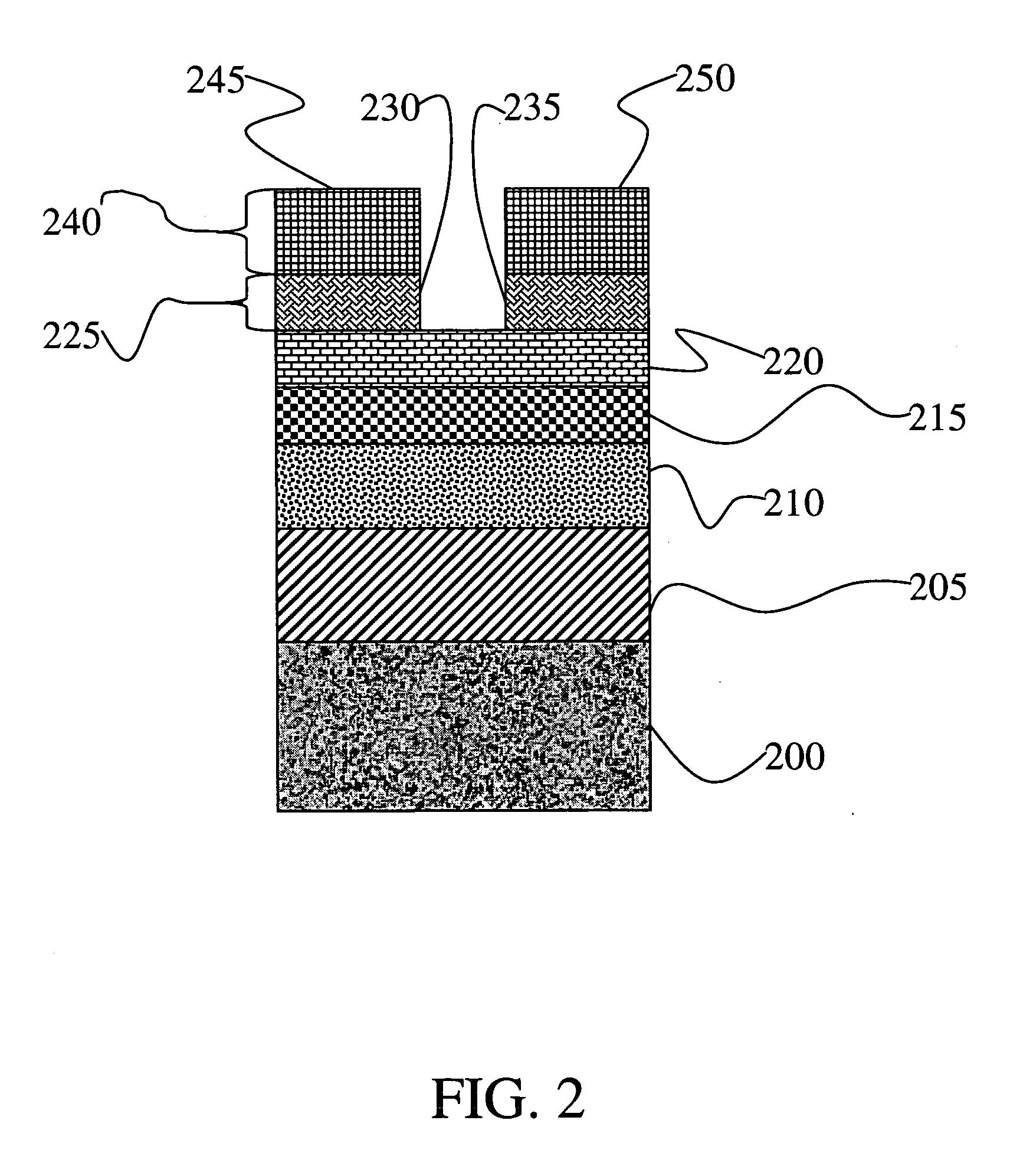
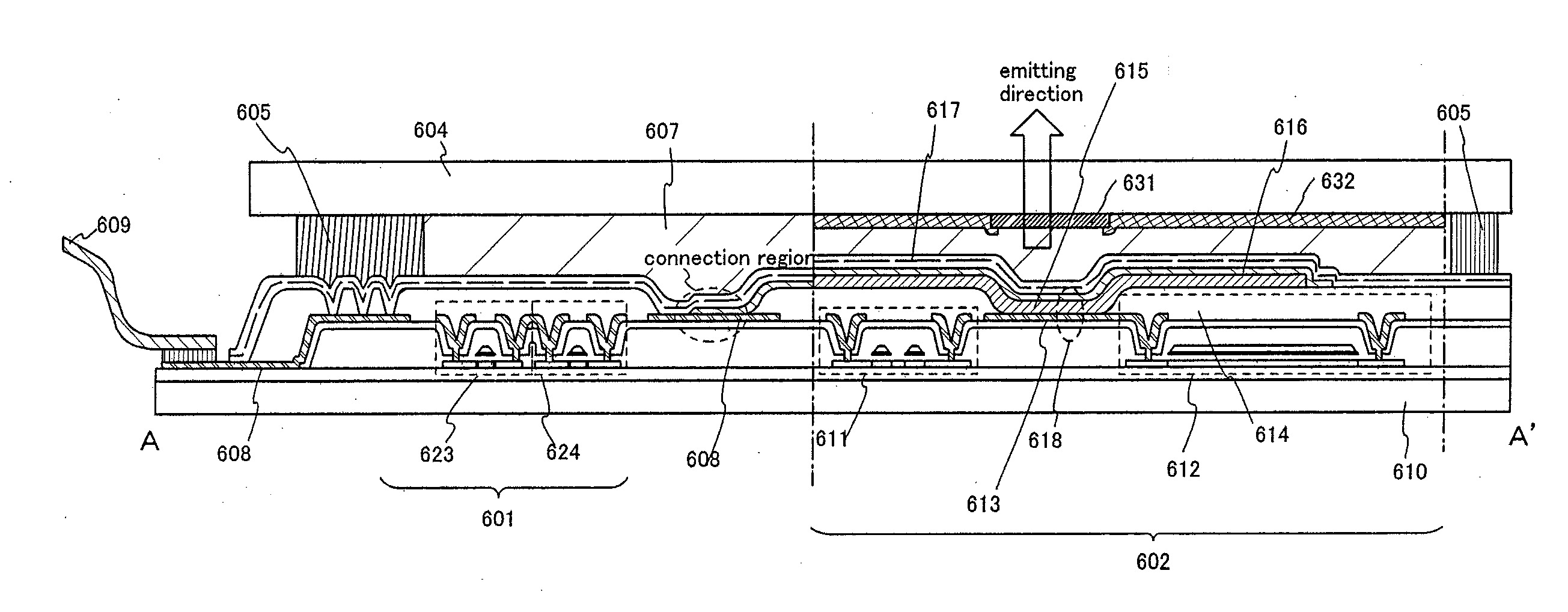
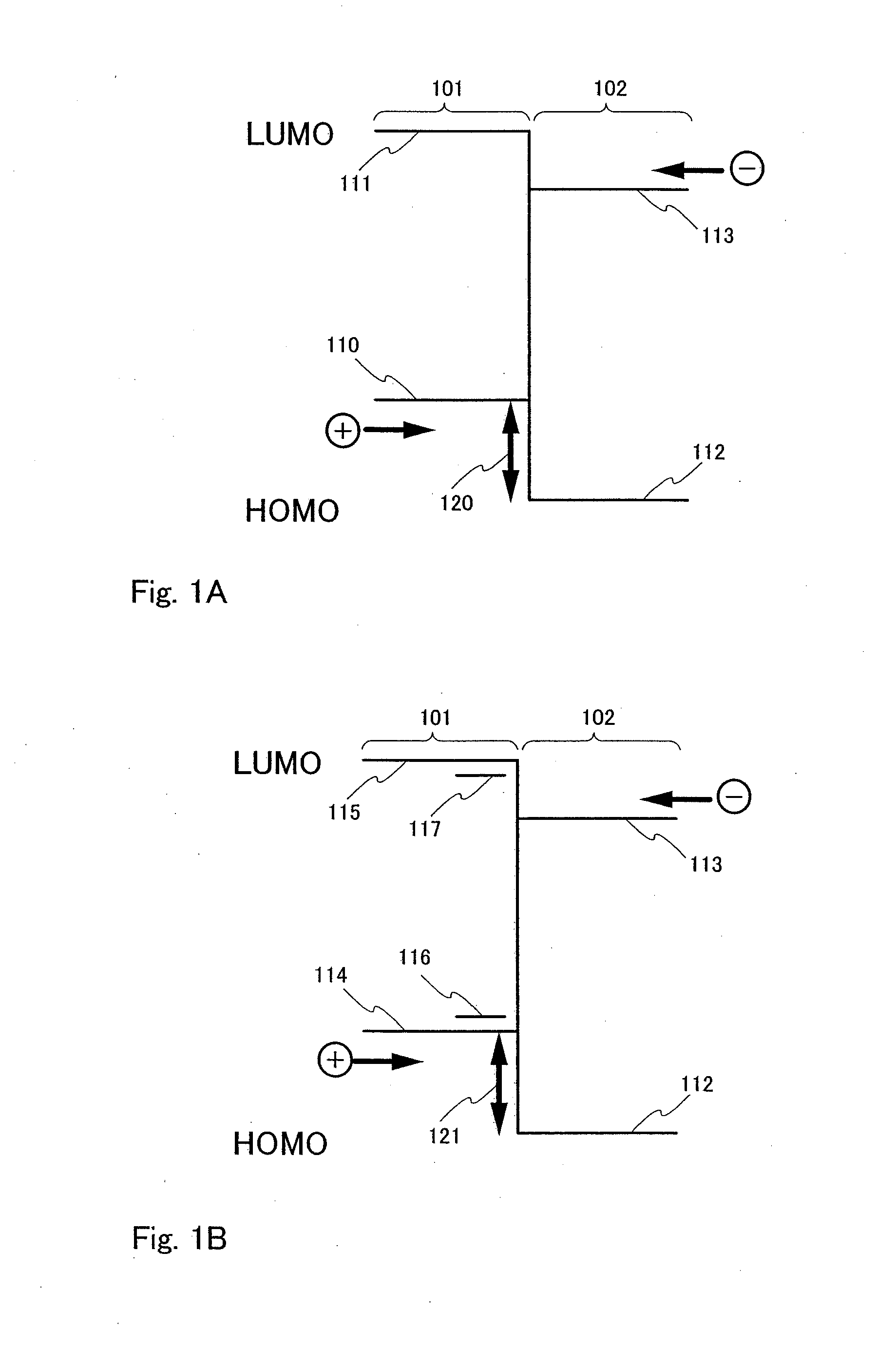
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
329 results about "Excimer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
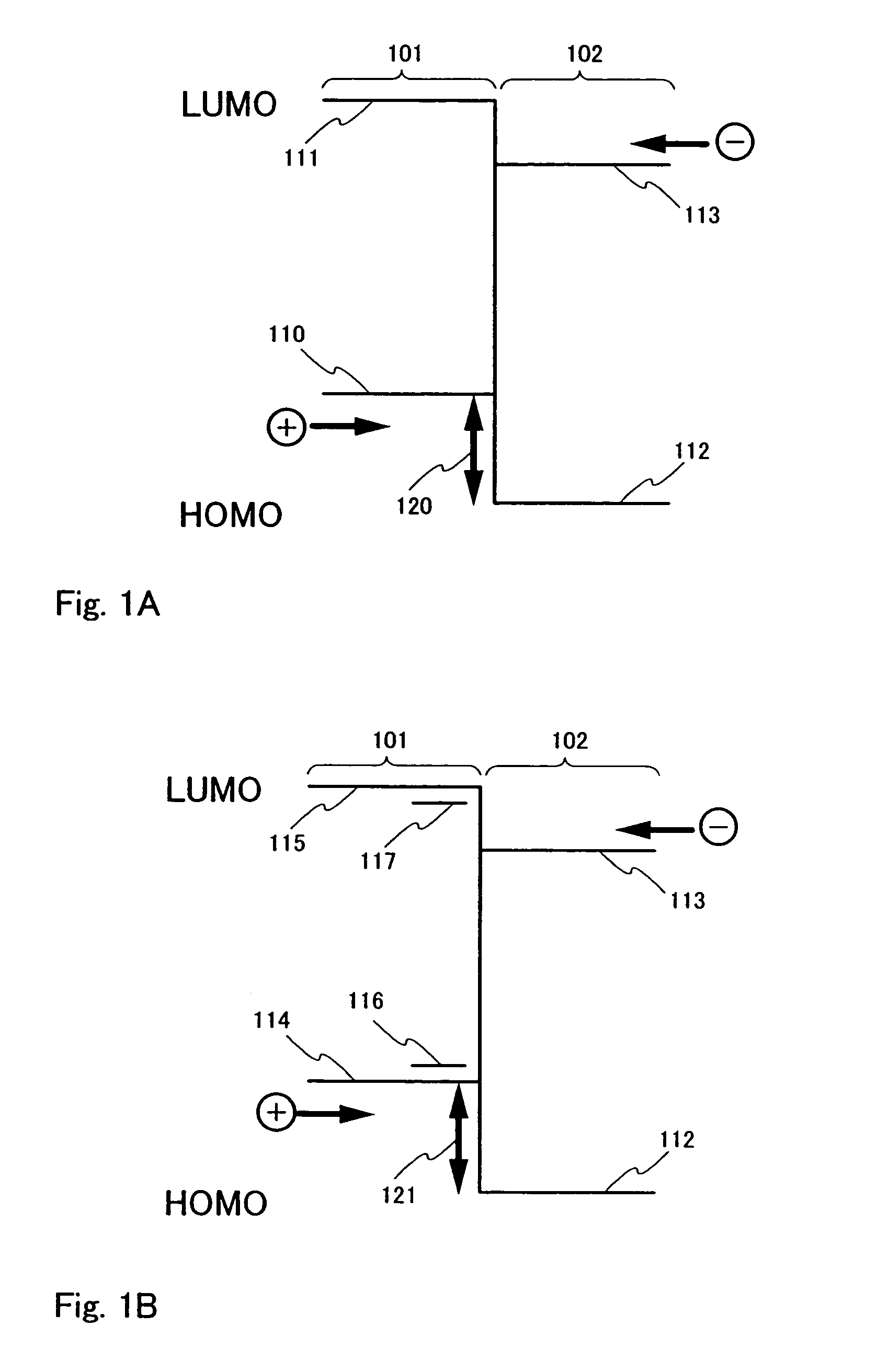
An excimer (originally short for excited dimer) is a short-lived dimeric or heterodimeric molecule formed from two species, at least one of which has completely filled valence shell by electrons (for example, noble gases). In this case, formation of molecules is possible only if such atom is in an electronic excited state. Heteronuclear molecules and molecules that have more than two species are also called exciplex molecules (originally short for excited complex). Excimers are often diatomic and are composed of two atoms or molecules that would not bond if both were in the ground state. The lifetime of an excimer is very short, on the order of nanoseconds. Binding of a larger number of excited atoms forms Rydberg matter clusters, the lifetime of which can exceed many seconds.
Discharge lamp
InactiveUS20100259152A1Irradiation of becomes intensiveImprove reliabilityIncadescent screens/filtersSolid cathode detailsCapacitanceGas-discharge lamp
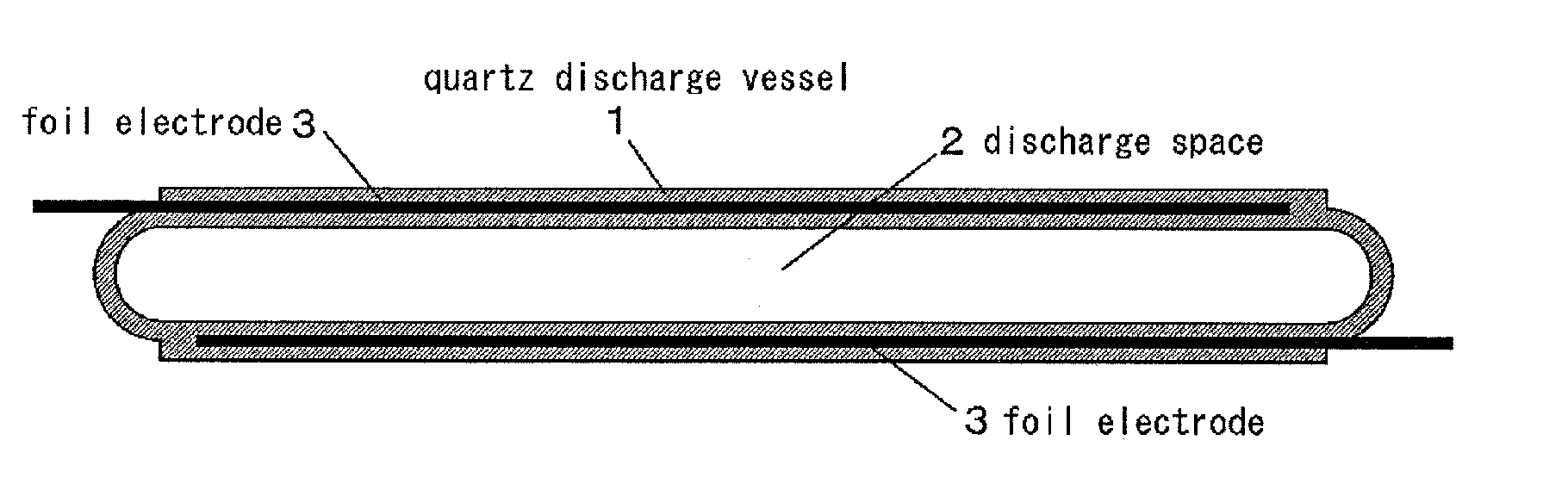
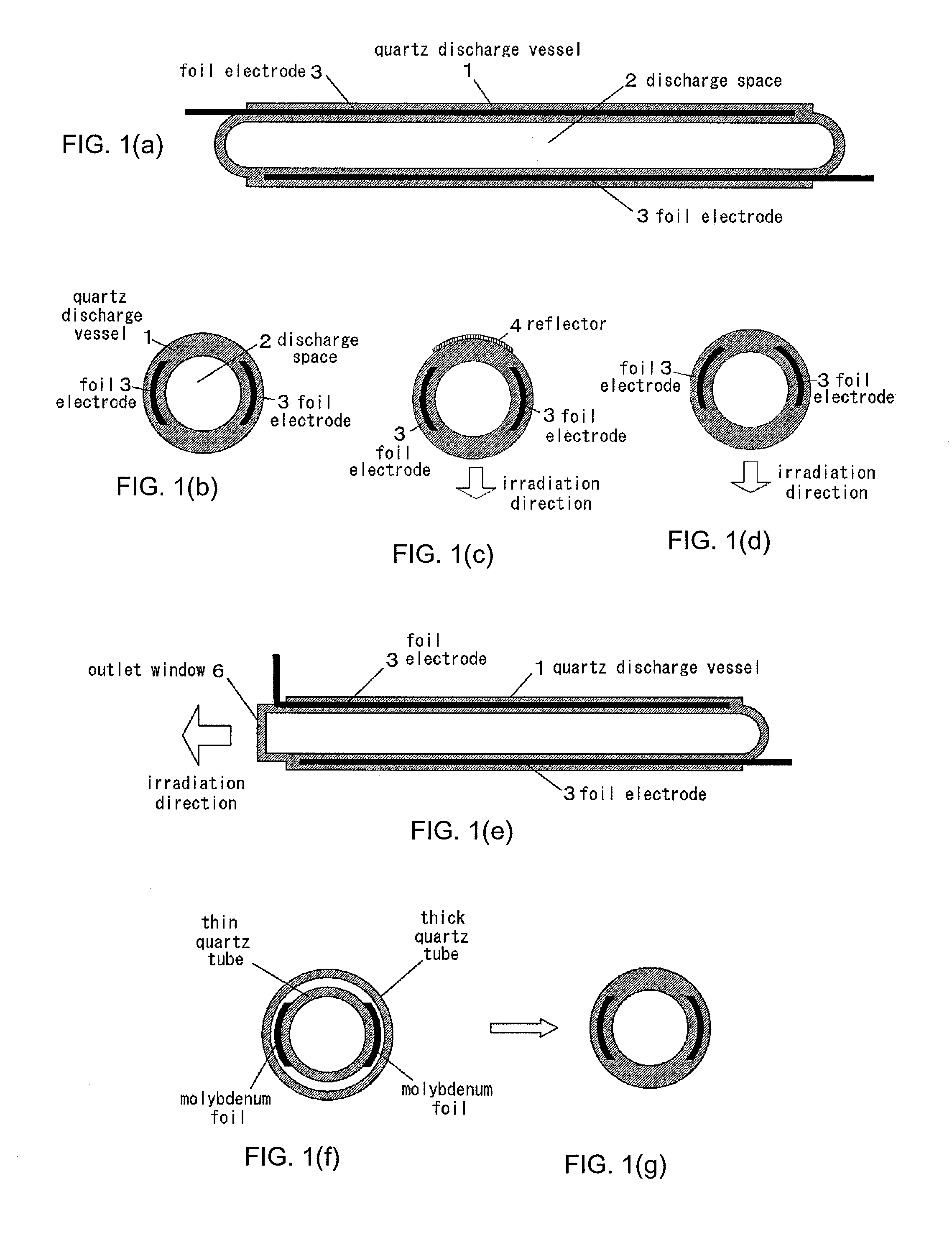
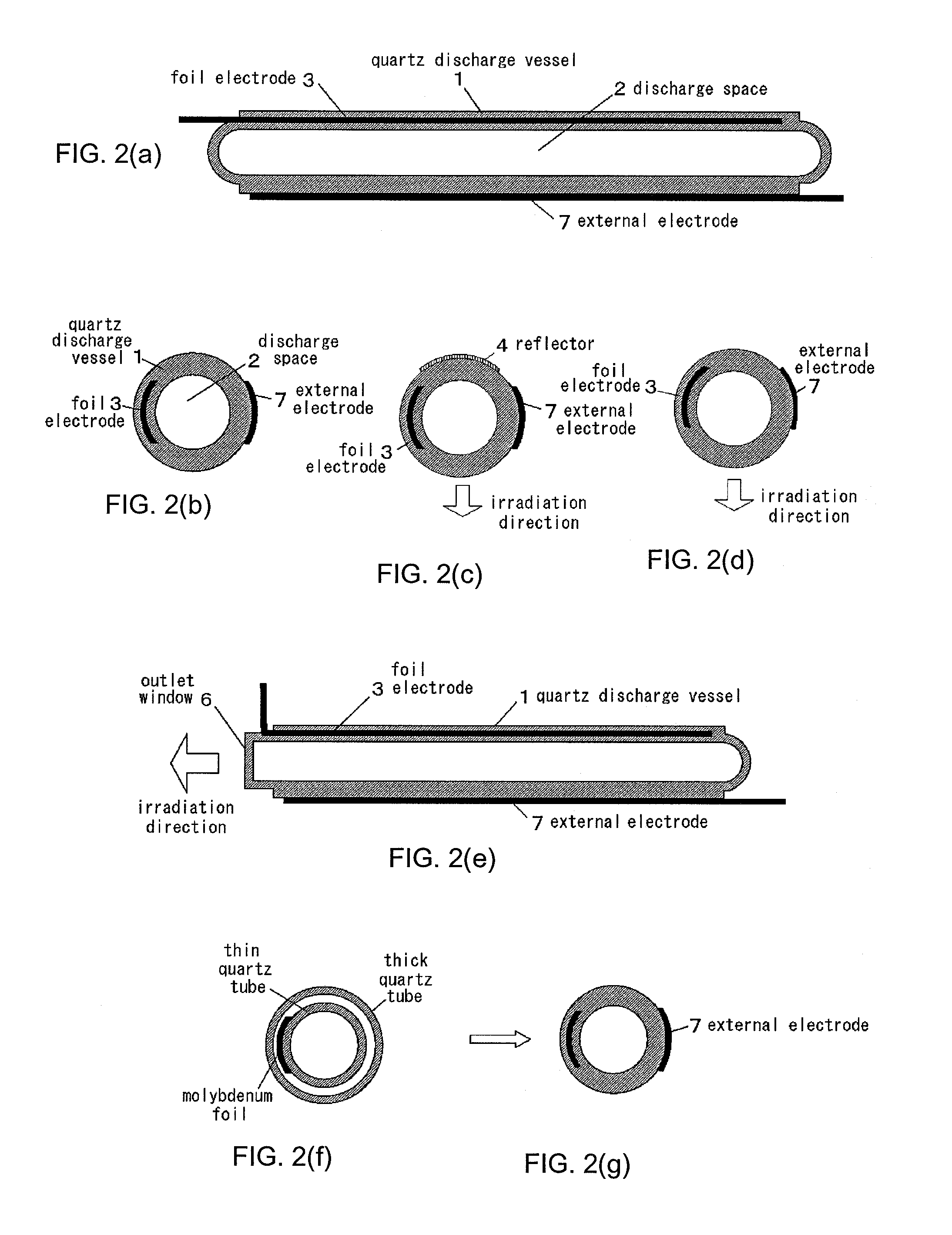
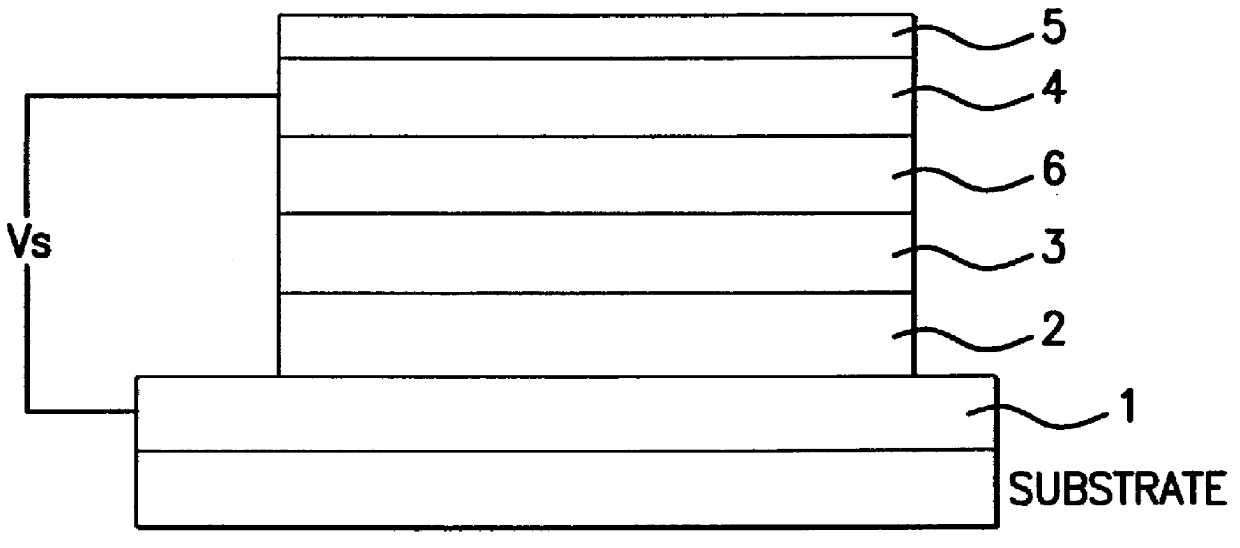
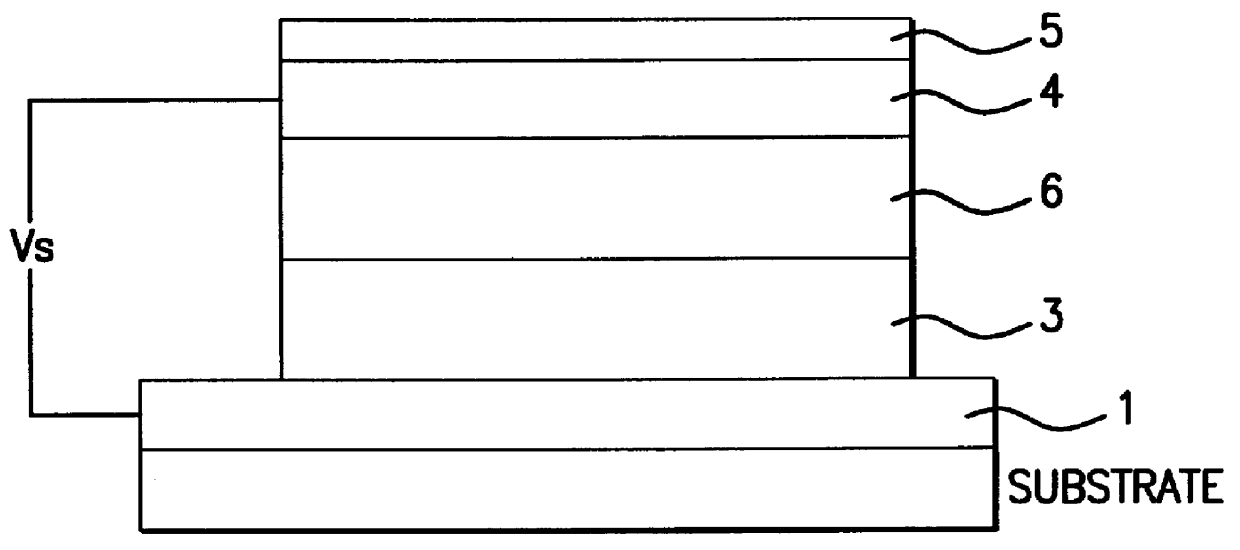
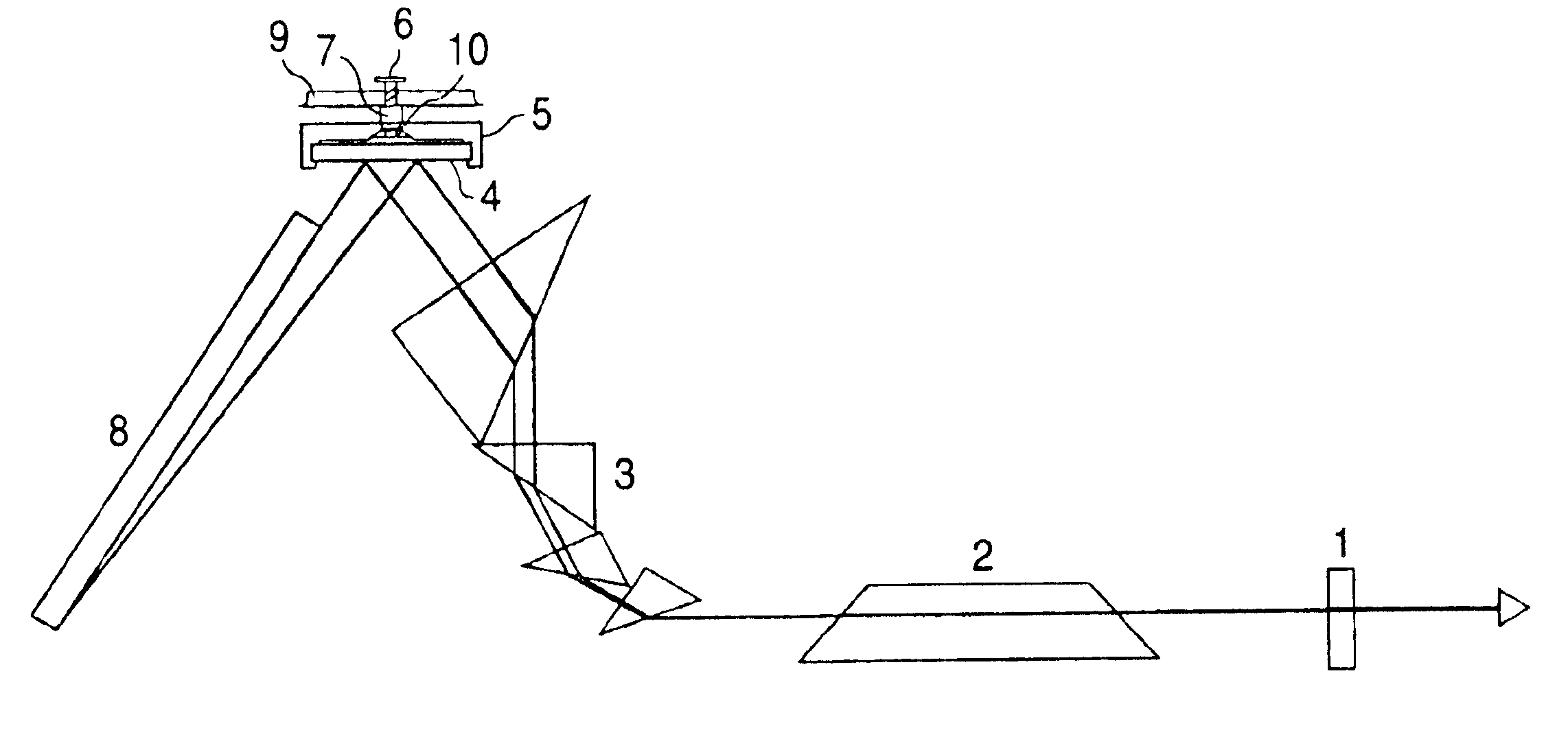
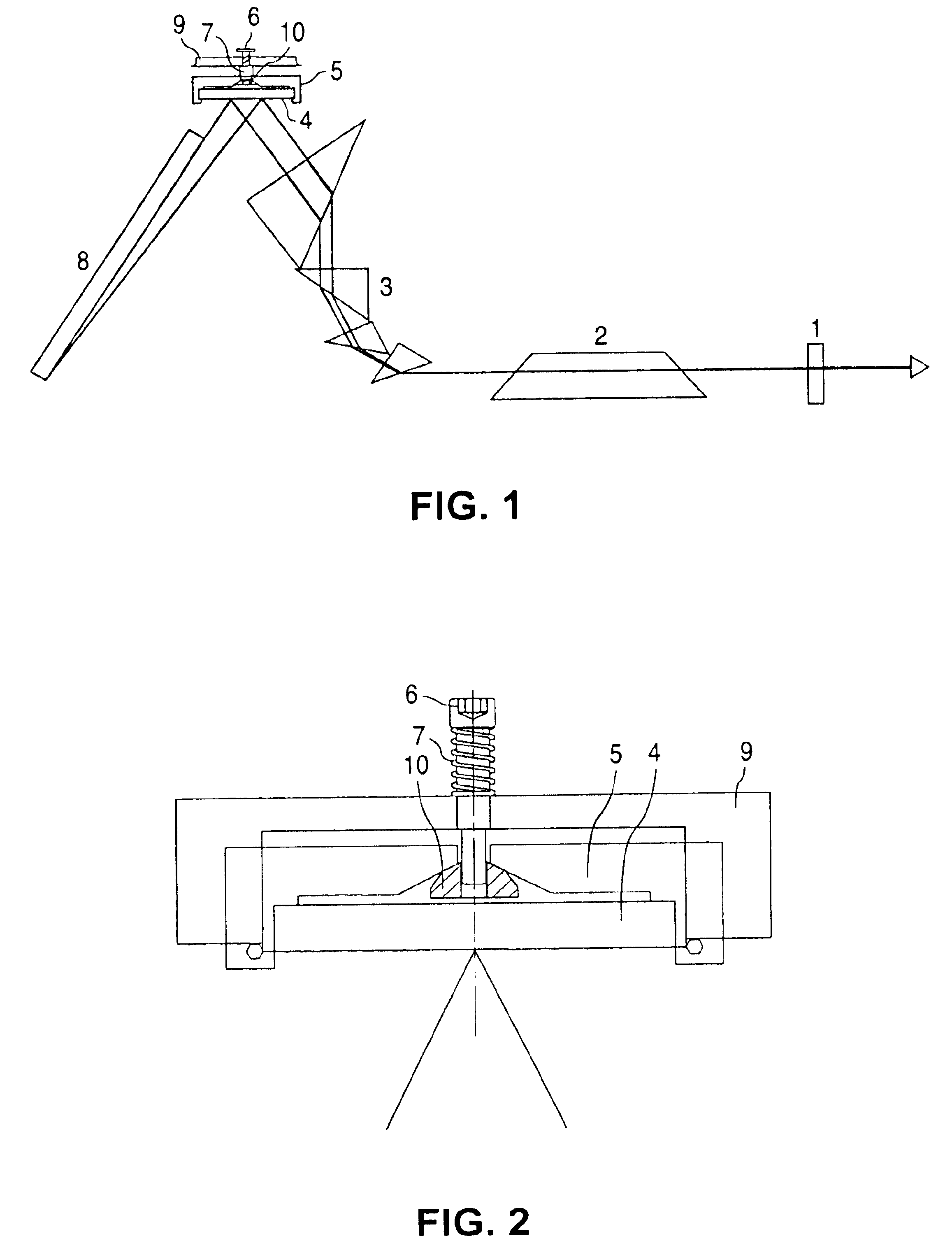
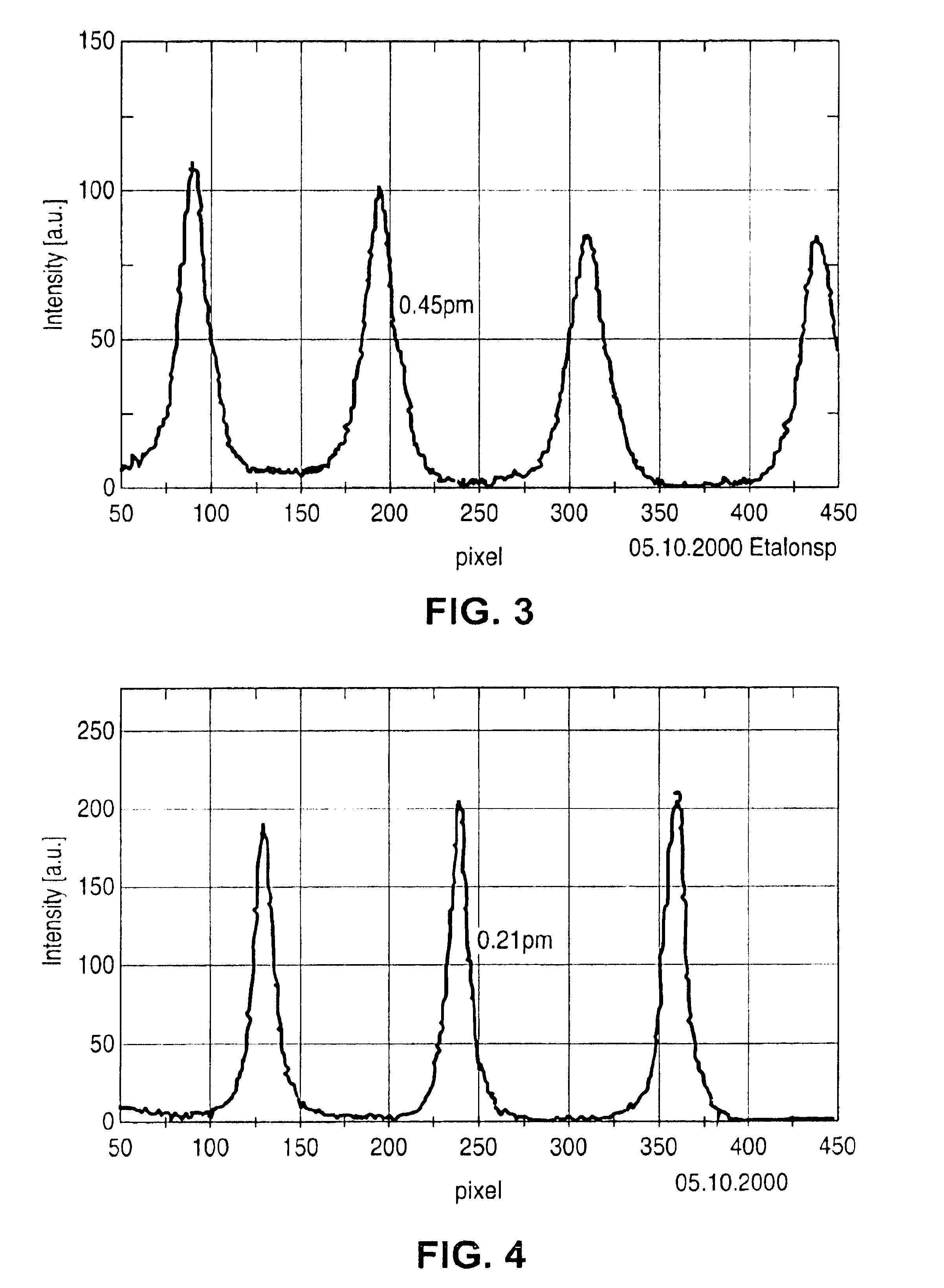
The object of this invention is to prevent surface discharge even when a high voltage is applied in a dielectric-barrier discharge lamp or a capacitively coupled high frequency discharge lamp with no electrodes in a discharge space. Ribbon foil electrodes 3 are embedded in the wall of a quartz discharge vessel 1. The discharge vessel 1 is disposed such that the foil electrodes 3 face each other on both sides of the axis of the quartz discharge vessel 1. It may be disposed such that the foil electrodes 3 have a truncated V-shaped cross-section. The single tube quartz discharge vessel 1 is filled with discharge gas to form excimer molecules by dielectric barrier discharge or capacitively coupled high-frequency discharge.
Owner:ORC MFG
Method of fabricating poly-crystalline silicon thin film and method of fabricating transistor using the same
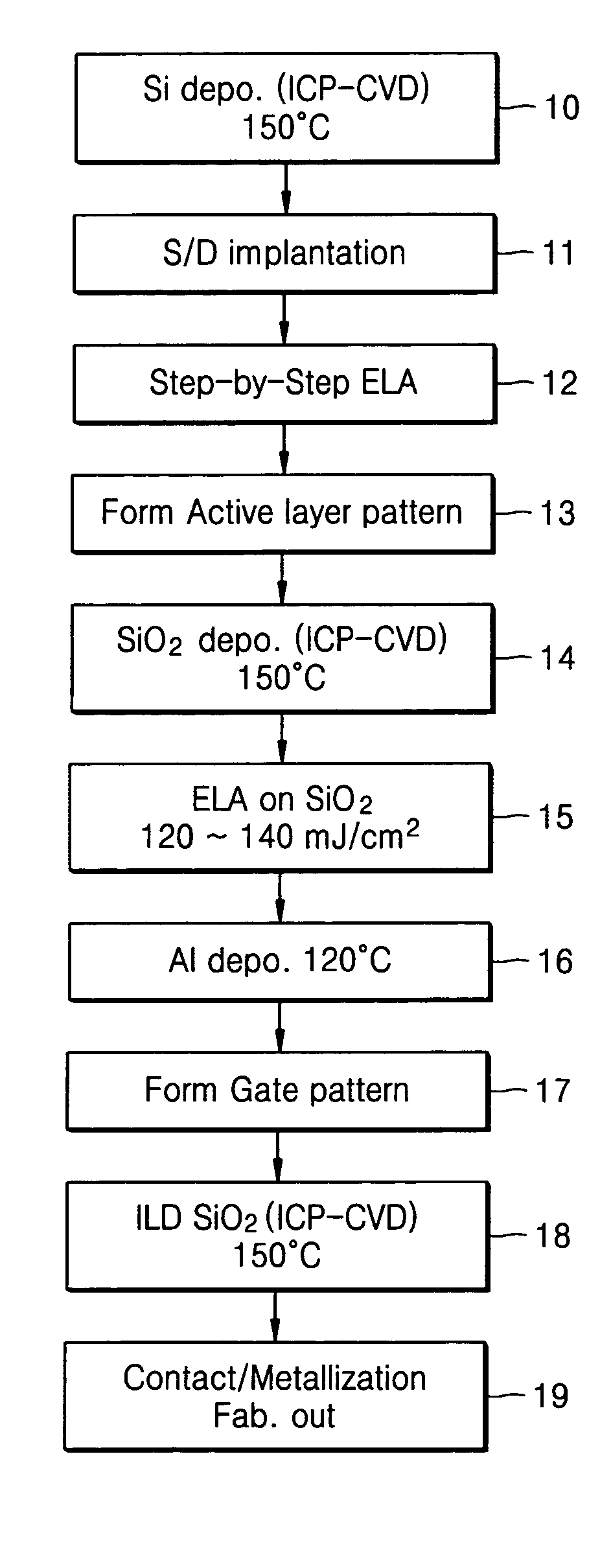
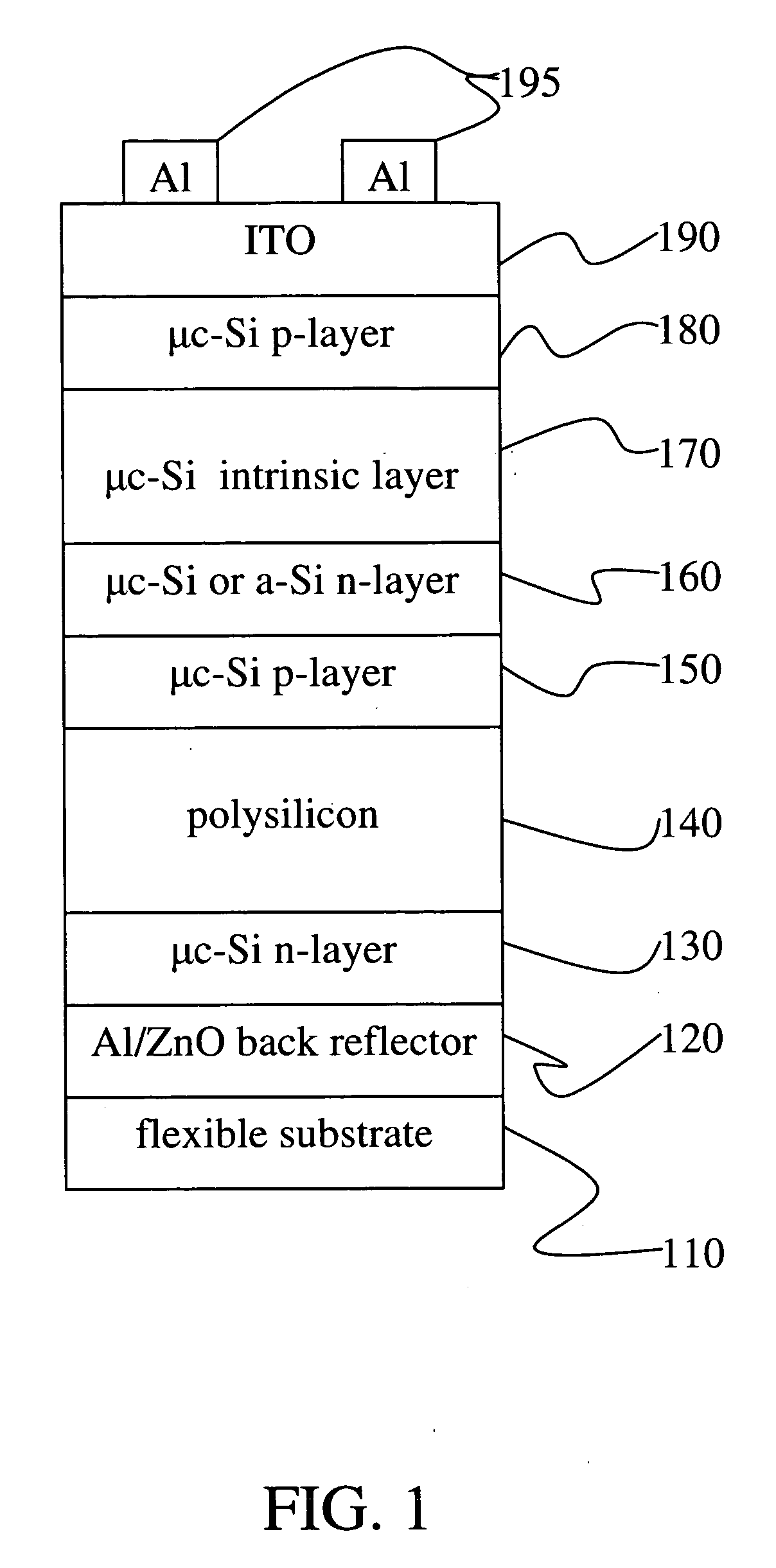
InactiveUS7563659B2Refined grain sizeHigh energyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInductively coupled plasmaSilicon thin film
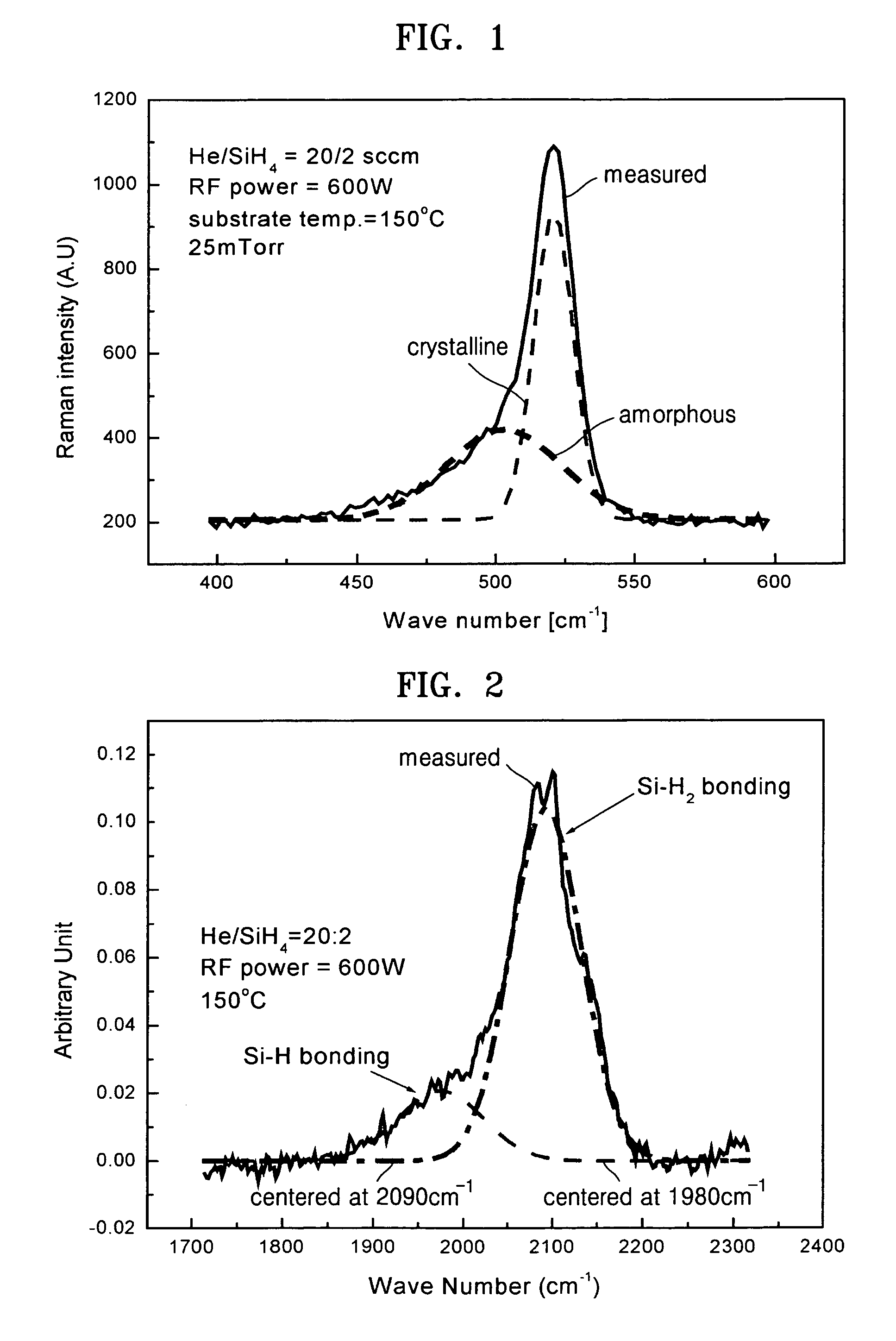
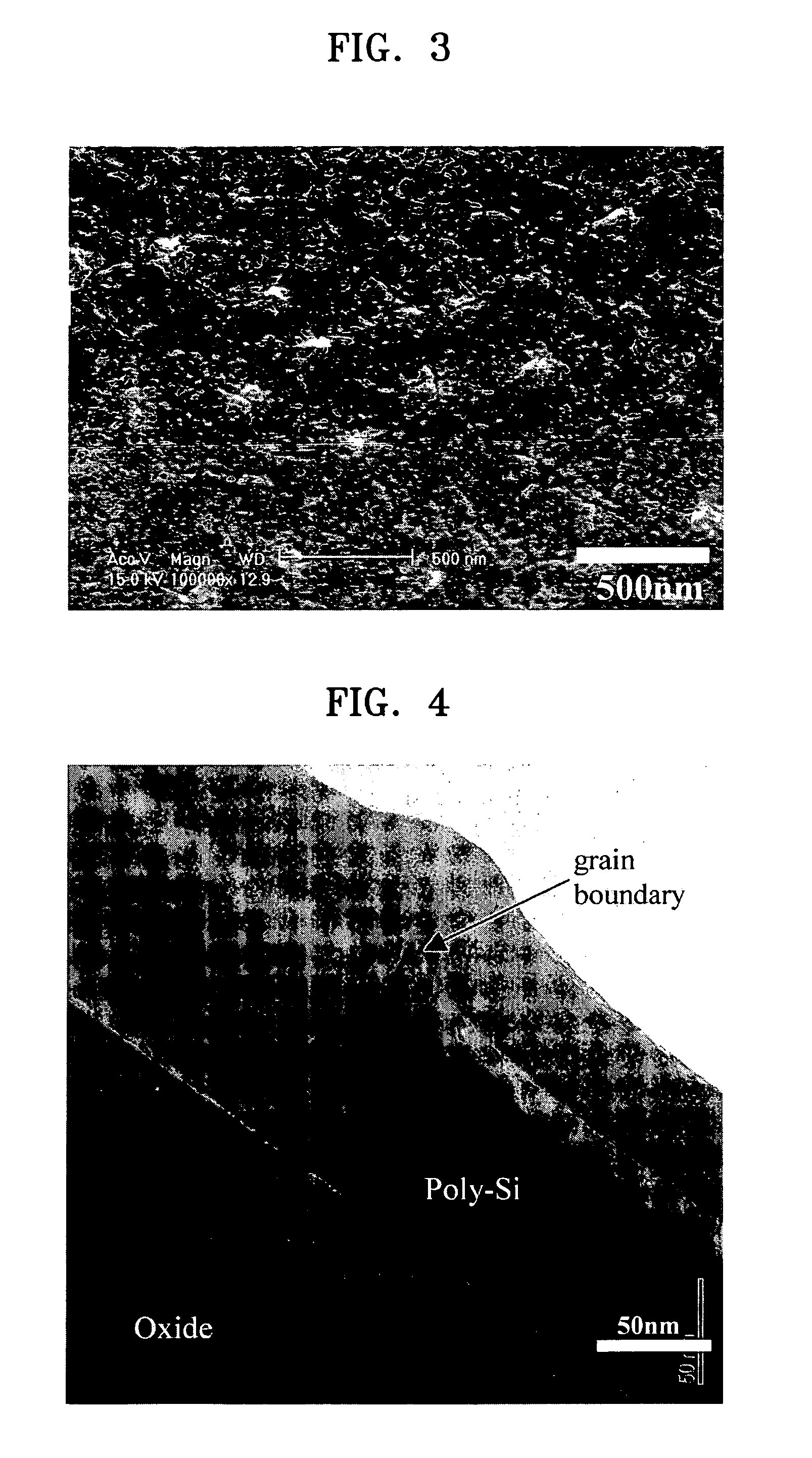
A method of fabricating a poly-Si thin film and a method of fabricating a poly-Si TFT using the same are provided. The poly-Si thin film is formed at a low temperature using inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition (ICP-CVD). After the ICP-CVD, excimer laser annealing (ELA) is performed while increasing energy by predetermined steps. A poly-Si active layer and a SiO2 gate insulating layer are deposited at a temperature of about 150° C. using ICP-CVD. The poly-Si has a large grain size of about 3000 Å or more. An interface trap density of the SiO2 can be as high as 1011 / cm2. A transistor having good electrical characteristics can be fabricated at a low temperature and thus can be formed on a heat tolerant plastic substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting element and light emitting device
InactiveUS7943925B2Improve light emission efficiencyImprove efficiencyLamination ancillary operationsDischarge tube luminescnet screensHigh concentrationPeak value
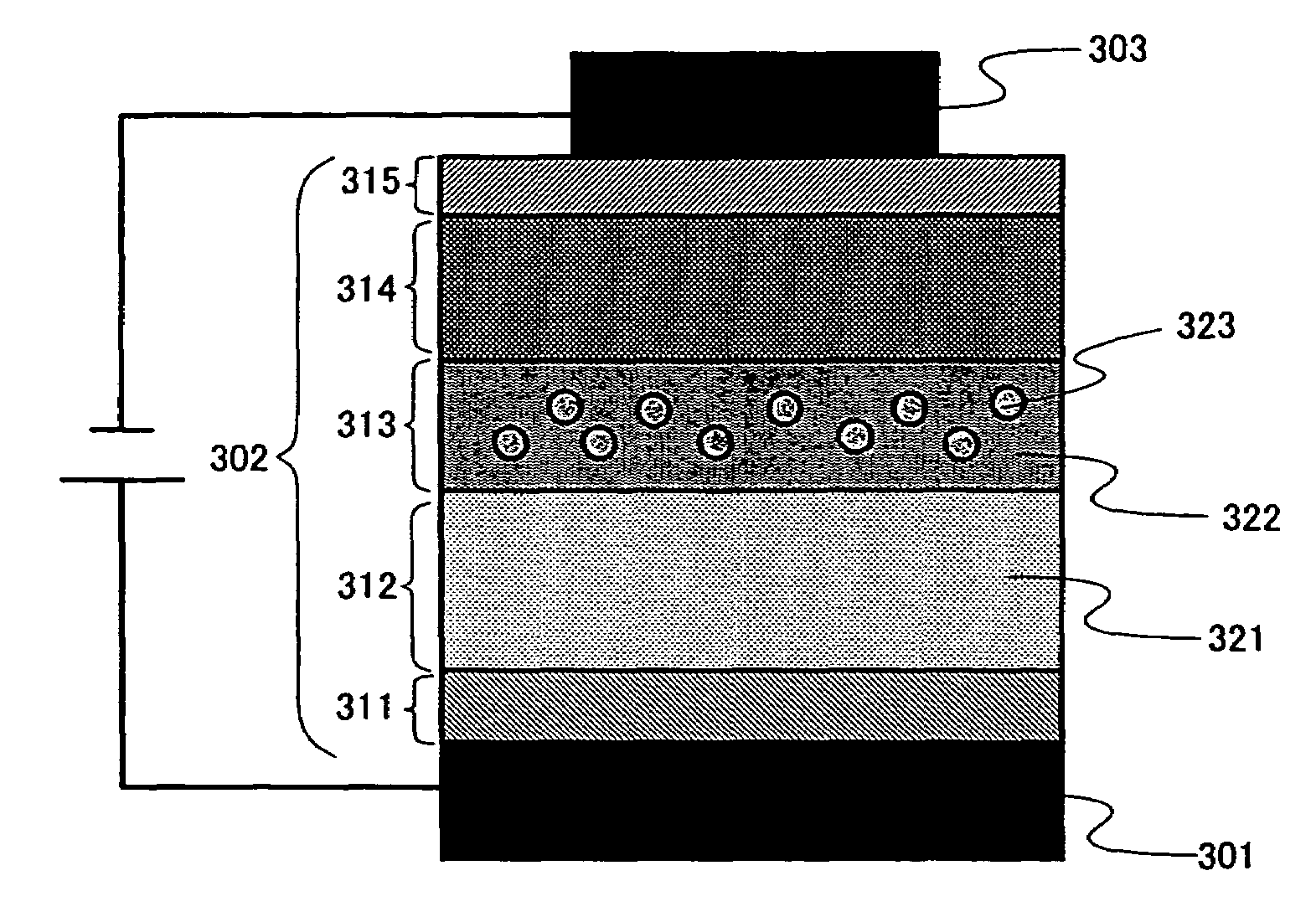
A high efficient white emission light emitting element having peak intensity in each wavelength region of red, green, and blue is provided. Specifically, a white emission light emitting element having an emission spectrum that is independent of current density is provided. A first light emitting layer 312 exhibiting blue emission and a second light emitting layer 313 containing a phosphorescent material that generates simultaneously phosphorescent emission and excimer emission are combined. In order to derive excimer emission from the phosphorescent material, it is effective to disperse a phosphorescent material 323 having a high planarity structure such as platinum complex at a high concentration of at least 10 wt % to a host material 322. Further, the first light emitting layer 312 is provided to be in contact with the second light emitting layer 313 at the side of an anode. Ionization potential of the second light emitting layer 313 is preferably larger by 0.4 eV than that of the first light emitting layer 312.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Excimer or molecular fluorine laser system with multiple discharge units
InactiveUS20030219094A1Handling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLaser arrangementsLithographic artistLight beam
A sub-310 nm lithography radiation source includes first and second beam generating modules for generating first and second pulsed beams, a beam combiner optic for producing a single combined beam from the first and second pulsed beams, and optics for directing each of the first and second pulsed beams to be incident upon the beam combiner.
Owner:LAMBDA PHYSIK
Method and system for fabricating an OLED
InactiveUS20040132228A1Solid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingOrganic light emitting deviceErbium lasers
A method and system for fabricating a layer of an organic light emitting device using pulsed laser deposition is provided. A pulsed laser source is used in the method for depositing an organic or coordination complex solid sample on a substrate. A plurality of coherent light wavelengths tuned at different frequencies from the laser and directed through an optical inlet of a vacuum chamber strike a sample to form a volatized sample for depositing on a substrate. Pulsed laser sources used in the method and system include YAG, excimer, alexandrite or combinations thereof. The system includes a pulsed laser source, a vacuum chamber, and an optical inlet for receiving at least two coherent light wavelengths tuned at different frequencies from a pulsed laser source. Alternative methods of deposition may also be performed within the same vacuum chamber.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Deposition methods for the formation of polycrystalline materials on mobile substrates
InactiveUS20060024442A1Solid-state devicesChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenMicrocrystalline silicon
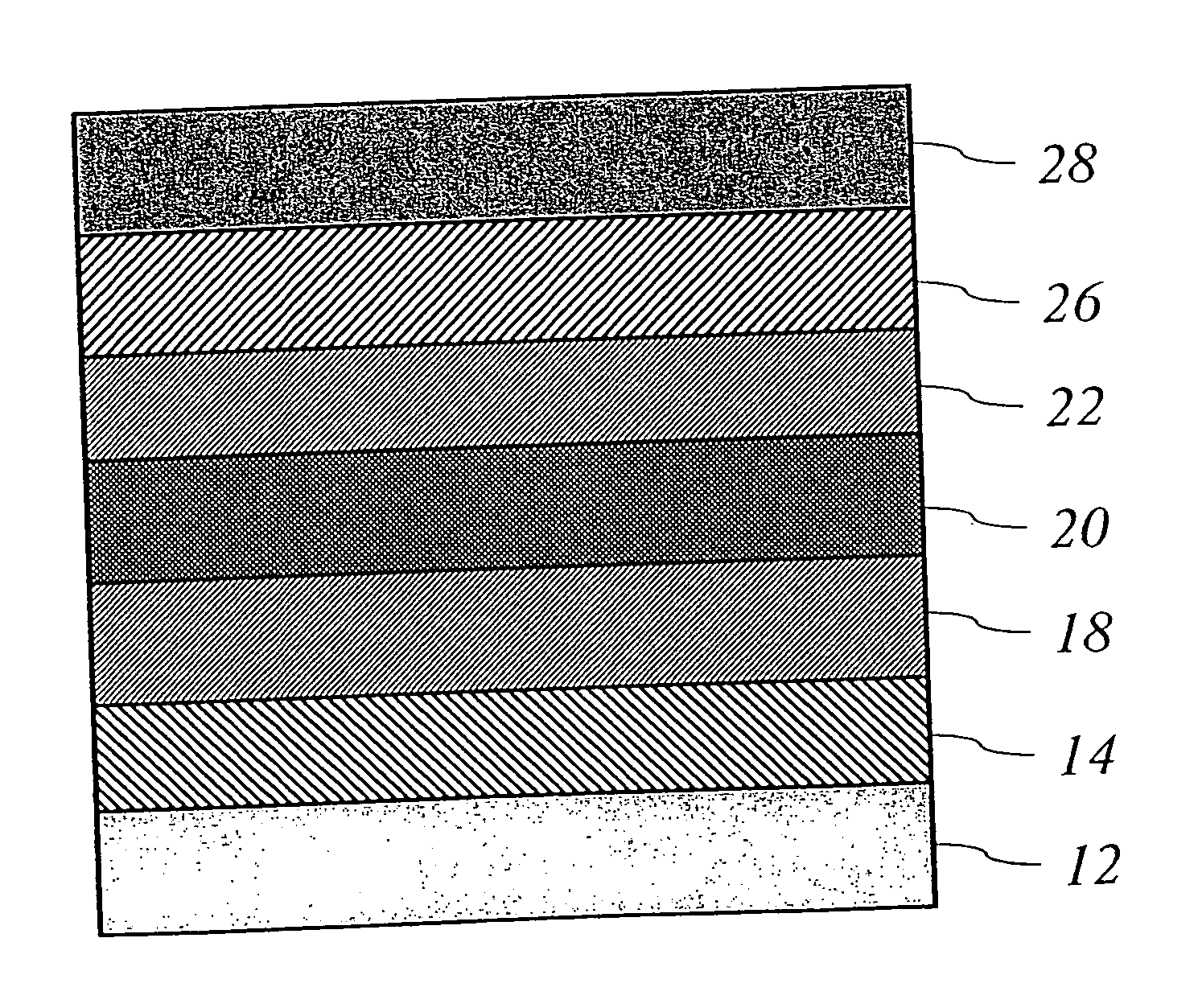
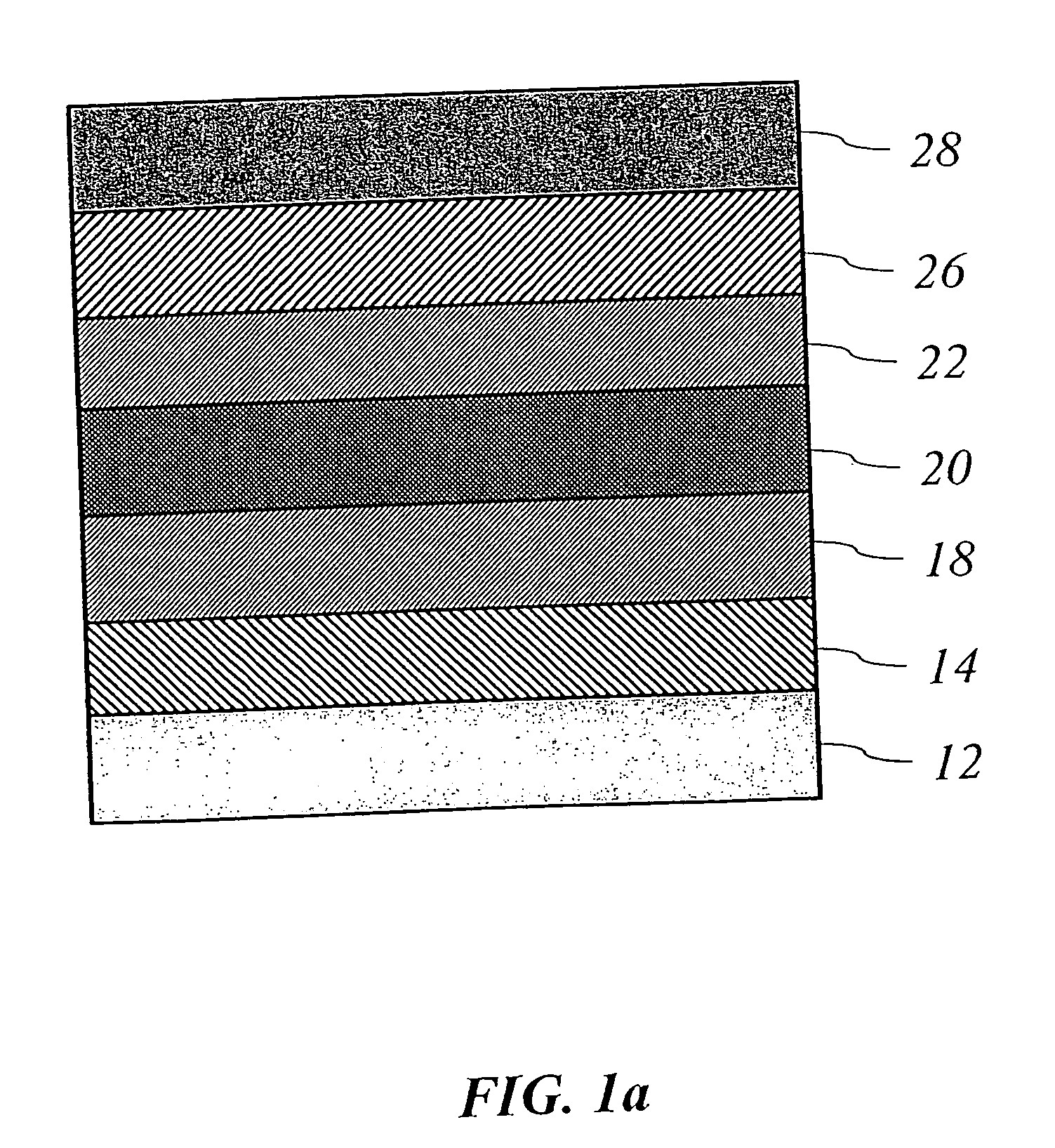
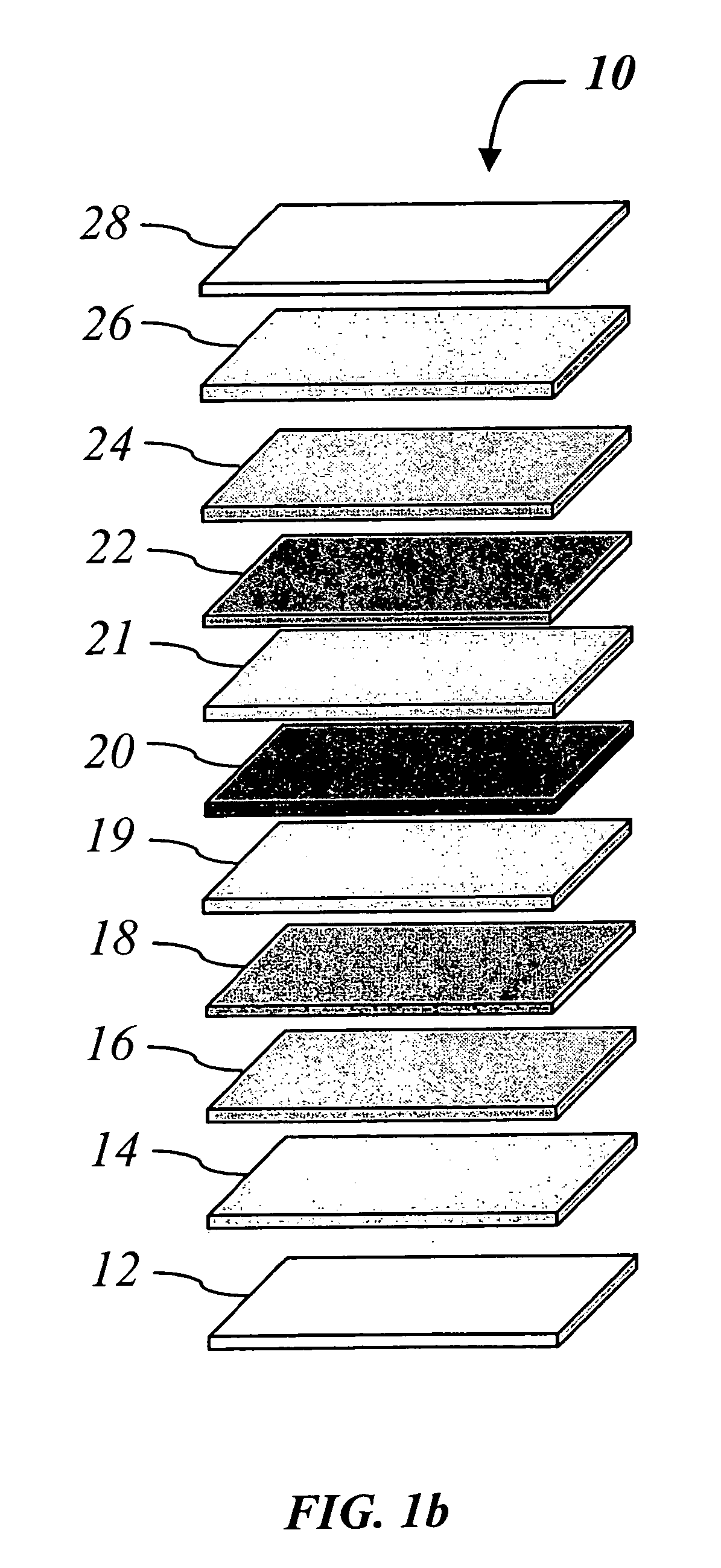
A deposition apparatus and method for continuously depositing a polycrystalline material such as polysilicon or polycrystalline SiGe layer on a mobile discrete or continuous web substrate. The apparatus includes a pay-out unit for dispensing a discrete or continuous web substrate and a deposition unit that receives the discrete or continuous web substrate and deposits a series of one or more thin film layers thereon in a series of one or more deposition or processing chambers. In a preferred embodiment, polysilicon is formed by first depositing a layer of amorphous or microcrystalline silicon using PECVD and transforming said layer to polysilicon through heating or annealing with one or more lasers, lamps, furnaces or other heat sources. Laser annealing utilizing a pulsed excimer is a preferred embodiment. By controlling the processing temperature, temperature distribution within a layer of amorphous or microcrystalline silicon etc., the instant deposition apparatus affords control over the grain size of polysilicon. Passivation of polysilicon occur through treatment with a hydrogen plasma. Layers of polycrystalline SiGe may similarly be formed. The instant deposition apparatus provides for the continuous deposition of electronic devices and structures that include a layer of a polycrystalline material such as polysilicon and / or polycrystalline SiGe. Representative devices include photovoltaic devices and thin film transistors. The instant deposition apparatus also provides for the continuous deposition of chalcogenide switching or memory materials alone or in combination with other metal, insulating, and / or semiconducting layers.
Owner:OVSHINSKY STANFORD R
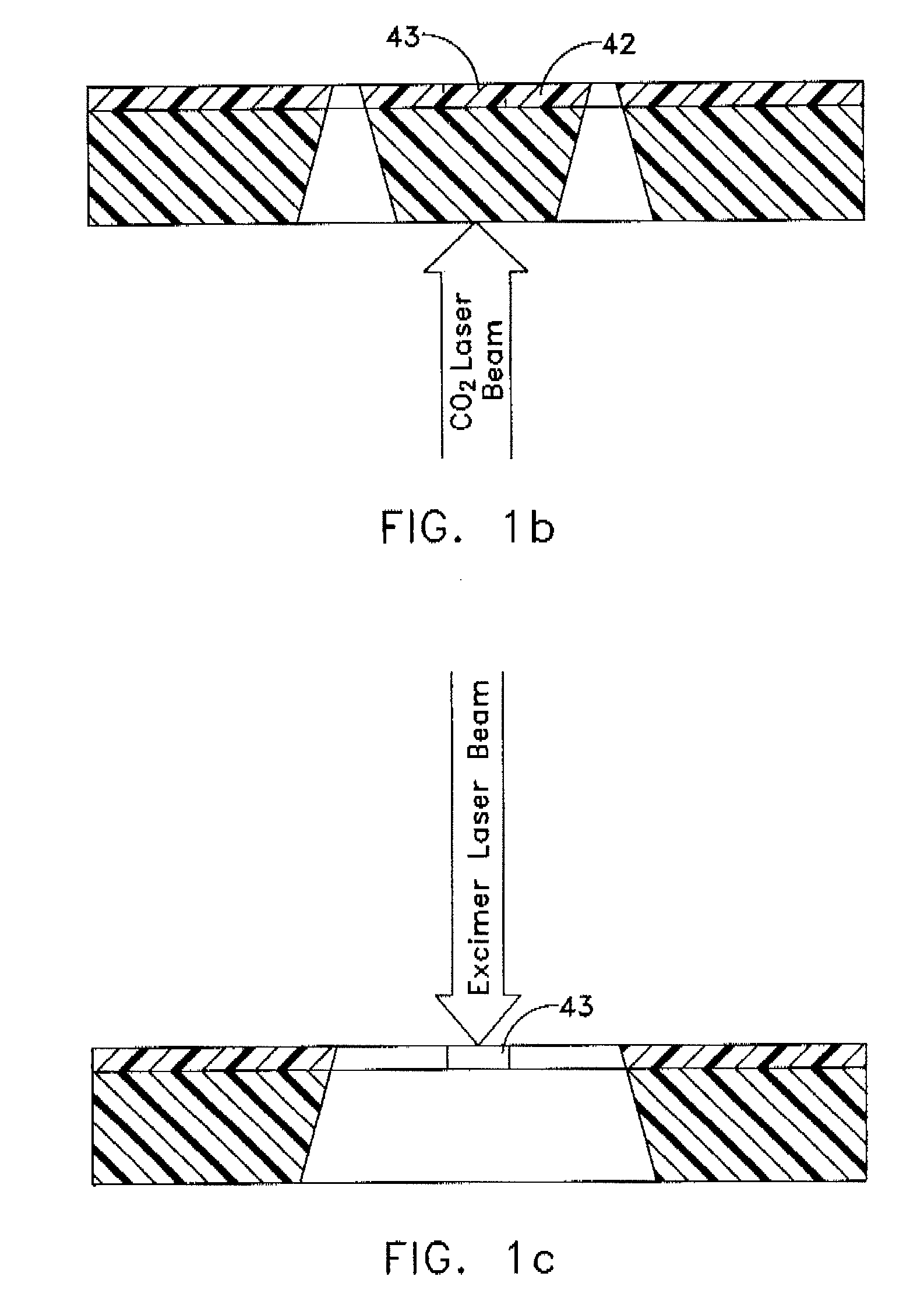
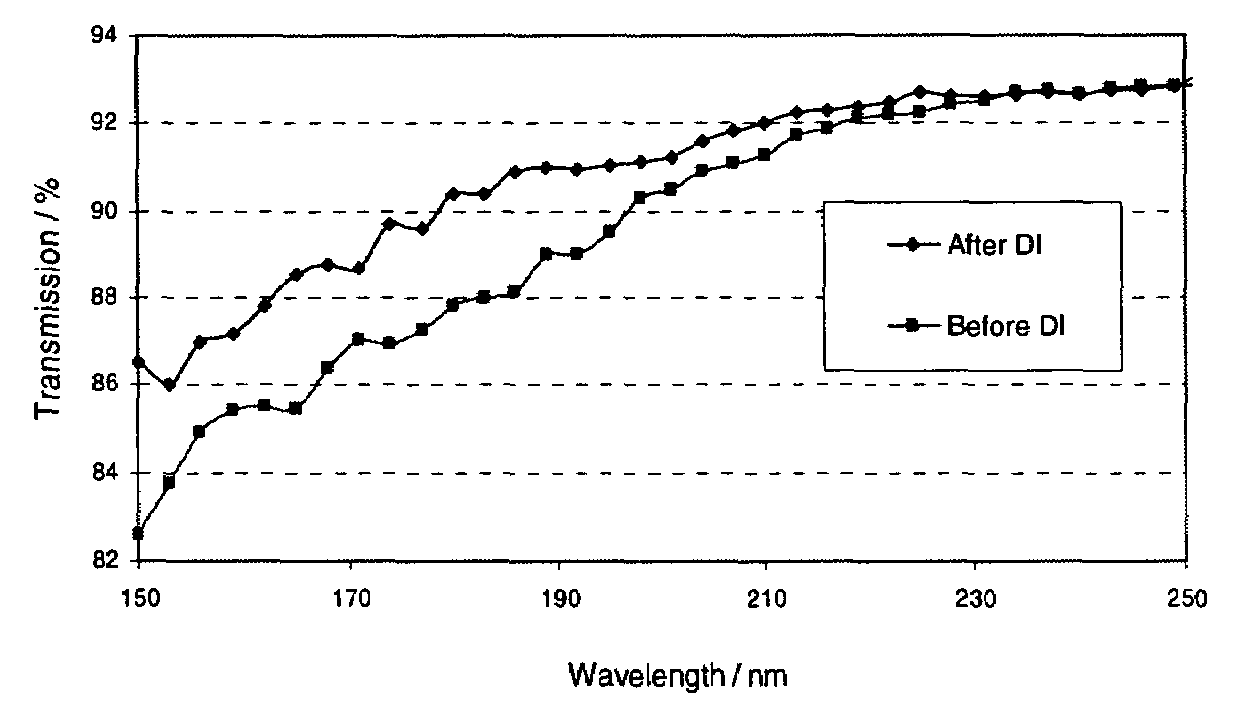
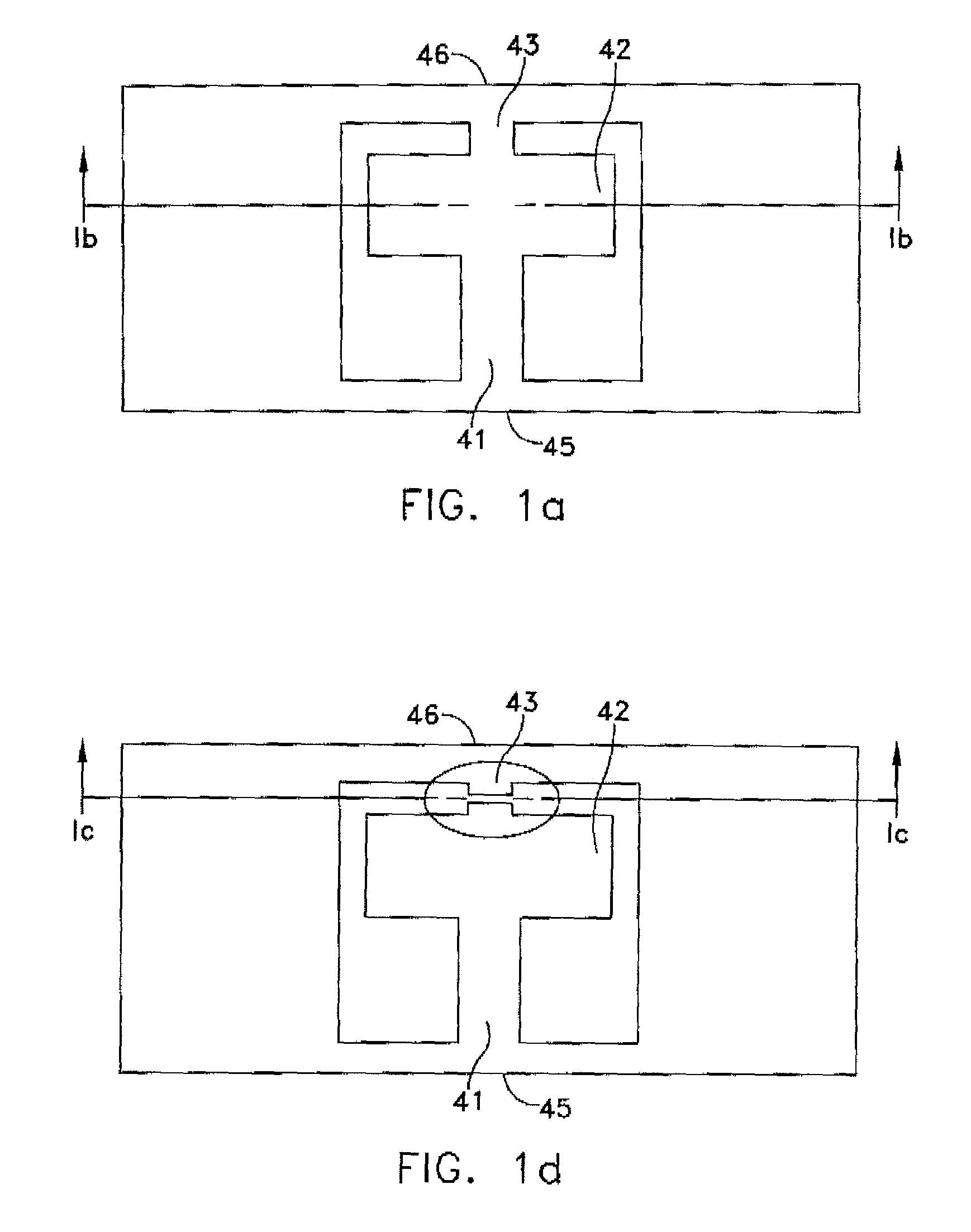
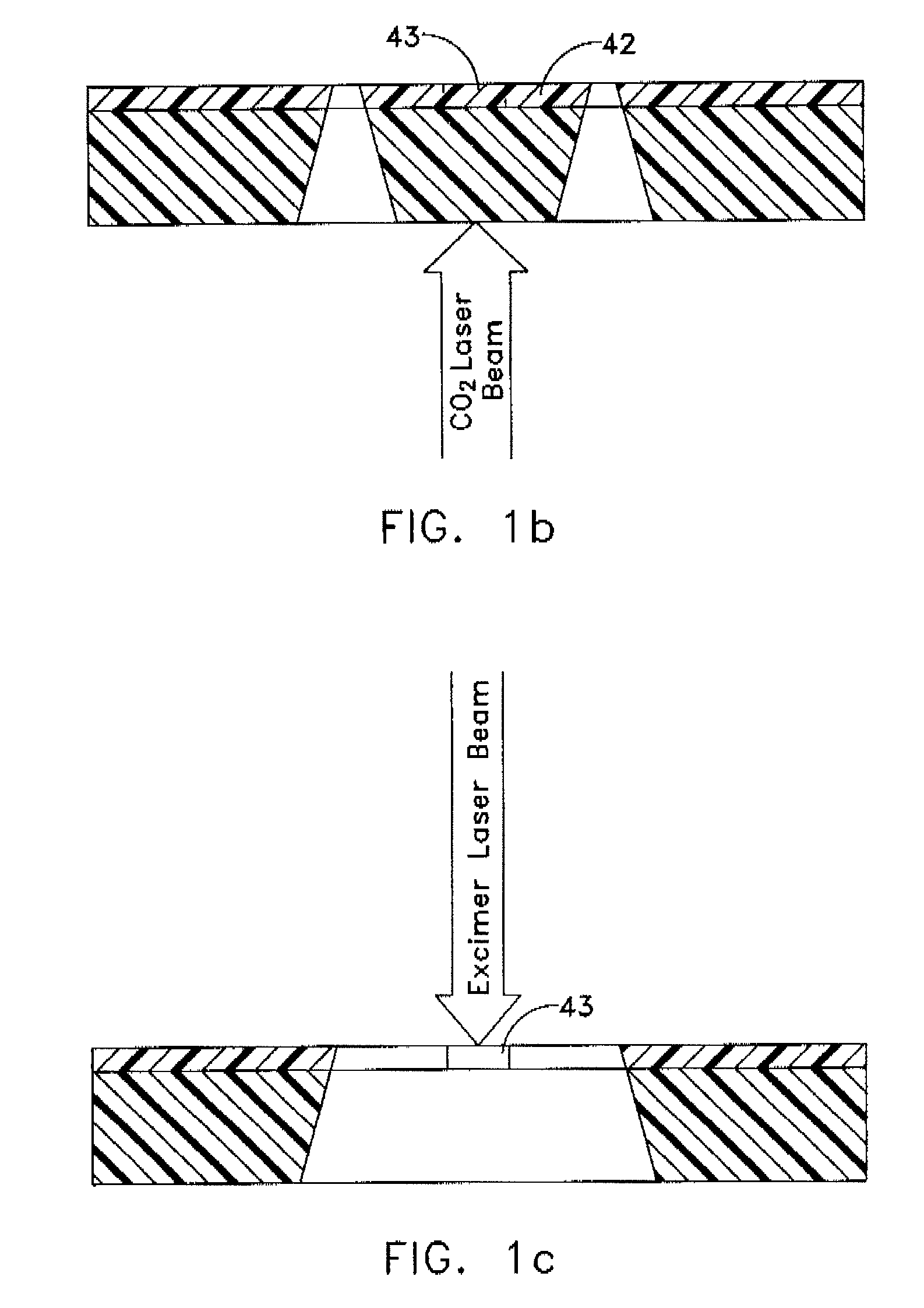
Surfacing of metal fluoride excimer optics
ActiveUS20060046099A1High purityEnhanced vapor depositionNatural mineral layered productsWater-setting substance layered productSingle crystalPrism
The invention is directed to improved coated metal fluoride single crystal optical elements suitable for use in below 250 nm optical lithography, and particularly below 200 nm lithography. The coated elements of the invention can be lenses, windows, prisms and other elements used in lithographic methods, including the laser sources used therein. The invention is also directed to a method of removing the quasi-Bielby layer formed when a shaped optical element is polished. Removal of the quasi-Bielby layer prior to coating results in improved durability and optical transmission characteristics of the coated lenses. The coating material can be any material that does not impede the transmission of below 250 nm electromagnetic radiation. Fluorine doped silicon dioxide is the preferred coating material.
Owner:CORNING INC
Light Emitting Element and Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20110204353A1Improve efficiencyEffective lightingLamination ancillary operationsElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh concentrationPeak value
A high efficient white emission light emitting element having peak intensity in each wavelength region of red, green, and blue is provided. Specifically, a white emission light emitting element having an emission spectrum that is independent of current density is provided. A first light emitting layer 312 exhibiting blue emission and a second light emitting layer 313 containing a phosphorescent material that generates simultaneously phosphorescent emission and excimer emission are combined. In order to derive excimer emission from the phosphorescent material, it is effective to disperse a phosphorescent material 323 having a high planarity structure such as platinum complex at a high concentration of at least 10 wt % to a host material 322. Further, the first light emitting layer 312 is provided to be in contact with the second light emitting layer 313 at the side of an anode. Ionization potential of the second light emitting layer 313 is preferably larger by 0.4 eV than that of the first light emitting layer 312.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Strongly quenching oligomeric excimer/quencher pairs for detection schemes
InactiveUS20100129820A1High efficiency quenchingEfficiently quenchedSaccharide with carbocyclic radicalsSugar derivativesOligomerPerylene
Compositions and systems are provided for the high efficiency quenching small water-soluble oligomers, or oligofluors, of from about 1-10 kd in size, where the oligofluors comprise multiple excimeric or exciplex forming fluorophores arranged on a scaffold, which are efficiently quenched by a quencher entity linked to the oligomer through a cleavable moiety. Fluorophores of interest include, without limitation, aromatic fluorophores such as pyrenes, e.g. benzopyrene, perylene, pyrene, etc. In some embodiments the oligofluor / quencher combination provides for a Stern-Vollmer constant (KSV) of greater than about 106 M−1, and may be greater than about 107 M−1, greater than about 108 M−1, or more. In some embodiments of the invention, the scaffold is a phosphodiester / glycoside backbone, e.g. an analog of a polynucleotide. The system of oligofluors and quenchers can be used in qualitative and quantitative screening and detection methods to detect any enzymatic, chemical or catalytic activity that can cleave the moiety between the quencher and scaffold.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Nanolithography method and nanolithography device
InactiveCN102866580AControl shapeRegulatory distributionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNanolithographyTwo-photon absorption
The invention discloses a nanolithography method and a nanolithography device in the technical field of nanolithography. The device comprises a femtosecond laser device, a light transmittance base plate, a photoetching mask plate, photoresist and a substrate. A specific super-diffraction limit graph is formed on the photoetching mask plate through the femtosecond laser device; a plasma excimer excitation structure on the upper surface of the photoetching mask plate is changed, and an exposure wavelength is adjusted by controlling the material of the photoetching mask plate, so that the shape, the distribution and the size of the super-diffraction limit graph can be controlled; moreover, a two-photon absorption phenomenon of the photoresist is introduced; and the line width of an exposure graph of the photoresist is controlled by controlling the power of a femtosecond laser exposure light source.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Organic electroluminescent element having an excimer light irradiated positive electrode and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6060826ALow luminescence starting potentialLuminous properties are stableSpark gapsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerOrganic electroluminescence
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an organic electroluminescent element having uniform surface luminescence, large luminescence intensity, and excellent stability over repeated use. The present invention provides a method of manufacturing an organic electroluminescent element using a positive electrode irradiated by excimer light when manufacturing an organic electroluminescent element comprising at least a substrate on which is sequentially formed a positive electrode, organic layer including an organic luminescent layer, and negative electrode, and an organic electroluminescent element manufactured by said method.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film and deposition method thereof, and semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20030039866A1Uniform film qualitySimple methodLaser detailsVacuum evaporation coatingLattice defectsDislocation
A Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film which can be deposited on any given substrate to have uniform film quality and excellent crystalline, and a deposition method thereof. A semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. A poly-crystalline Group III nitride compound thin film is deposited on a substrate by sputtering at a deposition rate of 15 to 200 nm / hour using a Group III nitride compound target in a plazma atmosphere of gas comprising 10 mole % or more nitrogen. Then, the poly-crystalline Group III nitride compound semiconductor thin film deposited on the substrate is irradiated with an excimer pulsed laser with an energy density of about 200 mJ / cm2, in an atmosphere of gas with an oxygen content of 2 mole % or less. Thereby, lattice defects such as grain boundaries or dislocations which occur in the thin film are removed.
Owner:MITAMURA SATOSHI
Miniature array spectral filter based on metallic surface plasma excimer
InactiveCN101256246AWide range of choicesPerformance indicators unchangedOptical filtersEtchingMedical diagnosis
The invention discloses a minitype array filter based on metal surface plasma excimer. A plurality of array units are provided on an optical substrate, a sub-wavelength hairline is set between the array units and a plurality of linear grid grooves of incidence plane, or emergence plane or incidence plane and emergence plane which are symmetrically distributed are set at the two sides of the sub-wavelength hairline in a space, wherein the distance of the linear grid groove is same to the width thereof. The invention has features: simple technique, compactness, and can be connected with the LED, photosensitive detection, optical imaging sensor to form a variety of filters and imaging spectrometer of sub-wavelength, with high resolution, high integrity and wide application foreground in photo etching, high density data storage, near-field optics, space exploration, and medical diagnosis. The minitype array filter can be used in microwave, infrared and visible light band.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
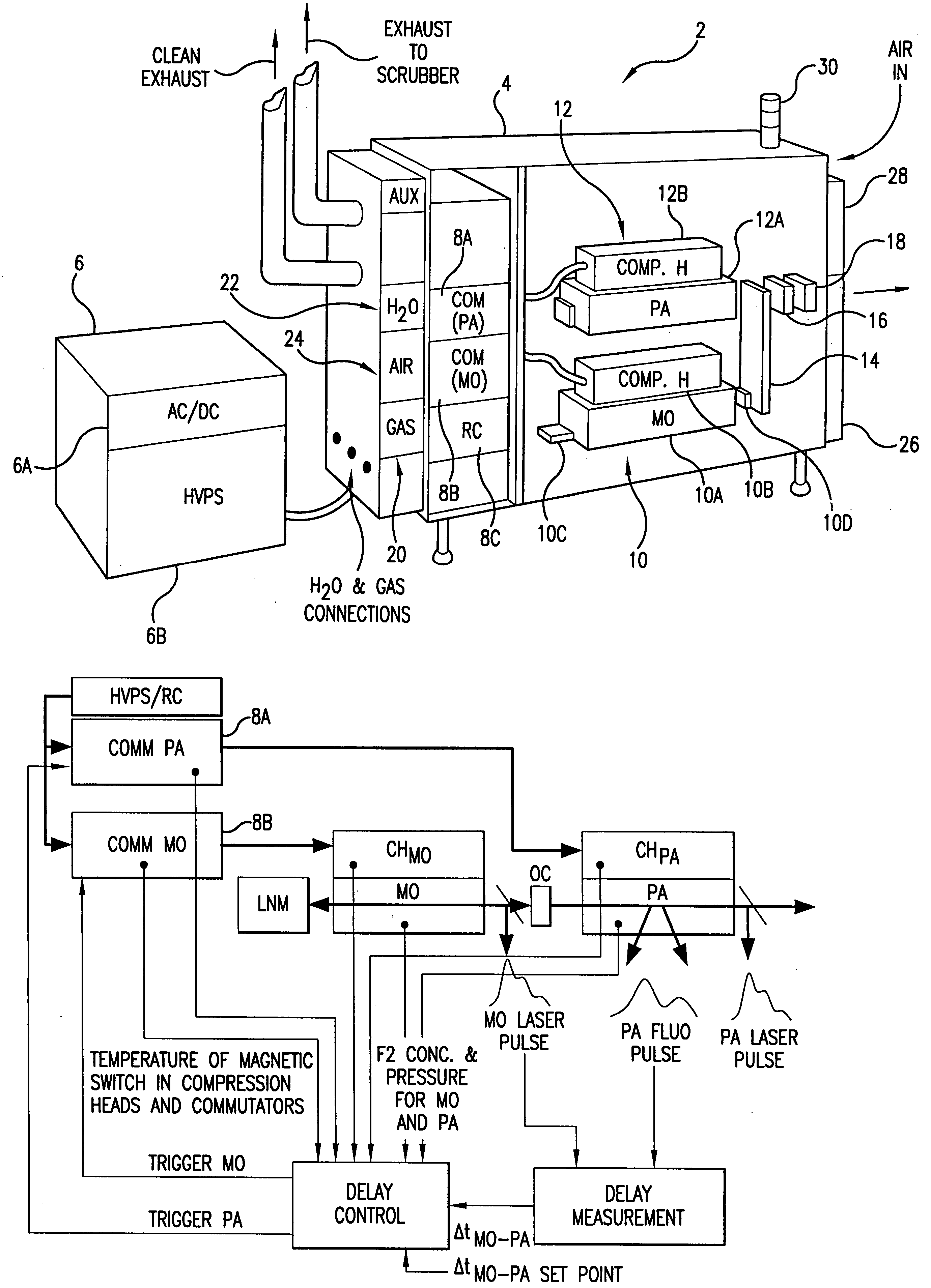
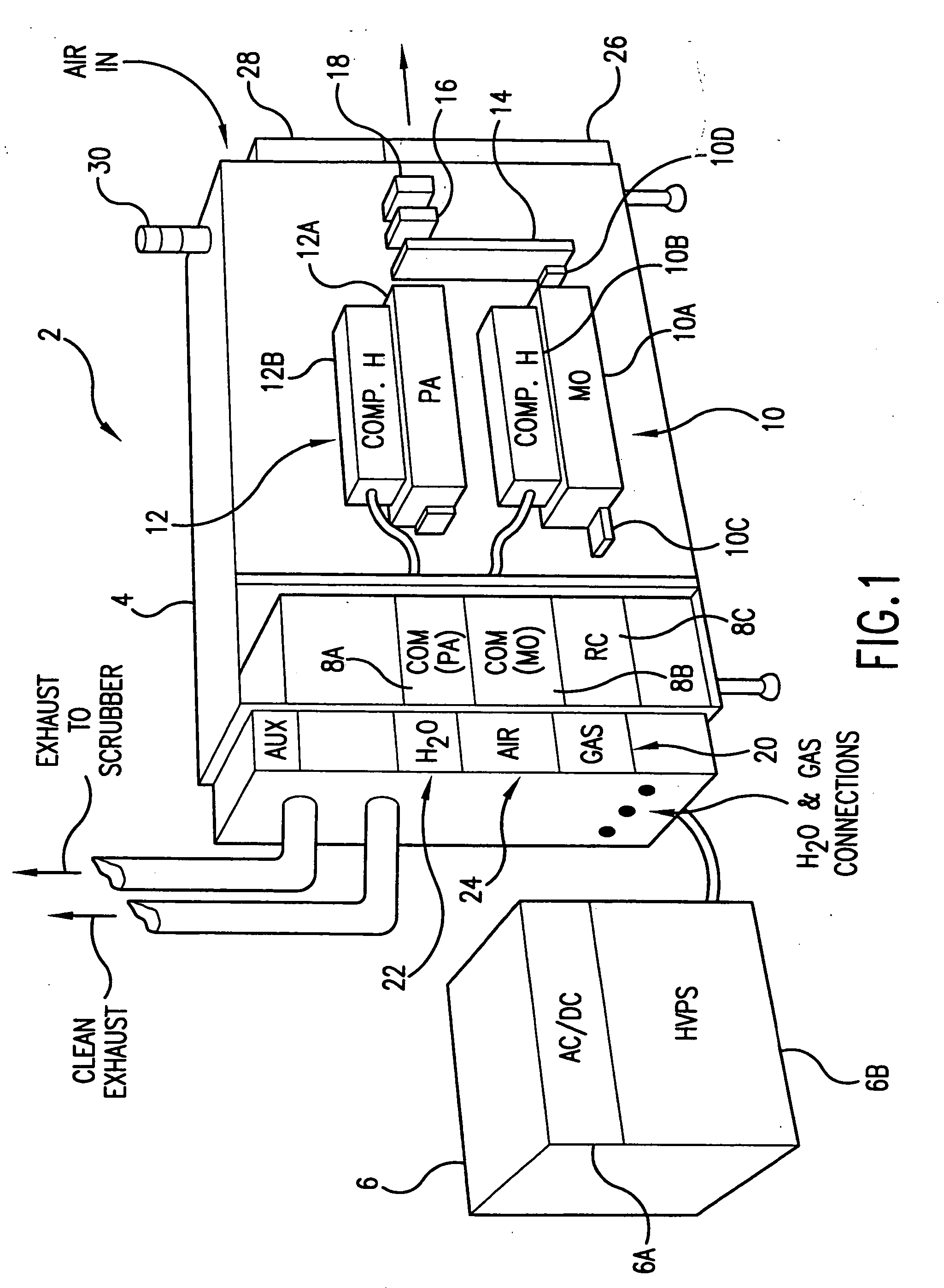
Very narrow band, two chamber, high rep-rate gas discharge laser system
InactiveUS20050271109A1Output powerBeam quality specificationOptical measurementsOptical resonator shape and constructionPulse beamSpectral bands
An oscillator-amplifier gas discharge laser system and method is disclosed which may comprise a first laser unit which may comprise a first discharge region which may contain an excimer or molecular fluorine lasing gas medium; a first pair of electrodes defining the first discharge region containing the lasing gas medium, a line narrowing unit for narrowing a spectral bandwidth of output laser light pulse beam pulses produced in said first discharge region; a second laser unit which may comprise a second discharge chamber which may contain an excimer or molecular fluorine lasing gas medium; a second pair of electrodes defining the second discharge region containing the lasing gas medium; a pulse power system providing electrical pulses to the first pair of electrodes and to the second pair of electrodes producing gas discharges in the lasing gas medium between the respective first and second pair of electrodes, and laser parameter control mechanism modifying a selected parameter of a selected laser output light pulse beam pulse produced by said gas discharge laser system by controlling the timing of the occurrence of the gas discharge between the first pair of electrodes and the occurrence of the gas discharge between the second pair of electrodes.
Owner:CYMER INC
Polymide substrate bonded to other substrate
Polyimide substrates, and polymer laminates for optical and electronic applications are described. Single or multi-layer waveguide structures are deposited on the polyimide substrates. Laminates including polymer or a hybrid organic / inorganic waveguiding film can be deposited on a polished polyimide substrate. The laminate can also include piezoelectric and metallic layers. Micromachined optical devices, such as cantilevered waveguide are fabricated by laser ablation using a combination of IR and UV lasers. A fiber-to-waveguide coupler with a laser-machined groove for holding the fiber is also disclosed. Holes are drilled with excimer and YAG laser in the polyimide substrate and metallized to provide continuous electrical contact between both sides of the substrate. Metallized polyimide substrates are bumped and stacked to provide high density interconnects. The polyimide substrate is bonded to a semiconductor wafer. Thin SOI or epitaxially grown layer with devices is transferred to the polyimide substrate by grinding and etching the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Surfacing of metal fluoride excimer optics
ActiveUS7128984B2Natural mineral layered productsWater-setting substance layered productSingle crystalPrism
The invention is directed to improved coated metal fluoride single crystal optical elements suitable for use in below 250 nm optical lithography, and particularly below 200 nm lithography. The coated elements of the invention can be lenses, windows, prisms and other elements used in lithographic methods, including the laser sources used therein. The invention is also directed to a method of removing the quasi-Bielby layer formed when a shaped optical element is polished. Removal of the quasi-Bielby layer prior to coating results in improved durability and optical transmission characteristics of the coated lenses. The coating material can be any material that does not impede the transmission of below 250 nm electromagnetic radiation. Fluorine doped silicon dioxide is the preferred coating material.
Owner:CORNING INC
Resonator arrangement for bandwidth control
A line-narrowed excimer or molecular fluorine laser system includes a discharge chamber filled with a gas mixture at least including molecular fluorine and a buffer gas, multiple electrodes within the discharge chamber connected to a discharge circuit for energizing the gas mixture, a resonator including a pair of resonator reflecting surfaces disposed on either side of the discharge chamber for generating a laser beam, and a line-narrowing / selection unit within the resonator for narrowing the bandwidth of the laser beam. The resonator further includes a third reflecting surface which is deformable and disposed between the pair of resonator reflecting surfaces. The line-narrowing / selection unit preferably includes a beam expander and a dispersive element, wherein the deformable third reflecting surface is disposed between the beam expander and the dispersive element.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Detonator excimer and detonator therewith
InactiveCN101029814AGuaranteed qualityAchieving standardized workExplosivesAmmunition fuzesDetonatorInterference fit
The invention belongs to the technique field of detonating equipment, the invention mainly relates to exciting equipment of detonator and detonator made by the equipment. The exciting equipment Comprises an open shell which is like a barrel, the surface of the shell is interference fit with inwall of the shell. It is filled with high explosive, amorce, igniting primer or delayed element, the height of high explosive layer, amorce layer, igniting primer or delayed element is separately 0.5~2 times ,0.25~2 times and 1~6 times of the external diameter of the shell. Charge density of the high explosive layer is 0.4~1.2 g / cm3, and charge density of the amorce layer is 0.5~2.5 g / cm3. Igniting primer or delayed element compromises a piece of metal whose shape is like a column. The surface of the metal is interference fit with inwall of its exteriority, there is a through hole inside the metal, else fill delayed explosive. The invention regards the exciting equipment as an individual element. It benefits to concentrating on producing and to dispersal use, it also benefits to industrial production continuously, moreover, many kinds of high-safety detonator according to its different use.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for producing optical film, optical film, polarizing plate and display
InactiveUS20100105830A1Eliminate poor peeling regionImprove productivityOptical articlesPolarising elementsTectorial membraneDisplay device
A method of manufacturing an optical film by a solution casting method, in which a poor peeling region of a metal support can be eliminated by casting a dope on the surface of the metal support after a surface treatment film is formed on the surface of the metal support by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment or excimer UV treatment. Consequently, limitation on the conditions of film production is reduced and productivity is enhanced. Furthermore, since peeling of the film is enhanced, lateral variation in peeling position is reduced and variation in retardation value is reduced sharply, and thereby an optical film having optical characteristics excellent in transparency and flatness can be manufactured. Consequently, a method for manufacturing an optical film, an optical film, a polarizing plate and a display device which meet the demands of a high quality thin and wide protective film for polarizing plate can be provided.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
System for analyzing a sample or a sample component and method for making and using same
InactiveUS20100118301A1Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyHigh pressureFluorescent light
A system and associated method are disclosed for analyzing a sample or sample component including species capable of producing fluorescent light when excited by a light source, where the light source comprises an excimer light source having a high voltage power supply with voltage and current regulation circuitry.
Owner:PETROLEUM ANALYZER COMPANY
Electroluminescent device using metal nanoparticles
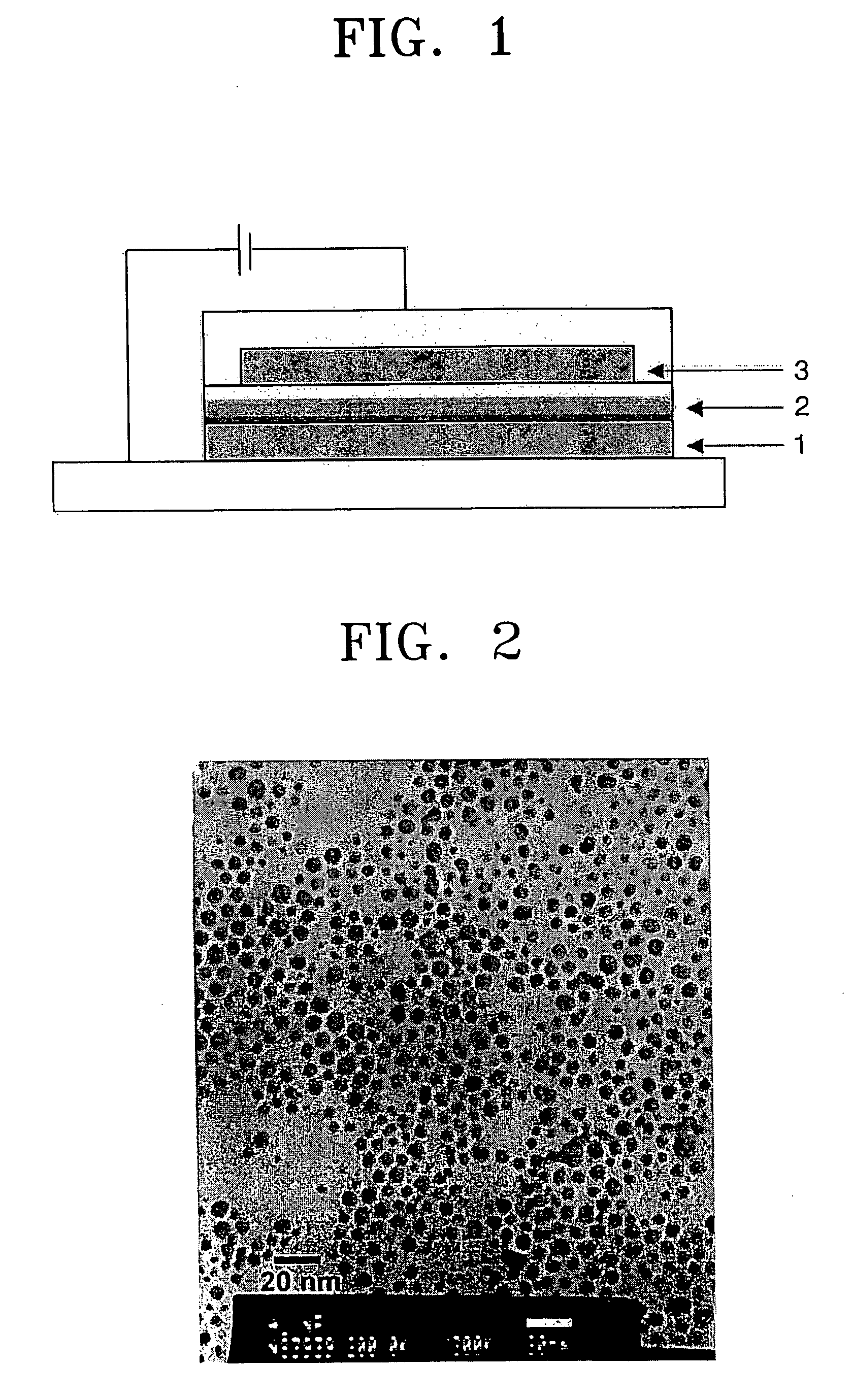
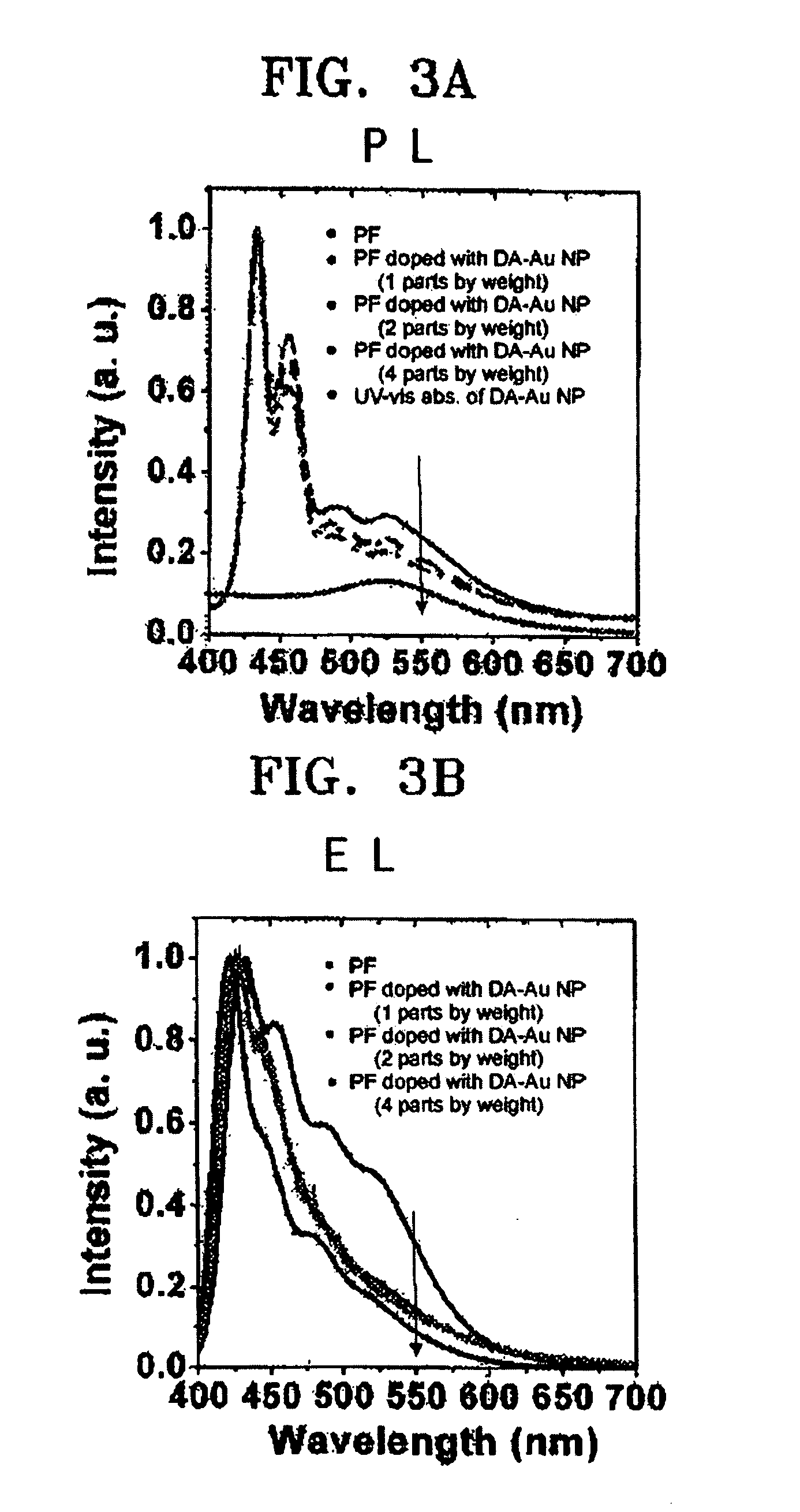
ActiveUS20050276993A1High color purityImprove emission efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesOrganic layerLength wave
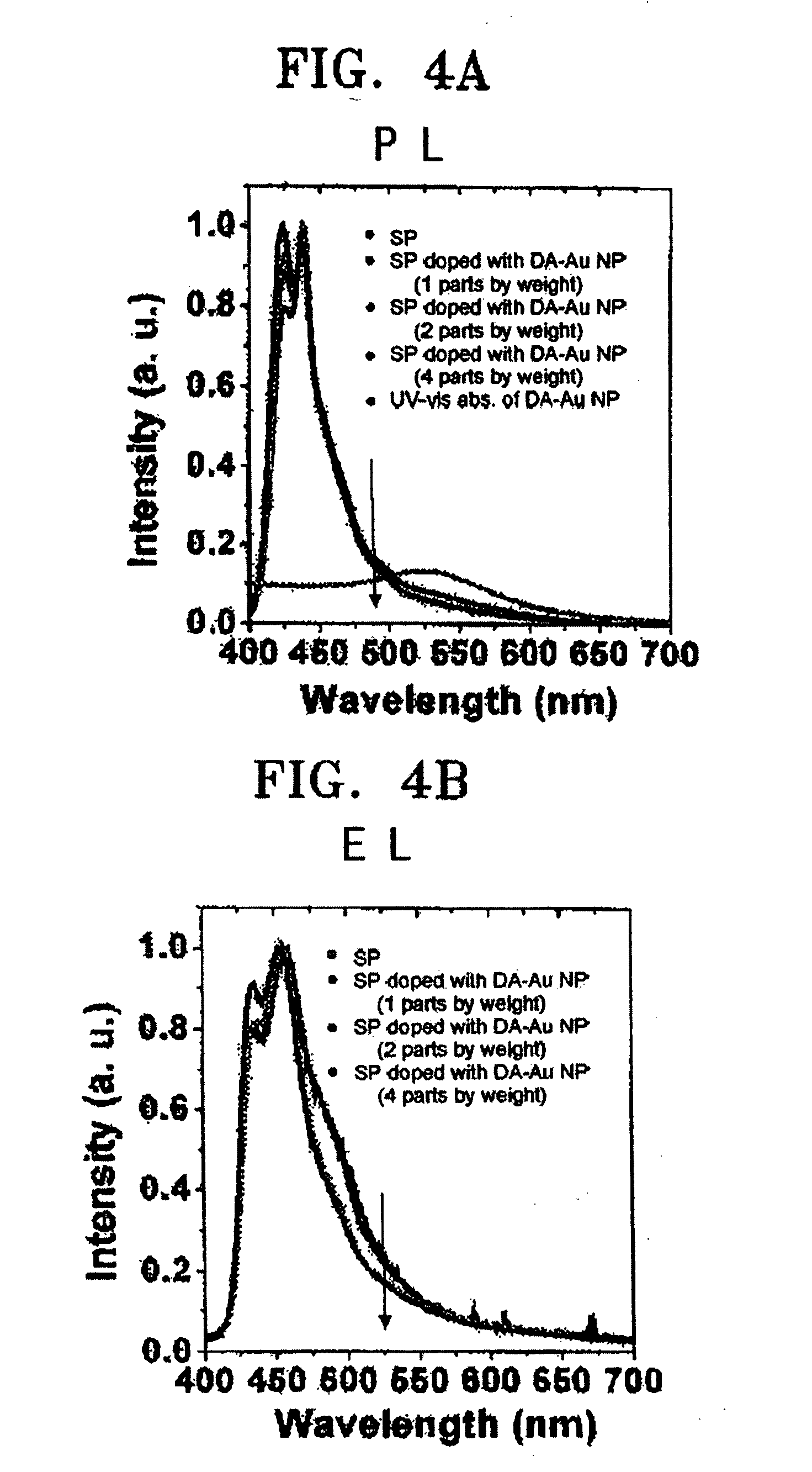
An electroluminescent (EL) device which has a light emitting layer including metal nanoparticles coated with an organic layer. The metal nanoparticles coated with the organic layer selectively remove an absorption band appearing at an excimer level without affecting a maximum absorption or emission wavelength, thereby enhancing the color purity and emission efficiency of the EL device.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Polymide substrate bonded to other substrate
Polyimide substrates, and polymer laminates for optical and electronic applications are described. Single or multi-layer waveguide structures are deposited on the polyimide substrates. Laminates including polymer or a hybrid organic / inorganic waveguiding film can be deposited on a polished polyimide substrate. The laminate can also include piezoelectric and metallic layers. Micromachined optical devices, such as cantilevered waveguide are fabricated by laser ablation using a combination of IR and UV lasers. A fiber-to-waveguide coupler with a laser-machined groove for holding the fiber is also disclosed. Holes are drilled with excimer and YAG laser in the polyimide substrate and metallized to provide continuous electrical contact between both sides of the substrate. Metallized polyimide substrates are bumped and stacked to provide high density interconnects. The polyimide substrate is bonded to a semiconductor wafer. Thin SOI or epitaxially grown layer with devices is transferred to the polyimide substrate by grinding and etching the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:FARAH JOHN
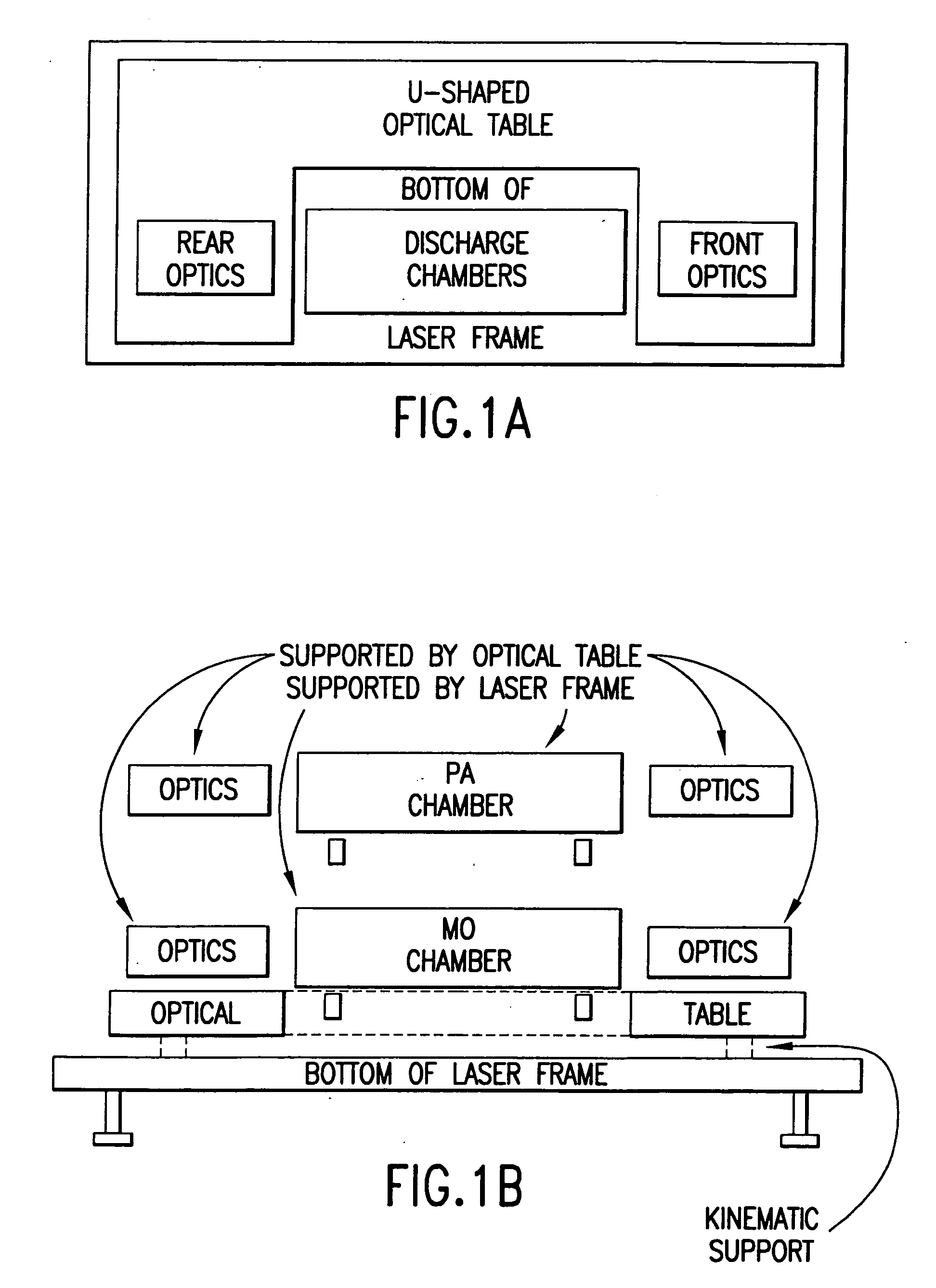
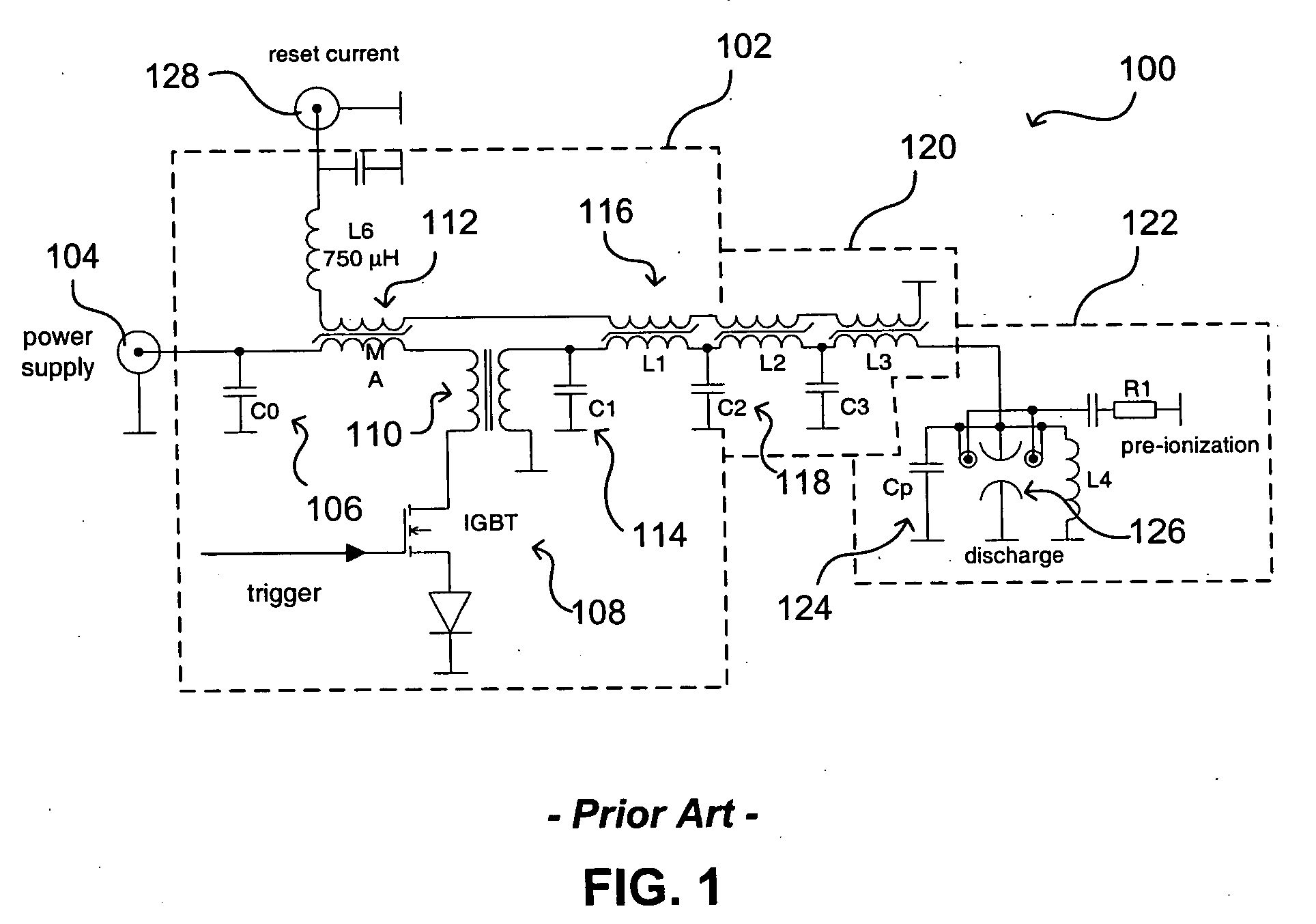
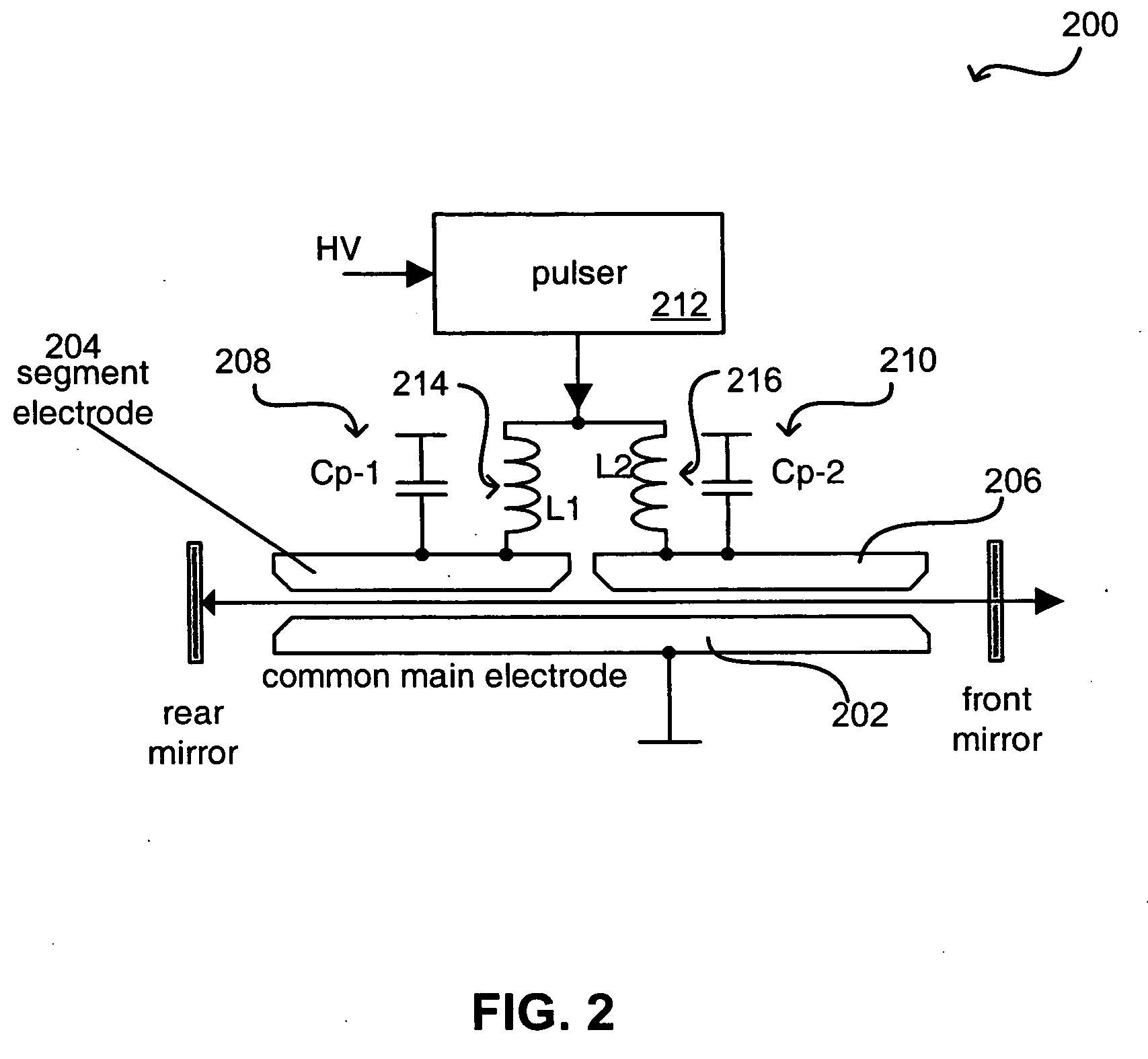
System and method for segmented electrode with temporal voltage shifting
The stability of a gas discharge in an excimer or molecular fluorine laser system can be improved by generating multiple discharge pulses in the resonator chamber, instead of a single discharge pulse. Each of these discharges can be optimized in both energy transfer and efficient coupling to the gas. The timing of each discharge can be controlled using, for example, a common pulser component along with appropriate circuitry to provide energy pulses to each of a plurality of segmented main discharge electrodes. Applying the energy to the segmented electrodes rather than to a standard discharge electrode pair allows for an optimization of the temporal shape of the resulting superimposed laser pulse. The optimized shape and higher stability can allow the laser system to operate at higher repetition rates, while minimizing the damage to system and / or downstream optics.
Owner:LAMBDA PHYSIK
Temperature stabilizing and controlling system of laser
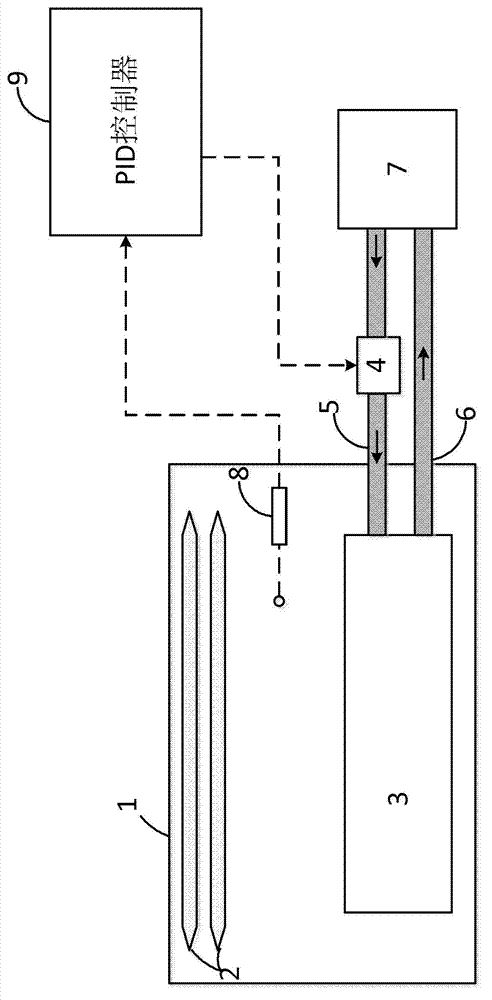
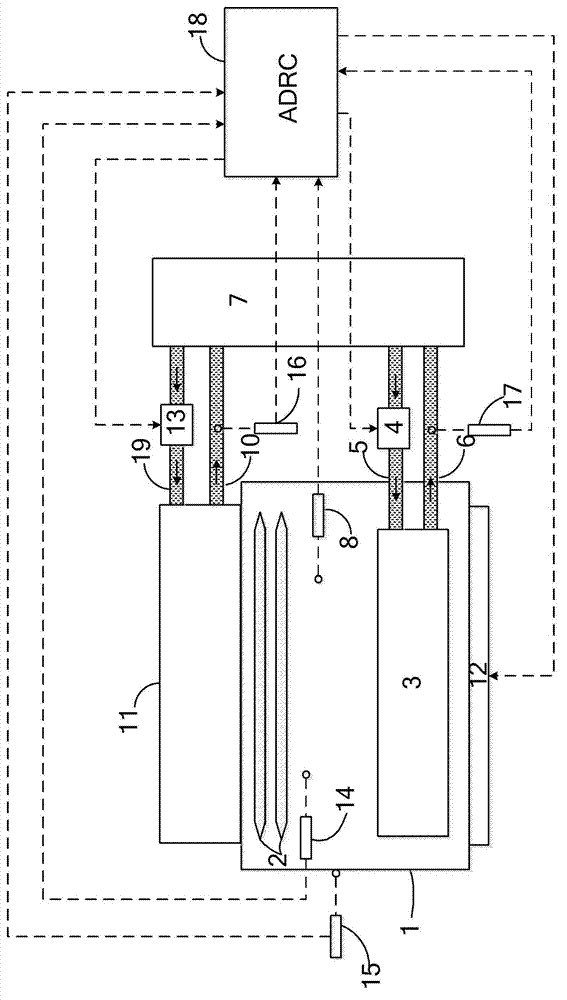
ActiveCN103092229AImprove temperature stabilityImprove flow uniformityLaser detailsTemperatue controlControl flowControl system
The invention discloses a temperature stabilizing and controlling system of a laser. The temperature stabilizing and controlling system of the laser comprises a first temperature sensor, a second temperature sensor, a third temperature sensor, a fourth temperature sensor and a fifth temperature sensor, wherein the first temperature sensor is located at the position of an air outlet in a discharge area inside a cavity body of a discharge cavity of the laser, the second temperature sensor is located at the position of an air inlet in the discharge area inside the cavity body of the discharge cavity, the third temperature sensor is located on the inner wall of the cavity body, the fourth temperature sensor is located in a water outlet pipeline of a heat exchange system, and the fifth temperature sensor is located in a water outlet pipeline of a cooling system of the cavity body. The first temperature sensor, the second temperature sensor, the third temperature sensor, the fourth temperature sensor and the fifth temperature sensor are respectively used for detecting temperature of the air outlet in the discharge area, the air inlet in the discharge area in the discharge cavity, the cavity body of the discharge cavity and cooling water in the water outlet pipelines, and are connected with an automatic digital recording and control (ADRC) through lines so that temperature signals detected by the temperature sensors are sent to the ADRC. The ADRC is used for controlling flow regulating valves on water inlet pipelines of the heat exchange system and the cooling system of the cavity body according to the temperature signals, and for controlling an electric heater, so that controlling on the laser is achieved. According to the temperature stabilizing and controlling system of the laser, temperature stability of an excimer gas laser system is improved.
Owner:RAINBOW SOURCE LASER RSLASER
High efficiency deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode
InactiveCN1921157AReduce difficultyImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorCharge carrier
The invention relates to a deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode structure. Wherein, said structure uses plasma excimer effect; the surface plasma excimer is the oscillating wave formed by coupled optical field and carrier at the surface of conductor; the activation and couple of surface plasma excimer are realize by metal film with periodical structure; and the metal film has electrode contact function; and the metal part of common MIS light-emitting diode uses periodical structure generating surface plasma excimer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser crystallization apparatus and crystallization method
InactiveUS20080073573A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiation therapyMolecular imagingLaser crystallization
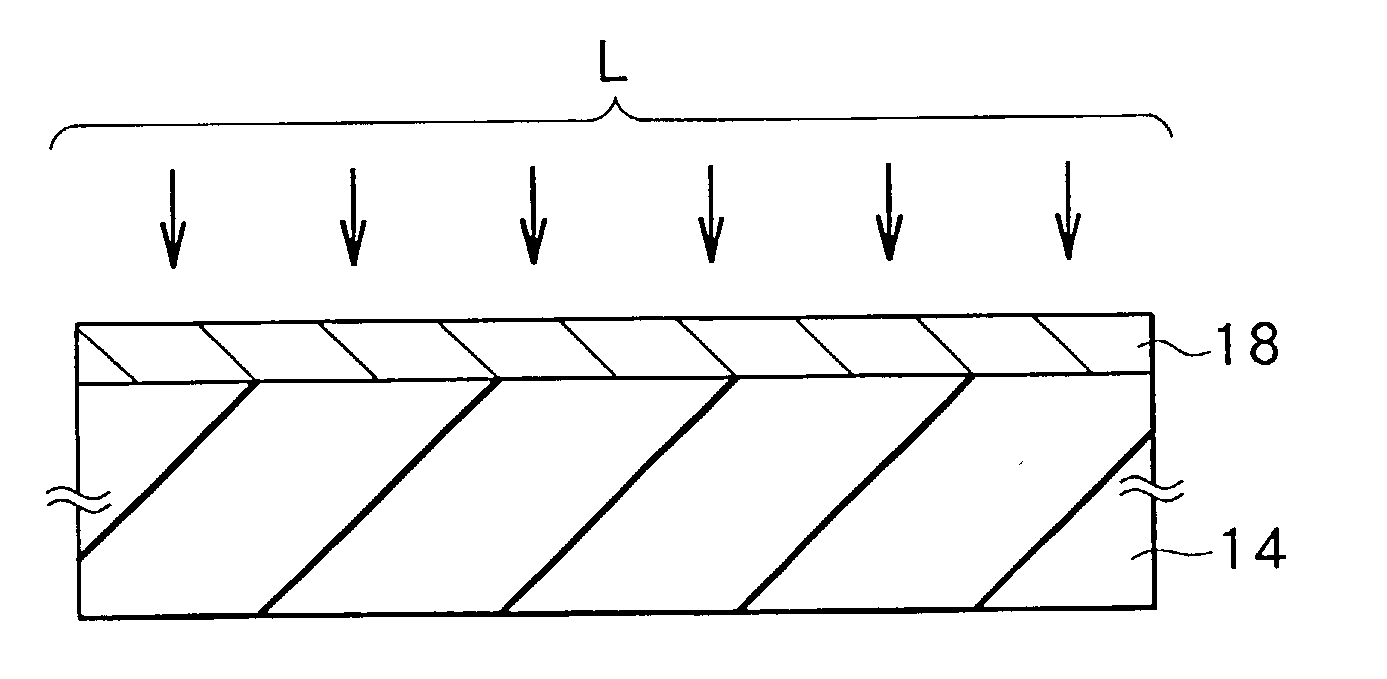
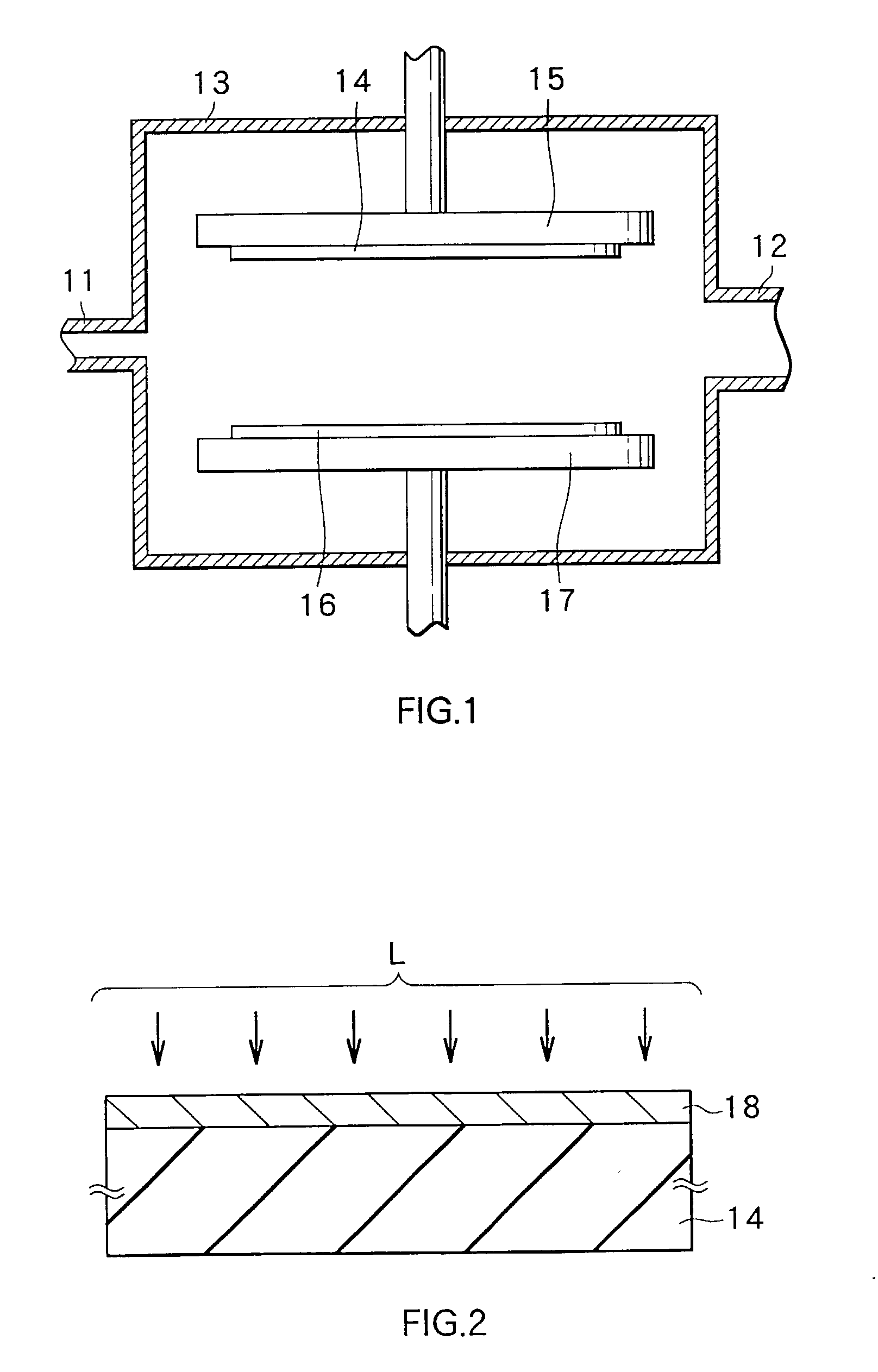
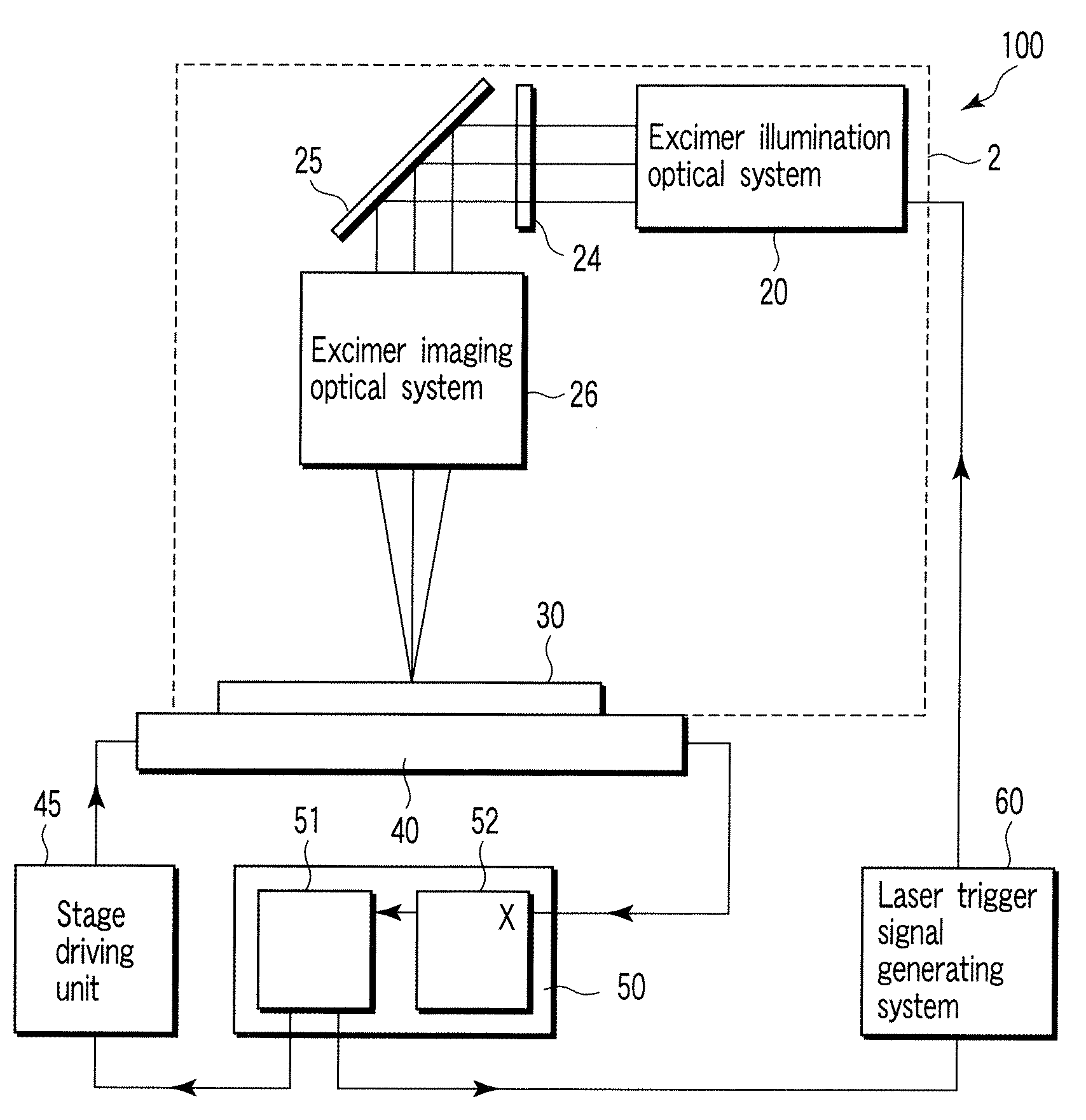
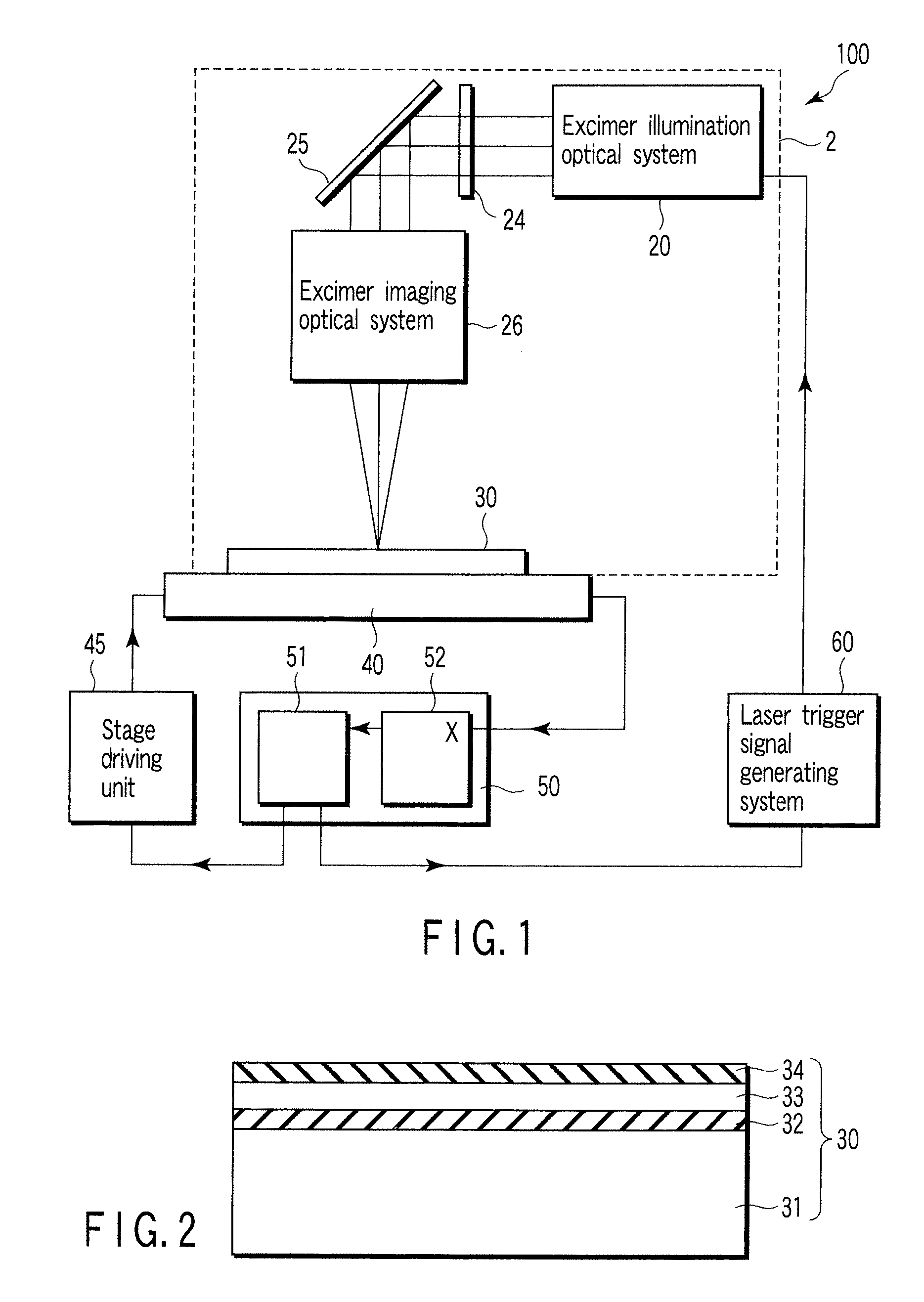
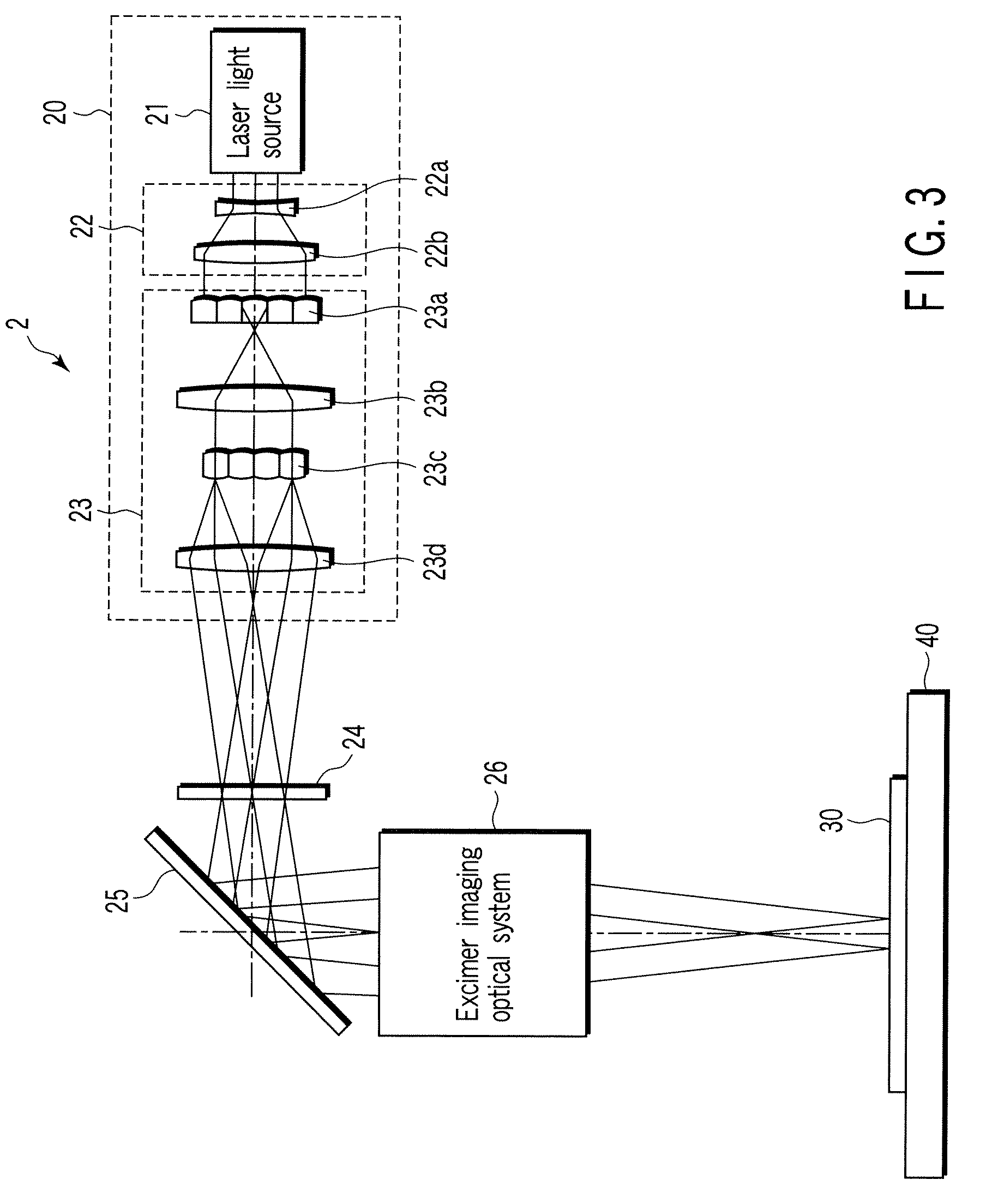
A laser crystallization apparatus and a crystallization method with a high throughput are provided. Laser light having a predetermined light intensity distribution is irradiated to a semiconductor film to melt and crystallize, wherein a irradiation position is placed very quickly and with a high positional accuracy, thereby forming the semiconductor film having a large crystal grain size. A laser crystallization apparatus according to one aspect of the present invention comprises a crystallizing laser light source, a phase shifter modulating pulse laser light to have the predetermined light intensity distribution, an excimer imaging optical system, a substrate holding stage mounting a processing substrate and continuously moving in the predetermined direction, a position measuring means, and a signal generating means indicating generation of the pulse laser light based on the position measurement of the stage by the position measuring means.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Joining apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060037997A1Efficient removalSimple structureWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSolid-state devicesUltravioletEngineering
The joining apparatus includes a suction nozzle for holding an electronic component, a board stage for holding a circuit board in opposition to the electronic component, and an excimer ultraviolet lamp placed at an irradiation position between the positioned electronic component and circuit board. In such a joining apparatus, ultraviolet irradiation to Au bumps of the electronic component and ultraviolet irradiation to board electrodes of the circuit board are performed concurrently by the excimer ultraviolet lamp to execute cleaning process of the two metallic portions. Thereafter, ultrasonic vibrations are imparted to the two metallic portions while those metallic portions are kept in contact with each other, by which metal joining between the two metallic portions is fulfilled.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
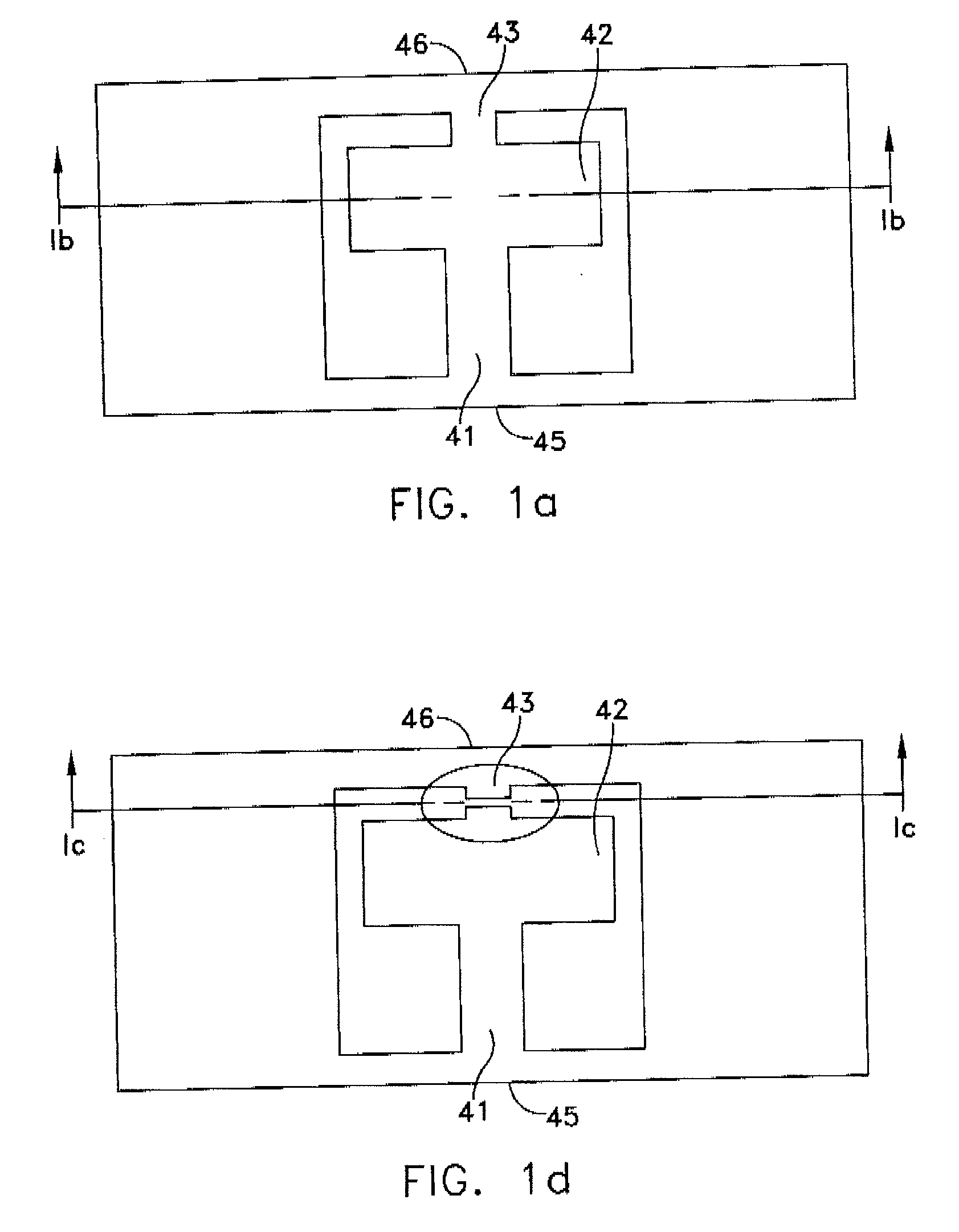
Low-loss medium loaded surface plasmon excimer optical waveguide
InactiveCN102169205AReduce transmission lossEnhanced field enhancement effectOptical waveguide light guideSurface plasmonRefractive index
The invention discloses a medium loaded surface plasmon excimer optical waveguide with low transmission loss and stronger light-field limiting ability. In the invention, the cross section of the waveguide structure comprises a metal basal layer (1), a high refractive index medium region (3) located on the metal basal layer, a low refractive index medium region (2) surrounded by the high refractive index medium region and the metal basal layer and a cladding (4), wherein the light-field distribution range of the waveguide structure can be obviously reduced by the high refractive index medium region on the metal basal layer so that the two-dimensional sub-wavelength constraint to a transmission light field is realized; and in the meantime, as the existence of the low refractive index medium region, the lower transmission loss of the waveguide can be maintained. By means of the optical waveguide structure, the contradiction of the light-field limiting ability and the transmission lost of a conventional medium loaded surface plasmon excimer optical waveguide is overcome and an ultrahigh integration level optical waveguide chip is possible to realize.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device for Generating Uvc Radiation
ActiveUS20080258601A1Promote absorptionAccelerate emissionsDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsUVC RadiationBismuth preparation
A device for generating ultraviolet radiation by means of an excimer discharge, which device is equipped with an at least partly UV-transparent discharge vessel whose discharge space is filled with a gas filling, with means for triggering and maintaining an excimer discharge in the discharge space, and with a luminescent material that contains a phosphor comprising a host lattice of general formula (Y1-x-y-z,Lux,Scy,Az)PO4 wherein 0≦x<1 and 0<y≦1 and 0≦z<0.05 and A is an activator selected from the group of bismuth, praseodymium and neodymium is useful for disinfection and purification of fluids and surfaces and provides improved germicidal action. The invention also relates to a UVC-phosphor comprising a host lattice of general formula (Y1-x-y-z,Lux,Scy,Az)PO4 wherein 0≦x<1 and 0<y≦1 and 0≦z<0.05 and A is an activator selected from the group of bismuth, praseodymium and neodymium comprising a improved emission spectrum. Such UV-C phosphors show a high quantum efficiency (>80%) and a strong absorption of 170 to 190 nm radiation. These phosphors emit UV-C radiation comprising a broadened band in the wavelength range between 225 and 275 nm.
Owner:USHIO EURO
Blue phosphorescent emitters employing functionalized imidazophenthridine and analogues
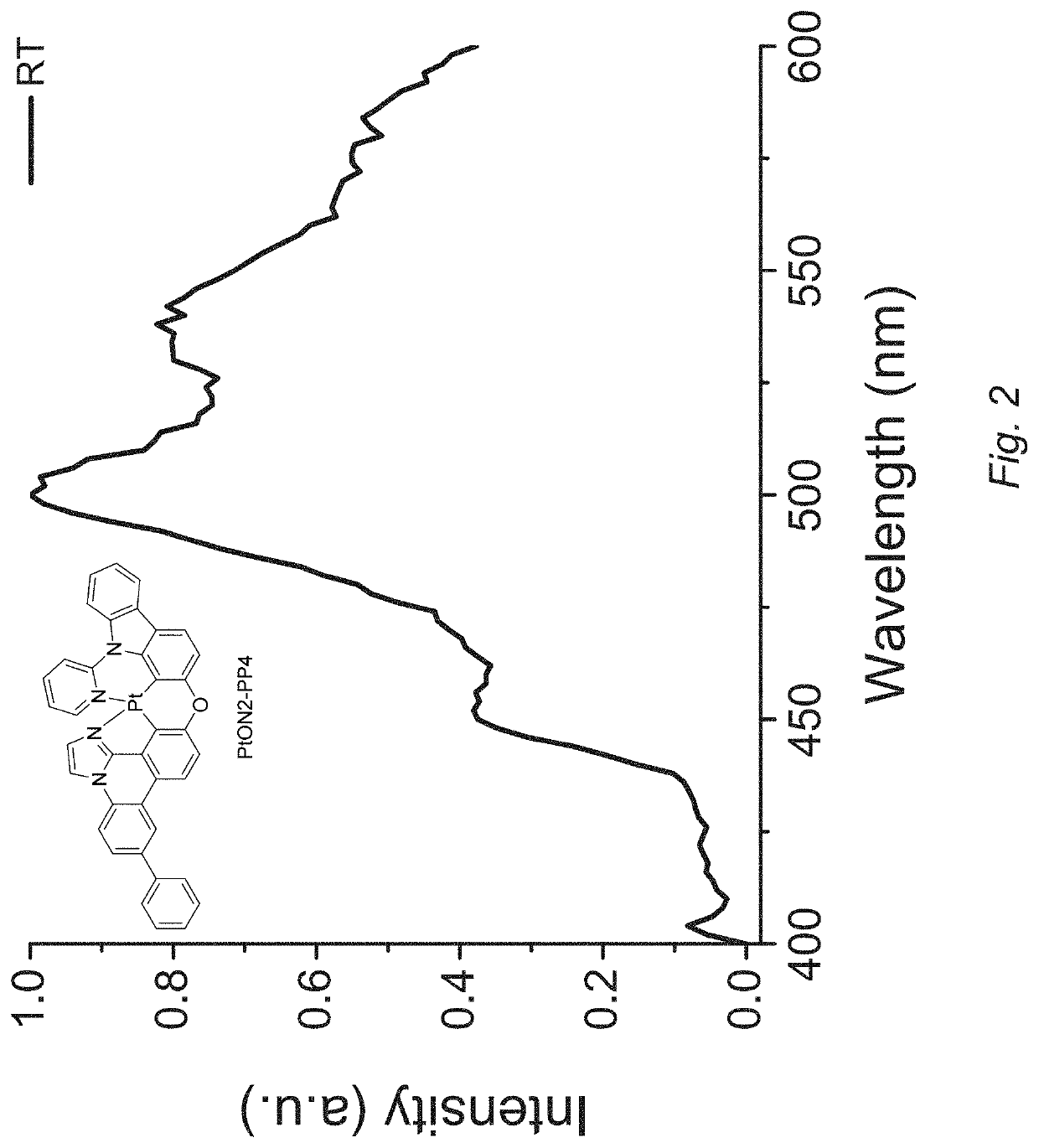
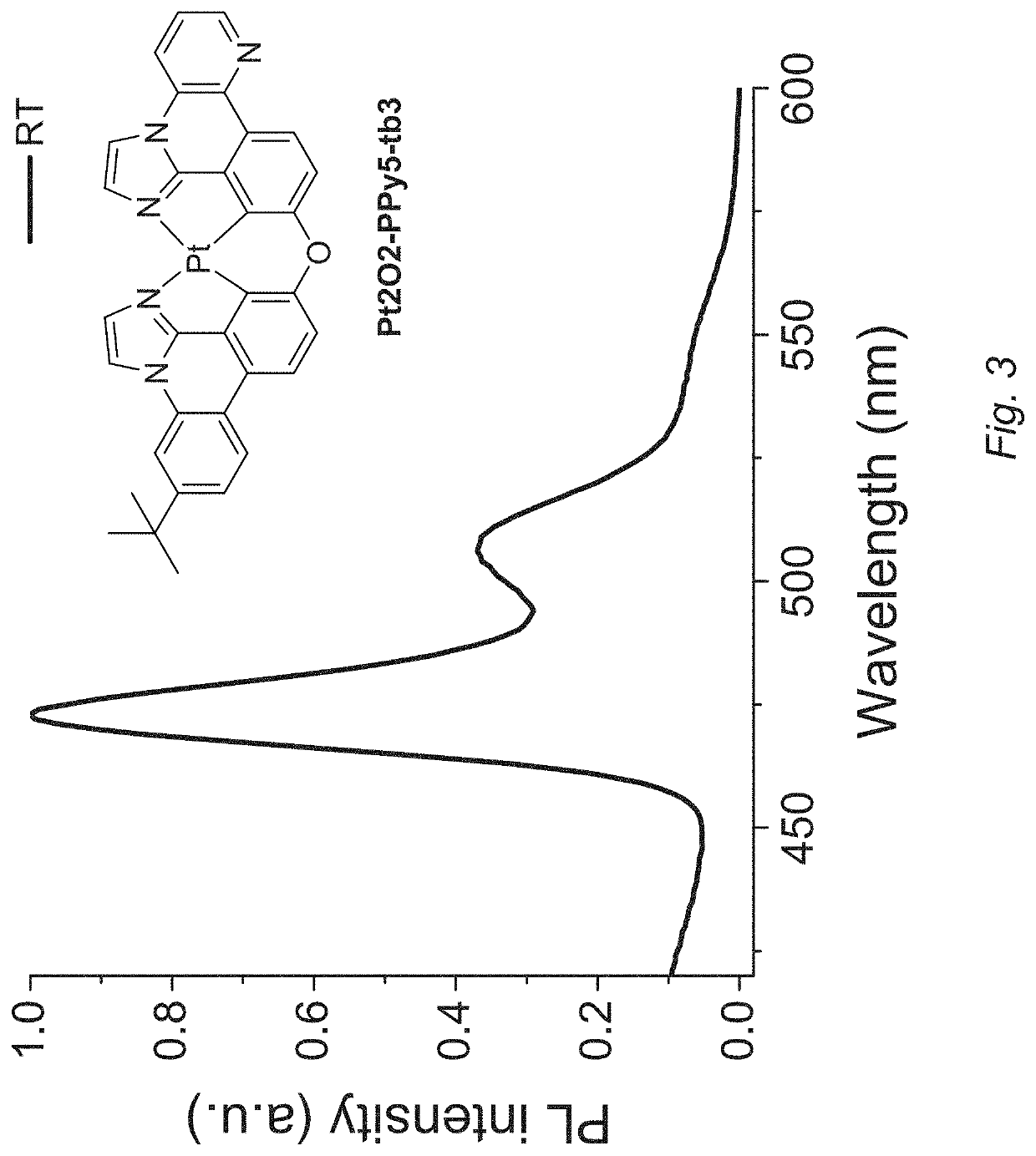
PendingUS20200239505A1Palladium organic compoundsSolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting devicePhenyl group
A series of functionalized imidazophenthridine analogue-based blue phosphorescent emitters have been designed, where bulky substituents (e.g., tetrabutyl, phenyl, mesityl, triisopropylbenzene, etc.) are introduced on an imidazophenthridine fragment of the emitters. Bulky substituents may suppress potential excimer formation, as well as improve the solubility of the complexes. This class of emitters may be utilized in luminescent labels, emitters for organic light emitting devices, and lighting applications.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com