Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2622 results about "Isotope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, and consequently in nucleon number. All isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in each atom.
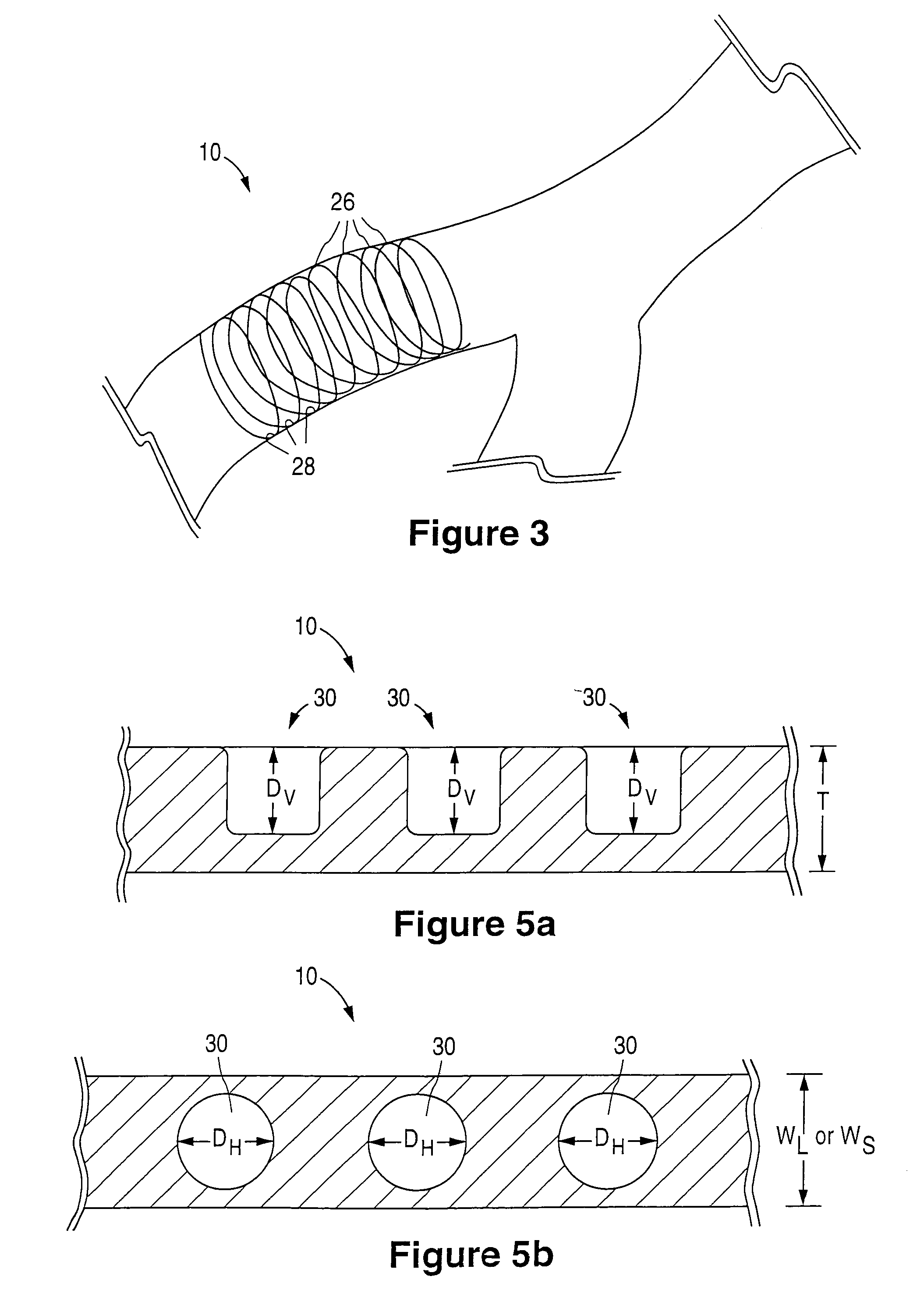
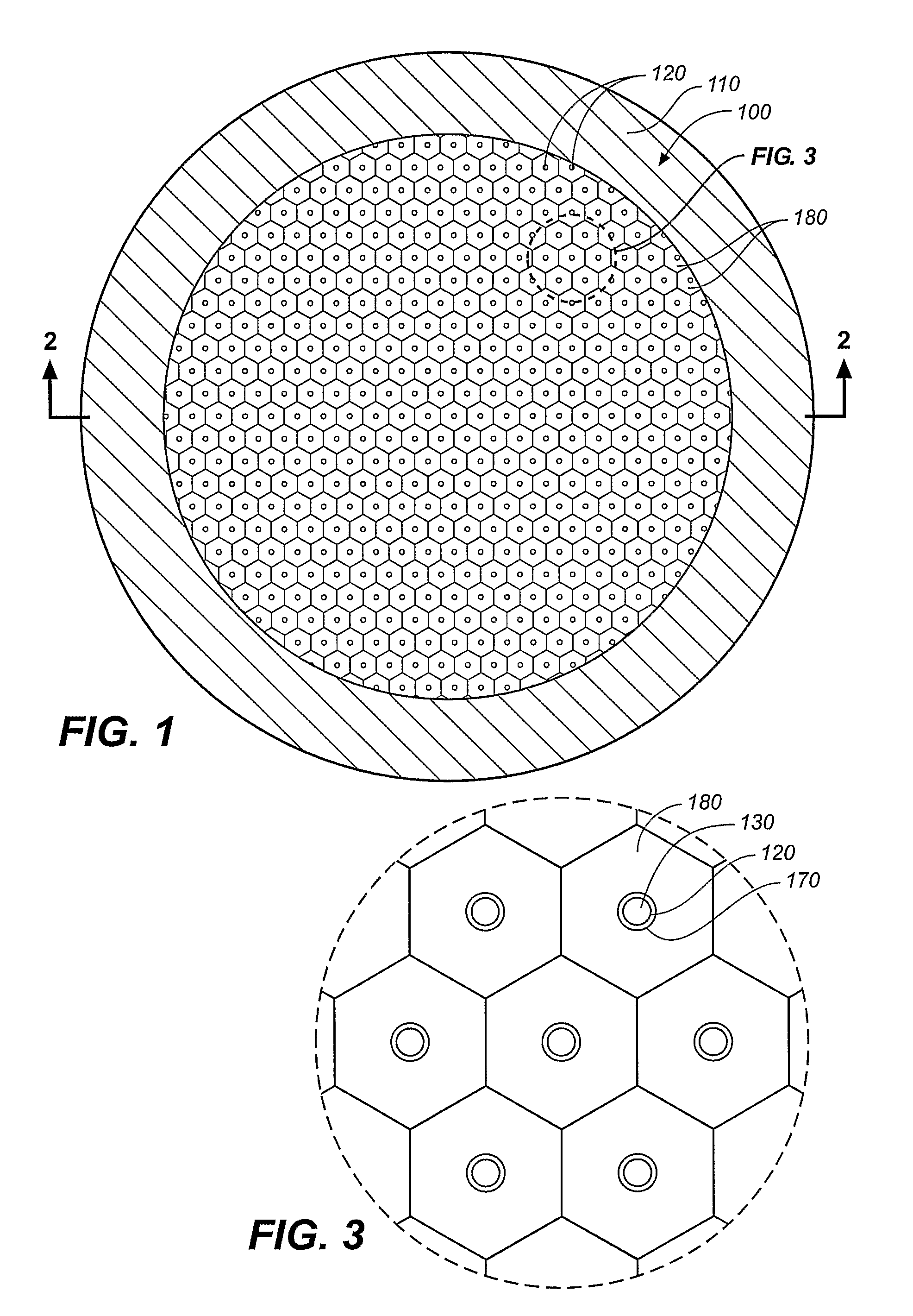
Microparticle coated medical device
A drug-loaded microparticle is applied to a medical device for subsequent application to biological tissues. A method of formulating a drug-loaded microparticle and applying it to the surface of a medical device, such as a stent, is disclosed. The drug-loaded microparticle is formulated by combining a drug with various chemical solutions. Specified sizes of the microparticles and amounts of drug(s) contained within the microparticles may be varied by altering the proportions of the chemicals / solutions. In addition to various drugs, therapeutic substances and radioactive isotopes may also be loaded into the microparticles. The drug-loaded microparticle are suspended in a polymer solution forming a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix may be applied to the entire surface or only selected portions of the medical device via dipping, spraying or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
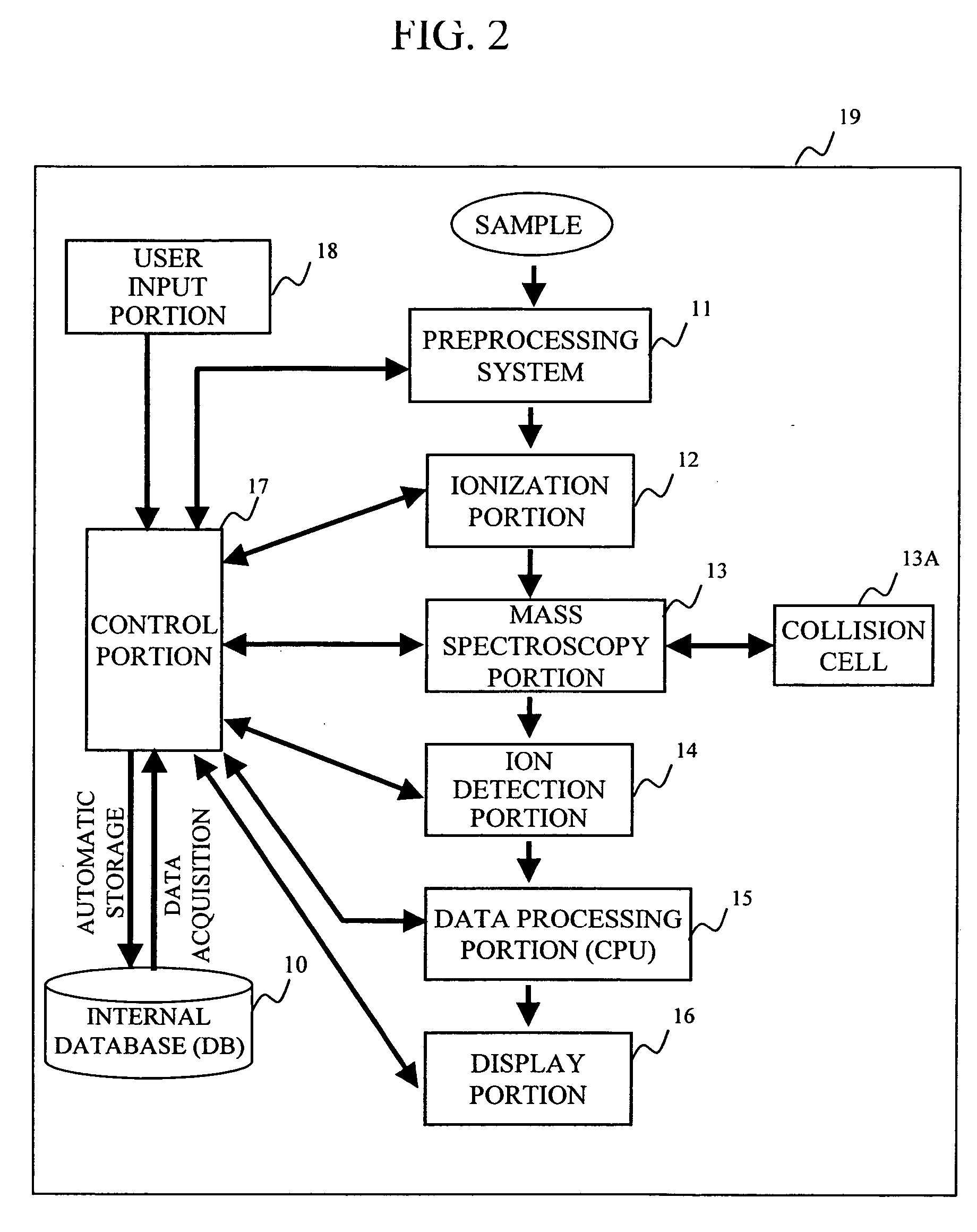
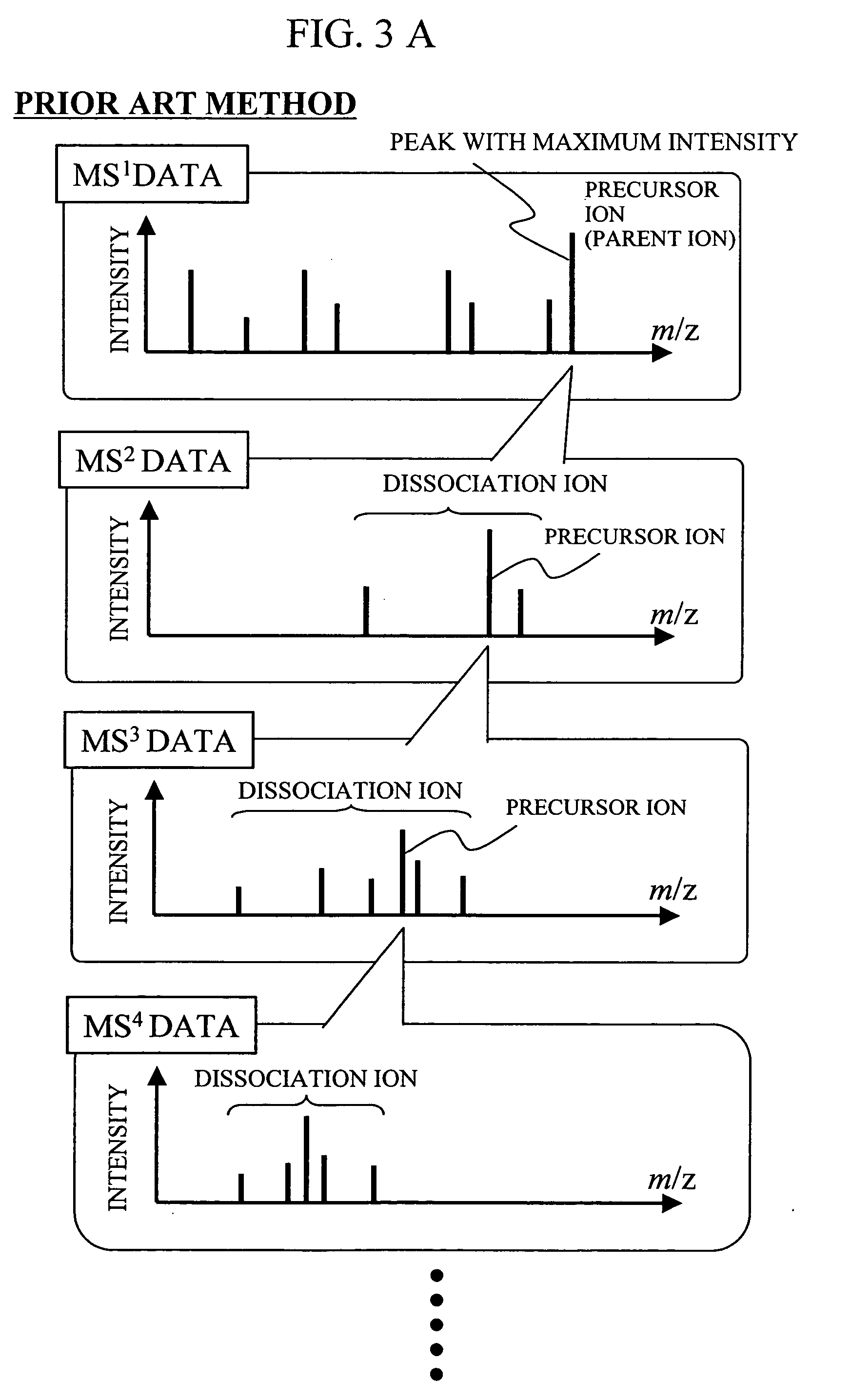
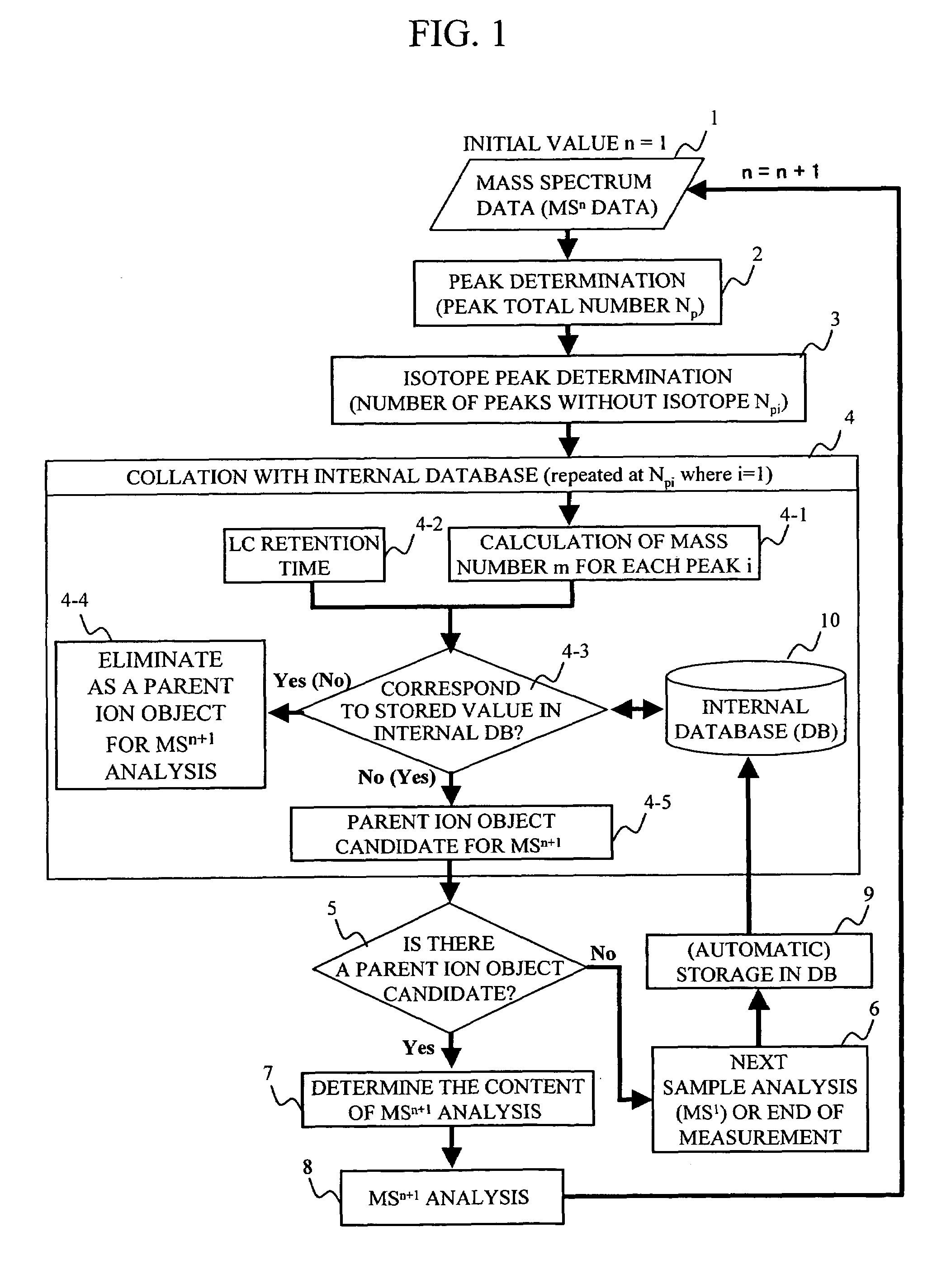
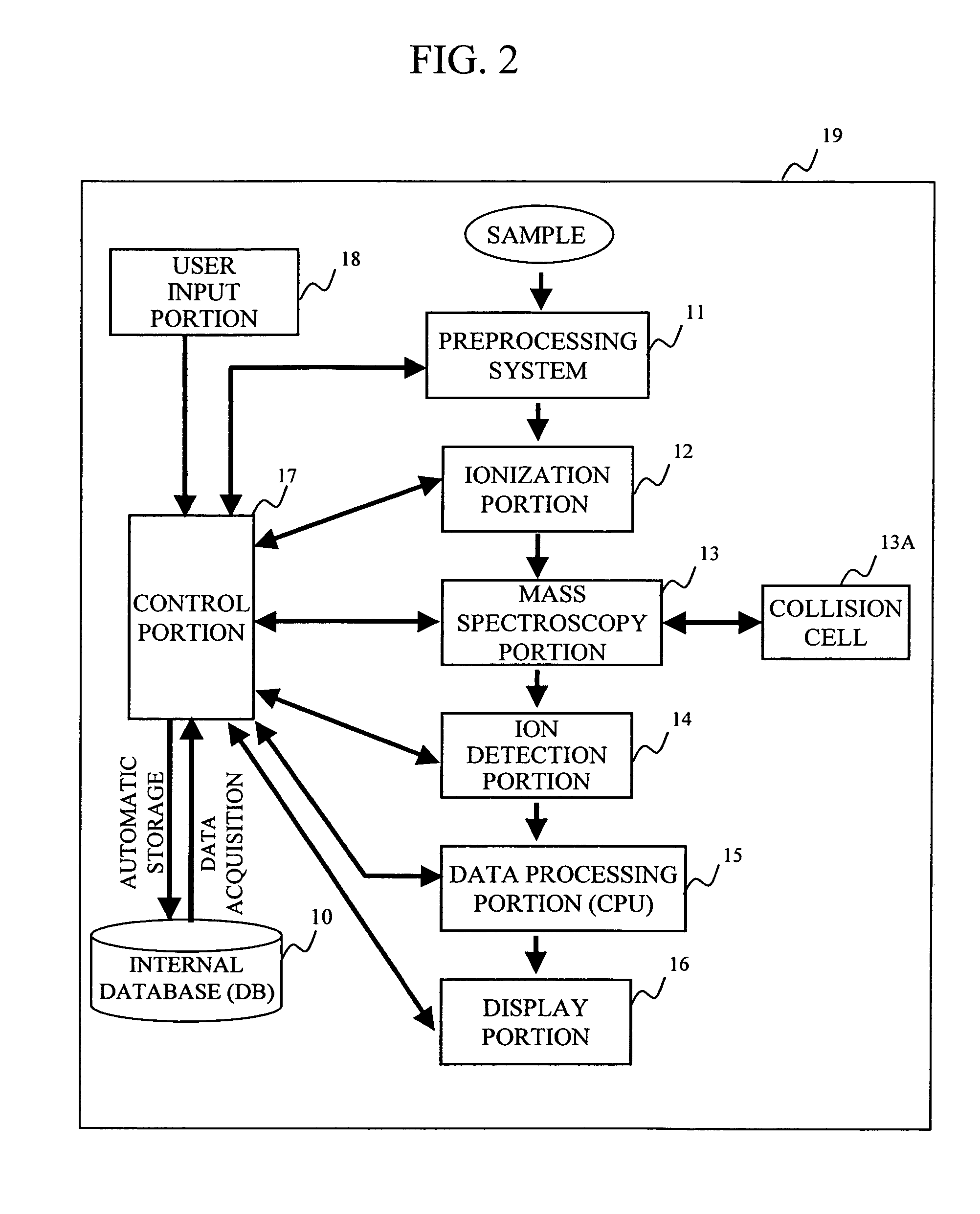
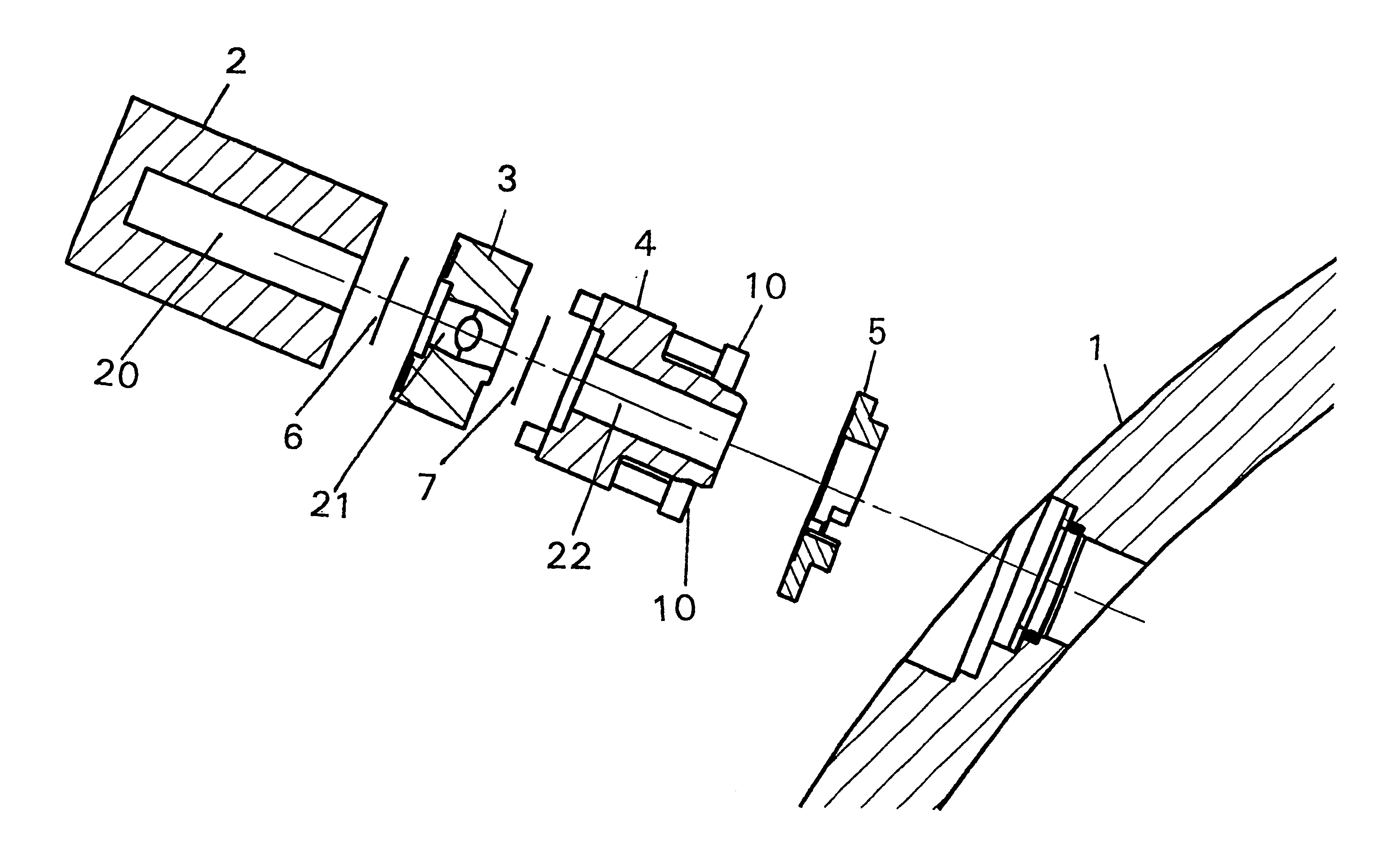
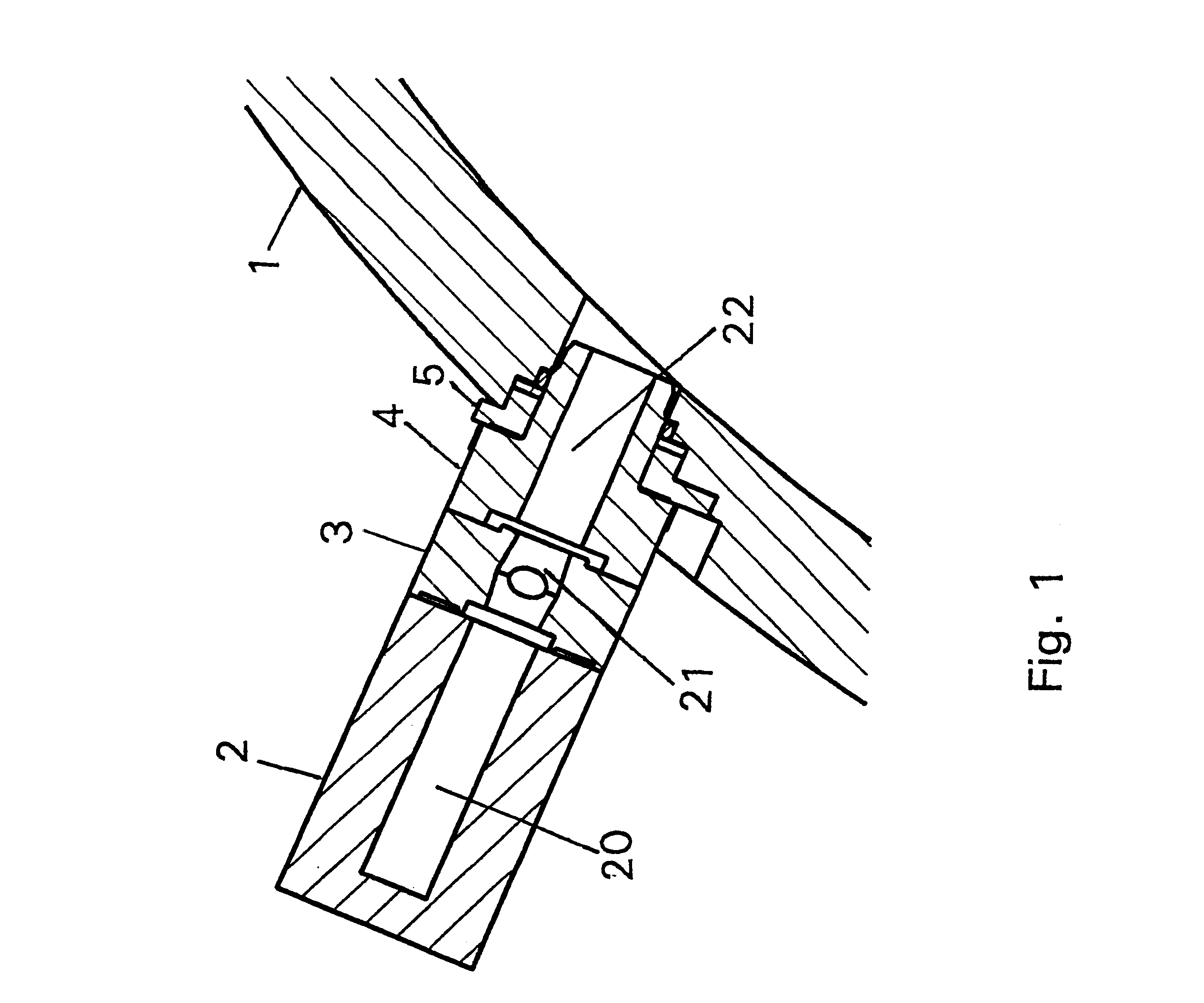
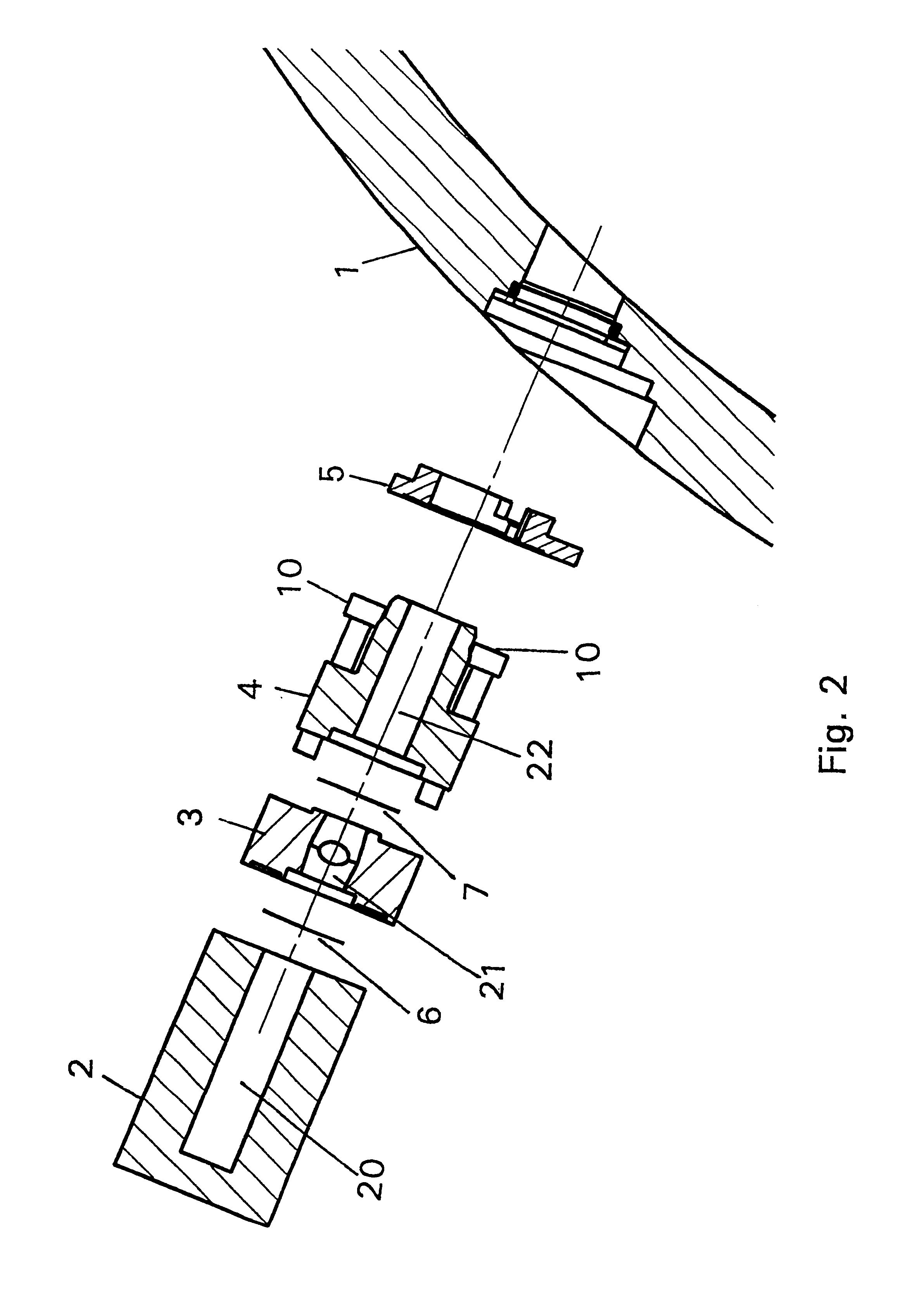
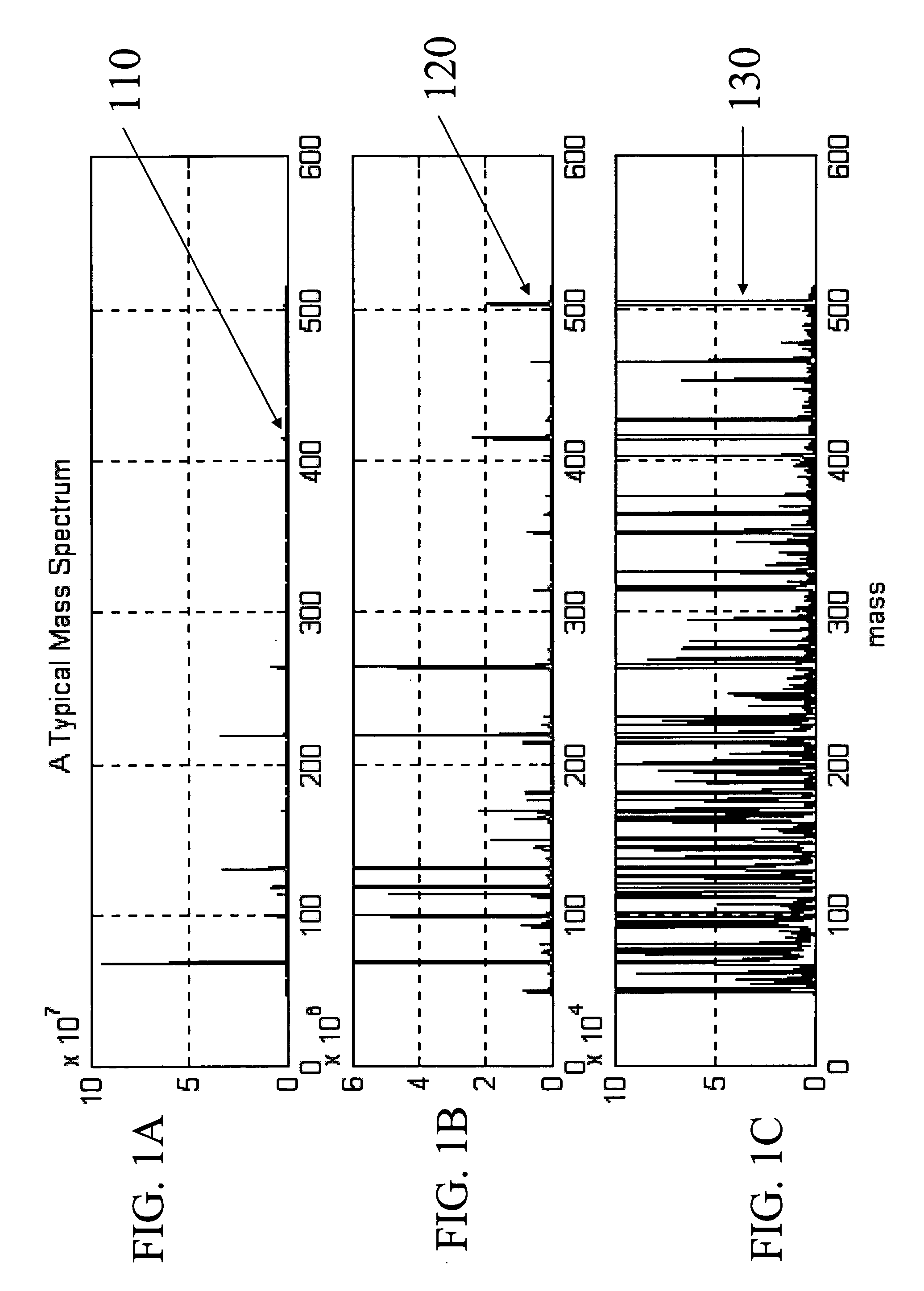
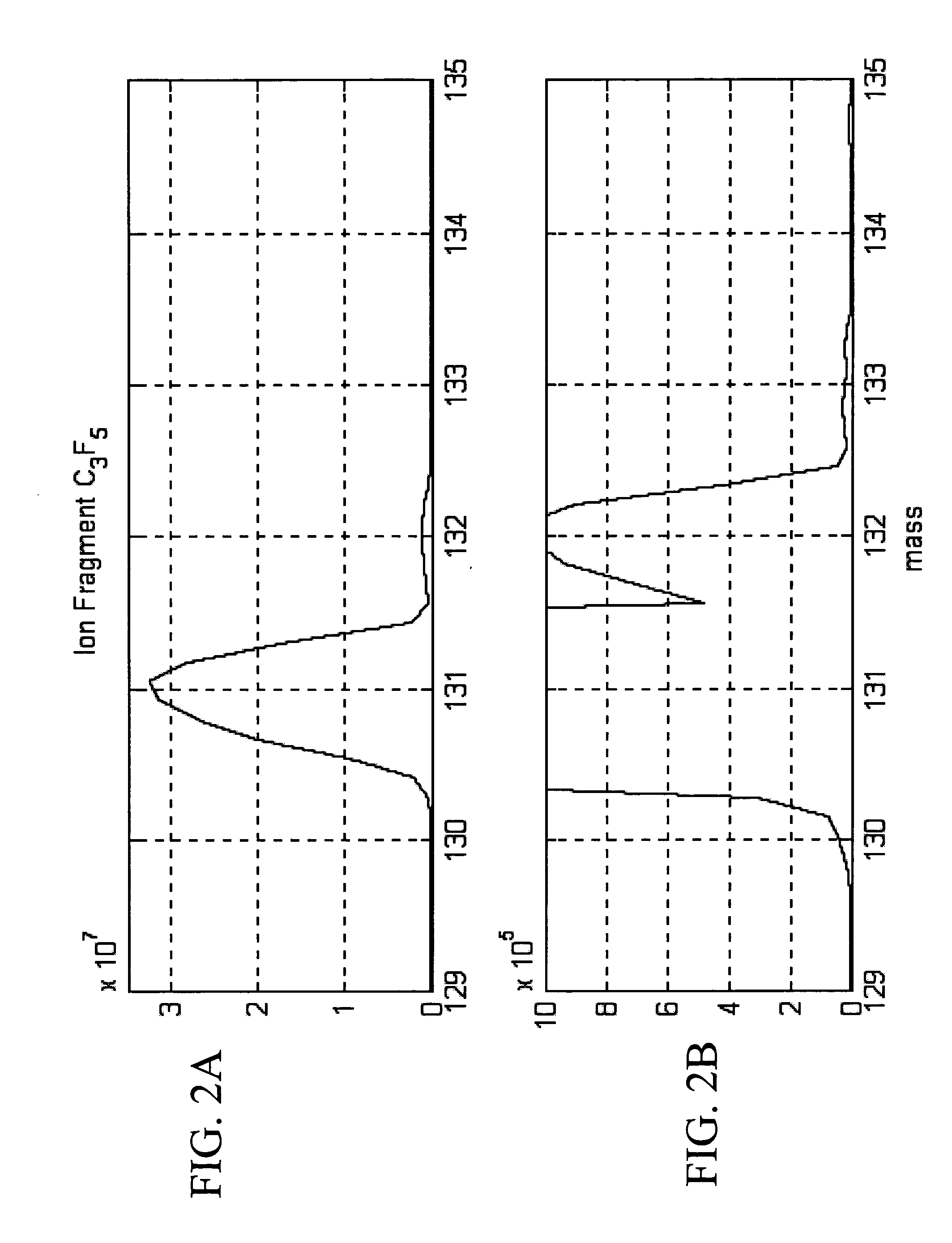
Mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS20050063864A1Reduce adverse effectsSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationStructure analysisSpectroscopy
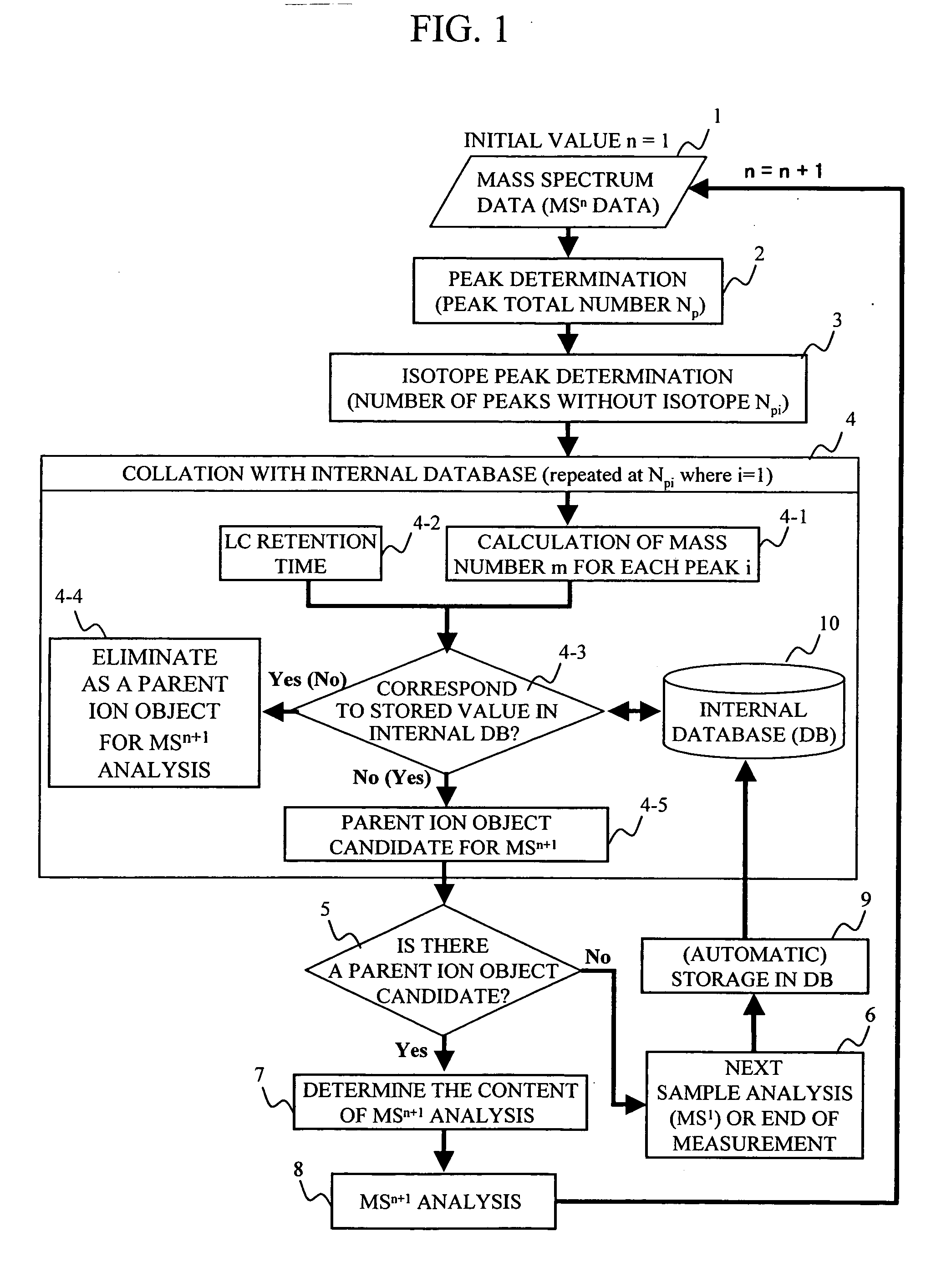
During the structural analysis of a protein or peptide by tandem mass spectroscopy, a peptide ion derived from a protein that has already been measured and that is expressed in great quantities is avoided as a tandem mass spectroscopy target. A peptide derived from a minute amount of protein, which has heretofore been difficult to analyze, can be automatically determined as a tandem mass spectroscopy target within the real time of measurement. Data concerning a protein that has already been measured and a peptide derived from the protein is automatically stored in an internal database. The stored data is collated with measured data with high accuracy to determine an isotope peak. In this way, the process of selecting a peptide peak that has not been measured as the target for the next tandem analysis can be performed within the real time of measurement and a redundant measurement of peptides derived from the same protein can be avoided. The information contained in the MSn spectrum is effectively utilized in each step of the MSn involving a multi-stage dissociation and mass spectroscopy (MSn), so that the flows for the determination of the next analysis content and the selection of the parent ion for the MSn+1 analysis, for example, can be optimized within the real time of measurement and with high efficiency and accuracy. Thus, a target of concern to the user can be subjected to tandem mass spectroscopy without wasteful measurement.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
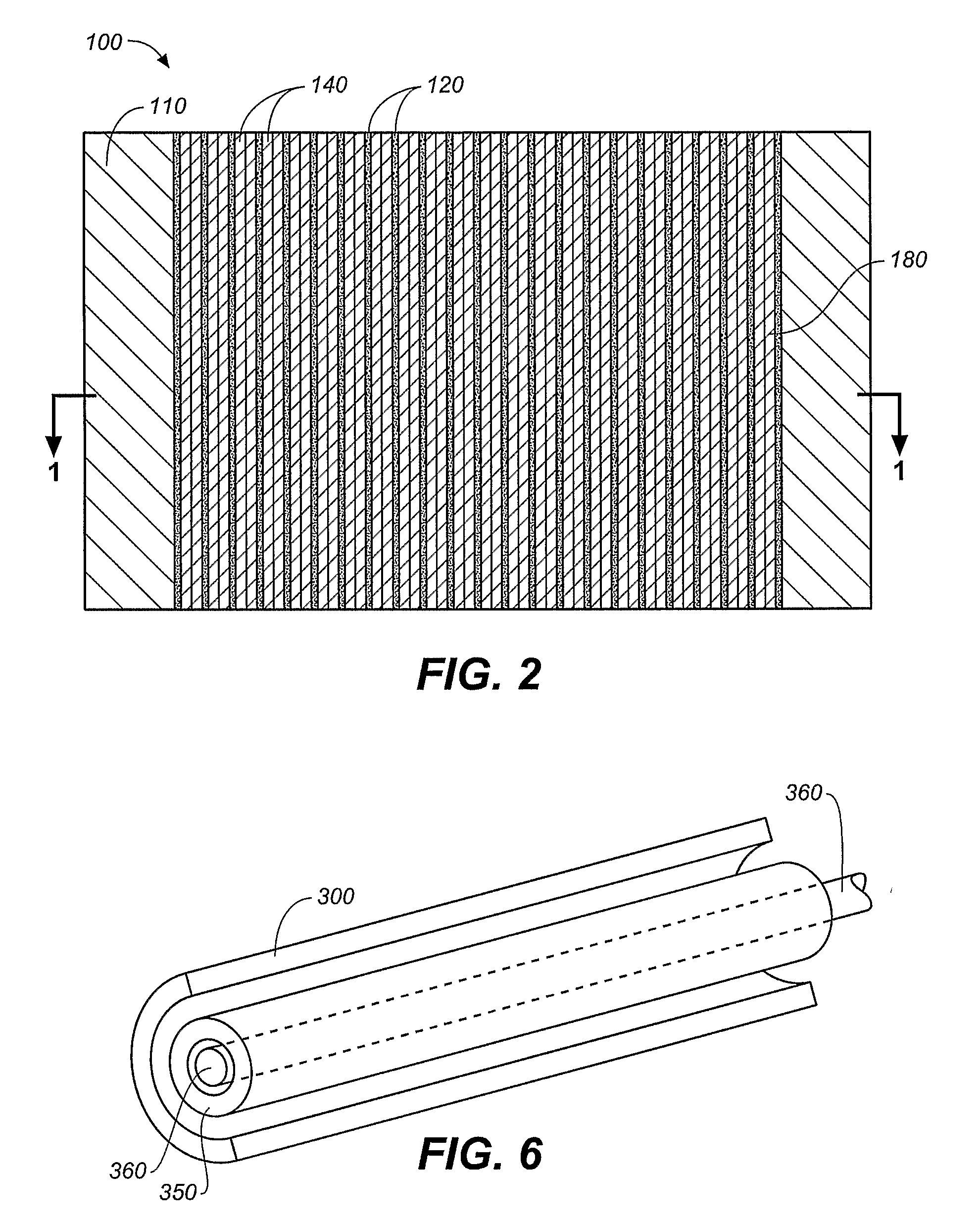
Increased drug-loading and reduced stress drug delivery device
InactiveUS7060093B2Eliminate and reduce breakEliminate and reduce and fractureStentsBlood vesselsMedicineIsotope
An implantable prosthesis, for example a stent, is provided having one or more elements that form the body structure of the prosthesis. The elements have a width that is variable from a nominal or conventional width to an increased width. The elements can have depots formed in the elements and are generally located at the increased width portions of the elements. Substances such as therapeutic substances, polymeric materials, polymeric materials containing therapeutic substances, radioactive isotopes, and radiopaque materials can be deposited into the depots.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
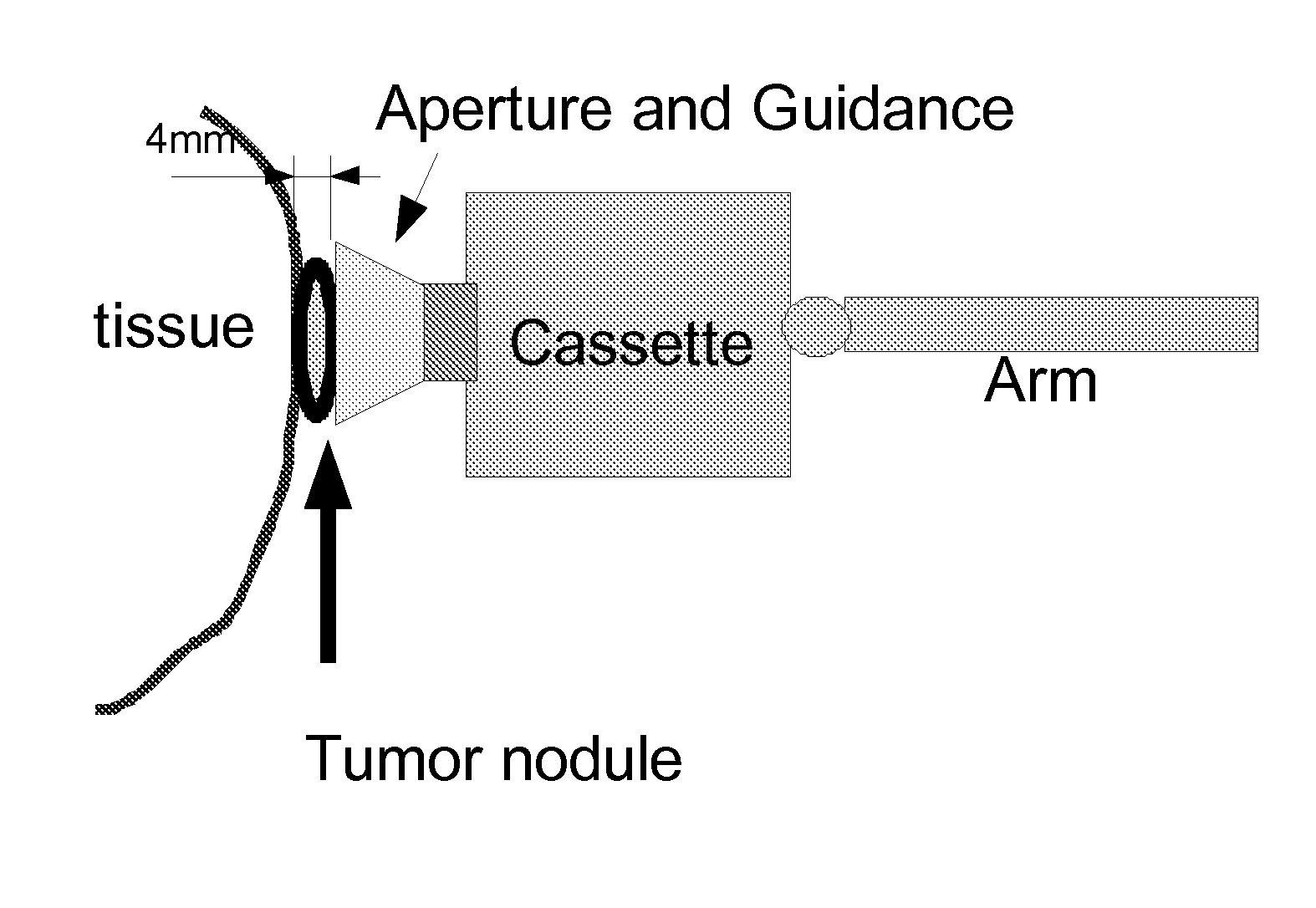
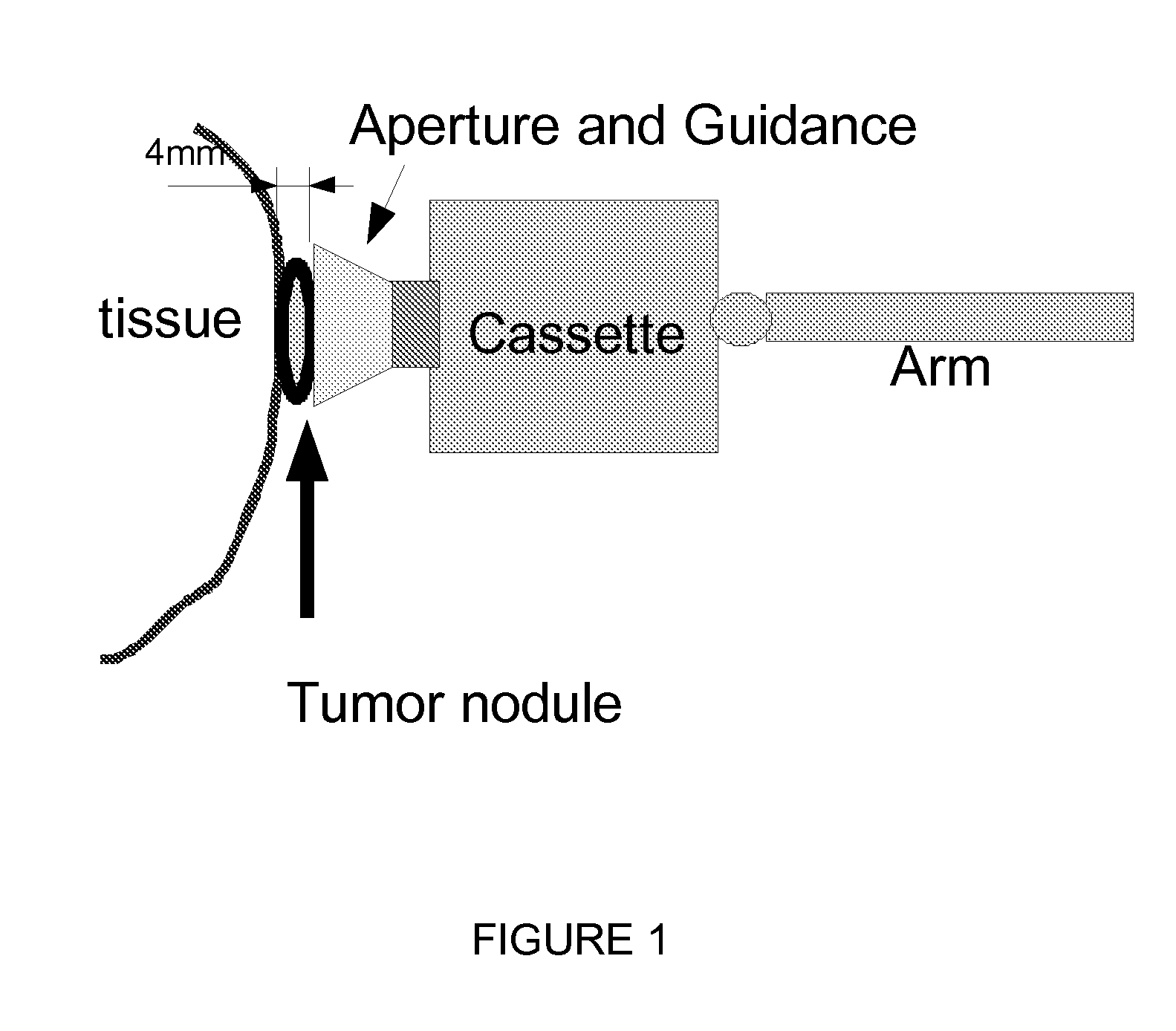
Direct visualization robotic intra-operative radiation therapy applicator device
ActiveUS8092370B2Increase probabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryX-rayTherapeutic effect
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:SRIORT
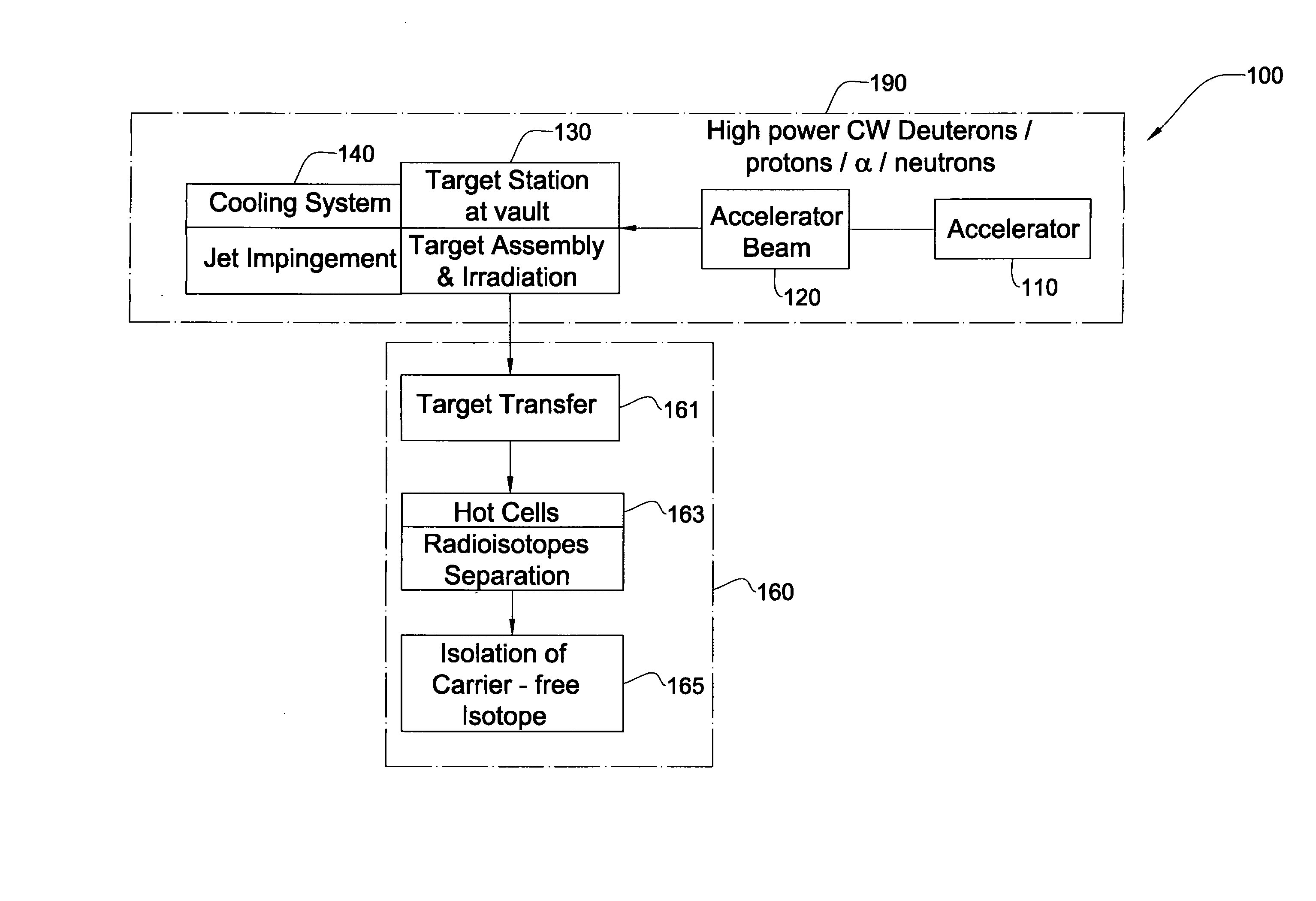
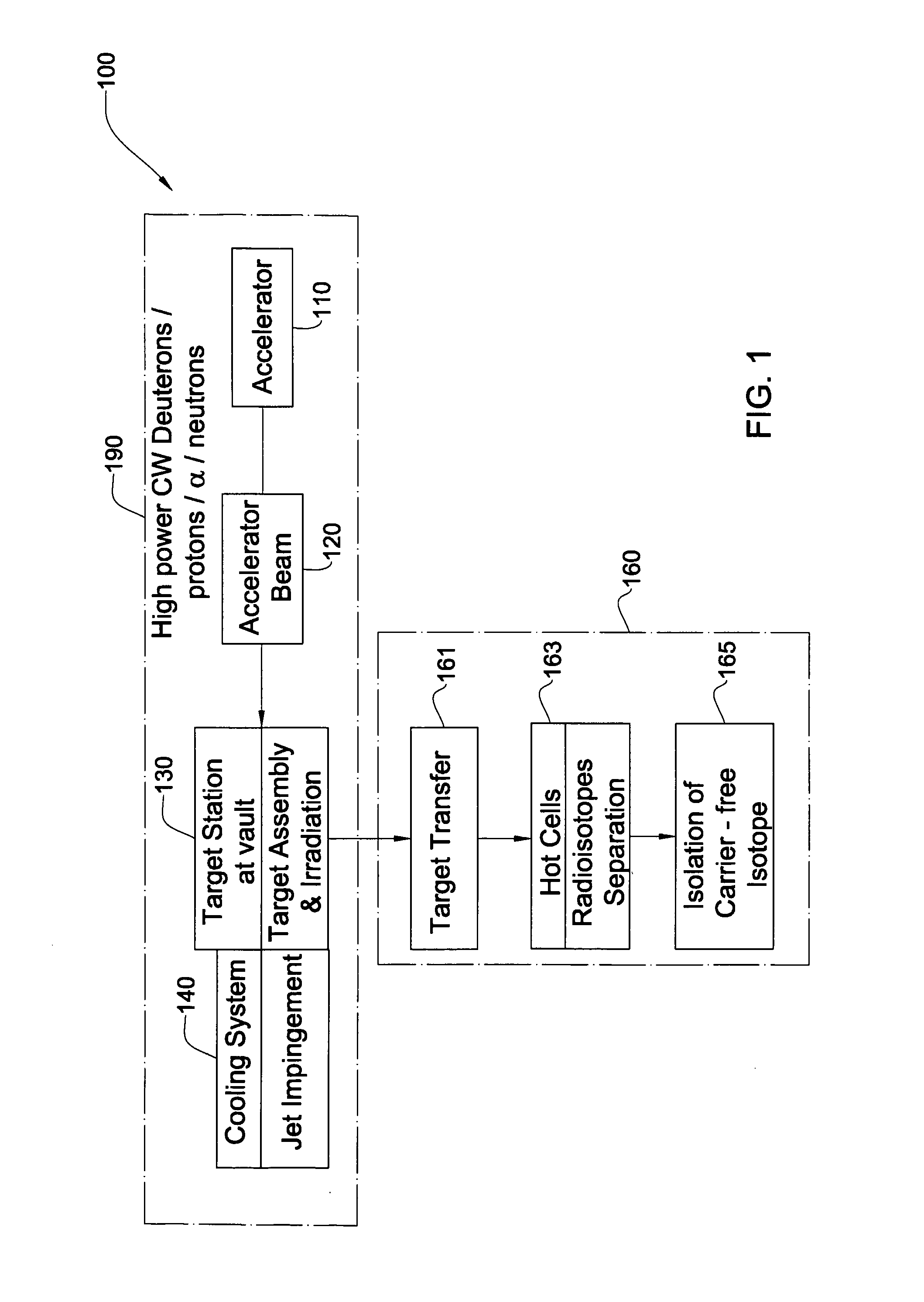
Method And System For Production Of Radioisotopes, And Radioisotopes Produced Thereby
InactiveUS20070297554A1Avoid communicationAvoid contaminationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsHeat fluxParticle beam
A system and method for the production of radioisotopes by the transmutation of target isotopic material bombarded by a continuous wave particle beam. An ion source generates a continuous wave ion beam, irradiating an isotope target, which is cooled by transferring heat away from the target at heat fluxes of at least about 1 kW / cm2.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION
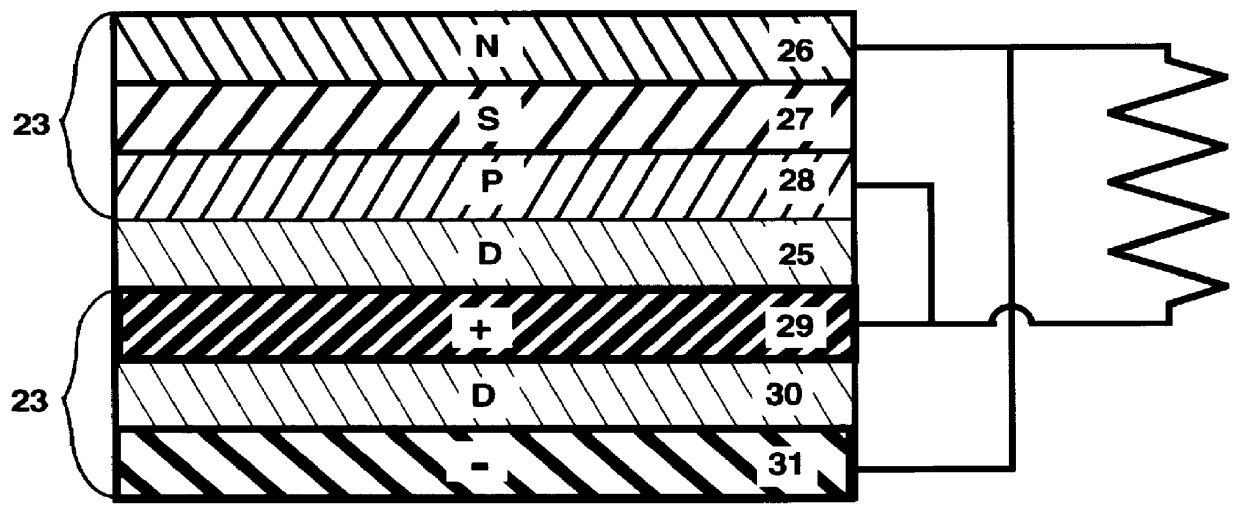
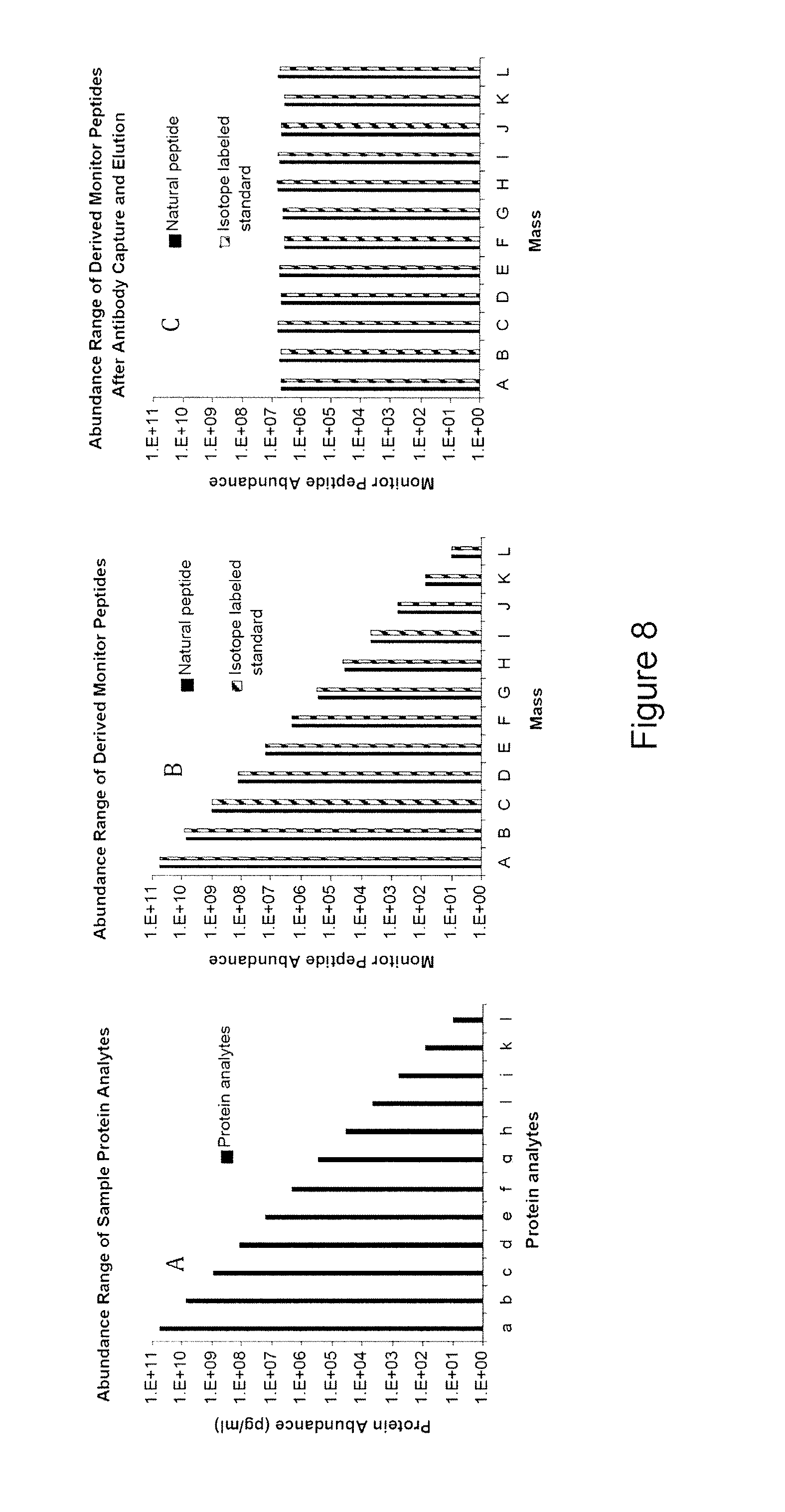
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20040072251A1Loss of substantial specific binding capacityReduce complexitySamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Rod assembly for nuclear reactors
A rod assembly for a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor may include an upper end piece, lower end piece and a plurality of rod segments attached between the upper and lower end pieces and to each other so as to form an axial length of the rod assembly. The rod assembly may include an adaptor subassembly provided at given connection points for connecting adjacent rod segments or a given rod segment with one of the upper and lower end pieces. The connection points along the axial length of the rod assembly may be located where the rod assembly contacts a spacer in the fuel bundle. One (or more) of the rod segments may include an irradiation target therein for producing a desired isotope when a fuel bundle containing one (or more) rod assemblies is irradiated in a core of the reactor.
Owner:NORDION (CANADA) INC
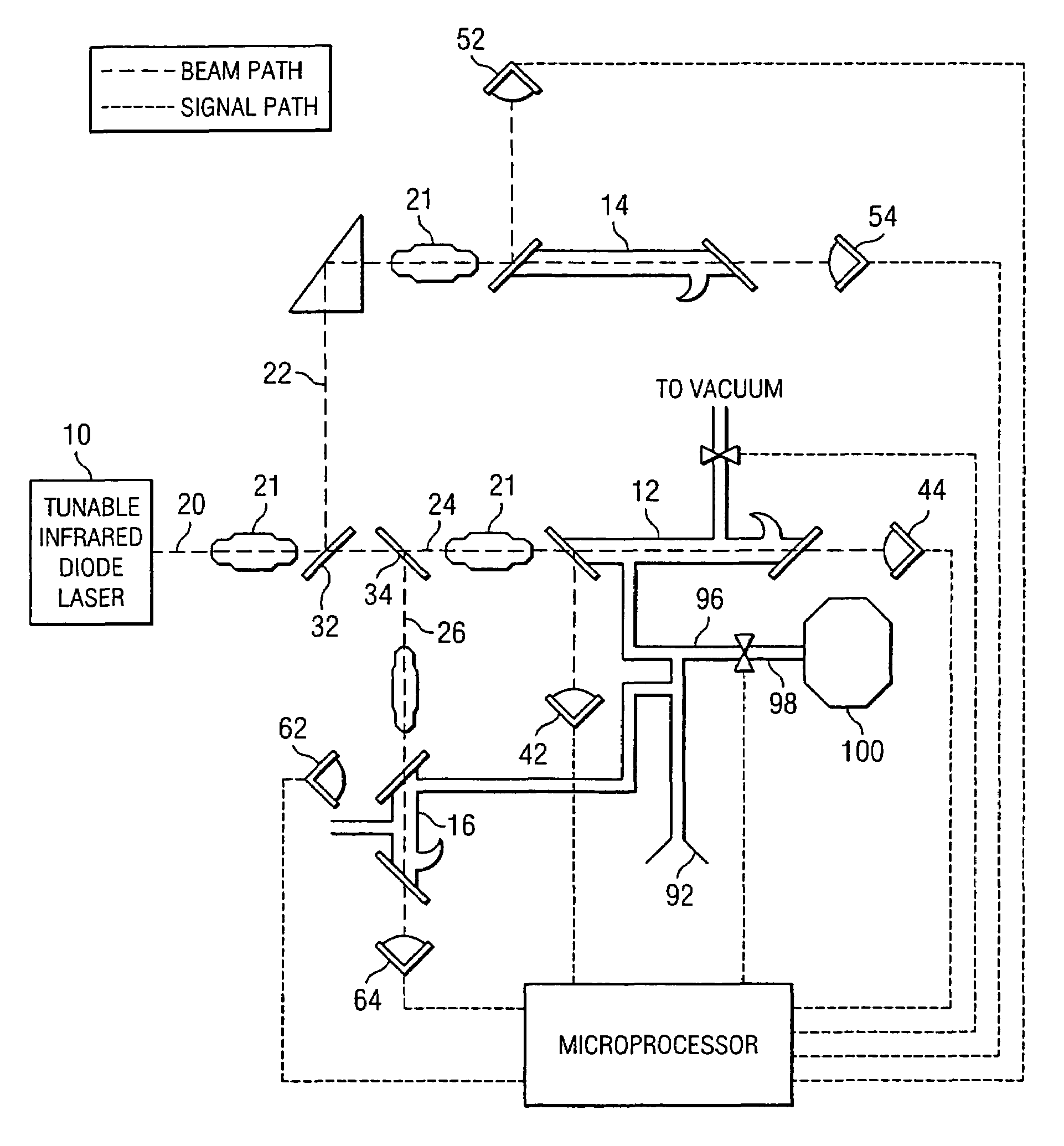
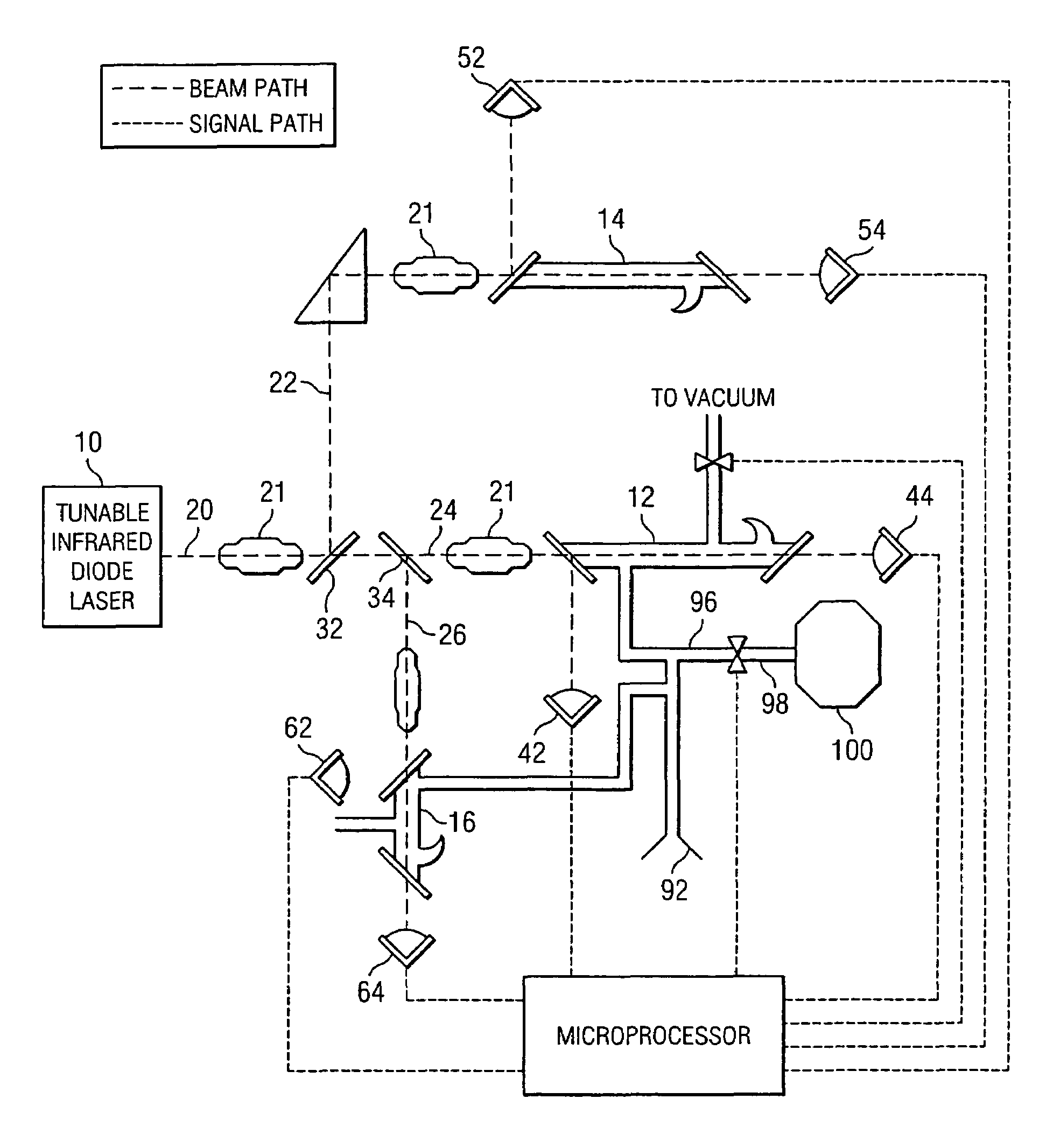
Method and apparatus for performing rapid isotopic analysis via laser spectroscopy
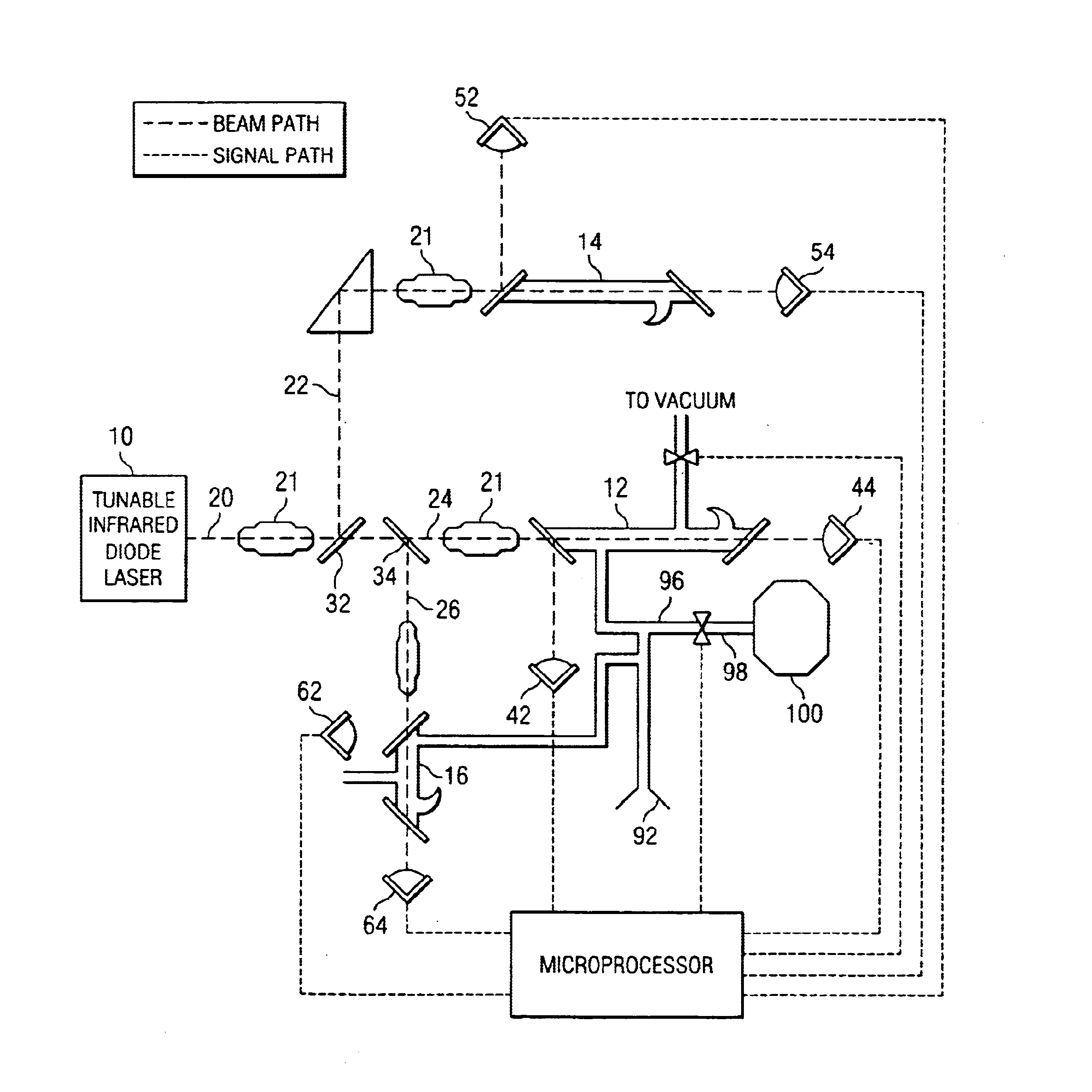
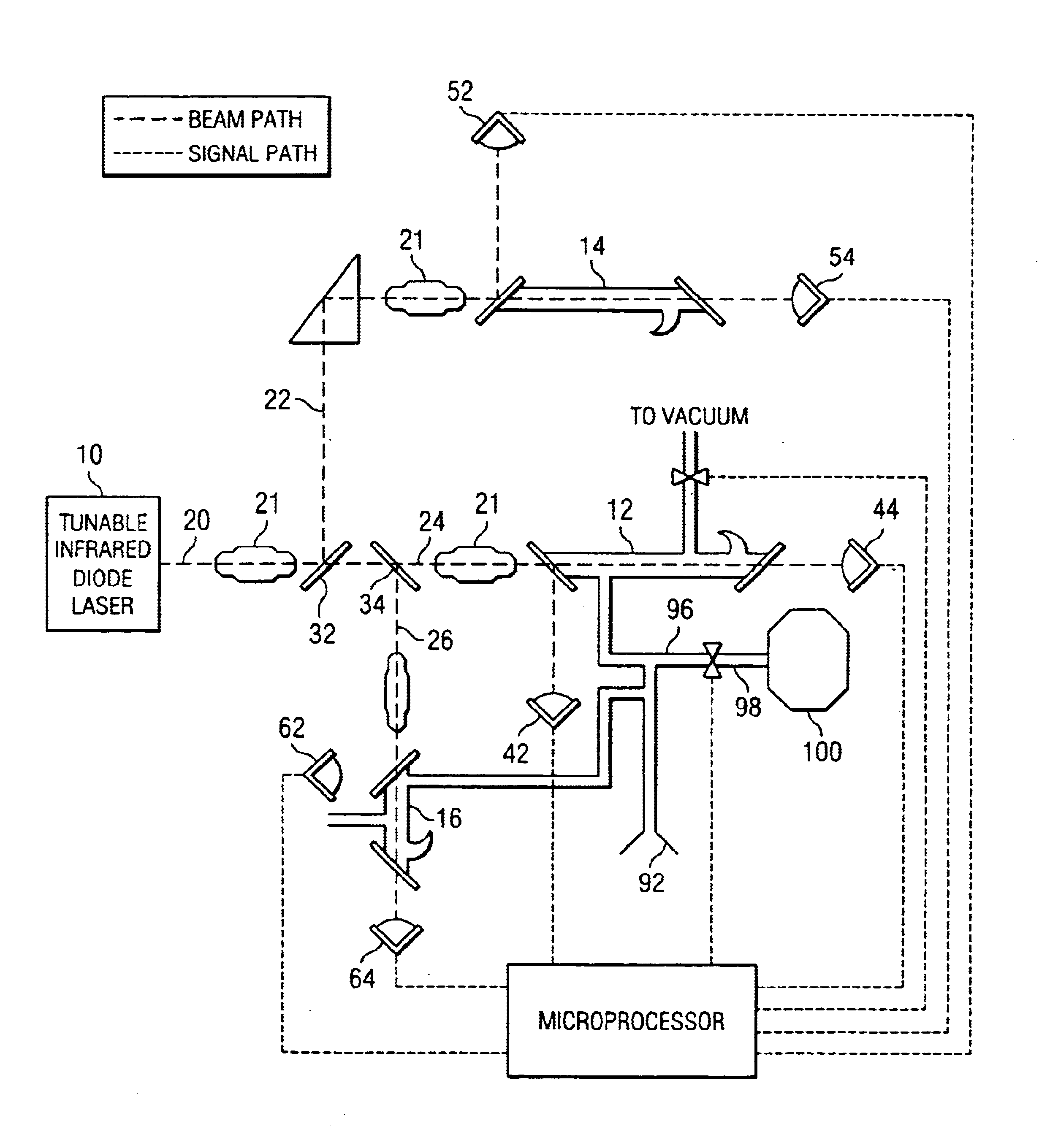
InactiveUS6888127B2Accurate and preciseAccurate and Precise MeasurementsRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsIsotopeLaser beams
Method and apparatus for providing real-time data indicative of the isotopic composition of formation fluids during drilling. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a reference fluid having a known isotopic composition in a reference cell; (b) capturing a sample of formation; (c) providing at least one laser beam; (e) passing a beam through the reference fluid, measuring the reference-measurement beam before and after it passes through the reference fluid; (f) and passing a beam through the sample, measuring the beam before and after it passes through the sample, and calculating a first isotope concentration from those measurements. The measurements can provide information relating to the carbon isotopic composition of individual compounds in hydrocarbon gas mixtures, with the individual compounds including methane, ethane, propane, iso- or normal butane, or iso- or normal pentane.
Owner:CALEB BRETT USA
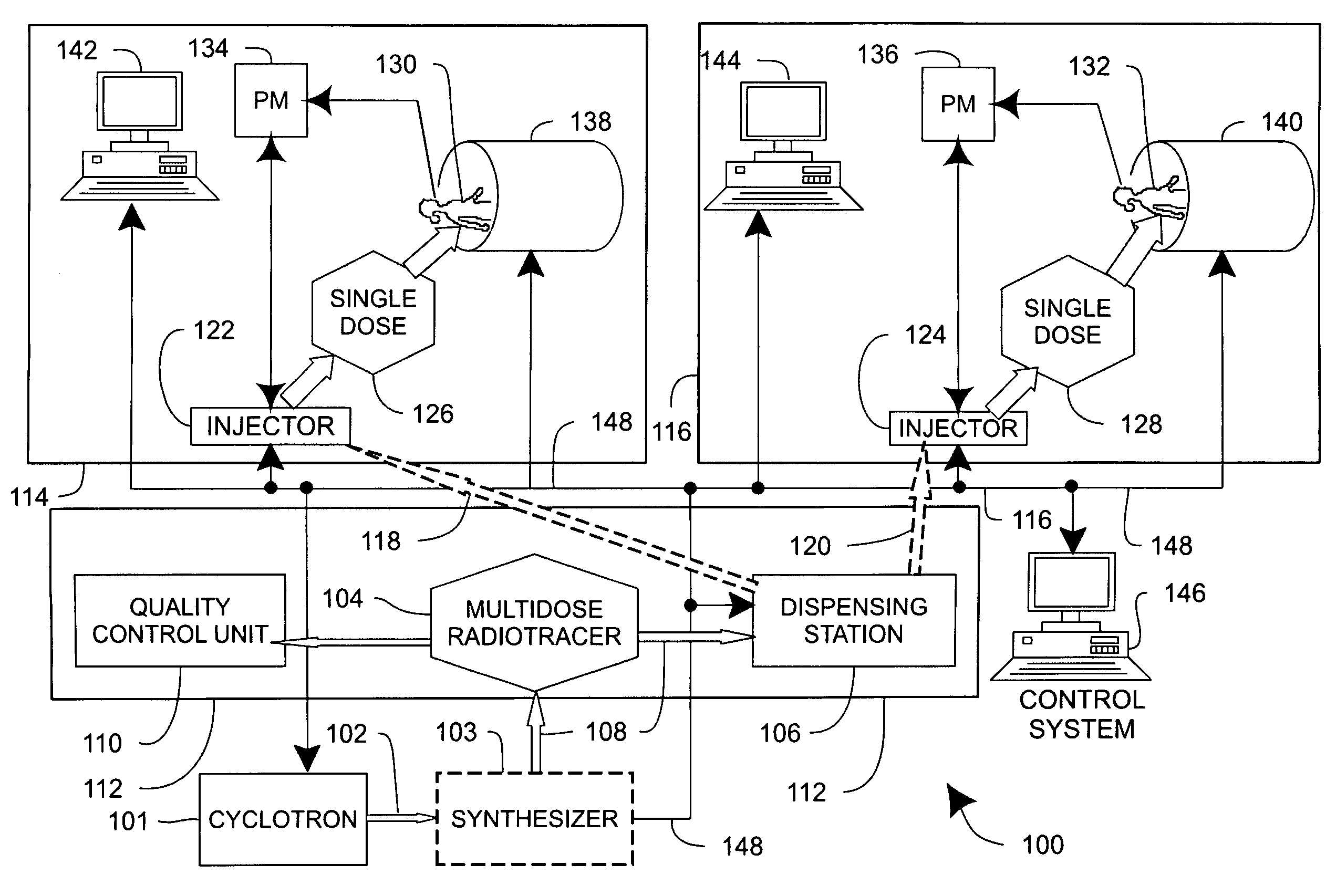
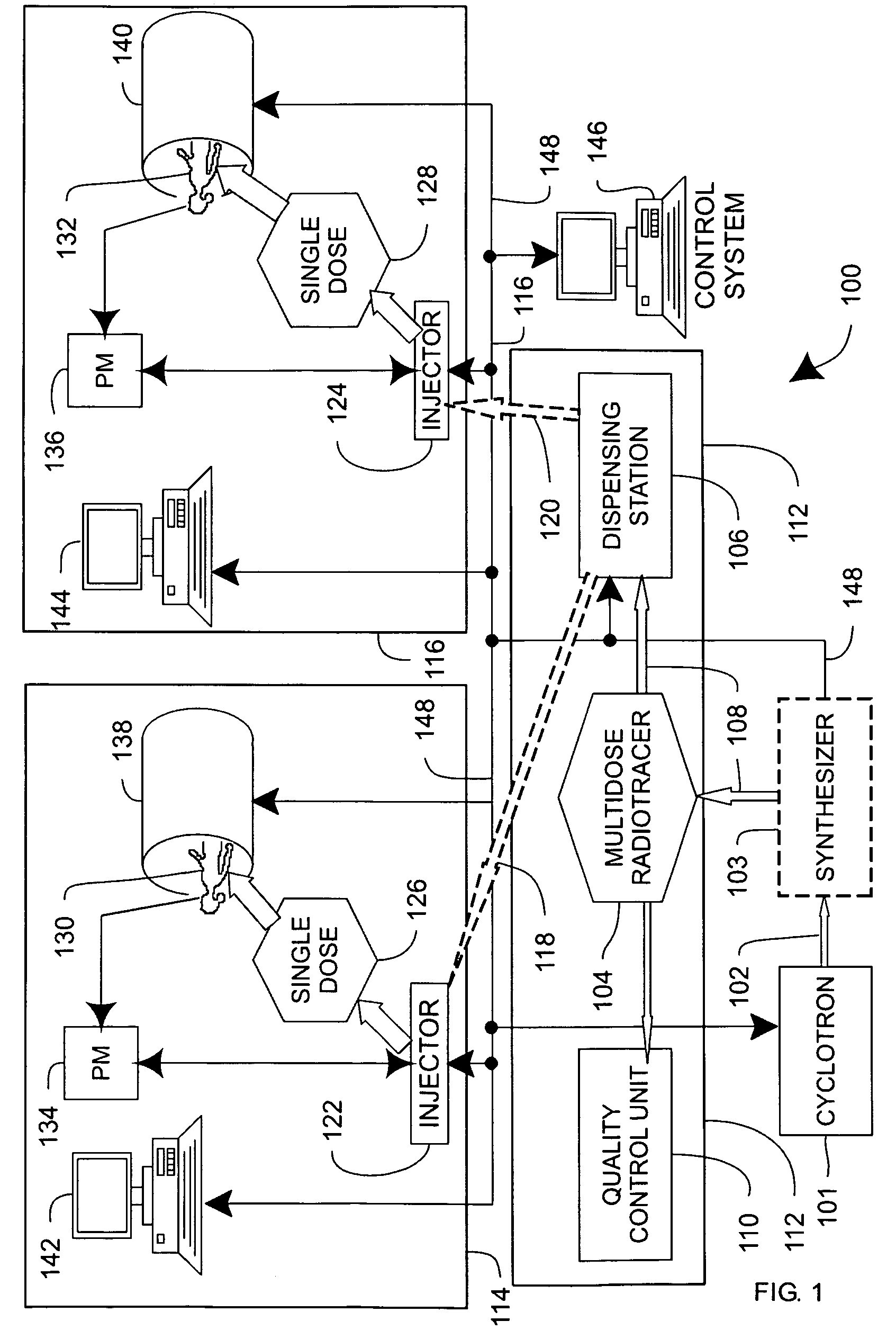
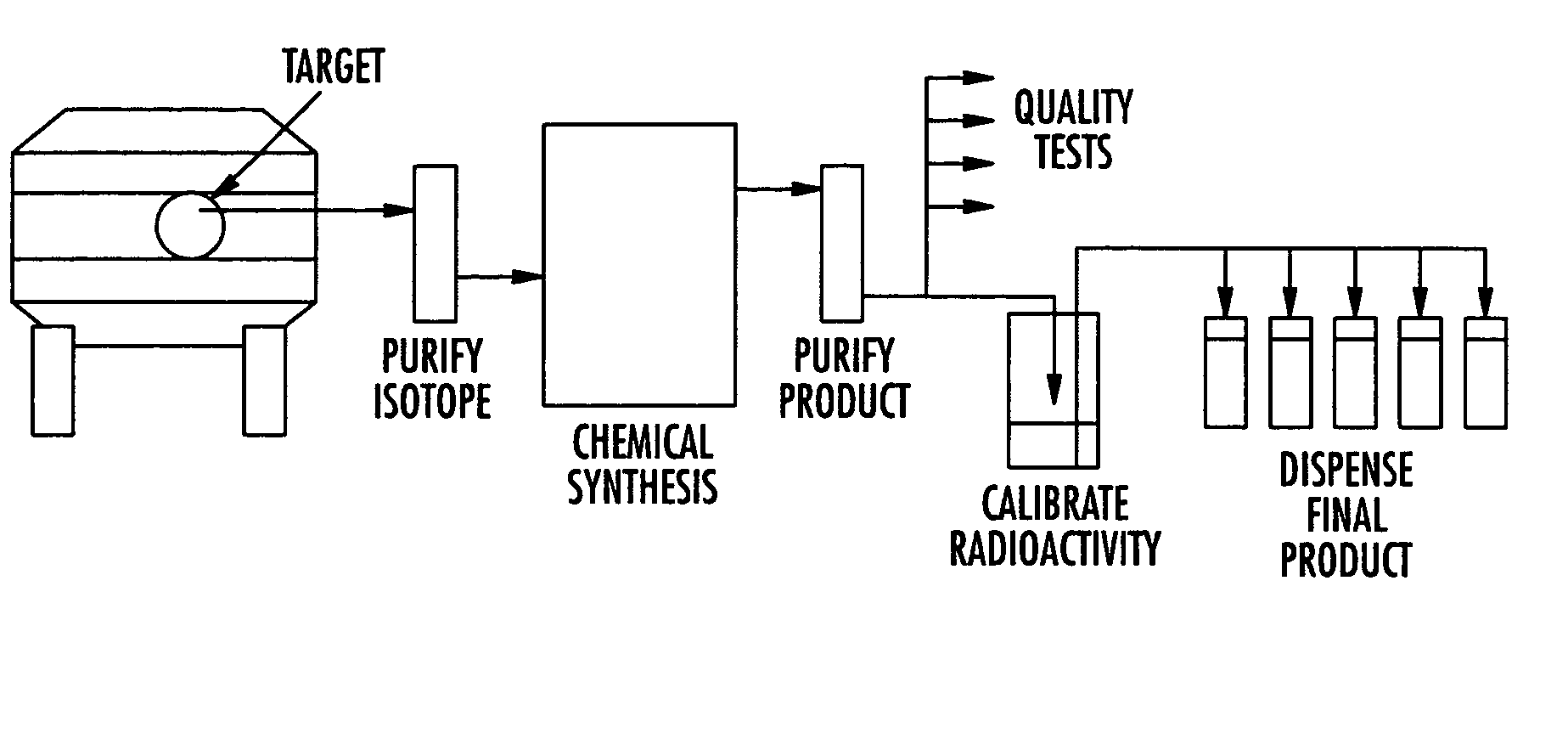
Systems, methods and apparatus for preparation, delivery and monitoring of radioisotopes in positron emission tomography
ActiveUS7734331B2Economy of scaleImprove distributionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsRadioactive tracerQuality control
In one aspect, systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a dispensing station dispenses a large quantity of a radiotracer to one or more positron emission tomography imaging stations. In some aspects a quality control unit verifies the quality of the radiotracer. In some embodiments, components of the system are coupled by a local area network. In some aspects, each positron emission tomography imaging station includes an injector system, a physiological monitoring device, and a positron emission tomography scanner. All of the devices can be controlled by a computer system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
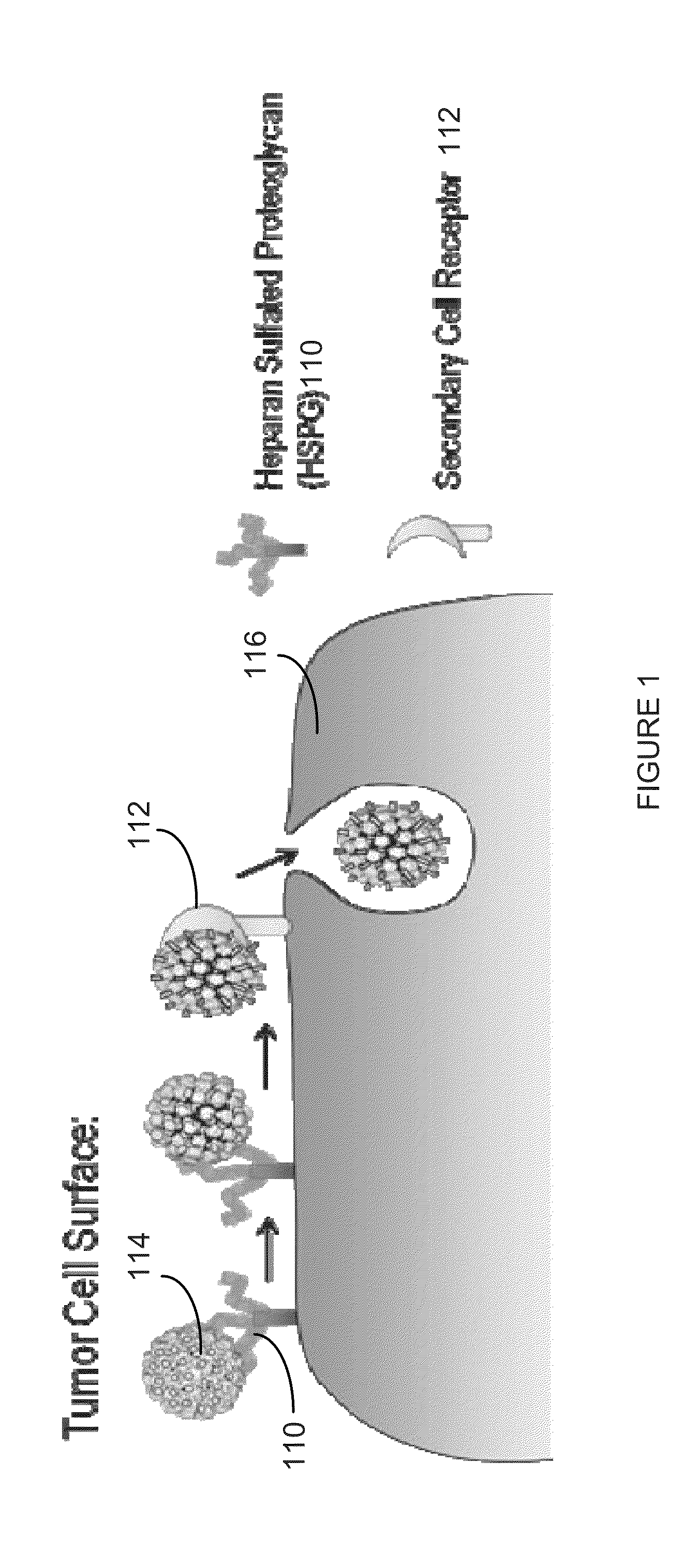
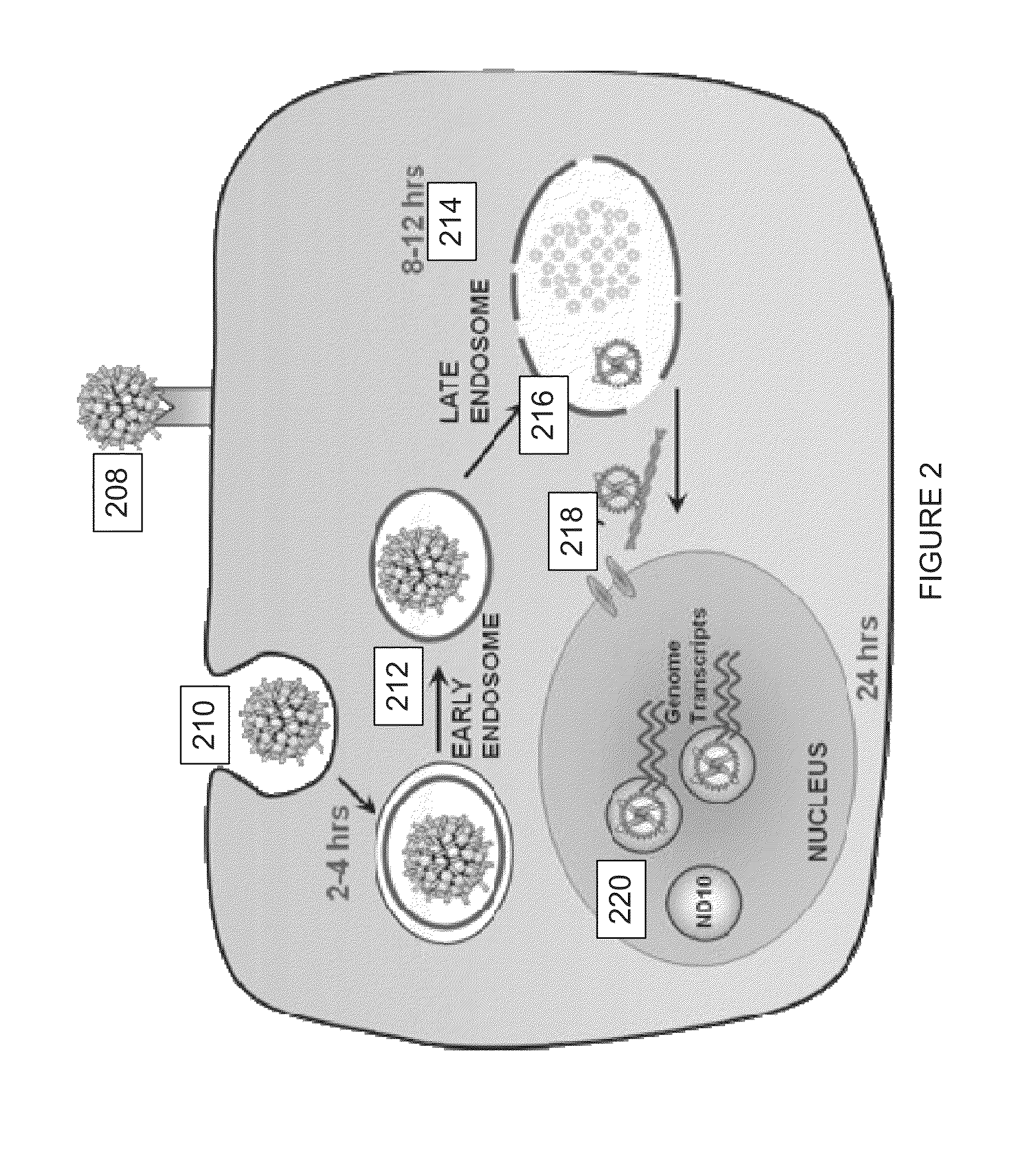
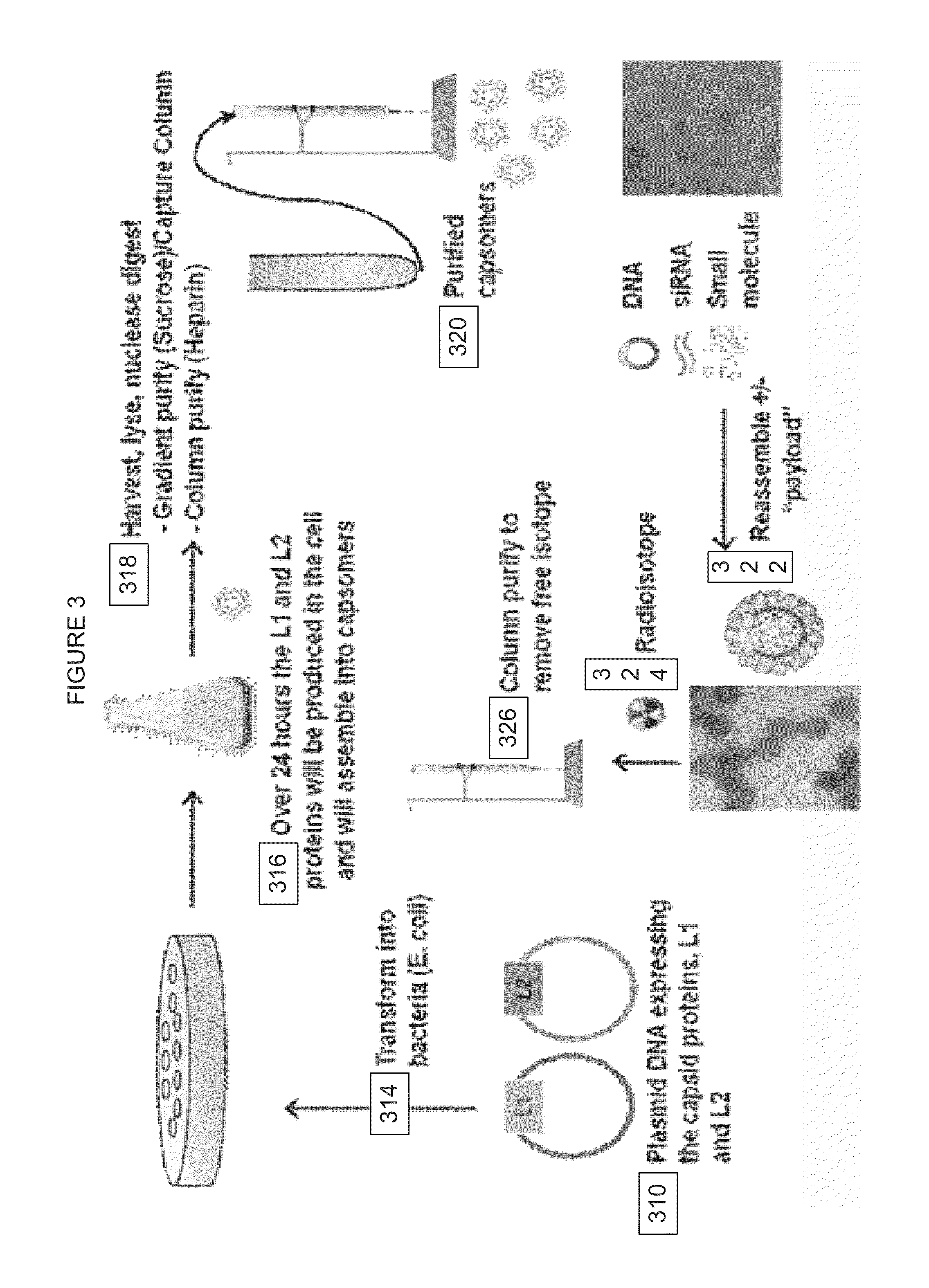
Virion Derived Protein Nanoparticles For Delivering Radioisotopes For The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Malignant And Systemic Disease And The Monitoring Of Therapy
InactiveUS20130116408A1Precise deliveryImproved imaging differentiationVirus peptidesDepsipeptidesTherapy monitoringIsotope
The invention is directed to novel compositions and methods utilizing virion derived protein nanoparticles for delivery of medical imaging agents and therapeutic agents for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant and systemic diseases. The nanoparticles of the present invention are designed to deliver radioactive isotopes suitable for imaging a tumor and its metastases. Additionally, the nanoparticles may deliver a radioisotope that is suitable for treating a tumor and its metastases by alpha, beta or gamma radiation. Alternatively, the virion derived nanoparticles may deliver a treatment agent for cancer or a combination of a radioisotope and a cancer treatment agent. Additionally the virion derived nanoparticle may include delivery of a drug that enhances the immune system's recognition of the tumor.
Owner:AURA BIOSCI
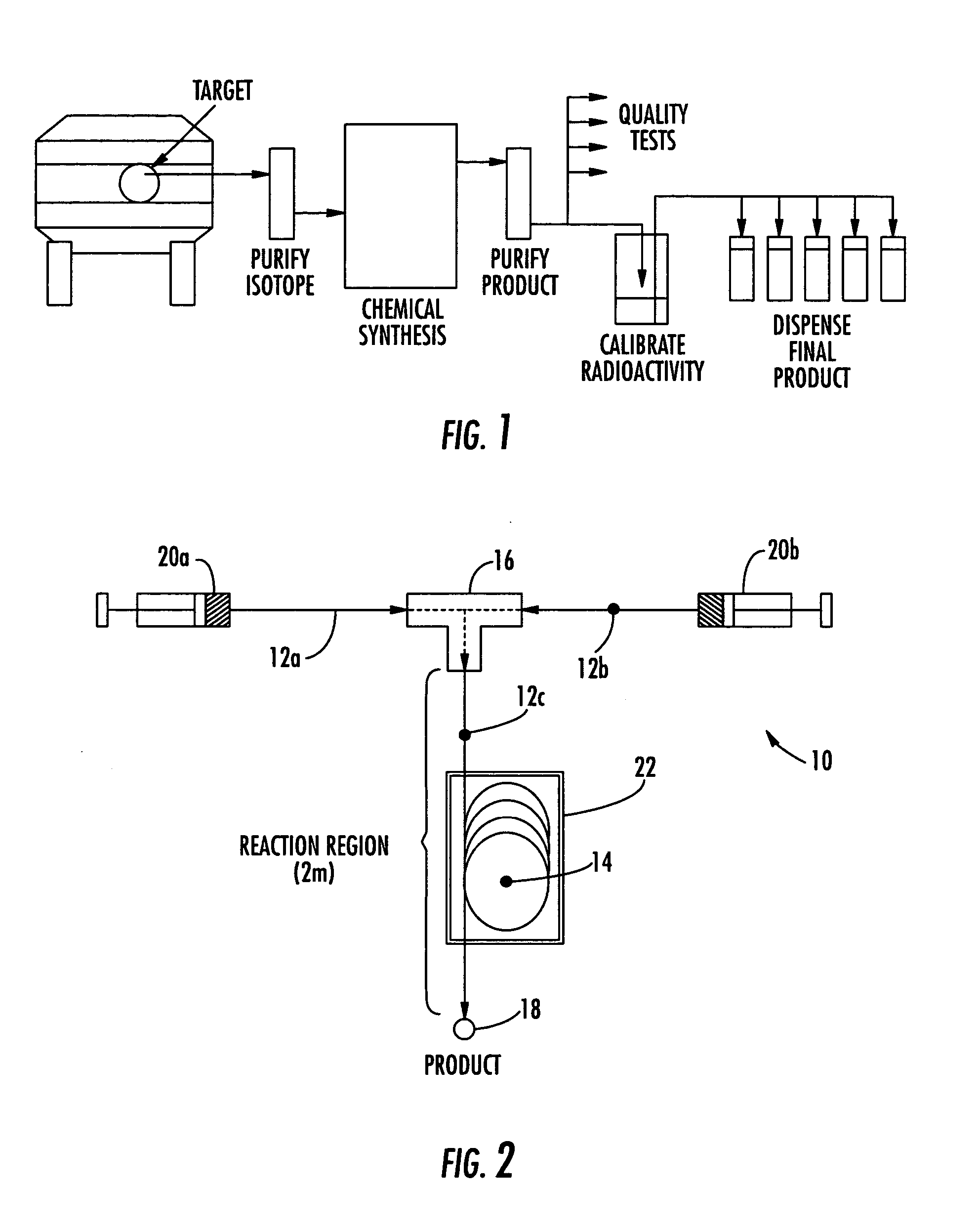
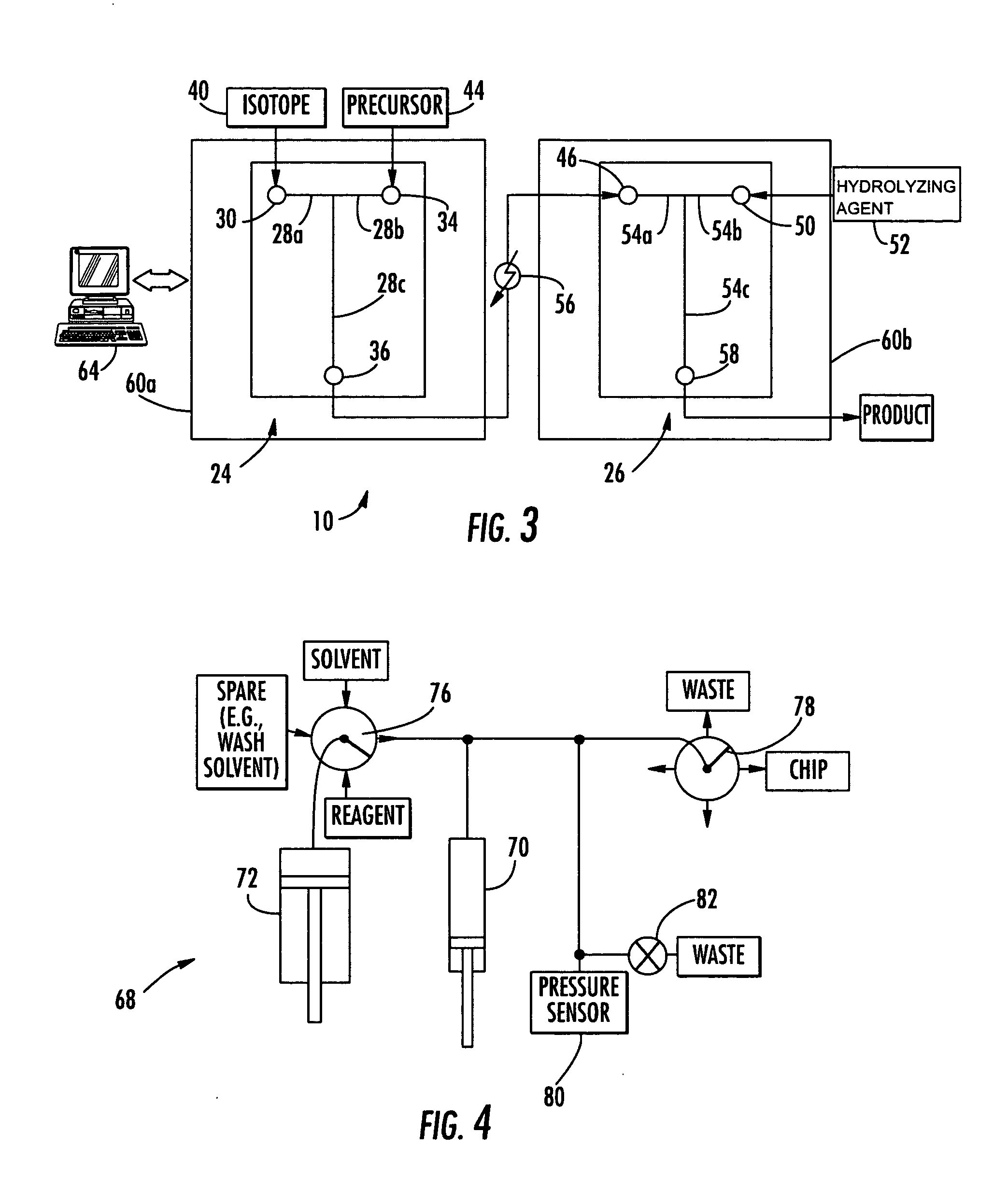
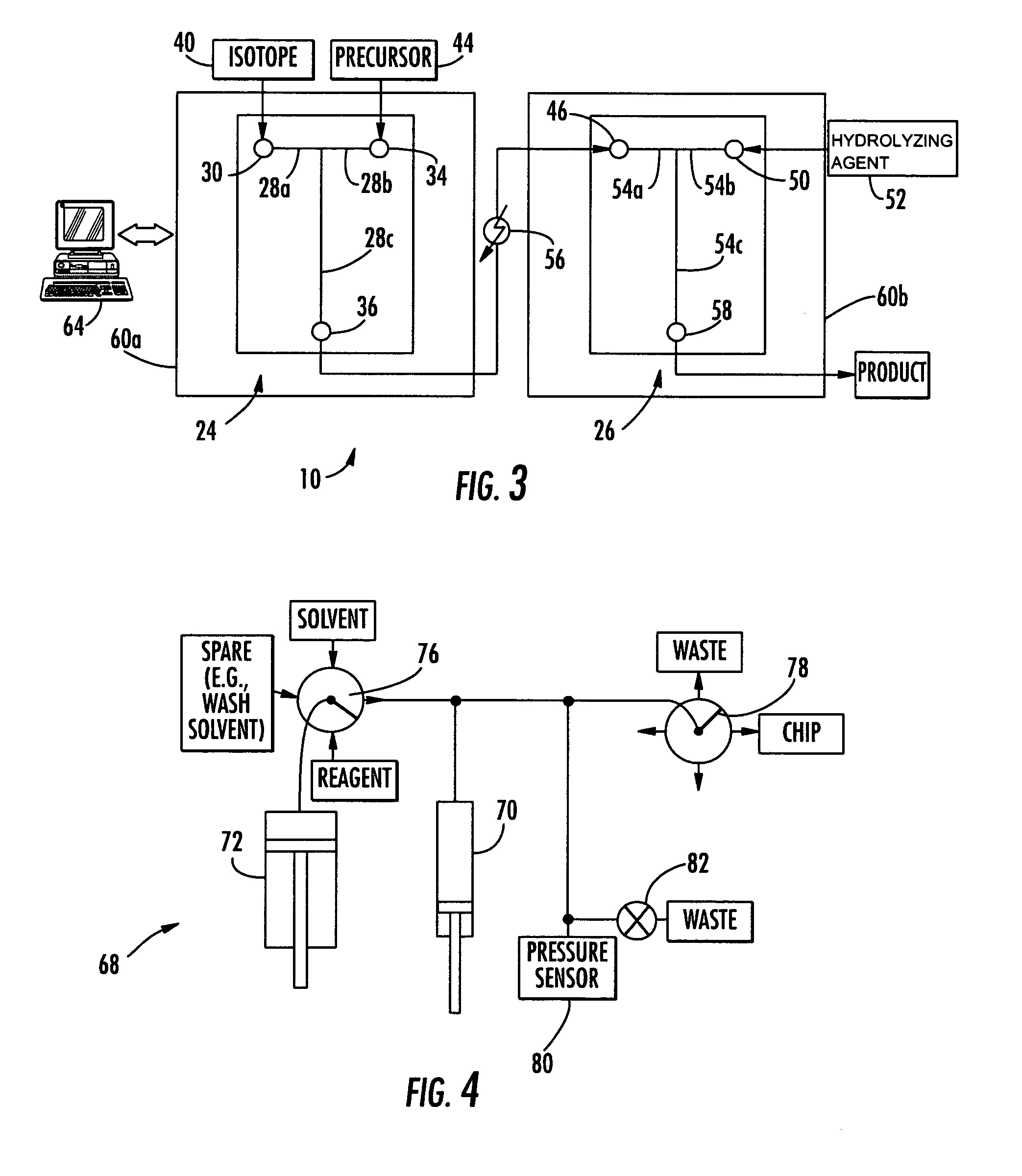
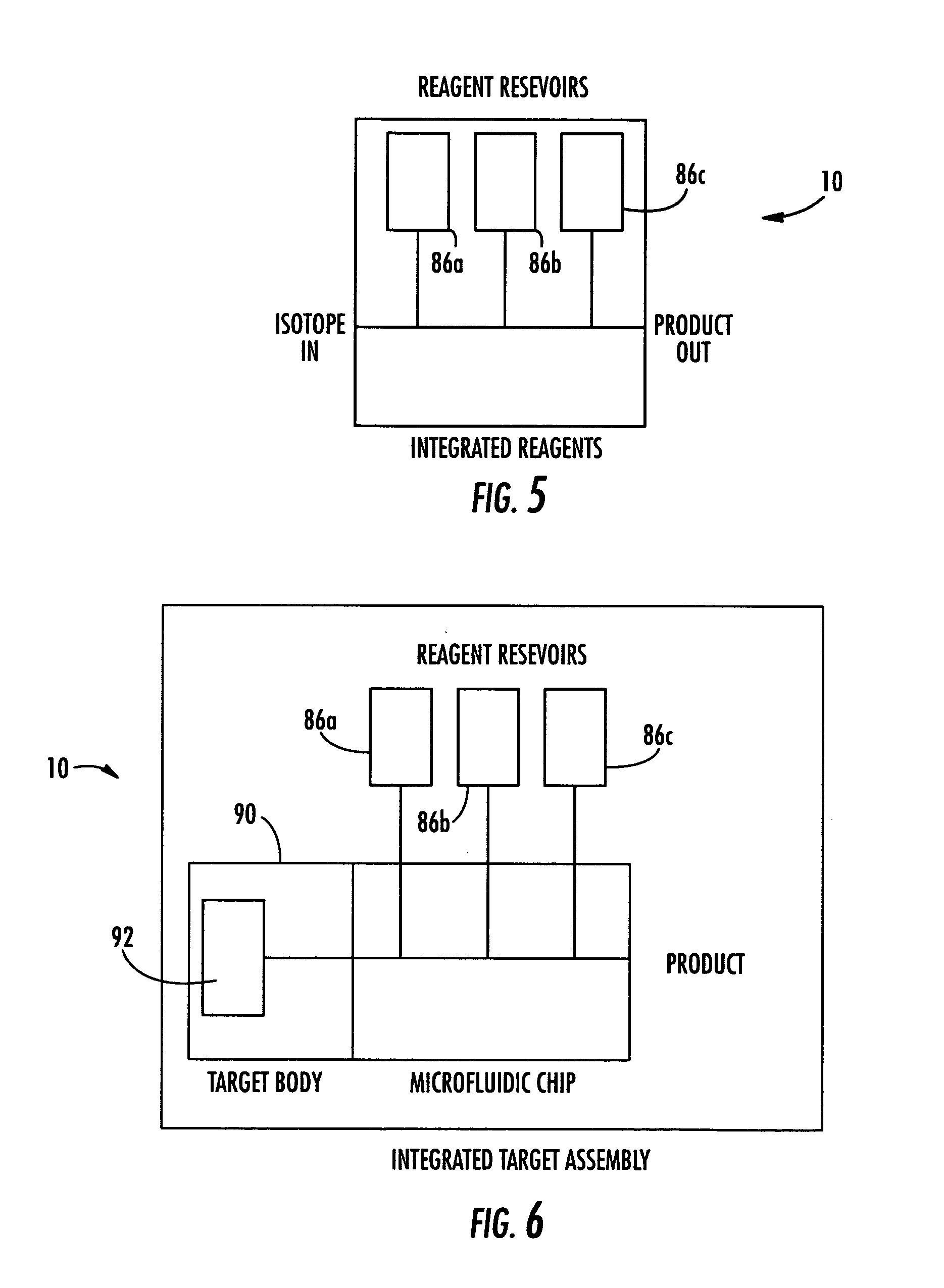
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20050232387A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals, such as PET molecular imaging probes, wherein the reaction step or steps that couple the radioactive isotope to an organic or inorganic compound to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe are performed in a microfluidic environment. The method for synthesizing a radiochemical in a microfluidic environment comprises: i) providing a micro reactor comprising a first inlet port, a second inlet port, an outlet port, and at least one microchannel in fluid communication with the first and second inlet ports and the outlet port; ii) introducing a reactive precursor into the first inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; iii) introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope into the second inlet port of the micro reactor; iv) contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in the microchannel of the micro reactor; v) reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, the reacting step resulting in formation of a radiochemical; and vi) collecting the radiochemical from the outlet port of the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
Microspheres capable of binding radioisotopes, optionally comprising metallic microparticles, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to a microsphere, comprising a hydrophilic polymer comprising a plurality of pendant anionic groups; a transition-metal, lanthanide or group 13-14 metal oxide, polyoxometalate or metal hydroxide or combination thereof; and a first radioisotope that emits a therapeutic β-particle. In certain embodiments, the microsphere further comprsies a second radioisotope that emits a diagnostic γ-ray; wherein the atomic number of the first radioisotope is not the same as the atomic number of the second radioisotope. In certain embodiments, the microsphere is composed of polymer impregnated with zirconia bound to 32p as the source of the therapeutic β-emissions and 67Ga as the source of the diagnostic γ-emissions. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the preparation of a microsphere impregnated with a radioisotope that emits therapeutic β-particles and a radioisotope that emits diagnostic β-emitting radioisotope and a γ-emitting radioistope; wherein the atomic number of the first radioisotope is not the same as the atomic number of the second radioisotope. In certain embodiments, said microspheres are administered to the patient through a catheter. In another embodiment, the microsphere is combined with the radioisotopes at the site of treatment.
Owner:BIOSPHERE MEDICAL INC
Non Proliferating Thorium Nuclear Fuel Inert Metal Matrix Alloys for Fast Spectrum and Thermal Spectrum Thorium Converter Reactors
InactiveUS20080144762A1Improve heat transfer performanceRobust assemblyOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationHigh energyEpithermal neutron
A set of alloy formulations is disclosed to use with thorium based nuclear fuels in a fast spectrum reactor; with thorium based nuclear fuels in existing thermal spectrum power reactors; for medical isotope production in the epithermal, the fast, the fission spectrum and the thermal spectra; and to use as fuel in test and experimental reactors that are non proliferative. The alloys form inert metal matrixes to hold fine particles of dispersed thorium containing fuel. The formulations also are useful for the production of medical and commercial isotopes in the high energy, fast and epithermal neutron spectra.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Breath test for detection of drug metabolism
InactiveUS6180414B1Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDrug metabolismMetabolite
A breath test for determining the rate of metabolism of a drug is described. First, a safe and effective amount of the drug, preferably appropriately labelled and most preferably isotopically-labelled, is administered to a subject. After a suitable time period, the exhaled breath of the subject is analyzed to determine the concentration of a metabolite. The concentration of the metabolite is then used to determine the rate of metabolism of the drug. A breath test kit is also described. Such a breath test kit would include an item or items necessary for performing at least one of the methods of determining the rate of metabolism of a drug in a subject. For example, such a breath test kit could include an isotopically-labelled drug to be administered to the subject.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL
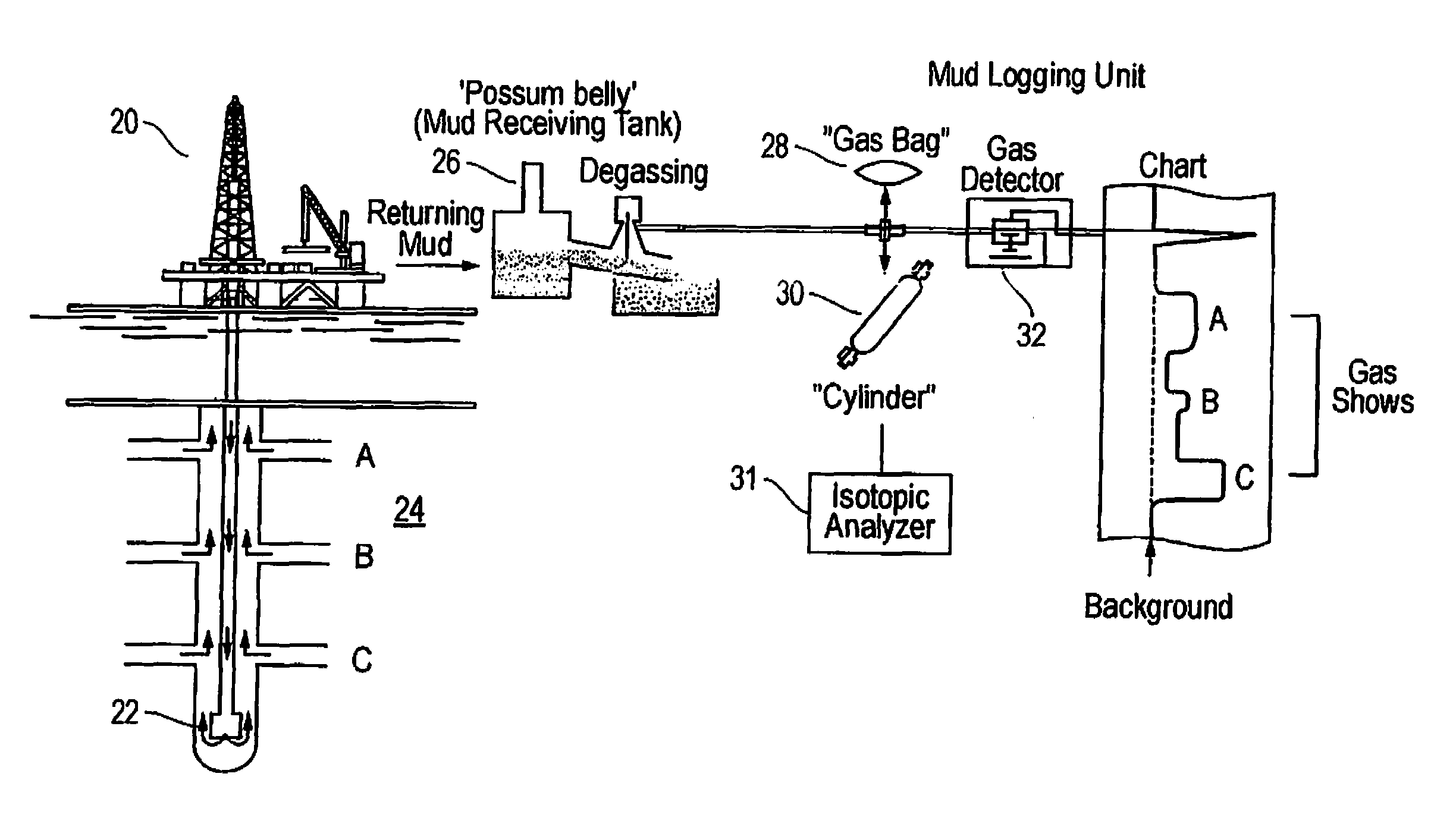
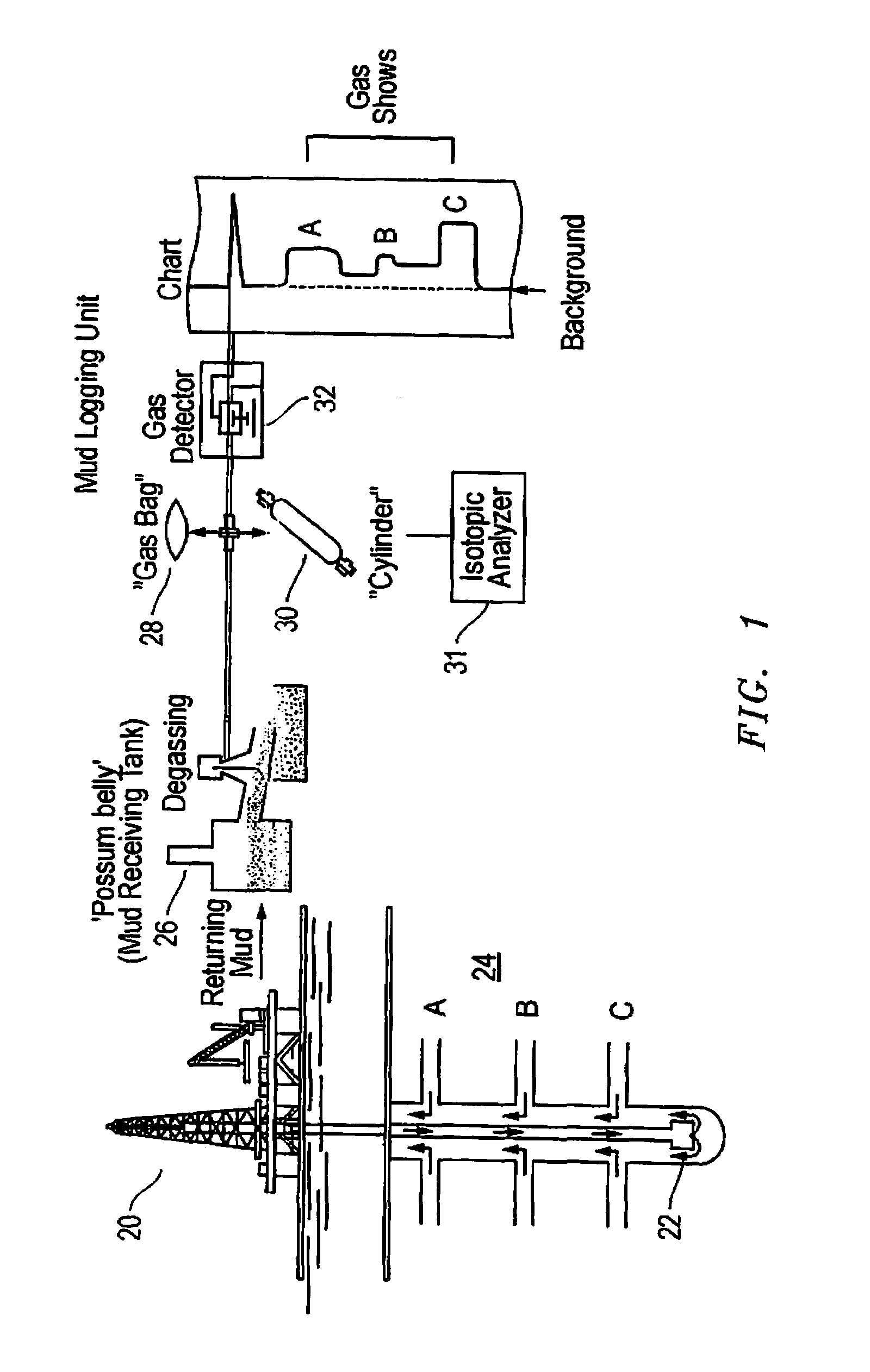
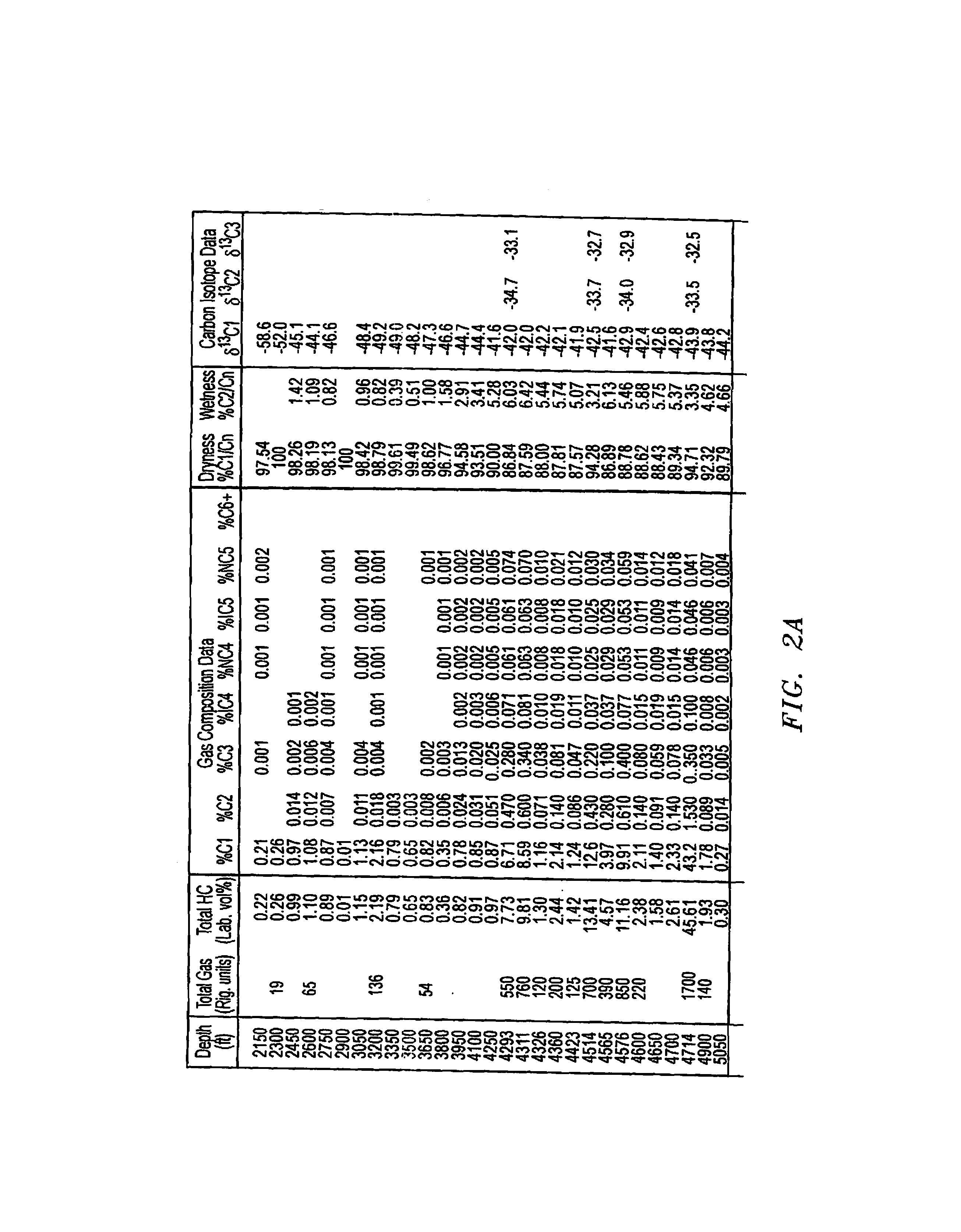
Method and system of processing information derived from gas isotope measurements in association with geophysical and other logs from oil and gas drilling operations
InactiveUS20080147326A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingProspecting/detection of underground/near-surface gasesWell loggingIsotopic composition
A system and method of interpreting well log isotopic information in a drilling operation of a target area. The method begins by inputting a template for indicating a trend from analyzed mud gas samplings into a computing system. Next, a plurality of mud gas samplings are profiled through a well bore at a plurality of incremental depths of the well bore. The plurality of gas samplings are analyzed to obtain a plurality of isotopic data points associated with hydrocarbon isotopic composition of the plurality of gas samplings. The plurality of isotopic data points includes data associated with a composition of ethane and methane or other gaseous components within each of the mud gas samplings. A trend associated with the template is determined by the computing system from the plurality of isotopic data points. The plurality of isotopic data points is analyzed to geochemically interpret the geological information.
Owner:ELLIS LEROY
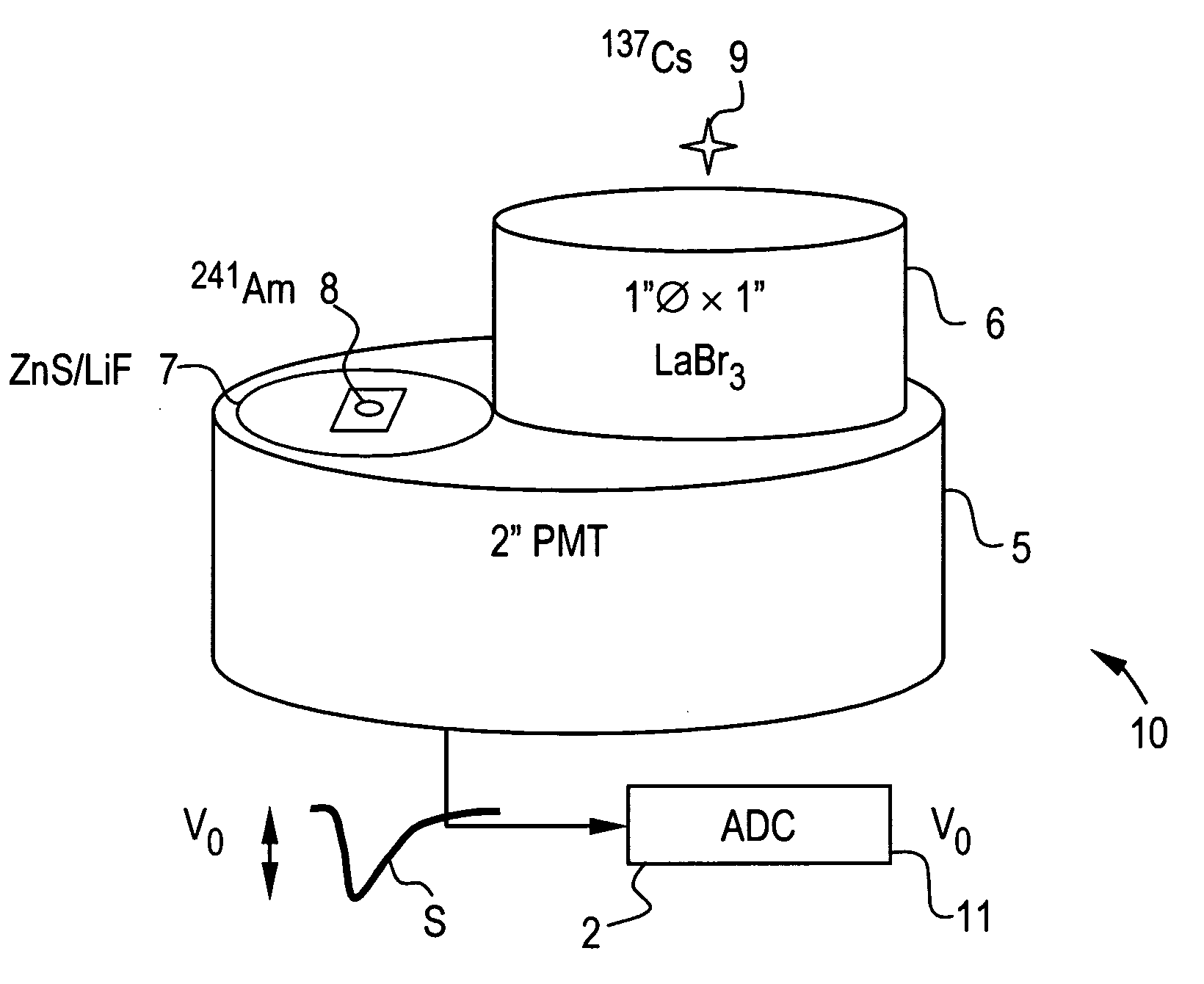
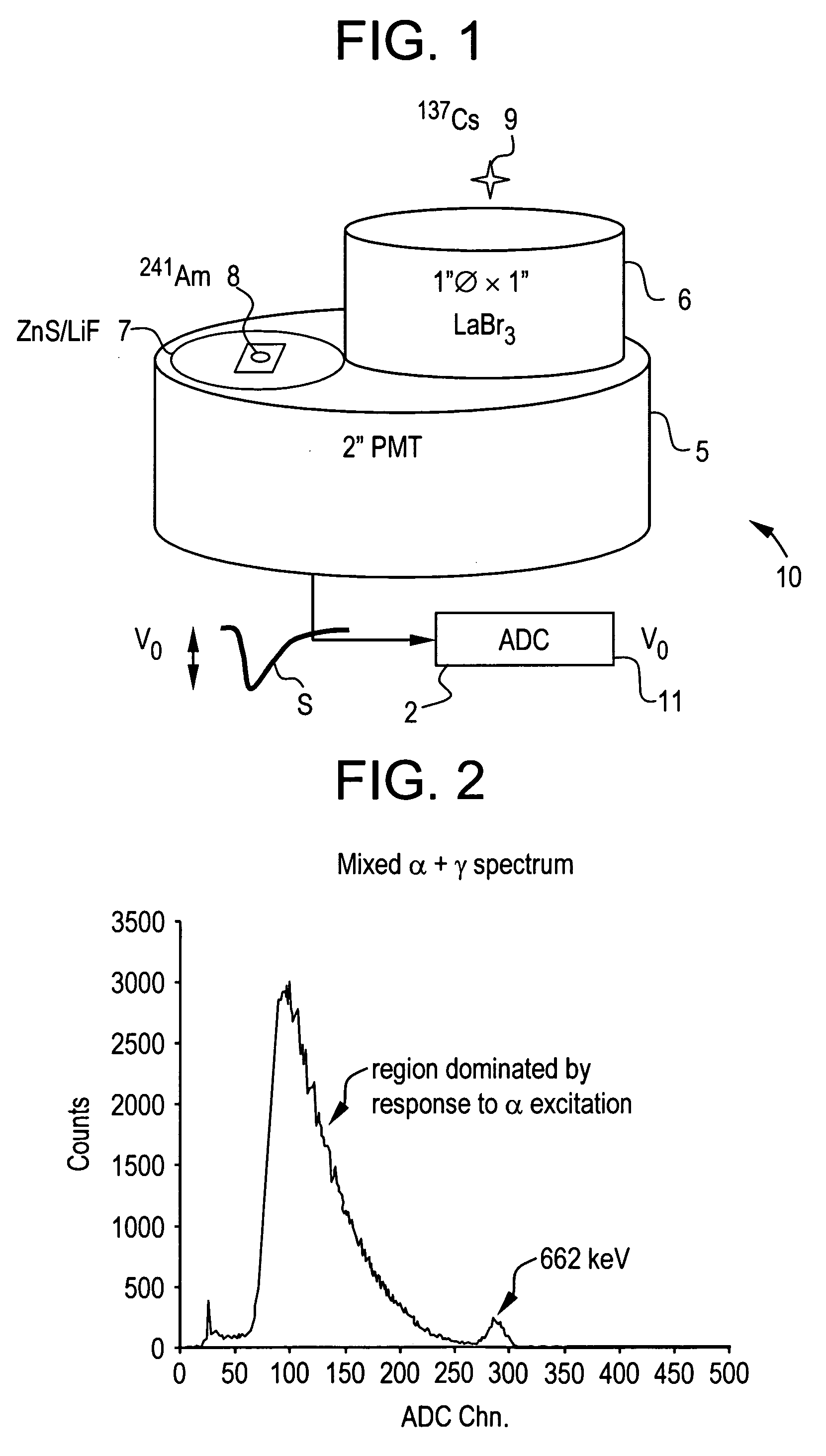
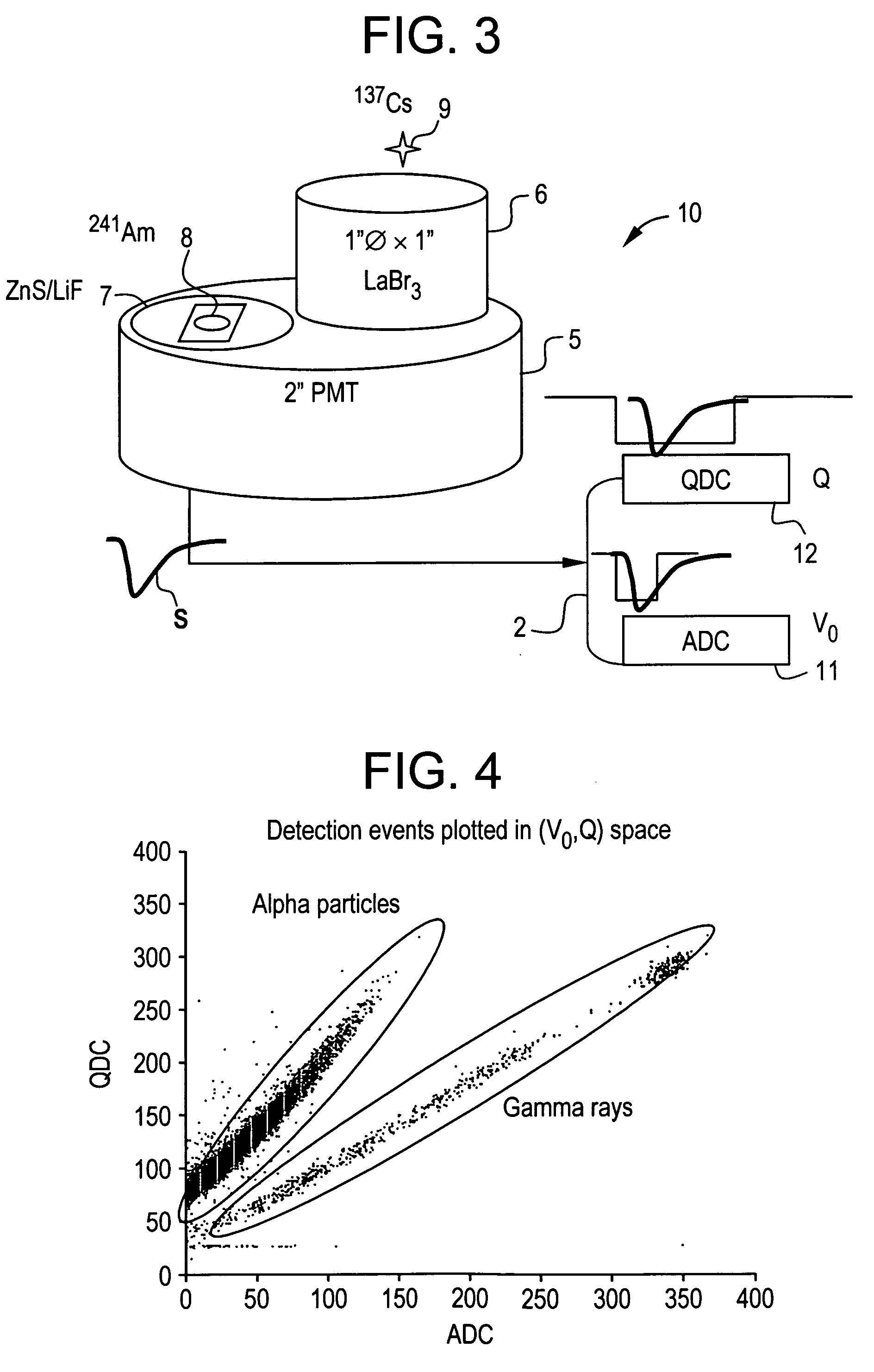
Pulse shape discrimination method and apparatus for high-sensitivity radioisotope identification with an integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector
InactiveUS20070290136A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacteristic energyGamma energy
A method and apparatus for discriminating the types of radiation interacting with an integrated radiation detector having of a pulse-mode operating photosensor which is optically coupled to a gamma-ray scintillator sensor and a neutron scintillator sensor and uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse processing provides for, among other things, faithful representation of the true energy spectrum of the gamma radiation field and allows for radioisotope identification by searching for the presence of characteristic energy lines in the gamma energy spectrum. The pulse shape discrimination method ensures that the high sensitivity and resolution of the isotope identification function is not affected during operation in mixed neutron-gamma fields.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Radioactive ion
InactiveUS20050118098A1Minimize difficultyEfficient methodIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMedicineInsertion stent
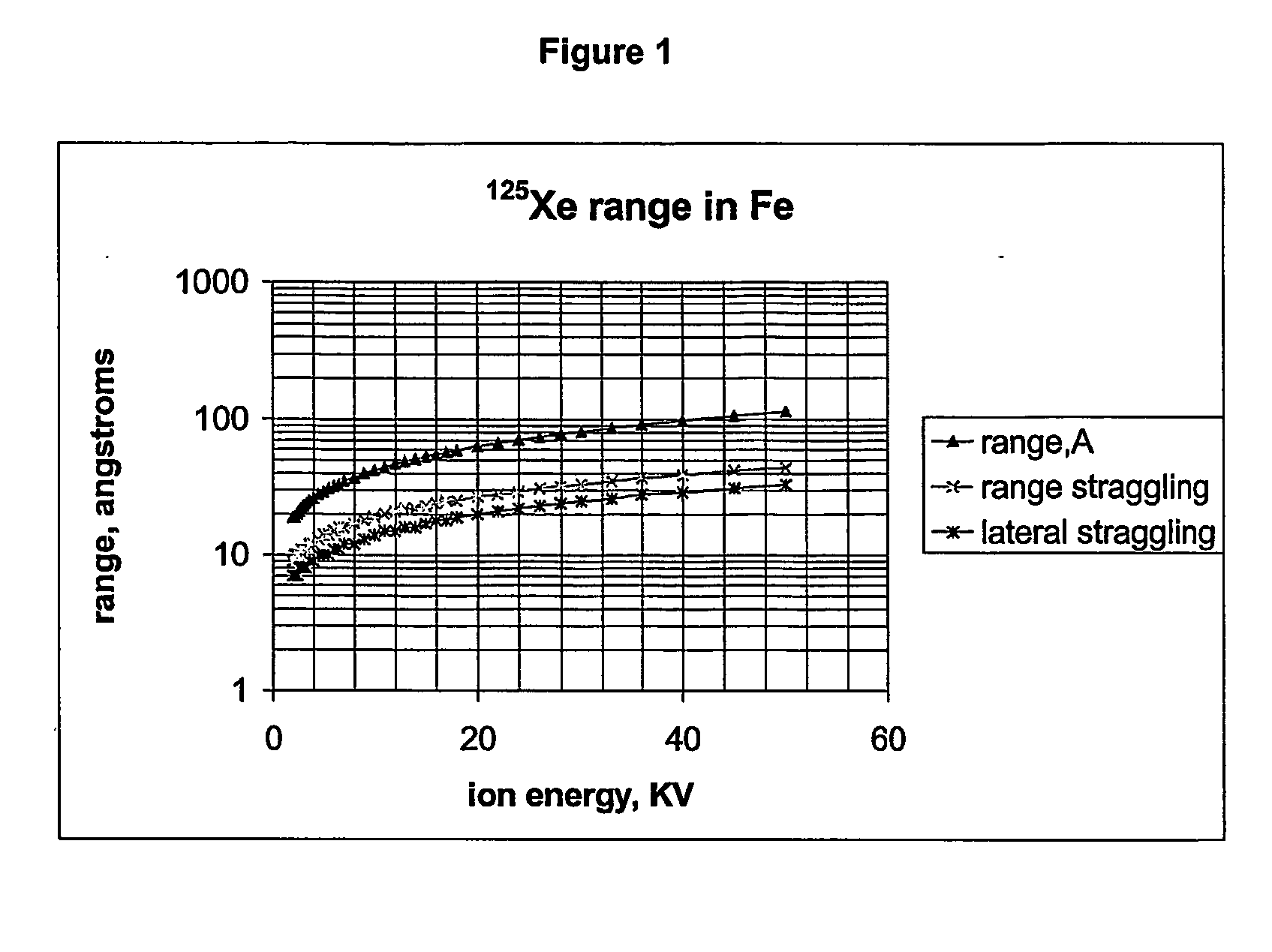
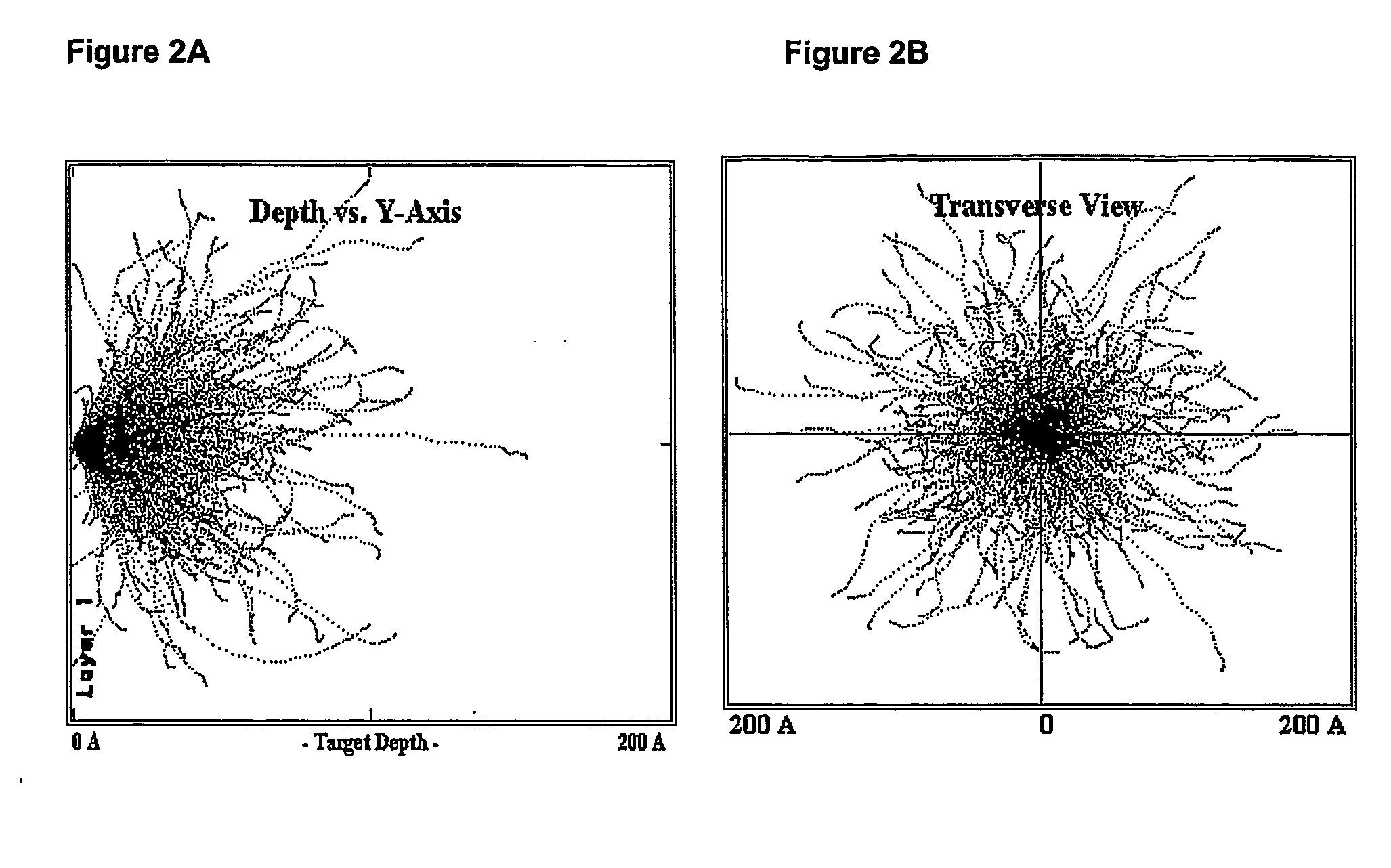
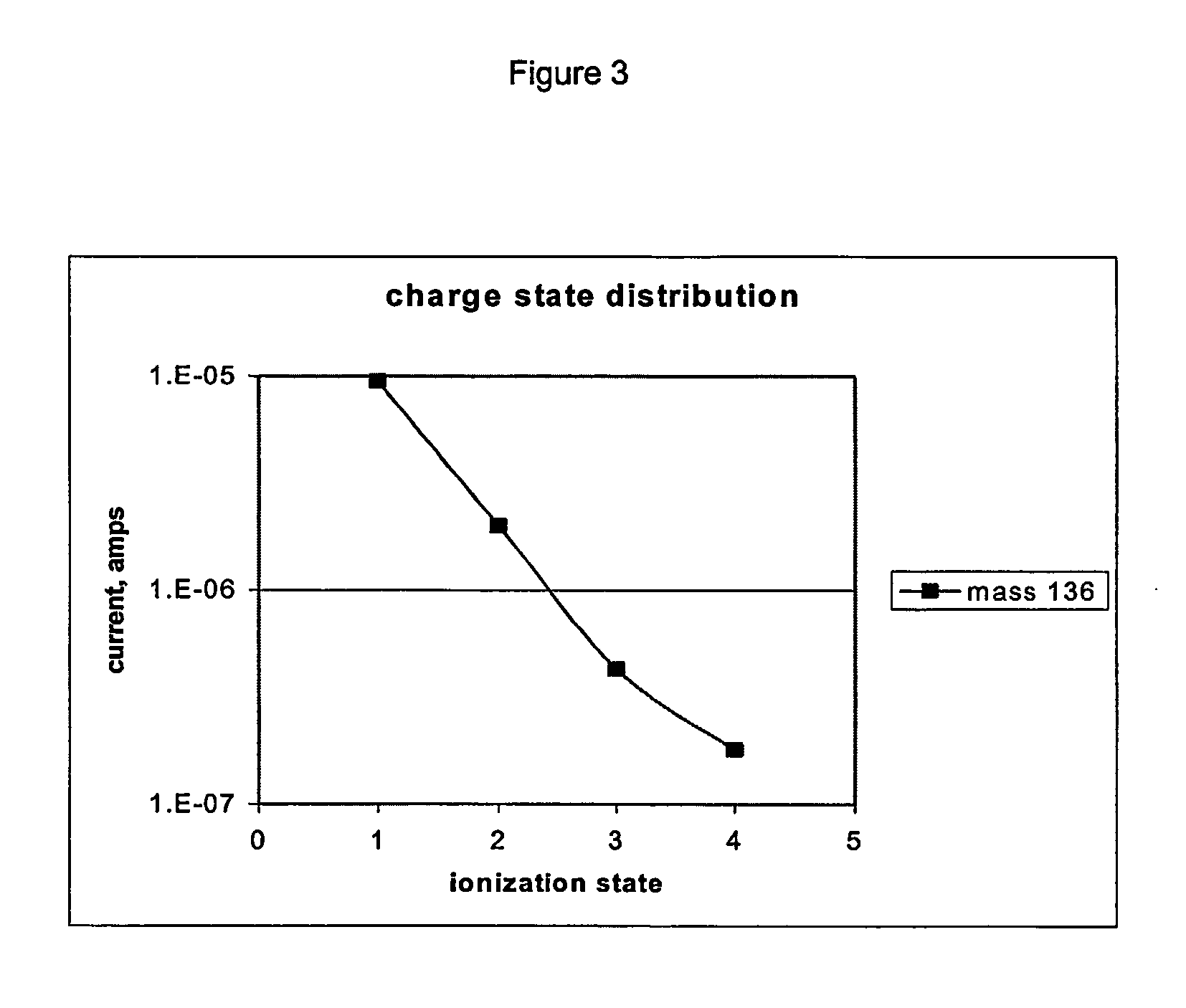
The present invention relates to a method for implantation of Xe isotopes in a matrix for production of 125I sources that do not shed radioactive atoms. 125Xe implanted at 12 kV in steel, titanium and gold does not evolve after more than 10 half-lives (380 h) and 125I from the decay of implanted 125Xe is equally stable for 2 half-lives (120 d). The matrix having radioxenon implanted is useful as a medical device, for instance as a “seed” for radiotherapeutic uses or in production of stents. Methods of treatment utilizing such devices are also encompassed by the present invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
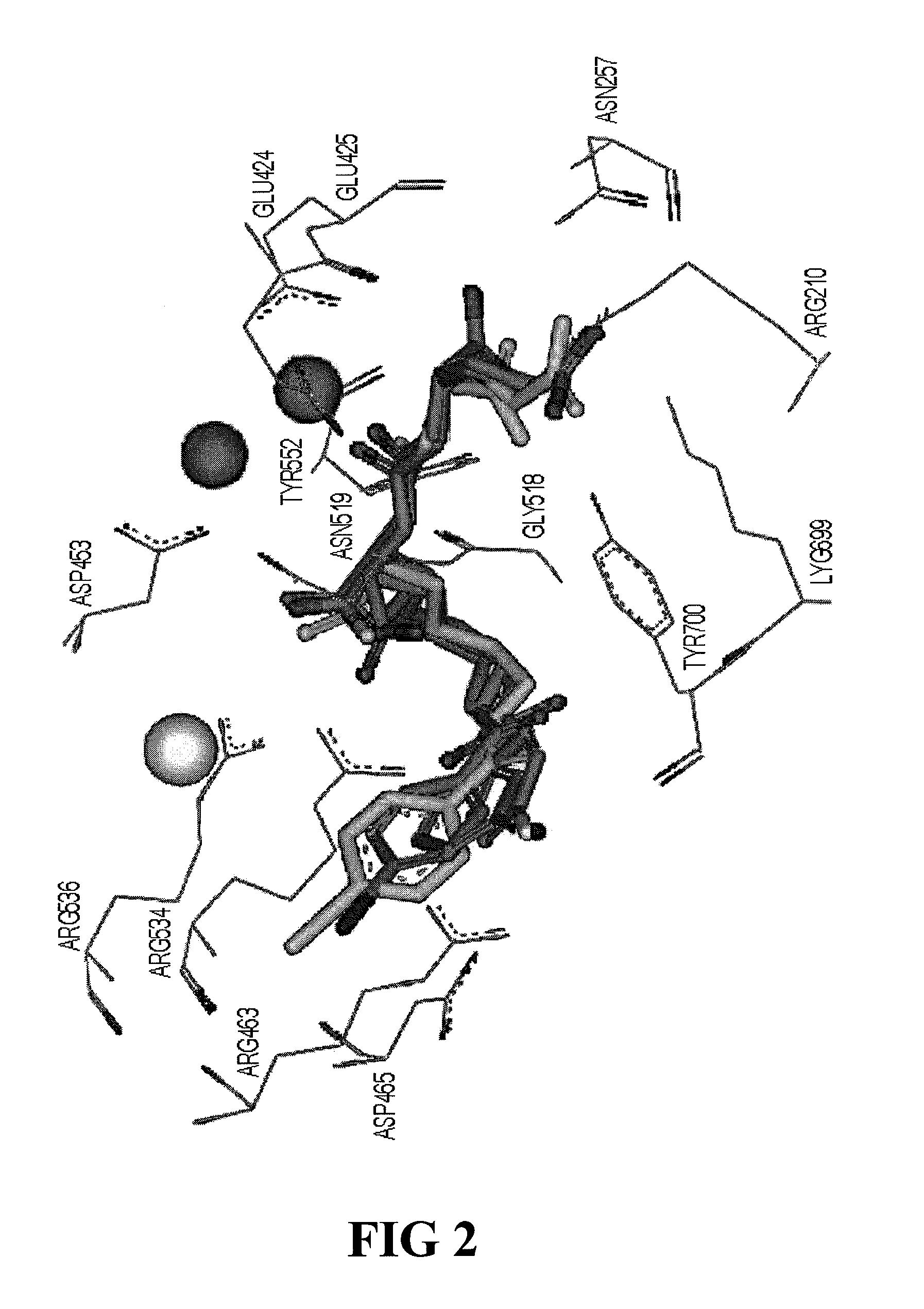
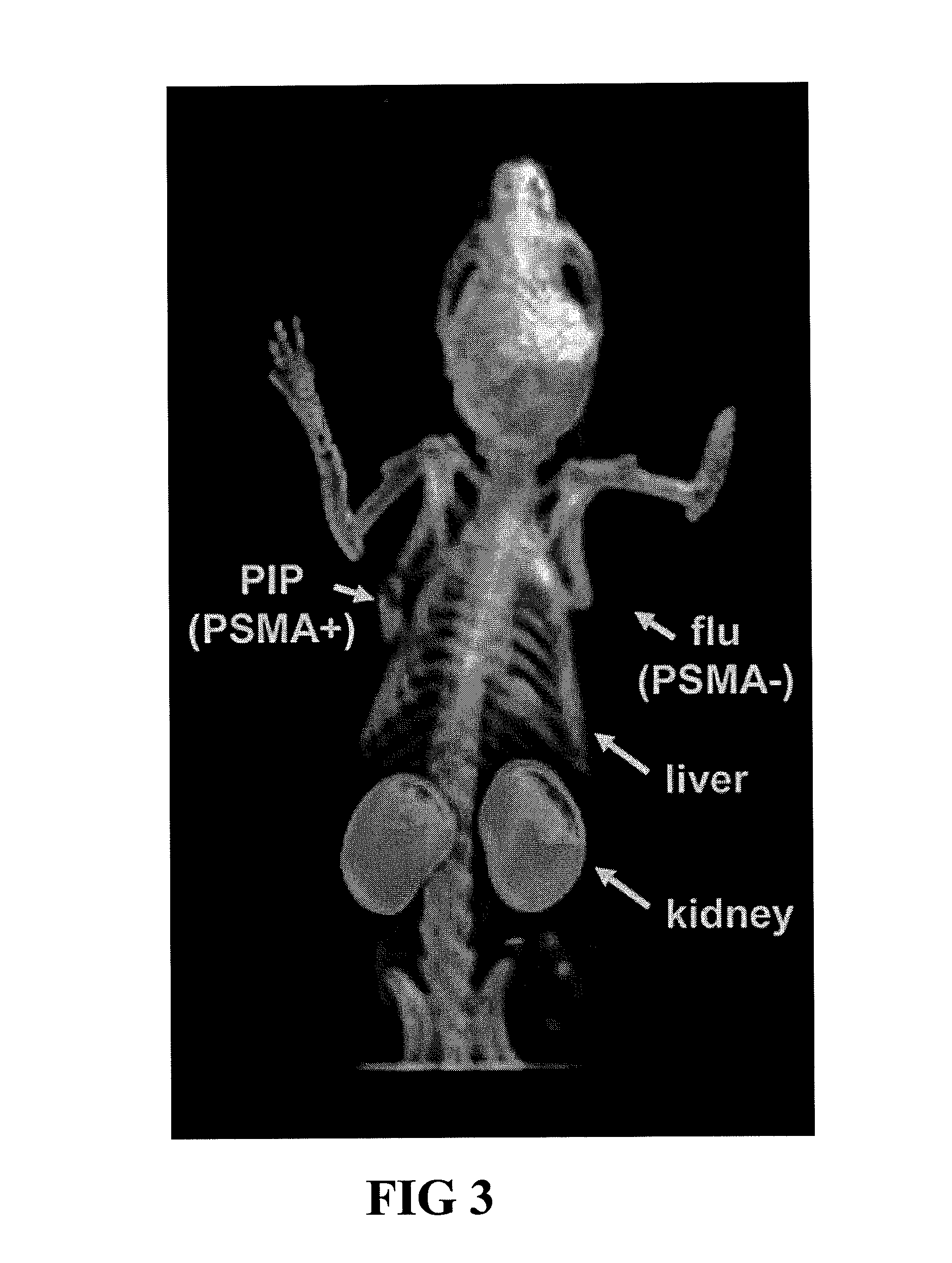
PSMA-binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS8778305B2Satisfies long standing and unmetSharp contrastGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsProstate cancer cellAntigen
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS7473892B2Reduce adverse effectsSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationPeptide ionsSpectroscopy
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
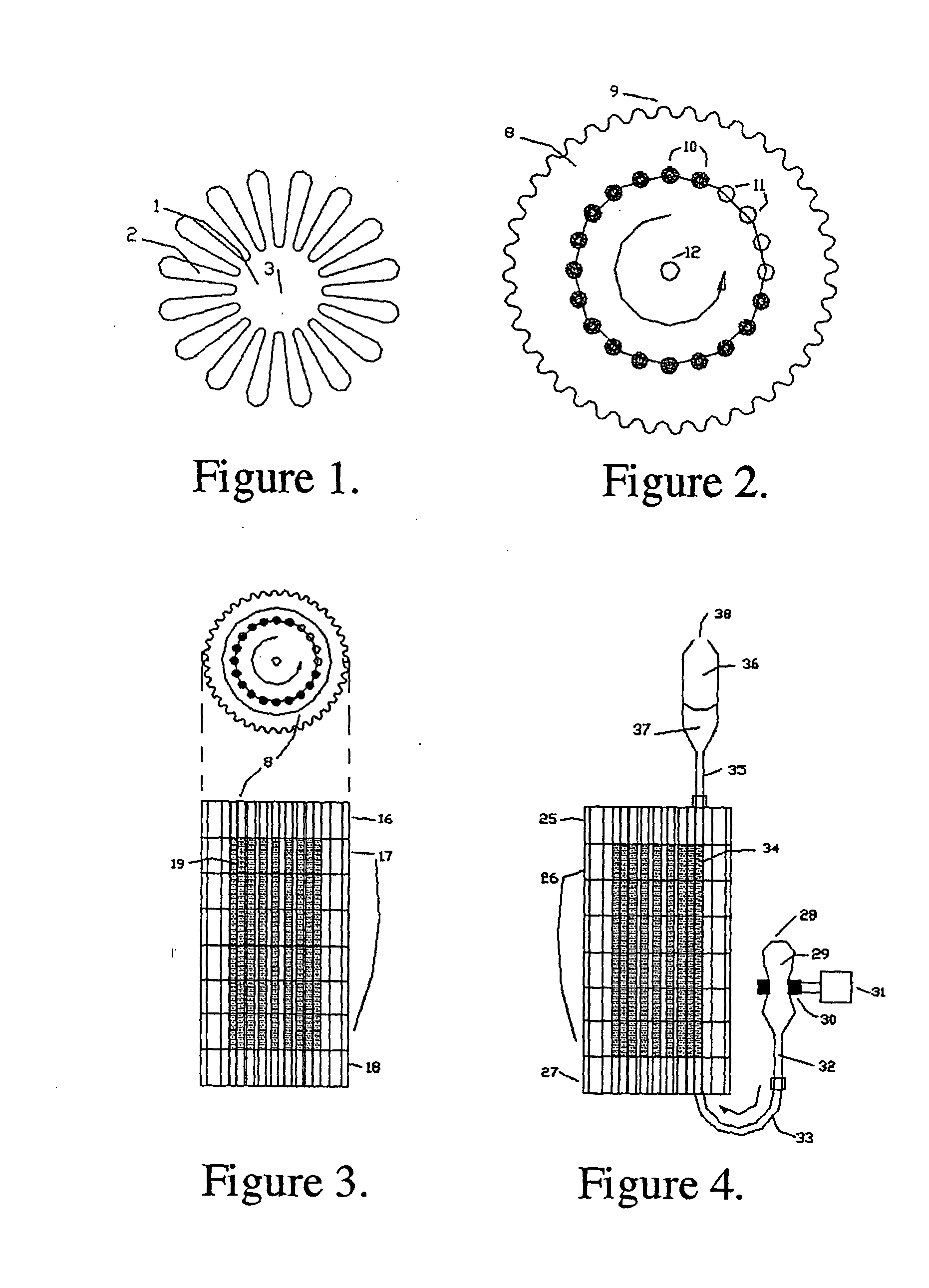
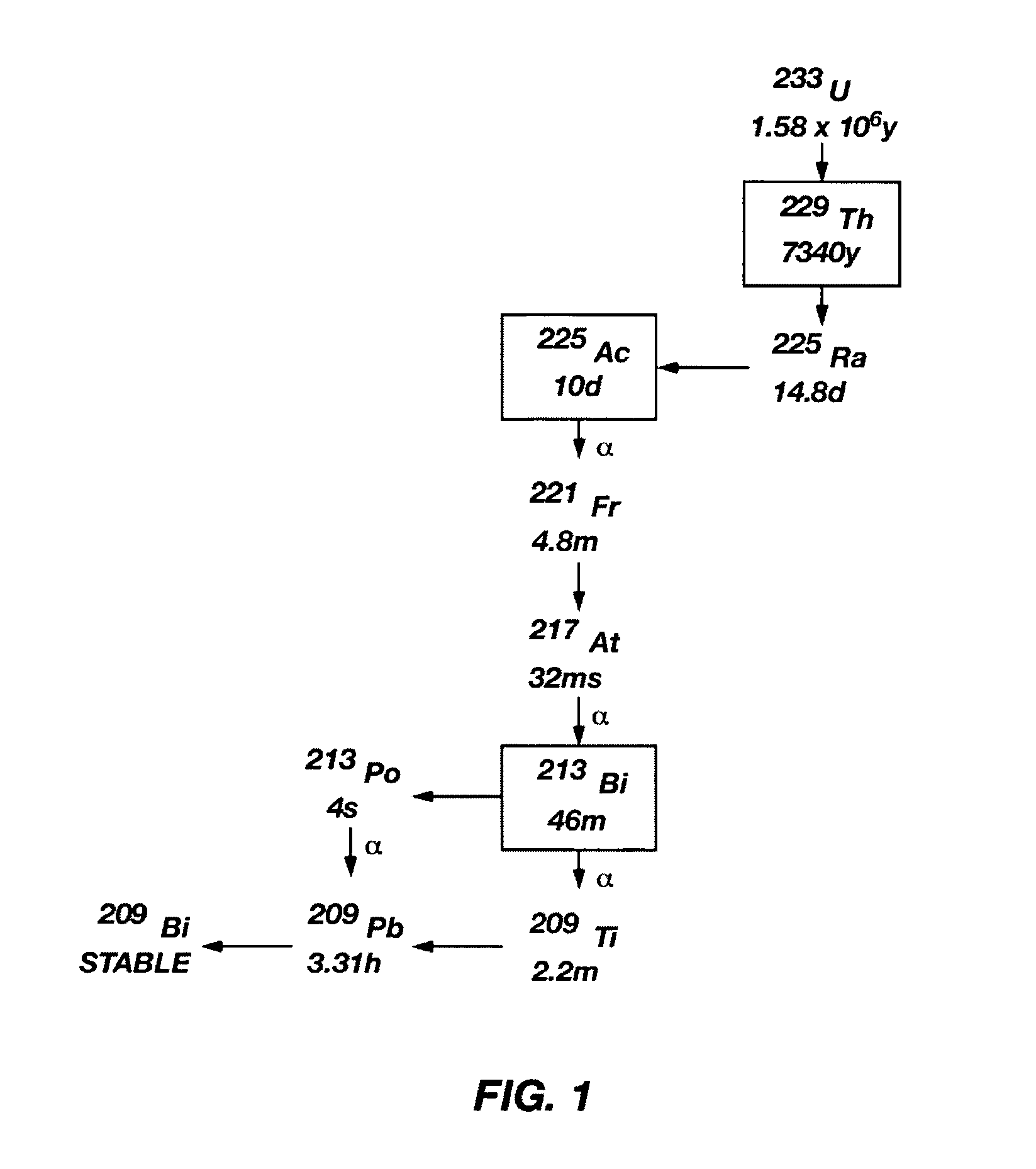
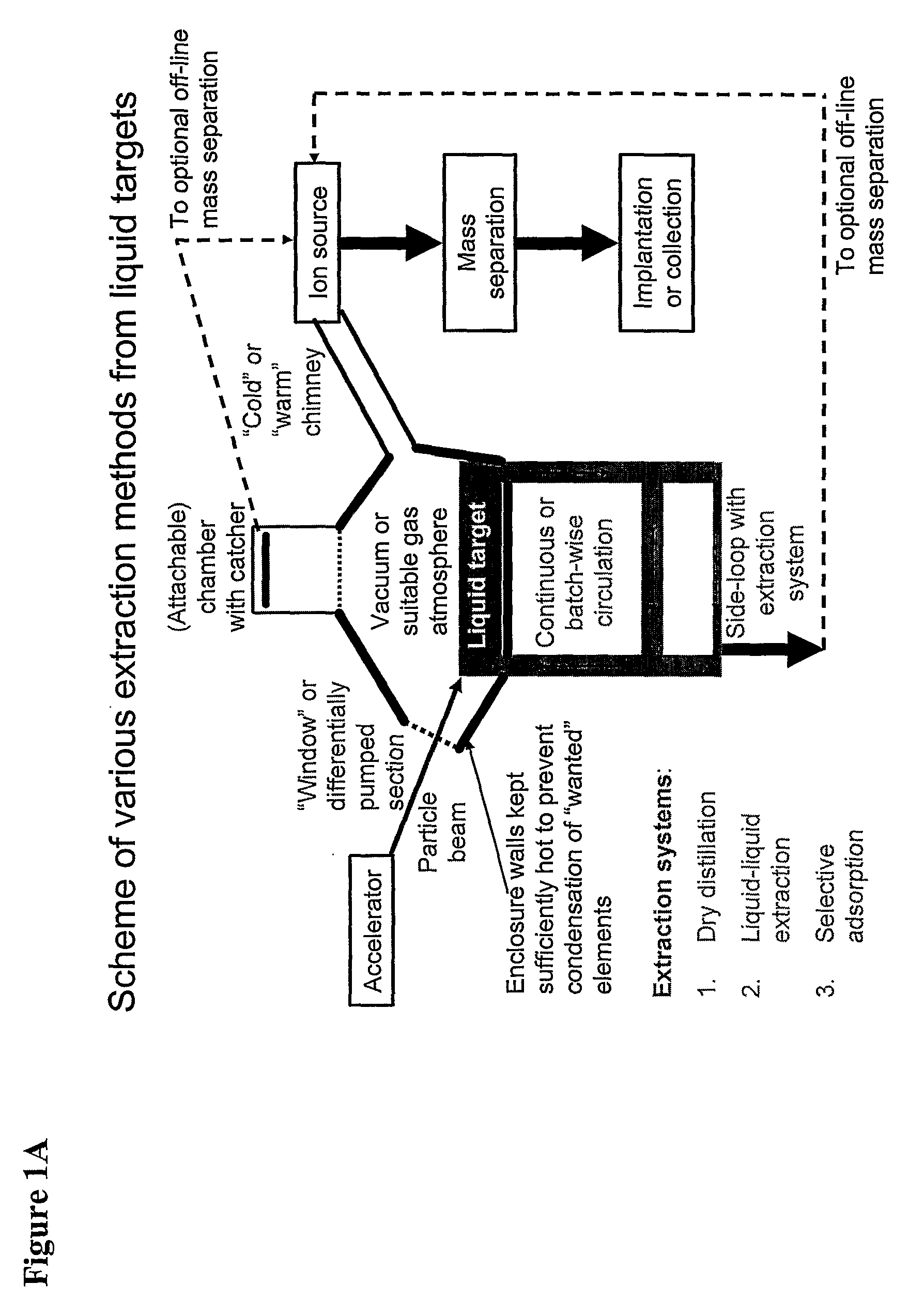
Process for radioisotope recovery and system for implementing same
A method of recovering daughter isotopes from a radioisotope mixture. The method comprises providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one parent isotope. The at least one parent isotope is extracted into an organic phase, which comprises an extractant and a solvent. The organic phase is substantially continuously contacted with an aqueous phase to extract at least one daughter isotope into the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase is separated from the organic phase, such as by using an annular centrifugal contactor. The at least one daughter isotope is purified from the aqueous phase, such as by ion exchange chromatography or extraction chromatography. The at least one daughter isotope may include actinium-225, radium-225, bismuth-213, or mixtures thereof. A liquid-liquid extraction system for recovering at least one daughter isotope from a source material is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Isotopic gas analyzer
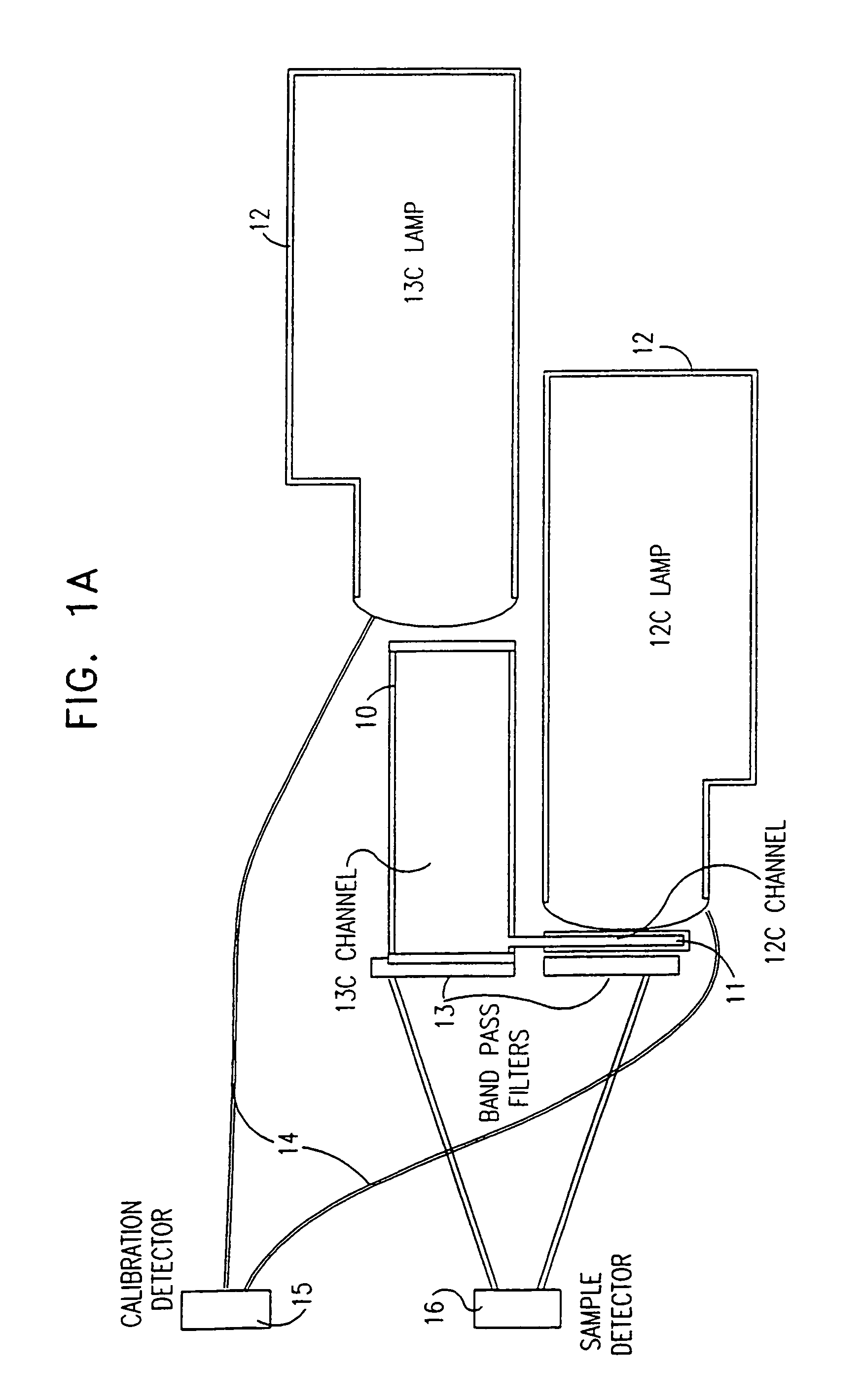
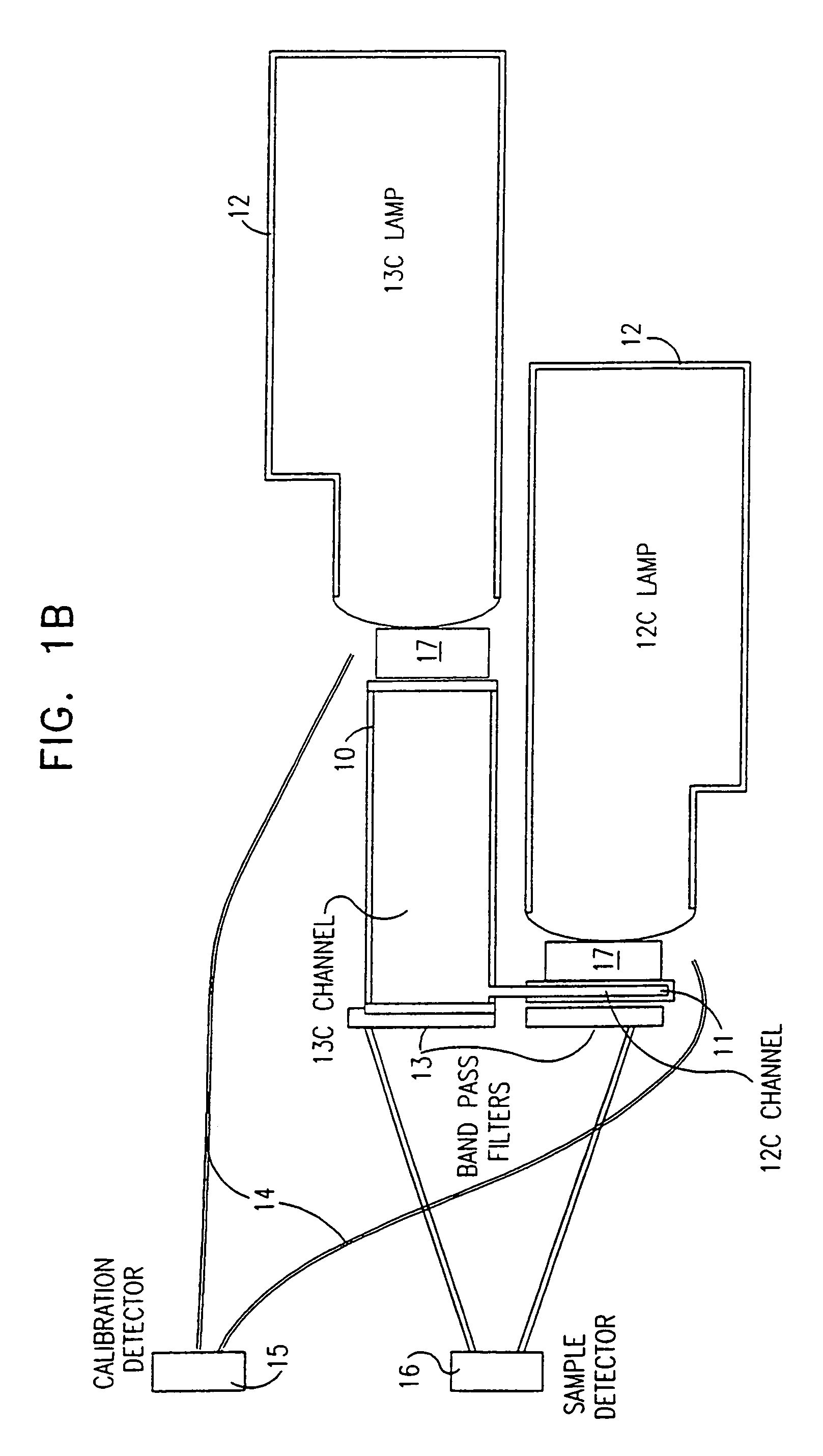
InactiveUS7063667B1Low costShort path lengthWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationCross sensitivityAbsorption cell
An NDIR spectrometer based on the use of wavelength specific lamp sources, whose emission spectrum consists of discrete, narrow lines characteristic of the isotope present in the lamp, and which it is desired to measure with the spectrometer. This allows very high intrinsic sensitivity, enabling the use of an extremely compact absorption cell with a very short path length. In addition, the source can be self-modulated, such that problems associated with external choppers are avoided. Furthermore, there is insignificant cross sensitivity between the isotopes themselves and between the isotopes and other ambient gases in the operating environment.
Owner:BREATHID 2006
Method for Production of Radioisotope Preparations and Their Use in Life Science, Research, Medical Application and Industry
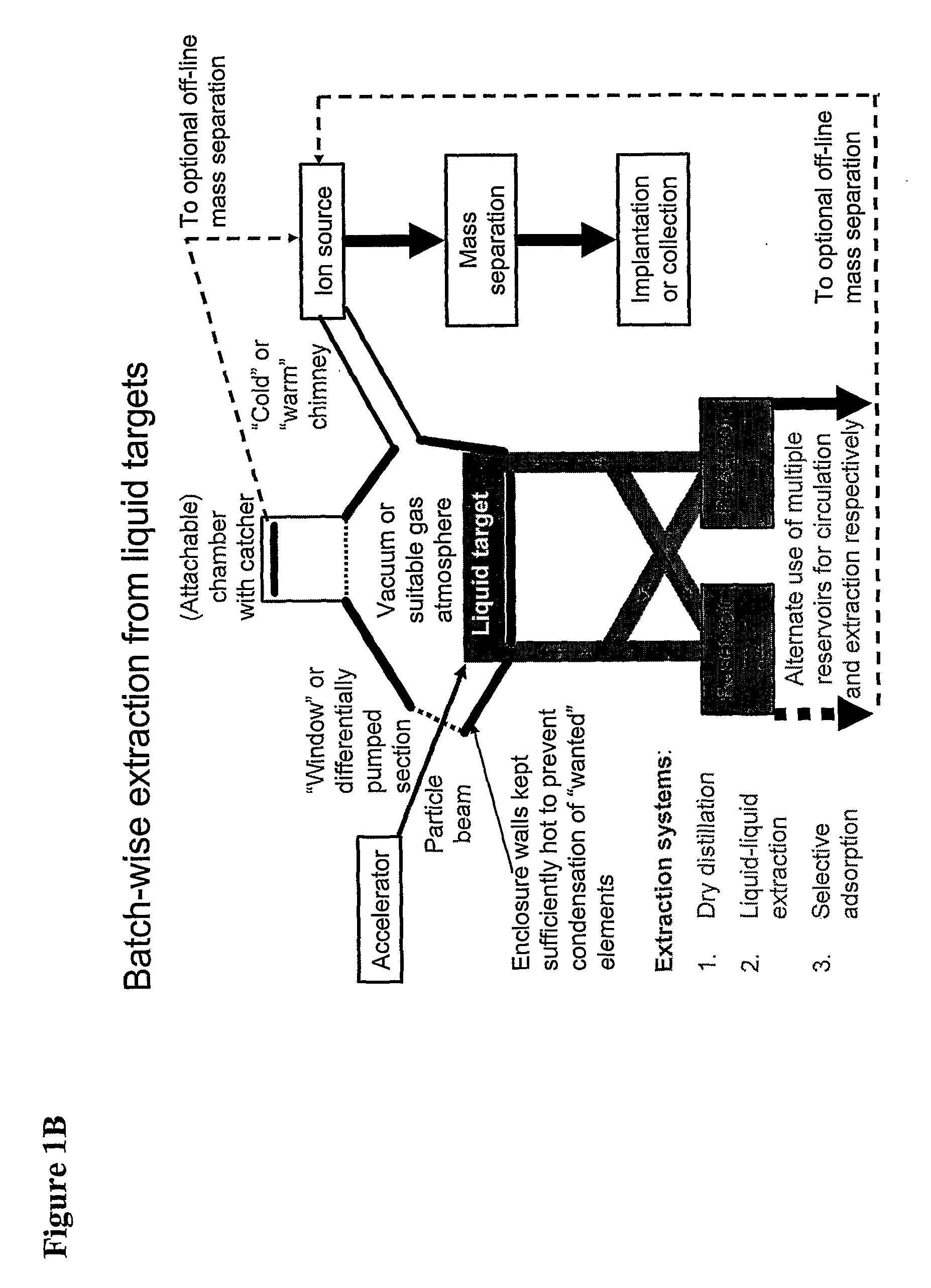
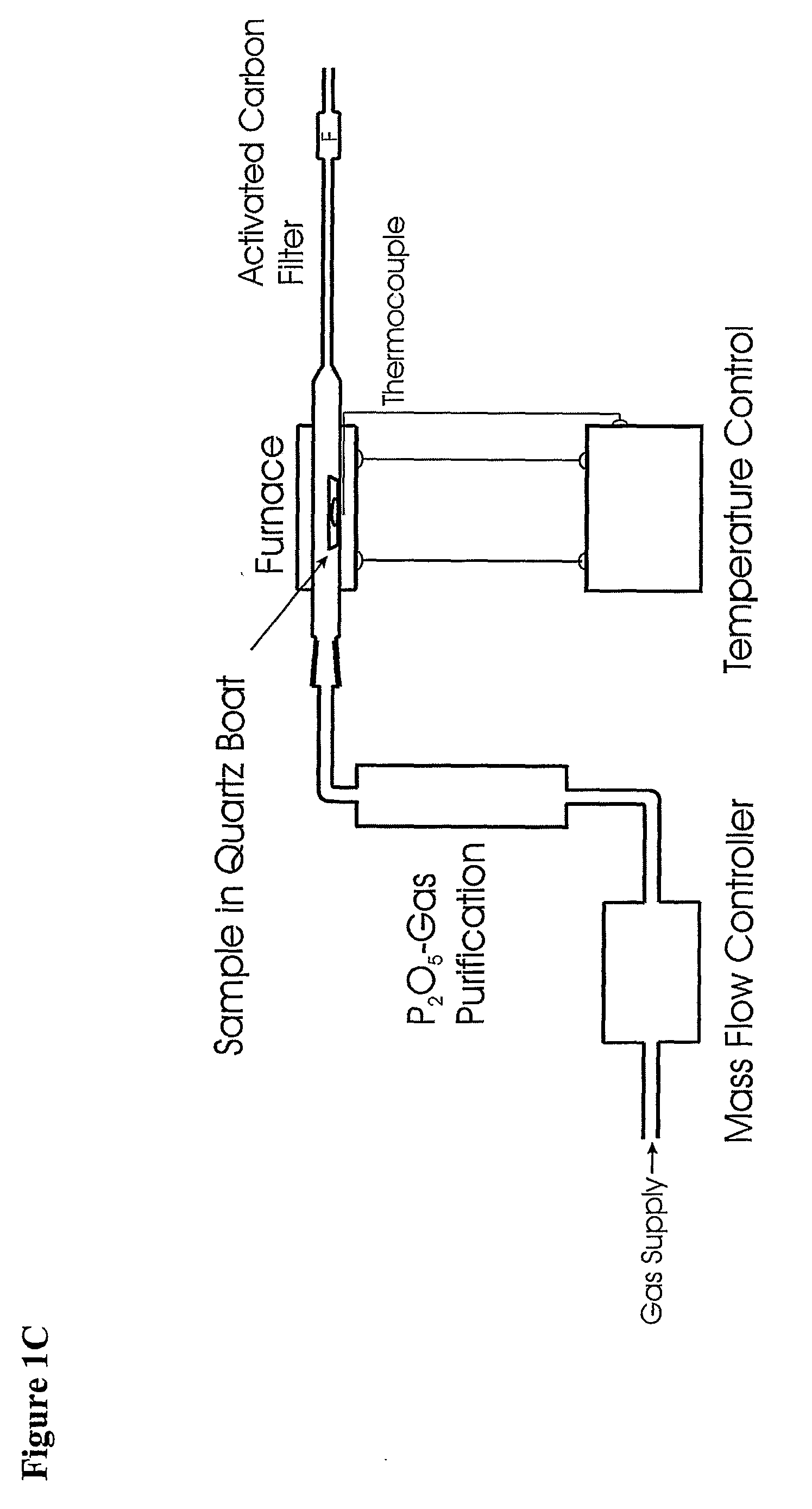
The present invention relates to an universal method for the large scale production of high-purity carrier free or non carrier added radioisotopes by applying a number of “unit operations” which are derived from physics and material science and hitherto not used for isotope production. A required number of said unit operations is combined, selected and optimised individually for each radioisotope production scheme. The use of said unit operations allows a batch wise operation or a fully automated continuous production scheme. The radioisotopes produced by the inventive method are especially suitable for producing radioisotope-labelled bioconjugates as well as particles, in particular nanoparticles and microparticles.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH +1
Layered metal foil semiconductor power device
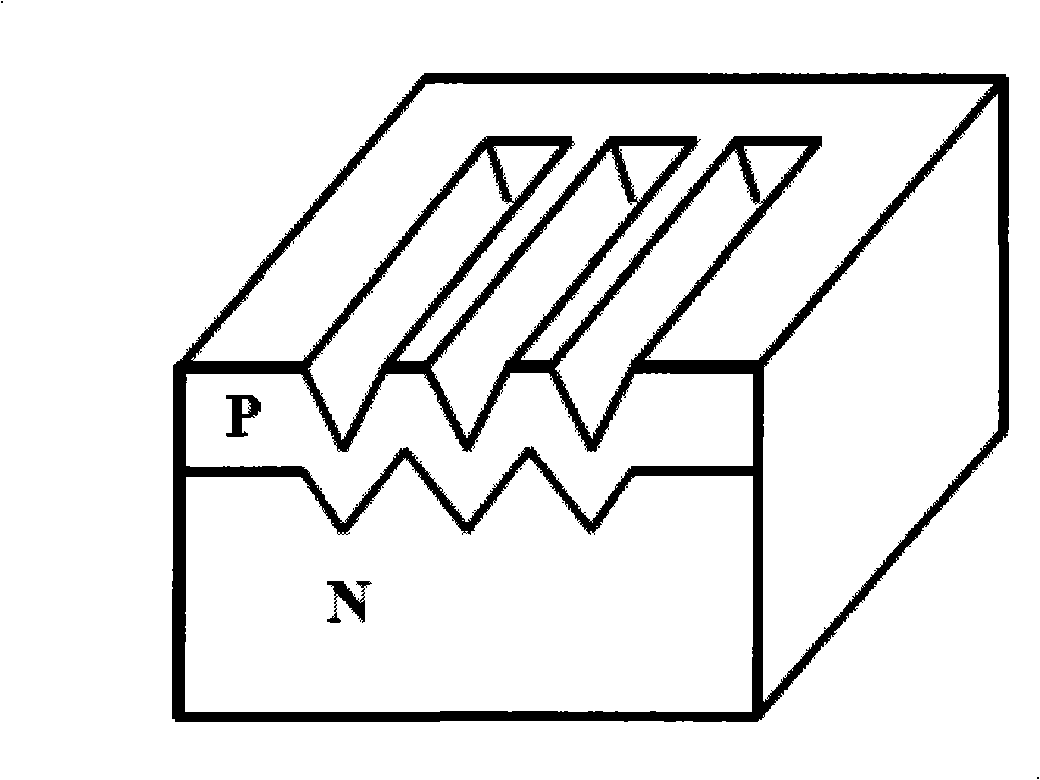
InactiveUS6118204AIncrease motivationGood energyRadiation electrical energyThermoelectric devicesSemiconductor materialsMetal foil
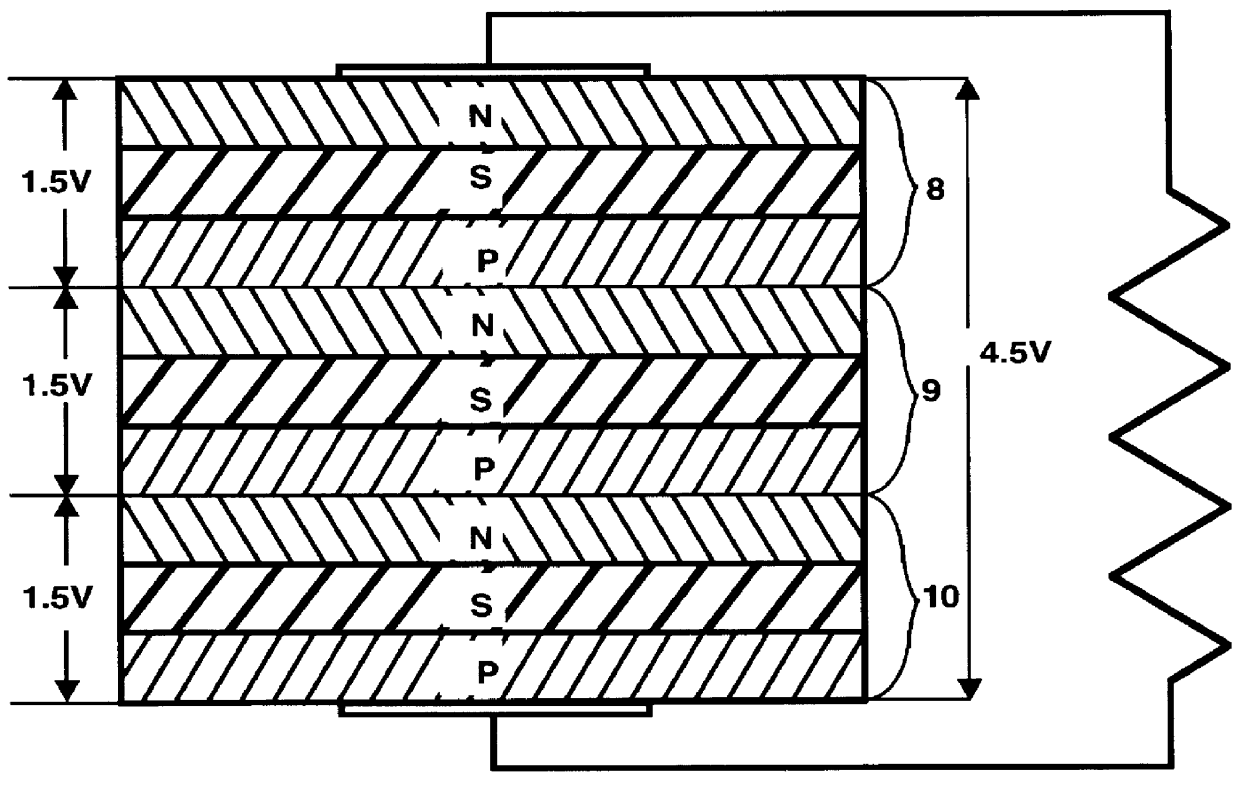
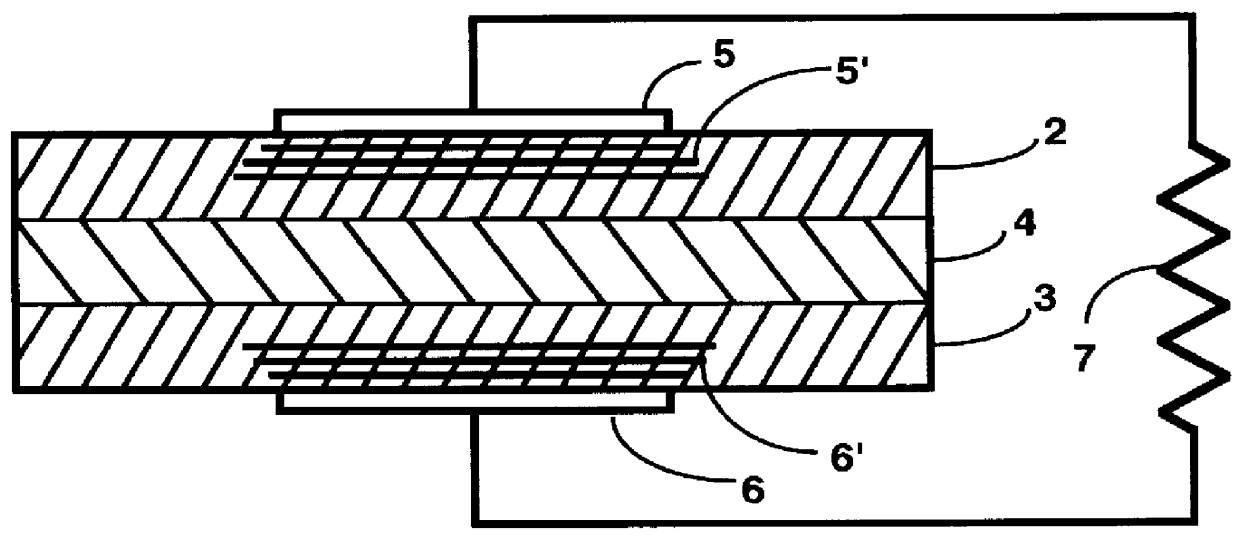
The present invention is a power cell for directly converting ionizing radiation into electrical energy. The invented isotopic electric converter provides an electrical power source that includes an electronegative material layered in a semiconductor, to form a first region that has a high density of conduction electrons, and an electropositive material also layered in the semiconductor material to form a second region with a high density of holes. Said N-layers region and P-layers region are separated by a neutral zone of semiconductor material doped with a radioactive isotope, such as, but not limited to, tritium. No junction is formed between the N and P layers regions. Rather, the potential gradient across the neutral zone is provided by the difference between the work functions of the electronegative and electropositive electrodes. Electrical contacts are affixed to the respective regions of the first and second type conductivity which become the anode and cathode of the cell, respectively. Beta particles emitted by the tritium generate electron-hole pairs within the neutral zone, which are swept away by the potential gradient between the first and second regions, thereby producing an electric current.
Owner:BROWN PAUL M
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7632686B2Reduce complexityOverwhelm resolutionSamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
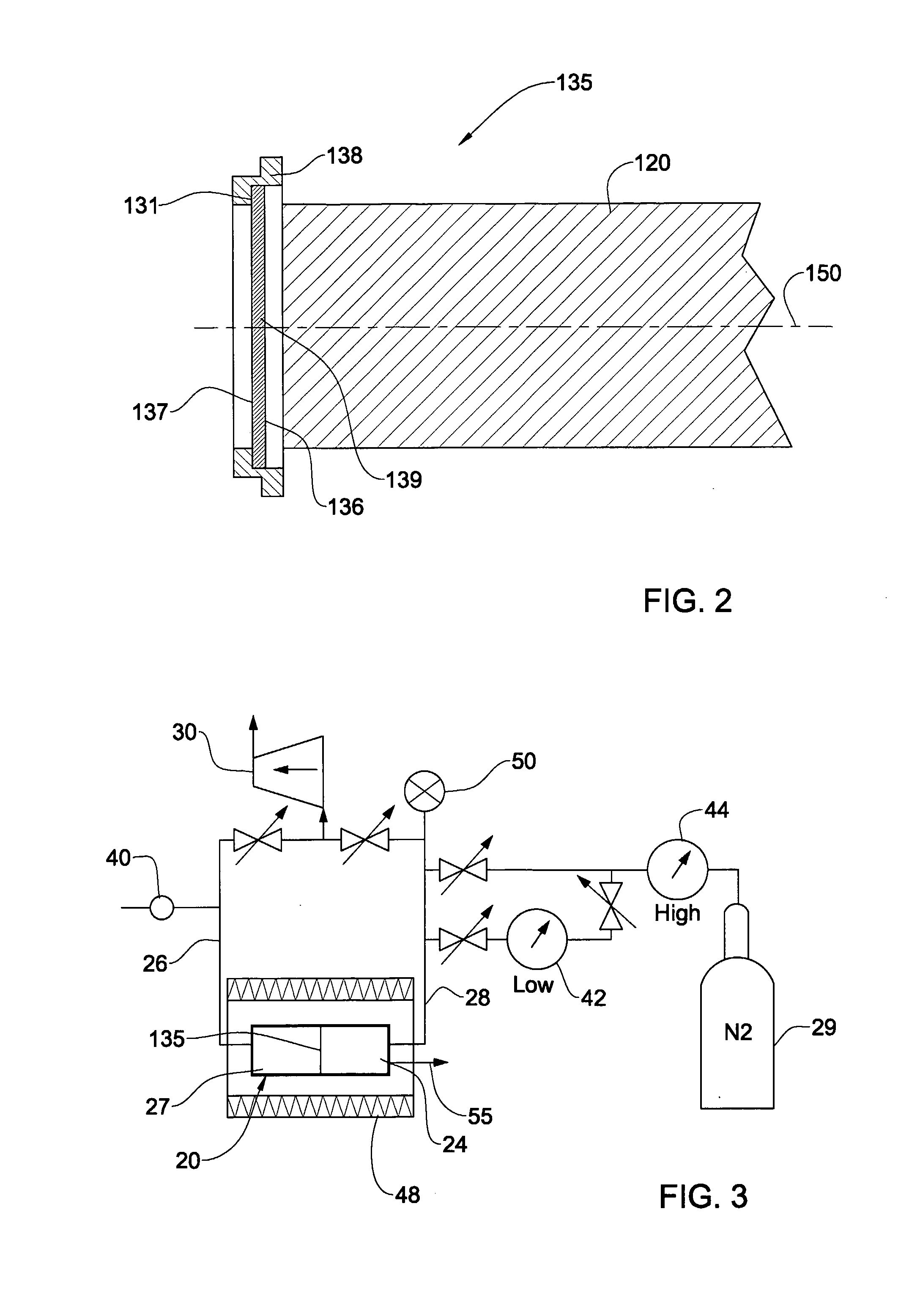
Device for fitting of a target in isotope production
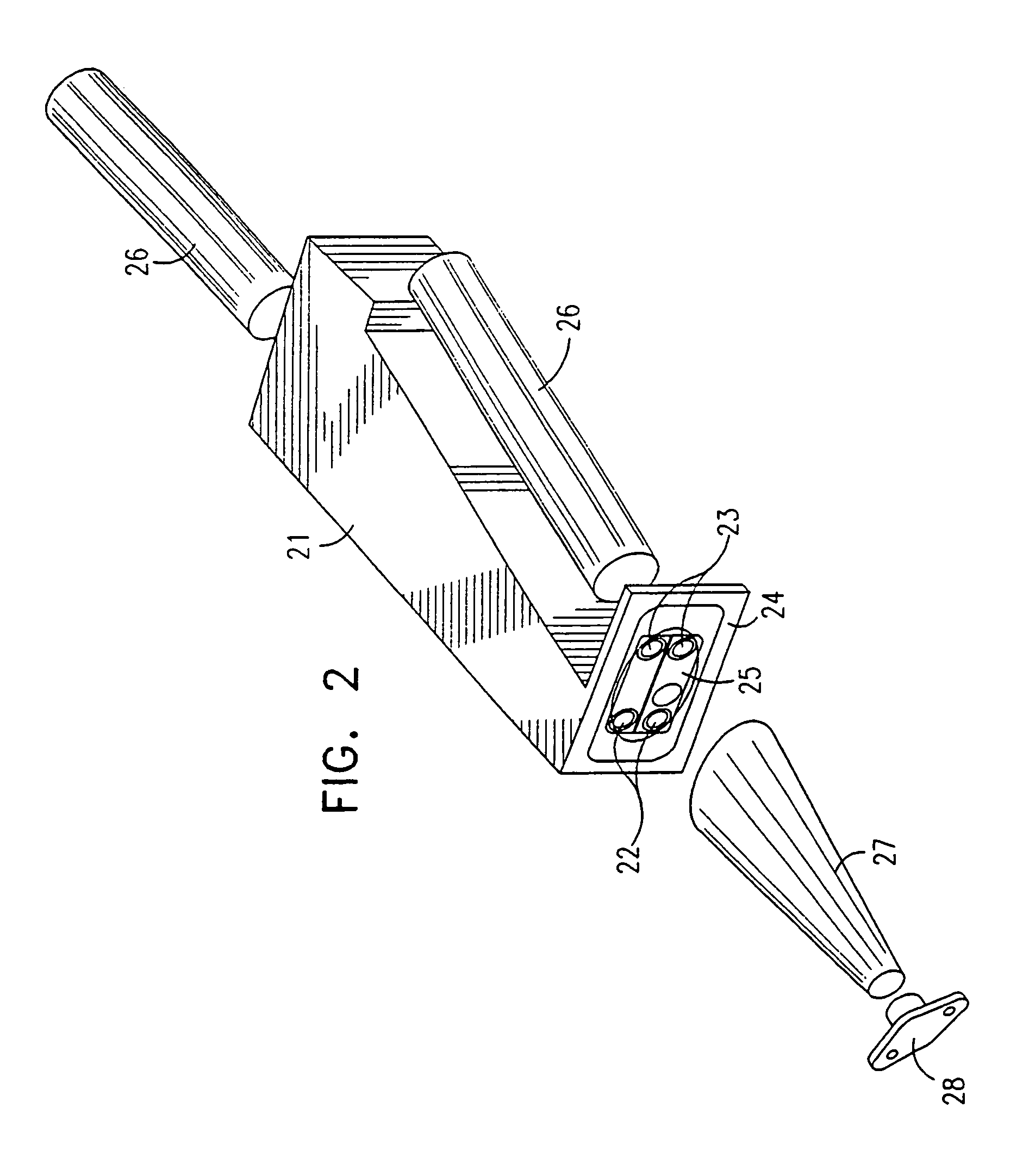
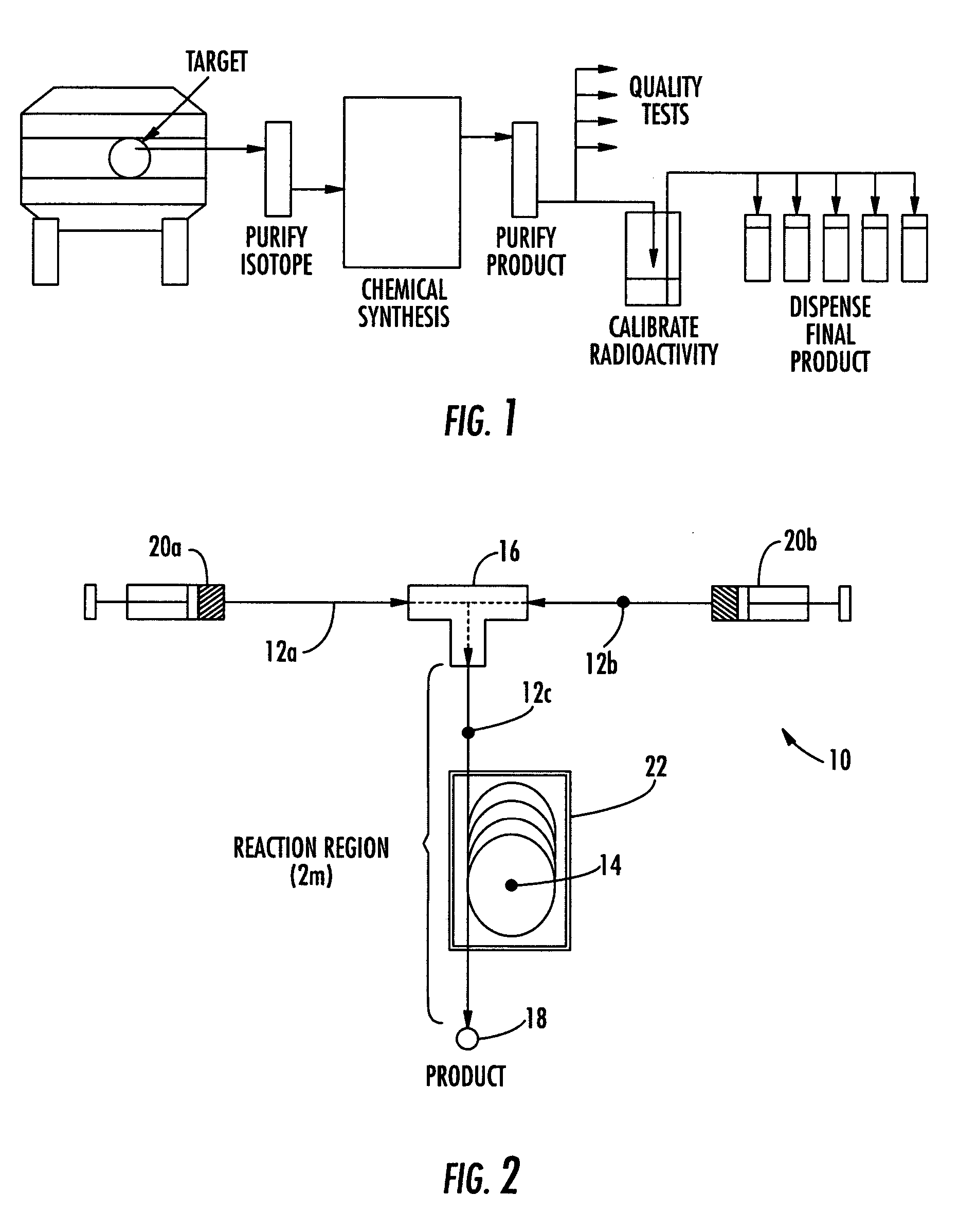
InactiveUS6433495B1Minimize radiationFit fastThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInterior spaceIsotope
A device is disclosed for simple and quick disconnection of a target assembly at a cyclotron accelerator producing an ion beam irradiating the target assembly for PET radioisotope production. The device consists of a target body presenting a target space for introduction of target media to be irradiated by the ion beam from the cyclotron accelerator. The target body is separated into three portions by means of two separation window foils. The first separation window separates the internal space of a first body portion from a further internal space portion of a second target body portion and the second separation window separates a further internal space of the second target body portion from an internal space of a third target body portion being in communication with the vacuum space of the cyclotron. This third body portion forms a bayonet fitting to a corresponding bayonet fitting fixed to the cyclotron vacuum casing at a position where the ion beam is extracted, whereby the corresponding bayonet fitting also constitutes an insulating member. The device can by a small twisting be quickly released from the vacuum casing of the cyclotron after the vacuum has been removed for necessary maintenance and service.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
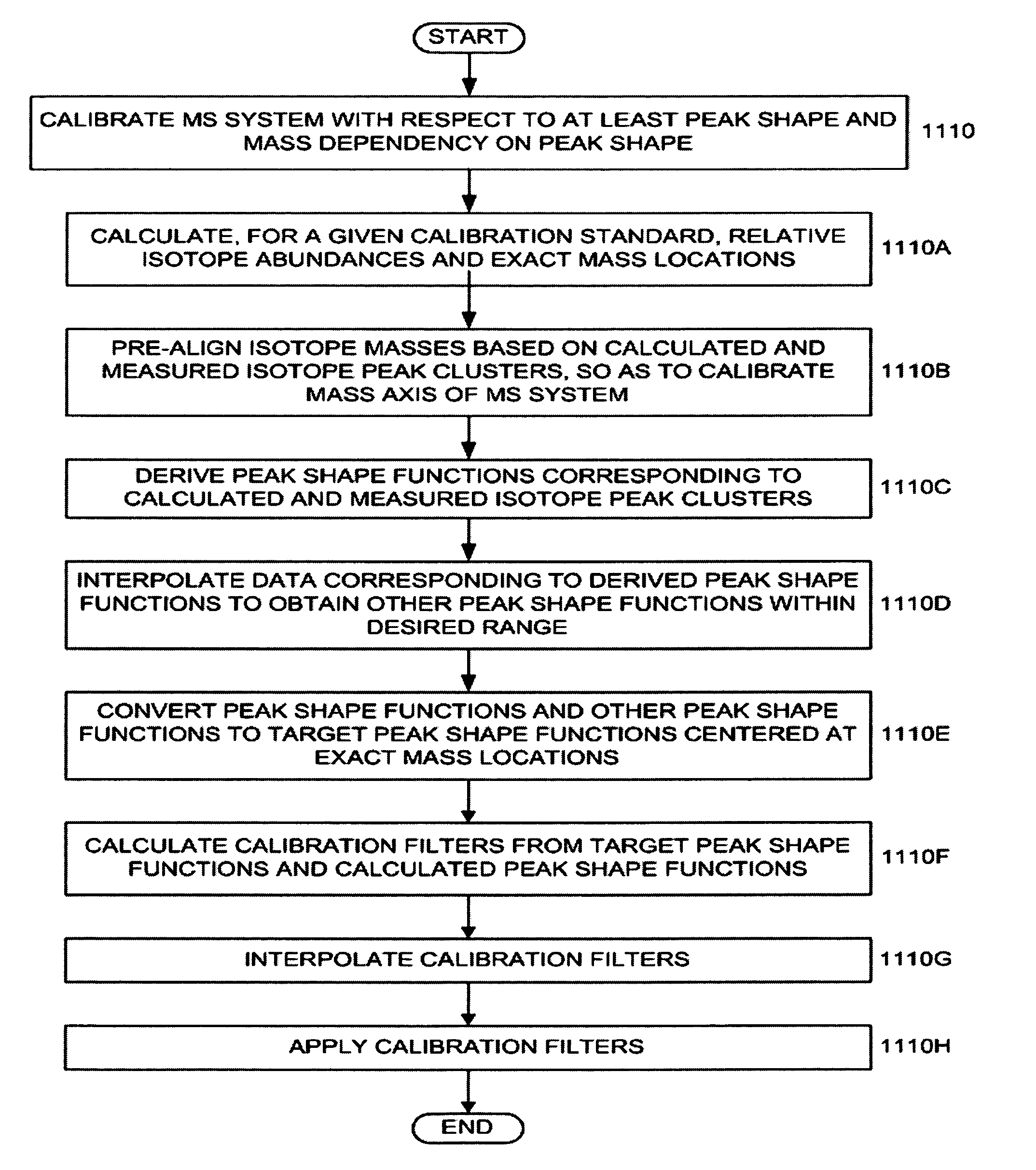
Methods for operating mass spectrometry (MS) instrument systems
ActiveUS20050086017A1Improve accuracyQuality improvementParticle separator tubesTesting/calibration apparatusClustered dataMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
There is provided a method for obtaining at least one calibration filter for a Mass Spectrometry (MS) instrument system. Measured isotope peak cluster data in a mass spectral range is obtained for a given calibration standard. Relative isotope abundances and actual mass locations of isotopes corresponding thereto are calculated for the given calibration standard. Mass spectral target peak shape functions centered within respective mass spectral ranges are specified. Convolution operations are performed between the calculated relative isotope abundances and the mass spectral target peak shape functions to form calculated isotope peak cluster data. A deconvolution operation is peformed between the measured isotope peak cluster data and the calculated isotope peak cluster data after the convolution operations to obtain the at least one calibration filter.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for performing rapid isotopic analysis via laser spectroscopy
Method and apparatus for providing real-time data indicative of the isotopic composition of formation fluids during drilling. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a reference fluid having a known isotopic composition in a reference cell; (b) capturing a sample of formation; (c) providing at least one laser beam; (e) passing a beam through the reference fluid, measuring the reference-measurement beam before and after it passes through the reference fluid; (f) and passing a beam through the sample, measuring the beam before and after it passes through the sample, and calculating a first isotope concentration from those measurements. The measurements can provide information relating to the carbon isotopic composition of individual compounds in hydrocarbon gas mixtures, with the individual compounds including methane, ethane, propane, iso- or normal butane, or iso- or normal pentane.
Owner:CALEB BRETT USA
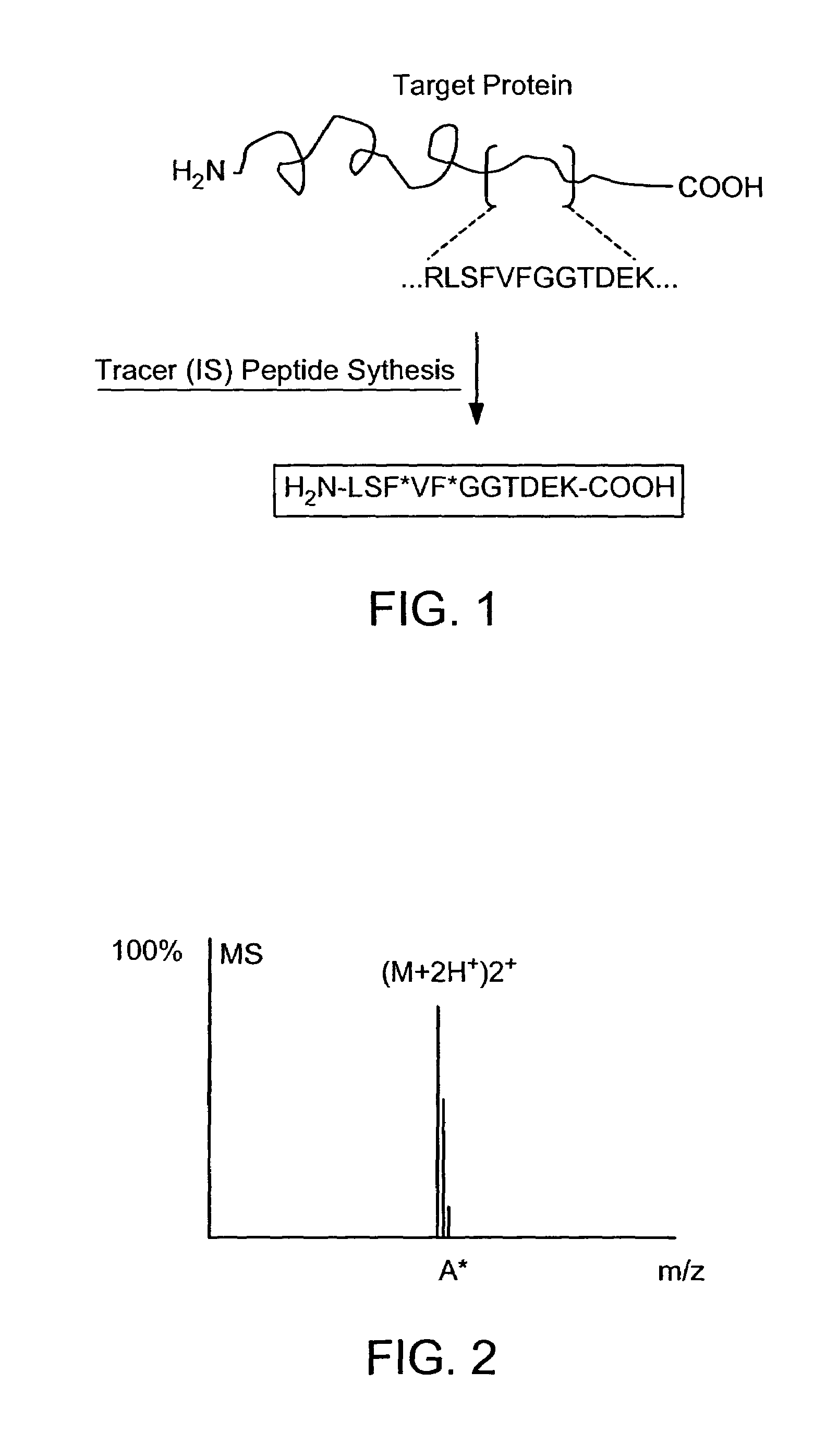
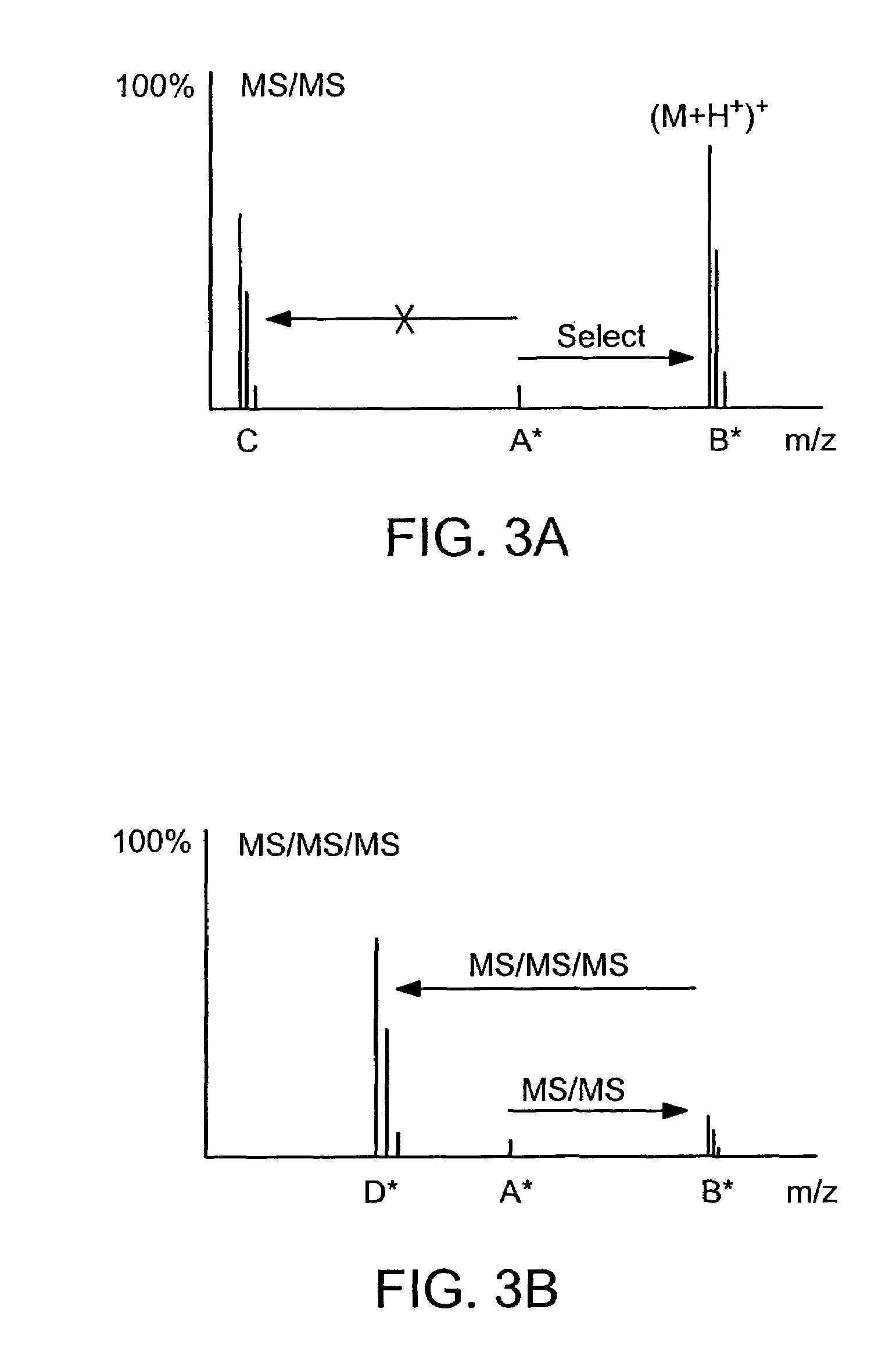
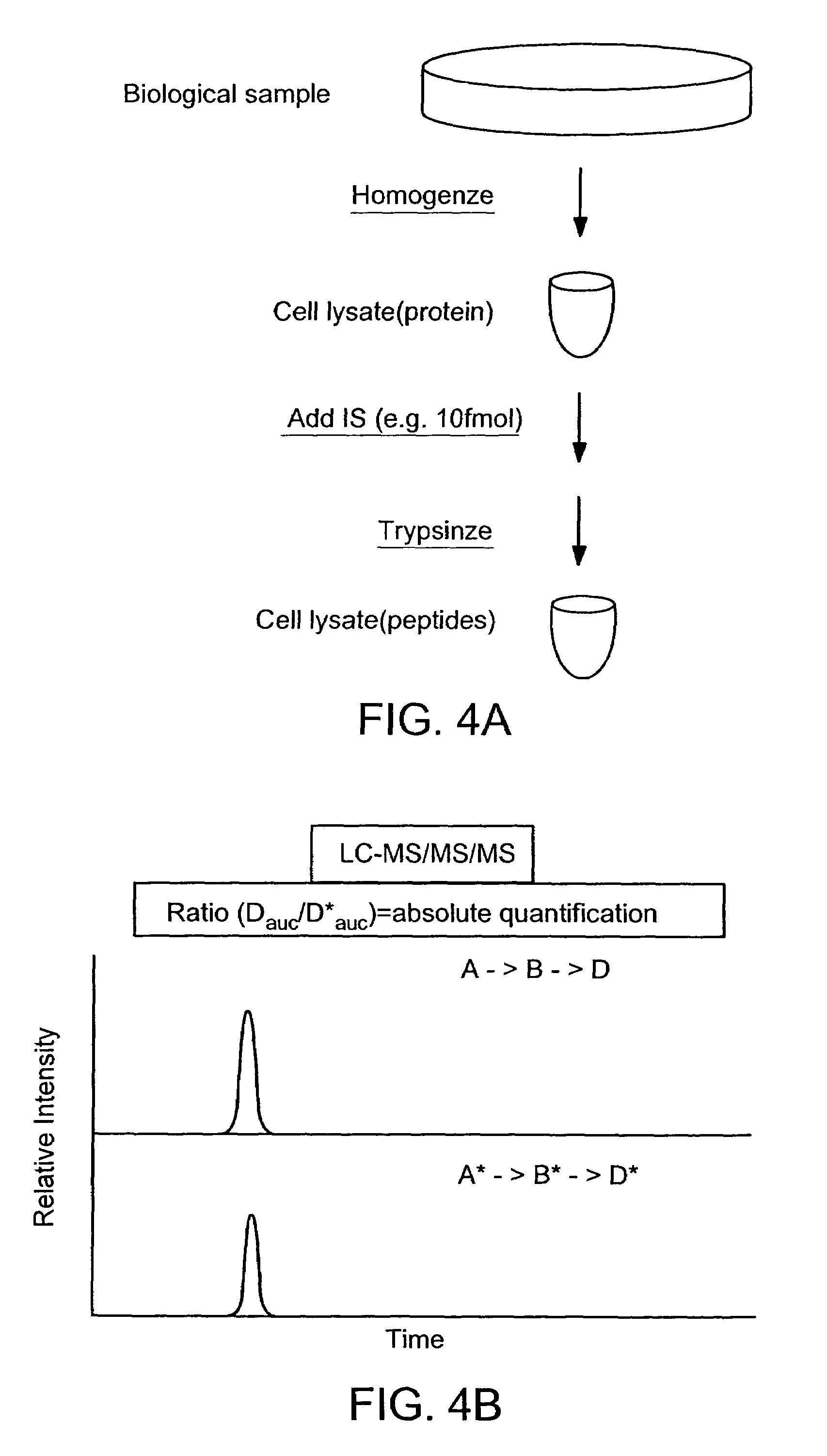
Absolute quantification of proteins and modified forms thereof by multistage mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7501286B2Rapid and high throughput analysisQuantitative precisionDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsStable Isotope LabelingIsotope
The invention provides reagents, kits and methods for detecting and / or quantifying proteins in complex mixtures, such as a cell lysate. The methods can be used in high throughput assays to profile cellular proteomes. In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide internal standard labeled with a stable isotope and corresponding in amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequence of a subsequence of a target polypeptide. In another aspect, the peptide internal standard is labeled at a modified amino acid residue and is used to determine the presence of, and / or quantitate the amount of a particular modified form of a protein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes including FDG
InactiveUS20050232861A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals wherein the reaction that couples the radioactive isotope to the reactive precursor to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe is performed in a microfluidic environment. The method comprises: providing a micro reactor; introducing a liquid reactive precursor dissolved in a polar aprotic solvent into an inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope dissolved in a polar aprotic solvent into another inlet port of the micro reactor; contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in a microchannel of the micro reactor; reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, wherein the reacting step is conducted at a temperature above the boiling point of the polar aprotic solvent at 1 atm and at a pressure sufficient to maintain the polar aprotic solvent in liquid form; and collecting the resulting radiochemical from the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
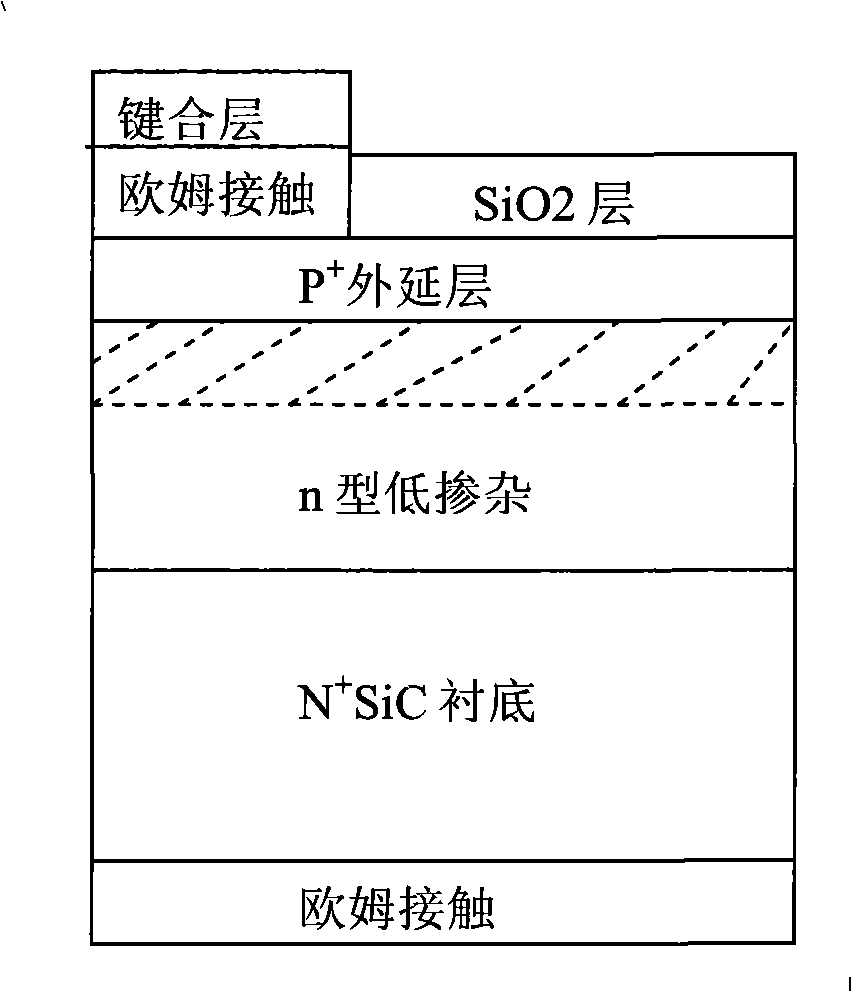
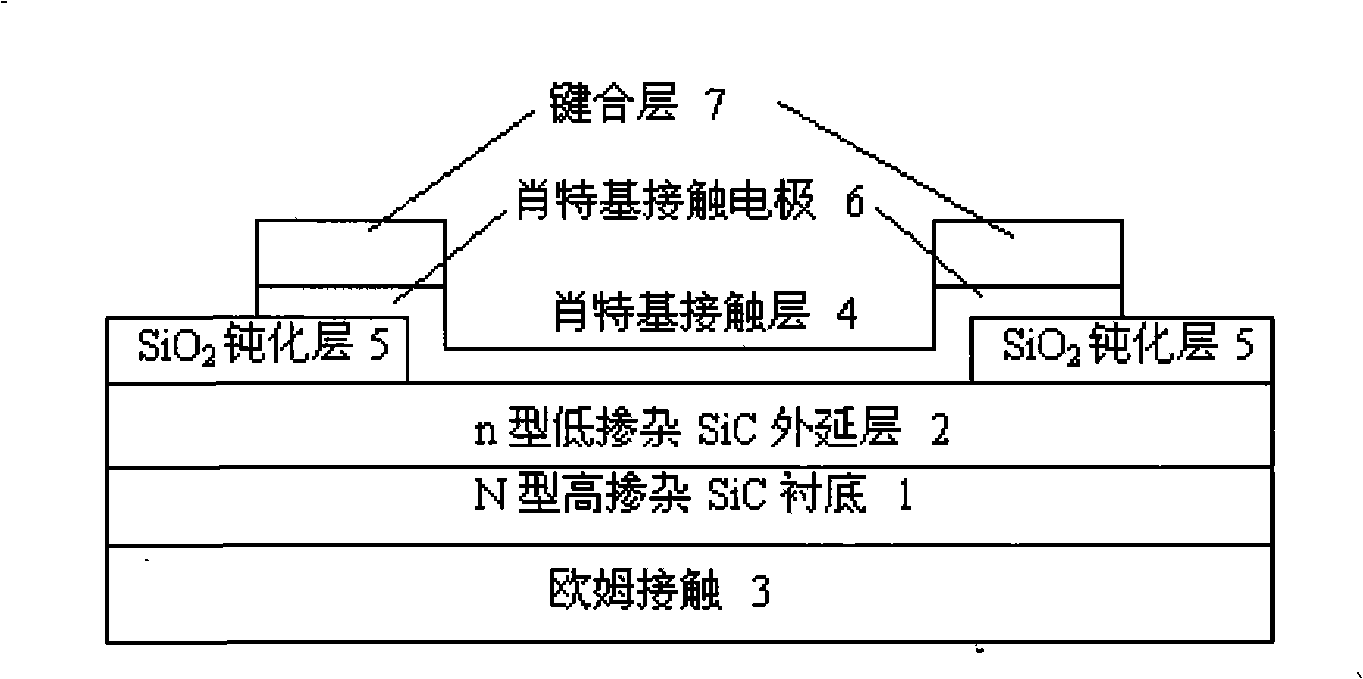
Minisize nuclear battery
InactiveCN101325093AReduce blockingIncrease the open circuit voltageRadiation electrical energyOhmic contactContact layer
The invention discloses a minitype nuclear battery, which mainly solves the problem that the nuclear battery manufacturing is easier than the SiC technology realization. A low doping epitaxial layer (2) and an ohmic contact electrode (3) are respectively arranged at the upper part and the lower part of an N-type high doping SiC substrate (1), wherein, a circular schottky contact layer (4) is deposited on the upper surface of the low doping epitaxial layer (2), and a SiO2 passivating layer (5) and a bonding layer (7) are arranged on the circumference at the outer edge of the schottky contact layer. The schottky contact layer (4) and a schottky contact electrode (6) are formed by adopting an identical technology, that is, a schottky contact hole is etched by adopting wet process in the center position of the SiO2 passivating layer (5), and Ni, Pt or Au with the thickness being 5 to 20 nm deposited on the SiO2 passivating layer on the hole or at the periphery of the hole, and the schottky contact layer (4) and the schottky contact electrode (6) are respectively formed after the SiO2 passivating layer is peeled off. The minitype nuclear battery has the advantages of simple technology and high conversion efficiency, and is applicable in directly converting the nuclear energy radiated by isotopes into the electric energy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com