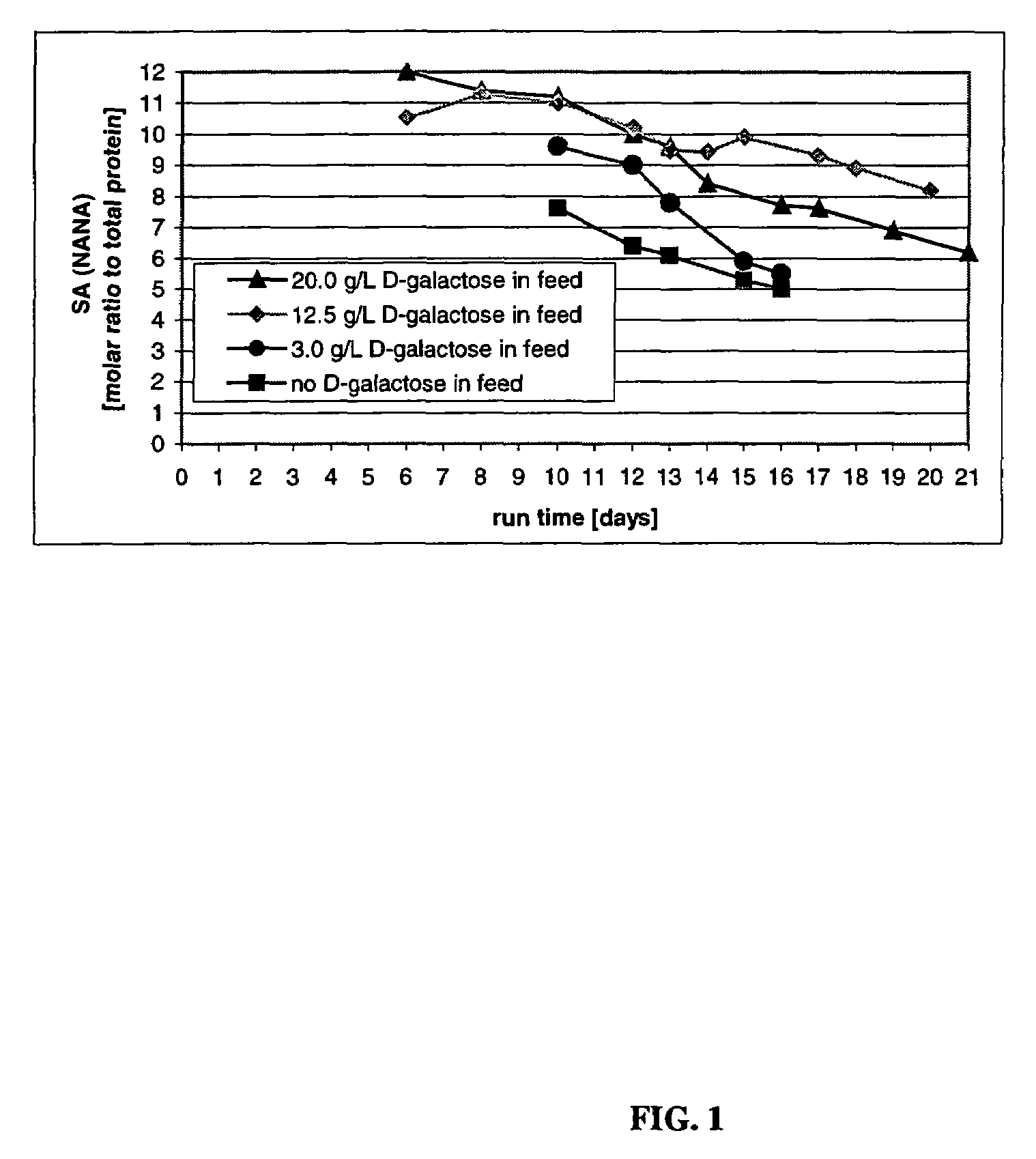
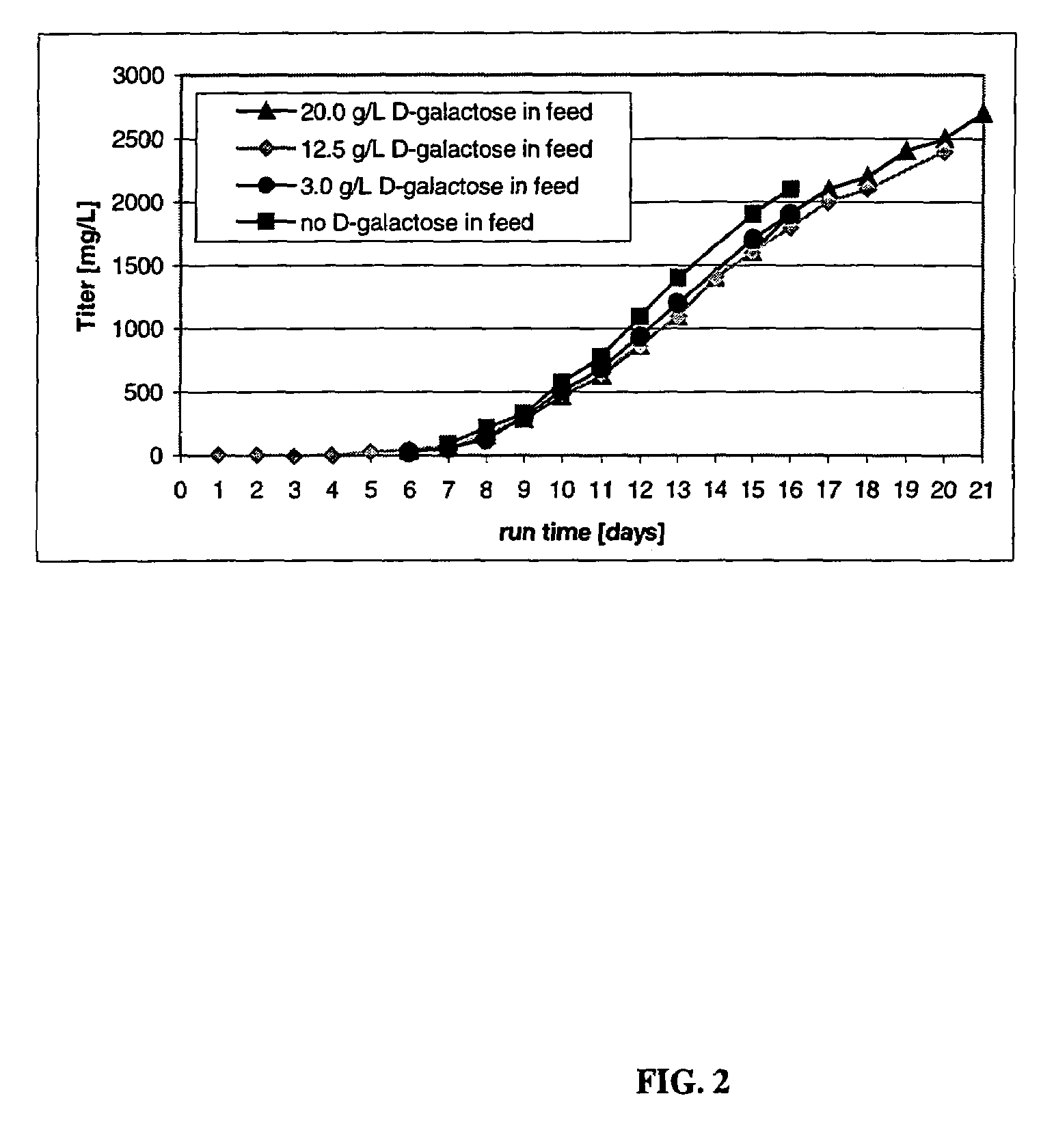
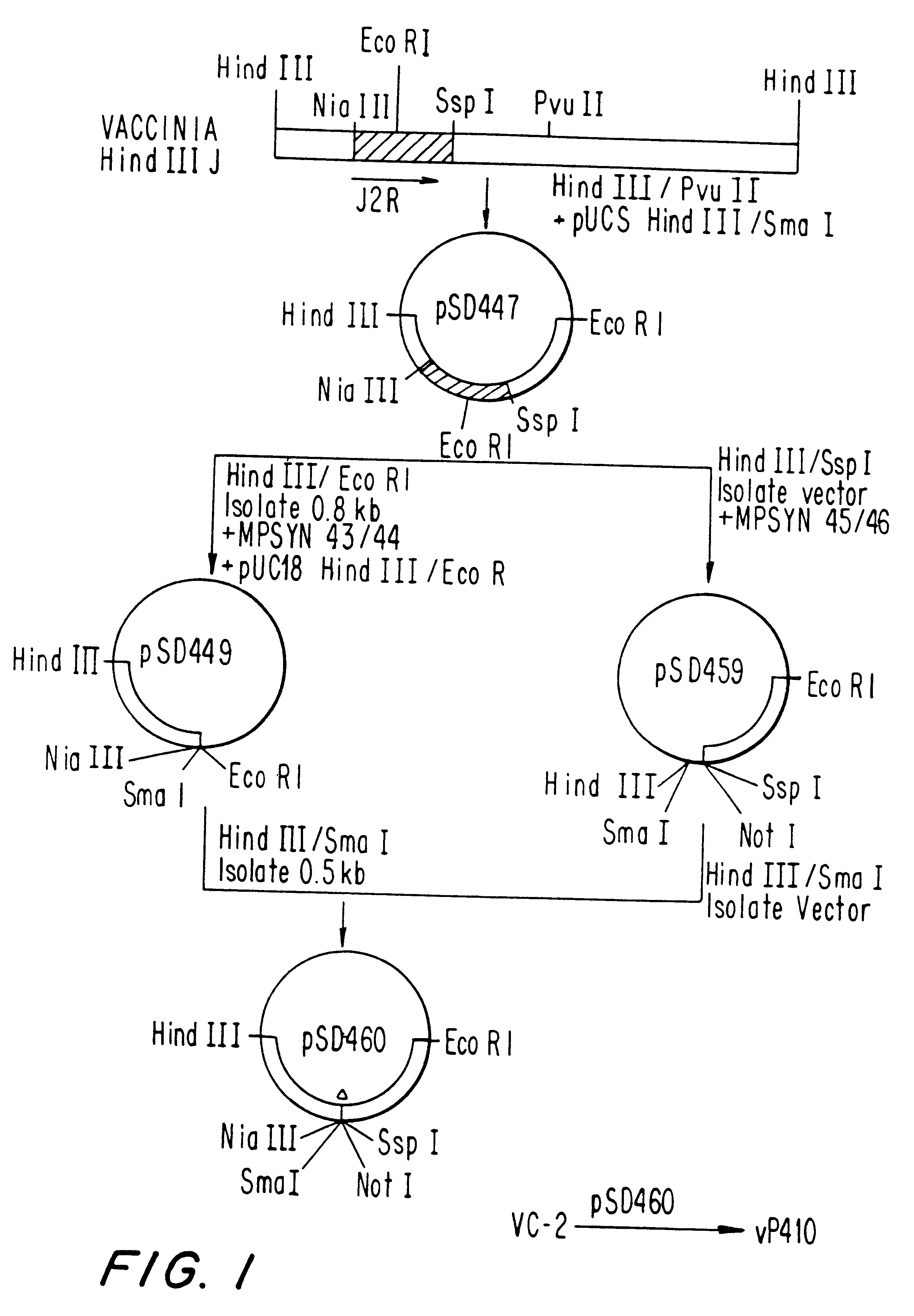
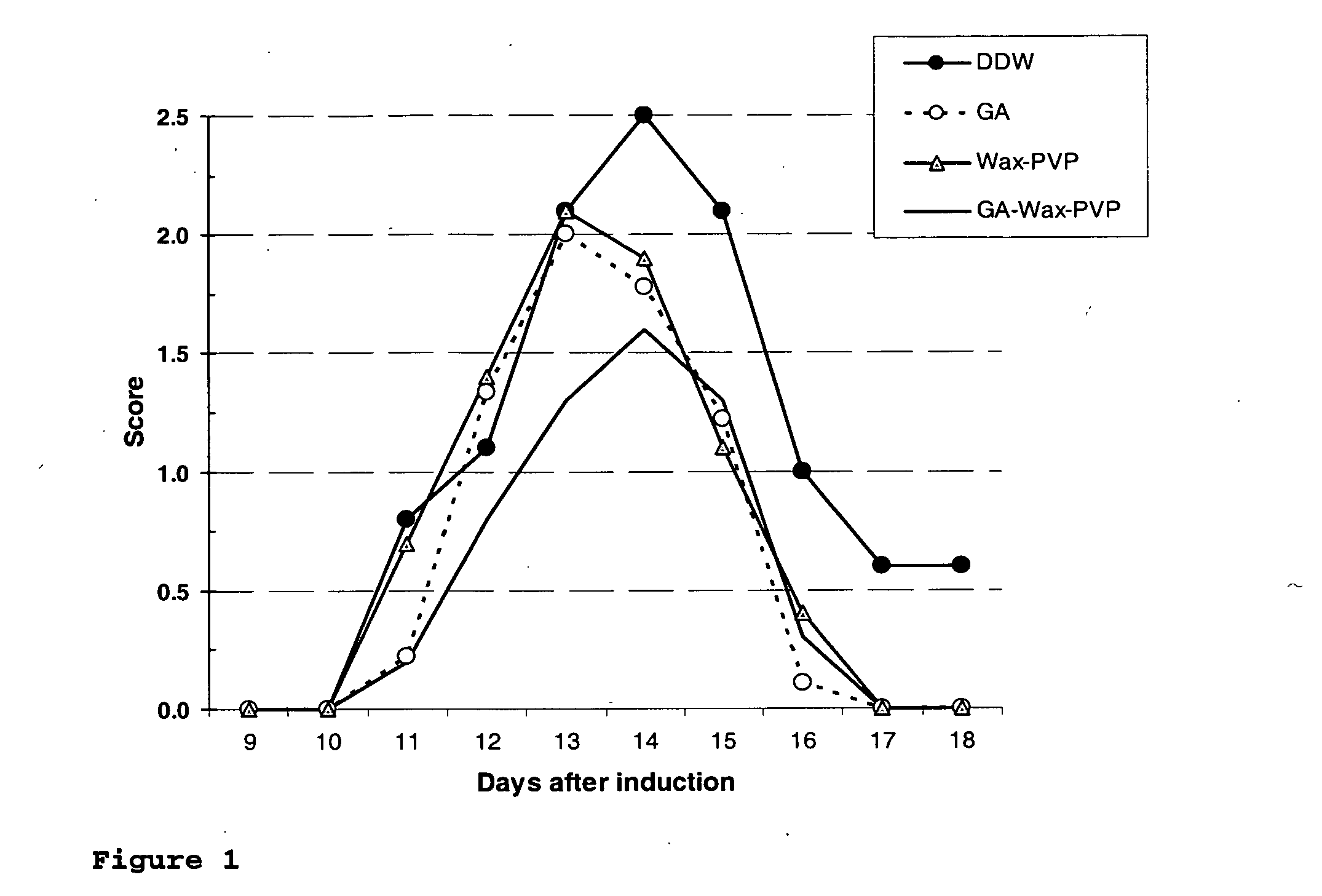
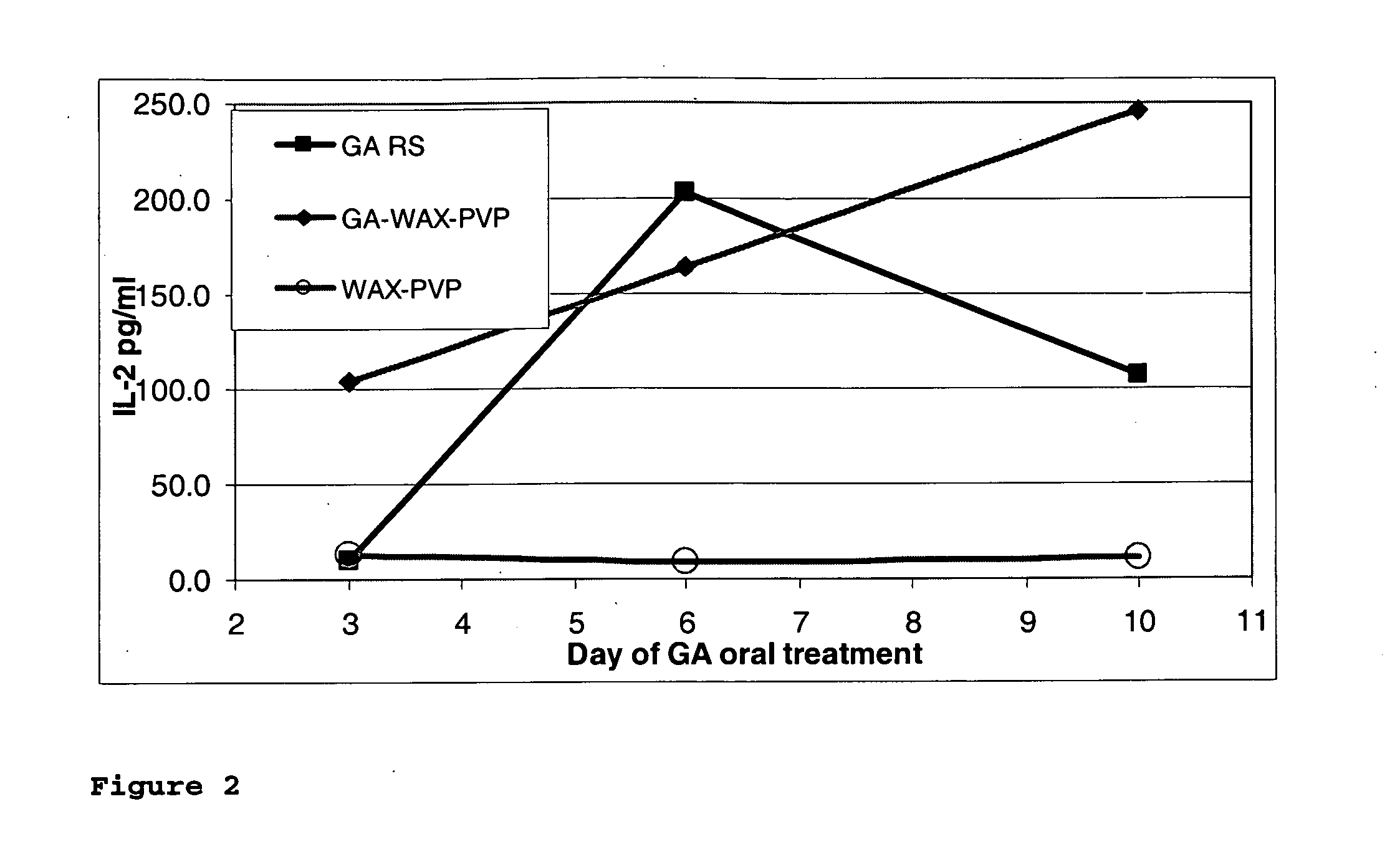
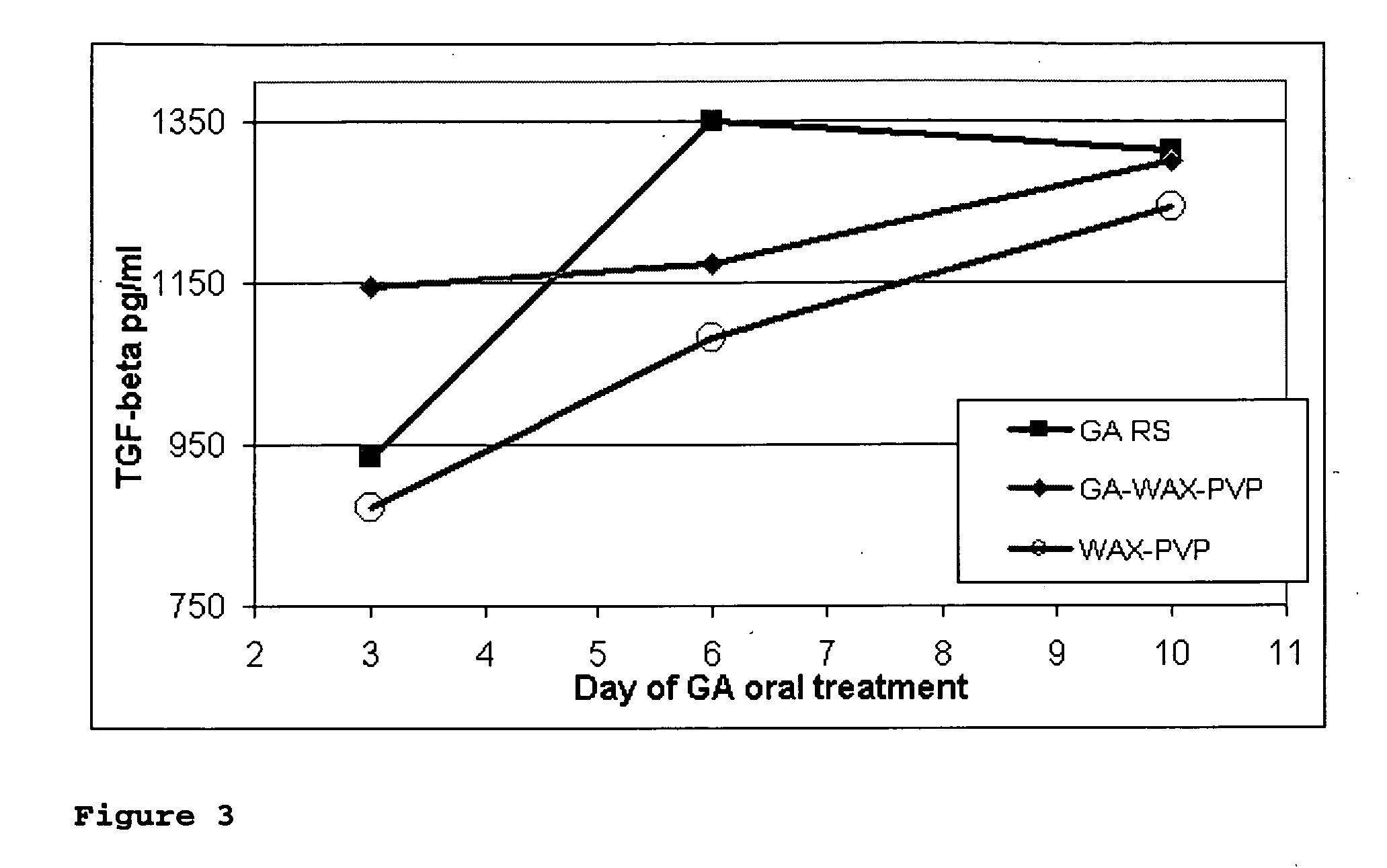
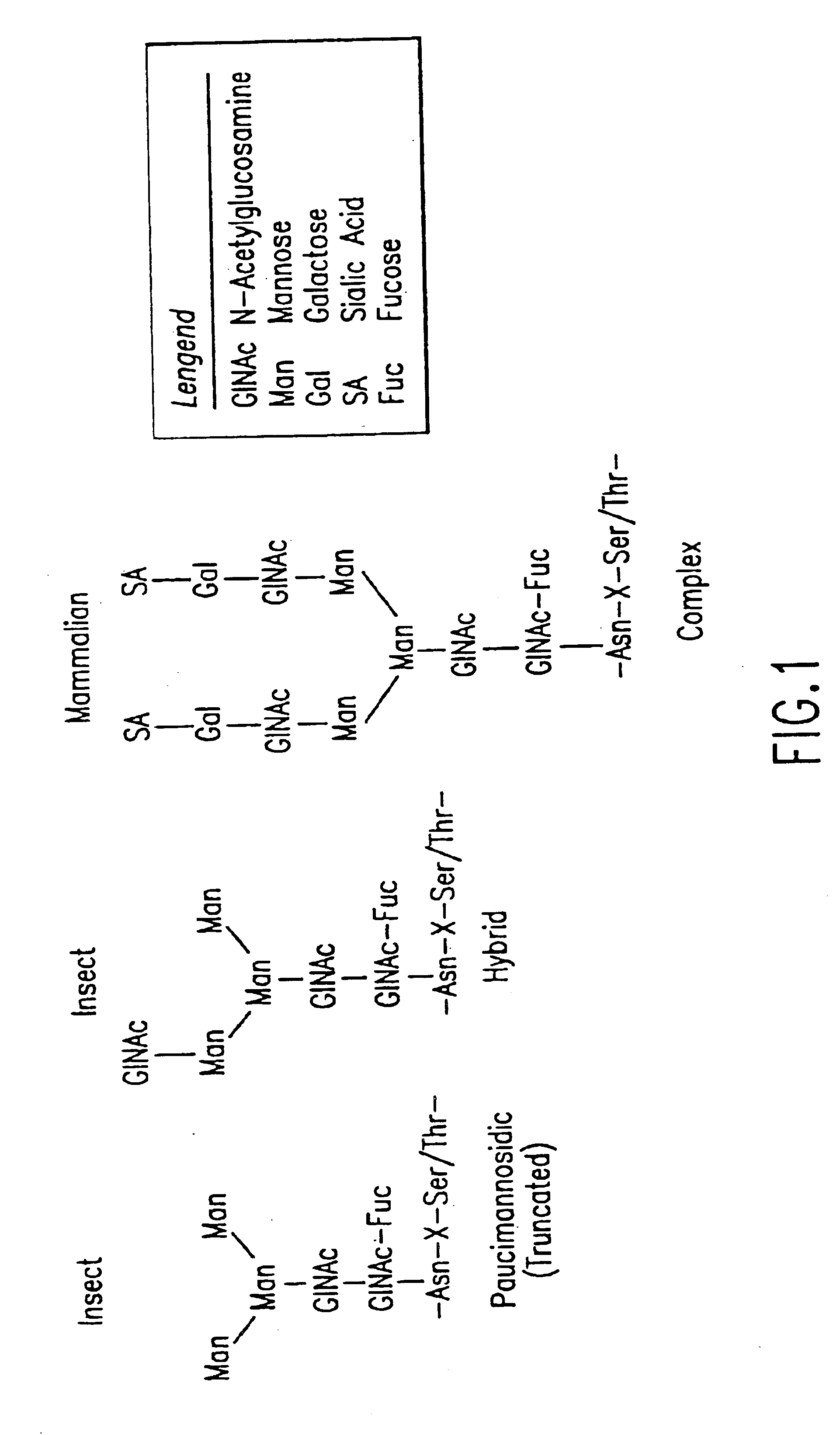
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2589 results about "Glycoprotein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated.
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
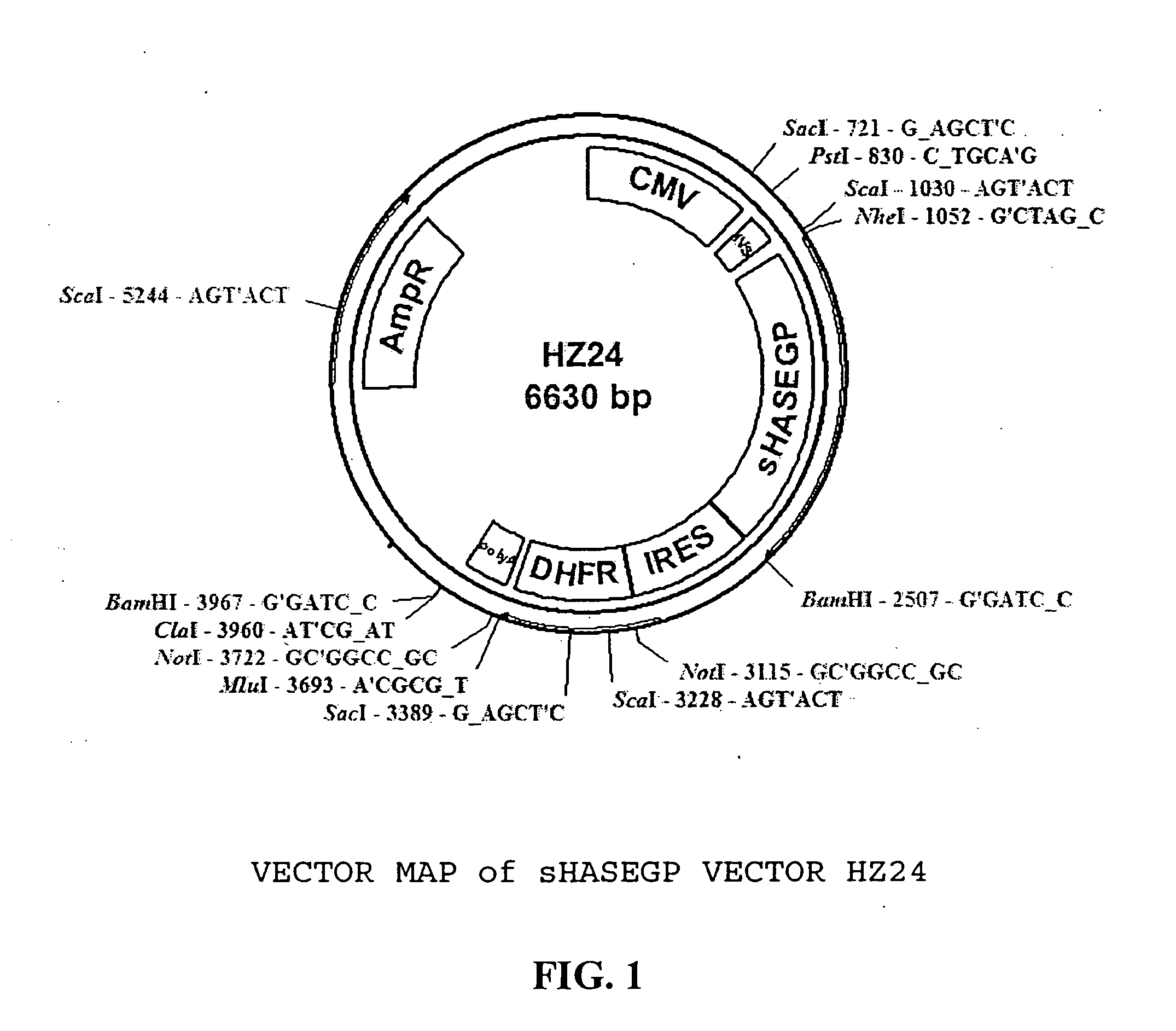
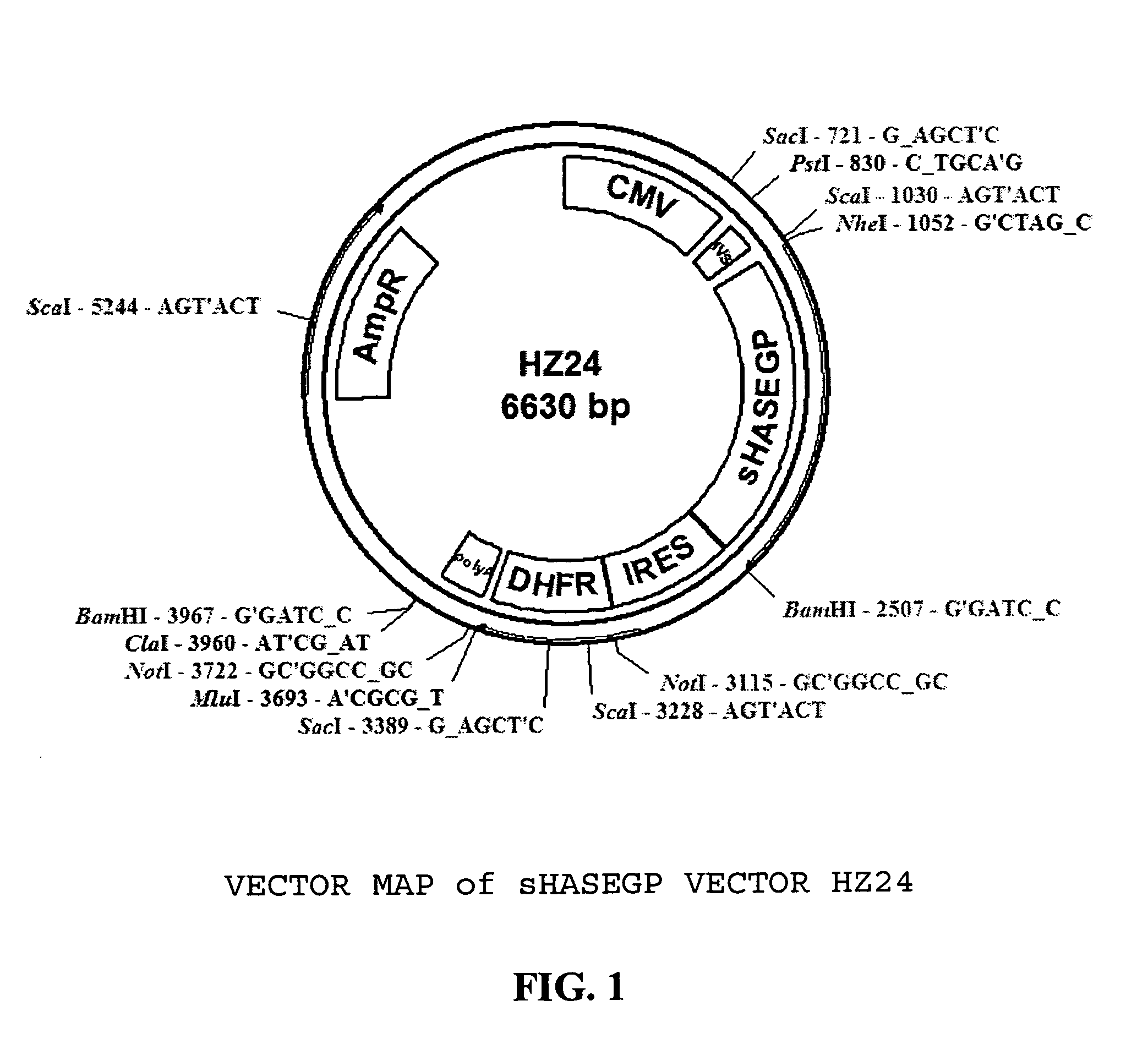
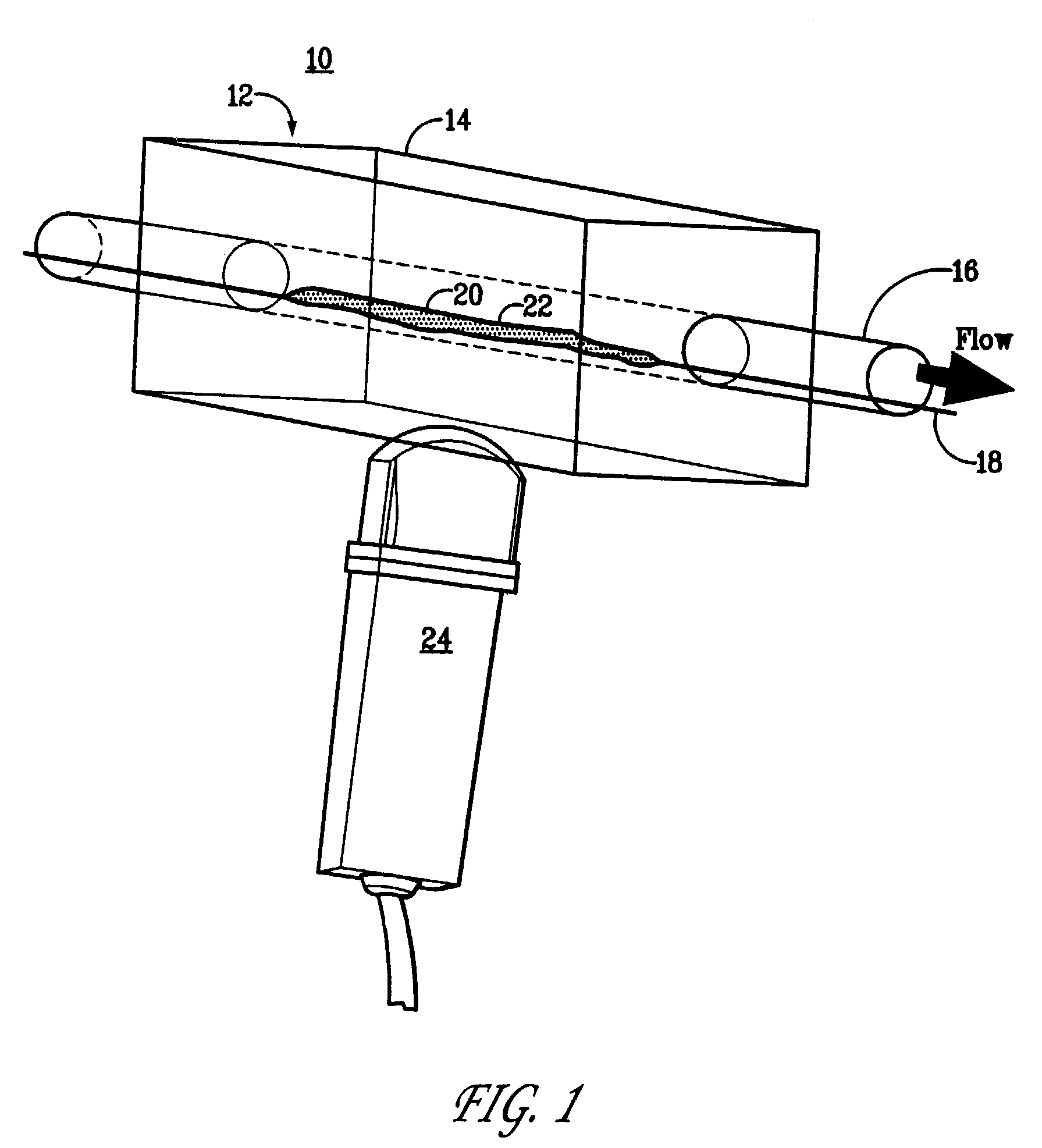
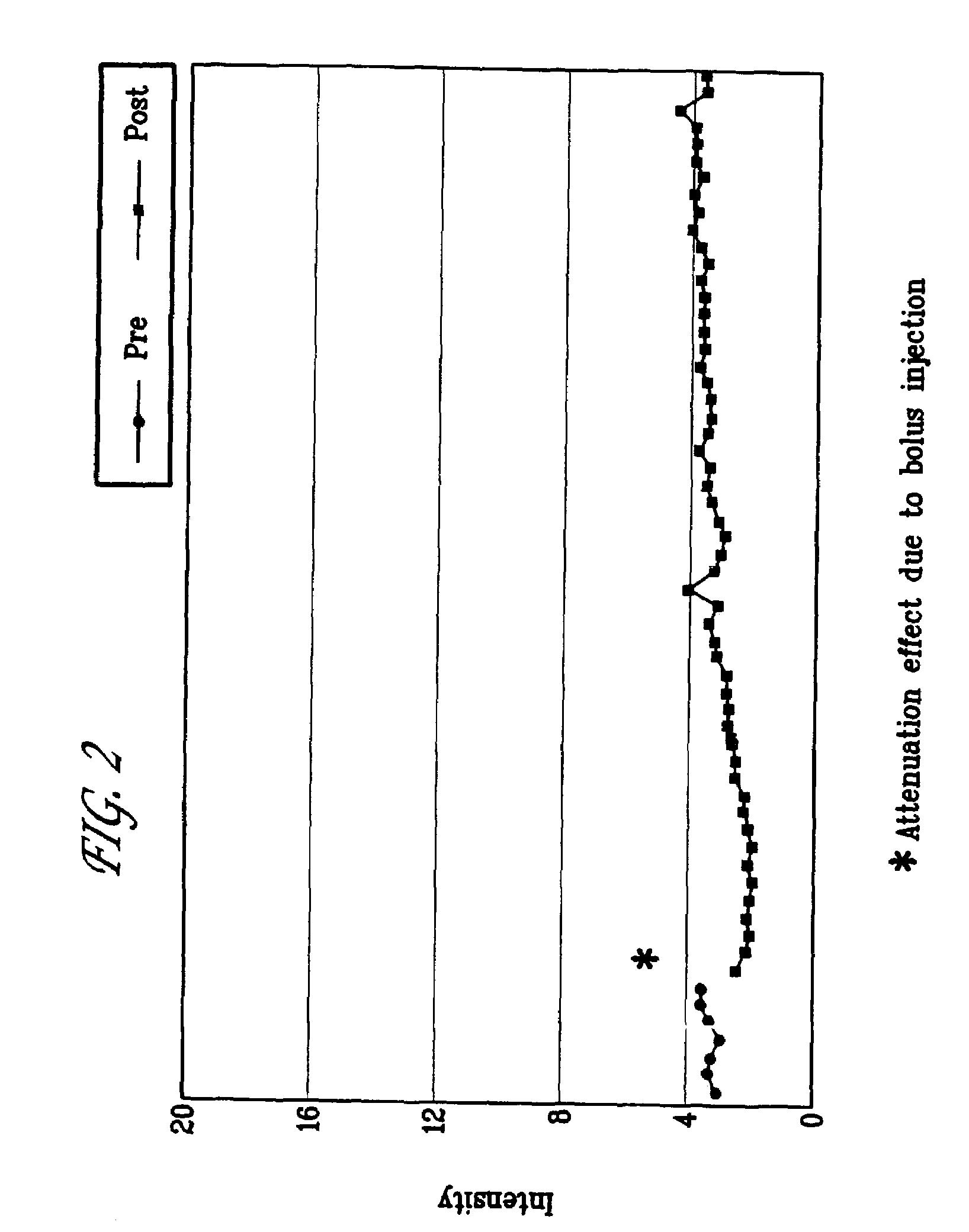
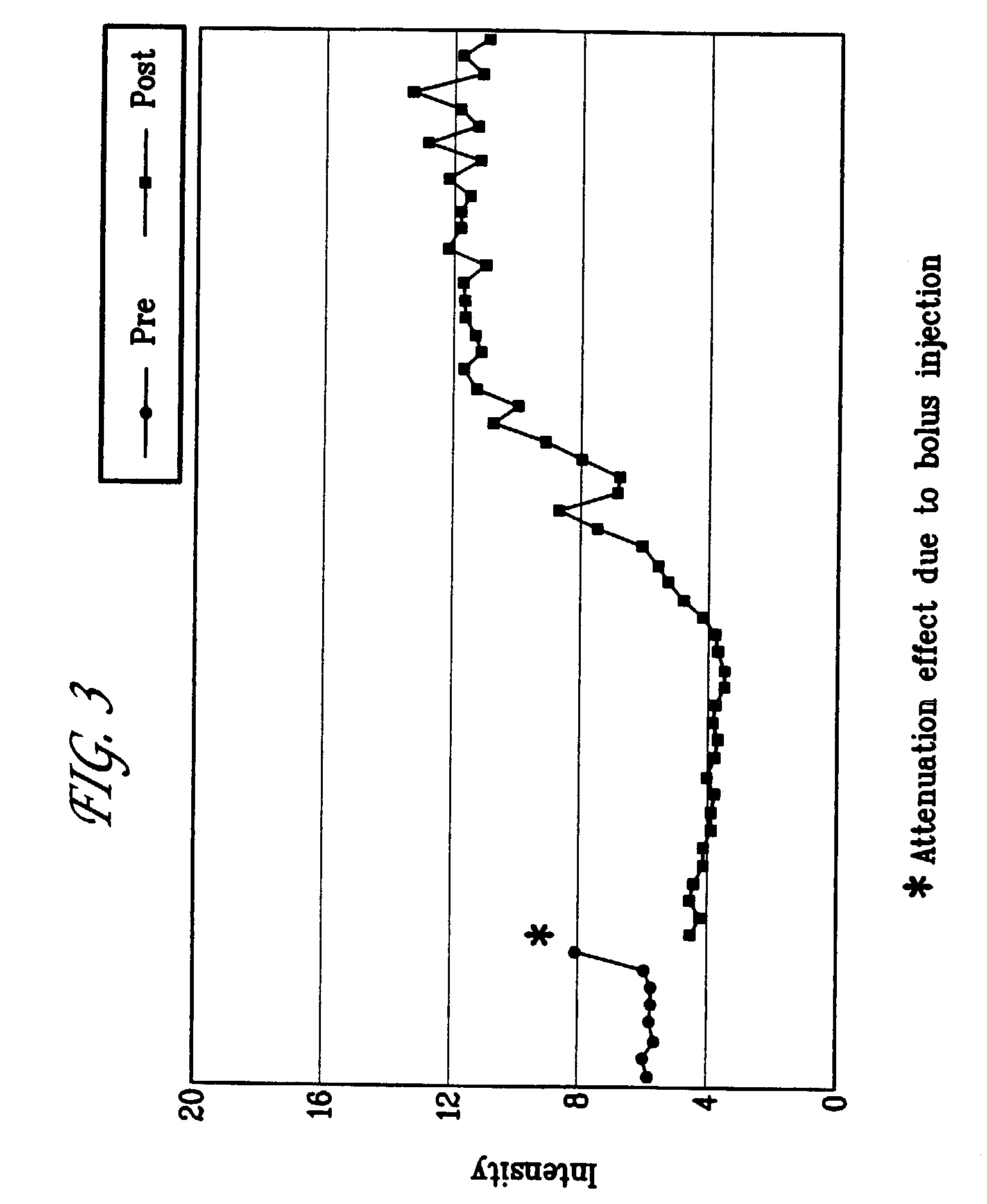
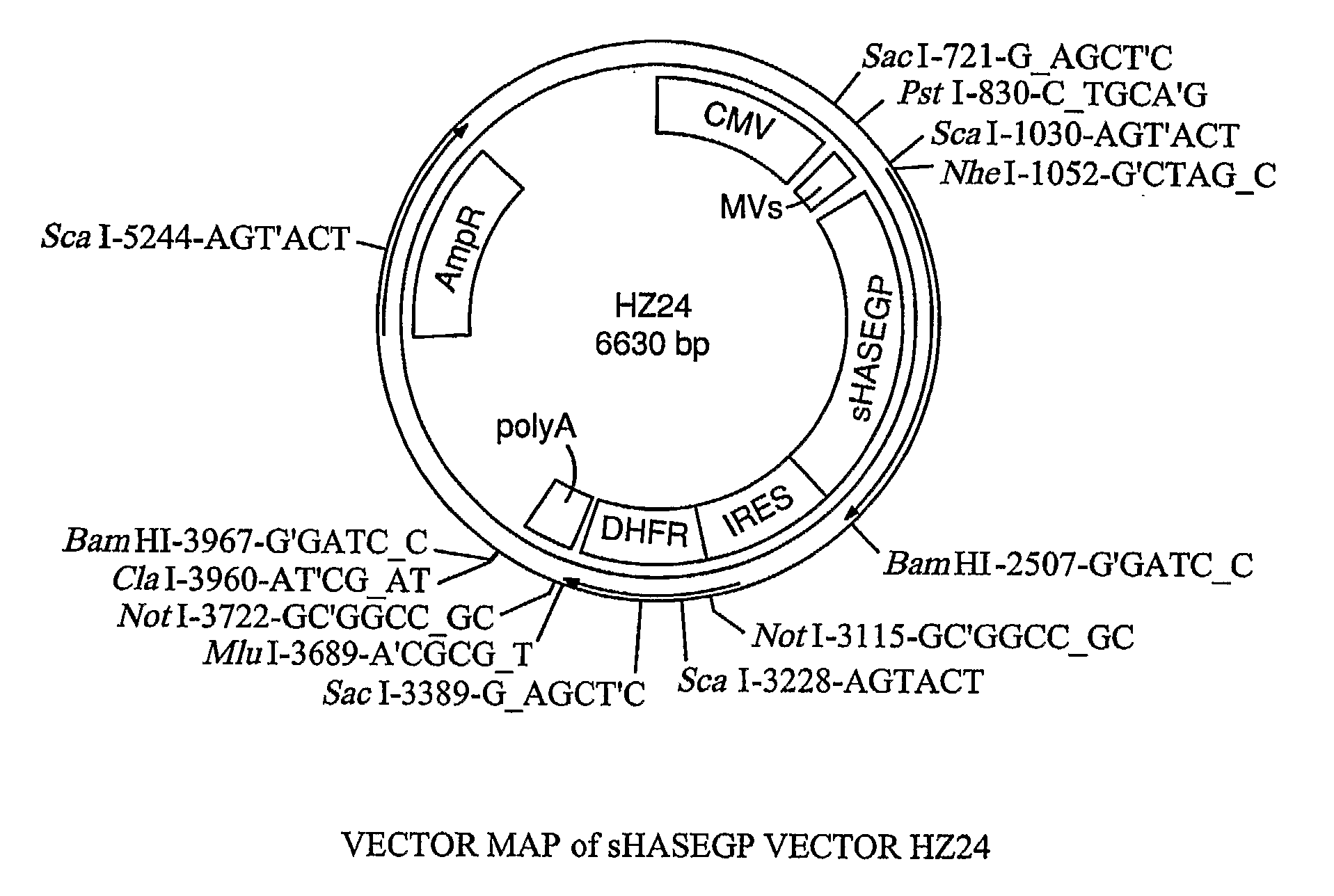
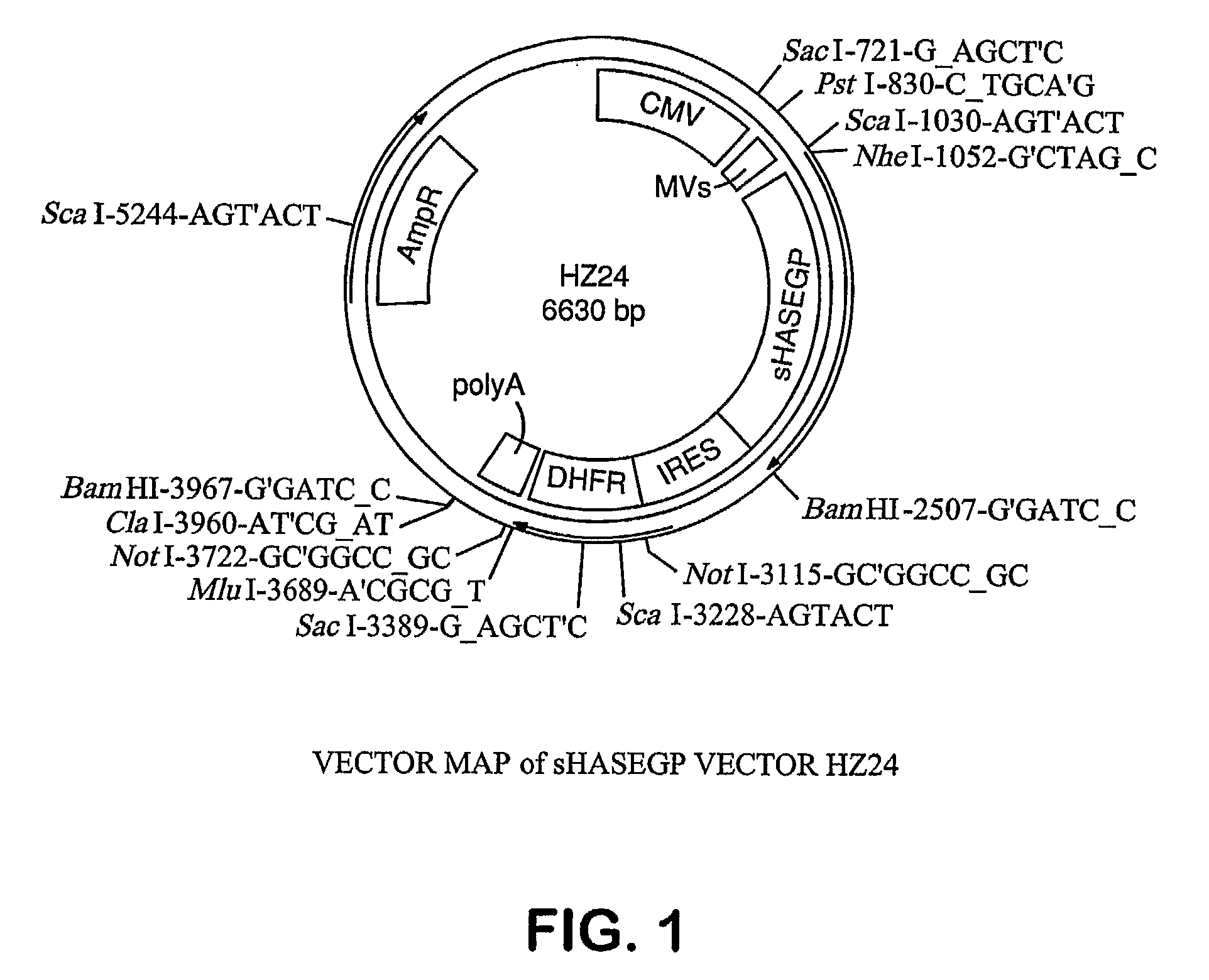
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Tissue-and serum-derived glycoproteins and methods of their use
InactiveUS20070099251A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood plasmaBiology
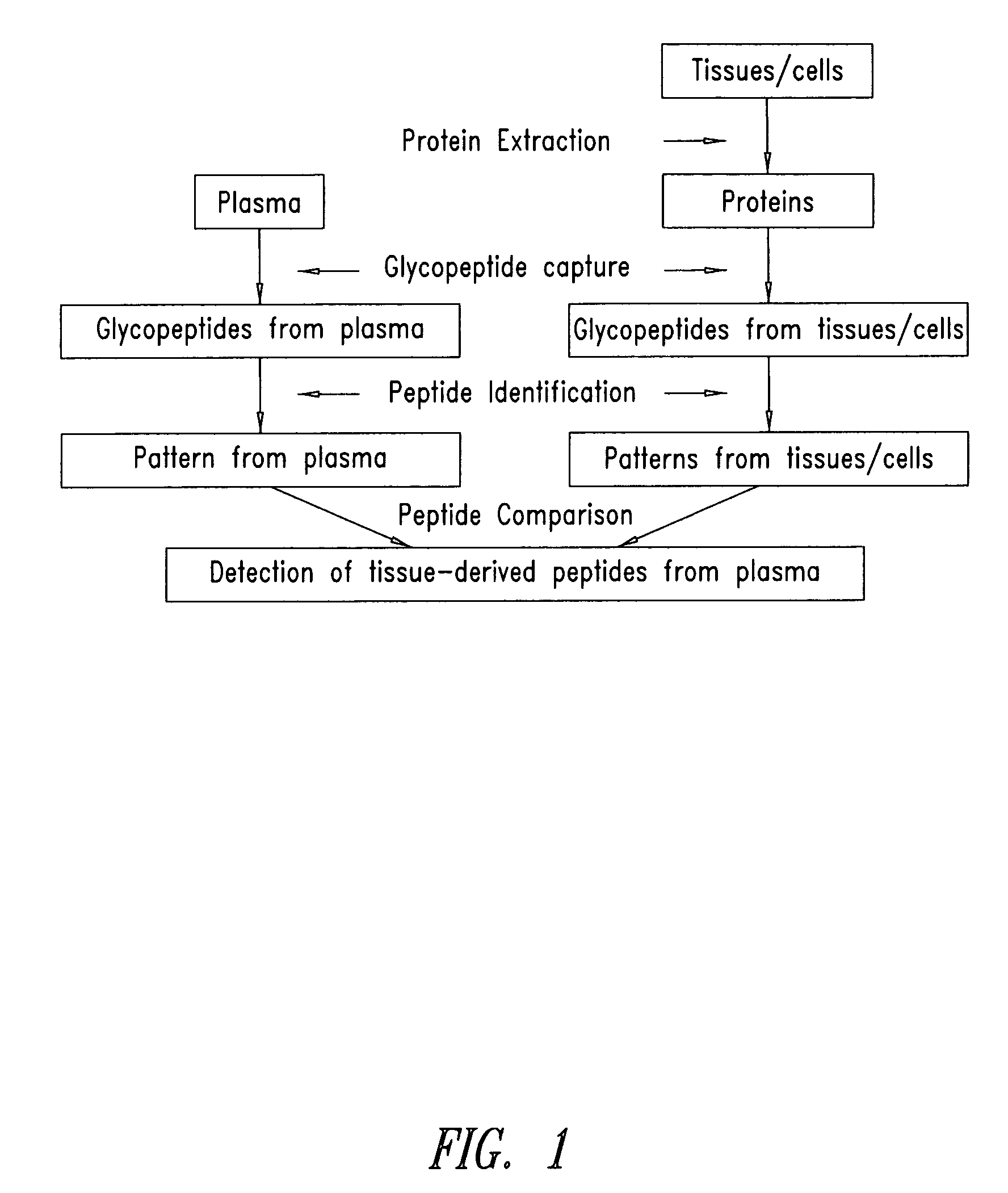
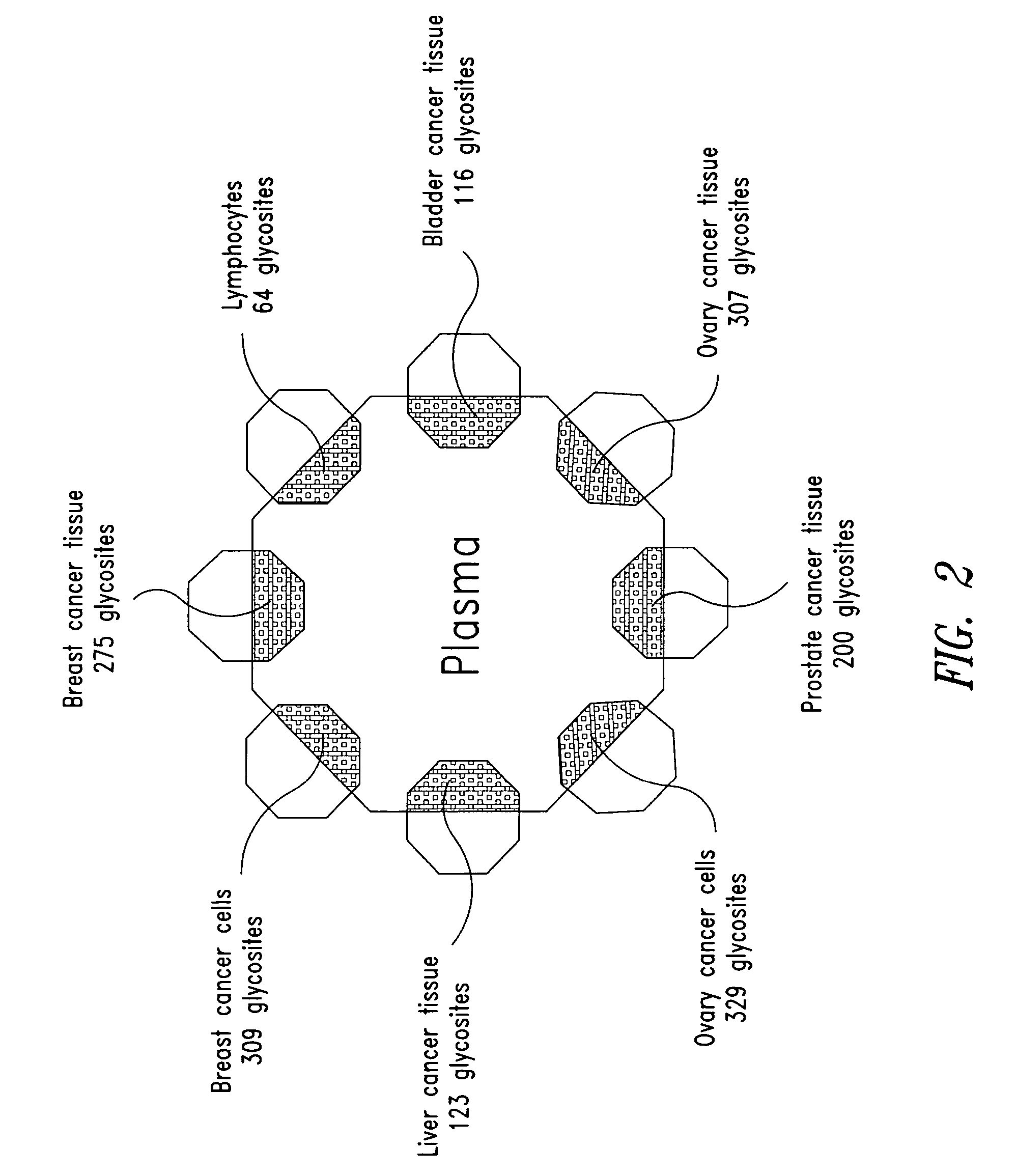
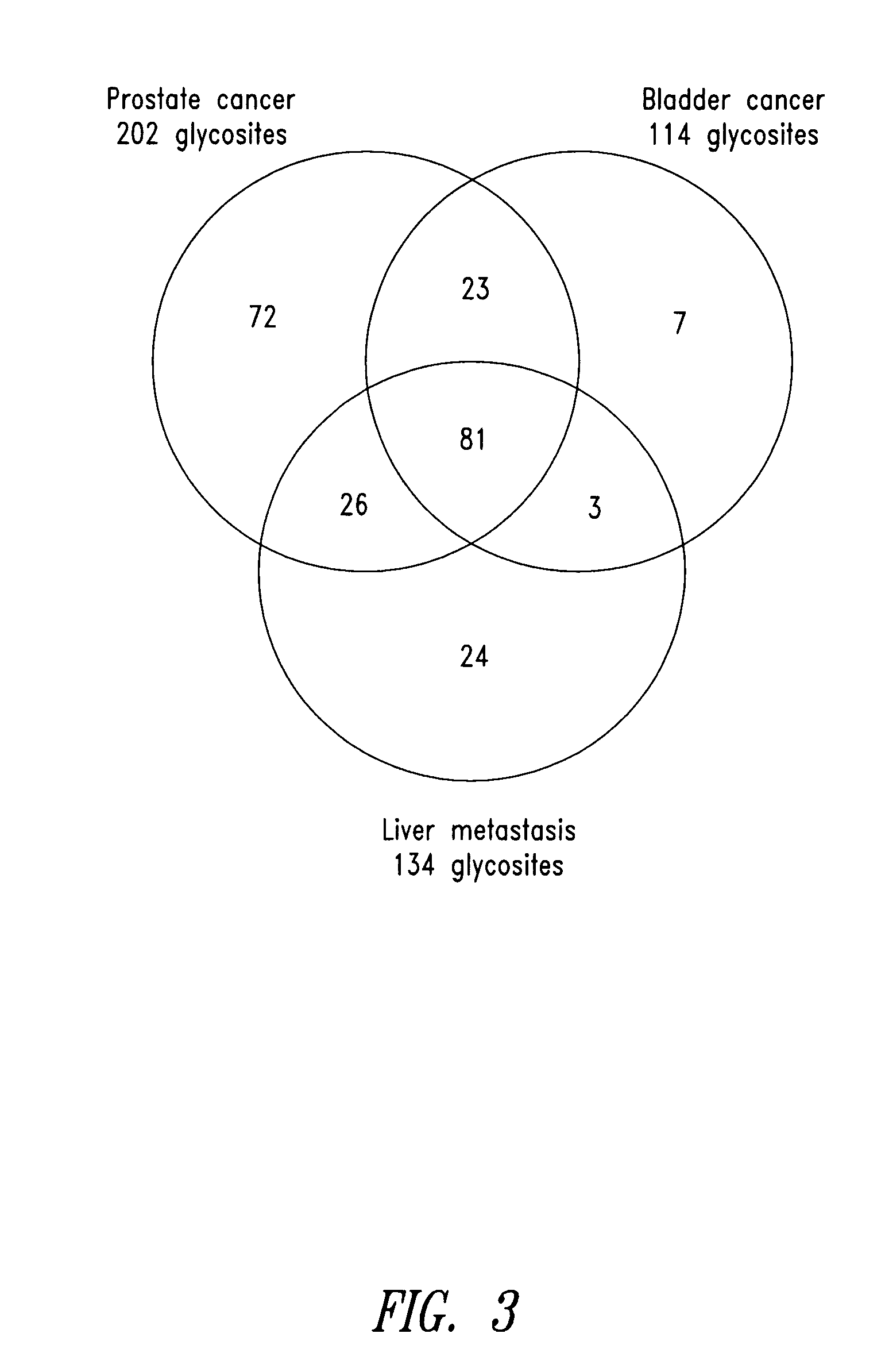
The present invention is directed generally to tissue-derived glycoproteins and glycosites detectable in plasma via mass spectrometric analysis of glycoproteins from both tissues and blood. The invention also provides methods for identifying tissue-derived glycoproteins and glycosites in plasma, panels of detection reagents for detecting same, as well methods for detecting disease using such panels. The invention further provides a database of tissue-derived glycoproteins and glycosites detectable in plasma.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
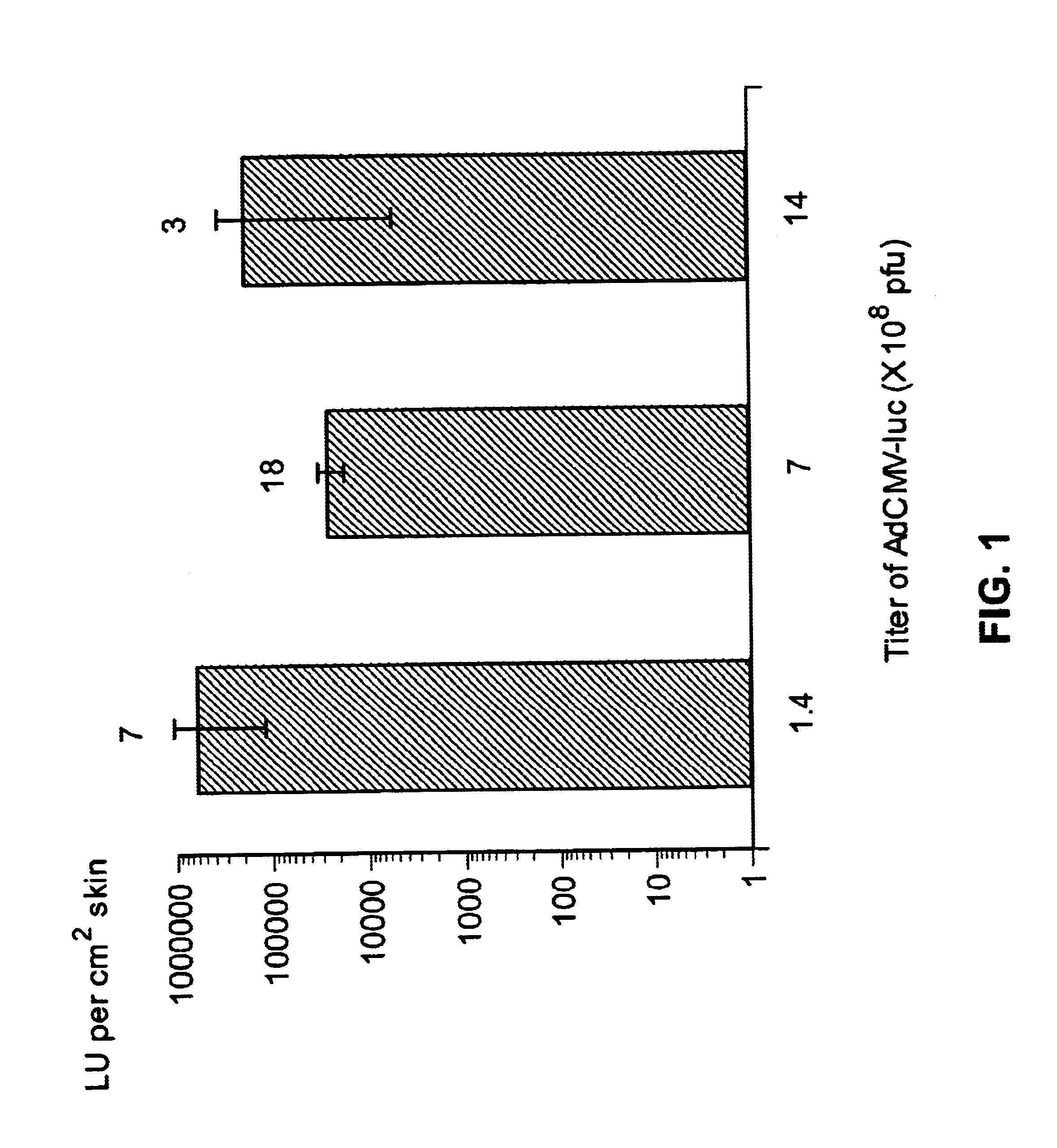
Vaccine and drug delivery by topical application of vectors and vector extracts
InactiveUS20040009936A1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient deliverySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideNeoplasmGlycoprotein
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive immunization and drug delivery in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal following topical application of non-replicative vectors, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. Also disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive immunization and drug delivery in an animal and / or a method of inducing a systemic immune response or systemic therapeutic response to a gene product comprising contacting skin of the animal with cell-free extracts in an amount effective to induce the response, wherein the extracts are prepared by filtration of disrupted cells, wherein the cell comprises and expresses a nucleic acid molecule. Preferably, the cell is temporarily disrupted by sonication, remaining intact and viable after the sonication. Also, methods are disclosed and claimed for enhancing the immunogenicity and efficacy of an epicutaneous vaccine for inducing a systemic immune response to an antigen, in an animal comprising contacting skin of the animal with vaccines admixed with heat-shock protein 27, in an amount effective to induce the response. The methods include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope or antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, influenza M2, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, anthrax germination factors, rabies glycoprotein, HBV surface antigen, HIV gp120, HIV gp160, human carcinoembryonic antigen, malaria CSP, malaria SSP, malaria MSP, malaria pfg, botulinum toxin A, and mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP; and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co- stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells including epidermal cells. The immune response can also be induced by antigens expressed from the nucleic acid molecule within the vector. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector. The animal can be a vertebrate, e.g., a mammal, such as human, a cow, a horse, a dog, a cat, a goat, a sheep or a pig; or fowl such as turkey, chicken or duck. The vector can be one or more of a viral vector, including viral coat, e.g., with some or all viral genes deleted therefrom, bacterial, protozoan, transposon, retrotransposon, and DNA vector, e.g., a recombinant vector; for instance, an adenovirus, such as an adenovirus defective in its E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 region(s) and / or all adenoviral genes.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
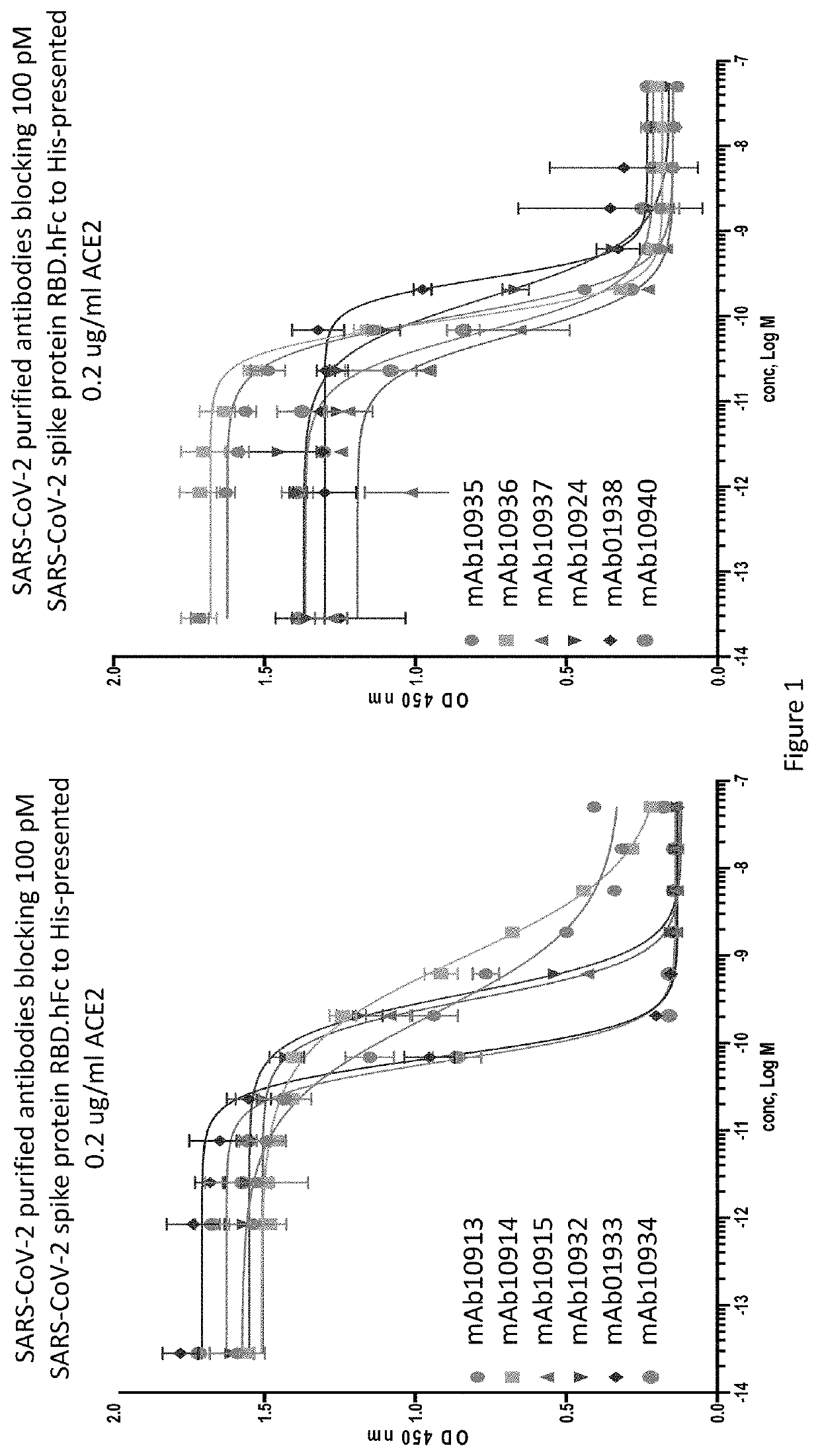
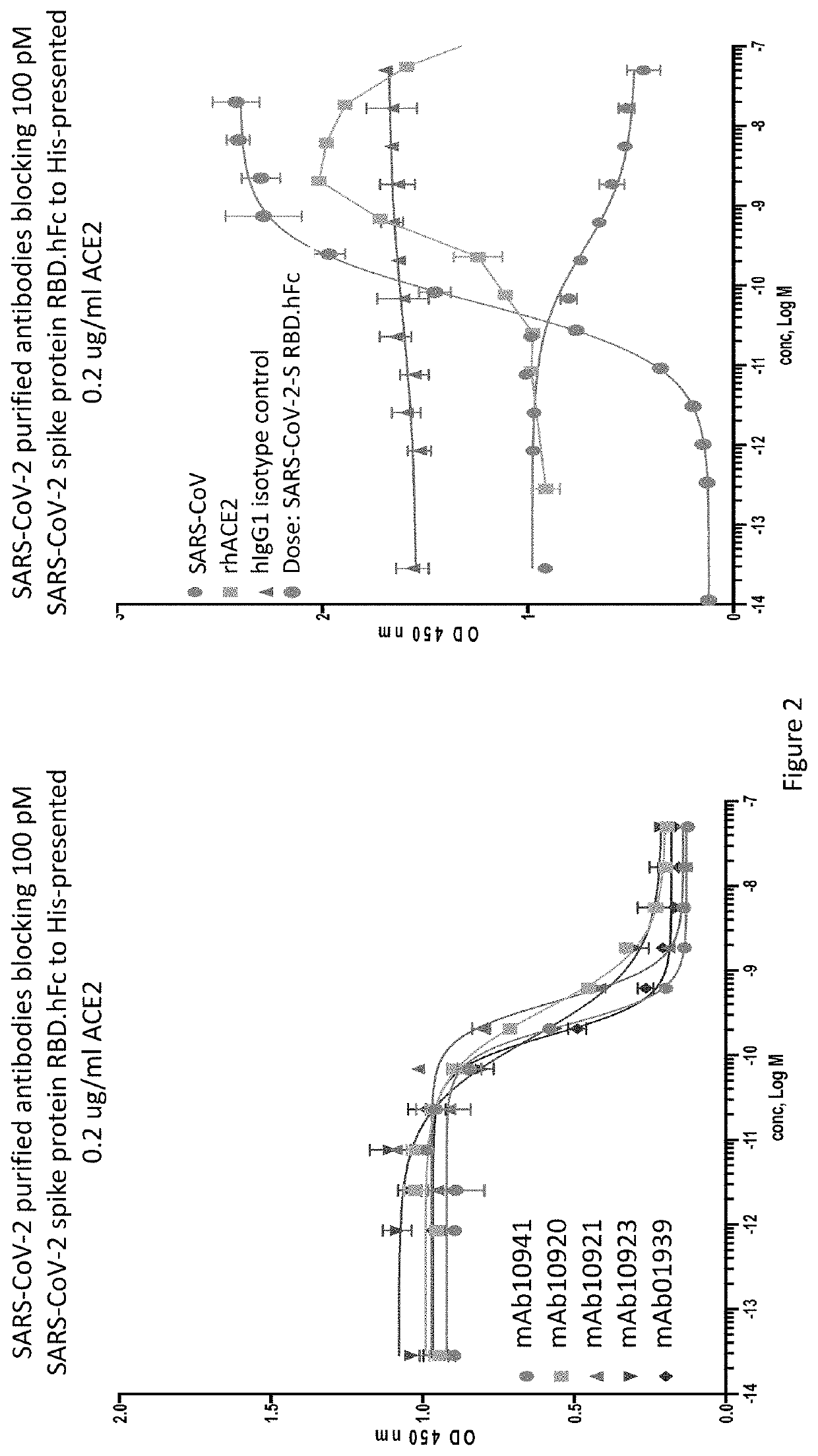
Anti-SARS-CoV-2-spike glycoprotein antibodies and antigen-binding fragments
ActiveUS10787501B1Growth inhibitionControl spreadViral antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenAntiendomysial antibodies
The present disclosure provides antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind specifically to a coronavirus spike protein and methods of using such antibodies and fragments for treating or preventing viral infections (e.g., coronavirus infections).
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Noninvasive genetic immunization, expression products therefrom, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6716823B1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideMalariaNon invasive
Disclosed and claimed are methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal. The vector can include and express an exogenous nucleic acid molecule encoding an epitope or gene product of interest. The systemic immune response can be to or from the epitope or gene product. The nucleic acid molecule can encode an epitope of interest and / or an antigen of interest and / or a nucleic acid molecule that stimulates and / or modulates an immunological response and / or stimulates and / or modulates expression, e.g., transcription and / or translation, such as transcription and / or translation of an endogenous and / or exogenous nucleic acid molecule; e.g., one or more of influenza hemagglutinin, influenza nuclear protein, influenza M2, tetanus toxin C-fragment, anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, rabies glycoprotein, HBV surface antigen, HIV gp 120, HIV gp 160, human carcinoembryonic antigen, malaria CSP, malaria SSP, malaria MSP, malaria pfg, and mycobacterium tuberculosis HSP; and / or a therapeutic, an immunomodulatory gene, such as co-stimulatory gene and / or a cytokine gene. The immune response can be induced by the vector expressing the nucleic acid molecule in the animal's cells. The animal's cells can be epidermal cells. The immune response can be against a pathogen or a neoplasm. A prophylactic vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine or an immunological composition can include the vector. The animal can be a vertebrate, e.g., a mammal, such as human, a cow, a horse, a dog, a cat, a goat, a sheep or a pig; or fowl such as turkey, chicken or duck. The vector can be one or more of a viral vector, including viral coat, e.g., with some or all viral genes deleted therefrom, bacterial, protozoan, transposon, retrotransposon, and DNA vector, e.g., a recombinant vector; for instance, an adenovirus, such as an adenovirus defective in its E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 region(s). The method can encompass applying a delivery device including the vector to the skin of the animal, as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can have all viral genes deleted therefrom. The vector can induce a therapeutic and / or an anti-tumor effect in the animal, e.g., by expressing an oncogene, a tumor-suppressor gene, or a tumor-associated gene. Immunological products generated by the expression, e.g., antibodies, cells from the methods, and the expression products, are likewise useful in in vitro and ex vivo applications, and such immunological and expression products and cells and applications are disclosed and claimed. Methods for expressing a gene product in vivo and products therefor and therefrom including mucosal and / or intranasal administration of an adenovirus, advantageously an E1 and / or E3 and / or E4 defective or deleted adenovirus, such as a human adenovirus or canine adenovirus, are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7332303B2Low production costQuality improvementAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHigh cellBiotechnology
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Anti liver disease drug R-YEEE and method of synthesizing branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins
The present invention provides a novel method of synthesizing branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins. A number of these glycoproteins have binding affinity to the asialoglycoprotein receptor. The present invention also provides novel conjugates having branched galactose-terminal glycoproteins that is complexed to a therapeutically effective agent, such as an isolated protein, polysacharides, lipids and radioactive isotope. These conjugates may be used to deliver the therapeutically effective agent to mammalian cells generally, and to hepatocytes specifically.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS20080085870A1Reduce in quantityDecreased immunological responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Devices and methods for obtaining mammary fluid samples for evaluating breast diseases, including cancer
InactiveUS6887210B2Reduce morbidityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgical needlesCellular componentBreast pump (device)
Biological samples of mammary fluid or components thereof are obtained using a breast pump device coupled with a solid phase sample collection medium, alternatively facilitated by administering oxytocin to the subject. The breast pump device stimulates expression of mammary fluid and provides for collection of diagnostic samples to evaluate breast disease, including cancer. The biological sample may include whole cells or cellular components, purified or bulk proteins, glycoproteins, peptides, nucleotides or other desired constituents comprising a breast disease marker. Methods, kits and adapter devices relating to the breast pump device are also provided. Yet additional methods, devices, accessories, and materials are provided for laboratory handling and processing of breast fluid samples and for related diagnostic methods.
Owner:ATOSSA THERAPEUTICS INC
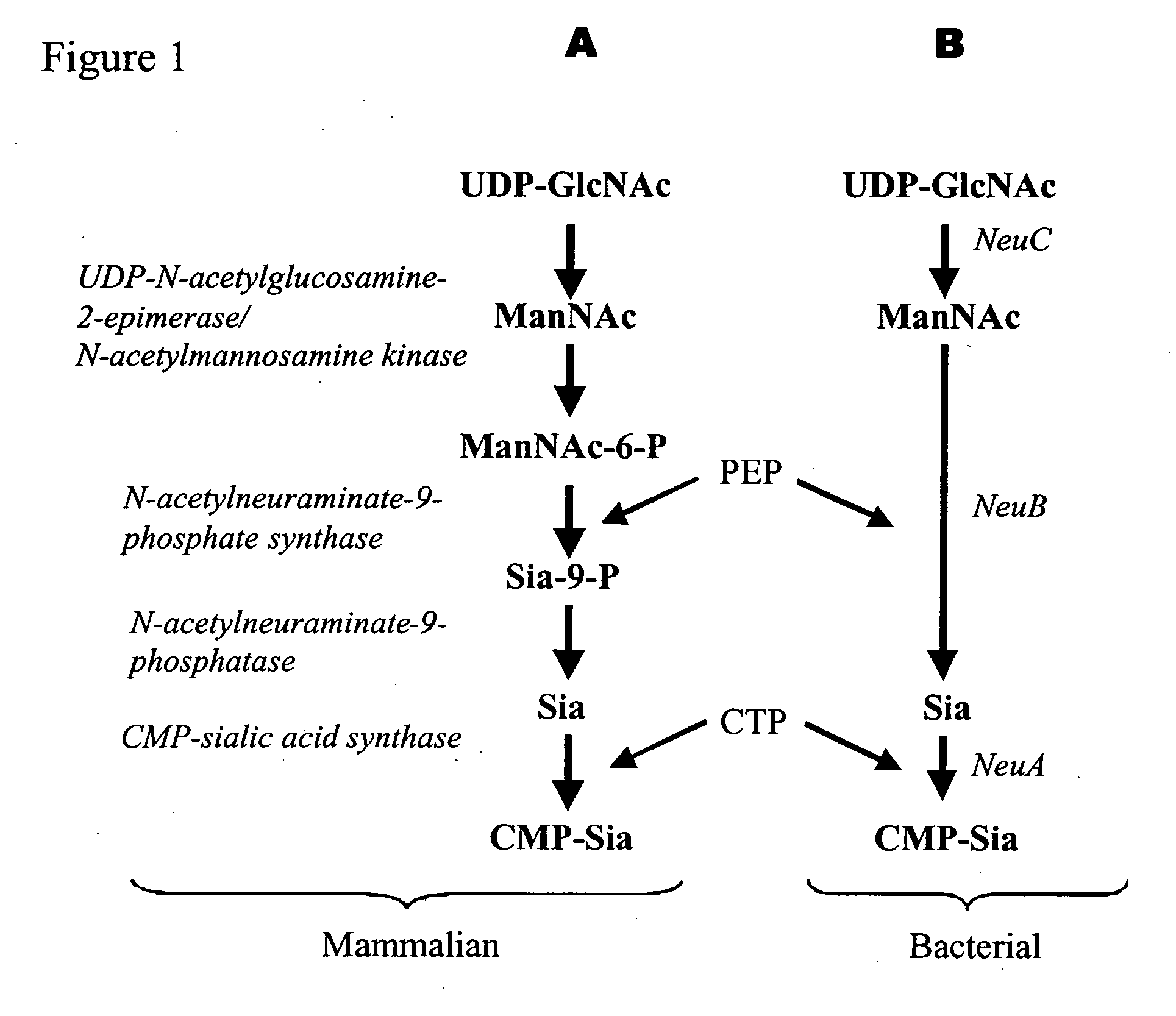
Method of engineering a cytidine monophosphate-sialic acid synthetic pathway in fungi and yeast
The present invention provides methods for generating CMP-sialic acid in a non-human host which lacks endogenous CMP-Sialic by providing the host with enzymes involved in CMP-sialic acid synthesis from a bacterial, mammalian or hybrid CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. Novel fungal hosts expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
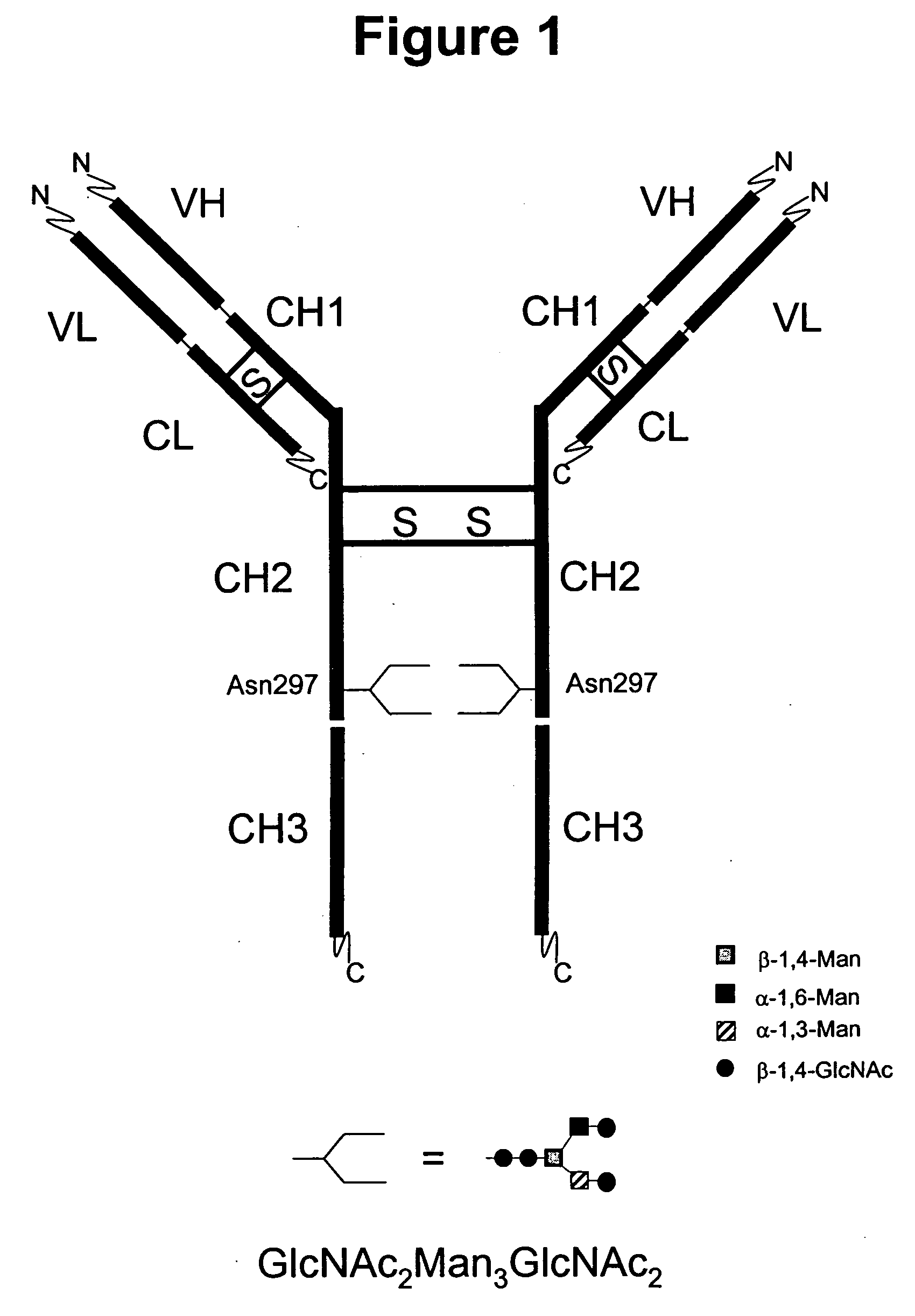
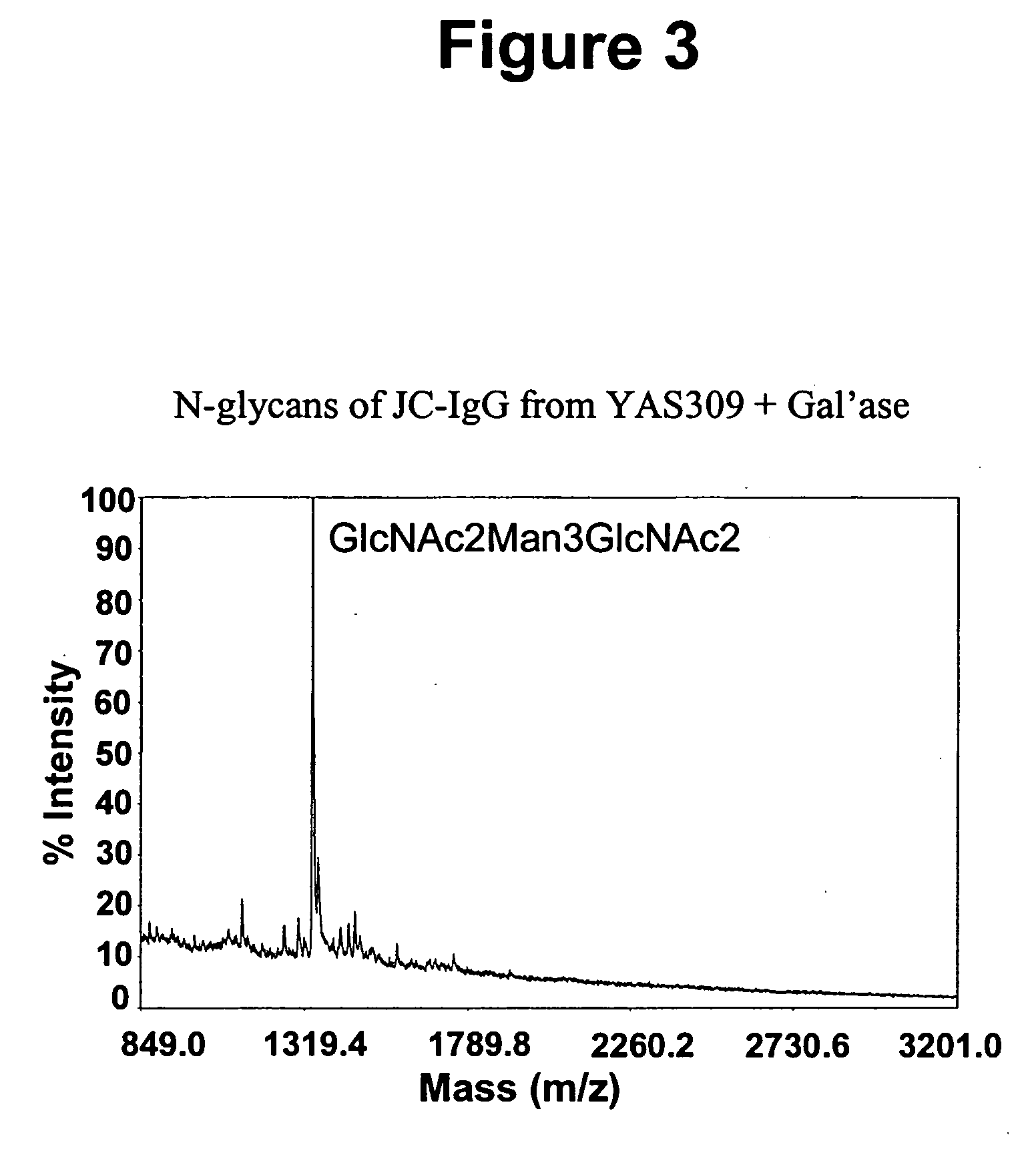
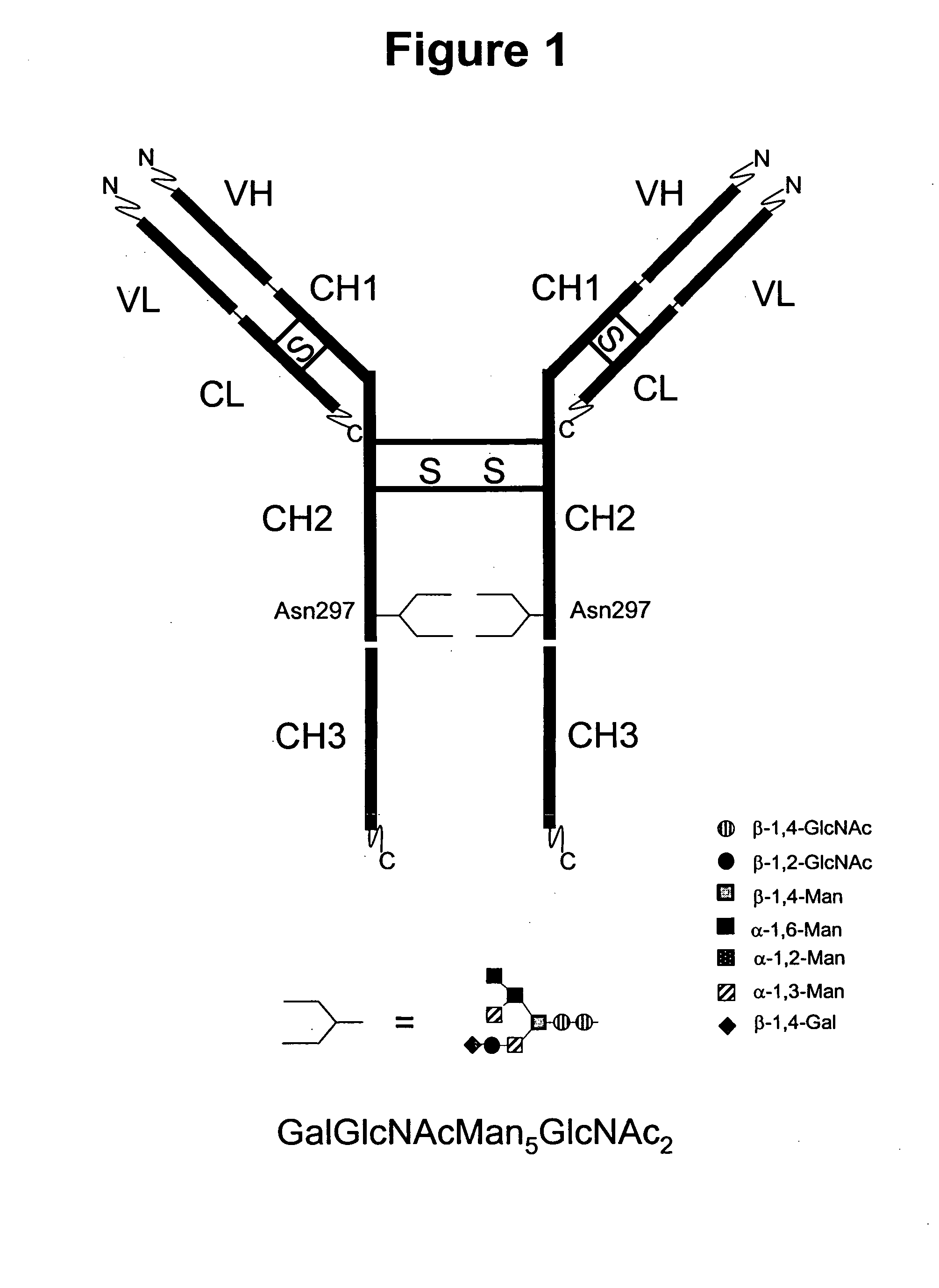
Immunoglobulins comprising predominantly a GlcNAc2Man3GlcNAc2 glycoform
InactiveUS20060029604A1Adverse effect can be minimized and avoidedEasily reproducibleAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGlucuronic acidGlycoprotein
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin glycoprotein compositions having predominant N-glycan structures on an immunoglobulin glycoprotein which confer a specific effector function. Additionally, the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antibody having a particular enriched N-glycan structure, wherein said N-glycan structure is GlcNAc2Man3GlcNAc2.
Owner:GLYCOFI
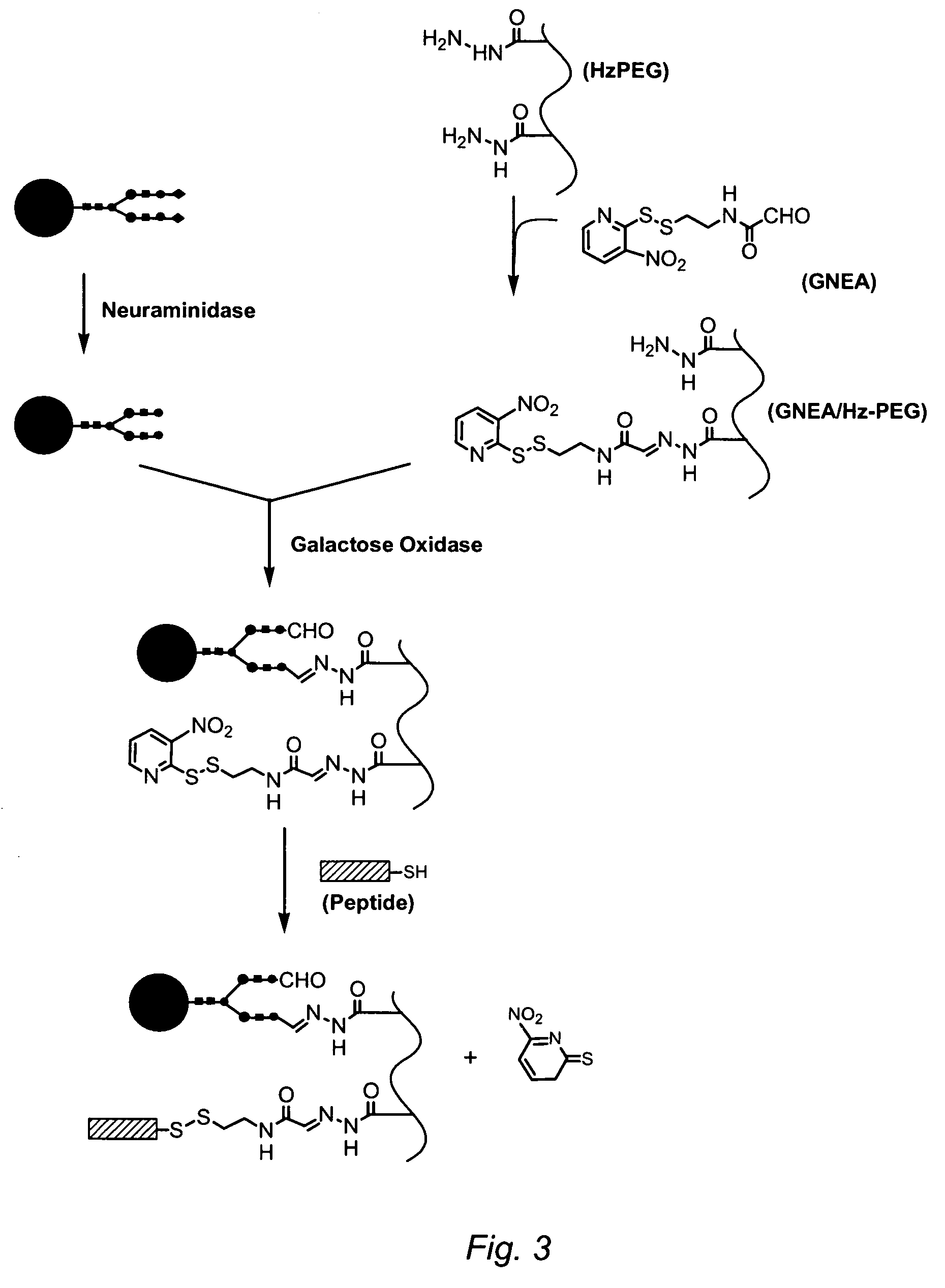
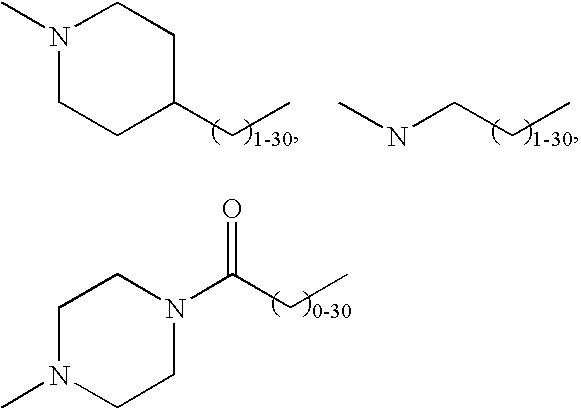
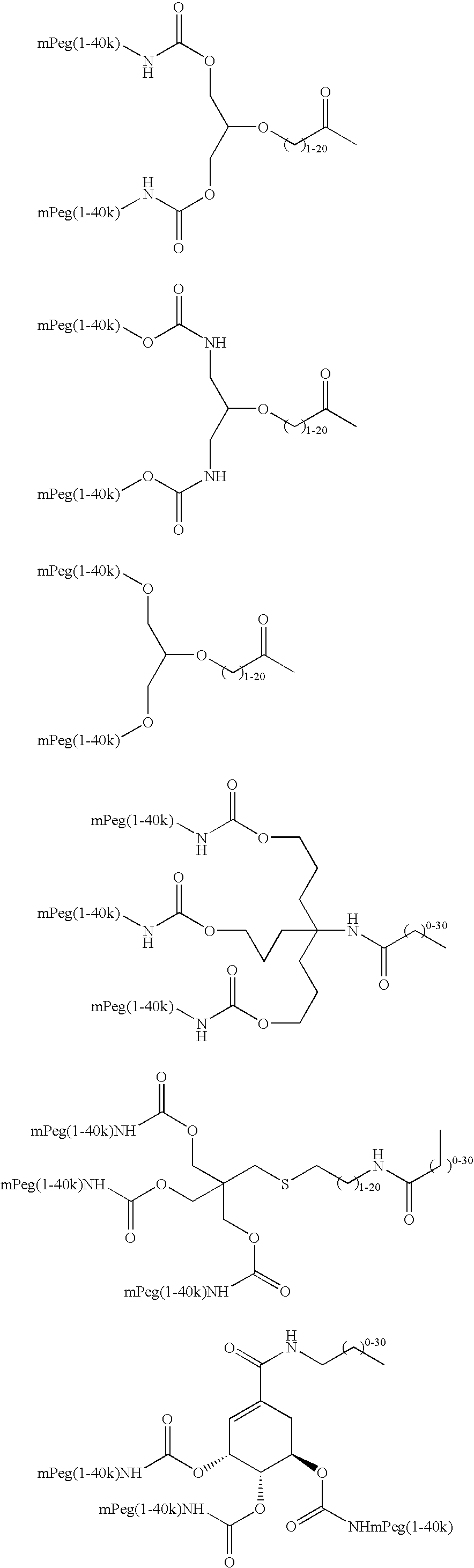
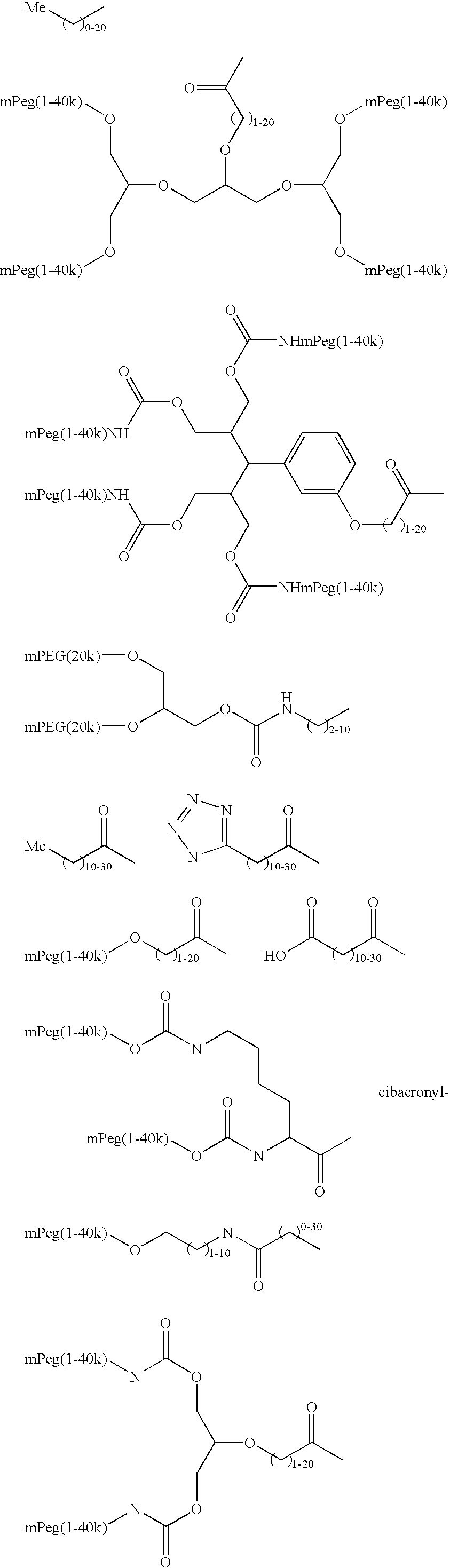
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
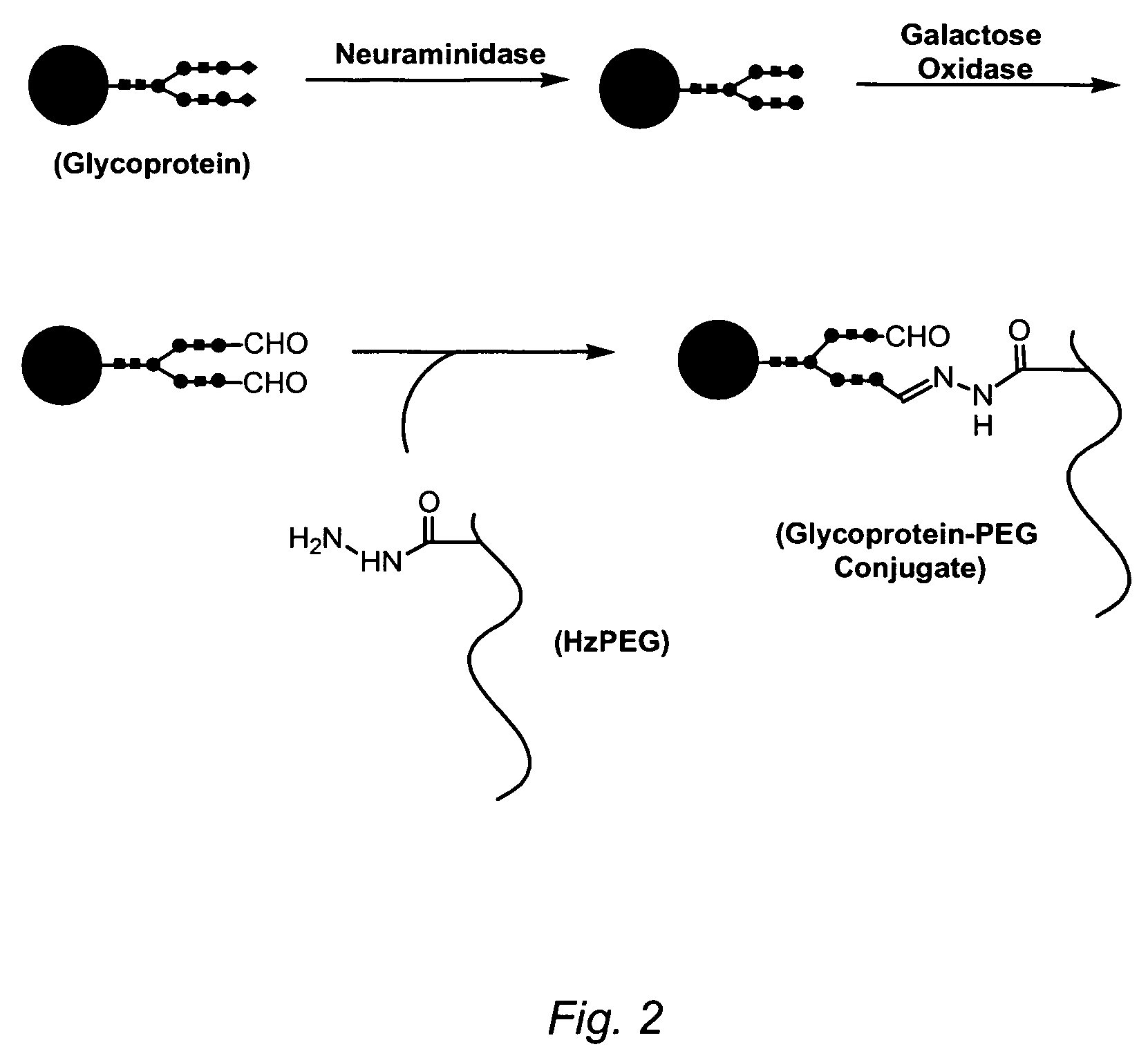
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Poxvirus-canine distemper virus (CDV) or measles virus recombinants and compositions and methods employing the recombinants
InactiveUS6309647B1Improve securityImprove security levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseHemagglutininCanine distemper virus Antigen
Attenuated recombinant viruses containing DNA coding for a canine distemper virus antigen or measles M or N antigen, as well as methods and compositions employing the viruses, are disclosed and claimed. The recombinant viruses can be NYVAC or ALVAC recombinant viruses. The DNA can code for at least one of: canine distemper virus fusion protein, canine distemper virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein, canine distemper nucleocaspid protein, canine distemper matrix protein, measles virus nucleocaspid protein, and measles virus matrix protein. The recombinant viruses and gene products therefrom are useful for eliciting protection against canine distemper virus and / or measles virus, and, the gene products and antibodies elicited thereby are useful in assays. Additionally, DNA from the recombinants is used for probes or for generating PCR primers.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
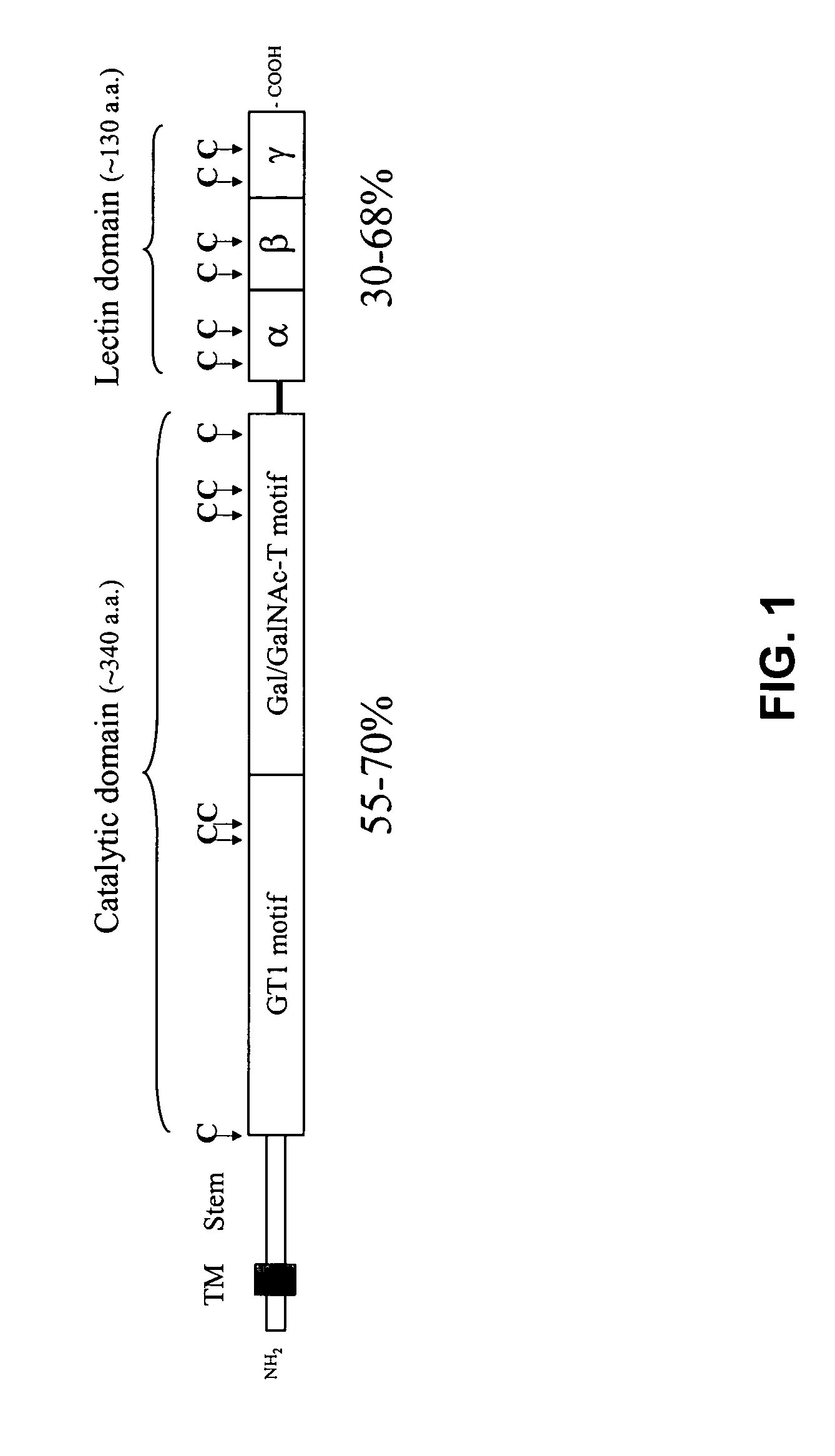
Methods to identify agents modulating functions of polypeptide galnac-transferases, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such agents and the use of such agents for preparing medicaments
Novel methods for identification of inhibitors or modulators of binding activities mediated by lectin domains of polypeptide GalNAc-transferases are disclosed. Direct binding activity of GalNAc-transferase lectins has been demonstrated for the first time and methods to measure lectin mediated binding of isolated lectins or enzymes with lectin domains are disclosed. The present invention specifically discloses a novel selective inhibitor of polypeptide GalNAc-transferase lectin domains, which provides a major advancement in that this inhibitor and related inhibitors sharing common characteristics of activity bind lectin domains without serving as acceptor substrate for glycosyltransferases involved in synthesis of O-glycans. This inhibitor is represented by the β-anomeric configuration of GalNAc-benzyl, GalNAcβ-benzyl. Methods for inhibiting intracellular transport, cell surface expression, and secretion of mucins and O-glycosylated glycoproteins without affecting O-glycosylation processing are disclosed using the novel selective inhibitor identified.
Owner:GLYCOZYM
Methods of imaging and treatment
InactiveUS7329402B2For signal receptionDecreasing background tissue signalTetrapeptide ingredientsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsThrombusTarget tissue
Novel ultrasound methods comprising administering to a patient a targeted vesicle composition which comprises vesicles comprising a lipid, protein or polymer, encapsulating a gas, in combination with a targeting ligand, and scanning the patient using ultrasound. The scanning may comprise exposing the patient to a first type of ultrasound energy and then interrogating the patient using a second type of ultrasound energy. The targeting ligand preferably targets tissues, cells or receptors, including myocardial cells, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, tumor cells and the glycoprotein GPIIbIIIa receptor. The methods may be used to detect a thrombus, enhancement of an old or echogenic thrombus, low concentrations of vesicles and vesicles targeted to tissues, cells or receptors.
Owner:IMARX PHARM CORP
Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases
InactiveUS20090123367A1Facilitated DiffusionEnhance convective transportBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME +6
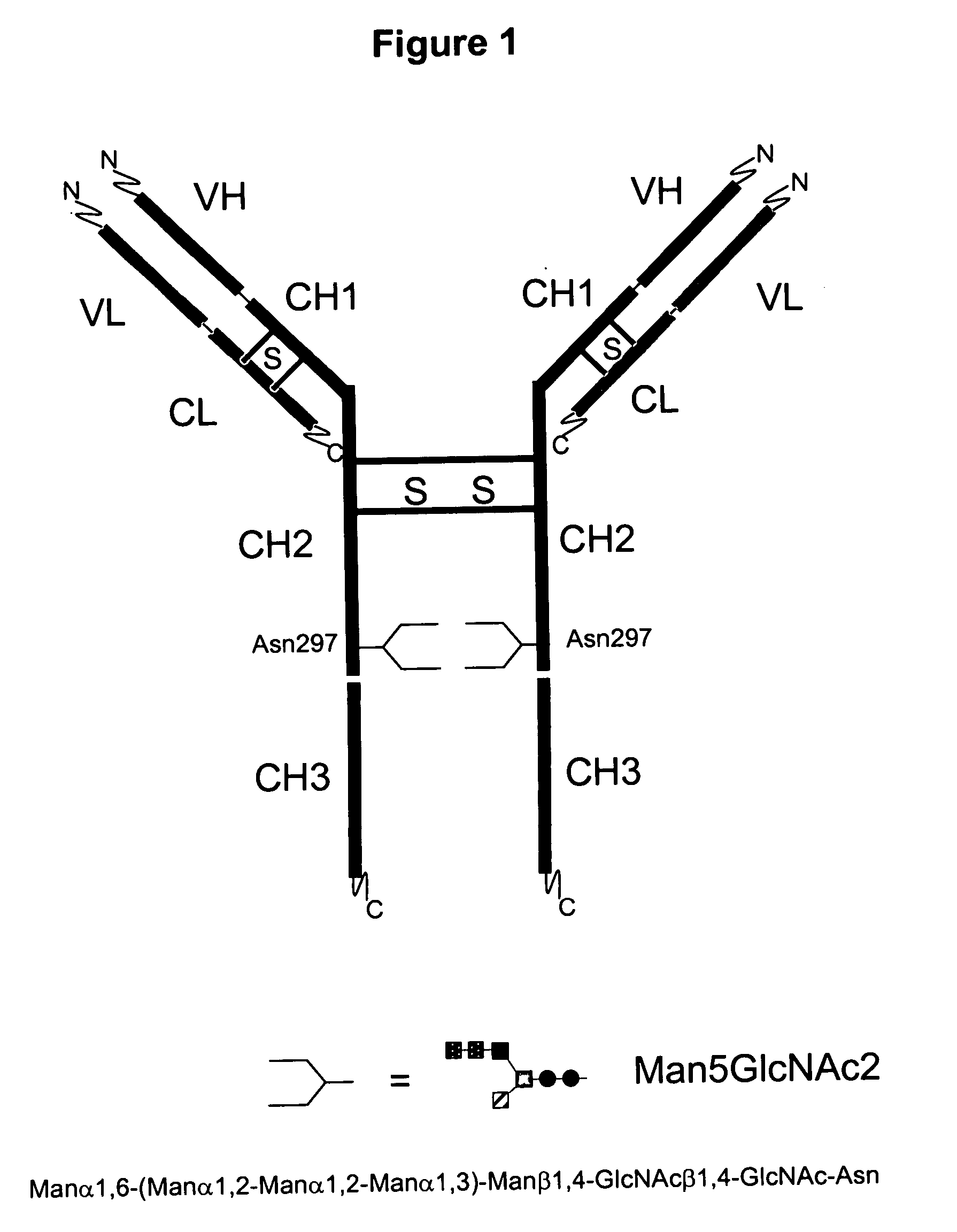
Immunoglobulins comprising predominantly a Man5GIcNAc2 glycoform
InactiveUS20060257399A1Easily reproducibleAdverse effect can be minimized and avoidedAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGlucuronic acidGlycoprotein
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin glycoprotein compositions having predominant N-glycan structures on an immunoglobulin glycoprotein which confer a specific effector function. Additionally, the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antibody having a particular enriched N-glycan structure, wherein said N-glycan structure is Man5GlcNAc2.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Stabilized glycoproteins
ActiveUS20040191265A1Increased in half lifeGood storage stabilitySnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainGlycoprotein i
The present invention provides stabilized immunoglobulin molecules that have increased storage stability and / or in vivo half-lives due to the mutation of one or more amino acids that would otherwise render the immunoglobulin molecules susceptible to degradation. In a preferred embodiment, the stabilized immunoglobulins of the invention have mutations at the heavy chain constant domain hinge region. Such stabilized immunoglobulin molecules, i.e., immunoglobulin molecules with increased storage stability have one or more of the following advantages they are more readily transported and / storable for longer periods and / or less stringent conditions than non-stabilized counterparts; that smaller amounts and or less frequent dosing is required in the therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic use of such stabilized molecules.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Nanoparticles for drug delivery
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a nanoparticle and any one of a peptide, a polysaccharide, or a glycoprotein, attached electrostatically thereto, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Uses of the composition and processes for its preparation.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
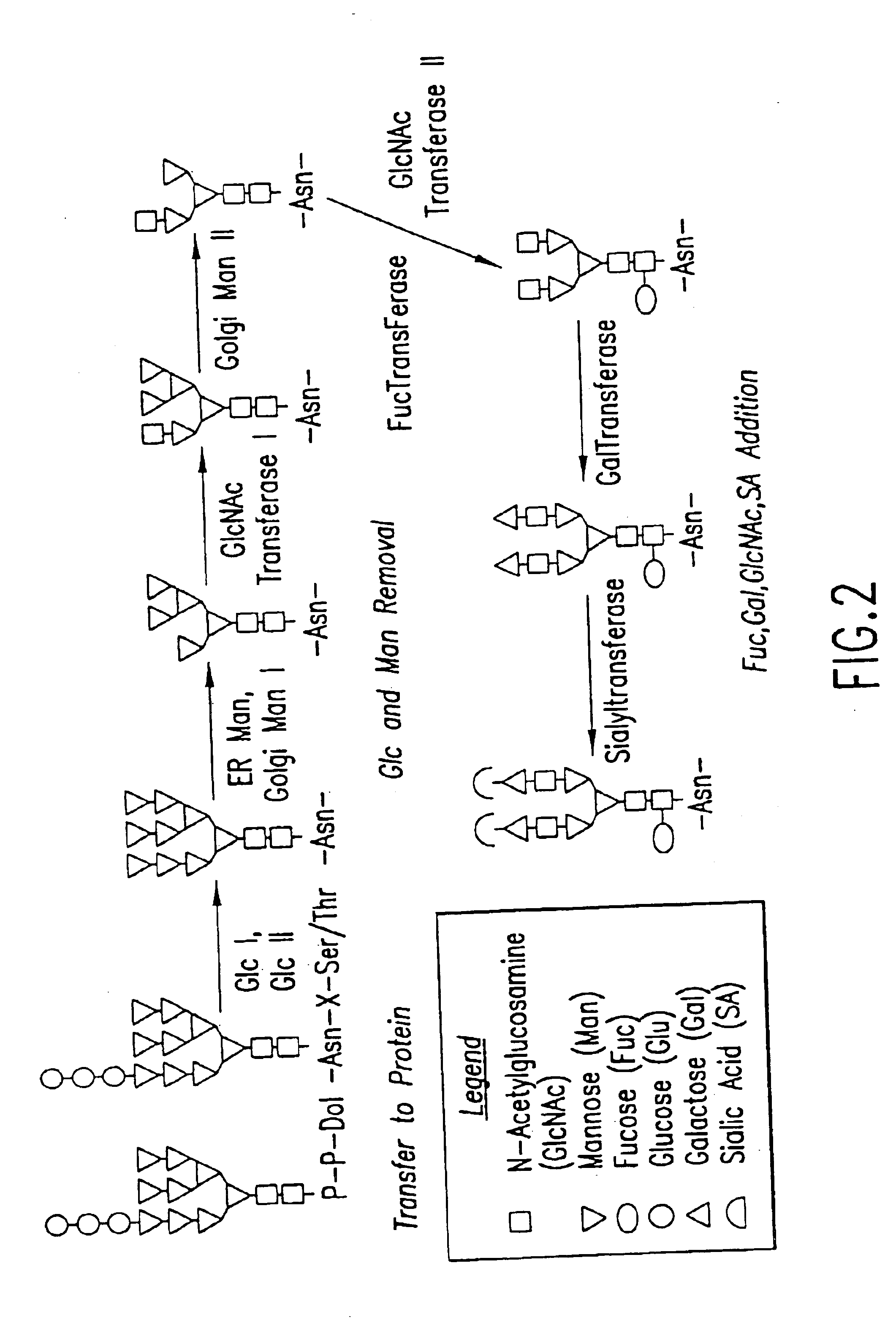
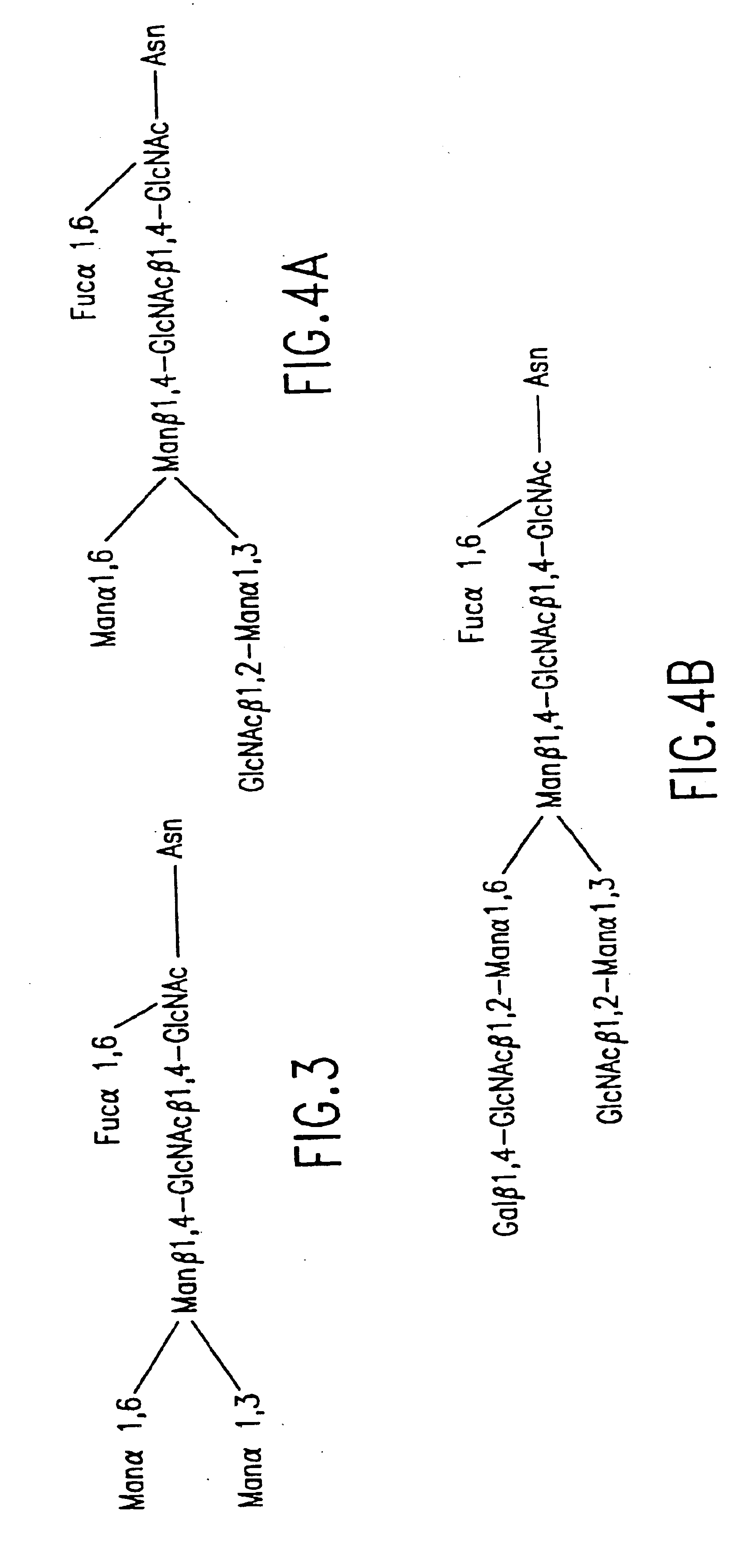
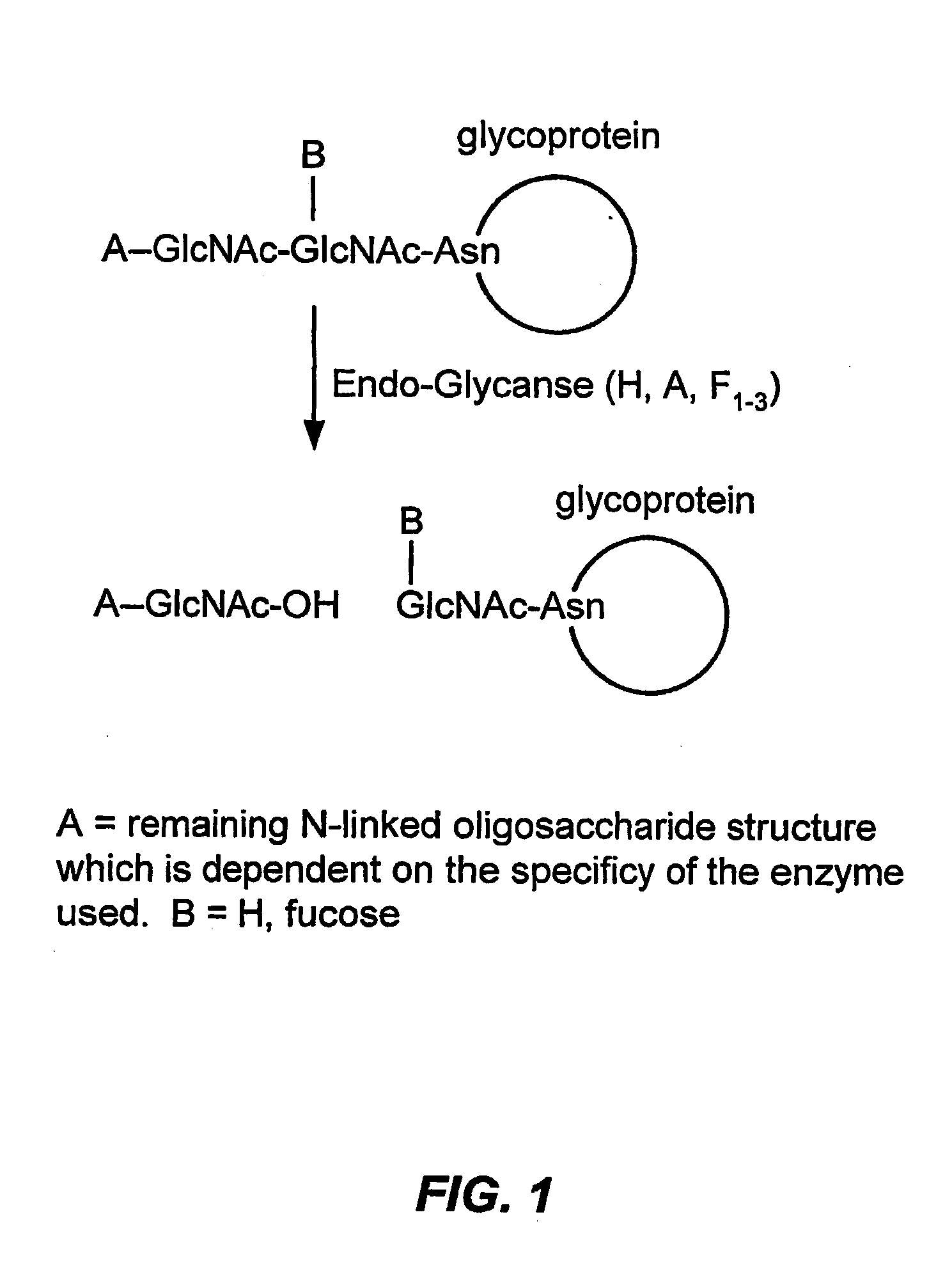
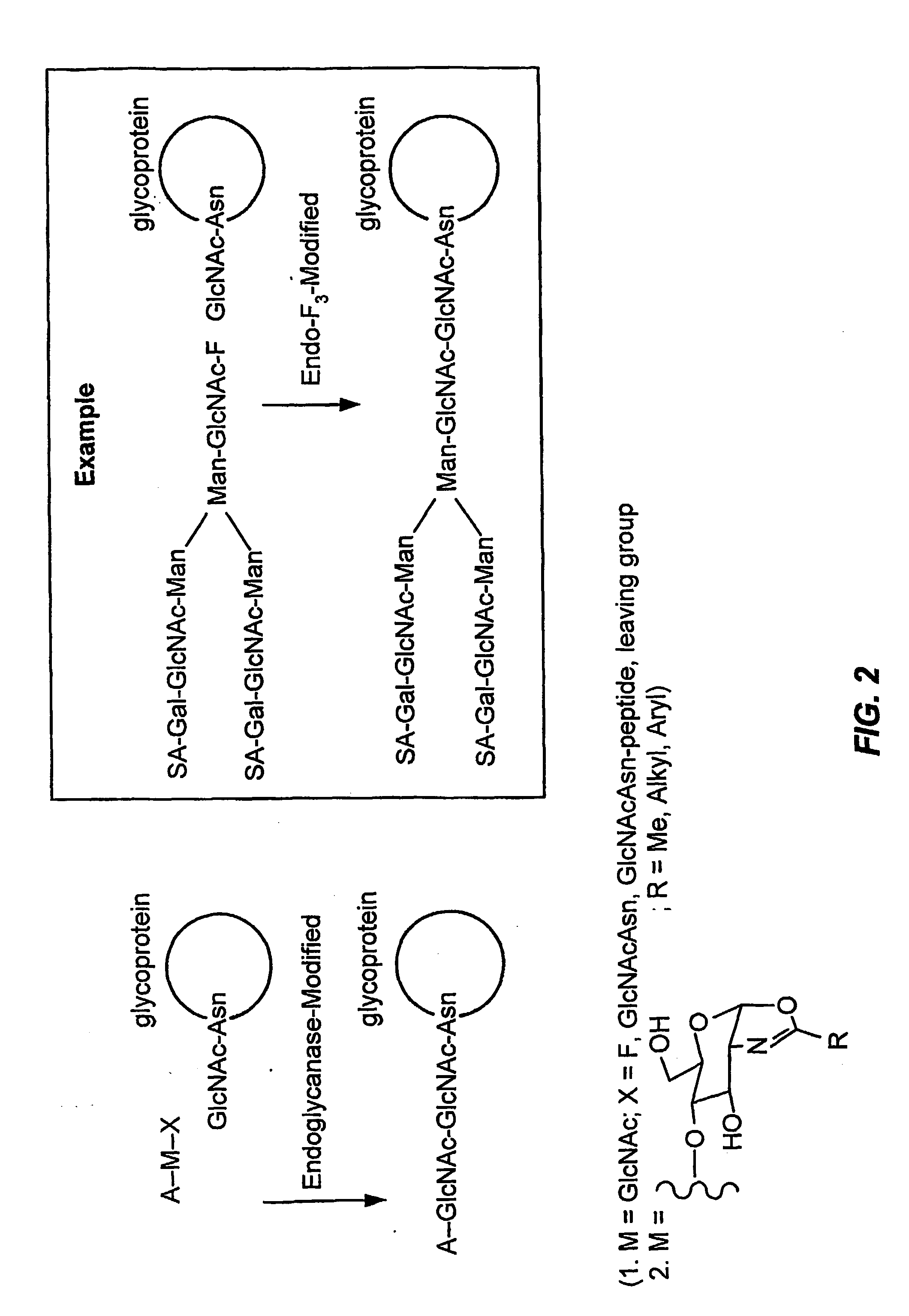
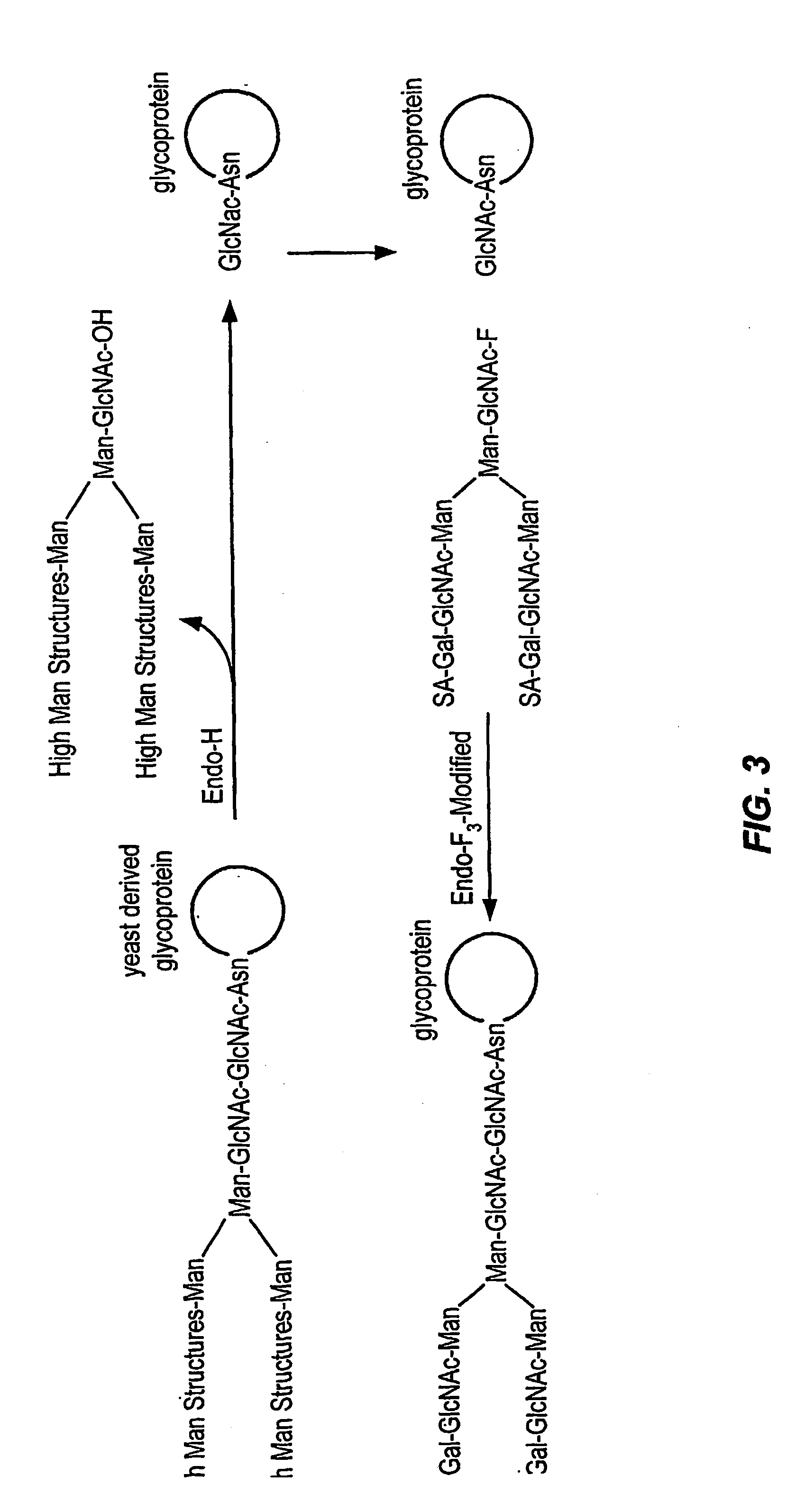
Glycoprotein remodeling using endoglycanases
This invention provides methods for modifying glycosylation patterns of glycoproteins, including recombinantly produced glycoproteins. Also provided are glycoprotein compositions in which the glycoproteins have a homogeneous glycosylation pattern.
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
Human Antibodies to Ebola Virus Glycoprotein
ActiveUS20160215040A1Inhibiting and neutralizing activityAvoid enteringImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsViral glycoproteinAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to Ebola virus glycoproteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing Ebola virus activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing Ebola virus infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the Ebola virus for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
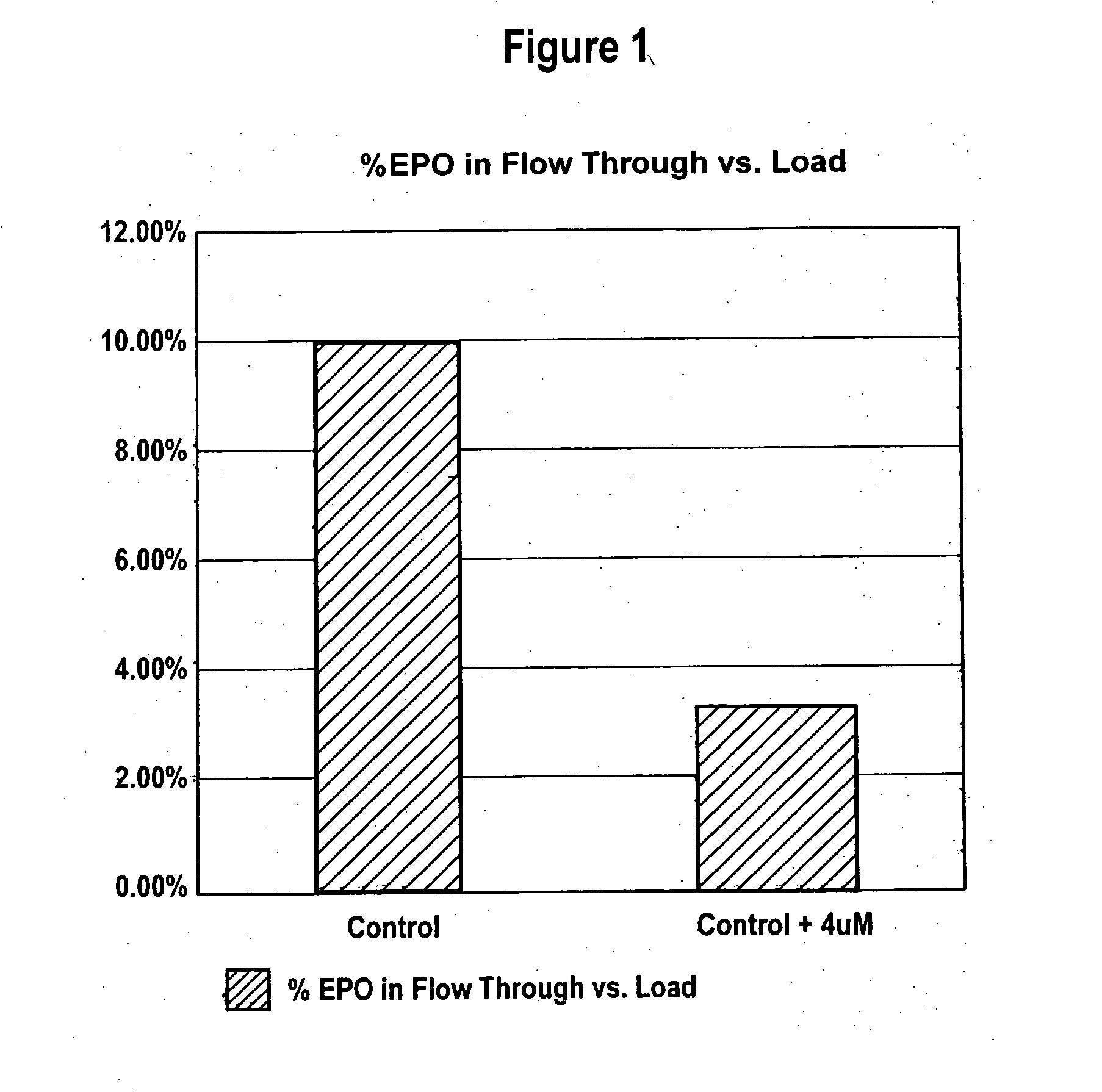
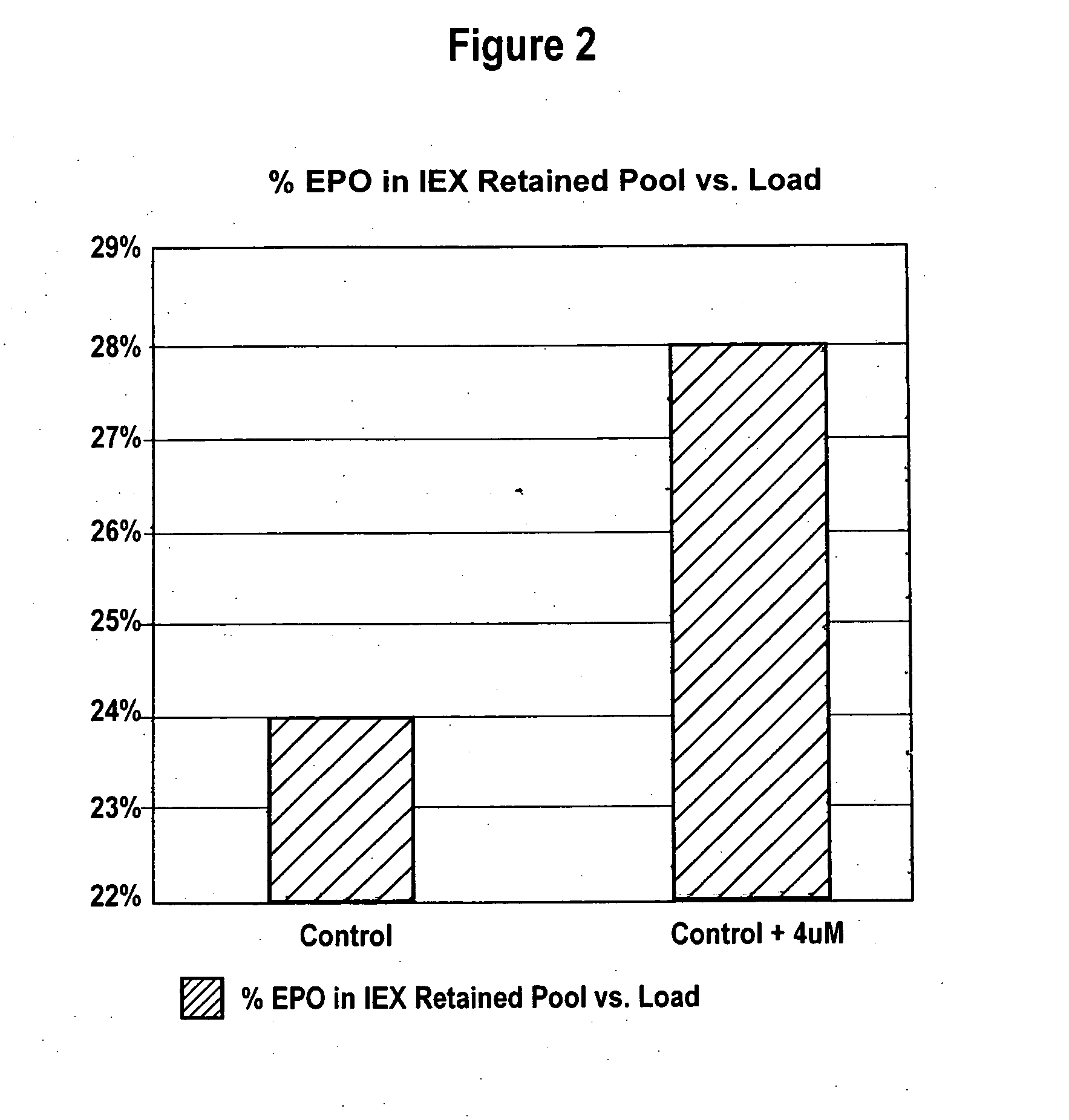
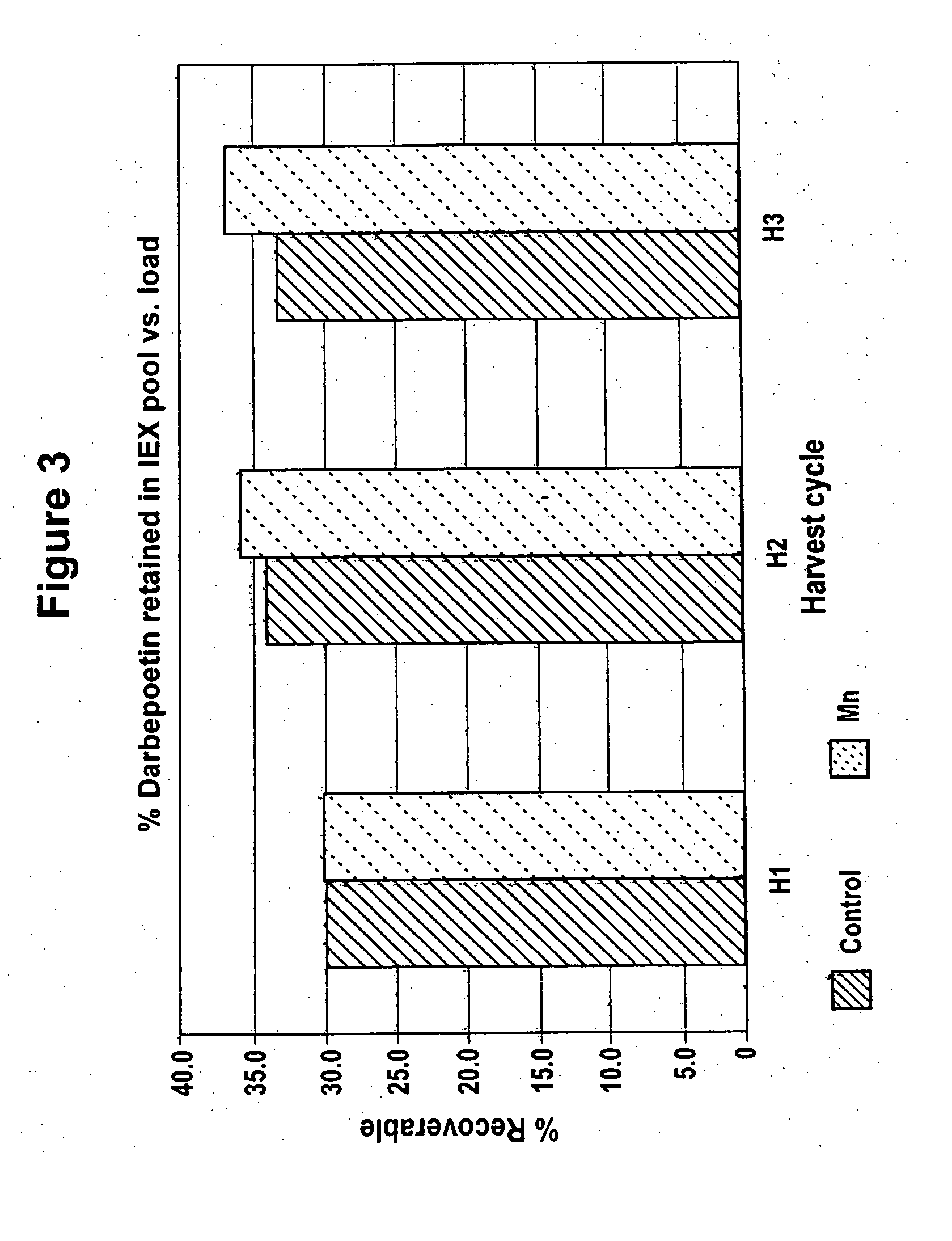
Production of glycoproteins using manganese
ActiveUS20070161084A1Increase sialylationProduced in advanceImmunoglobulinsFermentationSialic acid aldolaseBiotechnology
Culture media comprising manganese and methods of culturing cells to improve sialylation and glycosylation of glycoproteins are provided.
Owner:AMGEN INC
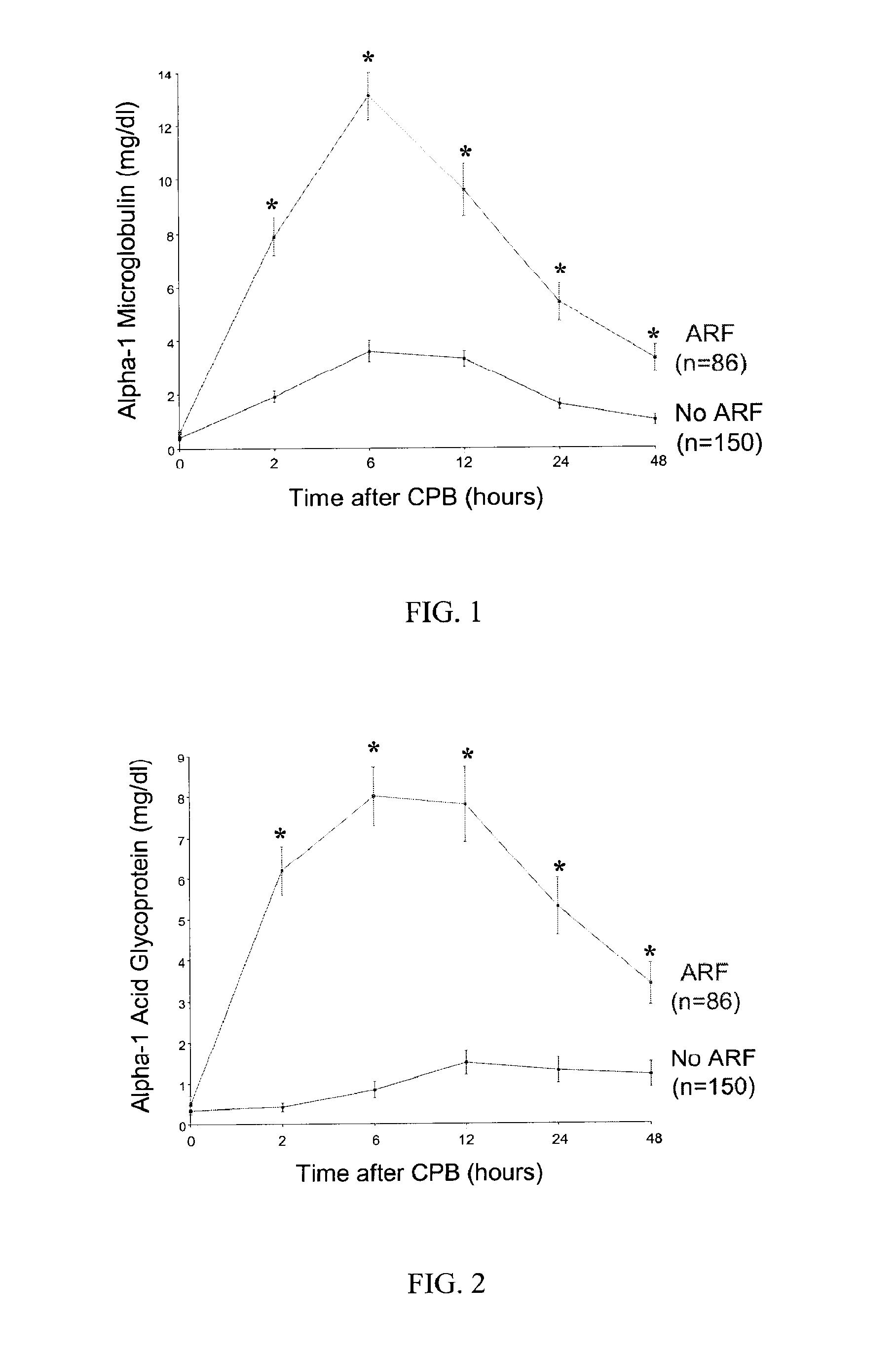
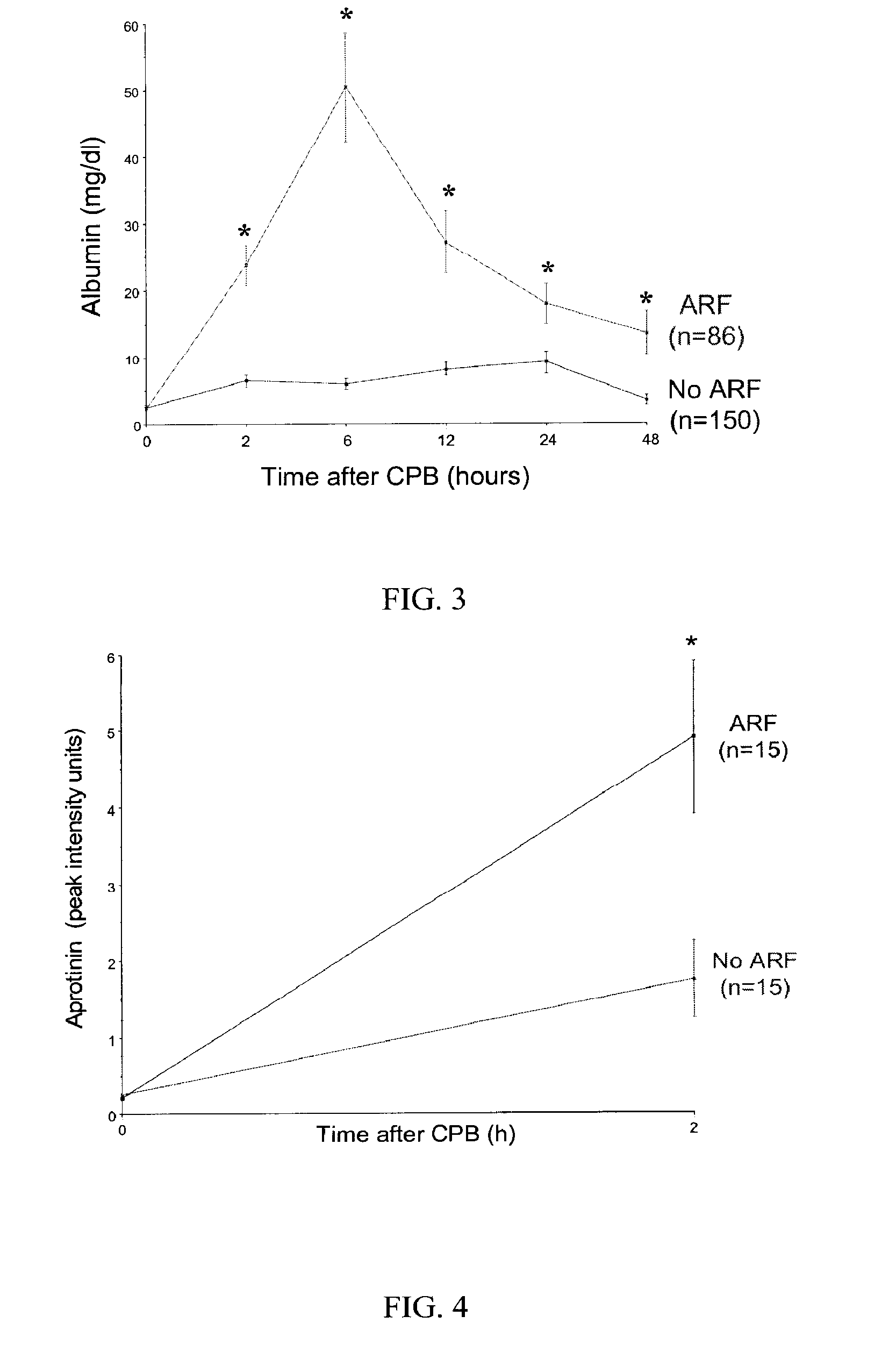
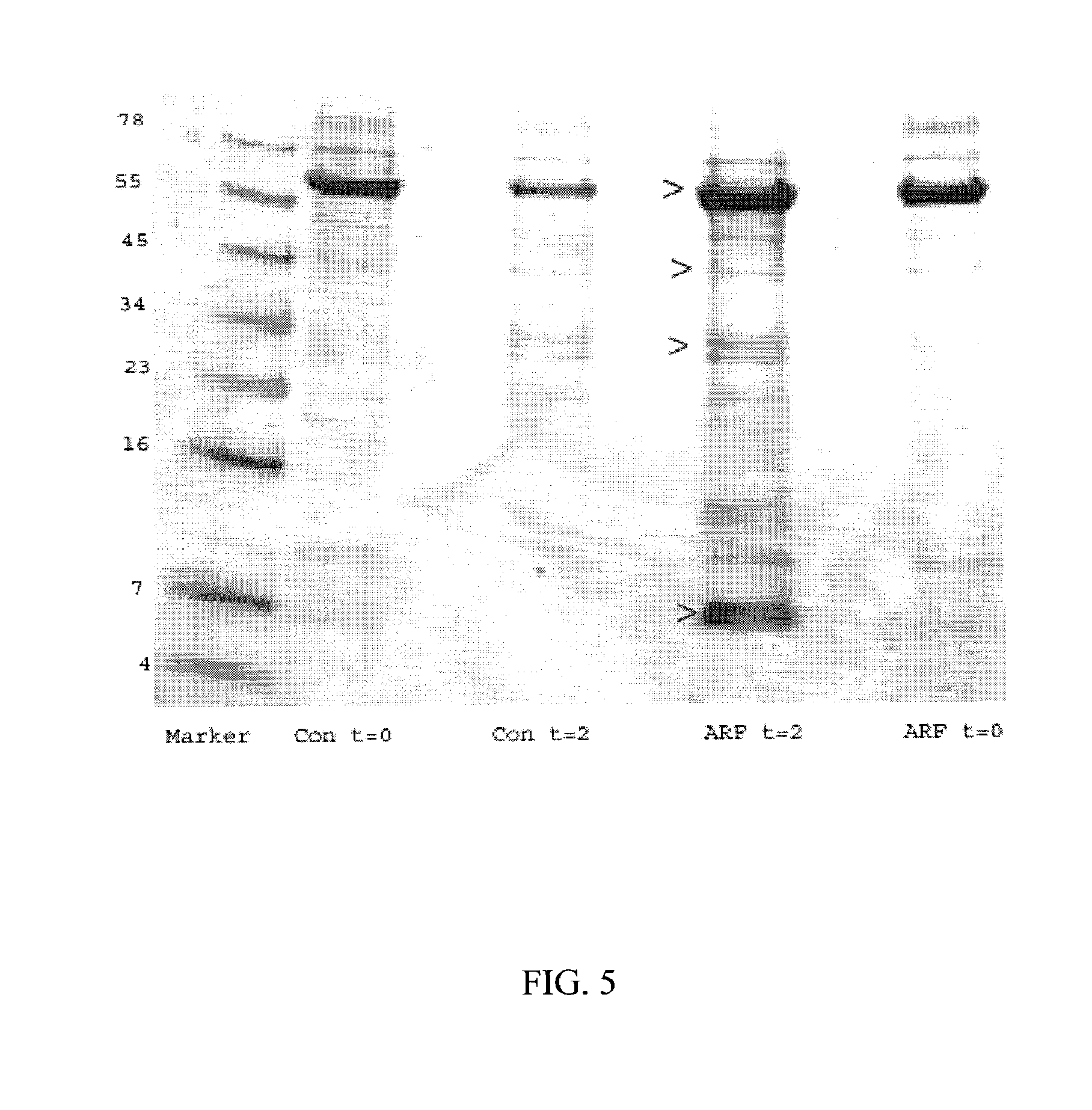
Method and Kit for the Early Detection of Impaired Renal Status
InactiveUS20070248989A1Pharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPoint of careExtracorporeal circulation
A method and kit for identifying the presence of an early biomarker of impaired renal status following a renal event in a mammalian subject. The method typically comprises (a) providing a body fluid sample obtained from a mammalian subject following a renal event; and (b) detecting in the provided sample the presence of a protein selected from the group consisting of aprotinin, alpha-1-microglobulin (A1M), alpha-1-acid-glycoprotein (A1AG), microalbumin, and combinations thereof, the presence thereof serving as an early biomarker of a change in renal status. The method can include a kit for point-of-care detection of the early biomarker of impaired renal status. Identification of the presence or absence of the early biomarker typically directs a caregiver's therapeutic decision regarding managing treatment of the subject for impaired renal status The invention also includes a method of assessing the administration of aprotinin during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery and provides for methods where the level of aprotinin in the subject's urine directs a caregiver's therapeutic decision regarding the intra-operative administration of aprotinin.
Owner:NIH
Composition and vaccine for treating lung cancer
InactiveUS20160168227A1High in proteinEffectively stimulating the (adaptive) immune systemOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAntigenDisease
The present invention relates to a composition comprising at least one mRNA encoding a combination of antigens capable of eliciting an (adaptive) immune response in a mammal, wherein the antigens are selected from the group consisting of 5T4 (Trophoblast glycoprotein, TPBG), Survivin (Baculoviral TAP repeat-containing protein 5; BIRC5), NY-ESO-1 (New York esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 1, CTAG1B), MAGE-C1 (Melanoma antigen family C1), MAGE-C2 (Melanoma antigen family C2), and MUC1 (Mucin 1). The invention furthermore relates to a vaccine comprising at least one mRNA encoding such a combination of antigens, and to the use of said composition (for the preparation of a vaccine) and / or of the vaccine for eliciting an (adaptive) immune response for the treatment of lung cancer, preferably of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and diseases or disorders related thereto. Finally, the invention relates to kits, particularly to kits of parts, containing the composition and / or the vaccine.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
Modified proteins
InactiveUS20100056428A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduce in quantityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycoprotein iOrganic chemistry
Method of conjugating glycoproteins by means of chemical modification is provided as well as new modified glycoproteins.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Immunoglobulins comprising predominantly a GalGlcNAcMan5GLcNAc2 glycoform
InactiveUS20060034830A1Adverse effect can be minimized and avoidedEasily reproducibleAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGlucuronic acidGlycoprotein
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin glycoprotein compositions having predominant N-glycan structures on an immunoglobulin glycoprotein which confer a specific effector function. Additionally, the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antibody having a particular enriched N-glycan structure, wherein said N-glycan structure is GalGlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS6639050B1Enhance molecular packingEasy to identifyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com