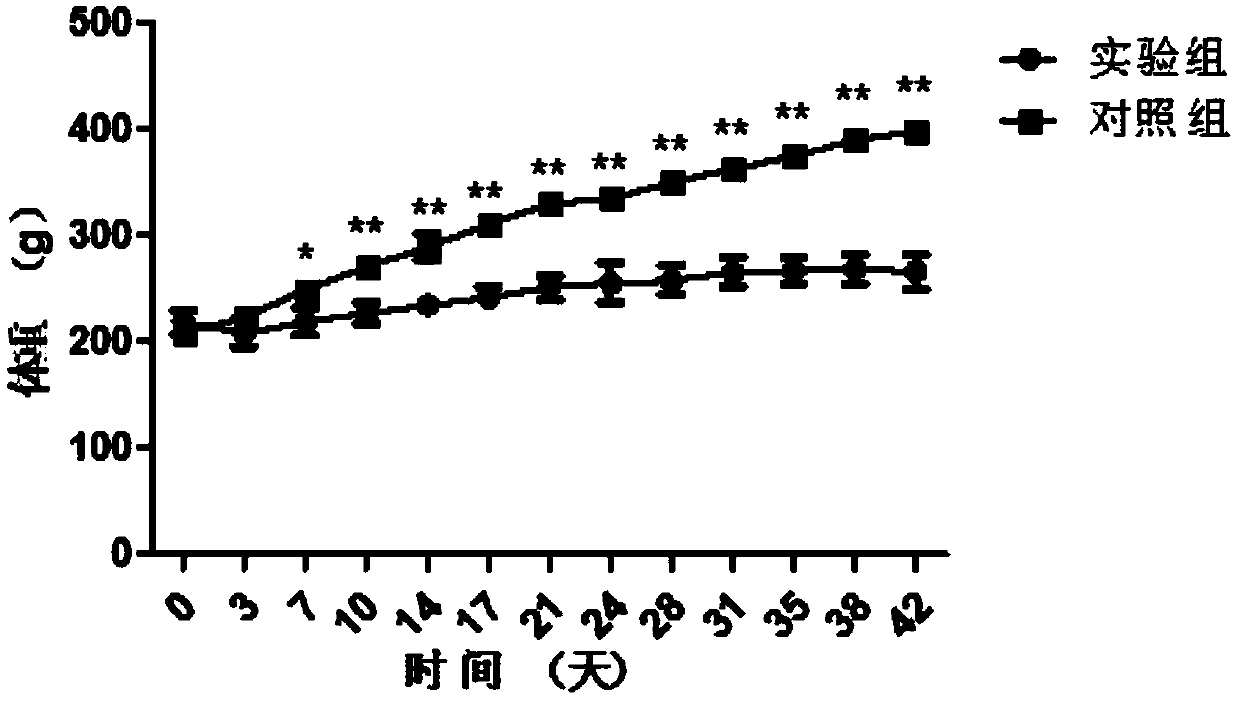
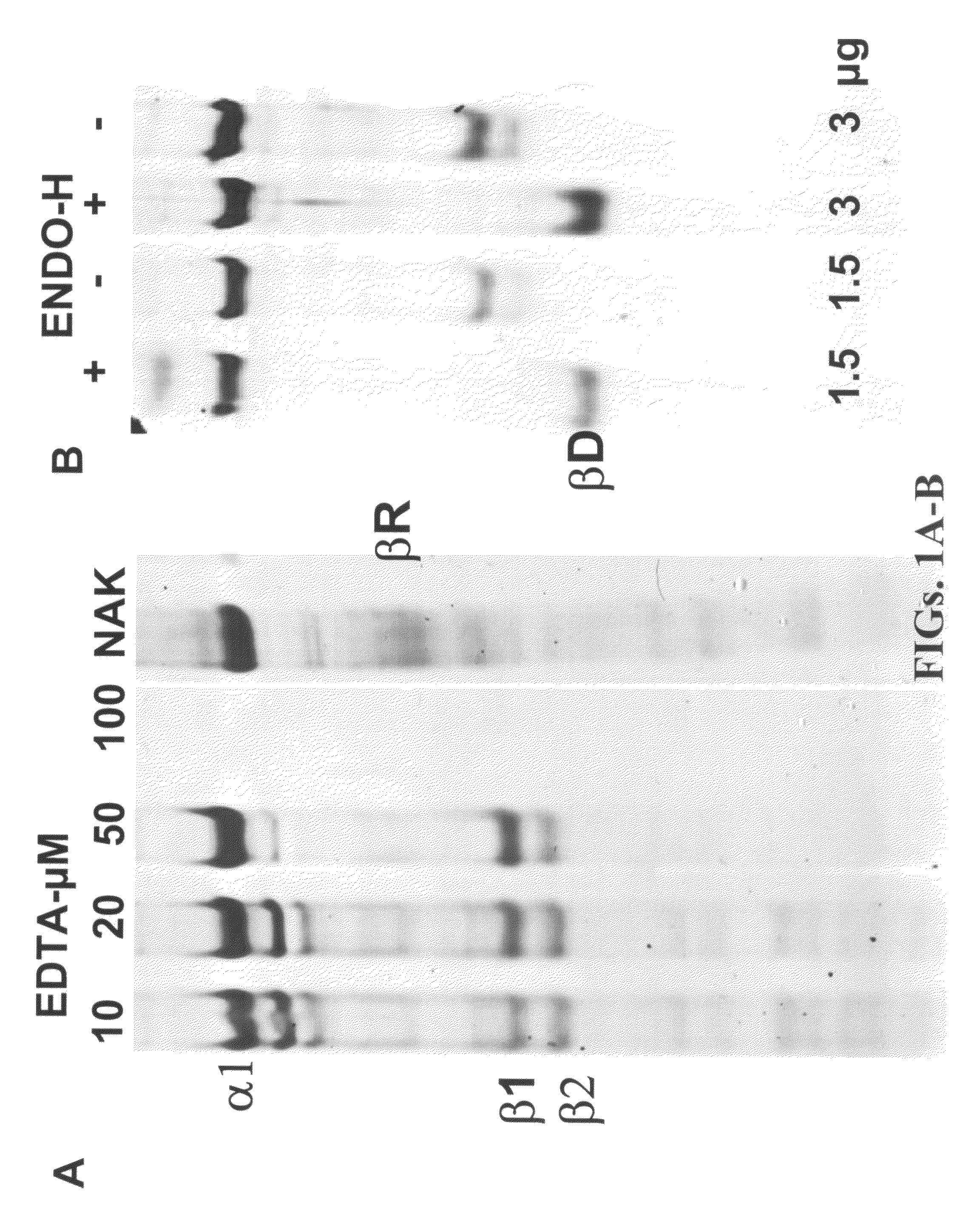
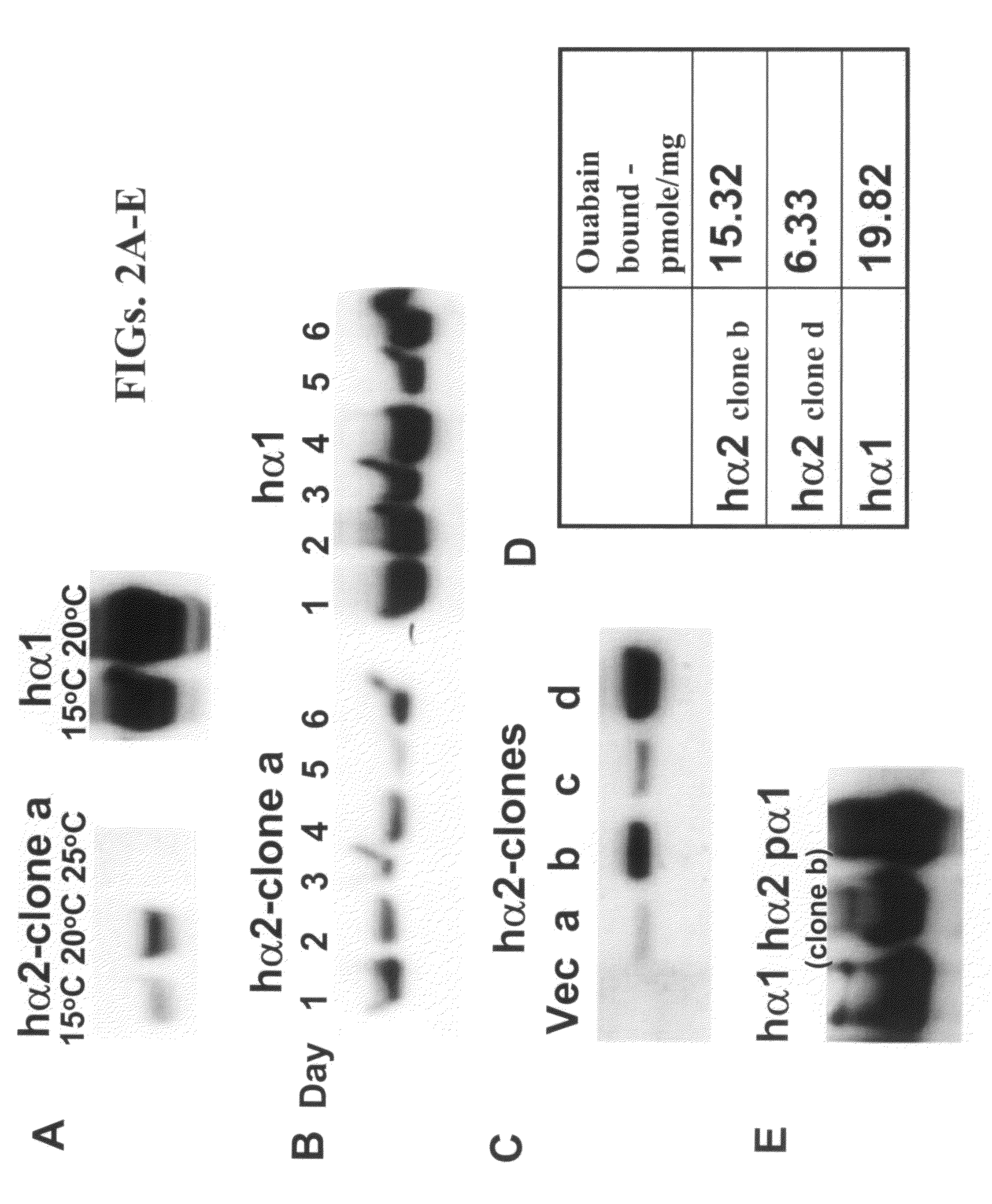
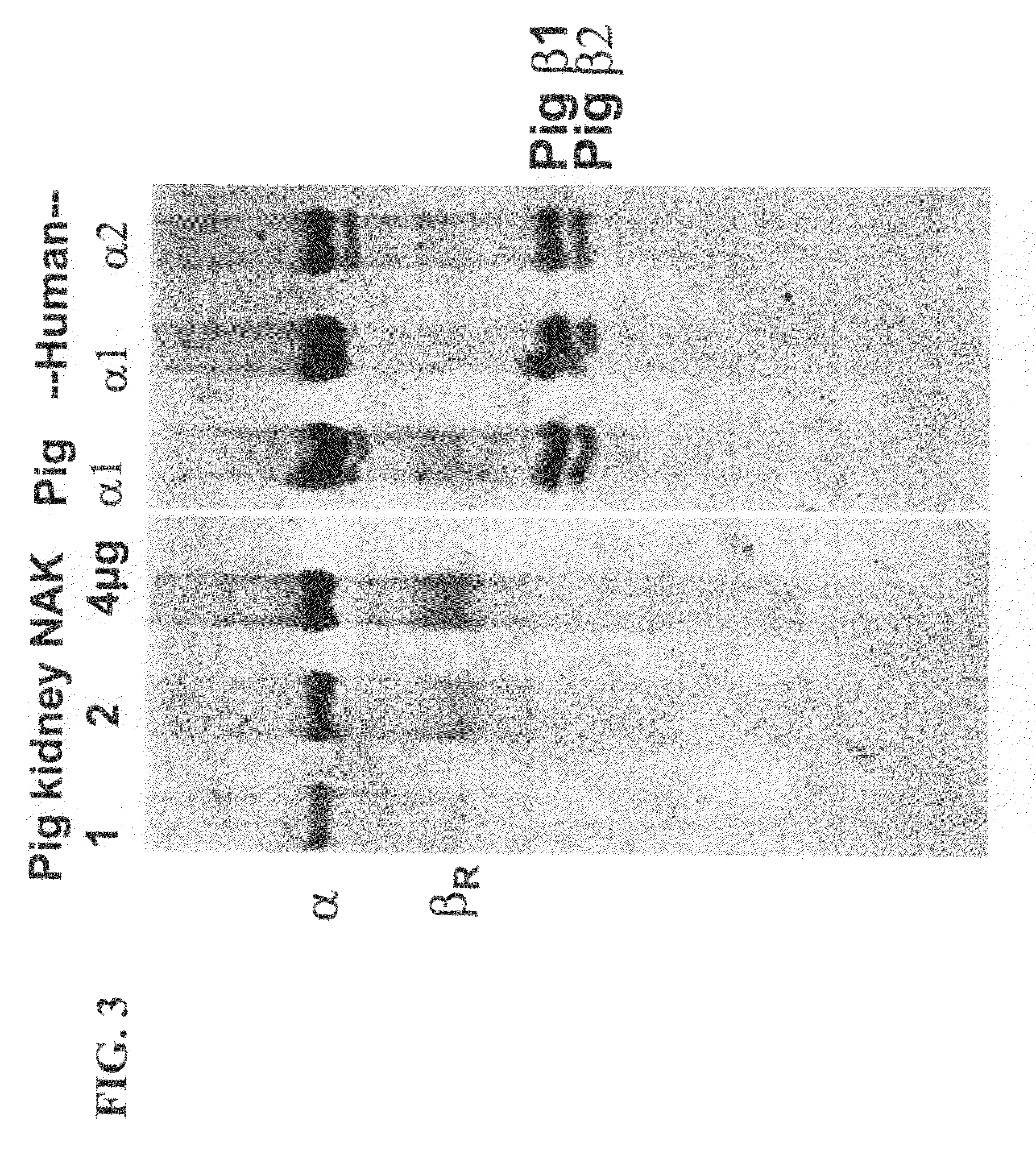
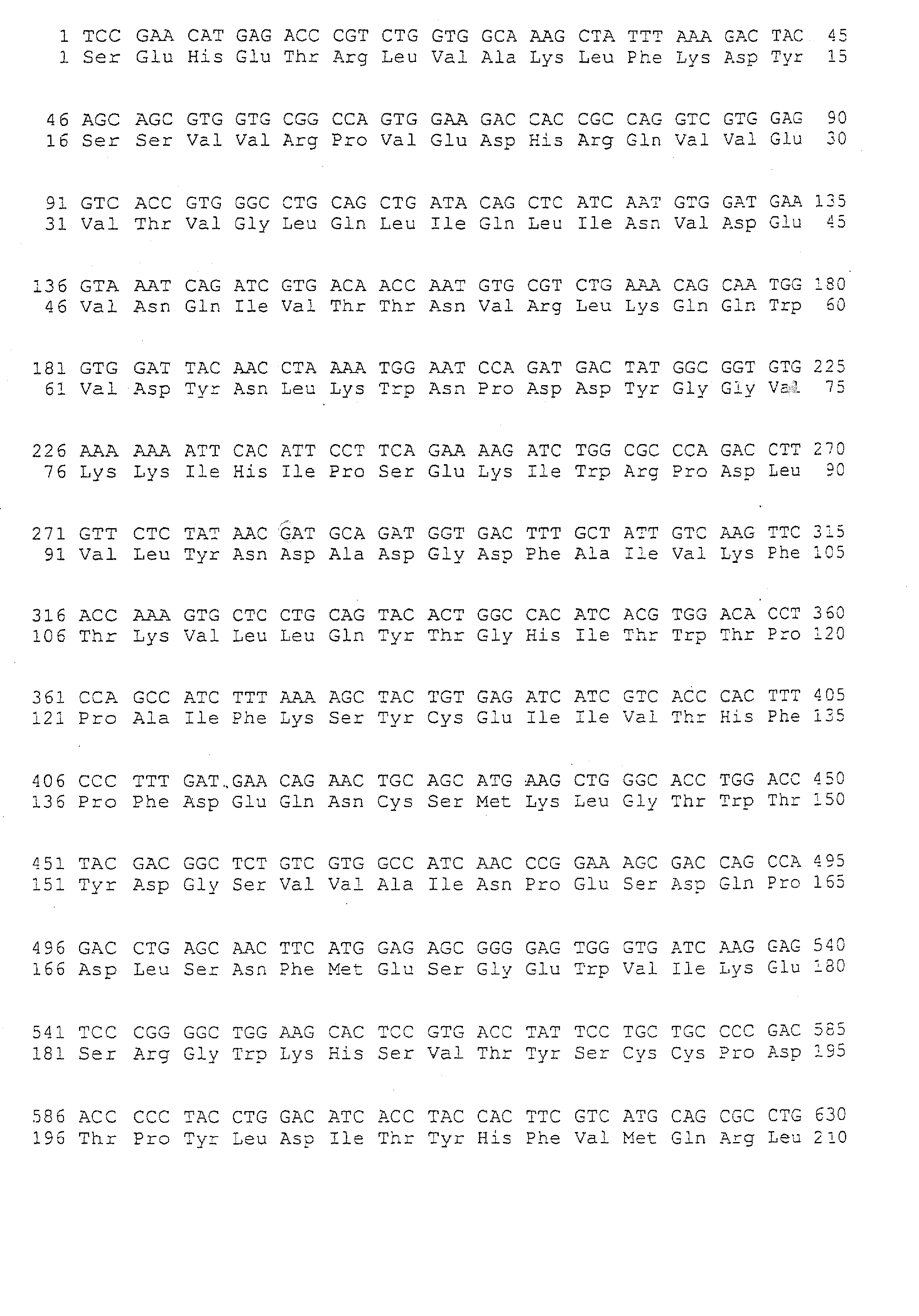
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101 results about "Β subunit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
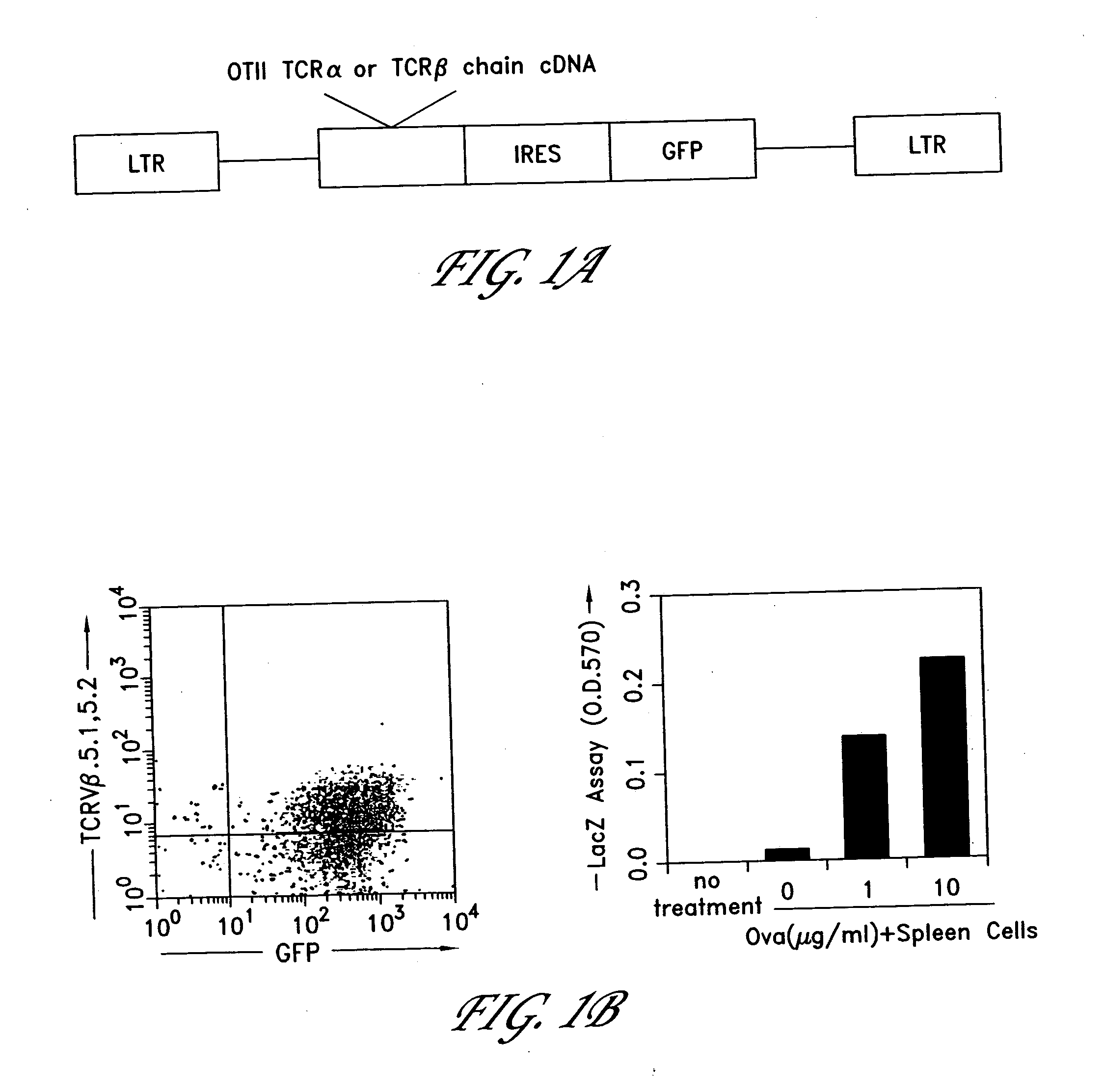
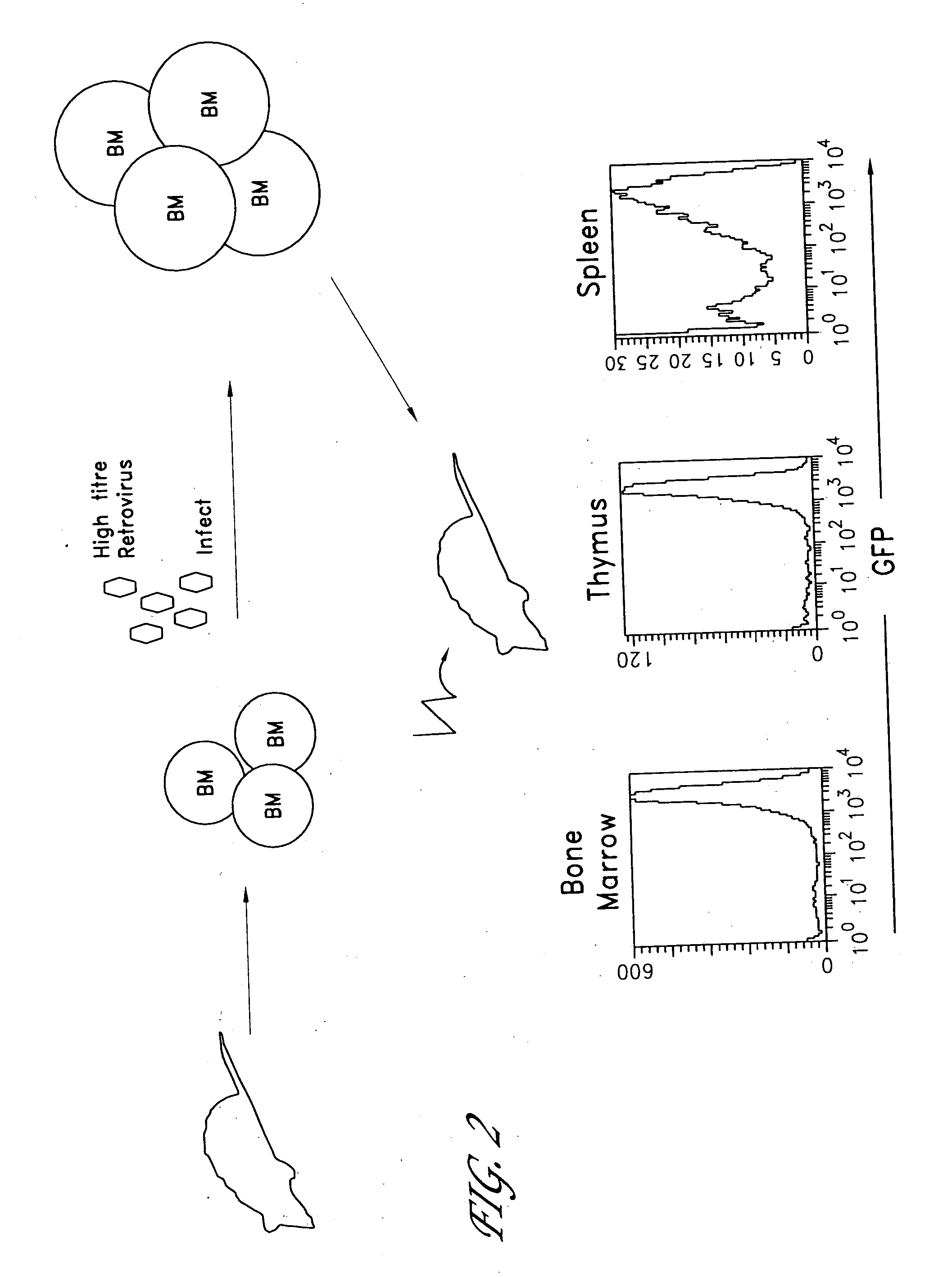
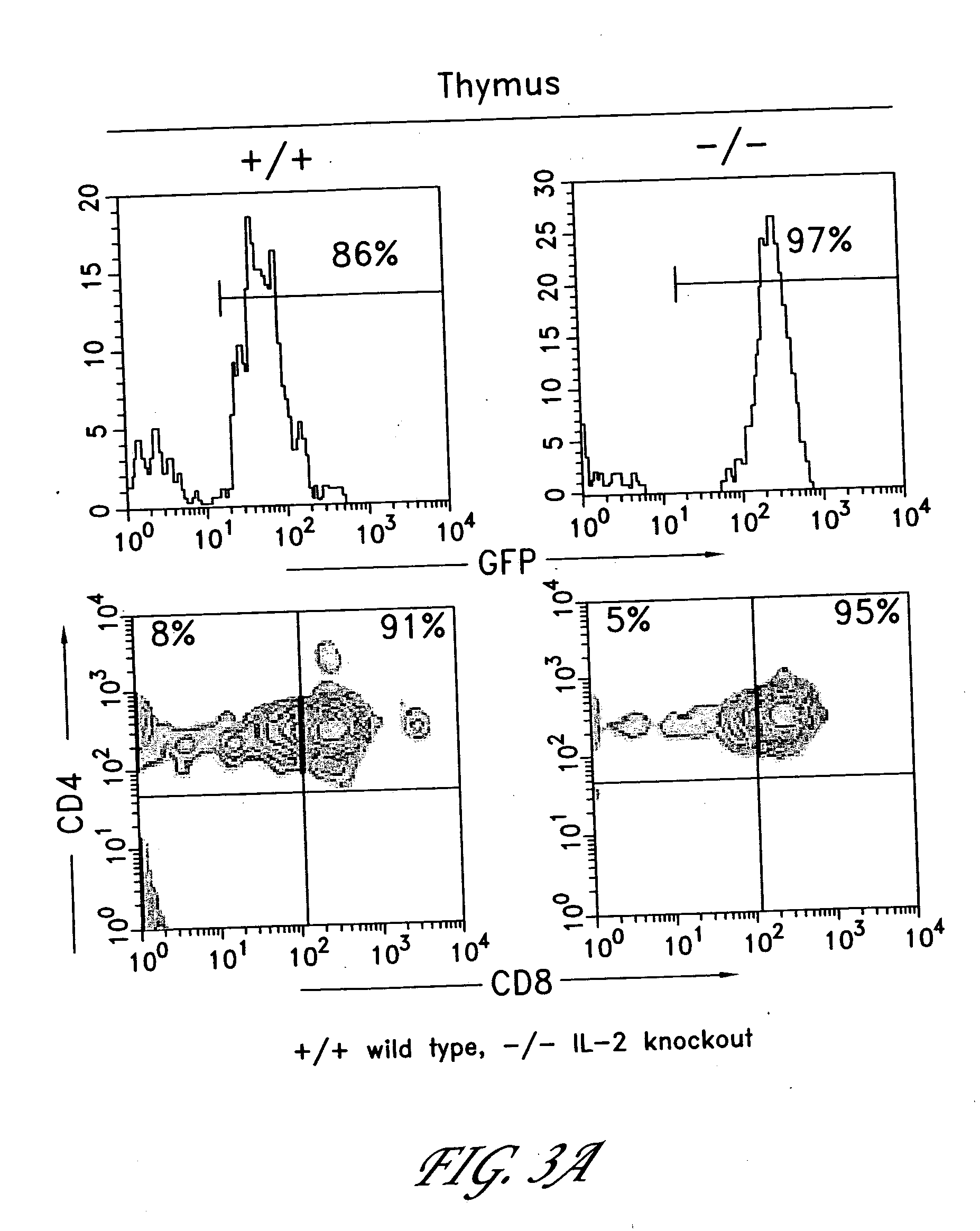
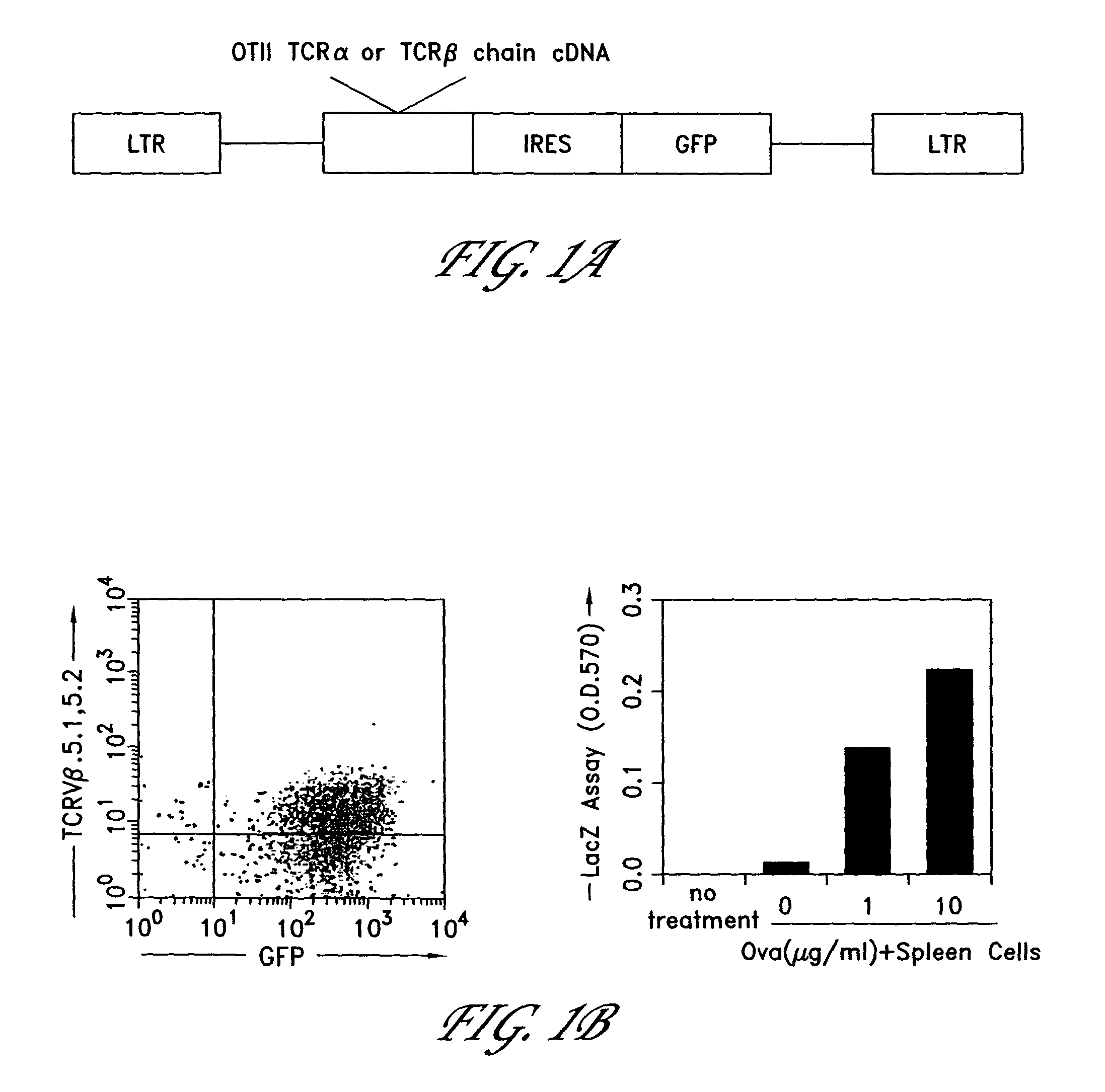
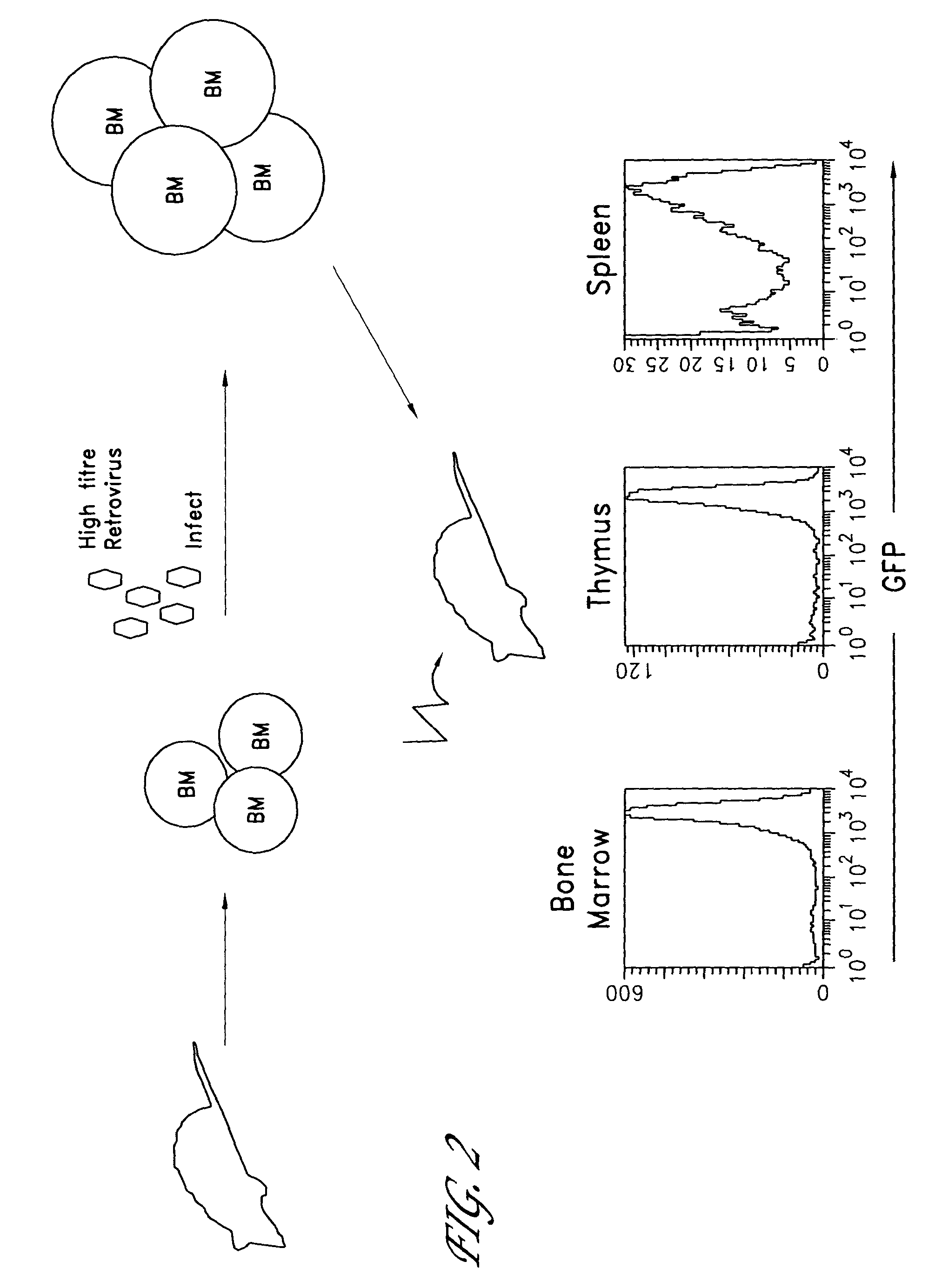
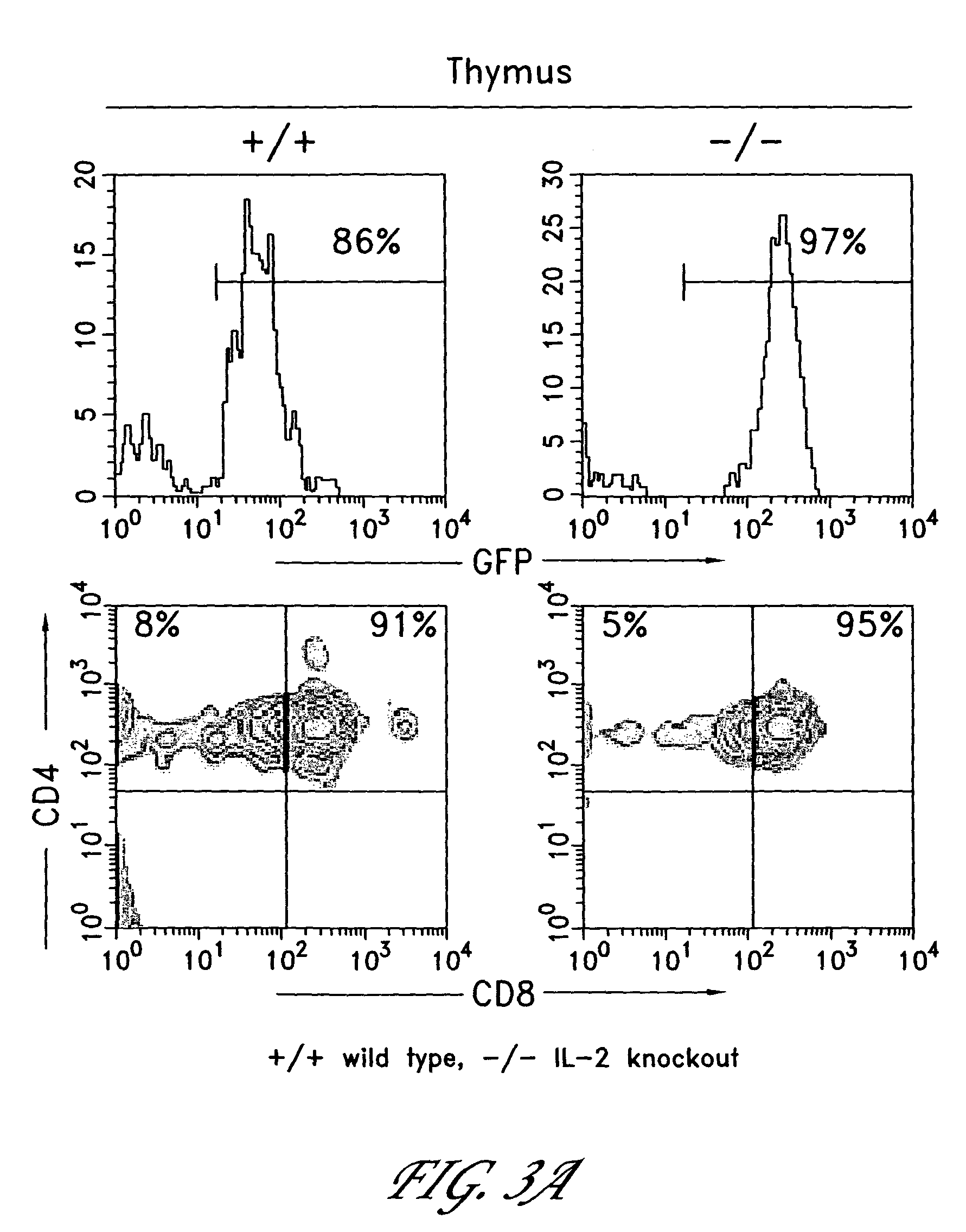
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS20070116690A1Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
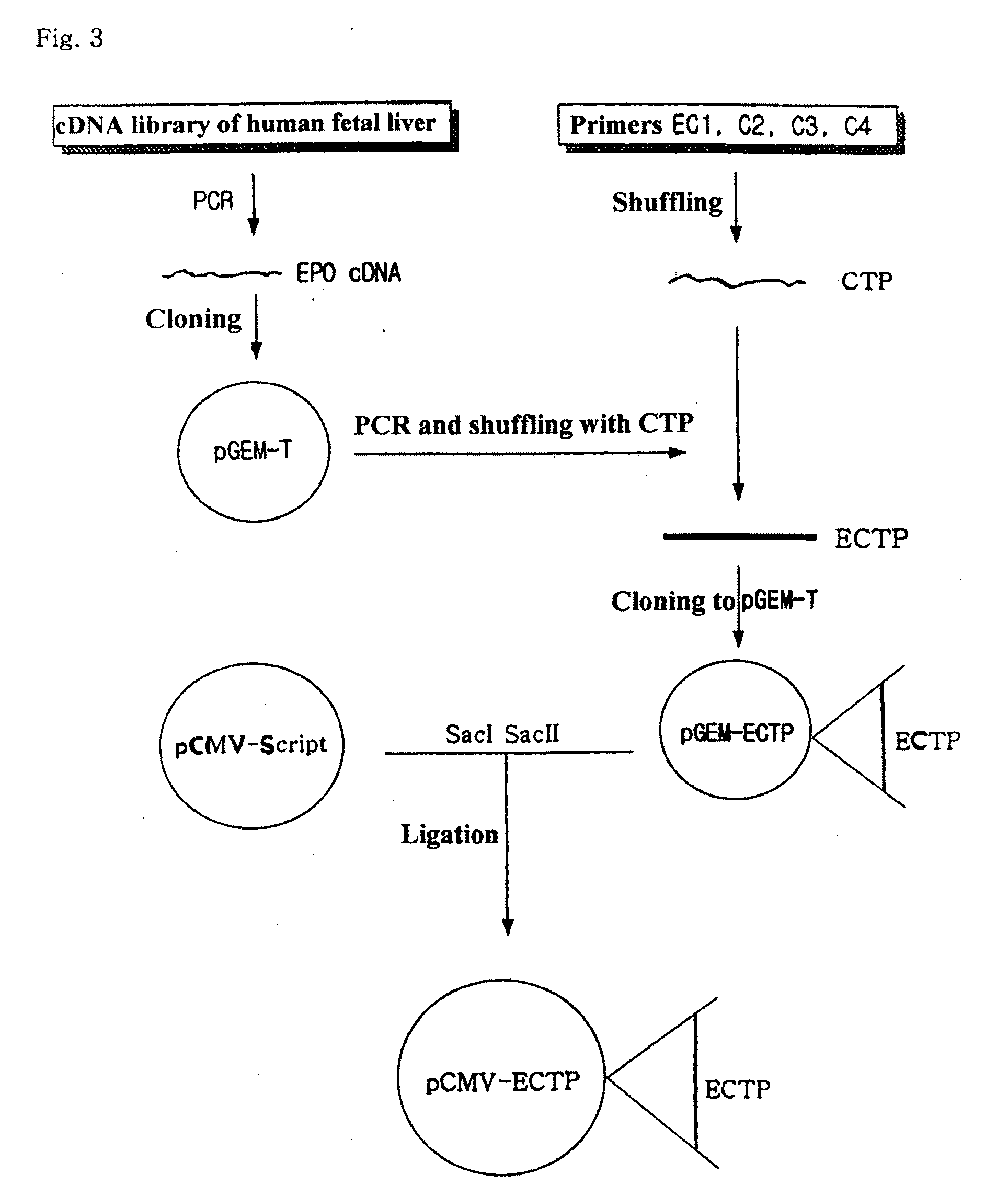
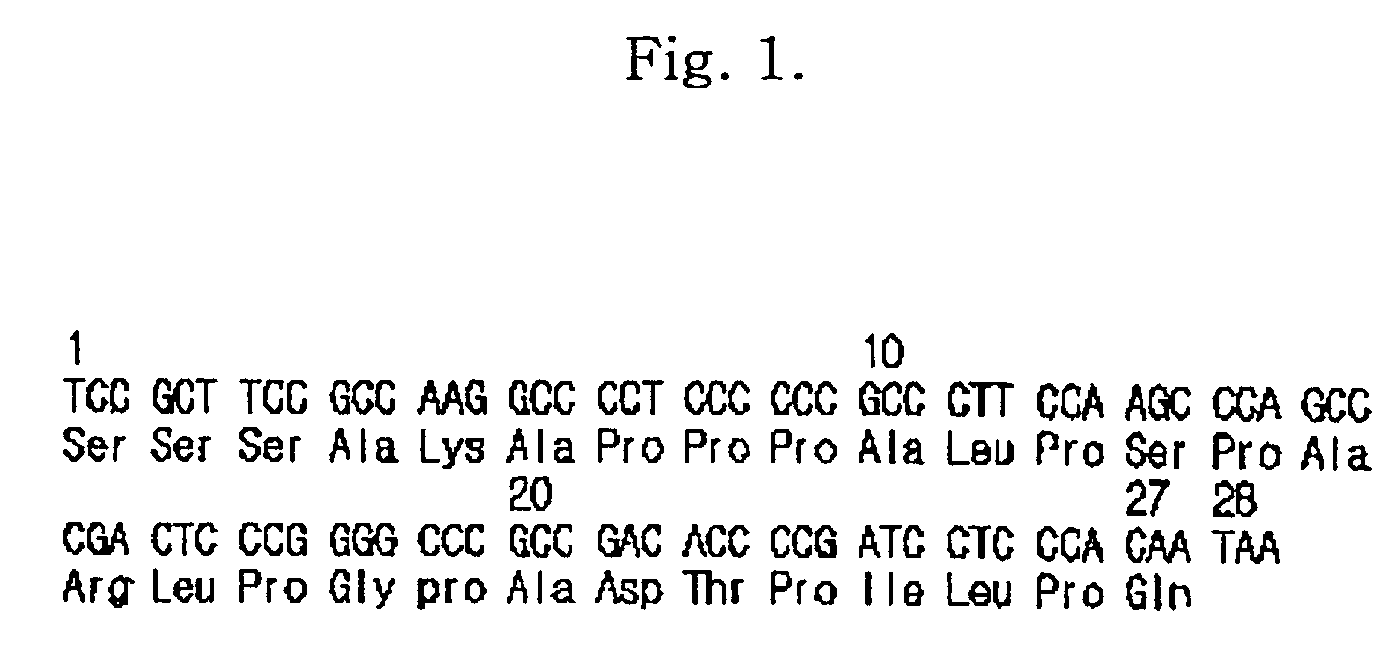
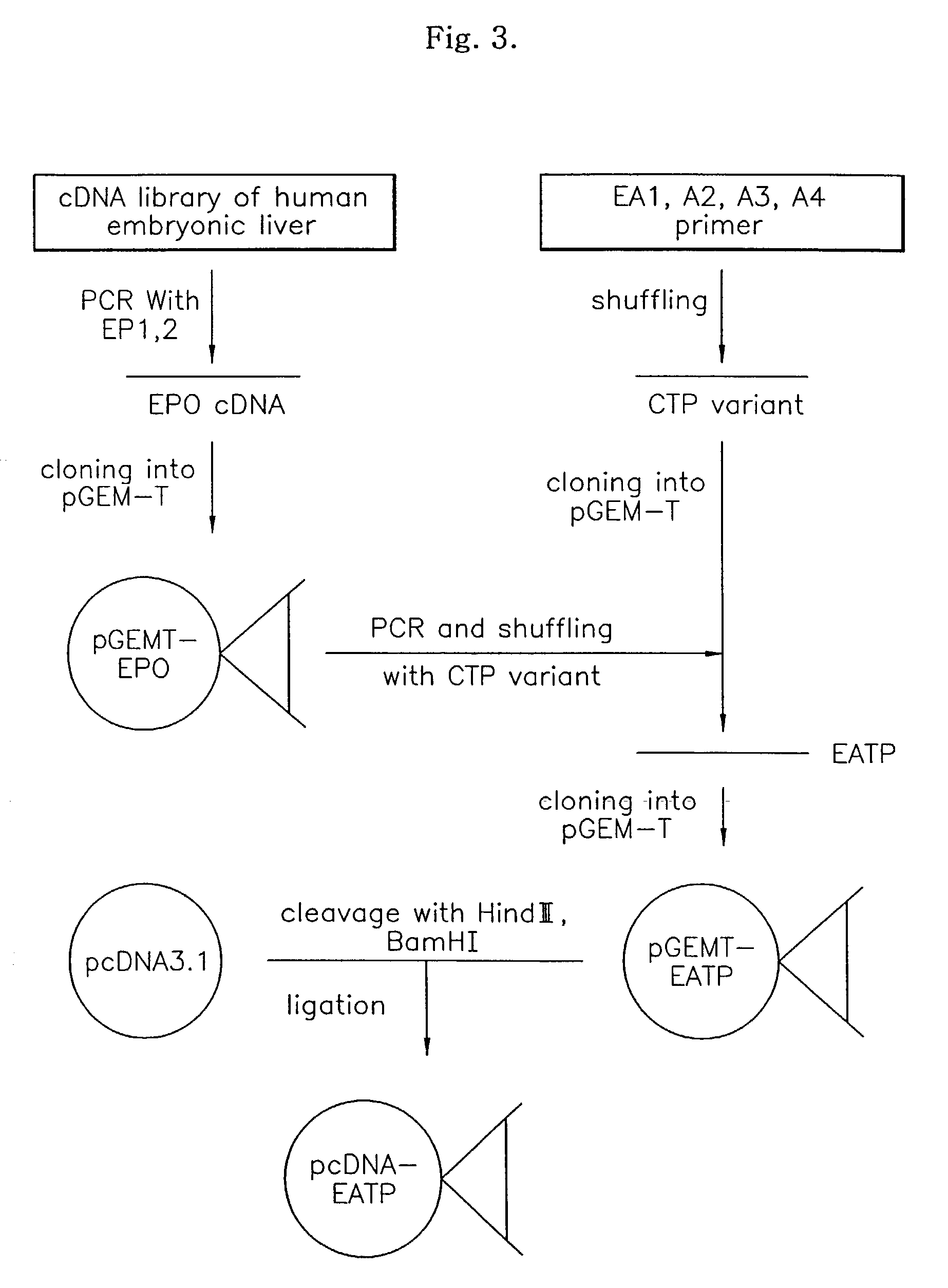
Fusion protein having the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin
InactiveUS20090221037A1High activityImprove in vivo activitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsΒ subunitRed blood cell
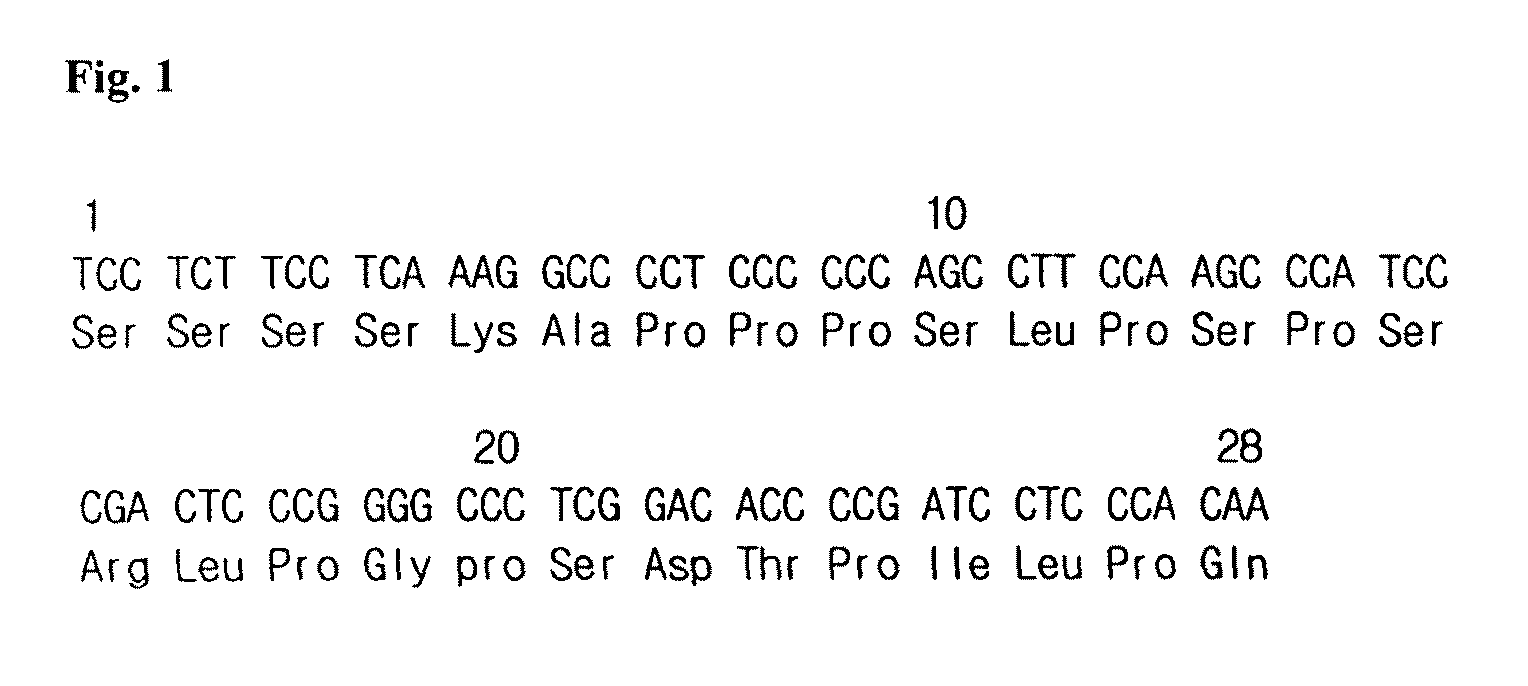
The present invention relates to a fusion protein in which a carboxy terminal of human erythropoietin (EPO) is fused with a carboxy terminal peptide fragment of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), to DNA encoding the fusion protein, and to a method for preparation of the fusion protein. The fusion protein has the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin.
Owner:CJ HEALTHCARE CORP
Fusion protein having the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin
InactiveUS8008454B2Improve in vivo activityExtended half-lifeSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsΒ subunitDna encoding
The present invention relates to a fusion protein in which a carboxy terminal of human erythropoietin (EPO) is fused with a carboxy terminal peptide fragment of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), to DNA encoding the fusion protein, and to a method for preparation of the fusion protein. The fusion protein has the enhanced in vivo activity of erythropoietin.
Owner:CJ HEALTHCARE CORP
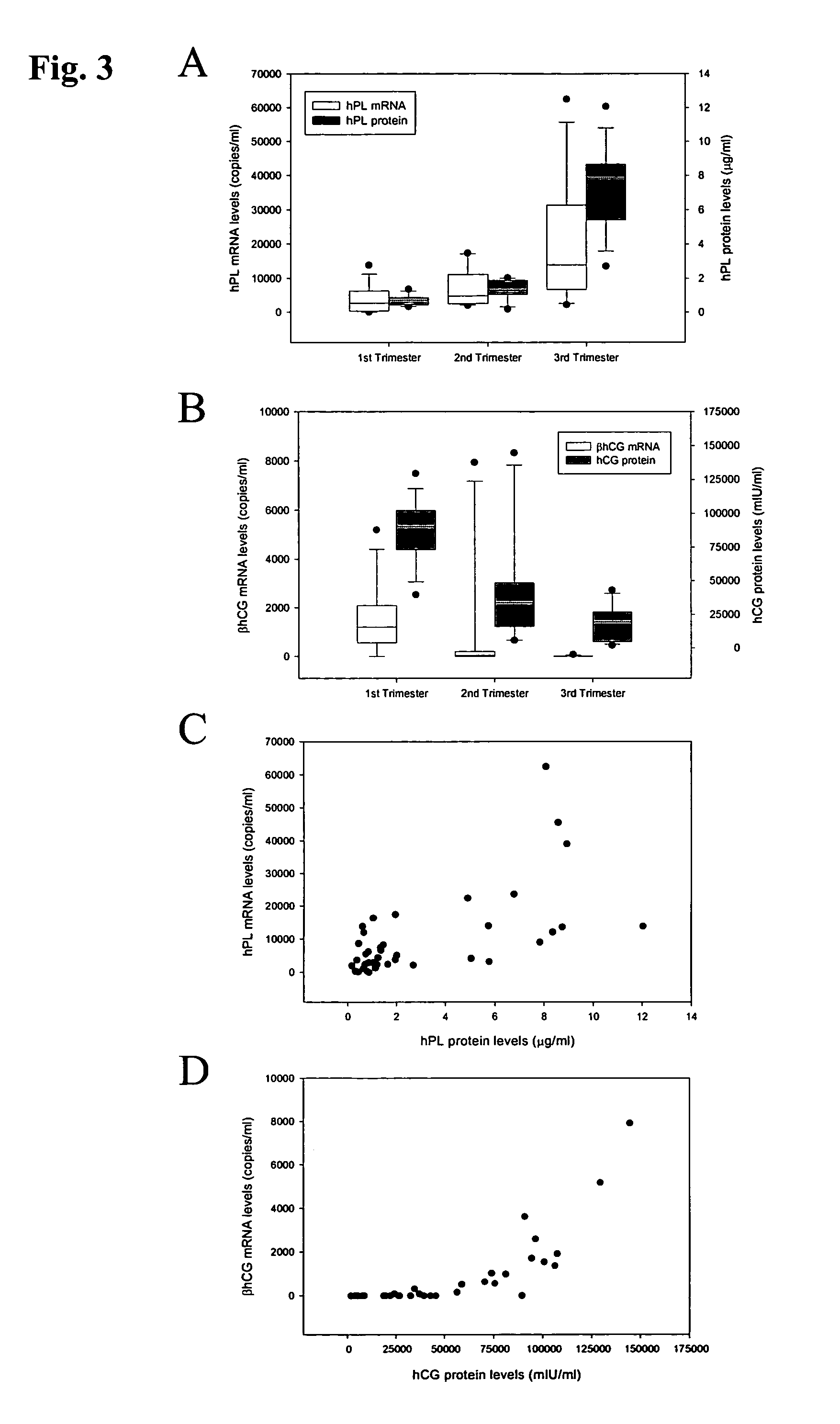
Method for diagnosing preeclampsia by detecting hCRH mRNA
ActiveUS7235359B2Increased risk of developingIncrease volumeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlyceraldehydeMetastasis suppressor
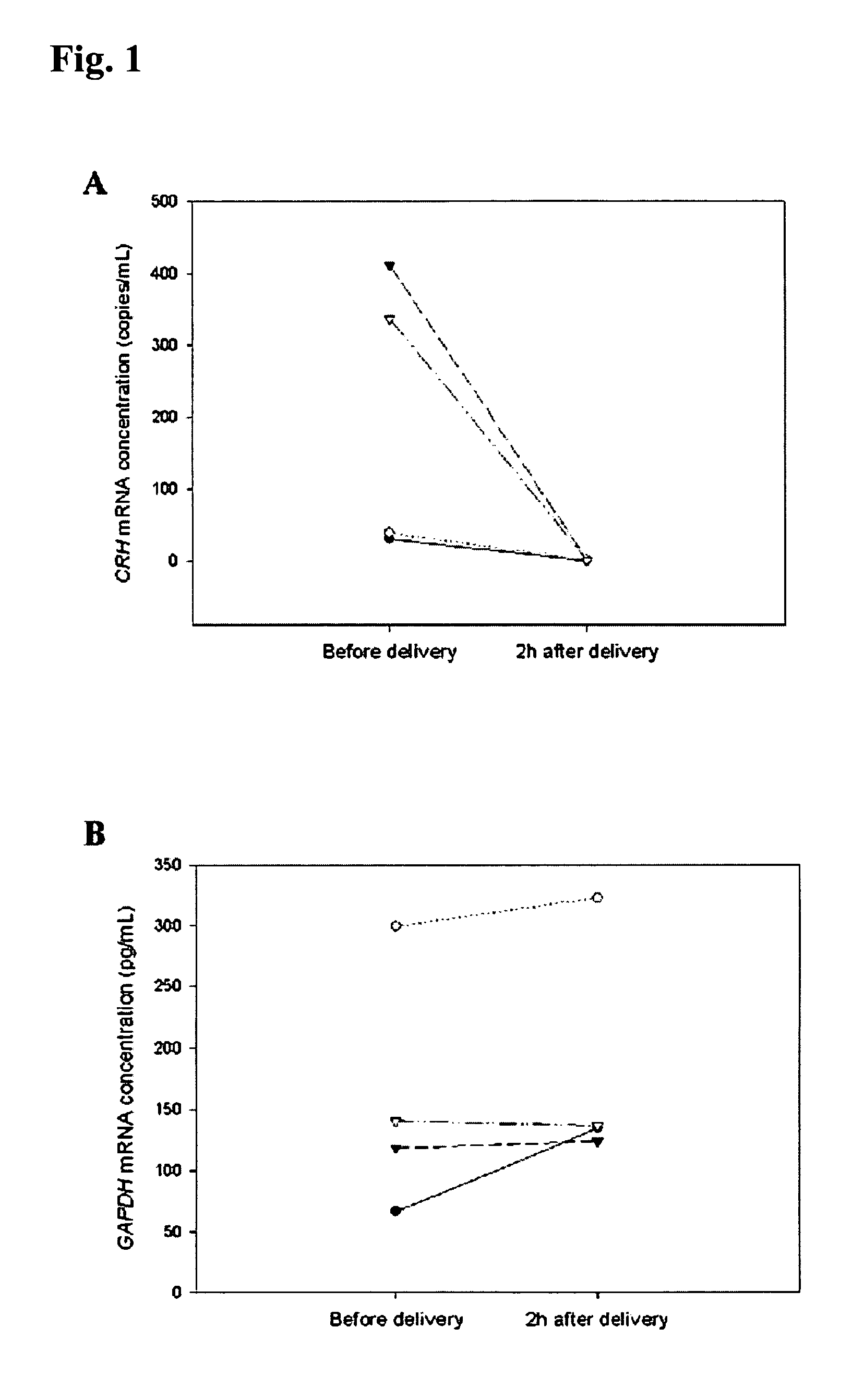
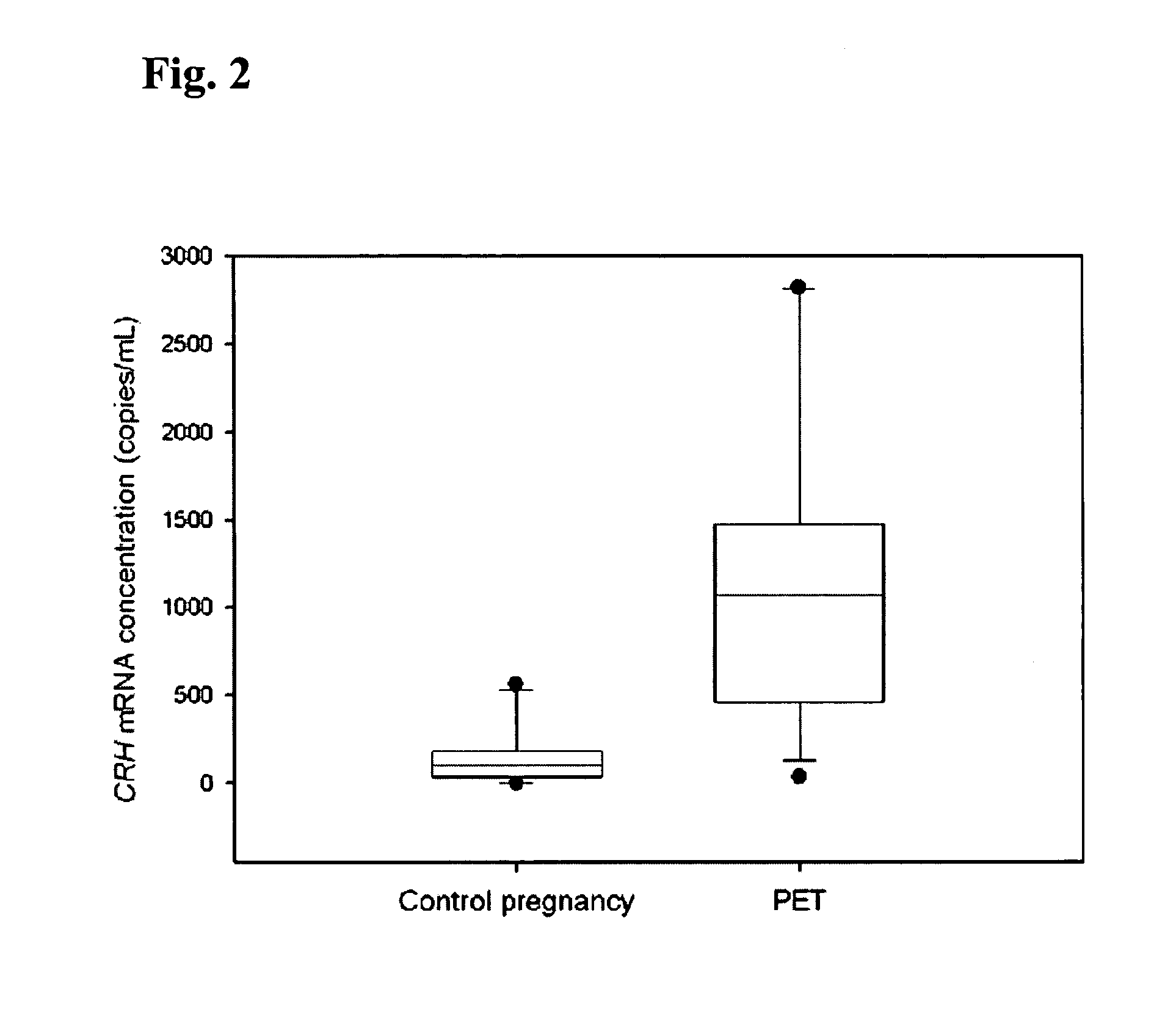
Methods and kits are provided for diagnosing, monitoring, or predicting the conditions of pre-eclaimpsia, fetal chromosomal aneuploidy, and pre-term labor in a pregnant woman, as well as for detecting pregnancy in a woman, by quantitatively measuring in the maternal blood the amount of one or more mRNA species encoding human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (hCG-β), human placental lactogen (hPL), human corticotropin releasing hormone (hCRH), KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor (KISS1), tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TPFI2), placenta-specific 1 (PLAC1), or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and comparing the amount of the mRNA species with a standard control.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
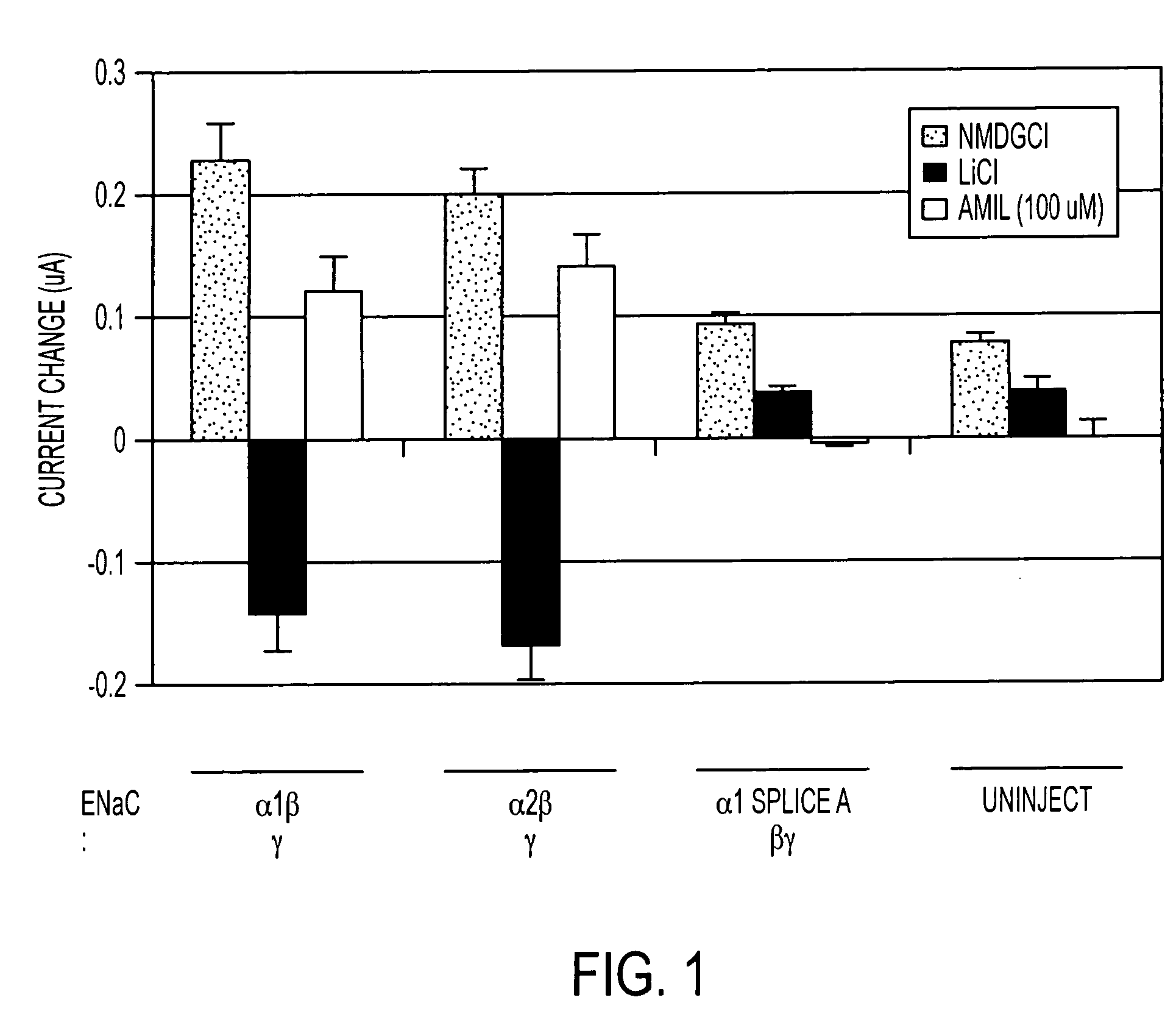
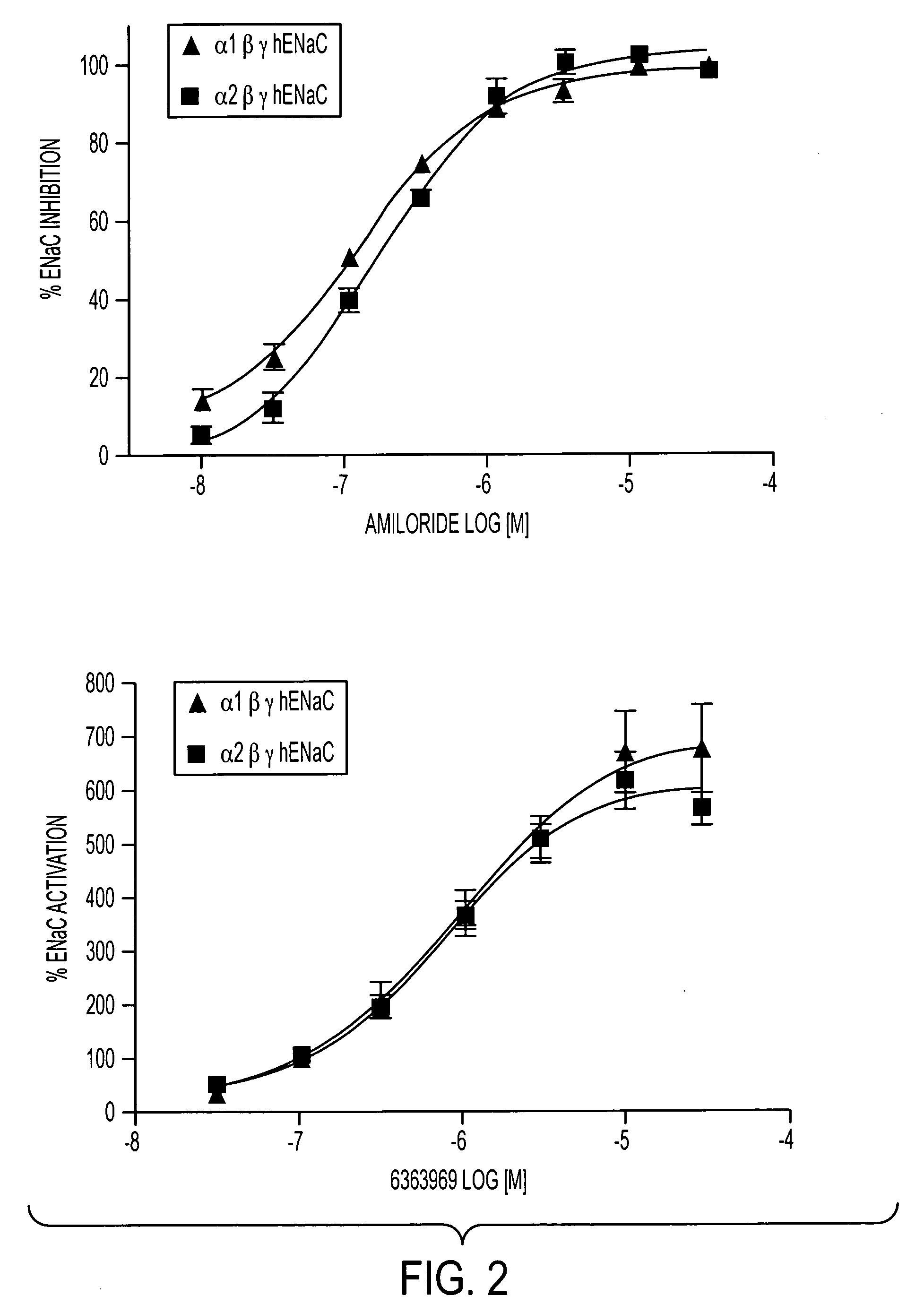
Novel splice variants of human epithelial sodium channel genes expressed in human taste tissue and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060223117A1Promote salt intensityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesEpithelial sodium channelSalty taste
Nucleic acid sequences encoding novel splice variants that encode subunits of an ENaC expressed in human taste tissue are provided. These splice variants when expressed in association with other ENaC subunits, i.e., α, β and γ subunits or α, β and Δ subunits may be used to produce amiloride-insensitive ENACs. The resultant amiloride-insensitive ENaCs are useful in in vitro assays for identifying ENaC modulators that modulate taste (enhance or inhibit), particularly human salty taste.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Method for the production of 1,3-propanediol by recombinant organisms comprising genes for coenzyme B12 synthesis
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding aquacobalamin reductase, cob(II)alamin reductase, cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase, glycerol dehydratase and 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase activities useful for the production of 1,3-propanediol from a variety of carbon substrates. More specifically the following nucleotide sequences are provided: btuR, encoding the E. coli cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; cobA, encoding the Salmonella typhimurium cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; cobO, encoding the Pseudomonas denitrificans cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase enzyme; dhaB1, encoding the α subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaB2, encoding the β subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaB3, encoding the γ subunit of the Klebsiella glycerol dehydratase enzyme; dhaT, encoding Klebsiella oxidoreductase enzyme; the yciK gene isolated from E. coli; the glucose isomerase promoter sequence from Streptomyces; and the N-terminal amino acid sequence for cob(II)alamin reductase from Pseudomonas denitrificans.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polynucleotides encoding GFRα3
InactiveUS7026138B1Facilitating identification and characterizationEasy to detectSugar derivativesTissue cultureNucleotideReceptor activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences, including expressed sequence tags (ESTs), oligonucleotide probes, polypeptides, vectors and host cells expressing, and immunoadhesions and antibodies to mammalian GFRα3, a novel α-subunit receptor of the GDNF (i.e. GFR) receptor family. It further relates to an assay for measuring activation of an α-subunit receptor by detecting tyrosine kinase receptor activation (i.e., autophosphorylation) or other activities related to ligand-induced α-subunit receptor homo-dimerization or homo-oligomerization.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for the generation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
InactiveUS7939059B2Function increaseEnhancing function of T cellBiocideVirusesDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The invention provides systems and methods for the generation of lymphocytes having a unique antigen specificity. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of virally infecting cells from bone marrow with one or more viral vectors that encode antigen-specific antibodies for the production of, for example B cells and T cells. In some embodiments, the viral vectors include an IRES or 2A element to promote separation of, for example, the α subunit and β subunit of a T cell receptor (TCR) or heavy and light chains of a B-cell antibody. The resulting lymphocytes, express the particular antibody that was introduced in the case of B cells and TCR in the case of T cells. The lymphocytes generated can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes including the treatment of various cancers and the generation of a desired immune response to viruses and other pathogens. The resulting cells develop normally and respond to antigen both in vitro and in vivo. We also show that it is possible to modify the function of lymphocytes by using stem cells from different genetic backgrounds. Thus our system constitutes a powerful tool to generate desired lymphocyte populations both for research and therapy. Future applications of this technology may include treatments for infectious diseases, such as HIV / AIDS, cancer therapy, allergy, and autoimmune disease.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fusion protein having enhanced in vivo erythropoietin activity
ActiveUS7091326B2Enhanced human EPO activityProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRed blood cellHalf-life
Provided is a fusion protein comprising, at its carboxy terminal of human erythropoietin (EPO), a mutant having one to four amino acid substitutions in the carboxy terminal peptide (CTP) fragment of a human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) β subunit, for increasing an in vivo half-life activity of EPO. The in vivo half-life can be greatly elongated while retaining the intrinsic activity of the EPO, without increasing the sugar chain content.
Owner:CJ HEALTHCARE CORP
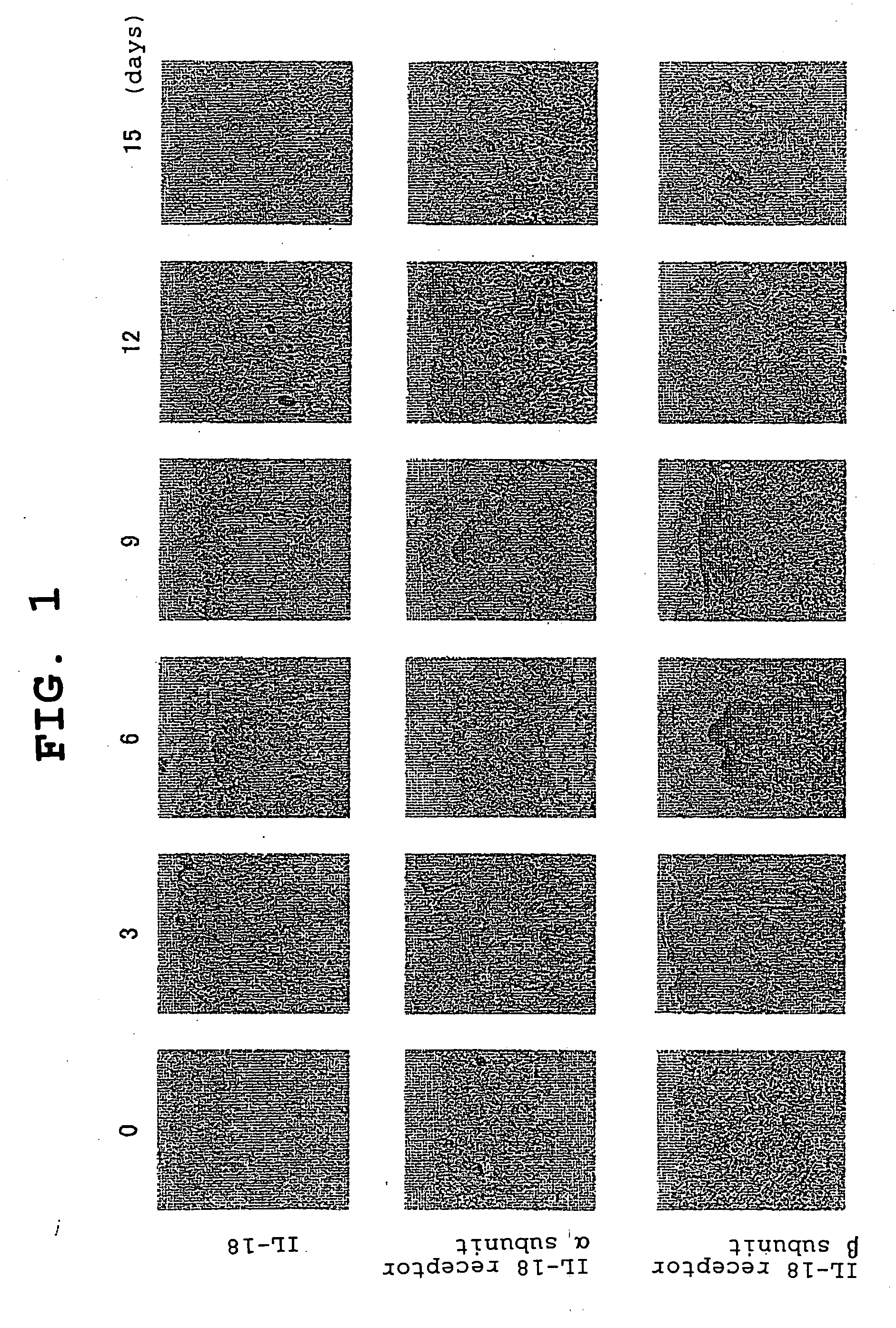
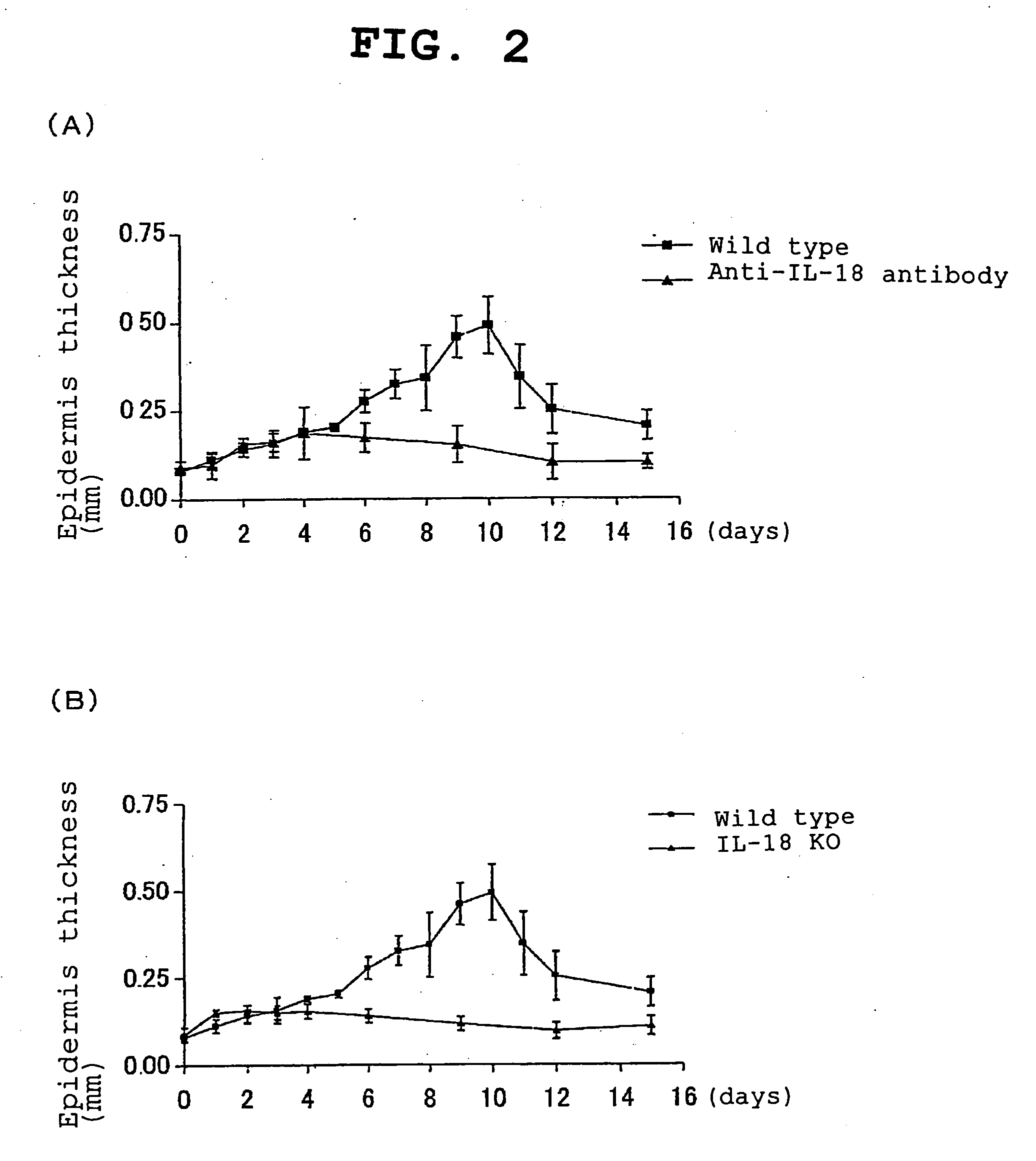
Il-18 Receptor Antagonist and Pharmaceutical Composition Containing the Antagonist
ActiveUS20080063644A1Inhibit functioningGuaranteed functionAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderΒ subunitAmino acid
Provided is an IL-18 receptor antibody usable for immunohistochemistry, which functions as an IL-18 receptor antagonist. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition and method for preventing and / or treating an IL-18-dependent disorder, particularly skin thickening caused by ultraviolet, using the antibody. An antibody against the IL-18 receptor α subunit, which is characterized by binding specifically to a polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1, or an antibody against the IL-18 receptor β subunit, which is characterized by binding specifically to a polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2, is prepared.
Owner:SEKIYAMA ATSUO
GFRalpha3 and its uses
InactiveUS20060216289A1Facilitating identification and characterizationEasy to detectFungiSenses disorderAutophosphorylationReceptor activation
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences, including expressed sequence tags (ESTs), oligonucleotide probes, polypeptides, vectors and host cells expressing, and immunoadhesions and antibodies to mammalian GFRα3, a novel α-subunit receptor of the GDNF (i.e. GFR) receptor family. It further relates to an assay for measuring activation of an α-subunit receptor by detecting tyrosine kinase receptor activation (i.e., autophosphorylation) or other activities related to ligand-induced α-subunit receptor homo-dimerization or homo-oligomerization.
Owner:DE SAUVAGE FREDERIC +3
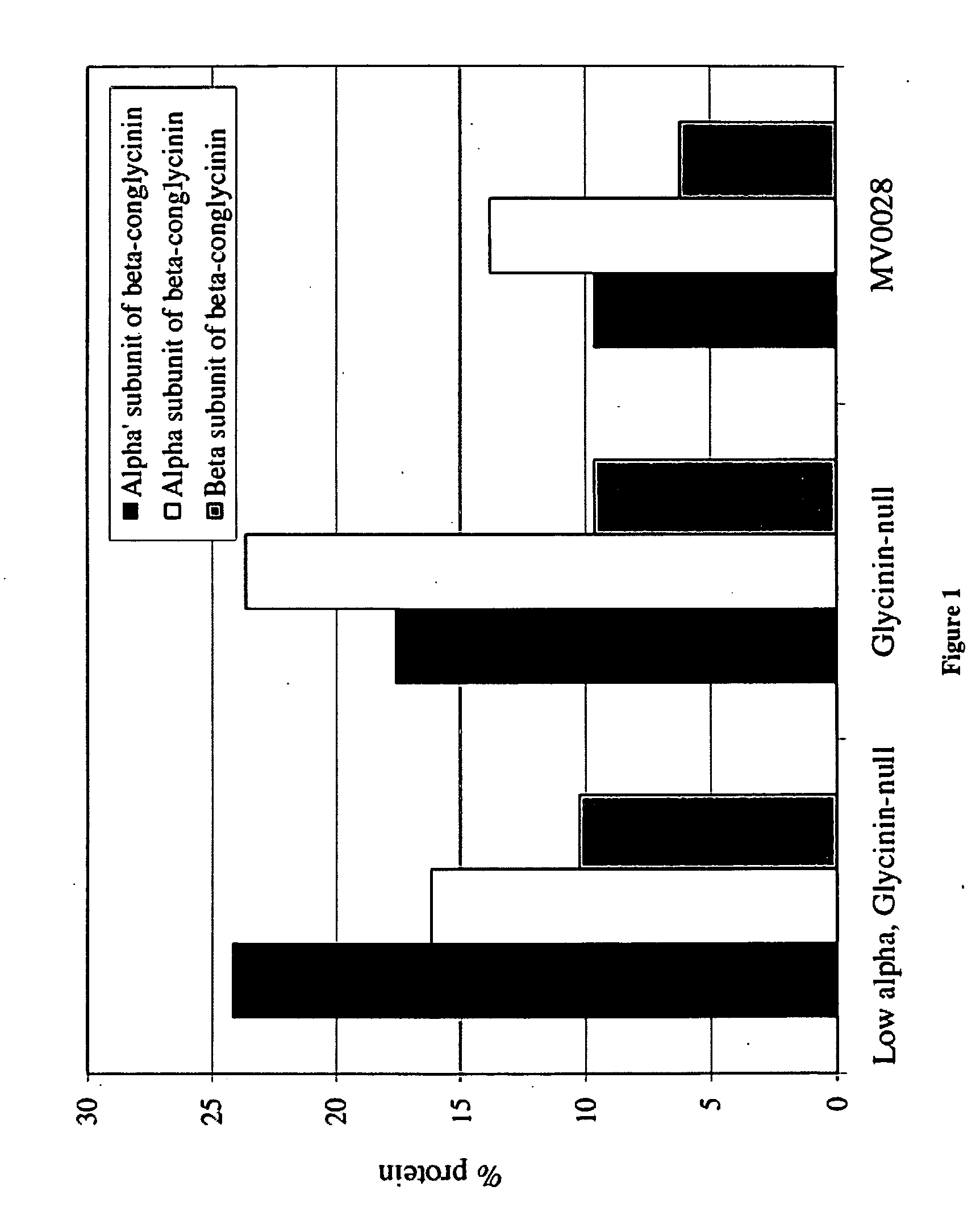
Increased alpha-prime beta-conglycinin soybeans
ActiveUS20090068337A1Increase productionAltered fatty acid compositionImmunoglobulinsFermentationNull phenotypeGlobulin
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the art by providing a soybean plant with non-transgenic mutations conferring decreased α-subunit of β-conglycinin content and increased α′-subunit content of β-conglycinin in seed. Moreover, the invention provides an agronomically elite soybean plant with non-transgenic mutations conferring a gyclinin null phenotype, increased β-conglycinin content, and increased α′-subunit content of β-conglycinin in the seed. The invention also provides derivatives, and plant parts of these plants and uses thereof. Methods for producing such plants are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Development of follicle stimulating hormone agonists and antagonists in fish
InactiveUS20070281883A1Improve metabolic activityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyDisulfide bond
The invention provides recombinant forms of piscine follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) with characteristic intramolecular disulfide bonds and modified glycosylation patterns in the β-subunit that enhance the stability and metabolic activity of the hormone. Also provided are recombinant materials to produce the FSH β and glycoprotein α-subunits singly or in combination to obtain complete heterodimeric hormone of regulated glycosylation pattern. The piscine FSH agonists of the invention are therapeutically useful to expedite the onset of puberty in captive fish and to alleviate reproductive dysfunctions in fish. Likewise, the piscine FSH antagonists of the invention will be therapeutically useful to halt gonadal development, thereby contributing to body weight gain of the fish,
Owner:FISHBREED
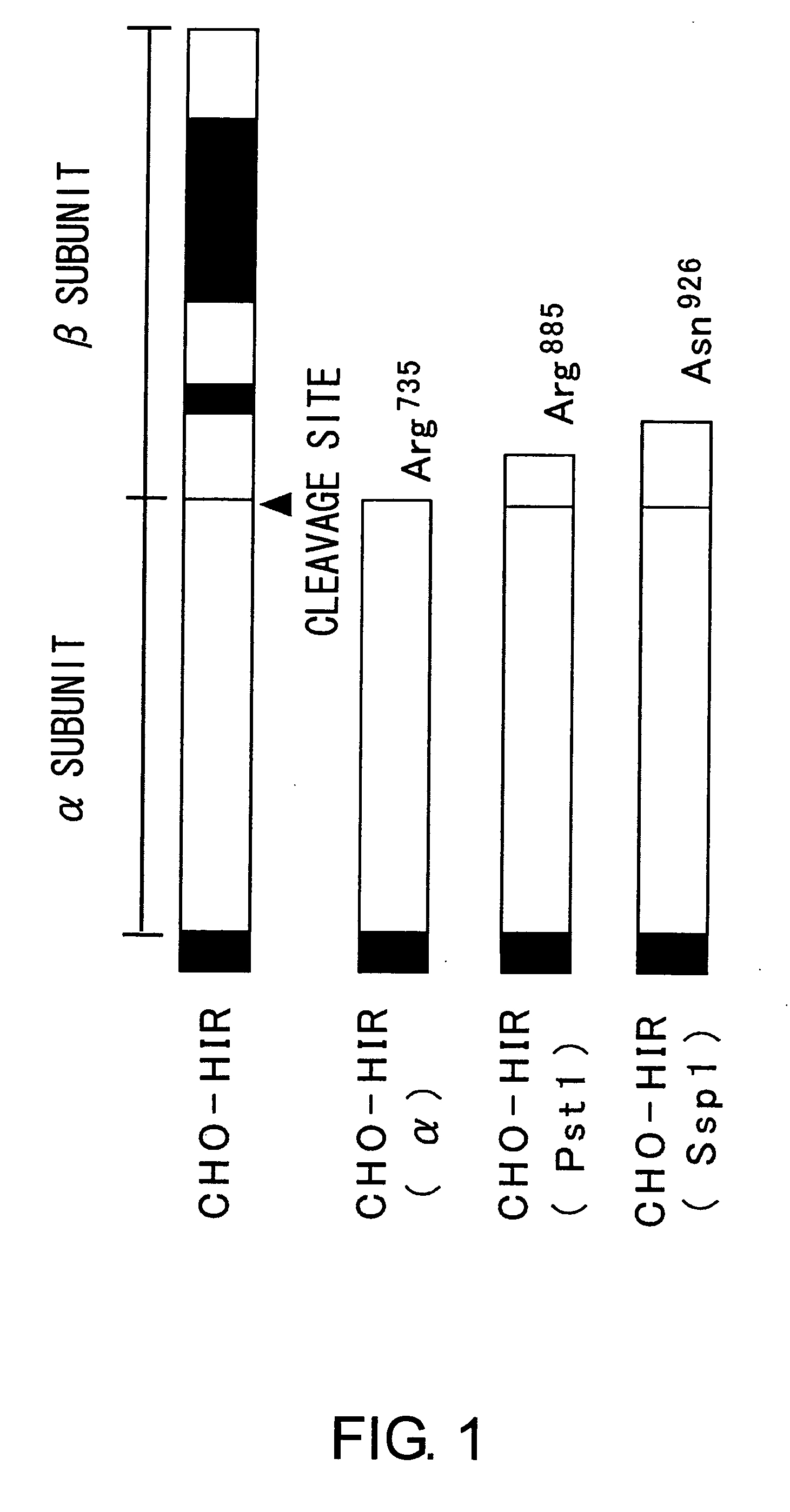
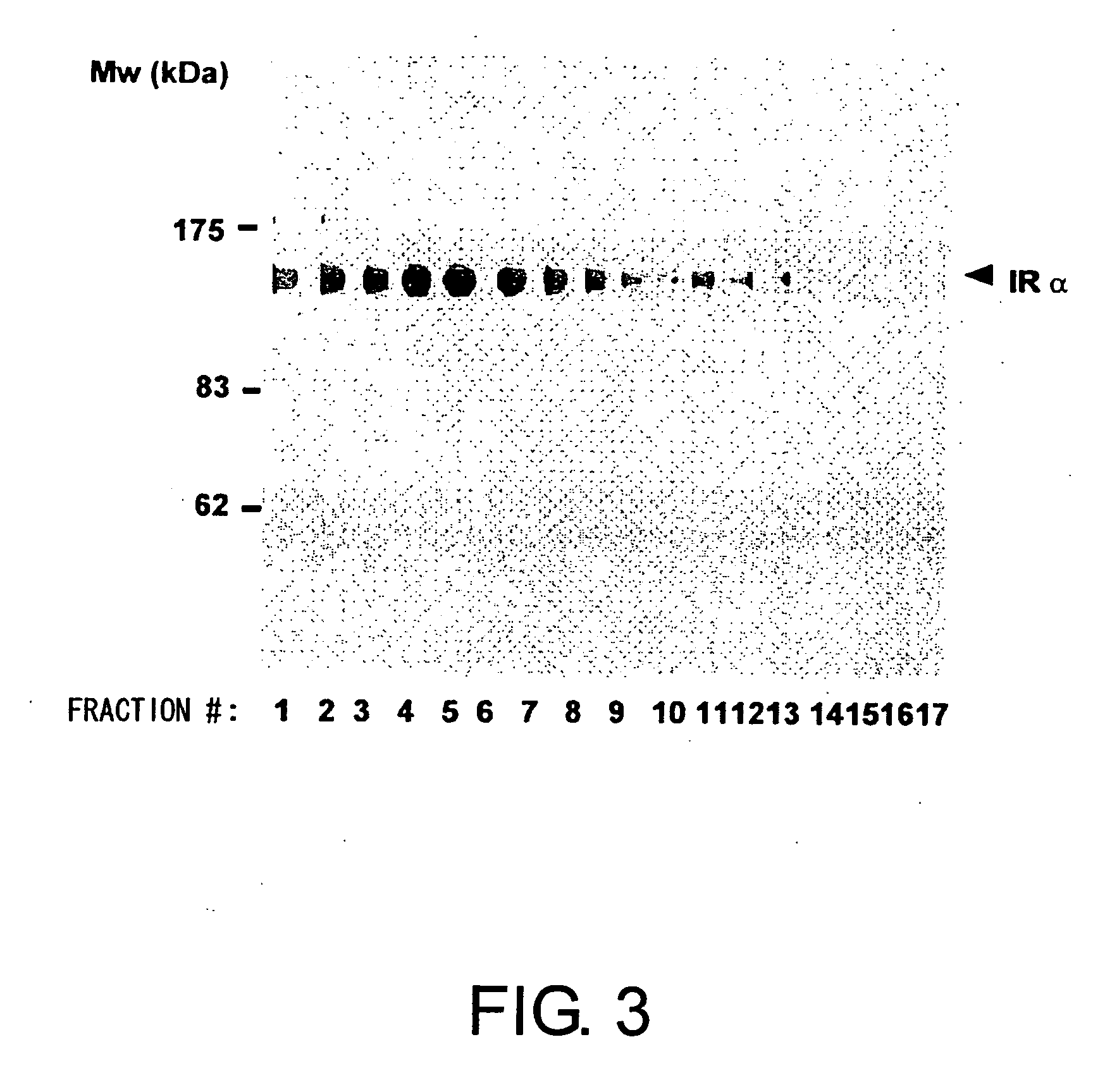
Methods for measuring the insulin receptor alpha subunit
ActiveUS20070059784A1Easy to collectEasy to synthesizeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisFree insulinInsulin Receptor alpha Subunit
Presence of free insulin receptor α-subunit in blood was discovered. Furthermore, methods for measuring the insulin receptor α-subunit was provided, the method comprising the steps of contacting the insulin receptor α-subunit in a blood sample with an antibody recognizing the insulin receptor α-subunit, and detecting the binding between the two. Measurement of the free insulin receptor α-subunit in the blood is useful for evaluating risk factors for diabetes. In addition, the measurement methods of the present invention showed that concentrations of the free insulin receptor α-subunit in the blood of diabetes or cancer patients are significantly high. Free insulin receptor α-subunit in blood is useful as a marker for diabetes or cancer.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
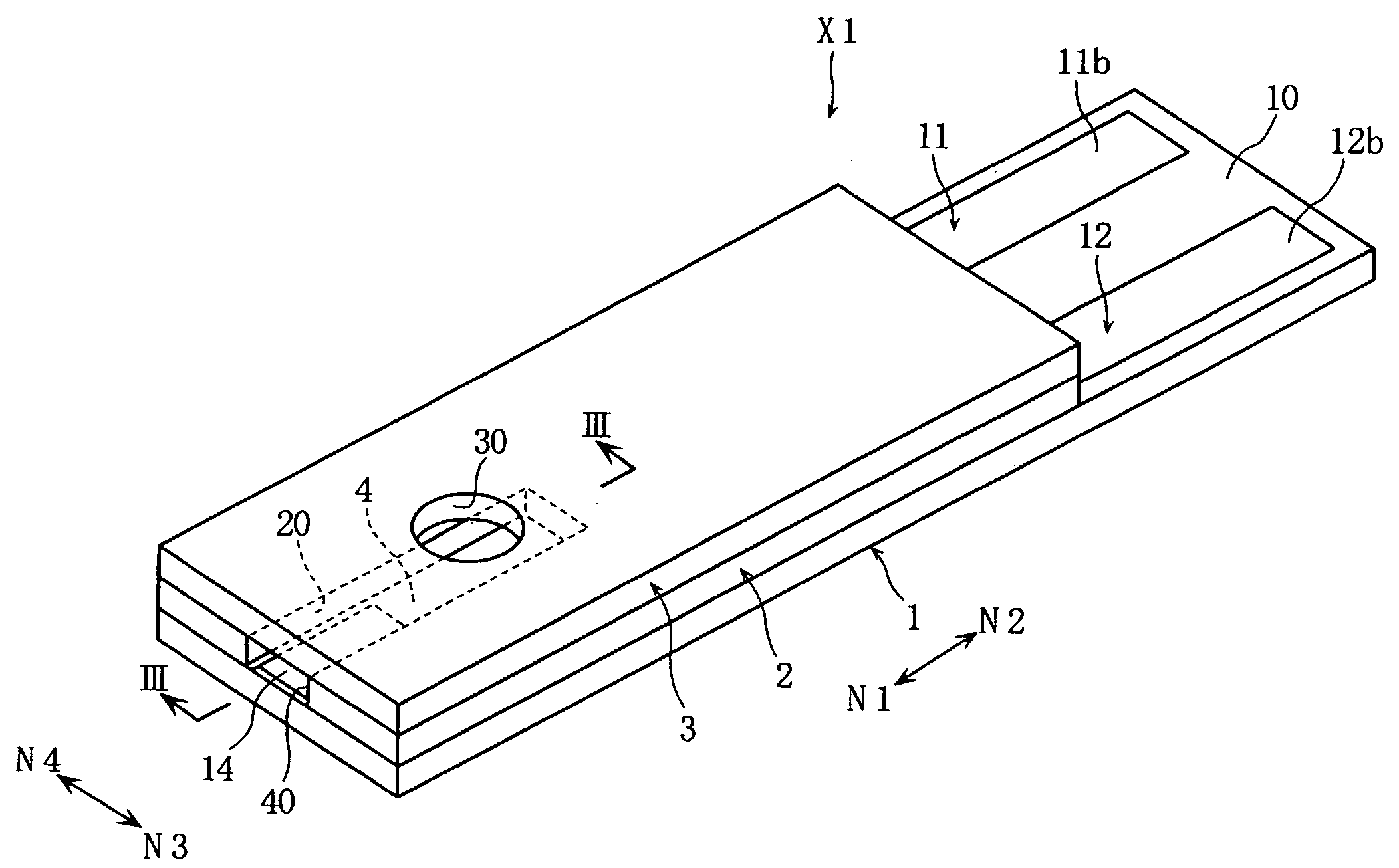
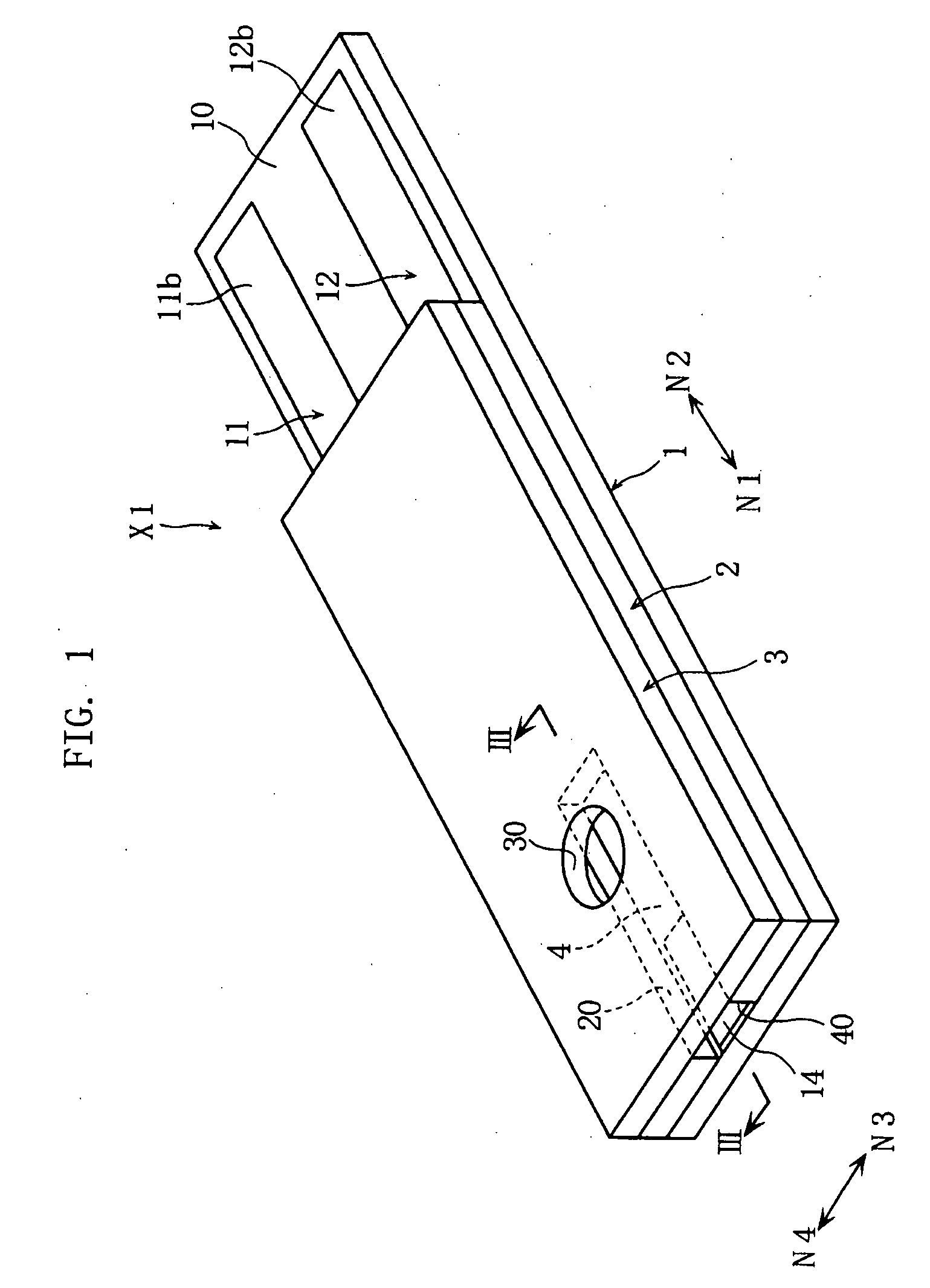
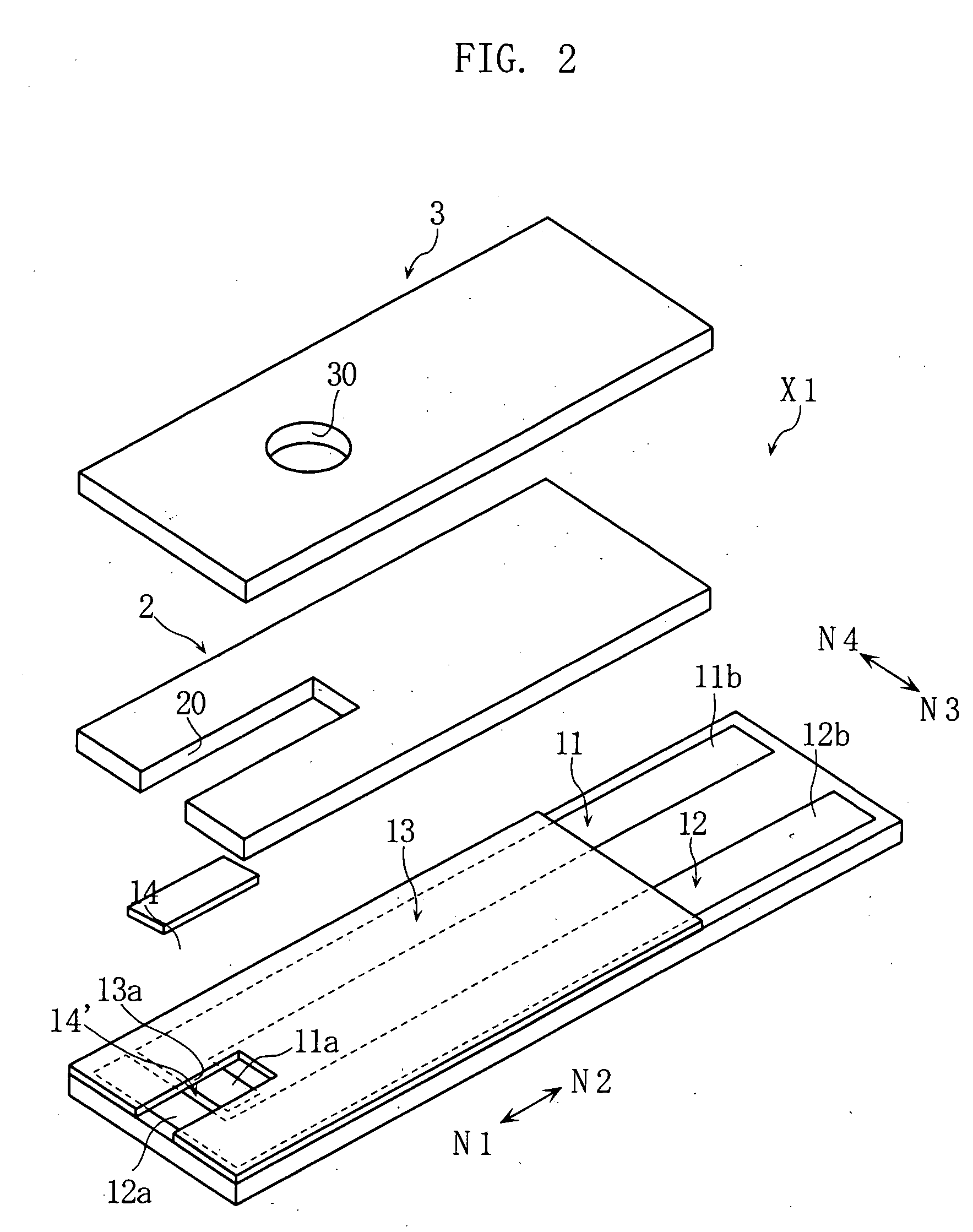
Protein-Immobilized membrane, method for immobilization of protein, enzyme-immobilized electrode, and biosensor
InactiveUS20090101499A1Precise positioningEffective activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlucose dehydrogenase activityCell membrane
The present invention relates to a protein-immobilized membrane (14) including a cell membrane homologous layer (14A) and a protein (14B) immobilized to the cell membrane homologous layer (14A), where the protein contains cytochrome or a cytochrome complex. The present invention also relates to a method for forming a protein-immobilized membrane (14), and an enzyme-immobilized electrode and a biosensor (X1) provided with a protein-immobilized membrane (14). Preferably, the cell membrane homologous layer (14A) may contain a phospholipid polymer, and the protein (14B) may be CyGDH including an α subunit having a glucose dehydrogenase activity and cytochrome C having a function of electron transfer.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
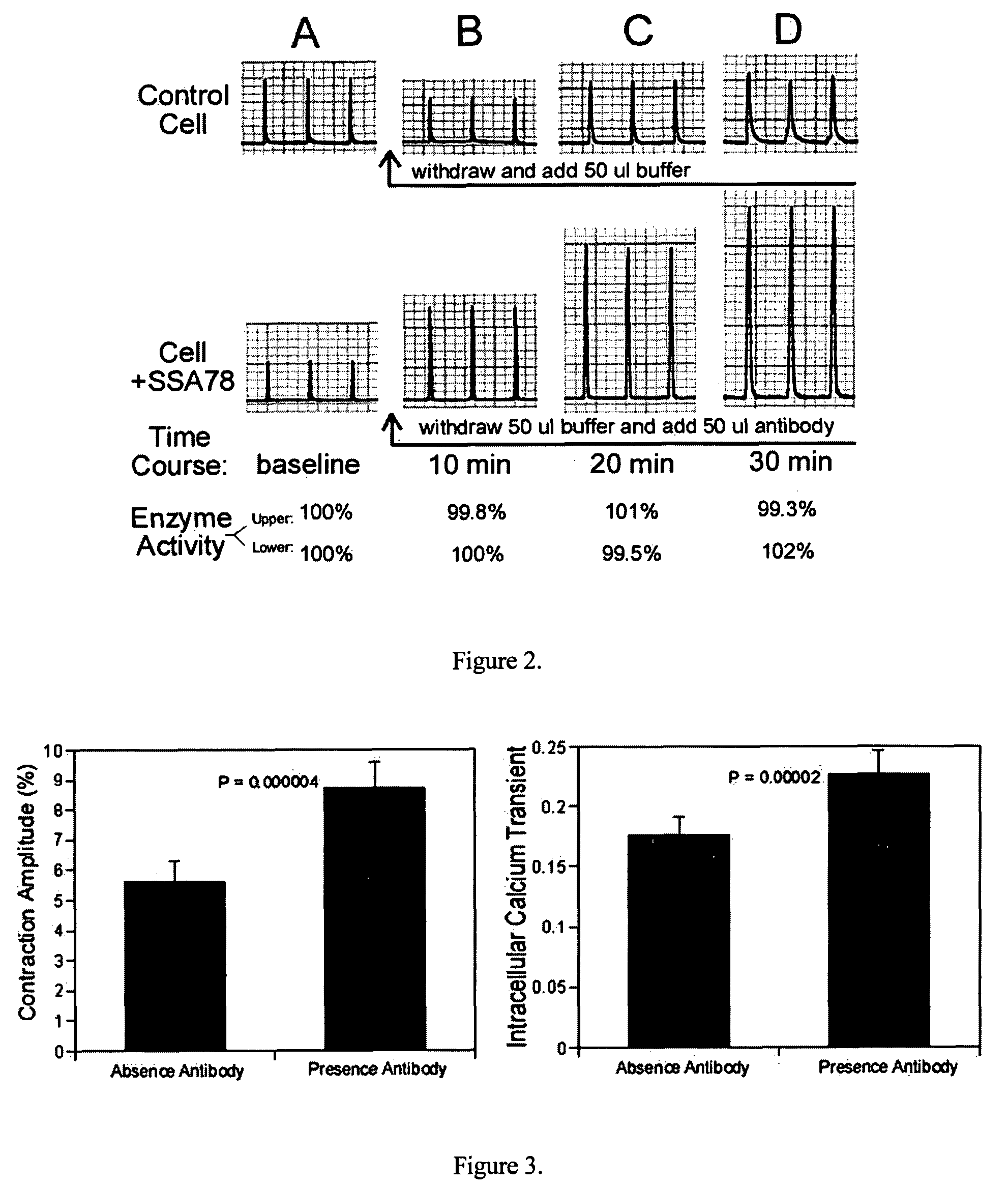
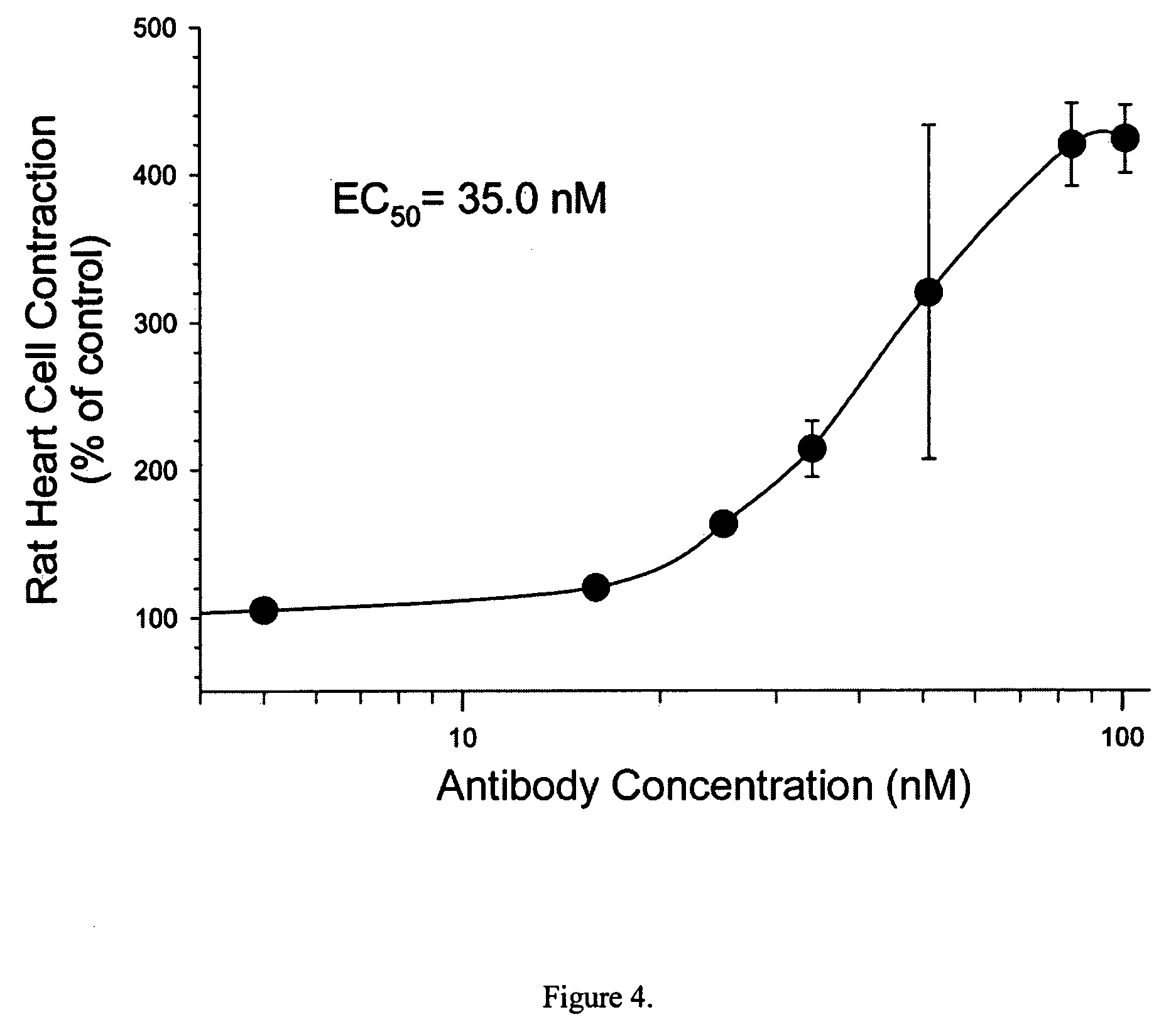
Inotropic antibodies and therapeutic uses thereof
ActiveUS7754210B2Physiological function is goodStable growthAntibody ingredientsFermentationATPaseΑ subunit
Antibodies binding to sites on the α-subunit (Na++K+)-ATPase increase cardiac contraction of both ventricular myocytes and mouse heart. In particular, antibodies binding to the RSATEEEPPNDD (SEQ ID NO: 1) or DVEDSYGQQWTYEQR (SEQ ID NO: 2) peptides (or isoforms / derivatives thereof) of the α-subunit of the (Na++K+)-ATPase, have been found to be highly inotropic. Both the antibodies and the peptides are important for the treatment of human heart failure and other contractile disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Continuous dosing regimen
Compositions comprising one or more cancer drugs, continuous oral dosing schedule with drugs which bind to the colchicine site of tubulin β-subunits, and methods of treating diseases using continuous dosing schedules are disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
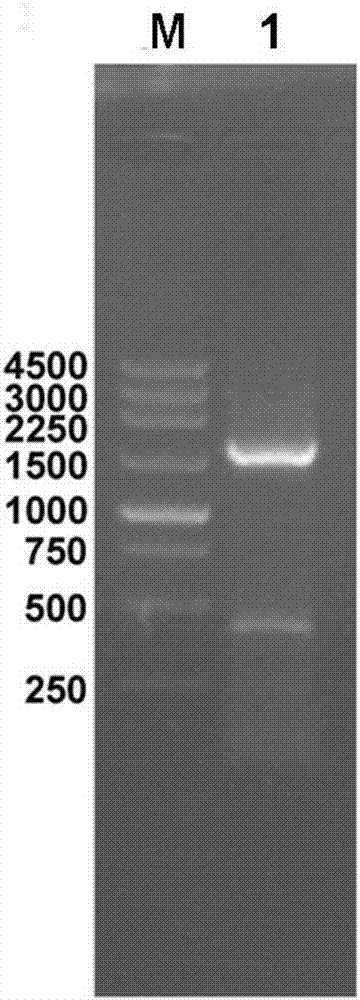
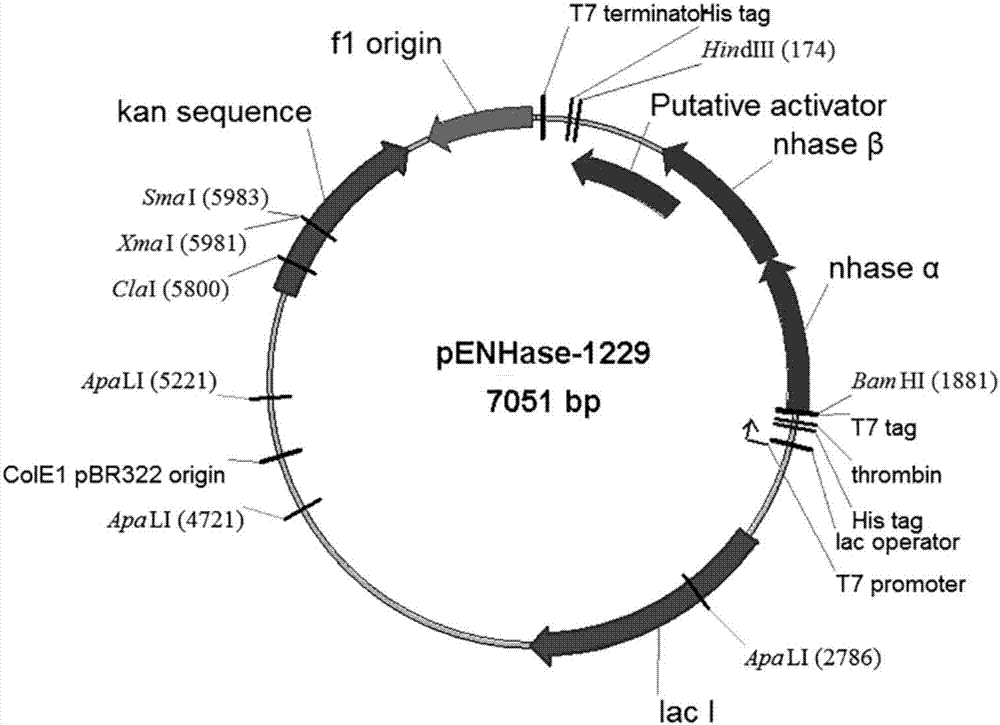
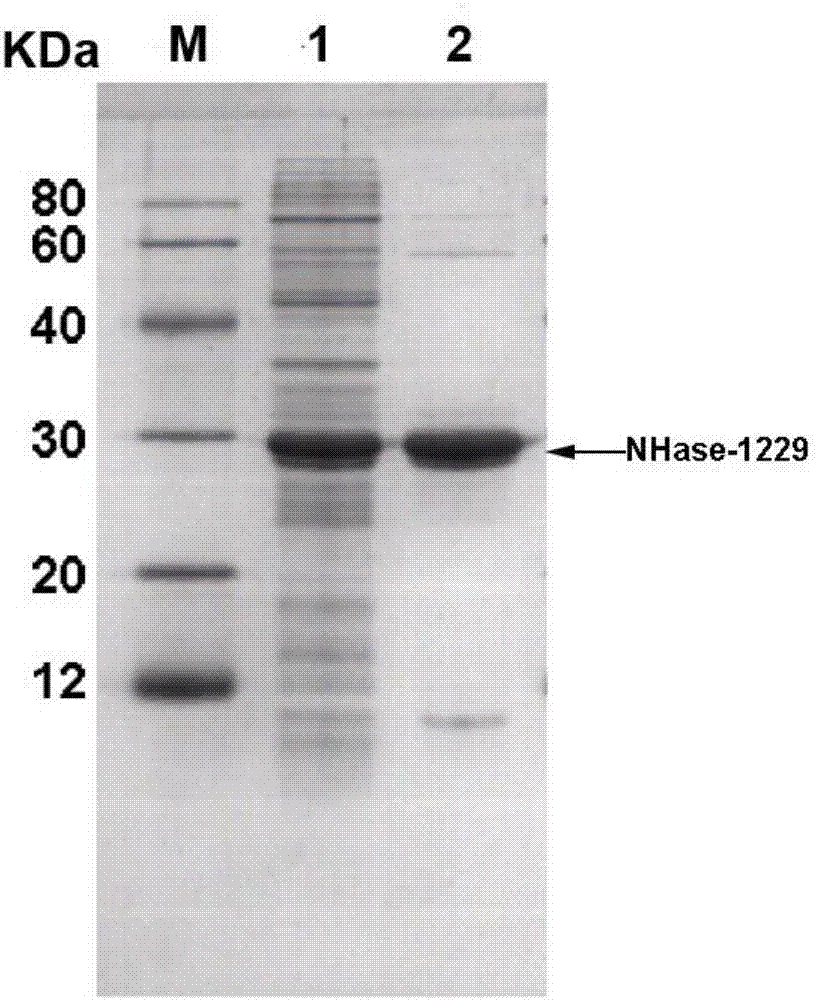
Heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds
InactiveCN107881163AHigh expressionHigh activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention discloses heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds. The heat-resistantnitrile hydratase contains alpha-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4, beta-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.5, and active element coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.6. The nitrile hydratase genes are cloned from aurantimonas manganoxydans SI859A and successfully subjected to heterologous expression in E. coli BL21 (DE3), so as to obtain nitrile hydratase with high expression quantity and high activity and proteins with specific activities reaching 404.5U / mg. The nitrile hydratase has high catalytic activity on aromatic nitrile compounds and aliphatic nitrile compounds, and is a kind of nitrile hydratase with wide substrate spectrum, high thermal stability and excellent industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Use of sodium channel blockers for the treatment of visceral pain or pain caused by cancer treatment
The invention provides methods for treating visceral pain and pain associated with therapy. The compounds useful in the methods of the invention are blockers of sodium ion channels, and in particular compounds that bind to the SS1 or SS2 extracellular mouth of the α-subunit thereof. Particularly useful compounds are saxitoxin and its derivatives and analogues and tetrodotoxin and its derivatives and analogues.
Owner:WEX MEDICAL LTD
Construction of expression system for RNA polymerase derived from influenza virus, crystallization of the RNA polymerase, and screening method for Anti-influenza agent
The present invention aims to express influenza virus RNA polymerase on a large scale, to crystallize the influenza virus RNA polymerase, and to provide a method for screening a substance capable of serving as an active ingredient in anti-influenza drugs which target a protein highly conserved among influenza virus species.The present invention provides a complex comprising a polypeptide consisting of an amino acid sequence at positions 239-716 of the RNA polymerase PA subunit in influenza A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 1934 H1N1 and a polypeptide consisting of an amino acid sequence at positions 1-81 of the RNA polymerase PB1 subunit in influenza A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 1934 H1N1, as well as a method for screening a substance capable of serving as an active ingredient in anti-influenza drugs, which comprises the step of selecting a substance which inhibits the interaction between α-subunit and β-subunit 1, each constituting influenza virus RNA polymerase, in the presence of a candidate substance.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA +1
Urine protein marker for chronic pancreatitis and application thereof
The present application relates to urinary protein markers for chronic pancreatitis and uses thereof. Specifically, this application relates to the use of urine protein markers obtained by using chronic pancreatitis disease models and mass spectrometry analysis in the early diagnosis of human chronic pancreatitis disease and the use of disease course monitoring. The urine protein markers are selected from Igγ‑1 chain C domain, nucleonectin‑2, beta‑2‑microglobulin, interleukin‑4 receptor alpha subunit, phosphoglycerate mutase 1, dipeptidyl peptidase 2, secreted pyrophosphoprotein 24, glycans Core protein, endothelial cell selective adhesion molecule, nestin-2, serum amyloid substance p, nerve cell adhesion molecule 1, etc. In this application, the obtained differential protein in urine provides a non-invasive and convenient option for early diagnosis and subsequent treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
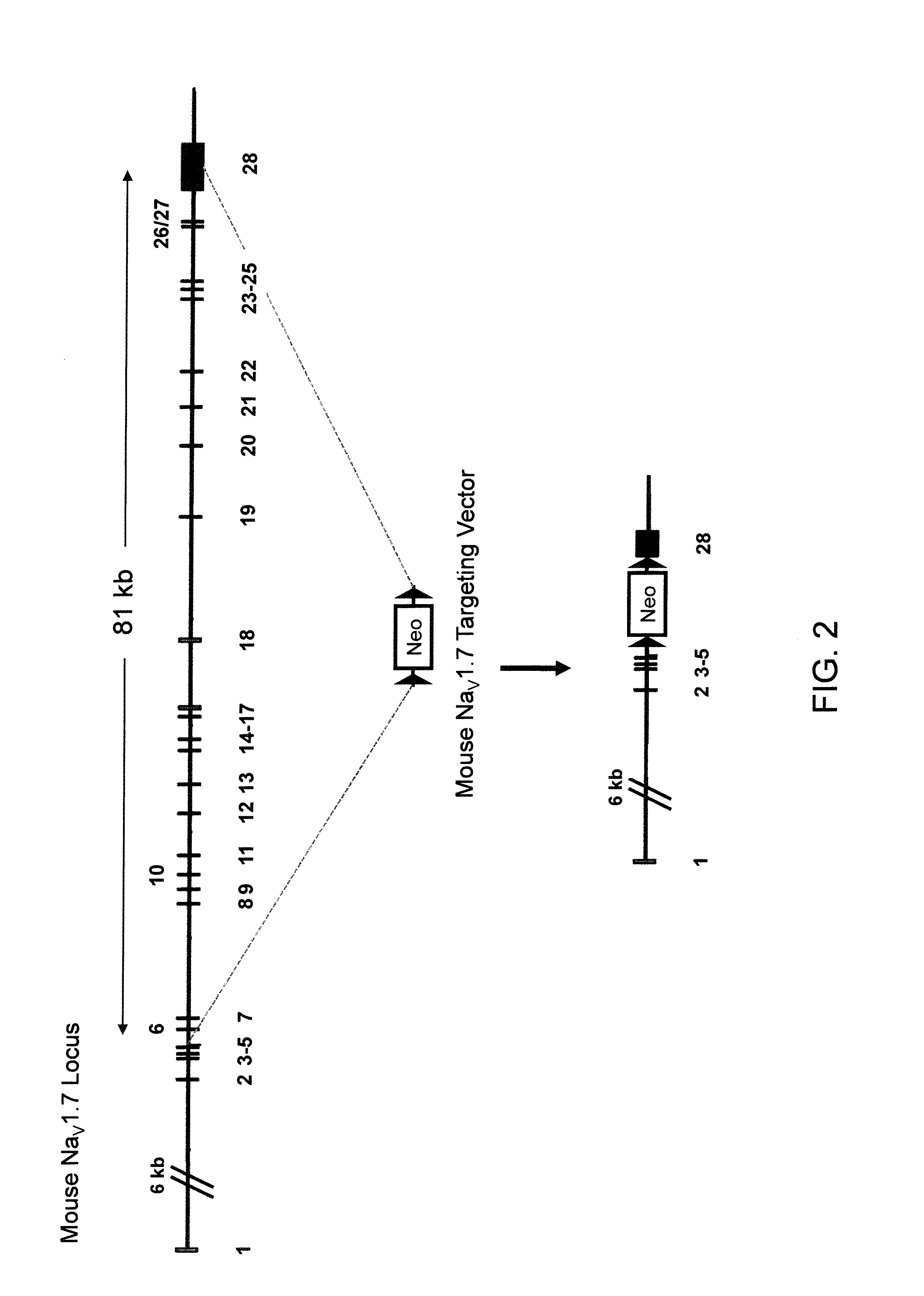
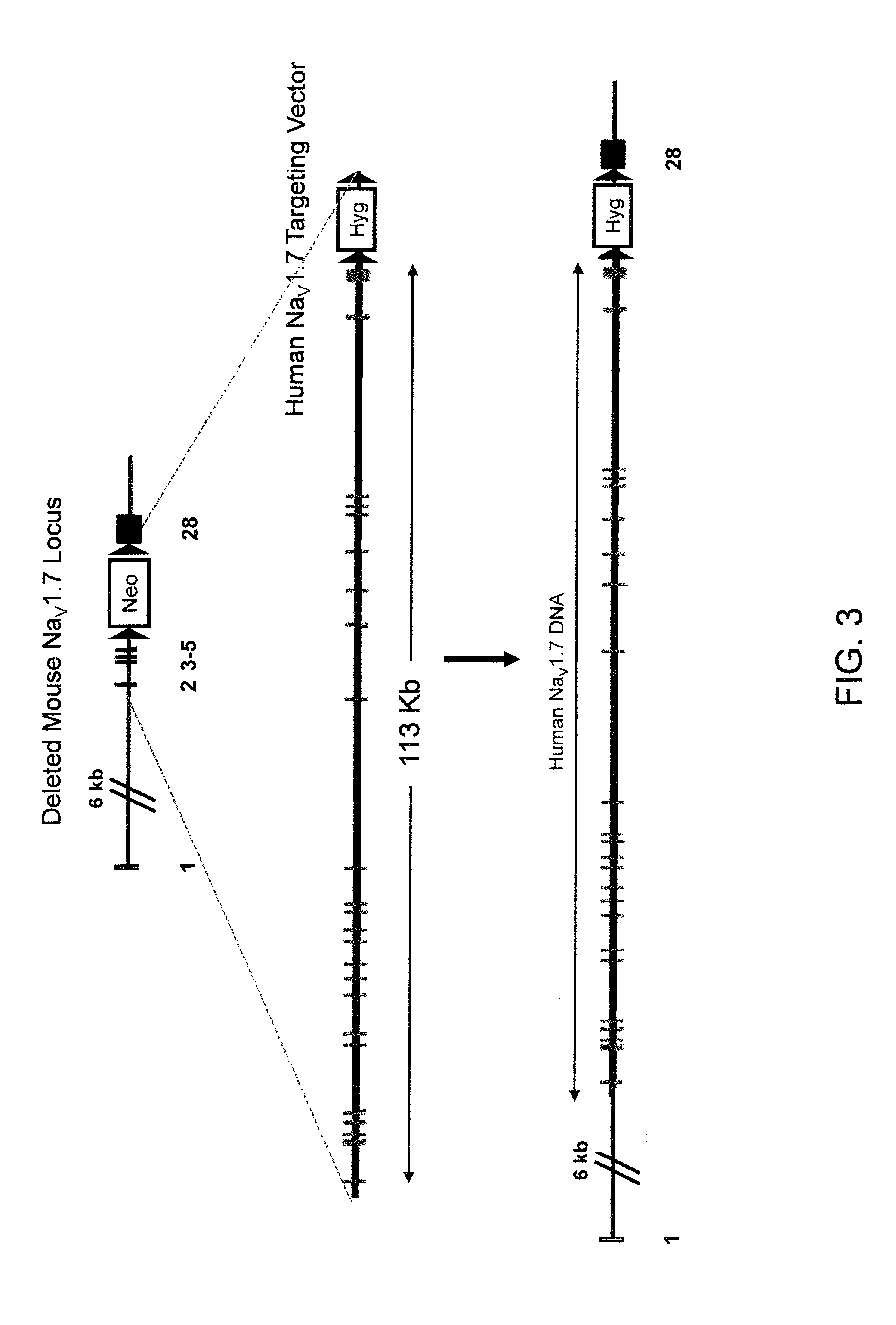
Mice expressing human voltage-gated sodium channels
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
B12 -dependent dehydratases with improved reaction kinetics
InactiveUS7410754B1Facilitated reaction kineticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide-Directed MutagenesisMutant
Sequences of B12-dependent dehydratases with improved reaction kinetics are presented. Use of these B12-dependent dehydratases reduce the rate of the enzyme's suicide inactivation in the presence of glycerol and 1,3-propanediol. The enzymes were created using error-prone PCR and oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis to target the DhaB1 gene, which encodes the α-subunit of glycerol dehydratase. Mutants with improved reaction kinetics were rapidly identified using high throughput assays.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
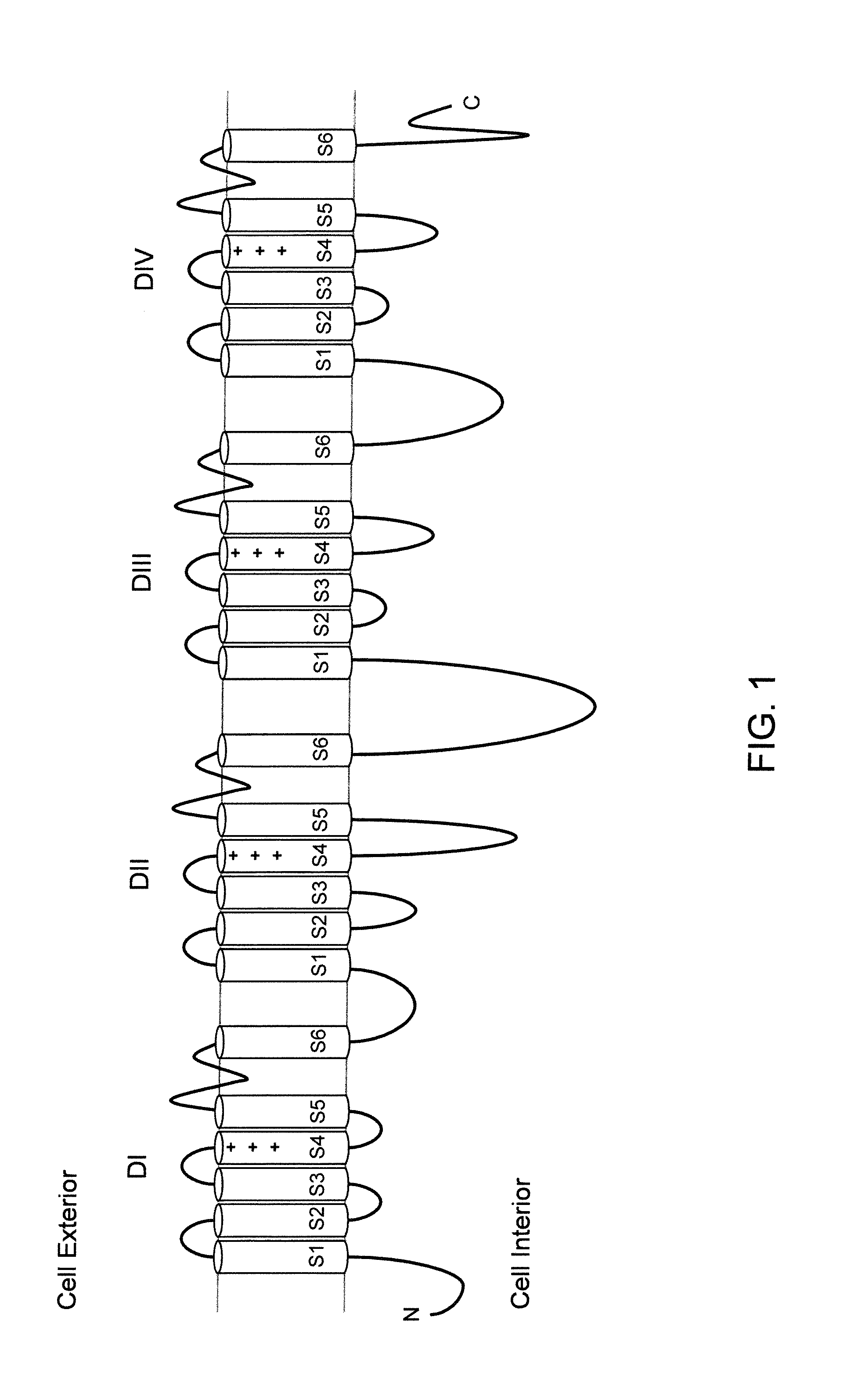
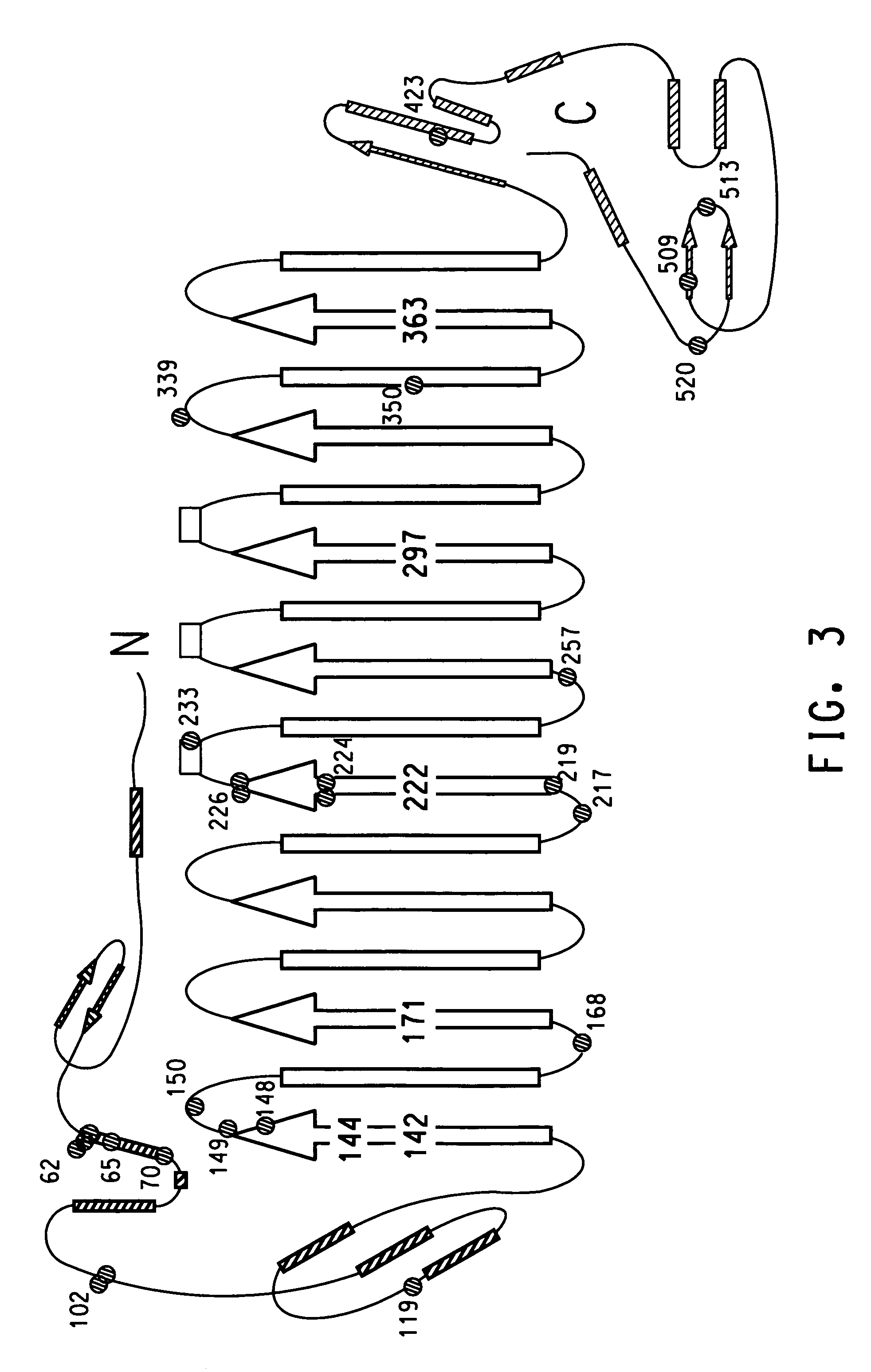
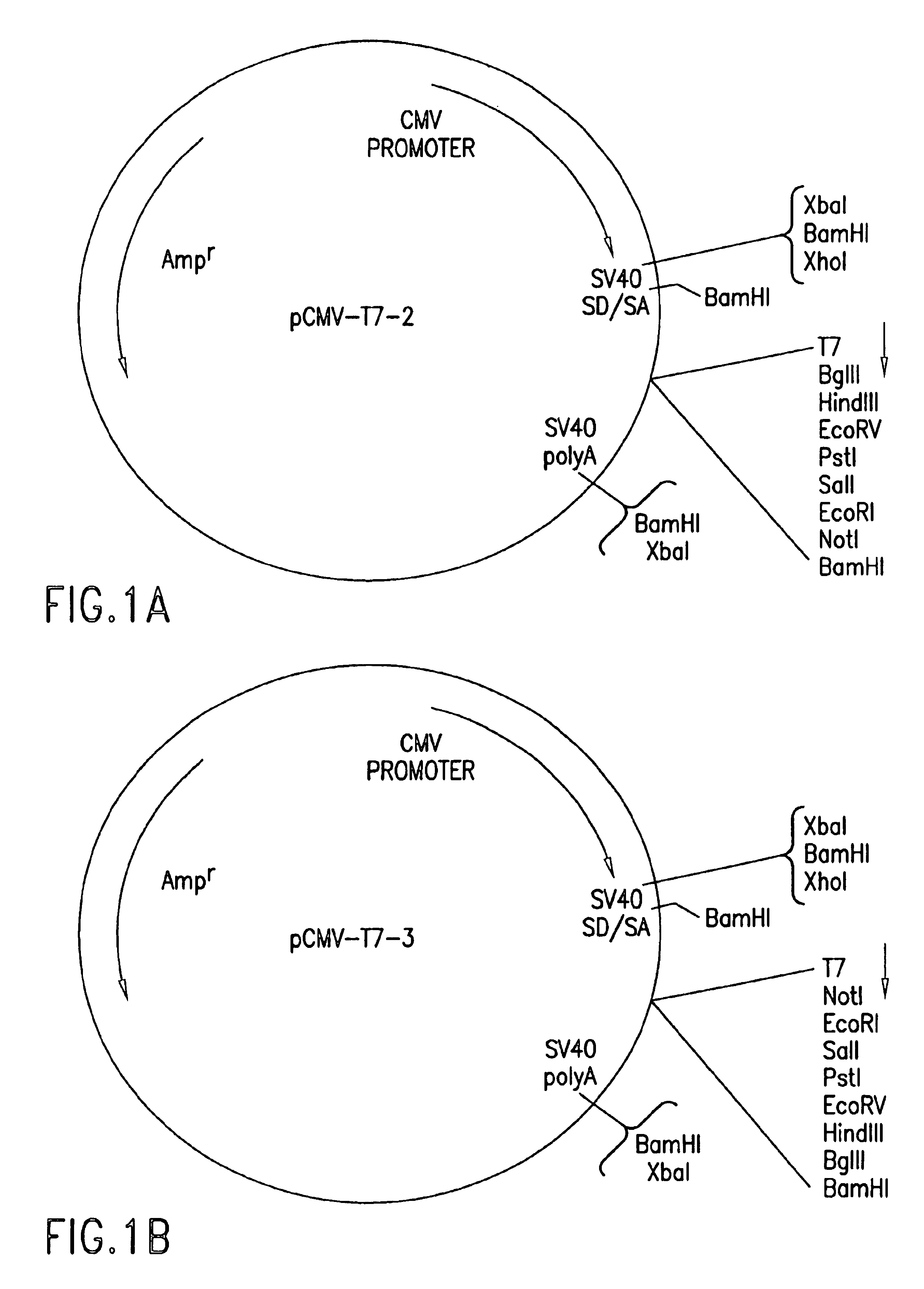
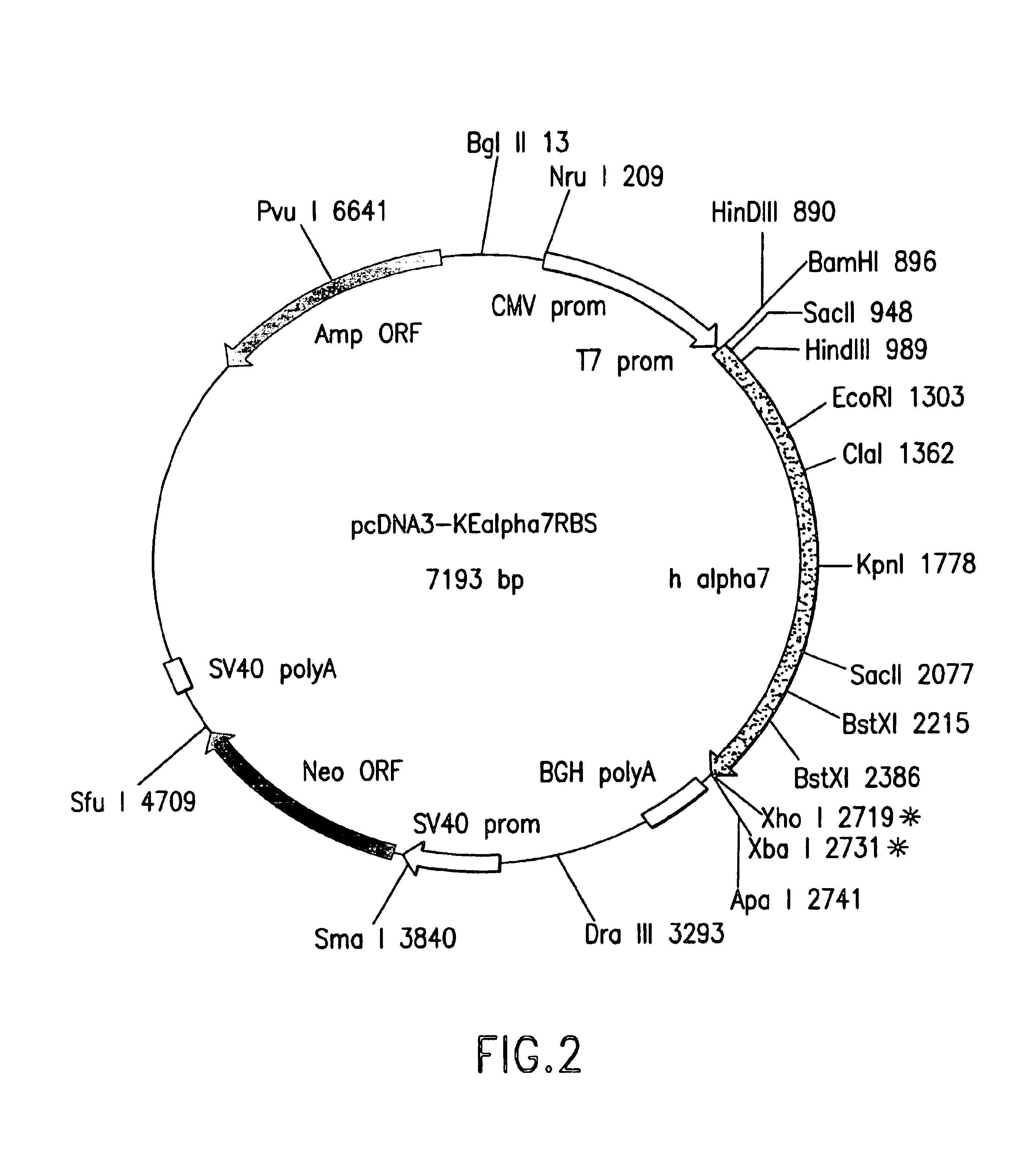
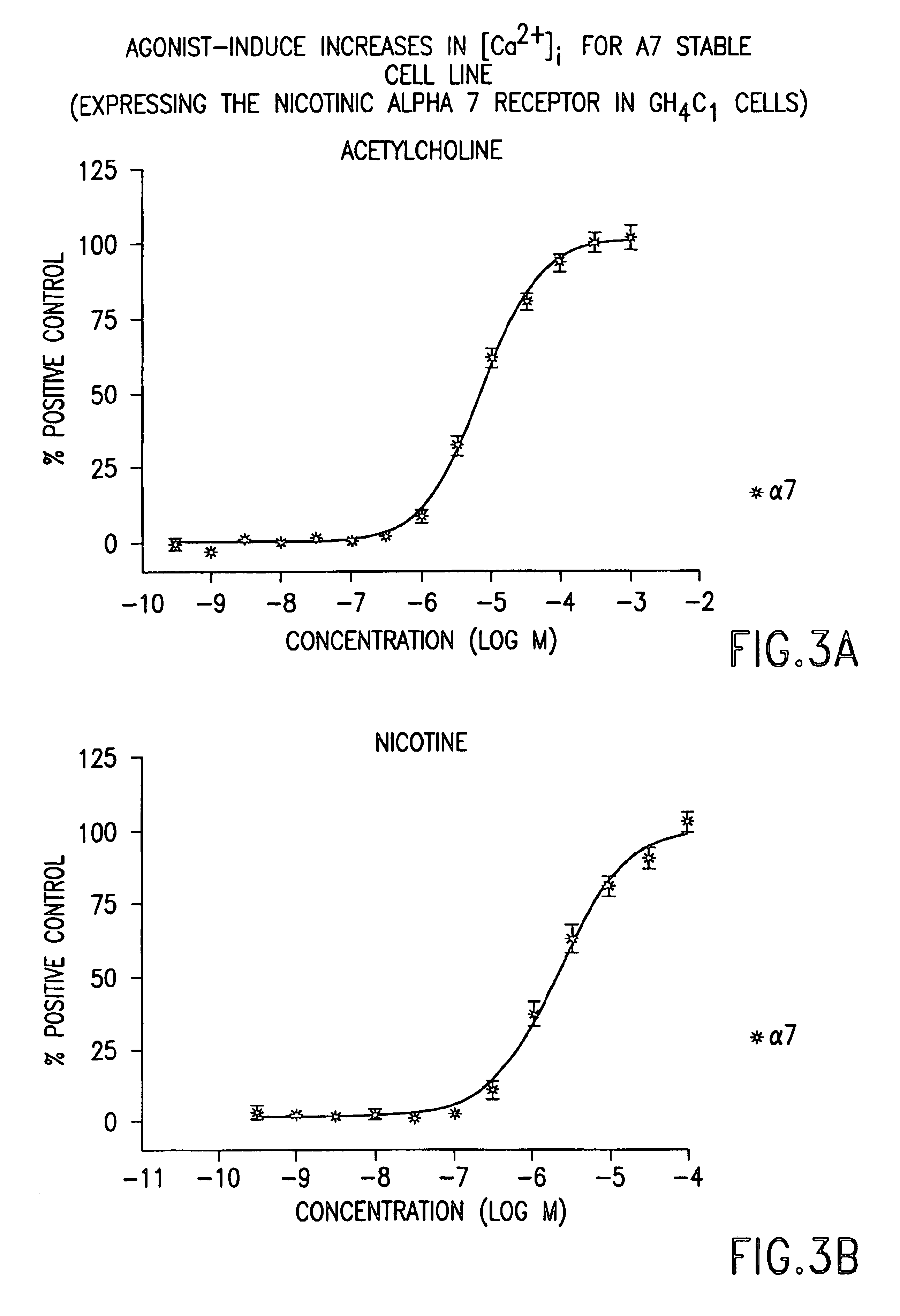
DNA encoding human α and β subunits of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, cells transformed therewith, and recombinant cell line expressing a human α and β subunit of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, i.e., DNA or RNA encoding human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha and beta subunits, mammalian and amphibian cells containing said DNA, methods for producing α and β subunits and recombinant (i.e., isolated or substantially pure) α subunits and β subunits are provided. In addition, cells expressing various multimeric combinations of subunits (i.e., α1, α2 α3 α4 α5 α6 and / or α7 in combination with at least one of an α and β subunit are also provided. A recombinant, non-human cell line expressing the human α7 subunit of nAChR is disclosed.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Human calcium channel compositions and methods
InactiveUS7414110B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesDna encodingCalcium channel activity
Isolated DNA encoding each of human calcium channel α1-, α2-, β- and γ-subunits, including subunits that arise as splice variants of primary transcripts, is provided. Cells and vectors containing the DNA and methods for identifying compounds that modulate the activity of human calcium channels are also provided.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Highly purified and stabilized Na,K-ATPase isoforms and methods of producing same
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Continuous dosing regimen
Compositions comprising one or more cancer drugs, continuous oral dosing schedule with drugs which bind to the colchicine site of tubulin β-subunits, and methods of treating diseases using continuous dosing schedules are disclosed.
Owner:GORDON GARY +3
Recombinant fragments of the human acetylcholine receptor and their use for treatment of myasthenia gravis
InactiveUS20070269865A1Modulating autoimmune responseSuppress diseaseBacteriaSugar derivativesAcetylcholine receptorAutoimmune responses
Polypeptides capable of modulating the autoimmune response of an individual to human acetylcholine receptor (hAChR), more particularly polypeptides corresponding entirely or partially to the extracellular domain of hAChR α-subunit, are useful in the diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis. Preferred polypeptides are polypeptides corresponding to amino acid residues 1-121 or 122-210 of the hAChR α-subunit sequence, and polypeptides corresponding to amino acid residues 1-121, 1-210 or 1-205 of the hAChR α-subunit sequence in which is inserted, between amino acid residues 58 and 59, a sequence of 25 amino acid residues encoded by the p3A exon of the hAChR α-subunit gene, and fragments, analogs, fused, soluble and denatured forms thereof. DNA molecules encoding said polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Novel high functional enzyme having modified substrate specificity of human ß-hexosaminidase b and exhibiting protease resistance
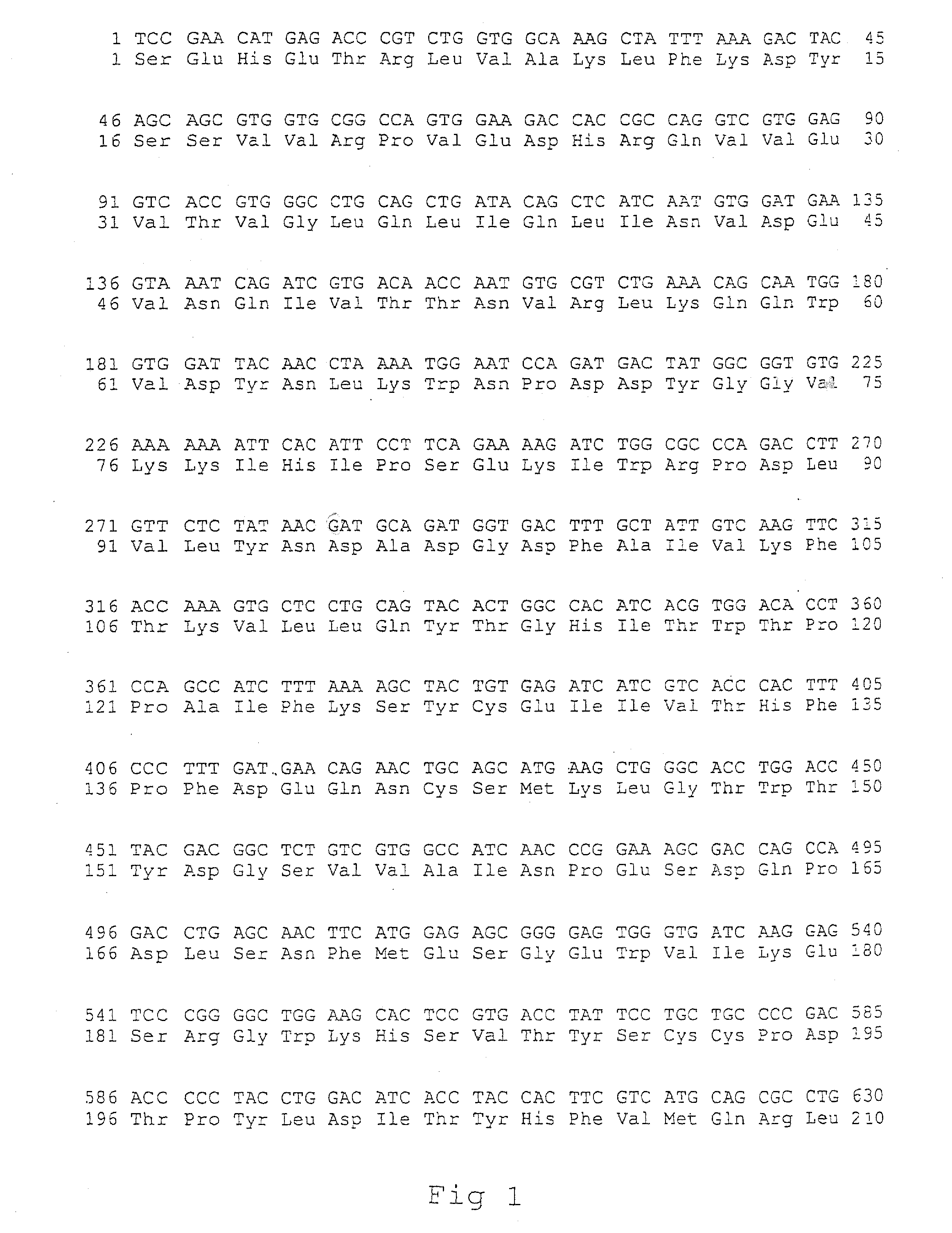
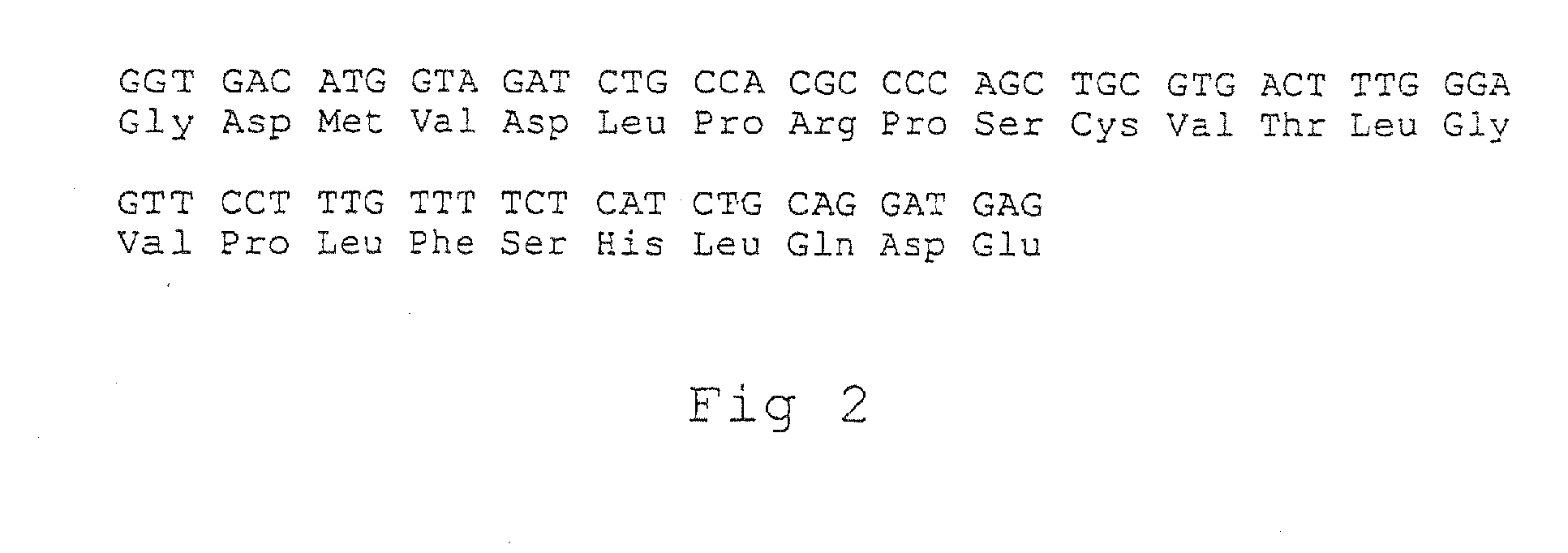
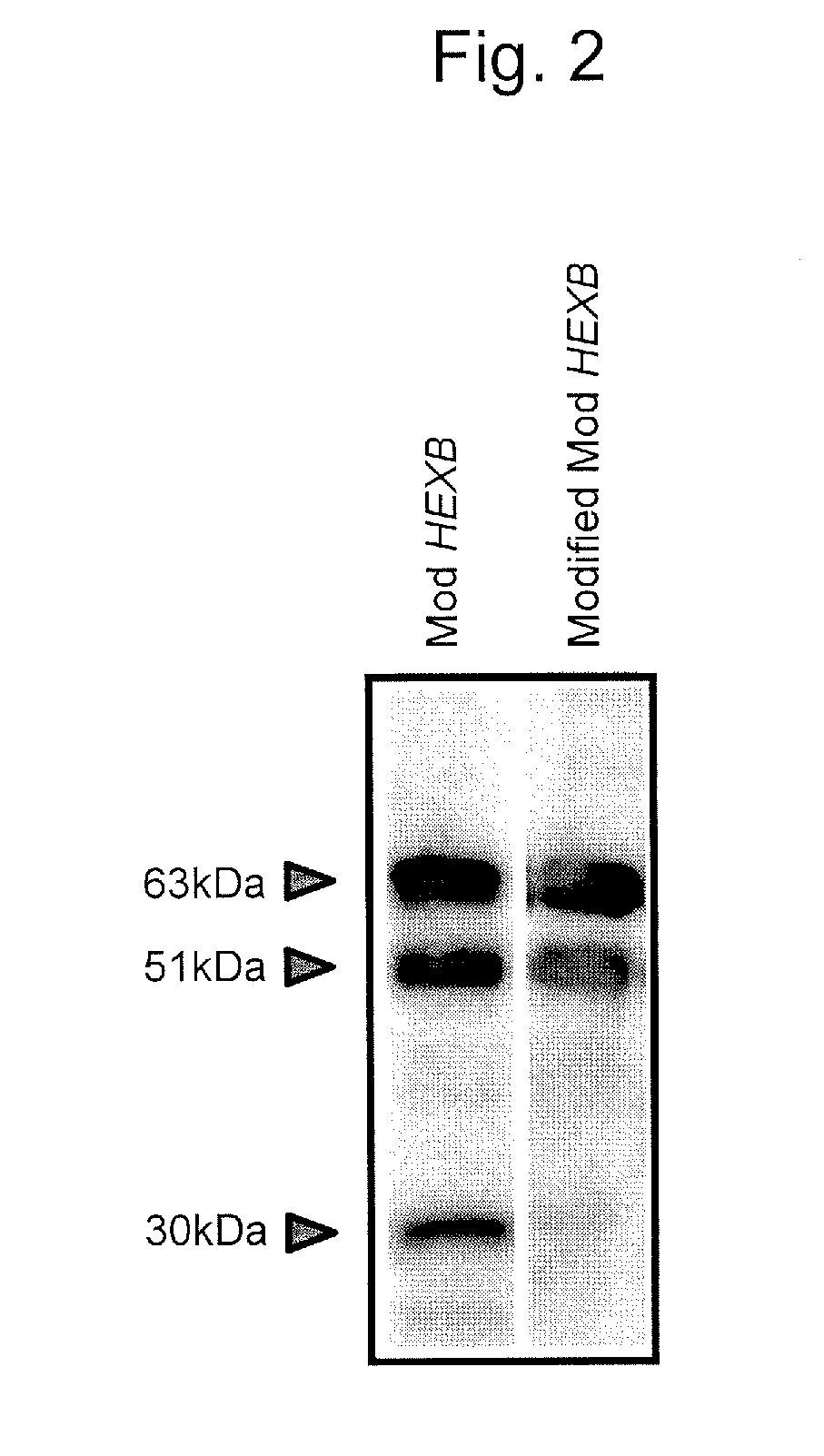
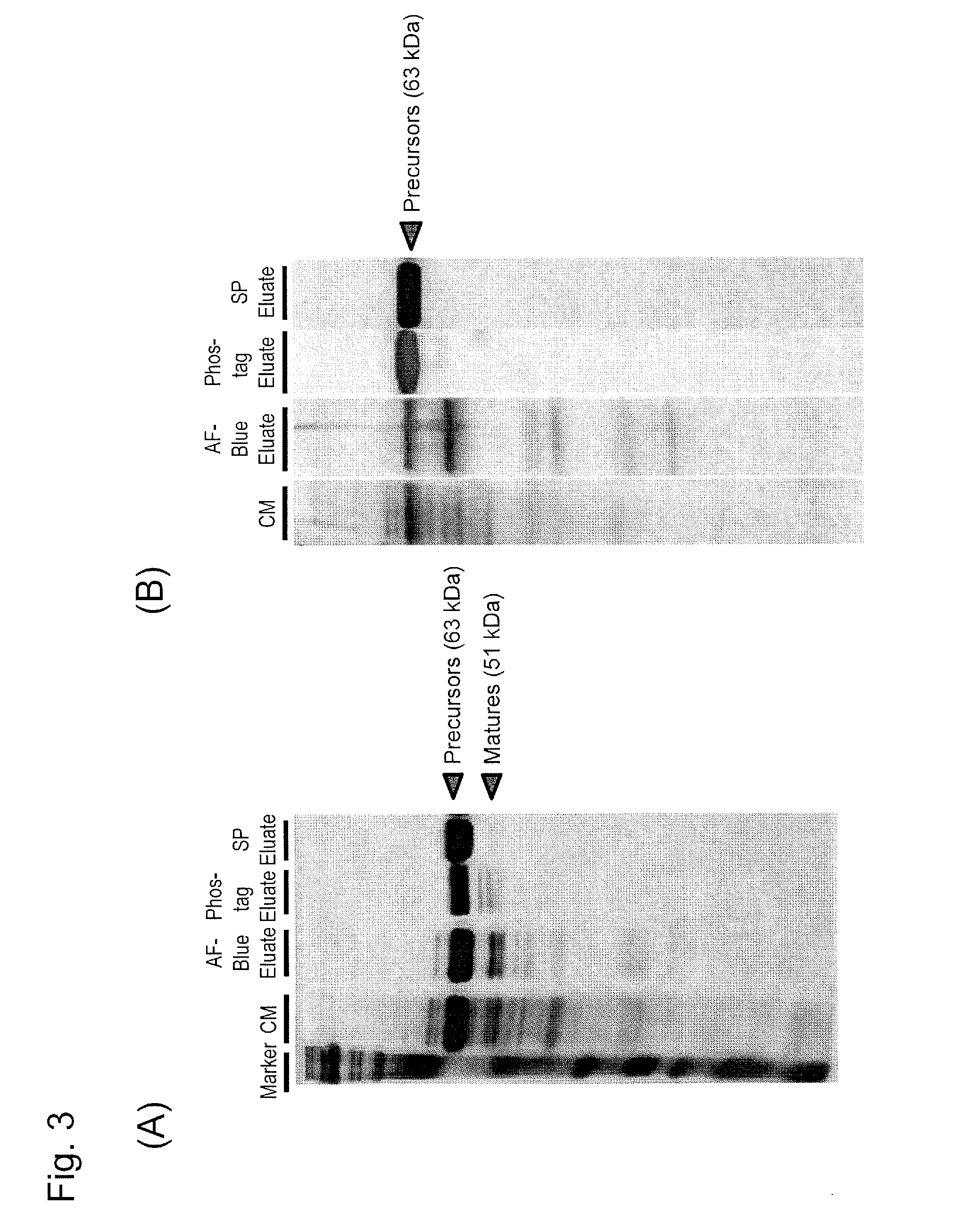
Provided is a modified β-subunit of human β-hexosaminidase which has the activity derived from the α-subunit of wild-type human β-hexosaminidase and has the resistance to protease. A protein comprising an amino acid sequence having substitutions of the 312th to the 318th amino acids with glycine, serine, glutamic acid, proline, serine, glycine and threonine in order, respectively, in an amino acid sequence of a β-subunit of wild-type human β-hexosaminidase.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOKUSHIMA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com