Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Sufficient dynamic range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
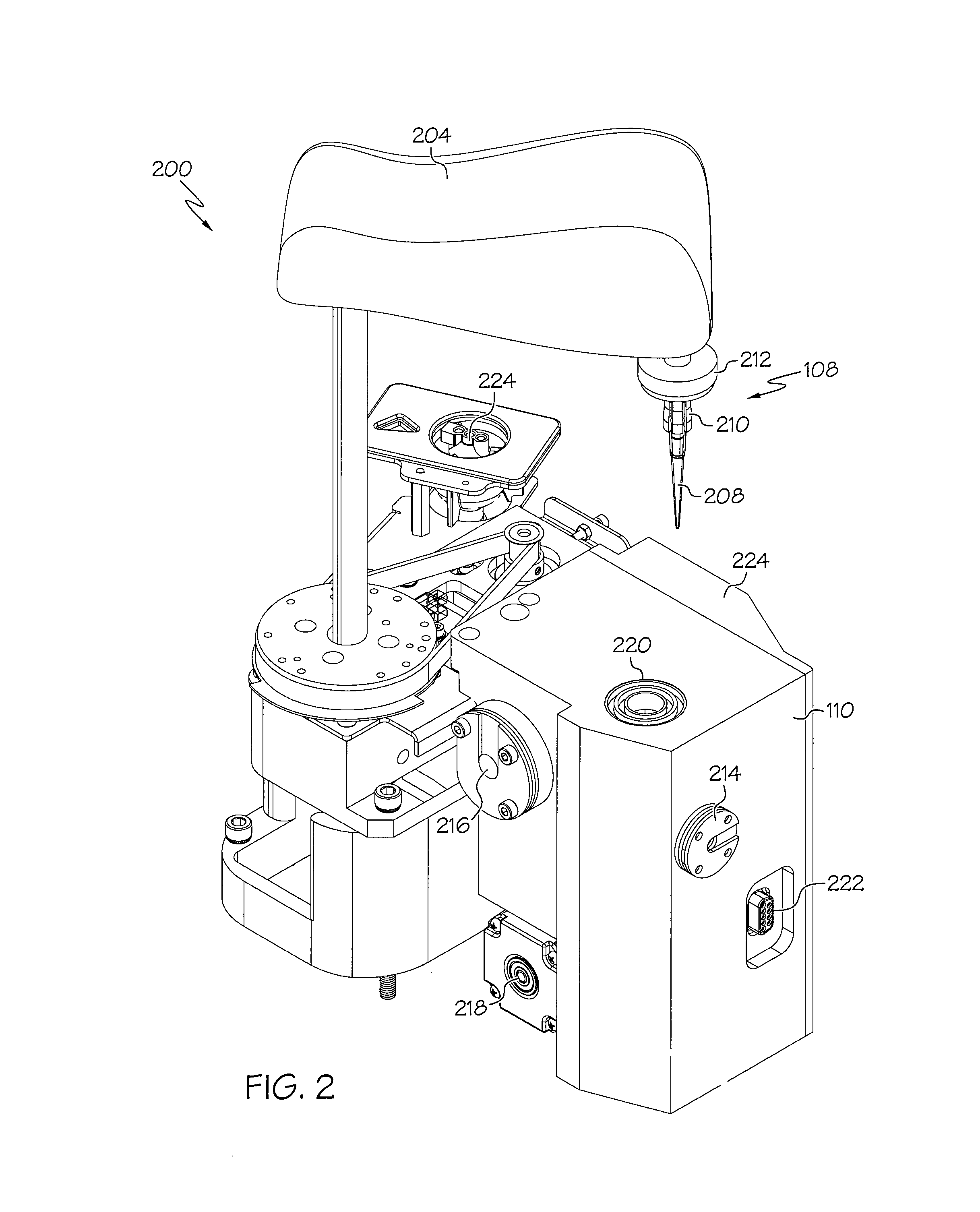
Magnetic gradiometer incorporating global feedback
InactiveUS6339328B1Minimizing energySufficient dynamic rangeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientGradiometer
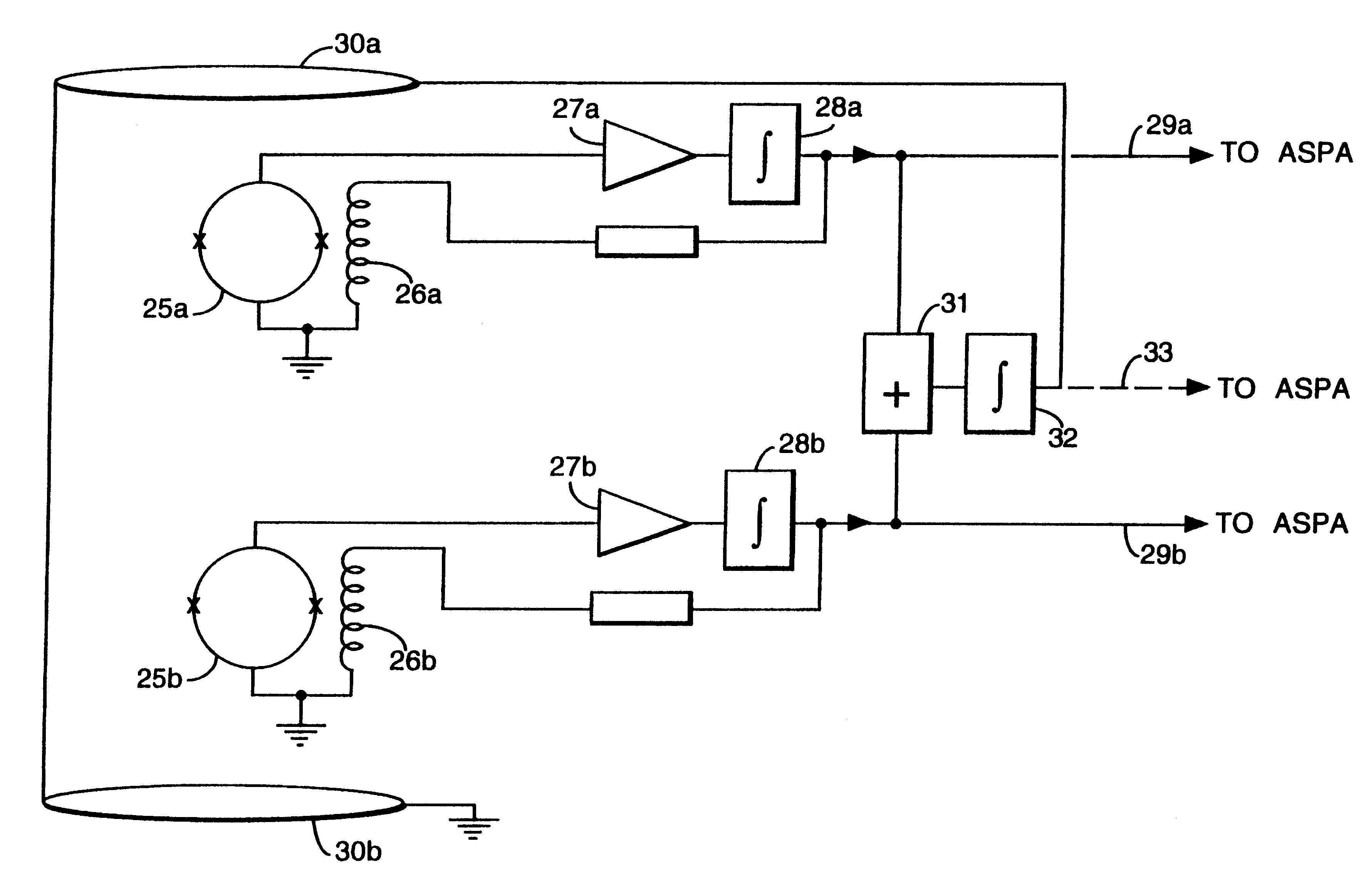
A gradiometer for measuring properties of a magnetic field and in particular, for measuring magnetic field gradient components, comprising at least two magnetic sensors wherein at least two of the magnetic sensors are arranged to sense the magnetic field component in substantially the same direction. The magnetic sensors may be super conducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometers, Hall probes, flux gates or magneto-resistive magnetometers. The gradiometer also includes a computer processor loaded with an adaptive signal-processing algorithm, for performing adaptive signal balancing of the magnetometer outputs. In a preferred embodiment the gradiometer may comprise at least eight magnetometers in a three-dimensional arrangement, and a set of three orthogonal global feedback coils, one for each direction x, y, z, such that the five independent magnetic field gradient components may be measured. The gradiometer may also be used to measure second or higher order magnetic field gradient components.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
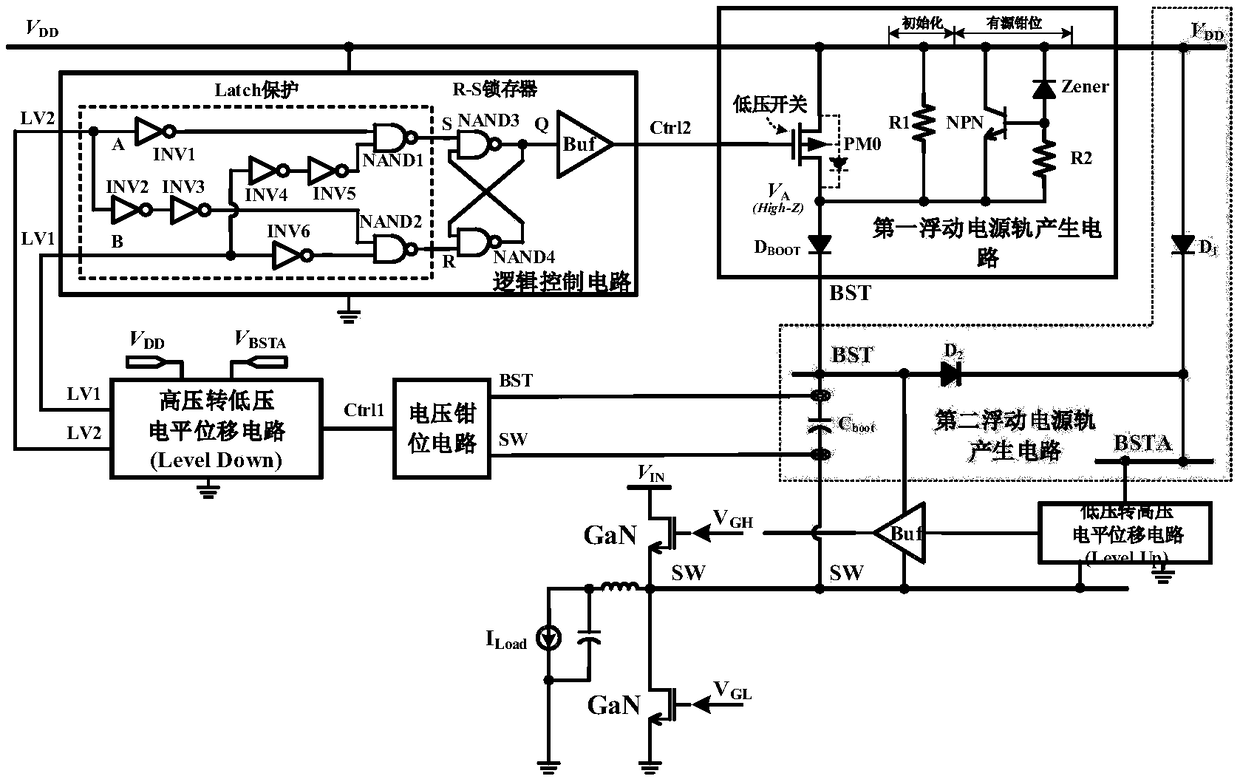
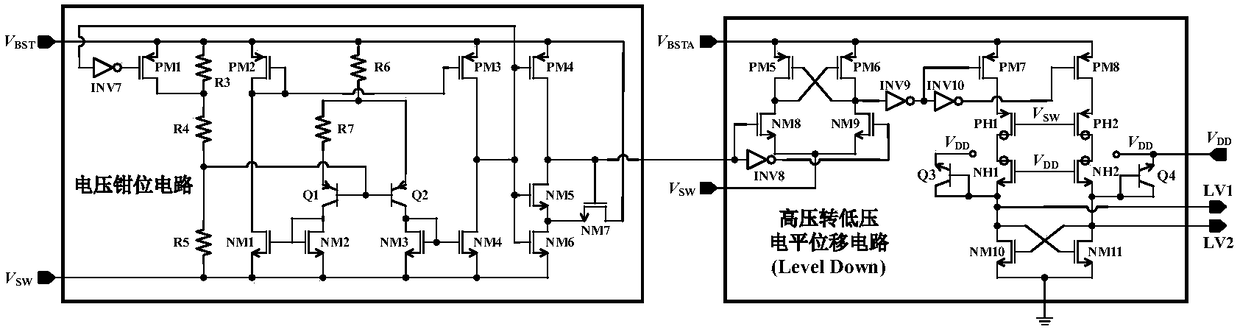
Floating power supply rail applicable to GaN high-speed gate driving circuit
ActiveCN108494234ASufficient dynamic rangeTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionLow voltageHemt circuits
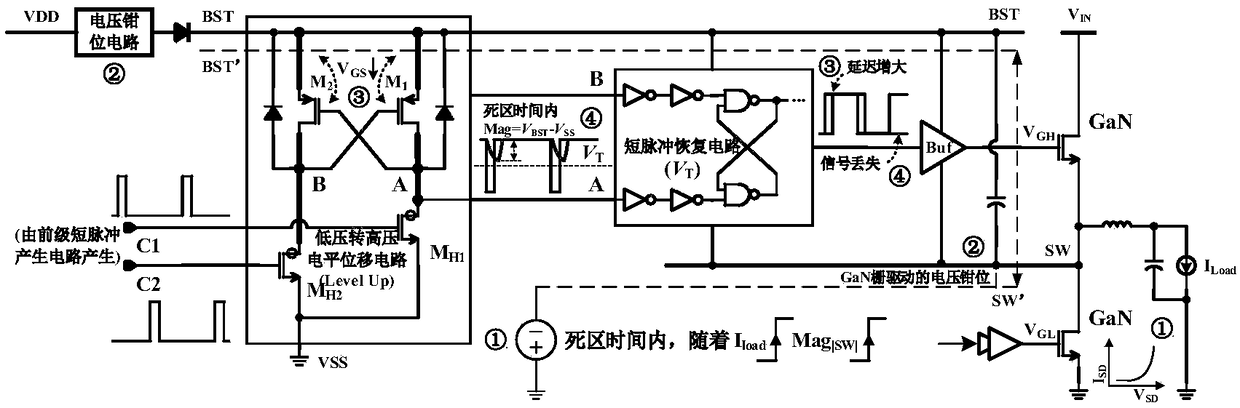
The invention relates to a floating power supply rail applicable to a GaN high-speed gate driving circuit, and belongs to the technical field of power management. With the design of dual floating power supply rails, a GaN power switch device can work within a safety voltage, and a low-voltage-to-high-voltage potential displacement circuit has enough dynamic range. A high-voltage-to-low-voltage potential displacement circuit, a voltage clamping circuit, a logic control circuit and a first floating power supply rail generation circuit form a closed loop, a BST for generating a first power supplyrail is used as a power supply rail of a buffer circuit in the GaN high-speed gate driving circuit, and a gate source voltage of the GaN power switch device can be enabled to be within a safety range; and a second floating power supply rail generation circuit forms a closed loop, a BSTA for generating a second power supply rail is used as a power supply rail of the low-voltage-to-high-voltage potential displacement circuit in the GaN high-speed gate driving circuit, and the GaN high-speed gate driving circuit can be enabled to have enough dynamic range.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
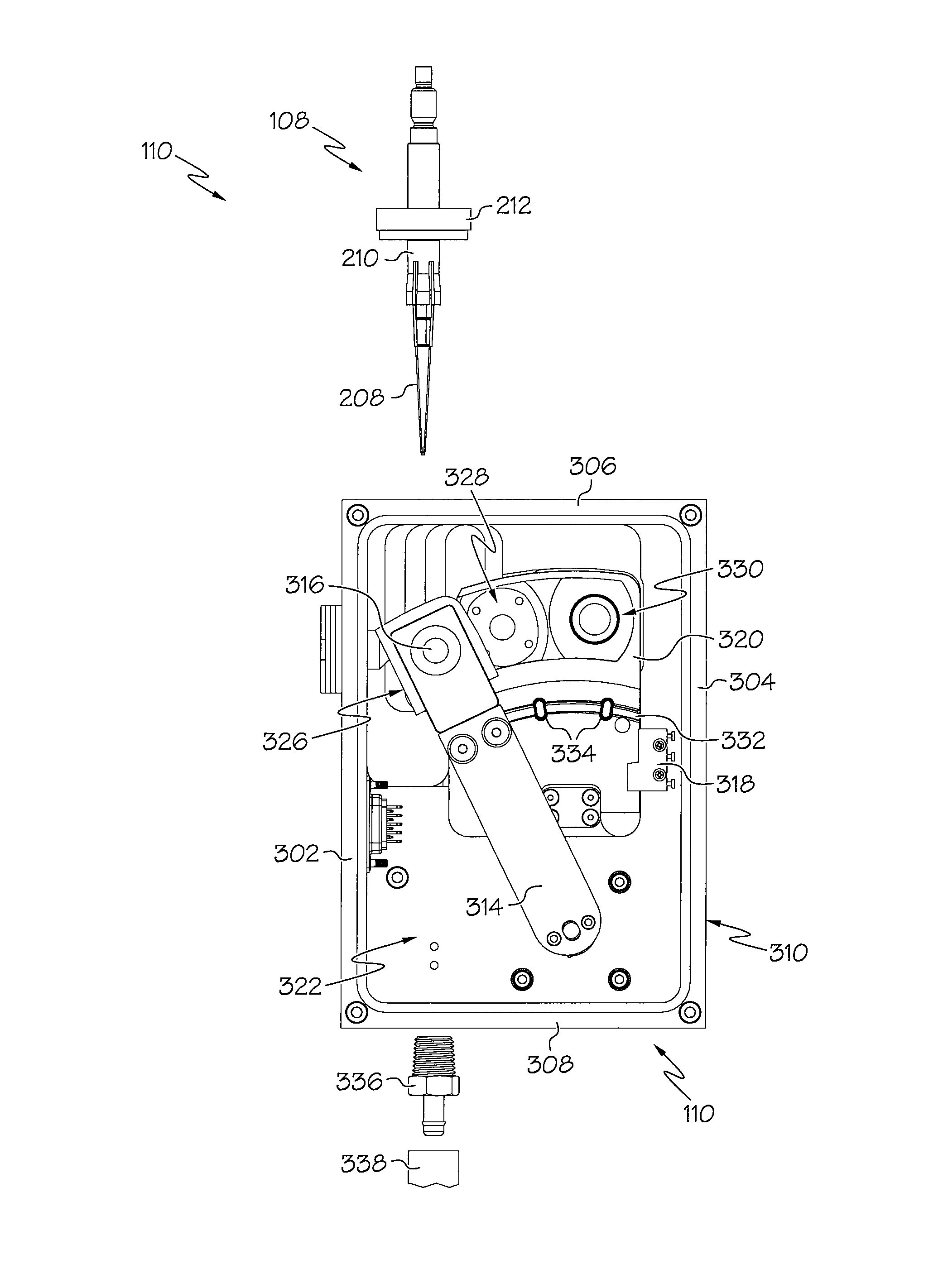
Device and associated methods for performing luminescence and fluorescence measurements of a sample
ActiveUS9075055B2Crosstalk from the fluorescence light source can be minimizedMinimize crosstalkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDisease diagnosisFluorescencePipette
An apparatus for measuring the luminescence and the fluorescence of a sample, comprising: a light tight optics box capable of receiving a pipette tip containing a sample; an optical sensor located within the optics box and capable of being disposed in both a luminescence reading position and a fluorescence reading position; an excitation light fiber optic bundle and a sample transmission fiber optic bundle; an excitation light assembly that projects excitation light onto a first terminus end of the excitation light fiber optic bundle; and an in-line filter located along the sample transmission fiber optic bundle.
Owner:HYCOR BIOMEDICAL LLC
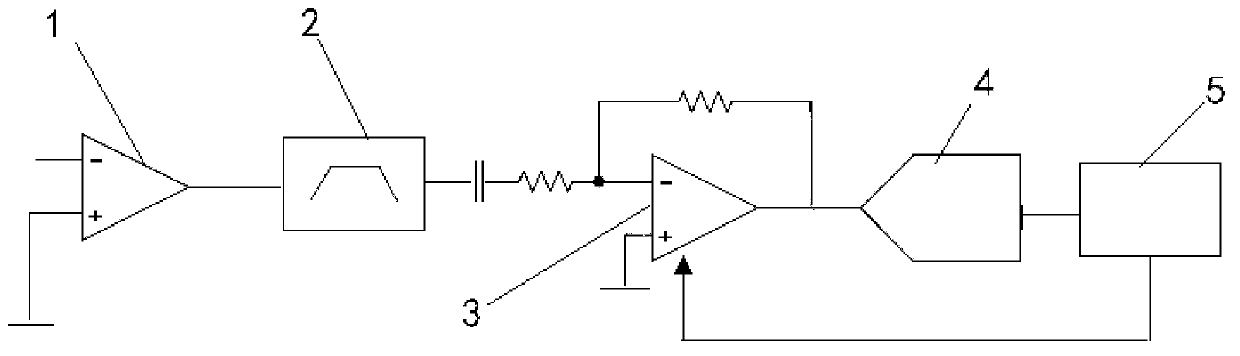
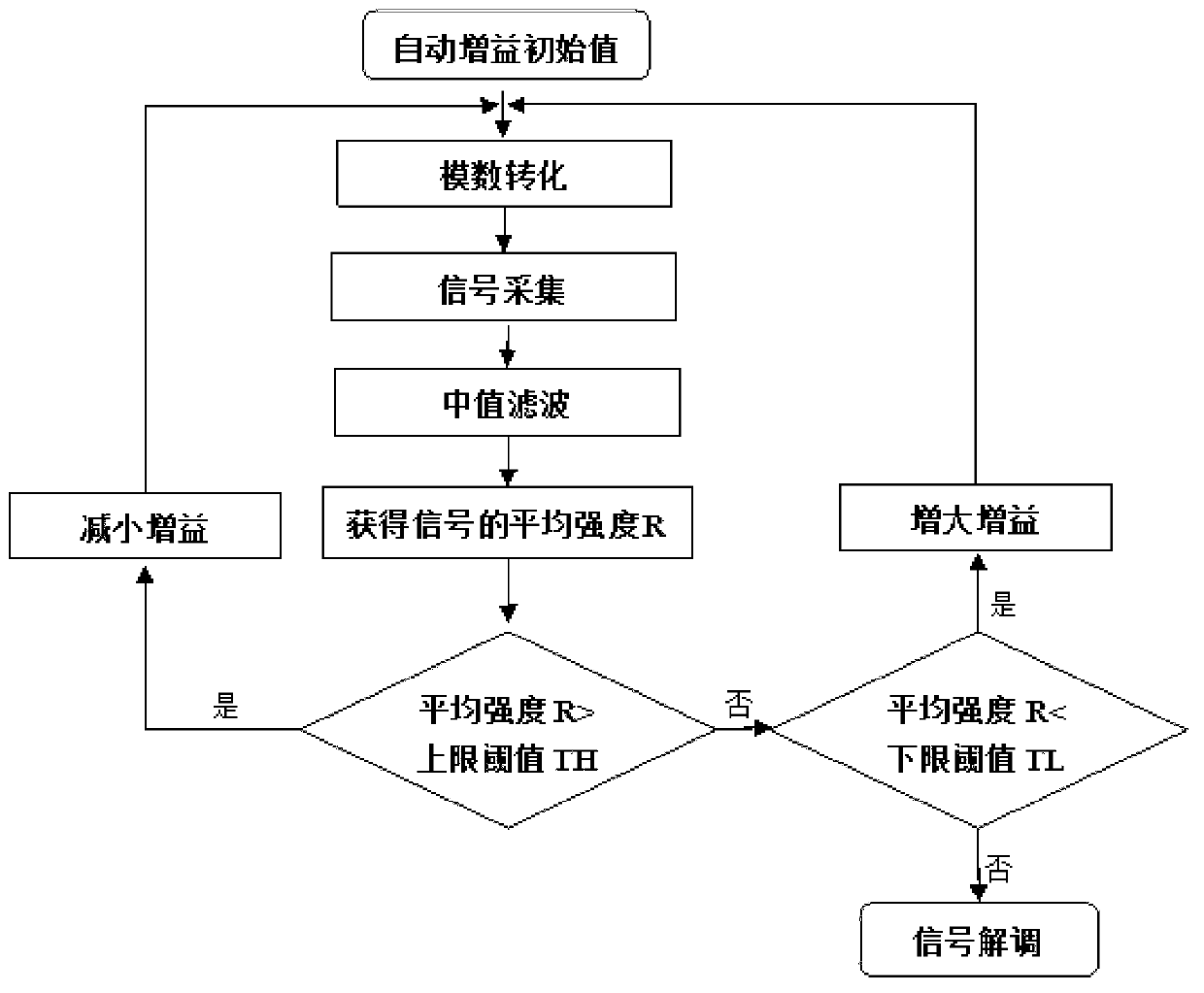
Control method of automatic gain in power line carrier communication network
ActiveCN103220018AImprove receiver sensitivitySufficient dynamic rangePower distribution line transmissionLow noiseBandpass filtering
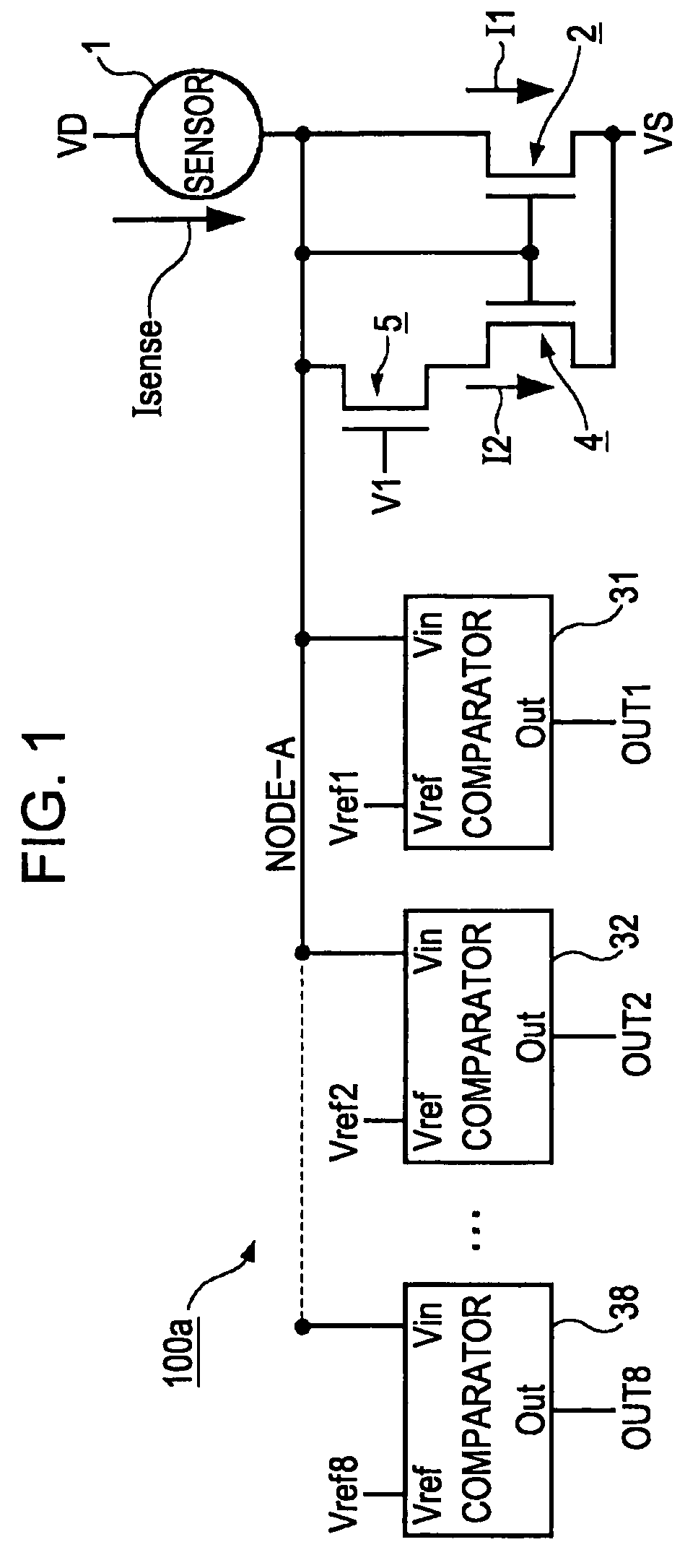
The invention discloses a control method of an automatic gain in a power line carrier communication network, and belongs to the technical field of power line carriers. The control method relates to a front end low noise amplifier, an active band-pass filter, a programmable gain amplifier, an analog-digital conversion unit and an automatic gain control unit. The method comprises the steps that an input carrier signal passes through the front end low noise amplifier, lower noise amplification is conducted on the input signal firstly, and after band-pass filtering, the carrier signal with a high signal-to-noise ratio is obtained; the carrier signal is amplified through the programmable gain amplifier, an initial gain value of the programmable gain amplifier is set to be the maximum value in a preset reference range, analog-digital conversion is conducted on the input carrier signal after the input carrier signal is amplified, sampling is conducted on the converted carrier signal, and median filtering is conducted on an obtained sampling signal to obtain average intensity of the carrier signal; and the gain of the programmable gain amplifier can be adjusted according to a difference between the average intensity of the carrier signal and the preset reference range.
Owner:北京中宸微电子有限公司
Blind i/q mismatch compensation with receiver non-linearity
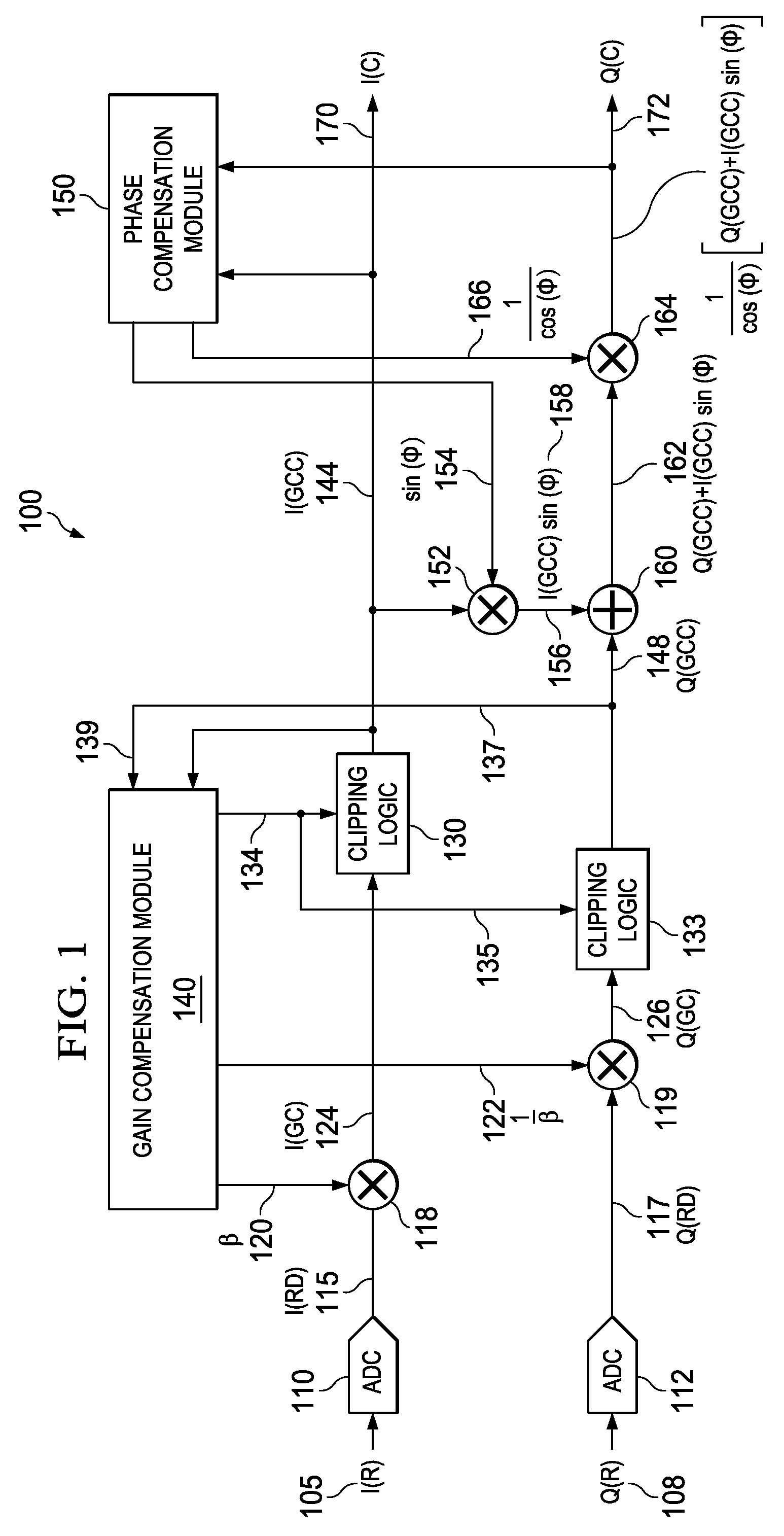
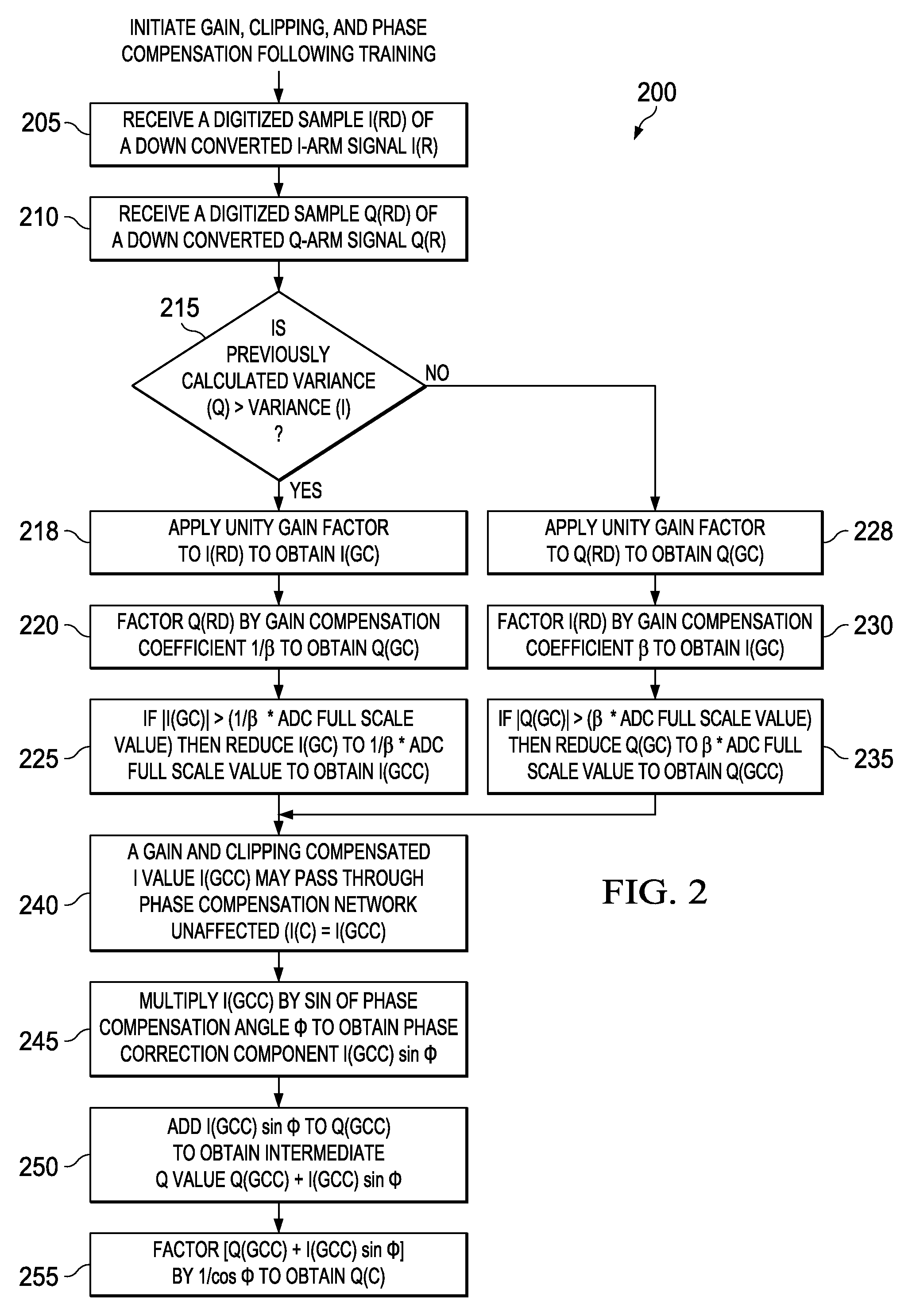
ActiveUS20140044158A1Sufficient dynamic rangeAvoid clippingError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionData streamEngineering
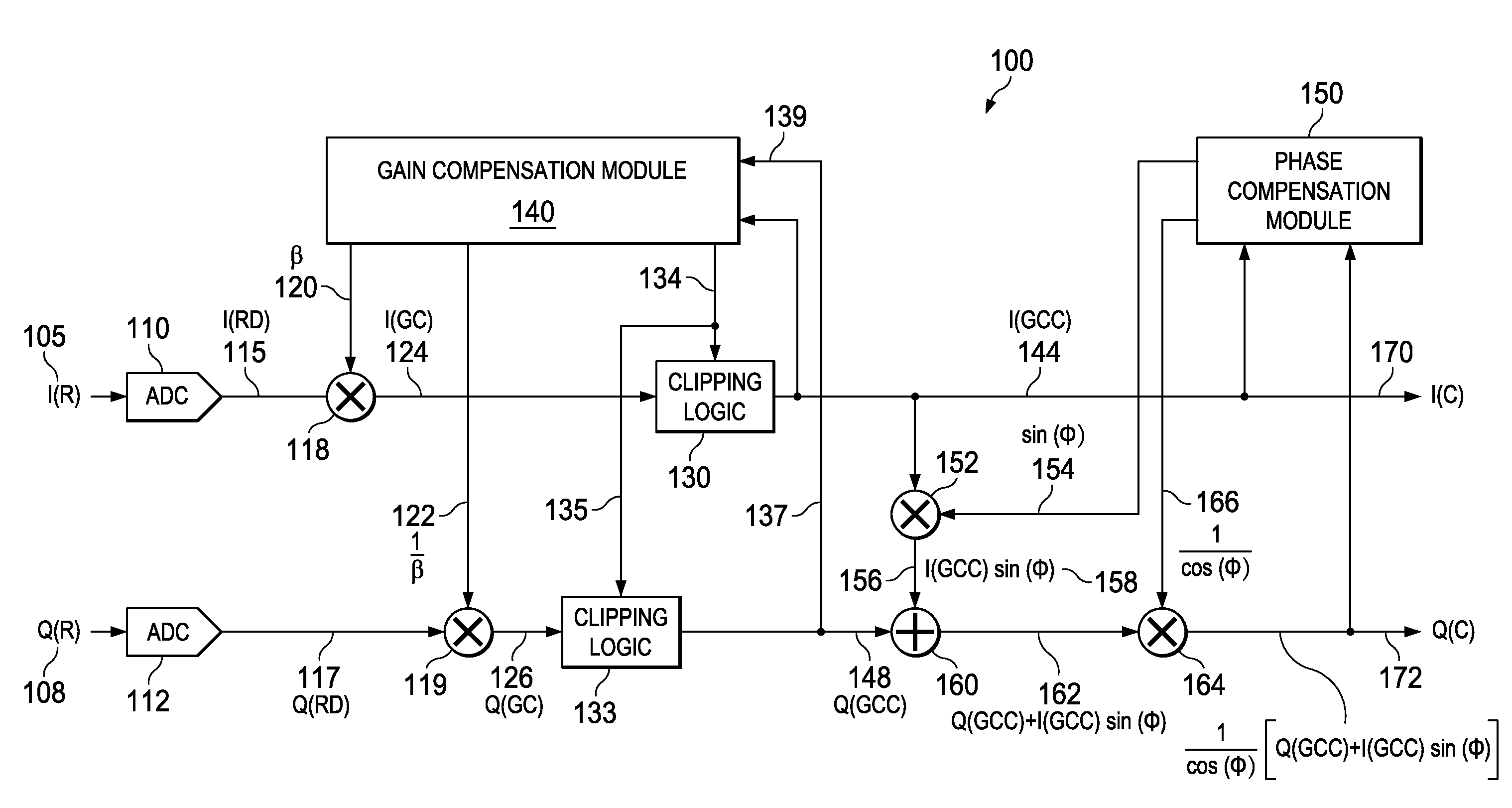
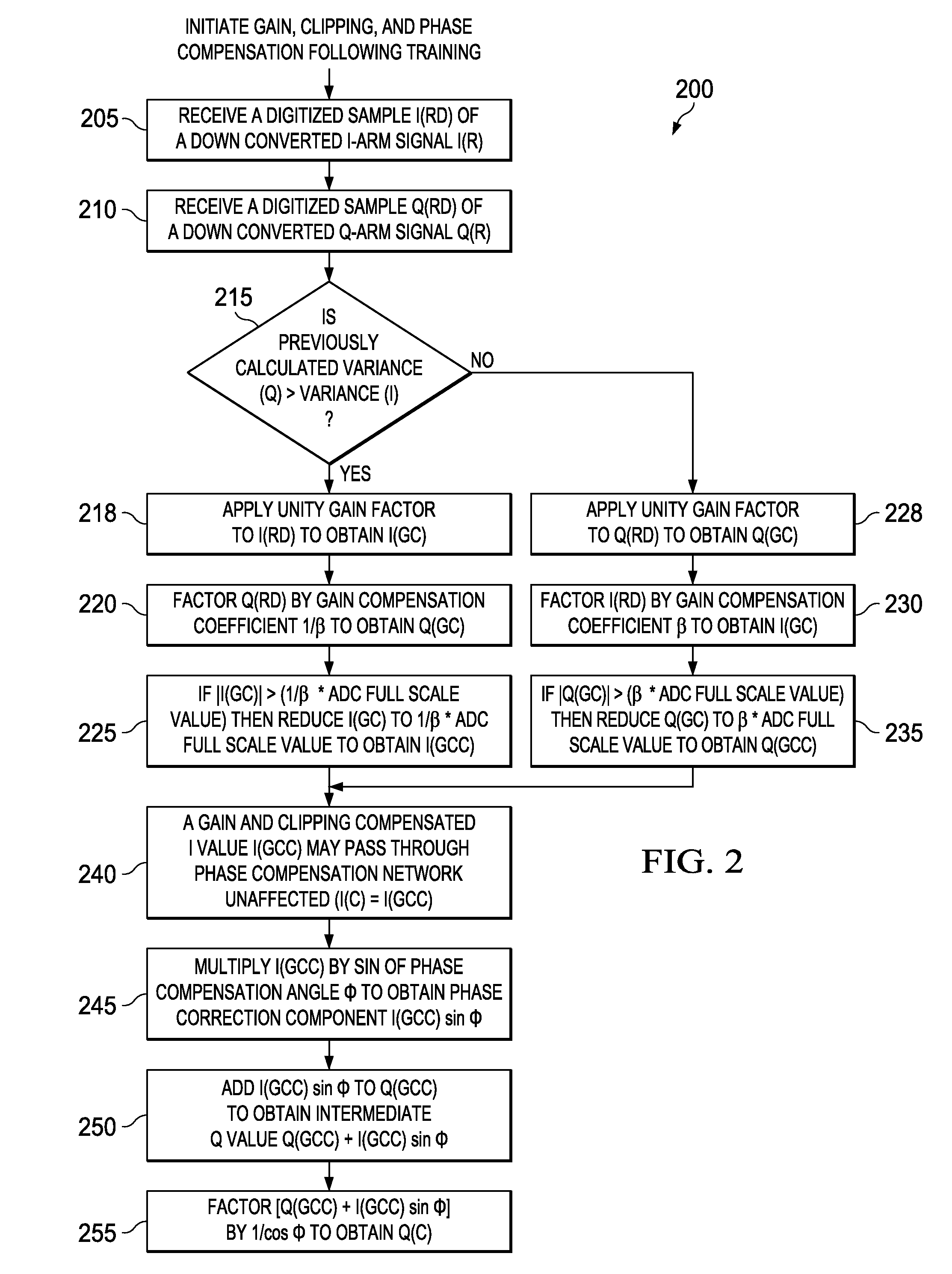
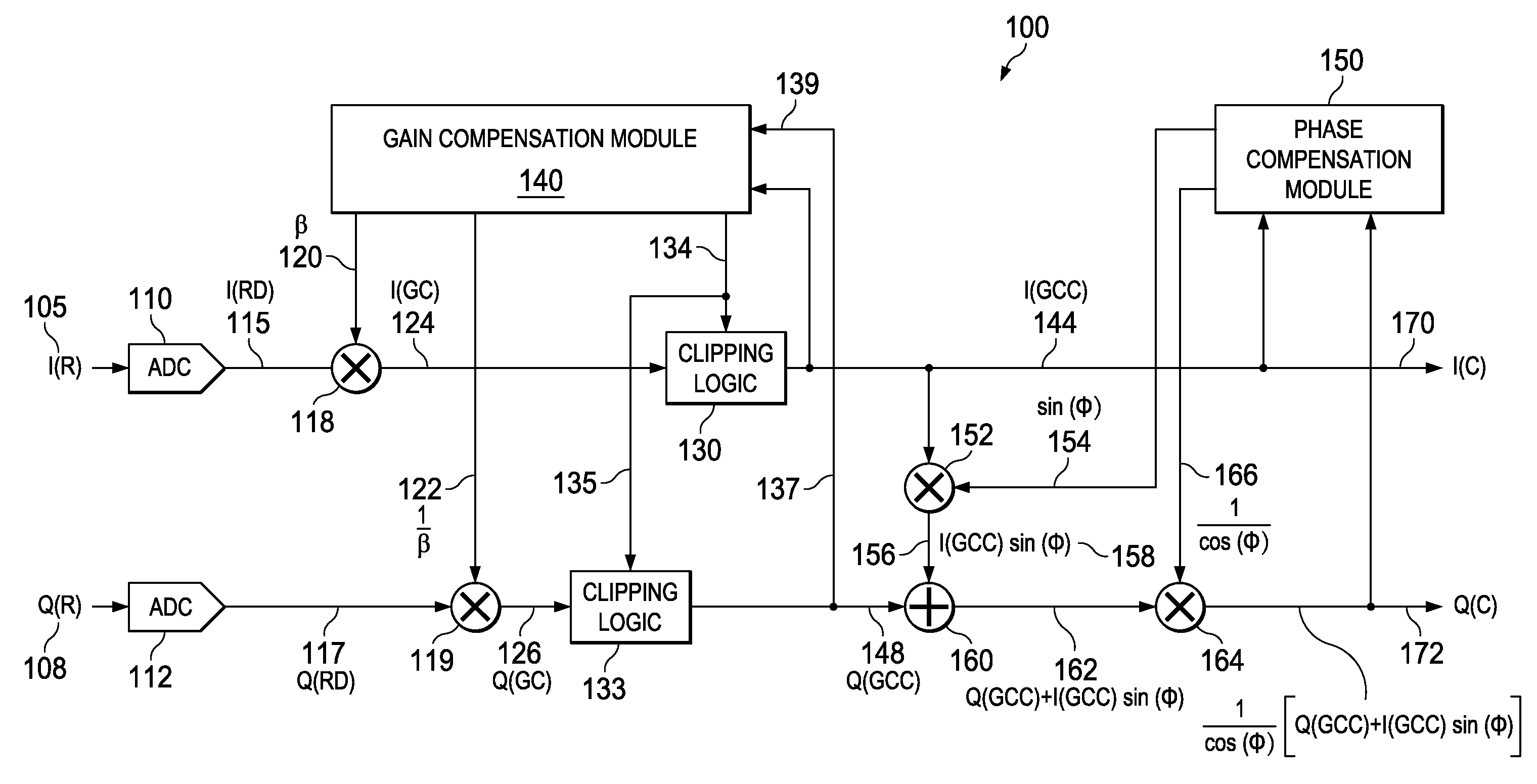
Apparatus and methods disclosed herein perform gain, clipping, and phase compensation in the presence of I / Q mismatch in quadrature RF receivers. Gain and phase mismatch are exacerbated by differences in clipping between I & Q signals in low resolution ADCs. Signals in the stronger channel arm are clipped differentially more than weaker signals in the other channel arm. Embodiments herein perform clipping operations during iterations of gain mismatch calculations in order to balance clipping between the I and Q channel arms. Gain compensation coefficients are iteratively converged, clipping levels are established, and data flowing through the network is gain and clipping compensated. A compensation phase angle and phase compensation coefficients are then determined from gain and clipping compensated sample data. The resulting phase compensation coefficients are applied to the gain and clipping corrected receiver data to yield a gain, clipping, and phase compensated data stream.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
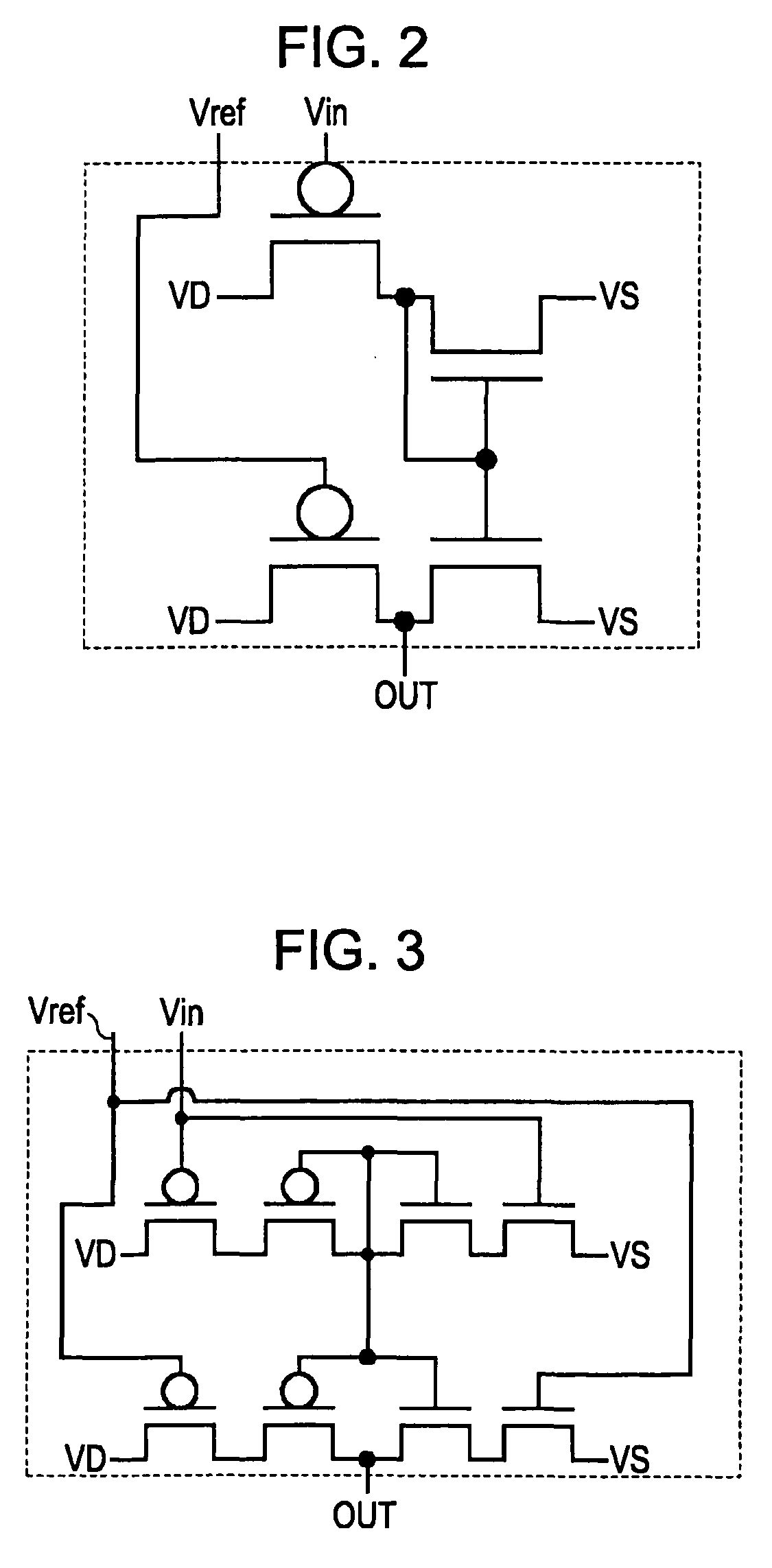
Electronic circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus including the same
InactiveUS7868882B2Sufficient dynamic rangeLow cost manufacturingMaterial analysis by optical meansCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitancePower flow
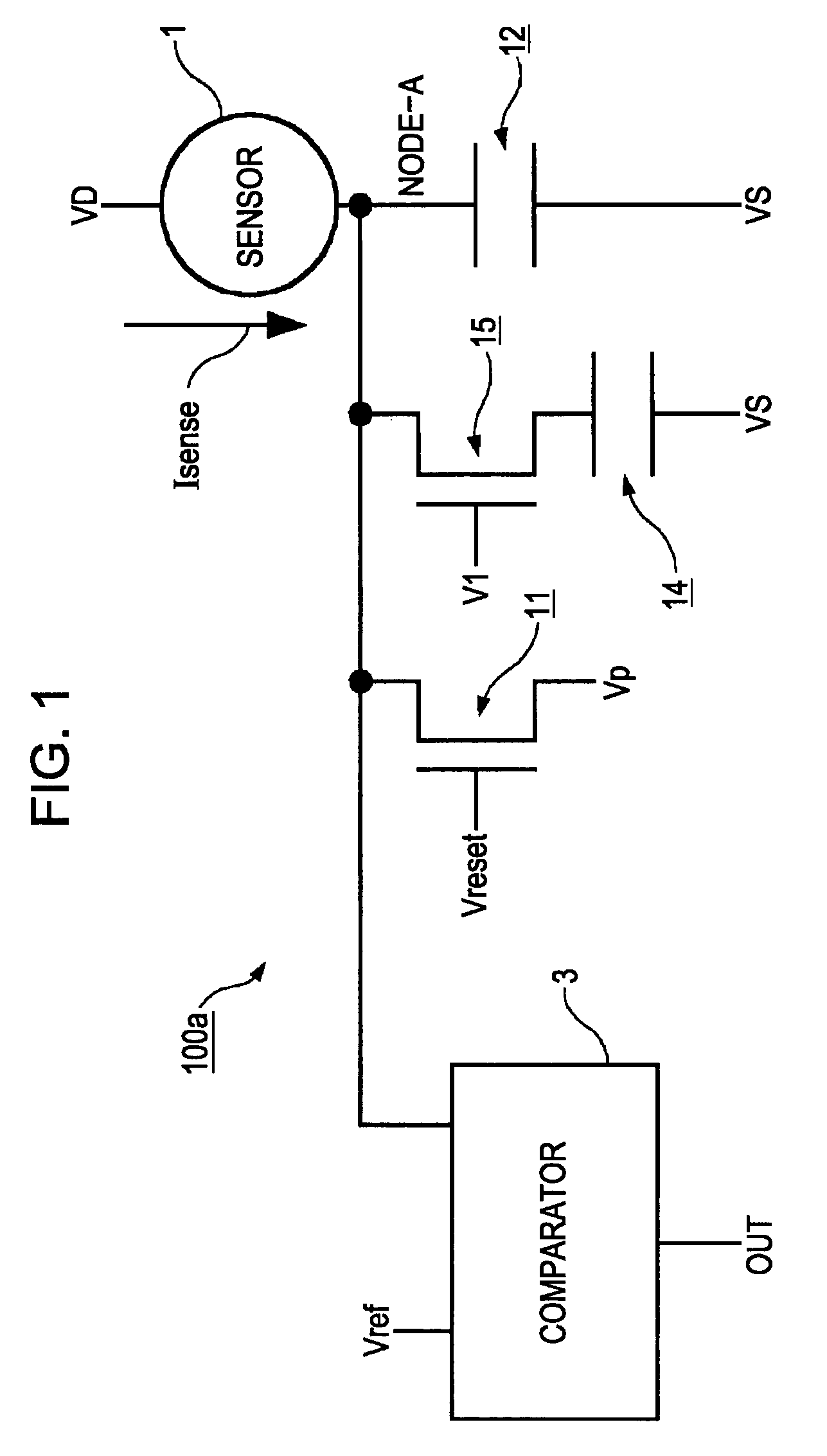
An electronic circuit, which has transistors disposed on a substrate, each transistor including an active layer made of thin-film polysilicon, includes a sensor that converts a measured quantity into a current value, a current-voltage conversion circuit that converts the current value into a voltage, and a voltage detection circuit that detects the voltage converted by the current-voltage conversion circuit and outputs a predetermined signal. The current-voltage conversion circuit includes a storage circuit and a range-switching circuit that switches a current-voltage conversion range of the current-voltage conversion circuit by switching the capacitance of the storage circuit.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Device and associated methods for performing luminescence and fluorescence measurements of a sample
ActiveUS20140273277A1Minimize crosstalkCrosstalk from the fluorescence light source can be minimizedChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDisease diagnosisFluorescencePipette
An apparatus for measuring the luminescence and the fluorescence of a sample, comprising: a light tight optics box capable of receiving a pipette tip containing a sample; an optical sensor located within the optics box and capable of being disposed in both a luminescence reading position and a fluorescence reading position; an excitation light fiber optic bundle and a sample transmission fiber optic bundle; an excitation light assembly that projects excitation light onto a first terminus end of the excitation light fiber optic bundle; and an in-line filter located along the sample transmission fiber optic bundle.
Owner:HYCOR BIOMEDICAL LLC
Device and associated methods for performing luminescence and fluorescence measurements of a sample
ActiveUS20150177146A1Crosstalk from the fluorescence light source can be minimizedMinimize crosstalkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationPipetteFluorescence
Apparatuses and methods of optically analyzing fluid within a pipette are described herein. In an embodiment, an optical reader subassembly includes a housing including an internal area, a container configured to hold a fluid sample at a sample position in a light tight manner within the internal area of the housing, a light source configured to project light onto the fluid sample within the container, and an optical sensor configured to move between different sensor positions while the fluid sample remains stationary at the sample position, the different sensor positions including at least two of: (i) a first sensor position for taking a luminescence reading of the fluid sample; (ii) a second sensor position for taking a dark current or other background measurement; and (iii) a third sensor position for taking a fluorescence reading of the fluid sample.
Owner:HYCOR BIOMEDICAL INC
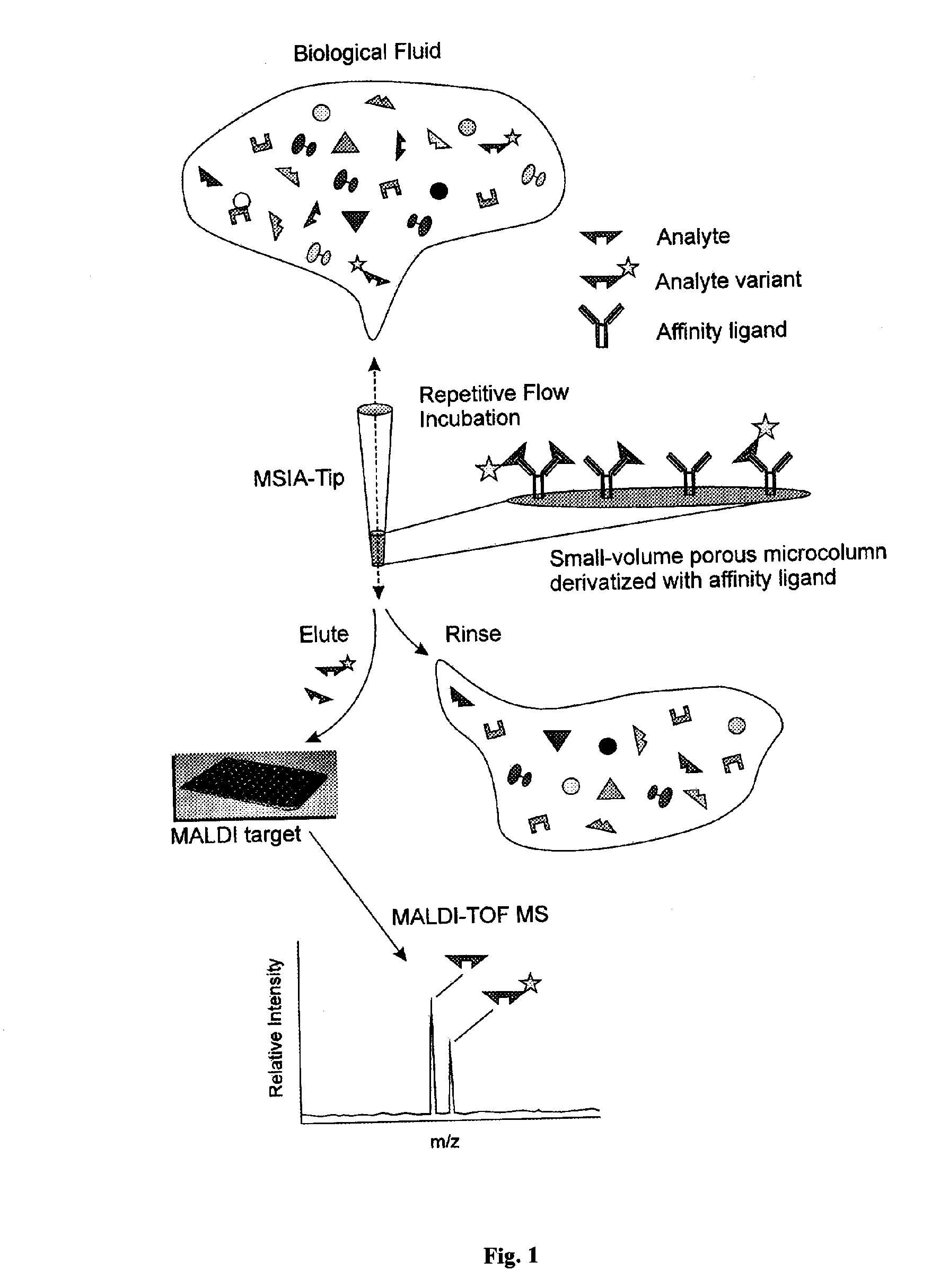
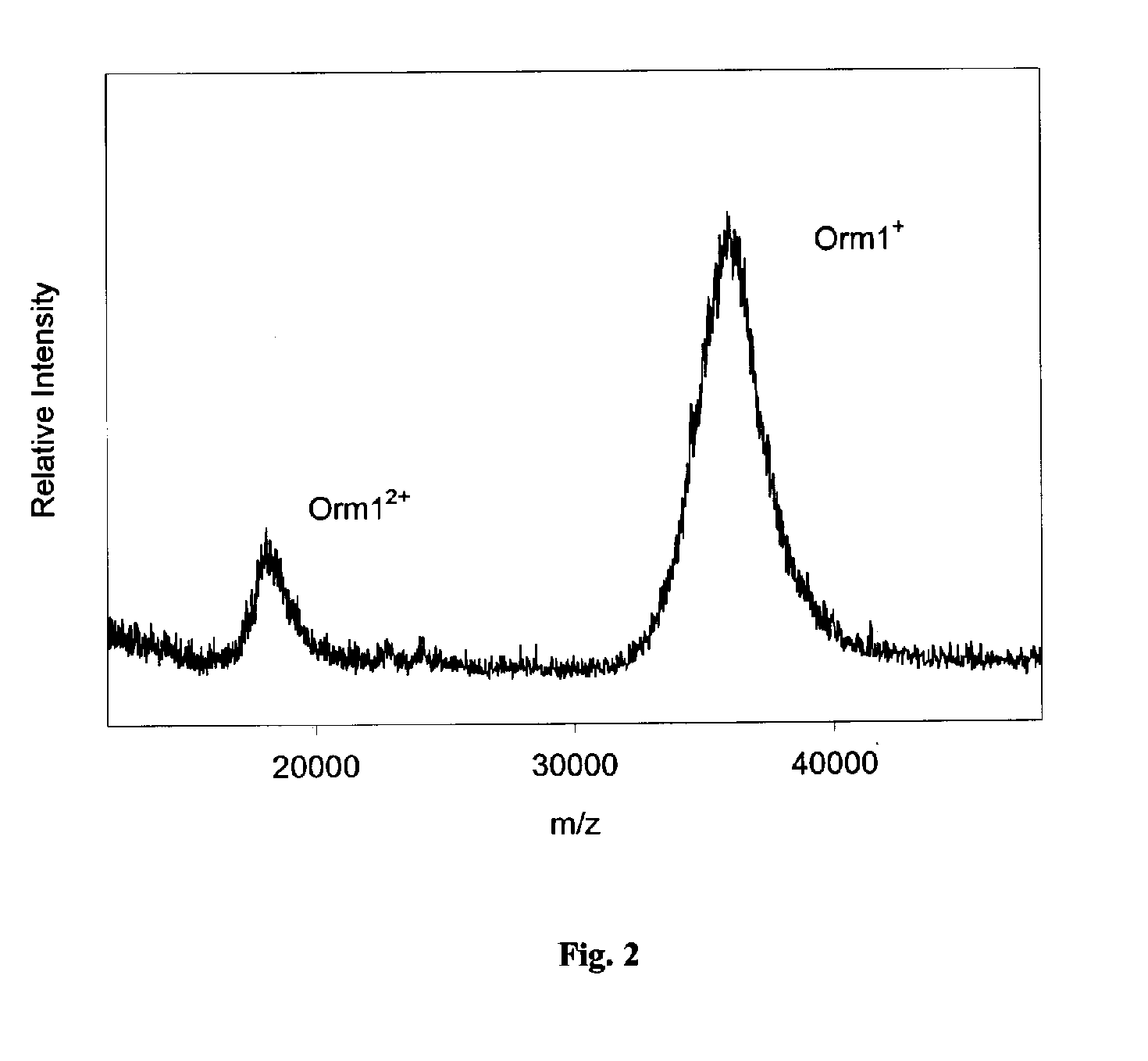
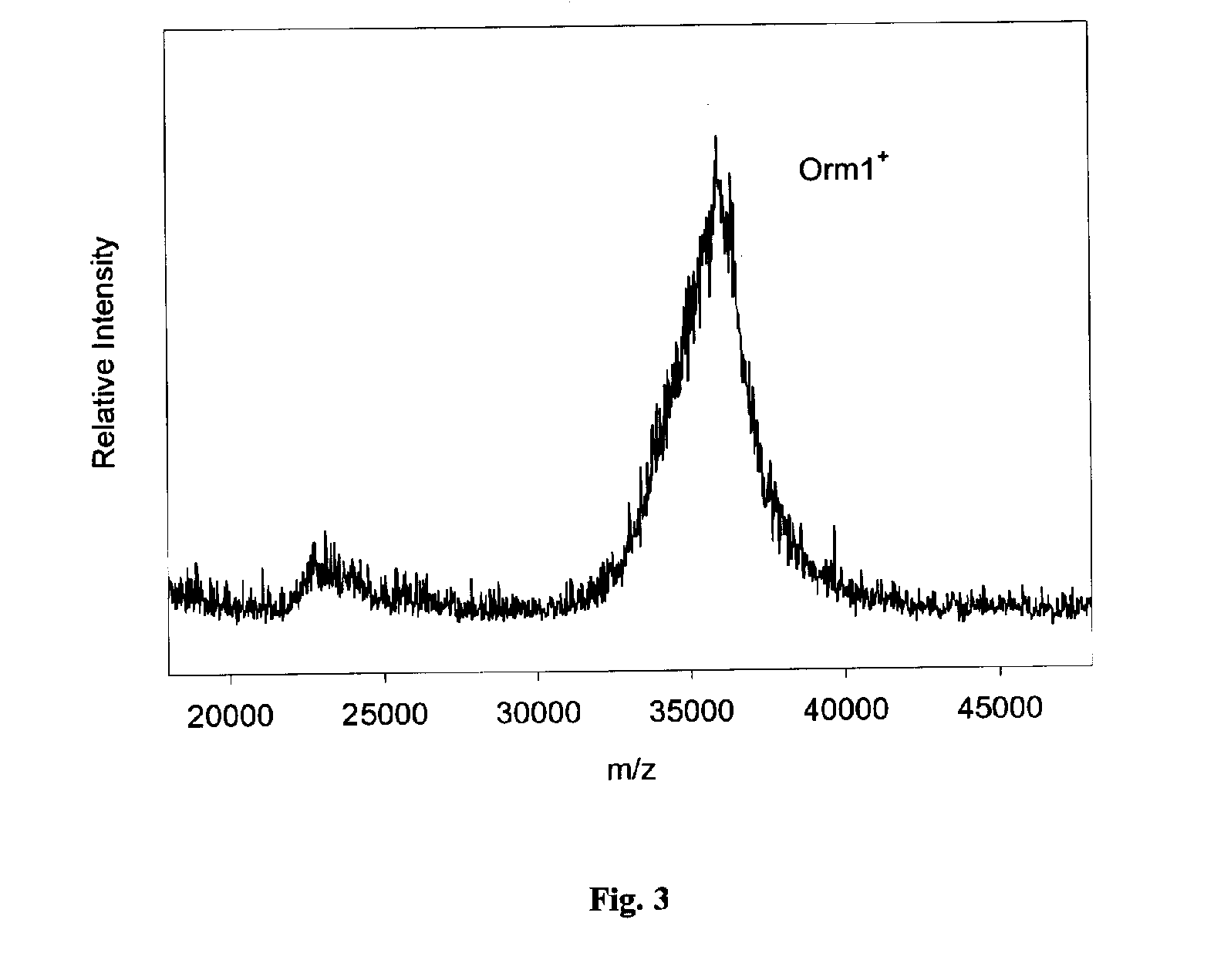
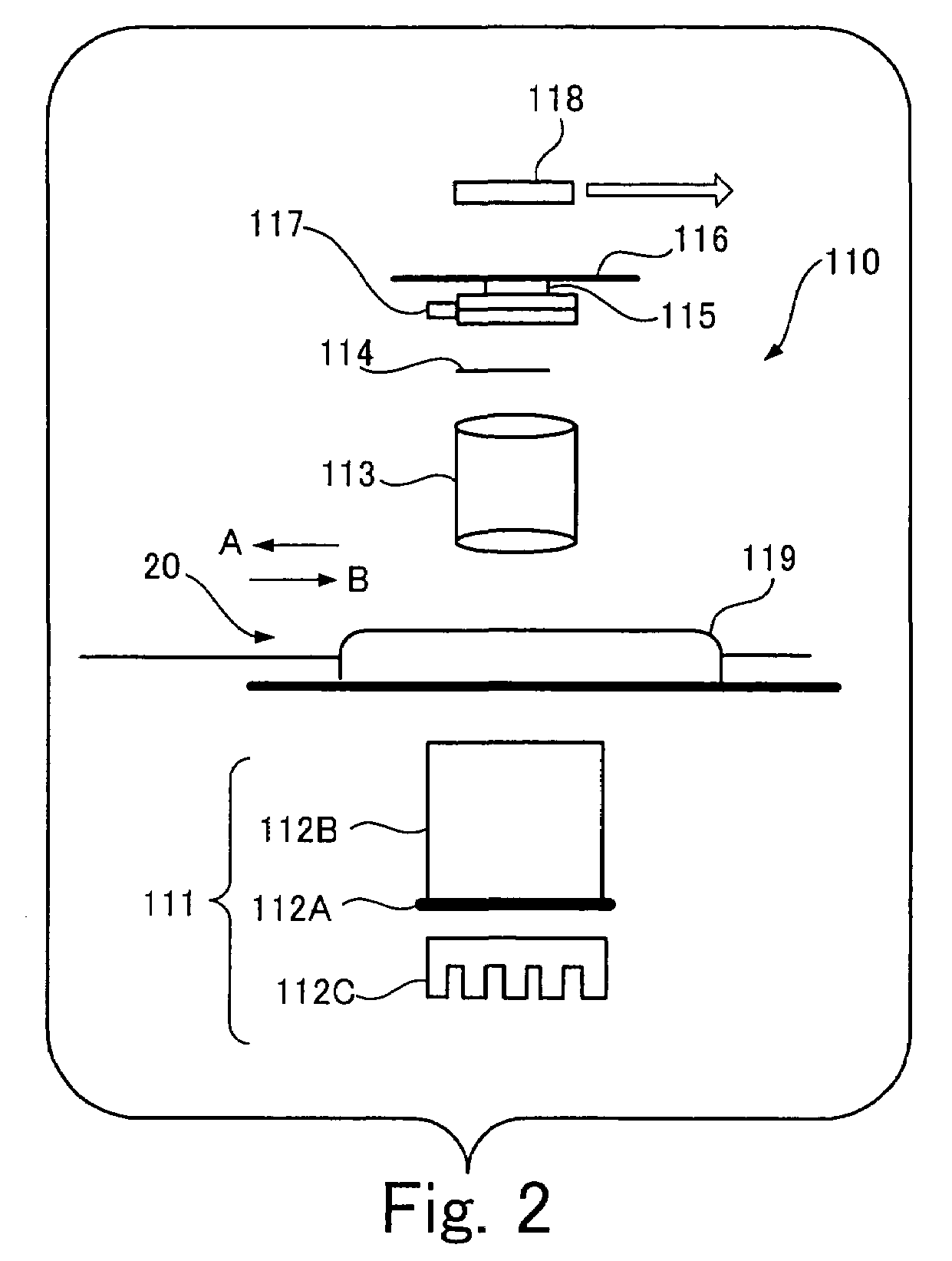
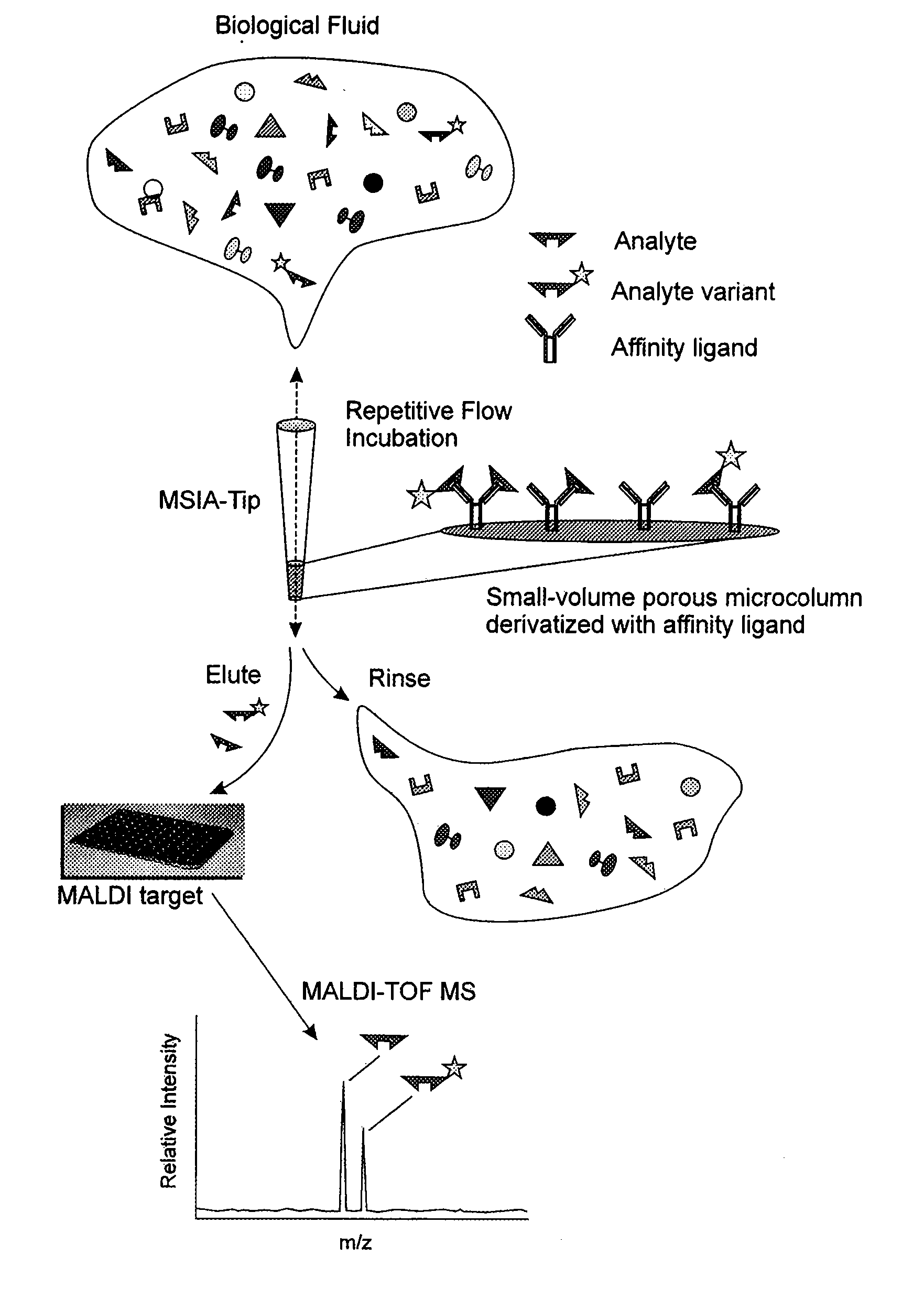
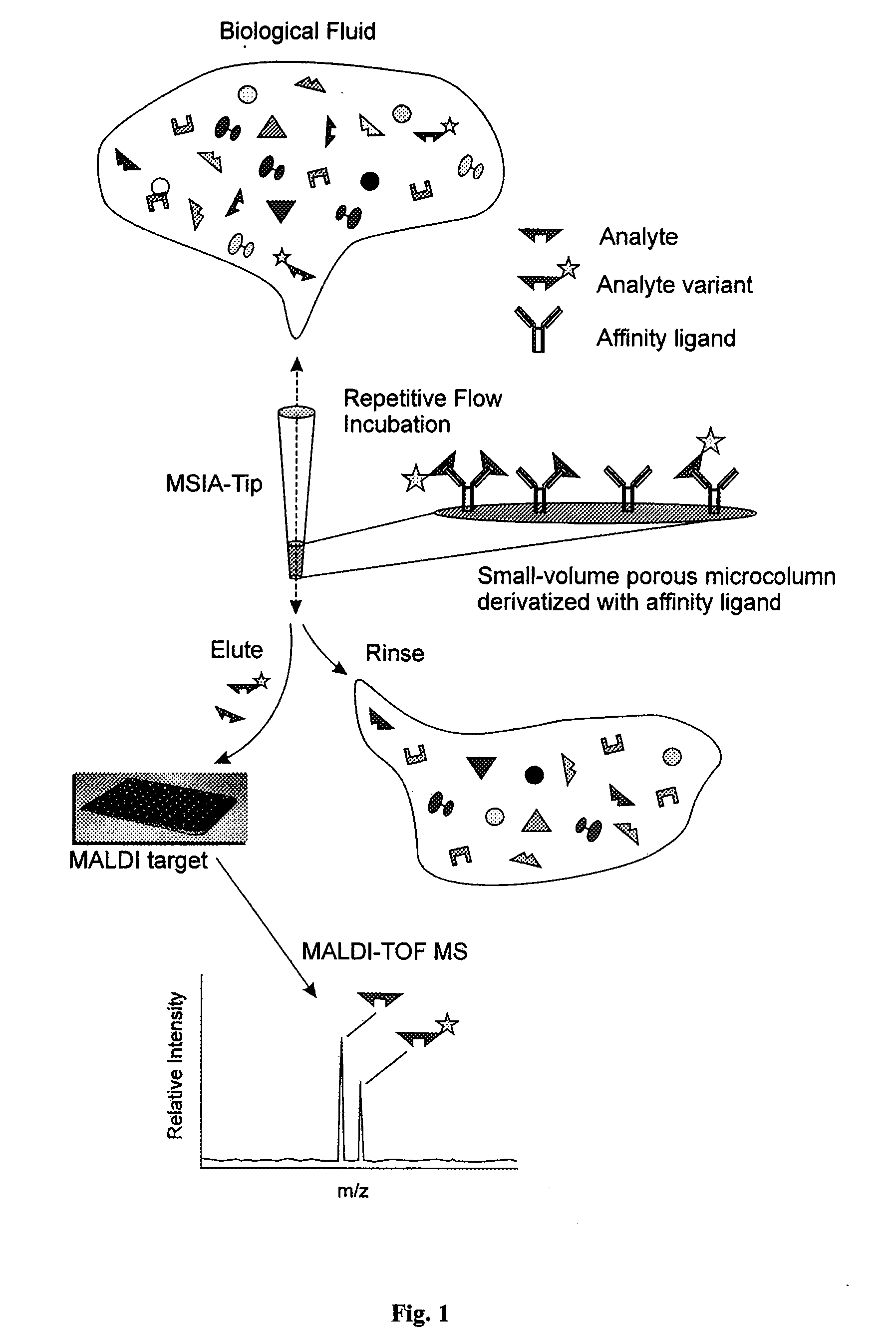
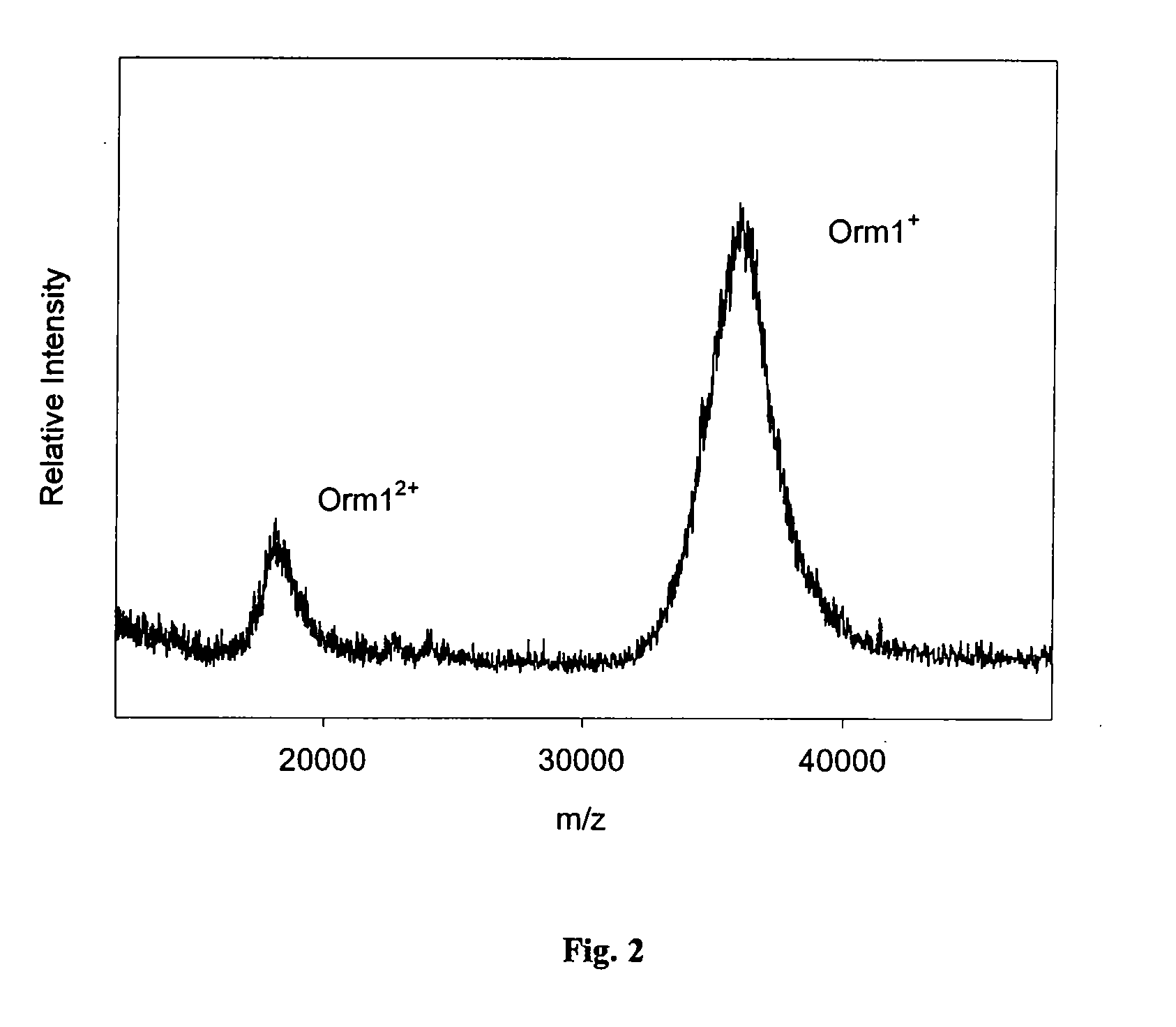
Method and apparatus for mass spectrometric immunoassay analysis of specific biological fluid proteins
InactiveUS20050164409A1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeSufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingProtein targetMass spectrometry
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins and their variants that are present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Device and associated methods for performing luminescence and fluorescence measurements of a sample
ActiveUS20150177145A1Crosstalk from the fluorescence light source can be minimizedMinimize crosstalkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationPipetteFluorescence
Owner:HYCOR BIOMEDICAL LLC
Electronic circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20070284509A1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeIncrease costMaterial analysis by optical meansCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceCurrent voltage
An electronic circuit, which has transistors disposed on a substrate, each transistor including an active layer made of thin-film polysilicon, includes a sensor that converts a measured quantity into a current value, a current-voltage conversion circuit that converts the current value into a voltage, and a voltage detection circuit that detects the voltage converted by the current-voltage conversion circuit and outputs a predetermined signal. The current-voltage conversion circuit includes a storage circuit and a range-switching circuit that switches a current-voltage conversion range of the current-voltage conversion circuit by switching the capacitance of the storage circuit.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Broadband high dynamic range digital receiving system for electromagnetic signals
ActiveUS8401134B1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeLow costPolarisation/directional diversityTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
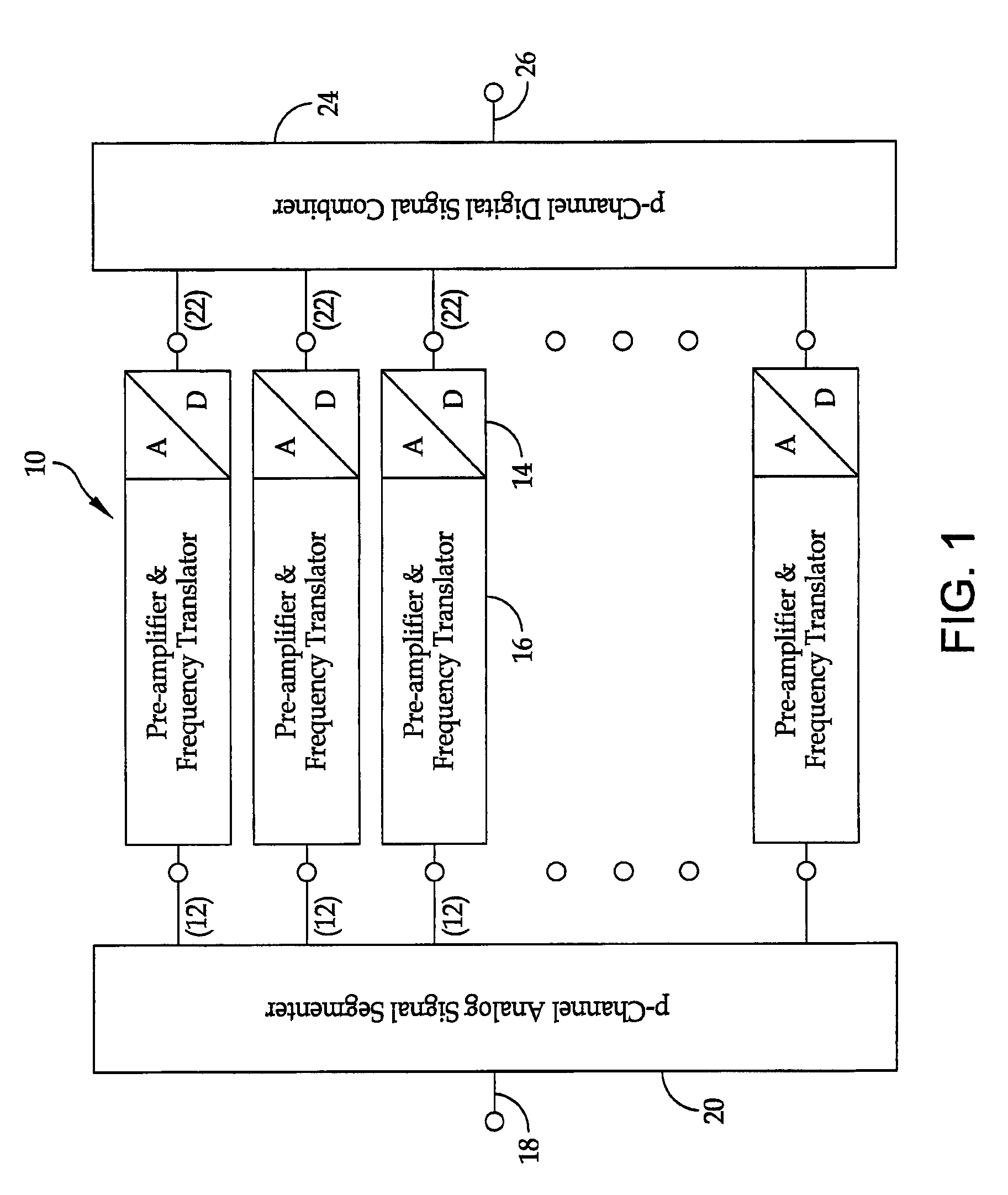
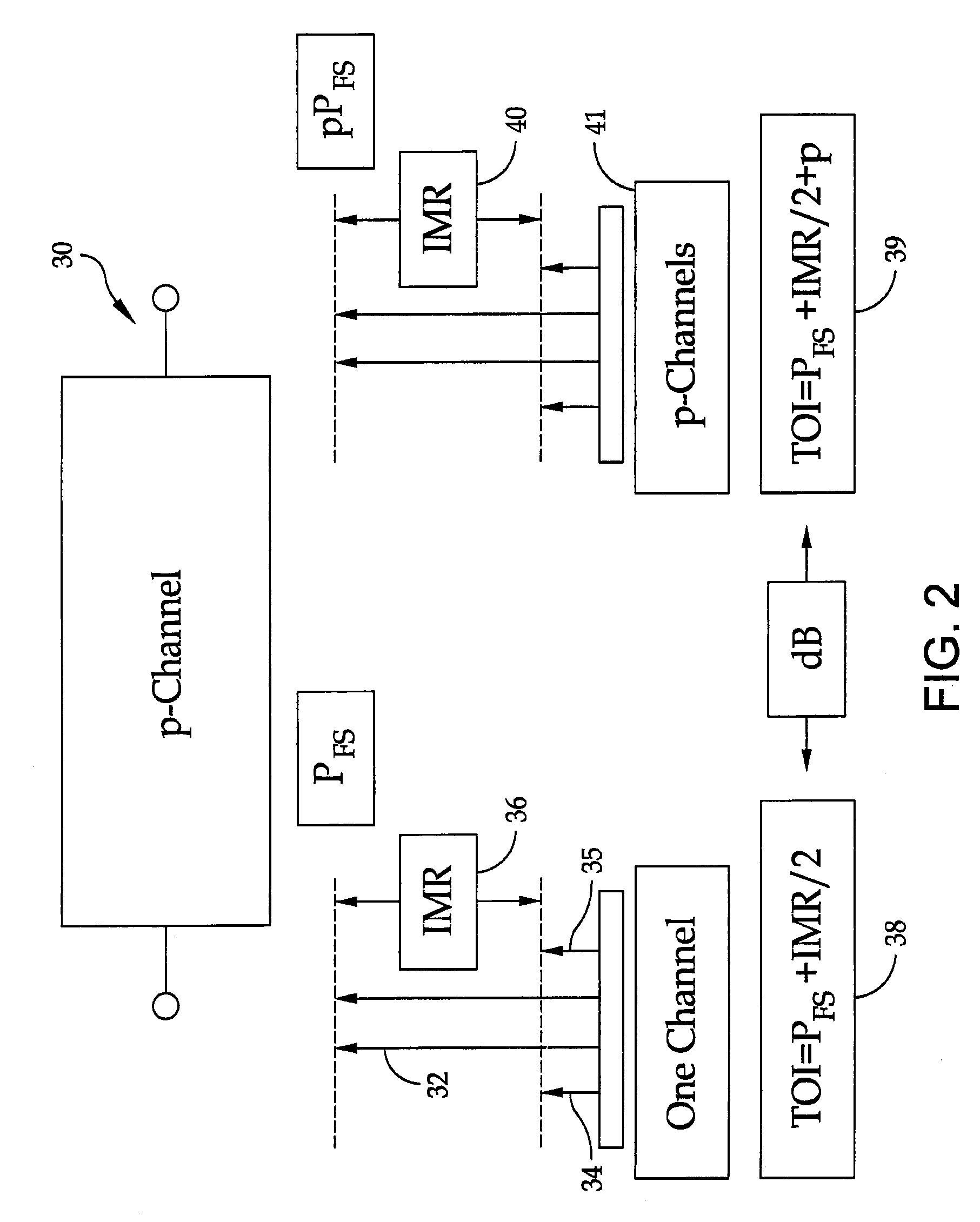
A method is provided for the design of a wide-band high dynamic-range electromagnetic signal receiving system. The method provides for receiving a plurality of analog signals, converting the plurality to a digital replica that can be processed to recover separate high-fidelity replicas of each individual signal in the received plurality. The method also provides increasing the signal dynamic range with a parallel architecture comprising “p” identical parallel analog-to-digital channels wherein the value of is determined by the ratio of the largest amplitude signal to the minimum detectable signal. Further, it is demonstrated that “p” is the fundamental limit on the number of parallel channels necessary to linearly process a specified plurality of signals containing a largest signal and a minimum detectable signal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
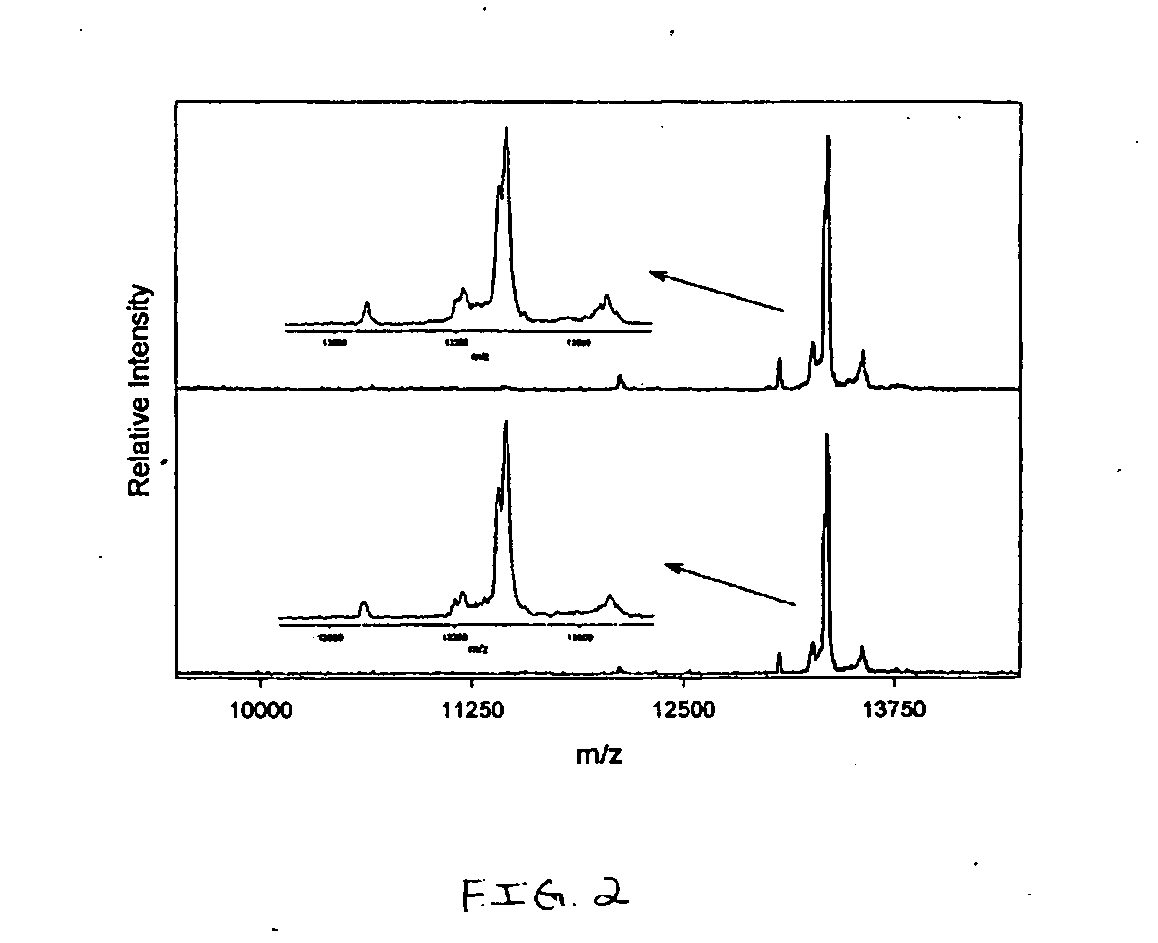
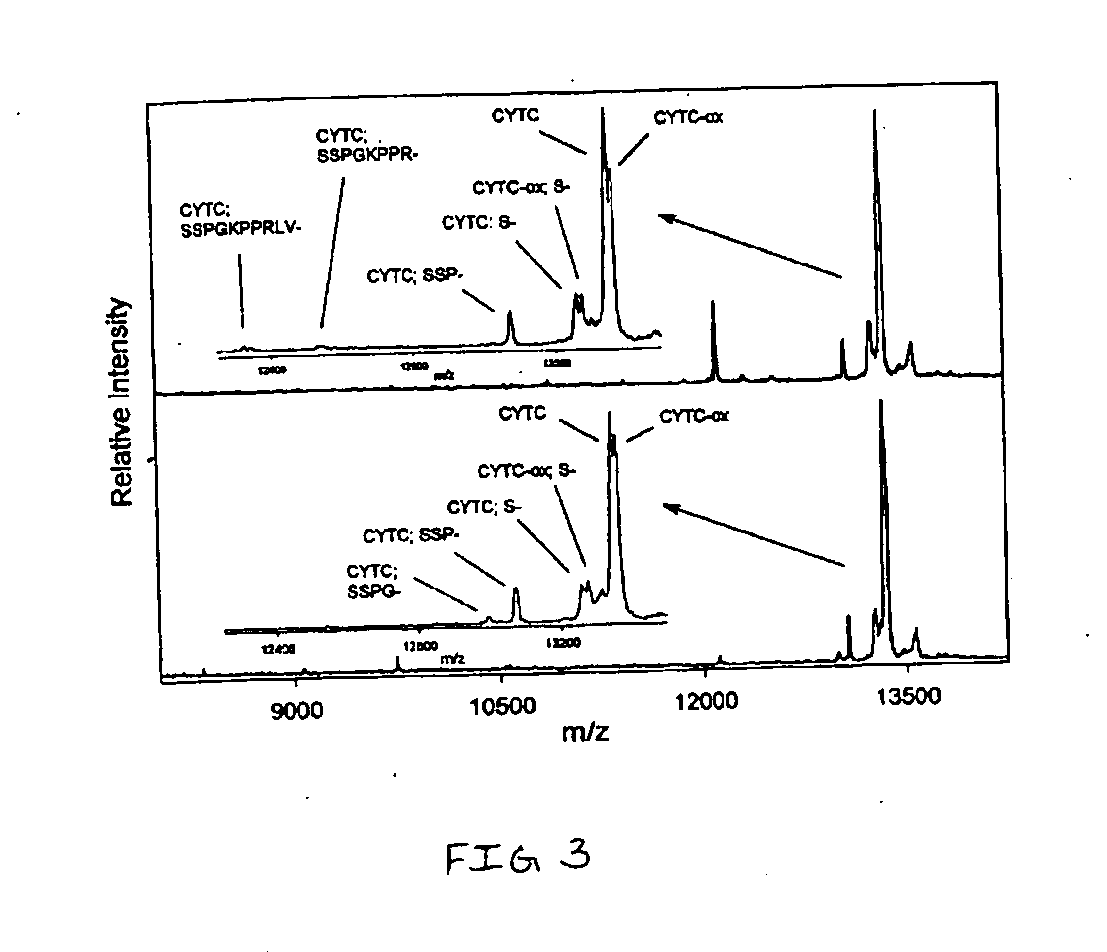
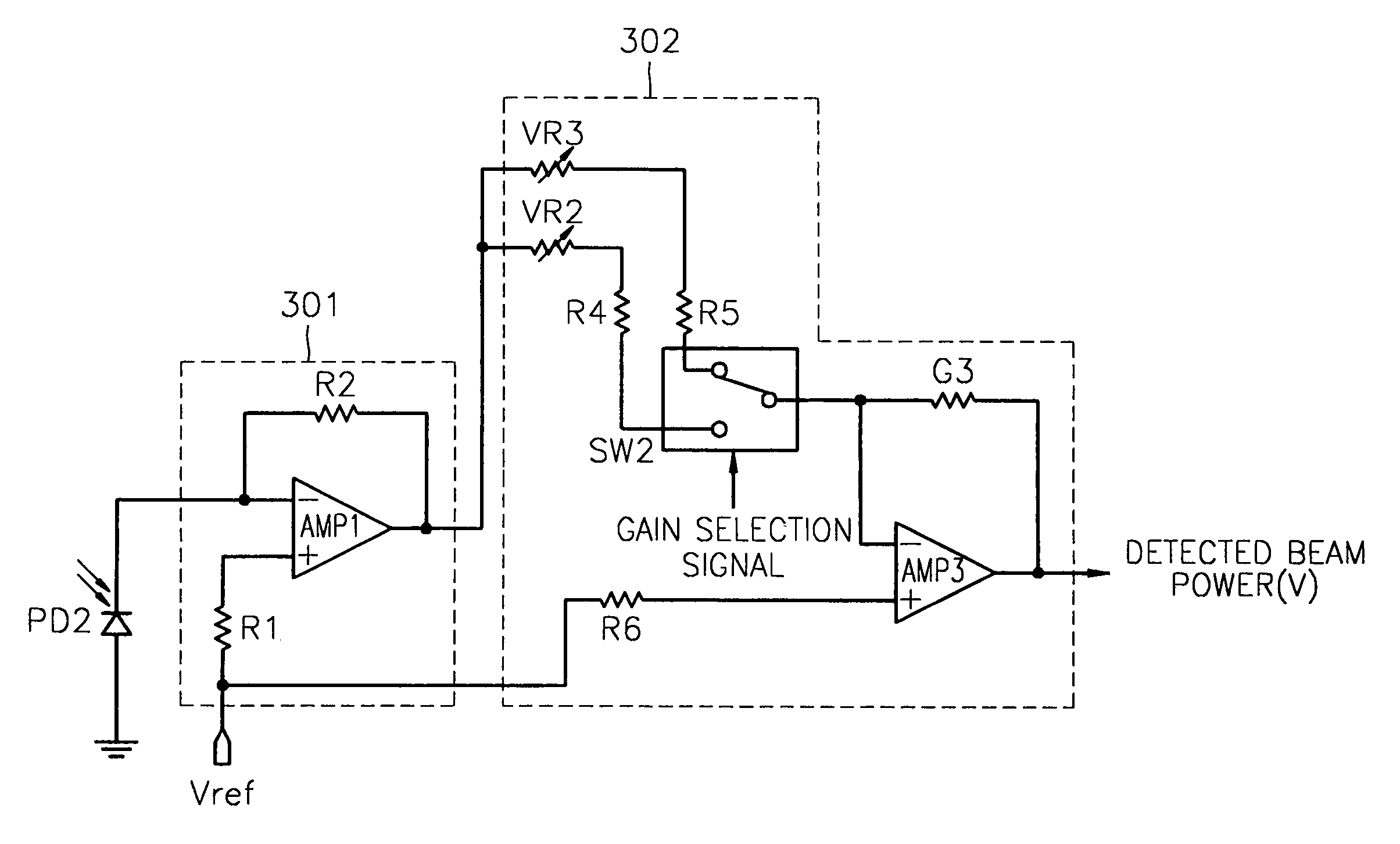
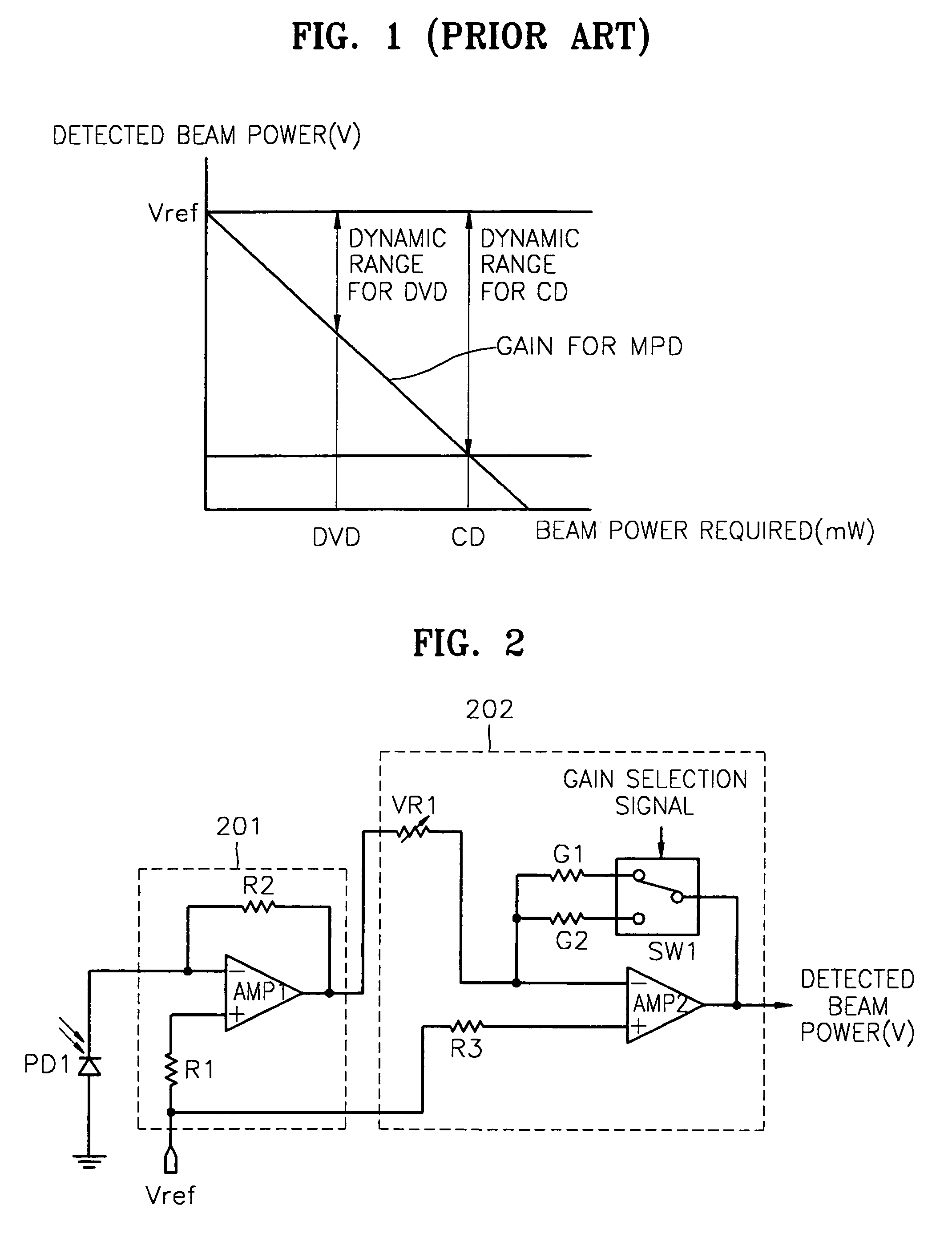
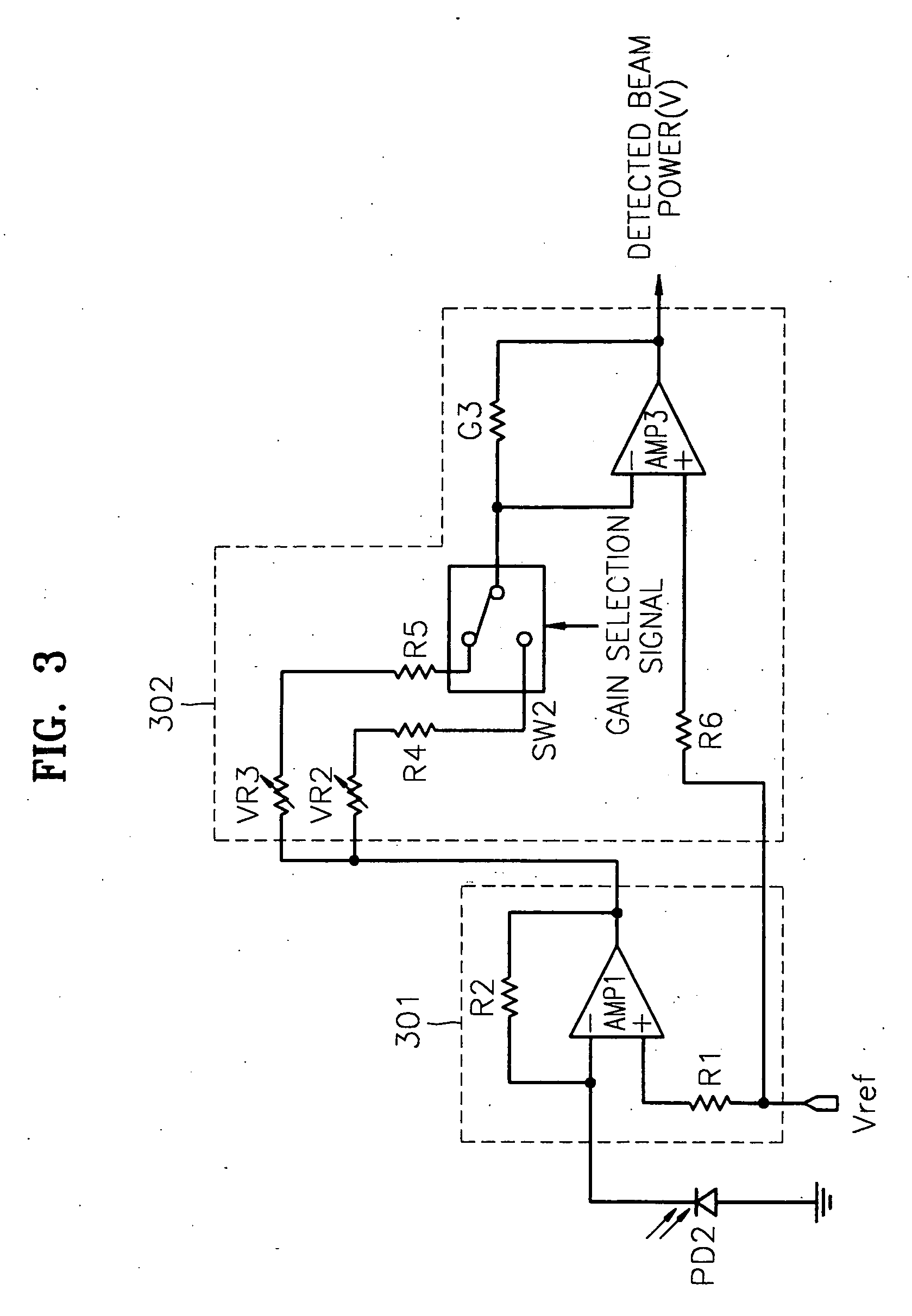
Apparatus and method for detecting beam power in optical drive
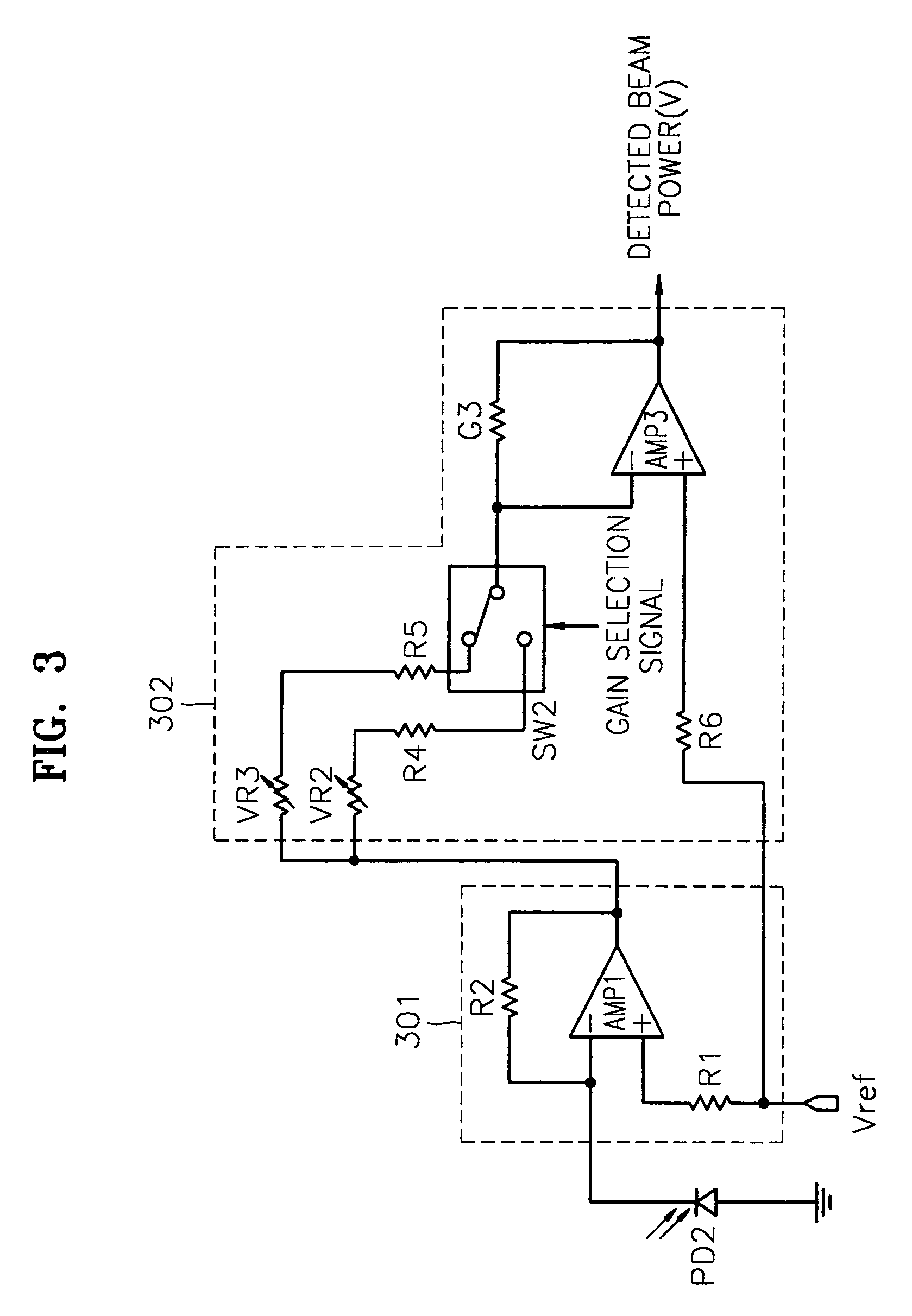
InactiveUS7068933B2Solve the lack of dynamic rangeSufficient dynamic rangeOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageLight beamDynamic range
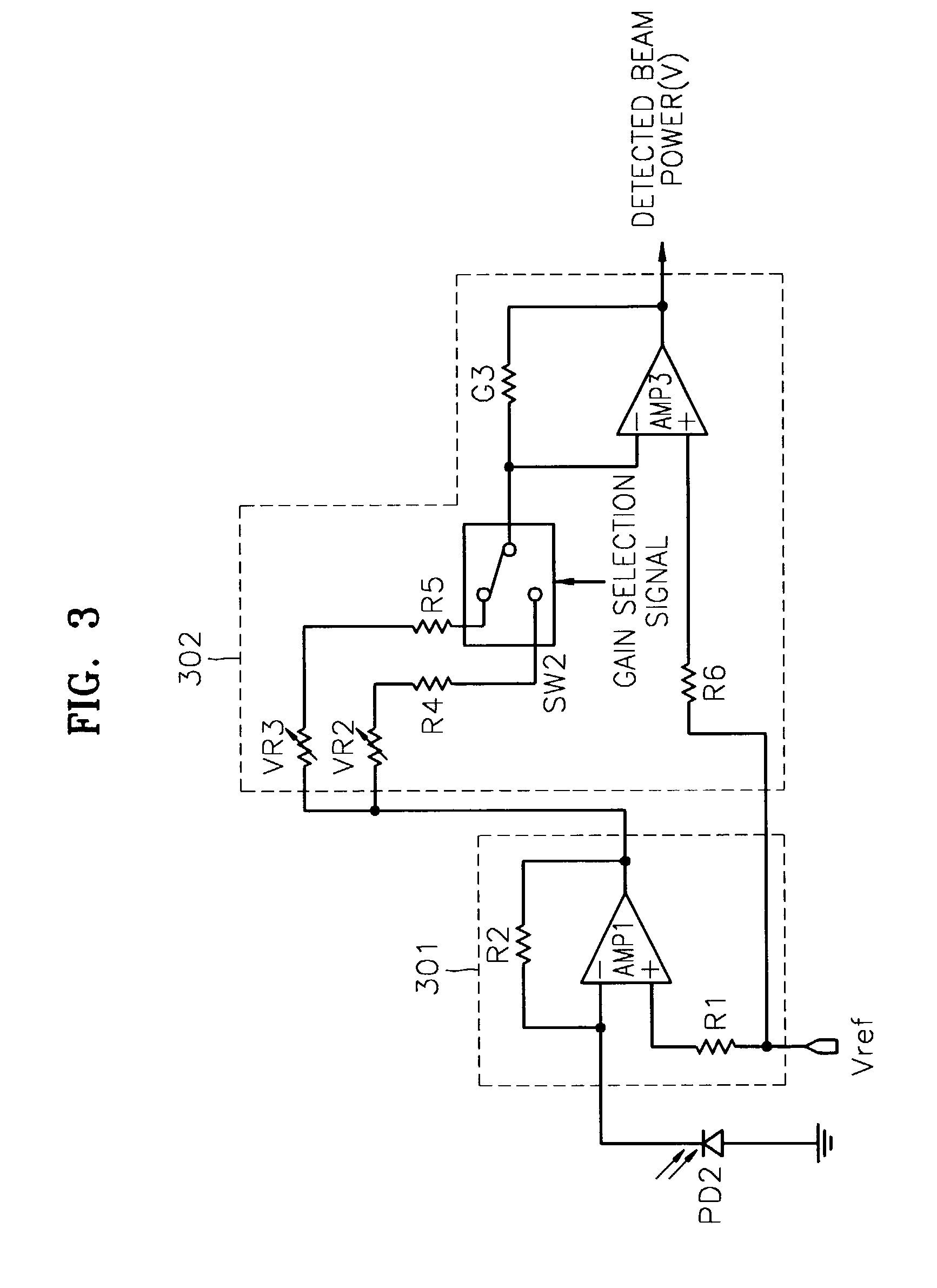
An apparatus and method for detecting beam power generated by a plurality of light sources, using a single device. The apparatus includes a light-receiving unit that receives the beam power generated by one of a plurality of light sources, and an amplifying unit that selects a gain, amplifies the beam power received by the light-receiving unit according to the selected gain, and outputs the beam power amplified as a detected beam power. According to the apparatus and method, received beam power (or amplification gain) is amplified by a gain determined according to the characteristics of the respective light sources. Thus, it is possible to provide the detected beam power in consideration of a sufficient dynamic range for the each light source, thereby realizing effective APC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electronic circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus including the same
ActiveUS7893932B2Sufficient dynamic rangeSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCurrent voltageActive layer
An electronic circuit, which has transistors disposed on a substrate, each transistor including an active layer made of thin-film polysilicon, includes a sensor that converts a measured quantity into a current value, a current-voltage conversion circuit that converts the current value into a voltage, and a voltage detection circuit that detects the voltage converted by the current-voltage conversion circuit and outputs a predetermined signal. The current-voltage conversion circuit includes a range-switching circuit that switches a current-voltage conversion range.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
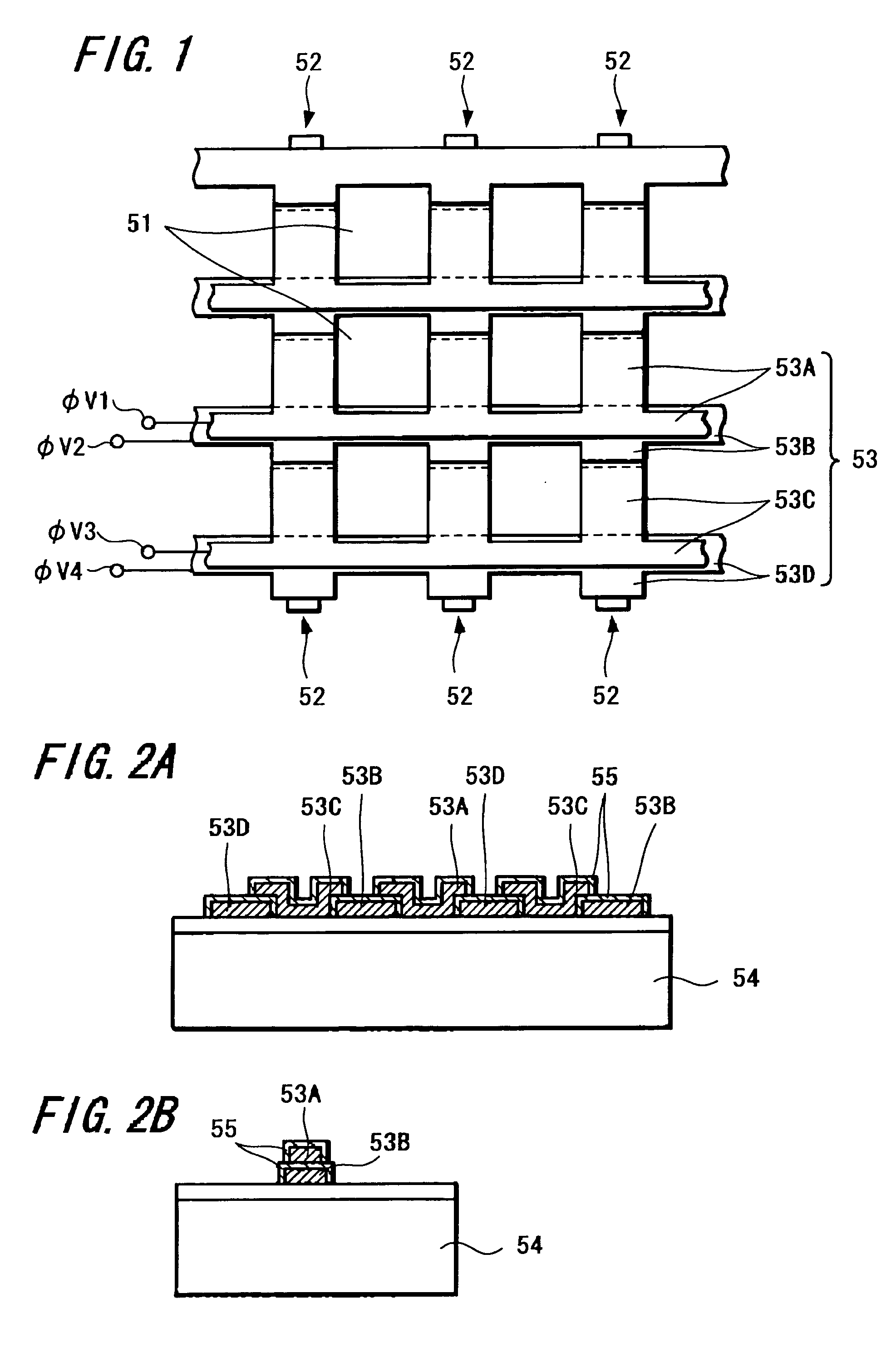
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing solid-state imaging device and method of driving solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20050247933A1Improve featuresAddressing Insufficient SensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringElectric charge
A solid-state imaging device capable of securing sufficient sensitivity and obtaining favorable characteristics is provided. The solid-state imaging device includes a charge-transfer portion 2 provided on one side of each column of light-receiving sensor portions 1, each forming a pixel, arranged in the form of a matrix and a transfer electrode of the charge-transfer portion 2 including a first transfer electrode formed of first electrode layers 3A and 3C and a second transfer electrode formed by electrically connecting first electrode layers 3B and 3D and a second electrode layer 4; the first electrode layers 3B and 3D in the second transfer electrode are independently formed in each of the charge-transfer portion 2; and the first transfer electrodes 3A and 3C and the second electrode layer 4 are laminated in a portion between pixels adjacent to each other in the direction of the charge-transfer portions 2.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
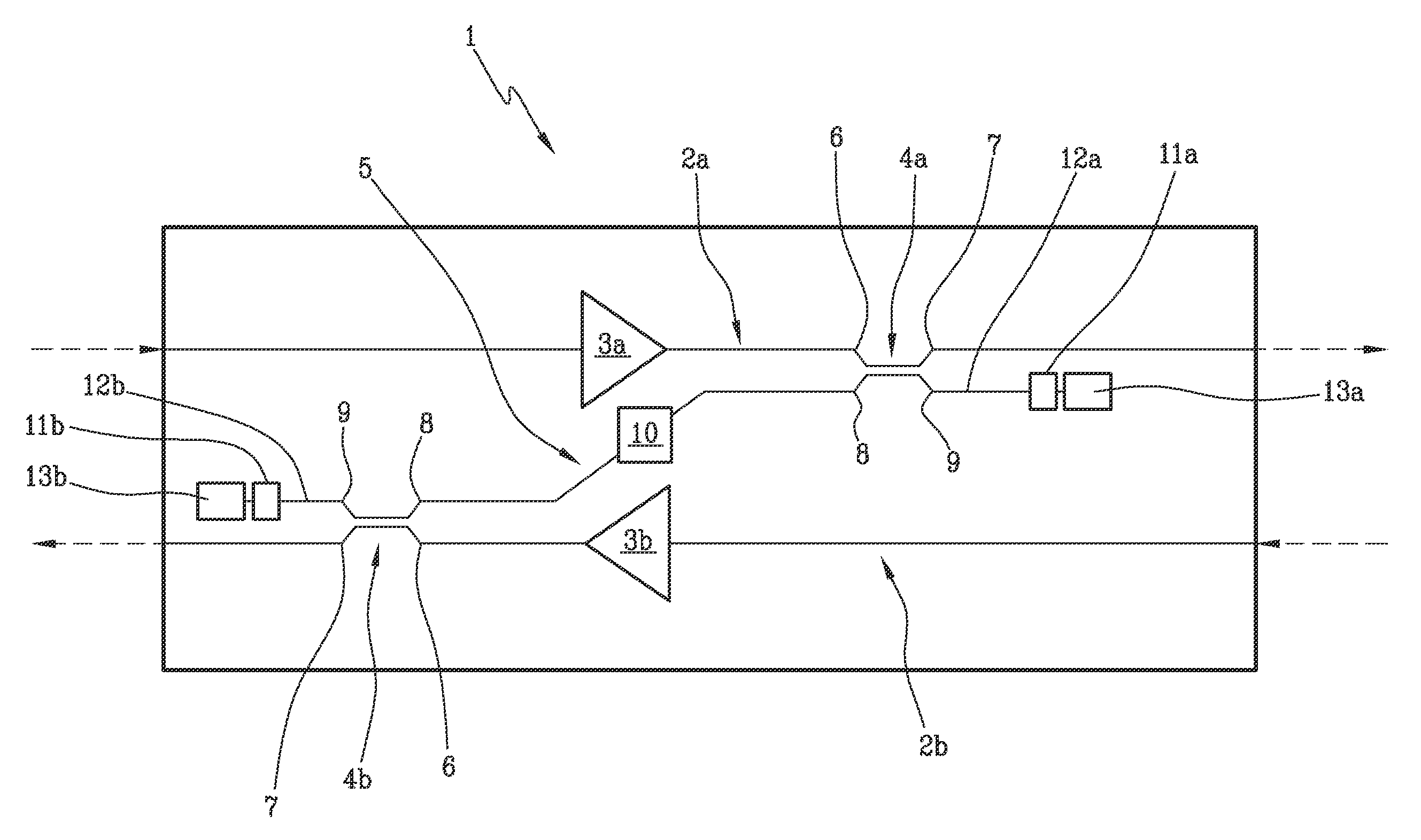
Optical amplification stage for OTDR monitoring and related method and system for OTDR monitoring of an optical communication link
ActiveUS9124362B2The process is simple and effectiveSimple structureElectromagnetic transmissionUltrasound attenuationOptical reflection
Optical amplification stage (1) for OTDR monitoring, comprising a first (2a) and a second optical signal path (2b), a first (3a) and a second optical amplifier (3b), a first optical coupler (4a) placed along the first optical signal path downstream the first optical amplifier, a second optical coupler (4b) placed along the second optical signal path downstream the second optical amplifier, an optical by-pass path (5) optically connecting the first and the second optical coupler, a first (11a) and a second optical reflector (11b) optically connected to respectively the first and second optical coupler, and an optical filter (10) placed along the optical by-pass path which has attenuation high on the whole WDM band and low at the OTDR wavelength(s).
Owner:SUBCOM BRASIL COMML LTDA
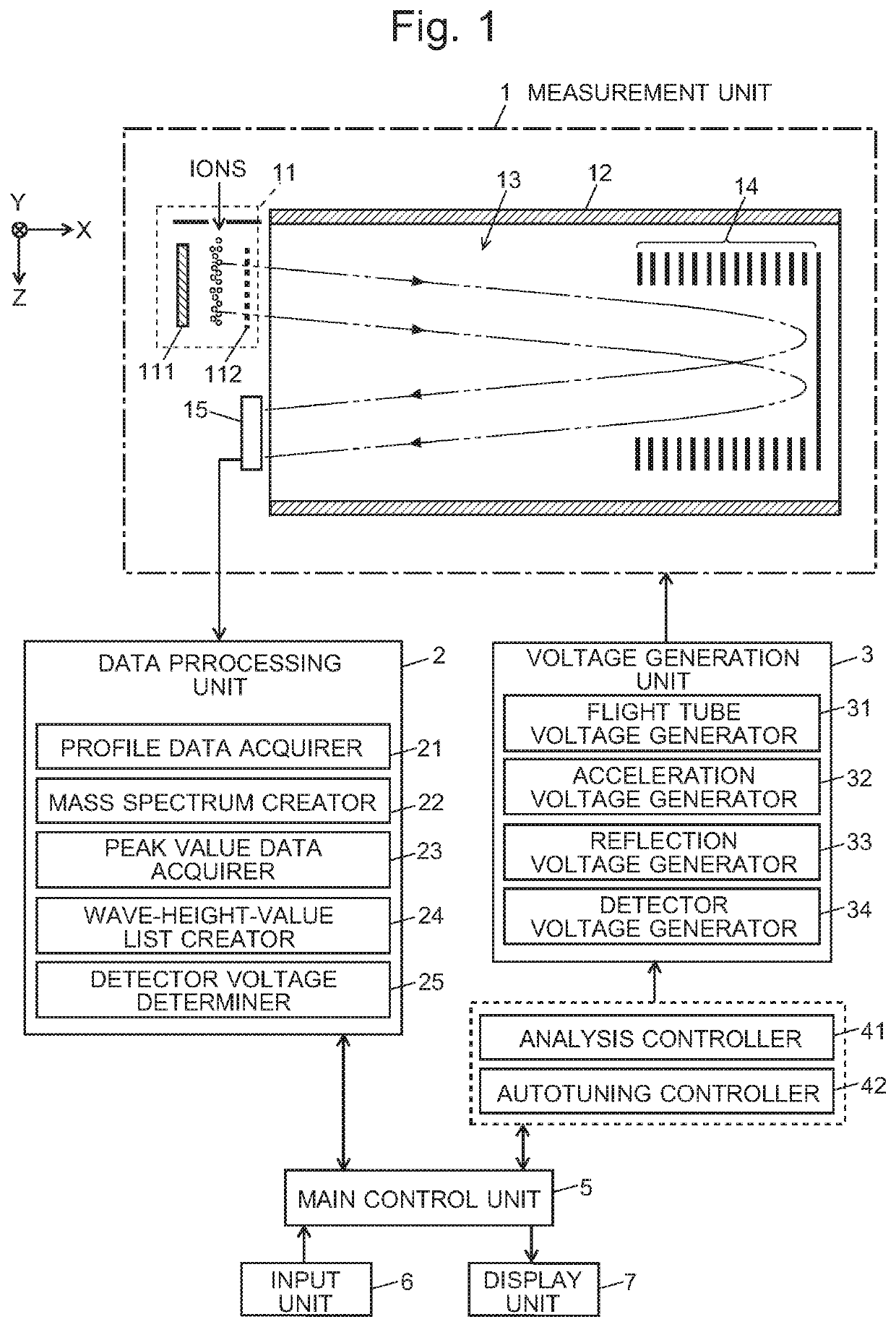
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer
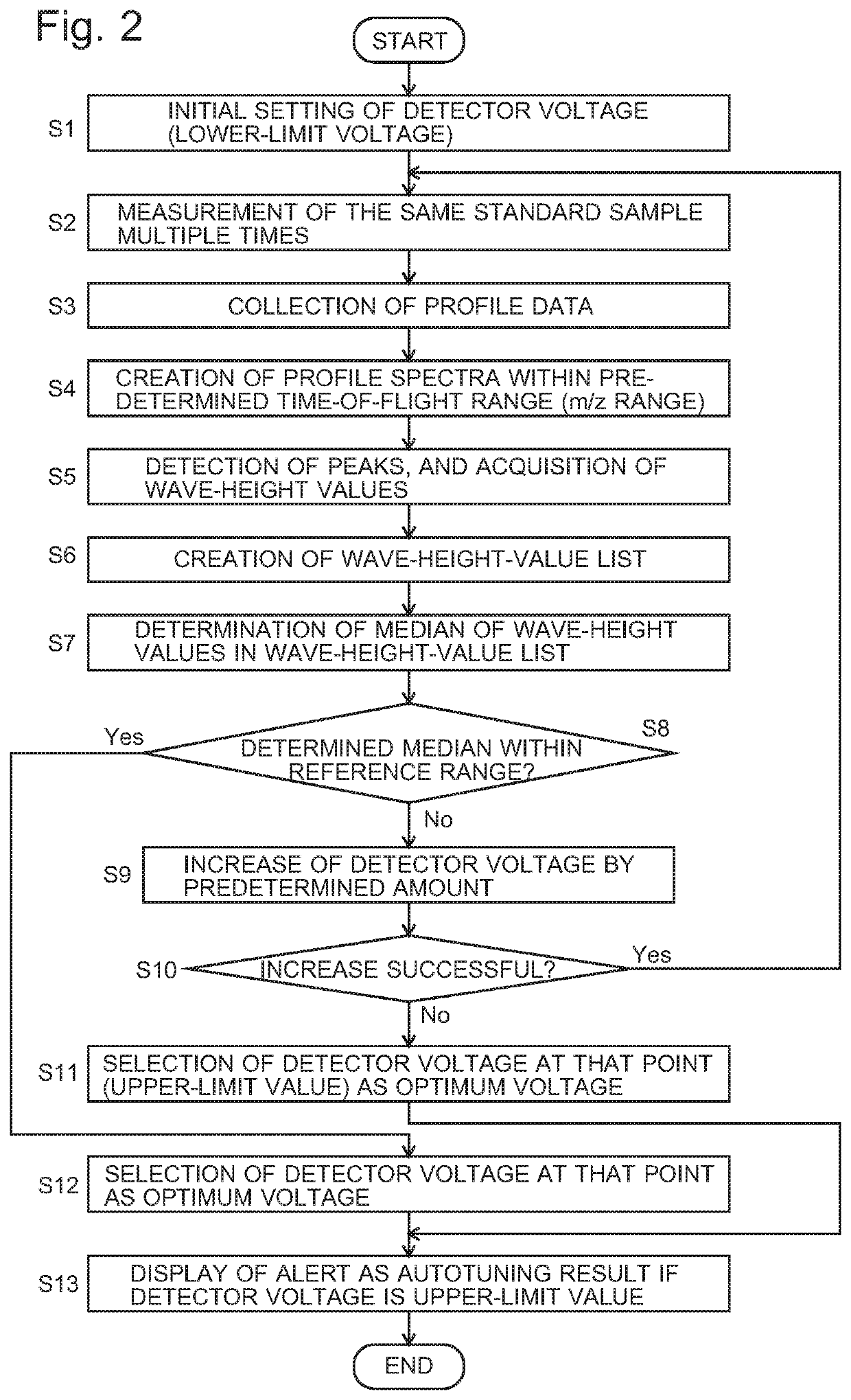
ActiveUS20210013019A1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeCondition is often affectedSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersVoltage generatorEngineering
For an automatic adjustment of a detector voltage, a measurement of a standard sample is performed, in which a reflection voltage generator under the control of an autotuning controller applies, to a reflector, voltages which are different from those applied in a normal measurement and do not cause temporal conversion of ions. Ions having the same m / z simultaneously ejected from an ejector are dispersed in the temporal direction and reach a detector. Therefore, a plurality of low peaks corresponding to individual ions are observed on a profile spectrum. A peak-value data acquirer determines a wave-height value of each peak. A wave-height-value list creator creates a list of wave-height values. A detector voltage determiner searches for a detector voltage at which the median of the wave-height values in the wave-height-value list falls within a reference range.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Communication Device
InactiveUS20090135960A1Prevent overflowPrevent digit lossNetwork traffic/resource managementEqualisersFrequency spectrumIdentification device
In a communication device for receiving signals from devices that become communication partners, received signals from the respective devices are identified. Each of the devices that become communication partners is provided with a frequency spectrum of a pattern specific to each of the devices. In the communication device, storage means stores correspondence between information identifying the devices that become communication partners and the frequency spectrums provided to the respective devices, acquisition means acquires a frequency spectrum contained in a received signal, identification means compares the frequency spectrum acquired by the acquisition means with the frequency spectrums stored by the storage means to identify a device corresponding to the frequency spectrum that coincides with the frequency spectrum acquired by the acquisition means and which is stored by the storage means.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
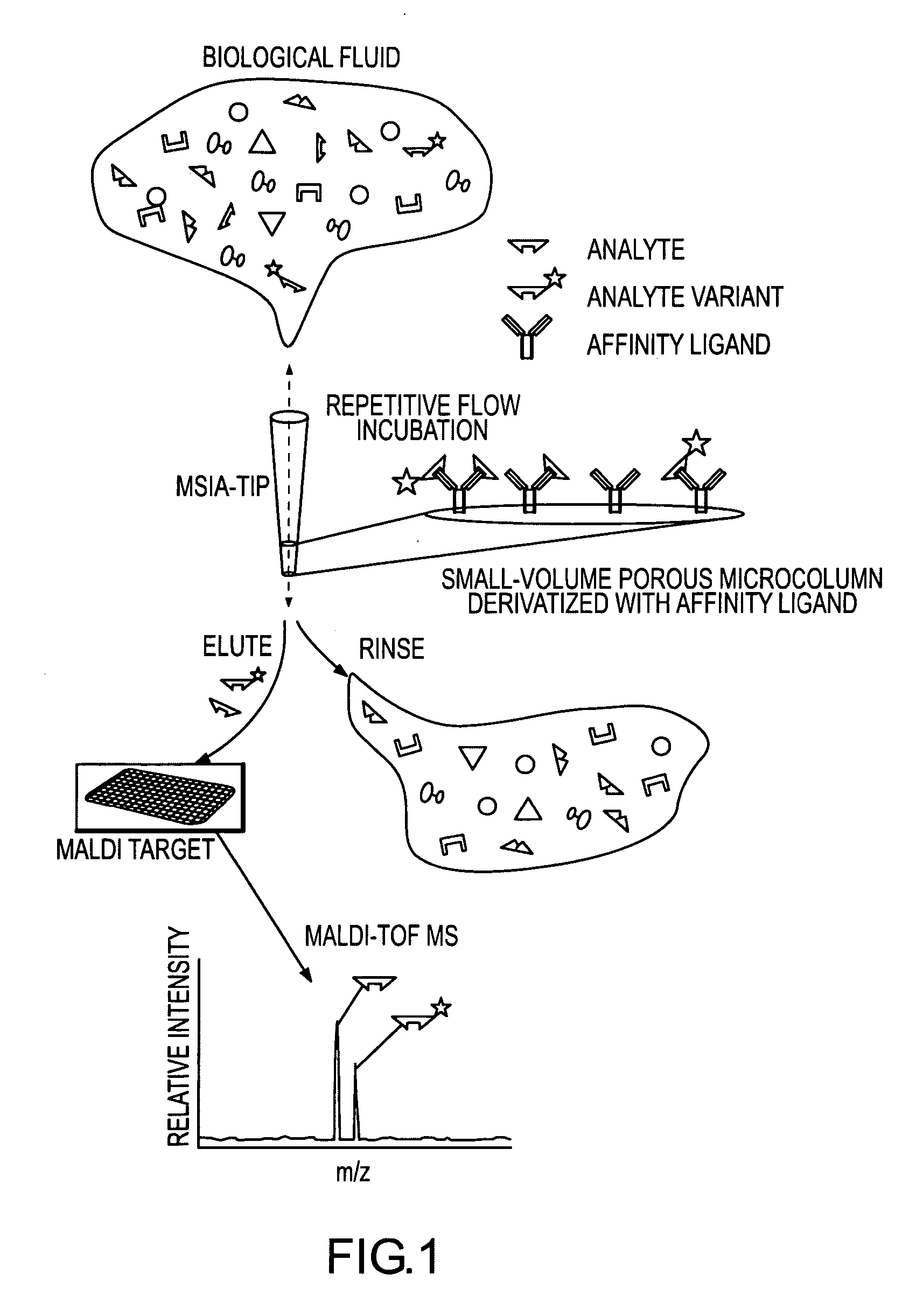
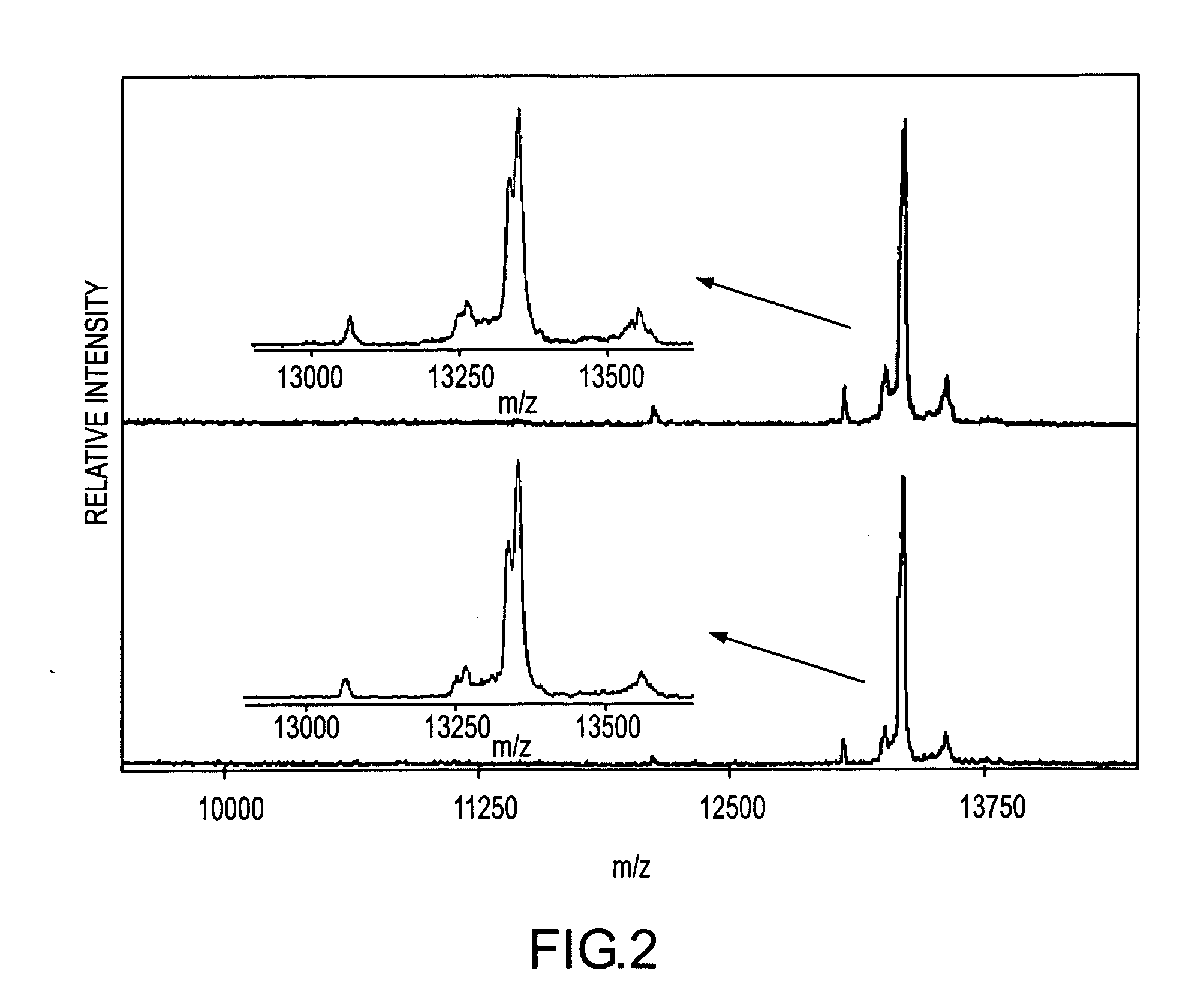
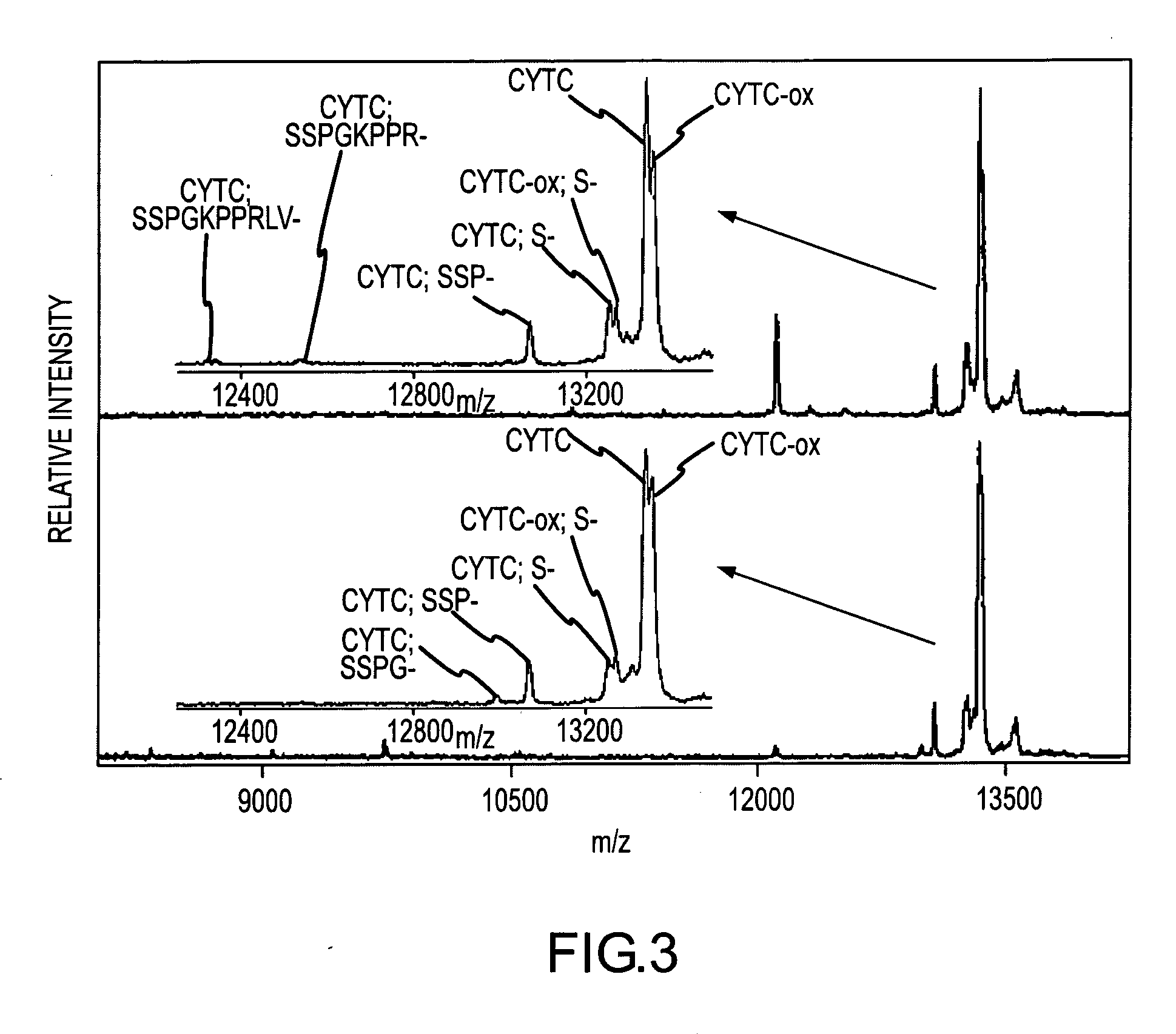
Analysis of proteins from biological fluids using mass spectrometric immunoassay
InactiveUS20060127948A1Sufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingImmunoassaysDrug targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
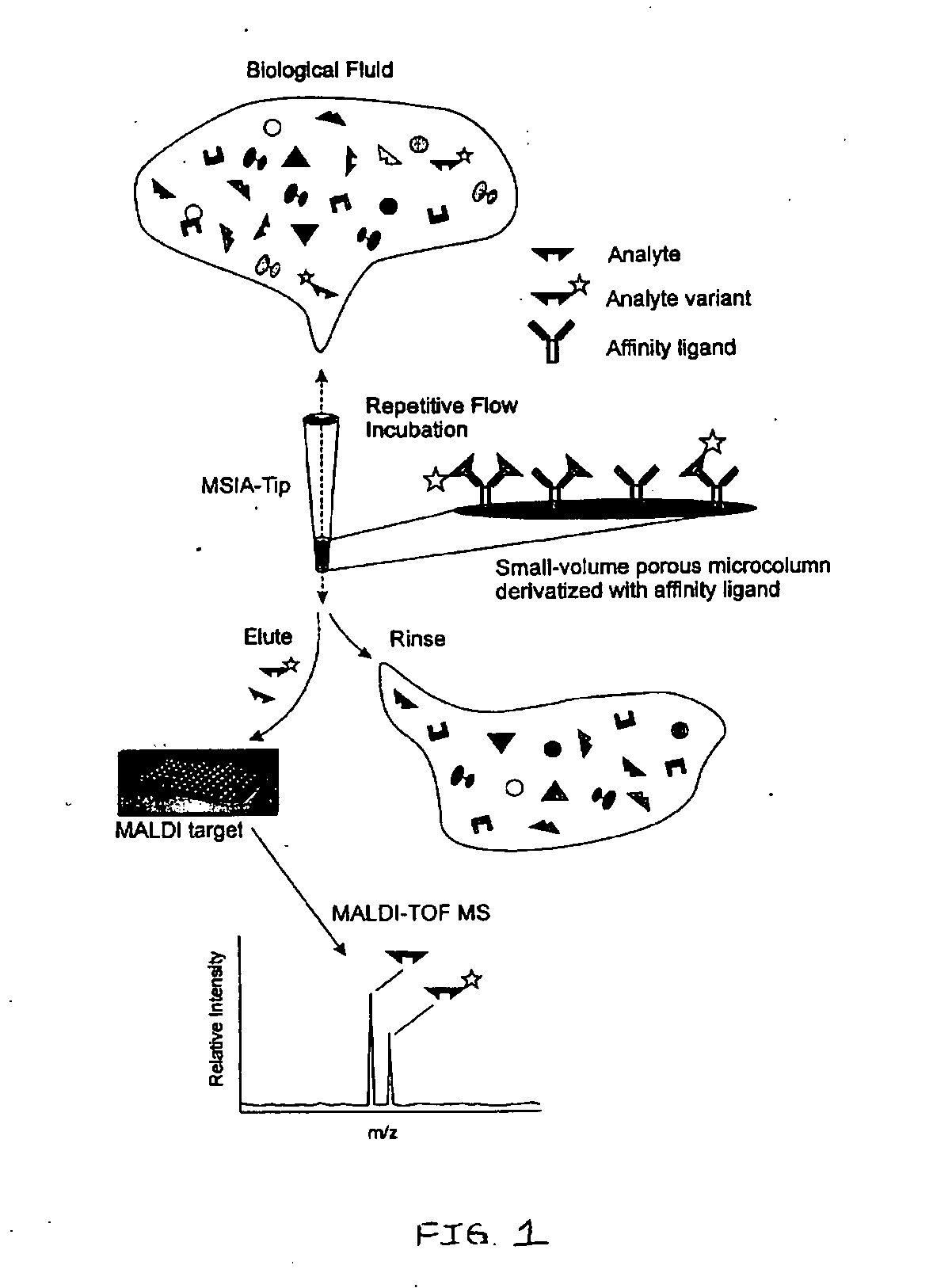
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Pipettor tips containing porous solid supports that are covalently derivatized with affinity ligand and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids. Nonspecifically bound compounds are rinsed from the extraction devices using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein (and / or its variants) are eluted directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to a working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants. Such MSIA devices, kits and methods have significant application in the fields of; basic research and development, proteomics, protein structural characterization, drug discovery, drug-target discovery, therapeutic monitoring, clinical monitoring and diagnostics, as well as in the high throughput screening of large populations to establish and recognize protein / variant patterns that are able to differentiate healthy from diseased states.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Apparatus and method for detecting beam power in optical drive
InactiveUS7343103B2Sufficient dynamic rangeOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageLight beamDynamic range
An apparatus and method for detecting beam power generated by a plurality of light sources, using a single device. The apparatus includes a light-receiving unit that receives the beam power generated by one of a plurality of light sources, and an amplifying unit that selects a gain, amplifies the beam power received by the light-receiving unit according to the selected gain, and outputs the beam power amplified as a detected beam power. According to the apparatus and method, received beam power (or amplification gain) is amplified by a gain determined according to the characteristics of the respective light sources. Thus, it is possible to provide the detected beam power in consideration of a sufficient dynamic range for the each light source, thereby realizing effective APC.
Owner:TS OPTICS CORP
Tuneable AWG device for multiplexing and demultiplexing signals and method for tuning said device
ActiveUS9239425B2Sufficient dynamic rangeOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMultiplexingAcoustic wave
The invention relates to a tuneable AWG device for multiplexing and demultiplexing signals and to a method for tuning said device. The inventive device is an integrated-optic device which enables a signal made up of a plurality of signals multiplexed by wavelength division to be injected through an input port such as to obtain, at the output, a demultiplexed signal with each component exiting via a different port. If the multiplexed signal is changed to another input port, the demultiplexed signals appear at different ports, but always according to a pre-determined relationship. The invention makes it possible to tune the AWG device by using stationary acoustic waves such that the acoustically excited optical guides are excited by a linear acoustic wave.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA +2
Blind I/Q mismatch compensation with receiver non-linearity
ActiveUS9042487B2Sufficient dynamic rangeAvoid clippingError preventionFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationData streamWeak signal
Apparatus and methods disclosed herein perform gain, clipping, and phase compensation in the presence of I / Q mismatch in quadrature RF receivers. Gain and phase mismatch are exacerbated by differences in clipping between I & Q signals in low resolution ADCs. Signals in the stronger channel arm are clipped differentially more than weaker signals in the other channel arm. Embodiments herein perform clipping operations during iterations of gain mismatch calculations in order to balance clipping between the I and Q channel arms. Gain compensation coefficients are iteratively converged, clipping levels are established, and data flowing through the network is gain and clipping compensated. A compensation phase angle and phase compensation coefficients are then determined from gain and clipping compensated sample data. The resulting phase compensation coefficients are applied to the gain and clipping corrected receiver data to yield a gain, clipping, and phase compensated data stream.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of manufacturing solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20100171857A1Improve featuresAddressing Insufficient SensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringElectric charge
A method of manufacturing a solid-state imaging device. Light-receiving sensor portions each constituting a pixel in the form of a matrix is arranged. The matrix has columns aligned in a vertical direction and rows aligned in a horizontal direction. Charge-transfer portions are formed on either side of the columns of said pixels. Transfer electrodes in said charge-transfer portions are formed to include a first transfer electrode formed of a first electrode layer and a second transfer electrode formed by electrically connecting the first electrode layer and a second electrode layer through a contact. The second transfer electrode being disposed in the vertical direction above the charge-transfer portion in a vicinity of the contact to decrease the width of the charge-transfer portions in the horizontal direction and increase the light receiving sensor portions in the vertical direction.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Apparatus and method for detecting beam power in optical drive
InactiveUS20060188269A1Sufficient dynamic rangeOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageLight beamDynamic range
Owner:TS OPTICS CORP
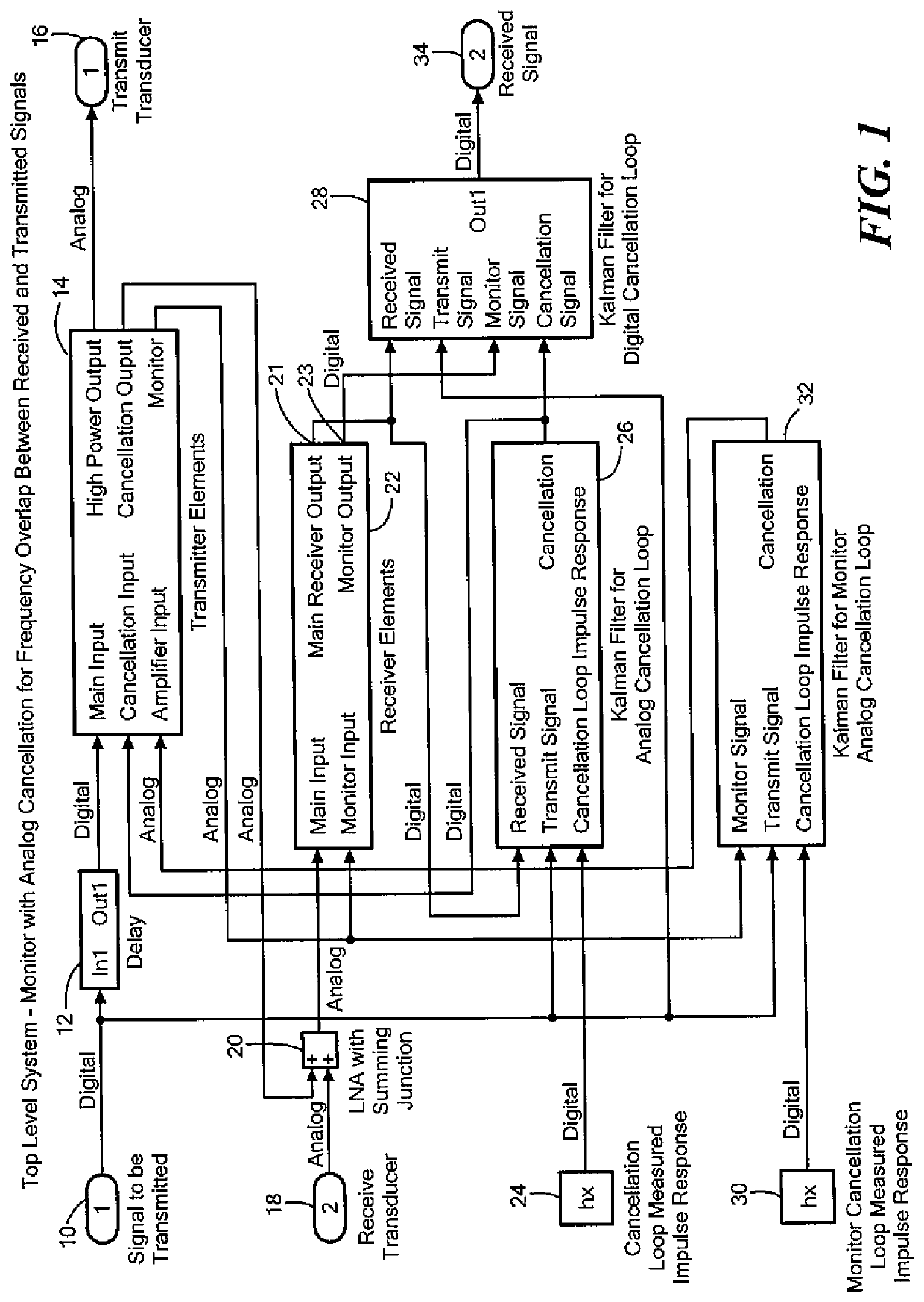
Acoustic and RF cancellation systems and methods
ActiveUS10586522B2Reduce complexitySufficient dynamic rangeSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSound producing devicesKaiman filterTransducer
A method of performing cancellation for acoustic or electromagnetic measurement or communications includes receiving an output signal to be applied to a transmit transducer, introducing a delay to the output signal to produce a delayed output signal, applying the delayed output signal to the transmit transducer, receiving an input signal from a receiving transducer, wherein the input signal comprises at least a portion of the delayed output signal, and iteratively solving a Kalman filter problem as a function of the input signal, the output signal, and the delay to produce a first filtered input signal.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER +1
Image reading apparatus
InactiveUS7342680B2Sufficient dynamic rangeExtension of timeDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationComputer scienceWide dynamic range
The present invention provides an image reading apparatus capable of reading images with a sufficiently wide dynamic range. An image reading apparatus of this invention has a light source, a reading section which generates image data based on light obtained from an original illuminated with light from the light source, a first level changing section which changes a light receiving level in the reading section in a first manner, a second level changing section which changes the light receiving level in a second manner different from the first manner, a control section in which plural light receiving levels are generated by synergistically changing a light receiving level, and a combining section which combines plural image data obtained by reading an image of an original at plural light receiving levels.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Analysis of proteins from biological fluids using mass spectrometric immunoassay
InactiveUS20060121533A1Solve the lack of dynamic rangeSufficient dynamic rangeBiological testingImmunoassaysDrug targetMass spectrometric immunoassay
Presented herein are methods, devices and kits for the mass spectrometric immunoassay (MSIA) of proteins present in complex biological fluids or extracts. Pipettor tips containing porous solid supports that are covalently derivatized with affinity ligand and used to extract specific proteins and their variants from various biological fluids. Nonspecifically bound compounds are rinsed from the extraction devices using a series of buffer and water rinses, after which the wild type protein (and / or its variants) are eluted directly onto a target in preparation for analysis such as matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Mass spectrometry of the eluted sample then follows with the retained proteins identified via accurate molecular mass determination. Protein and variant levels can be determined using quantitative methods in which the protein / variant signals are normalized to signals of internal reference standard species (either doped into the samples prior to the MSIA analysis, or other endogenous protein co-extracted with the target proteins) and the values compared to a working curves constructed from samples containing known concentrations of the protein or variants. Such MSIA devices, kits and methods have significant application in the fields of; basic research and development, proteomics, protein structural characterization, drug discovery, drug-target discovery, therapeutic monitoring, clinical monitoring and diagnostics, as well as in the high throughput screening of large populations to establish and recognize protein / variant patterns that are able to differentiate healthy from diseased states.
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
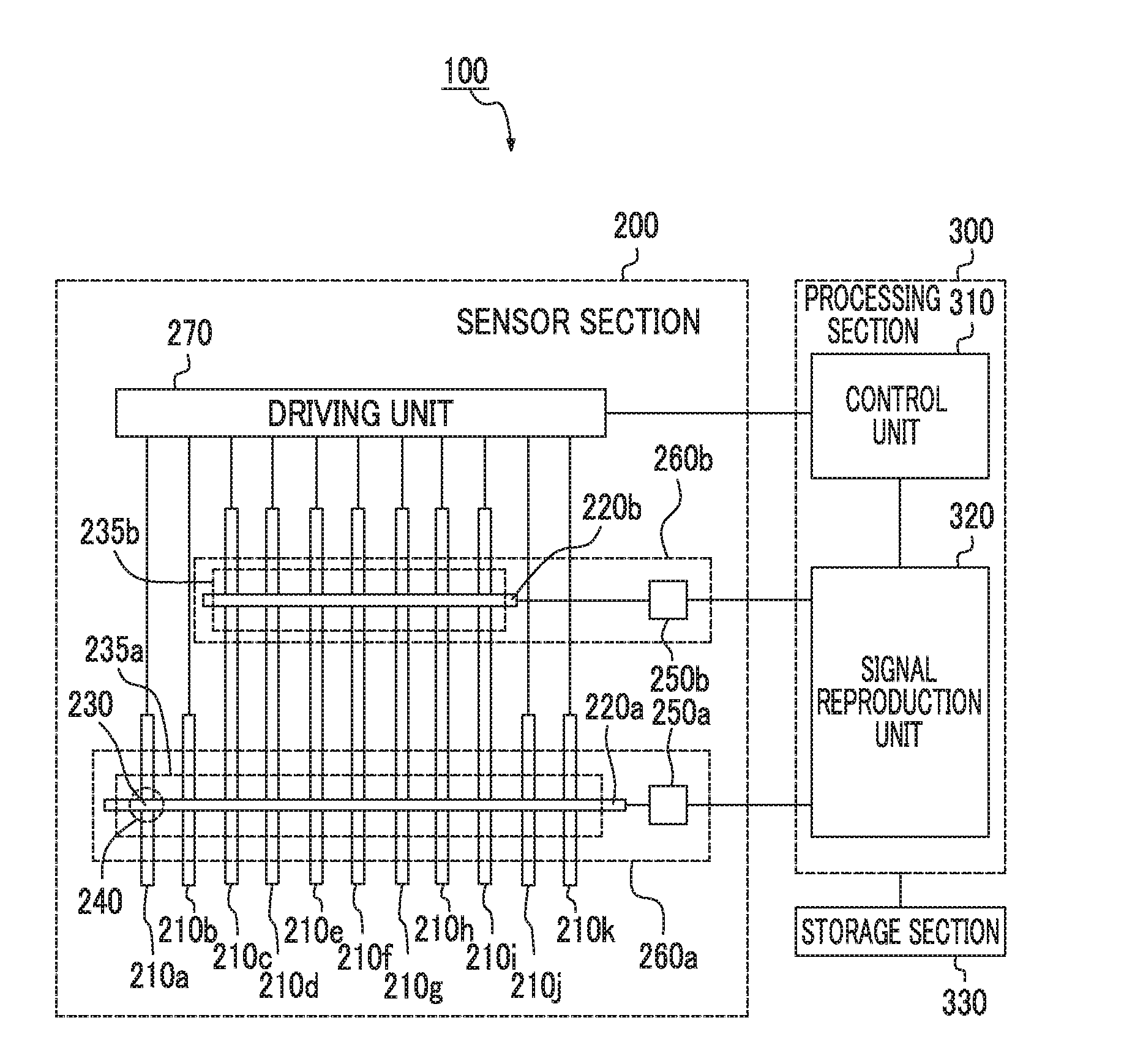
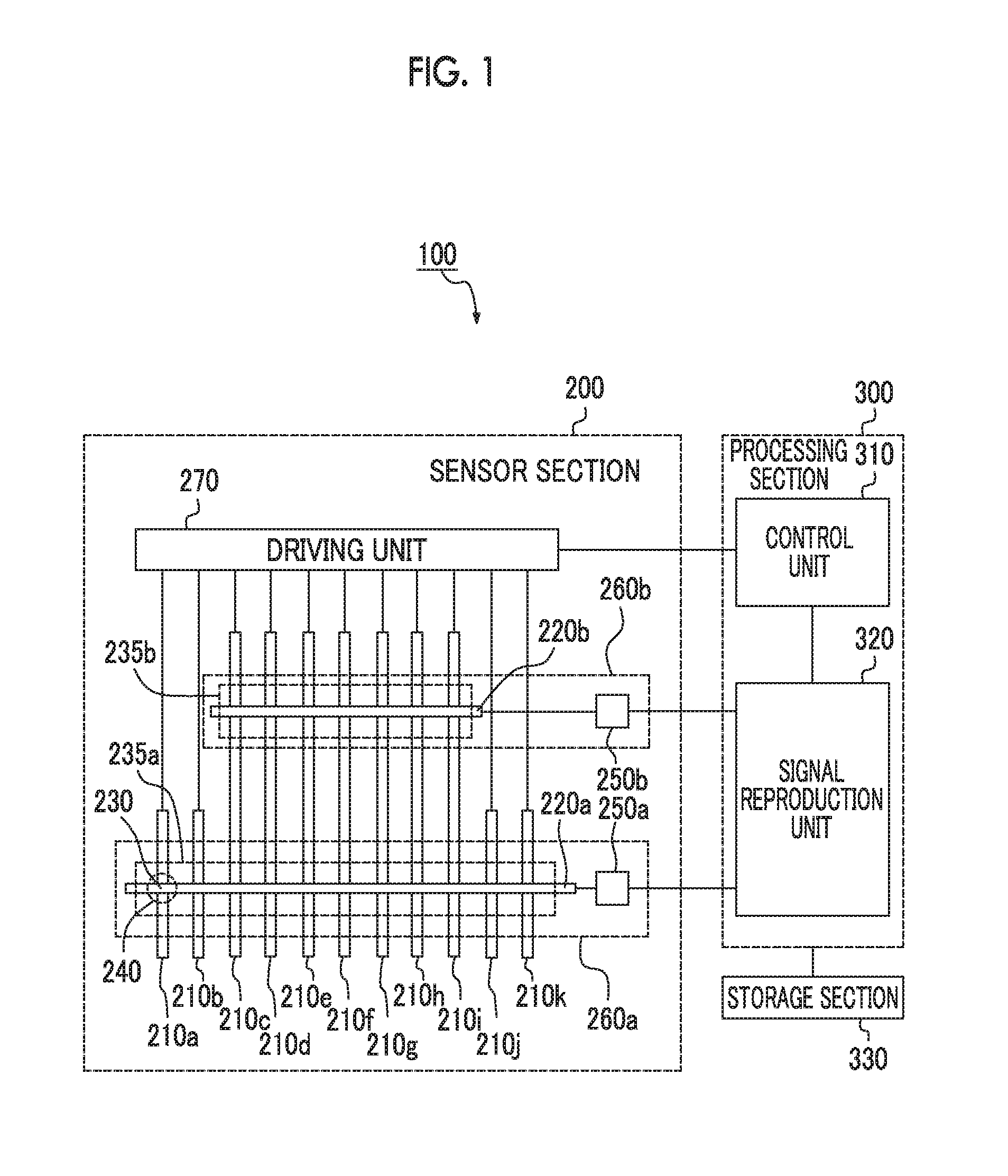
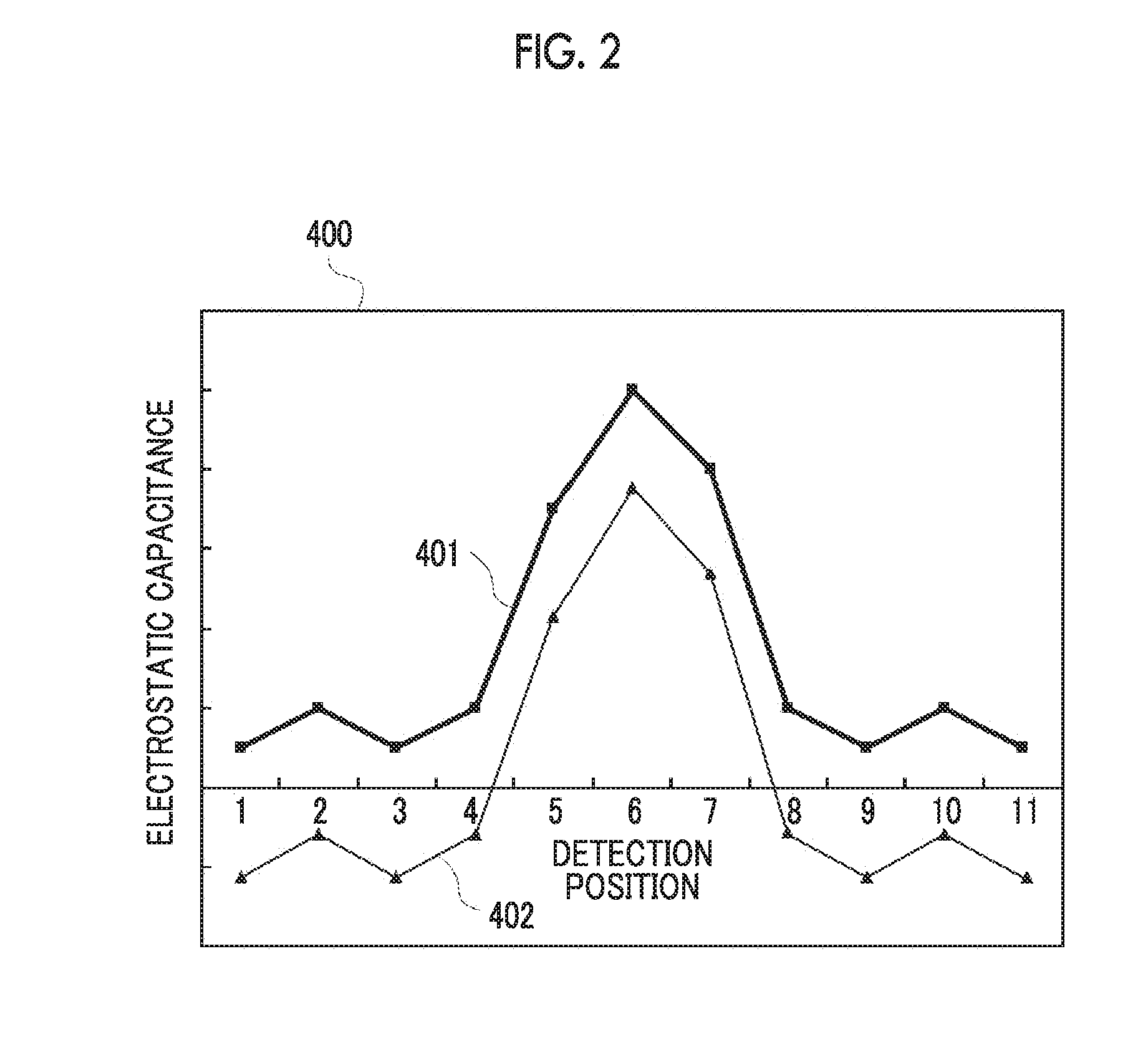
Input apparatus, control method for input apparatus, apparatus and program causing computer to execute control method for input
ActiveUS20160342264A1Increase degree of freedomHigh sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingSignal onEngineering
An input apparatus includes a sensor section configured to include a plurality of detection units, and to control positive and negative polarities of a detection signal at each detection position, a control unit configured to generate a group of combined detection signals in which polarity patterns are different from each other, and a signal reproduction unit configured to reproduce signal levels of a group of detection signals on the basis of a group of combined detection signals and a group of polarity patterns, in which at least some of the plurality of detection units differ in the number of detection positions, and the control unit selects the group of polarity patterns according to the number of detection positions so that the number of positive polarities and the number of negative polarities included in each of the polarity patterns are similar to each other.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Method and apparatus for mass spectrometric immunoassay analysis of specific biological fluid proteins
Owner:INTRINSIC BIOPROBES
Portable reflectometer and method for characterising the mirrors of solar thermal power plants
InactiveUS20130169950A1Sufficient dynamic rangeAvoid insufficient thicknessRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesData acquisitionDiffuse reflection
The invention relates to a portable reflectometer and to a method for characterizing the collector mirrors used in solar power plants for the in-field characterization of reflection coefficients. The equipment includes all of the components required for this measurement, such as a module to measure the reflection coefficient of the mirror, an electronic data acquisition and processing system, a system for processing data and controlling the equipment, a system for storing the data of interest, a user interface system, and a system allowing communication between the aforementioned systems and an outer casing. The equipment can be used to characterize the specular reflection coefficient of flat or curved mirrors of different thicknesses, without requiring adjustments to be made to the equipment, minimizing the influence of diffuse reflection on the measurement.
Owner:ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECH SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com