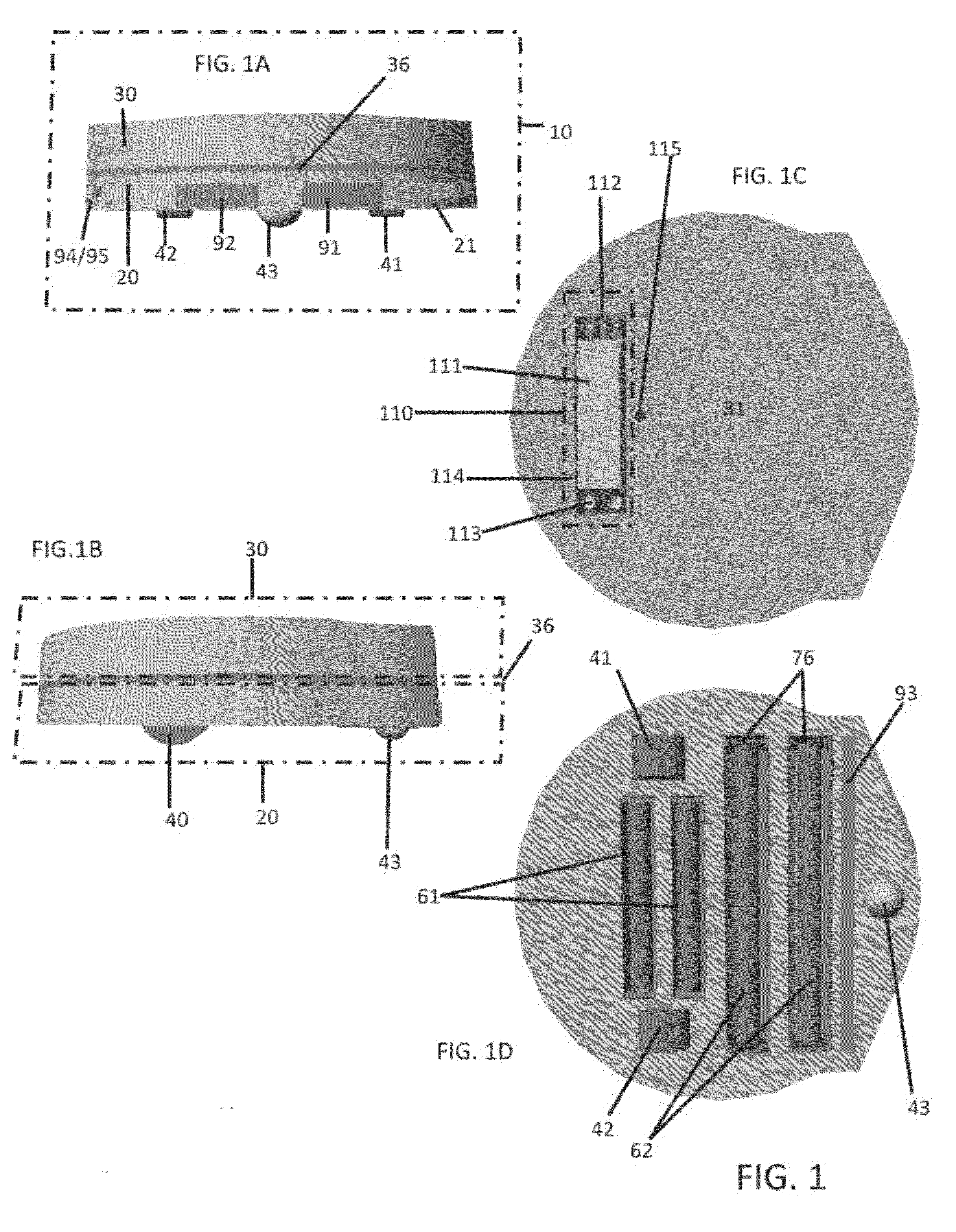
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4564 results about "Light irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
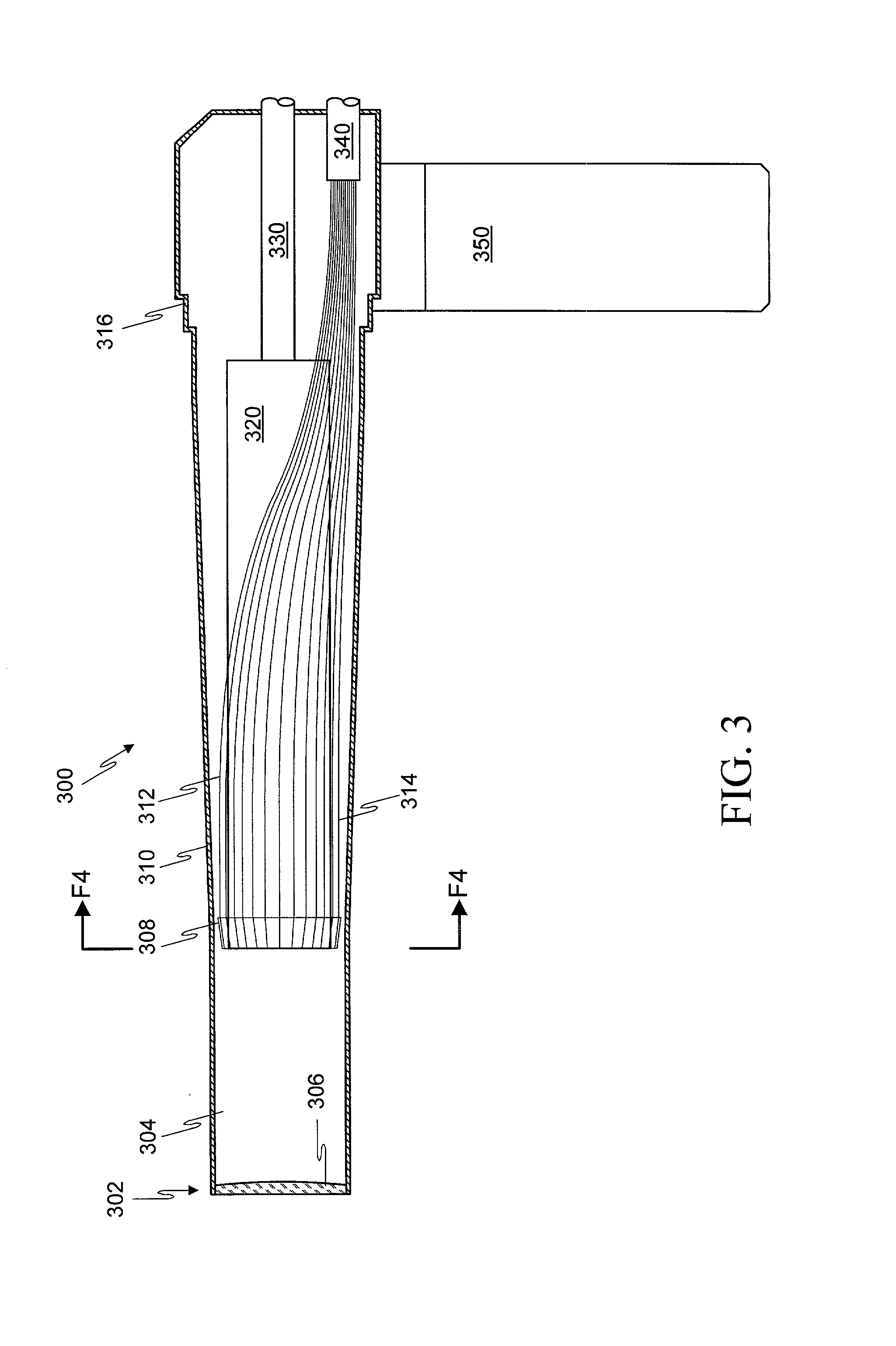
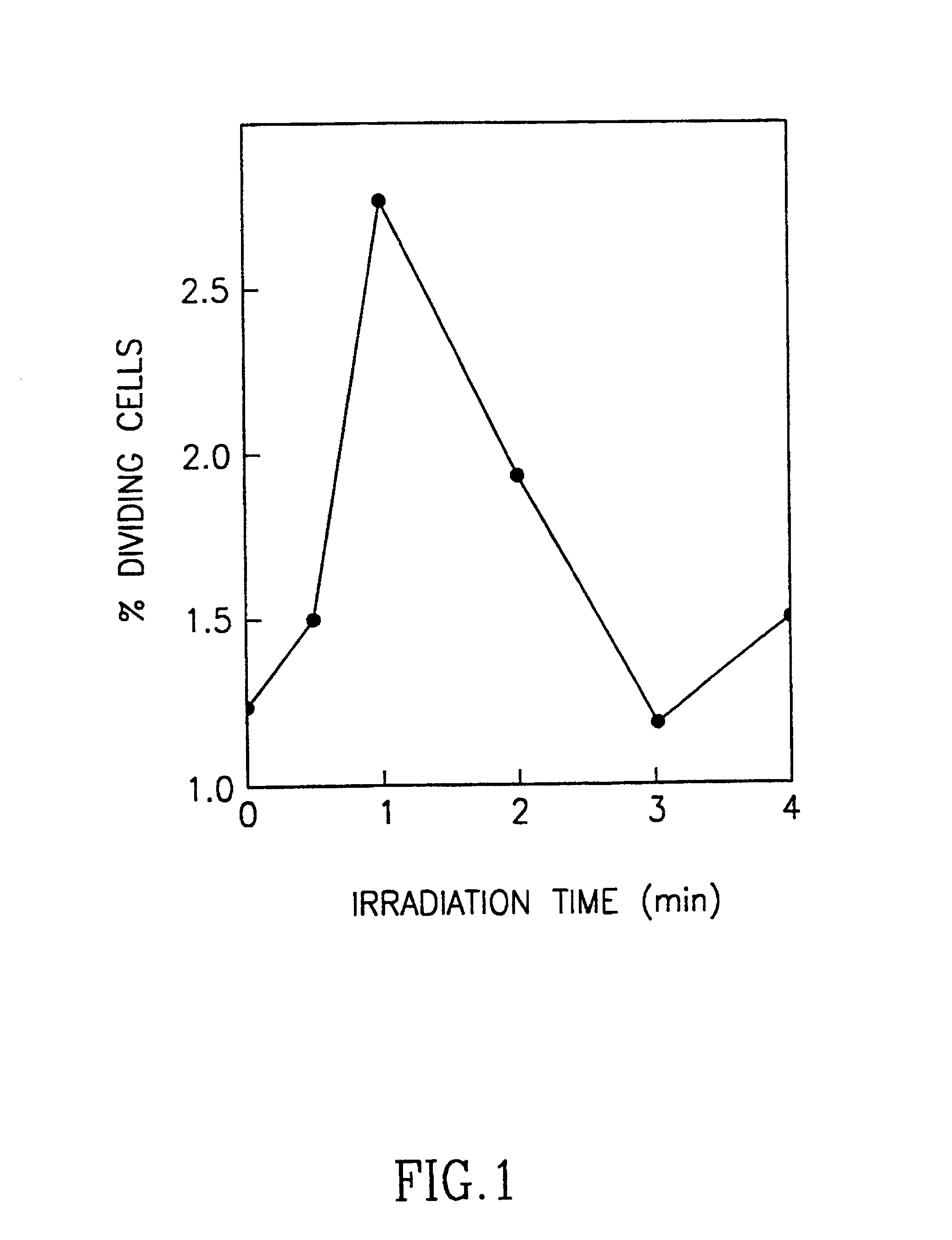
Light irradiation of molecules is the most popular method for the formation of active species. Light absorption can result in either the excitation of particles or photodissociation of molecules to form atoms and radicals. Both continuous and pulse light sources are used.
UV light irradiating apparatus with liquid filter
ActiveUS7763869B2High mechanical strengthHigh energyMirrorsOptical filtersLiquid layerLight irradiation
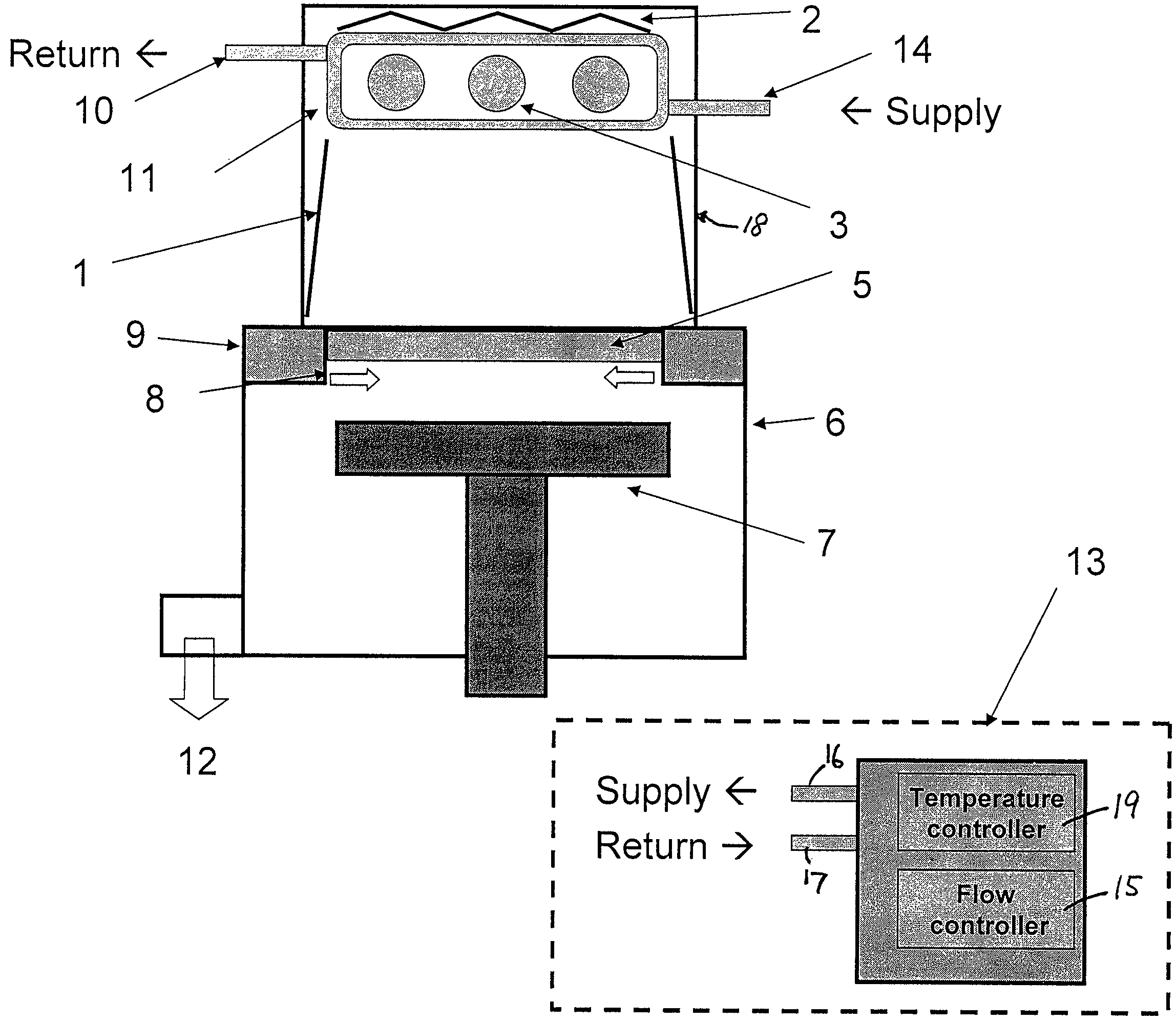
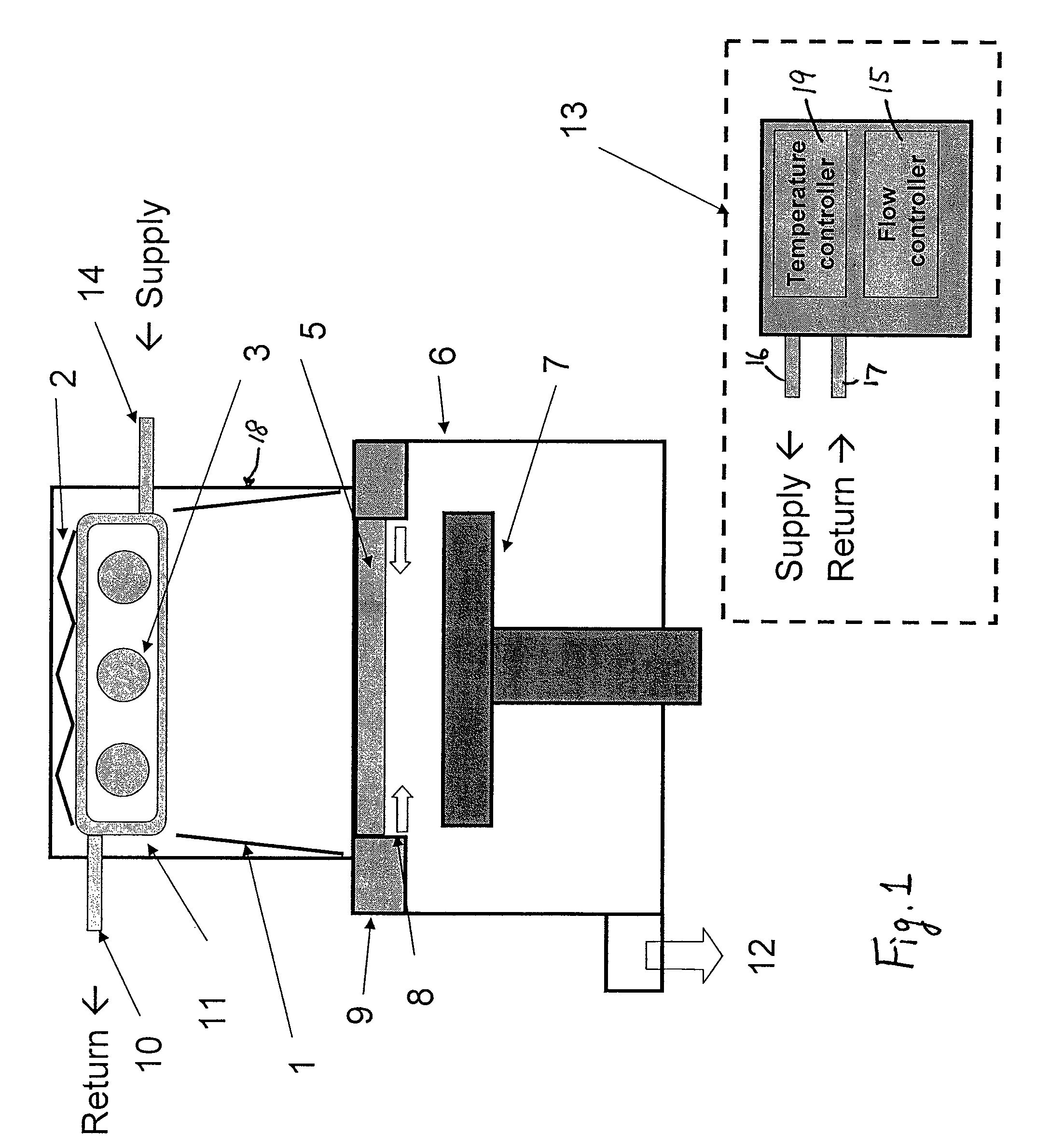
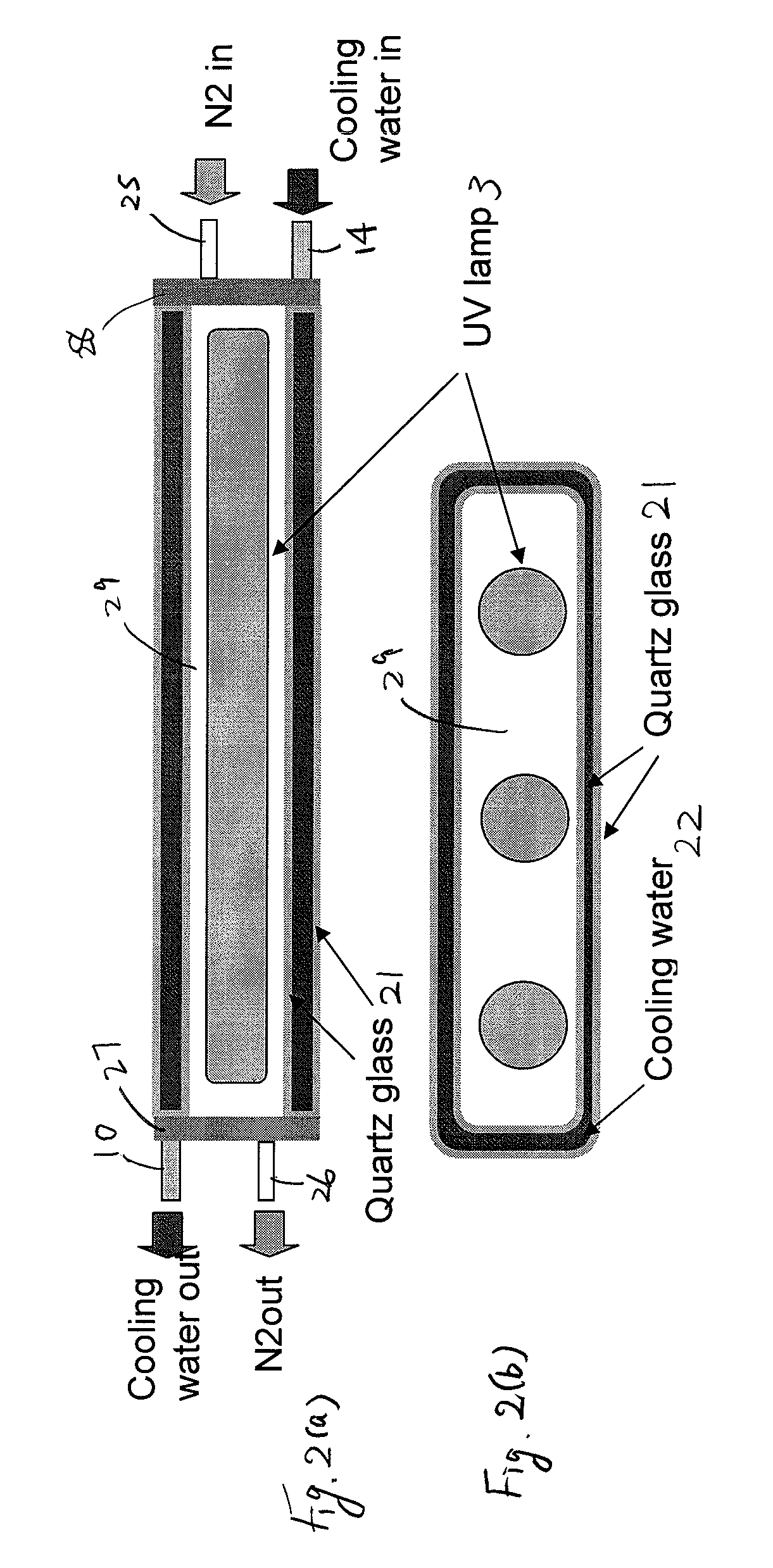
A UV light irradiating apparatus for irradiating a semiconductor substrate with UV light includes: a reactor in which a substrate-supporting table is provided; a UV light irradiation unit connected to the reactor for irradiating a semiconductor substrate placed on the substrate-supporting table with UV light through a light transmission window; and a liquid layer forming channel disposed between the light transmission window and at least one UV lamp for forming a liquid layer through which the UV light is transmitted. The liquid layer is formed by a liquid flowing through the liquid layer forming channel.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
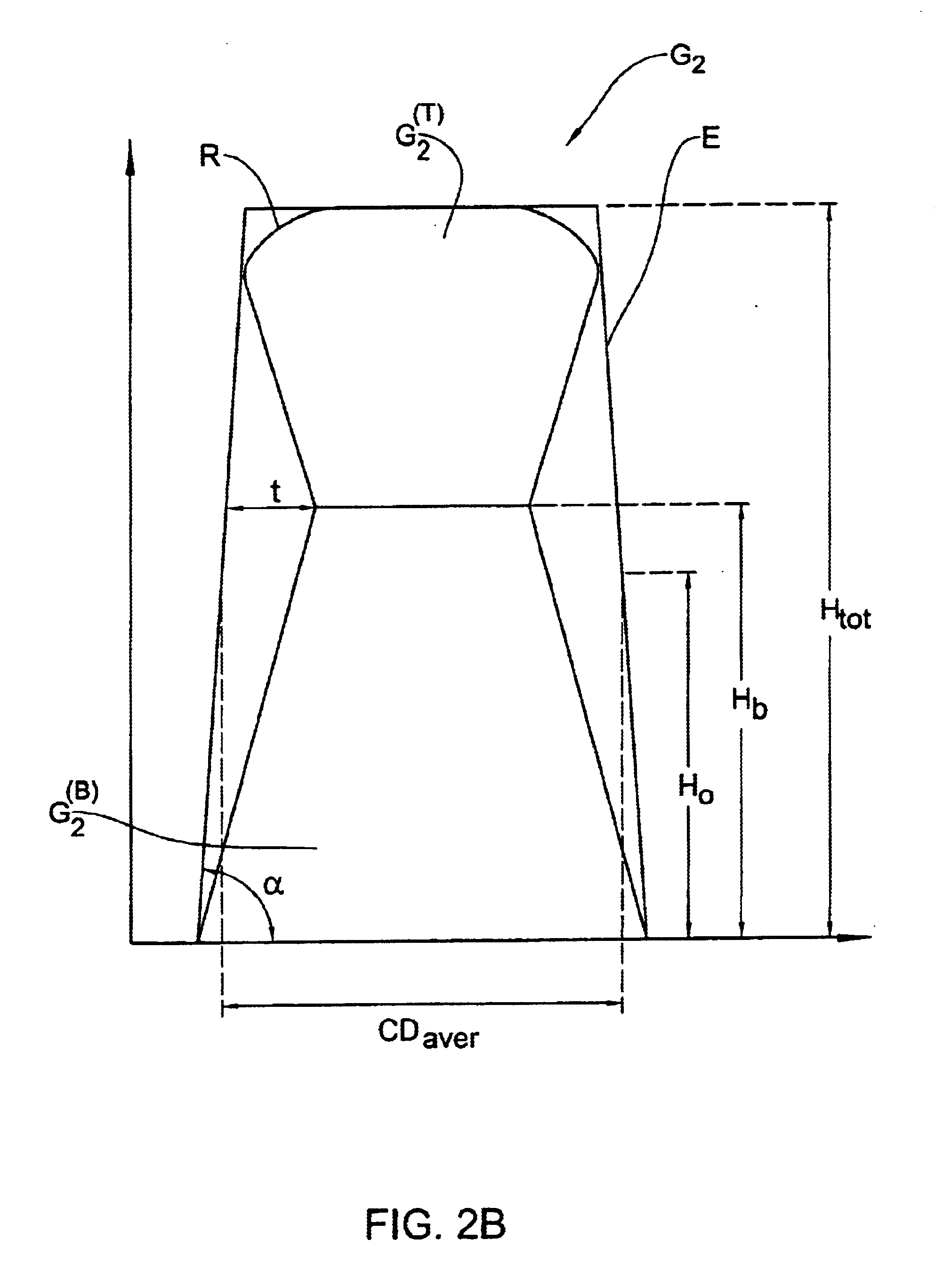
Method and system for measuring patterned structures
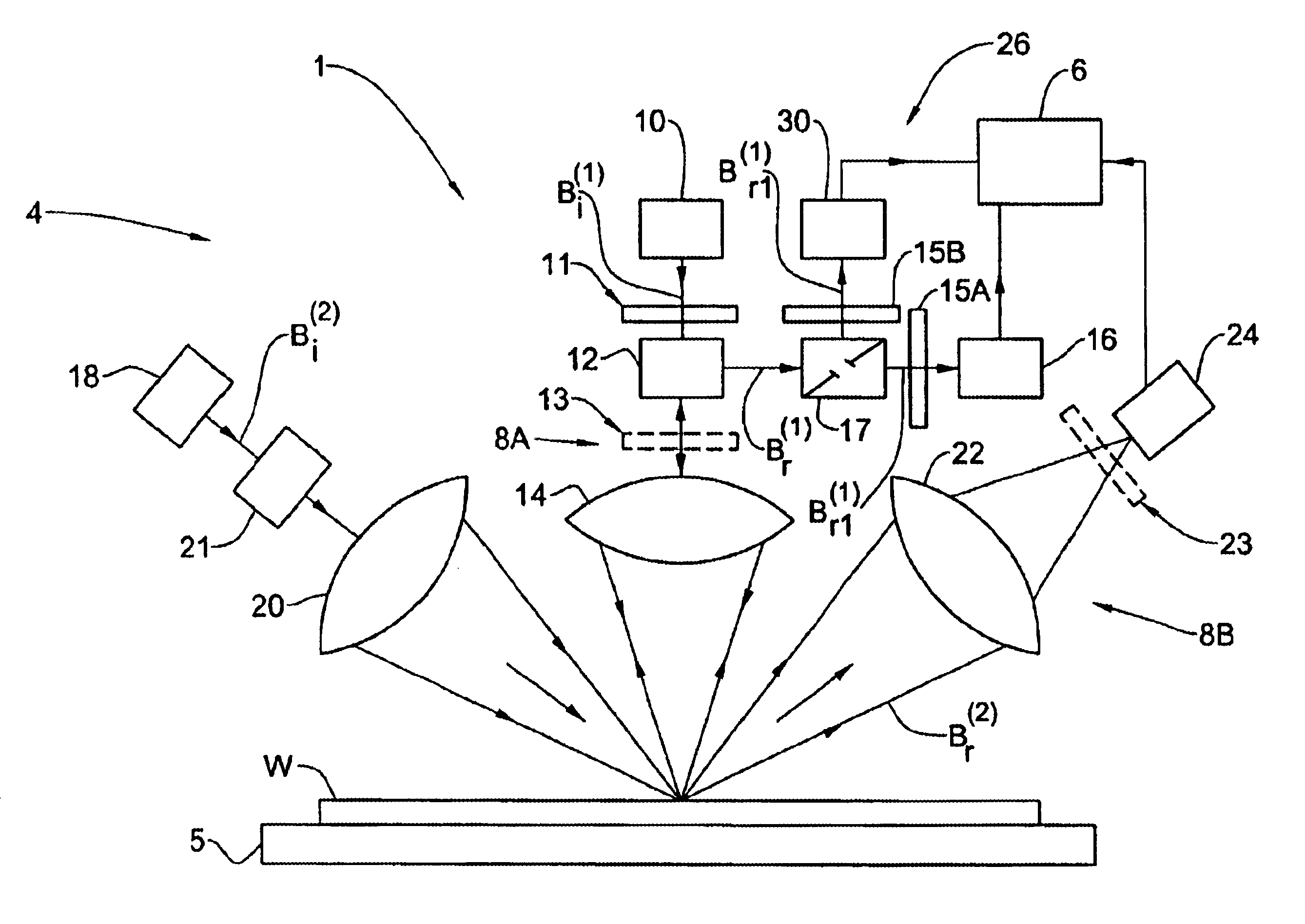
InactiveUS6657736B1Good chanceConfidence in resultRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidenceWavelength band
A method and system are presented for determing a line profile in a patterned structure, aimed at controlling a process of manufacture of the structure. The patterned structure comprises a plurality of different layers, the pattern in the structure being formed by patterned regions and un-patterned regions. At least first and second measurements are carried out, each utilizing illumination of the structure with a broad wavelengths band of incident light directed on the structure at a certain angle of incidence, detection of spectral characteristics of light returned from the structure, and generation of measured data representative thereof. The measured data obtained with the first measurement is analyzed, and at least one parameter of the structure is thereby determined. Then, this determined parameter is utilized, while analyzing the measured data obtained with the second measurements enabling the determination of the profile of the structure.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTR LTD
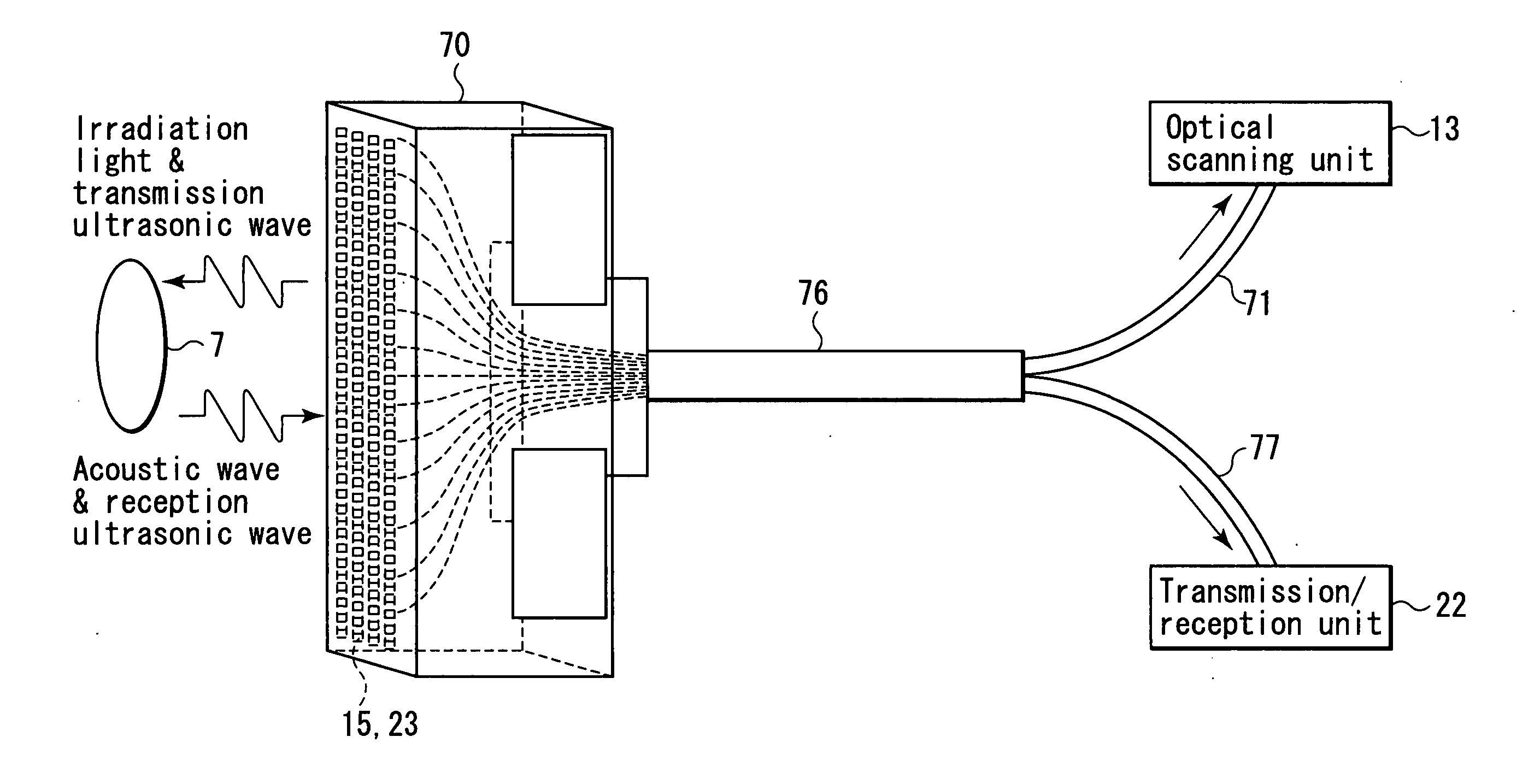
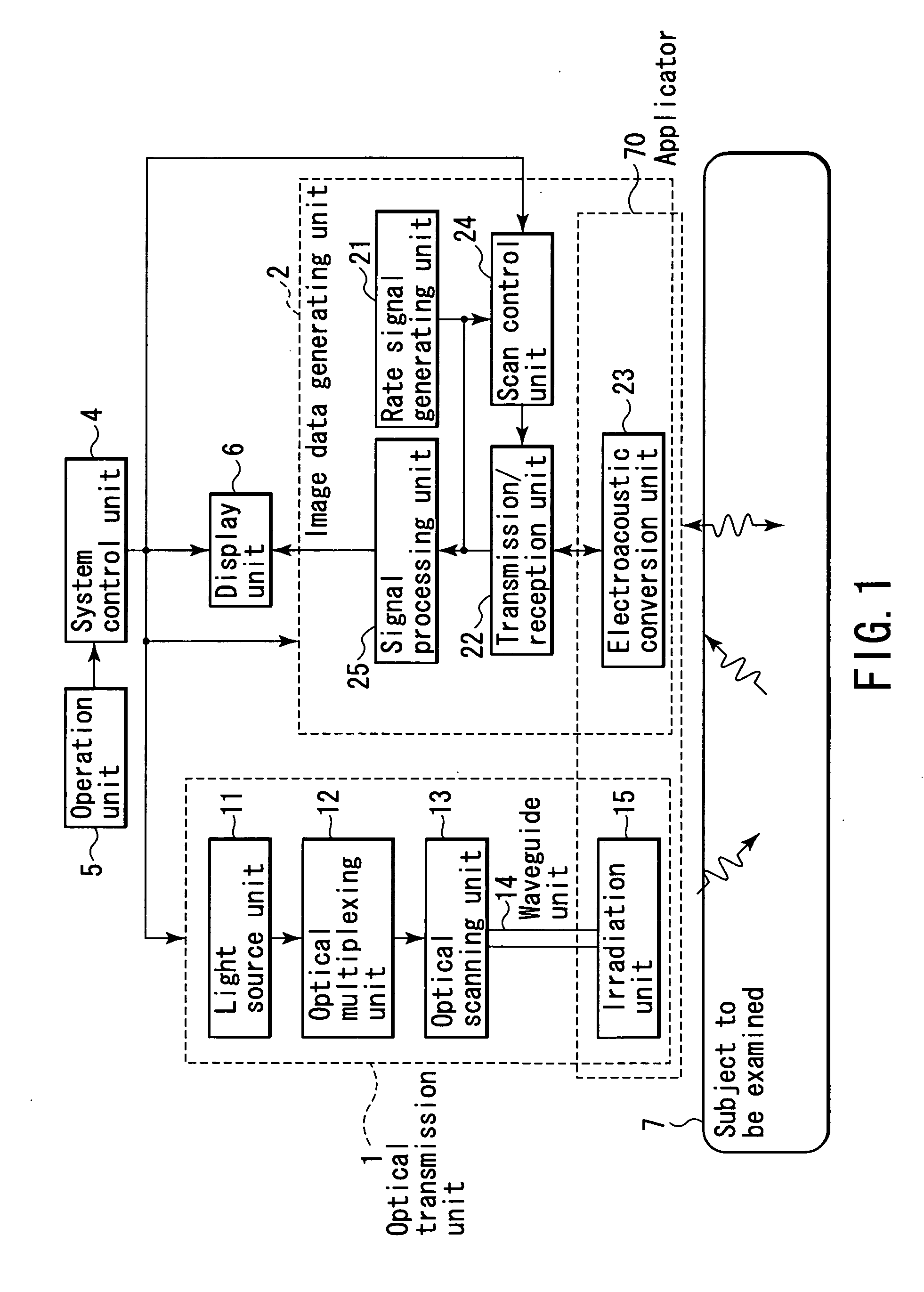
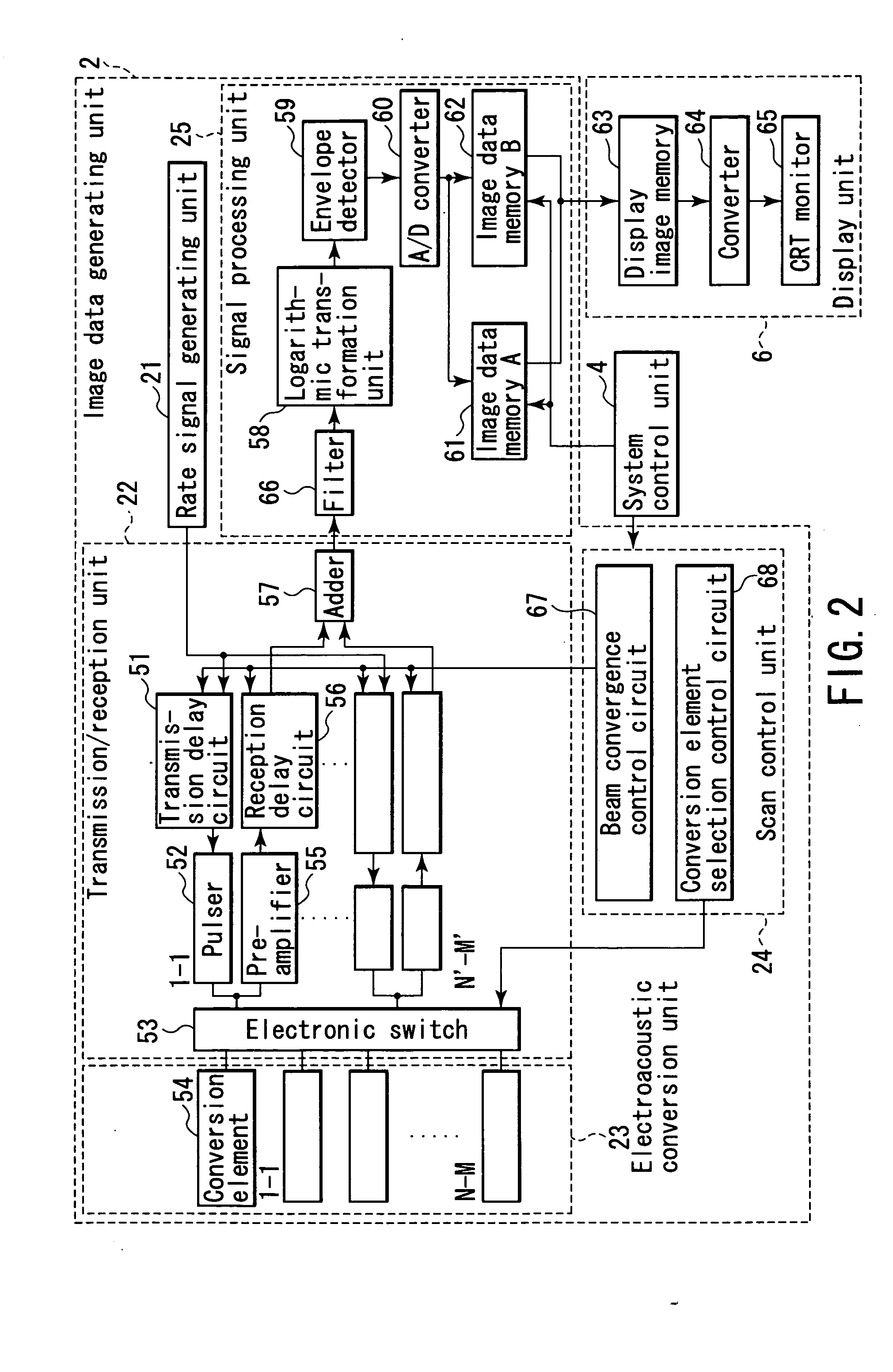
Non-invasive subject-information imaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050187471A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansLight irradiationTransducer
A non-invasive subject-information imaging apparatus according to this invention includes a light generating unit which generates light containing a specific wavelength component, a light irradiation unit which radiates the generated light into a subject, a waveguide unit which guides the light from the light generating unit to the irradiation unit, a plurality of two-dimensionally arrayed electroacoustic transducer elements, a transmission / reception unit which transmits ultrasonic waves to the subject by driving the electroacoustic transducer elements, and generates a reception signal from electrical signals converted by electroacoustic transducer elements, and a signal processing unit which generates volume data about a living body function by processing a reception signal corresponding to acoustic waves generated in the subject by light irradiation, and generates volume data about a tissue morphology by processing a reception signal corresponding to echoes generated in the subject upon transmission of the ultrasonic waves.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Optical probe for detecting or irradiating light and near-field optical microscope having such probe and manufacturing method of such probe
InactiveUS6215114B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight irradiationNear field optical microscope
An optical prove for detecting or irradiating evanescent light is manufactured by forming a film having a regulated film thickness on a substrate, then forming a recess from the rear surface of the substrate, and forming a through hole in the film from the side of the recess by etching. The obtained optical probe has a micro-aperture at the tip of the through hole and usually, a plurality of optical probes each having a micro-aperture of uniform profile are formed on a single substrate. In the recess, light-receiving or light-irradiating means may be provided.
Owner:CANON KK
Phosphor film, lighting device using the same, and display device
InactiveUS20060268537A1Solution to short lifeEfficient wide color reproduction rangePlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsLight irradiationLiquid-crystal display
The invention realizes a phosphor film that has a fluorescent characteristic excellent in resistance to humidity and provides, using the phosphor film, a liquid crystal display device that is excellent in resistance to humidity and has satisfactory calorimetric property and color mixture property. Phosphor particles that are excited by incident light and emit light having a wavelength different from the incident light are mixed in a binder. The binder mixed with the phosphor particles is sandwiched between a translucent film and a non-permeable layer as a phosphor layer to form a phosphor film. This phosphor film is provided at least in one place among a place between a light source and a light guide of a lighting device, a place on a light irradiation surface of the light guide, and a place between the light guide and a reflection plate. Moreover, the phosphor particles have a characteristic that a wavelength absorbed by a color filter of a display element is set as an excitation wavelength and a luminescent wavelength is in a region transmitted by the color filter. With this phosphor film, it is possible to realize a display device that has extremely high luminance efficiency and color reproducibility.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Method and device for determining a light transport parameter in a biological matrix
ActiveUS7315752B2Easy to separateEasy to useDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsMean free pathLight irradiation
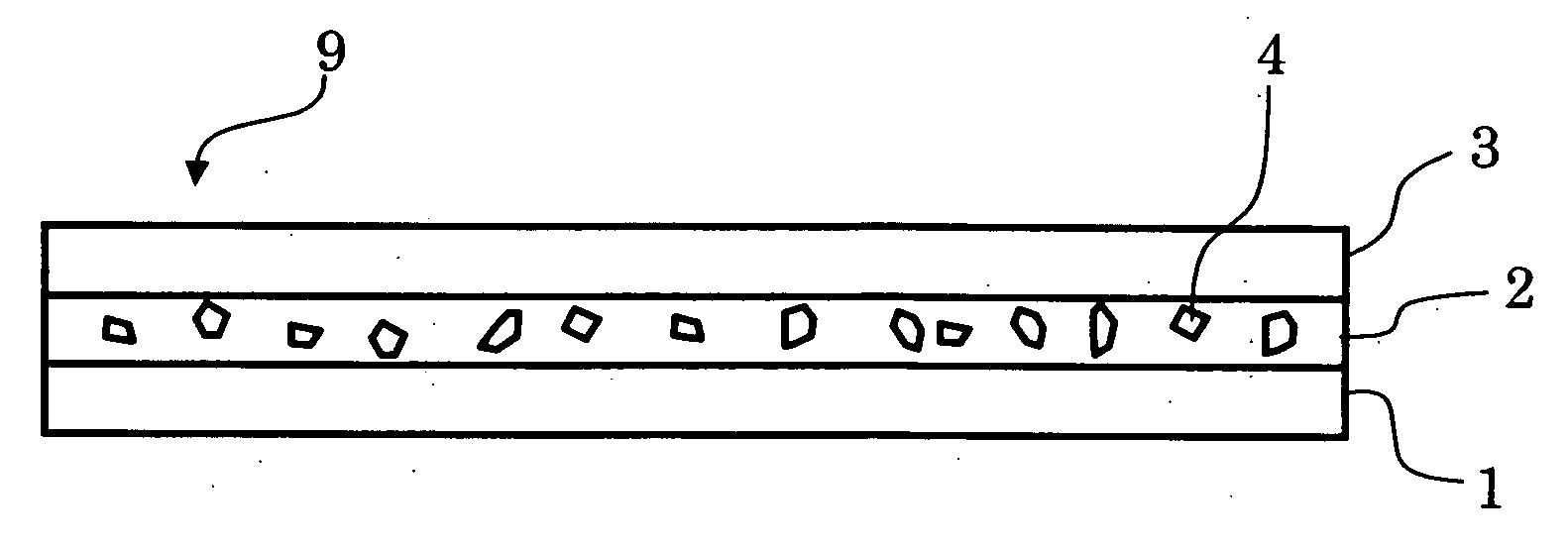
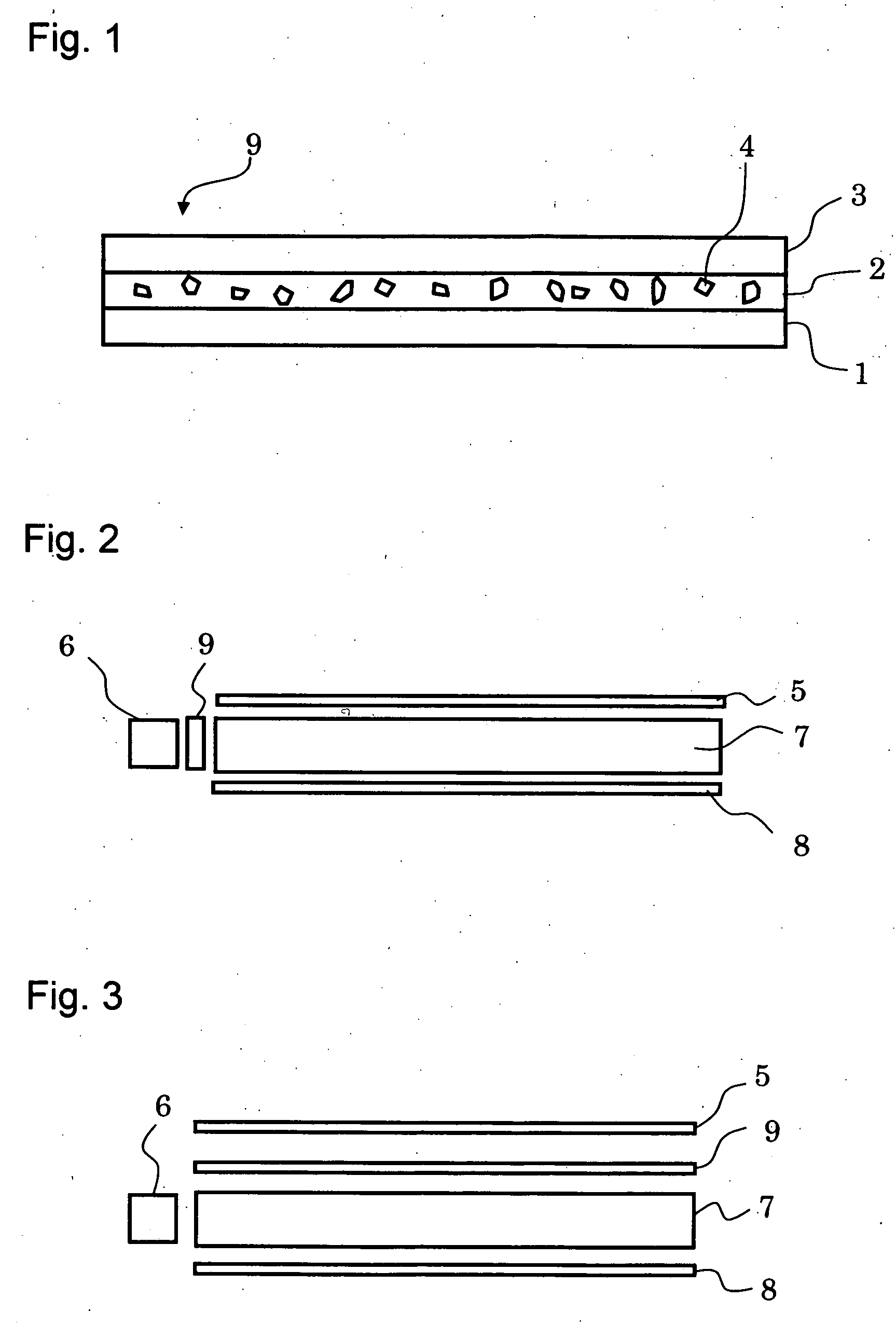
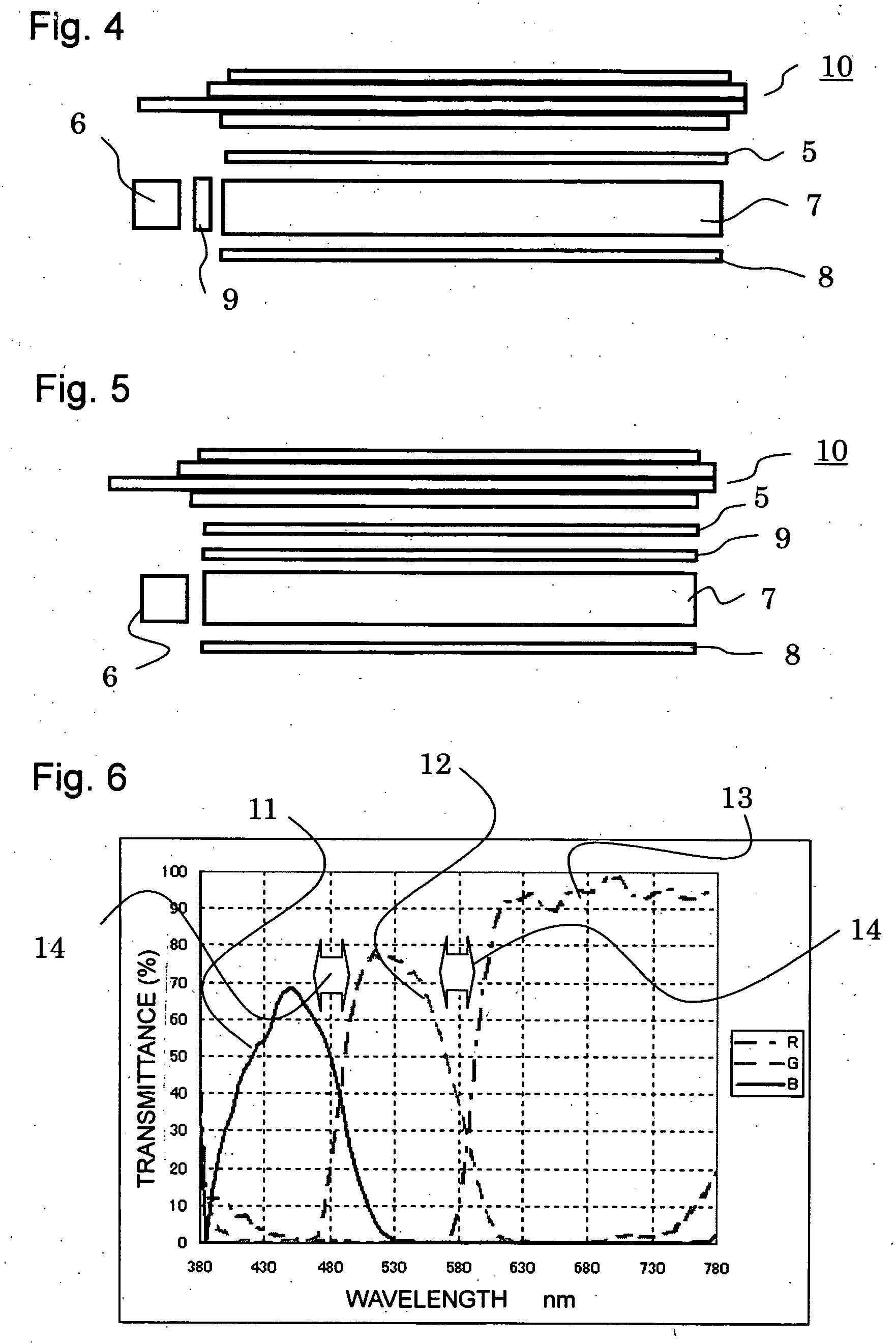
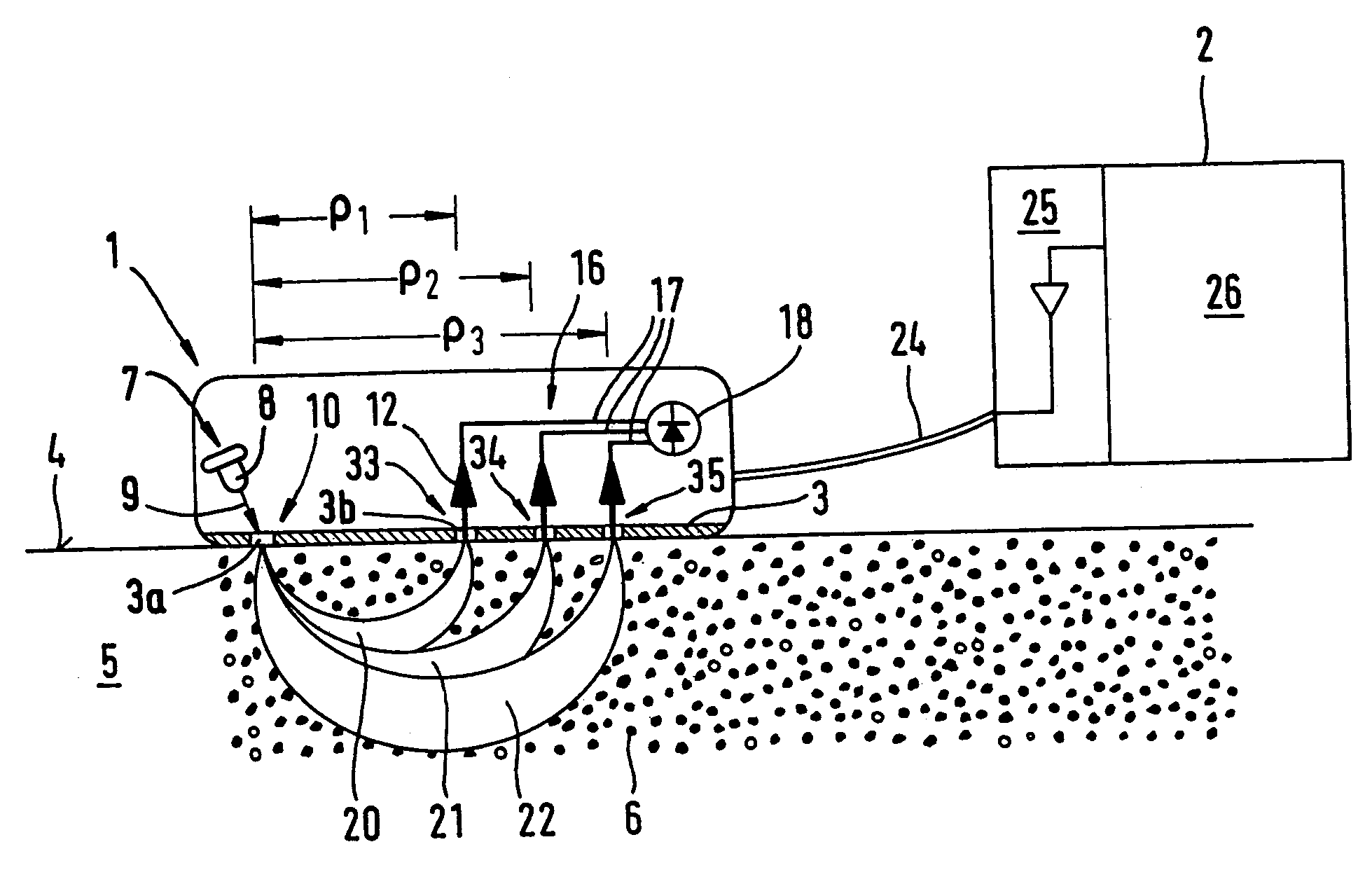
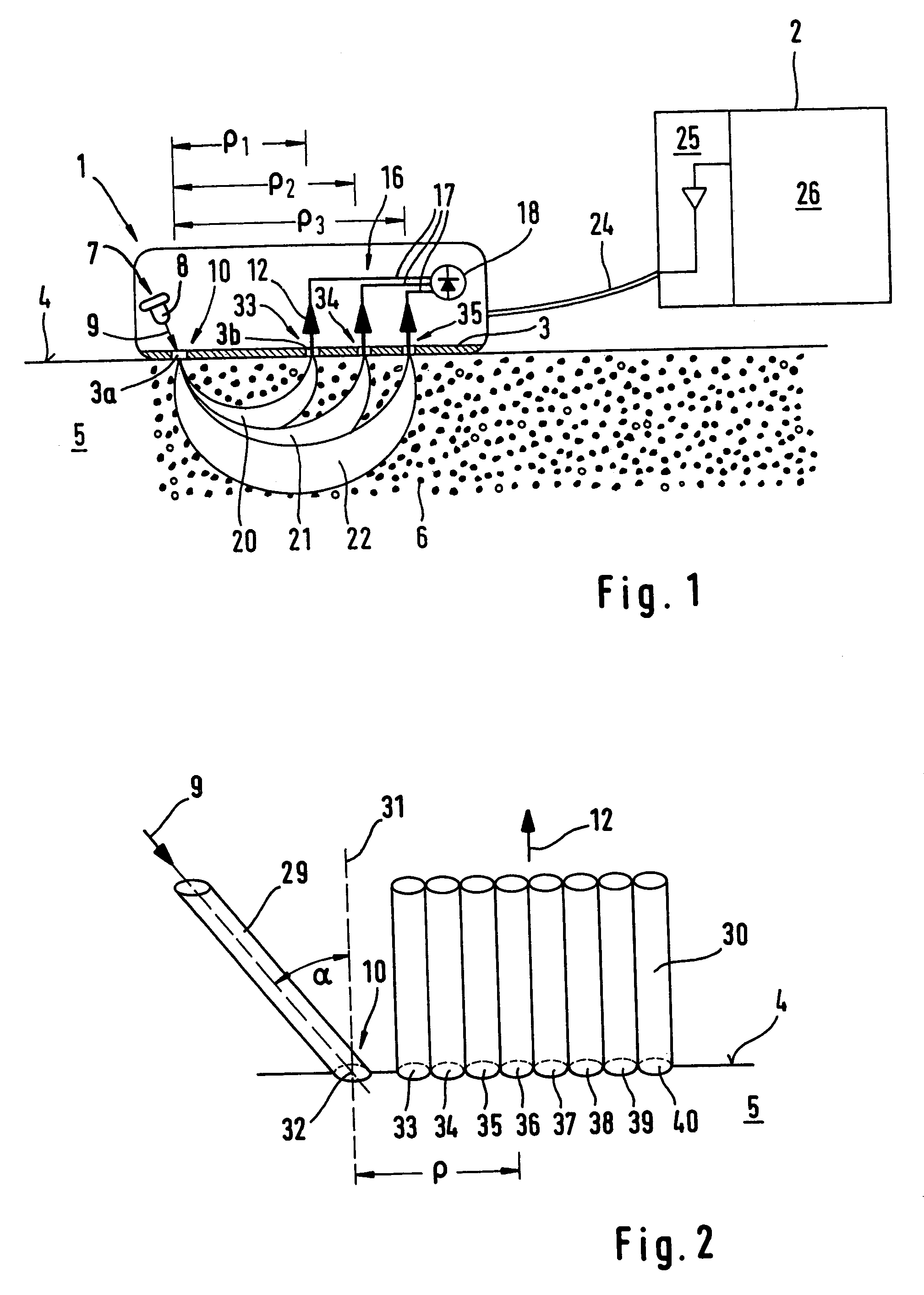
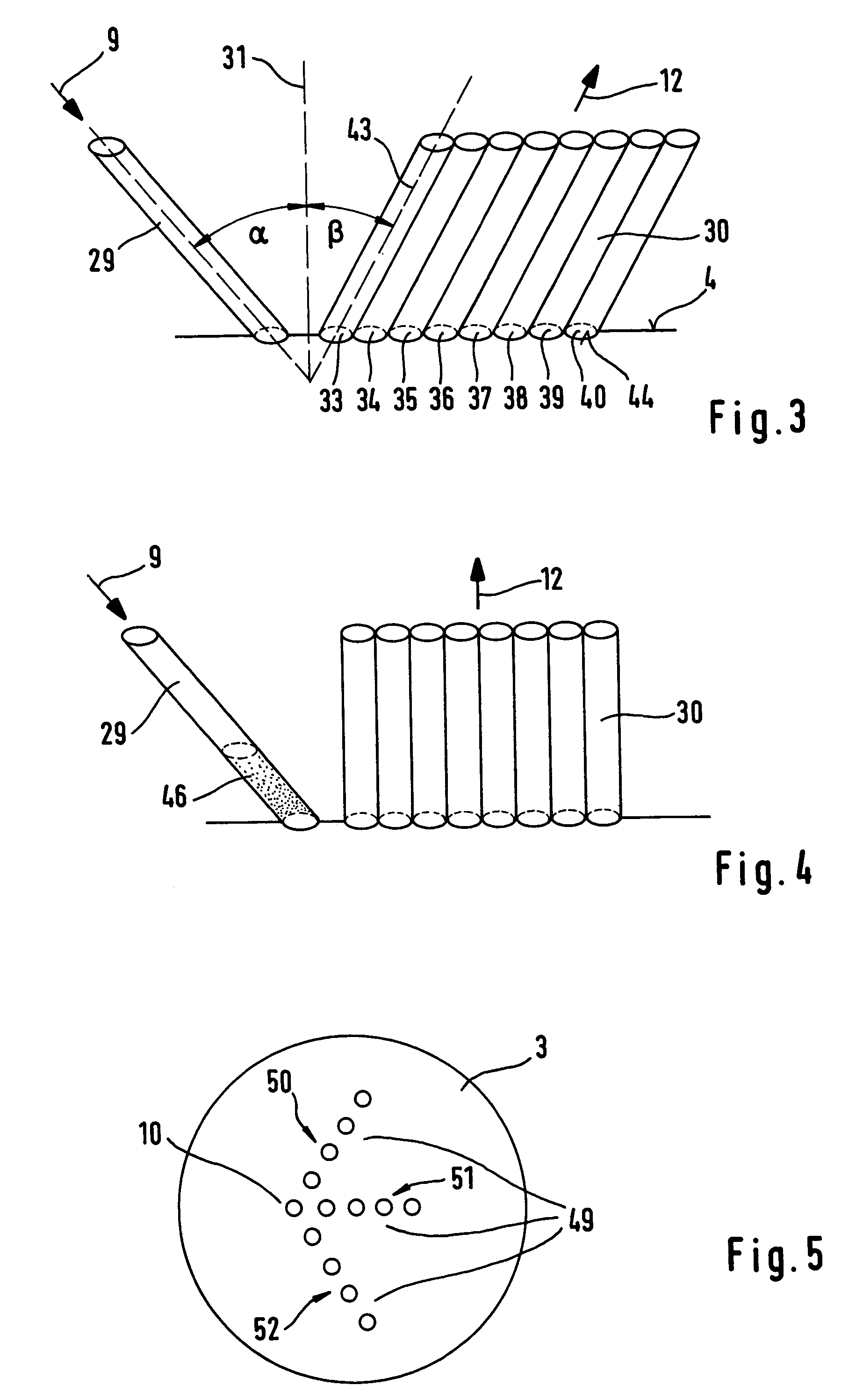
A method for the selective determination of the scattering index μs of a scattering biological matrix, in particular for the purpose of non-invasive determination of the concentration of glucose in the skin, by means of detection measurements, in each of which light in the form of primary light (9) is irradiated into the biological matrix (5) and an intensity measurement value of secondary light (12) exiting at a detection site (33-40) that is located at different measuring distances (ρ) from the respective light irradiation site (10) during the detection measurements is measured. In order to improve the quality and selectivity of the determination of μs, the primary light is irradiated obliquely at an angle between 5° and 85° using a contacting light-guiding element. In at least two detection measurements, the measuring distance (ρ) between the respective light irradiation site (10) and the respective detection site (33-40) corresponds to no more than five times the mean free path length of the light propagating in the biological matrix.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
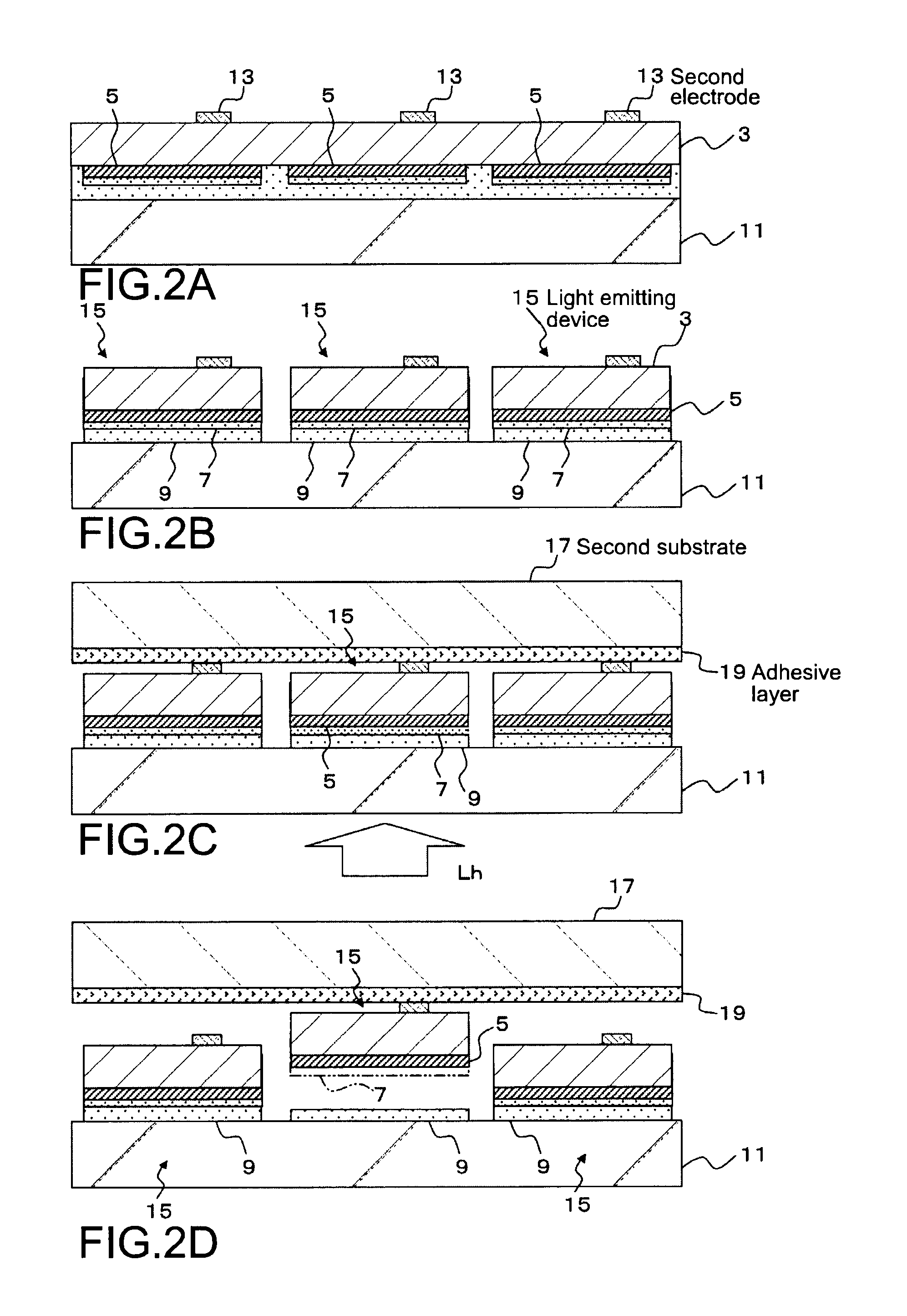
Method of transferring a device and method of manufacturing a display apparatus
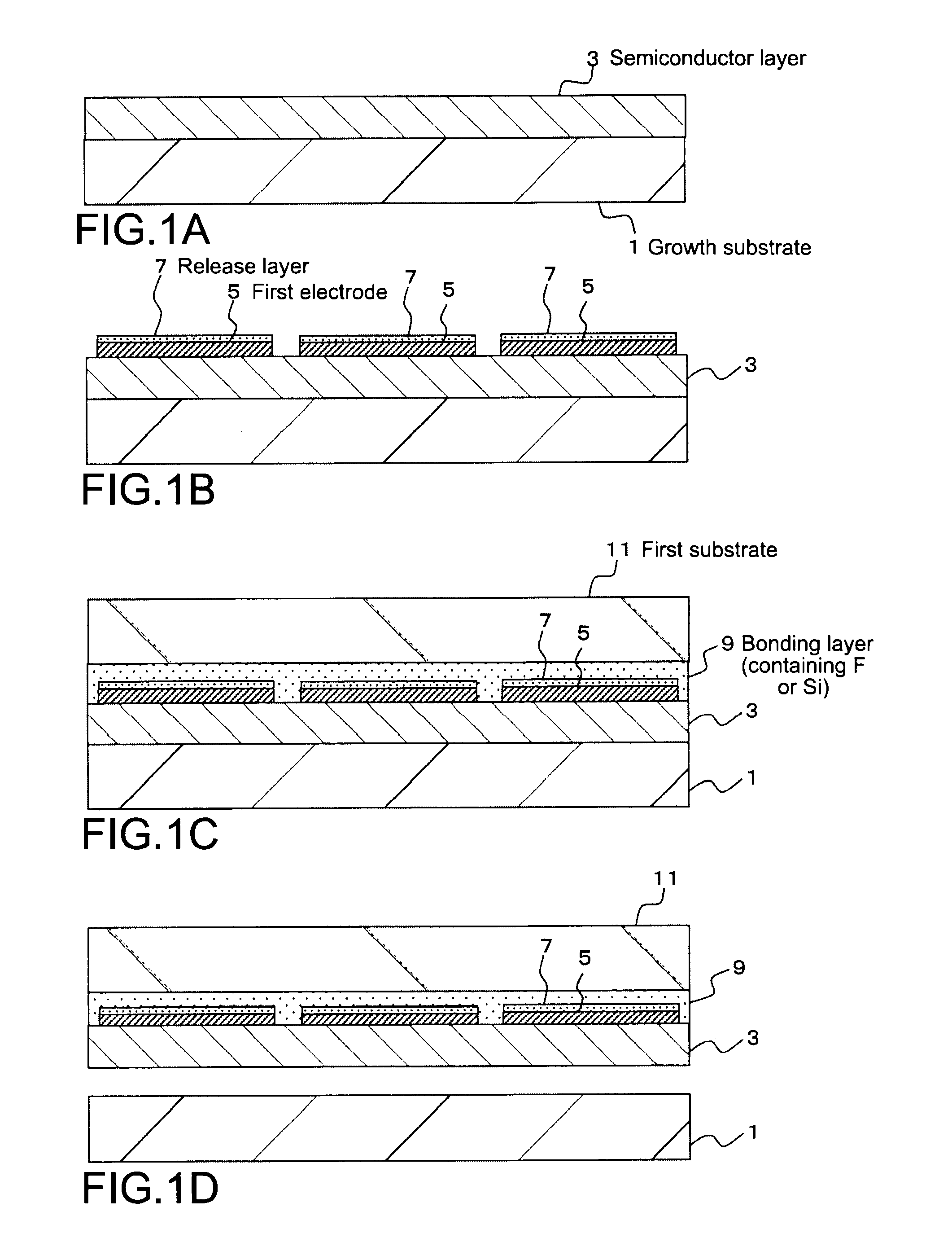
InactiveUS20100186883A1Easily ablatedSufficient bonding propertyOrnamental structuresSolid-state devicesLight irradiationOptoelectronics
A method of transferring a device includes: arranging a release layer and a device in the stated lamination order on a first substrate having light transmitting property via a bonding layer having light transmitting property; arranging an adhesive layer formed on a second substrate so that the adhesive layer is opposed to a surface of the first substrate on which the device is arranged; and ablating the release layer by performing light irradiation on the release layer from the first substrate side and transferring the device onto the second substrate with the bonding layer being left on the first substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
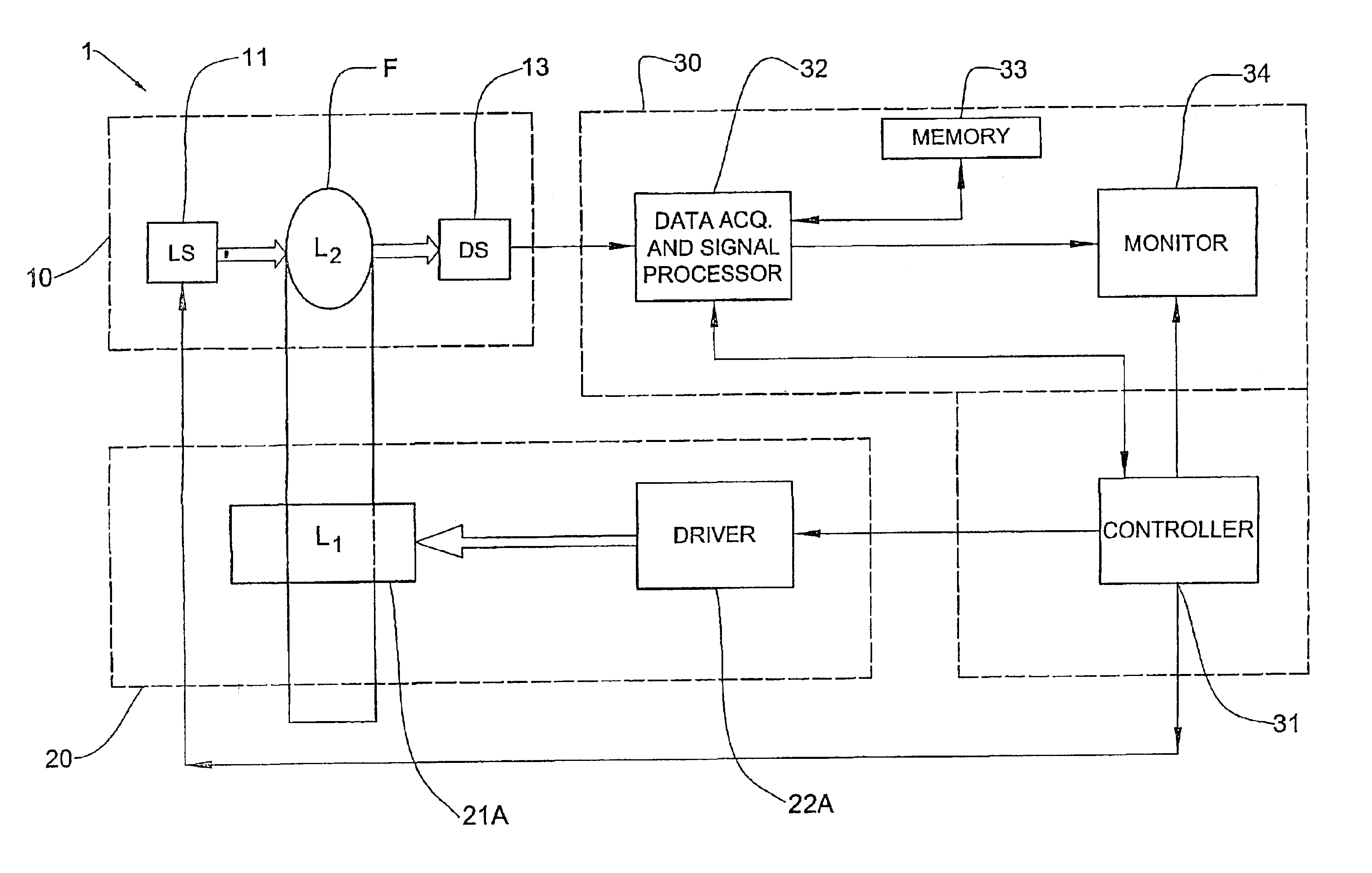
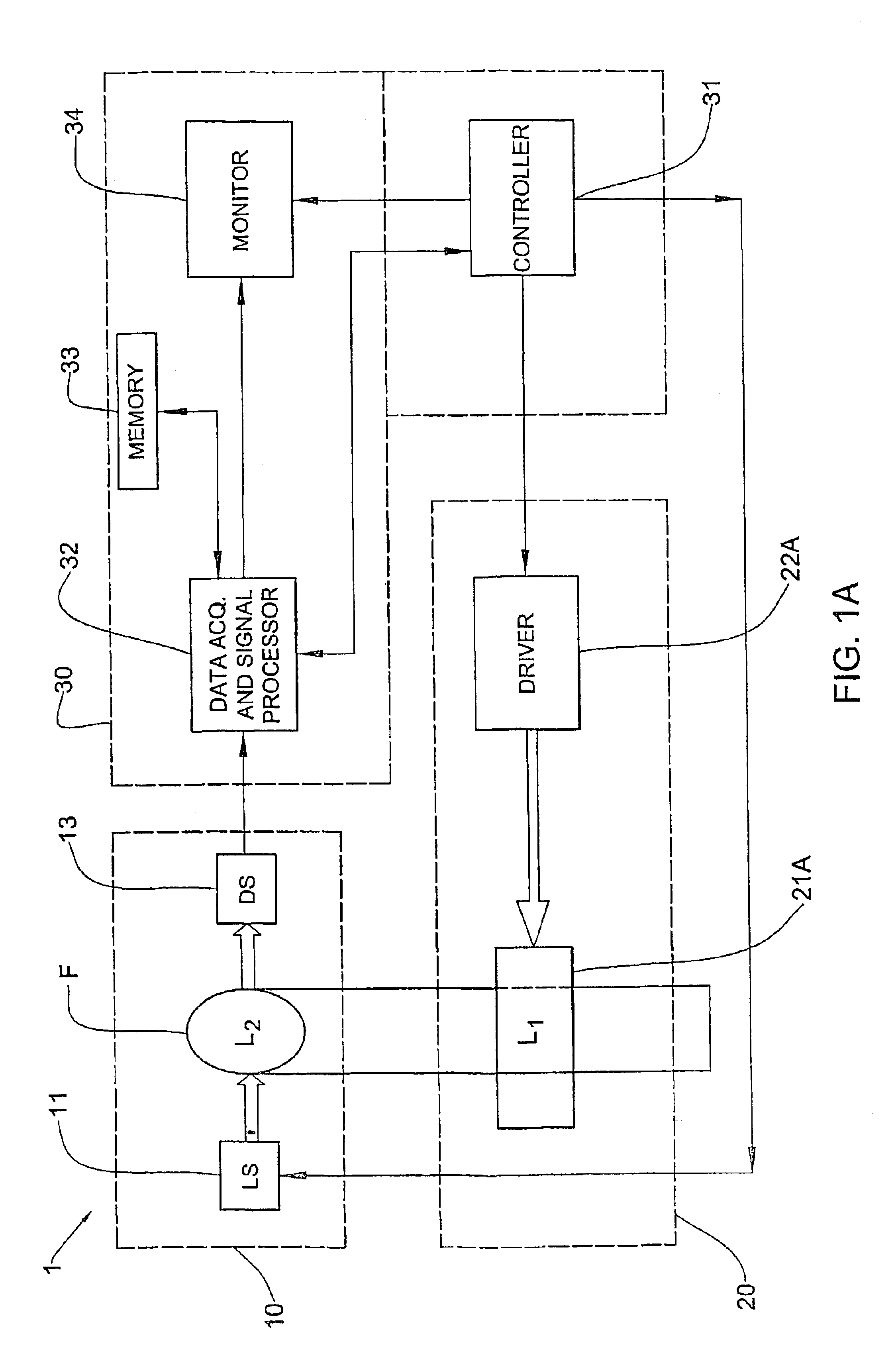
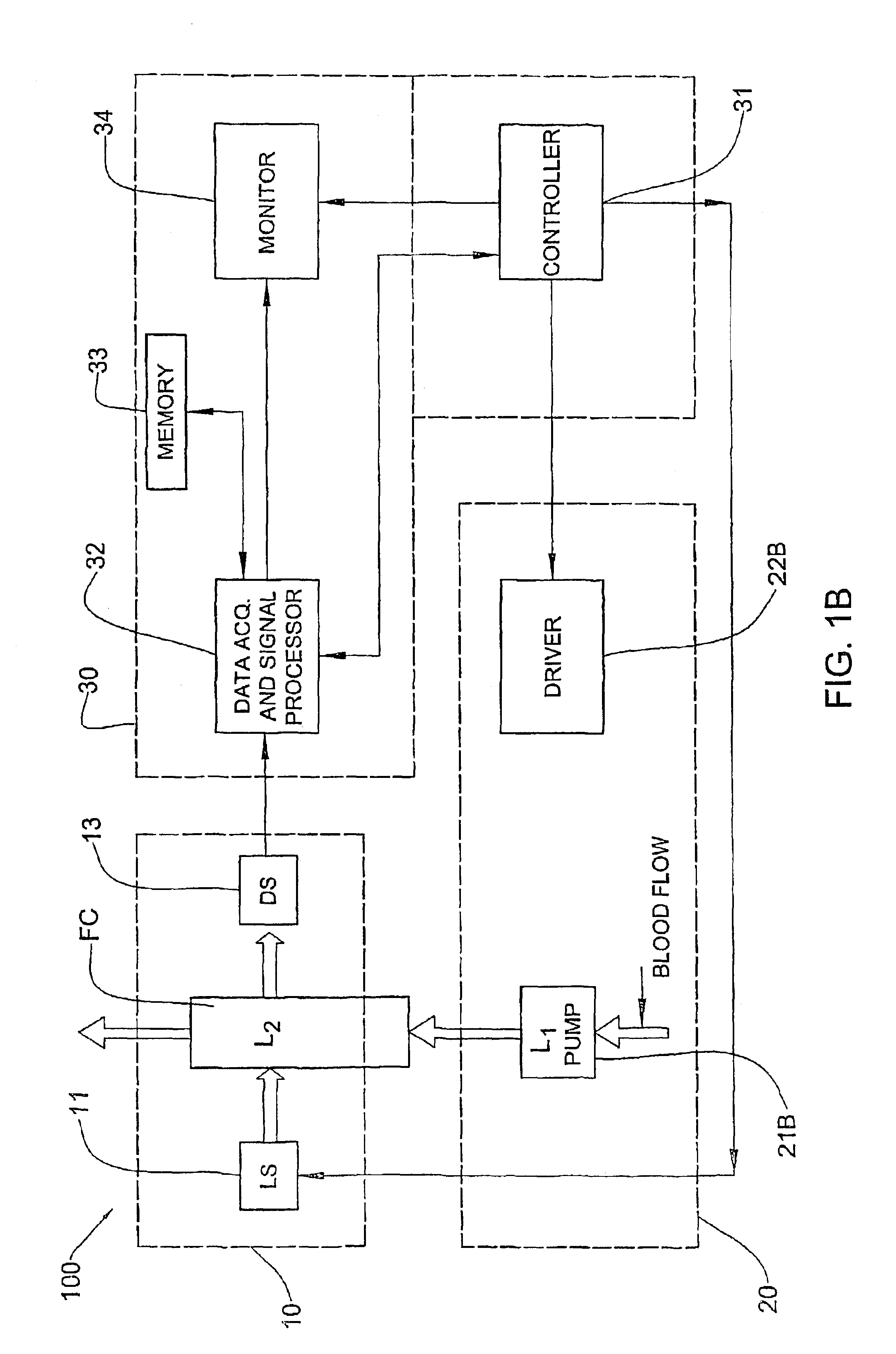
Method and device for measuring concentration of glucose or other substances in blood
InactiveUS6804002B2Diagnostics using pressurePolarisation-affecting propertiesLight irradiationGlucose polymers
A method and device for optical measurements are presented for determining the concentration of a substance in patient's blood. Optical measurement sessions are applied to a measurement location in a blood containing medium during certain time period. The optical measurements include illumination of the measurement location with incident light of at least one selected wavelength, detection, at each measurement session, of at least two light responses of the medium characterized by at least two different polarization states of detected light, respectively, and generation of data representative thereof. Measured data so obtained is in the form of at least two time variations of the light responses of the medium characterized by different polarization states of detected light, respectively, a relation between the time variations being indicative of the concentration of the substance in blood.
Owner:ORSENSE LTD
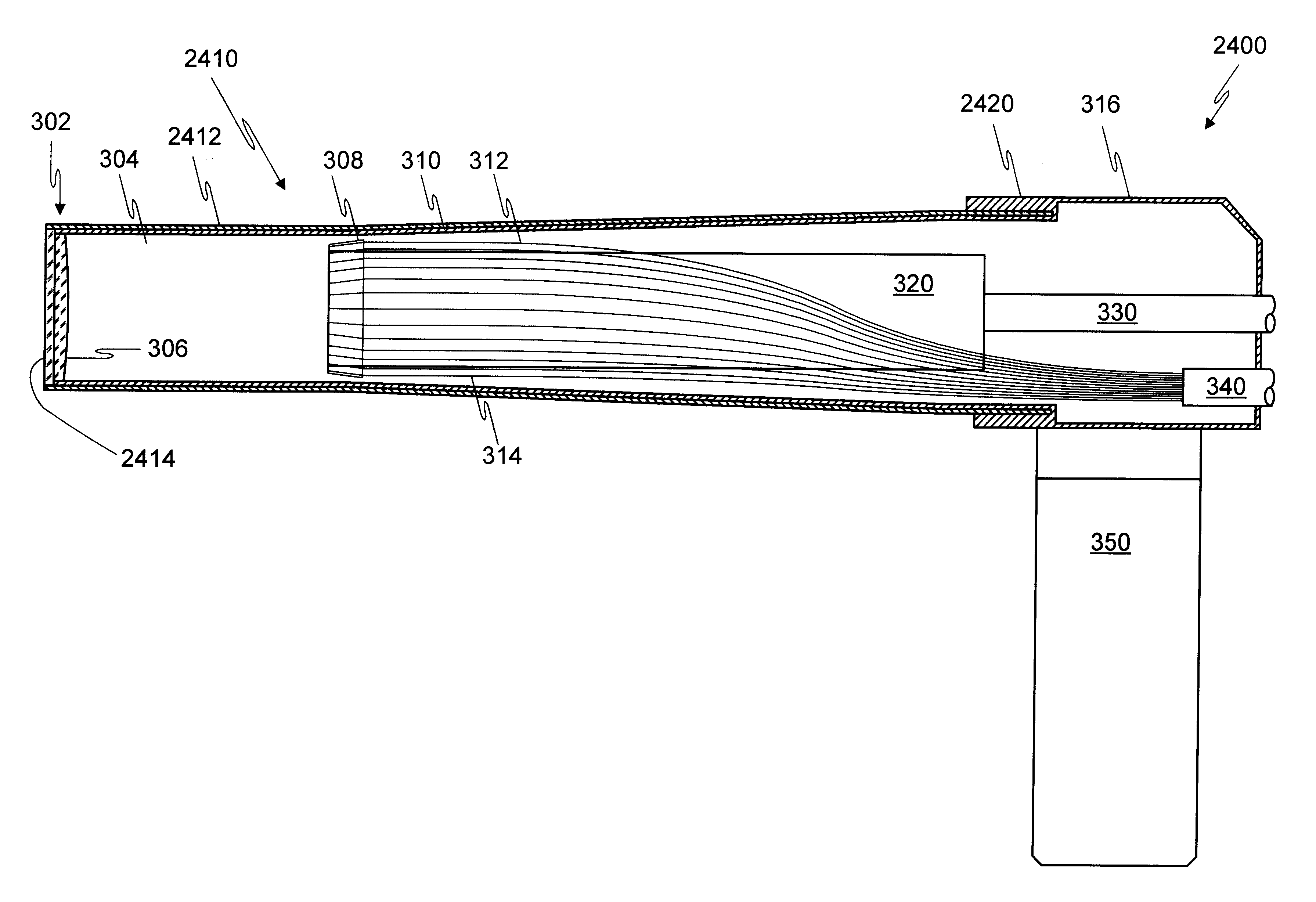
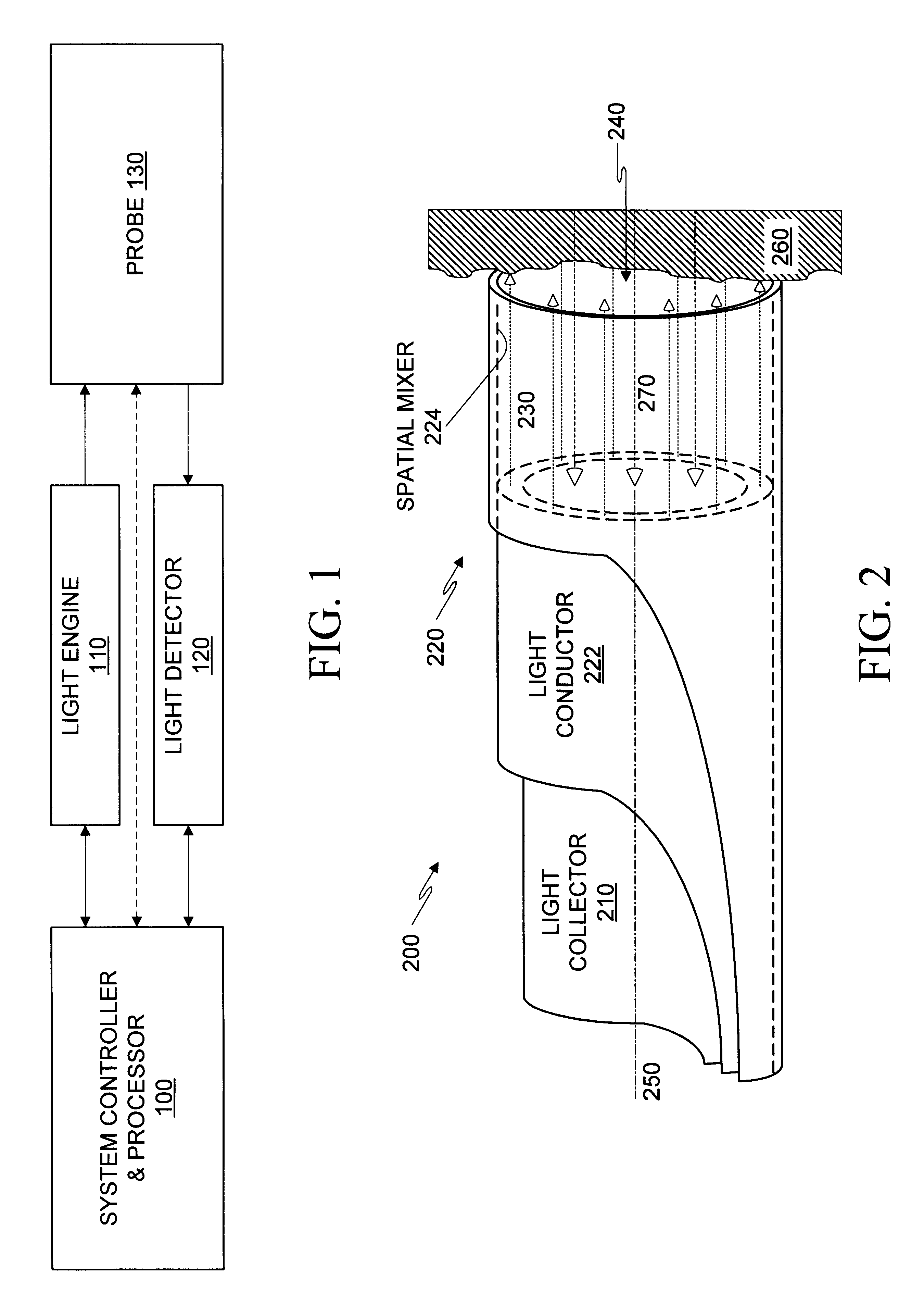
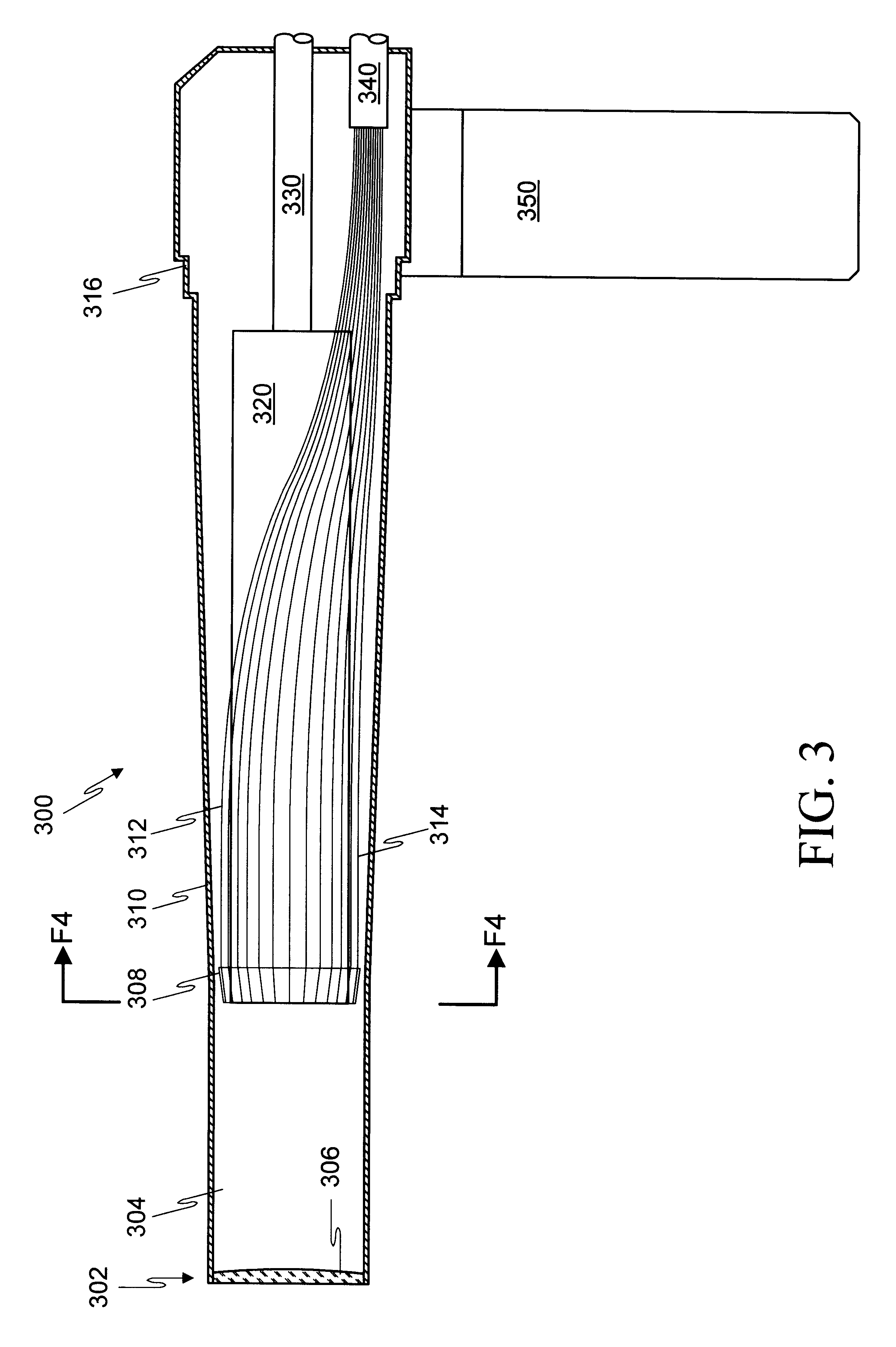
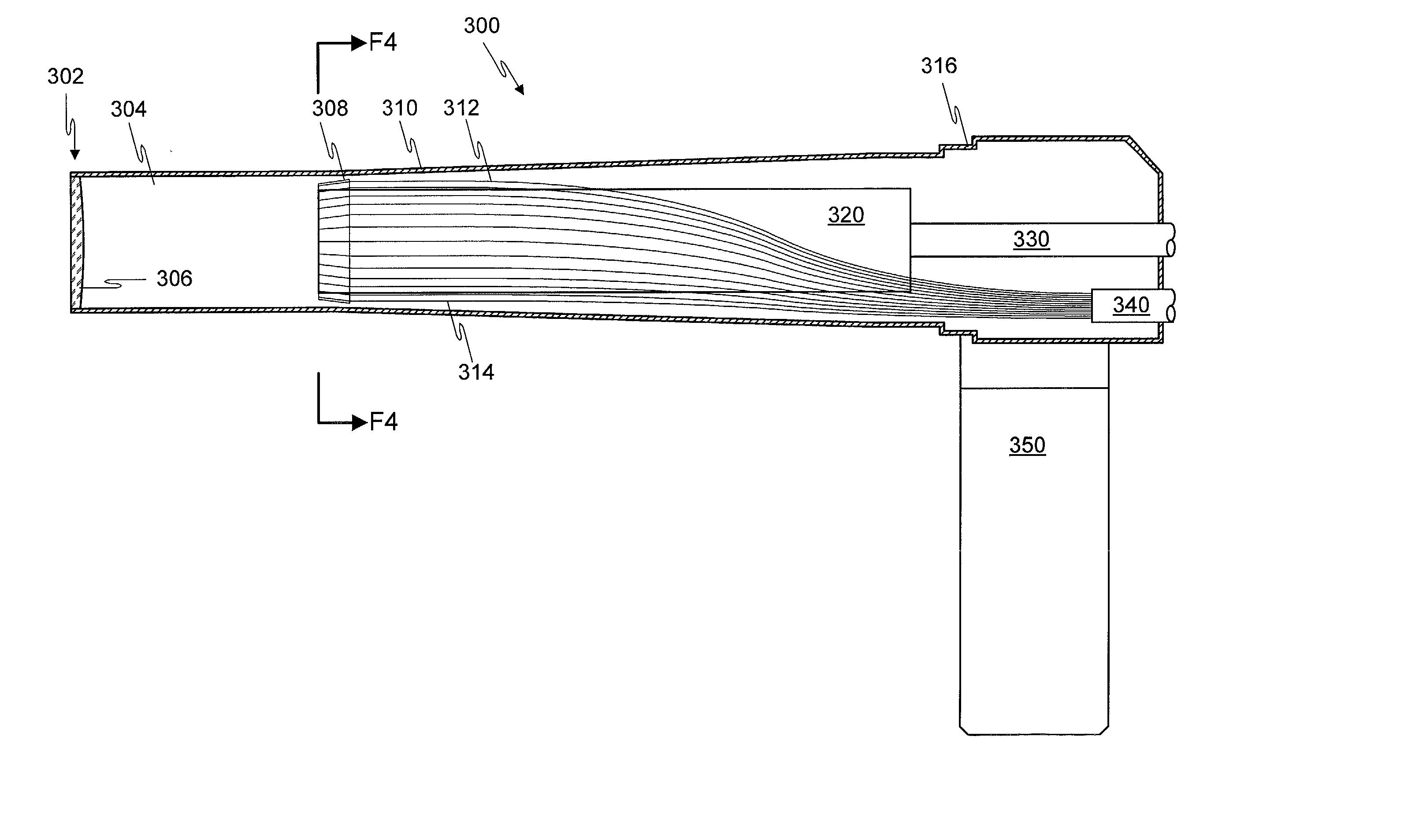
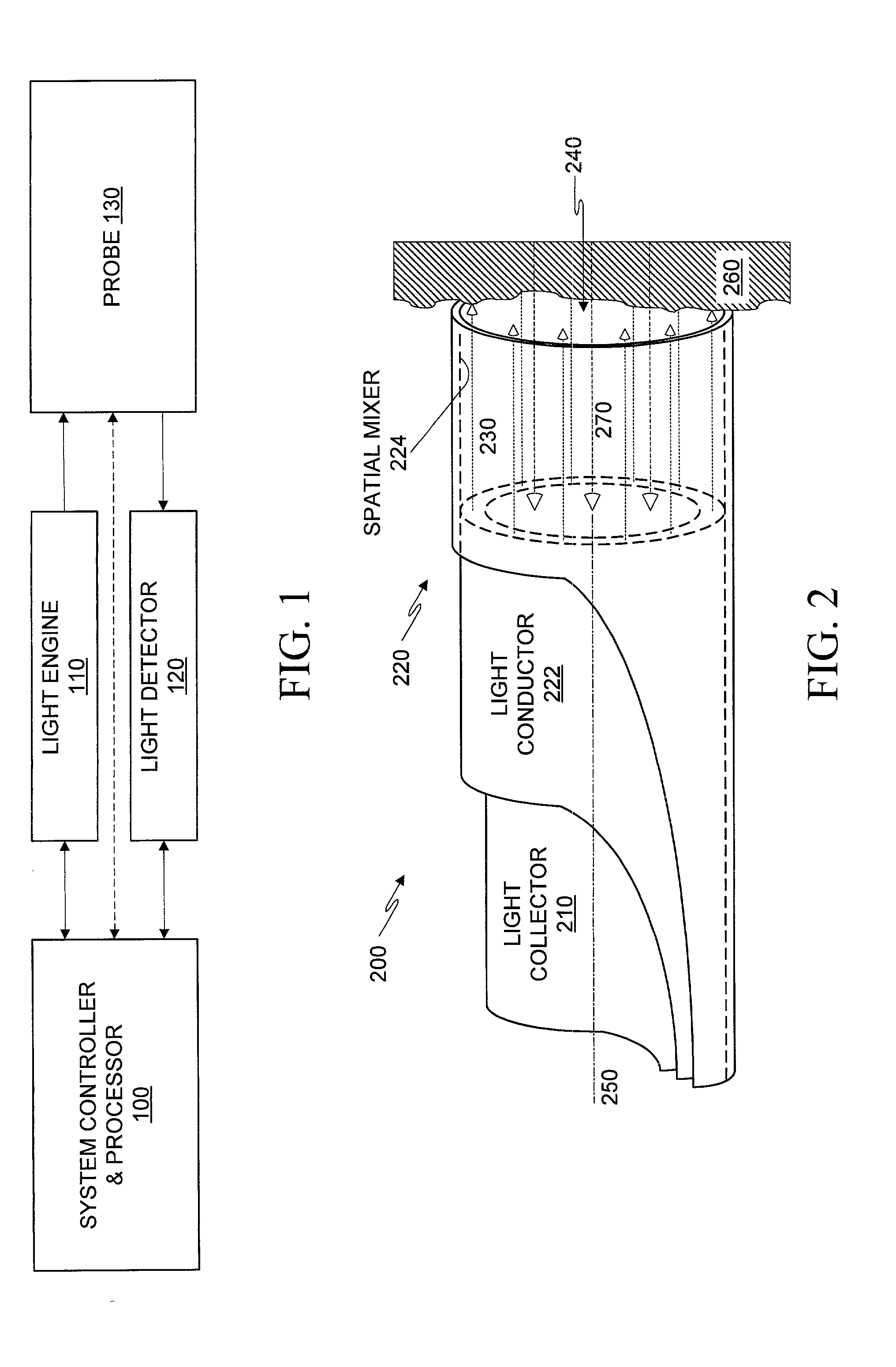
Optical probe having and methods for difuse and uniform light irradiation
A variety of optical probes and methods have utility in the examination of various materials, especially materials in the interior of cavities having restricted access through orifices or passageways. One type of such optical probe is elongated and includes a distal optical window, a divergent light source, a spatial mixer, and a light collector. Light from the light source is mixed in the spatial mixer to achieve uniform diffuse light in the vicinity of the optical window. The light collector receives light from the target through the spatial mixer. The optical probe may be made of two sections, a reusable section and a disposable. The disposable is elongated and contains a mounting section, an inside surface suitable for the spatial mixing of light, and an optical element which helps to seal the reusable probe section from the target.
Owner:LIFESPEX
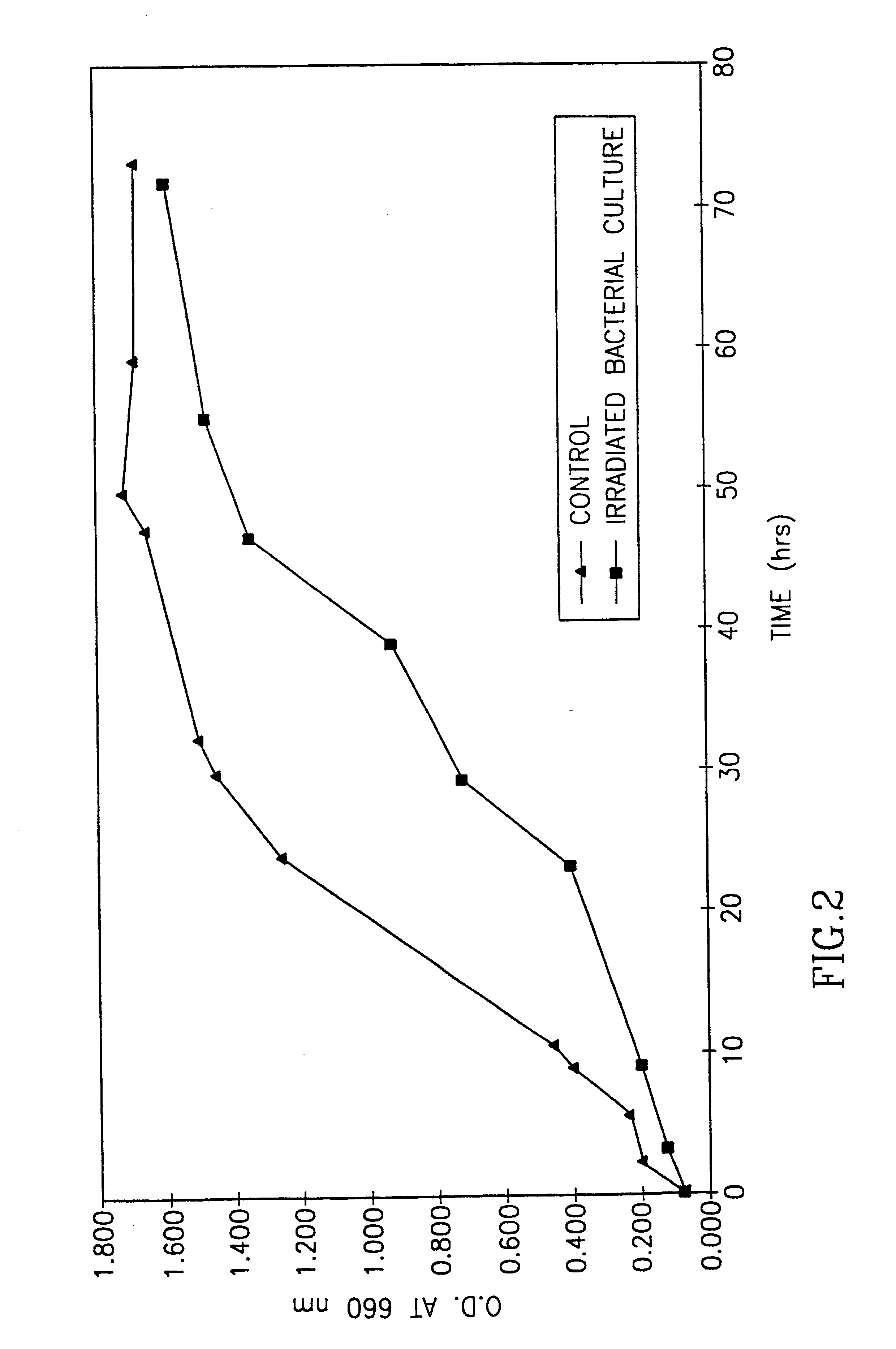
Sterilization system with ultraviolet emitter for eradicating biological contaminants
ActiveUS20120223216A1Effectively destroyEffective sterilizationAutomatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
An exemplary sterilization system includes a self-propelled robotic mobile platform for locating and eradicating infectious bacterial and virus strains on floors (and objects thereon), walls, cabinets, angled structures, etc., using one or more ultraviolet light sources. A controller allows the system to adjust the quantity of ultraviolet light received by a surface by, for example, changing the intensity of energy input to a ultraviolet light source, changing a distance between a ultraviolet light source and a surface being irradiated, changing the speed / movement of the mobile platform to affect time of exposure, and / or by returning to contaminated areas for additional passes. The mobile platform may include a sensor capable of detecting fluorescence of biological contaminants irradiated with ultraviolet light to locate contaminated areas. The system is thus capable of “seek and destroy” functionality by navigating towards contaminated areas and irradiating those areas with ultraviolet light accordingly.
Owner:FLAHERTY KAREN
Thin tube which can be hyperflexed by light
InactiveUS20080021416A1Prevent leakageMechanism is complicatedSurgeryEndoscopesLight irradiationMedicine
A thin tube is provided that is inserted into a lumen of a living body so as to be used, which can detect the flexed direction of the forward end of itself with the use of a sensor disposed at such forward end upon light irradiation. The forward end of the thin tube is allowed to be flexed to a desired direction with the use of an actuator disposed at such forward end. Such thin tube for medical use is inserted into the lumen of a living body so as to be used for internal observation or internal treatment and contains a device for sensing light irradiation and / or an actuator that is operated via light irradiation at its forward end and a light transmission means, such light transmission means being used for irradiating the device and / or the actuator with light and such device or actuator functioning for monitoring and / or controlling the degree of flection of the forward end of such thin tube, is provided.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
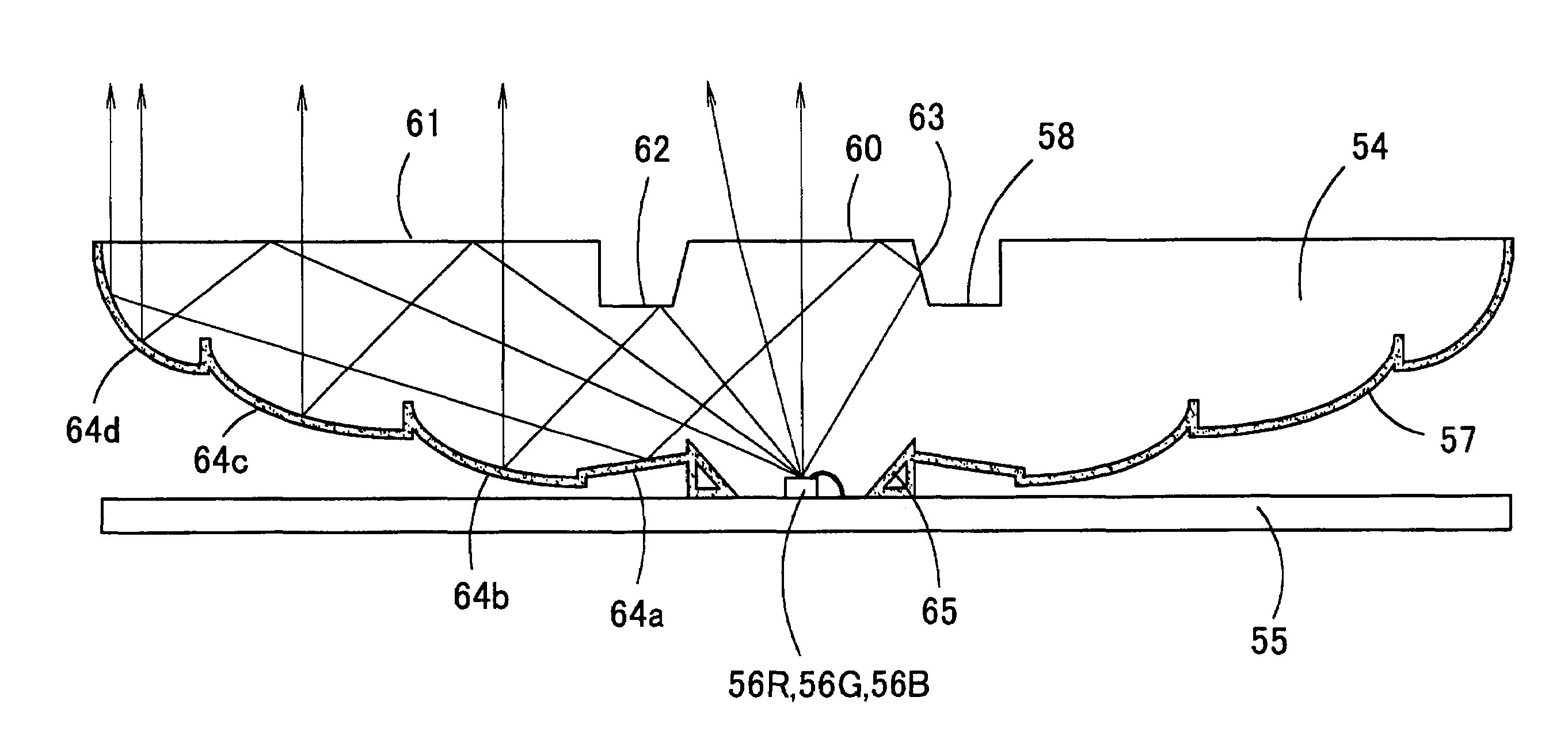
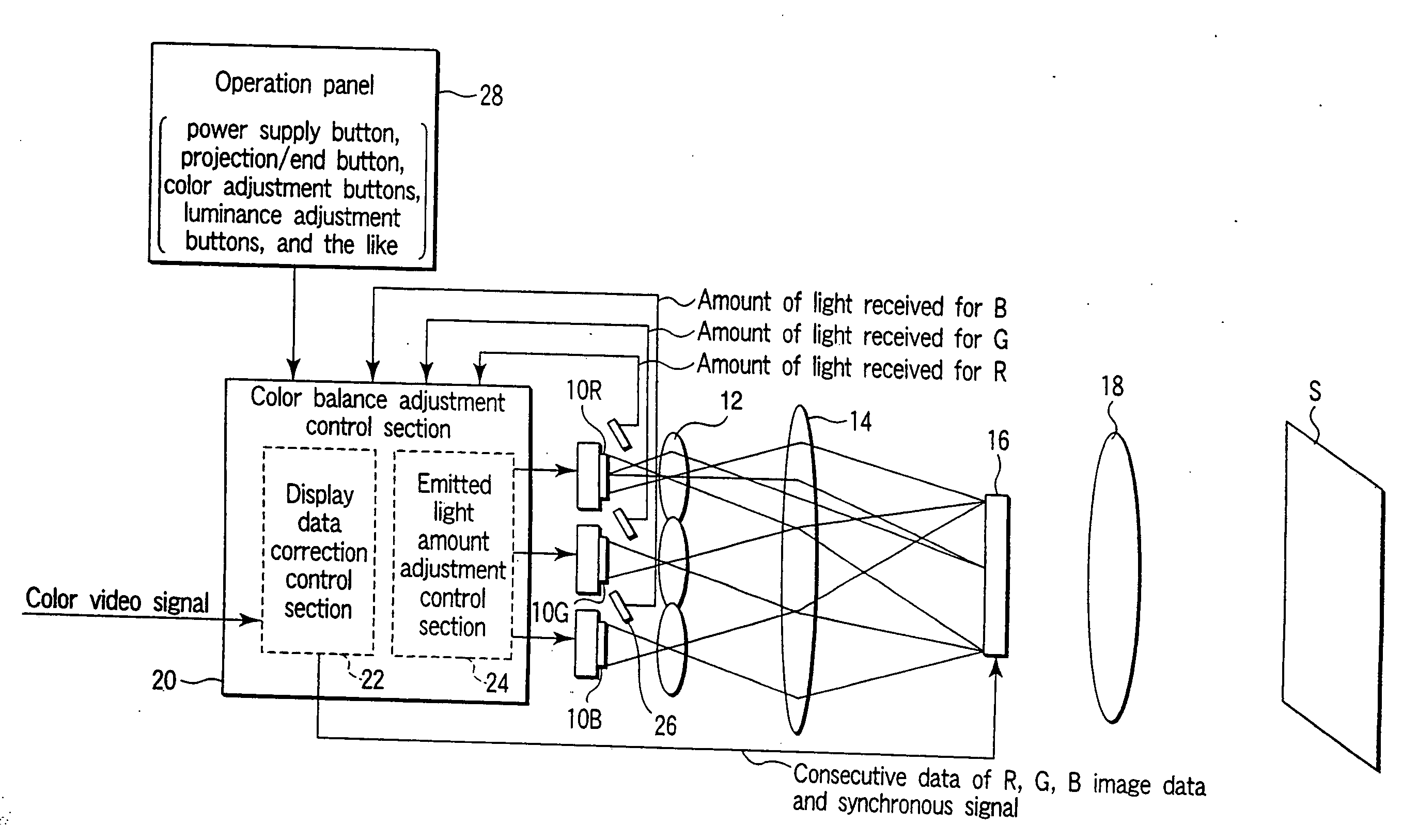
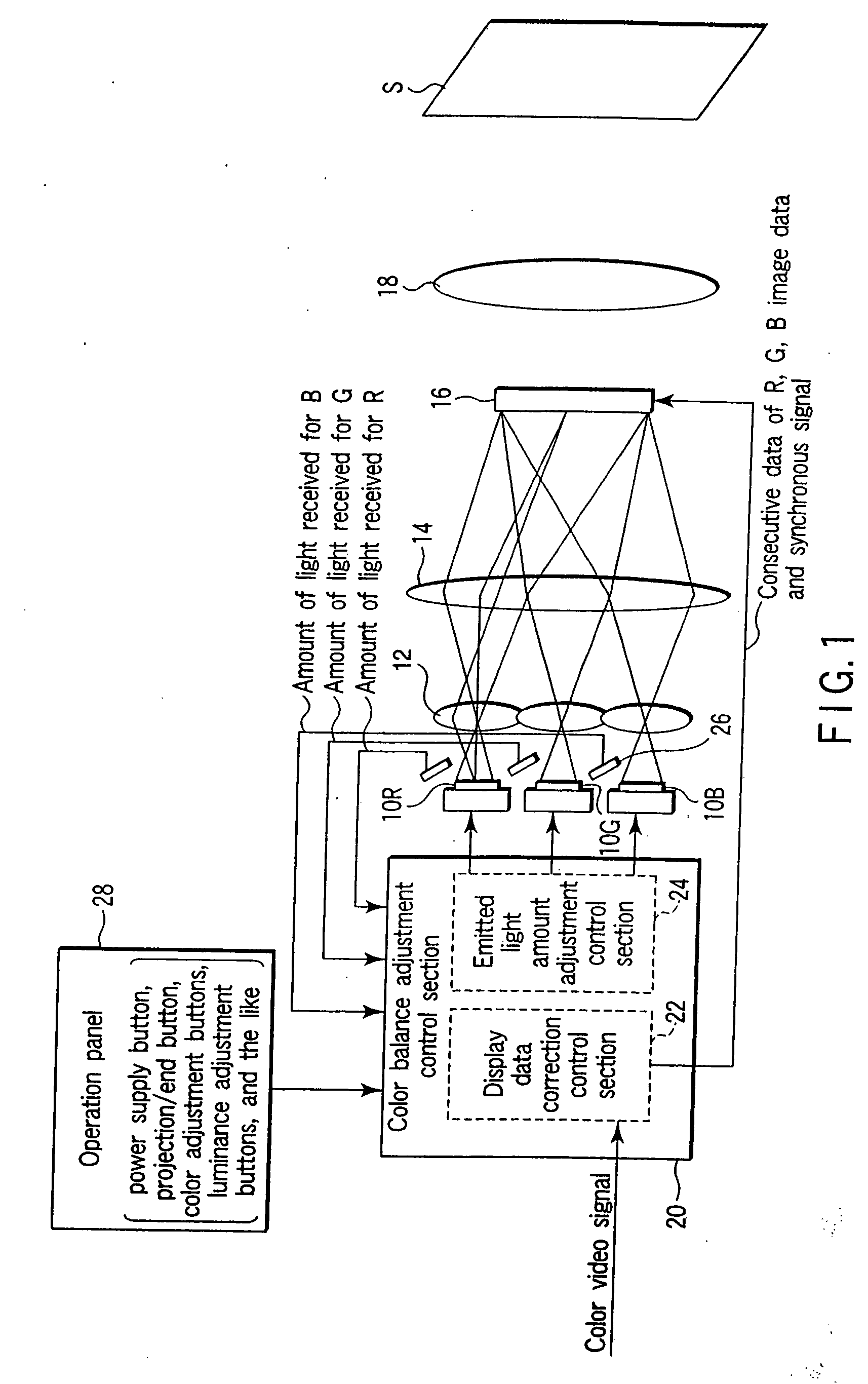
Display apparatus, light source device, and illumination unit
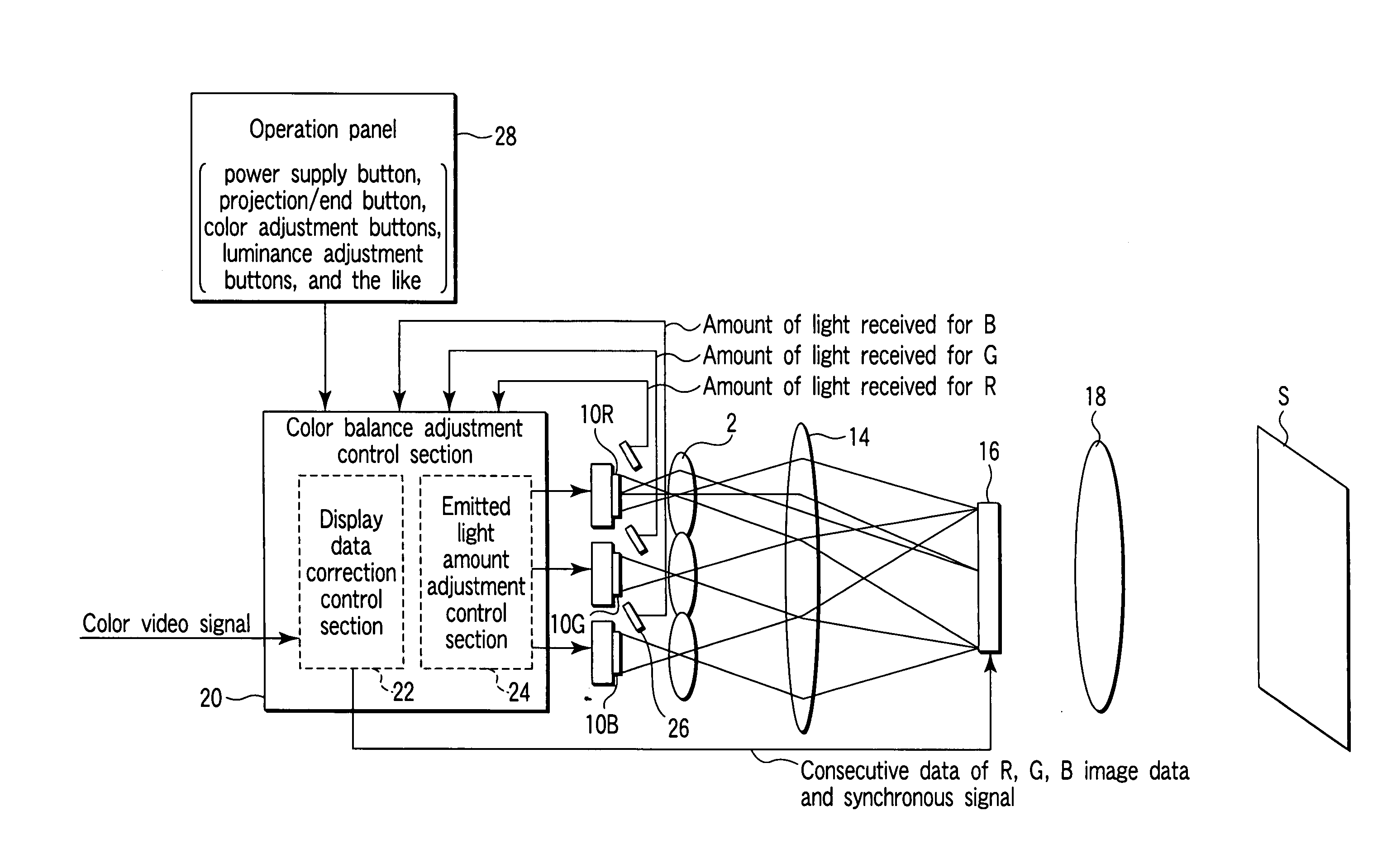
InactiveUS7052138B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight irradiationLight-emitting diode
A display apparatus capable of illuminating a light modulation device with a light from a light emitting body to display an image on a display plane comprises a plurality of light emitting bodies (R, G, B) different from one another in emitted light color, a light receiving device configured to detect the light from the light emitting bodies and to output an amount of light received, and a color balance adjustment control section configured to adjust and control a color balance in the display plane in accordance with the amount of light received by the light receiving device. The color balance adjustment control section is configured to be capable of identifying the emitted light color of the light emitting body relating to the amount of light received.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method for nucleotide detection
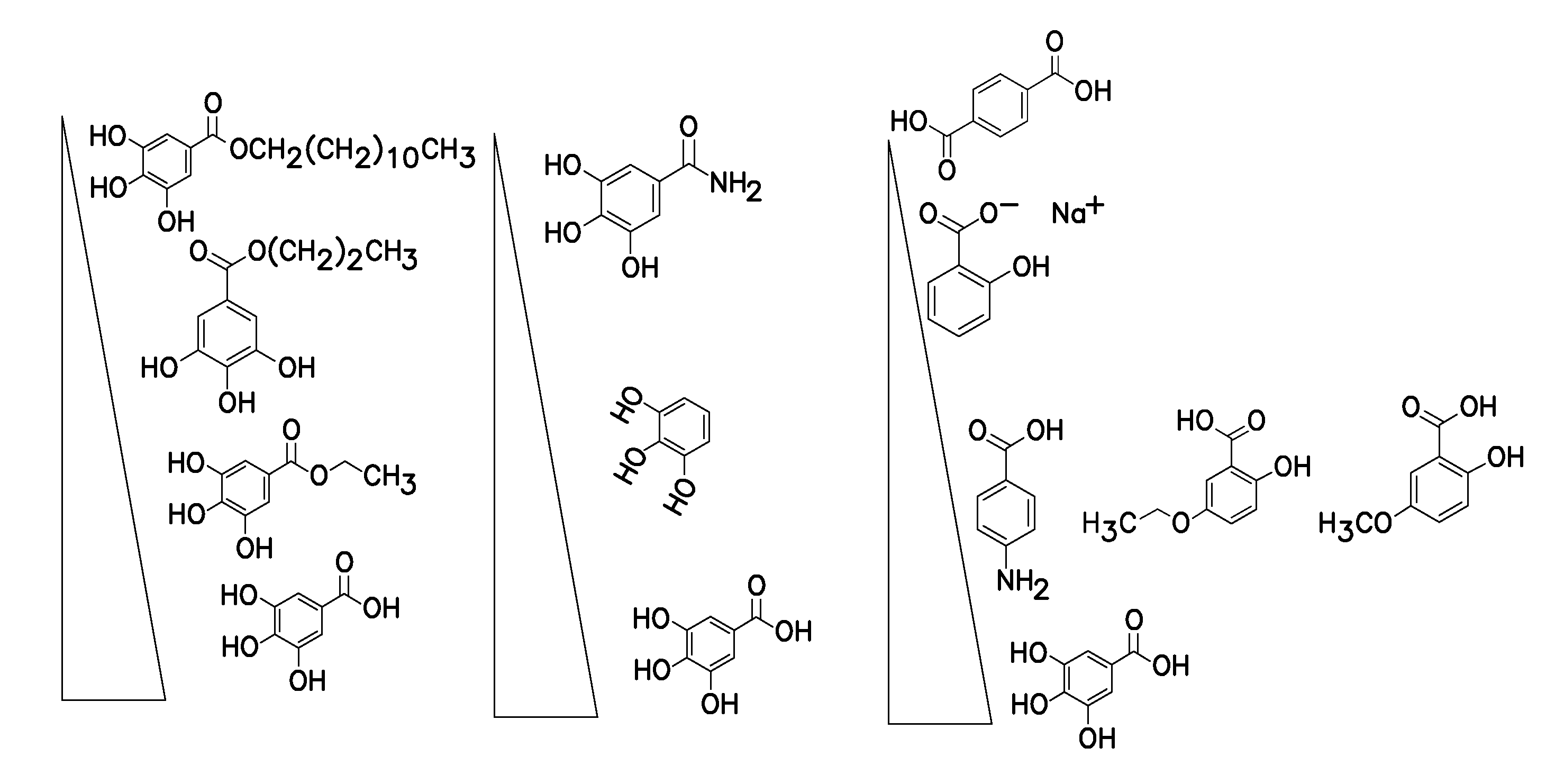
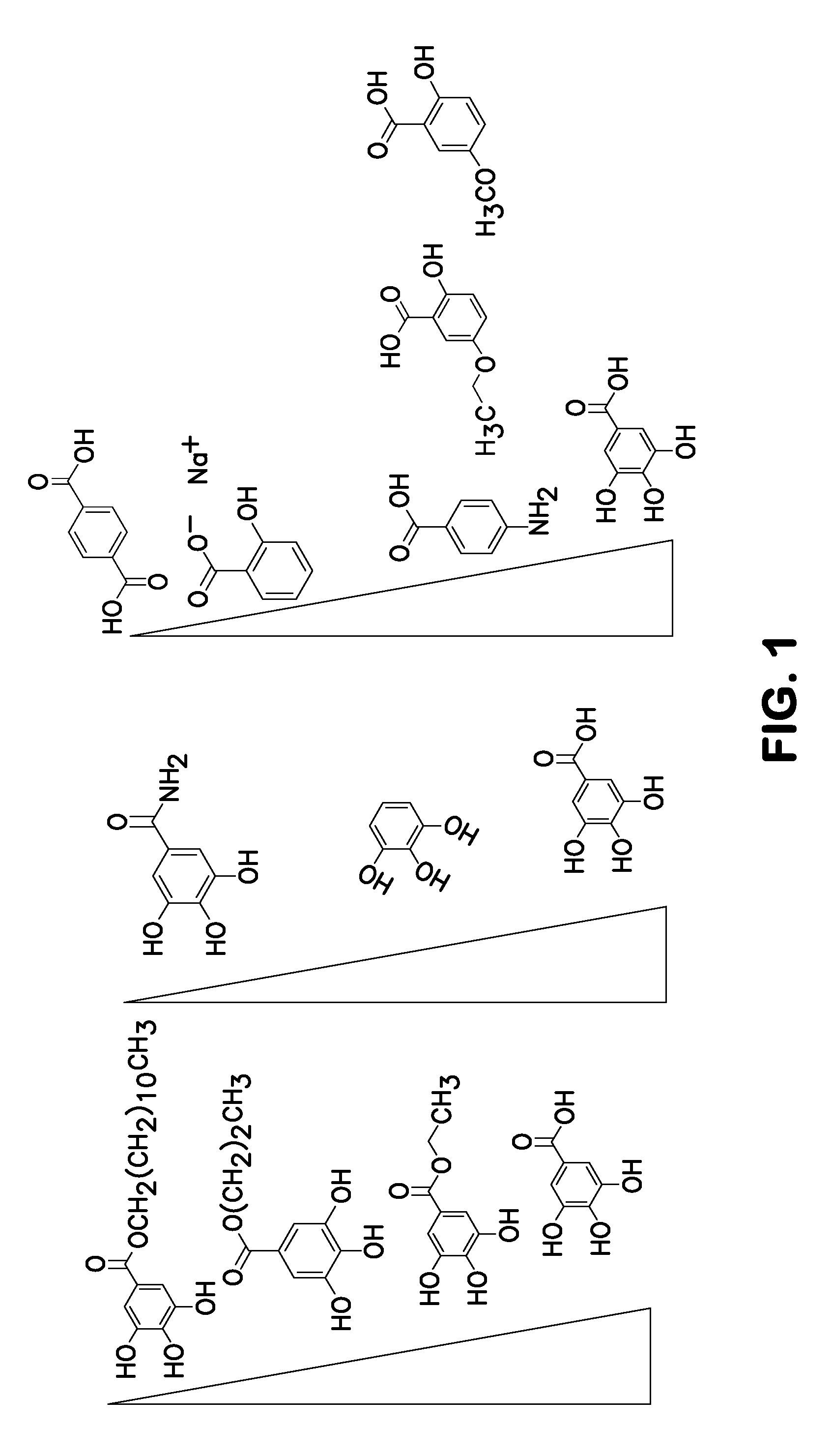
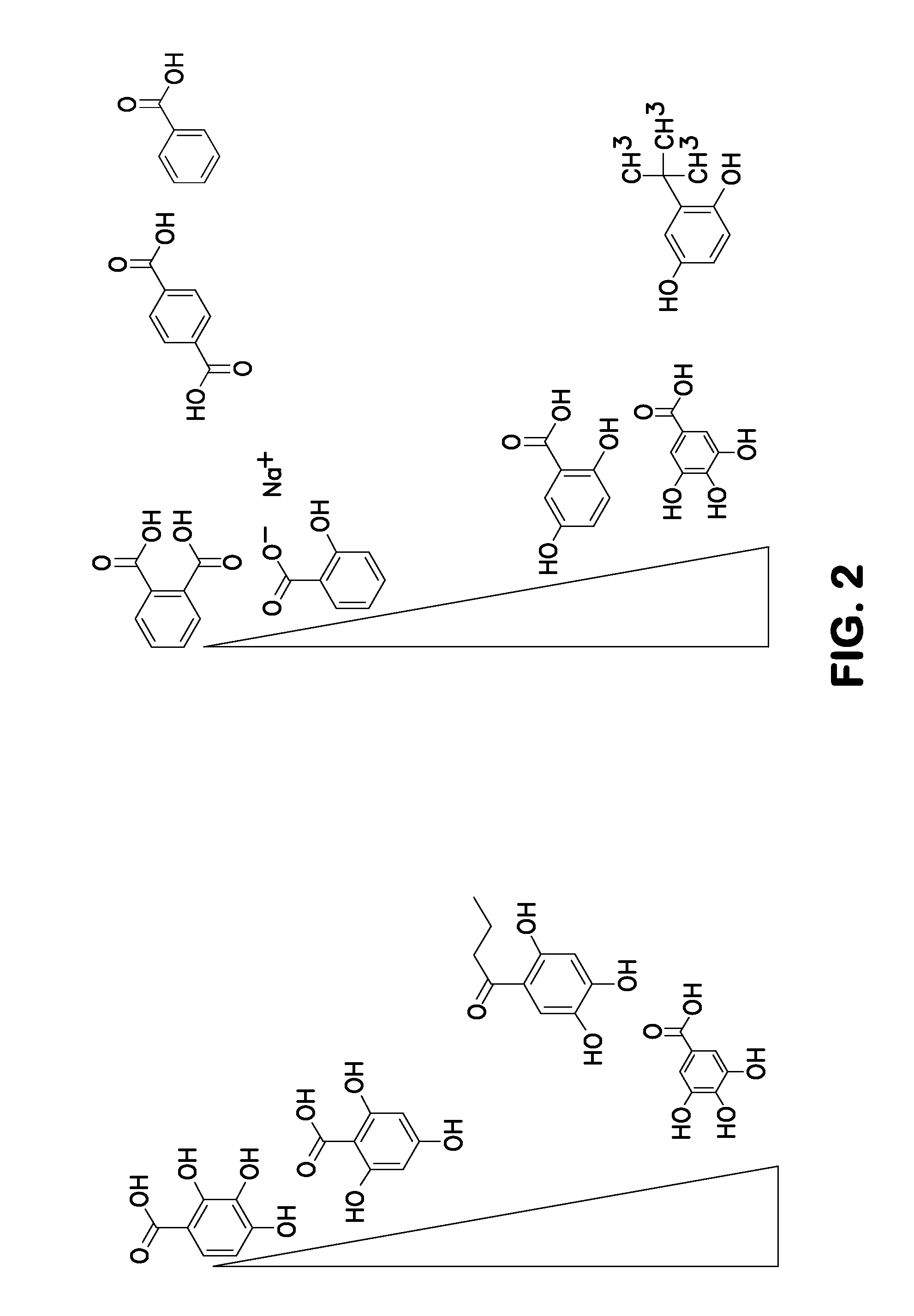
ActiveUS20120196758A1Prevent degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGallic acid esterNucleic acid detection
A method of inhibiting light-induced degradation of nucleic acids includes irradiating a portion of the nucleic acids in the presence of a detection solution comprising a polyphenolic compound. A method of detecting a nucleic acid having a fluorescent tag includes irradiating at least a portion of the nucleic acid with light of a suitable wavelength to induce a fluorescence emission and detecting the fluorescence emission. Optionally, the polyphenolic compound is gallic acid, a lower alkyl ester thereof, or mixtures thereof. A kit includes one or more nucleotides, an enzyme capable of catalyzing incorporation of the nucleotides into a nucleic acid strand and a polyphenolic compound suitable for preparing a detection solution.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Measuring condition setting jig, measuring condition setting method and biological information measuring instrument
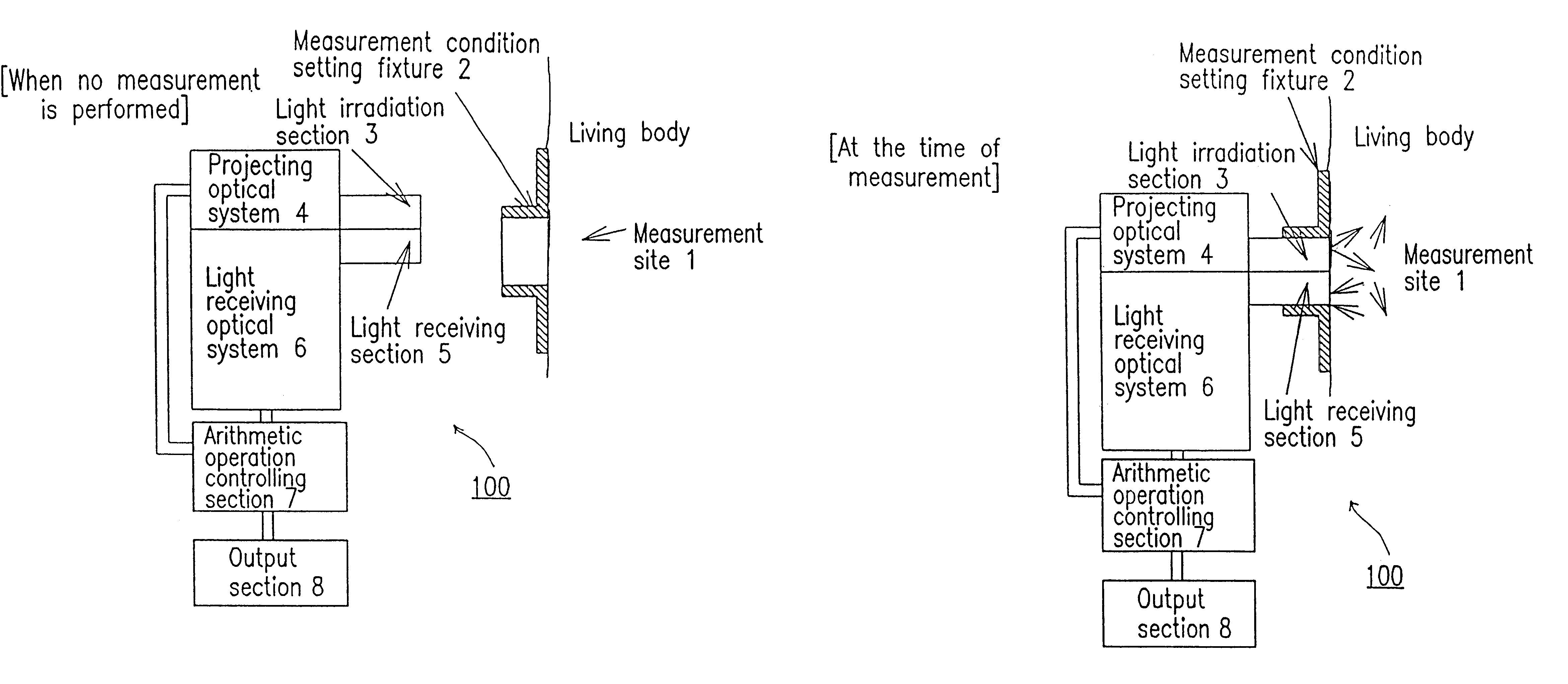
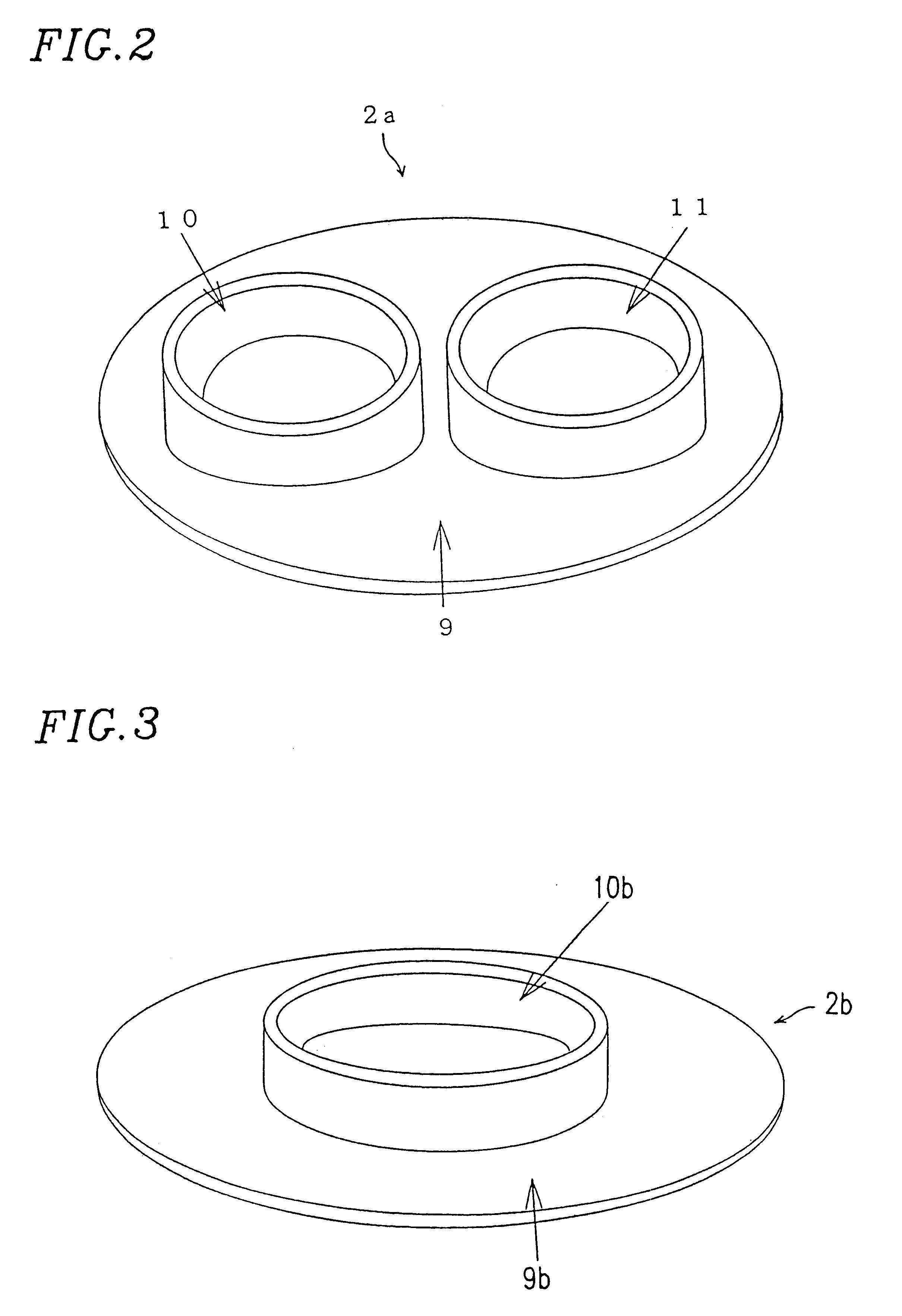
InactiveUS6381489B1Easily and accurately reproducedHighly precise measurement valueDiagnostics using lightSurgeryLight irradiationMeasuring instrument
A measurement condition setting fixture 2 is secured to a measurement site 1 of a living body prior to the measurement. At the time of measurement, a light irradiation section 3 and a light receiving section 5 of a measuring optical system are respectively attached and secured to a light irradiation section securing section 10 and a light receiving section securing section 11 of the measurement condition setting fixture 2. Thus, the measurement site 1 and the measuring optical system are secured to each other, and desirable measurement conditions can be realized. Moreover, the measurement conditions can be maintained throughout the measurement. After the measurement is completed, the measurement site 1 can be removed from the measuring optical system by detaching the light irradiation section 3 and the light receiving section 5 from the light irradiation section securing section 10 and the light receiving section securing section 11. When the measurement is performed again, the desirable measurement conditions can be reproduced merely by attaching the light irradiation section 3 and the light receiving section 5 to the light irradiation section securing section 10 and the light receiving section securing section 11.
Owner:KYOTO DAICHI KAGAKU
Optical probe having and methods for difuse and uniform light irradiation
A variety of optical probes and methods have utility in the examination of various materials, especially materials in the interior of cavities having restricted access through orifices or passageways. One type of such optical probe is elongated and includes a distal optical window, a divergent light source, a spatial mixer, and a light collector. Light from the light source is mixed in the spatial mixer to achieve uniform diffuse light in the vicinity of the optical window. The light collector receives light from the target through the spatial mixer. The optical probe may be made of two sections, a reusable section and a disposable. The disposable is elongated and contains a mounting section, an inside surface suitable for the spatial mixing of light, and an optical element which helps to seal the reusable probe section from the target.
Owner:LIFESPEX
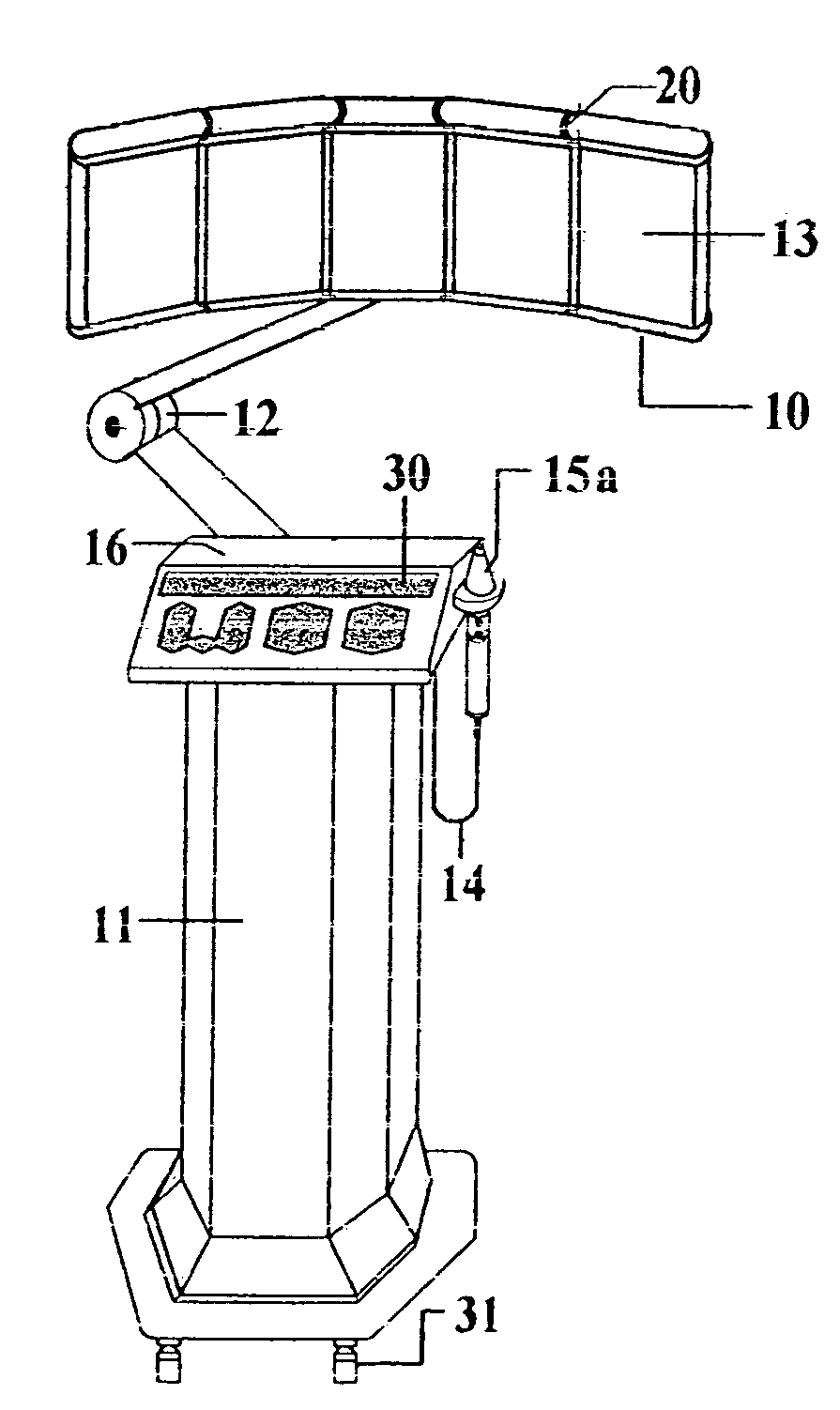
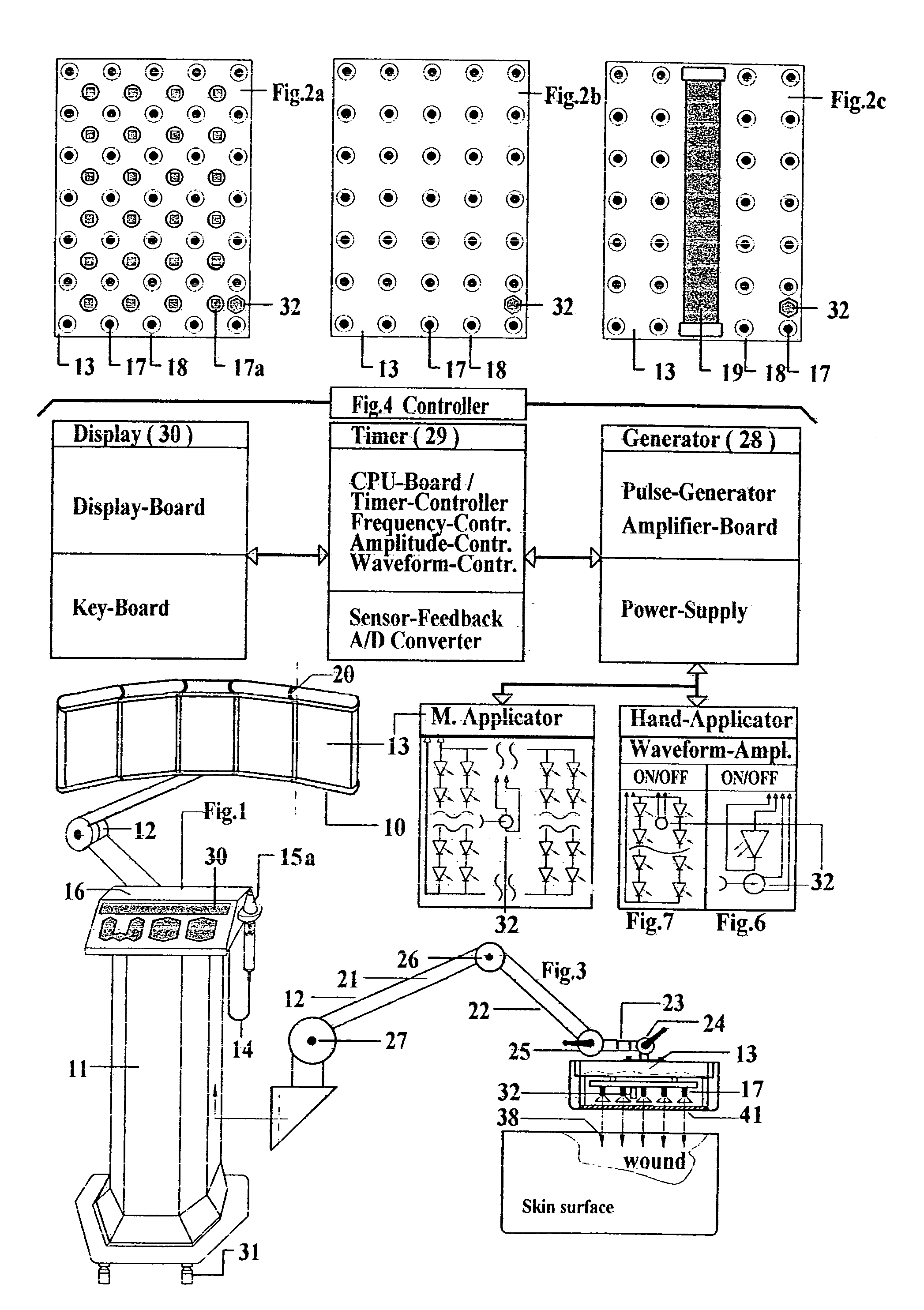
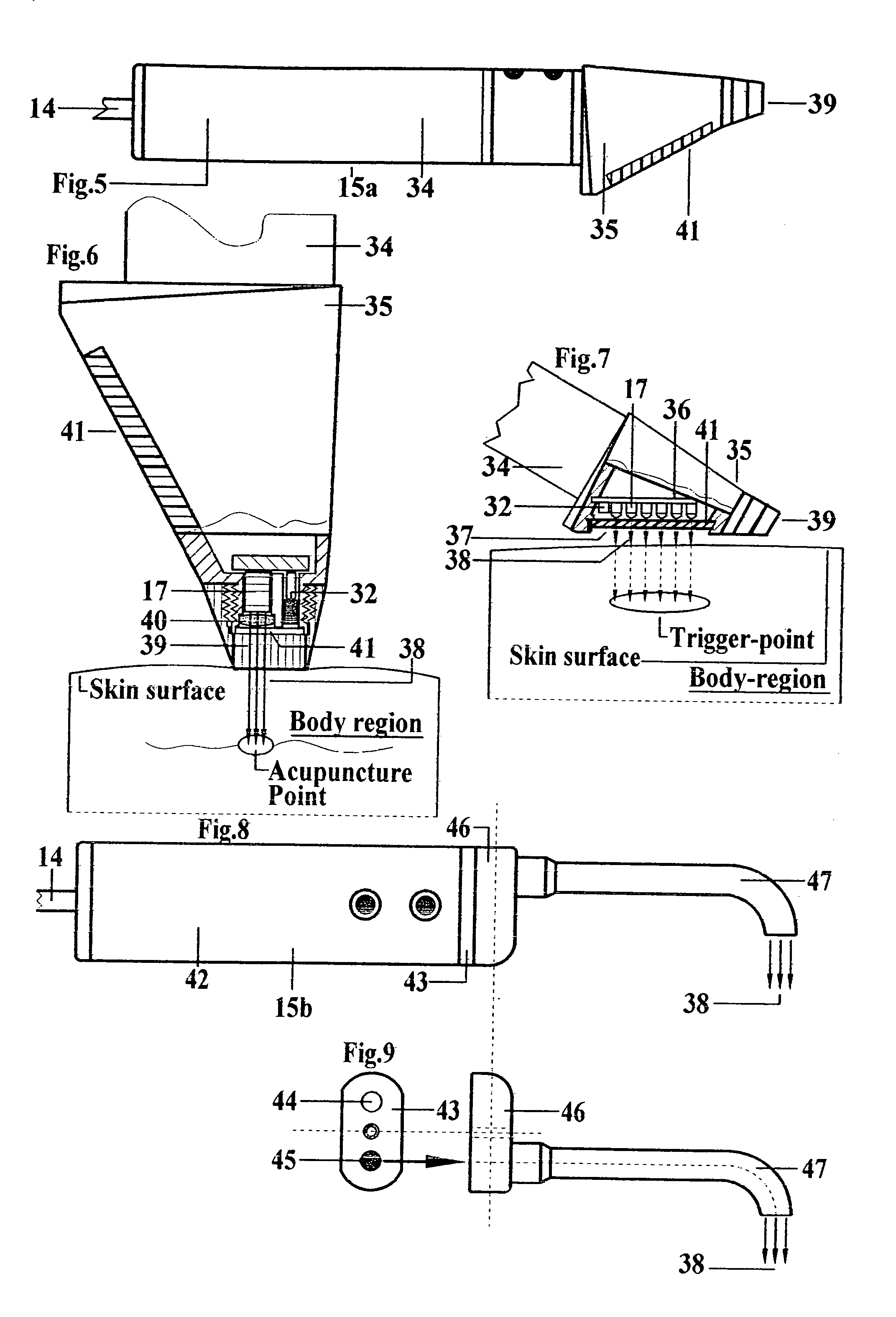
Photodynamic stimulation device and method
InactiveUS7033381B1Promote breathingEnhancing therapeutic capability of deviceDentistrySurgeryTreatment teamOperation mode
A treatment device which uses cold red and infrared radiation for the photodynamic stimulation of cells, especially cells of human tissue. The described device produces a constant energy radiation by the use of semiconductor and / or laser diodes, which furthermore radiate light in several separate wavelengths due to a special operation mode. With help of sensors the advanced controller system is able to test the patients for the needed radiation doses in order to avoid overstimulation. Furthermore the radiation openings in the applicators are advantageously covered with a polarization filter, whereby the absorption in the irradiated tissue is increased. The basic equipment consists of a standpillar, with which machine applicators are connected with a jointed arm. The machine applicators are adapted for the treatment of large area tissues, for example, the back of humans. The standpillar is freely movable on wheels and includes a control mechanism, whereby the various parameters for therapy can be adjusted and switched ON and OFF. The standpillar is also connected to a hand applicator designed for the treatment of small tissue areas, e.g., acupuncture points. Another version of the hand applicator is especially devised for dental treatment, whereby the head piece of the hand applicator can be connected with an expander containing an optical fiber. Photodynamic substances are introduced into tissue to be treated, which enhances the effects of light irradiation by the inventive device.
Owner:LARSEN ERIK
Method of treating semiconductor element
InactiveUS8084331B2Little influenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight irradiationLength wave
In a method of treating a semiconductor element which at least includes a semiconductor, a threshold voltage of the semiconductor element is changed by irradiating the semiconductor with light with a wavelength longer than an absorption edge wavelength of the semiconductor. The areal density of in-gap states in the semiconductor is 1013 cm−2eV−1 or less. The band gap may be 2 eV or greater. The semiconductor may include at least one selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Zn and Sn. The semiconductor may be one selected from the group consisting of amorphous In—Ga—Zn—O (IGZO), amorphous In—Zn—O (IZO) and amorphous Zn—Sn—O (ZTO). The light irradiation may induce the threshold voltage shift in the semiconductor element, the shift being of the opposite sign to the threshold voltage shift caused by manufacturing process history, time-dependent change, electrical stress or thermal stress.
Owner:CANON KK
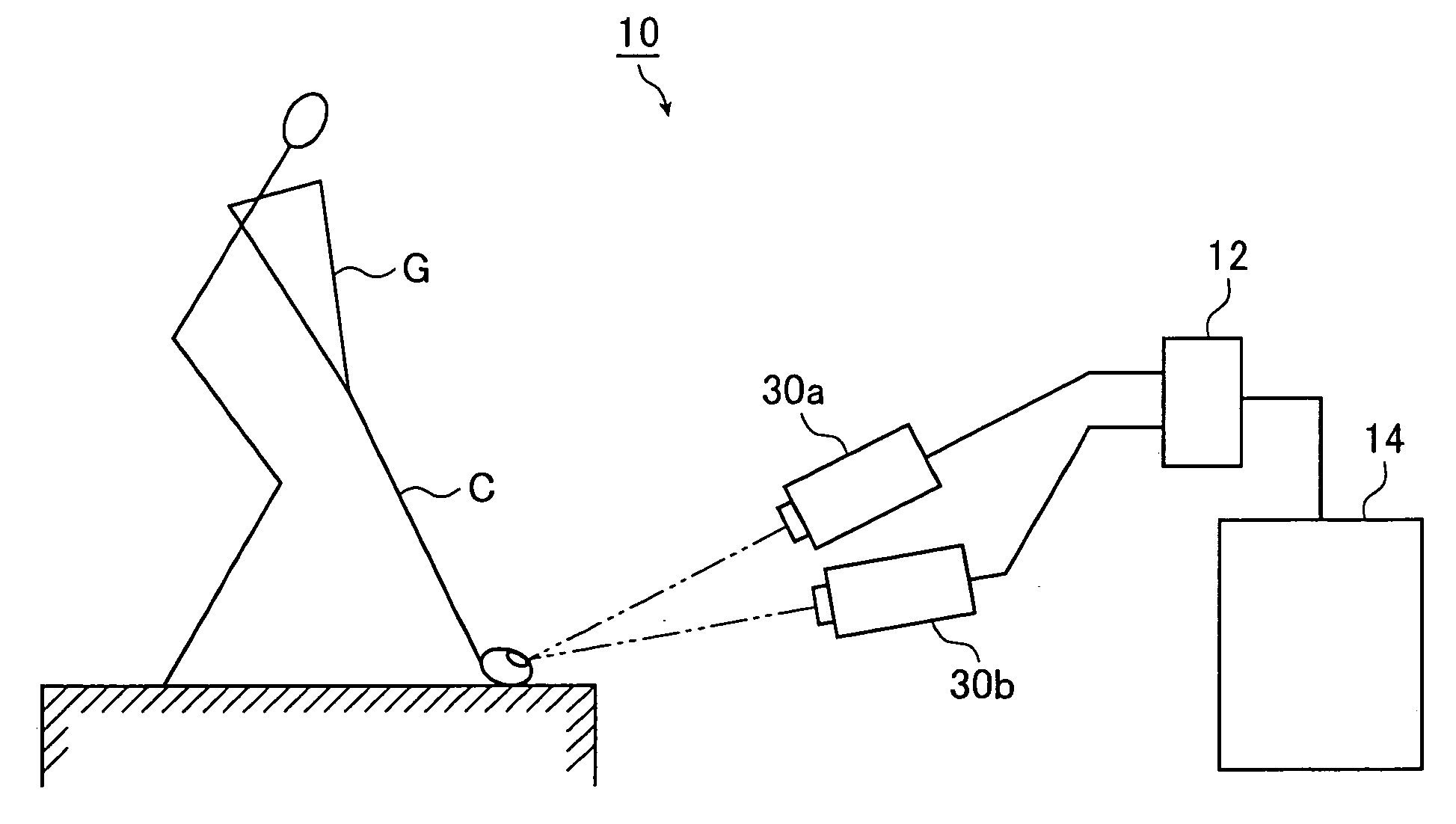
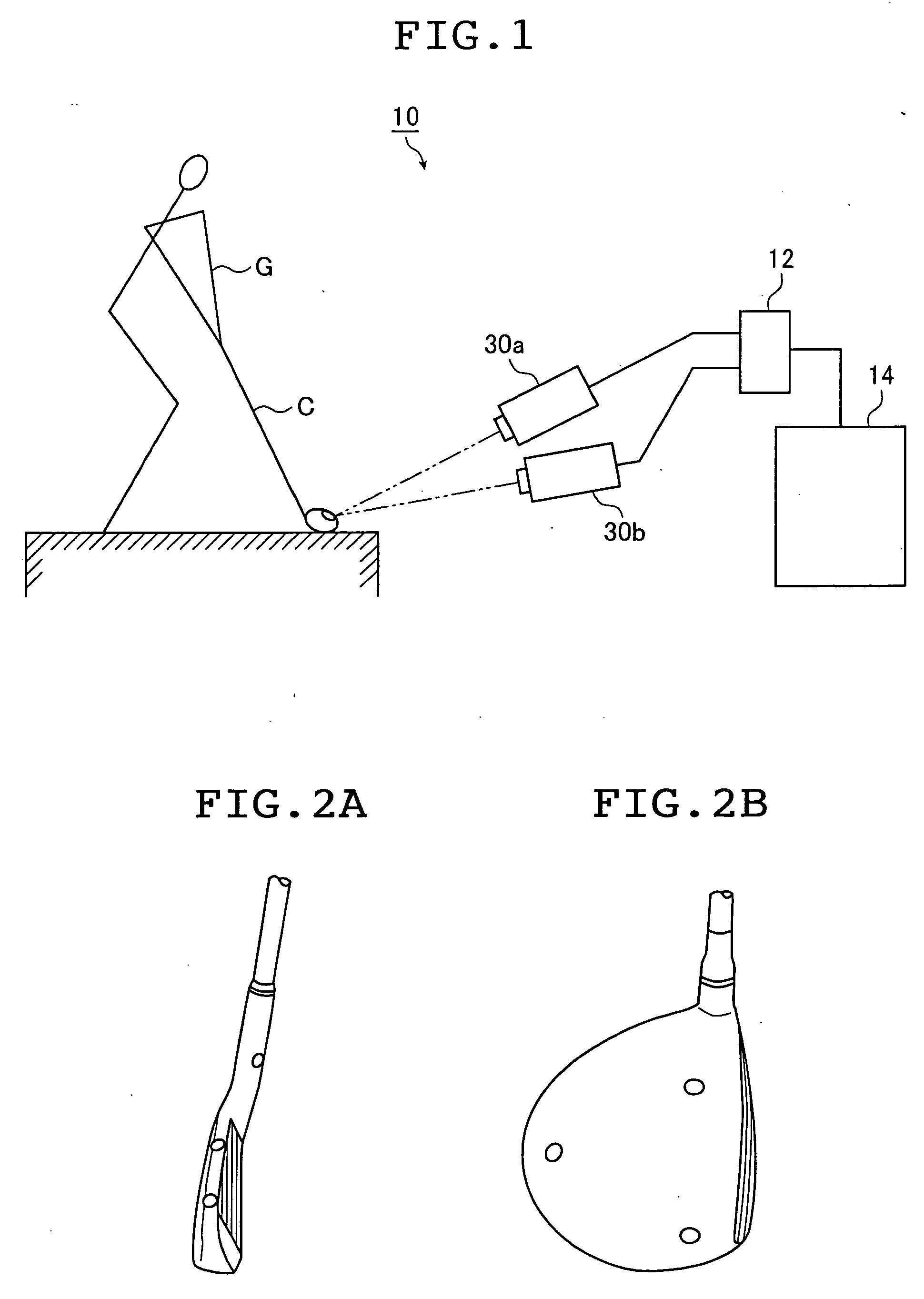
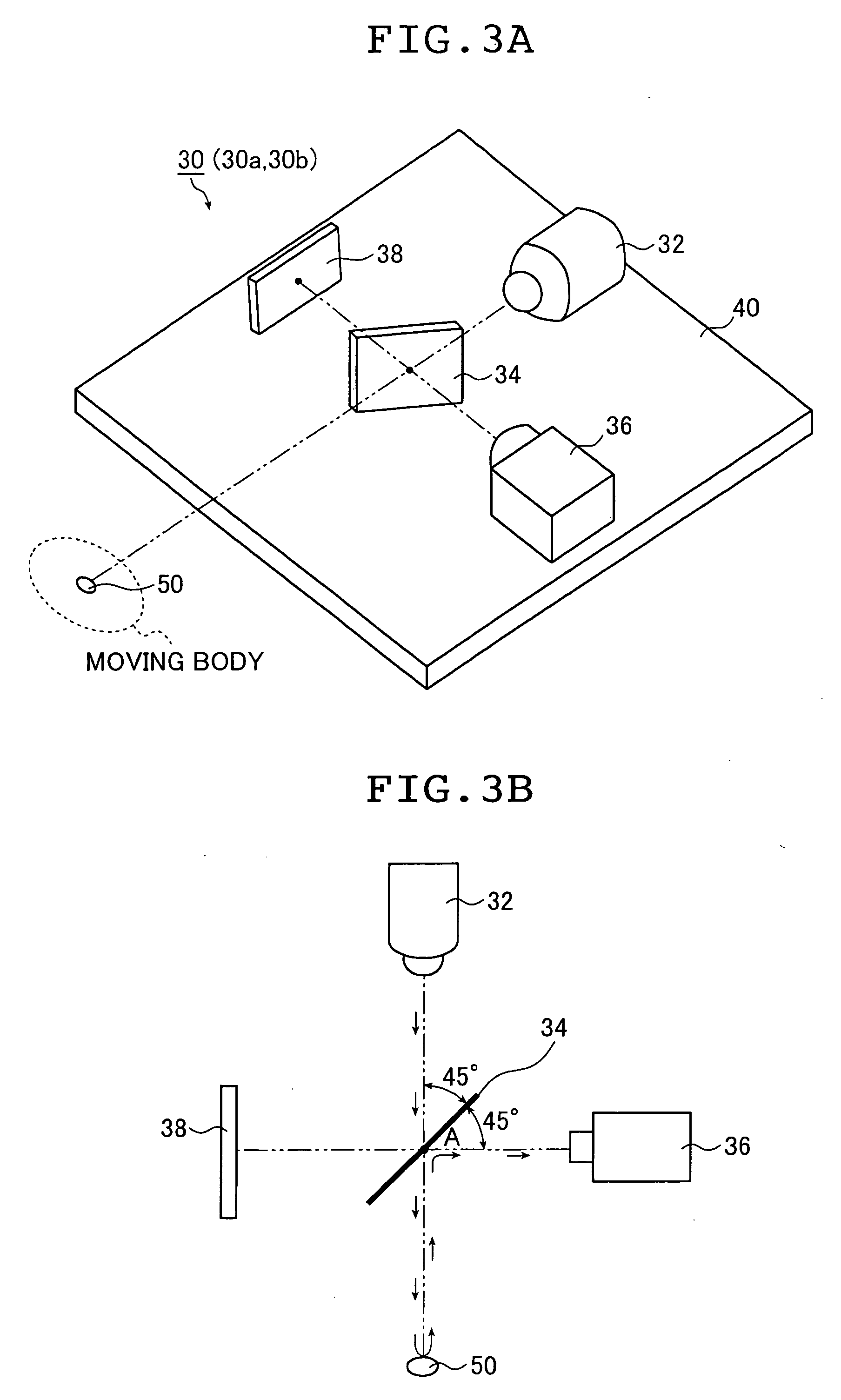
Moving body measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20050213076A1Improve accuracyIncrease contrastGymnastic exercisingUsing optical meansLight irradiationTransmitted light
A moving body measuring apparatus of the invention measures movement information of a moving body as an object to be measured. The apparatus has an optical member having a boundary surface on which light is incident, the optical member being adapted to transmit light entering the boundary surface from one side and to reflect light entering the boundary surface from the other side; an irradiation light source that emits light toward the optical member and irradiates light outgoing from the optical member onto the moving body; a camera that photographs via the optical member an image of light reflected from a reflection marker provided on a surface of the irradiated moving body; and a movement information computation portion that computes movement information for the moving body based on the image of the light reflected by the reflection marker and photographed by the camera, wherein arrangement of the irradiation light source, the camera, and the optical member is adjusted such that an outgoing angle of the irradiation light outgoing from the boundary surface substantially coincides with an incoming angle at which the light reflected by the reflection marker enters the boundary surface.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Lighting unit, display device, and phosphor film
ActiveUS20060255711A1Improve efficiencyLong life-timeDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesLight irradiationPhosphor
To provide a lighting unit which: does not greatly affect the design of a light guide plate; and has a long lifetime, high efficiency, and a wide color reproduction range by means of a phosphor. In view of the foregoing, the lighting unit of the present invention is constituted in such a manner that a phosphor bead or a phosphor film is arranged on at least one of the light irradiation plane of a light guide plate, the rear surface of the light guide plate, and the light incidence plane of the light guide plate. In addition, a phosphor film is constituted by using: a phosphor bead formed of a phosphor particle and a water-impervious material with which the phosphor particle is coated so that the particle is confined in the material; and a polymer film holding the phosphor bead.
Owner:DAWNCREST IP LLC
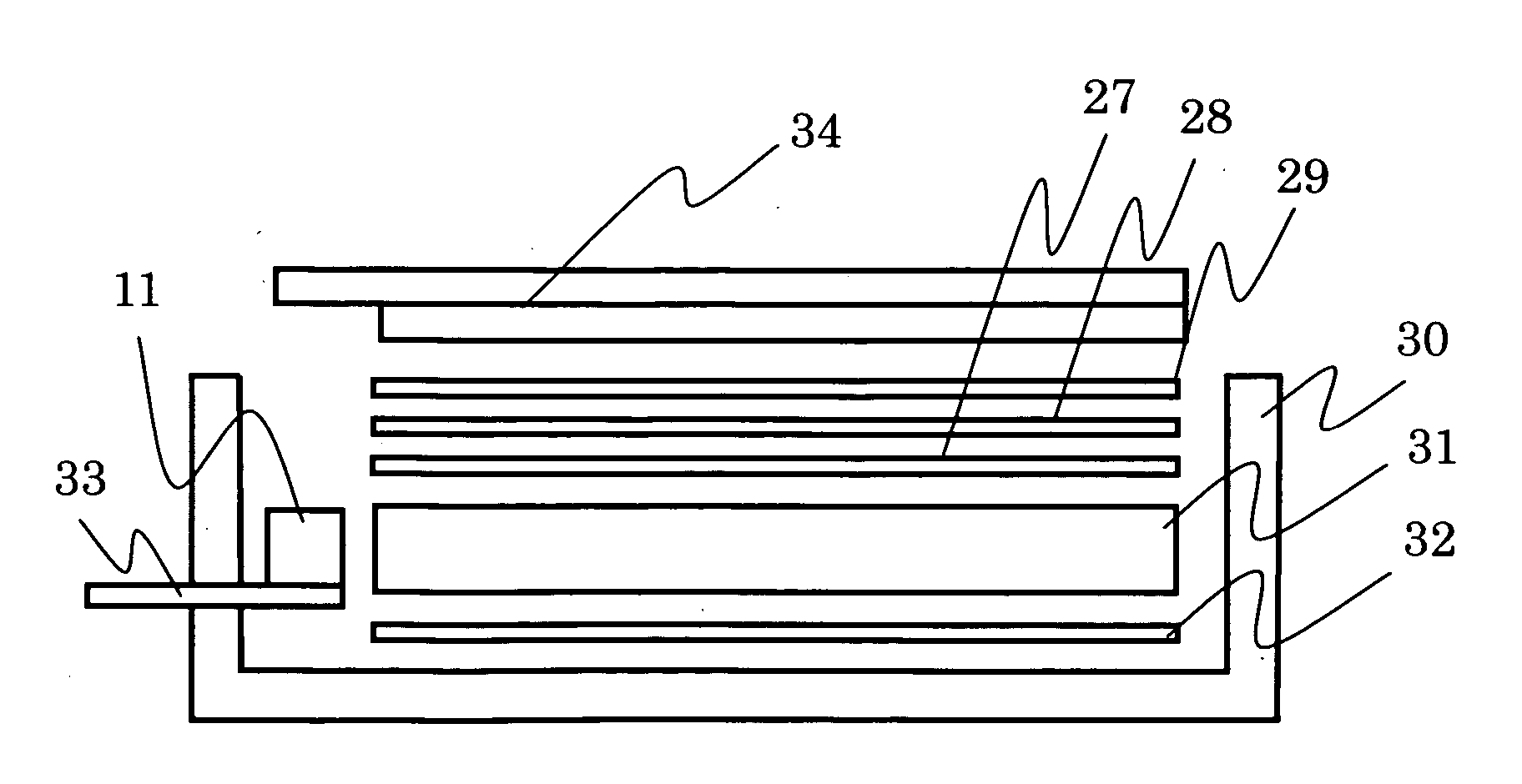
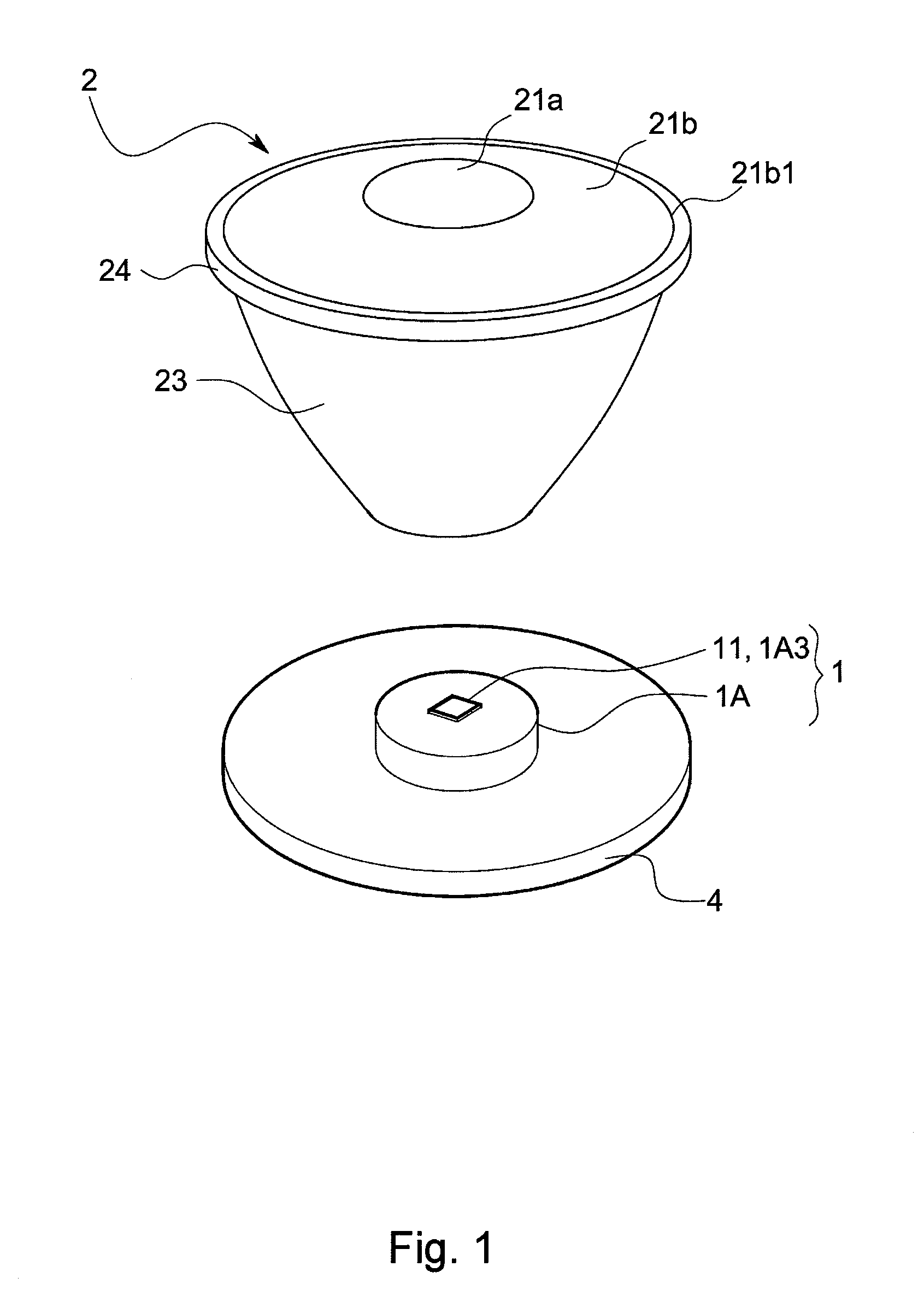
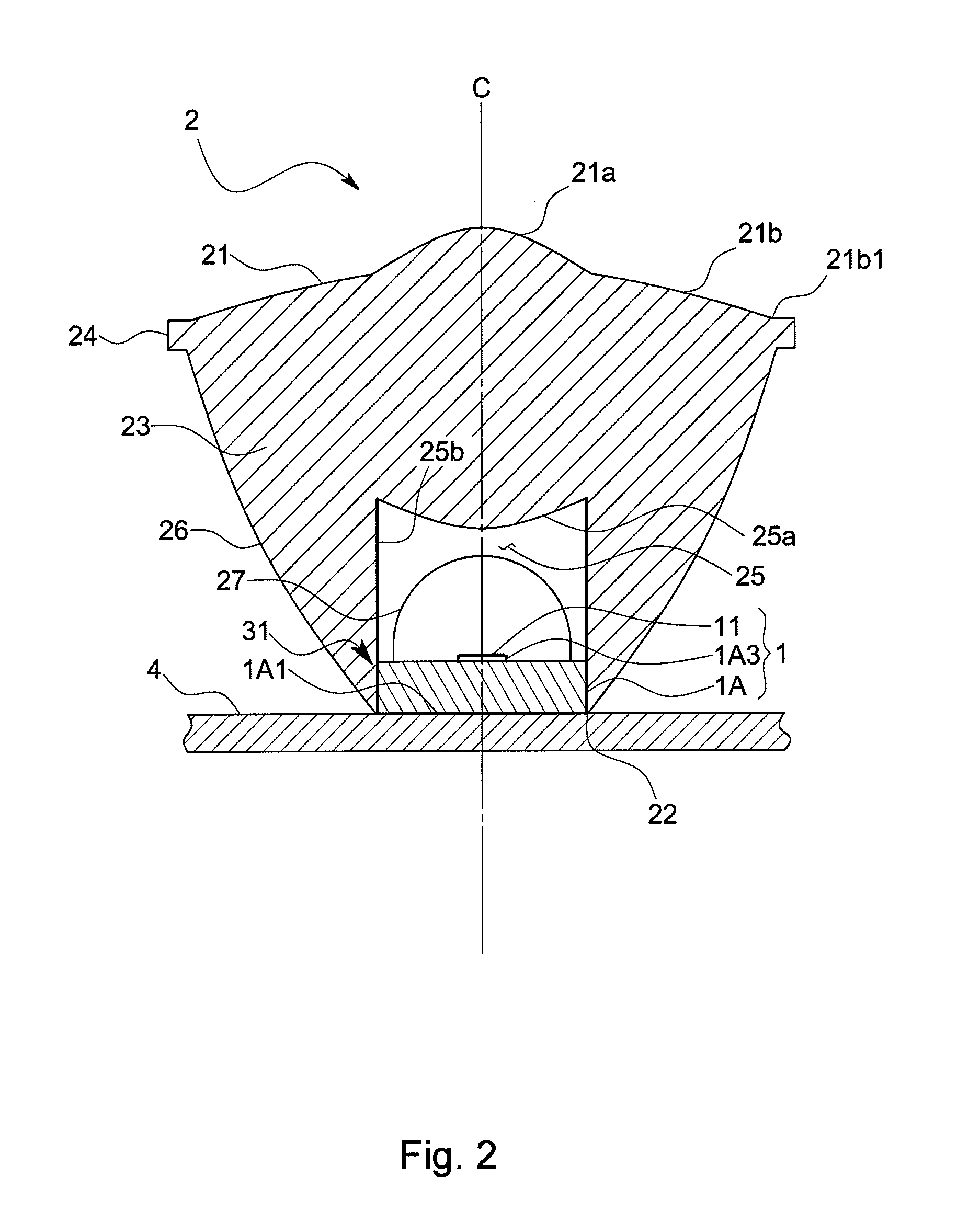
Light irradiation apparatus
The invention provides a light irradiation apparatus that can adjust widening / narrowing of a light irradiation area and can guide almost whole of light emitted from an LED to the light irradiation area.The apparatus has an LED 11 and an optical unit 2 for making light for the LED 11 pass through itself and emit from its apical surface 21, and is equipped further with a supporting body 1A for holding the LED on the apical surface and a position adjustment mechanism for adjusting a relative position of the optical unit 2 to the LED 11 along an optical axis C direction. The apparatus is configured so that the potion adjustment mechanism make the optical unit 2 move relative to the LED 11 between a proximity position P1 at which a part or the whole of the supporting body 1A is housed in a base end recess 25 and a clearance position P2 at which substantially whole of the supporting body 1A comes out of the base end recess 25 so that the apical surface of the supporting body 1A and a base end face 22 of the optical unit 2 become substantially the same height.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Image forming apparatus and method
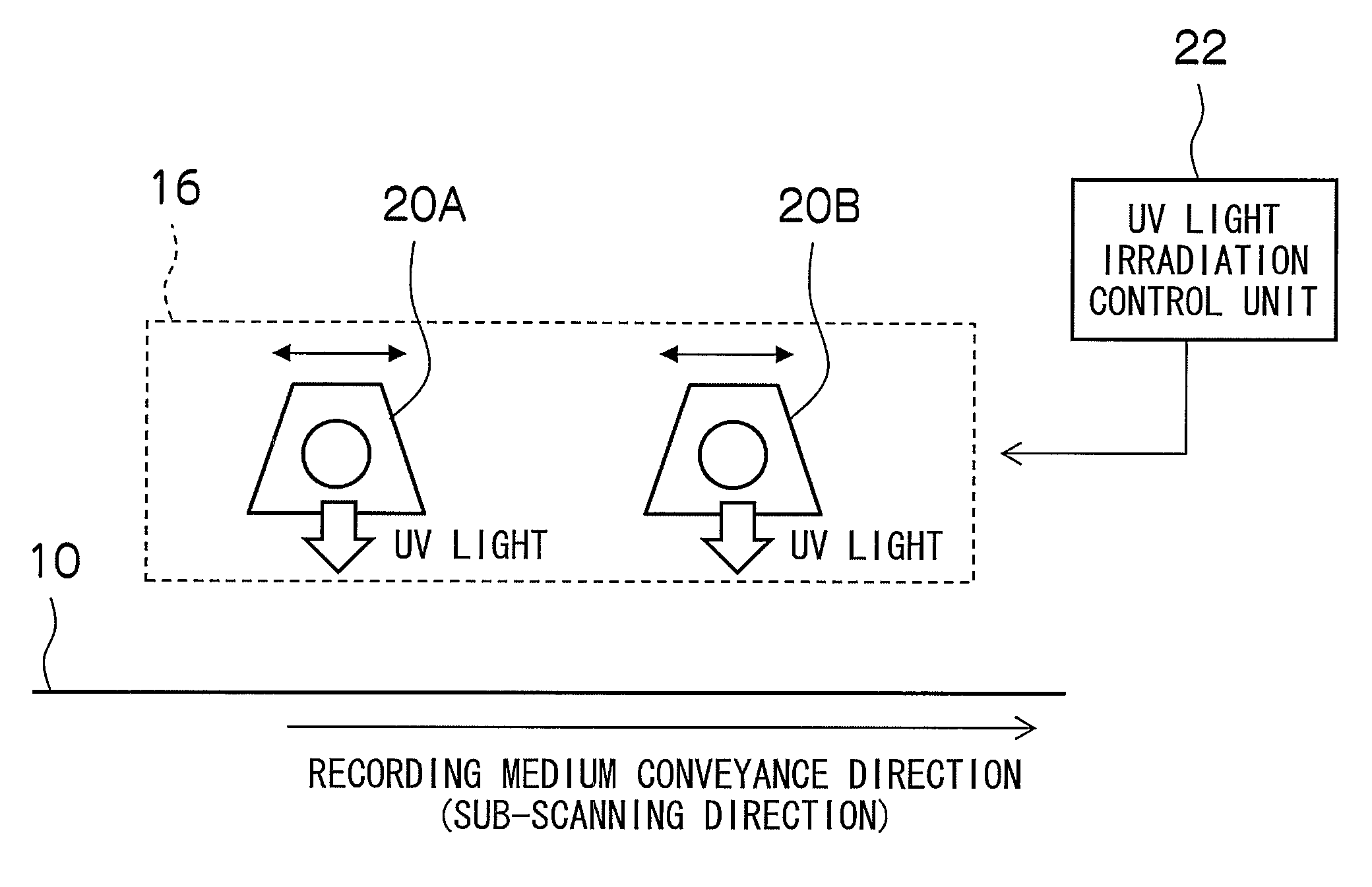
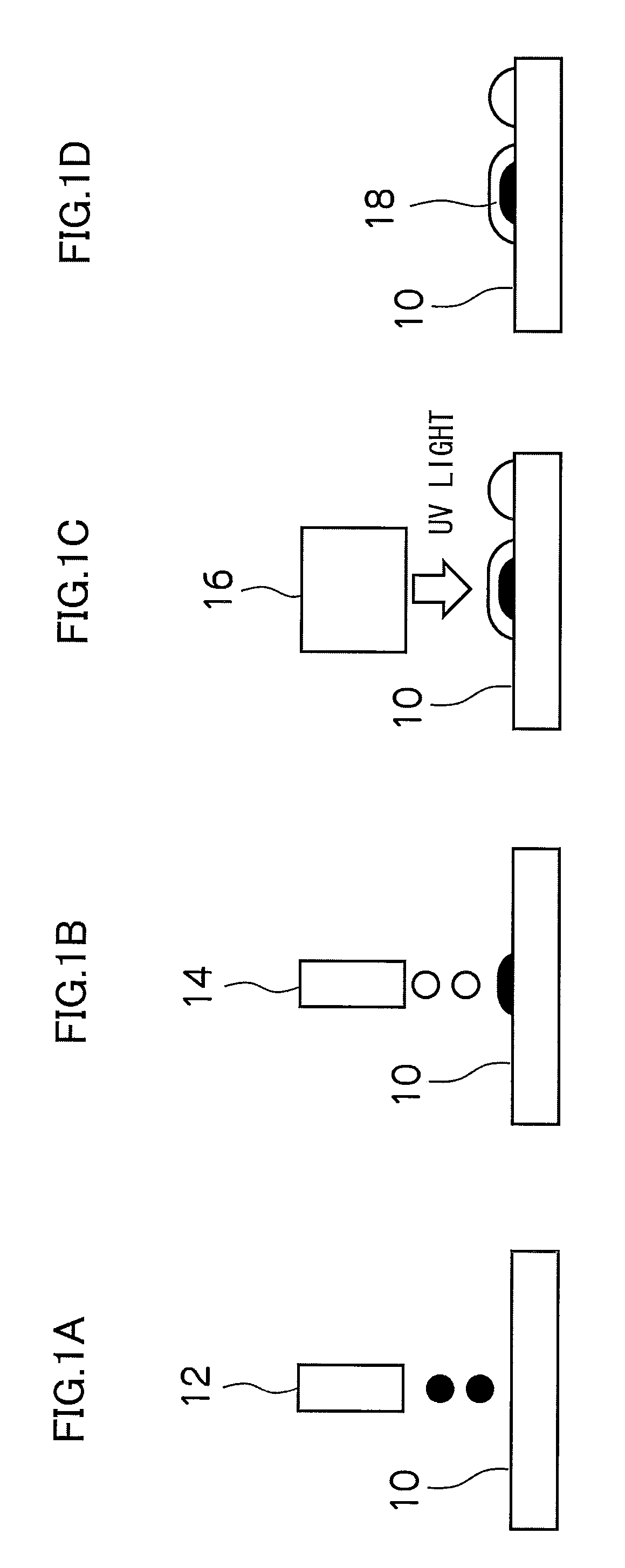
InactiveUS20090225143A1Gloss level can be made rapidly and efficientlyDifferent gloss levelInking apparatusElectrographic process apparatusLight irradiationImage formation
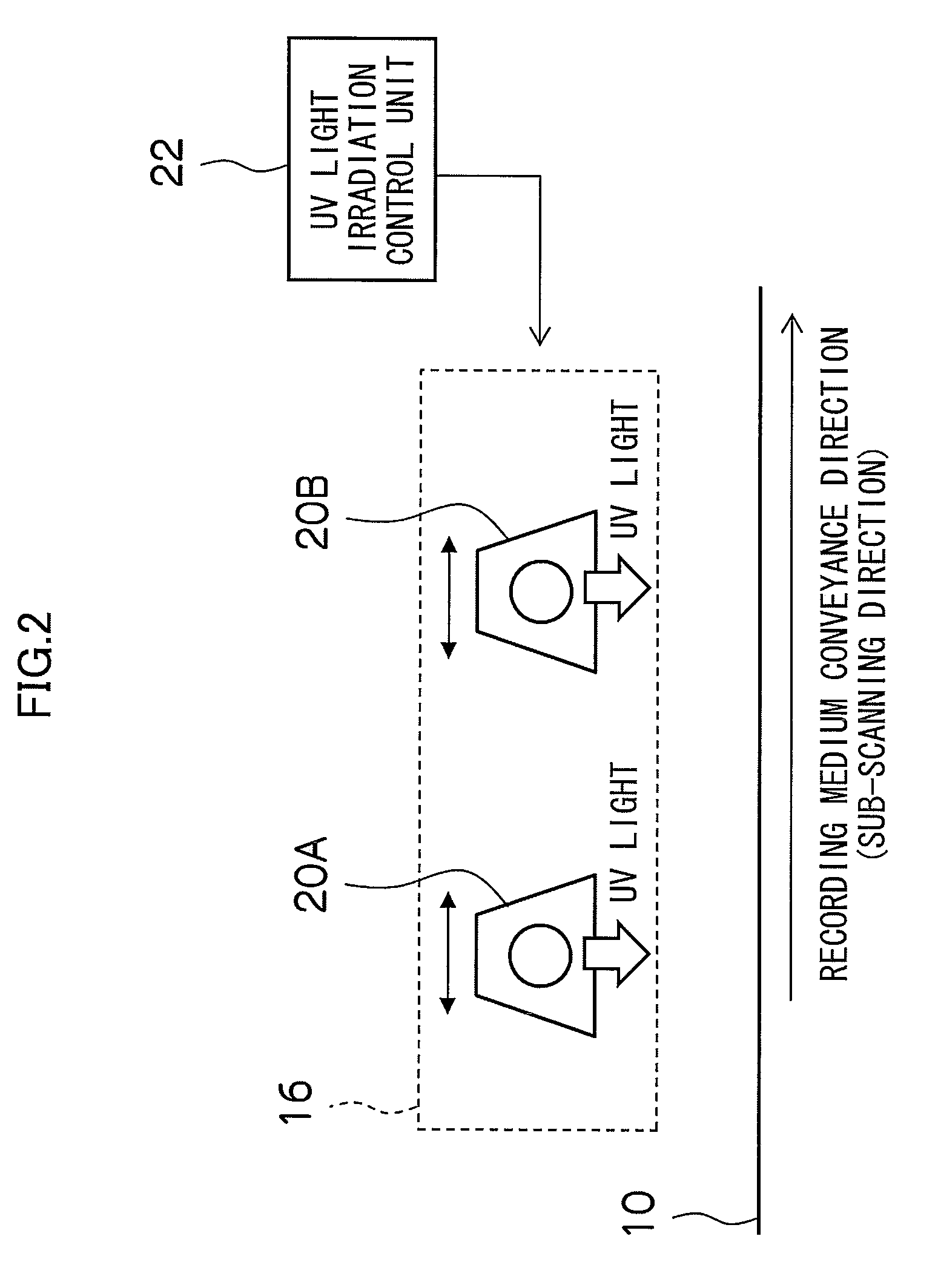
The image forming apparatus includes: an image forming device which forms an image on a recording medium; a transparent UV ink droplet ejection device which ejects and deposits droplets of transparent UV ink onto the recording medium; a UV light irradiation device which irradiates UV light onto the transparent UV ink having been deposited on the recording medium; a gloss condition setting device which sets a gloss condition of the image; and a UV light irradiation control device which controls an irradiation timing of the UV light irradiated from the UV light irradiation device in accordance with the gloss condition.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
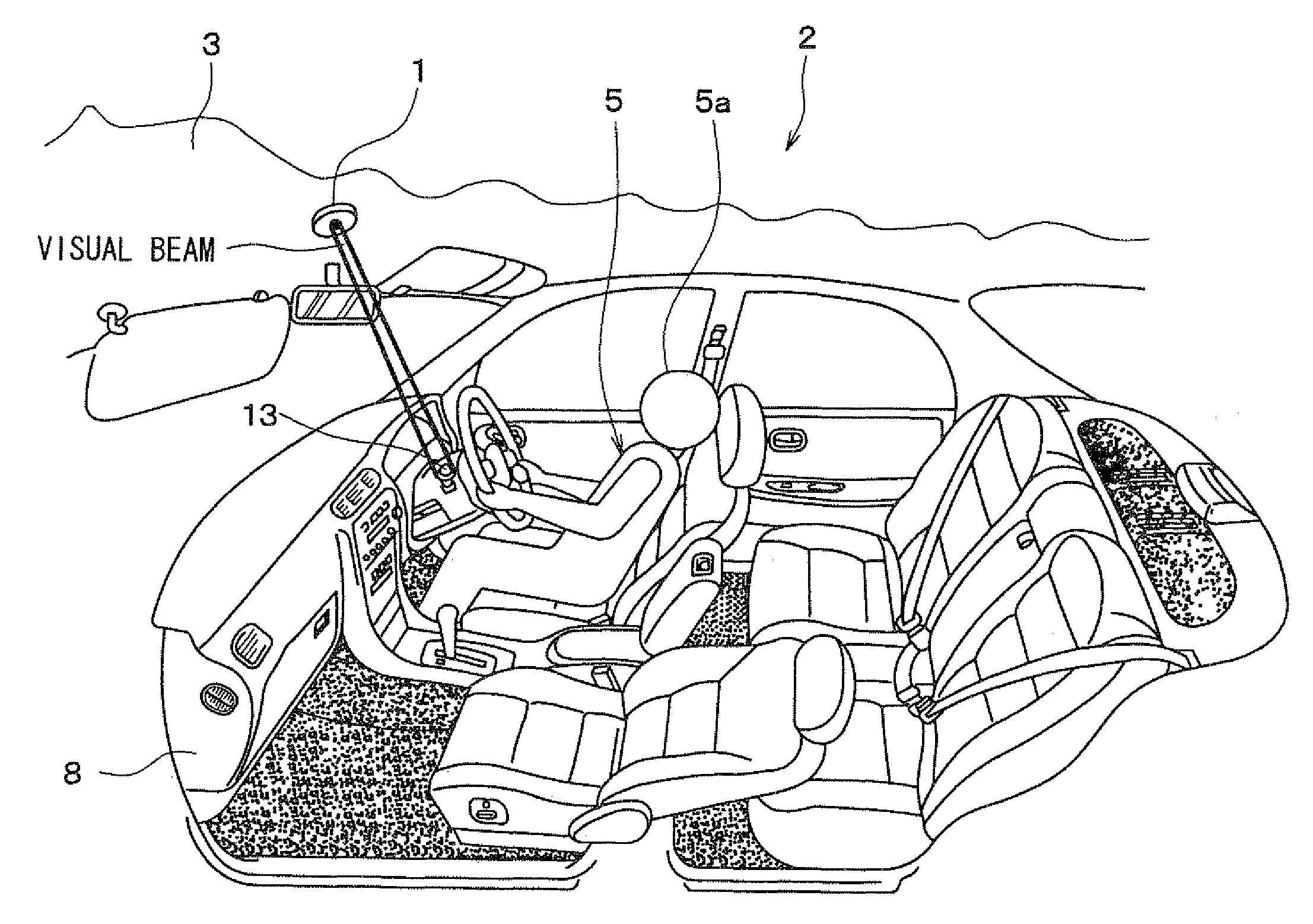
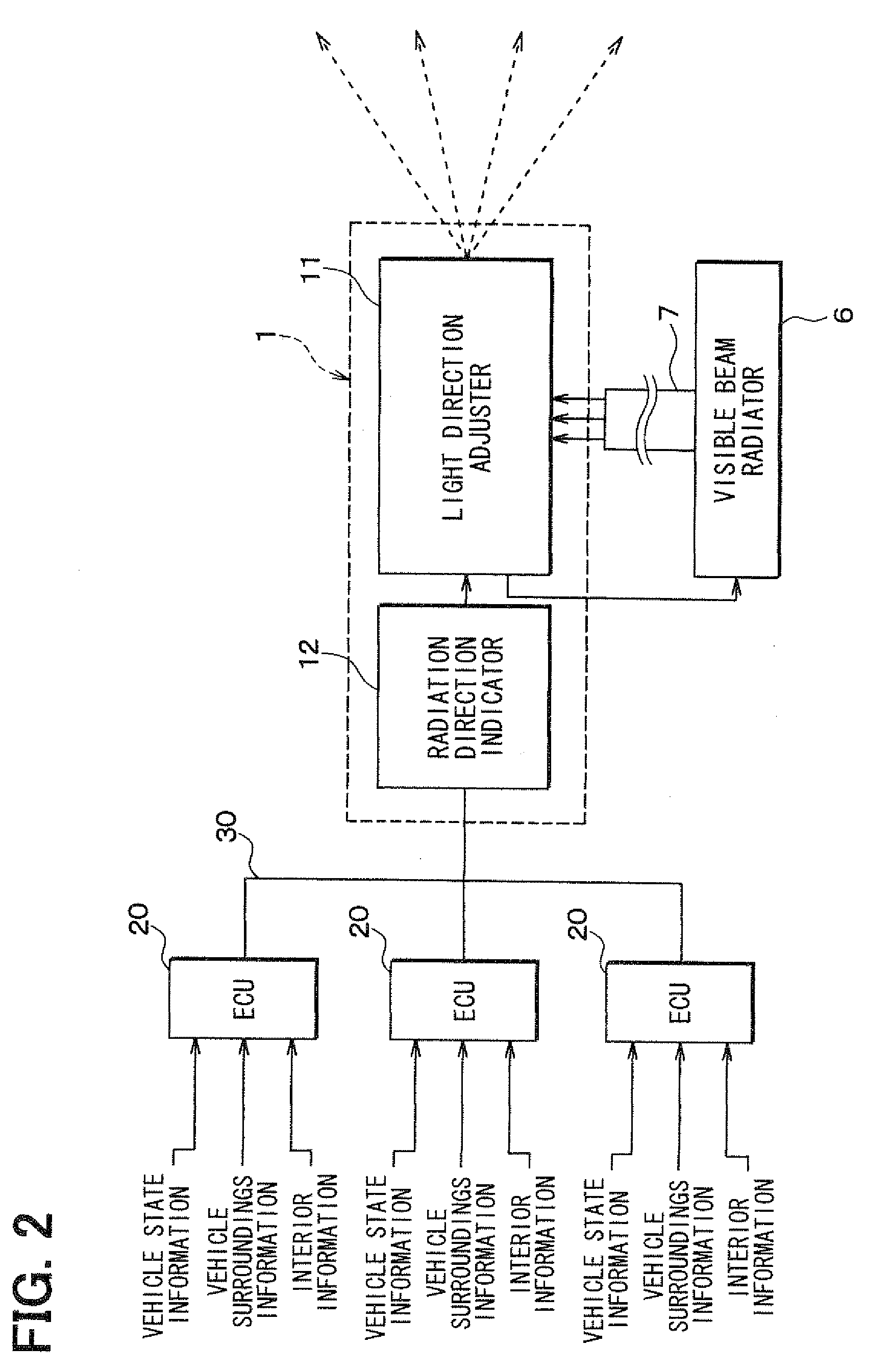
Interior information display apparatus and light irradiation apparatus used for the same
ActiveUS20100295670A1Raise the possibilityEffective displaySteering partsDashboard lighting devicesLight irradiationEngineering
Information is displayed by irradiating a visible light on a specific position based on at least one of vehicle state information, vehicle surrounding information, and vehicle interior information. For example, the visible light is irradiated on a target switch based on signals indicating an on / off state of a headlamp operation switch and an on / off state of a key switch. A user 5 can easily confirm the target switch and unerringly operate the target switch. A visible light irradiator 6 is arranged in a vehicle compartment and irradiates the visible light to display information in the vehicle compartment. The information can be provided for the user 5 in a novel manner.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Device for light irradiation onto tissue
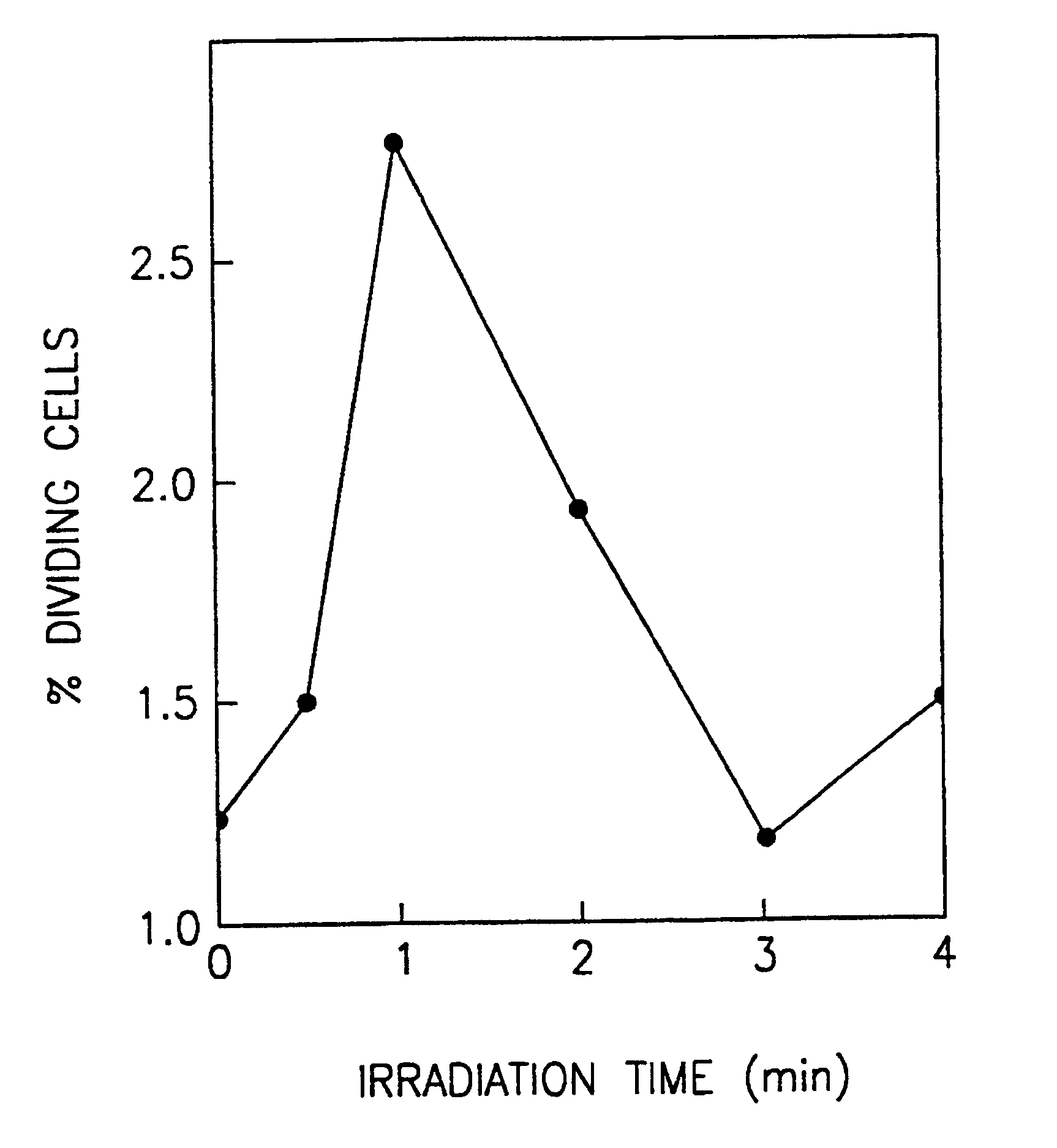
A method and device for inducing or promoting growth and proliferation of skin cells or tissue or for controlling bacterial skin infection is described. The skin cells are irradiated with a low-intensity broad spectrum light at a wavelength of between about 340 to 3,000 nm. The increase in rate of cultivated cells is useful for example to obtain skin-like tissue needed for skin grafts or for promoting healing of skin wounds or lesions. Light-induced skin bacteria control is useful for example in the treatment of bacterial infections of the skin.
Owner:QRAY
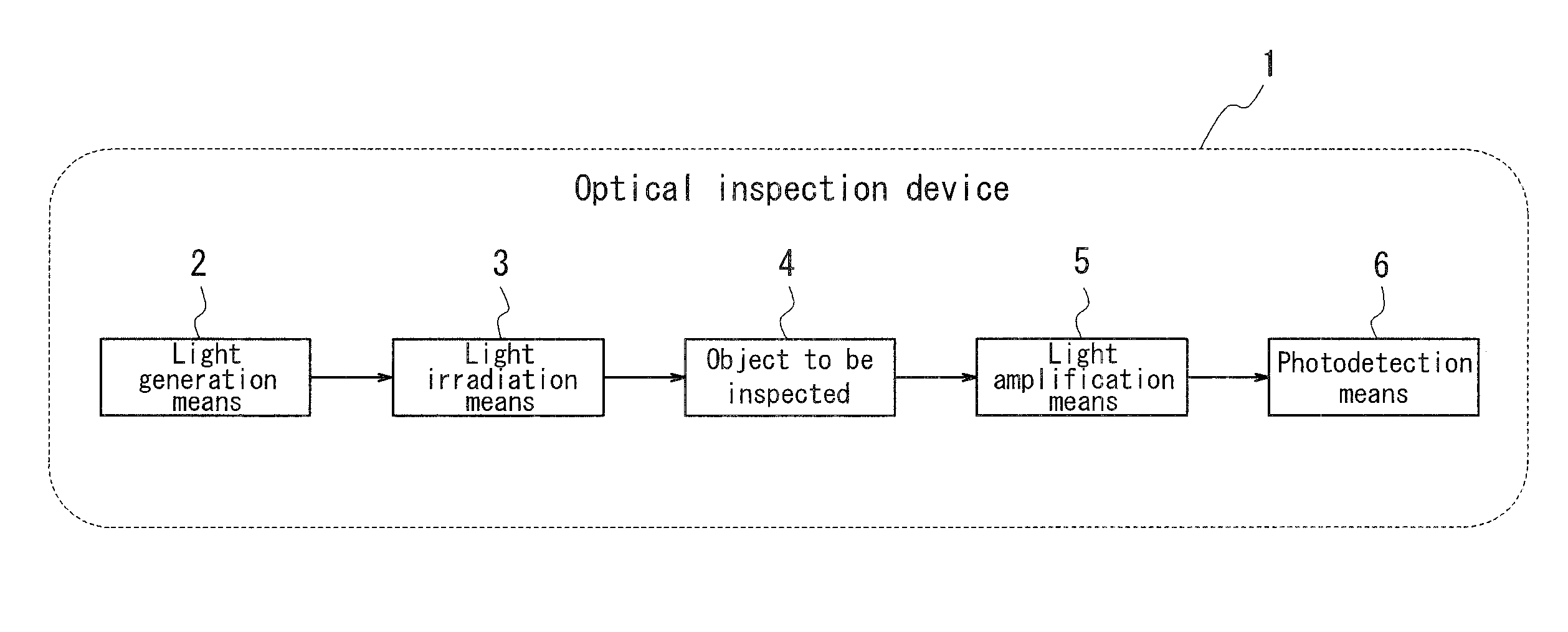
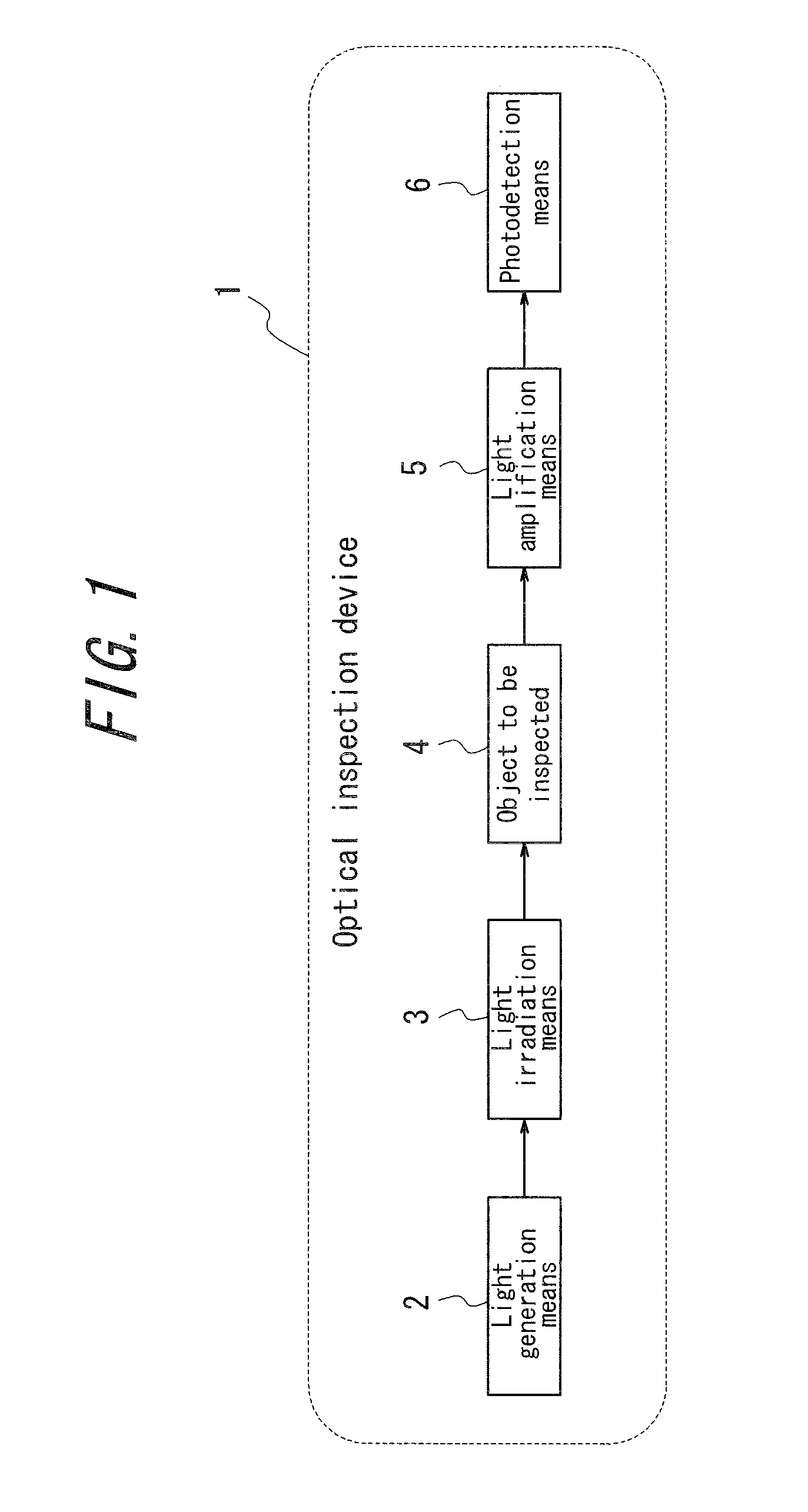
Optical inspection device, electromagnetic wave detection method, electromagnetic wave detection device, organism observation method, microscope, endoscope, and optical tomographic image generation device
ActiveUS20100210952A1High sensitivityIncrease light intensityOptical radiation measurementRadiation measurementBiological bodyLight irradiation
An optical inspection device 1, comprising a light generation means 2, a light irradiation means 3 irradiating an object to be inspected 4 with light generated from the light generation means 2 and a photodetection means 6 photoelectrically converting signal light obtained from the object to be inspected 4 through irradiation of light by the light irradiation means 3, and inspecting the object to be inspected 4 based on output from the photodetection means 6, wherein a light amplification means 5 amplifying signal light obtained from the object to be inspected 4 is provided. There is thus provided an optical inspection device capable of photoelectrically converting signal light from the object to be inspected with high sensitivity and promptly with its inexpensive configuration without increasing the intensity of light with which the object to be inspected is irradiated and without using an expensive low-noise and high-sensitivity photodetector.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ink jet printer and image recording method
InactiveUS20040041892A1Improve curing effectIncrease temperatureOther printing apparatusPrinting after-treatmentLight irradiationCationic polymerization
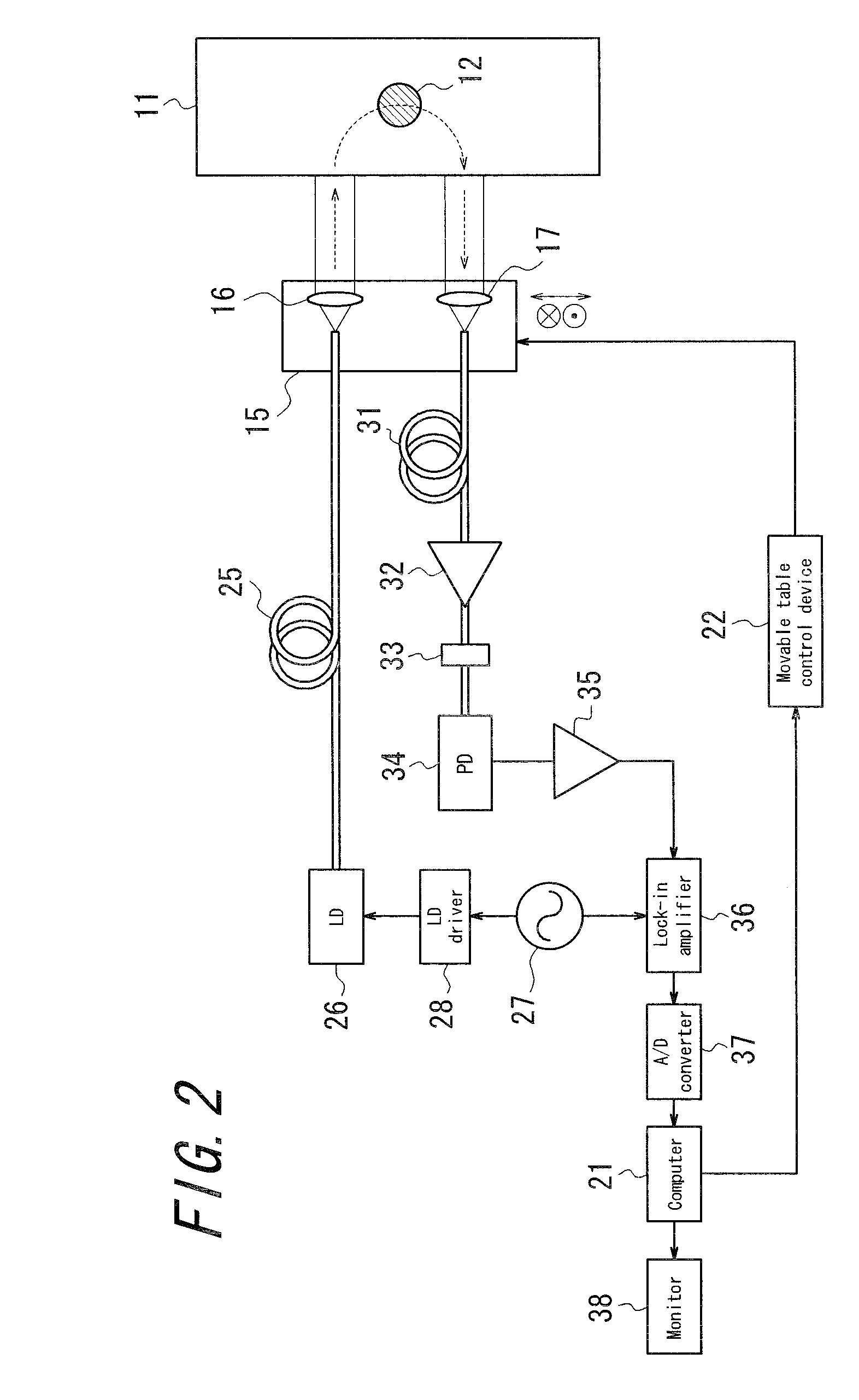
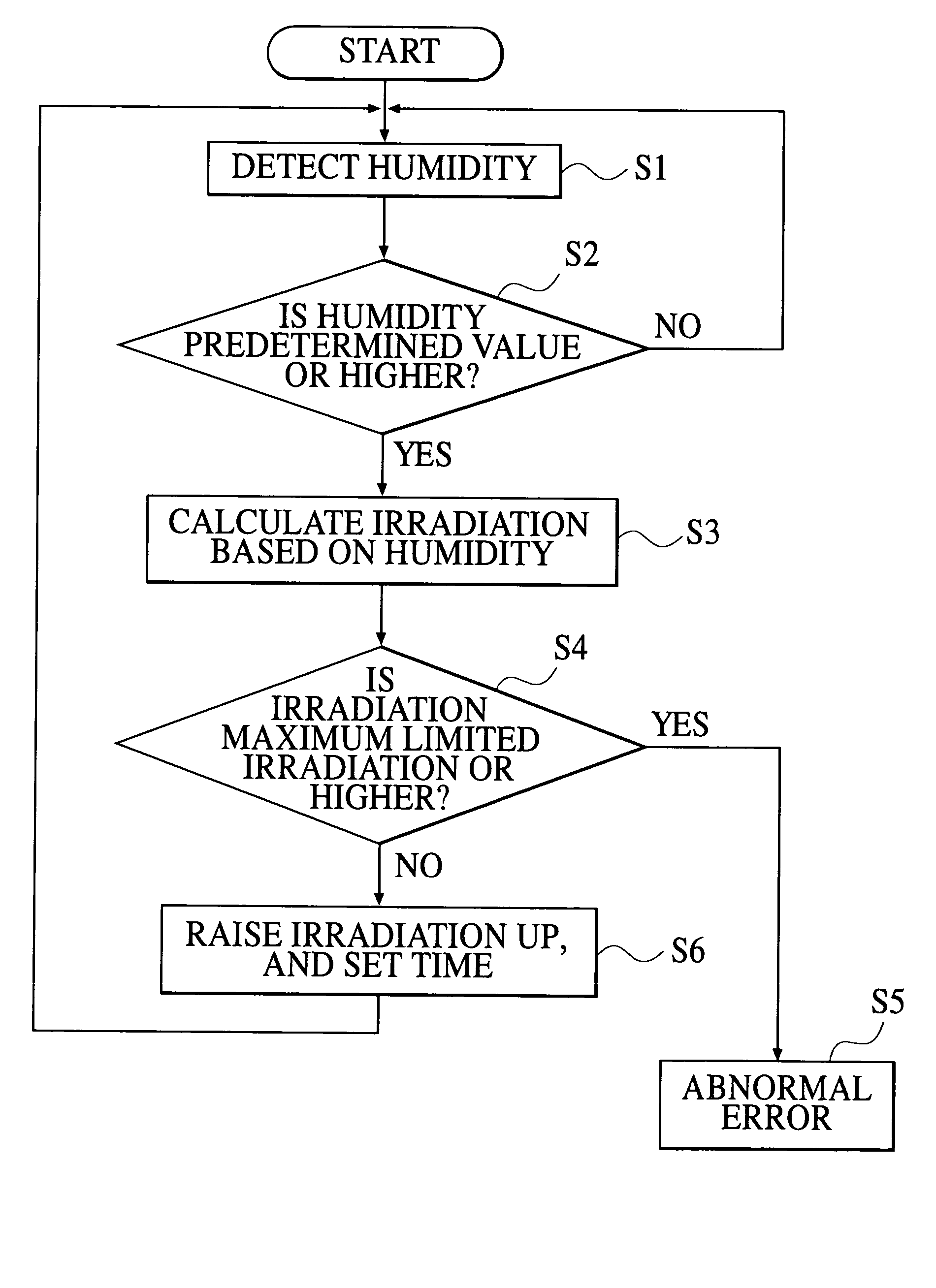
An ink jet printer capable of enhancing curability of cationic polymerization ink in a state that a raise in temperature of a recording medium is prevented as possible. The ink jet printer for recording a desired image on a recording medium by ejecting ink which includes a cationic polymerization component and which is curable when irradiated with light to the recording medium, has: a recording head for ejecting the ink to the recording medium; a light irradiation section for irradiating the light to the ink placed on the recording medium; a humidity detecting section for detecting humidity around the ink placed on the recording medium; and a controller for controlling irradiation of the light to be irradiated from the light irradiation section on the basis of detected humidity detected by the humidity detecting section.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Light emitting source and a light emitting source array
InactiveUS7399108B2High color reproductionUniform colorSolid-state devicesLight guides for lighting systemsLight irradiationLight emitting device
On the rear surface of a transparent molded unit is provided a reflecting member. In a central part of the molded unit are encapsulated light emitting devices. In the vicinity of the central part of the reflecting member is formed a reflecting area that is angularly inclined to the rear surface as it moves to the outer circumferential direction. A toric channel is provided on a light irradiation surface of the molded unit, and a slope total reflection area is provided in its inner circumferential side. Light emanating from the light emitting devices is reflected at the slope total reflection area, and further reflected at the direct output area. Then, after being further reflected at the reflecting area of the reflecting member, the light is guided to the outer circumferential end of the reflecting member, and is outputted forward from the total reflection area by being reflected at the outer circumferential end of the reflecting member.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Spectral characteristic obtaining apparatus, image evaluation apparatus and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20110299104A1Digitally marking record carriersRadiation pyrometrySensor arrayLight irradiation
A spectral characteristic obtaining apparatus including a light irradiation unit configured to emit light onto a reading object; a spectroscopic unit configured to separate at least a part of diffused reflected light from the light emitted onto the reading object by the light irradiation unit into a spectrum; and a light receiving unit configured to receive the diffused reflected light separated into the spectrum by the spectroscopic unit and to obtain a spectral characteristic. In at least one example embodiment, the light receiving unit is configured to be a spectroscopic sensor array including plural spectroscopic sensors arranged in a direction, and the spectroscopic sensors include a predetermined number of pixels arranged in the direction to receive lights with different spectral characteristics from each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
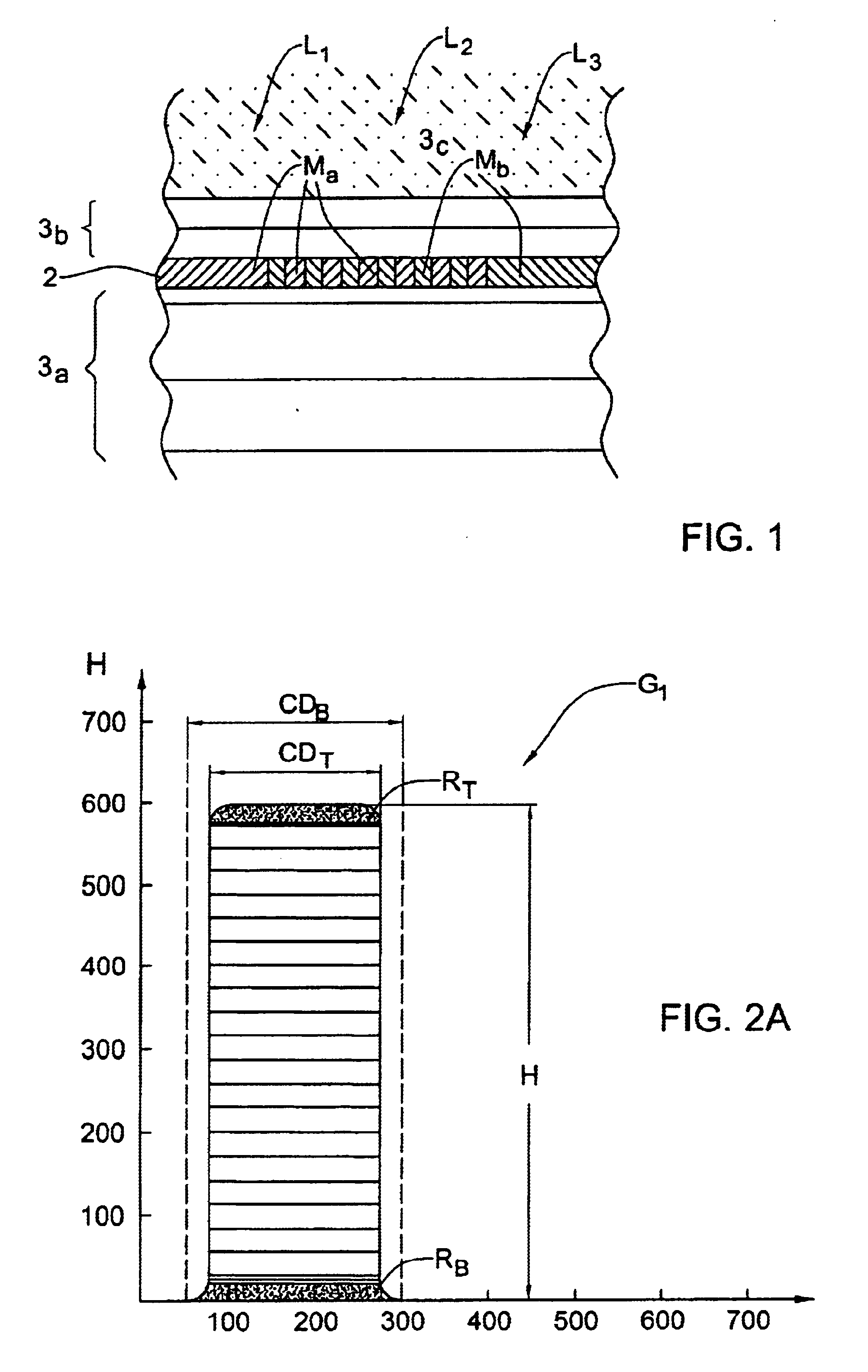
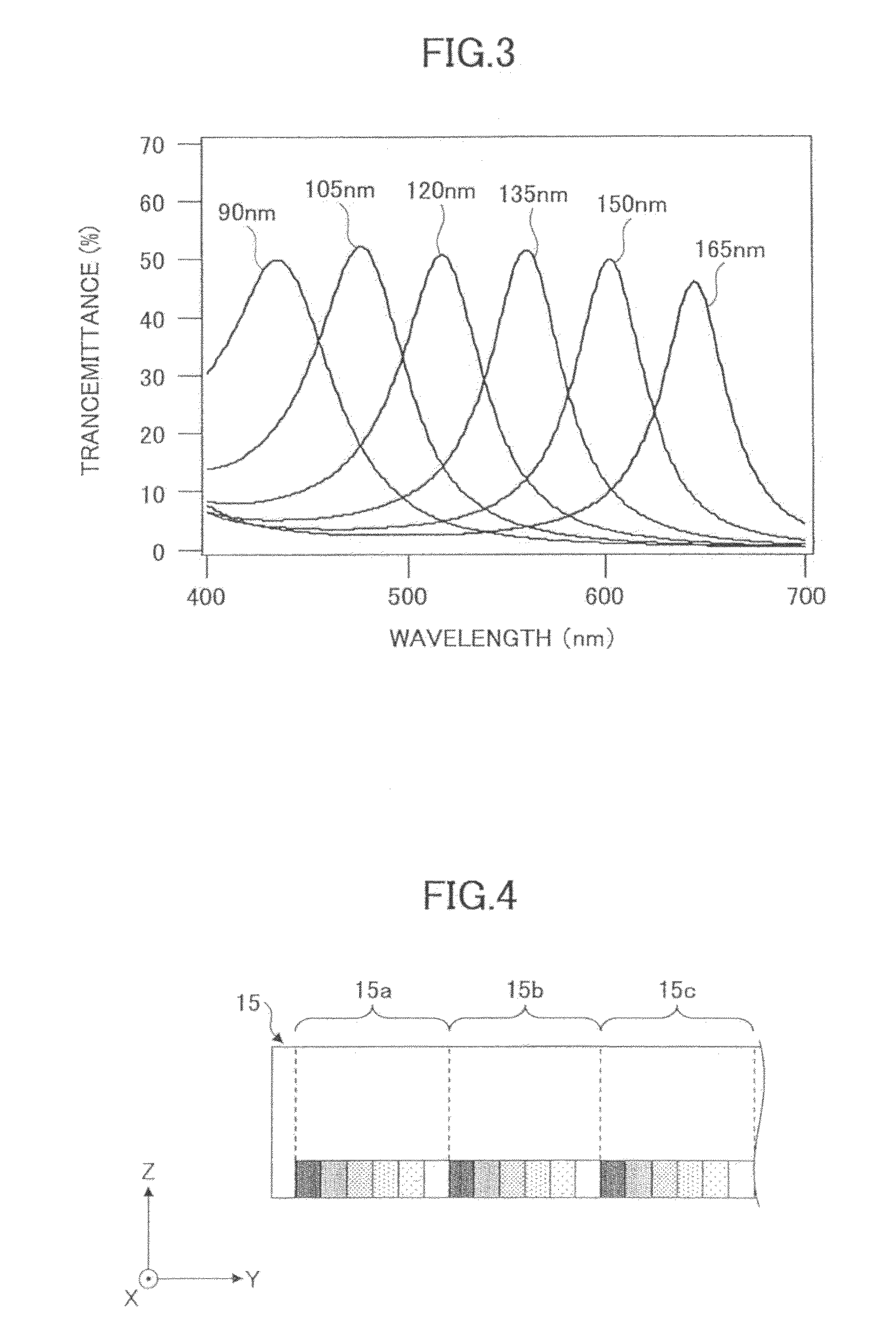
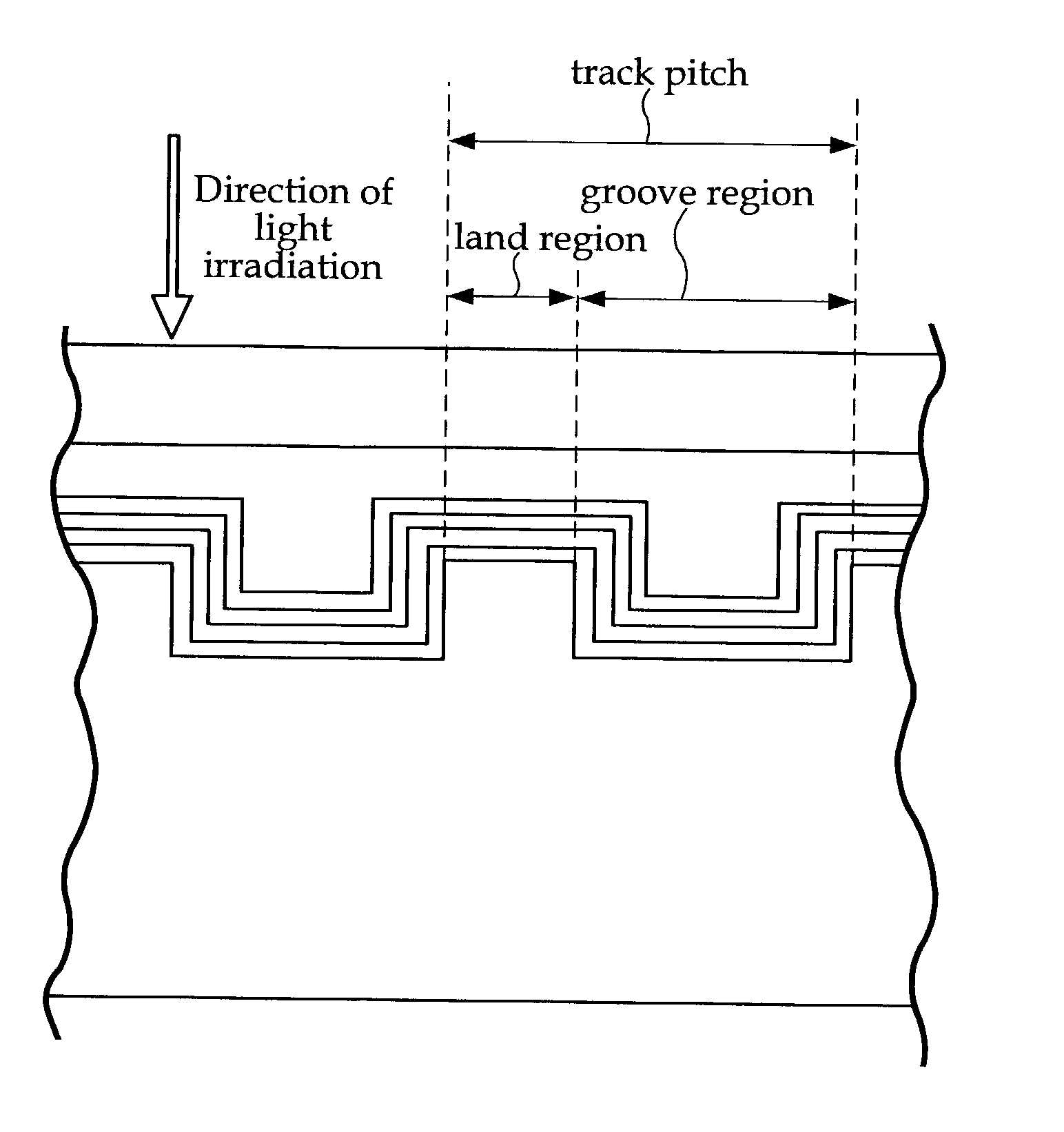
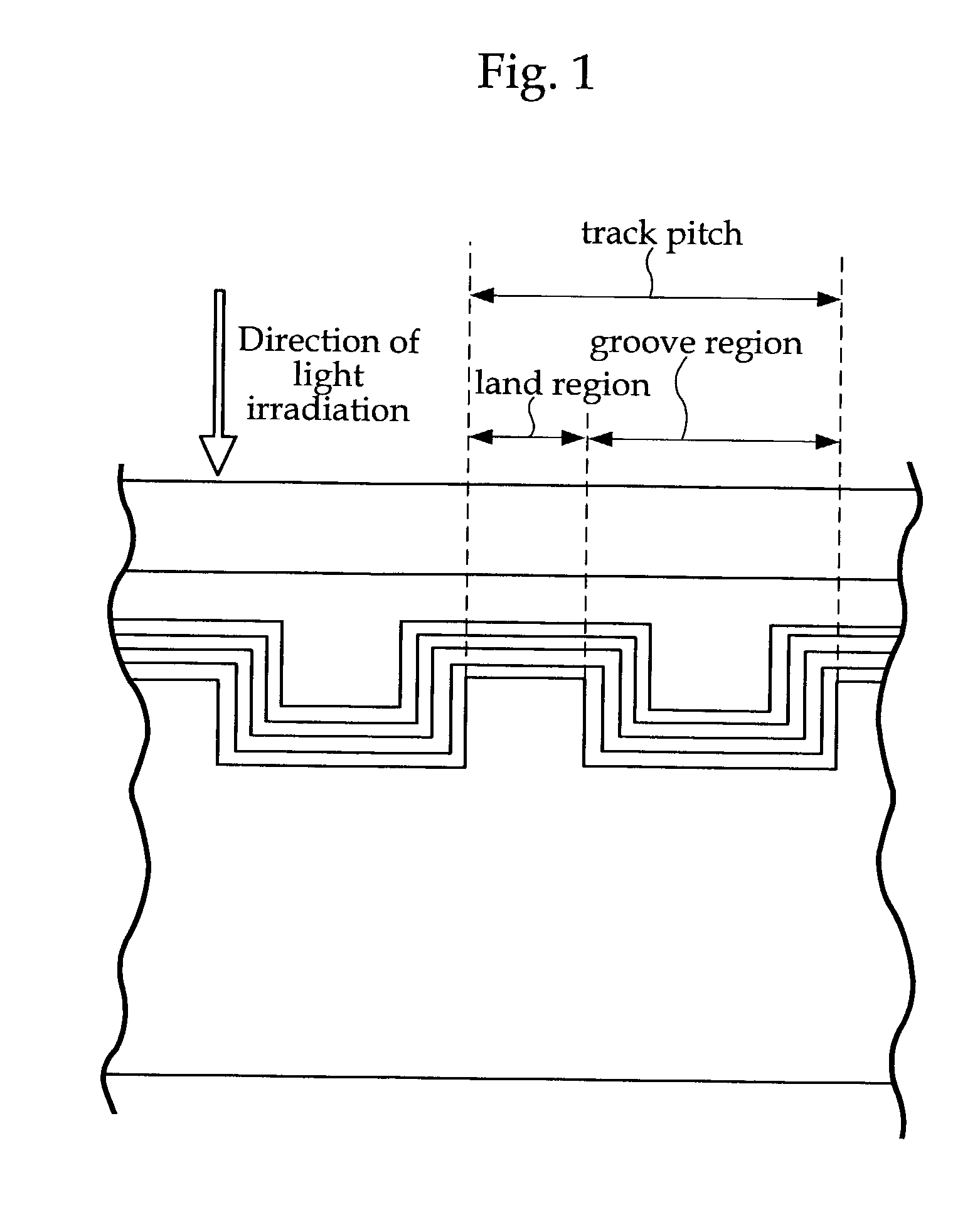
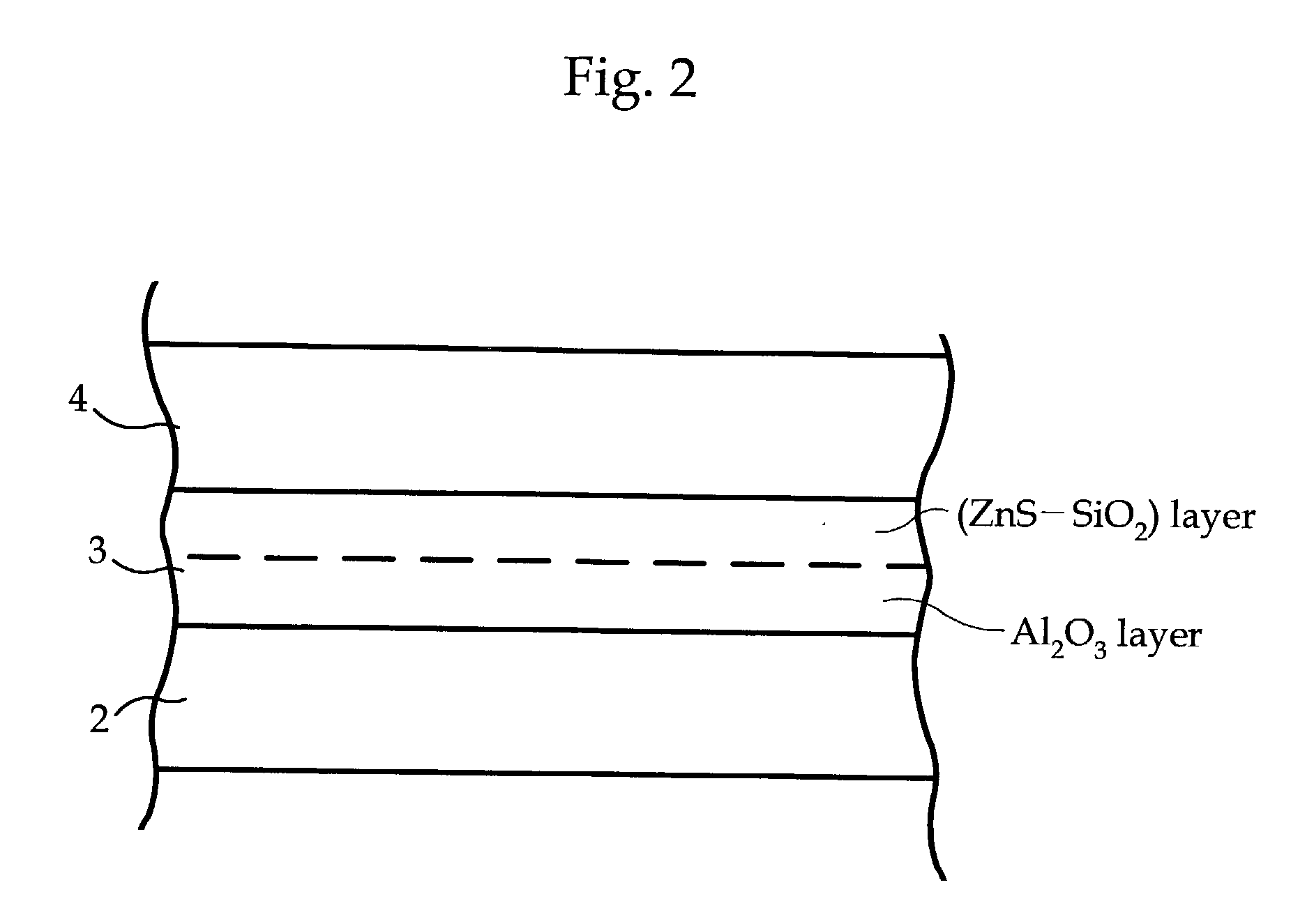
Information recording medium
InactiveUS20030081537A1Shorten speedHigh densityRadiation applicationsLayered productsLight irradiationLight reflection
An optical recording medium configured with a light reflection layer; a first protection layer; a recording layer containing a phase-change material which changes between crystalline and amorphous phases by a light irradiation; a second protection layer; and one of a cover layer and a protective coating layer disposed on a substrate in this order; and in which the light reflection layer is formed of one of an Al alloy and an Ag alloy; the first protection layer has a ZnS-SiO2 mixture layer which contains a mixture of ZnS and SiO2, and a intermediate layer having higher thermal conductivity than the ZnS-SiO2 mixture layer; the intermediate layer is formed on the side of the light reflection layer; the recording layer comprises Ge, Sb, and Te as main elements; and the second protection layer comprises a mixture of ZnS and SiO2.
Owner:RICOH KK
Automatic optical detection method and automatic optical detection system
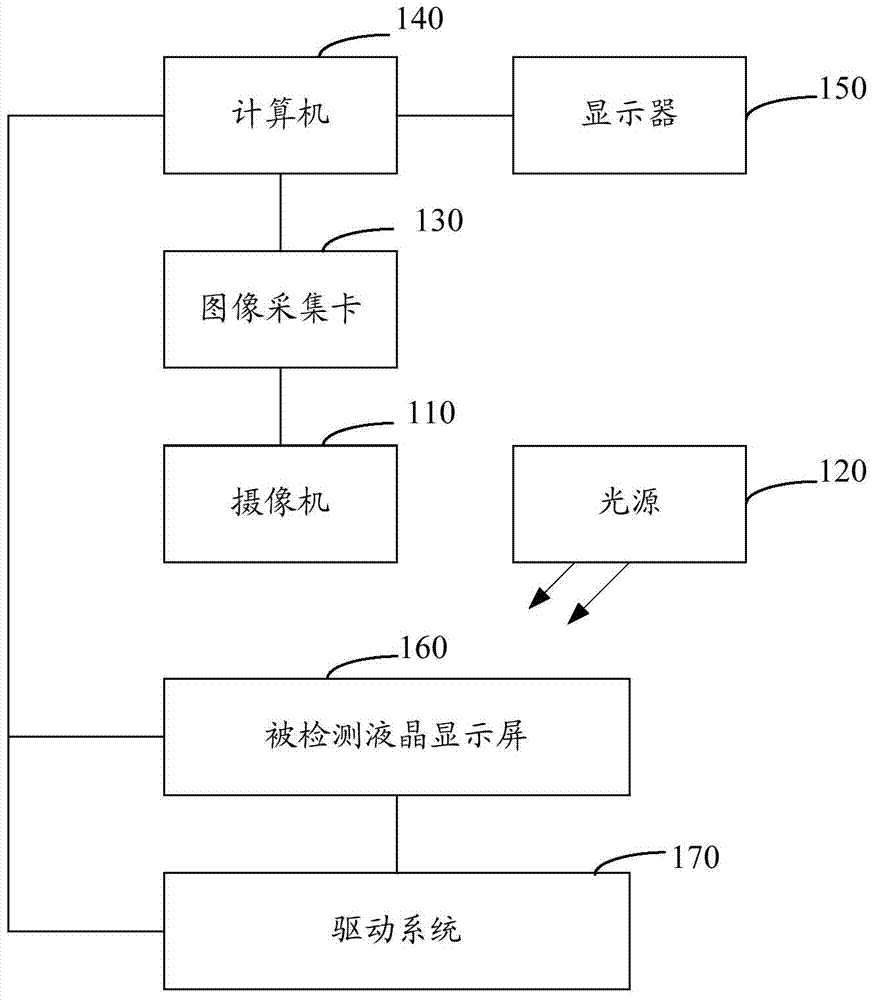
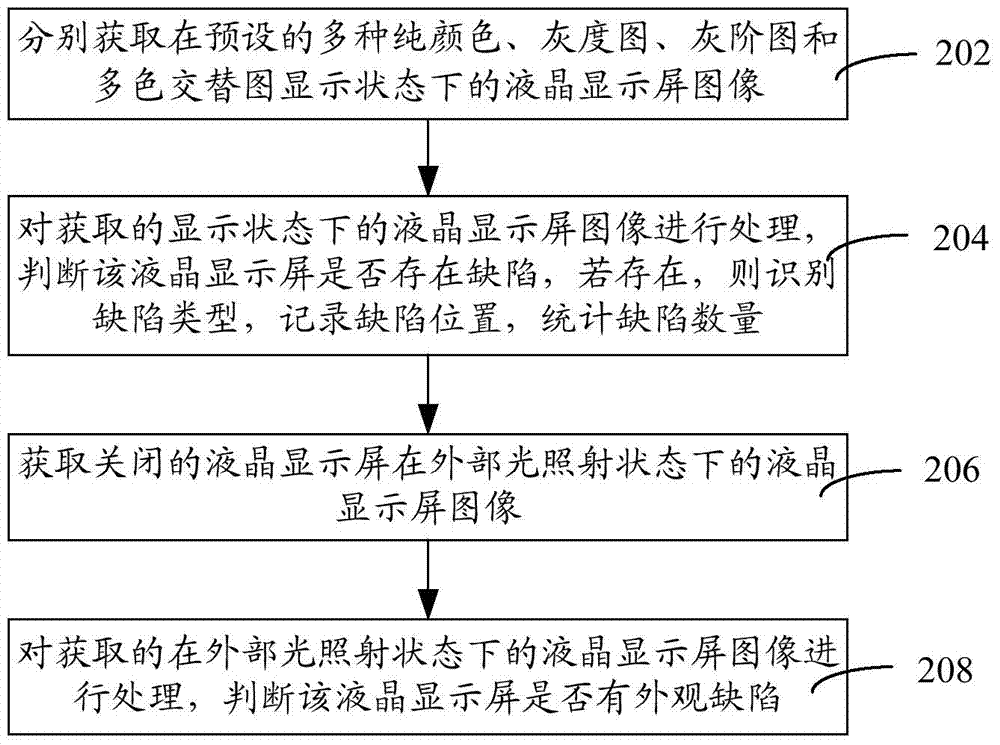
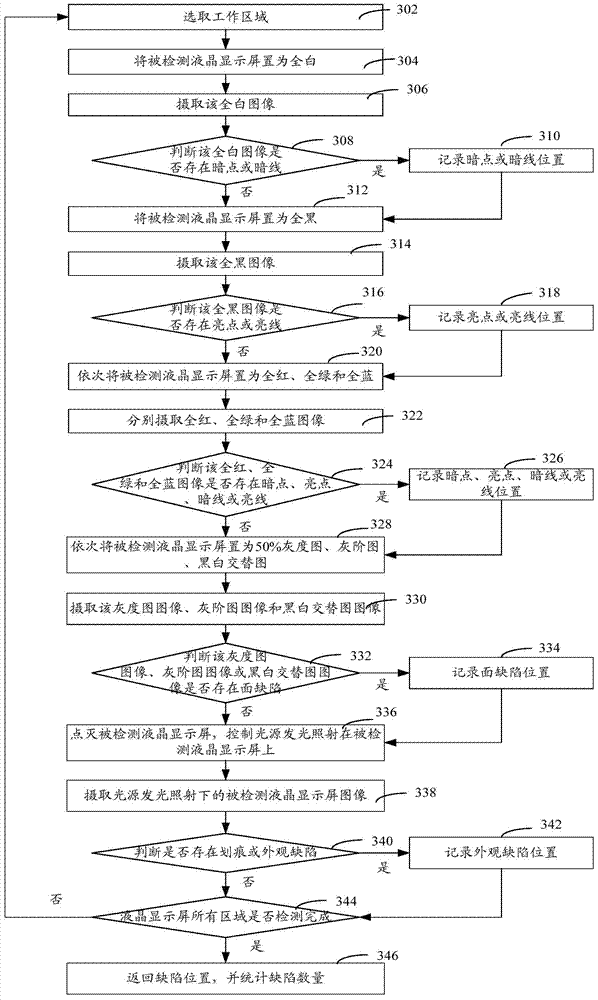
ActiveCN104749184AQuality improvementImprove yieldOptically investigating flaws/contaminationNon-linear opticsProduction lineLight irradiation
The invention relates to an automatic optical detection method and an automatic optical detection system. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining liquid crystal screen images in preset display states of multiple pure colours, grey-scale images, grey-level images and multi-colour alternating images respectively; processing the liquid crystal screen images in the obtained display states, judging whether a liquid crystal screen has defects or not, if so, then identifying the types of the defects, recording the positions of the defects, and counting the number of the defects; obtaining the liquid crystal screen images of the turned-off liquid crystal screen in an external light irradiation state; processing the liquid crystal screen images in the obtained external light irradiation state, and judging whether the liquid crystal screen has appearance defects or not. According to the automatic optical detection method and the automatic optical detection system provided by the invention, brightness, dark spots, bright lines, dark lines, surface defects and appearance defects can be detected, defect detection types are increased, unqualified products are reduced, the quality of the liquid crystal screen is improved, a production line can be improved, and the production yield of the liquid crystal screen can be increased.
Owner:EVOC SMART IOT TECH CO LTD
Display apparatus, light source device, and illumination unit
InactiveUS20060170883A1Color signal processing circuitsStatic indicating devicesLight irradiationLight-emitting diode
A display apparatus capable of illuminating a light modulation device with a light from a light emitting body to display an image on a display plane comprises a plurality of light emitting bodies (R, G, B) different from one another in emitted light color, a light receiving device configured to detect the light from the light emitting bodies and to output an amount of light received, and a color balance adjustment control section configured to adjust and control a color balance in the display plane in accordance with the amount of light received by the light receiving device. The color balance adjustment control section is configured to be capable of identifying the emitted light color of the light emitting body relating to the amount of light received.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com