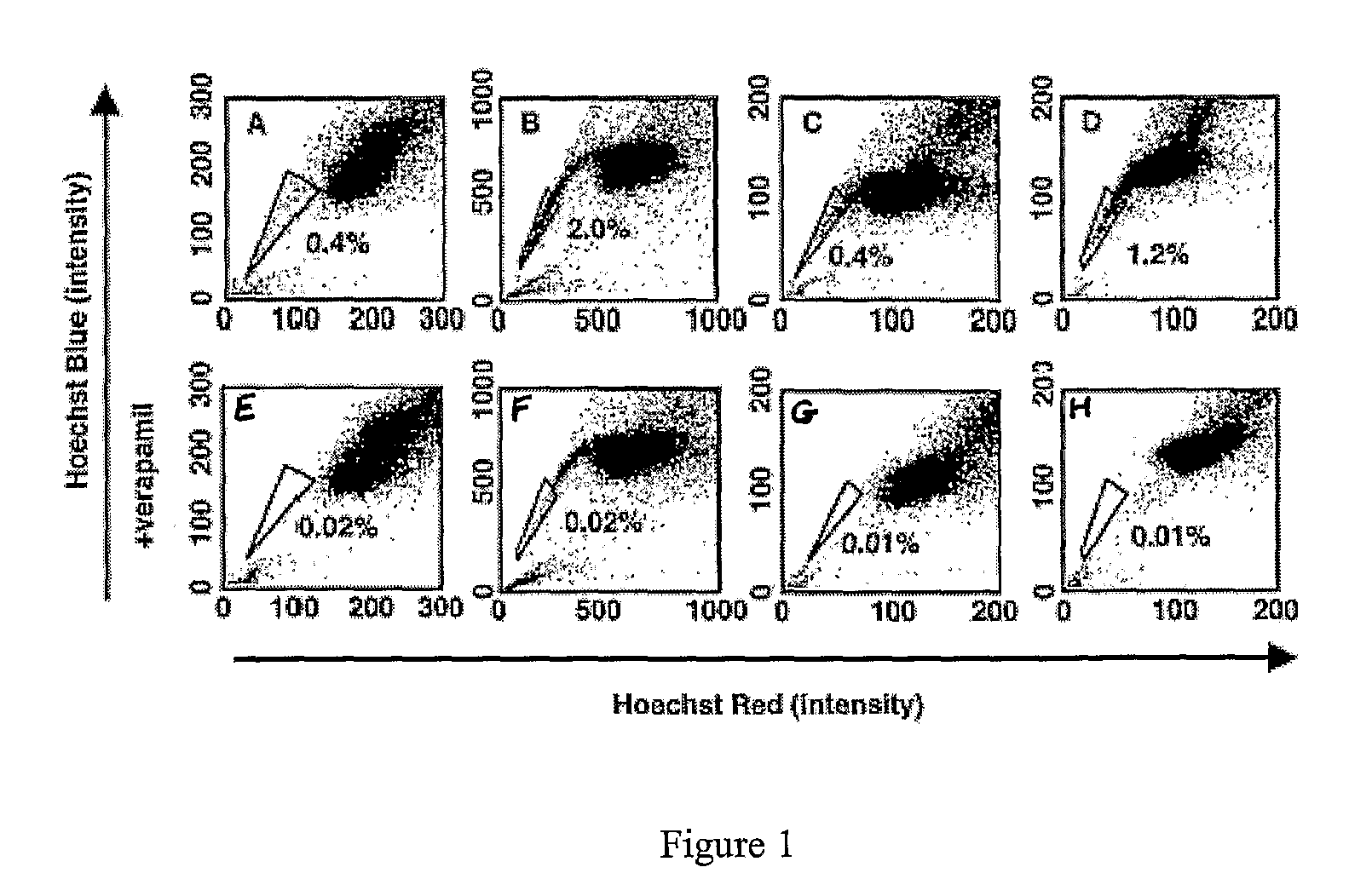
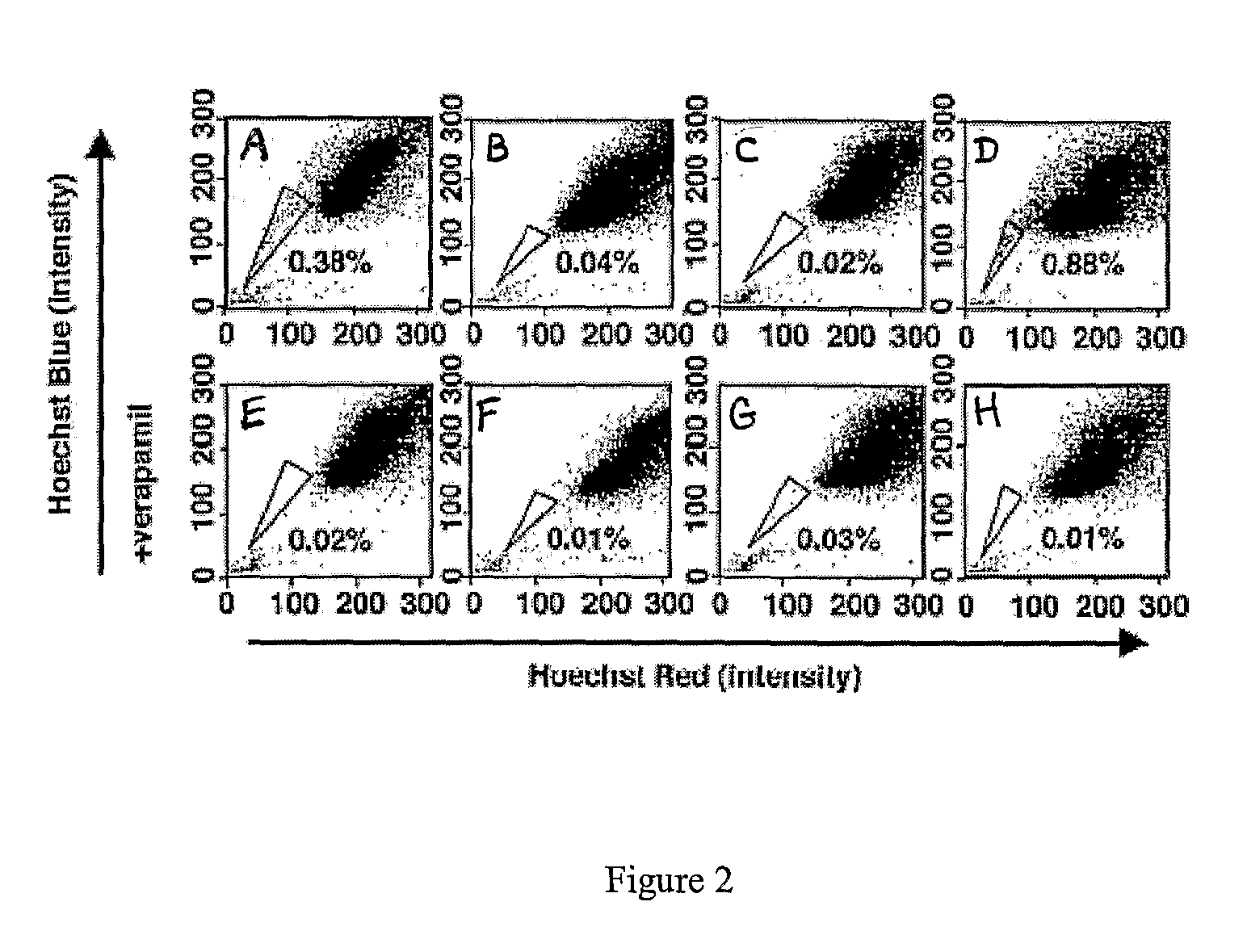
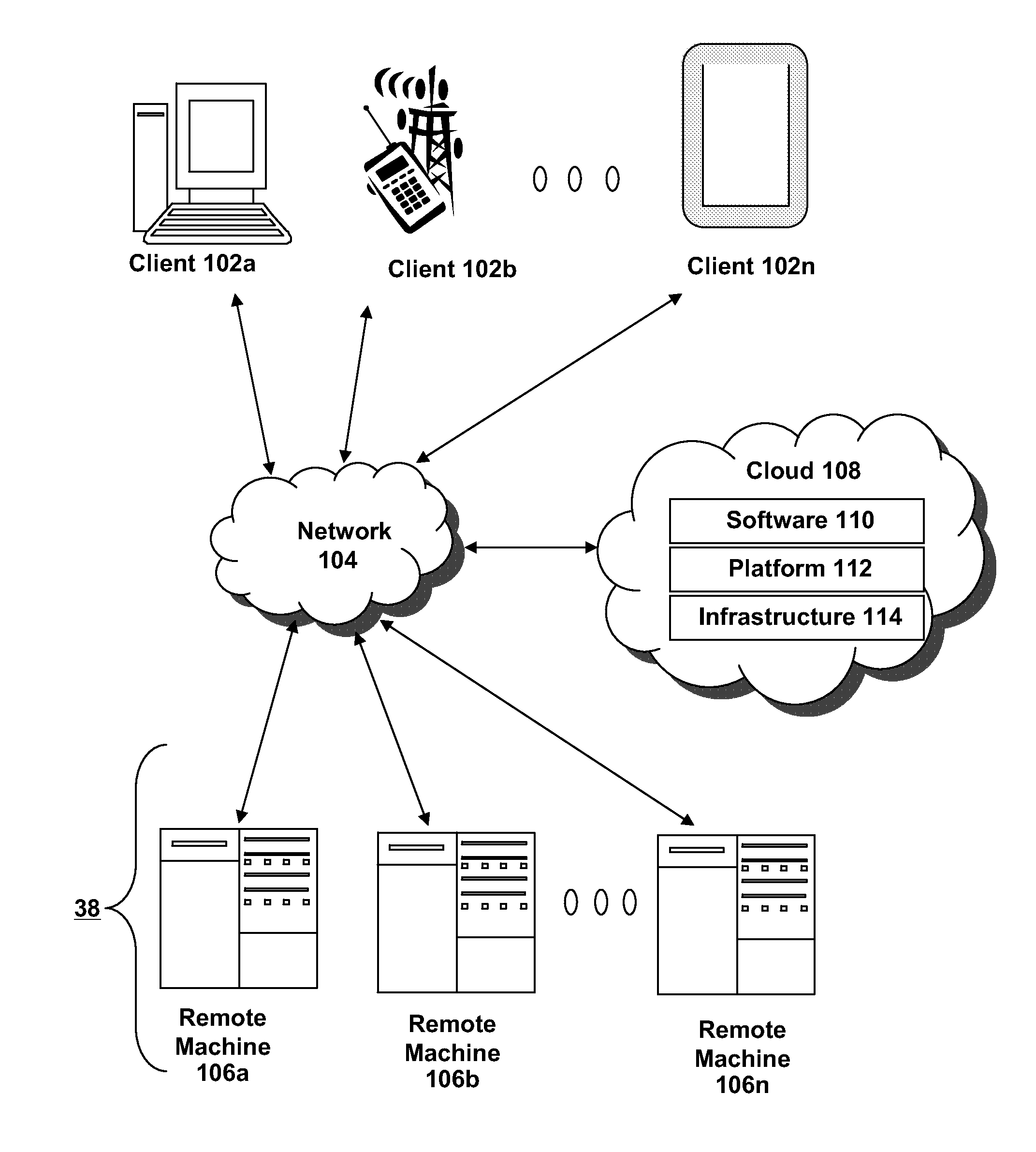
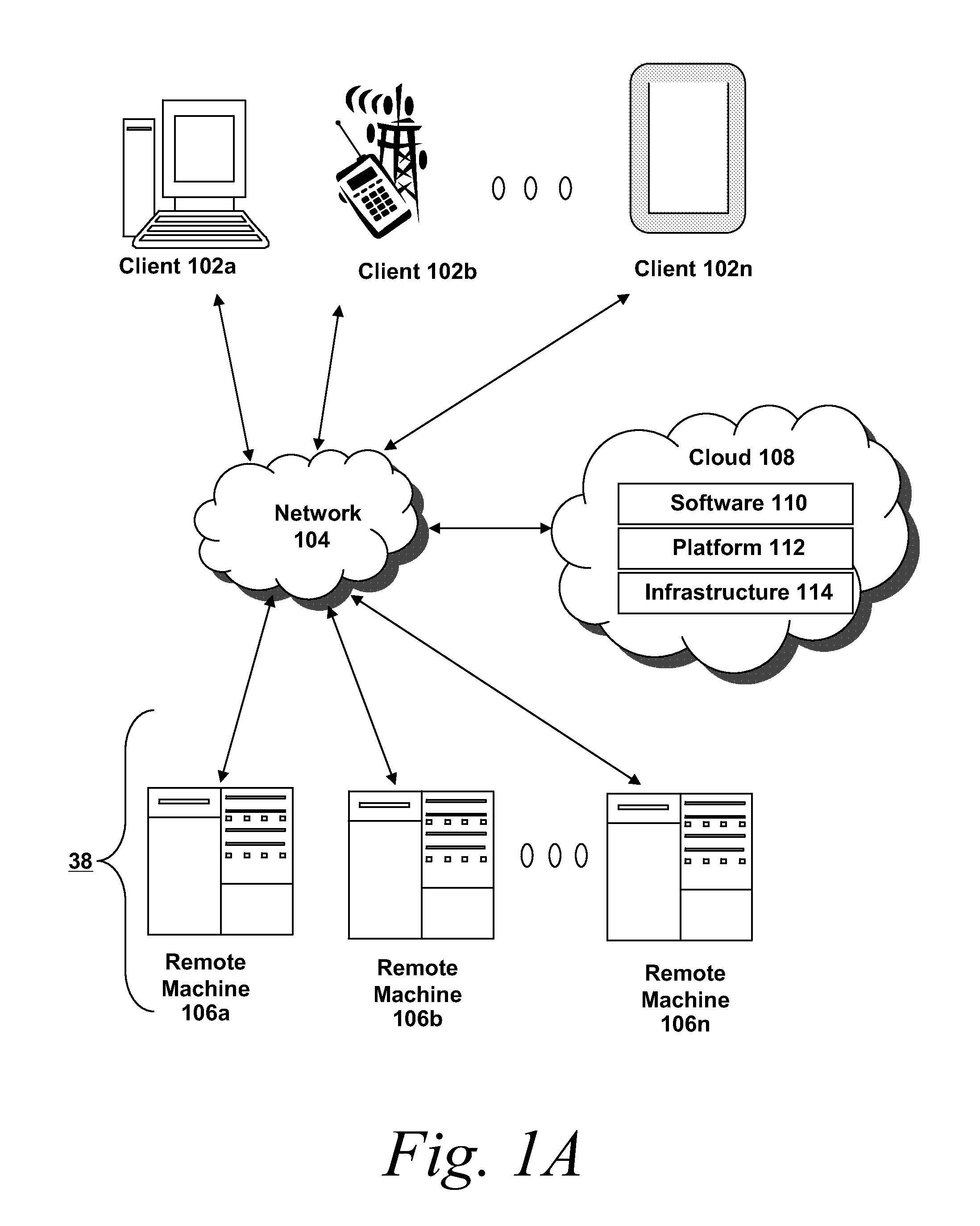
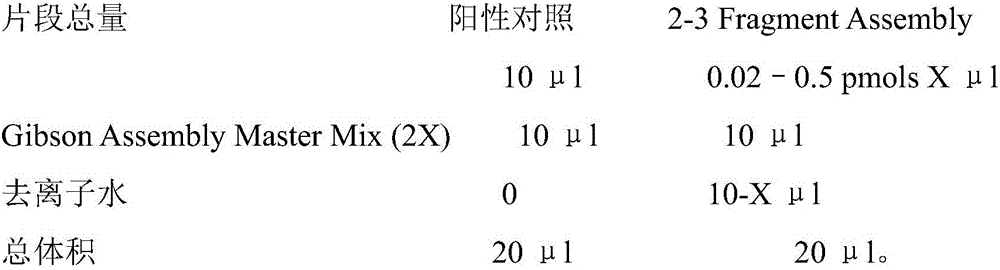
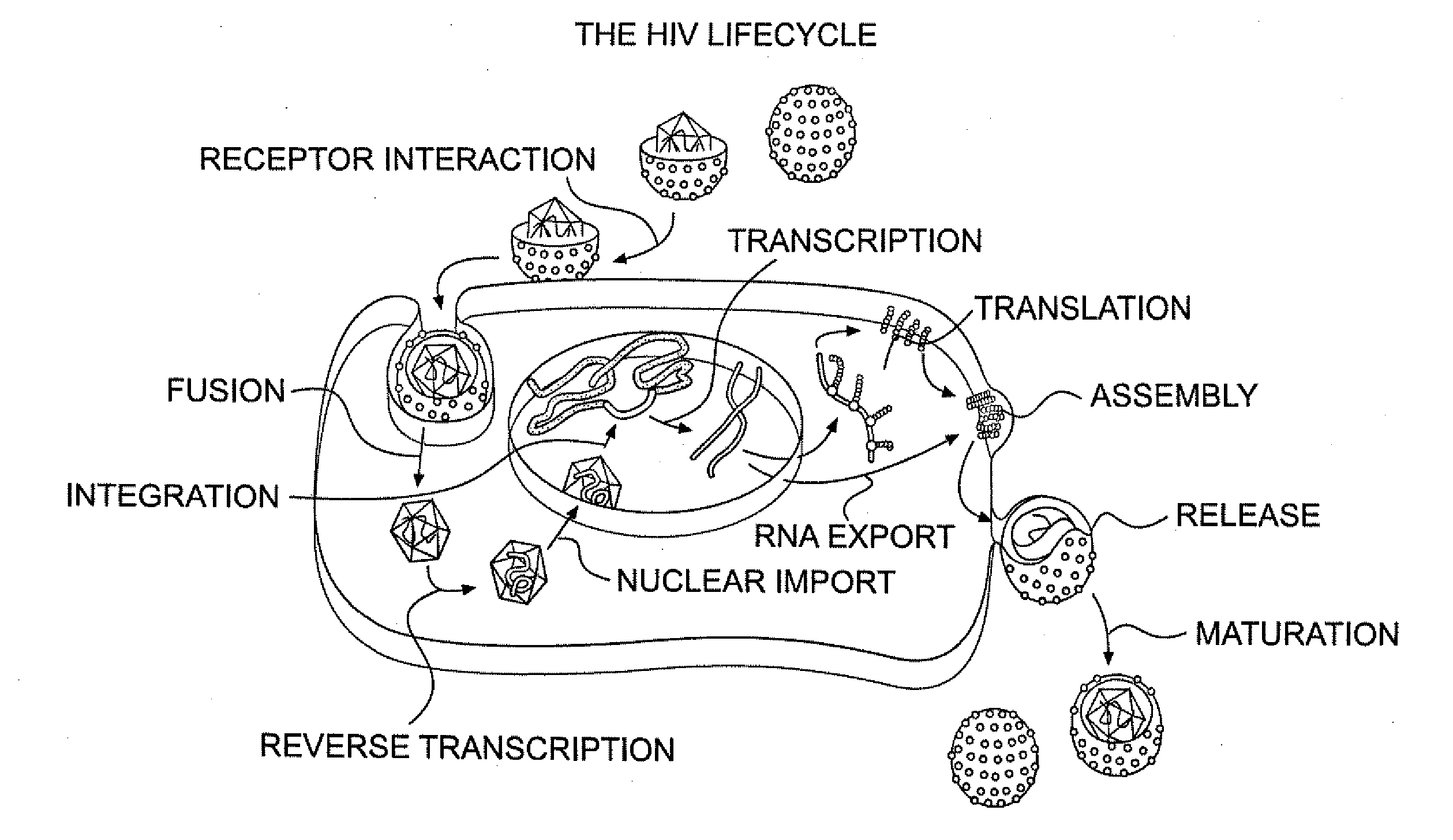
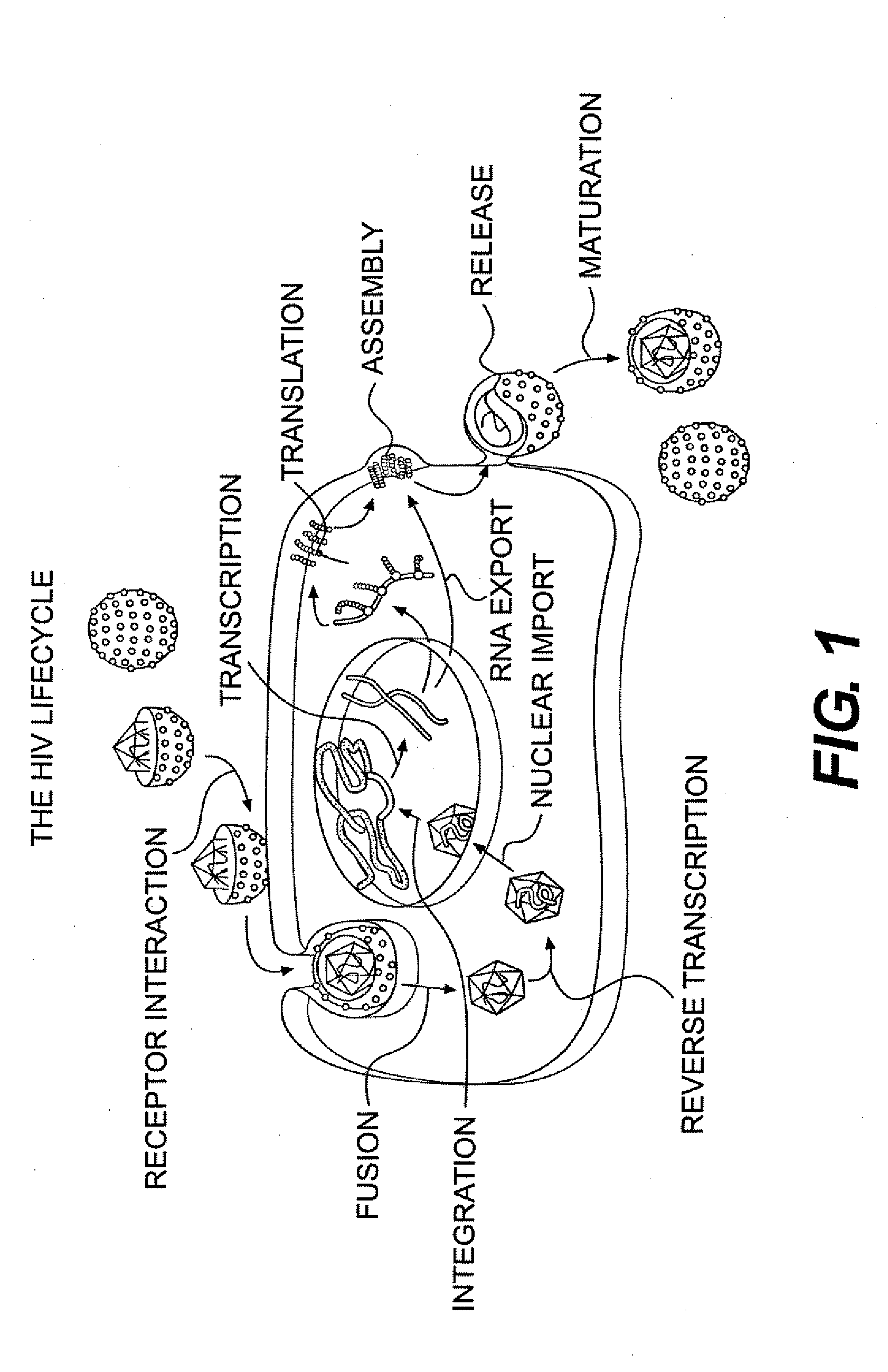
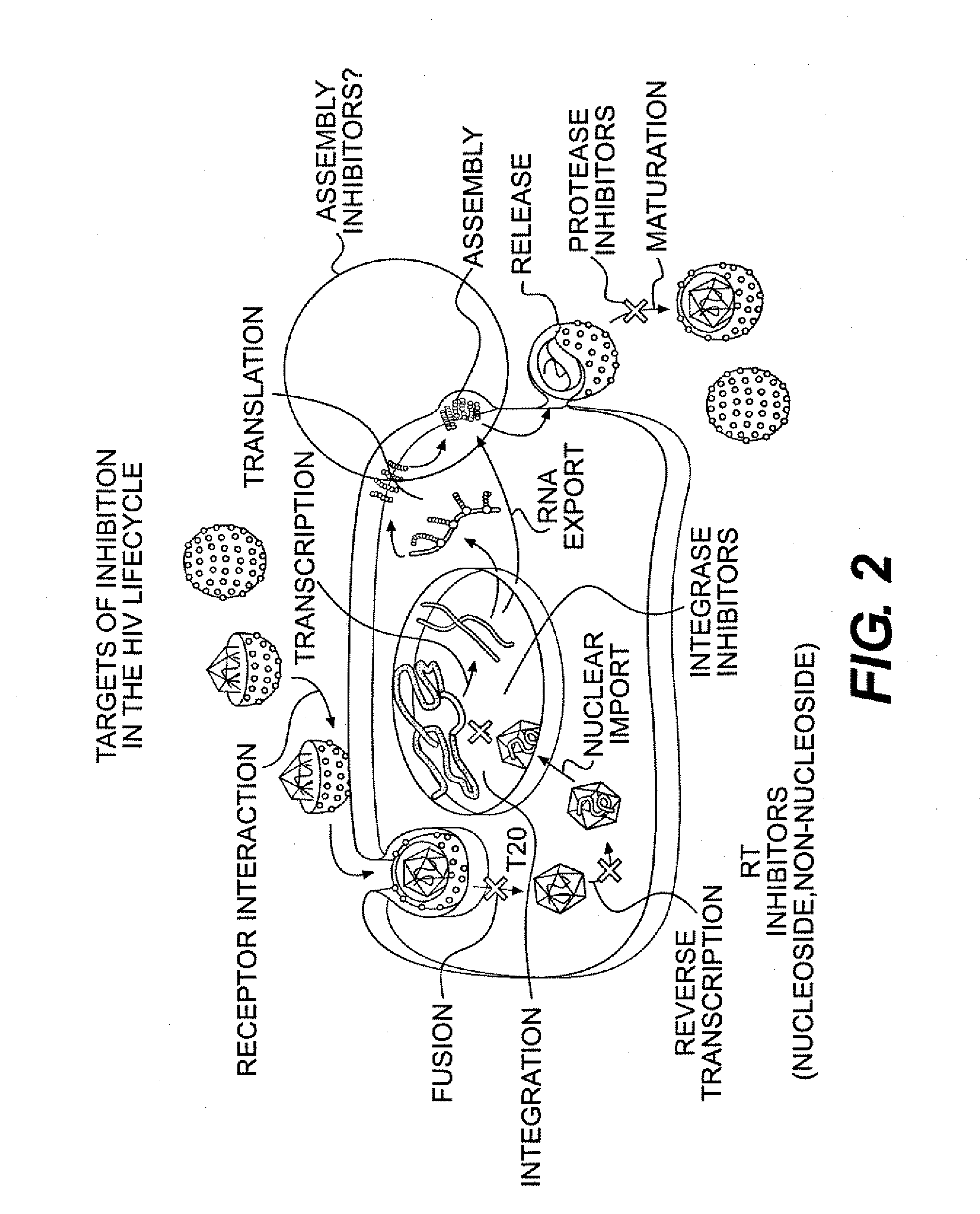
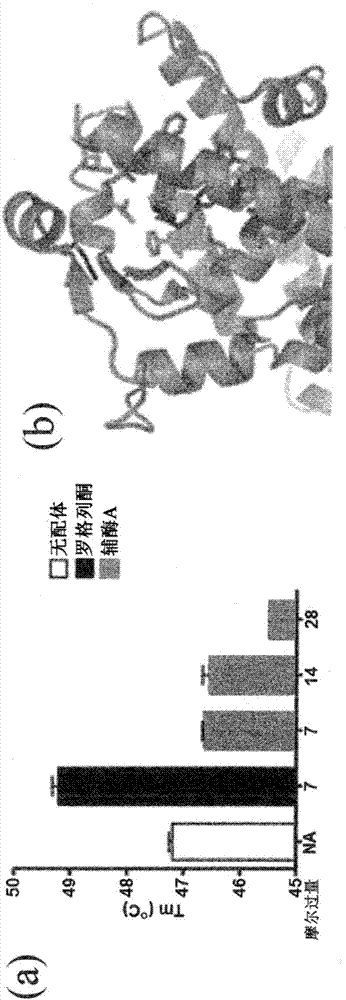
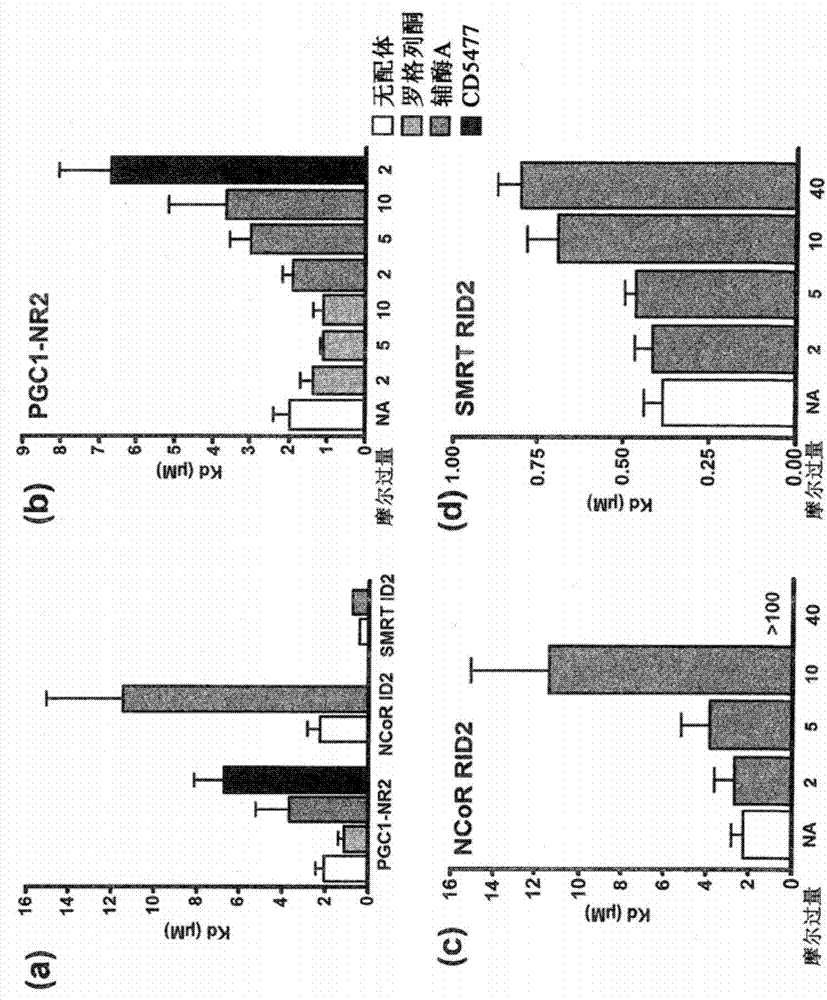
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1558 results about "Drug target" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drug Target. A drug target is a molecule in the body, usually a protein, that is intrinsically associated with a particular disease process and that could be addressed by a drug to produce a desired therapeutic effect.
Single cell gene expression for diagnosis, prognosis and identification of drug targets
InactiveUS20100255471A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDrug targetDisease status
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for drug target screening
InactiveUS6165709AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyProtein targetProtein activity
The present invention provides methods for identifying targets of a drug in a cell by comparing (i) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell, (ii) the effects on a wild-type cell of modifications to a putative target of the drug, and (iii) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell which has had the putative target modified of the drug. In various embodiments, the effects on the cell can be determined by measuring gene expression, protein abundances, protein activities, or a combination of such measurements. In various embodiments, modifications to a putative target in the cell can be made by modifications to the genes encoding the target, modification to abundances of RNAs encoding the target, modifications to abundances of target proteins, or modifications to activities of the target proteins. The present invention also provides methods for drug development based on the methods for identifying drug targets.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Method and apparatus treating tissue adjacent a bodily conduit with thermocompression and drugs
InactiveUS7833220B2Guaranteed functionAvoid heatElectrotherapyDrug compositionsSufficient timeHeat sensitive
Owner:MEDIFOCUS
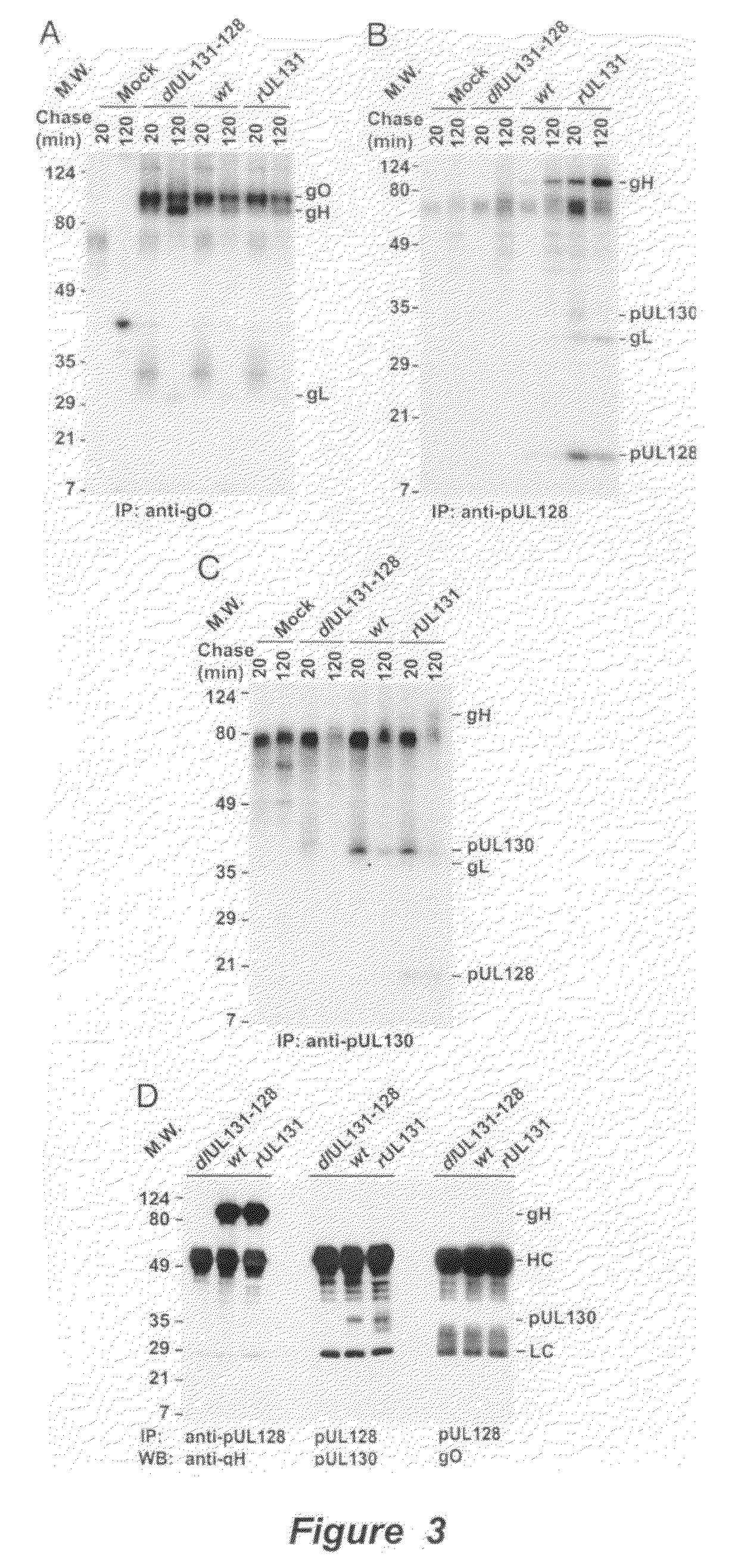
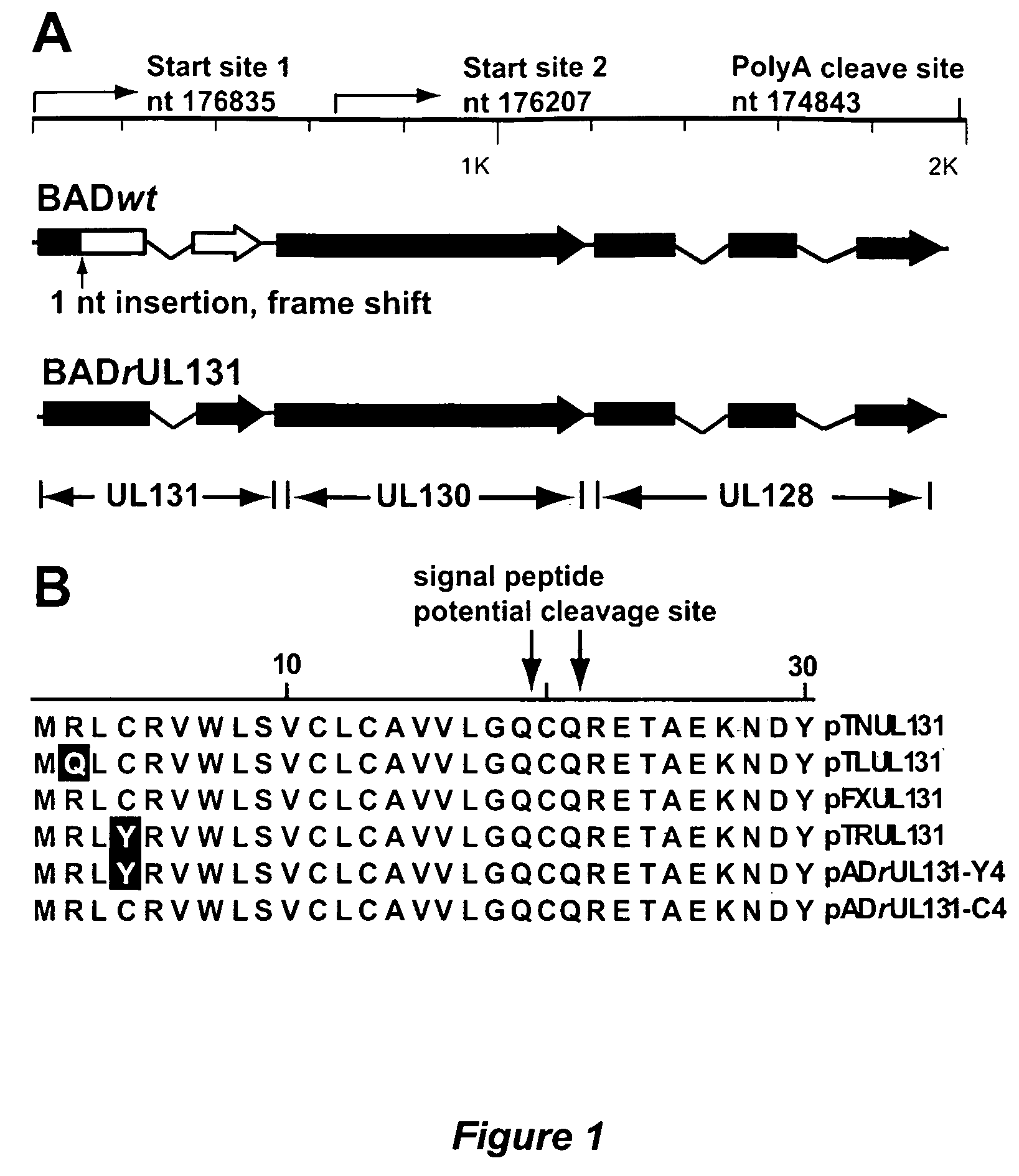
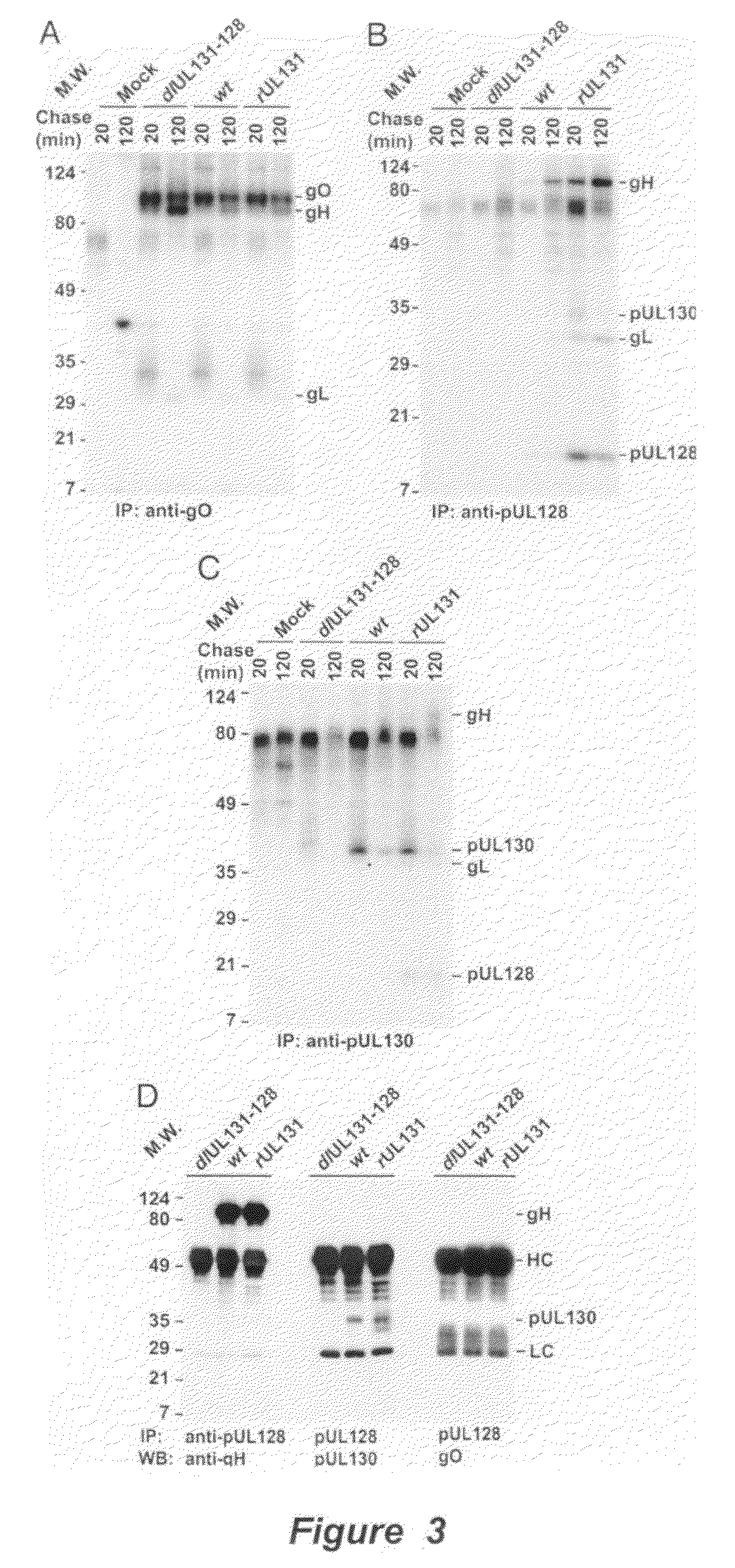
Cytomegalovirus surface protein complex for use in vaccines and as a drug target
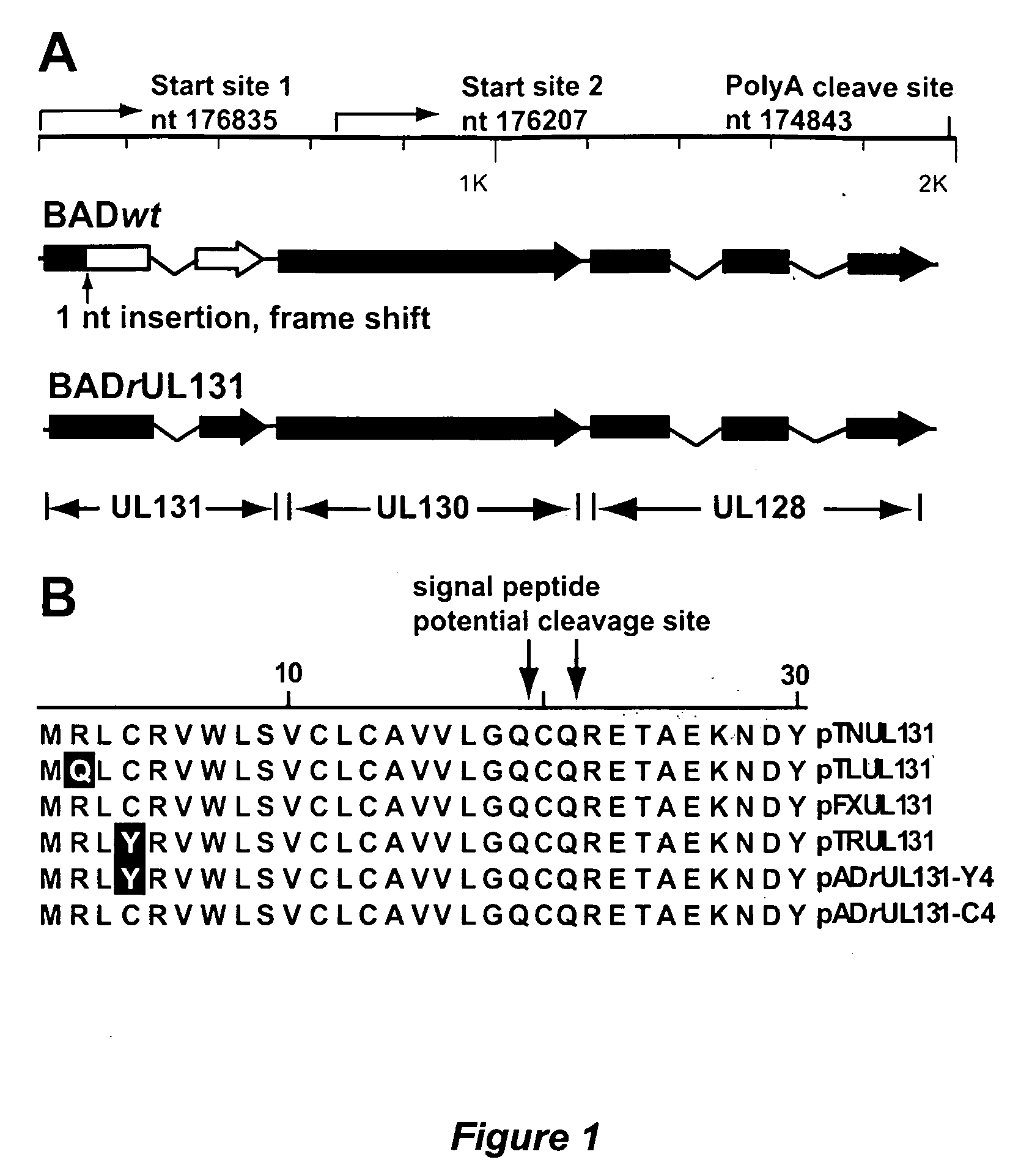
Immunogenic compositions and prophylactic or therapeutic vaccines for use in protecting and treating against human cytomegalovirus (CMV) are disclosed. Subunit vaccines comprising a human CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, and nucleic acid vaccines comprising at least one nucleic acid encoding a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130 are described. Also disclosed are therapeutic antibodies reactive against a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, as well as methods for screening compounds that inhibit CMV infection of epithelial and endothelial cells, methods for immunizing a subject against CMV infection, methods for determining the capability of neutralizing antibodies to inhibit human CMV infection of cell types other than fibroblasts, and methods of diminishing an CMV infection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Response element
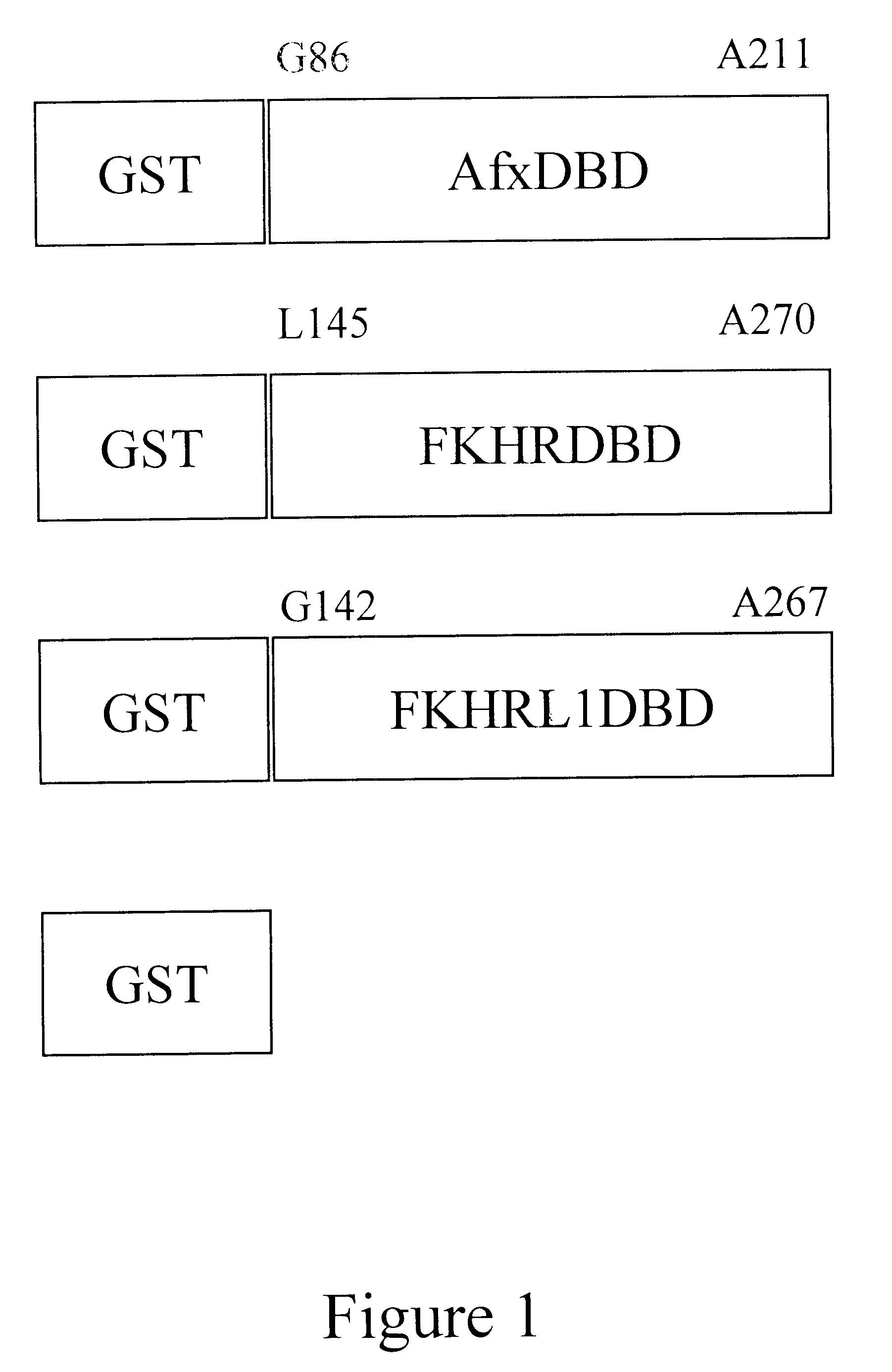
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
Microarray gene expression profiling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma : prognosis and drug target identification
InactiveUS20060088823A1Easy to detectEasy to optimizeMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationAbnormal tissue growthNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe or a novel set of such probes in a microarray is provided. The probe or probe set is useful in the prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CC-RCC), wherein aggressive and non-agressive CC-RCC tumor types are characterized by differential expression profiles of genes that hybridize with one or more of these probes. Microarrays and kits
Owner:HAAB BRIAN +3
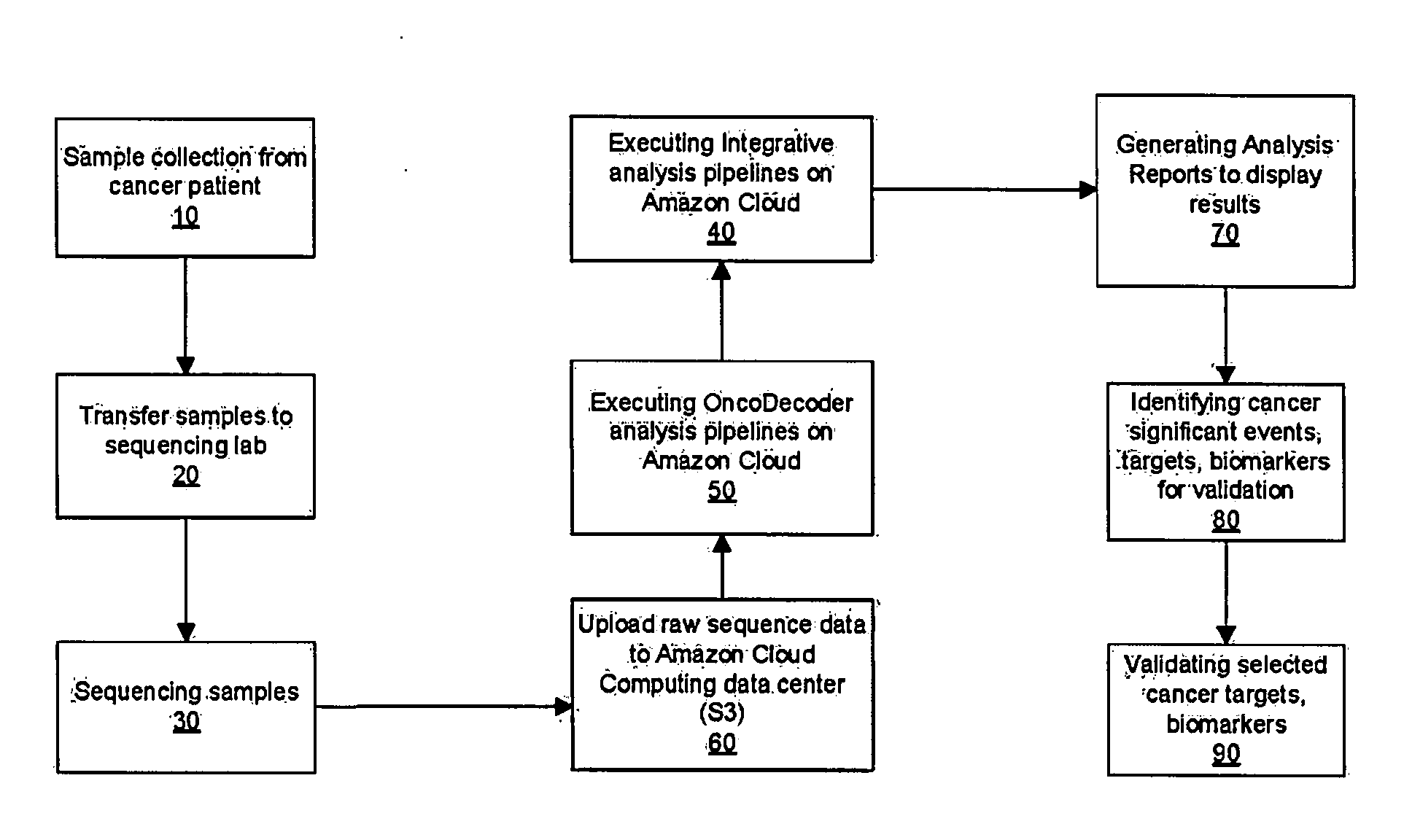
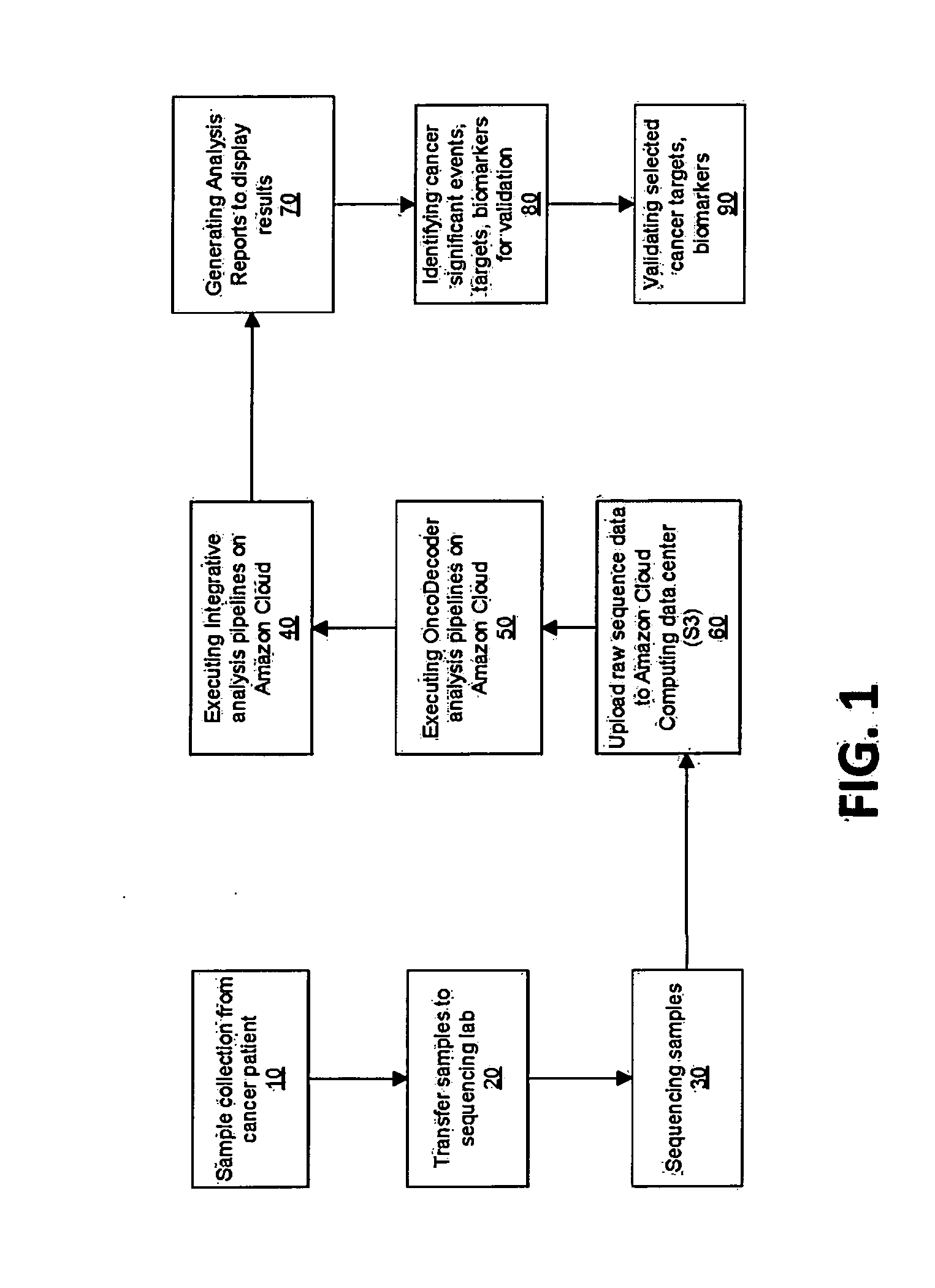
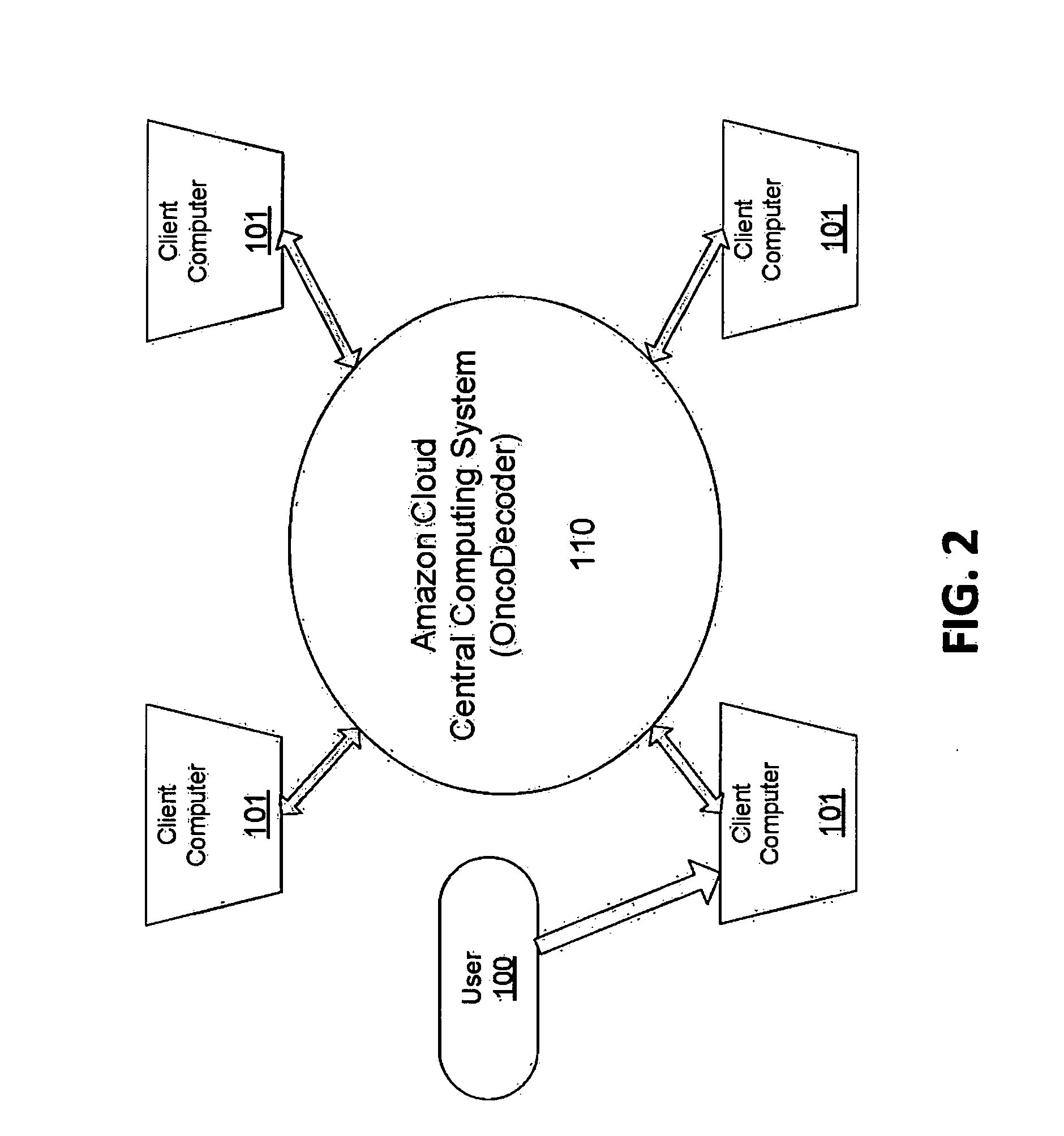
Systems and methods for cancer-specific drug targets and biomarkers discovery
InactiveUS20130184999A1Improve throughputMinimal hardware requirementProteomicsGenomicsHuman cancerBiomarker discovery
The present invention provides users with cloud-based high throughput computing system for integrative analyses of next generation sequencing genomic data, such that human cancer biomarkers and drug targets can be accurately and quickly identified. Advantageously, the present invention harness a comprehensive systematic analysis pipelines for all types of next generation sequencing genomic data, advanced genomic variants calling algorithms and modeling, variant data correlation and integration, and identification of cancer specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Thus, the present invention will aid users so that less of their time and efforts are required in order to obtain precisely the desired information for which they are analyzing.
Owner:DING YAN
Methods And Means Related To Cancer Stem Cells
ActiveUS20080132423A1Promote more developedPromote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCancer cellPresent method
This invention relates to the methods for the identification and isolation of cancer stem cells from cultured cancer cell lines. Cell line-derived cancer stem cells isolated using the present methods may be useful, for example, in assays to screen compounds for anti-cancer stem cell activity and in target discovery methods for identifying novel expressed genes and druggable targets. The invention also relates to the screening of compounds for activity against cell line-derived cancer stem cells.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Systems and methods for disease knowledge modeling
InactiveUS20130268290A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsTreatment choicesTreatment options
Systems and methods are described herein for disease knowledge modeling and clinical treatment decision support, and the prioritization of possible treatment options based on tumor or other disease biomarkers. Disease or indication information, including identification of biomolecular entities associated with the indication may be culled through text data mining to create a knowledge model of the indication. In some embodiments, the knowledge model may comprise a network of associations between molecular entities, including such drug targets and biomakers, genes, pathways. The model may be combined with patient-specific variant information and historical treatment records to identify and prioritize treatment decisions and allow for the prediction of disease drivers and provide treatment options tailored to a patient's genetic data.
Owner:MOLECULAR HEALTH
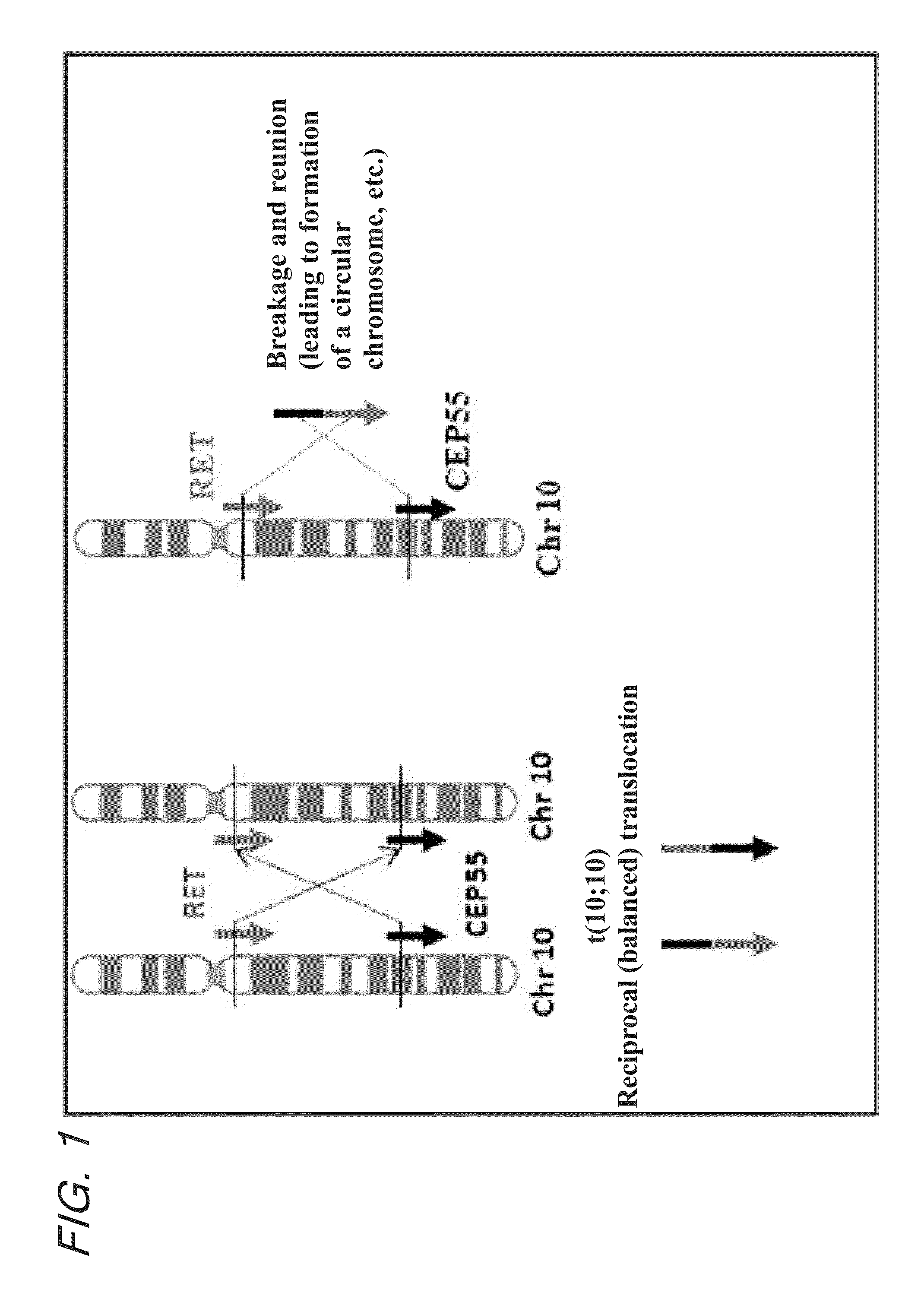
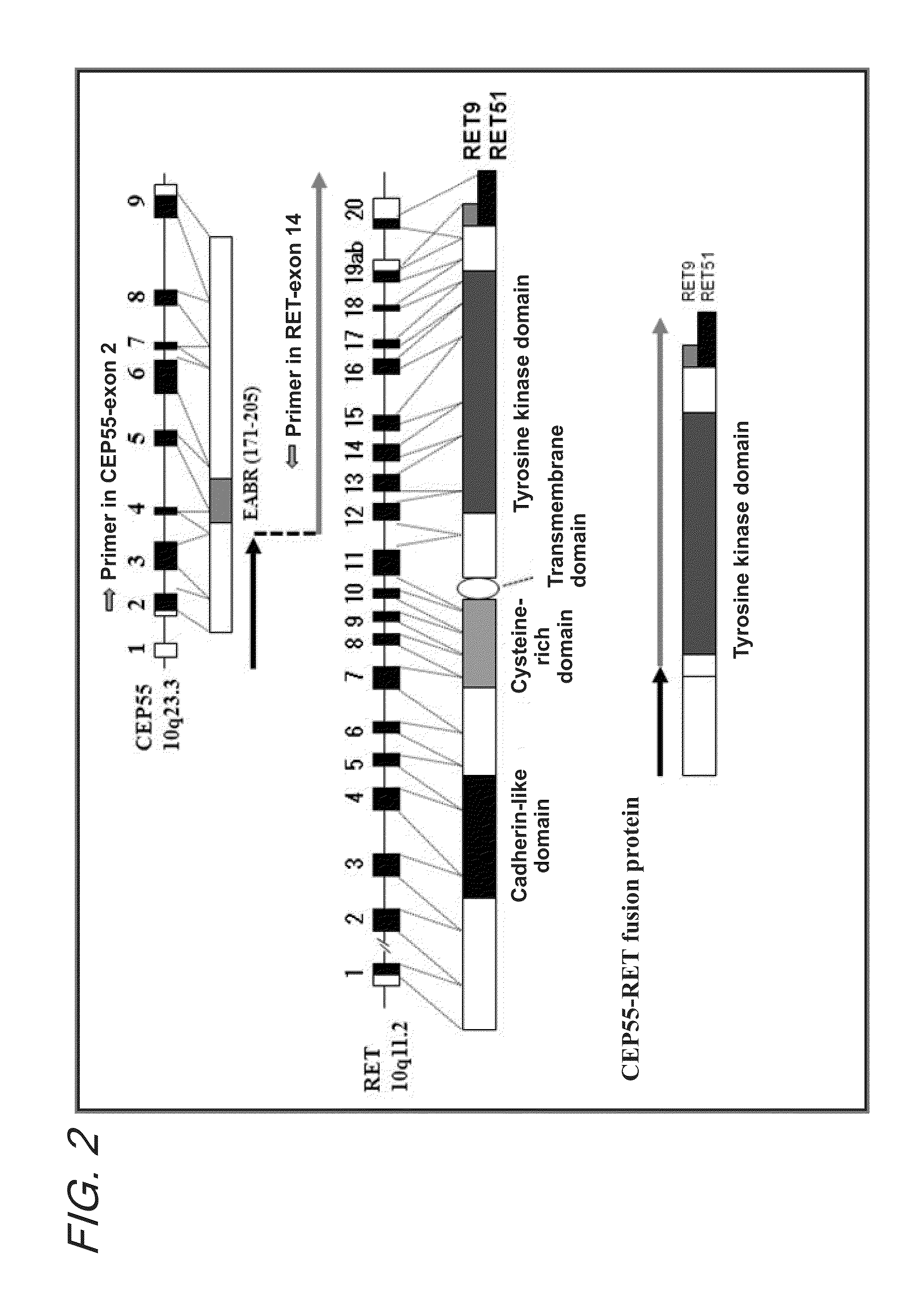
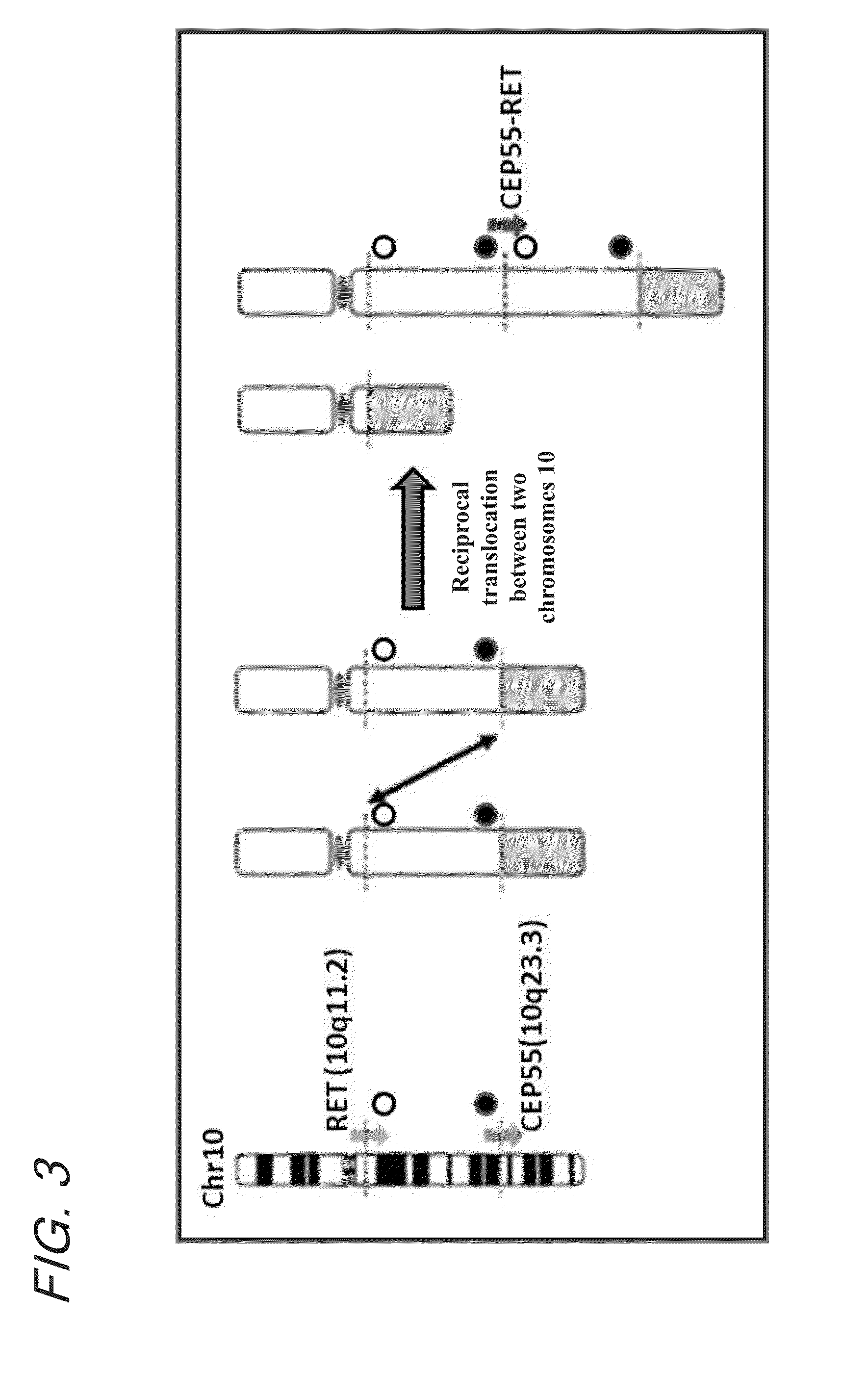
Fusion gene of cep55 gene and ret gene
InactiveUS20150177246A1Efficient detectionEffective treatment of cancerBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRet geneTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
In order to identify genes that can serve as indicators for predicting the effectiveness of drug treatments in cancers and provide novel methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatments with drugs targeting said genes, transcriptome sequencing was performed of diffuse-type gastric cancer. As a result, in-frame fusion transcripts between the CEP55 gene and the RET gene were identified. It was also found that said gene fusions induce activation of RET protein, thereby causing canceration of cells. Further, it was demonstrated that the RET protein activation and canceration caused by said gene fusion can be suppressed by using a RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and that treatments with a RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor are effective in patients with detection of said gene fusion.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT +1
Nucleic acid arrays for monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes
InactiveUS20050221354A1Reagent cost per experimentRobust overall probe set signal valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug targetPolynucleotide
The present invention provides nucleic acid arrays and methods of using the same for detecting or monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes. Non-limiting examples of drug target genes include kinase genes, phosphatase genes, protease genes, G-protein coupled receptor genes, nuclear hormone receptor genes, and ion channel genes. The present invention also provides methods of using nucleic acid arrays for the identification or validation of drugs or drug targets. In one embodiment, a nucleic acid array of the present invention is concentrated with probes for drug target genes. These probes constitute a substantial portion of all of the polynucleotide probes that are stably attached to the nucleic acid array, and can hybridize under stringent or nucleic acid array hybridization conditions to the tiling sequences selected from Attachment C, or the complements thereof.
Owner:WYETH
Method and systems for high throughput single cell genetic manipulation
InactiveUS20180312873A1Strong specificityUptake of the reagent into the cell is facilitatedMicroencapsulation basedBiological pathwayDrug target
Provided herein are methods and systems for introducing nucleic acid manipulation agents into single cells. Such high throughput delivery of nucleic acid manipulation reagents into single cells and subsequent genetic manipulation of such cells allow for large scale genetic analysis that can be useful, for example, for the study of biological pathways and drug target discovery.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Single cell gene expression for diagnosis, prognosis and identification of drug targets
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cytomegalovirus surface protein complex for use in vaccines and as a drug target
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
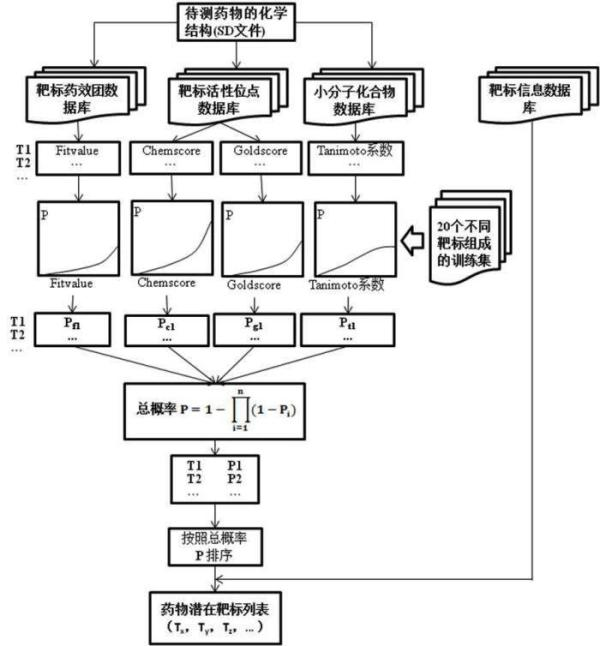
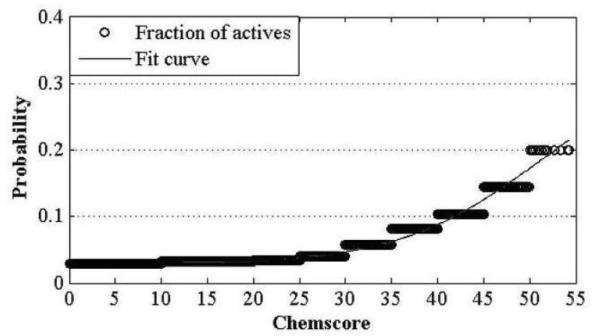
Construction and prediction method of integrated drug target prediction system
InactiveCN102663214AOvercoming the problem of low forecasting accuracySpecial data processing applicationsPharmacophoreEngineering
The invention discloses a construction and prediction method of an integrated drug target prediction system. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing a protein crystal structure database; selecting the protein bound with the drug-like ligand small molecule or the protein with the small molecule ligand binding potential as a target point, and building a crystal structure database of targets; for these targets, collecting the information of the targets related to diseases, the biology type and the active small molecule ligand information, and integrating a comprehensive target screening database composed of an active site database, a pharmacophore database, a small molecular compound database and a target basic information database. Based on the comprehensive target screening database, the construction of the integrated drug target prediction system is realized through a script program or a PipelinePilot flow, and the probability of target prediction accuracy of the method is provided. The method provided by the invention exerts the three above technical advantages to provide the probability of target prediction, thereby providing effective basis for further experimental verification.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Polylactide nanoparticles
InactiveUS8003128B2Easy to produceHigh molecular weightOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNanoparticleLactide
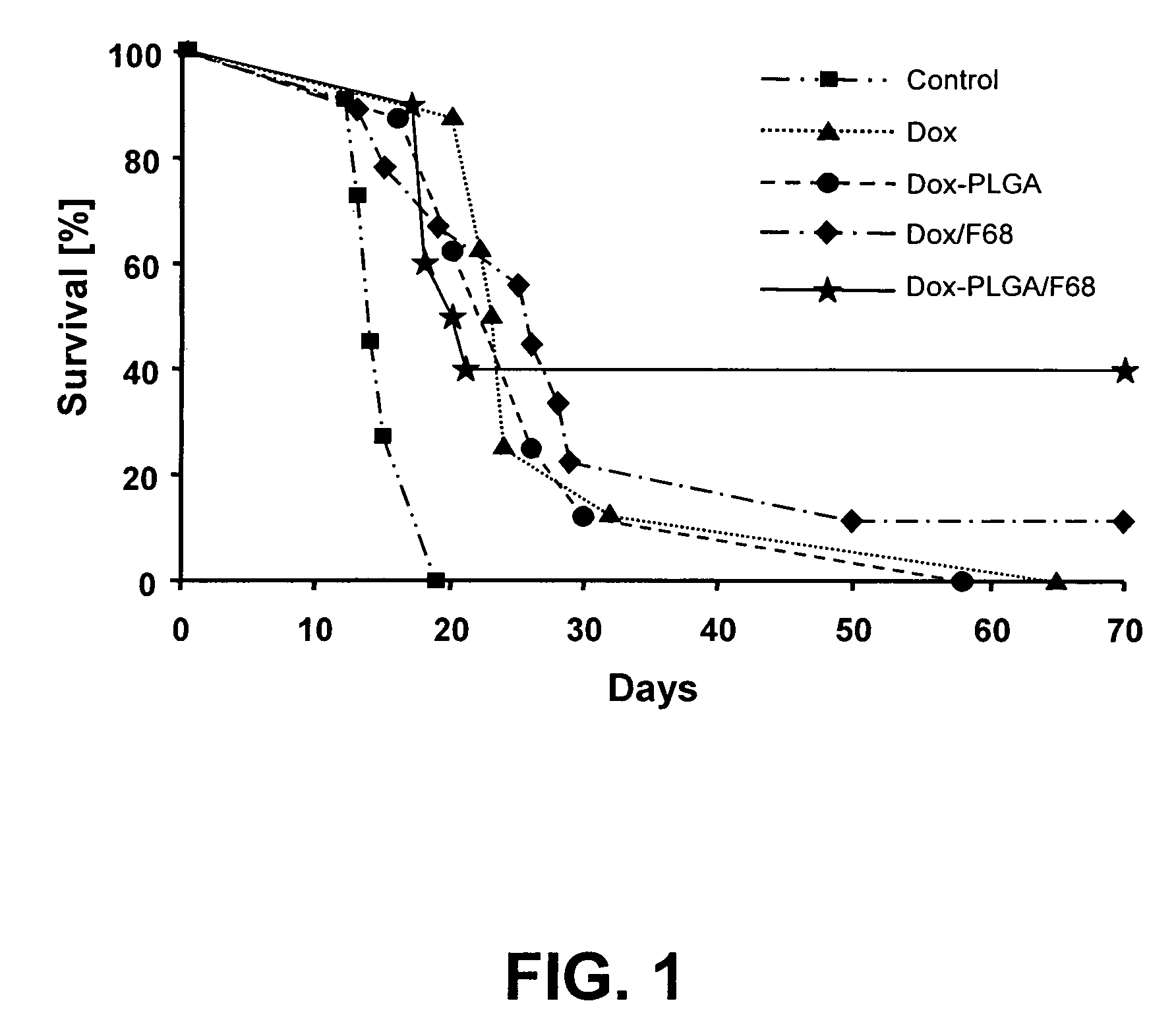
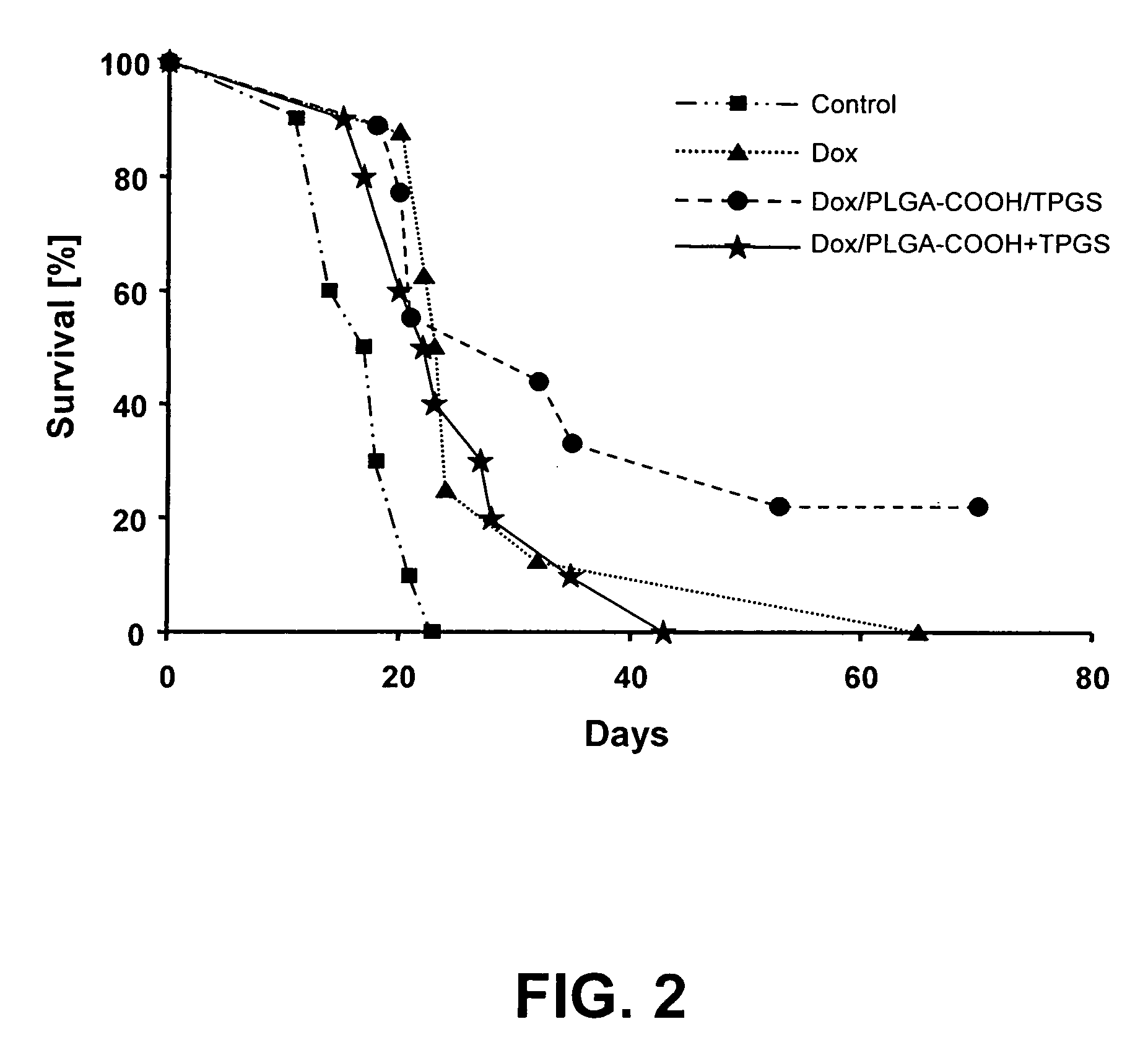
A drug targeting system for administering a pharmacologically active substance to the central nervous system of a mammal across the animal's blood brain barrier. The drug targeting system comprises nanoparticles made of poly(DL-lactide) and / or poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide), a pharmacologically active substance which is absorbed to, adsorbed to, and / or incorporated into the nanoparticles, and either contains TPGS or comprises a pluronic 188 surfactant coating deposited on the drug-loaded nanoparticles.
Owner:DAPHOT ENTERPRISES
Method and apparatus treating tissue adjacent a bodily conduit with thermocompression and drugs
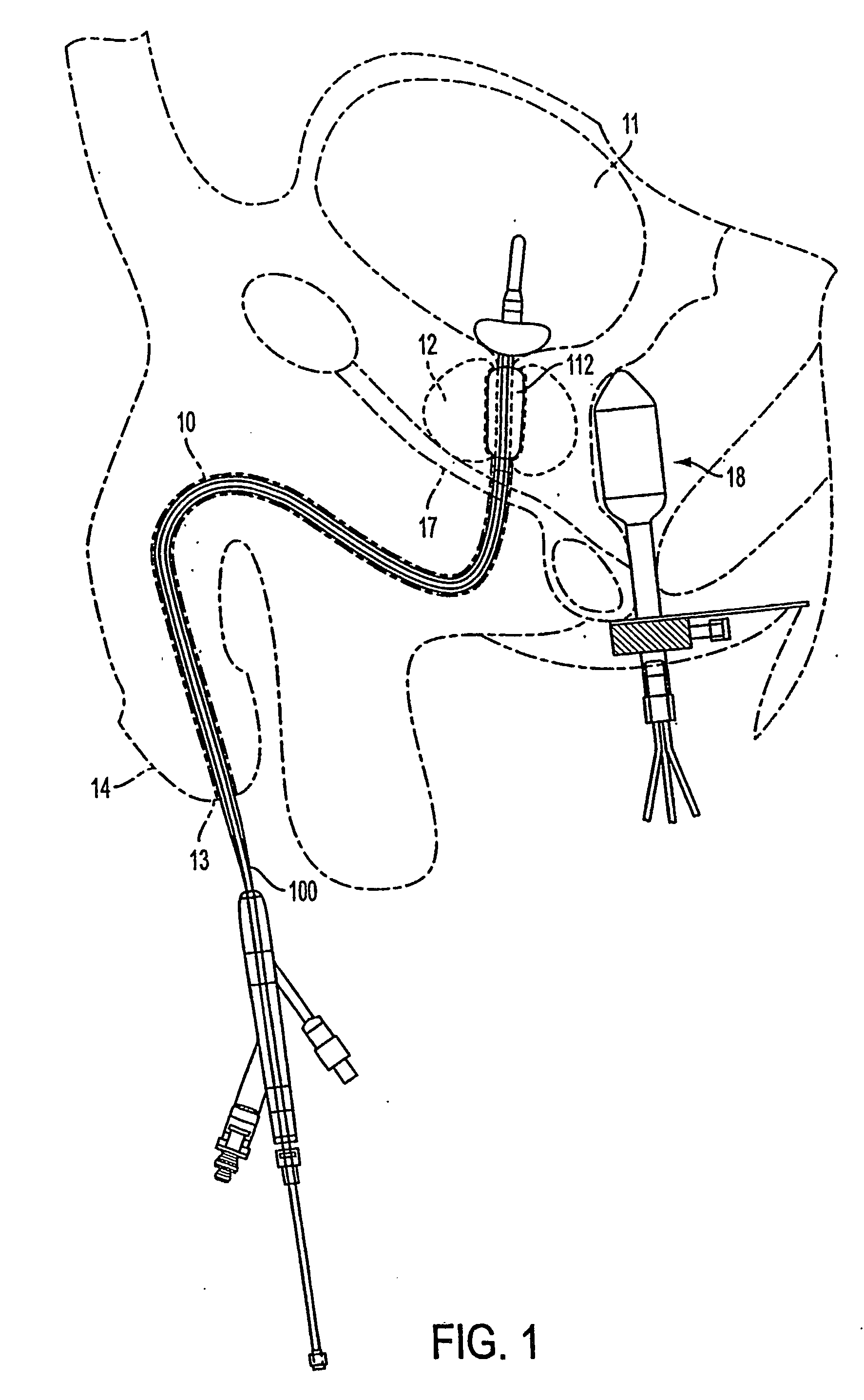
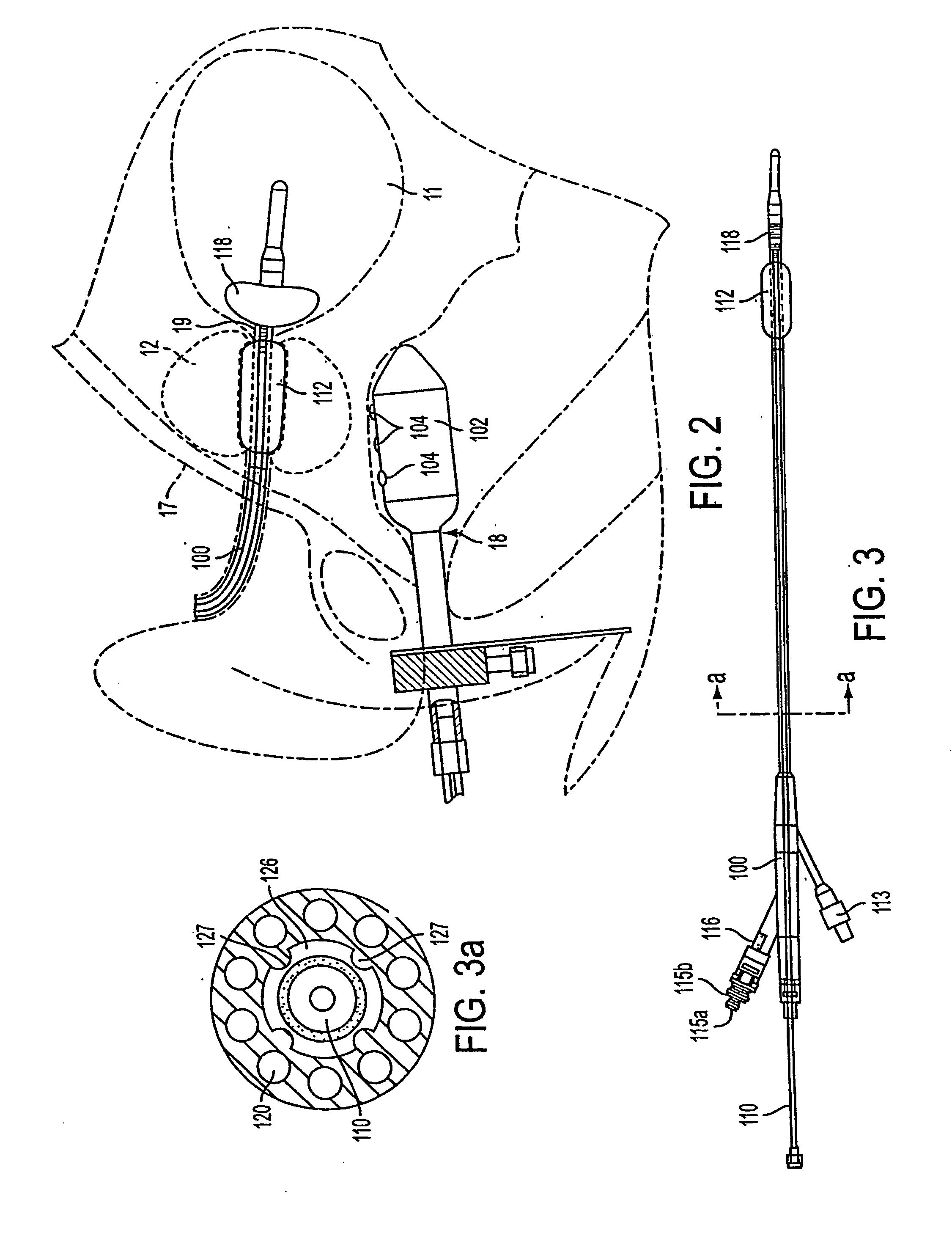
InactiveUS20050203498A1Efficient transferImprove drug deliveryElectrotherapyDrug compositionsInsertion stentHeat sensitive
A method and apparatus (100) of treating tissue adjacent a bodily conduit using thermotherapy, while preventing obstructions of the bodily conduit due to edema, includes injection of a drug-encapsulated within a heat-sensitive carrier, such as a liposome, within a region of tissue to be treated. The heat produced by the energy-emitting source (110) heats a portion of the tissue surrounding the bodily conduit to a temperature of approximately 43° C. for a time sufficient to destroy the heated portion of the tissue. In addition, the heat produced by the energy-emitting source (110) activates the heat-sensitive carrier to activate the release of the encapsulated drug and the drug targets the tissue to be heated. The focused energy of the energy-emitting source together with the compression acting on the target area can assist in delivering drugs to the target area so that a natural stent has a long term efficacy.
Owner:MEDIFOCUS
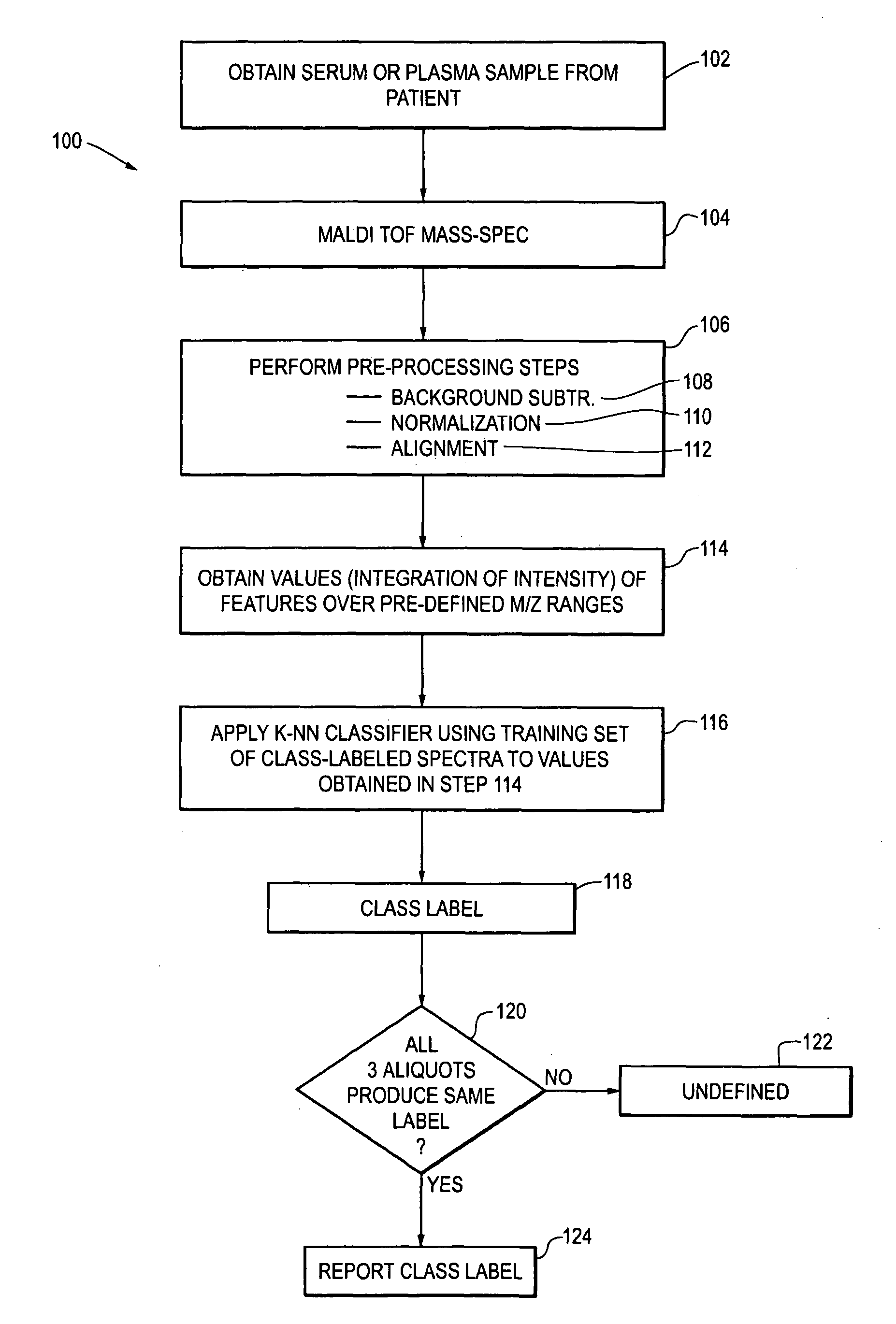
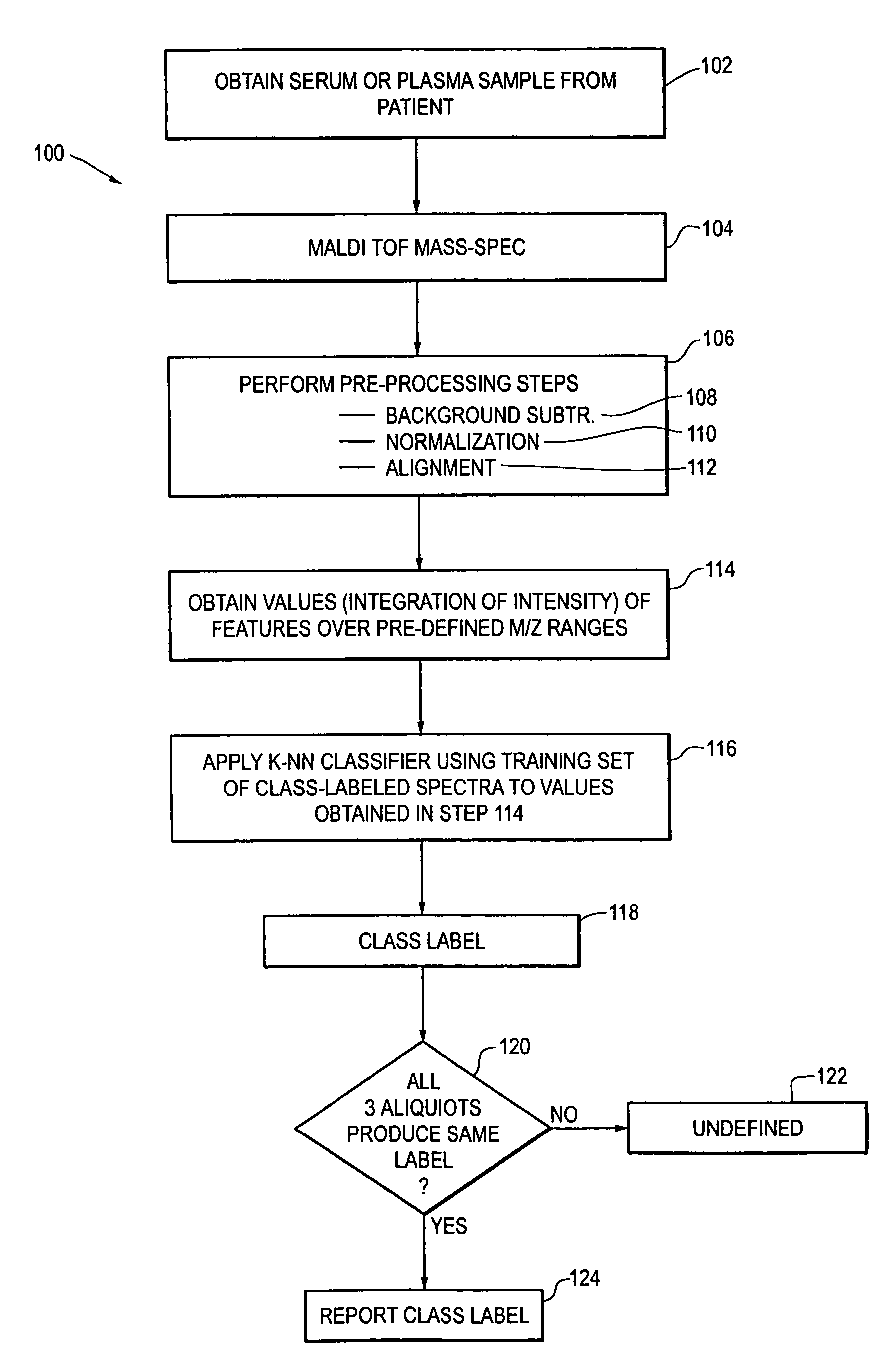
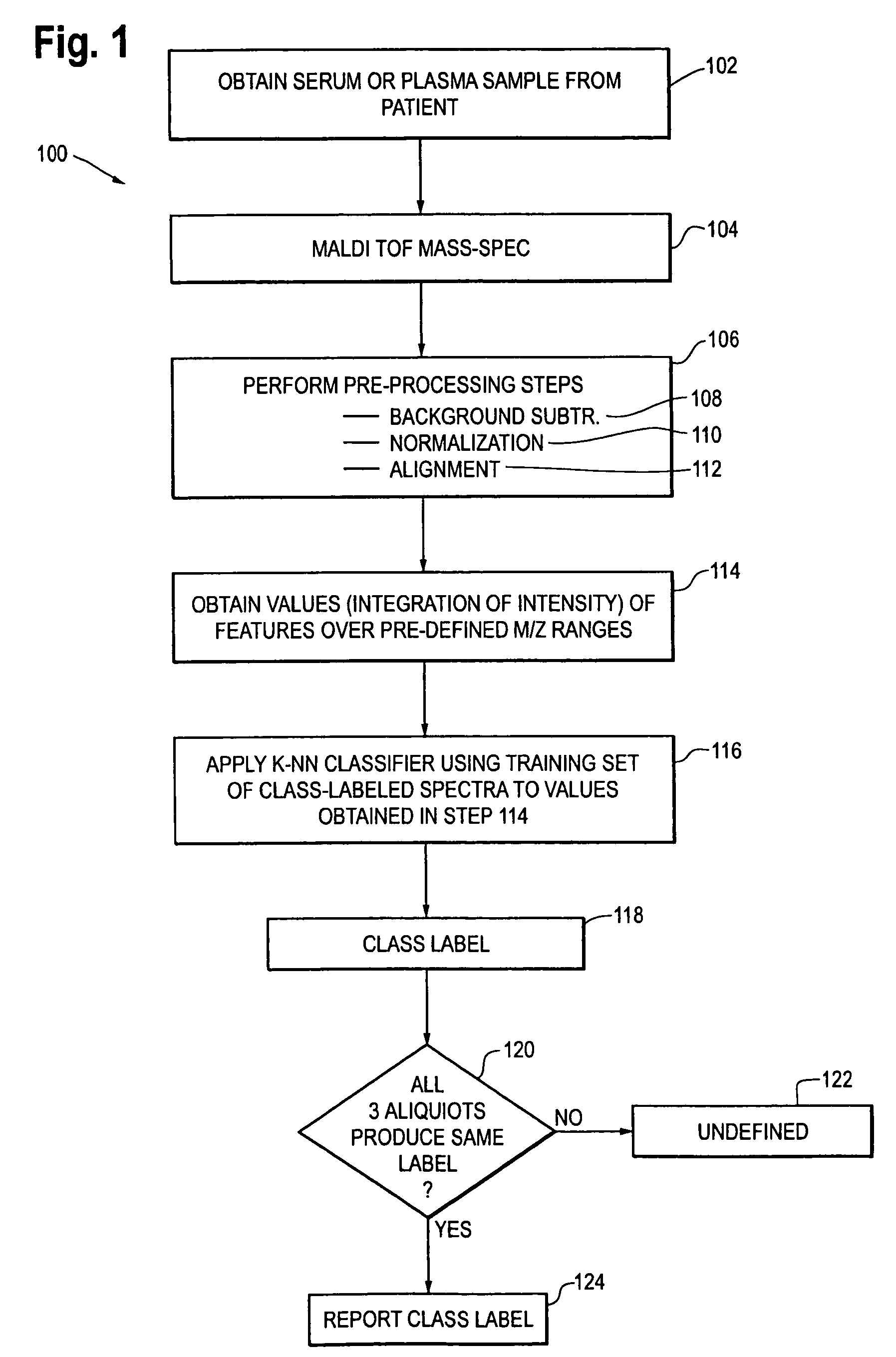
Selection of non-small-cell lung cancer patients for treatment with monoclonal antibody drugs targeting EGFR pathway
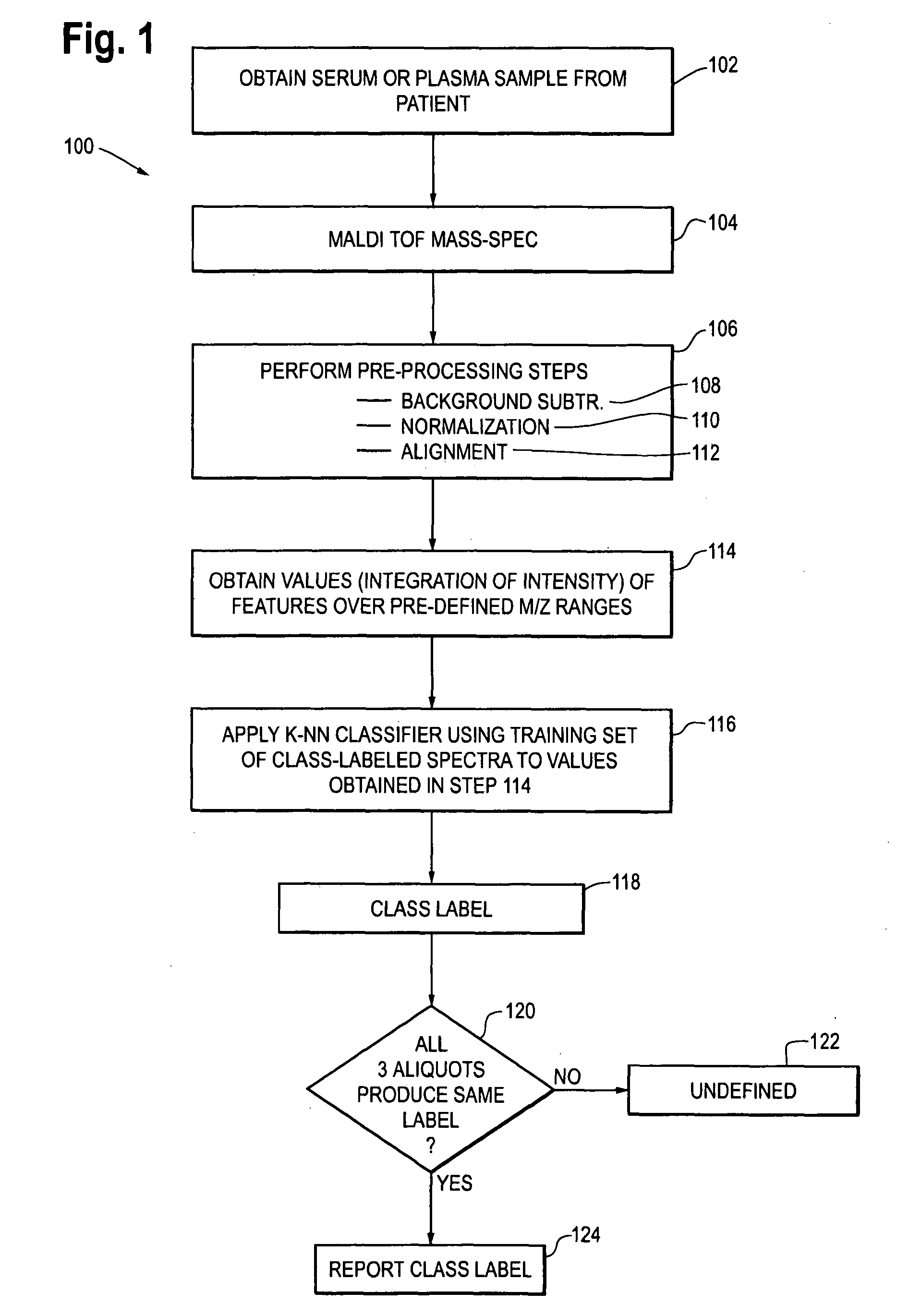
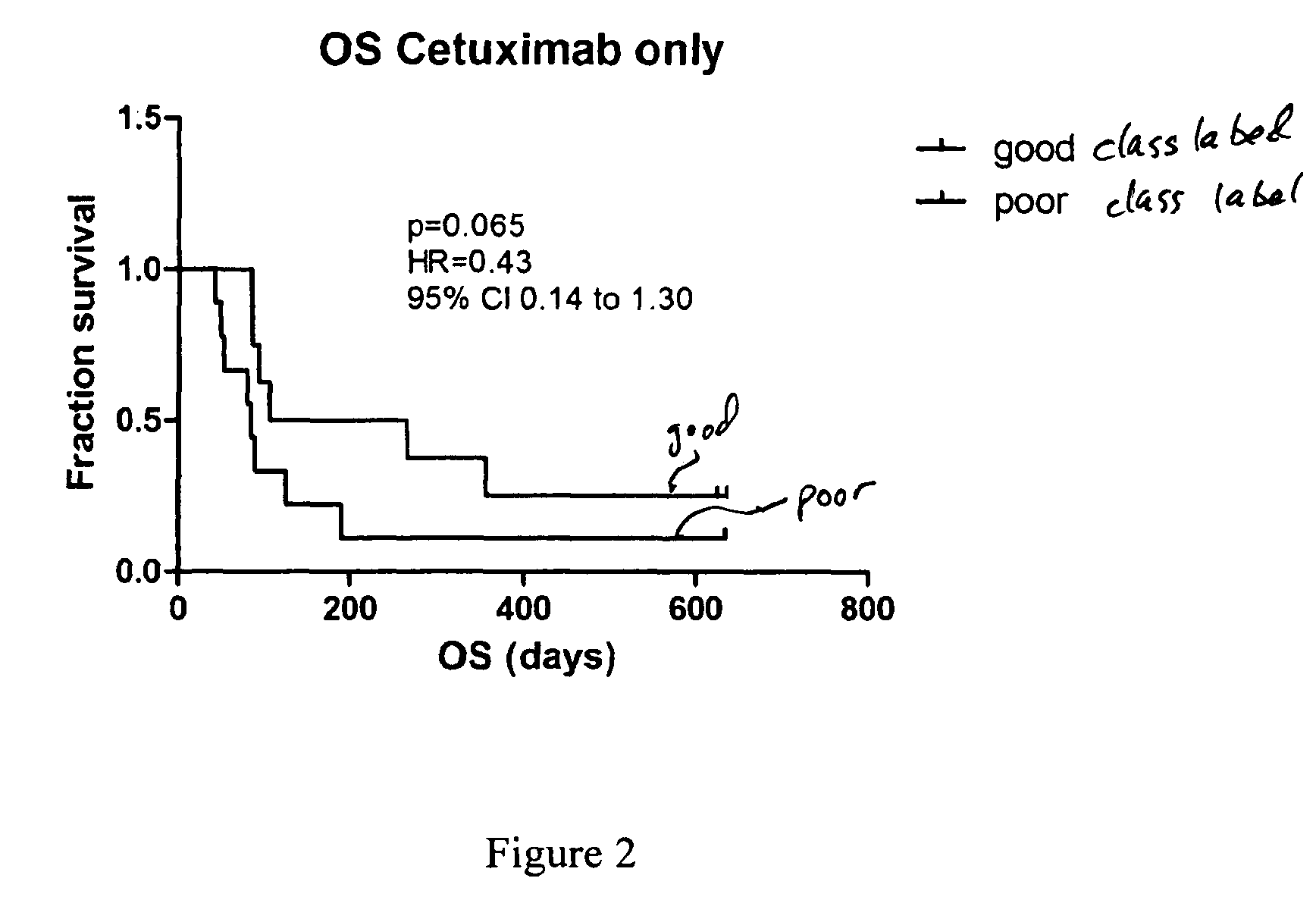
Methods using mass spectral data analysis and a classification algorithm provide an ability to determine whether a non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient is likely to benefit from a monoclonal antibody drug targeting an epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. A mass spectrum is obtained from a sample (e.g. blood sample) from the patient. One or more predefined pre-processing steps are performed on the mass spectrum. Values of selected features in the spectrum at one or more predefined m / z ranges are obtained after the pre-processing steps have been performed. Such values are used in a classification algorithm using a training set comprising class-labeled spectra produced from samples from other patients to identify the patient as being likely to benefit from treatment with the drug.
Owner:BIODESIX
Built-in drug target interaction prediction method based on heterogeneous network
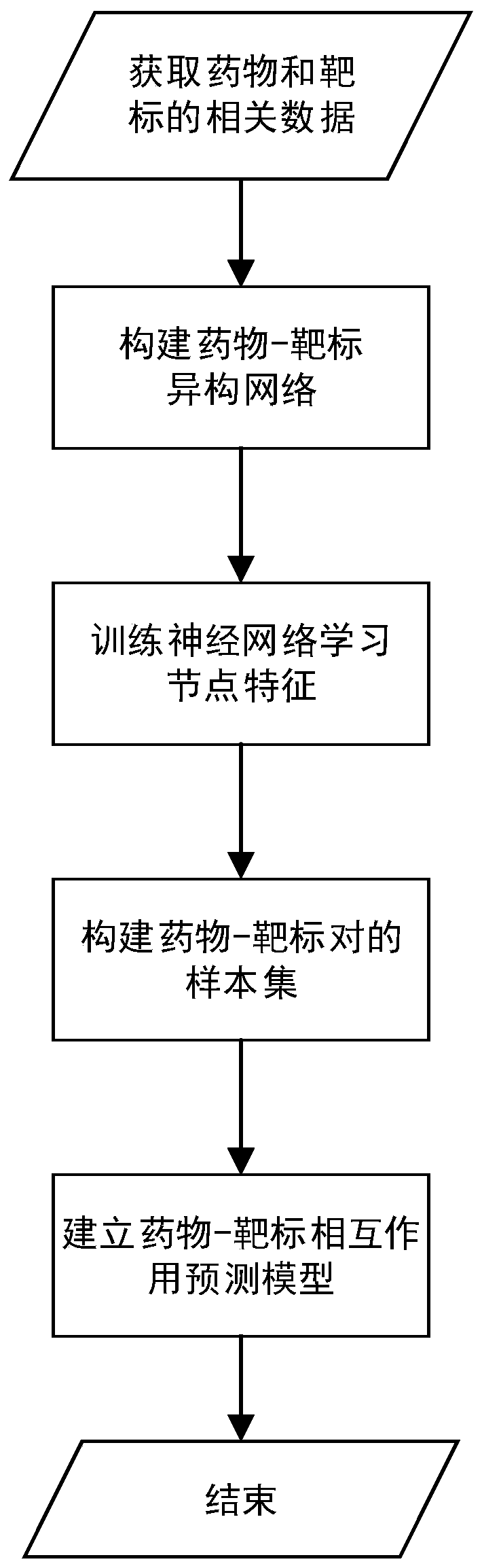
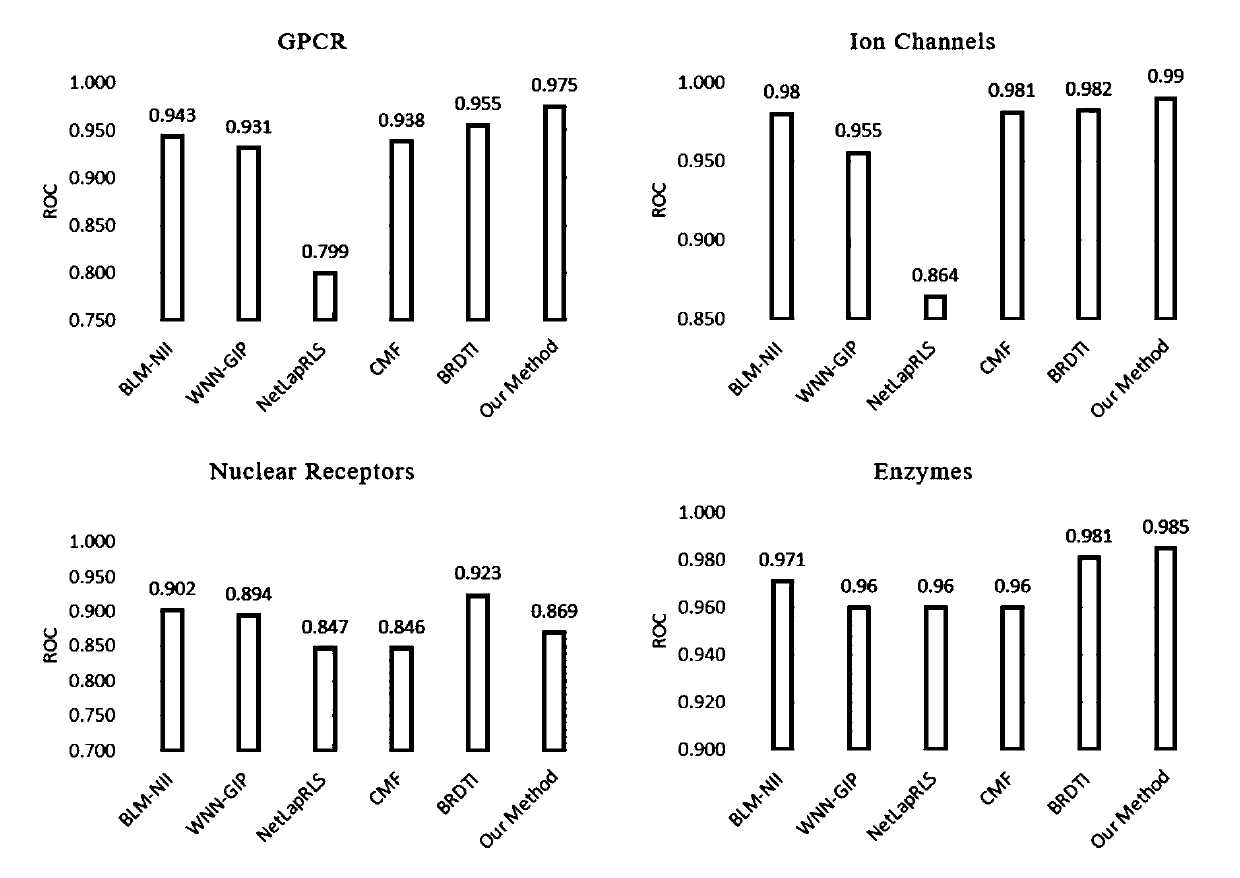
The invention discloses a built-in drug target interaction prediction method based on a heterogeneous network. The built-in drug target interaction prediction method includes the steps: based on the assumption that a chemically similar drug can often interact with a similar target, combining a drug-drug similarity network, a target-target similarity network, and a drug-target interaction network into a drug-target heterogeneous network; using a starting-node-based migrating sequence, constructing a neural network classification model, taking the migrating sequence as input of the neural network classification model, training the classification model and learning to obtain vector representation of all nodes; and for prediction of drug-target interaction, giving a pair of drug-target pairs,extracting vector representation of the corresponding drug and target from the node vectors obtained from learning, performing Hadamard product operation on the two vectors, and taking the obtained result as the input of a random forest classifier to obtain the final prediction result. According to the experimental verification, the built-in drug target interaction prediction method based on a heterogeneous network has preferable prediction effect and applicability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for screening drug target genes based on CRISPR/Cas9 high-throughput technology
InactiveCN106399377ADetermining infection efficiencyDetermine the MOI valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a method for screening drug target genes based on a CRISPR / Cas9 high-throughput technology. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a sgRNA library; secondly packaging the sgRNA library by using slow viruses, and collecting the viruses; thirdly screening the sgRNA library in a cancer cell line; fourthly extracting cells obtained by screening and genome DNA of the cells before screening; and finally enriching sgRNA in genome DNA. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that a CRISPR / Cas cell screening process is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined with a simple and convenient method by utilizing puromycin resistance of infected cells, and MOI values of the viruses are determined; more importantly, a virus packaging method is greatly optimized, so that the virus packaging efficiency is improved to be more than 5 times that of a conventional method, and large-scale drug target screening cost can be greatly reduced; and the method is used for promoting industrialization of cancer drug target screening.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Drug repositioning method based on multi-information fusion and random walk model
ActiveCN107506591AEfficient miningTake advantage ofMolecular designSpecial data processing applicationsData setHeterogeneous network
The invention discloses a drug repositioning method based on multi-information fusion and a random walk model. According to the method, disease-target-drug heterogeneous network is constructed through integrating existing disease data, drug data, target data, disease-drug associated data, disease-gene associated data and drug-target associated data; the basic random walk model is extended to the constructed heterogeneous network; and candidate therapeutic drugs are recommended for diseases through effectively utilizing global network information. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and effective; and compared with other methods and proved by tests on a standard data set, the method has good prediction performance in the aspect of drug repositioning.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Small molecule inhibitors of hiv-1 capsid assembly
InactiveUS20090176776A1Inhibit HIV replicationInhibition formationBiocideOrganic chemistryDrug targetChemical library
The present invention provides novel methods of treating HIV infections employing small molecule inhibitors identified by chemical library (DIVERSet™ library). These small molecule inhibitors may specifically bind to HIV-1 capsid protein thereby interfering with capsid assembly. The small molecule inhibitors of the present invention can be potential drug targets in the treatment of HIV infection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
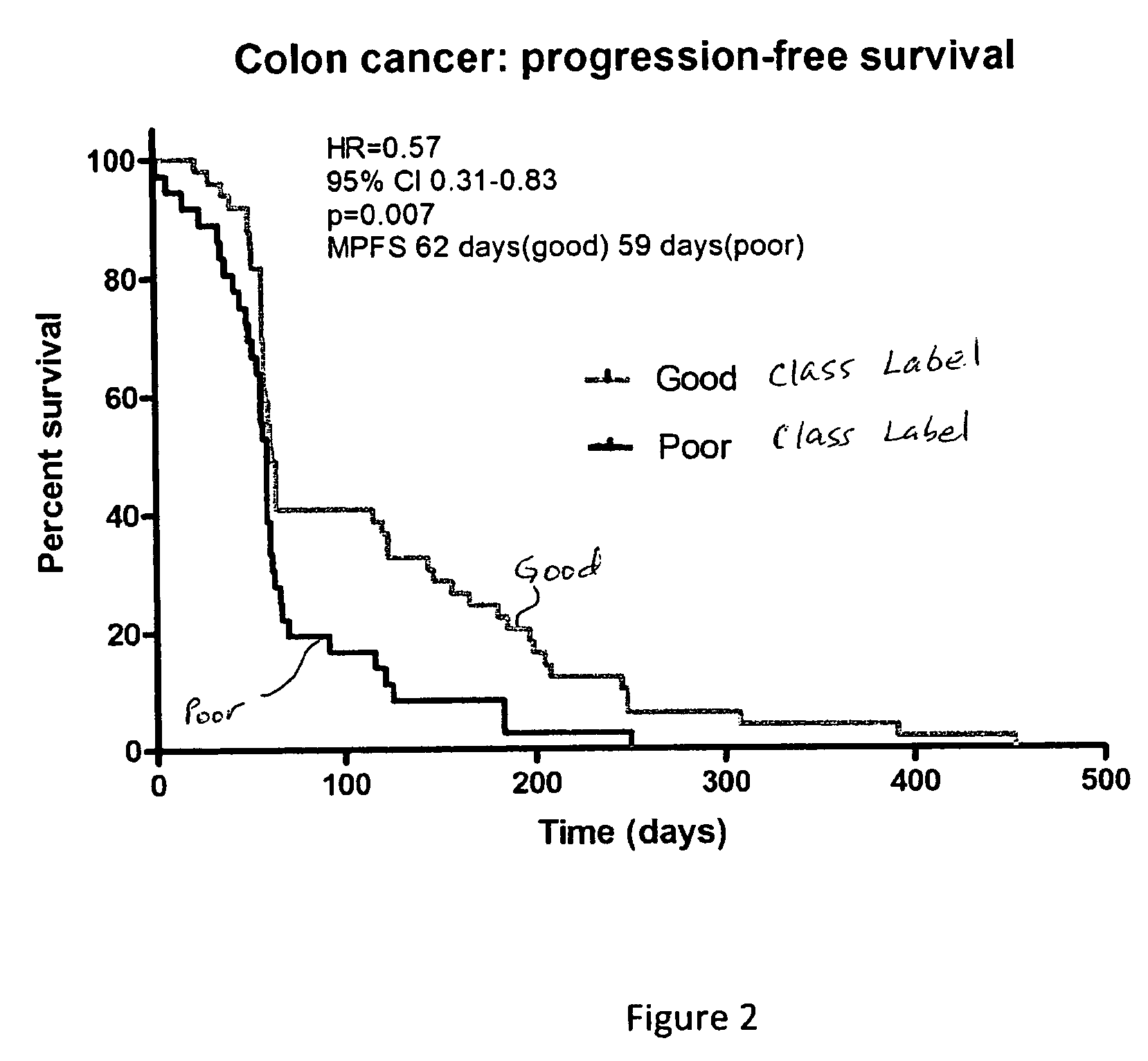
Selection of colorectal cancer patients for treatment with drugs targeting EGFR pathway
Owner:BIODESIX
Drug targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders
InactiveUS20060084071A1Increased toxicityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
Methods of screening candidate agents to identify potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of a neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease and methods for identifying a mutation in, or changes in expression of, a gene associated with neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease, are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Screening for ligand binding at specific target sites
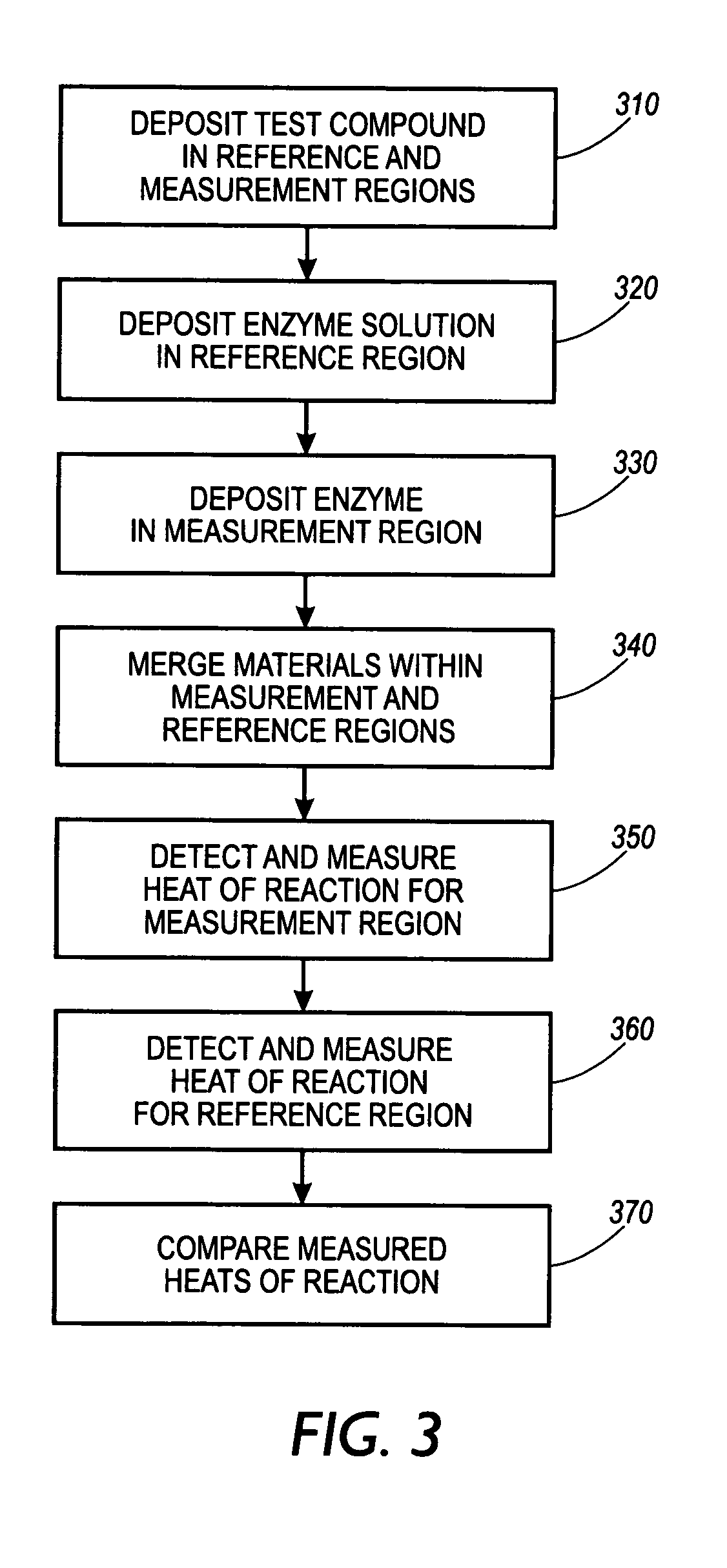
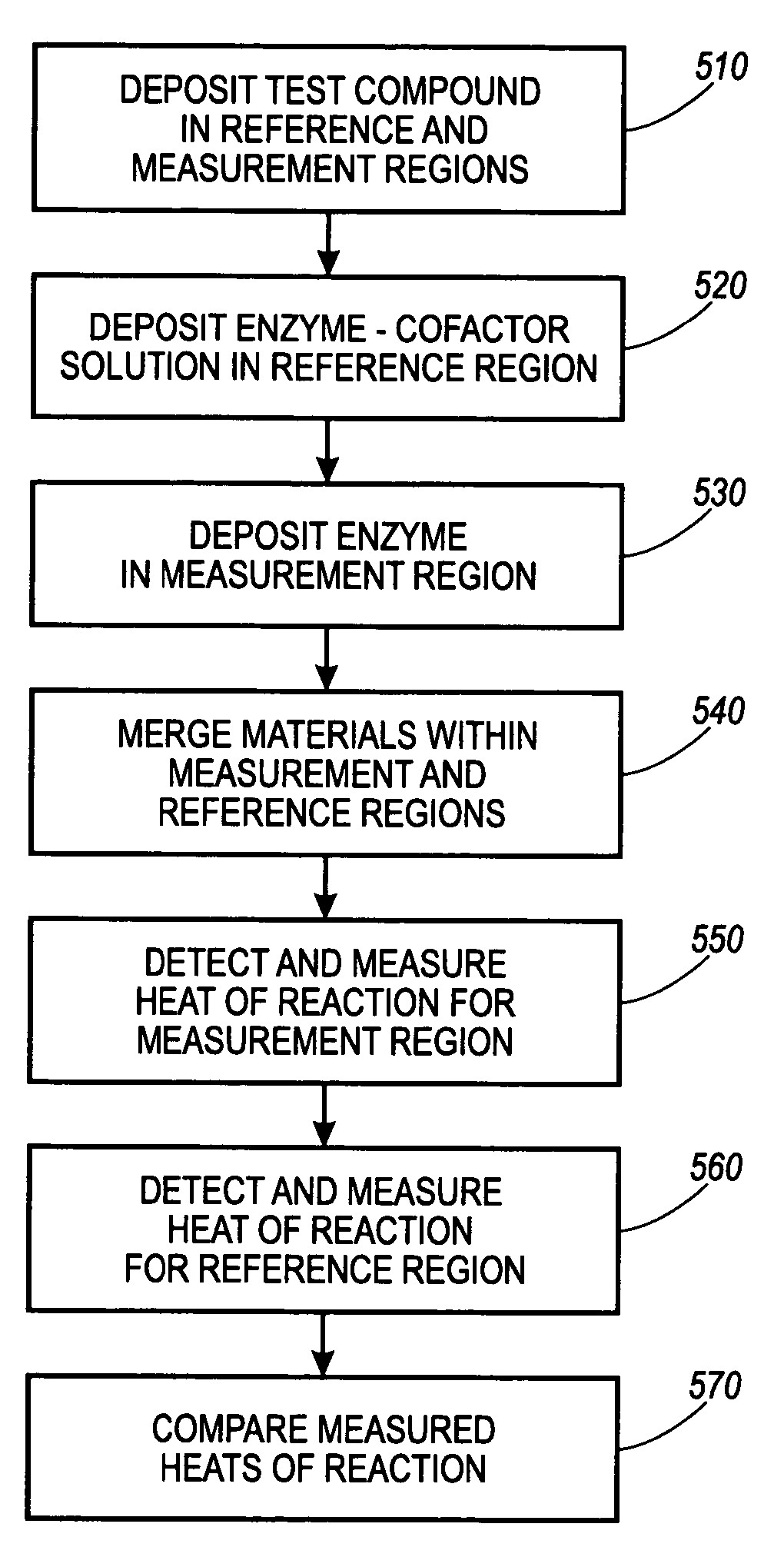
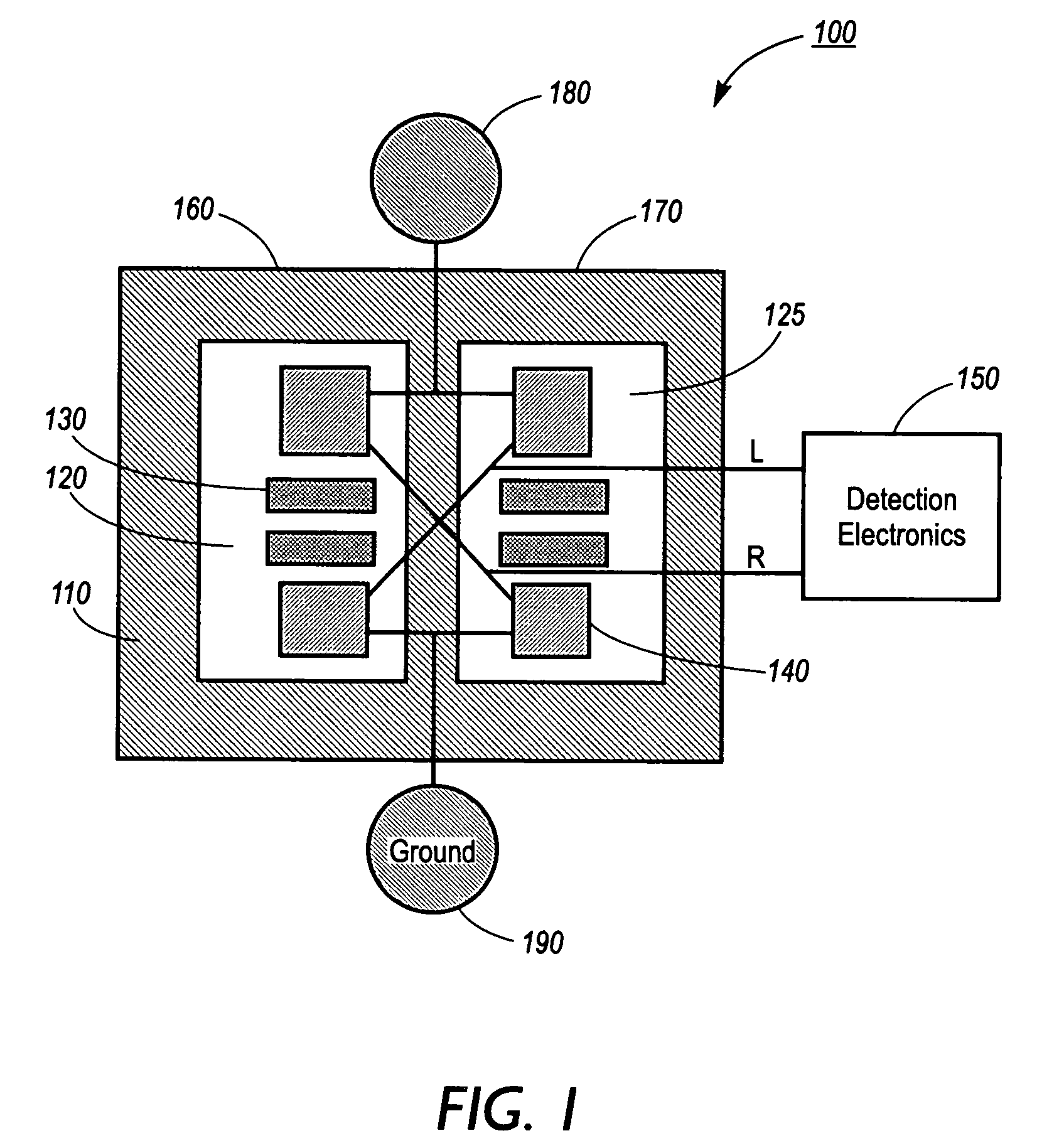
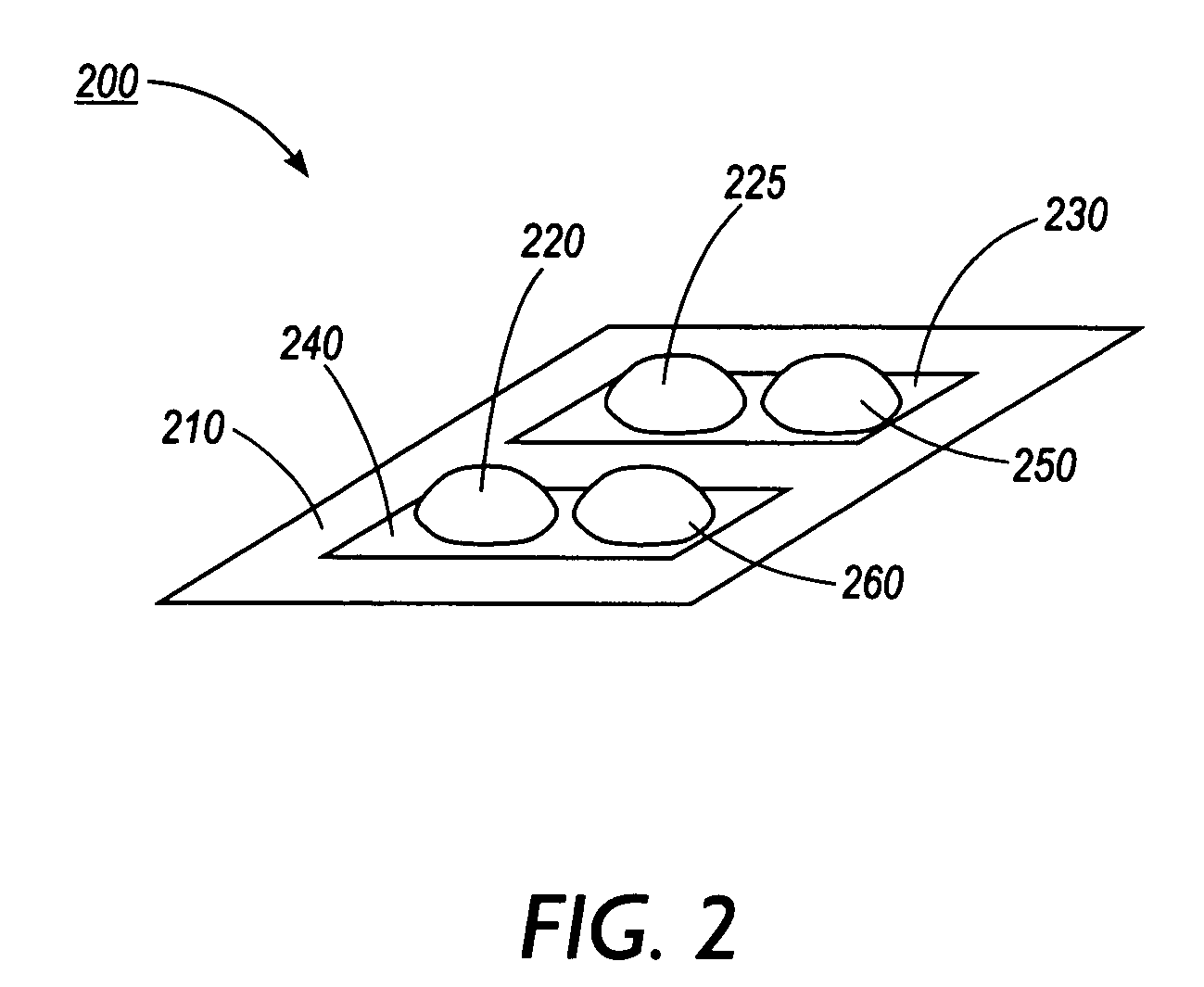
ActiveUS20050112710A1Material heat developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteDrug target
A method for screening of compounds for binding differentiation at various drug target binding sites is used with a device measuring the enthalpy of reaction for the binding. The method includes merging test ligand with target compound and merging test ligand with target compound in the presence of at least one blocking agent. A first heat of reaction is detected for the merged test ligand and target compound solution and a second heat of reaction is detected for the merged test ligand and target compound solution in the presence of a blocking agent. The two heats of reaction are compared to determine whether a reaction has occurred.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Screening for ligand binding at specific target sites
ActiveUS7419835B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial heat developmentBinding siteDrug target
A method for screening of compounds for binding differentiation at various drug target binding sites is used with a device measuring the enthalpy of reaction for the binding. The method includes merging test ligand with target compound and merging test ligand with target compound in the presence of at least one blocking agent. A first heat of reaction is detected for the merged test ligand and target compound solution and a second heat of reaction is detected for the merged test ligand and target compound solution in the presence of a blocking agent. The two heats of reaction are compared to determine whether a reaction has occurred.
Owner:XEROX CORP
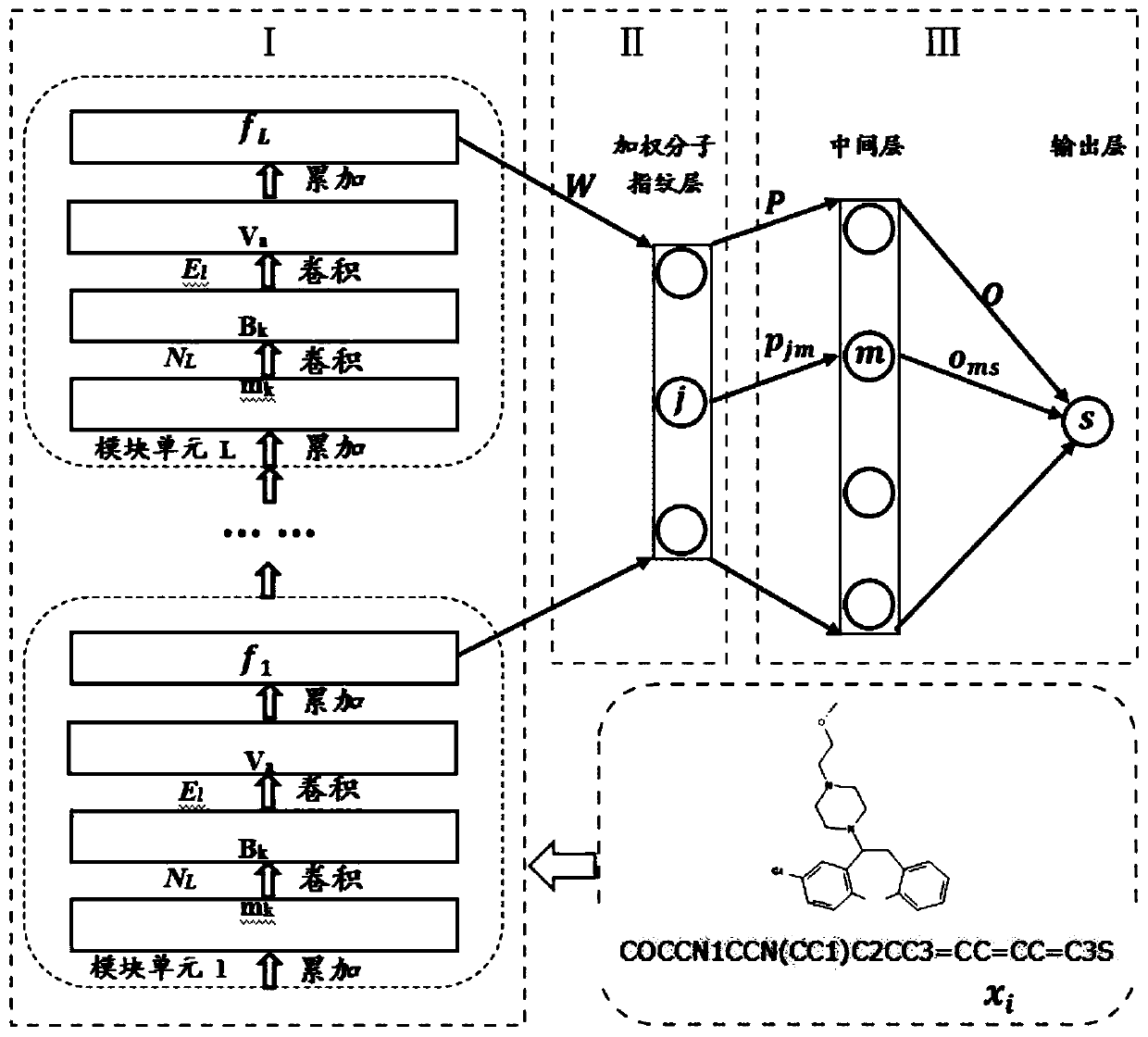
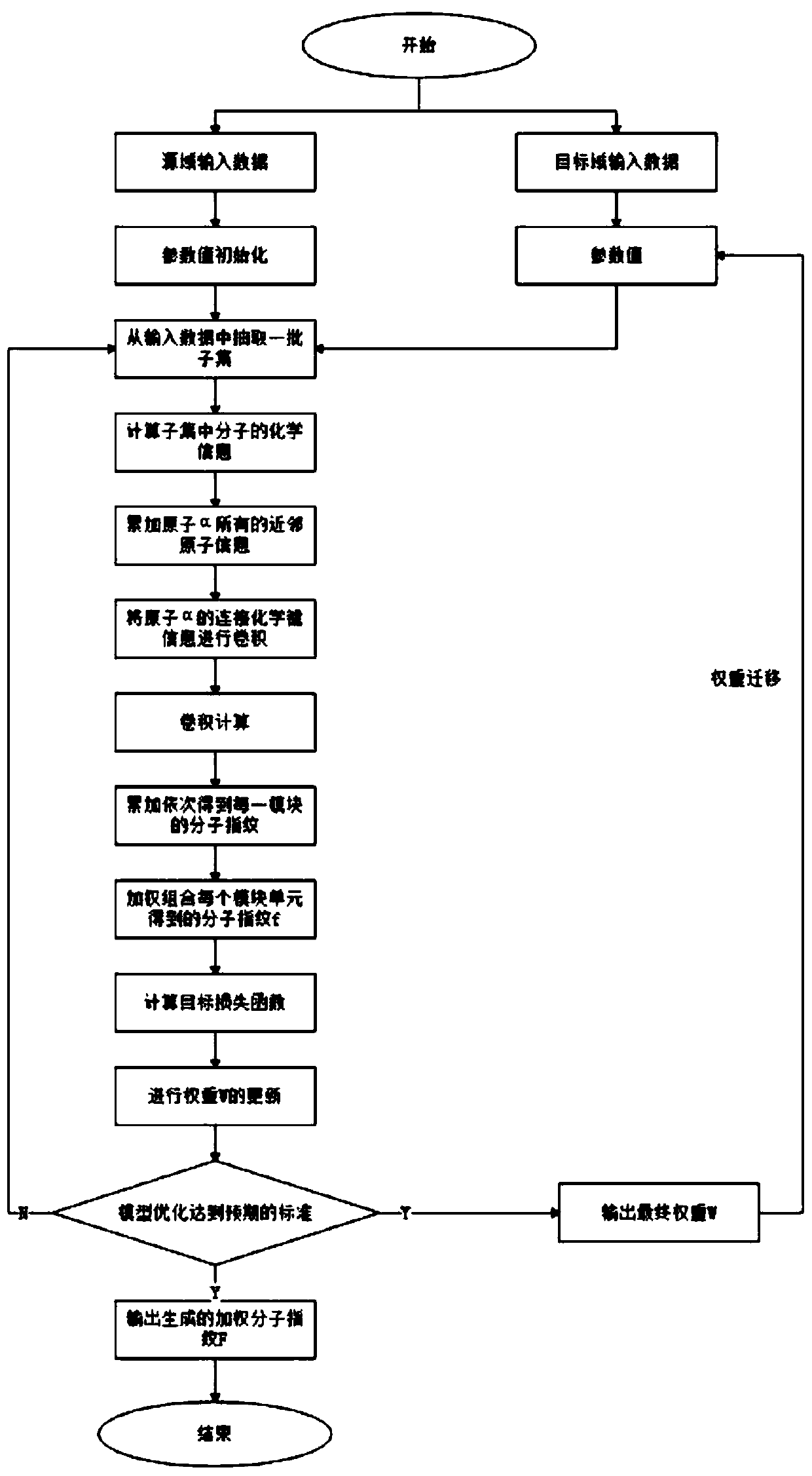
Small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof
ActiveCN110459274AImplement the buildMolecular designChemical machine learningDrug targetDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a small molecule drug virtual screening method based on deep migration learning and application thereof. A source domain is used as an input to be trained, converged and derived to obtain a weight matrix; a target domain is input into an improvement tool to serve as the initialization weight of the target domain; fine adjustment, training and convergence are conducted on the initialization weight and data in the target domain sequentially; a biological activity value of interaction of a lead compound and a drug target in the target domain is predicted, a target domain molecular fingerprint and a predicted value are obtained, and an evaluation index root mean square error and a correlation coefficient of a predicted result are output; the target domain is subjected to fine adjustment by repeating above steps, and the weight matrix of the source domain helps the target domain build a model. According to the small molecule drug virtual screening method and the application thereof, the effective virtual screening model can still be obtained under the condition that the information of a known active ligand sample is insufficient, and does not need to rely on a large number of data samples.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Novel purified FabI polypeptides from fransicella tularensis
The present invention relates to novel drug targets for pathogenic bacteria. Accordingly, the invention provides purified protein comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also provides biochemical and biophysical characteristics of the polypeptides of the invention.
Owner:DEBIOPHARM INTERNATIONAL SA
Methods and systems for identifying ligand-protein binding sites
ActiveCN107111691AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBinding siteComputerized system
The invention provides a novel integrated structure and system-based approach for drug target prediction that enables the large-scale discovery of new targets for existing drugs Novel computer-readable storage media and computer systems are also provided. Methods and systems of the invention use novel sequence order-independent structure alignment, hierarchical clustering, and probabilistic sequence similarity techniques to construct a probabilistic pocket ensemble (PPE) that captures even promiscuous structural features of different binding sites for a drug on known targets. The drug's PPE is combined with an approximation of the drug delivery profile to facilitate large-scale prediction of novel drug- protein interactions with several applications to biological research and drug development.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ductus side-entry jackets and prosthetic disorder response systems
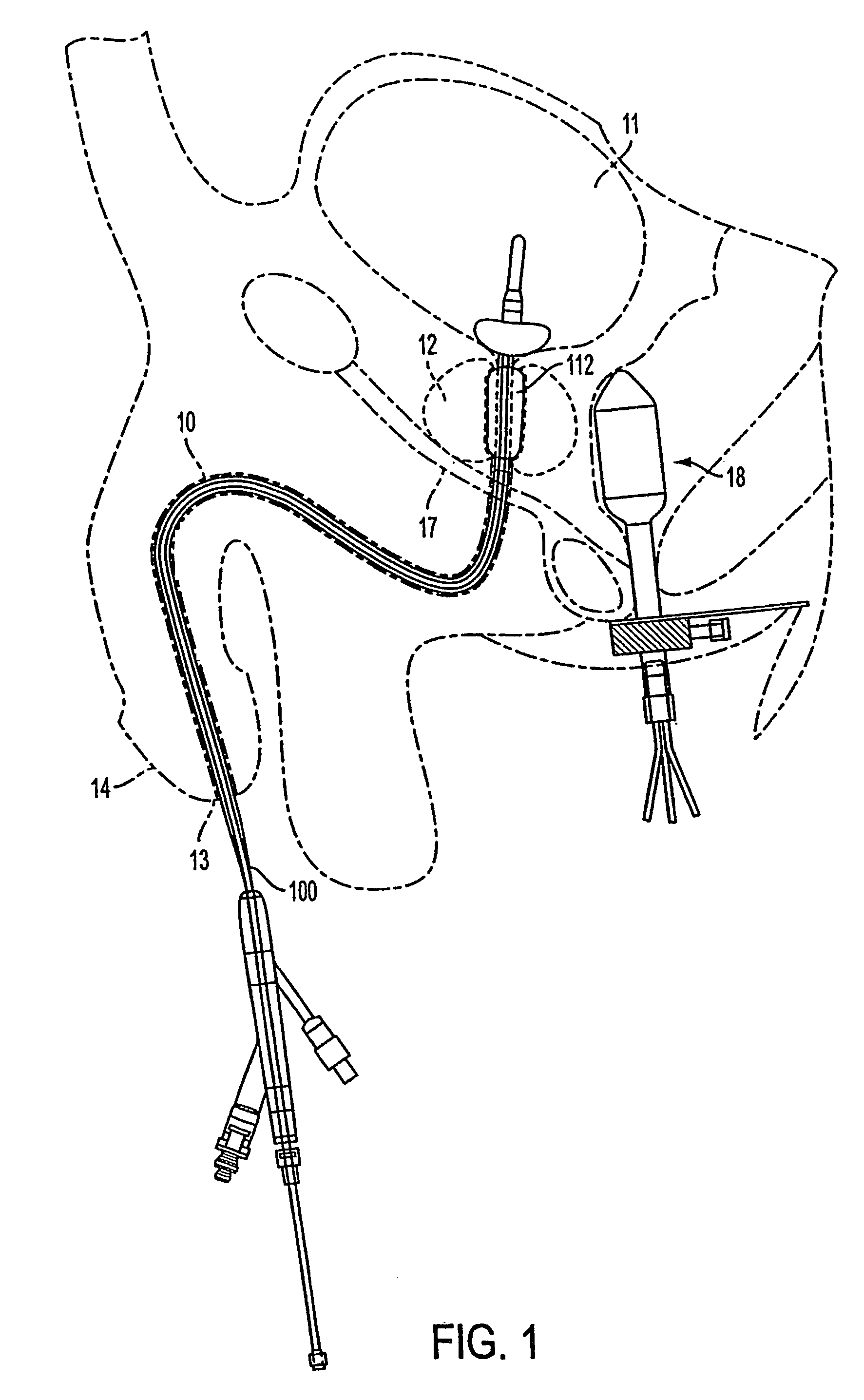
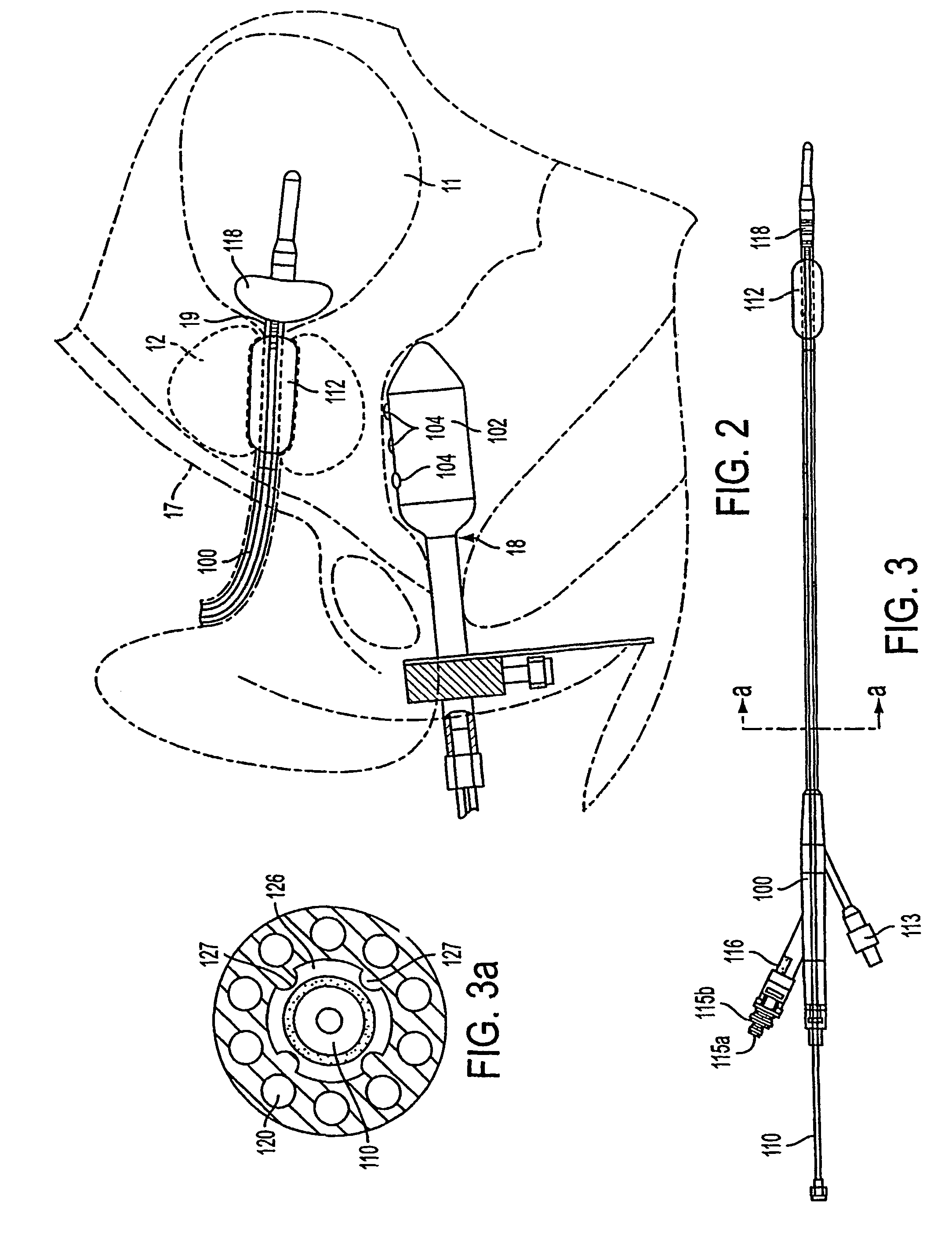
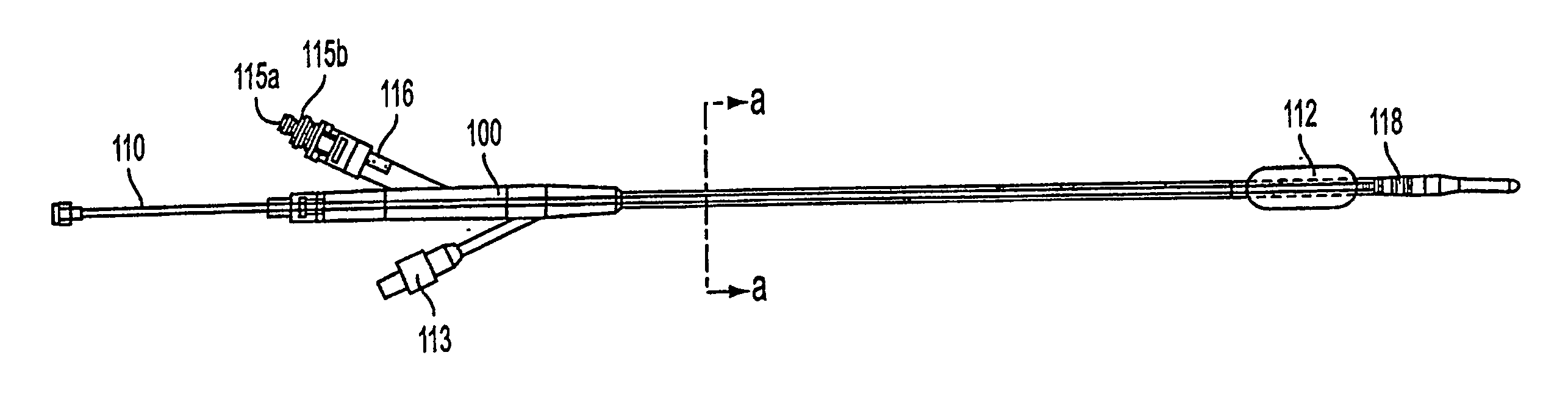
Provided are means for the direct and continuous connection of a catheter to the lumen of any tubular anatomical structure, or ductus, without medically significant leakage. A port implanted at the body surface with piping to a periductal collar allows drug or radionuclide delivery that bypasses the upstream lumen. The port allows injection, infusion, or attachment of an automatic ambulatory pump. A superparamagnetic nanoparticle carrier-bound drug, for example, can be introduced into the lumen to pass downstream until the carrier particles, with or without the drug still bound, are drawn into the lumen wall by a magnetized jacket surrounding the ductus. Such constitutes a method of drug targeting whereby a segment of a vessel or the territory supplied by a branch of that segment can be circumscribed for exposure to the drug. A jacket with side-entry connector positioned in surrounding relation to a lesion requiring treatment can itself be magnetized.
Owner:GOLDSMITH DAVID S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com