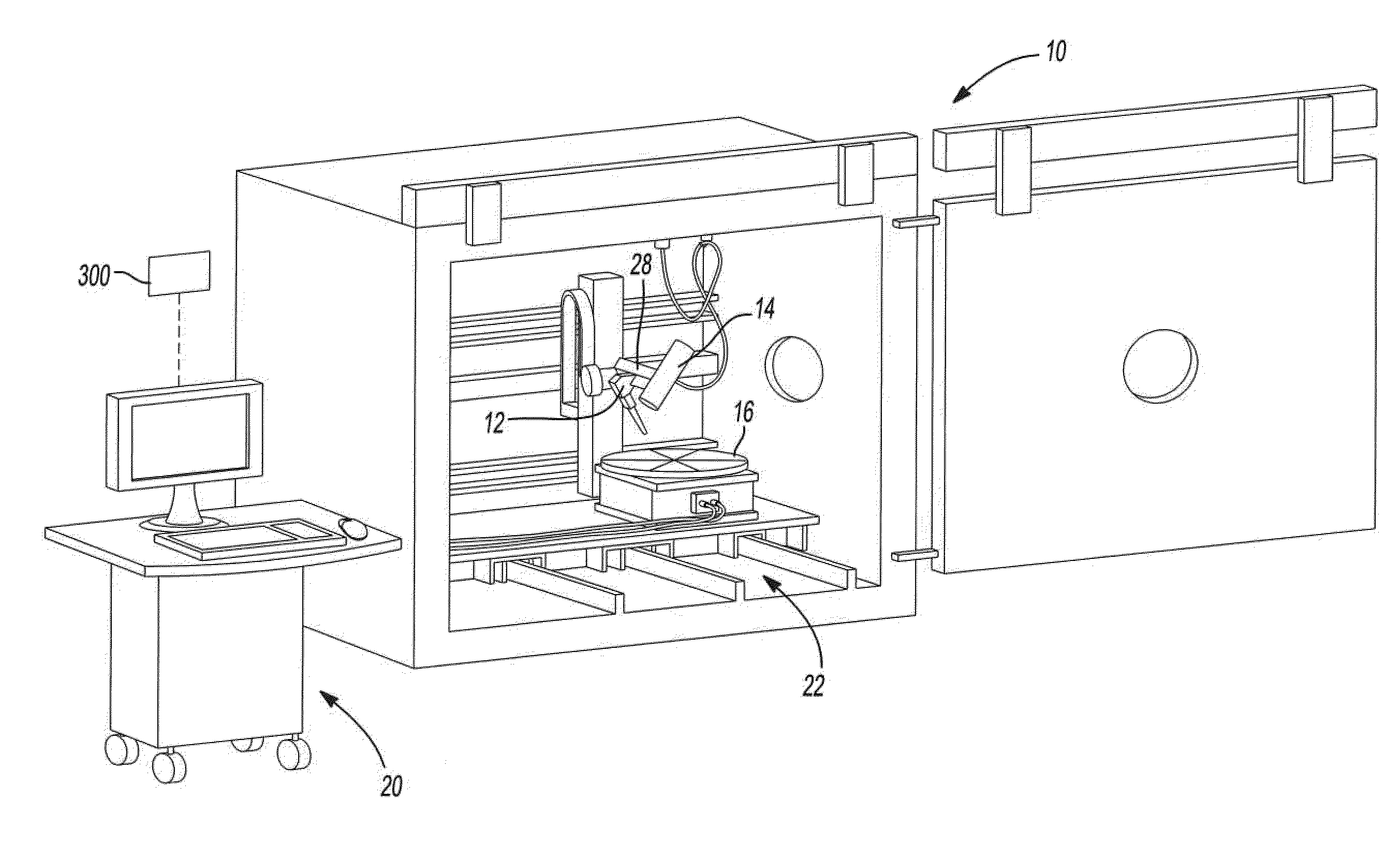
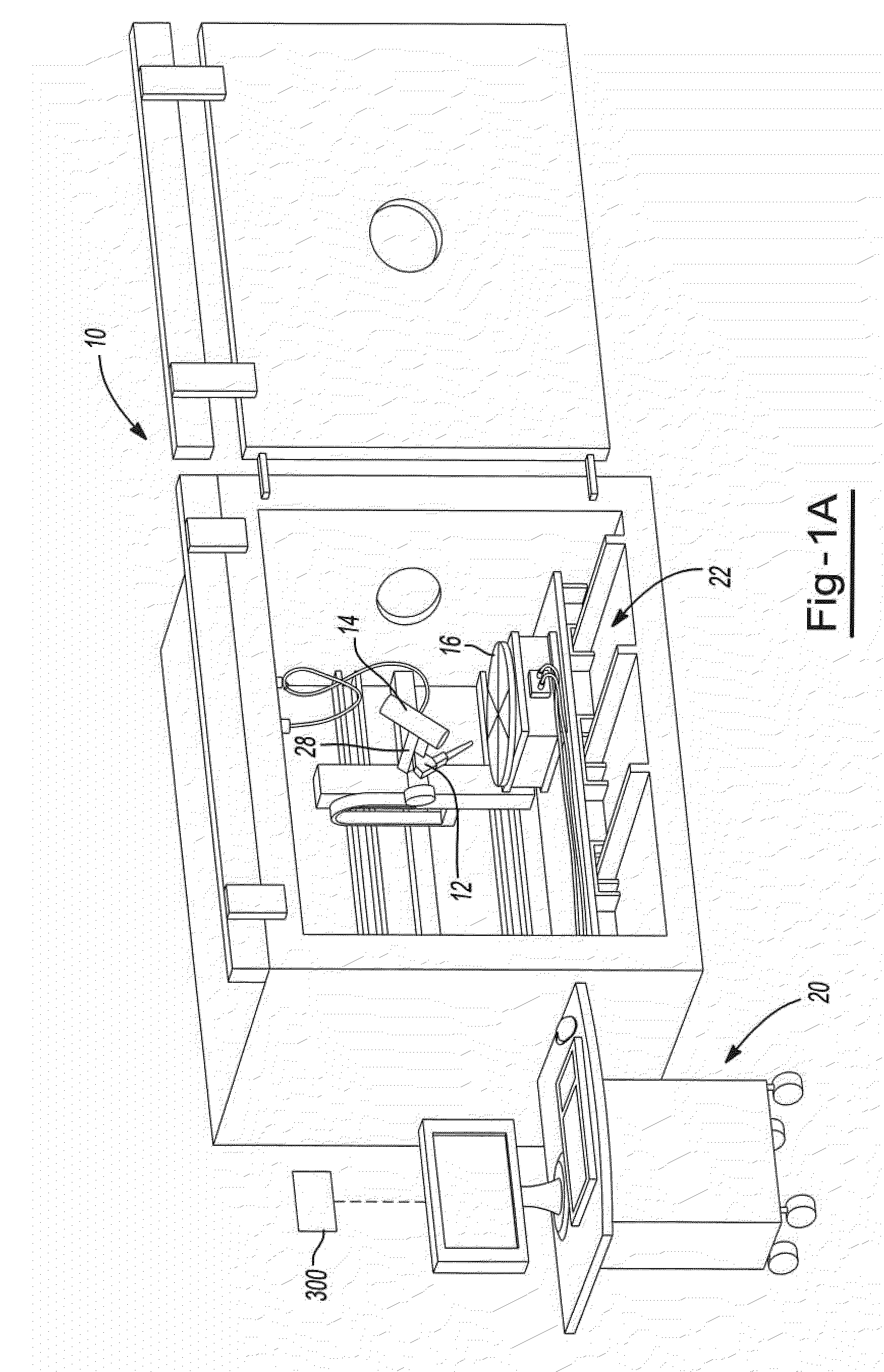
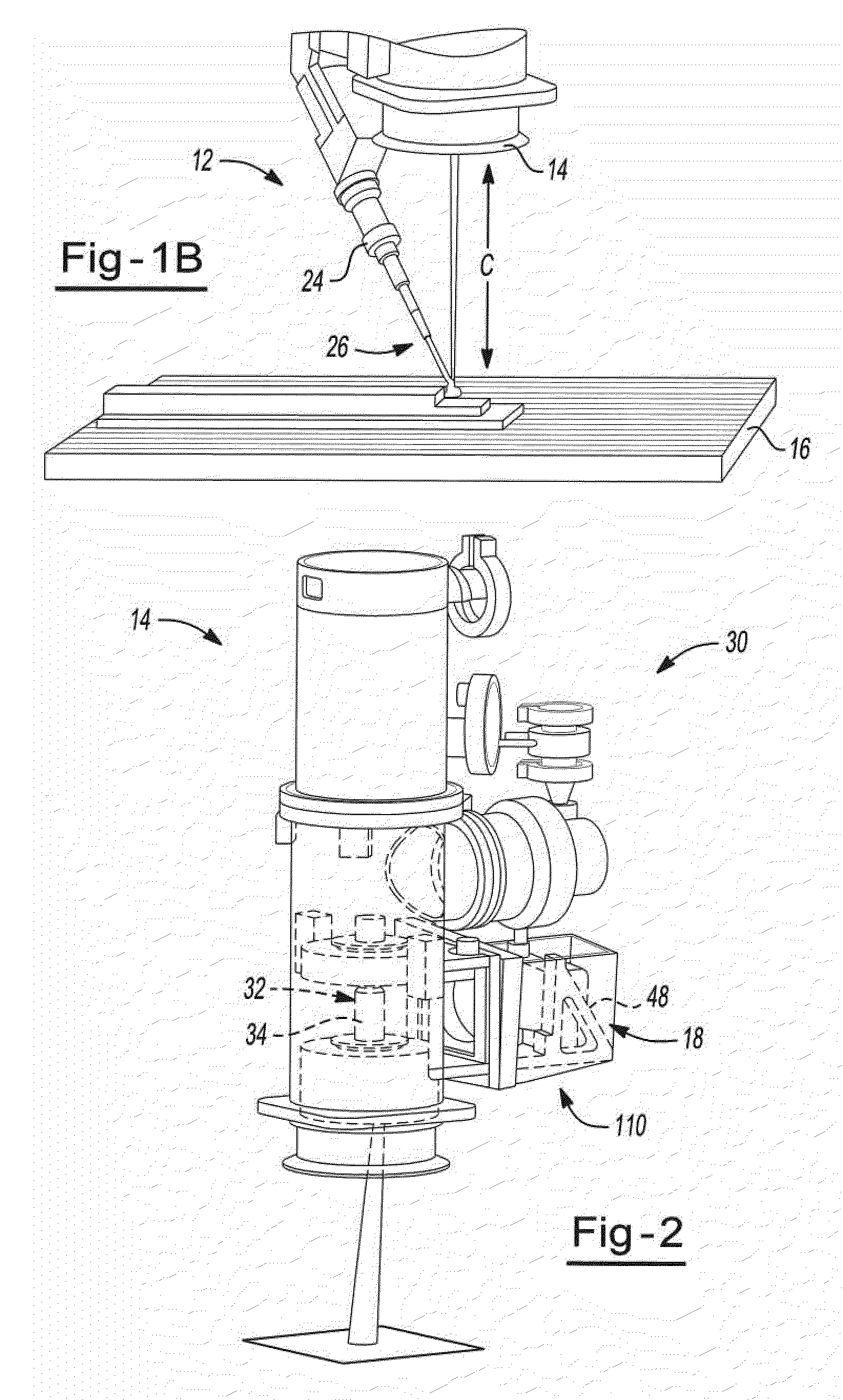
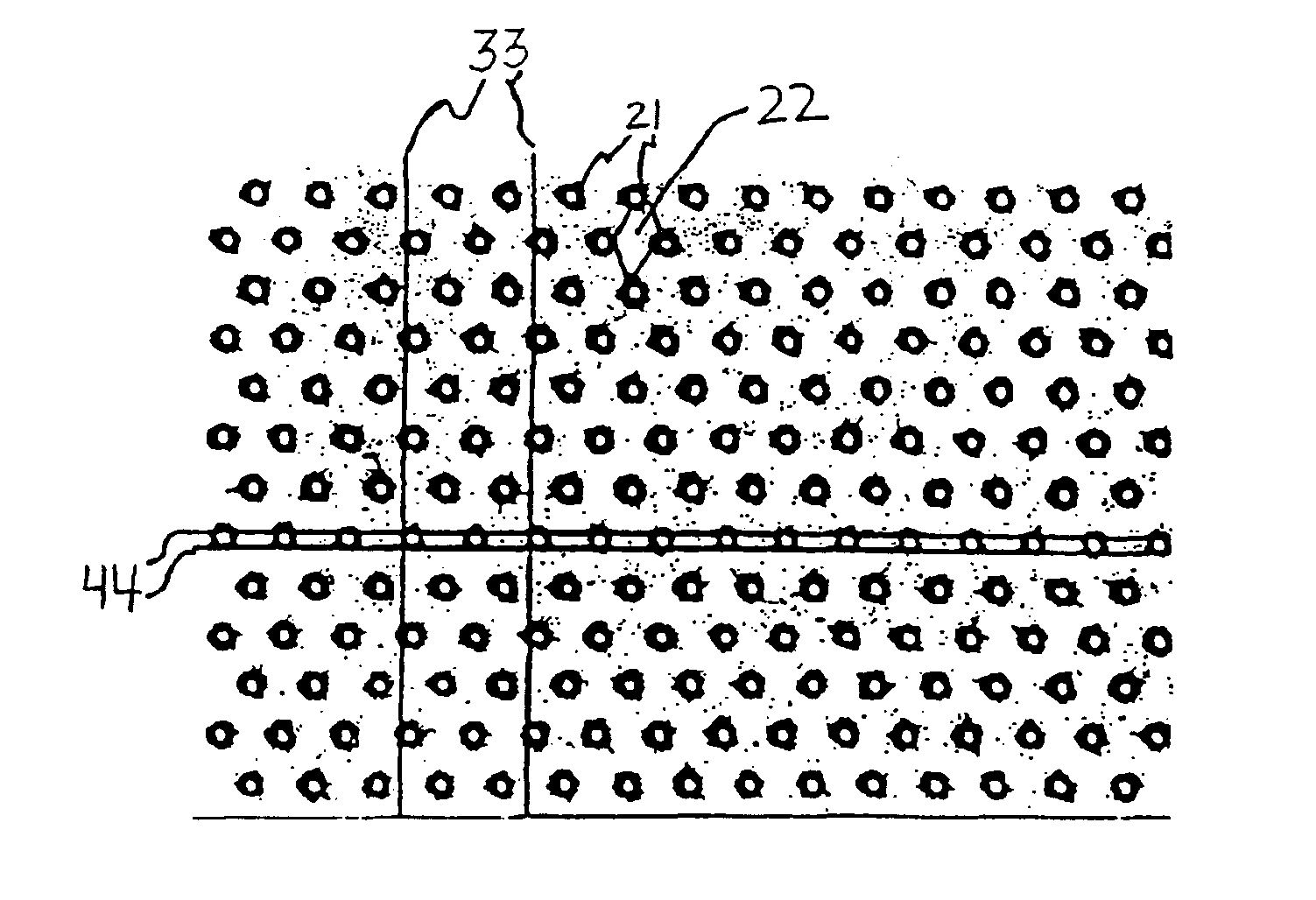
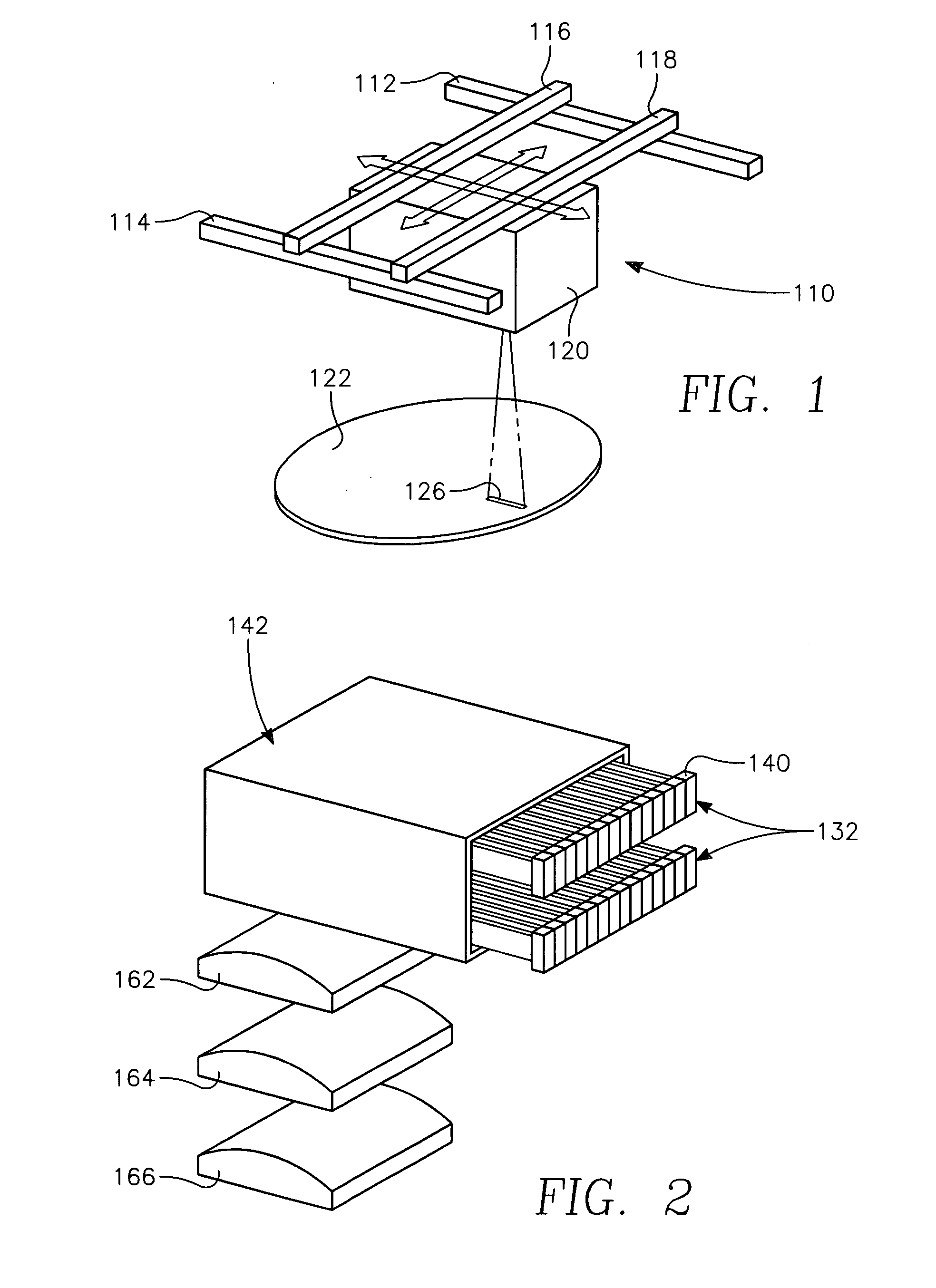
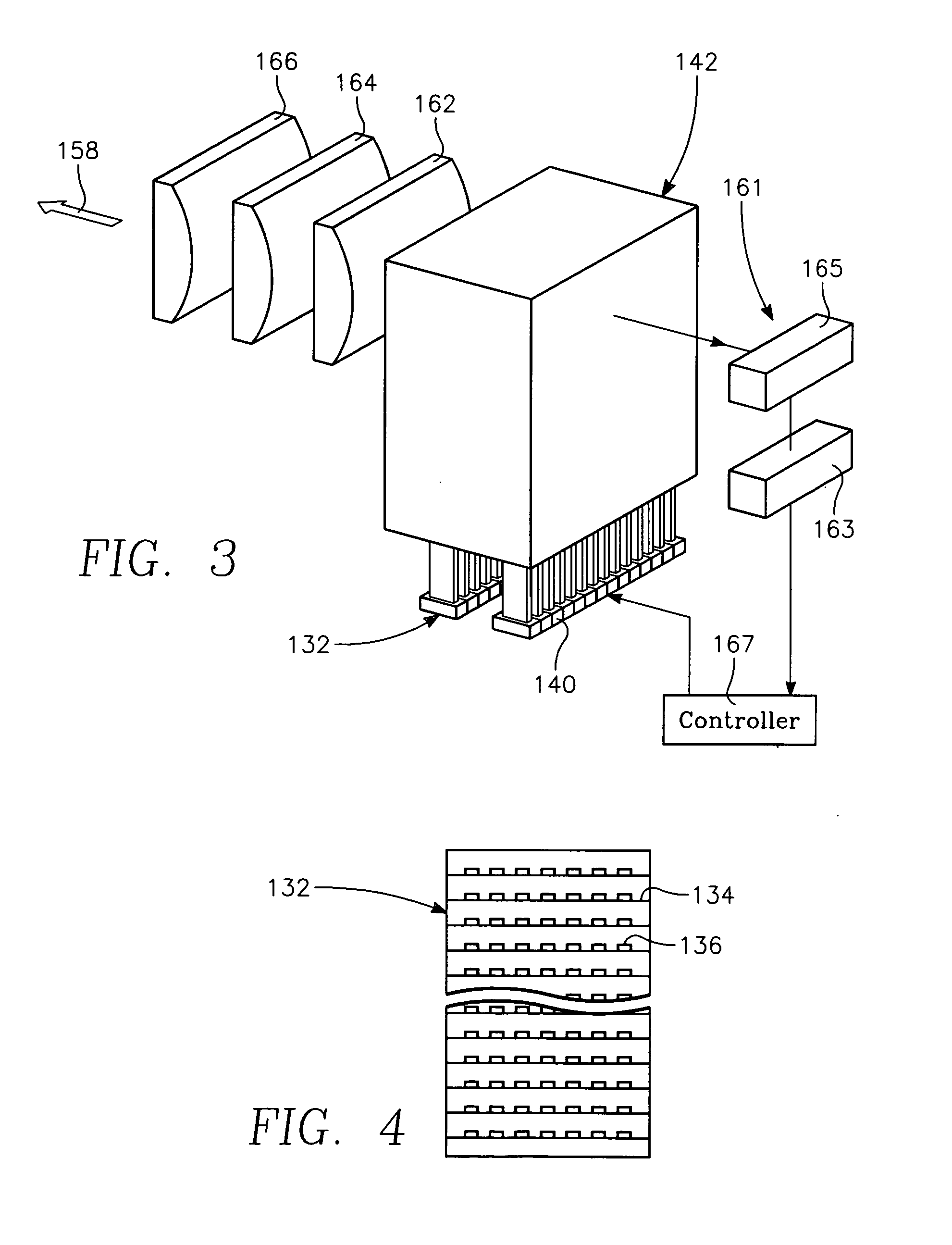
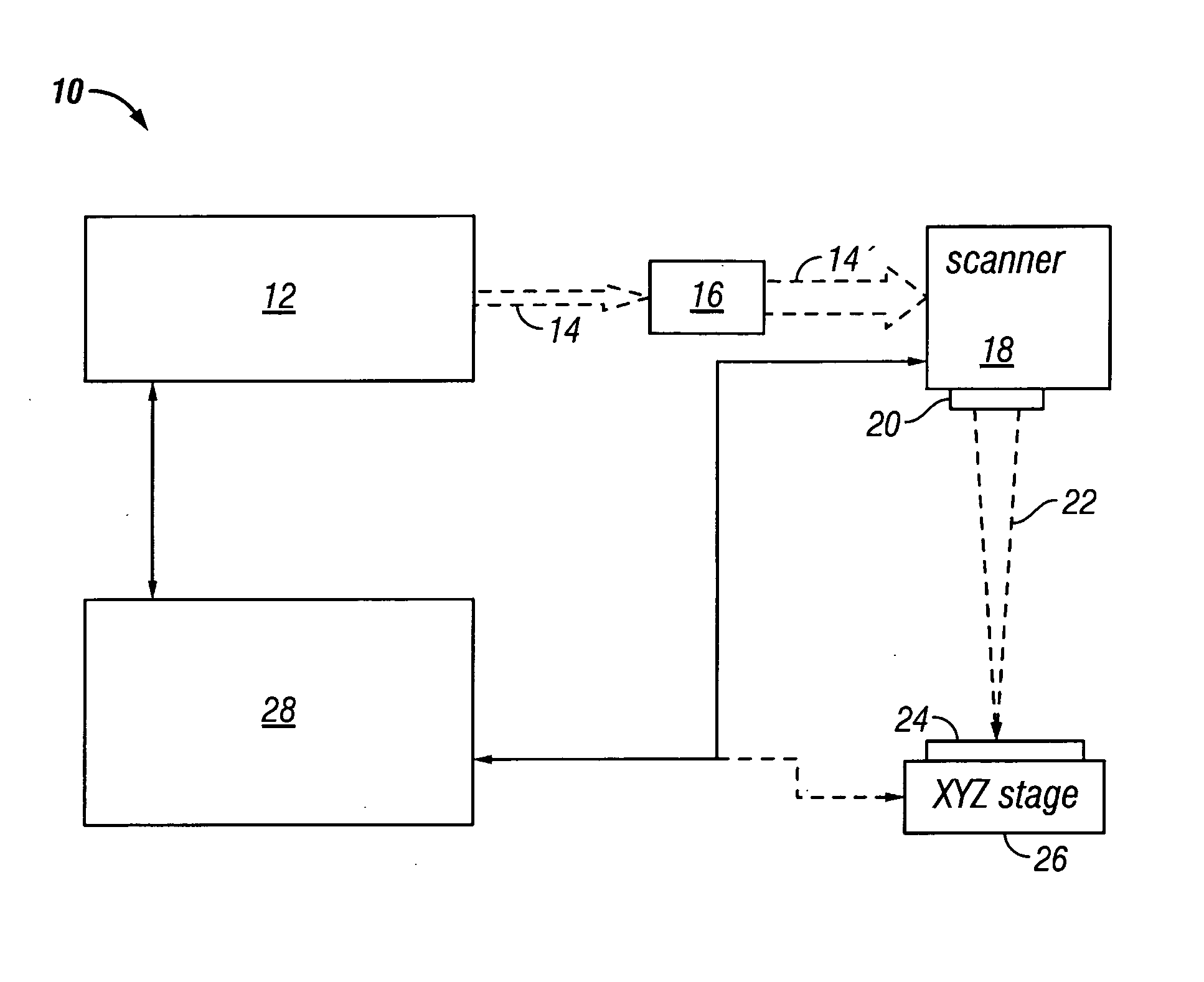
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
20934results about "Welding/soldering/cutting articles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
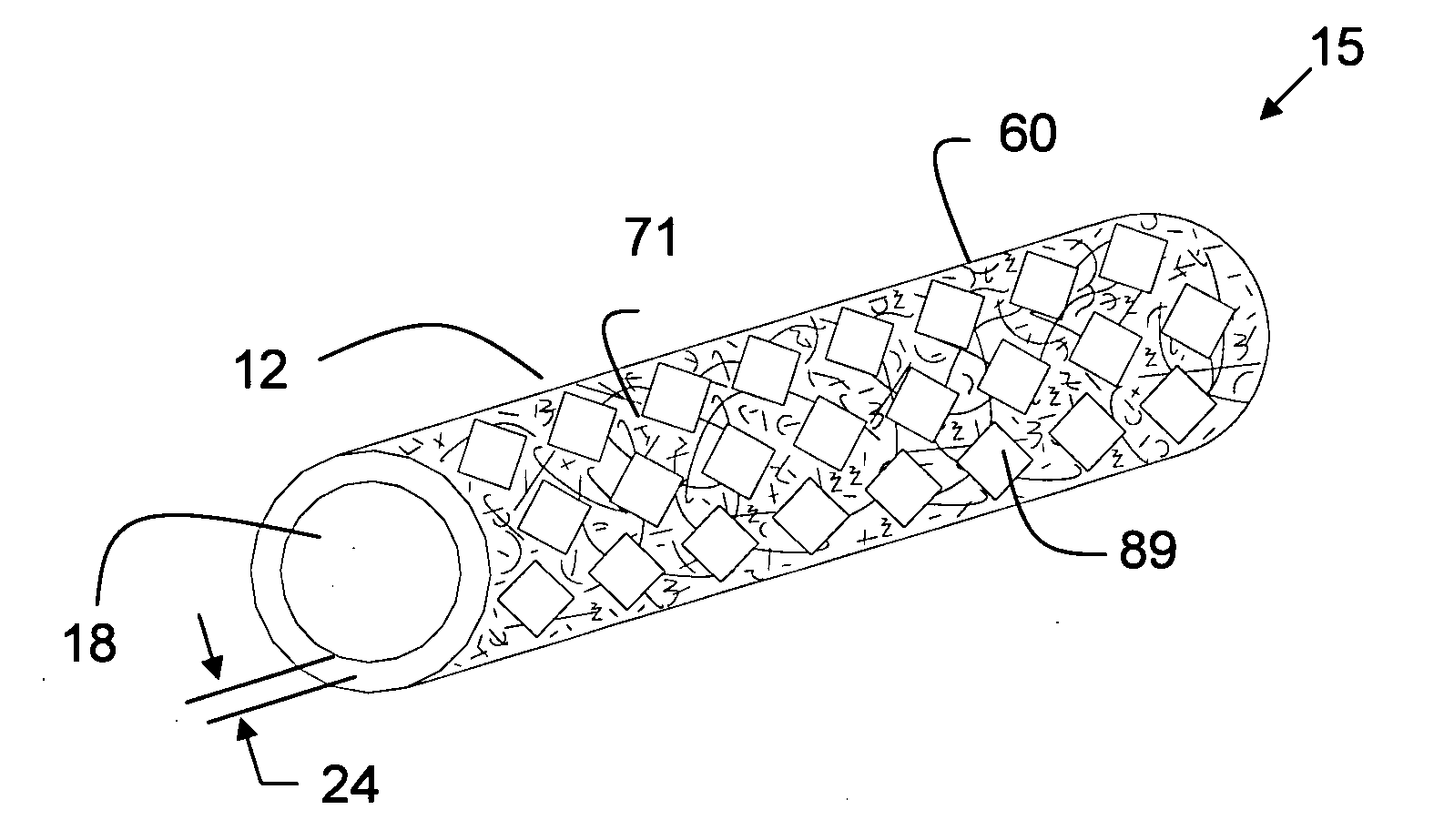
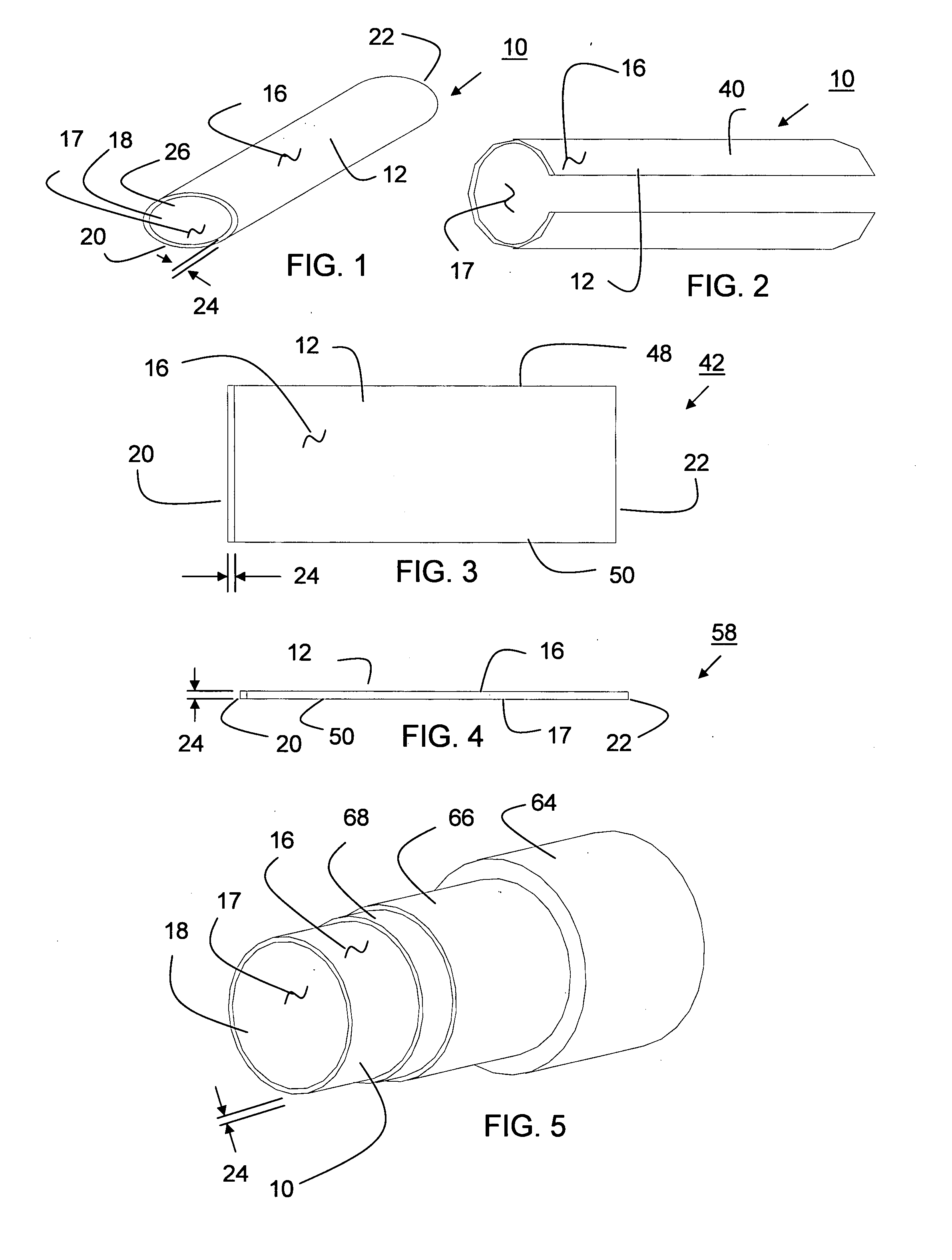
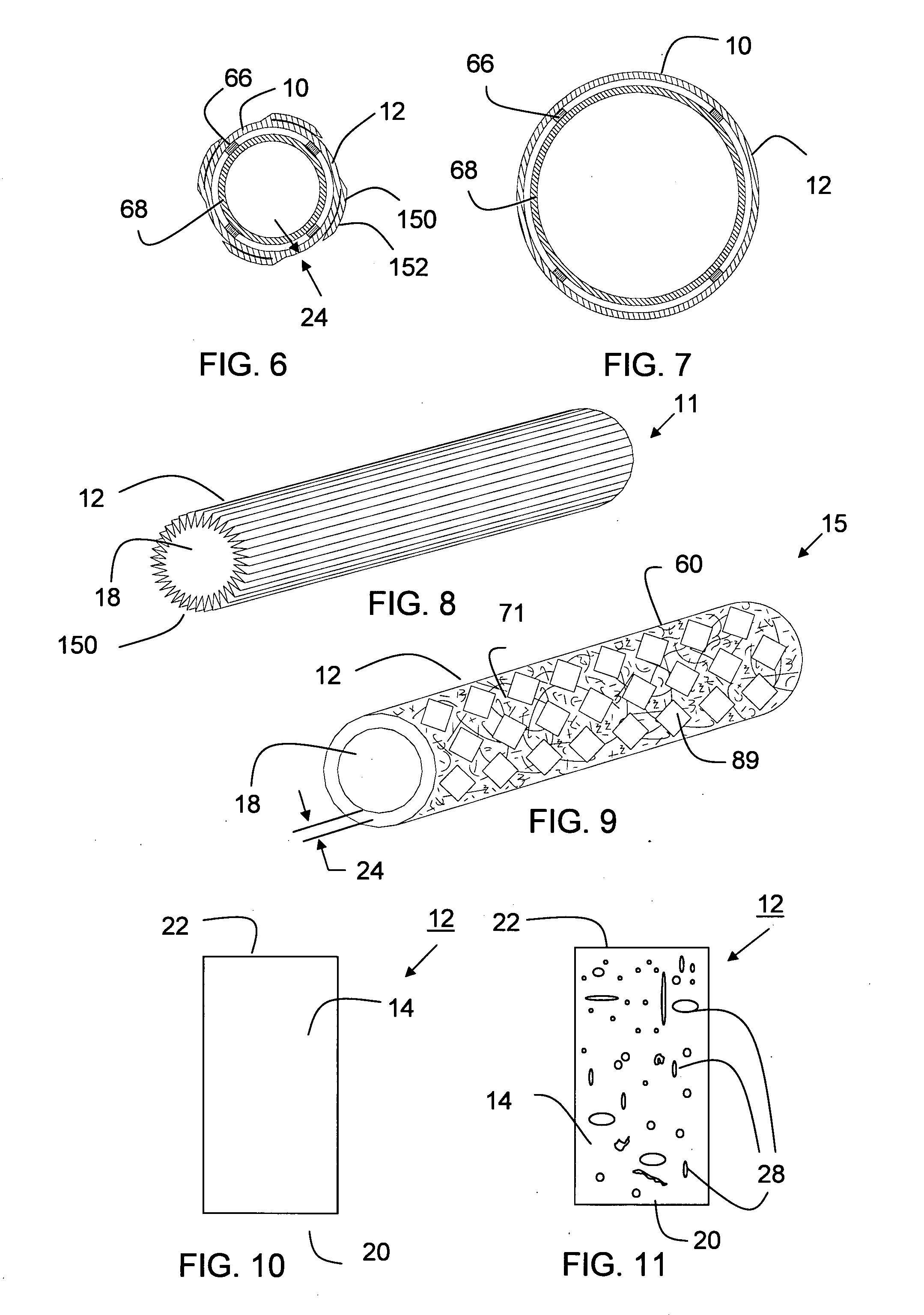
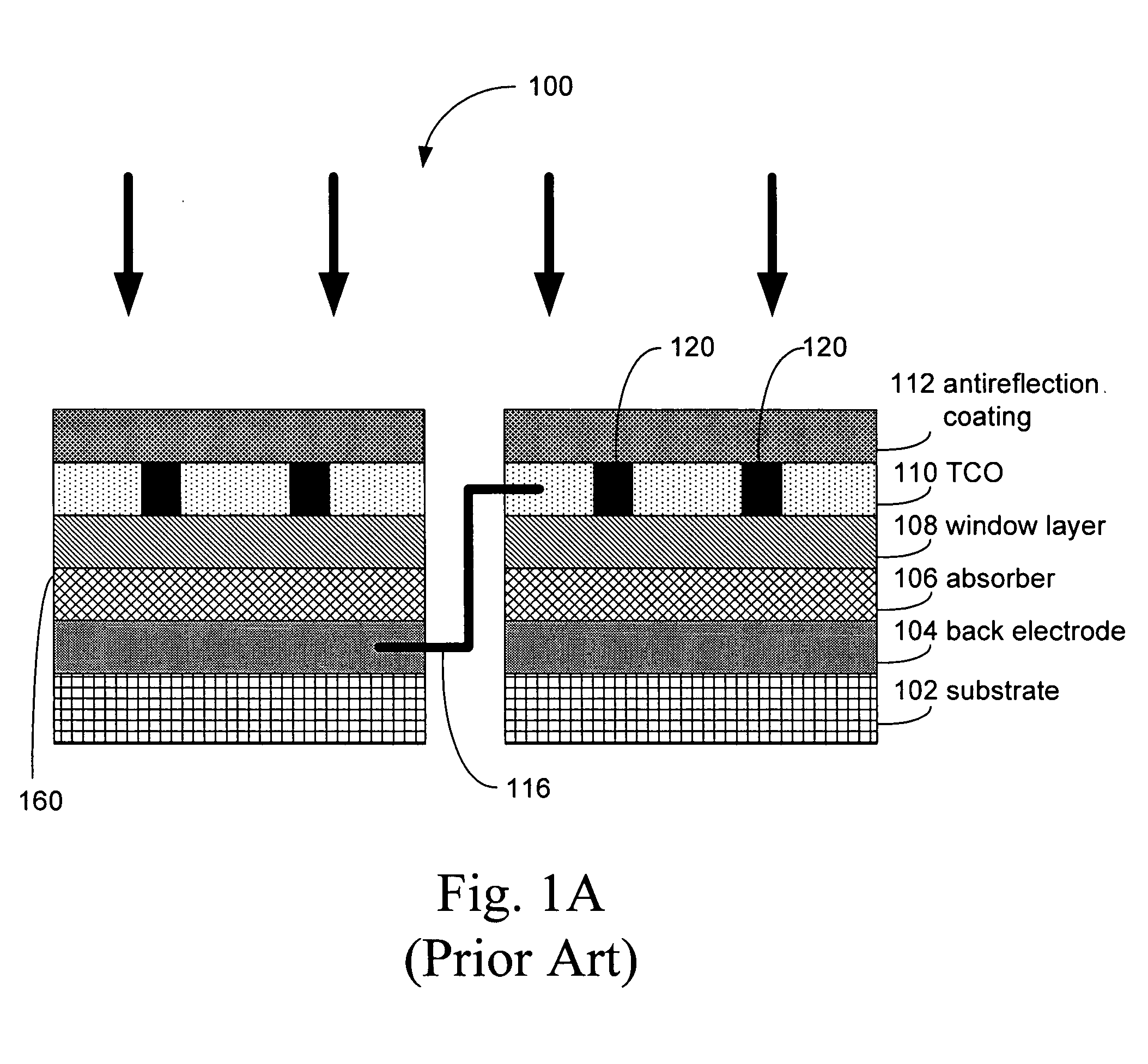
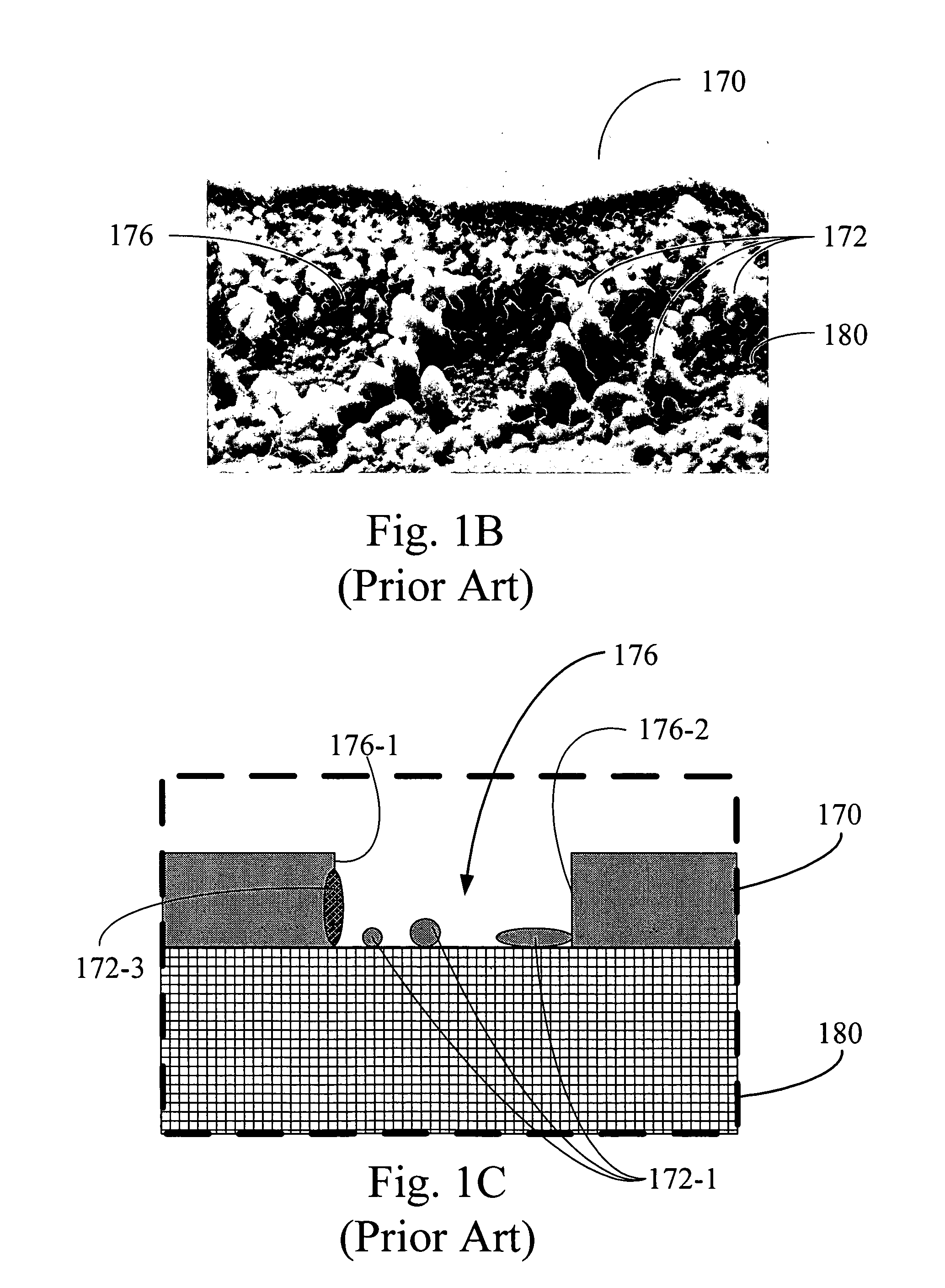
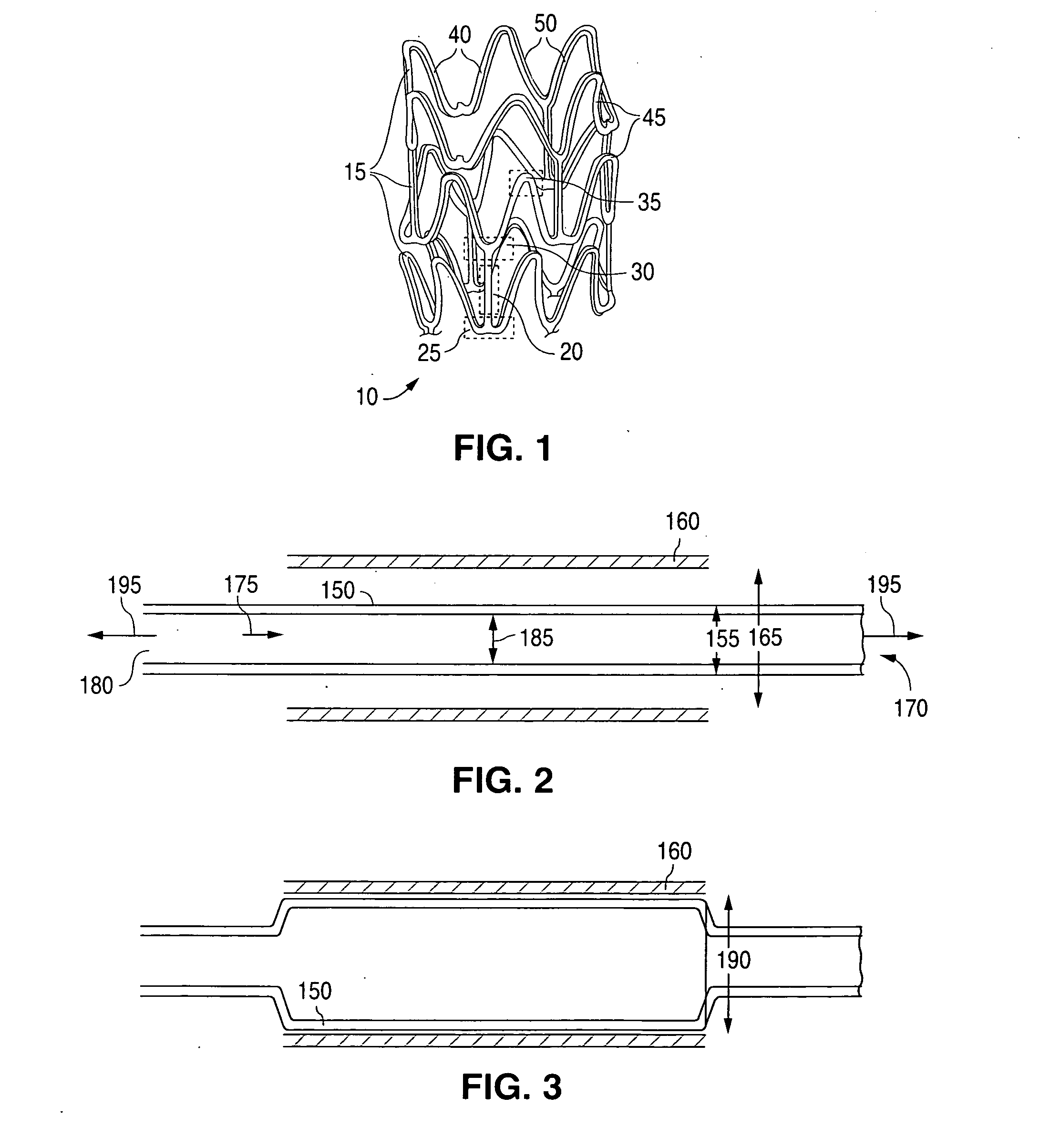
Tear and abrasion resistant expanded material and reinforcement
InactiveUS20070207186A1Increase flexibilityLess complex manufacturing processStentsSurgeryDiseaseEngineering
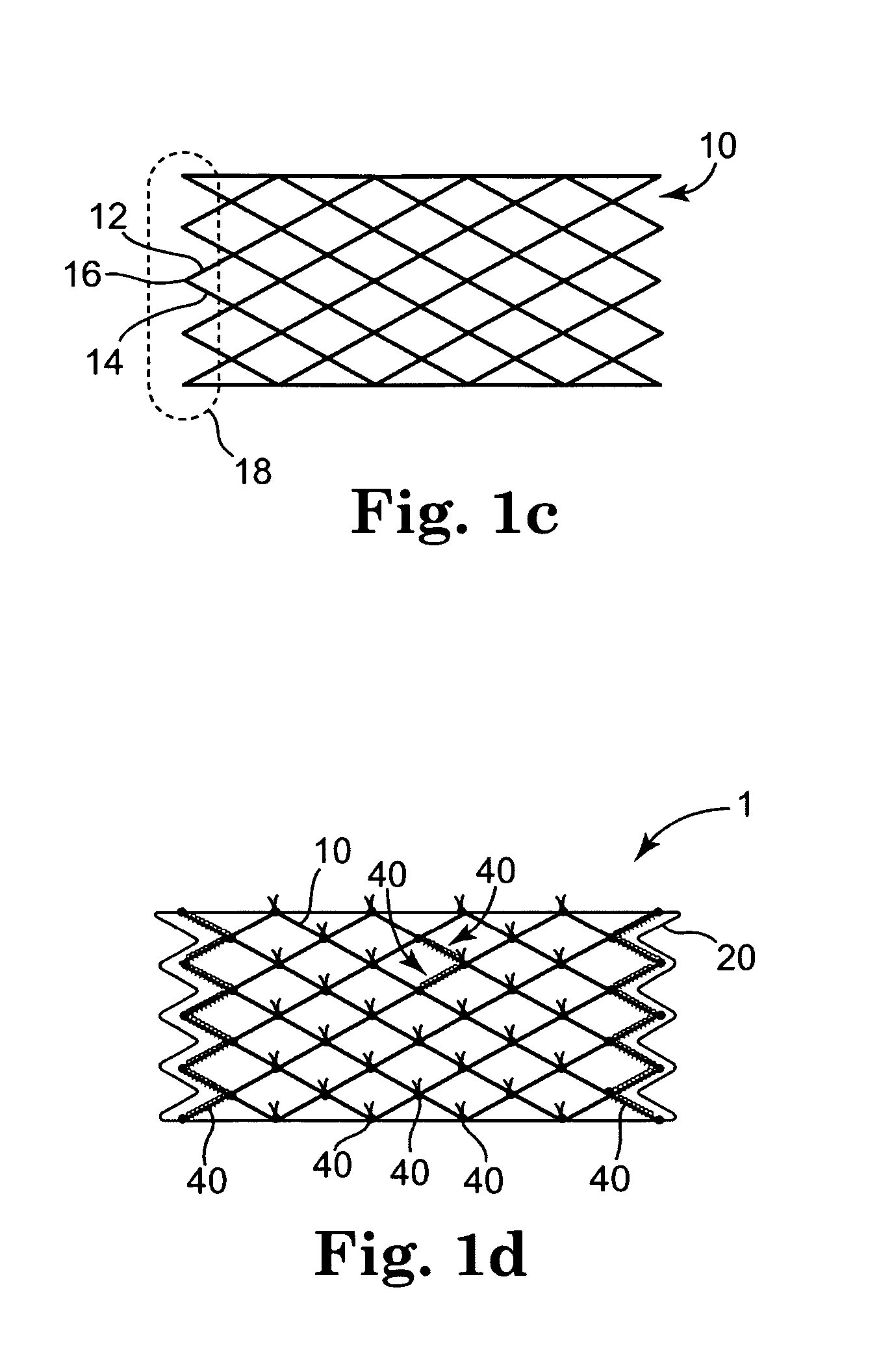
The present invention is a more durable expanded material that enables thinner wall thicknesses and a more flexible reinforcement suitable for stenting. The present invention is especially useful in the construction of grafts, stents, and stent-grafts which are used, for example, in repairing or replacing blood vessels that are narrowed or occluded by disease, aneurismal blood vessels, or other medical treatments. The inventive material and configurations allow expansion or contraction in size or adjustment in size in an incremental manner so that the optimum size, shape, and fit with other objects can be obtained. The present invention is also optionally capable of more accurately delivering one or more active ingredients such as drugs over longer periods of time. The present invention optionally includes surface modifications and additives that increase the surface adhesion of active ingredients, coatings, or combinations thereof. Finally, the present invention optionally includes growing cells on the inventive material so that the expanded material, reinforcement, or combinations thereof are useful, for example, in producing lab-grown blood vessels or organs.
Owner:SCANLON JOHN JAMES +1
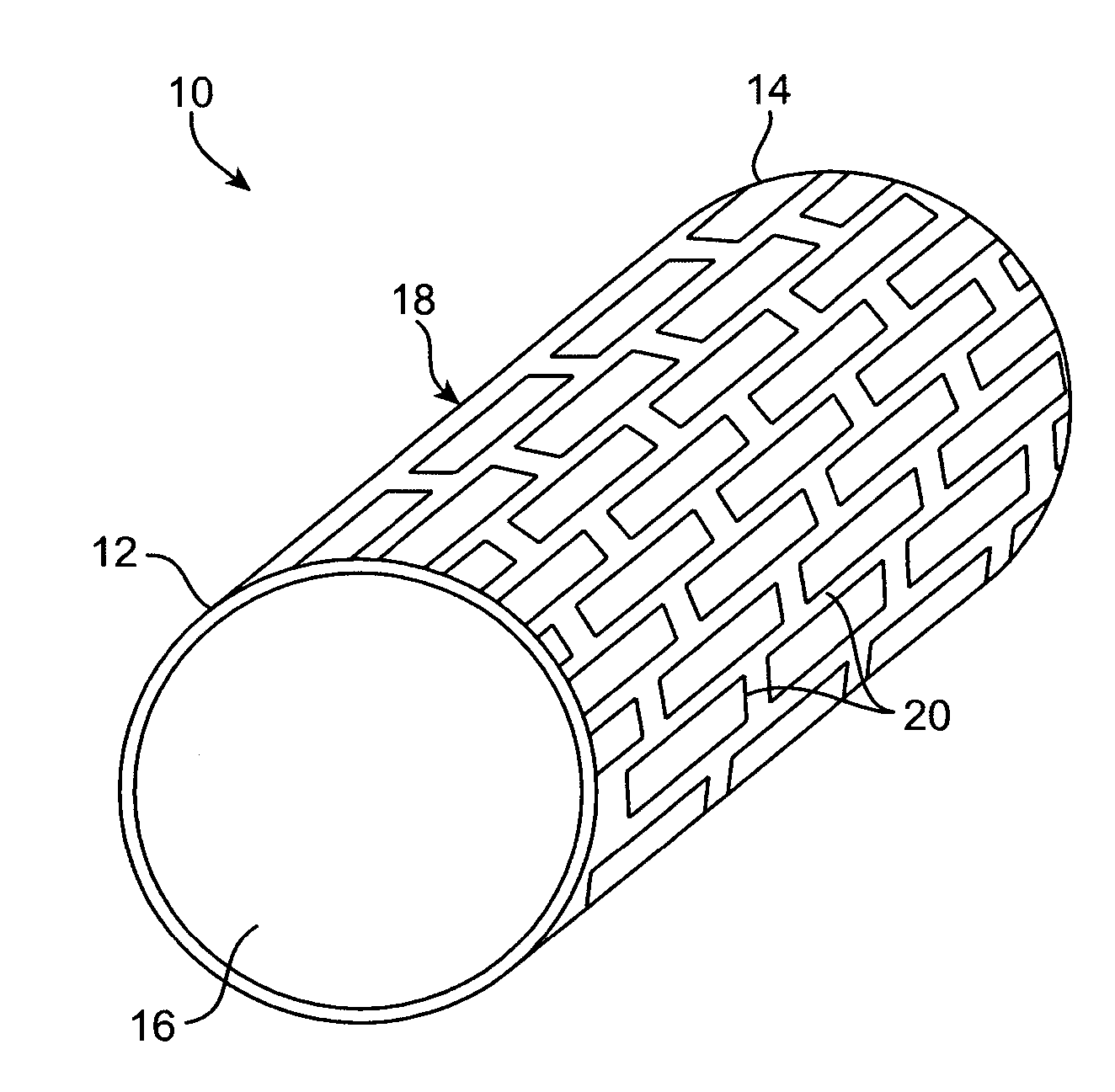
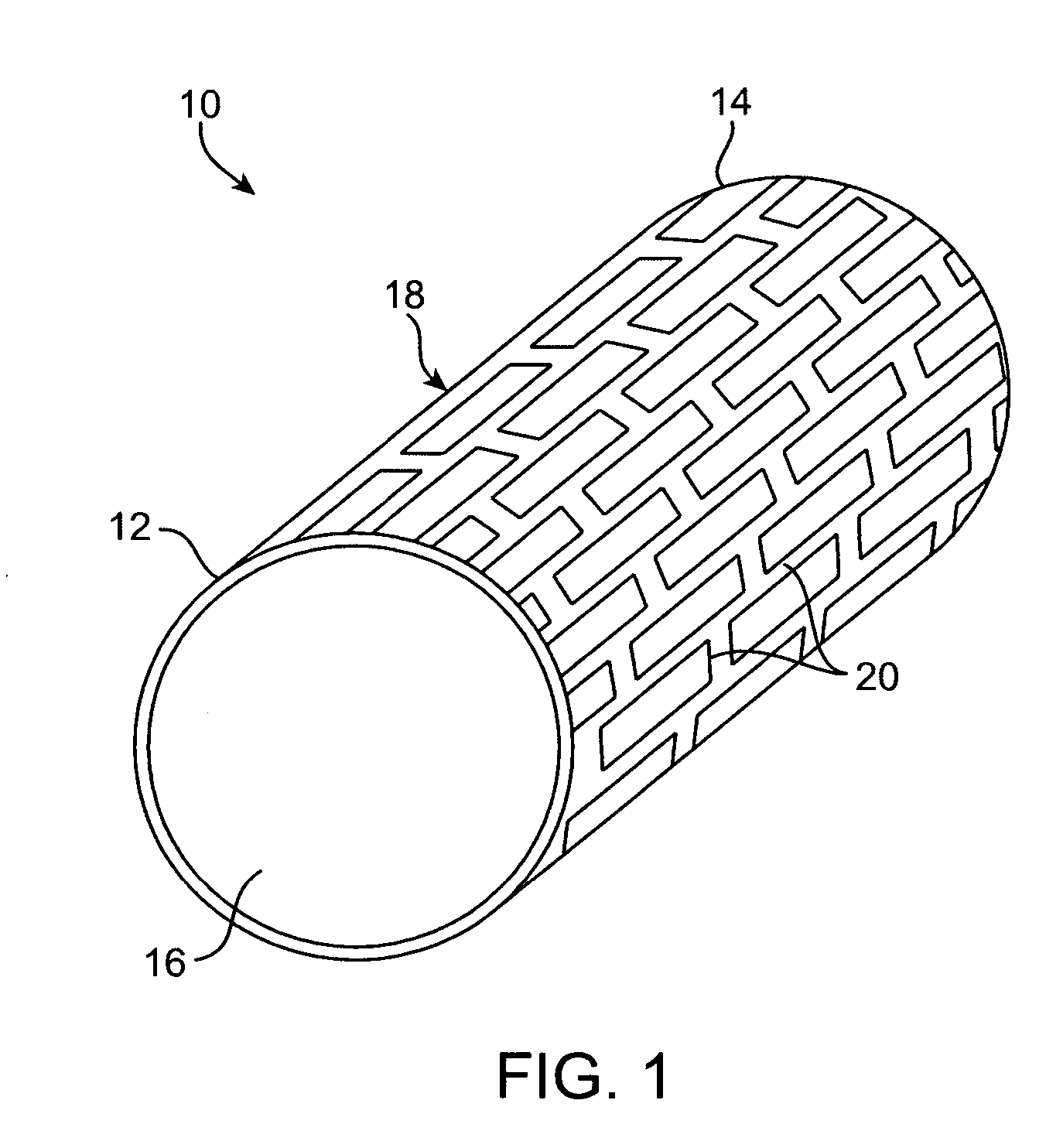
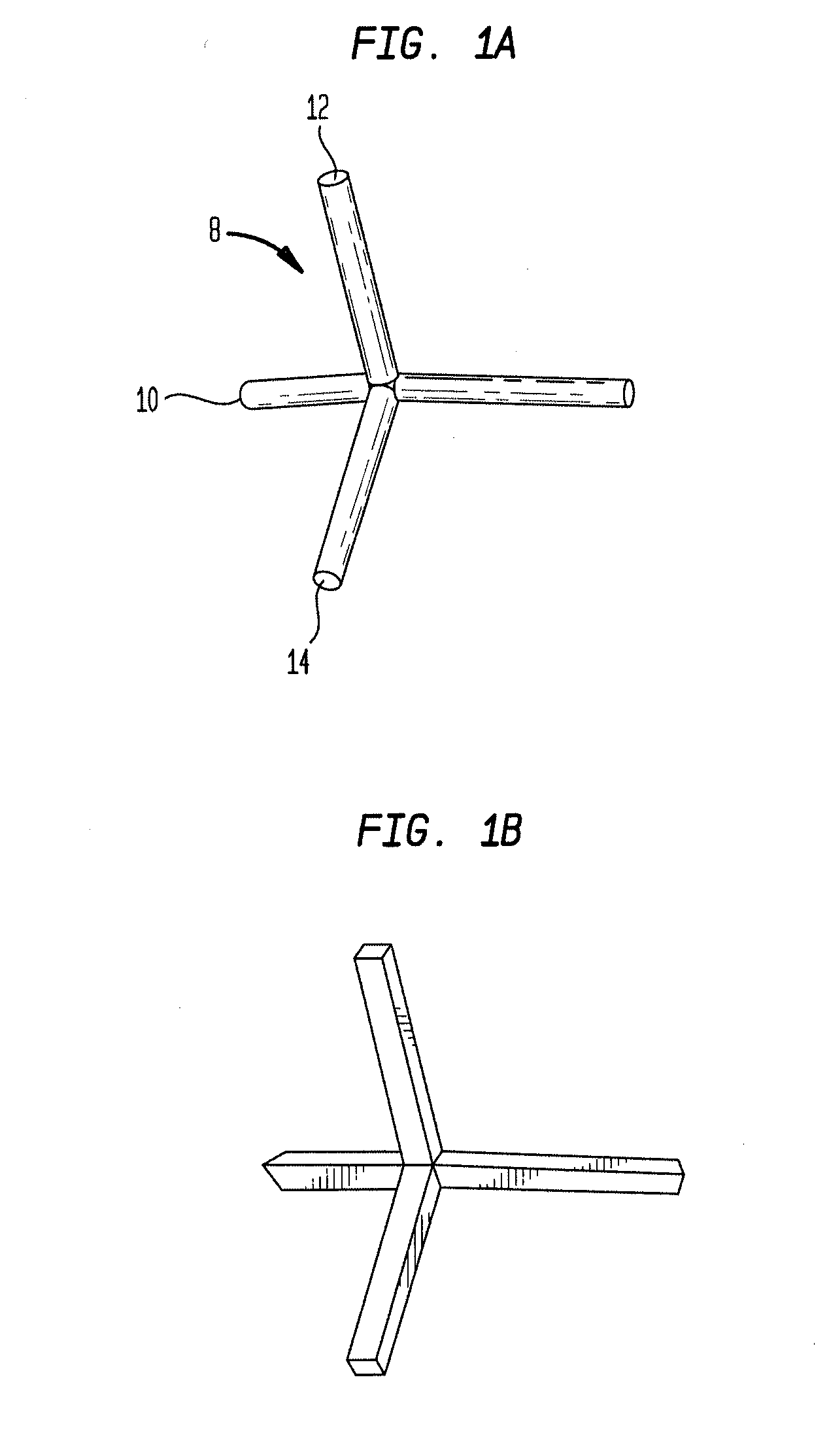
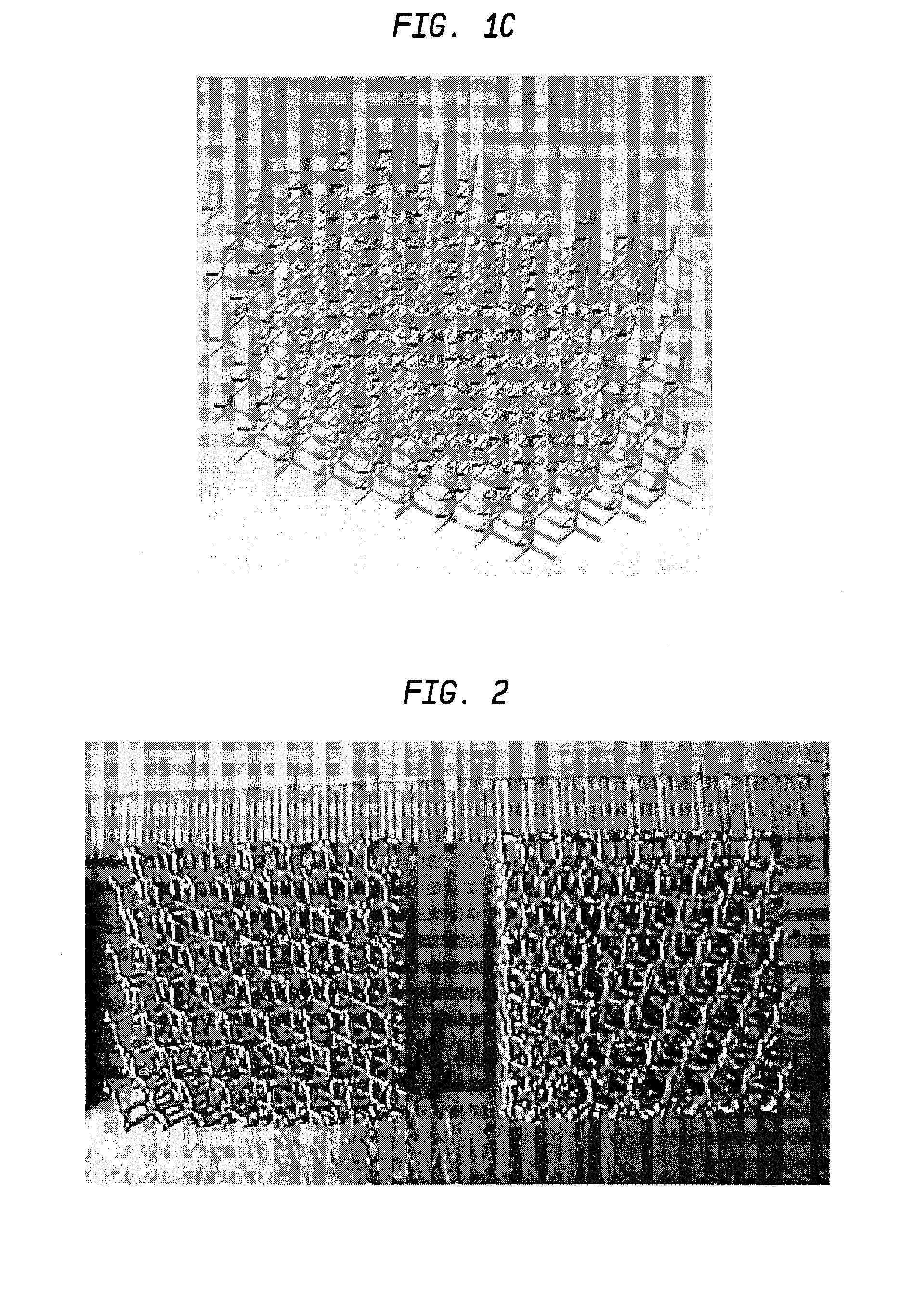
Laser-produced porous structure
The present invention disclosed a method of producing a three-dimensional porous tissue in-growth structure. The method includes the steps of depositing a first layer of metal powder and scanning the first layer of metal powder with a laser beam to form a portion of a plurality of predetermined unit cells. Depositing at least one additional layer of metal powder onto a previous layer and repeating the step of scanning a laser beam for at least one of the additional layers in order to continuing forming the predetermined unit cells. The method further includes continuing the depositing and scanning steps to form a medical implant.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL +1
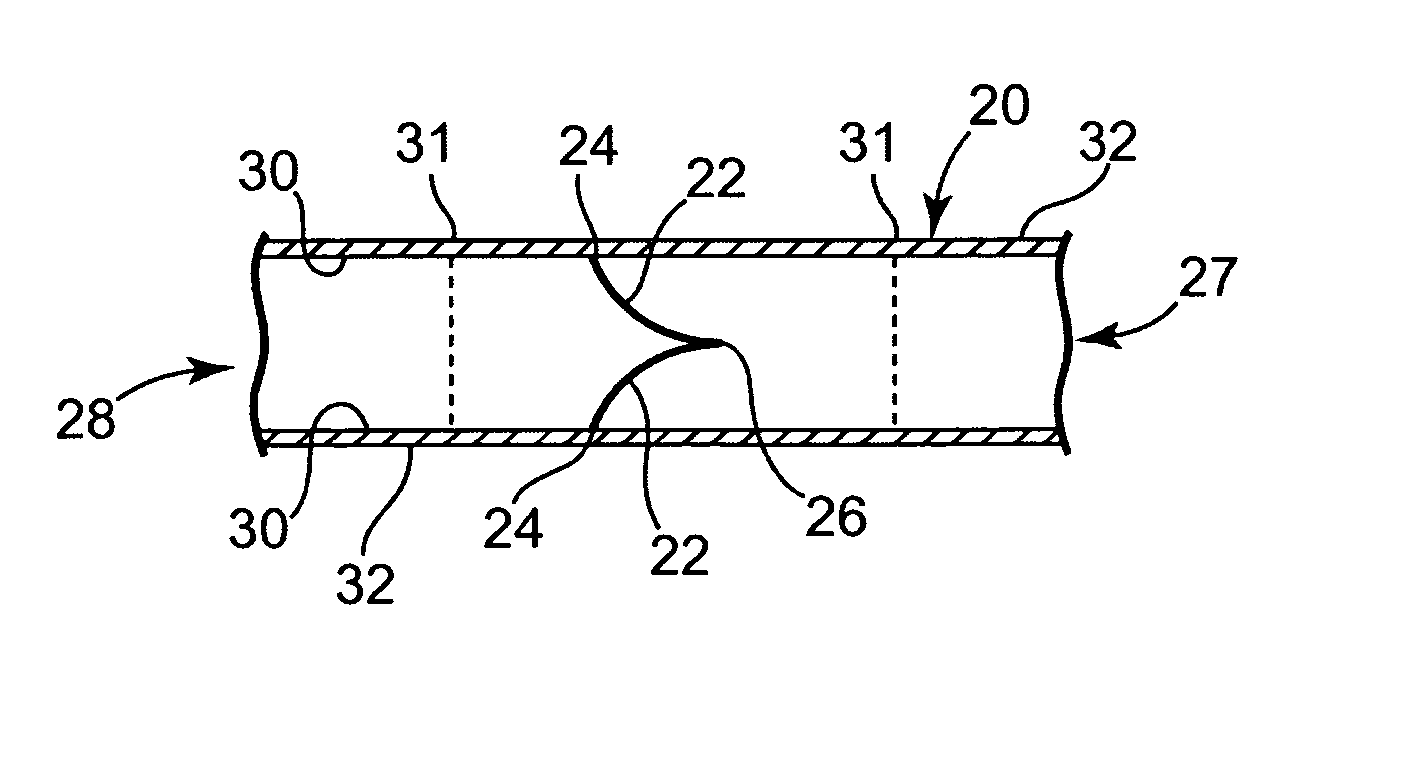
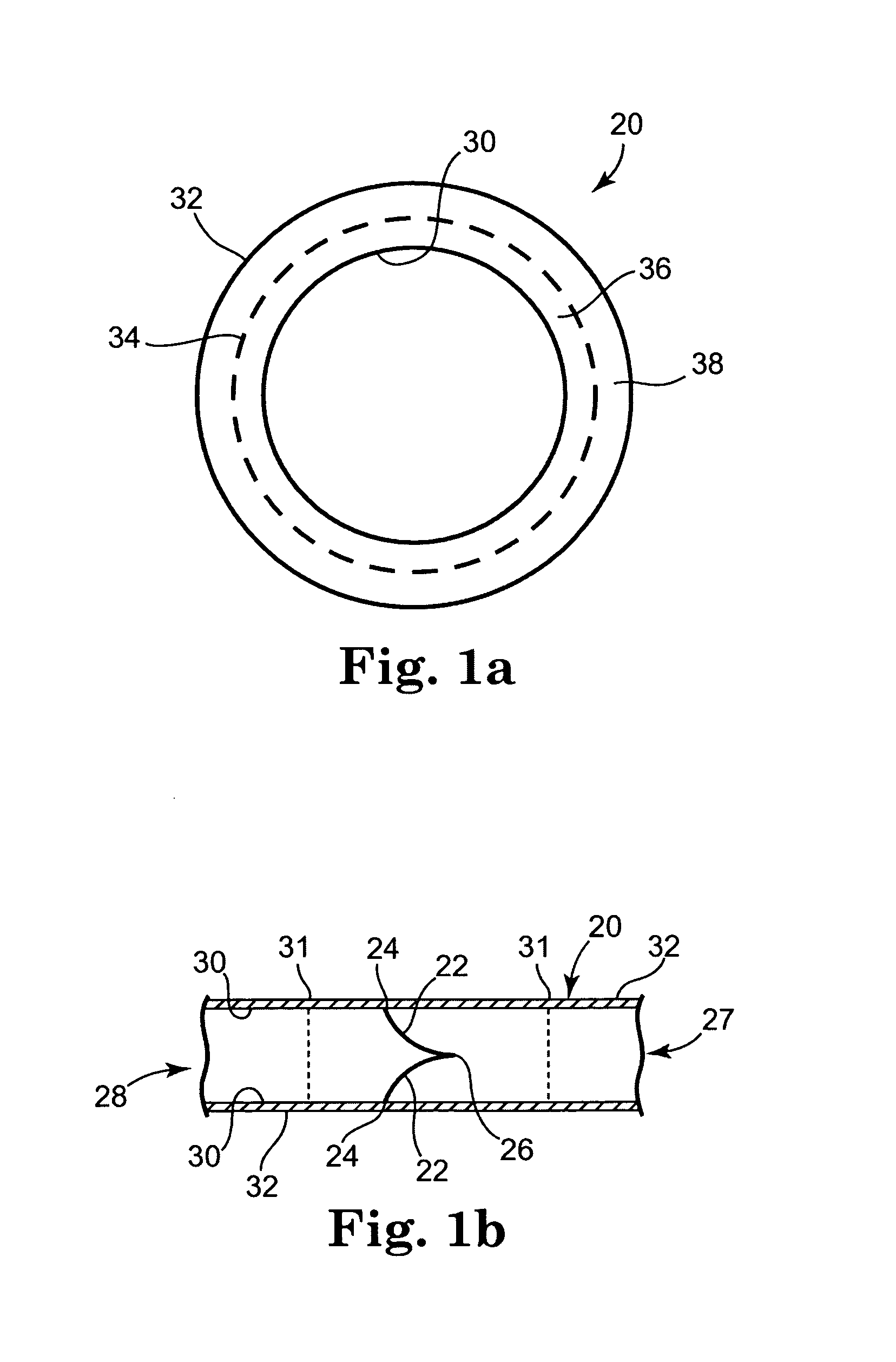
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
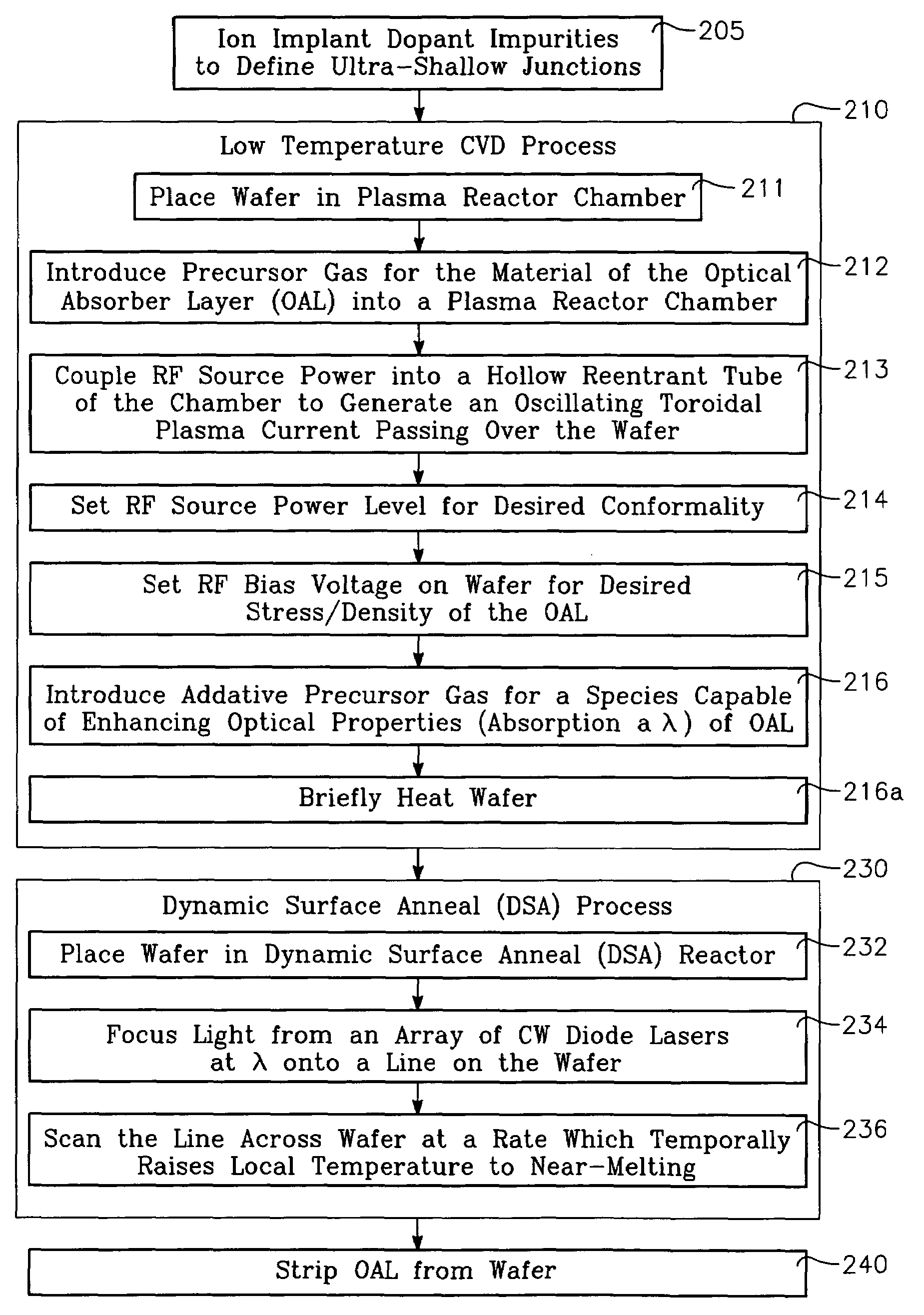
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS7335611B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorLow temperature deposition
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Degradable implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060229711A1Reduce probabilityLower resistanceStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantBlood vessel
Devices and methods are provided for an implantable medical device which is degradable over a clinically relevant period of time. The medical devices may have the form of implants, graft implants, vascular implants, non vascular implants, wound closure implants, sutures, drug delivery implants, biologic delivery implants, urinary tract implants, inter-uterine implants, organ implants, bone implants including bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, spinal disks, or the like. In preferred embodiments, the implantable medical device comprises an implantable luminal prosthesis, such as vascular and non-vascular stents and stents grafts.
Owner:ELIXIR MEDICAL CORP
Method for controlling configuration of laser induced breakdown and ablation
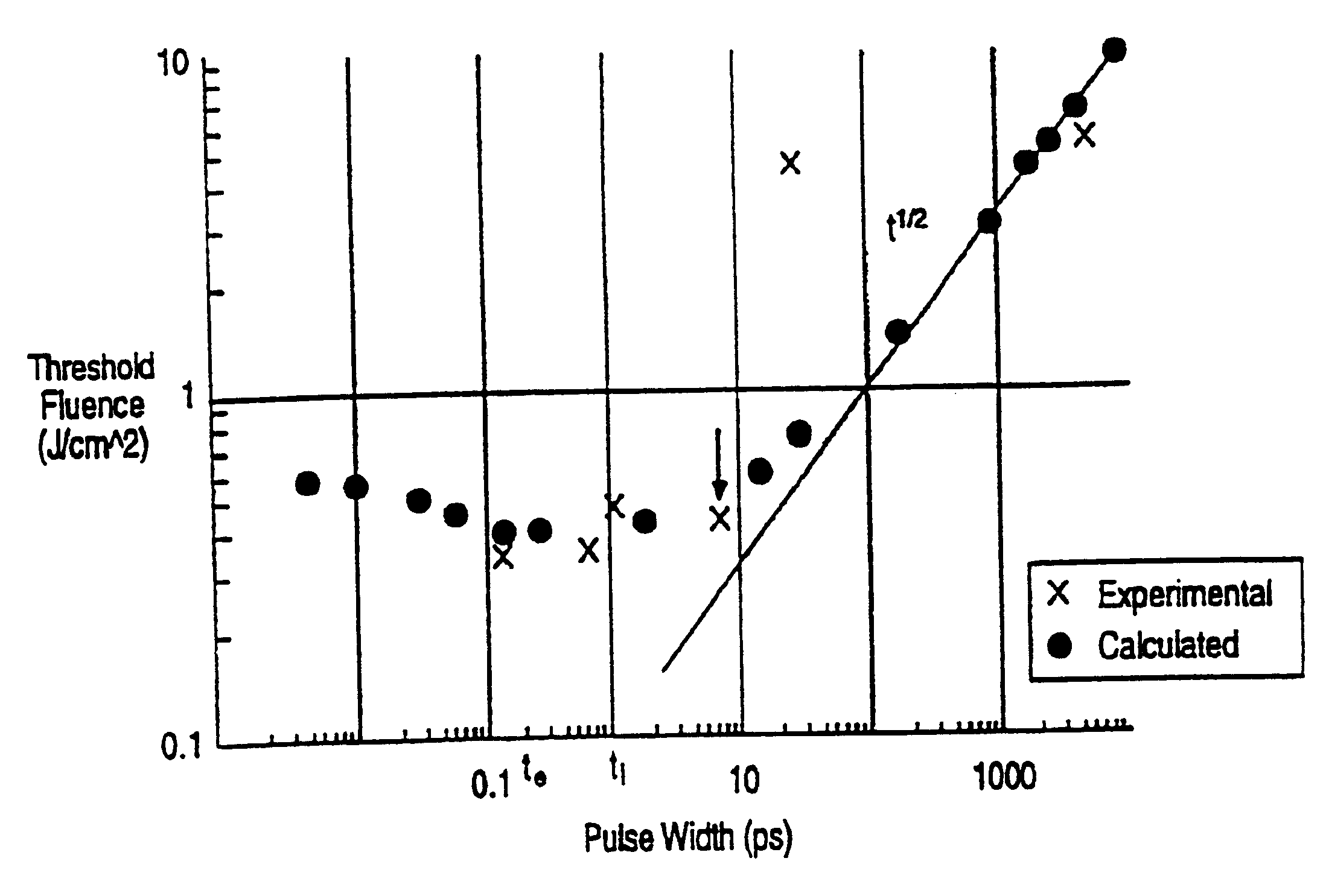
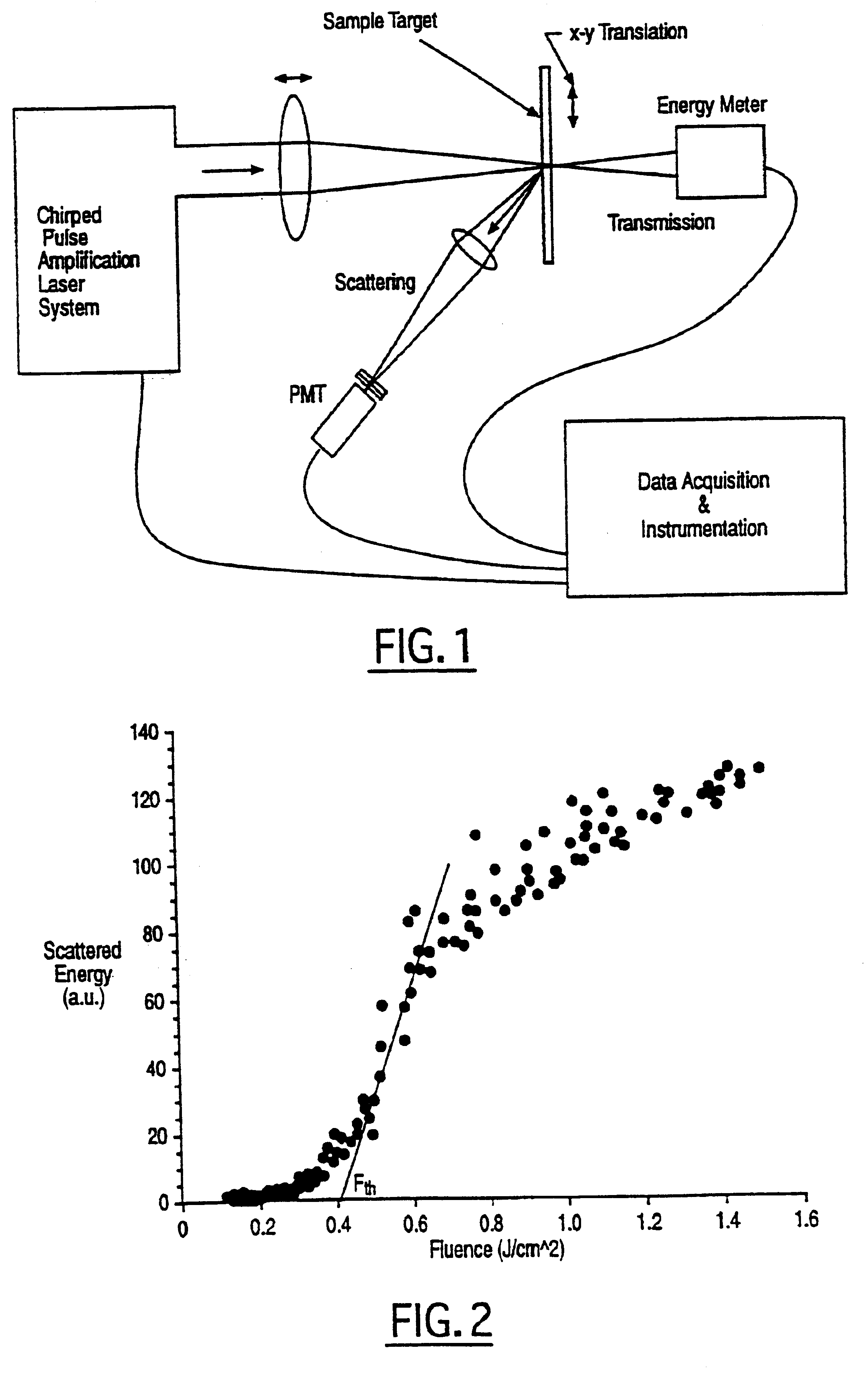
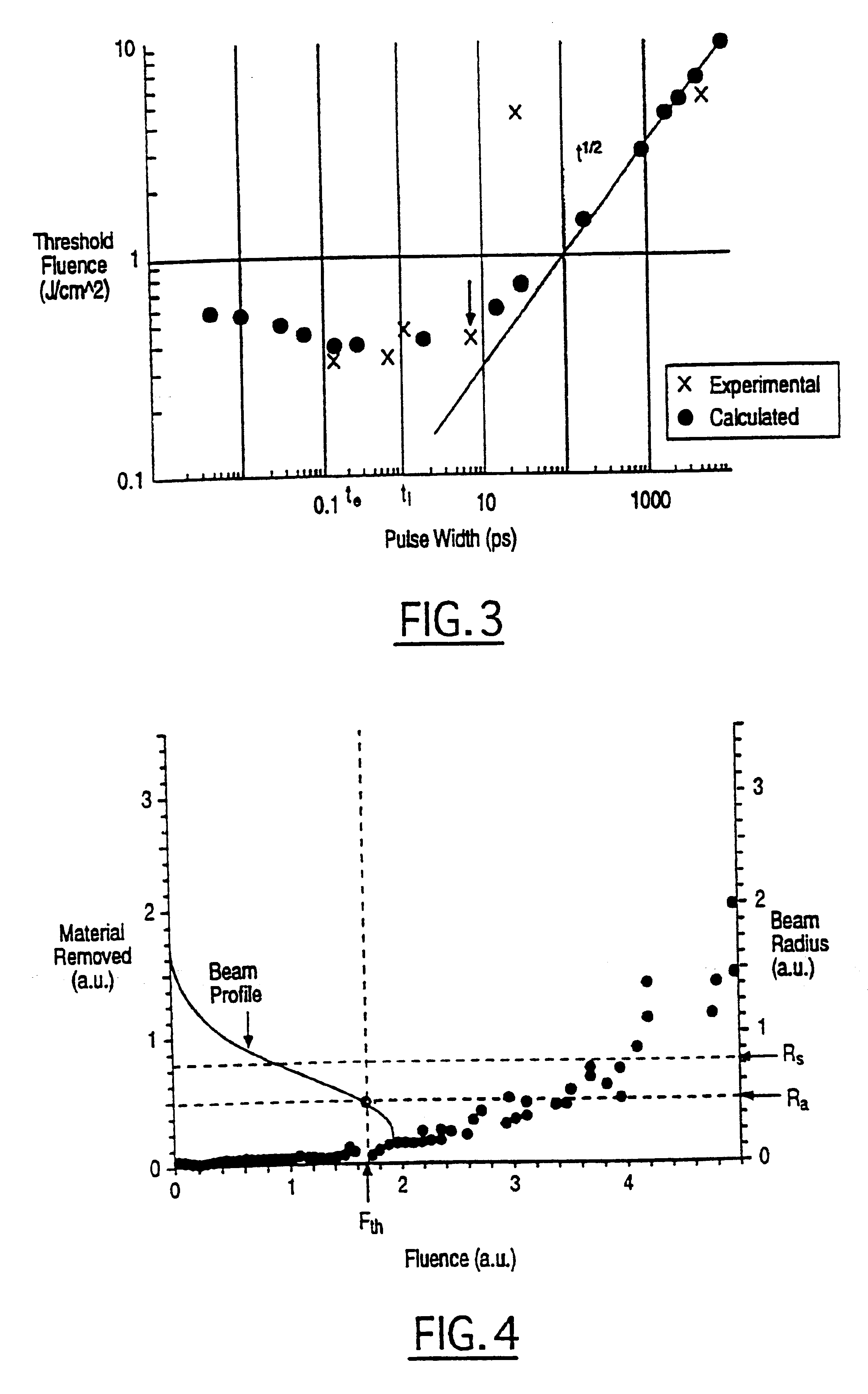
In one aspect the invention provides a method for laser induced breakdown of a material with a pulsed laser beam where the material is characterized by a relationship of fluence breakdown threshold (Fth) versus laser beam pulse width (T) that exhibits an abrupt, rapid, and distinct change or at least a clearly detectable and distinct change in slope at a predetermined laser pulse width value. The method comprises generating a beam of laser pulses in which each pulse has a pulse width equal to or less than the predetermined laser pulse width value. The beam is focused to a point at or beneath the surface of a material where laser induced breakdown is desired.The beam may be used in combination with a mask in the beam path. The beam or mask may be moved in the x, y, and Z directions to produce desired features. The technique can produce features smaller than the spot size and Rayleigh range due to enhanced damage threshold accuracy in the short pulse regime.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Methods for producing ultrasonic waveguides having improved amplification
InactiveUS20070130771A1High magnificationReduce stressElectrical transducersMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcousticsWaveguide
Methods for manufacturing ultrasonic waveguides having improved velocity gain are disclosed. Additionally, methods for manufacturing ultrasonic medical devices including the ultrasonic waveguides are disclosed. Specifically, the ultrasonic waveguides comprises a first material having a higher acoustic impedance and a second material having a lower acoustic impedance.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
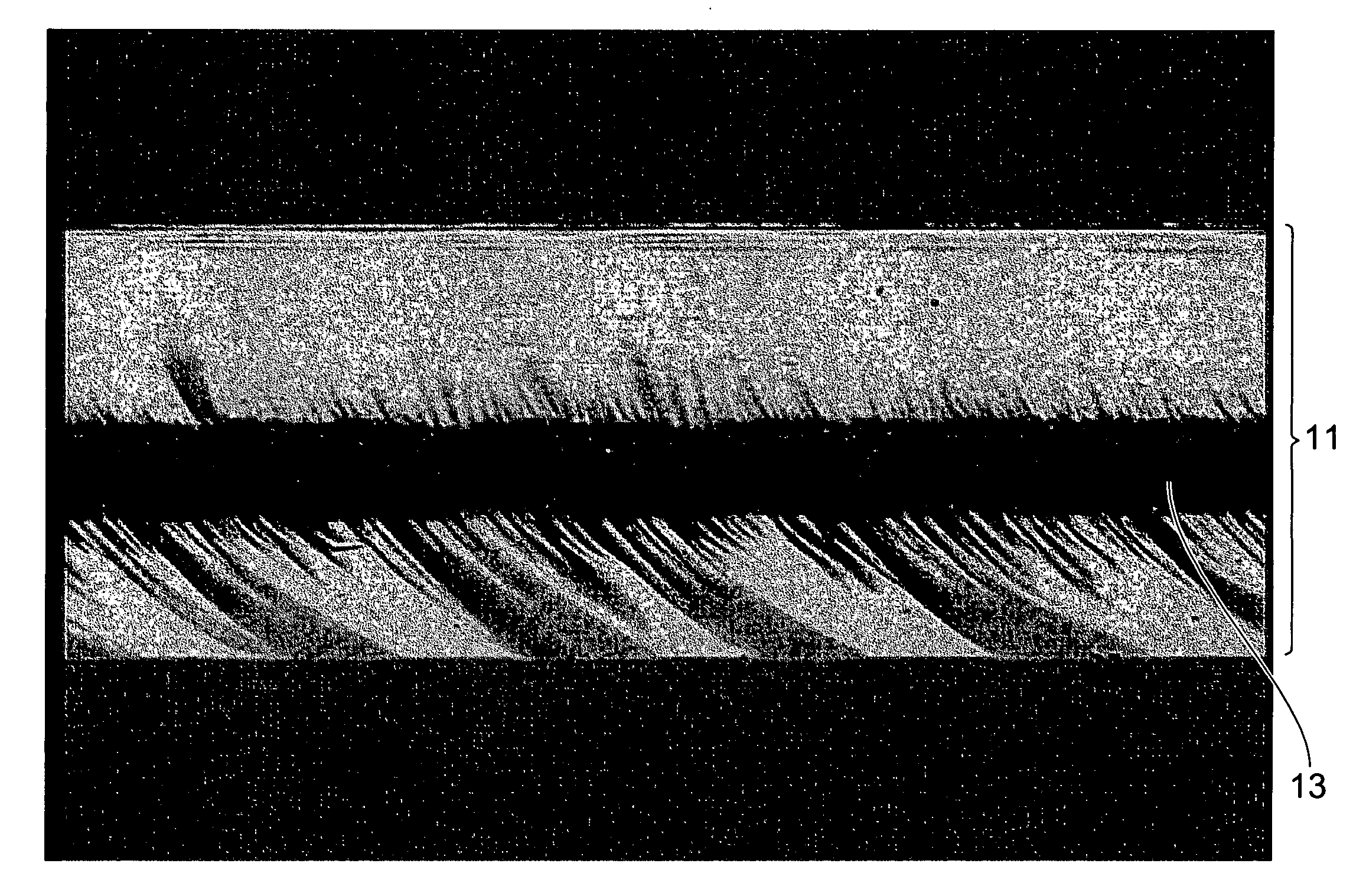
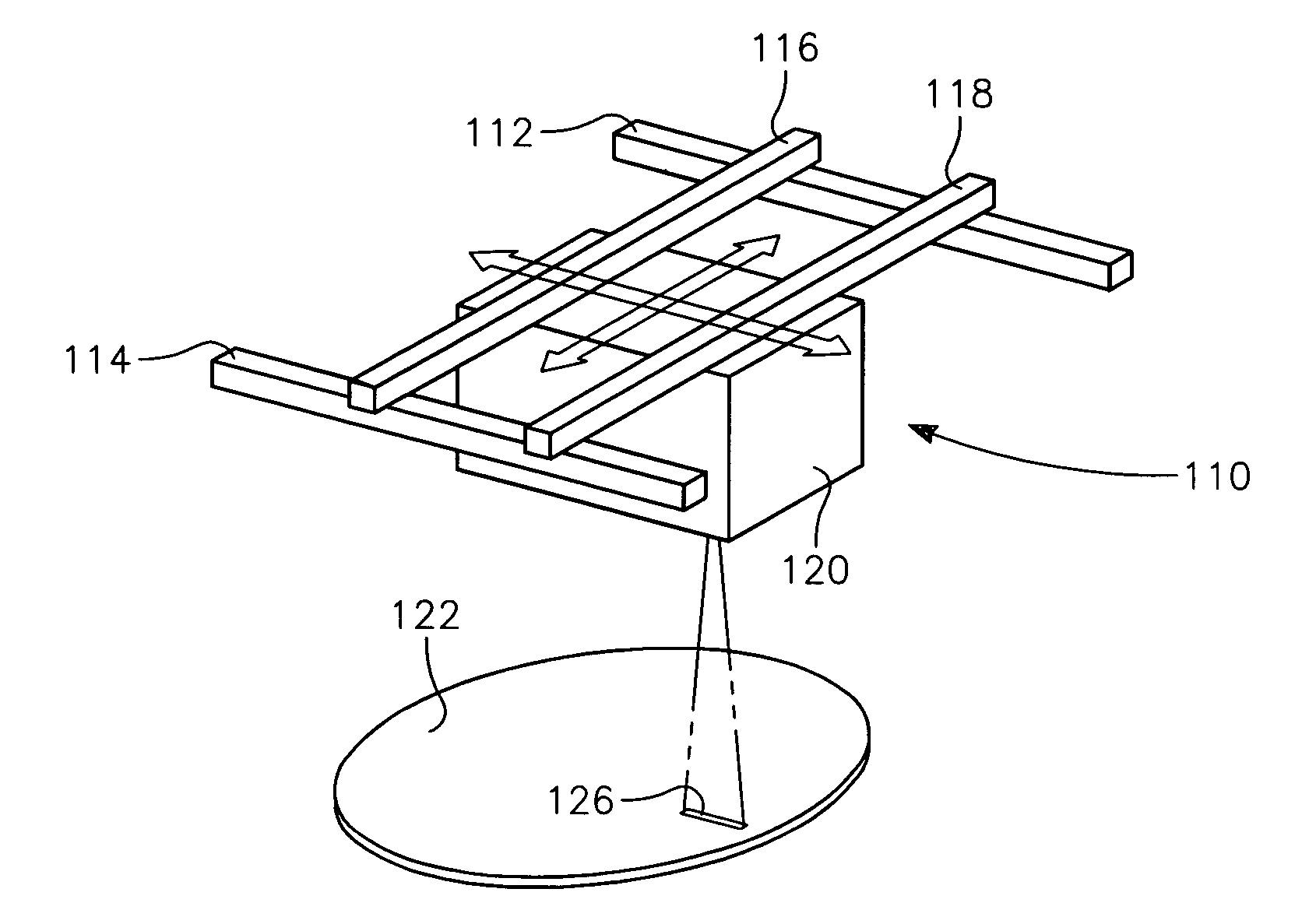
Method for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS6042774AShorten production timeAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresIrradiationMaterials science
A method of producing an object by successive solidification of layers of a powder material is disclosed. The method provides a preformed base plate having a metal plate with a solidified layer of a powder material formed thereon. Then, successive layers of said powder material are applied and solidified on the solidified layer of the base plate to form the object. In further detail, the method for produces a three-dimensional by providing a support and a preformed base plate having an upper surface for supporting the object. The base plate is removably attached to the support. Means are provided for adjusting the elevation of said upper surface. A layer of the powder material is applied to the upper surface of the base plate. The powder material is solidified at points corresponding to a cross-section of the object by irradiation with electromagnetic or particle radiation. Then, the applying and solidifying steps are repeated for completing the object.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
Formation of heteroepitaxial layers with rapid thermal processing to remove lattice dislocations
InactiveUS20160155629A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesReaction temperatureGallium nitride
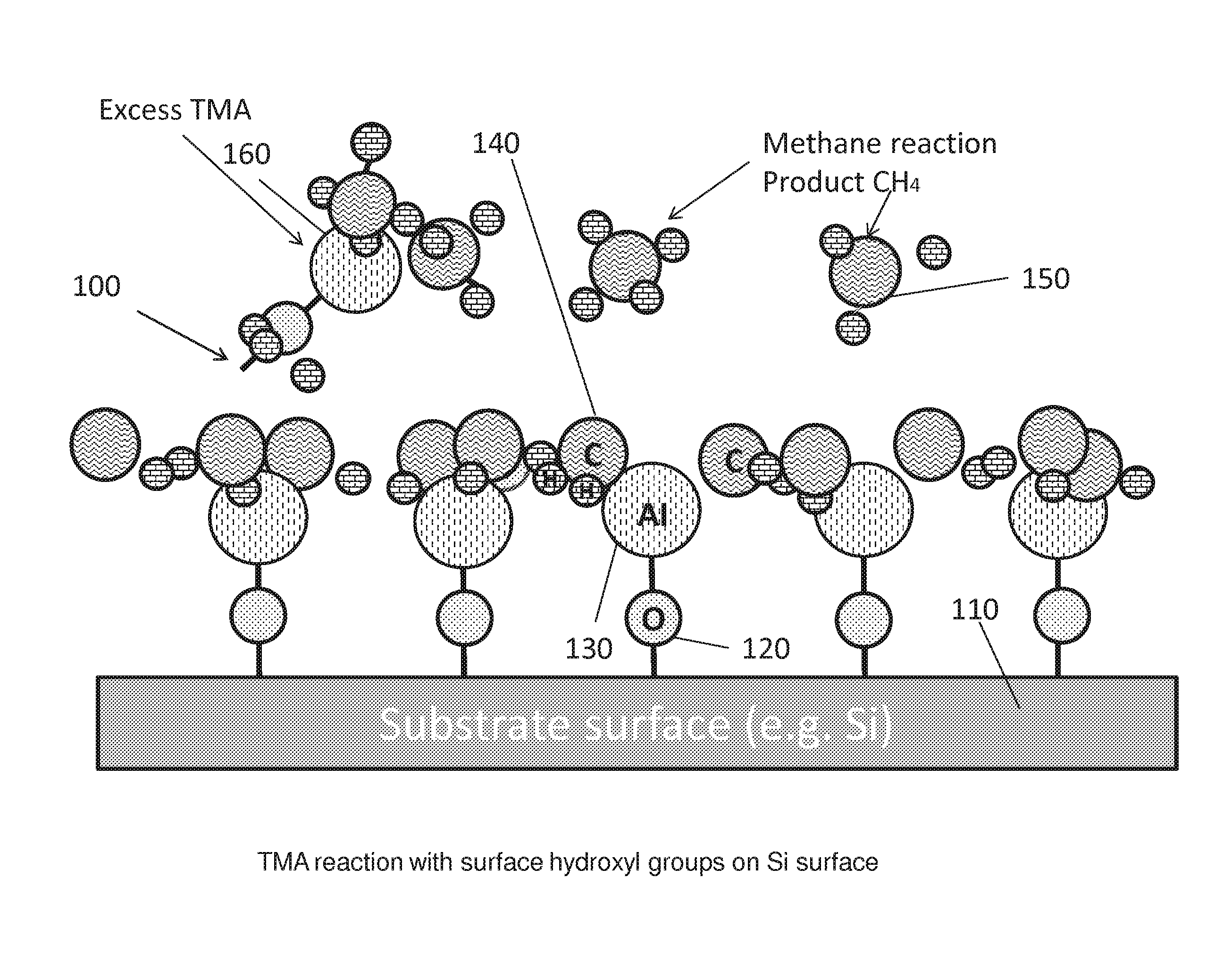
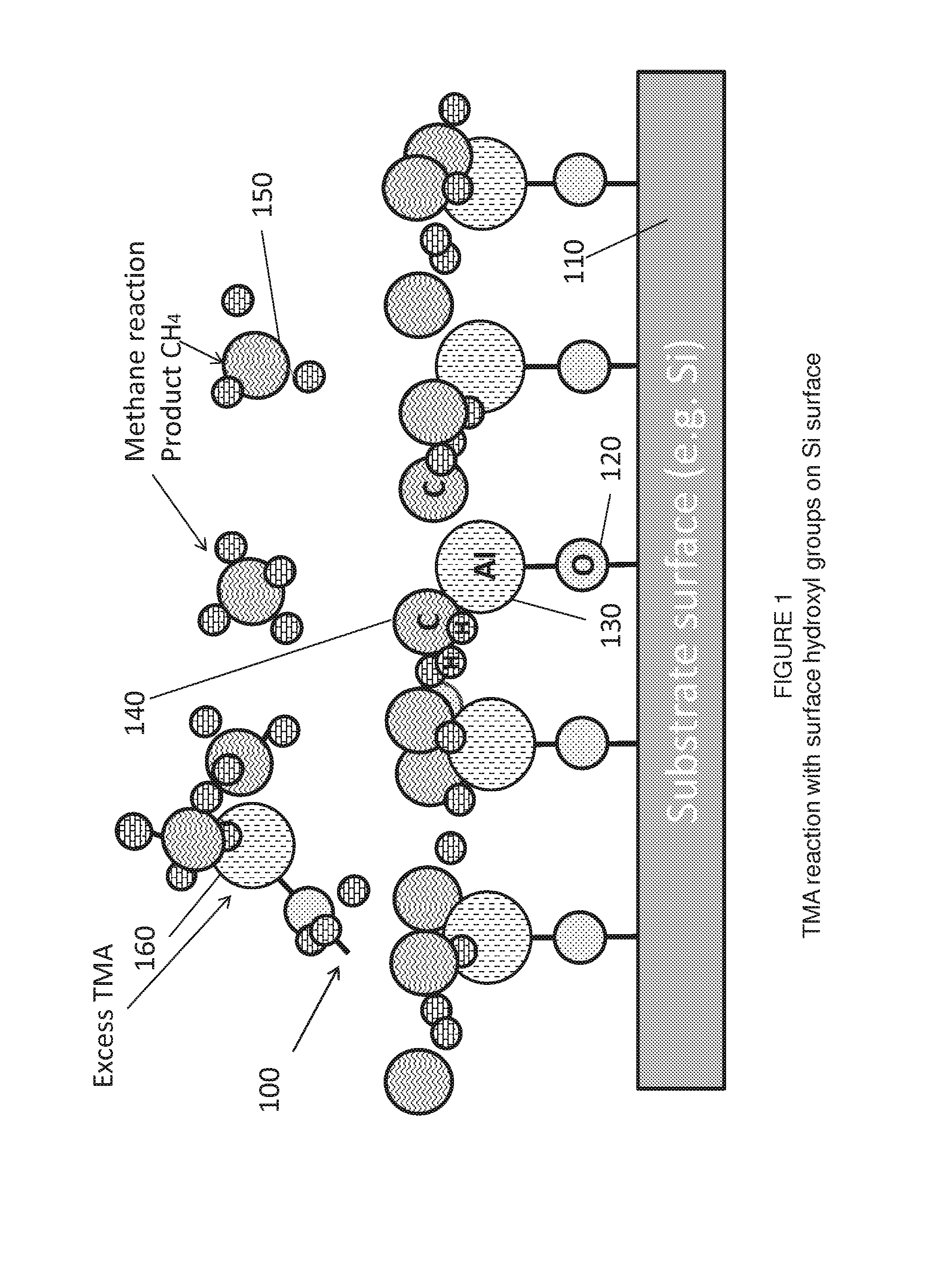
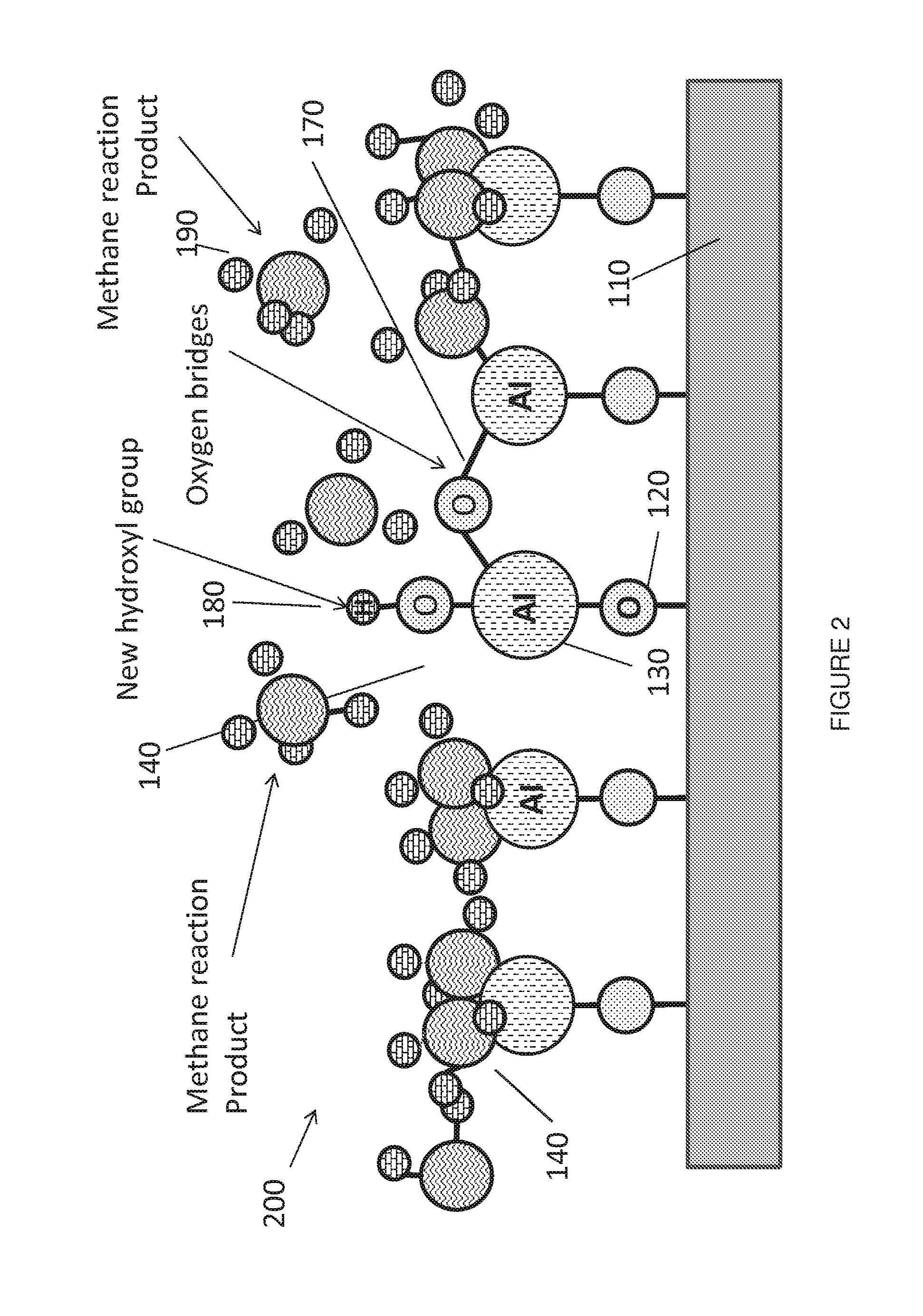
Method and devices are disclosed for device manufacture of gallium nitride devices by growing a gallium nitride layer on a silicon substrate using Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) followed by rapid thermal annealing. Gallium nitride is grown directly on silicon or on a barrier layer of aluminum nitride grown on the silicon substrate. One or both layers are thermally processed by rapid thermal annealing. Preferably the ALD process use a reaction temperature below 550° C. and preferable below 350° C. The rapid thermal annealing step raises the temperature of the coating surface to a temperature ranging from 550 to 1500° C. for less than 12 msec.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS20100025387A1Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
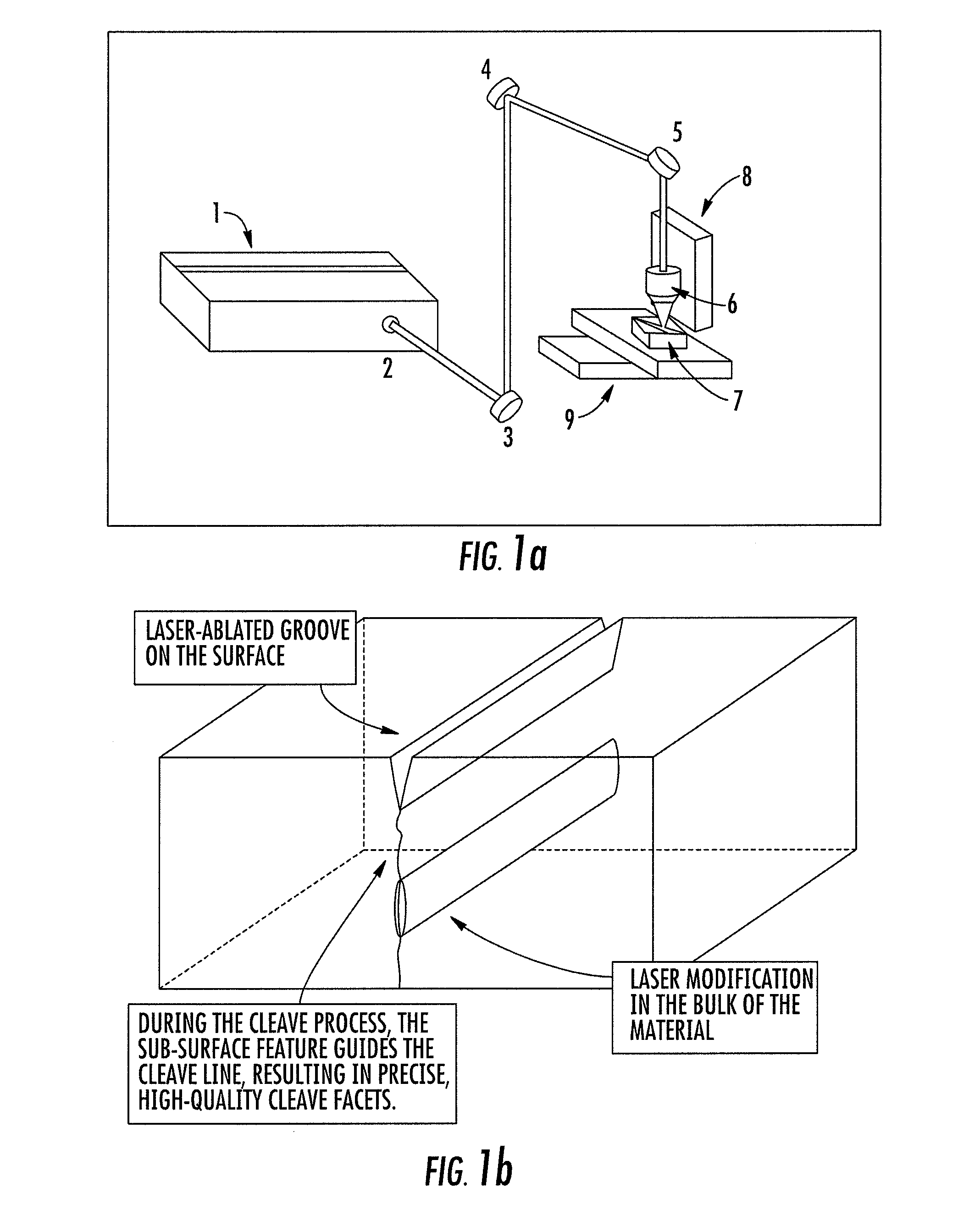
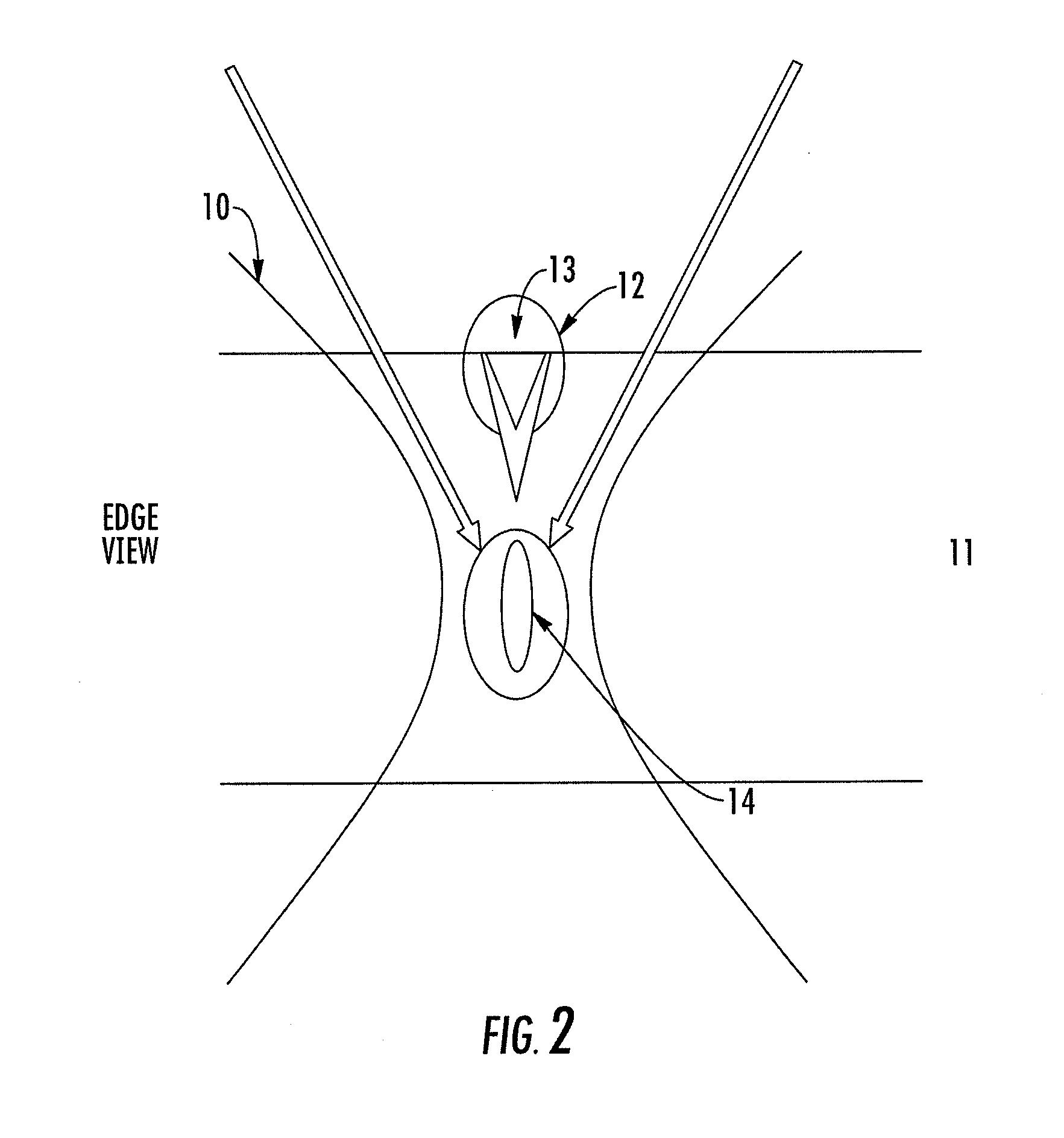
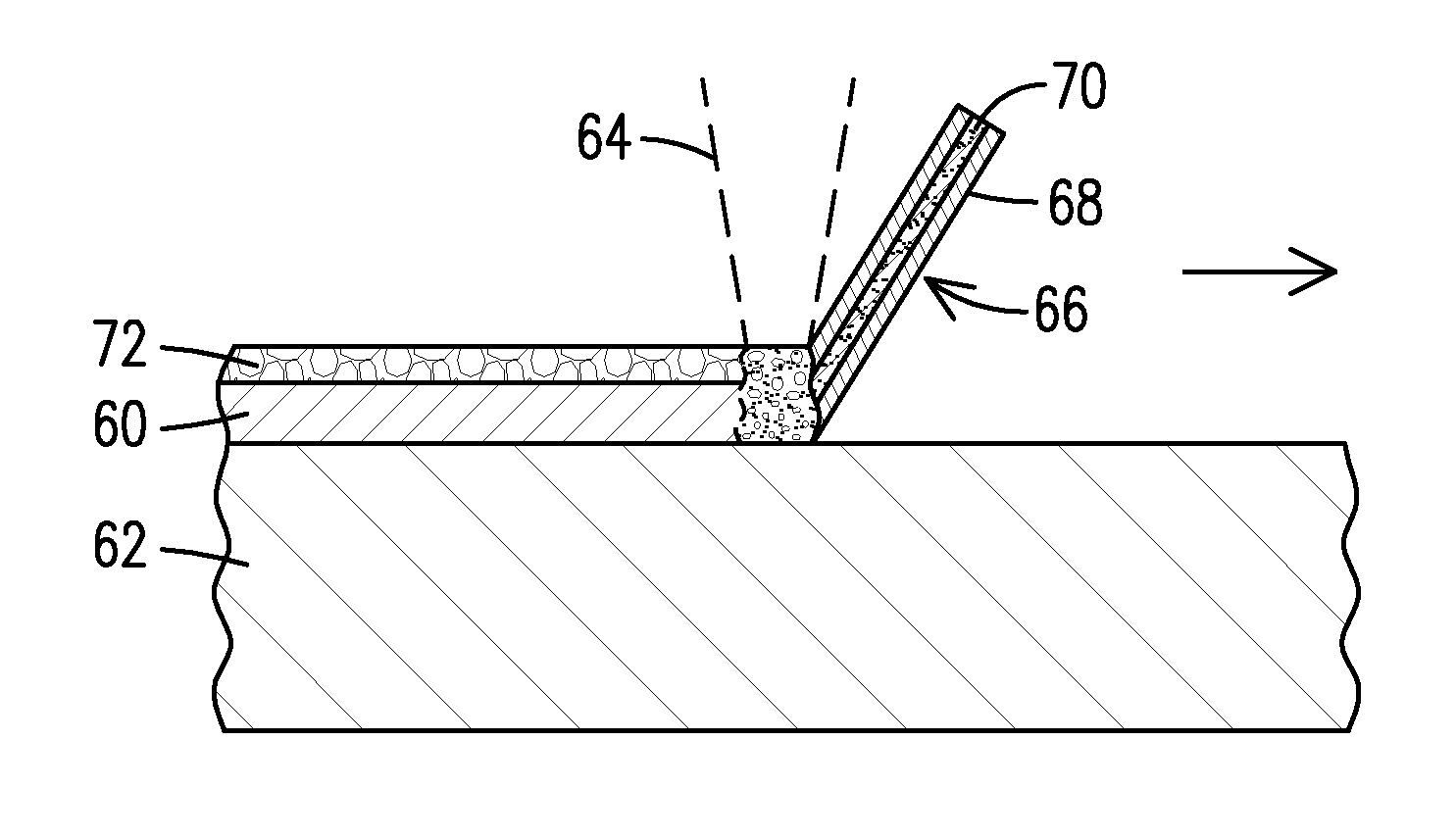
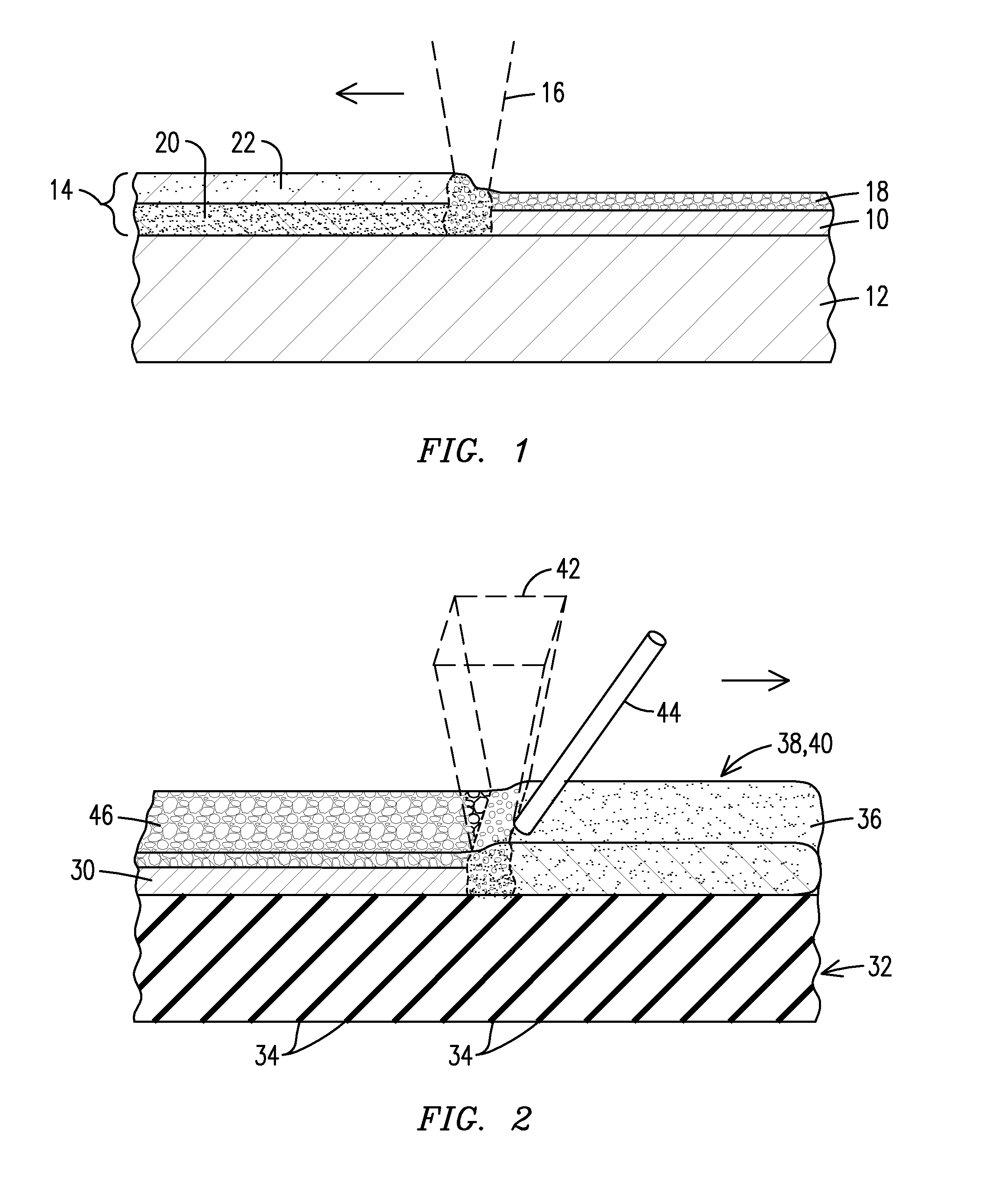
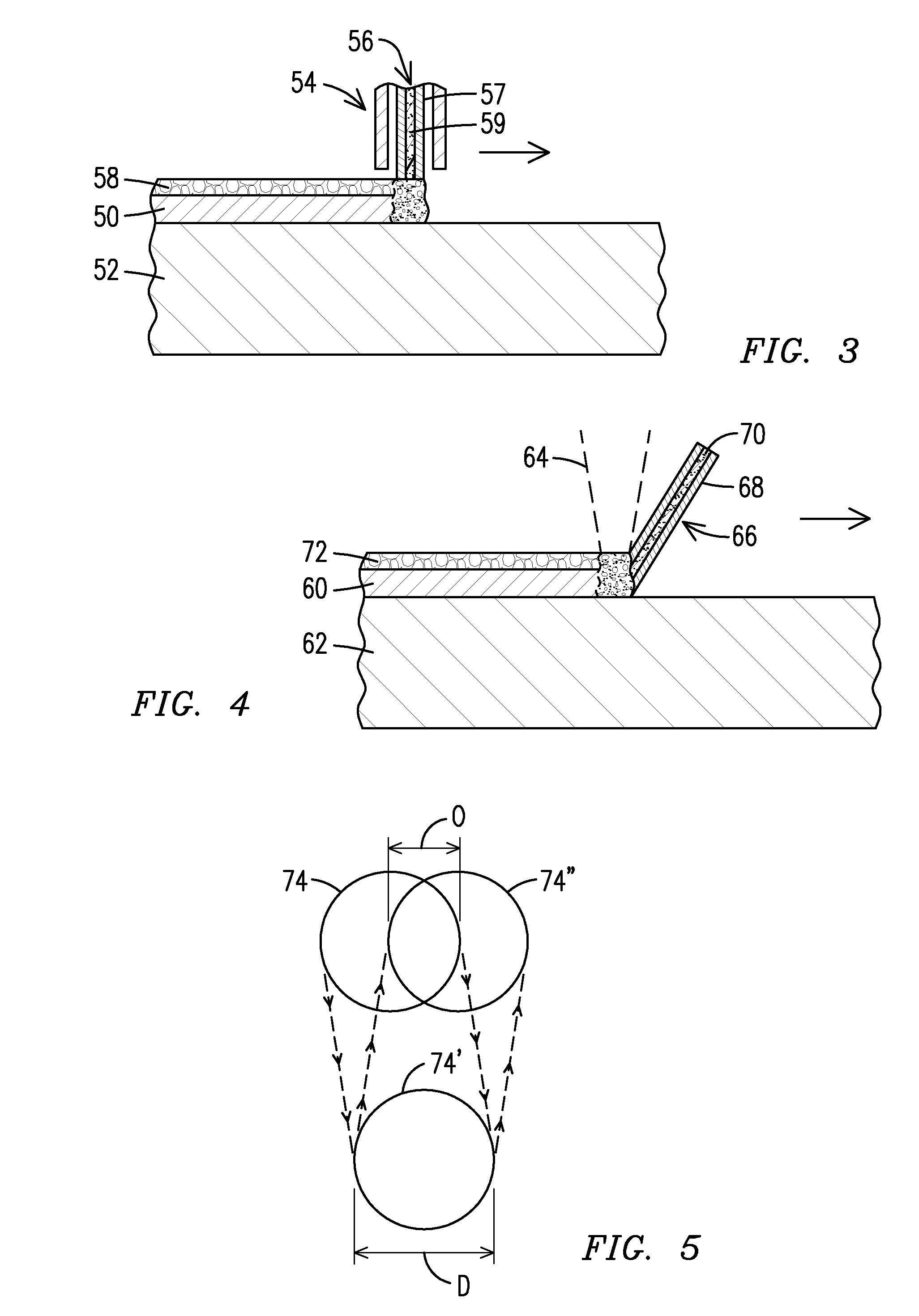
Methods, devices, and systems for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials are disclosed, with example applications in scribing, marking, welding, and joining. For example, ultrashort laser pulses create scribe features with one pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with correctly aligned illumination. Reflective marks may also be formed with control of laser parameters. A transparent material other than glass may be utilized. A method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. In some embodiments of transparent material processing, a multifocus beam generator simultaneously forms multiple beam waists spaced depthwise relative to the transparent material, thereby increasing processing speed.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
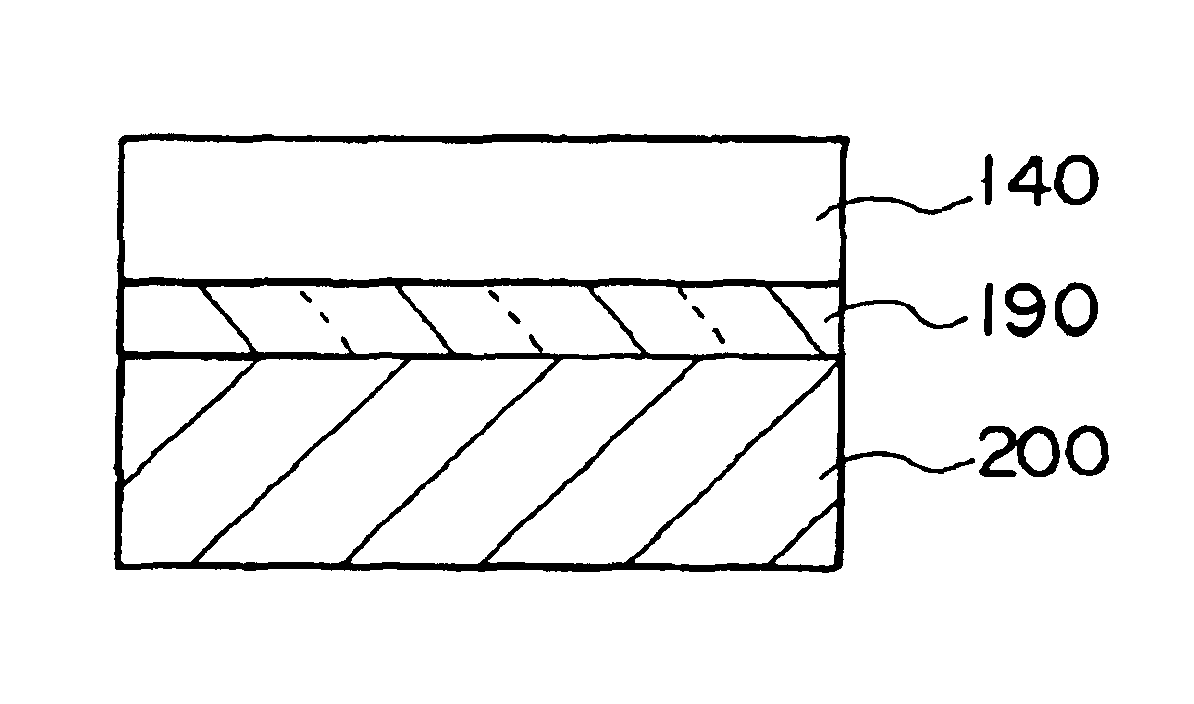
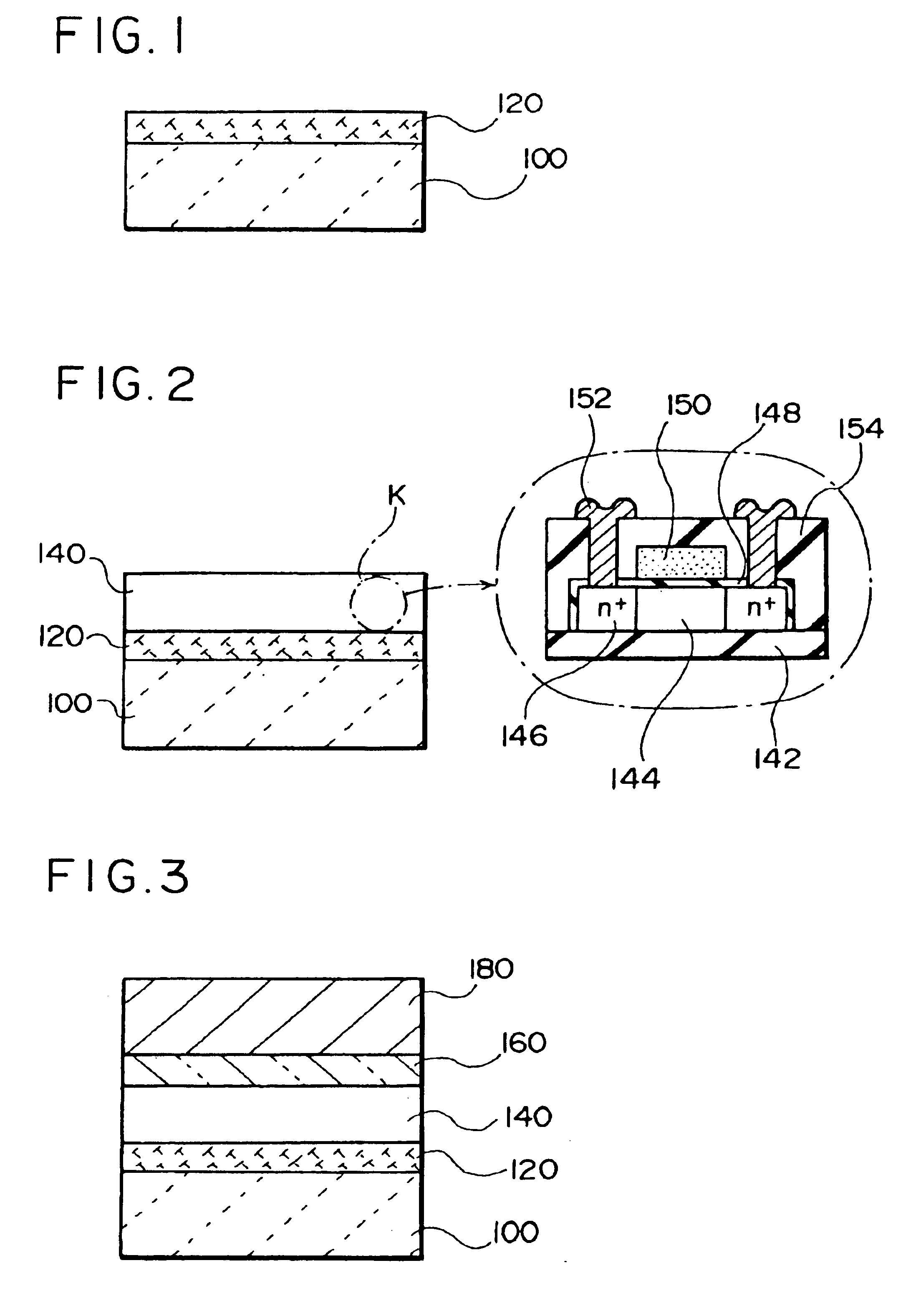
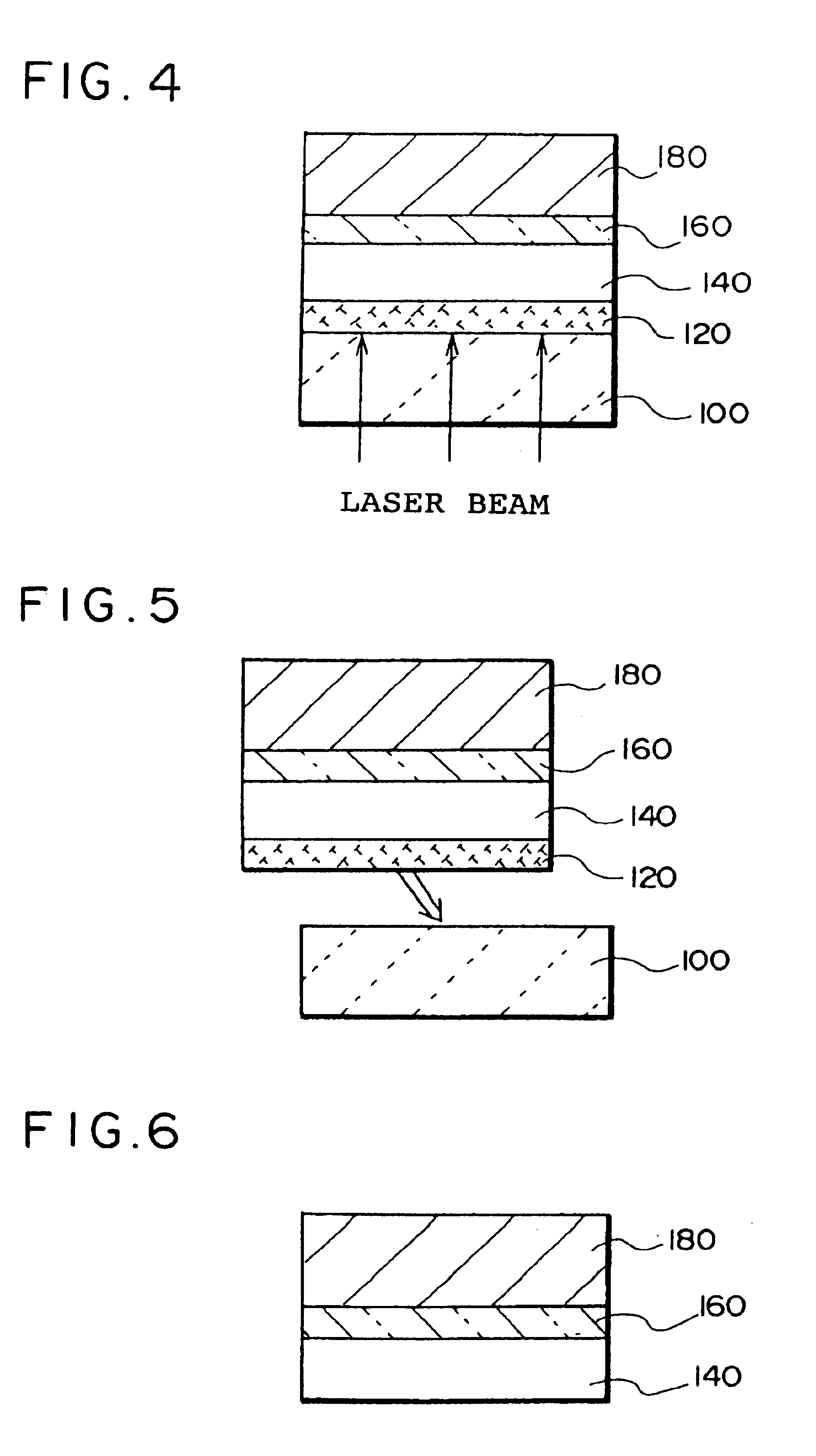
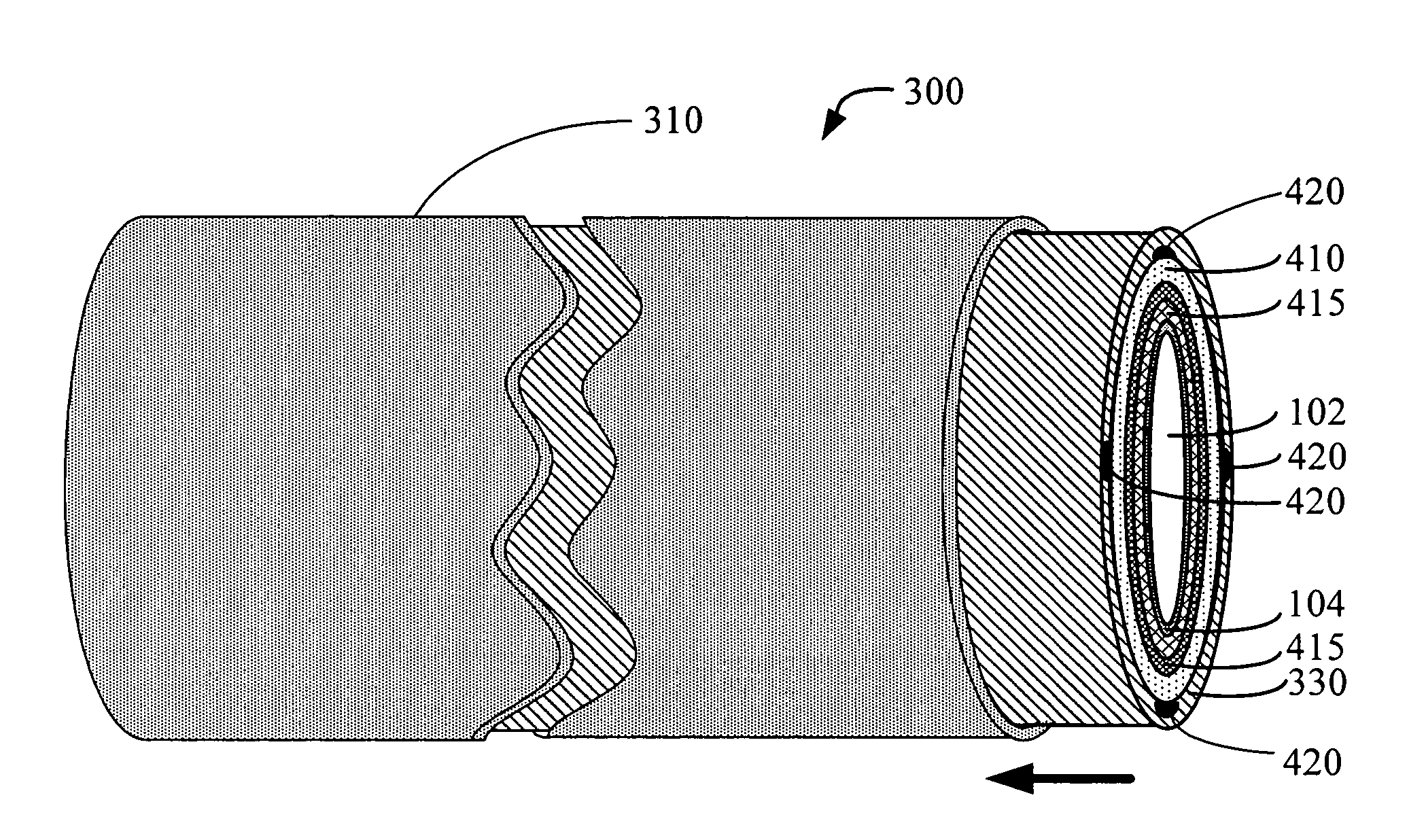
Thin film device transfer method, thin film device, thin film integrated circuit device, active matrix board, liquid crystal display, and electronic apparatus
A thin film device fabrication method in which a thin film device formed on a substrate are transferred to a primary destination-of-transfer part and then the thin film device is transferred to a secondary destination-of-transfer part. A first separation layer (120) made of such a material as amorphous silicon is provided on a substrate (100) which allows passage of laser. A thin film device (140) such as TFTs are formed on the substrate (100). Further, a second separation layer (160) such as a hot-melt adhesive layer is formed on the thin film devices (140), and a primary destination-of-transfer part (180) is mounted thereon. The bonding strength of the first separation layer is weakened by irradiation with light, and the substrate (100) is removed. Thus, the thin film device (140) is transferred to the primary destination-of-transfer part. Then, a secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) is attached onto the bottom of an exposed part of the thin film device (140) via an adhesive layer (190). Thereafter, the bonding strength of the second separation layer is weakened by such means as thermal fusion, and the primary destination-of-transfer part is removed. In this manner, the thin film device (140) can be transferred to the secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) while maintaining layering relationship with respect to the substrate (100).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electron beam layer manufacturing
ActiveUS20110061591A1Obstruct passageProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusFree formClosed loop
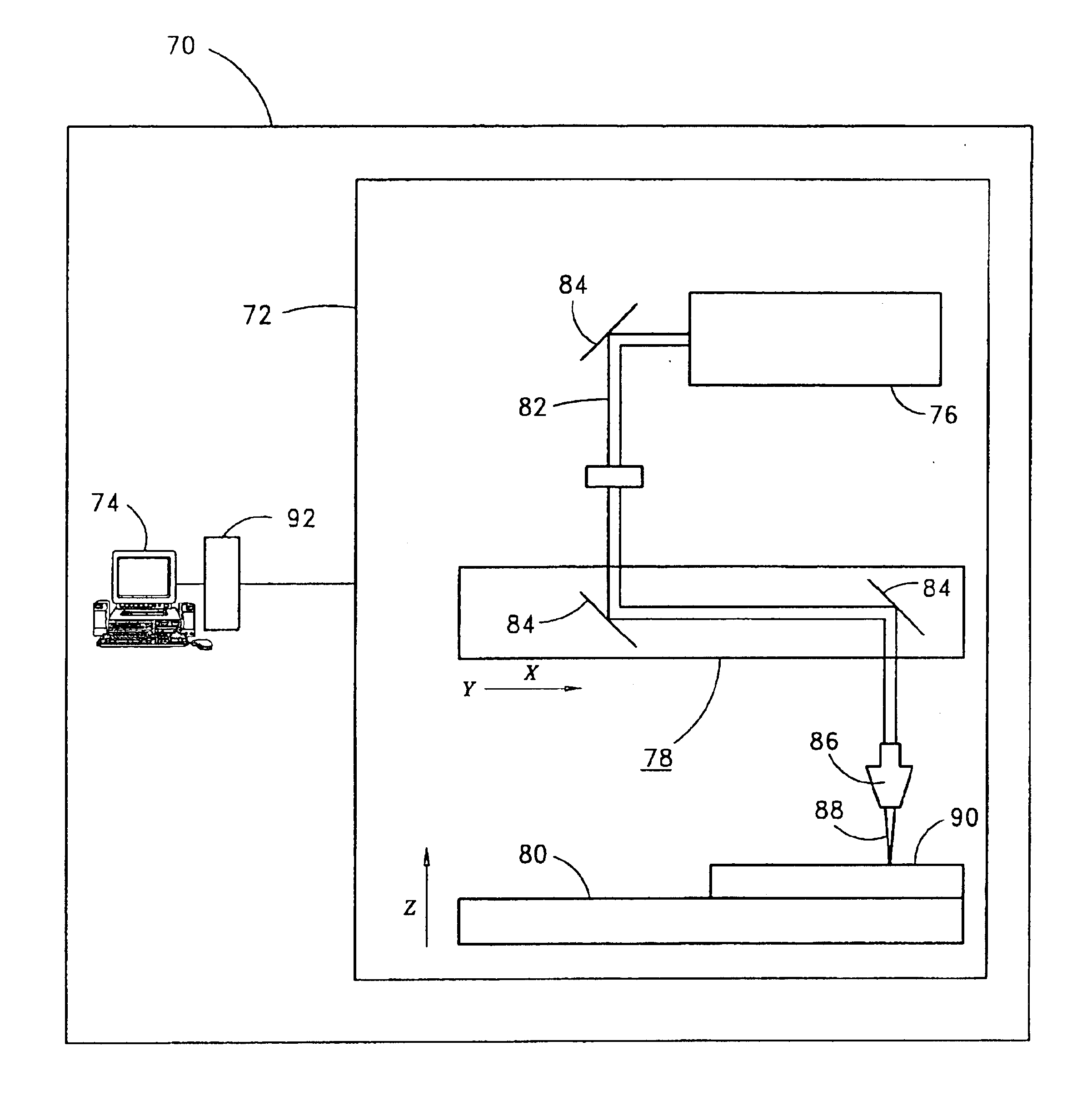
A process and apparatus for free form fabrication of a three-dimensional work piece comprising (a) feeding raw material in a solid state to a first predetermined location; (b) depositing the raw material onto a substrate as a molten pool deposit under a first processing condition; (c) monitoring the molten pool deposit for a preselected condition; (d) comparing information about the preselected condition of the monitored molten pool deposit with a predetermined desired value for the preselected condition of the monitored molten pool deposit; (e) solidifying the molten pool deposit; (f) automatically altering the first processing condition to a different processing condition based upon information obtained from the comparing step (d); and repeating steps (a) through (f) at one or more second locations for building up layer by layer a three-dimensional work piece. The apparatus is characterized by a detector that monitors a preselected condition of the deposited material and a closed loop electronic control device for controlling operation of one or more components of the apparatus in response to a detected condition by the detector.
Owner:SCIAKY SA
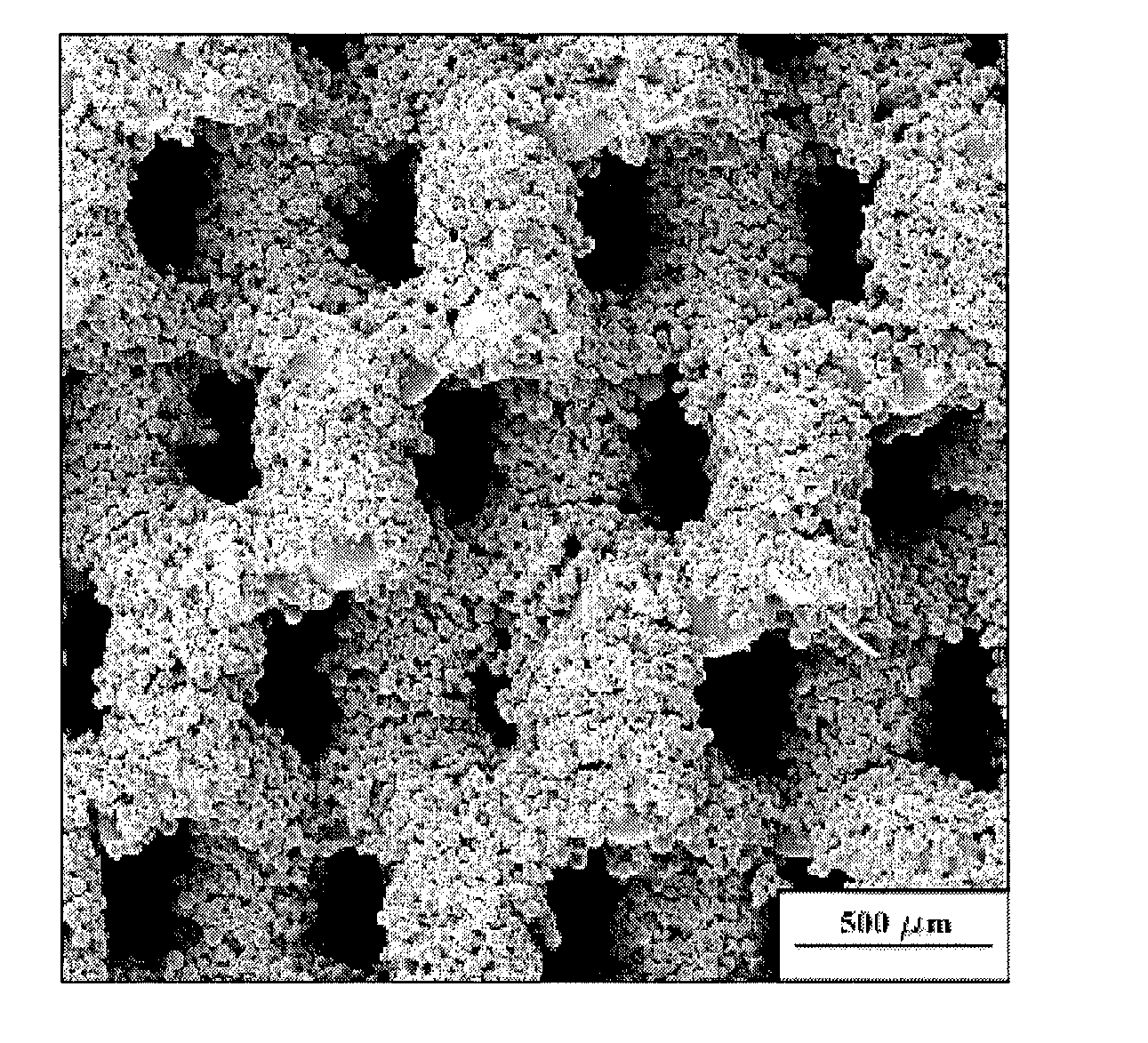
Neovascularization promoting membrane for bioimplants
A method of producing a biocompatible microporous membrane comprising the steps of providing a biocompatible membrane and using an energy beam to form a set of pores having a minor axis of less than 15 μm through the biocompatible membrane. One embodiment includes the steps of producing a first layer of material, defining a first set of pores; producing a second layer of material, defining a second set of pores and wherein the second set of pores is defined so as to cooperatively engage the first set of pores; and aligning and joining the first layer of material to the second layer of material to form a laminated membrane, having through-passageways formed by the first set of pores at least partially aligned with the second set of pores.
Owner:WAVEFORM TECH INC
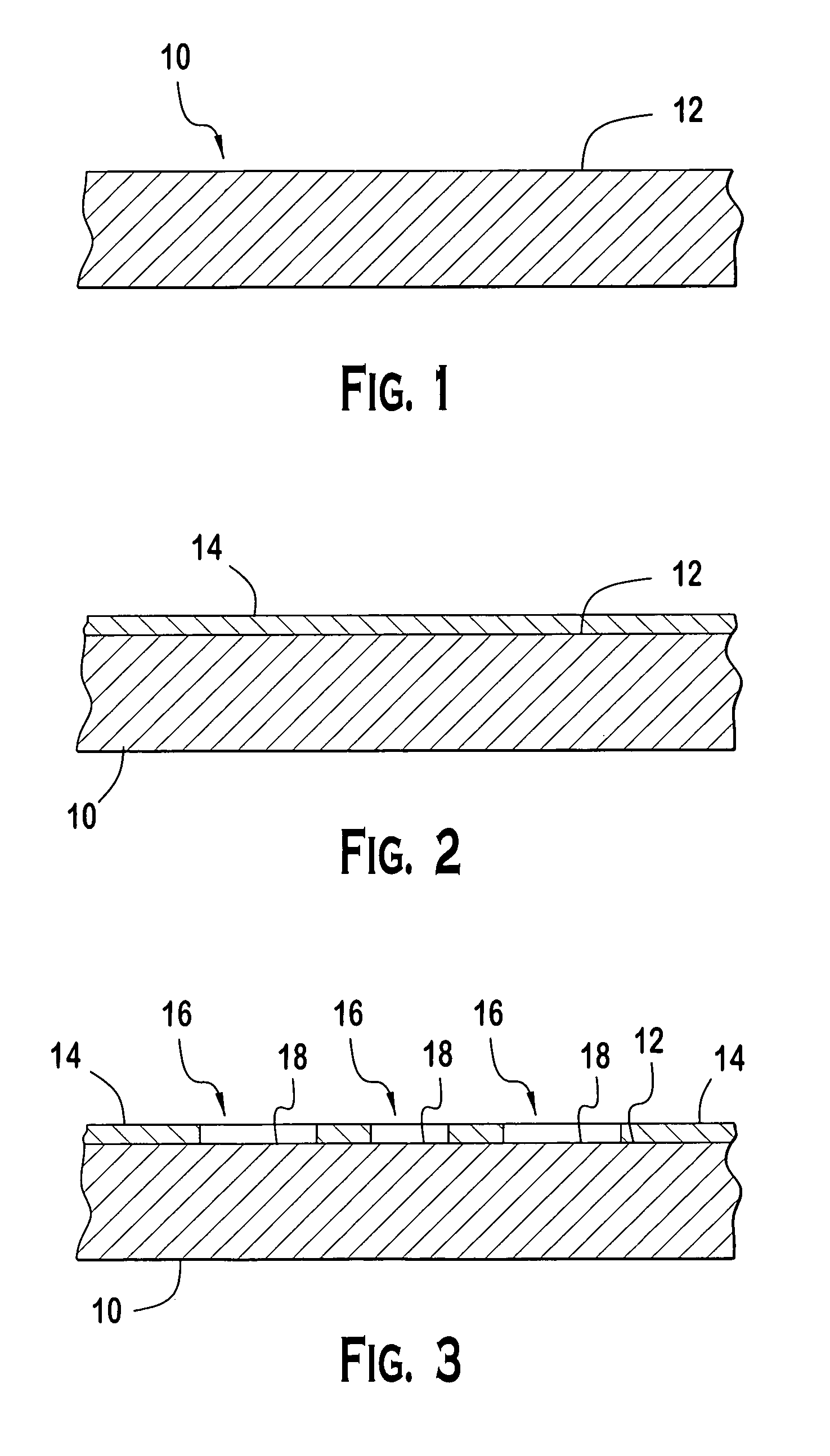
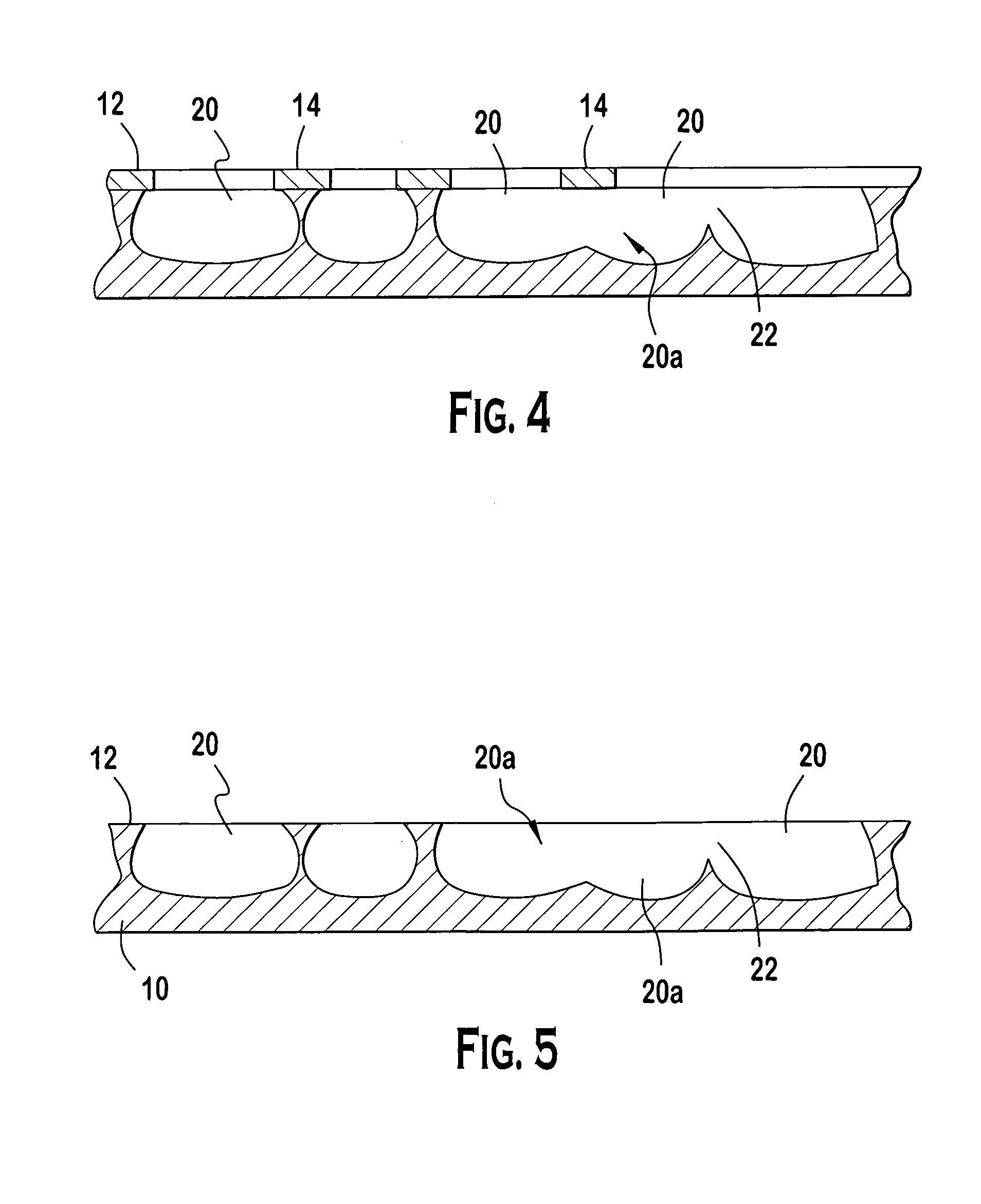
Laser scribing apparatus, systems, and methods
InactiveUS20080029152A1Final product manufactureWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser scribingEngineering
Apparatus, systems, and methods for forming a photovoltaic cell from a common layer on a substrate are provided. A first pass is made with a first laser beam over an area on the common layer. The first pass forms a groove in the common layer. The first pass forms within the common layer a first edge and a second edge. The first edge is separated from the second edge by the groove. The groove provides a first level of electrical isolation between the first edge and the second edge. A second pass is made with a second laser beam over approximately the same area on the common layer. The second pass provides a second level of electrical isolation between the first edge and the second edge. The second level of electrical isolation is greater than the first level of electrical isolation.
Owner:SOLYNDRA
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS20070032095A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorEngineering
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for laser texturing of surfaces of a substrate
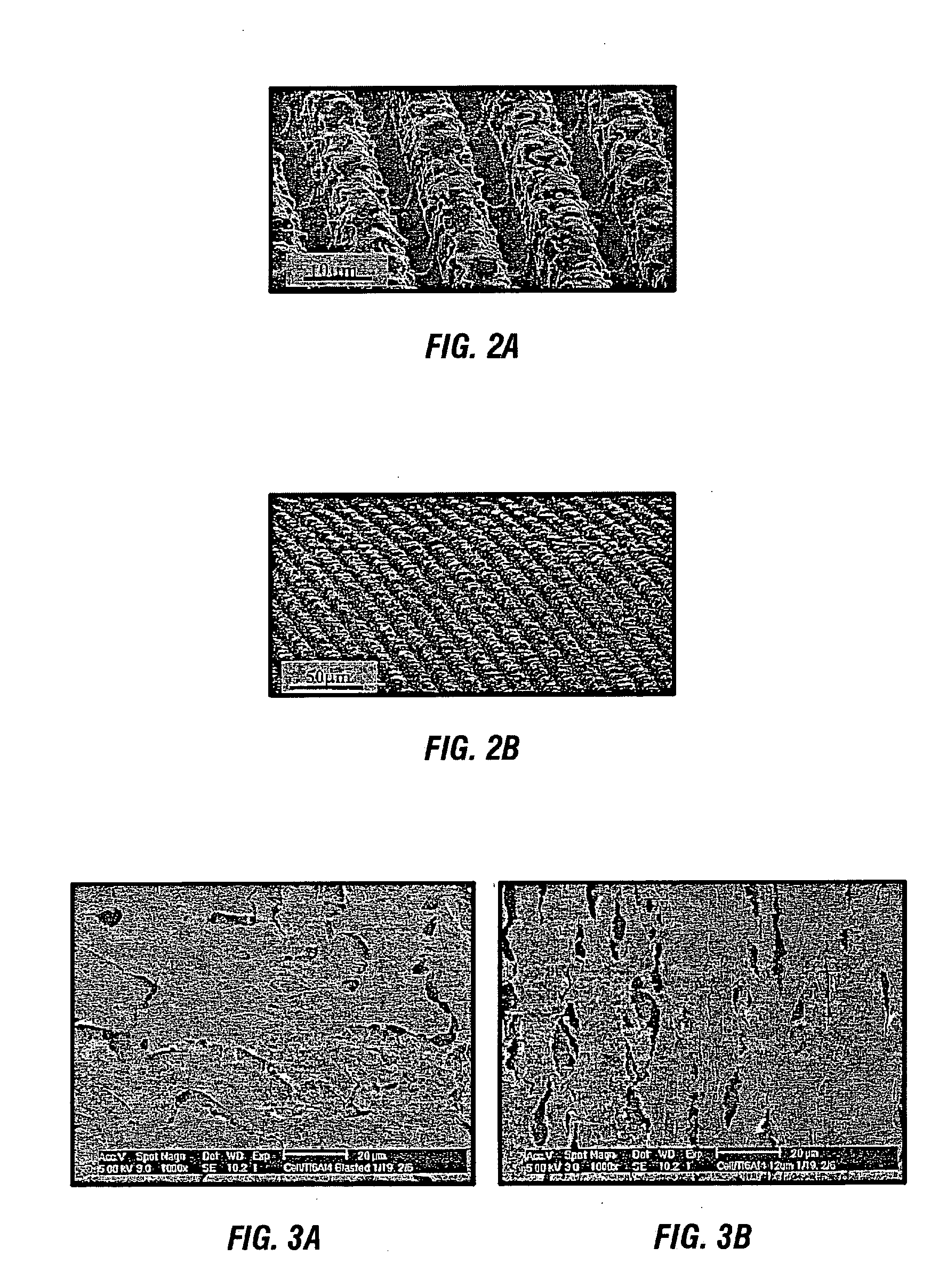
The present application is directed to a method of modifying a surface of an article and includes irradiating pulsed laser light output at repetition rates in excess of about 1kHz, directing the laser light to a spot on the surface, and producing micro-grooved surfaces having one or more grooves formed thereon, the grooves having groove depths in the range of about 1 μm to about 100 μm.
Owner:SPECTRA PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
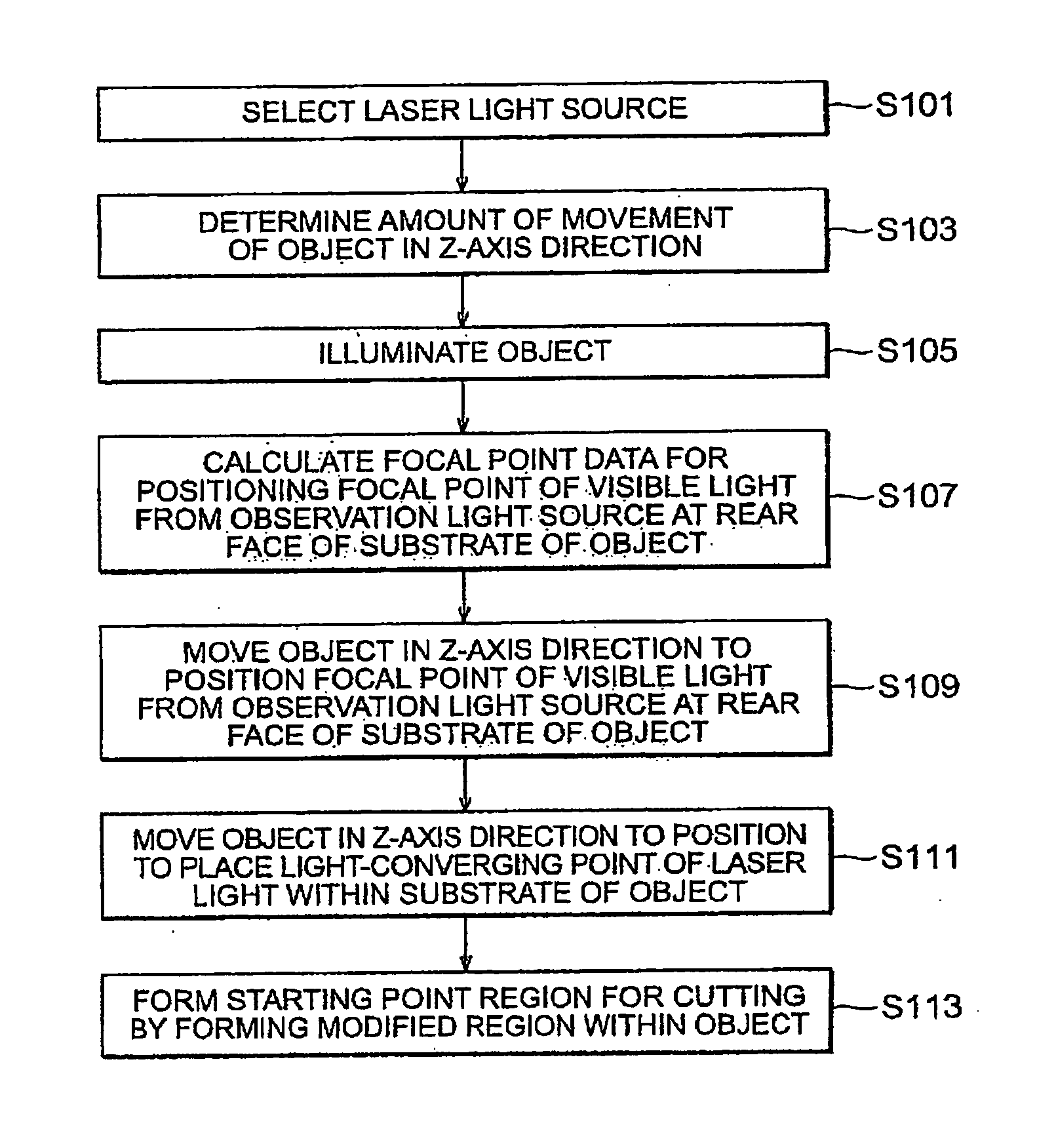
Laser processing method
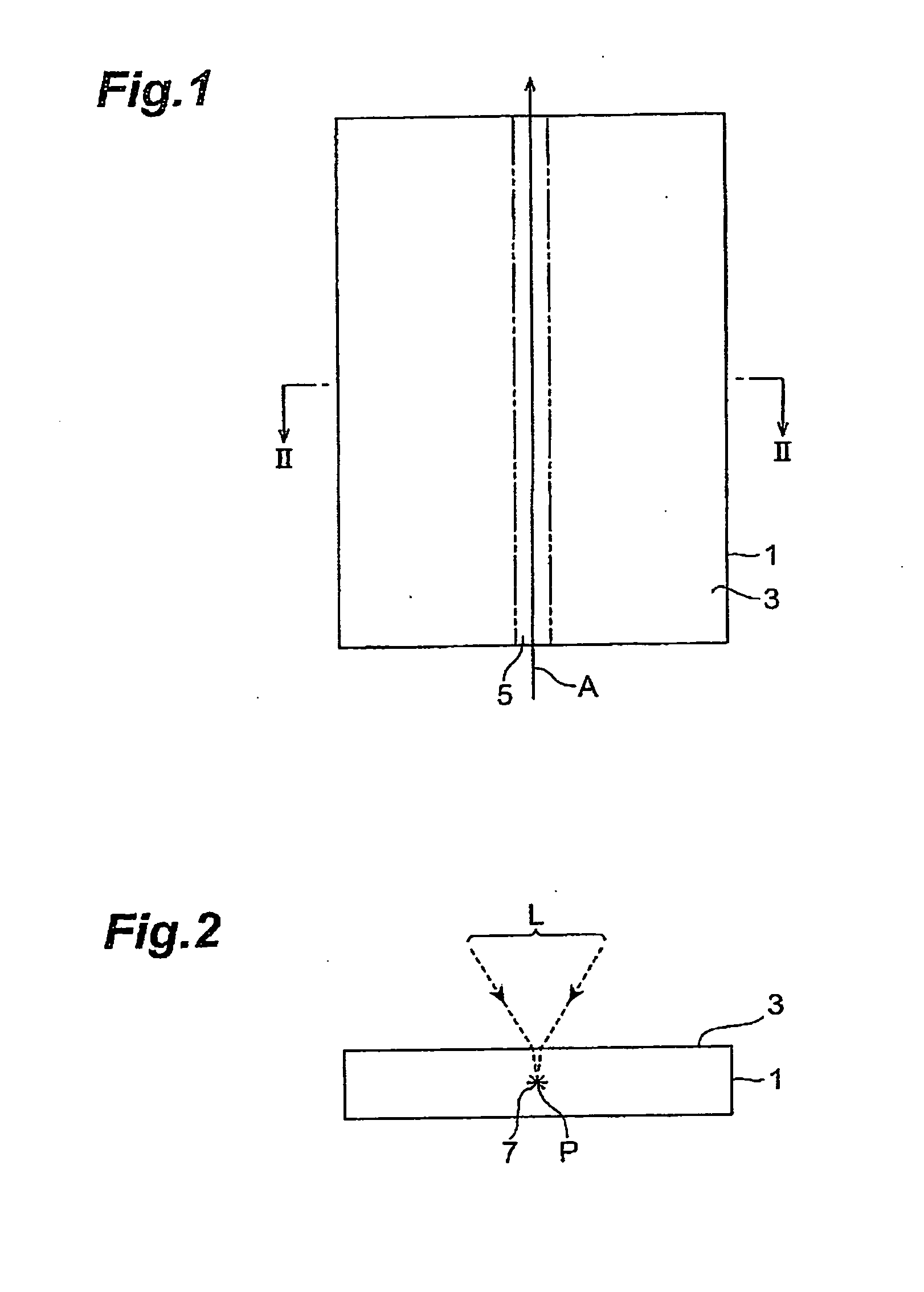
ActiveUS20050202596A1Force is smallImprove accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser processingLaser light
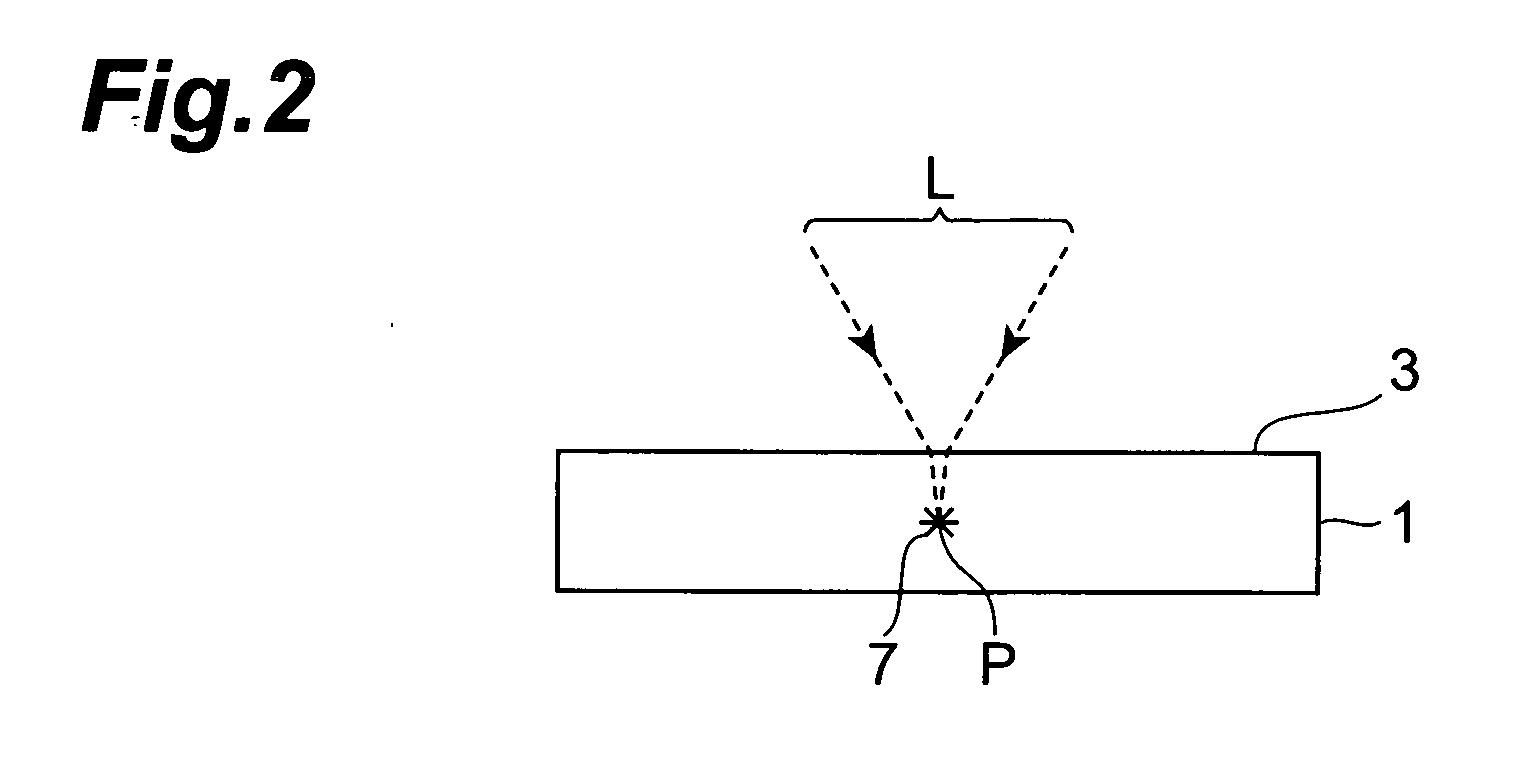
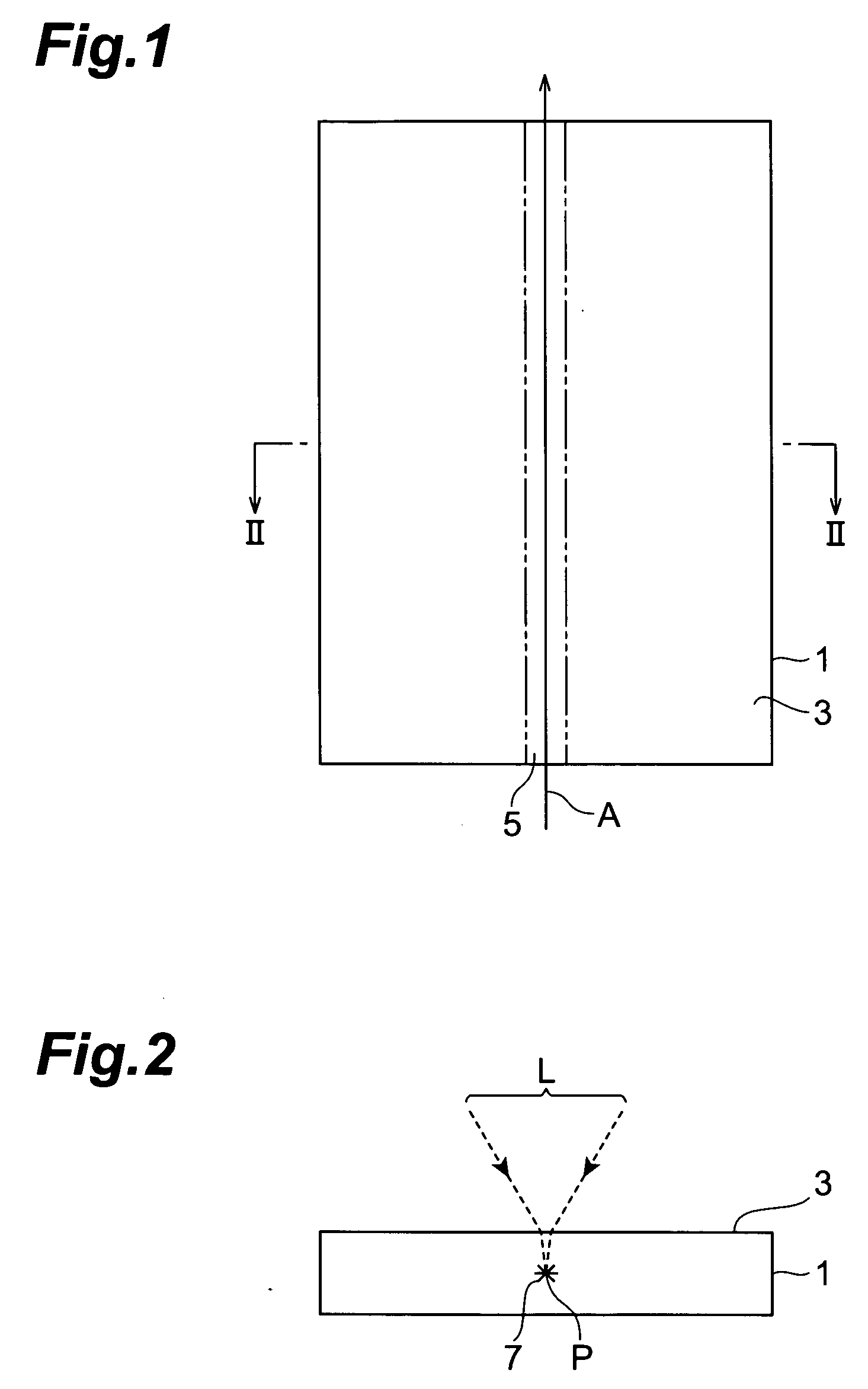
A laser processing method which can highly accurately cut objects to be processed having various laminate structures is provided. An object to be processed comprising a substrate and a laminate part disposed on the front face of the substrate is irradiated with laser light L while a light-converging point P is positioned at least within the substrate, so as to form a modified region due to multiphoton absorption at least within the substrate, and cause the modified region to form a starting point region for cutting. When the object is cut along the starting point region for cutting, the object 1 can be cut with a high accuracy.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Strengthened glass substrate sheets and methods for fabricating glass panels from glass substrate sheets
Owner:CORNING INC
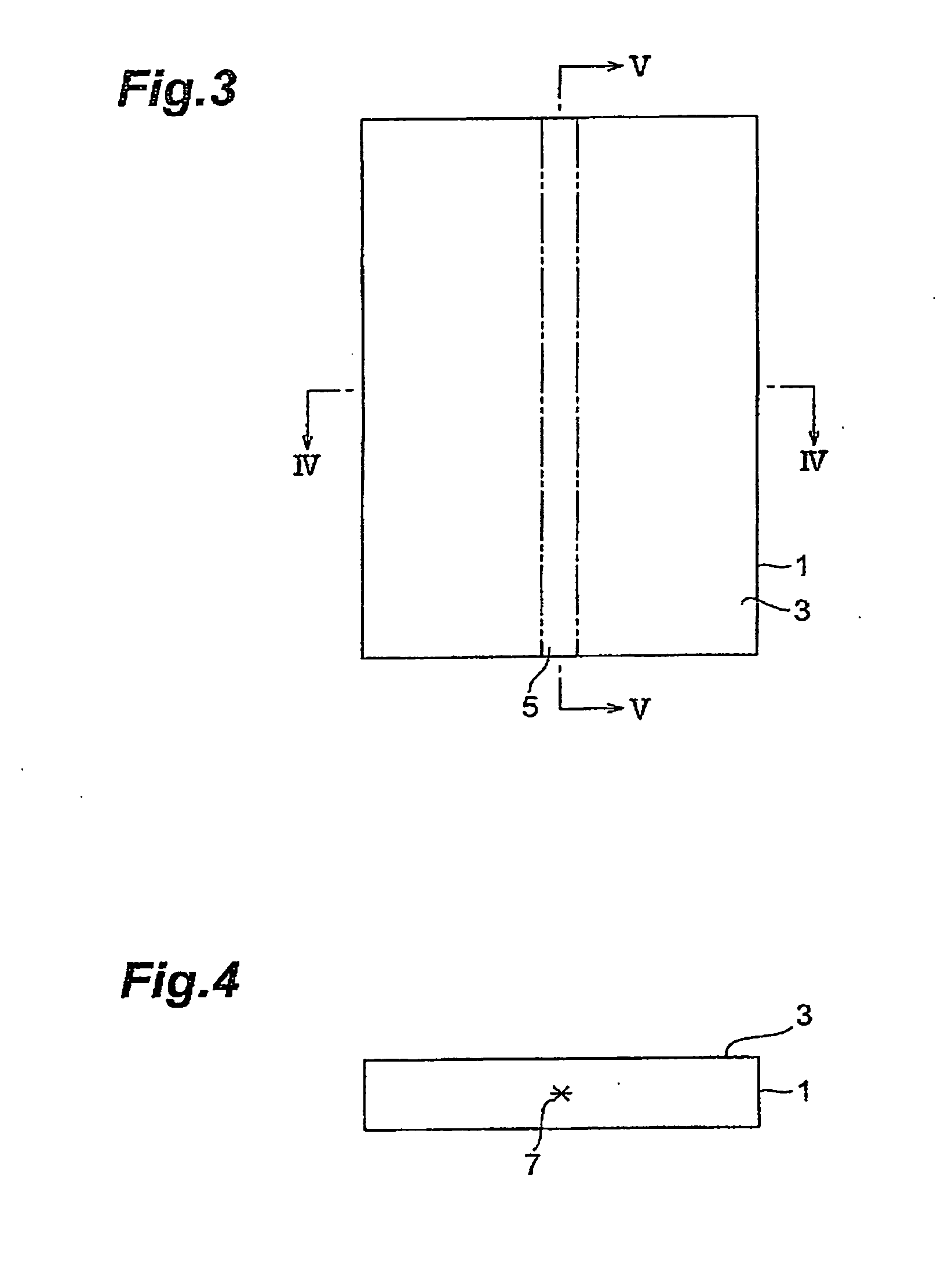
Method of cutting processed object
InactiveUS20060011593A1Precise cuttingPrevent unnecessary fracturesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingClassical mechanicsLaser light
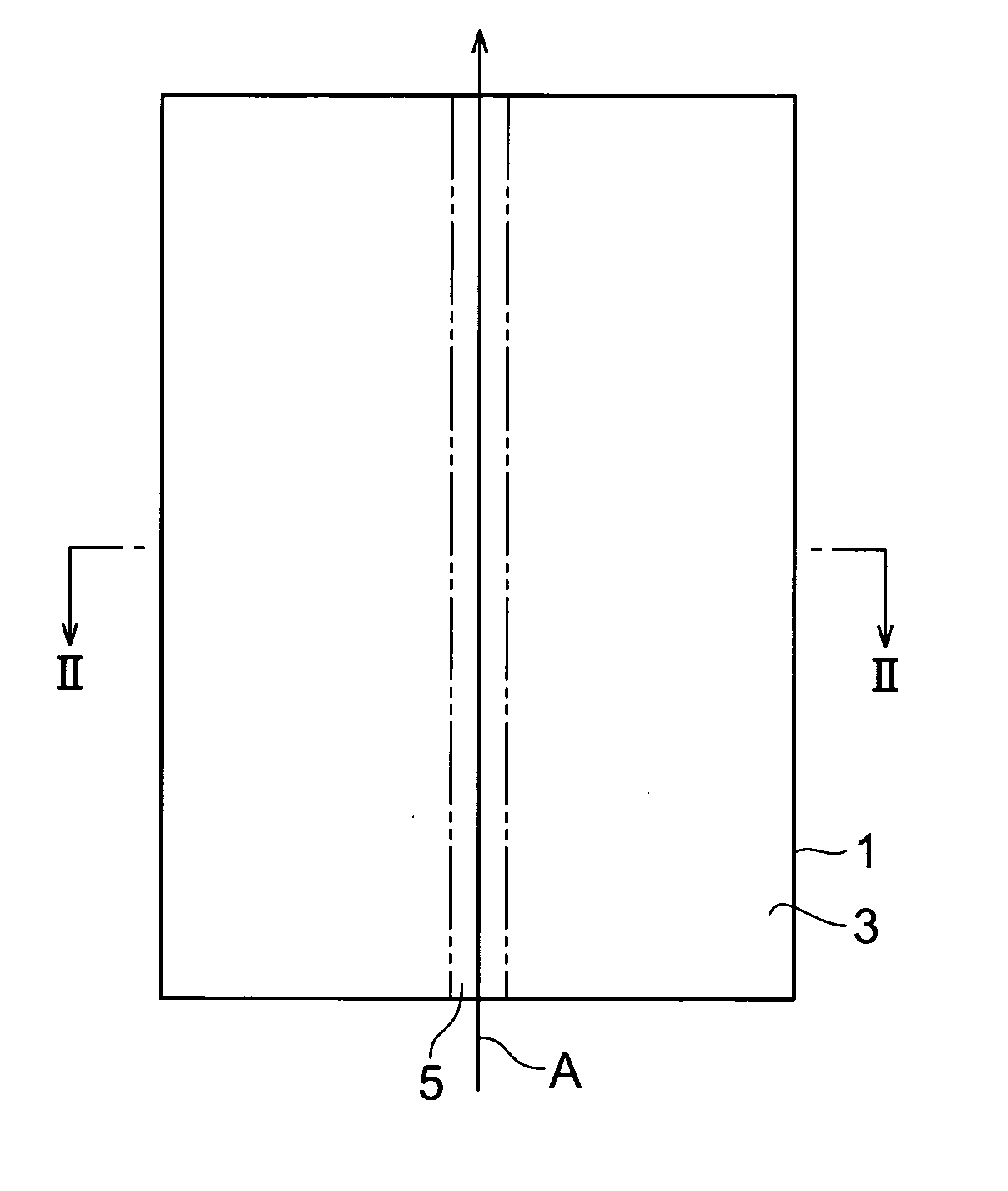
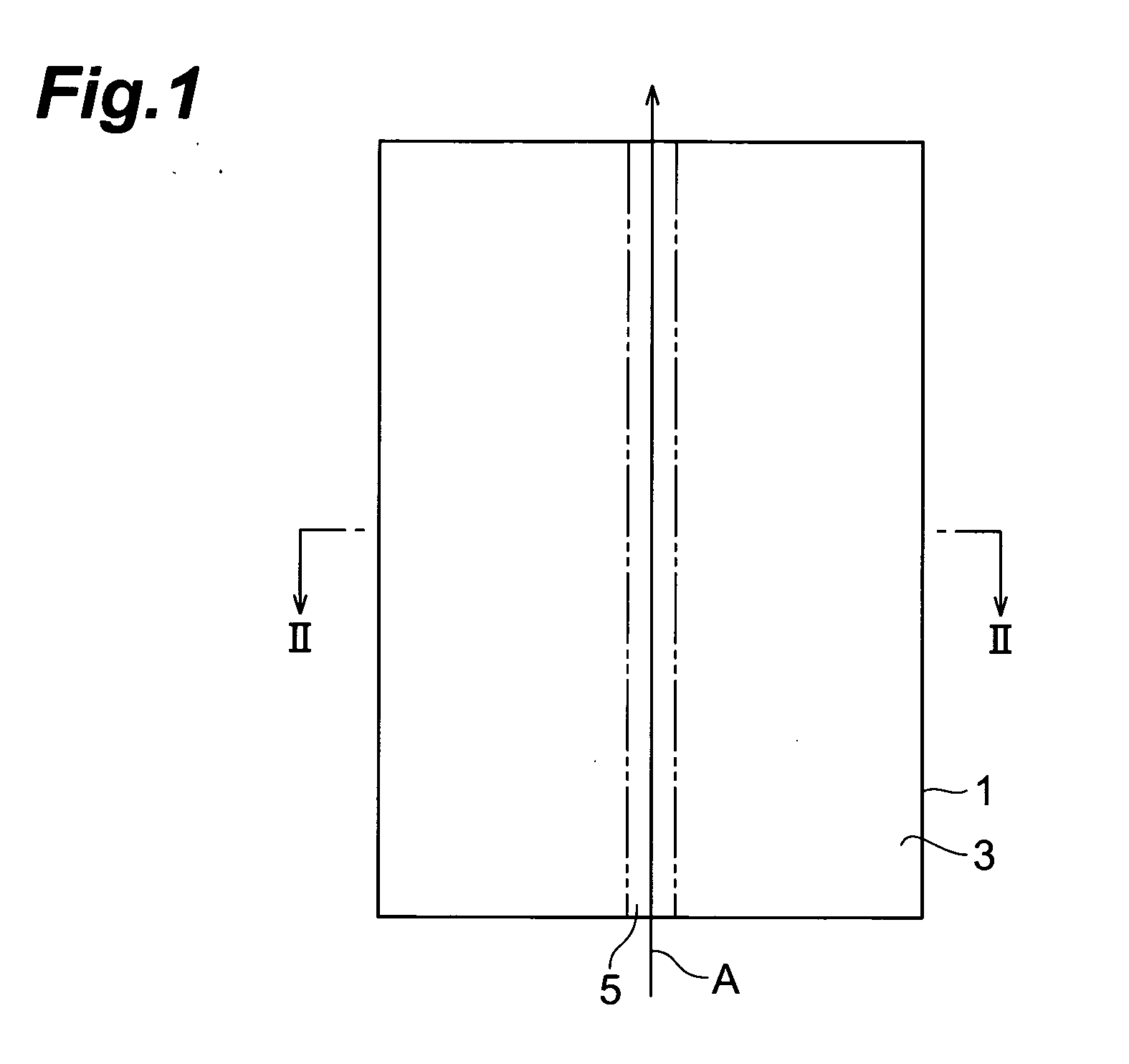
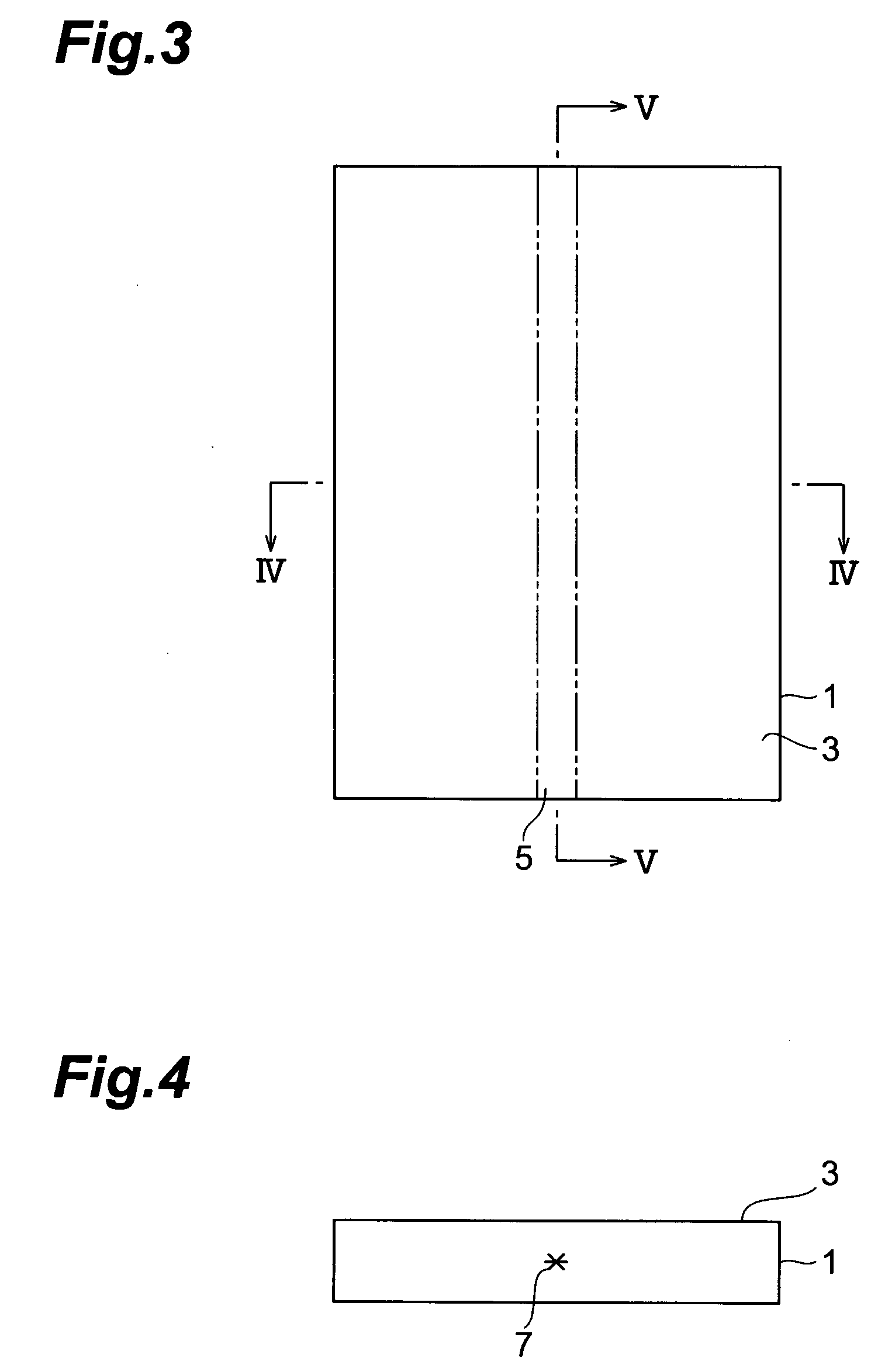
A method of cutting an object which can accurately cut the object is provided. An object to be processed 1 such as a silicon wafer is irradiated with laser light L while a light-converging point P is positioned therewithin, so as to form a modified region 7 due to multiphoton absorption within the object 1, and cause the modified region 7 to form a starting point region for cutting 8 shifted from the center line CL of the thickness of the object 1 toward the front face 3 of the object 1 along a line along which the object should be cut. Subsequently, the object 1 is pressed from the rear face 21 side thereof. This can generate a fracture from the starting point region for cutting 8 acting as a start point, thereby accurately cutting the object 1 along the line along which the object should be cut.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Methods of making medical devices
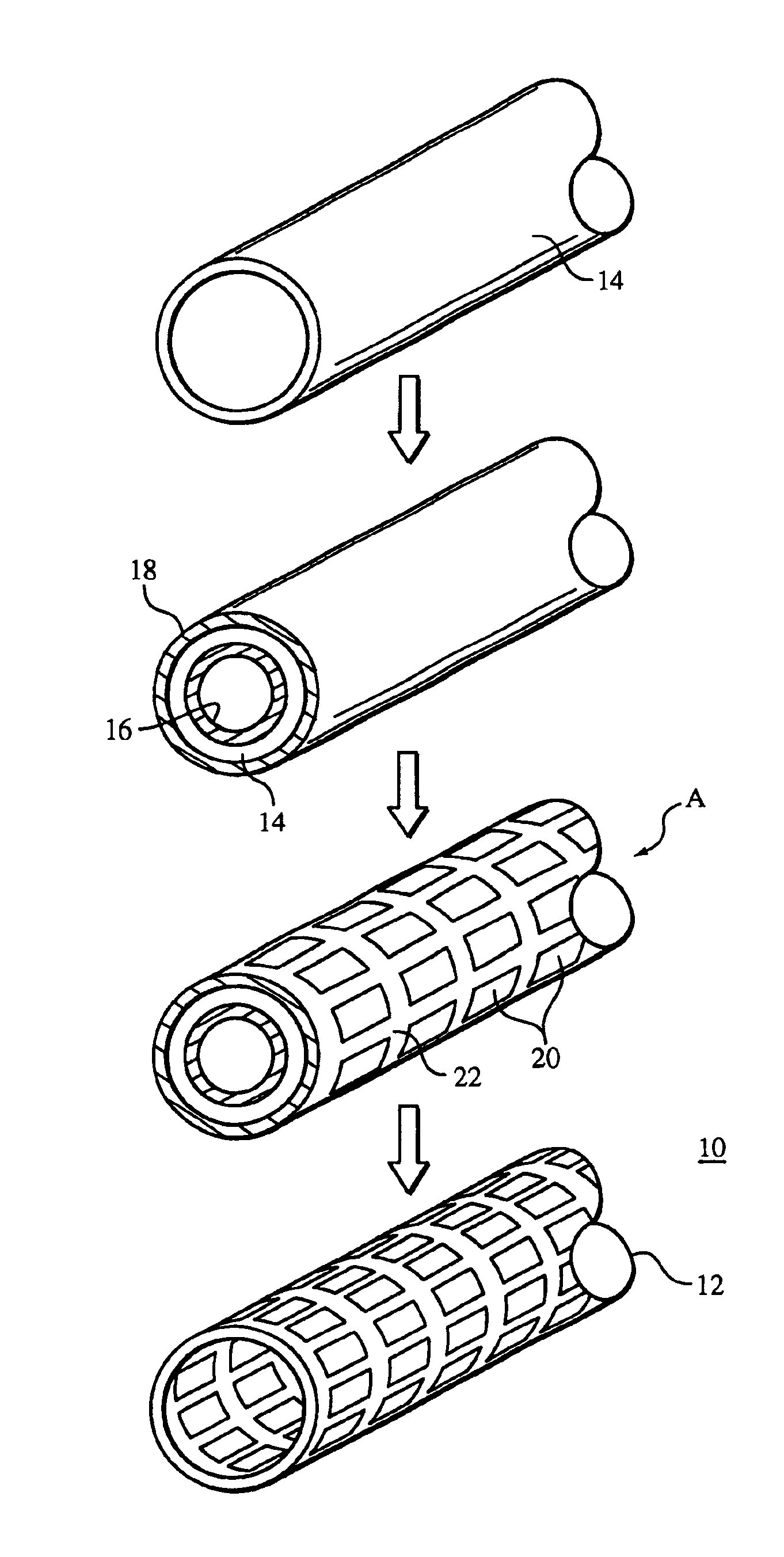
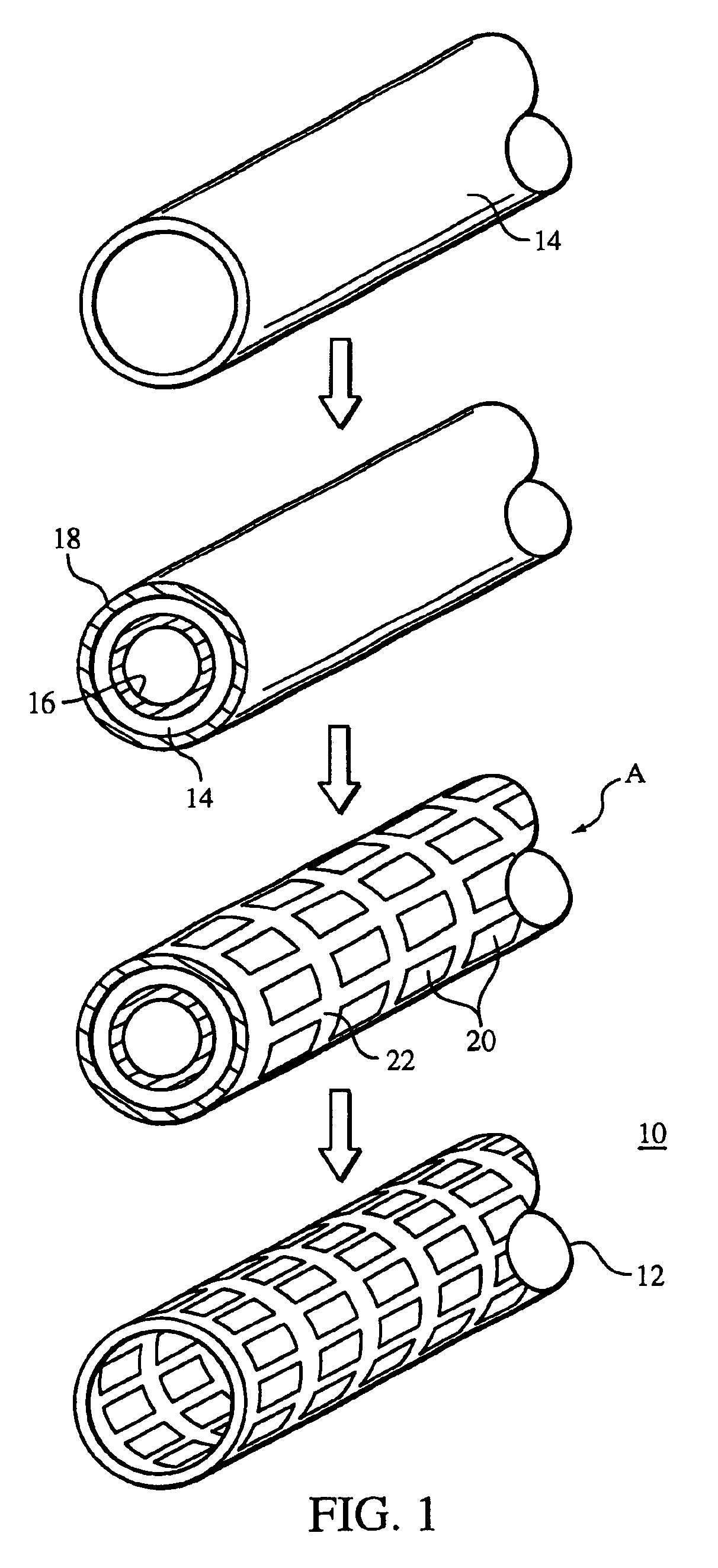
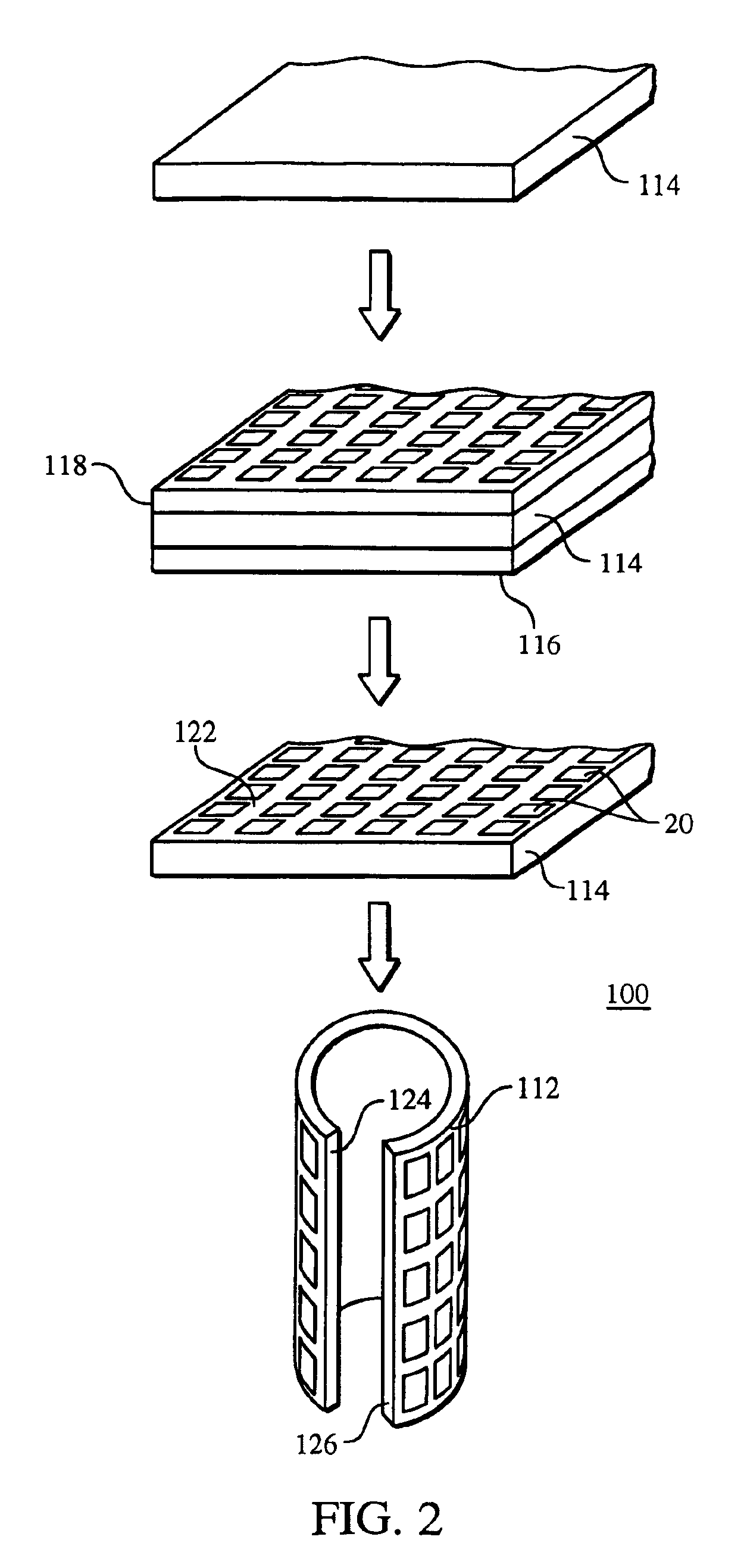
InactiveUS6865810B2Reduce the amount requiredEasy to disassemblePretreated surfacesAntithrombogenic treatmentInsertion stentMedical device
A method of making a stent includes providing a tubular member having a first layer, the first layer and the tubular member having different compositions, removing a portion of the tubular member, and removing a portion of the first layer from the tubular member.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Drug-eluting Biodegradable Stent and Delivery Means
A biodegradable stent comprising a luminal surface portion with a second degree of crosslink, an outer surface portion with a first degree of crosslink, and a body between the luminal and outer surface portions, wherein the body comprises a crosslinked material characterized by the first degree of crosslink not less than the second degree of crosslink.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Manufacturing process for polymeric stents
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR +1
Composite heart valve apparatus manufactured using techniques involving laser machining of tissue
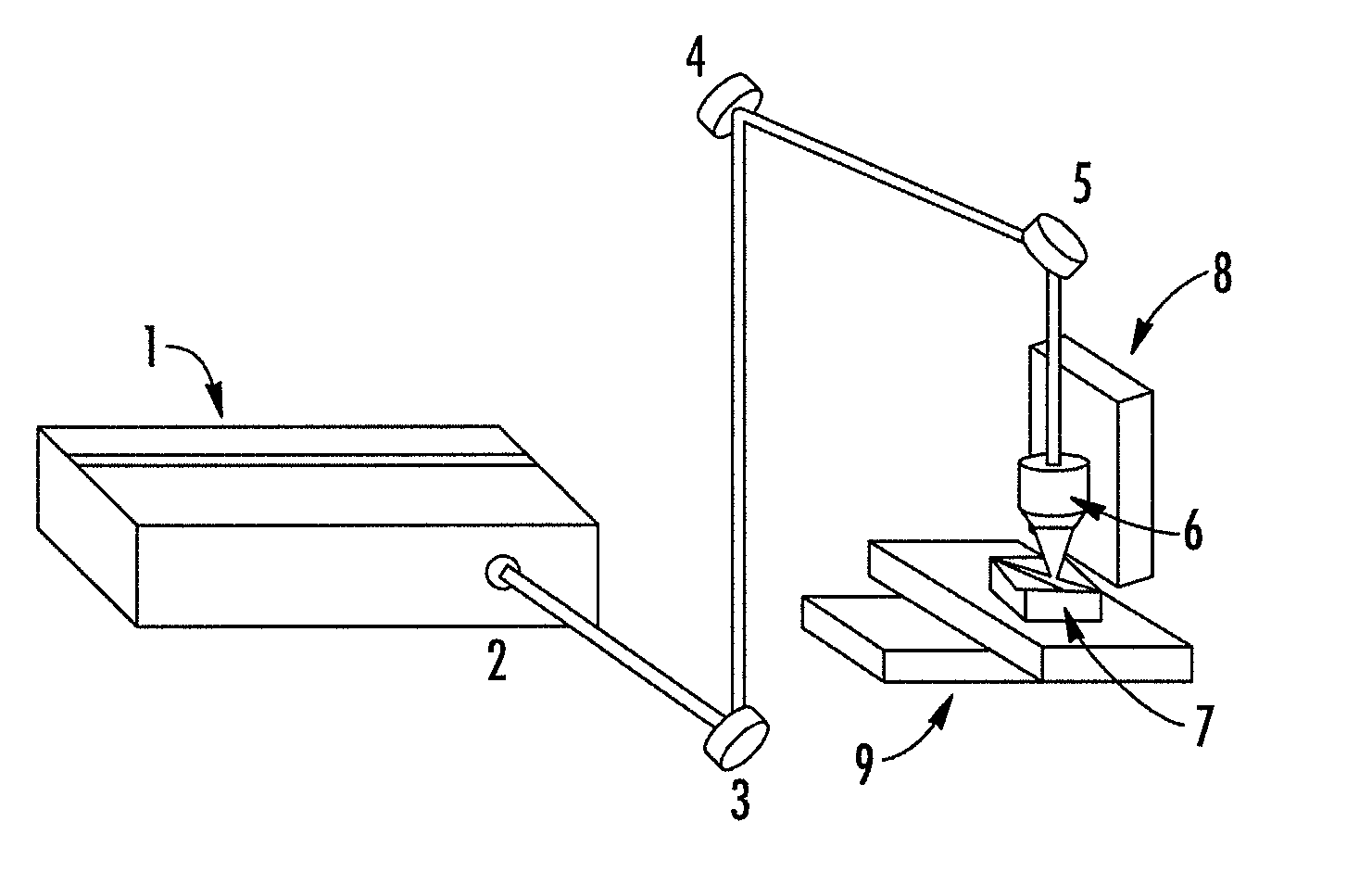
ActiveUS20070073392A1Modifies tissue much fasterLow scrap rateTubular organ implantsVenous valvesVeinLaser processing
Methodology for using laser machining techniques to modify a tissue for use in a medical device. In a representative mode of practice, relatively low energy laser machining is used to thin down at least a portion of a valved jugular vein. The thinned down vein may then be sutured to, or otherwise integrated with, a corresponding stent to make a percutaneous heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Laser-produced porous structure
The present invention disclosed a method of producing a three-dimensional porous tissue in-growth structure. The method includes the steps of depositing a first layer of metal powder and scanning the first layer of metal powder with a laser beam to form a portion of a plurality of predetermined unit cells. Depositing at least one additional layer of metal powder onto a previous layer and repeating the step of scanning a laser beam for at least one of the additional layers in order to continuing forming the predetermined unit cells. The method further includes continuing the depositing and scanning steps to form a medical implant.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL +1
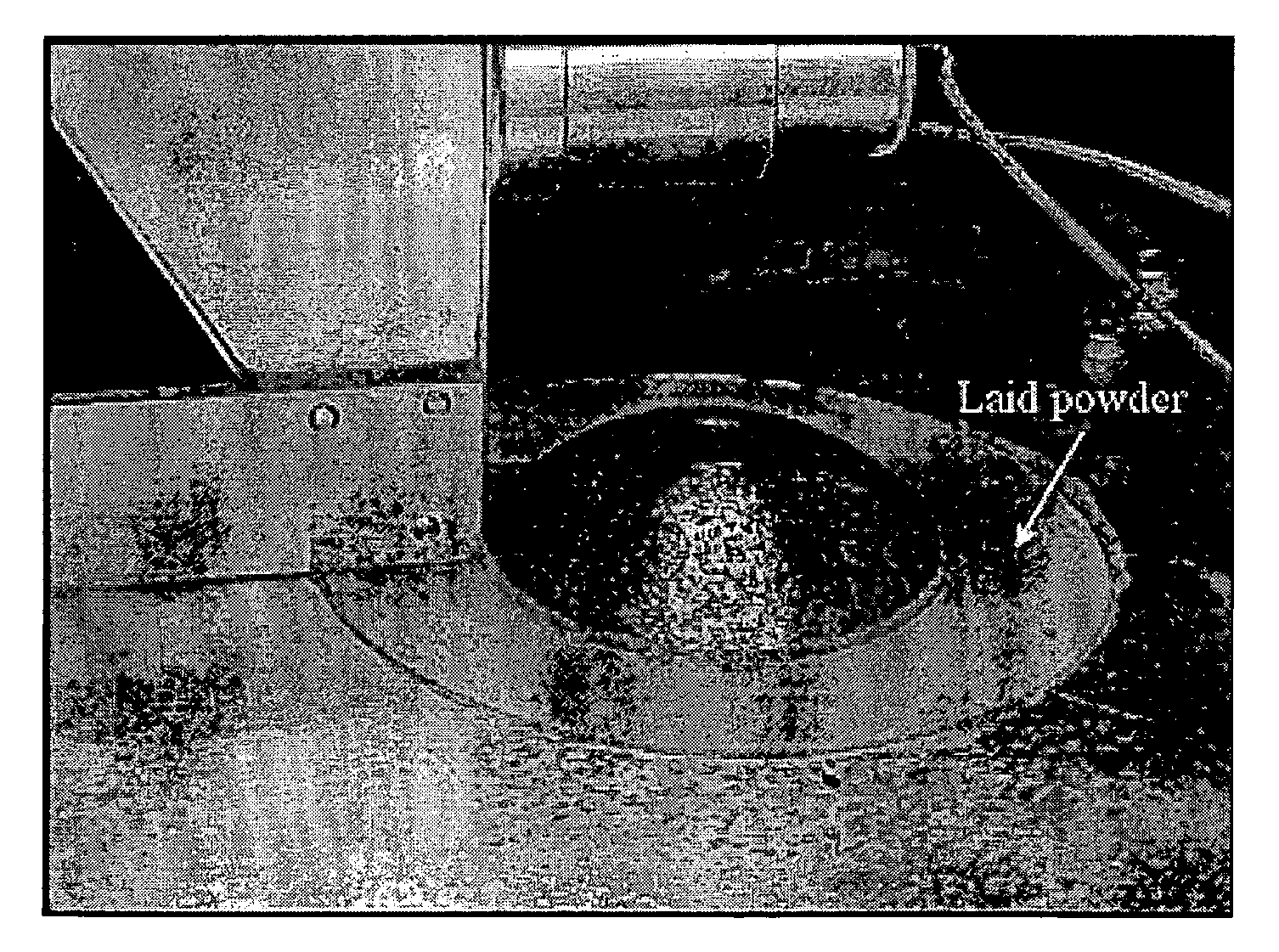
Selective laser melting / sintering using powdered flux
InactiveUS20130136868A1TurbinesRadiation applicationsSelective laser meltingSelective laser sintering
An additive manufacturing process (110) wherein a powder (116) including a superalloy material and flux is selectively melted in layers with a laser beam (124) to form a superalloy component (126). The flux performs a cleaning function to react with contaminants to float them to the surface of the melt to form a slag. The flux also provides a shielding function, thereby eliminating the need for an inert cover gas. The powder may be a mixture of alloy and flux particles, or it may be formed of composite alloy / flux particles.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method for dicing substrate
ActiveUS20050272223A1Improve transverse breaking strengthAvoid chippingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProcess regionLaser light
A substrate dividing method which can thin and divide a substrate while preventing chipping and cracking from occurring. This substrate dividing method comprises the steps of irradiating a semiconductor substrate 1 having a front face 3 formed with functional devices 19 with laser light while positioning a light-converging point within the substrate, so as to form a modified region including a molten processed region due to multiphoton absorption within the semiconductor substrate 1, and causing the modified region including the molten processed region to form a starting point region for cutting; and grinding a rear face 21 of the semiconductor substrate 1 after the step of forming the starting point region for cutting such that the semiconductor substrate 1 attains a predetermined thickness.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Imaged article on polymeric substrate
InactiveUS6203952B1Increasing the thicknessSmooth peelingAntenna supports/mountingsLoop antennasResistPolymer substrate
Patterned articles, such as RFID antenna, are made by subablation, a process comprising the steps of:A. providing a substrate having a coating, such as a metal or metal oxide, and an interface comprising the thin region where the coating and the substrate are closest to each other;B. exposing at least one part of the total area of the coating to a flux of electromagnetic energy, such as a focused excimer laser beam, sufficient to disrupt the interface but insufficient to ablate the coating; andC. removing the parts of the coating in registry with the portion of the interface area that was disrupted, by means such as ultrasonic agitation.The process has advantages over photo-resist processes in that there is no residual chemical resist left on the product and no undercutting of the pattern or image. It has advantages over laser ablation processes in that higher throughput is possible at the same energy level and there is no microscopic debris left on the product surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com