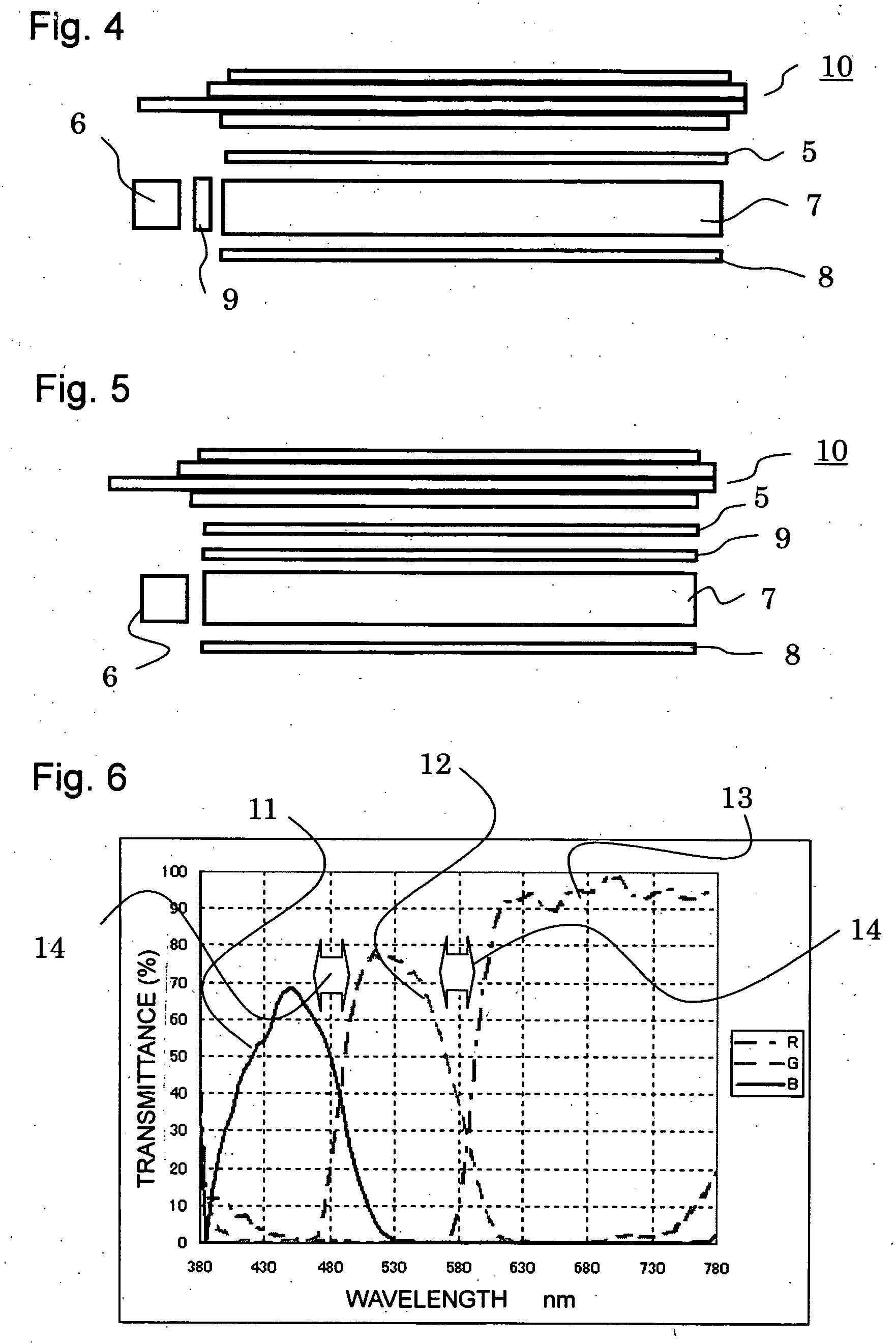
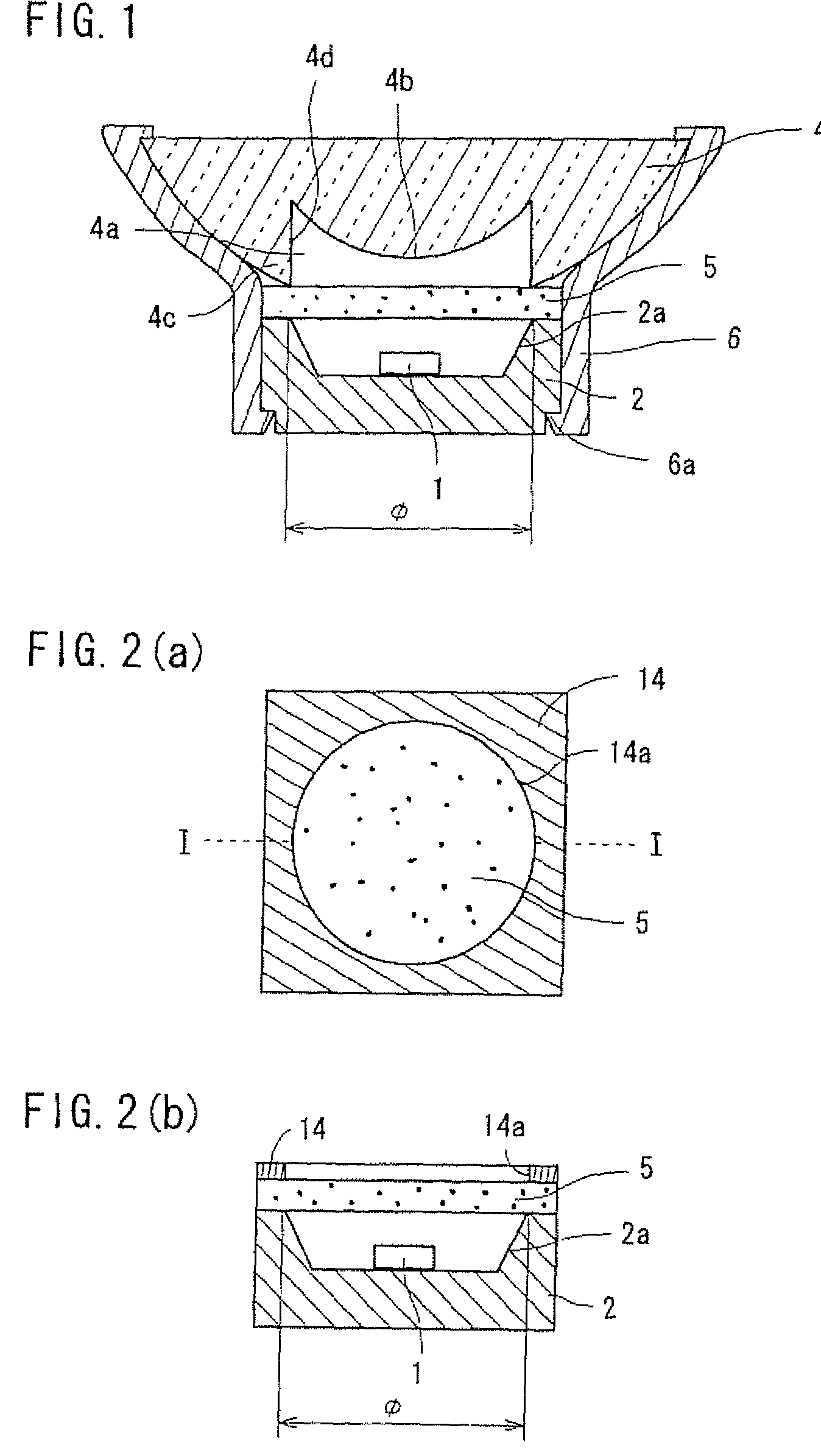
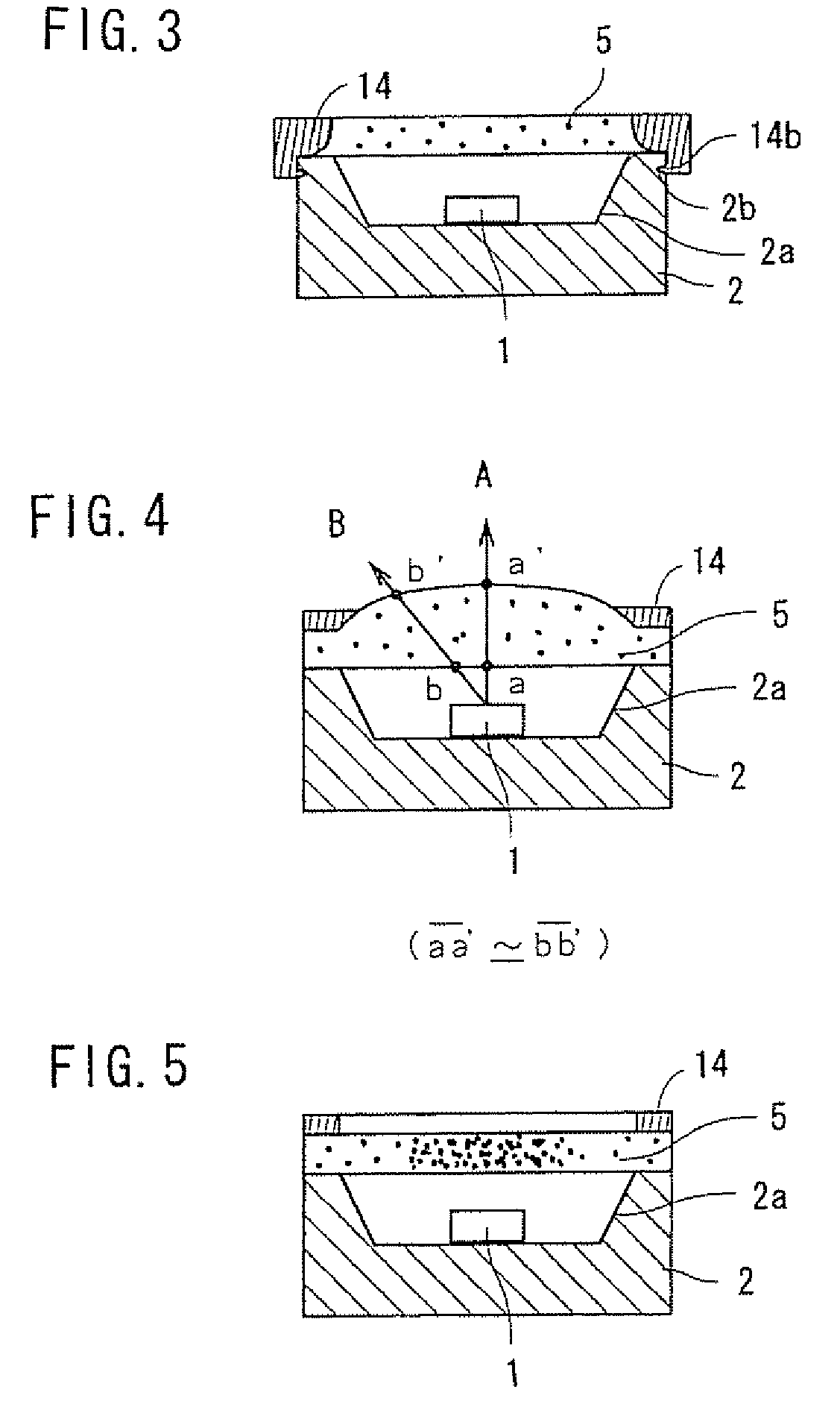
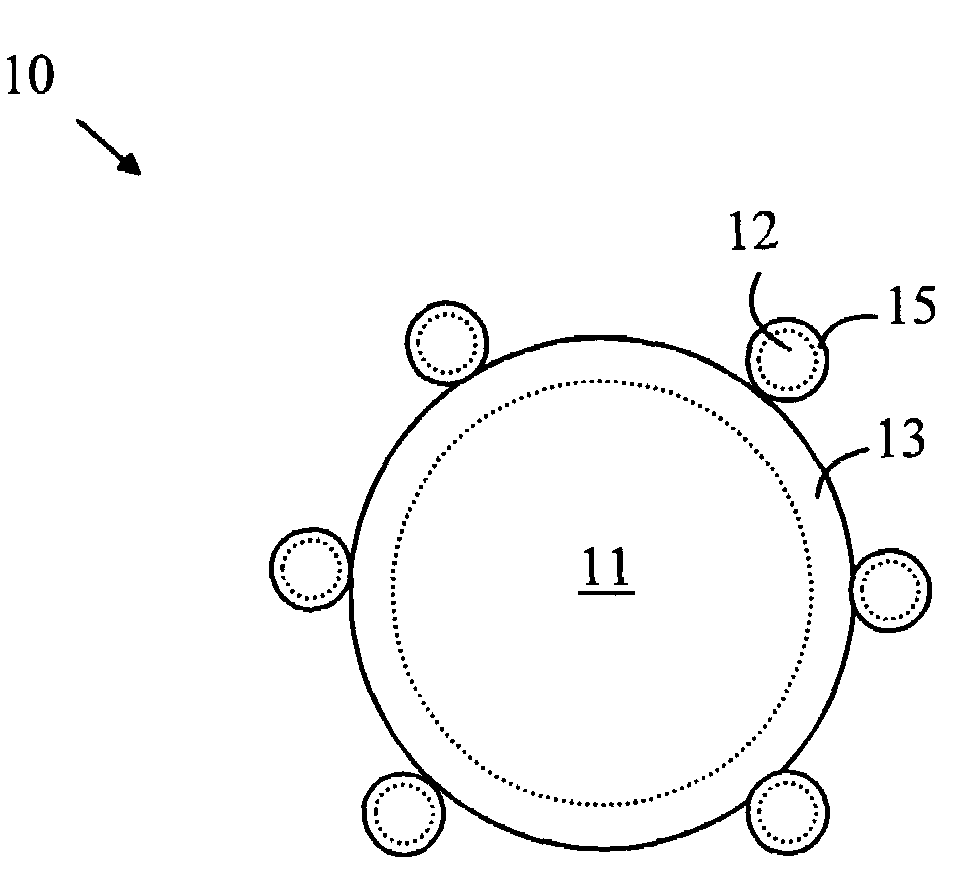
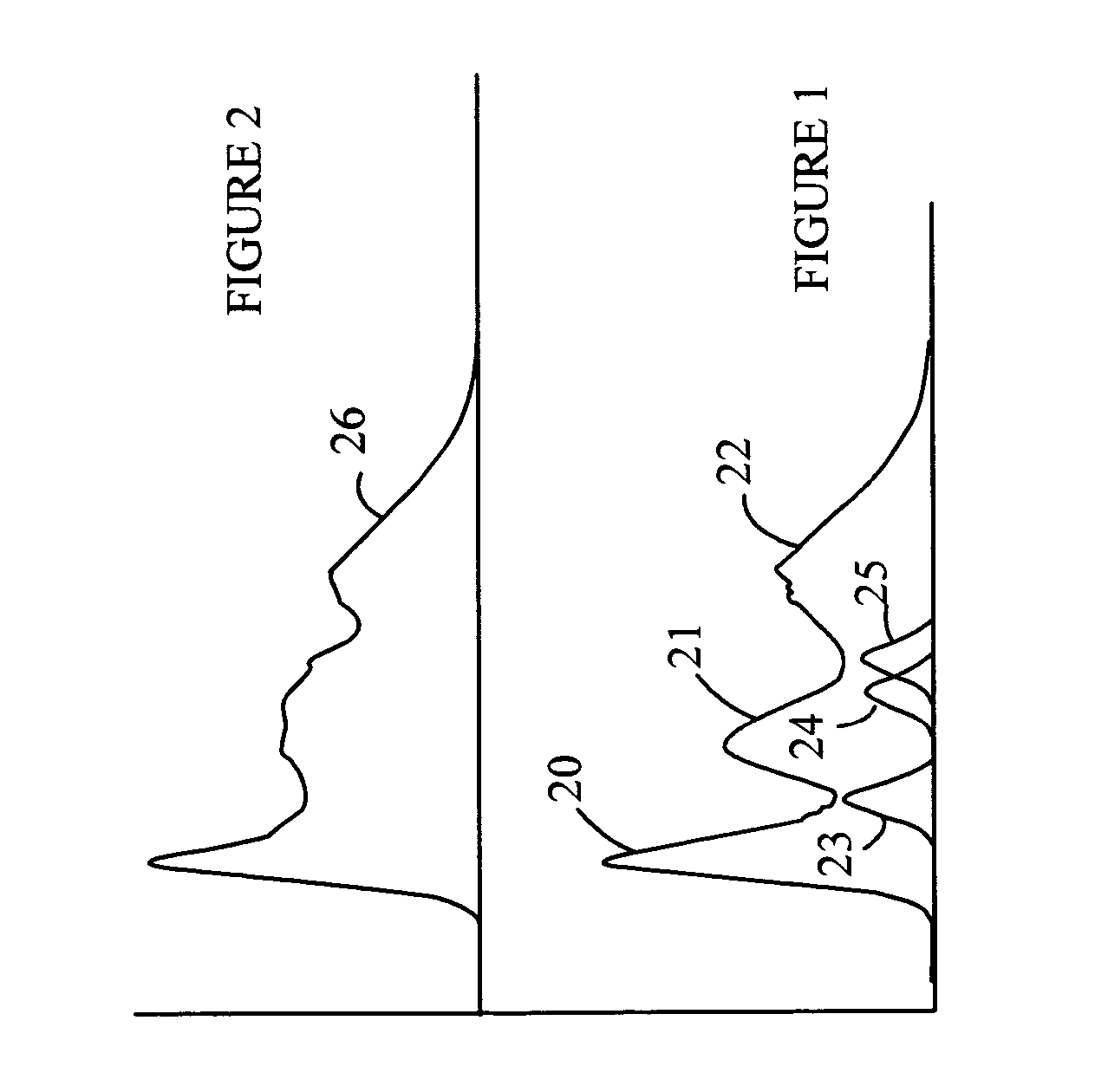
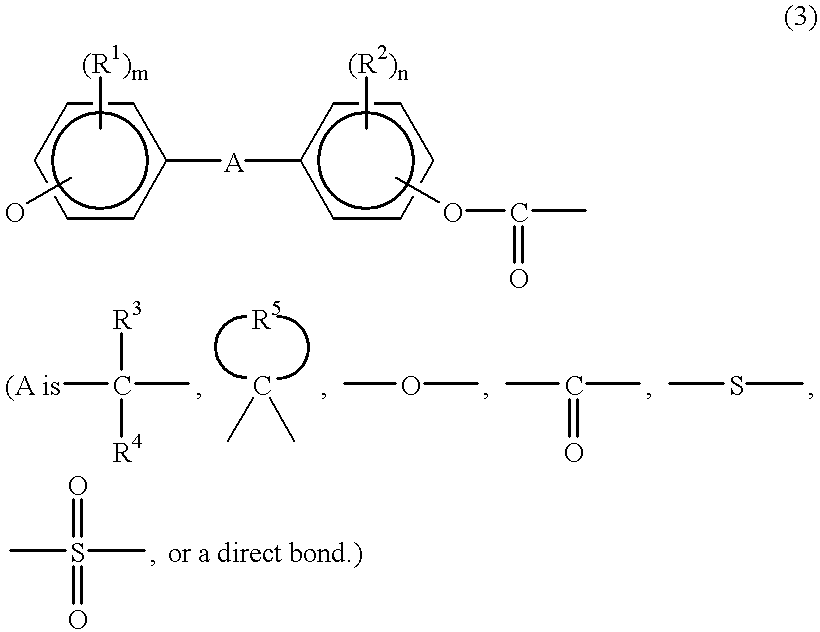Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1767 results about "Excitation wavelength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
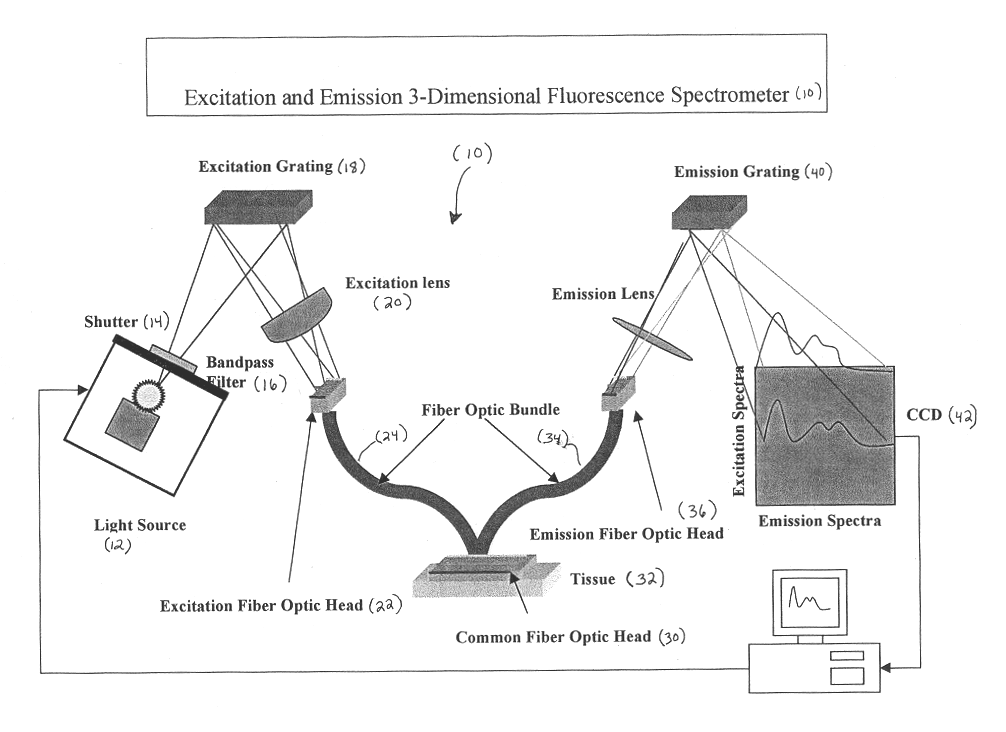
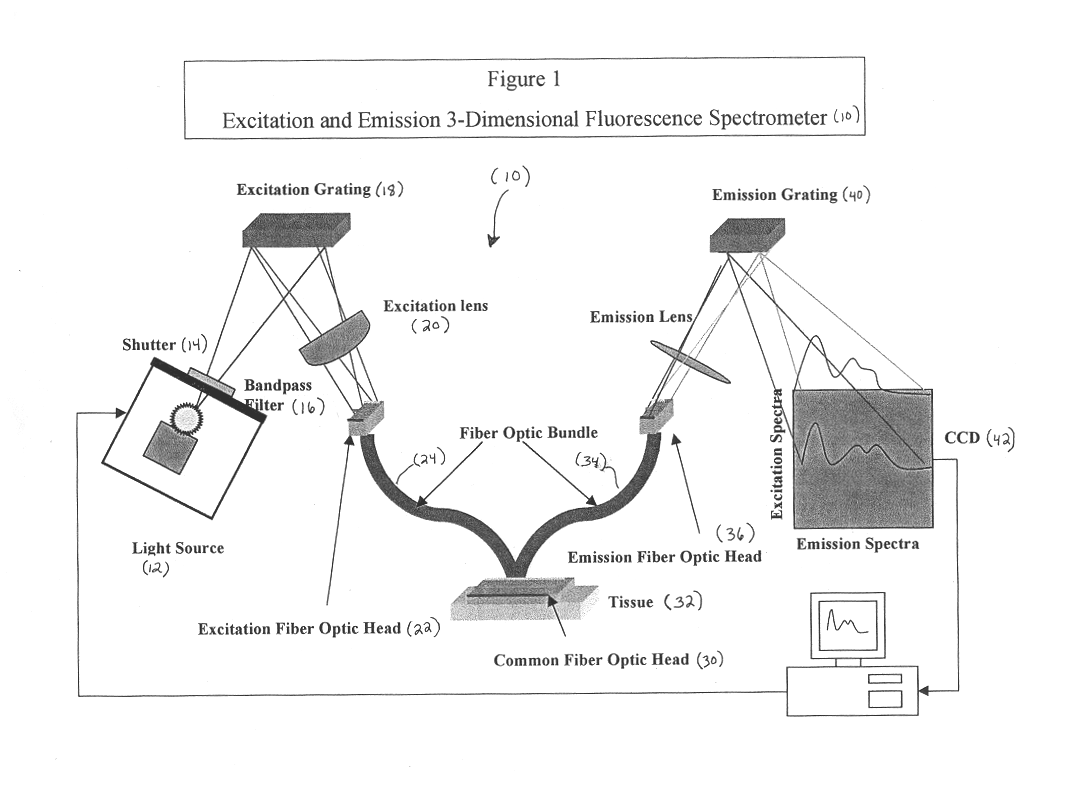
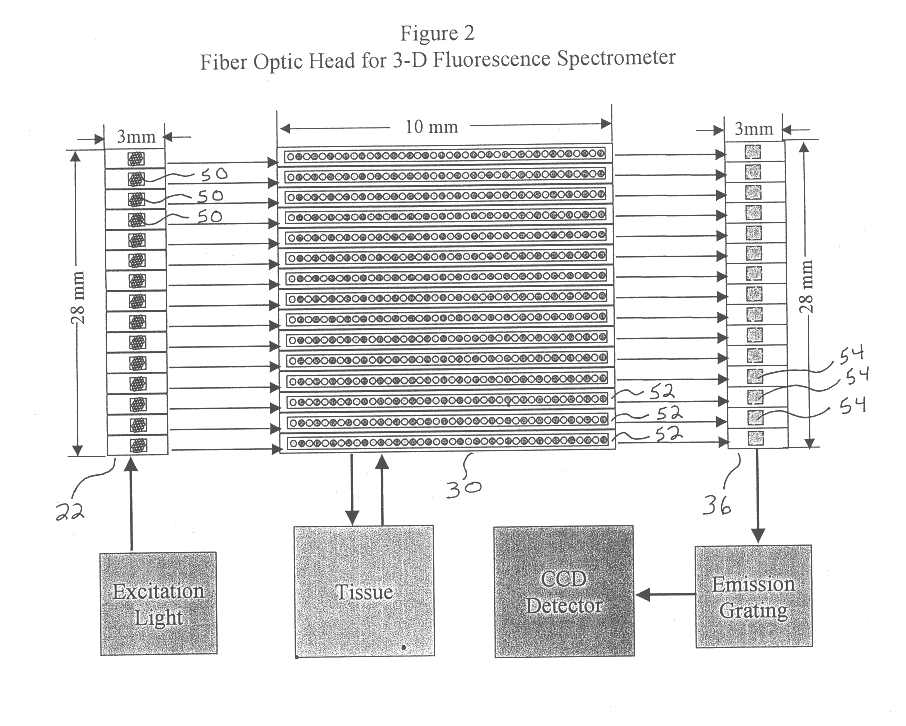
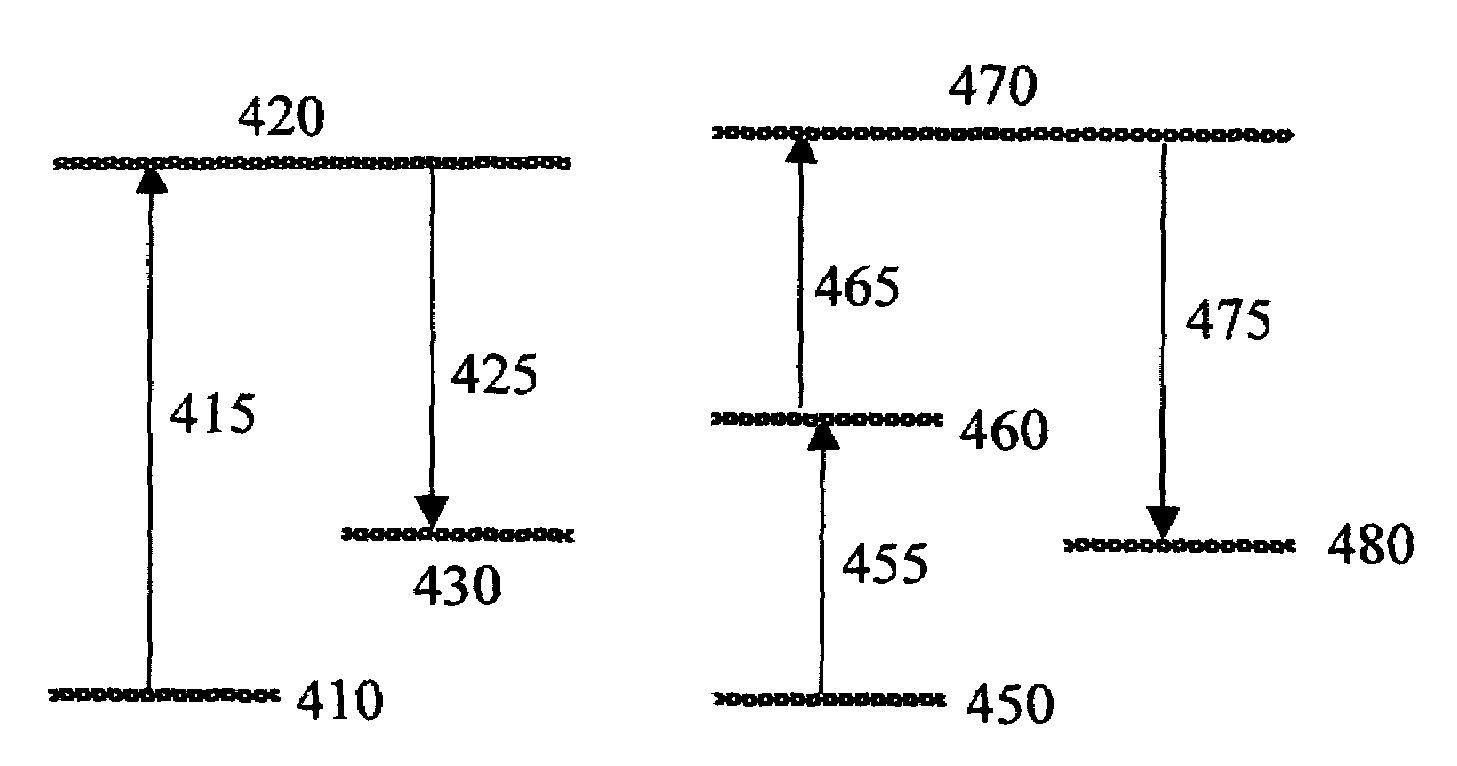
Generation of spatially-averaged excitation-emission map in heterogeneous tissue
An instrument for evaluating fluorescence of a heterogeneous tissue includes means for exciting a two-dimensional portion of the tissue surface with excitation radiation at a plurality of excitation wavelengths, means for collecting emission radiation from the two-dimensional portion of the tissue surface simultaneously with excitation of the portion, and means for forming a two-dimensional excitation-emission map of the excitation radiation and the simultaneously collected emission radiation and spatially averaging the excitation and emission radiation.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
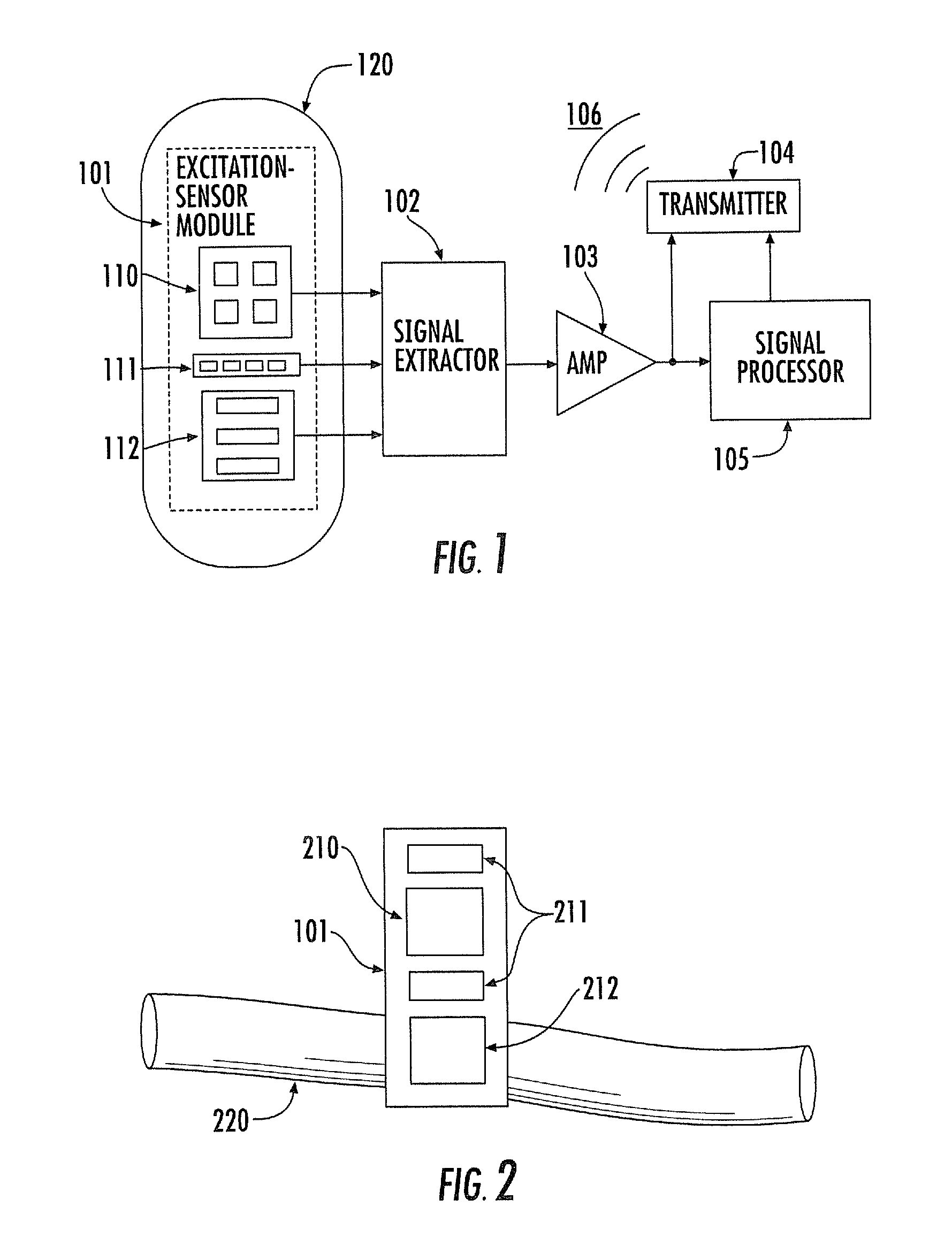
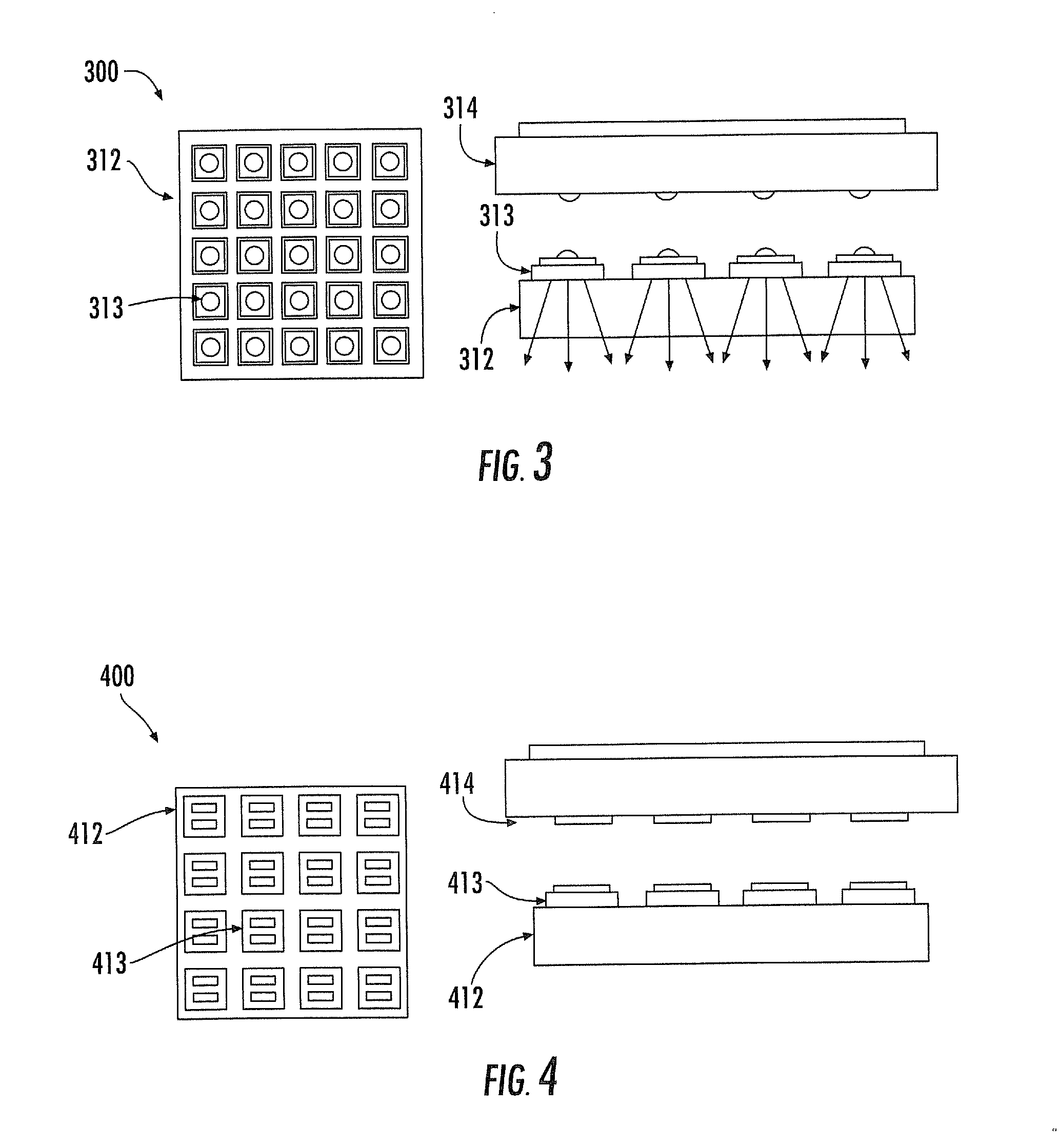
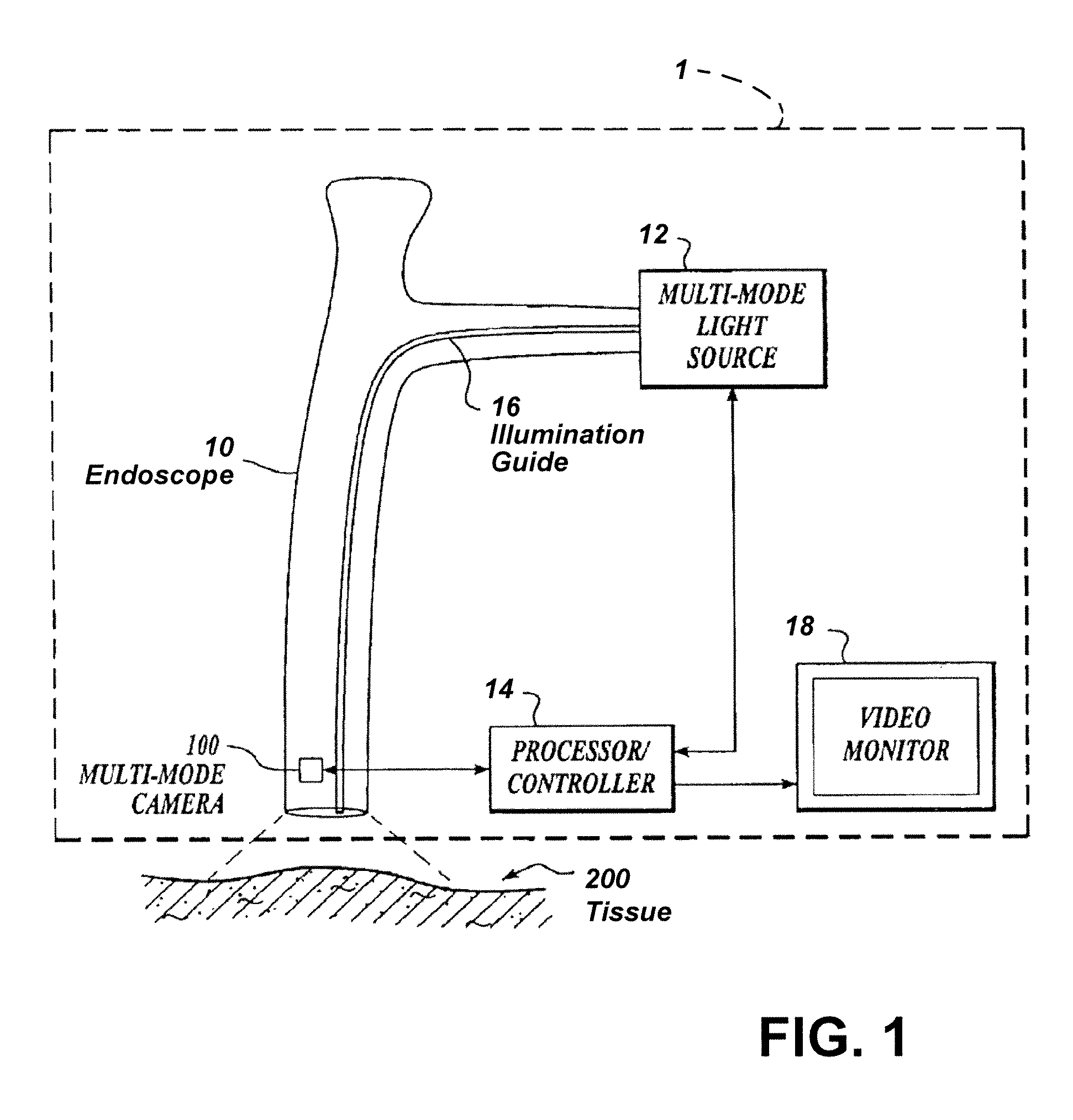
Noninvasive physiological analysis using excitation-sensor modules and related devices and methods
Methods and apparatus for qualifying and quantifying excitation-dependent physiological information extracted from wearable sensors in the midst of interference from unwanted sources are provided. An organism is interrogated with at least one excitation energy, energy response signals from two or more distinct physiological regions are sensed, and these signals are processed to generate an extracted signal. The extracted signal is compared with a physiological model to qualify and / or quantify a physiological property. Additionally, important physiological information can be qualified and quantified by comparing the excitation wavelength-dependent response, measured via wearable sensors, with a physiological model.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
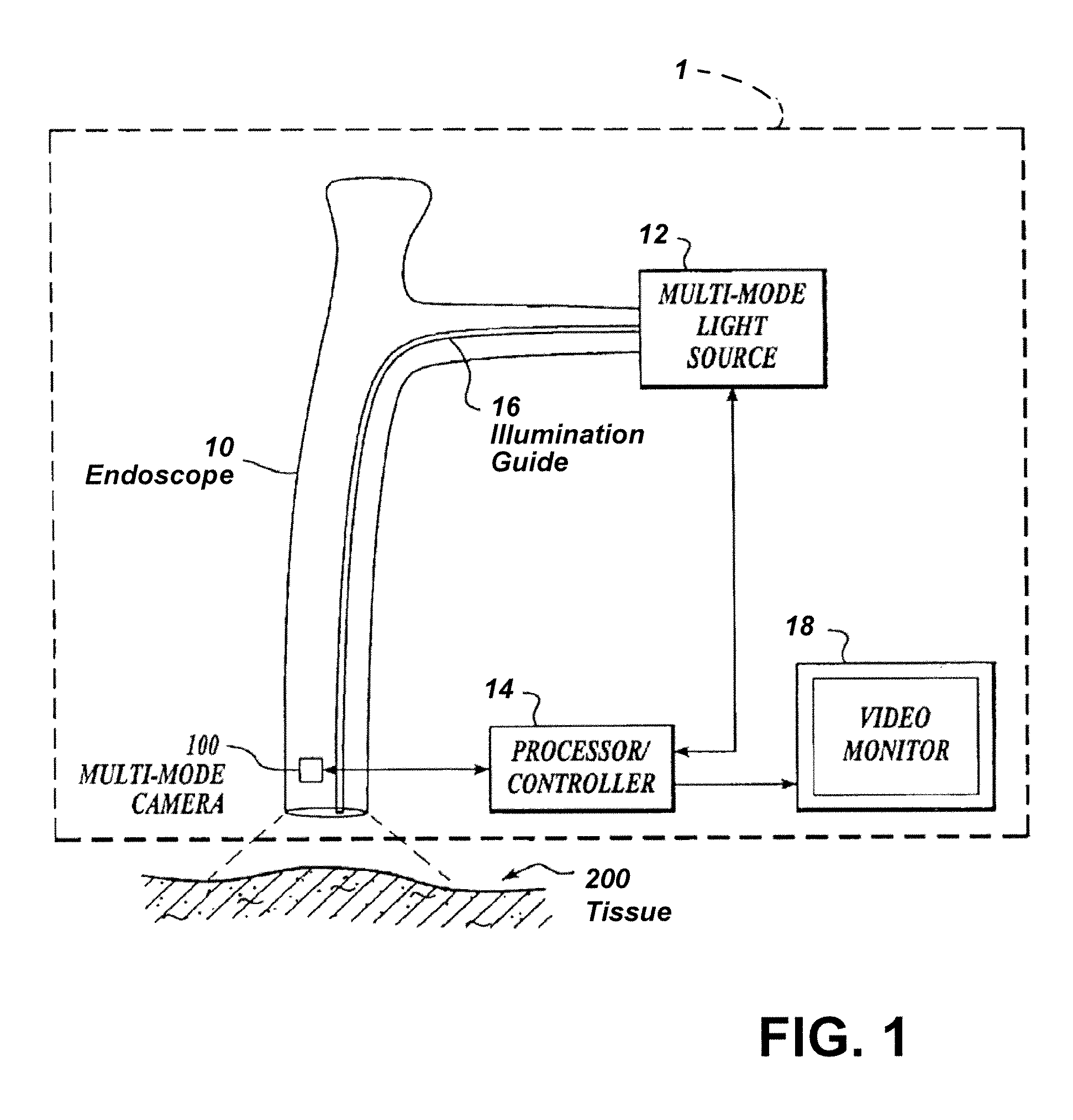
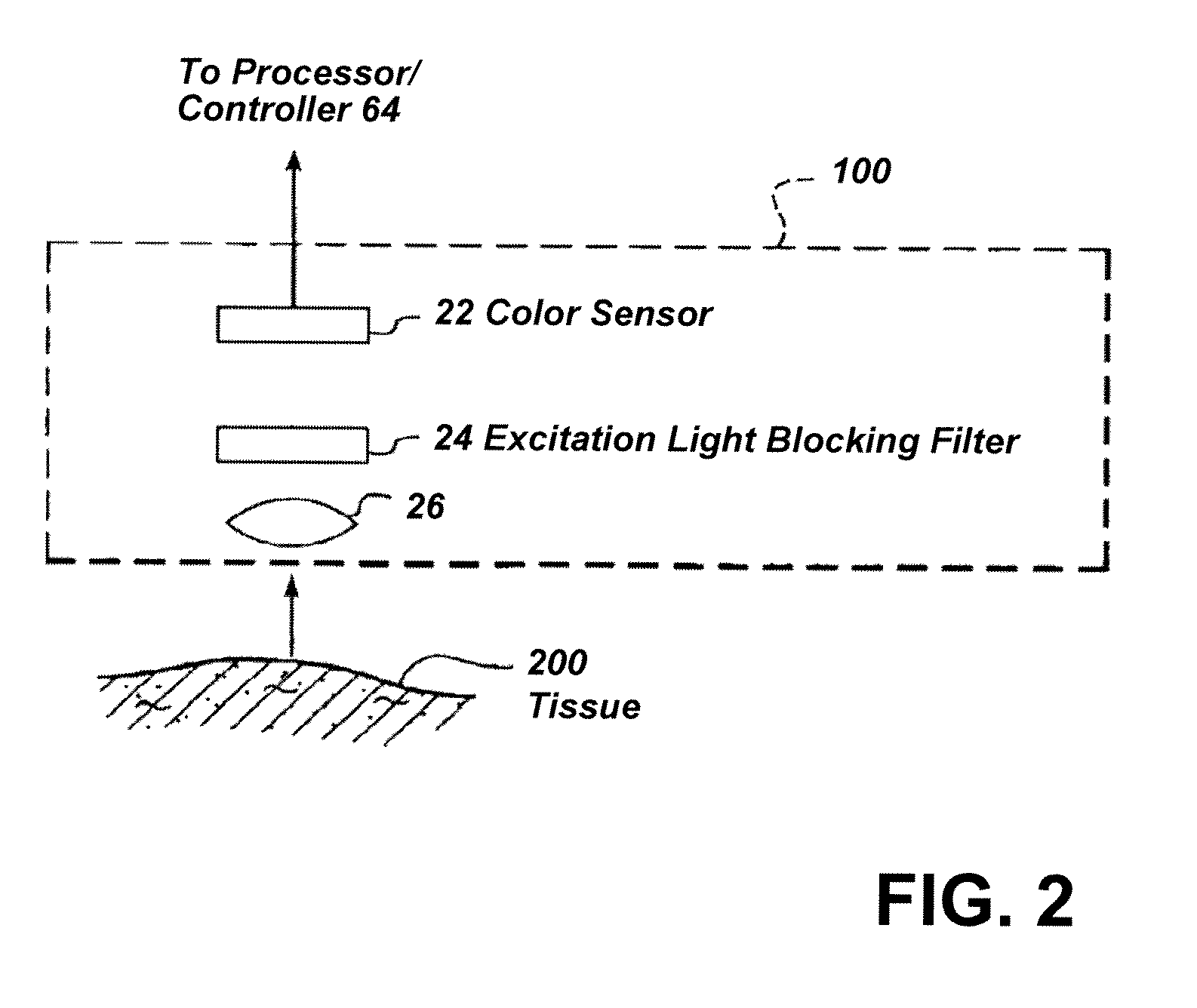
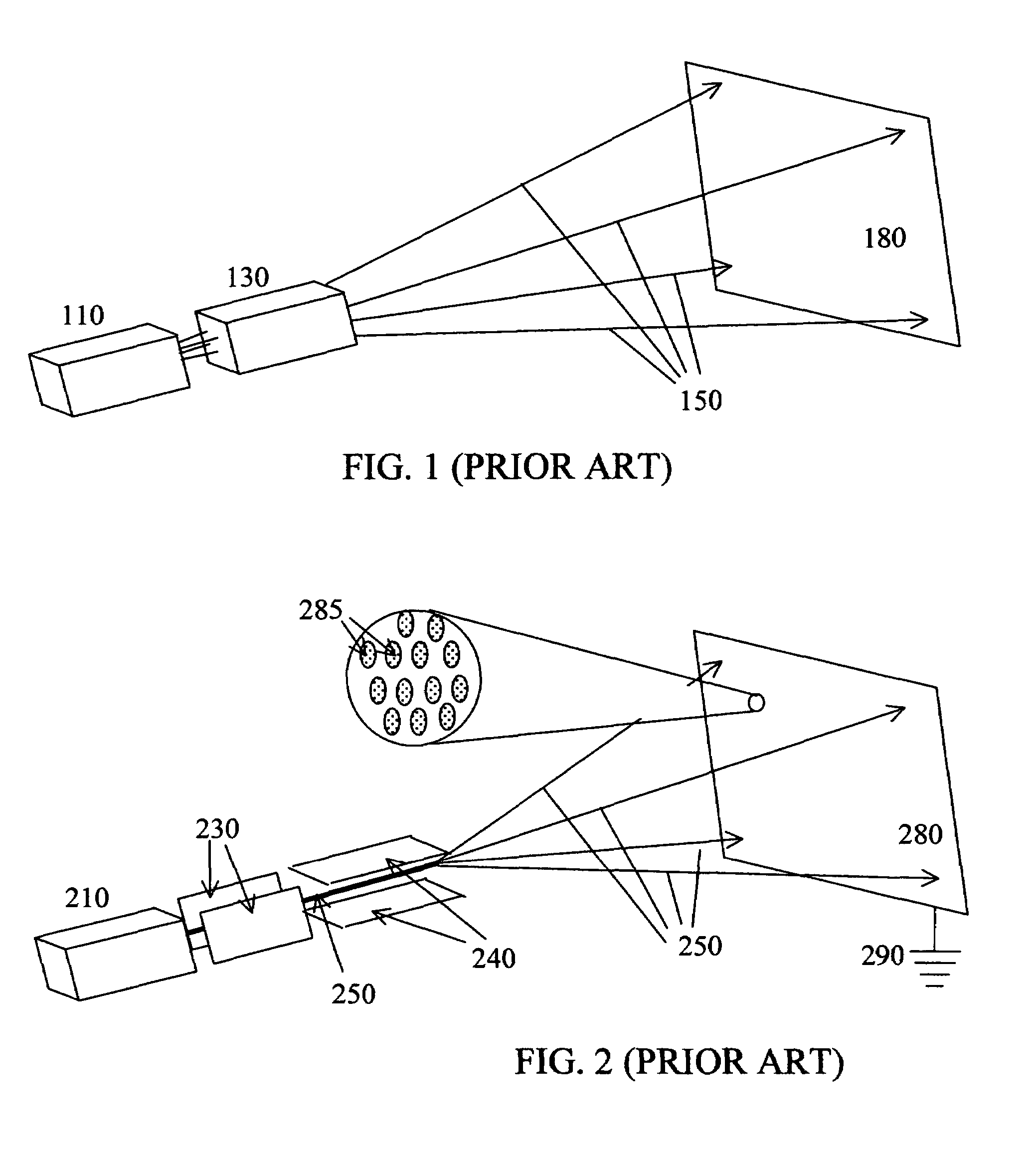
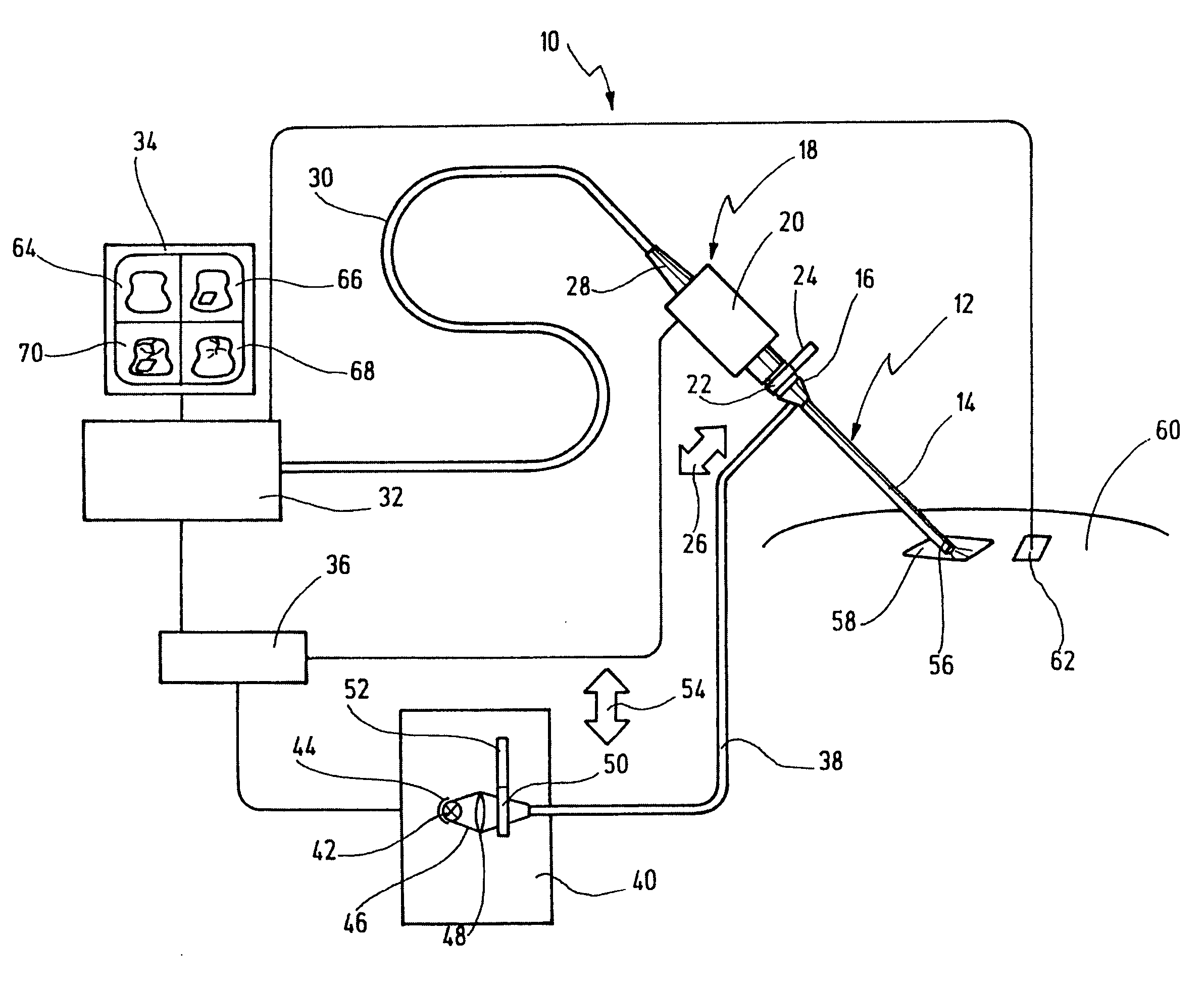
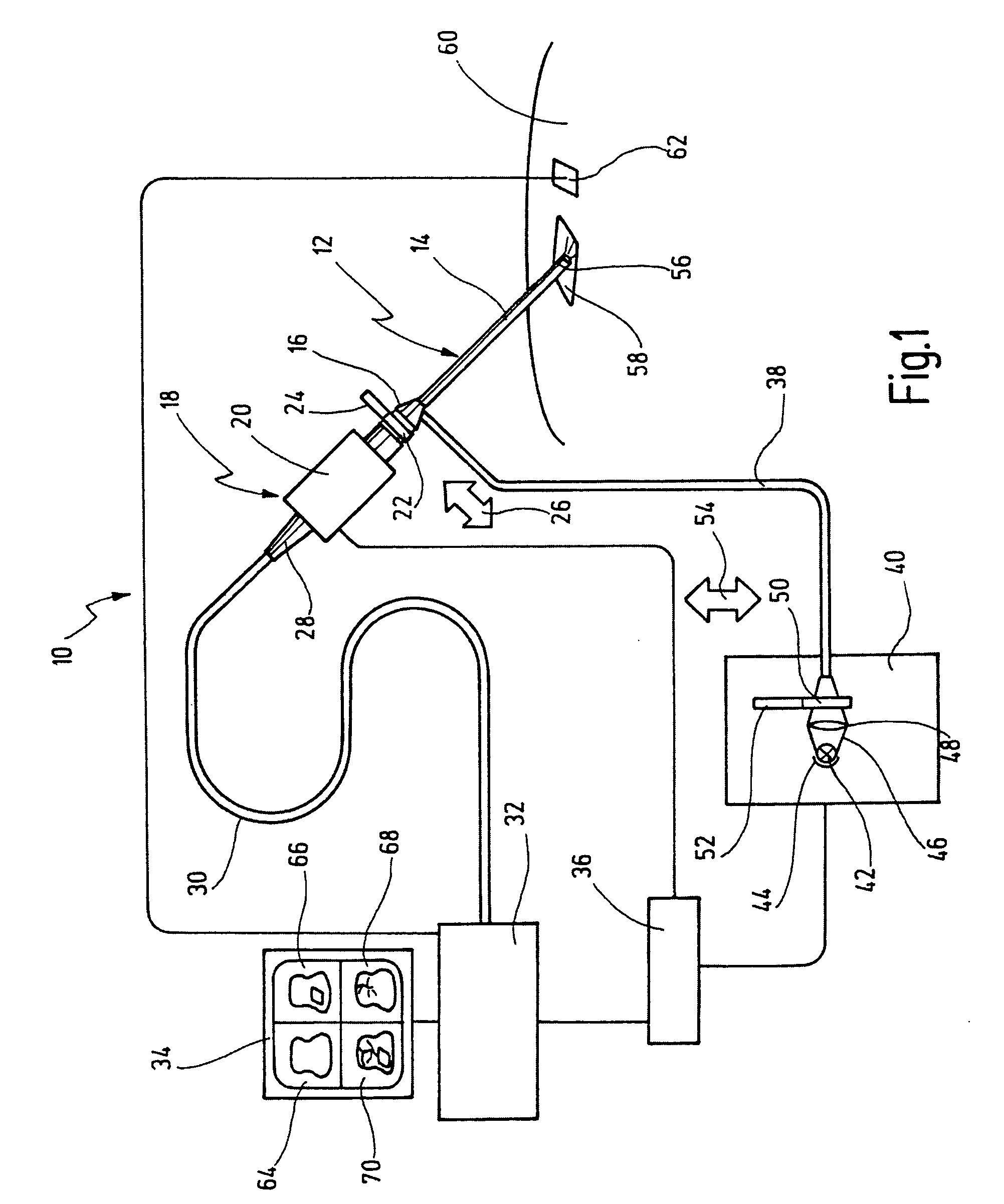
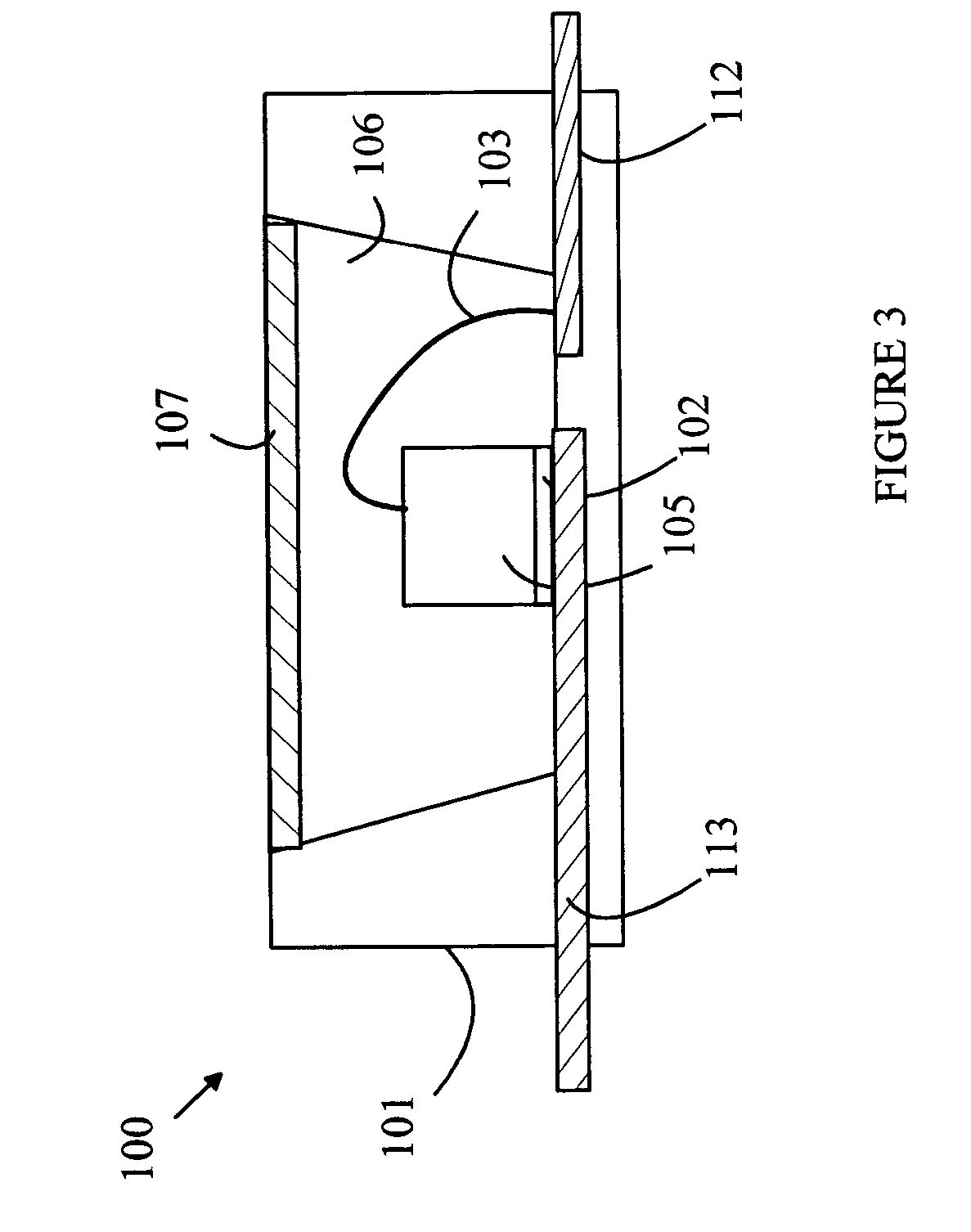
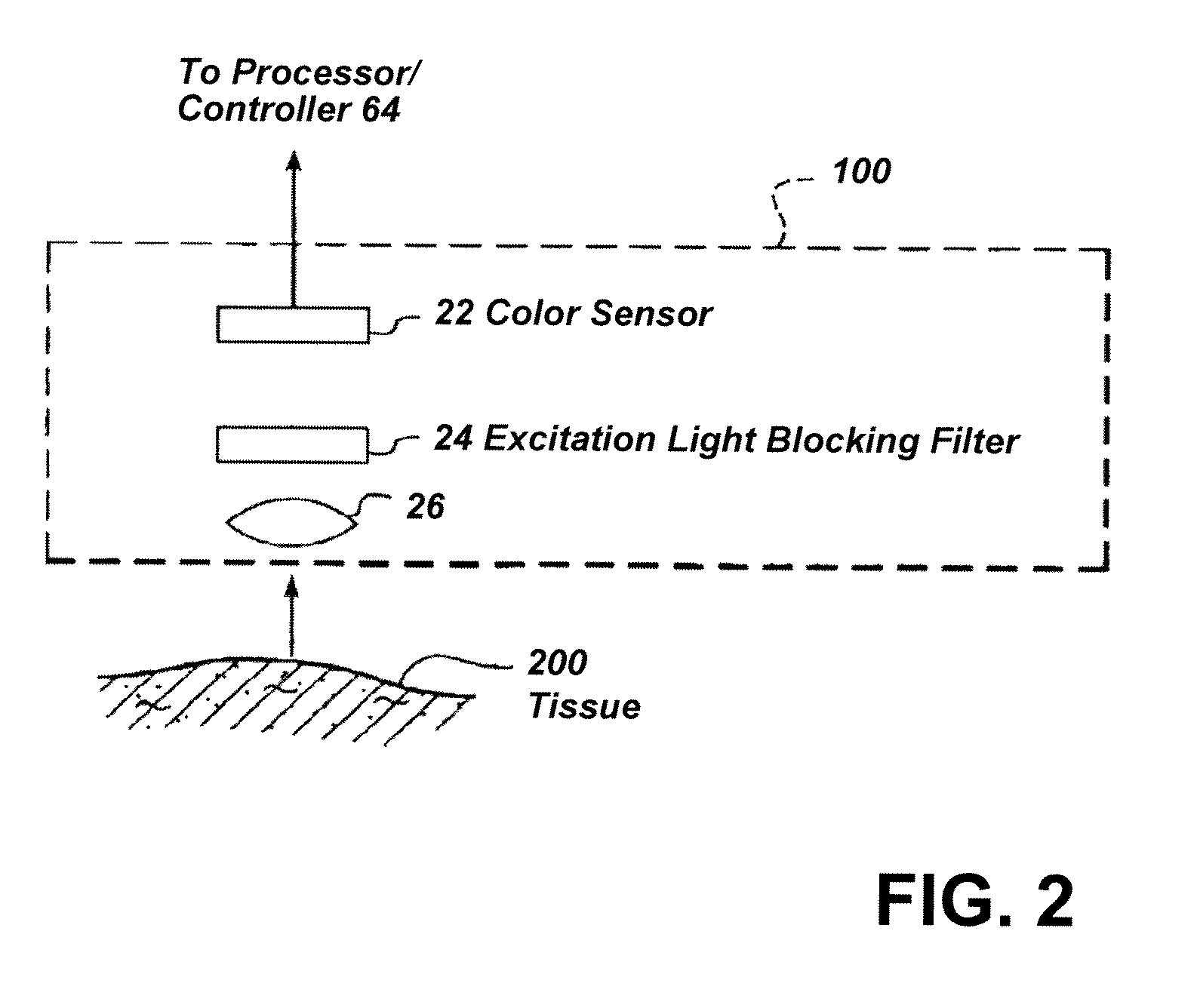
Imaging system with a single color image sensor for simultaneous fluorescence and color video endoscopy
ActiveUS20080239070A1Enhanced attainable spatial resolutionHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsSurgeryVideo rateMonochrome Image
An endoscopic video system and method using a camera with a single color image sensor, for example a CCD color image sensor, for fluorescence and color imaging and for simultaneously displaying the images acquired in these imaging modes at video rates in real time is disclosed. The tissue under investigation is illuminated continuously with fluorescence excitation light and is further illuminated periodically using visible light outside of the fluorescence excitation wavelength range. The illumination sources may be conventional lamps using filters and shutters, or may include light-emitting diodes mounted at the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
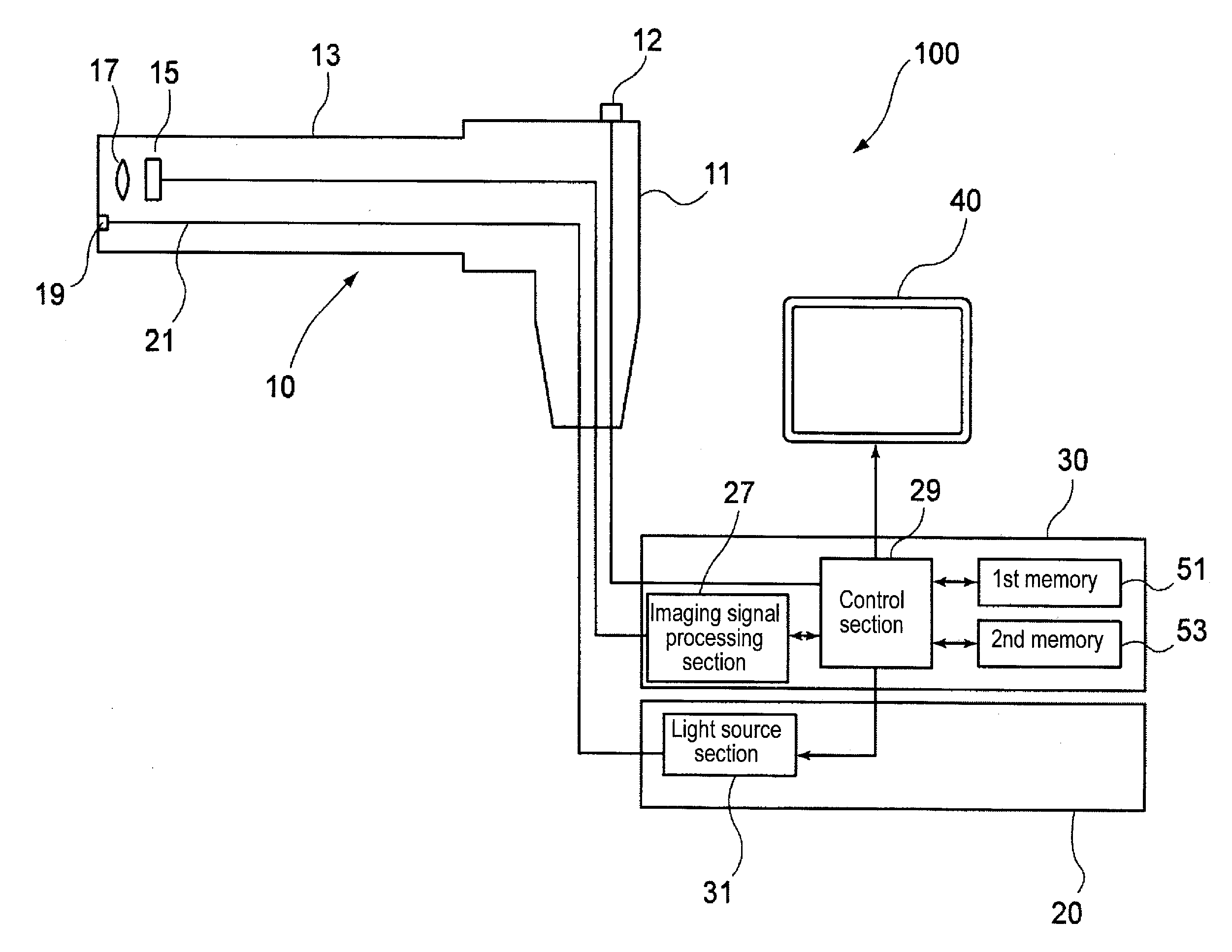
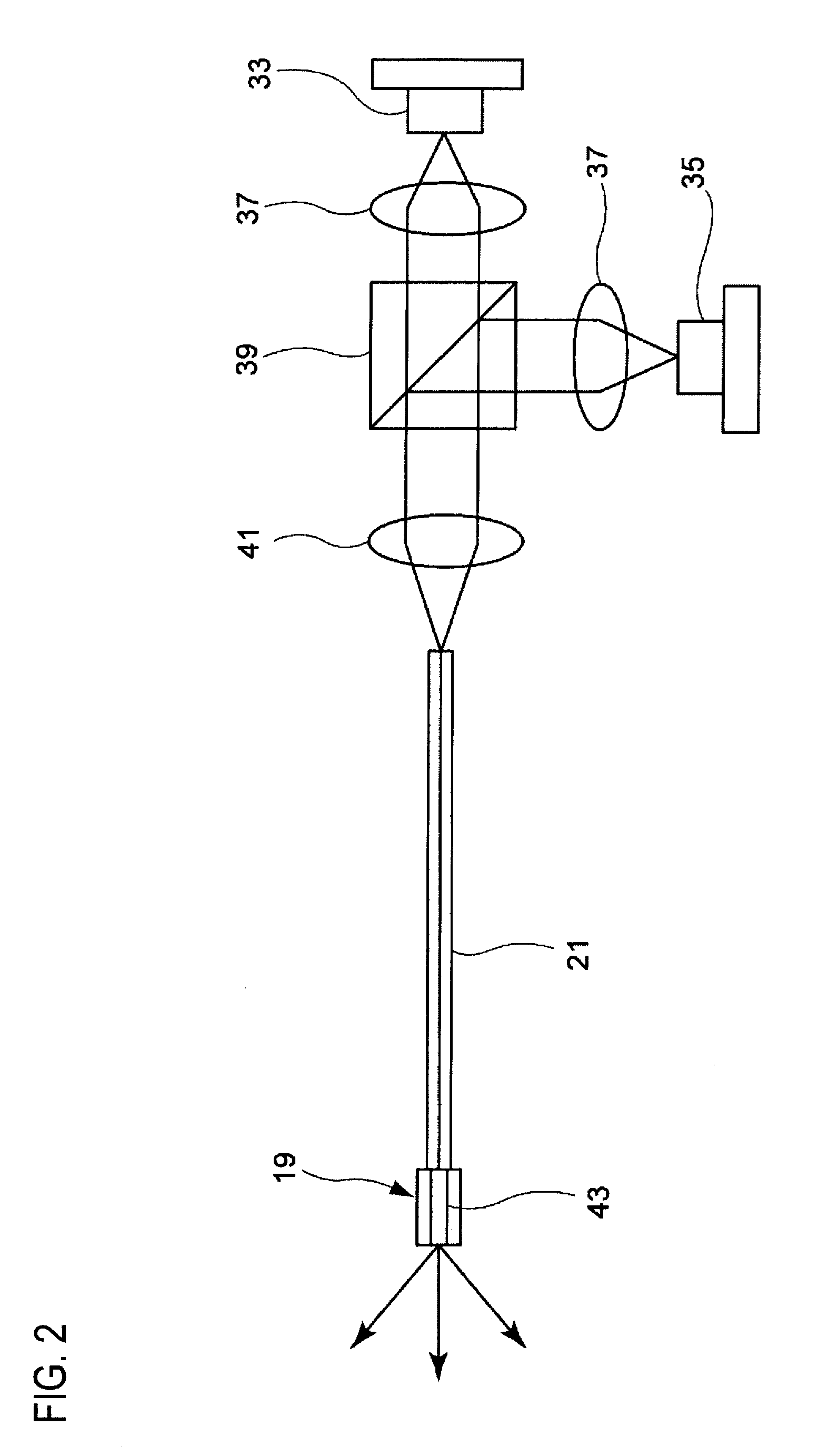
Light source device, imaging apparatus and endoscope apparatus
A light source device includes a first light source, a second light source having an emission wavelength that is different from the first light source, and a phosphor that is disposed to be distant from the first light source and the second light source and absorbs light in a predetermined excitation wavelength band to emit fluorescence. The phosphor is disposed on an emission light optical path that is shared by the first light source and the second light source. The emission wavelength of the first light source is in the predetermined excitation wavelength band. The emission wavelength of the second light source is outside of the predetermined excitation wavelength band.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nano particles and molecules
ActiveUS7090355B2Avoid viewingDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsColor imageWavelength filter
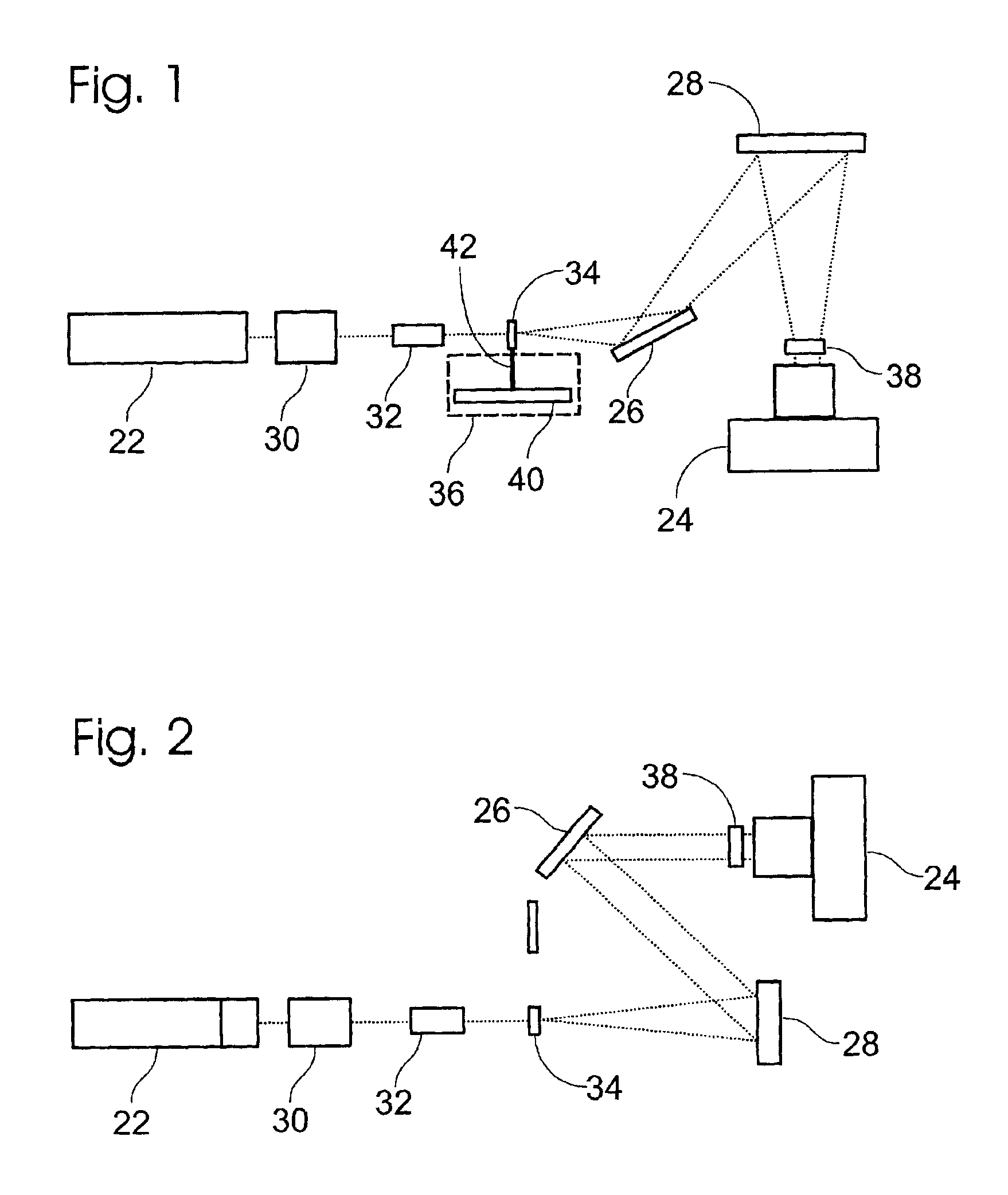
A system and a method of a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion (FC) of nano-particles and molecules are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a color image display system consists of a light source equipped with two-dimensional scanning hardware and a FC display screen board. The FC display screen board consists of a transparent fluorescence display layer, a wavelength filtering coating, and an absorption substrate. In another preferred embodiment, two mechanisms of light excitation are utilized. One of the excitation mechanisms is up-conversion where excitation light wavelength is longer than fluorescence wavelength. The second mechanism is down-conversion where excitation wavelength is shorter than fluorescence wavelength. A host of preferred fluorescence materials for the FC screen are also disclosed. These materials fall into four categories: inorganic nanometer sized phosphors; organic molecules and dyes; semiconductor based nano particles; and organometallic molecules. These molecules or nano-particles are incorporated in the screen in such a way that allows the visible transparency of the screen. Additionally, a preferred fast light scanning system is disclosed. The preferred scanning system consists of dual-axes acousto-optic light deflector, signal processing and control circuits equipped with a close-loop image feedback to maintain position accuracy and pointing stability of the excitation beam.
Owner:SUN INNOVATIONS
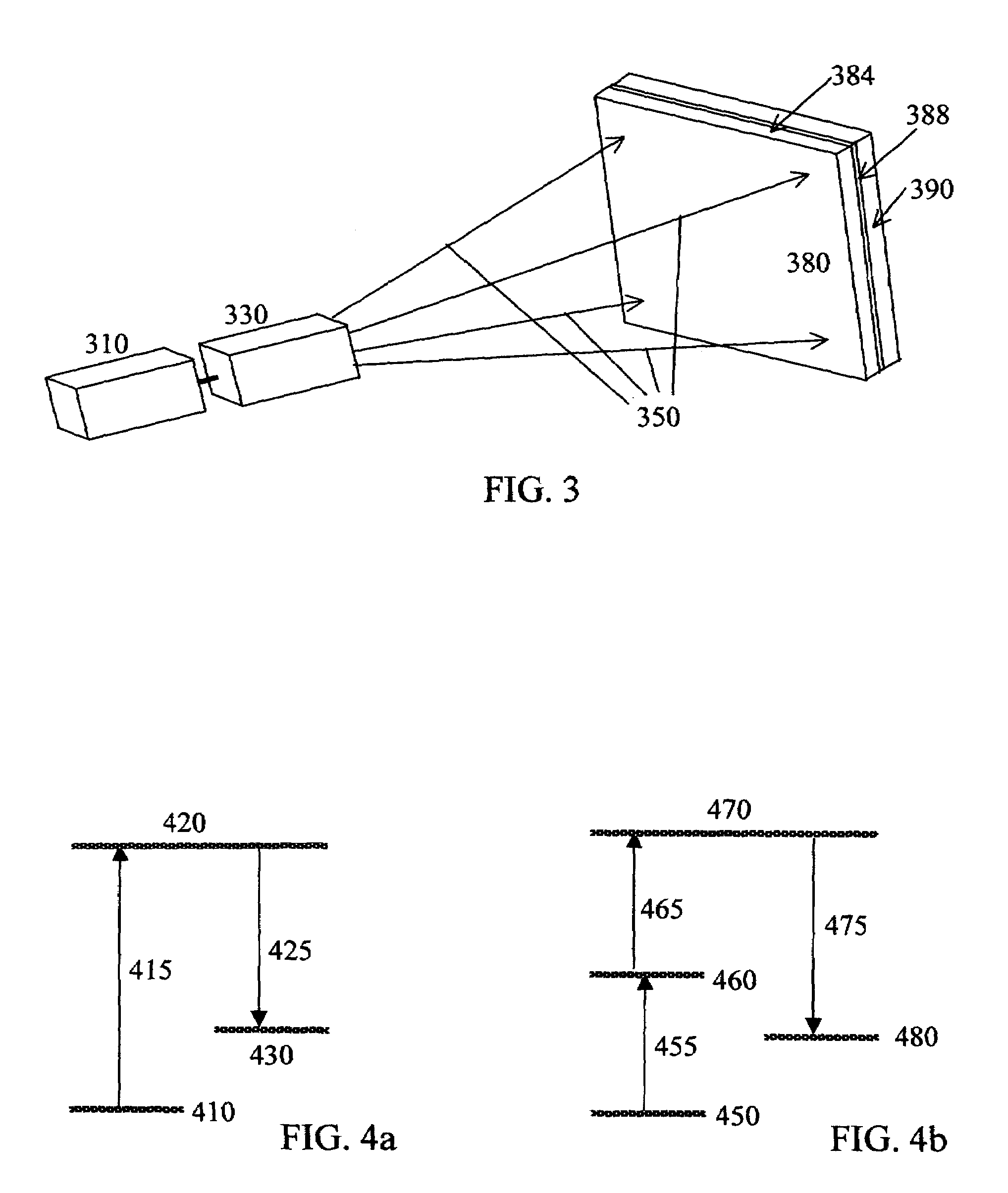
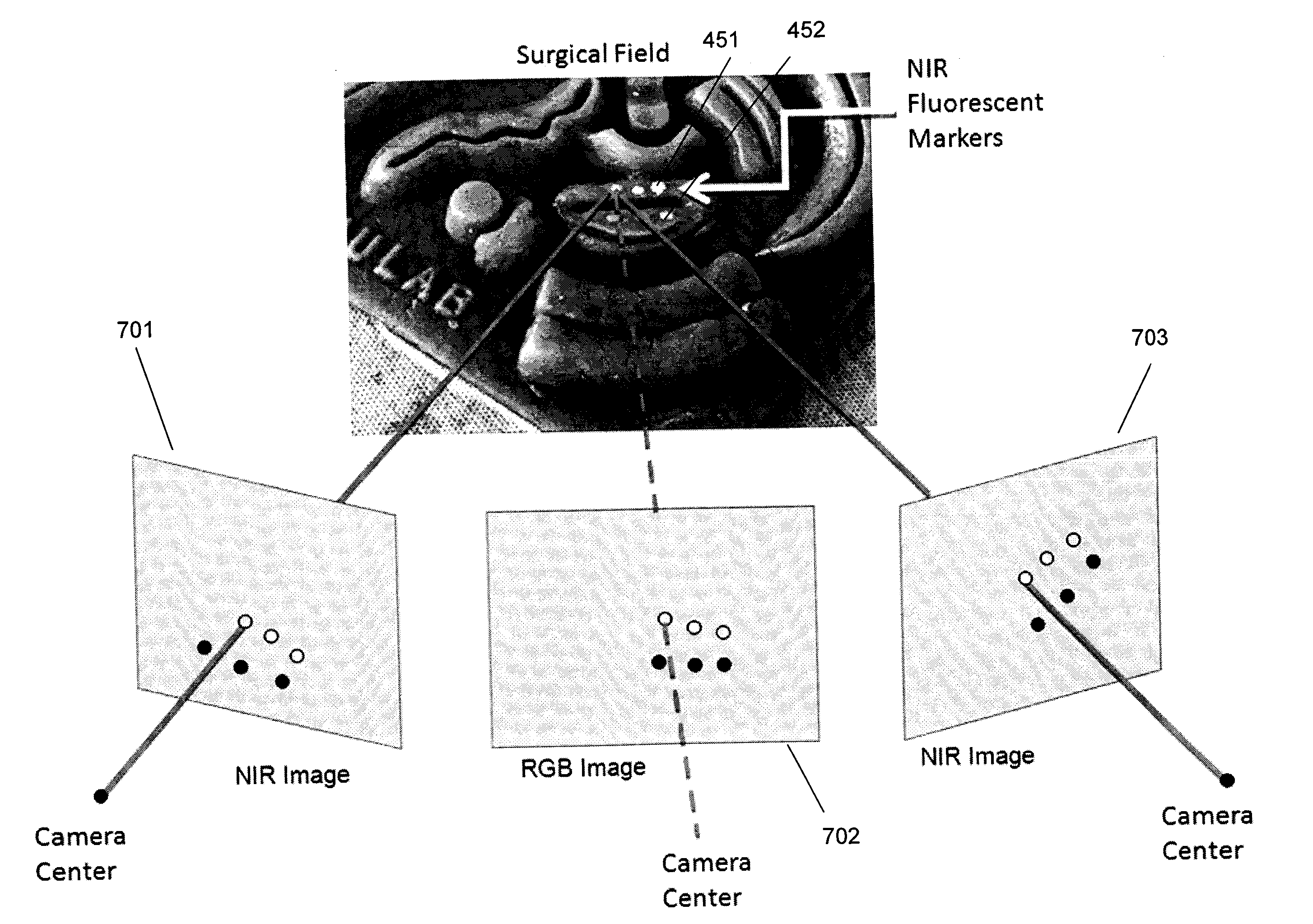
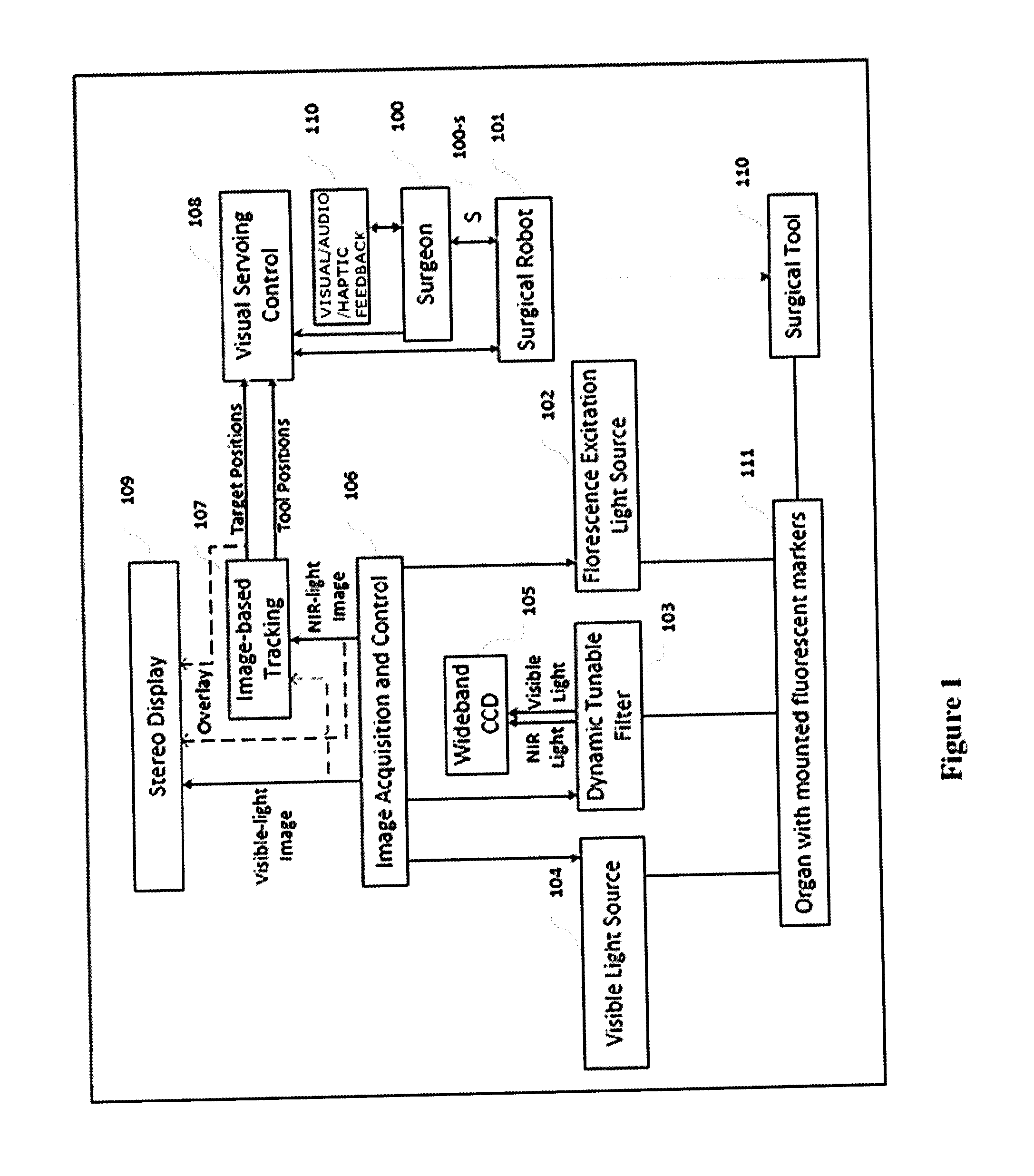
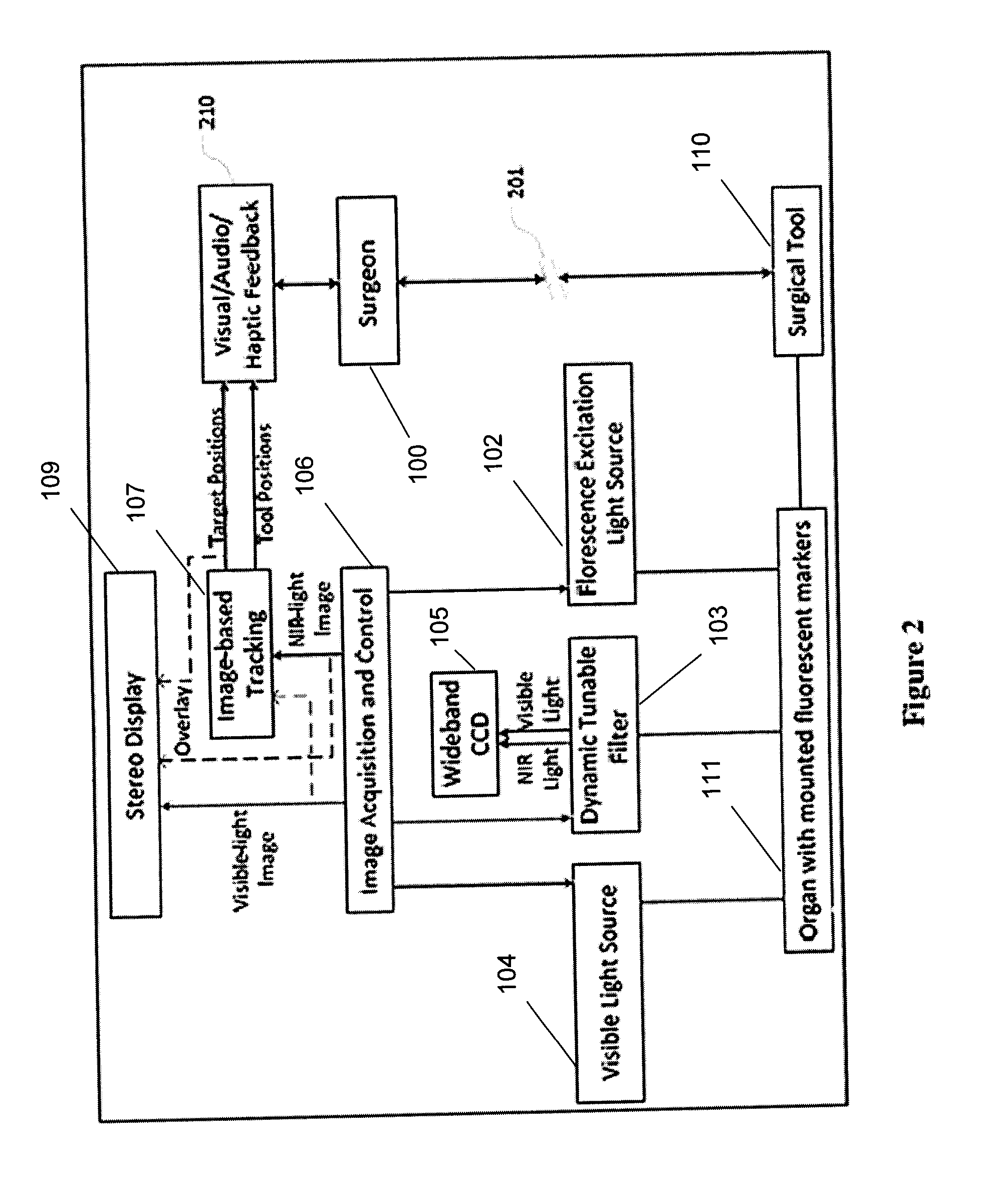
Dual-mode stereo imaging system for tracking and control in surgical and interventional procedures
InactiveUS20130274596A1Change is minimalSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostics using spectroscopyDual modeFluorescent light
System and method for tracking and control in medical procedures. The system including a device that deploys fluorescent material on at least one of an organ under surgery and a surgical tool, a visual light source, a fluorescent light source corresponding to an excitation wavelength of the fluorescent material, an image acquisition and control element that controls the visual light source and the fluorescent light source, and captures and digitizes at least one of resulting visual images and fluorescent images, and an image-based tracking module that applies image processing to the visual and fluorescent images, the image processing detecting fluorescent markers on at least one of the organ and the surgical tool.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
Phosphor film, lighting device using the same, and display device
InactiveUS20060268537A1Solution to short lifeEfficient wide color reproduction rangePlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsLight irradiationLiquid-crystal display
The invention realizes a phosphor film that has a fluorescent characteristic excellent in resistance to humidity and provides, using the phosphor film, a liquid crystal display device that is excellent in resistance to humidity and has satisfactory calorimetric property and color mixture property. Phosphor particles that are excited by incident light and emit light having a wavelength different from the incident light are mixed in a binder. The binder mixed with the phosphor particles is sandwiched between a translucent film and a non-permeable layer as a phosphor layer to form a phosphor film. This phosphor film is provided at least in one place among a place between a light source and a light guide of a lighting device, a place on a light irradiation surface of the light guide, and a place between the light guide and a reflection plate. Moreover, the phosphor particles have a characteristic that a wavelength absorbed by a color filter of a display element is set as an excitation wavelength and a luminescent wavelength is in a region transmitted by the color filter. With this phosphor film, it is possible to realize a display device that has extremely high luminance efficiency and color reproducibility.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Nanocrystal taggants
ActiveUS7917298B1Improve emission efficiencyNarrow bandwidthMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by optical meansNanocrystalExcitation wavelength
The compositions, methods and systems of the invention provide nanocrystal taggants for unobtrusive monitoring of objects. Objects can be tagged with nanocrystal taggant compositions for detection of informative invisible emissions on illumination with appropriate excitation wavelengths.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
Device for supporting chromophore elements
ActiveUS20050201899A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMeasuring signalMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalysis by electrical excitationSurface layerPhotoluminescence
A device for supporting chromophore elements suitable for emitting fluorescence in response to light excitation, the device comprising a substrate having a surface layer carrying the chromophore elements, forming a planar waveguide, and containing photoluminescent constituents which emit guided luminescence at the excitation wavelength(s) of the chromophore elements when they are excited by primary excitation light illuminating the surface layer. The invention is particularly applicable to biochip type devices.
Owner:GENEWAVE SAS
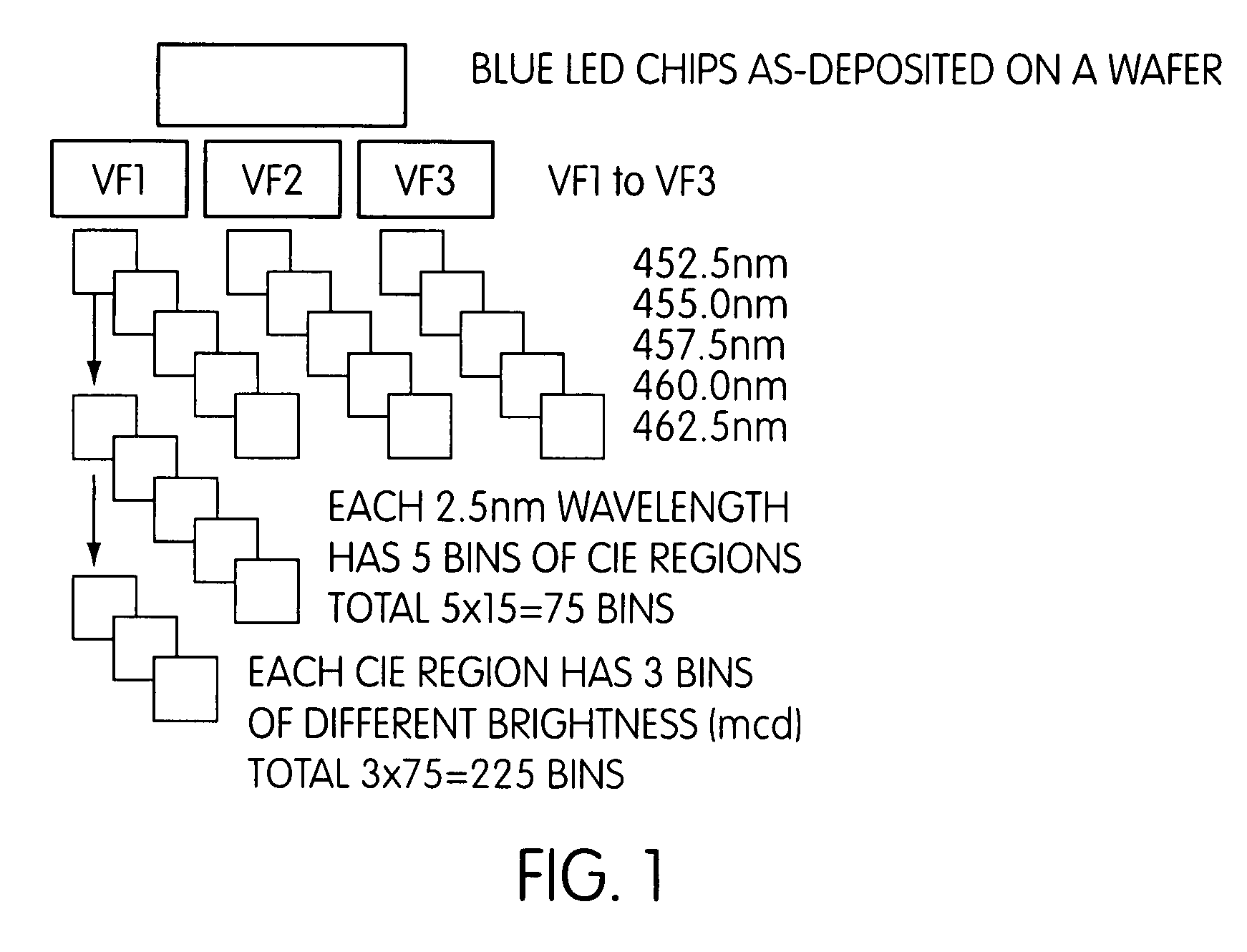
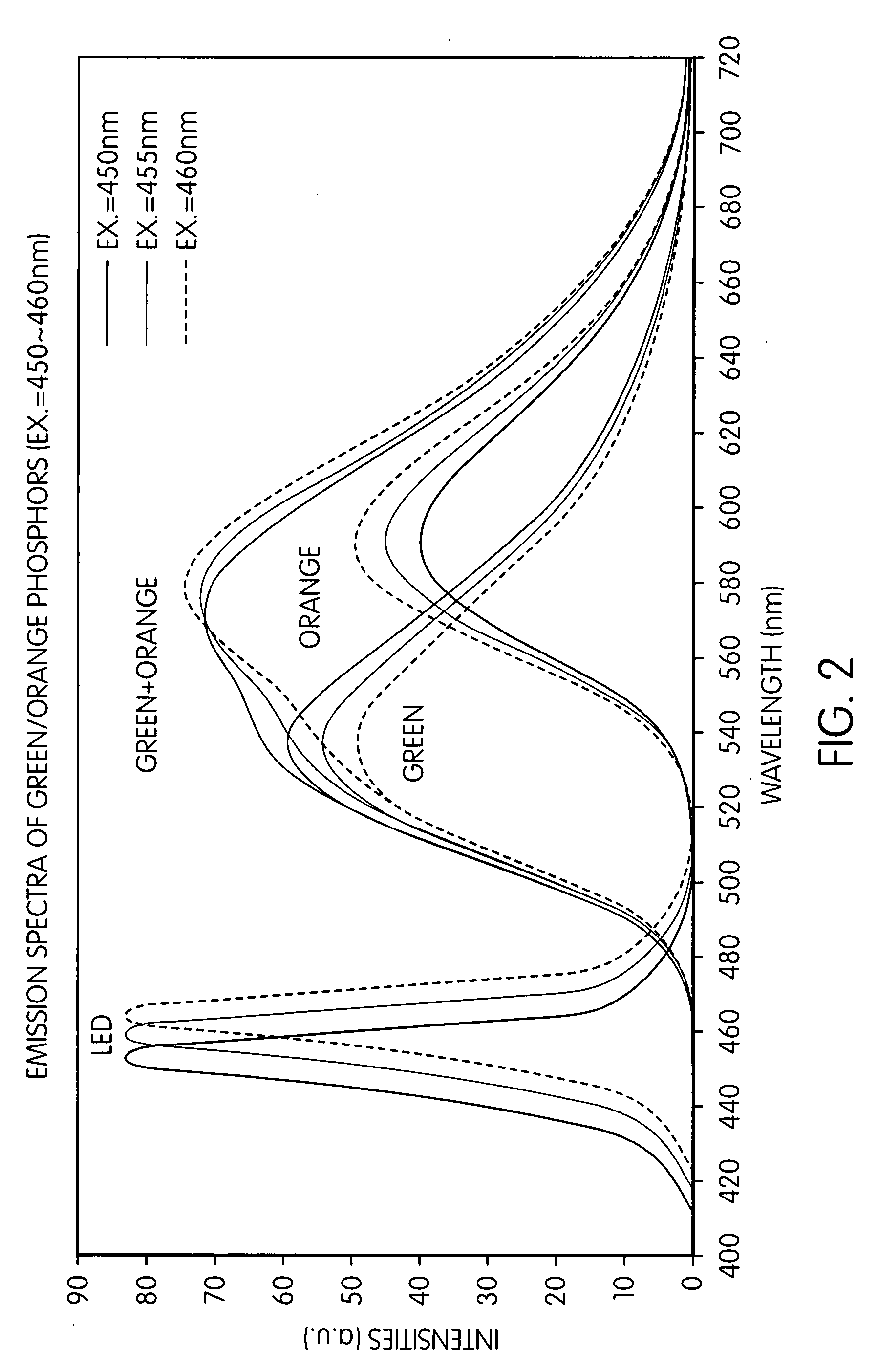
Two-phase yellow phosphor with self-adjusting emission wavelength
InactiveUS20080036364A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorLength wave
Disclosed herein are “smart” phosphor compositions capable of regulating the chromaticity of their emission to substantially constant values even with variations in the excitation radiation they receive to induce photoluminescence. One phosphor of the smart composition demonstrates an increase in emission intensity increases as the wavelength of the excitation radiation is increased. The other phosphor shows a decrease in emission intensity with increasing excitation wavelength. Constant chromaticity in this context is defined as a change in CIE x or y coordinate of less than about five percent over a 10 nm range of excitation wavelengths.
Owner:INTEMATIX
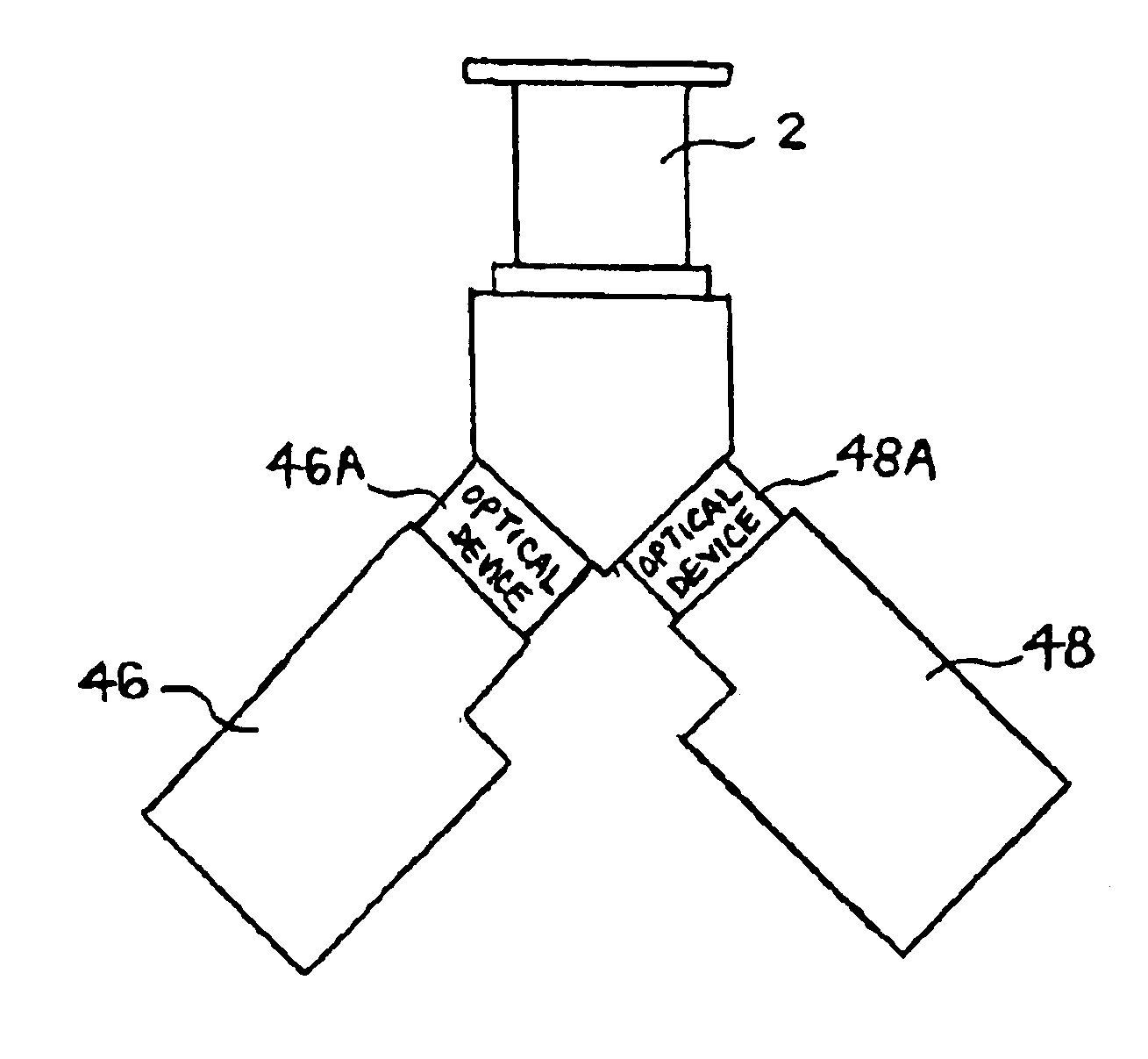
Multi-channel optical detection system
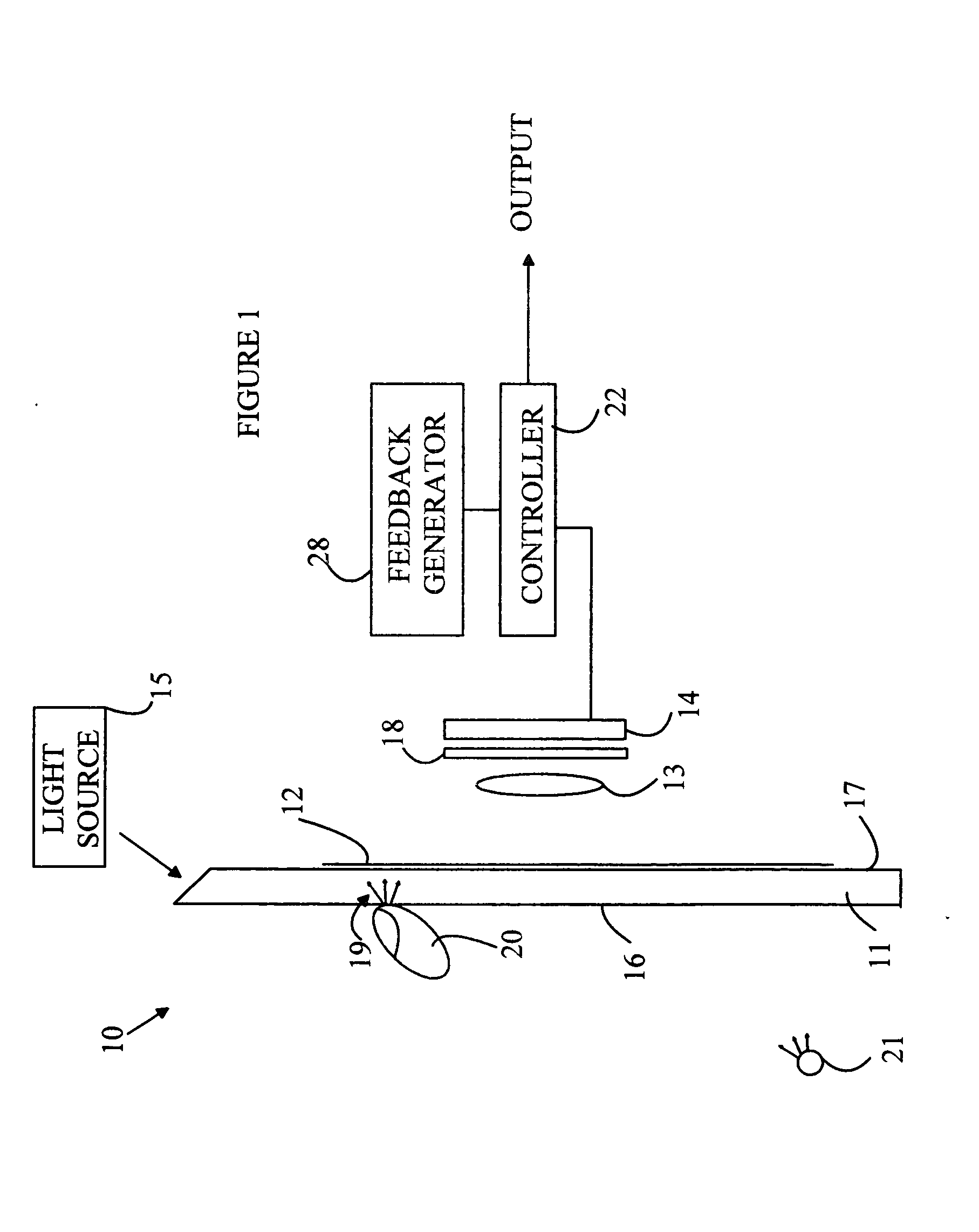
InactiveUS6940598B2Low costReduce maintenanceOptical radiation measurementHeating or cooling apparatusExcitation beamAnalyte
An apparatus for thermally controlling and optically interrogating a reaction mixture includes a vessel [2] having a chamber [10] for holding the mixture. The apparatus also includes a heat-exchanging module [37] having a pair of opposing thermal plates [34A, 34B] for receiving the vessel [2] between them and for heating / and or cooling the mixture contained in the vessel. The module [37] also includes optical excitation and detection assemblies [46,48] positioned to optically interrogate the mixture. The excitation assembly [46] includes multiple light sources [100] and a set of filters for sequentially illuminating labeled analytes in the mixture with excitation beams in multiple excitation wavelength ranges. The detection assembly [48] includes multiple detectors [102] and a second set of filters for detecting light emitted from the chamber [10] in multiple emission wavelength ranges. The optics assemblies [46,48] thus provide a multi-channel system for detecting a plurality of different target analytes in the mixture.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Noninvasive physiological analysis using excitation-sensor modules and related devices and methods
Methods and apparatus for qualifying and quantifying excitation-dependent physiological information extracted from wearable sensors in the midst of interference from unwanted sources are provided. An organism is interrogated with at least one excitation energy, energy response signals from two or more distinct physiological regions are sensed, and these signals are processed to generate an extracted signal. The extracted signal is compared with a physiological model to qualify and / or quantify a physiological property. Additionally, important physiological information can be qualified and quantified by comparing the excitation wavelength-dependent response, measured via wearable sensors, with a physiological model.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
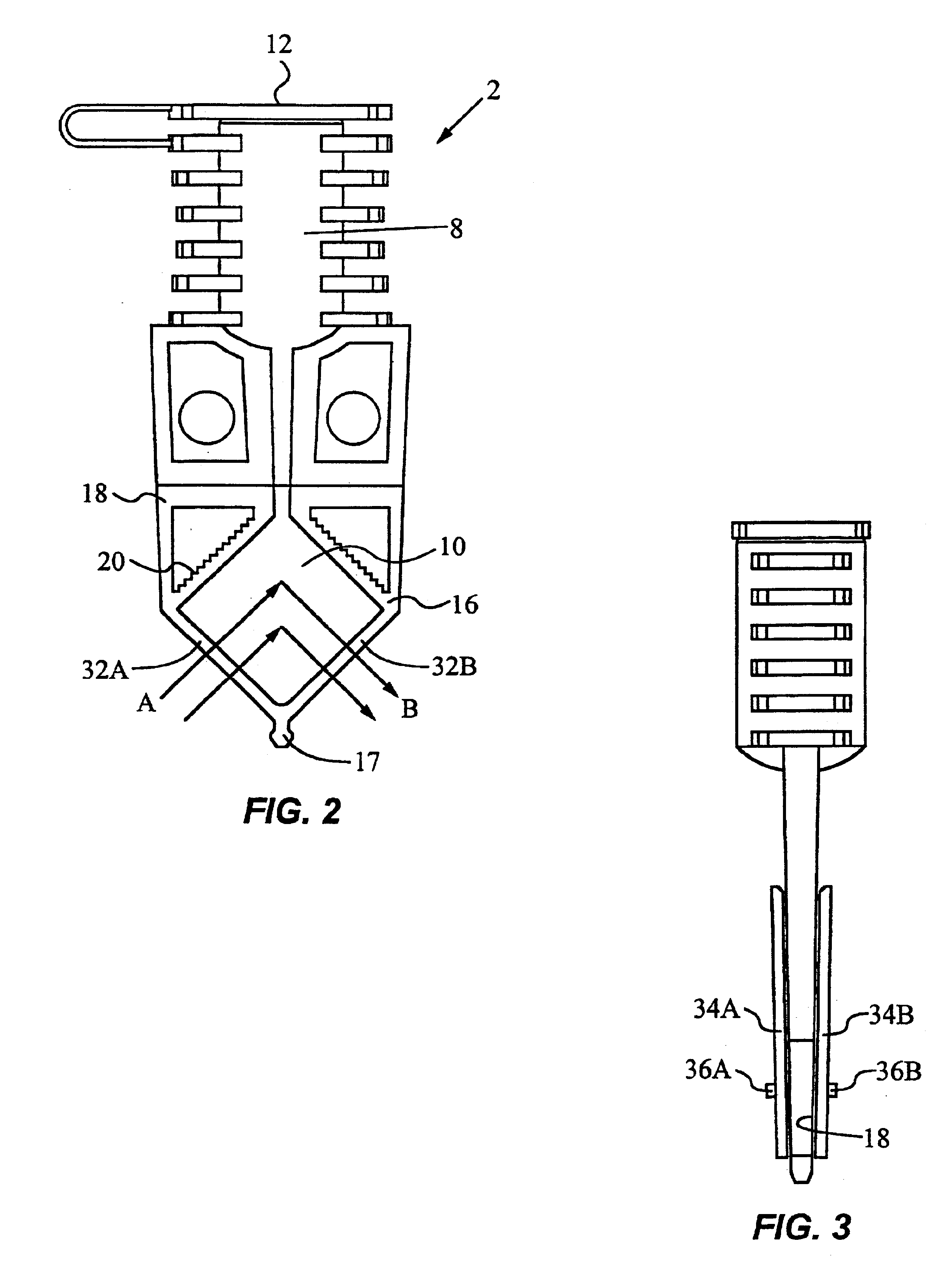
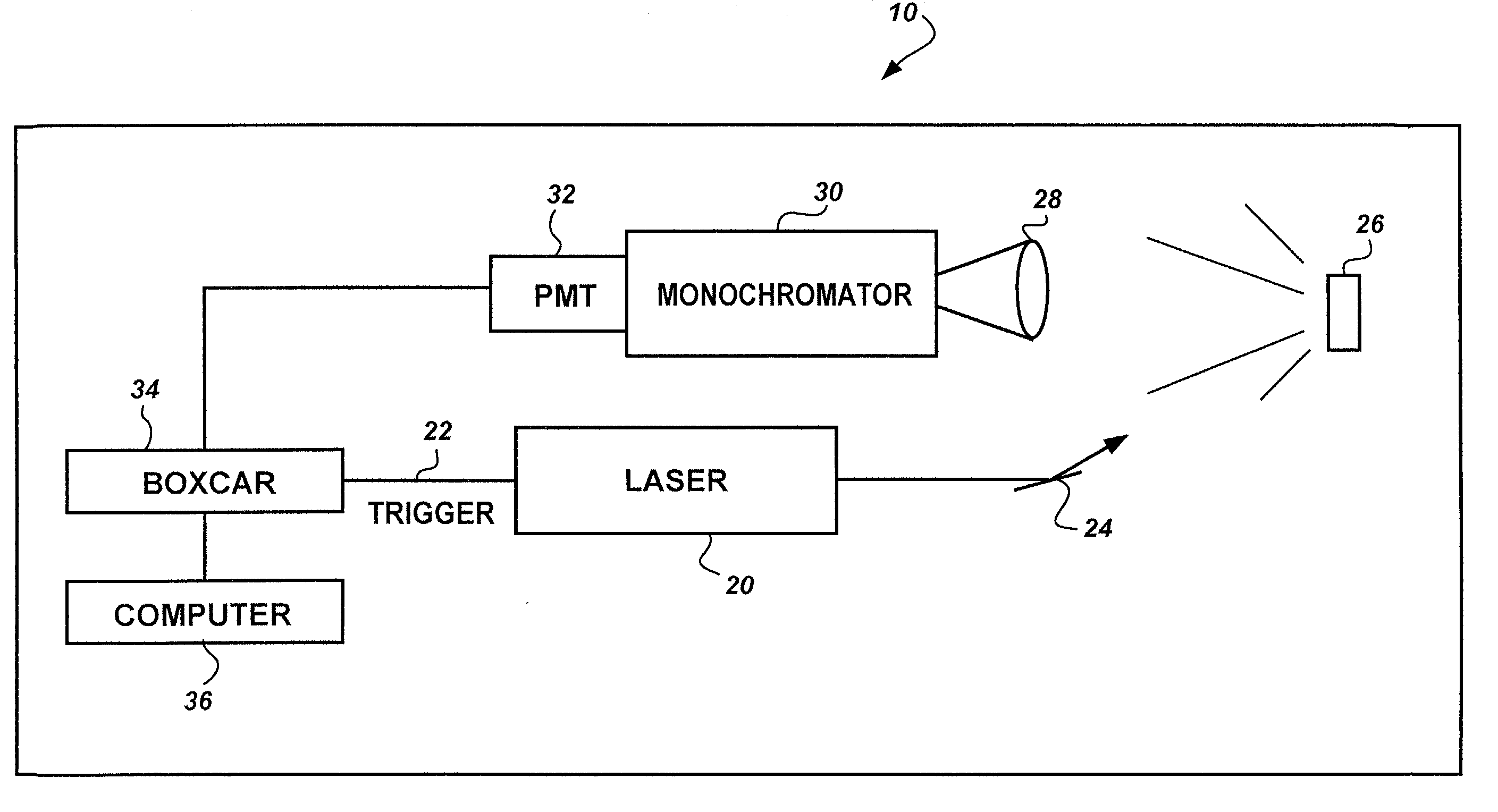
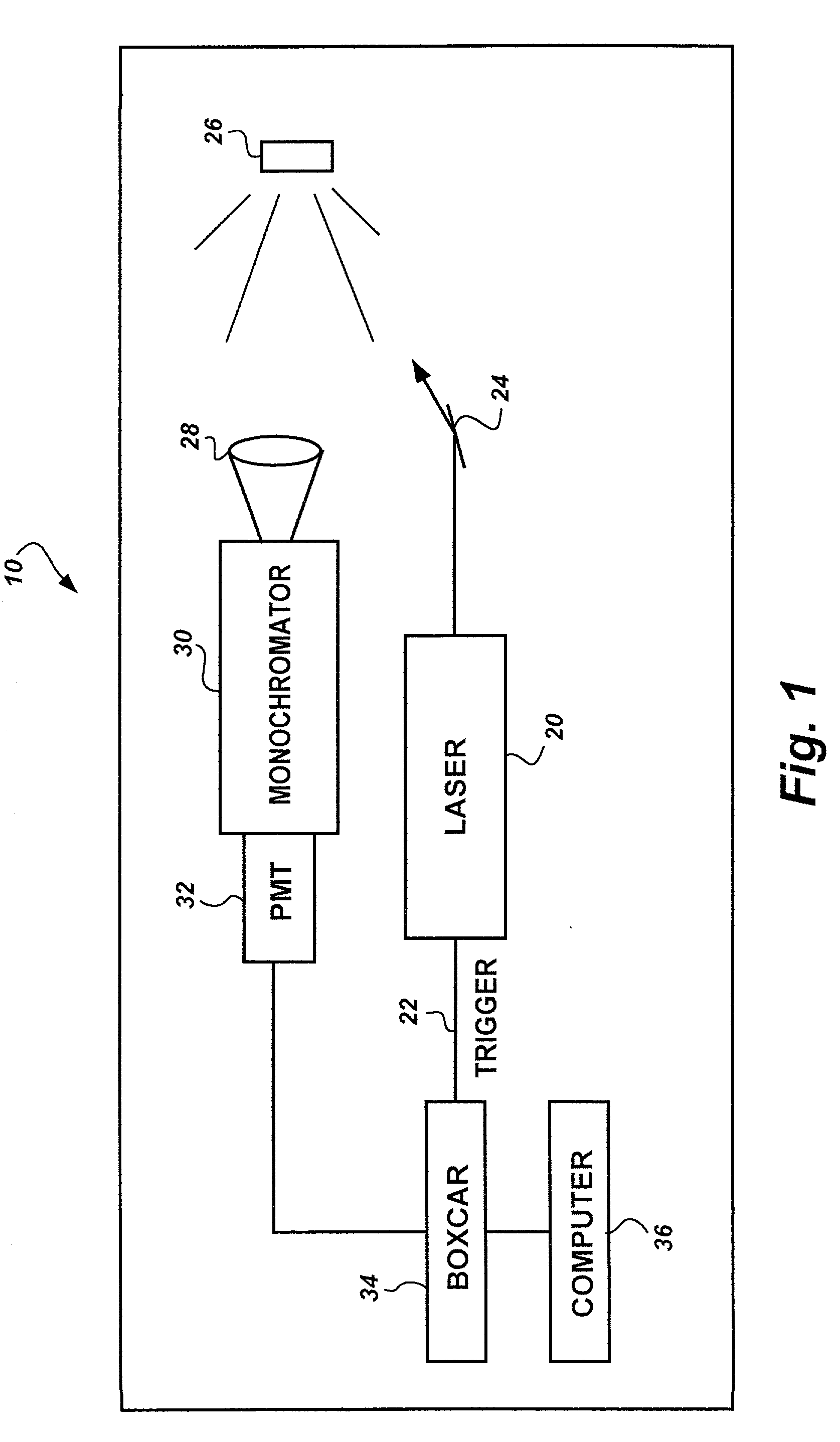
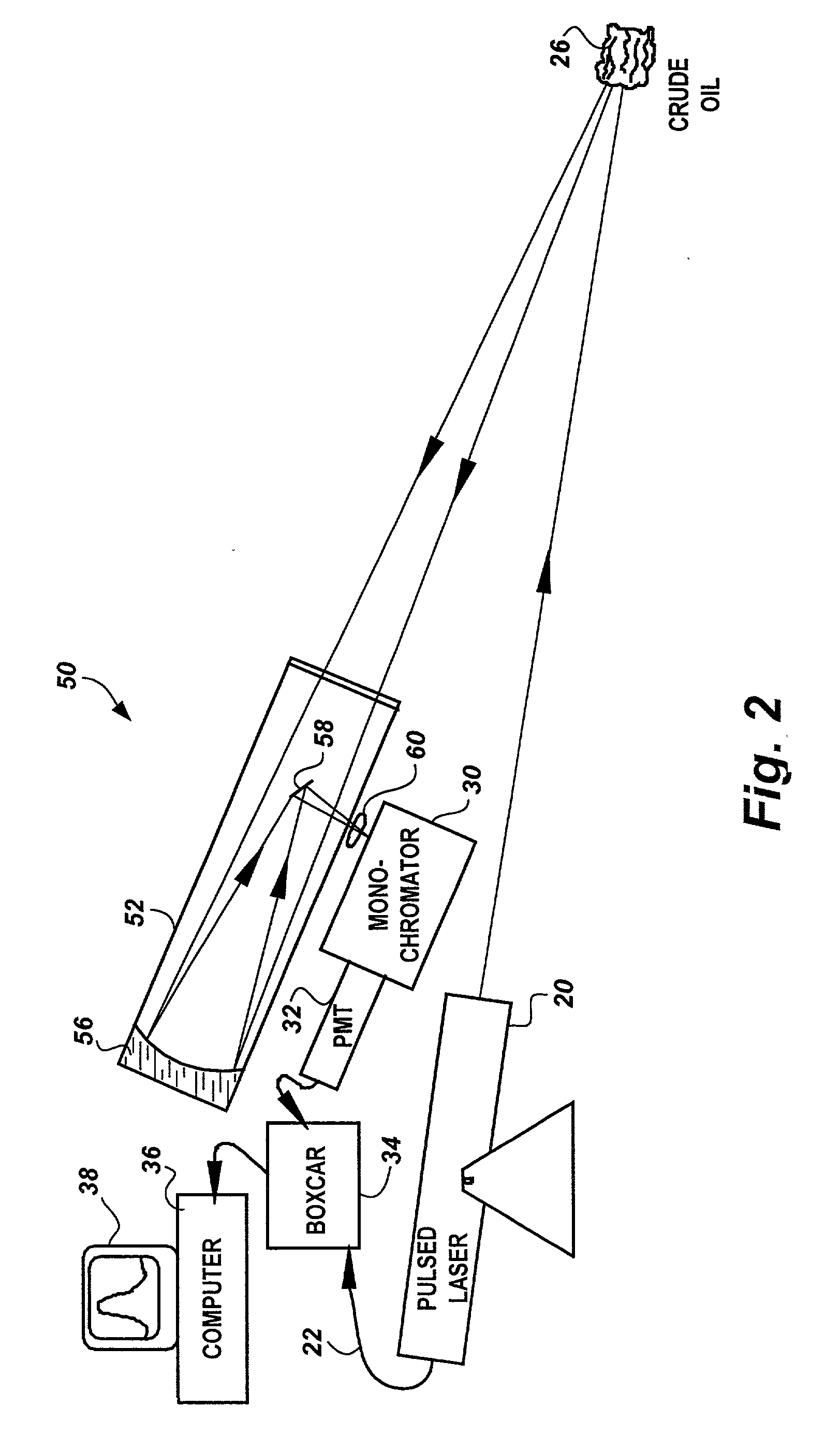
Method for characterization of petroleum oils using normalized time-resolved fluorescence spectra
A method based on time-resolved, laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy for the characterization and fingerprinting of petroleum oils and other complex mixtures. The method depends on exciting the wavelength-resolved fluorescence spectra of samples using ultraviolet pulsed laser radiation, measuring them at specific time gates within the temporal response of the excitation laser pulse, and comparing them in terms of their shapes alone without taking into account their relative intensities. The method provides fingerprints of crude oils without resorting to any kind of approximation, for distinguishing between closely similar crude oils of the same grade, and is useful in remote and non-remote setups, along with applications in fingerprinting blended and non-blended crude oils using different ultraviolet excitation wavelengths. Applications include estimating °API gravity of crude oils and monitoring degradation of mineral oils.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
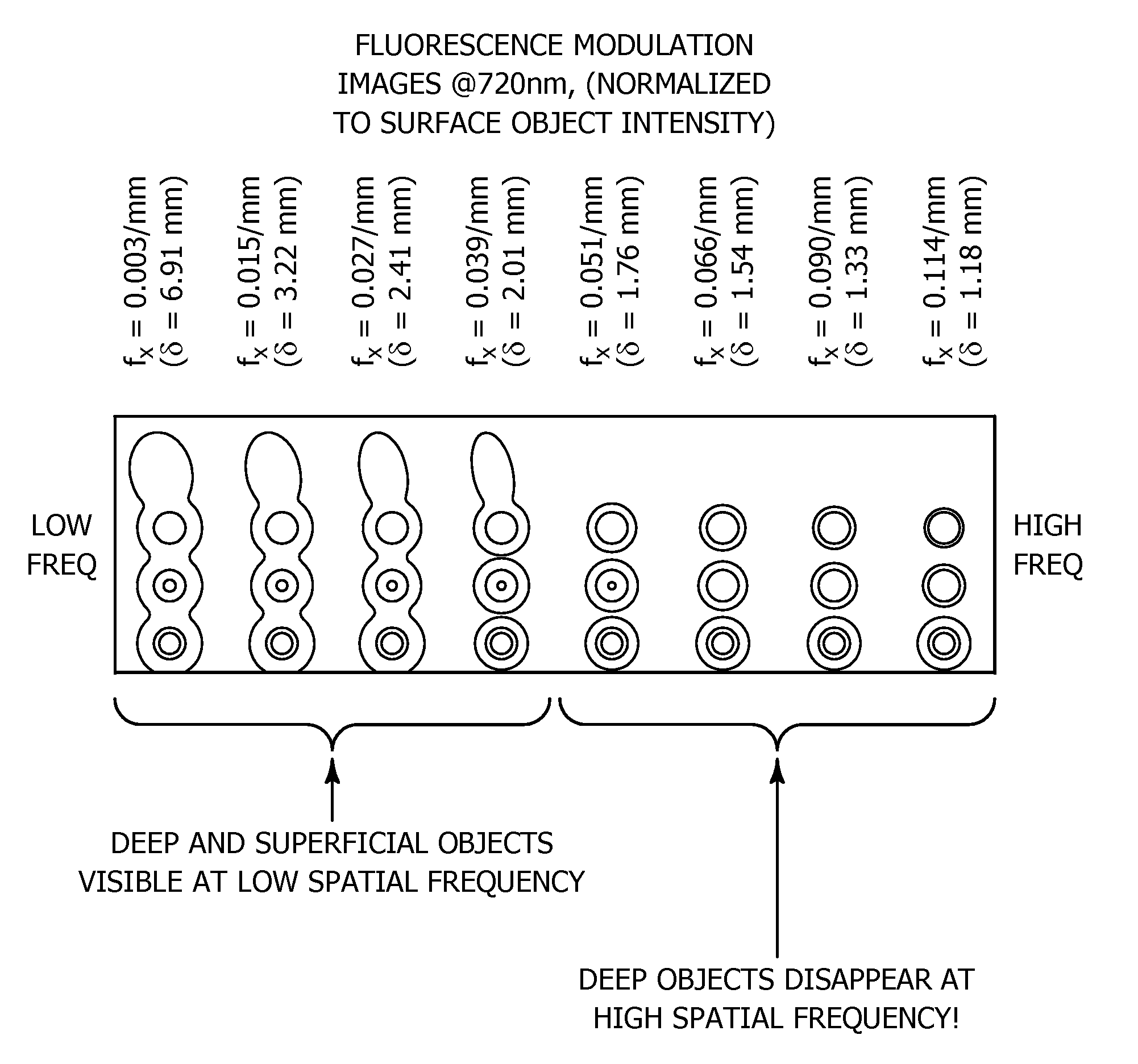
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multifunctional fluorescence diagnosis system
ActiveUS20060241499A1Increase contrastSharp contrastEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging processingObservation system
A fluorescence diagnosis system has a viewing system at least one light source and a camera system. The at least one light source can be operated in three modes, a first generating white light, a second with a first fluorescence excitation light of a first excitation wavelength and a third in which a second fluorescence excitation light of a second excitation wavelength is generated producing a fluorescence image in the NIR range. The camera system is sensitive at least in the visible and the NIR range. The system further comprises an image processing system for converting the fluorescence image in the NIR range into a visible image.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
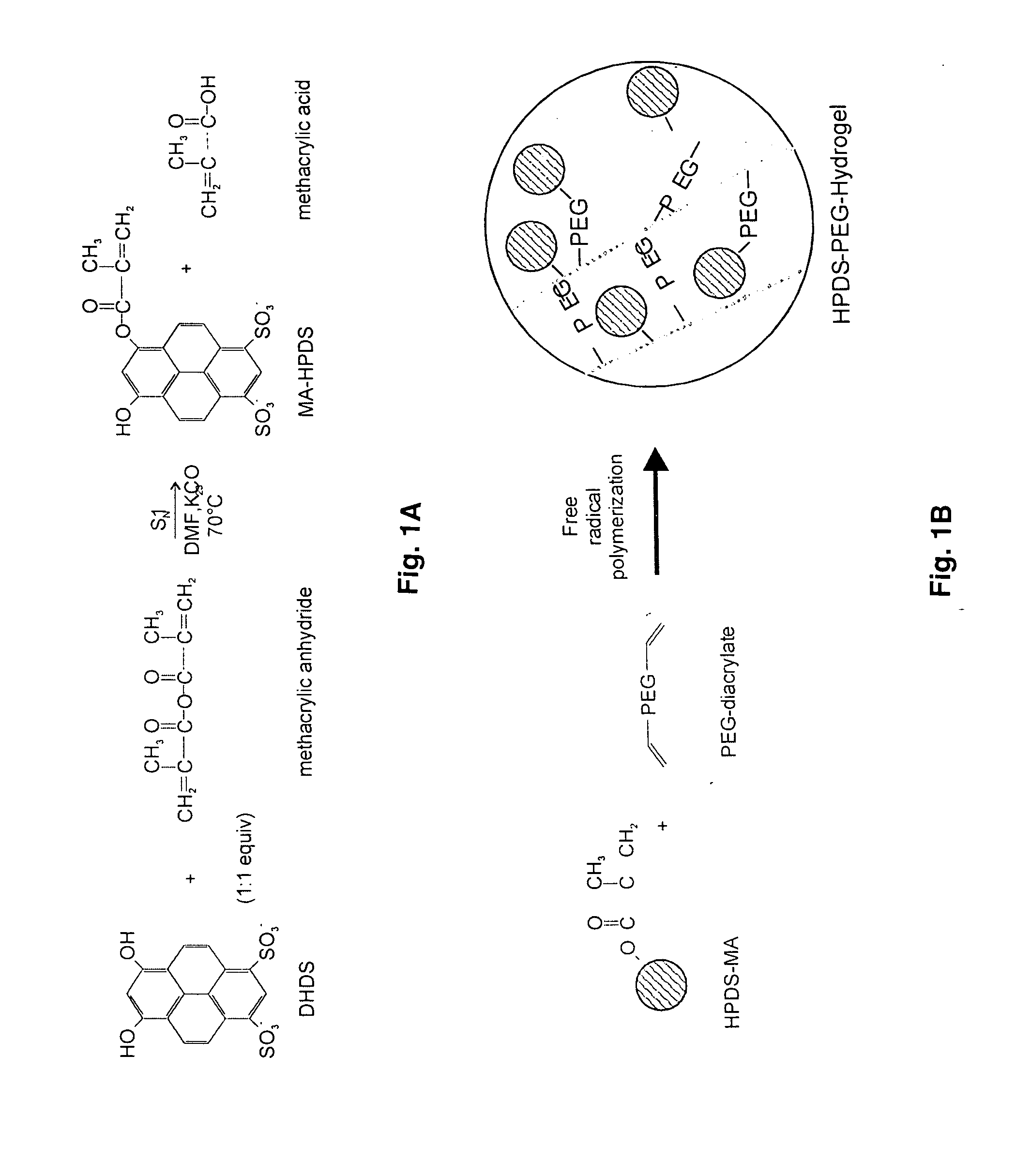
Ratiometric fluorescent pH sensor for non-invasive monitoring
InactiveUS20050090014A1Chemical analysis using titrationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNon invasiveLocal environment
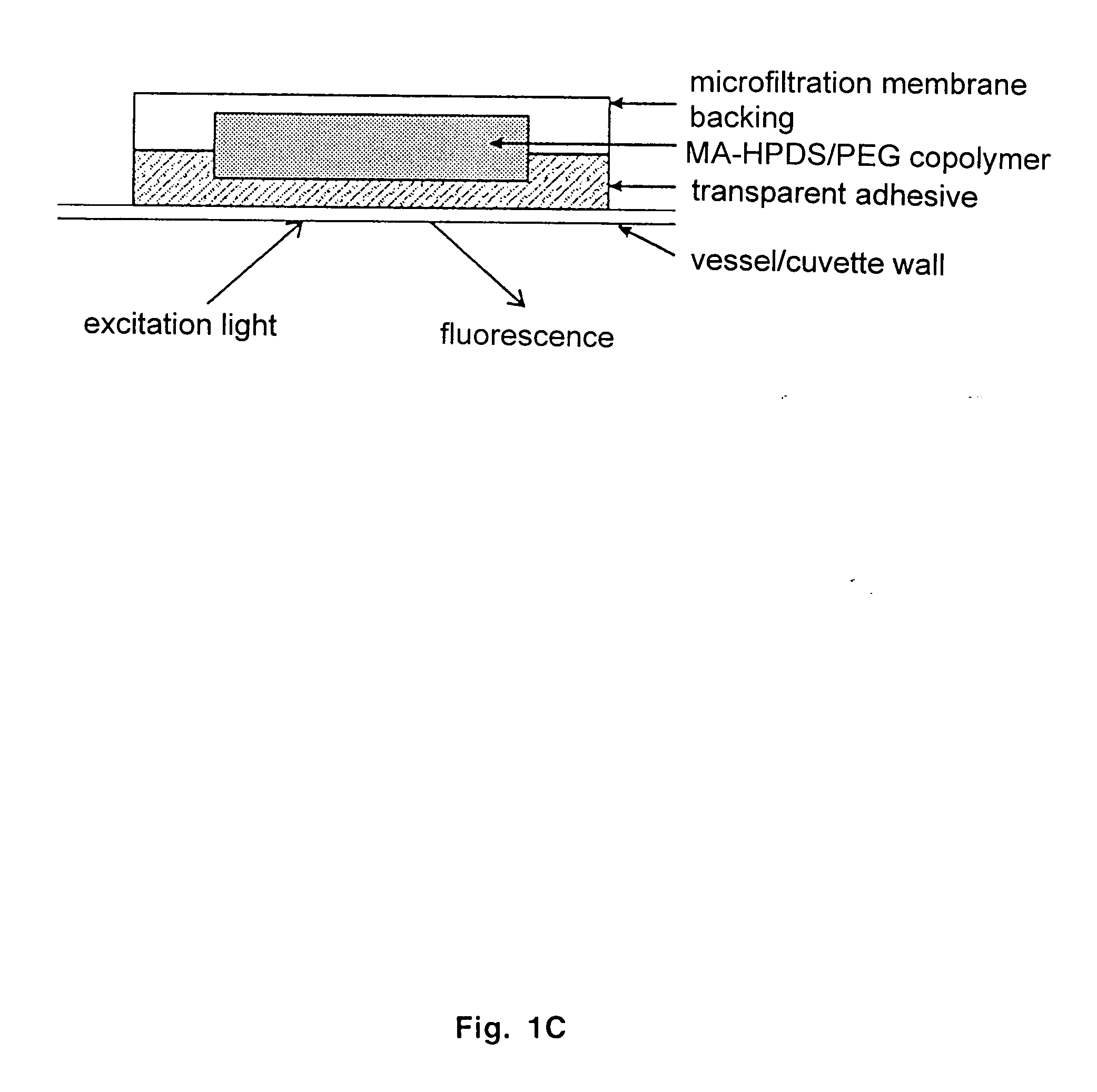
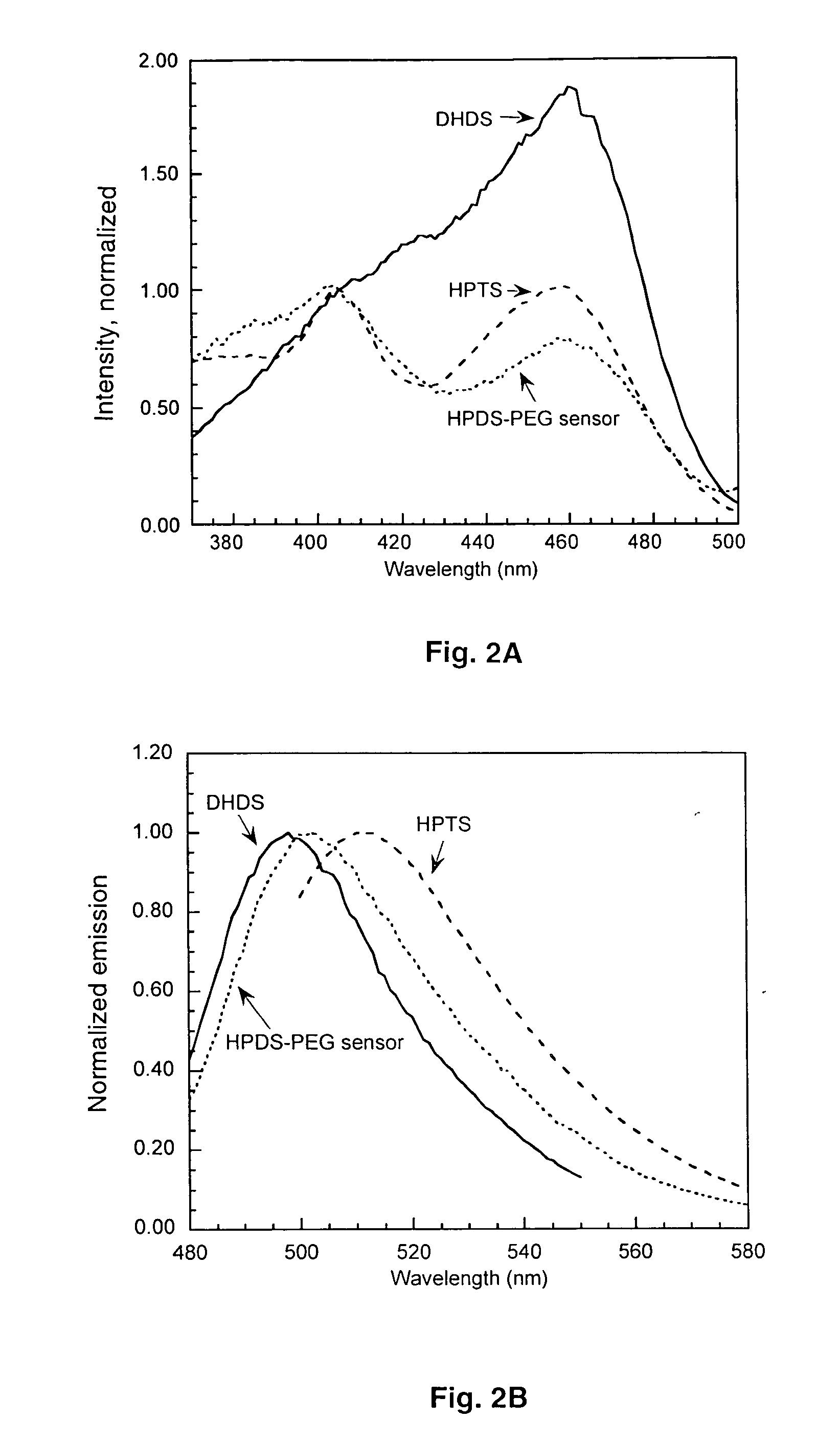
The present invention provides ratiometric fluorescent pH sensors for non-invasive, continuous monitoring of pH in such applications as fermentation processes. The ratiometric fluorescent pH sensors comprise a fluorescent dye that exhibits a shift in excitation wavelength with a corresponding shift in pH in the local environment of said fluorescent dye. Ratiometric measurements of the emission intensities at dual excitation maxima correlate to pH. Also provided is a fluorescent dye 6-methacryloyl-8-hydroxy-1,3-pyrene disulfonic acid (MA-HPDS). Further provided are systems and methods to non-invasively and continuously monitor pH.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Luminescence assay using cyclical excitation wavelength sequence
A method for the conduct of a measurement of proximity between luminescent species based on detection of transfer of excitation energy between them. A first photoluminescent species (the "donor") and a second photoluminescent species (the "acceptor") are provided and are such that the donor species and the acceptor species have at least some excitation spectral regions which differ and that at least a part of the emission spectrum of the donor overlaps with at least a part of the excitation spectrum of the acceptor. The donor species is excited with a cyclical temporal sequence of wavelength bands, optionally provided as pulses or modulated in intensity, giving rise to a characteristic temporal fluctuation in emission therefrom and emission in at least one wavelength band characteristic of the acceptor is analyzed to detect the presence of the said characteristic fluctuation or a subcomponent thereof and optionally also to detect a fluctuation characteristic of direct excitation of the acceptor.
Owner:PHOTONIC RES SYST
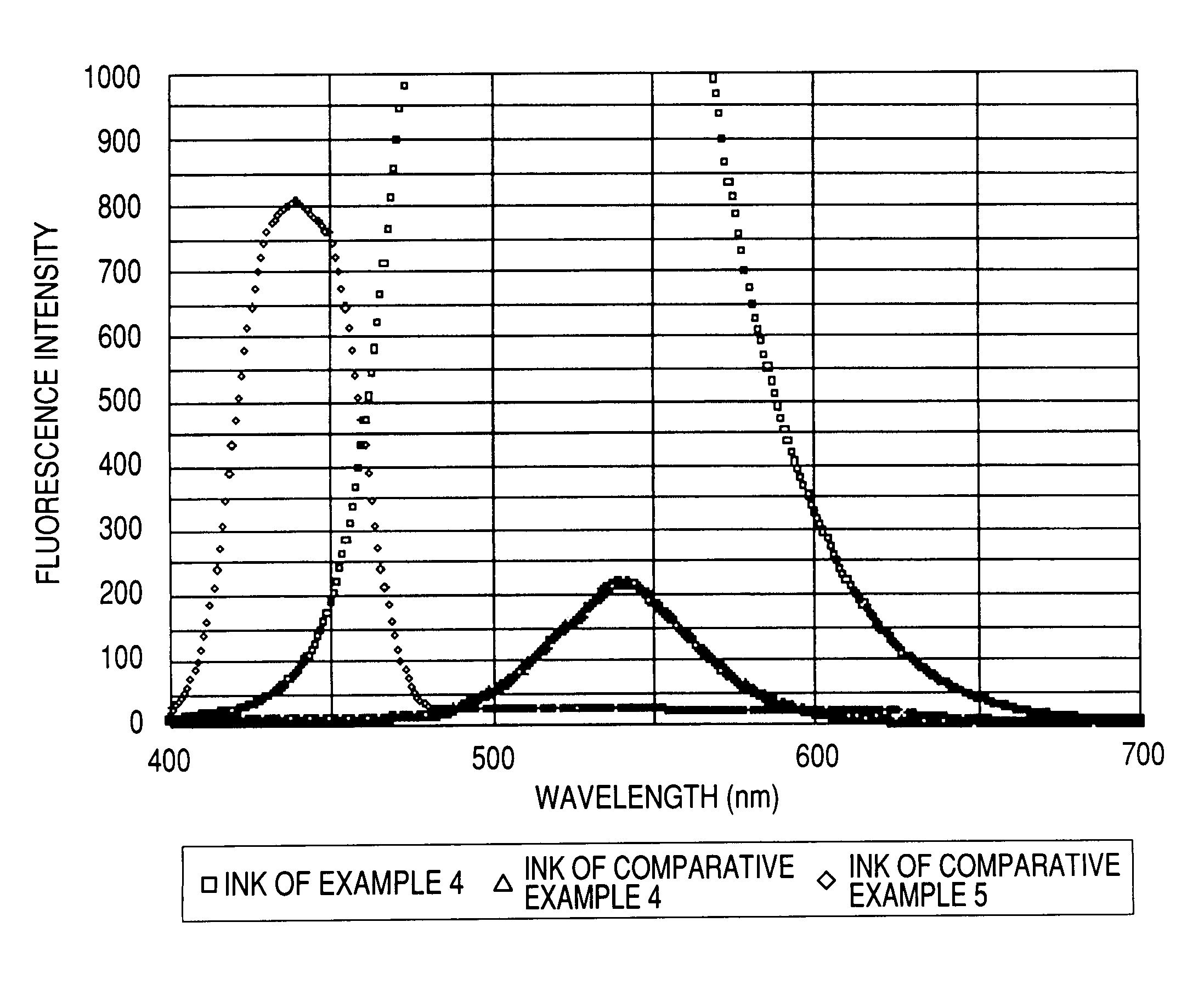
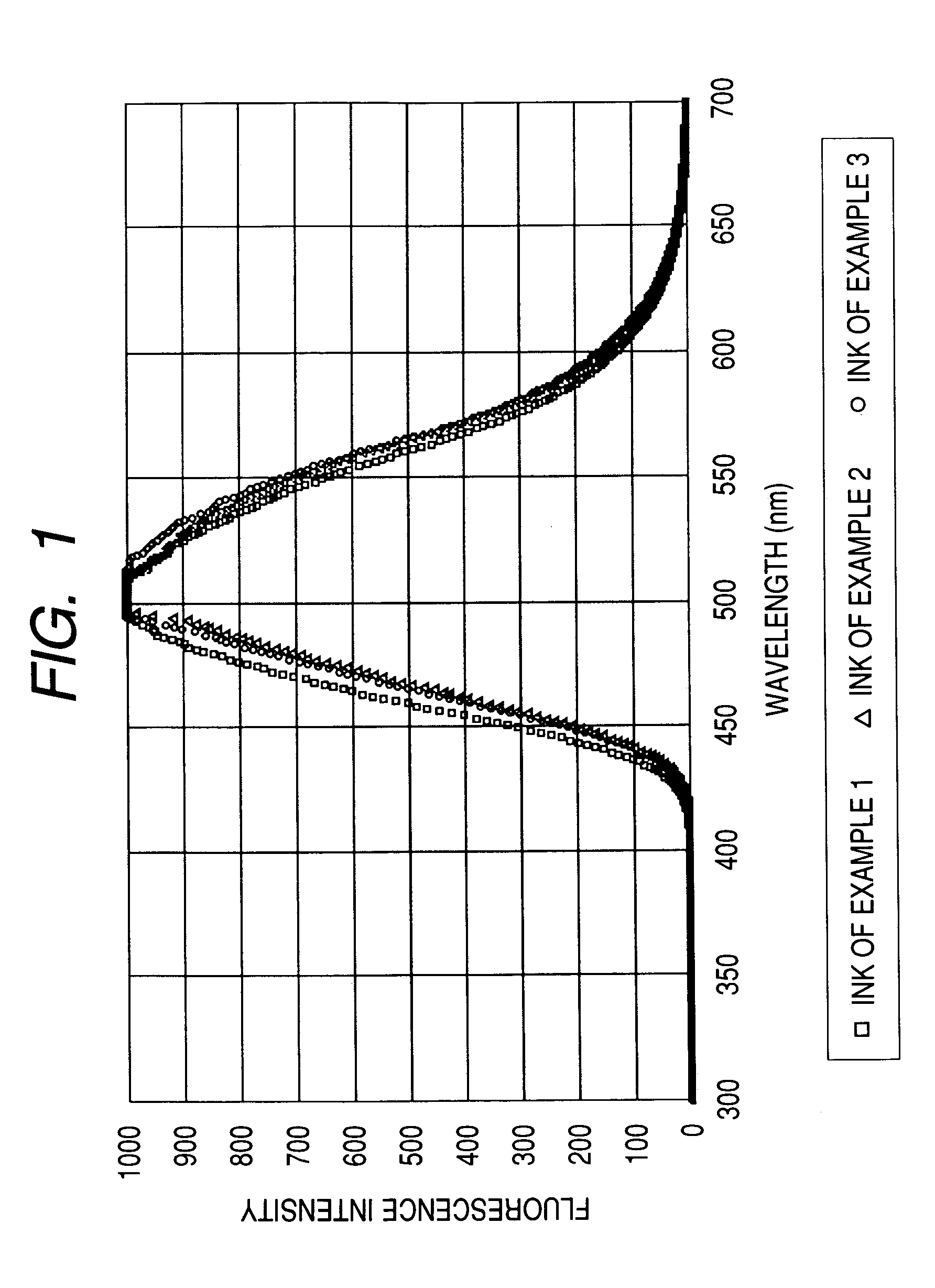
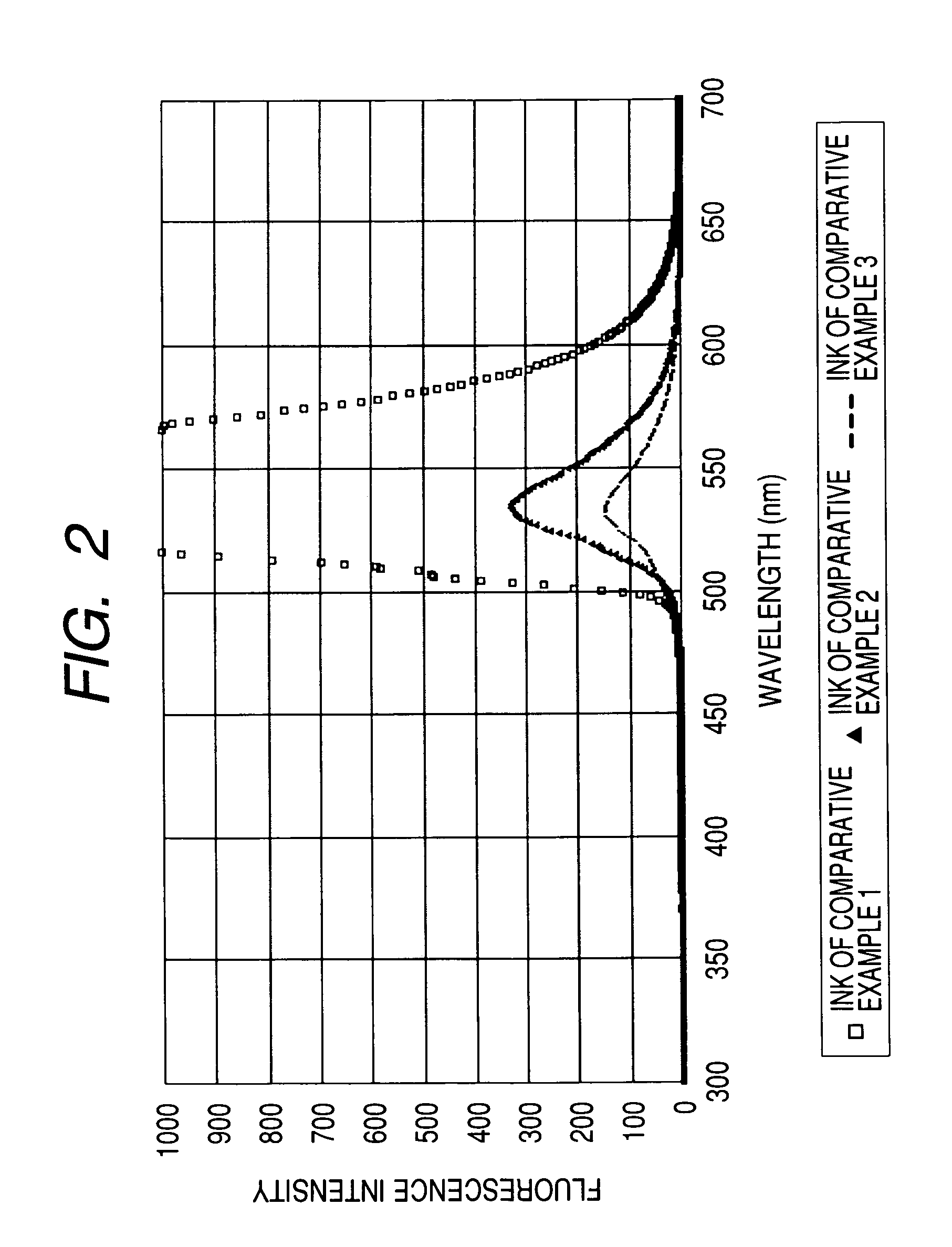
Water-based fluorescent ink, recorded image using the same, and judging method
The present invention relates to a water-based fluorescent ink for the purpose of measurement or judgment of the fluorescence emission in a visible light region by an excitation wavelength in a predetermined ultraviolet range, containing water, a coloring material dissolved or dispersed in water, and an organic solvent, having a plurality of fluorescent groups in the coloring material structure of the coloring material, and using a water-soluble coloring material having a sulfonic acid group as the water-soluble group in the state of a free acid, capable of improving the water resistance and the light resistance, dramatically increasing the content of the fluorescent coloring material in the ink, which has conventionally been included only by a small amount in the ink due to the concentration quenching problem, obtaining preferable fluorescence emission and water resistance of the recorded image, and providing preferable adhesion resistance to the recording medium of the coloring material and reliability.
Owner:CANON KK
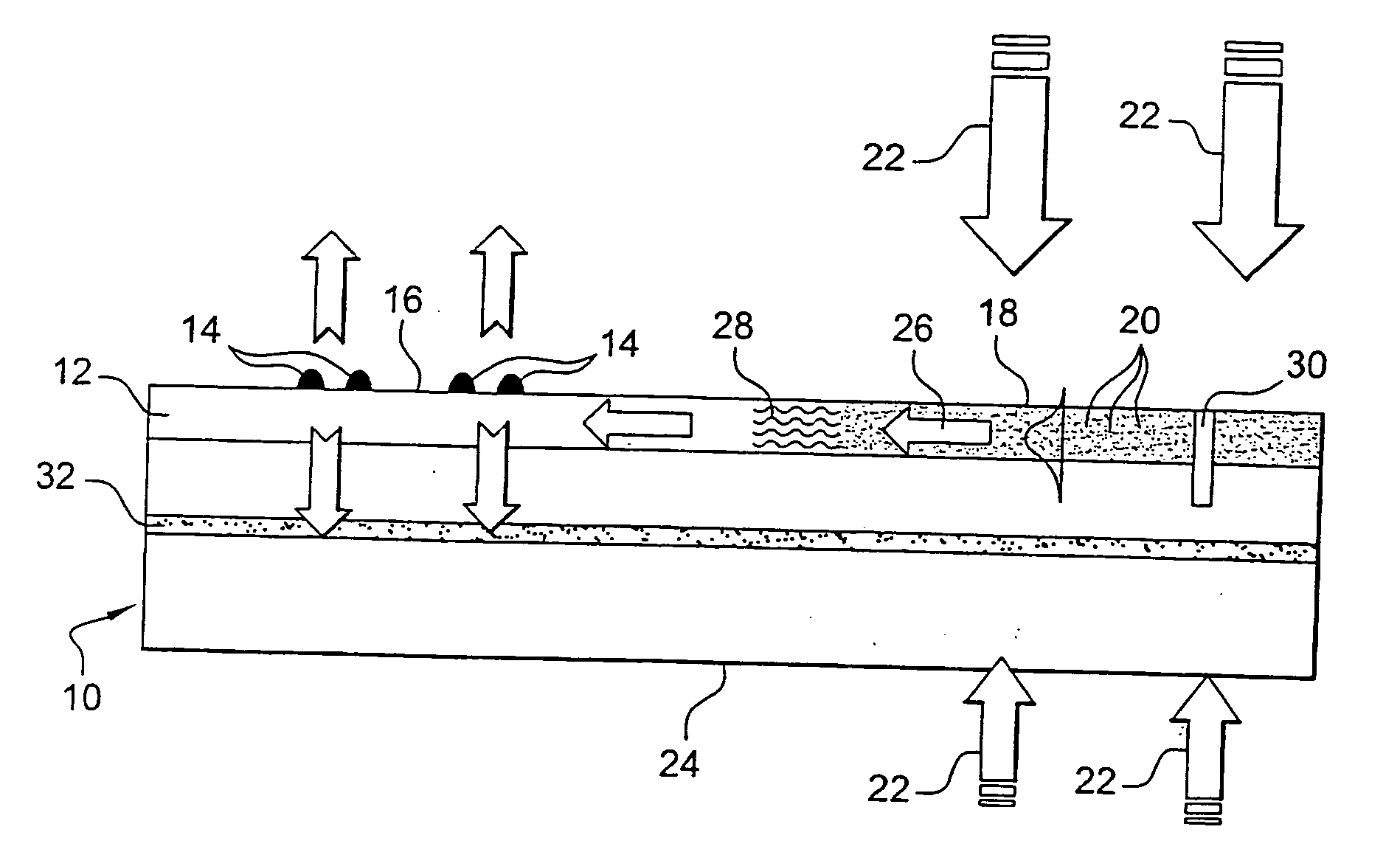
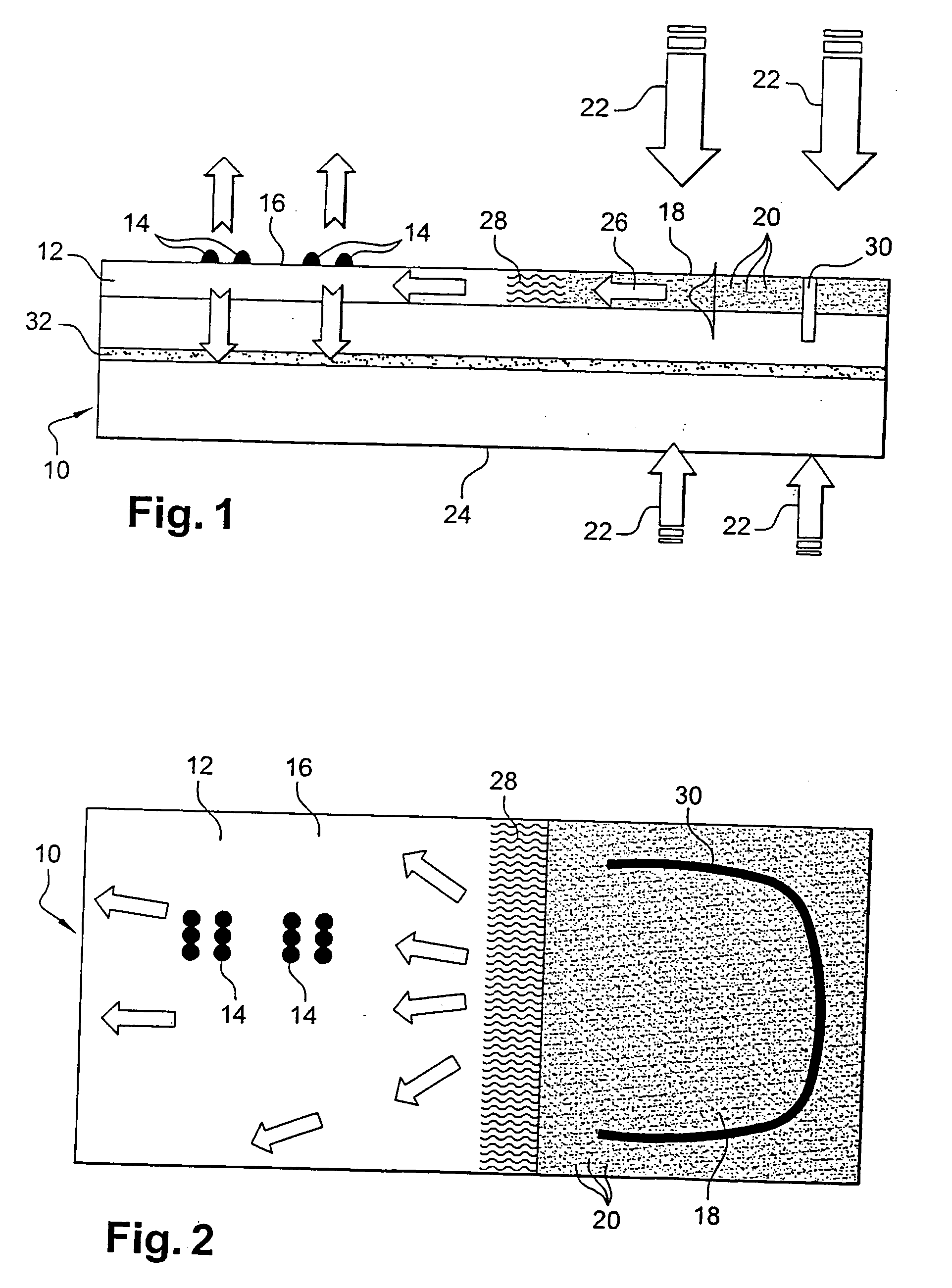
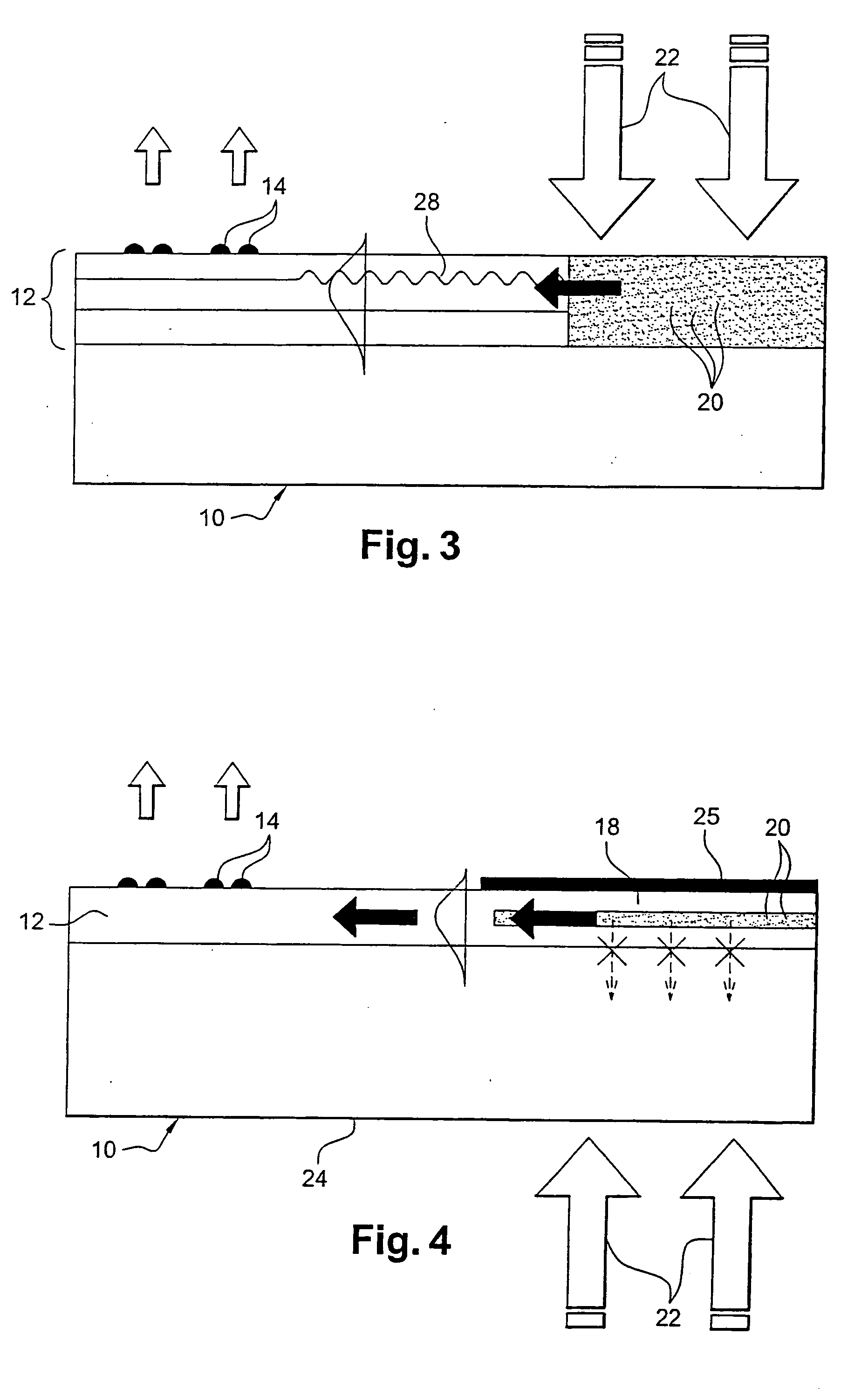
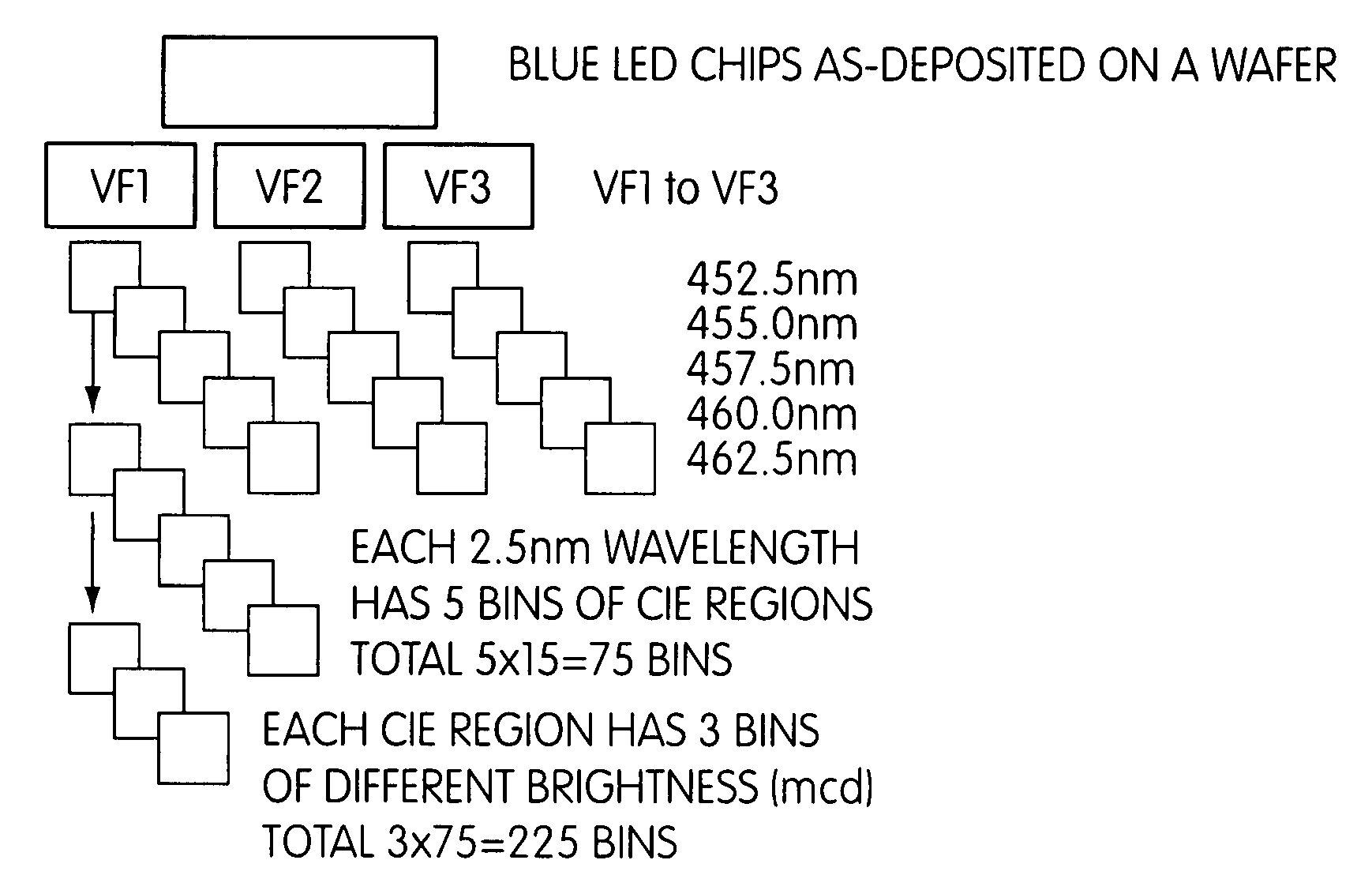
Light emitting device using light emitting diode chip
ActiveUS7717589B2Reduce unevennessSmall surface areaDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLength waveIrradiation
A light emitting device comprises: an LED chip mounted in a recess formed in a mounting substrate; a wavelength converting member that is disposed so as to cover the recess and the edge area around the recess and that is excited by light emitted from the LED chip to emit light of a wavelength different from an excitation wavelength; and an emission control member disposed at a light output side of the wavelength converting member so as to allow emission of light coming from an area of the wavelength converting member that corresponds to the recess and to prevent emission of light coming from an area of the wavelength converting member that corresponds to the edge area around the recess. This can prevent variations in color between light emitted from the central part of the wavelength converting member and light emitted from the part of the wavelength converting member that is located on the edge area around the recess of the mounting substrate, thereby reducing unevenness of color on the irradiation surface.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Phosphor based on a combination of quantum dot and conventional phosphors
A phosphor composition and a light source constructed therefrom are disclosed. The phosphor composition includes first and second phosphors. The first phosphor includes first phosphor particles that convert light of an excitation wavelength to light having a first spectrum characterized by an intensity of light that varies as a function of wavelength. The first phosphor particles are chosen such that the first spectrum is independent of the size of the particles. The second phosphor includes particles of a QD phosphor that convert the excitation light to light in a QD phosphor spectrum. The first phosphor particles and the QD phosphor particles are present in a ratio of concentrations. The ratio, the first phosphor particles, and the QD phosphor particles are chosen such that a combined spectrum has an intensity that is more uniform as a function of wavelength than either the QD phosphor spectrum or the first spectrum.
Owner:DOCUMENT SECURITY SYST
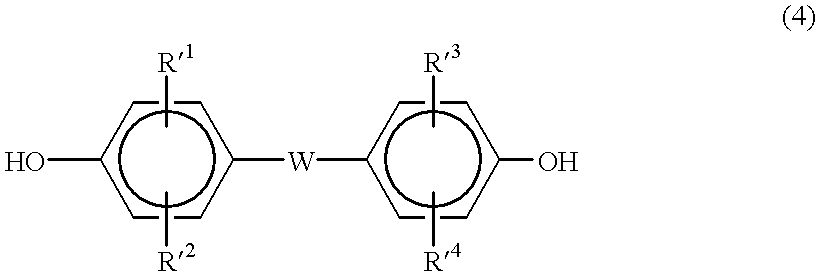
Stabilized aromatic polycarbonate
The relative intensity of fluorescent light of a melt-polycondensed aromatic polycarbonate produced by the transesterification process (melt polymerization process) of an aromatic dihydroxy compound and a carbonic acid diester in the presence of a catalyst comprising a basic nitrogen compound and / or a basic phosphorus compound in combination with an alkali metal compound is suppressed to 4.0x10-3 or below at a wavelength of 465 nm based on a standard substance in a fluorescent light spectrum obtained by the excitation wavelength of 320 nm. An aromatic polycarbonate having good color stability, especially good stability to the deterioration of the chip color during storage of the chip in air at room temperature can be produced by the present invention.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Imaging system with a single color image sensor for simultaneous fluorescence and color video endoscopy
An endoscopic video system and method using a camera with a single color image sensor, for example a CCD color image sensor, for fluorescence and color imaging and for simultaneously displaying the images acquired in these imaging modes at video rates in real time is disclosed. The tissue under investigation is illuminated continuously with fluorescence excitation light and is further illuminated periodically using visible light outside of the fluorescence excitation wavelength range. The illumination sources may be conventional lamps using filters and shutters, or may include light-emitting diodes mounted at the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
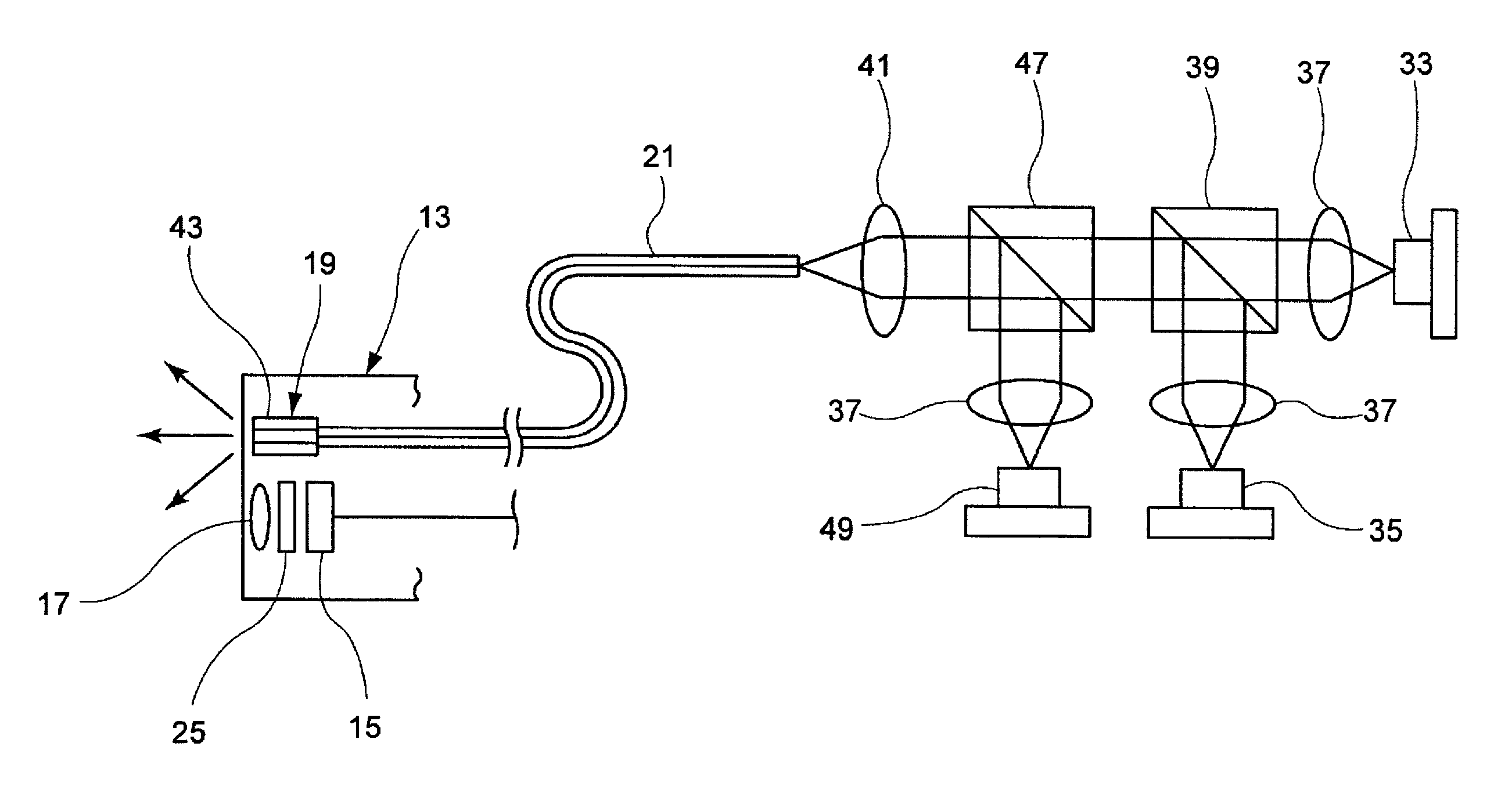
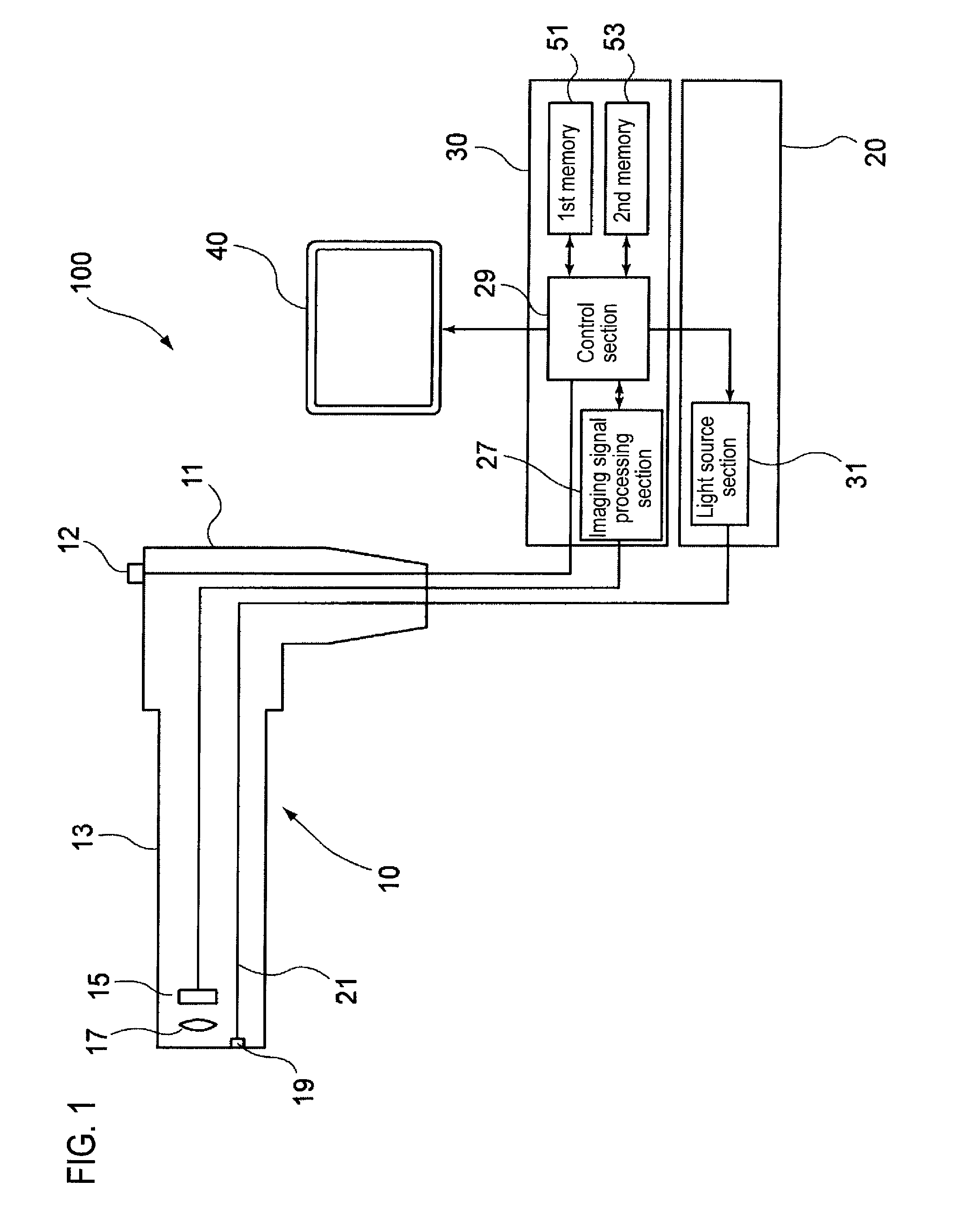
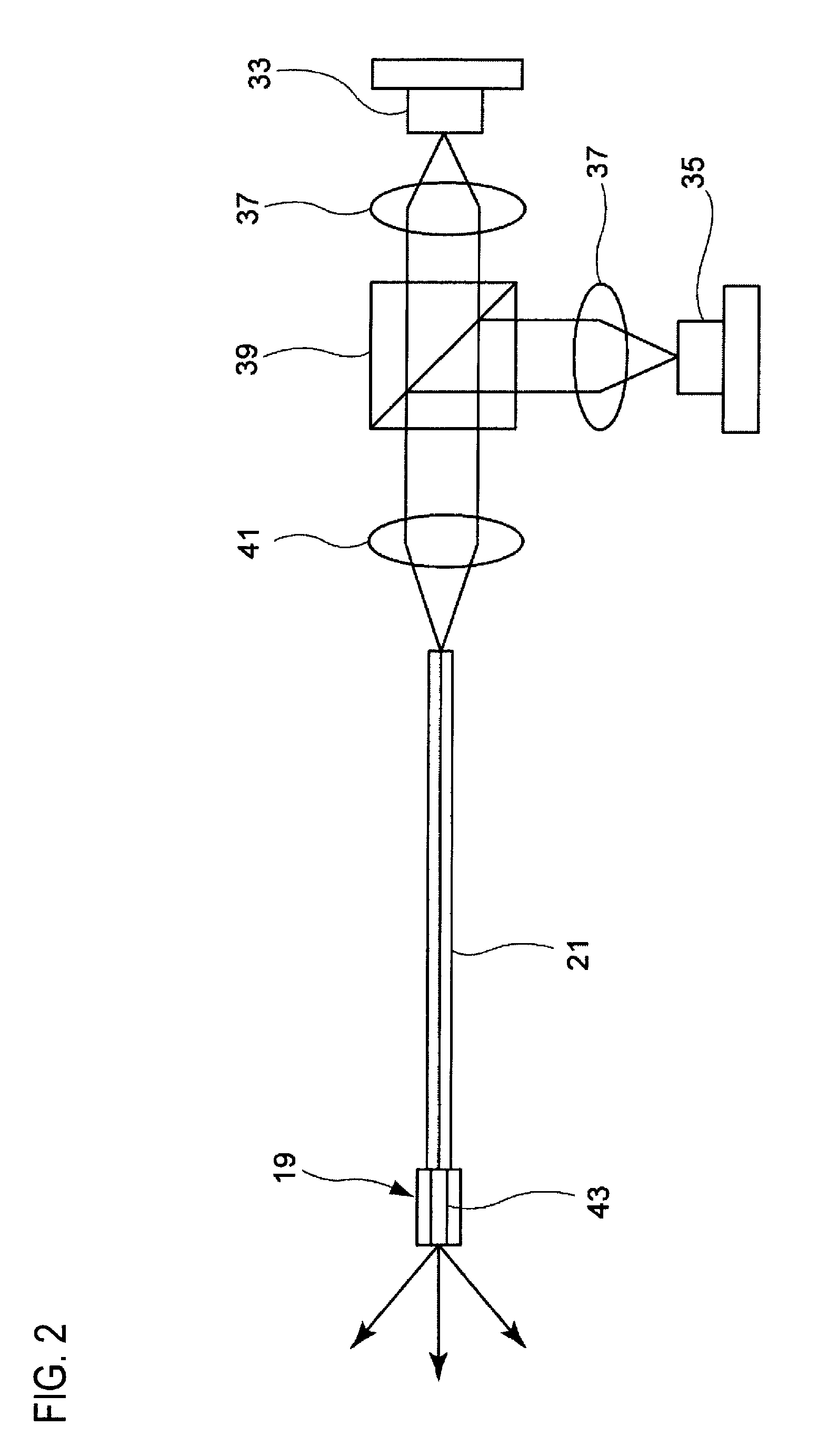
Light source device, imaging apparatus and endoscope apparatus
InactiveUS20090312607A1Improve accuracySimple designTelevision system detailsCladded optical fibrePhosphorLength wave
A light source device includes a first light source 33, a second light source 35 having an emission wavelength that is different from the first light source 33, and a phosphor 43 that is disposed to be distant from the first light source 33 and the second light source 35 and absorbs light in a predetermined excitation wavelength band to emit fluorescence. The phosphor 43 is disposed on an emission light optical path that is shared by the first light source 33 and the second light source 35. The emission wavelength of the first light source 33 is in the predetermined excitation wavelength band. The emission wavelength of the second light source 35 is outside of the predetermined excitation wavelength band.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
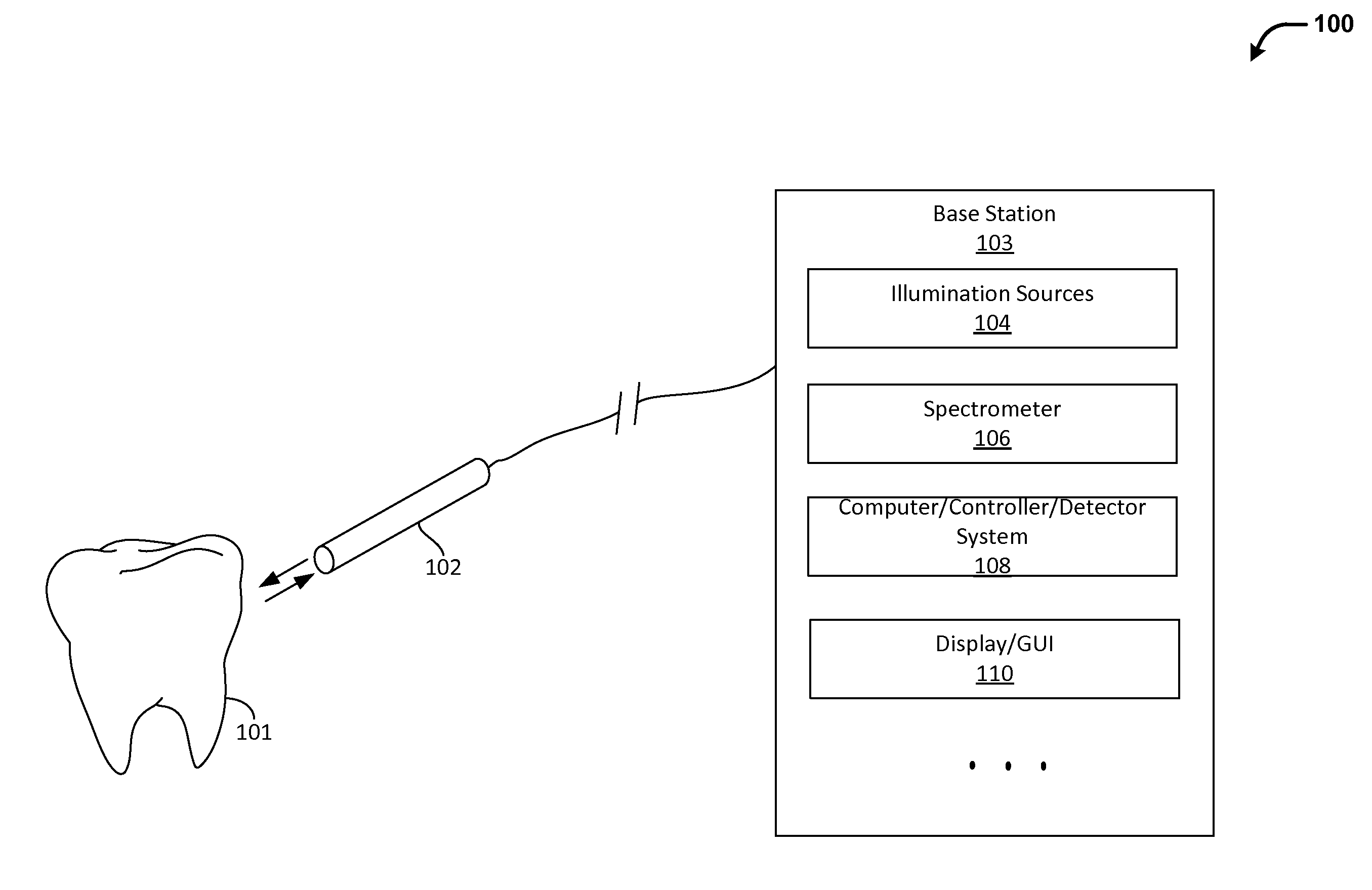
Dental demineralization detection, methods and systems
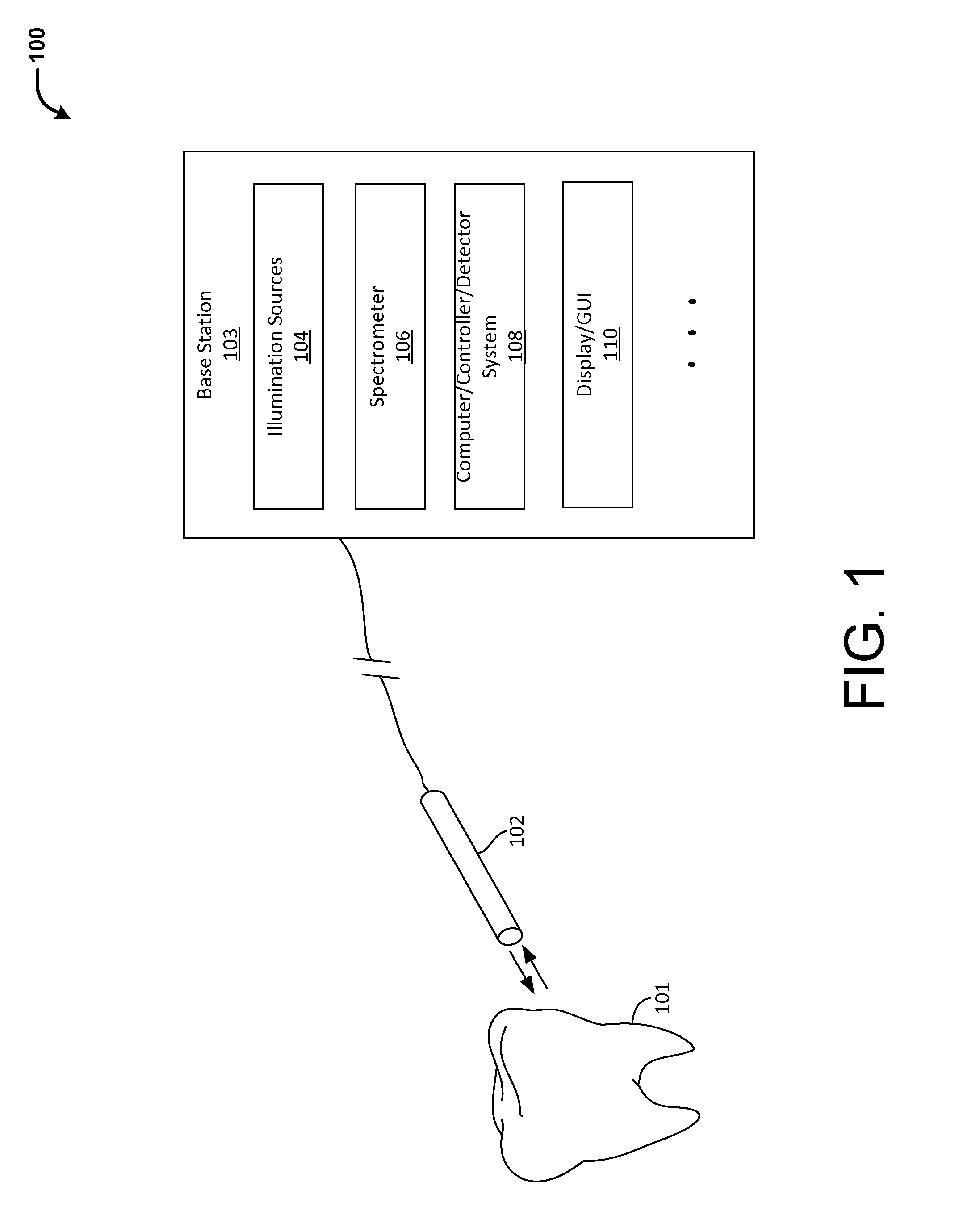
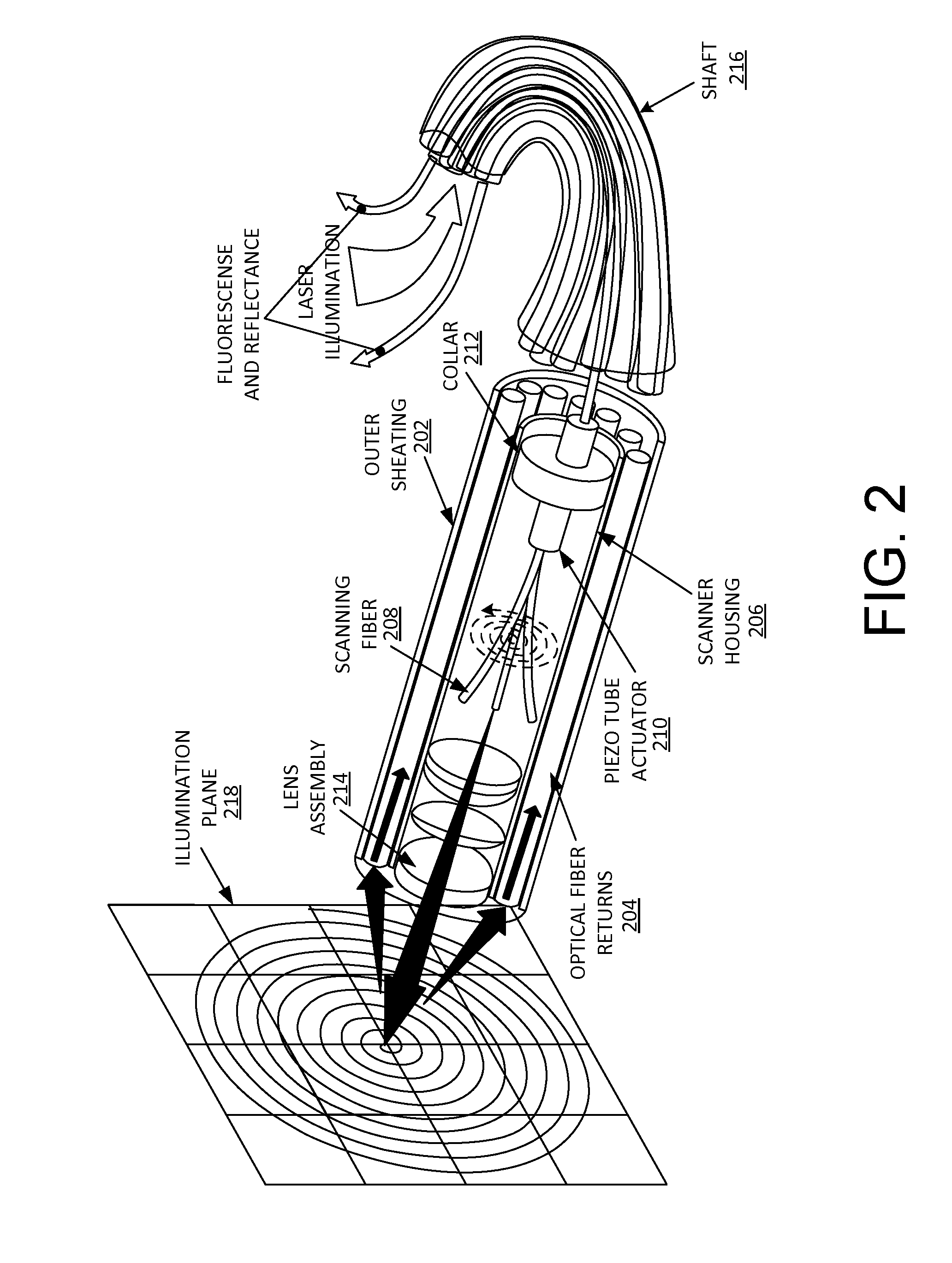
Methods and systems for detecting early stage dental caries and decays are provided. In particular, in an embodiment, laser-induced autofluorescence (AF) from multiple excitation wavelengths is obtained and analyzed. Endogenous fluorophores residing in the enamel naturally fluoresce when illuminated by wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet into the visible spectrum. The relative intensities of the AF emission changes between different excitation wavelengths when the enamel changes from healthy to demineralized. By taking a ratio of AF emission spectra integrals between different excitation wavelengths, a standard is created wherein changes in AF ratios within a tooth are quantified and serve as indicators of early stage enamel demineralization. The techniques described herein may be used in conjunction with a scanning fiber endoscope (SFE) to provide a reliable, safe and low-cost means for identifying dental caries or decays.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
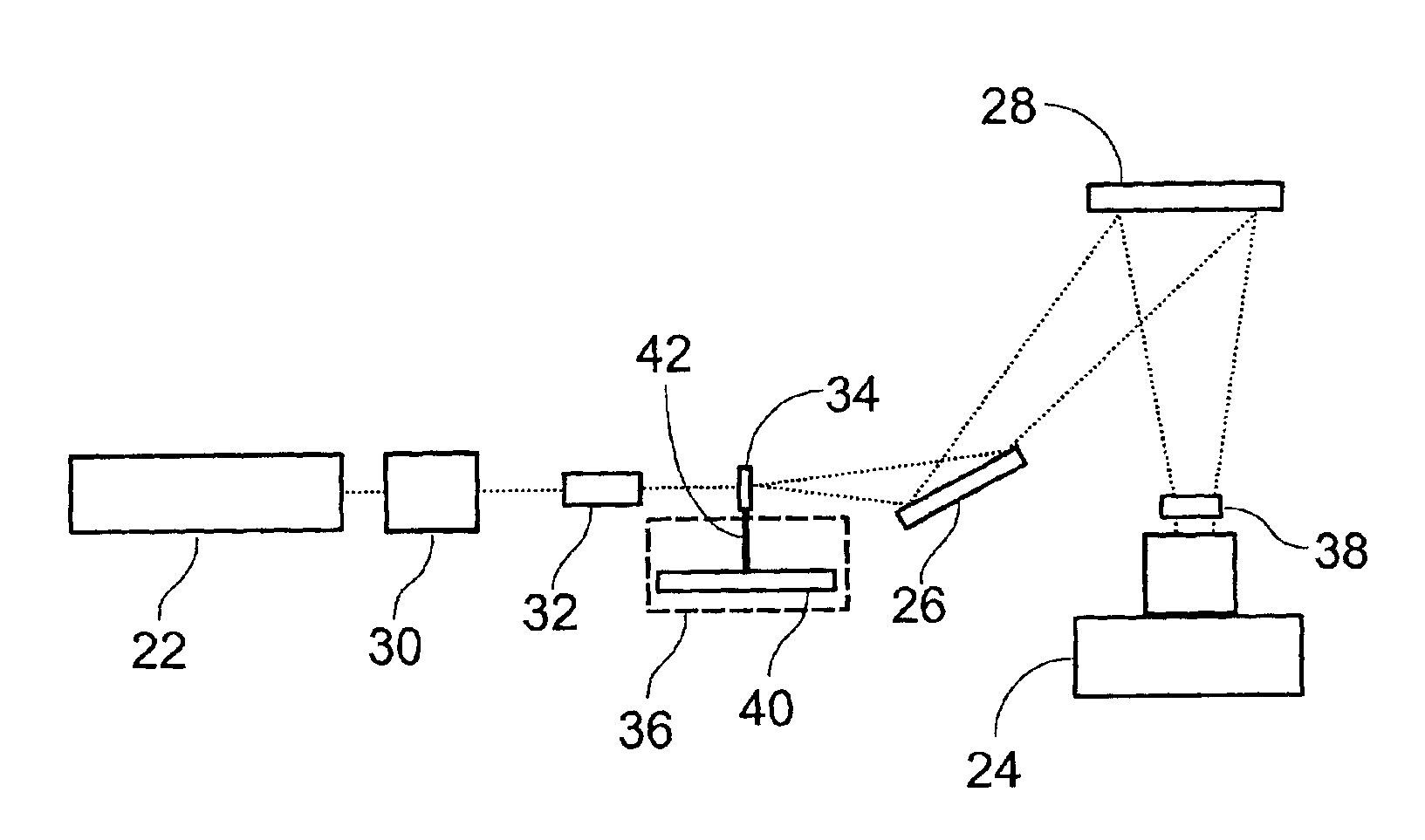
Light detection device
InactiveUS6930314B2Increase flexibilityImprove reading speedSpectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsGenomicsMicroscope slide
Apparatus and methods for optical illumination and / or detection with improved flexibility and / or read speed. The apparatus and methods may include mechanisms for selecting and switching between multiple excitation wavelengths and / or simultaneously reading from a plurality of sample sites. The apparatus and methods may be used with microplates, PCR plates, cell culture plates, biochips, chromatography plates, microscope slides, and other substrates for high-throughput screening, genomics, SNPs analysis, pharmaceutical research and development, life sciences research, and other applications.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Optical generic switch panel
InactiveUS20080006766A1Material analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsRefractive indexExcitation wavelength
A switch panel having a touch plate, light converter, and light analyzer are disclosed. The touch plate includes an optically transparent layer having first and second surfaces, and having an index of refraction greater than that of air. The touch plate conducts light of an excitation wavelength between the first and second surfaces and emits part of that light through the second surface at one of a plurality of emission locations depending on the position at which pressure is applied to the first surface. The light converter is positioned to receive the light emitted through the second surface and generates light having a plurality of distinct location-specific spectra, one of the location-specific spectra corresponding to each of the emission locations. The light analyzer generates a signal indicative of which of the location-specific spectra was generated by the light converter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH GENERAL IP SINGPAORE PTE LTD
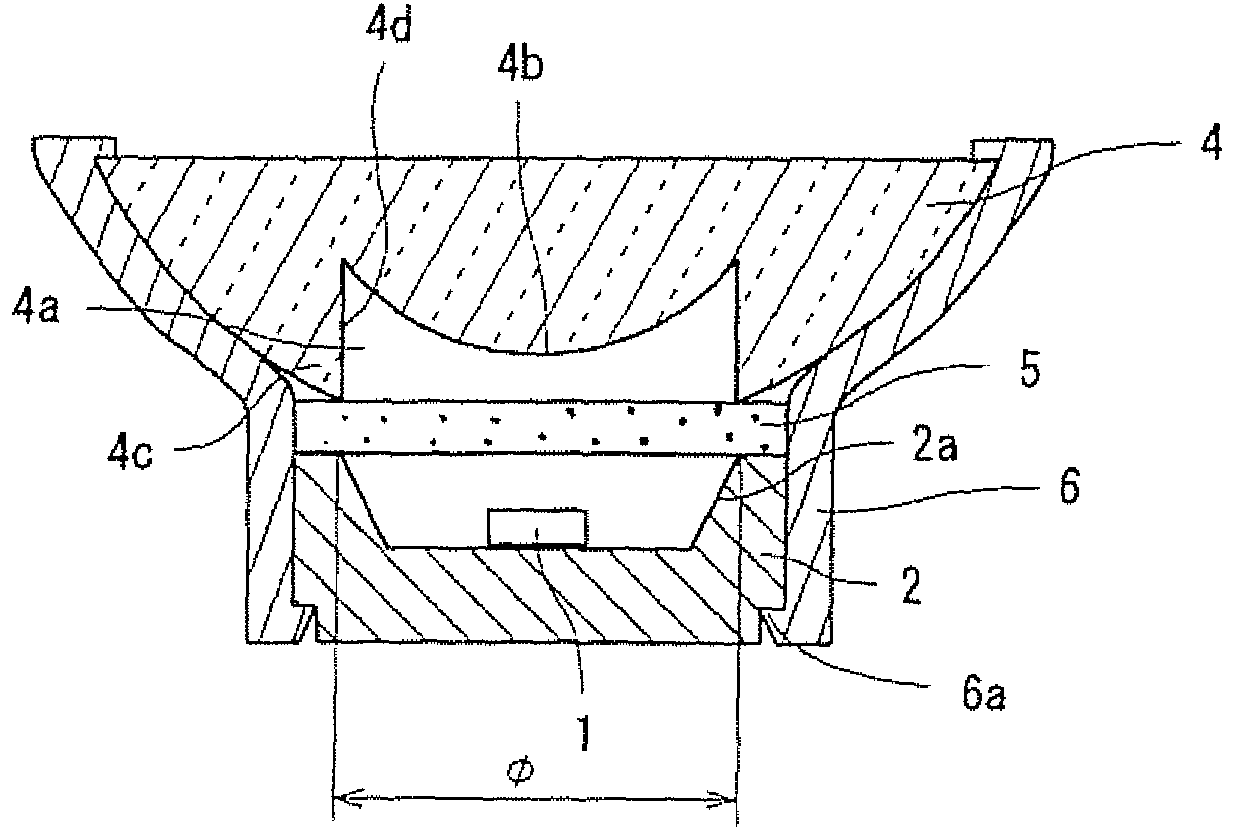
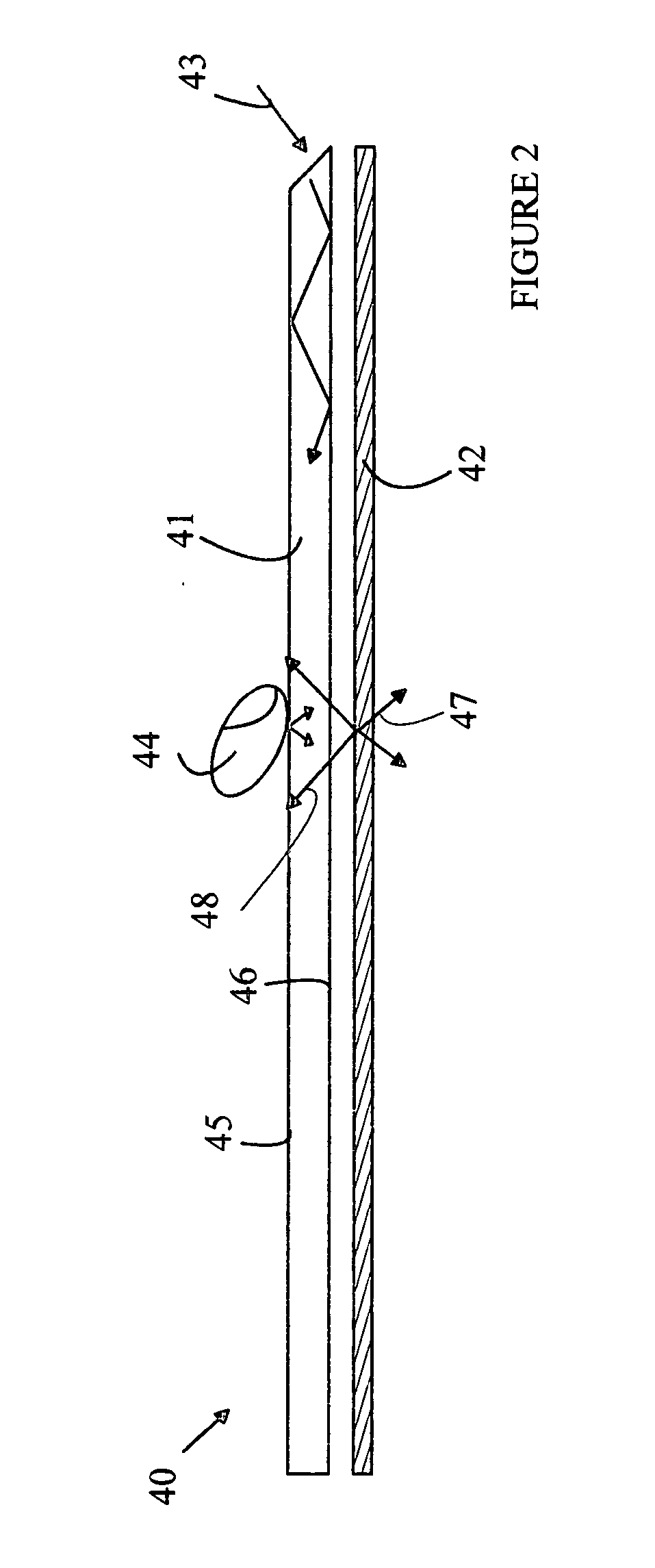
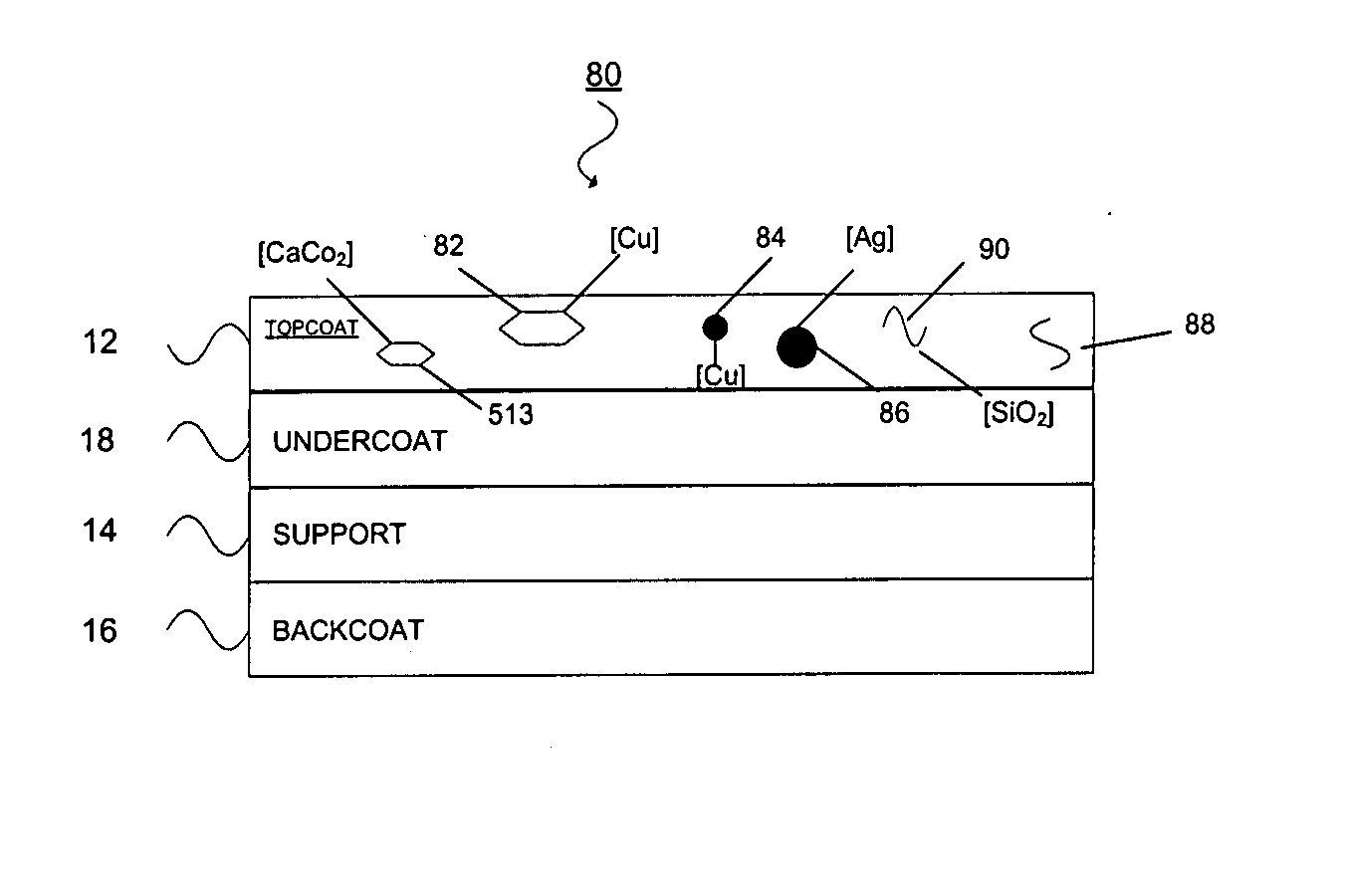
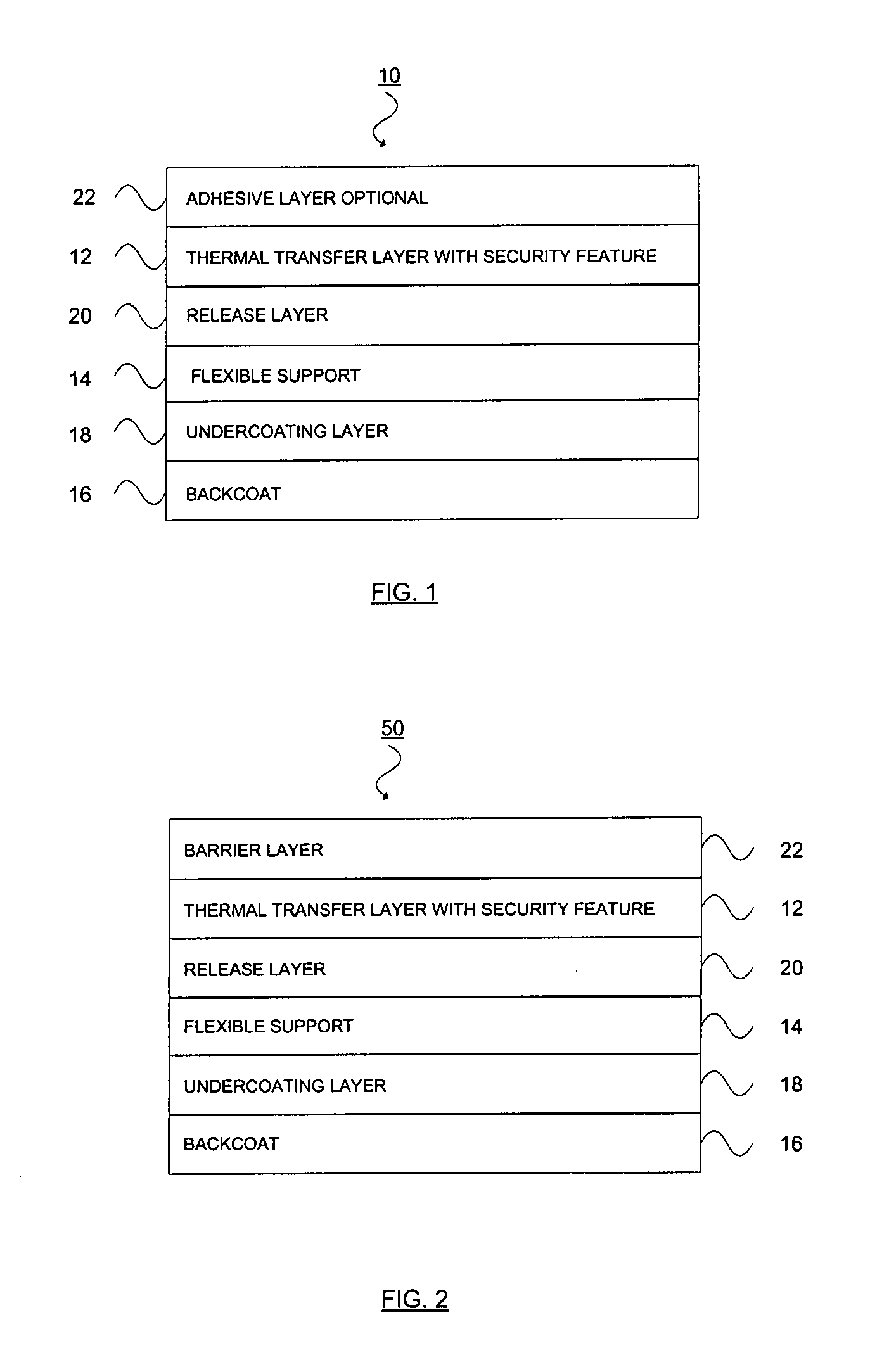
Thermal transfer ribbon
A thermal transfer printing medium that contains a thermal transfer layer which contains a first taggant and colorant, wherein: the first taggant comprises a fluorescent compound with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths of greater than 700 nanometers. When the thermal transfer layer is printed onto a white polyester substrate with a gloss of at least about 84, a surface smoothness Rz value of 1.2, and a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of 1.91 and (b) of −6.79 and a lightness (L) of 95.63, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system, and when such printing utilizes a printing speed of 2.5 centimeters per second and a printing energy of 3.2 joules per square centimeter, a printed substrate with certain properties is produced. The printed substrate has a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of from −15 to 15 and (b) from −18 to 18, and the printed substrate has a lightness (L) of less than about 35, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system. When the printed substrate is illuminated with light source that excites the first taggant with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths greater than 700 nanometers, the printed substrate produces a light fluorescence with a wavelength of from about 300 to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:INT IMAGING MATERIALS
Systems and techniques for generating Bessel beams
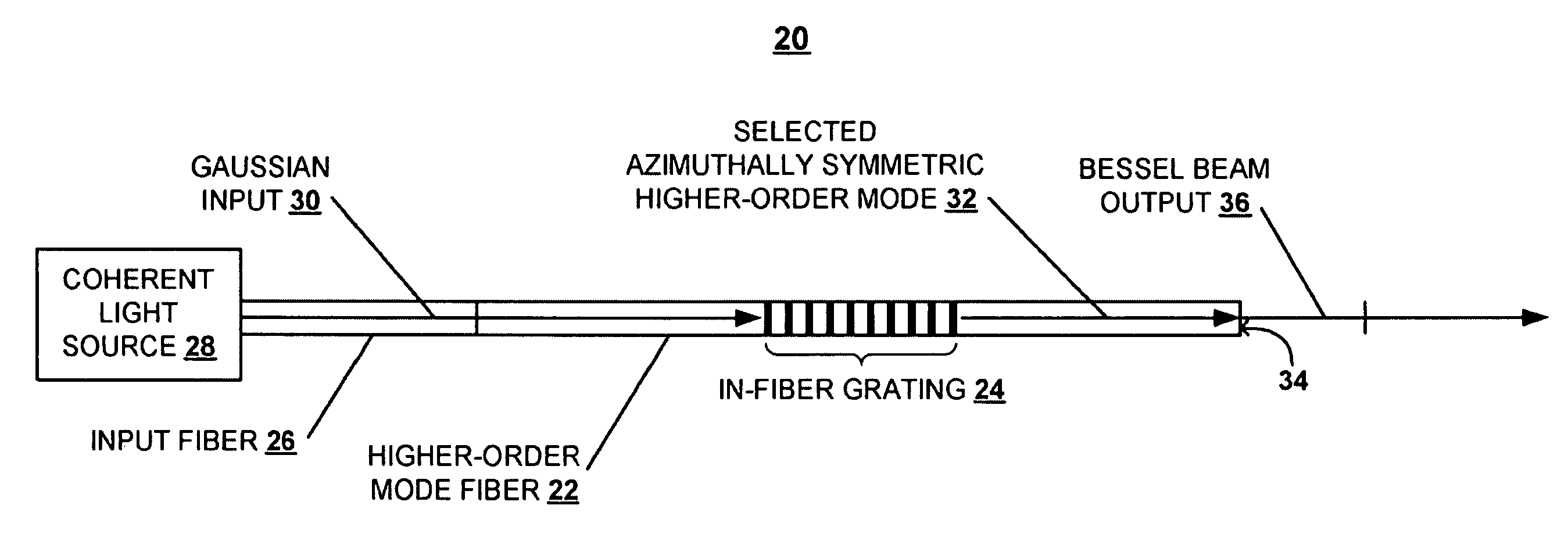
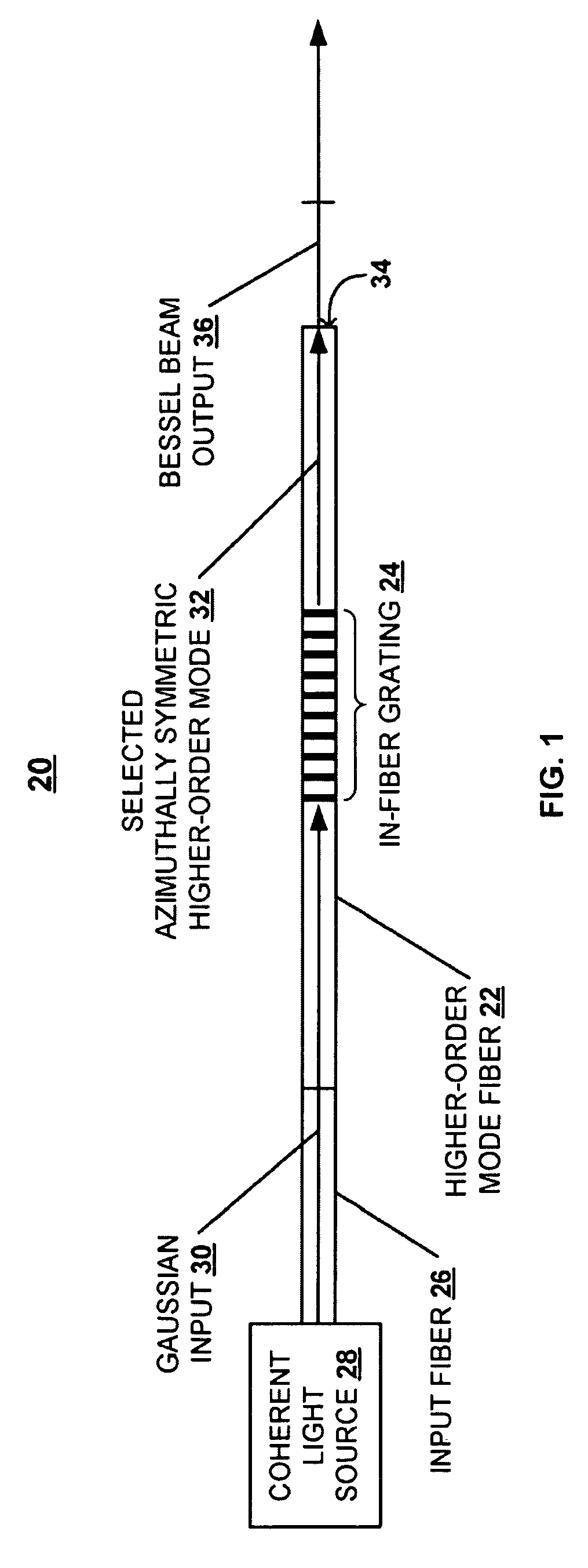
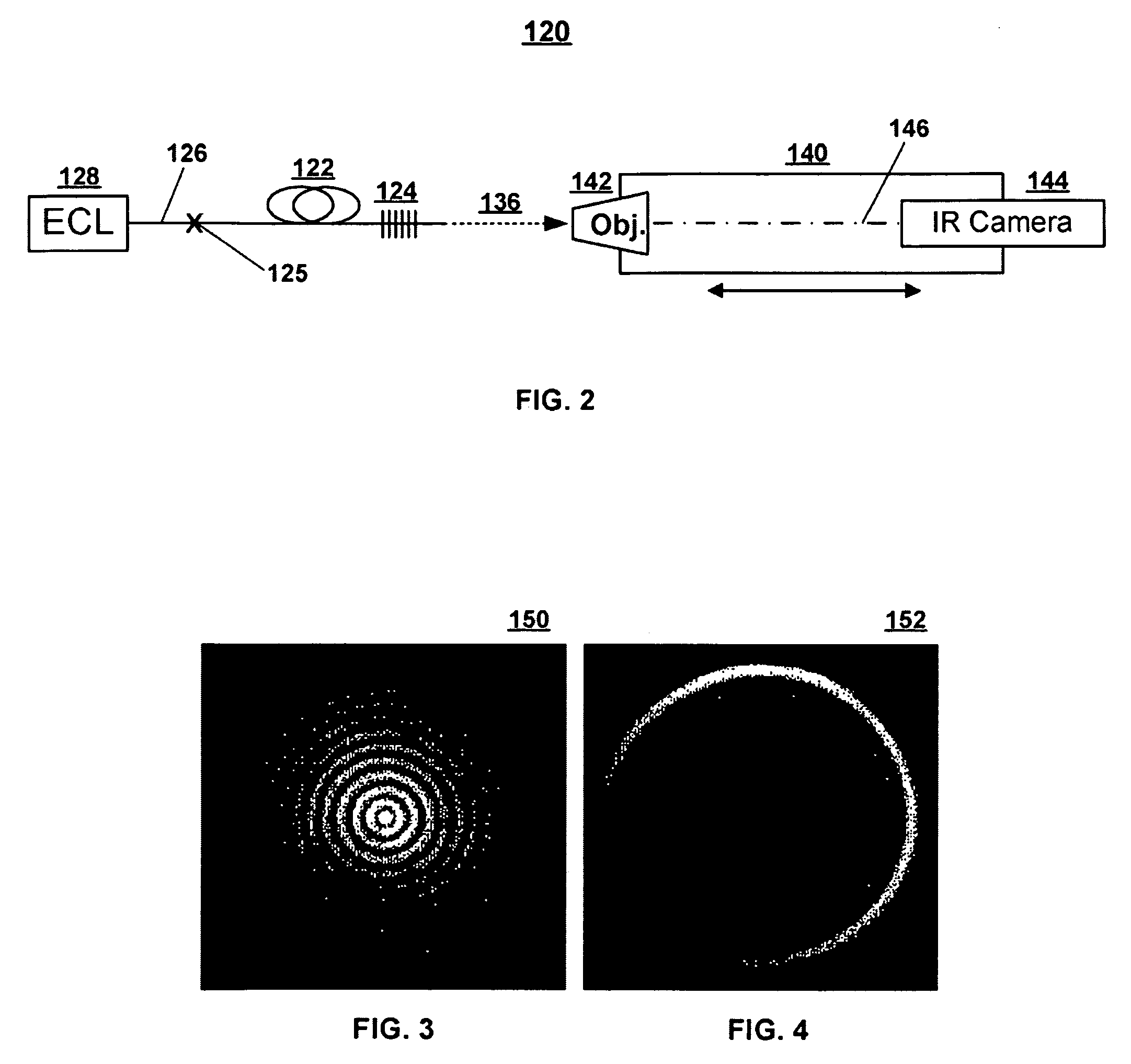
A technique is described for generating a Bessel beam. An input optical fiber is provided that supports propagation in the fundamental mode. The input fiber is connected to a fiber mode converting device that provides phase matching, at a predetermined excitation wavelength, between the fundamental mode and a selected azimuthally symmetric higher-order mode. As an input to the fiber mode converting device, a coherent light beam is fed through the input optical fiber to provide a fundamental mode input at the excitation wavelength. The fiber mode converting device resonantly excites the selected azimuthally symmetric mode. The azimuthally symmetric mode is provided as a beam output from an endface of the fiber mode converting device to approximate a Bessel beam.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
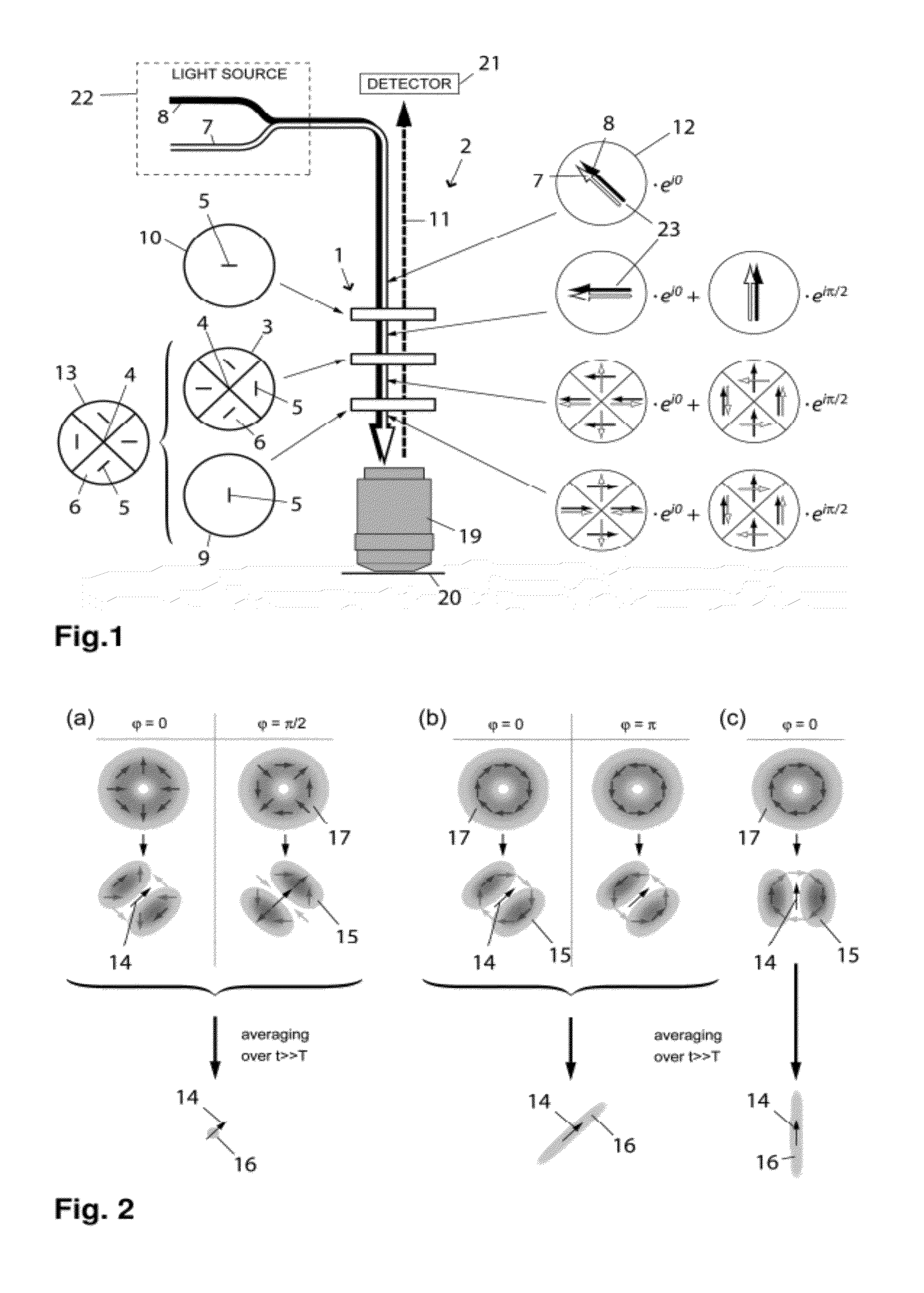
Fluorescence Light Scanning Microscope Having a Birefringent Chromatic Beam Shaping Device
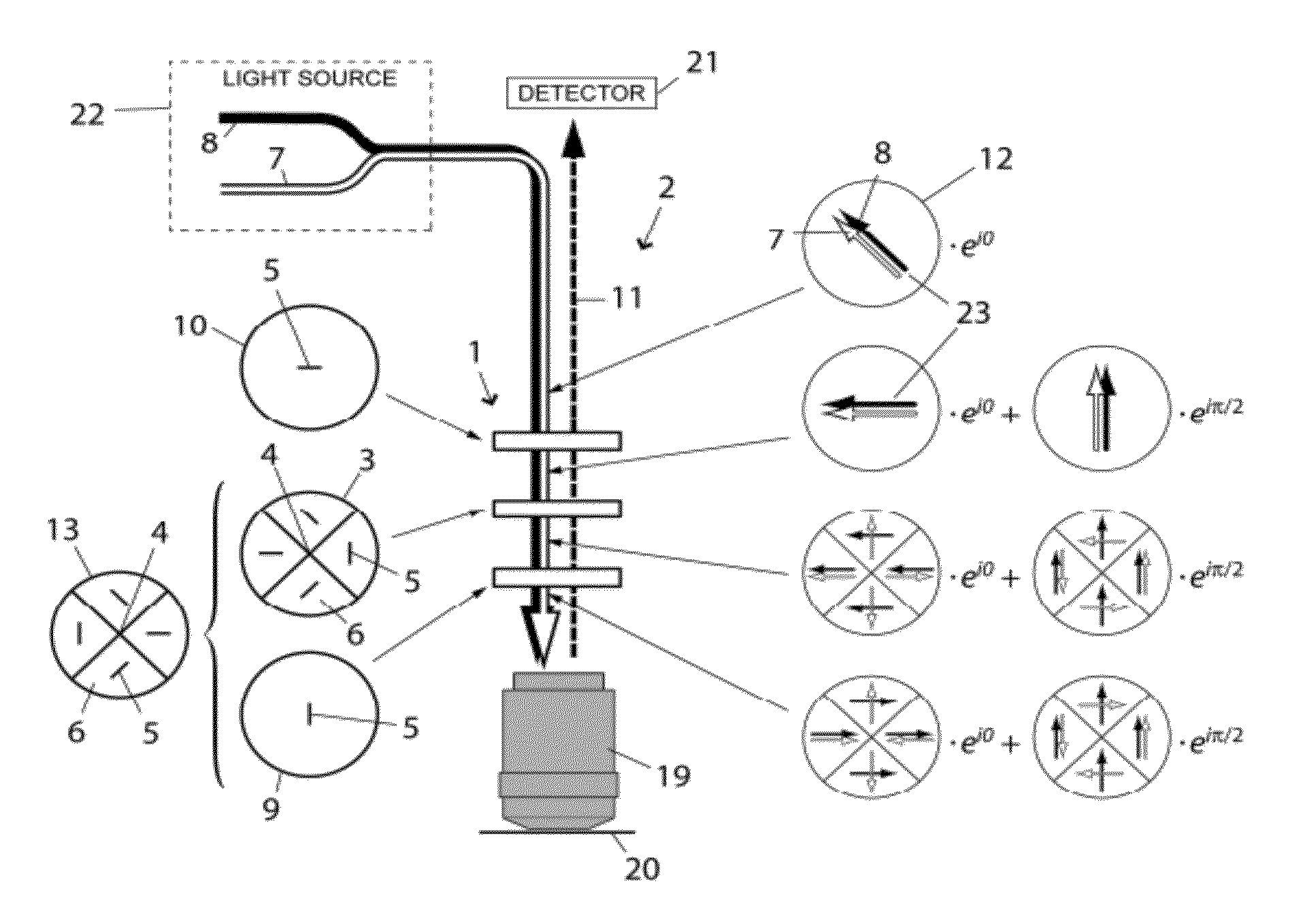
A fluorescence light scanning microscope (2) comprises a light source providing excitation light (8) for exciting a fluorophore in a sample to be imaged for spontaneous emission of fluorescence light, and suppression light (7) for suppressing spontaneous emission of fluorescence light by the fluorophore on a common optical axis (4), the suppression wavelength differing from the excitation wavelength; an objective (19) focusing both the excitation (8) and the suppression (7) light to a focus point; a detector (21) detecting fluorescence light (11) spontaneously emitted by the fluorophore; and a chromatic beam shaping device (1) arranged on the common optical axis (4), and including a birefringent chromatic optical element (3) adapted to shape a polarization distribution of the suppression light (7) such as to produce an intensity zero at the focus point, and to leave the excitation light such as to produce a maximum at the focus point.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com