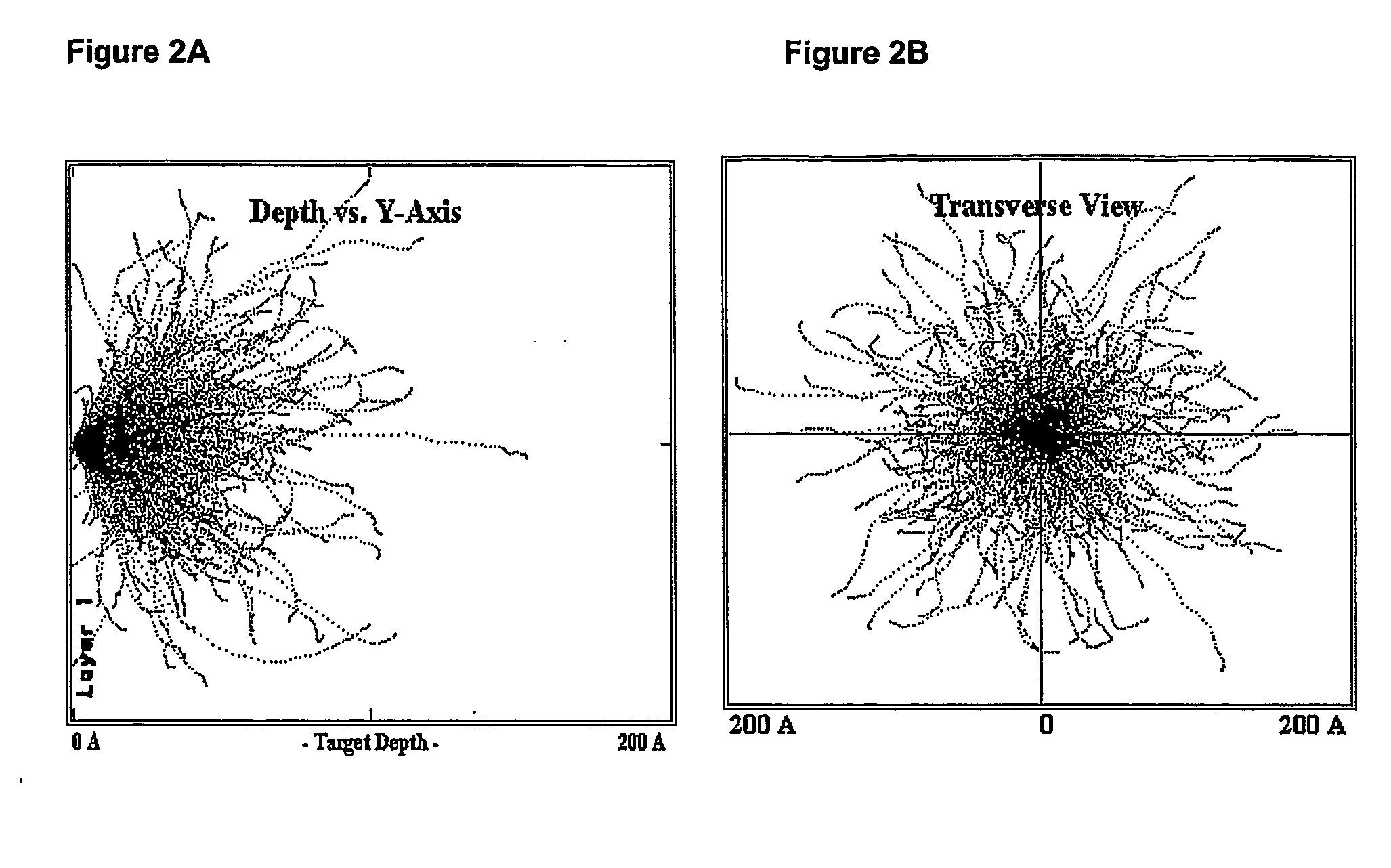
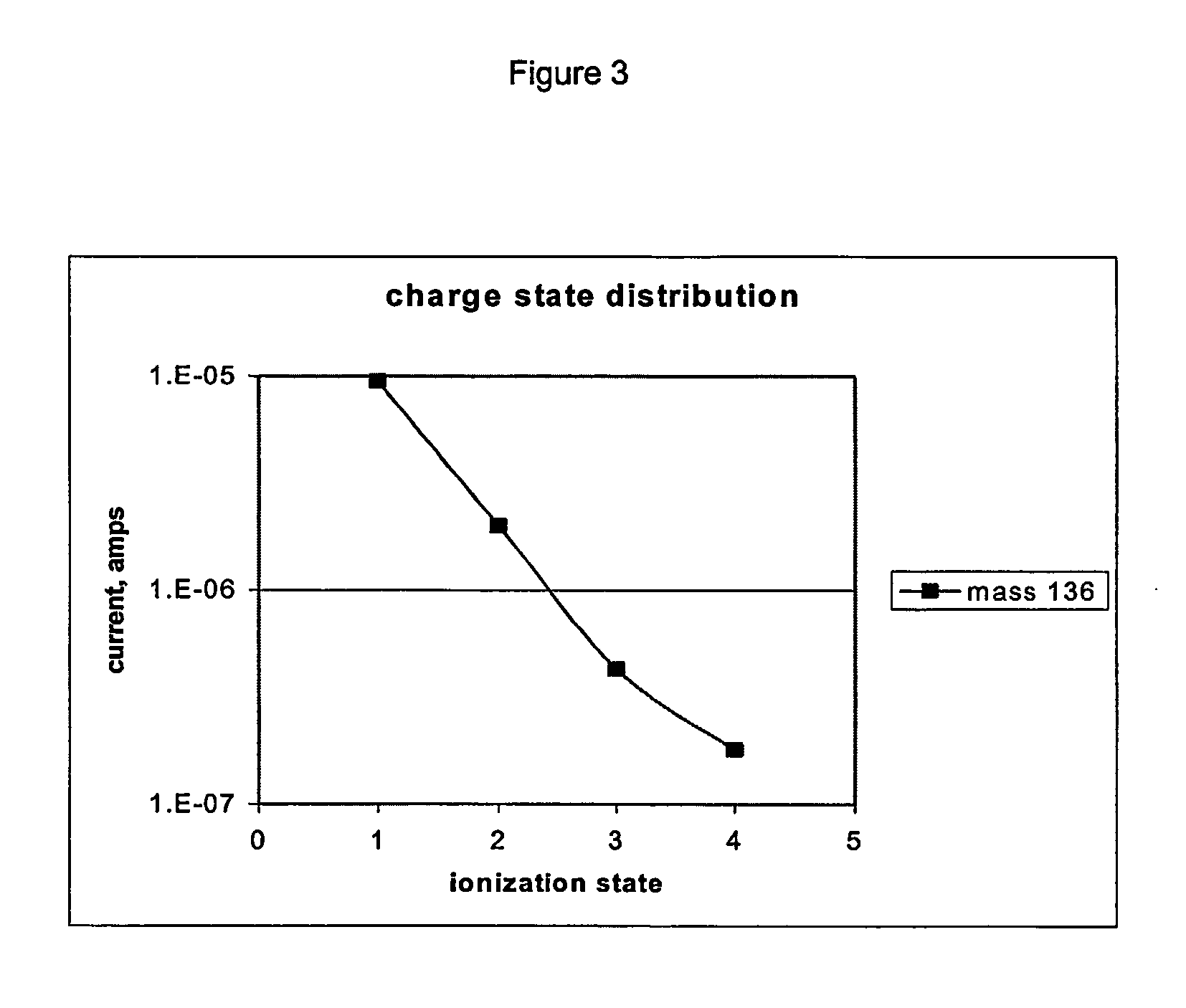
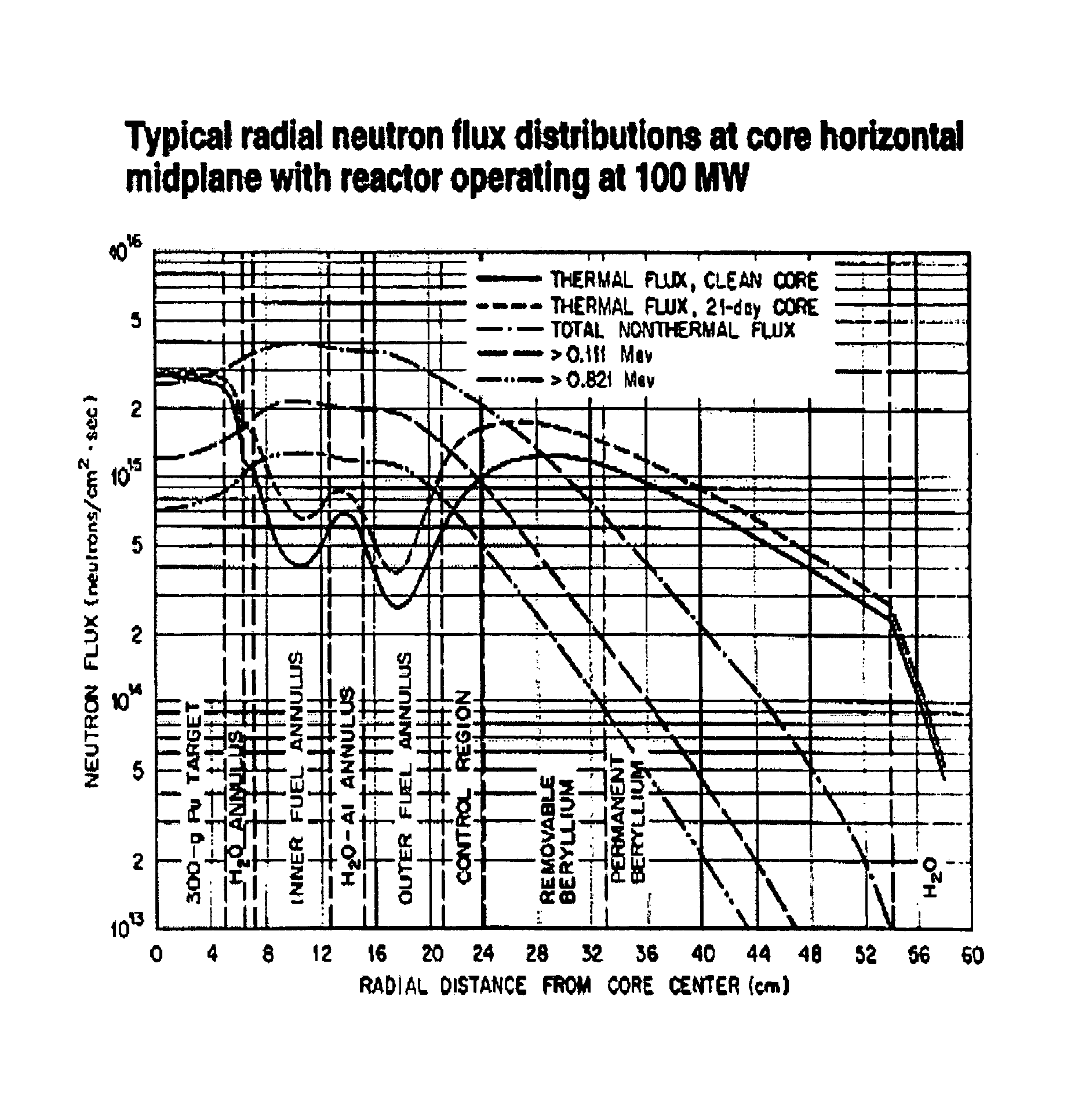
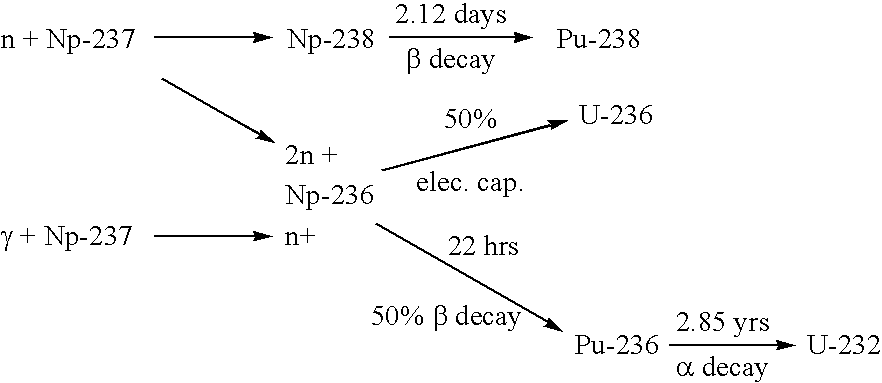
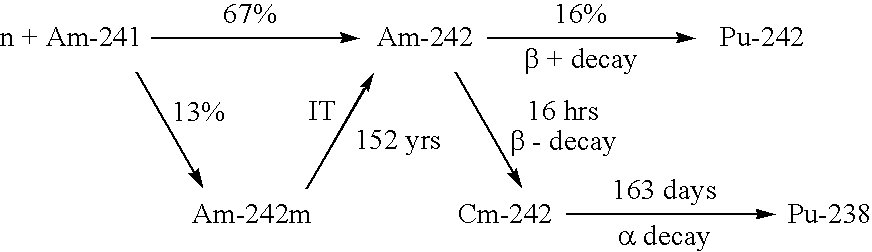Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
632results about "Conversion outside reactor/accelerators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
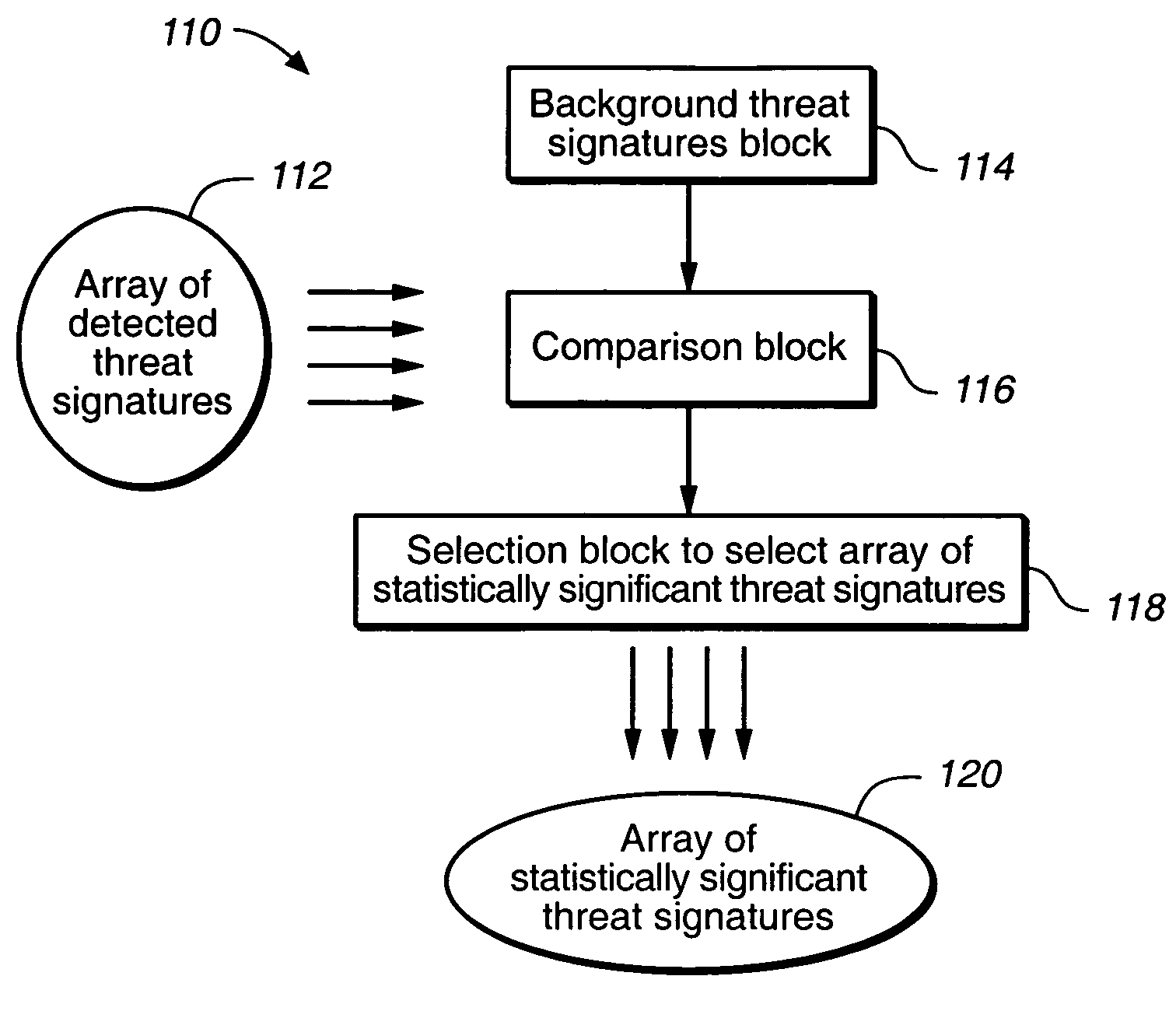
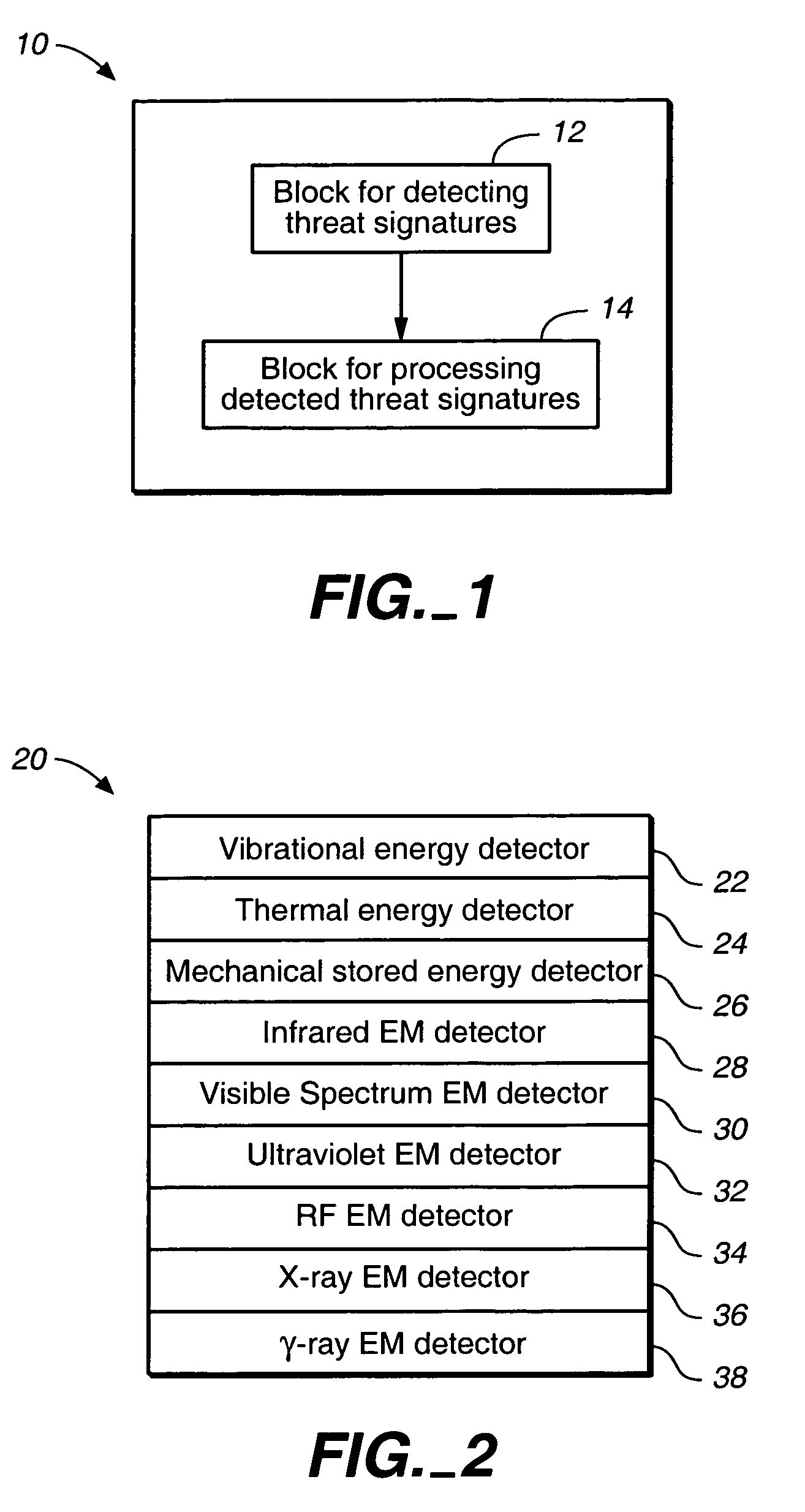
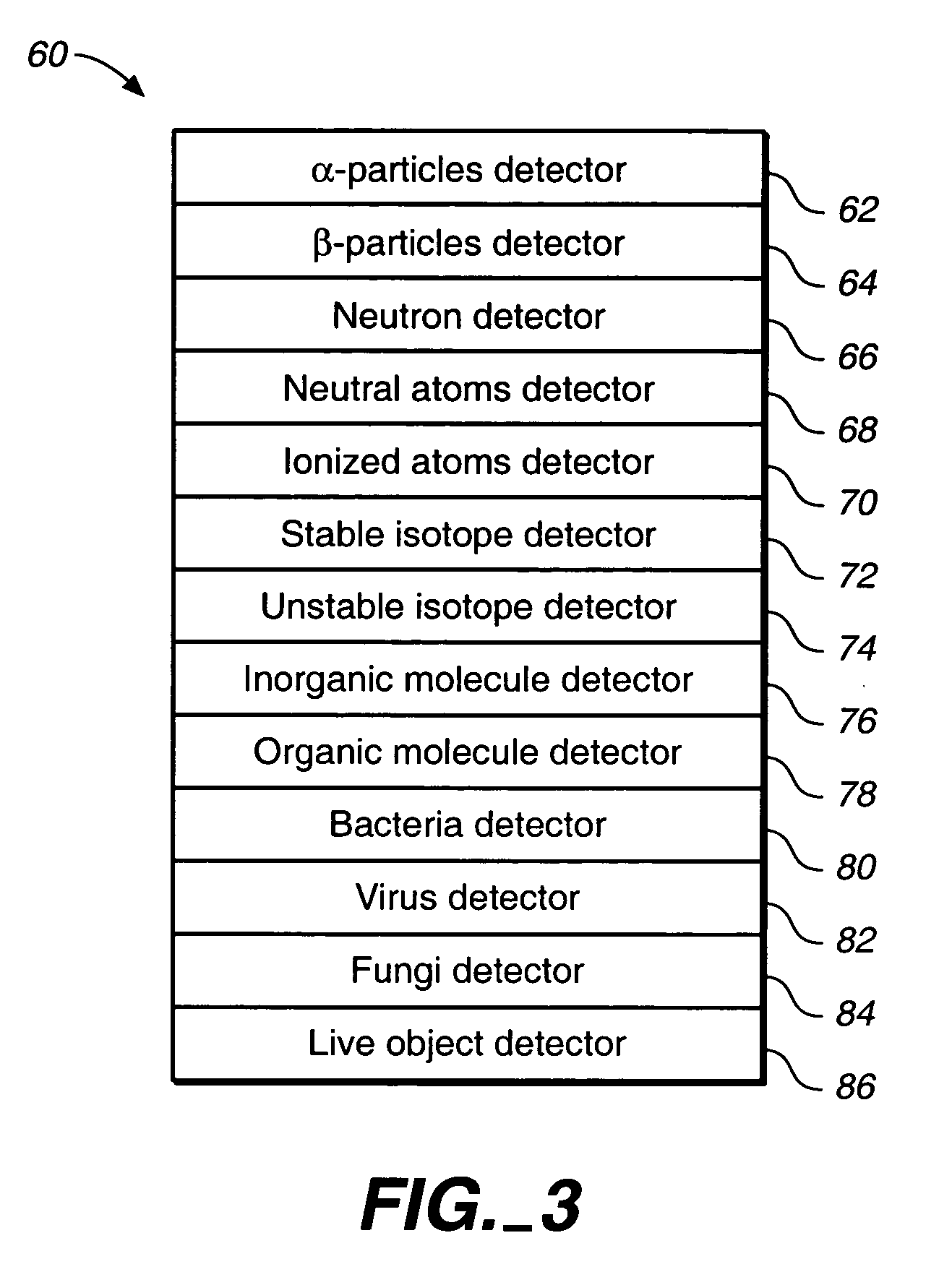
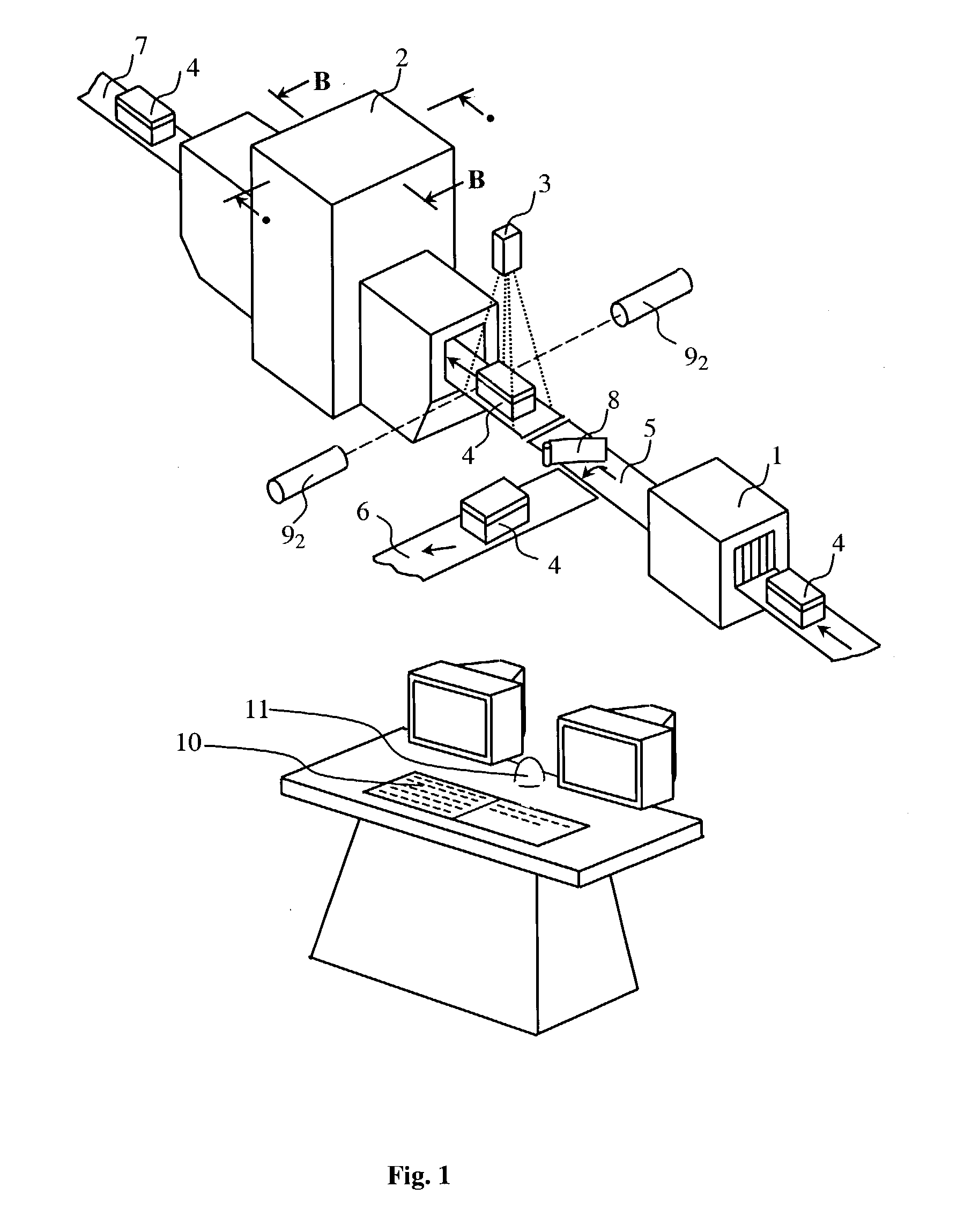
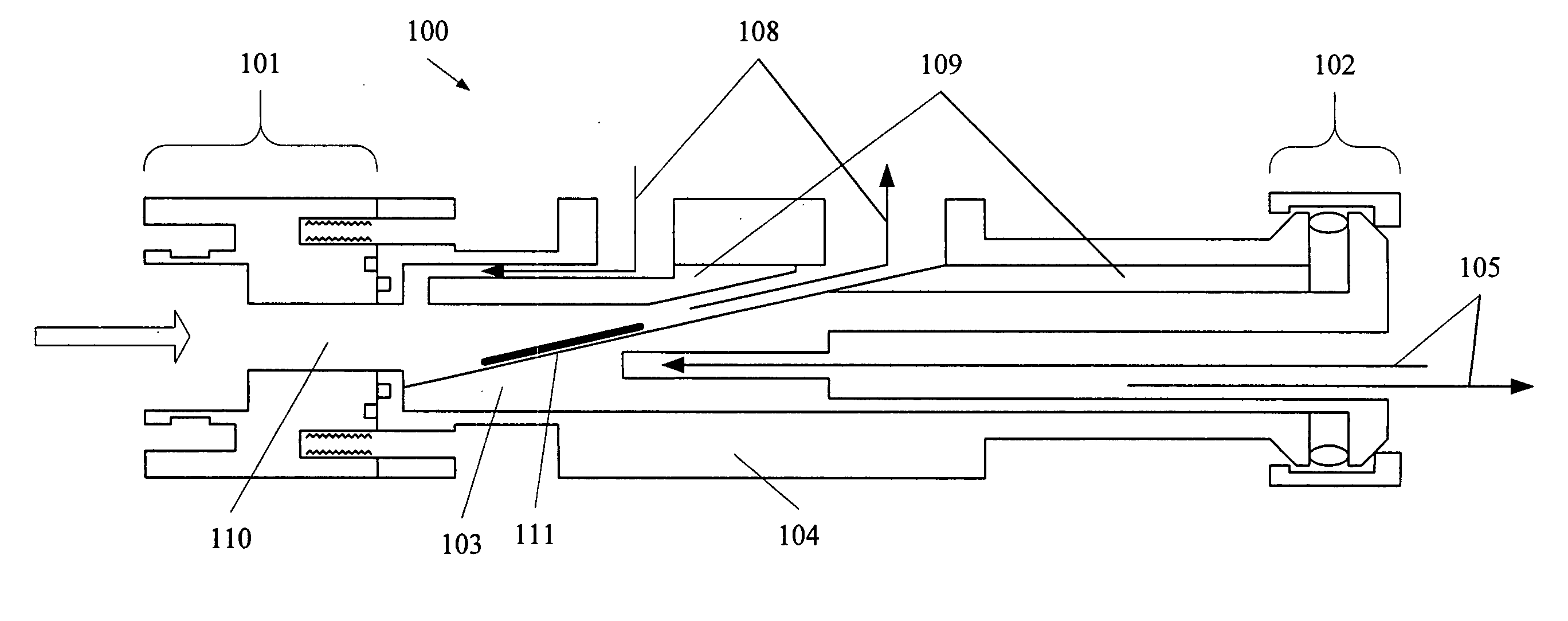
Detection and identification of threats hidden inside cargo shipments
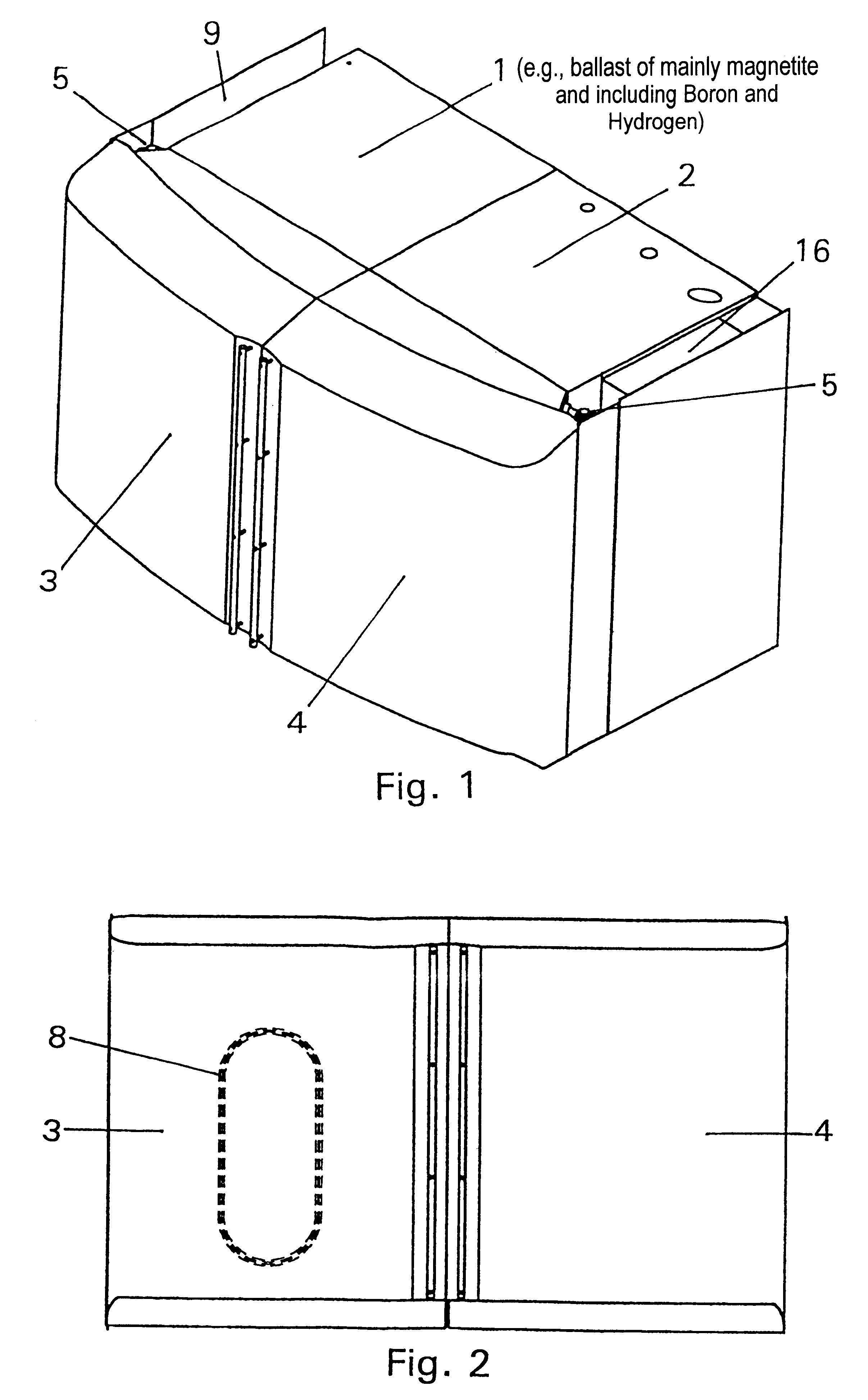
InactiveUS7151447B1Continuous processConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansHomeland securityCargo container
A method for identifying at least one threat to the homeland security. Each threat is either hidden inside at least one cargo container before transit, or is placed inside at least one cargo container while in transit. Each threat while interacting with its surrounding generates a unique threat signature.The method comprises the following steps: (A) detecting at least one threat signature; and (B) processing each detected threat signature to determine a likelihood of at least one threat to become a threat to the homeland security.
Owner:ERUDITE
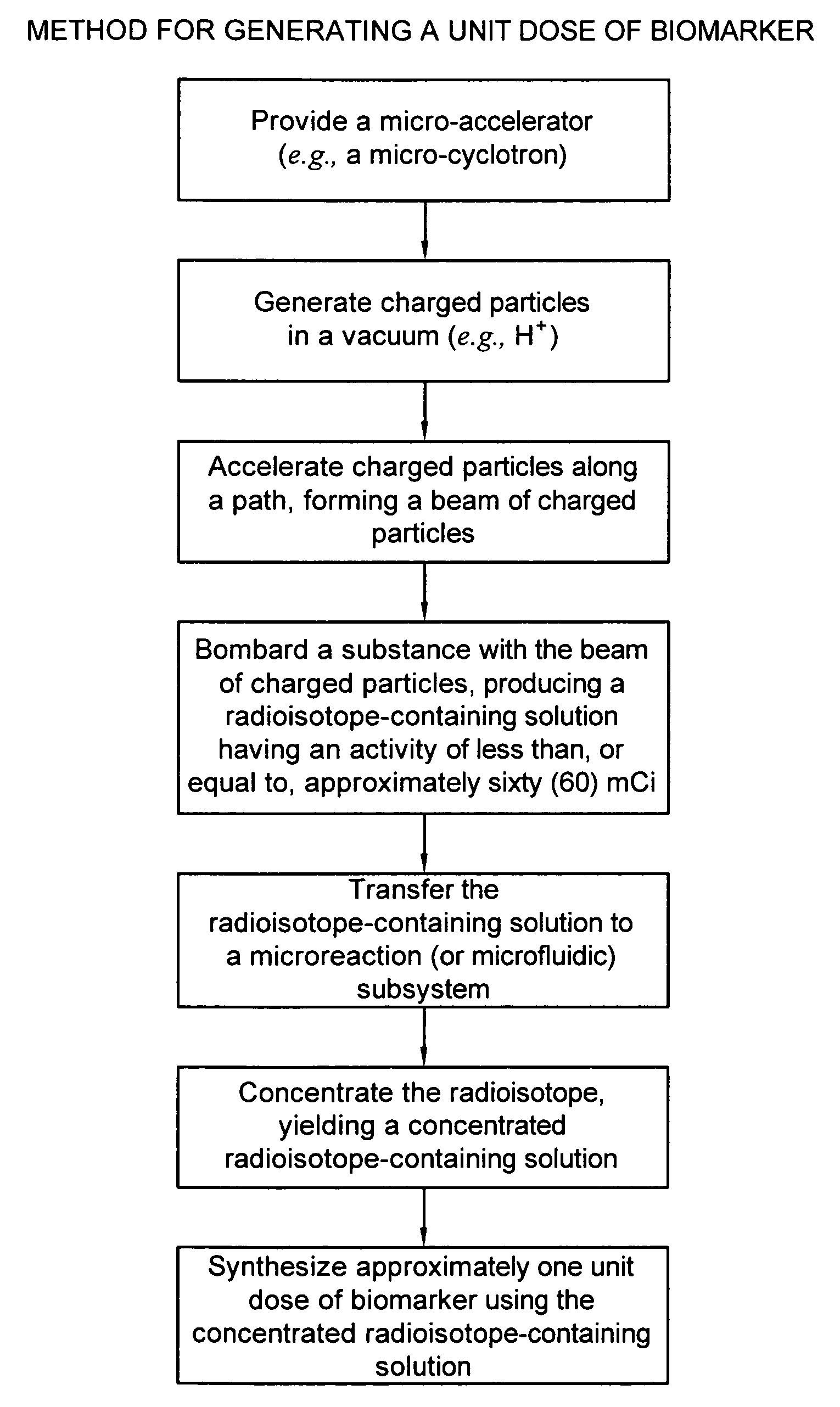
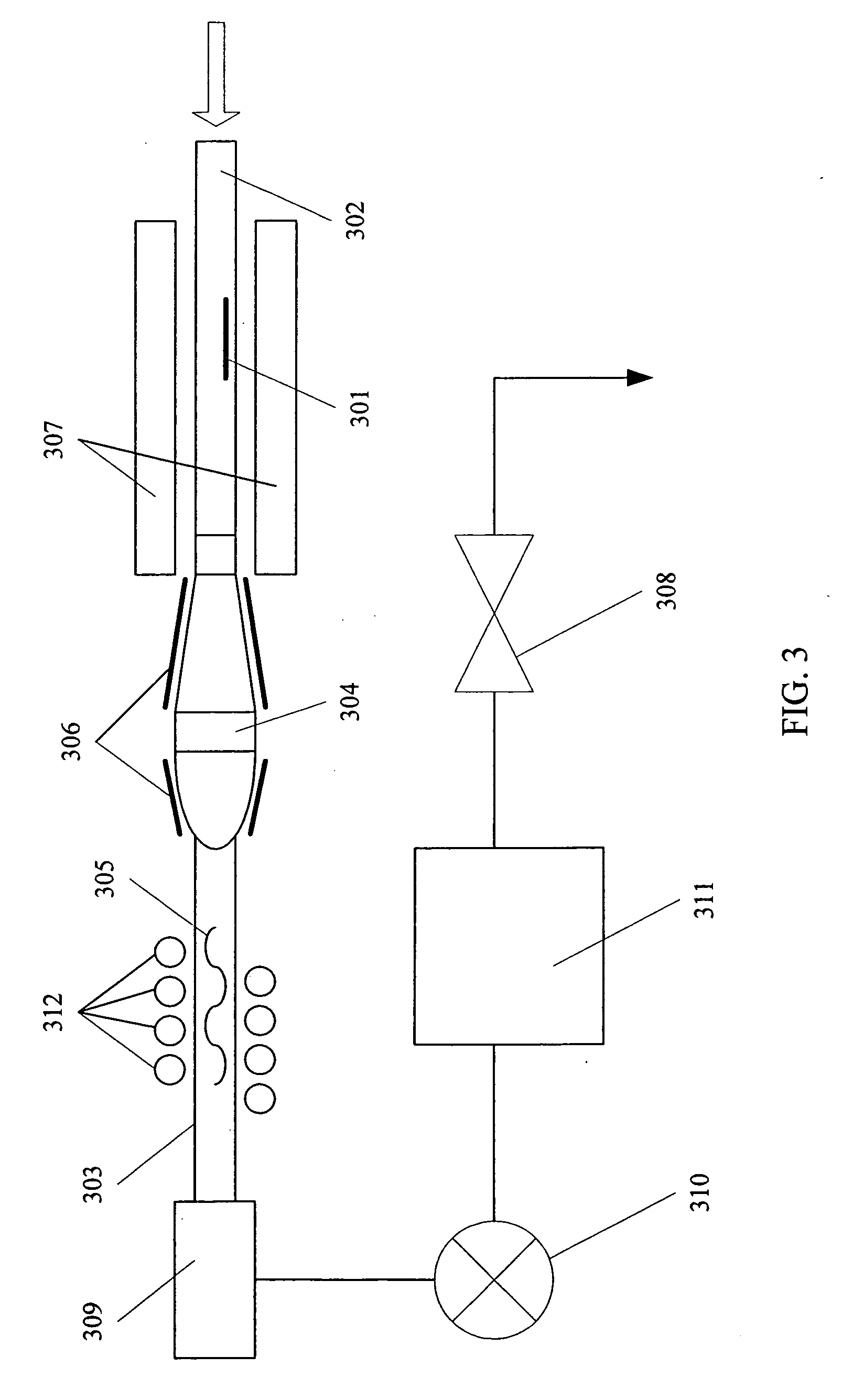
Biomarker generator system
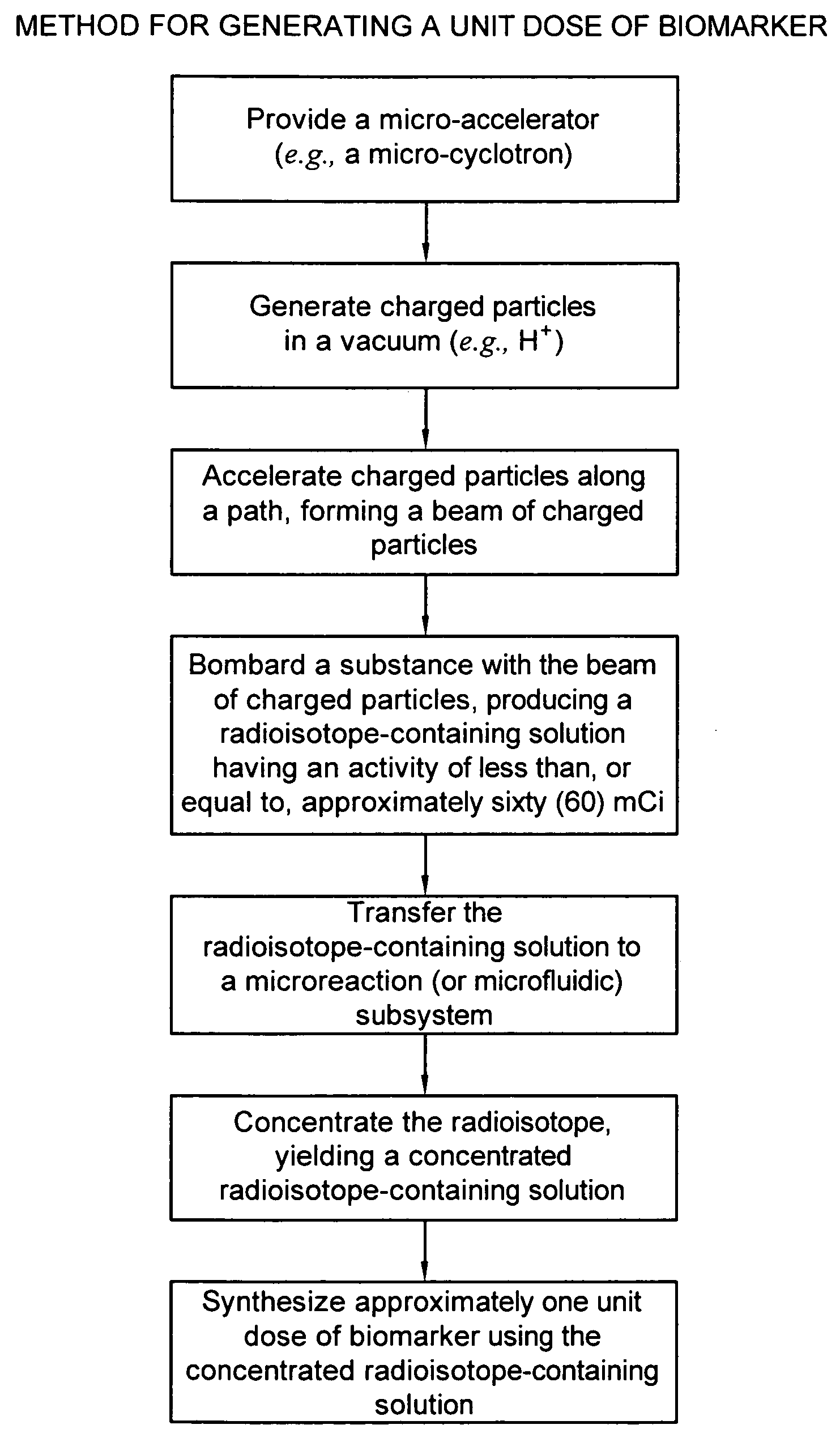
ActiveUS7476883B2Efficient dosingEfficient productionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope delivery systemsChemical synthesisMicroreactor
A biomarker generator system for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker. The biomarker generator system includes a small, low-power particle accelerator (“micro-accelerator”) and a radiochemical synthesis subsystem having at least one microreactor and / or microfluidic chip. The micro-accelerator is provided for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a radioactive substance, such as a substance that emits positrons. The radiochemical synthesis subsystem is provided for receiving the radioactive substance, for receiving at least one reagent, and for synthesizing the approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker.
Owner:BEST ABT INC
Method And System For Production Of Radioisotopes, And Radioisotopes Produced Thereby
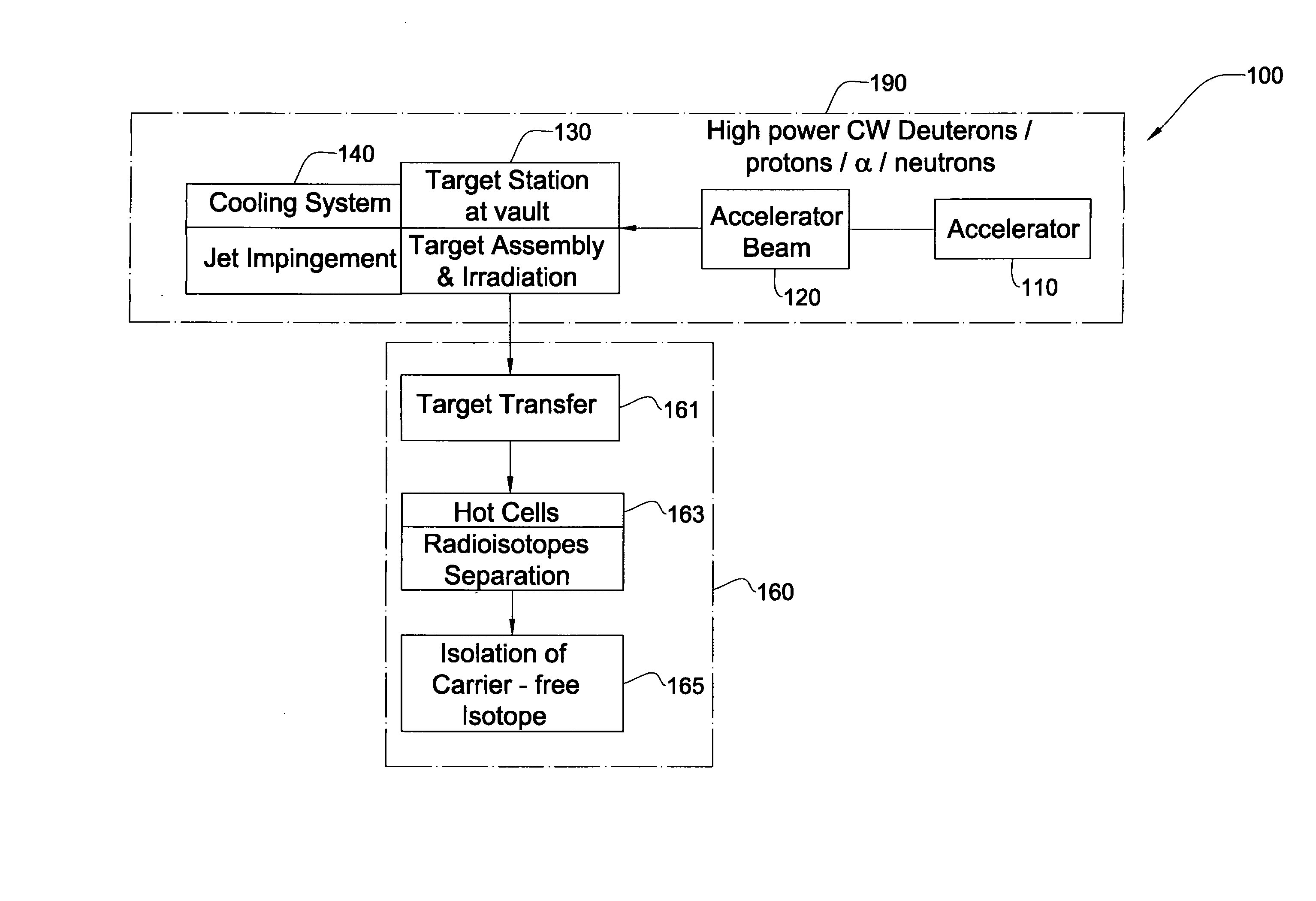
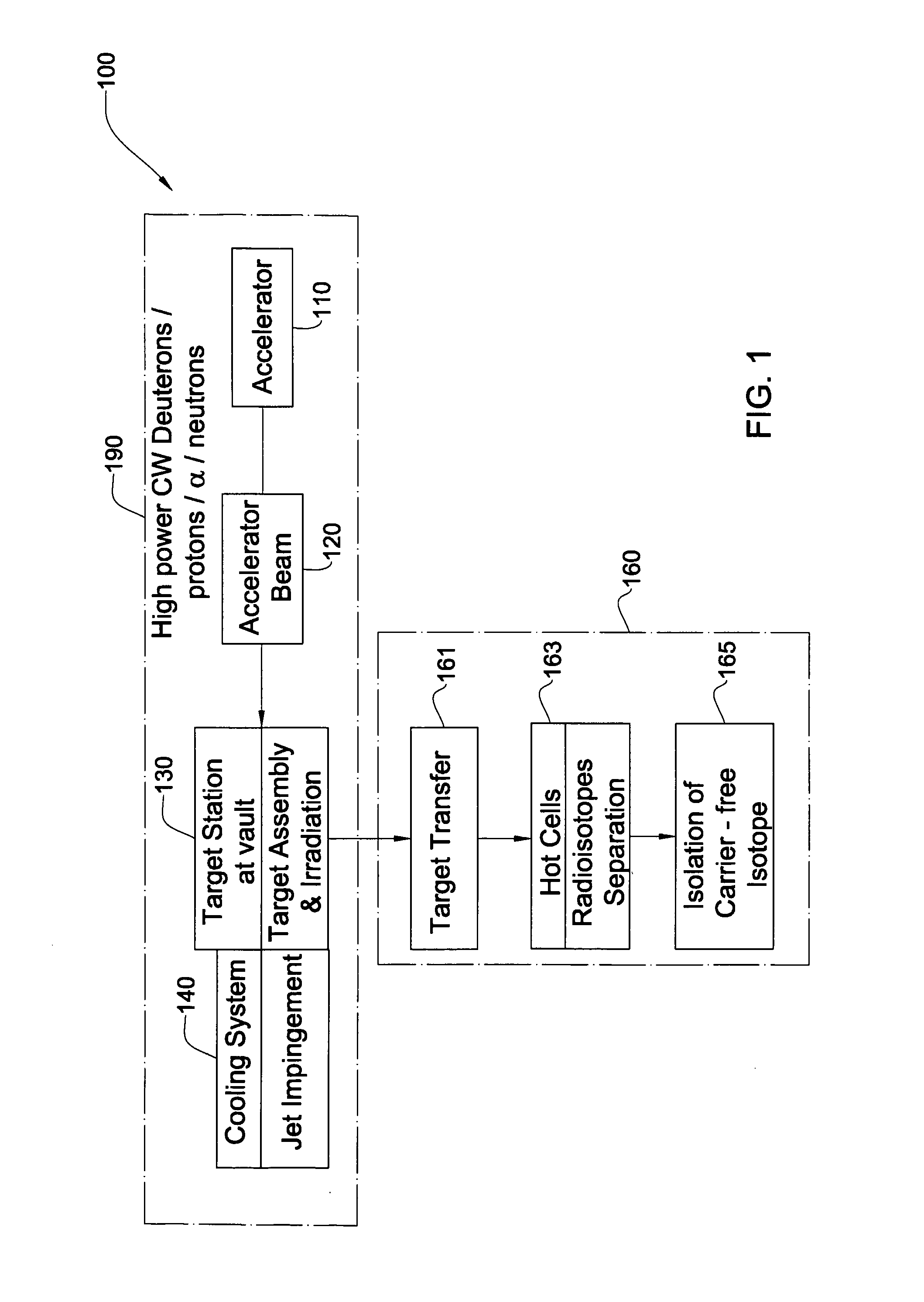
InactiveUS20070297554A1Avoid communicationAvoid contaminationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsHeat fluxParticle beam
A system and method for the production of radioisotopes by the transmutation of target isotopic material bombarded by a continuous wave particle beam. An ion source generates a continuous wave ion beam, irradiating an isotope target, which is cooled by transferring heat away from the target at heat fluxes of at least about 1 kW / cm2.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION
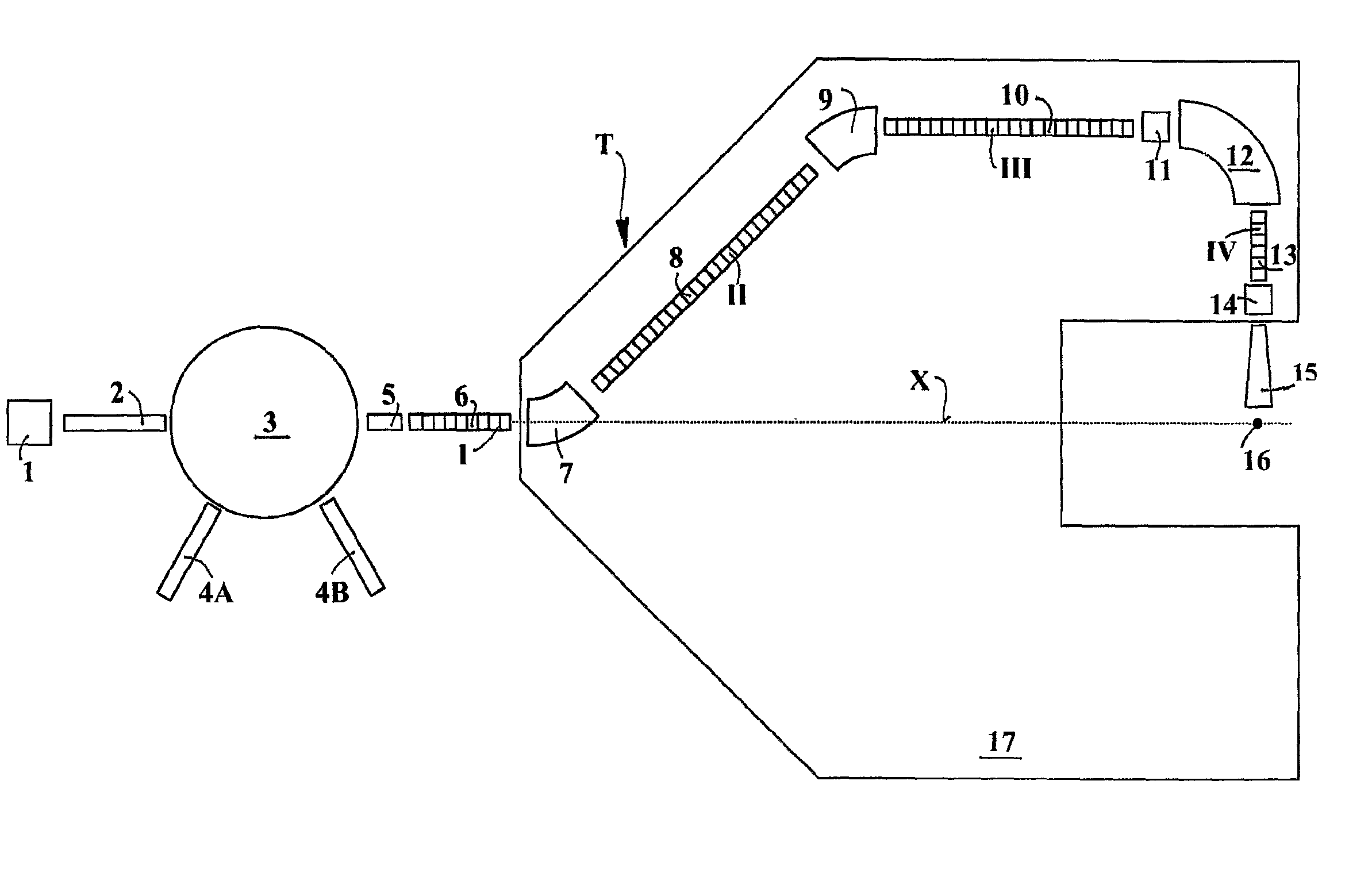
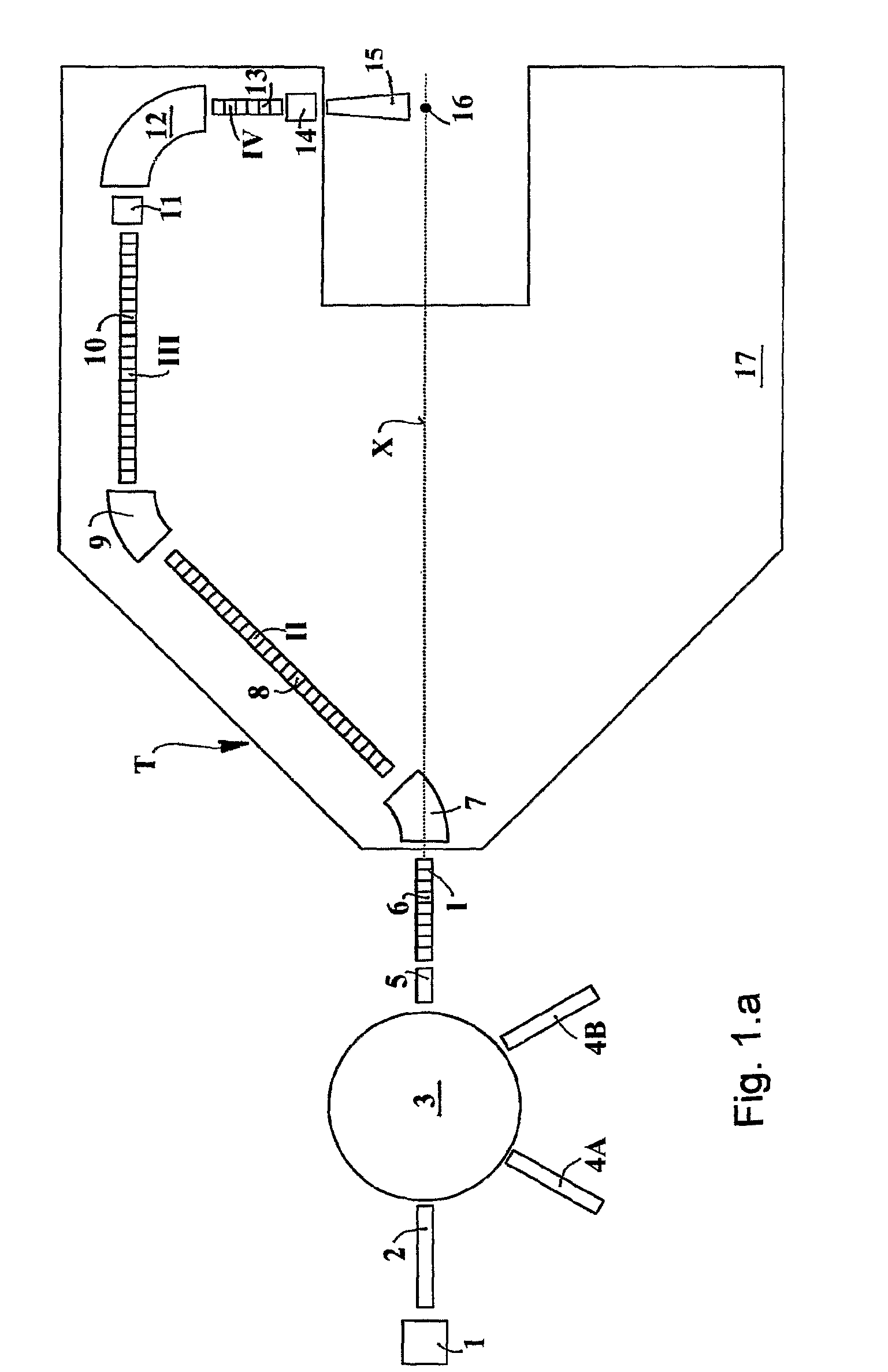
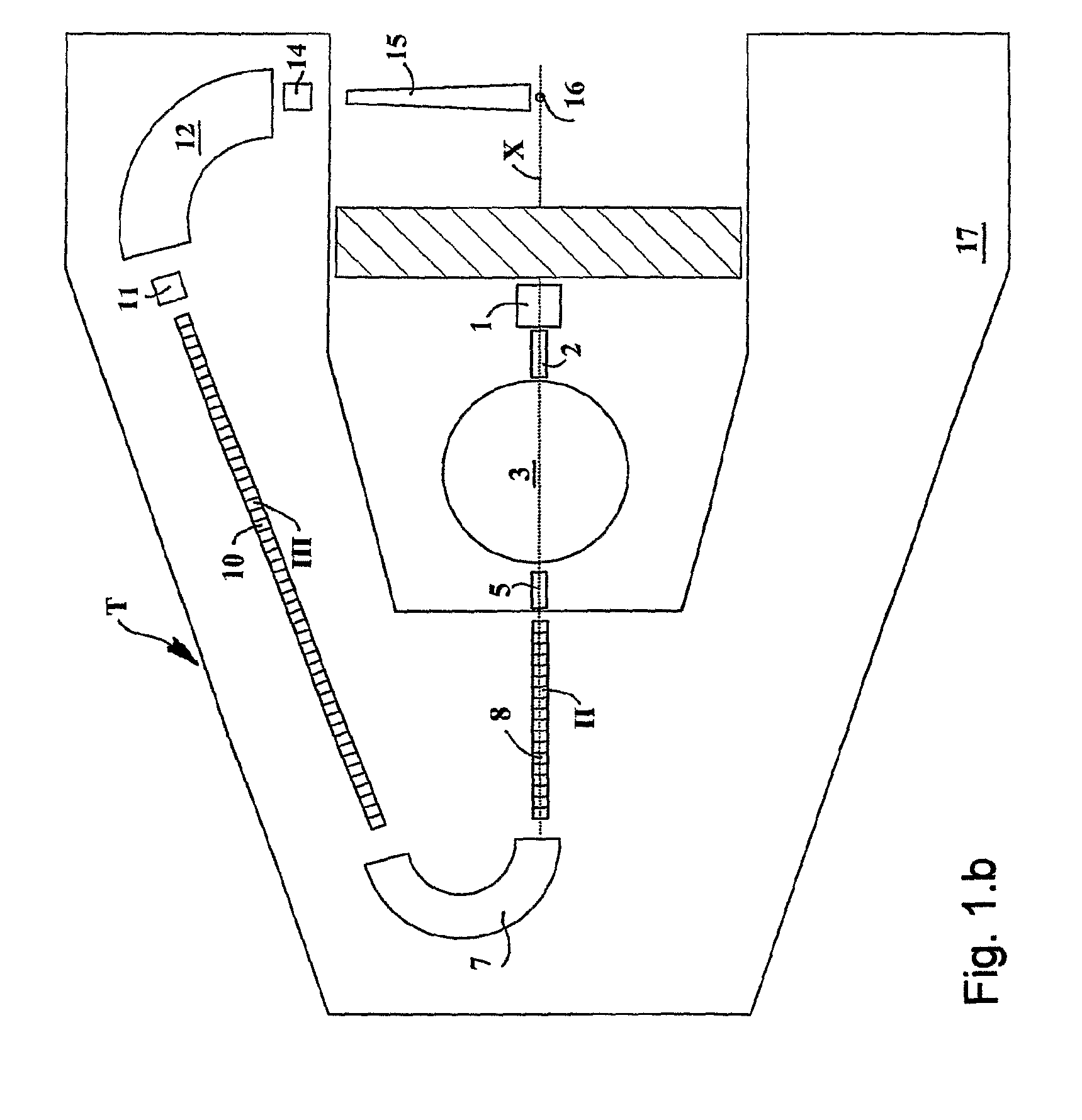
Ion acceleration system for medical and/or other applications
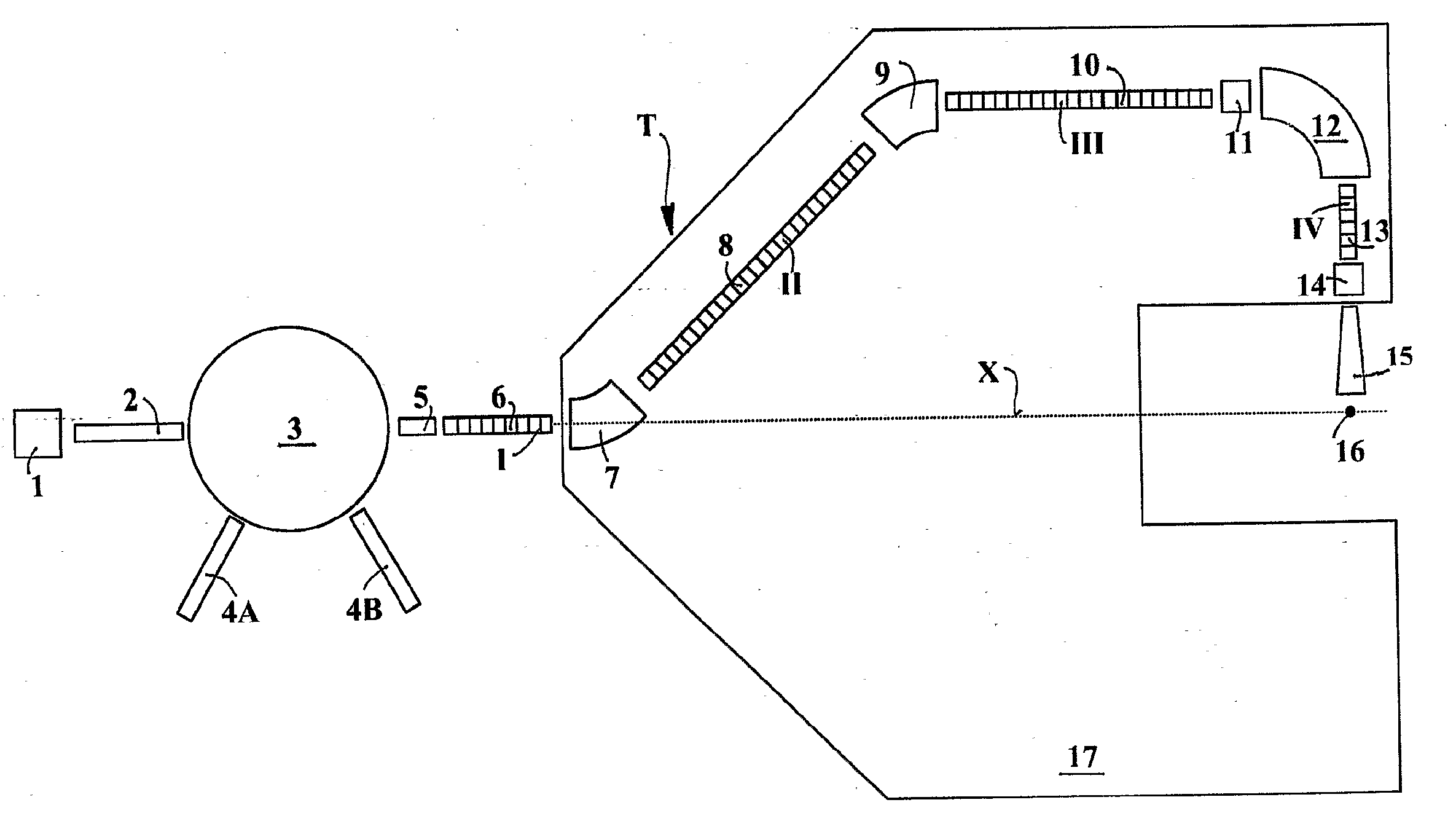
ActiveUS8405056B2Enhanced couplingWeaken energyStability-of-path spectrometersConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMedicineEngineering
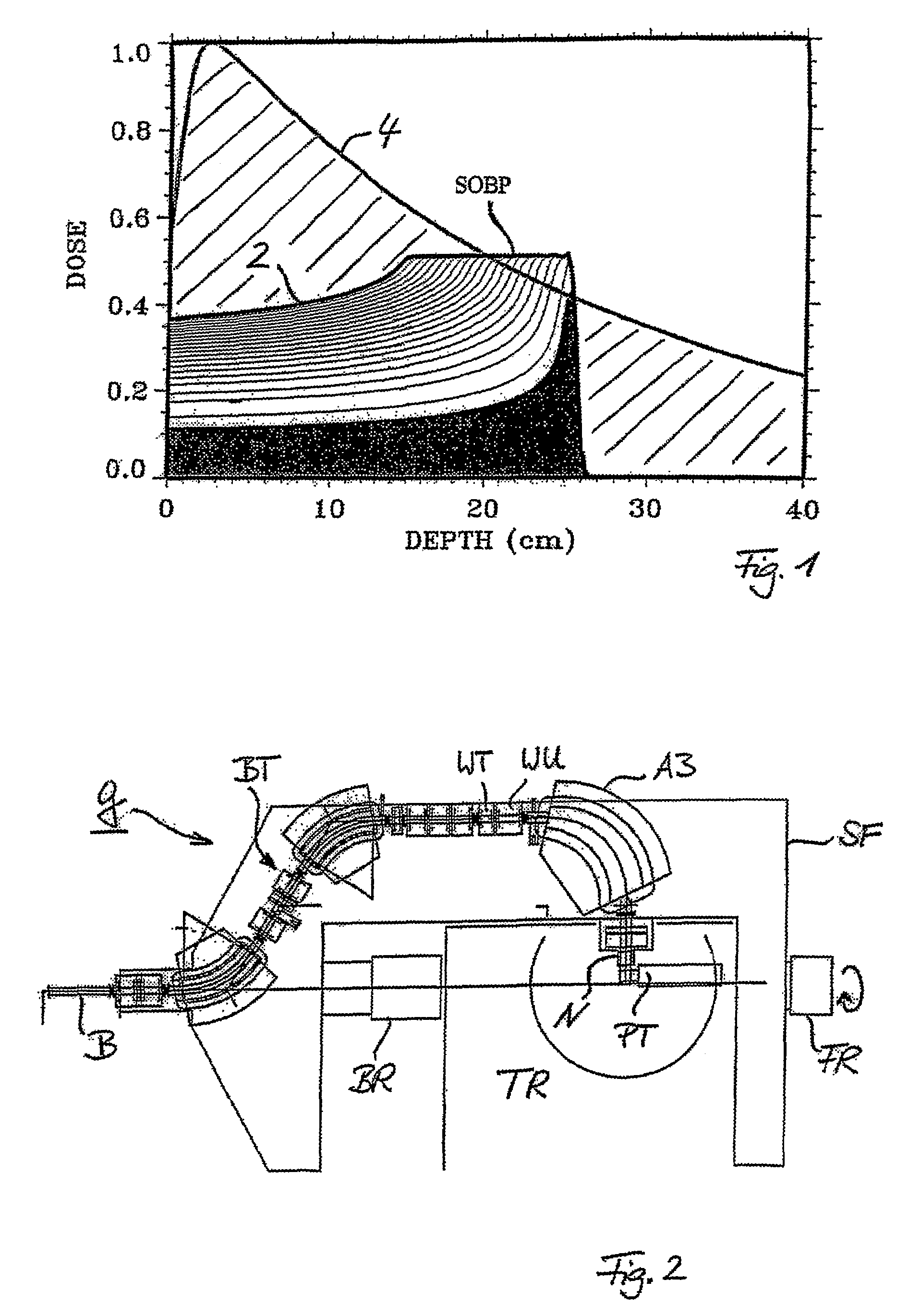
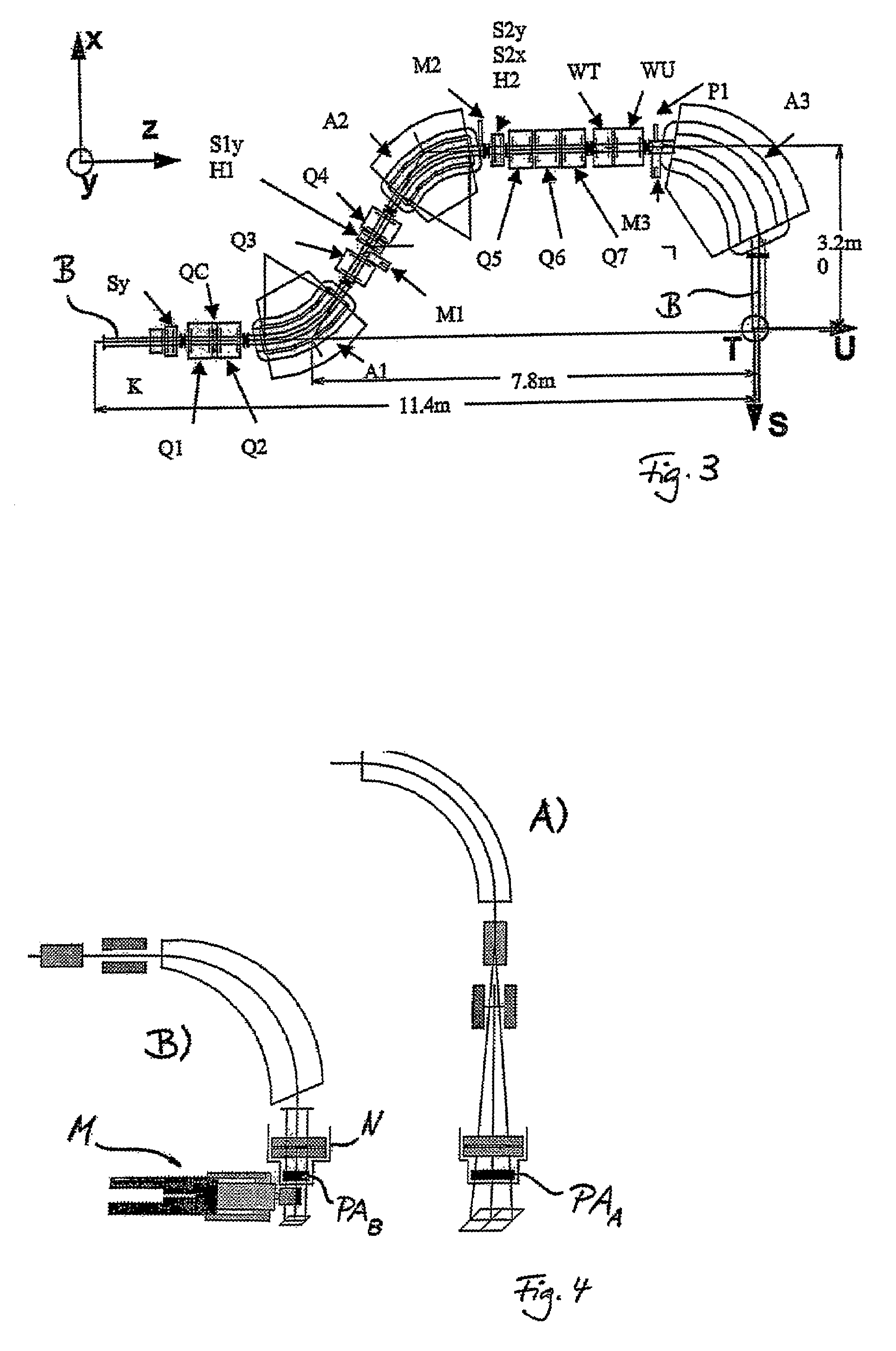
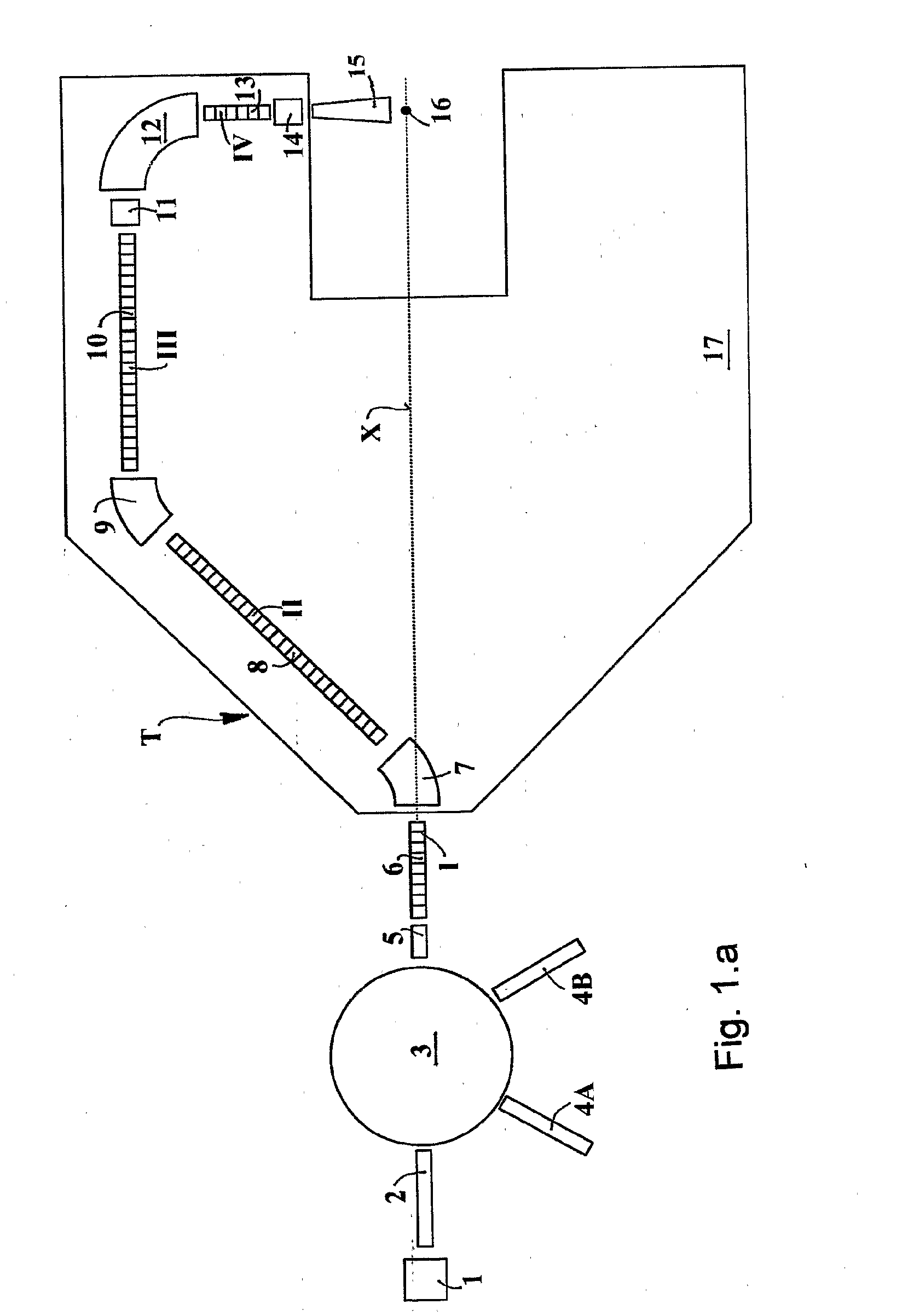
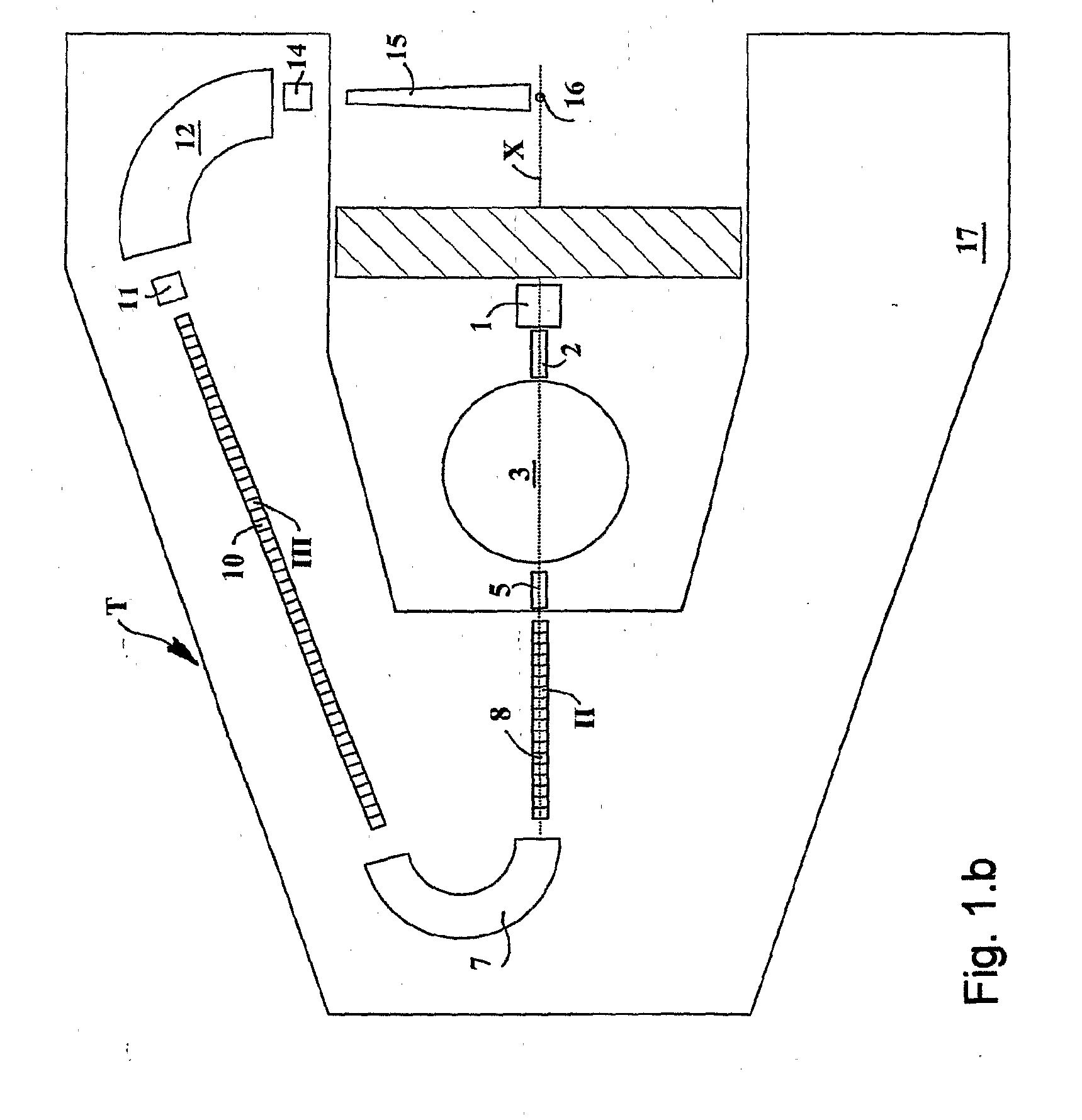
The ion acceleration system or complex (T) for medical and / or other applications is composed in essence by an ion source (1), a pre-accelerator (3) and one or more linear accelerators or linacs (6, 8, 10, 13), at least one of which is mounted on a rotating mechanical gantry-like structure (17). The isocentrical gantry (17) is equipped with a beam delivery system, which can be either ‘active’ or ‘passive’, for medical and / or other applications. The ion source (1) and the pre-accelerator (3) can be either installed on the floor, which is connected with the gantry basement, or mounted, fully or partially, on the rotating mechanical structure (17). The output beam can vary in energy and intensity pulse-by-pulse by adjusting the radio-frequency field in the accelerating modules of the linac(s) and the beam parameters at the input of the linear accelerators.
Owner:ADVANCED ONCOTHERAPY PLC
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20050232387A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals, such as PET molecular imaging probes, wherein the reaction step or steps that couple the radioactive isotope to an organic or inorganic compound to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe are performed in a microfluidic environment. The method for synthesizing a radiochemical in a microfluidic environment comprises: i) providing a micro reactor comprising a first inlet port, a second inlet port, an outlet port, and at least one microchannel in fluid communication with the first and second inlet ports and the outlet port; ii) introducing a reactive precursor into the first inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; iii) introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope into the second inlet port of the micro reactor; iv) contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in the microchannel of the micro reactor; v) reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, the reacting step resulting in formation of a radiochemical; and vi) collecting the radiochemical from the outlet port of the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
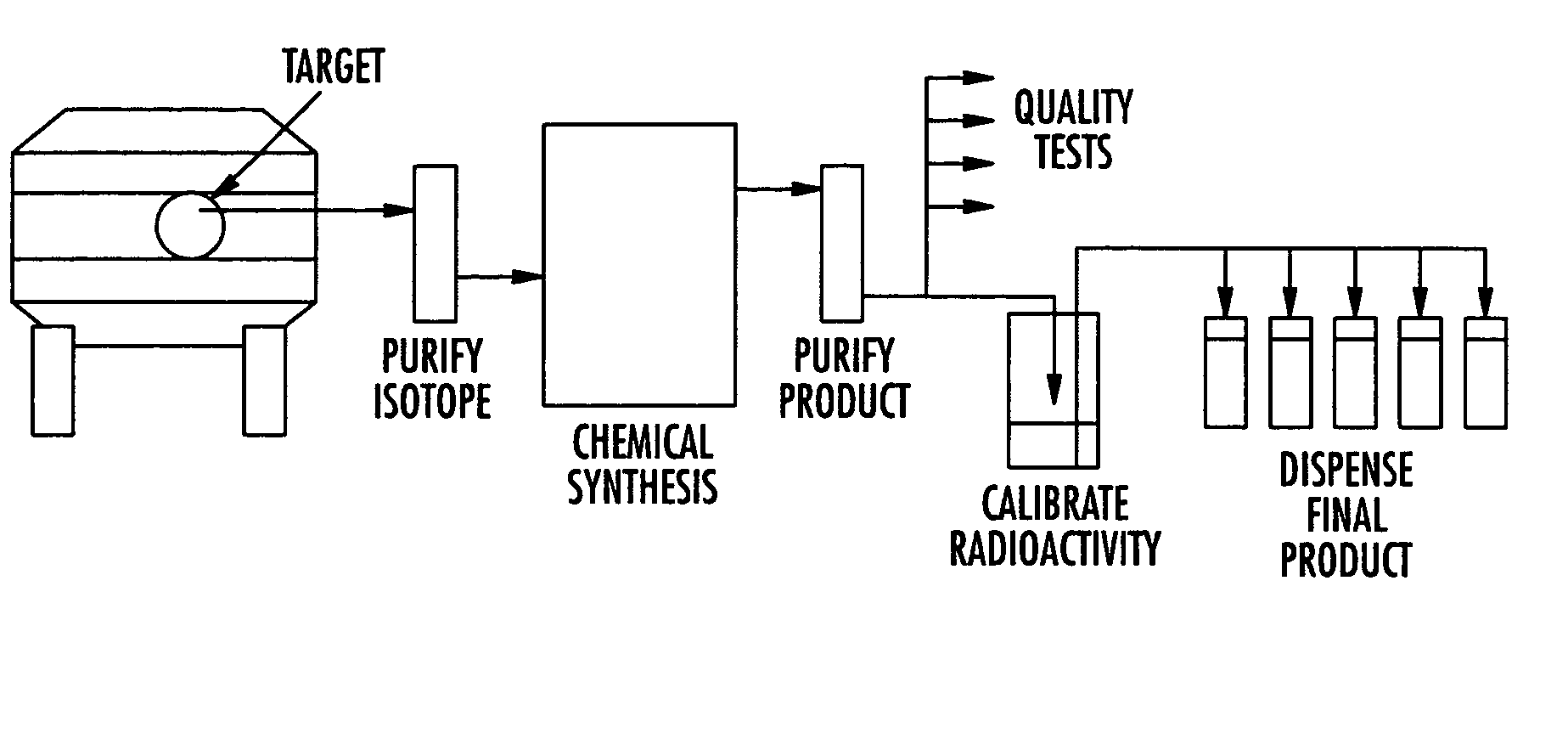
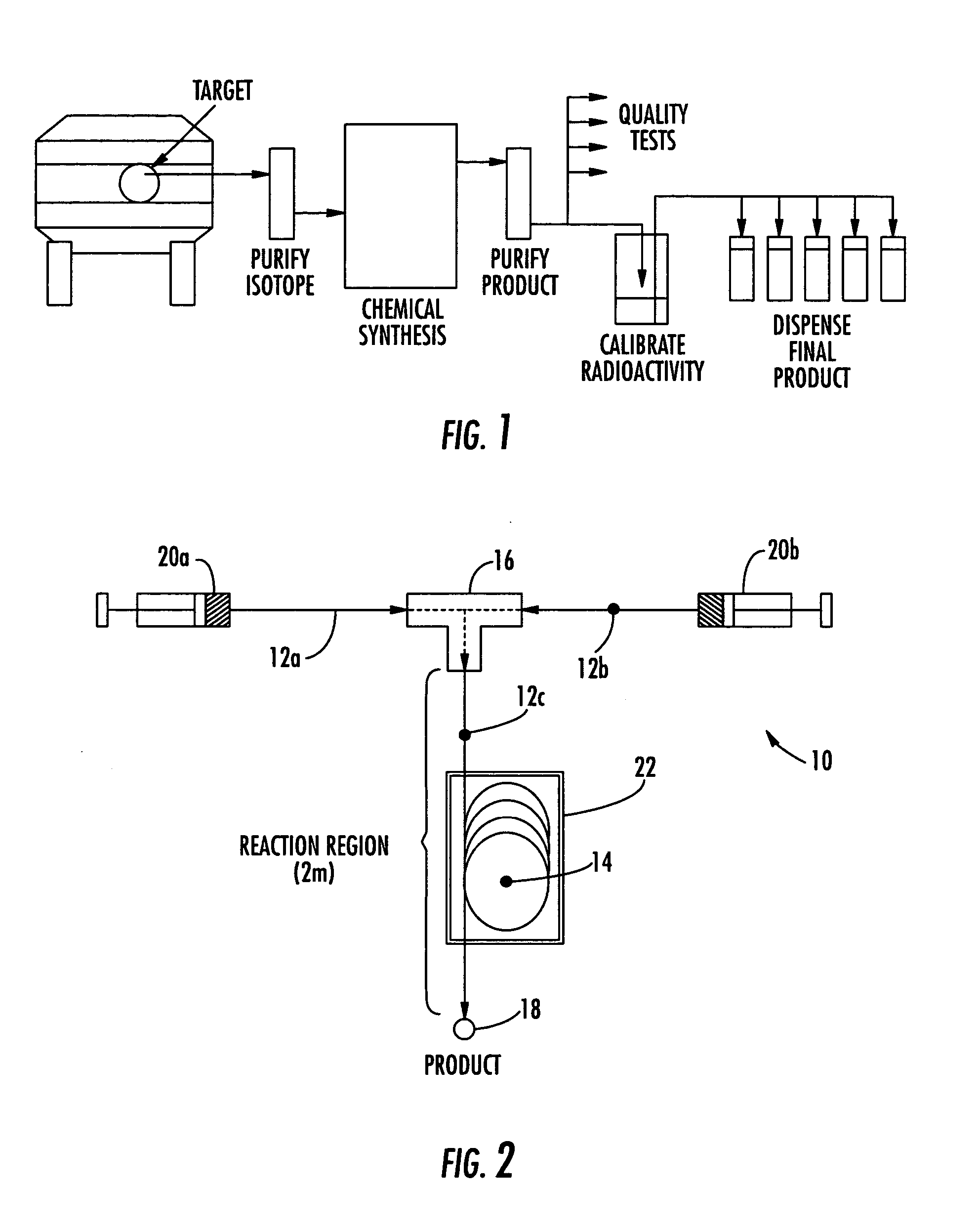
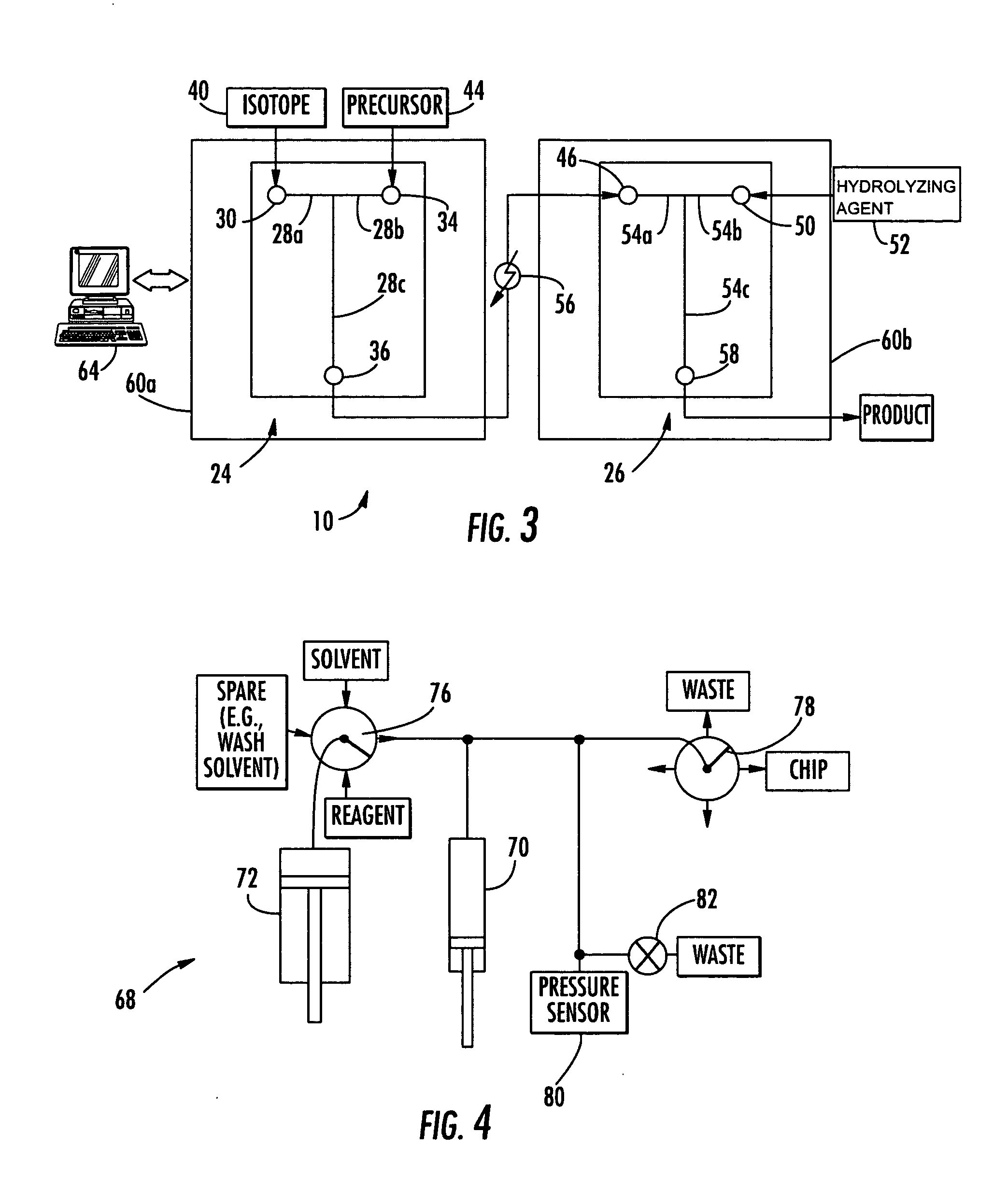
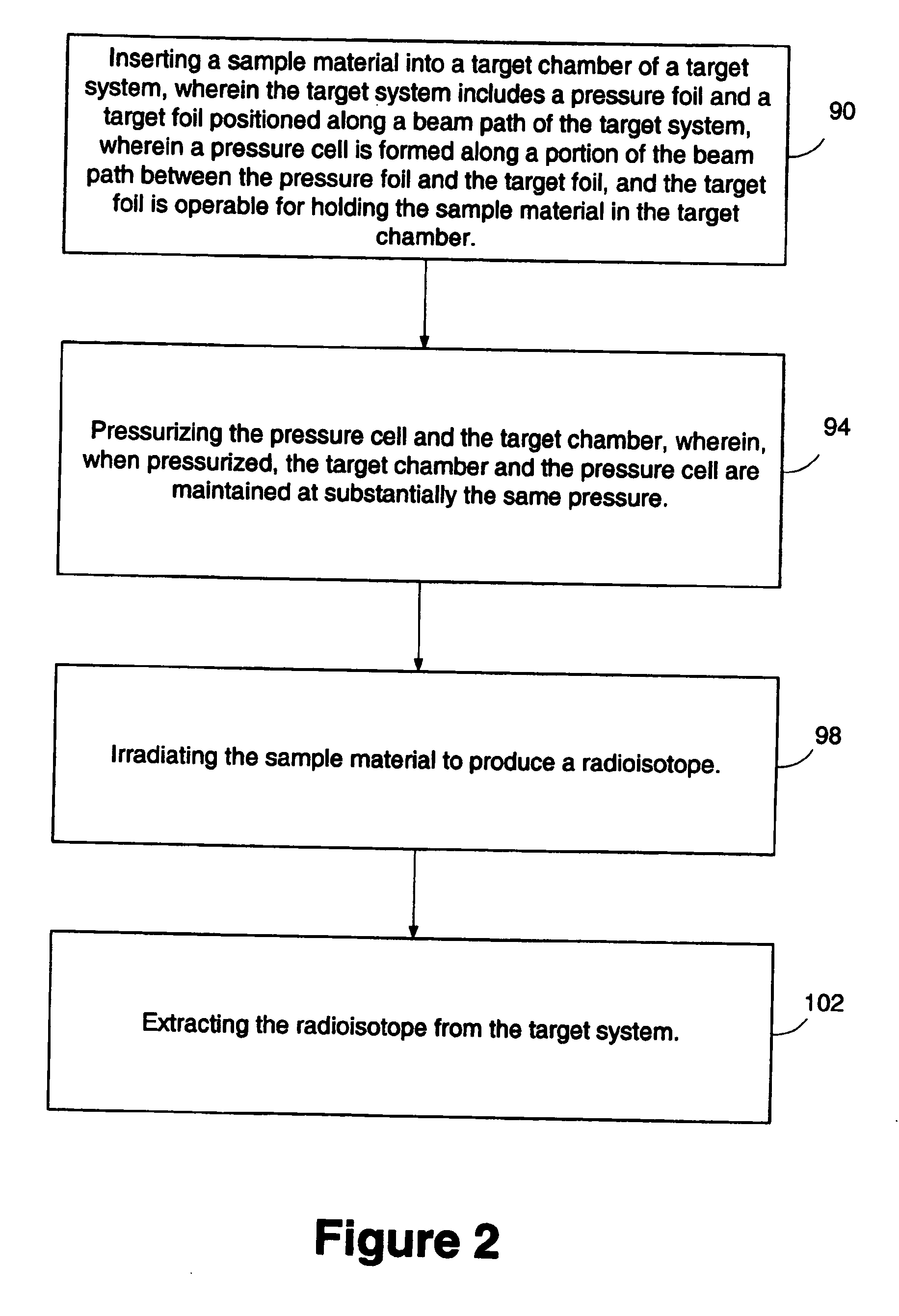
Method and apparatus for the production of radioisotopes
InactiveUS20060062342A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsParticle beamPressure cell
A target system includes a beam path for receiving a particle beam and a target chamber for housing a sample material. A target foil is operable for holding the sample material in the target chamber. A pressure cell is formed along a portion of the beam path between the target foil and a pressure foil. When irradiating the sample material with the particle beam, the pressure inside the target chamber and the pressure cell is increased and maintained at substantially the same pressure. A method includes inserting a sample material into a target chamber of a target system. The target system includes a pressure cell formed along a portion of a beam path between a pressure foil and a target foil, adjacent the target chamber. The pressure cell and the target chamber are pressurized and maintained at substantially the same pressure. The sample material is irradiated to produce a radioisotope.
Owner:HOUSTON CYCLOTRON PARTNERS
Assembly for transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material
InactiveUS6233299B1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationRadioactive agentTechnetium-99
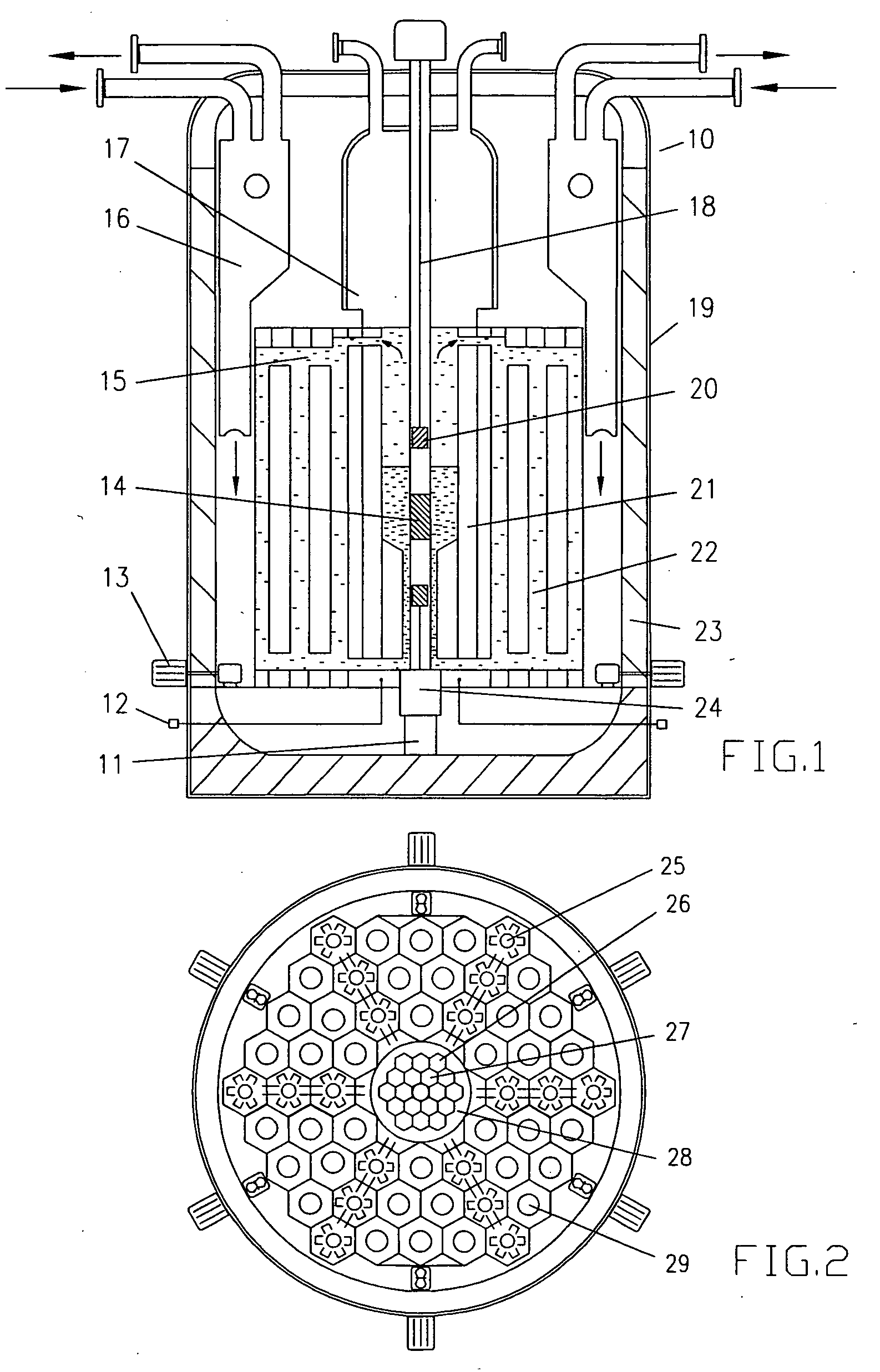
A new transmutation assembly permits an efficient transmutation of a long-lived radioactive material (long-lived FP nuclides such as technetium-99 or iodine-129) which was produced in the nuclear reactor. Wire-type members of a long-lived radioactive material comprised of metals, alloys or compounds including long-lived FP nuclides are surrounded by a moderator material and installed in cladding tubes to form FP pins. The FP pins, and nothing else, are housed in a wrapper tube to form a transmutation assembly. The wire-type members can be replaced by thin ring-type members. The transmutation assemblies can be selectively and at least partly loaded into a core region, a blanket region or a shield region of a reactor core in a fast reactor. From a viewpoint of reducing the influence on the reactor core characteristics, it is optimal to load the transmutation assemblies into the blanket region.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
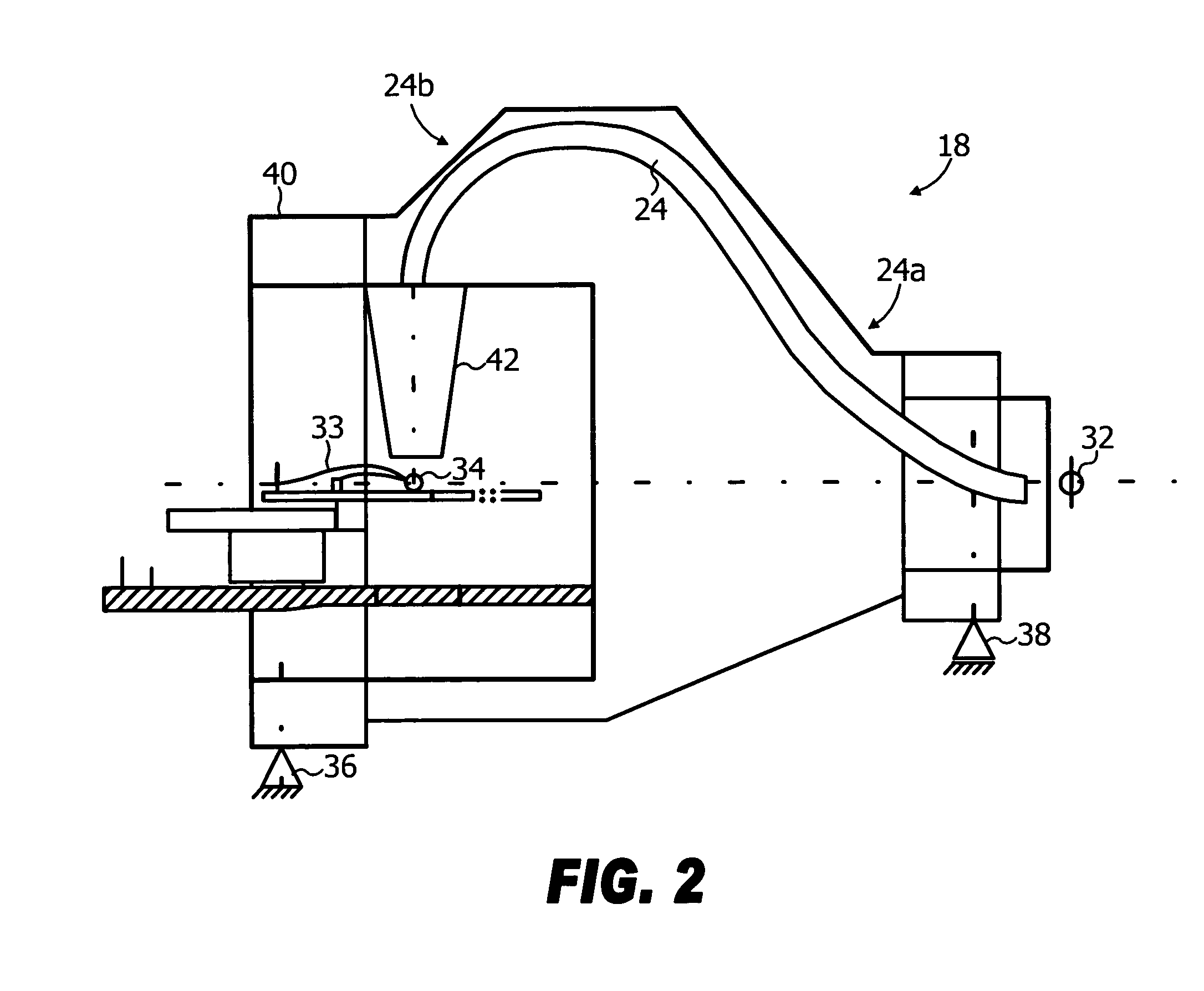
System for the delivery of proton therapy
InactiveUS7560715B2Avoid the broadening of the beam due MCSIncrease rangeThermometer detailsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsProtonLight beam
A process for an intensity-modulated proton therapy of a predetermined volume within an object includes discretising the predetermined volume into a number of iso-energy layers each corresponding to a determined energy of the proton beam. A final target dose distribution is determined for each iso-energy layer. The final target dose distribution or at least a predetermined part of this final target dose distribution is applied by parallel beam scanning by controlling the respective beam sweepers, thereby scanning one iso-energy layer after the other using an intensity-modulated proton beam while scanning a predetermined iso-energy layer.
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Reactor tray vertical geometry with vitrified waste control
InactiveUS20060171498A1Reduce the amount of wasteNegative environmental impactConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationThermal energyVitrification
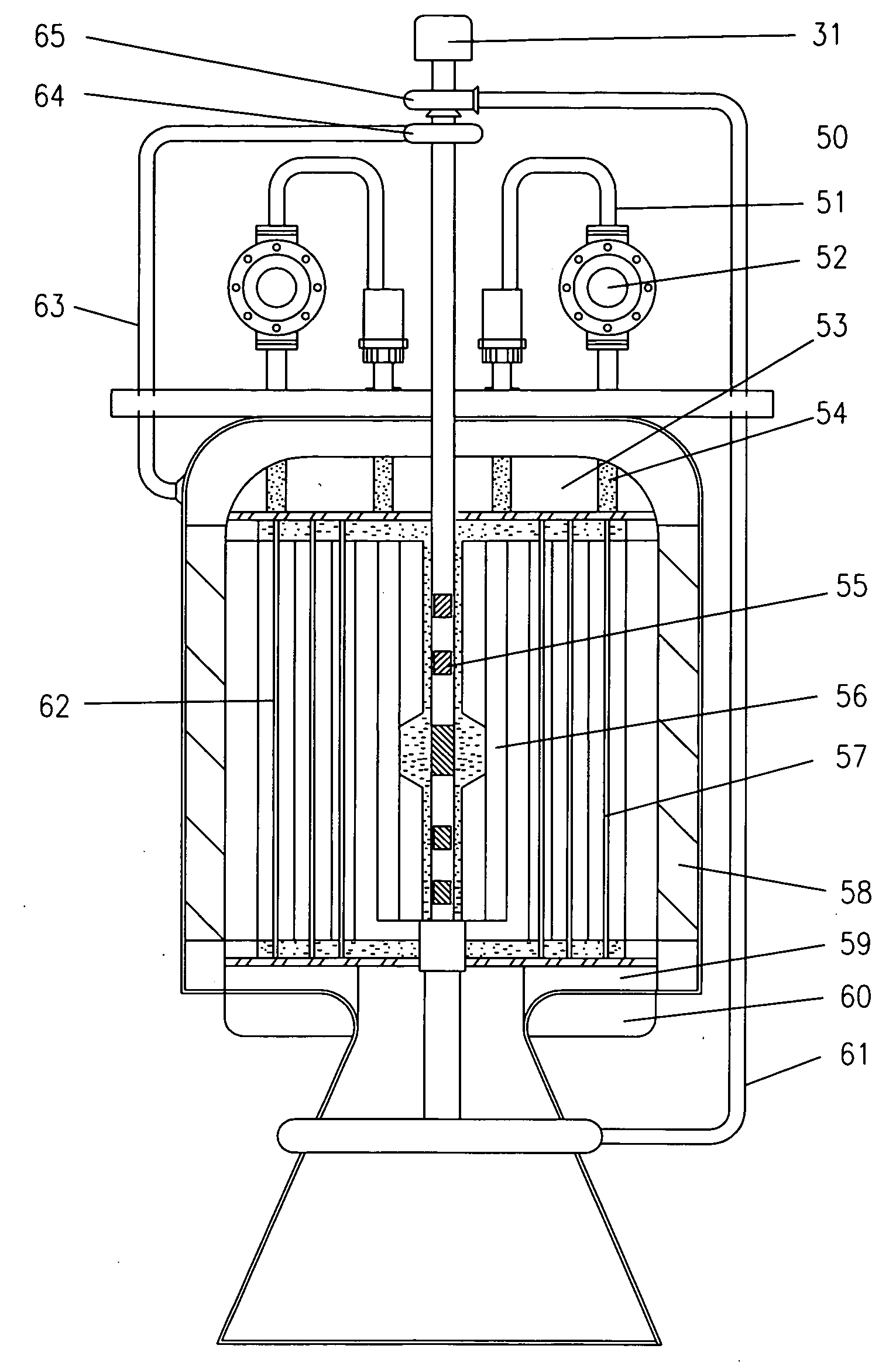
A nuclear-powered plant for systems of up to about 100 MWs with a confinement section where the reaction takes place in a core having a reactive thorium / uranium-233 composition, and where an external neutron source is used as a modulated neutron multiplier for the reactor core output. The core is housed in a containment structure that radiates thermal energy captured in a multiple-paths heat exchanger. The exchanger heat energy output is put to use in a conventional gas-to-water heat exchanger to produce commercial quality steam.
Owner:D B I CENTURY FUELS & AEROSPACE SERVICES
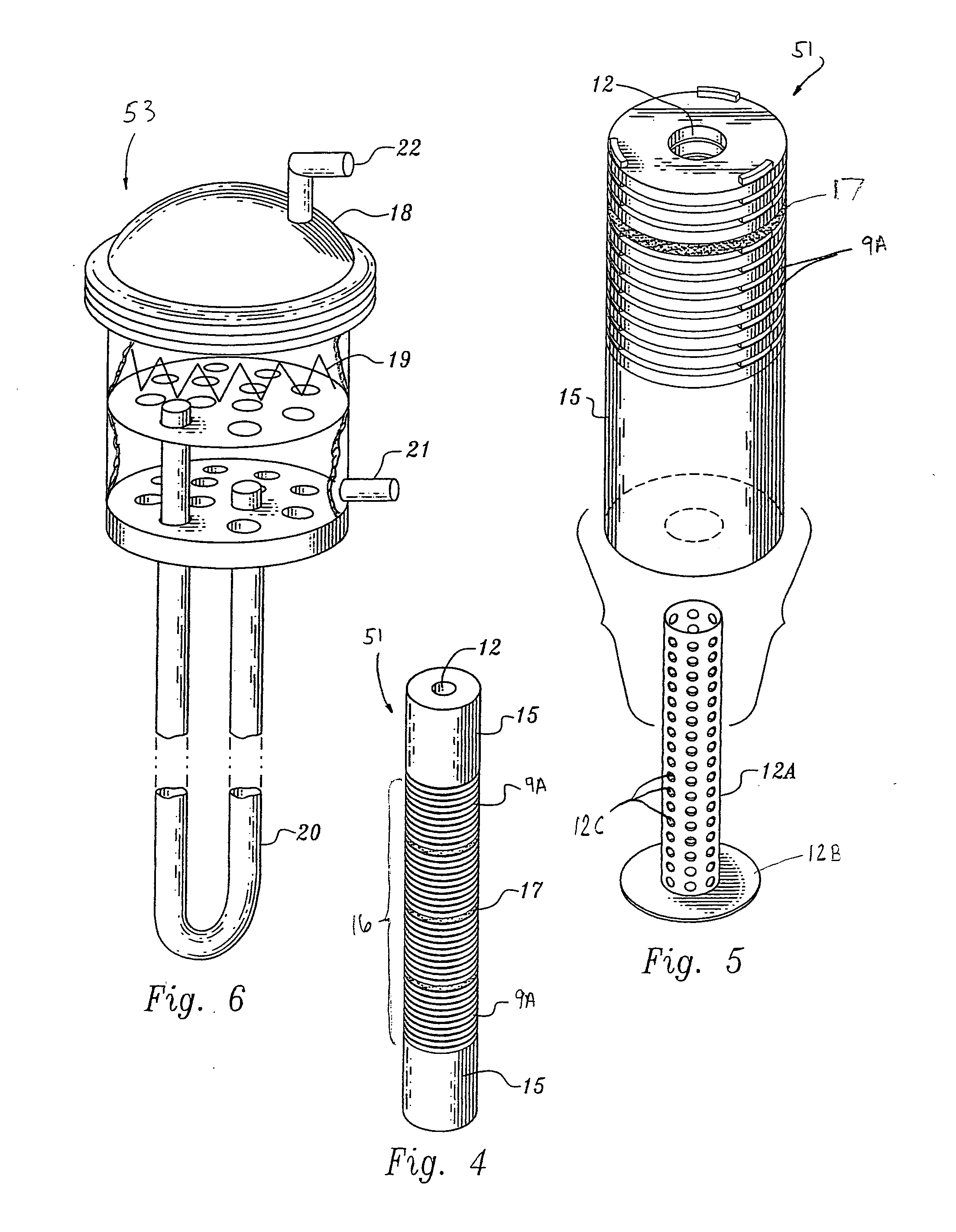
Internal circulating irradiation capsule for iodine-125 and method of producing iodine-125 using same
InactiveUS20060126774A1Reduce neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron irradiationIodine
A present invention provides an internal circulating irradiation capsule available for the production of iodine-125 and a related production method. The irradiation capsule filled with xenon gas has a lower irradiation part, an upper irradiation part, and a neutron control member. The lower irradiation part is inserted into an irradiation hole of a reactor core and irradiated with a large quantity of neutron directly. When neutron is radiated to the xenon gas, iodine-125 is produced from xenon gas. The upper irradiation part protrudes from the irradiation hole, and iodine-125 is transferred to the upper irradiation part by convection and solidified in the upper part. The neutron control member reduces neutron in the upper part to produce iodine-125 of high purity and radioactivity in a large quantity.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Nonintrusive method for the detection of concealed special nuclear material
ActiveUS20050220247A1Overcome problemsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringNeutron pulseRadiation damage
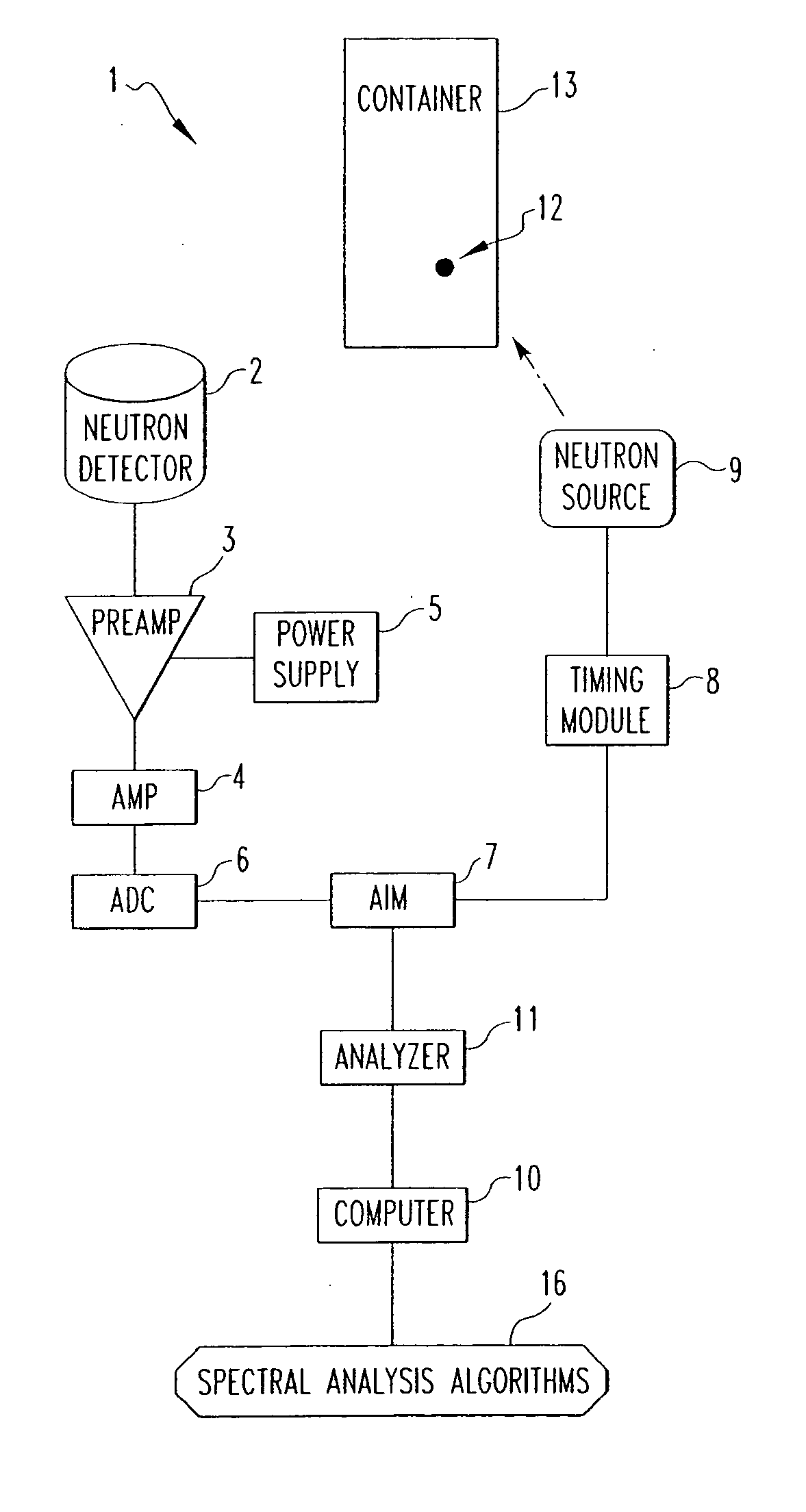
A method and associated apparatus for detecting concealed fissile, fissionable or special nuclear material in an article, such as a shipping container, is provided. The article is irradiated with a source of fast neutrons, and fast neutrons released by the fissile or fissionable material, if present, are detected between source neutron pulses. The method uses a neutron detector that can detect and discriminate fast neutrons in the presence of thermal neutrons and gamma radiation. The detector is able to process high count rates and is resistant to radiation damage, and is preferably a solid state neutron detector comprised of silicon carbide.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Multiple energy x-ray source for security applications
InactiveUS20050117683A1X-ray/infra-red processesConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsX-rayFissile material
An x-ray inspection system for identifying fissile material includes one or more sources of penetrating radiation that generate first, second, and third instantaneous spectra where the object is exposed to the second only if there is no penetration of the first and the object is exposed to the third only if there is no penetration of the second. Further, the sources of the second and the third spectra are pulsed. Consequently, ambient levels of radiation may be held below cabinet levels while identifying objects containing fissile material.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
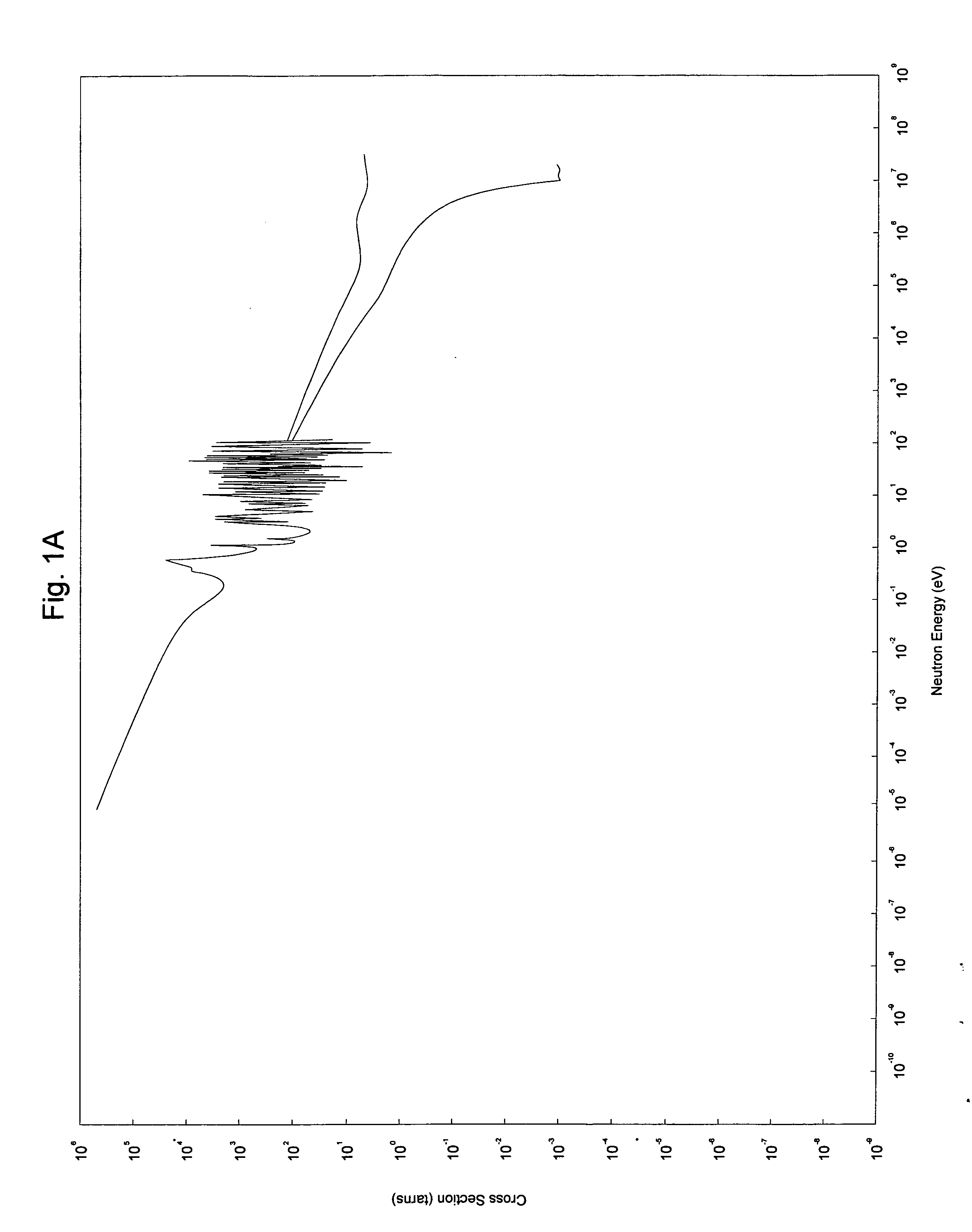
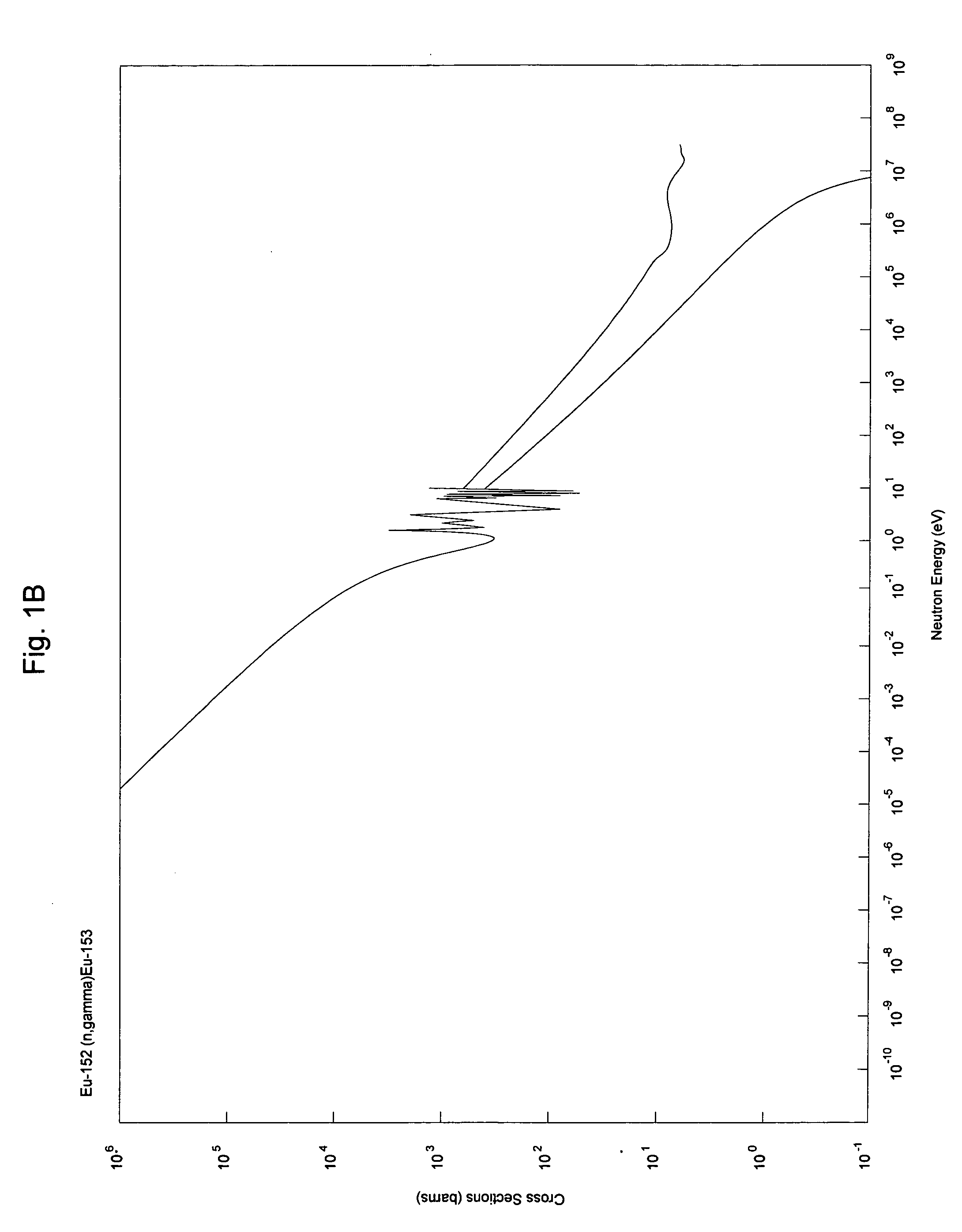
Method of producing europium-152 and uses therefor
InactiveUS20080076957A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesMedical physicsBrachytherapy
Provided herein is a method of producing europium-152 as a radiotherapeutic source for external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy using existing containment or capsule devices for the radionuclide. The method comprises irradiating a europium-151 enriched target with neutrons confined to a range of neutron energies effective to drive the reaction 151Eu(n,γ)152Eu. Also provided are methods of treating a subject using external beam radiation therapy or brachytherapy using europium-152.
Owner:ADELMAN STUART LEE
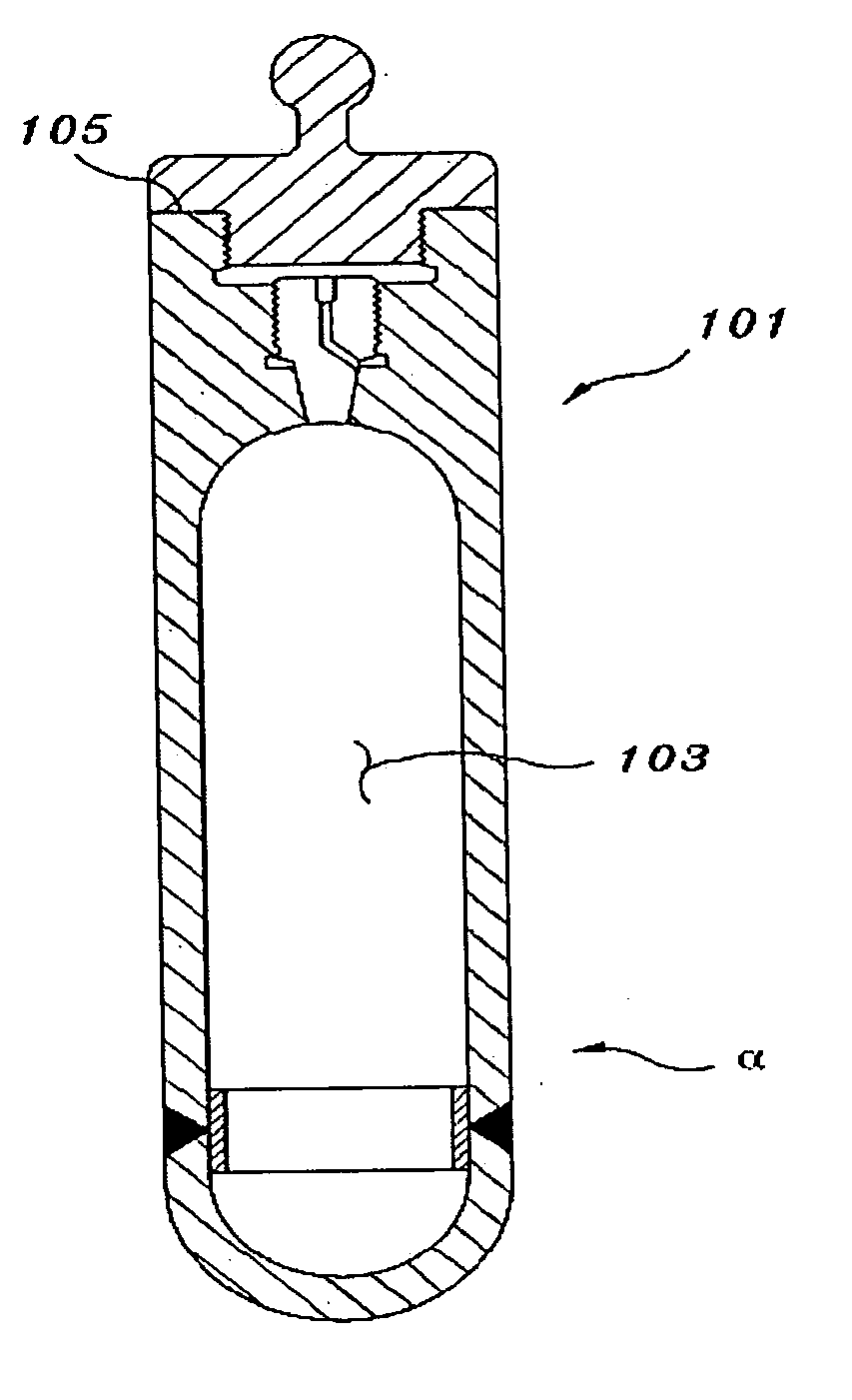
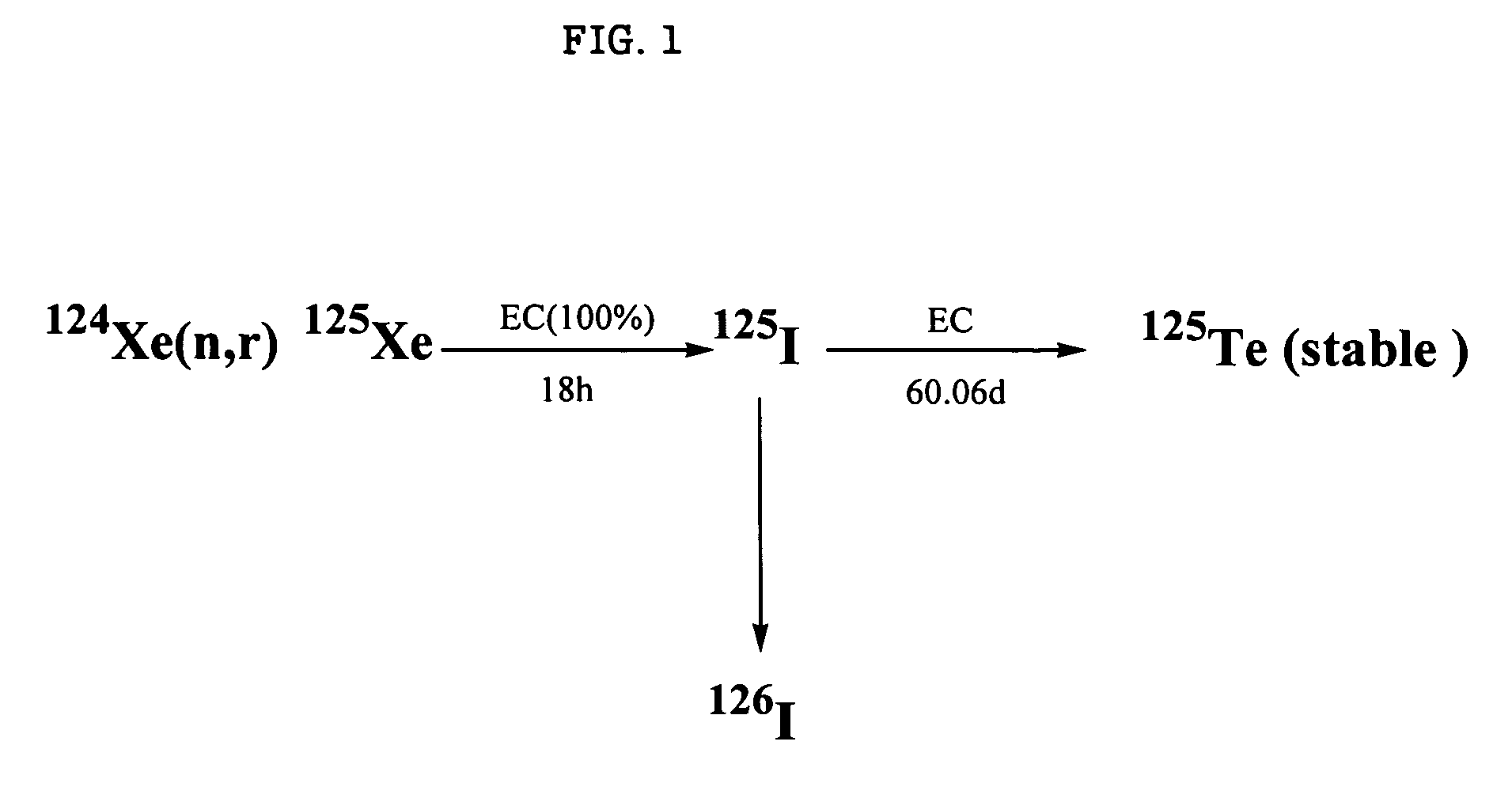
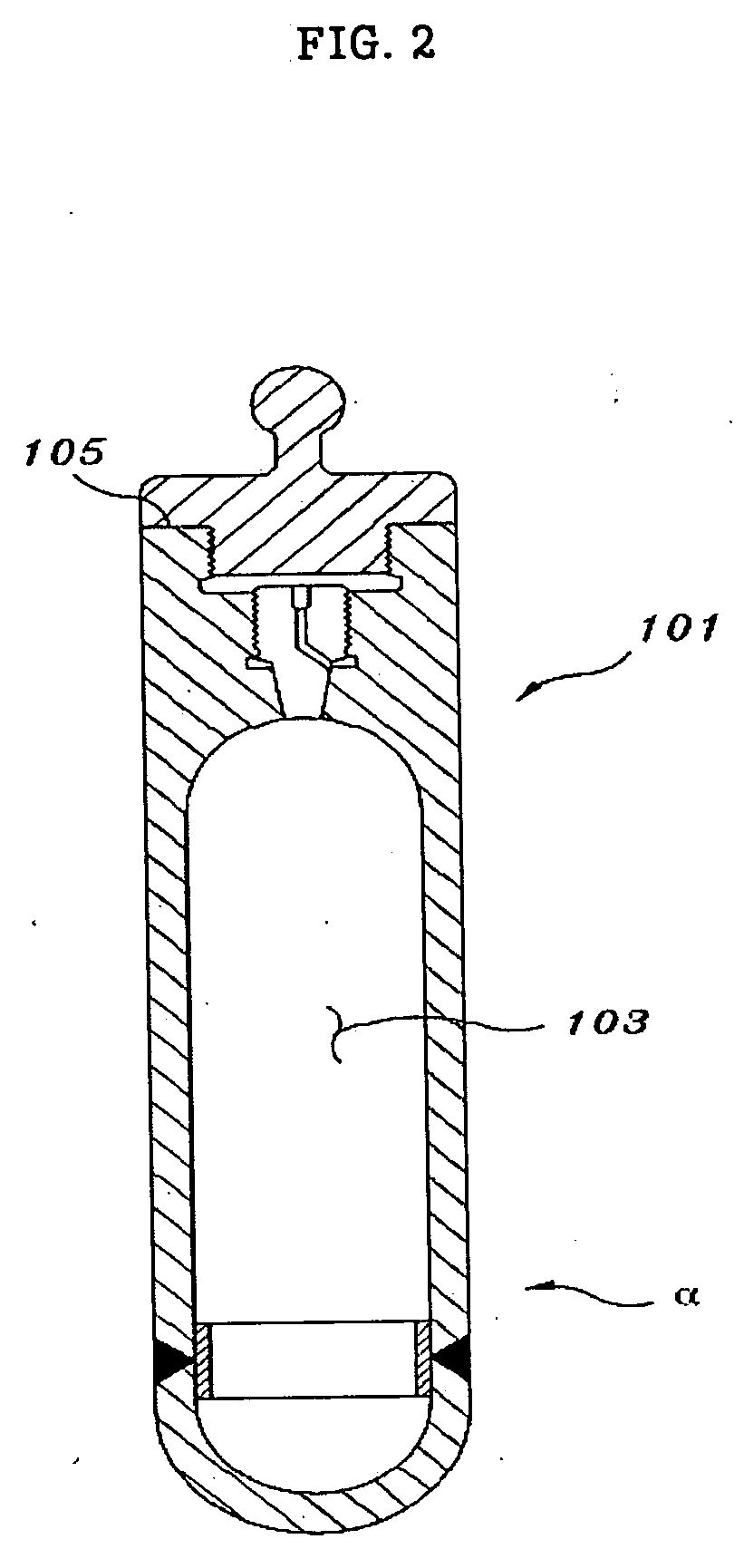
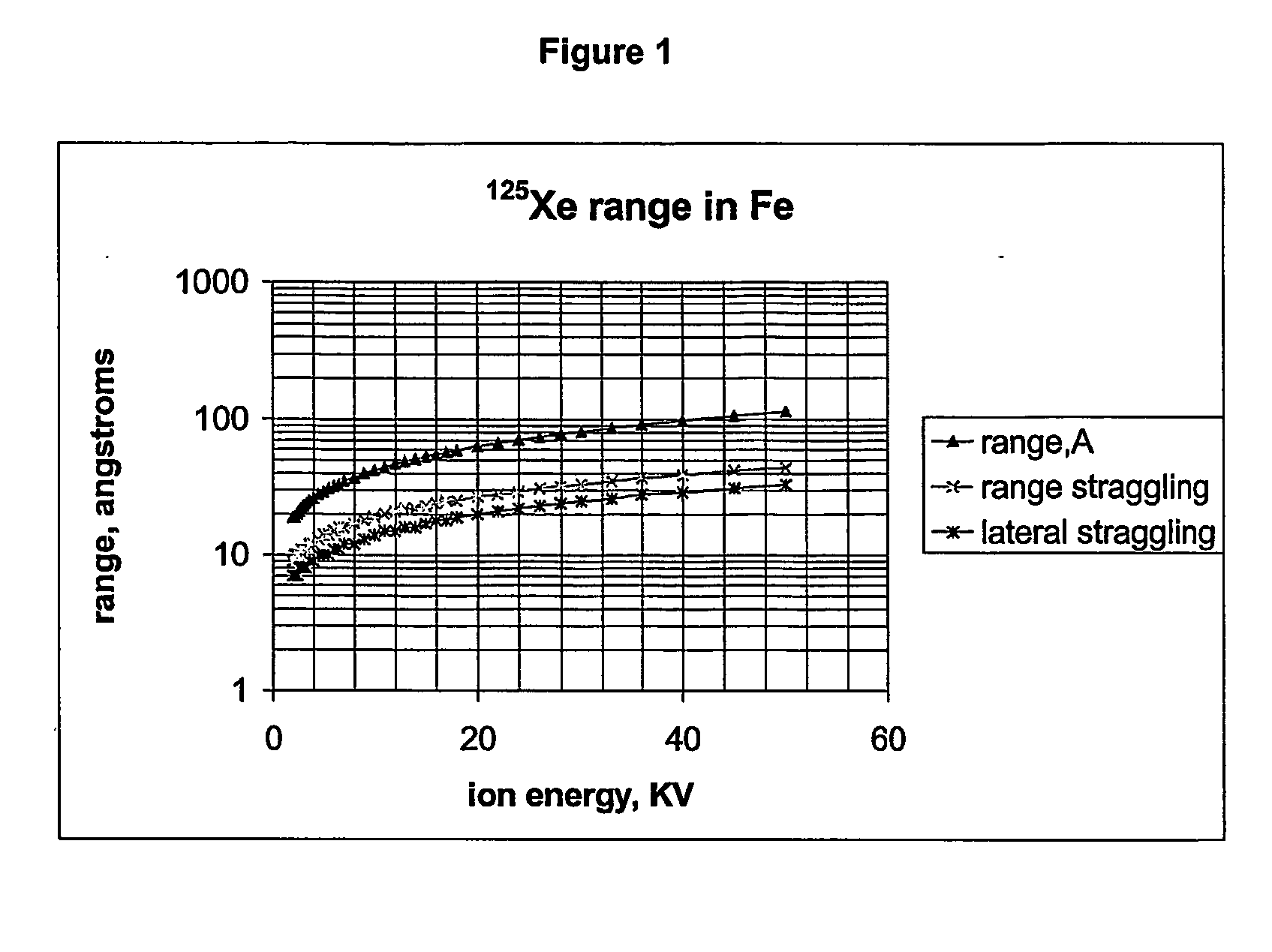
Radioactive ion
InactiveUS20050118098A1Minimize difficultyEfficient methodIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMedicineInsertion stent
The present invention relates to a method for implantation of Xe isotopes in a matrix for production of 125I sources that do not shed radioactive atoms. 125Xe implanted at 12 kV in steel, titanium and gold does not evolve after more than 10 half-lives (380 h) and 125I from the decay of implanted 125Xe is equally stable for 2 half-lives (120 d). The matrix having radioxenon implanted is useful as a medical device, for instance as a “seed” for radiotherapeutic uses or in production of stents. Methods of treatment utilizing such devices are also encompassed by the present invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
Process for producing ultra-pure plutonium-238
InactiveUS6896716B1Efficient productionEasy to separateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationDecay productThermal neutron flux
A method for producing ultra-pure Pu-238 is provided. The method comprises the steps of short-term irradiating Am-241 targets with a high, thermal neutron flux greater than 6.5×1014 neutrons cm−2 s−1 and more preferably greater than 1×1015 neutrons cm−2 s−1 for a predetermined period of time preferably from 20 days to 30 days and more preferably approximately 25 days to convert a substantial fraction of the Am-241 to Cm-242, e.g., approximately 0.555 g of Cm-242 per g of Am-241 charged, thereafter promptly chemically separating the produced Cm-242, preferably within 10 days to 20 days of the irradiation cycle of the Am-241 targets and more preferably within about 15 days of the irradiation cycle of the Am-241 targets, and recovering the ultra-pure Pu-238 decay product of the separated Cm-242.
Owner:WOOD ROSE C +1
Rubidium generator for cardiac perfusion imaging and method of making and maintaining same
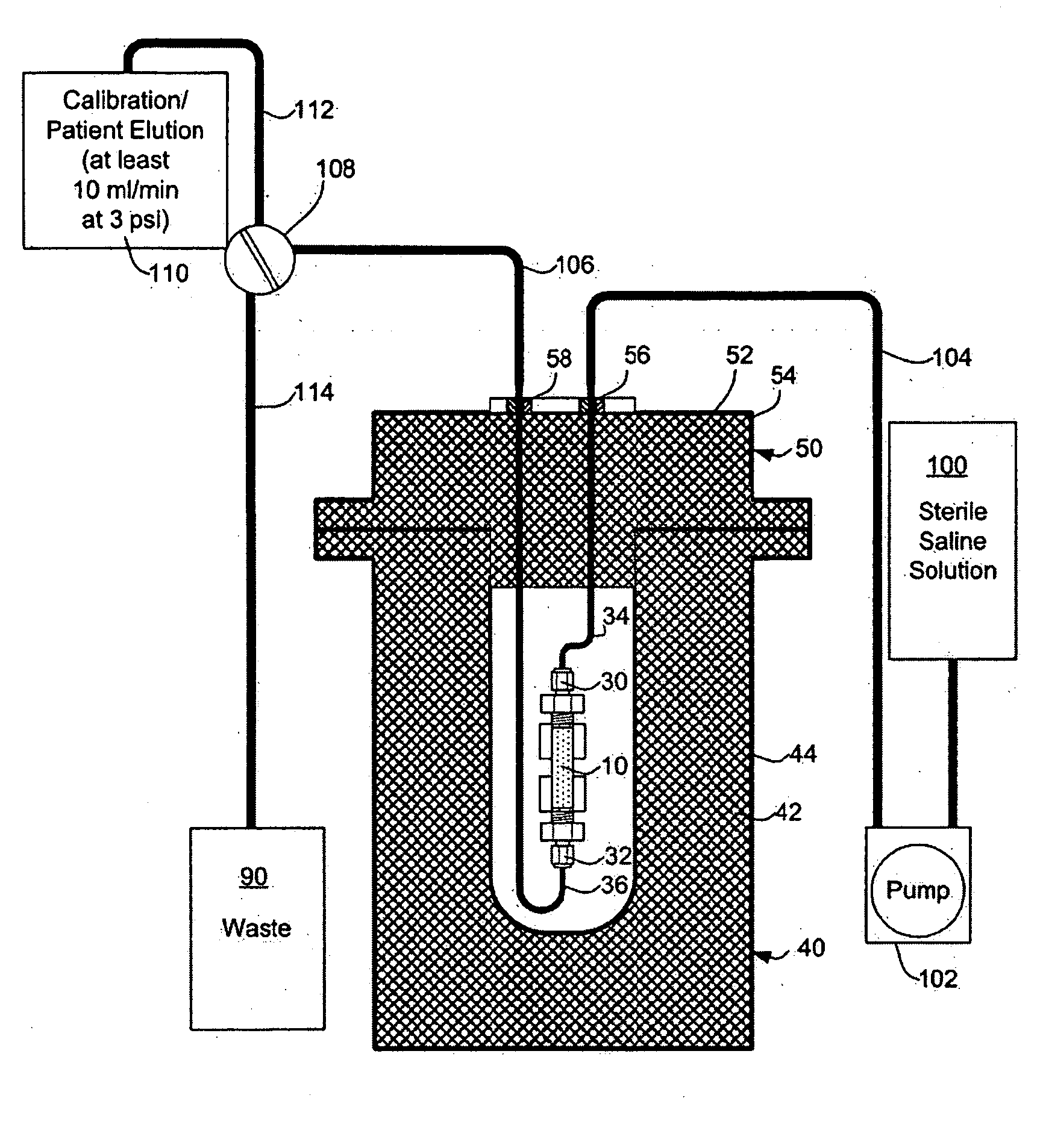
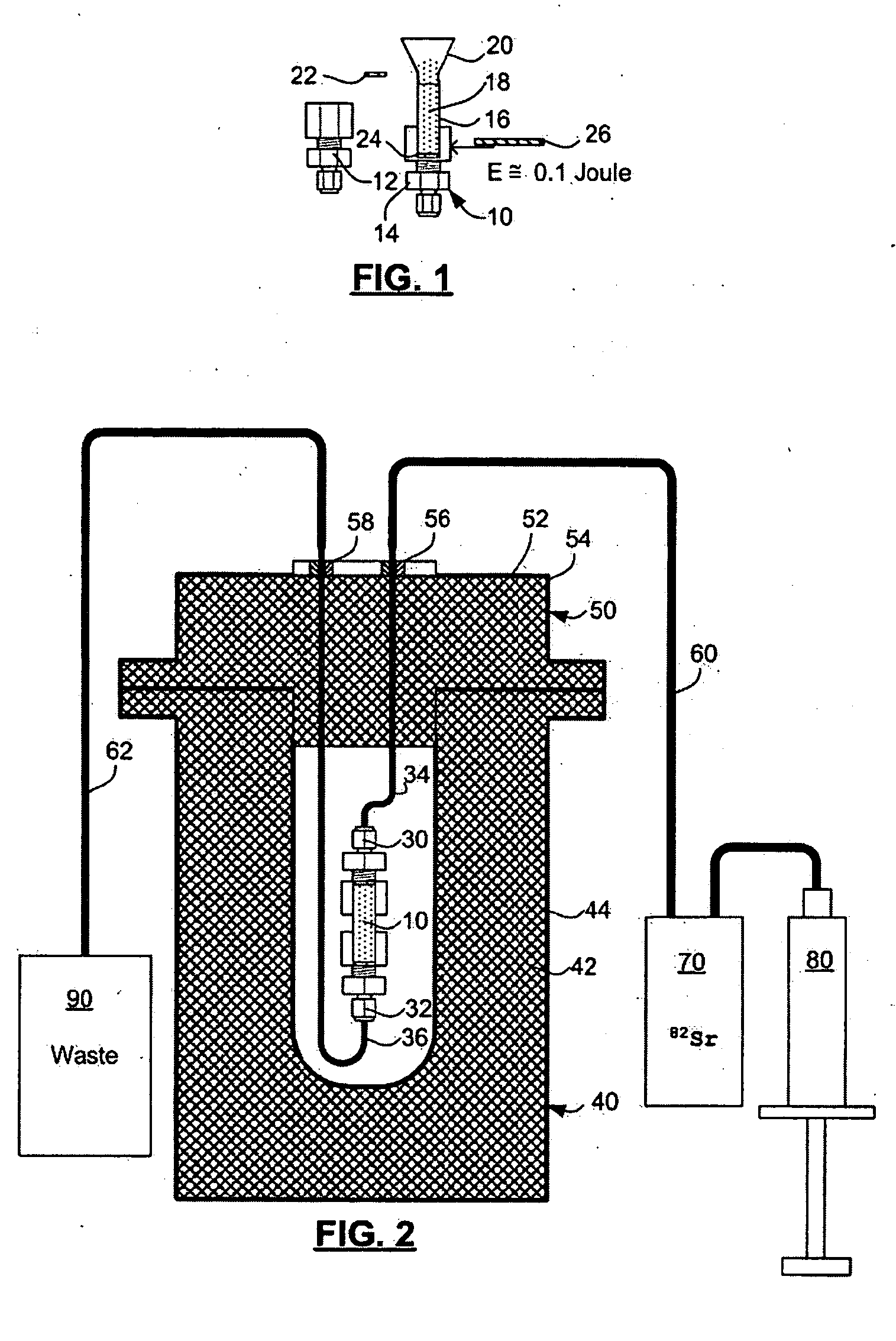
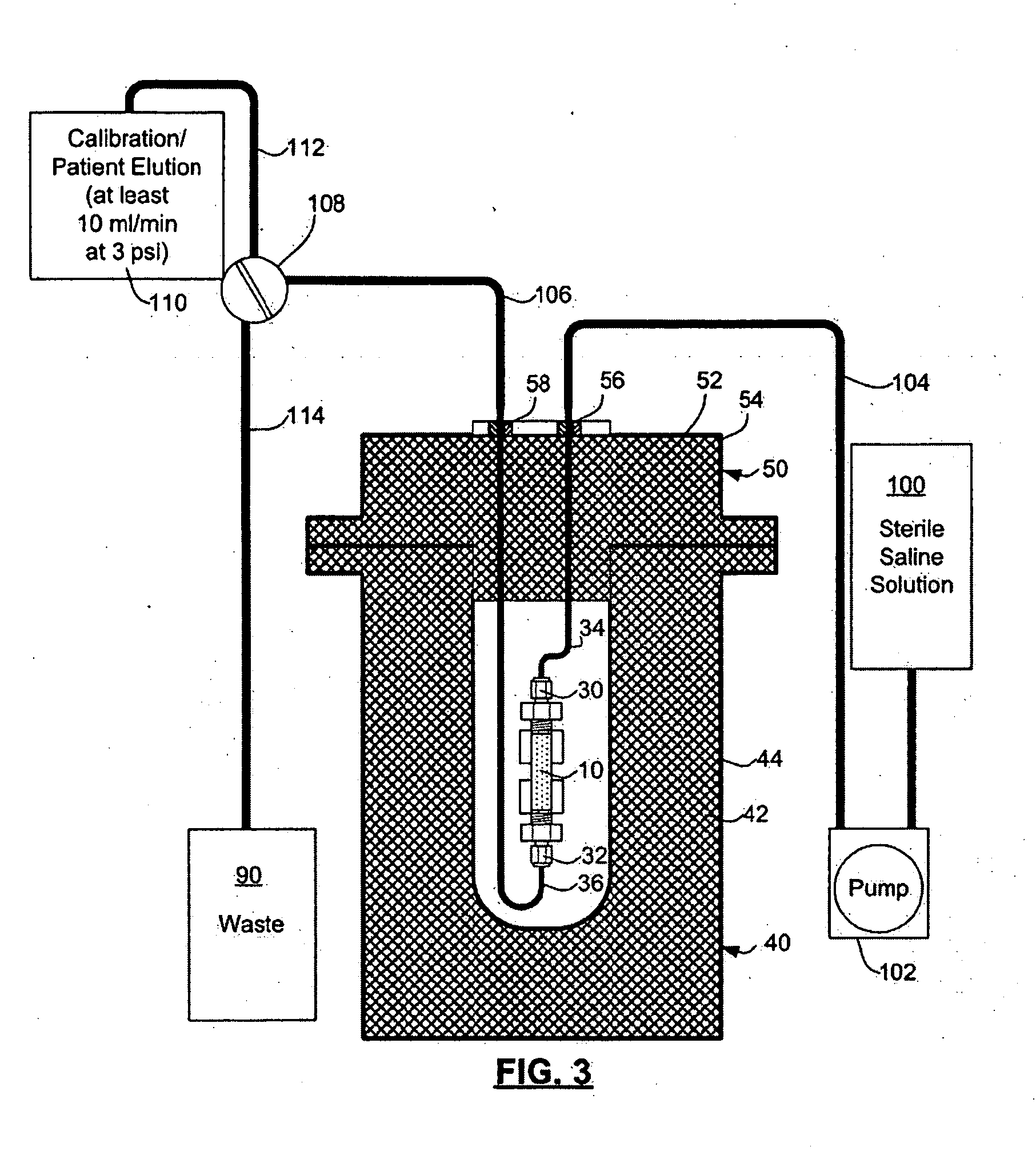
ActiveUS20070140958A1Low pressure elutionFacilitates precision flow controlIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsFractographyRubidium
An 82Sr / 82Rb generator column is made using a fluid impervious cylindrical container having a cover for closing the container in a fluid tight seal, and further having an inlet for connection of a conduit for delivering a fluid into the container and an outlet for connection of a conduit for conducting the fluid from the container. An ion exchange material fills the container, the ion exchange material being compacted within the container to a density that permits, the ion exchange material to be eluted at a rate of at least 5 ml / min at a fluid pressure of 1.5 pounds per square inch (10 kPa). The generator column can be repeatedly recharged with 82Sr. The generator column is compatible with either three-dimensional or two-dimensional positron emission tomography systems.
Owner:OTTAWA HEART INST RES
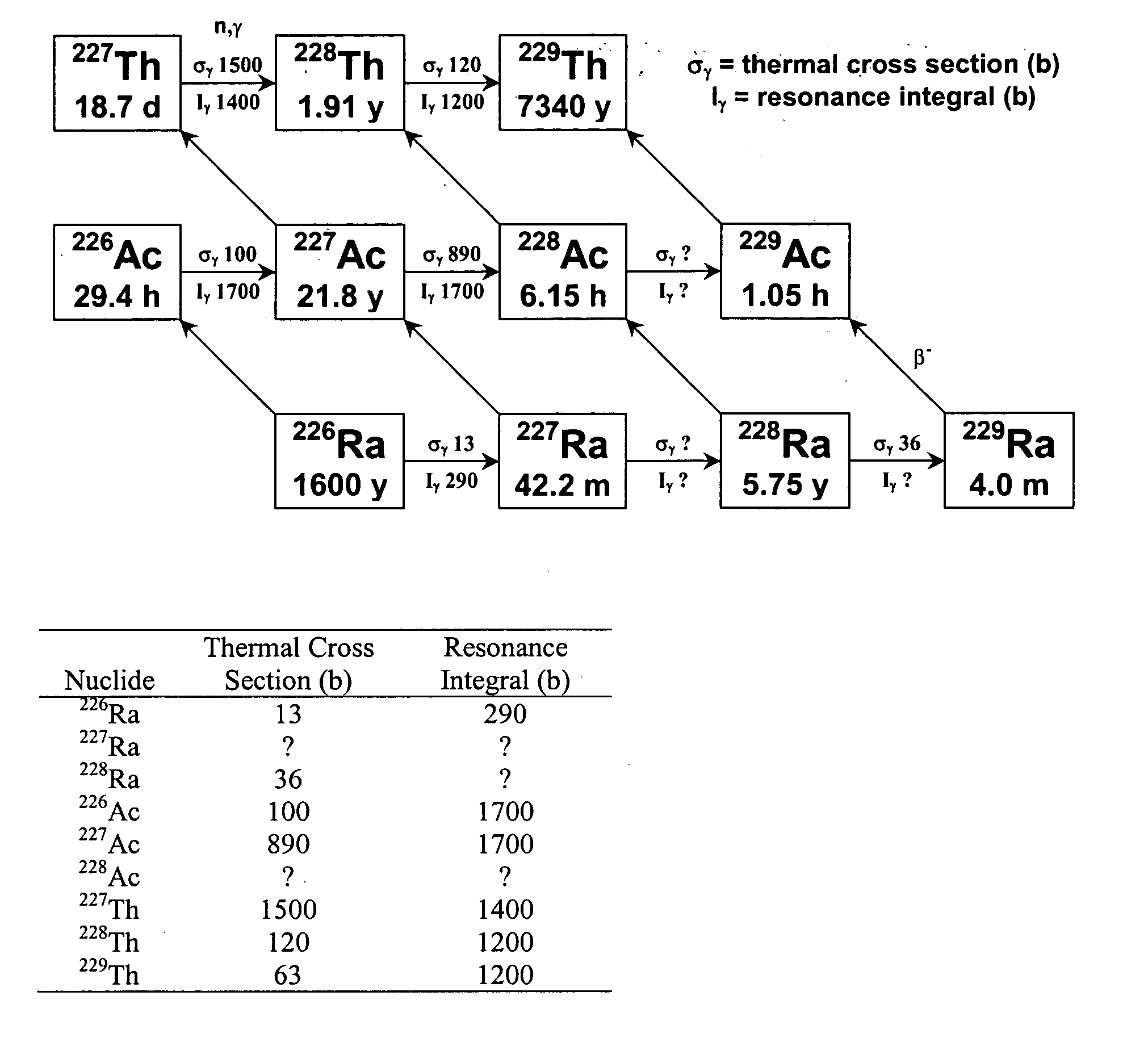
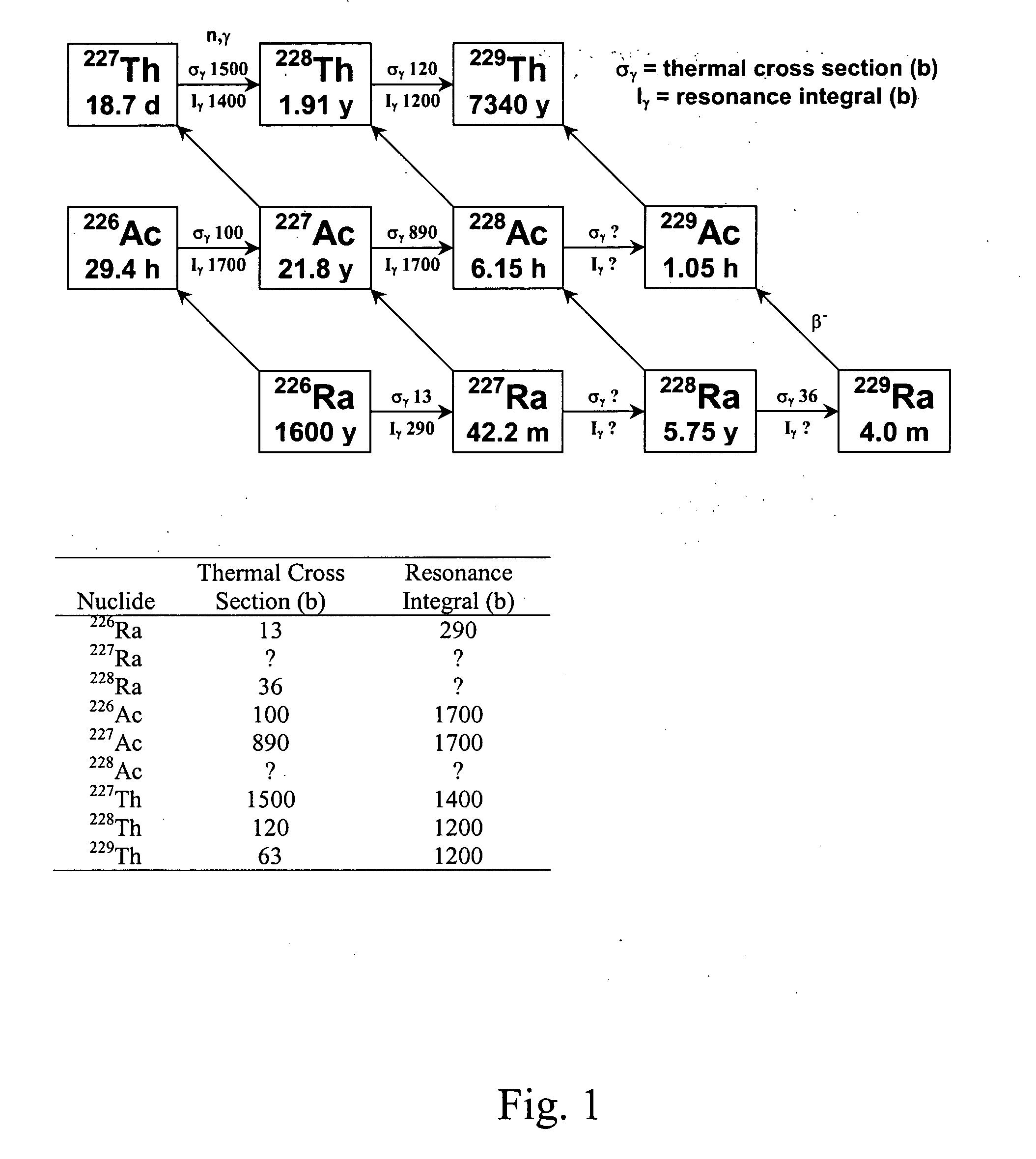
Production of thorium-229
InactiveUS20050105666A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesNeutron captureAlpha particle
A method for producing 229Th includes the steps of providing 226Ra as a target material, and bombarding the target material with alpha particles, helium-3, or neutrons to form 229Th. When neutrons are used, the neutrons preferably include an epithermal neutron flux of at least 1×1013 n s−1·cm−2. 228Ra can also be bombarded with thermal and / or energetic neutrons to result in a neutron capture reaction to form 229Th. Using 230Th as a target material, 229Th can be formed using neutron, gamma ray, proton or deuteron bombardment.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
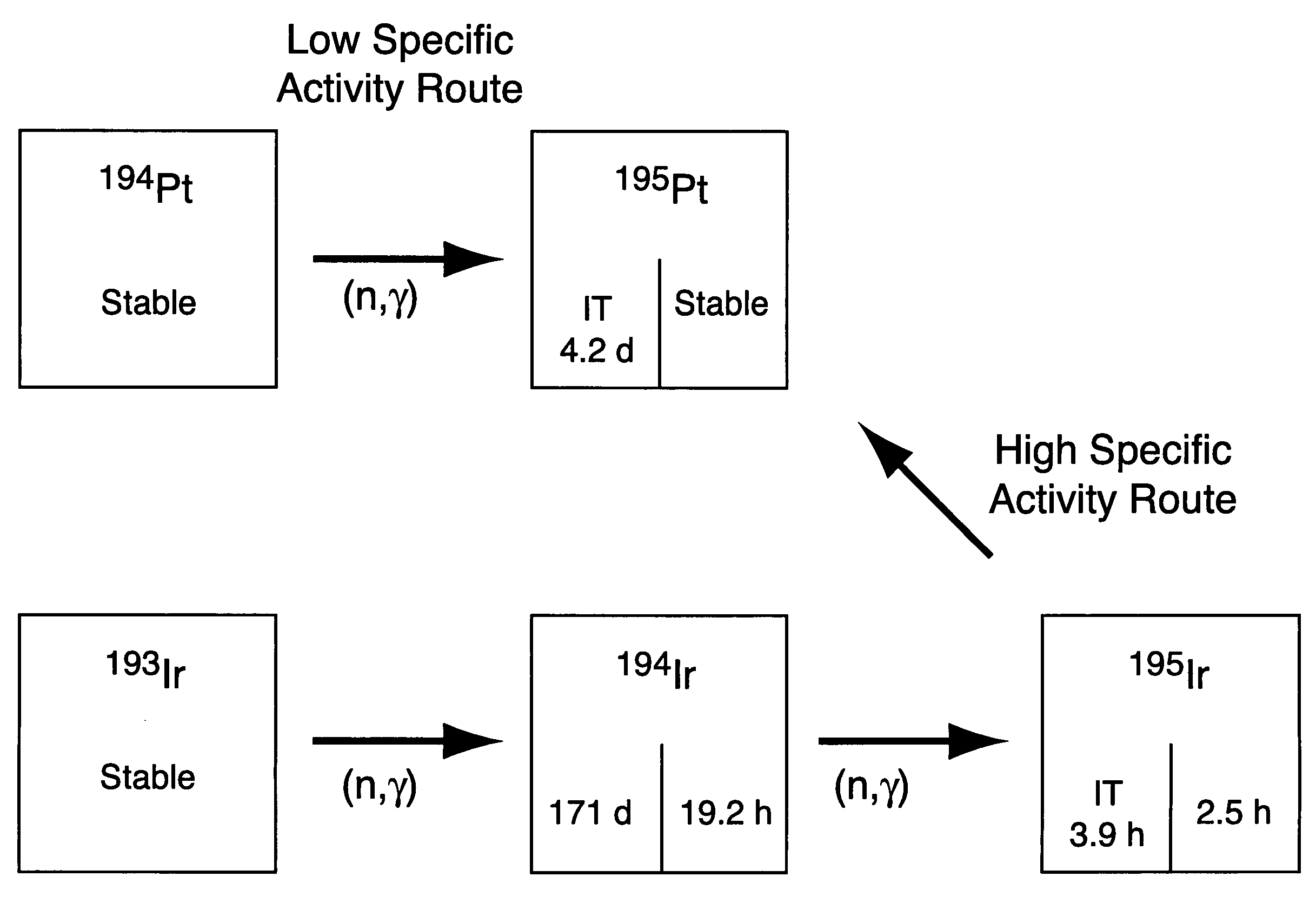
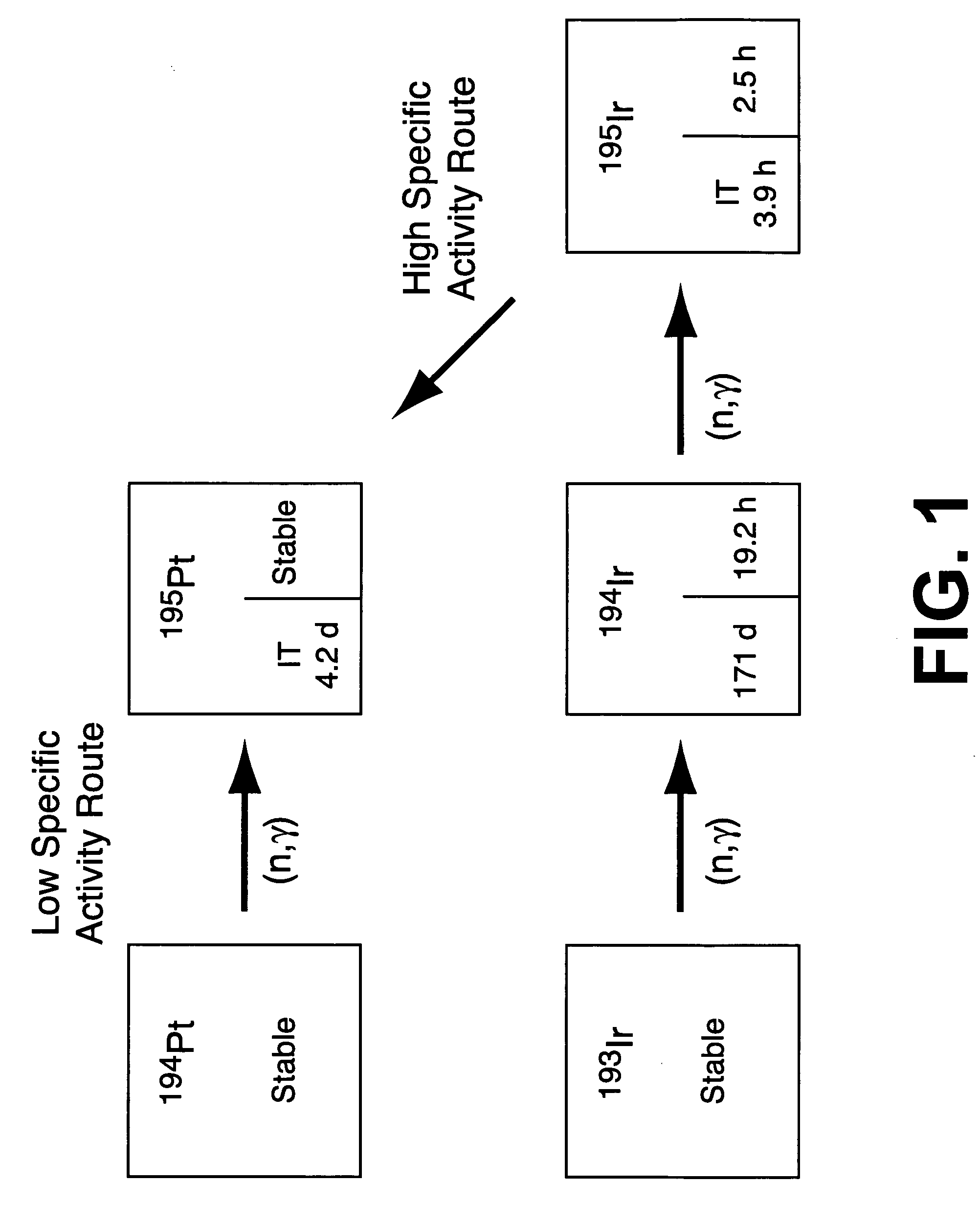
High specific activity platinum-195m
InactiveUS20040196942A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsPlatinumIrradiated materials
A new composition of matter includes <195m>Pt characterized by a specific activity of at least 30 mCi / mg Pt, generally made by method that includes the steps of: exposing <193>Ir to a flux of neutrons sufficient to convert a portion of the <193>Ir to <195m>Pt to form an irradiated material; dissolving the irradiated material to form an intermediate solution comprising Ir and Pt; and separating the Pt from the Ir by cation exchange chromatography to produce <195m>Pt.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for Production of Radioisotope Preparations and Their Use in Life Science, Research, Medical Application and Industry
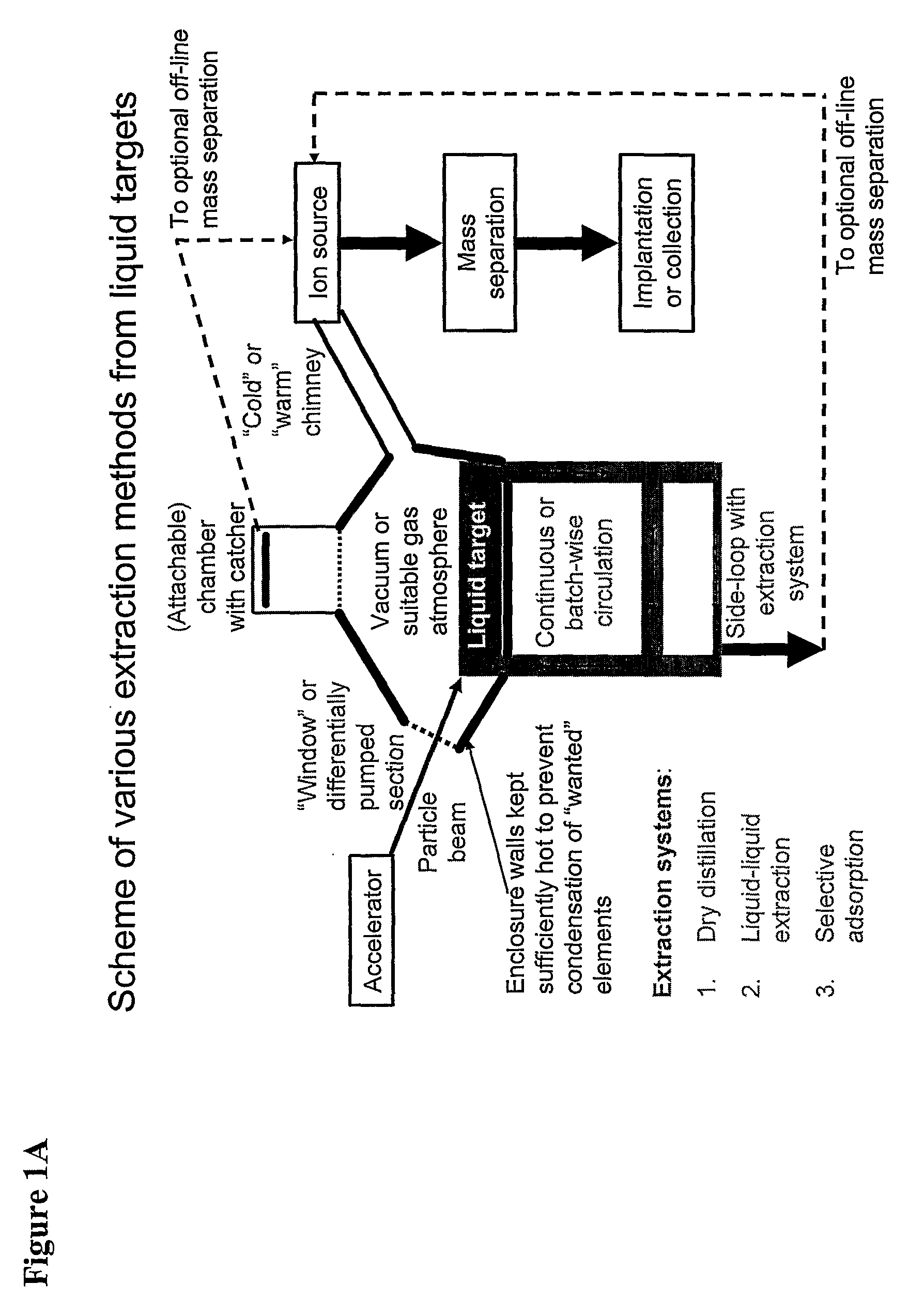
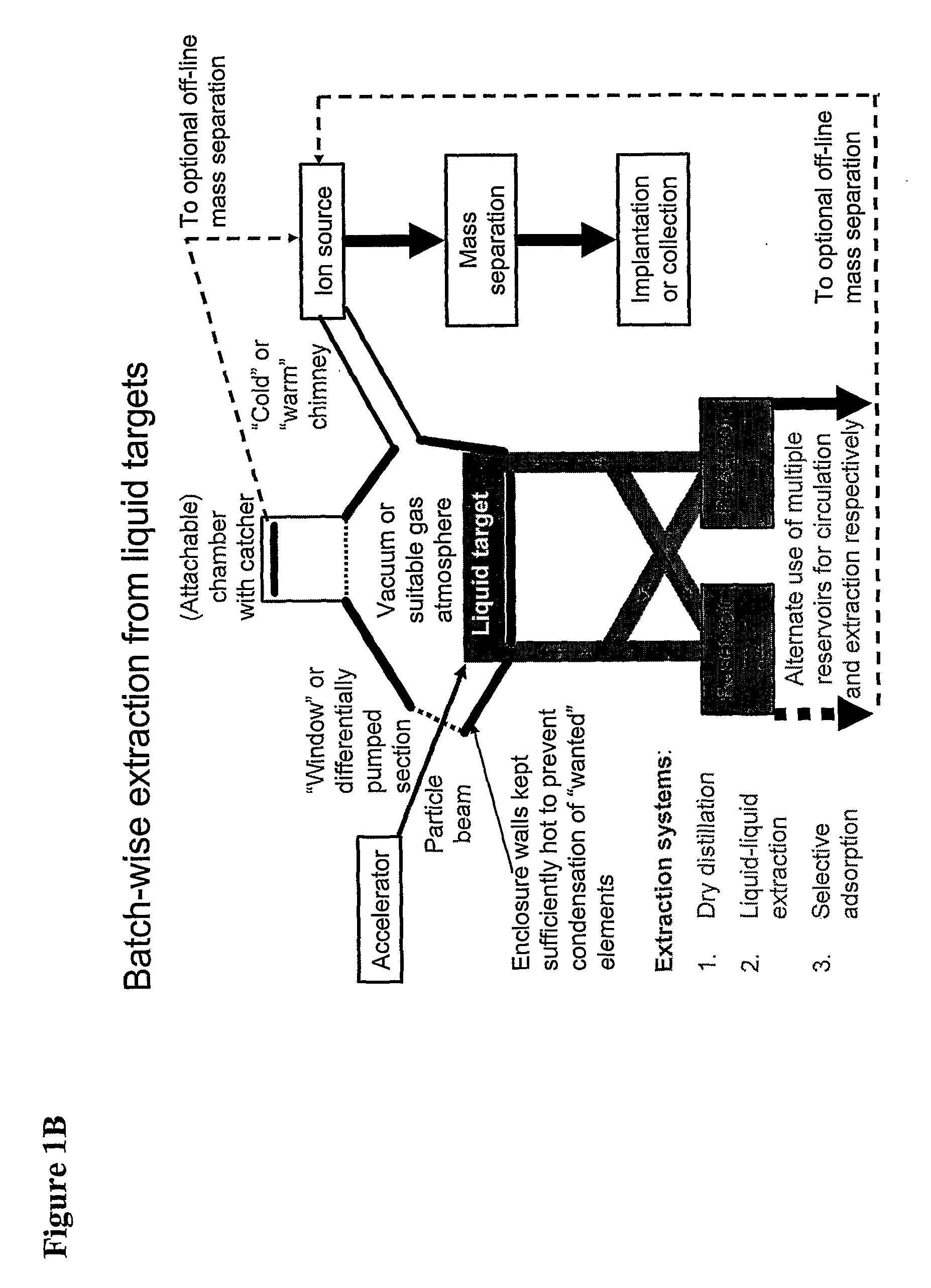
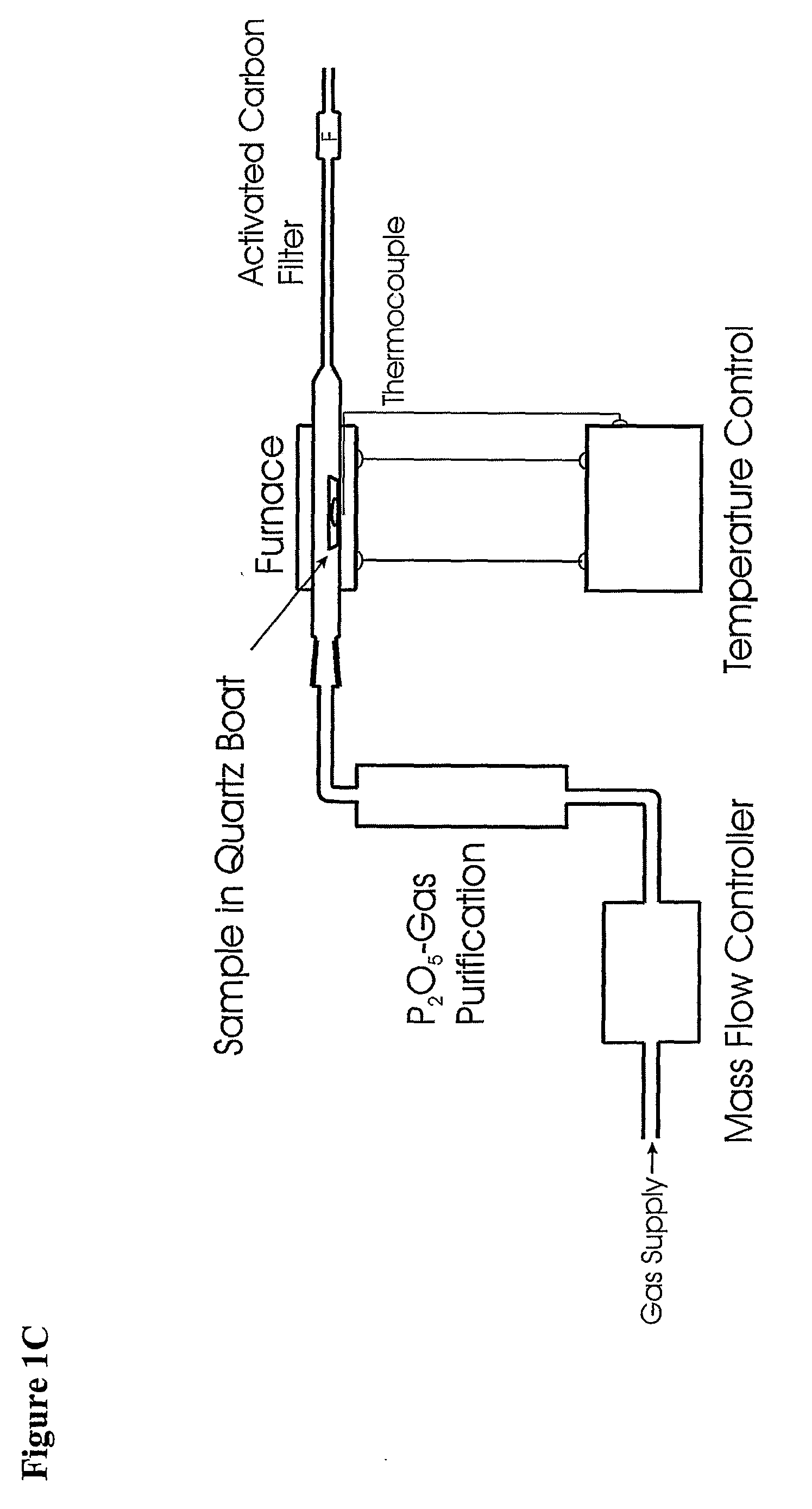
The present invention relates to an universal method for the large scale production of high-purity carrier free or non carrier added radioisotopes by applying a number of “unit operations” which are derived from physics and material science and hitherto not used for isotope production. A required number of said unit operations is combined, selected and optimised individually for each radioisotope production scheme. The use of said unit operations allows a batch wise operation or a fully automated continuous production scheme. The radioisotopes produced by the inventive method are especially suitable for producing radioisotope-labelled bioconjugates as well as particles, in particular nanoparticles and microparticles.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH +1
Ion acceleration system for medical and/or other applications
ActiveUS20100320403A1Minimal volumeEasy to installConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsElectrode and associated part arrangementsBasementEngineering
The ion acceleration system or complex (T) for medical and / or other applications is composed in essence by an ion source (1), a pre-accelerator (3) and one or more linear accelerators or linacs (6, 8, 10, 13), at least one of which is mounted on a rotating mechanical gantry-like structure (17). The isocentrical gantry (17) is equipped with a beam delivery system, which can be either ‘active’ or ‘passive’, for medical and / or other applications. The ion source (1) and the pre-accelerator (3) can be either installed on the floor, which is connected with the gantry basement, or mounted, fully or partially, on the rotating mechanical structure (17). The output beam can vary in energy and intensity pulse-by-pulse by adjusting the radio-frequency field in the accelerating modules of the linac(s) and the beam parameters at the input of the linear accelerators.
Owner:ADVANCED ONCOTHERAPY PLC
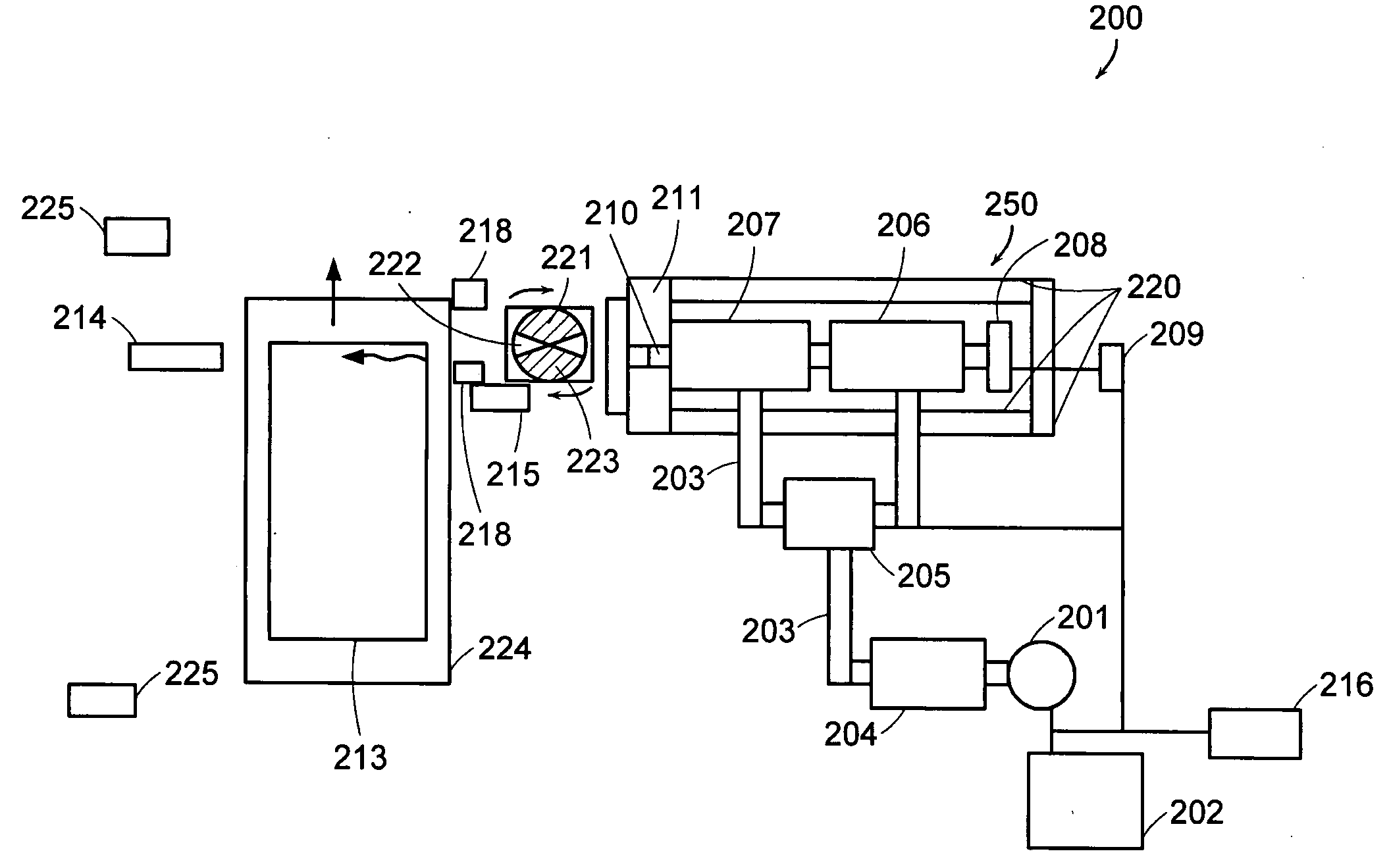
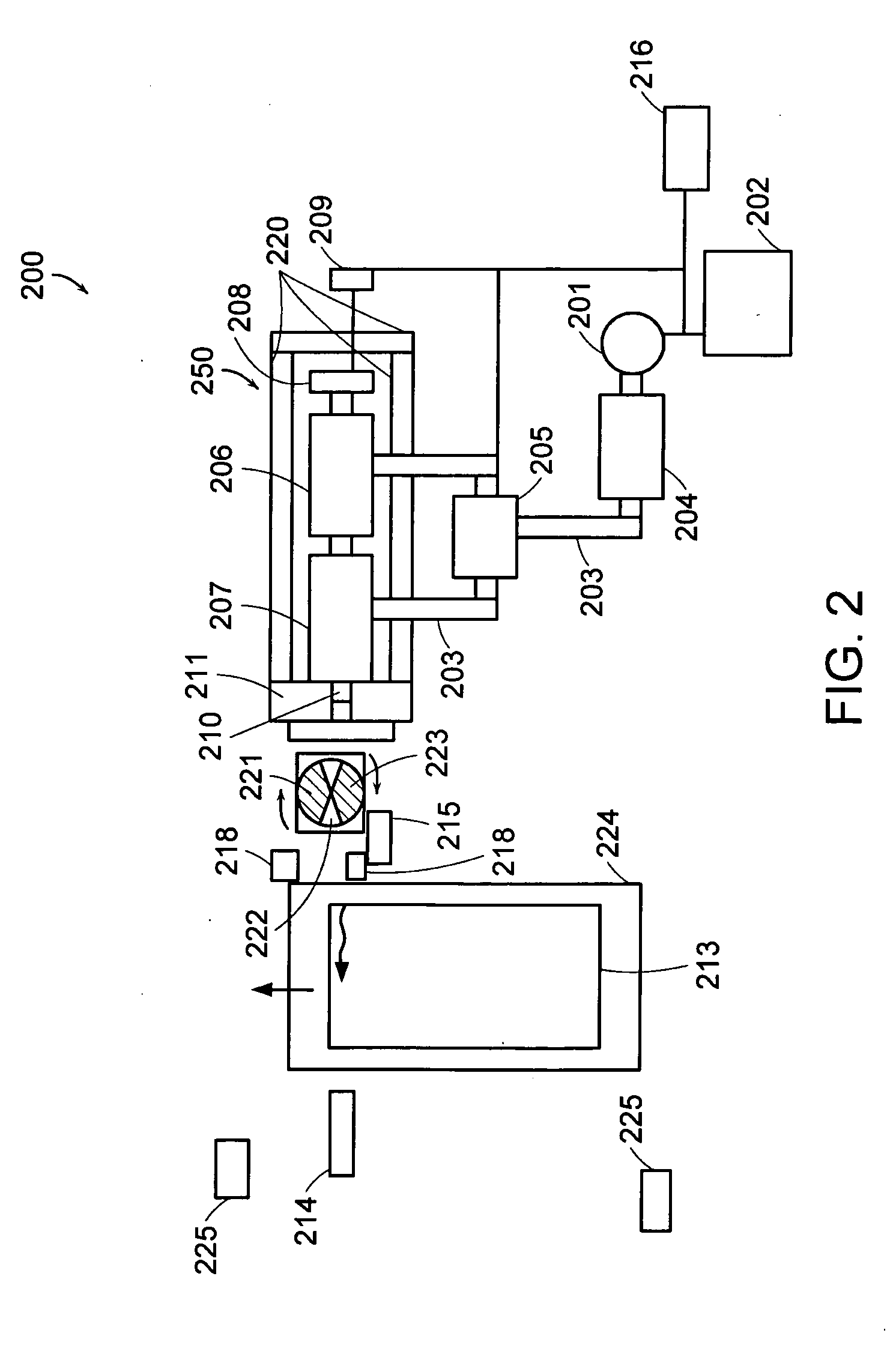
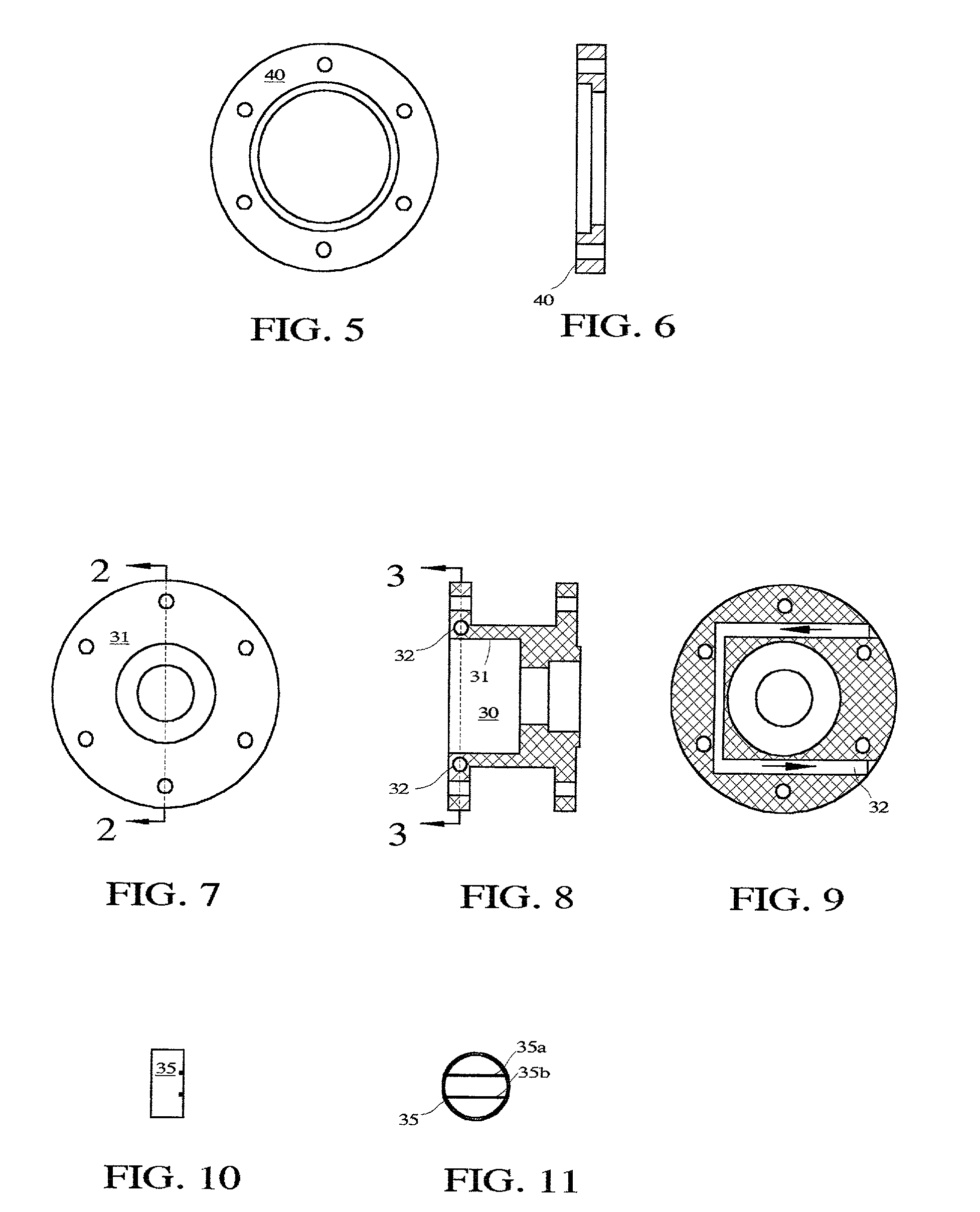
Device for fitting of a target in isotope production
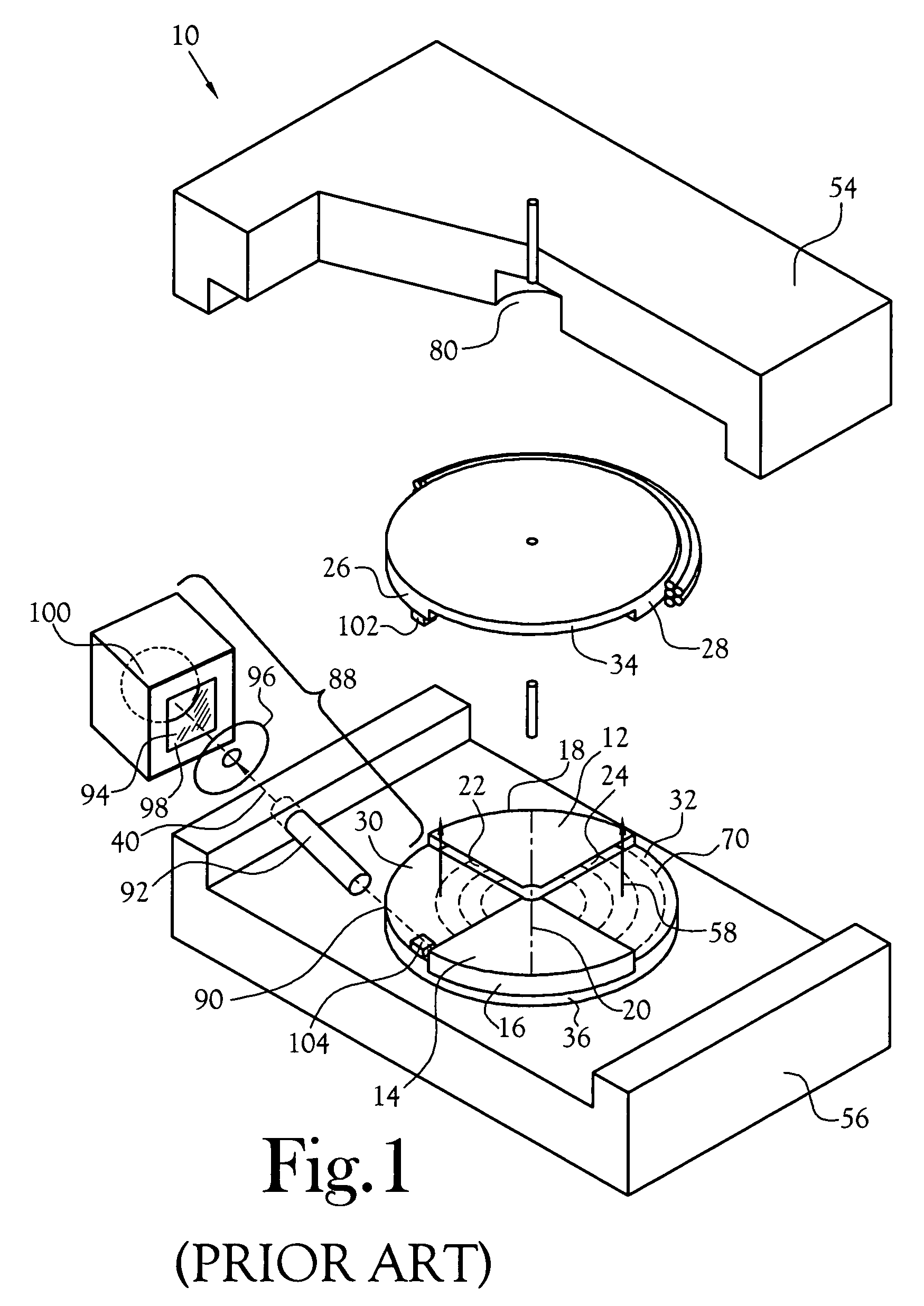
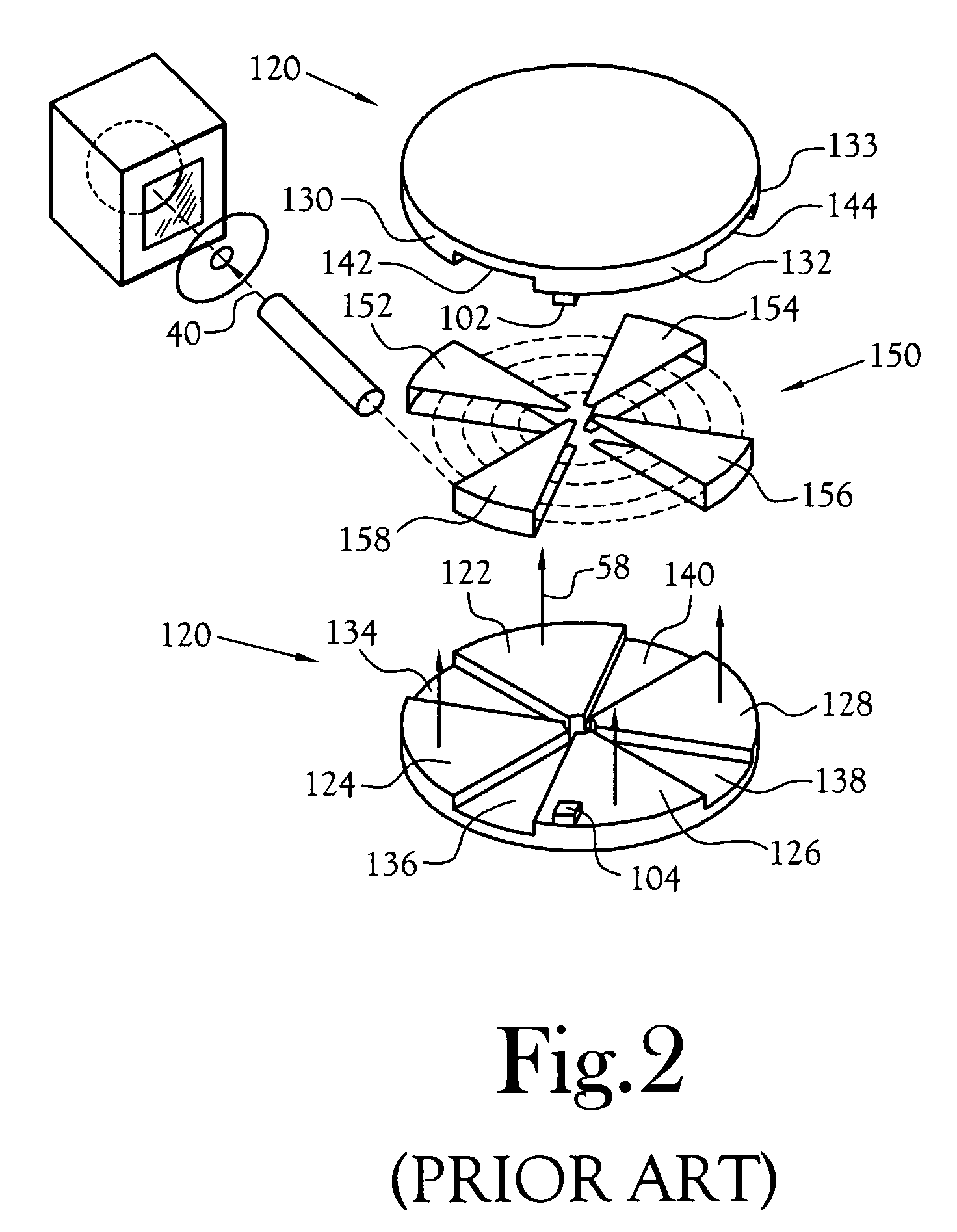
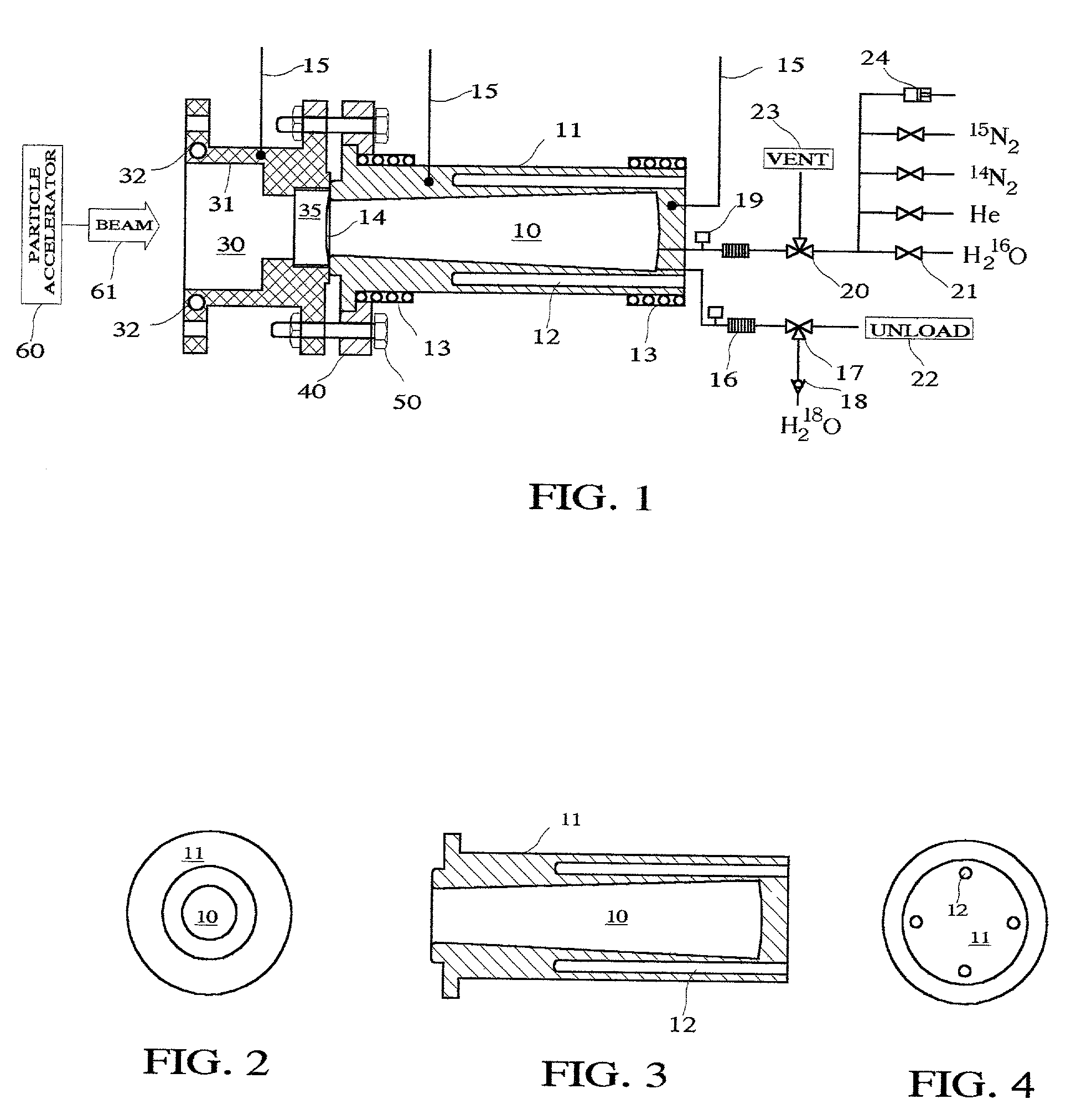
InactiveUS6433495B1Minimize radiationFit fastThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInterior spaceIsotope
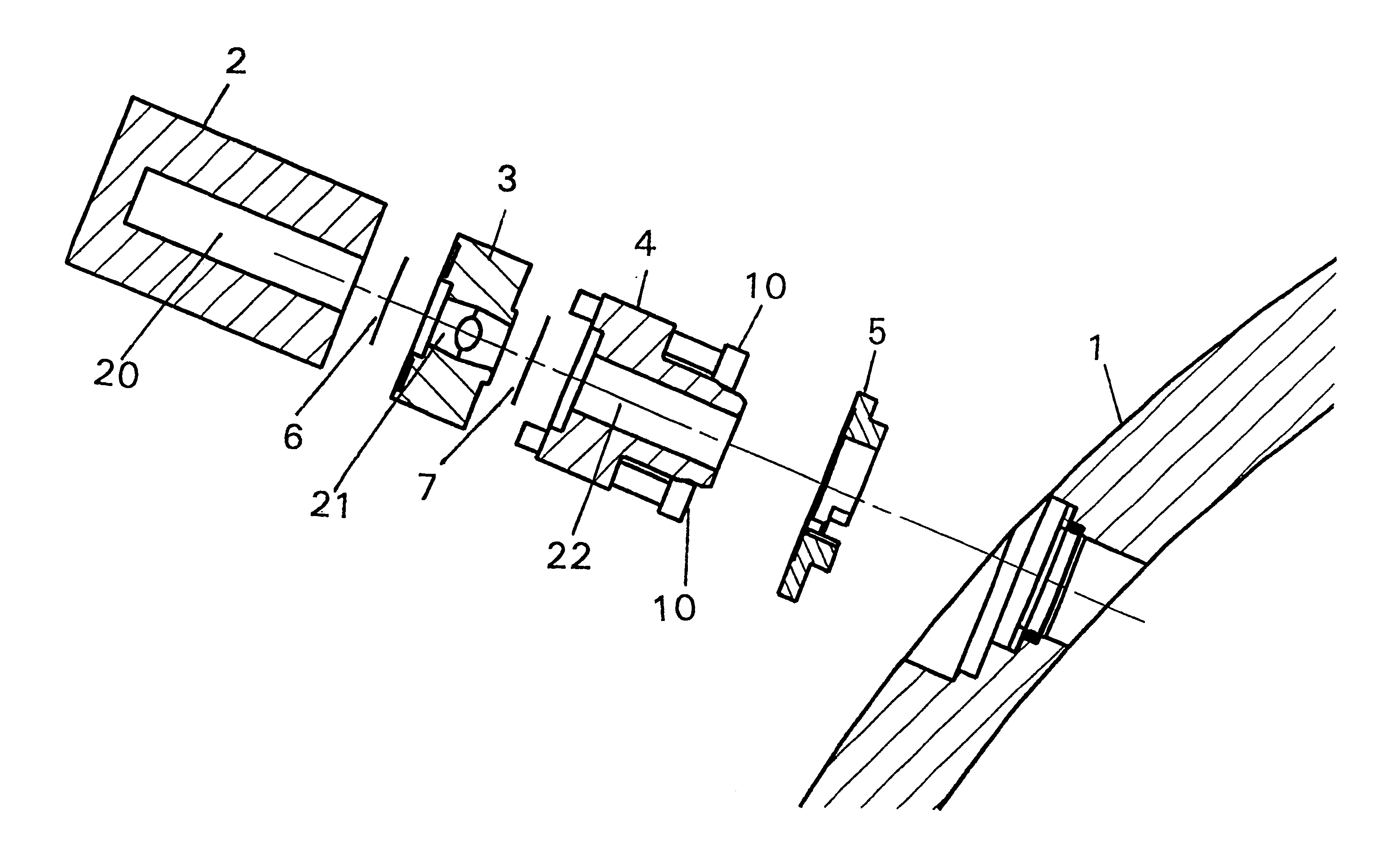
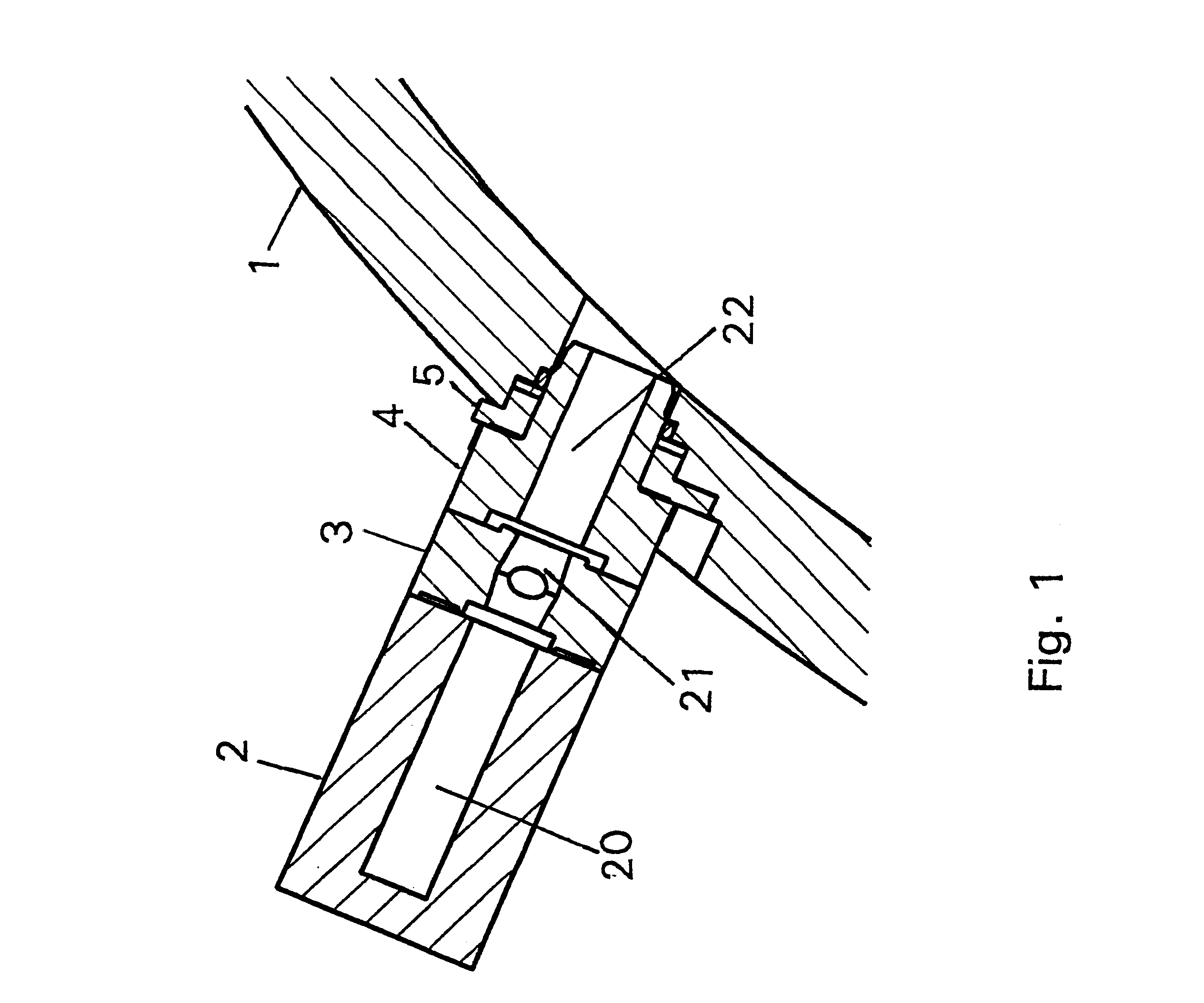
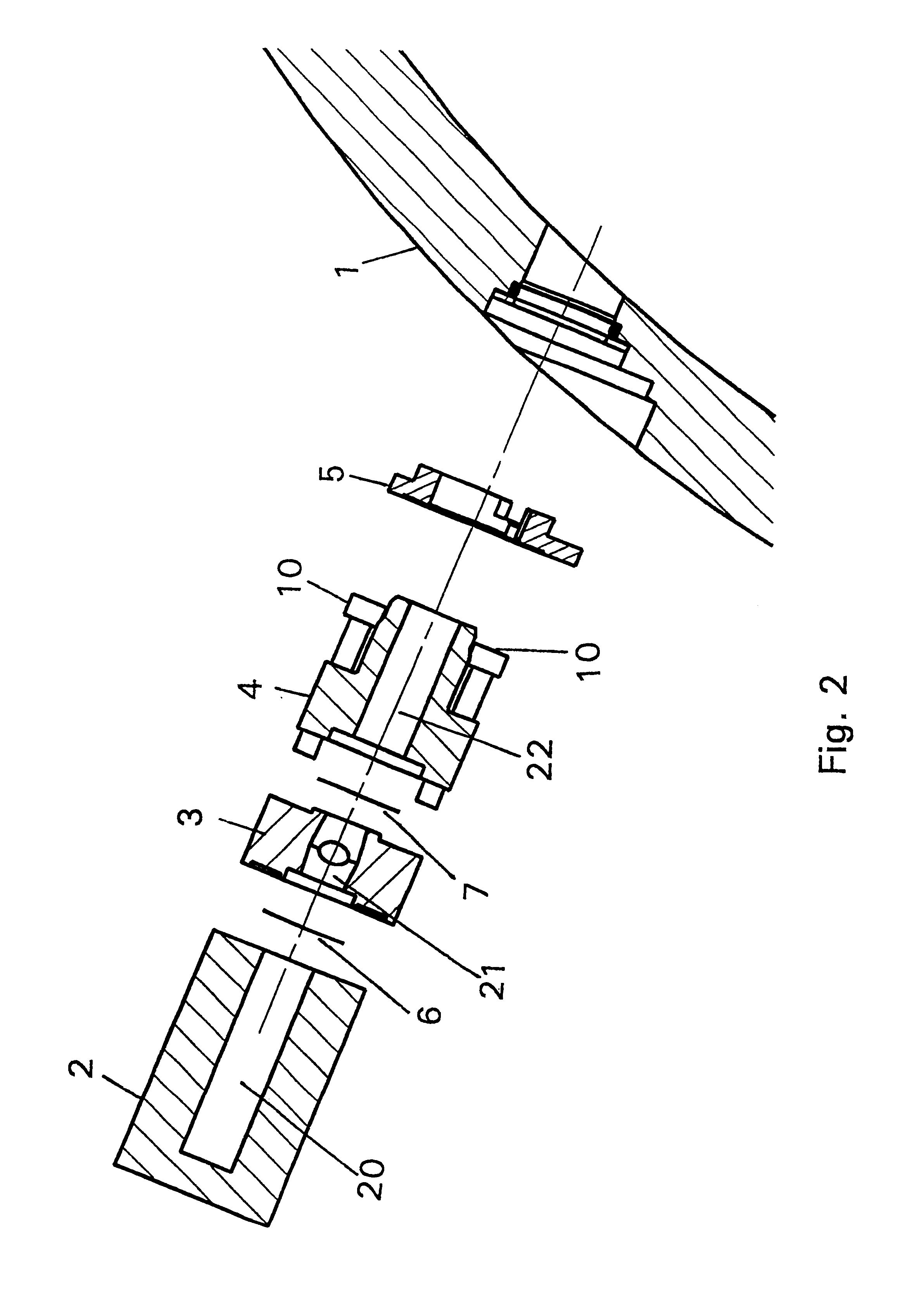
A device is disclosed for simple and quick disconnection of a target assembly at a cyclotron accelerator producing an ion beam irradiating the target assembly for PET radioisotope production. The device consists of a target body presenting a target space for introduction of target media to be irradiated by the ion beam from the cyclotron accelerator. The target body is separated into three portions by means of two separation window foils. The first separation window separates the internal space of a first body portion from a further internal space portion of a second target body portion and the second separation window separates a further internal space of the second target body portion from an internal space of a third target body portion being in communication with the vacuum space of the cyclotron. This third body portion forms a bayonet fitting to a corresponding bayonet fitting fixed to the cyclotron vacuum casing at a position where the ion beam is extracted, whereby the corresponding bayonet fitting also constitutes an insulating member. The device can by a small twisting be quickly released from the vacuum casing of the cyclotron after the vacuum has been removed for necessary maintenance and service.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
Particle therapy system
InactiveUS20050139787A1Time to setLow efficiencyThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTransport systemExcitation current
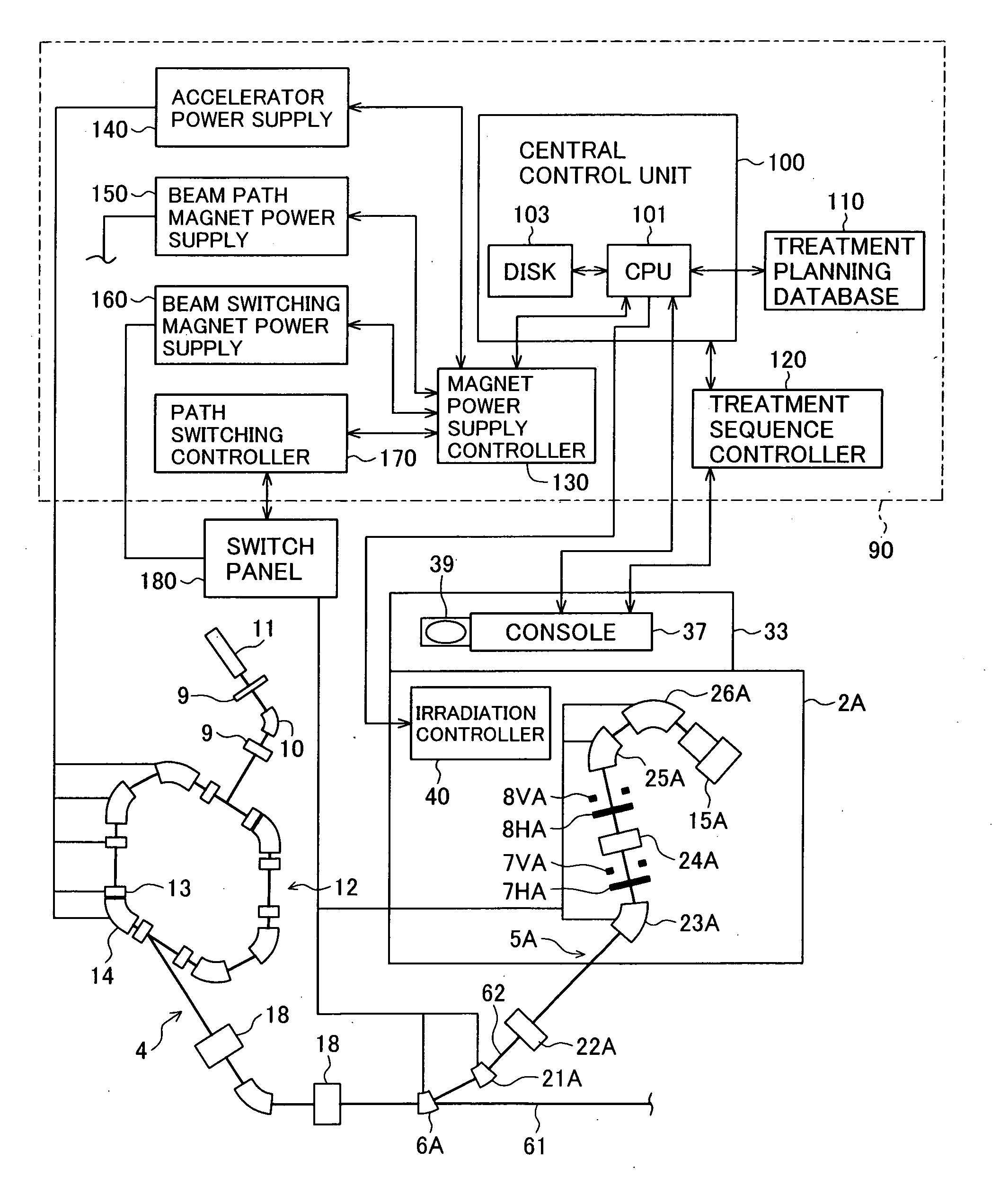
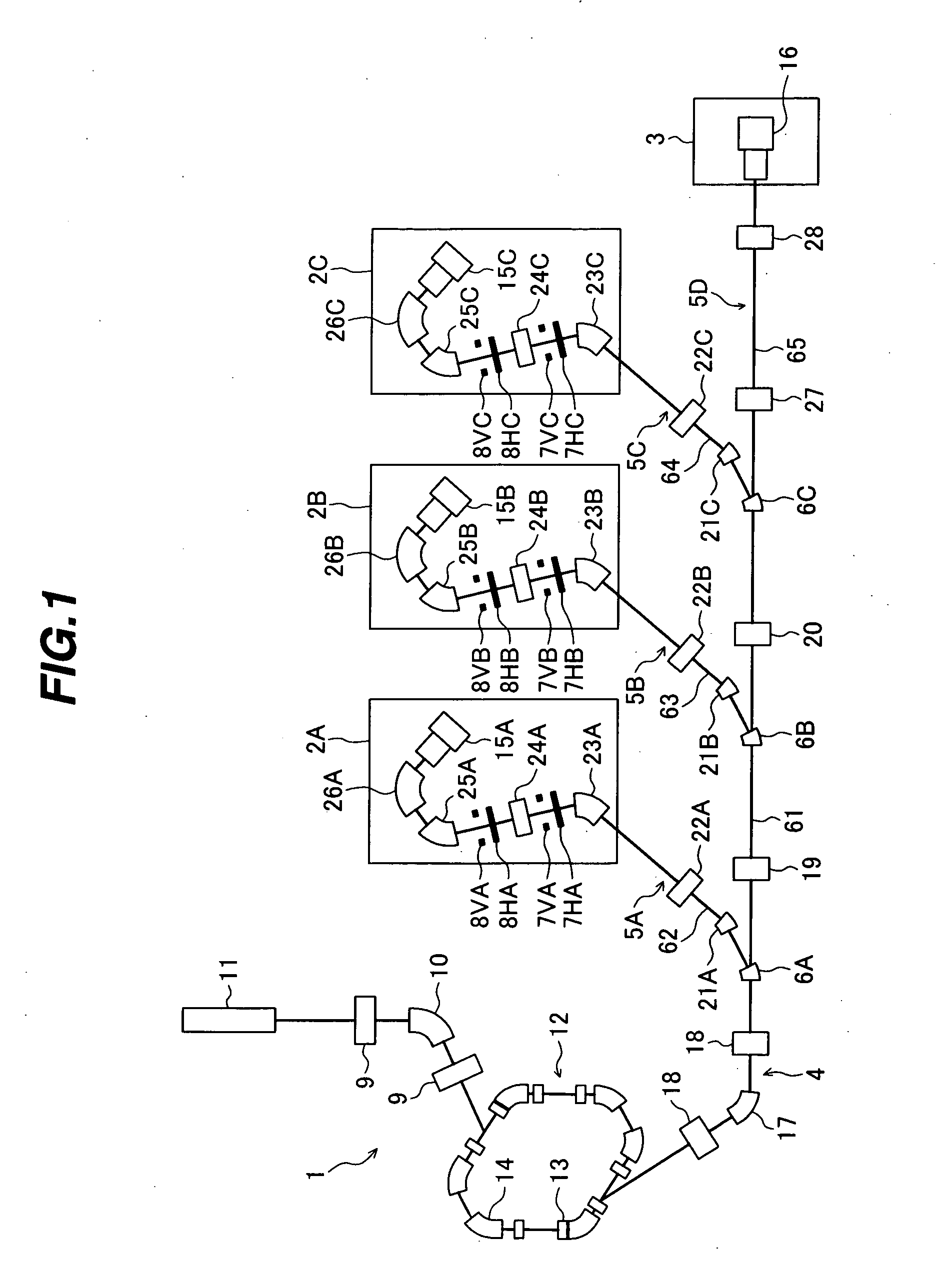
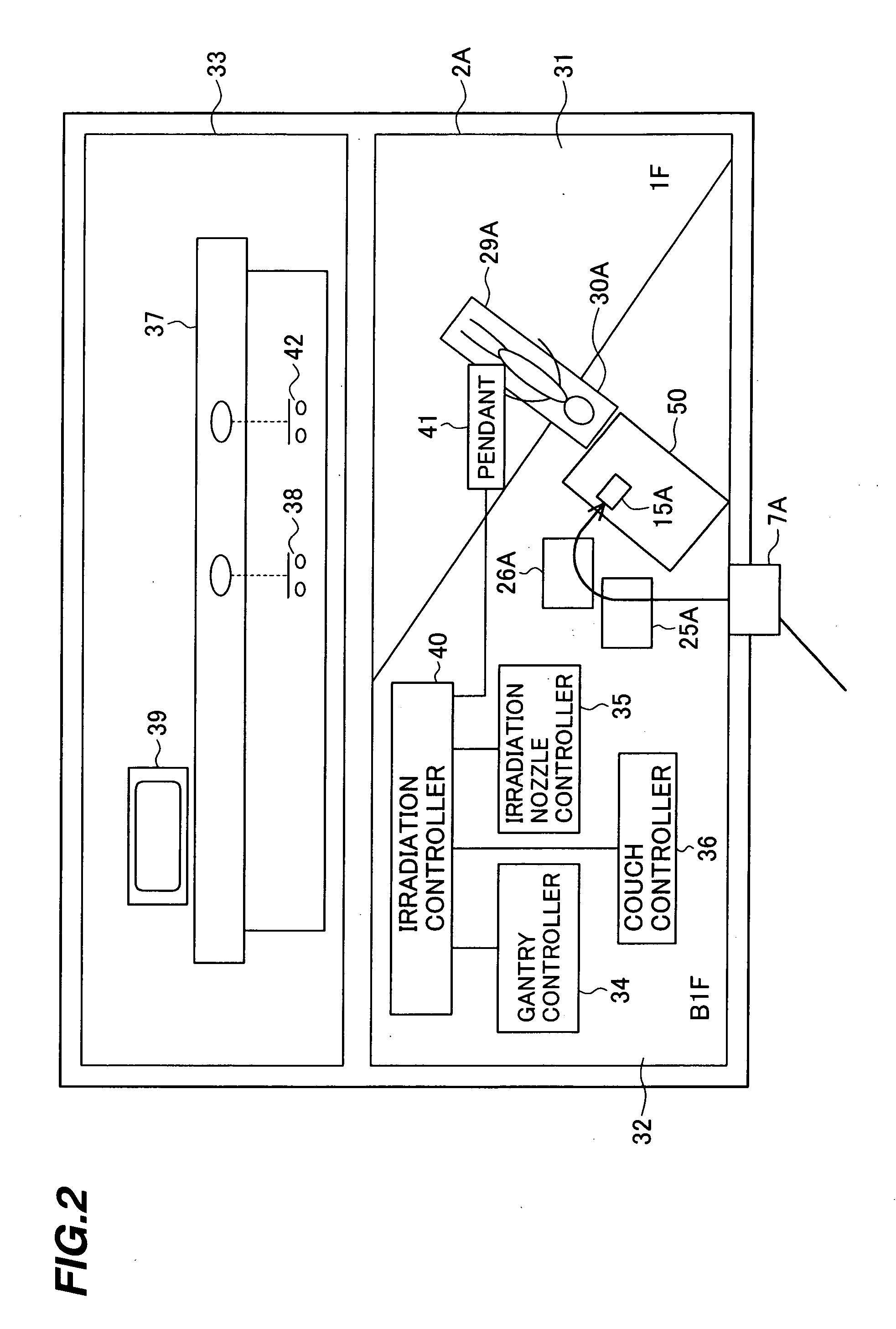
A particle therapy system capable of increasing the number of patients treated in one treatment room per unit time. The particle therapy system comprises a charged particle beam generator for generating an ion beam, an irradiation apparatus for irradiating the ion beam extracted from the charged particle beam generator to an irradiation target, a beam transport system for transporting the ion beam extracted from the charged particle beam generator to the irradiation apparatus, and a central control unit for producing a set of command data to command excitation currents for magnets disposed in the charged particle beam generator and the beam transport system, the set of command data being classified into group-1 data and group-2 data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Biomarker generator system
ActiveUS20080067413A1Efficient dosingEfficient productionIsotope delivery systemsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroreactorParticle accelerator
A biomarker generator system for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker. The biomarker generator system includes a small, low-power particle accelerator (“micro-accelerator”) and a radiochemical synthesis subsystem having at least one microreactor and / or microfluidic chip. The micro-accelerator is provided for producing approximately one (1) unit dose of a radioactive substance, such as a substance that emits positrons. The radiochemical synthesis subsystem is provided for receiving the radioactive substance, for receiving at least one reagent, and for synthesizing the approximately one (1) unit dose of a biomarker.
Owner:BEST ABT INC
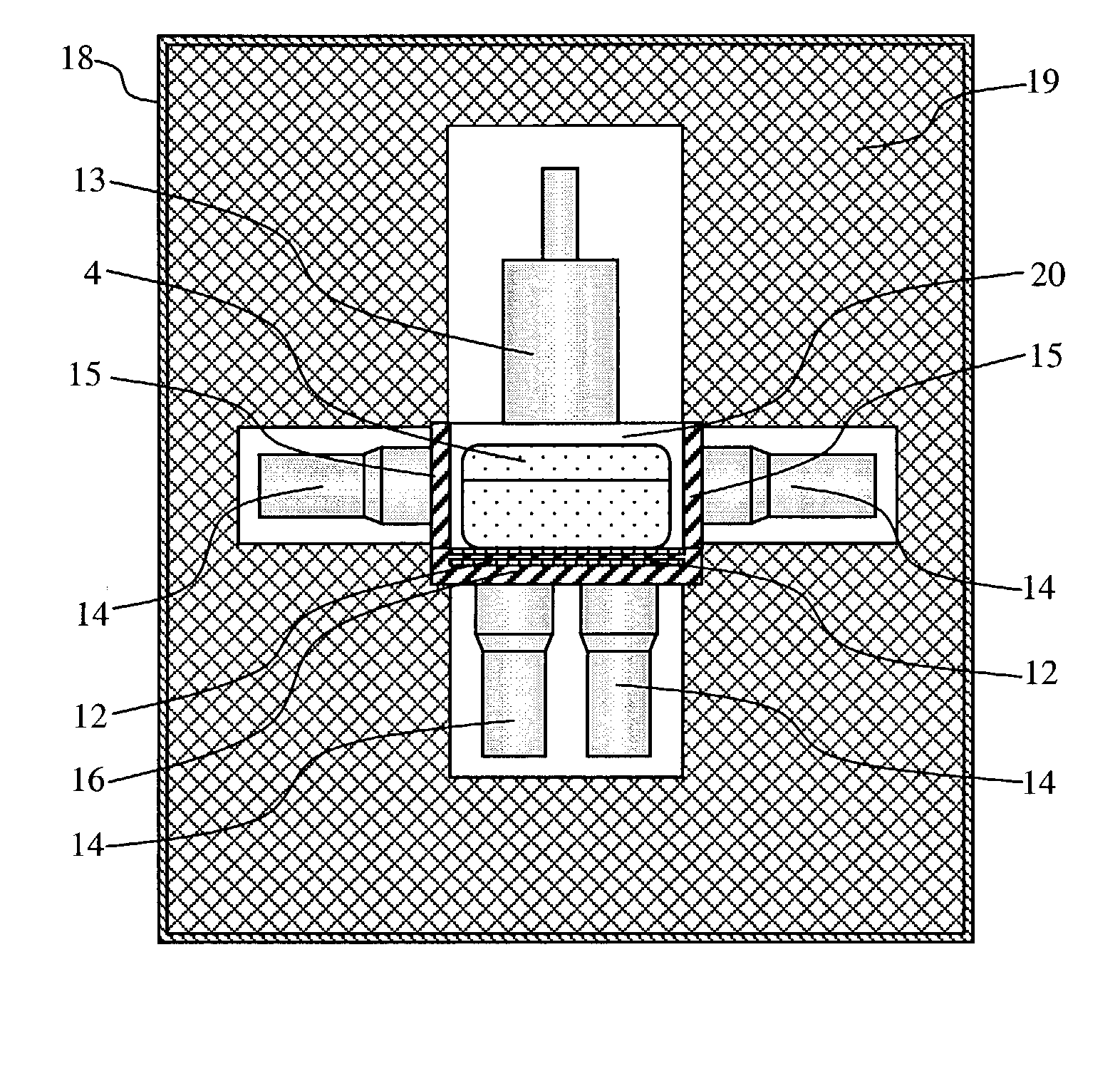
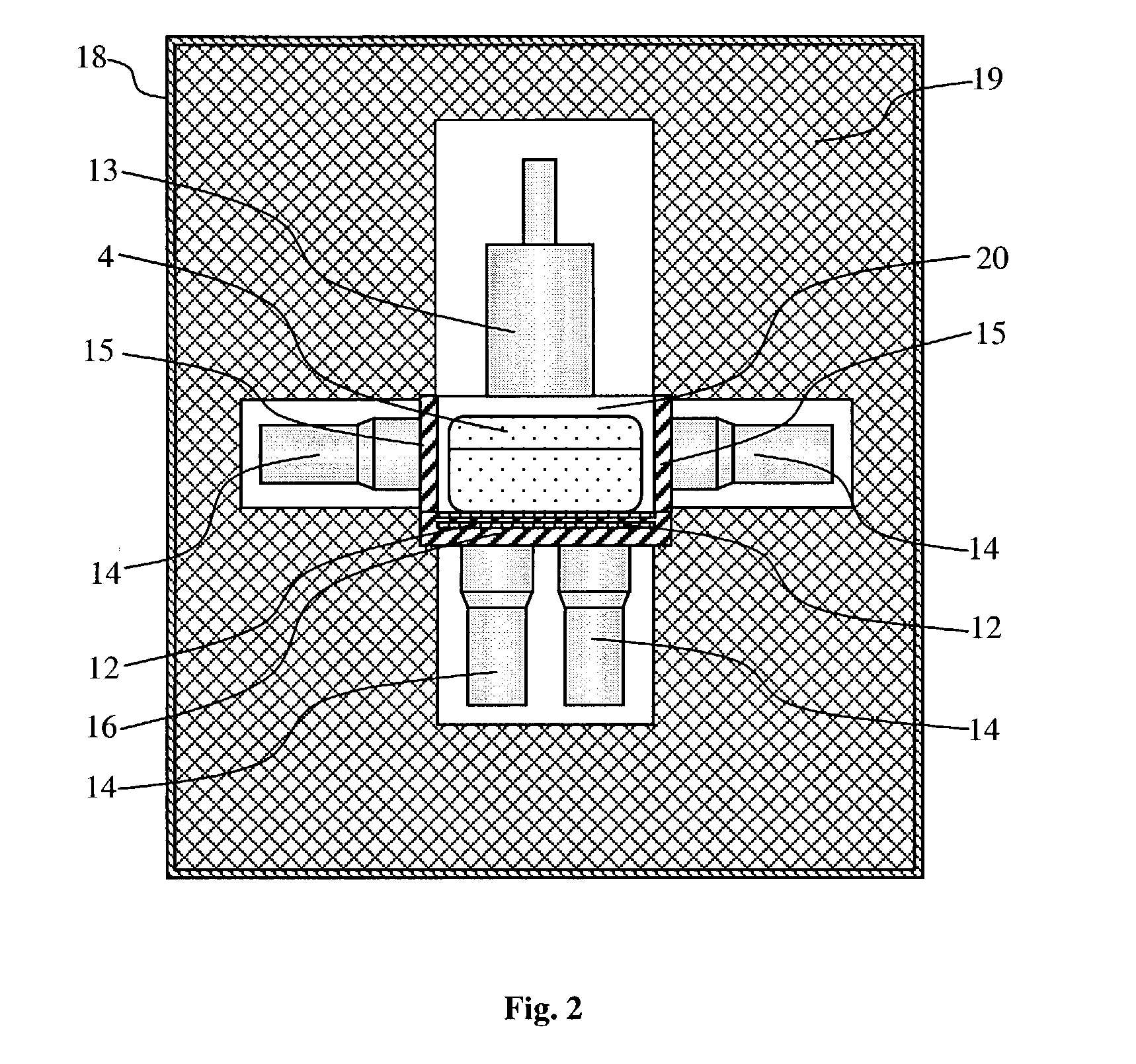
Integrated radiation shield
InactiveUS6392246B1Environment safetyEasy to integrateConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsPortable shielded containersEngineeringIsotope
An apparatus is disclosed that forms a basic integrated radiation shield for a PET isotope production system to create a safe environment. The apparatus and the system combine several subsystems to provide a high degree of integration and a nice aesthetic impression. The apparatus contains a cyclotron system and contains integrated target media handling for gas targets and water dispensing systems for water targets. A compartment including first and second additional radiation shields, respectively, that contains additional processing systems. The apparatus forms a closed radiation-proof system by means of a casing formed of four molded sections. A first and second section constitute a main body containing;the cyclotron system and a third and a fourth section constituting a pair of tight doors for encompassing the cyclotron into a sealed radiation shield. The first section additionally contains a Waste Gas Delay Line embedded in its shielding material.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
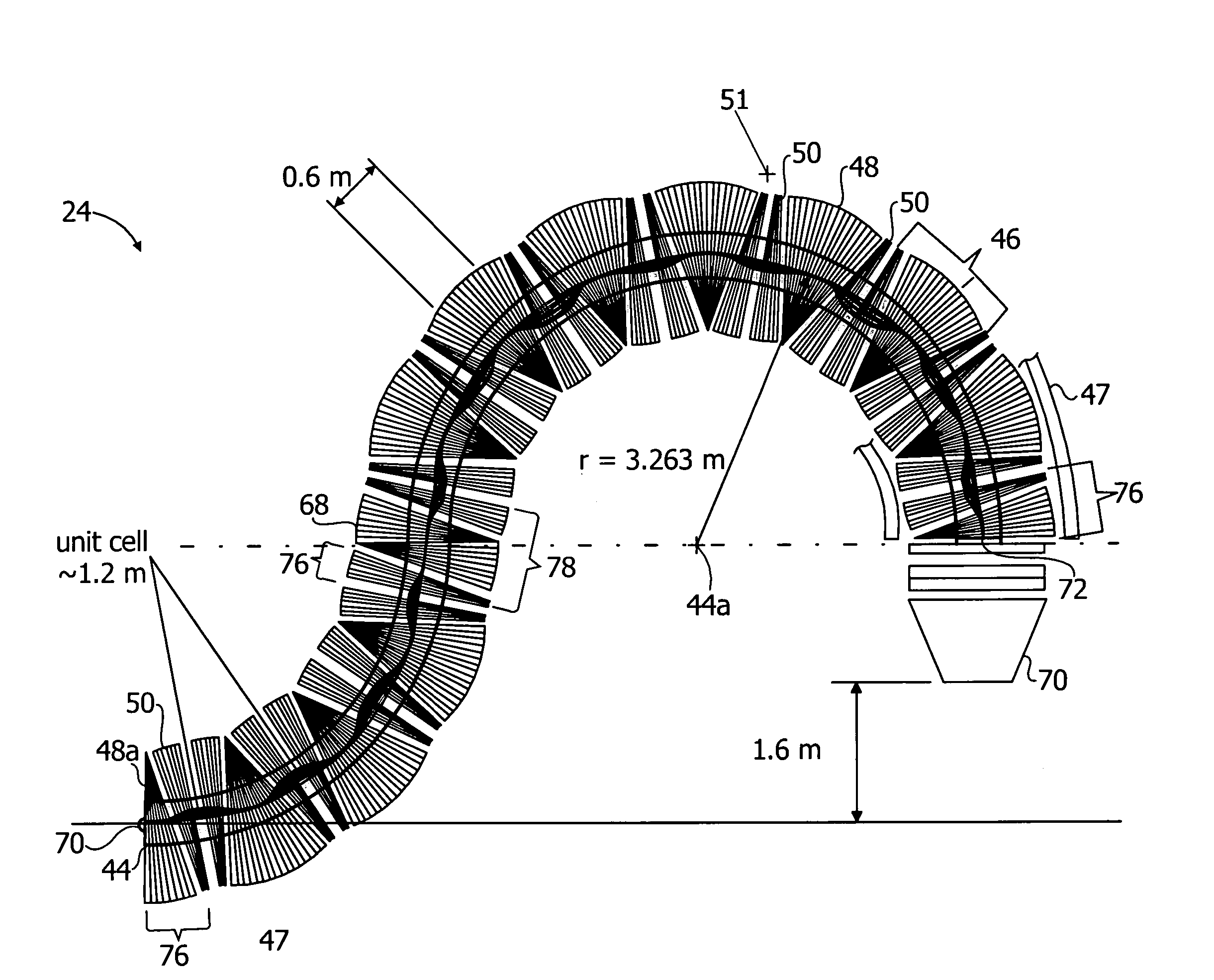
Gantry for medical particle therapy facility
ActiveUS7582886B2Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle beamBeam tube
A particle therapy gantry for delivering a particle beam to a patient includes a beam tube having a curvature defining a particle beam path and a plurality of fixed field magnets sequentially arranged along the beam tube for guiding the particle beam along the particle path. In a method for delivering a particle beam to a patient through a gantry, a particle beam is guided by a plurality of fixed field magnets sequentially arranged along a beam tube of the gantry and the beam is alternately focused and defocused with alternately arranged combined function focusing and defocusing fixed field magnets.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
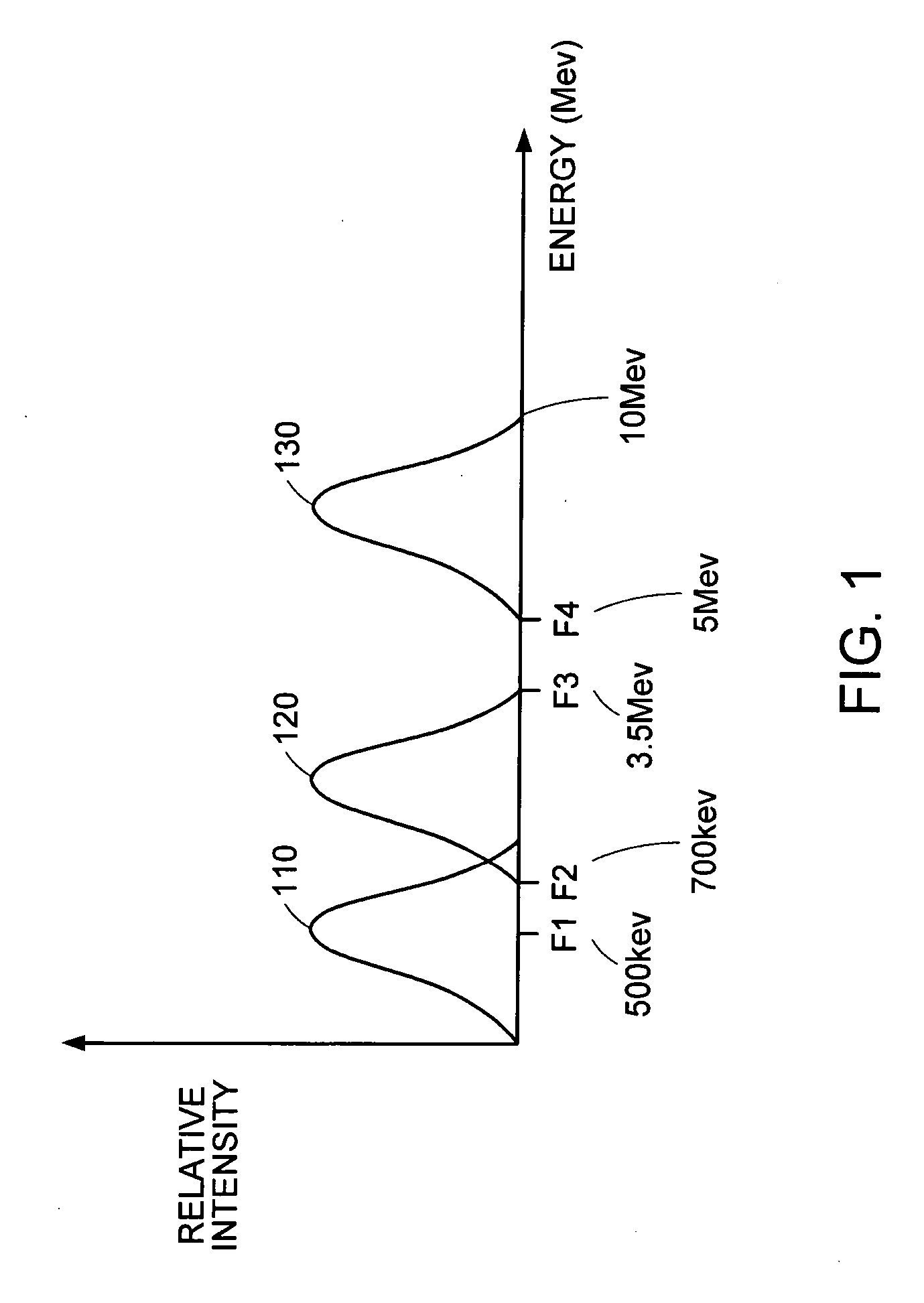
InactiveUS20030147484A1Increases radiation levelReduce riskConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
High flux sub-critical reactor for nuclear waste transmulation
InactiveUS20080232533A1Improve distributionImprove economyConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationHigh fluxPu element
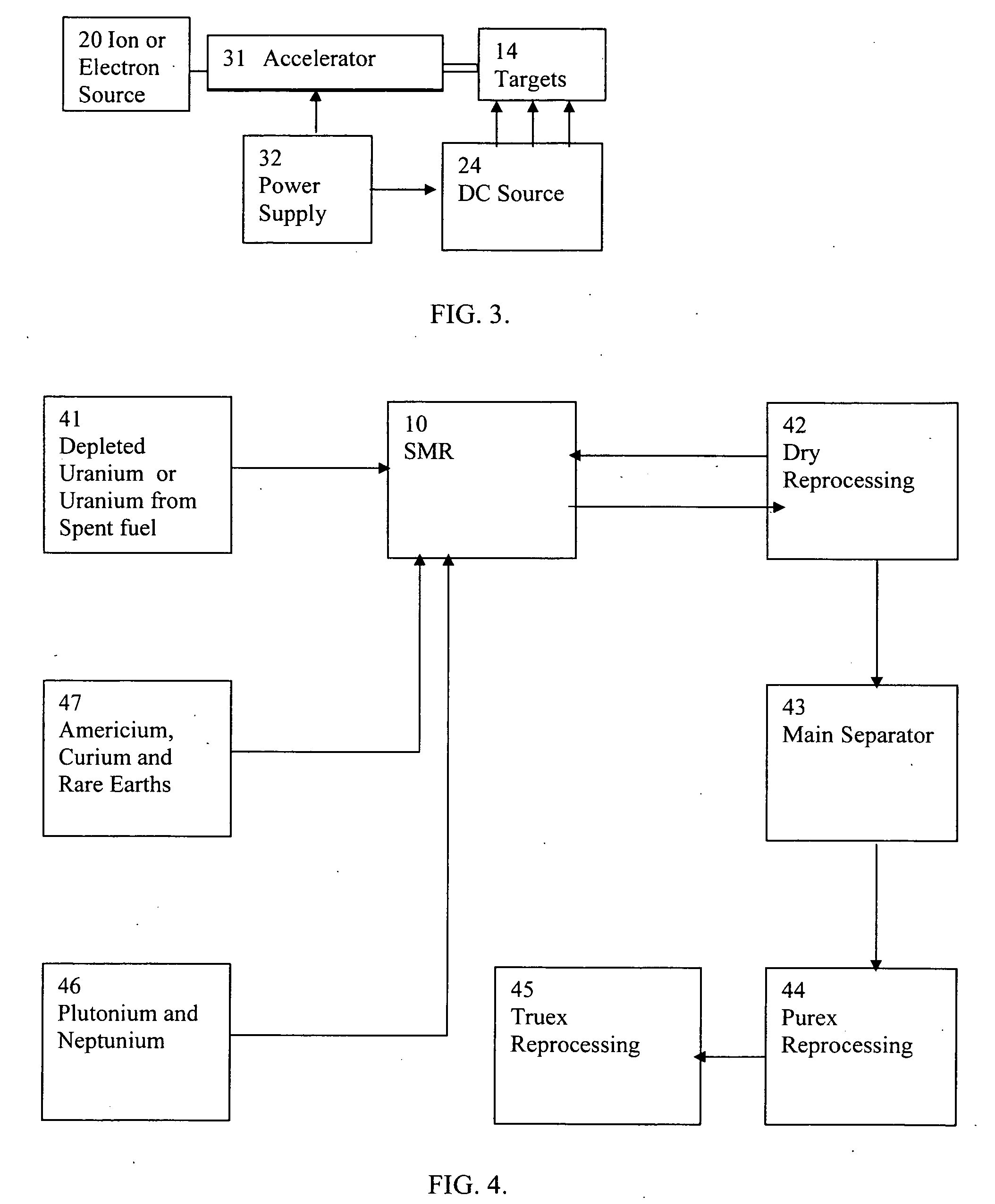
A process to safely convert about 95% of the nuclear waste into a usable fuel source is disclosed. The process, involving a sub-critical power reactor and a proliferation-resistant fuel cycle, consumes depleted uranium or thorium fuel with fissionable fuel, including reactor or weapons-grade plutonium. The reactor is comprised of coaxial neutron and energy-amplifying regions separated by moderating and thermal neutron absorbing layers. Control of the water or gas-cooled reactor is provided by plutonium-helium loops with a variable volume flow rate and an external source of neutrons that quickly reacts to any fluctuations of the reactor parameters. A second embodiment of the invention is a compact sub-critical propulsion reactor utilizing fission electric cell and thermo-acoustic technology for electrical power generation.
Owner:BLANOVSKY ANATOLY
High power high yield target for production of all radioisotopes for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20050061994A1Avoid low densitySuppress instabilityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringCoolant flowInstability
A high power high yield target for the positron emission tomography applications is introduced. For production of Curie level of Fluorine-18 isotope from a beam of proton it uses about one tenth of Oxygen-18 water compared to a conventional water target. The target is also configured to be used for production of all other radioisotopes that are used for positron emission tomography. When the target functions as a water target the material sample being oxygen-18 water or oxygen-16 water is heated to steam prior to irradiation using heating elements that are housed in the target body. The material sample is kept in steam phase during the irradiation and cooled to liquid phase after irradiation. To keep the material sample in steam phase a microprocessor monitoring the target temperature manipulates the flow of coolant in the cooling section that is attached to the target and the status of the heaters and air blowers mounted adjacent to the target. When the target functions as a gas target the generated heat from the beam is removed from the target by air blowers and the cooling section. The rupture point of the target window is increased by a factor of two or higher by one thin wire or two parallel thin wires welded at the end of a small hollow tube which is held against the target window. One or two coils are used to produce a magnetic filed along the beam path for preventing the density depression along the beam path and suppression of other instabilities that can develop in a high power target.
Owner:AMINI BEHROUZ
Systems and methods for the cyclotron production of iodine-124
ActiveUS20070064858A1Good physical propertiesSimple processConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDistillationIodine
The present invention relates to targets, systems and methods for the cyclotron production of 124I from aluminum telluride (Al2Te3) targets. The systems and methods utilize low energy proton cyclotrons to produce 124I by the 124Te(p,n) reaction from enriched Al2Te3 glassy melts. The 124I is recovered in high yield from the glassy melt by adapted methods of common thermal distillation techniques.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
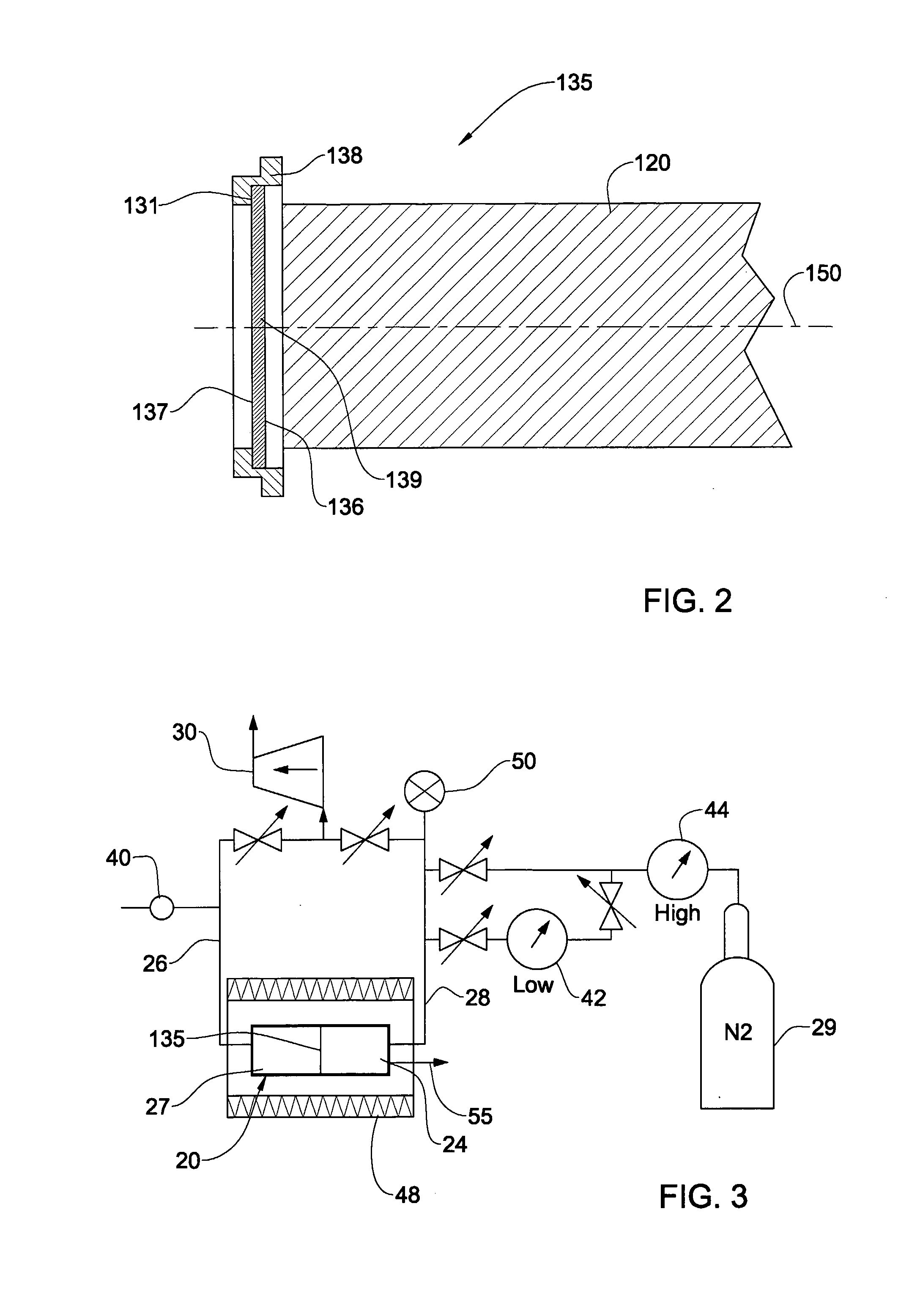
Method and apparatus for ion source positioning and adjustment
ActiveUS20050283199A1ElectrotherapyConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention is directed to a method and apparatus for ion source positioning and adjustment. According to one embodiment, the invention relates to an apparatus for ion source positioning and adjustment. The apparatus comprises a bottom plate, a middle plate and a top plate, wherein the top plate is coupled to the middle plate by at least one adjustment member for causing the top plate to move in a first direction, wherein the at least one adjustment member positions the top plate in a predetermined position with respect to the middle plate; and the middle plate is coupled to the bottom plate by a worm gear assembly for causing the middle plate to move in a second direction with respect to the bottom plate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com