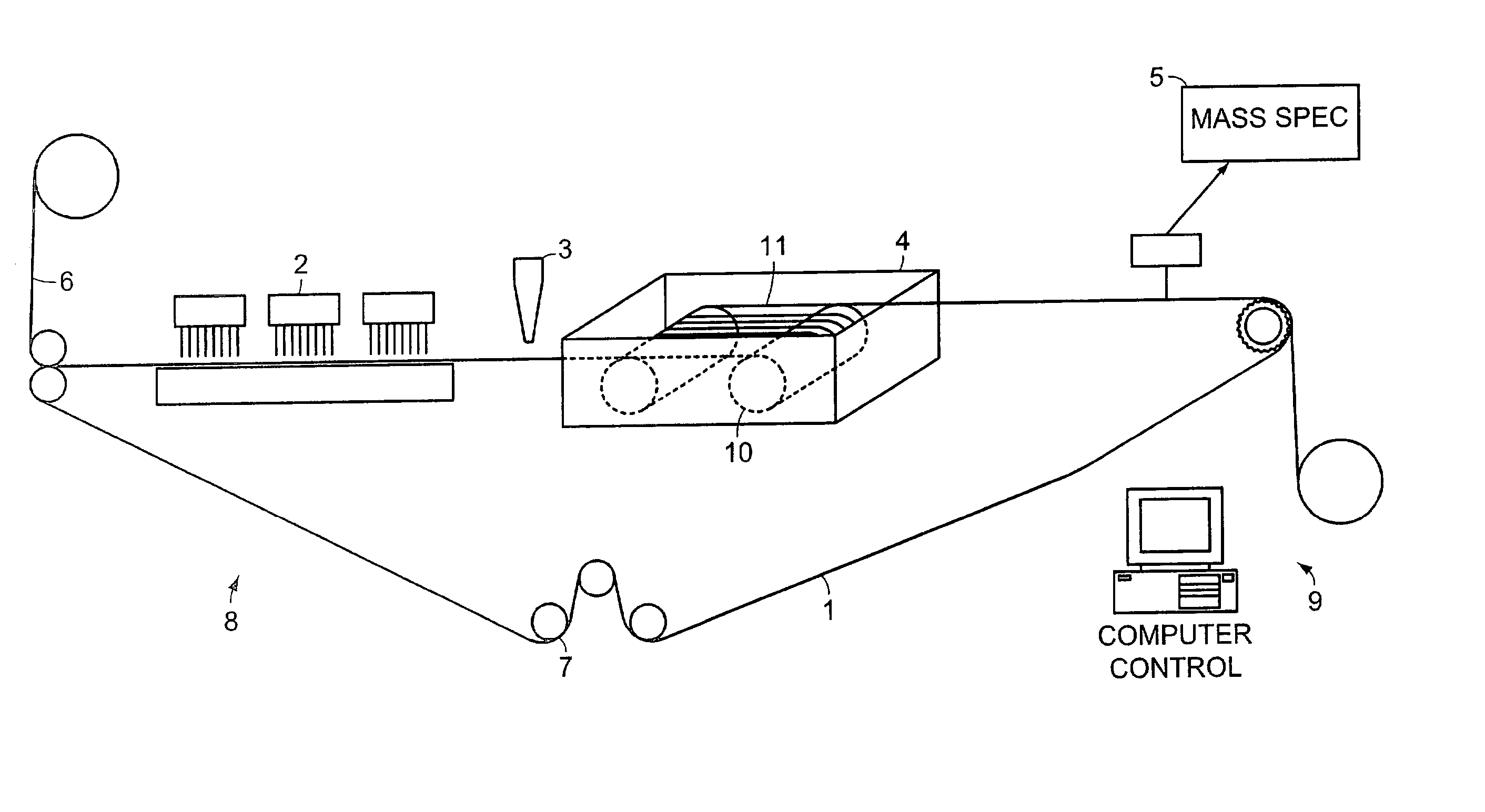
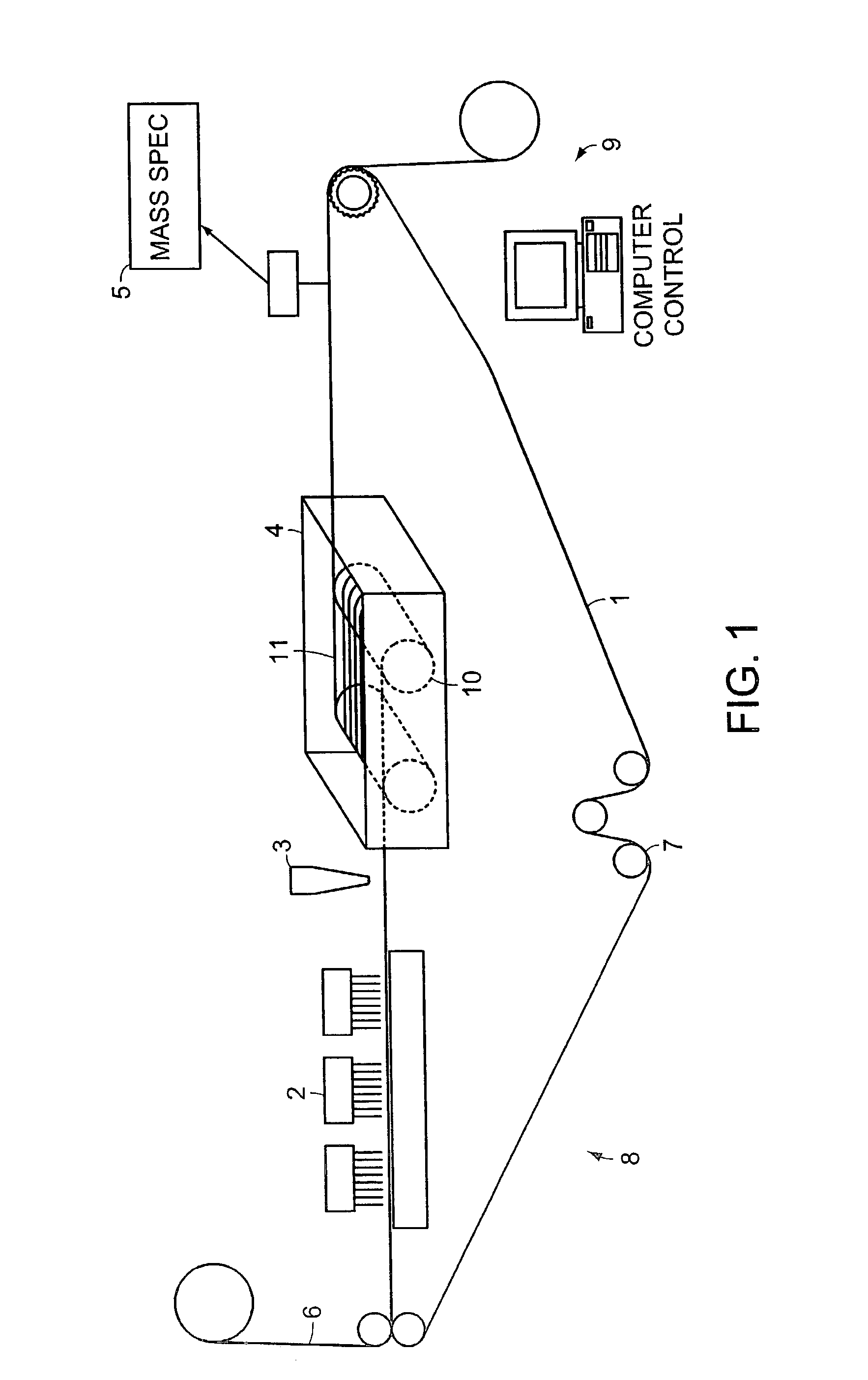
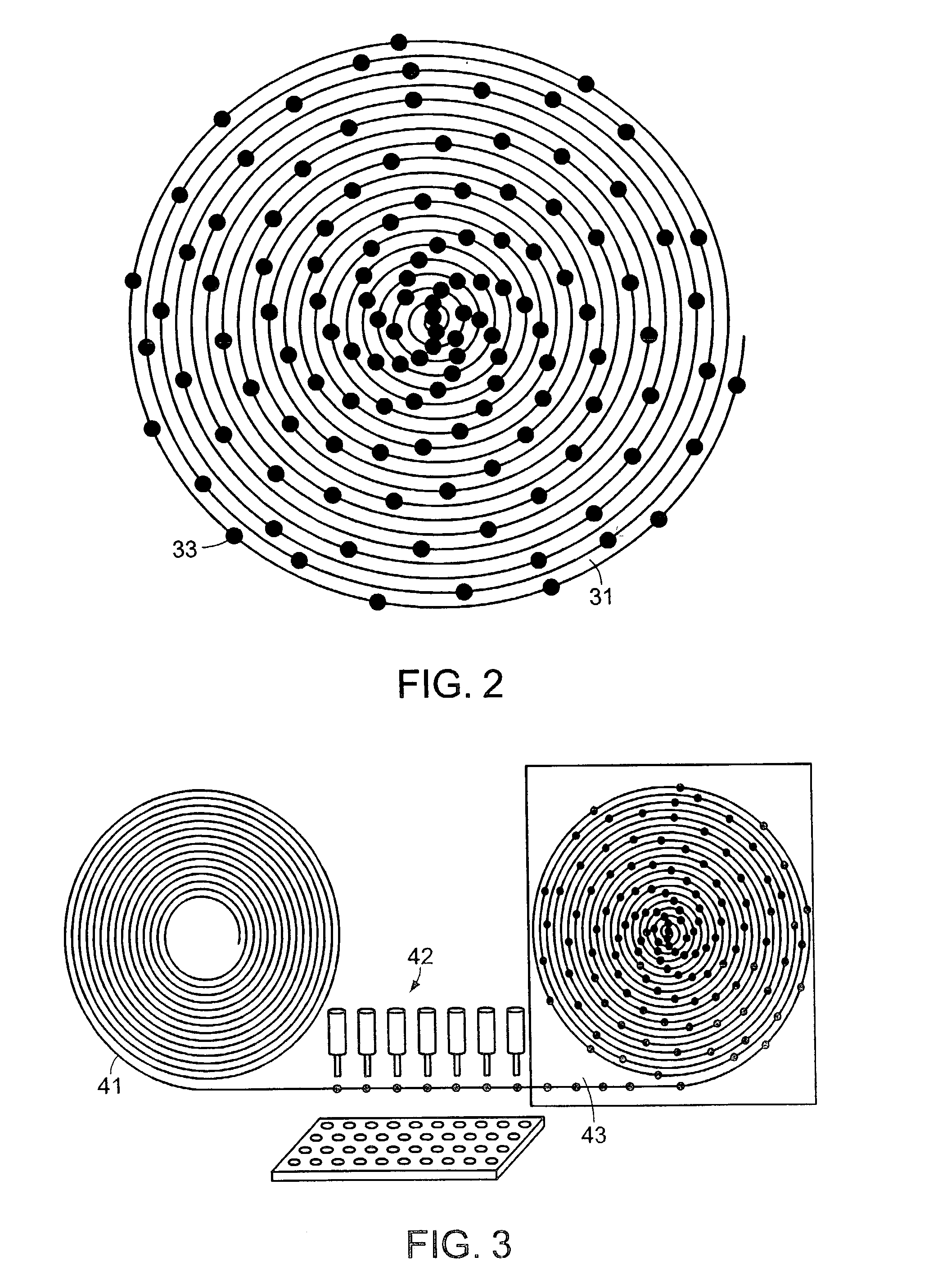
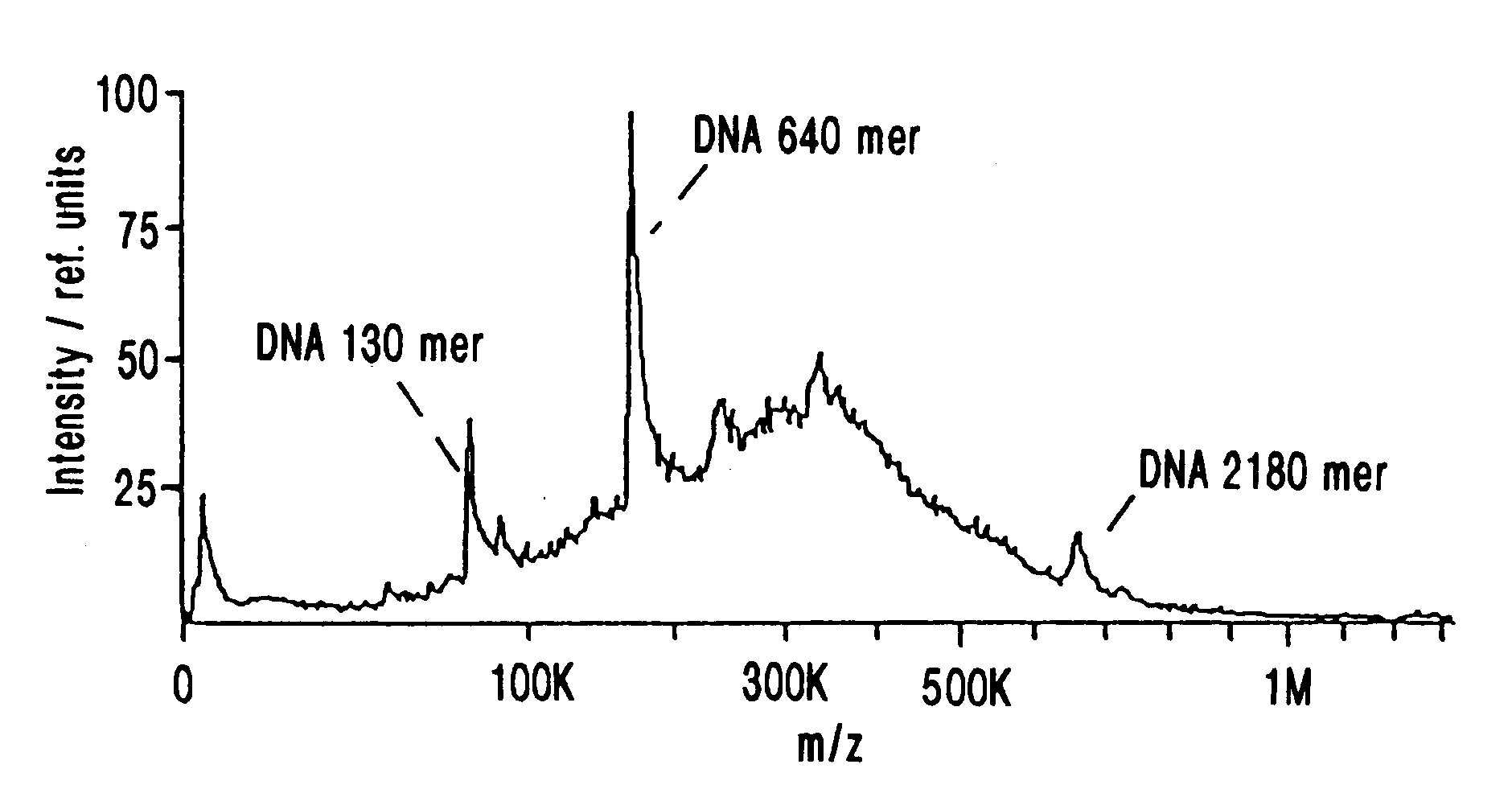
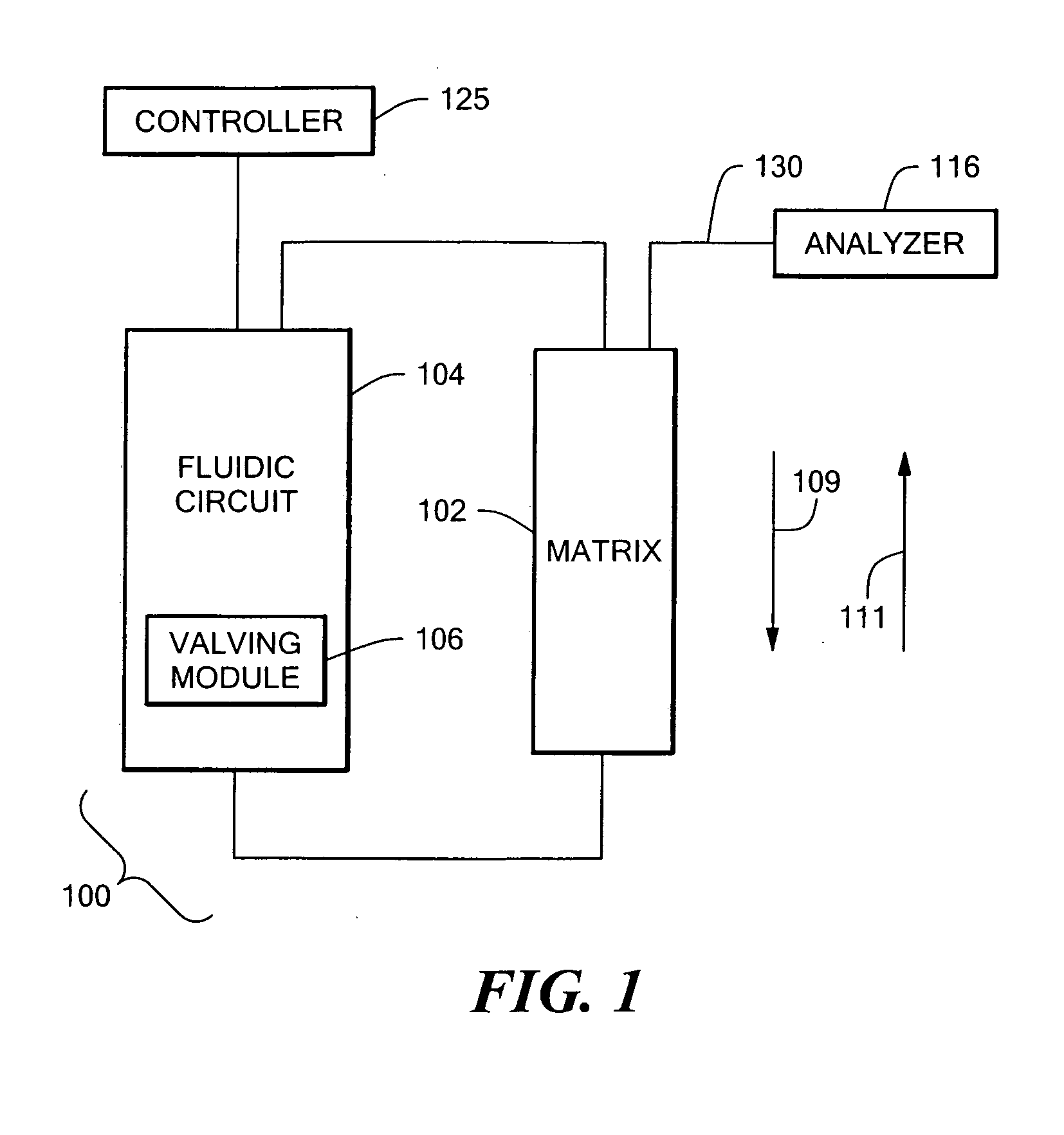
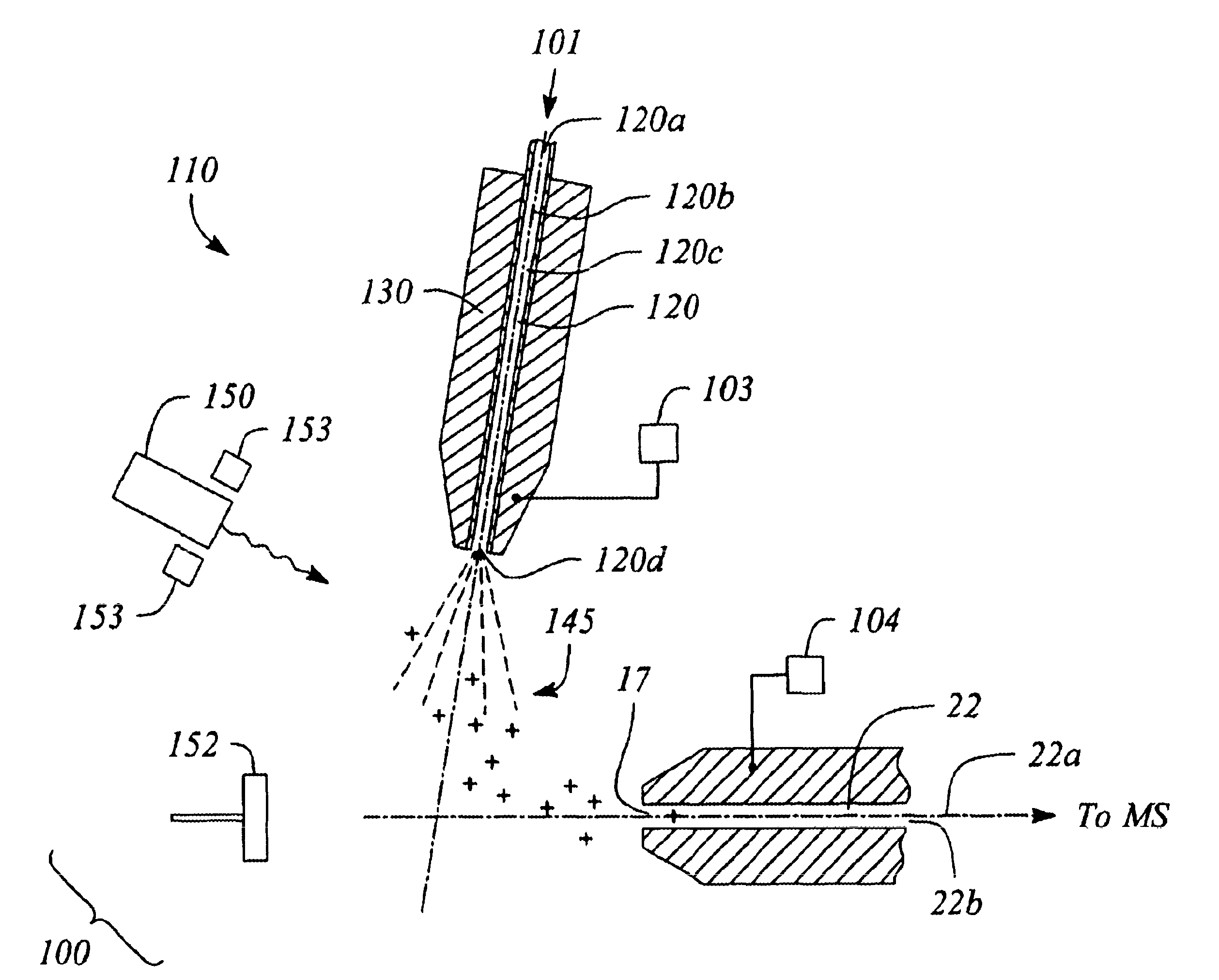
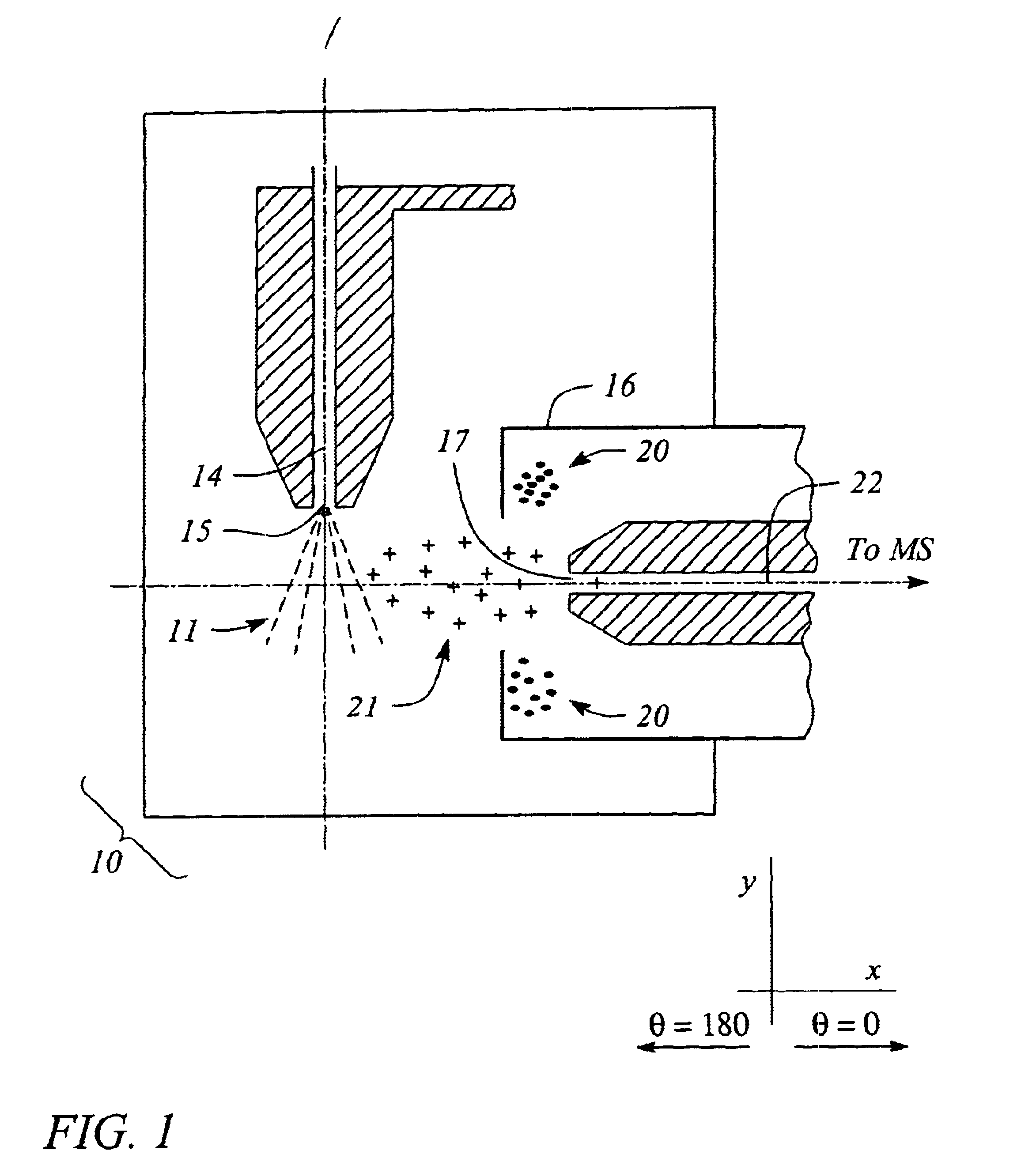
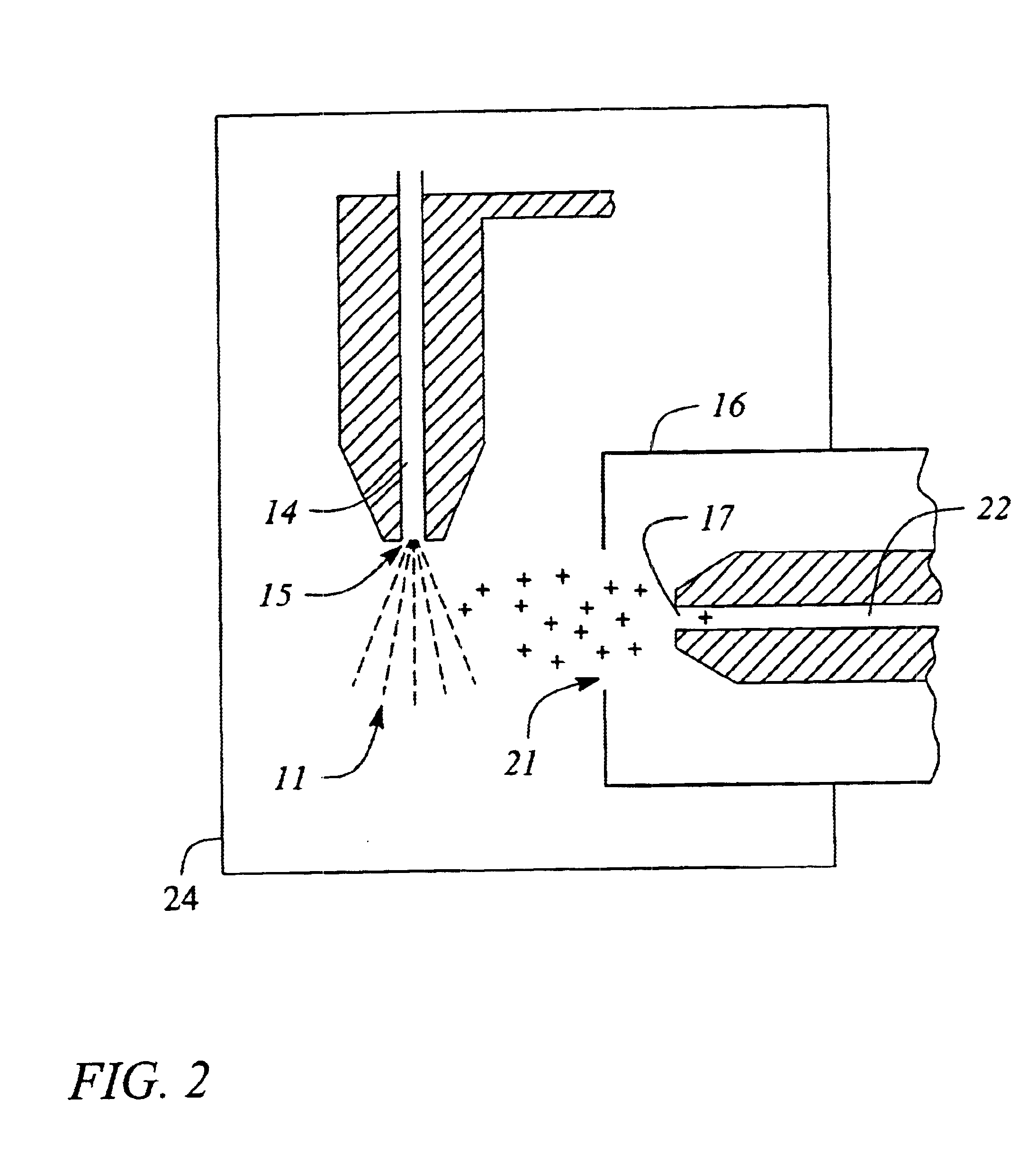
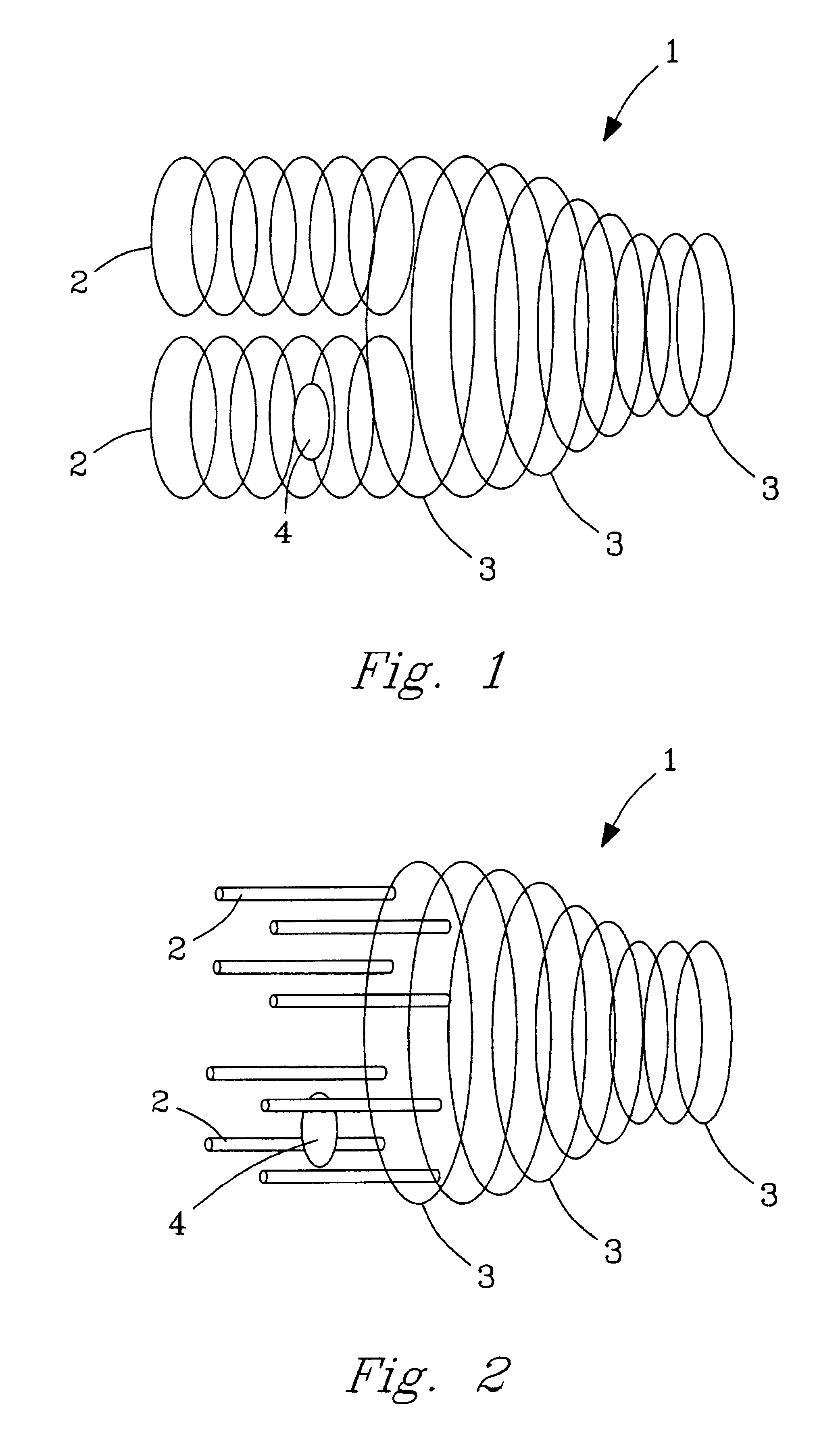
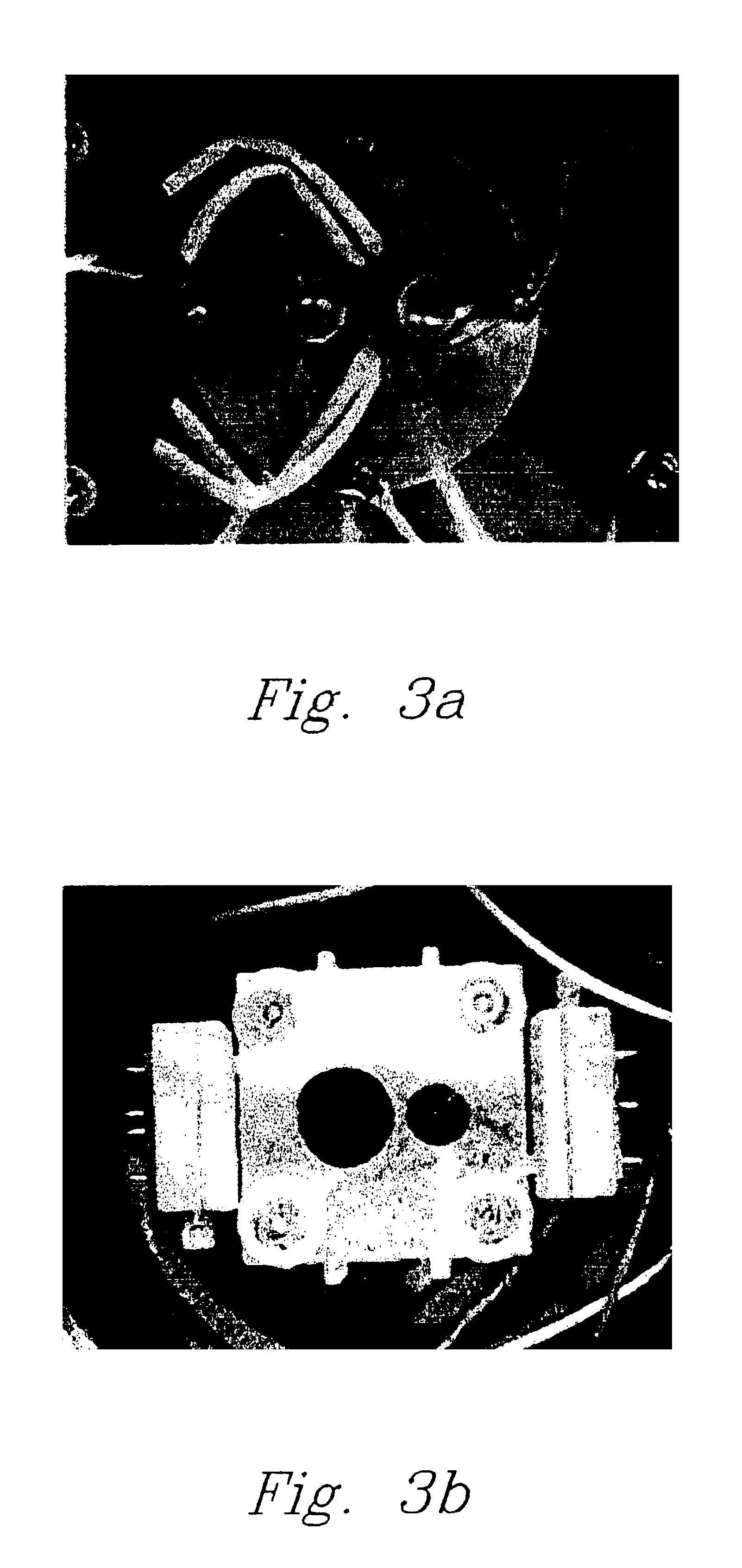
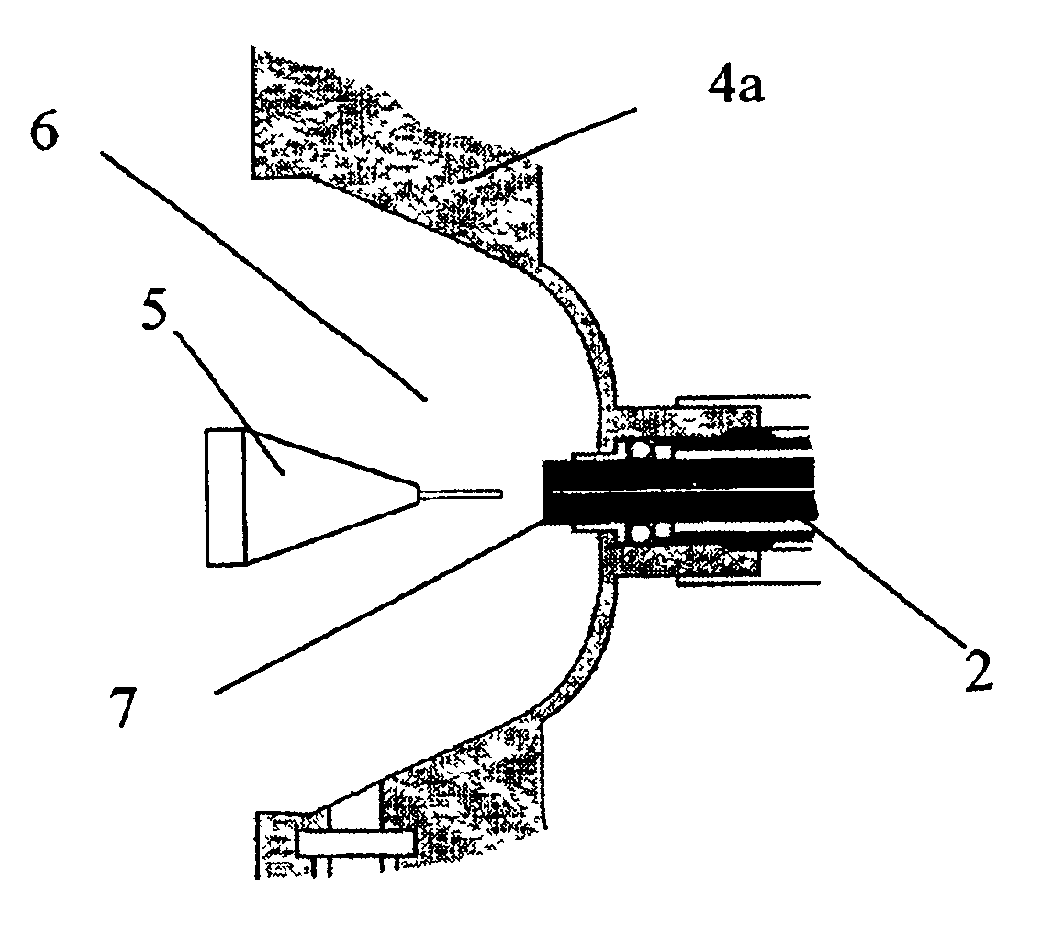
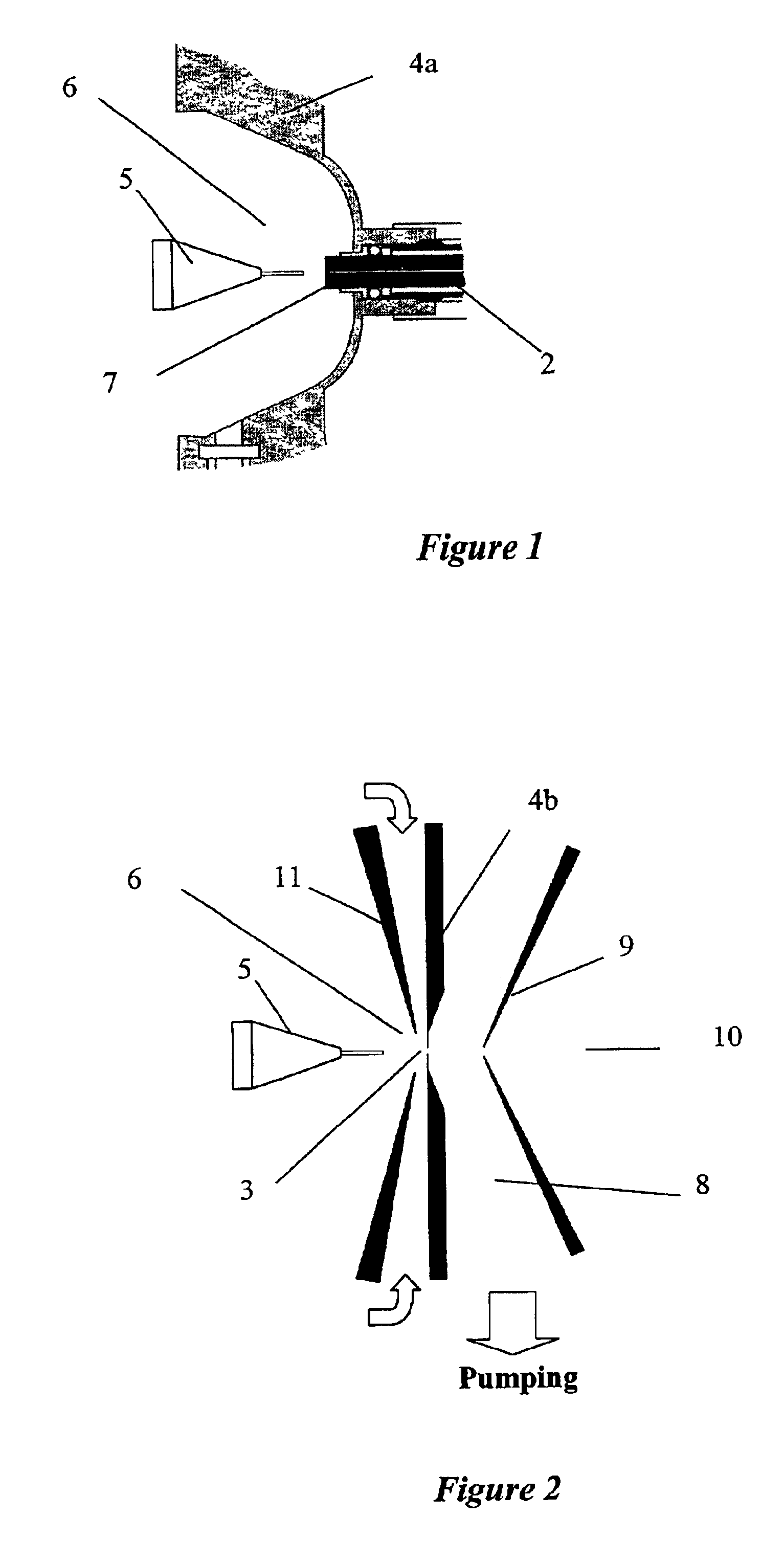
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2201results about "Samples introduction/extraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
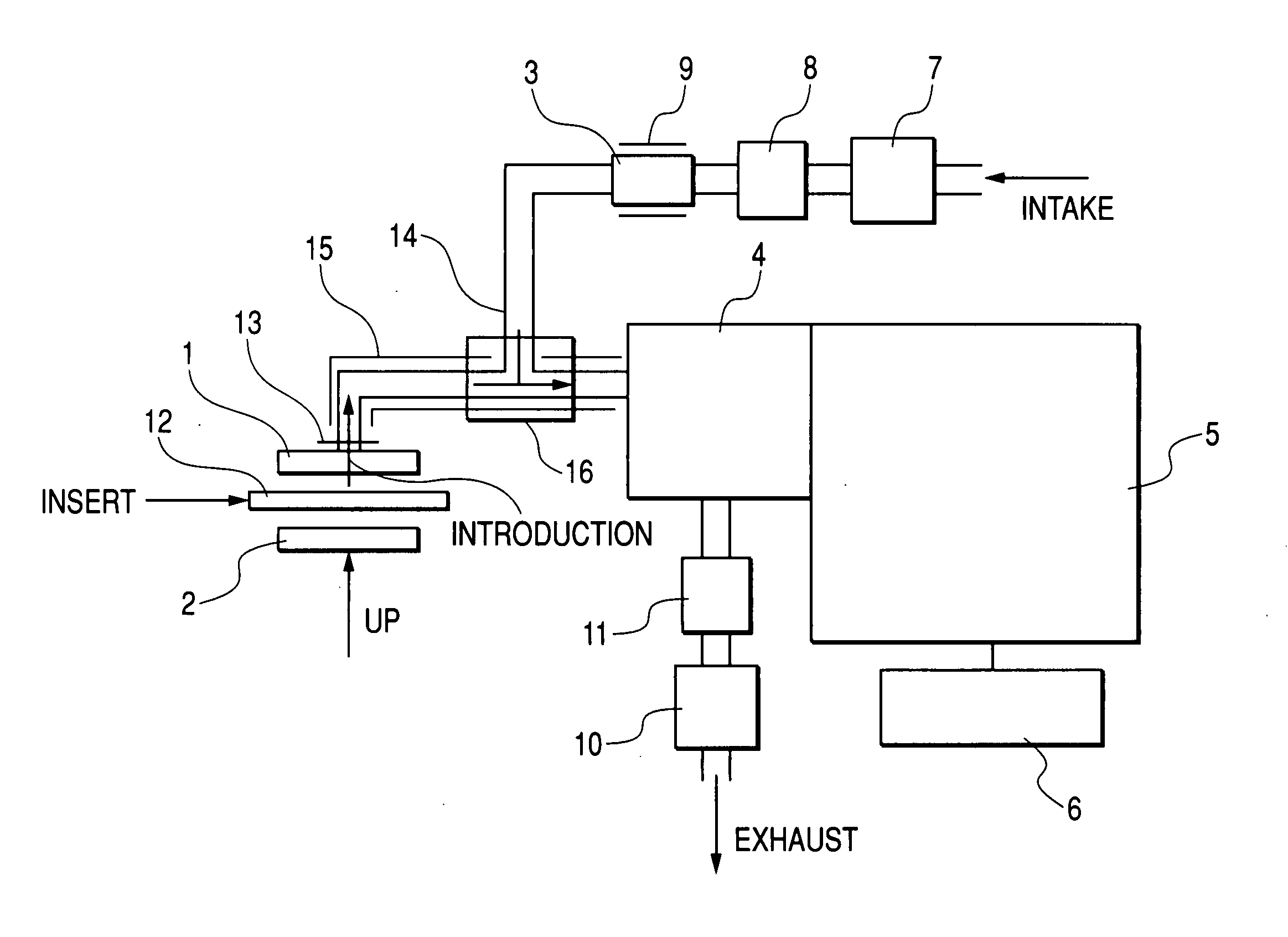
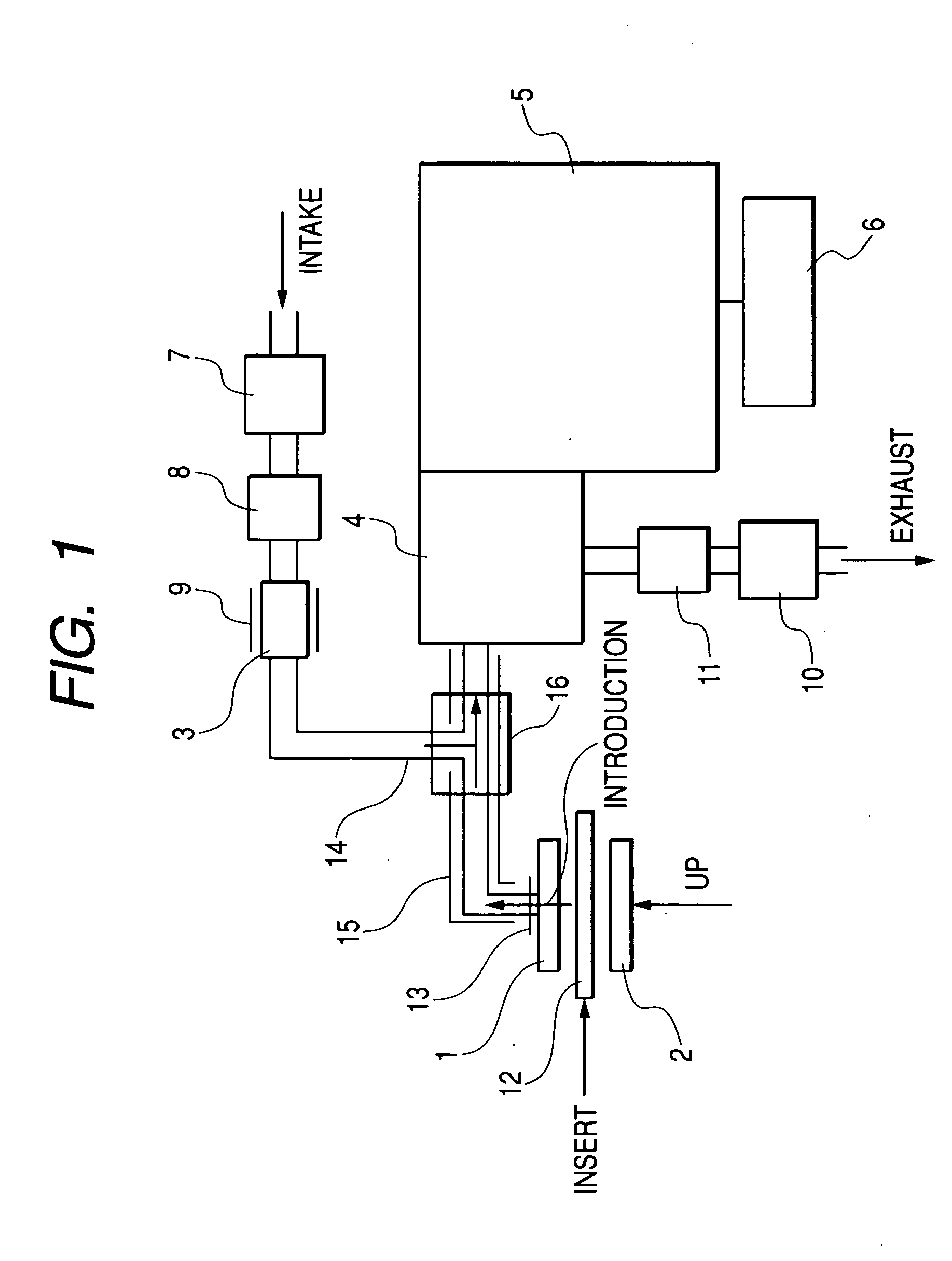
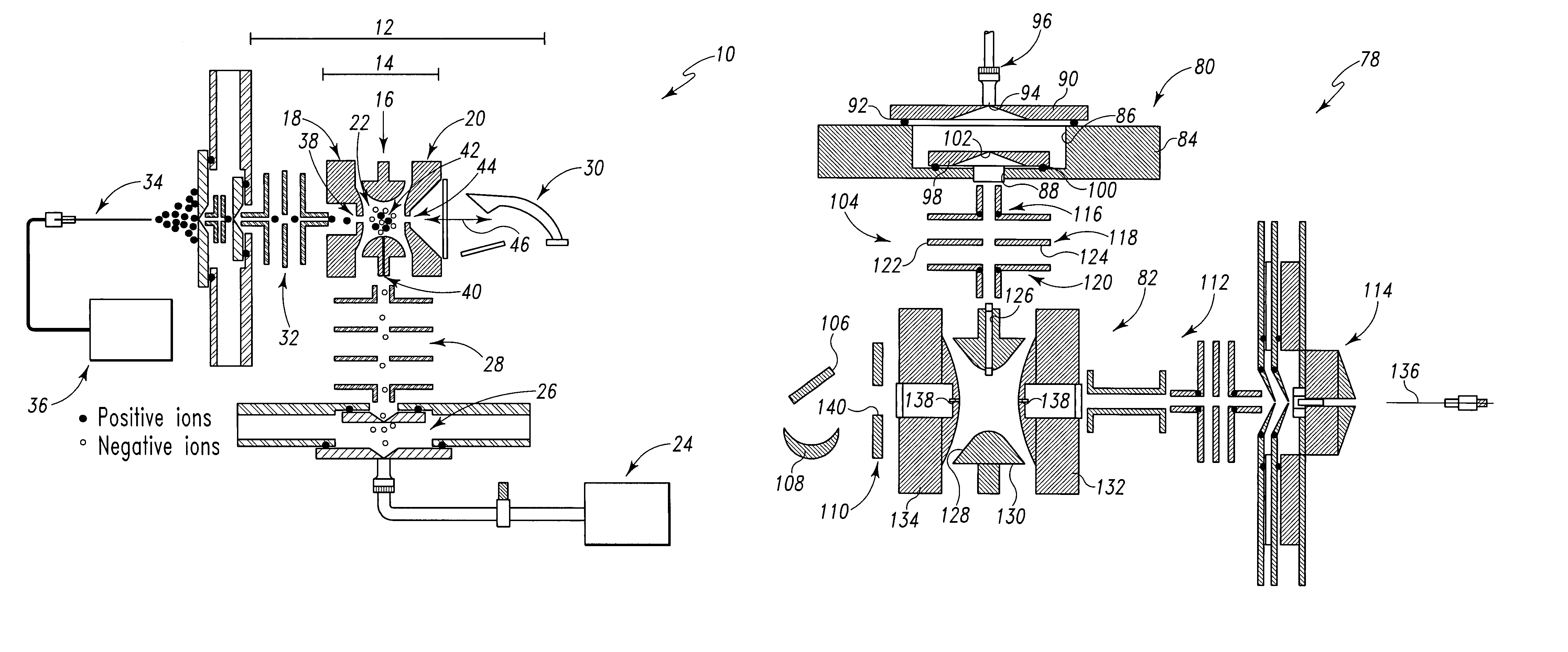
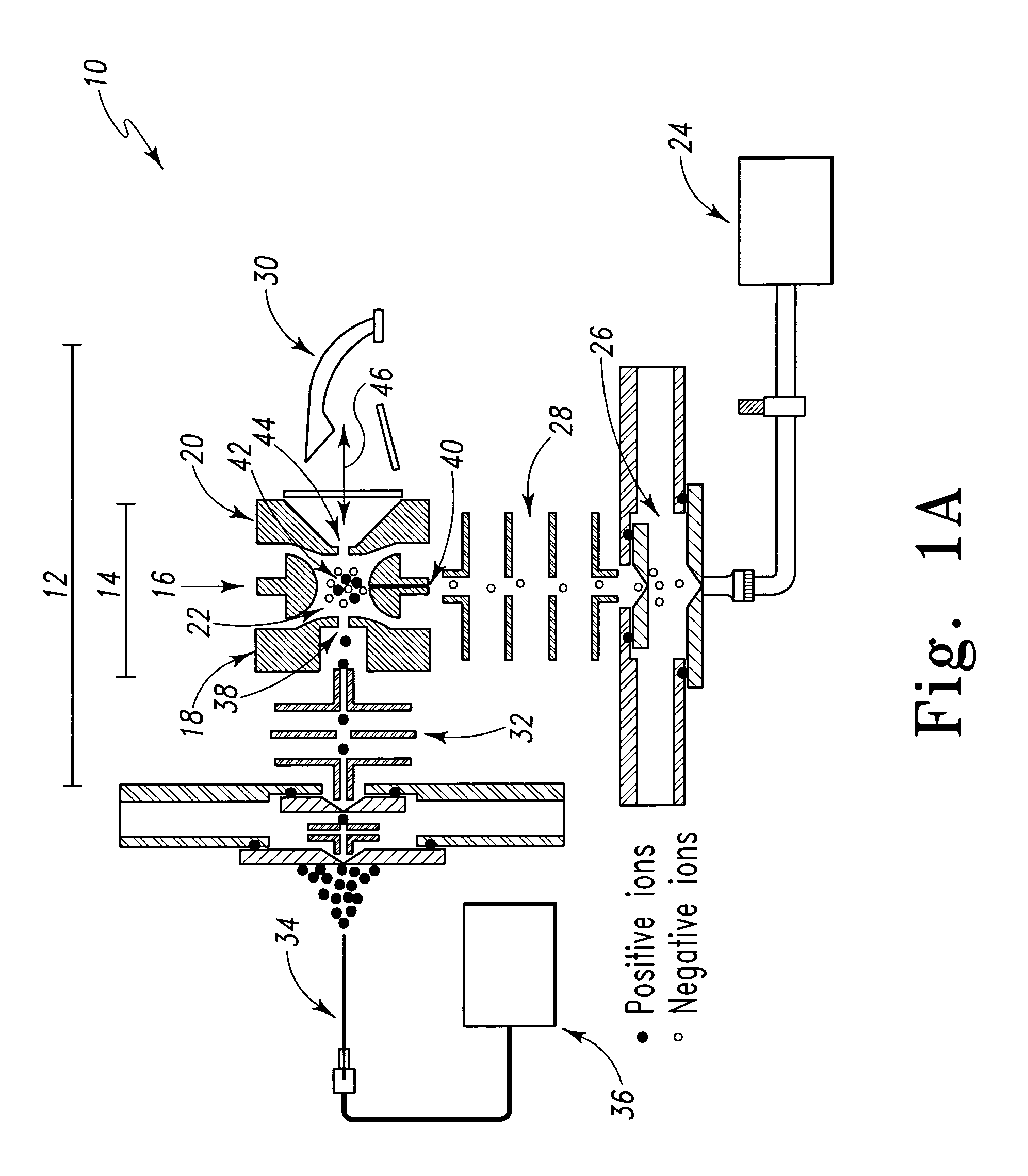
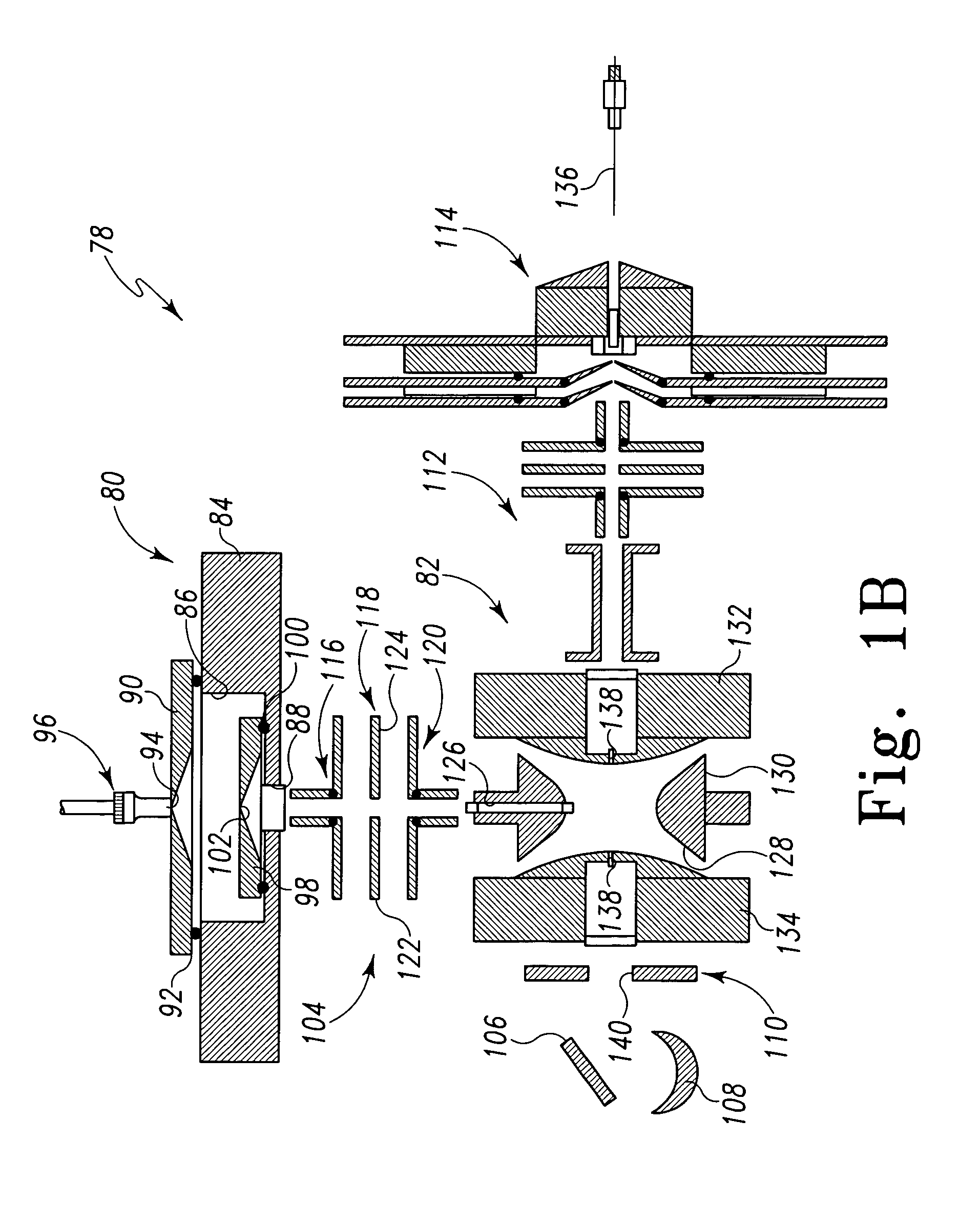
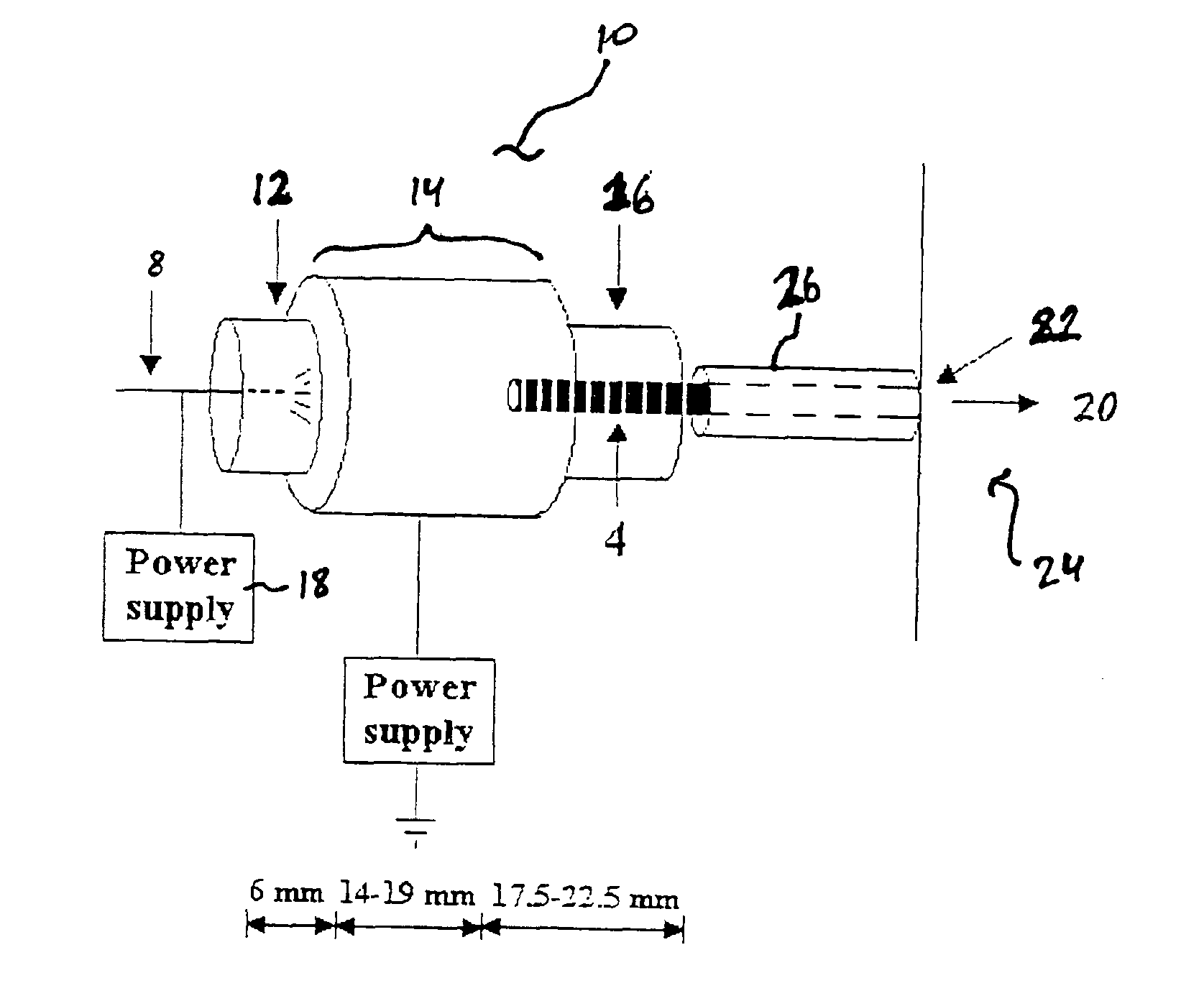
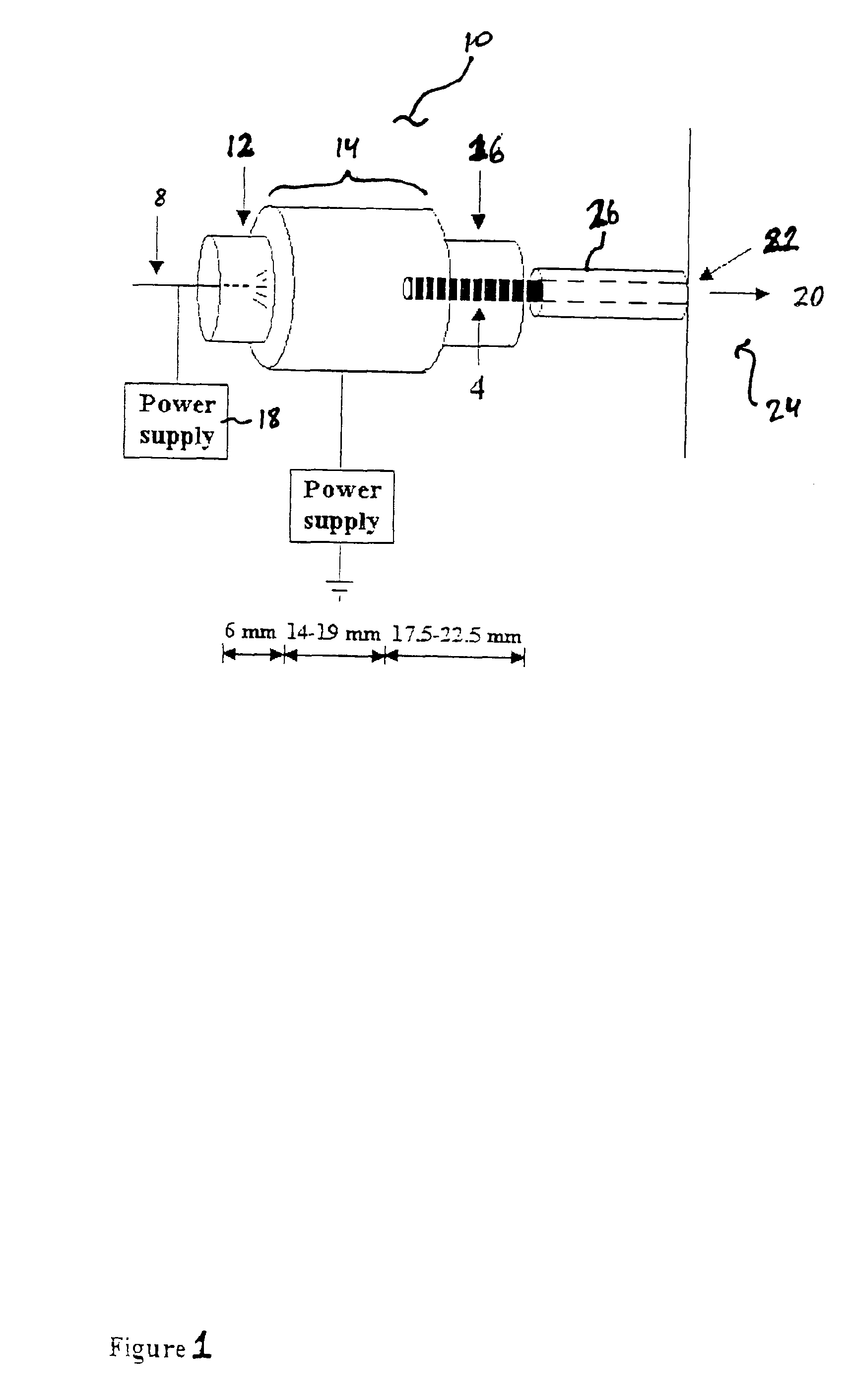
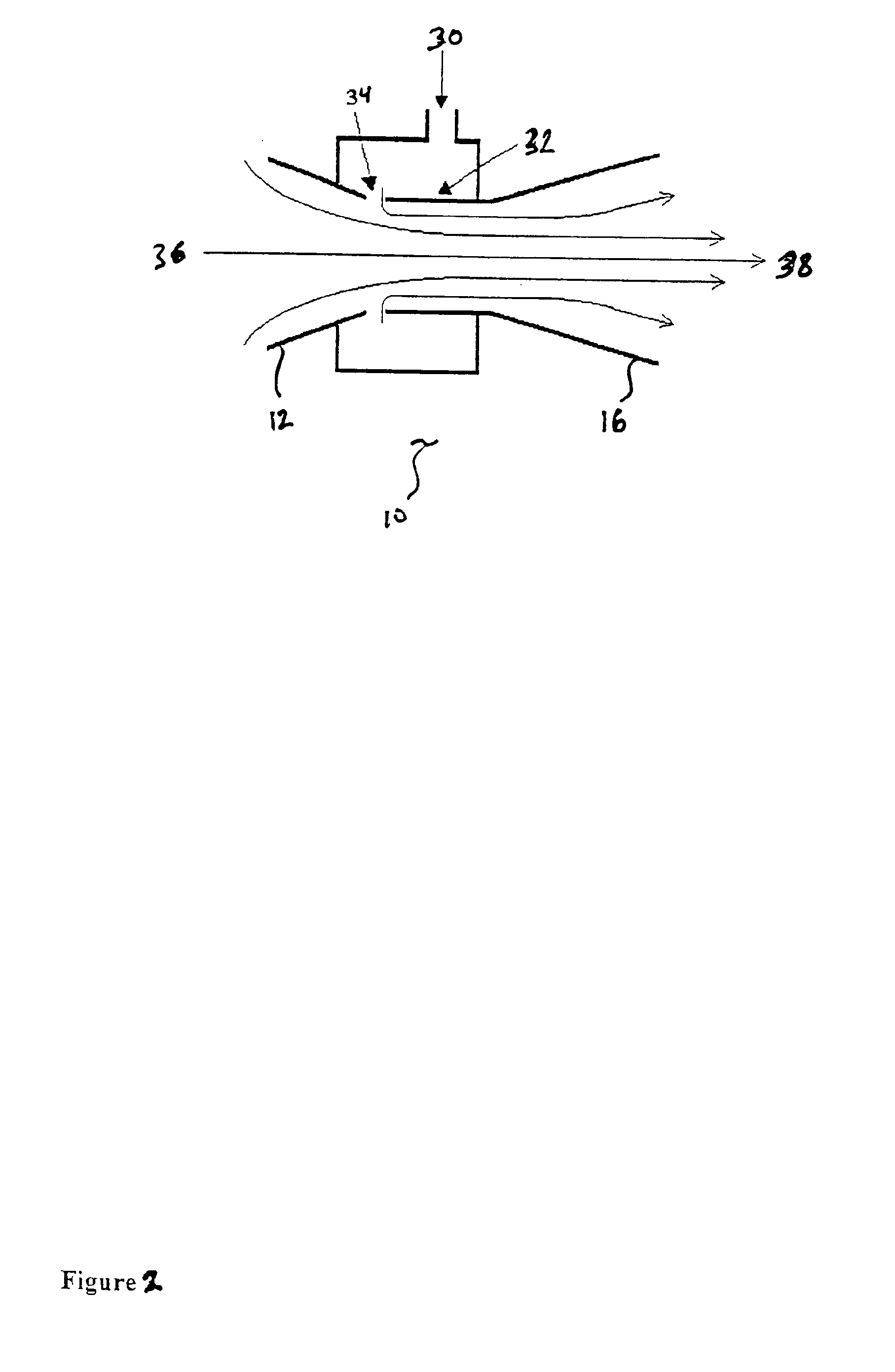
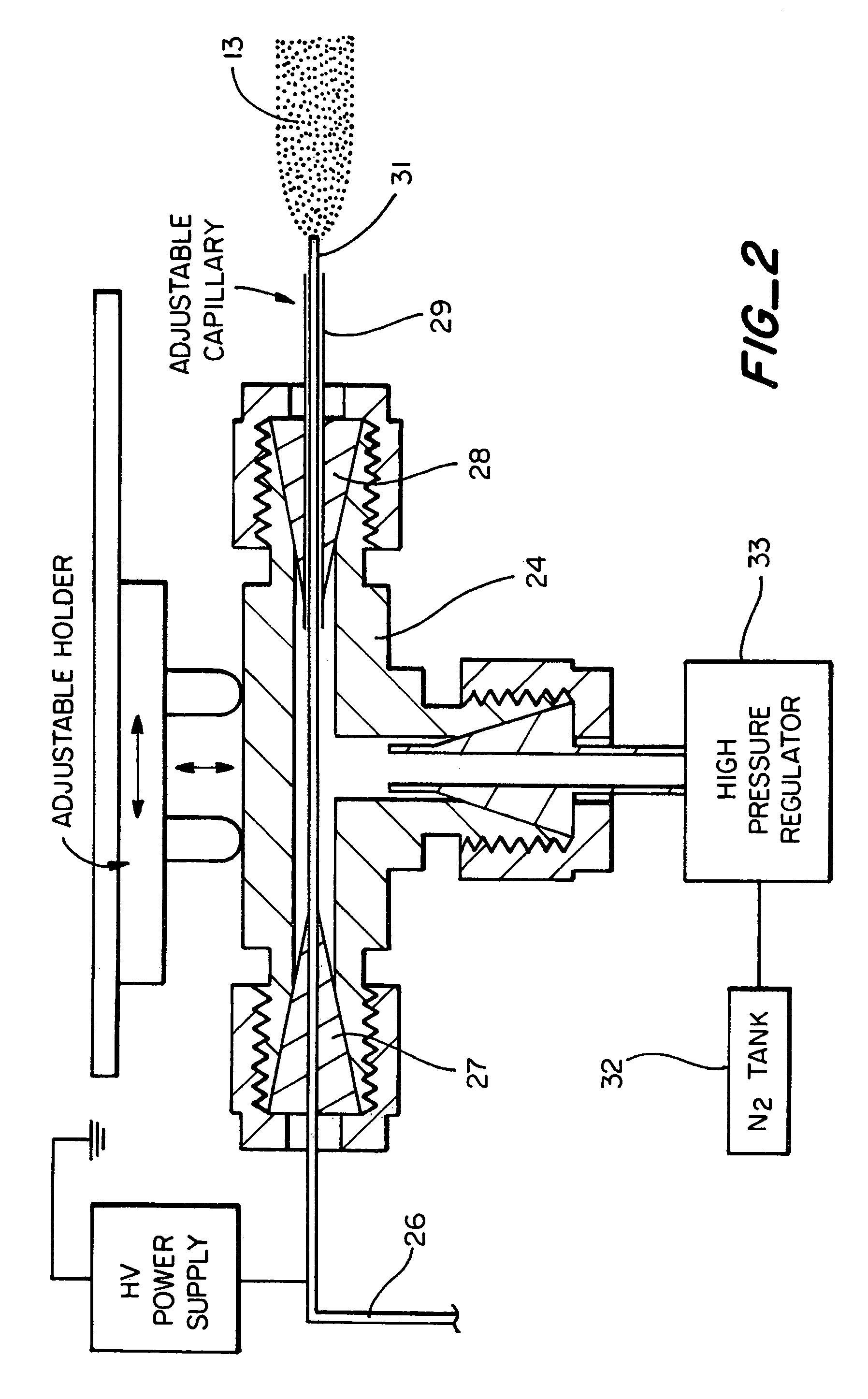
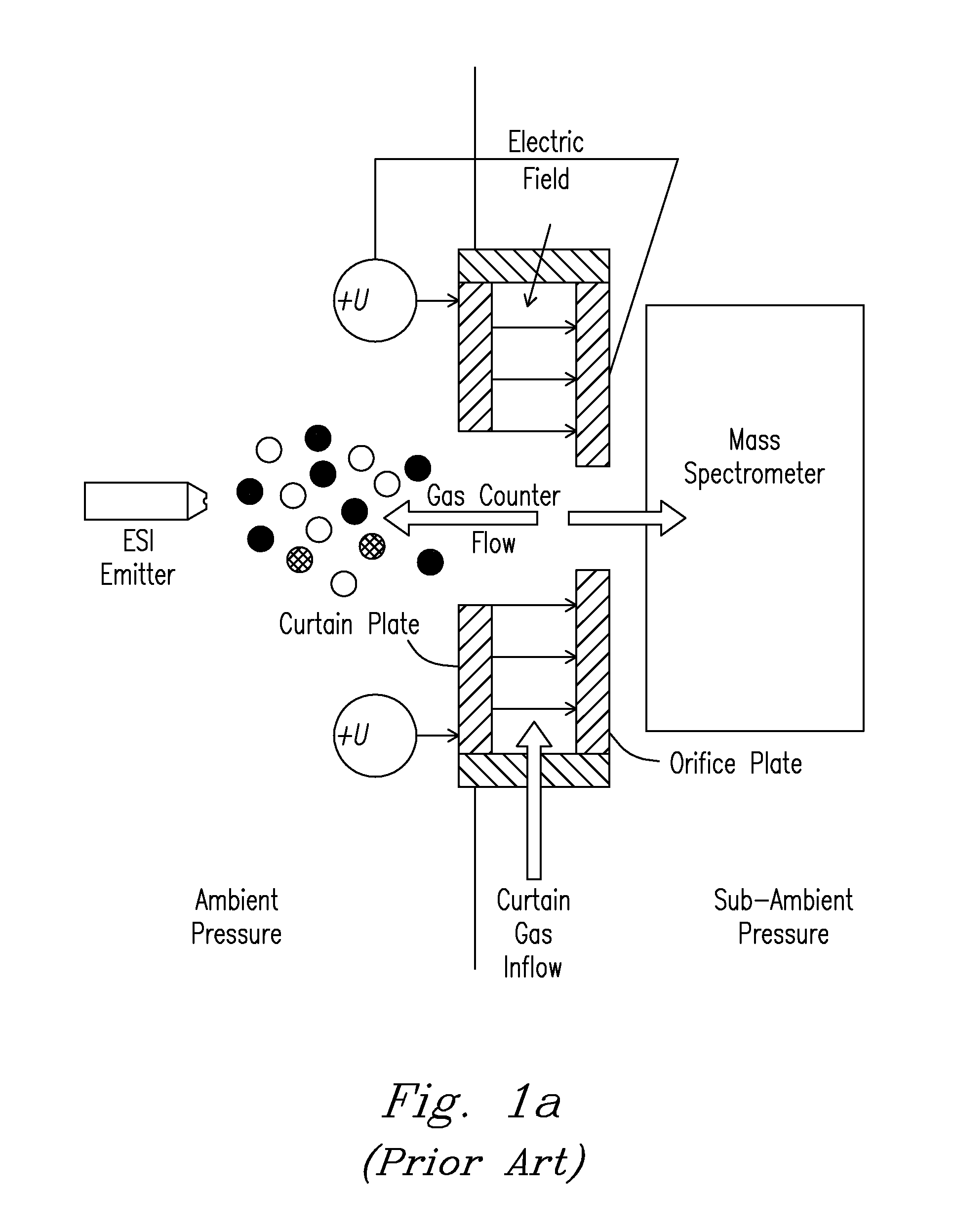
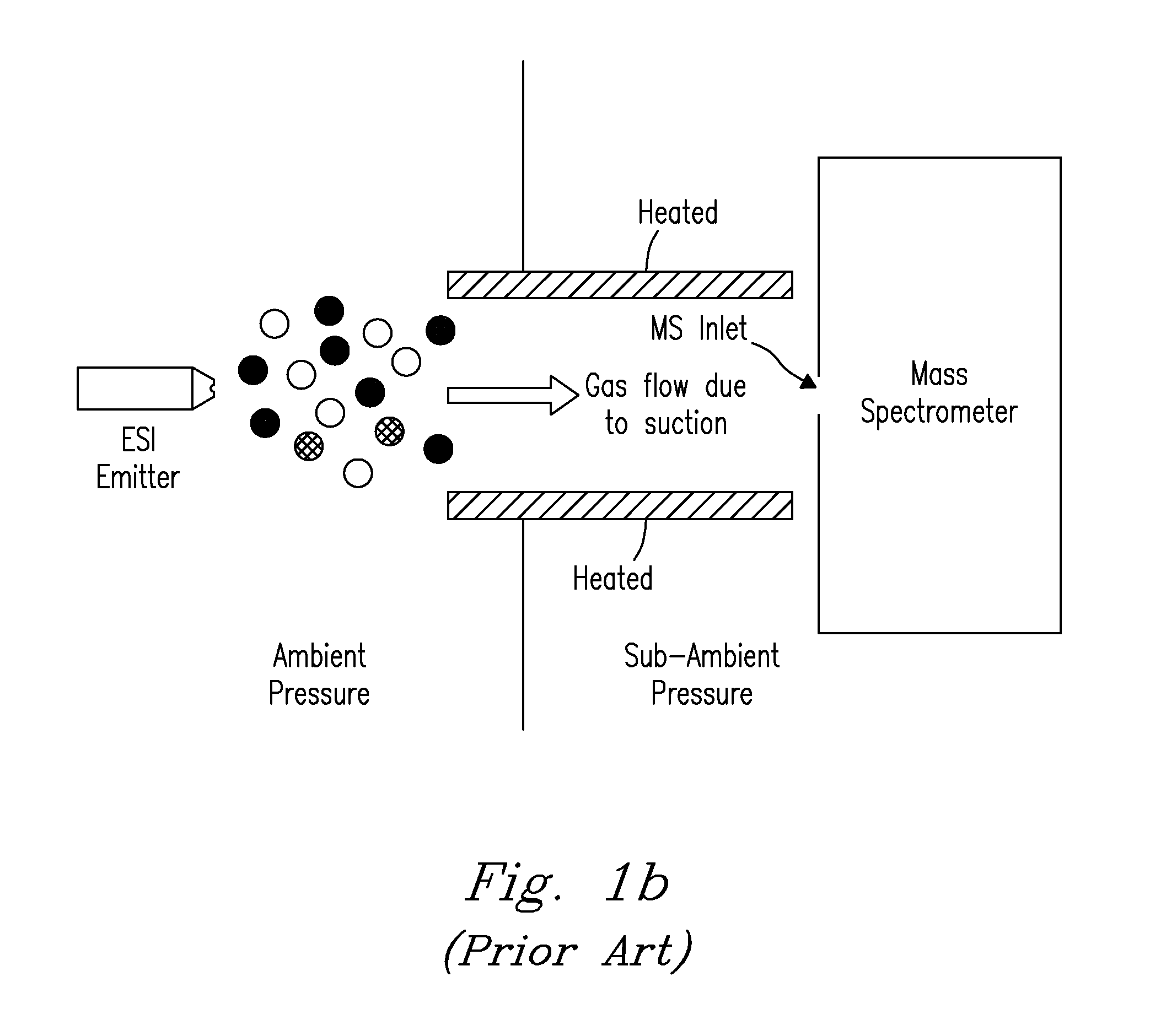
Apparatus for detecting chemical substances and method therefor
ActiveUS20050061964A1High detection sensitivityPrevent false detectionStability-of-path spectrometersAnalysis using chemical indicatorsNon detectionData treatment
An apparatus for detecting chemical substances which is high in sensitivity and selectivity is provided. An organic acid or an organic acid salt is used to generate an organic acid gas from an organic acid gas generator 3 to be mixed with a sample gas for introduction into an ion source 4 for ionization, thereby obtaining a mass spectrum by a mass analysis region 5. A data processor 6 determines the detection or non-detection of a specific m / z of an organic acid adduct ion obtained by adding a molecule generated from the organic acid to a molecule with specific m / z generated from a target chemical substance to be detected based on the obtained mass spectrum. When there is an ion peak with the m / z of the organic acid adduct ion, the presence of the target chemical substance to be detected is determined, and an alarm is sounded. False detection can be prevented.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
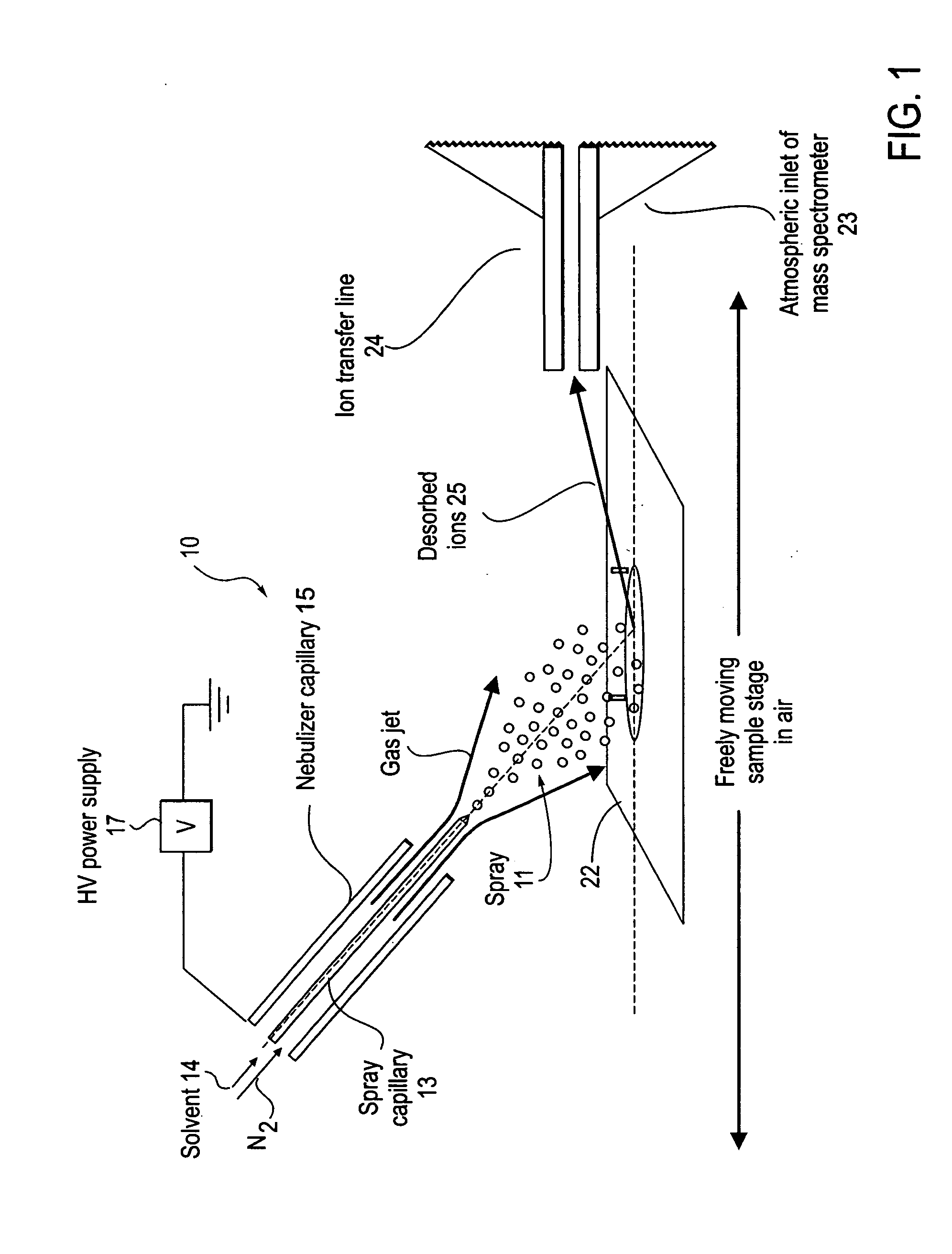
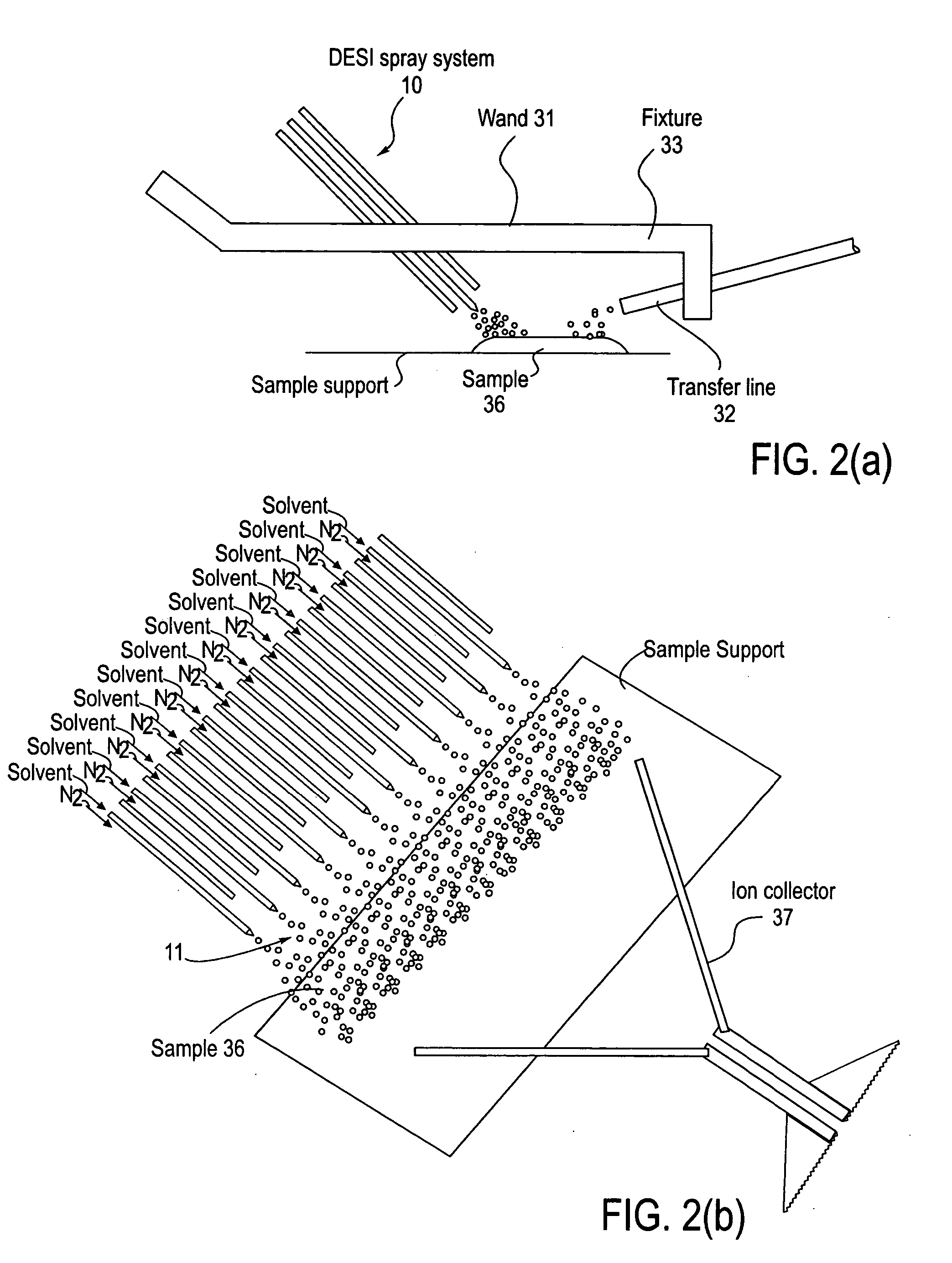
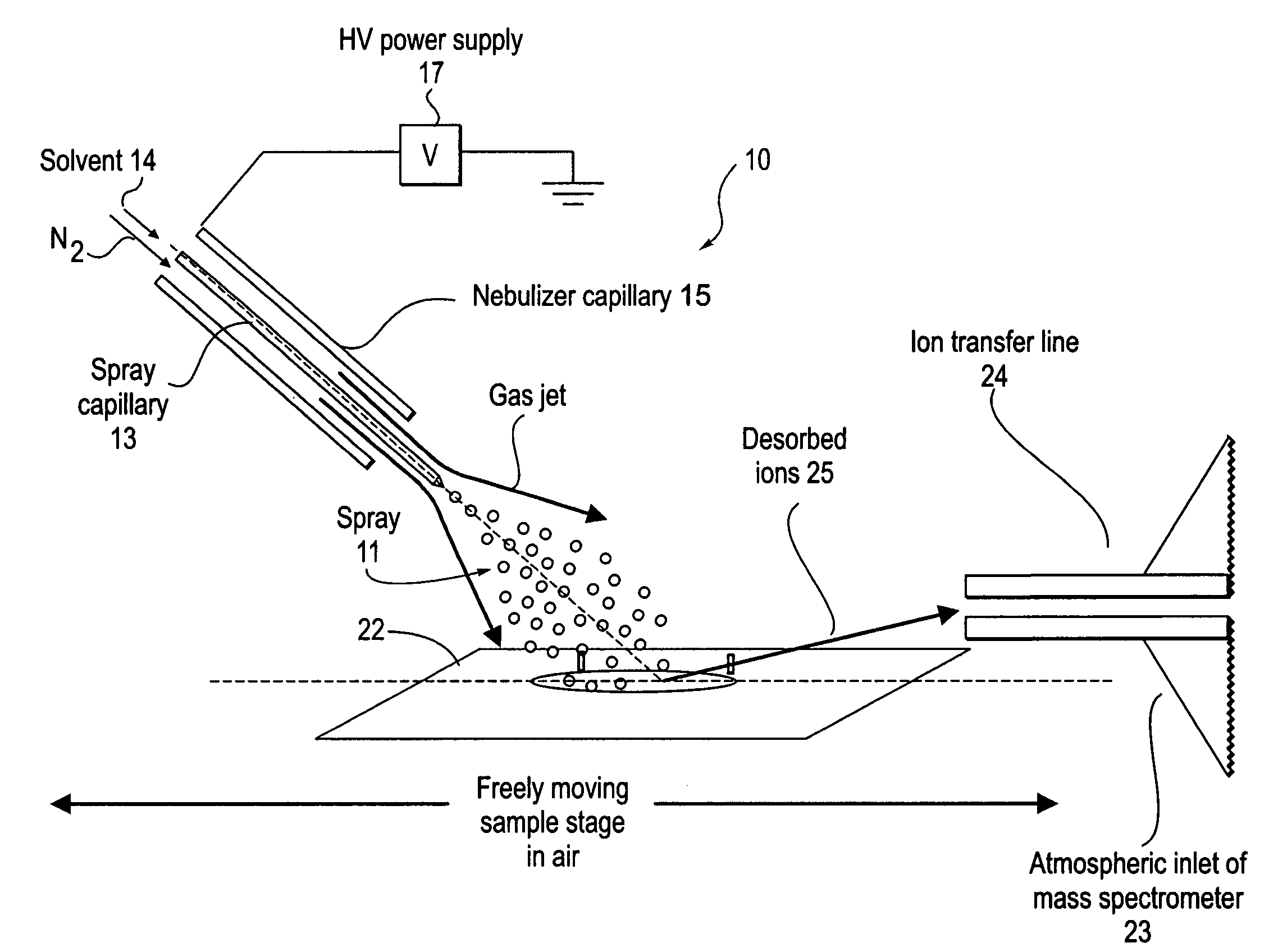
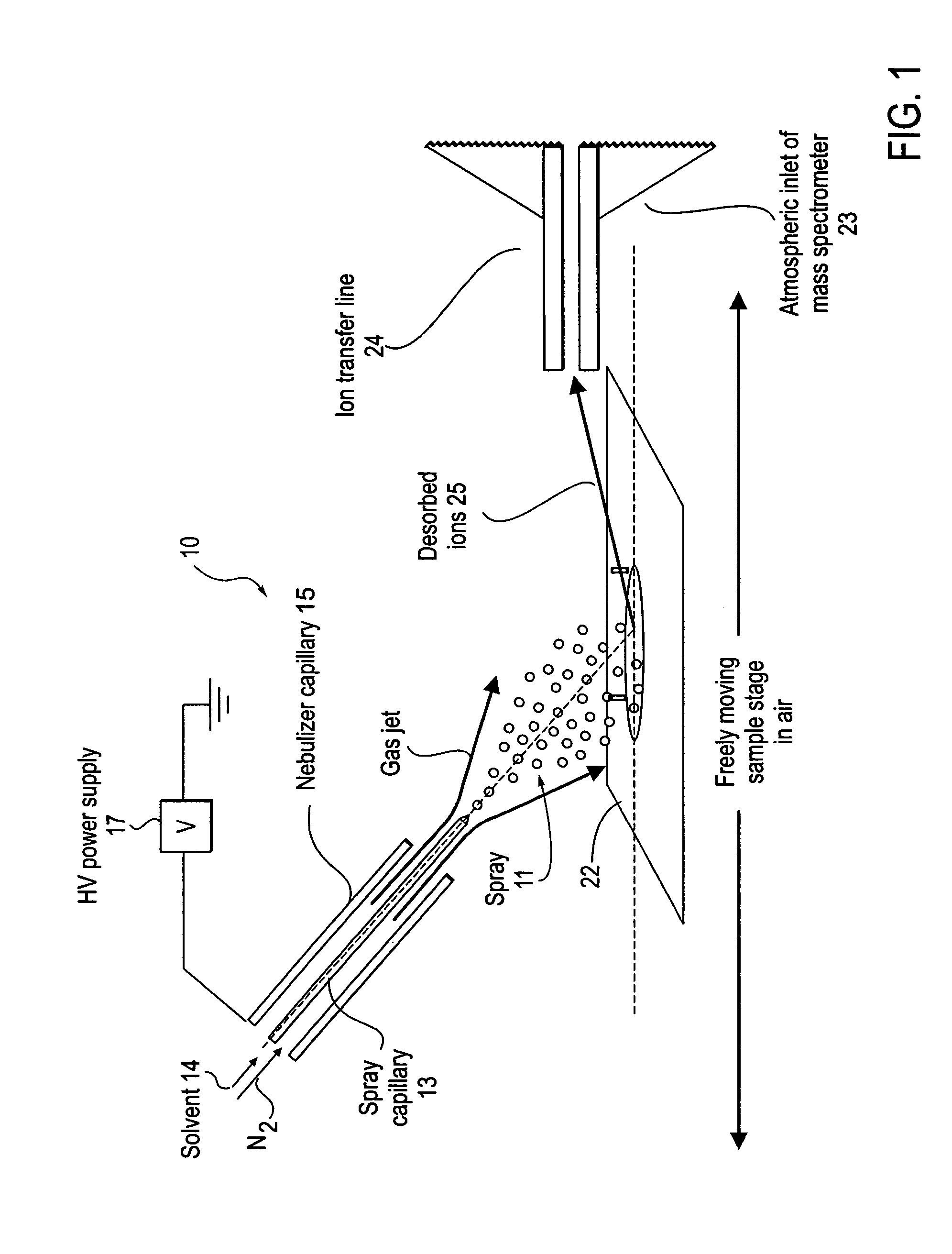
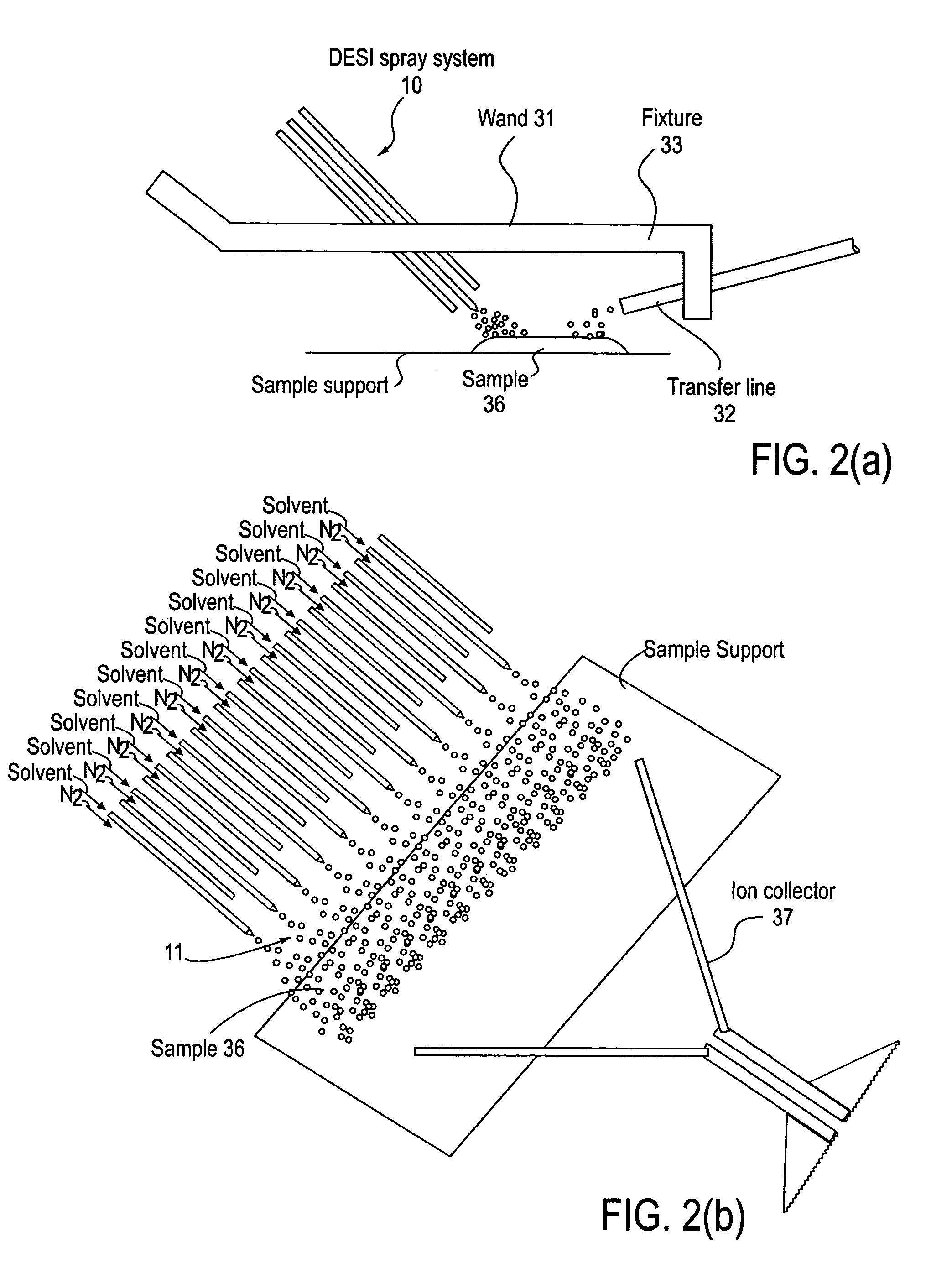
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS20050230635A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansIonizationDesorption electrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS7335897B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLycopeneElectrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
System and method for high throughput screening of droplets
InactiveUS20030119193A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh flux
A system and method for high throughput screening of fluid samples. A reduced pressure is applied, via an injection valve, to a sample aspiration tube. A first fluid and a second fluid are alternatively aspirated, via the sample aspiration tube, the first fluid for filling a sample loop with samples, the second fluid for flushing the sample aspiration tube. Excess fluid aspirated from the first fluid source and all fluid aspirated from the second fluid source is captured in an inline trap.
Owner:BIOCIUS LIFE SCI
IR-MALDI mass spectrometry of nucleic acids using liquid matrices
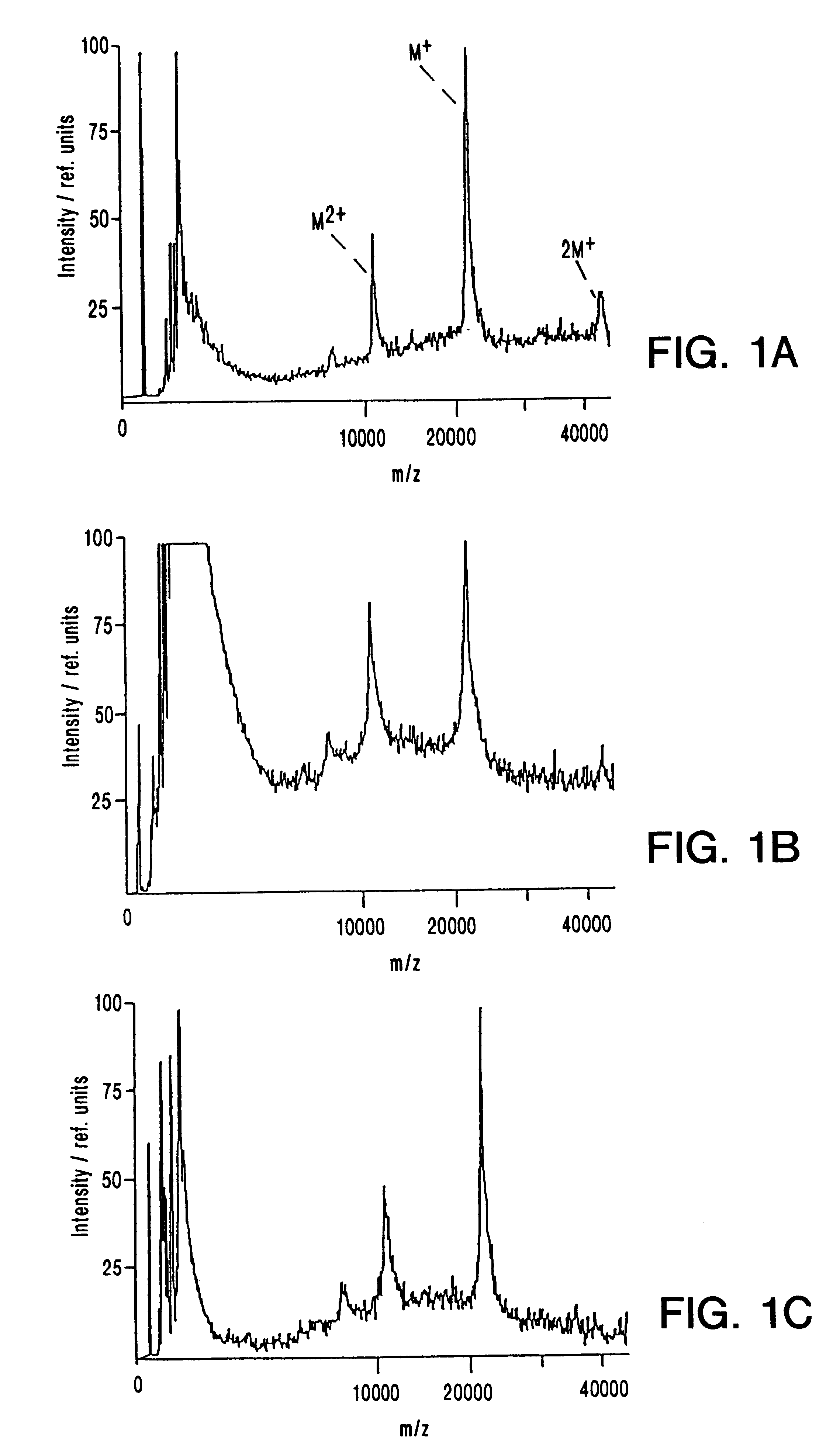
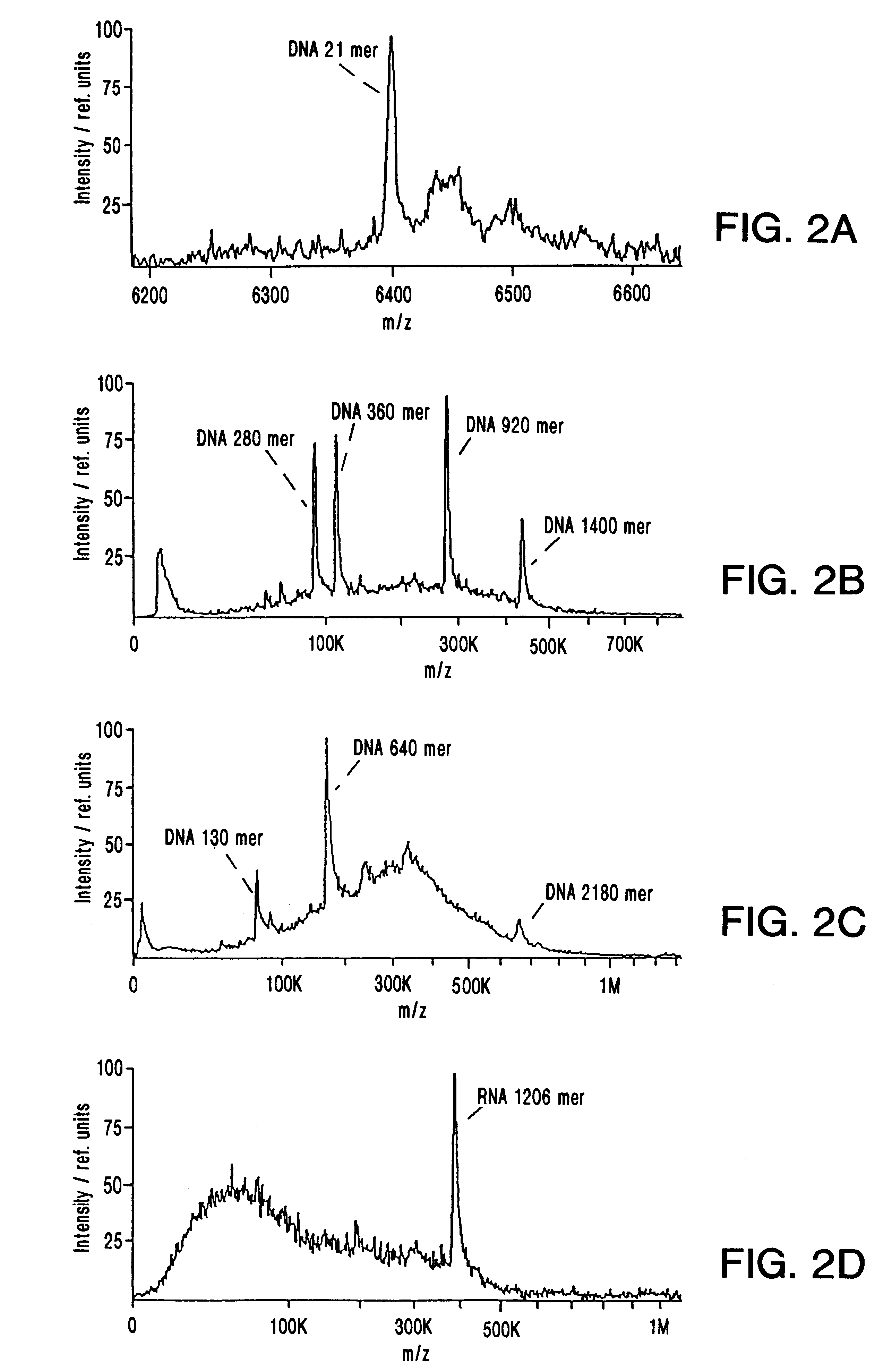
InactiveUS6706530B2Rapidly and accurately massOptimize allocationNanostructure manufactureSamples introduction/extractionMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMatrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
Mass spectrometry of large nucleic acids by infrared Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization (MALDI) using a liquid matrix is reported.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Volatile matrices for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6104028AEasy to spreadReduce formationSamples introduction/extractionWithdrawing sample devicesThermal ionization mass spectrometryRoom temperature
A sample preparation method is disclosed for volatilization and mass spectrometric analysis of nonvolatile high molecular weight molecules. Photoabsorbing molecules having significant sublimation rates at room temperature under vacuum, and preferably containing hydroxy functionalities, are disclosed for use as matrices in matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry. The samples are typically cooled in the mass spectrometer to temperatures significantly below room temperature.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS20050063864A1Reduce adverse effectsSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationStructure analysisSpectroscopy
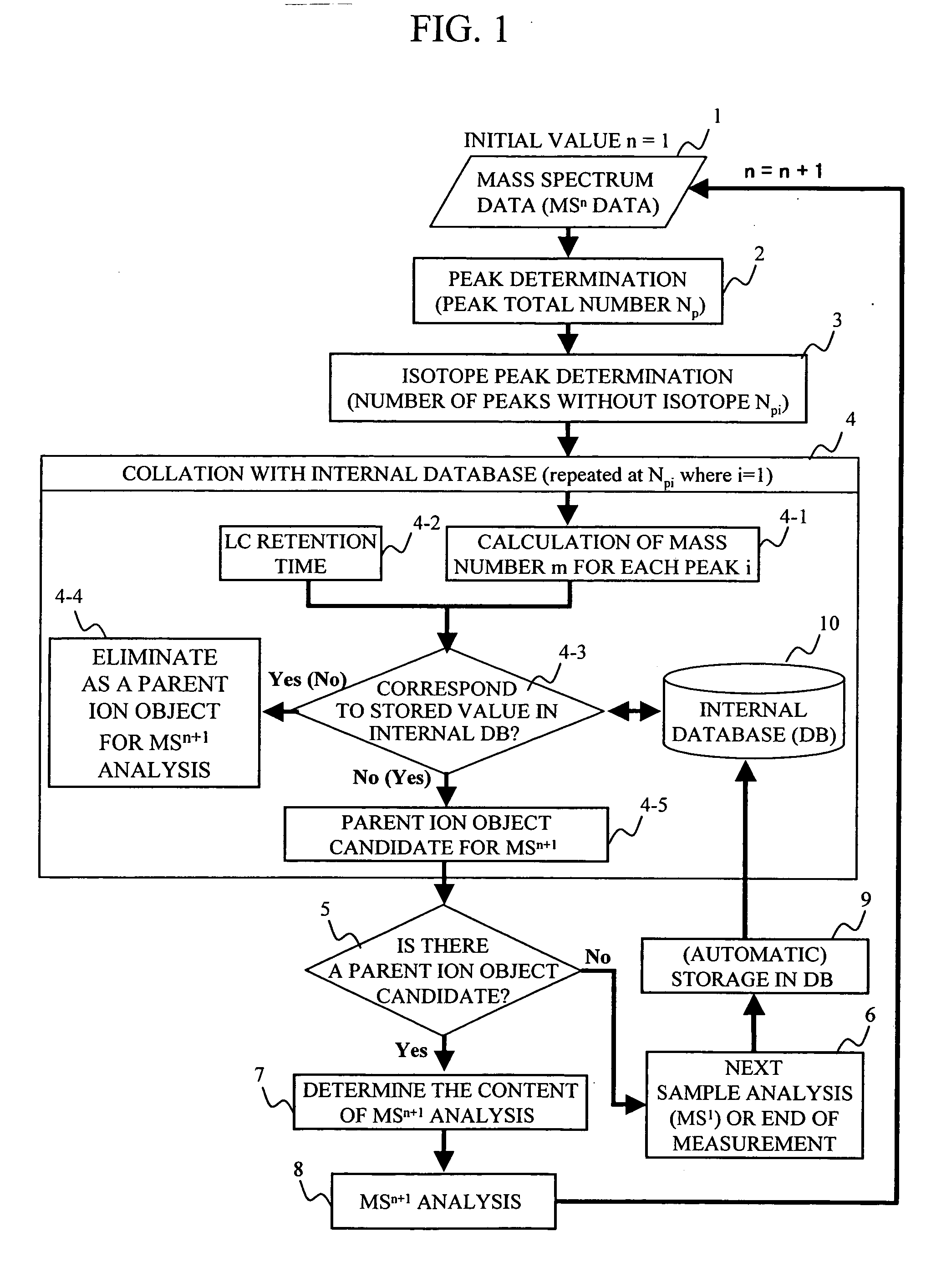
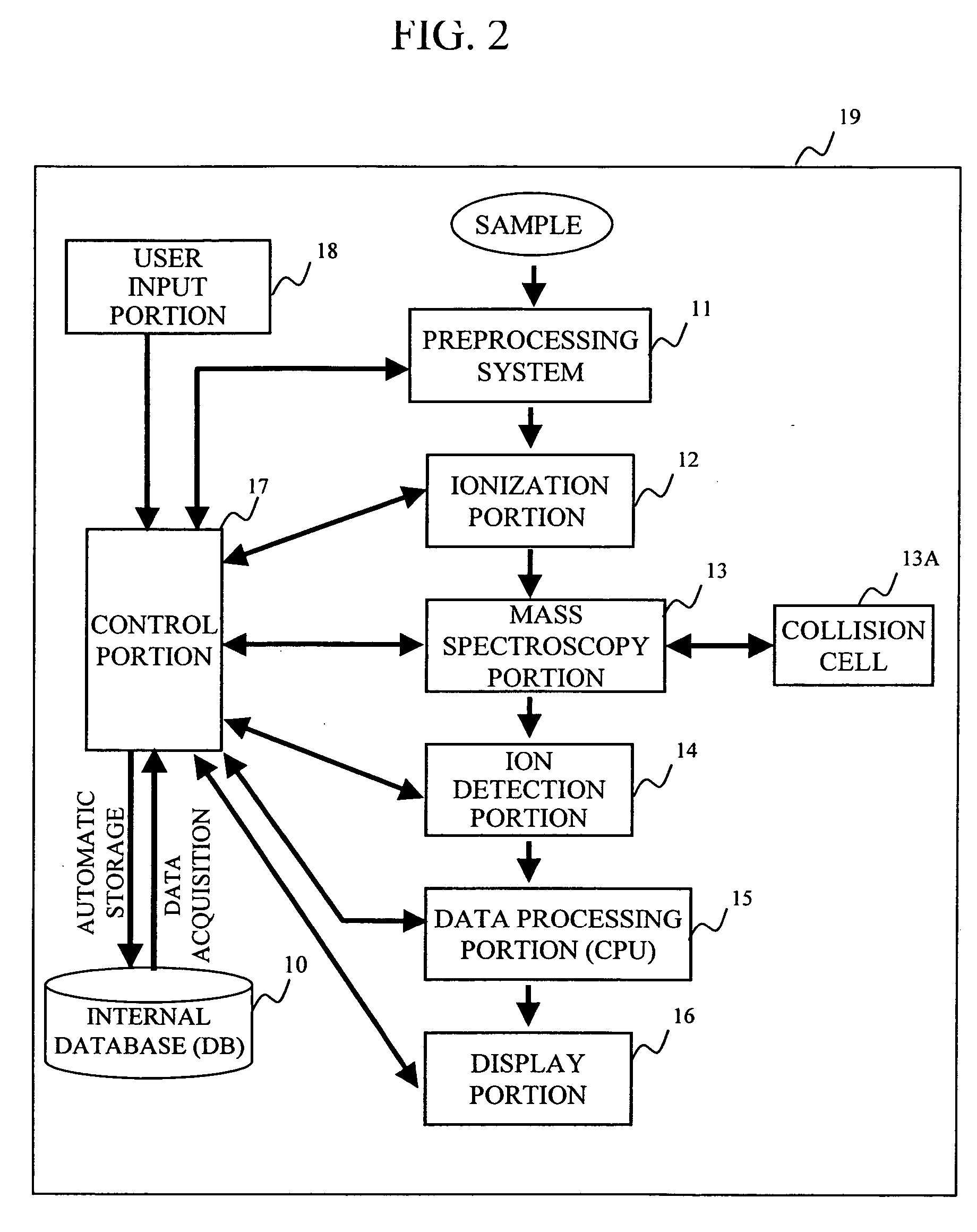
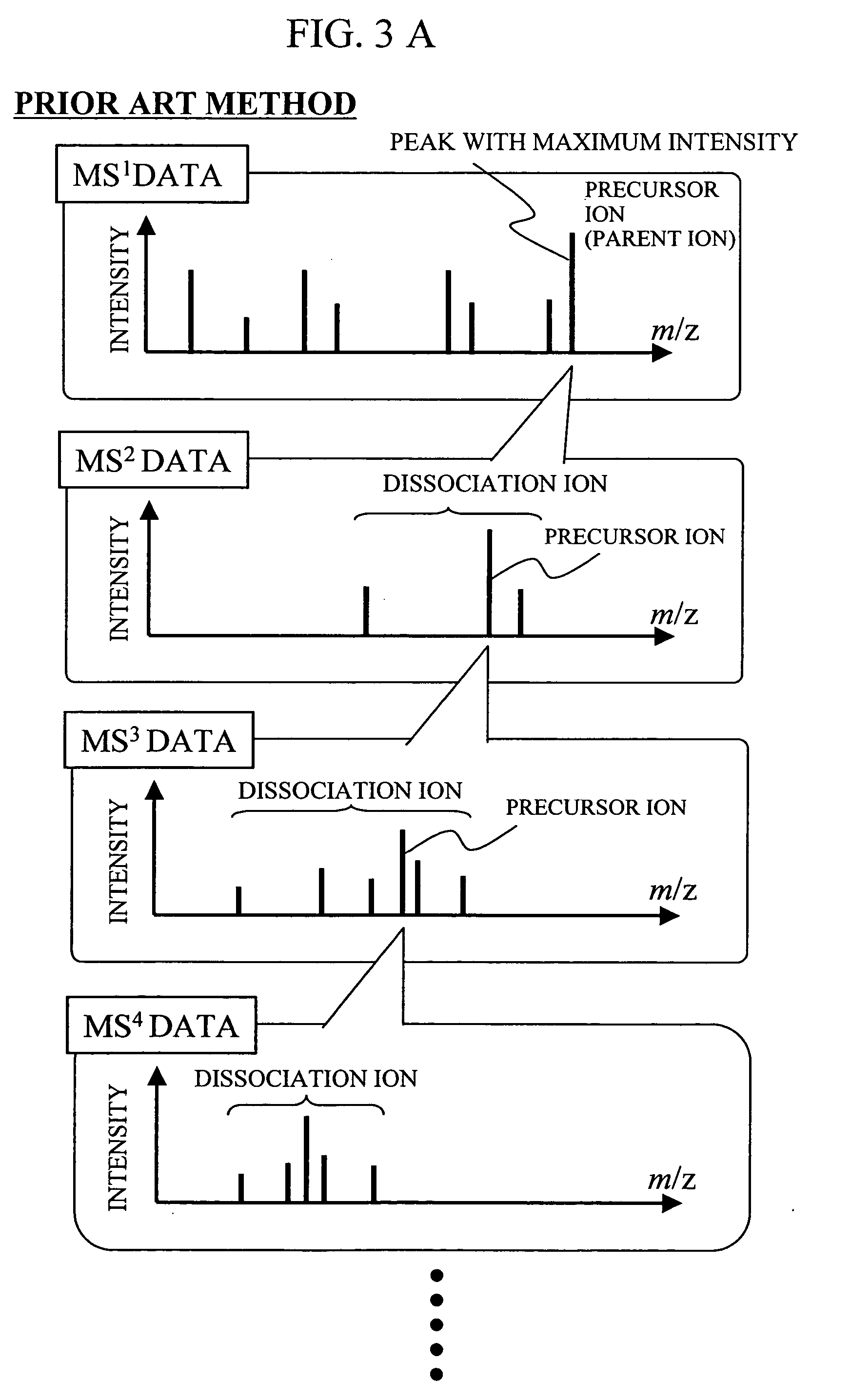
During the structural analysis of a protein or peptide by tandem mass spectroscopy, a peptide ion derived from a protein that has already been measured and that is expressed in great quantities is avoided as a tandem mass spectroscopy target. A peptide derived from a minute amount of protein, which has heretofore been difficult to analyze, can be automatically determined as a tandem mass spectroscopy target within the real time of measurement. Data concerning a protein that has already been measured and a peptide derived from the protein is automatically stored in an internal database. The stored data is collated with measured data with high accuracy to determine an isotope peak. In this way, the process of selecting a peptide peak that has not been measured as the target for the next tandem analysis can be performed within the real time of measurement and a redundant measurement of peptides derived from the same protein can be avoided. The information contained in the MSn spectrum is effectively utilized in each step of the MSn involving a multi-stage dissociation and mass spectroscopy (MSn), so that the flows for the determination of the next analysis content and the selection of the parent ion for the MSn+1 analysis, for example, can be optimized within the real time of measurement and with high efficiency and accuracy. Thus, a target of concern to the user can be subjected to tandem mass spectroscopy without wasteful measurement.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Surface-enhanced affinity capture for desorption and detection of analytes
InactiveUS6027942AFacilitate desorption/ionizationAccurately determineTime-of-flight spectrometersComponent separationAnalyteDesorption
This invention relates generally to a mass spectrometer probe and a method of using said probe for desorption and ionization of analytes. The sample probe comprises an affinity reagent on the probe surface, wherein the affinity reagent is capable of selectively binding an analyte. An analyte bound to the affinity reagent can be desorbed by a high energy source and detected in the mass spectrometer. The probe and methods are useful in detection and analysis of macromolecules such as proteins or other biomolecules.
Owner:HUTCHENS T WILLIAM
Method and apparatus for embedded heater for desorption and ionization of analytes
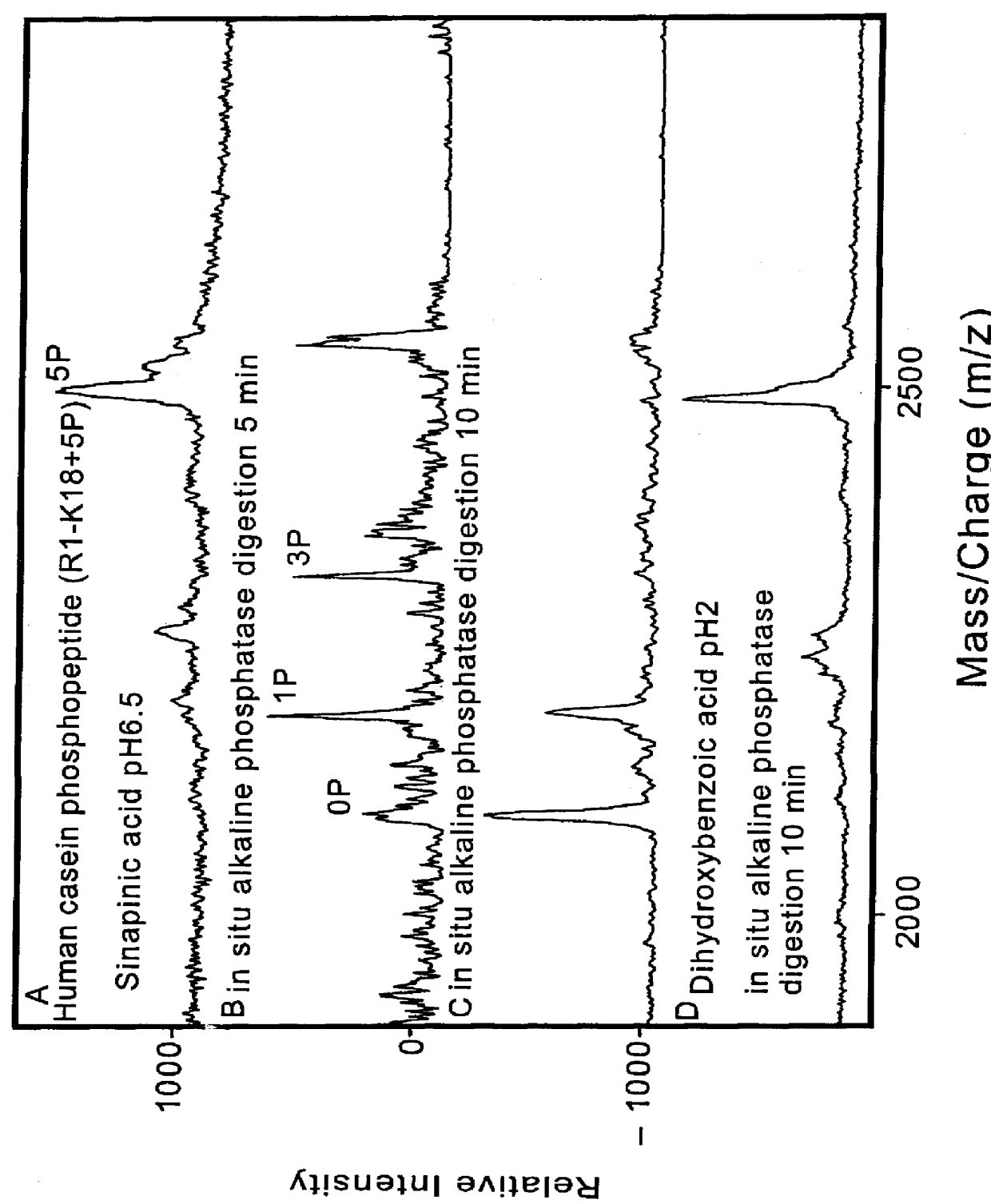
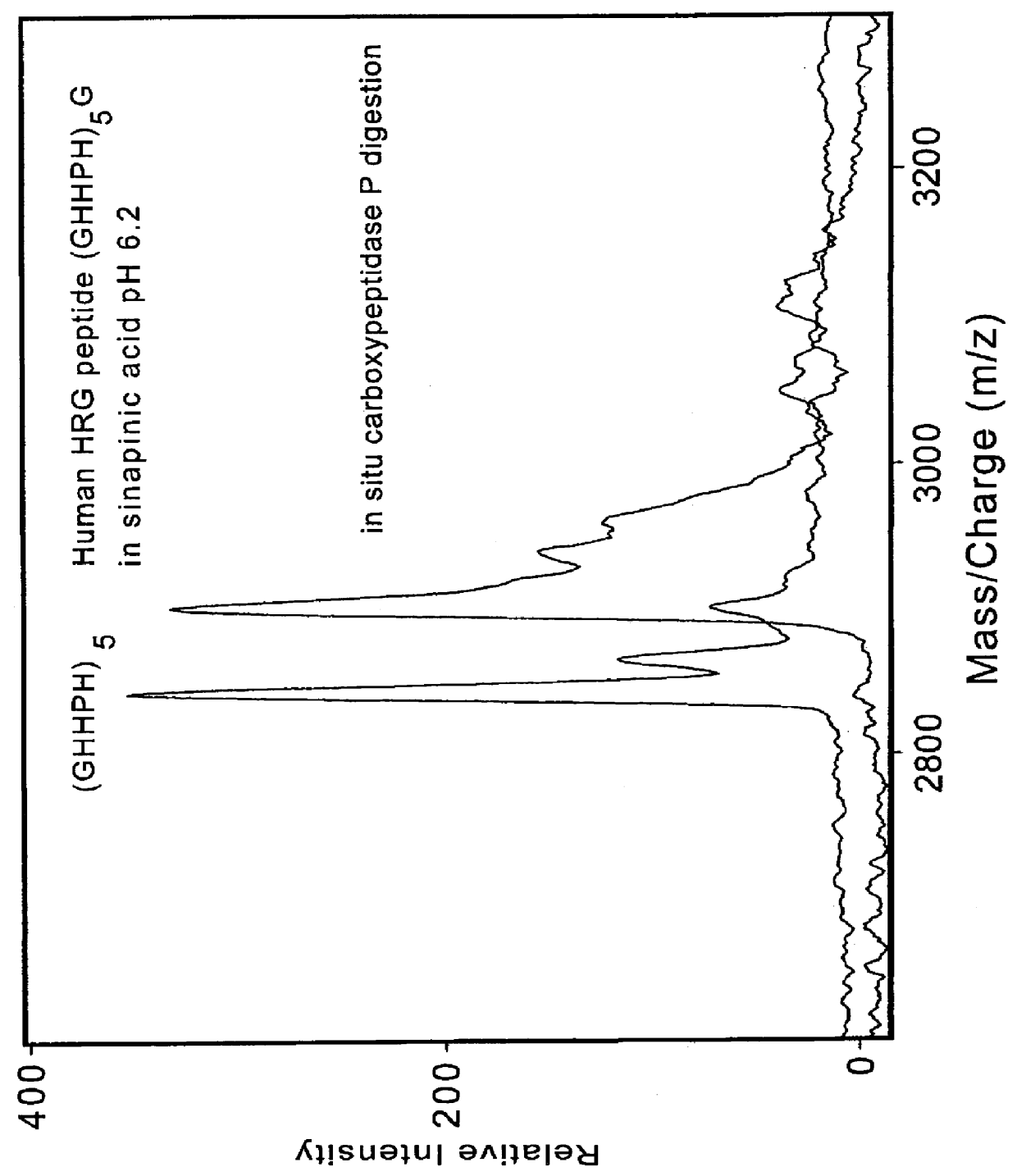
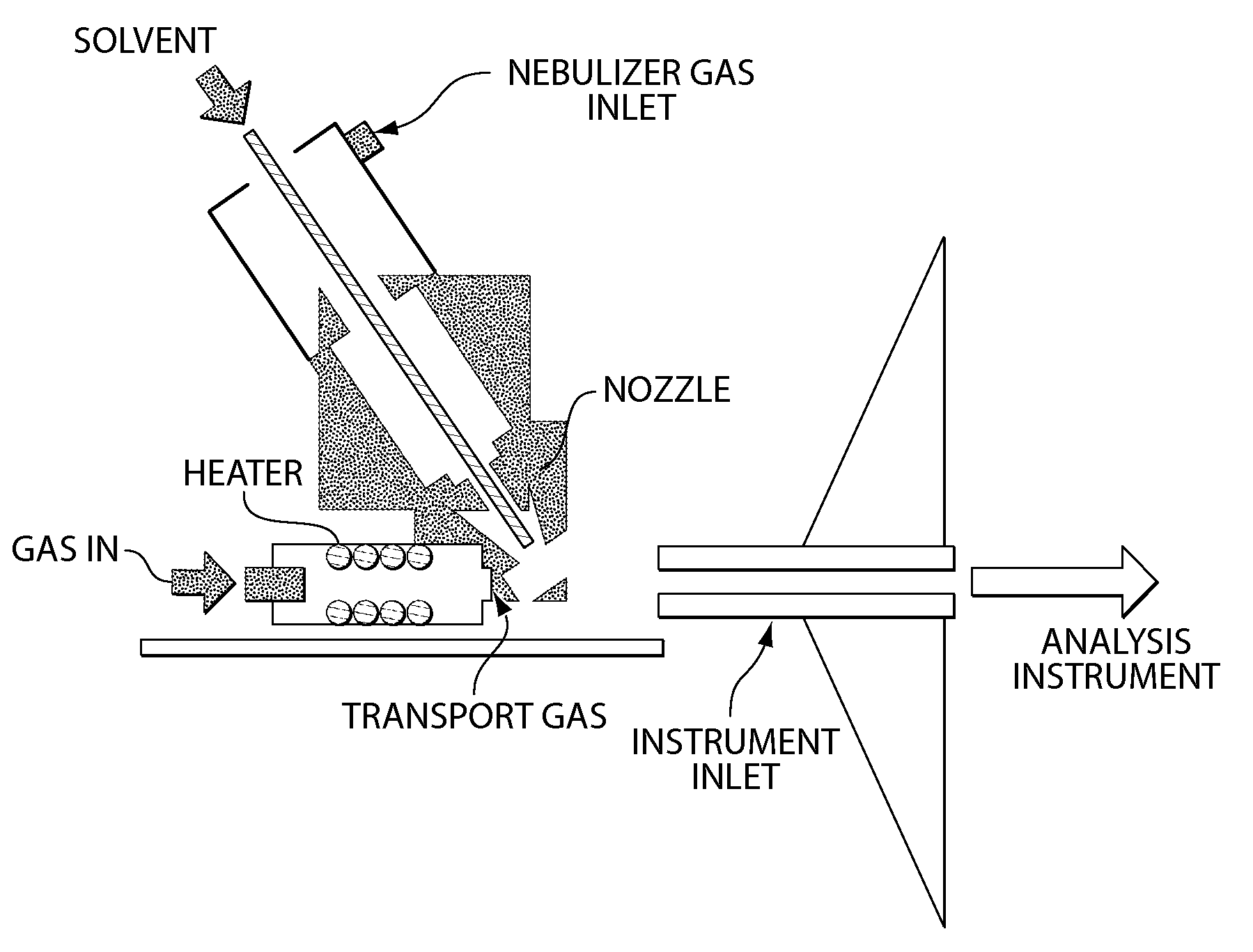
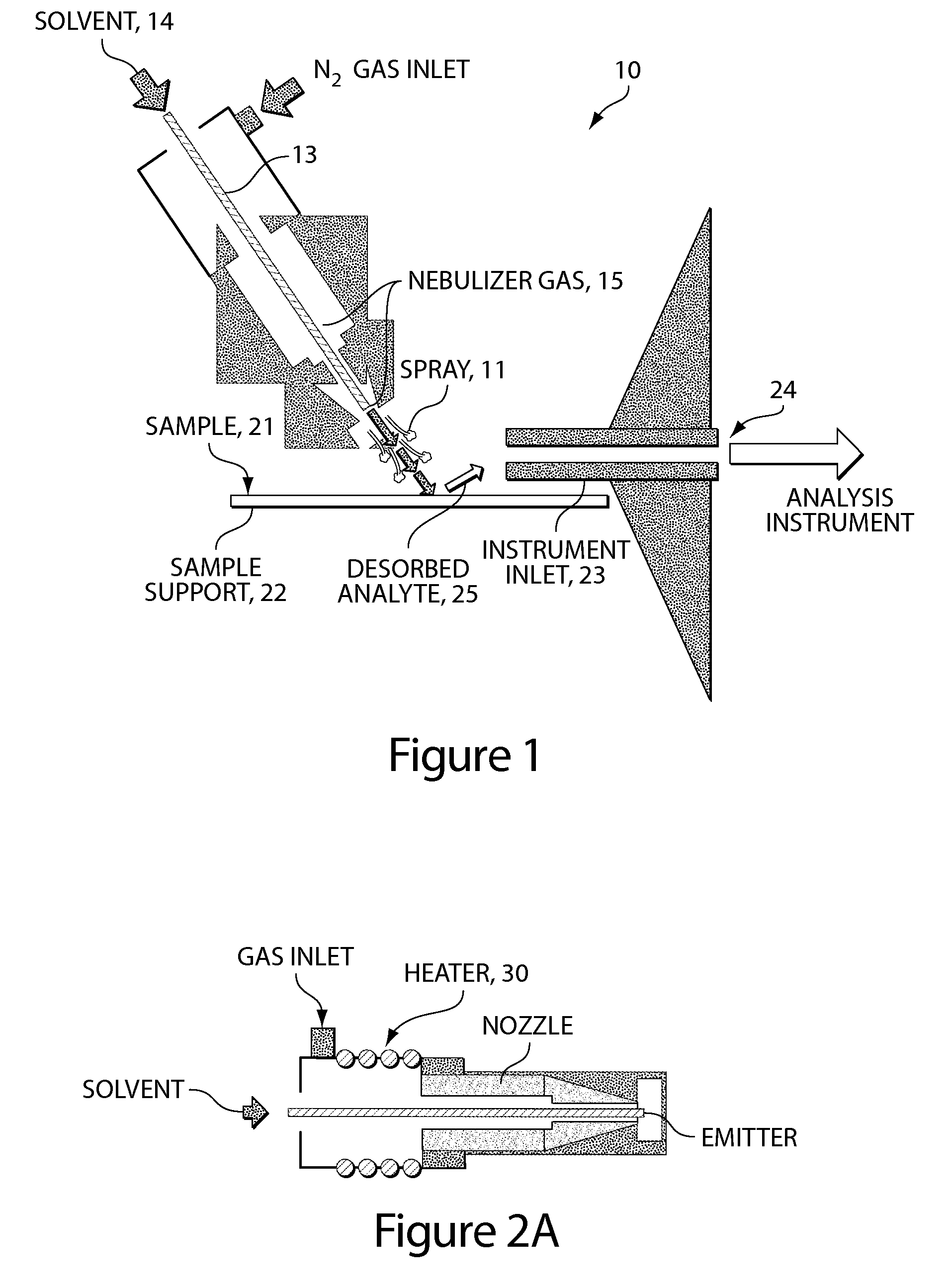
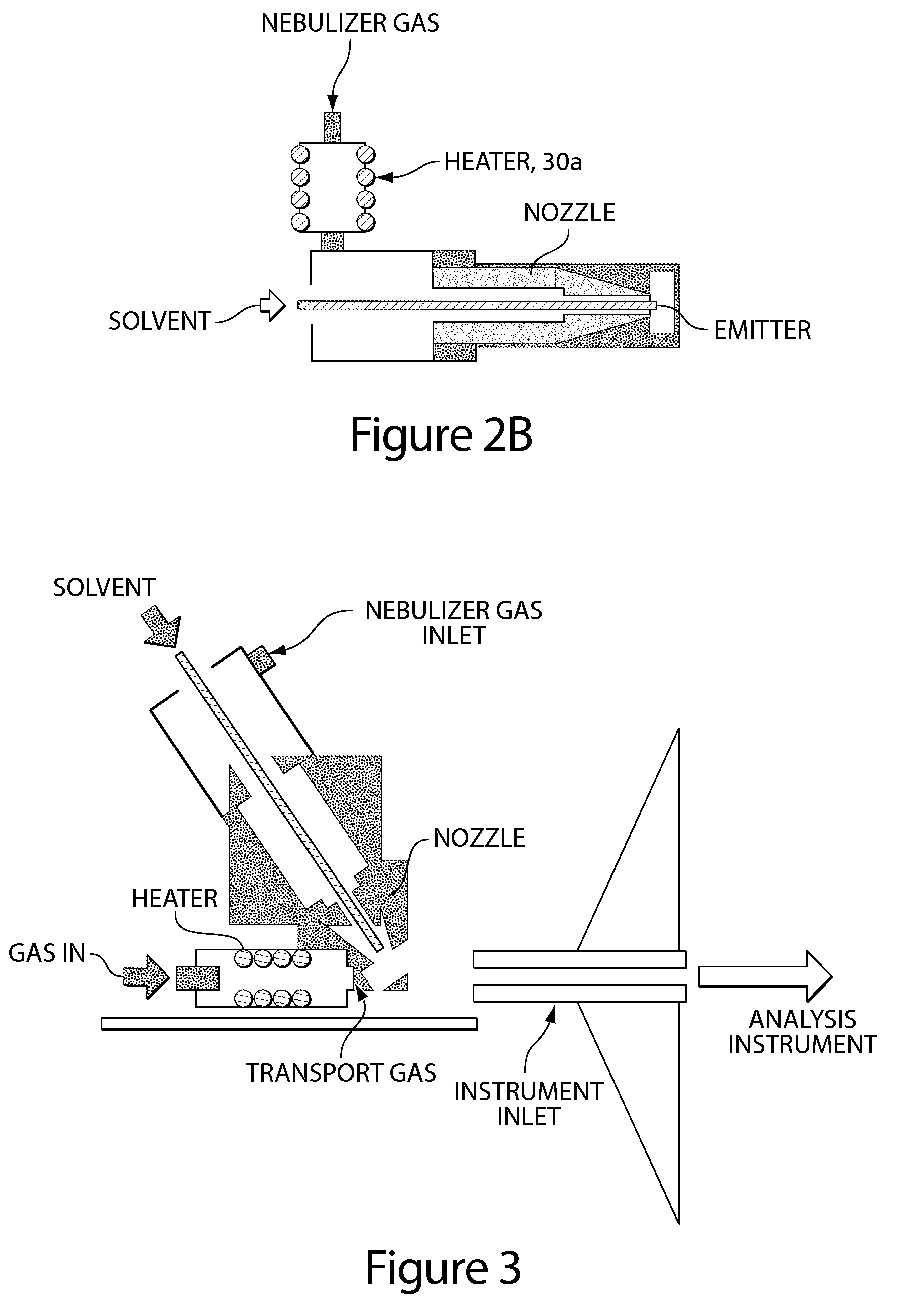
ActiveUS20100078550A1Enhance spot resolutionSmall sizeTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionDesolvationInstrumentation
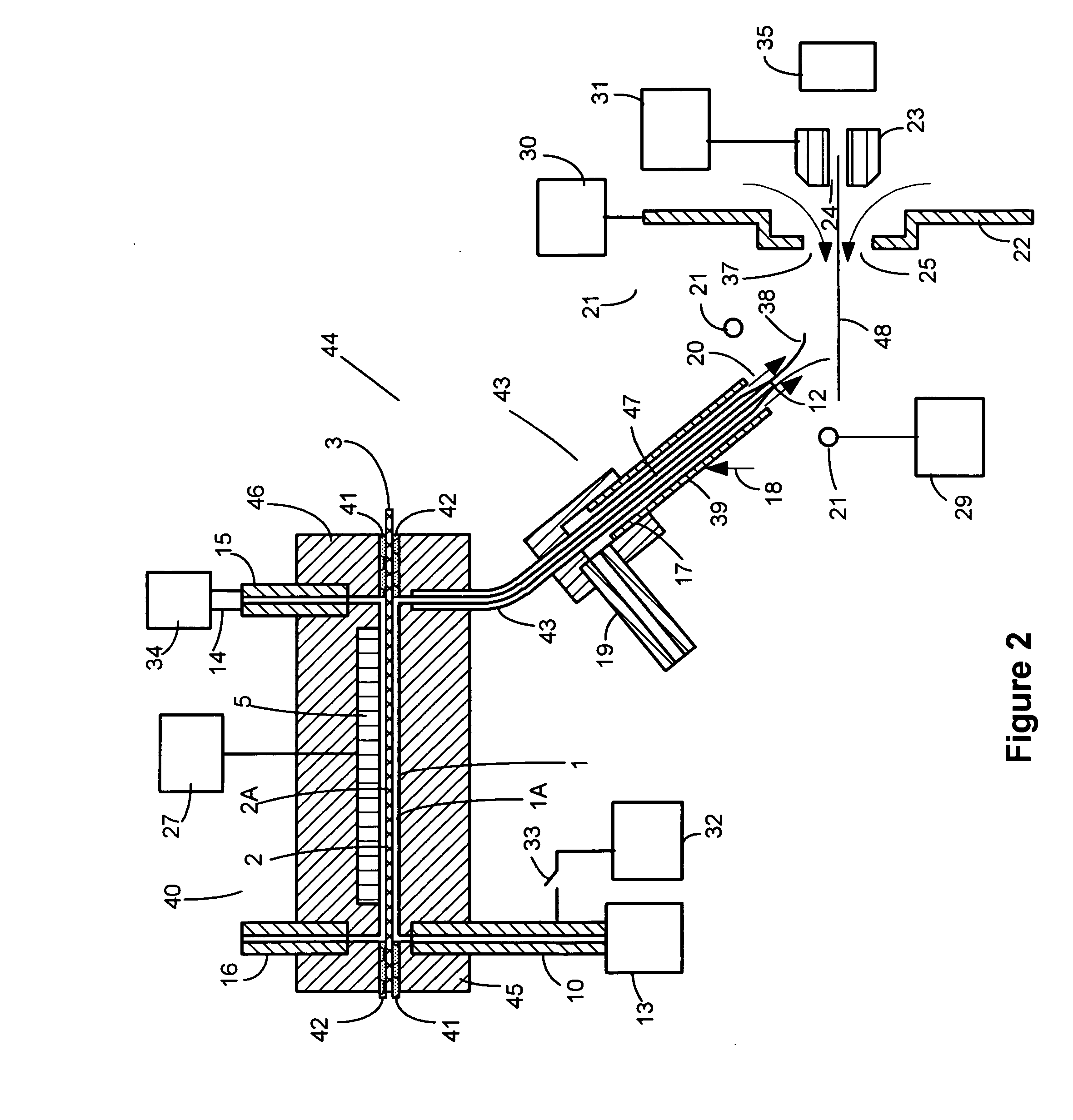
A heated DESI spray device provides improved resolution or control of analyte desorption at a target locus on a sample. Heating controls spot size and enhances resolution in an imaging mode without impairing signal level. Additionally or alternatively the heated DESI spray may control desorption kinetics of a target analyte or otherwise control analyte discrimination in detection mode. One embodiment of the DESI spray is heated by heating nebulizing gas that accompanies the electrosprayed solvent. Another embodiment heats a separate gas stream that transports or directs desorbed material to the ion aperture of an analysis instrument. Heating may reduce size of primary droplets, alter the impact dynamics or the energy delivered by the spray to the surface, reduce size of secondary droplets and / or assure desolvation, improve species selectivity or otherwise affect sampling and enhance the ion signal level.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Ionization by droplet impact
ActiveUS20060108539A1Minimize the numberIncrease kinetic energySamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermal energyMass spectrometric
The invention relates to methods and instruments for ionizing analyte molecules, preferably biomolecules, which are dissolved in liquids or firmly adsorbed on surfaces. Liquids are nebulized at atmospheric pressure by electrospraying. Highly charged microdroplets, which enter the vacuum of the mass spectrometer through the inlet capillary, strike an impact plate when energy is fed in. The repulsive Coulomb force of the charges, the absorption of additional thermal energy and / or the conversion of their kinetic energy into thermal energy cause the microdroplets to burst and evaporate. Analyte molecules which are located in the nebulized liquid or on the impact plate are released in charged form and can be fed to the mass spectrometer for analysis by the extraction and collection effect of an ion funnel operated with RF and DC voltages.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
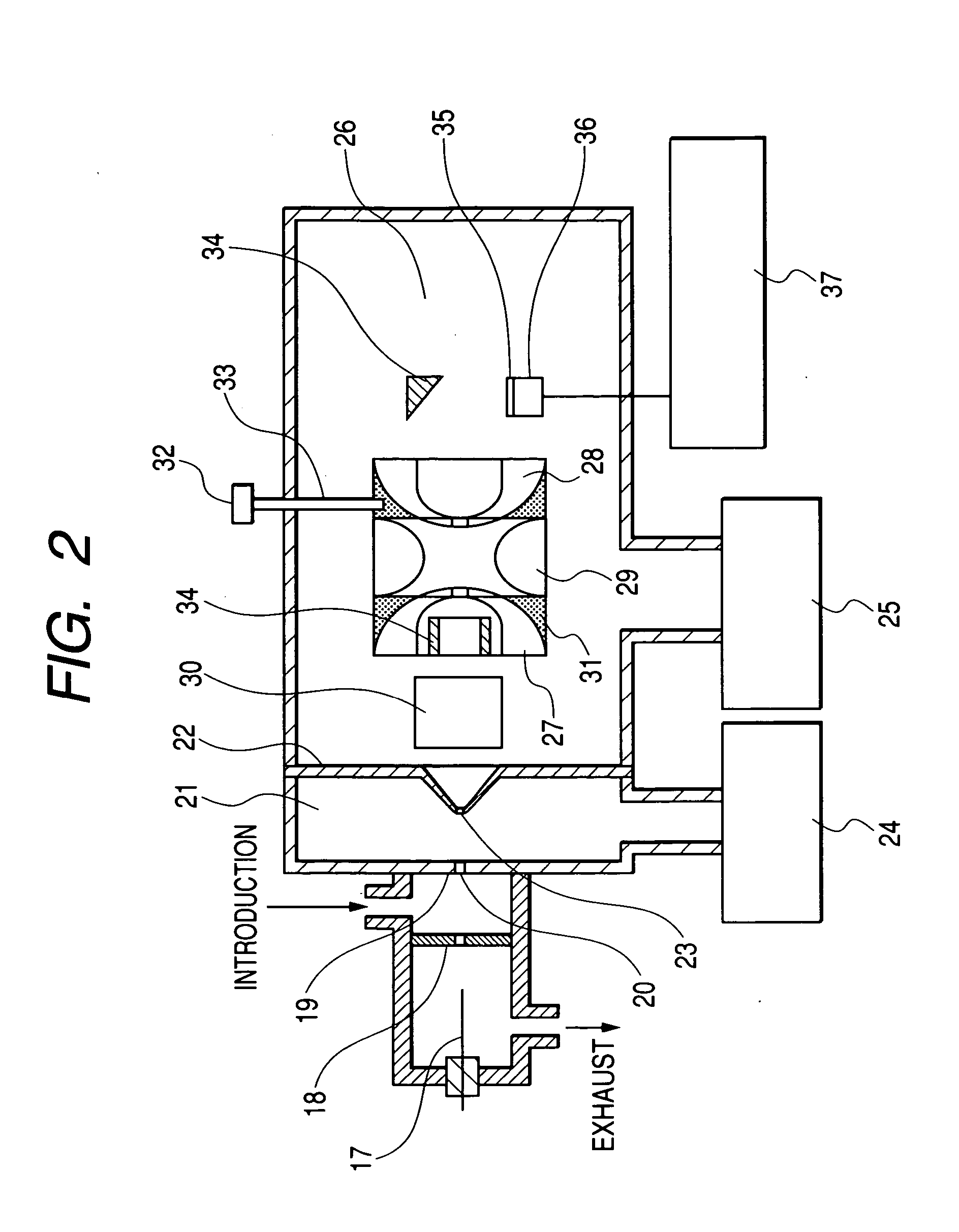
System and method for identification of biological tissues
ActiveUS20120156712A1Easy to detectOverall light weightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCombined useTissue sample
The present invention provides for a system, method, and device for analyzing, localizing and / or identifying tissue types. The method includes analyzing, localizing and / or identifying one or more tissue samples, characterized in that the method comprises: (a) generating gaseous tissue particles from a site in the one or more tissue samples, (b) transporting the gaseous tissue particles from the site to an analyser, (c) using the analyser for generating tissue-related data based on the gaseous tissue particles, and (d) analyzing, localizing and / or identifying the one or more tissue samples based on the tissue-related data. The invention can either be used in close conjunction with a surgical procedure, when one or more surgical tools are an integrated part of ionization, or as a separate mass spectrometric probe for the analysis of one or more tissue parts.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD +1
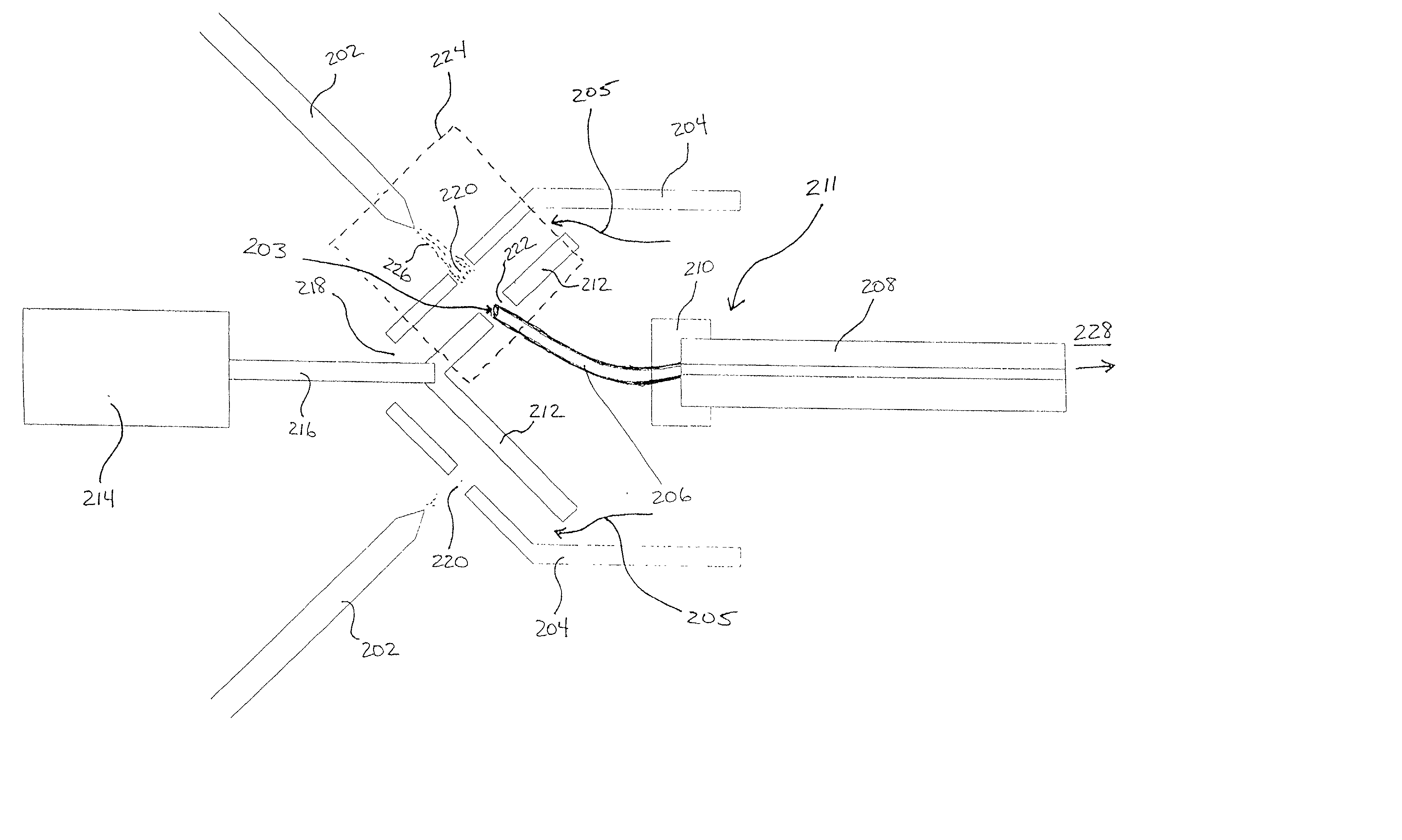
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6744041B2Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
Charged droplet sprayers
ActiveUS20050258360A1Improve performanceOptimize charged droplet spray performanceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesSprayerElectric field
Charged droplet spray is formed from a solution with all or a portion of the charged droplet spray current generated from reduction or oxidation (redox) reactions occurring on surfaces removed from the first or sample solution flow path. In one embodiment of the invention, two solution flow channels are separated by a semipermeable membrane. A first or sample solution flowing through the first solution flow channel exchanges cation or anion charged species through the semipermeable membrane with a second solution or gas flowing through the second flow channel. Charge exchange is driven by the electric field applied at the charged droplet sprayer sample solution outlet. Redox reactions occur at an electrode surface in contact with the second solution. The invention increases the control and range of the Electrospray ionization process during ES / MS operation. Alternative embodiments of the invention provide for conducting redox reactions on conductive surfaces removed from the first or sample solution flow path but not separated by semipermeable membranes.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Apparatus and methods for parallel processing of micro-volume liquid reactions
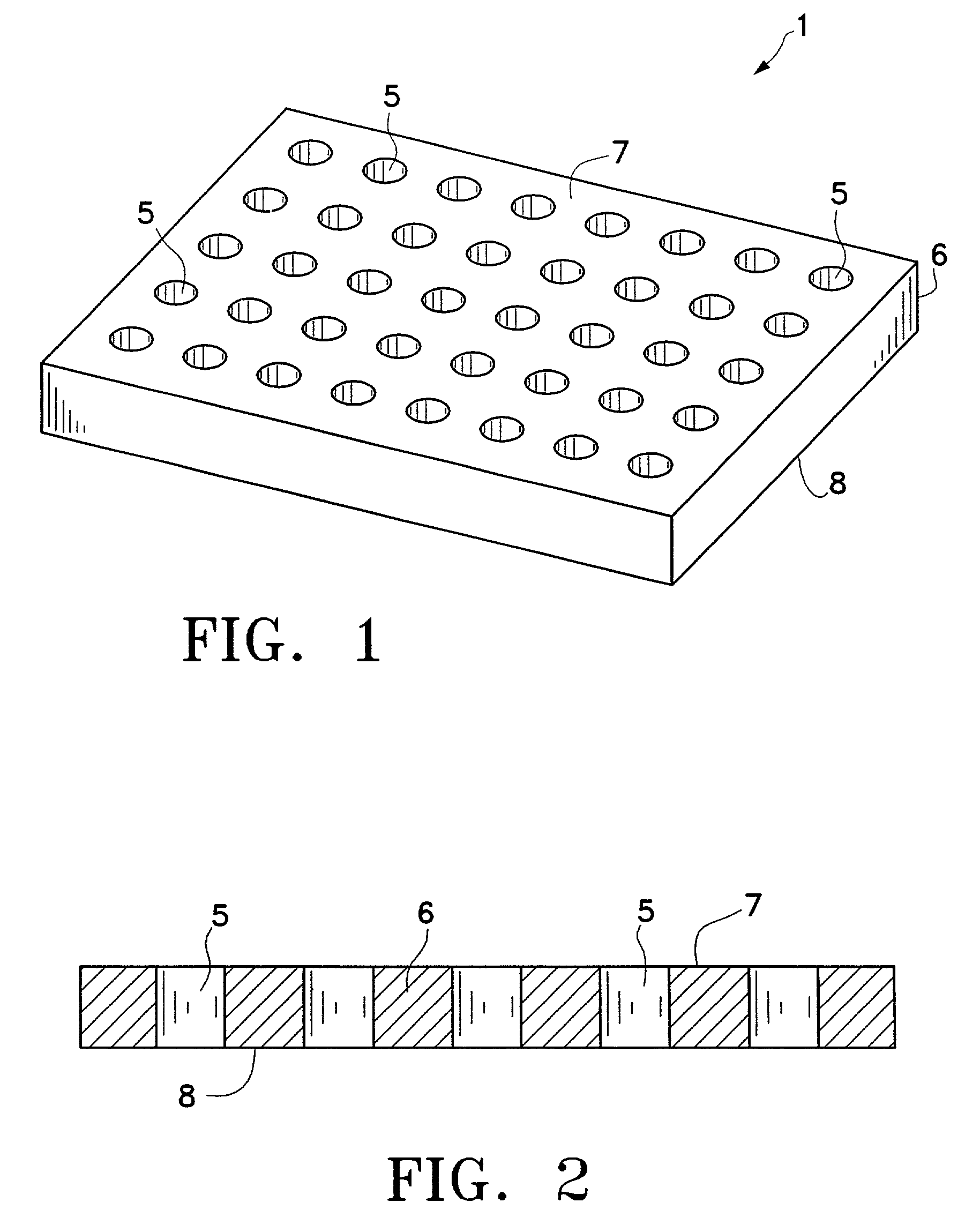
InactiveUS7332271B2Easy to displayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParallel processingMicrochemistry
Disclosed herein are apparatuses and methods for conducting multiple simultaneous micro-volume chemical and biochemical reactions in an array format. In one embodiment, the format comprises an array of microholes in a substrate. Besides serving as an ordered array of sample chambers allowing the performance of multiple parallel reactions, the arrays can be used for reagent storage and transfer, library display, reagent synthesis, assembly of multiple identical reactions, dilution and desalting. Use of the arrays facilitates optical analysis of reactions, and allows optical analysis to be conducted in real time. Included within the invention are kits comprising a microhole apparatus and a reaction component of the method(s) to be carried out in the apparatus.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of selectively inhibiting reaction between ions
InactiveUS7064317B2Avoid reactionSimple methodStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMass-to-charge ratioResonance excitation
A method of inhibiting the reaction between ions of opposite polarity is disclosed. The method includes exposing a population of ions to a resonance excitation frequency during a mass-to-charge altering reaction between a first subpopulation of ions and a second subpopulation of ions, the resonance excitation frequency being tuned to inhibit the mass-to-charge altering reaction between an ion of the first subpopulation of ions having a predetermined mass-to-charge ratio and an ion of the second subpopulation of ions so that when an ion of the first subpopulation of ions attains the predetermined mass-to-charge ratio, the ion having the predetermined mass-to-charge ratio is selectively inhibited from reacting with ions of the second subpopulation of ions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
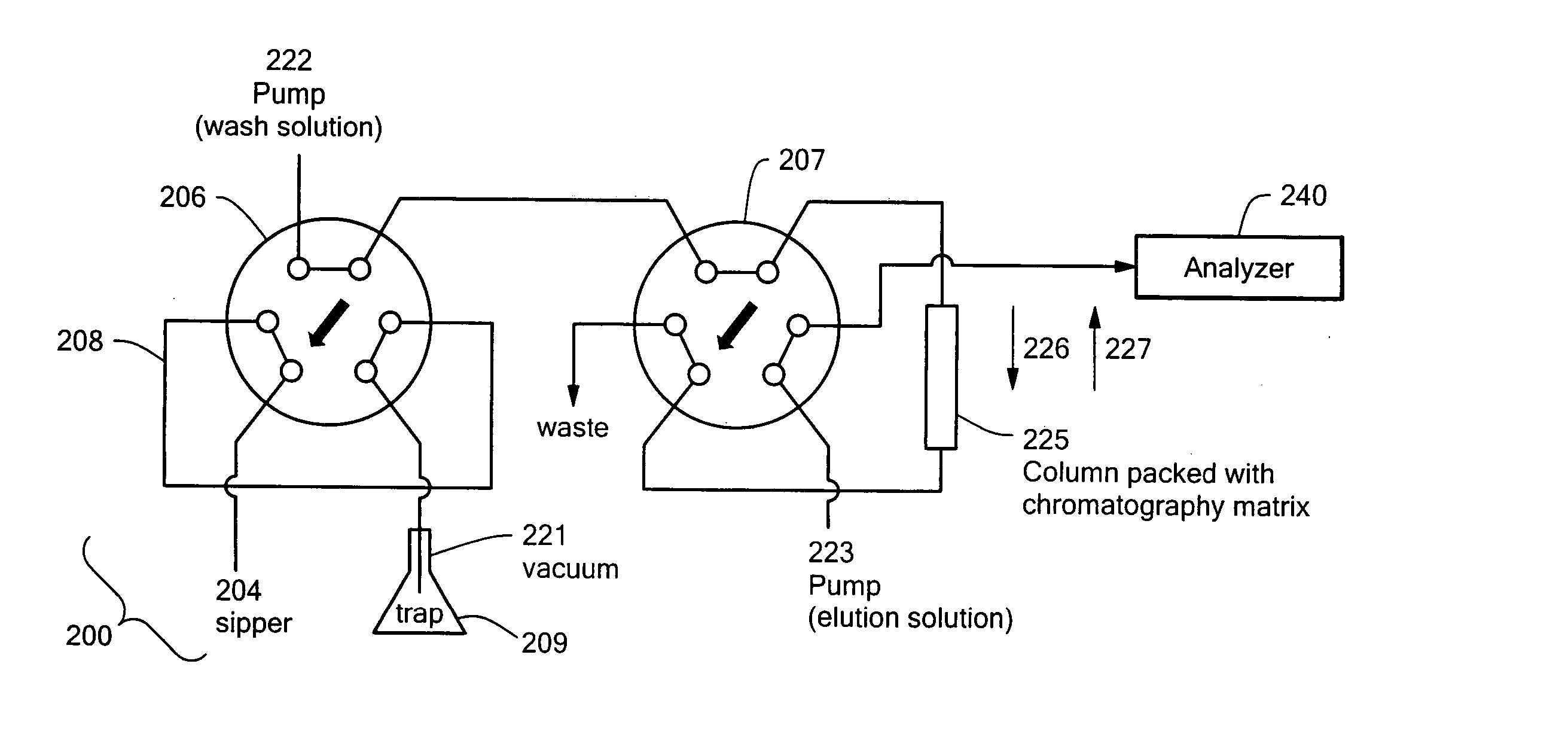
High throughput autosampler
InactiveUS20050194318A1Improve throughputMinimizes sample carryoverSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationAutosamplerHigh flux
An auto-injection system provides high throughput screening of fluidic samples. A sample injection valve has a first position which applies a reduced pressure to a sample sipper tube for aspirating a fluidic sample into the sample sipper tube, and a second position which delivers the fluidic sample to a sample supply loop. A column control valve has a first position which delivers the fluidic sample from the sample supply loop to a sample chromatography column, and a second position which reverses direction of fluid flow through the sample chromatography column to deliver the fluidic sample to a sample analyzer. A wash control valve has a first position which supplies a wash buffer solution to the sample chromatography column in a forward fluid flow direction, and a second position which supplies elution solvent to flush the sample supply loop.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
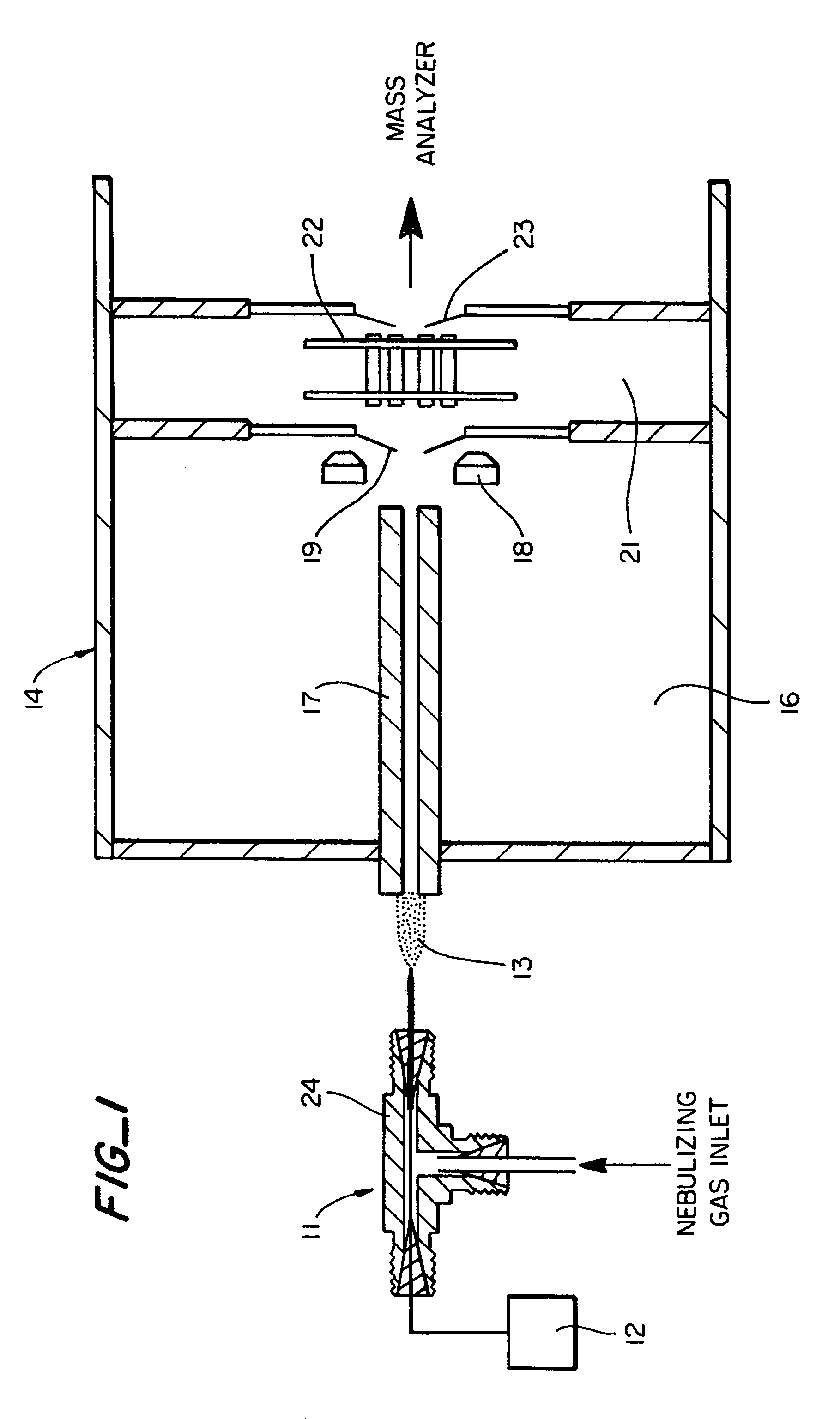
Ion sampling for APPI mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6653626B2Component separationSamples introduction/extractionMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPhysical chemistry
An atmospheric pressure ion source, e.g. for a mass spectrometer, that produces ions by atmospheric pressure photoionization (APPI). It includes a vaporizer, a photon source for photoionizing vapor molecules upon exit from the vaporizer, a passageway for transporting ions to, for example, a mass spectrometer system, and a means for directing the ions into the passageway. The center axis of the vaporizer and the center axis of the passageway form an angle that may be about 90 degrees. Included in the invention is a method for creating ions by atmospheric pressure photoionization along an axis and directing them into a passageway oriented at an angle to that axis.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for aerodynamic ion focusing
InactiveUS6992299B2High sensitivityIncrease the number ofThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersDesolvationHigh velocity
A method and apparatus for focusing ions for delivery to an ion detection device using an aerodynamic ion focusing system that uses a high-velocity converging gas flow at an entrance aperture to focus an ion plume by reducing spreading and increasing desolvation of ions, and wherein a voltage is applied to at least a portion of the aerodynamic ion focusing system to assist in the focusing and delivery of ions to the ion detection device.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Method and apparatus for interfacing separations techniques to MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060266941A1No significant loss in spatial resolution occursAccurate locationSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationThin layerConductive materials
A sample plate for MALDI-TOF mass spectrography is provided which consists of a collimated hole structure intimately connected to a frame. The frame and at least one surface of the collimated hole structure are electrically conductive. The collimated hole structure may be formed from any material including glass, plastic, and metal and at least one surface may be rendered conductive by application of a thin layer of an electrically conductive material such as a metal, metal oxide, carbon, or organic or inorganic conductor or semi-conductor. The conductive surface is maintained in good electrical conduct with the conductive frame.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
Gold implantation/deposition of biological samples for laser desorption three dimensional depth profiling of tissues
ActiveUS20050035284A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionDesorptionIon implantation
The present invention enhances the laser desorption of biological molecular ions from surfaces by creating a surface localized MALDI particle matrix by ion implantation of low energy ionized clusters (gold, aluminum, etc.) or chemically derivatized clusters into the near surface region of the sample. MALDI analysis of the intact biomolecules on the surface or within a narrow subsurface region defined by the implantation range of the ions can then be performed by laser desorption into a mass spectrometer or, in a preferred embodiment, into a combined ion mobility orthogonal time of flight mass spectrometer.
Owner:IONWERKS
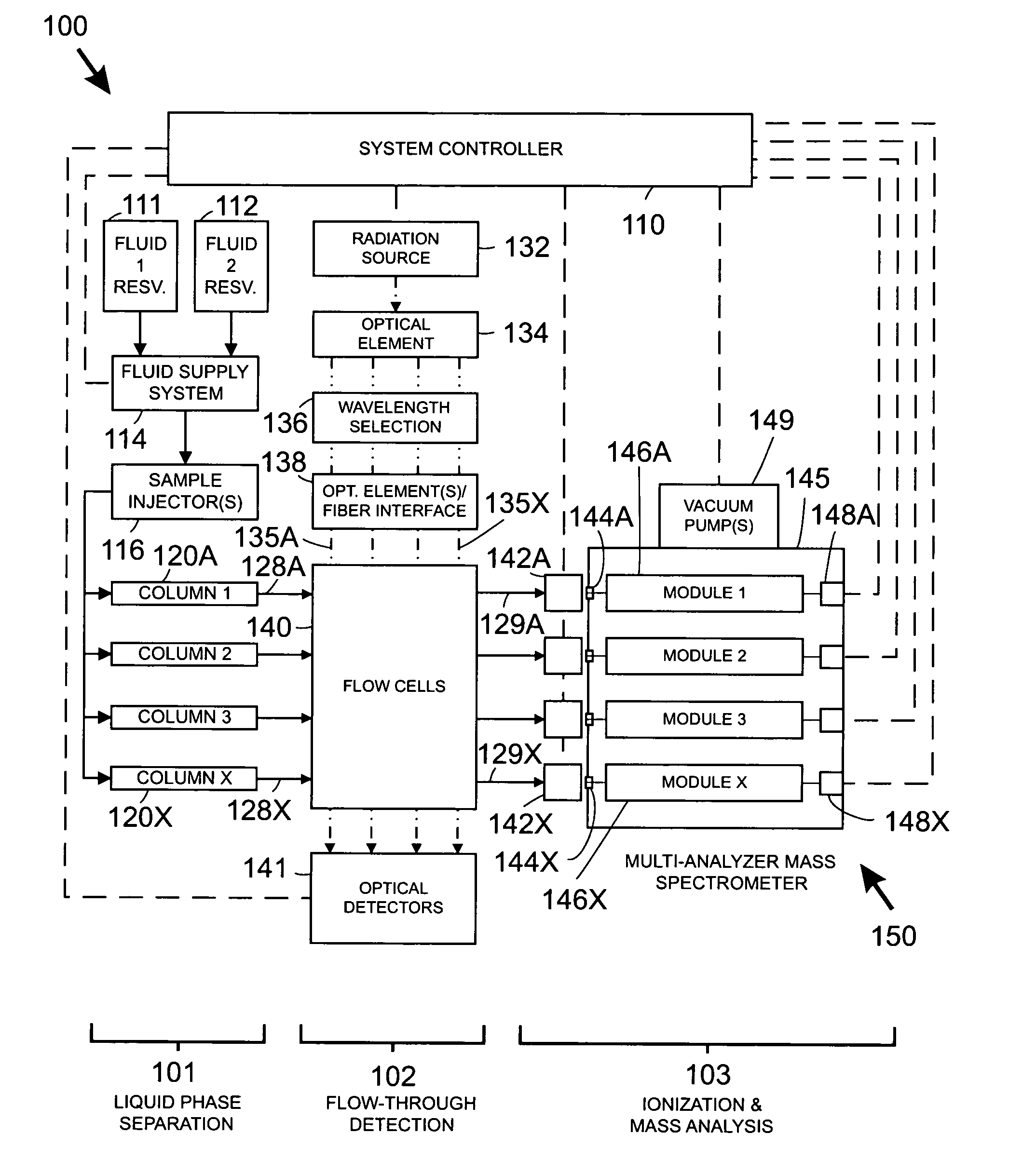
High throughput systems and methods for parallel sample analysis
Systems and methods for analyzing multiple samples in parallel using mass spectrometry preferably coupled with fluid phase separation techniques are provided. A modular mass spectrometer includes a vacuum enclosure, multiple sample inlets, multiple common vacuum pumping elements, and multiple mass analysis modules disposed substantially within the enclosure, with each module preferably including a mass analyzer and a transducer. In one embodiment, the modules mate with the vacuum enclosure to define multiple sequential vacuum regions, with each vacuum region having an associated common vacuum pumping element. At least one multi-pole ion transfer optic element is preferably associated with each module. Fluid phase separation devices may include microfluidic devices utilizing chromatographic, electrophoretic, or other separation methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
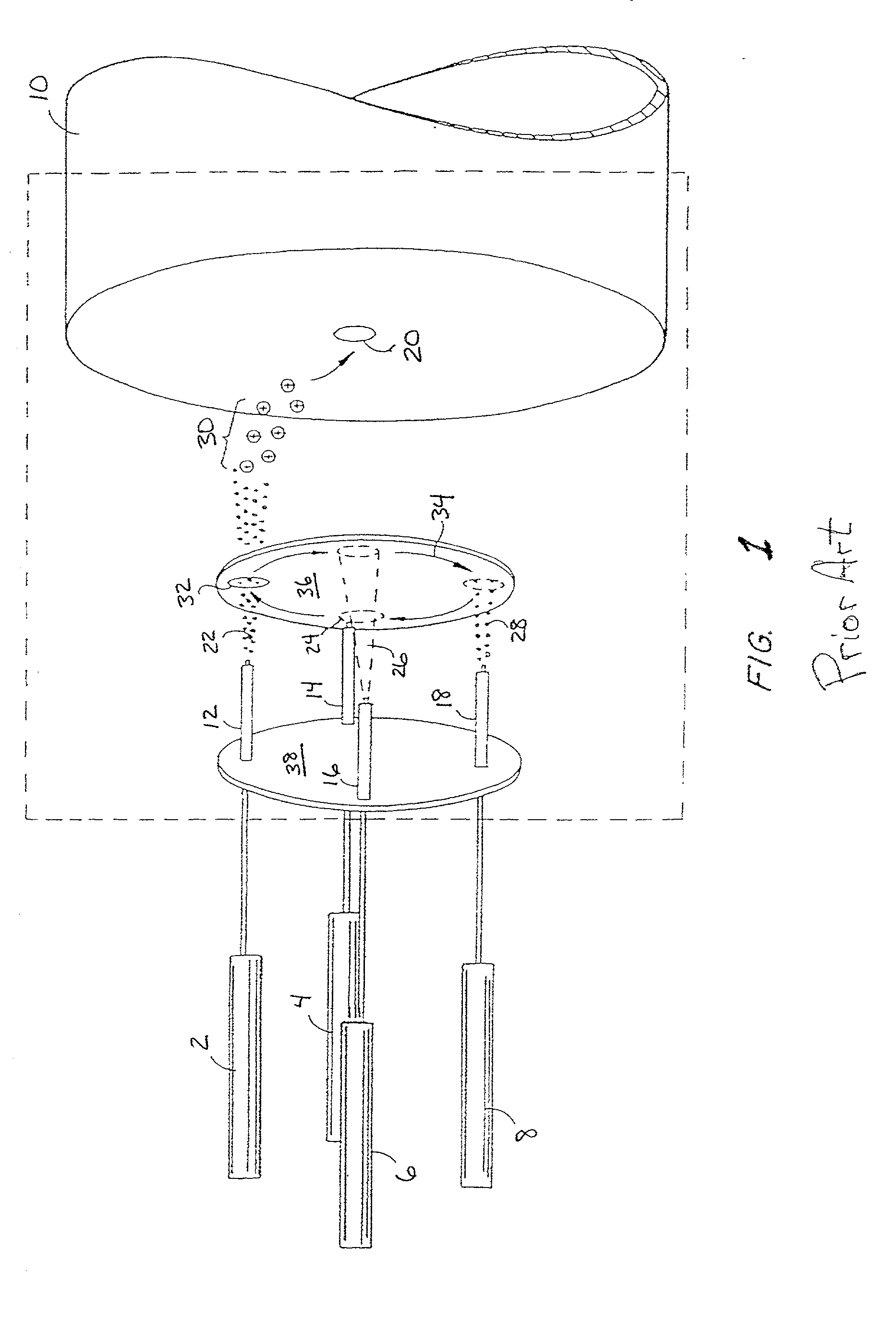
Multi-source ion funnel
InactiveUS6979816B2Enhance ion conductanceMany limitationStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsHigh pressureDc voltage
A method for introducing ions generated in a region of relatively high pressure into a region of relatively low pressure by providing at least two electrospray ion sources, providing at least two capillary inlets configured to direct ions generated by the electrospray sources into and through each of the capillary inlets, providing at least two sets of primary elements having apertures, each set of elements having a receiving end and an emitting end, the primary sets of elements configured to receive a ions from the capillary inlets at the receiving ends, and providing a secondary set of elements having apertures having a receiving end and an emitting end, the secondary set of elements configured to receive said ions from the emitting end of the primary sets of elements and emit said ions from said emitting end of the secondary set of elements. The method may further include the step of providing at least one jet disturber positioned within at least one of the sets of primary elements, providing a voltage, such as a dc voltage, in the jet disturber, thereby adjusting the transmission of ions through at least one of the sets of primary elements.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Capillary ion delivery device and method for mass spectroscopy
InactiveUS6806468B2Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometrySpectroscopy
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Probes for a gas phase ion spectrometer
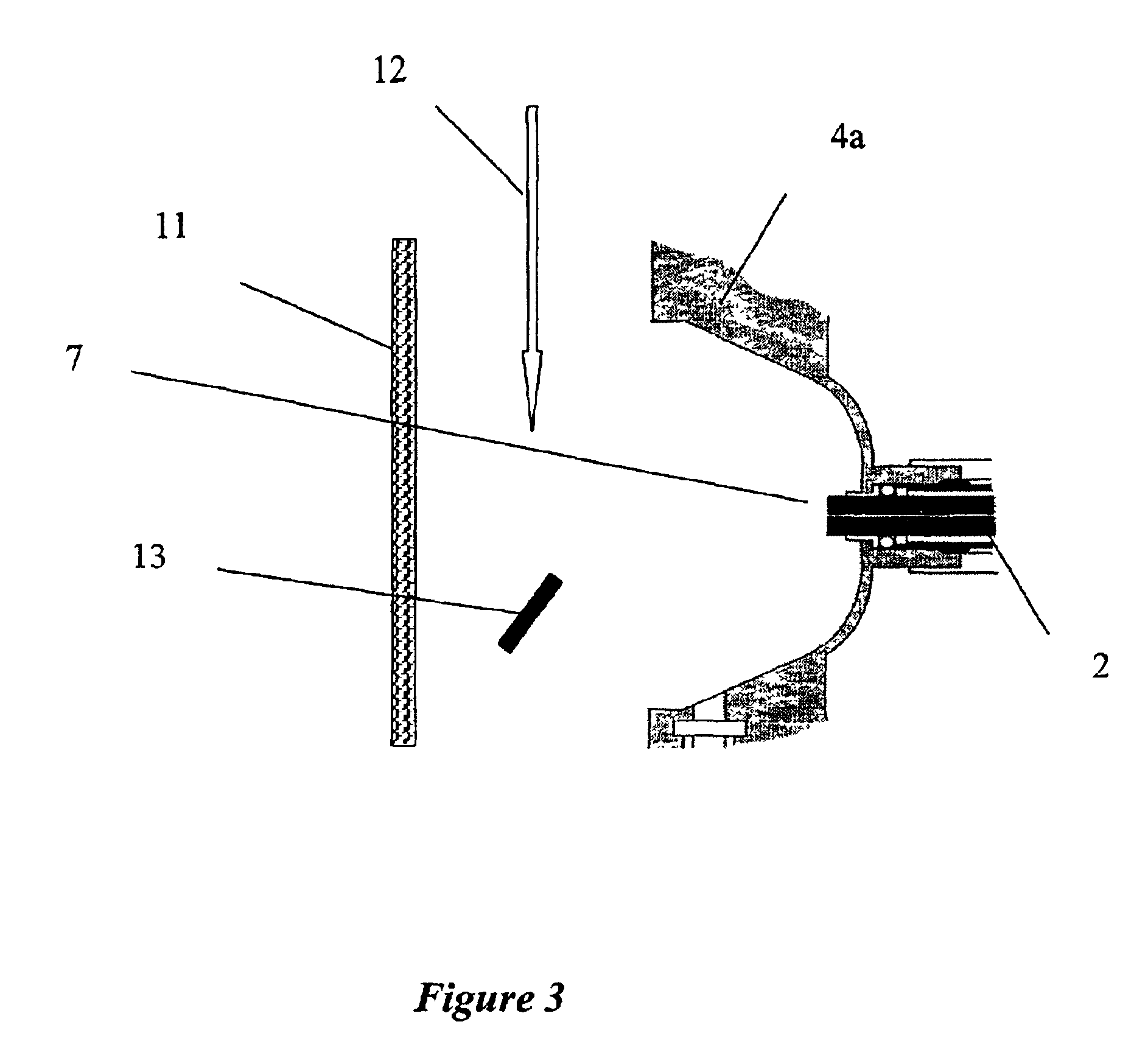
InactiveUS6897072B1Large capacityHigh detection sensitivitySamples introduction/extractionPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteGas phase
The invention provides a probe and a method of making the probe that is removably insertable into a gas phase ion spectrometer, the probe comprising a substrate having a surface and a hydrogel material on the surface, the hydrogel material comprising binding functionalities for binding with an analyte detectable by the gas phase ion spectrometer. The invention also provides a probe and a method of making the probe that is removably insertable into a gas phase ion spectrometer, the probe comprising a substrate having a surface and a plurality of particles that are uniform in diameter on the surface, the particles comprising binding functionalities for binding with an analyte detectable by the gas phase ion spectrometer. Further, the invention provides a system comprising the probe of the present invention and a gas phase ion spectrometer comprising an energy source that directs light to the probe surface to desorb an analyte and a detector in communication with the probe surface that detects the desorbed analyte. The invention also provides a method for desorbing an analyte from a probe surface, the method comprising exposing the binding functionalities to a sample containing an analyte under conditions to allow binding between the analyte and the binding functionalities, and desorbing the analyte from the probe by gas phase ion spectrometry.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
High throughput systems and methods for parallel sample analysis
Systems for analyzing multiple samples in parallel using mass spectrometric preferably coupled with fluid phase separation techniques are provided. A multi-analyzer mass spectrometer includes multiple inlets, multiple mass analyzers, and multiple transducers to conduct mass analyses of multiple samples in parallel. A modular mass analyzer may include a vacuum enclosure, a chassis, and multiple mass analysis modules disposed within the chassis. Modules are preferably disposed in a spatially compact two-dimensional array. A common multi-stage vacuum system may be utilized in conjunction with baffles or partitions disposed within and between modules to maintain differential vacuum conditions within the spectrometer utilizing a minimum number of pumps. Common control inputs may be provided to multiple modules or other components within a multi-analyzer spectrometer. Fluid phase separation devices for use with a multi-analyzer spectrometer may be microfluidic devices utilizing chromatographic, electrophoretic, or other separation methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
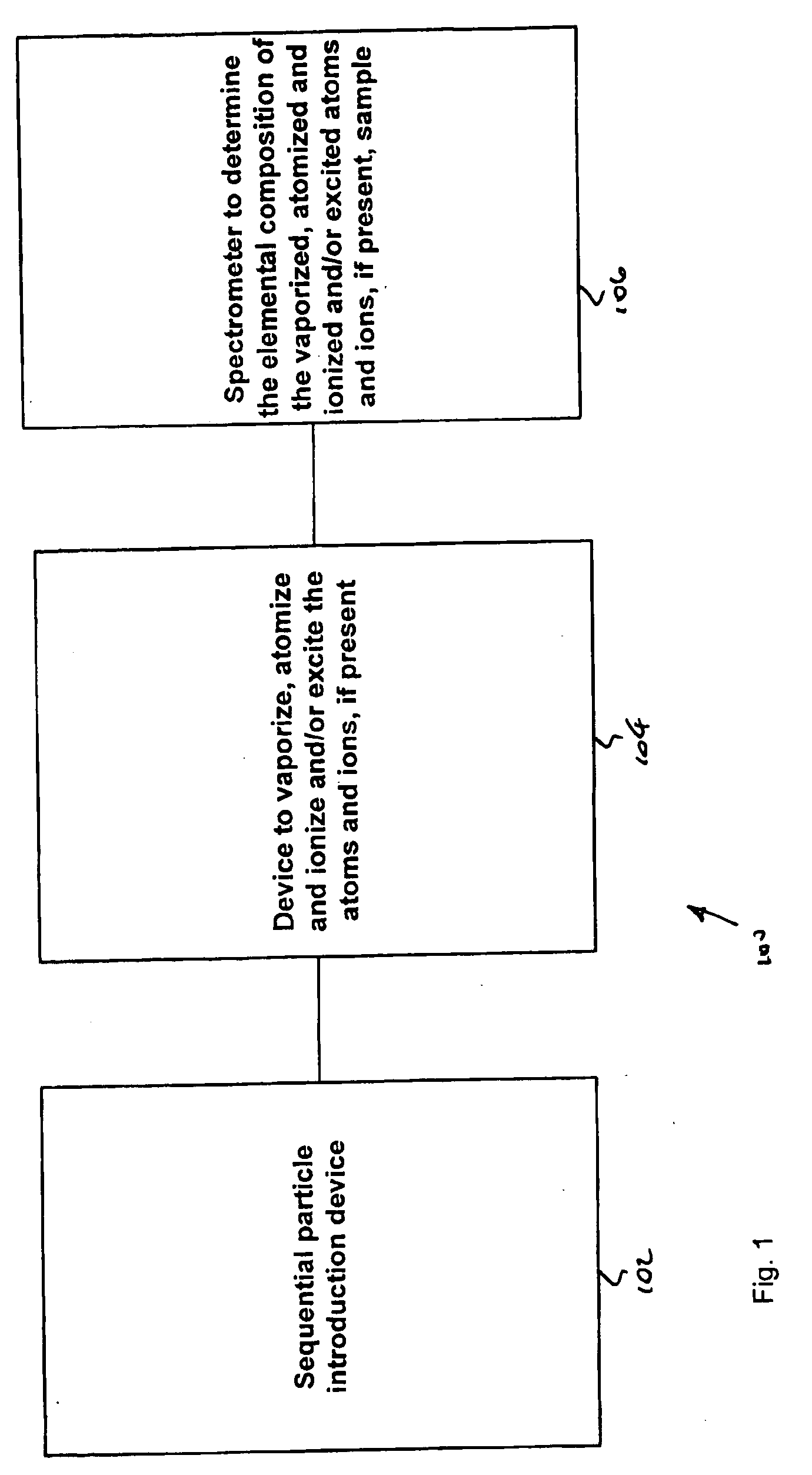
Method and apparatus for flow cytometry linked with elemental analysis
An apparatus (100) for sequentially analyzing particles such as single cells or single beads, by spectrometry. The apparatus, an elemental flow cytometer, includes means (102) for sequential particle introduction, means (104) to vaporize, atomize and excite or ionize the particles, or an elemental tag associated with an analyte on the particles, and means (106) to analyze the elemental composition of the vaporized, atomized and excited or ionized particles, or an elemental tag associated with the particles. Methods for sequentially analyzing particles such as singe cells or single beads by spectrometry are also described.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
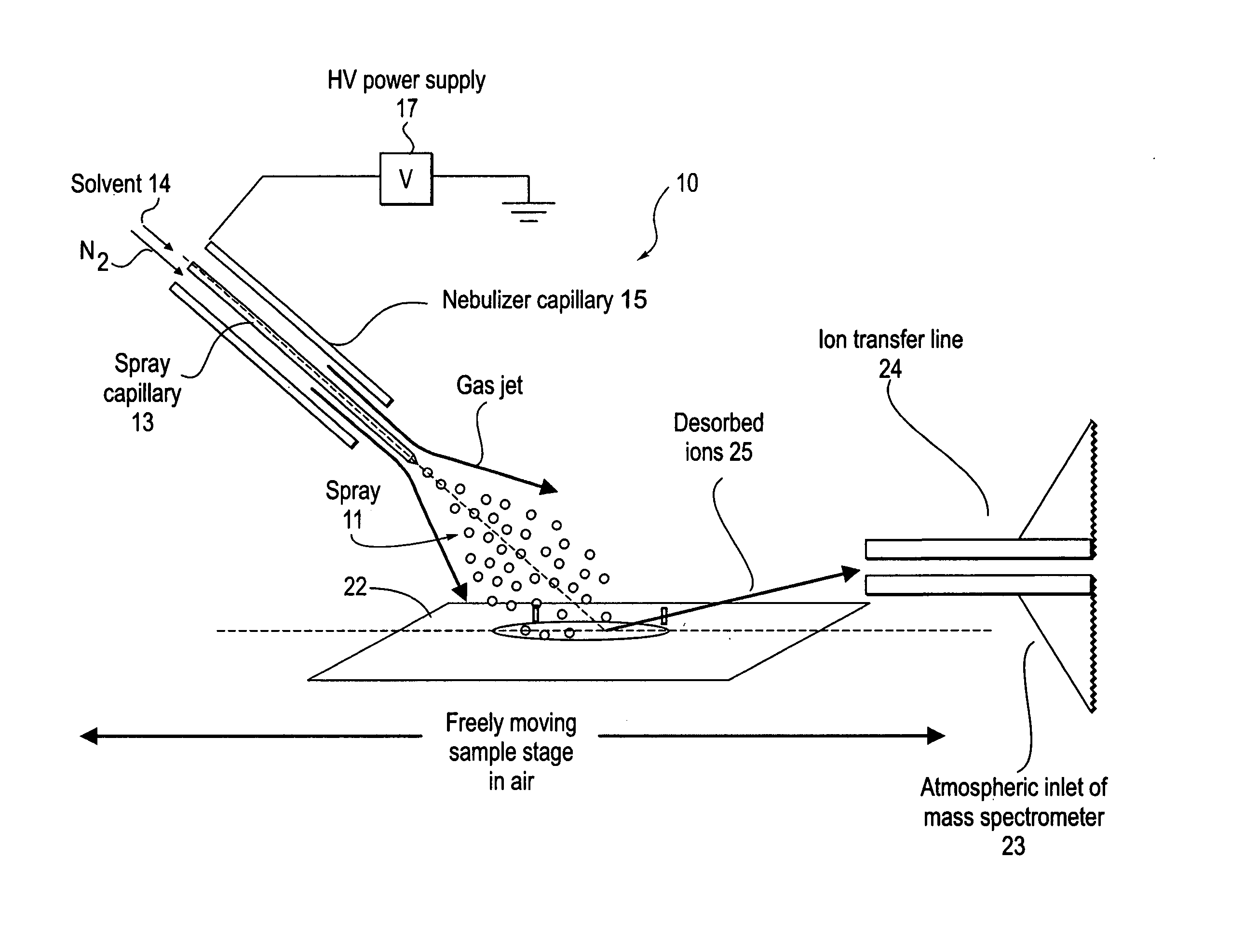
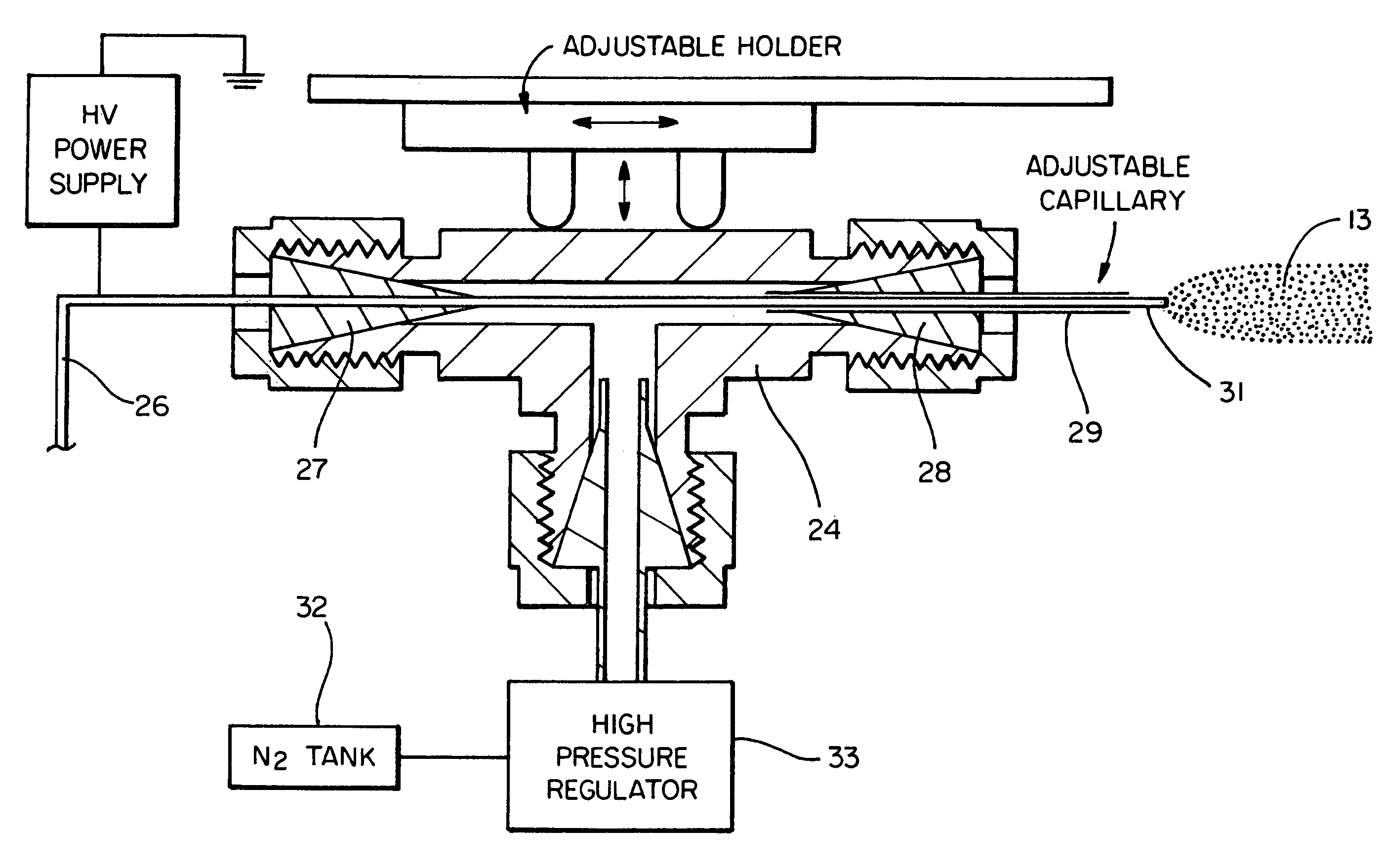
Electrosonic spray ionization method and device for the atmospheric ionization of molecules
There is described a device and method for generating gaseous ions of a sample material such as molecules in solution at atmospheric pressure. The device includes a conduit for receiving a solution containing the material to be ionized and form a stream. A jet of gas at supersonic velocity is directed at the stream and interacts therewith. Droplets are formed and by the adiabatic expansion of the gas and vigorous evaporation of the solution gaseous ions are generated. In the method a stream of the sample solution is delivered from a conduit with an electric potential. A gas jet at supersonic velocity interacts with the delivered solution and through the action of adiabatic expansion of the gas and evaporation of the solution gaseous ions are formed.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Means and method for multiplexing sprays in an electrospray ionization source
InactiveUS20020121598A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationESI mass spectrometryMultiplexing
A means and method are disclosed for multiplexing a plurality of samples from multiple sprayer devices to be efficiently transferred to a mass analyzer for subsequent analysis. Sample sprays are formed from a plurality of sprayers, which are desolvated to form the sample ions. The sample ions are then selected from one of the sprayers for transportation into a mass analyzer. To accomplish this, the apparatus of the invention comprises a multi-part capillary wherein a first section thereof is connected to a motor which is able to move this first section from one sprayer to the next. This first section may be a flexible tube-like structure loosely mounted in an aperture of a cone-shaped end of a motor which rotates such that the sampling orifice may be aligned with different sprayers at different times to sequentially and repetitively sample ions produced by each of the plurality of sprayers.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
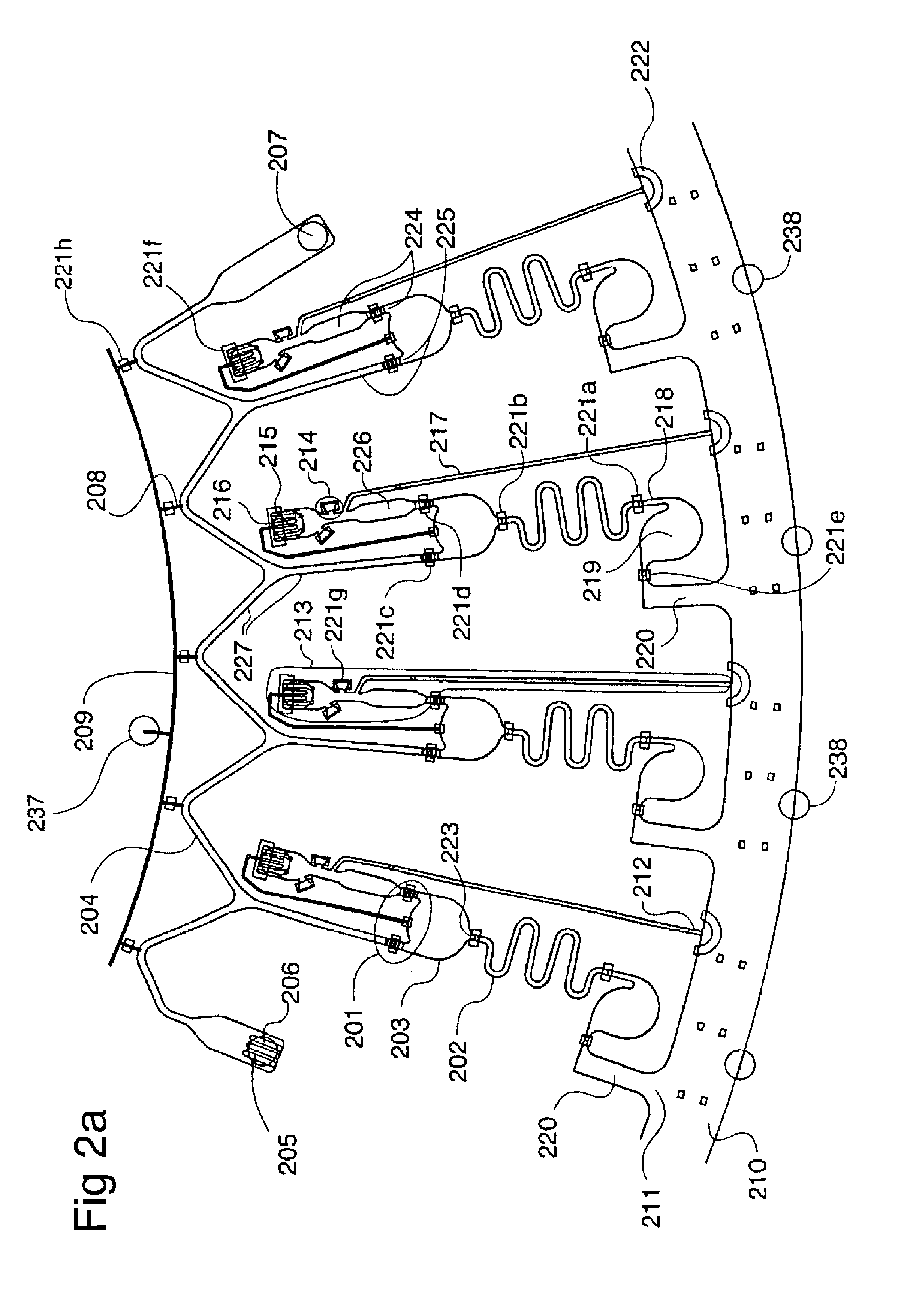
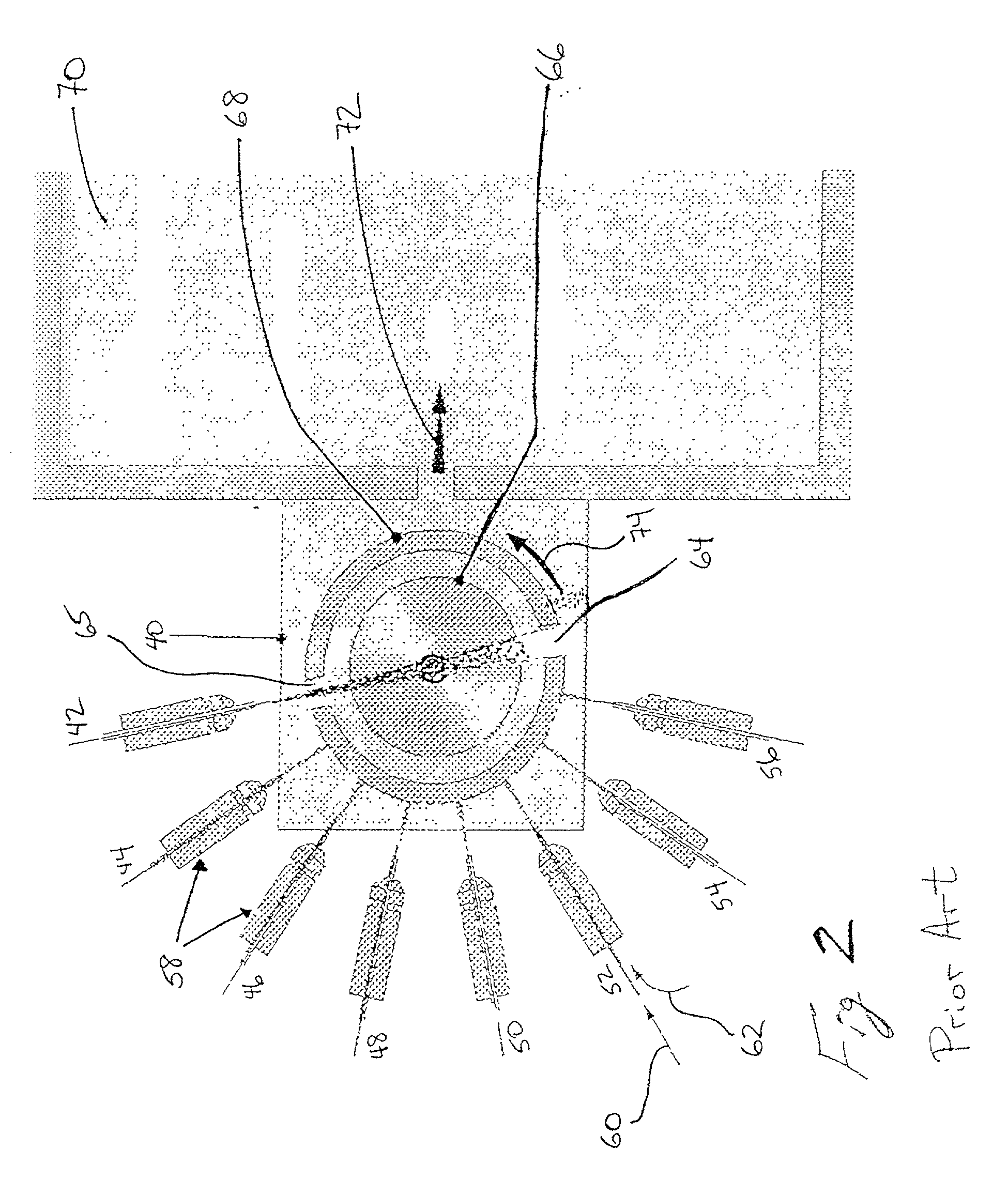
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
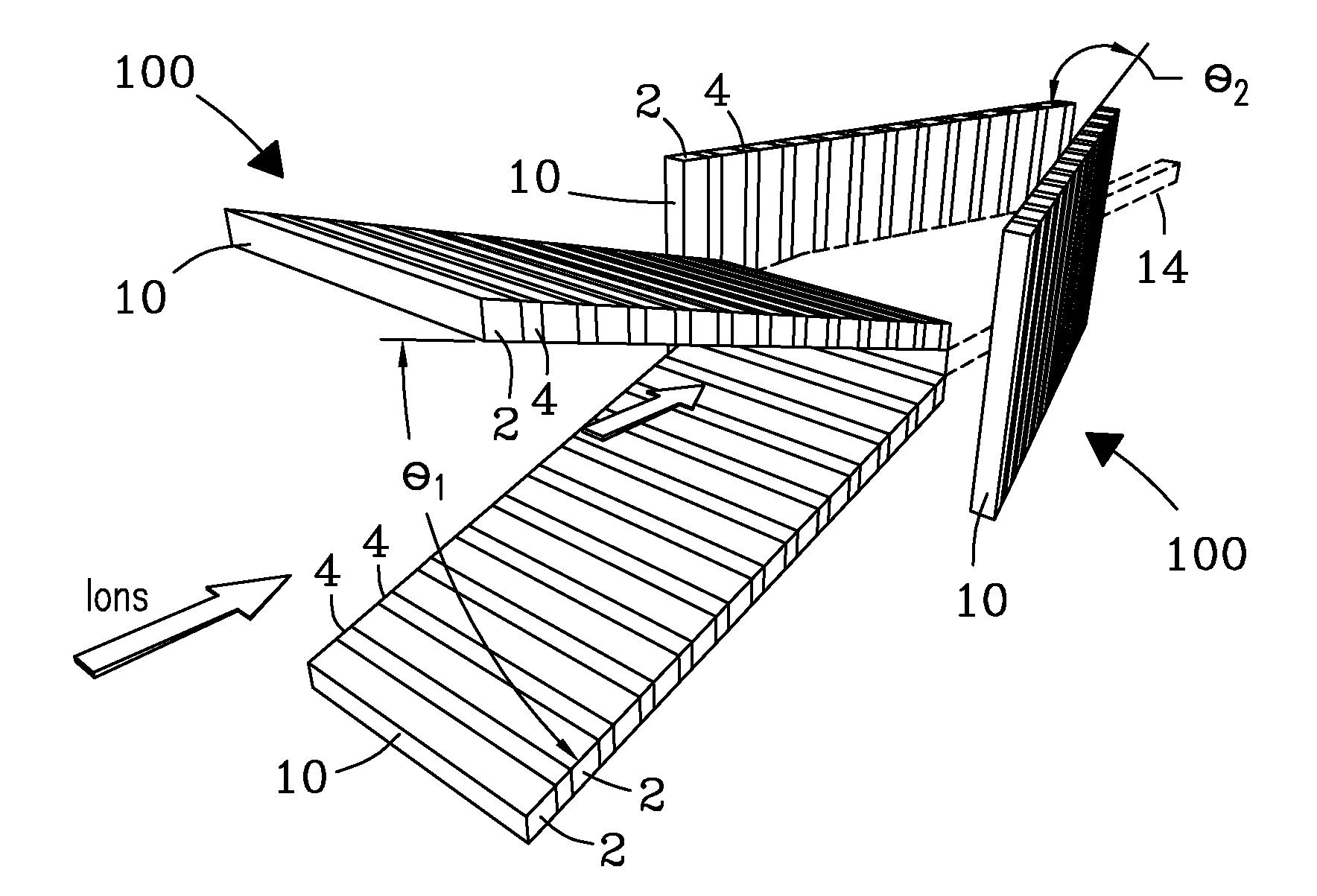
ActiveUS20120261570A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
Electrodynamic on funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective on focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and on mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress on beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com