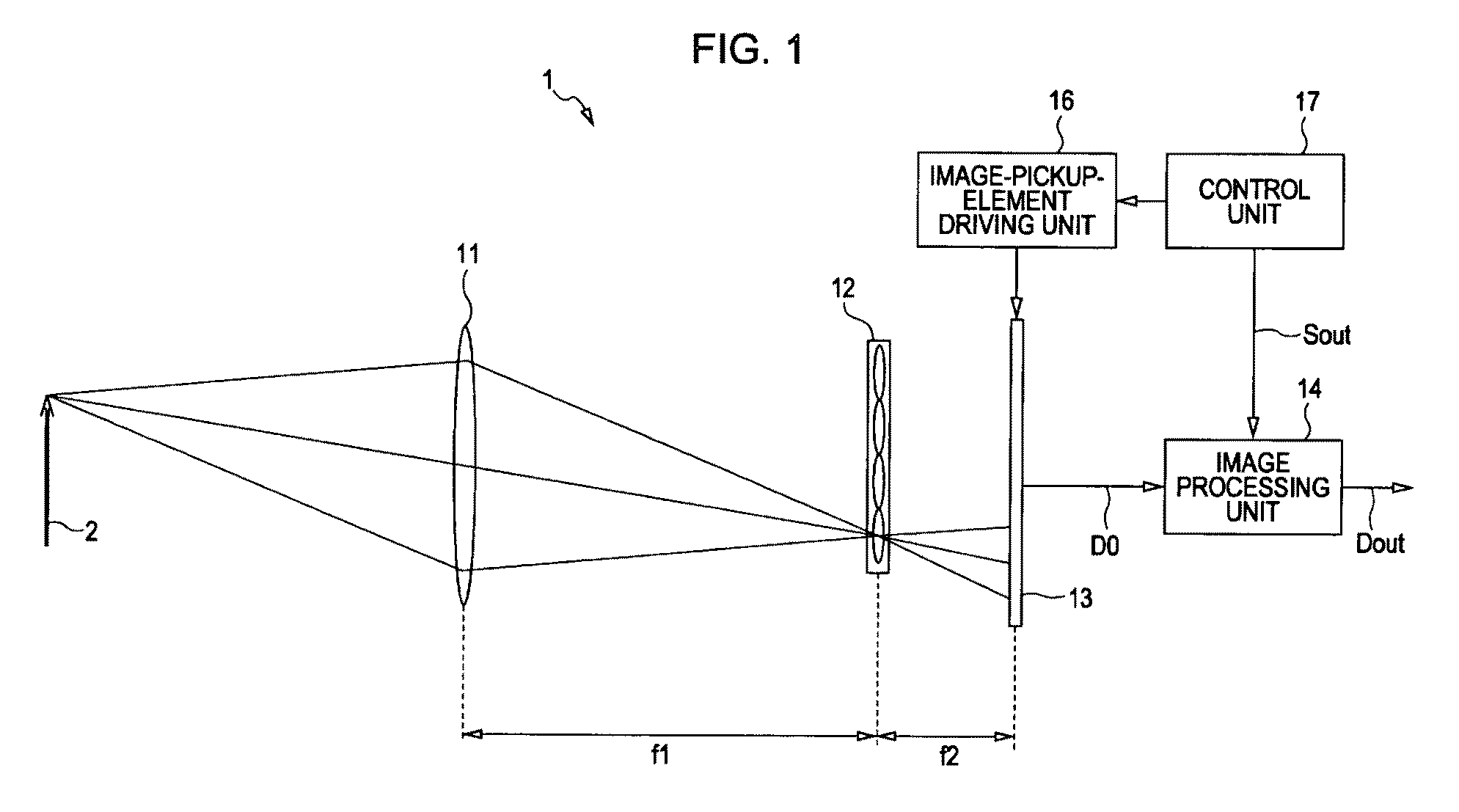
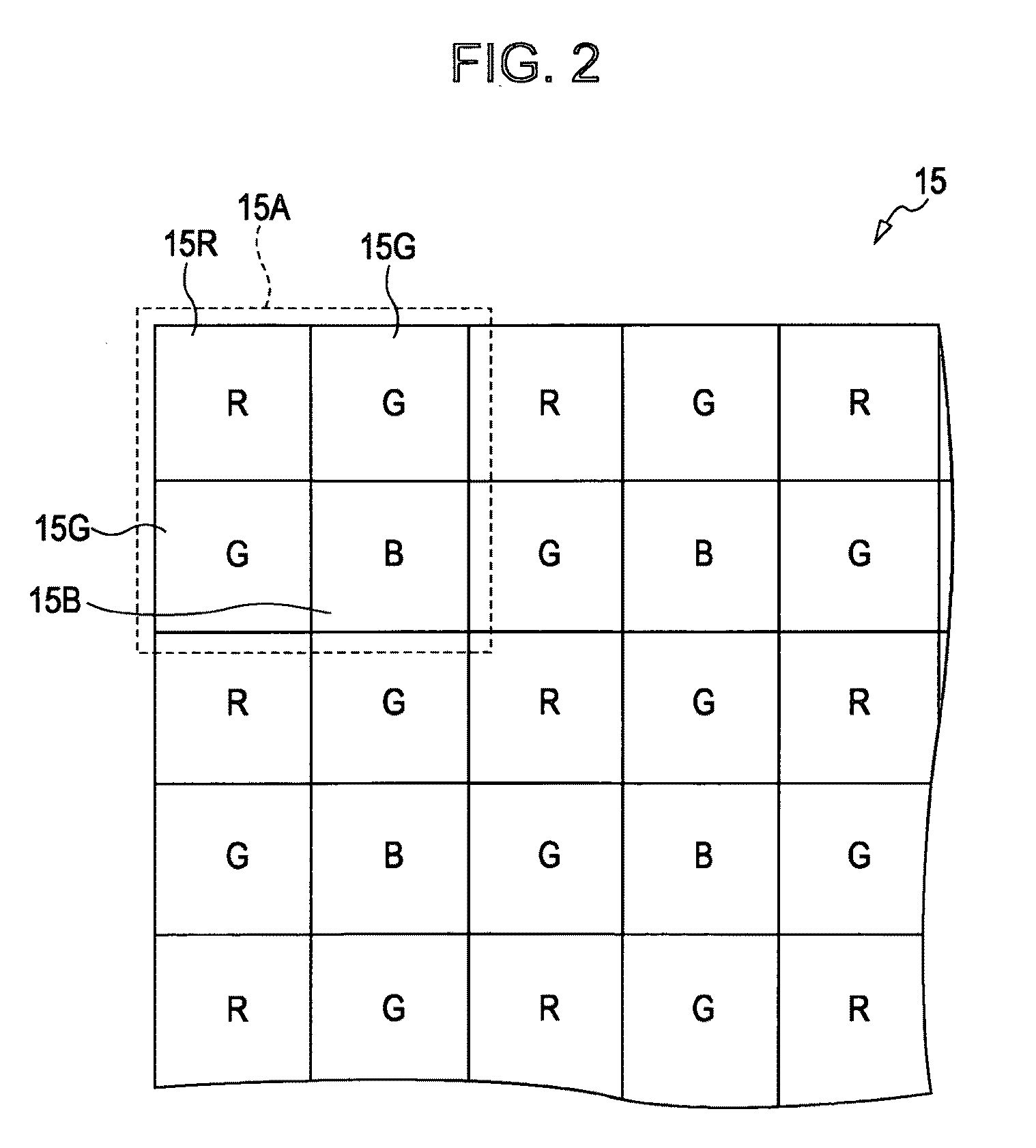
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20090128658A1Accurate brightnessPrevent color balanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsParallaxImaging processing
An image pickup apparatus includes an image-pickup lens having an aperture diaphragm, an image-pickup element that has a color filter which is periodically allocated colors in units of a predetermined unit array and that generates picked-up image data including pixel data of colors using received light, the color filter being adjacent to a light receiving surface, a microlens array unit that is arranged on an image forming surface of the image-pickup lens and whose microlenses are each allocated a plurality of pixels of the image-pickup element, and an image processing unit that performs image processing on the picked-up image data generated by the image-pickup element. The image processing unit includes a parallax component image generation unit that generates a plurality of parallax component images and an interpolation processing unit that performs color interpolation processing for each of the parallax component images.
Owner:SONY CORP
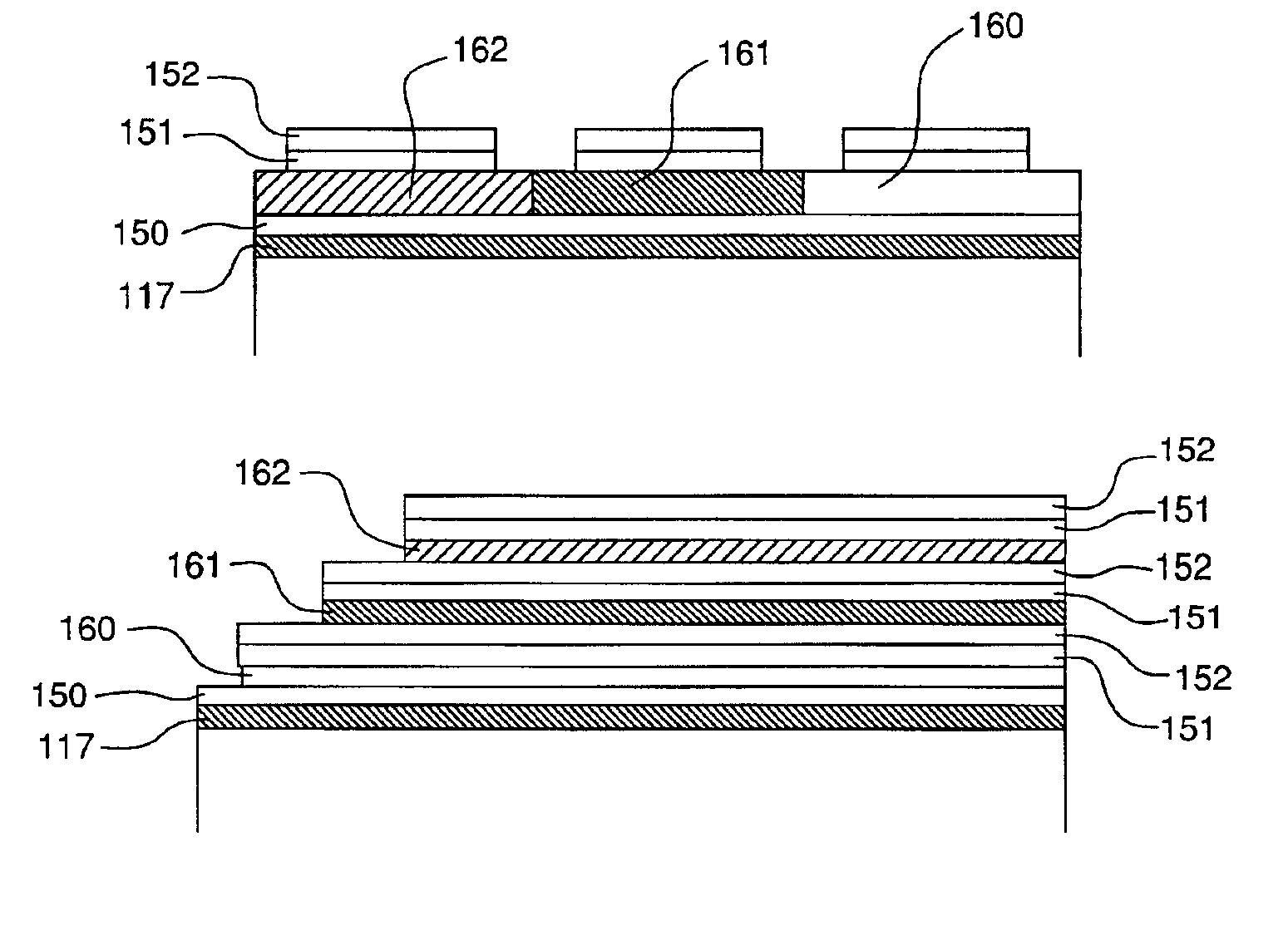
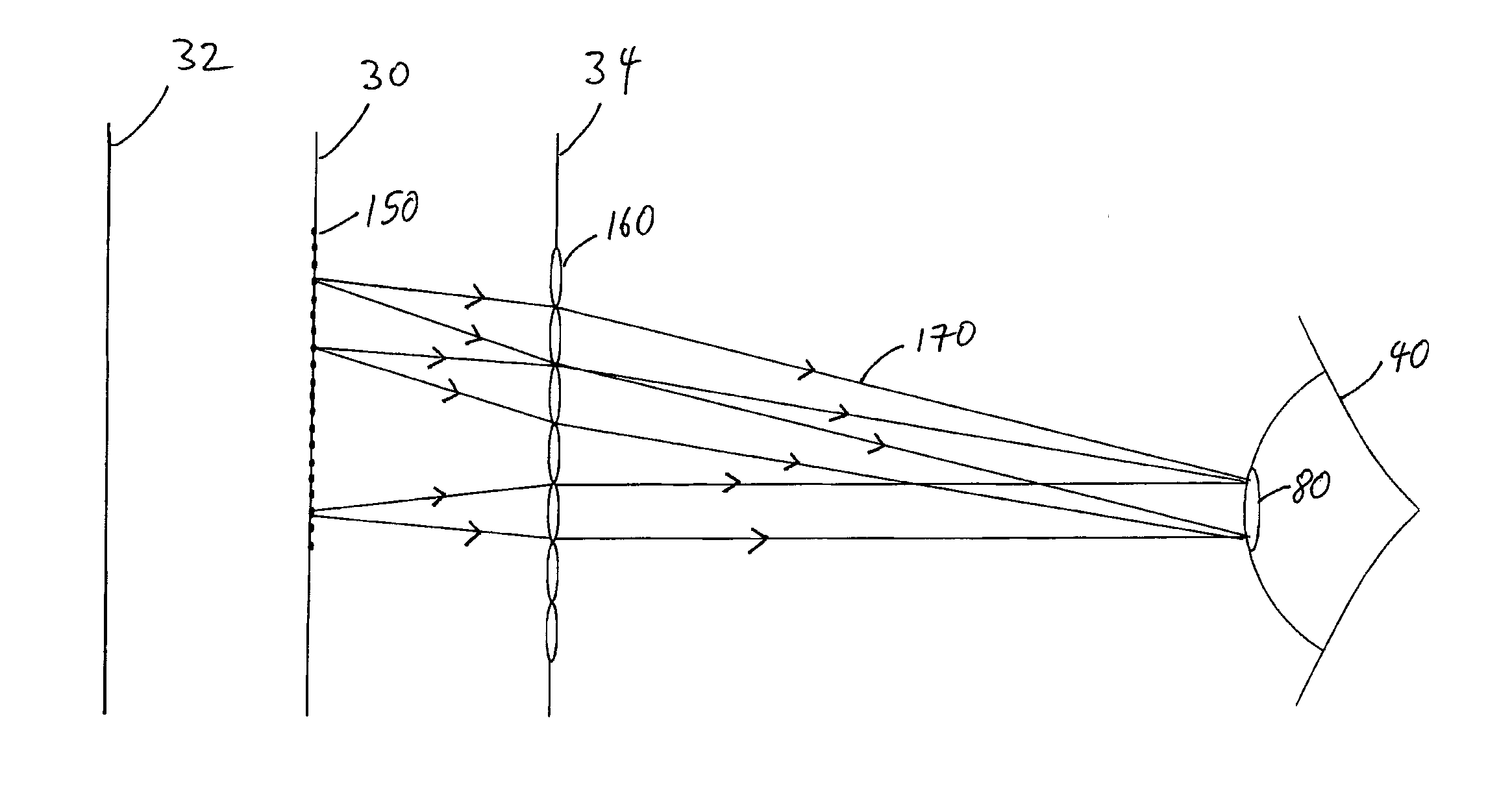
Display assembly
A display assembly, comprising: a display device (30); a microlens array (34); and an eye tracker (8), for example a pupil tracker (8), and / or a head tracker; wherein plural pixels (150) or sub-pixels of the display device (30) are provided for each microlens (160) of the microlens array (34). The display may be adapted such that only certain pixels / sub-pixels (150) are activated / selected for any particular determined pupil / eye / head position, for example such that for each microlens (160), only one respective pixel / sub-pixel (150) is activated / selected for any particular determined pupil / eye / head position. The display device (30) may be a transparent display device (30), the microlens array (34) may be a switchable microlens array (34), and the display assembly may further comprise a light blocking device (32) that is switchable between a substantially light blocking state and a substantially light passing state.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Microelectrical mechanical structure (MEMS) optical modulator and optical display system
InactiveUS20050002086A1Eliminating light attenuation of lightEliminating expenseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPlanar substrateActuator
A MEMS optical display system includes an illumination source for providing illumination light, a collimating lens for receiving the illumination light and forming from it collimated illumination light, and a converging microlens array having an array of lenslets that converge the collimated illumination light. The converging microlens array directs the illumination light to a microelectrical mechanical system (MEMS) optical modulator. The MEMS optical modulator includes, for example, a planar substrate through which multiple pixel apertures extend and multiple MEMS actuators that support and selectively position MEMS shutters over the apertures. A MEMS actuator and MEMS shutter, together with a corresponding aperture, correspond to pixel. The light from the converging microlens array is focused through the apertures and is selectively modulated according to the positioning of the MEMS shutters by the MEMS actuators, thereby to impart image information on the illumination light. The light is then passed to a diffused transmissive display screen by a projection microlens array.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
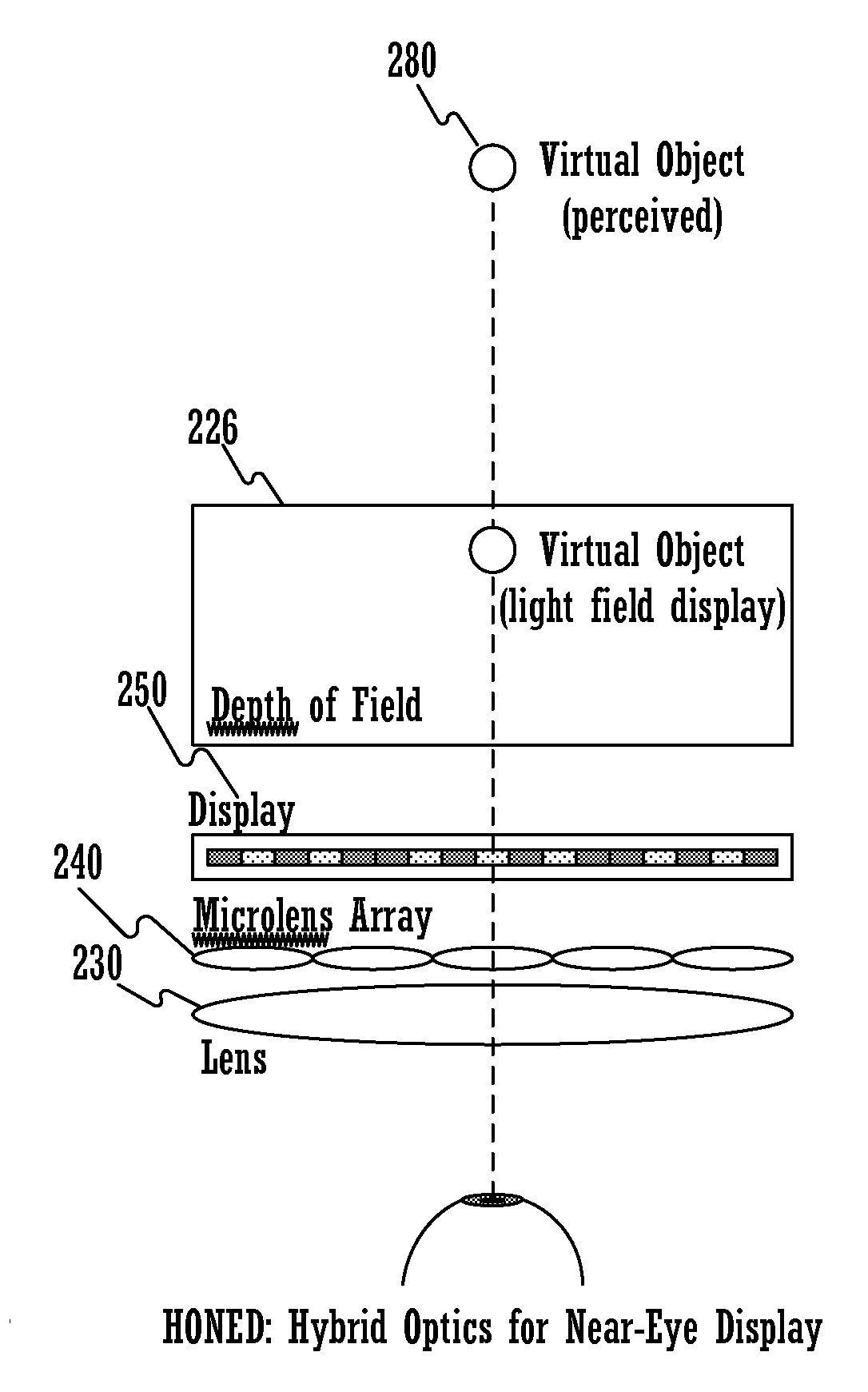
Hybrid optics for near-eye displays
ActiveUS20150049390A1Reduce depthGreat percentageStatic indicating devicesDetails for portable computersImage resolutionDisplay device
A method for displaying a near-eye light field display (NELD) image is disclosed. The method comprises determining a pre-filtered image to be displayed, wherein the pre-filtered image corresponds to a target image. It further comprises displaying the pre-filtered image on a display. Subsequently, it comprises producing a near-eye light field after the pre-filtered image travels through a microlens array adjacent to the display, wherein the near-eye light field is operable to simulate a light field corresponding to the target image. Finally, it comprises altering the near-eye light field using at least one converging lens, wherein the altering allows a user to focus on the target image at an increased depth of field at an increased distance from an eye of the user and wherein the altering increases spatial resolution of said target image.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
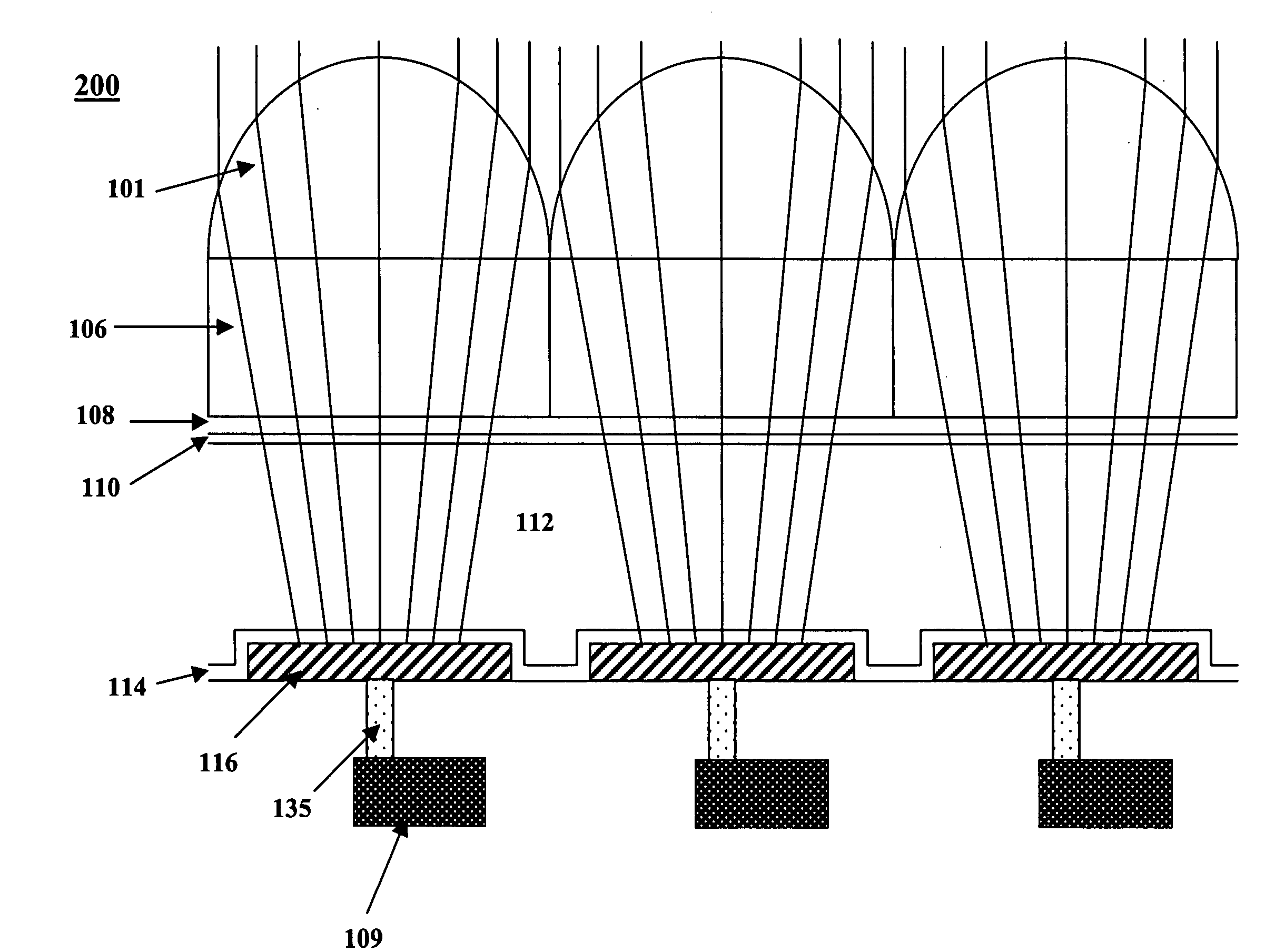
MOS or CMOS sensor with micro-lens array
InactiveUS20060249765A1Small pixelsMinimize and eliminate pixel to pixel crosstalkSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOS sensorHigh-definition television
A MOS or CMOS sensor with a multi-layer photodiode layer covering an array of active pixel circuits. The multi-layer photodiode layer of each pixel is fabricated as continuous layers of charge generating material on top of the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits so that extremely small pixels are possible with almost 100 percent packing factors. The sensor includes special features to minimize or eliminate pixel to pixel crosstalk. A micro-lens array with a micro-lens positioned above each pixel directs light illuminating the pixel toward the central portion of the pixel and away from its edges. Also, preferably carbon is added to doped amorphous silicon N or P bottom layer of the multi-layer photodiode layer to increase the electrical resistivity in the bottom layer to further discourage crosstalk. In preferred embodiments each of the pixels define a tiny surface area equal to or larger than about 3.24 square microns and smaller than or equal to about 25 square microns. Detailed descriptions are provided for two general types of sensors. The first type has a pixel count of about 0.3 to 1.9 million pixels and are especially suited for sues such as cell phone cameras. The second type with pixel count of between about 1.9 million pixels to more than 5 million pixels is especially suited for high definition television cameras.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com