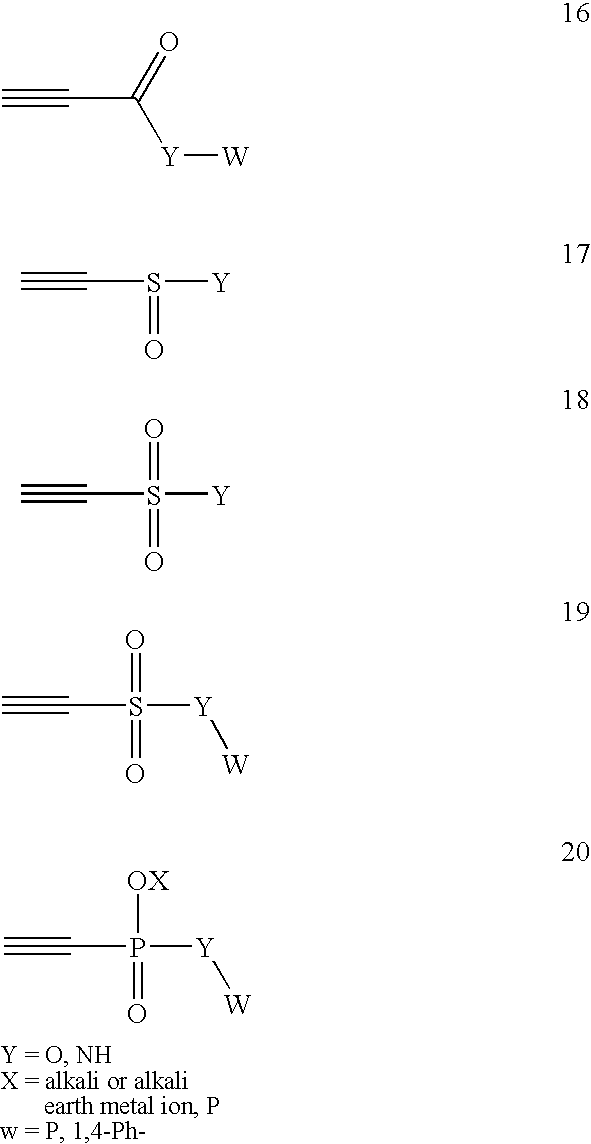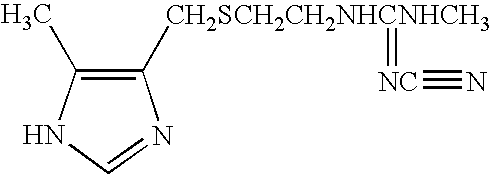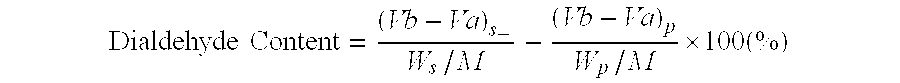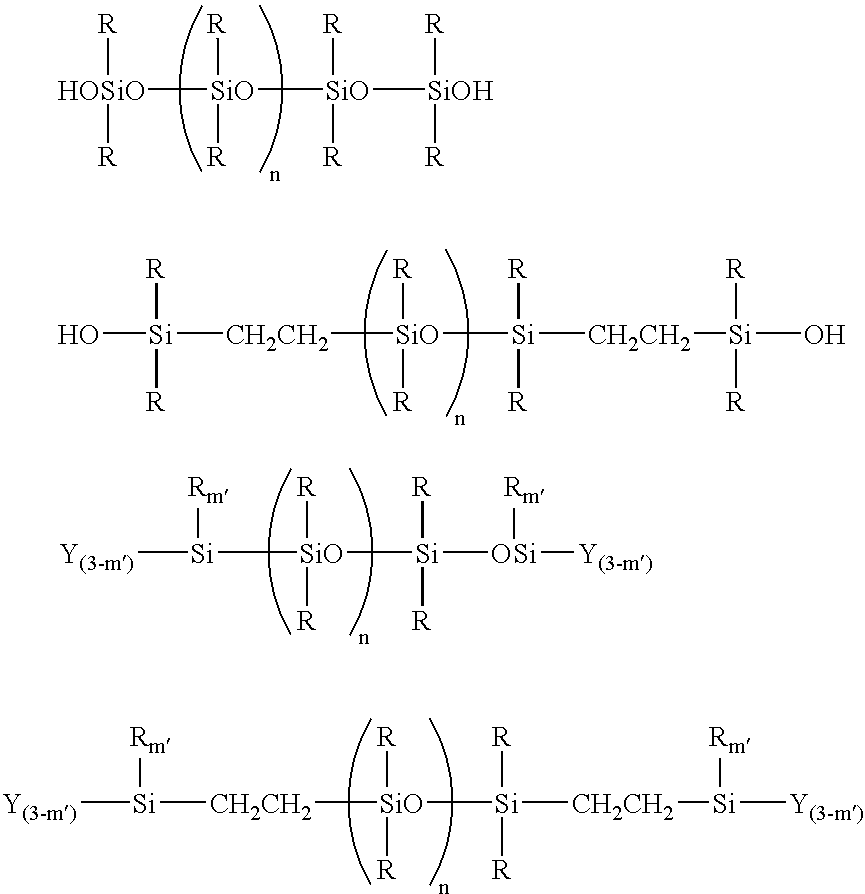Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3566results about How to "Prevent adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
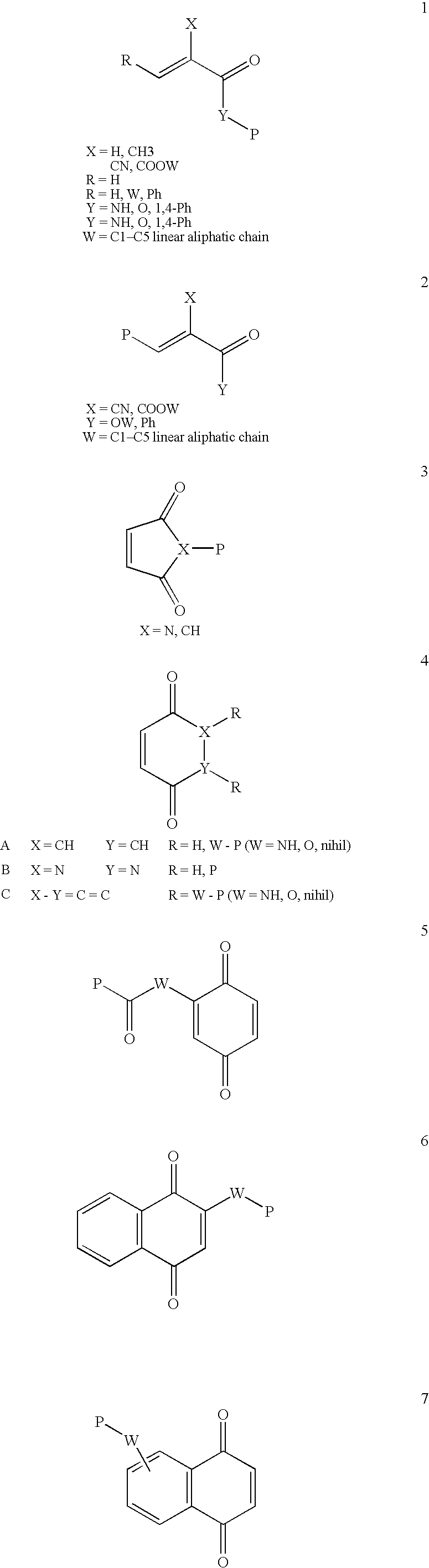
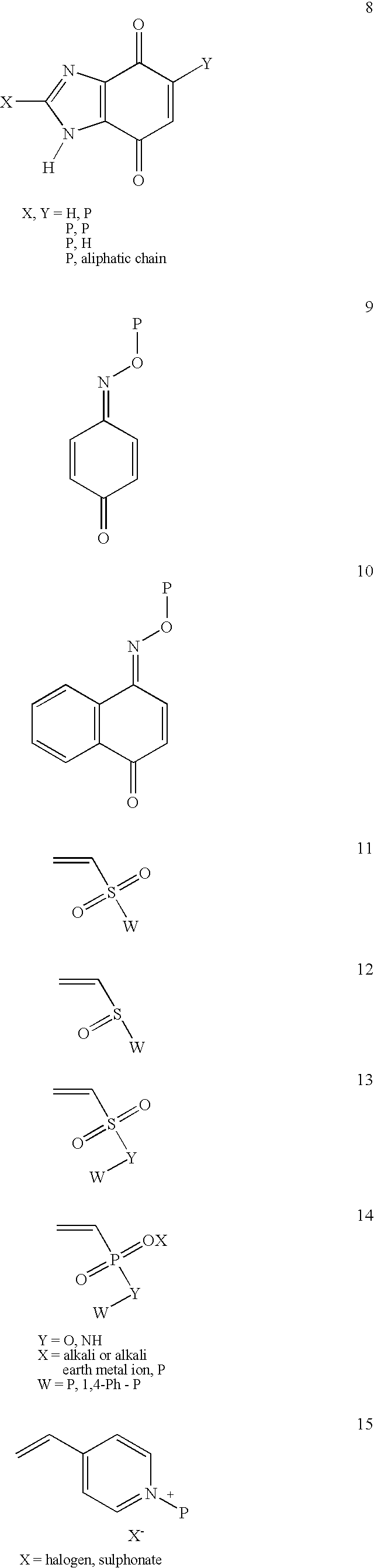
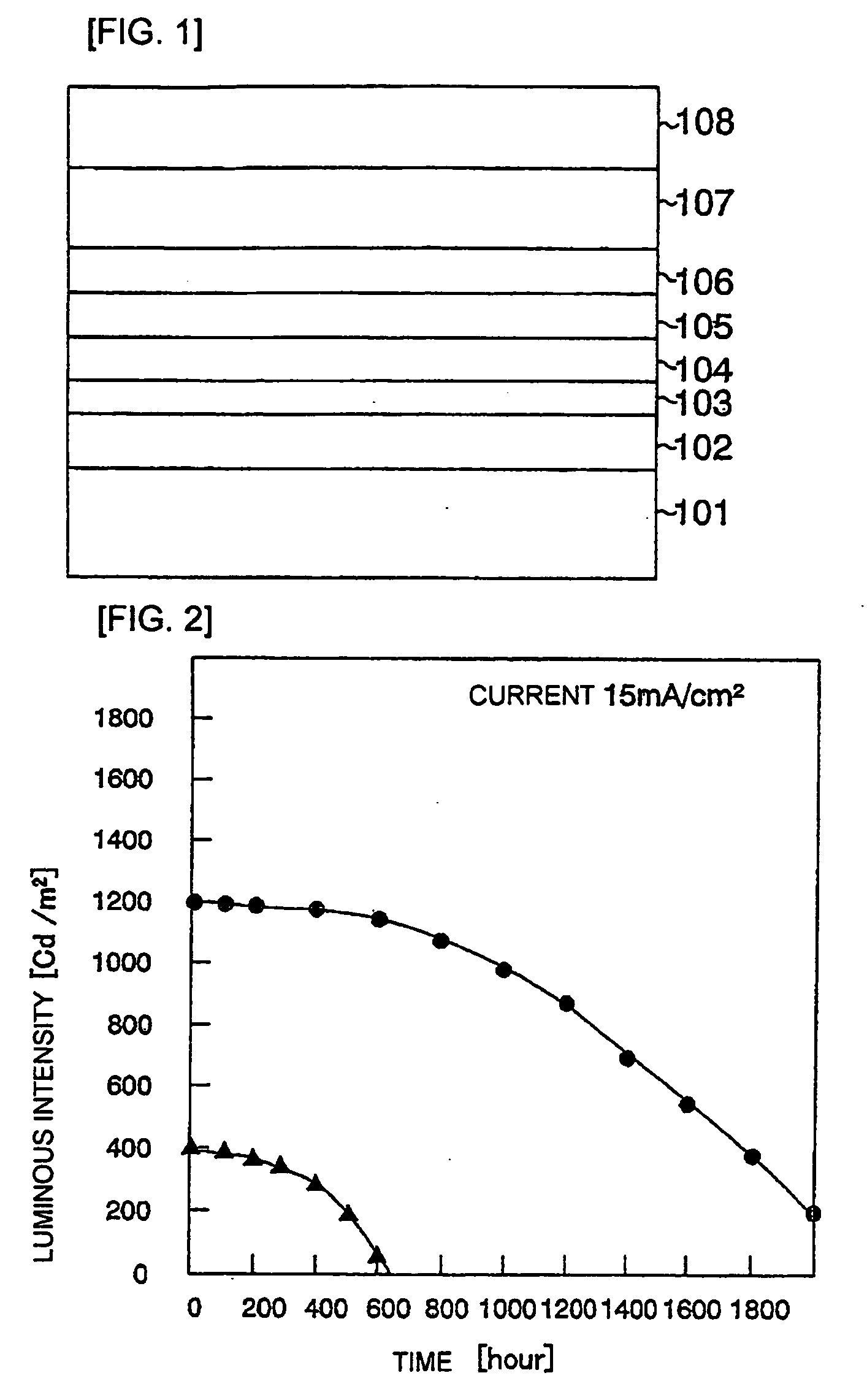
Conjugate addition reactions for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutically active compounds
InactiveUS6958212B1Reducing and delaying onsetGood water solubilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological materialsPolymer
The invention features polymeric biomaterials formed by nucleophilic addition reactions to conjugated unsaturated groups. These biomaterials may be used for medical treatments.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Oral care compositions containing combinations of anti-bacterial and host-response modulating agents
InactiveUS20070053849A1Potent anti-inflammatory activityPromote progressAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsWhole bodyOral bacterial infection
The present invention encompasses topical oral care compositions comprising the combination of an anti-bacterial agent with an anti-inflammatory agent in an orally acceptable carrier for effective treatment and prevention of bacteria-mediated diseases and conditions in the oral cavity and for modulating host reaction to bacterial pathogens present in the oral cavity and to the toxins, endotoxins, inflammatory cytokines and mediators released by or prompted by these pathogens. The present invention also encompasses methods of use of these compositions comprising topical application to the oral cavity. The benefits of the present compositions and methods extend beyond treating and preventing oral bacterial infections in the oral cavity to promoting whole body or systemic health.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive for medical use
ActiveUS20060078536A1Prevent adhesionAvoid stickingSurgical adhesivesEther/acetal active ingredientsAnti adhesiveTissue adhesives
Tissue adhesives formed by reacting an oxidized polysaccharide with a water-dispersible multi-arm polyether amine, wherein at least three of the arms are terminated by primary amine groups, are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; anti-adhesive applications; and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Antimicrobial coating for inhibition of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation
InactiveUS20080063693A1Increased coating antimicrobial efficacyPrevent bacterial adhesionBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsWater insolubleMetallic materials
The present invention provides antimicrobial coatings for coating substrate surfaces, particularly medical devices, for preventing bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation by inhibiting microbial growth and proliferation on the coating surface. The antimicrobial coatings are composed of a hydrogel and a bioactive agent including a substantially water-insoluble antimicrobial metallic material that is solubilized within the coating. Antimicrobial coating formulations for obtaining such coatings, and coating methods are also described.
Owner:BACTERIN
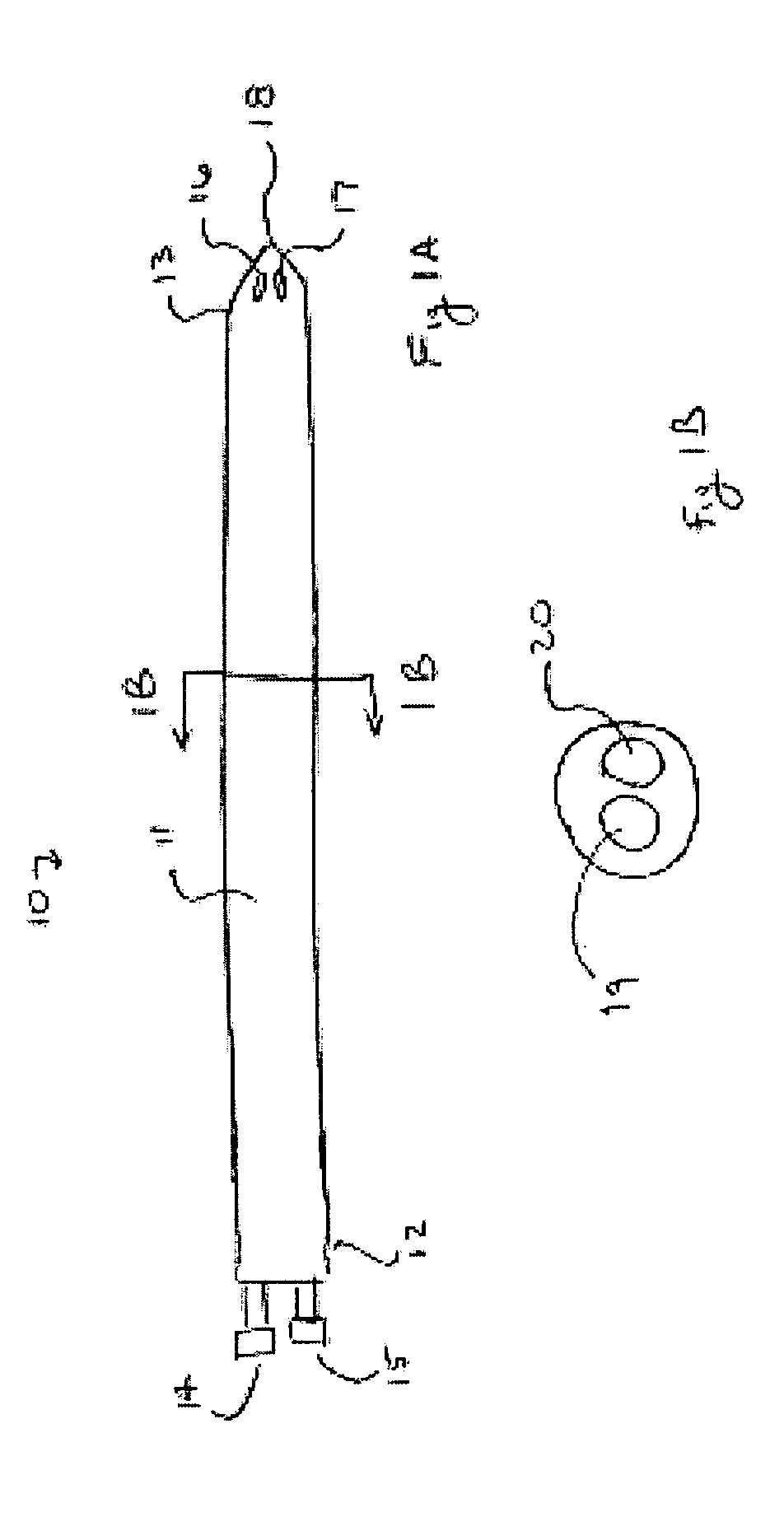
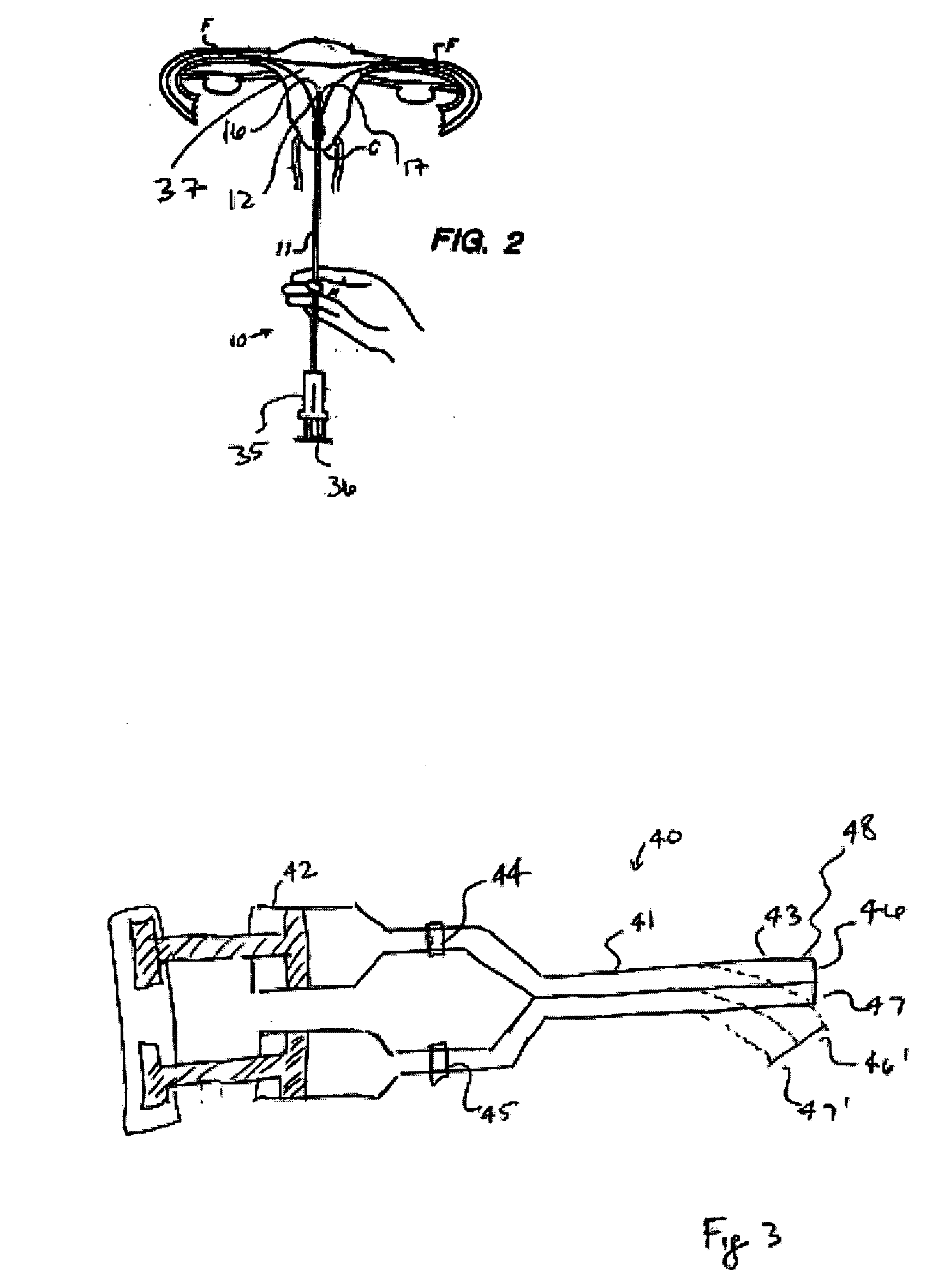
Intrauterine applications of materials formed in situ
InactiveUS20050266086A1Reduce bleedingPrevent adhesionOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryChemistryCovalent bond
Certain embodiments herein are directed to method of preventing adhesions in a uterus by introducing a flowable material into a uterus to tamponade a surface of the uterus. Such a material may be a hydrogel. The hydrogel may be formed in situ from at least one precursor, for example, a hydrophilic polymer with functional groups for forming covalent bonds.
Owner:CONFLUENT SURGICAL
Super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface preparation technology
The invention discloses super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface preparation technology. In the preparation technology, aluminum or aluminum alloy sheets are subjected to two-step electrochemical treatment, and then are modified by using perfluorinated octadecyl trichlorosilane or perfluorinated polymethacrylate to prepare the super-hydrophobic and super-oleophobic surface. The surface has super-hydrophobic property on aqueous solution of which the pH value is between 1 and 14 and super-oleophobic property on various oil drops, wherein a contact angle of the surface on water is 171 degrees, and a rolling angle is less than 1 degree; the surface expresses the super-oleophobic property on various oil drops except for perfluorinated polymer liquid, and all contact angles between the oil drops and the surface are more than 150 degrees, and rolling angles are generally less than 10 degrees; and the surface can also be put in air for a long time and can still maintain the super-hydrophobic property and super-oleophobic property.
Owner:中科润泉(烟台)工业科技有限公司
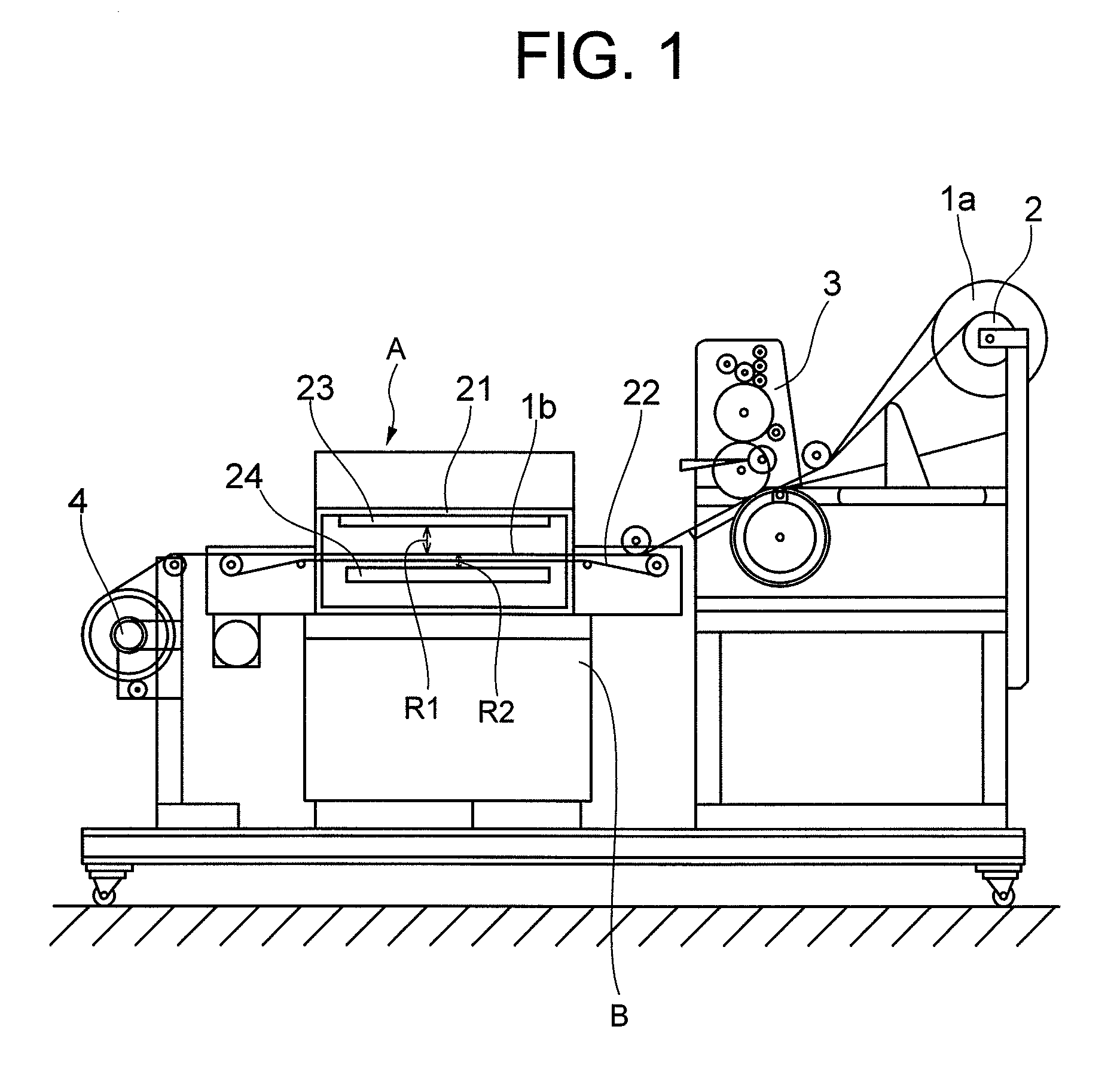
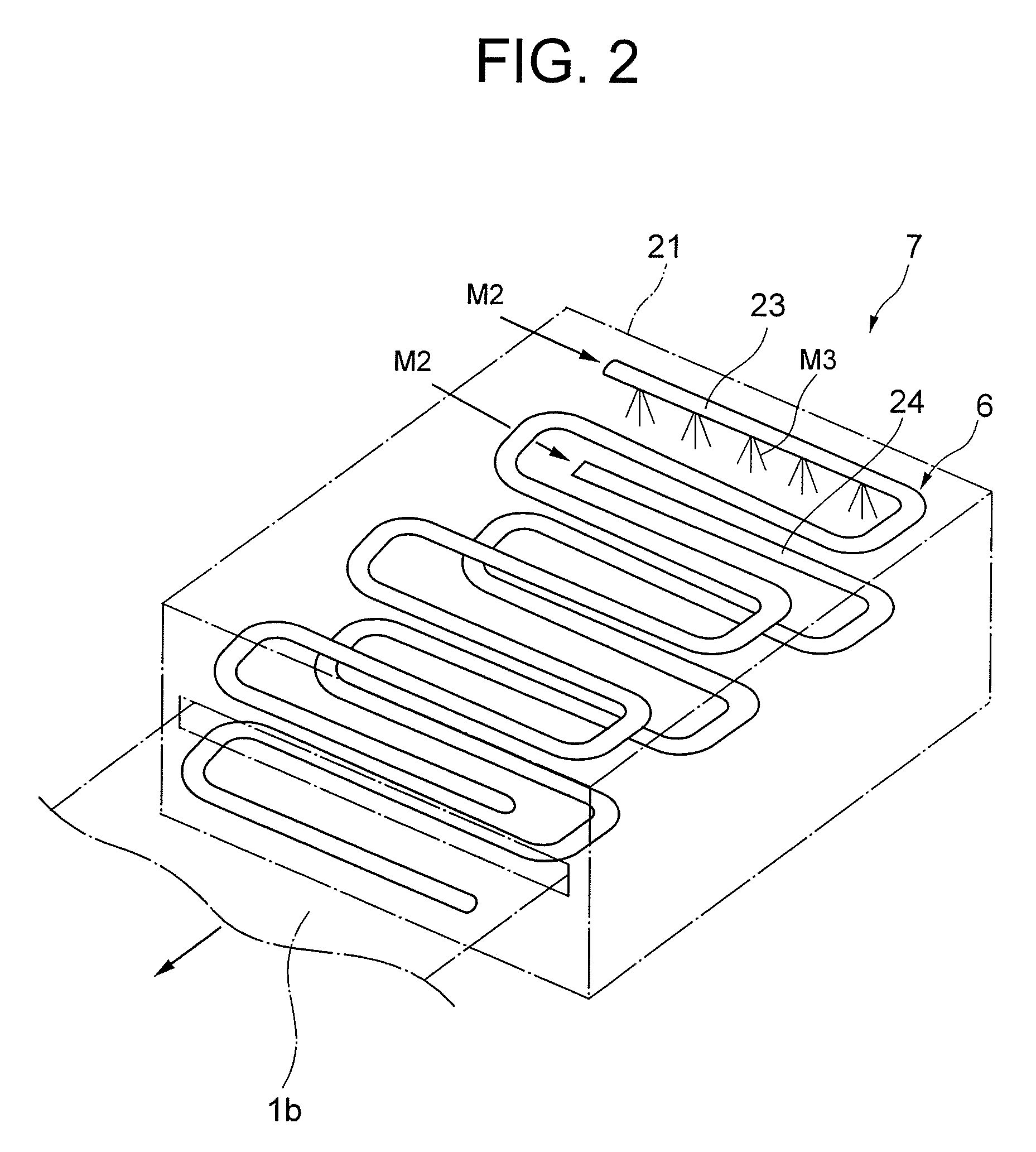
Method of drying printed material and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20100192402A1Avoid stickingFast dryingDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsFiberNano size
To carry out drying of printing ink with the use of Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam. Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam being clustered on Nano oder is generated and jetted to the print side of printed material so that the Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam imparts intramolecular vibrational energy to ink of the print side. Consequently, the Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam being clustered on Nano oder not only passes through fiber pores in the printed material but also collides with the ink of the print side. The Nano sized high-temperature dryness steam having collided with the ink of the print side imparts thermally excited energy as intramolecular vibrational energy to the ink containing polar molecules. The ink is dried by the intramolecular energy.
Owner:DAIDO SANGYO
Absorbent multilayer hydrogel wound dressings
ActiveUS20060200063A1Acceptable water uptake speedGood flexibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
The invention provides wound dressings comprising an absorbent (porous) hydrogel composition comprising a foam portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having an internal cellular structure, and a continuous portion which comprises a flexible plasticised hydrophilic polymer matrix having relatively continuous internal structure. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition includes apertures providing fluid flow communication through the continuous portion between an external surface of the continuous portion and the foam portion whereby the foam portion can take up external water or other fluid into the cellular structure through the apertures of the continuous portion. The continuous portion of the hydrogel composition may be tacky to the skin, allowing its use as a bioadhesive.
Owner:KCI USA
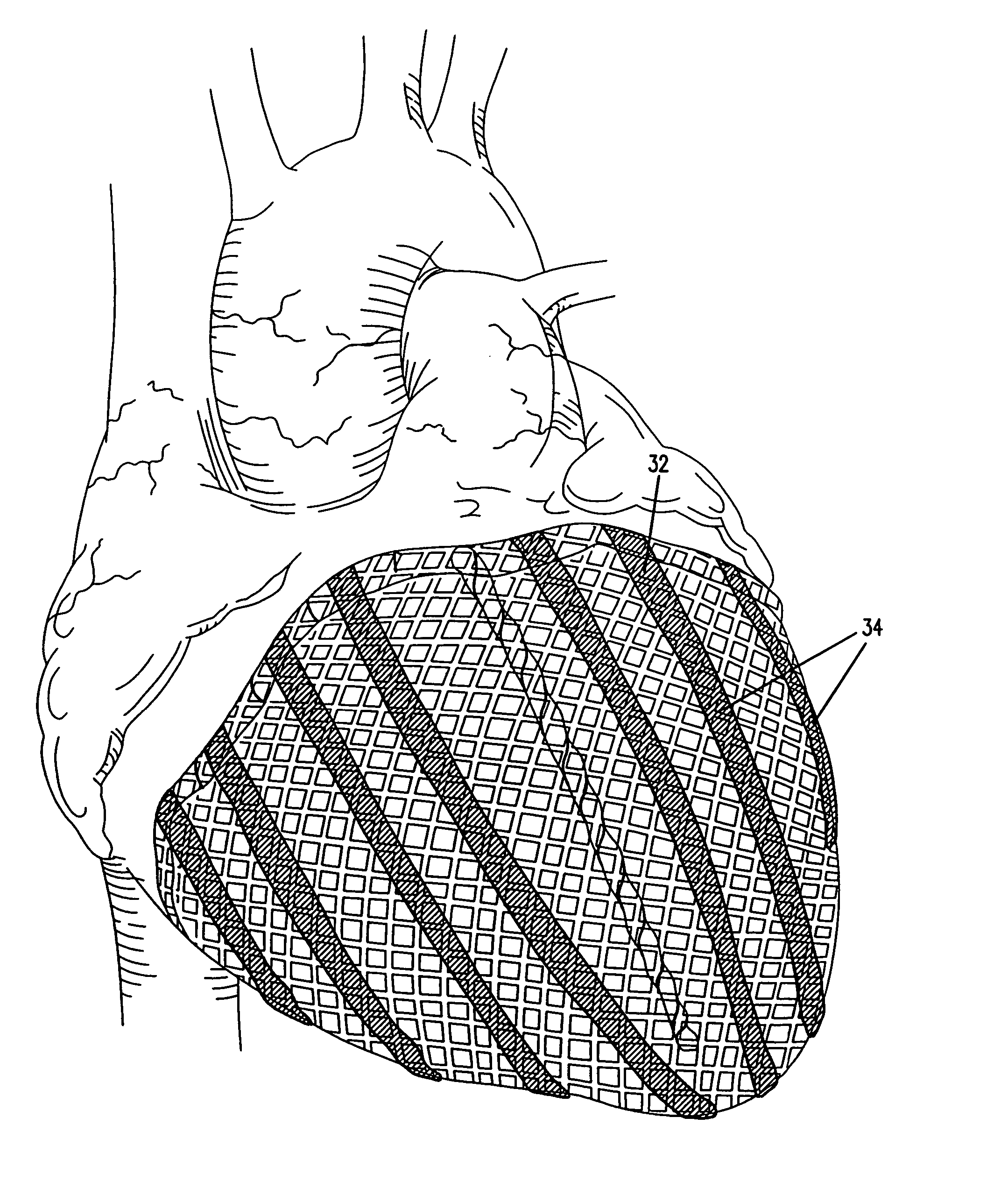
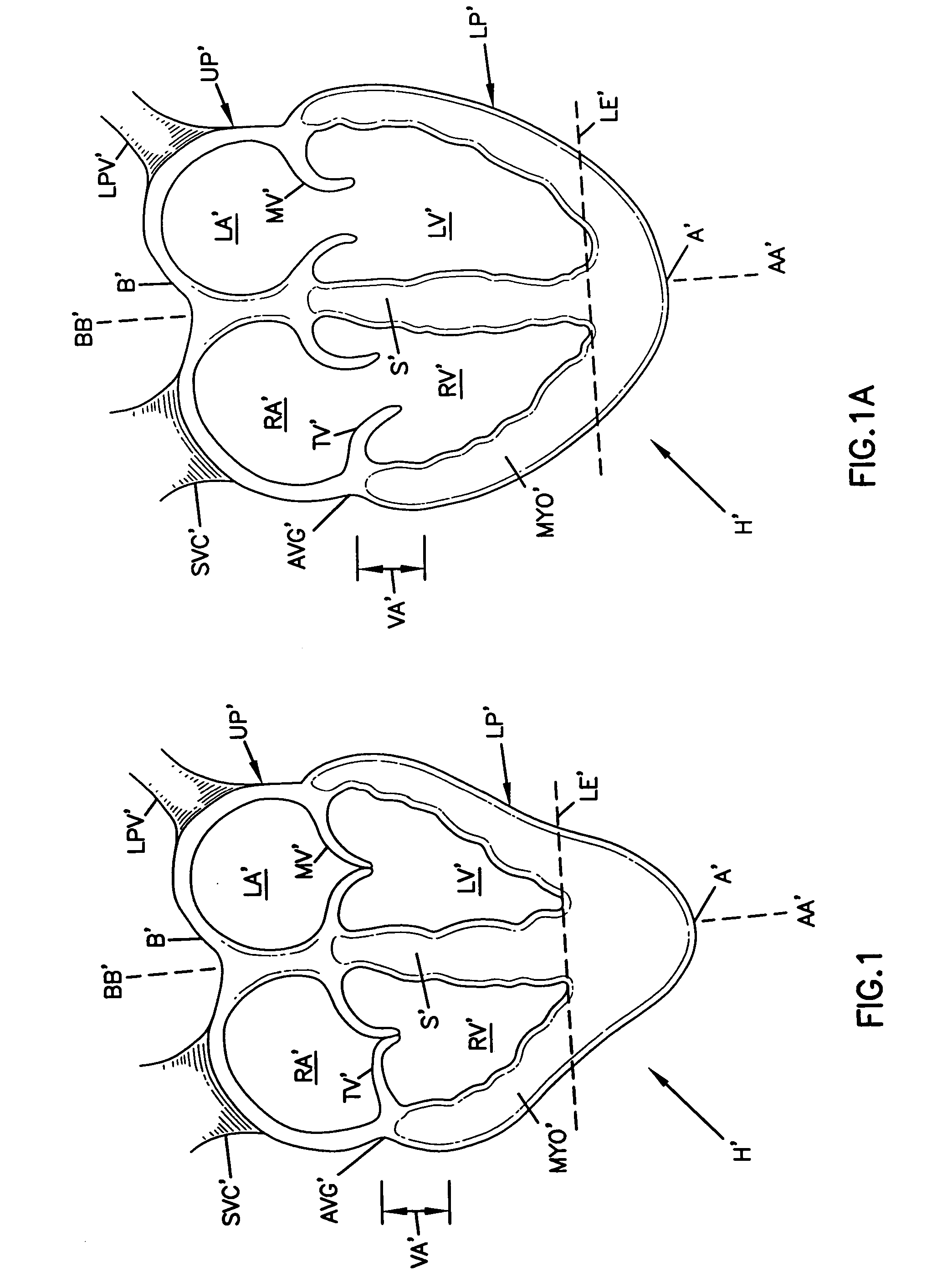
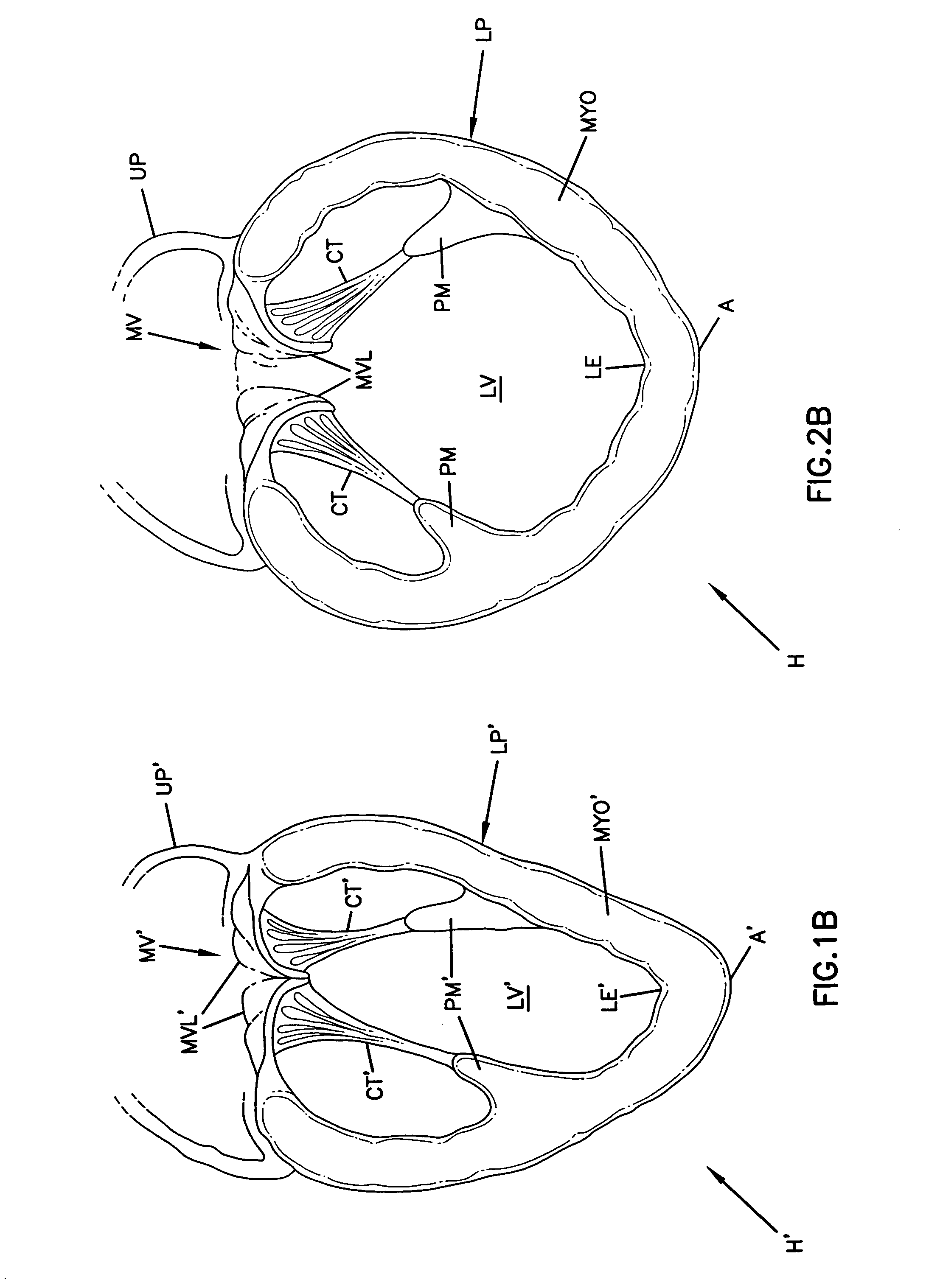
Cardiac disease treatment and device
A device for treating cardiac disease of a heart having an upper portion and a lower portion divided by an A-V groove, the device including a jacket adapted to be secured to the heart, and a non-adherent material in association with the jacket. The jacket is fabricated from a flexible material defining a volume between an upper and a lower end, the jacket being adapted to be adjusted on the heart to snugly conform to an external geometry of the heart and assume a maximum adjusted volume for the jacket to constrain expansion of the heart beyond the maximum adjusted volume during diastole and permit substantially unimpeded contraction of the heart during systole. As a result of the flexible material, the jacket allows unimpeded diastolic filling of the heart. Also described is a method for treating cardiac disease including surgically accessing the heart, applying the treatment device of the invention, securing the treatment device to the heart, and surgically closing access to the heart while leaving the treatment device on the heart.
Owner:MARDIL
Production of electrolytic water
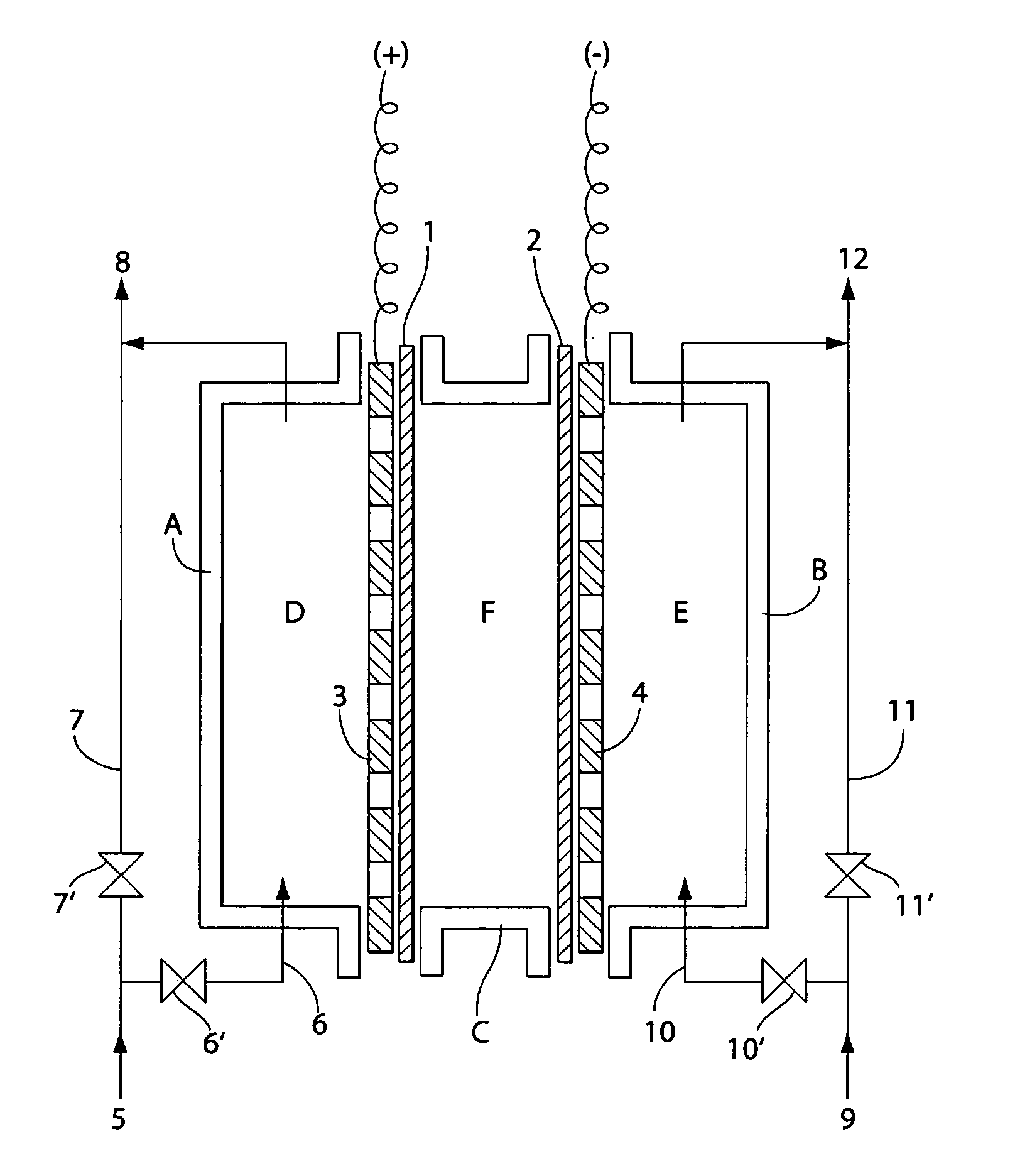
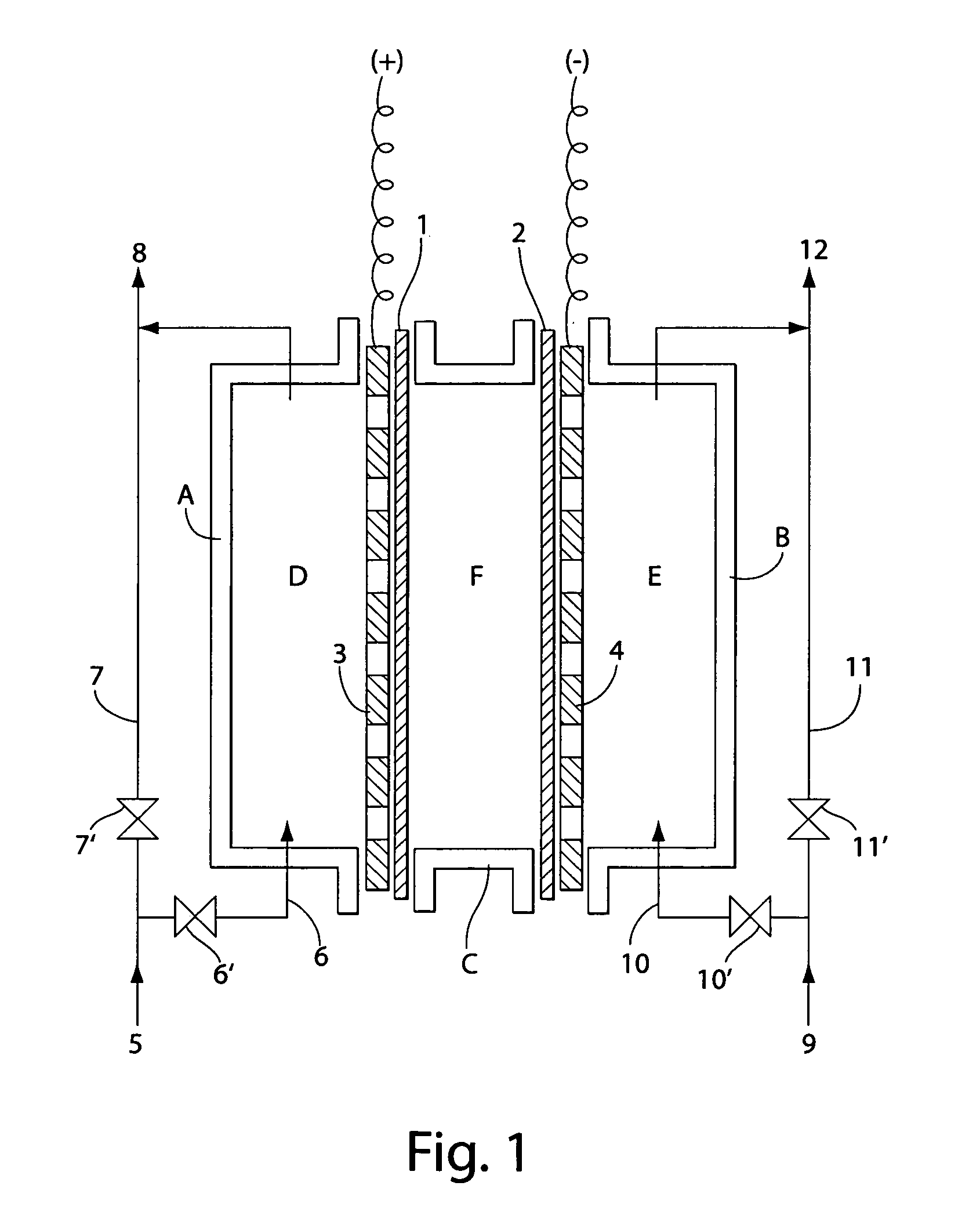
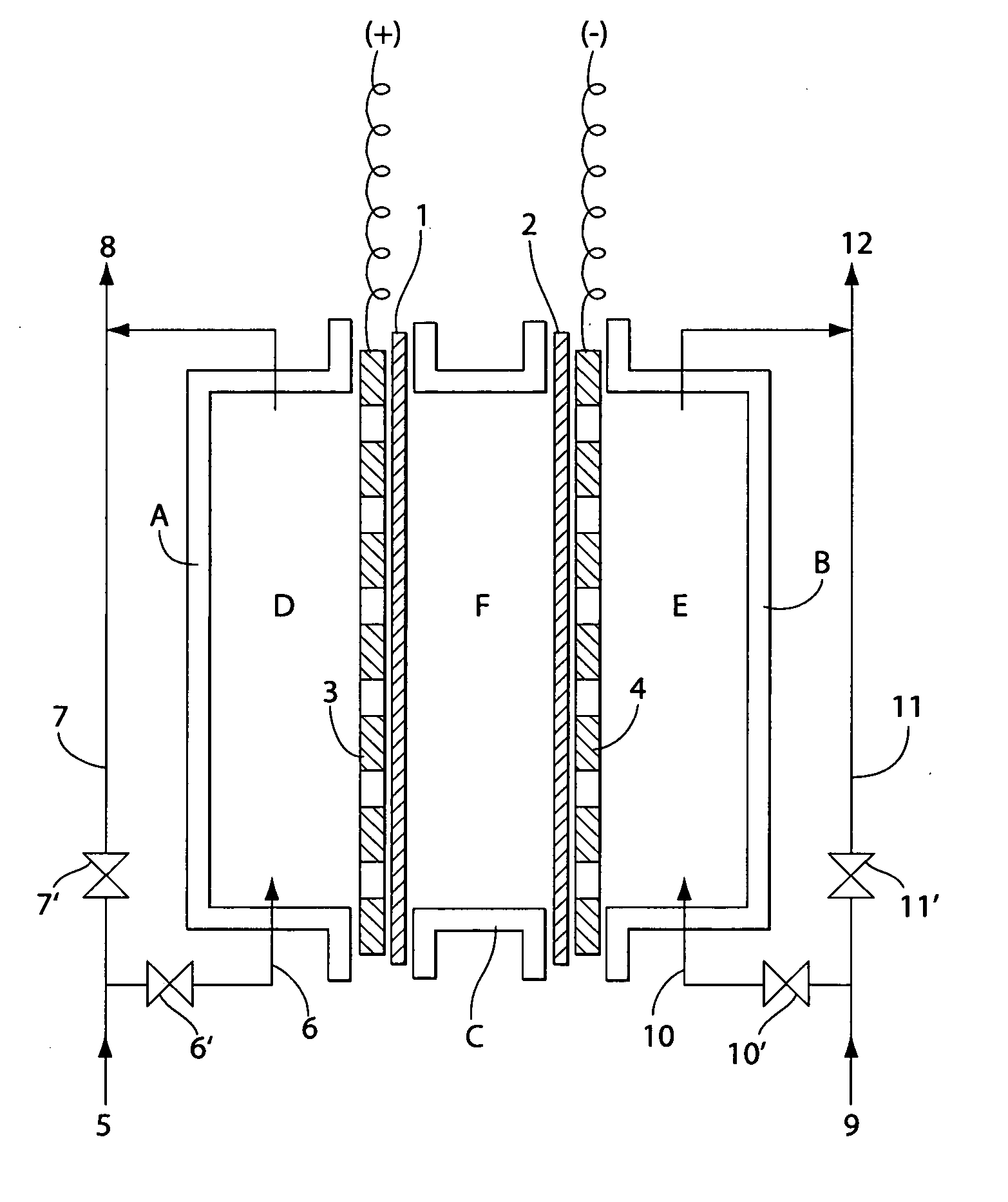
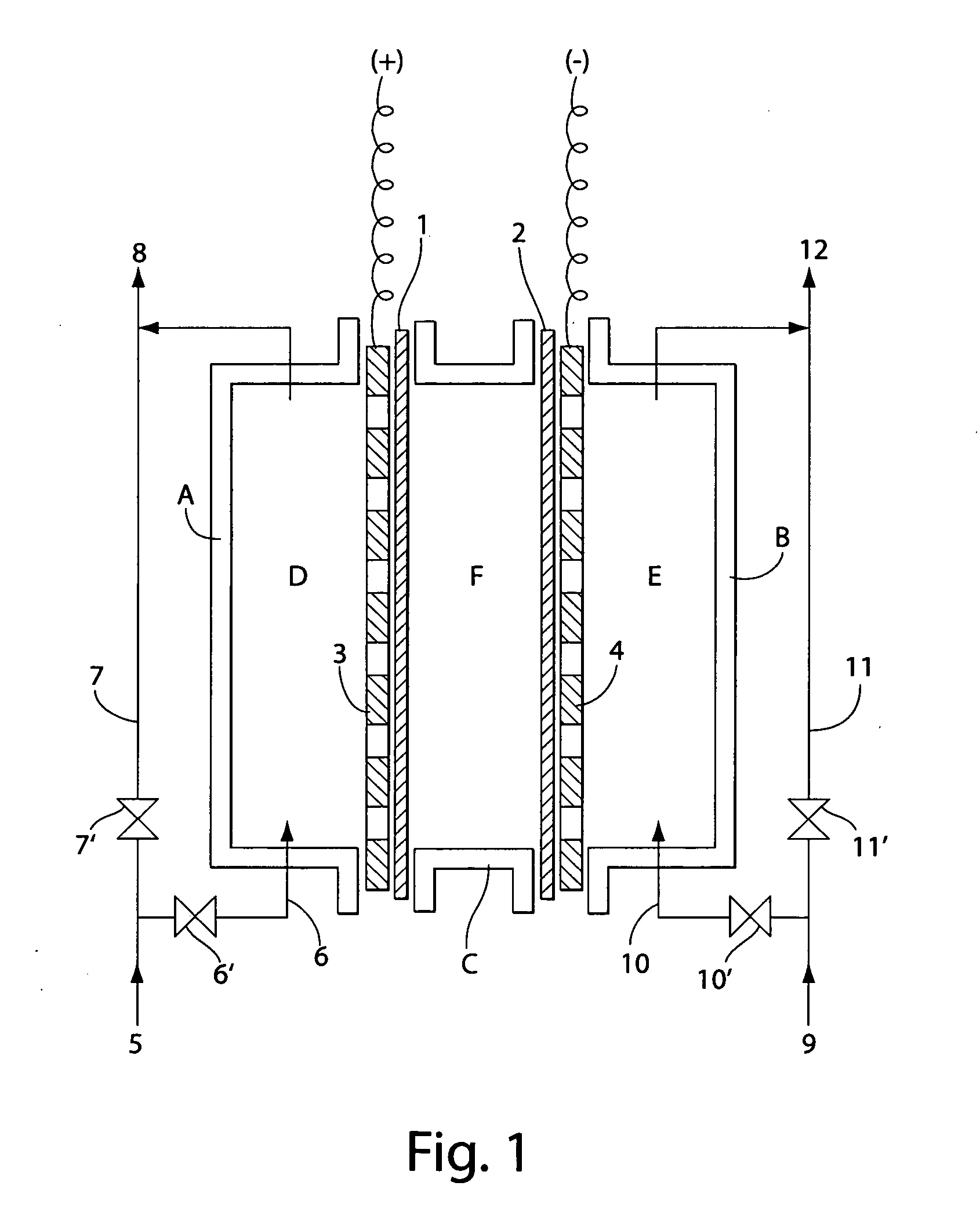
InactiveUS7238272B2Prevent adhesionIncrease productivityCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Shingle with dual sealant
InactiveUS20150089895A1Good adhesionHigh strengthRoof covering using tiles/slatesBuilding repairsEngineeringSealant
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to articles, systems, methods of use, methods of manufacturing, and methods of packing roofing shingles with dual sealants. A shingle may comprise, in some embodiments, a headlap region comprising a top headlap surface and a back headlap surface; a buttlap region comprising a top buttlap surface and a back buttlap surface. A top headlap surface may comprise a first sealant and / or a back headlap surface may comprise a second sealant.
Owner:BUILDING MATERIALS INVESTMENT
Production of electrolytic water
InactiveUS20050189237A1Increase free chlorine production efficiencyPrevent adhesion of scaleCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
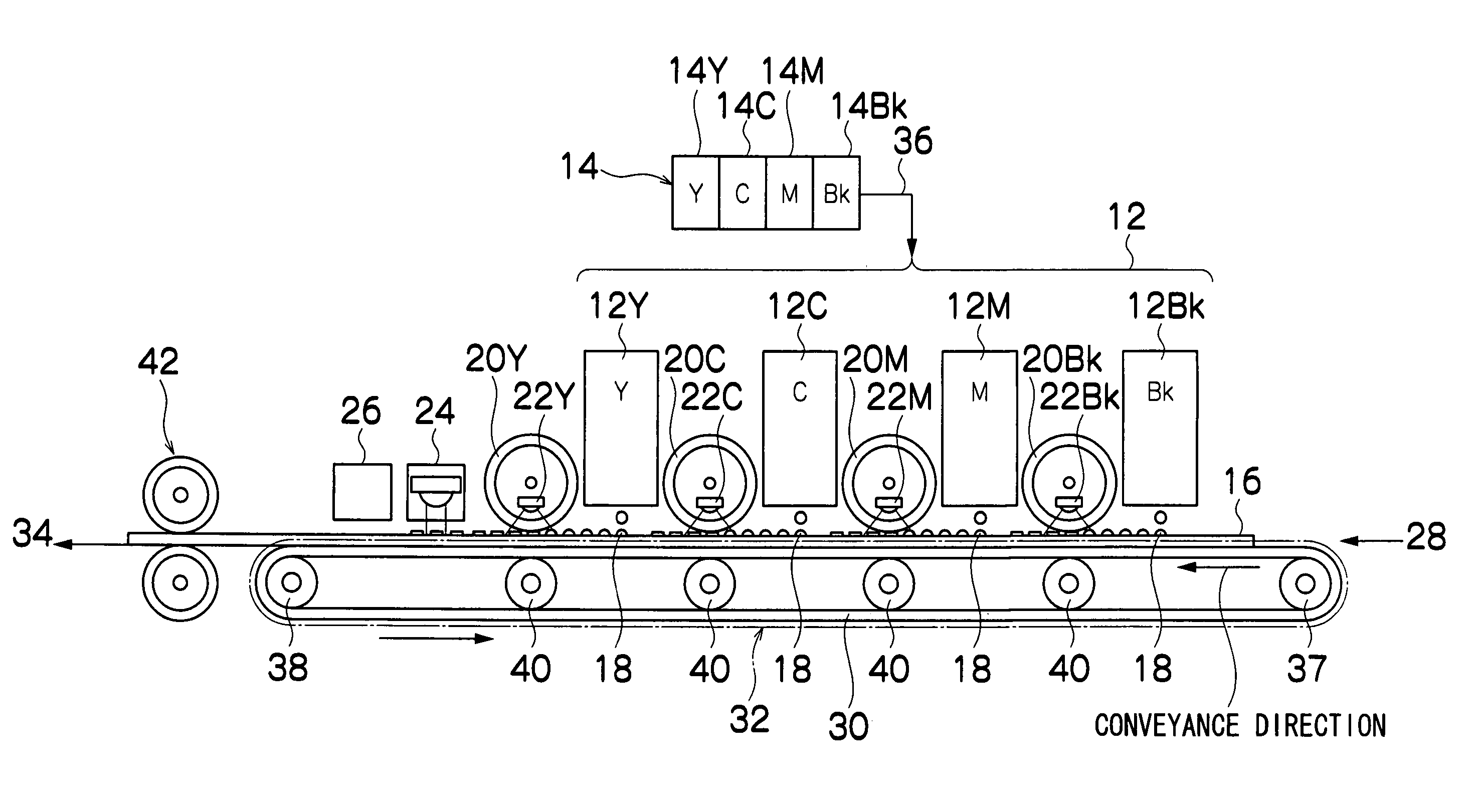
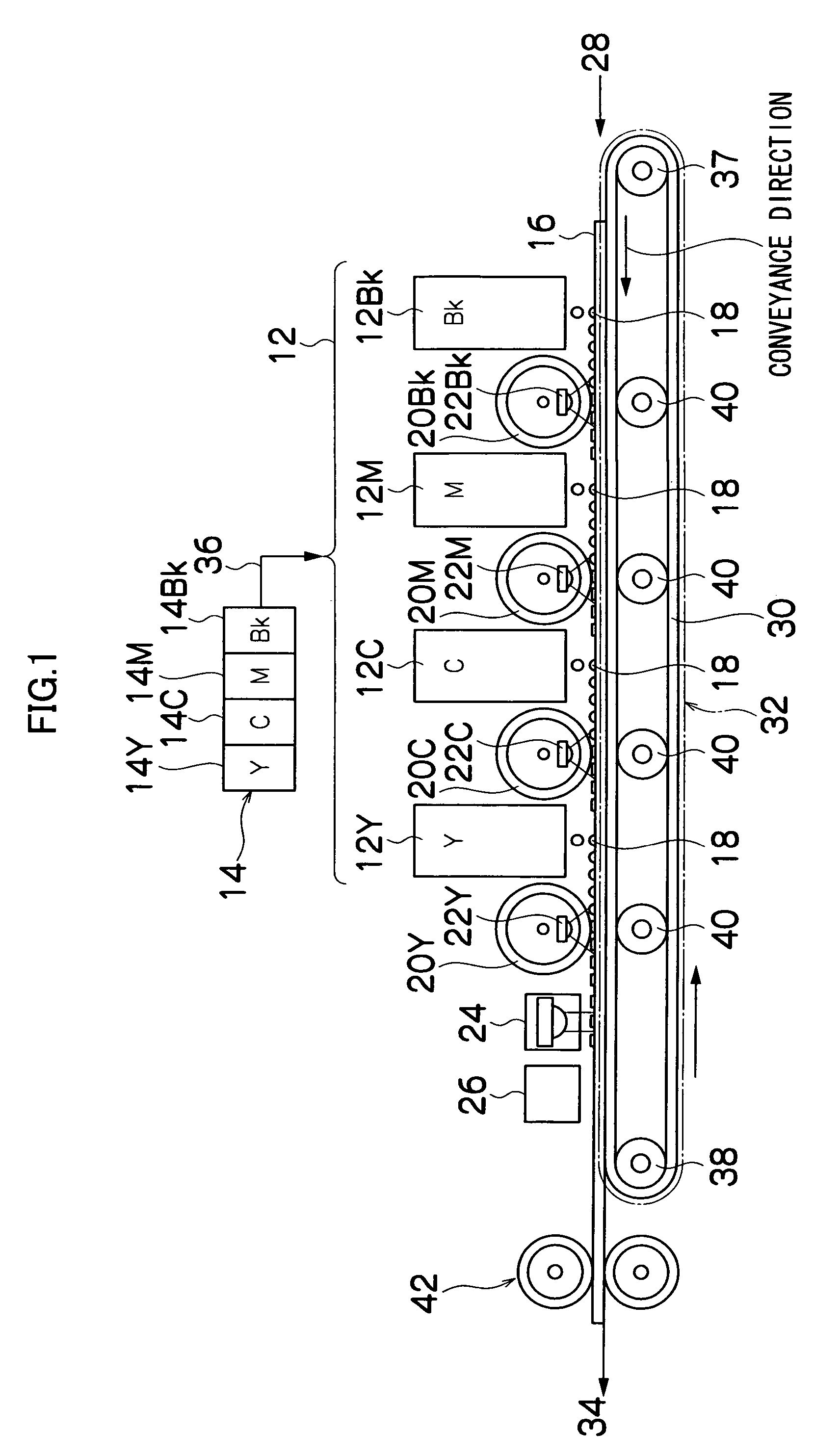
Image recording apparatus and image recording method
InactiveUS20060066703A1Prevent adhesionPrevent steppingOther printing apparatusRadiation exposureRecording head
The image recording apparatus comprises: a recording head which ejects a recording liquid having properties of being cured by irradiation of radiation, onto a recording medium; a relative conveyance device which causes the recording head and the recording medium to move relatively to each other in a relative conveyance direction; a radiation irradiating device which irradiates the radiation onto recording liquid deposited on the recording medium; and a pressurization device which pressurizes the recording liquid which has been irradiated with the radiation, the pressurization device being provided on a downstream side of the recording head in the relative conveyance direction of the relative conveyance device, the pressurization device having the radiation irradiating device provided inside thereof and having one of a transmissive member capable of transmitting the radiation emitted from the radiation irradiating device to exterior and a structure capable of transmitting the radiation to the exterior, wherein a pressurization start position of the pressurization device at which pressurization of the recording liquid on the recording medium starts is situated further to the downstream side of the recording head in the relative conveyance direction of the relative conveyance device than an irradiation start position of the radiation irradiating device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and apparatus for mounting
A method and an apparatus for mounting: the method for bonding a plurality of objects to each other, comprising the steps of disposing, apart from each other, a first object, a second object and a holding means therefor, and a backup member having a reference positioning surface in this order, adjusting the parallelism of the second object or the holding means therefor relative to the reference positioning surface, adjusting the parallelism of the first object or the holding means therefor relative to the second object or the holding means therefor, bringing the first object into contact with the second object to temporarily bond both objects to each other, bringing the holding means for the second object into contact with the reference positioning surface of the backup member, and pressing both objects against each other for final bonding, whereby, finally, a highly reliable and accurate bonding state can be achieved.
Owner:TORAY ENG CO LTD +1
Laser cutting device, laser cutting method and laser cutting system
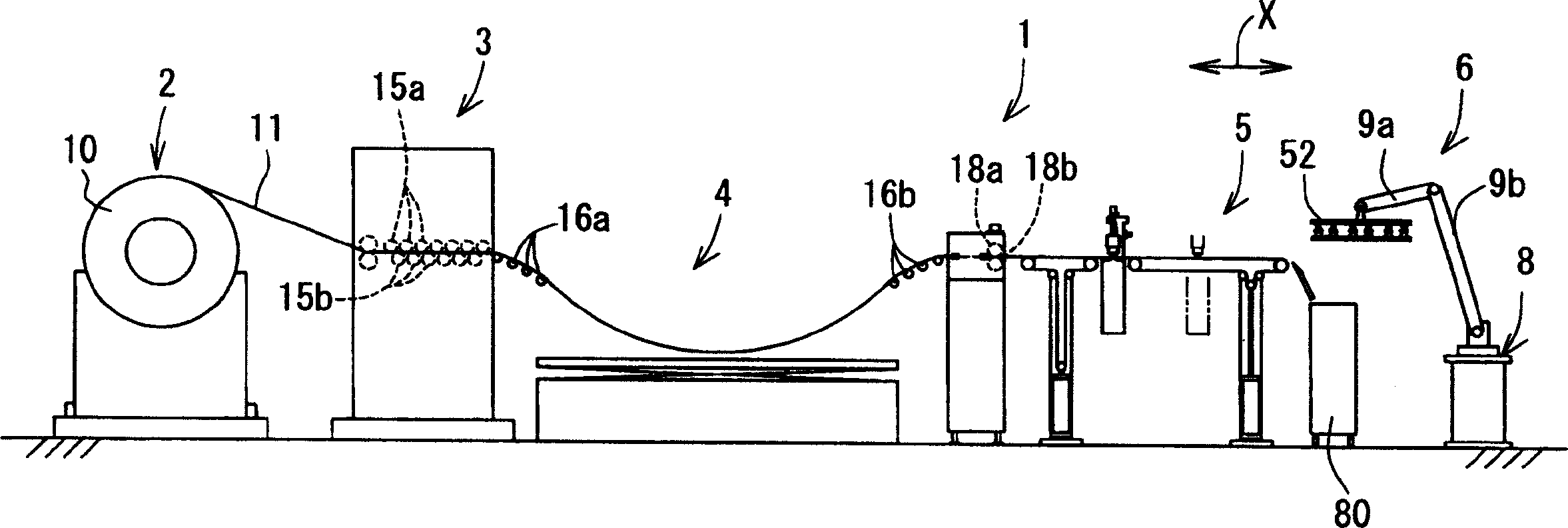
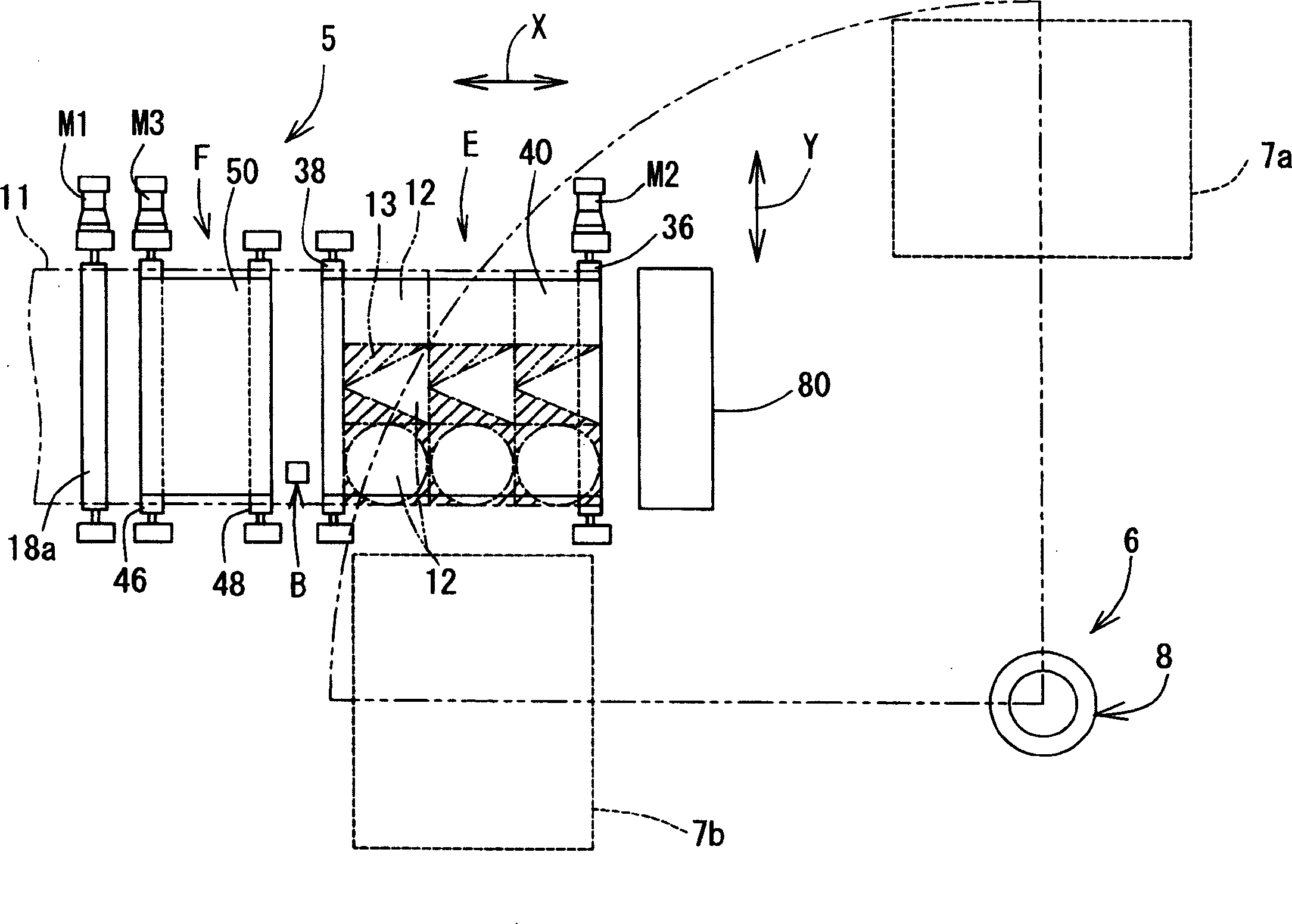
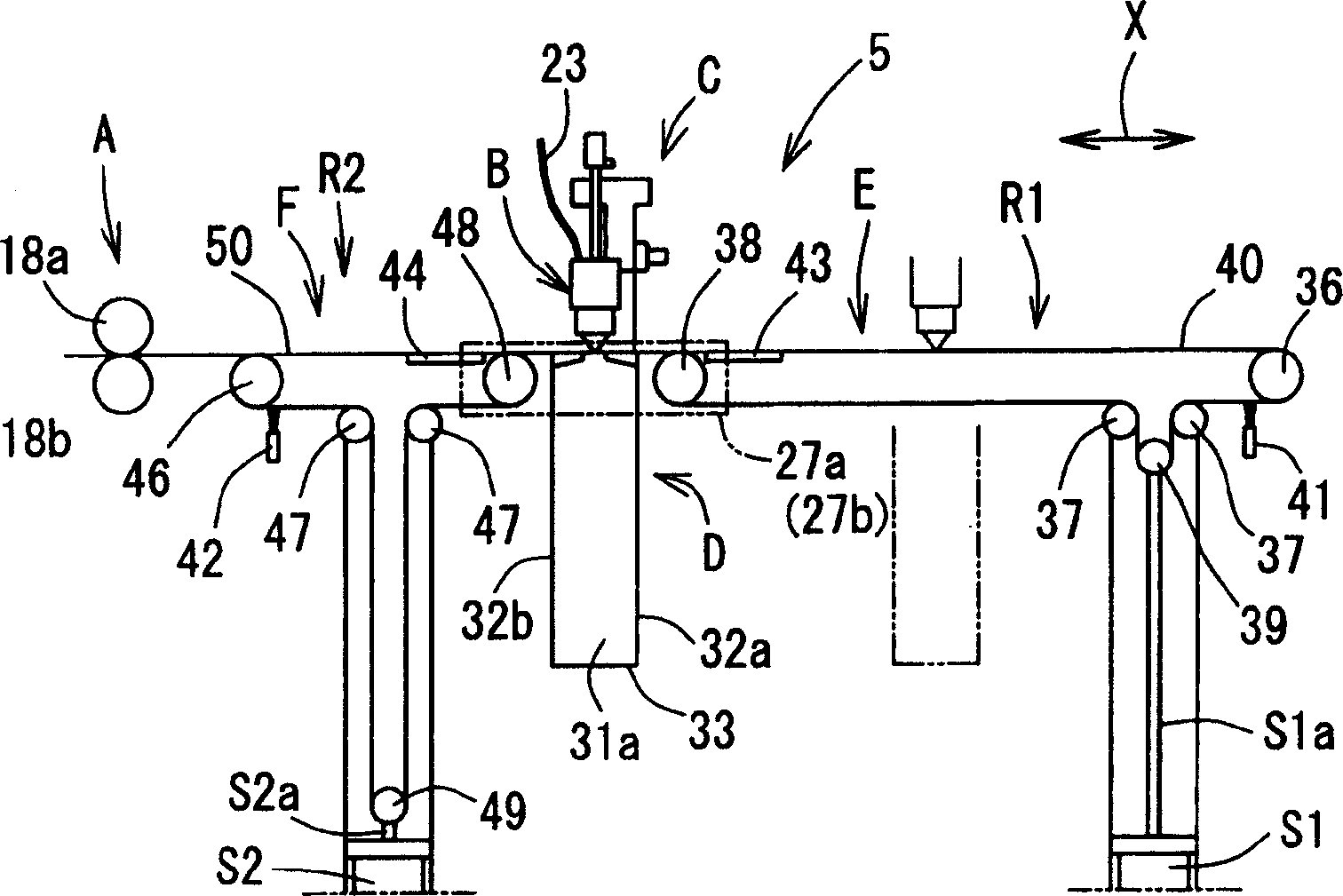
InactiveCN1652895APrevent adhesionReliable supportConveyorsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEngineeringLaser cutting
A laser cutting device, comprising a material feeding means for feeding a sheet-like material in a feeding direction, a processing head capable of radiating laser beam toward the material, a head moving means for moving the processing head in a material feeding direction X and a material lateral direction Y, an upstream side support means (belt conveyor mechanism F) for supporting the material on the upstream side of the lower part of the processing head and increasing / decreasing the support area (R2) of the material in the feeding direction according to the movement of the processing head in the feeding direction, and a downstream side support means (belt conveyor mechanism E) for supporting a part cut on the processing side lower part of the processing head and increasing / decreasing the support area (R1) of the cut part in the feeding direction according to the movement of the processing head in the feeding direction.
Owner:TOYOTA STEEL CENT CO LTD
Method of manufacturing MEMS sensor and MEMS sensor
InactiveUS20100096714A1Prevent adhesionPreventing undesired etching of a protective filmAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTransducer detailsMetallic materialsOptoelectronics
A method of manufacturing an MEMS sensor according to the present invention includes the steps of: forming a first sacrificial layer on one surface of a substrate; forming a lower electrode on the first sacrificial layer; forming a second sacrificial layer made of a metallic material on the first sacrificial layer to cover the lower electrode; forming an upper electrode made of a metallic material on the second sacrificial layer; forming a protective film made of a nonmetallic material on the substrate to collectively cover the first sacrificial layer, the second sacrificial layer and the upper electrode; and removing at least the second sacrificial layer by forming a through-hole in the protective film and supplying an etchant to the inner side of the protective film through the through-hole.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
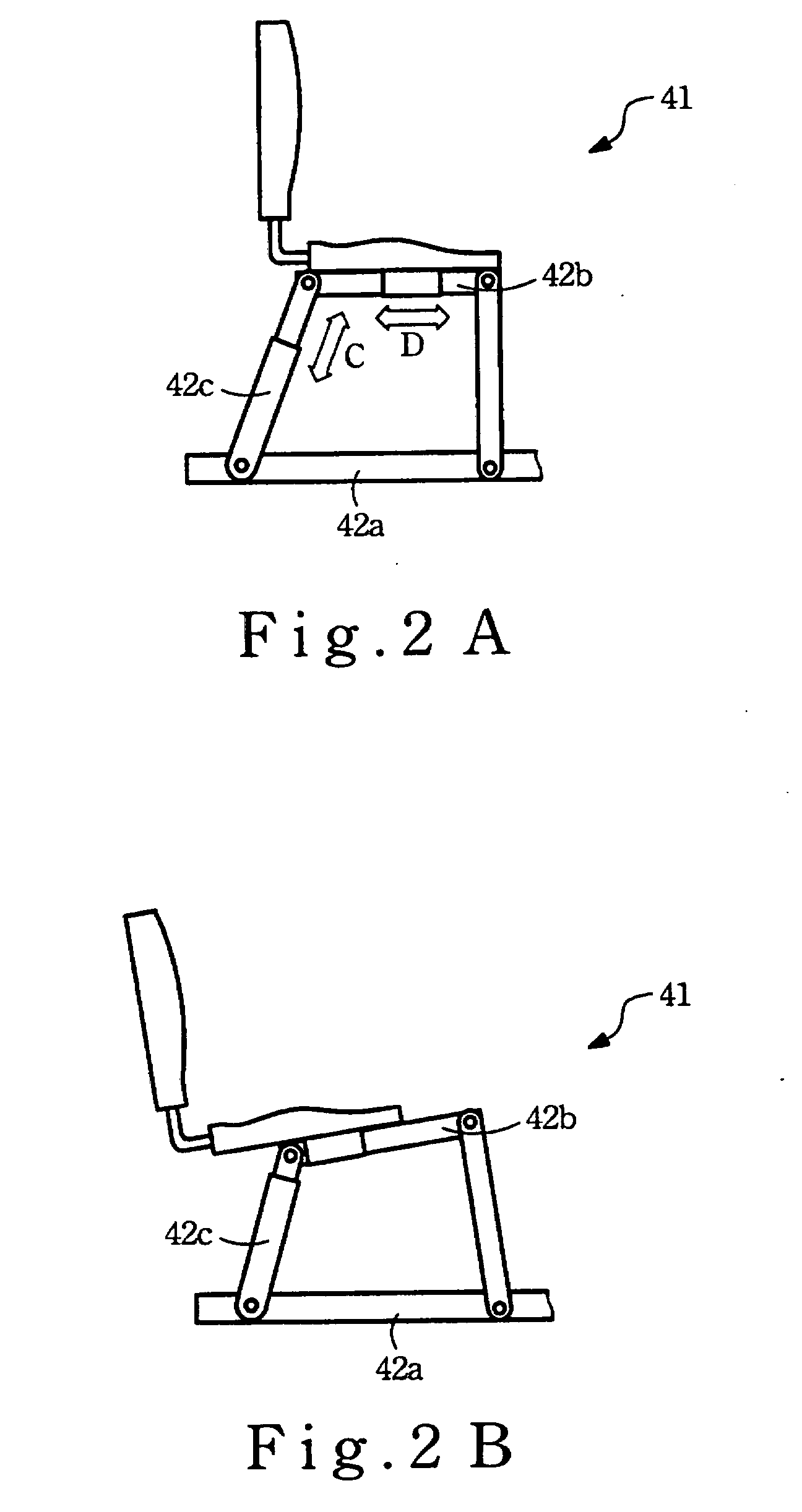
Multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) muscle training machine
InactiveUS20080085819A1Enhance coordinationPrevent adhesionSpace saving gamesFrictional force resistorsMuscle trainingMulti degree of freedom
A MDOF muscle training machine is provided in the present invention. The training machine has multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) being able to be set by users to make various cyclic motions with respect to various groups of muscle to be trained. The training machine comprises an adjustable frame and a cyclic motion device. The adjustable frame has MDOF being able to be adjusted with respect to the various cyclic motions. The cyclic motion device is assembled on the adjustable frame. The adjustable frame can be adjusted to decide a specific position of the cyclic motion device with respect to specific groups of muscle. Both arms (legs) of the user are constrained by the cyclic motion device. The user has to coordinate the specific groups of muscle to drive the cyclic motion device.
Owner:YANG TIAN FANG
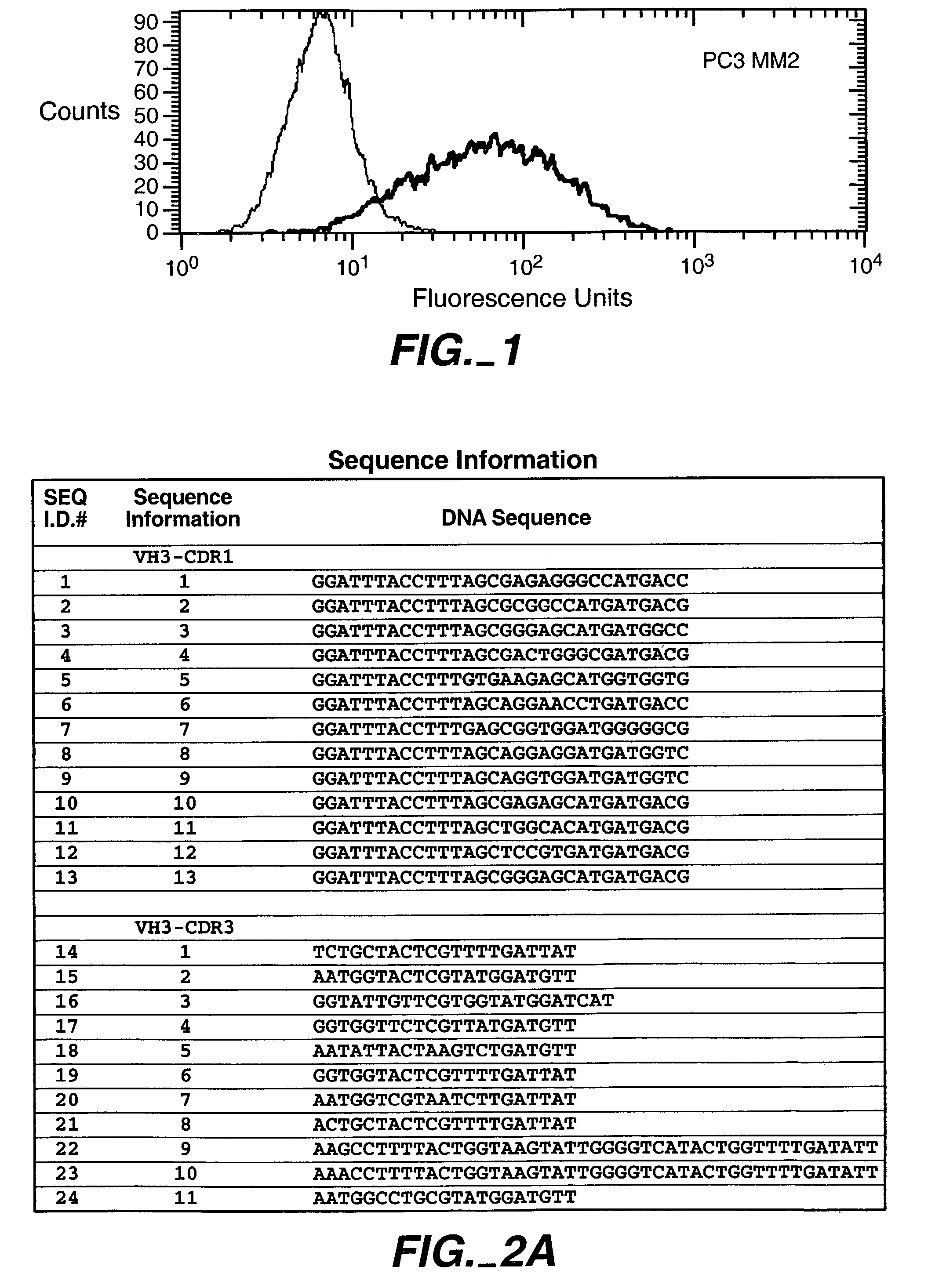
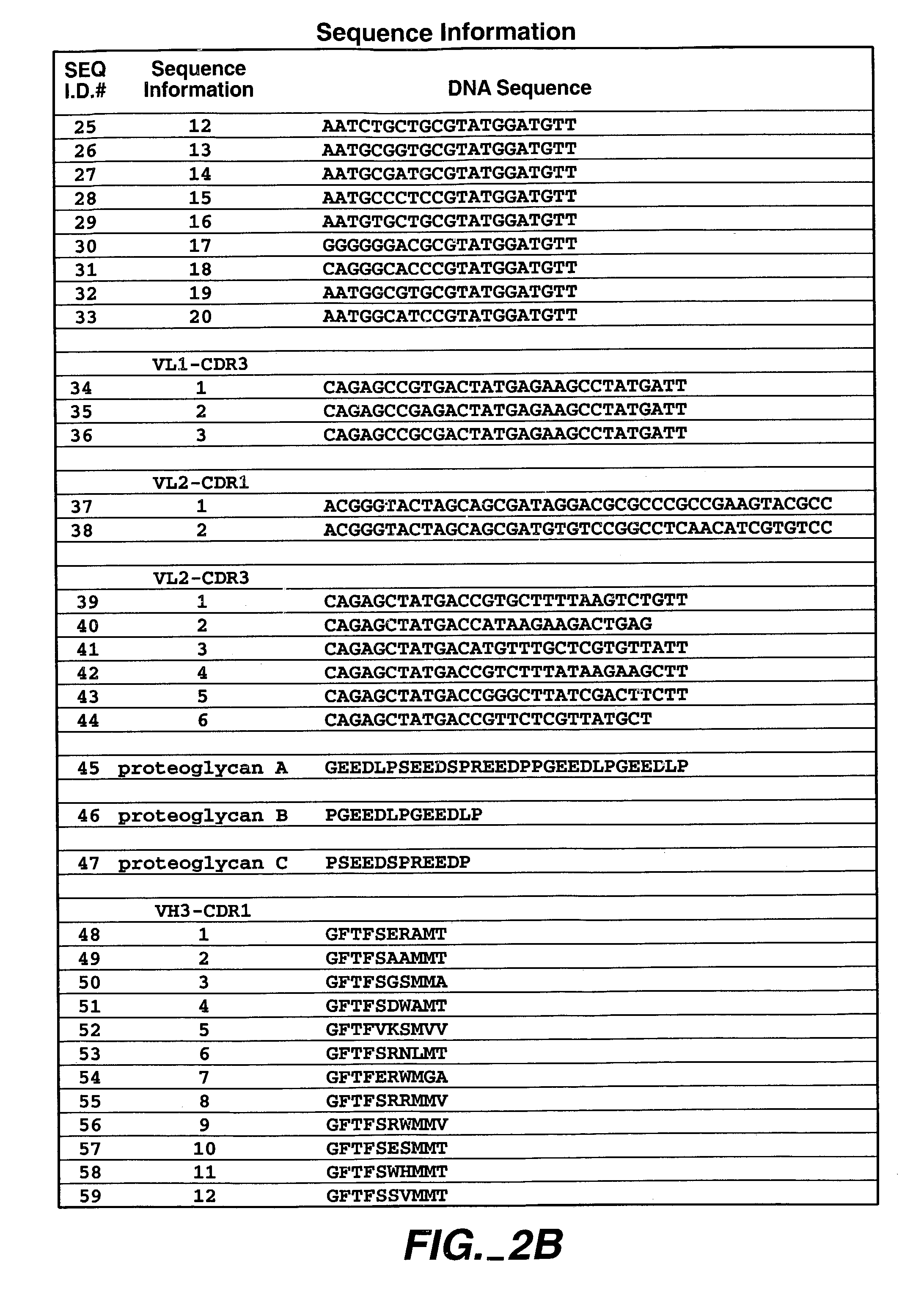
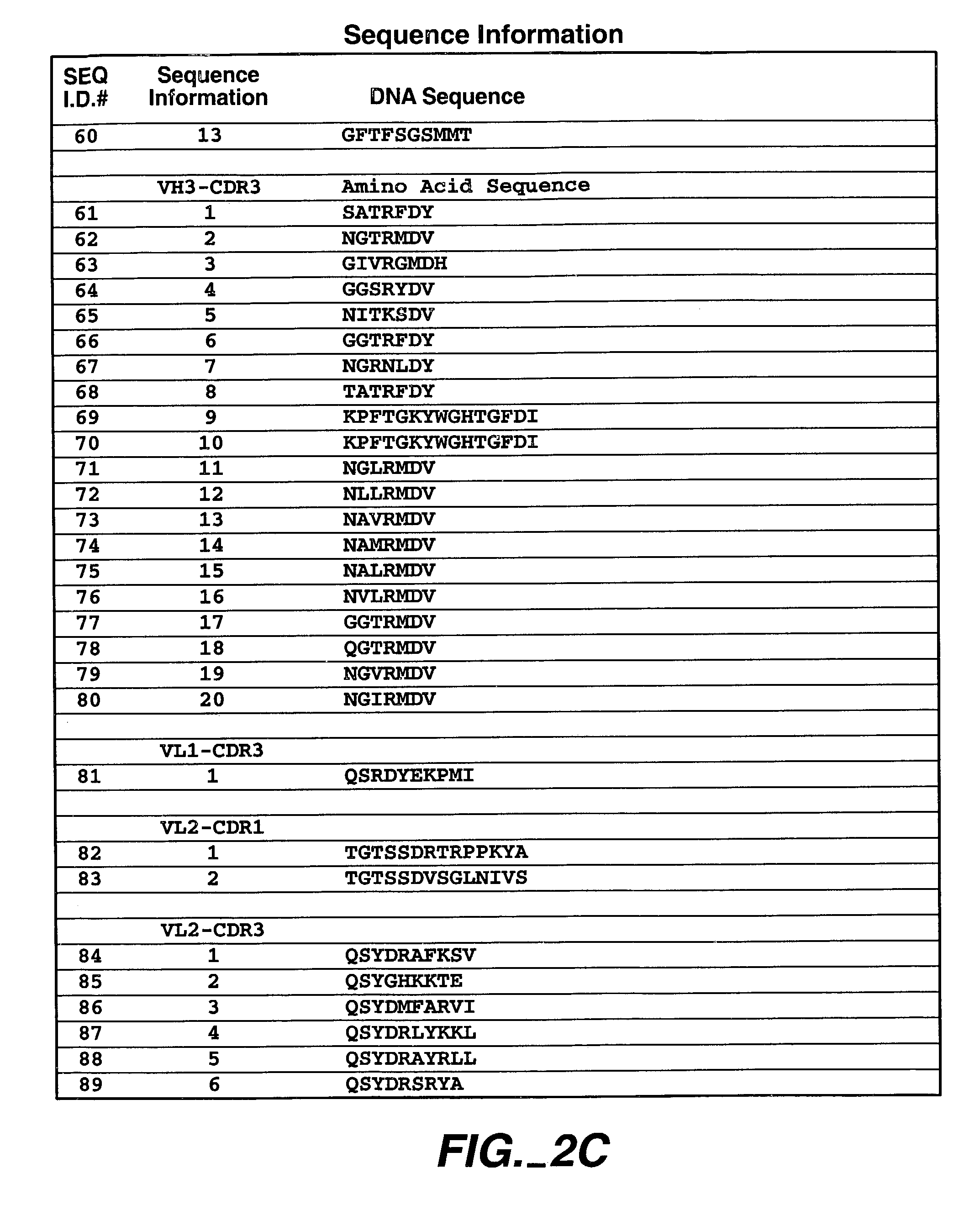
Human antibodies that have MN binding and cell adhesion-neutralizing activity
The invention is composed of monoclonal human MN antibodies or MN antibody fragments that target the GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeat within the proteoglycan domain. The proteoglycan domain of the MN cell surface protein contains four of these identical GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeats. Binding to the desired epitope is verified by competition ELISA, where ELISA signal can be attenuated by co-incubation with a peptide containing this repeat (PGEEDLPGEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 119)). This inhibition of binding can also be verified using Biacore assays, where binding of desired antibodies to immobilized MN or proteoglycan peptides can be inhibited by the peptide repeat. In addition to binding to the peptide repeat, human anti-MN antibodies can inhibit the cell adhesion of CGL-1 cells to MN coated plastic plates. Human anti-MN antibodies have been used to diagnose and quantify MN expression in cancer cells and tumors using FACS and immunohistochemical methods. An example is also provided where a human anti-MN IgG1 mediates tumor cell lysis though antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, these antibodies will be useful for the treatment of cancers in which MN is upregulated or can be useful for the diagnosis of cancers in which MN is upregulated.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Film-Forming Apparatus And Film-Forming Method
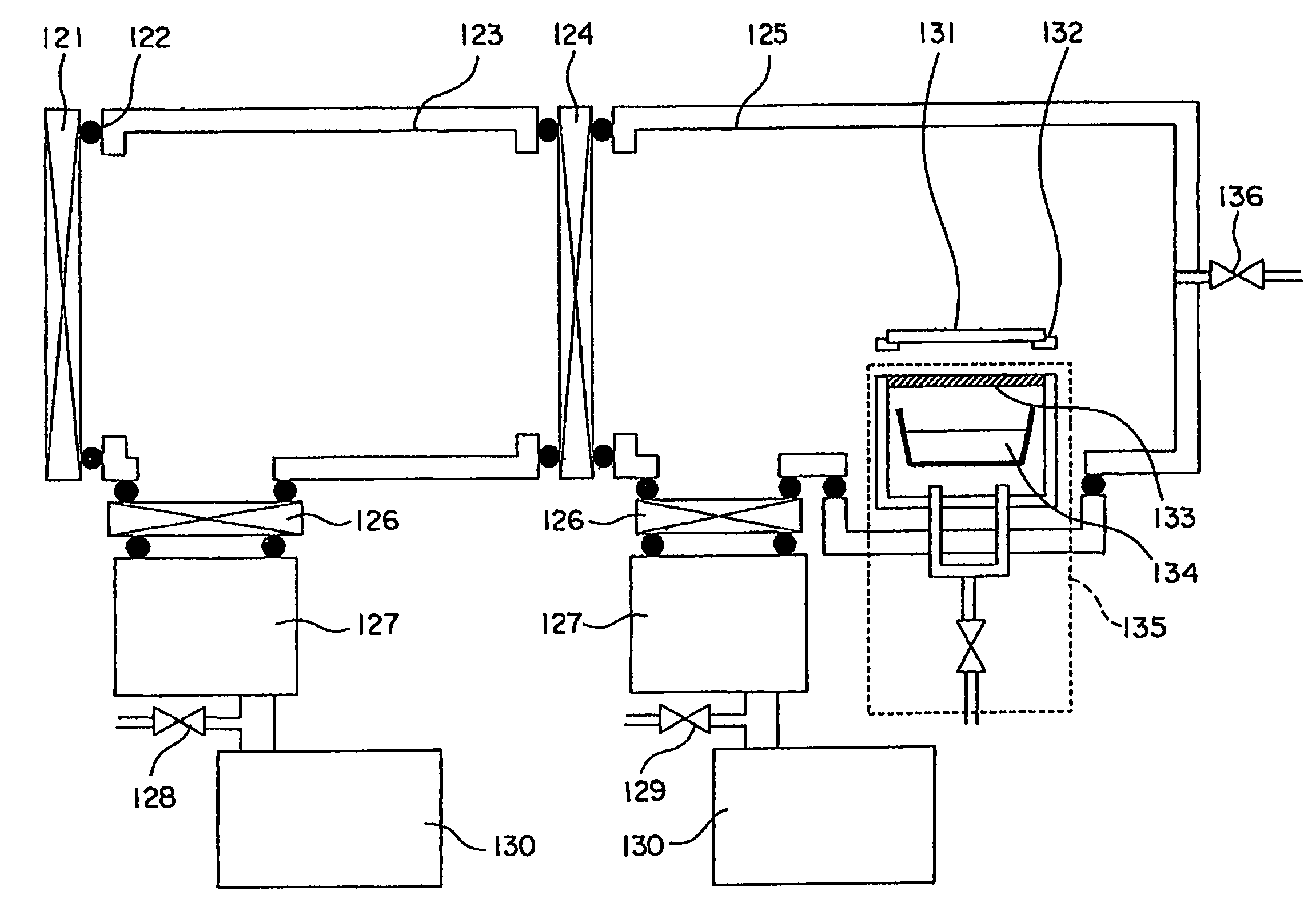
InactiveUS20080241587A1High film forming rateUniform film formationDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringRaw material
For increasing the film-forming rate and enabling uniform film formation and waste elimination of raw material, a film-forming method and a film-forming apparatus can reach an evaporated film-forming material to a surface of a substrate by the flow of a transport gas so as to control the film-forming conditions by the flow of the gas. Thereby a uniform thin film can be deposited on the large-area substrate. That is, by directing the evaporated raw material toward the substrate, it is possible to increase the film-forming rate and achieve uniform film formation.
Owner:OHMI +1
Systems and methods relating to polymer foams
InactiveUS20110202016A1Prevent and limit bleedingPrevent adhesionSurgical adhesivesMedical devicesBody fluidPolymer
Systems and methods related to polymer foams are generally described. Some embodiments relate to compositions and methods for the preparation of polymer foams, and methods for using the polymer foams. The polymer foams can be applied to a body cavity and placed in contact with, for example, tissue, injured tissue, internal organs, etc. In some embodiments, the polymer foams can be formed within a body cavity (i.e., in situ foam formation). In addition, the foamed polymers may be capable of exerting a pressure on an internal surface of a body cavity and preventing or limiting movement of a bodily fluid (e.g., blood, etc.).
Owner:ARSENAL MEDICAL
Workpiece surface wiping device and workpiece surface wiping method
InactiveCN103611694ACause scratchesQuality improvementCleaning using toolsArticle deliveryEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:株式会社雷恩工业
Nose pad cushion and applicator for respiratory mask
InactiveUS20110209701A1Prevent sore and sore spotAvoid Insufficient SealingRespiratory masksBreathing masksNoseAdhesive
A removable nose pad cushion adherable to a medical face mask and more particularly to a positive pressure ventilation mask approximately where the mask rests on the upper nose area of a wearer's face providing a cushioning seal between the mask and wearer's nose. The nose pad cushion can be impregnated with medication to be adsorbed by the skin of the patient. The surface of the nose pad cushion which contacts the skin of the user is soft and pliable and selected to removably adhere only to dry skin and is incapable of sticking to a moist wound bed or sores formed on the bridge of the nose. The area covered by the cushion primarily covers the upper nose area but could cover the entire interface between the mask and the face of a user. The cushion can be pre-shaped to be applied to the desired area of the mask. The adhesive which holds the cushion to the mask is of a type such that the cushion can be removed cleanly and replaced with another cushion periodically.
Owner:DERRINGER LAURA +1
Surface-finishing agent and finished material and method of surface finishing
InactiveUS20060266258A1Developing surfaceHigh water slipping propertyOther chemical processesFibre treatmentSoil propertiesSlurry
The present invention provides a surface-treating agent to form fine roughness on the surface of a material and more specifically a surface treating-agent which forms fine roughness on the surface of a material and is easy to process, thereby being useful for materials for highly water-repellent glass, lenses and fabric, materials with an excellent anti-soiling property, panels having an excellent light scattering property, illumination of optical fiber and the like, materials and coatings to prevent accumulation and adhesion of snow or icicle formation on antennas, wires and steel towers, and roughness formation on the surface of semiconductor substrates; the treated materials; and a method of surface treatment to develop the roughness. The surface-treating agent of the present invention has an average primary particle diameter in the range of 1-50 nm, contains fine particles in the range of 5-60% by mass of the total amount of the surface-treating agent in a slurry of nanoparticles which are treated for water repellency and mechanically dispersed in a solvent containing a volatile solvent, and forms a roughness structure with upward protrusions having a spatial periodicity of 0.1-50 μm on the surface of a material by volatilizing the solvent or dipping repeatedly in water upon treating the surface of the material.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
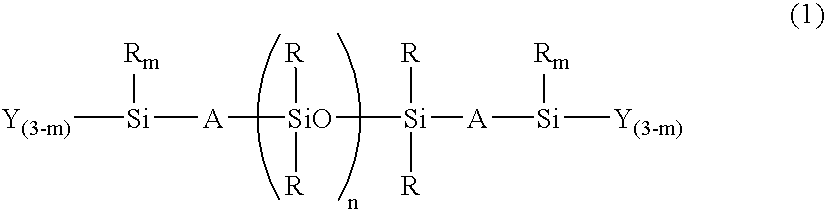
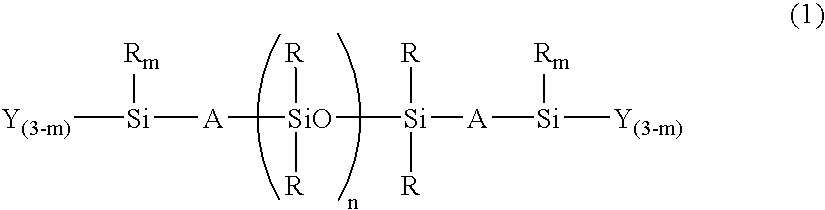
Room-temperature curable organopolysiloxane composition
InactiveUS6906161B2Superior long-term endurance of antifoulingPrevent adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPartial hydrolysisLong term durability
A room-temperature curable organopolysiloxane composition is provided, which includes (A) an organopolysiloxane with the terminals blocked with a hydroxyl group, a hydrolysable group, or both these types of groups, and (B) an organosilicon compound containing a hydrolysable group, a partial hydrolysis-condensation product thereof, or a mixture of the two, and (C) a polysiloxane containing an oxyalkylene group bonded to a silicon atom via, for example, a C—C—Si linkage. Application of this composition to an underwater structure is able to generate an antifouling coating that is effective in preventing the adhesion and growth of aquatic organisms on the surface of the underwater structure, and displays superior long term endurance of this antifouling effect.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Oral care compositions containing combinations of anti-bacterial and host-response modulating agents
InactiveUS8283135B2Potent anti-inflammatory activityPromote progressAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDiseaseOral bacterial infection
The present invention encompasses topical oral care compositions comprising the combination of an anti-bacterial agent with an anti-inflammatory agent in an orally acceptable carrier for effective treatment and prevention of bacteria-mediated diseases and conditions in the oral cavity and for modulating host reaction to bacterial pathogens present in the oral cavity and to the toxins, endotoxins, inflammatory cytokines and mediators released by or prompted by these pathogens. The present invention also encompasses methods of use of these compositions comprising topical application to the oral cavity. The benefits of the present compositions and methods extend beyond treating and preventing oral bacterial infections in the oral cavity to promoting whole body or systemic health.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
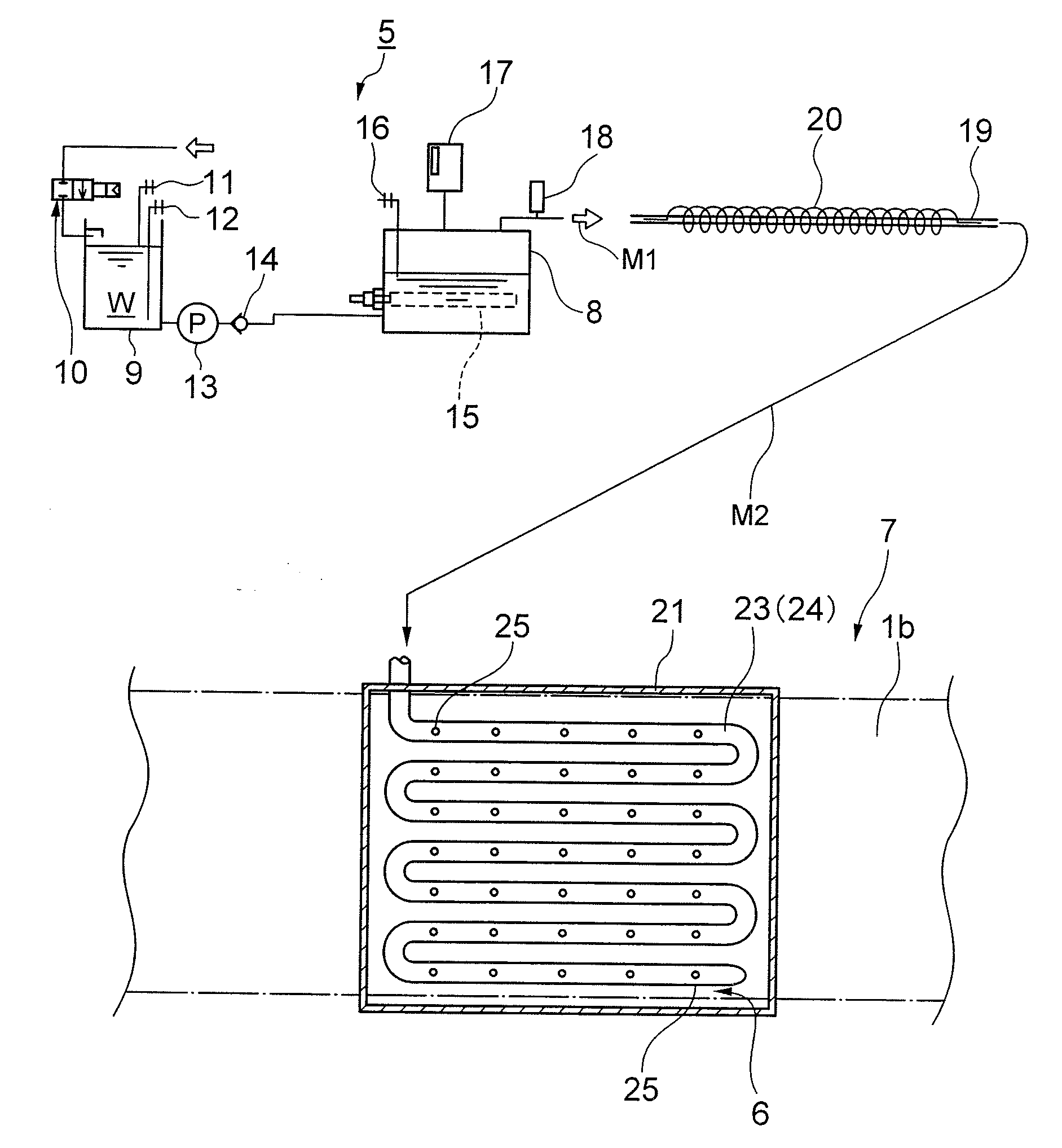
Heat exchanger tube
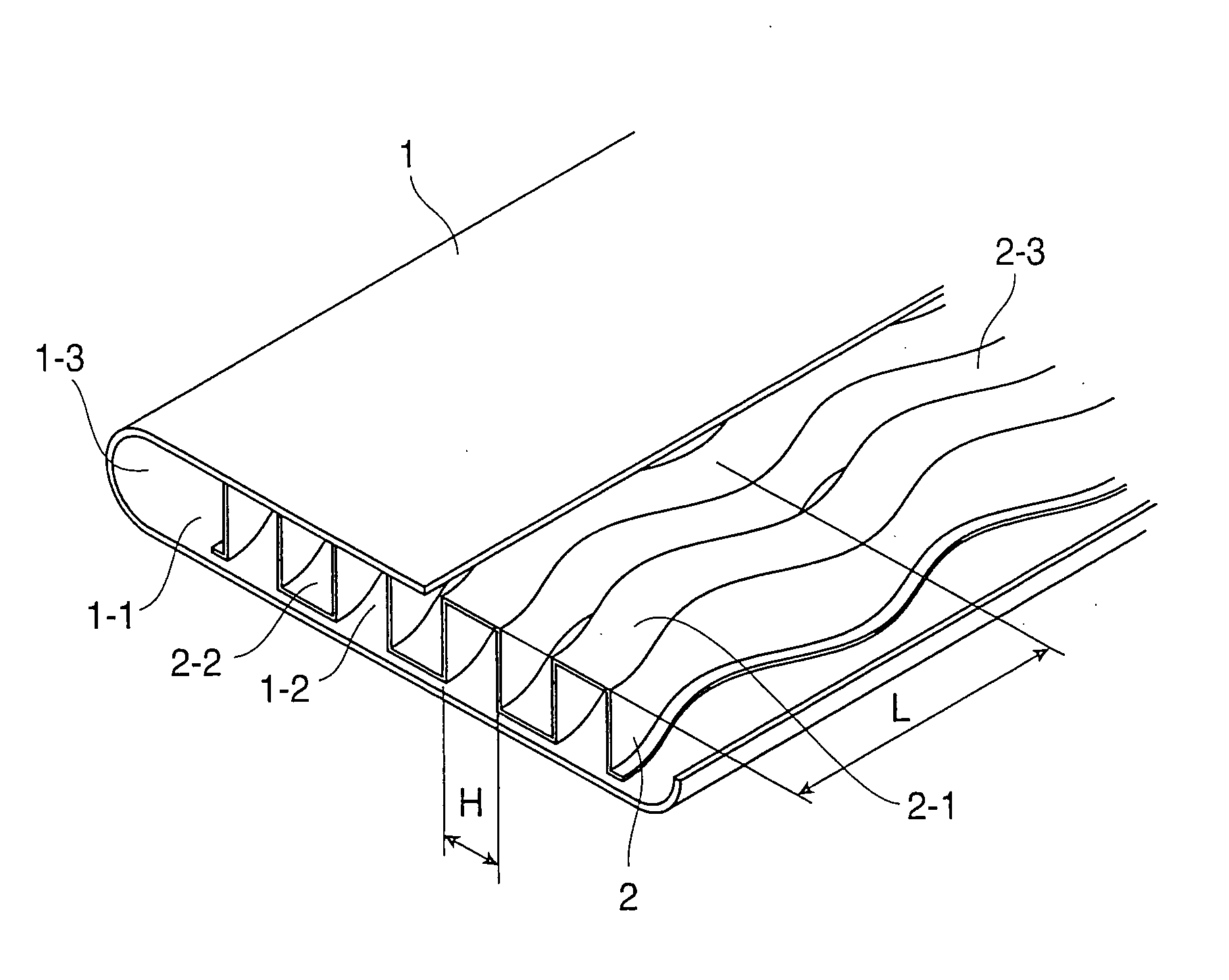
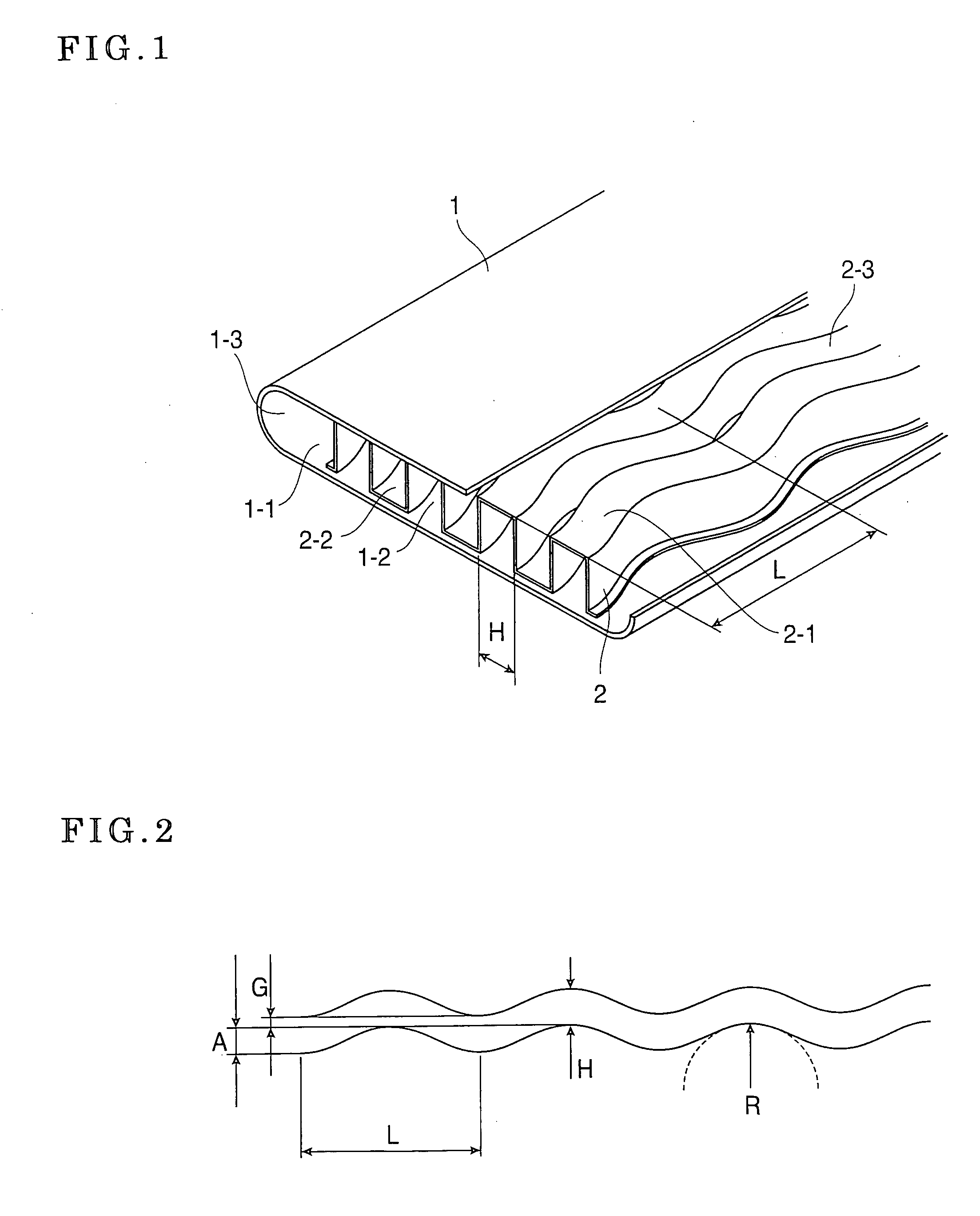
InactiveUS20070056721A1Improve cooling effectImprove heat transfer performanceRecuperative heat exchangersExhaust gas recirculationWave shapeEngineering
A heat exchanger tube has an inner peripheral surface serving as an exhaust gas flow path with a flat cross-sectional shape. A thin structure is incorporated in the heat exchanger tube and has a substantially rectangular channel-shaped waveform in cross section. The corrugated fin structure has a curved surface forming waveform meandering with a predetermined wavelength in the lengthwise direction. The wave width of the channel-shaped waveform is H, the wavelength of the waveform meandering in the lengthwise direction is L and the amplitude of the waveform meandering in the lengthwise direction is A. The heat exchanger tube is formed so that H / L is set at 0.17 to 0.20 and the ration (G / H) of a gap G determined by H-A to H is set at −0.21 to 0.19.
Owner:USUI KOKUSAI SANGYO KAISHA LTD
Biodegradable polymer adhesion barriers
InactiveUS20070299155A1Prevent adhesionAvoid stickingCosmetic preparationsImpression capsSolventOpen surgery
The present invention provides adhesion barrier compositions based on a solution of at least one of a biodegradable polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), or polyester urea (PEU) polymers, dissolved in a biocompatible solvent. The compositions can be applied to a tissue surface, such as in open surgery, as a viscous liquid which forms an adhesive film upon being sprayed or painted onto the tissue surface. Alternatively, the composition can be applied to the tissue surface as a preformed solid layer or double layer (either porous or non-porous) that adheres to the tissue surface. In open surgery, the invention adhesion barrier compositions are used to separate opposing tissue surfaces or tissue-organ surfaces while injured tissues heal, for example in the abdomen or pelvis
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
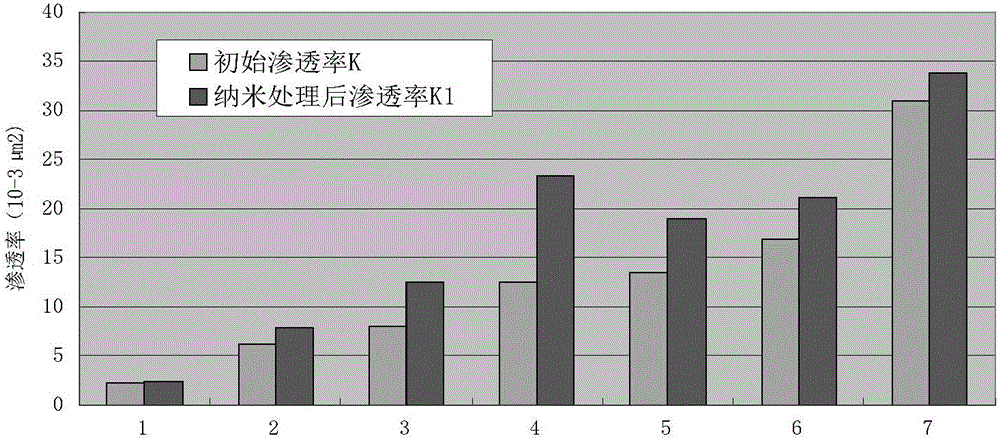
Pressure-reducing and injection-increasing agent for water injection well of low-permeability oilfield, and preparation method and application thereof
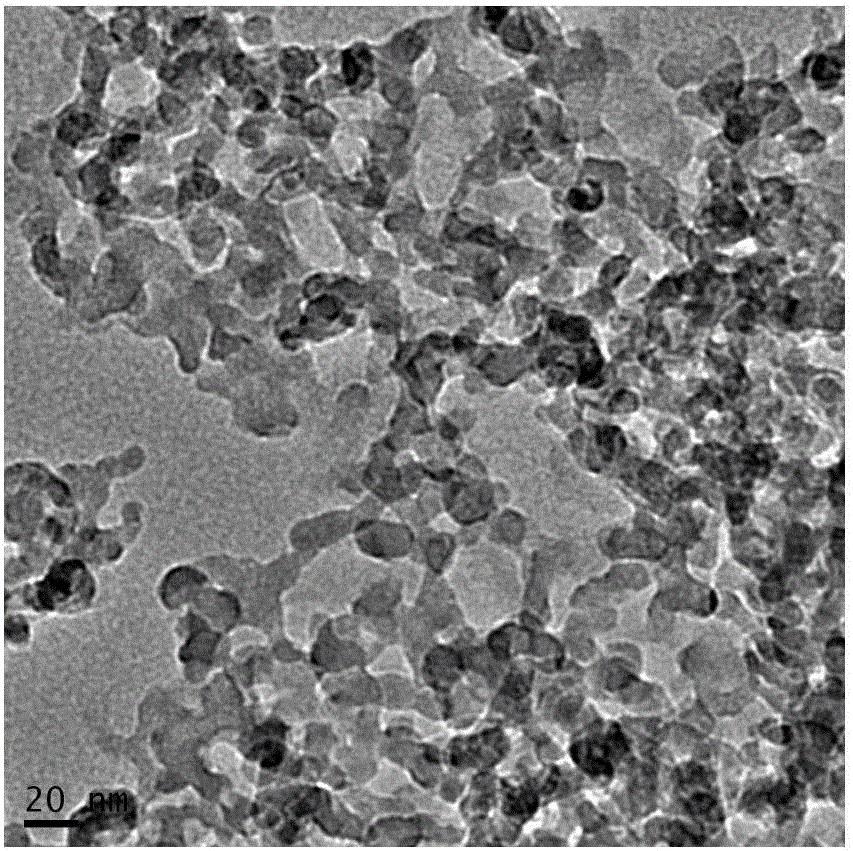
InactiveCN106085401ALarge specific surface areaReduce thicknessFluid removalDrilling compositionNanometreChemistry
The invention relates to a pressure-reducing and injection-increasing agent for a water injection well of a low-permeability oilfield, and a preparation method and application thereof. The pressure-reducing and injection-increasing agent is prepared from the following components by weight: 2.0 to 6.5% of a multifunctional surface treating agent, 0.75 to 3.15% of hydrophobic nanometer silica or nanometer poly-silicon and 2 to 8% of a pH conditioning agent, with the balance being deionized water, wherein the multifunctional surface treating agent comprises, by weight, 30 to 80% of a nonionic surfactant, 2 to 25% of an anionic surfactant and 10 to 50% of an ampholytic surfactant. The pressure-reducing and injection-increasing agent is free of pollution to strata and can overcome the problems of high water injection pressure, unqualified injection allocation of a water injection rate and a short action period of injection increase in the later stage of development. The preparation method is simple in process, free of emission of pollutants and easy for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:郑州东申石化科技有限公司
Anti-fouling ship paint with low biological surface energy
InactiveCN1810903ANo pollutionPrevent adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesSurface oceanWeather resistance
The anti-fouling ship paint with low biological surface energy consists of low surface energy resin, biological extract micro capsule, nanometer titania, microporous silica and solvent. The present invention has biological extracts chitin, capsaicin as anti-fouling agent through micro capsule slow releasing treatment and nanometer modified low surface energy paint and multiple anti-fouling performances. The present invention has the advantages of self-cleaning performance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, weather resistance, etc and is used for ship as well as bridge, marine engineering member, etc.
Owner:JIANGSU GEMEIGAO DEV CO LTD
Substrate processing system and substrate cleaning apparatus
InactiveCN101276739AReduce gravityReliable removalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsForeign matterGas phase
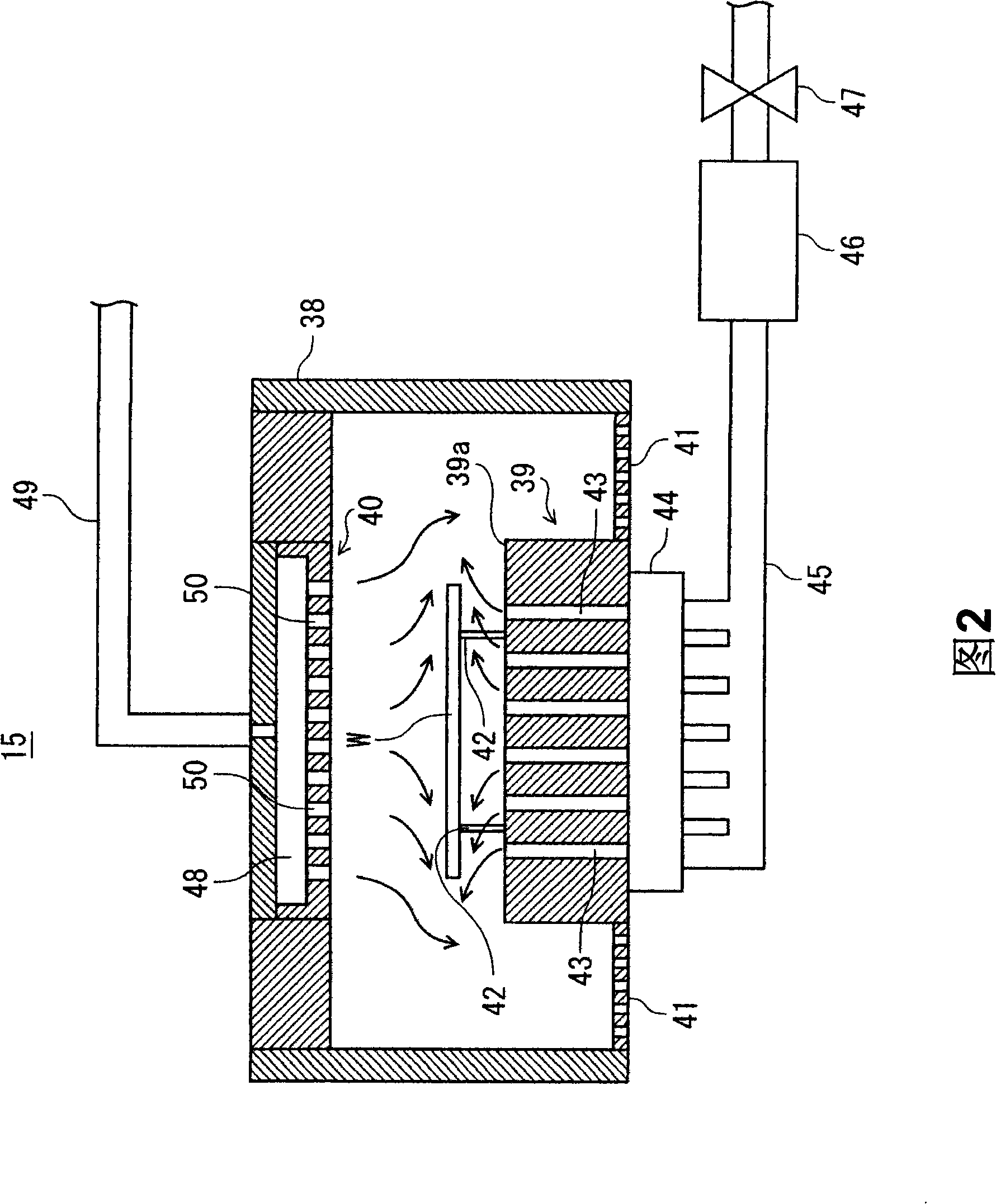
This invention provides a substrate processing system that enables foreign matter adhered to a rear surface or a periphery of a substrate to be completely removed. A processing assembly (15) of a substrate cleaning apparatus of the substrate processing system (10) including: a chamber (38) for accepting a wafer (W); a holding table (39) configured at the bottom of the chamber (38) and for placing the wafer W; a spray head configured at the top in the chamber (38) and opposite to the holding table (39).The holding table (39) jets the mixed cleaning agent of cleaning substrate (such as pure water) and inactive gas (such as N2) in two phases of a gas phase and a liquid phase at the back side or edge part facing to the wafer (W). The spray head (40) generates the down-flow facing to the surface of the wafer (W).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com