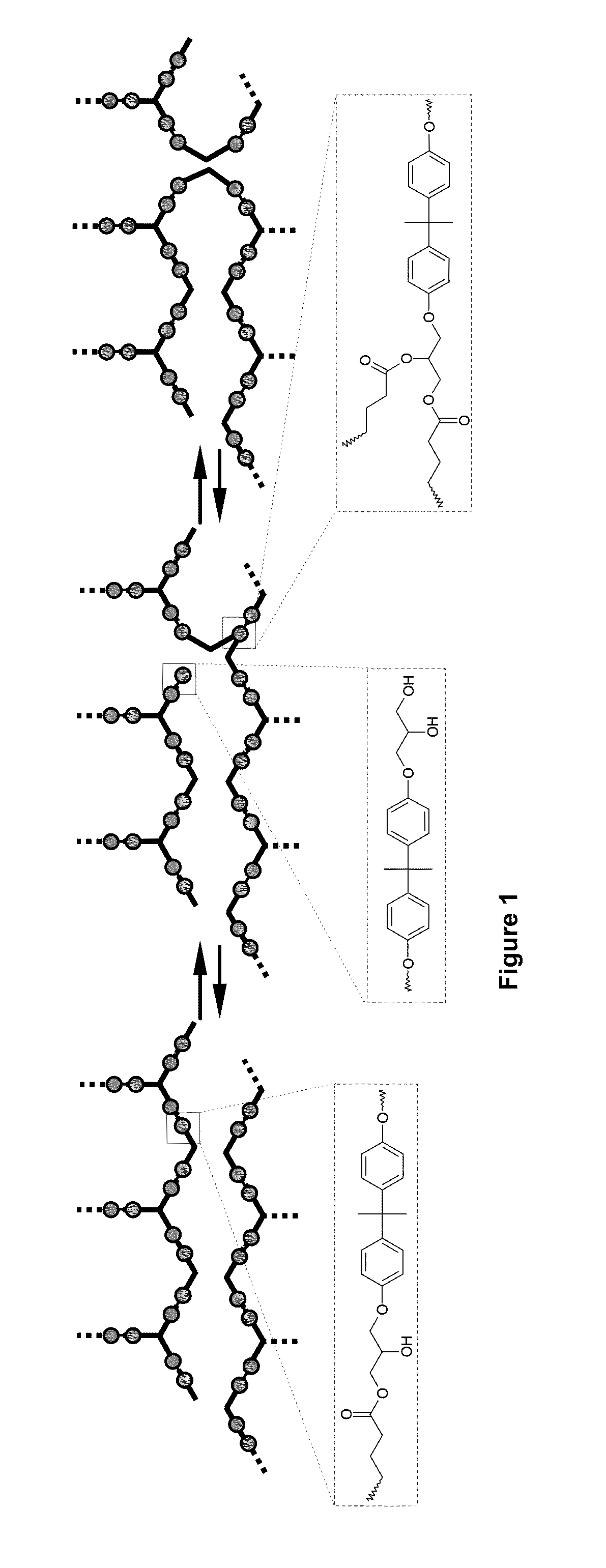
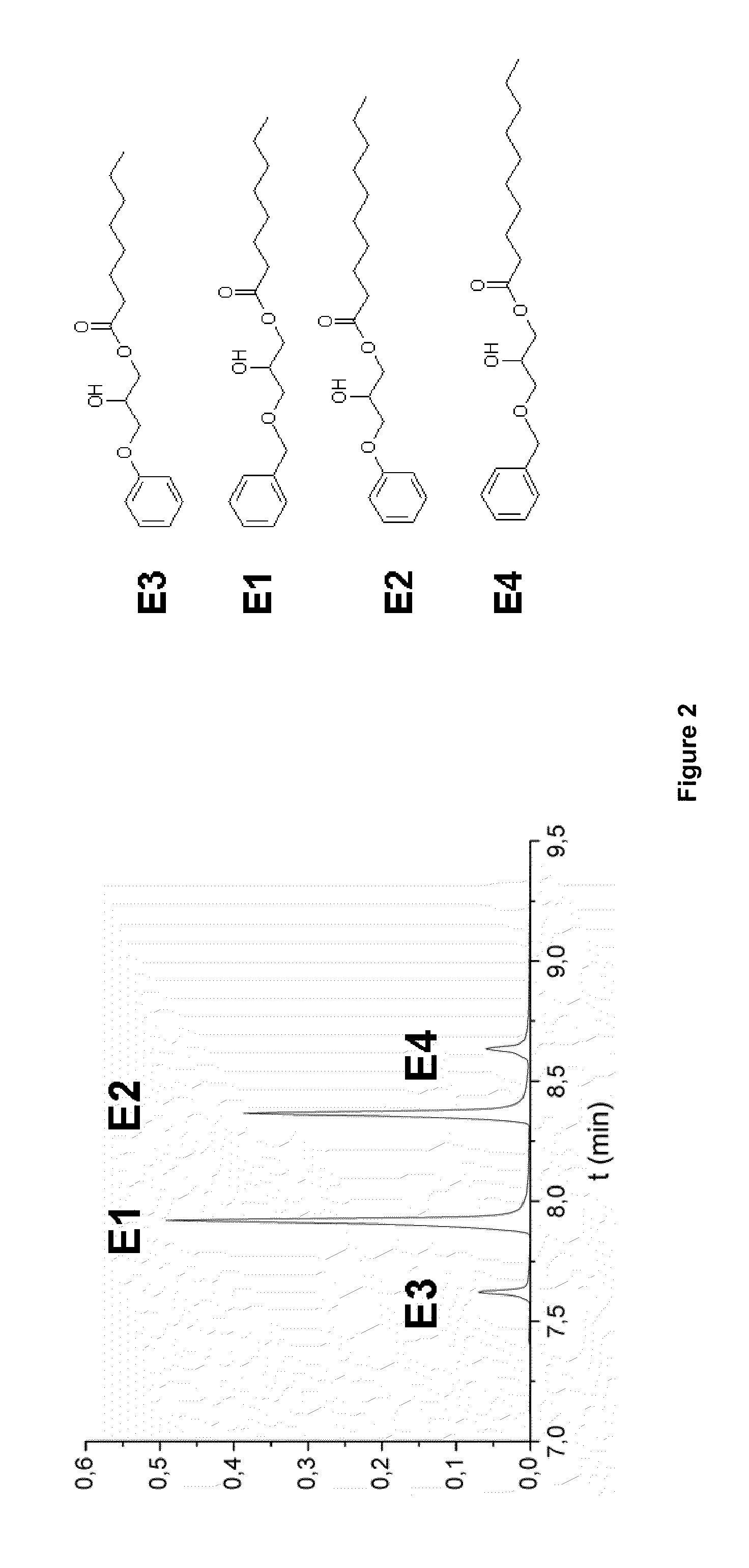
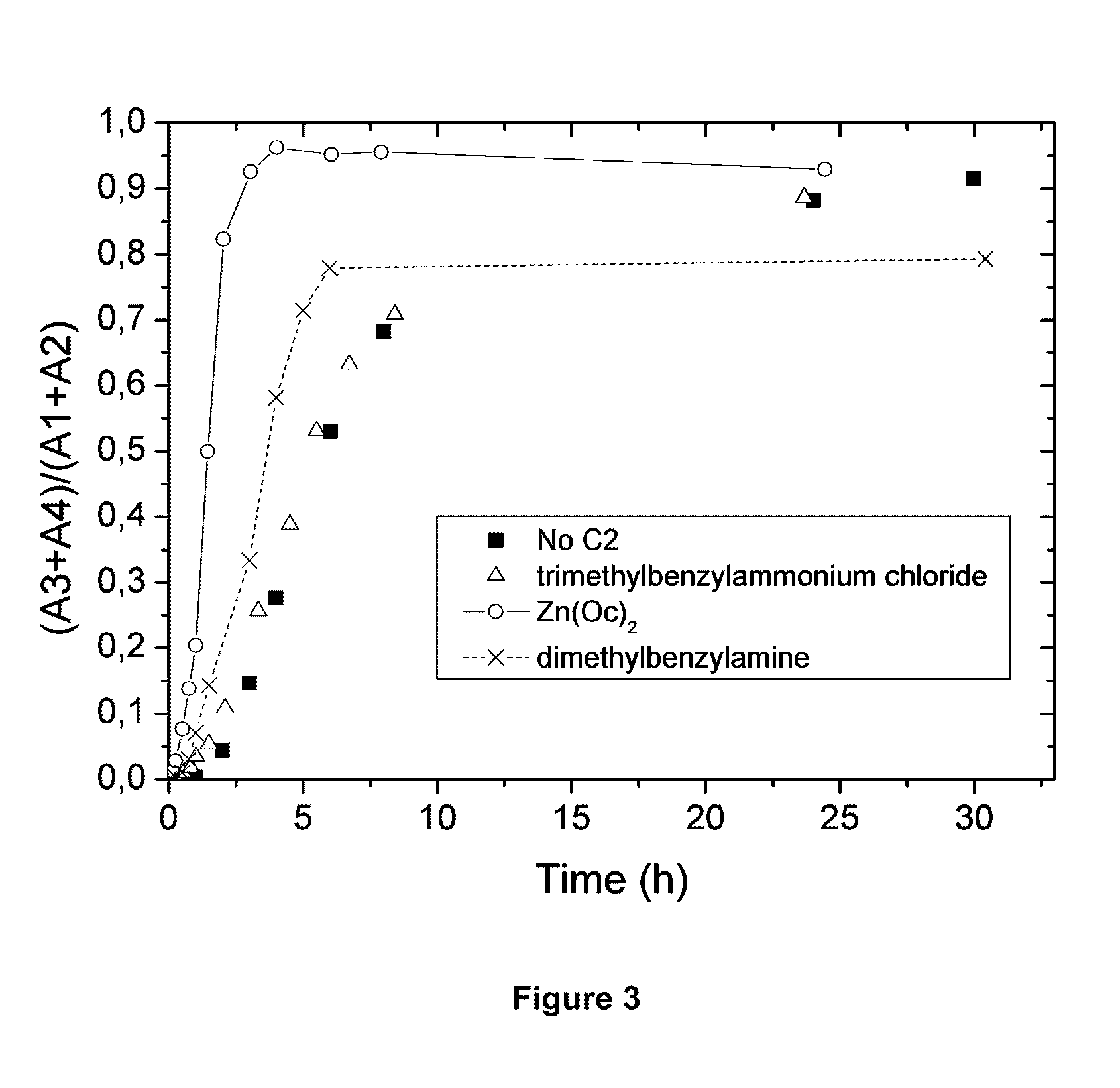
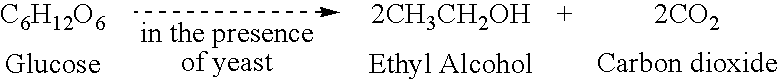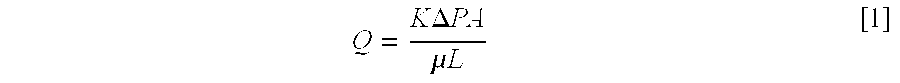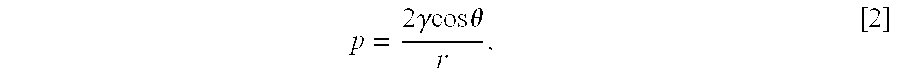Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2308 results about "Transesterification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
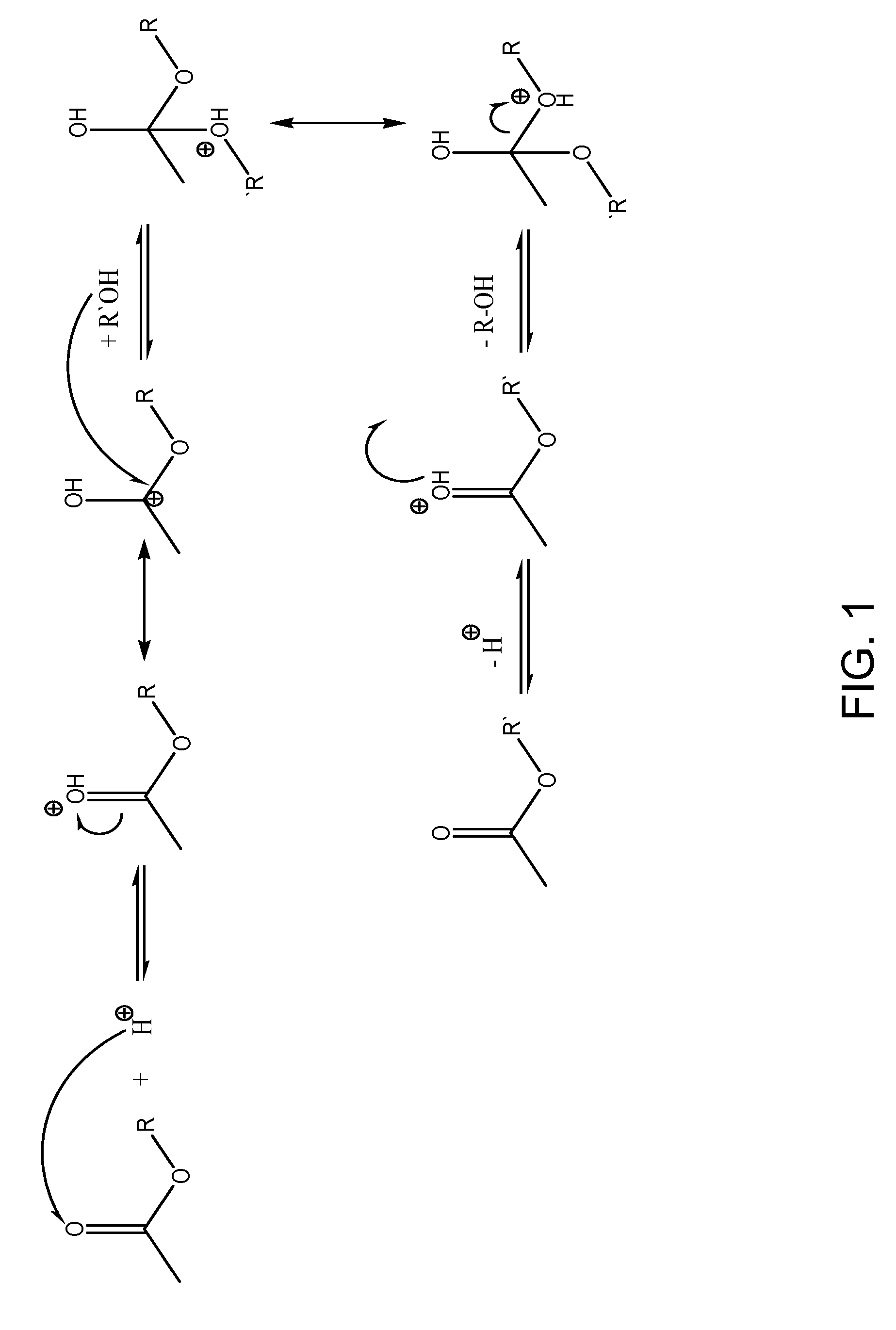
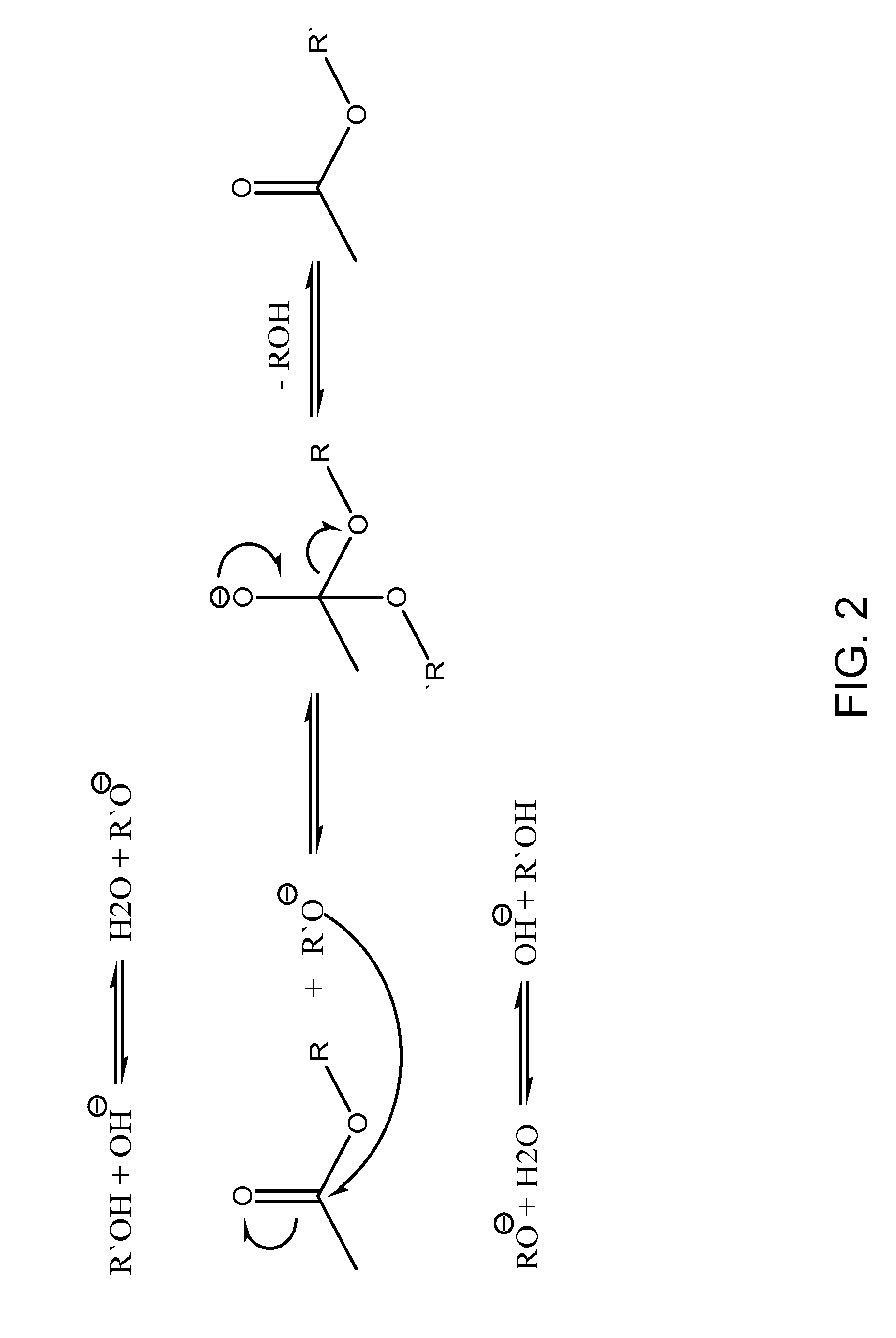
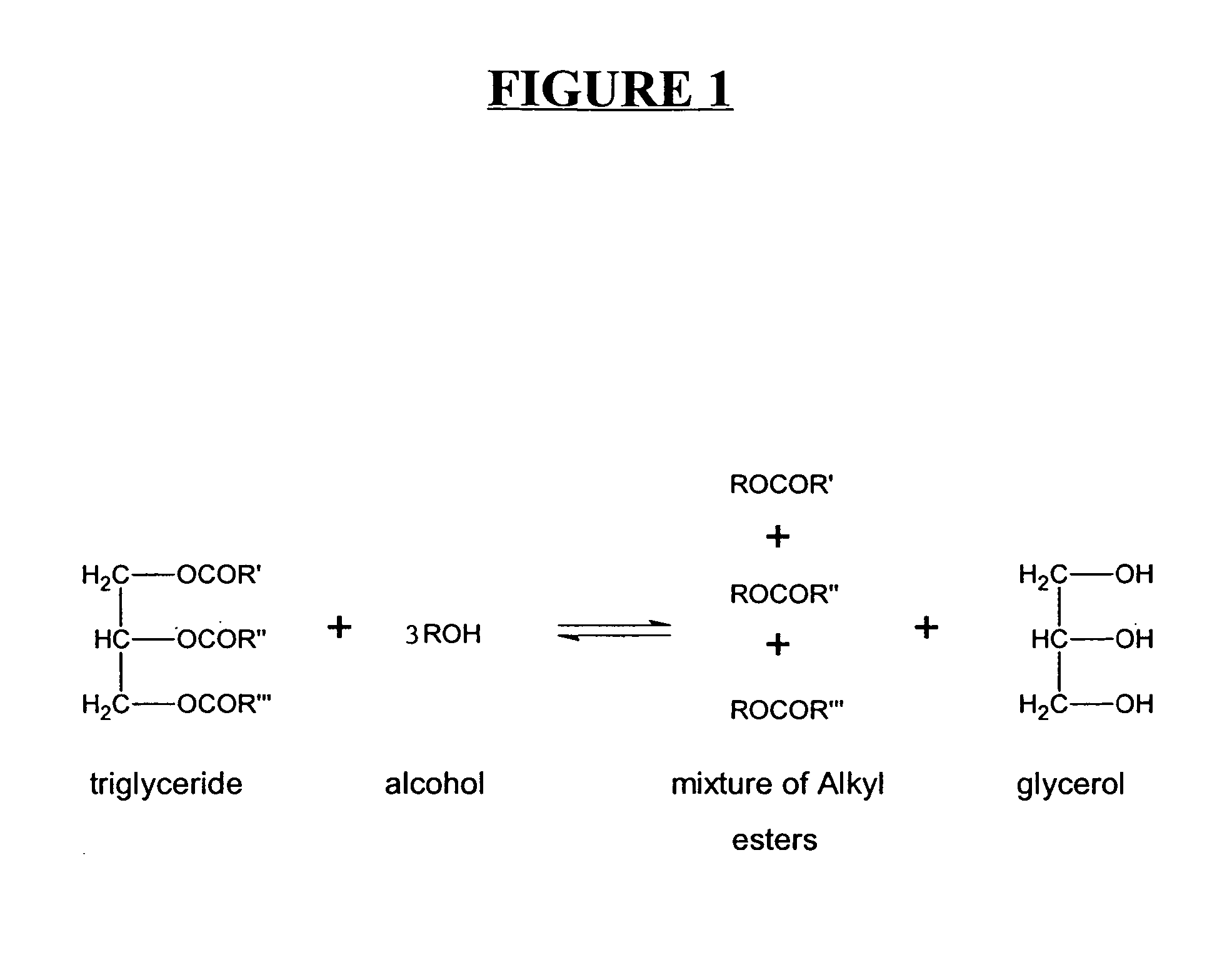
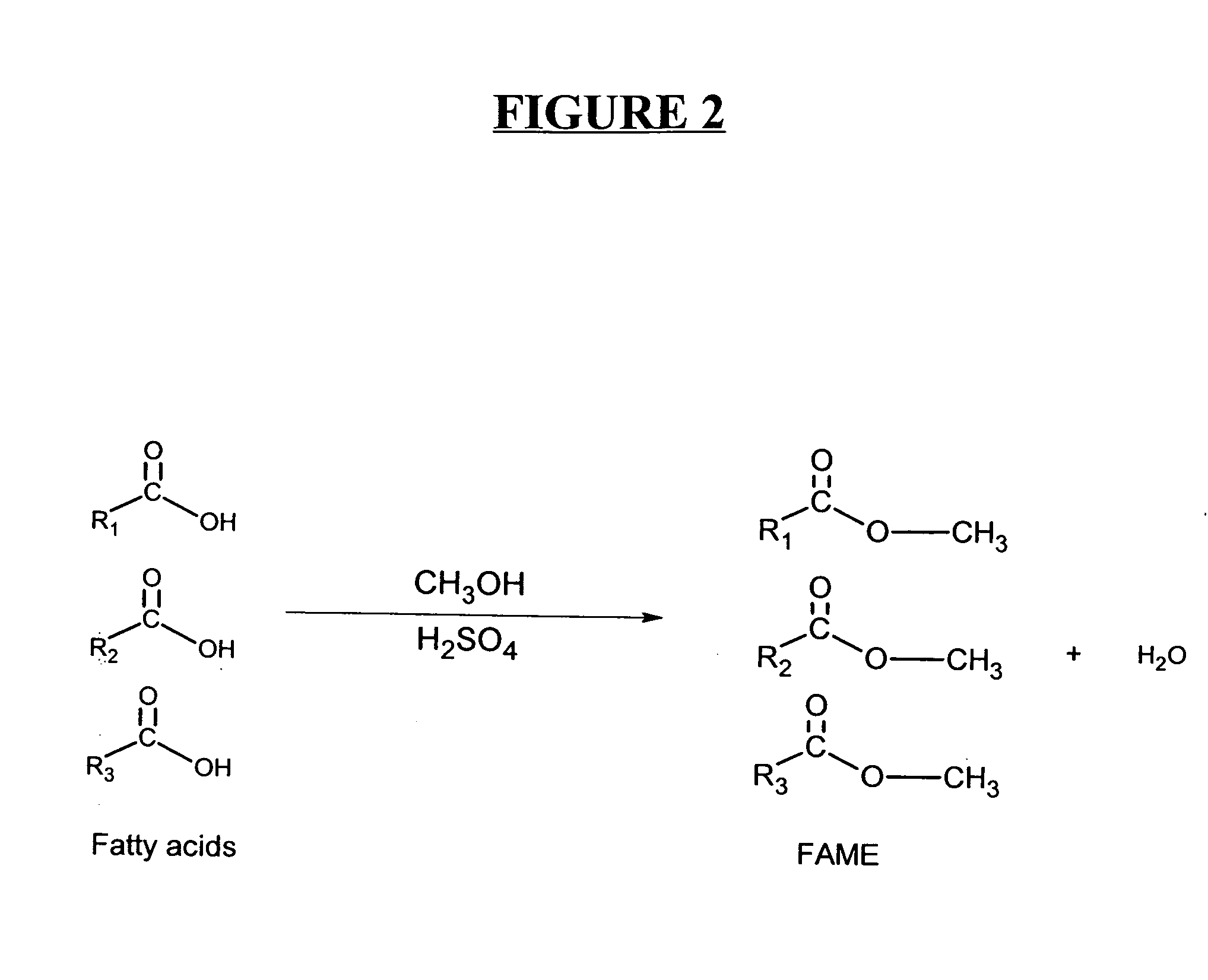
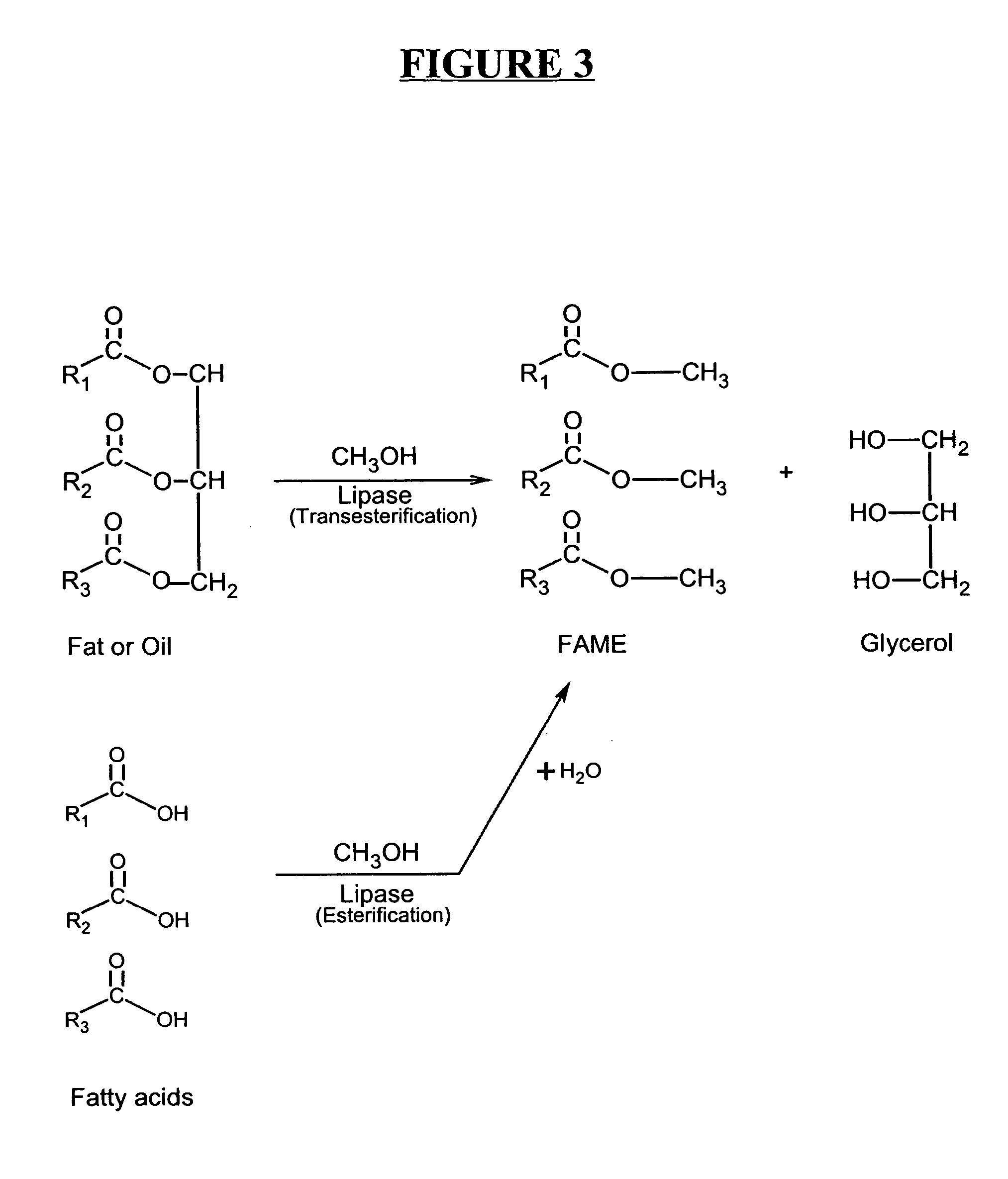
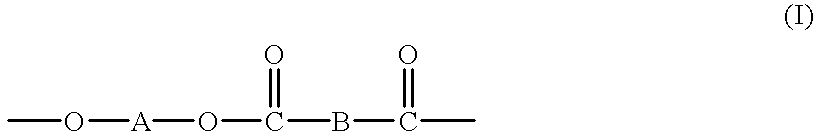
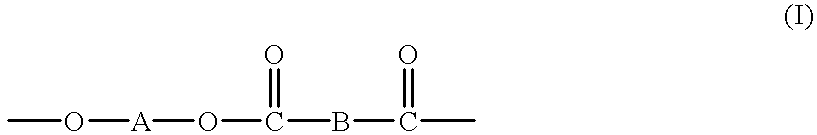
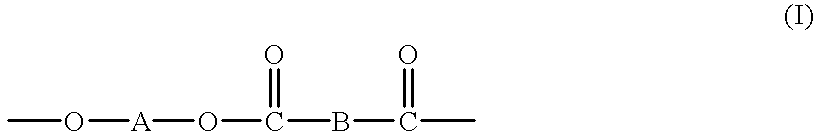
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R′ of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of enzymes (biocatalysts) particularly lipases (E.C.3.1.1.3).
Oxygen scavenging condensation copolymers for bottles and packaging articles
Compositions for scavenging oxygen are disclosed. These compositions comprise condensation copolymers comprising predominantly polyester segments and an oxygen scavenging amount of polyolefin oligomer segments. The polyester segments comprise segments derived from typical bottling and packaging polyesters such as PET and PEN. The copolymers are preferably formed by transesterification during reactive extrusion and typically comprise about 0.5 to about 12 wt % of polyolefin oligomer segments. The copolycondensates are capable of absorbing at least 0.4 cc of oxygen per gram of copolymer in the solid state at ambient temperatures and are typically used as layers in films, liners, cups, wraps, bottles, etc. Use of these oxygen scavenging compositions in bottles provides a clear and rigid bottle similar in appearance to unmodified polyester bottles. In a series of preferred embodiments, bottles fabricated with the oxygen scavenging copolycondensates of this invention are over 99.4 wt % polyester and suitable for recycle with other polyester bottles.
Owner:COLORMATRIX HLDG
Methods and compositions for extraction and transesterification of biomass components
InactiveUS20090234146A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationBiofuel
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the direct transesterification and extraction of bio-lipids and bio-oils in the production of biofuel, particularly fatty acid methyl ester products.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Process for preparing a polymer having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone and such (CO)polymers
A process for preparing a polymer having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone and having a number average molecular weight of at least 10,000 (as determined by GPC based on polystyrene standards) includes a first step where a prepolymer is made having the 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone, followed in a second step by a polycondensation reaction. In the first step a 2,5-furandicarboxylate ester is transesterified with a compound or mixture of compounds containing two or more hydroxyl groups, in the presence of a tin(IV) based transesterification catalyst. In the second step at reduced pressure and under melt conditions the prepolymer prepared in the first step is polycondensed in the presence of a tin (II) based polycondensation catalyst until the polymer is obtained. This polymer may then be subjected to Solid State Polycondensation. Polymers so produced may have a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone, and having a number average molecular weight of at least 20,000 (as determined by GPC based on styrene standards), and an absorbance as a 5 mg / mL solution in a dichloromethane:hexafluoroisopropanol 8:2 at 400 nm of below 0.05.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
Glycerol Feedstock Utilization for Oil-Based Fuel Manufacturing
InactiveUS20090004715A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid chemical modificationMicroorganismTransesterification
The invention provides methods of manufacturing biodiesel and other oil-based compounds using glycerol and combinations of glycerol and other feedstocks as an energy source in fermentation of oil-bearing microorganisms. Methods disclosed herein include processes for manufacturing high nutrition edible oils from non-food feedstock materials such as waste products from industrial waste transesterification processes. Also included are methods of increasing oil yields by temporally separating glycerol and other feedstocks during cultivation processes. Also provided herein are oil-bearing microbes containing exogenous oil production genes and methods of cultivating such microbes on glycerol and other feedstocks.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Methods for producing biodiesel
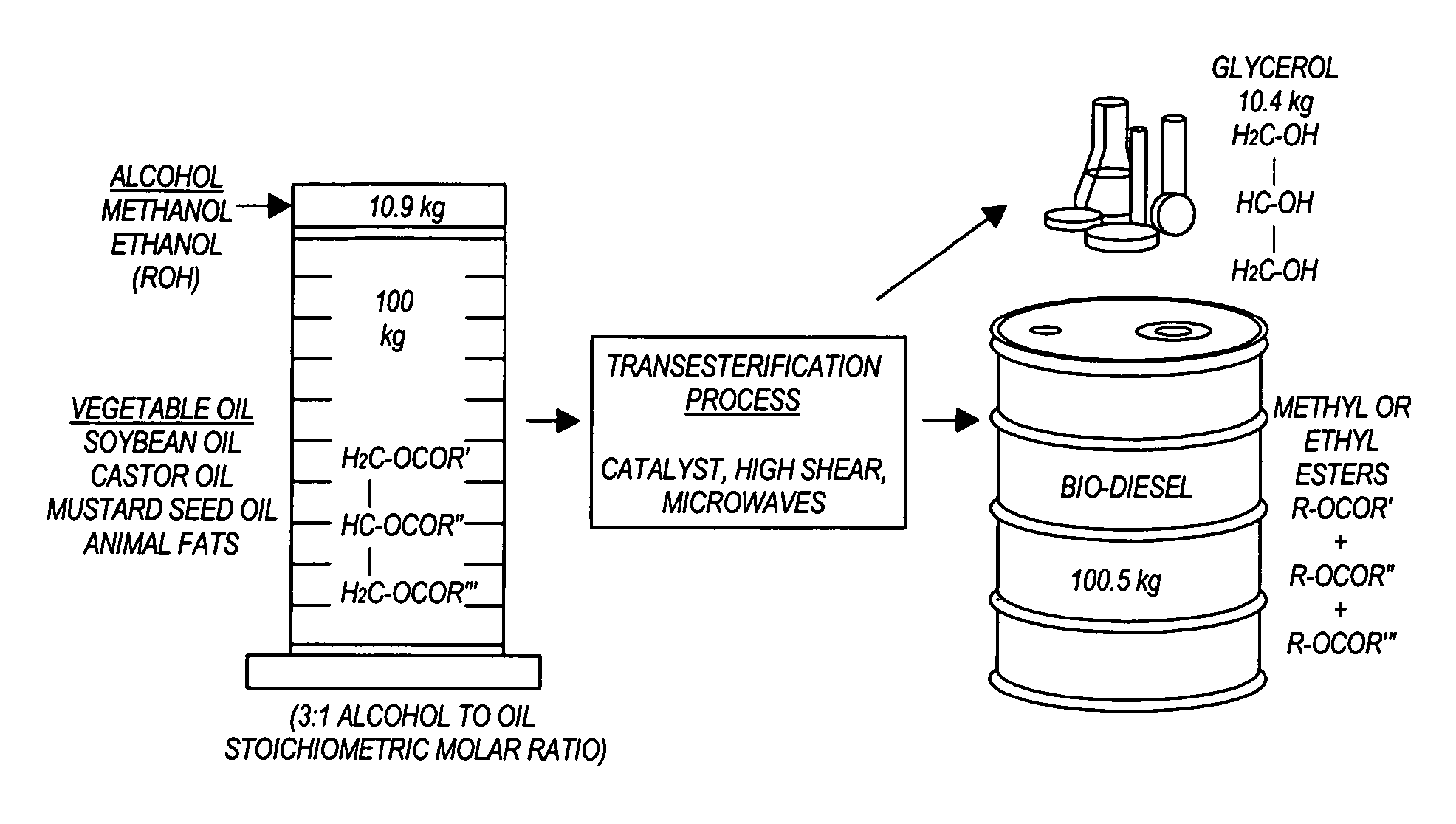
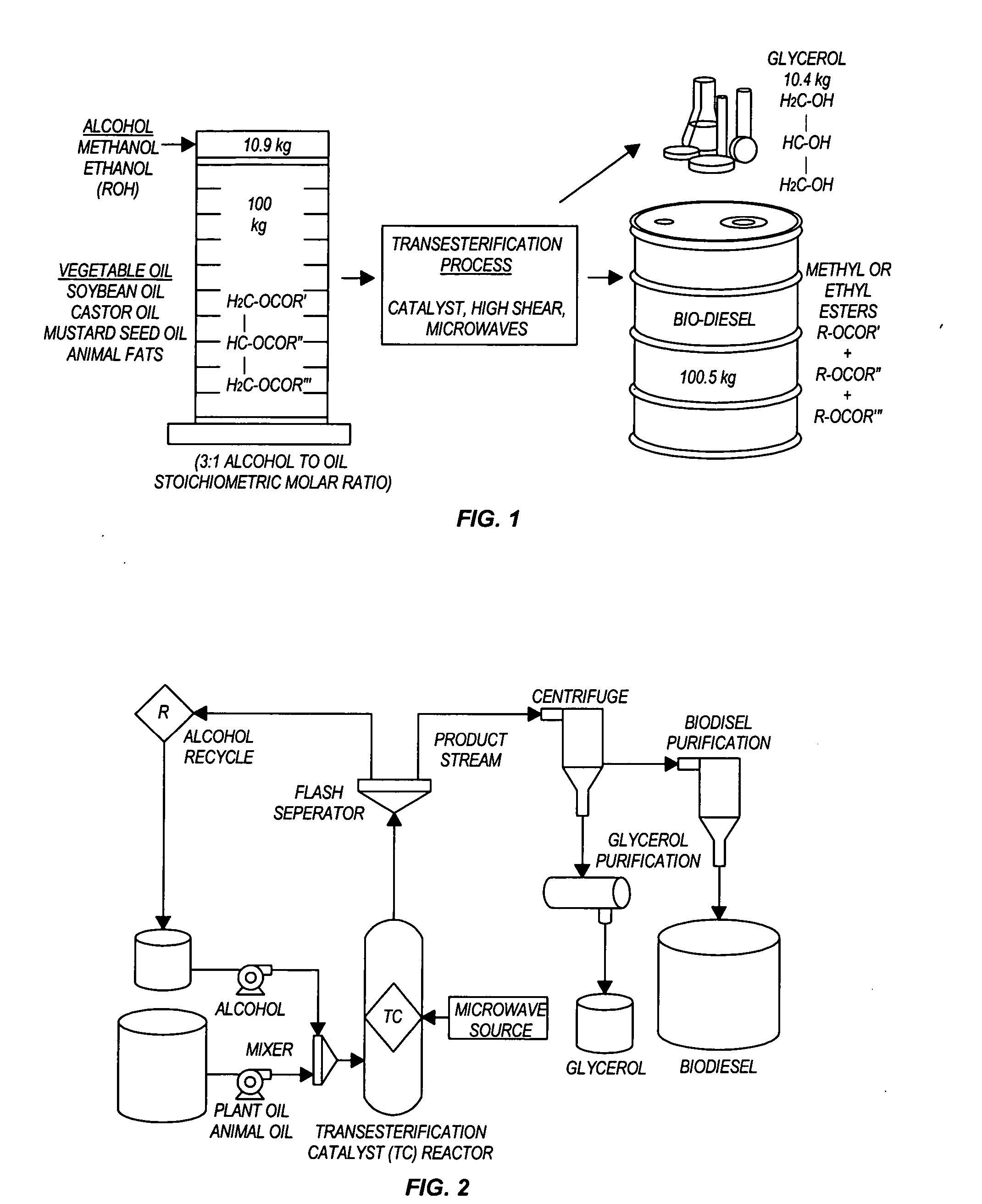
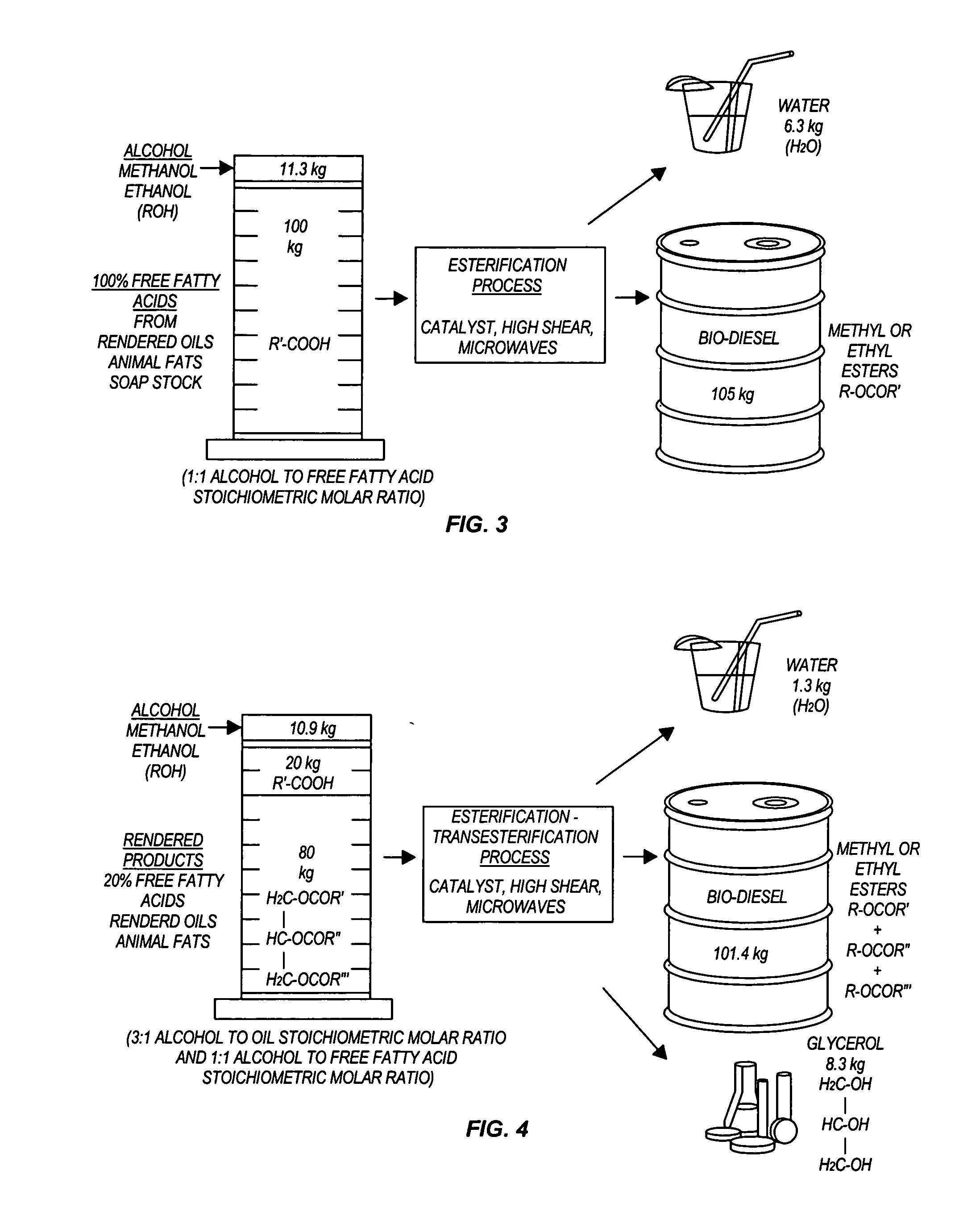
InactiveUS20050274065A1Fatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionMicrowaveTransesterification
Transesterification, esterification, and esterification-transesterification (both one-step and two-step) for producing biofuels. The process may be enhanced by one or more of the following: 1) applying microwave or RF energy; 2) passing reactants over a heterogeneous catalyst at sufficiently high velocity to achieve high shear conditions; 3) emulsifying reactants with a homogeneous catalyst; or 4) maintaining the reaction at a pressure at or above autogeneous pressure. Enhanced processes using one or more of these steps can result in higher process rates, higher conversion levels, or both.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
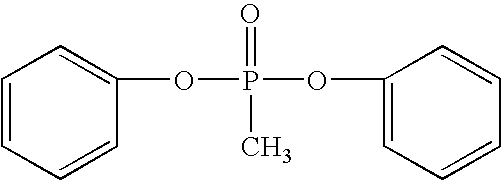
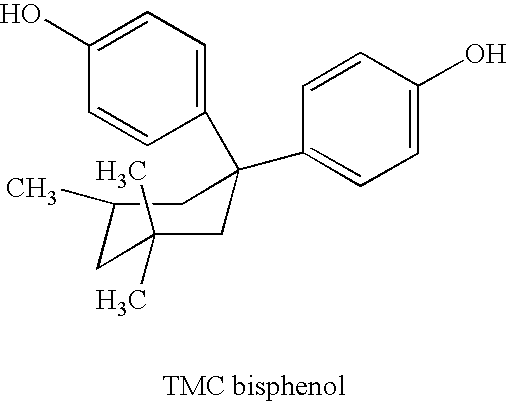
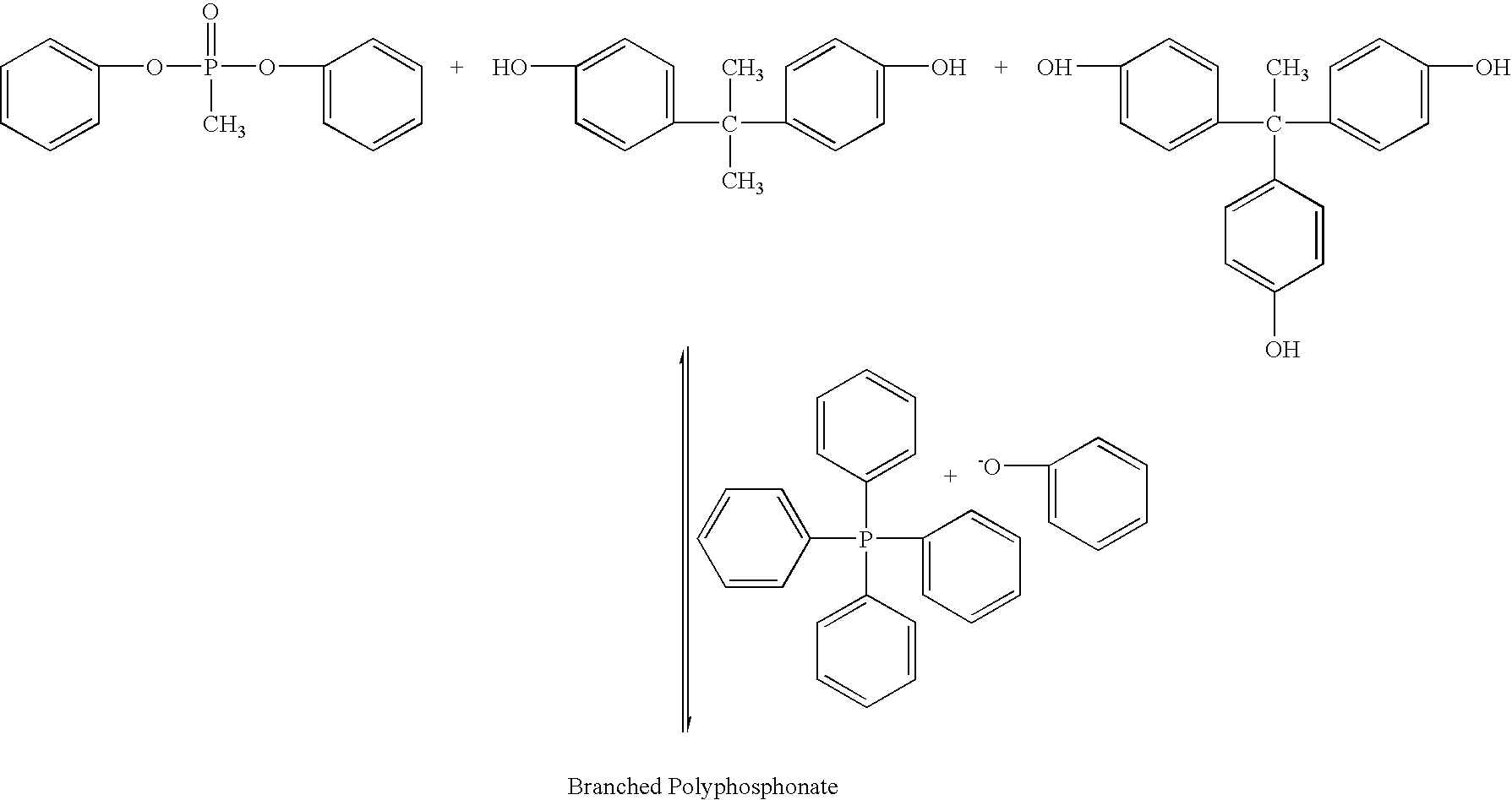
Branched polyphosphonates that exhibit an advantageous combination of properties, and methods related thereto
Disclosed are branched polyphosphonates produced via a superior transesterification process, and methods related thereto. These branched polyphosphonates exhibit a unique and advantageous combination of properties, such as outstanding fire resistance, improved heat stability, improved toughness, and superior processing characteristics. Also disclosed are polymer compositions that comprise these branched polyphosphonates and at least one other polymer, wherein the resulting polymer compositions exhibit flame retardant properties. Further disclosed are articles of manufacture produced from these polymers, such as fibers, films, coated substrates, moldings, foams, fiber-reinforced articles, or any combination thereof; these articles may be coated with a moisture barrier to enhance their moisture resistance properties.
Owner:FRX POLYMERS LLC
Production of biodiesel and other valuable chemicals from wastewater treatment plant sludges
ActiveUS20050112735A1Reduce the environmentPromote digestionBio-organic fraction processingByproduct vaporizationLipid formationSludge
A process for producing biodiesel has been invented by first extracting lipids from the sludges generated during primary and / or biological treatment of municipal, agricultural, and industrial wastewaters using primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments followed by the transesterification of the extracted lipids using transesterification conversion into alcohol-based esters. The resulting products from this process include biodiesel, glycerol, lipid-free proteins, various other useful chemicals and an aqueous-based substrate well suited for optimized digestion within subsequent biological digestion (either aerobic or anaerobic). The lipids extracted from the sludges containing high levels of microorganisms are phospholipids which can also be directly used as lecithin. The extraction of the lipids from the sludges will be performed using chemical extraction techniques with the transesterification of the extracted lipids accomplished using basic, acidic, and / or a combination of the two transesterification techniques.
Owner:MISSISSPPI STATE UNIV RES & TECH
Purification of glycerin
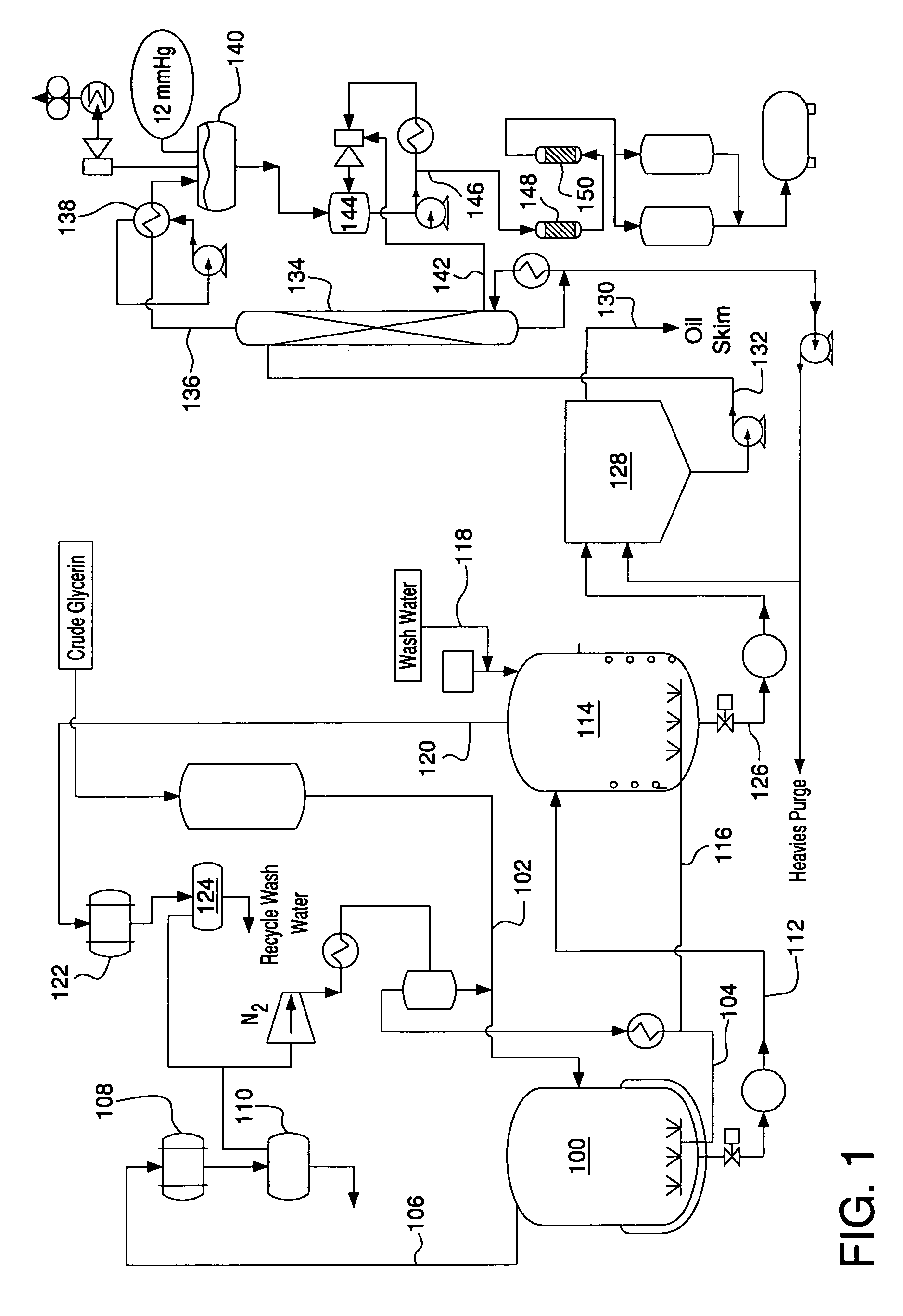
InactiveUS7126032B1Low costEfficient recyclingOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds purification/separationAlcoholWash water
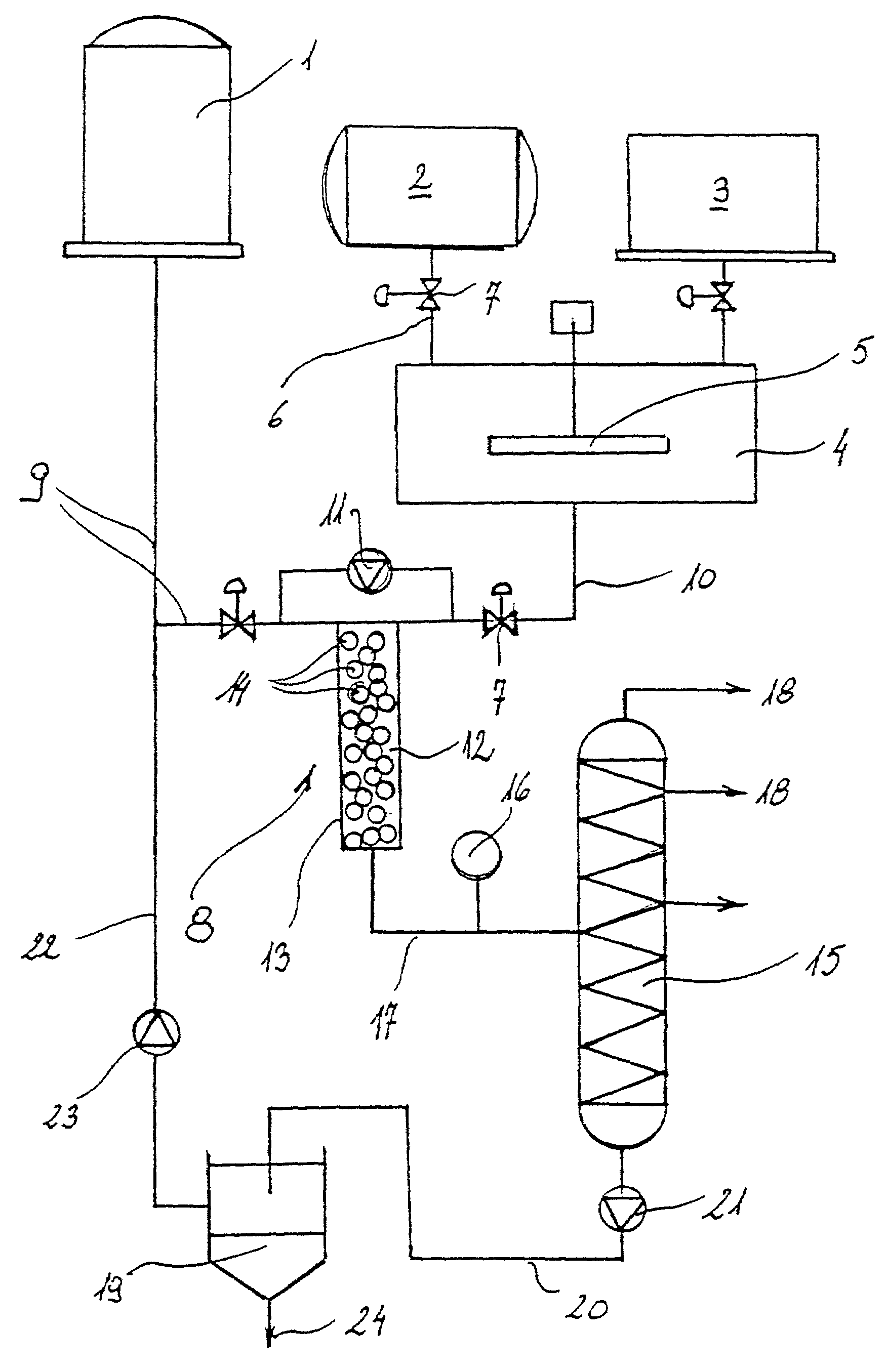
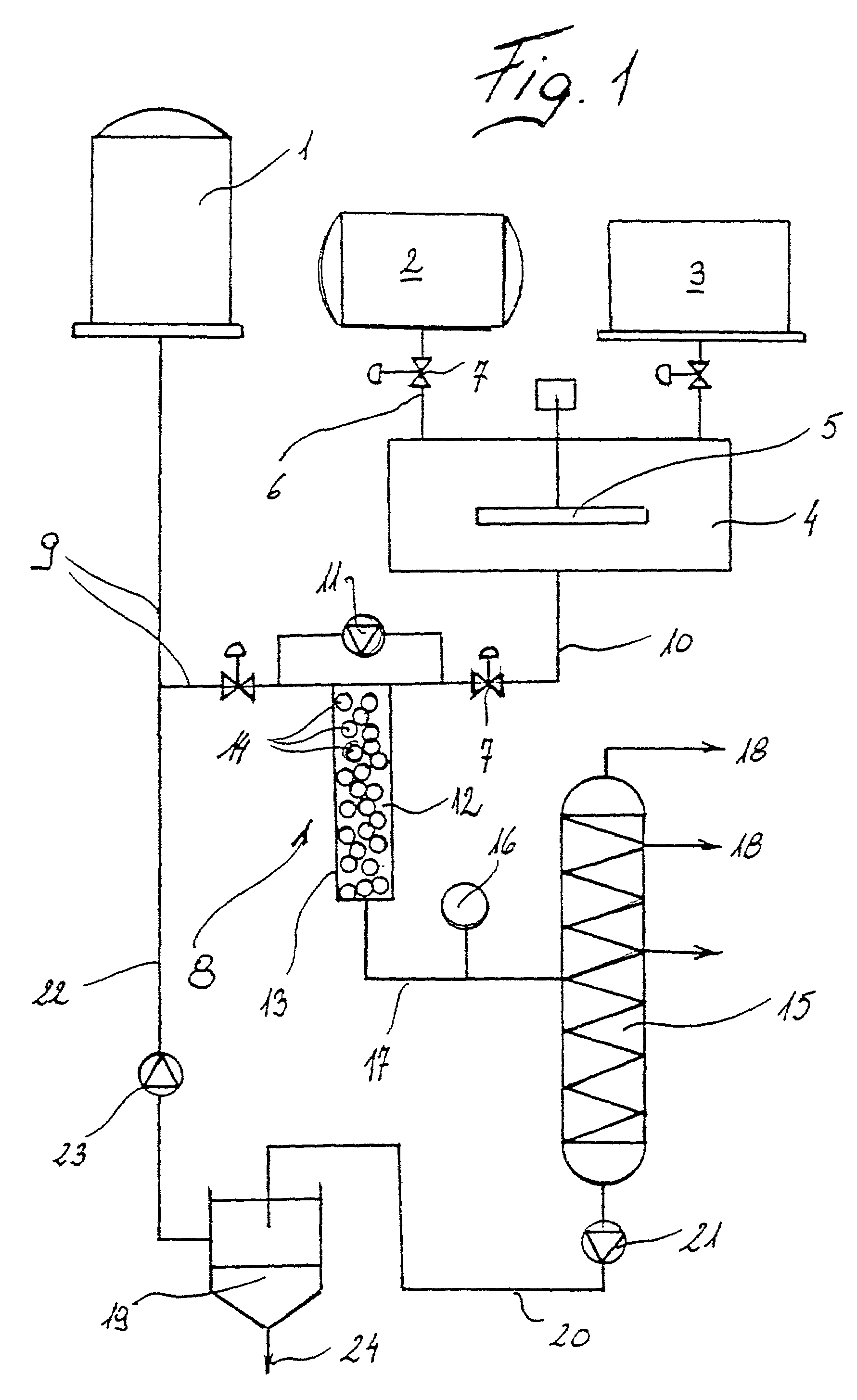
A process for purifying glycerin recovered as a byproduct of biodiesel production comprises heating a glycerin effluent stream containing a low molecular weight alcohol, water and fatty acid esters of the low molecular weight alcohol to cause transesterification of the fatty acid esters to glycerides and additional low molecular weight alcohol. The reaction mixture is sparged with nitrogen to help remove water and low molecular weight alcohol, which drives the transesterification reaction towards glyceride formation. A wash water stream may also be added to the recovered glycerin stream from biodiesel production. Either before or following the transesterification reaction, an oil layer can be separated from the recovered glycerin stream by reducing the pH of the stream to below 7. Following separation of the oil layer and transesterification the glycerin stream is flash distilled to separate glycerin from water, salts, and glycerides.
Owner:SUNOCO INC (R&M)
Method for producing biodiesel from an alga
InactiveUS20090298159A1Avoid Microbial ContaminationOrganic chemistryFatty acid esterificationMembrane lipid metabolismOrganism
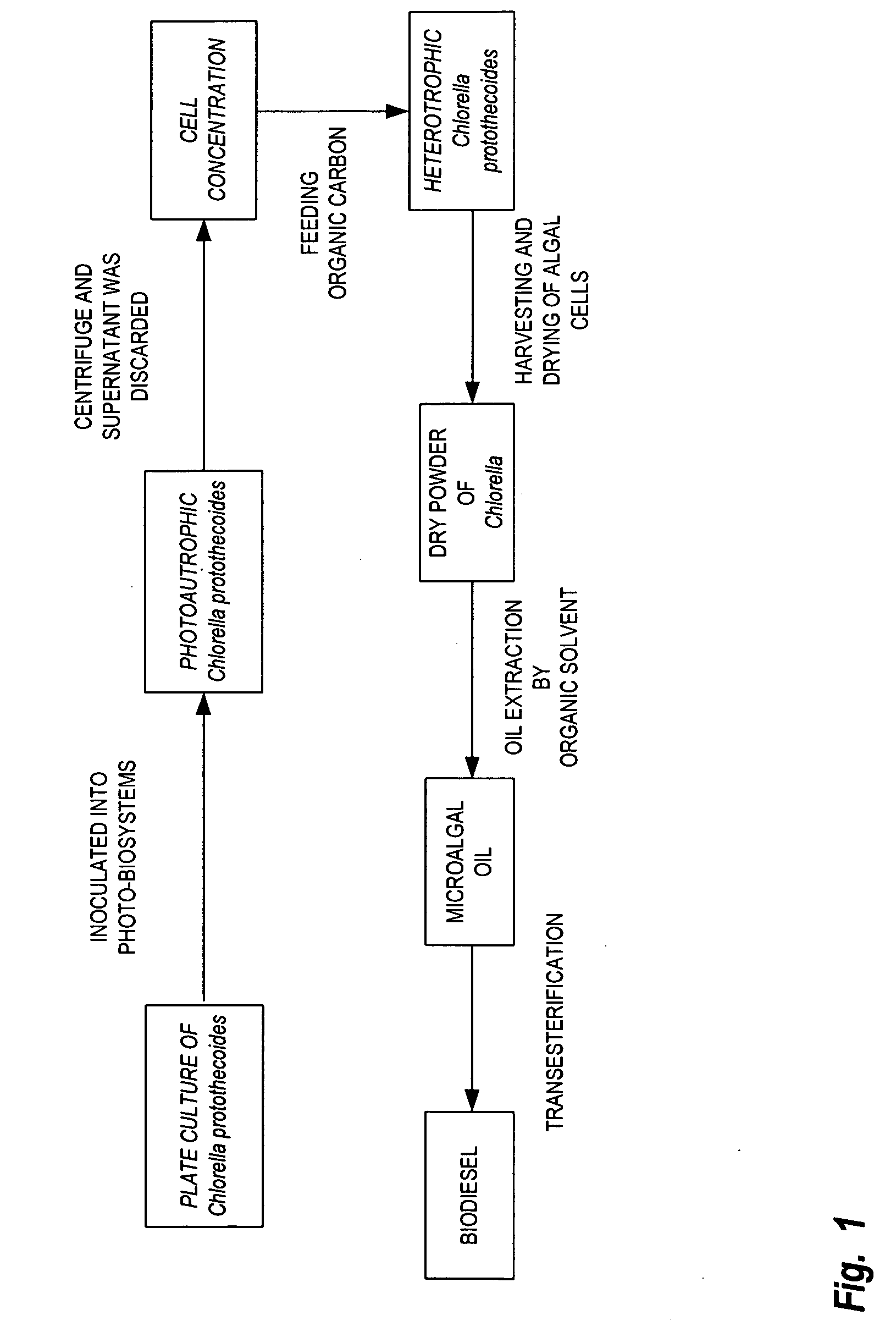
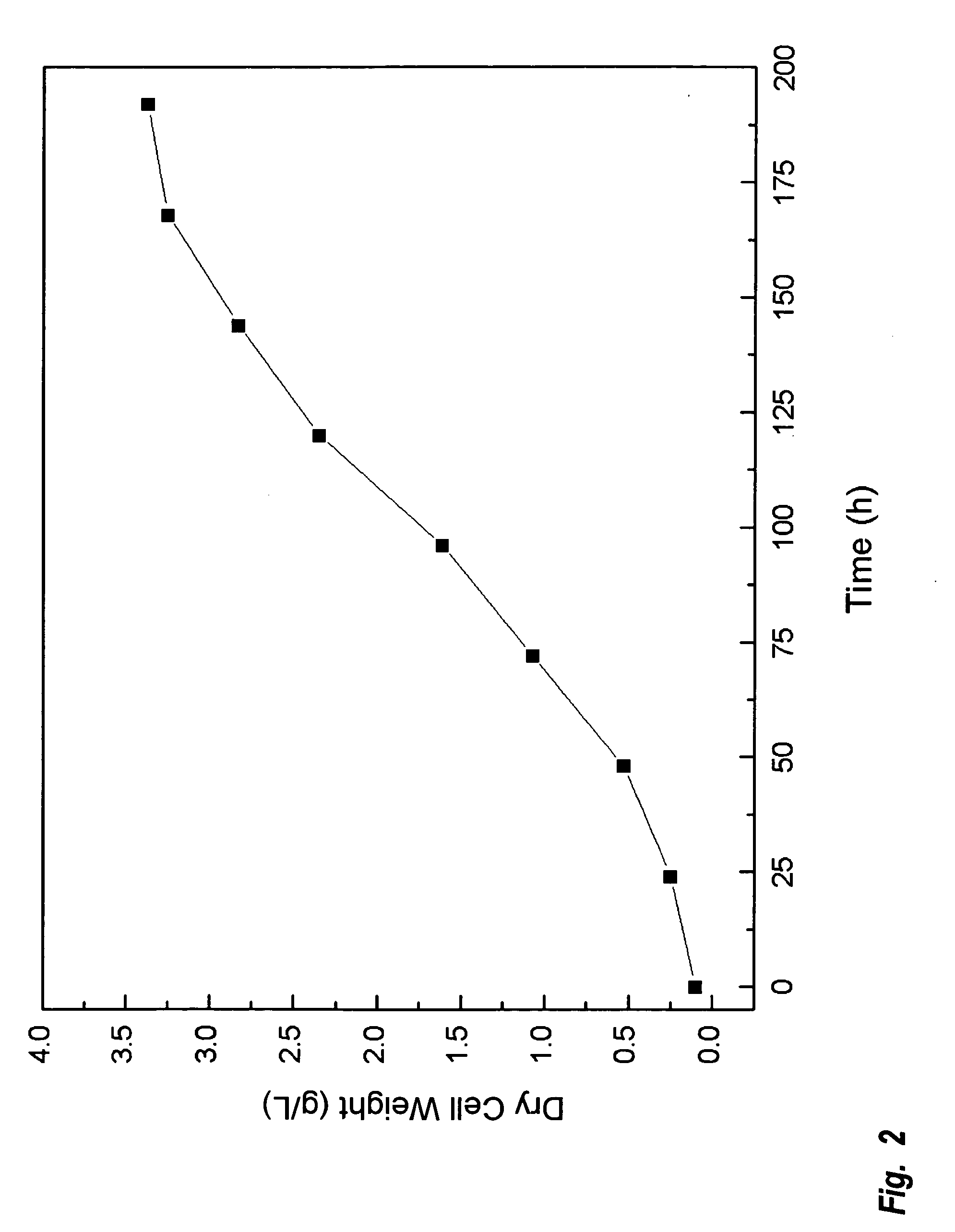
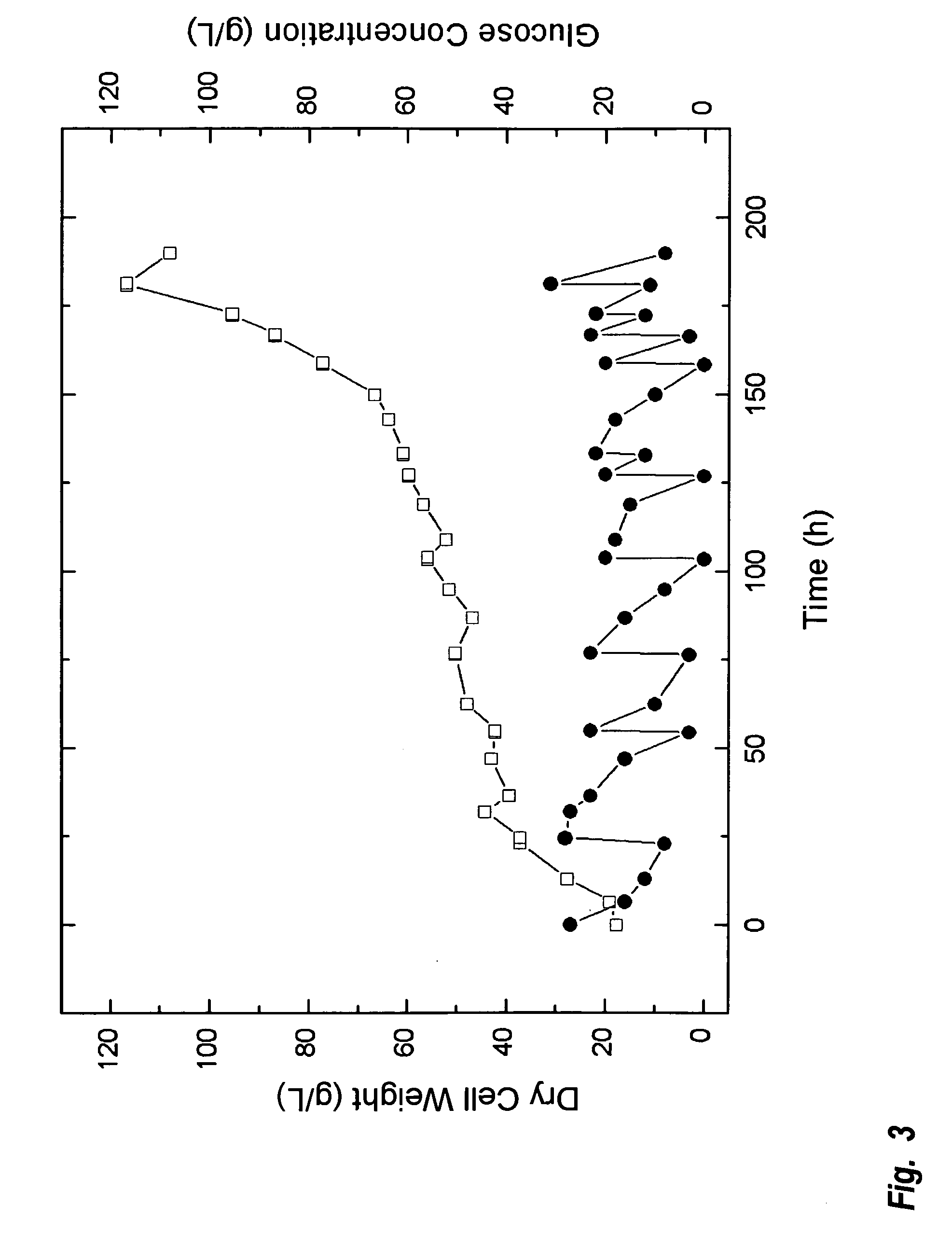
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a two-stage, autotrophic and heterotrophic cultivations of chlorella for biodiesel production. This method includes a sequence of procedures: cultivating photoautotrophic algae, concentrating cells and then transferring them to a fermentor for heterotrophic cultivation. During the photoautotrophic cultivation stage, the culture is exposed to a light source, such as sunlight with carbon dioxide obtained from a carbon dioxide source or from air. antibacterial agents may be added to prevent contamination from undesired microorganisms. Organic carbons are added during heterotrophic cultivation stage. Fermentation conditions are optimized for maximizing lipid synthesis. High biomass is achieved to about 108 g / L with lipid content reaching about 52% of dry cell weight. After cultivation, biodiesel is made through extraction and transesterification of algae lipids.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester and equipment for realizing the same
InactiveUS7045100B2Avoid disadvantagesRational productionPressurized chemical processFatty acid esterificationAlcoholTransesterification
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester, including compounding saturated and unsaturated higher fatty substances from at least one of vegetable and animal with an alkaline solution dissolved in alcohol to form a mixture. The method also includes emulsifying the mixture to reach a chemical balance state in a reaction section, wherein fats are transesterified into fatty acid methyl ester, wherein border surfaces of the mixture are enlarged by dynamic turbulence in the reaction section and the transesterification is performed under pressure, and wherein the pressure is reduced during transesterification. The method further includes after reaching a chemical balance state, separating residues from the fatty acid methyl ester in a phase separation section. Apparatus for producing fatty acid methyl ester.
Owner:AMERICAN RENEWABLE FUELS
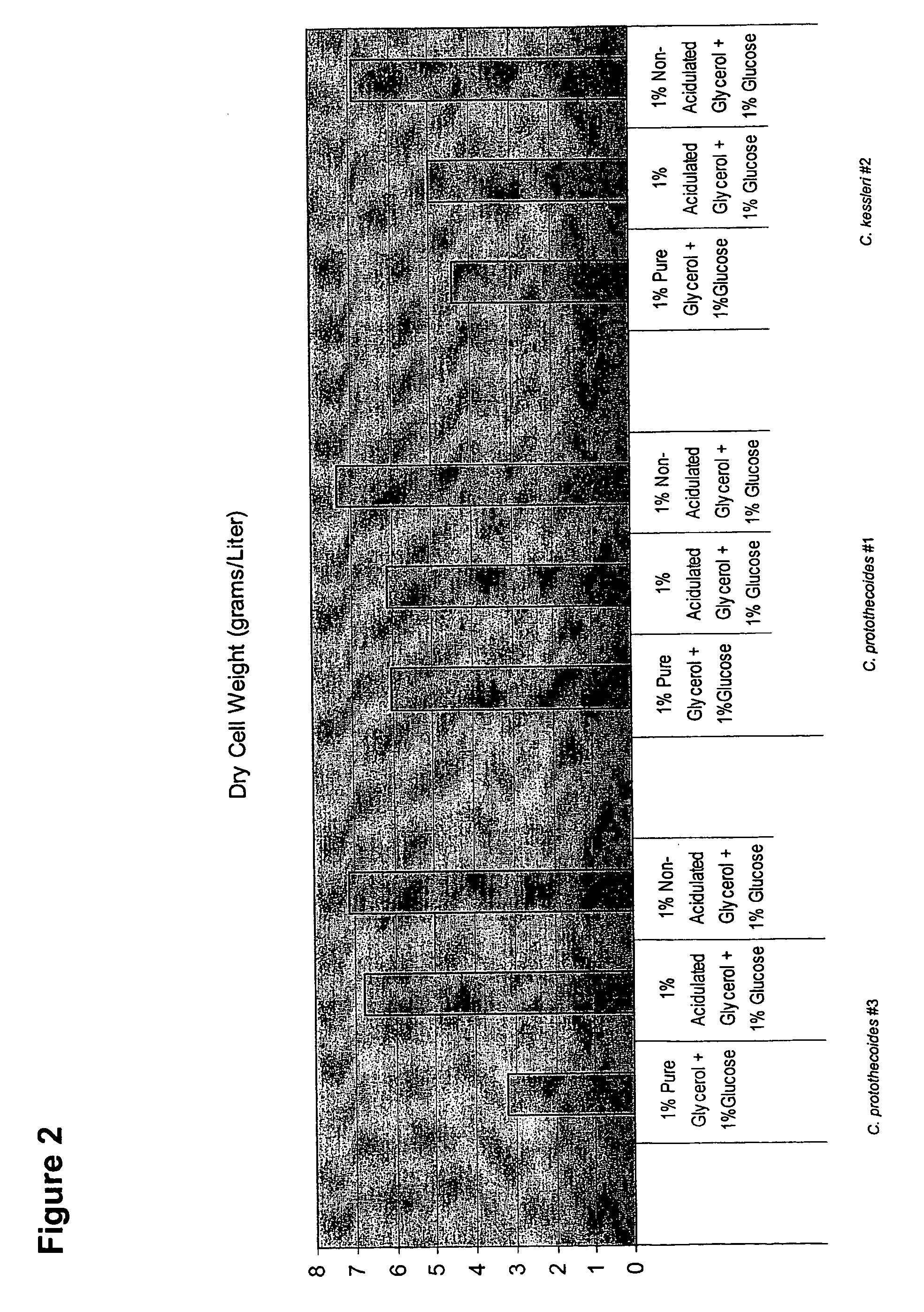
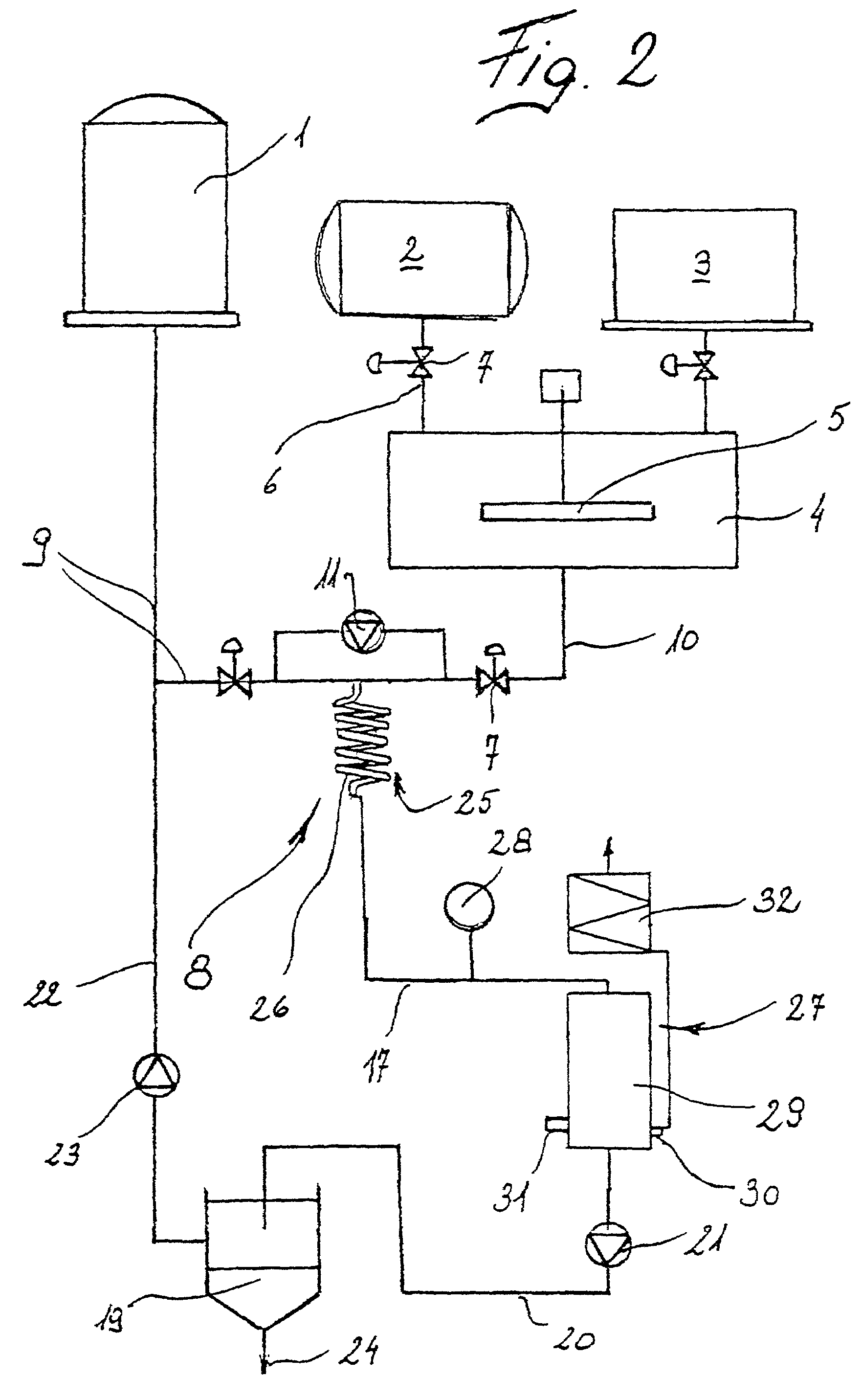
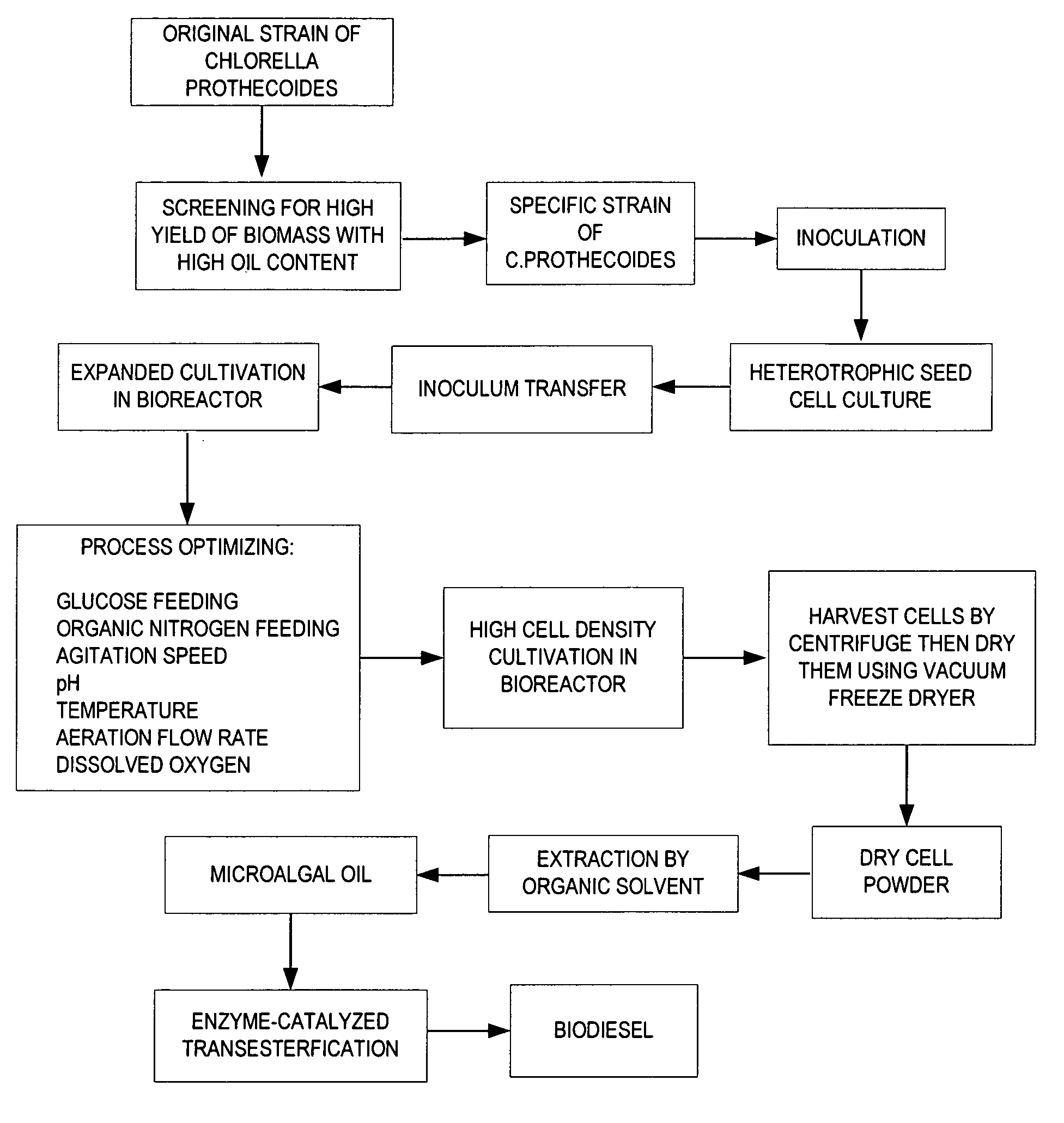
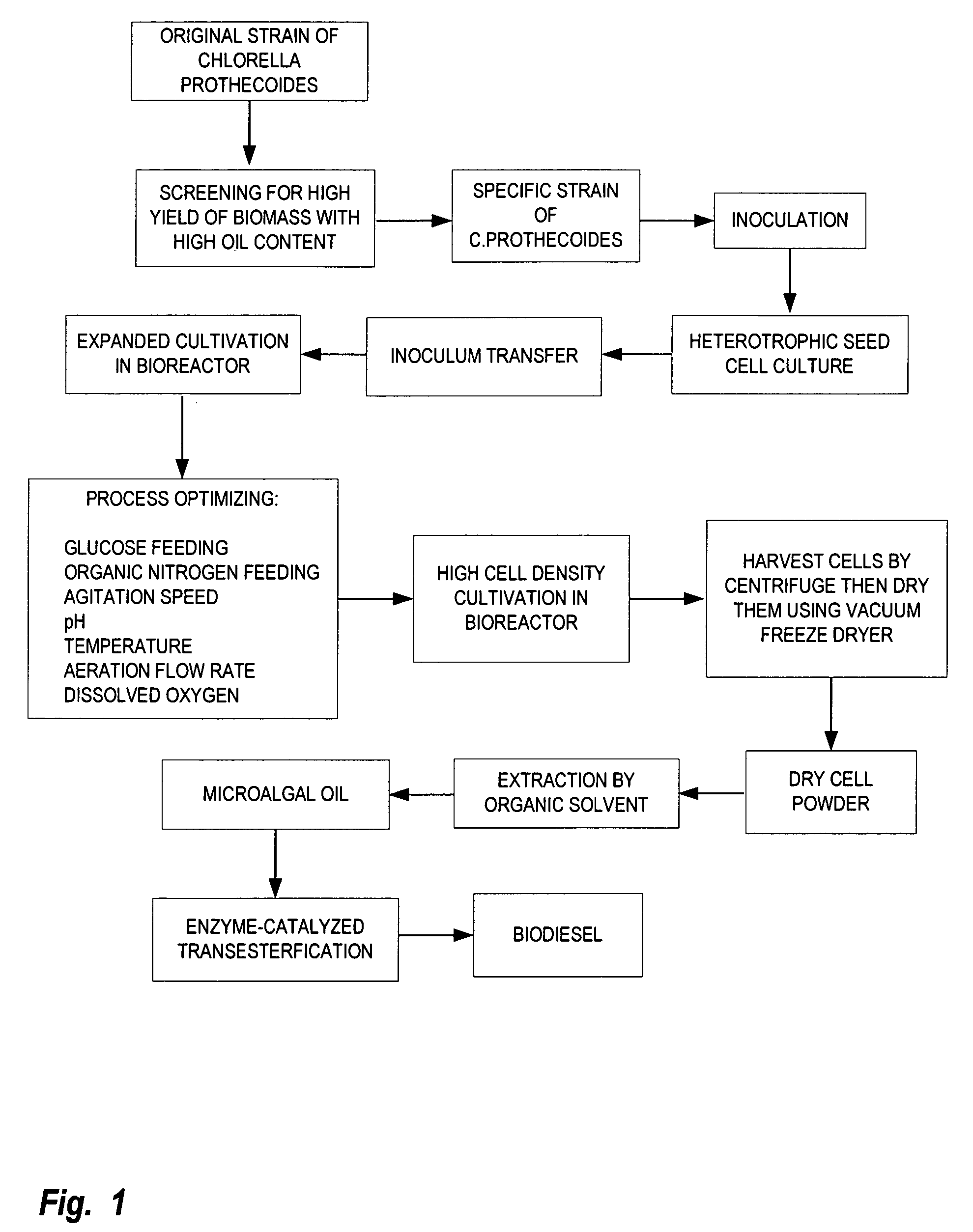
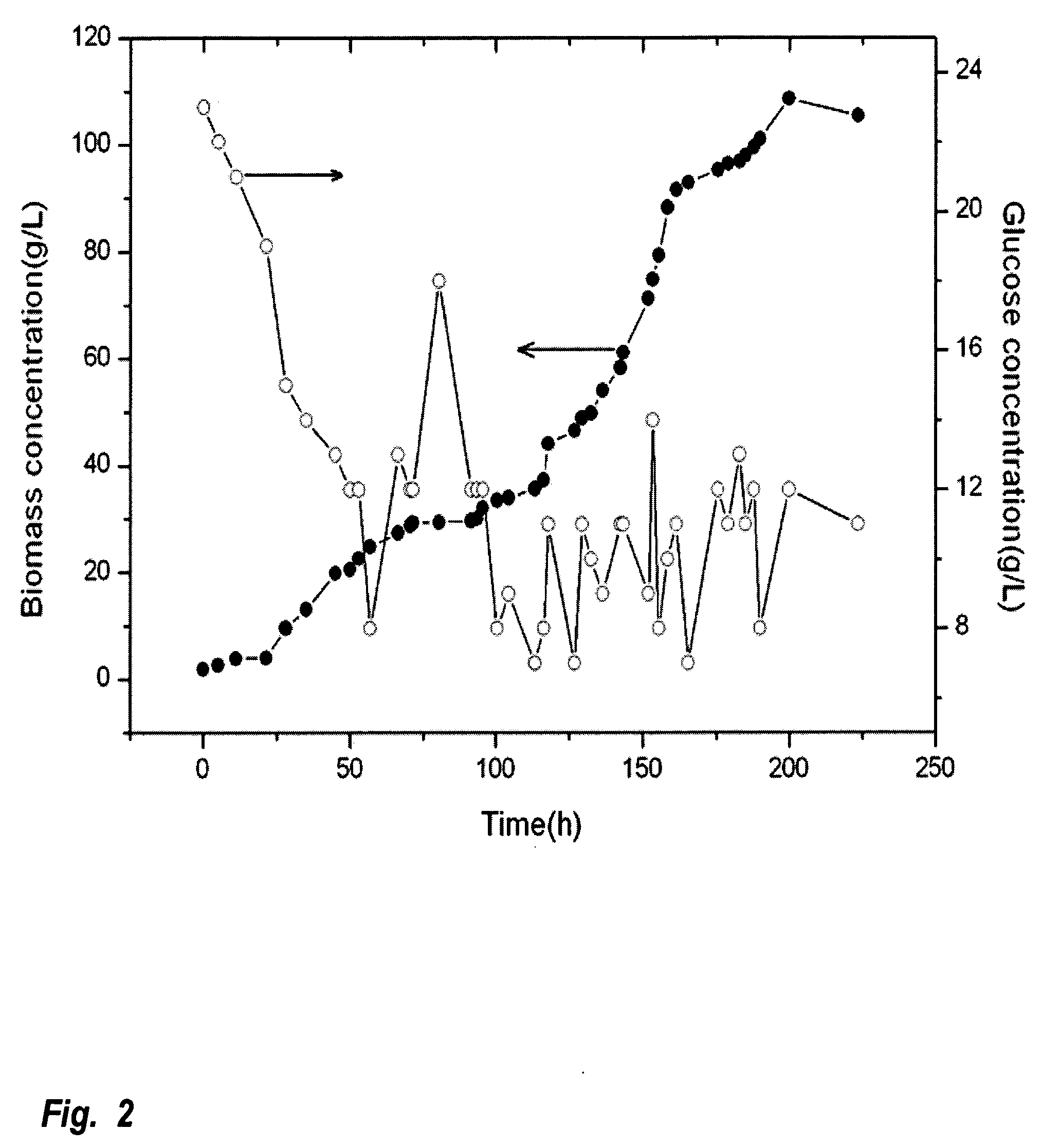
Method for producing biodiesel using high-cell-density cultivation of microalga Chlorella protothecoides in bioreactor
InactiveUS20090211150A1Reduce acidityAdjust pHFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeHigh cellHigh density
A method is provided to produce biodiesel from algae using a strain of microalga chlorella protothecoids, by screening a specific strain with characteristics of high yield of biomass and high oil content, cultivating the screened strain for high-cell-density growth for up to 108 grams of dry cell weight per liter of the suspension in a bioreactor using solutions containing carbohydrates as feed, harvesting and drying the high density cultivated algal cells to extract oil from the dried algal cells, and producing the biodiesel by reaction of catalyzed transesterification using the extracted oil as feedstock.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
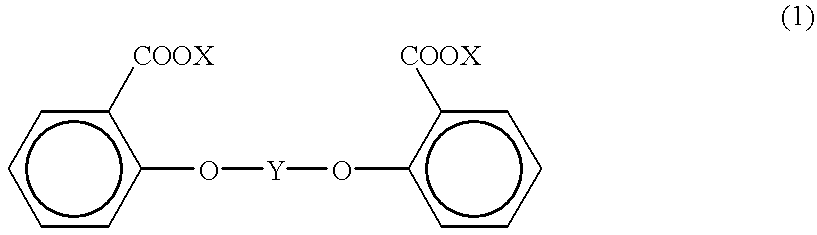
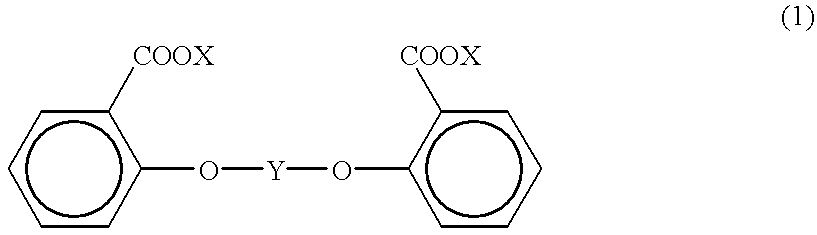
Process for producing aromatic polycarbonate
An aromatic polycarbonate and an active-hydrogen compound are subjected to the transesterification reaction in the presence of a transesterification catalyst under a reduced pressure condition followed by reaction with a salicylic acid ester derivative expressed by the following chemical formula (1),{wherein X is methyl or ethyl, and Y is a carbonyl group or a divalent functional group expressed by the following formula (2),(where Z is an alkylene group having a carbon number of 1 to 30, an arylene group having a carbon number of 6 to 30 or an aralkylene group having a carbon number of 7 to 30)}.An aromatic polycarbonate having a high molecular weight can be produced by this process.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Process for producing alkyl esters from a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol
InactiveUS6878837B2High purityImpact on overall process costFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationAluminateTransesterification
Alkyl esters of fatty acids, and high purity glycerin, are produced using a process comprising a set of transesterification reactions between a vegetable or animal oil and an aliphatic monoalcohol employing a heterogeneous catalyst, for example based on zinc aluminate, the water content in the reaction medium being controlled to a value that is below a given limiting value.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
High molecular weight copolyesters from macrocyclic oligoesters and cyclic esters
InactiveUS6420048B1Synthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingTransesterificationCopolyester
High molecular weight copolyesters have been prepared from macrocyclic oligoesters and cyclic esters in the presence of a transesterification catalyst. The invention generally features a method of making a copolyester, a method of making a block copolymer of copolyester, and a copolyester prepared from macrocyclic oligoesters and cyclic esters.
Owner:CYCLICS CORP
Production of biodiesel from combination of corn (maize) and other feed stocks
InactiveUS20070099278A1Increase Biodiesel production outputStable year round productionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationProcess systemsSodium Bentonite
A method and system to produce biodiesel from a combination of corn (maize) and other agro feedstock may be simarouba, mahua, rice, pongamia etc. Germ is separated (either by wet process or dry process) from corn, crude corn oil extracted from germ and corn starch milk / slurry is heated and cooked in jet cooker to about 105 degree Celsius, enzymes added to convert starch into fermentable sugars in liquification and saccharification process and rapidly cooled down to about 30 degree Celsius. Simarouba fruits syrup, mahua syrup is mixed with corn starch milk (after saccharification). When yeast is added the fermentation takes place for about 72 hours. Thereafter the fermented wash is distilled to produce ethanol. Water consumed in dry process is very less compared to traditional wet process system. Corn oil and mixture of other oils is fed into transesterification (reaction) vessels where ethanol with catalyst, usually sodium hydroxide is added and reaction takes place for about a period of 2-8 hours. Crude biodiesel and crude glycerin as by-products is produced. Excess ethanol removed by distillation process. Crude biodiesel washed with warm water to remove residual soaps or unused catalyst, dried and biodiesel stored for commercial use. Oil extracted from spent bleach mud (used sodium bentonite), a waste product of edible oil refineries may also be utilized for economical production of biodiesel in combination of corn oil and ethanol.
Owner:AARE PALANISWAMY RAMASWAMY
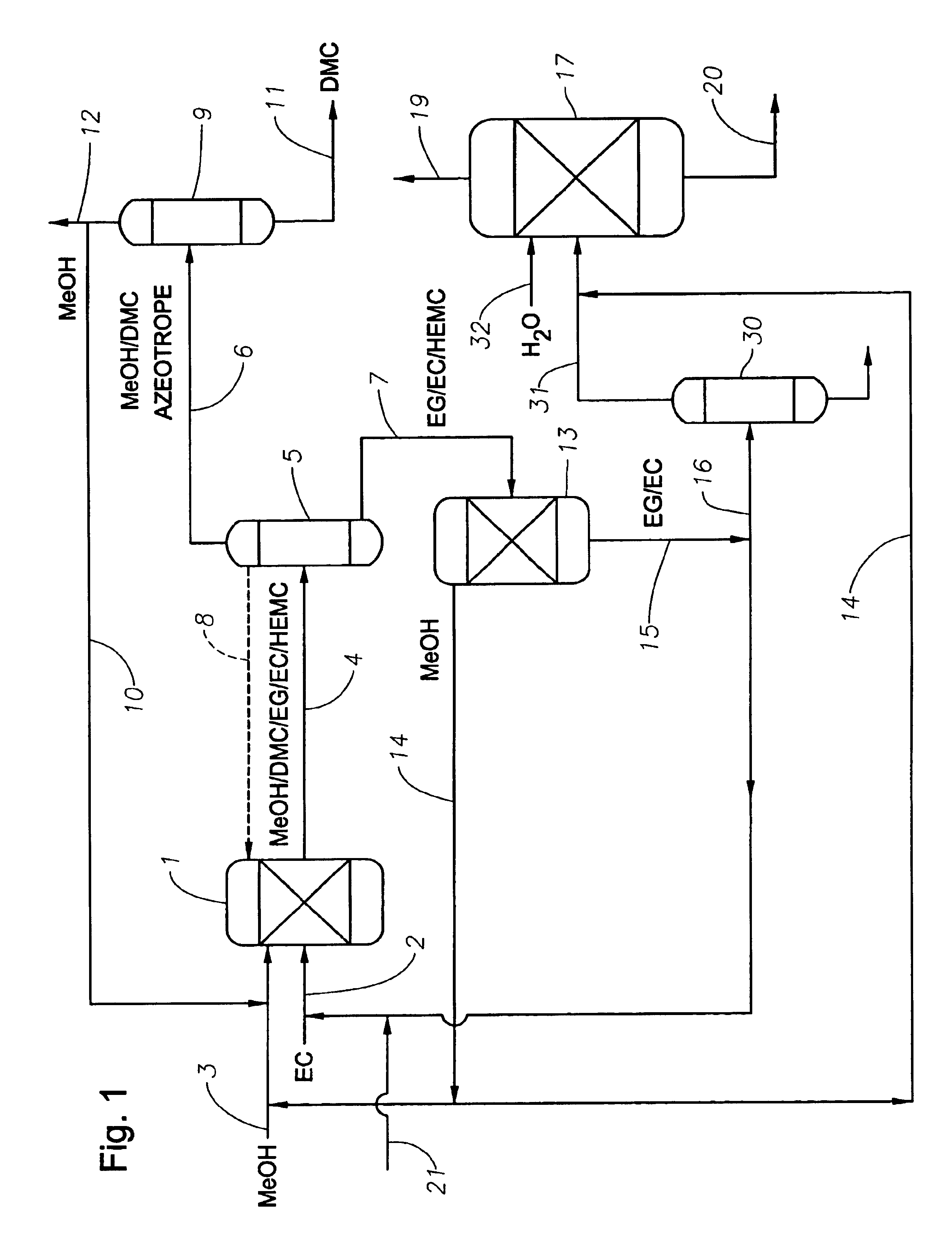
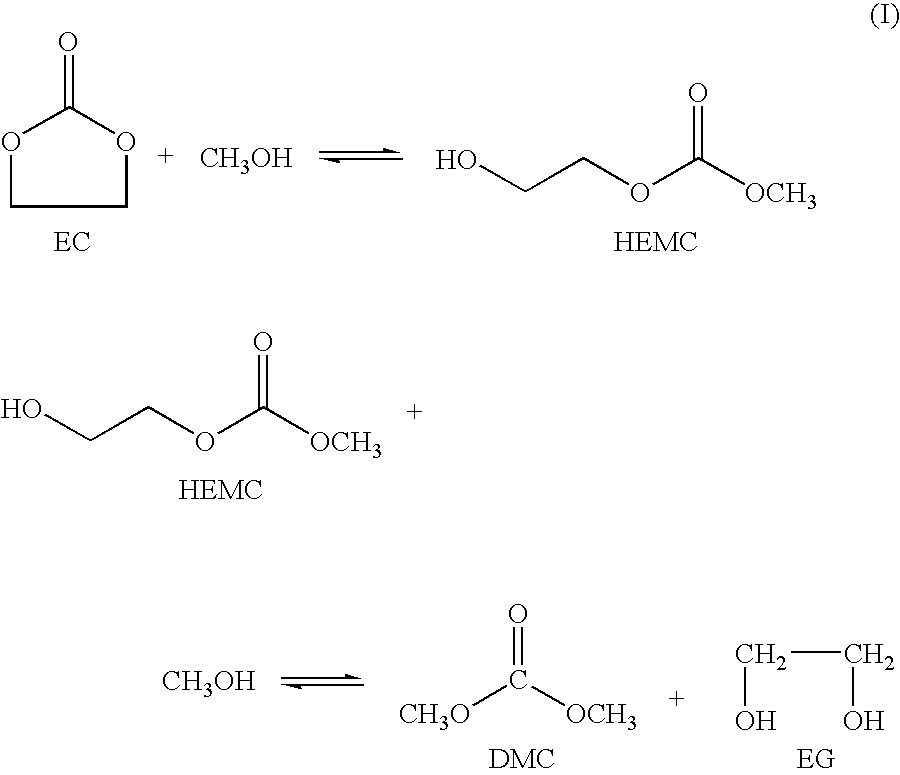
Process for the production of unsymmetric and/or symmetric dialkyl carbonates and diols
InactiveUS6930195B2High yieldOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholTransesterification
A process for the production of a dialkyl carbonate and a diol, such as dimethyl carbonate and ethylene glycol, by reacting a feed containing a cyclic carbonate, a hydroxy alkyl carbonate and an aliphatic monohydric alcohol in the presence of a transesterification catalyst is described. In another aspect, a process is described which is particularly useful for producing unsymmetric dialkyl carbonates, such as ethyl methyl carbonate.
Owner:BADGE LICENSING LLC
Method of producing fatty acid lower alkylester from fat and oil
InactiveUS6090959AImprove reaction efficiencySimplify eliminate needFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningAlcoholTransesterification
In a method of producing a fatty acid lower alkylester according to the invention, a fat & oil and a lower alcohol are caused to react with each other in the presence of a catalyst, in which triglyceride contained in the fat & oil undergoes a transesterification. The catalyst to be used in the reaction is a solid basic catalyst consisting essentially of a potassium compound and iron oxide, of a calcium compound and iron oxide, or of a potassium compound and zirconium oxide. It is possible to produce the fatty acid lower alkylester at a high reaction efficiency by this method as well as to simplify or eliminate the need of catalyst separation and recovery processes.
Owner:GREENTECH SOLUTION
Process for the preparation of fatty acid methyl ester from triglyceride oil by transesterification
InactiveUS20060080891A1Produced cost-effectivelyReduce water contentFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationUnit operation
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of biodiesel from triglyceride oils through transesterification, particularly the fatty acid methyl ester of oil mechanically expelled from whole seeds of Jatropha curcas, a plant with potential for cultivation on wastelands in India and other countries, all unit operations being carried out at ambient temperature.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Catalytic cracking process for the production of diesel from vegetable oils
The present invention relates to a thermo catalytic process to produce diesel oil from vegetable oils, in refineries which have two or more Catalytic Cracking (FCC) reactors. At least one reactor processes heavy petroleum or residue in conventional operation conditions while at least one reactor processes vegetable oils in proper operation conditions to produce diesel oil. This process employs the same catalyst employed in the FCC process, which processes conventional feedstocks simultaneously. This process transforms high heat content raw materials into fuel hydrocarbons. It may improve efficiency for the obtainment of highly pure products and may not yield glycerin, one by-product of the transesterification process. The diesel oil produced by said process may have superior qualities and / or a cetane number higher than 40. Once cracking conditions occur at lower temperatures, it may form a less oxidized product, which is consequently purer than those obtained by existent technology.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Polycarbonate diol and producing method thereof, and polyurethane and active energy ray-curable polymer composition both formed using same
ActiveUS20130109804A1Improves stain resistanceHigh hardnessOrganic chemistryPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesMethacrylateElastomer
A novel polycarbonate diol is useful as a raw material for producing a polycarbonate diol-based polyurethane with a high degree of hardness, superior abrasion resistance, and superior hydrophilicity. The polyurethane is useful in paints, coating agents, synthetic leathers, artificial leathers, and highly-functional elastomers, or the like. The polycarbonate diol is also useful for producing an active-energy radiation curable polymer composition giving a cured film having superior contamination resistance and high degree of hardness. The curable polymer composition contains a urethane(meth)acrylate oligomer obtained from the polycarbonate diol. The polycarbonate diol is obtained, for example, by reacting two specific types of diols with diester carbonate in the presence of a transesterification catalyst. The catalyst has a metal of Group 1 or 2 on the periodic table. A metal content of the transesterification catalyst is 100 weight ppm or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Apparatus and method for the production of fatty acid alkyl ester
InactiveUS20050027137A1Eliminate operationShort possible reaction timeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAlcoholVegetable oil
An apparatus and method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters from fatty acids derived from vegetable oils and animal fats with an alkaline solution dissolved in stoichiometric or near stoichiometric levels of a monoalkyl alcohol to form a mixture. The method further comprises emulsifying the mixture as a means to reach a completed chemical reaction state in a reactor section, wherein the oils or fats are transesterified into fatty acid alkyl esters. The transesterification occurs when the natural boundary surfaces of the immiscible mixture are enlarged by ultrasonic cavitation in the reaction section and the transesterification is performed at, or near atmospheric pressure. The method finally includes, after reaching the chemical reaction state, separating residues from the fatty acid alkyl ester in a gravitational phase separation section.
Owner:HOOKER JEFFREY D
A process for preparing a polymer product having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone to be used in bottle, film or fibre applications
A process for preparing a polymer having a 2,5-furandicarboxylate moiety within the polymer backbone, and having a number average molecular weight of at least 25,000, includes a transesterification step, a polycondensation step, a drying and / or crystallizing step, and a step where the polymer is subjected to post condensation conditions, and to a polyester-containing bottle or film or fibre-containing woven or non-woven object made from melt-processing poly(ethylene-2,5-furandicarboxylate), where the poly(ethylene-2,5-furandicarboxylate) is obtainable by the process of the invention.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
Stabilized aromatic polycarbonate
The relative intensity of fluorescent light of a melt-polycondensed aromatic polycarbonate produced by the transesterification process (melt polymerization process) of an aromatic dihydroxy compound and a carbonic acid diester in the presence of a catalyst comprising a basic nitrogen compound and / or a basic phosphorus compound in combination with an alkali metal compound is suppressed to 4.0x10-3 or below at a wavelength of 465 nm based on a standard substance in a fluorescent light spectrum obtained by the excitation wavelength of 320 nm. An aromatic polycarbonate having good color stability, especially good stability to the deterioration of the chip color during storage of the chip in air at room temperature can be produced by the present invention.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
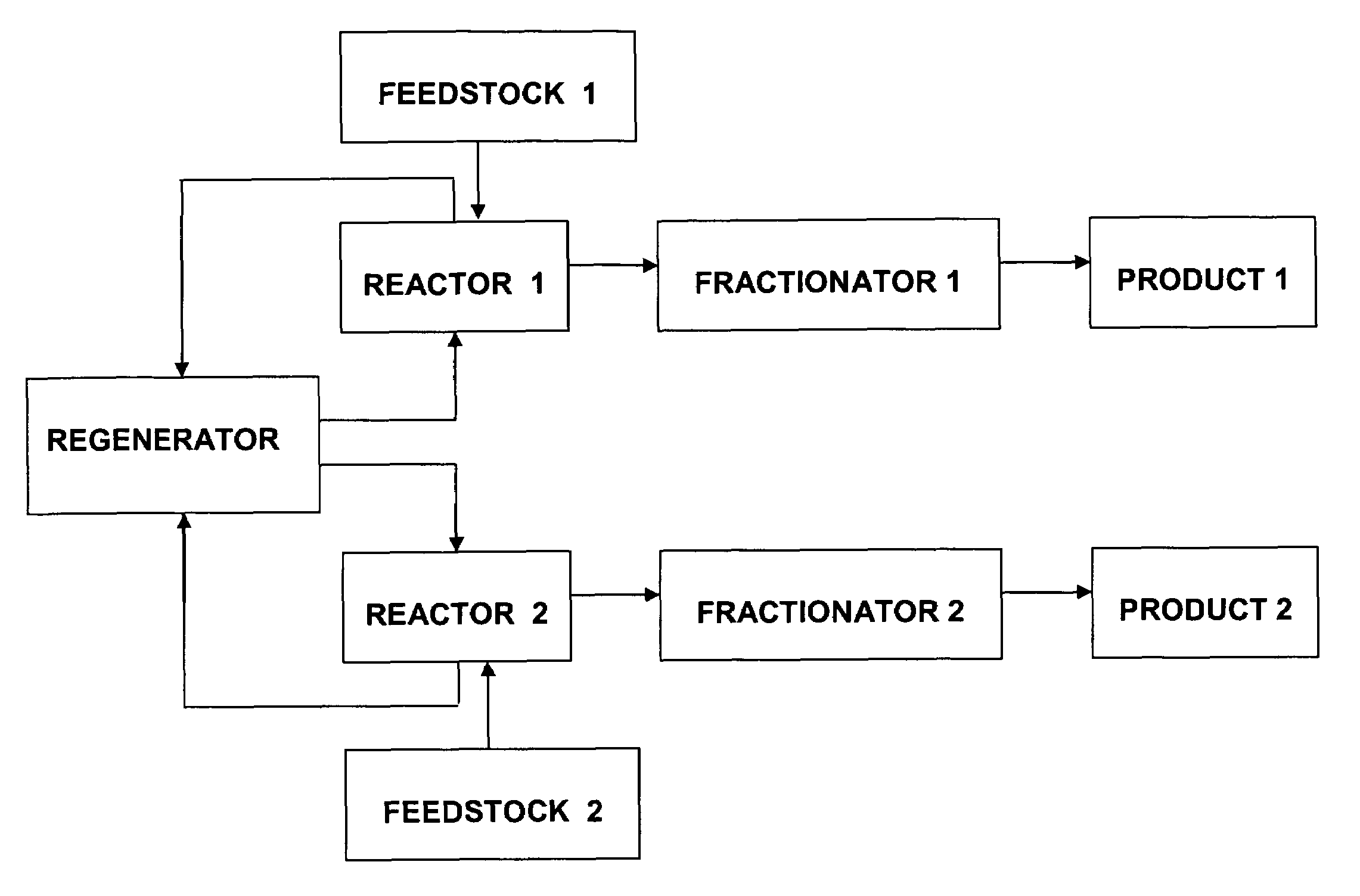
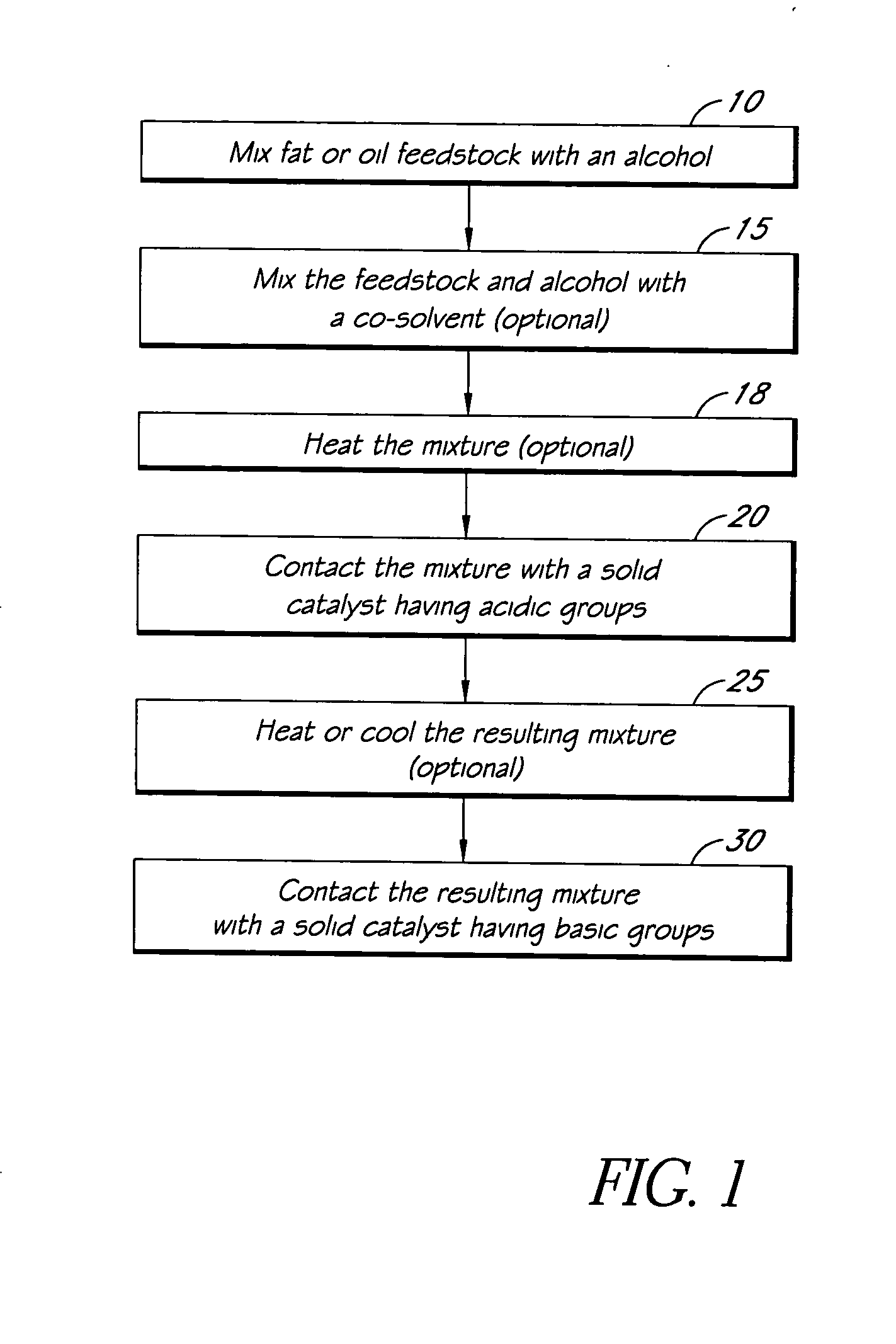
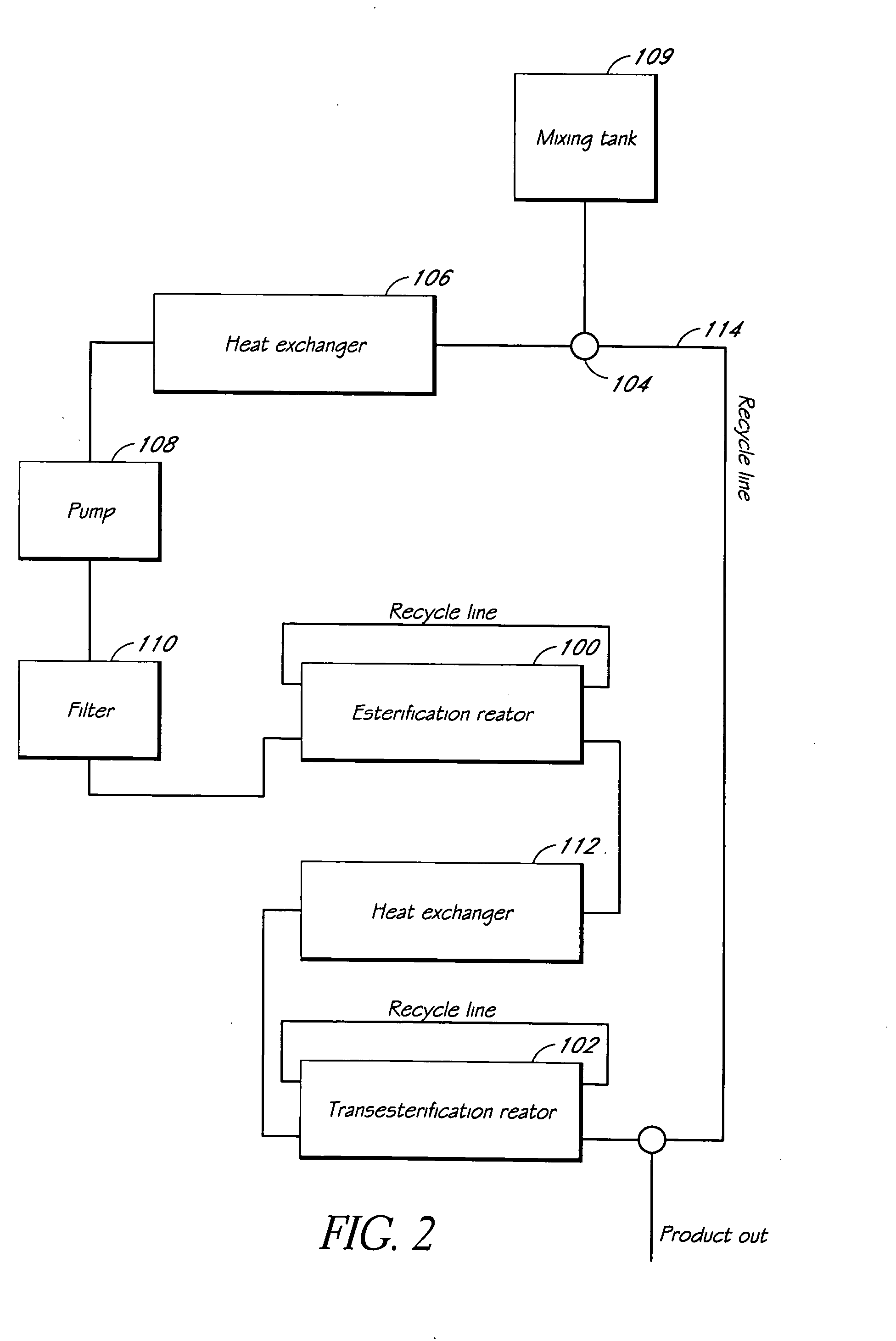
Systems and methods for esterification and transesterification of fats and oils
InactiveUS20060293533A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationAlcoholTransesterification
Esterification and transesterification of fats and oils is conducted using one or more heterogeneous solid catalysts in the presence of an alcohol and a cosolvent. In one example, esterification of free fatty acids in fats and oils feedstock is conducted by contacting the feedstock with a solid catalyst having acidic groups. Transesterification of triglycerides in the feedstock is conducted by contacting the feedstock with a solid catalyst having basic groups. Single train continuous plant designs are described for near complete conversion of fats and oils by sequentially contacting the feedstock with heterogeneous acidic solid catalyst and basic solid catalyst.
Owner:BIOSPHERE ENVIRONMENTAL ENERGY
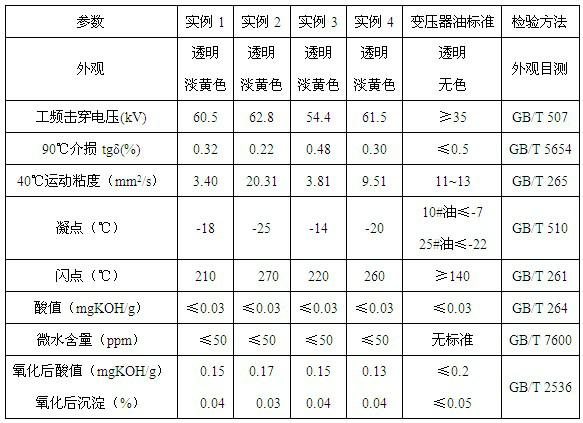
Vegetable insulating oil, and preparation method of vegetable insulating oil
InactiveCN102682869AImprove performanceReduce the temperatureLiquid organic insulatorsBase-materialsVegetable oilAnti oxidant
The invention relates to vegetable insulating oil based on vegetable oil, and a preparation method of the vegetable insulating oil. The insulating oil is prepared by the steps of using refined vegetable oil as raw material, carrying out ester exchange reaction on low-molecular alcohol, refining and washing after the reaction, rinsing, distilling under reduced pressure in order to remove water and alcohol, de-coloring, de-acidifying, filtering, de-watering deeply, finally adding antioxidant and pour point depressant. The insulating oil prepared by the method has the characteristics of high flashing point, low viscosity, low pour point, low acidity, low brackish water content, excellent dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and high breakdown voltage and has good physical and chemical performance and electrical performance.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Epoxy Acid Thermoset Resins and Composites that Can Be Hot-Fashioned and Recycled
Resins and thermoset composites comprising them, these materials being able to be hot-fashioned. These compositions resulting from placing at least one thermosetting resin precursor, this thermosetting resin precursor comprising hydroxyl functions and / or epoxy groups, and optionally ester functions, in contact with at least one hardener chosen from carboxylic acids, in the presence of at least one transesterification catalyst whose total molar amount is between 5% and 25% of the total molar amount of hydroxyl and epoxy contained in the thermosetting resin precursor. Process for manufacturing these materials, process for transforming and process for recycling these materials. New solid forms of resins and of thermoset composites that may be used in the implementation of these processes.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Process for branching thermoplastic linear polycarbonate resins
Linear polyesters are branched by transesterification with resins having the formula: wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Methods of using modified natural products as dewatering aids for fine particles
InactiveUS6375853B1Reduce moistureHigh degreeDrying solid materials without heatSolid fuelsNatural productTransesterification
Naturally occurring lipids of vegetable and animal origin are broken into smaller molecules, and used as dewatering aids. The process of breaking the molecules include transesterification, interesterification, and saponification followed by acidulation. The modified lipid molecules can adsorb on the surface of the particles to be dewatered and greatly enhance their hydrophobicity, which will help increase the rate of dewatering and hence reduce cake moisture. The modified lipids are more effective dewatering aids than the naturally occurring unmodified lipids, possibly because they can more readily form close-packed monolayers of hydrophobes on the surface of the particles.
Owner:YOON ROE HOAN
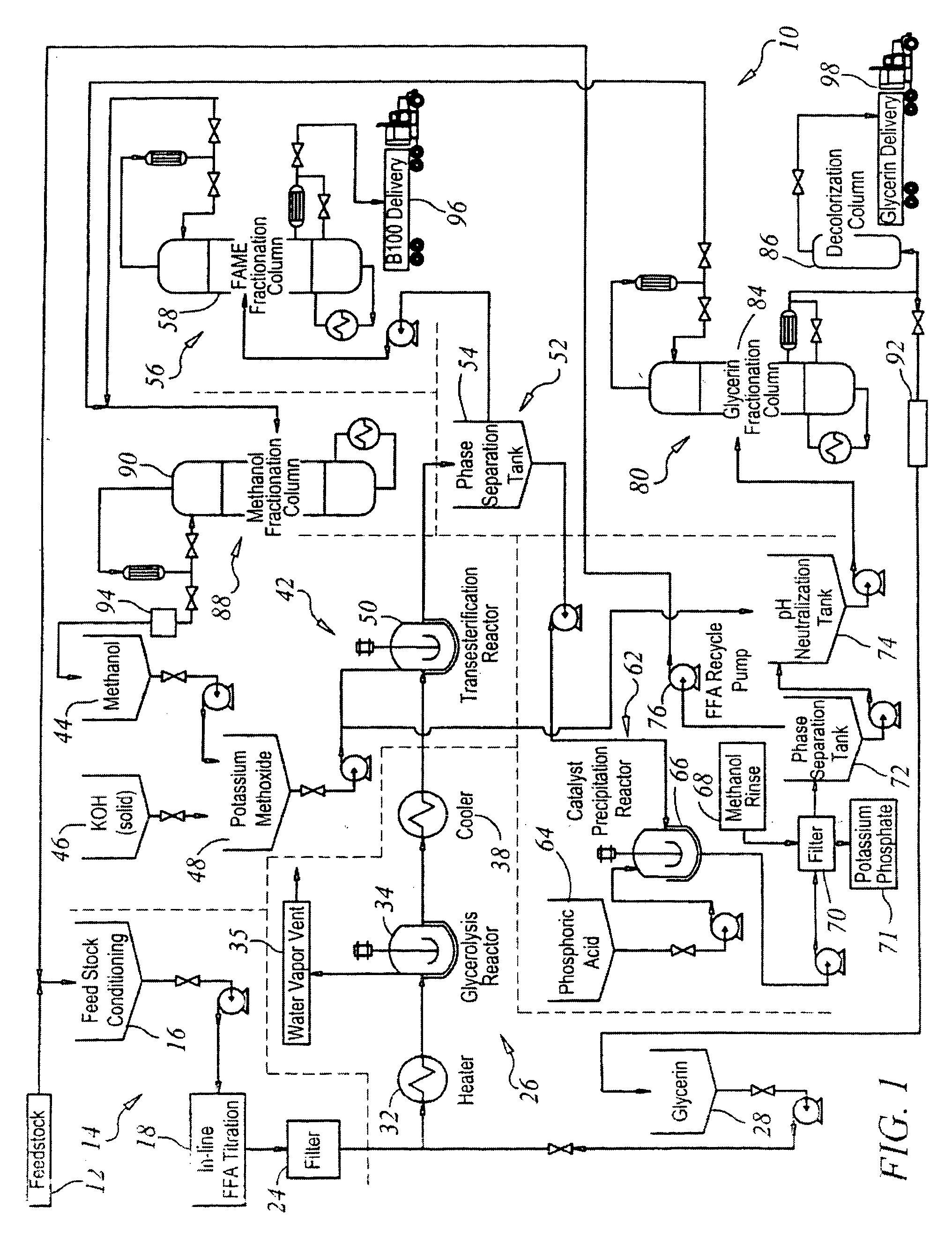
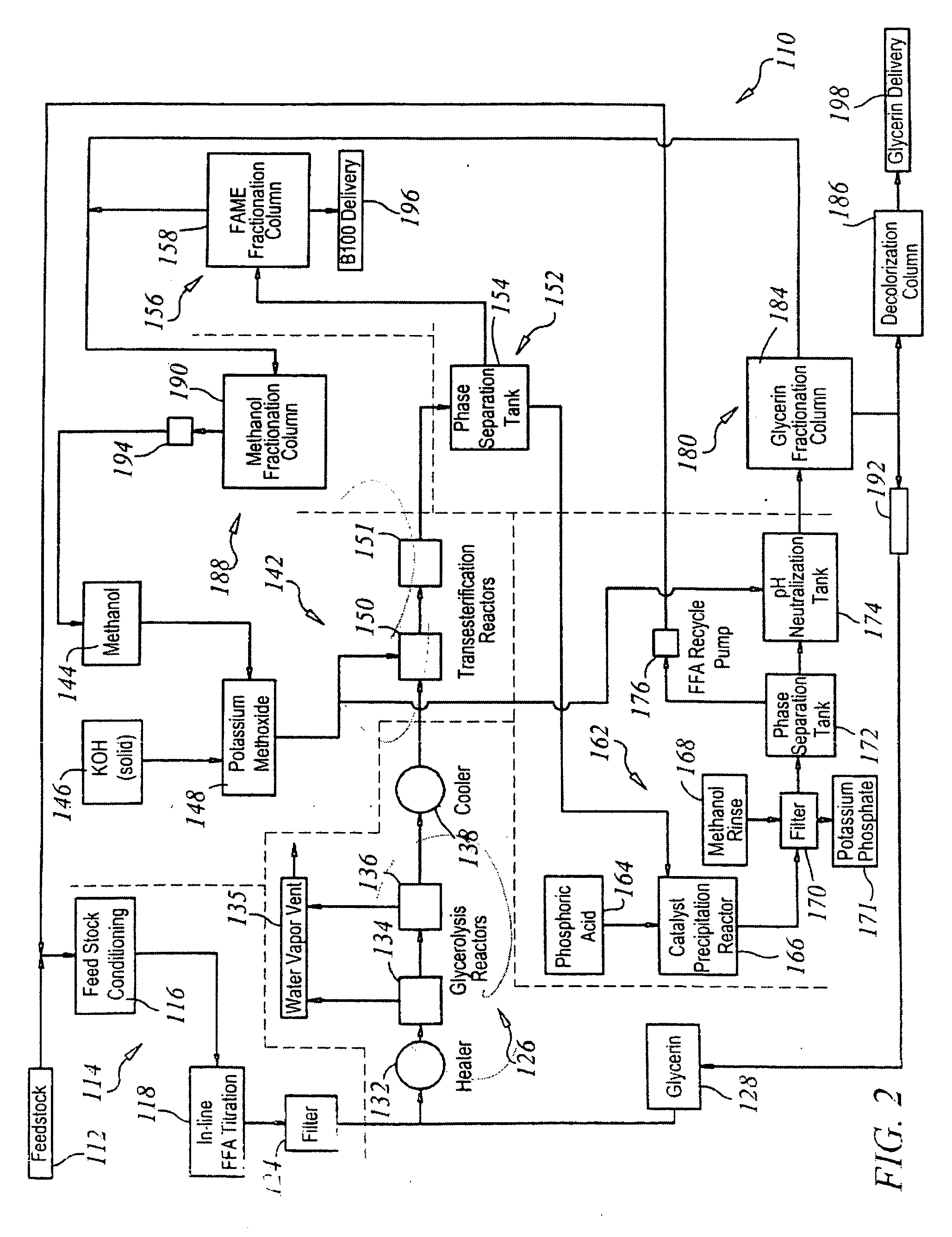
Production of biodiesel and glycerin from high free fatty acid feedstocks
ActiveUS20070277430A1Increase productionHigh purityFatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic acidChemical reaction
A system and method for the conversion of free fatty acids to glycerides and the subsequent conversion of glycerides to glycerin and biodiesel includes the transesterification of a glyceride stream with an alcohol. The fatty acid alkyl esters are separated from the glycerin to produce a first liquid phase containing a fatty acid alkyl ester rich (concentrated) stream and a second liquid phase containing a glycerin rich (concentrated) stream. The fatty acid alkyl ester rich stream is then subjected to distillation, preferably reactive distillation, wherein the stream undergoes both physical separation and chemical reaction. The fatty acid alkyl ester rich stream is then purified to produce a purified biodiesel product and a glyceride rich residue stream. The glycerin rich second liquid phase stream may further be purified to produce a purified glycerin product and a (second) wet alcohol stream. Neutralization of the alkaline stream, formed during the alkali-catalyzed transesterfication process, may proceed by the addition of a mineral or an organic acid.
Owner:REG SENECA LLC +3
Method for producing fats or oils
ActiveUS20050014237A1Extended half-lifeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationEnzyme
The present invention is directed to improving productivity of an enzymatic method for making esterified, transesterified or interesterified products. Specifically, a method that can greatly improve the productivity of enzymatic transesterification or esterification by deodorization alone, or by deodorization and purification of the initial substrate to extend the useful life of the enzyme is disclosed.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com