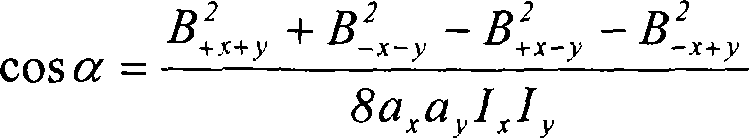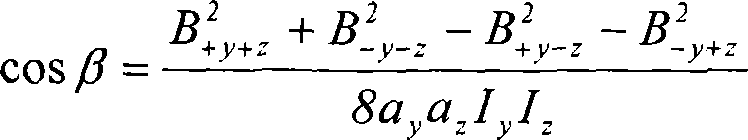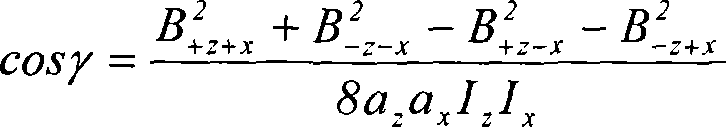Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
386 results about "Magnetic gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
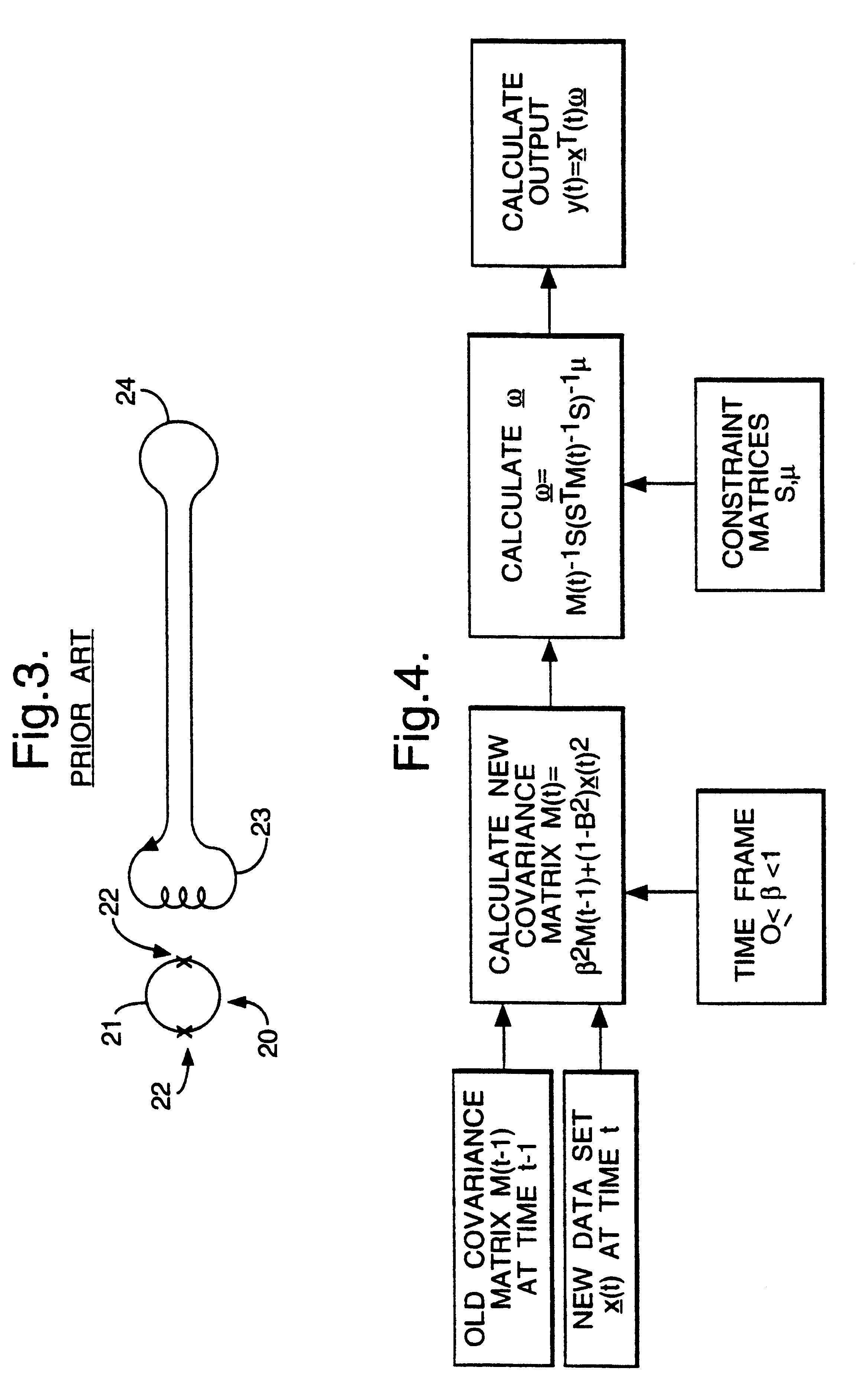
A magnetic field gradient is a variation in the magnetic field with respect to position. A one-dimensional magnetic field gradient is a variation with respect to one direction, while a two-dimensional gradient is a variation with respect to two.
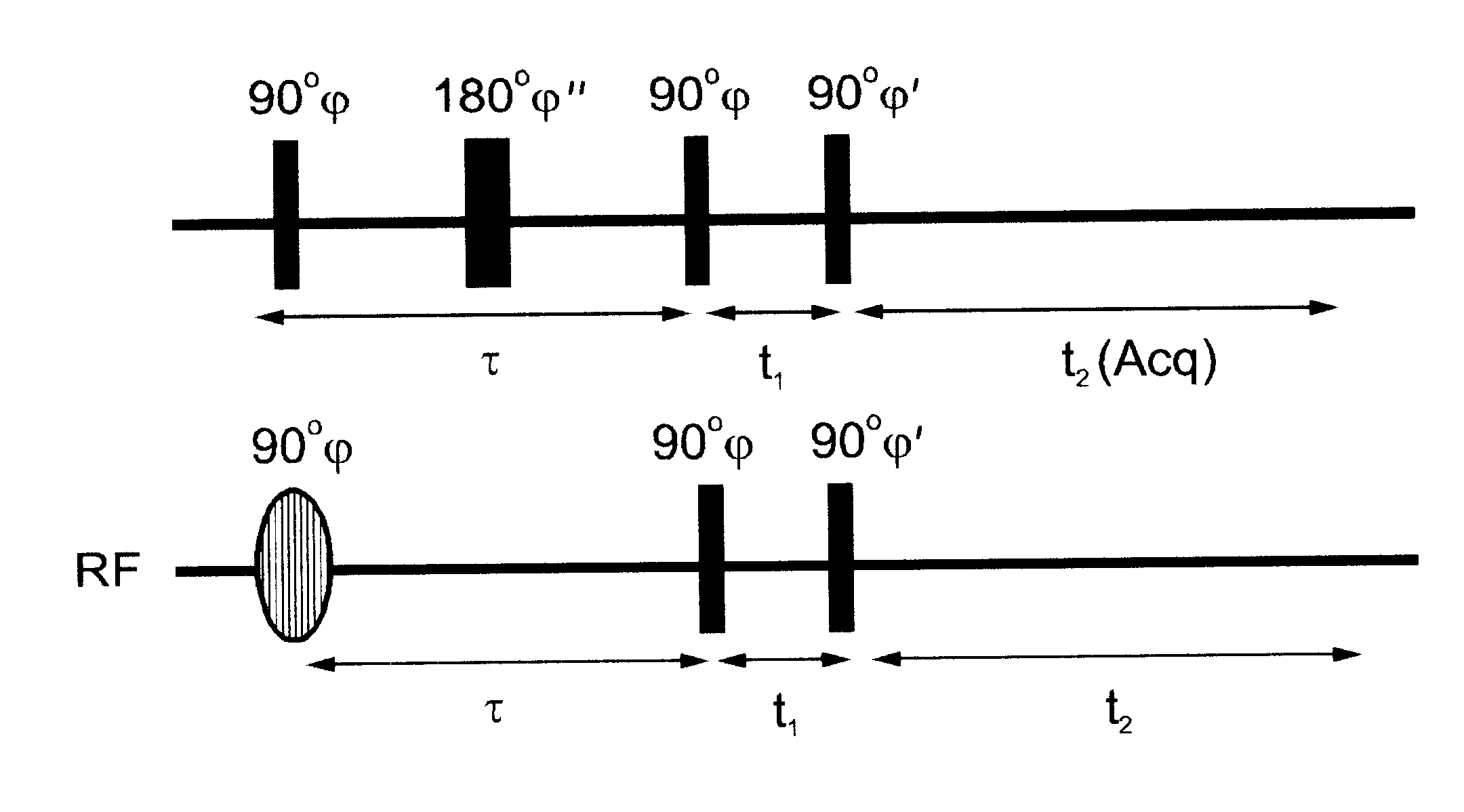
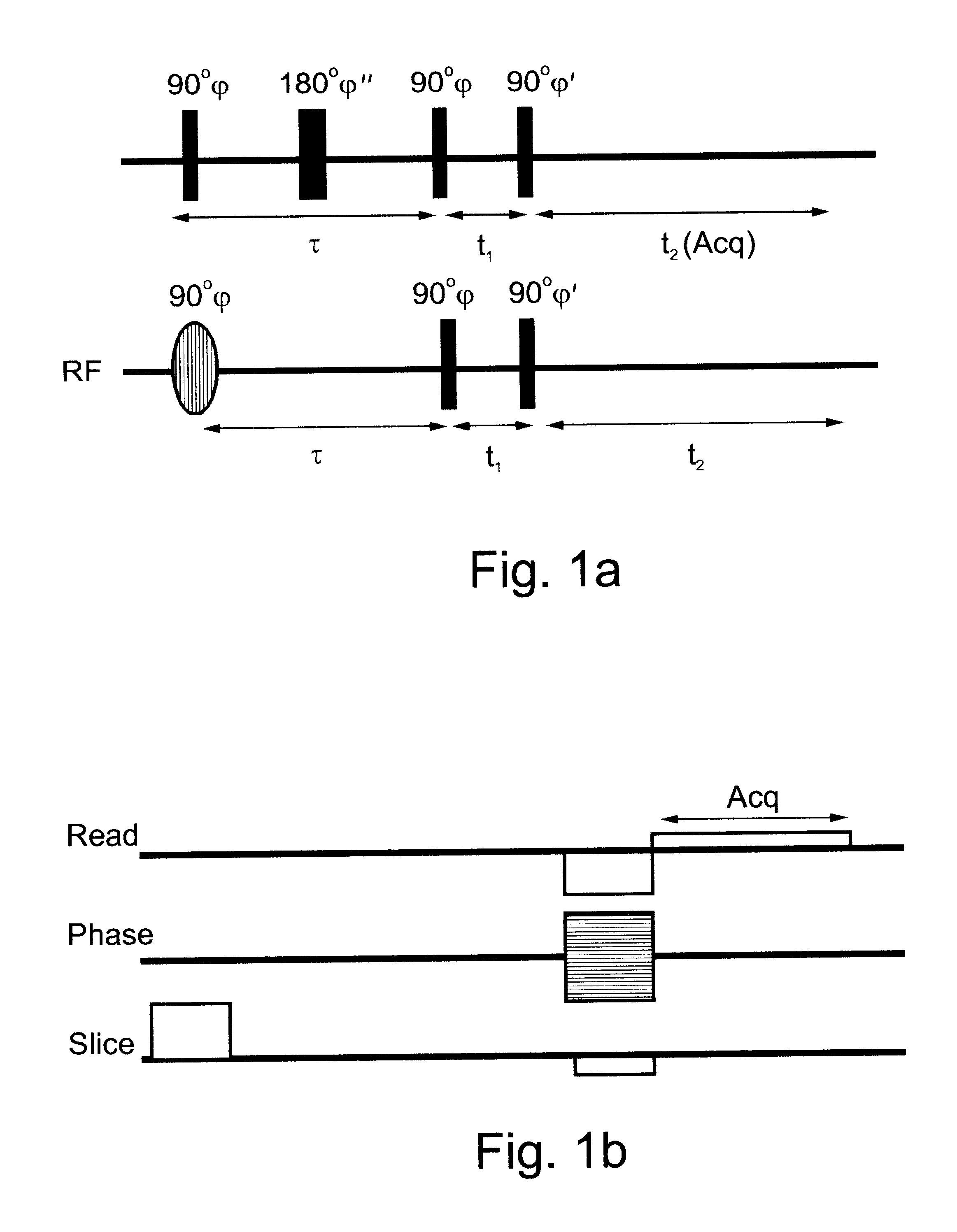
Method of magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6373250B1Reduce leakageReduce repetitionsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientResonance
A method of slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance imaging of an object is disclosed. The method is effected by implementing the steps of (a) applying a radiofrequency pulse sequence selected so as to select a coherence of an order n to the object, wherein n is zero, a positive or a negative integer other than ±1; (b) applying magnetic gradient pulses, so as to select a slice of the object to be imaged arid to create an image; and (c) acquiring a radiofrequency signal resulting from the object, so as to generate a magnetic resonance slice image of the object. The method provides slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance images of yet unprecedented quality in terms of contrast. The method is particularly useful for imaging connective tissues.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA +1
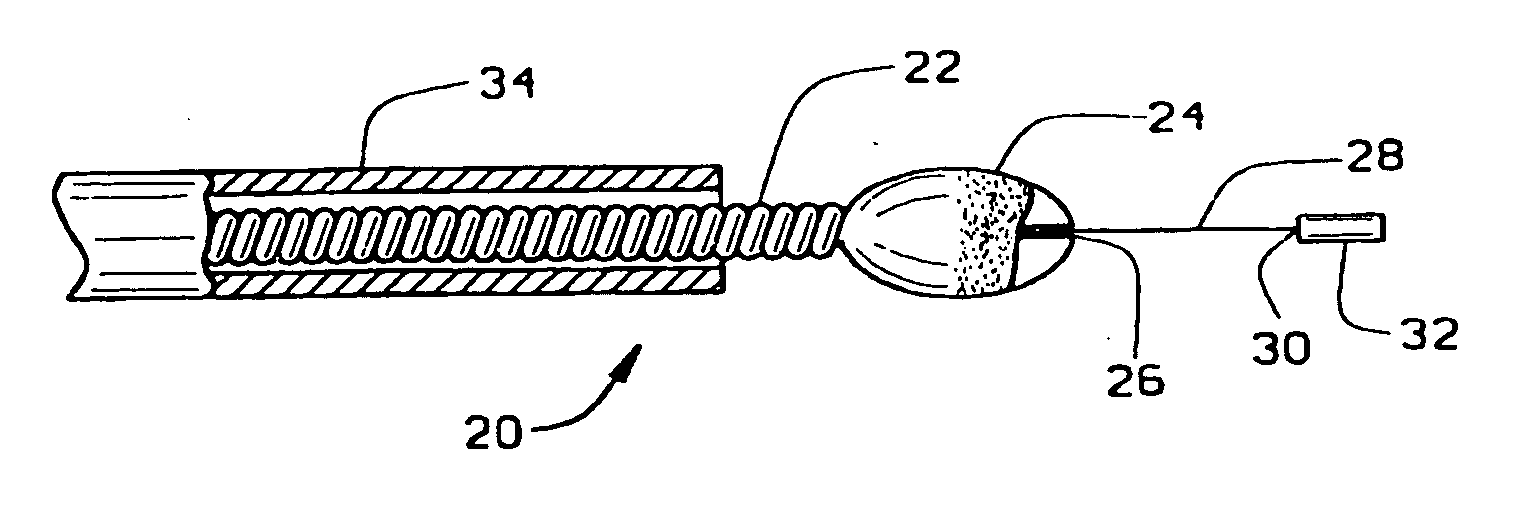
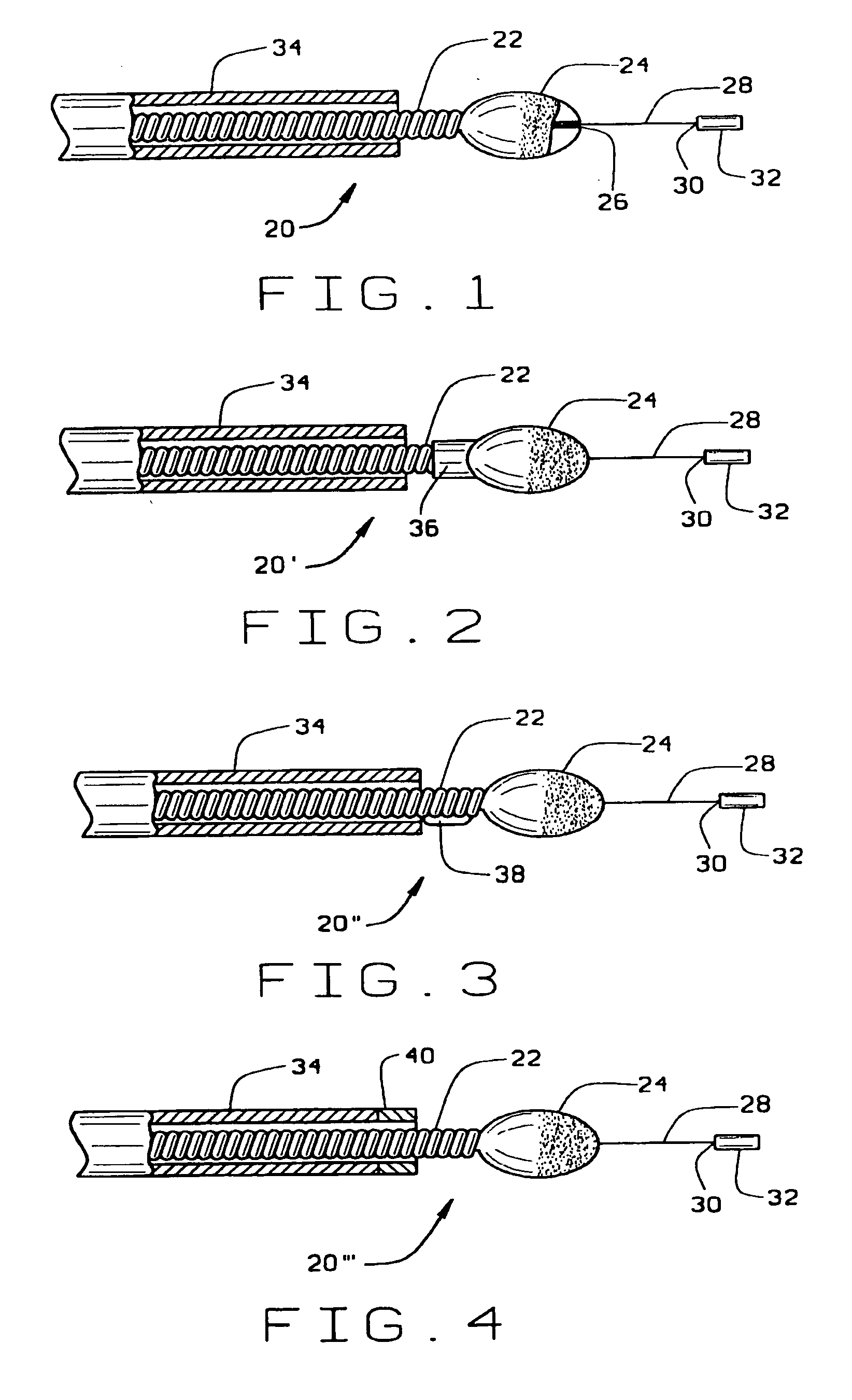
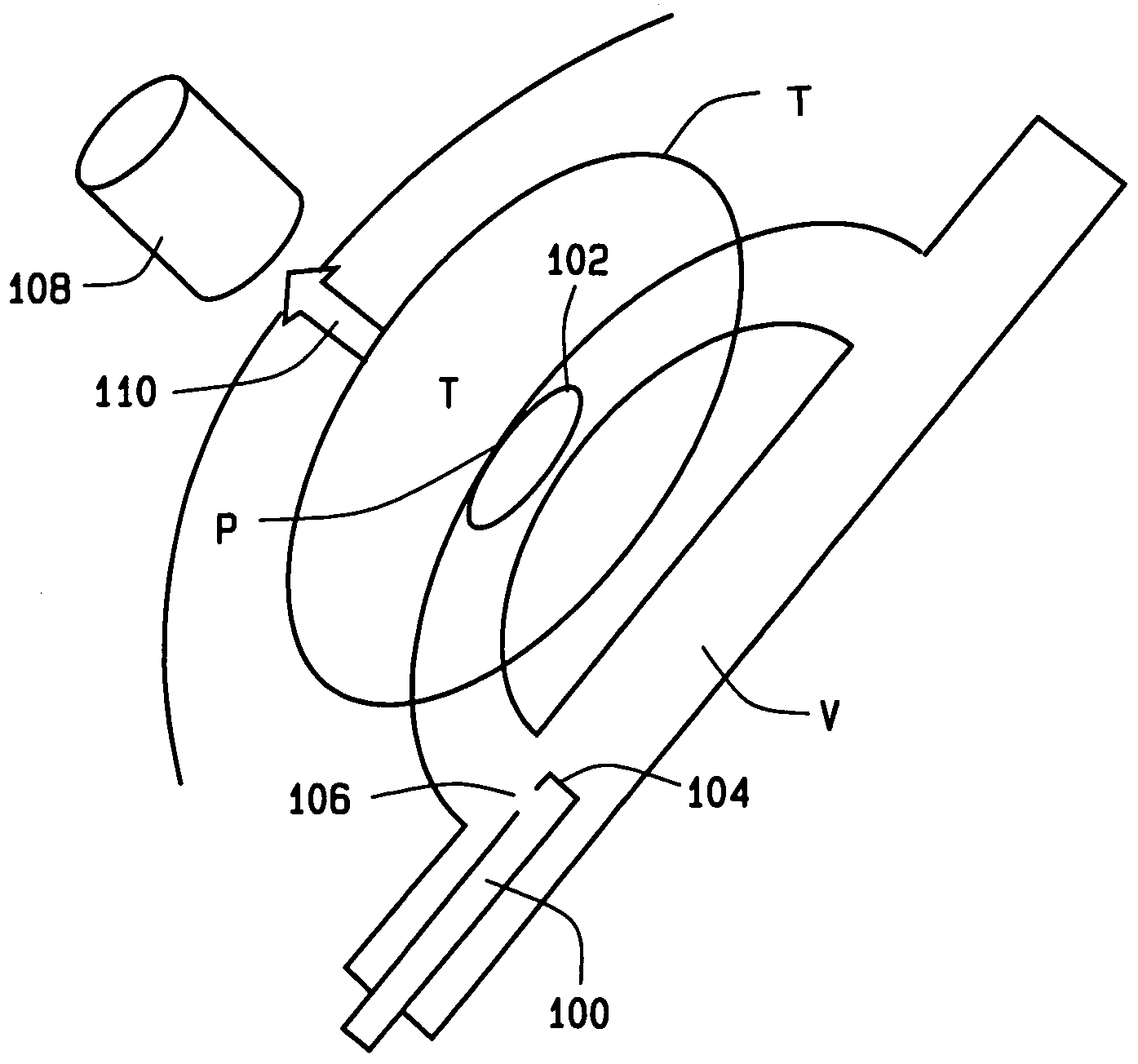
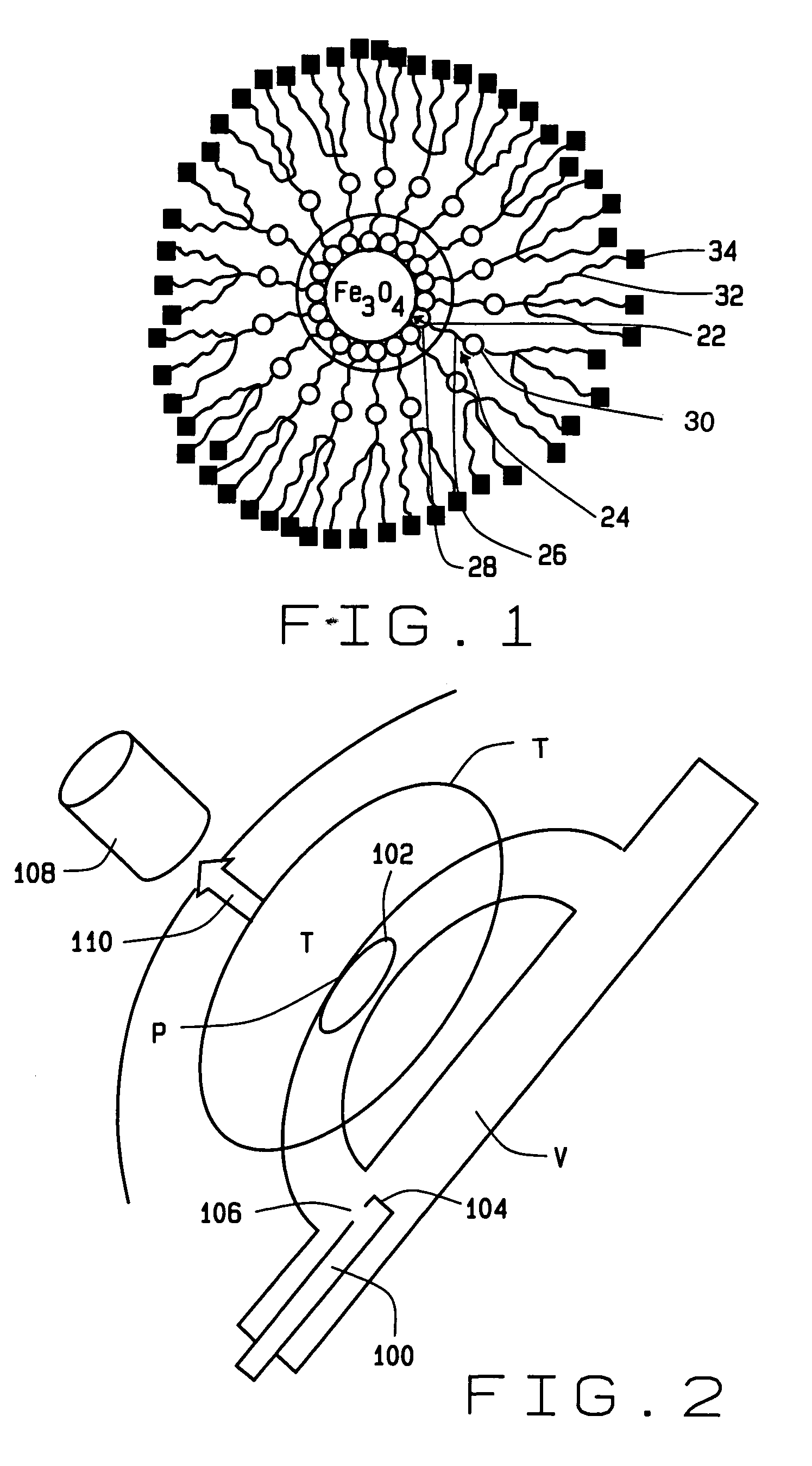
Magnetically navigable and/or controllable device for removing material from body lumens and cavities
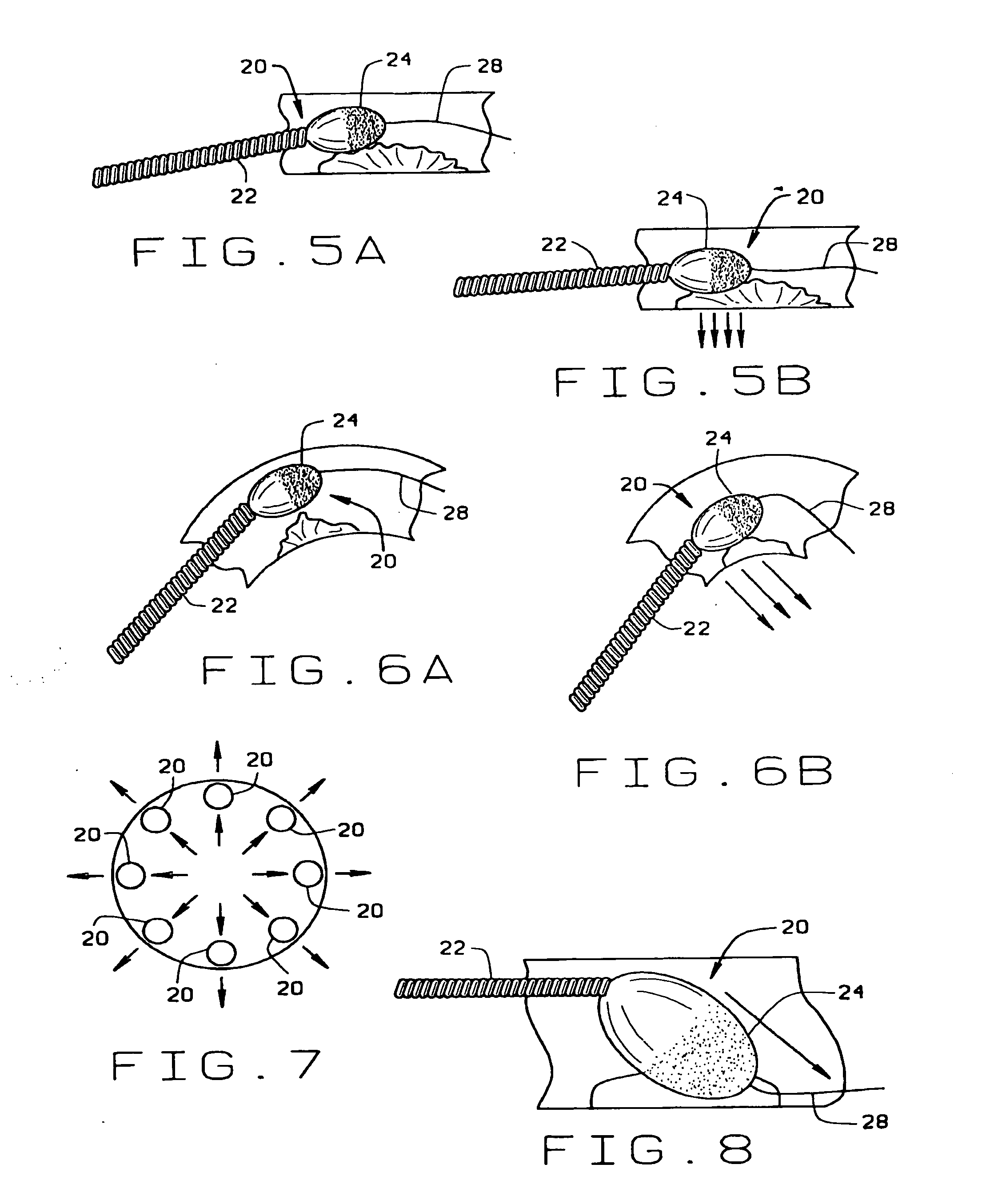
A magnetically navigable atherectomy device includes a cutting head, a flexible drive shaft having a proximal and a distal end, with the cutting device on the distal end, and a magnet associated with the cutting head, the magnet of sufficient size to allow the cutting head to be oriented by an externally applied magnetic field. The magnet may be a portion of the cutting head made from a magnetically permeable or permanent magnetic material, a portion of the drive shaft made from a magnetically permeable or permanent magnetic material; a separate magnet between the cutting head and the drive shaft, a portion a magnet on a sheath covering the drive shaft. Alternatively a guide wire can provided with a magnetic material on its distal end. Through the application of a magnetic field and / or a magnetic gradient, the artherectomy device can be guided to the location of the atheromatous material in the body. Once at the site of atheromatous material, through the application of a magnetic field or magnetic gradient, the device can be manipulated into proximity to the atheromatous material to remove the material.
Owner:HALL ANDREW F +3
Magnetically-controllable delivery system for therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20060041182A1Enhanced magnetizationReduce penetrationStentsElectrotherapyMagnetic gradientMagnetization
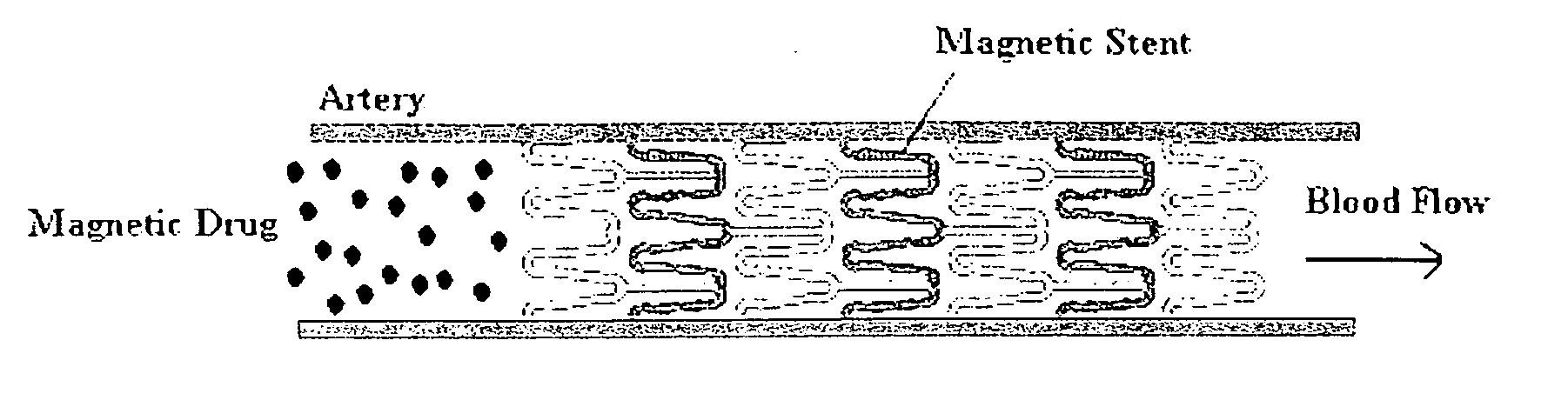
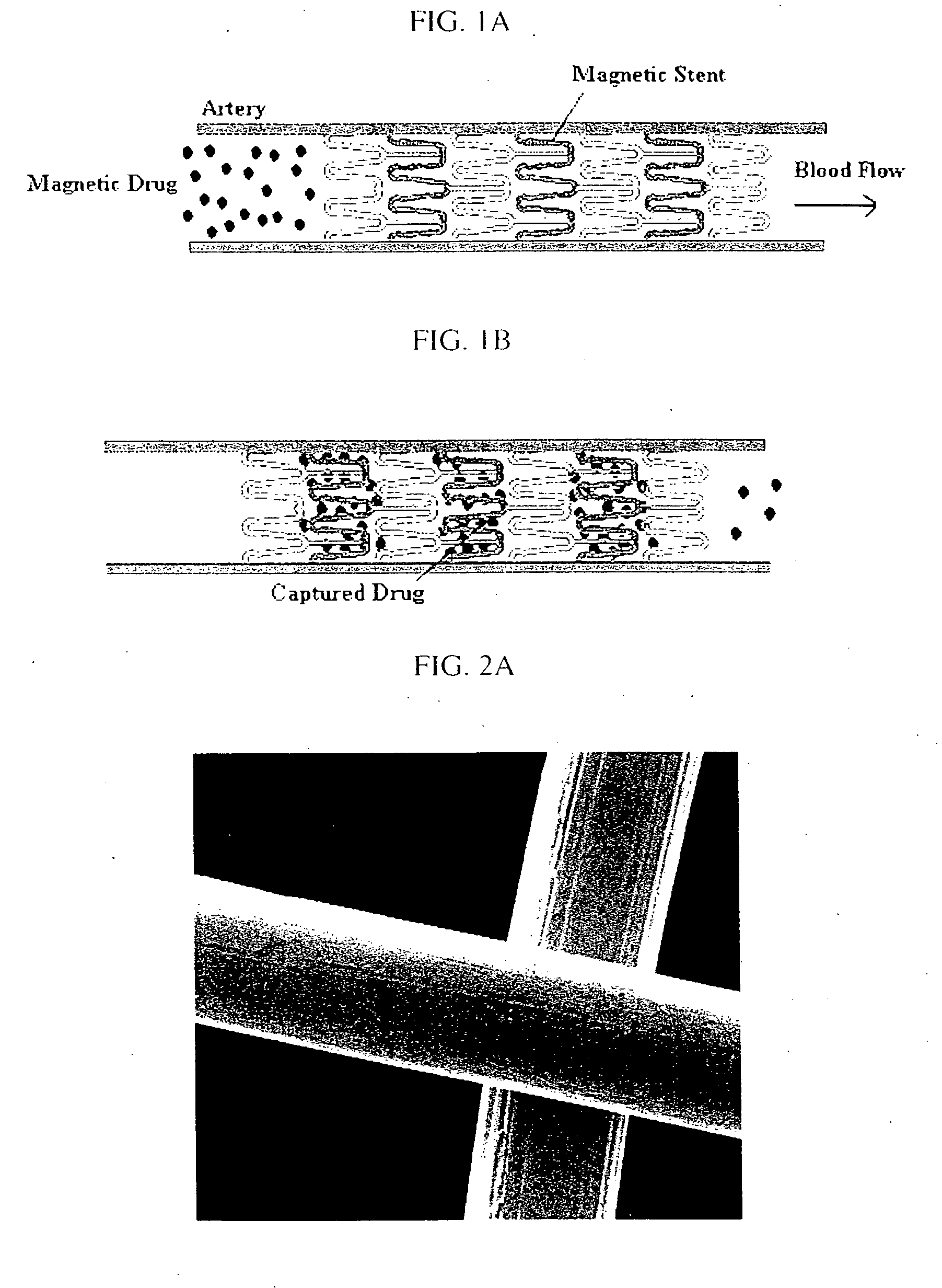
A magnetic delivery system for delivering a magnetizable particle to a location in a body, the device includes a magnetizable object implanted in the body, wherein the magnetizable object includes a plurality of segments distributed throughout the magnetizable object and wherein the segments are configured to provide a magnetic gradient for attracting the magnetizable particle and an external source of a magnetic field capable of (i) magnetizing the magnetizable particle and (ii) increasing a degree of magnetization of the magnetizable object and thereby creating the magnetic gradient. A drug delivery system including the magnetic delivery system and a magnetizable particle associated with a therapeutic agent and / or a cell. A cell delivery system based on the magnetic delivery system and a magnetizable particle associated with a cell. A method of using the magnetic delivery system for delivery of a therapeutic agent and / or a cell to a targeted location in a body.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Magnetically guidable carriers and methods for the targeted magnetic delivery of substances in the body
InactiveUS7189198B2Facilitated releaseLess hydrophobicPowder deliveryElectrotherapyMagnetic gradientGene delivery
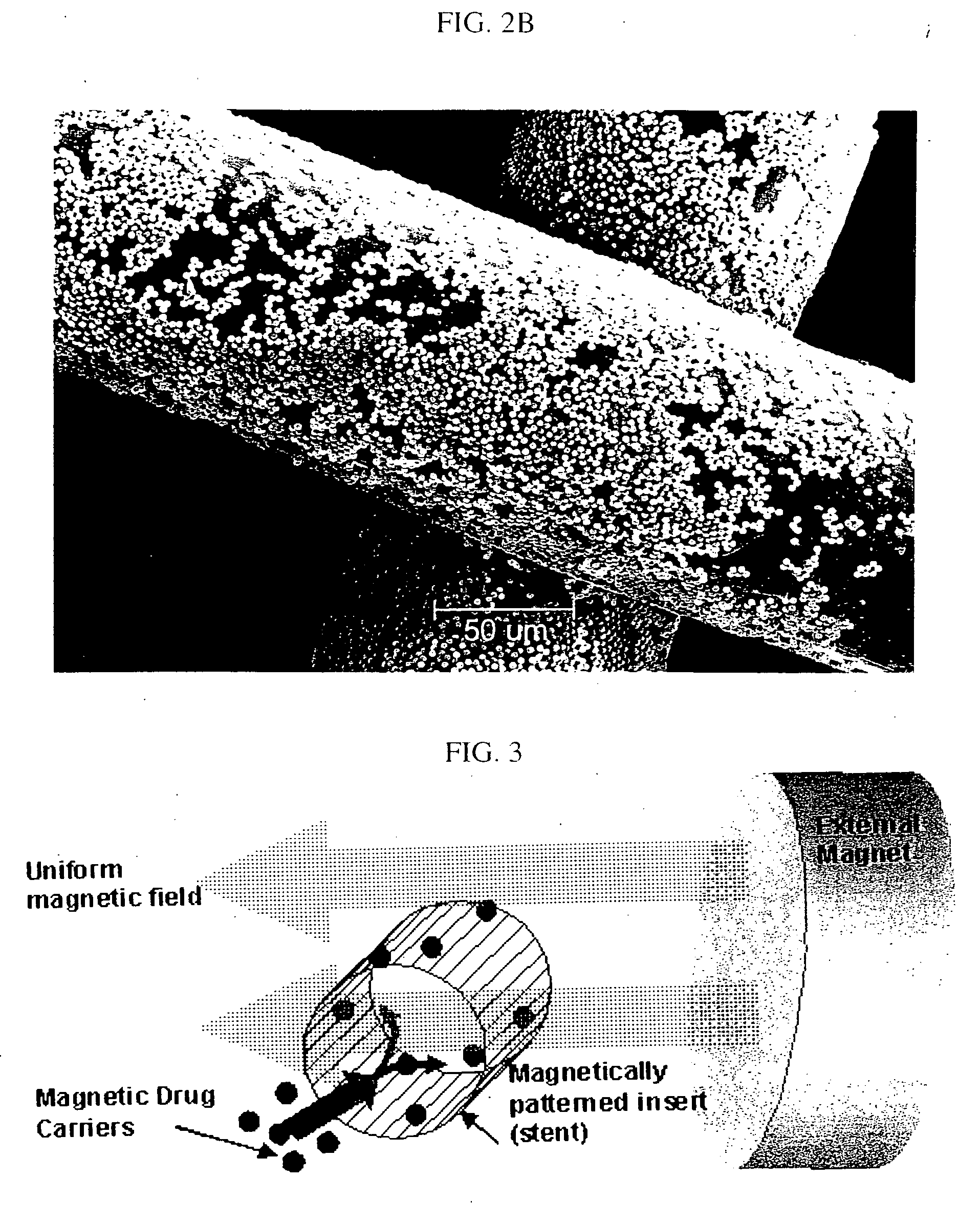
A method of delivering a substance to targeted tissue comprising the steps of: delivering a plurality of magnetically responsive particles which are carrying the substance and have a hydrophobic coating into the patient's vasculature upstream of the targeted tissue; and applying a magnetic gradient in the vicinity of the targeted tissue to draw the magnetically responsive particles against the wall of the patient's vasculature in the vicinity of the targeted tissue, to allow the substance on the magnetic particles to migrate through the wall of the patent's vasculature to targeted tissue.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
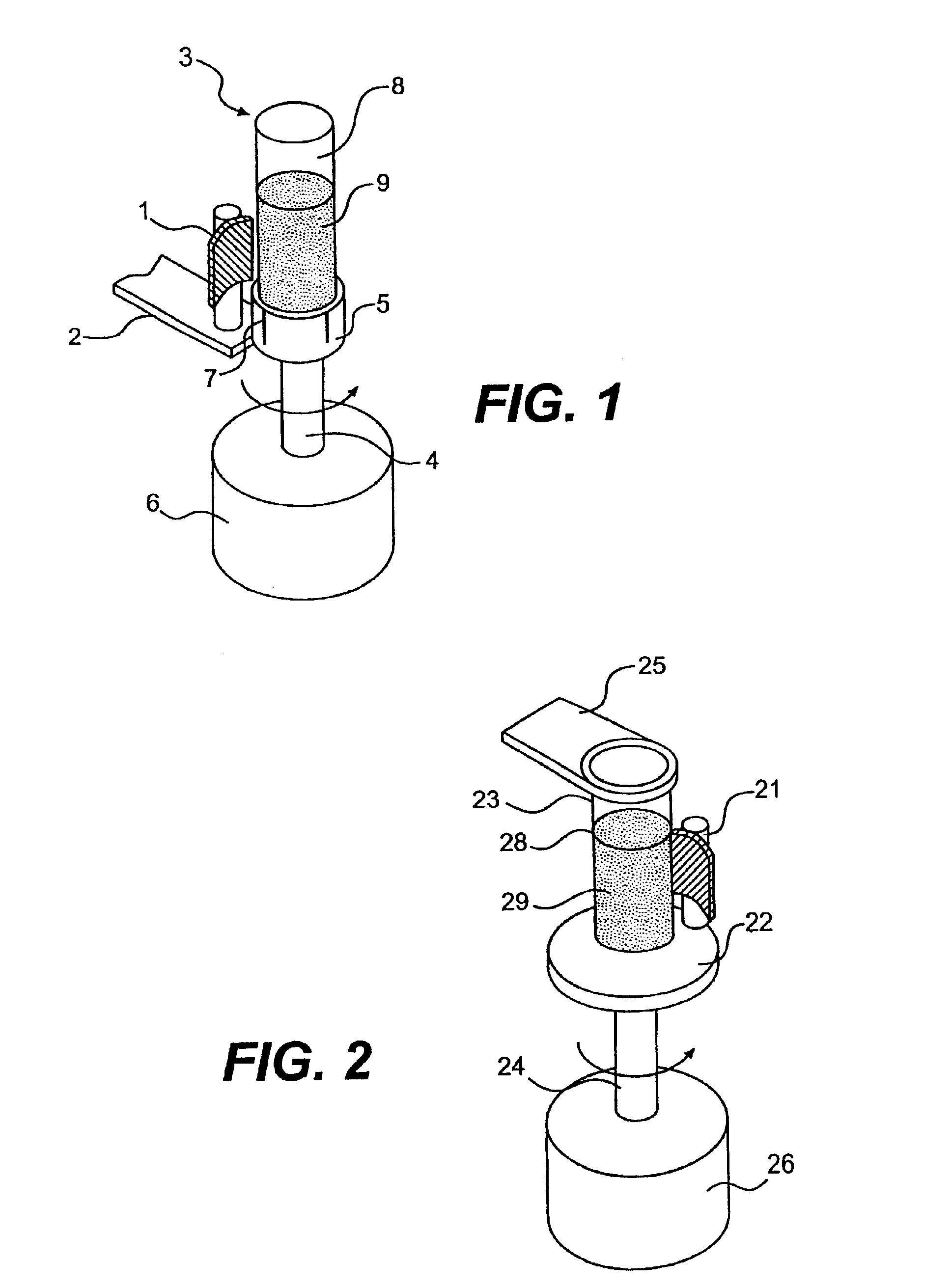
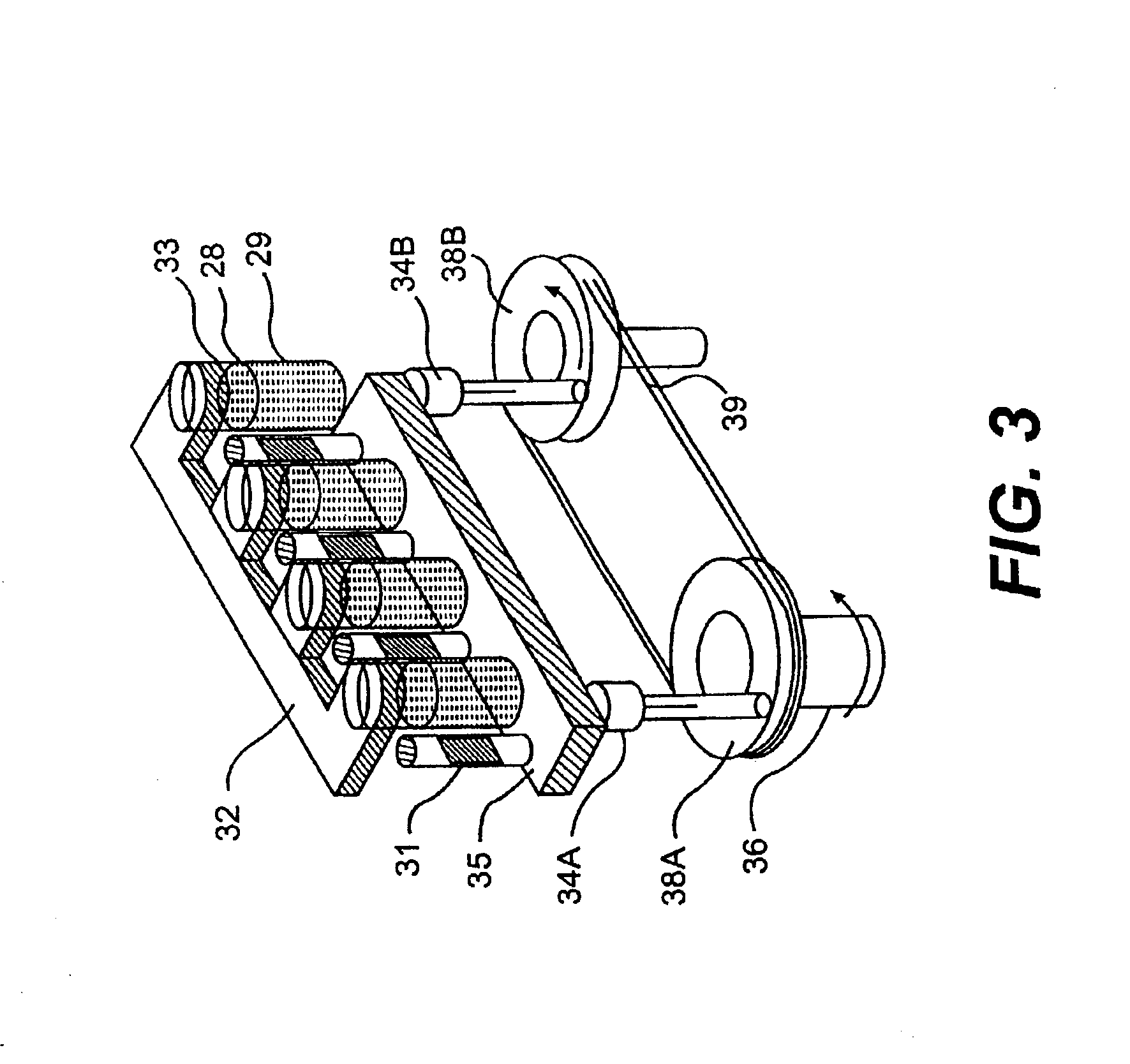
Apparatus and method for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS6884357B2Promote specific affinity binding reactionEfficient scanningElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingMagnetMagnetic gradient
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
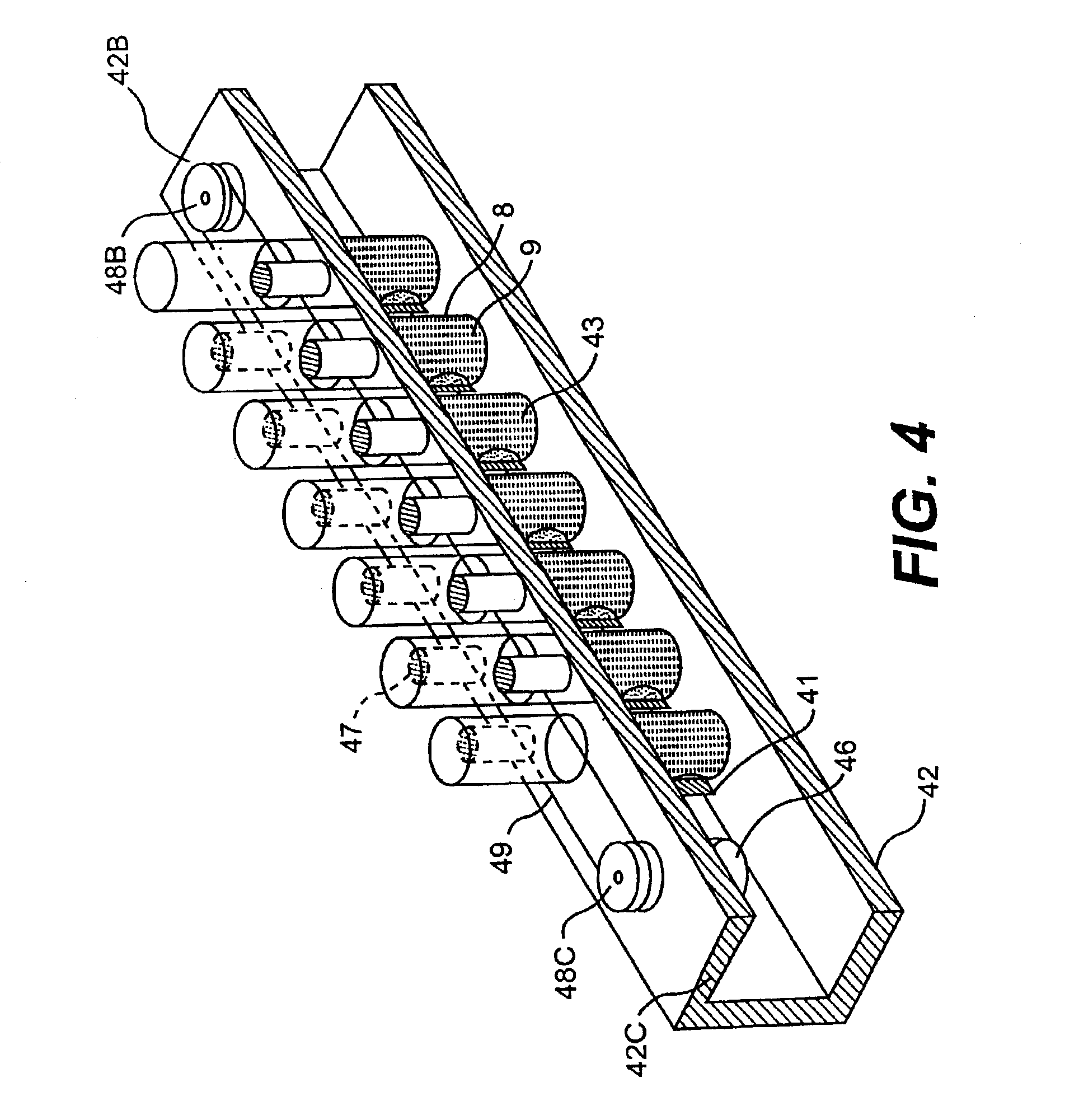
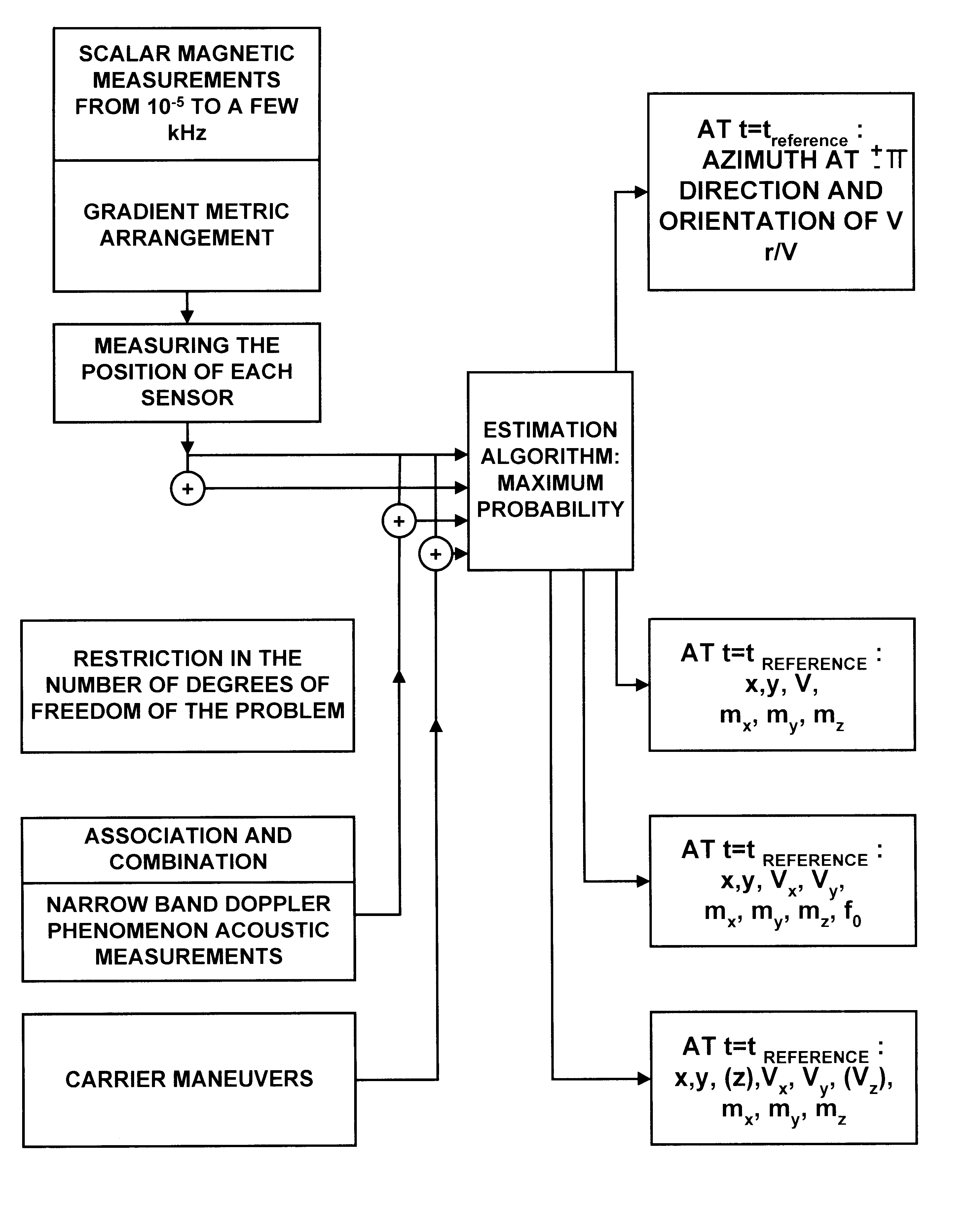
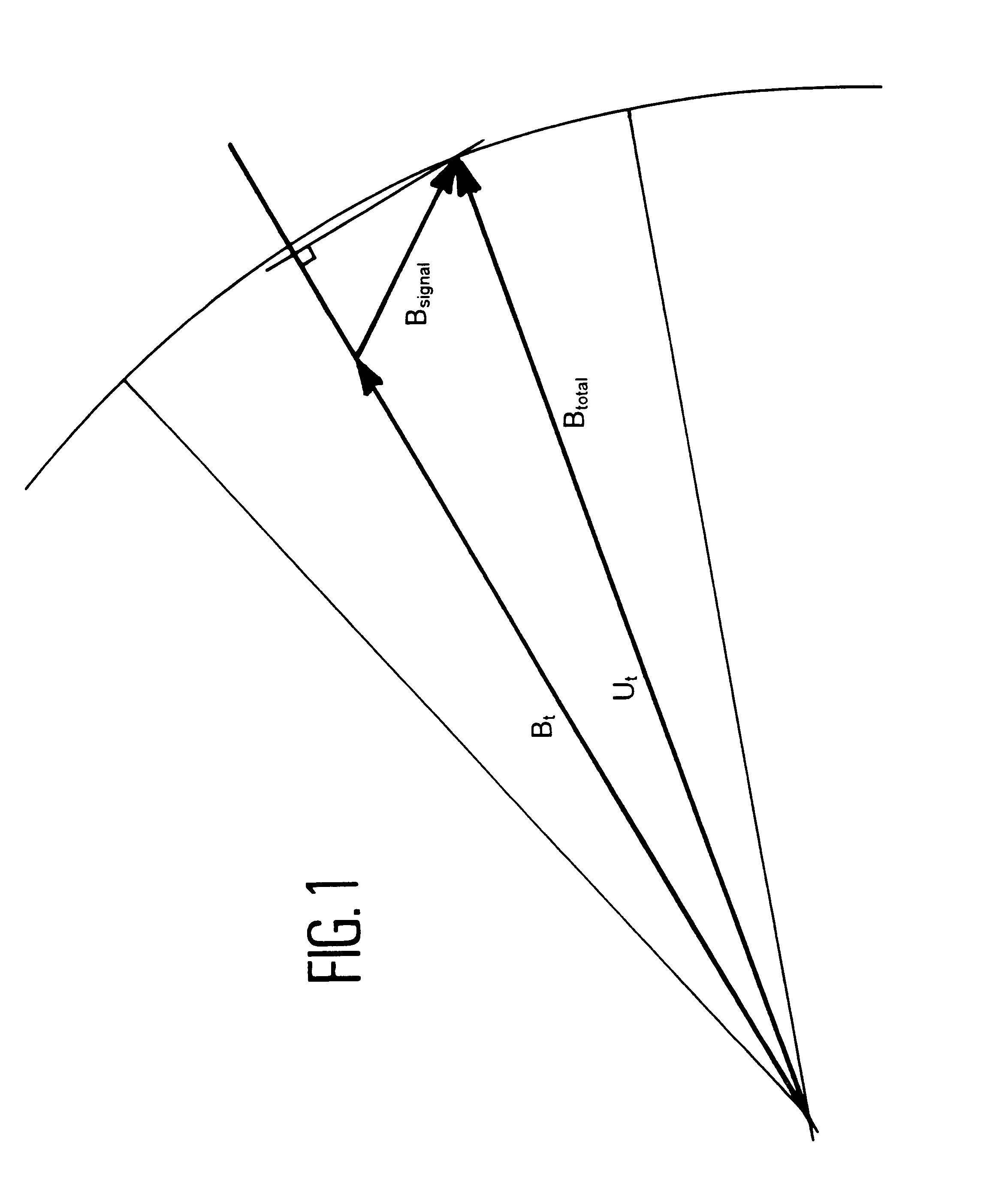
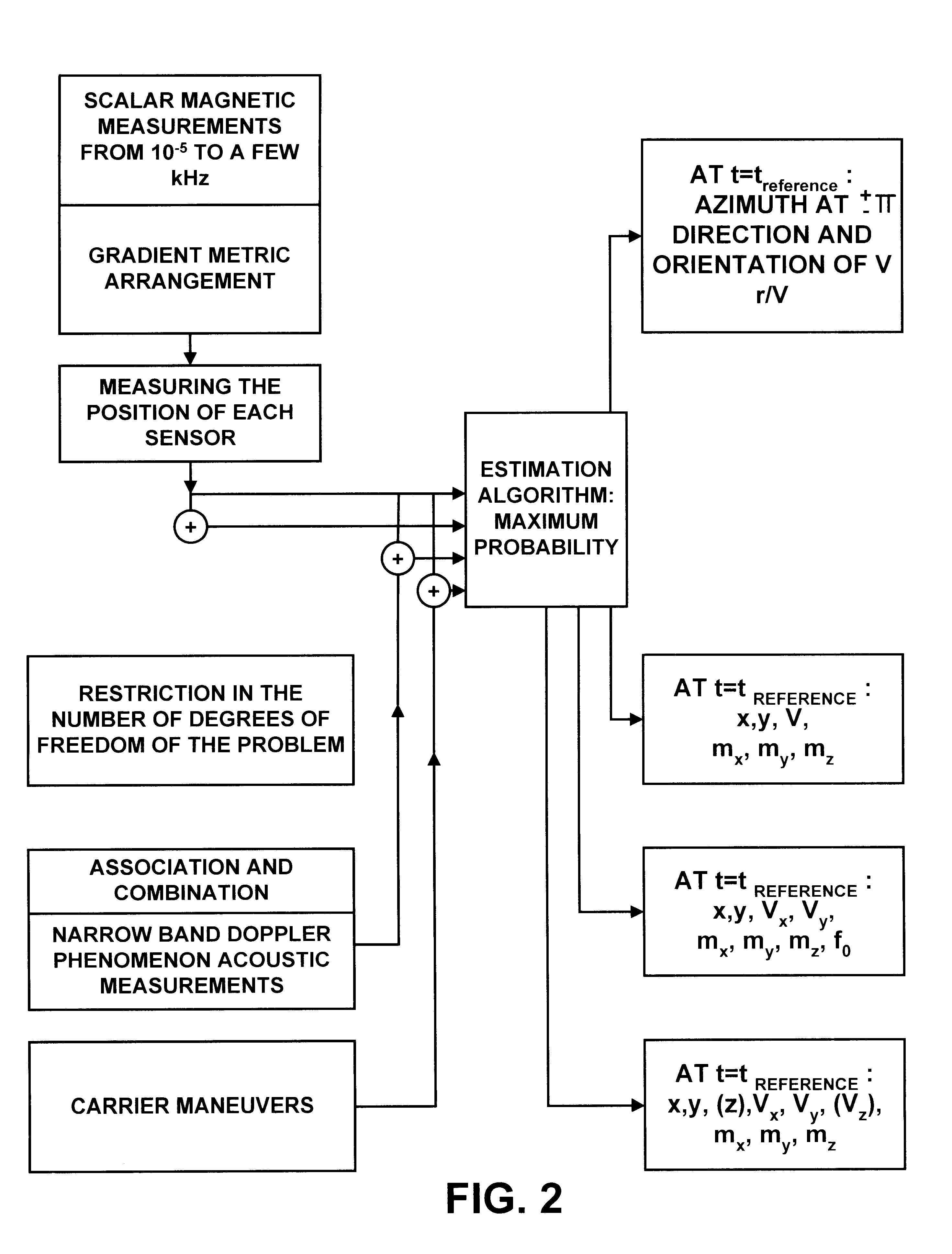
Process for determining the position of a moving object using magnetic gradientmetric measurements
InactiveUS6539327B1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMagnetic gradientElectromagnetic interference
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Magnetic anomaly sensing-based system for tracking a moving magnetic target
InactiveUS7342399B1Accurately determineUsing electrical meansDevices using time traversedMagnetic gradientSystem usage
A system for tracking a moving magnetic target uses a magnetic anomaly sensing system to continually determine magnetic gradient tensors associated with the target and converts the magnetic gradient tensors to gradient contraction scalars. A processor uses the magnetic gradient tensors and gradient contraction scalars to determine a minimum of bearing and range to the target. A velocity of the target is determined using the determined bearing and range at two points in time as the target is moving. To continually track with the moving target, the processor determines adjustments in elevation and azimuth using the magnetic gradient tensors and gradient contraction scalars along with bearing, range and determined velocities of the target. The processor can include a routine that determines range while accounting for asphericity errors introduced by the aspherical nature of constant magnetic gradient contours associated with the target.
Owner:NAVY USA AS REPRESENED BY THE SEC OF THE
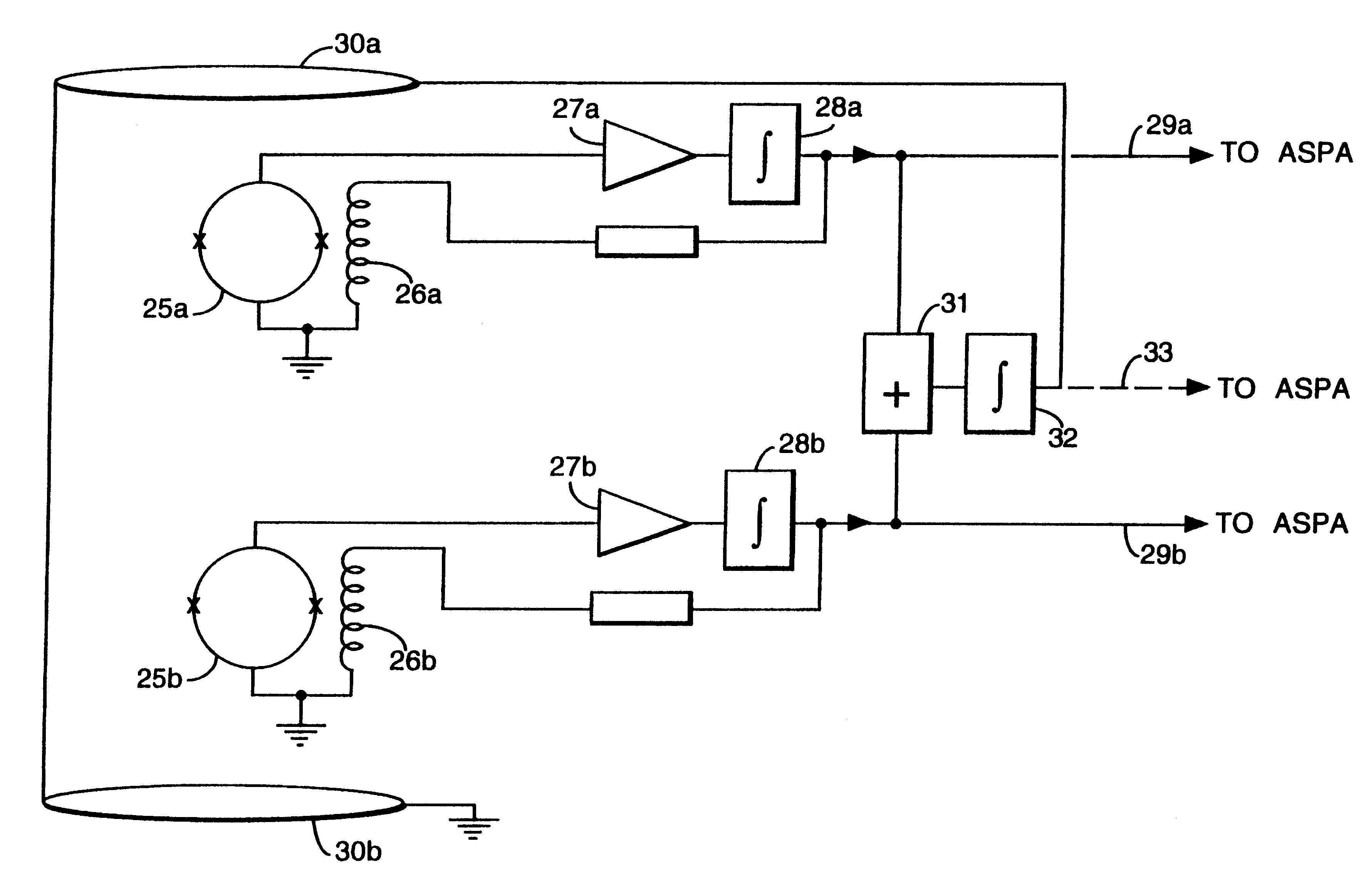
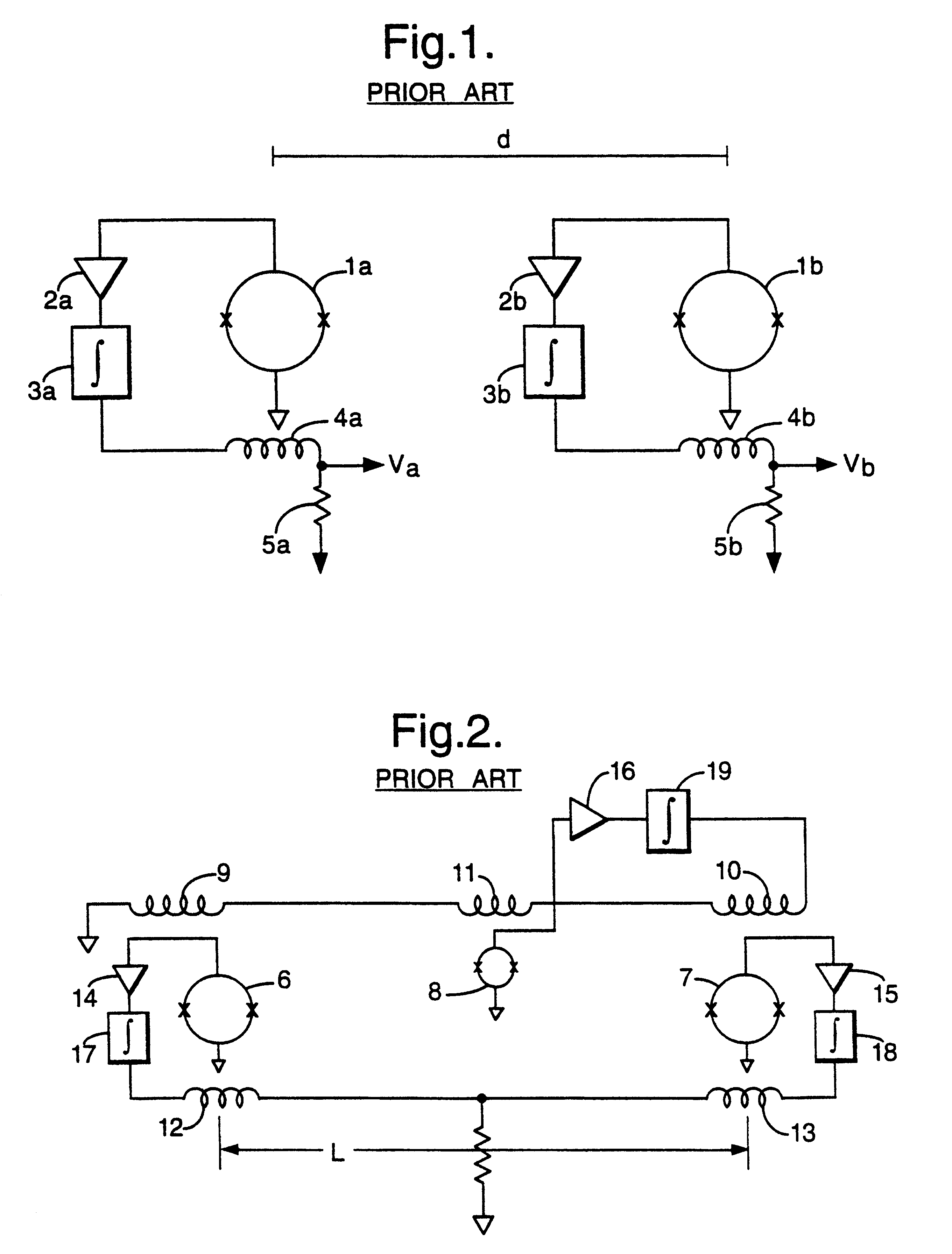
Magnetic gradiometer incorporating global feedback
InactiveUS6339328B1Minimizing energySufficient dynamic rangeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientGradiometer
A gradiometer for measuring properties of a magnetic field and in particular, for measuring magnetic field gradient components, comprising at least two magnetic sensors wherein at least two of the magnetic sensors are arranged to sense the magnetic field component in substantially the same direction. The magnetic sensors may be super conducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometers, Hall probes, flux gates or magneto-resistive magnetometers. The gradiometer also includes a computer processor loaded with an adaptive signal-processing algorithm, for performing adaptive signal balancing of the magnetometer outputs. In a preferred embodiment the gradiometer may comprise at least eight magnetometers in a three-dimensional arrangement, and a set of three orthogonal global feedback coils, one for each direction x, y, z, such that the five independent magnetic field gradient components may be measured. The gradiometer may also be used to measure second or higher order magnetic field gradient components.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Method of locating magnetic target based on tri-axial vector magnetic sensor array
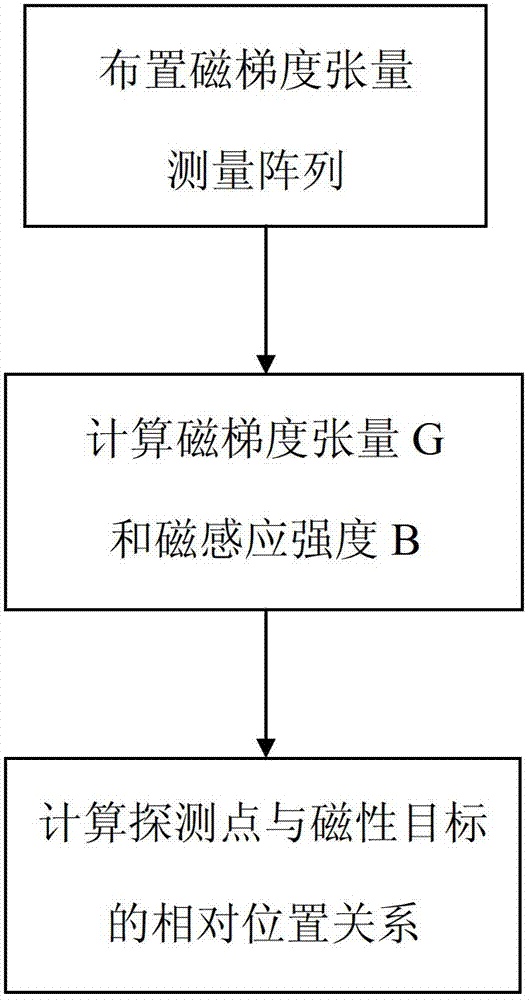
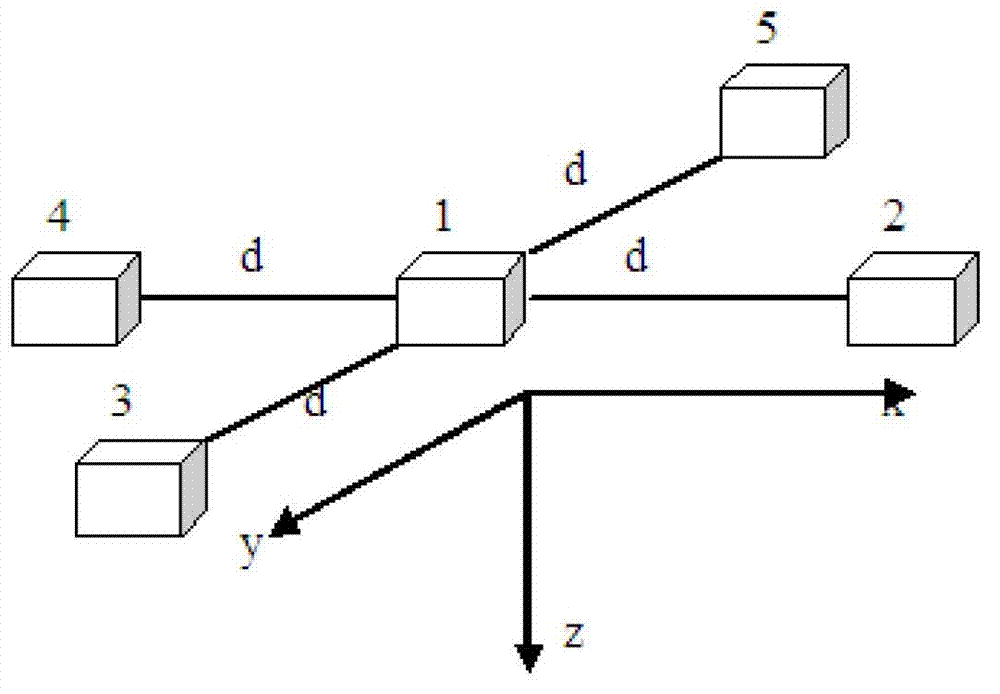
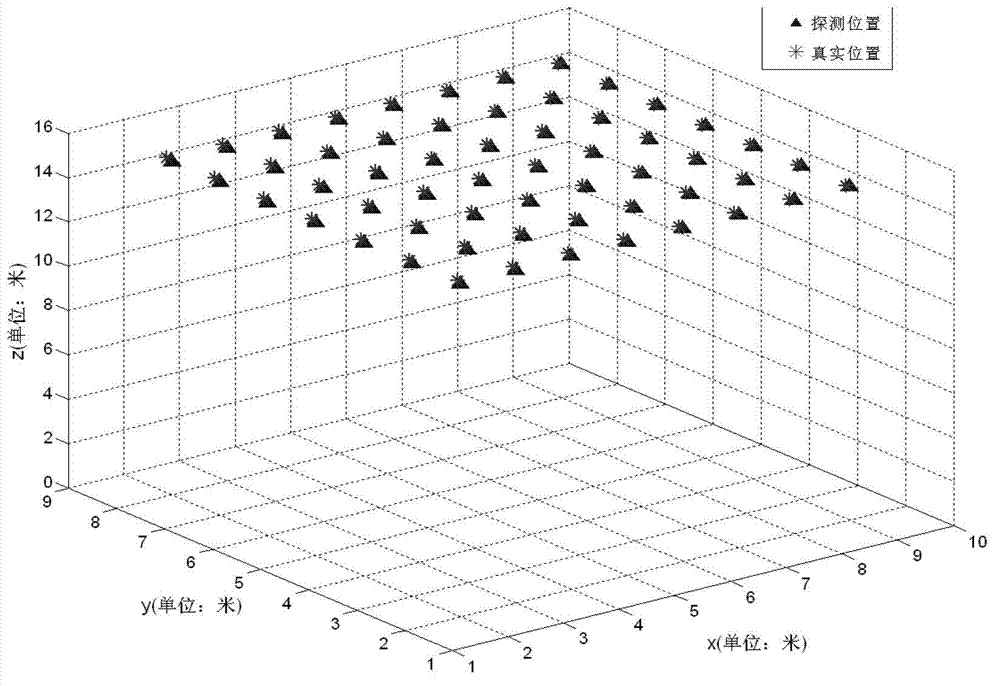
InactiveCN102927981AThe positioning method is simpleThe positioning method is practicalNavigation instrumentsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientSensor array
The invention discloses a method of locating a magnetic target based on a tri-axial vector magnetic sensor array. According to the method, the magnetic target is located by a magnetic gradient tensor measuring array formed by five tri-axial vector magnetic sensors at high locating precision. The specific scheme of the method comprises the following steps of: at first, measuring the magnetic gradient tensor of any point on the periphery of the magnetic target by utilizing the magnetic gradient tensor measuring array; secondly, resolving a relative distance between the magnetic target and the magnetic measuring array and relative coordinates by utilizing the magnetic tensor; and at last, locating the magnetic target according to the resolved relative distance and the relative position coordinates. The locating method has the advantages of simplicity, practicability and high locating precision.
Owner:710TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Three-axial magnetometer correcting method and three-axial magnetic gradient correcting method
InactiveCN101251584AImprove work efficiencyReasonable designElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic disturbance
The invention relates to a magnetometer correcting method and a magnetic gradiometer correcting method, in particular to a three axis magnetometer correcting method and a three axis magnetic gradiometer correcting method. Under the conditions of no standard three-axis coil, no standard magnetic field and no normalized three-axis magnetometer, the invention corrects the error and carrier magnetic interference generated due to the inconsistent nonorthogonality, interaxial coupling and sensitivity of the three axis magnetometer and the three axis magnetic gradiometer. The invention adopts an ordinary three-axis coil, a scalar quantity magnetometer and a high precision current source to form a correcting device which has the correcting precision at the same order of magnitude as the single axis test precision of a corrected three axis magnetometer. The invention does not need to turn a corrected three axis magnetometer and a corrected three axis magnetic gradiometer during correcting, thereby having a simple operation process and high correcting precision and improving the test precision of magnetic field vector by the three axis magnetometer and the three axis magnetic gradiometer.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
‘Thermal spring’ magnetic recording media for writing using magnetic and thermal gradients
InactiveUS6881497B2Avoid thermal instabilityRapid coolingSoldering apparatusRecord information storageMagnetic gradientMagnetic media
A thermal spring magnetic medium is provided having first and second stacks providing two exchange coupled ferromagnetic layers having different Curie temperatures. The first stack has a high magneto-crystalline anisotropy, a relatively low saturation magnetization and a low Curie temperature. The second stack has a relatively low magneto-crystalline anisotropy, a high saturation magnetization and a high Curie temperature. Preferably the first stack includes an alloy of Fe—Pt or Co—Pt, and the second stack includes an allow of Co—Pt or Co—Pd. A disk drive system having the novel medium is also provided.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Apparatus and method for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20030127396A1Simple construction operationMaximizes mixing efficiencyElectrostatic separationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic source
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8405395B2Reliable separationLarge possible separationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Diagnostic and therapeutic magnetic propulsion capsule and method for using the same
InactiveUS20110301497A1Reduced field generator powerImprove art of robotic guidanceVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEndoscopesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
A guided medical propulsion capsule driven by strong electro-magnetic interaction between an external AC / DC magnetic gradient-lobe generator and a set of uniquely magnetized ferrous-conductive elements contained within the capsule. The capsule is navigated through the lumens and cavities of the human body wirelessly and without any physical contact for medical diagnostic, drug delivery, or other procedures with the magnetically guiding field generator external to the human body. The capsule is equipped with at least two sets of magnetic rings, disks and / or plates each possessing anisotropic magnetic properties. The external magnetic gradient fields provide the gradient forces and rotational torques on the internal conductive and magnetic elements needed to make the capsule move, tilt, and rotate in the body lumens and cavities according to the commands of an operator.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP +1
Magnetically-Controllable Delivery System for Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20100204674A1Enhanced magnetizationSaturation magnetizationStentsElectrotherapyMagnetic gradientMagnetization
A magnetic delivery system for delivering a magnetizable particle to a location in a body, the device includes a magnetizable object implanted in the body, wherein the magnetizable object includes a plurality of segments distributed throughout the magnetizable object and wherein the segments are configured to provide a magnetic gradient for attracting the magnetizable particle and an external source of a magnetic field capable of (i) magnetizing the magnetizable particle and (ii) increasing a degree of magnetization of the magnetizable object and thereby creating the magnetic gradient. A drug delivery system including the magnetic delivery system and a magnetizable particle associated with a therapeutic agent and / or a cell. A cell delivery system based on the magnetic delivery system and a magnetizable particle associated with a cell. A method of using the magnetic delivery system for delivery of a therapeutic agent and / or a cell to a targeted location in a body.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
System and method for measuring a magnetic gradient field
ActiveUS10088535B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEfficient detectionMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic field gradientPhotodetector
A system and method is described to measure the magnetic field gradient using an optically pumped magnetometer configured as an intrinsic gradiometer. Atoms are prepared in a freely precessing coherent superposition of the magnetically sensitive hyperfine ground states in two or more physically separated locations. A probe laser beam is used to interrogate atoms in both locations. As the probe light beam passes through the coherent atoms, optical sidebands are self-generated at the ground state hyperfine frequency of the magnetically sensitive states. Each of the two sets of atoms produces distinct sidebands at a frequency separation proportional to the magnetic field experienced by each set of atoms. The probe light is captured using a photodetector. The self-generated probe optical sidebands interfere to produce a beat note whose frequency is proportional to the magnetic field gradient between the two sets of atoms. Measuring the frequency of the beat note therefore provides an accurate reading of the magnetic field gradient. An optical filter or a polarizer can be additionally used to remove the central frequency of the probe light, thus removing the noise produced by the residual probe beam.
Owner:QUSPIN
Gradient Field Optically Pumped Magnetometer
InactiveUS20180238974A1Measurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
A system and method to measure a magnetic gradient field with an optically-pumped magnetometer is described. Atoms are spin polarized at two locations. Larmor frequencies are, induced and the spin frequency is detected. The frequencies are proportional to the total magnetic field at the locations of the atoms. The magnetic field gradient is extracted from the beat frequency of the two Larmor frequencies.
Owner:QUSPIN
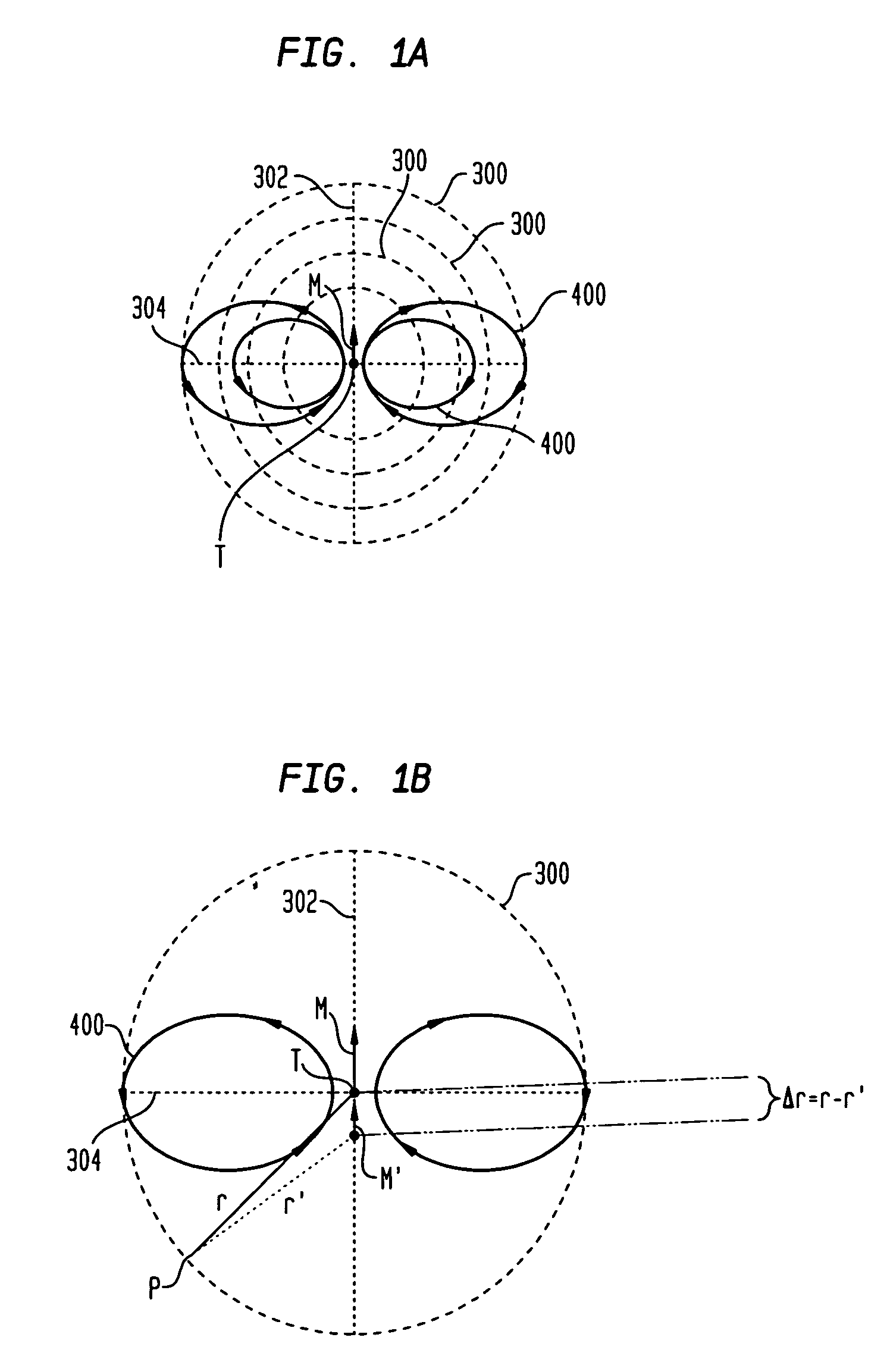
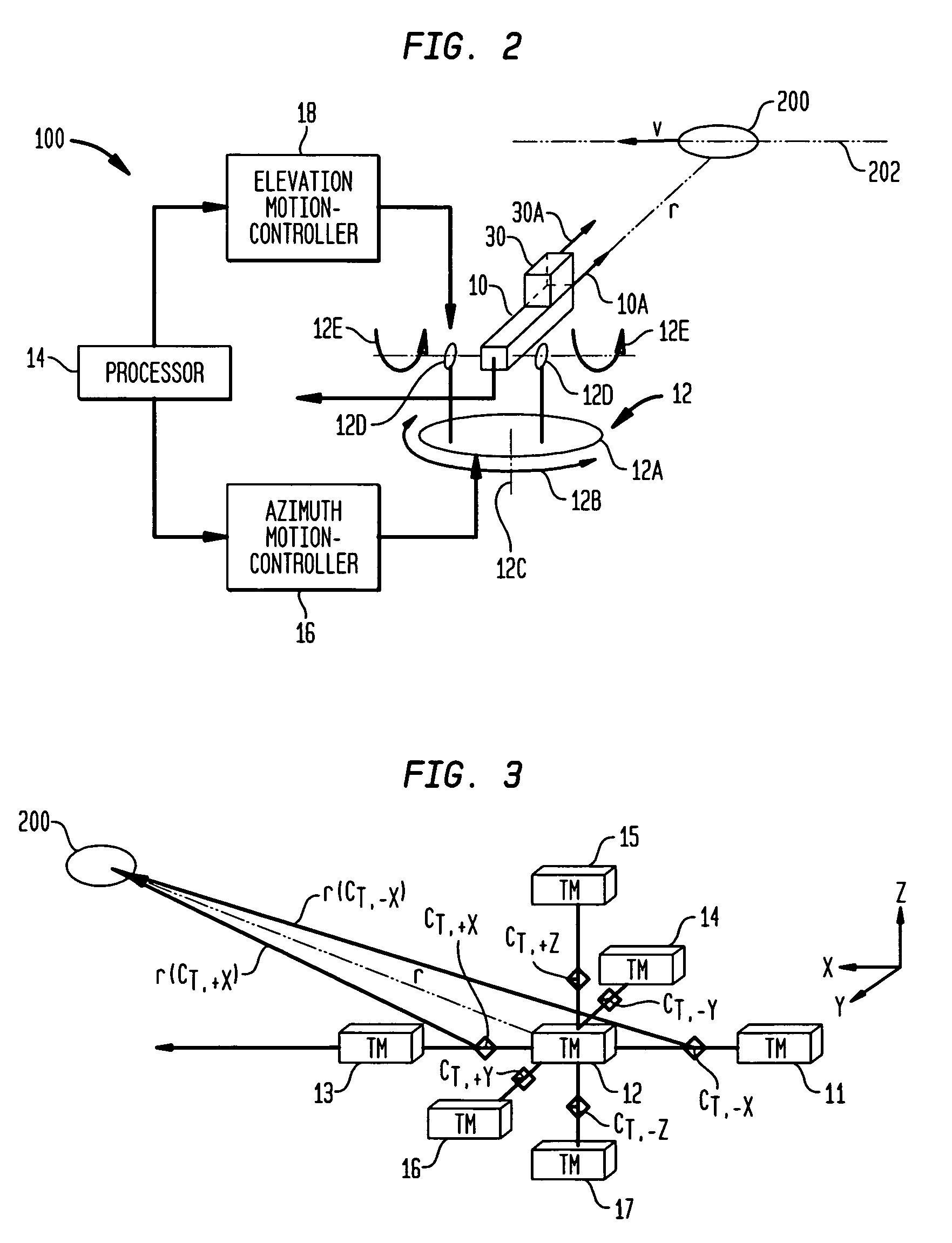
Magnetic anomaly homing system and method using rotationally invariant scalar contractions of magnetic gradient tensors
InactiveUS7038458B1Electric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic gradientGuidance control
A magnetic anomaly homing system and method utilize an array of four triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors coupled to a non-magnetic platform. The four TM sensors are positioned at the vertices of a rectangular parallelogram. The magnetic field sensed at the four TM sensors is processed to generate complete gradient tensors and corresponding scalar gradient contractions thereof for four two-axis gradiometers formed by the array. The scalar gradient contractions define guidance control parameters used to steer the platform toward the magnetic anomaly.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Screening method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070052411A1Easy to detectReduce chanceMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysicsRegion of interest
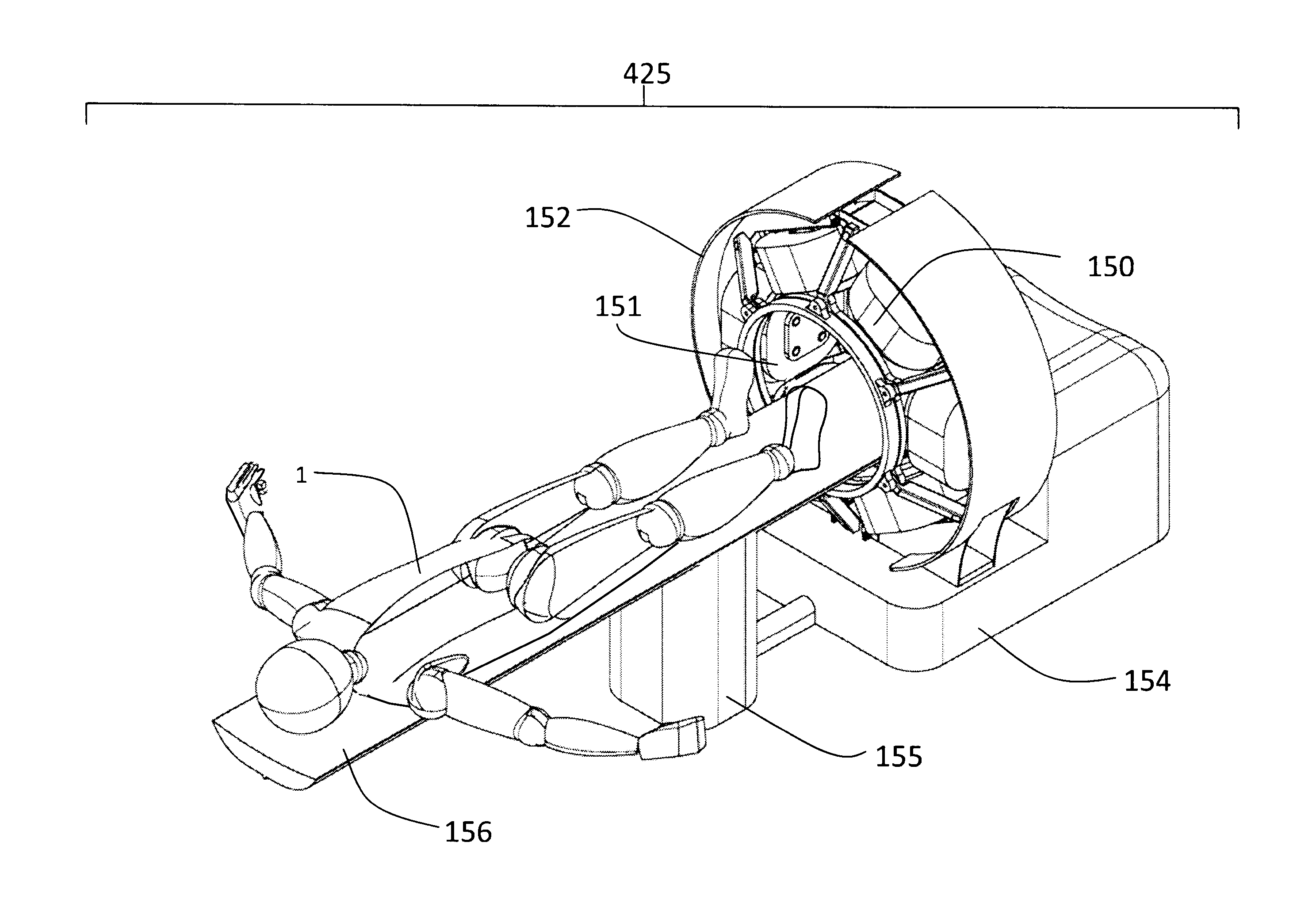
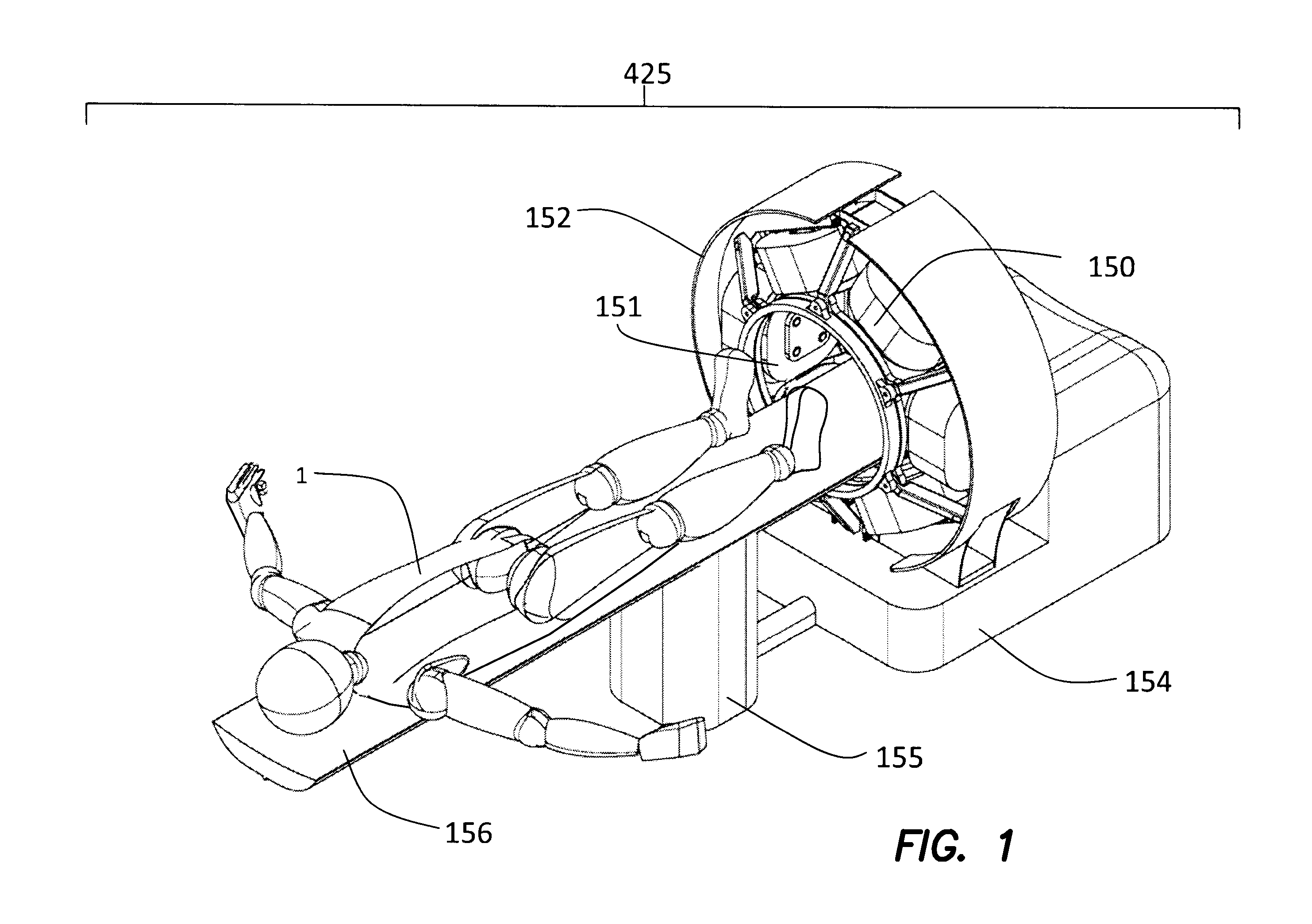
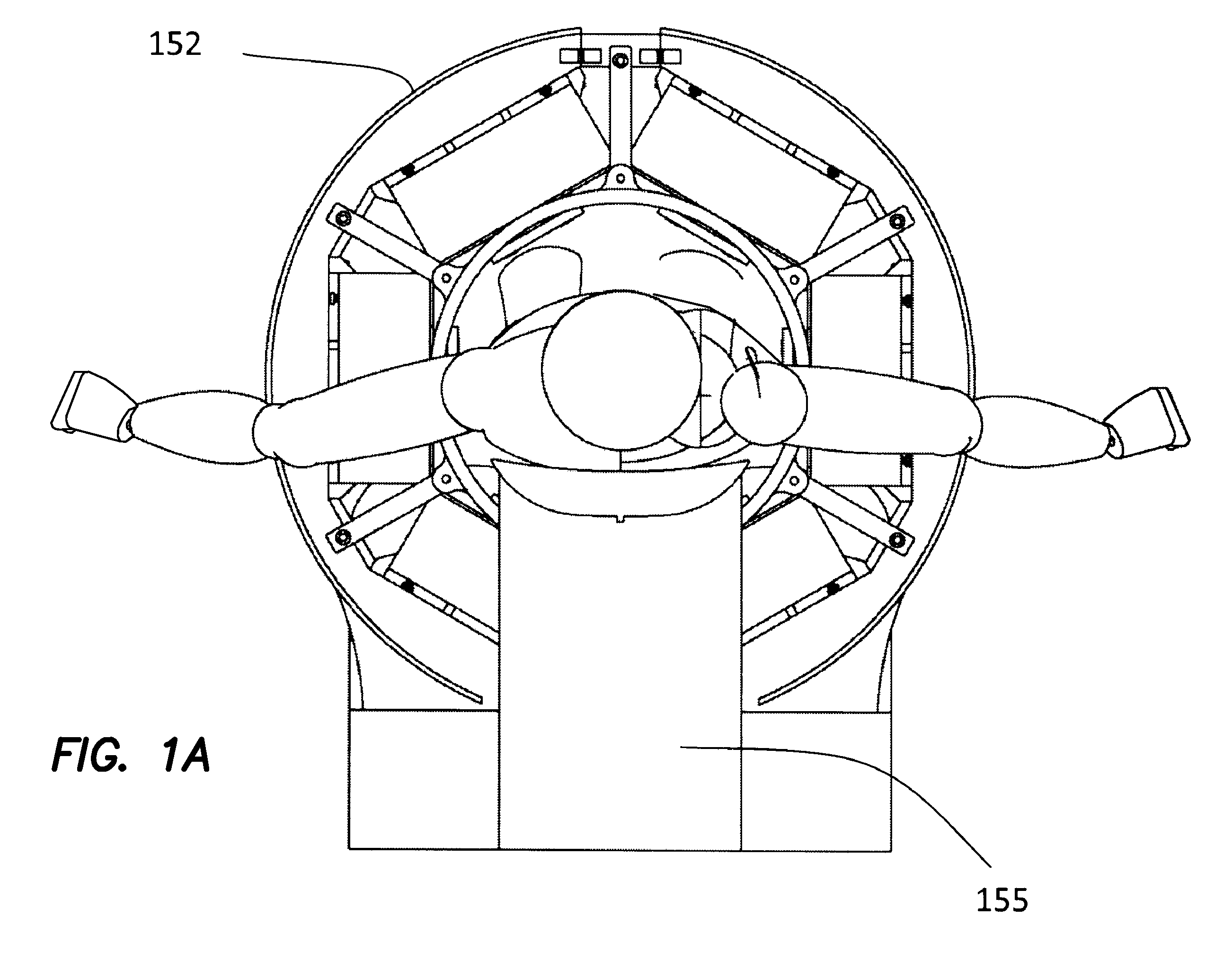
A method and an apparatus are disclosed, to screen patients or other areas for ferromagnetic objects, particularly for use intra-operatively in an operating room. The device comprises at least one magnetic field source, at least one magnetic gradiometer, and the associated electronics. The field source and the gradiometer are supported by an arm structure which can be manipulated to position the field source and the gradiometer at one or more positions near areas of interest, such as areas on a patient or other subject, and to orient the field source and the gradiometer so that the axis of the magnetic field is arranged along three different non-parallel, non-coplanar, axes to ensure detection of any ferromagnetic object regardless of its shape and orientation. The device can be manipulated to place the sensor arrays in close proximity to selected parts of a subject's body, for screening purposes. Two field sources and two gradiometers can be provided, for positioning on two sides of a portion of the subject's body, such as the head.
Owner:KOPP DEV
Movable type location method based on magnetic gradient tensor and geomagnetic vector measurement
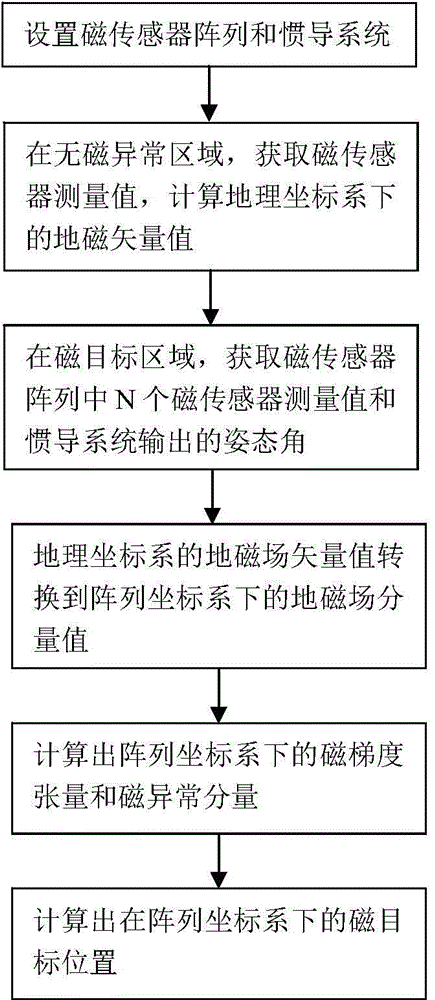
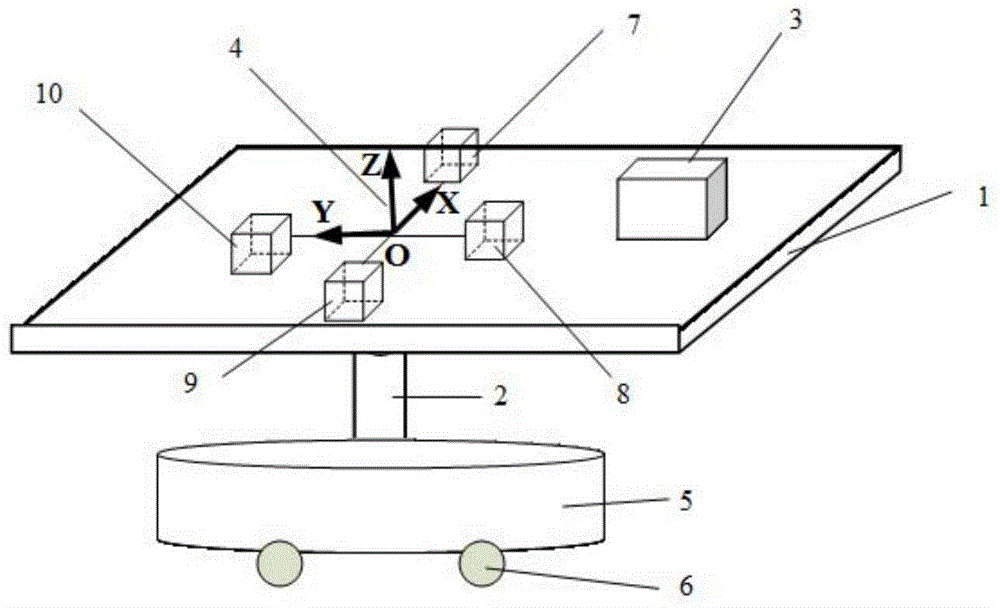
ActiveCN104535062AOvercome component variation effectsAvoid geomagnetic vector inaccuracy problemsNavigation by terrestrial meansSensor arrayMagnetic gradient
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic measurement, and particularly relates to a movable type location method based on magnetic gradient tensor and geomagnetic vector measurement. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) setting a magnetic sensor array and an inertial navigation system; (S2) in a nonmagnetic abnormal area, acquiring a measured value of a magnetic sensor and calculating a geomagnetic vector value in a geographic coordinate system; (S3) allowing a nonmagnetic moving device to move in a magnetic target area to acquire the measured value of the magnetic sensor and an attitude angle output by the inertial navigation system; (S4) calculating a geomagnetic field component value in an array coordinate system; (S5) calculating the magnetic gradient tensor and a magnetic abnormal component in the array coordinate system; and (S6) calculating the position of a magnetic target in the array coordinate system according to the magnetic gradient tensor and the magnetic abnormal component in the array coordinate system. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for achieving movable type real-time location, overcoming the requirement for immobility of the array in static location and acquiring the projection of a magnetic field in a magnetic sensor coordinate system more accurately by attitude conversion.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Apparatus for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20050155921A1Promote specific affinity binding reactionLength and efficiencyElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
Magnetic resonance imaging method using a partial parallel acquisition technique with non-cartesian occupation of k-space
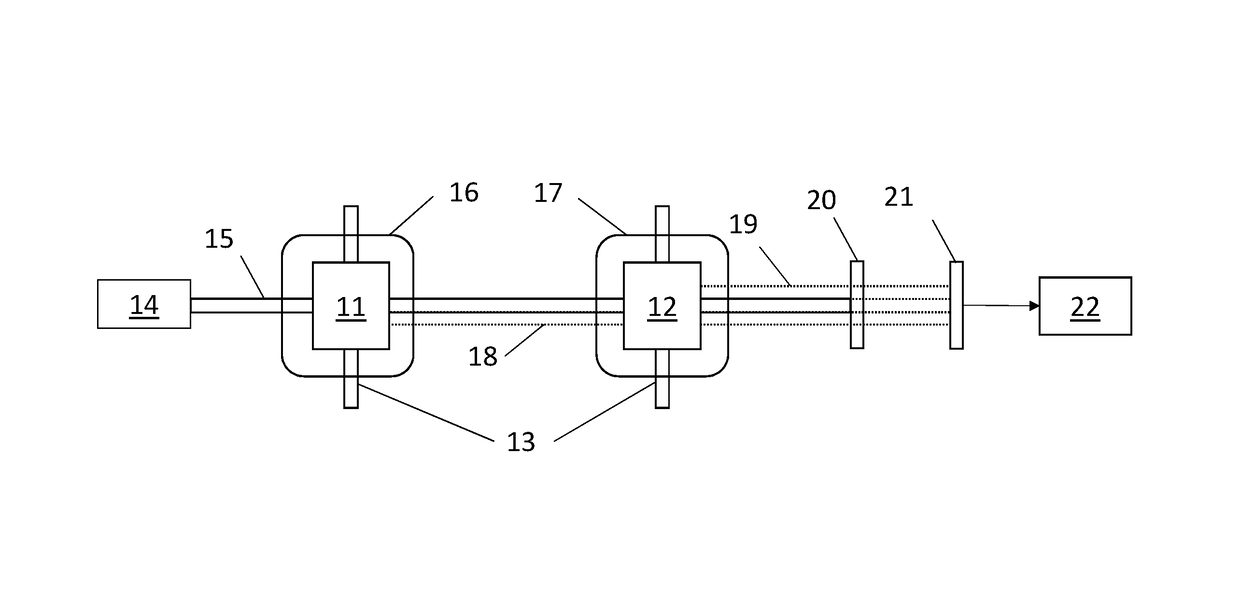
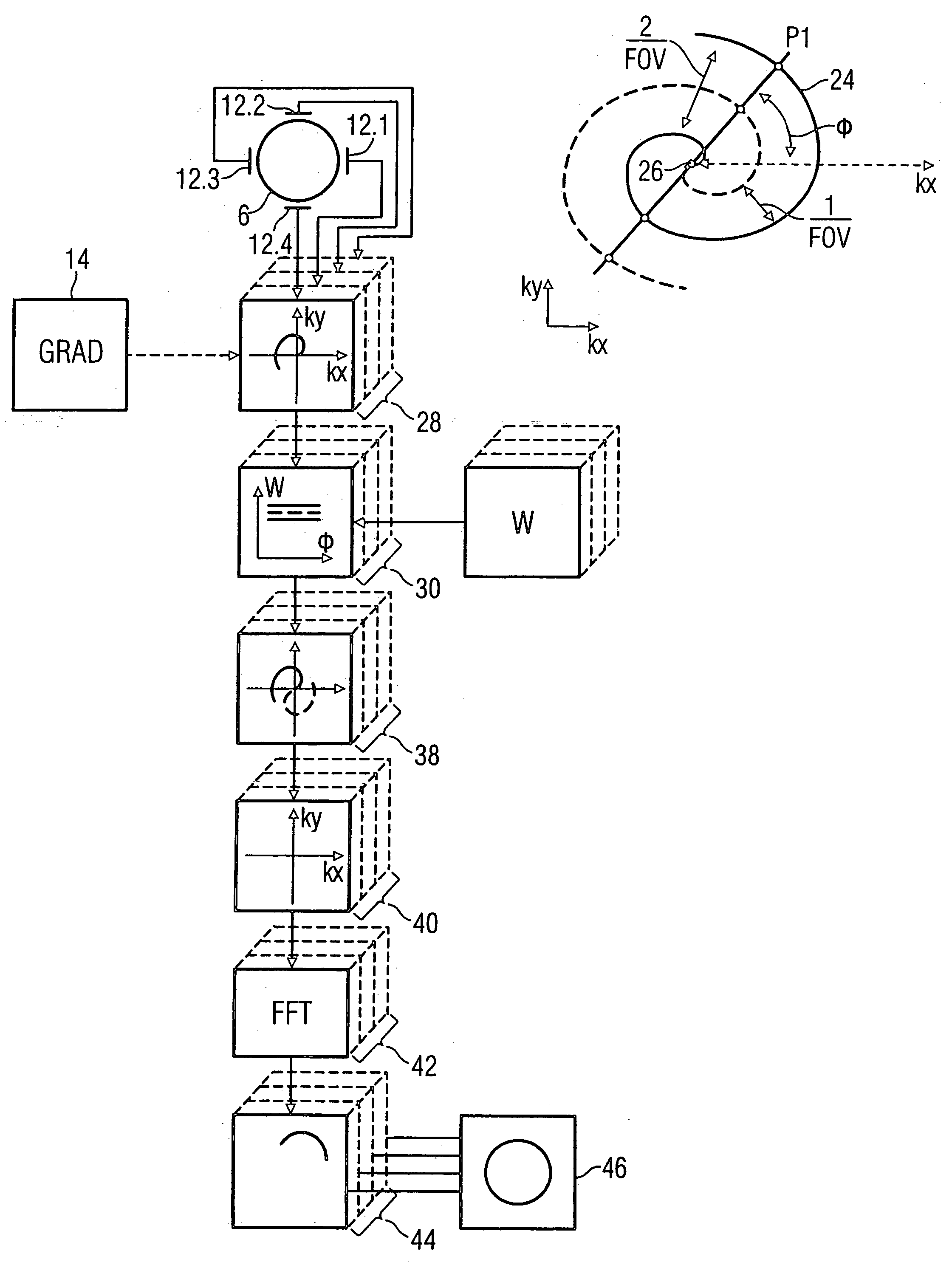
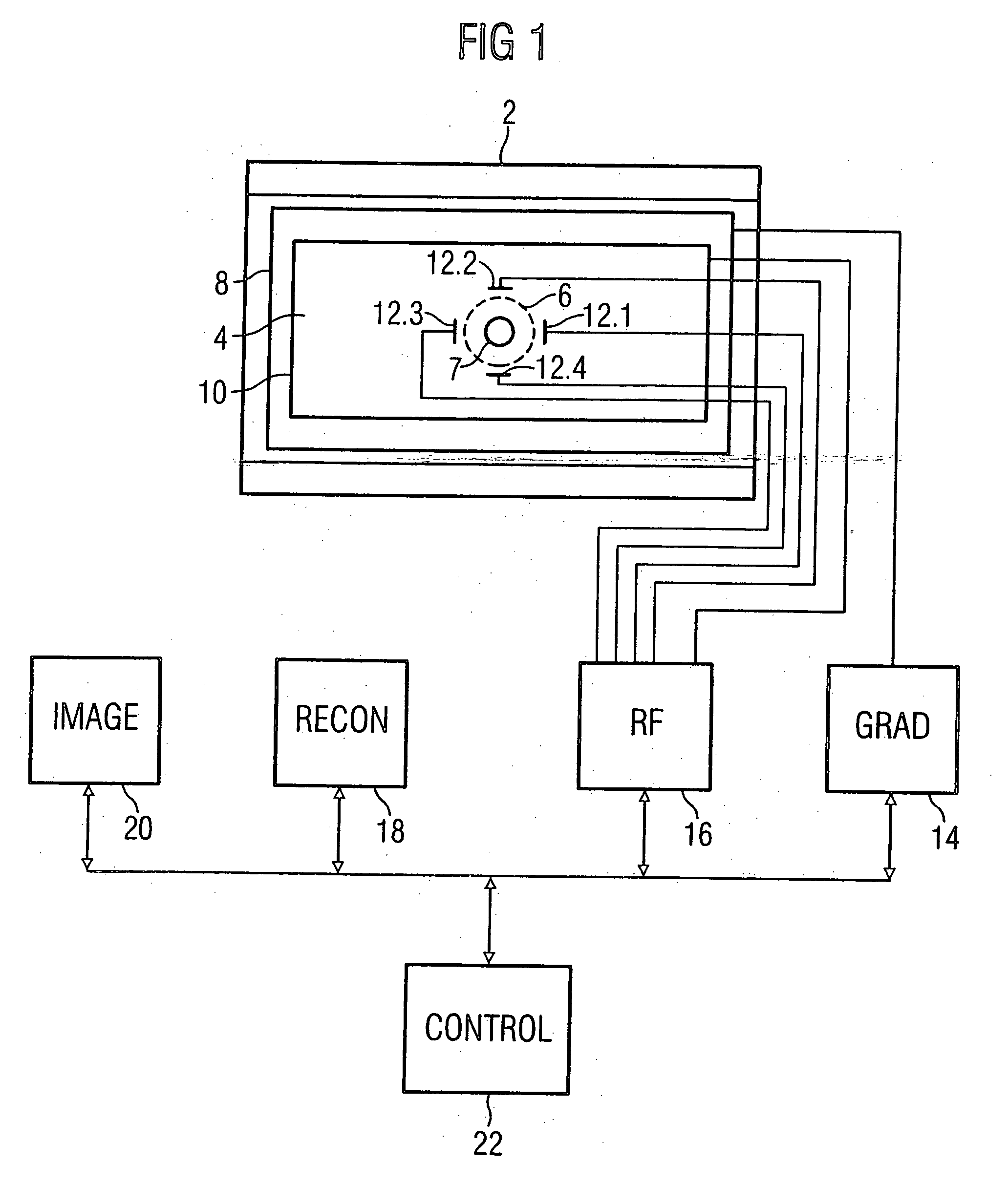
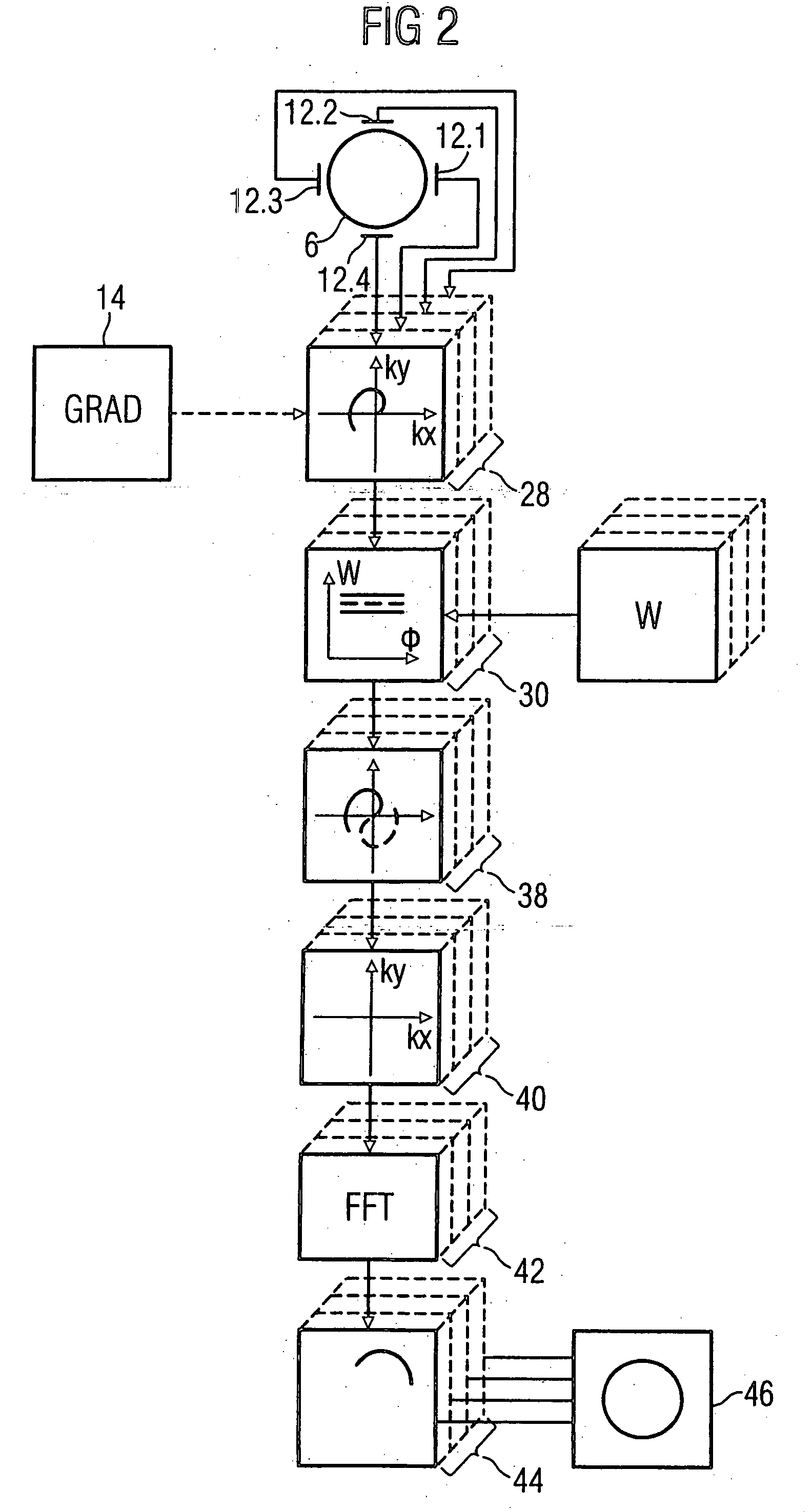
InactiveUS20050264287A1Less effortSimplify the rebuild processMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientAcquisition technique
In a method for magnetic resonance imaging using a partial parallel acquisition technique with a non-Cartesian occupation of k-space, a number of antennas disposed around an imaging volume for reception of magnetic resonance signals and the magnetic resonance signals in the imaging volume are spatially coded by magnetic gradient fields, such that k-space for each antenna is only incompletely occupied with magnetic resonance signals with at least one trajectory proceeding around the origin of k-space. From the reception signals of each antenna, missing sample values of the trajectory that lie on a straight-line segment extending from the origin are determined in k-space according to a weighting with weighting factors from sample values of the trajectory that likewise lie on the straight lines, such that each k-space is completely occupied. A partial image of the imaging area is generated from each completely occupied k-space by means of a Fourier transformation. An image of the imaging volume is generated from the partial images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
High-efficient ion source with improved magnetic field
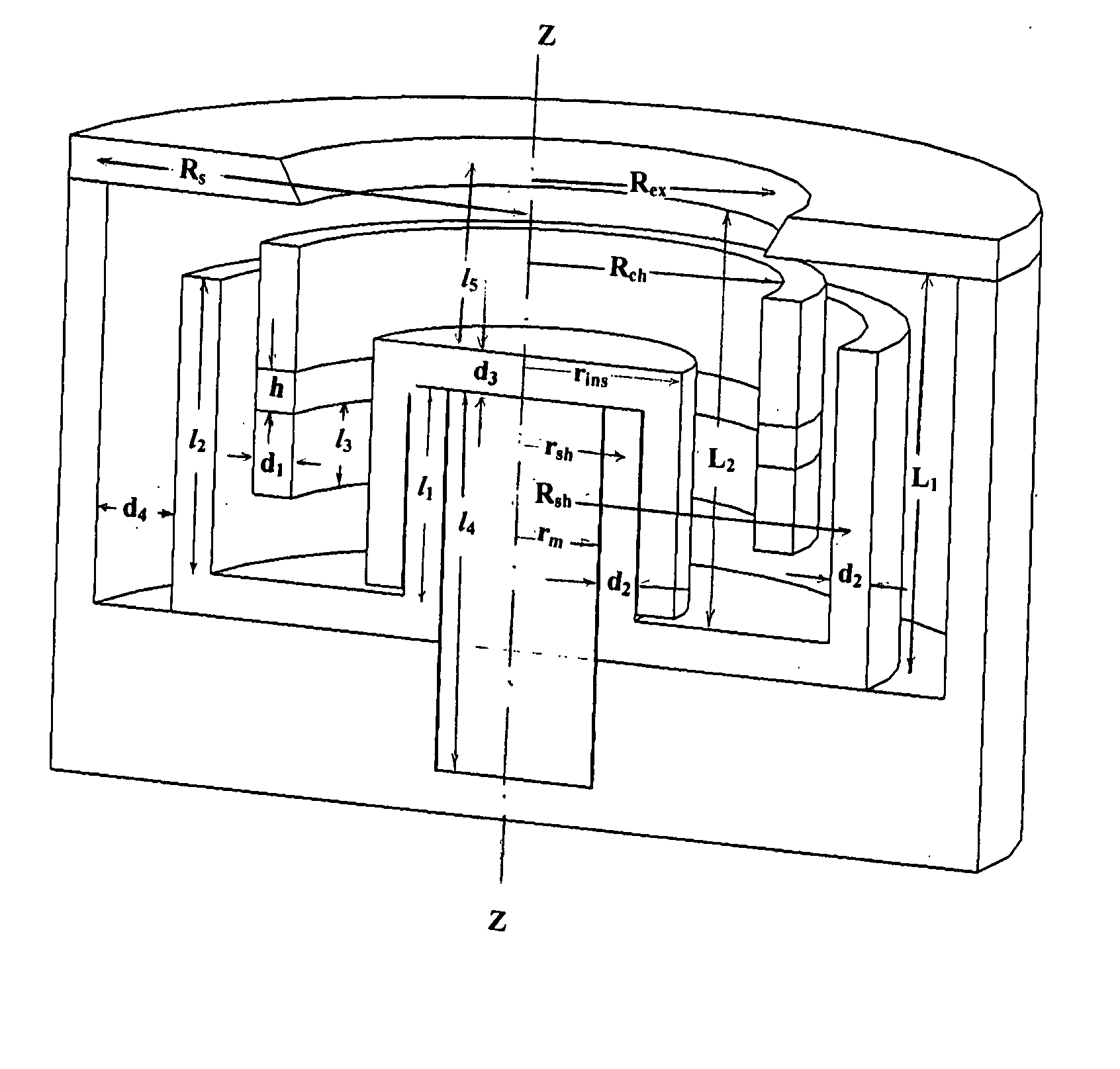
InactiveUS20050237000A1Improve operating conditionsWide rangeMaterial analysis by optical meansElectric arc lampsMagnetic gradientIon beam
A Hall-type ion source for generation of ion beams for technological applications presents itself a hybrid ion source, where properties of closed drift systems and end-Hall ion sources are combined for more efficient operation. An ion source has shorter central magnetic pole than regular closed drift ion source with magnetic screens that provide positive magnetic gradient in an ion source's discharge channel. An ion source with these combined properties has higher ratio of ion beam current to discharge current than end-Hall ion source and wider range of discharge parameters than closed drift ion source.
Owner:ZHURIN VIACHESLAV V
Aircraft hanging-type fluxgate magnetic gradient tensor instrument correction method
InactiveCN105891755AGuaranteed correctnessOvercoming the problem of changing calibration parametersElectrical measurementsCorrection algorithmMagnetic field gradient
The invention relates to an aircraft hanging-type fluxgate magnetic gradient tensor instrument correction method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a single fluxgate error model; 2) establishing a magnetic gradient tensor component error correction model; 3) collecting correction data in a uniform magnetic field region at high altitude; 4) correcting errors of tensor components; 5) collecting correction data in non-uniform magnetic field region on the ground; 6) solving scale factor error of the tensor components; 7) combining correction coefficients obtained through high-altitude correction and ground correction; and 8) fully calculating magnetic gradient tensor after correction. Compared with a conventional aircraft magnetic field gradient tensor correction algorithm, the correction method in the invention not only corrects a single tensor component, but also corrects the tensor as a whole, so that the tensor component and the whole correction results are allowed to be more accurate, and meanwhile, application conditions thereof meet actual aircraft magnetic gradient tensor detection region geological conditions better.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Arterial spin labeling with pulsed radio frequency sequences
In one aspect, a method for imaging fluid flow and / or perfusion using spin labeling is provided. The method comprises applying a first magnetic gradient sequence at least to a labeling region, applying a first pulsed radio frequency (RF) sequence to the labeling region to label the fluid, the first pulsed RF sequence comprising a first plurality of pulses wherein an amplitude envelope is non-zero, the first plurality of pulses each separated by a respective first plurality of intervals wherein the amplitude envelope is substantially zero, and acquiring at least one first signal emitted from an imaging region a predetermined delay after applying the first pulsed RF sequence.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Motion type magnetic target locating method based on vector magnetic gradiometer
InactiveCN106405658AReduce measurement errorAccurately obtainedElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationVector magnetographNuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a motion type magnetic target locating method based on a vector magnetic gradiometer. The motion type magnetic target locating method comprises the following steps that (1) the structural error of two sets of vector magnetometers forming the vector magnetic gradiometer is compensated so that the signal output of the two sets of vector magnetometers is maintained to be consistent; (3) the vector magnetic gradiometer is enabled to rotate around a vertical axis in a magnetic abnormal space, the magnetic field direction gradient data of the magnetic gradiometer at the rotating azimuth angle are acquired, and magnetic field full tensors are acquired according to the relation between the direction gradient and the azimuth angle; and (3) magnetic target locating is performed by using the magnetic field full tensors. According to the motion type magnetic target locating method, the structural error compensation problem of the vector magnetic gradiometer is solved by using the mode of triaxial coefficient compensation so that the output of the two sets of vector magnetometers forming the magnetic gradiometer is enabled to be correspondingly consistent; and the structural error is eliminated so that high-resolution detection can be realized.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Device and method for obtaining relevant parameters of aviation superconductive full-tensor magnetic gradient measuring system
InactiveCN104345348AReduce computational difficultyImprove computing efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationAviationMagnetic gradient
The invention relates to an aviation geophysic magnetic type exploration data processing method. The method is characterized in that the baseline direction unit vectors and sensor plane normal vectors, corresponding to an inertia navigation coordinate system, and the sensor plane normal vectors, corresponding to a three-component magnetic instrument coordinate system, of five plane superconductive magnetic gradient sensors can be accurately obtained, and then the premise is provided for accurately obtaining five independent components of a full-tensor magnetic gradient corresponding to a geographic coordinate system; the five independent components of the full-tensor magnetic gradient are calculated by a coordinate system conversion method, the middle process of calculating the attitude angles, corresponding to the coordinate system, of the five plane superconductive magnetic gradient sensors is not needed, the inertial navigation coordinate system is used as the coordinate system of the measurement system, and the attitude data measured by inertial navigation are converted by the one-time coordinate system, so as to obtain the five independent components of the full-tensor magnetic gradient corresponding to the geographic coordinate system. The method has the advantages that the calculation difficulty is decreased, the calculation efficiency is improved, and the method is more suitable for measuring the attitude time varying of measuring platforms, such as aviation magnetic measuring.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +1
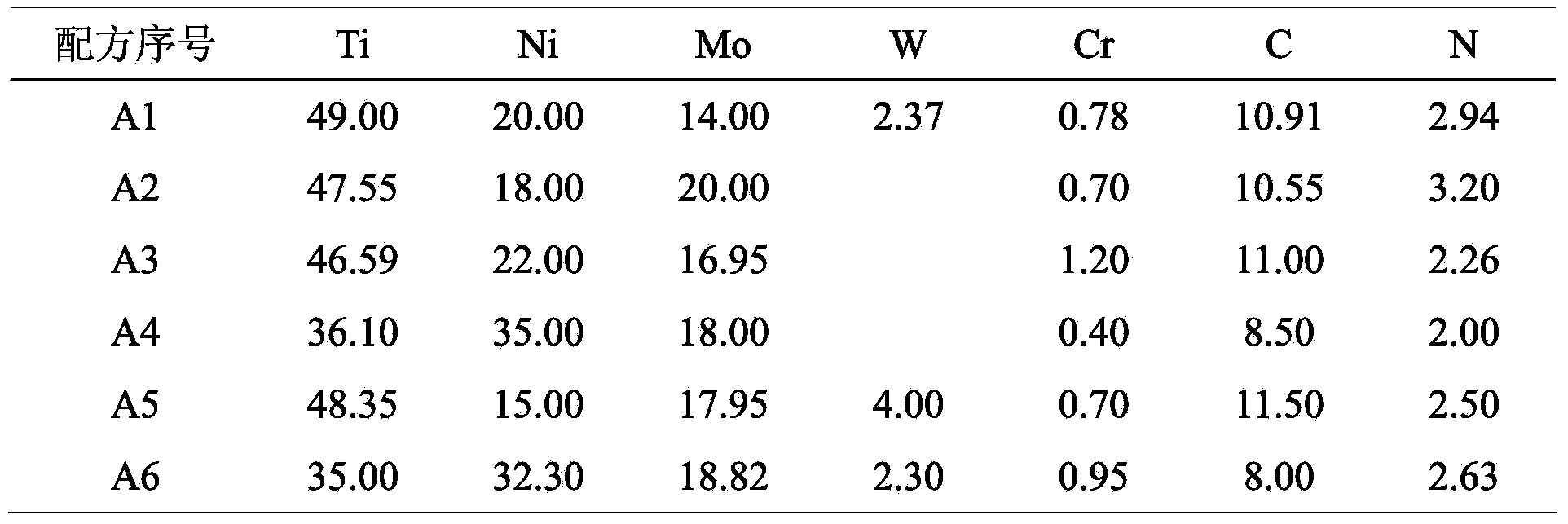
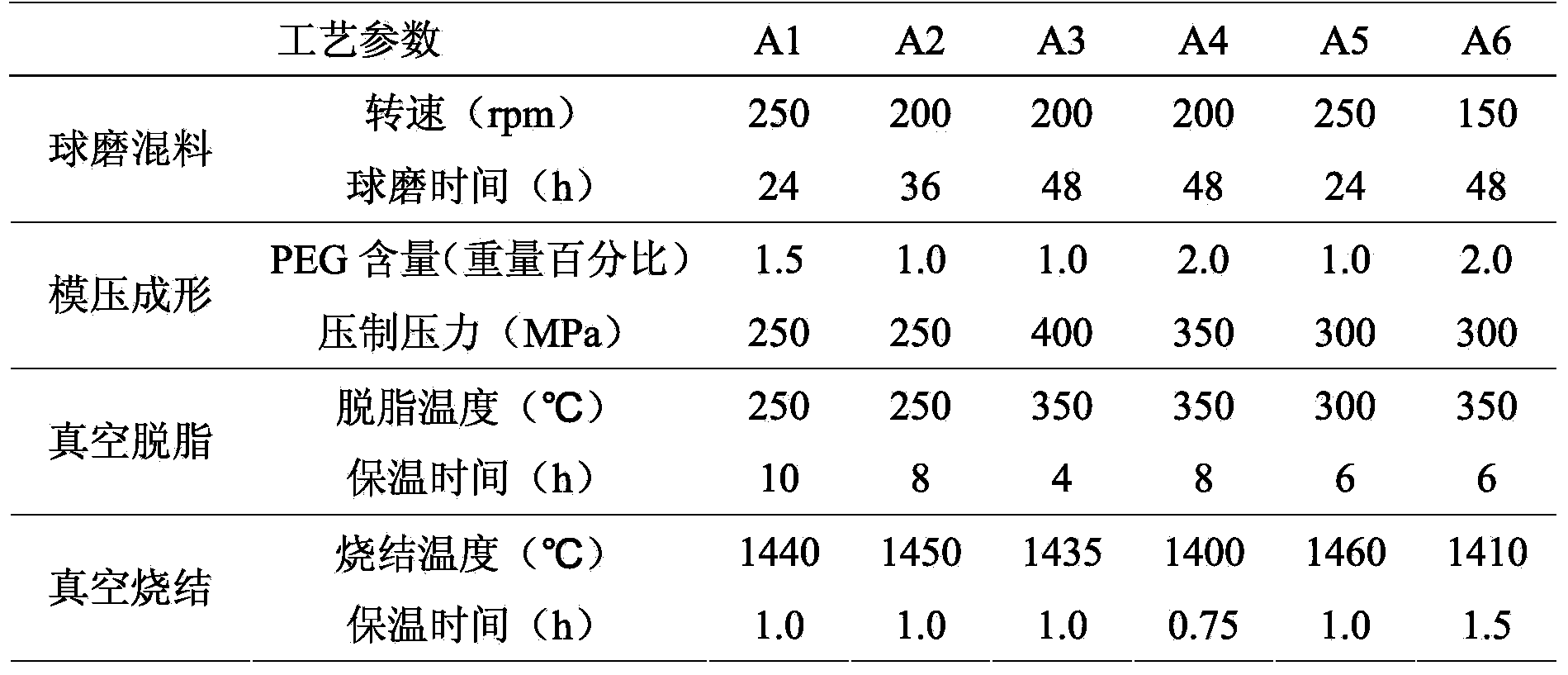
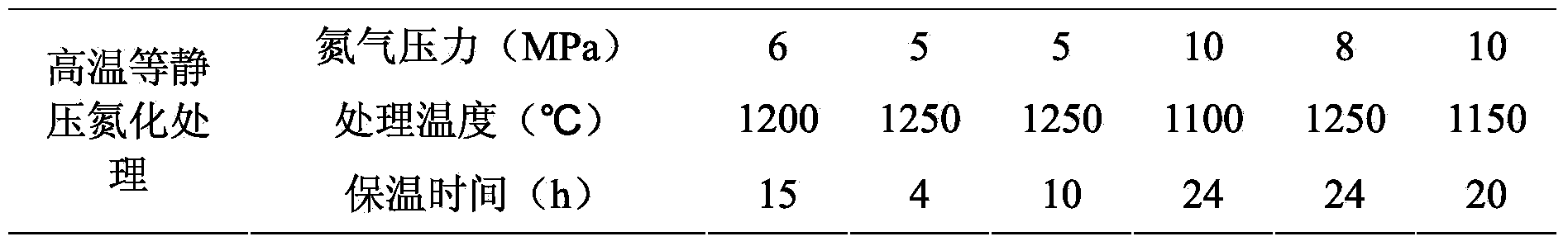
Non-magnetic Ti(C, N) base cermet with gradient structure and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a non-magnetic Ti(C, N) base cermet with a gradient structure and a preparation method thereof, belonging to Ti(C, N) base cermets and solving the problem of contradictions between strong toughness and no magnetism of existing Ti(C, N) base cermets, so that the Ti(C, N) base cermet simultaneously has strong toughness and no magnetism. The non-magnetic Ti(C, N) base cermet with the gradient structure is prepared by using TiC, TiN, Ni, Mo2C, WC and Cr3C2 powder as the raw materials and carrying out ball-milling and mixing, die forming, vacuum degreasing, vacuum sintering and hot isostatic pressing surface nitriding. The non-magnetic Ti(C, N) base cermet has good wear resistance, red hardness, impact resistance and chemical stability, has low coefficients of friction with the materials such as iron and steel, silicon carbide and the like, has bending strength not less than 1800MPa, core matrix hardness of 86.0-92.5HRA and surface hardening layer Vickers microhardness of 1800-2050kg / mm<2>, is especially suitable for manufacturing non-magnetic cutting tools, non-magnetic dies and non-magnetic wear-resistant parts, has widened application range and has good popularization and application prospects in the industries such as tools and dies, national defences, military projects and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for positioning the focus of a gradient field and treatment facility
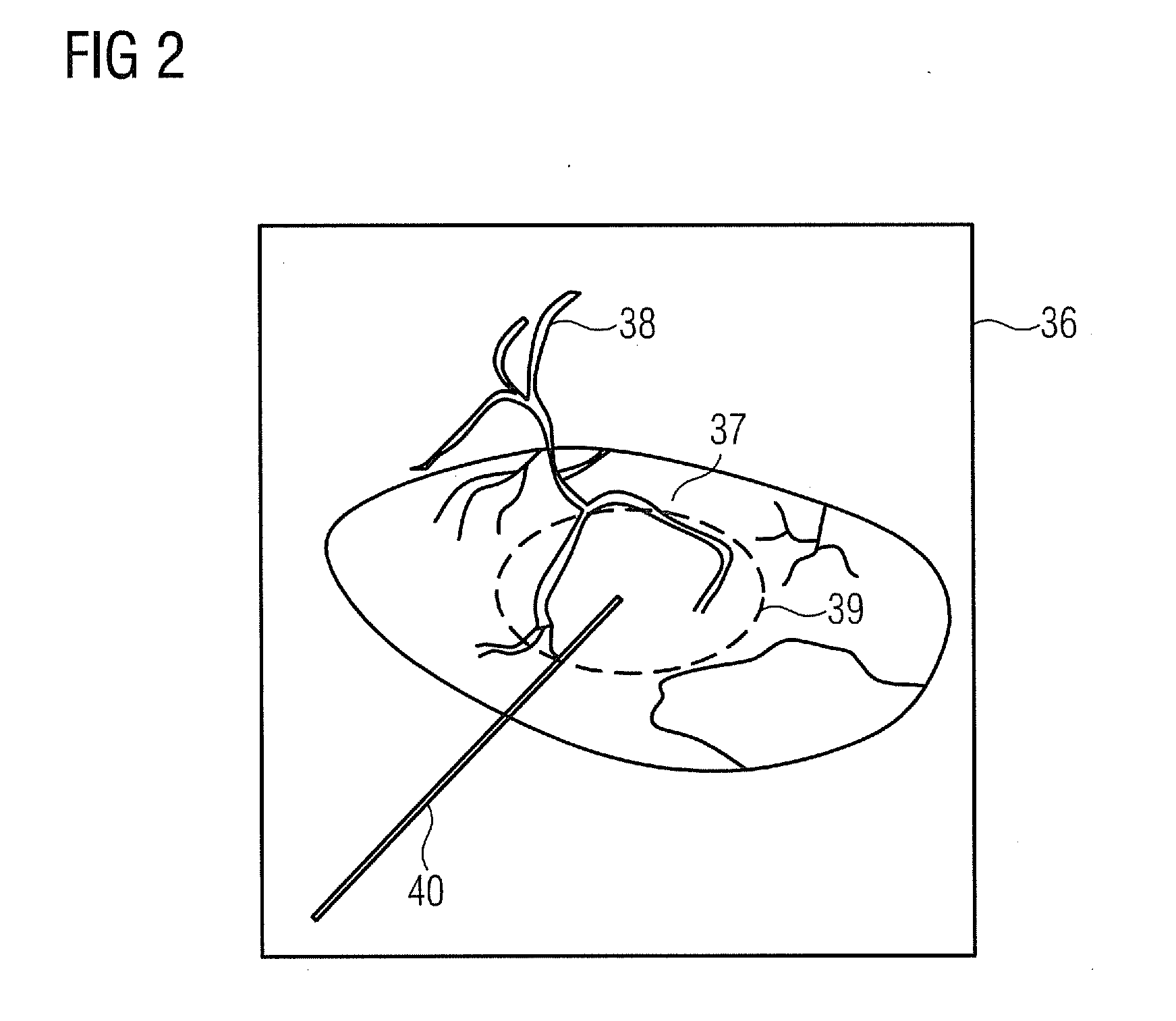
InactiveUS20110282184A1Easy to optimizeSafer and rapid concentrationElectrotherapyMagnetic measurementsMagnetic gradientNanoparticle
A method for guiding nanoparticles to a target location by a magnetic gradient field and / or holding them at the target location is proposed. The magnetic gradient field is generated by a magnet system with at least one magnet. A focus of the magnet system is registered with an X-ray device. At least one three-dimensional image dataset showing the target location is captured by the X-ray device. The position of the target location is determined manually and / or automatically in the image dataset or in an image dataset determined therefrom and is positioned automatically based on the registration of the focus so that the focus coincides with the position of the target location.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com