Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Direct binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Direct binding. Direct binding is a feature of the linker and dynamic linker on Solaris and OpenSolaris. It provides a method to allow libraries to directly bind symbols to other libraries, rather than weakly bind to them and leave the dynamic linker to figure out which library contains the symbol.
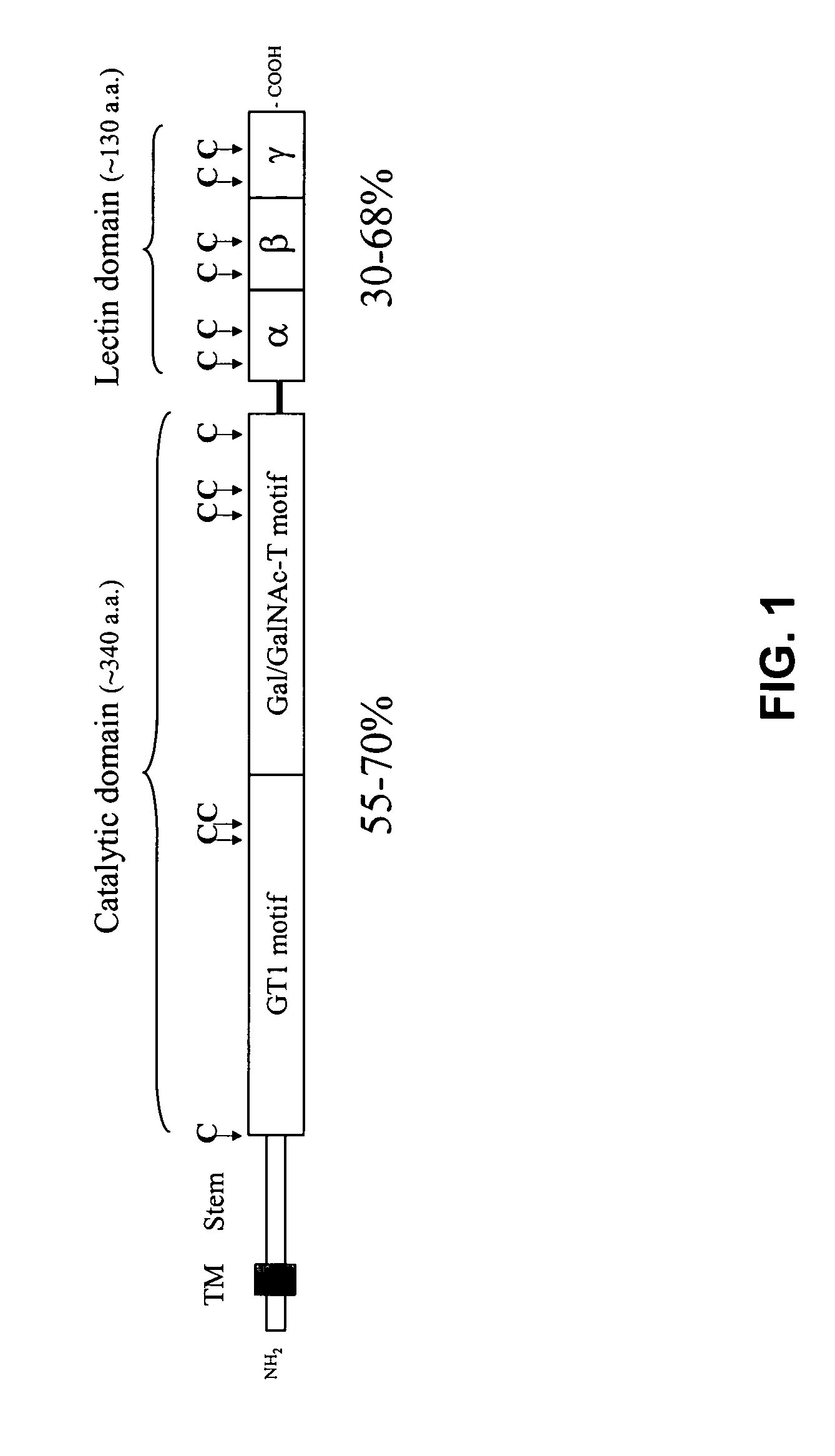
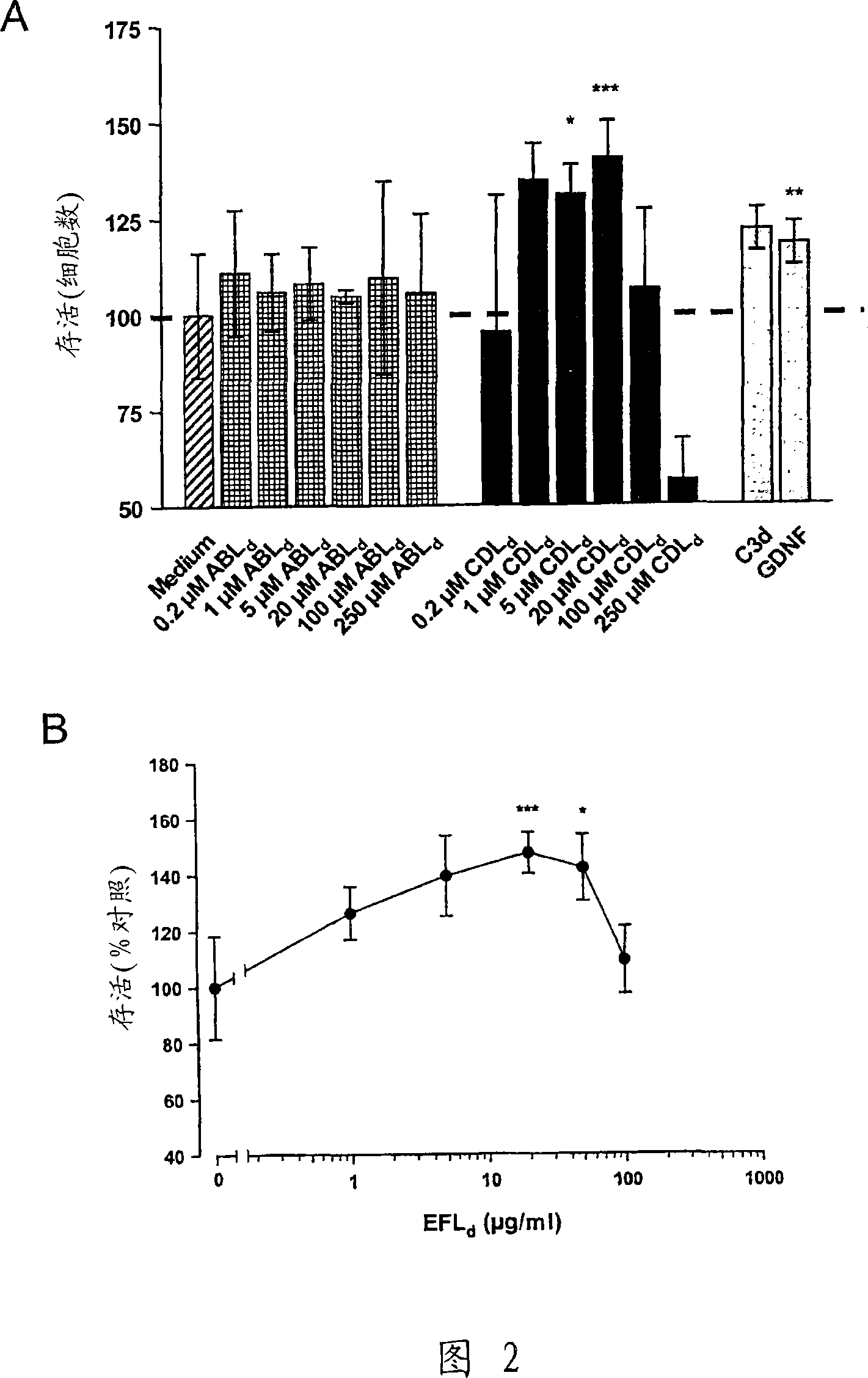
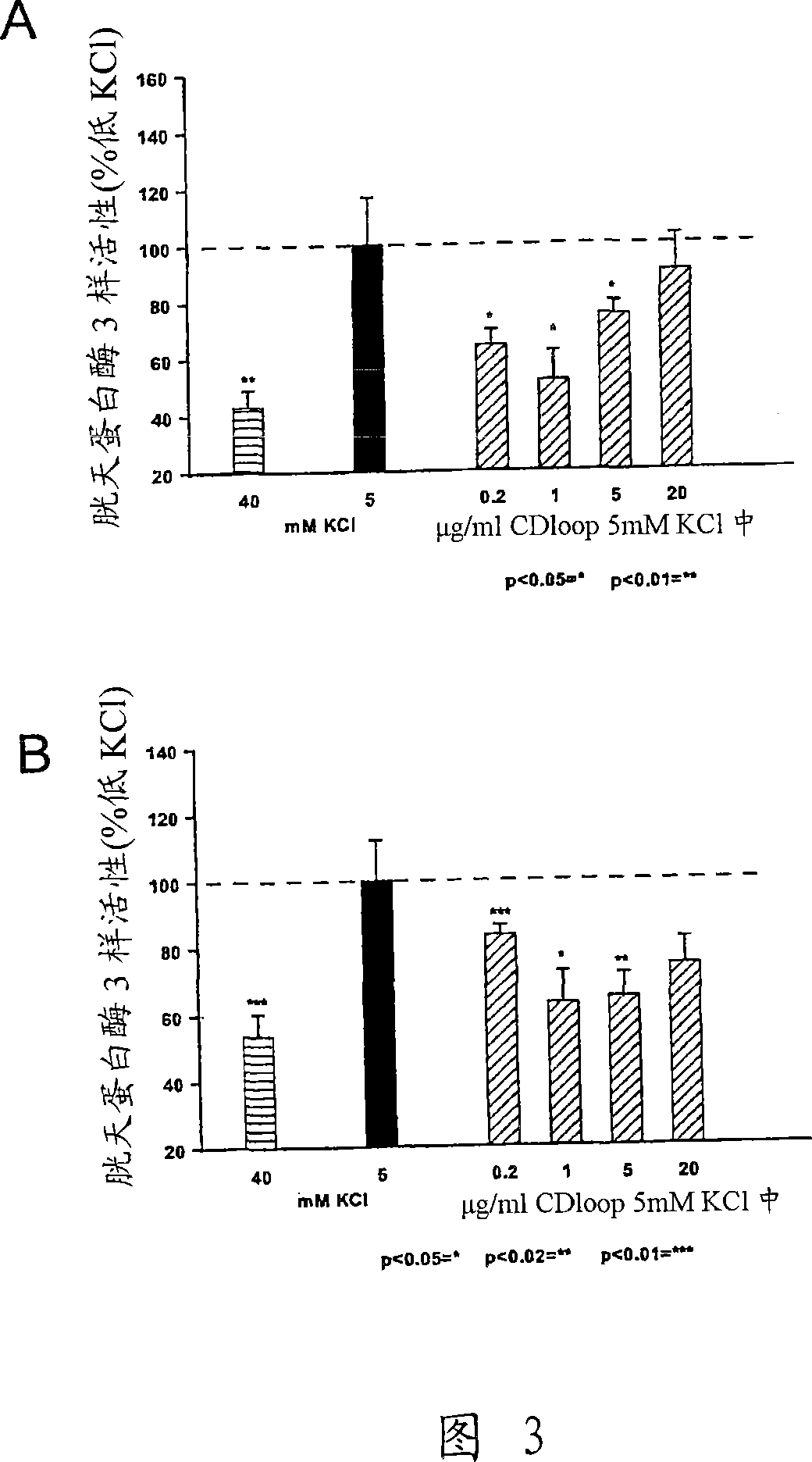
Methods to identify agents modulating functions of polypeptide galnac-transferases, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such agents and the use of such agents for preparing medicaments
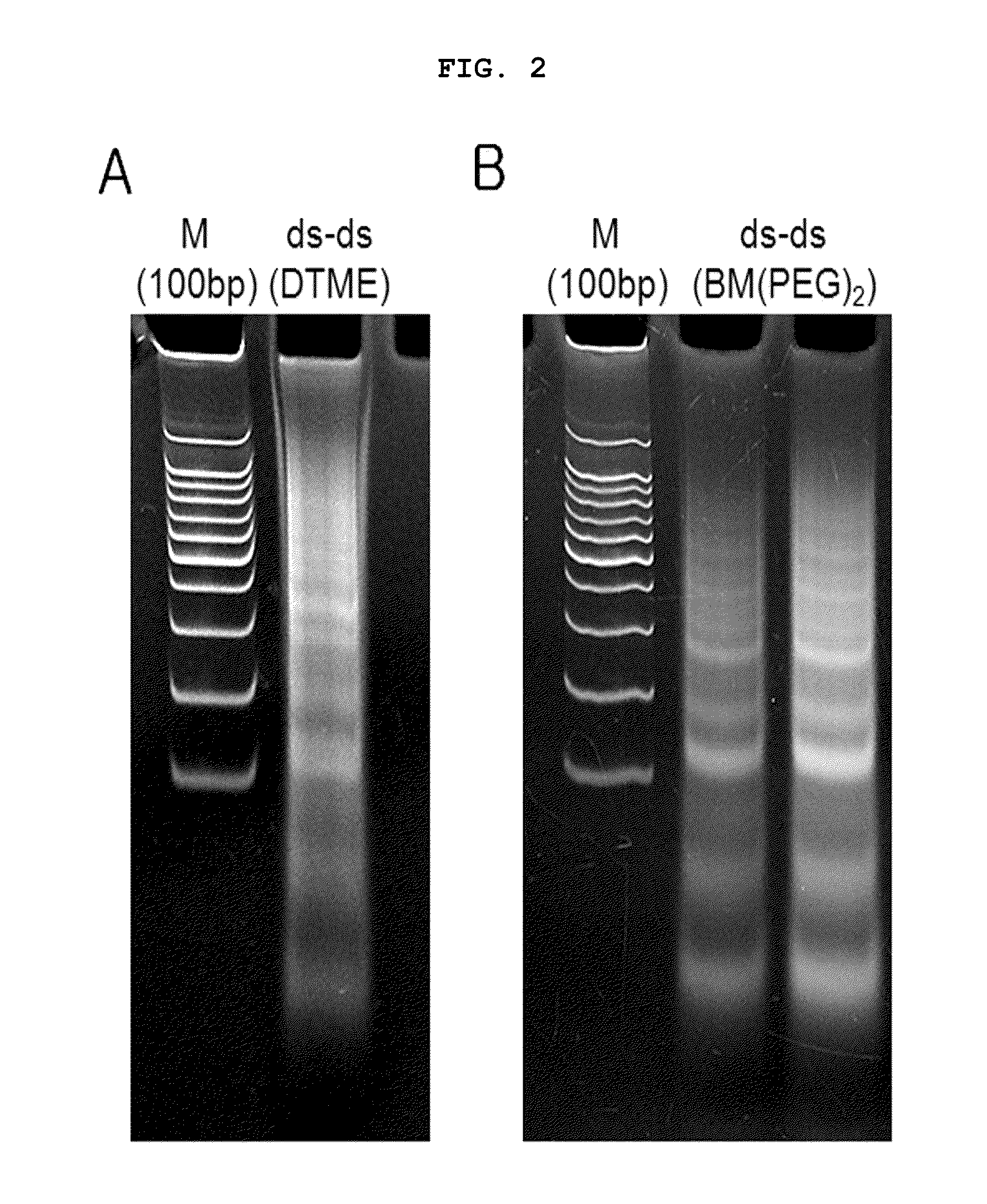
Novel methods for identification of inhibitors or modulators of binding activities mediated by lectin domains of polypeptide GalNAc-transferases are disclosed. Direct binding activity of GalNAc-transferase lectins has been demonstrated for the first time and methods to measure lectin mediated binding of isolated lectins or enzymes with lectin domains are disclosed. The present invention specifically discloses a novel selective inhibitor of polypeptide GalNAc-transferase lectin domains, which provides a major advancement in that this inhibitor and related inhibitors sharing common characteristics of activity bind lectin domains without serving as acceptor substrate for glycosyltransferases involved in synthesis of O-glycans. This inhibitor is represented by the β-anomeric configuration of GalNAc-benzyl, GalNAcβ-benzyl. Methods for inhibiting intracellular transport, cell surface expression, and secretion of mucins and O-glycosylated glycoproteins without affecting O-glycosylation processing are disclosed using the novel selective inhibitor identified.
Owner:GLYCOZYM
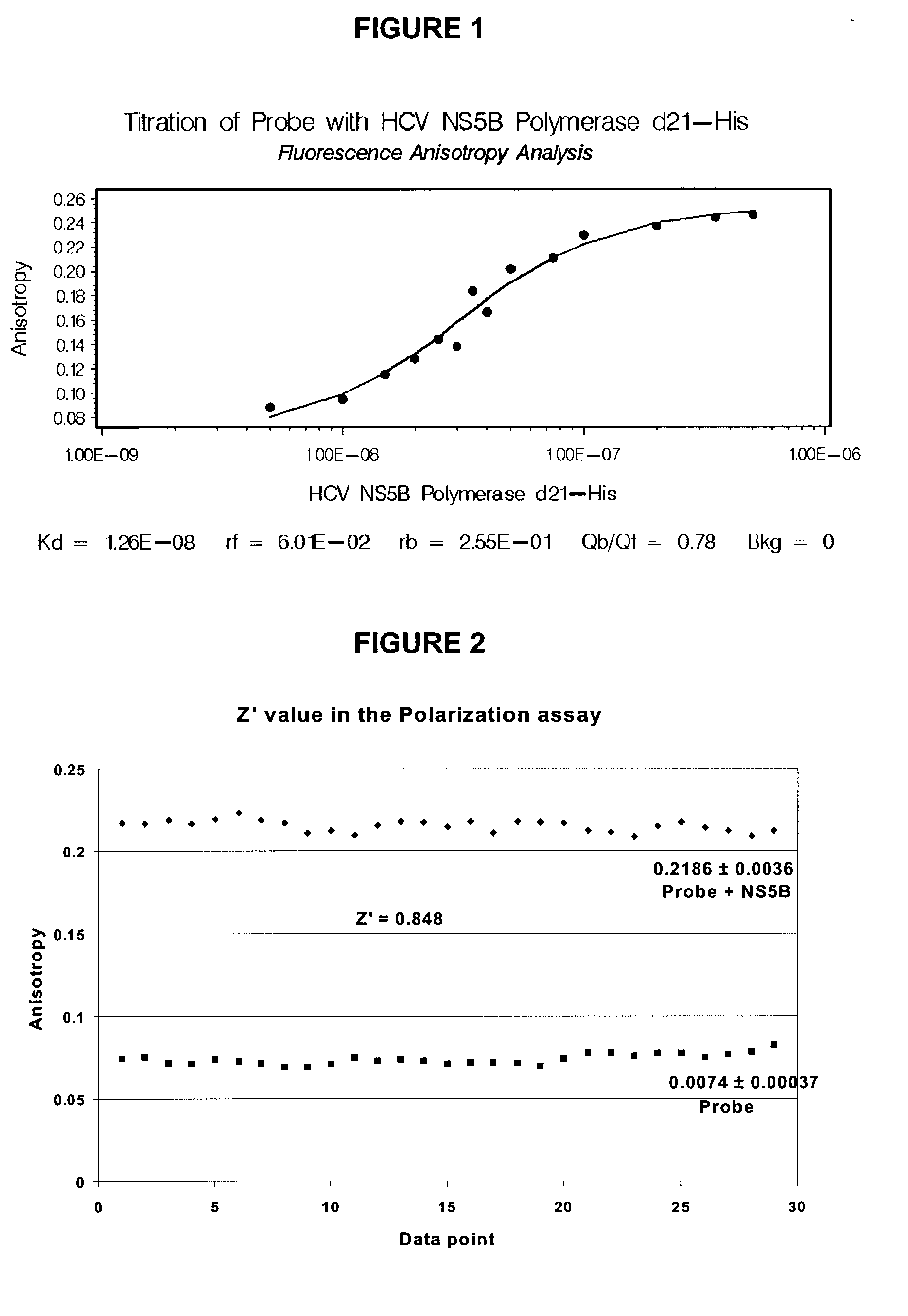
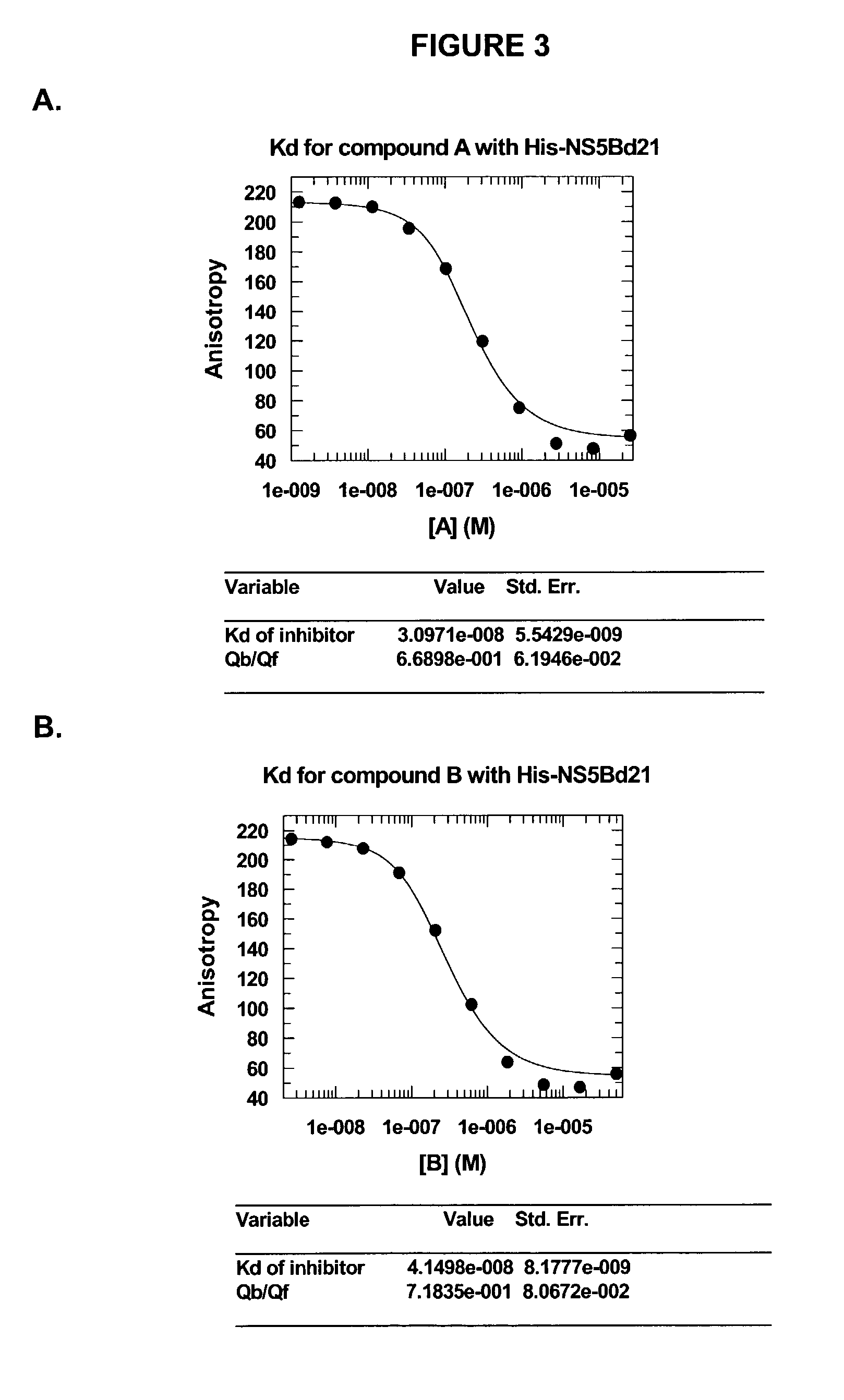
Direct binding assay for identifying inhibitors of HCV polymerase
A method for identifying compounds binding to HCV polymerase comprising the steps of: contacting said HCV polymerase or an analog thereof with a probe formula I:wherein A is O, S, N, NR1, or CR1, wherein R1 is defined herein;----- represents either a single or a double bond;R2 is selected from: H, halogen, R21, OR21, SR21, COOR21, SO2N(R22)2, N(R22)2, CON(R22)2, NR22C(O)R22 or NR22C(O)NR22 wherein R21 and each R22 is defined herein;B is NR3 or CR3, wherein R3 is defined herein;with the proviso that, when A is not N, then one of A or B is either CR1 or CR3,K is N or CR4, wherein R4 is defined herein;L is N or CR5, wherein R5 has the same definition as R4 defined above;M is N or CR7, wherein R7 has the same definition as R4 defined above;R5 is C(Y1)Z wherein Y1 is O or S; andZ is N(R6a)R6 or OR6, wherein R6a is H or alkyl or NR61R62 wherein R61 and R62 are defined herein; and R6 is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, Het, alkyl-aryl, alkyl-Het; or R6 iswherein R7 and R8 and Q are as defined herein;Y2 is O or S;R9 is H, (C1-6 alkyl), (C3-7)cycloalkyl or (C1-6)alkyl-(C3-7)cycloalkyl, aryl, Het, (C1-6)alkyl-aryl or (C1-6)alkyl-Het, all of which optionally substituted with R90; or R9 is covalently bonded to either of R7 or R8 to form a 5- or 6-membered heterocycle; or a salt thereof; where the probe comprises a detectable label attached to any suitable position, whereby said probe binds to an HCV polymerase or an analog thereof and is capable of being displaced by an inhibitor thereof.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM CANADA LTD
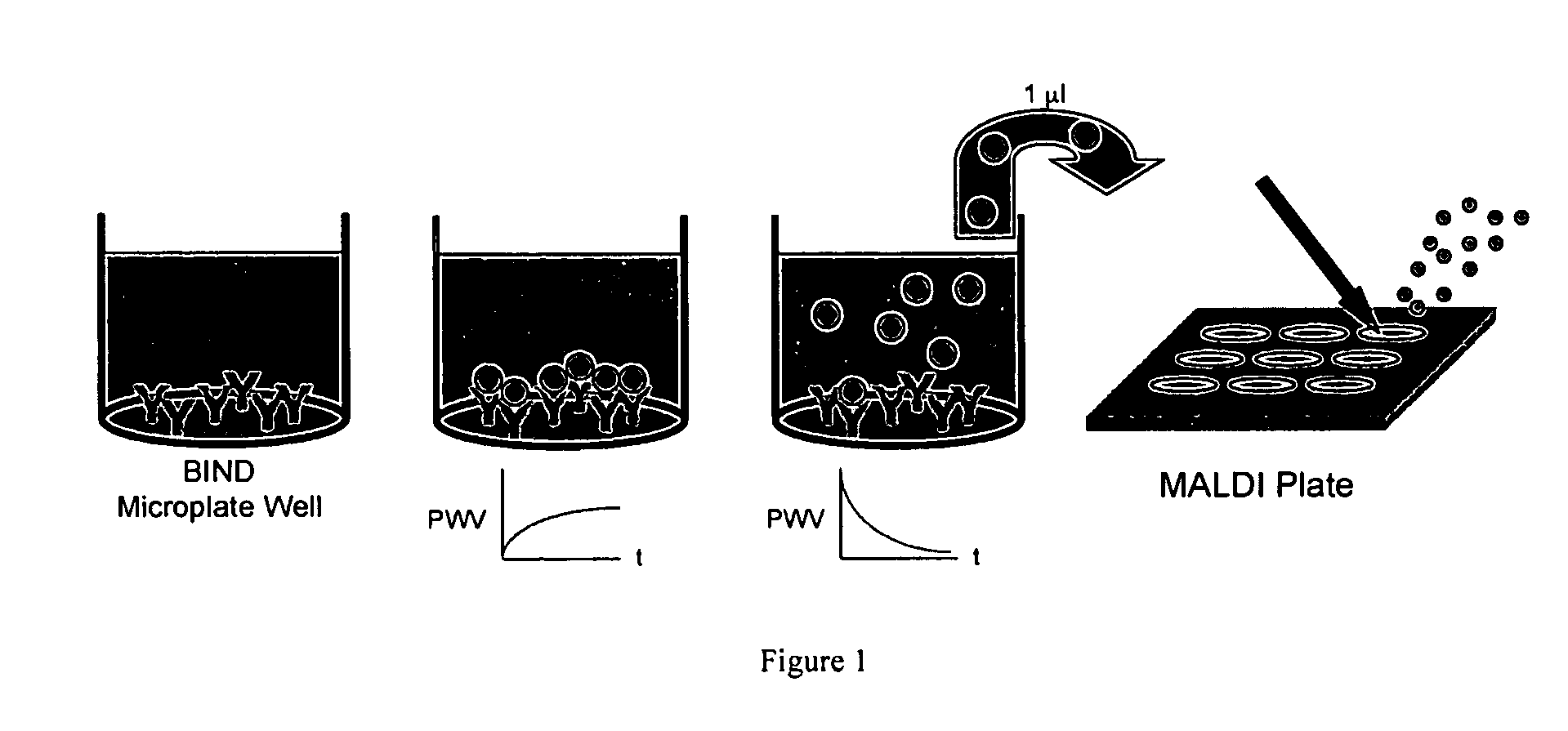
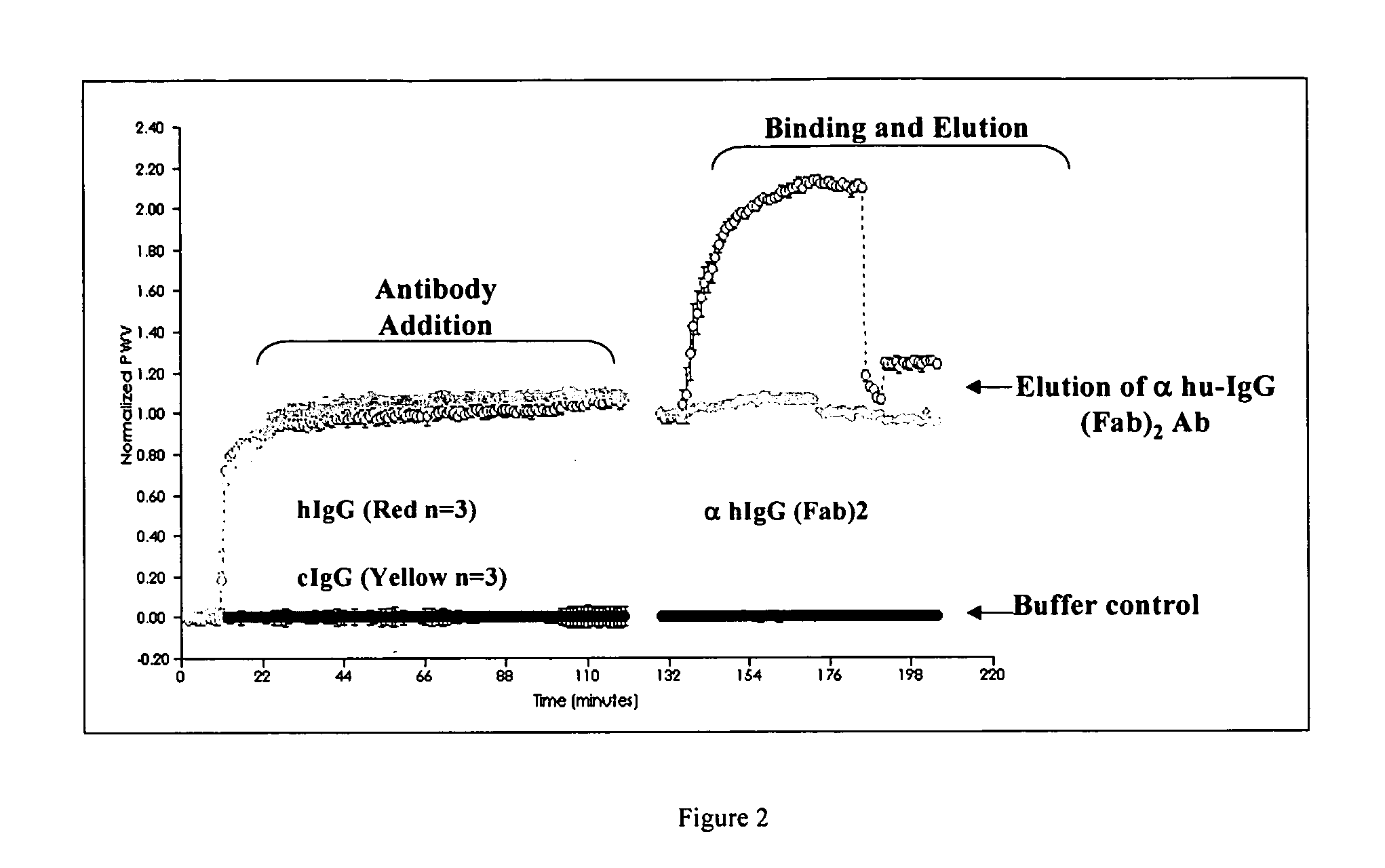
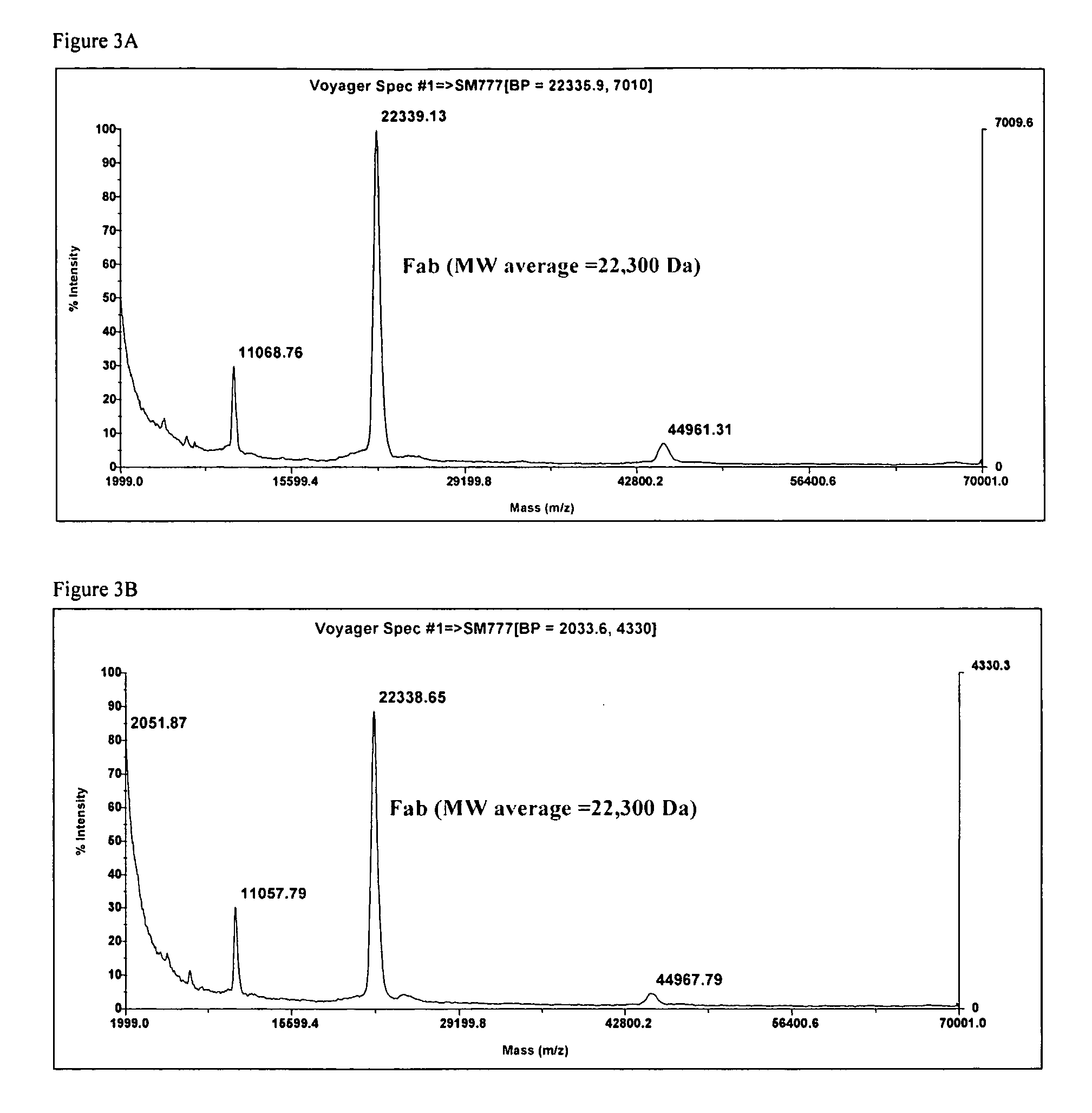
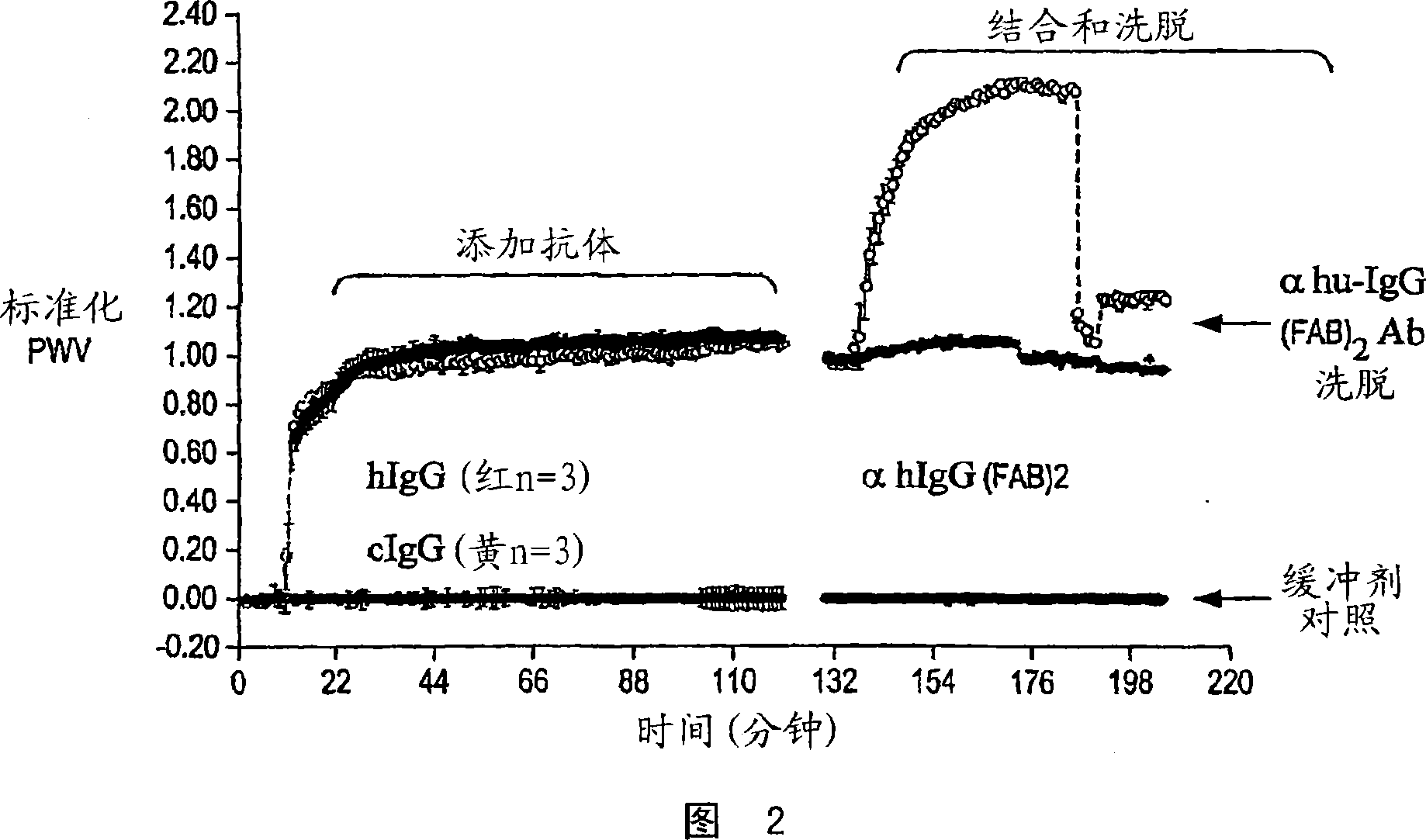
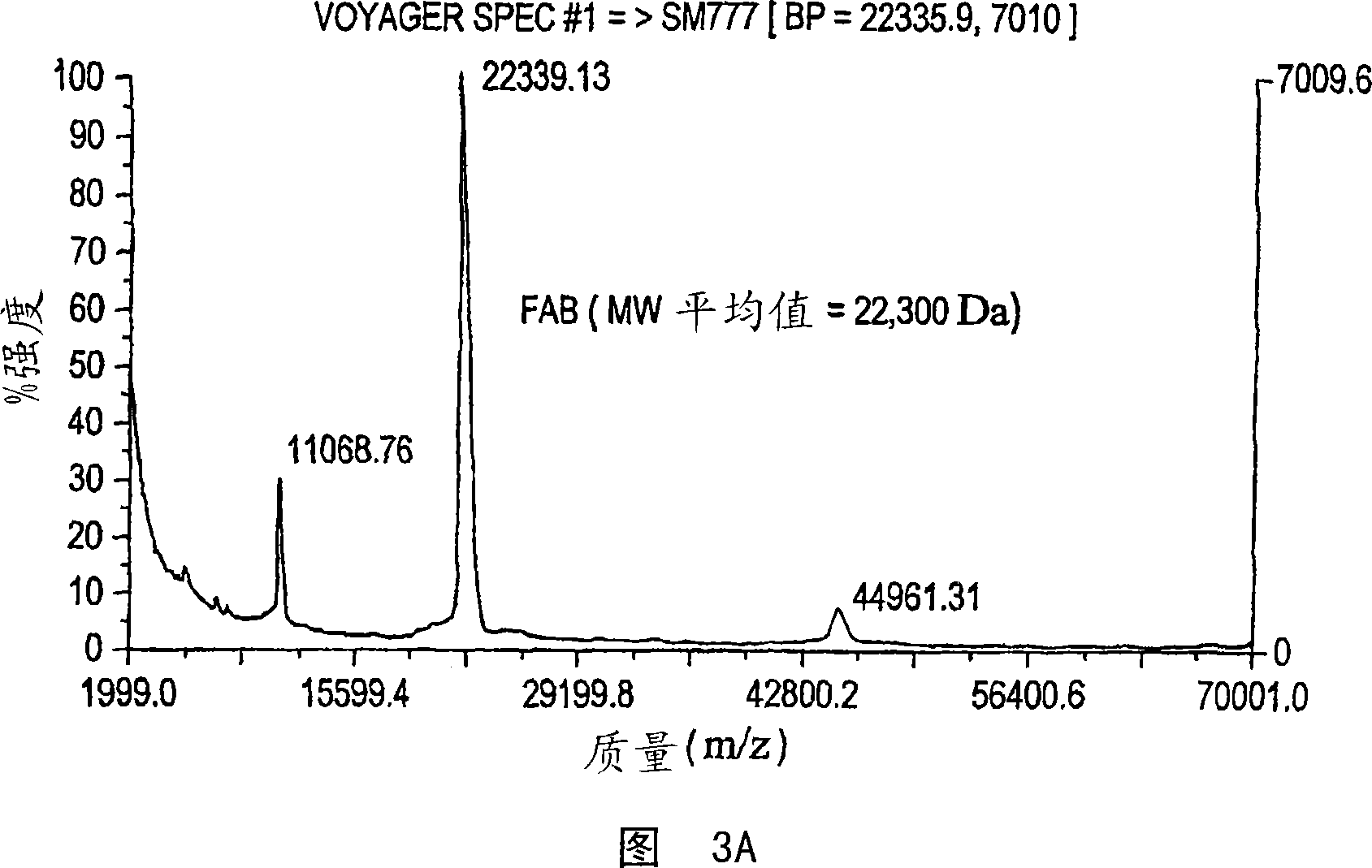
Integration of direct binding label-free biosensors with mass spectrometry for functional and structural characterization of molecules
InactiveUS20060003372A1Microbiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCombined methodMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention provides methods for the detection, quantification, identification and structural analysis of one or more molecules. Mass spectrometry (MS) is not a universal detector as all molecules do not ionize equally well leading to poor signal to quantity information. MS can be optimized to identify the specific mass of a binding component when the presence of a material is known. Colorimetric resonant reflectance optical sensors provide a universal mass detector in that nearly all biological masses give equally proportional signals. The combined methods allow selection and or detection with quantification of all masses binding to the sensor with the ability to identify specific molecules by their individual masses and structure analyses.
Owner:SRU BIOSYST
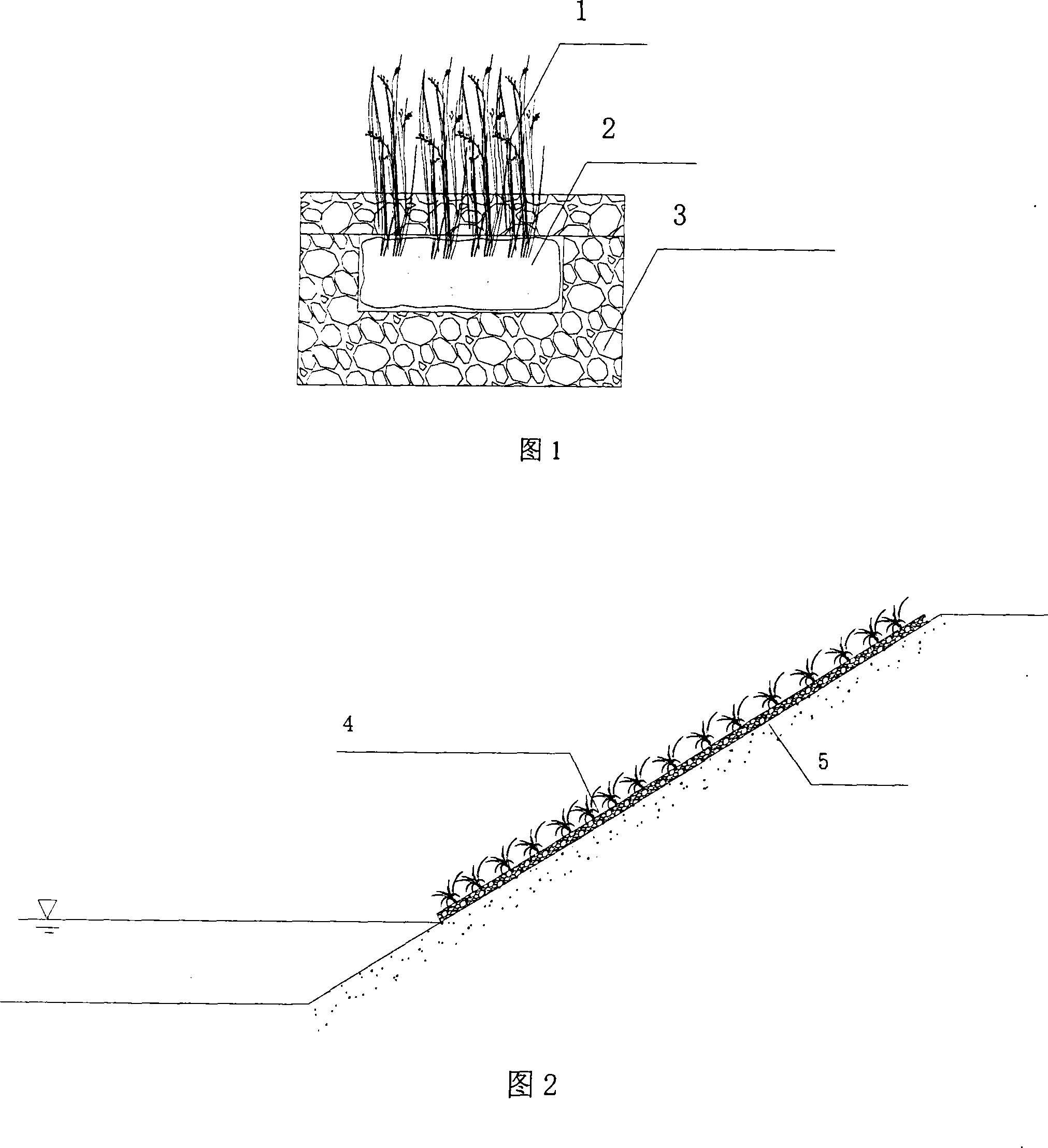
Porous concrete ecological capsule slope protection method
InactiveCN101235631AGuaranteed water permeabilityGuaranteed breathabilityCoastlines protectionCultivating equipmentsFiberNormal growth
The invention relates to a porous concrete ecological capsule slop protection process, which comprises making ecological capsules which are braided by fiber material such as palm ropes and twines and the like, storing doras, water-retention material, slow-release fertilizer, insecticide and plant seeds, placing the ecological capsules in the grooves of the porous concrete ecological capsule blocks, matching an upper and a lower porous concrete ecological capsule blocks through the way of bolt or direct binding, placing the porous concrete ecological capsule blocks on hard slope protection, connecting each porous concrete ecological capsule block with bolts or jump rings, and binding the space between the porous concrete ecological capsule blocks with cement and wholly hinging on the top portion of the slop protection. The advantages are that solving the difficulty of the ecological repair of the hard slop protection, guaranteeing the normal growth of plants which are covered on the hard slop protection, and purifying water and increasing water landscape. The process is applied on the hard slop protection project of river and lakes, which solves the problems of plant growing stroma loss which is caused by scouring, plant growing difficulty and reducing flood control function which is caused by the improper reconstruction for the original slop protection.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
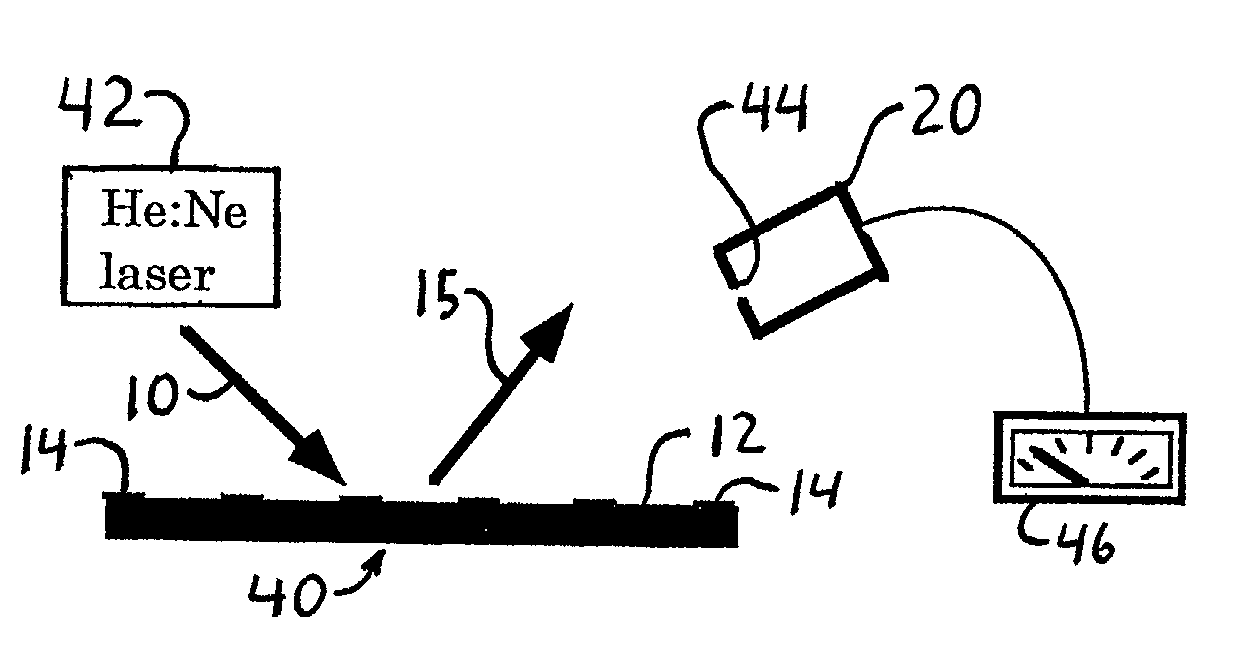
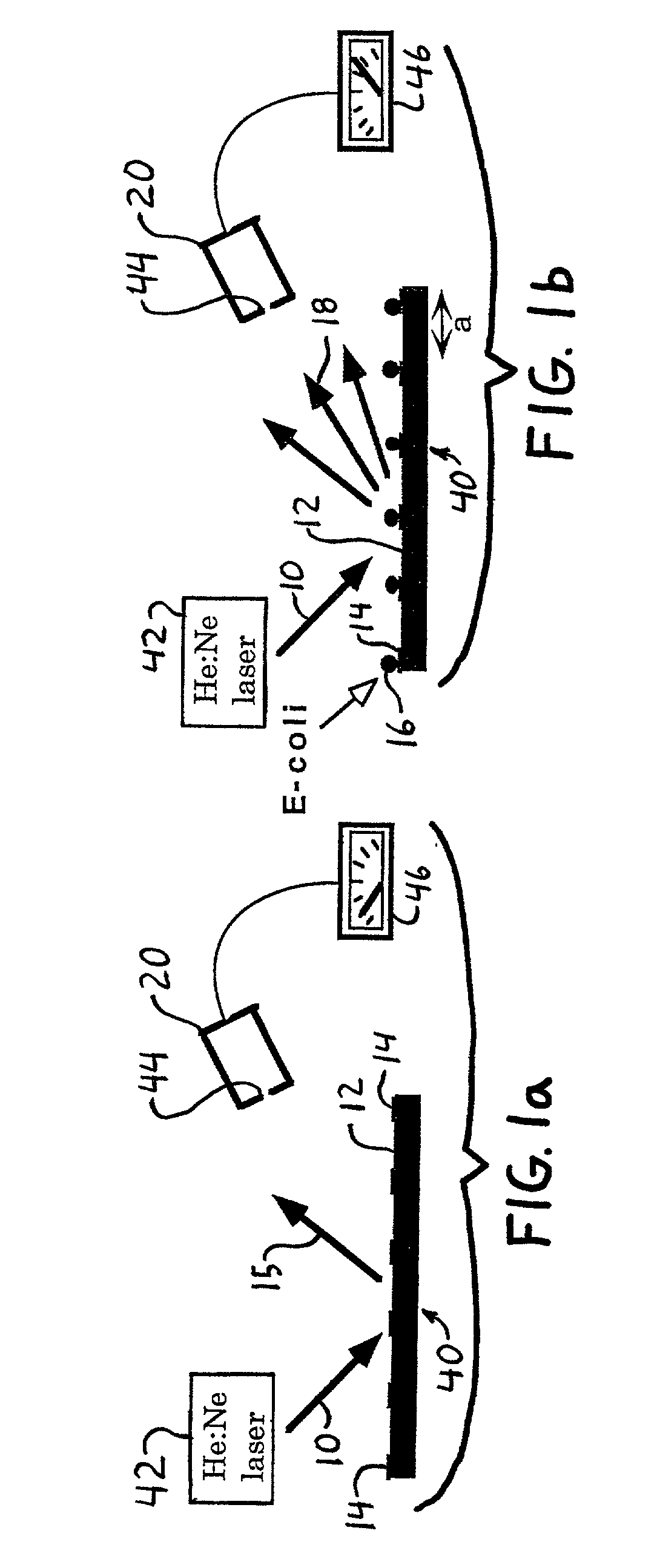
Diffraction-based cell detection using a micro-contact-printed antibody grating
InactiveUS20020037593A1Material nanotechnologyScattering properties measurementsMicrocontact printingEscherichia coli
An optical biological detector is able to bind specific targeted bacterial cells by stamping an antibody grating pattern onto a silicon surface. The antibody grating alone produces insignificant optical diffraction, but upon immunocapture of the targeted cells, the optical phase change produces a diffraction pattern. Micro-contact printing provides a method for placing the antibody grating pattern directly onto a substrate surface with no additional processes or binding chemicals. Antibodies or other biologically active material may be stamped directly onto clean native oxide silicon substrates with no other chemical surface treatments. Direct binding of the antibodies to the silicon occurs in a way that still allows them to function and selectively bind antigen. The performance of the sensor was evaluated by capturing Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells on the antibody-stamped lines and measuring the intensity of the first order diffraction beam resulting from the attachment of cells. The diffraction intensity increases in proportion to the cell density bound on the surface.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Super-hydrophobic coating capable of being used underwater and preparation and application method thereof
ActiveCN105647290APrevent adhesionAttach to resistLiquid surface applicatorsChloropene polymer coatingsOrganic solventHigh humidity
The invention discloses a super-hydrophobic coating capable of being used underwater and a preparation and application method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of super-hydrophobic coatings. The super-hydrophobic coating is formed by a backing material and a hydrophobic material. The backing material is prepared from, by mass, 5% to 30% of sealing rubber, 5% to 30% of petroleum resin, 1% to 10% of flatting agent and 30% to 89% of organic solvent A. The backing material and the hydrophobic material are used in combination, and on the basis of guaranteeing super-hydrophobic performance, the backing material is utilized for increasing the direct binding strength of a super-hydrophobic coating and a base material; damage of water flow / steam and the like to the super-hydrophobic coating can be effectively reduced, use strength is increased, the super-hydrophobic state can be maintained in the underwater / high-humidity environment for a long time, the service life can be prolonged, and great significance is achieved on oceangoing voyage, underwater exploration and the like.
Owner:BEIJING NEATRITION TECH CO LTD
Novel ligand detecting method
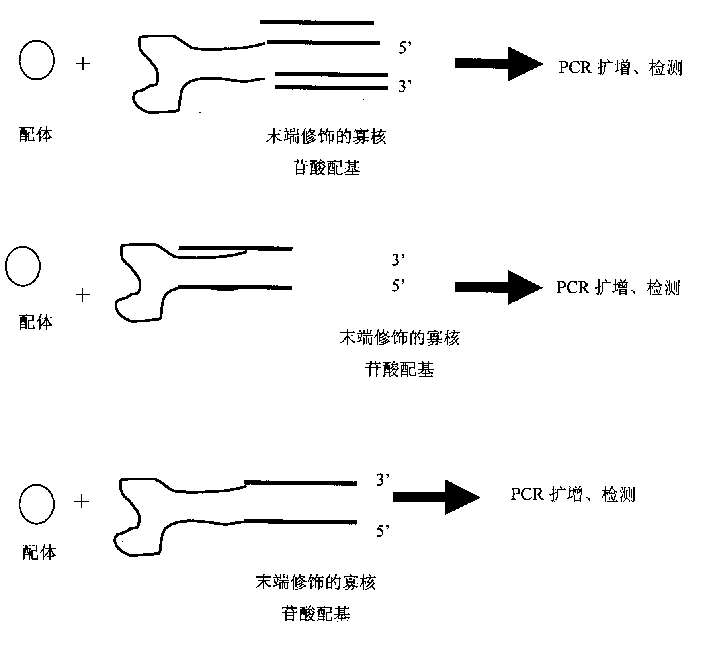
InactiveCN1521272AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingDirect binding
The present invention relates to one new kind o detecting ligand of nucleic acid aglucone. The method utilizes nucleic acid sequence modified ligand to specify oligonucleotide aglucone for direct binding with ligand and converting ligand signal into nucleic acid aglucone signal. The ligand is then determined via subsequent PCR proliferation and amplification and detection. The method of detecting ligand has the features of fast speed, high sensitivity, powerful specificity multi-ligand microarray detection.
Owner:甘肃省医学科学研究院
Cherkasky fusion proteins containing antibody-, antigen- and microtubule-binding regions and immune response-triggering regions
The invention relates to the fields of tumour physiology and biotechnology. The object of the invention is to develop effective and selective novel fusion proteins and fusion protein-antibody complexes against various types of leukaemia and solid tumours. Selectivity is achieved by cell-specific or tumour-specific ligands of the fusion proteins or by antibodies of the fusion protein-antibody complexes. Effectiveness is achieved on the one hand by the direct binding of the microtubules or cytoskeleton elements to the microtubule-binding regions and on the other hand by induction, as well as by the reinforcement of the immune reaction by regions that trigger the immune reaction on the target cells.
Owner:CHERKASKY ALEXANDER
PEPTIDES WITH THE CAPACITY TO BIND TO TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR beta 1 (TGF-beta 1)
InactiveUS20100222280A1Inhibitory activitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCorneal fibrosis
The described peptides possess the capacity to bind to Transforming Growth Factor TGF-β1 (TGF-β1), and are potential inhibitors of the biological activity of TGF-β1 through direct binding to this cytokine. These peptides can be used in the treatment of diseases or pathological alterations based on excessive or deregulated TGF-β1 expression, e.g., liver fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, corneal fibrosis and haze.
Owner:DIGNA BIOTECH +1
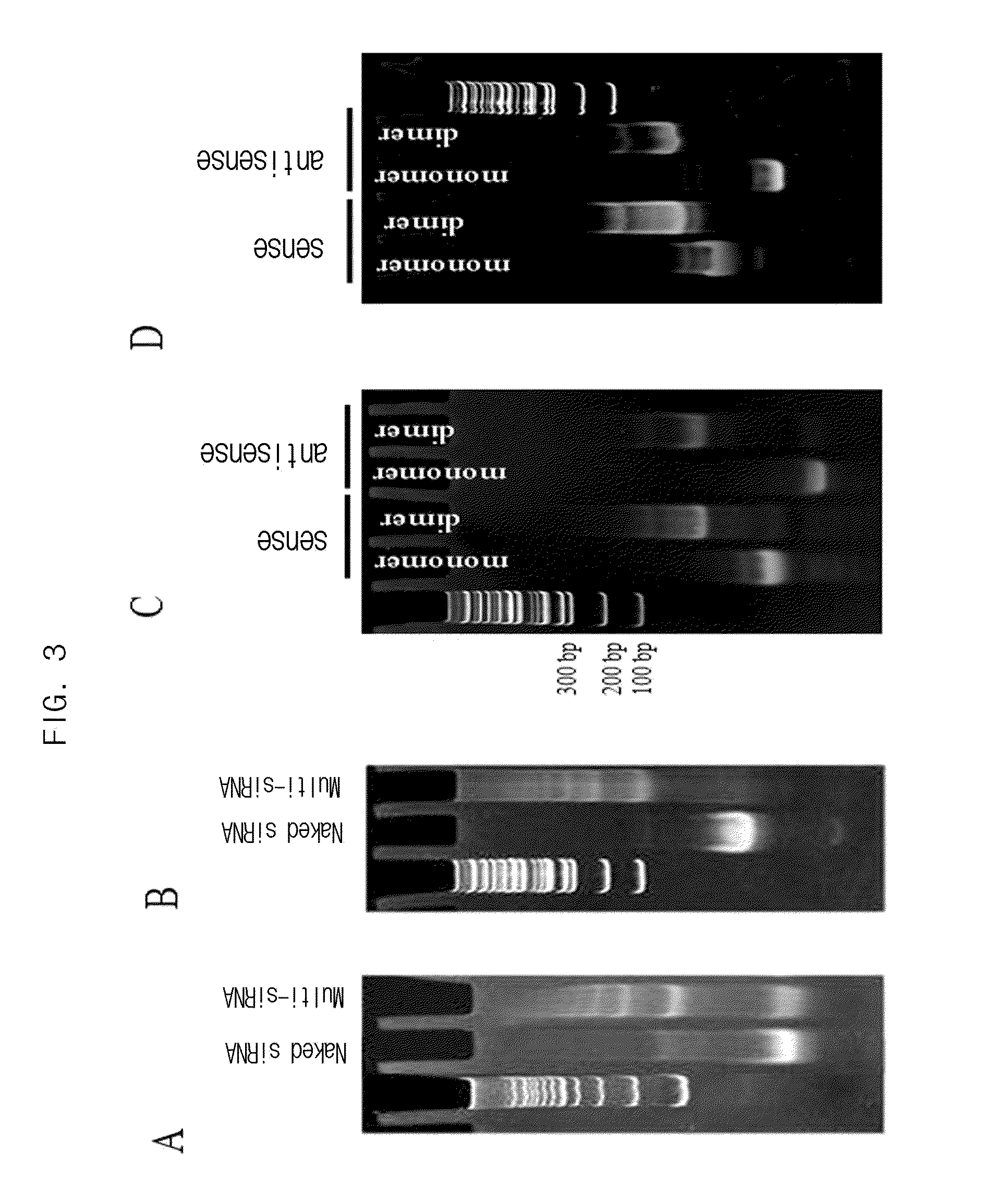
Multi-conjugate of siRNA and preparing method thereof
The present invention relates to a multi-conjugate of small interfering RNA (siRNA) and a preparing method of the same, more precisely a multi-conjugate of siRNA prepared by direct binding of double stranded sense / antisense siRNA monomers or indirect covalent bonding mediated by a cross-linking agent or a polymer, and a preparing method of the same. The preparing method of a siRNA multi-conjugate of the present invention is characterized by simple and efficient reaction and thereby the prepared siRNA multi-conjugate of the present invention has high molecular weight multiple times the conventional siRNA, so that it has high negative charge density, suggesting that it has excellent ionic interaction with a cationic gene carrier and high gene delivery efficiency.
Owner:KAIST IP
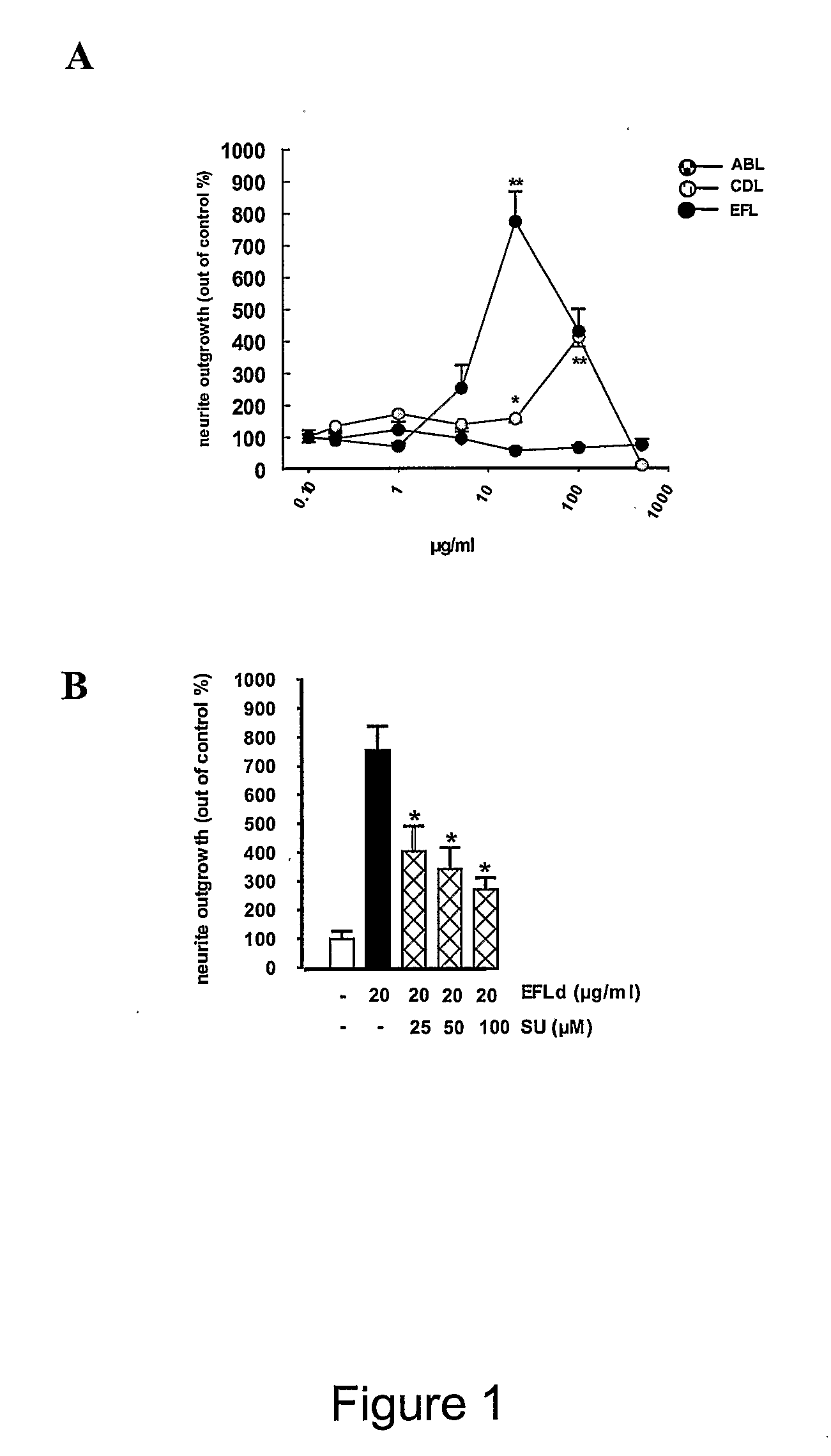
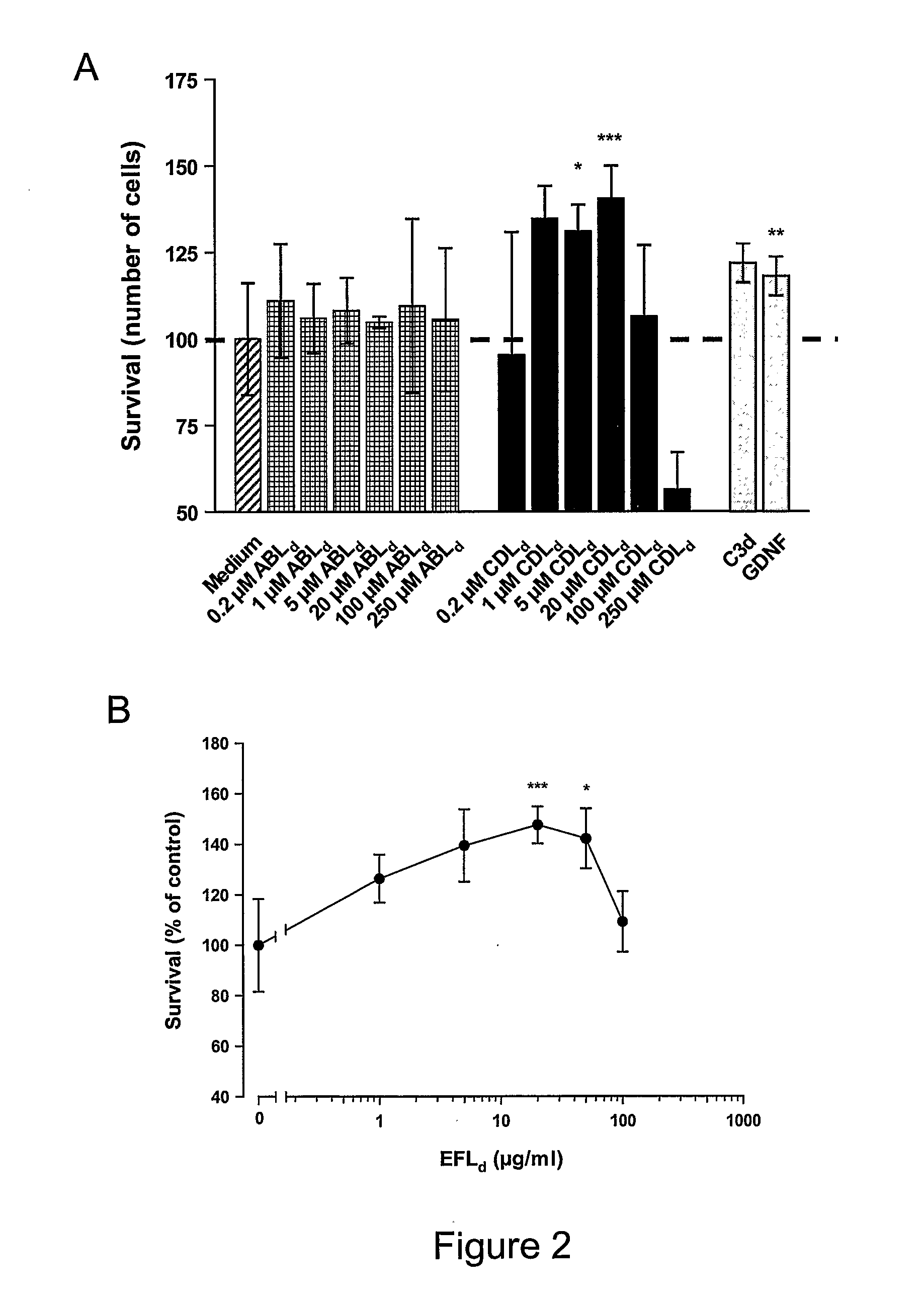
Fgfr binding peptides
InactiveUS20090074774A1Stimulating neurite outgrowthConducive to survivalImmunoglobulin superfamilyNervous disorderDiseaseNeural cell
The present invention relates to new peptide compounds capable of direct binding to fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and activating said receptor. The compounds of the invention comprise peptide fragments of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) derived from the fibronectin type-III module 1 (F3, 1) of NCAM. Peptide sequences of the invention are capable of stimulating learning and memory and / or neurite outgrowth and / or neural cell survival. Peptide sequences and compounds comprising thereof, according to the invention, may be beneficially used for treatment and / or prevention of different pathological conditions wherein FGFR and / or NCAM play a role in pathology and / or recovery from disease. Accordingly, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the peptide sequences and compounds of the invention are also in the scope of protection.
Owner:ENKAM PHARMA
Integration of direct binding sensors with mass spectrometry for functional and structural characterization of molecules
InactiveCN101057131AColor/spectral properties measurementsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryStructural analysis
The invention provides methods for the detection, quantification, identification and structural analysis of one or more molecules. Mass spectrometry (MS) is not a universal detector as all molecules do not ionize equally well leading to poor signal to quantity information. MS can be optimized to identify the specific mass of a binding component when the presence of a material is known. Colorimetric resonant reflectance optical sensors provide a universal mass detector in that nearly all biological masses give equally proportional signals. The combined methods allow selection and or detection with quantification of all masses binding to the sensor with the ability to identify specific molecules by their individual masses and structure analyses.
Owner:SRU BIOSYST
Multi-conjugate of sirna and preparing method thereof
ActiveUS20110044931A1Improve responseImprove efficiencyTripeptide ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCross-linkGene delivery
The present invention relates to a multi-conjugate of small interfering RNA (siRNA) and a preparing method of the same, more precisely a multi-conjugate of siRNA prepared by direct binding of double stranded sense / antisense siRNA monomers or indirect covalent bonding mediated by a cross-linking agent or a polymer, and a preparing method of the same. The preparing method of a siRNA multi-conjugate of the present invention is characterized by simple and efficient reaction and thereby the prepared siRNA multi-conjugate of the present invention has high molecular weight multiple times the conventional siRNA, so that it has high negative charge density, suggesting that it has excellent ionic interaction with a cationic gene carrier and high gene delivery efficiency.
Owner:KAIST IP
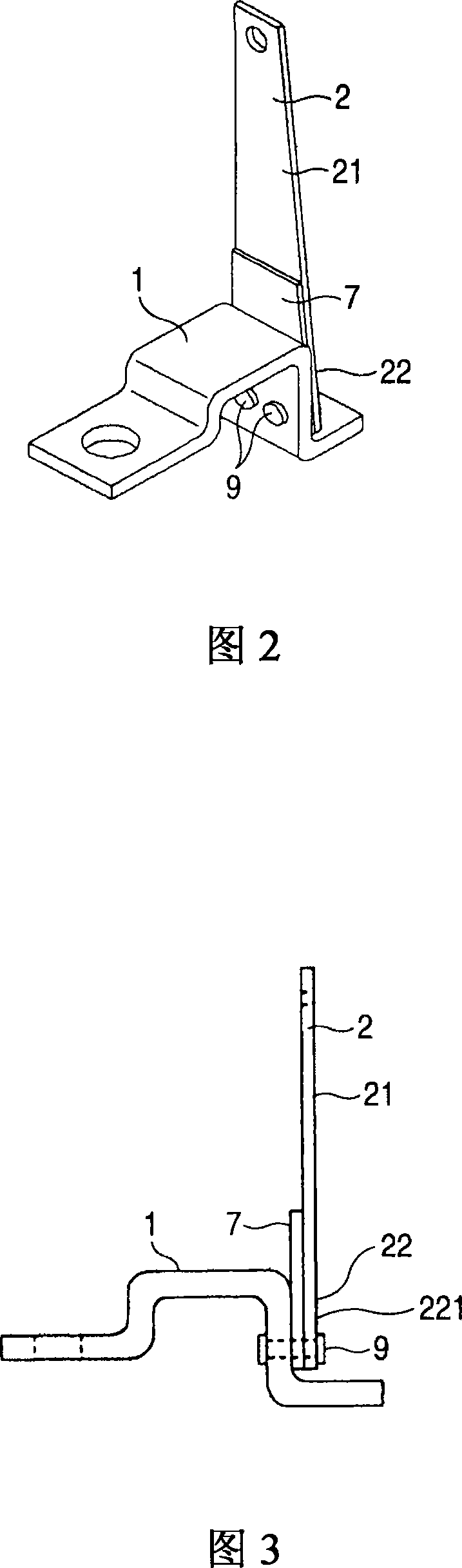
Circuit breaker and thermal trip
InactiveCN101147224AWill not affect tripping characteristicsHigh temperature measurementProtective switch detailsElectrothermal relaysContact typeDirect binding
A thermal tripping device, on a heater (1) as a fixed terminal, a bimetal strip (2) with one end as an action end (21) and the other end as a fixed end (22) The above-mentioned fixed end (22) is fastened to the above-mentioned heater (1) in a cantilever shape, and when the above-mentioned heater (1) is overheated by energizing the above-mentioned heater (1), the above-mentioned moving end of the above-mentioned bimetal (2) (21) Bending, and on the fastening part (221) where the above-mentioned bimetal strip is fastened to the above-mentioned heater, integrally and directly bond the temperature measuring member (7), which is obtained from the above-mentioned bimetal strip (2) and the above-mentioned heater (1) are exposed so as to be in contact with the contact temperature measuring device (8).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
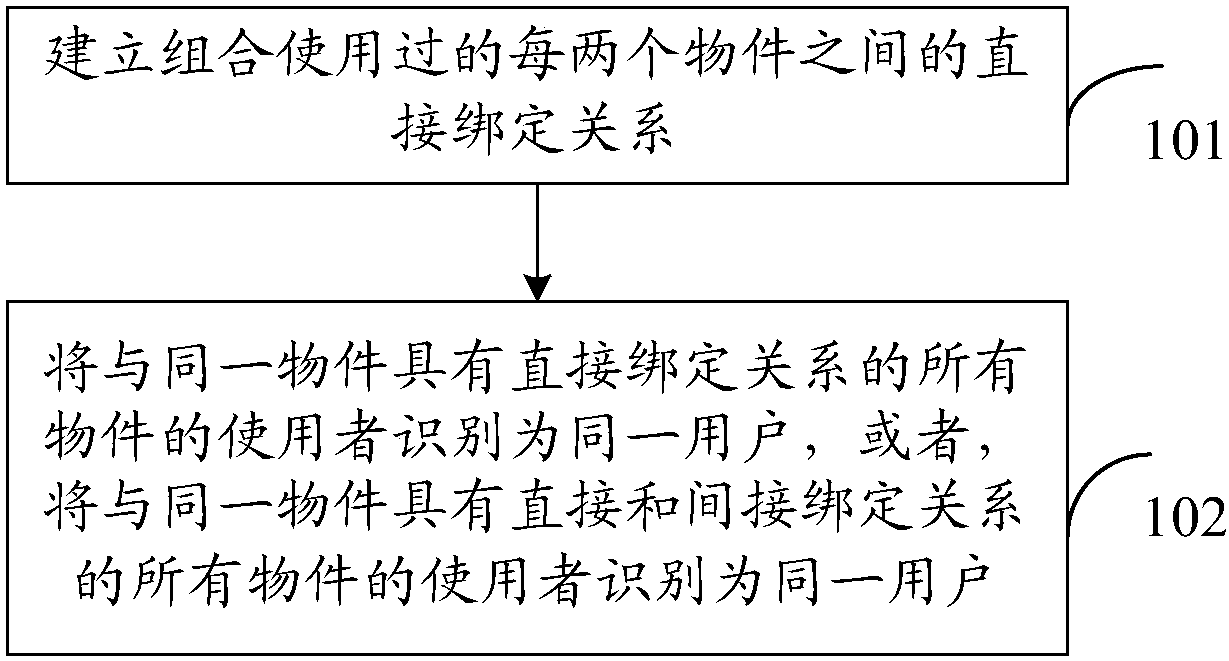
Method and device for identifying same user
ActiveCN108076450AReduce the problem of identifying as different usersImprove accuracyNetwork data managementDirect bindingData science
The invention discloses a method for identifying a same user. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a direct binding relationship between every two articles which are used in a combined manner; and identifying a user of all the articles which have the direct binding relationships with the same article as the same user, or identifying a user of all the articles which have the direct binding relationships and indirect binding relationships with the same article as the same user. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention has the advantage that the article user can bemore accurately identified.
Owner:BEIJING GRIDSUM TECH CO LTD
Toll-like receptor agonists and antagonists and methods of use thereof
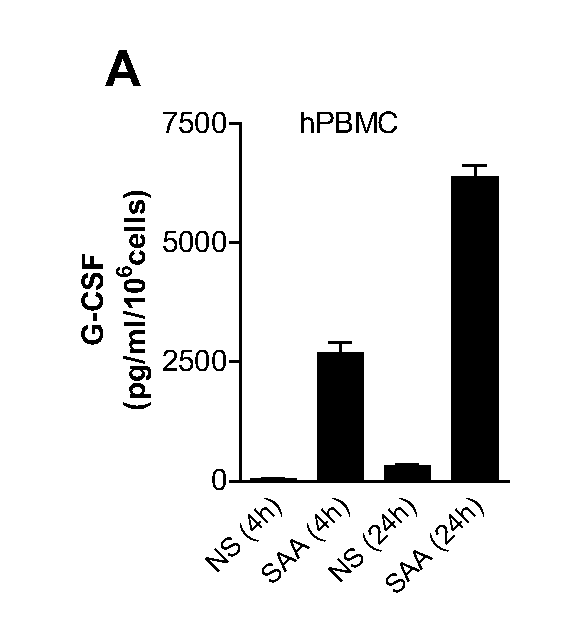
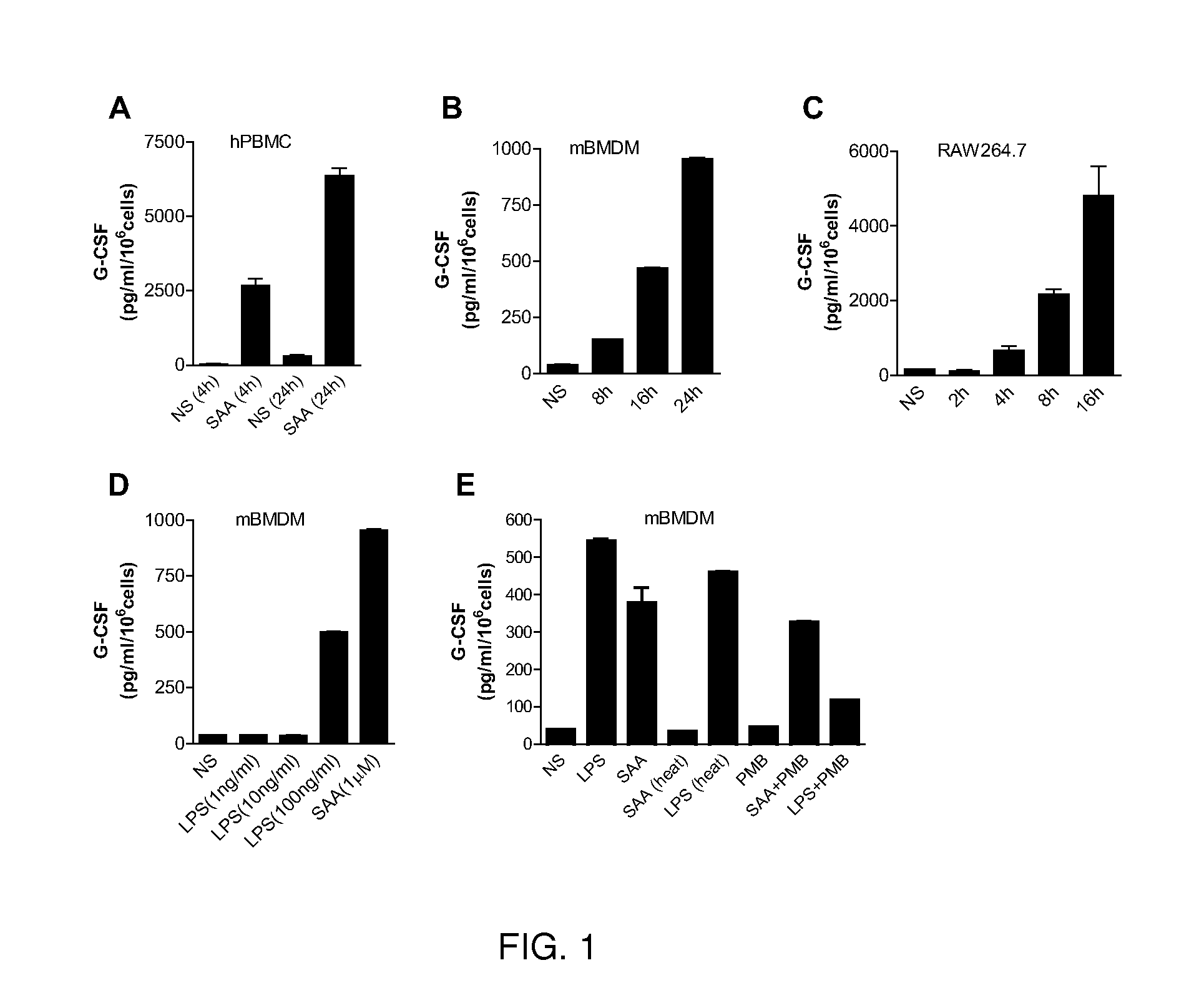
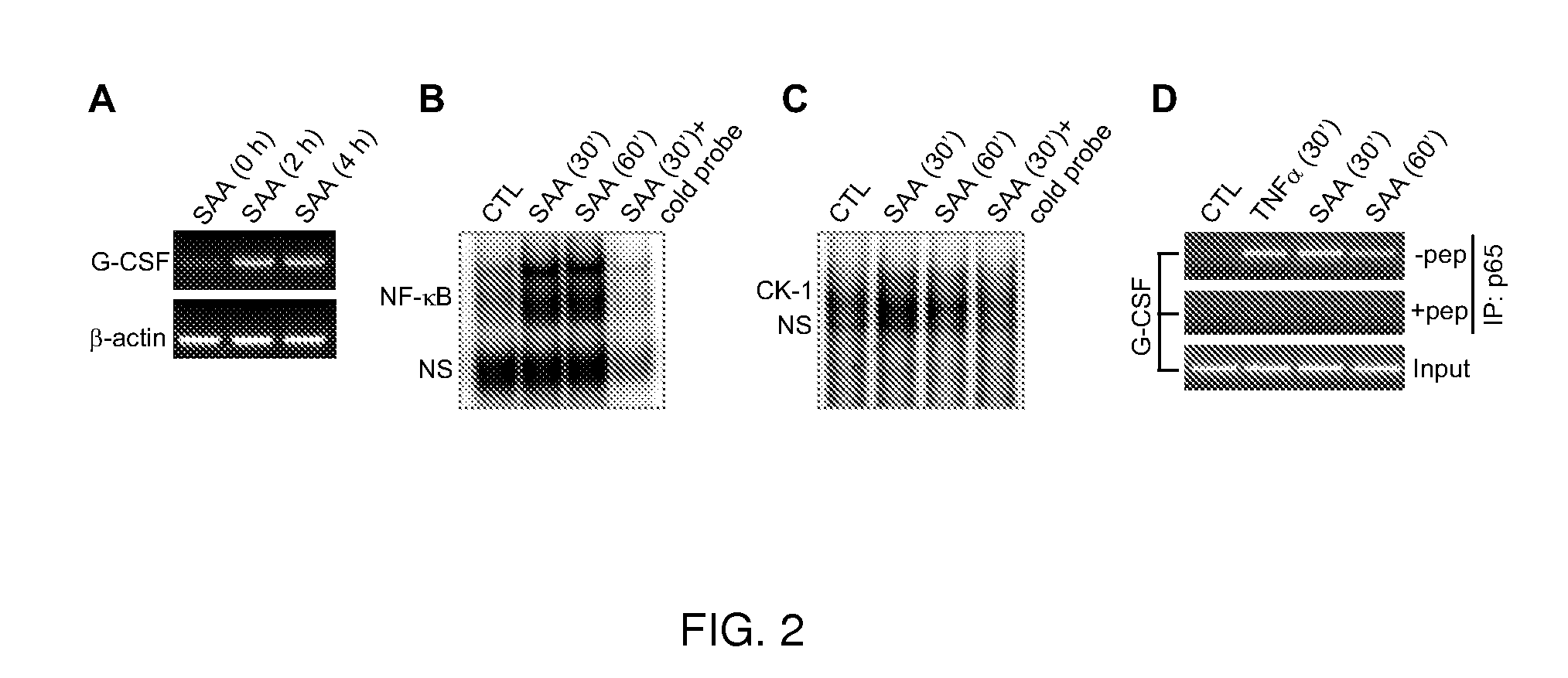
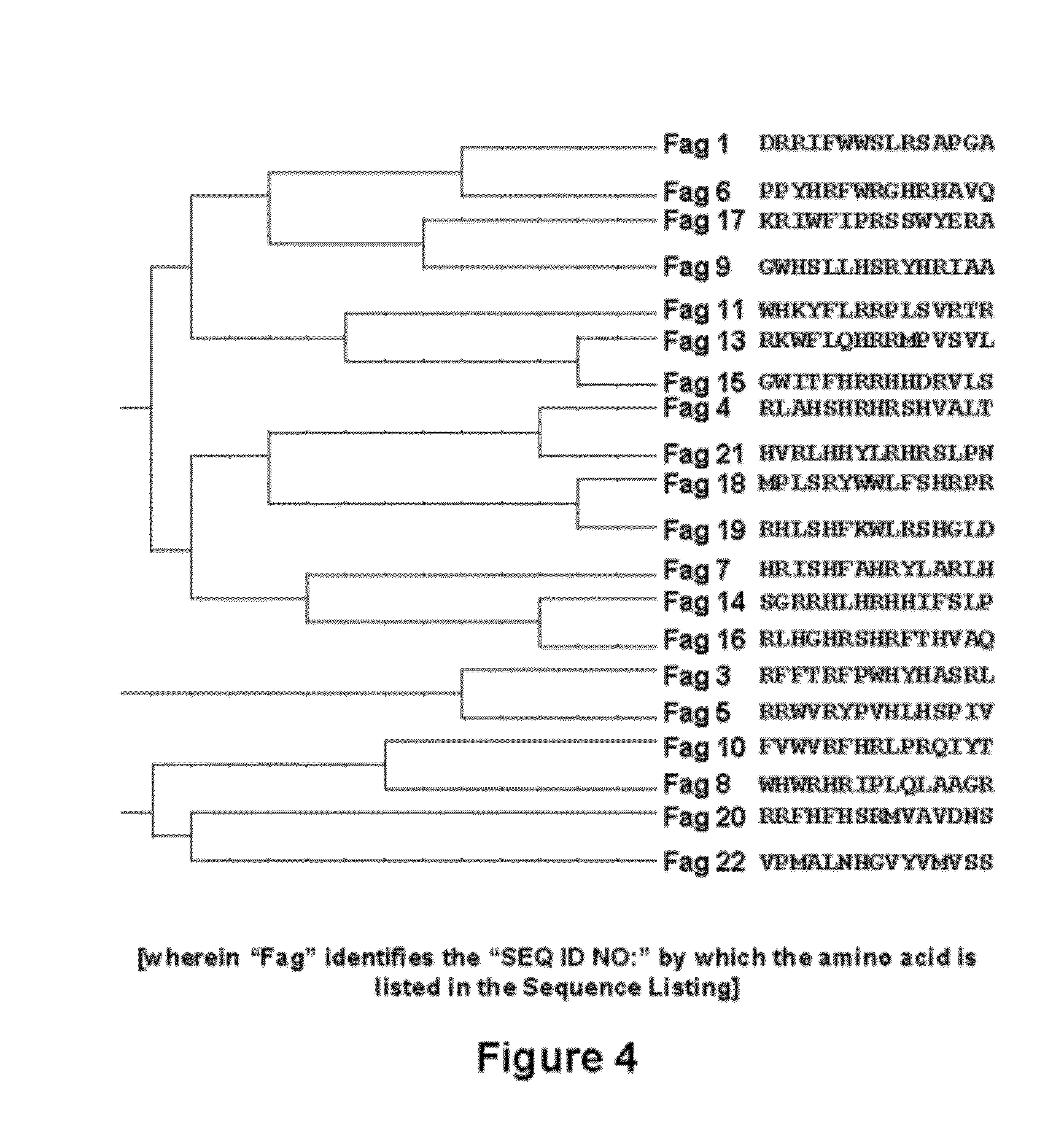
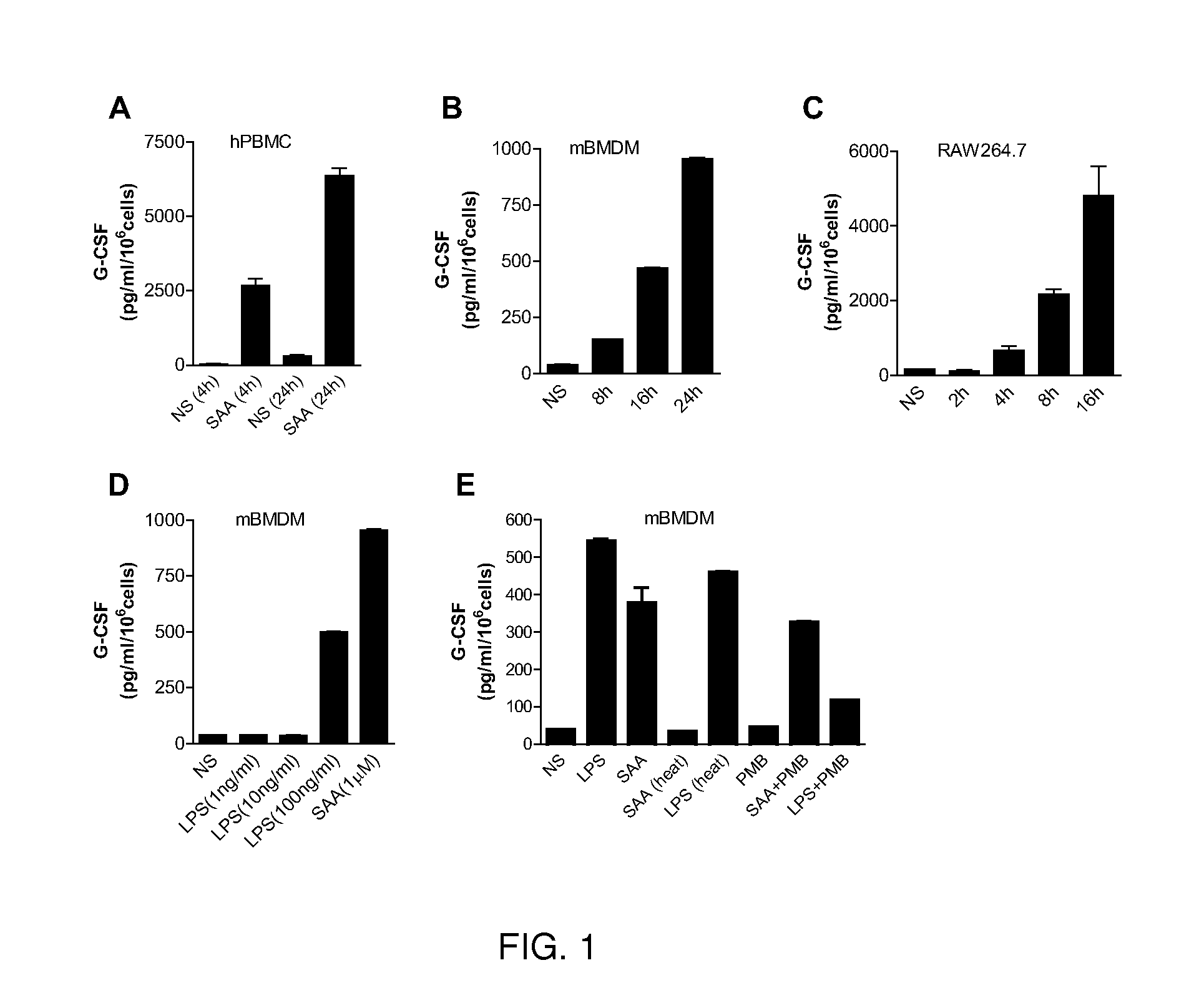
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods of modulating inflammatory and immune responses through binding of SAA to TLR2 in a subject (e.g., human, non-human primate, rodent, etc.), and compositions and methods for screening TLR2 agonists and antagonists. In the studies described herein, a potential role of SAA in neutrophilia was investigated and the results demonstrated that SAA is a potent inducer for macrophage secretion of G-CSF, which leads to neutrophilia in mice. Using G-CSF− / − and TLR2− / − mice, it was found that the SAA-induced neutrophilia is dependent on TLR2-mediated production of G-CSF. Based on direct binding assay and gain-of-function studies in TLR2-transfected cells, SAA was identified as a novel ligand for TLR2 and a link between increased SAA concentration and TLR2-mediated inflammatory responses such as neutrophilia was established. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
A capacitive touch screen and terminal equipment
PendingCN109683752AAvoid damage to silver nanowiresImprove protectionMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSilver pasteLaser etching
The invention relates to the field of touch screens, in particular to a capacitive touch screen. The capacitive touch screen comprises a base material and a silver nanowire conducting layer coated onthe base material, wherein the silver nanowire conducting layer comprises a visible area and a binding area, OCA optical cement is attached to the visible area, a connecting circuit is printed from the inner edge of the visible area to the binding area, and the silver nanowire conducting layer is connected with the flexible circuit board through the connecting circuit. According to the invention,the silver nanowires are used as the conductive layer, and the connection line is printed in the conductive layer binding area, so that the connection between the conductive layer and the flexible circuit board is realized, and the phenomenon that the silver nanowires are damaged due to the direct binding between the flexible circuit board and the conductive layer is avoided; And the printed silver paste does not need to be etched, so that the problem of environmental pollution caused by destructive particles generated by laser etching or acid-base etching is avoided. And by printing a connecting circuit, the protection of the silver nanowires from the conductive layer binding region to the visible region can be realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUAKE COMM TECH CO LTD
Peptides with the capacity to bind to transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)
The described peptides possess the capacity to bind to Transforming Growth Factor TGF-β1 (TGF-β1), and are potential inhibitors of the biological activity of TGF-β1 through direct binding to this cytokine. These peptides can be used in the treatment of diseases or pathological alterations based on excessive or deregulated TGF-β1 expression, e.g., liver fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, corneal fibrosis and haze.
Owner:DIGNA BIOTECH +1
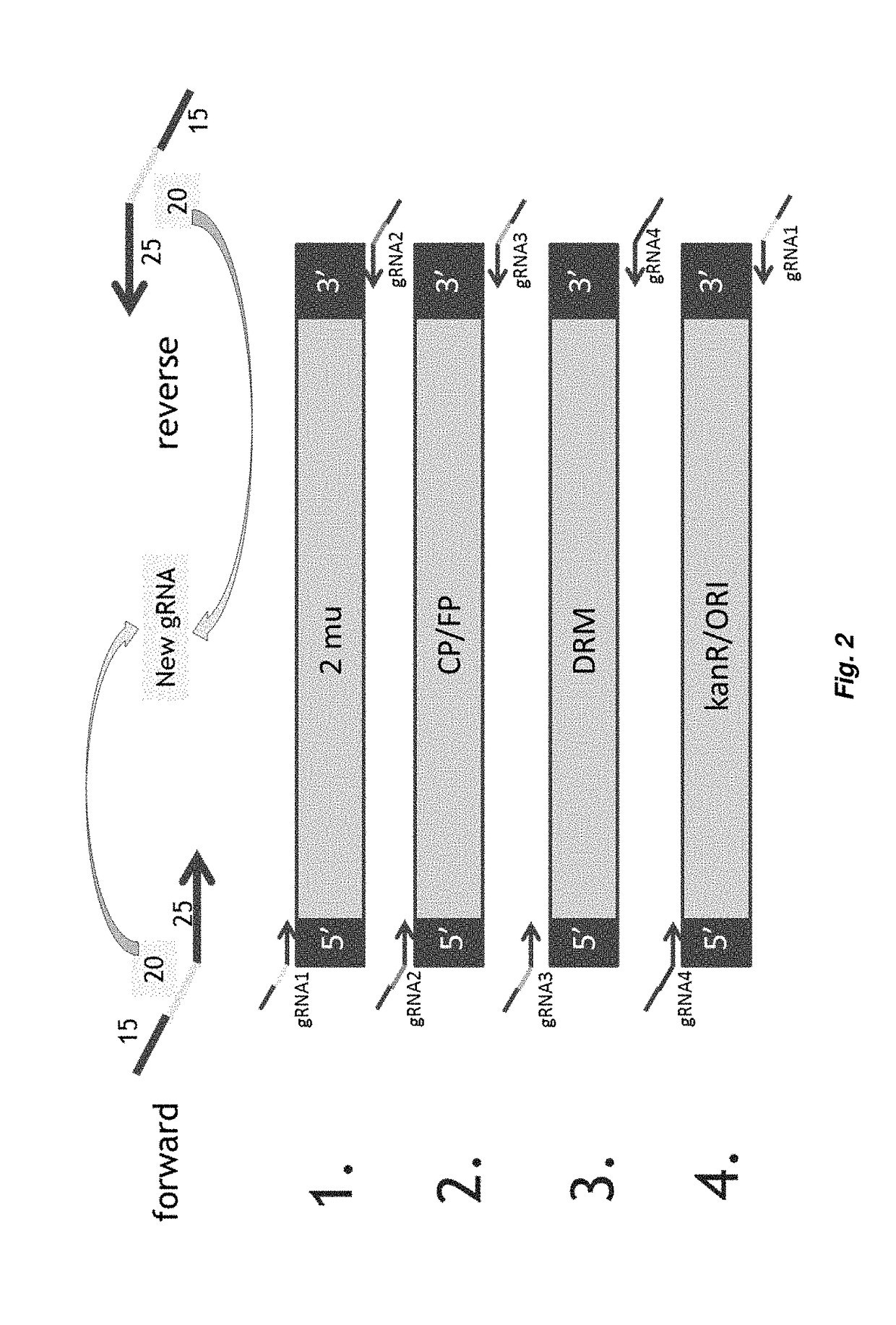
Guide RNA assembly vector
InactiveUS20190055544A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionIn vivoDirect binding
The present invention relates relates to a CRISPR-CAS system for a host cell, in particular to a method to produce a circular vector comprising one or more guide-polynucleotide expression cassettes, wherein said one or more guide-polynucleotide expression cassettes comprise a polynucleotide encoding a guide-polynucleotide operably linked to one or more control sequences which direct the expression of said guide-polynucleotide in a host cell, wherein said guide-polynucleotide comprises a guide-sequence that essentially is the reverse complement of a target-polynucleotide in a host cell and wherein the guide-polynucleotide can direct binding of a Cas protein at a target-polynucleotide in a host cell to form a CRISPR-Cas complex, in vivo.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
FGFR binding peptides
InactiveCN101027320AStimulate survivalStimulate neuroplasticityImmunoglobulin superfamilyNervous disorderDiseaseNeural cell
The present invention relates to new peptide compounds capable of direct binding to fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and activating said receptor. The compounds of the invention comprise peptide fragments of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) derived from the fibronectin type-III module 1 (F3, 1) of NCAM. Peptide sequences of the invention are capable of stimulating learning and memory and / or neurite outgrowth and / or neural cell survival. Peptide sequences and compounds comprising thereof, according to the invention, may be beneficially used for treatment and / or prevention of different pathological conditions wherein FGFR and / or NCAM play a role in pathology and / or recovery from disease. Accordingly, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the peptide sequences and compounds of the invention are also in the scope of protection.
Owner:ENKAM PHARMA
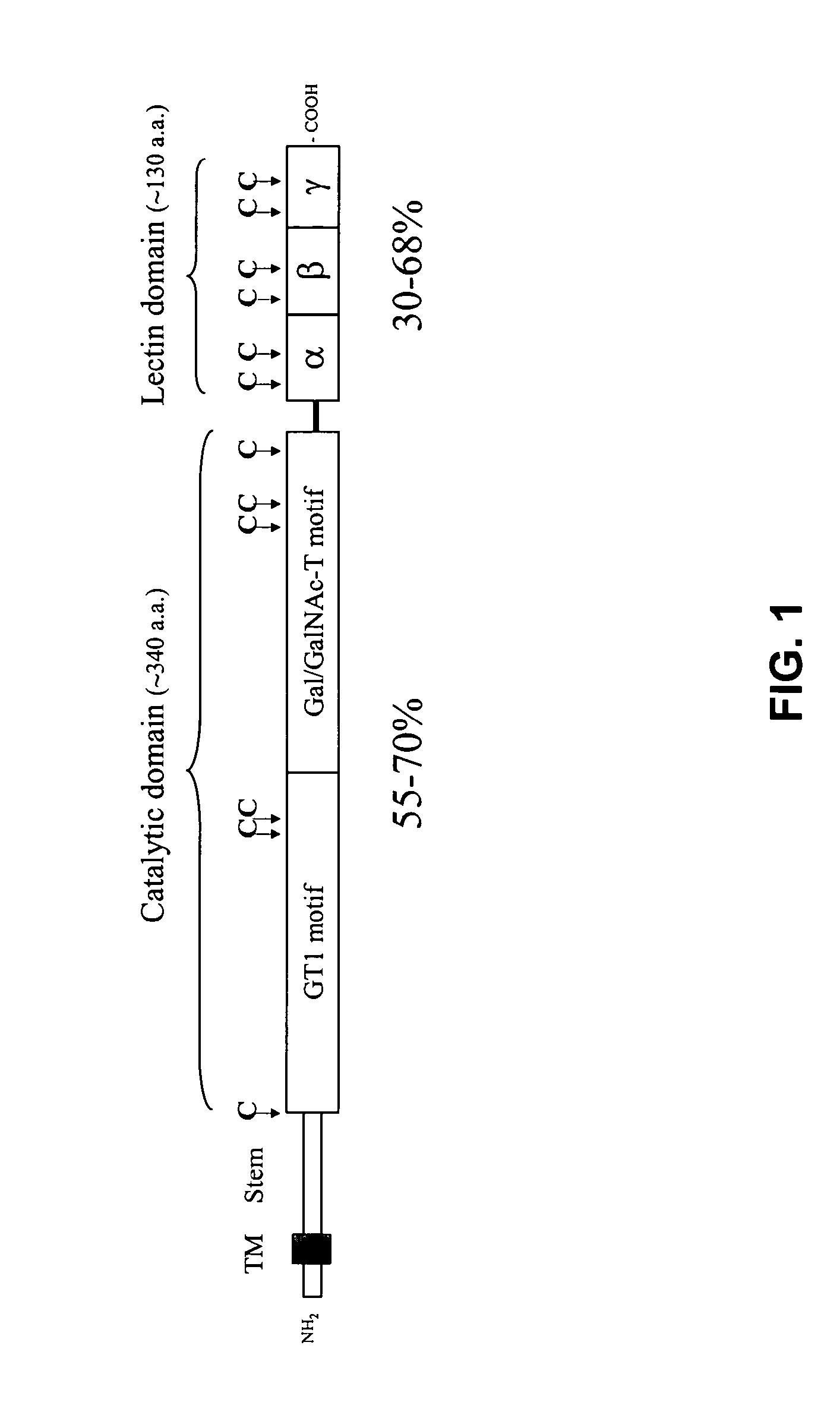
ISOLATED LECTIN POLYPEPTIDES CONSISTING OF TRUNCATED MAMMALIAN UDP-GalNAc:POLYPEPTIDE N- ACETYLGALACTOSAMINYLTRANSFERASES
Owner:GLYCOZYM
Biocidal molecules, macromolecular targets and methods of production and use
InactiveUS20060240494A1Restrains essential movementInhibit activity of proteinCompound screeningBiocideScreening methodDirect binding
A method for identifying a compound that has a biocidal effect against a selected organism involves screening from among known or unknown peptide or non-peptide molecules, a test molecule that binds selectively to a target sequence of a multi-helical lid of a heat shock protein of the organism. The binding of the test compound inhibits the protein folding activity of the protein. A specific embodiment of such a method is useful for identifying or designing a pharmaceutical or veterinary biocidal or antibiotic compound, preferably a pathogen and / or strain-specific compound. For this purpose, the compound does not bind to a heat shock protein that is homologous to the mammalian subject to be treated with the compound. Screening methods can encompass direct binding or competitive assays. Molecules or compounds identified by these methods are employed as biocides for pharmaceutical, veterinary, pesticide, insecticide and rodenticide uses, among others.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY +1
Manufacturing method of field termination type insulated gate type bipolar transistor
InactiveCN103700589ASimple processLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDirect binding
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a field termination type insulated gate type bipolar transistor. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: forming a first substrate, forming a termination layer on the back side of the first substrate, binding the first substrate with a second substrate of specified thickness through the termination layer in a direct binding mode, thinning the first substrate, forming a front side structure of IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator) on the first substrate, removing the second substrate by taking the termination layer as the key point, and removing the termination layer. The method provided by the invention can be compatible with the conventional ordinary process, and is simple in process and high in efficiency, no special equipment is needed, and the process cost can be greatly lowered.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
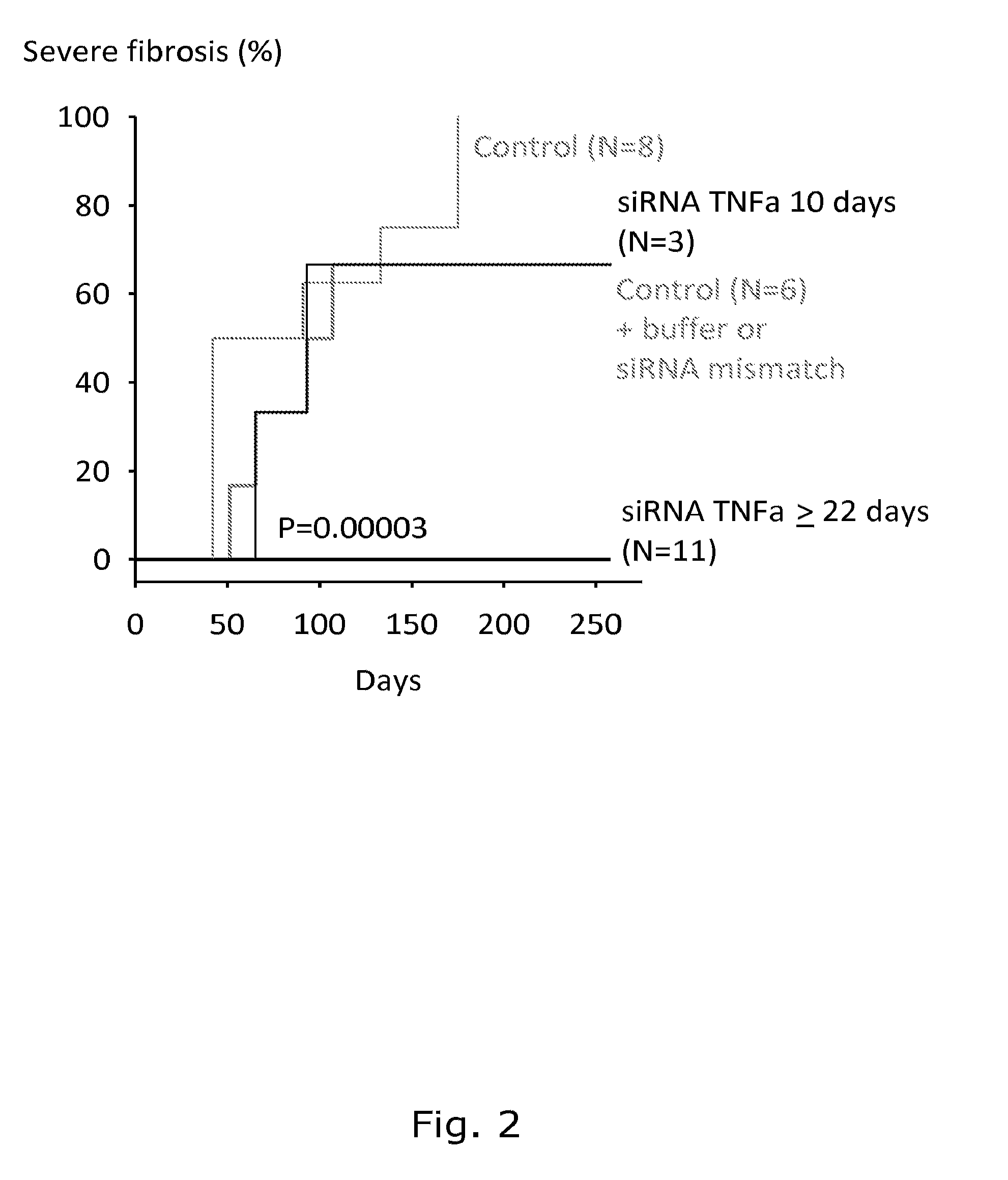
Treatment of radiation-induced fibrosis
InactiveUS20120040004A1Reduce the impactIncrease dosePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsRadiation induced fibrosisNanoparticle
The present invention relates to treatment or prevention of radiation induced fibrosis using TNF-alpha antagonism. Preferably, TNF-alpha is antagonized by direct binding or by inhibition of synthesis. In a preferred embodiment, the invention comprises intraperitoneal administration of a chitosan-siRNA nanoparticle, wherein the siRNA is targeted to the mRNA encoding TNF-alpha.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV +1
Peptides with the capacity to bind to transforming growth factor b1 (tgf-b1)
InactiveUS20070142275A1High diffusion potentialShort half-lifeSenses disorderSsRNA viruses positive-senseDirect bindingCytokine
The described peptides possess the capacity to bind to Transforming Growth Factor TGF-β1 (TGF-β1), and are potential inhibitors of the biological activity of TGF-β1 through direct binding to this cytokine. These peptides can be used in the treatment of diseases or pathological alterations based on excessive or deregulated TGF-β1 expression.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
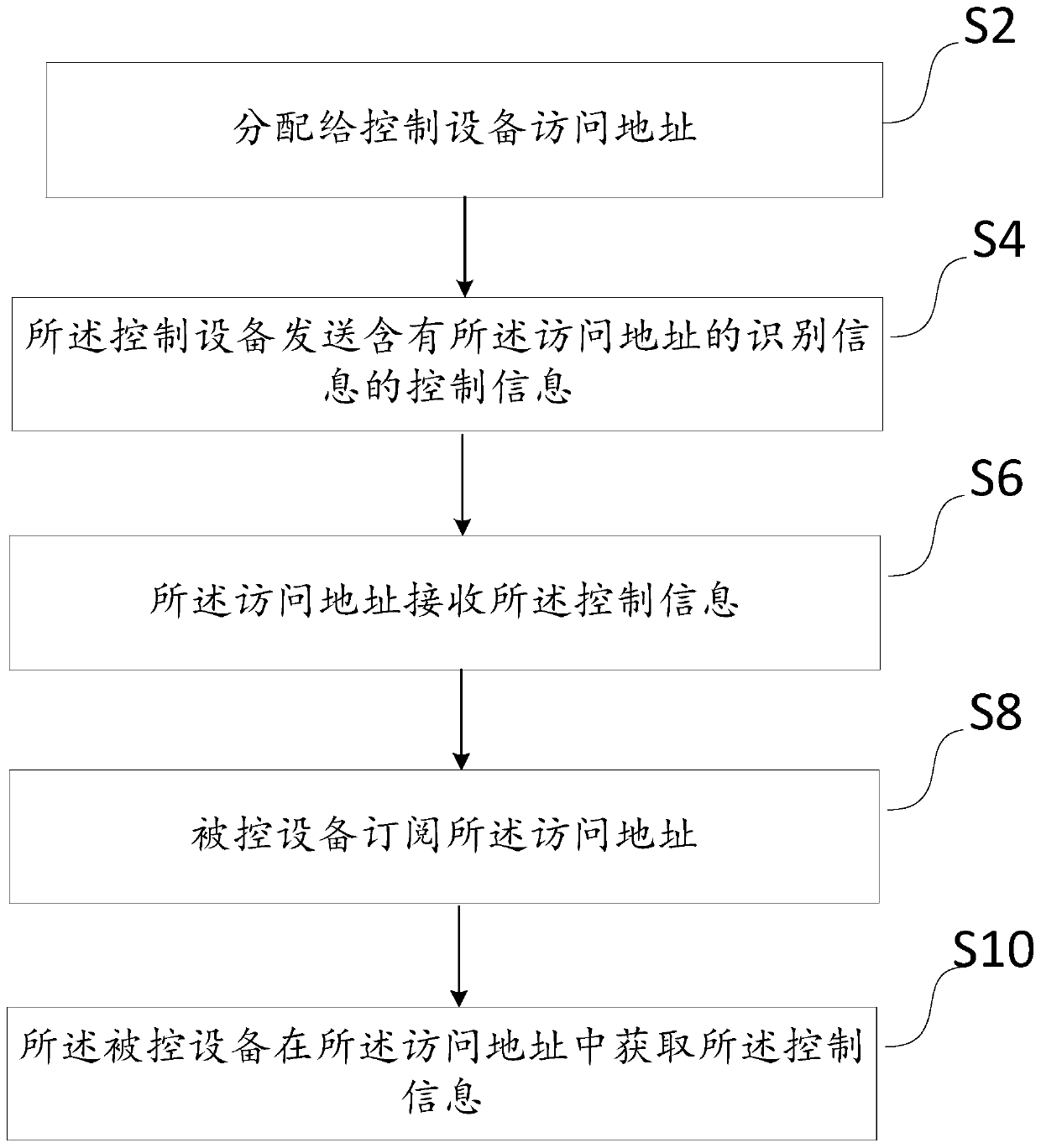
Local device binding method and system
PendingCN111065079AAchieve direct controlRealize flexible linkage control functionTransmission systemsNetwork topologiesControl mannerDirect binding
The invention discloses a local device binding method. The method comprises the following steps: allocating an access address to a control device; enabling the control device to send control information containing the identification information of the access address; enabling the access address to receive the control information; enabling a controlled device to subscribe the access address; and the controlled device to acquire the control information from the access address. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following advantages that the relates to the local binding and control technology based on the BLE mesh technology; when a remote controller or a sensor and intelligent equipment such as a lamp or a socket are in the same network, the directional control over the intelligent equipment can be achieved through direct binding of the remote controller or the sensor and the intelligent equipment, an APP can check and modify the binding relation, and a more flexible andsafer control mode is achieved; moreover, a flexible linkage control function between the sensor and the intelligent equipment is realized, the necessity of the gateway is reduced, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU TUYA INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Reinforced fiber laminate sheet, fiber-reinforced resin molded body, and method for manufacturing reinforced fiber laminate sheet
ActiveCN108367531AEquivalent form stabilityGood formabilityLayered product treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsFiber bundleDirect binding
The present invention provides a reinforced fiber sheet exhibiting a stable shape and favorable bulking properties, a method for manufacturing same, and a fiber-reinforced resin molded body. The reinforced fiber sheet according to the present invention comprises a plurality of reinforced fiber bundles that are arranged in one direction, wherein first and second reinforced fiber bundle layers, in which there is no direct binding force between reinforced fiber bundles within a layer, are disposed so as to have mutually distinct fiber orientations, and are integrally formed by being fastened together using fastening elements, satisfying conditions (i) and (ii). (i) Fastening surfaces of the first and second reinforced fiber bundle layers have fastening sections that include at least one fastening element, and an average surface area S1 of 100 mm2. (ii) In the fastening sections, the surface area ratio of the fastening elements to the fastening section is 0.1% to 80%, inclusive.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Peptides with the capacity to bind to transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)
InactiveUS7666841B2High diffusion potentialShort half-lifeSenses disorderSsRNA viruses positive-senseDiseaseDirect binding
The described peptides possess the capacity to bind to Transforming Growth Factor TGF-β1 (TGF-β1), and are potential inhibitors of the biological activity of TGF-β1 through direct binding to this cytokine. These peptides can be used in the treatment of diseases or pathological alterations based on excessive or deregulated TGF-β1 expression.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
Toll-like receptor agonists and antagonists and methods of use thereof
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods of modulating inflammatory and immune responses through binding of SAA to TLR2 in a subject (e.g., human, non-human primate, rodent, etc.), and compositions and methods for screening TLR2 agonists and antagonists. In the studies described herein, a potential role of SAA in neutrophilia was investigated and the results demonstrated that SAA is a potent inducer for macrophage secretion of G-CSF, which leads to neutrophilia in mice. Using G-CSF− / − and TLR2− / − mice, it was found that the SAA-induced neutrophilia is dependent on TLR2-mediated production of G-CSF. Based on direct binding assay and gain-of-function studies in TLR2-transfected cells, SAA was identified as a novel ligand for TLR2 and a link between increased SAA concentration and TLR2-mediated inflammatory responses such as neutrophilia was established. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Air valve surface strengthening treatment method
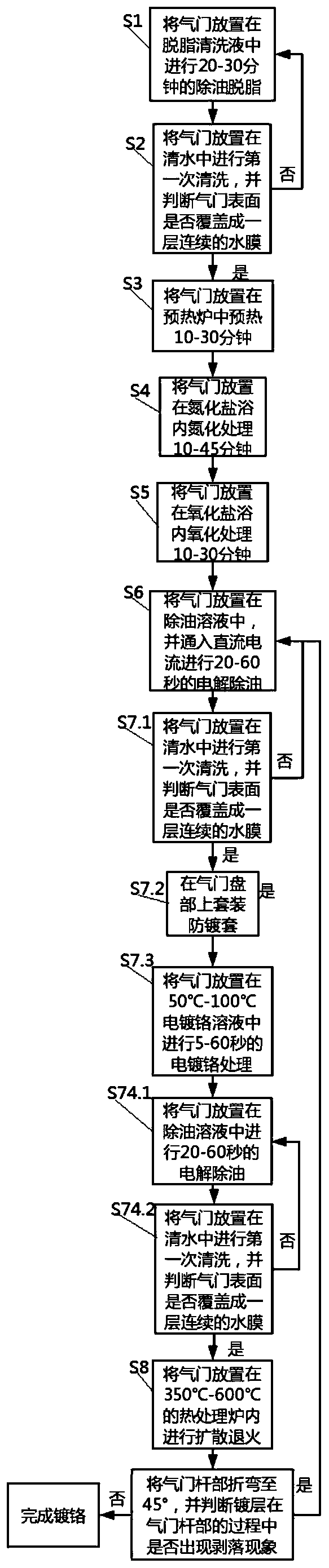
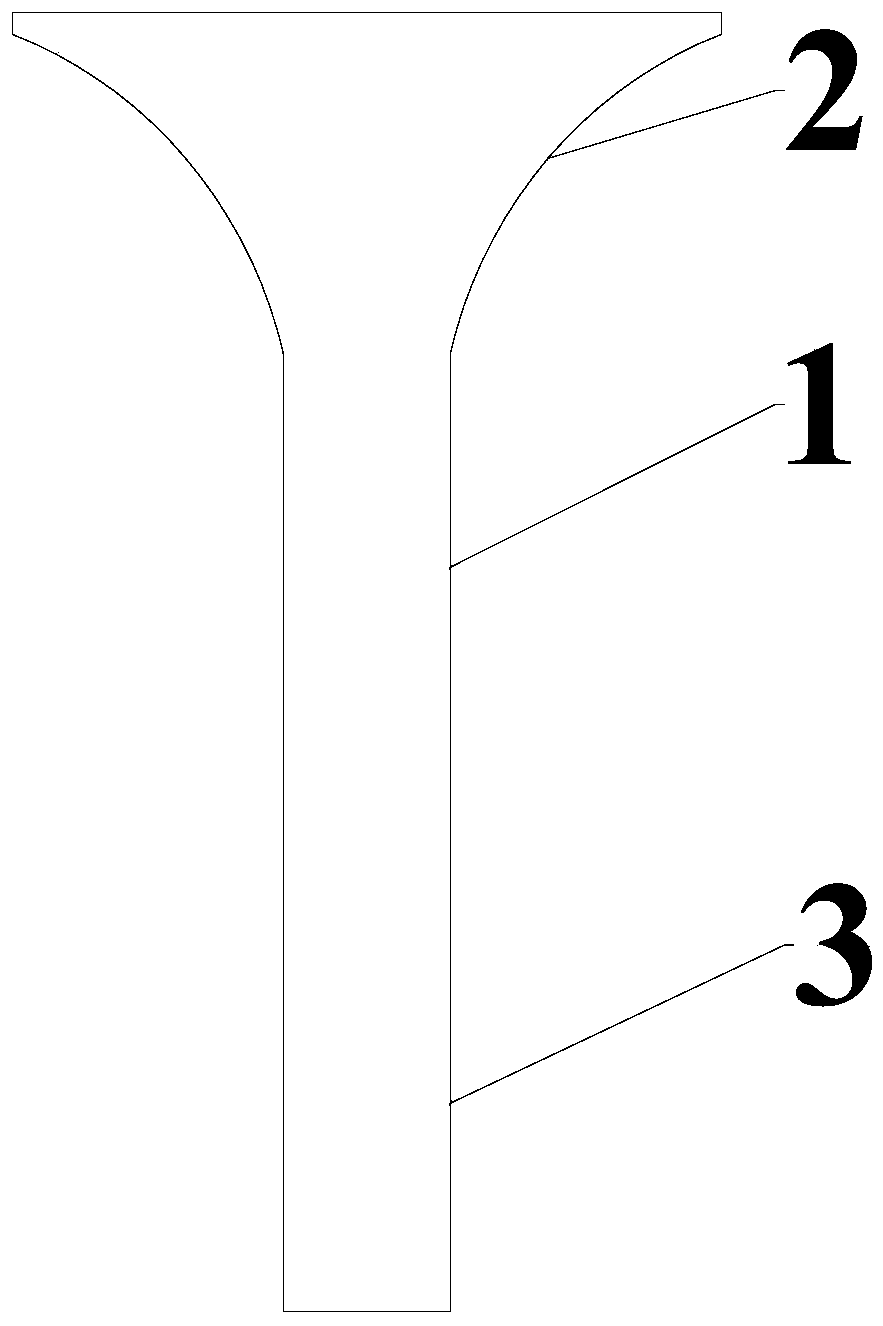
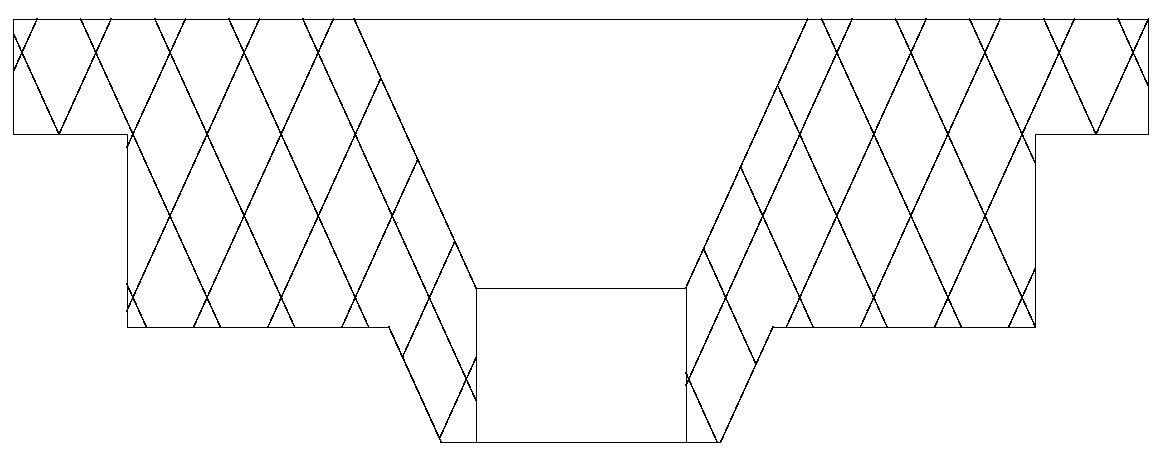
InactiveCN111074198AReduce the effect of microcracksImprove bindingSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesCrazingChromium coating
Owner:HUAI JI DENG YUE VALVE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com