Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
679 results about "Molecular imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular imaging originated from the field of radiopharmacology due to the need to better understand fundamental molecular pathways inside organisms in a noninvasive manner.
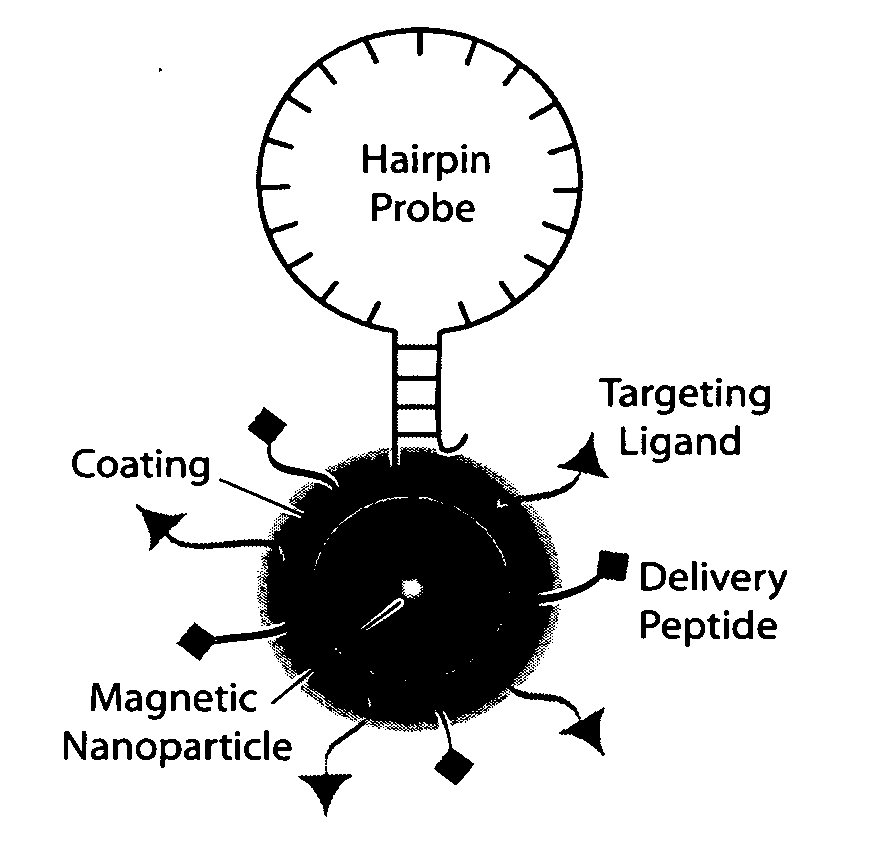
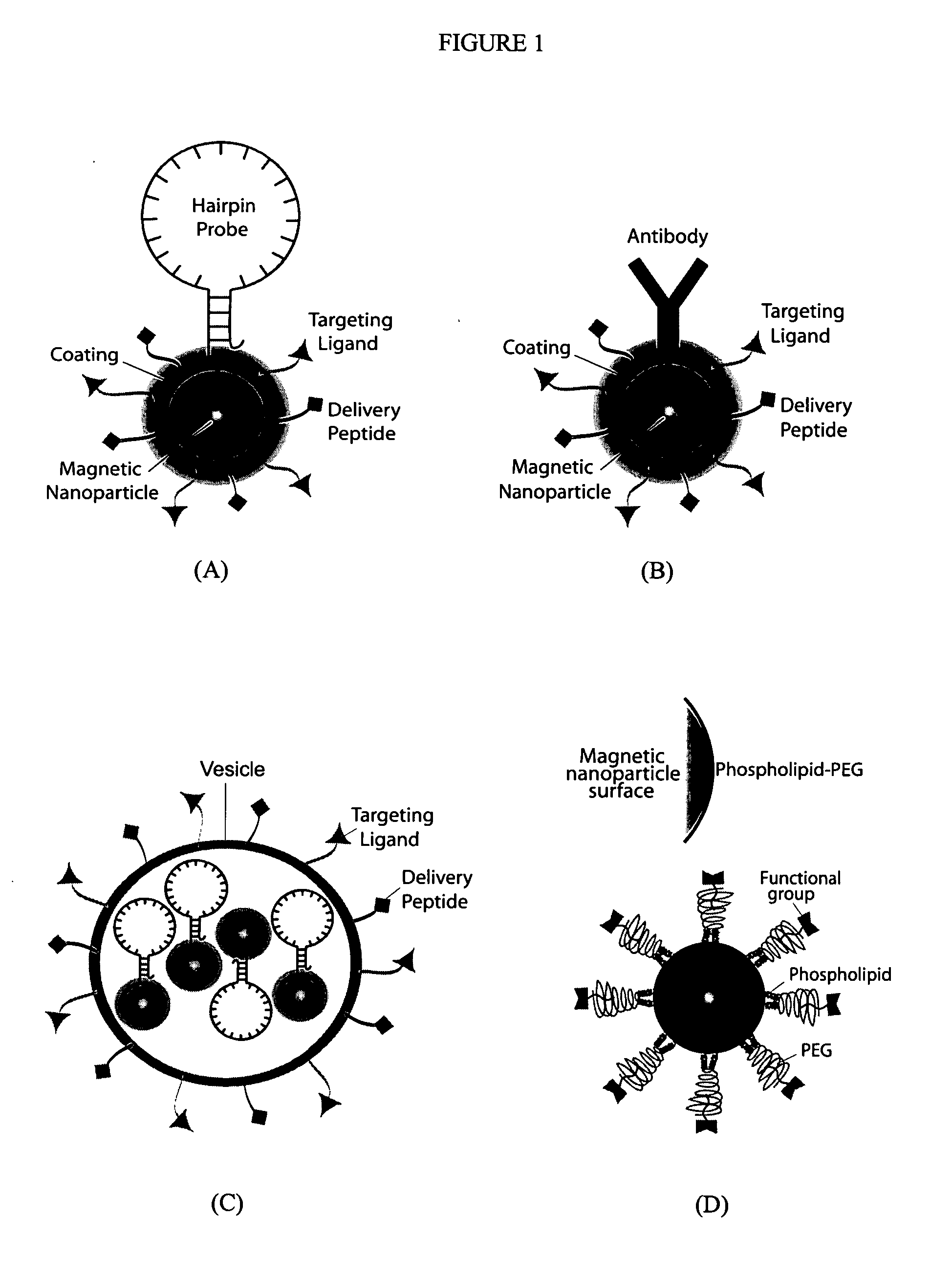
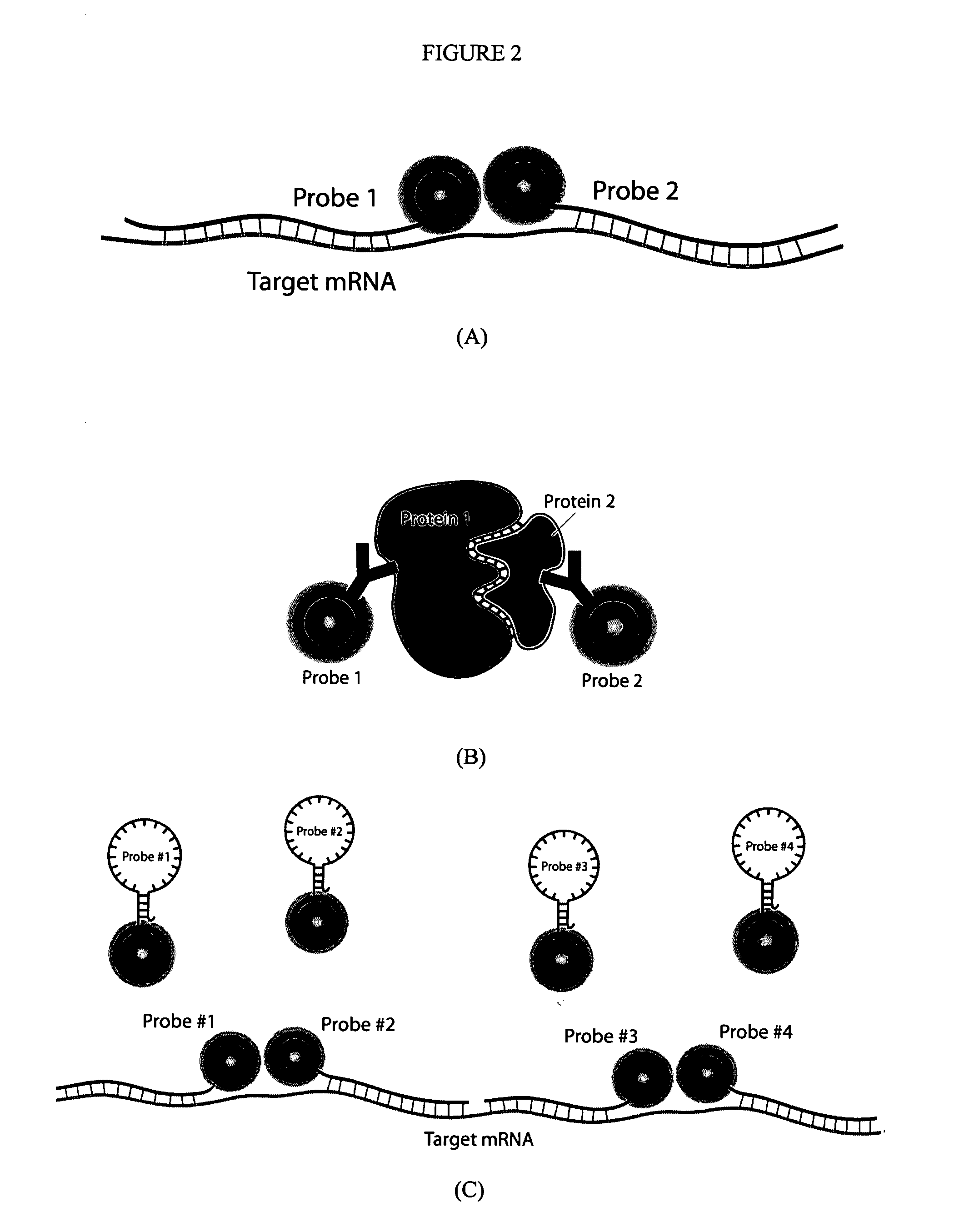
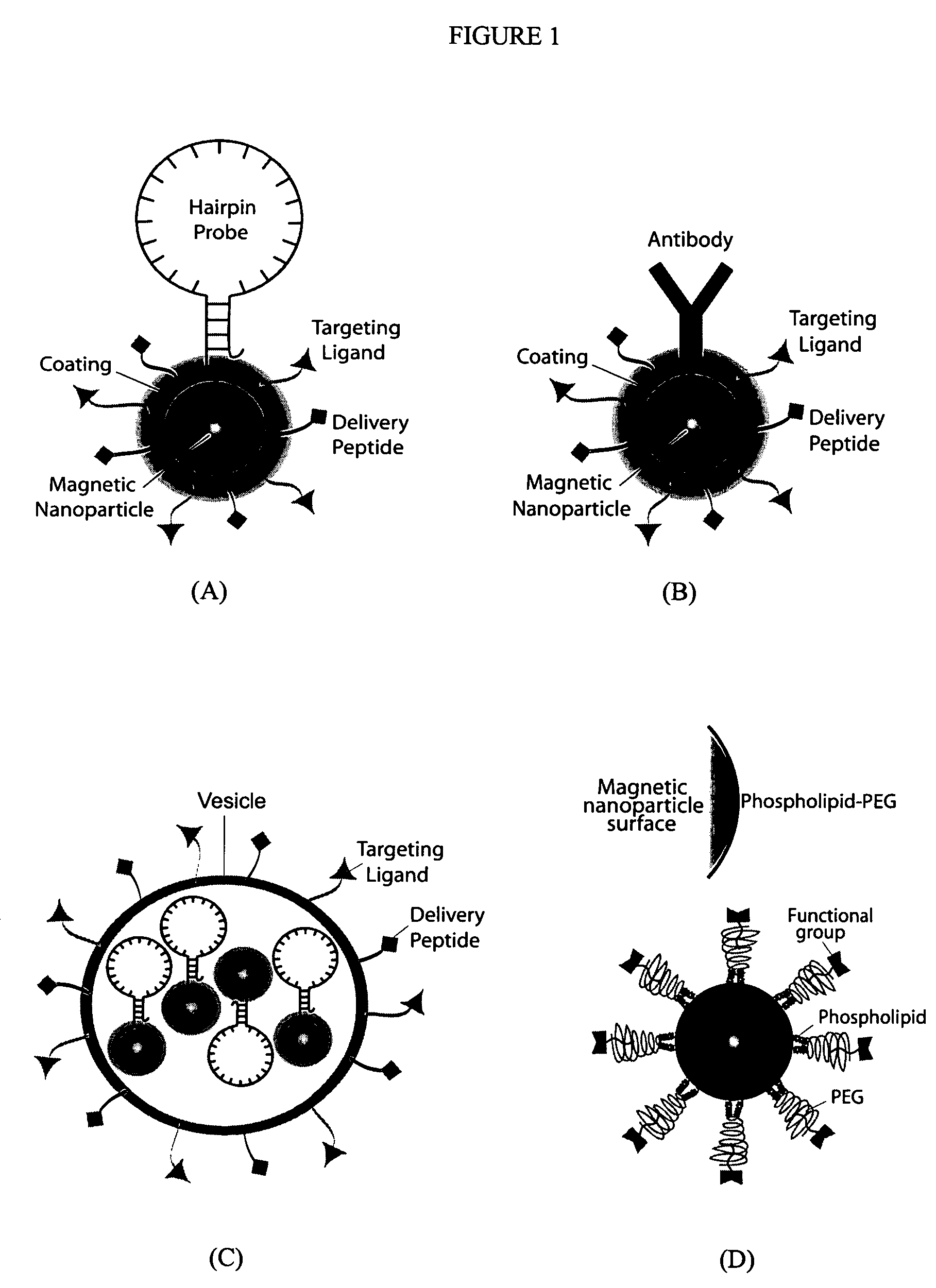
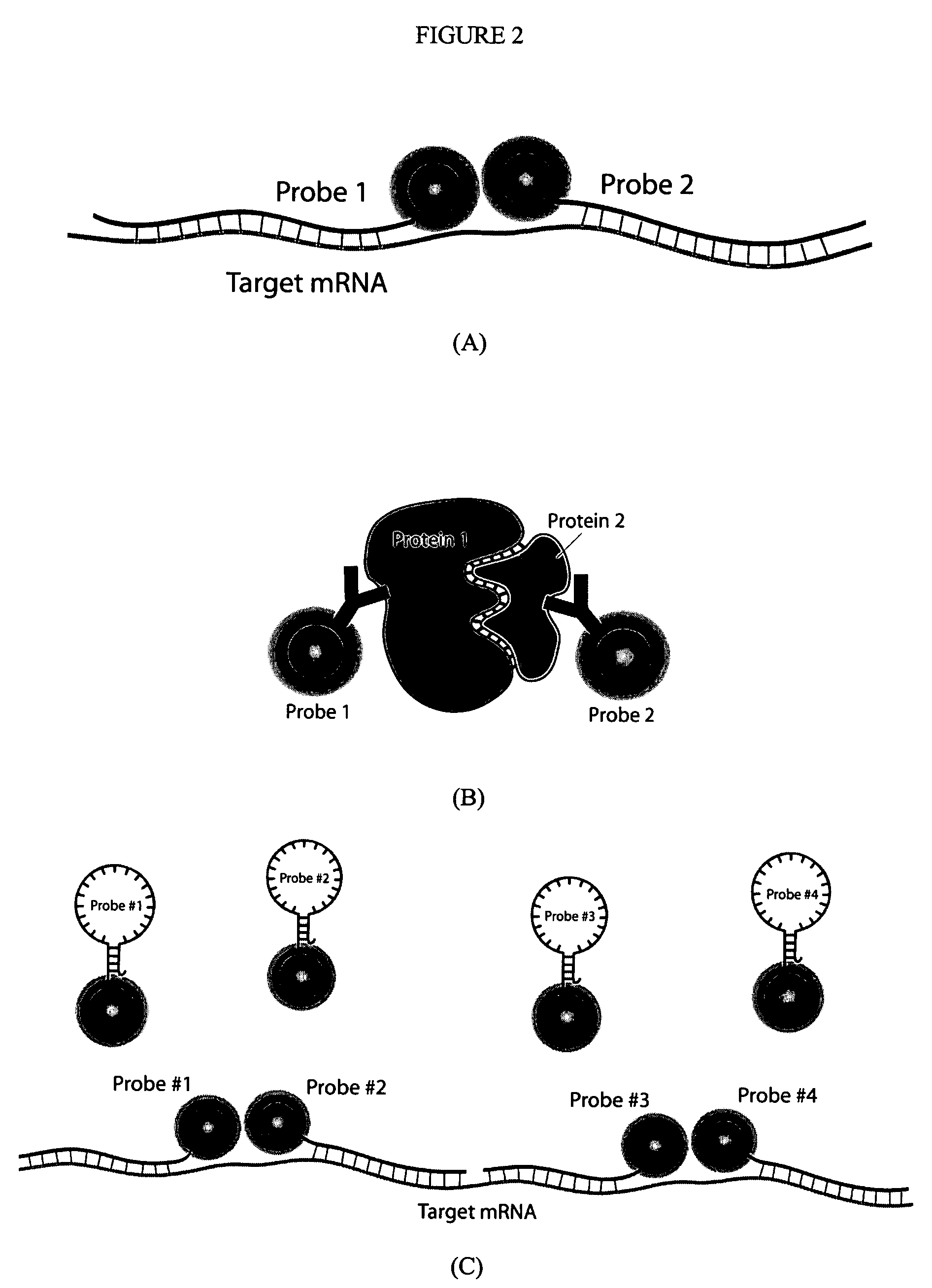
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS20050130167A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS7459145B2Efficient internalizationHigh sensitivityBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
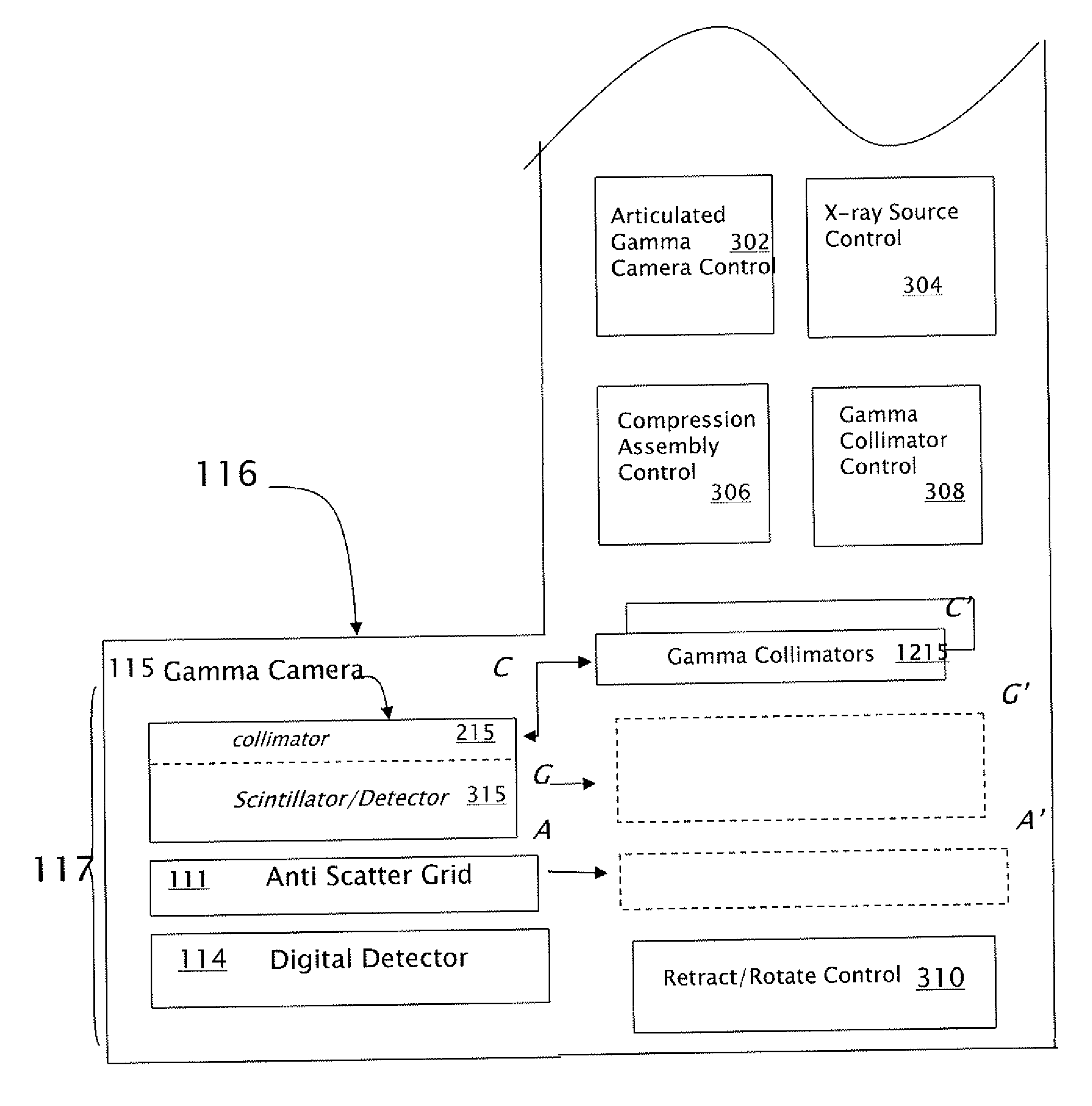
Multi-Dimensional Image Reconstruction and Analysis for Expert-System Diagnosis
ActiveUS20080033291A1Maximize obtainedAvoid saturationMedical automated diagnosisComputerised tomographsDosimetry radiationMulti dimensional
The present invention relates to the capabilities of a highly sensitive radioactive-emission camera, a result of a meticulous search for the many different effects that combine synergistically to increase sensitivity and spatial, spectral, and time resolutions. The new camera opens a new realm in SPECT-type imaging, making it viable for dynamic studies, the use of radiopharmaceutical cocktails, molecular imaging, dosimetry and other studies requiring the high sensitivity and resolutions. In particular, the new camera opens the door to SPECT expert system, examples for which are provided. The expert system relates to defining disease signatures for automatic diagnosis, preferably, based on a multi-parameter vector, preferably, based on kinetic radiopharmaceutical values. Additionally or alternatively, based on simultaneous administration of multiple isotopes.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
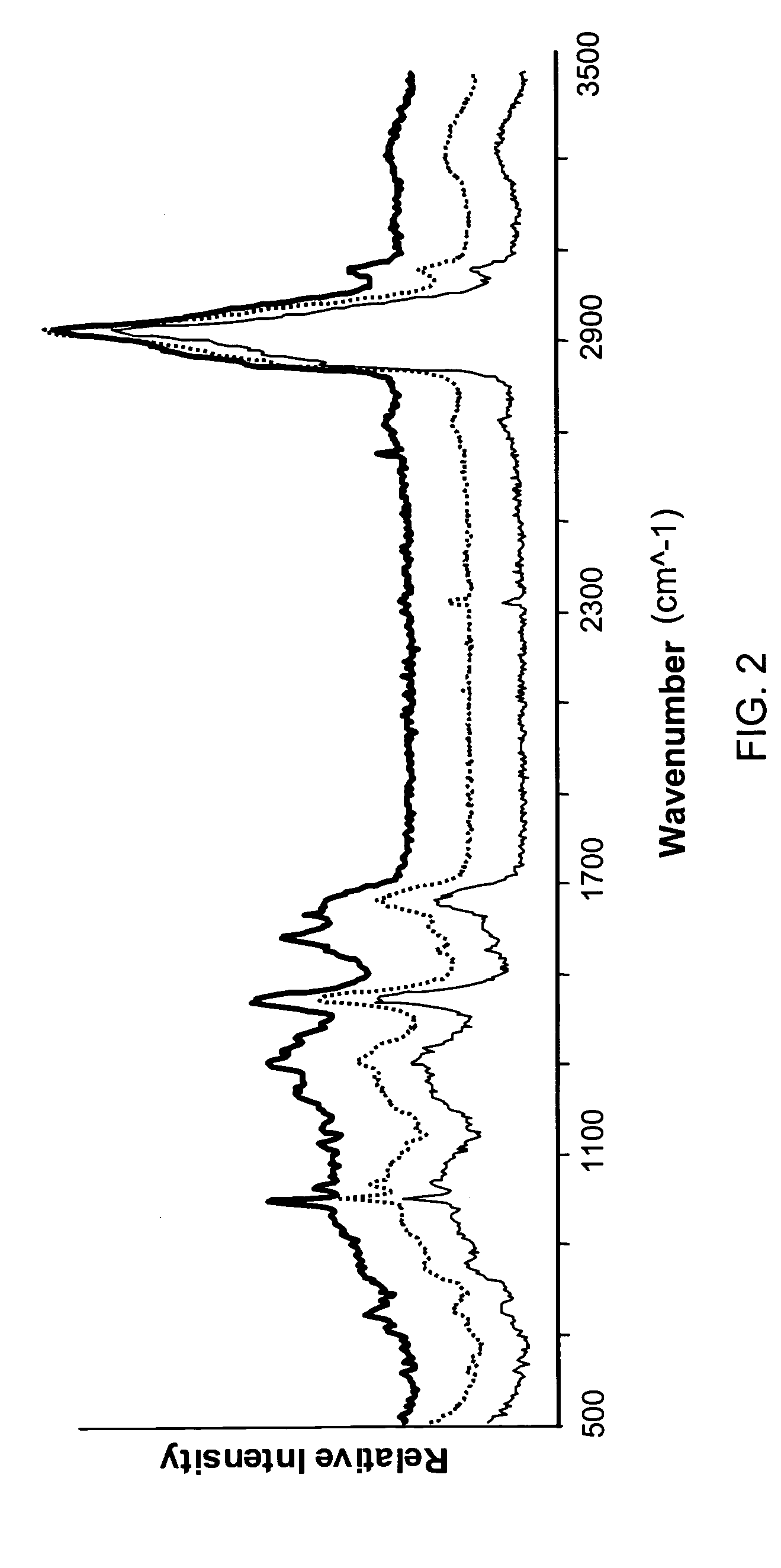
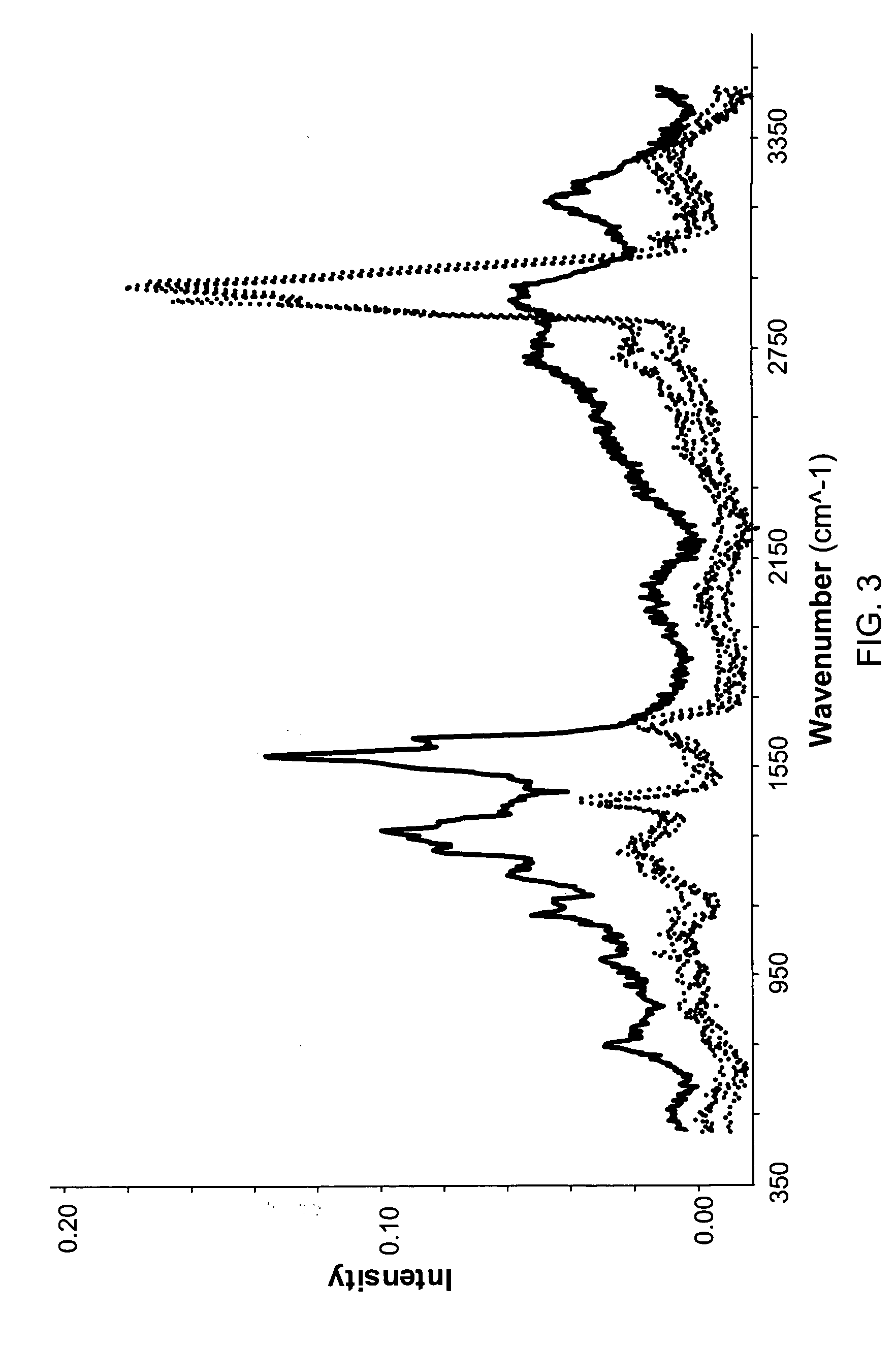
Cytological methods for detecting a disease condition such as malignancy by Raman spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20060281068A1Superior resolution and intensitySensitive assessmentRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitheliumCancer cell
Raman molecular imaging (RMI) is used to detect mammalian cells of a particular phenotype. For example the disclosure includes the use of RMI to differentiate between normal and diseased cells or tissues, e.g., cancer cells as well as in determining the grade of said cancer cells. In a preferred embodiment benign and malignant lesions of bladder and other tissues can be distinguished, including epithelial tissues such as lung, prostate, kidney, breast, and colon, and non-epithelial tissues, such as bone marrow and brain. Raman scattering data relevant to the disease state of cells or tissue can be combined with visual image data to produce hybrid images which depict both a magnified view of the cellular structures and information relating to the disease state of the individual cells in the field of view. Also, RMI techniques may be combined with visual image data and validated with other detection methods to produce confirm the matter obtained by RMI.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
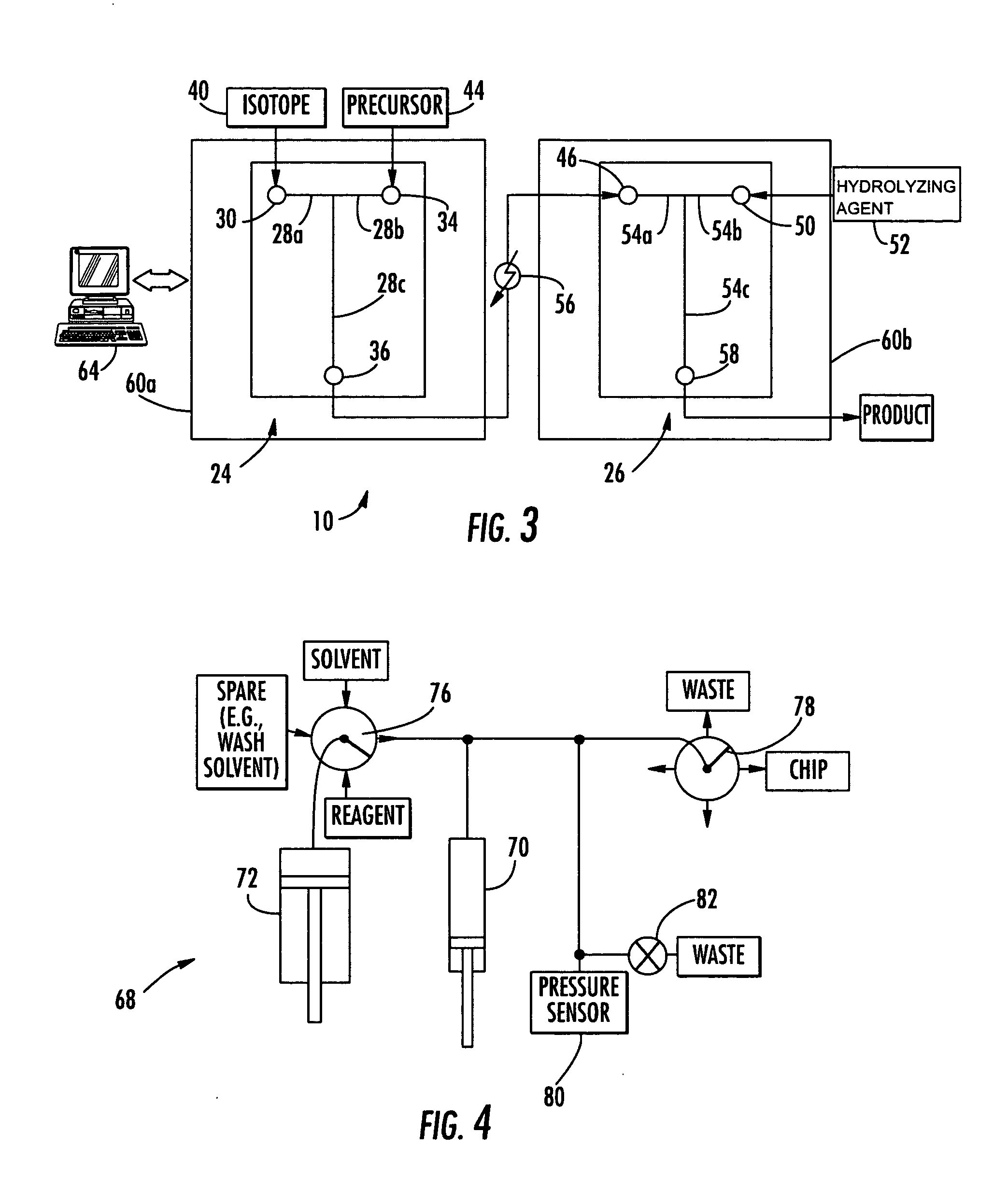
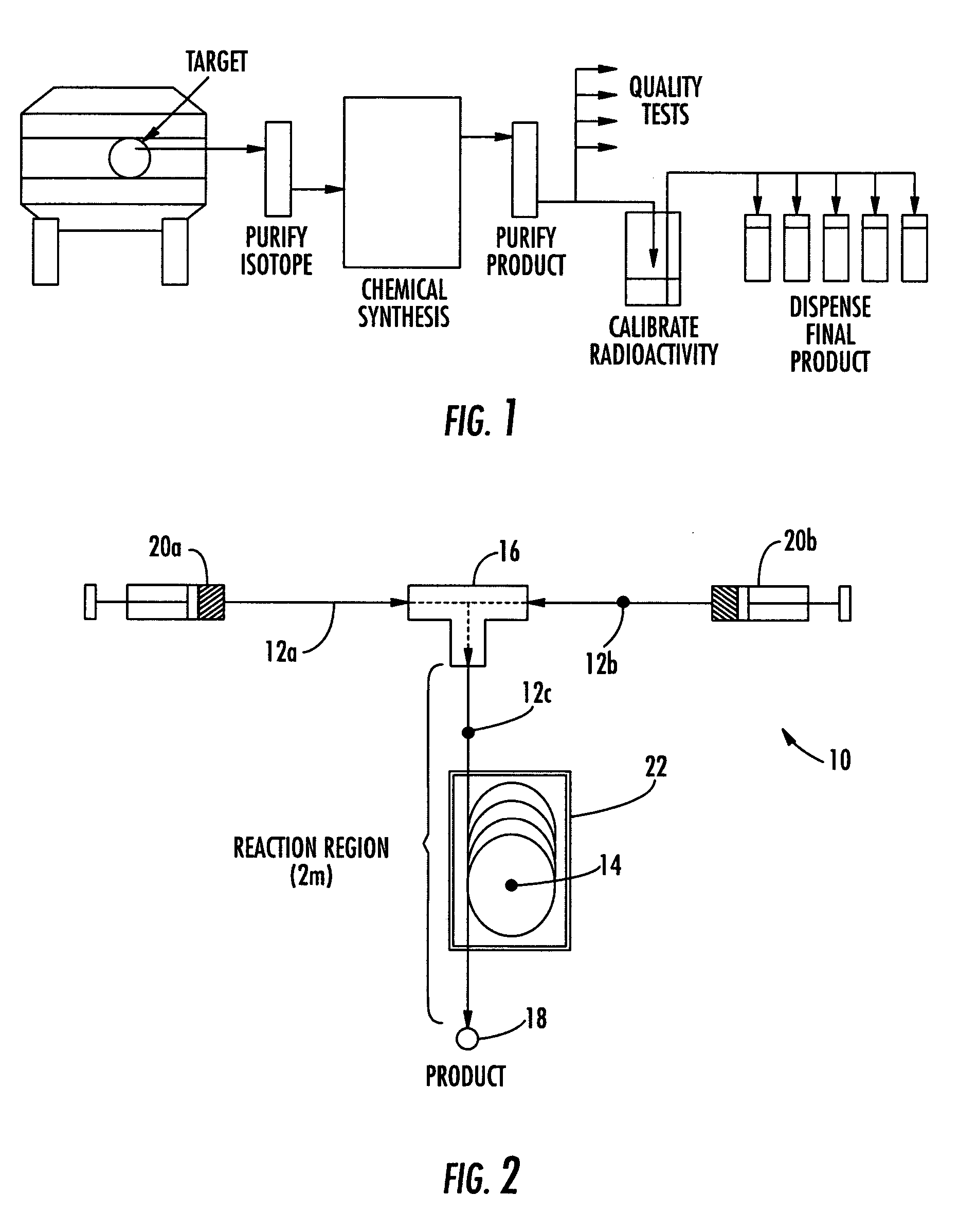
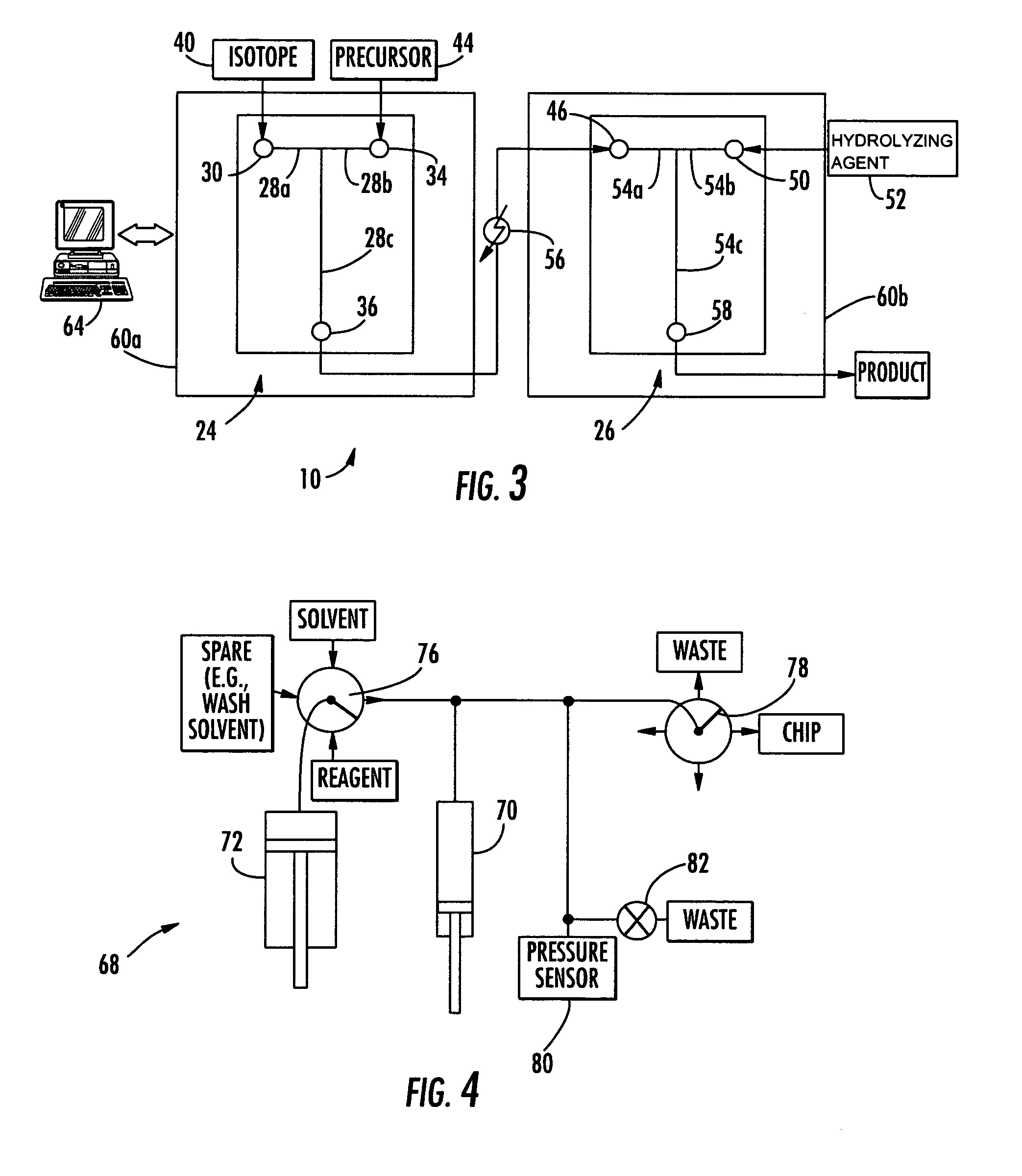
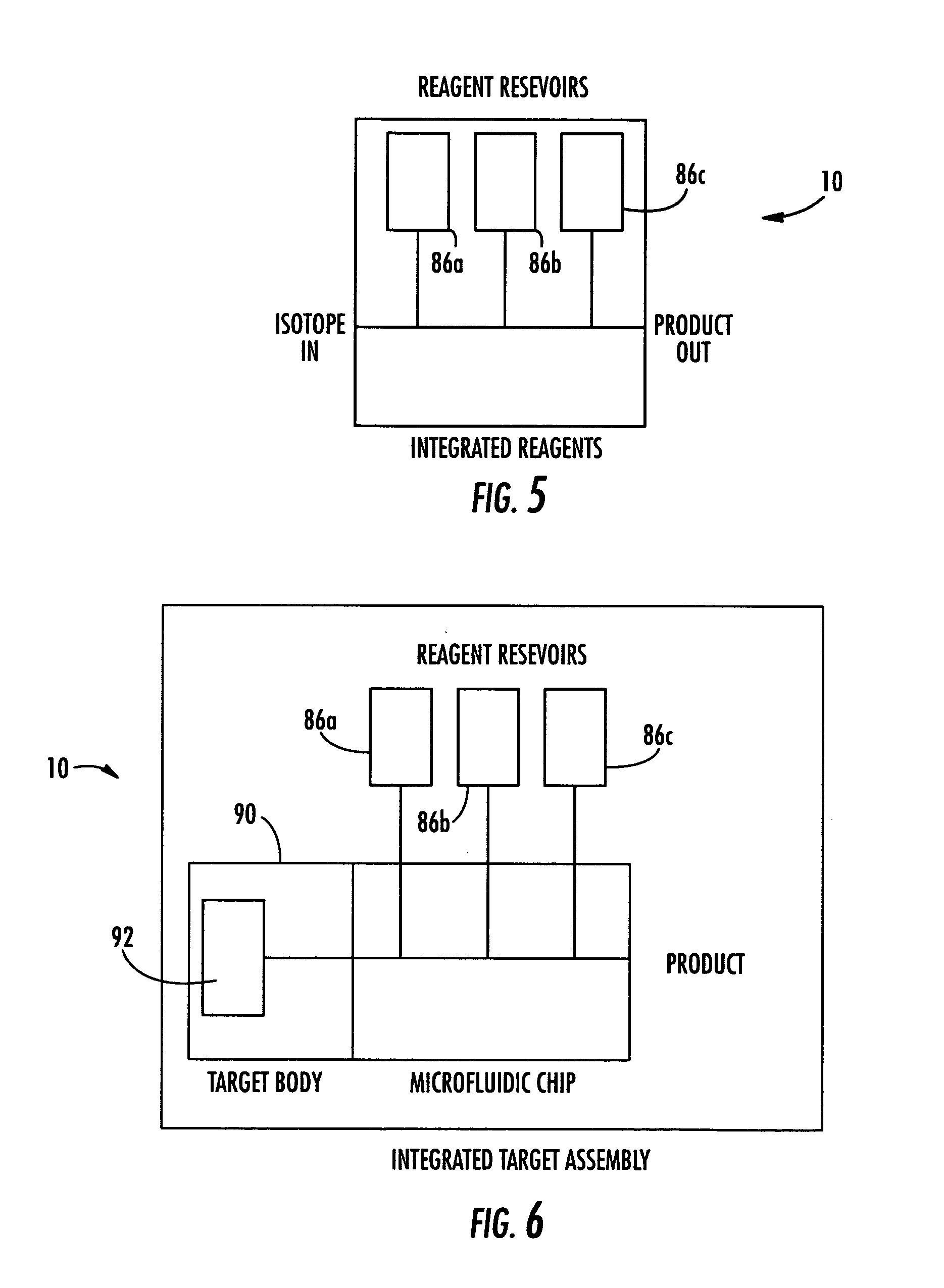
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20050232387A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals, such as PET molecular imaging probes, wherein the reaction step or steps that couple the radioactive isotope to an organic or inorganic compound to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe are performed in a microfluidic environment. The method for synthesizing a radiochemical in a microfluidic environment comprises: i) providing a micro reactor comprising a first inlet port, a second inlet port, an outlet port, and at least one microchannel in fluid communication with the first and second inlet ports and the outlet port; ii) introducing a reactive precursor into the first inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; iii) introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope into the second inlet port of the micro reactor; iv) contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in the microchannel of the micro reactor; v) reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, the reacting step resulting in formation of a radiochemical; and vi) collecting the radiochemical from the outlet port of the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20060147379A1Maximize signal-to-background ratioUseful in therapyCompounds screening/testingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseCellular respiration
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes including FDG
InactiveUS20050232861A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals wherein the reaction that couples the radioactive isotope to the reactive precursor to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe is performed in a microfluidic environment. The method comprises: providing a micro reactor; introducing a liquid reactive precursor dissolved in a polar aprotic solvent into an inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope dissolved in a polar aprotic solvent into another inlet port of the micro reactor; contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in a microchannel of the micro reactor; reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, wherein the reacting step is conducted at a temperature above the boiling point of the polar aprotic solvent at 1 atm and at a pressure sufficient to maintain the polar aprotic solvent in liquid form; and collecting the resulting radiochemical from the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
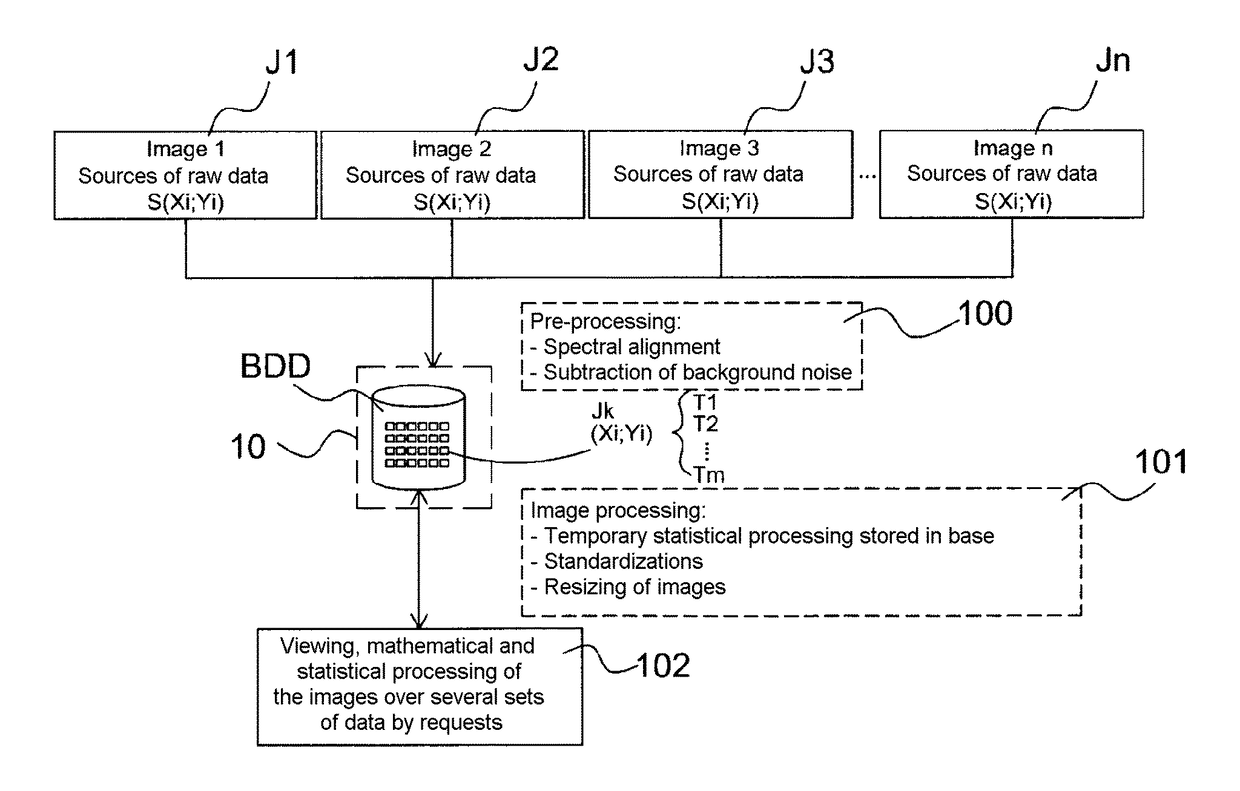
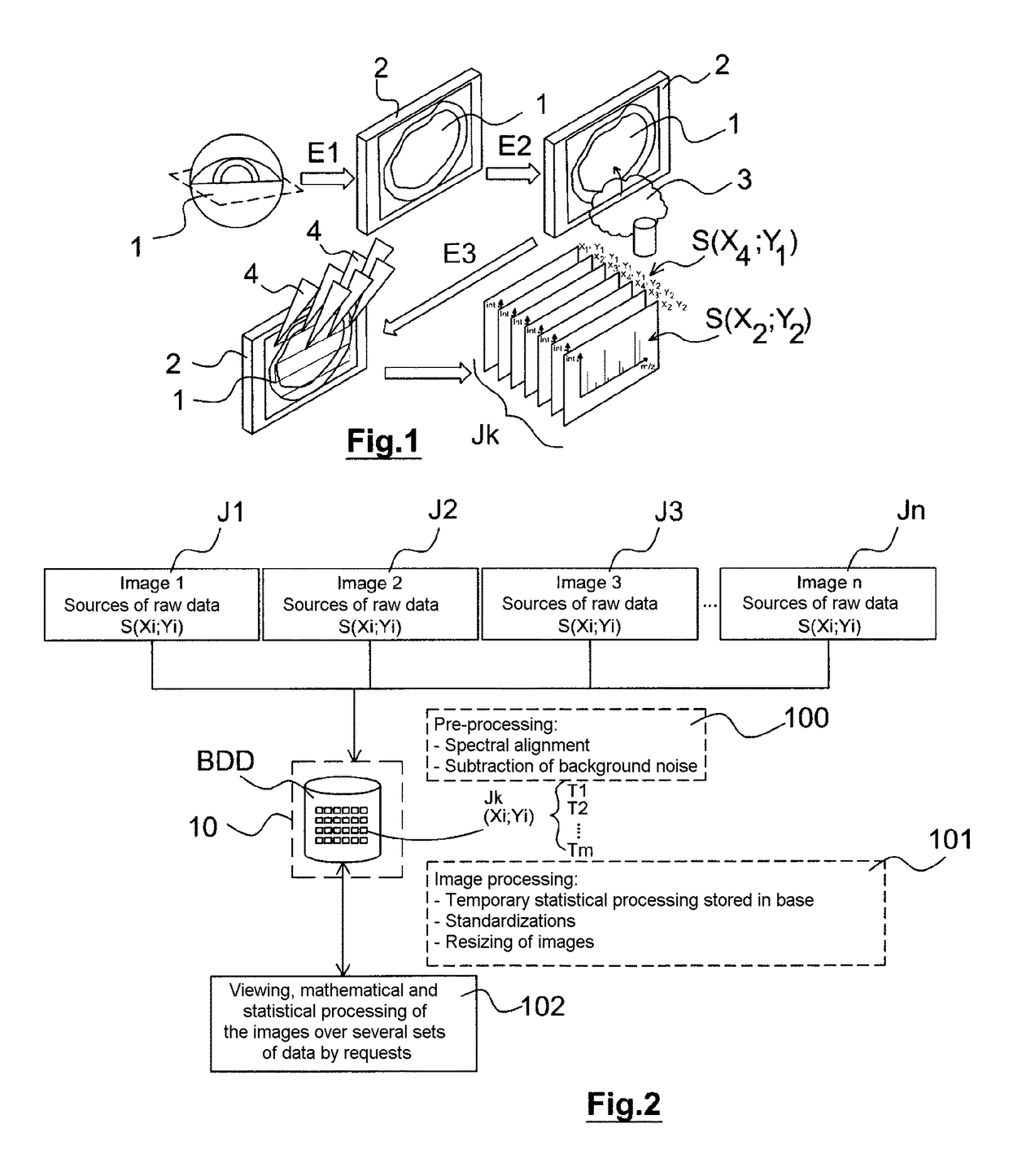
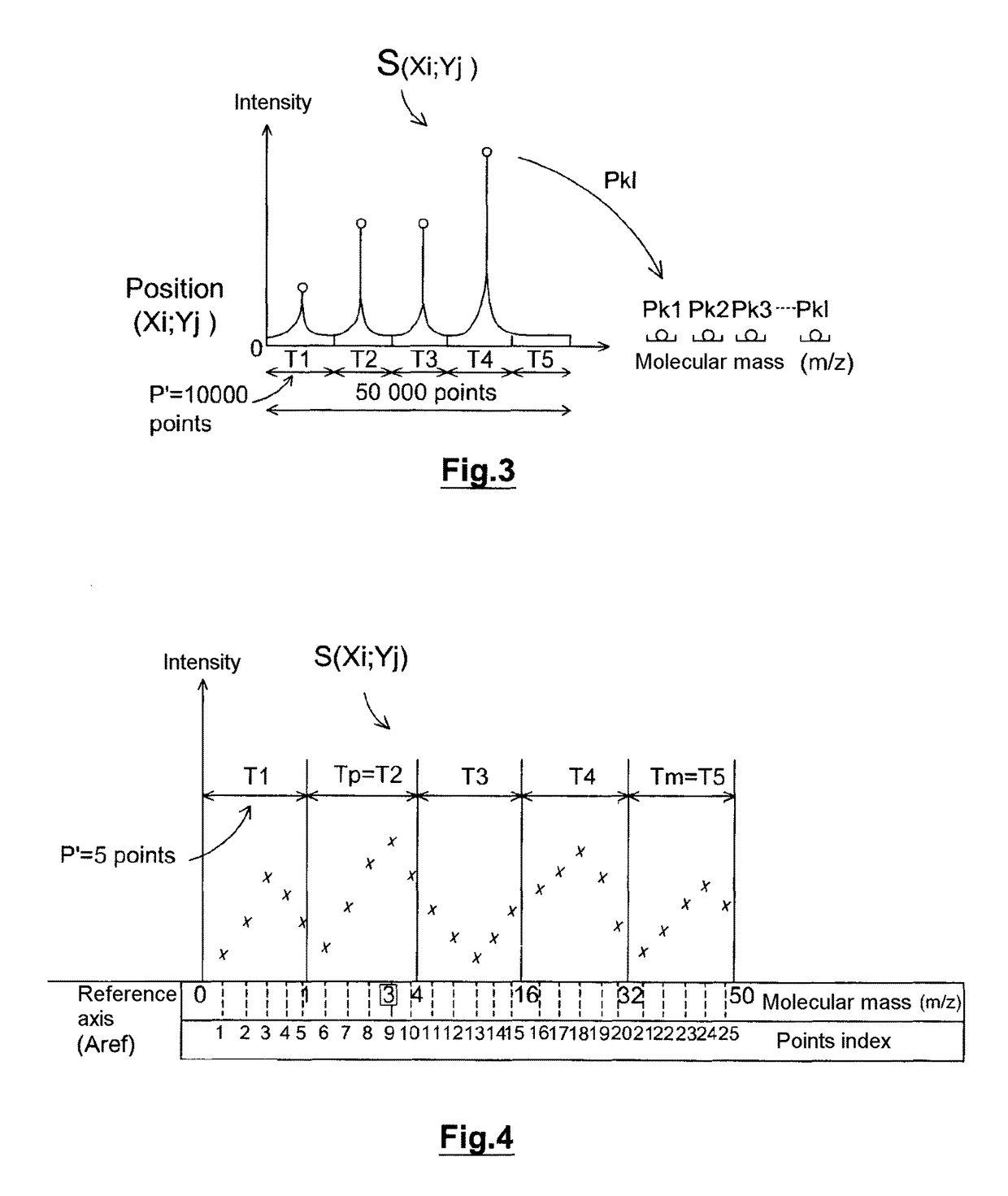
Method for processing molecular imaging data and corresponding data server
A method for processing a plurality of spectral datasets (J1-Jn) intended for being used by a molecular imaging method or a method for recording a plurality of spectral datasets (J1-Jn), each spectral dataset (J1-Jn) being defined by a set of spatial positions (Xi, Yj) each of which is associated with a molecular spectrum with at least two dimensions containing a set of molecular information (S(Xi, Yj)), the method including in particular the following steps: for each dataset (J1-Jn), cutting the molecular spectrum associated with each position (Xi, Yj) into a plurality of spectrum segments (T1-Tm); inserting the segments (T1-Tm) obtained for each position (Xi, Yj) of each dataset (J1-Jn) into a database (BDD); selecting in the database (BDD), following a request relating to molecular information of interest, the one or more segments (T1-Tm) containing the molecular information of interest; and selecting, within each segment (T1-Tm), the molecular information of interest.
Owner:IMABIOTECH
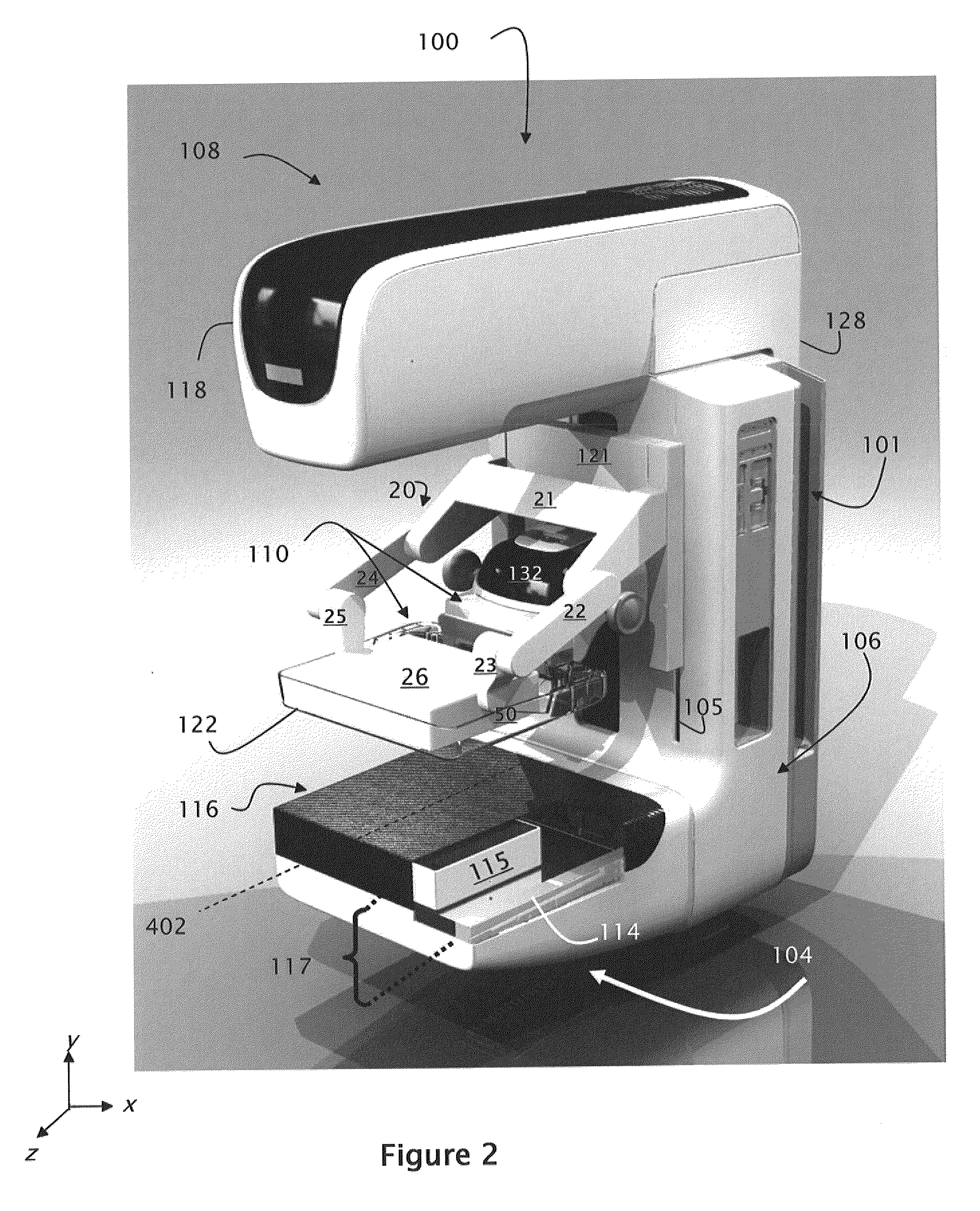
Integrated Breast X-Ray and Molecular Imaging System
ActiveUS20100260316A1Increase speedImprove accuracyTomosynthesisMaterial analysis by optical meansTomosynthesisMolecular imaging
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
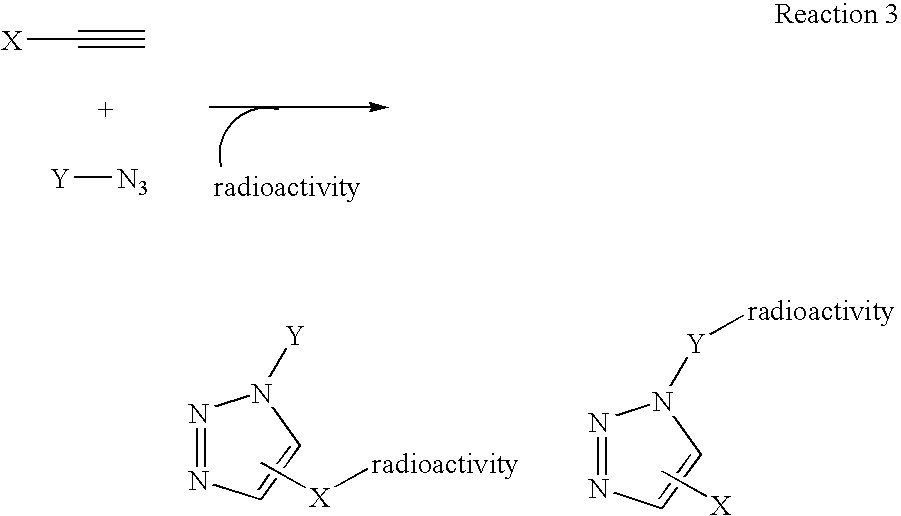
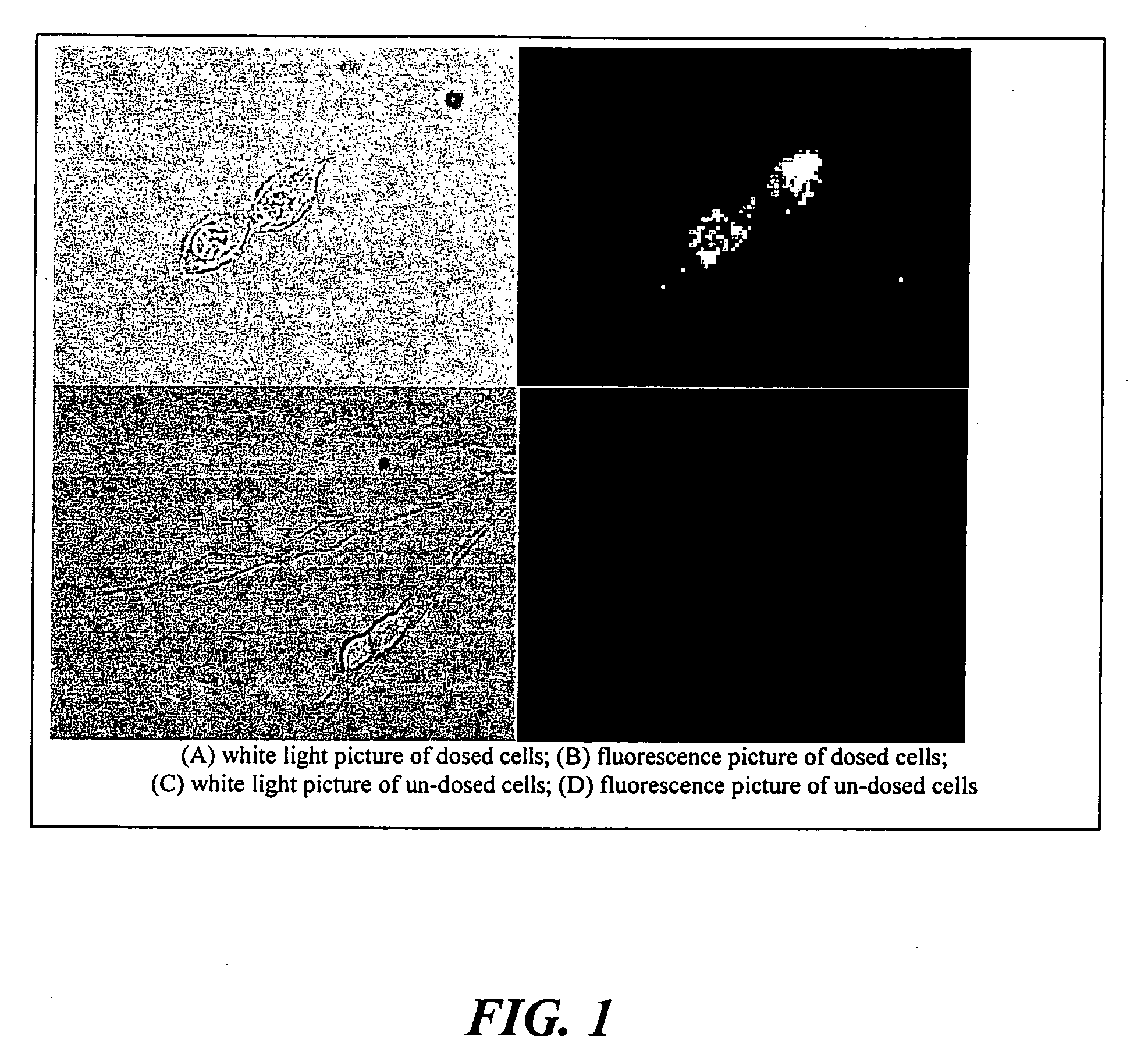
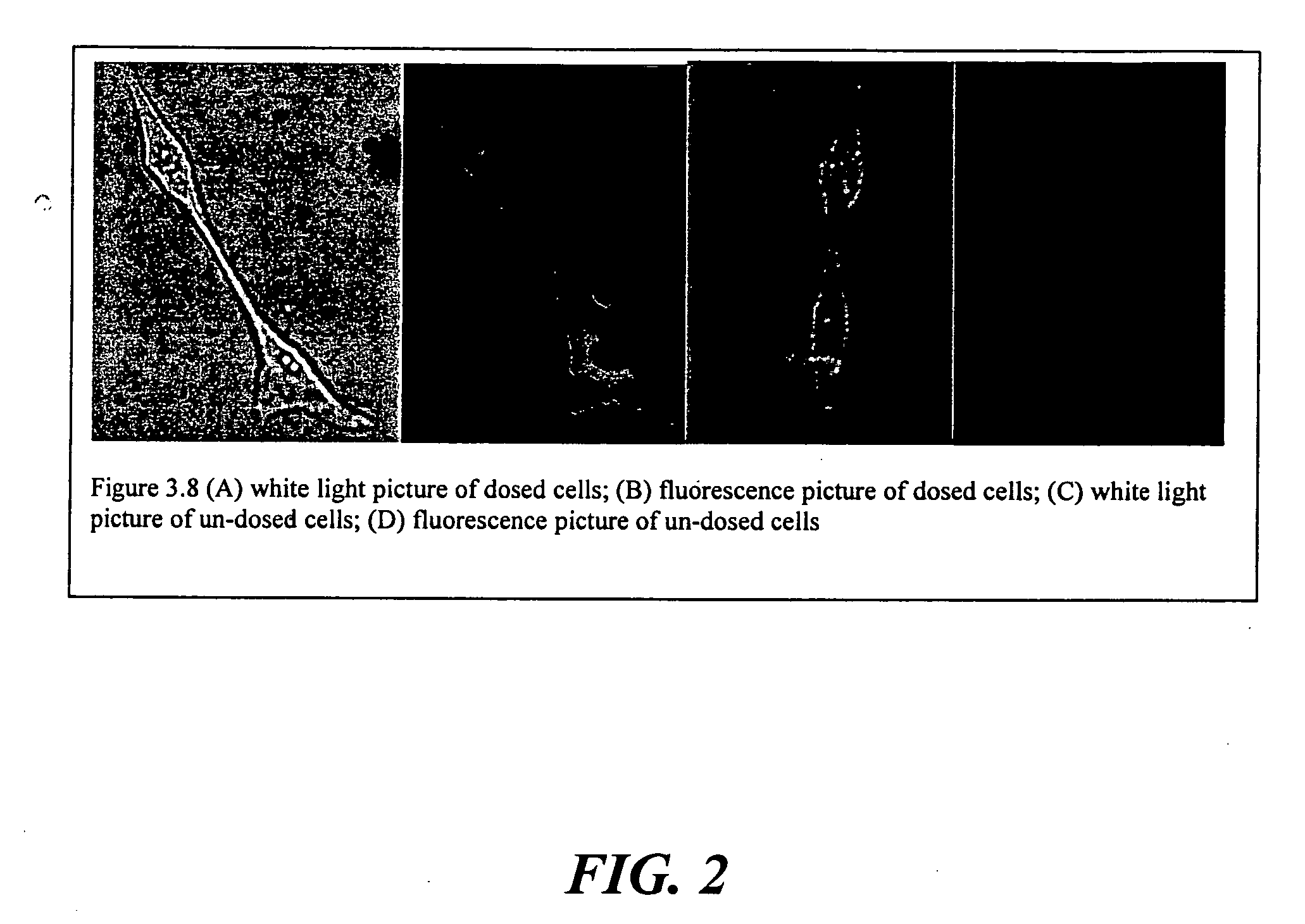
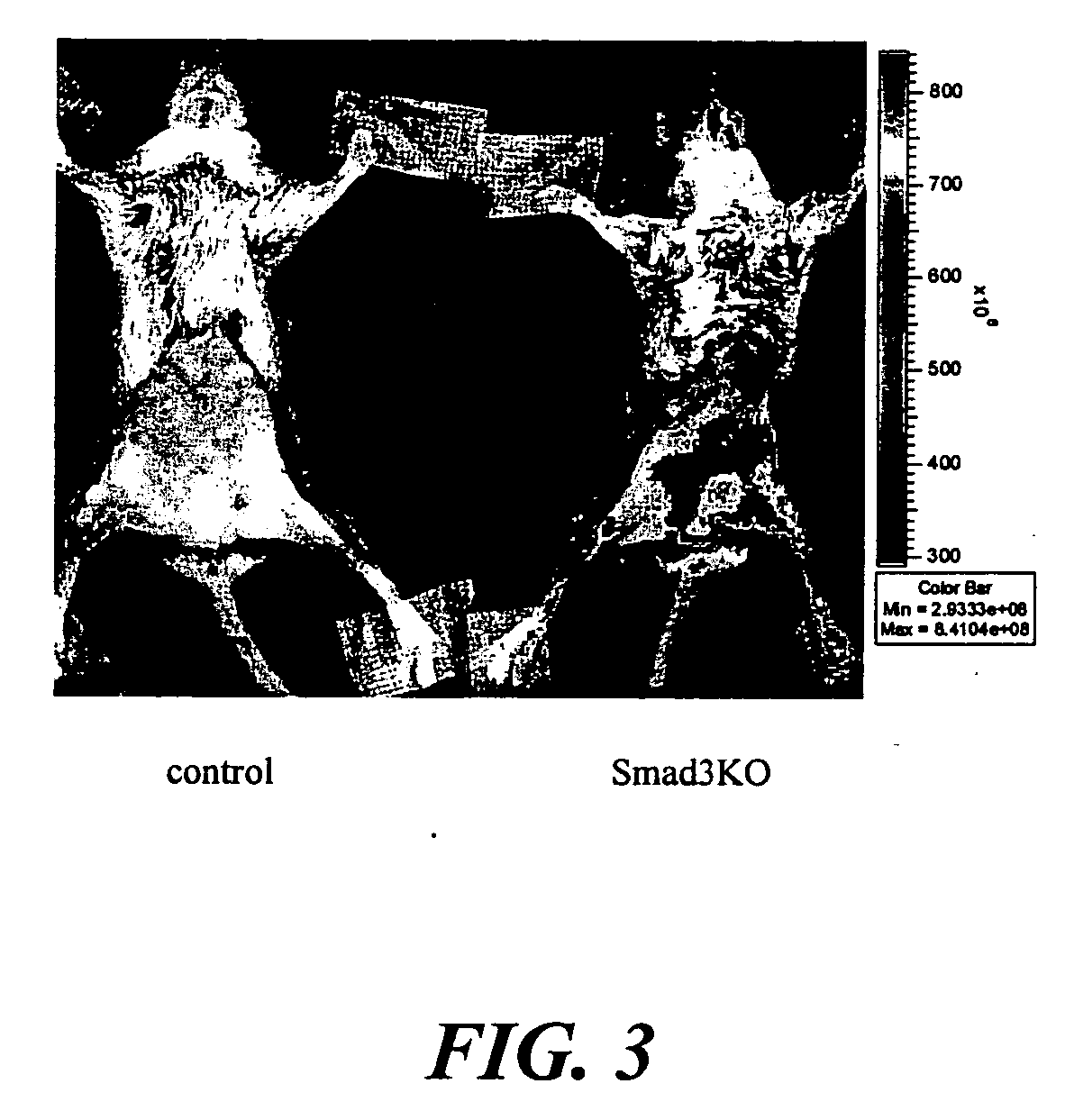
Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition
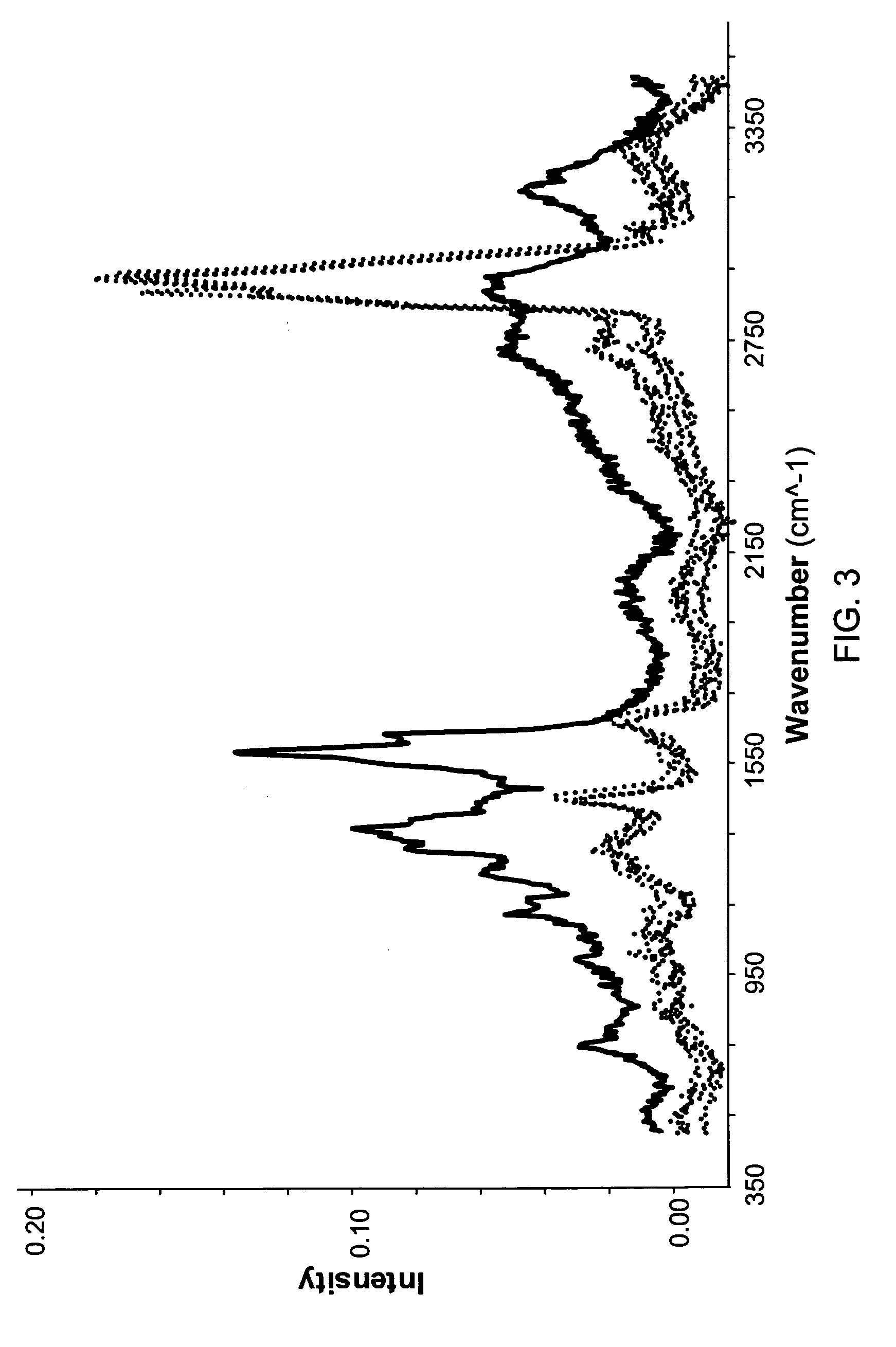
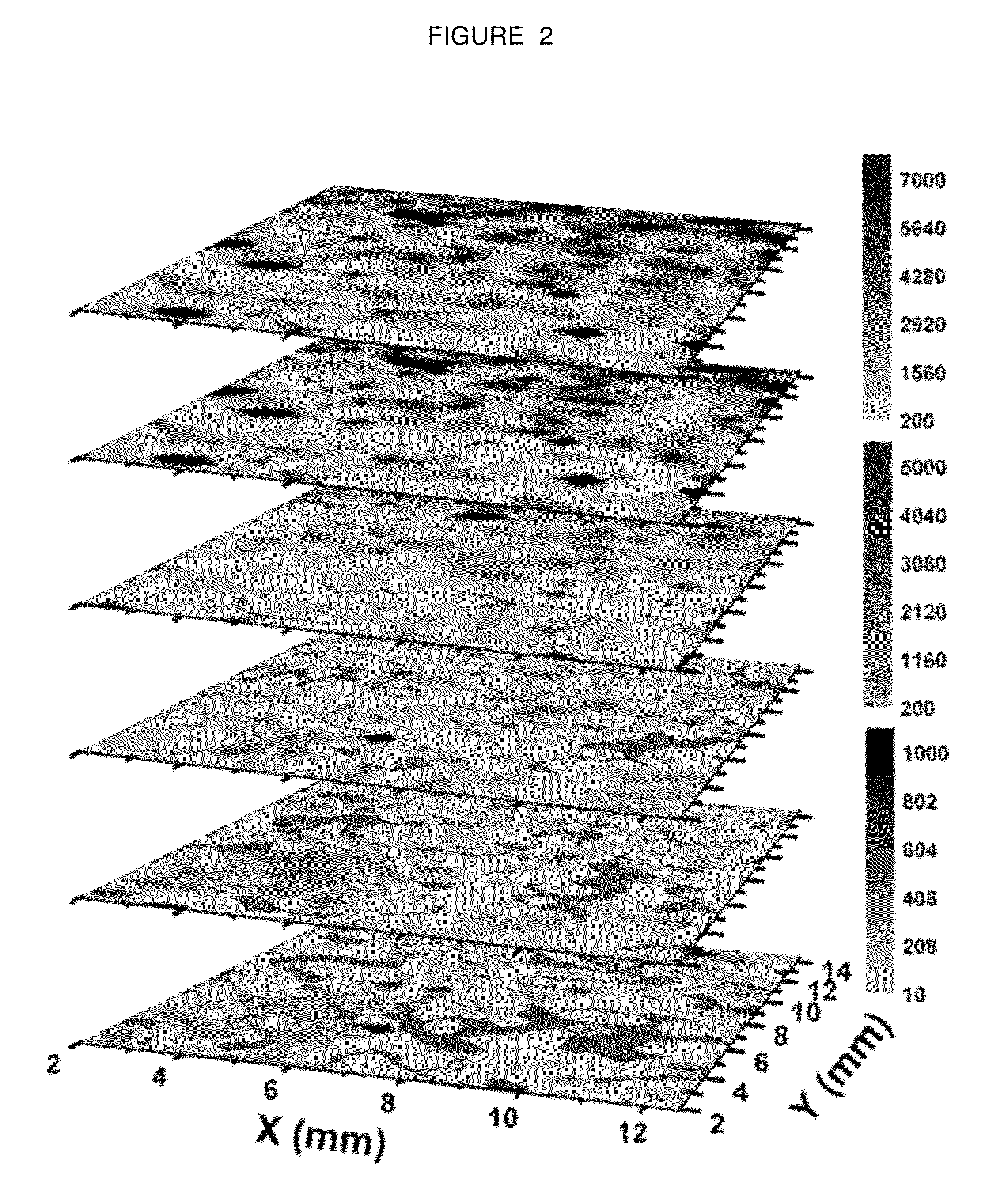
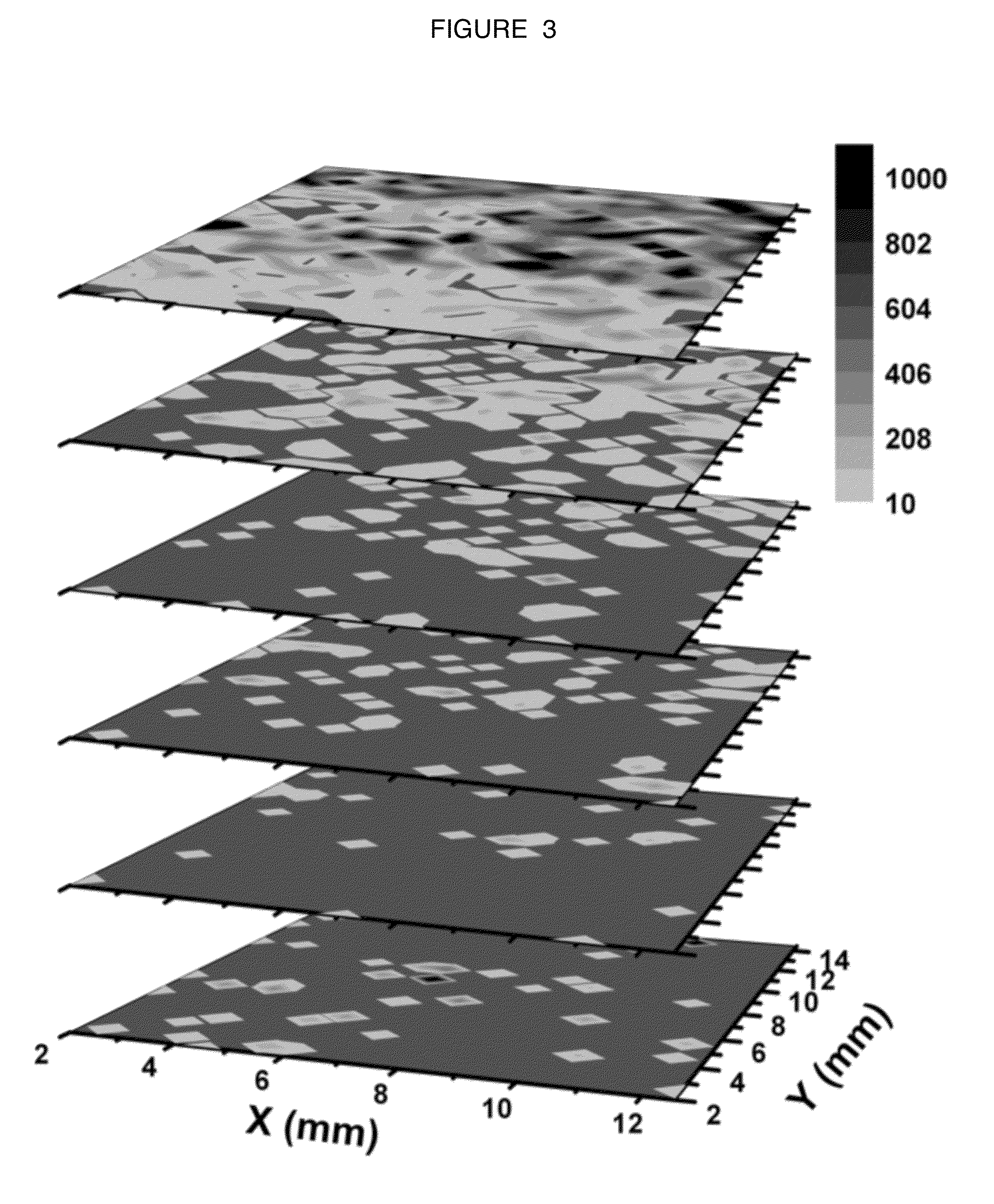
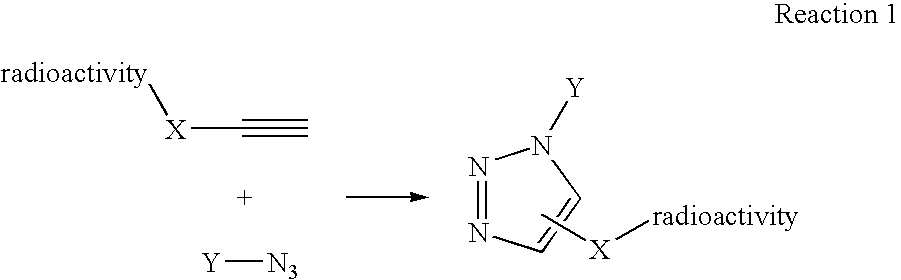
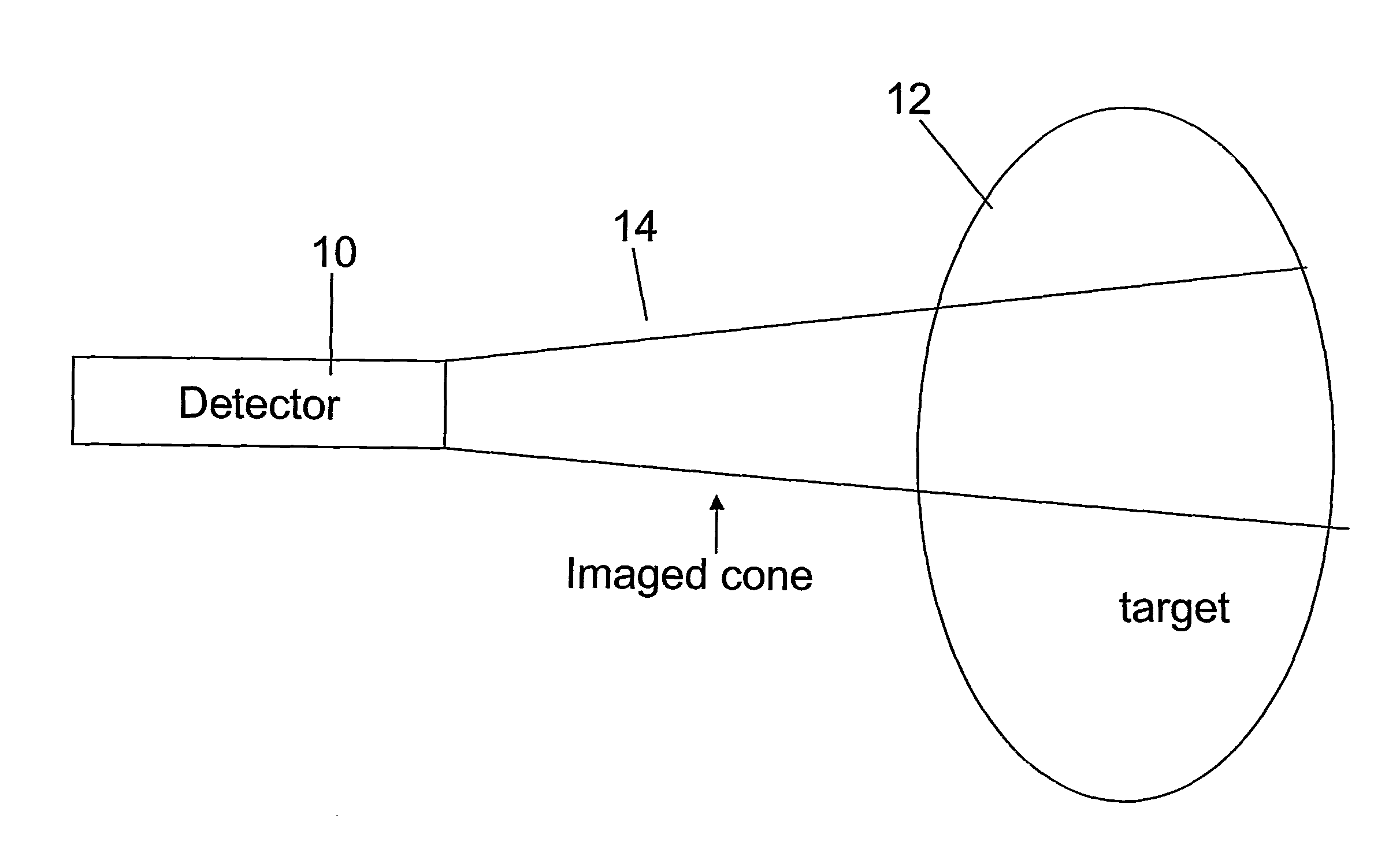
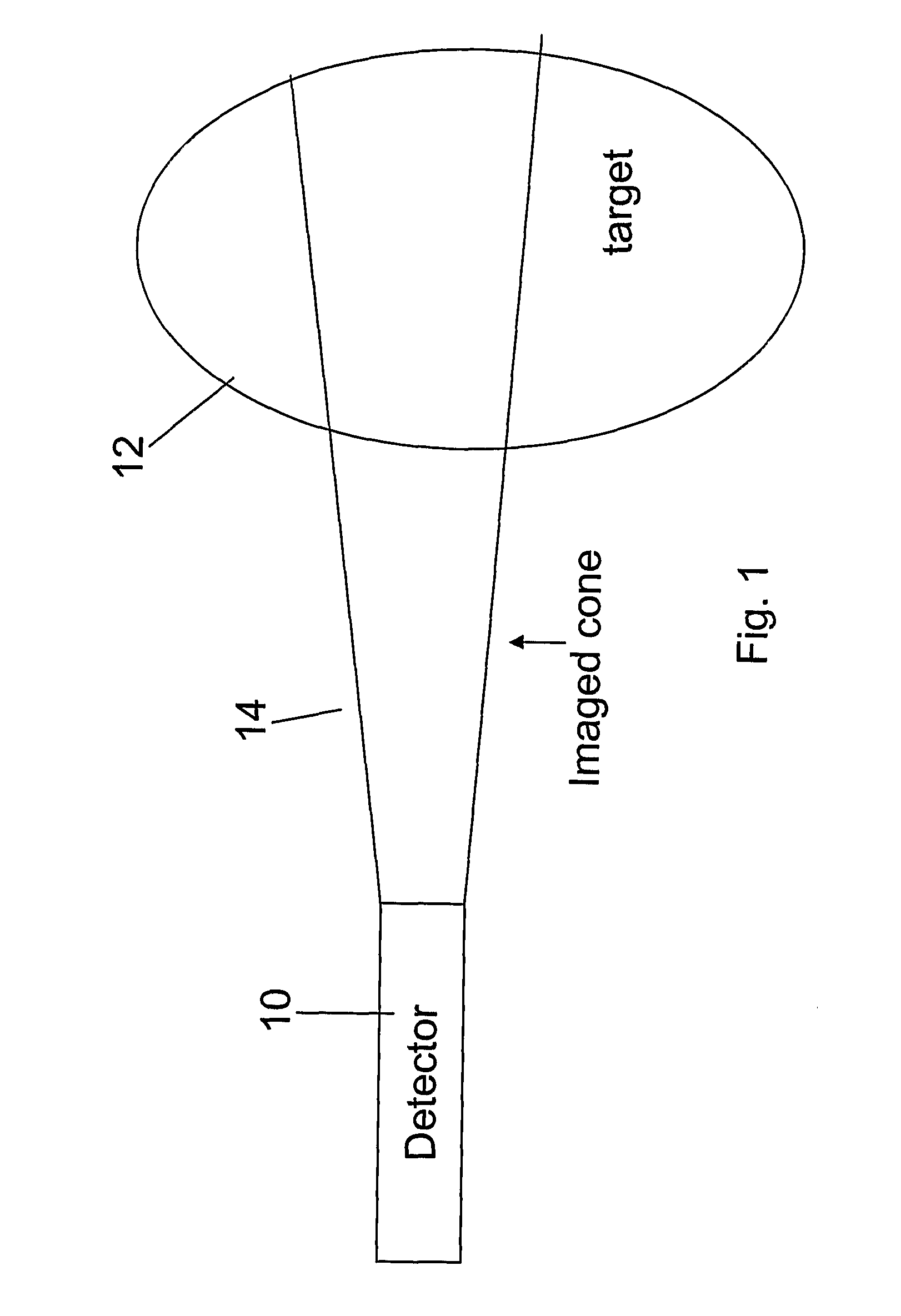
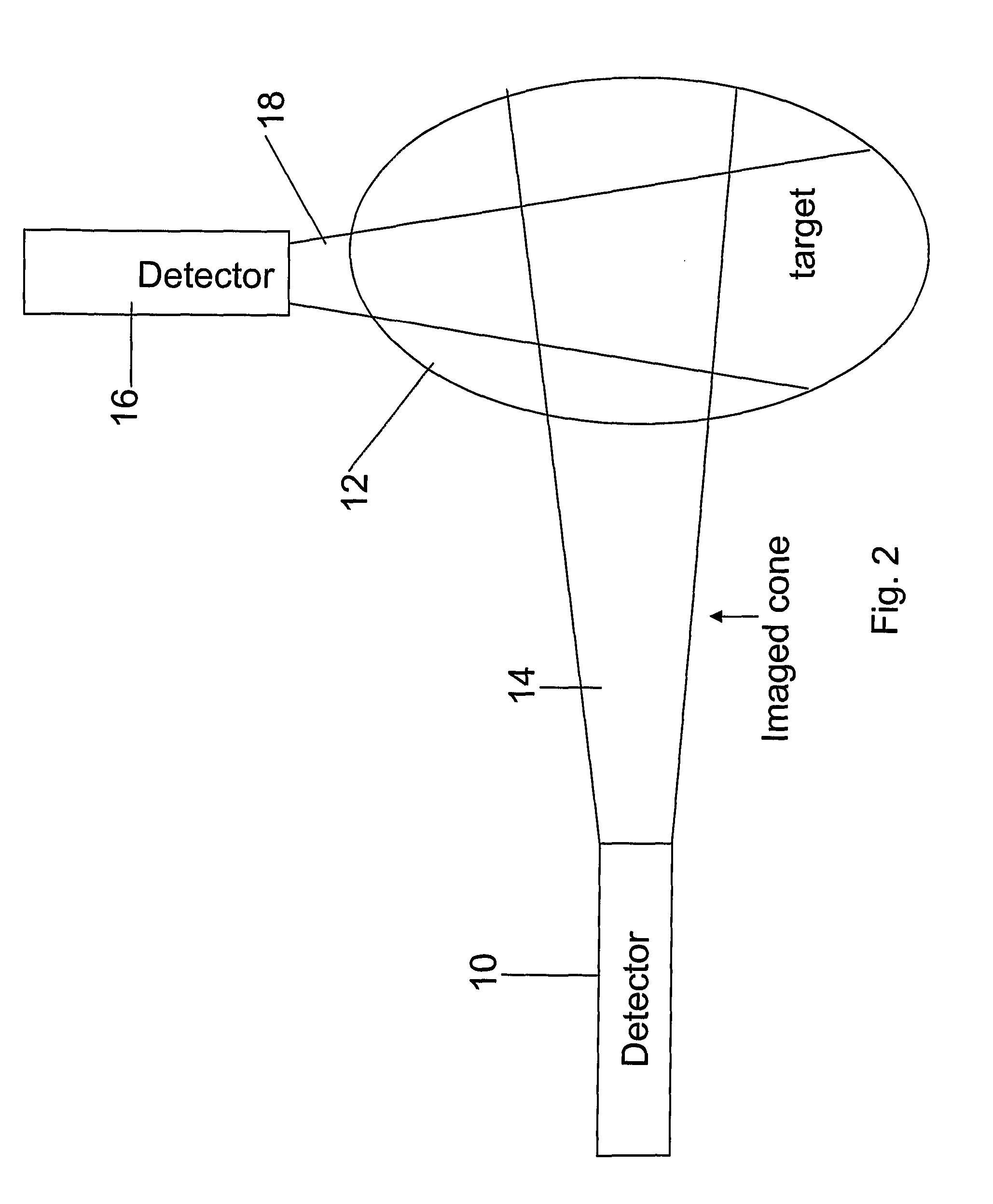
InactiveUS20080267878A1NanomedicineRadioactive preparation carriersBiotin-streptavidin complexMolecular imaging
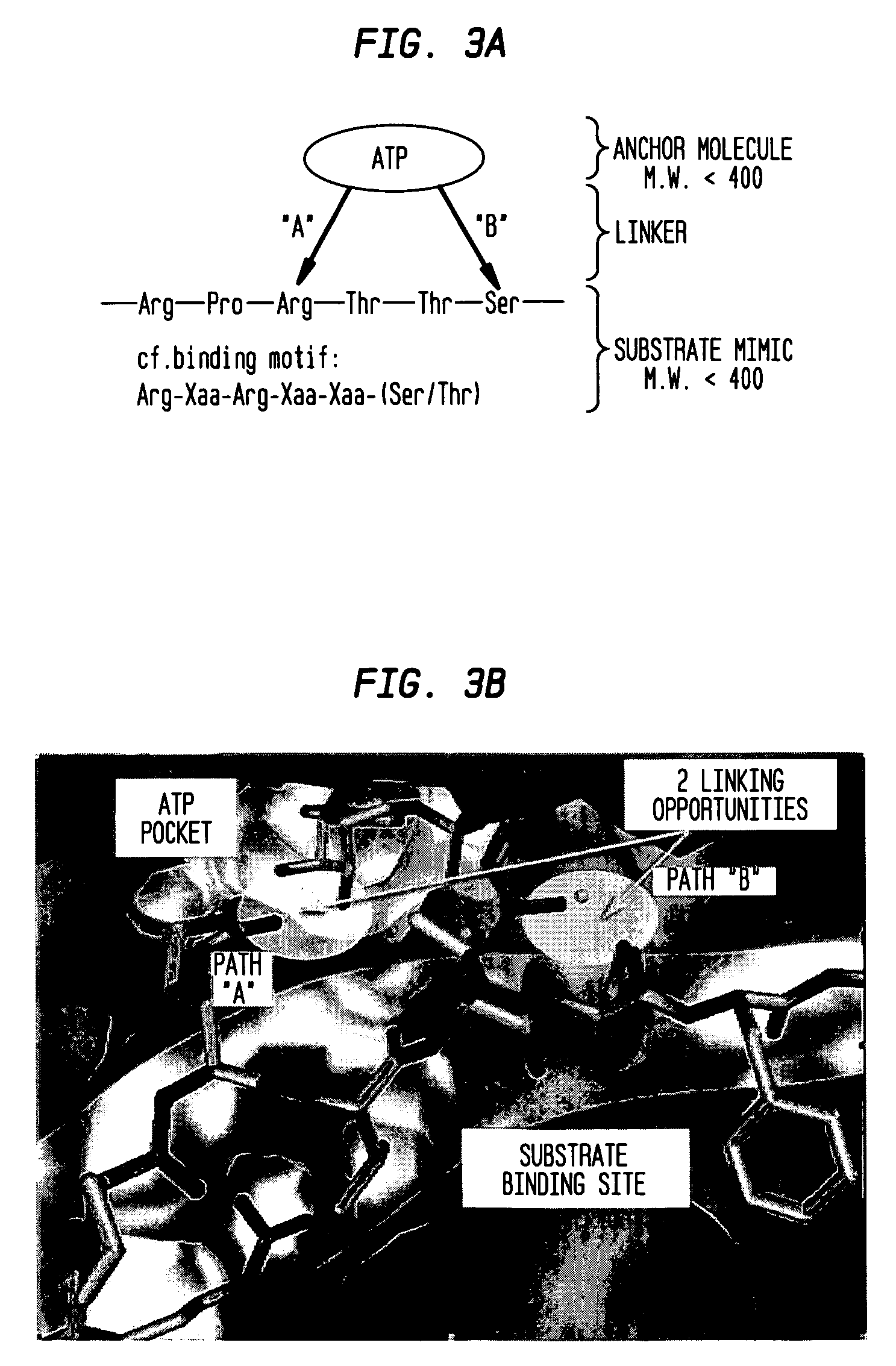
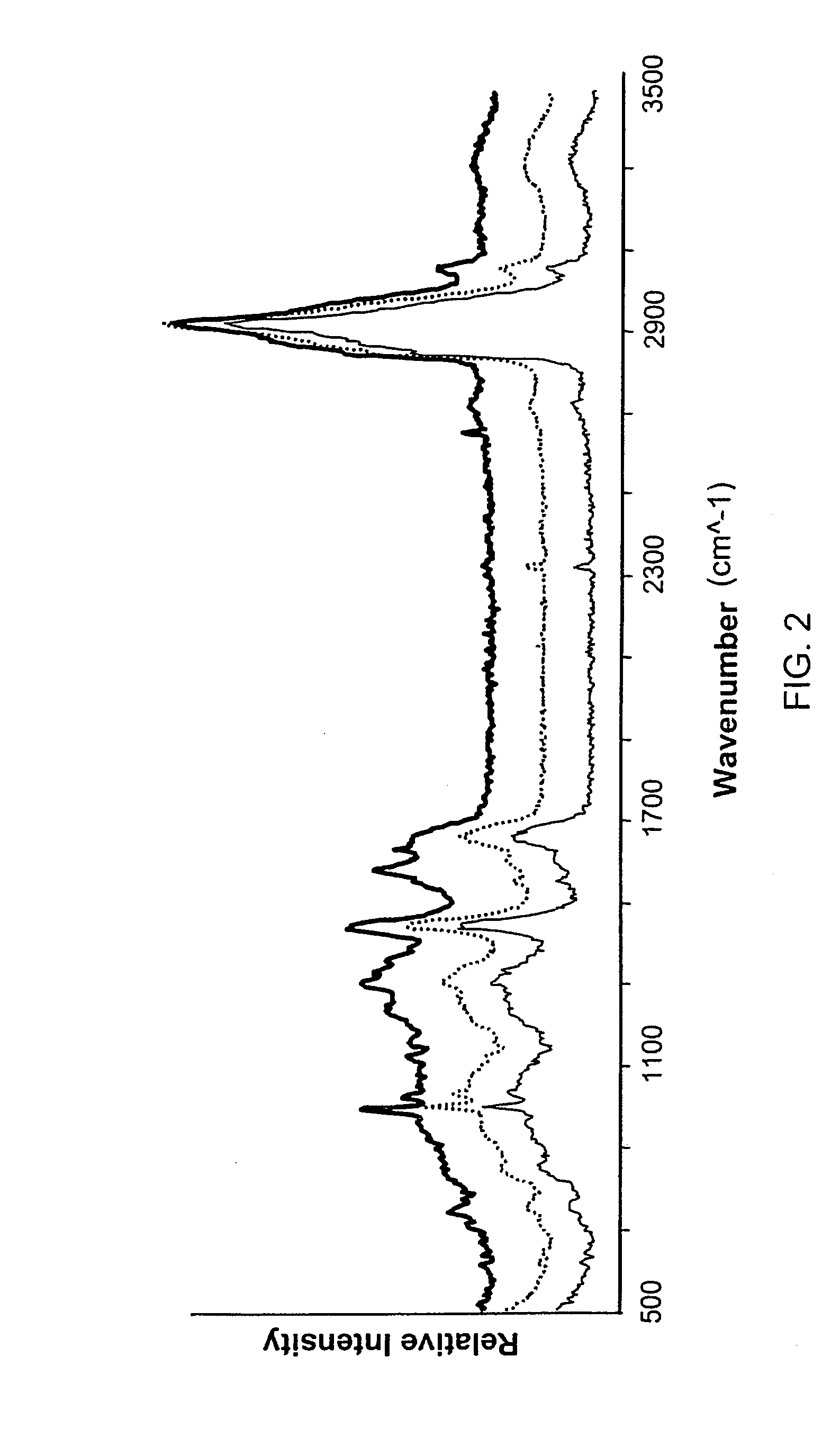
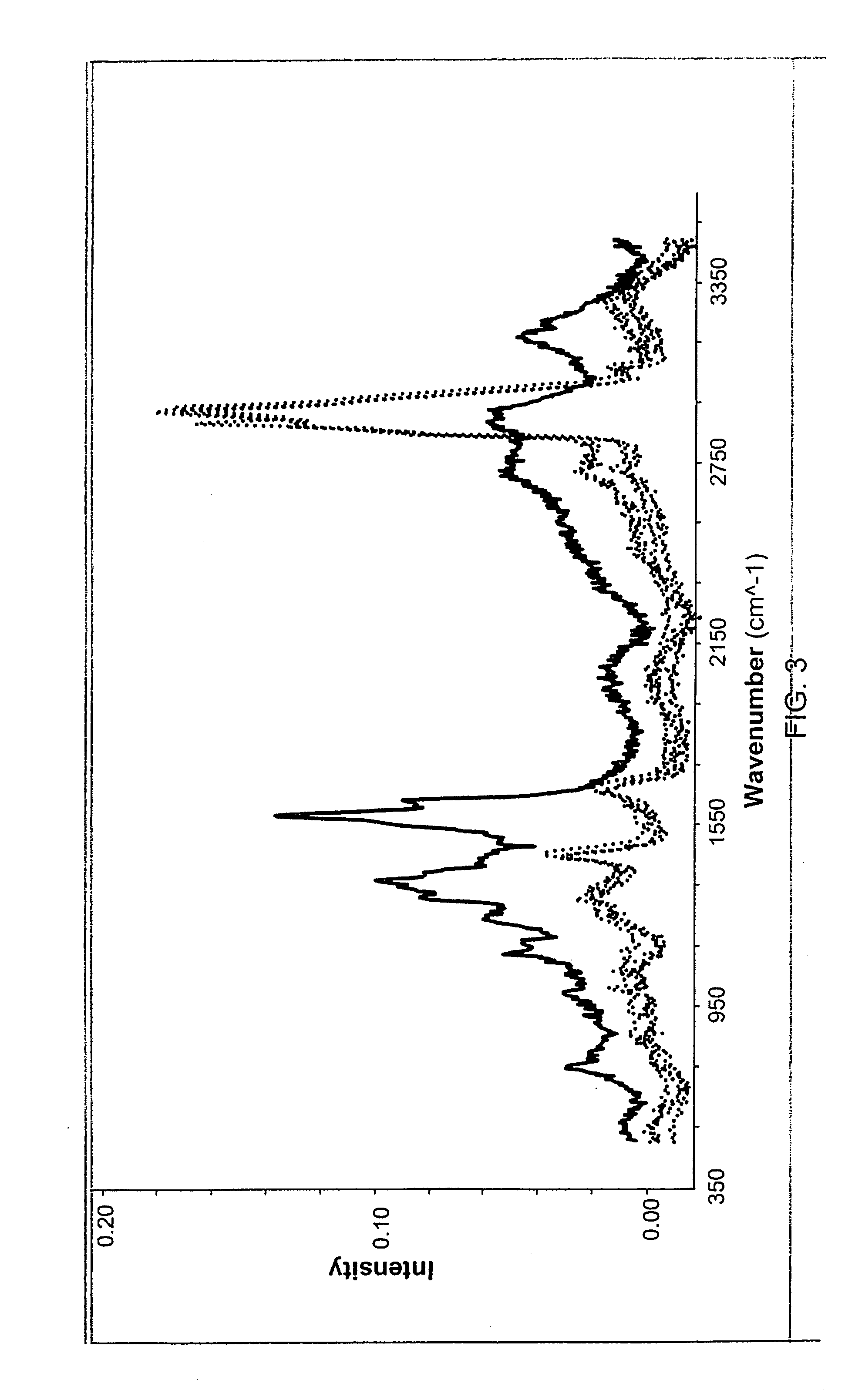
The use of a selective chemical and bioorthogonal reaction providing a covalent ligation such as the [3+2] cycloaddition, in targeted molecular imaging and therapy is presented, more specifically with interesting applications for pre-targeted imaging or therapy. Current pre-targeted imaging is hampered by the fact that it relies solely on natural / biological targeting constructs (biotin / streptavidin). Size considerations and limitations associated with their endogenous nature severely limit the number of applications. The present invention describes how the use of an abiotic, bio-orthogonal reaction which forms a stable adduct under physiological conditions, by way of a small or undetectable bond, can overcome these limitations.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Cytological analysis by raman spectroscopic imaging
Raman molecular imaging is used to differentiate between normal and diseased cells or tissue. For instance benign and malignant lesions of bladder and other tissues can be distinguished, including epithelial tissues such as lung, prostate, kidney, breast, and colon, and non-epithelial tissues, such as bone marrow and brain. Raman scattering data relevant to the disease state of cells or tissue can be combined with visual image data to produce hybrid images which depict both a magnified view of the cellular structures and information relating to the disease state of the individual cells in the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
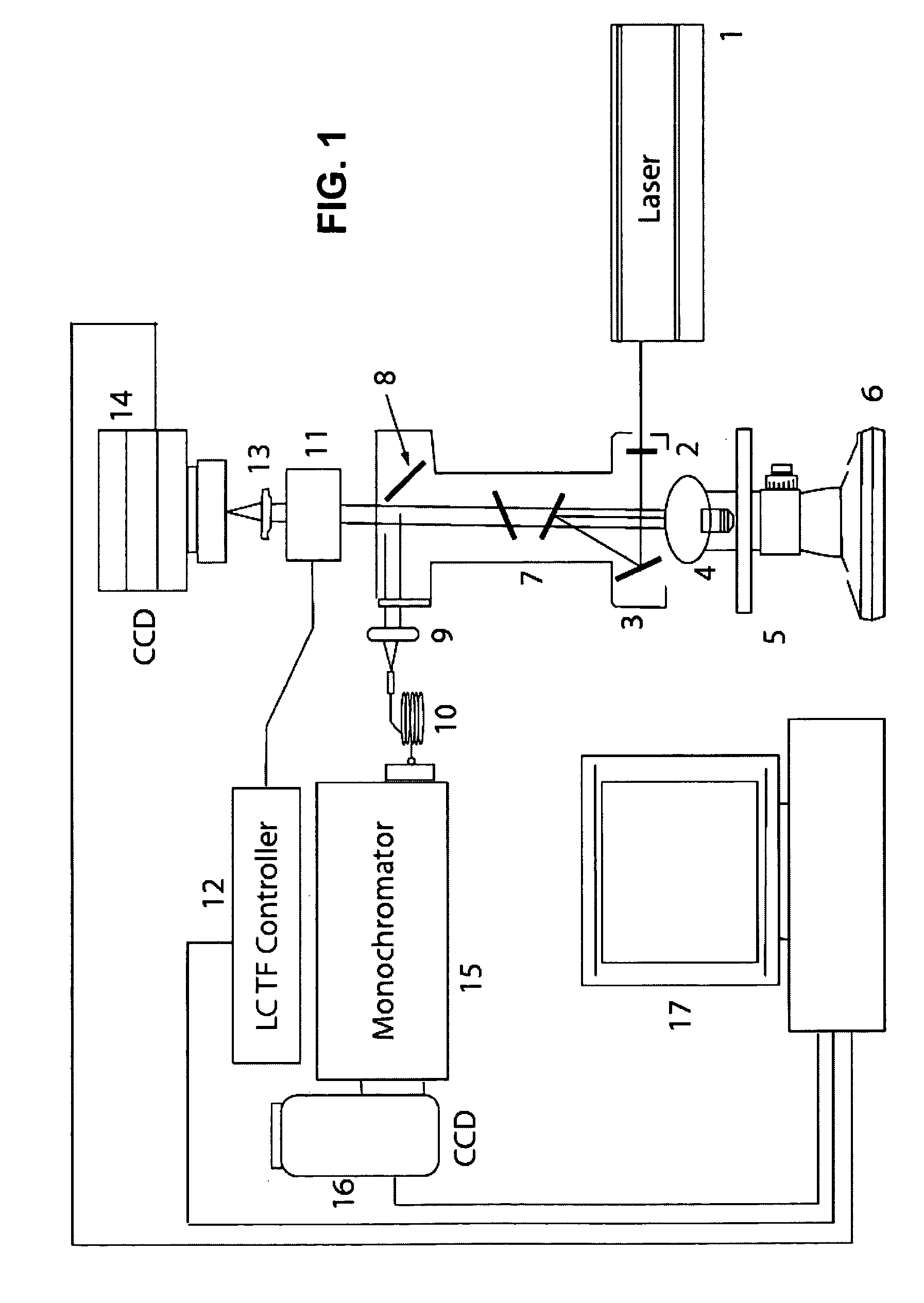
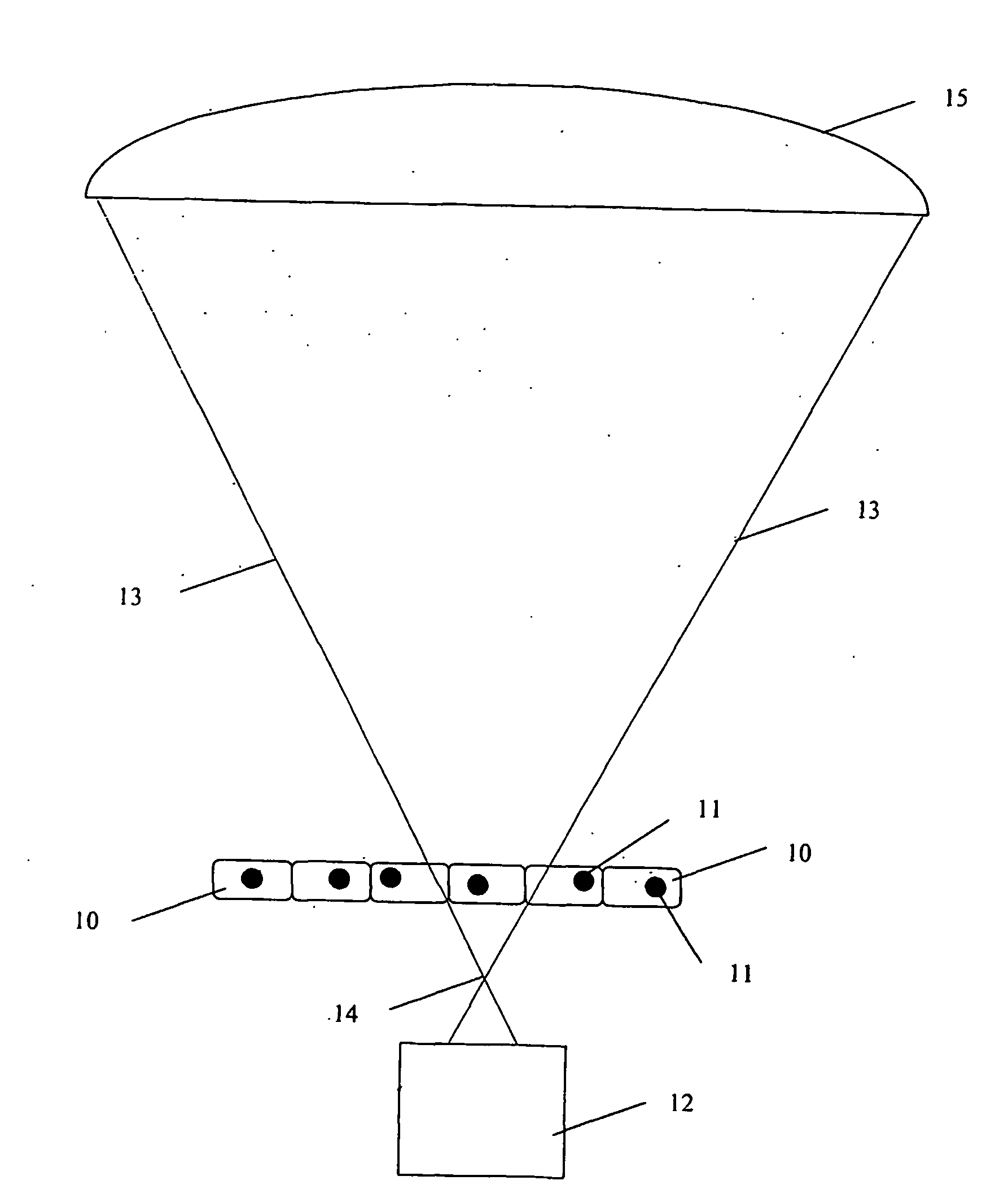
System for molecular imaging
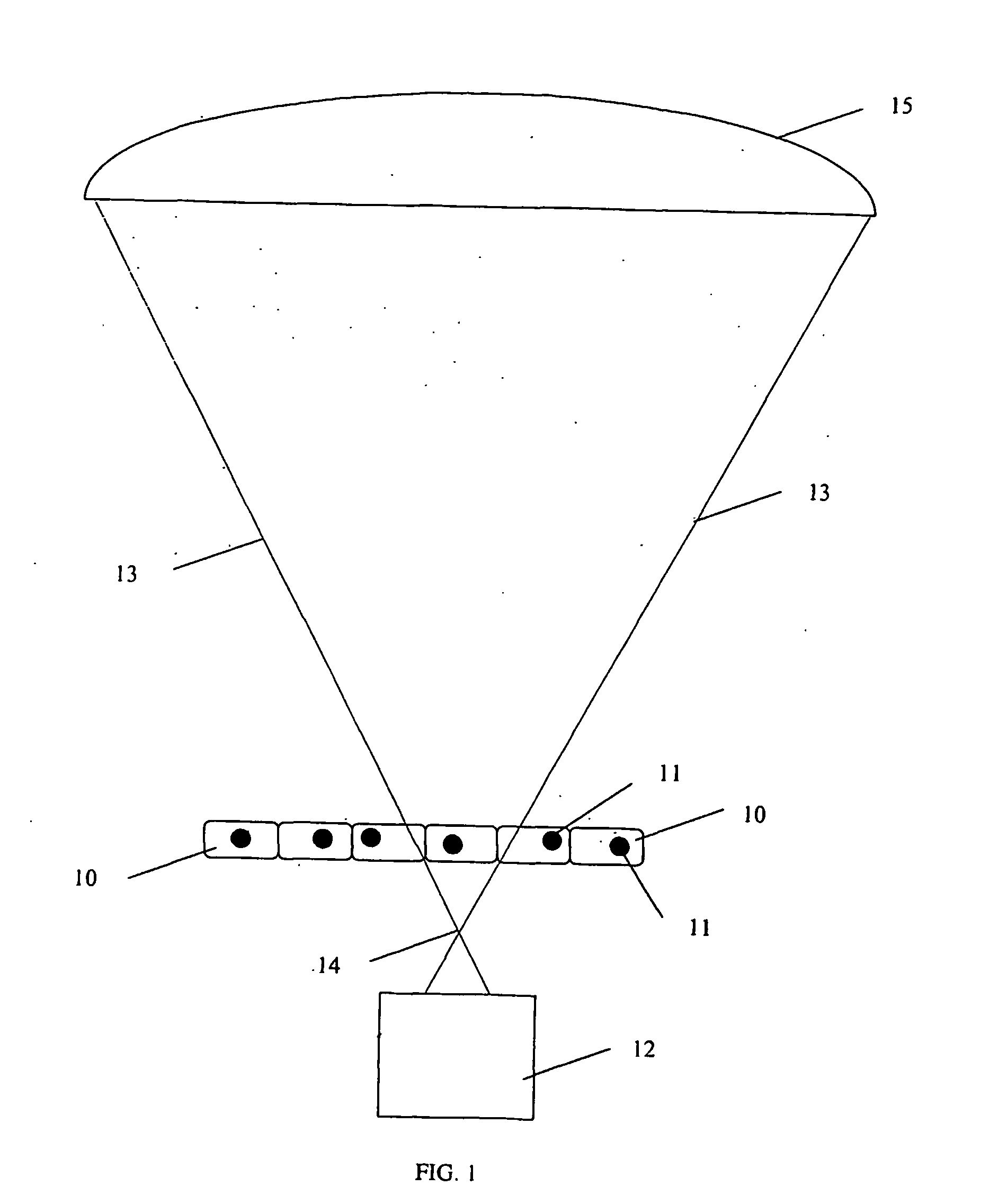
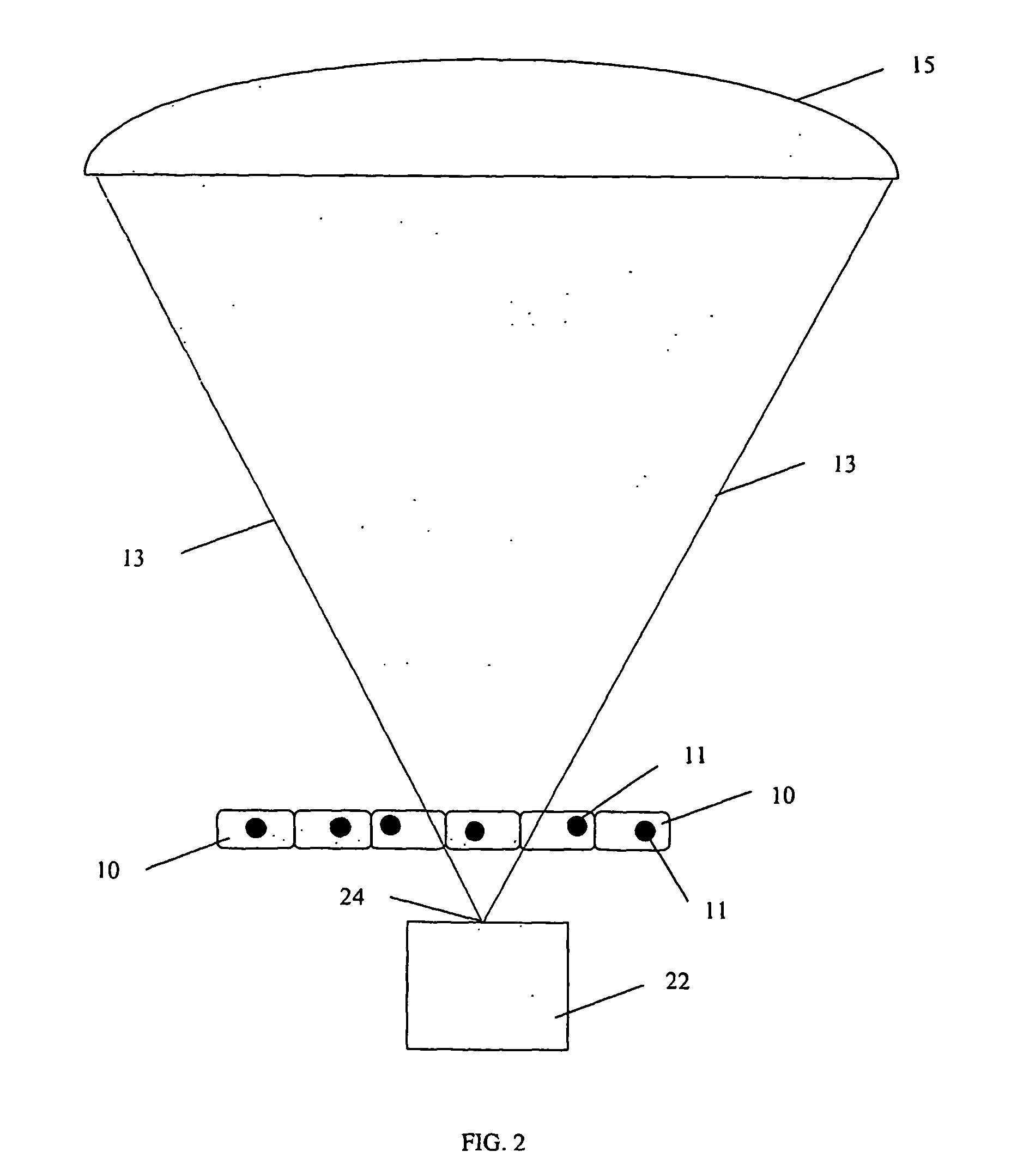
InactiveUS20070025504A1Promote recoveryMass extinctionDiagnostics using lightMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayPhotonics
Charged and neutral particles, photons (13), photonic optics, detectors (15) and sensor arrays are used for application to molecular imaging, communication with biological organisms and monitoring and learning biological activity inside living organisms. The living organisms include among others living tissue, biological organs, cells (10), eukaryotes, prokaryotes, viruses and phages. Molecular imaging can be an effective new tool to understand the mechanisms of life and communicate, modify and control it. Techniques, methods and devices are described to achieve these aims. The probes used in molecular imaging described above will include the full spectrum of photons; charged and uncharged particles (13); chemicals; and biological probes.
Owner:TUMER TUMAY O
Ionization method and apparatus using electrospray
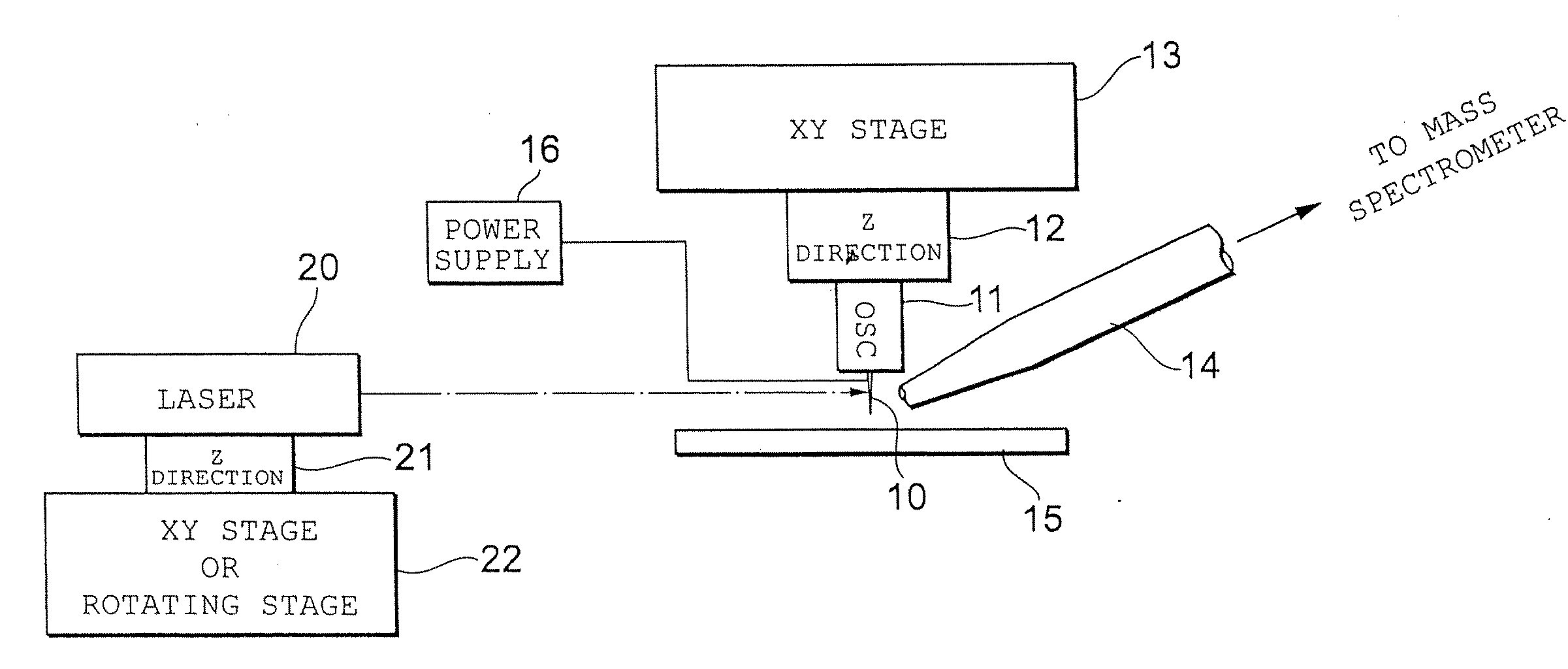
ActiveUS20090140137A1Efficient productionSamplingComponent separationImage resolutionMolecular imaging
A biological sample can be subjected to measurement, description and ionization of ions is possible under atmospheric pressure without undergoing pretreatment. Imaging having a resolution on the nanometer order can be performed. An STM needle (probe) of an XYZ-axis-drive piezoelectric element is oscillated along the Z axis to contact the sample to a depth on the nanometer order and capture molecules at the needle tip. A pulsed high voltage is applied to the needle, achieving needle electrospray. The sample molecules are then desorbed and ionized, and mass spectrometry is carried out. The needle is swept in the XY directions, oscillation is repeated and an image obtained by molecular imaging of a nanometer area of the biological sample is measured. The probe may be brought into contact with a droplet produced at the tip of a capillary connected to the outlet port of a liquid chromatograph to capture a sample.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
Cytological analysis by raman spectroscopic imaging
Raman molecular imaging is used to differentiate between normal and diseased cells or tissue. For instance benign and malignant lesions of bladder and other tissues can be distinguished, including epithelial tissues such as lung, prostate, kidney, breast, and colon, and non-epithelial tissues, such as bone marrow and brain. Raman scattering data relevant to the disease state of cells or tissue can be combined with visual image data to produce hybrid images which depict both a magnified view of the cellular structures and information relating to the disease state of the individual cells in the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
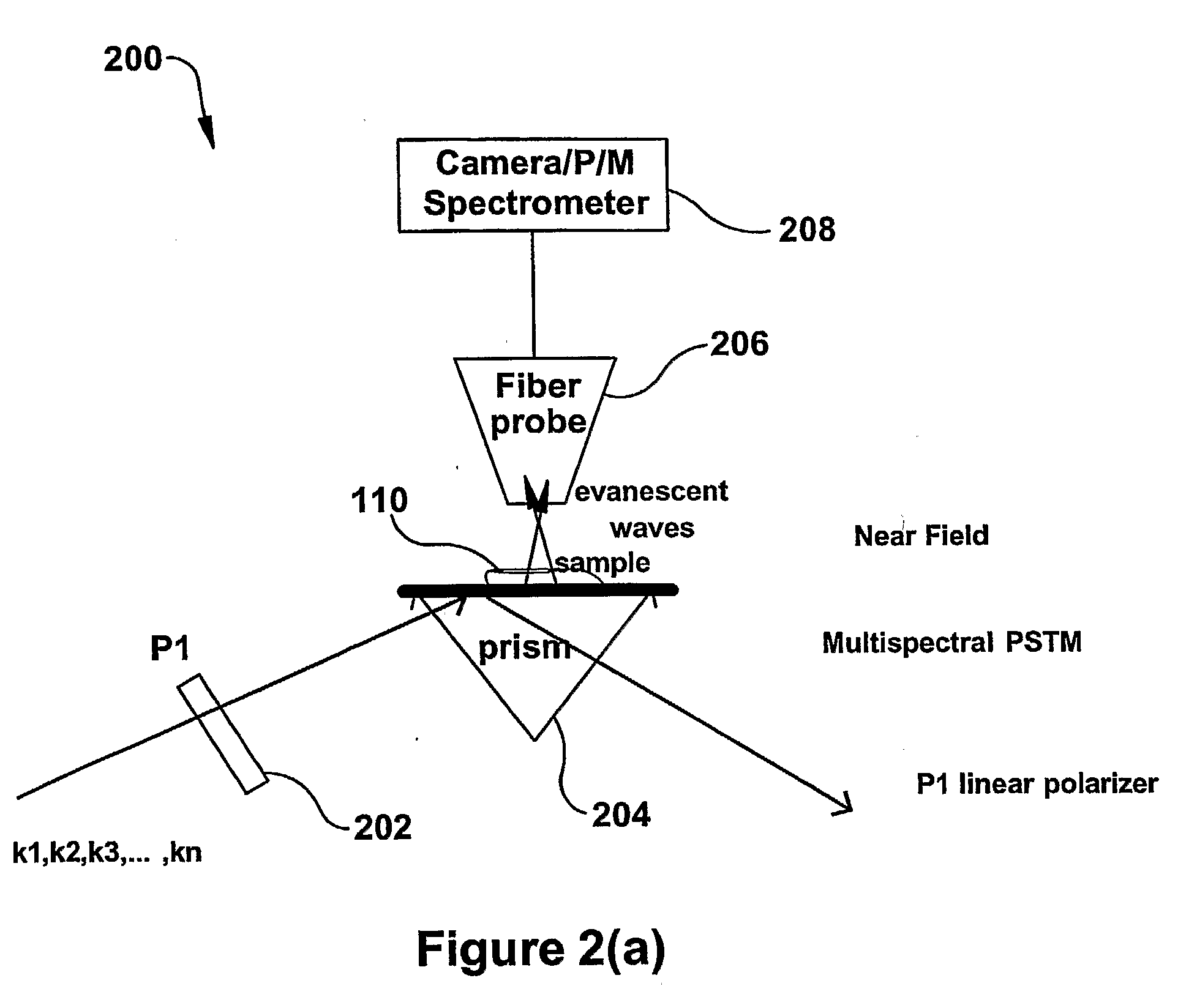
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
InactiveUS20090119808A1Enhanced sub-surfaceEnhanced in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesSurface/boundary effectDepth imagingImage resolution
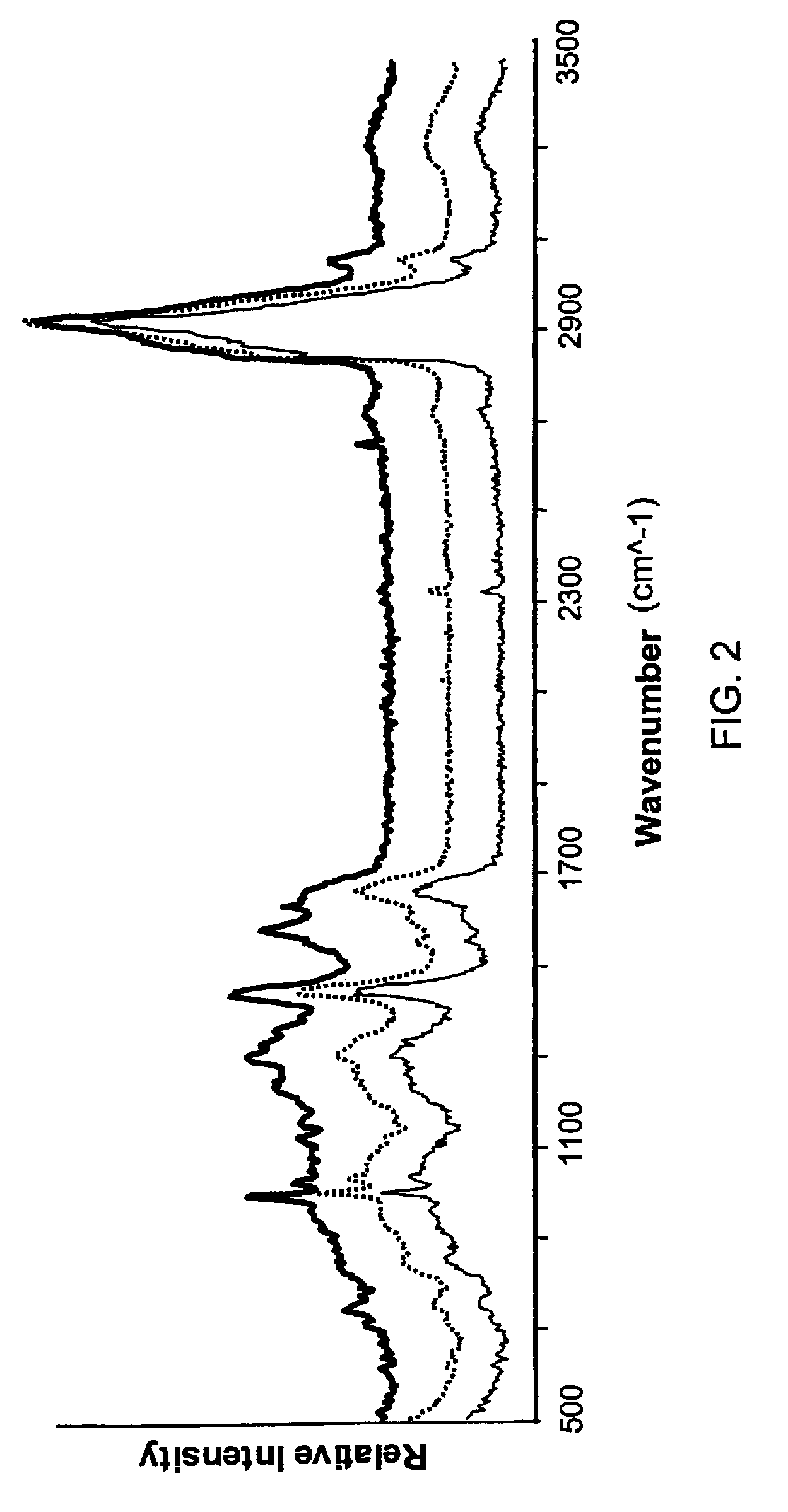
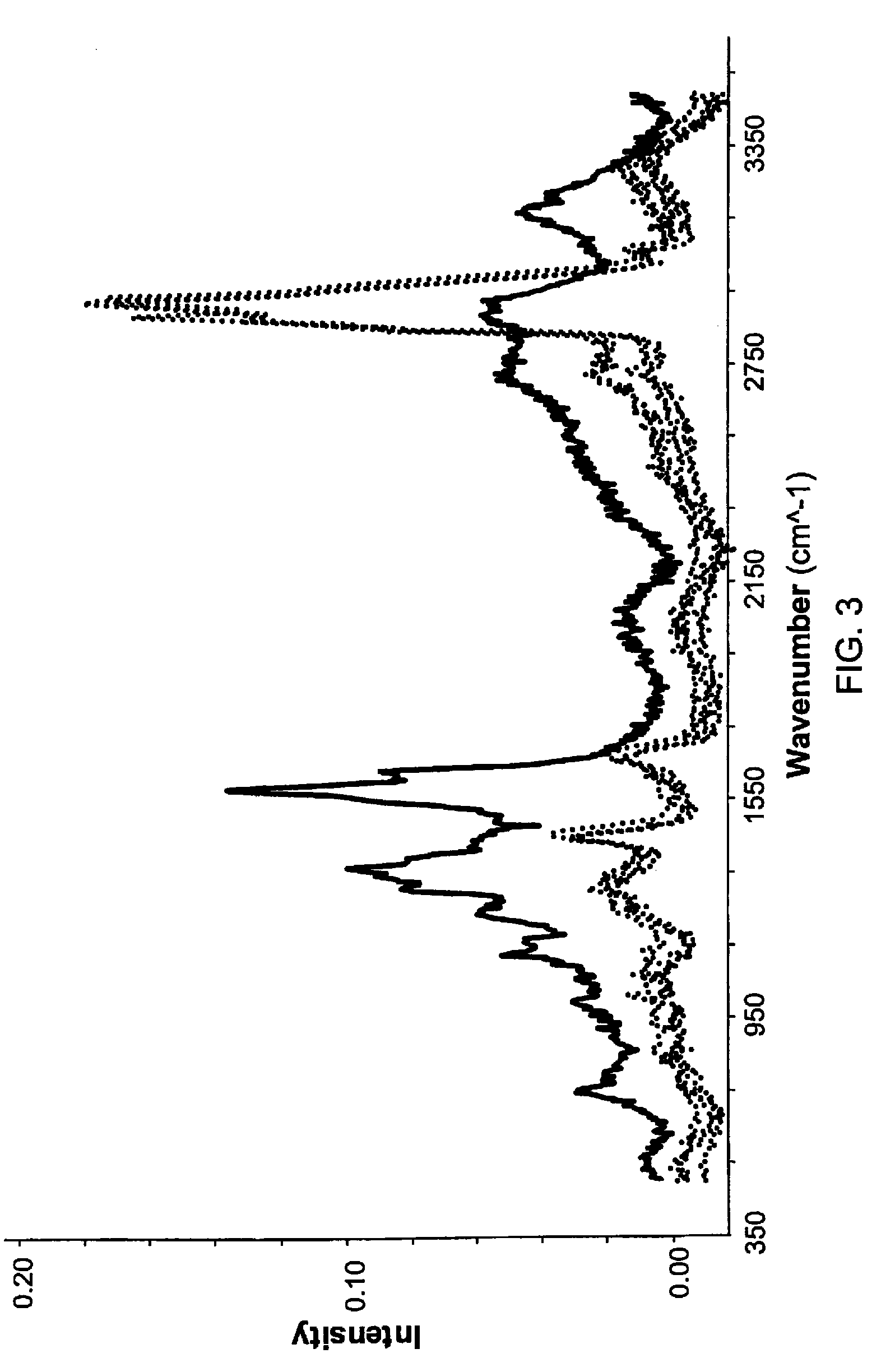
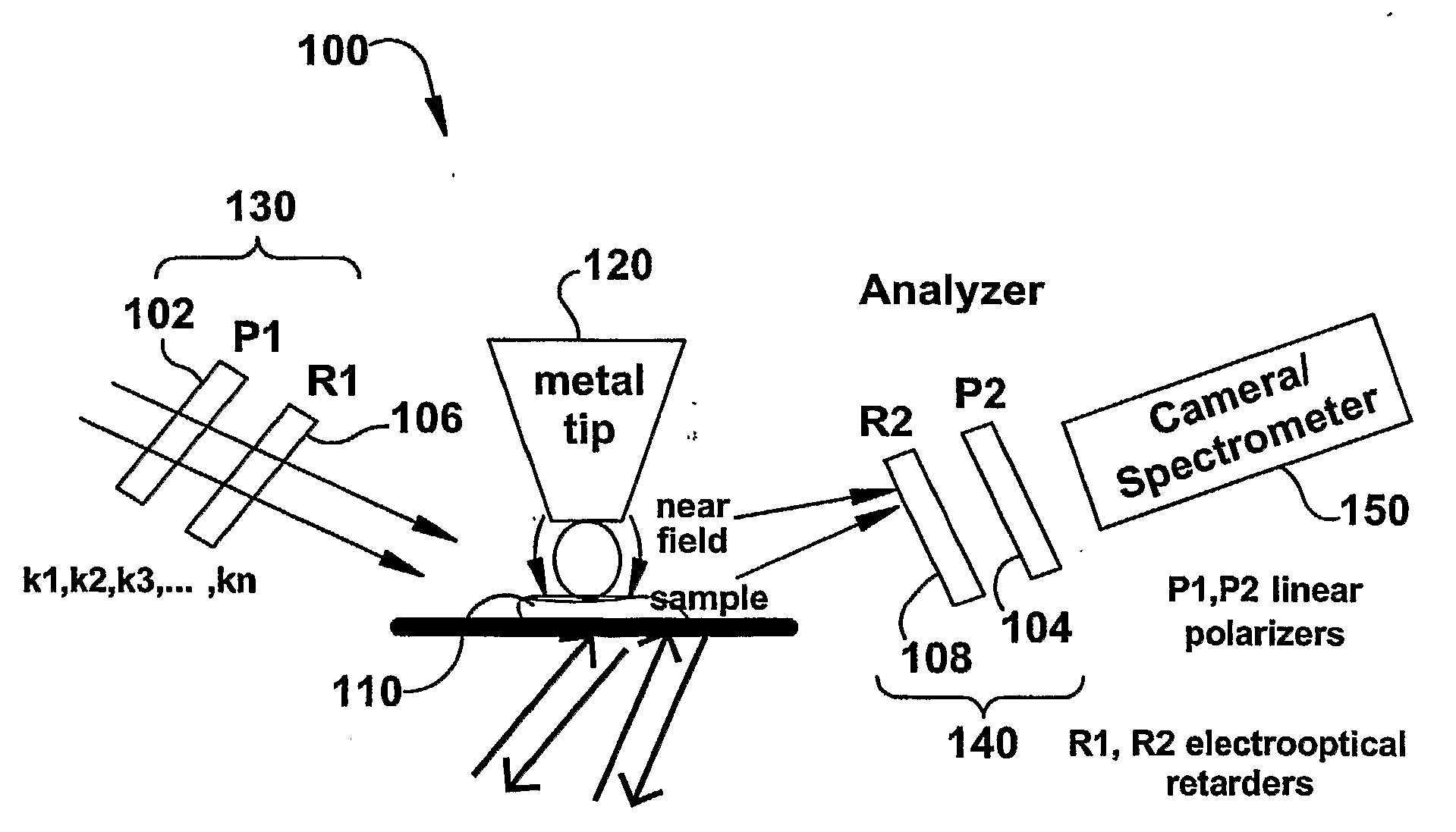
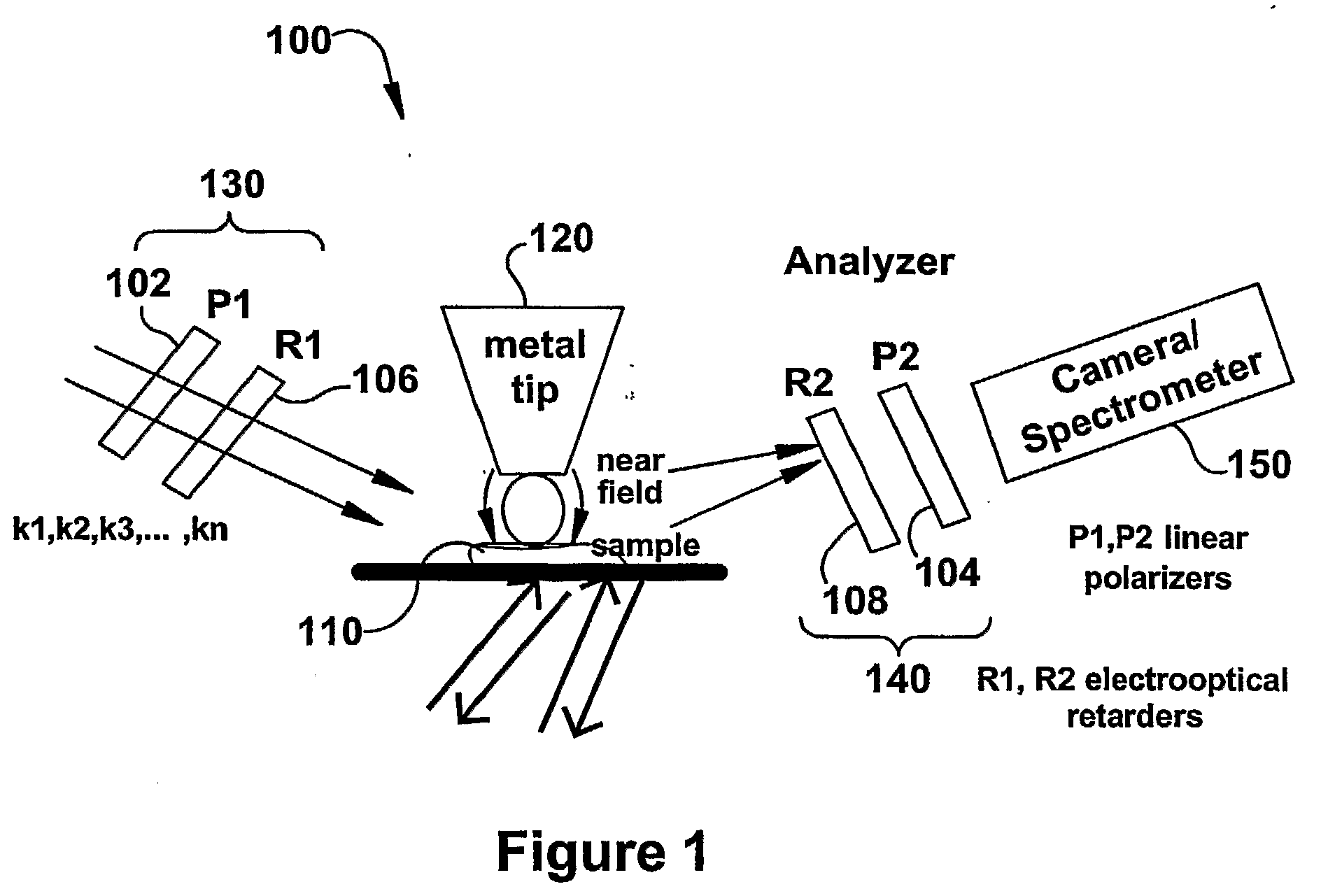
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
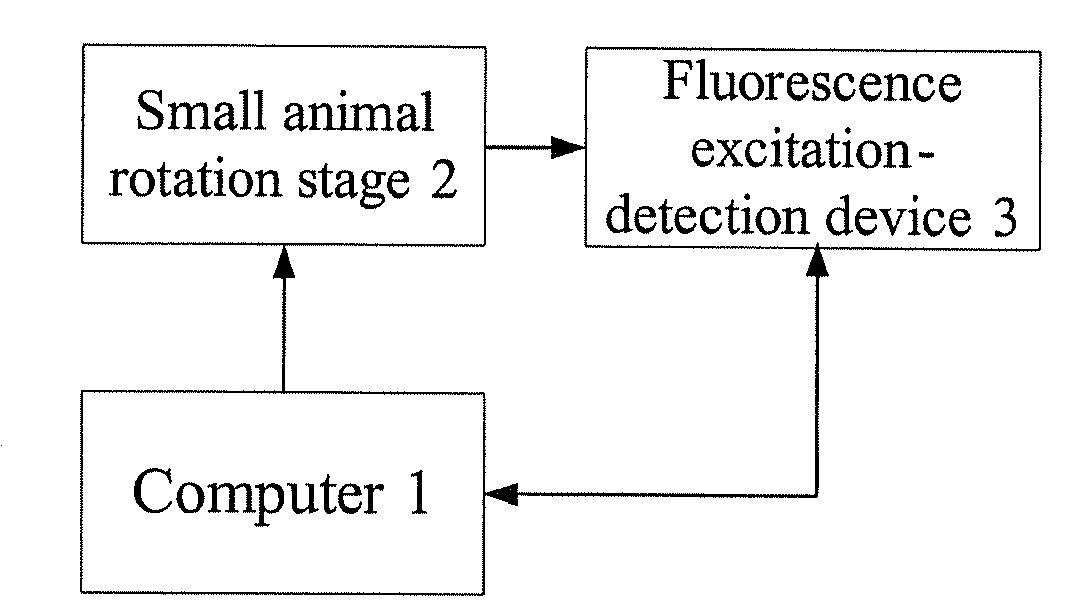
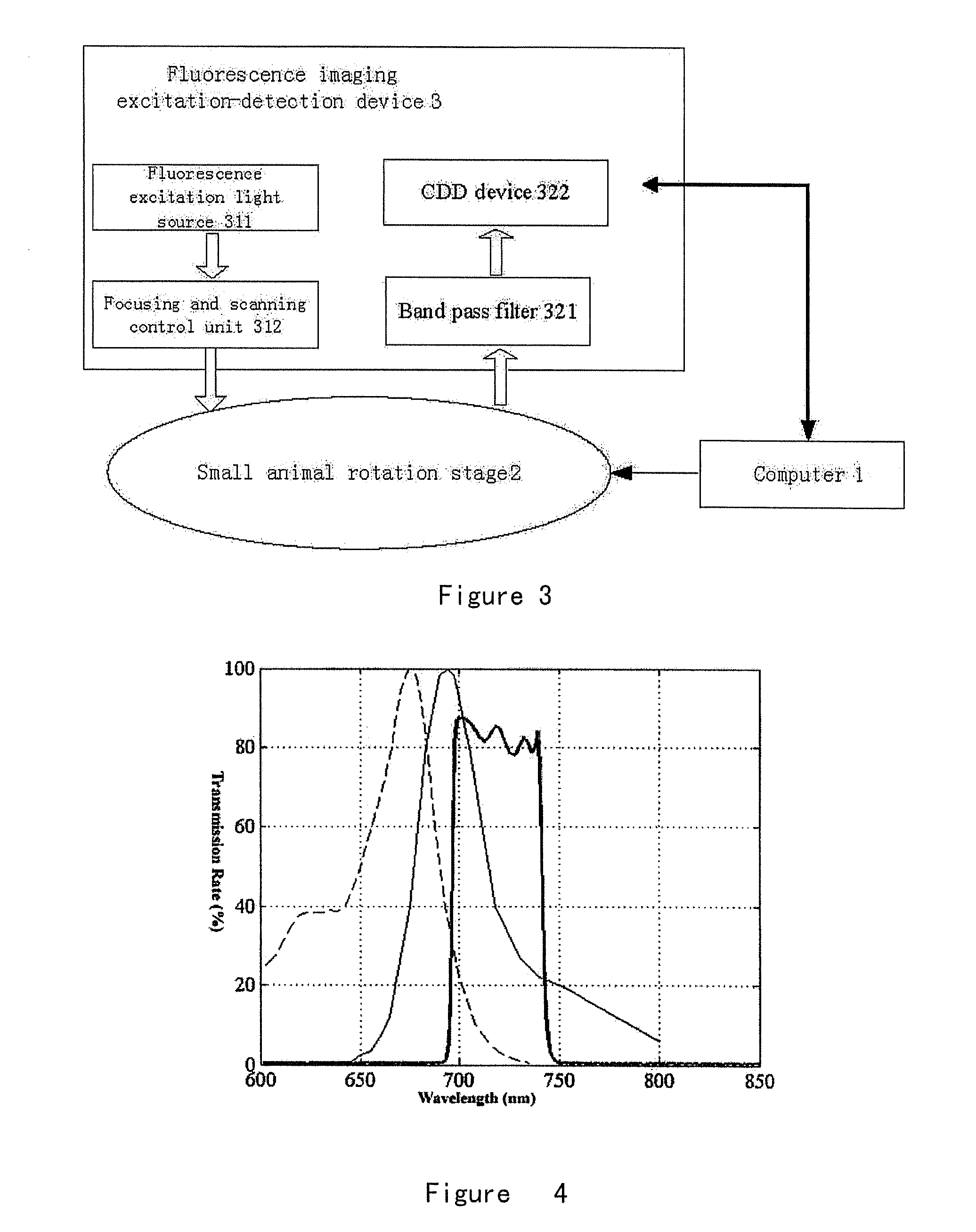
Dynamic Sampling System and Method for In Vivo Fluorescent Molecular Imaging
InactiveUS20090018451A1High throughput imaging technologyStable imaging techniqueMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographySmall animalMolecular imaging
A dynamic dada sampling system and method is disclosed for in vivo small animal fluorescence molecular imaging and dual-modality molecular imaging. The system comprises a computer, a rotation stage for animal suspension driven by a motor, and a fluorescence excitation-detection apparatus. The fluorescence excitation-detection apparatus comprises a fluorescence excitation module and a fluorescence detection module. The CCD device of the fluorescence detection module is connected to a computer through an interface controller. The motor is connected to a computer through RS232 interface. The process of dynamic data acquisition is as follows: a fluorescent probe is injected into a small animal in order to target specific cells or tissues; a small animal is vertically hung on a rotation stage after anesthesia; the fluorescence imaging detection module acquires the emitting light continuously. The present invention can provide 360 degree imaging quickly, efficiently, and non-invasively.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
In-vivo optical imaging method including analysis of dynamic images
ActiveUS20090252682A1Enhance the imageGenerate imageImage analysisDiagnostics using lightAnatomical structuresData set
In-vivo optical molecular imaging methods for producing an image of an animal are described. A time series of image data sets of an optical contrast substance in the animal is acquired using an optical detector Each image data set is obtained at a selected time and has the same plurality of pixels, with each pixel having an associated value. The image data sets are analyzed to identify a plurality of distinctive time courses, and respective pixel sets are determined from the plurality of pixels which correspond to each of the time courses. In one embodiment, each pixel set is associated with an identified anatomical or other structure, and an anatomical image map of the animal can be generated which includes one or more of the anatomical structures.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
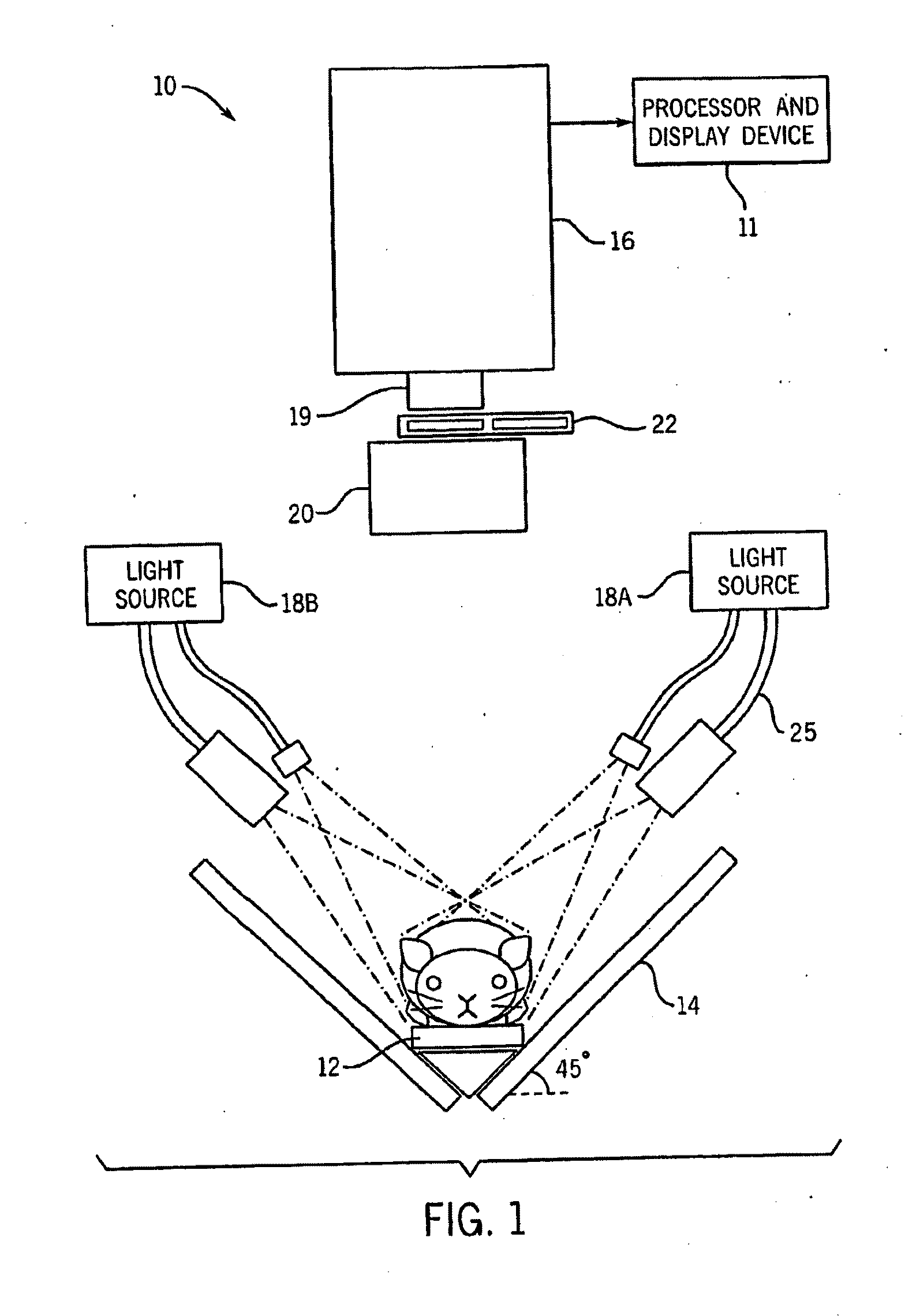
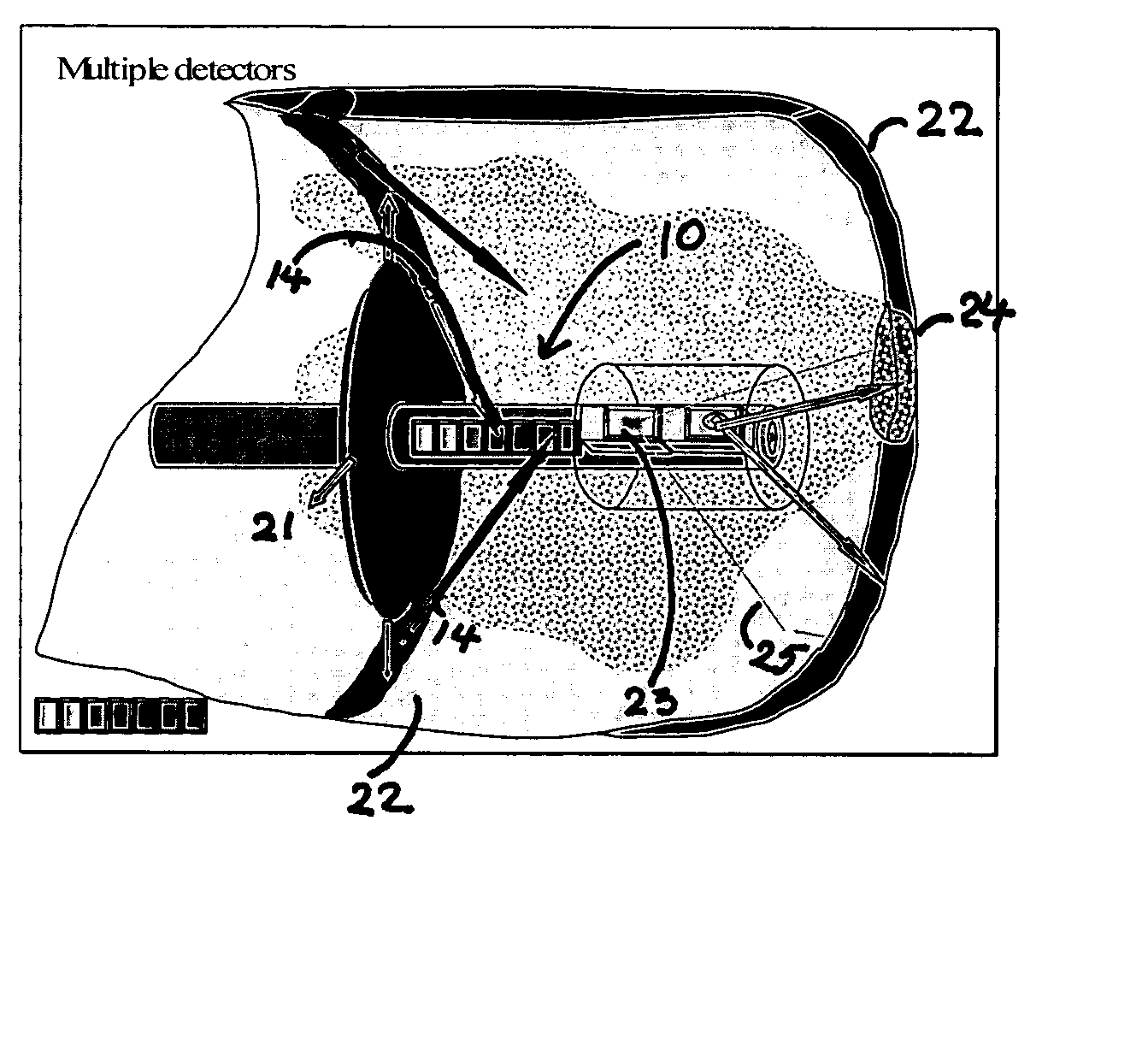
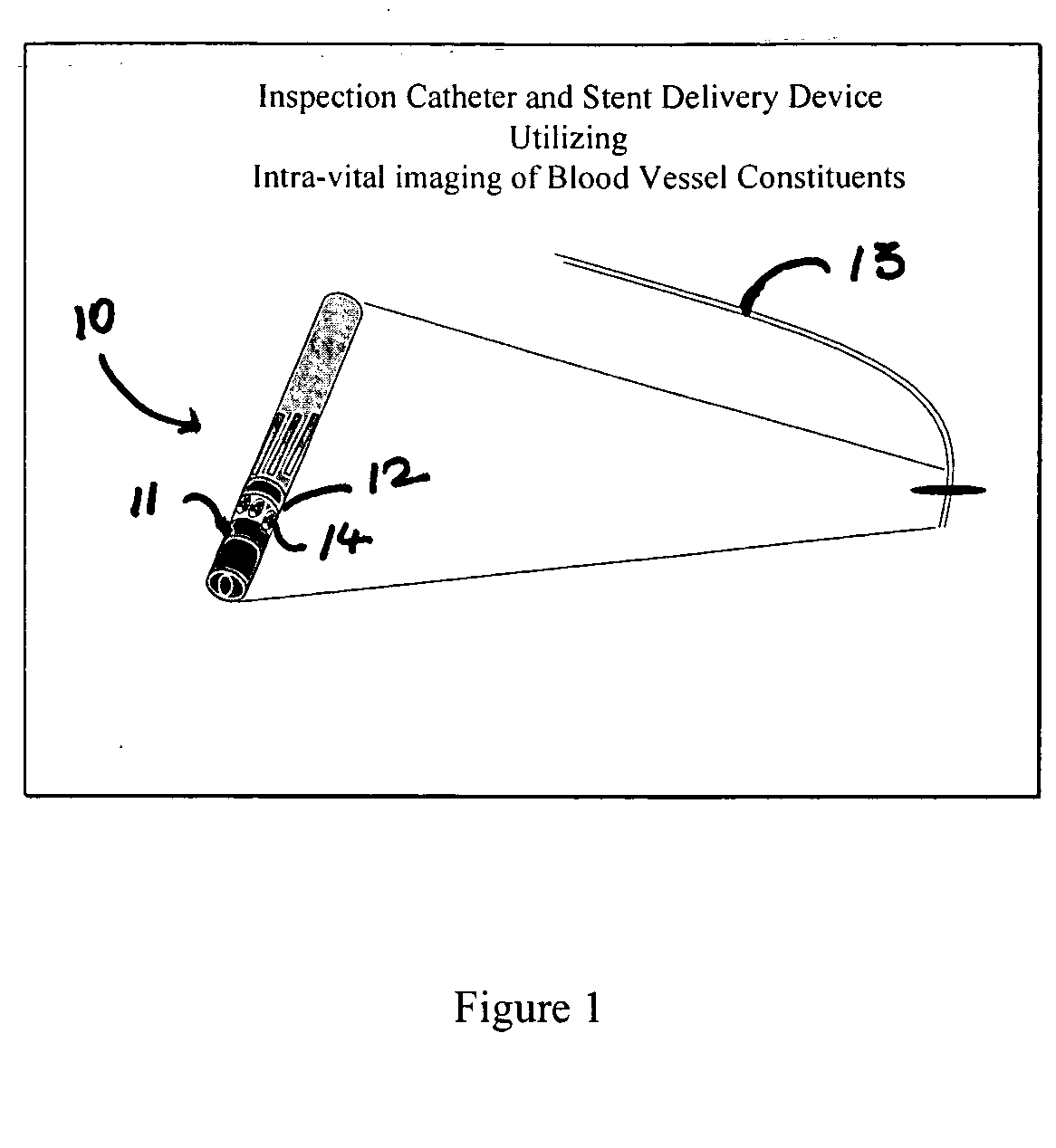
Intravascular imaging device and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060041199A1High sensitivityEasy diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryProbe typeMolecular imaging
The invention is directed to a probe-type imaging device useful to visualize interior surfaces, e.g., the lumen of blood vessels. Specifically, the probe-type device is particularly useful for direct tissue imaging in the presence or absence of molecular imaging agents.
Owner:ELMALEH DAVID R
Non-invasive diagnostic agents of cancer and methods of diagnosing cancer, especially leukemia and lymphoma
The present invention is directed to novel non-invasive diagnostic tools to image cancers, especially, leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL) with minimal toxicity in vivo. The present invention represents a clear advance in the art which presently relies on tissue biopsy for diagnoses of these cancers. The novel imaging probe is capable of detecting precancerous cells, as well as their metastatic spread in tissues. This represents a quantum step forward in the diagnosis and staging of NHL using non-invasively molecular imaging techniques. This novel probe will also be useful to monitor patients response to chemotherapy treatments and other interventions or therapies used in the treatment of NHL. Compounds according to the present invention may be used as diagnostic tools for a number of conditions and diseases states as well as therapeutic agents for treating such conditions and disease states.
Owner:STC UNM
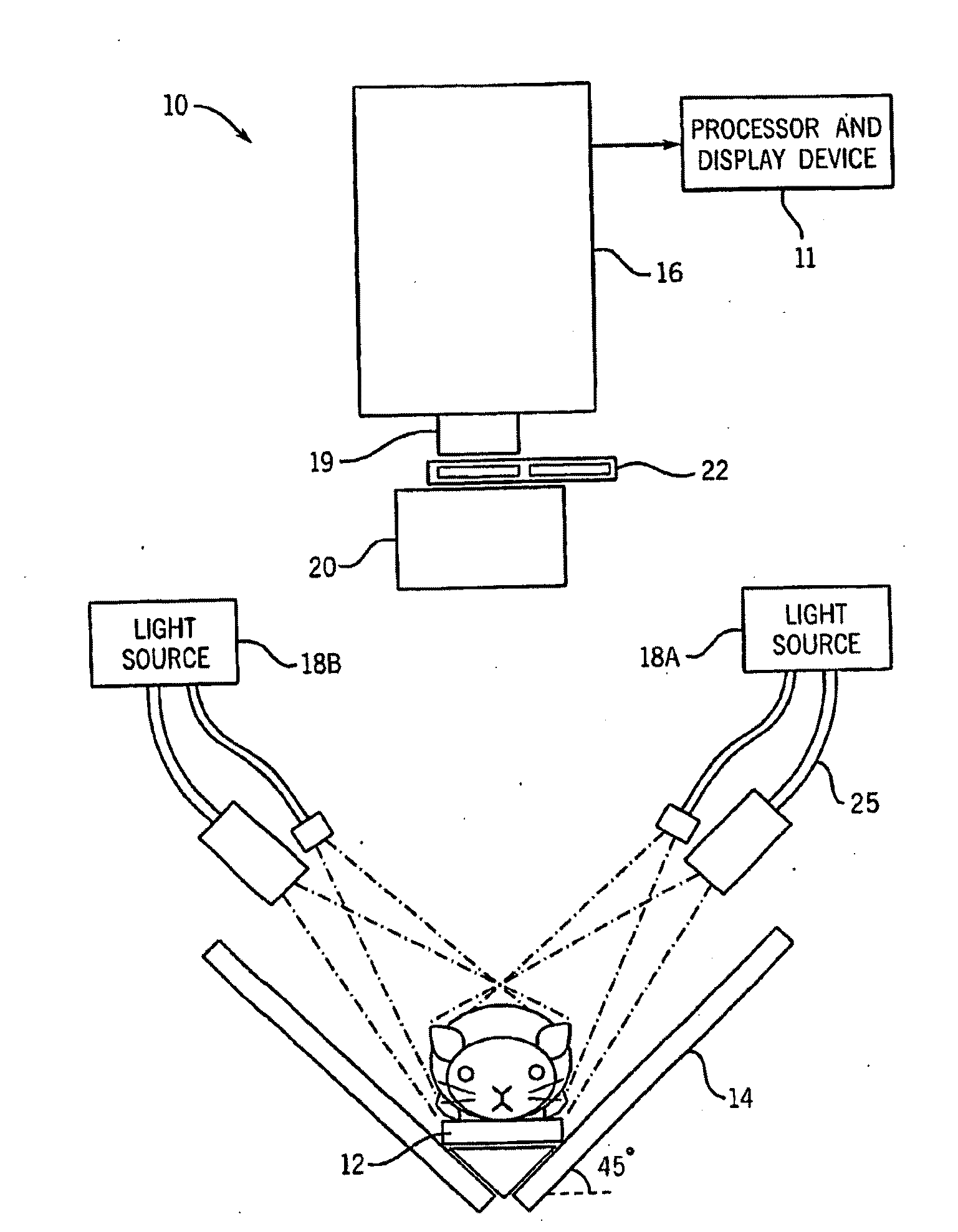
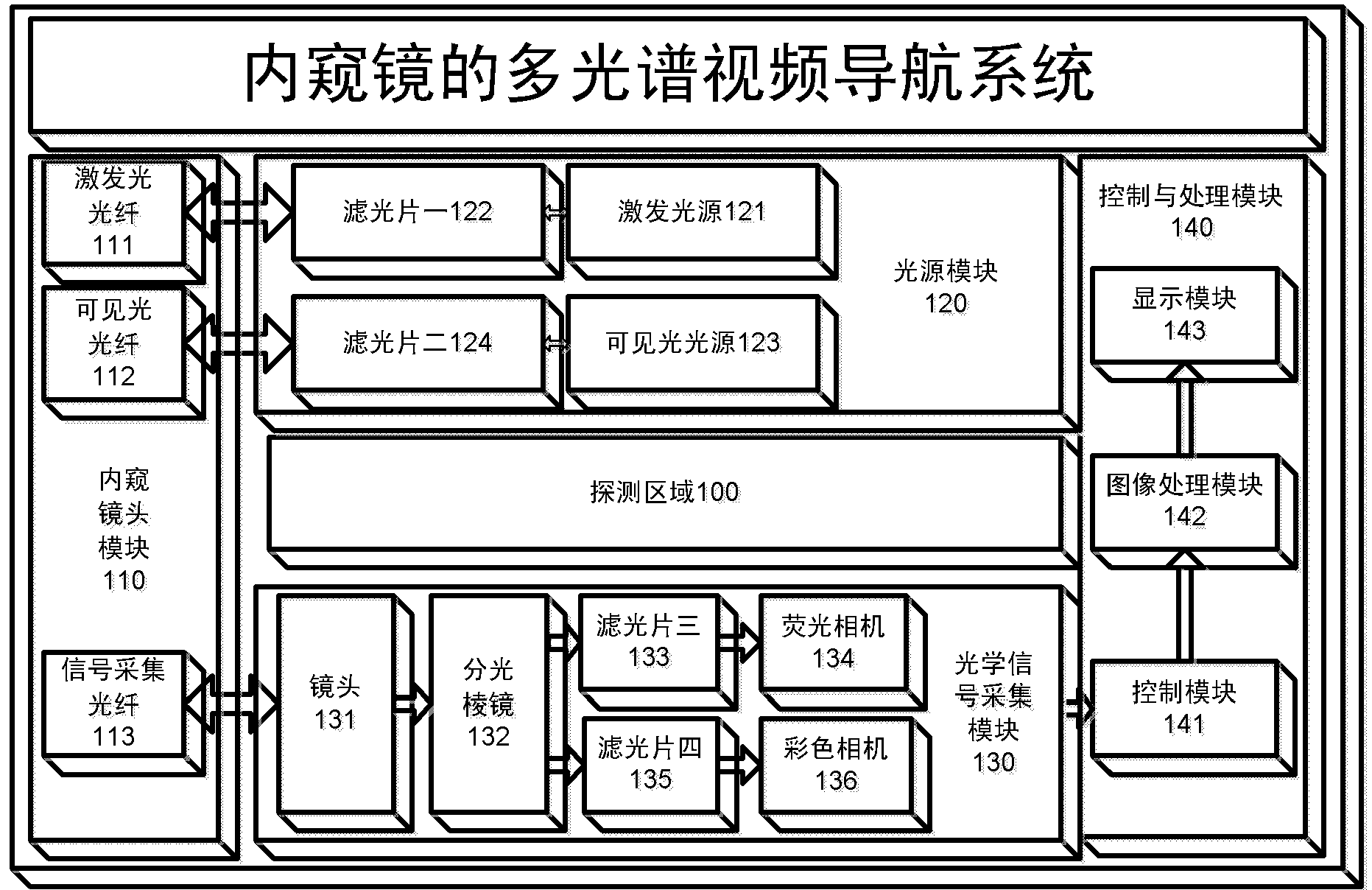
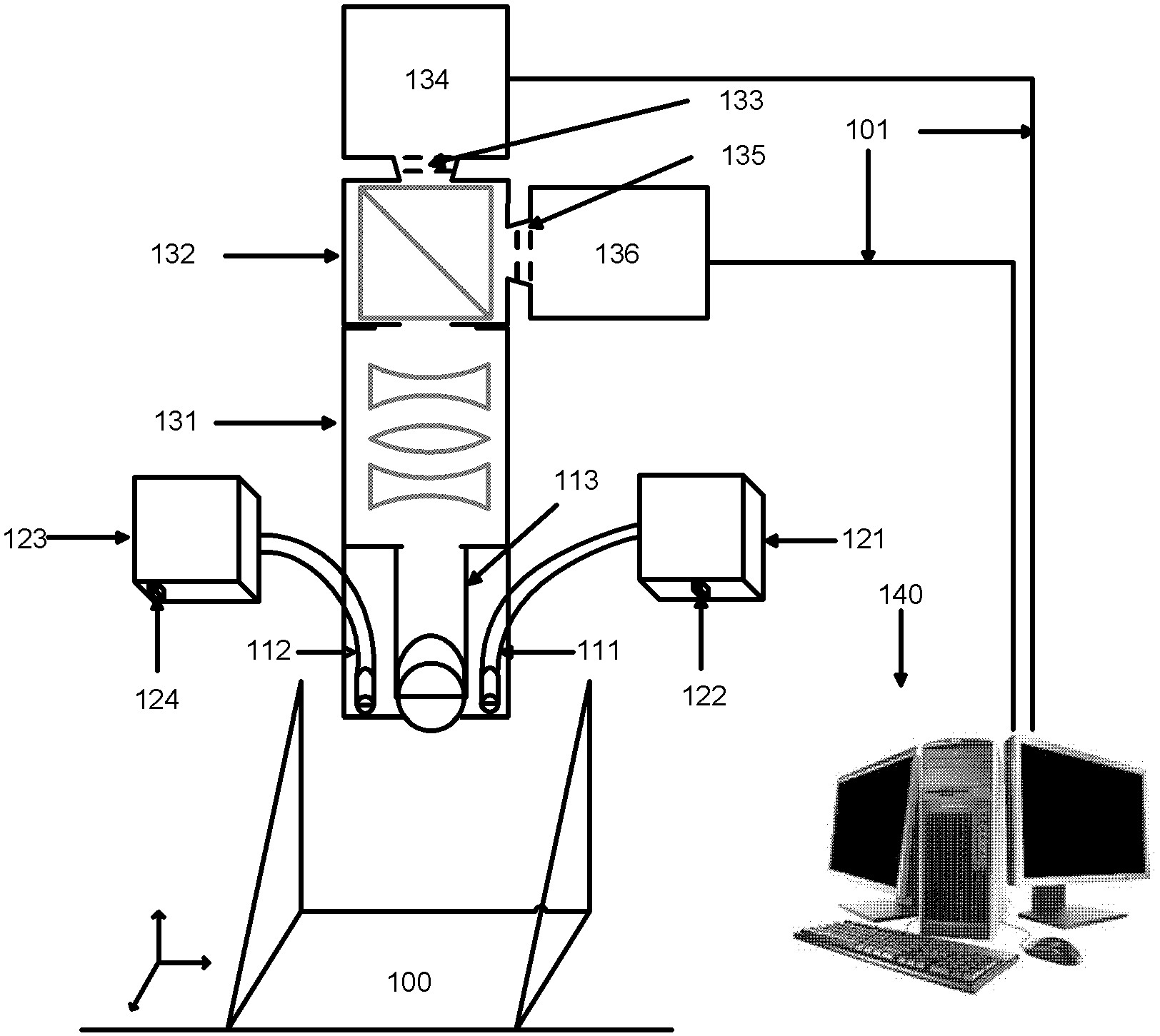
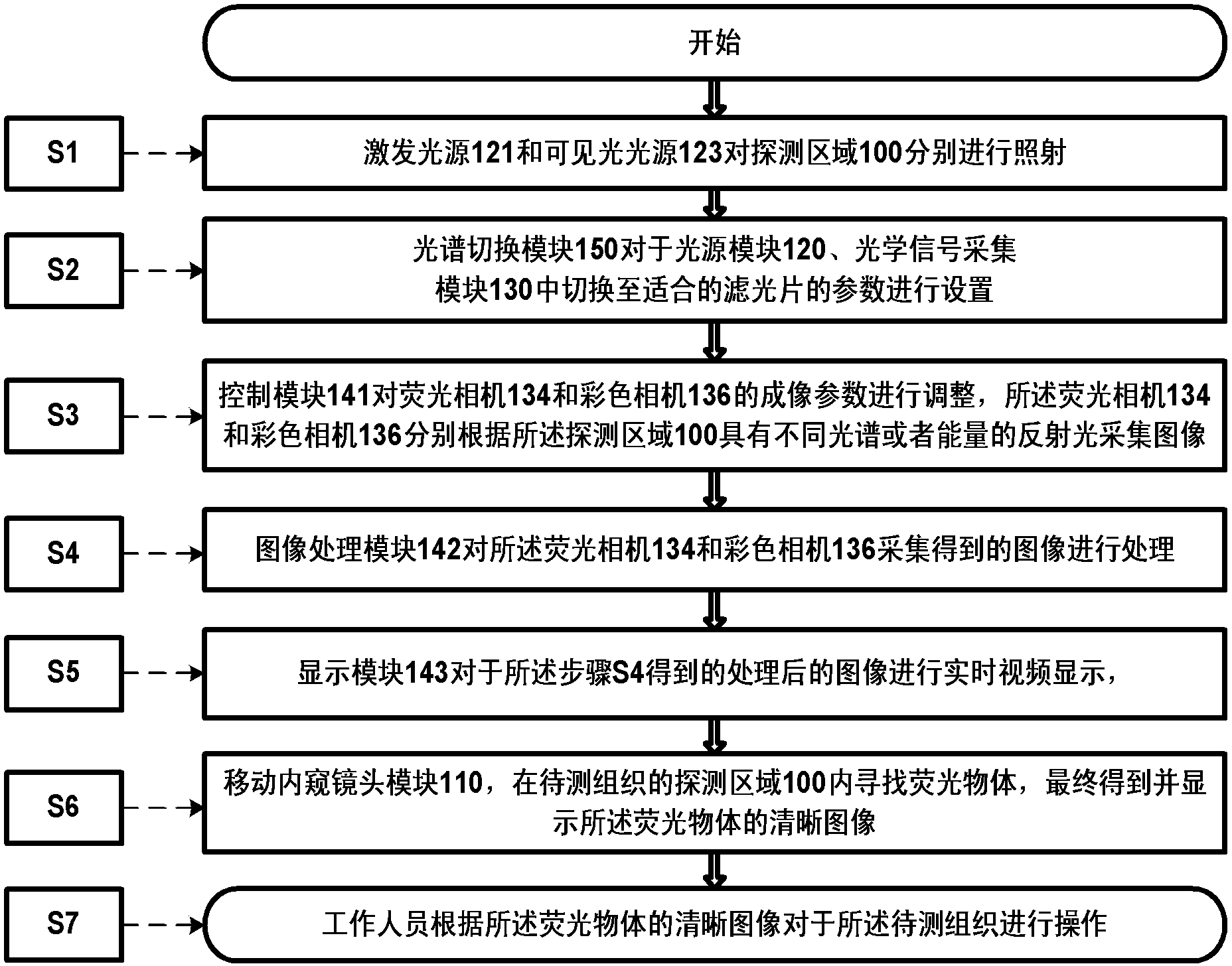
Endoscope-based multispectral video navigation system and method
InactiveCN103300812ARealize acquisitionBreak the technological monopolyEndoscopesFluorescenceMolecular imaging
The invention discloses an endoscope-based multispectral video navigation system and method. The system comprises an endoscope head module used for internal inspection, a light source module used for providing near infrared and visible light sources, an optical signal acquisition module used for acquiring near infrared and visible light images, a multispectral conversion module used for imaging different spectrum segments, and a controlling and processing module used for controlling a camera and processing the acquired images to achieve video navigation. The invention also discloses a method utilizing the system to achieve multispectral video navigation. By adopting the system and the method, the problem that at present, most endoscope fluorescent products can only see fluorescent images or visible light images but not multispectral images is solved, technical monopoly of foreign companies in China is broken through, the imaging research threshold of the multispectral endoscope is lowered, the selection space of optical molecular imaging probes is expanded, and the optical molecular imaging research and application ranges are extended.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Agents for therapy efficacy monitoring and deep tissue imaging
InactiveUS20080031823A1Limited applicationImprove clinical efficacyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideCellular respirationFunctional imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Novel molecular assembly, molecular probe for molecular imaging and molecular probe for drug delivery system using the same, and molecular imaging system and drug delivery system
InactiveUS20110104056A1The method is simple and safeHighly safe for a living bodyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryBiological bodyMolecular imaging
The present invention provides a molecular assembly which is less likely to accumulate in tissue other than cancer tissue, is highly safe for a living body, and can be prepared by a simple and safe method and whose particle size can be easily controlled. The present invention provides a molecular imaging system and a molecular probe useful for the system, and a drug delivery system and a molecular probe useful for the system. The present invention provides a method for preparing molecular assembly, by which the particle size of molecular assembly having a signal group or a drug can be arbitrarily controlled in order to allow the molecular assembly to effectively accumulate in cancer tissue by utilizing EPR effect. A molecular assembly comprising: an amphiphilic block polymer A comprising a hydrophilic block chain and a hydrophobic block chain having 10 or more lactic acid units; a hydrophobic polymer A2 having at least 10 or more lactic acid units; and / or a labeled polymer B comprising at least 10 or more lactic acid units and a labeling group.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
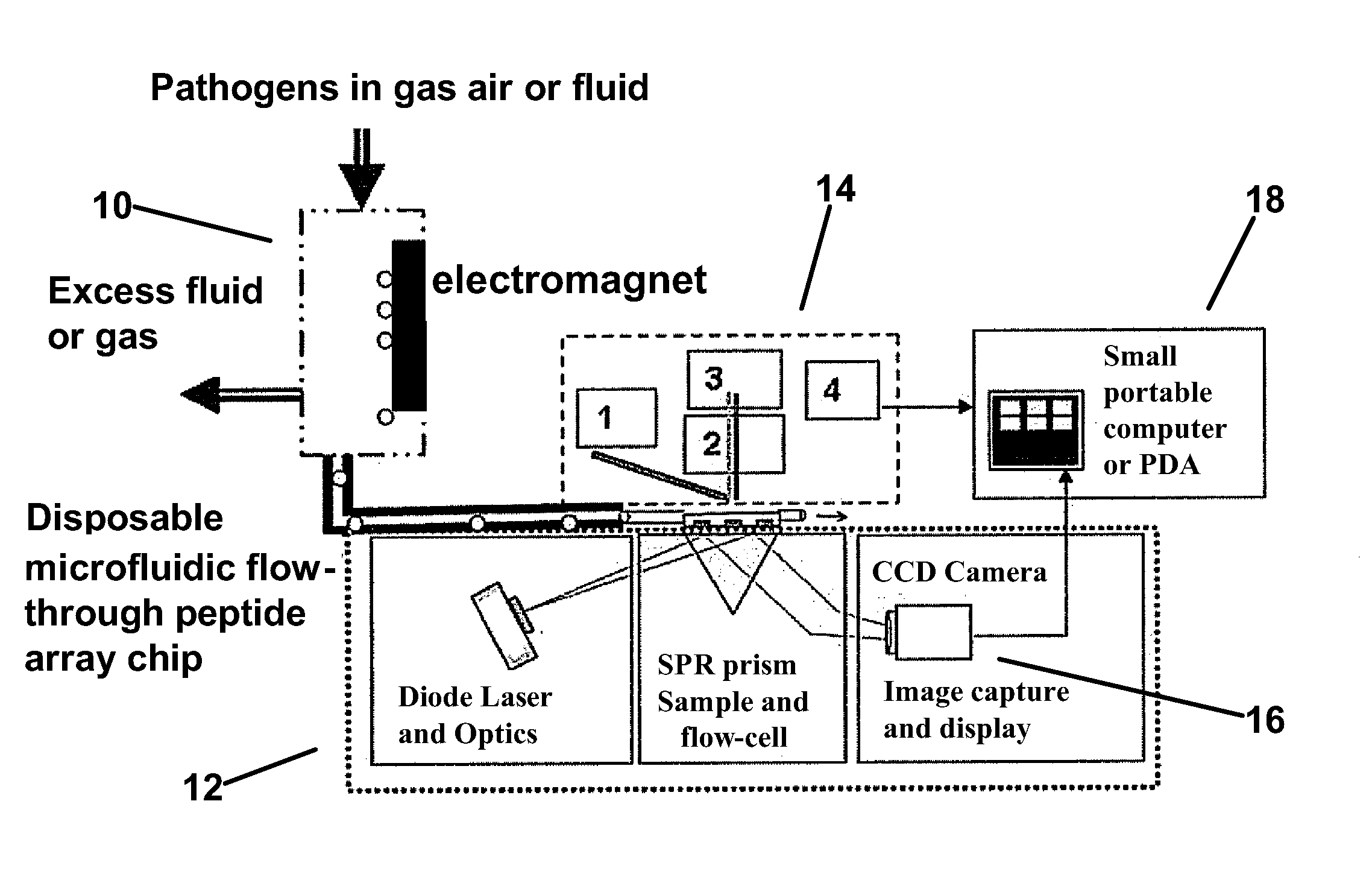
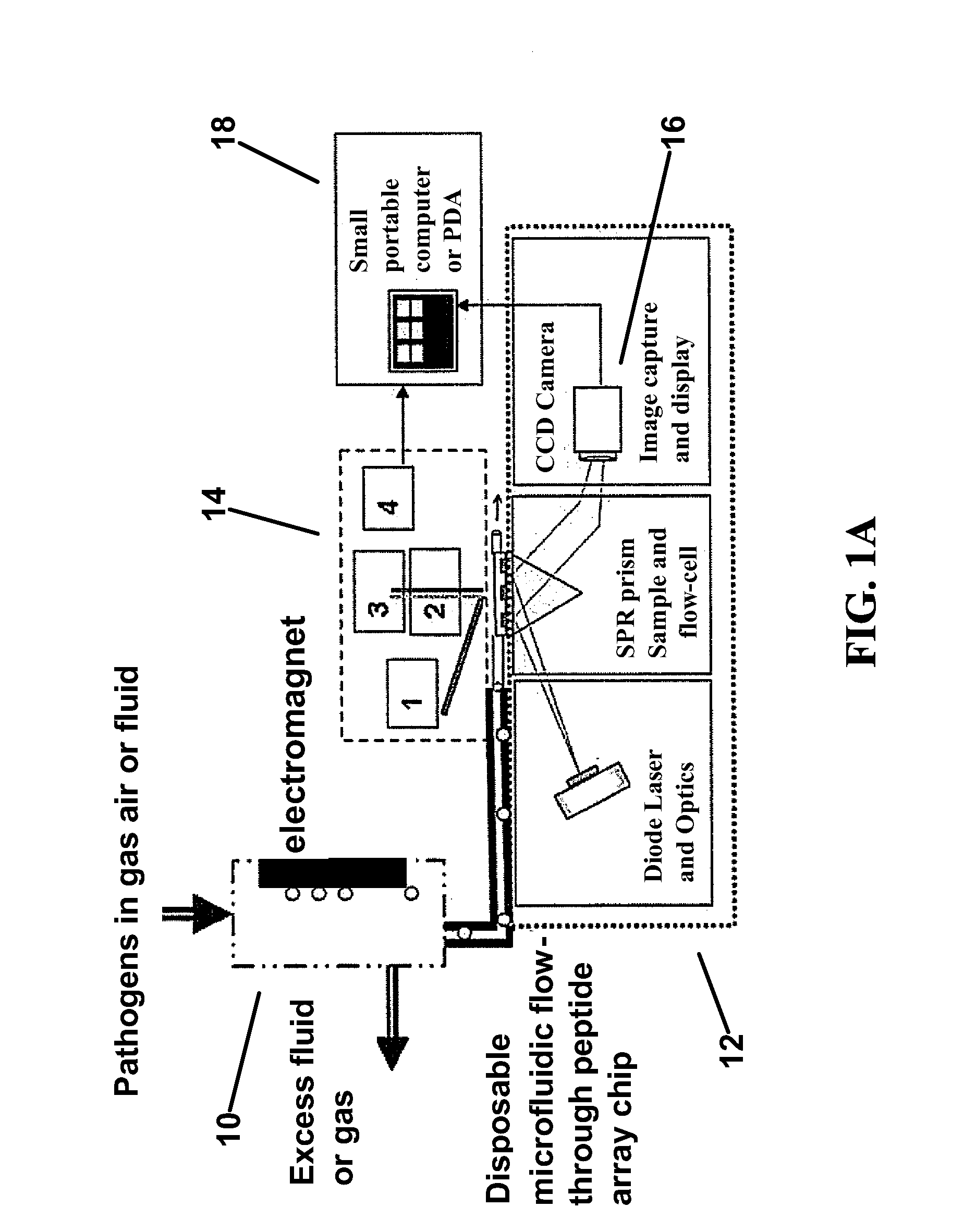
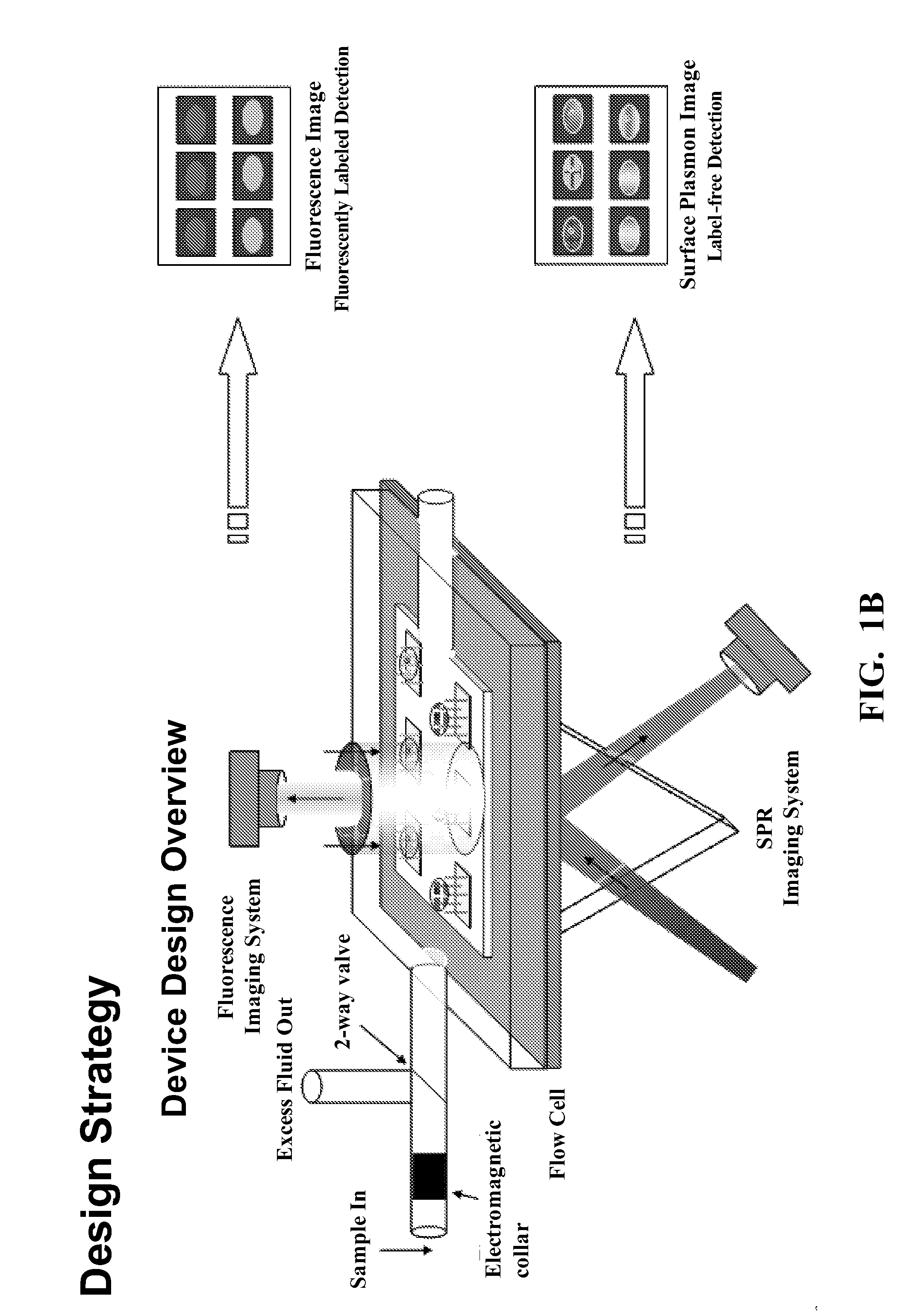
Hybrid microfluidic spr and molecular imaging device
InactiveUS20110039280A1High sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidicsMolecular imaging
A hybrid microfluidic biochip designed to perform multiplexed detection of singled- celled pathogens using a combination of SPR and epi-fluorescence imaging. The device comprises an array of gold spots, each functionalized with a capture biomolecule targeting a specific pathogen. This biosensor array is enclosed by a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic flow chamber that delivers a magnetically concentrated sample to be tested. The sample is imaged by surface plasmon resonance on the bottom of the biochip, and epi- fluorescence on the top.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
In situ click chemistry method for screening high affinity molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20060269942A1High expressionPeptide librariesOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisChemical reaction
The invention provides a method for identifying a candidate imaging probe, the method comprising: a) contacting a first library of candidate compounds with a target biomacromolecule, b) identifying a first member from the first library exhibiting affinity for the first binding site; c) contacting the first member identified from the first library affinity for the first binding site with the target biomacromolecule; d) contacting a second library of candidate compounds with the first member and the target biomacromolecule, e) reacting the complementary first functional group with the second functional group via a biomacromolecule induced click chemistry reaction to form the candidate imaging probe; f) isolating and identifying the candidate imaging probe; g) preparing the candidate imaging probe by chemical synthesis; and h) for imaging applications, converting the candidate imaging probe into an imaging probe.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Targeted, NIR imaging agents for therapy efficacy monitoring, deep tissue disease demarcation and deep tissue imaging
Compounds and methods related to NIR molecular imaging, in-vitro and in-vivo functional imaging, therapy / efficacy monitoring, and cancer and metastatic activity imaging. Compounds and methods demonstrated pertain to the field of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor imaging, metabolic imaging, cellular respiration imaging, cellular proliferation imaging as targeted agents that incorporate signaling agents.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Raman molecular imaging for detection of bladder cancer
InactiveUS20050250091A1Easy to compareDiagnostics using lightMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitheliumKidney
Raman molecular imaging is used to differentiate between normal tissue and benign and malignant lesions of bladder and other tissues, including epithelial tissues such as lung, prostate, kidney, breast, and colon, and non-epithelial tissues, such as bone marrow and brain. Raman scattering data relevant to the cancerous state of cells can be combined with visual image data to produce hybrid images which depict both a magnified view of the cellular structures and information relating to the cancerous state of the individual cells in the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Three-Dimensional Molecular Imaging By Infrared Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20100012831A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationESI mass spectrometryMolecular imaging
The field of the invention is atmospheric pressure mass spectrometry (MS), and more specifically a process and apparatus which combine infrared laser ablation with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Click chemistry method for synthesizing molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20060263293A1High reaction specificityEfficiently labeledSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLeaving groupChemical reaction
The present disclosure provides a method for preparing a radioactive ligand or radioactive substrate having affinity for a target biomacromolecule, the method comprising: (a) reacting a first compound comprising a first functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction, with a radioactive reagent under conditions sufficient to displace the leaving group with a radioactive component of the radioactive reagent to form a first radioactive compound; (b) providing a second compound comprising a second complementary functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction with the first functional group; (c) reacting the first functional group of the first radioactive compound with the complementary functional group of the second compound via a click chemistry reaction to form the radioactive ligand or substrate; and (d) isolating the radioactive ligand or substrate.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
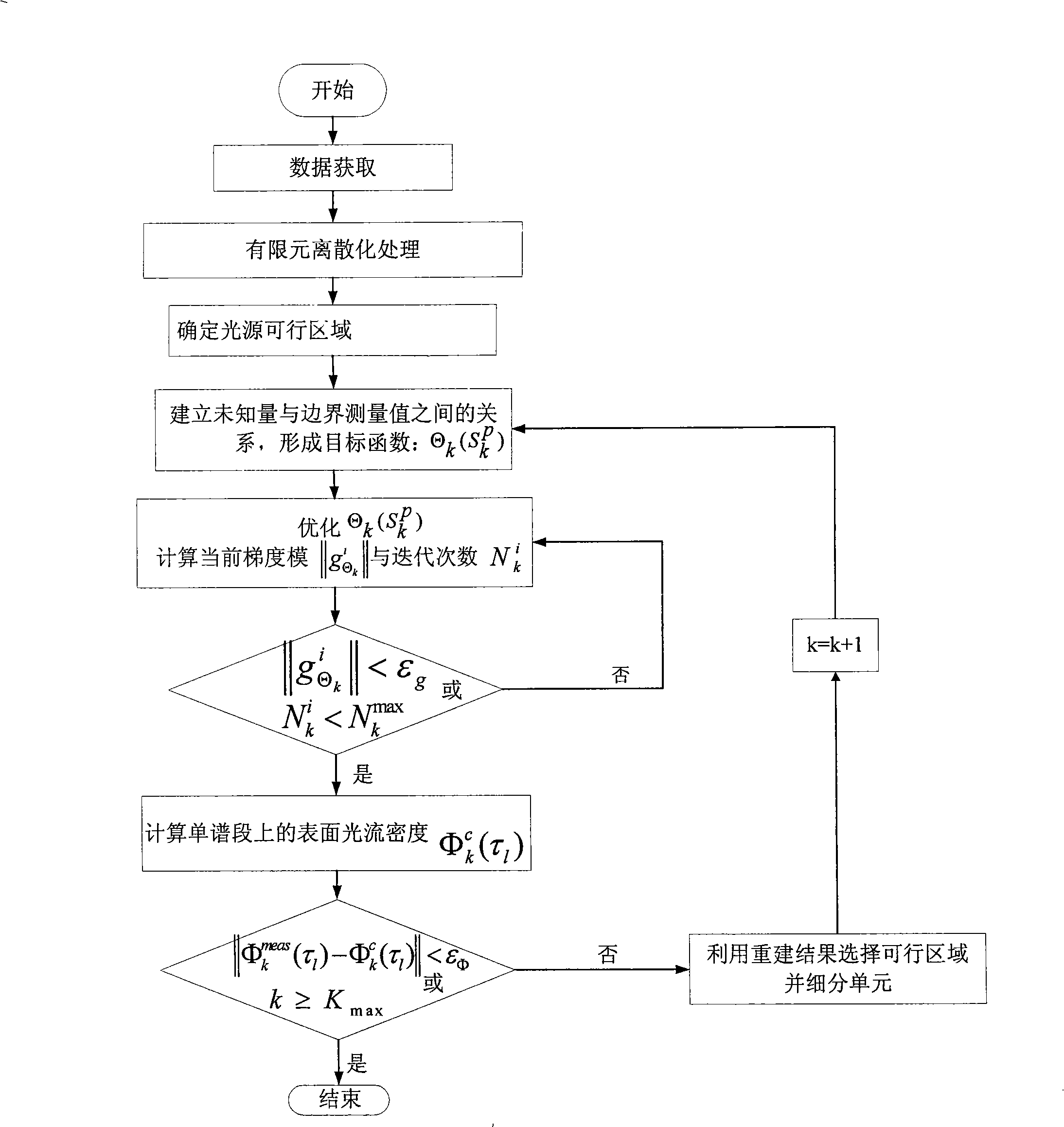
Multi-optical spectrum autofluorescence dislocation imaging reconstruction method based on single view
InactiveCN101342075ASolve inaccurateHigh speedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReconstruction methodData acquisition
The invention relates to a multi-spectrum auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method based on single view, which belongs to the optical molecular imaging field. The method is based on the diffusivity equation model, considers the uneven characteristics of small animal body, and simultaneously also considers the spectrum and the practical application characteristics of the auto fluorescence light source. In order to achieve the purpose, the multi-spectrum auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method based on single view comprises the flowing steps: firstly, data acquisition; secondly, the dispersing processing of finite element; thirdly, the optimization of the selection of the feasible light source zone; fourthly, the reconstruction of the light source. The method overcomes the defects that the reconstruction light source of the auto fluorescence fault imaging reconstruction method is inaccurate, the reconstruction speed is low, the real-time processing is not convenient, and error can exist during the multi-spectrum data acquisition.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
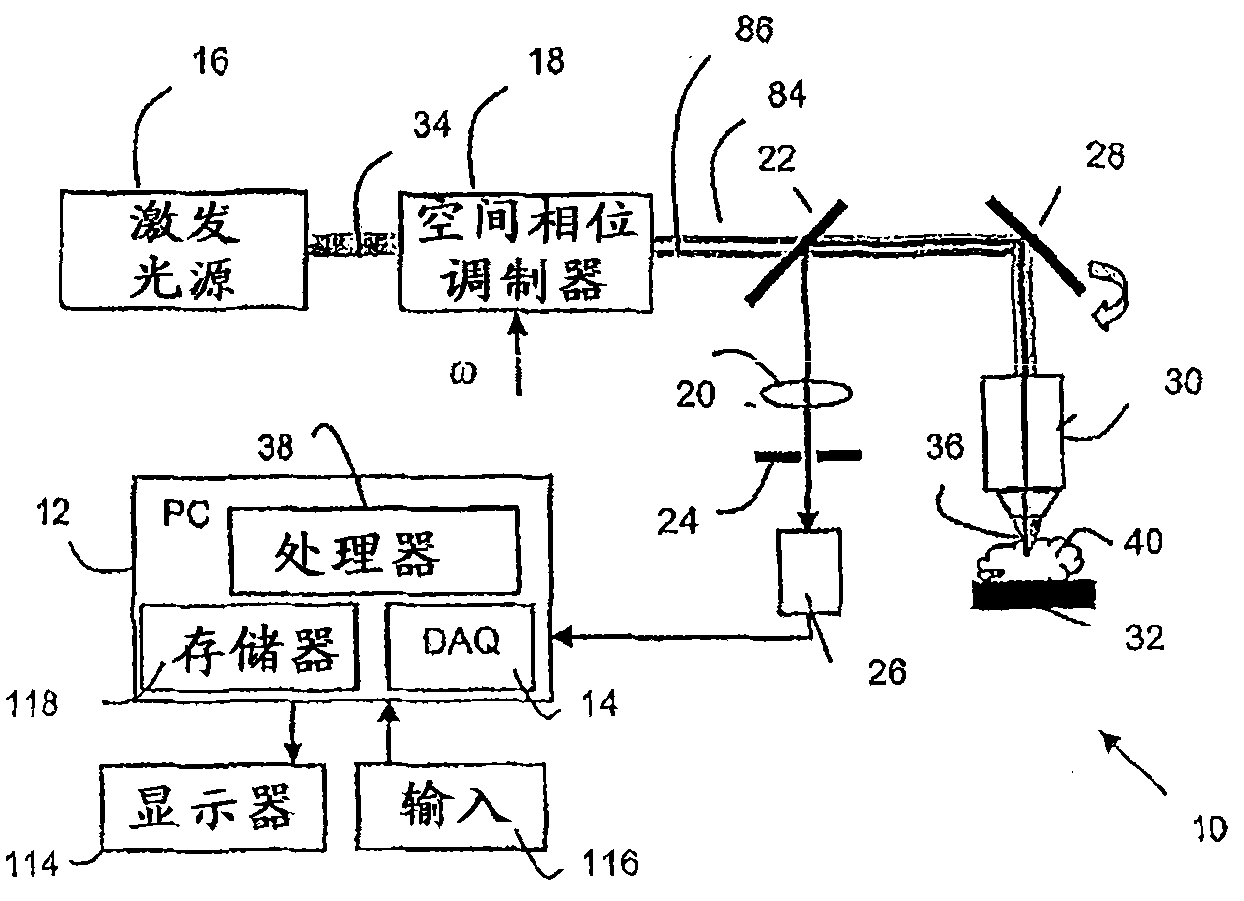
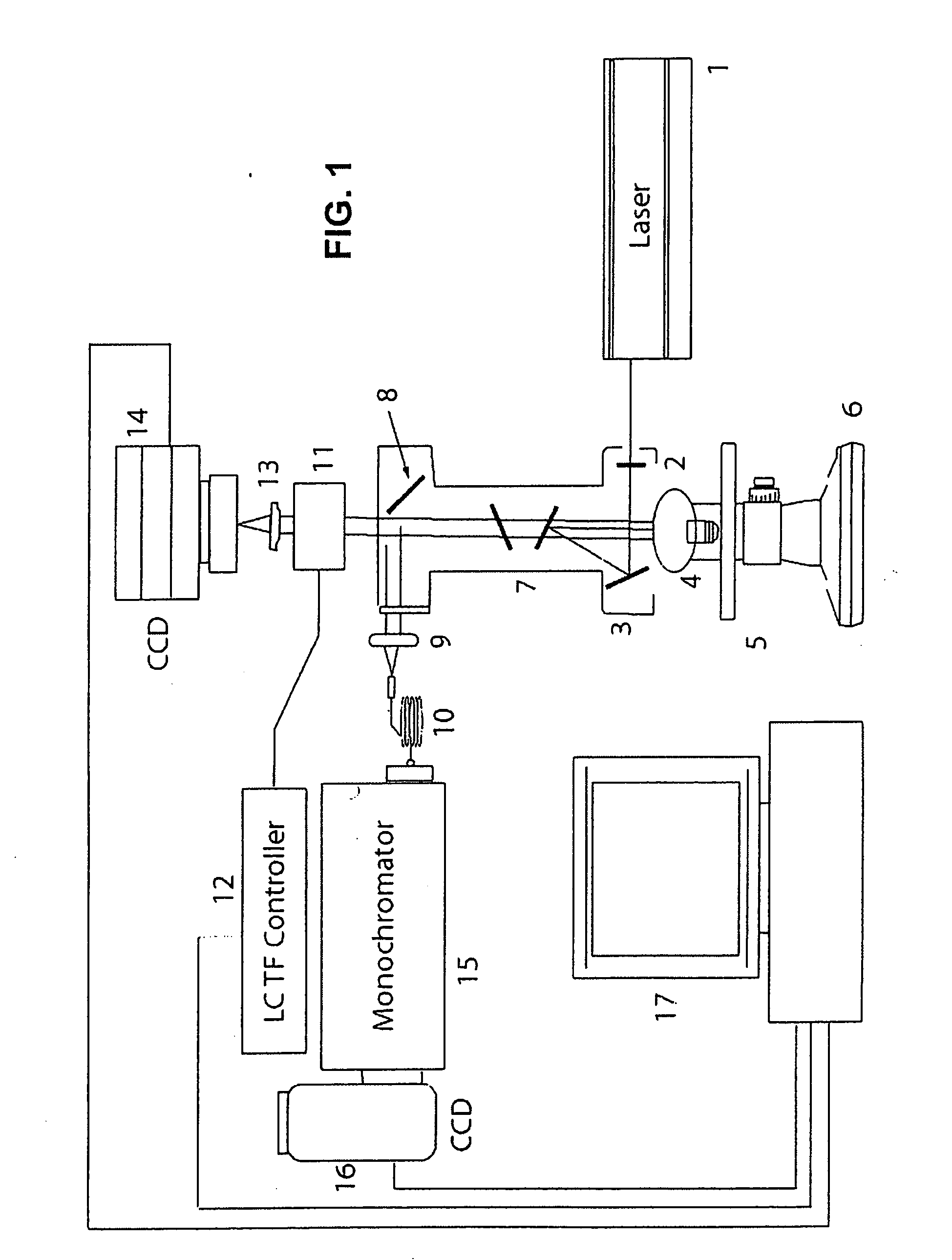
Fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system and method
A fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system (10) and method (200) is disclosed for high resolution molecular imaging of thick biological tissues (40) with single photon excited fluorescence. Optical sectioning and diffraction limited spatial resolution are retained for imaging inside a multiple-scattering medium by the use of focal modulation, a technique for suppressing the background fluorescence signal excited by the scattered light. The focal modulation microscopy system has a spatial phase modulator (18) inserted in the excitation light path (34), which varies the spatial distribution of coherent excitation light around the focal volume periodically at a preset frequency. A fluorescence focal modulation image (122,142) is formed on a display (114) with the demodulated fluorescence, while a confocal image (120,140) is available simultaneously.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f254bdb1-9433-4d65-8b75-909a30cbb9ed/US20080267878A1-20081030-D00000.png)
![Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f254bdb1-9433-4d65-8b75-909a30cbb9ed/US20080267878A1-20081030-D00001.png)
![Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition Targeted Imaging And/Or Therapy Using The [3+2] Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f254bdb1-9433-4d65-8b75-909a30cbb9ed/US20080267878A1-20081030-D00002.png)