Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Irradiated materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Irradiated Materials Laboratory. The Irradiated Materials Laboratory (IML) in Argonne's Nuclear Engineering Division is used to conduct research on the behavior of commercial nuclear reactor materials, including fuel, pressure vessels, and other in-reactor components.
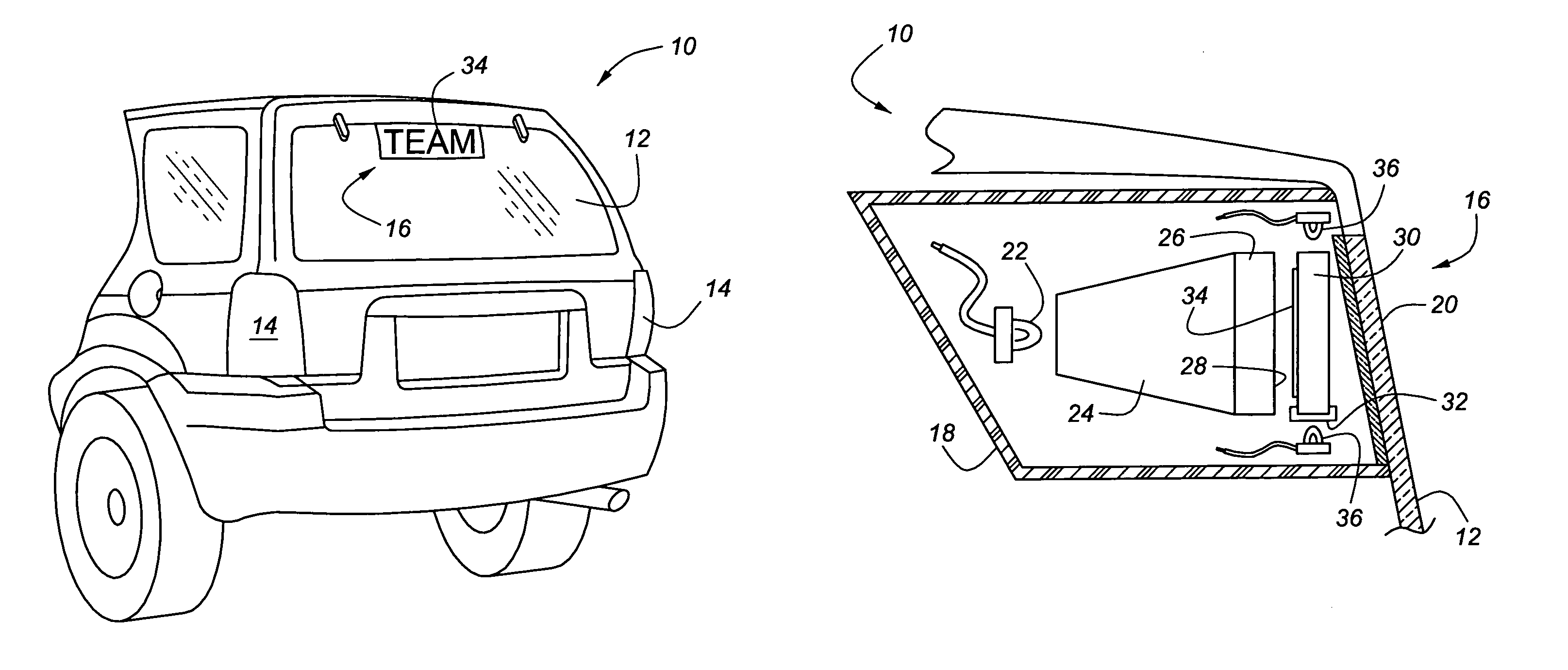
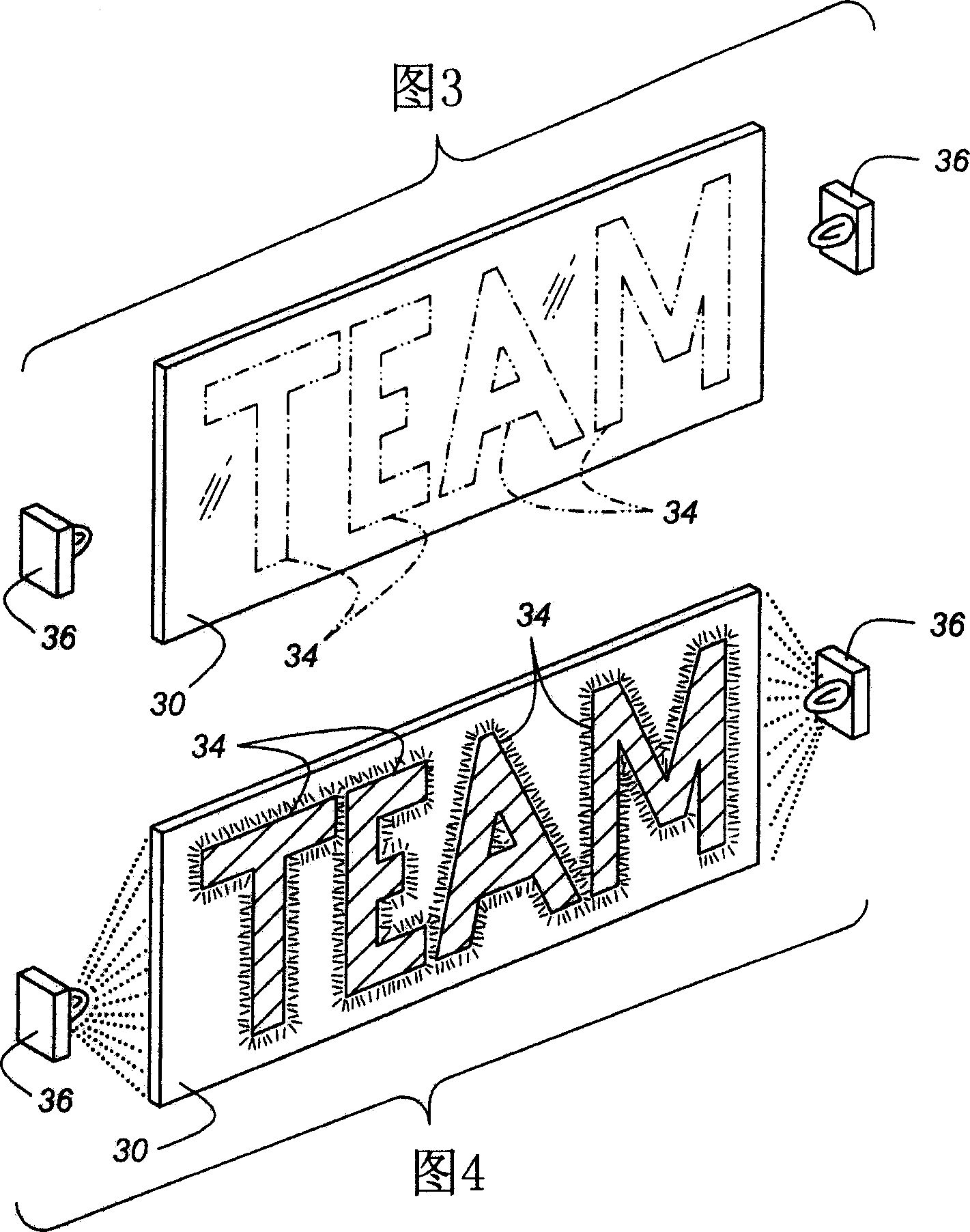
Vehicular lighting fixture with non-directional dispersion of light
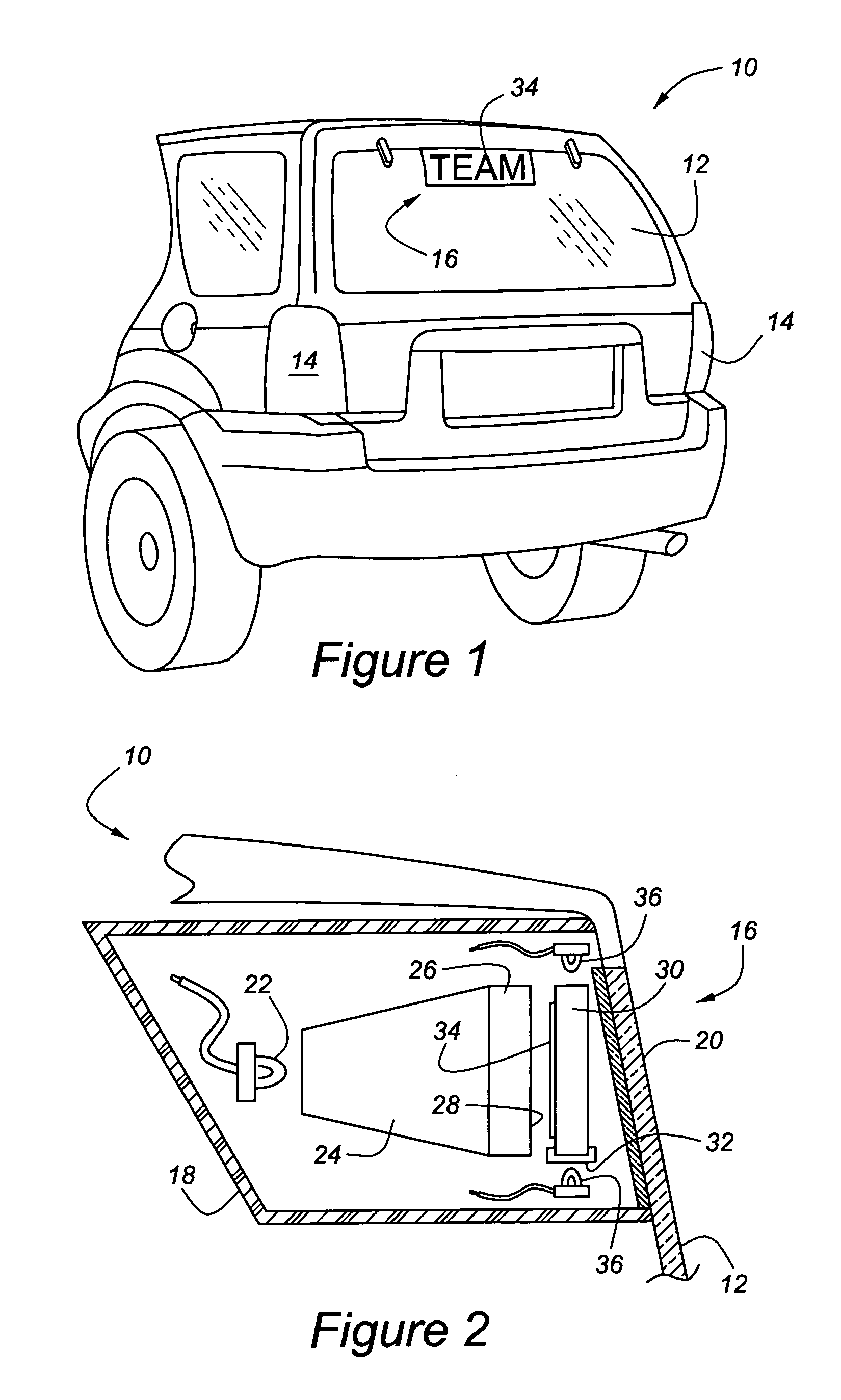
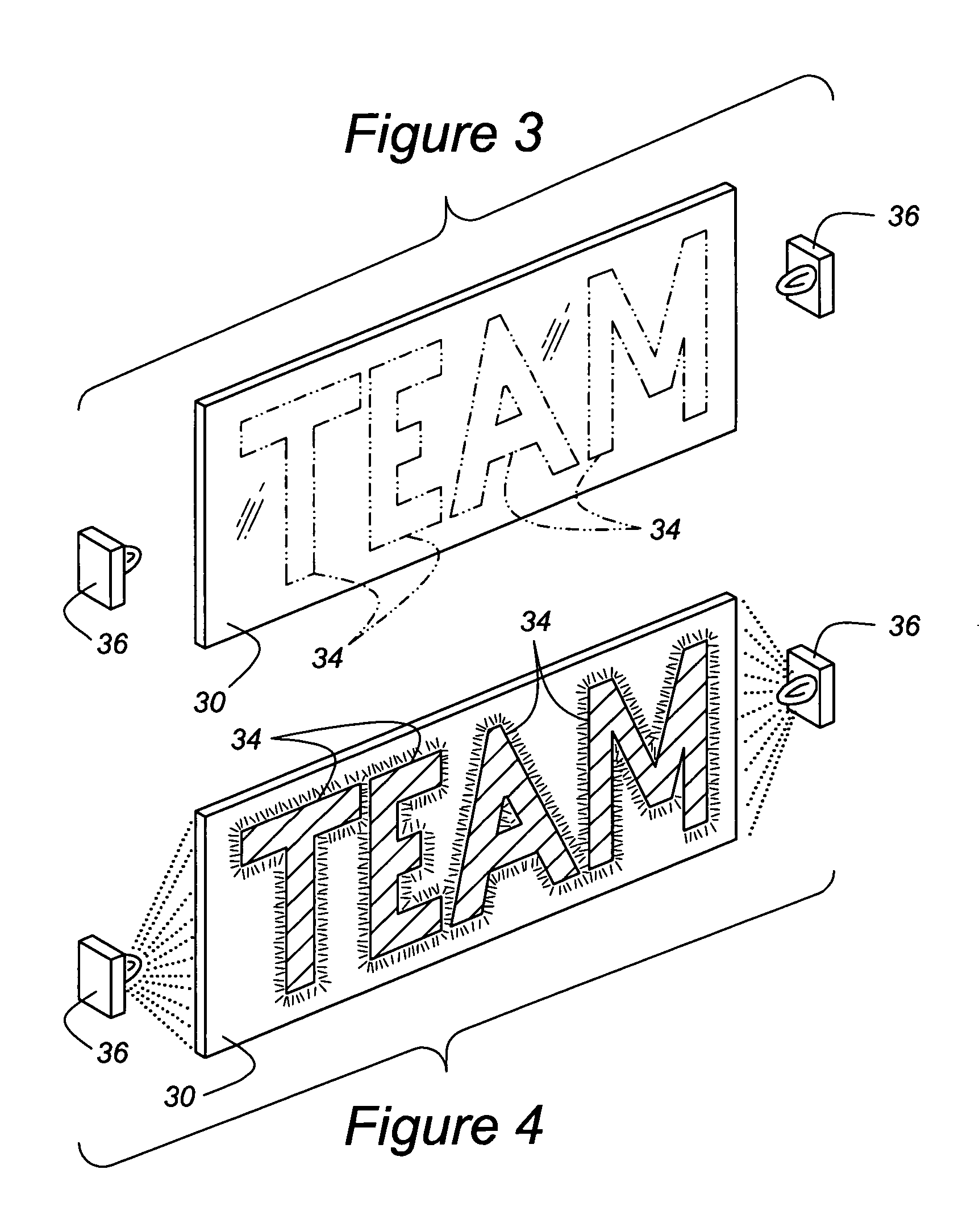
A CHMSL (16) or other lighting system feature of an automobile (10) includes a feature for presenting personal expressions in the form of words or symbols but is automatically deactivated when the regular vehicle lighting system is in use. The personal expression is fixed in a tangible medium by way of phosphor-coated indicia (34) placed within a UV impervious housing (18). A secondary UV light source (36) selectively energizes the phosphor-coated indicia (34) so that the irradiated material glows and is visible through a light transmissive screen (20). The light transmissive screen (20) is provided with a UV blocking agent so that harmful UV rays do not escape the housing (18). The phosphor-coated indicia (34) can be mounted on a removable transparent plate (30), on light dispersion optics (24, 26), or on the inner face of the light transmissive screen (20). A control circuit (42″) manages the primary light source (22) and the secondary UV light source (36) so that only one of the light sources can be energized at any one time.
Owner:REBO LIGHTING & ELECTRONICS LLC
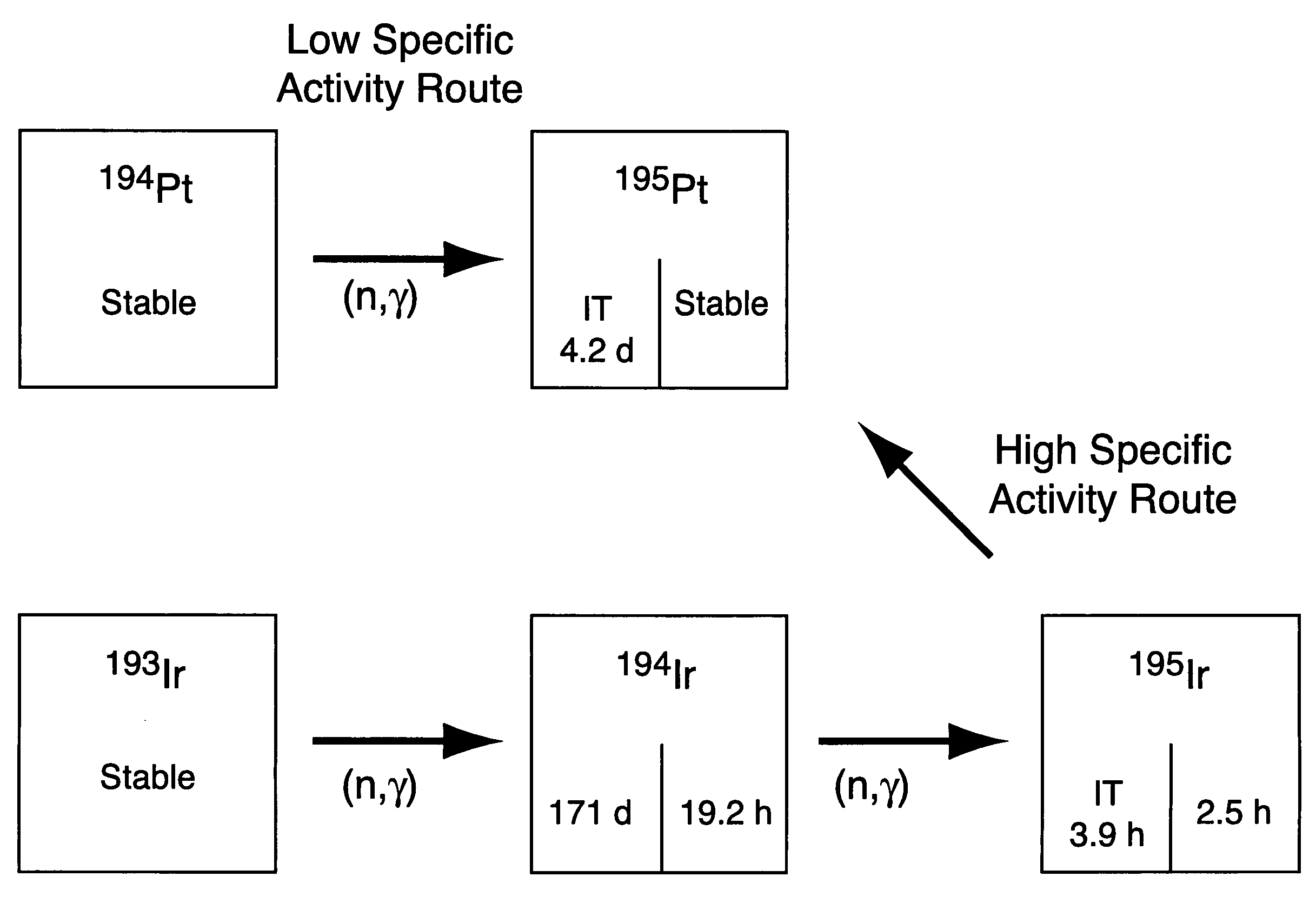
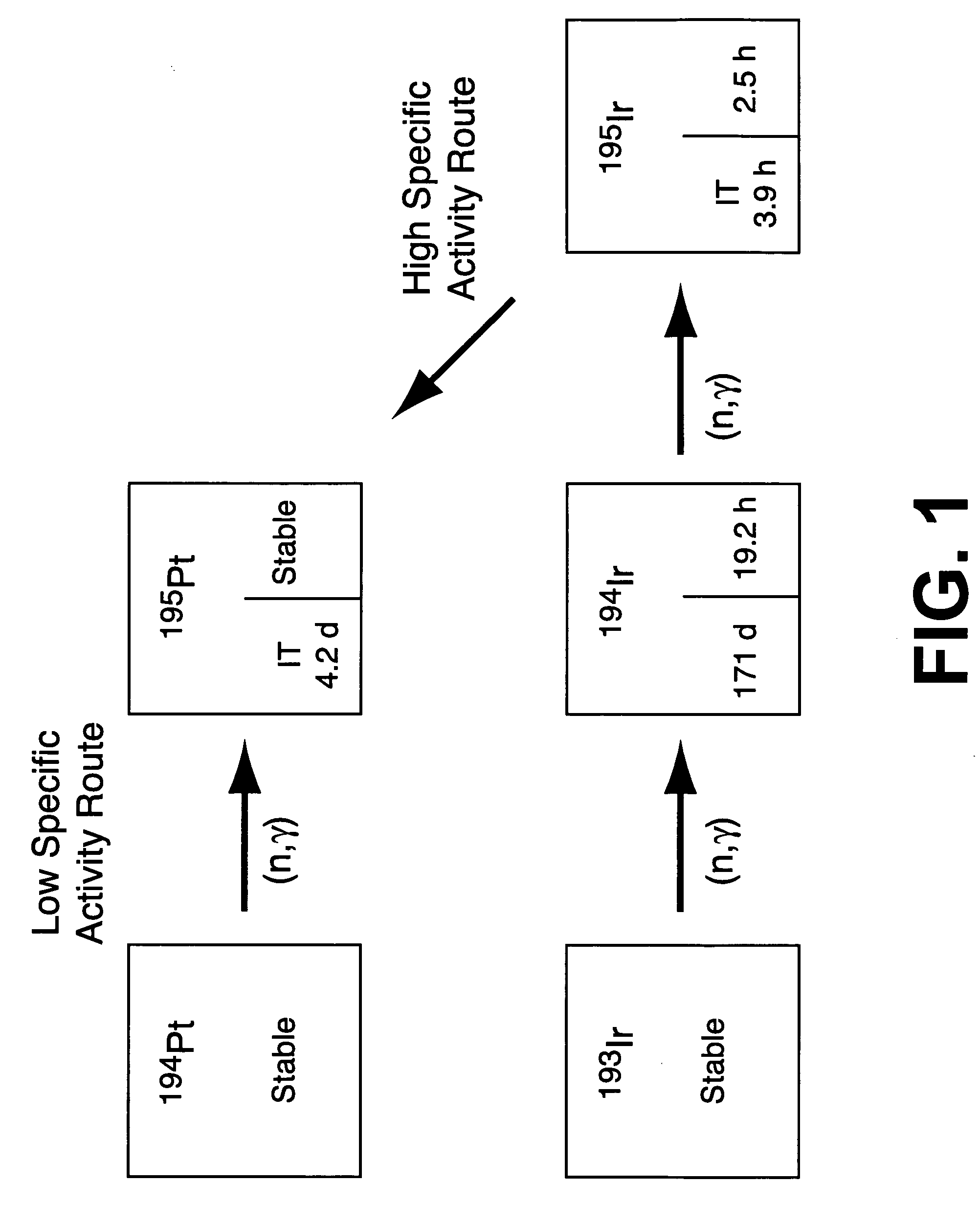
High specific activity platinum-195m
InactiveUS20040196942A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsPlatinumIrradiated materials
A new composition of matter includes <195m>Pt characterized by a specific activity of at least 30 mCi / mg Pt, generally made by method that includes the steps of: exposing <193>Ir to a flux of neutrons sufficient to convert a portion of the <193>Ir to <195m>Pt to form an irradiated material; dissolving the irradiated material to form an intermediate solution comprising Ir and Pt; and separating the Pt from the Ir by cation exchange chromatography to produce <195m>Pt.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Radiation sensitive film including a measuring scale
An article of manufacture comprising a radiation sensitive material, and a measuring scale that is part of the radiation sensitive material. A method of measuring at least one parameter relating to an irradiated material is also described. A radiation sensitive material including a measuring scale is exposed to radiation and at least one parameter relating to one or more exposed areas of the material is measured by reference to the measuring scale on the material.
Owner:ISP INVESTMENTS LLC
Compositions of high specific activity SN-117M and methods of preparing the same
ActiveUS8257681B2Easily appearNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsIrradiated materialsHigh specific activity
Compositions of high specific activity 117mSn with specific activity of greater than 100 Ci / g Sn and methods of producing the same. The method includes exposing 116Cd to an α-particle beam of sufficient incident kinetic energy and duration to convert a portion of the 116Cd to 117mSn to form an irradiated material. The irradiated material is dissolved to form an intermediate solution containing 117mSn and 116Cd. The 117mSn is separated from the 116Cd to yield high specific activity 117mSn.
Owner:SNIP HLDG
System for causing ablation of irradiated material of living tissue while not causing damage below a predetermined depth
InactiveUSRE36872E1Surgical instrument detailsLaser beam welding apparatusIrradiated materialsBiomedical engineering
Owner:LASER INDS
Vehicular lighting fixture with non-directional dispersion of light
A CHMSL (16) or other lighting system feature of an automobile (10) includes a feature for presenting personal expressions in the form of words or symbols but is automatically deactivated when the regular vehicle lighting system is in use. The personal expression is fixed in a tangible medium by way of phosphor-coated indicia (34) placed within a UV impervious housing (18). A secondary UV light source (36) selectively energizes the phosphor-coated indicia (34) so that the irradiated material glows and is visible through a light transmissive screen (20). The light transmissive screen (20) is provided with a UV blocking agent so that harmful UV rays do not escape the housing (18). The phosphor-coated indicia (34) can be mounted on a removable transparent plate (30), on light dispersion optics (24, 26), or on the inner face of the light transmissive screen (20). A control circuit (42″) manages the primary light source (22) and the secondary UV light source (36) so that only one of the light sources can be energized at any one time.
Owner:REBO LIGHTING & ELECTRONICS LLC
Vehicular lighting fixture with non-directional dispersion of light
InactiveCN101056781AImprove bindingControl conflictOptical signallingMobile visual advertisingLight dispersionLight equipment
A CHMSL (16) or other lighting system feature of an automobile (10) includes a feature for presenting personal expressions in the form of words or symbols but is automatically deactivated when the regular vehicle lighting system is in use. The personal expression is fixed in a tangible medium by way of phosphor-coated indicia (34) placed within a UV impervious housing (18). A secondary UV light source (36) selectively energizes the phosphor-coated indicia (34) so that the irradiated material glows and is visible through a light transmissive screen (20). The light transmissive screen (20) is provided with a UV blocking agent so that harmful UV rays do not escape the housing (18). The phosphor-coated indicia (34) can be mounted on a removable transparent plate (30), on light dispersion optics (24, 26), or on the inner face of the light transmissive screen (20). A control circuit (42'') manages the primary light source (22) and the secondary UV light source (36) so that only one of the light sources can be energized at any one time.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL CORP
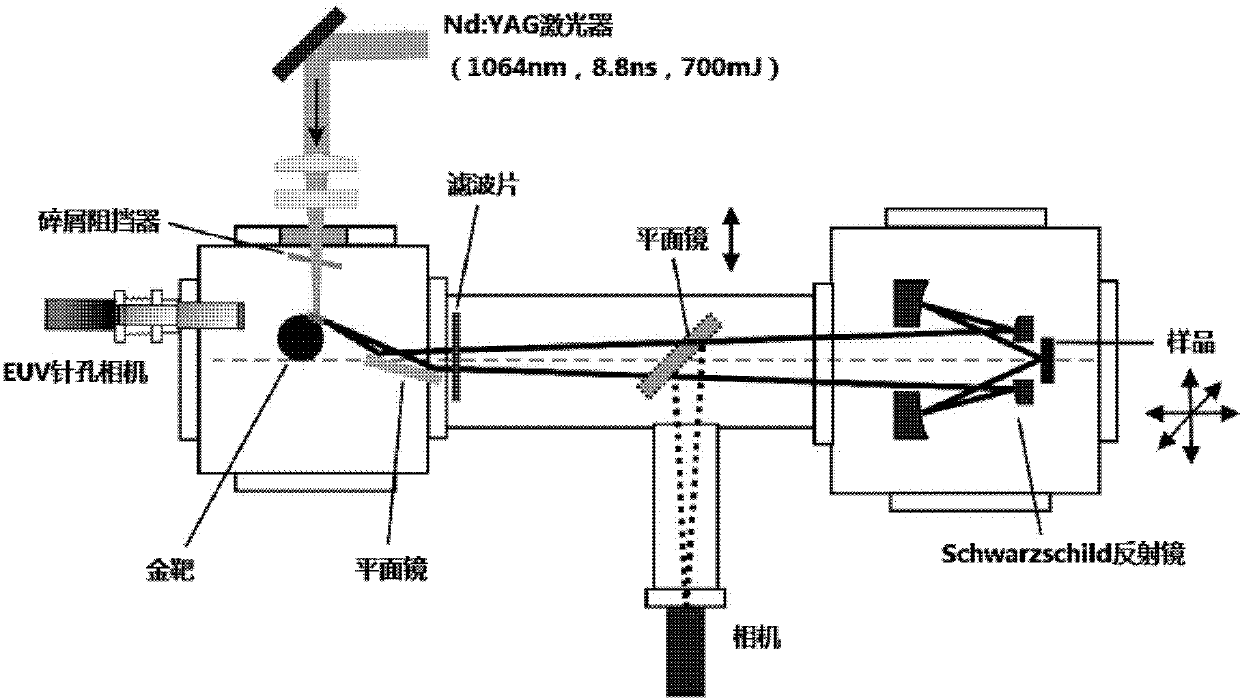
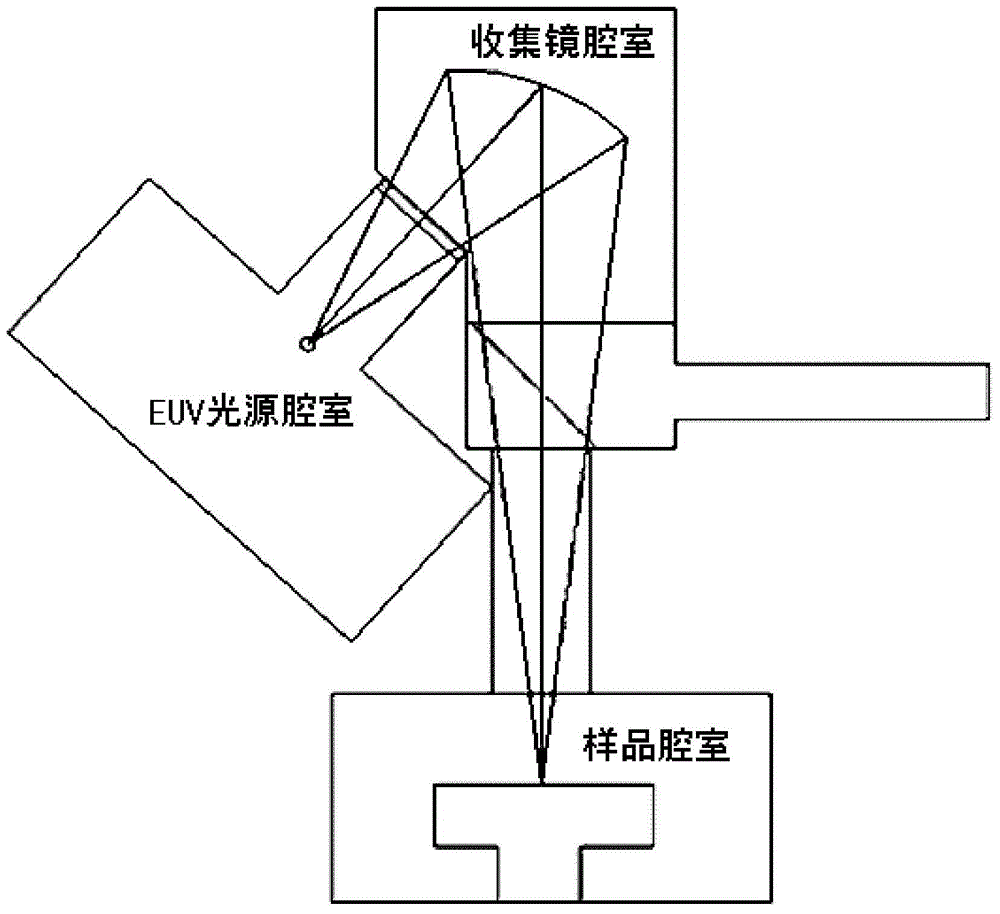
Test system for extreme ultraviolet radiation material
The invention discloses a test system for extreme ultraviolet radiation material. The system comprises a EUV light source chamber, which is used for accommodating a EUV light source which is used to give off wide spectrum near soft X-ray; a filter plate chamber, which is used for placing a filter plate which is used to filter the wide spectrum near soft X-ray to narrow spectrum EUV radiation; a collecting mirror chamber, which is used for placing a collecting mirror which is used for gathering the EUV radiations to a sample chamber; a spectrum detection chamber, which is used for installing a reflector and a spectrometer, wherein the reflector is used to reflect the EUV radiations from the collecting mirror chamber to the spectrometer; and a sample chamber, which is used for accommodating a sample to be tested, a CCD and an energy meter and can make the sample, the CCD and the energy meter move in turn to a same position where the sample, the CCD and the energy meter can be radiated by EUV radiation. The test system can obtain extreme ultraviolet radiation damage conditions of various samples.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
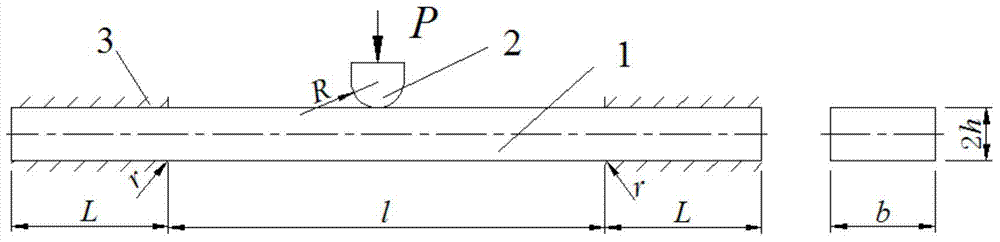
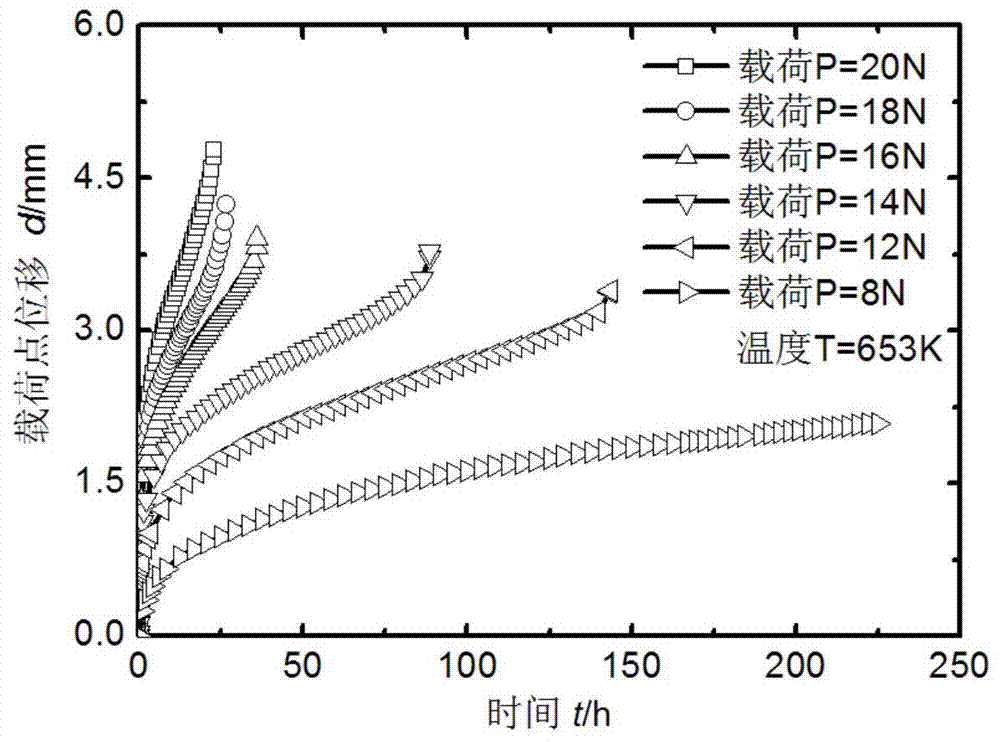
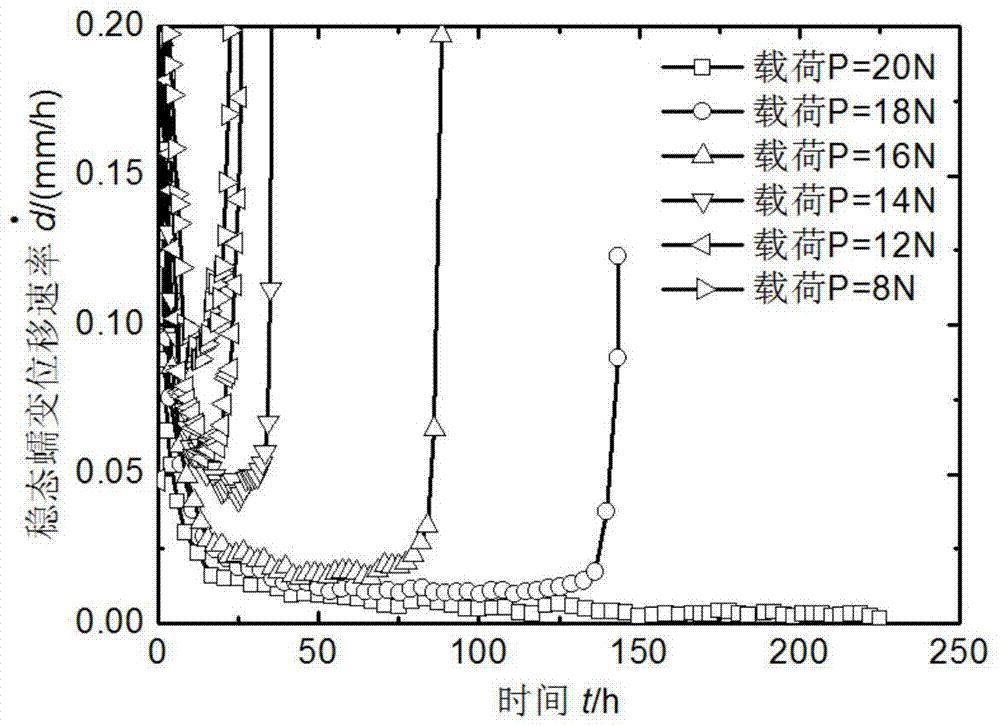
Clamped straight rod small sample creep testing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN103487336ASimple and fast operationImprove test accuracyInvestigating material ductilitySmall sampleComputer module
The invention provides a clamped straight rod small sample creep testing method and an apparatus thereof. The testing apparatus comprises a heating module, a loading module, a clamping module, a displacement measuring module and an external support; and the testing method comprises the following steps: designing and making a clamped straight rod small sample, carrying out multiple creep tests of a material at a same temperature under different loads, establishing a steady state creep rate curve, obtaining a Kachanov-Rabotnov creep damage constitutive equation, and adopting a finite element to carry out parameter optimization. The small sample creep testing method provided by the invention solves the problems of difficult data parse and many testing influence factors of present small sample technologies, has the advantages of simple operation, high testing precision and low cost, and provides basic data for the exploitation of a new material, the high-temperature integrity evaluation of a service member and the performance evaluation of an irradiated material.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for forming optical materials and devices
InactiveUS7026634B2Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureNanoinformaticsImage pickup tubesSolubilityRefractive index
The invention provides a process for forming optical components and new optical materials utilizing electron beam irradiation. The process comprises selectively irradiating optical materials to alter their index of refraction gradient three dimensionally. With the inventive process, new optical materials can be created that have enhanced optical properties over the un-irradiated material. The invention also provides a process in which optical components can be fabricated without requiring a planar / multiple layer process, thereby simplifying the fabrication of these optical components. The inventive process uses a controlled electron beam to alter the properties of optical materials. By using the radiation of a controlled electron beam, controlled changes in the index of refraction gradient of optical materials can be obtained. Further, radiation of the electron beam can be used to create new optical materials from materials not previously believed to be suitable for optical applications. This is based not only on the refractive index change created in the material, but also upon the change in other material properties such as elimination of melt and reduced solubility in normal solvents. In these cases, the electron beam modifies and creates a new networks structure within the material, which enhances its optical properties and allows for the formation of useful physical properties necessary for the fabrication of useful devices (i.e., resulting in wholly new optical materials). It is also disclosed that the inventive process can be used to produce a spatially graded index of refraction within a material to enhance the performance of an optical waveguide which can lead to a number of novel structures.
Owner:EBEAM & LIGHT
Radiation sensitive film including a measuring scale
Owner:ISP INVESTMENTS LLC
Sample component and method for nuclear power plant reactor pressure container irradiation inspection test
ActiveCN106644681AOptimal adjustment of loading quantityConsiderable loading spacePreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesReduction ratioIrradiated materials
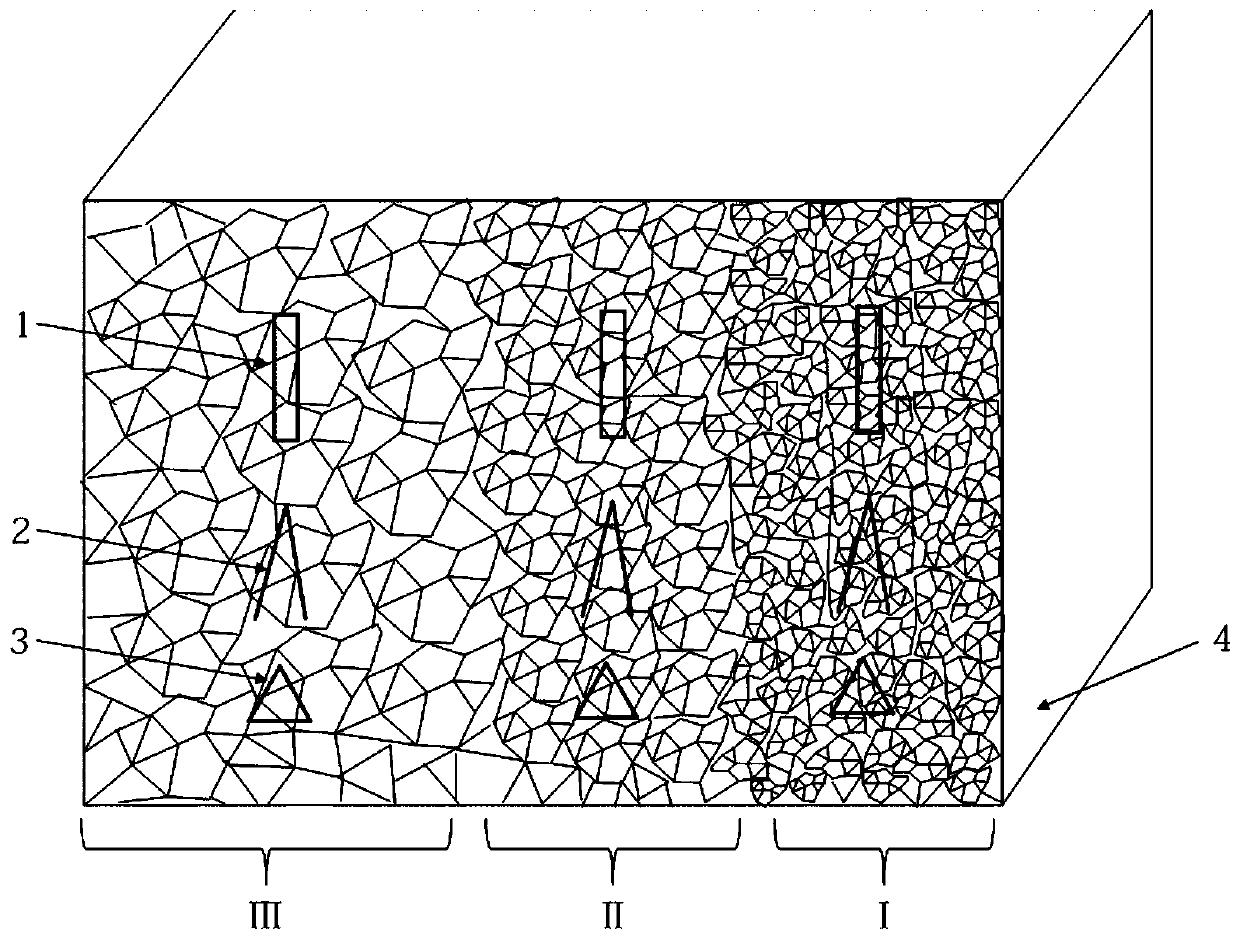
The invention discloses a sample component and method for a nuclear power plant reactor pressure container irradiation inspection test. The component comprises a tensile sample, an impact sample and a compact tensile sample, wherein the tensile sample is used for acquiring the tensile strength, the yield strength, the elongation and the cross section reduction ratio of irradiated materials, the impact sample is used for acquiring impact toughness of the irradiated materials, the compact tensile sample is used for acquiring fracture toughness of the irradiated materials and provided with notches, circular portions and side grooves which are sequentially formed in a first side face and a second side face from top to bottom, and the notch with an isosceles trapezoidal section, the circular portions and the notch with a V-shaped bottom jointly form an extensometer placement space. The method includes the steps of sample preparation, sample loading, sample testing and result evaluation. Arrangement of a bent sample is canceled, the quantity proportion of the other samples is optimized, the shape of the compact tensile sample is optimally improved, and test failure risks in fracture toughness testing are decreased.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Low energy big flow and strong irradiation device for materials
ActiveCN104157321AImprove defectsEffective simulationIrradiation devicesVacuum extractionNuclear fusion
The invention discloses a low energy big flow and strong irradiation device for materials. The key points of the technical scheme of the device are as follows: the device comprises an air supply system, an air pressure monitoring device 2, a plasma generation system, a sample table 13, a laser heating system 6, a temperature measurement system 9, a vacuum extraction system 5, a water-cooling circulating system 4 and a power supply system. When the material surface is processed by the device, the irradiation environment of a nuclear fusion reactor can be effectively simulated, and further, changes of characteristic, structure and function of the irradiated material can be studied.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
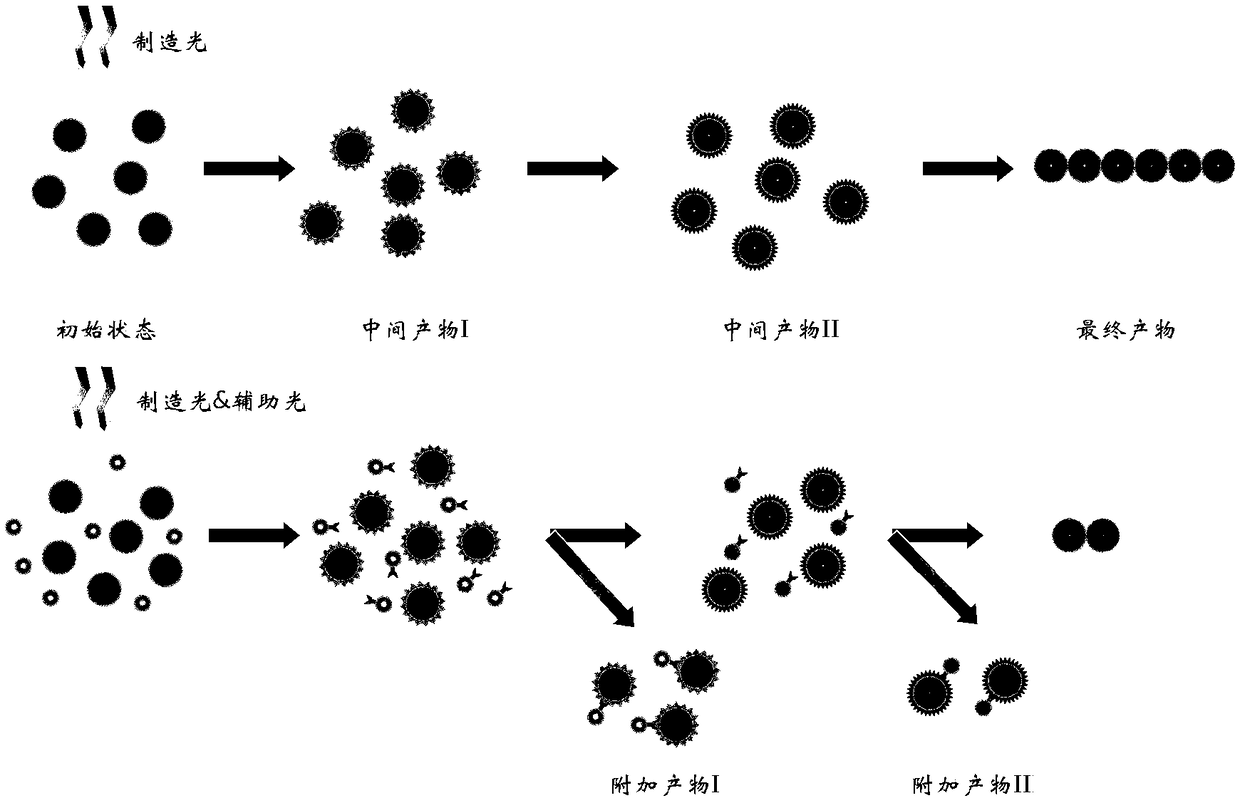
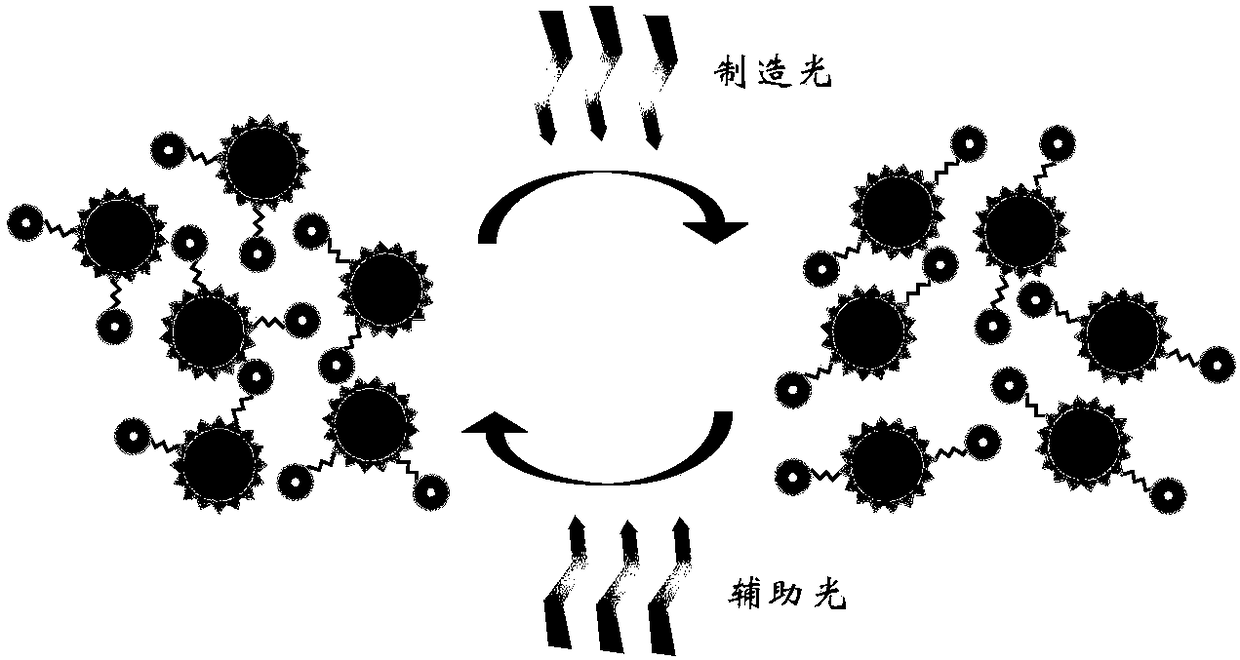
Double-light beam micro/nano optical manufacturing method
ActiveCN108279550ASmall feature sizeHigh resolutionPhotomechanical apparatusNanotechnologyImage resolutionLight beam
The invention relates to a double-light beam micro / nano optical manufacturing method which comprises the following steps: S1, providing manufacturing light according to the material properties of a to-be-irradiated processing material, so that the material properties of the to-be-irradiated processing material is changed under the irradiation of the manufacturing light; S2, providing auxiliary light according to the material properties of the to-be-irradiated processing material, wherein the auxiliary light can hinder the change in the material properties of the to-be-irradiated material underthe irradiation of the manufactured light; S3, regulating and controlling the manufacturing light and the auxiliary light, so that focal points distributed on a first local light field and a second local light field and formed by the manufacturing light and the auxiliary light on the to-be-irradiated material overlap in space, and a processing light field which is not superimposed by the second local light field and acts on the to-be-irradiated processing material is formed in the range of the first local light field. The manufacturing method provided by the invention can realize smaller feature size and higher resolution ratio, and a pattern and a structure manufactured have better mechanical property.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing surface porous metal material
The invention discloses a method for preparing multi-aperture metal materials, and the invention is disclosed for solving the problem of instability of the present preparation technology of the multi-aperture metal materials and the problem of the difficult controlling of size and density of pores. The producing characteristics of the method are that high-current pulse electronic beam (HCPEB) is employed to irradiate the metal materials, the working parameters of the high-current pulse electronic beam are that the energy of the electronic beam is 18-28 kilo electron volt, the pulse time is 3.5 microseconds, the energy density is about 2-4Jcm-2, and the air pressure of a vacuum chamber is about 10-5Torr. According to the requirements of pore size, distribution density and the like, technology parameters of grain size of materials needed to be irradiated, the energy of pulse electronic beam and the irradiating times are properly selected, and thereby different index requirements are met. The preparation technology disclosed by the invention is stable, and is capable of obtaining the metal materials of multi-pores on the surface, and the quantity and the distribution of the pores are controllable.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Vacuum acquisition device for EUV irradiation material test system and corresponding test method
ActiveCN104597115AStop the spreadMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas analysisVacuum pressure
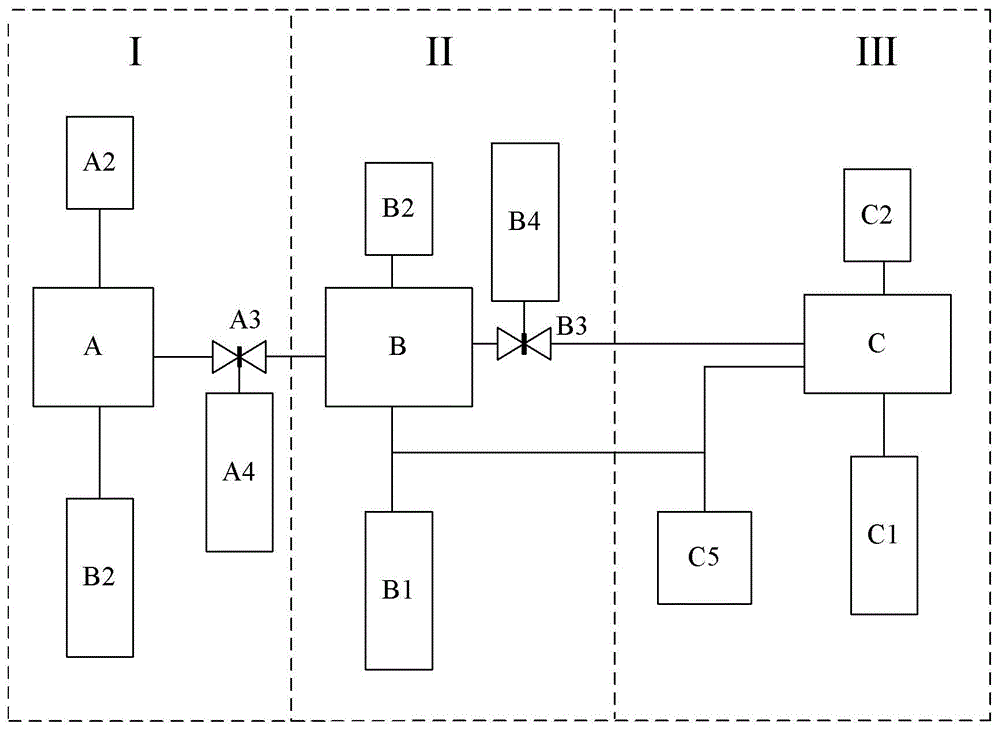
The invention discloses a vacuum acquisition device for an EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) irradiation material test system and a corresponding test method, wherein the test system comprises an EUV light source chamber (A), a collection mirror chamber (B) and a sample chamber (C); the vacuum acquisition device comprises a vacuum pump unit and a vacuum gauge unit that are respectively connected to each chamber, a first gate valve and a second gate valve (A3, B3) that are connected between the chambers, a first gas source and a second gas source (A4, B4) that are used for communicating the first gate valve and the second gate valve (A3, B3), as well as a gas analysis unit (C5) that is connected with the vacuum pump unit (B1) of the collection mirror chamber (B) by a valve. The invention can evacuate each part of the test system, effectively prevent pollutants from dispersing from the EUV light source chamber and the sample chamber to the collection mirror chamber, and can measure the gas components in the sample chamber and the partial pressure when the vacuum pressure is unmatched.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electromagnetic energy assisted drilling system and method
A drill bit, system and method for penetrating a material such as a mineral bearing rock or the like. The system comprises a drill bit comprising a cutting face comprising at least one cutting tool, an emitter of microwaves positioned behind the cutting face, wherein at least a portion of the microwaves are emitted in a direction away from the cutting face, and a reflector for directing the portion to the cutting face. In operation the emitted microwaves irradiate the material prior to the irradiated material being removed by the at least one cutting tool.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Portable radiant energy sterilizer
InactiveCN1638813AEffective sterilizationProtection against radiationRadiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesTransformerLow voltage
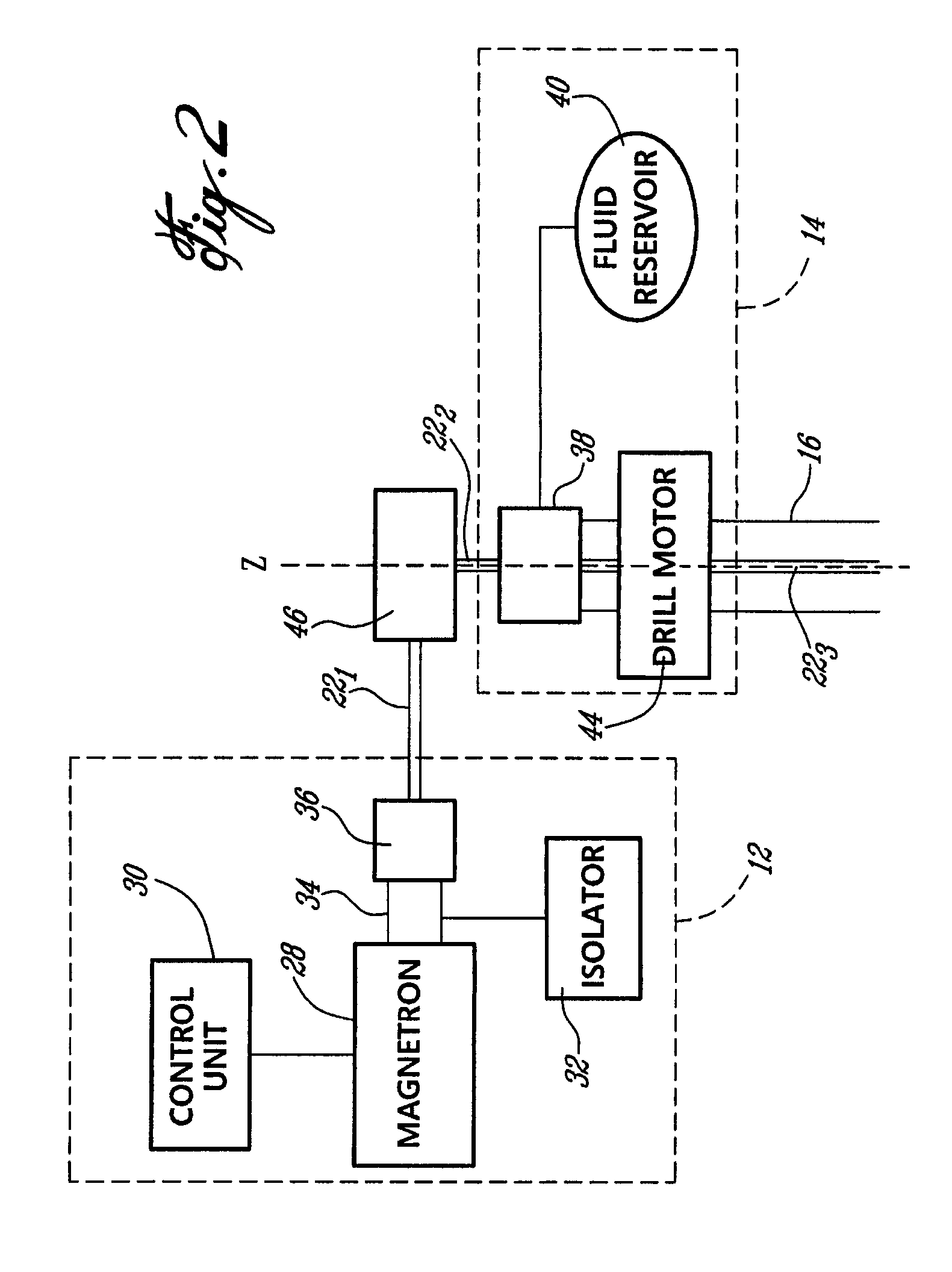
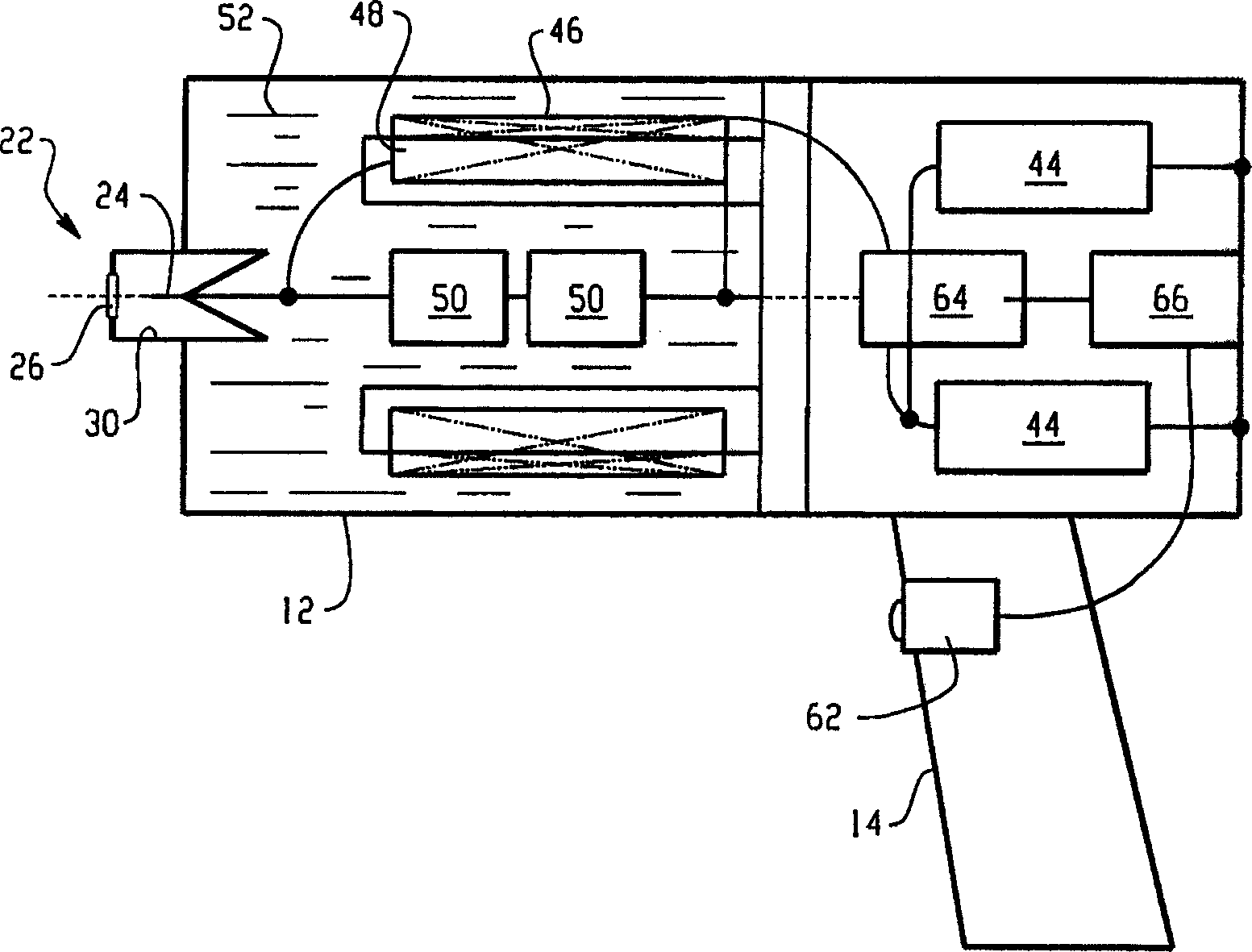
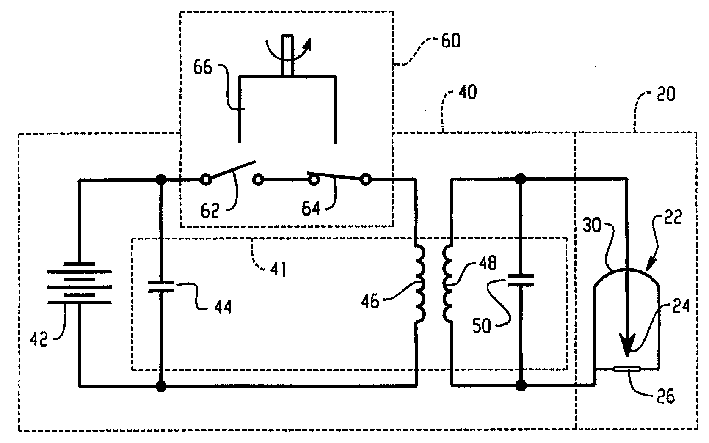
The present invention provides a portable radiation generating device for generating high energy electron beam radiation and X-rays from a low voltage power source such as a battery (42). The pulse high voltage generator (40) includes a power supply (42) and a Tesla transformer (41). The Tesla transformer has at least one first capacitor (44), a primary coil (46), a secondary coil (48), and at least one second capacitor (50). The at least one second capacitor is disposed axially within the secondary coil. A control system (60) is connected to the pulsed high voltage generator (40) for selectively controlling the energy transfer from the pulsed high voltage generator (40) to the radiation generating device (22). The radiation generating means are used to generate pulses of electrons and X-rays. Each pulse has a duration of approximately 100 nanoseconds. The electrons and X-rays generated by the radiation generating device can be used to inactivate microbial contaminants or irradiate various materials.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
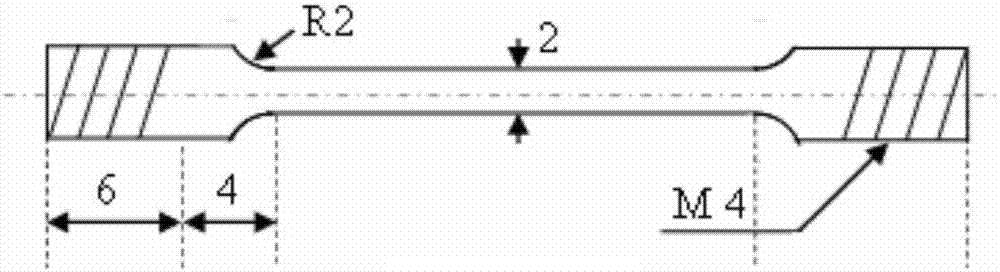
Stress corrosion tensile sample adopting ion irradiation to simulate neutron irradiation and preparation method of stress corrosion tensile sample
PendingCN107462451AUniform exposure to ion irradiationHighlight the effects of radiationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeutron irradiationChemical composition
The invention belongs to the field of the preparation of stress corrosion tensile samples, and particularly relates to a stress corrosion tensile sample adopting ion irradiation to simulate neutron irradiation and a preparation method, which is used for studying stress corrosion sensitivity of an irradiated material so as to evaluate the service performance of the material in a high-temperature high-pressure water environment of a nuclear power plant. The tensile sample comprises parallel portion scale distance section with a rectangular cross section, a tangential transitional arc portion and a threaded connection clamping portion. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (a) preparing a sample unit body; (b) grinding by using abrasive paper; (c) manually polishing; (d) ultrasonically cleaning; (e) pre-observing; and (f) performing EBSD detection. The stress corrosion tensile sample provided by the invention can uniformly receive the ion irradiation, and can effectively enable the influence of the irradiation to be prominent; the preparation method is simple, the practicability is high, and the cost is low; and the preparation method can effectively avoid the change of chemical components on the surface of the sample.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method of preparing high specific activity platinum-195m
InactiveUS20040032923A1High radiotoxicityHigh usefulnessHeavy metal active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPlatinumIrradiated materials
A method of preparing high-specific-activity <195m>Pt includes the steps of: exposing <193>Ir to a flux of neutrons sufficient to convert a portion of the <193>Ir to <195m>Pt to form an irradiated material; dissolving the irradiated material to form an intermediate solution comprising Ir and Pt; and separating the Pt from the Ir by cation exchange chromatography to produce <195m>Pt.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Comprehensive judgment method for performance irradiation ageing damage of elastomer for nuclear power
InactiveCN105973792AAccurately determine the cause of performance damageAccurately determine the phenomenon of radiation agingWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElastomerFailure prevention
The invention relates to a comprehensive judgment method for performance irradiation ageing damage of an elastomer for nuclear power. The comprehensive judgment method particularly comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out macro-performance test on an elastomer material, and preliminarily evaluating the ageing condition of each macro-performance of the irradiated material; (2) carrying out appearance observation on an irradiation sample, and judging the fracture mode is one or more reasons of ductile fracture, brittle fracture and the like by combining with a test result of the mechanical performance of the step (1); and (3) carrying out system analysis and testing on parts such as a tensile fracture surface and the interior of the material by virtue of multiple detection measures, and accurately judging the reasons of the ageing damage of the material by combining with a fracture appearance observation result of the step (2). By virtue of rapid analysis on typical modified rubber for the nuclear power under a ray irradiation condition, the reasons of the ageing damage of the elastomer material are accurately judged, and therefore, the targeted failure prevention and life prediction can be carried out. The comprehensive judgment method has application values in the evaluation on the service performance of other elastomer polymer materials in the fields of nuclear power, thermal power and petrochemicals, and the effective reference basis is provided for the selection and quality evaluation of materials in practical engineering application.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Fluorescent water treatment compounds and method of use
ActiveUS20170355628A1Easy to prepareImprove compatibilityWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment parameter controlWater sourceFluorescence
Disclosed herein are graphene quantum dot tagged water source treatment compounds or polymers, and methods of making and using. Also described herein are tagged compositions including an industrial water source treatment compound or polymer combined with a graphene quantum dot tagged water source treatment compound or polymer. The tagged materials are tailored to fluoresce at wavelengths with minimized correspondence to the natural or “background” fluorescence of irradiated materials in industrial water sources, enabling quantification of the concentration of the water source treatment compound or polymer in situ by irradiation and fluorescence measurement of the water source containing the tagged water source treatment compound or polymer. The fluorescence measurement methods are similarly useful to quantify mixtures of tagged and untagged water source treatment compounds or polymers present in an industrial water source.
Owner:CHAMPIONX USA INC
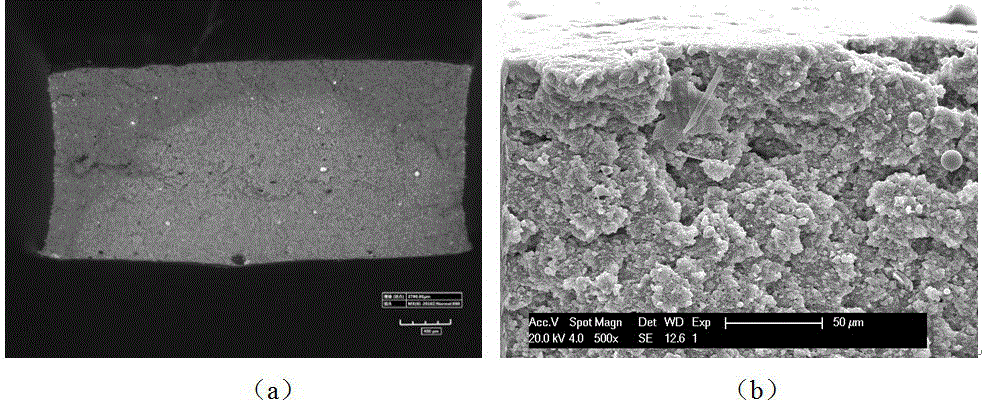
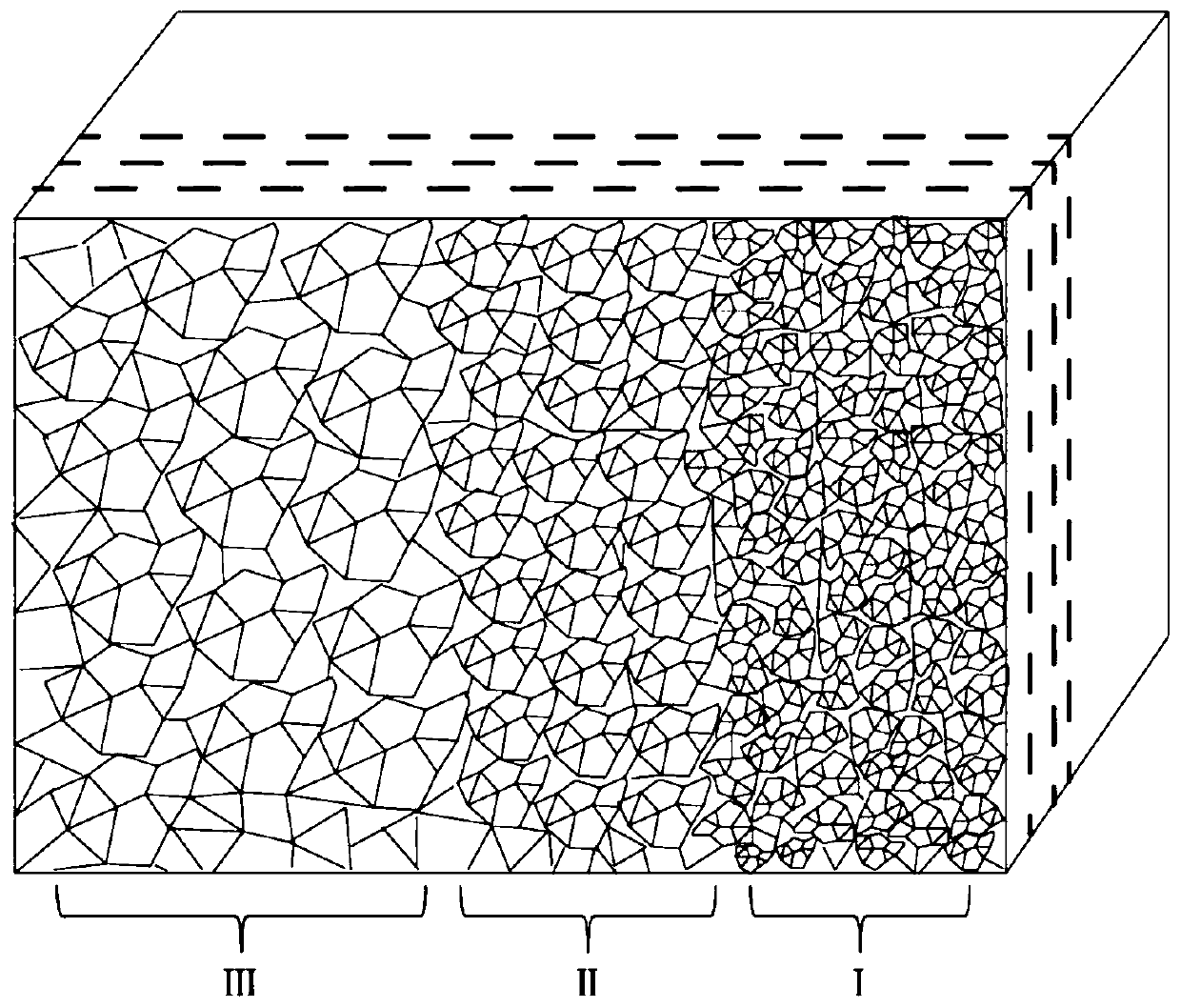
Method of screening irradiation-damage-resistant material by utilizing gradient structure
ActiveCN110346271AReduce in quantityImprove production efficiencyWeather/light/corrosion resistancePreparing sample for investigationIon beamElectron microscope
The invention belongs to the field of irradiation damage resistance of materials, and particularly relates to a method of screening an irradiation-damage-resistant material by utilizing a gradient structure. The method comprises the following steps of (1), preparing a gradient structure material; (2), performing an irradiation experiment on the surface with different grain sizes of the gradient structure material; (3), performing mechanical property testing on samples in different grain size regions by utilizing nanoindentation and convergent ion beams for the irradiated material, and automatically preparing a microstructure characterization sample; and (4), performing transmission electron microscope and three-dimensional atom probe analysis. With the adoption of the method, the differentgrain sizes can be prepared on one sample, and then the irradiation experiment is performed, therefore, the quantity of samples required for researching an influence of the different grain sizes on irradiation damage can be reduced; the efficiency of preparation of the microstructure characterization sample can be improved; and the efficiency of screening of the irradiation-damage-resistant material can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of irradiation degrading crop stalk to prepare edible fungus culturing material
InactiveCN1887047ABio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationDose uniformityOrganism
The present invention belongs to the field of irradiation treating technology, and is especially method of irradiation degrading crop stalk to prepare edible fungus culturing material. The present invention opens one new way of utilizing crop stalk. The method includes cutting stalk into 3-5 cm long, mixing with 1 / 20 concentration lime water to alkalize, piling to ferment for 15-25 days, compounding with supplementary material determined based on the variety of edible fungus to be cultured, hermetically packing and irradiating in the irradiation dose of 12-15 kGy and irradiation dose uniformity within 1.5, and using the irradiated material for culturing edible fungus. Or, the crop stalk is fermented preferably in a fermenting tank before compounding material, irradiation degrading and sterilizing to produce the edible fungus culturing material.
Owner:宁波超能科技股份有限公司
Method for etching surface material with induced chemical reaction by focused electron beam on surface
InactiveCN1479175AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
The invention refers to a procedure for etching of materials at the surface by focussed electron beam induced chemical reactions at said surface. The invention is characterized in that in a vacuum atmosphere the material which is to be etched is irradiated with at least one beam of molecules, at least one beam of photons and at least one beam of electrons, whereby the irradiated material and the molecules of the beam of molecules are excited in a way that a chemical reaction predetermined by said material and said molecules composition takes place and forms a reaction product and said reaction product is removed from the material surface - irradiation and removal step.
Owner:NAWOTEC +1
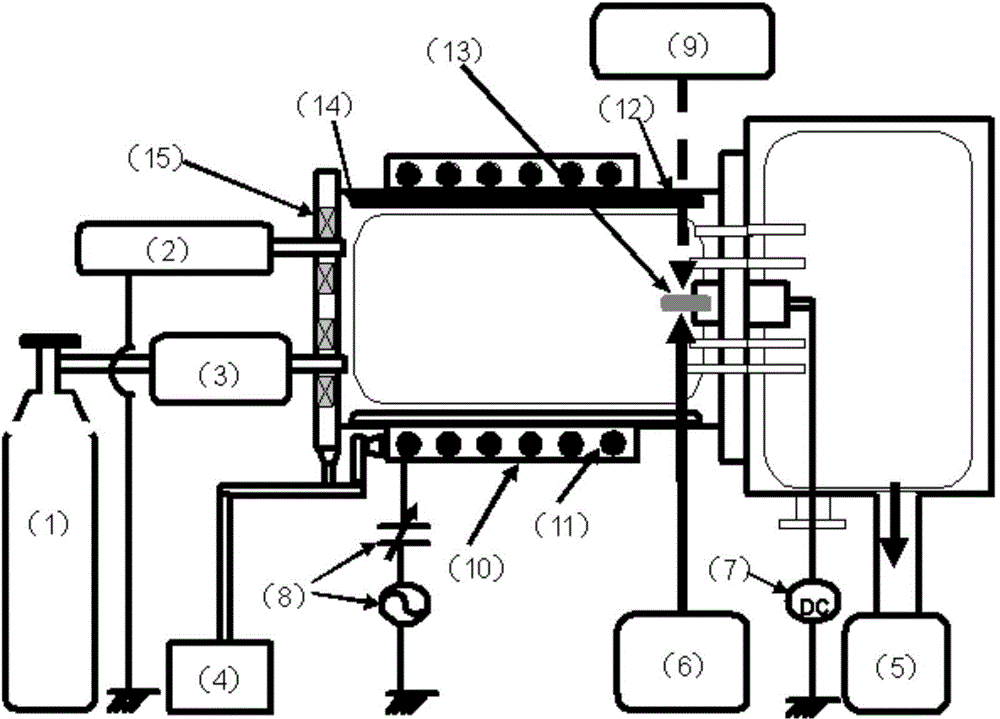
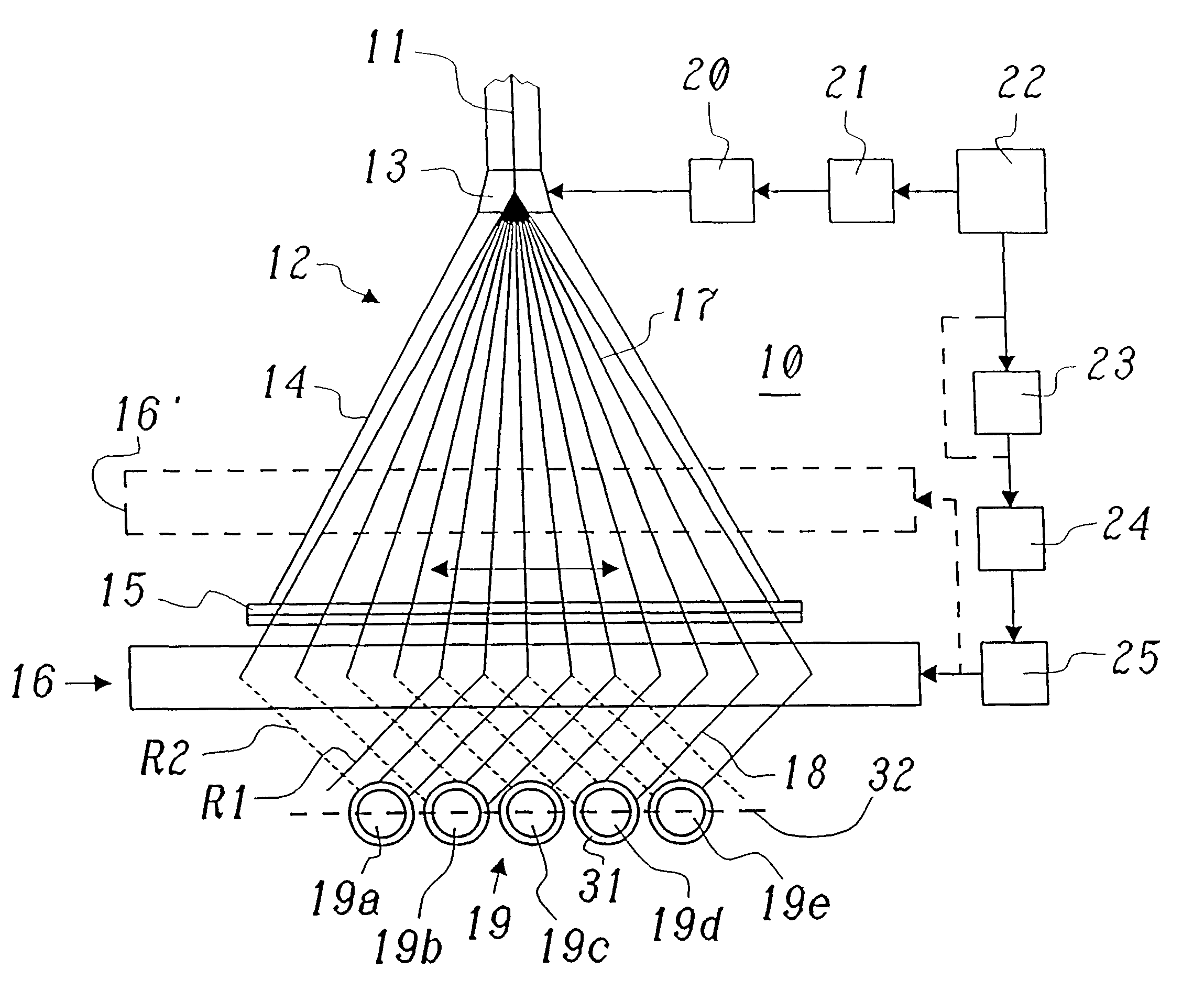
Process for the irradiation of strand-shaped irradiated material, and an irradiating device for the performance of the said process
InactiveUS6479831B1Achieve the cross-firing process simply and economicallyHomogenous magnetic field can be created relatively simplyElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyEngineeringScan angle
In a process for the irradiation of strand-shaped irradiated material (19; 19a-e), in particular cable insulation or sheathing (31) capable of being cross-linked by irradiation, or tubes, hoses, or profile elements capable of being cross-linked by irradiation, with electron beams impinging transversely to the longitudinal axis of the irradiated material (19; 19a-e), which strike the irradiated material (19; 19a-e) from two fixed irradiation directions (R1, R2), located at an angle to one another which is other than zero and for preference is a right angle, a uniform irradiation is achieved in a simple manner in that a scanned electron beam (17) is created from an electron beam (11) in a scanner (12) by means of a scan device (13), which by means of a temporally-actuated back-and-forth slewing movement in a prescribed angle range creates a radiation fan transversely to the longitudinal direction of the irradiated material, and that the scanned electron beam (17) is deflected by a deflection magnet (16, 16') arranged between the scan device (13) and the irradiated material (19; 19a-e) in such a way for each scan angle of the irradiation field that it impinges on the irradiation material (19; 19a-e) to be treated from one of the two fixed irradiation directions (R1, R2).
Owner:RADIATION DYNAMICS INC
Laser phase transition hardening method and bionic camshaft with hard phase prepared by method
ActiveCN107201427AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSurface layerHigh energy
The invention relates to a laser phase transition hardening method and a bionic camshaft with a hard phase prepared by the method. The laser phase transition hardening method comprises the steps: the surface of a workpiece is scanned by a laser beam with high-energy density, so that the surface temperature of the irradiated material rises to 10-20 DEG C higher than the solidus at high speed, and the surface of the heated area is heated to a semisolid state and then is rapidly cooled by a parent, thus a bionic unit body of which the microstructure is fine martensite is obtained, and the hardness can reach 690-770HV. A wearing surface layer with a soft and hard striped structure can be prepared on the cam surface of the camshaft by the method, and the hardness and the wear resistance of the cam surface are improved. The laser phase transition hardening method has the advantages of simple operation, little workpiece deformation and no defect, is suitable for the strengthening treatment of the camshaft, and is also suitable for the surface strengthening treatment of other workpieces made of 40Cr materials such as gears, sleeves, etc.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of coal-based mesoporous activated carbon
ActiveCN110451508ALarge specific surface areaHigh mesoporosityCarbon compoundsBulk chemical productionActivated carbonNitrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of coal-based mesoporous activated carbon. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing raw coal to obtain pulverized coal, adding the pulverized coal, an activator, ethanol and a ball-milling ball into a planetary ball mill, and performing ball milling to obtain a mixture; activating the bal-milled mixture in a nitrogen atmosphere toobtain an activated material; adding the activated material into a supercritical device, soaking the activated material in a supercritical acetone-water system, then filtering, washing and drying theobtained system, adding the dried material into an alkaline solution, and performing ultrasonic soaking; and filtering and drying the ultrasonically soaked material, placing the dried material in a sealed glass tank, irradiating the material with an electron beam irradiation device, washing the irradiated material with water, and drying the washed material to obtain the coal-based activated carbon. The coal-based mesoporous activated carbon obtained by the preparation method has a high specific surface area and a high mesoporosity, and has a high adsorption value for methylene blue.
Owner:新疆同力和环材科技有限公司
Low-energy and high-current material irradiation device
ActiveCN104157321BImprove defectsEffective simulationIrradiation devicesVacuum extractionNuclear fusion
The invention discloses a low energy big flow and strong irradiation device for materials. The key points of the technical scheme of the device are as follows: the device comprises an air supply system, an air pressure monitoring device 2, a plasma generation system, a sample table 13, a laser heating system 6, a temperature measurement system 9, a vacuum extraction system 5, a water-cooling circulating system 4 and a power supply system. When the material surface is processed by the device, the irradiation environment of a nuclear fusion reactor can be effectively simulated, and further, changes of characteristic, structure and function of the irradiated material can be studied.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy plasma facing material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114150206AReduce retentionImprove the ability to resist neutron radiationNuclear energy generationChemical vapor deposition coatingNeutron irradiationHigh entropy alloys
The invention discloses a tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy plasma facing material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of nuclear fusion energy application. The tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy is provided with columnar crystal grains with (001) orientation, and the grain size ranges from 10 micrometers to 70 micrometers. The high-entropy alloy comprises, by atomic percent, 20%-35% of W, 10%-25% of Ta, 10%-25% of Cr, 10%-20% of V, 5%-20% of Ti and 5%-20% of Y. The density of the tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy can reach 99% or above, the purity of the tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy exceeds 99.9%, the size of the columnar crystal can be controlled to be 10-70 microns, and fuel retention in a material after irradiation can be remarkably reduced. According to the tungsten-based columnar crystal high-entropy alloy, due to the high-entropy effect, the migration energy of interstitials and vacancies in the irradiated material is closer, so that the recombination rate of the interstitials and the vacancies is higher, and the neutron irradiation resistance of the material can be remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com