Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7670results about "Irradiation devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
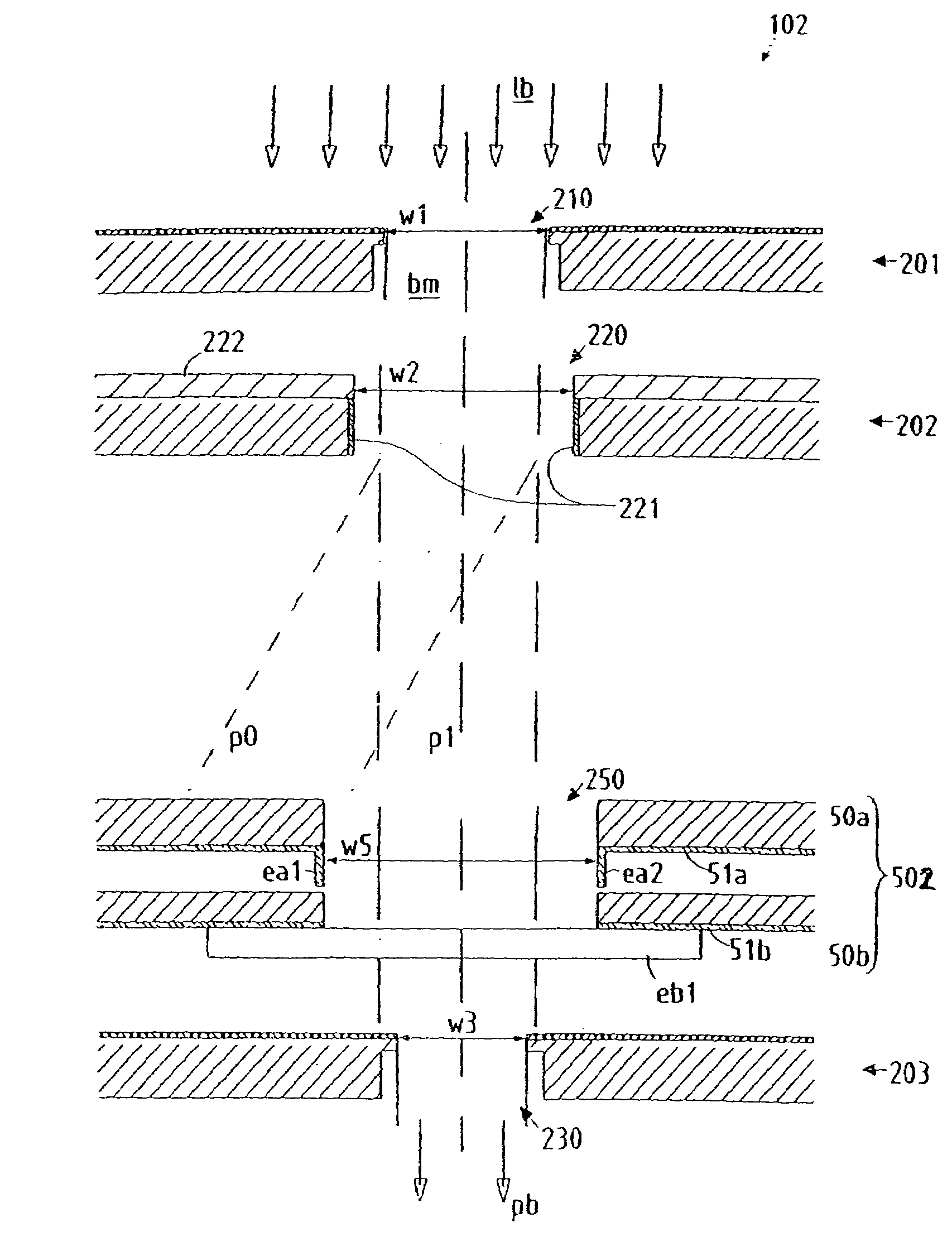
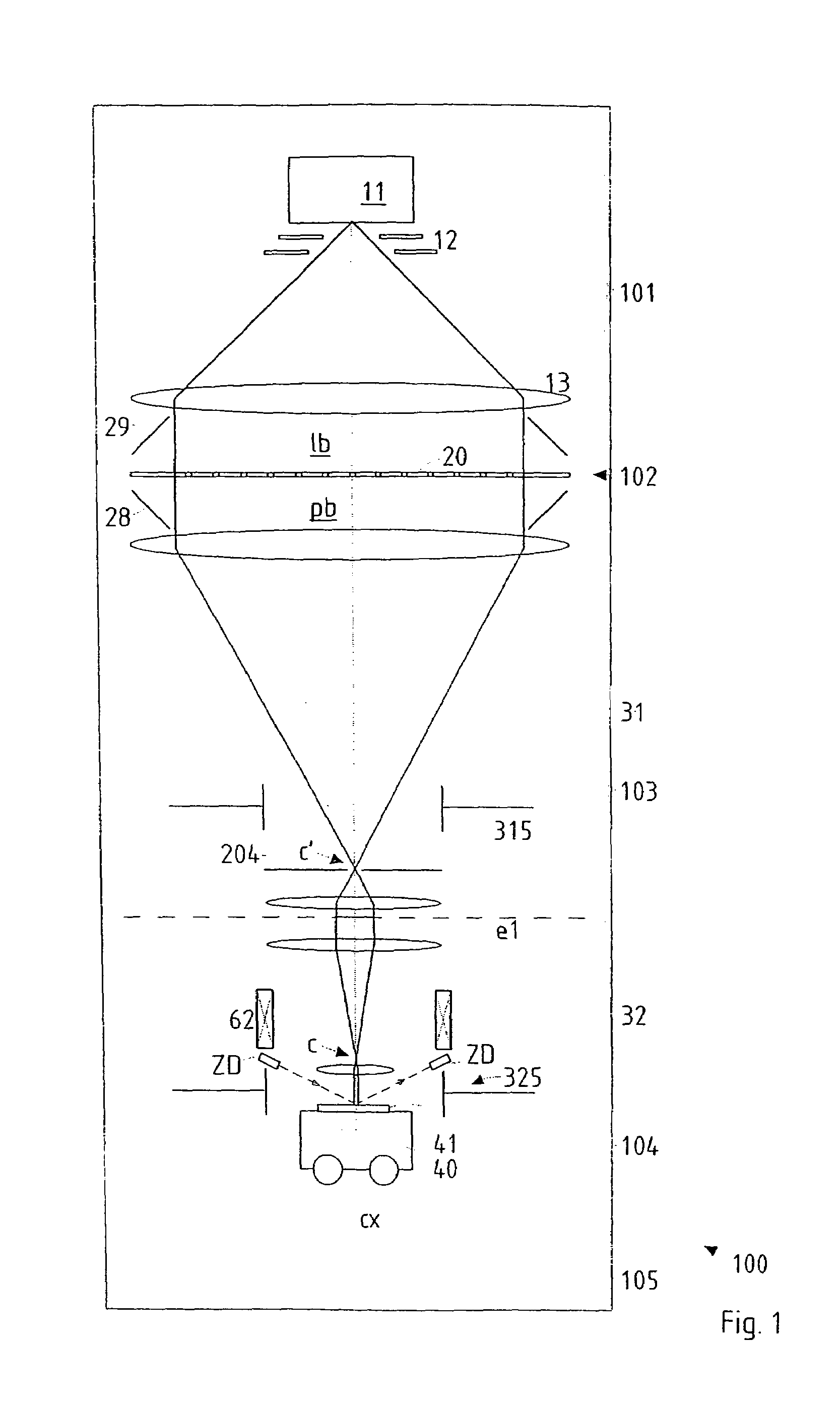
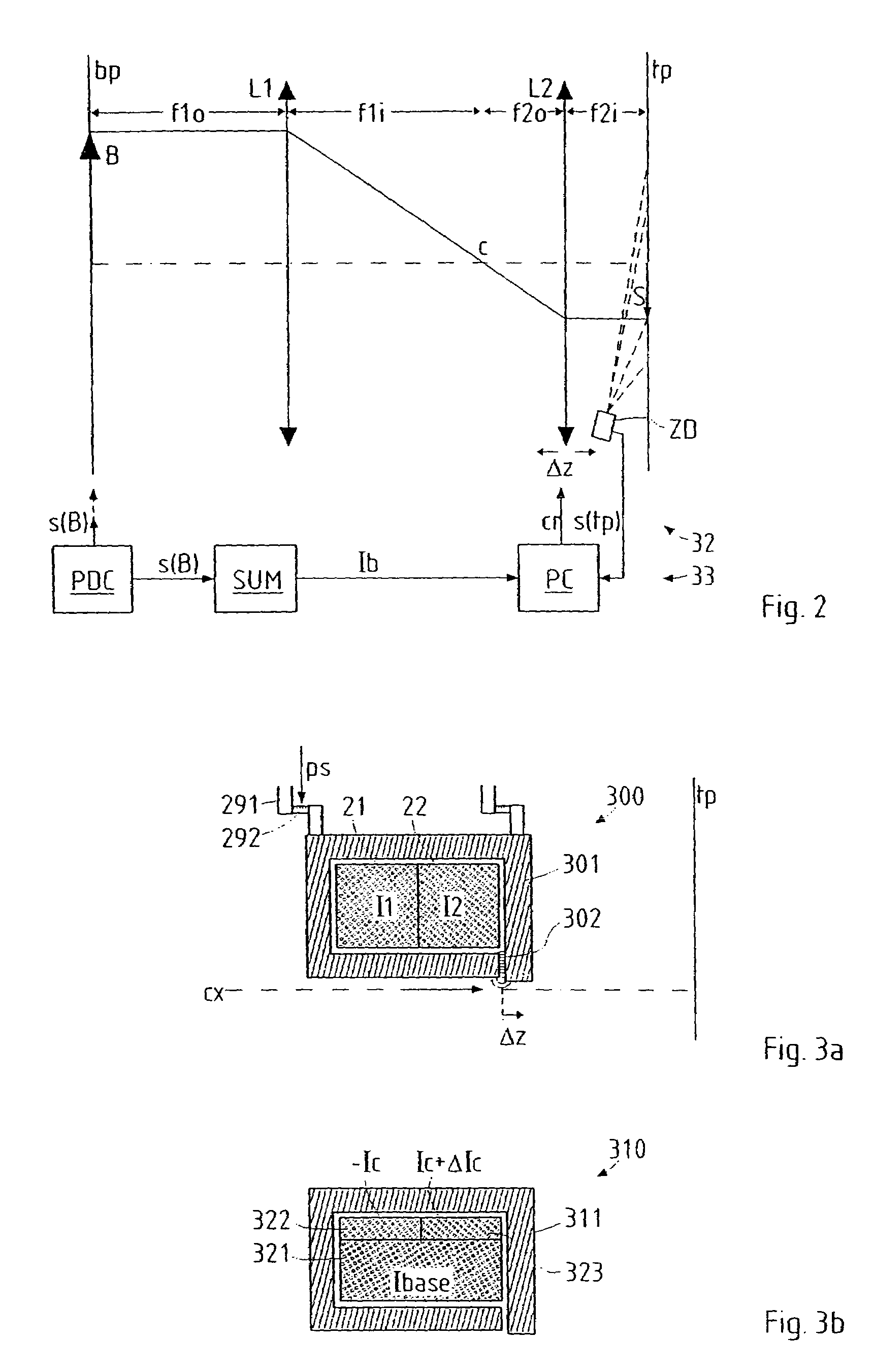
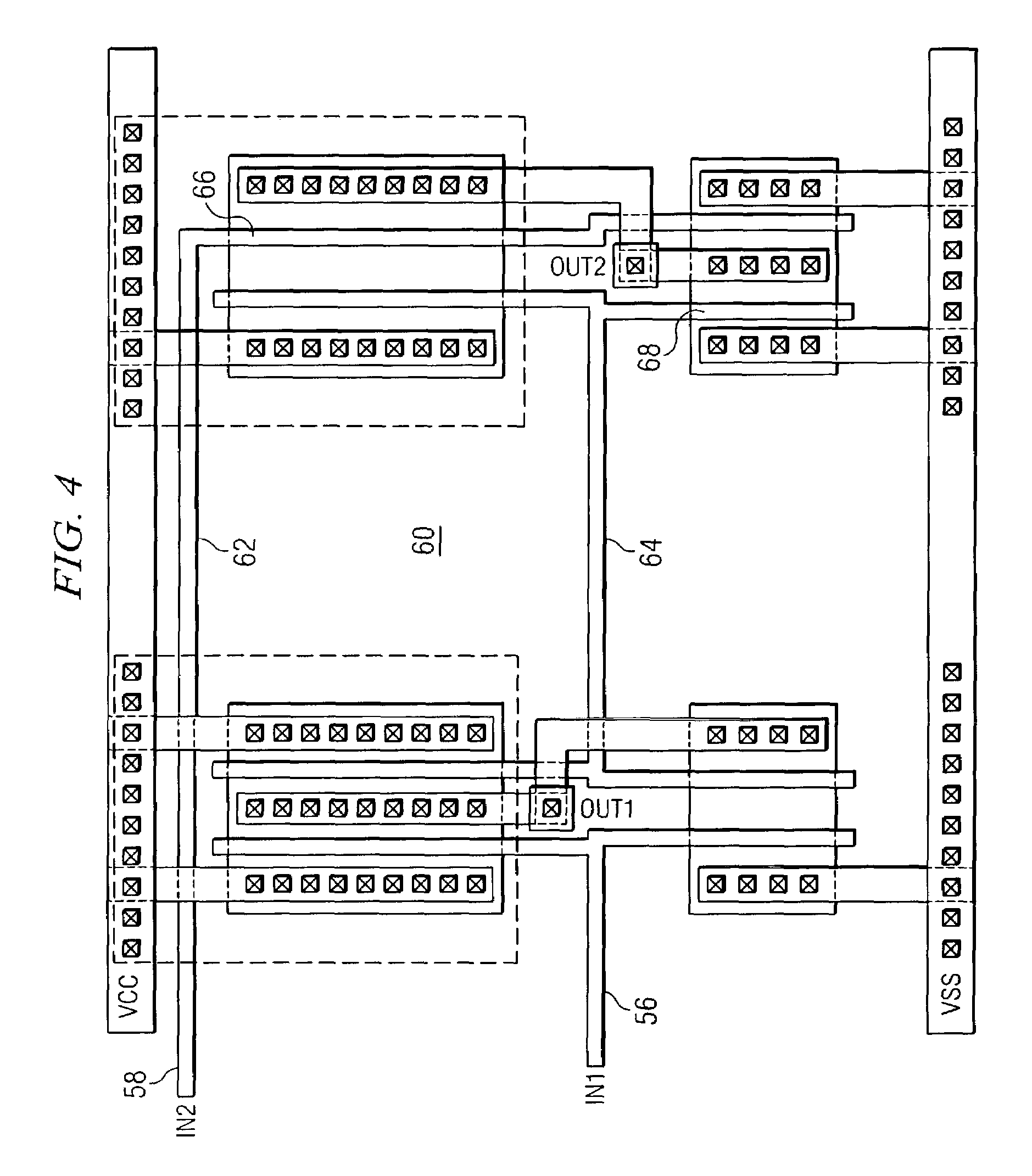
Particle-optical projection system
ActiveUS7388217B2Minimize distortionCompensation deviationElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsOptical axisProjection system
In a particle-optical projection system a pattern is imaged onto a target by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over; it is imaged into an image with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image position from the actual positioning of the target (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis), without changing the size of the image, the system includes a position detector for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target, and a controller for calculating modifications of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Method and system for drying a substrate
ActiveUS20050046934A1Good pattern uniformityImprove uniformityMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCooking & bakingThin membrane
A method and system is described for drying a thin film on a substrate following liquid immersion lithography. Drying the thin film to remove immersion fluid from the thin film is performed prior to baking the thin film, thereby reducing the likely hood for interaction of immersion fluid with the baking process. This interaction has been shown to cause non-uniformity in critical dimension for the pattern formed in the thin film following the developing process.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
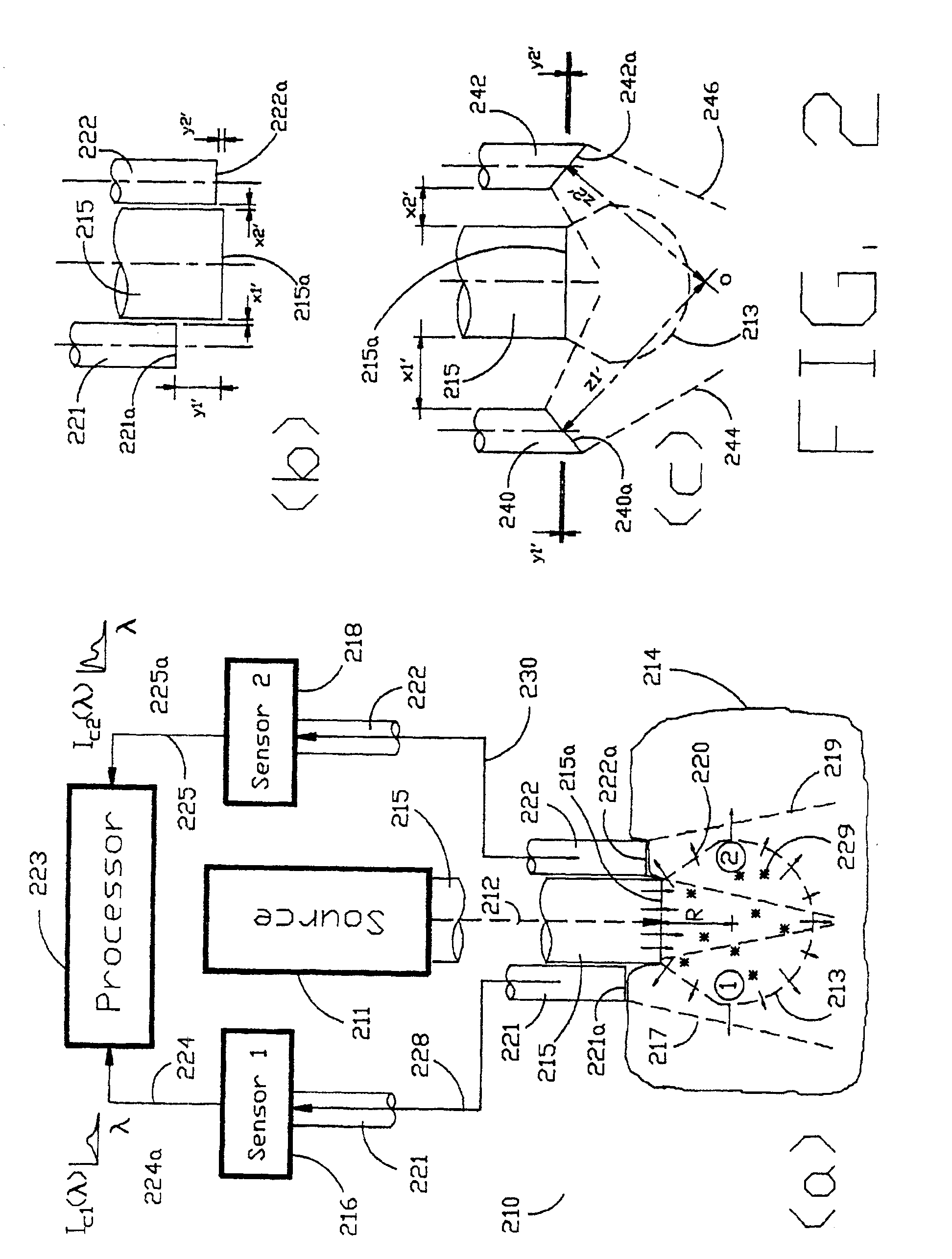
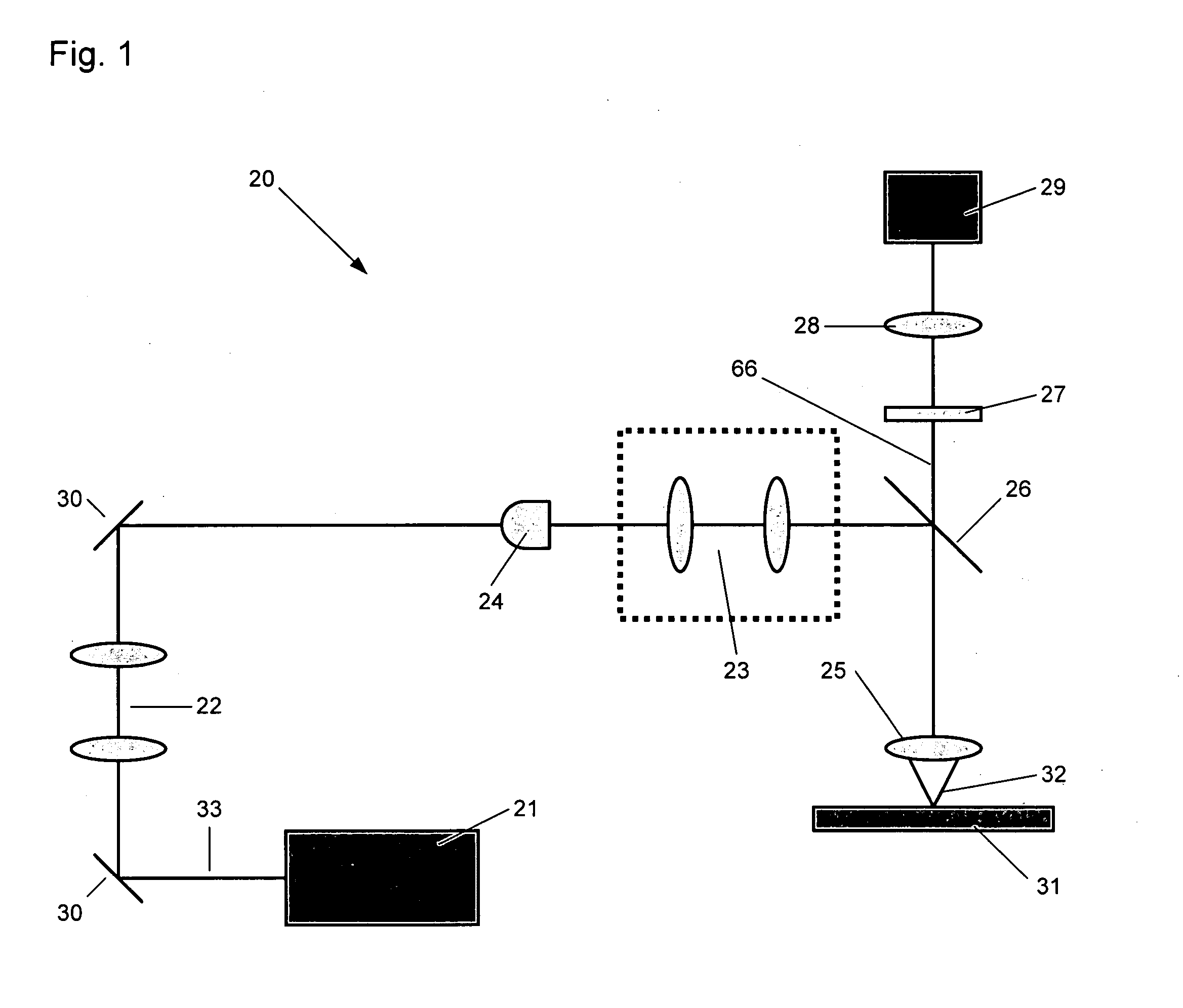
Method and devices for laser induced fluorescence attenuation spectroscopy
InactiveUSRE39672E1Large signal to noise ratioSurgeryScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpectroscopy
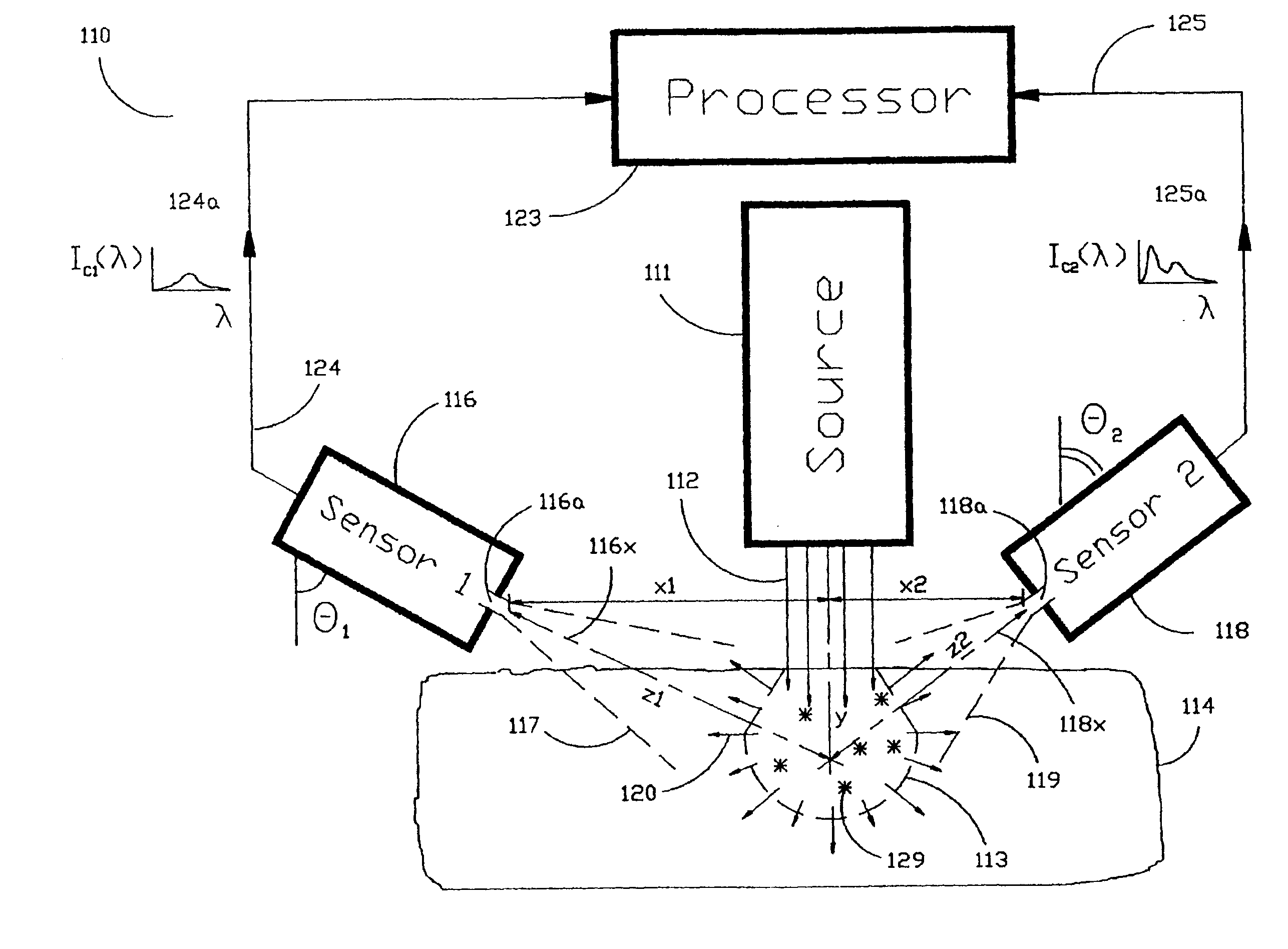
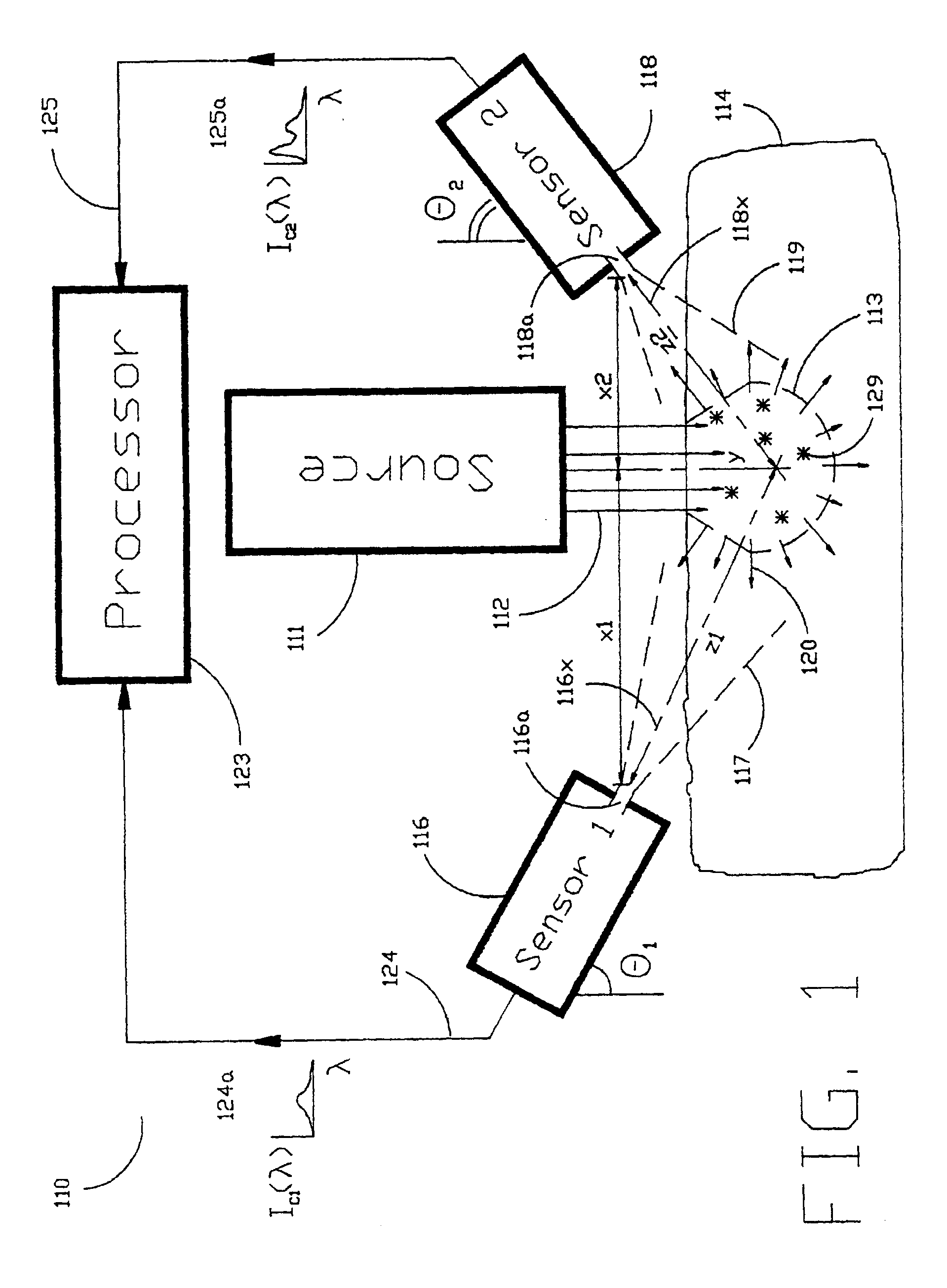
The Laser Induced Fluorescence Attenuation Spectroscopy (LIFAS) method and apparatus preferably include a source adapted to emit radiation that is directed at a sample volume in a sample to produce return light from the sample, such return light including modulated return light resulting from modulation by the sample, a first sensor, displaced by a first distance from the sample volume for monitoring the return light and generating a first signal indicative of the intensity of return light, a second sensor, displaced by a second distance from the sample volume, for monitoring the return light and generating a second signal indicative of the intensity of return light, and a processor associated with the first sensor and the second sensor and adapted to process the first and second signals so as to determine the modulation of the sample. The methods and devices of the inventions are particularly well-suited for determining the wavelength-dependent attenuation of a sample and using the attenuation to restore the intrinsic laser induced fluorescence of the sample. In turn, the attenuation and intrinsic laser induced fluorescence can be used to determined a characteristic of interest, such as the ischemic or hypoxic condition of biological tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
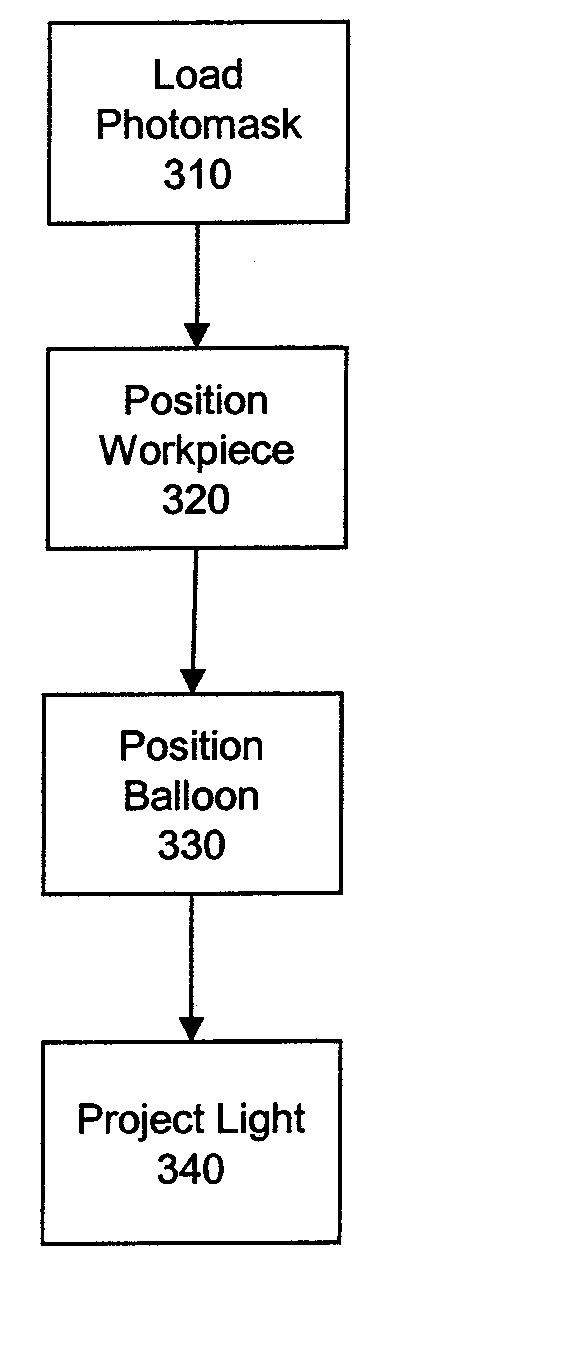
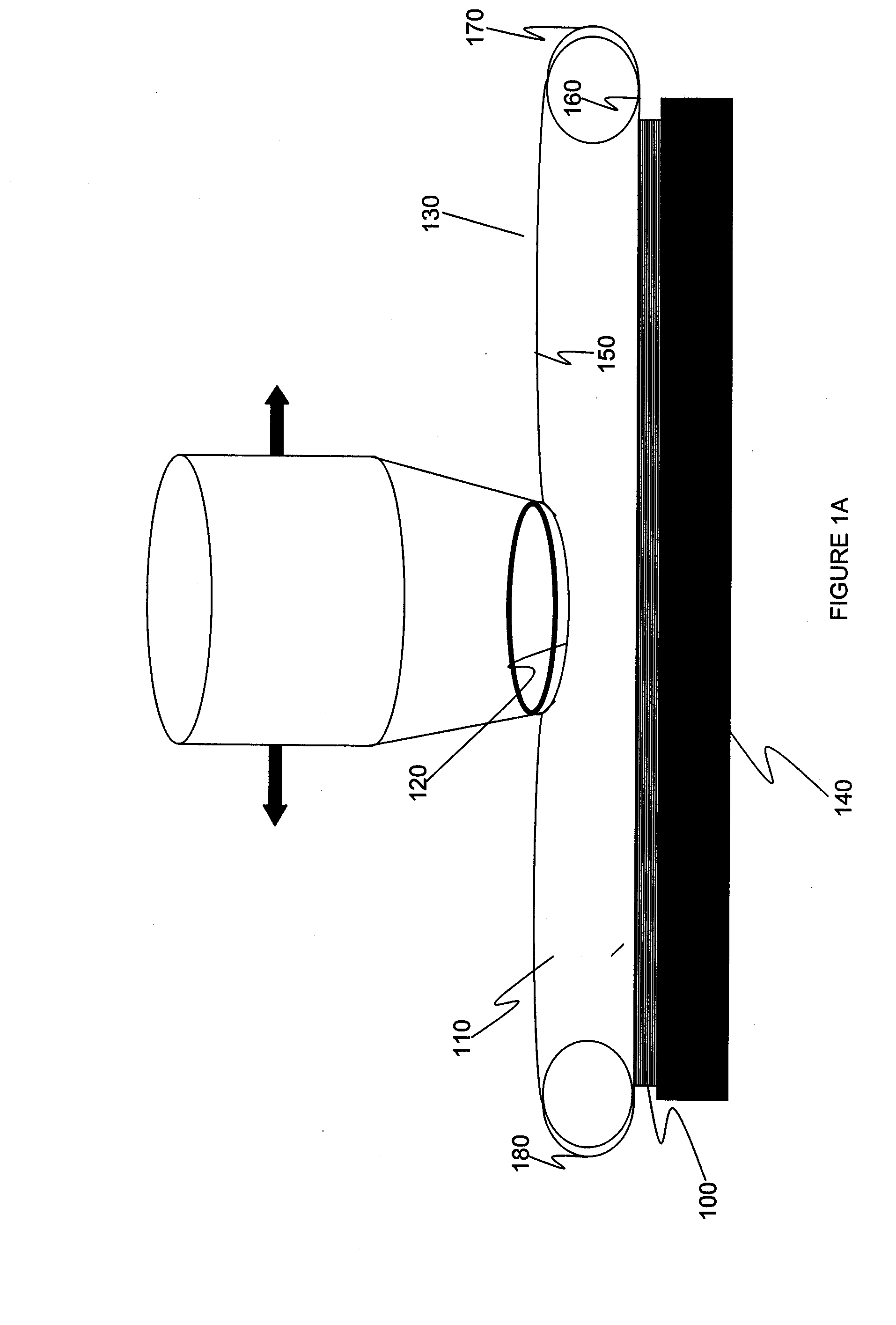
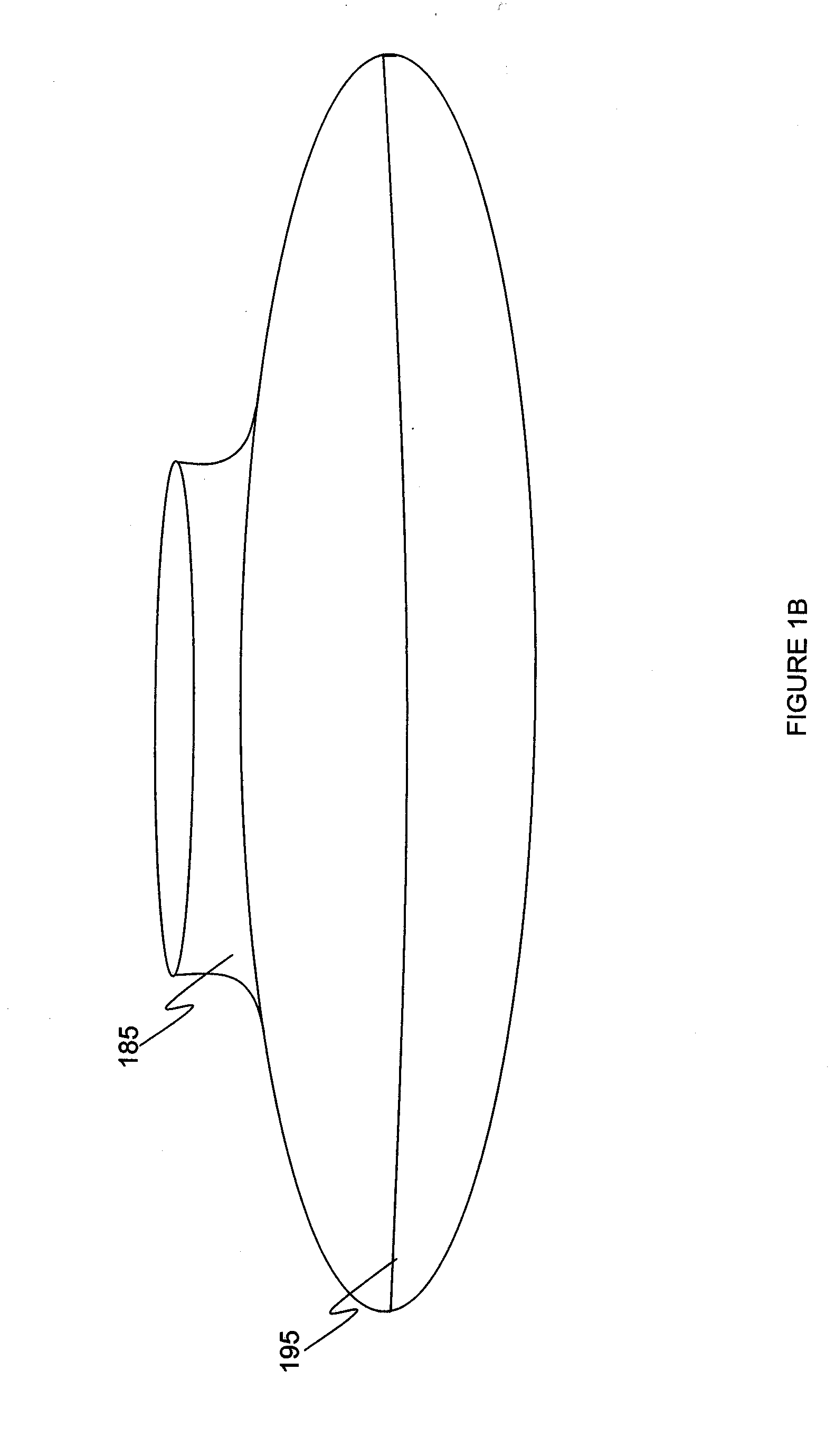
Liquid-filled balloons for immersion lithography
ActiveUS20050158673A1Suitable optical propertyPhotoprinting processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical propertySemiconductor structure
A liquid-filled balloon may be positioned between a workpiece, such as a semiconductor structure covered with a photoresist, and a lithography light source. The balloon includes a thin membrane that exhibits good optical and physical properties. Liquid contained in the balloon also exhibits good optical properties, including a refractive index higher than that of air. Light from the lithography light source passes through a mask, through a top layer of the balloon membrane, through the contained liquid, through a bottom layer of the balloon membrane, and onto the workpiece where it alters portions of the photoresist. As the liquid has a low absorption and a higher refractive index than air, the liquid-filled balloon system enhances resolution. Thus, the balloon provides optical benefits of liquid immersion without the complications of maintaining a liquid between (and in contact with) a lithographic light source mechanism and workpiece.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Apparatus for treating the surface with neutral particle beams
InactiveUS6935269B2Wide effective cross sectionImprove throughputRadiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesTarget surfaceMetal
The present invention relates to an apparatus for treating the surface with neutral particle beams comprising an antenna container, a plasma generating part, a neutral particle beam generating part and a treating part, wherein the antenna container comprises antennas connected to high frequency electric power supply through which high frequency electric power supplies, the plasma generating part transfers gases from a gas injector into plasmas with the supplied power, the neutral particle beam generating part reverts the obtained plasmas to neutral particle beams via the collision thereof with metal plates, and the treating part treats the surface of a target with the neutral particle beams.
Owner:SEM TECH CO LTD +1
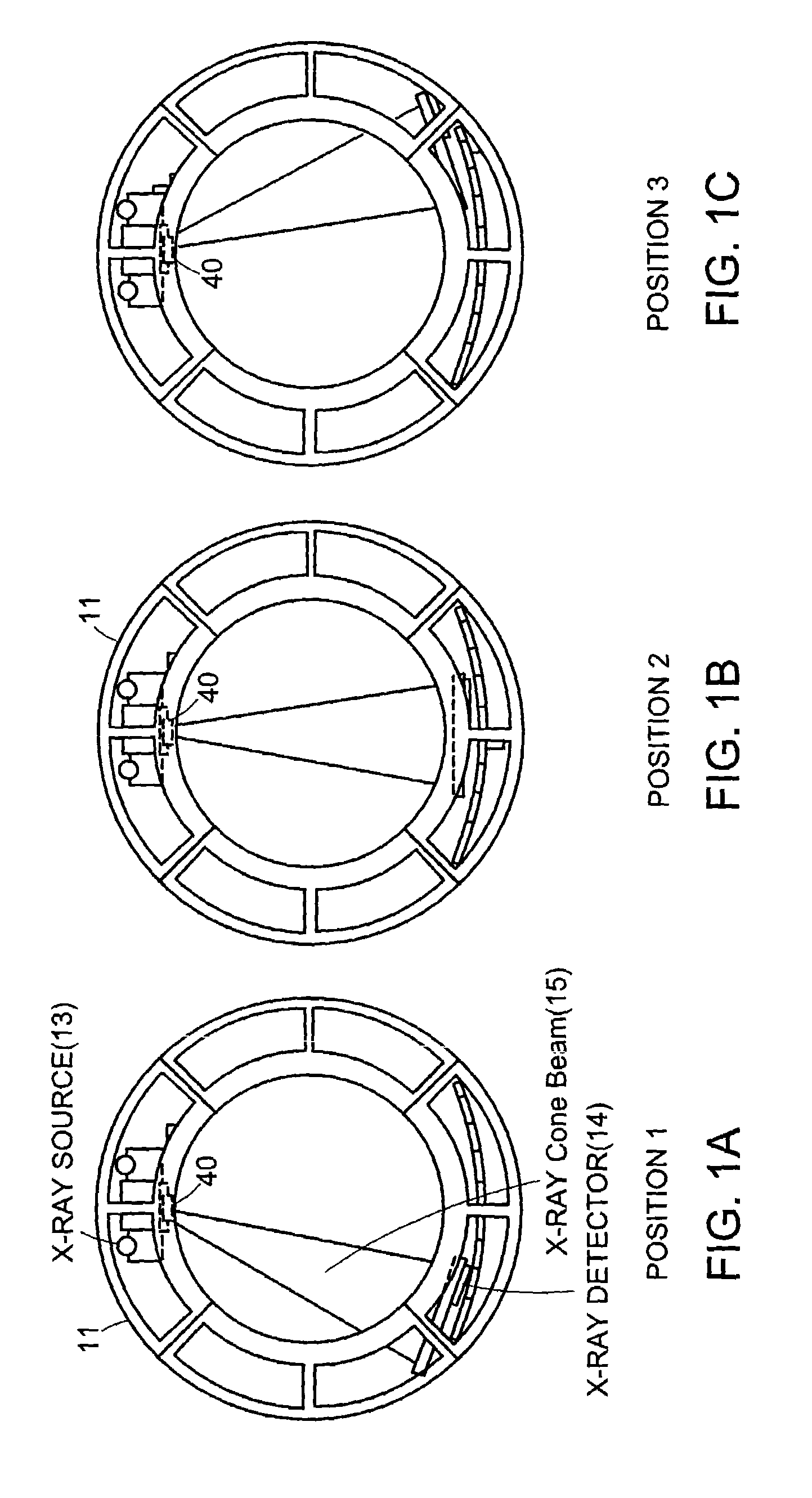
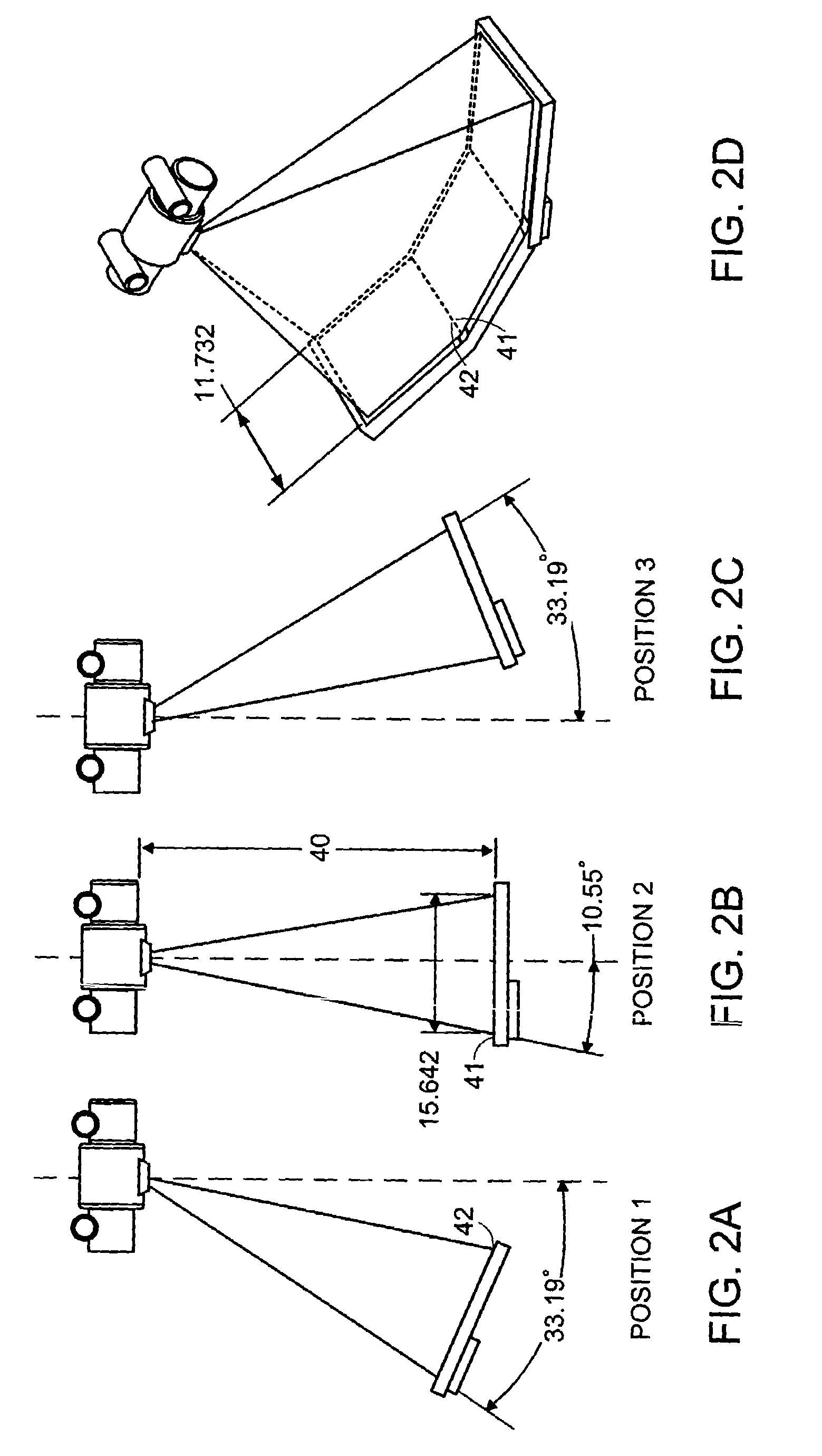
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
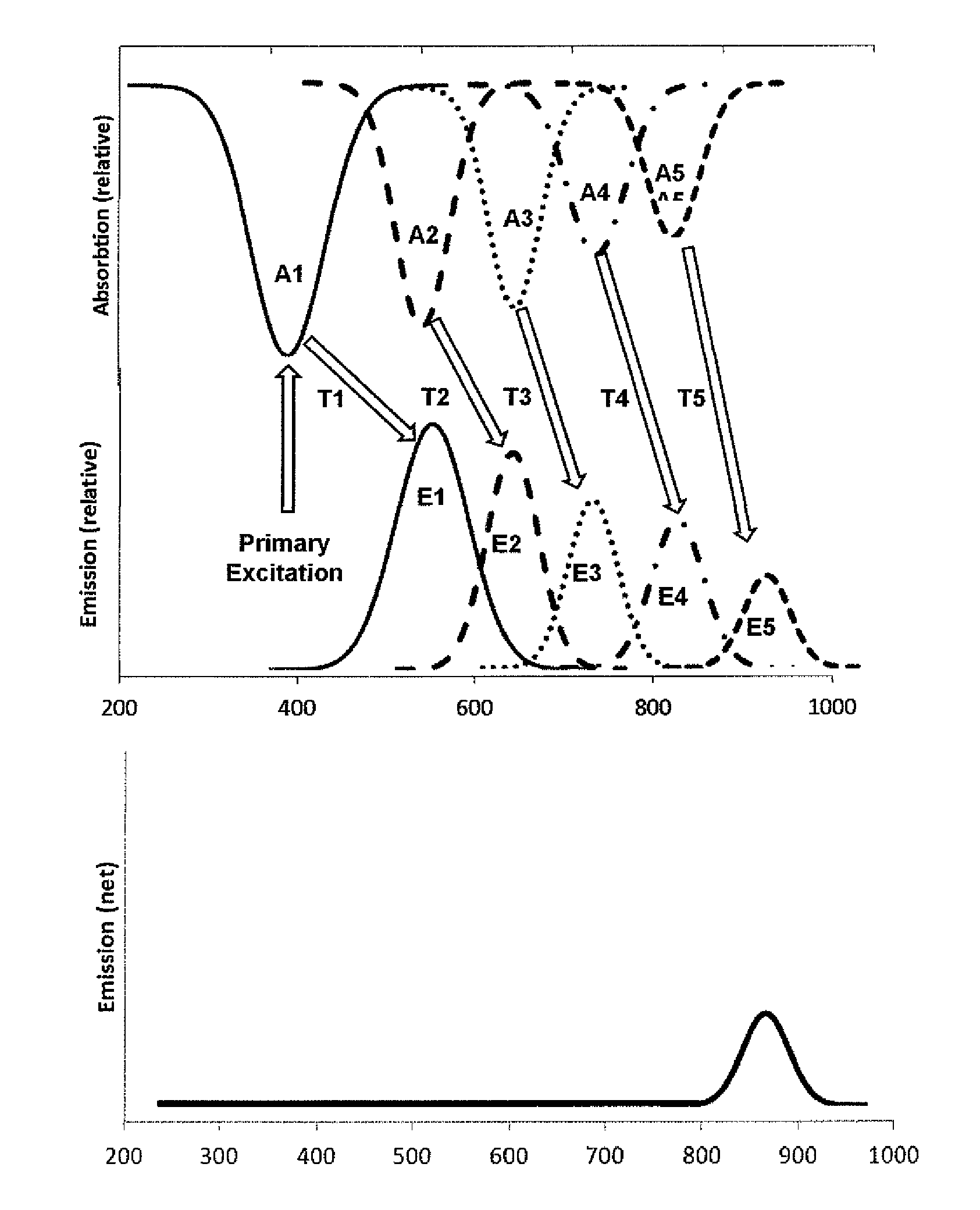
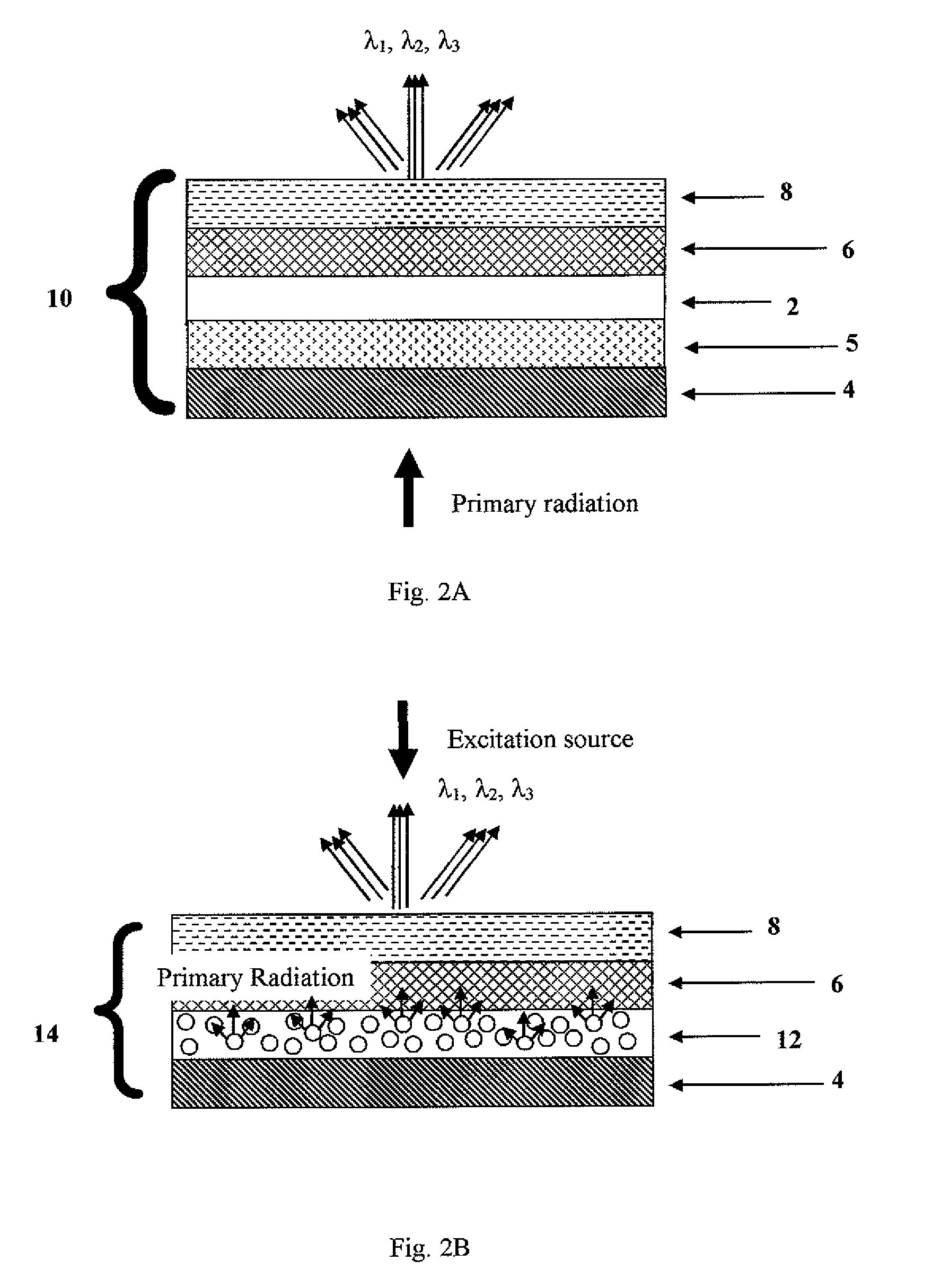
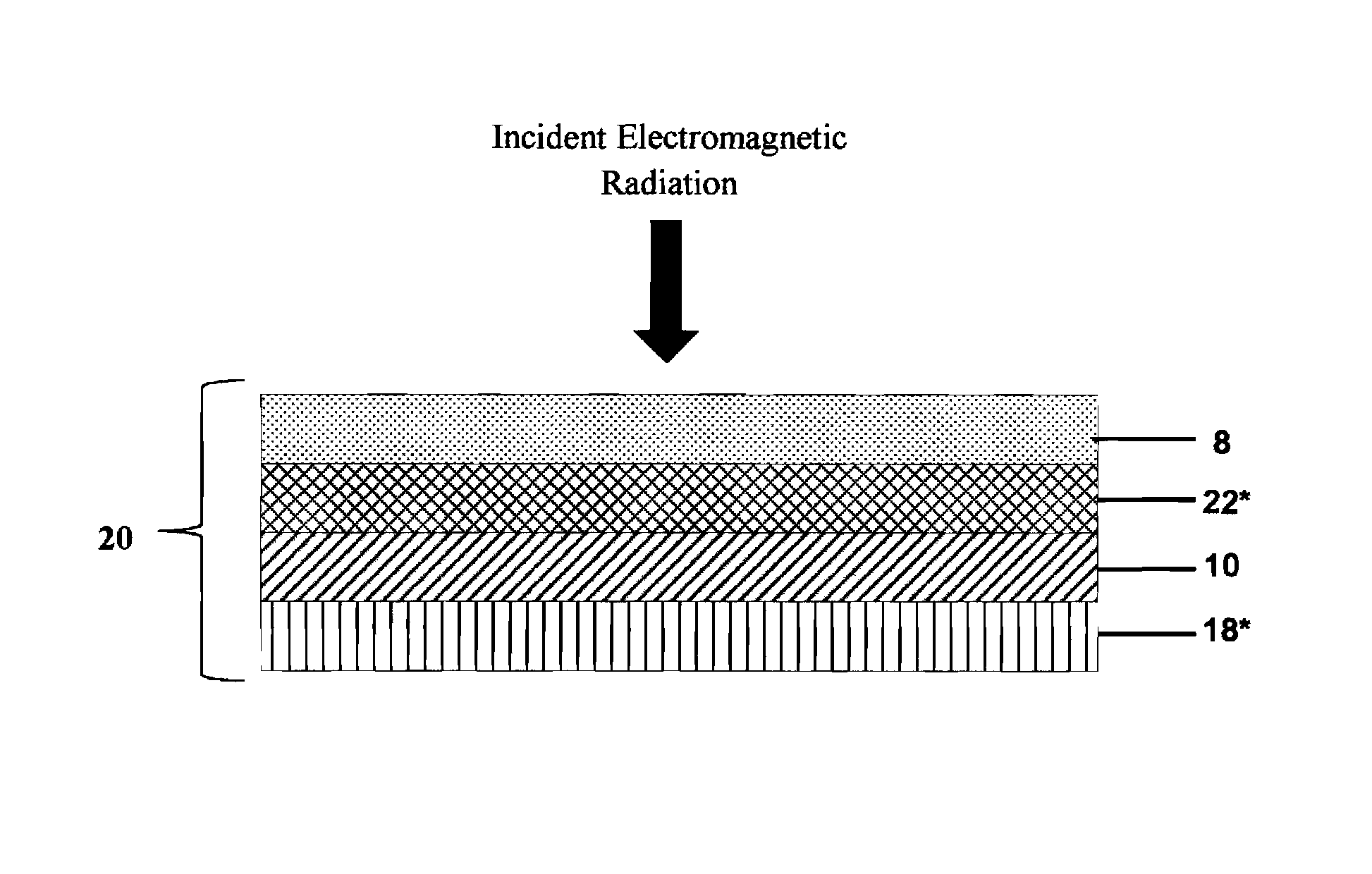
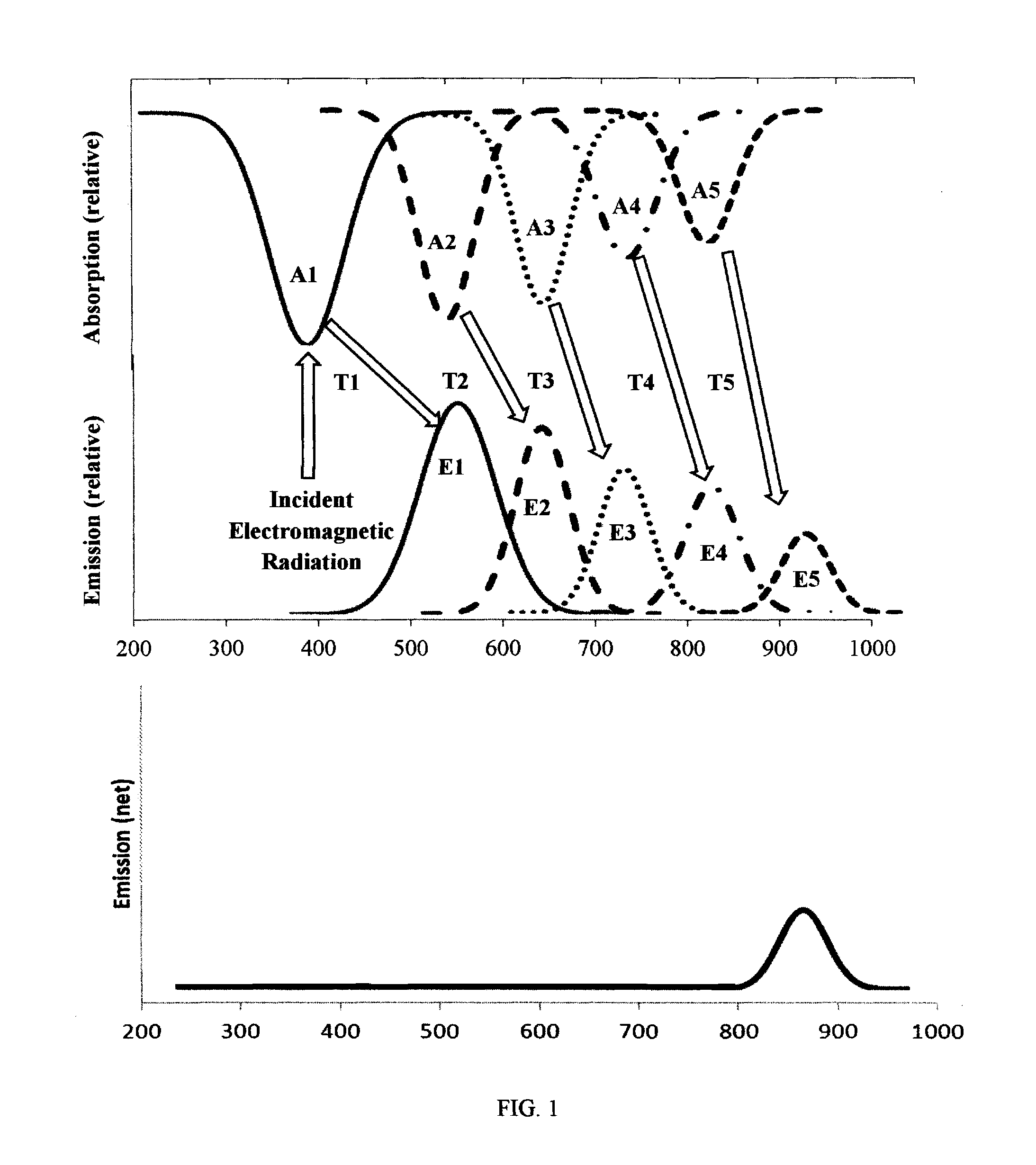
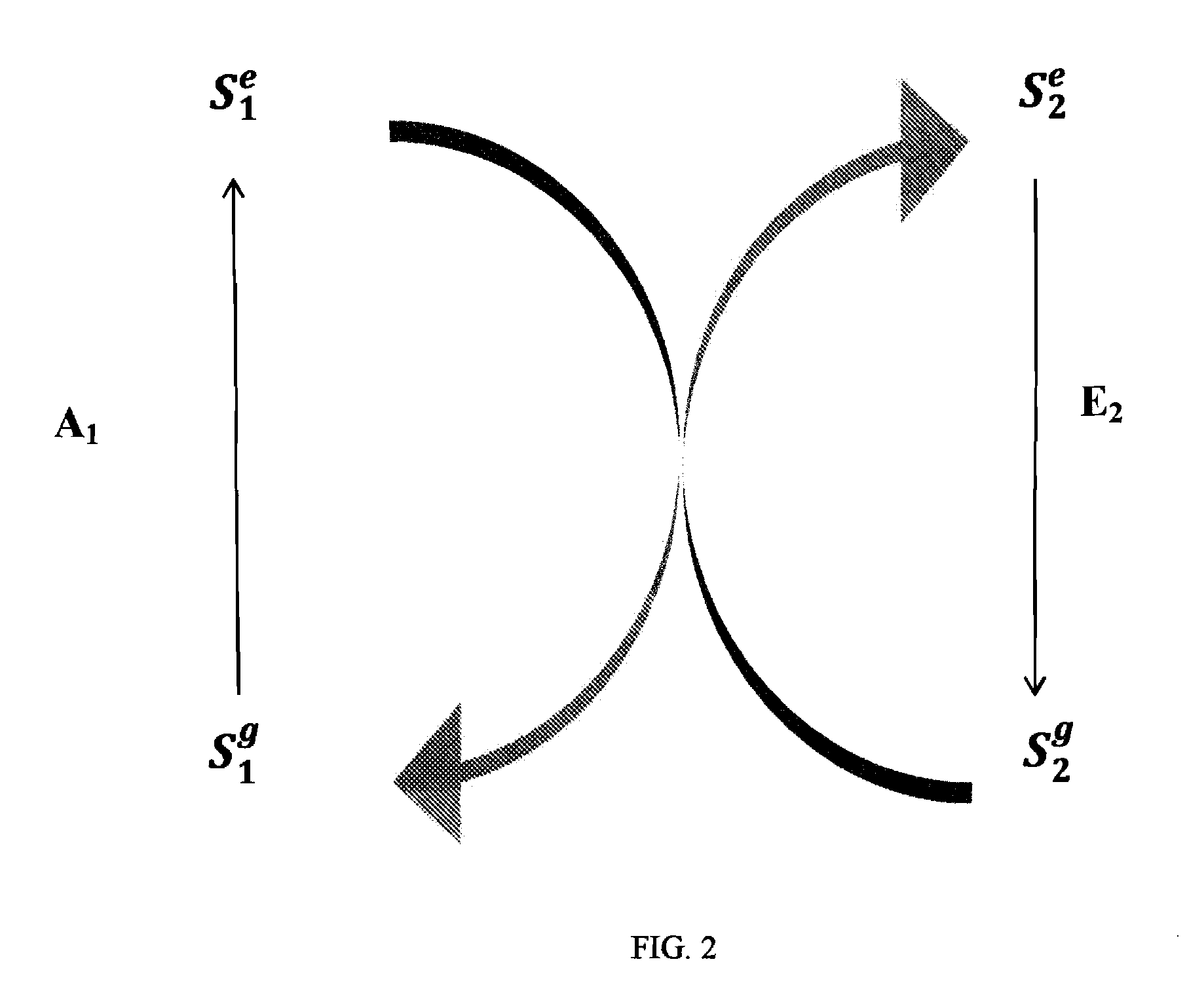
Photolytically and environmentally stable multilayer structure for high efficiency electromagnetic energy conversion and sustained secondary emission
ActiveUS8519359B2Increases photolytic and thermal stabilityEnhanced light scatteringPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersSecondary emissionPhotoluminescence
Disclosed is a method for converting a primary electromagnetic radiation to a longer output wavelength that includes providing an energy conversion layer having a first photoluminescent material and a second photoluminescent material, exposing the energy conversion layer to the primary electromagnetic radiation, and transferring at least a portion of absorbed energy from the first photoluminescent material to the second photoluminescent material by dipolar coupling, such that the second photoluminescent material subsequently emits the longer output wavelength.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
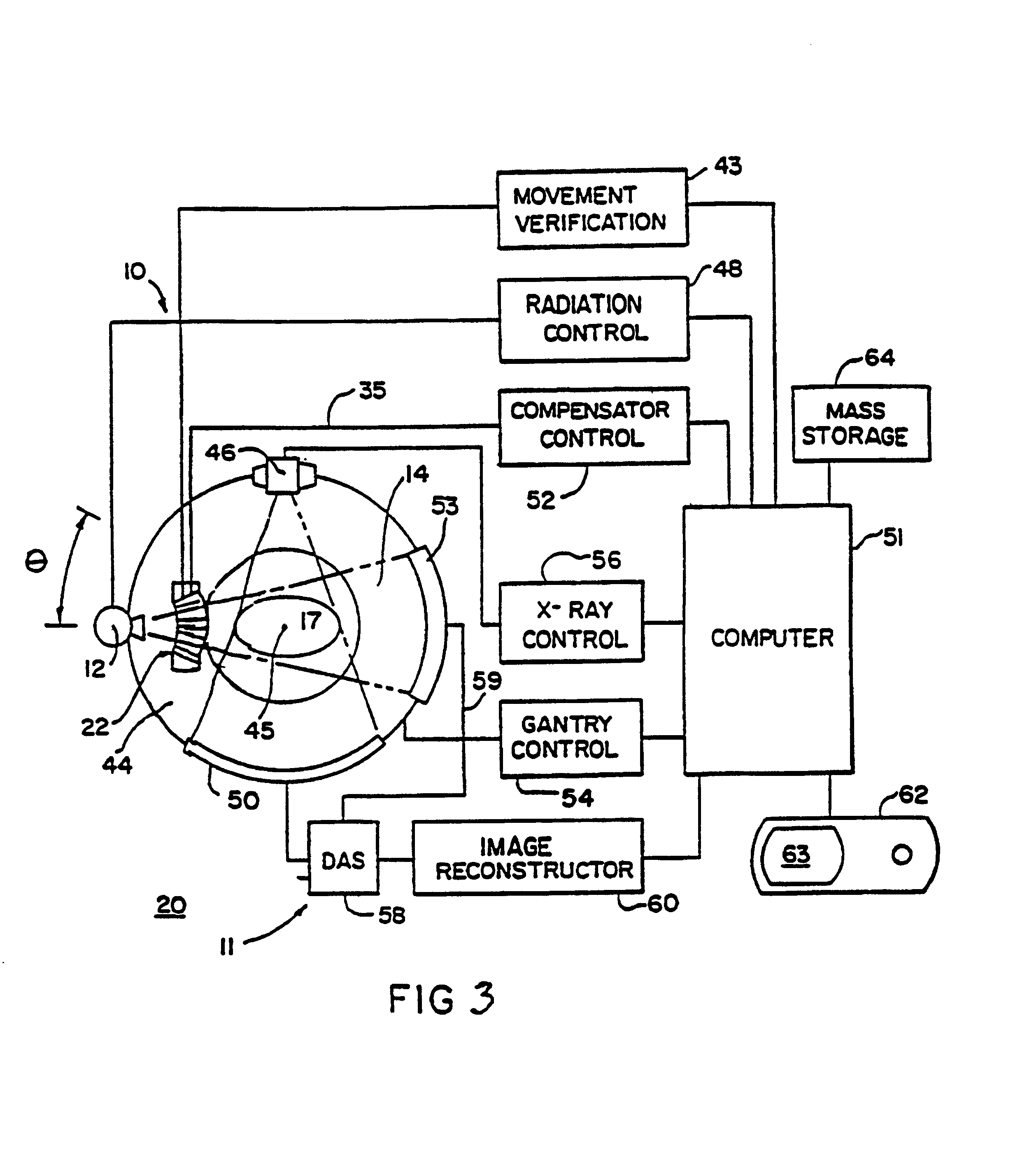
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Low rare earth mineral photoluminescent compositions and structures for generating long-persistent luminescence
InactiveUS8952341B2Improve stabilityGeneration of luminanceLayered productsPhotometryMaterials scienceRare-earth mineral
A low rare earth mineral photoluminescent structure for generating long-persistent luminescence that utilizes at least a phosphorescent layer comprising one or more phosphorescent materials having substantially low rare earth mineral content of less than about 2.0 weight percent, and one or more fluorescent layers is disclosed. Further disclosed are methods for fabricating and using the inventive low rare earth mineral photoluminescent structure. A low rare earth mineral photoluminescent composition for generating long-persistent luminescence that utilizes at least one or more phosphorescent materials having substantially low rare earth mineral content of less than about 2.0 weight percent and one or more fluorescent materials is also disclosed, as well as, the methods for fabricating and using the inventive low rare earth mineral photoluminescent composition.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
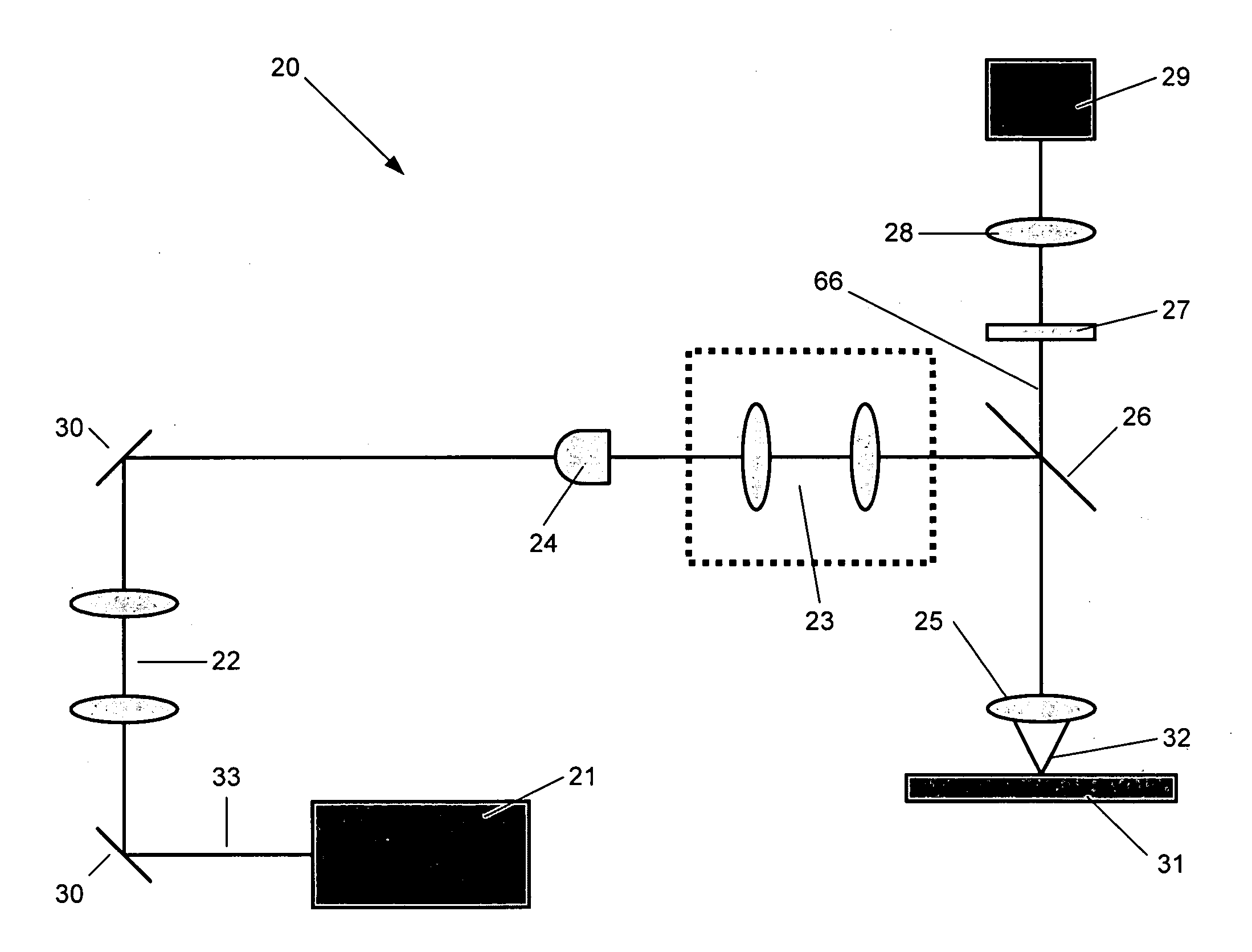
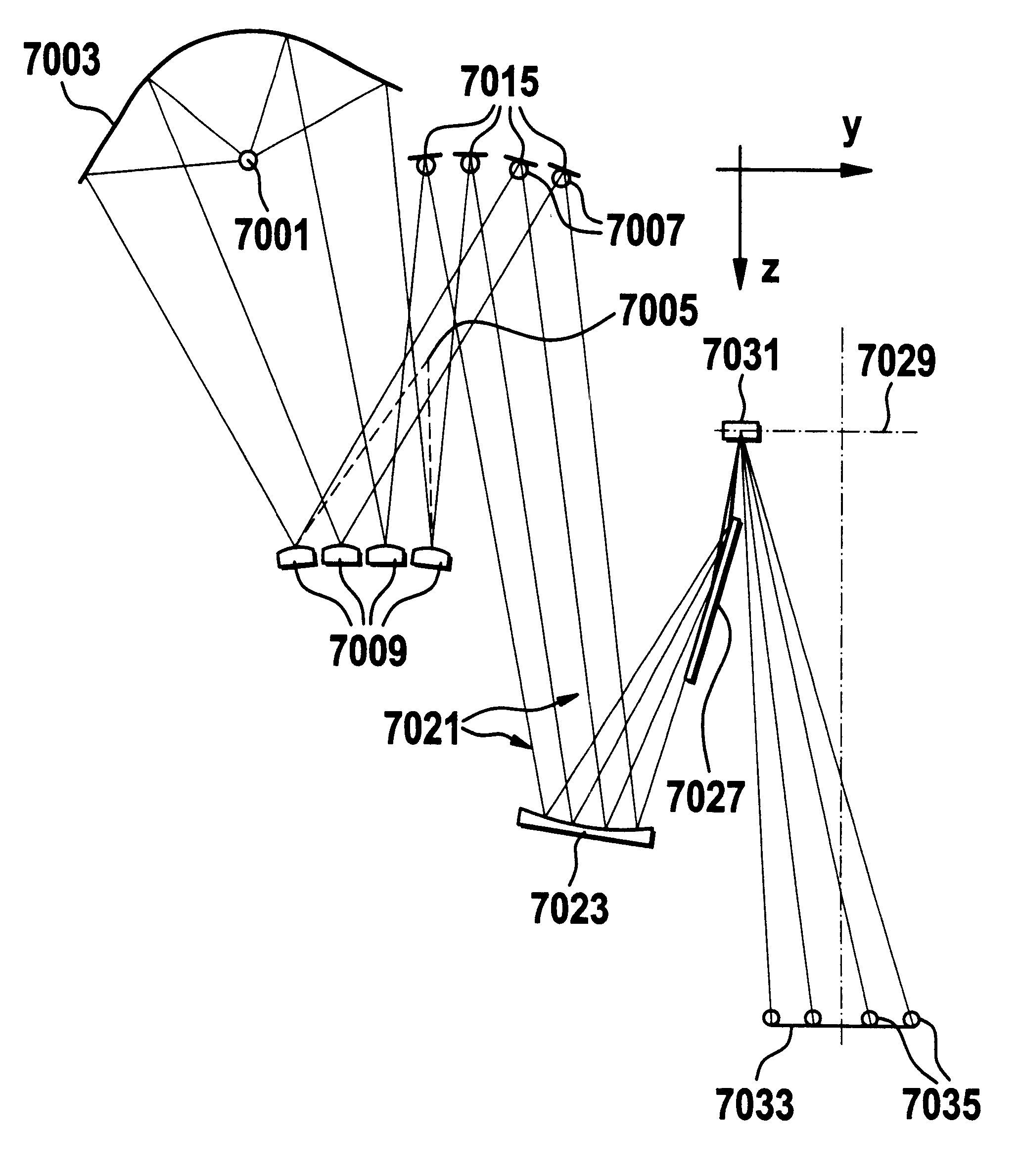
Confocal imaging methods and apparatus
The invention provides imaging apparatus and methods useful for obtaining a high resolution image of a sample at rapid scan rates. A rectangular detector array having a horizontal dimension that is longer than the vertical dimension can be used along with imaging optics positioned to direct a rectangular image of a portion of a sample to the rectangular detector array. A scanning device can be configured to scan the sample in a scan-axis dimension, wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array and the shorter of the two rectangular dimensions for the image are in the scan-axis dimension, and wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array is short enough to achieve confocality in a single axis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
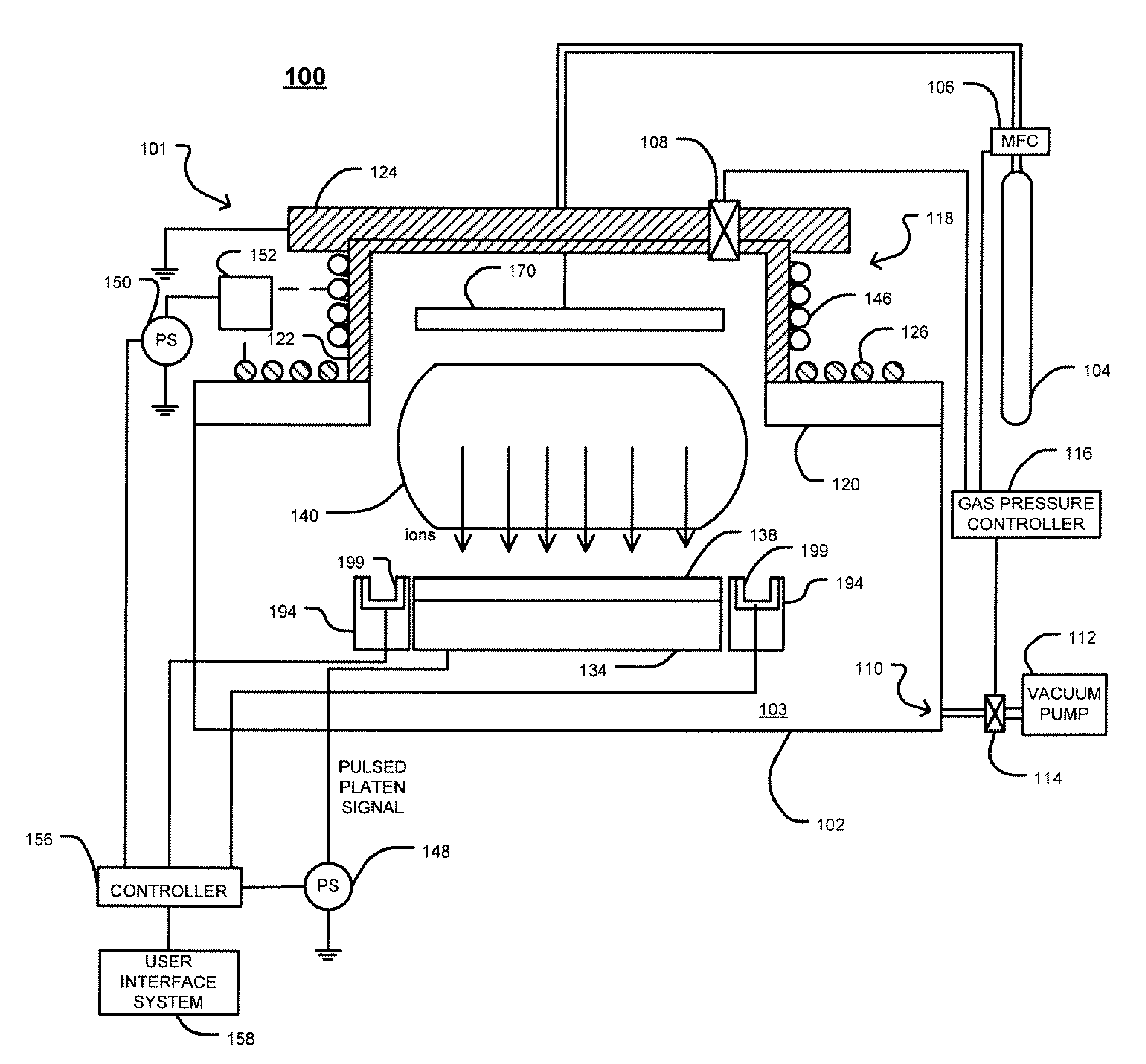
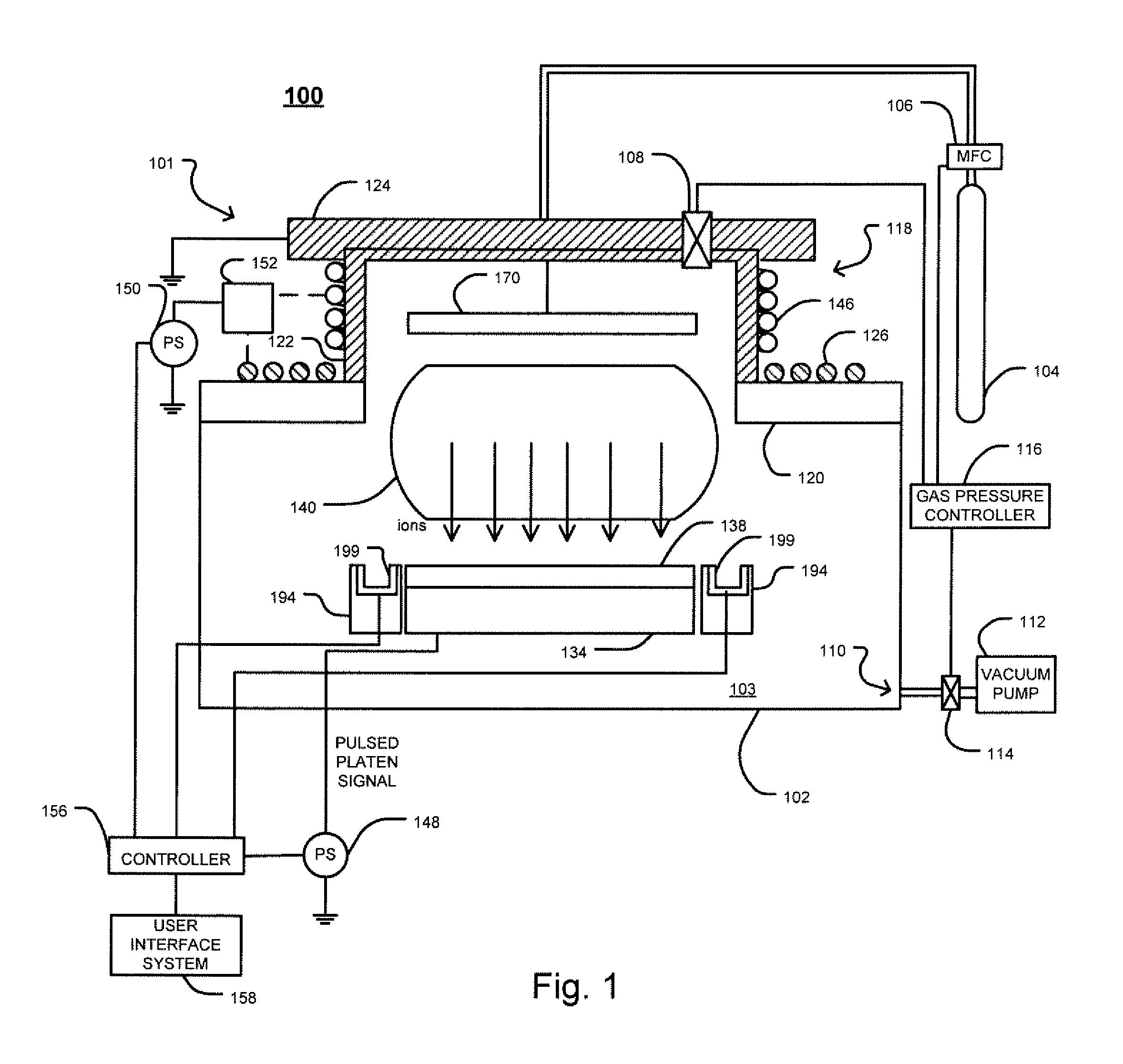
Techniques for cold implantation of carbon-containing species
InactiveUS20090200494A1Increase strainElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon implantationMaterials science
Techniques for cold implantation of carbon-containing species are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for ion implantation including a cooling device for cooling a target material to a predetermined temperature, and an ion implanter for implanting the target material with a carbon-containing species at the predetermined temperature to improve at least one of strain and amorphization.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
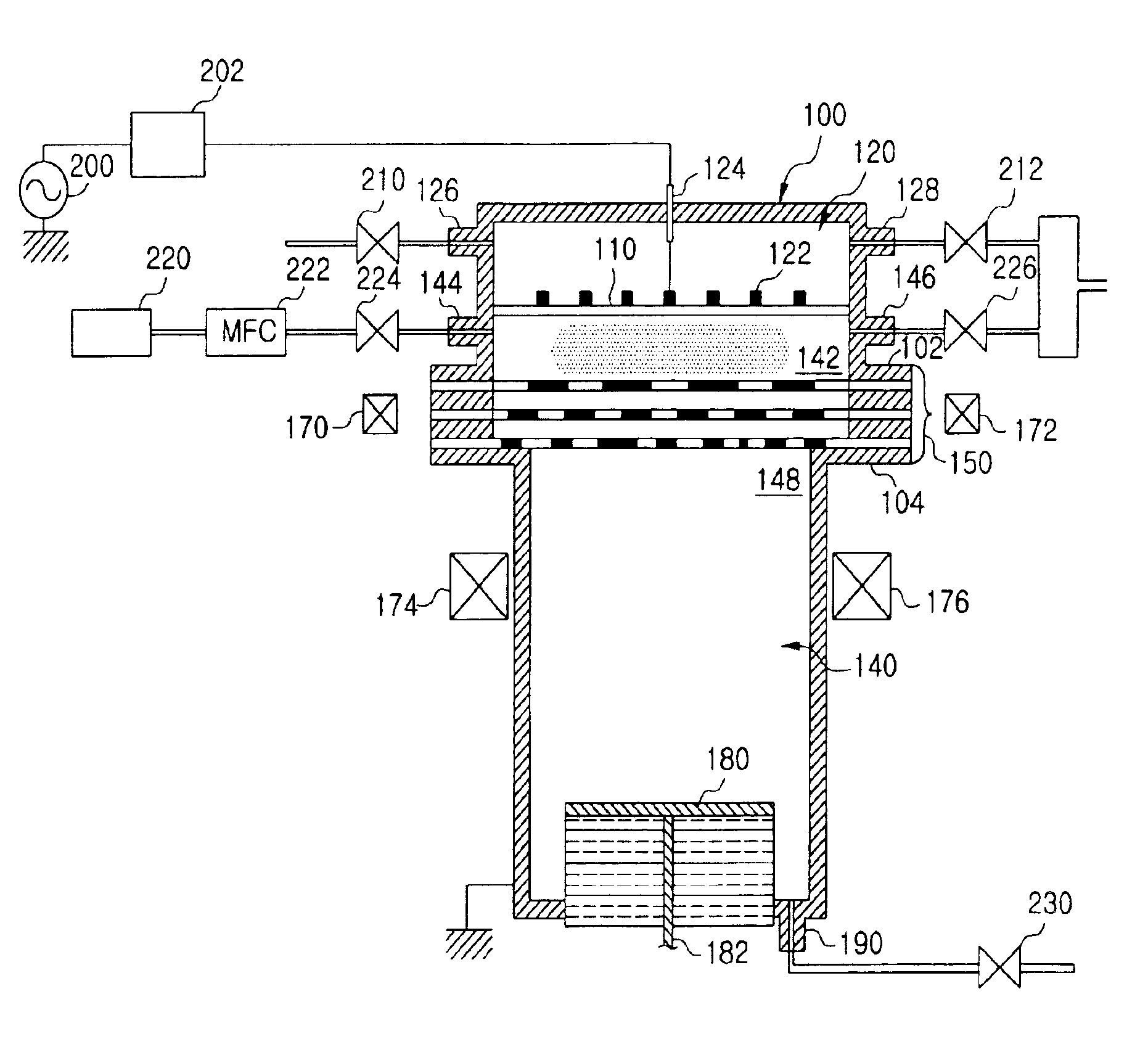
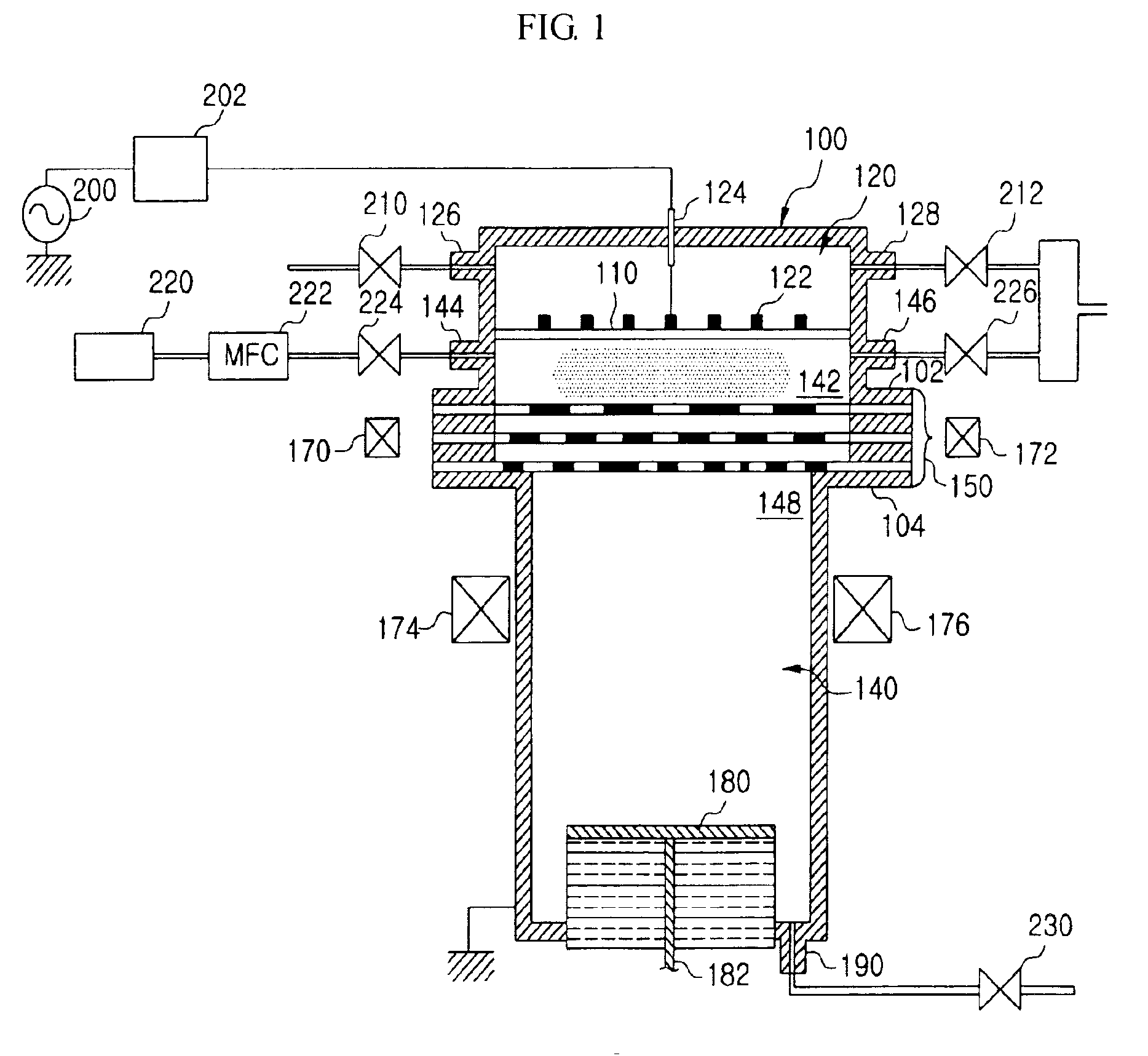
Method for supplying gas with flow rate gradient over substrate
ActiveUS8664627B1Reduce gradientIncrease concentrationMaterial analysis by optical meansPipeline systemsReaction chamberChemistry
A method for supplying gas over a substrate in a reaction chamber wherein a substrate is placed on a pedestal, includes: supplying a first gas from a first side of the reaction chamber to a second side of the reaction chamber opposite to the first side; and adding a second gas to the first gas from sides of the reaction chamber other than the first side of the reaction chamber so that the second gas travels from sides of the substrate other than the first side in a downstream direction.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
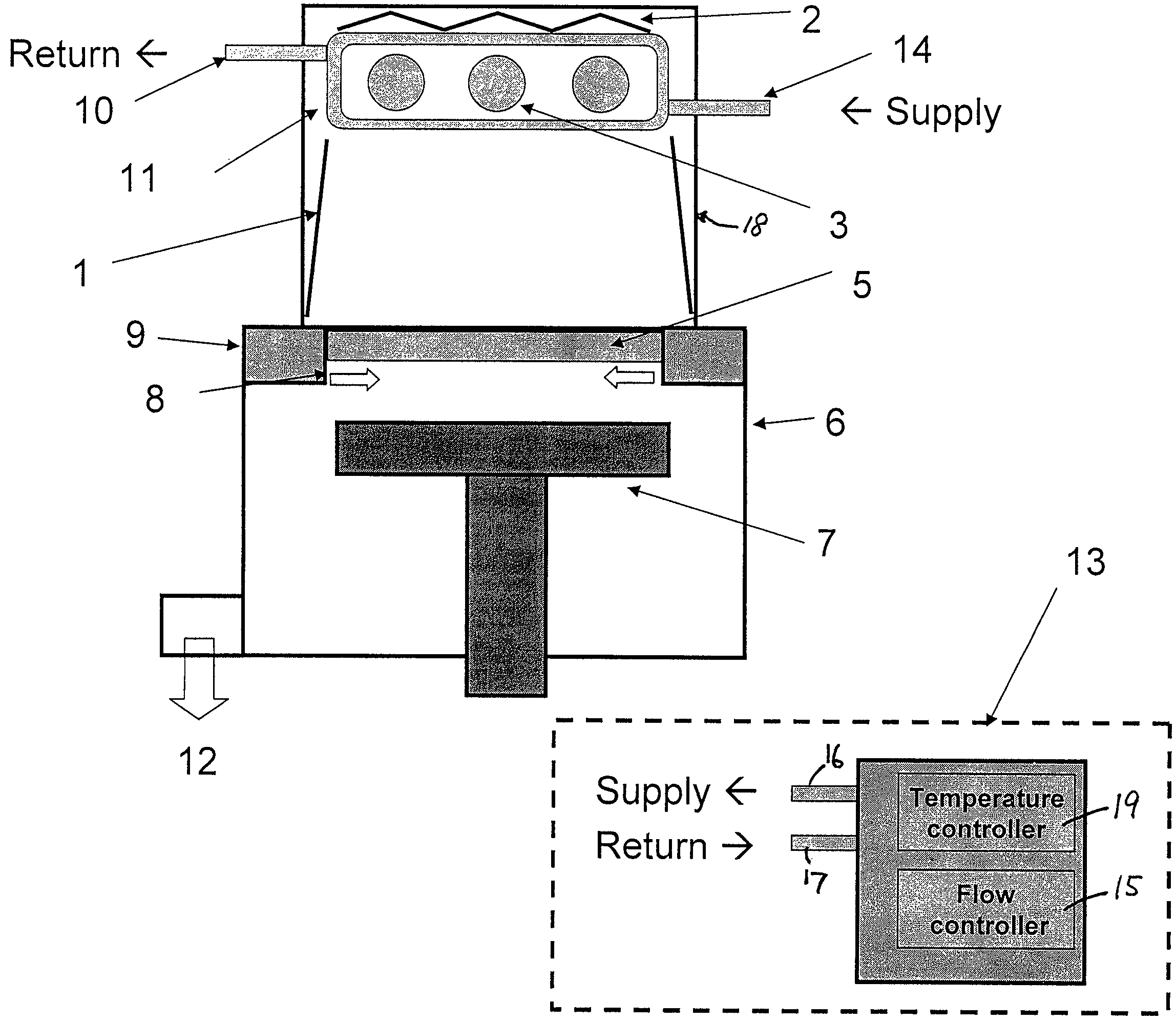
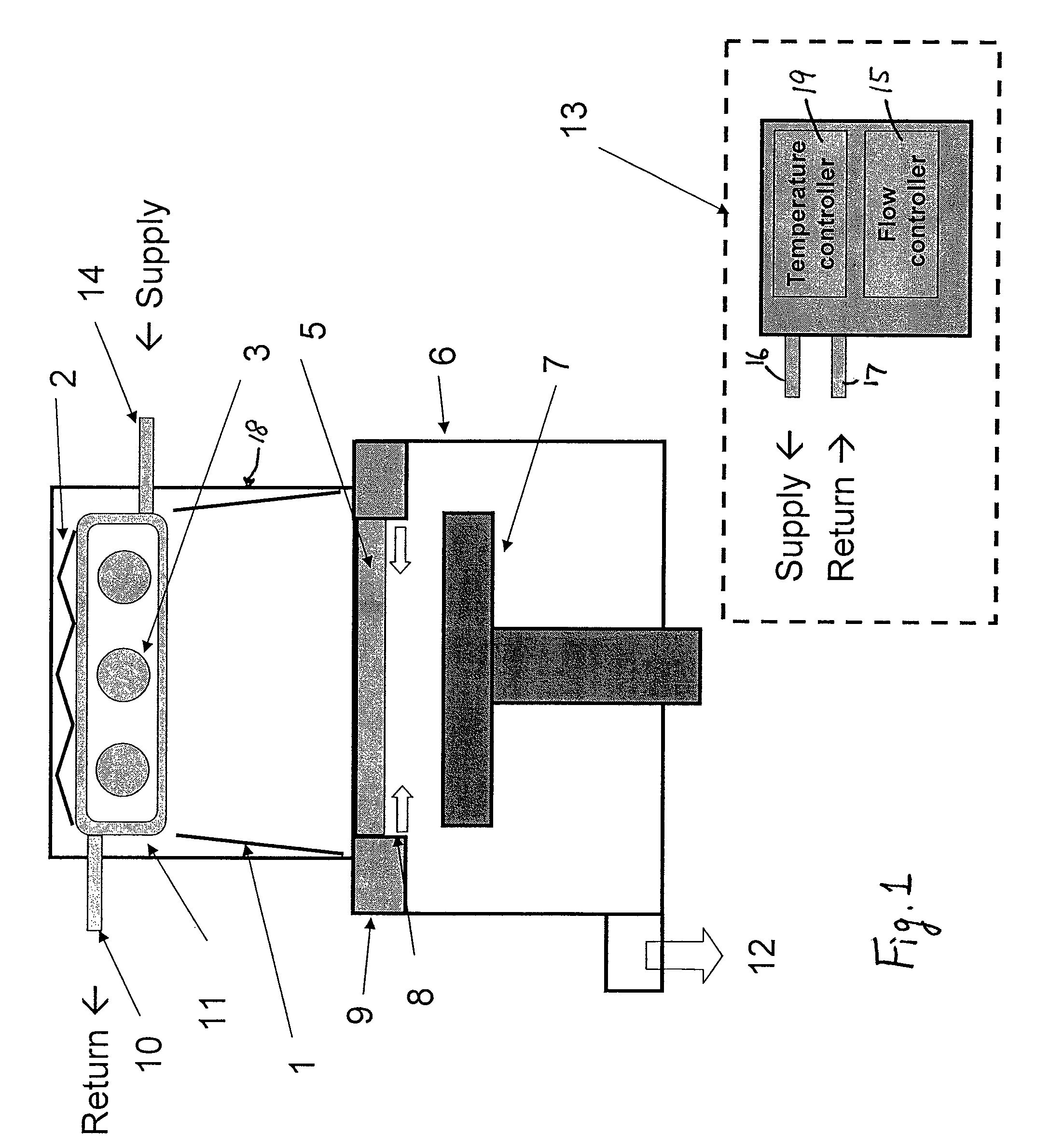
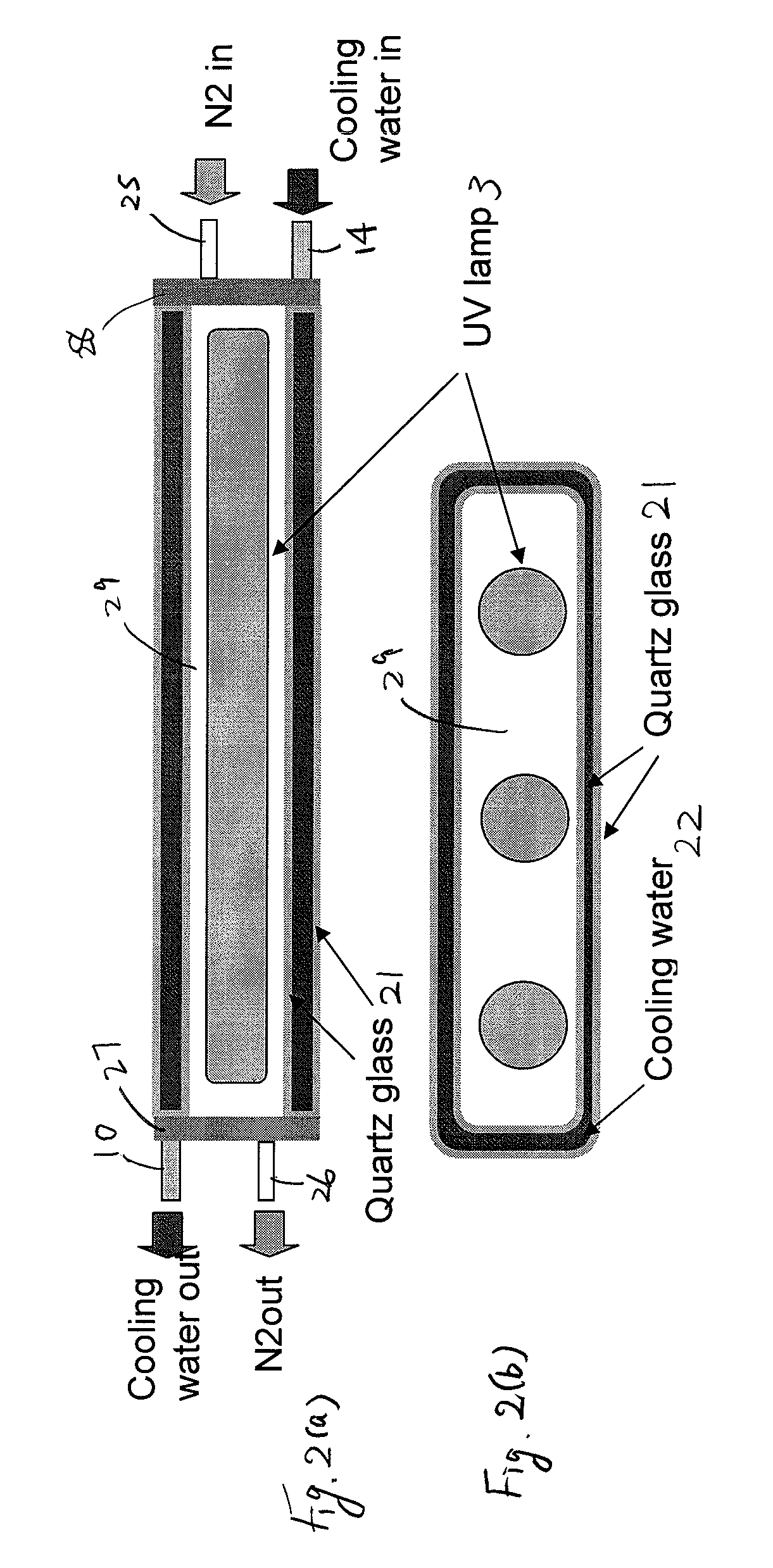
UV light irradiating apparatus with liquid filter
ActiveUS7763869B2High mechanical strengthHigh energyMirrorsOptical filtersLiquid layerLight irradiation
A UV light irradiating apparatus for irradiating a semiconductor substrate with UV light includes: a reactor in which a substrate-supporting table is provided; a UV light irradiation unit connected to the reactor for irradiating a semiconductor substrate placed on the substrate-supporting table with UV light through a light transmission window; and a liquid layer forming channel disposed between the light transmission window and at least one UV lamp for forming a liquid layer through which the UV light is transmitted. The liquid layer is formed by a liquid flowing through the liquid layer forming channel.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Multiplexed fluorescent detection in microfluidic devices
An optical detection and orientation device is provided comprising housing having an excitation light source, an optical element for reflecting the excitation light to an aspherical lens and transmitting light emitted by a fluorophore excited by said excitation light, a focussing lens for focusing the emitted light onto the entry of an optical fiber, which serves as a confocal aperture, and means for accurately moving said housing over a small area in relation to a channel in a microfluidic device. The optical detection and orientation device finds use in identifying the center of the channel and detecting fluorophores in the channel during operations involving fluorescent signals.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
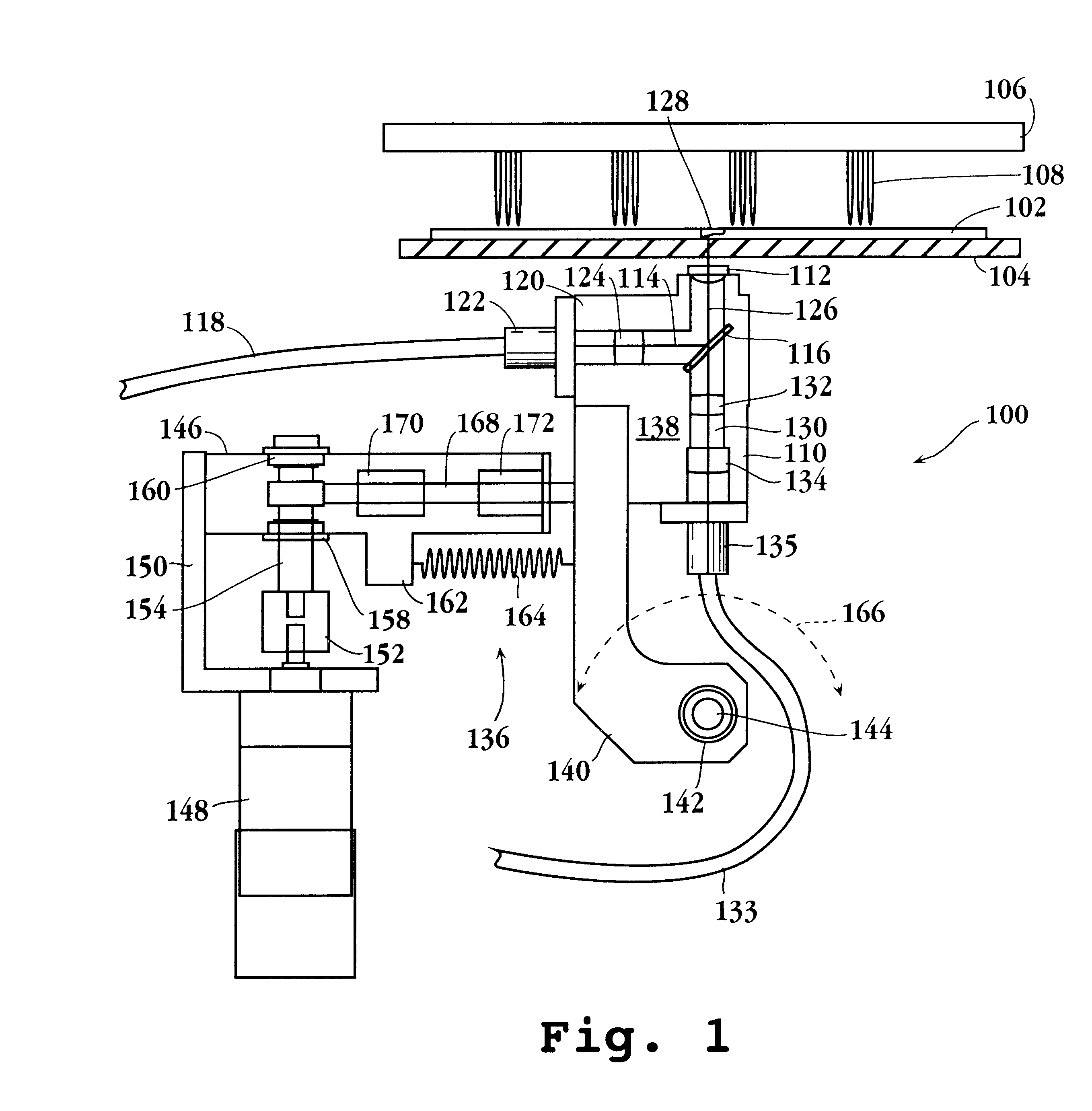
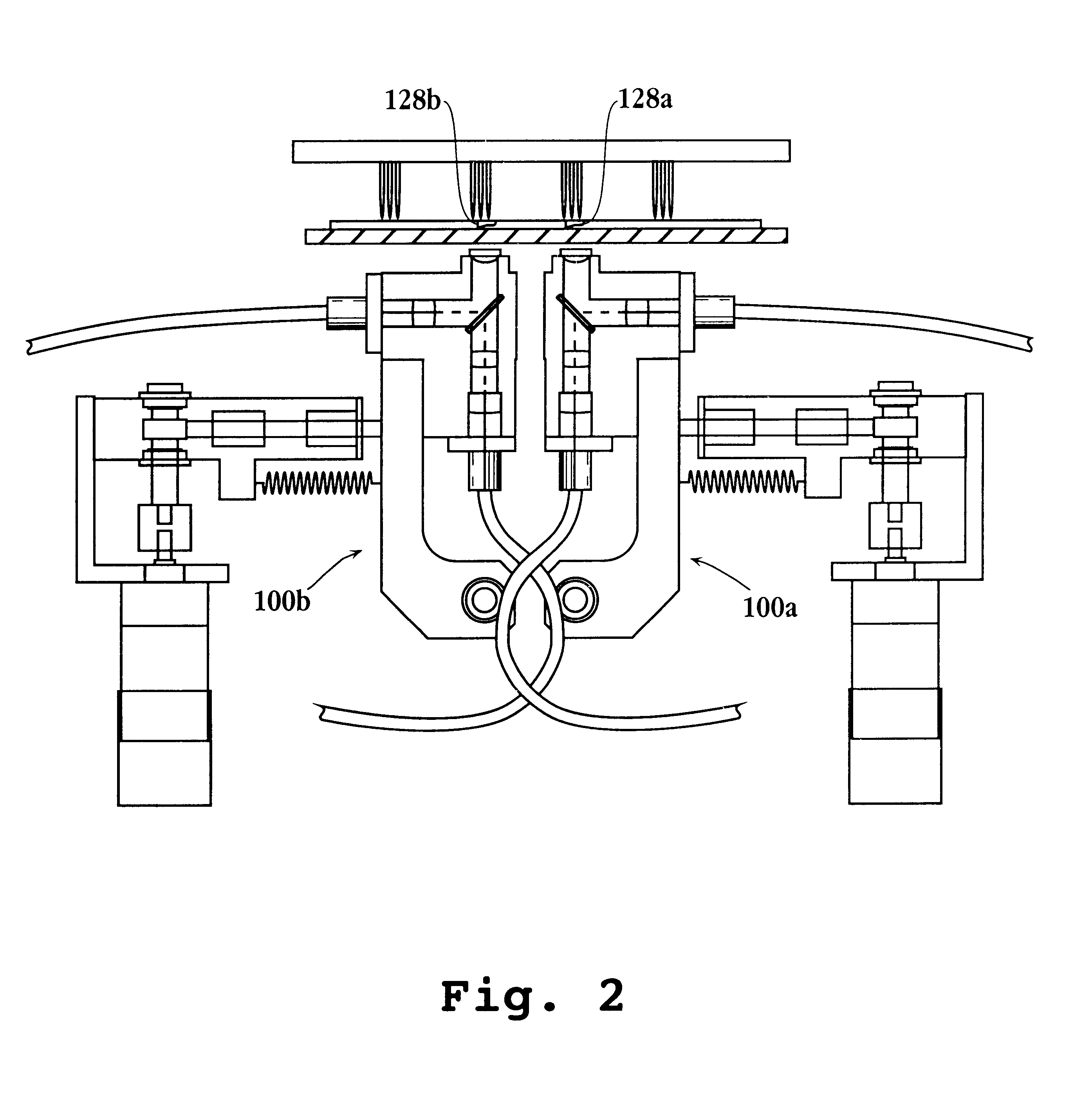
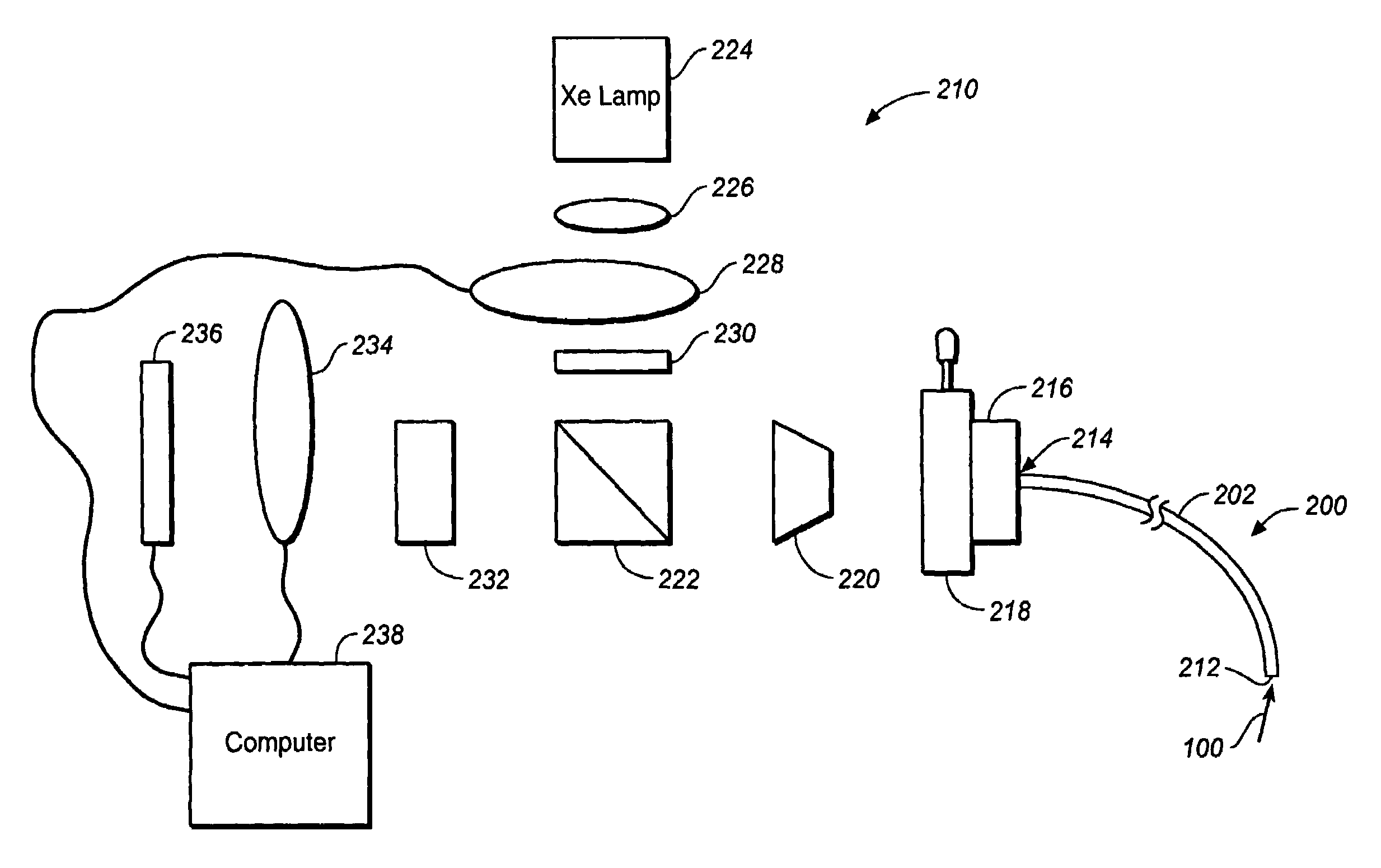
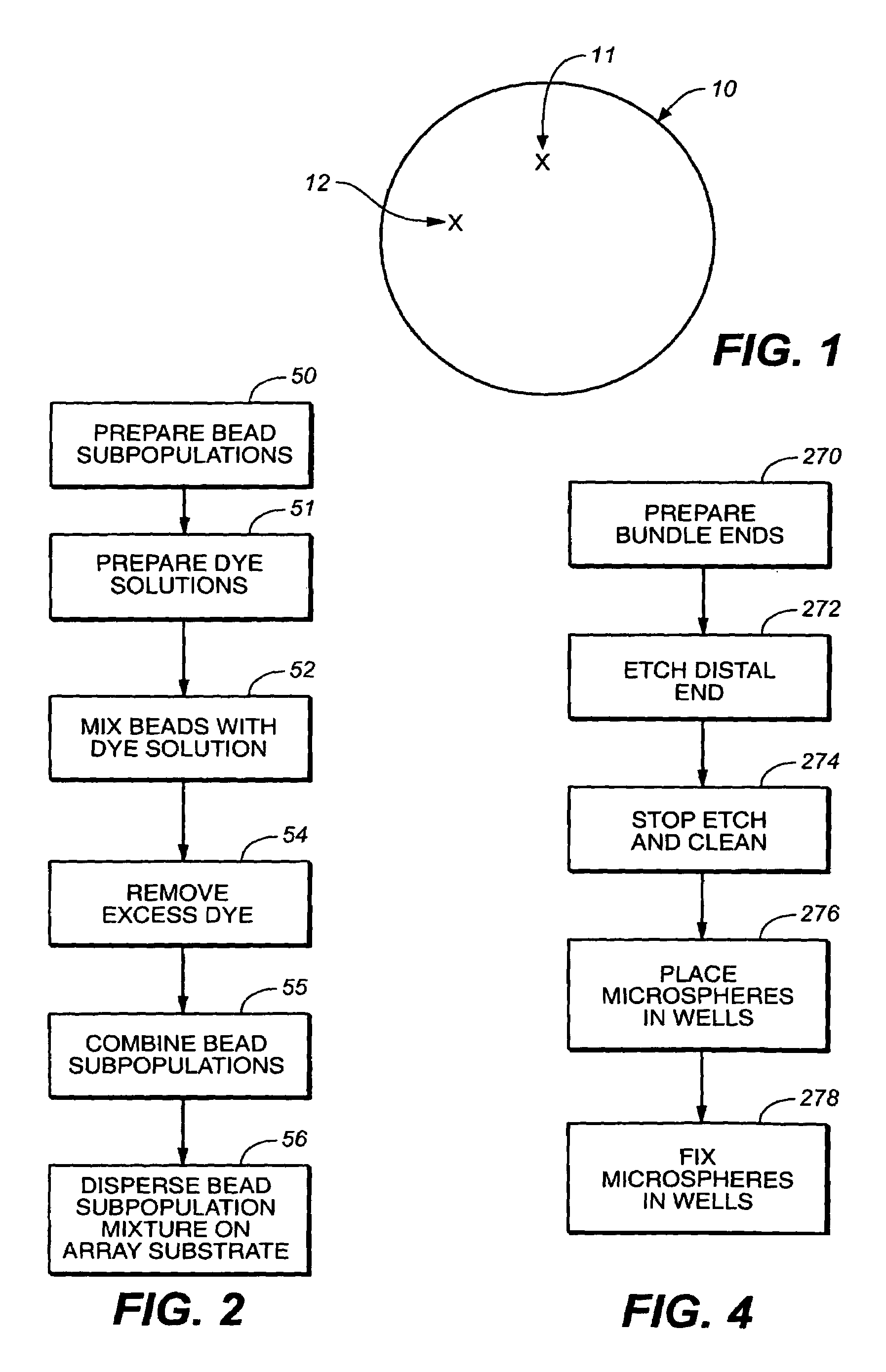
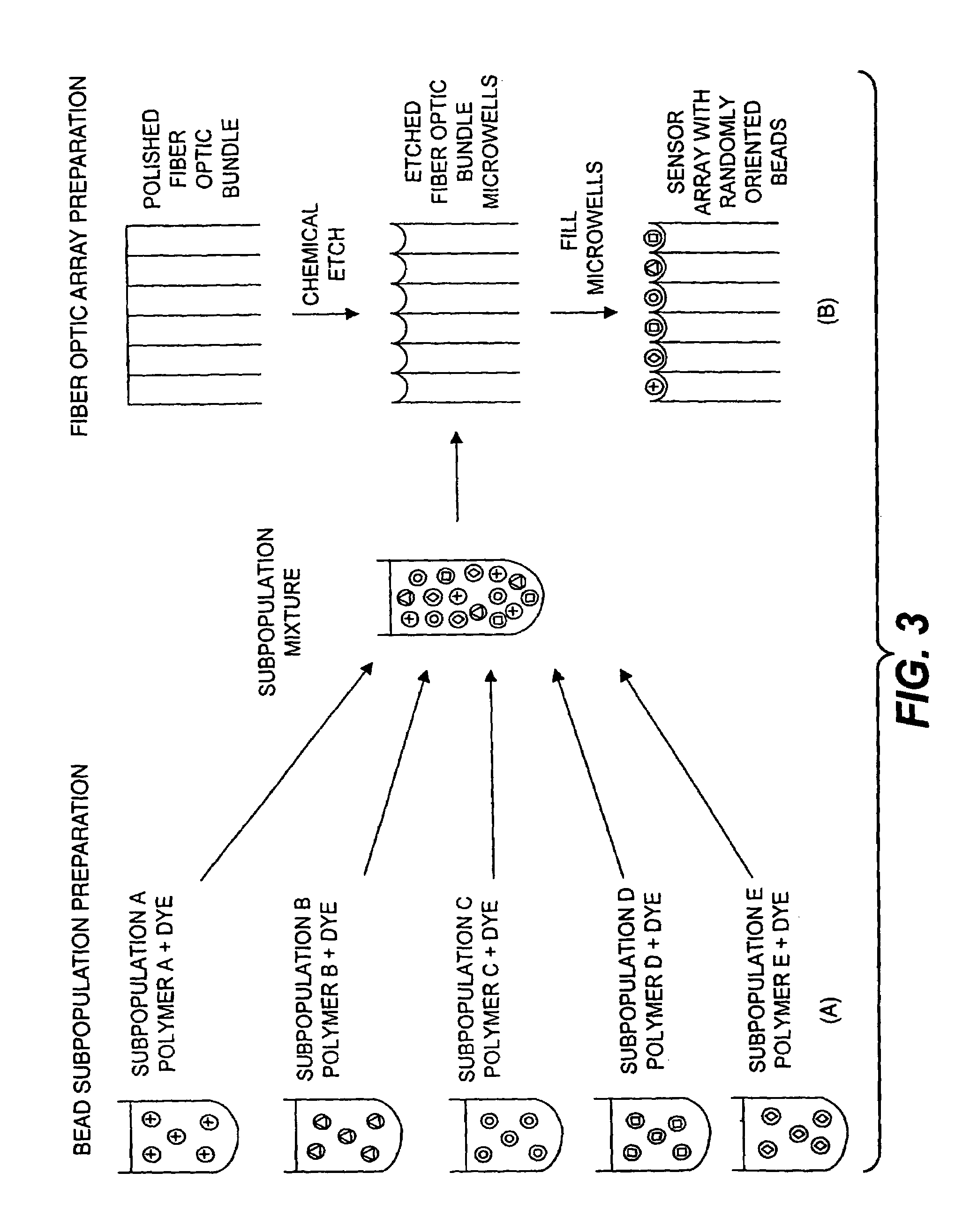
Self-encoding fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS7115884B1Overcome limitationsEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayLight energy
Self-encoding microspheres having distinct characteristic optical response signatures to specific target analytes may be mixed together while the ability is retained to identify the sensor type and location of each sensor in a random dispersion of large numbers of such sensors in a sensor array using an optically interrogatable encoding scheme, resulting in a microsphere-based analytic chemistry system. Individual microsphere sensors are disposed in microwells at a distal end of a fiber bundle and are optically coupled to discrete fibers or groups of fibers within the bundle to form an optical fiber bundle sensor. The identities of the individual sensors in the array are self-encoded by exposing the array to a reference analyte while illuminating the array with excitation light energy. A single sensor array may carry thousands of discrete sensing elements whose combined signal provides for substantial improvements in sensor detection limits, response times and signal-to-noise ratios.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
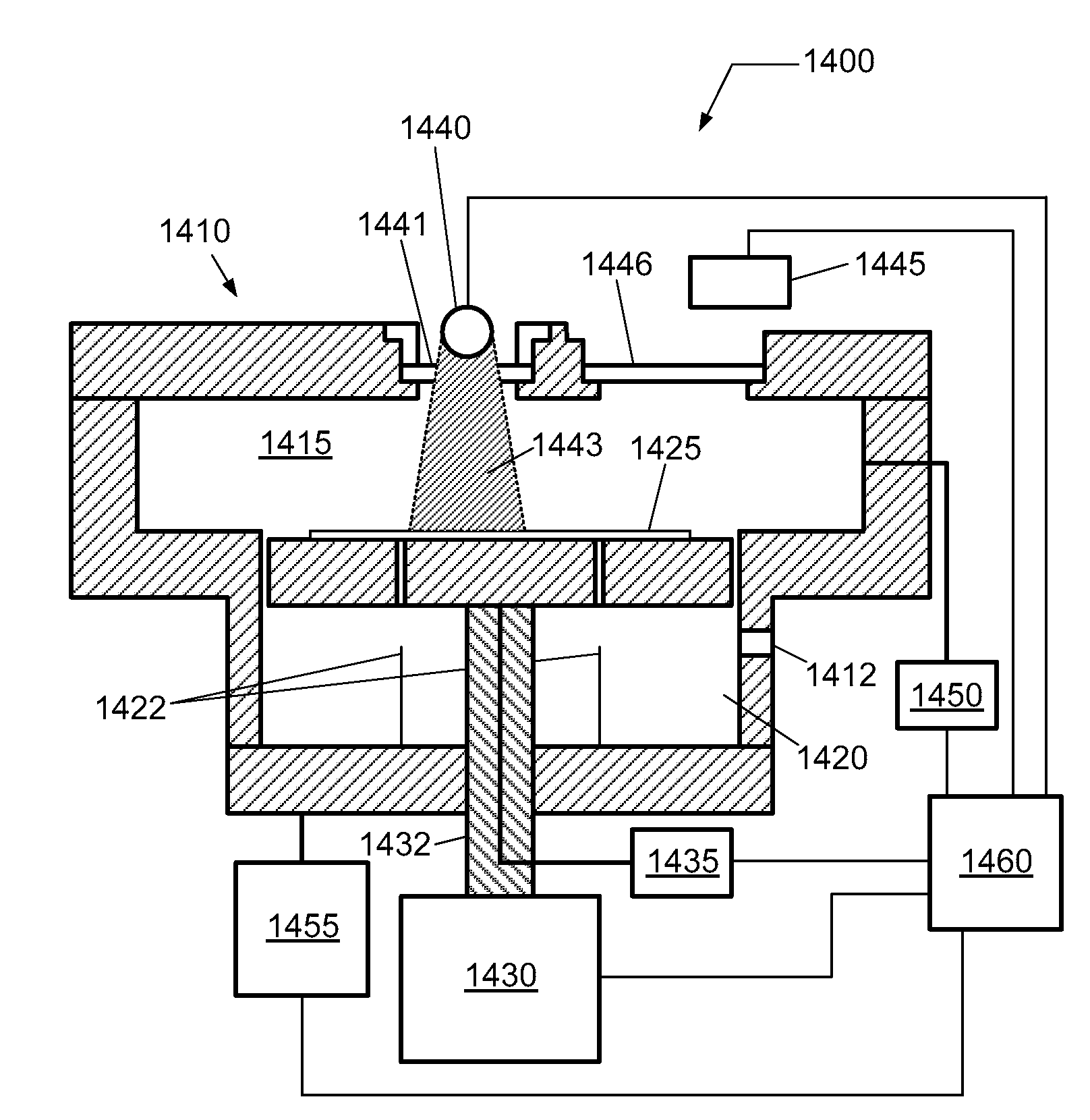
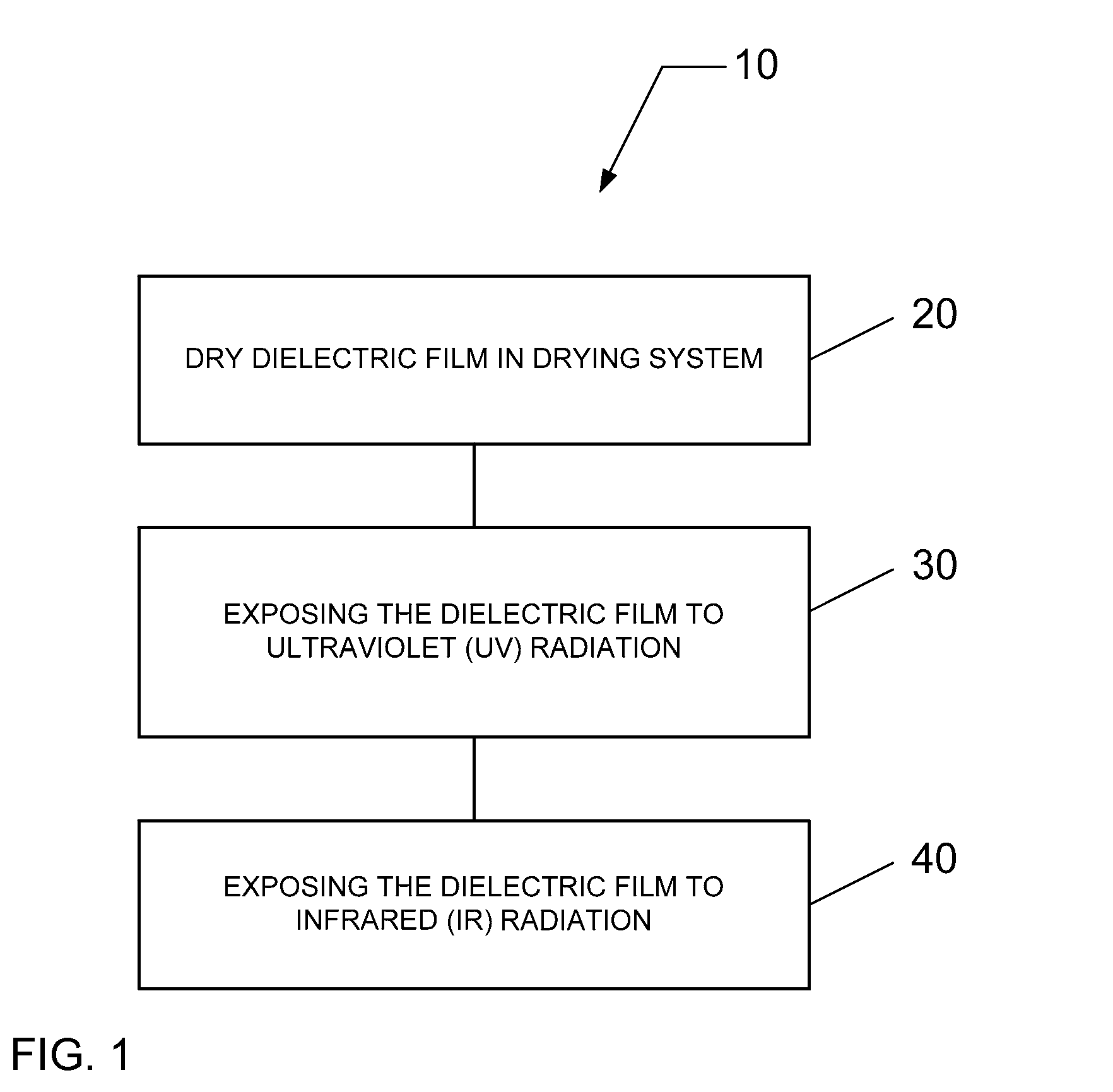
Dielectric material treatment system and method of operating
InactiveUS20100065758A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiation therapyProcess moduleUltraviolet
A system for curing a low dielectric constant (low-k) dielectric film on a substrate is described, wherein the dielectric constant of the low-k dielectric film is less than a value of approximately 4. The system comprises one or more process modules configured for exposing the low-k dielectric film to electromagnetic (EM) radiation, such as infrared (IR) radiation and ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
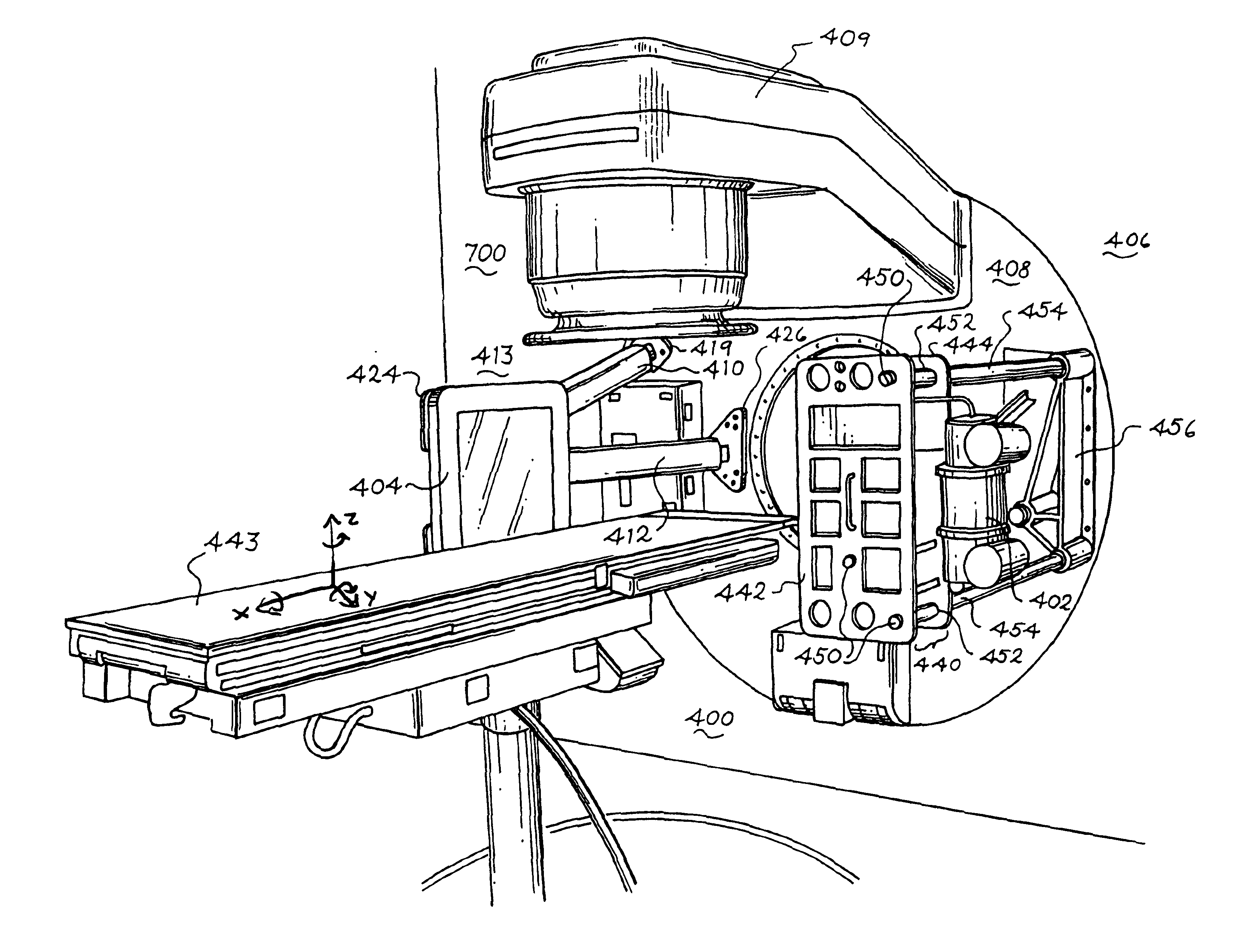
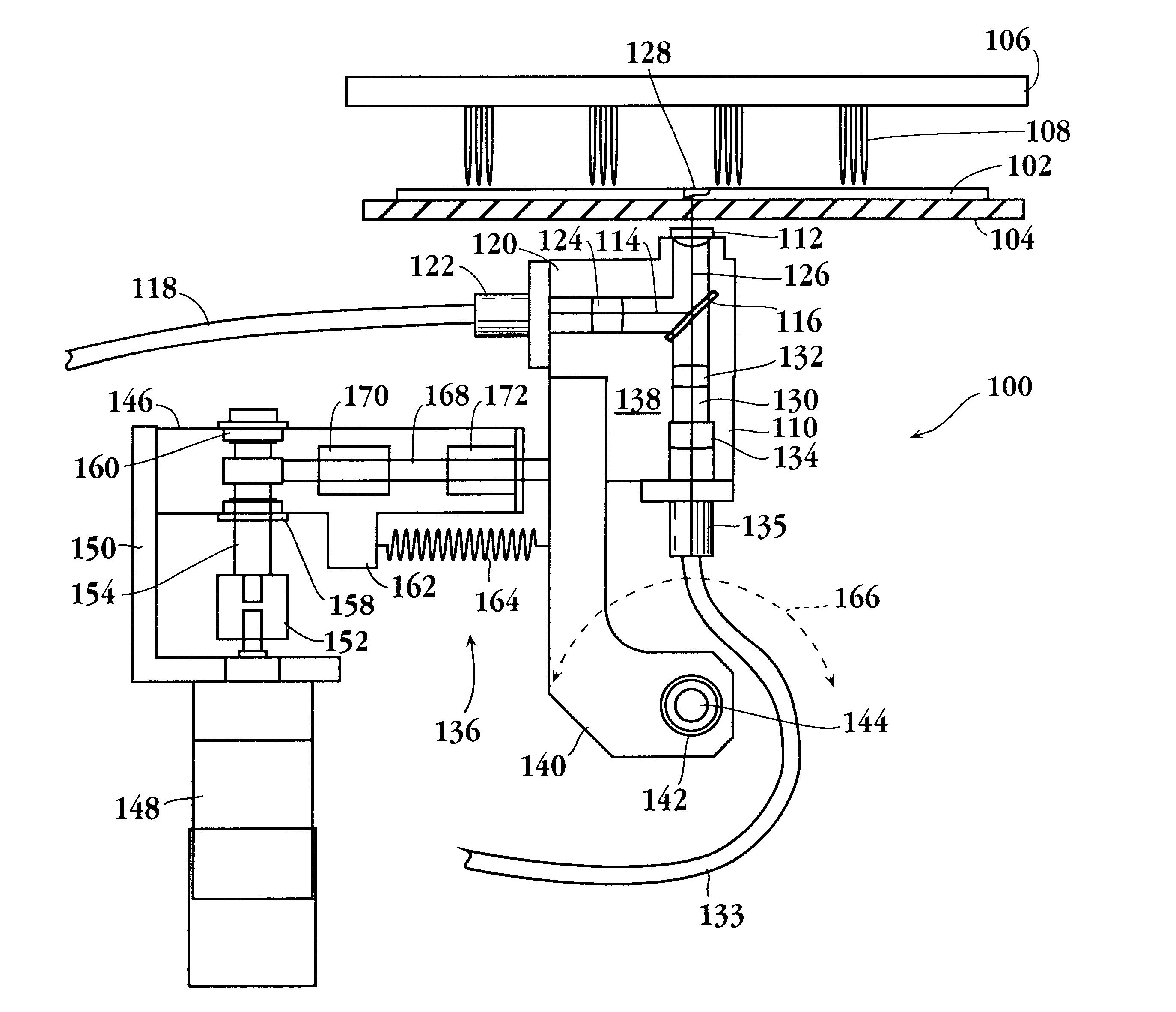
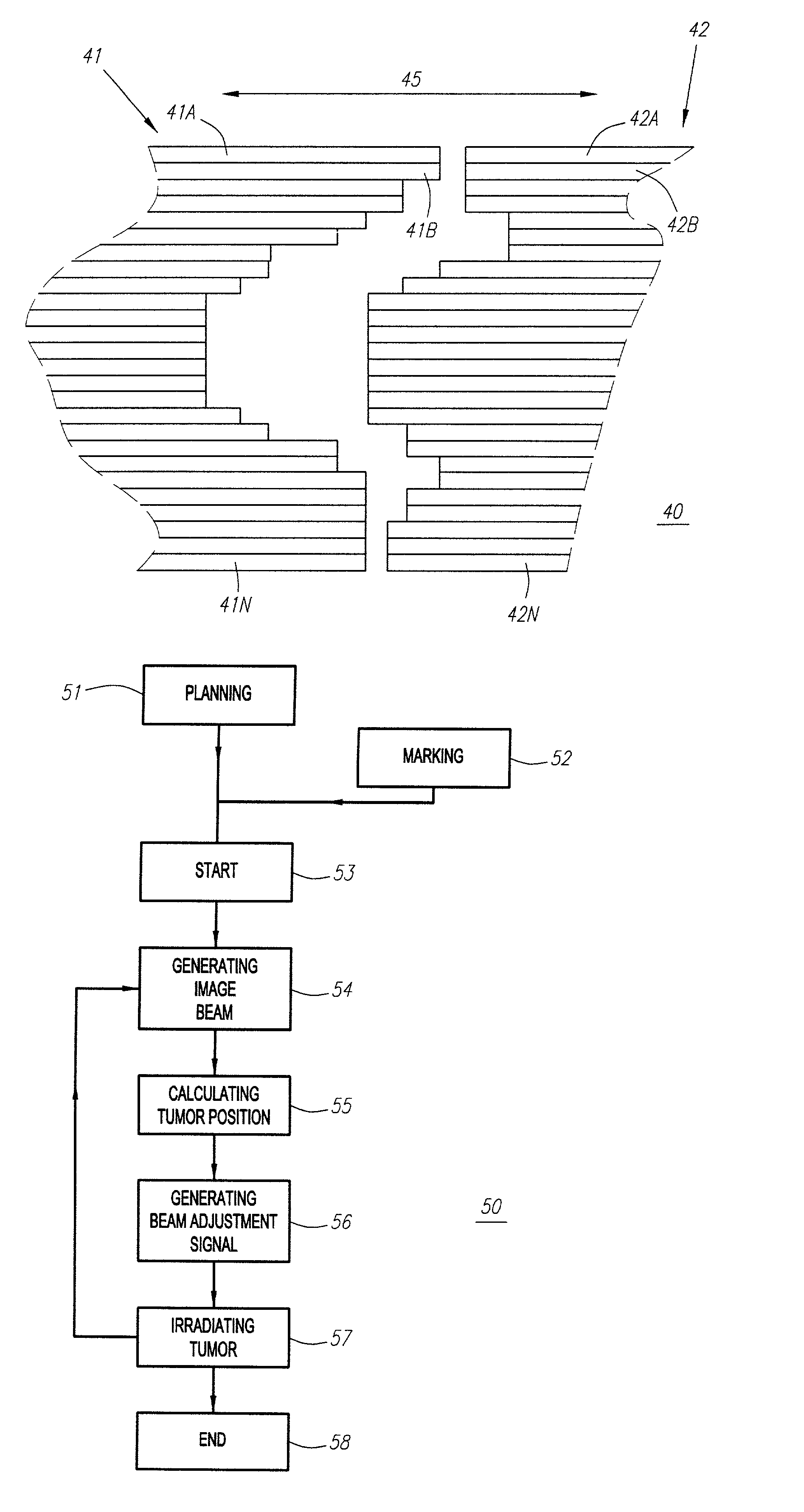
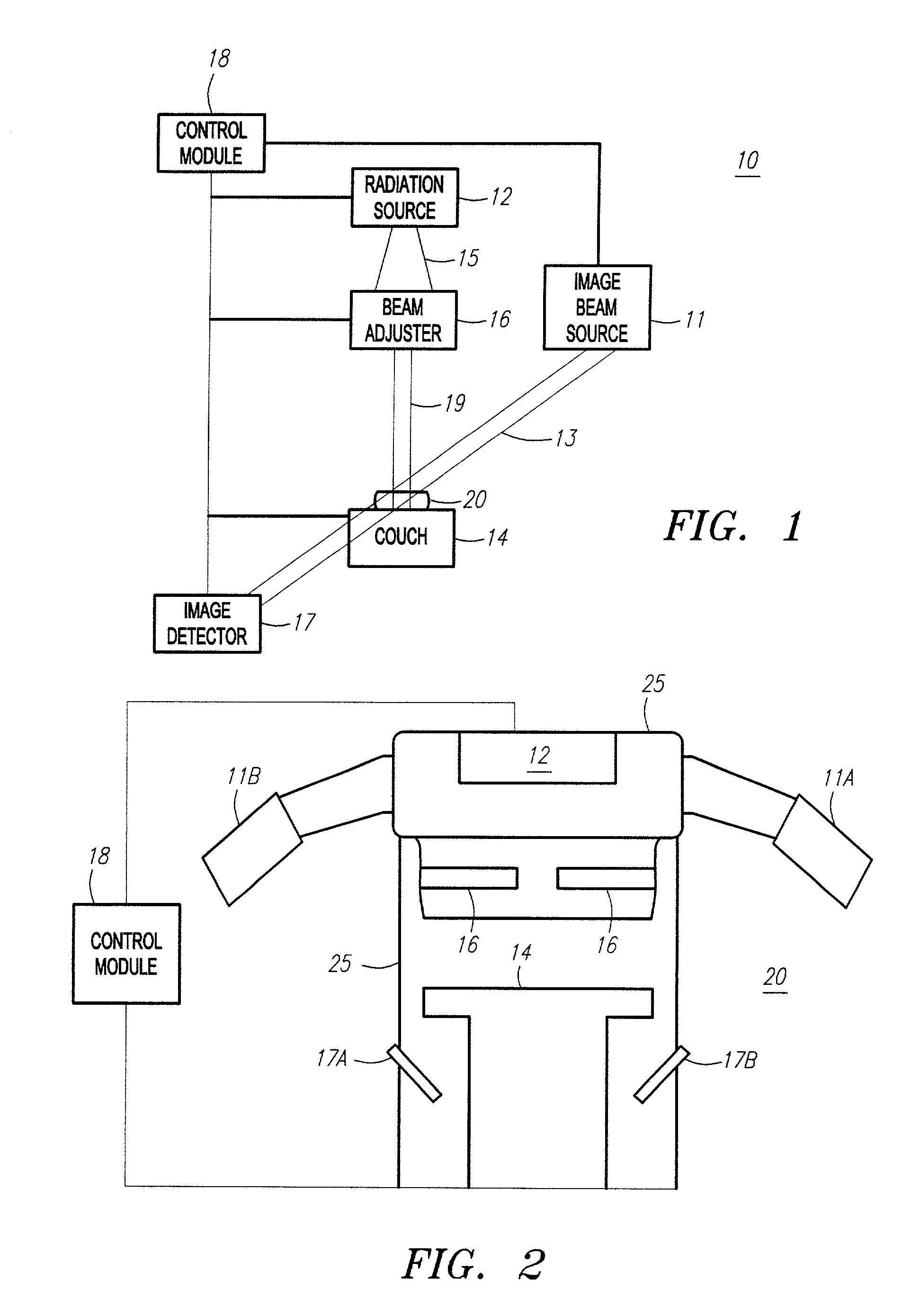
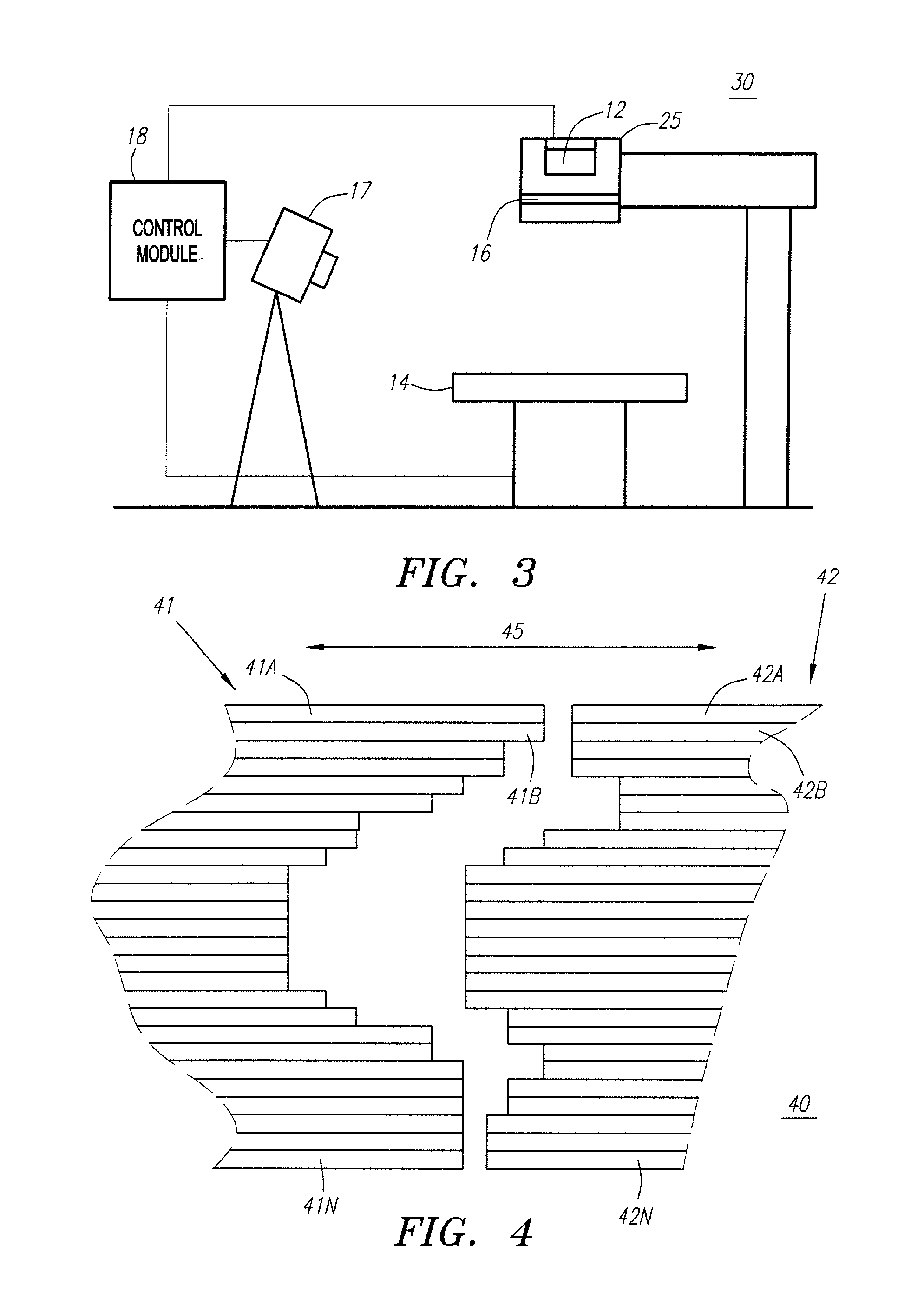
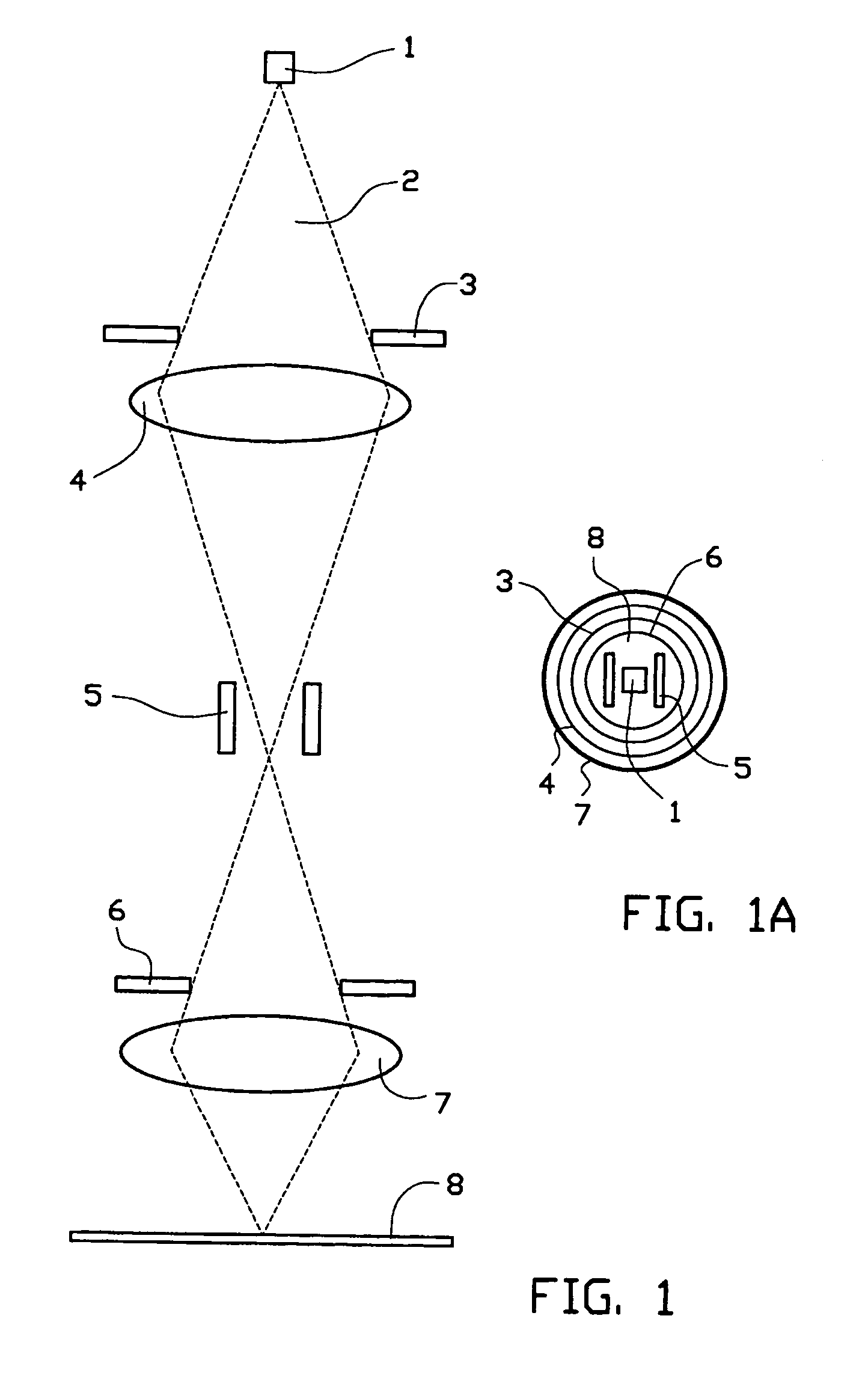
Method and apparatus for irradiating a target
An apparatus (10) for irradiating a target includes a radiation source (12) for generating a radiation beam and a multiple leaf beam adjuster (16) for collimating and adjusting the shape of the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) that would be projected on the target. An image detector (17) detects generates an image signal of the target. In response to the image signal, a control module (18) generate a beam adjustment signal for controlling the beam adjuster (16), thereby enabling the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) to track the movement of the target.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
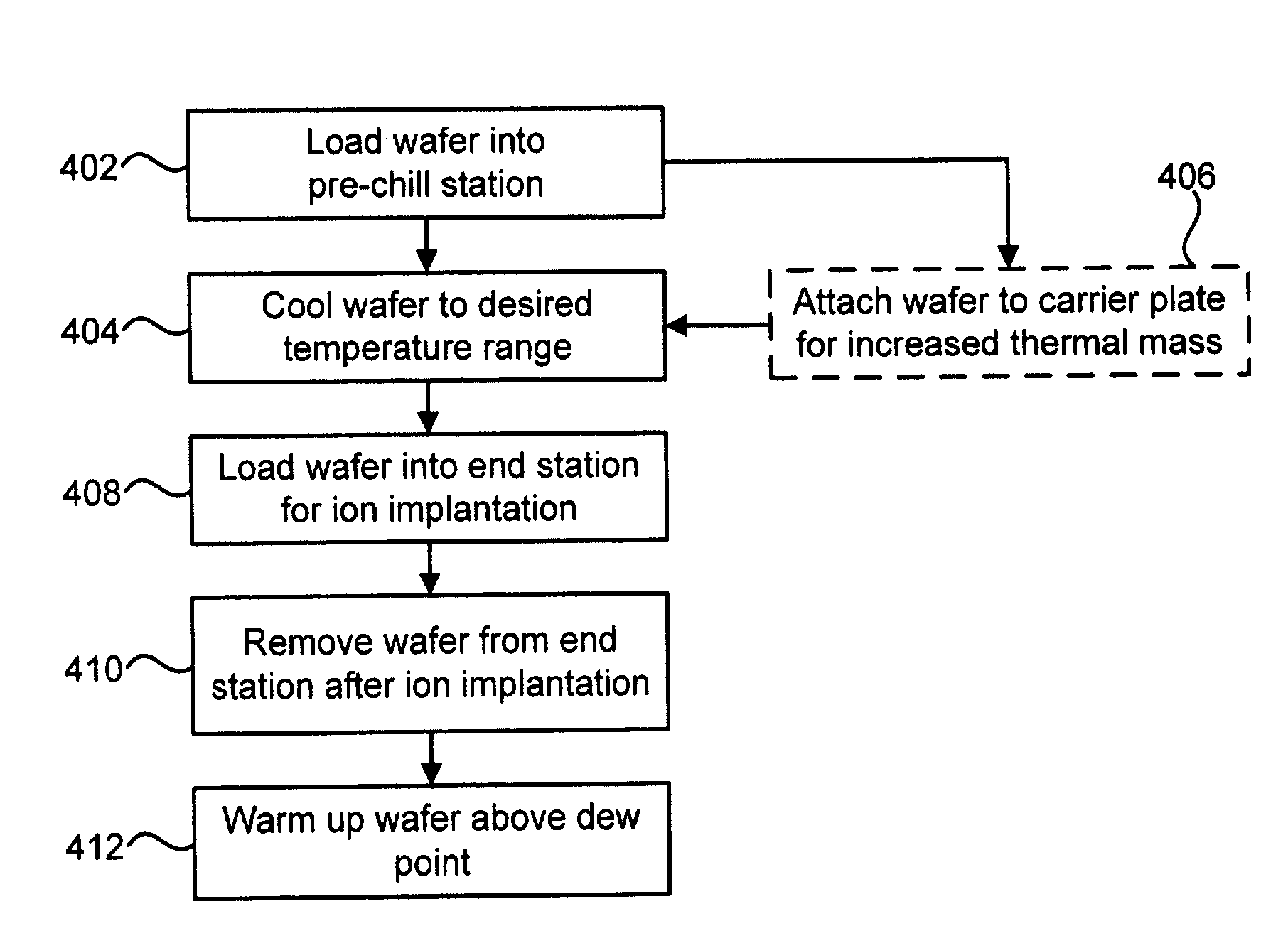
Technique for low-temperature ion implantation
ActiveUS20080044938A1Avoid overall overheatingFacilitate tilting and rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesEngineeringIon implantation
A technique for low-temperature ion implantation is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as an apparatus for low-temperature ion implantation. The apparatus may comprise a pre-chill station located in proximity to an end station in an ion implanter. The apparatus may also comprise a cooling mechanism within the pre-chill station. The apparatus may further comprise a loading assembly coupled to the pre-chill station and the end station. The apparatus may additionally comprise a controller in communication with the loading assembly and the cooling mechanism to coordinate loading a wafer into the pre-chill station, cooling the wafer down to a predetermined temperature range, and loading the cooled wafer into the end station where the cooled wafer undergoes an ion implantation process.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Process window based optical proximity correction of lithographic images
InactiveUS6578190B2Maximize rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProcess windowPlanographic printing
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method for preparing a radiation therapy plan
InactiveUS6560311B1Simple calculationFast executionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryDose profileIndividual dose
A method for determining a radiation treatment plan for a radiotherapy system providing multiple individual rays of intensity modulated radiation iteratively optimized the fluence of an initial set of such rays by a function that requires knowledge of only the prescribed dose and the dose resulting from the particular ray fluences. In this way, the need to store individual dose distributions of each ray are eliminated.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
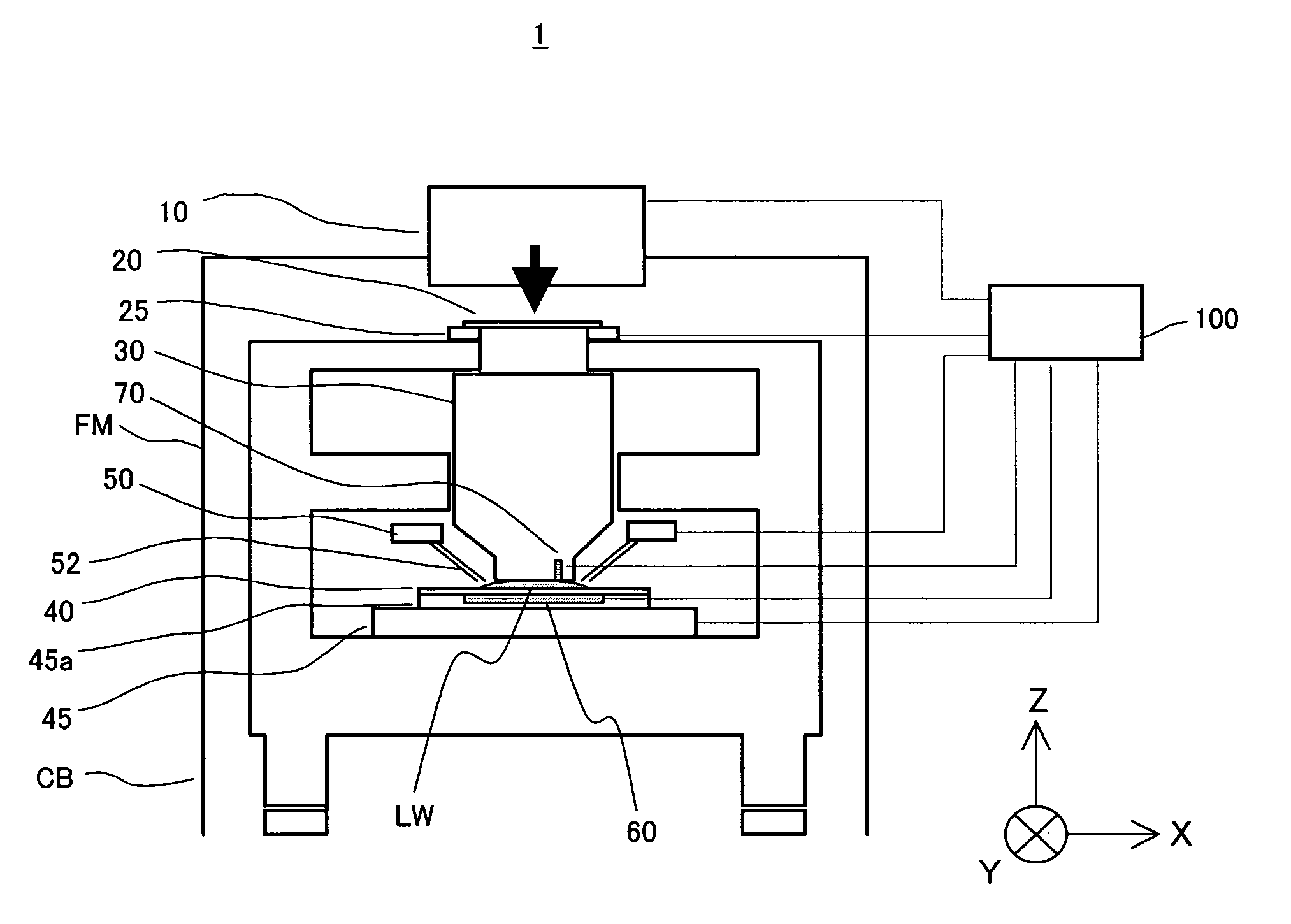
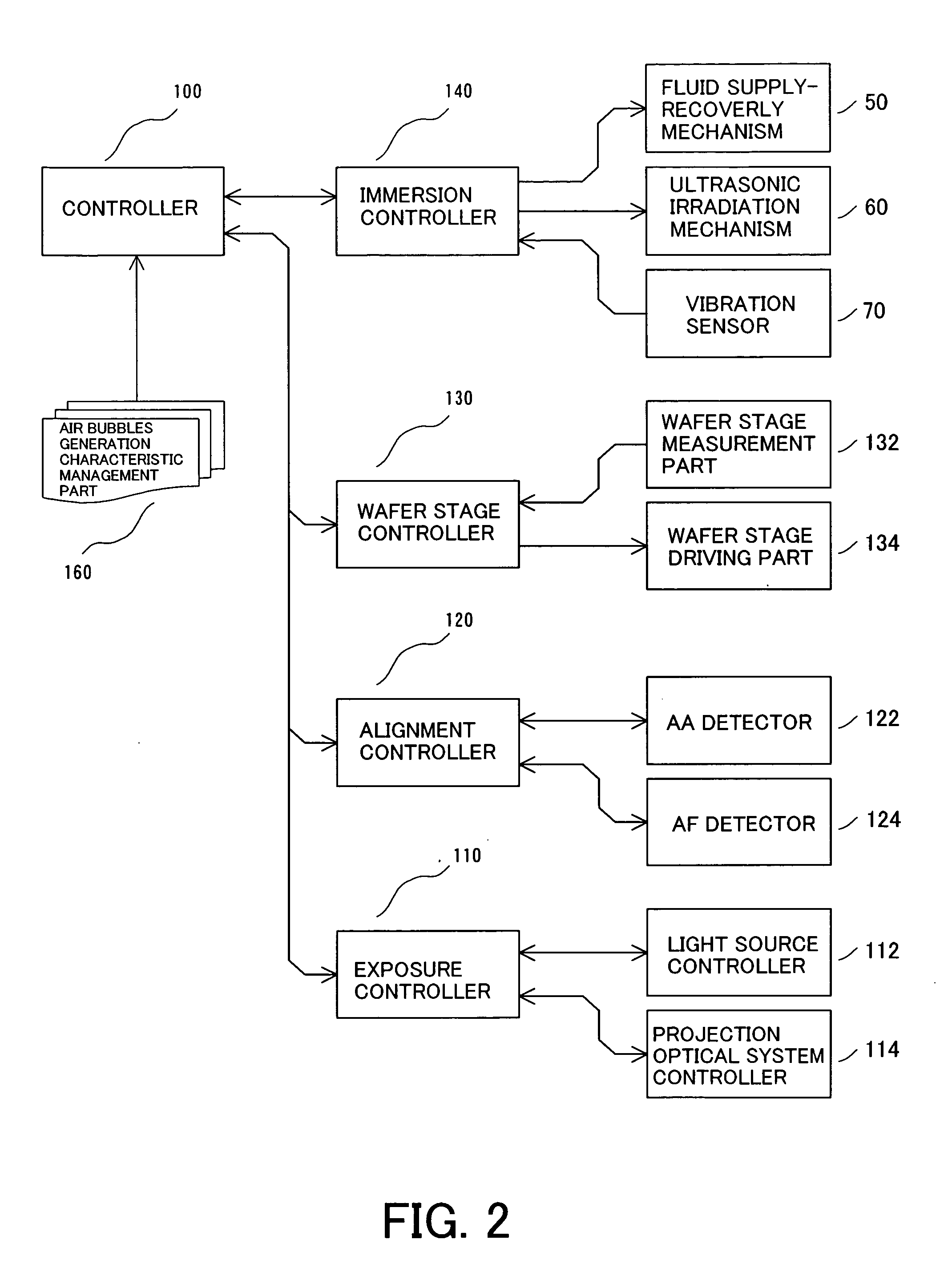
Exposure apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050213065A1Efficient removalInhibit deteriorationRailway vehiclesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReticleOptics
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting an image of a pattern of a reticle onto an object, via a fluid that is filled in a space between said projection optical system and the object, a vibrator part for vibrating at least one of the fluid, the object, and the projection optical system, and a controller for controlling the vibrator part so that the vibration of at least one of the fluid, the object, and the projection optical system becomes a tolerance during a processing of the object.
Owner:CANON KK
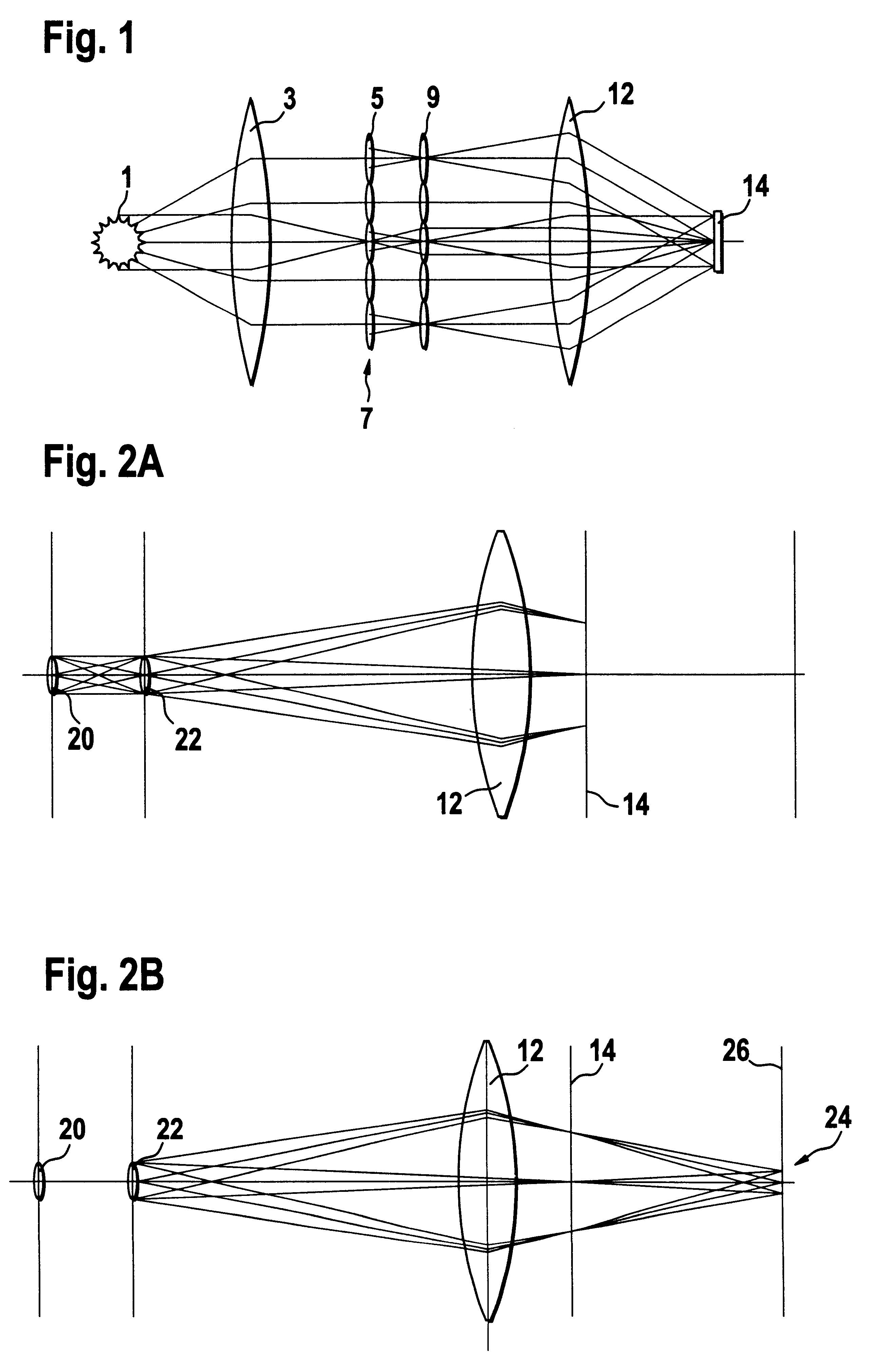
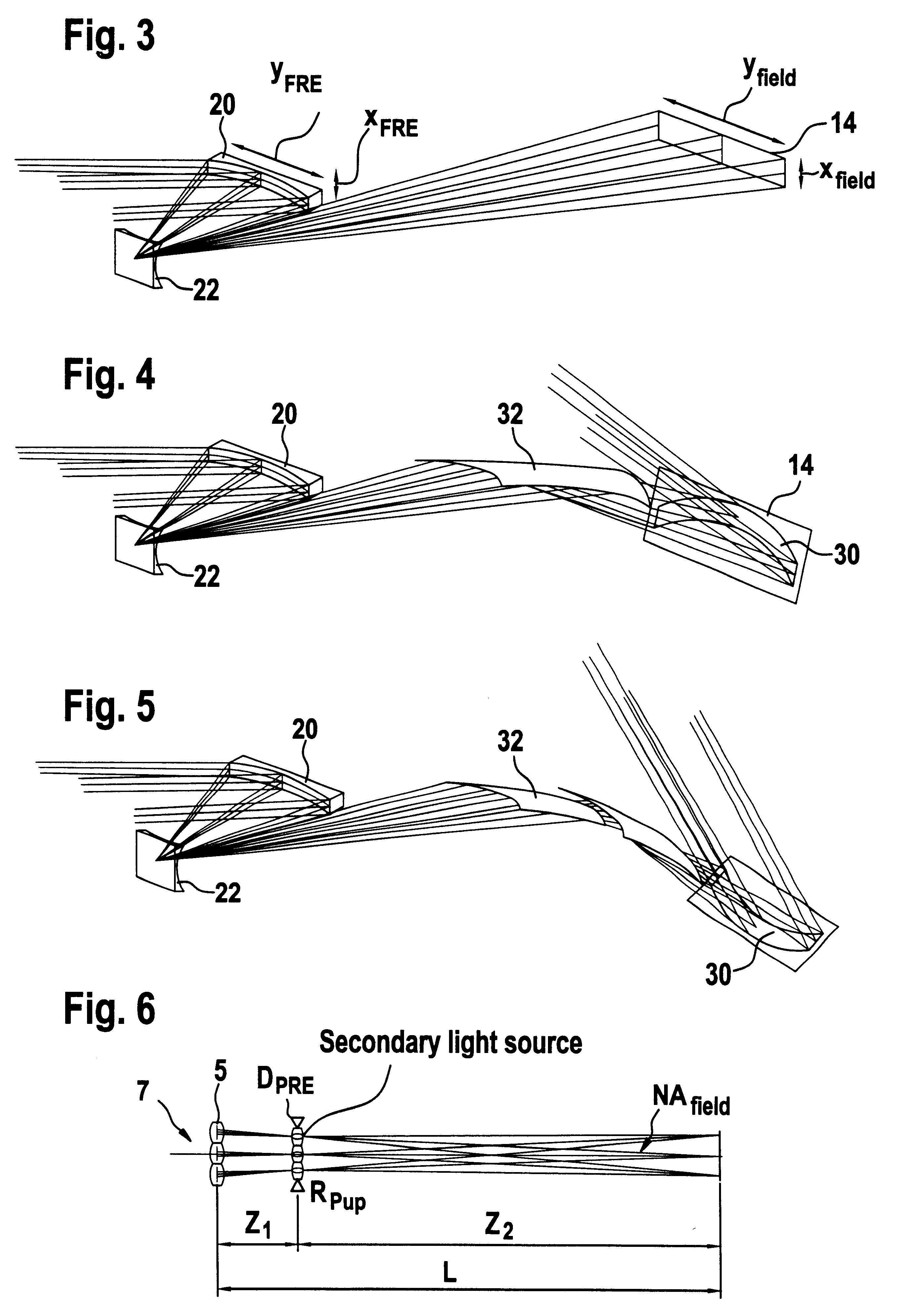
Illumination system with variable adjustment of the illumination
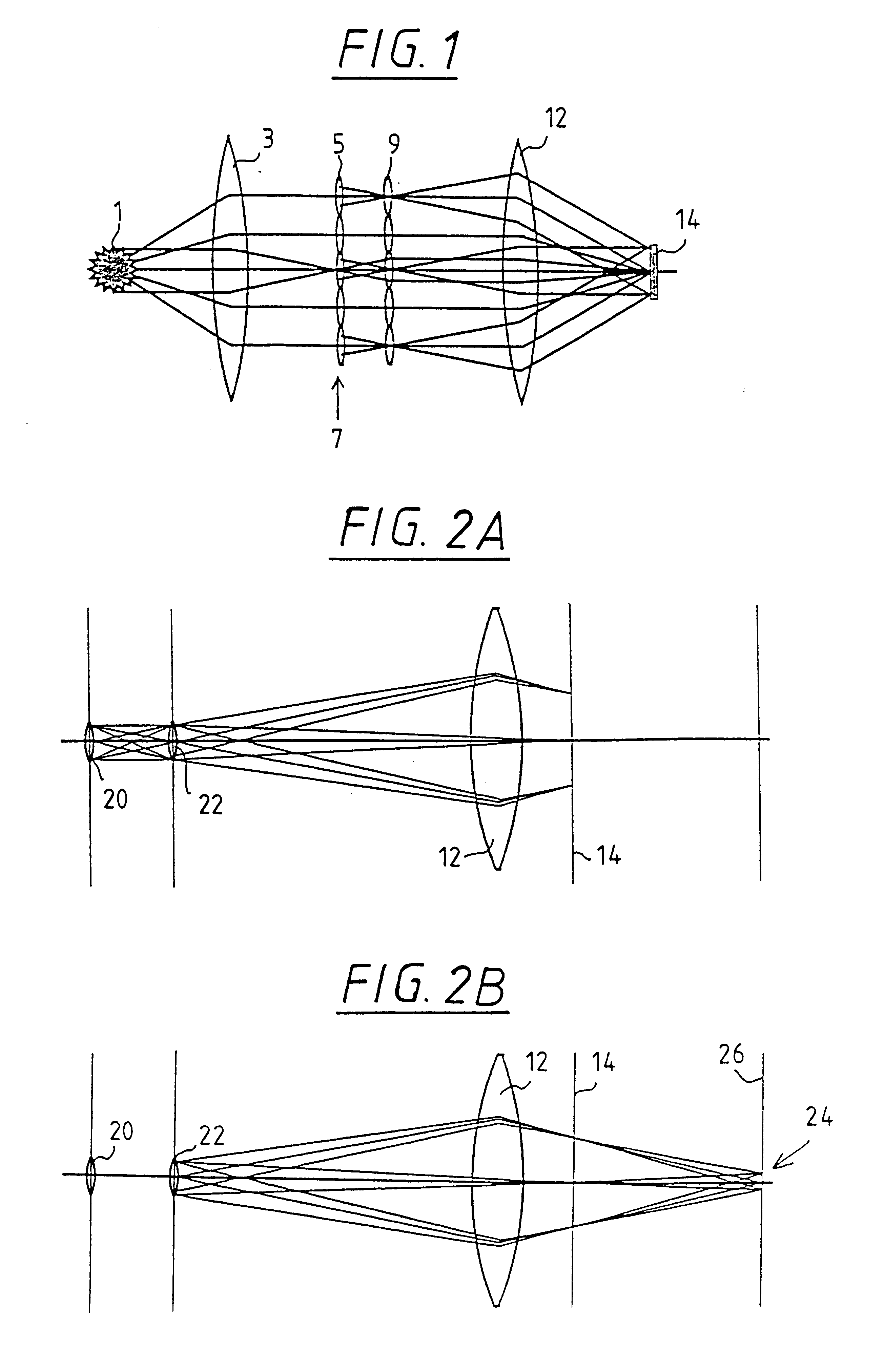
InactiveUS6658084B2Avoid lostSimple wayNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGratingExit pupil
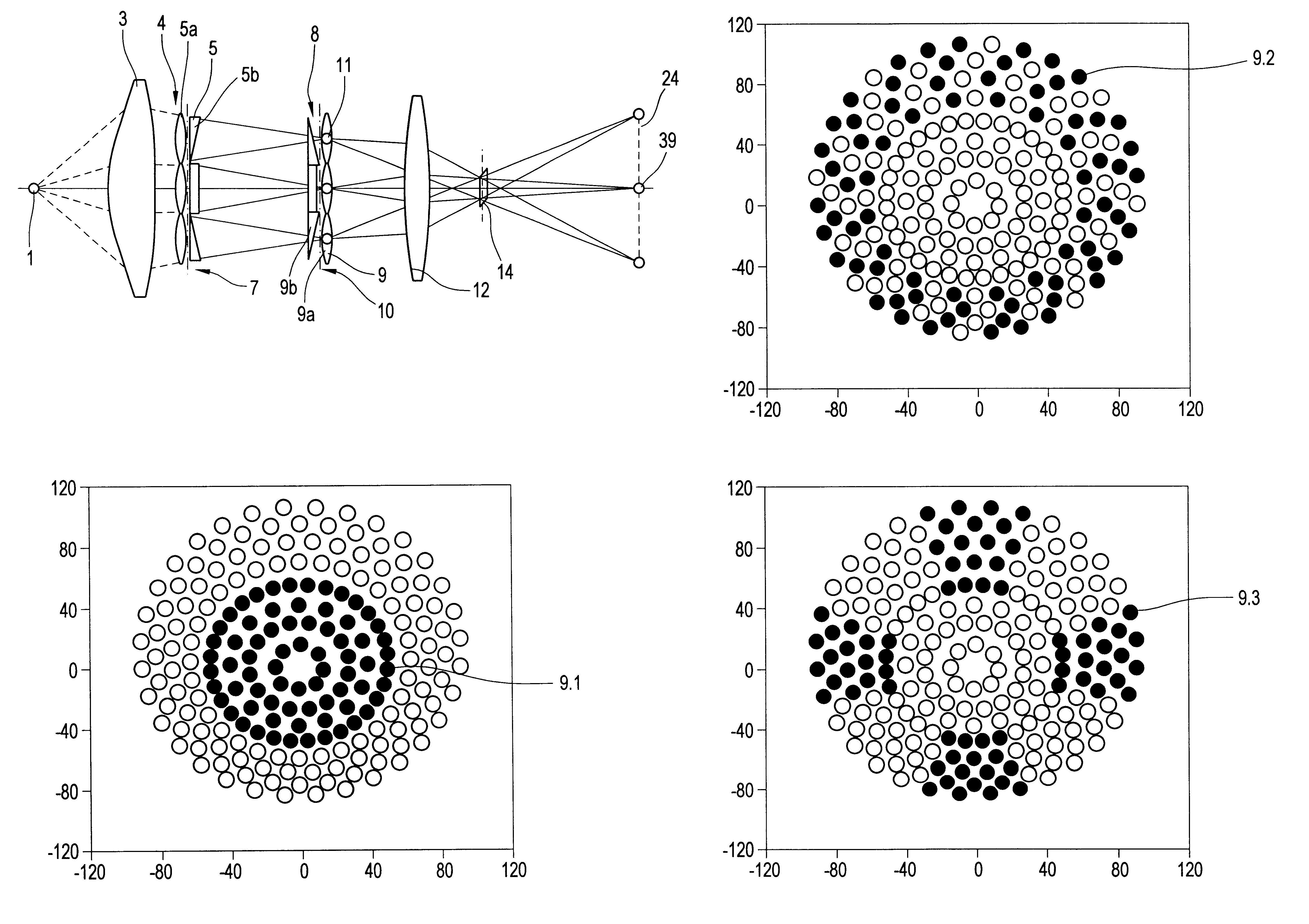
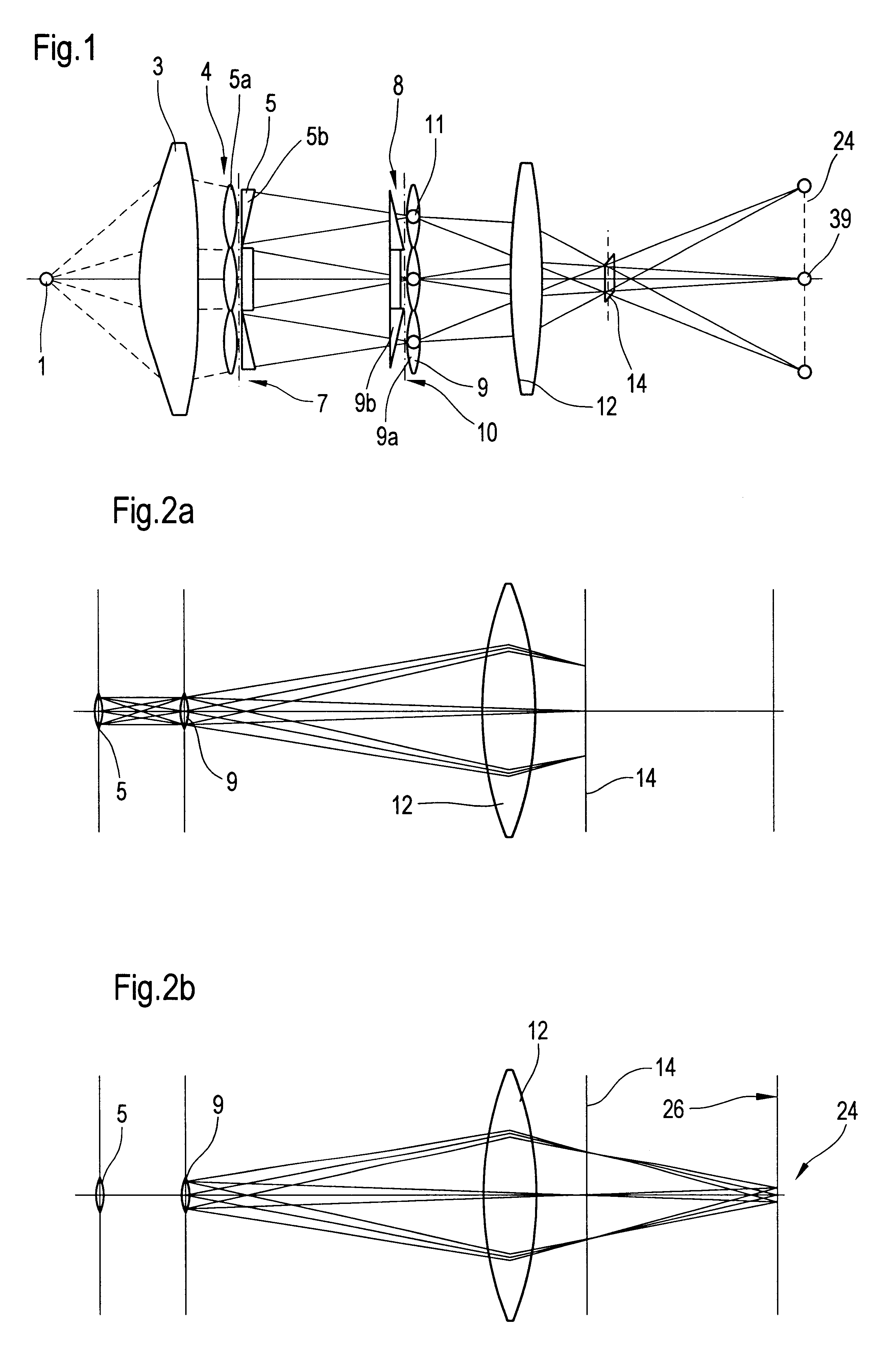
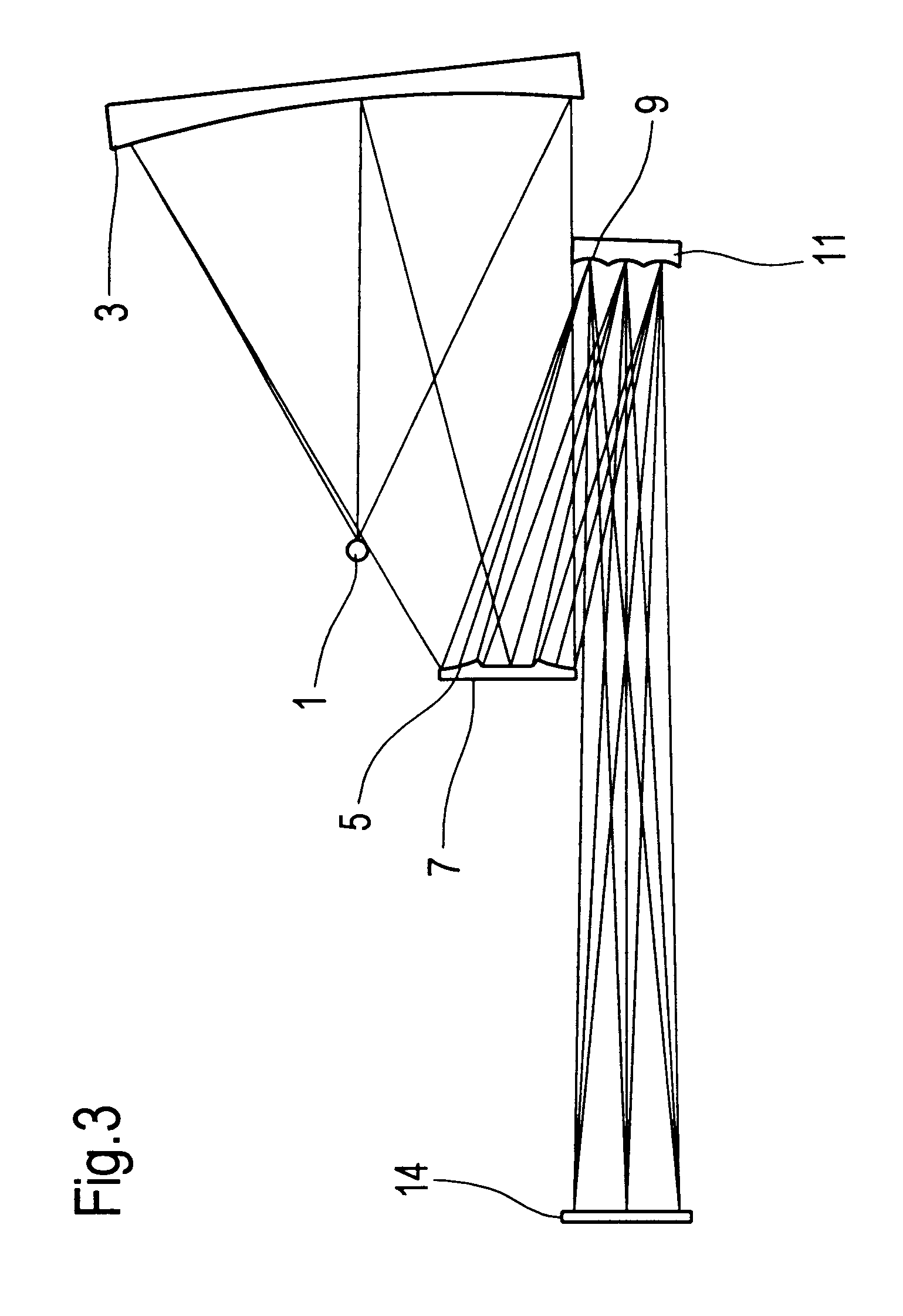
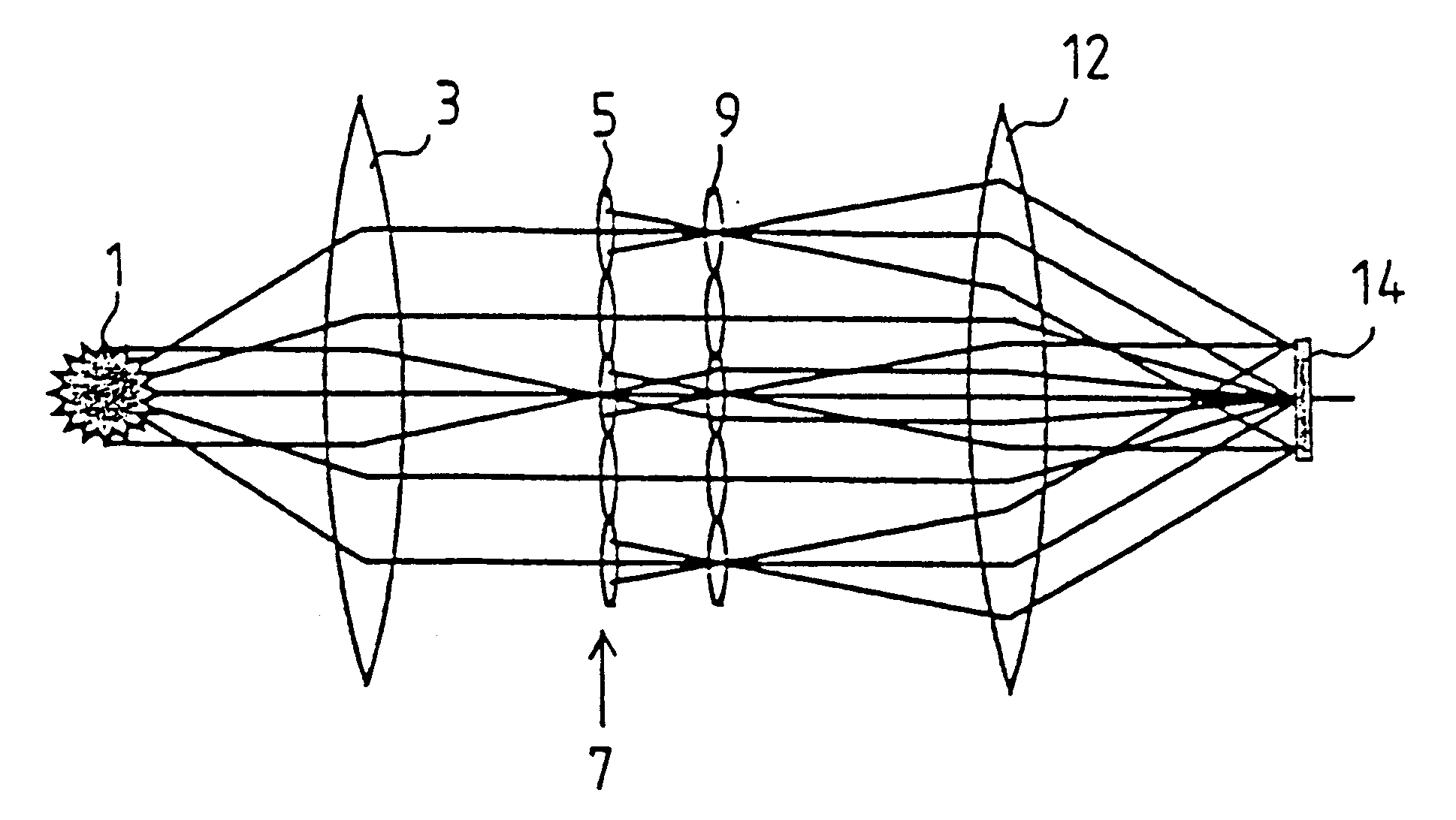
An illumination system comprises (a) a first optical element upon which a light beam impinges, where the first optical element has first raster elements that partition said light beam into light channels; (b) a second optical element that receives said light channels, where the second optical element has a second raster elements; (c) an object plane that receives said light channels via said second optical element; and (d) an exit pupil that is provided with an illumination via said object plane. The system is characterized by an assignment of a member of said first raster elements and a member of said second raster elements to each of said light channels to provide a continuous beam path from said first optical element to said object plane for each of said plurality of light channels. The assignment is changeable to provide an adjustment of said illumination in said exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Illumination system particularly for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6198793B1Etendu can be effectively increasedAvoid blurringsNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionCamera lensGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, particularly for EUV lithography, with at least one light source, which has an illumination A in a predetermined surface; at least one device for producing secondary light sources; at least one mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements; one or more optical elements, which are arranged between the mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements and the reticle plane, whereby the optical elements image the secondary light sources in the exit pupil of the illumination system.The illumination system is characterized by the fact that the raster elements of the one or more mirror or lenses are shaped and arranged in such a way that the images of the raster elements cover by means of the optical elements the major portion of the reticle plane and that the exit pupil defined by aperture and filling degree is illuminated.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Photomask for eliminating antenna effects in an integrated circuit and integrated circuit manufacture with same
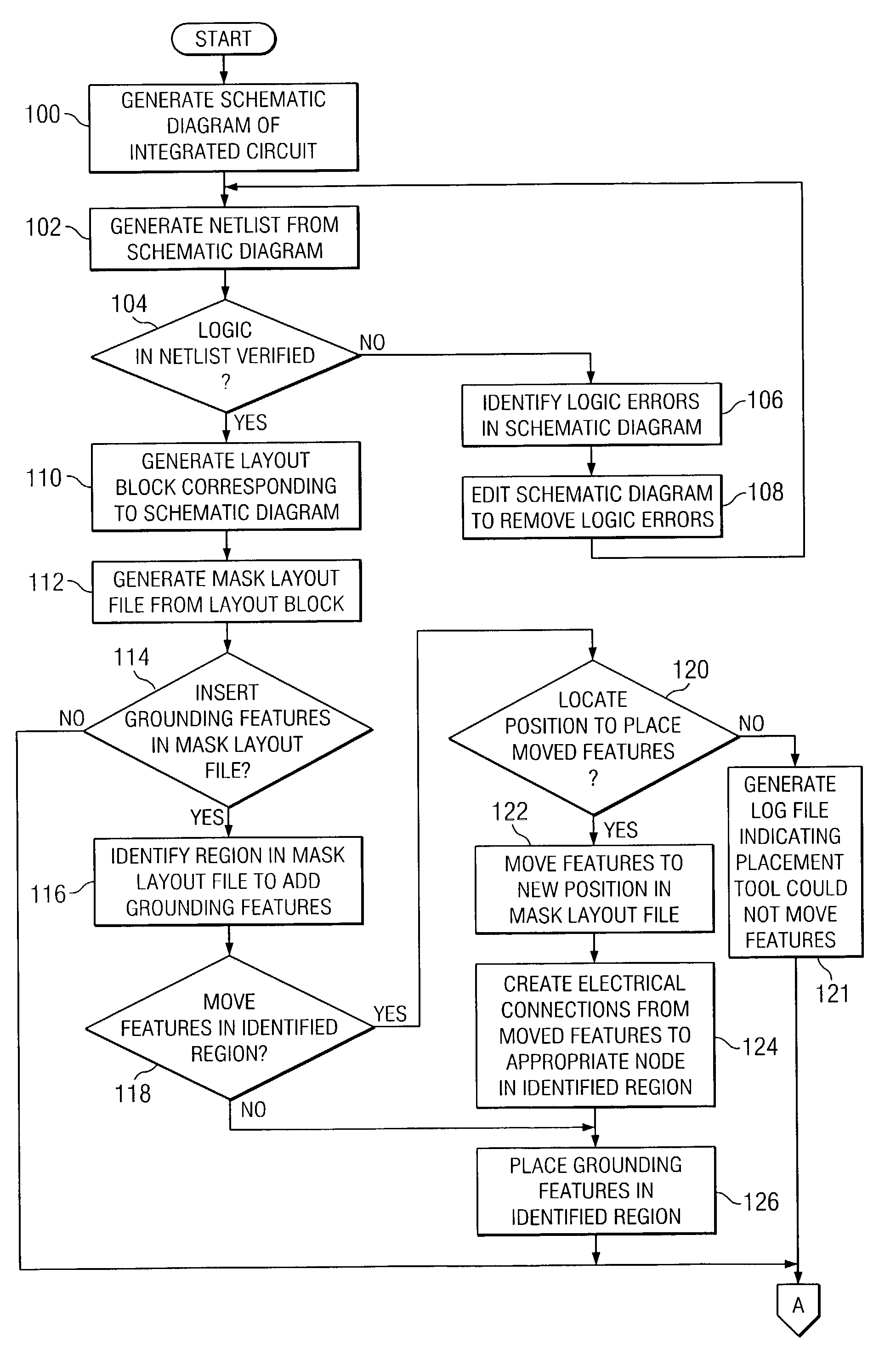
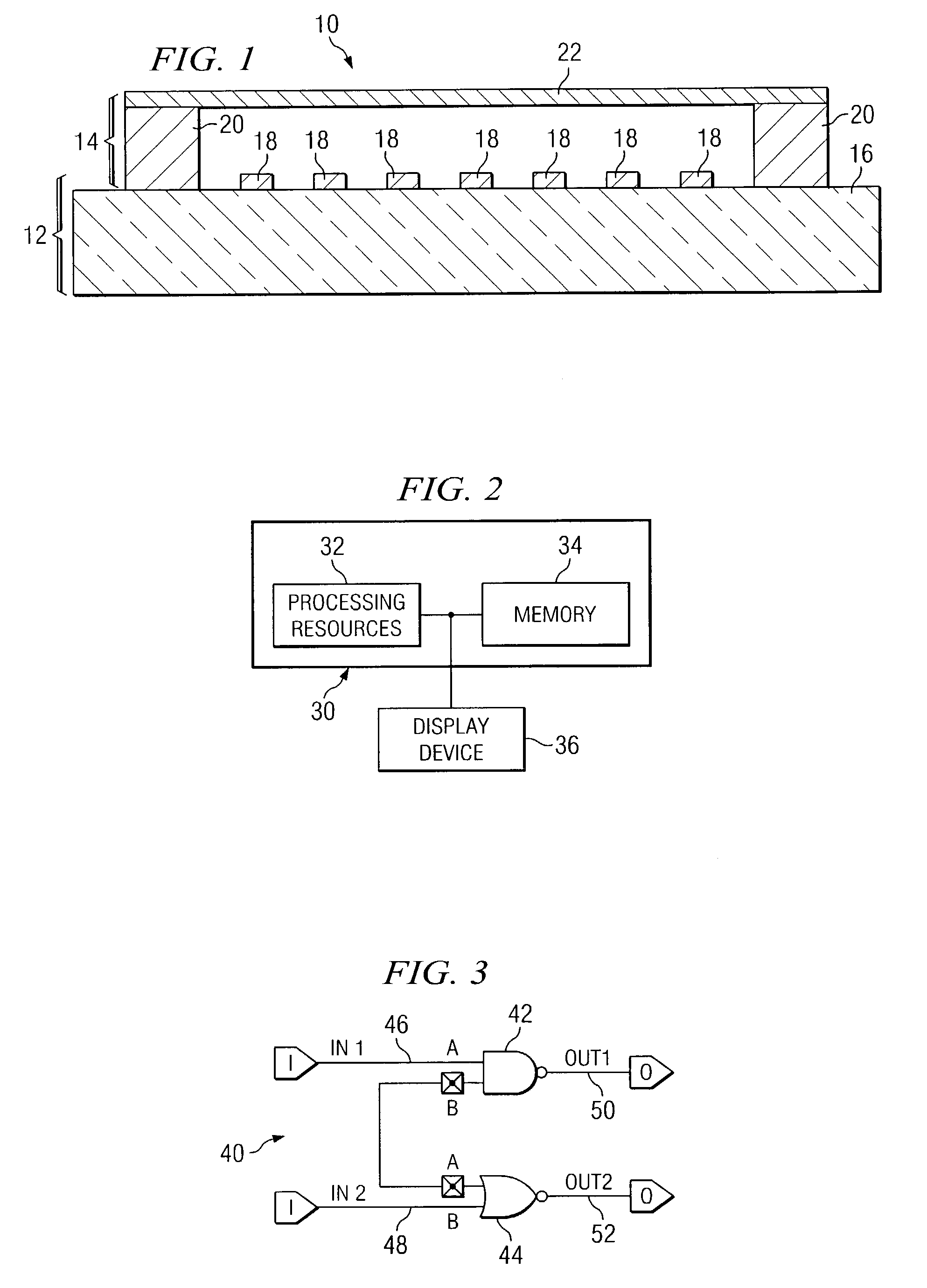
InactiveUS6978437B1Increase antenna ratioRaise the ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAntenna effectEngineering
A photomask for eliminating antenna effects in an integrated circuit and integrated circuit manufactured with the photomask are disclosed. The photomask includes a substrate and a patterned layer formed on at least a portion of the substrate. The patterned layer may be formed using a mask pattern file created by analyzing a pattern in a mask layout file to identify a region including an antenna ratio less than a first design rule. A feature located in the identified region is moved based on a second design rule from a first position to a second position in the mask layout file to create a space in the identified region. A grounding feature is placed in the space and automatically connected to a gate feature in the mask layout file such that the antenna ratio is increased to greater than or approximately equal to the first design rule.
Owner:CELERICS TECH
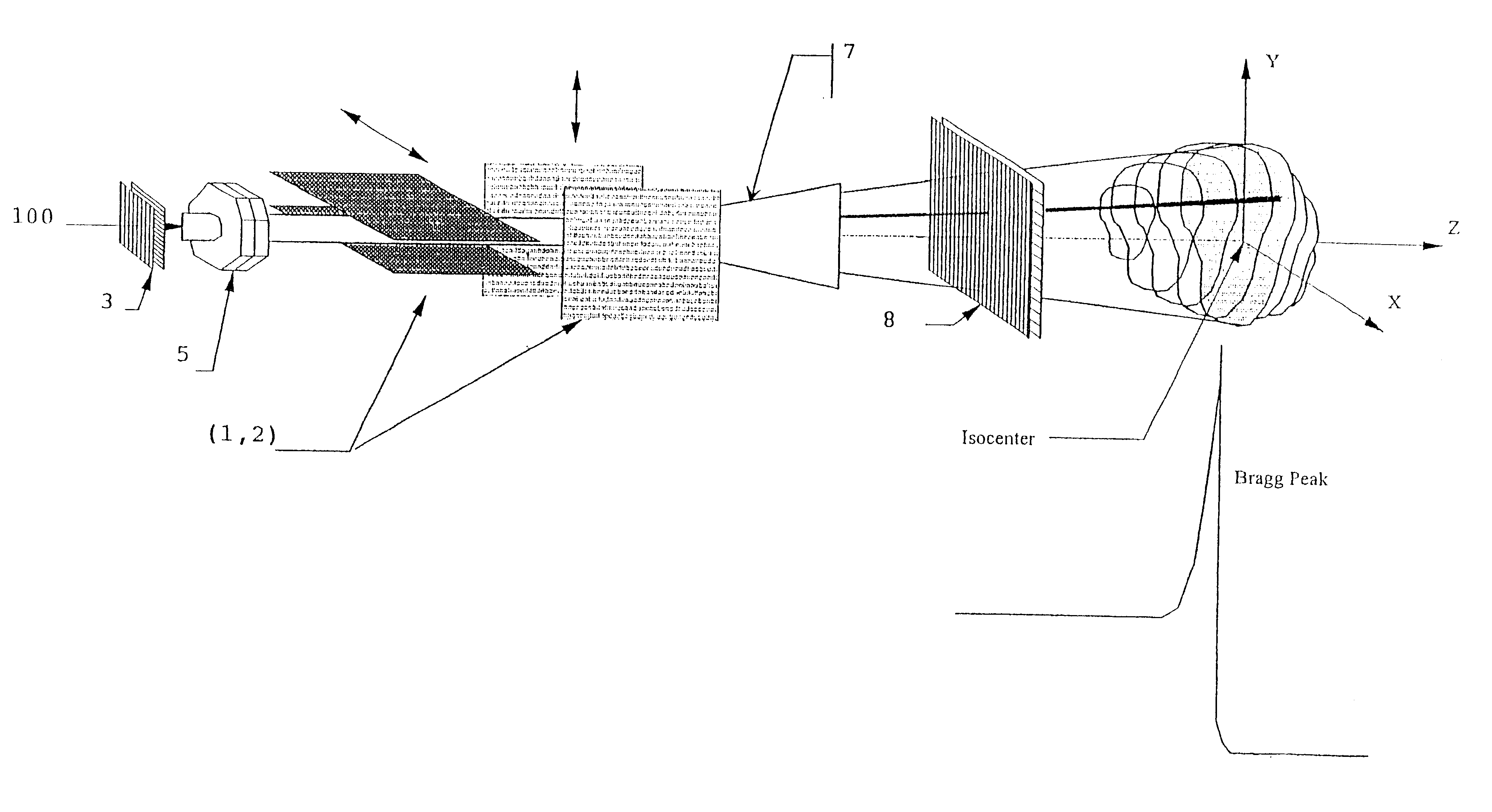
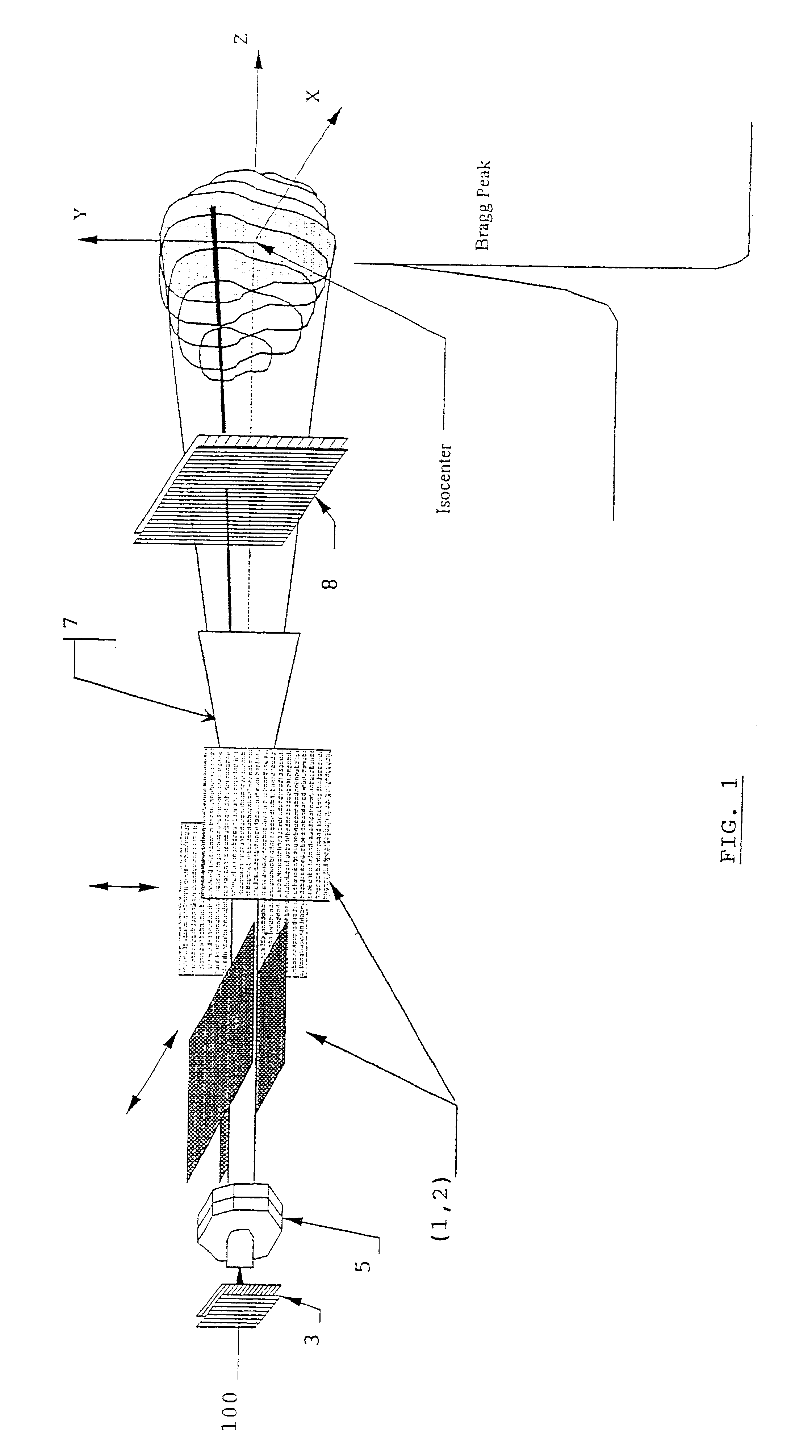
Method for treating a target volume with a particle beam and device implementing same
InactiveUS6717162B1Good flexibilityPossible to obtainRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsParticle beamParticle physics
The invention concerns a method for treating a target volume with a particle beam, in particular a proton beam, which consists in generating said particle beam using an accelerator and in producing from said beam a narrow spot directed towards the target volume, characterized in that said spot sweeping speed and the particle beam intensity are simultaneously varied.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
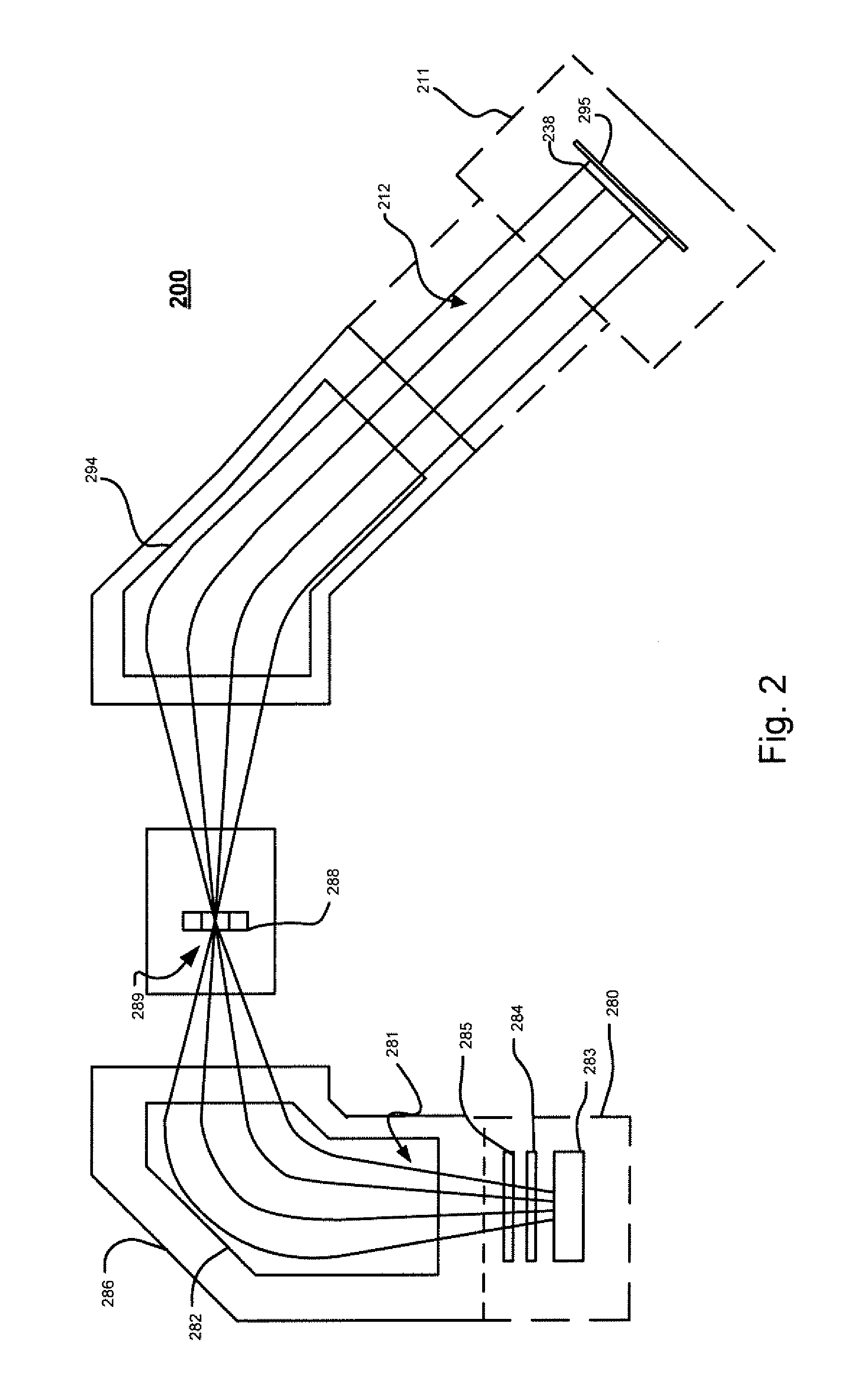
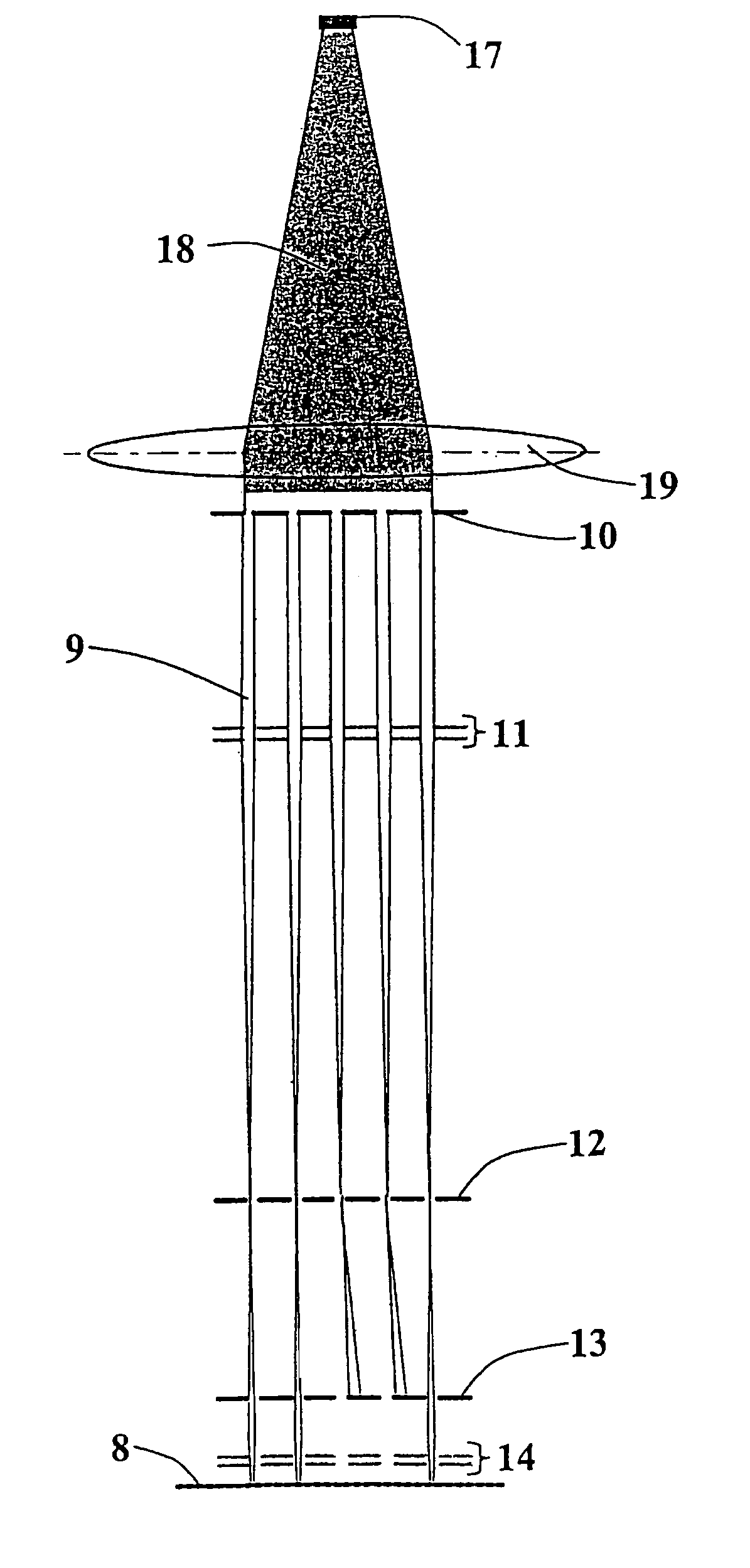
Charged particle beamlet exposure system
InactiveUS7084414B2Improve speed and stabilityOvercome problemsElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsControl signalMolecular physics
The invention relates to a charged-particle-optical system for a charged particle beam exposure apparatus, said system comprising:a first aperture means comprising at least a first substantially round aperture for partially shielding an emitted charged particle beam for forming a charged particle beamlet;a lens system comprising at least one lens for focussing a charged particle beamlet from said first aperture within or in the vicinity of an image focal plane of said lens;a deflector means, substantially located in said image focal plane, comprising at least one beamlet deflector for the deflection of a passing charged particle beamlet upon the reception of a control signal, anda second aperture means comprising at least one second substantially round aperture positioned in the conjugate plane of the first aperture, and said second aperture being aligned with said first aperture and said beamlet deflector for blocking said charged particle beamlet upon deflection by said beamlet deflector and to transmit it otherwise.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Neutral particle beam processing apparatus
InactiveUS6861642B2Inexpensive and compact structureImprove neutralization efficiencyLaser detailsVacuum evaporation coatingDielectricPlasma generator
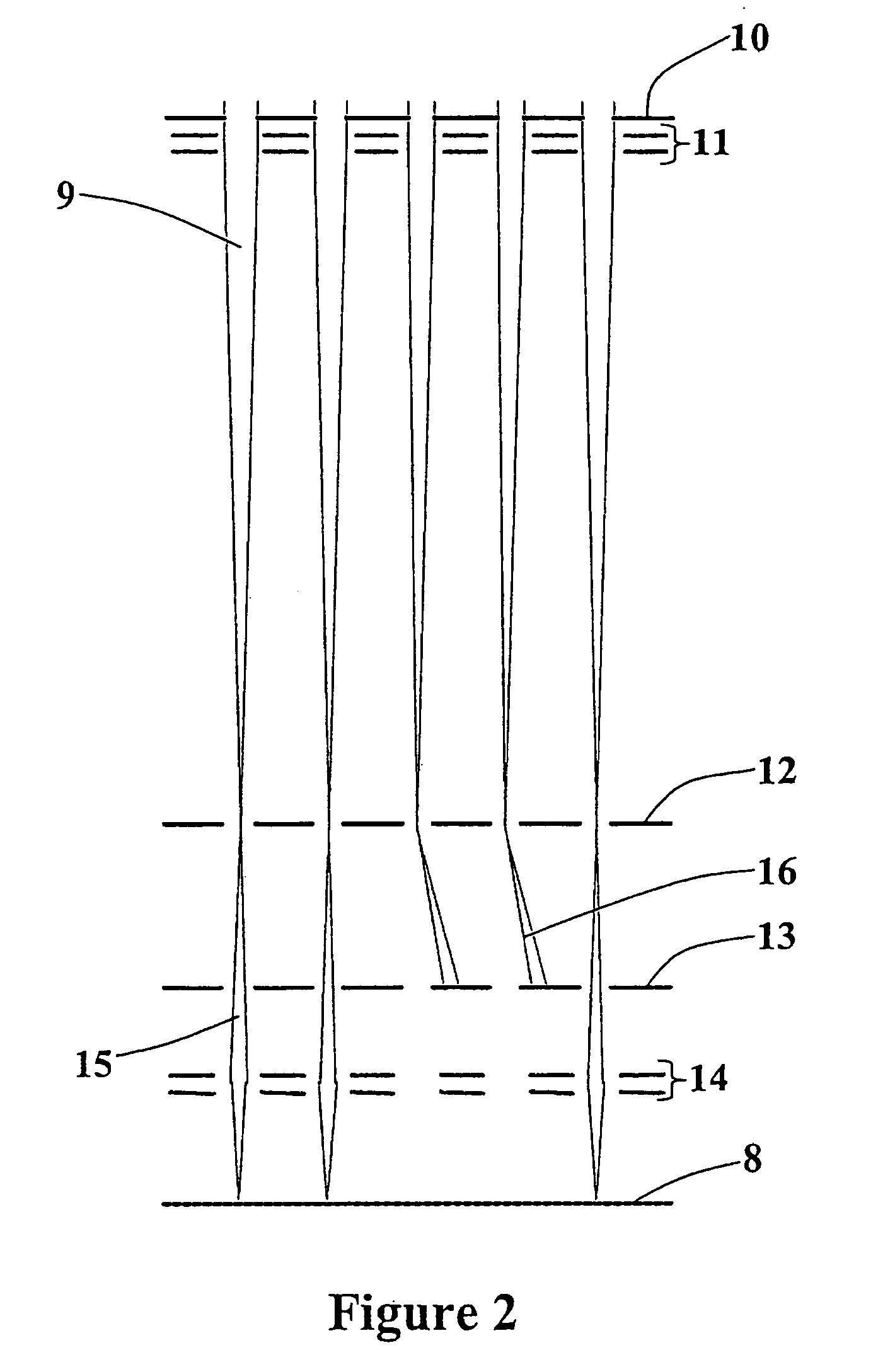
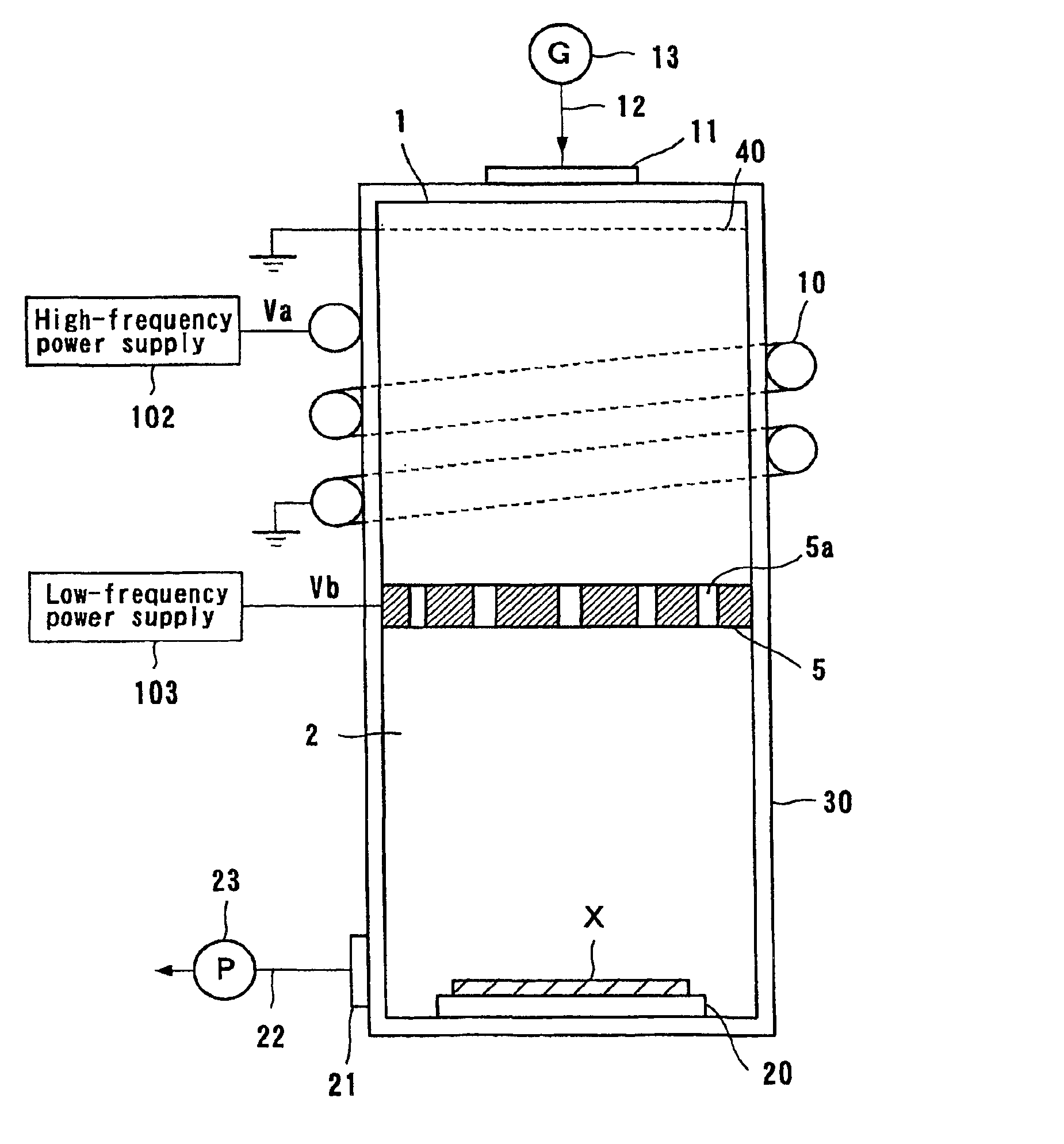
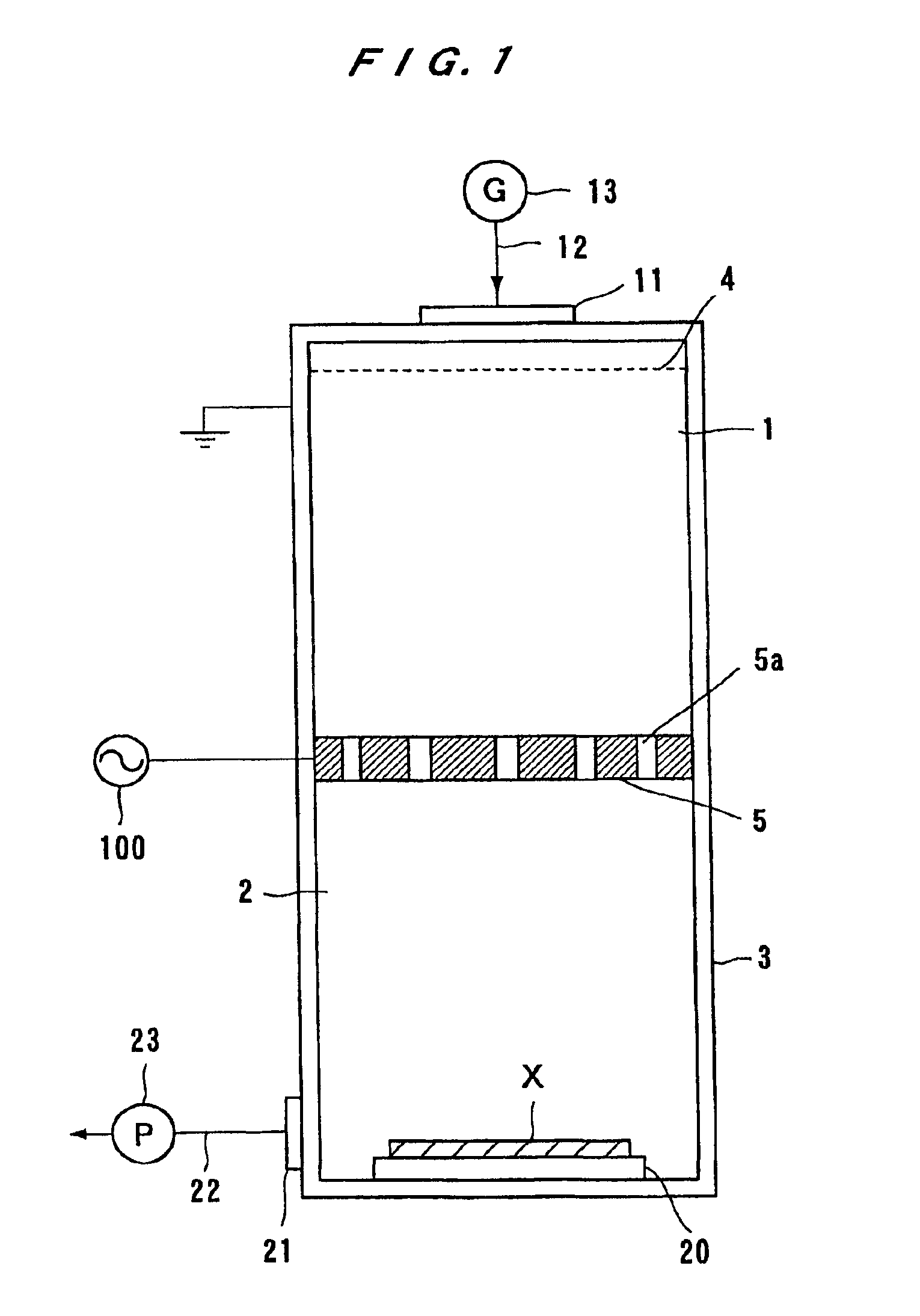
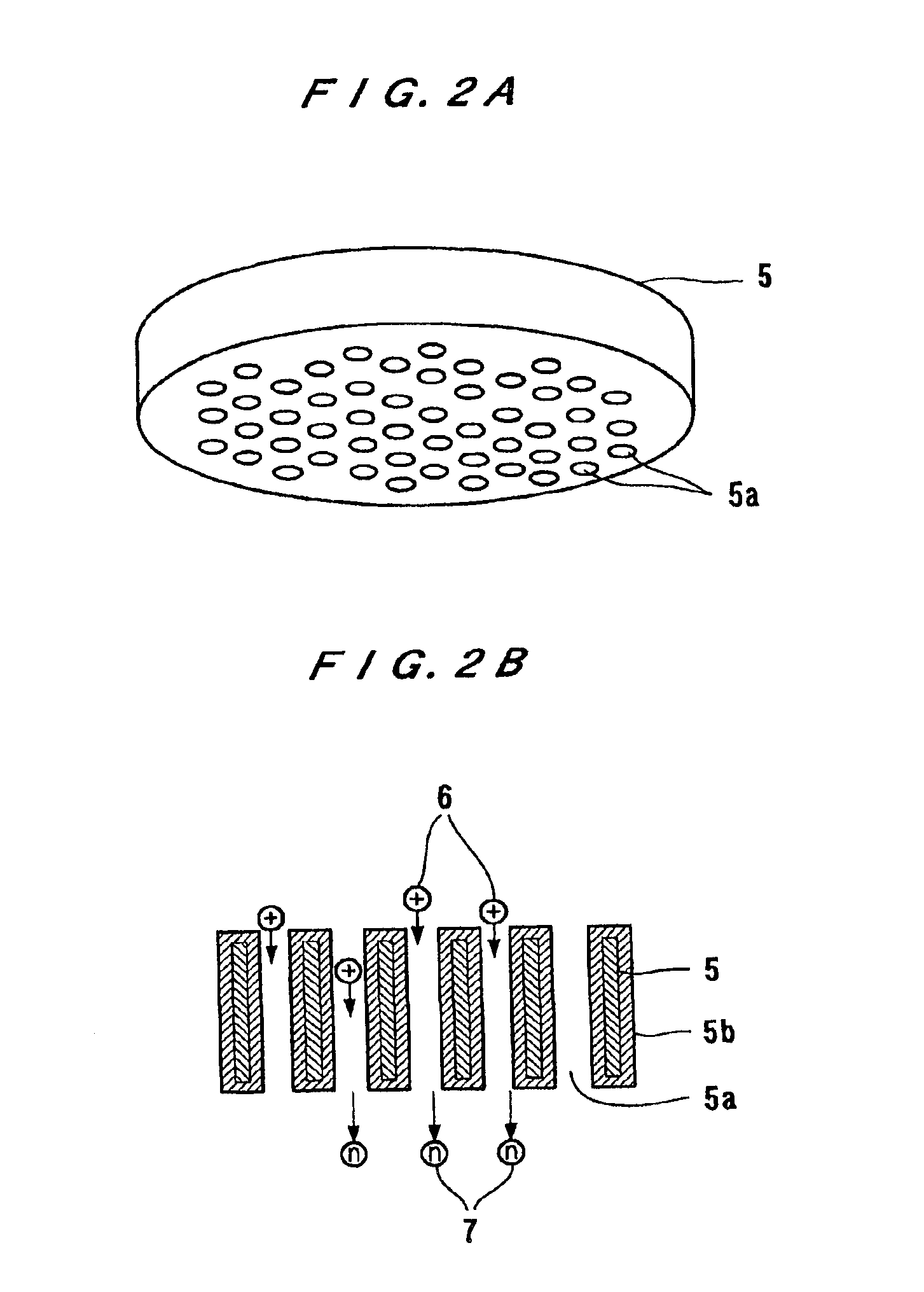
A neutral particle beam processing apparatus comprises a workpiece holder (20) for holding a workpiece (X), a plasma generator for generating a plasma in a vacuum chamber (3), an orifice electrode (5) disposed between the workpiece holder (20) and the plasma generator, and a grid electrode (4) disposed upstream of the orifice electrode (5) in the vacuum chamber (3). The orifice electrode (5) has orifices (5a) defined therein. The neutral particle beam processing apparatus further comprises a voltage applying unit for applying a voltage between the orifice electrode (5) and the grid electrode (4) via a dielectric (5b) to extract positive ions from the plasma generated by the plasma generator and pass the extracted positive ions through the orifices (5a) in the orifice electrode (5).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Cone-beam computerized tomography with a flat-panel imager
InactiveUS20030007601A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAmorphous siliconX-ray
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Ion beam therapy system and its couch positioning method
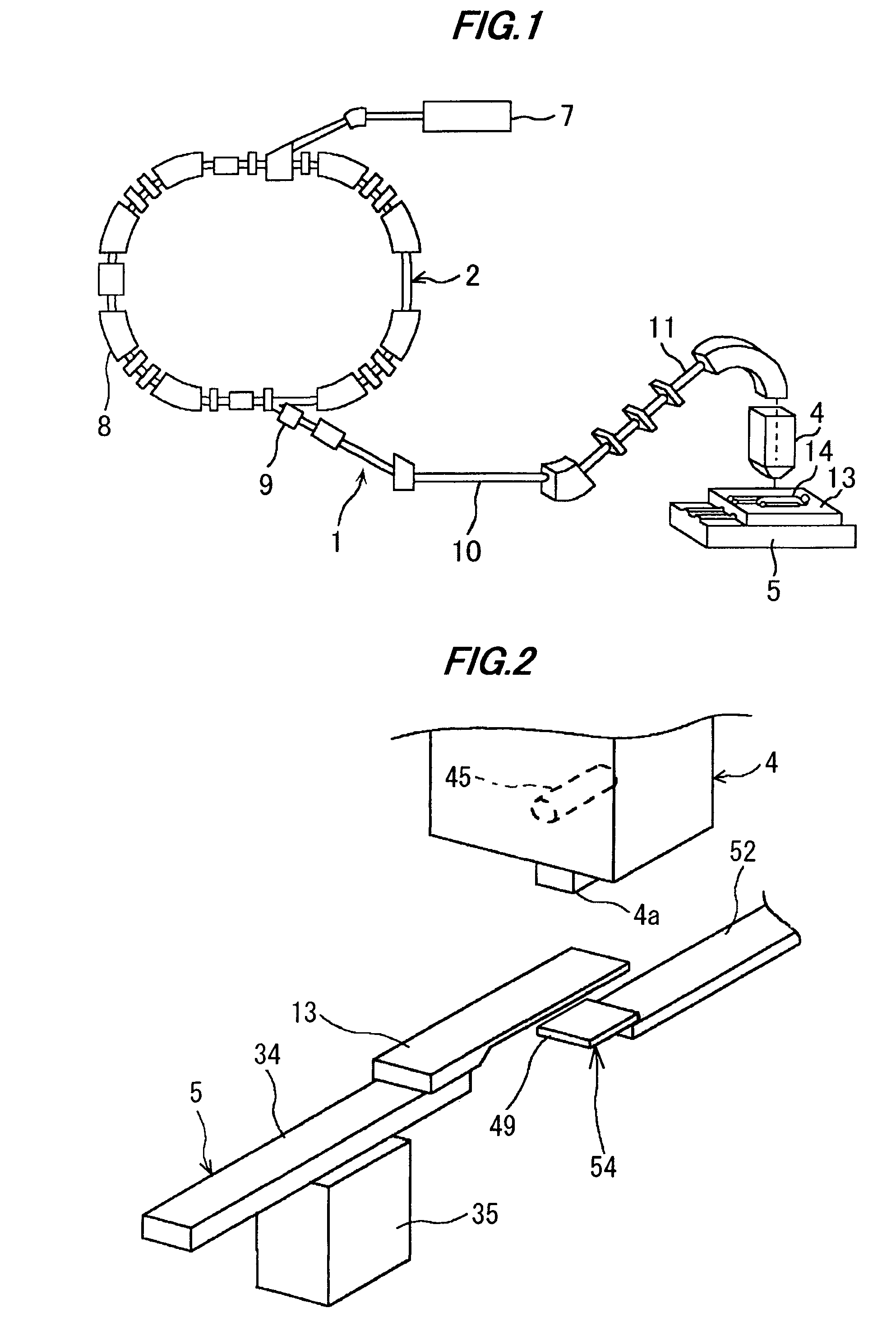
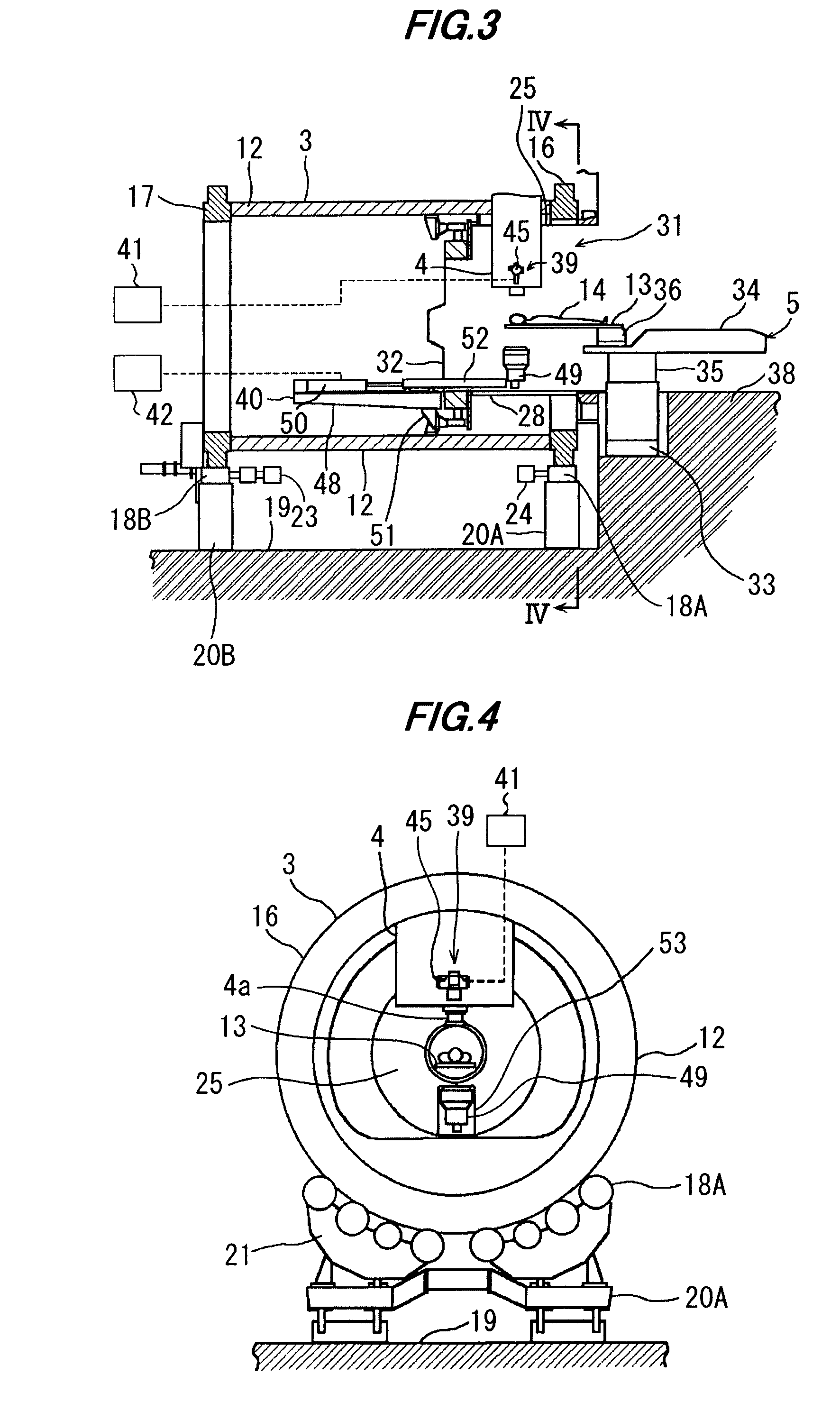
ActiveUS7193227B2Improve accuracyExtension of timeRadiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesIon beamX-ray
A therapy system using an ion beam, which can shorten the time required for positioning a couch (patient). The therapy system using the ion beam comprises a rotating gantry provided with an ion beam delivery unit including an X-ray tube. An X-ray detecting device having a plurality of X-ray detectors can be moved in the direction of a rotation axis of the rotating gantry. A couch on which a patient is lying is moved until a tumor substantially reaches an extension of an ion beam path in the irradiating unit. The X-ray tube is positioned on the ion beam path and the X-ray detecting device is positioned on the extension of the ion beam path. With rotation of the rotating gantry, both the X-ray tube emitting an X-ray and the X-ray detecting device revolve around the patient. The X-ray is emitted to the patient and detected by the X-ray detectors after penetrating the patient. Tomographic information of the patient is formed based on signals outputted from the X-ray detectors. Information for positioning the couch is generated by using the tomographic information.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com