Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1031results about How to "Produced cost-effectively" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
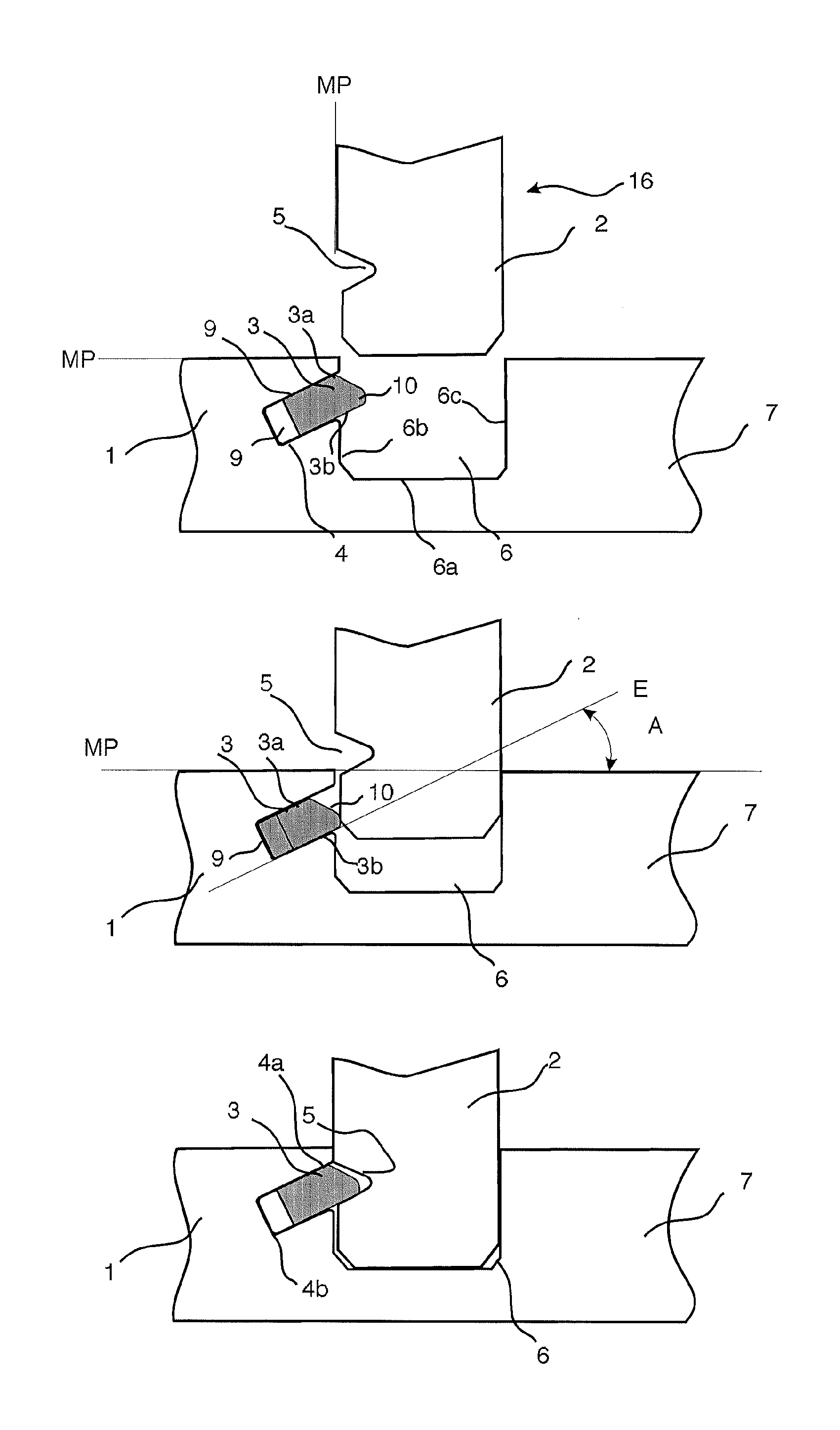
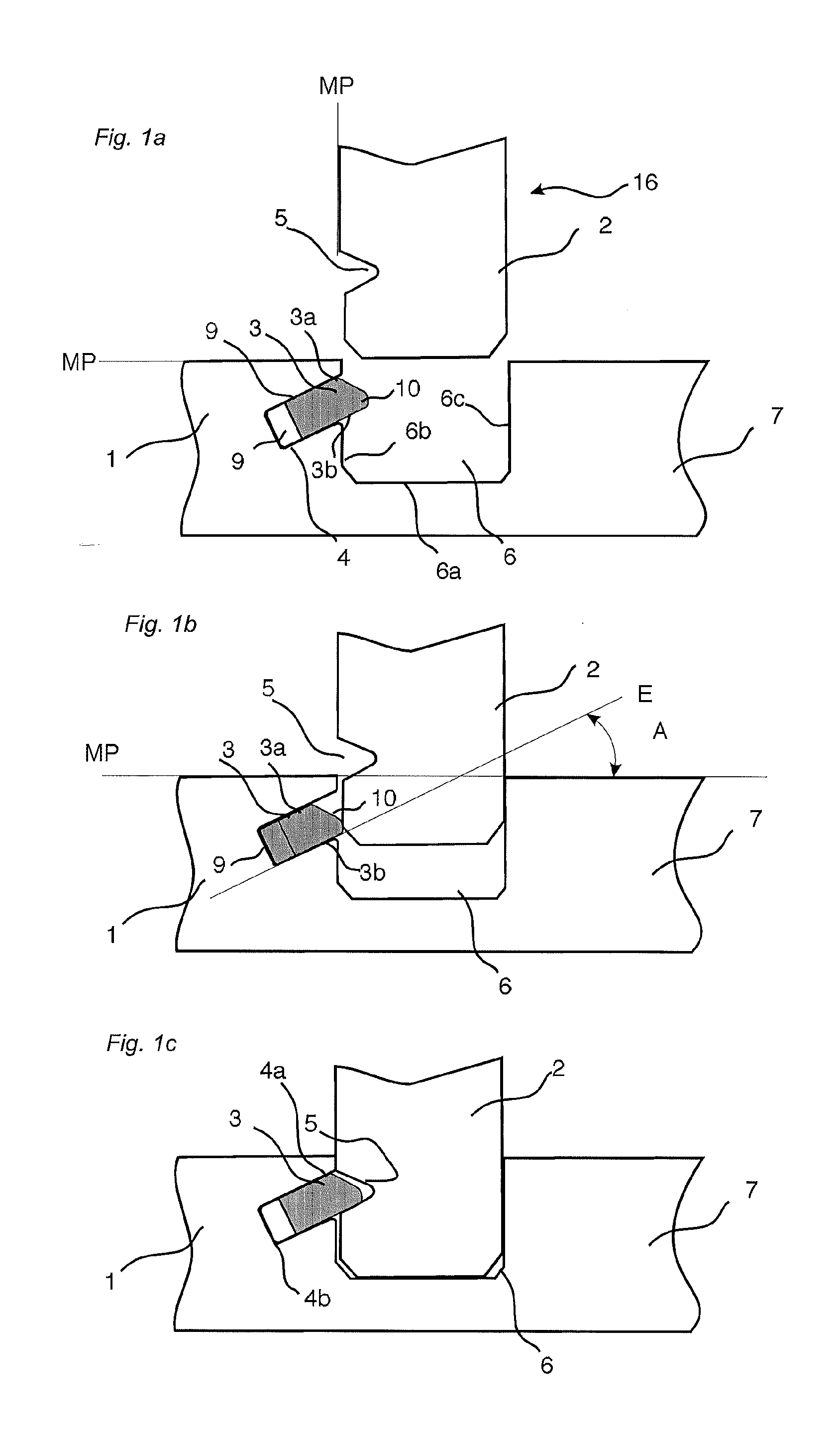
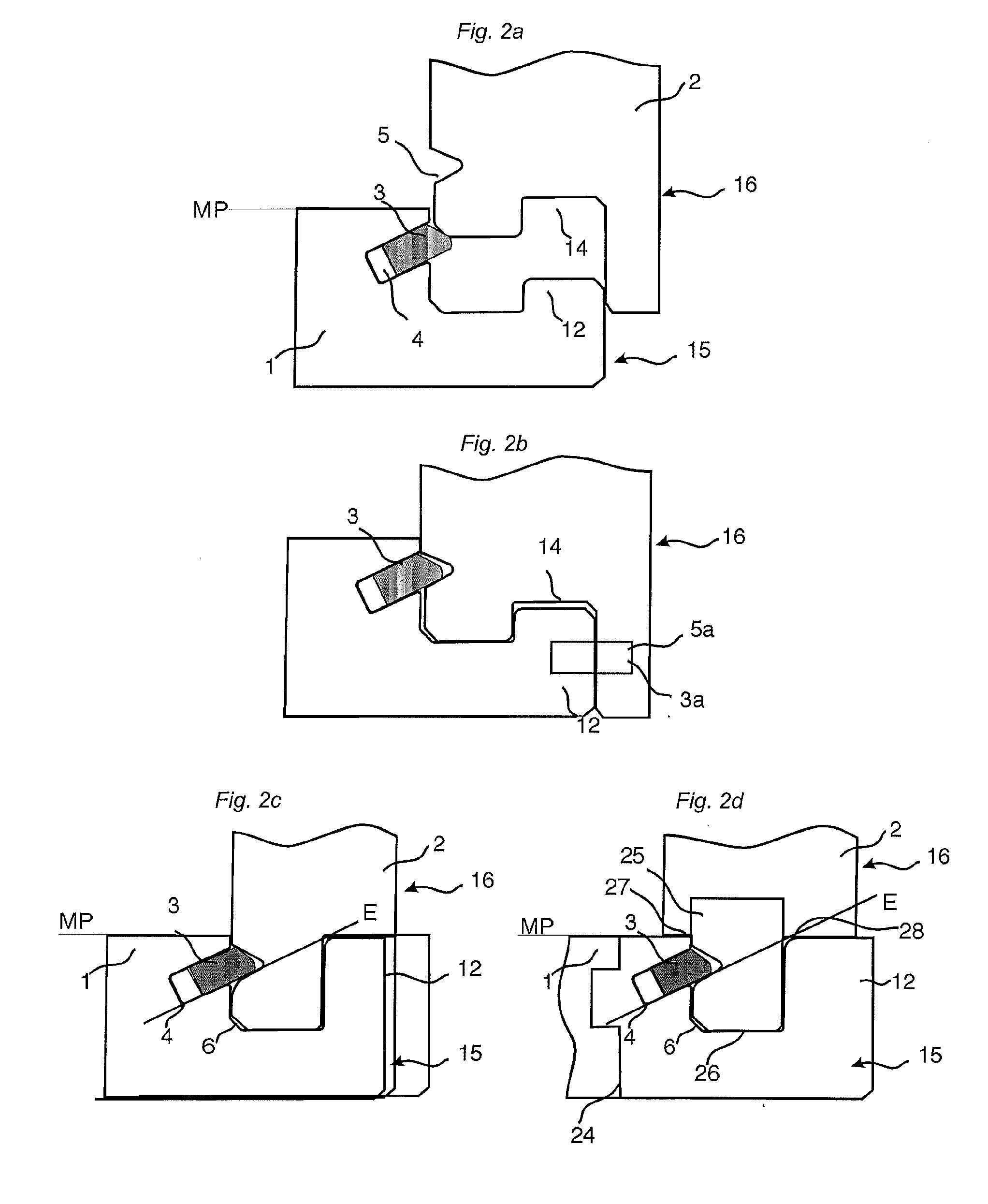
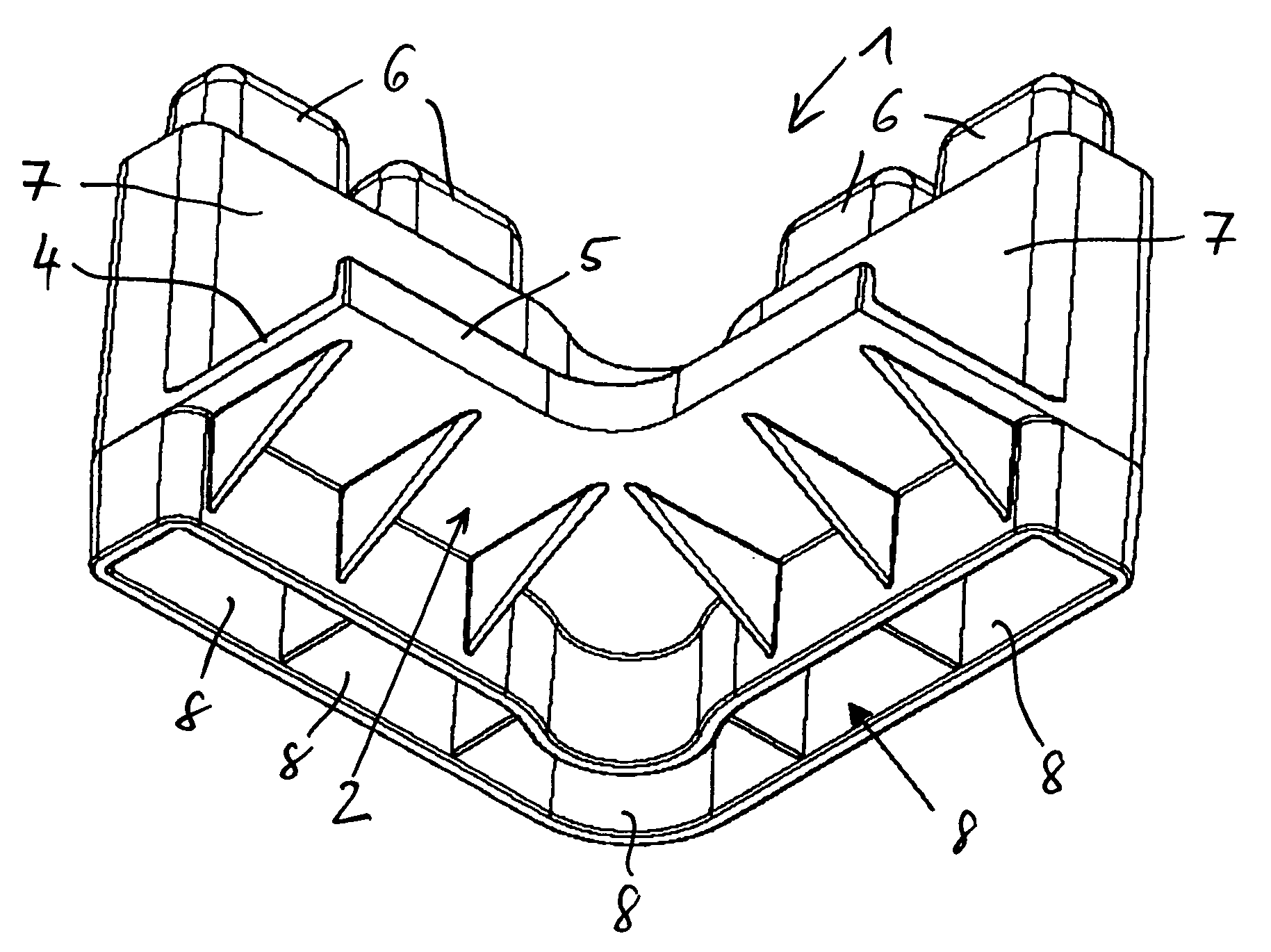
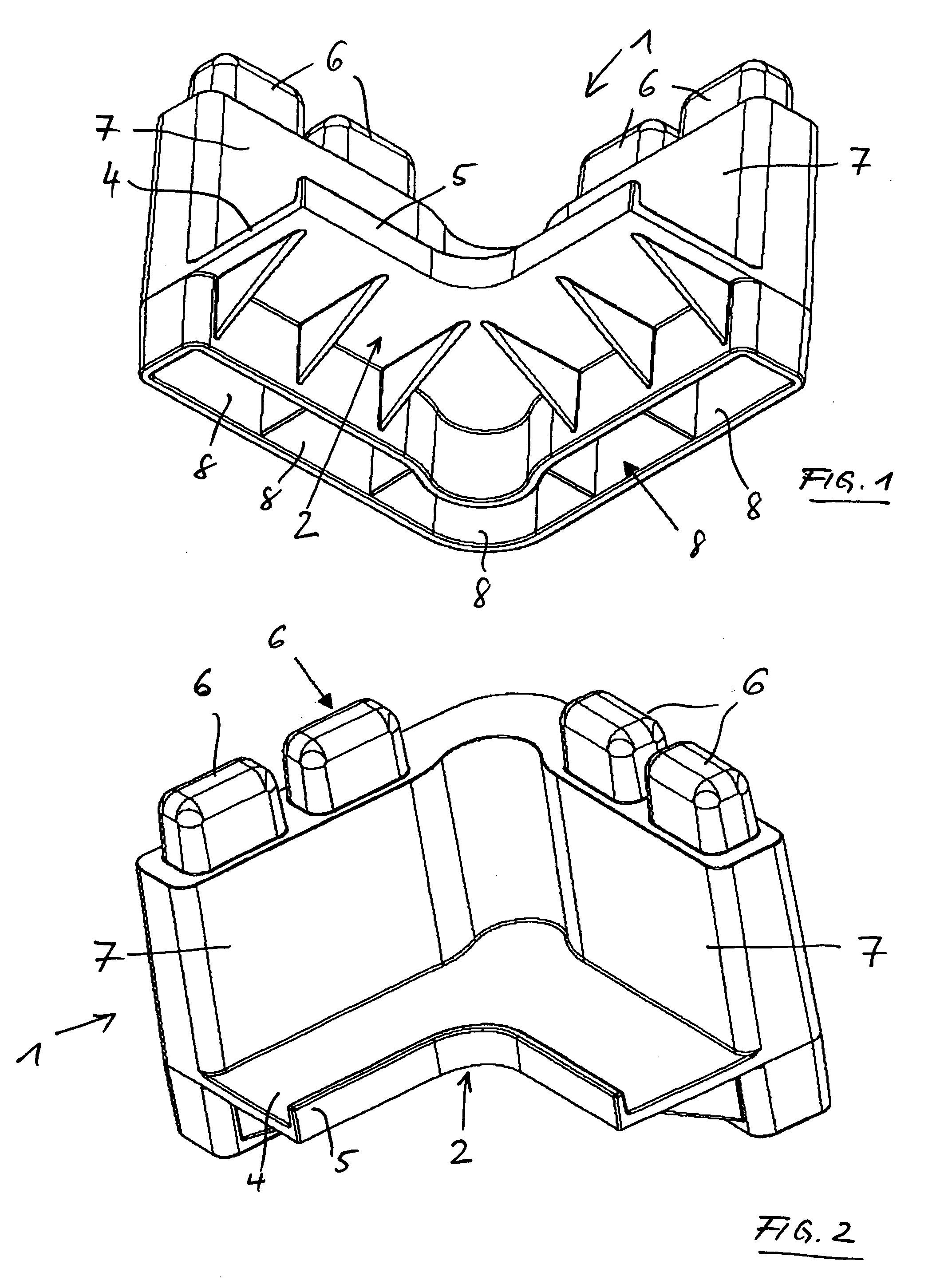
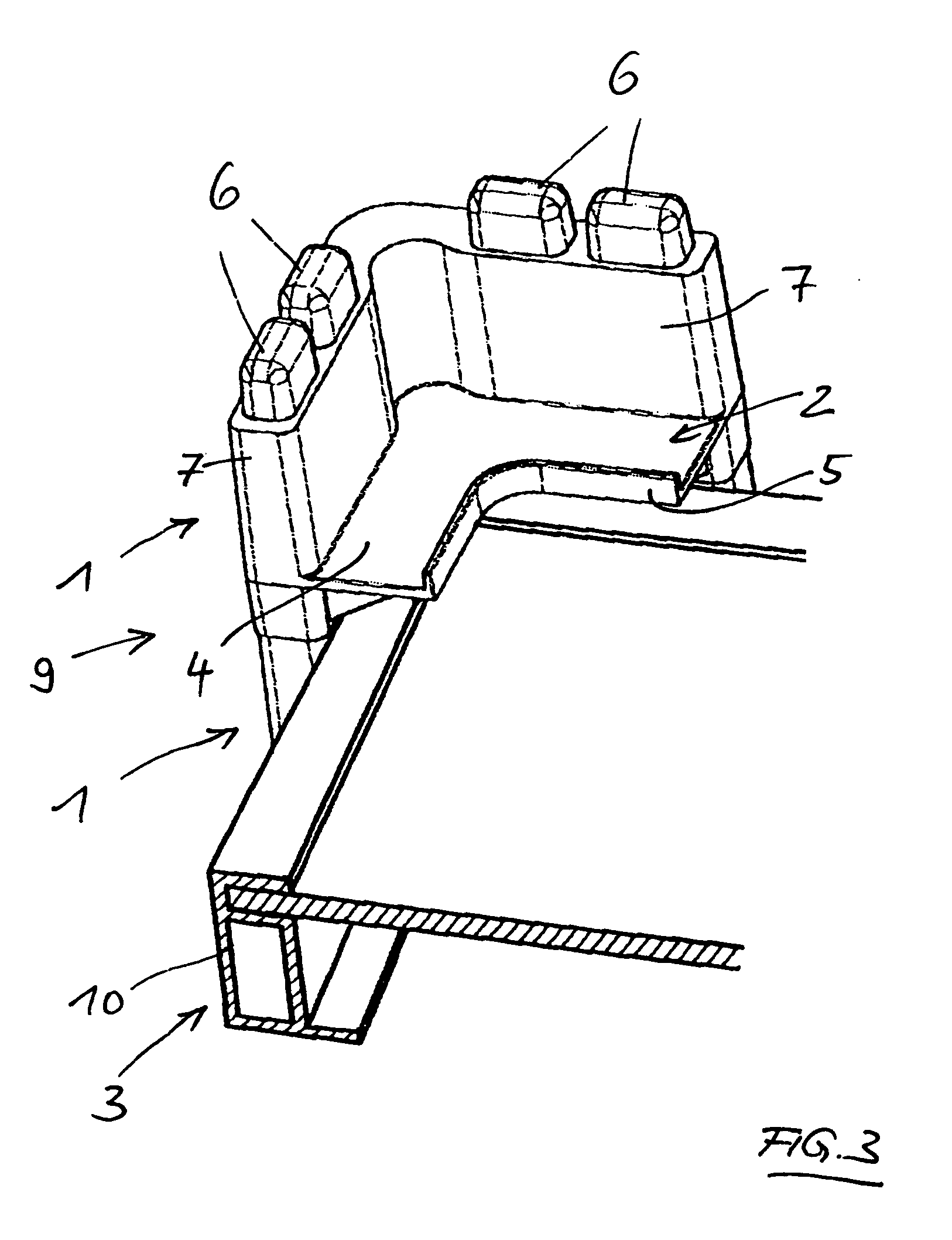
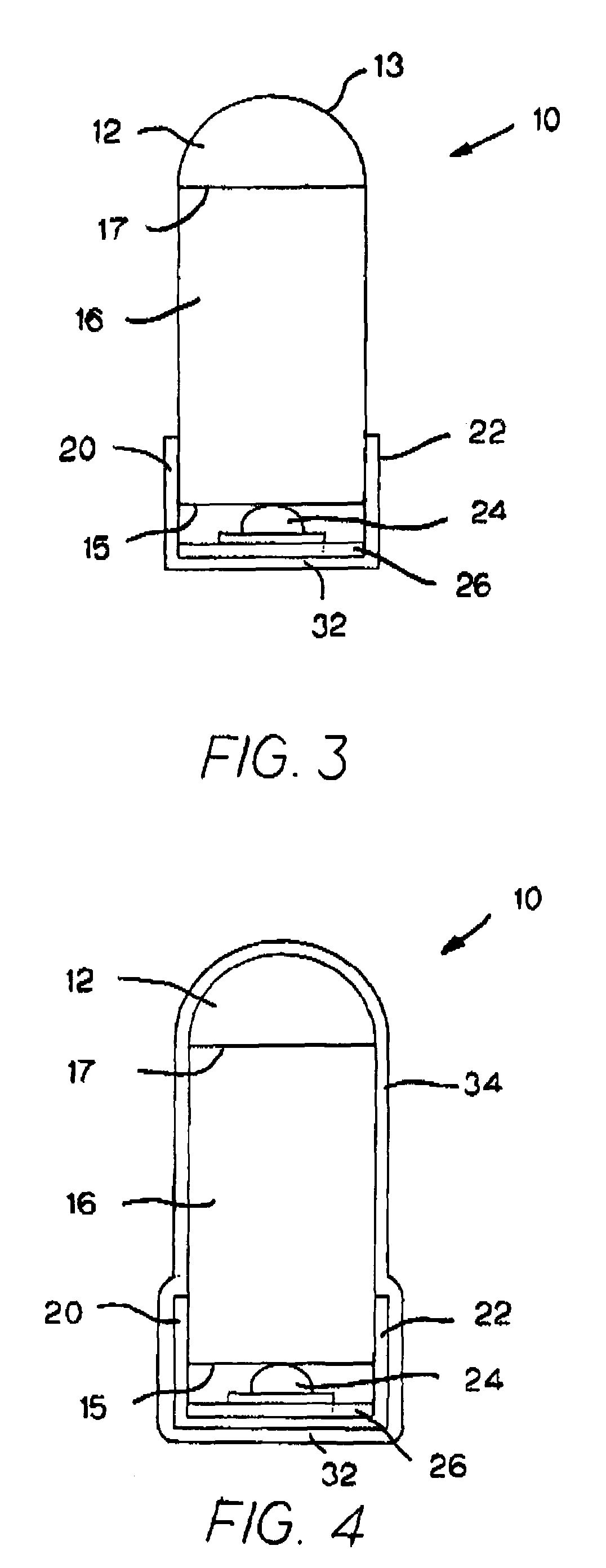
Mechanical locking system for building panels
ActiveUS20120279161A1Simple wayProduced cost-effectivelySheet joiningBuilding componentsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Panels are shown which are provided with a mechanical locking system allowing perpendicular connection with a snap action.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
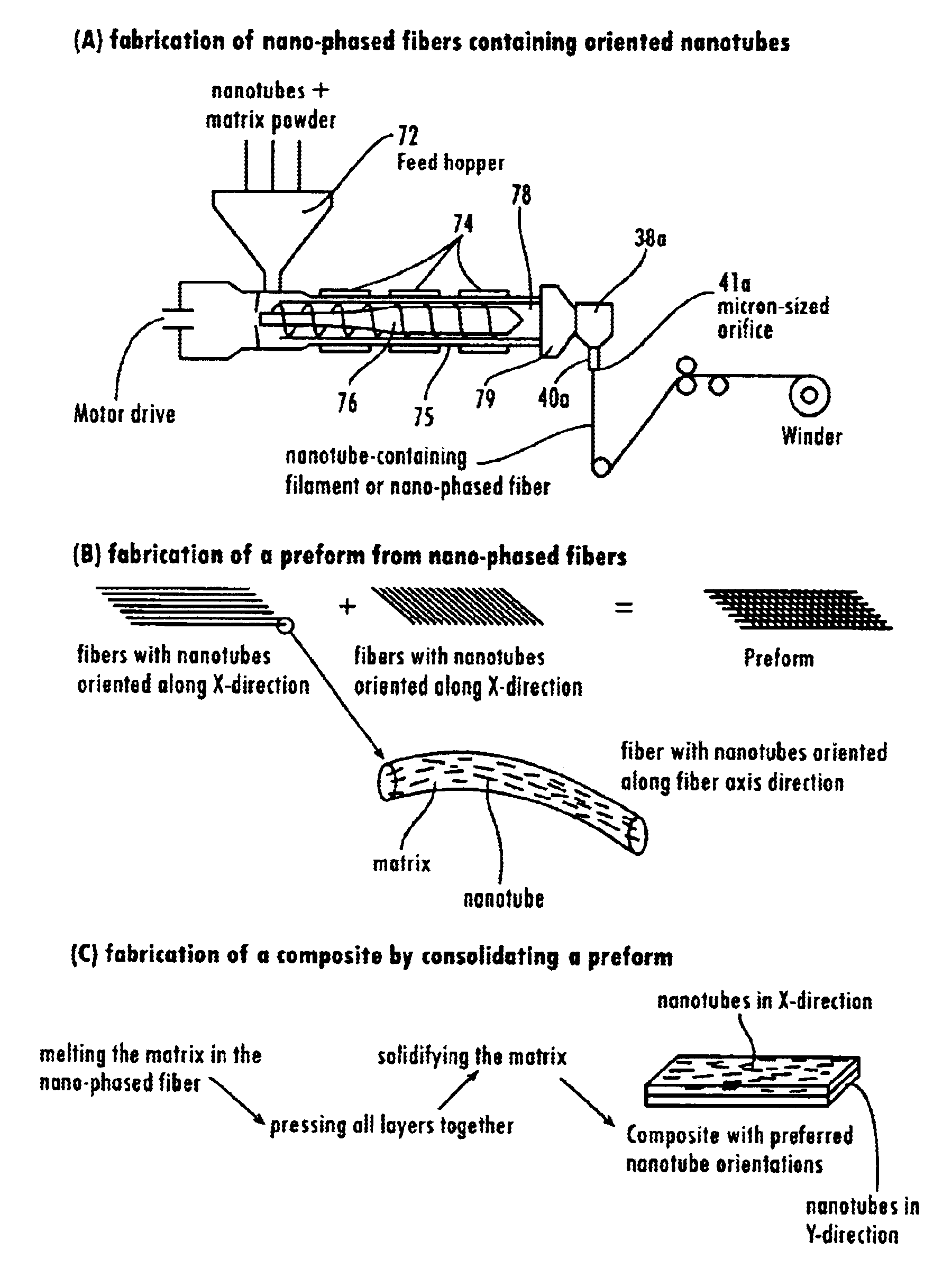
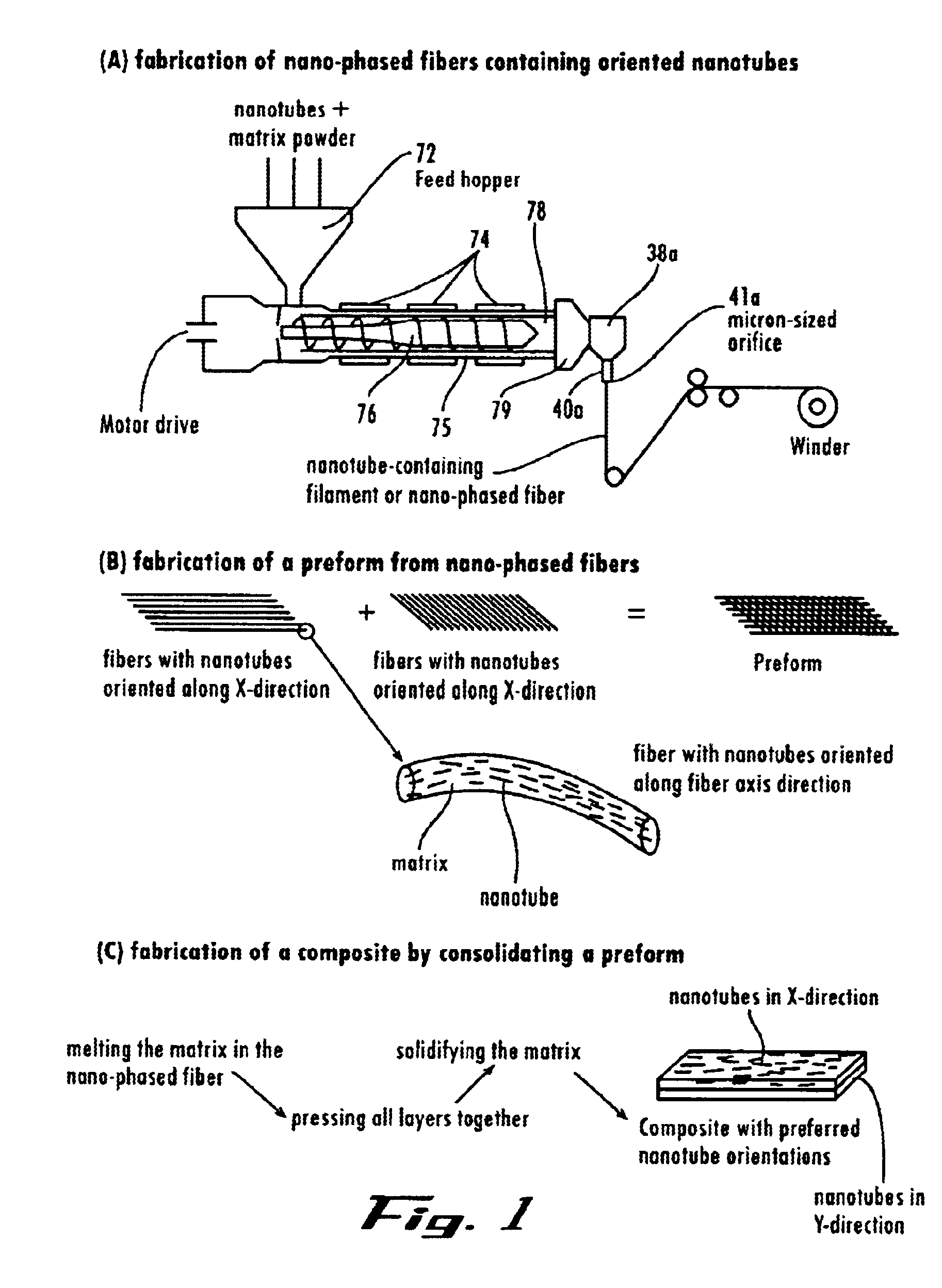
Nanotube fiber reinforced composite materials and method of producing fiber reinforced composites
InactiveUS6934600B2Requires minimizationGenerate efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiber-reinforced compositeMotion controller
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
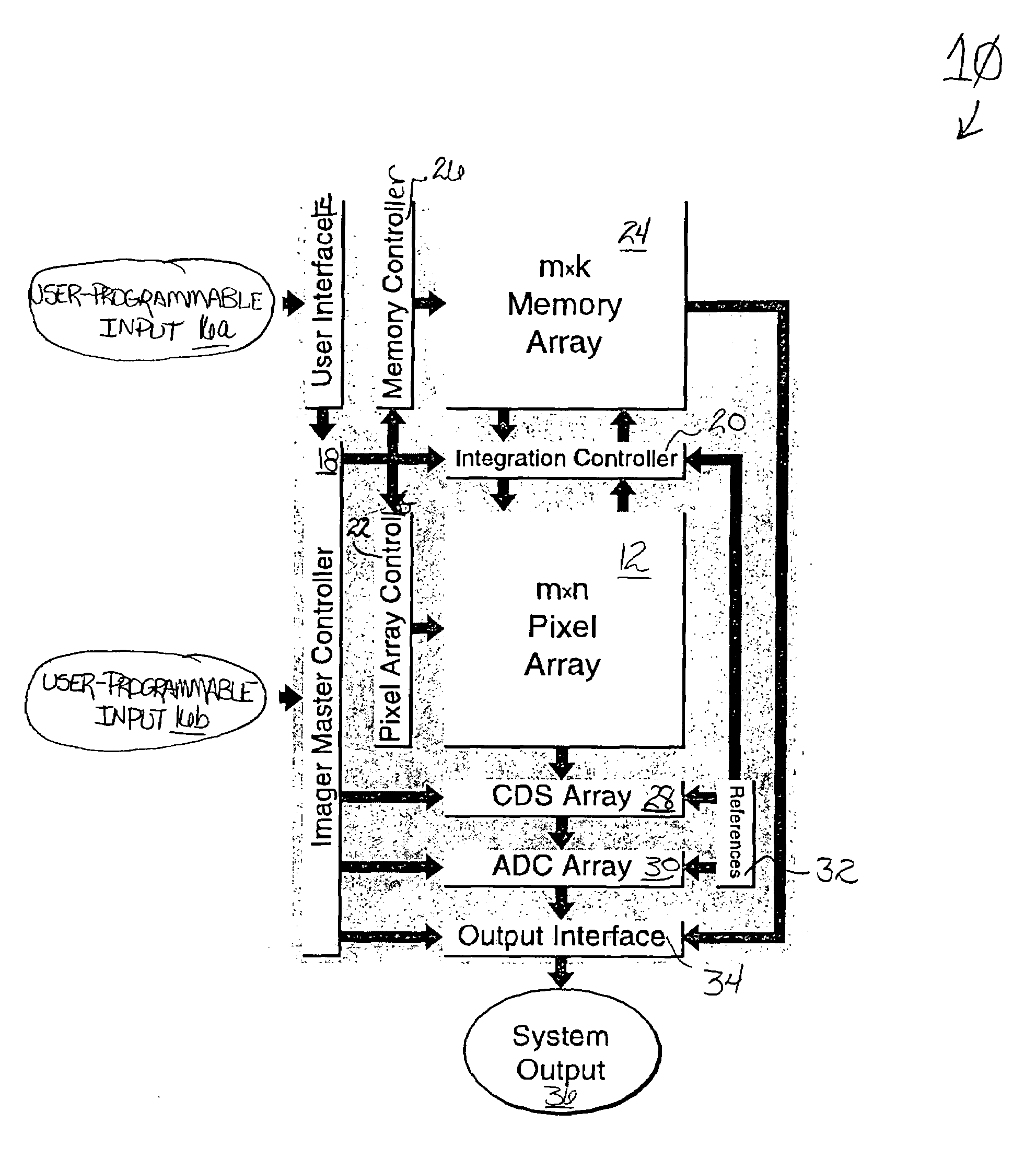
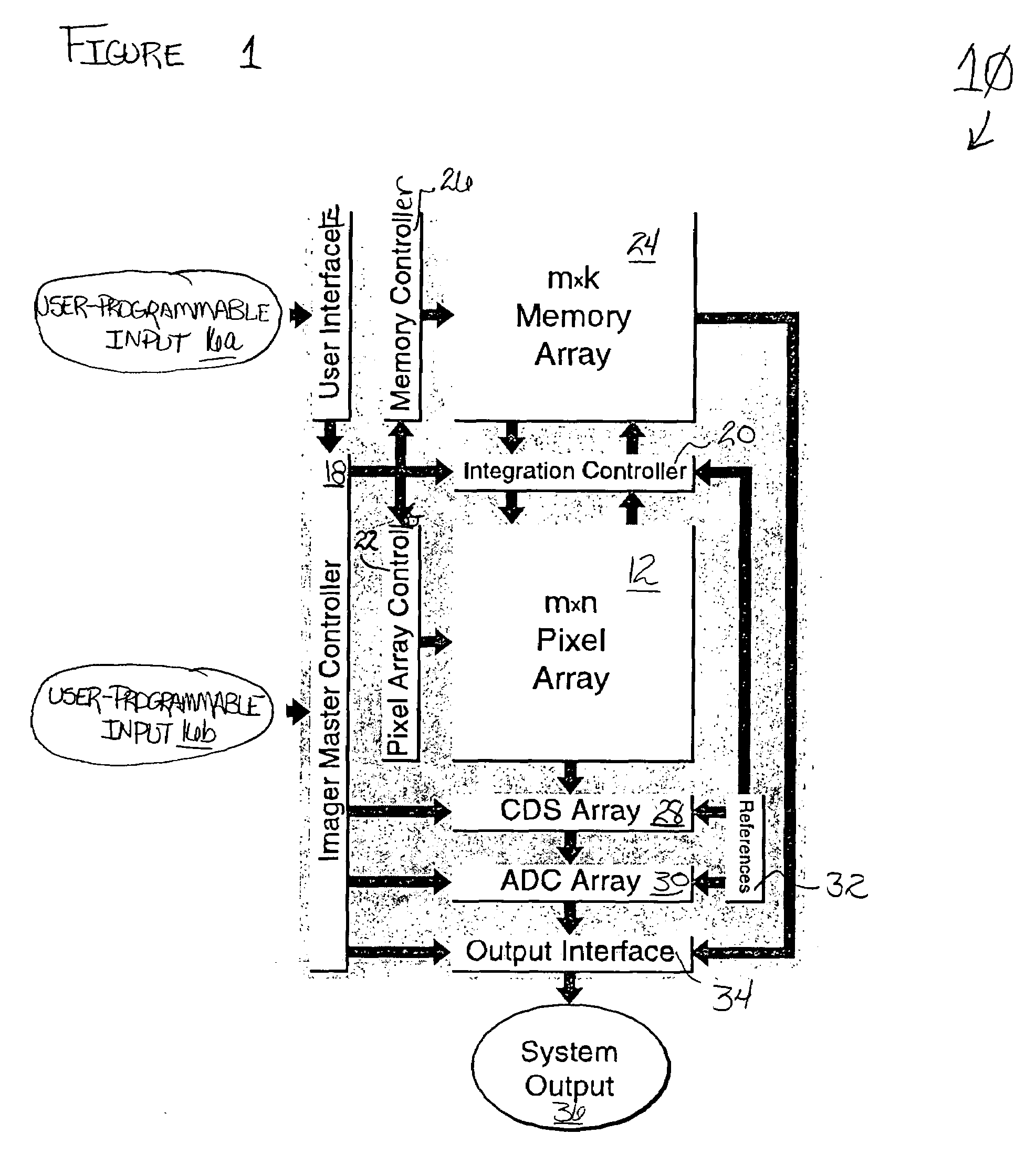
Single-chip imager system with programmable dynamic range
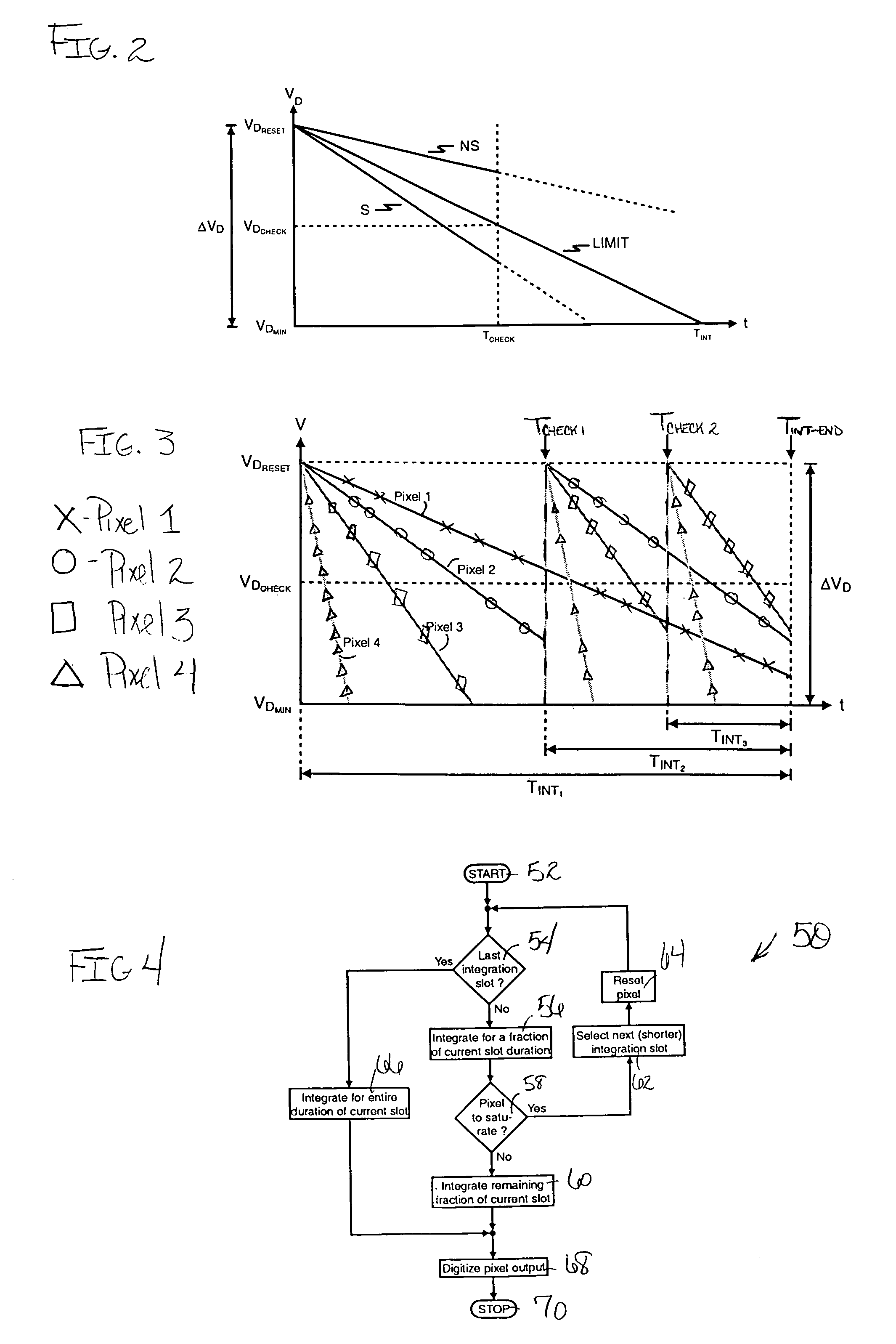
InactiveUS6977685B1Elegantly simple input/output connectionProduced cost-effectivelyTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl signalEngineering
The imager system of the invention, provided in a semiconductor substrate, includes a plurality of photosensitive, charge integrating pixels that are arranged in rows and columns of a pixel array for capturing illumination of a scene to be imaged. Each pixel includes a photogenerated charge accumulation region of the semiconductor substrate and a sense node at which an electrical signal, indicative of pixel charge accumulation, can be measured without discharging the accumulation region. Pixel access control circuitry is connected to pixel array rows and columns to deliver pixel access signals generated by the access control circuitry for independently accessing a selected pixel in the array. An input interface circuit is connected to accept a dynamic range specification input for the array pixels. Integration control circuitry is connected to access a selected pixel of the array to read the sense node electrical signal of the selected pixel, and configured to generate pixel-specific integration control signals delivered to the selected pixel, independent of other pixels, based on dynamic range specification input provided by the input interface circuit. An output interface circuit is connected to the pixel array to produce output image data based on sense node electrical signals from the pixel array.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
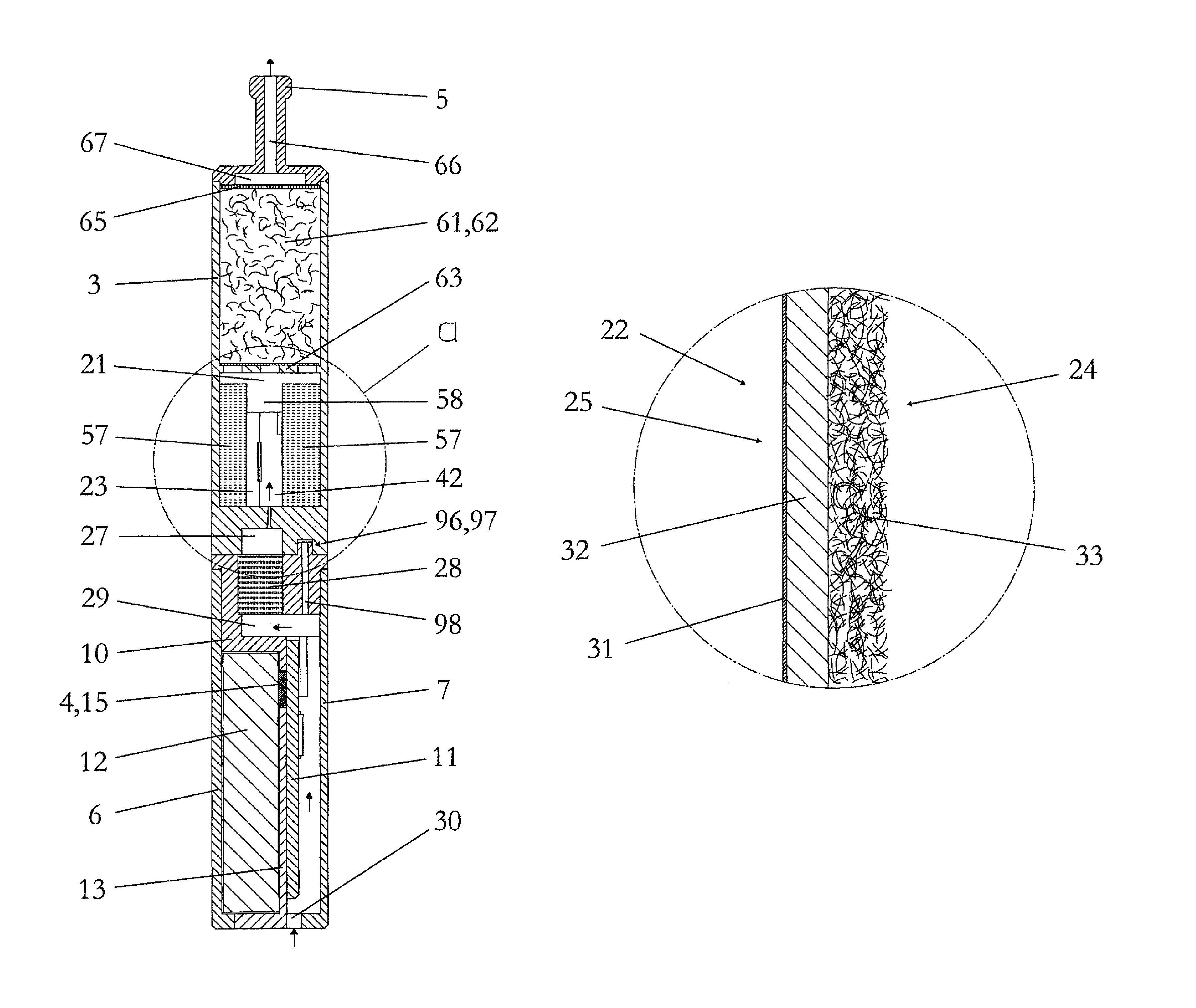
Inhaler
ActiveUS8833364B2High specific evaporative capacityHigh evaporator efficiencyRespiratorsOrganic active ingredientsEngineeringInhaler
The present disclosure relates to an inhaler component for producing a steam / air mixture or / and condensation aerosol in an intermittent and inhalation- or pull-synchronous manner, the inhaler component including: a housing; a chamber arranged in the housing; an air inlet opening for the supply of air from the surroundings to the chamber; an electrical heating element for evaporating a portion of a liquid material; and a wick having a capillary structure, which wick forms a composite structure with the heating element and automatically supplies the heating element with fresh liquid material after evaporation.
Owner:NICOVENTURES TRADING LTD
Injection device
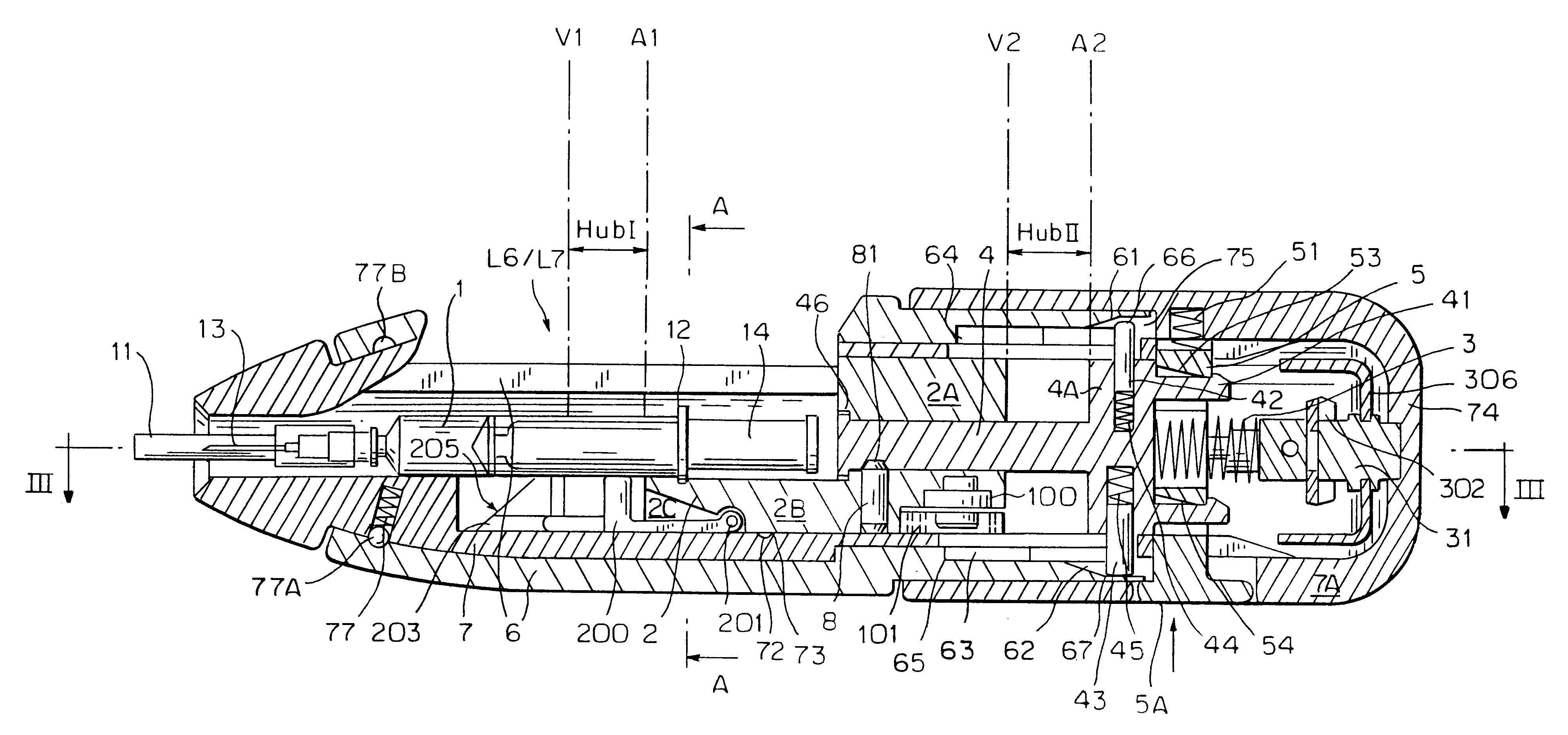
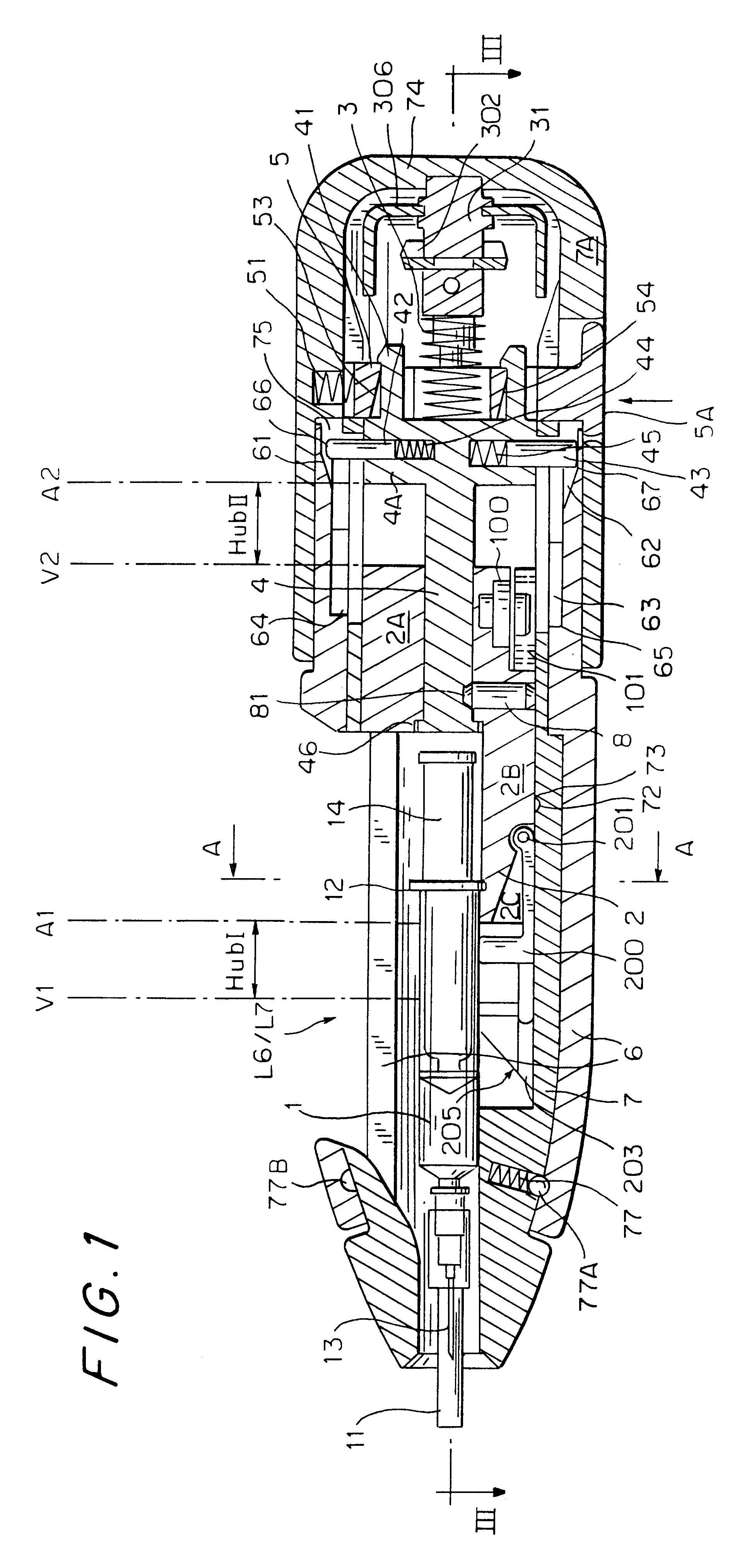
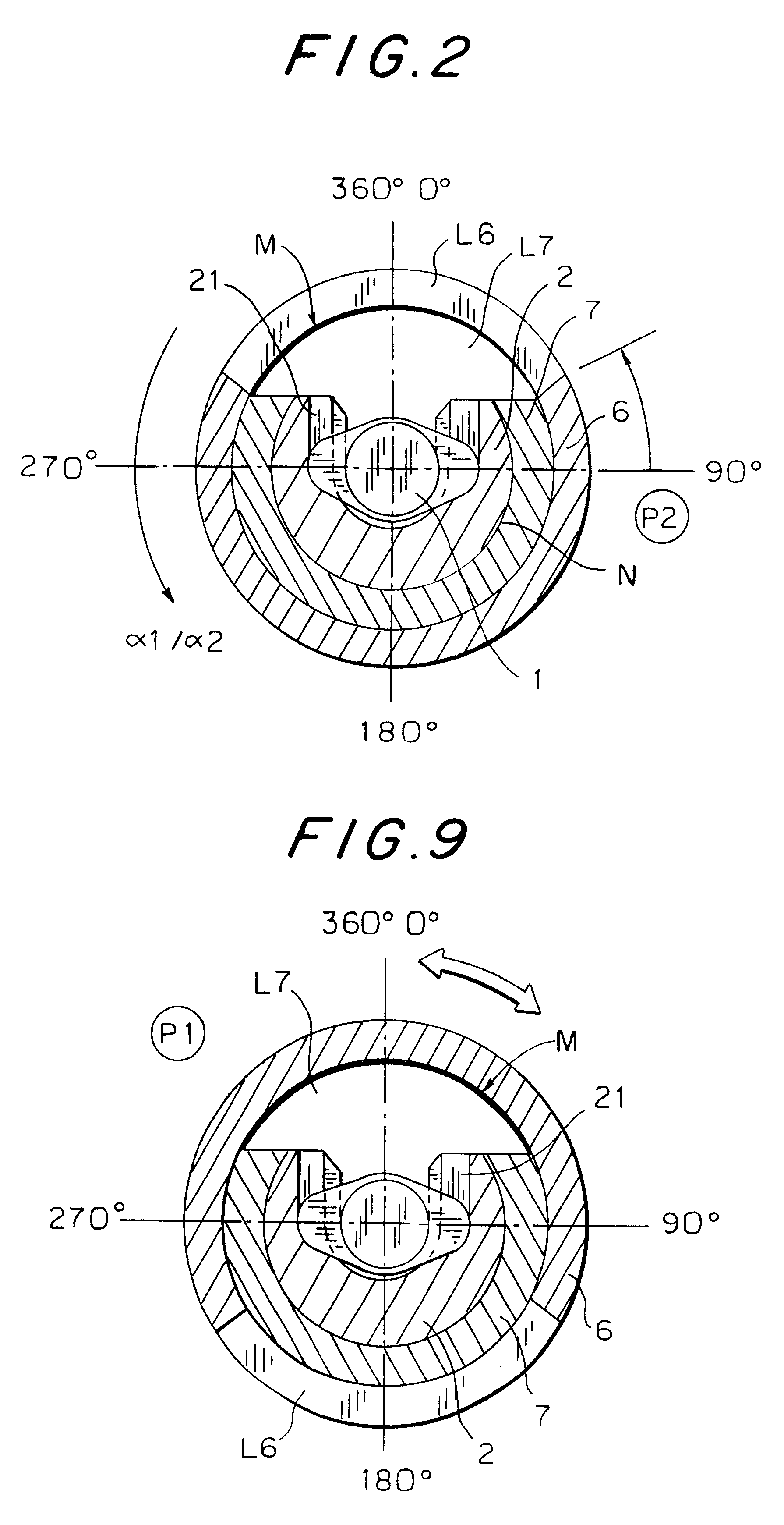
InactiveUS6454743B1Simplify mechanical designMinimal requirementAutomatic syringesMedical devicesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
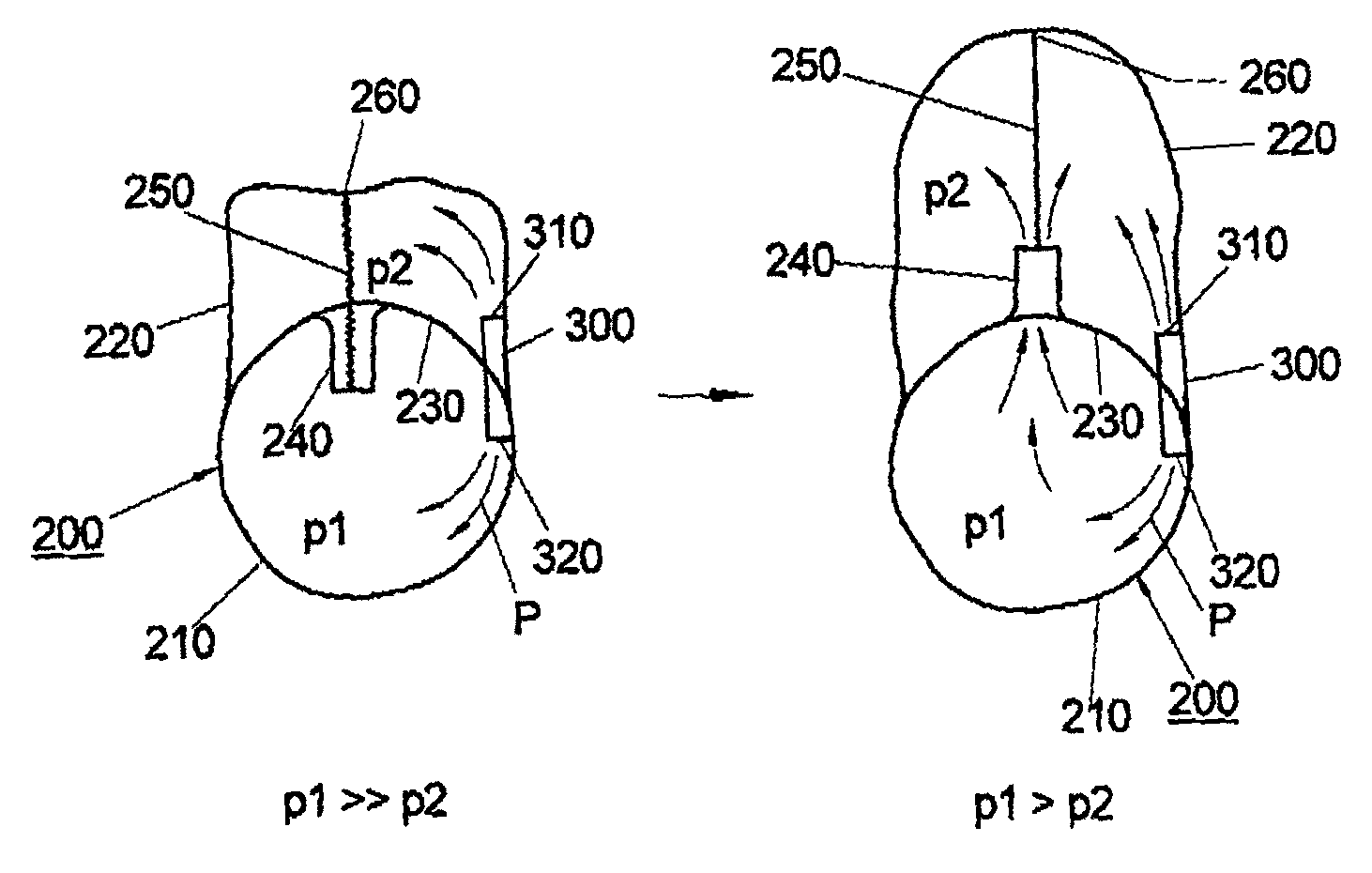
An injection device that is used with a syringe, wherein the injection needle of the syringe is initially introduced into the skin and the injection fluid is injected afterwards. The injection device is essentially driven and controlled by a control sleeve (6) which can be displaced and / or rotated in relation to the housing (7) and which can be moved between a closing and functional position (P1) and an open and safety position (P2). In the closing and functional position, the control sleeve prevents access to the syringe and activates a release device for the injection process. In the open and safety position, a syringe (1) can be removed or inserted. A plurality of components carrying out the injection process (a slide (2) in which the syringe (1) is placed and a plunger (4) that impinges upon the syringe piston) are moved or controlled depending on the movement and position of the control sleeve or supported (for example, an ejection device for the syringe or a signaling device informing that injection has been completed). The device enables full-automatic injection that can be reliably carried out by patients themselves with few handling procedures.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Device for the Treatment of Wounds Using a Vacuum
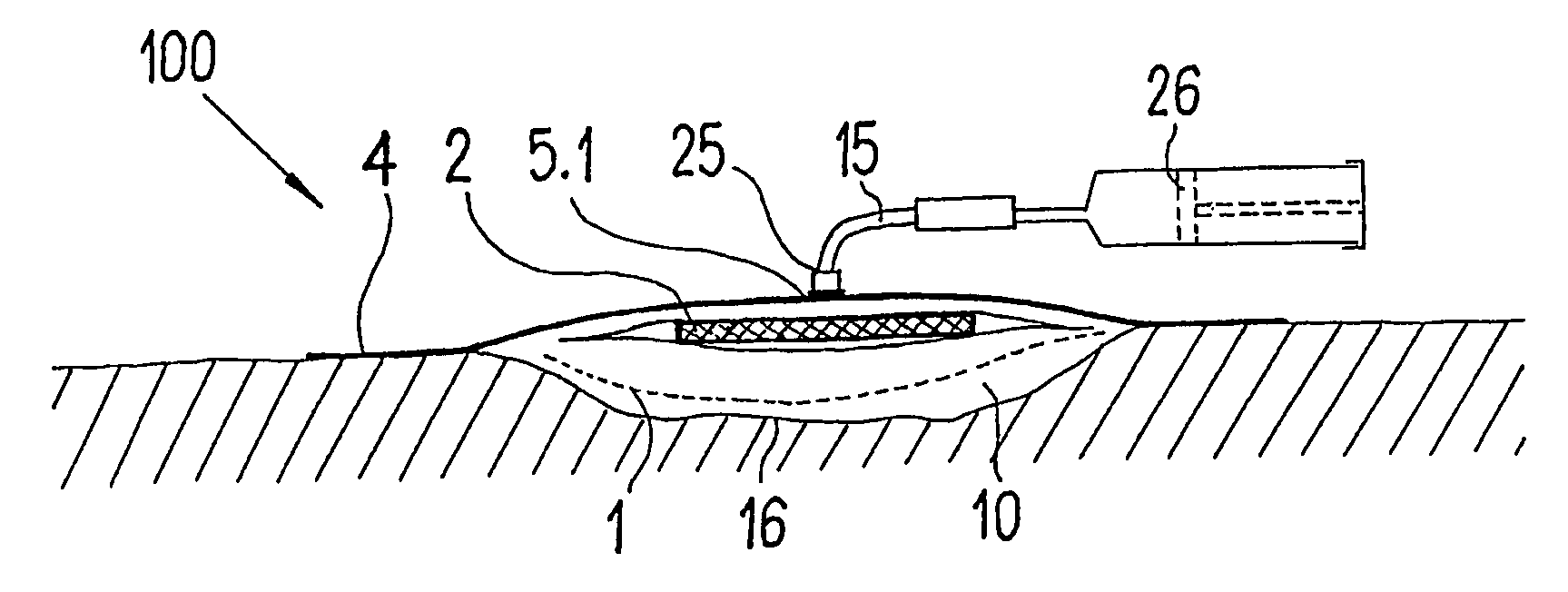
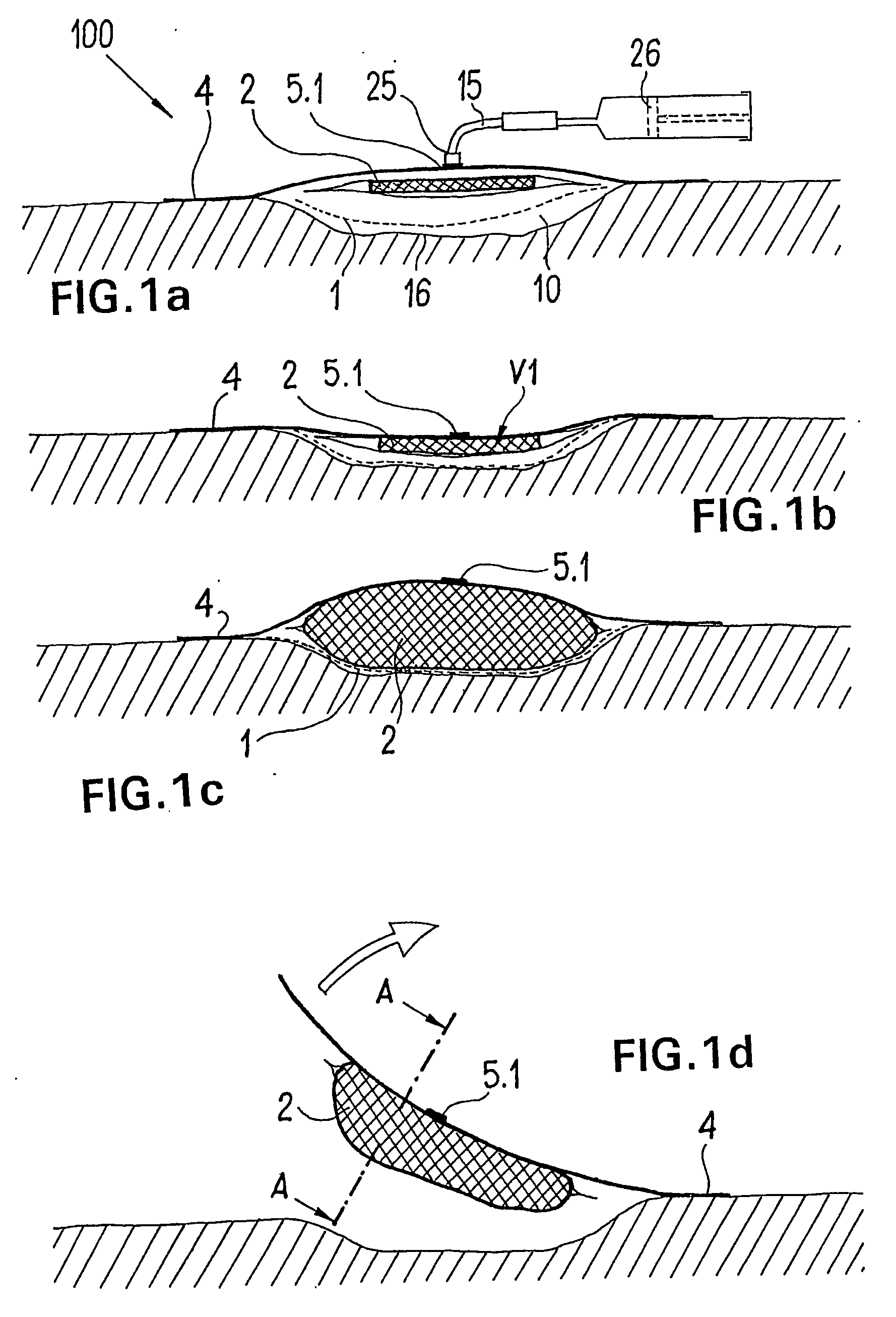
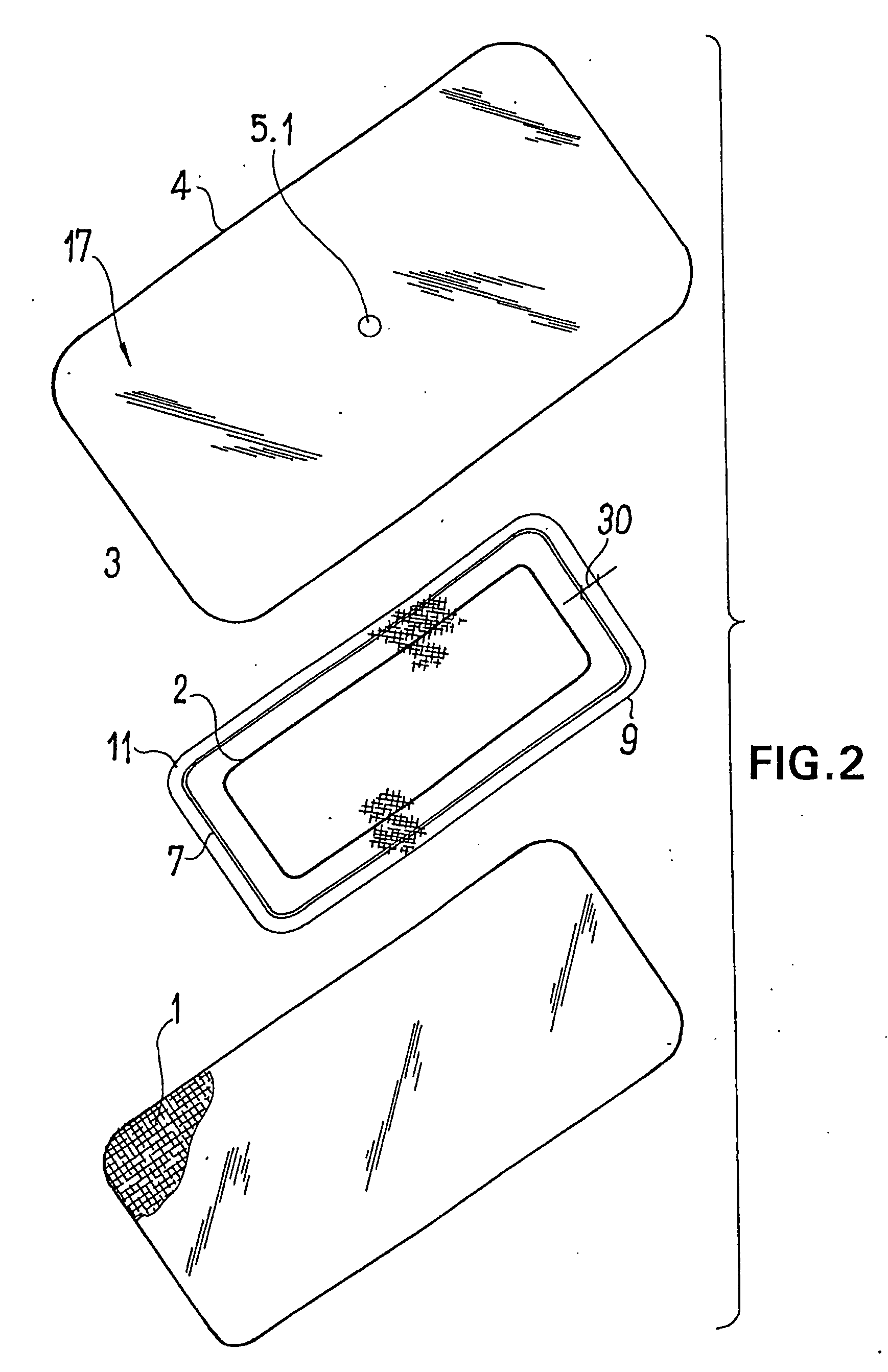
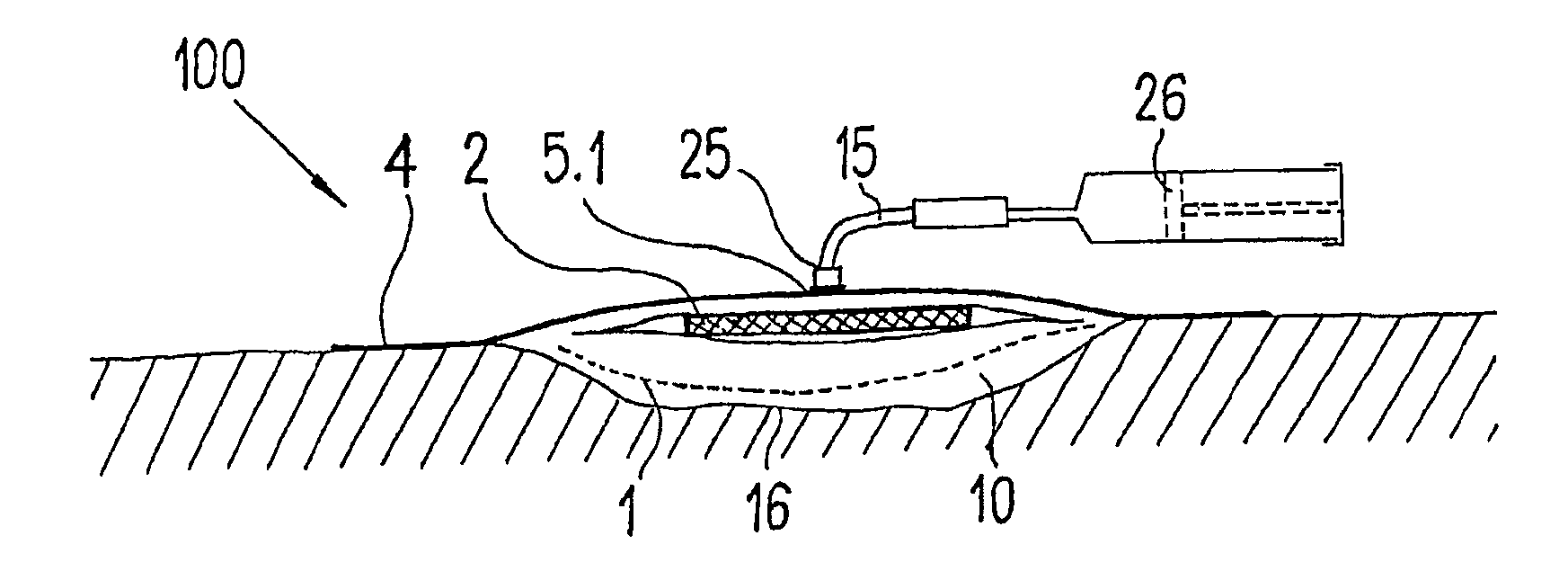
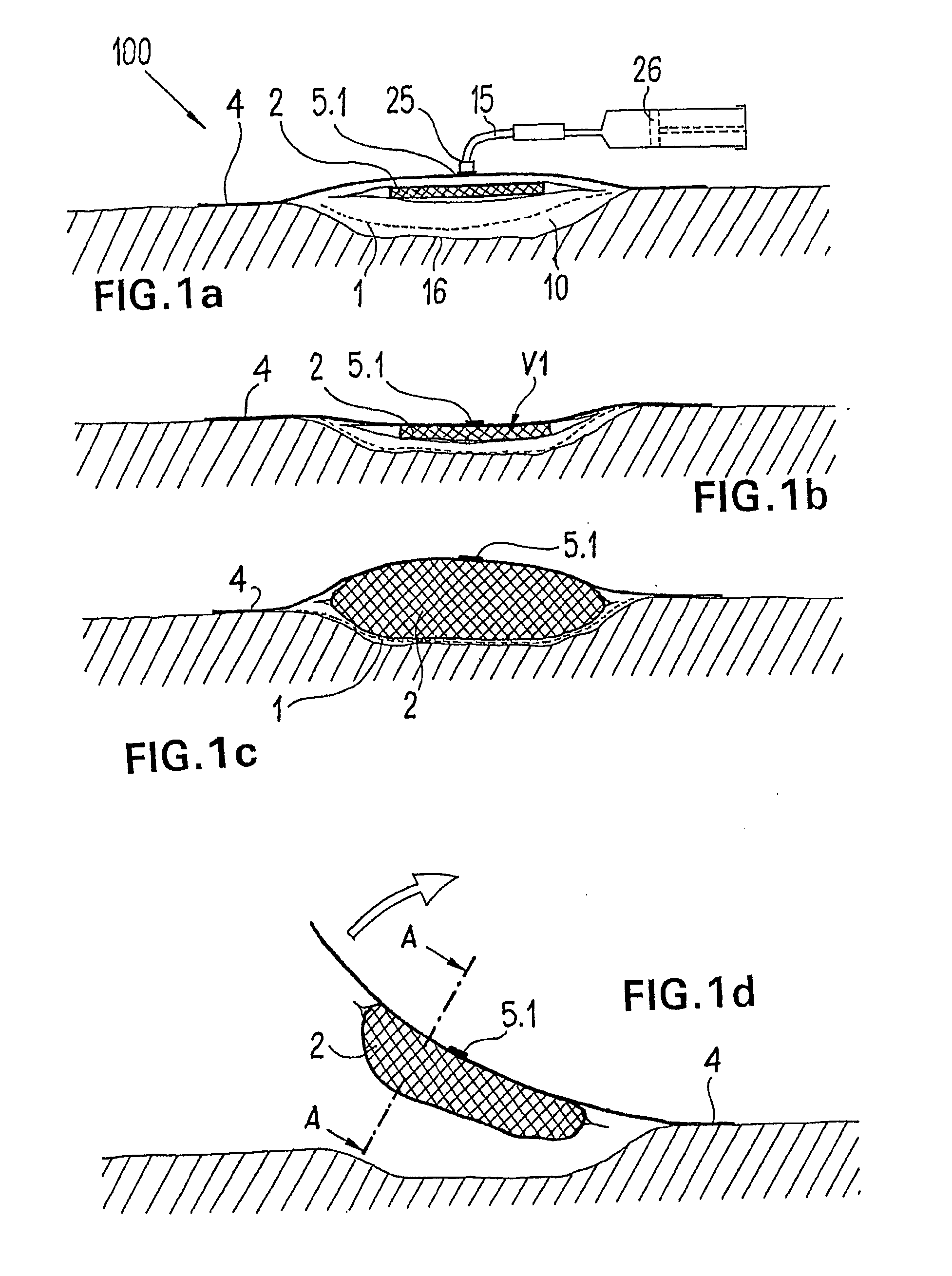
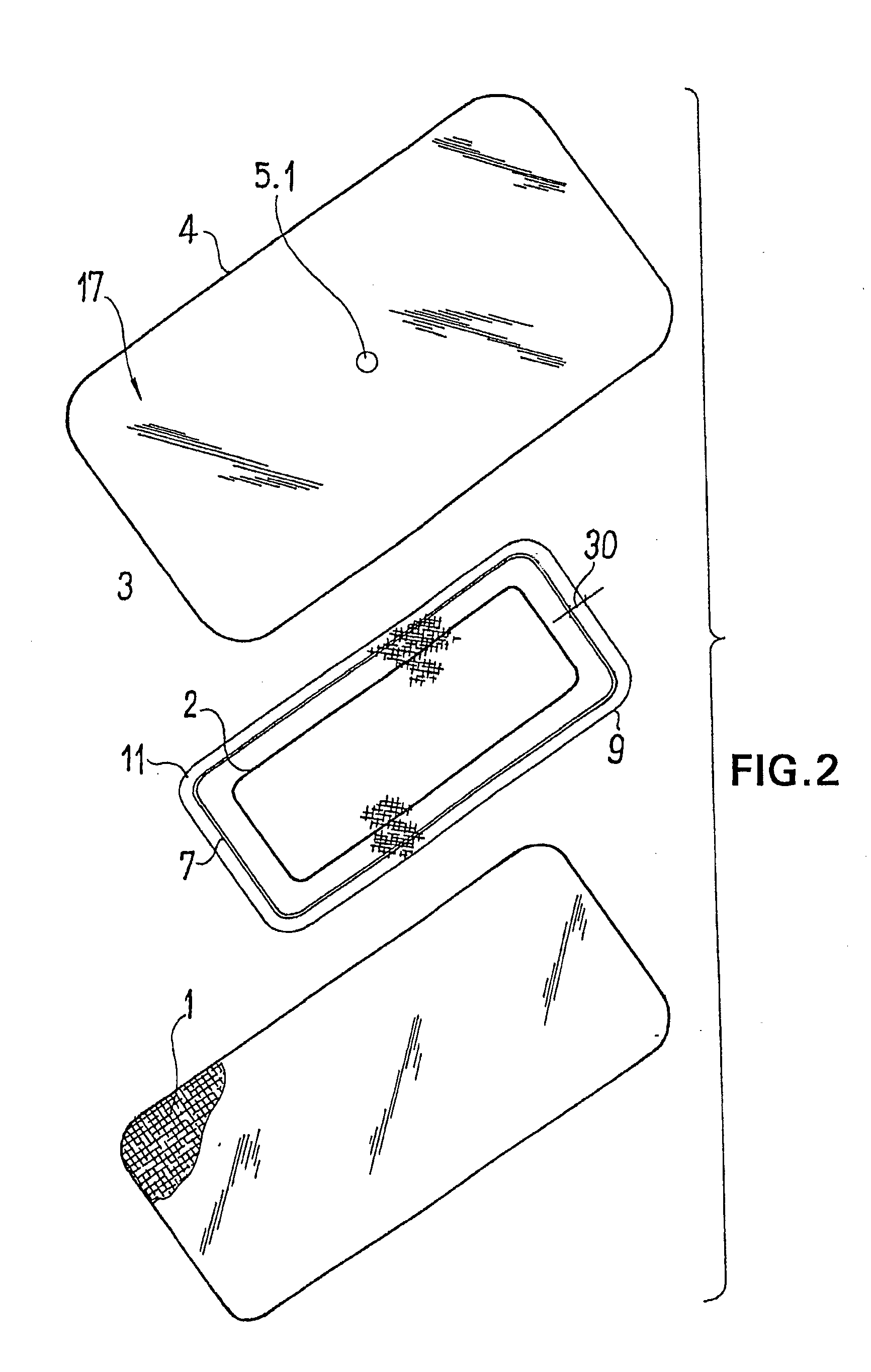
ActiveUS20080009812A1Cost effectiveSimple designNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersSecretionSecreted substance
The invention relates to a device (100) for treating wounds of the human or animal body using a vacuum and having a gas-tight wound-covering element (4), which, when placed in contact with the body of the patient, forms a wound space (10) between the respective wound and the wound-covering element, at least one connecting site (5.1; 5.2), which is in contact with the wound space (10), an absorption body (2), which is a layer, enclosed in an envelope, of a textile section, interspersed with super-absorbing particles, the envelope being permeable to liquids and having pores, the size of which does not exceed that of the super-absorbing particles. The absorption body (2), which is to be inserted in the wound space (10), has an initial volume, which enlarges in the course of the absorption process, and a final volume, so that, due to the size of the pores of the envelope, the absorbed wound secretions remain within the absorption body (2) and, with that, below the wound-covering element, until the absorption body is removed from the wound space.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
Method and Apparatus For a Variable User Interface
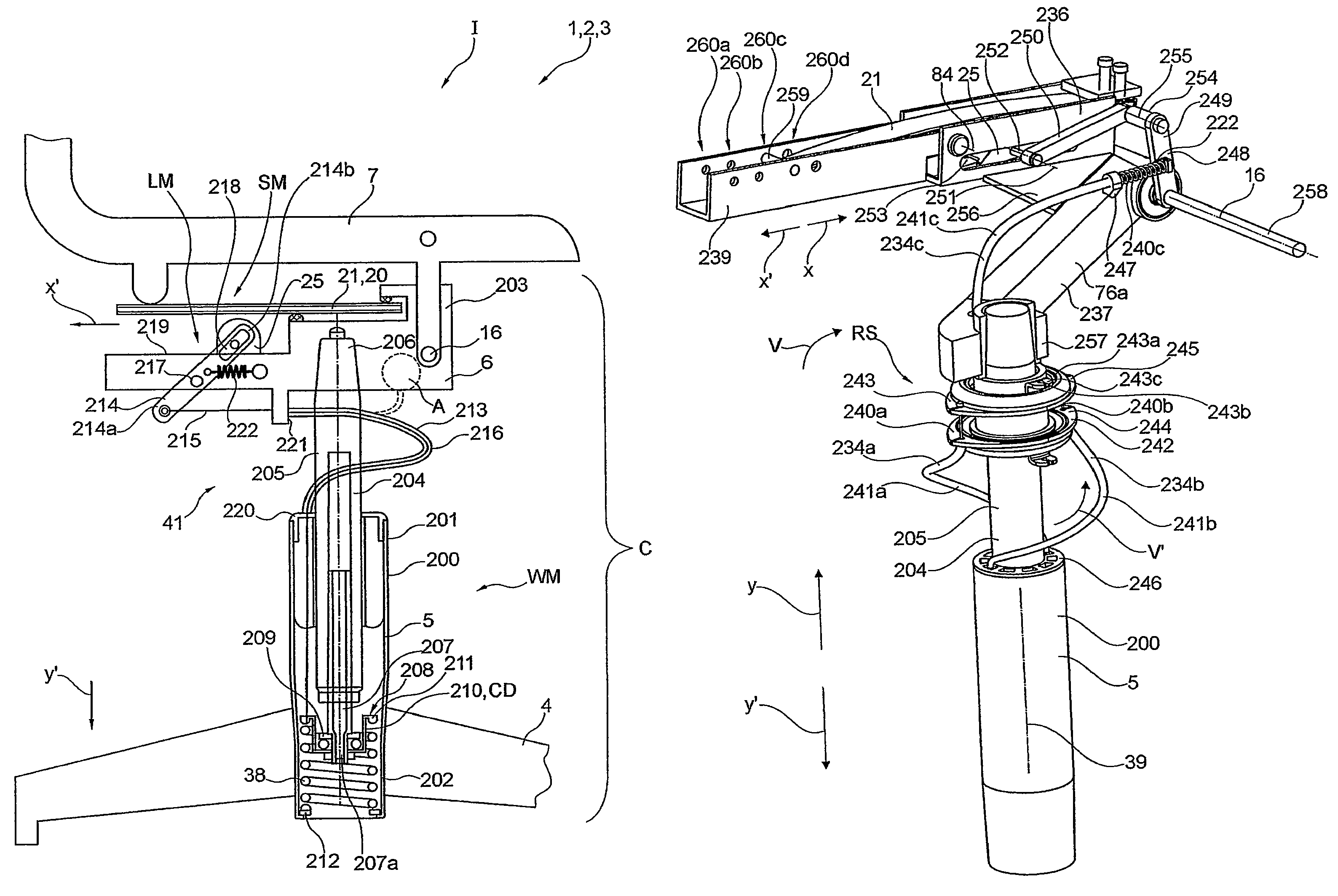
ActiveUS20080194987A1Economy of scaleGrow with diabeticCatheterSensorsAnalyteGraphical user interface
An analyte monitoring system is provided. The system may include a housing (200) and a visual display (206) on the housing (200), the visual display (206) having at lease one visual indicator position next to a corresponding marking (208, 210, 212, 214 and 216) on the housing (200). The system may include a processor (60) driving the visual display (206), wherein the processor (60) runs software that is modifiable to provide a variable user interface on the visual display (206). The system may include a wireless communication to allow applets or programs to be down-loaded by the processor (60).
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Method of component manufacture
InactiveUS6372542B1Produced cost-effectivelyEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a method of producing an electric, electronic, electromechanical and / or mechanical component (12), where the component substrate is given a three-dimensional structure (3'') or configuration, and where said substrate is adapted for further treatment or processing to form the component (12). The substrate is formed by shaping said substrate against a die or mold, such as by molding, pressing, extruding or embossing said substrate, wherewith the precision necessary with respect to said component in the three-dimensional structure is achieved by means of a micromechanical working process when producing the die or mold.
Owner:CRIMSON INT ASSETS LLC
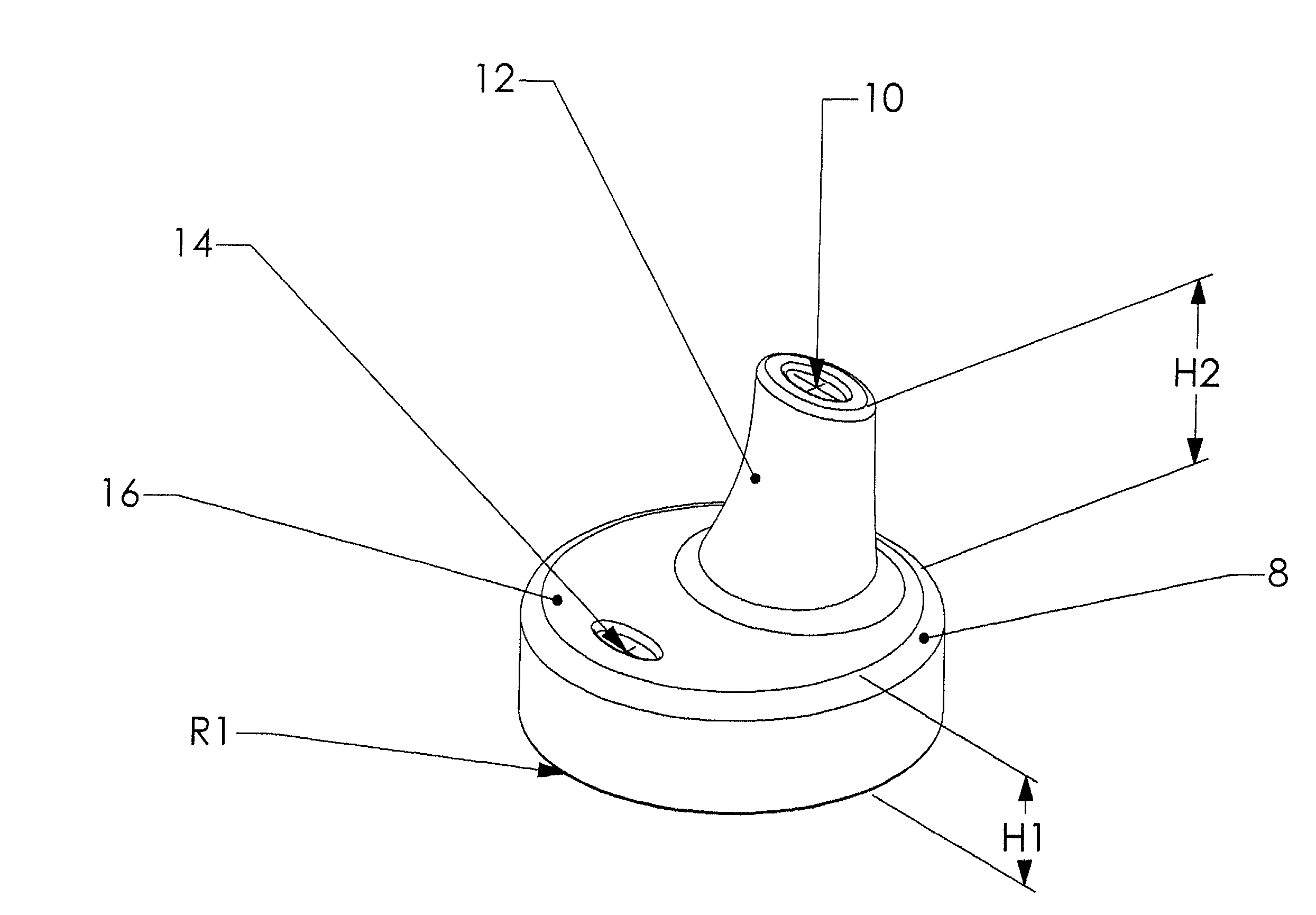
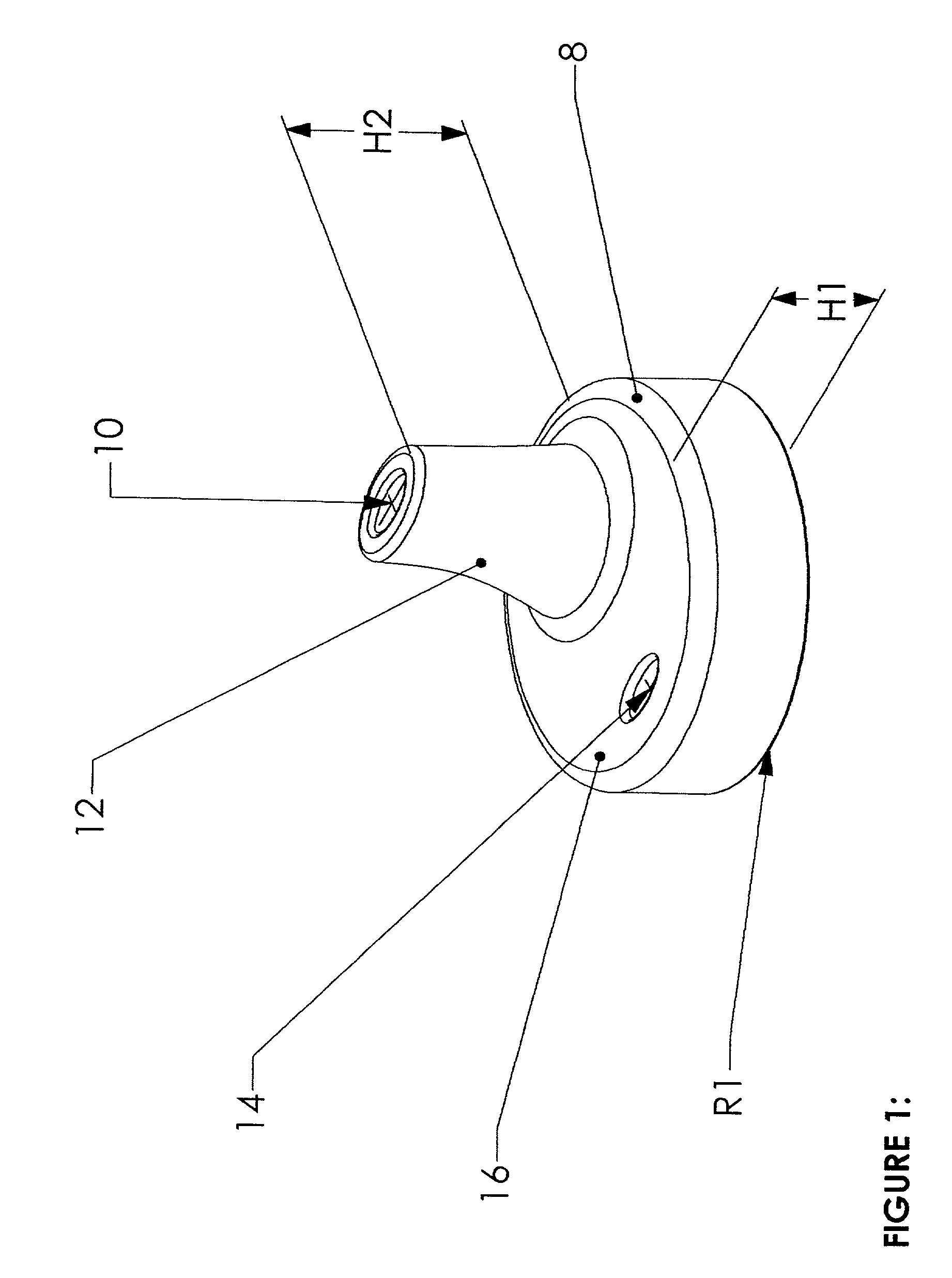
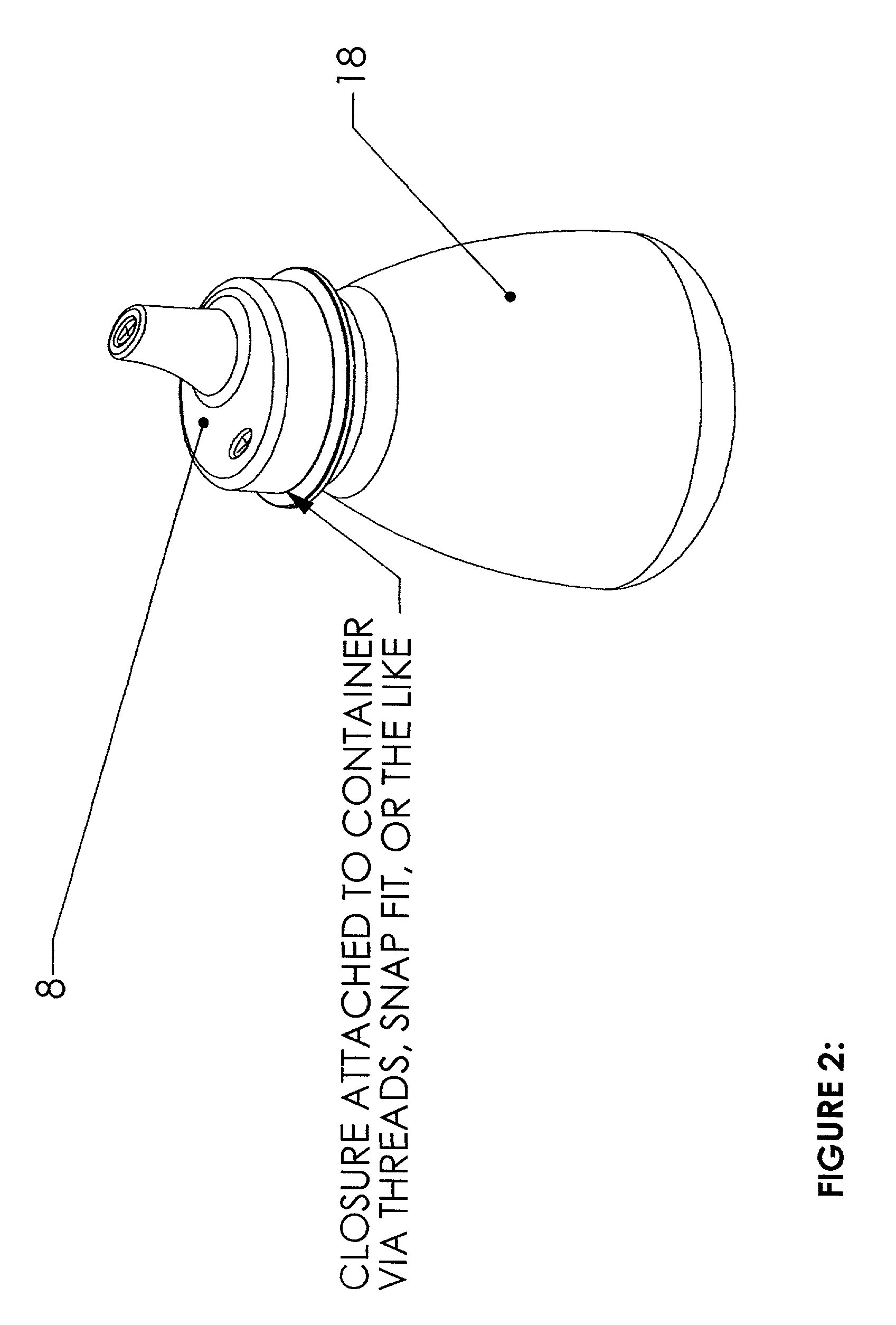
One material, one piece spill-proof closure
InactiveUS20020158075A1Prevent and limit leakageOvercome disadvantagesDrinking vesselsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CALDICOTT ROBERT JOHN +1
Smart card and method for manufacturing a smart card
InactiveUS7237724B2Improve protectionEasy to adaptPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsSmart cardThermosetting polymer
A smart card and a method for manufacturing the same wherein the smart card is composed of a printed circuit board, having a top surface and a bottom surface, a plurality of circuit components attached to the top surface of the printed circuit board, a filler board, attached to the top surface of the printed circuit board, a bottom overlay attached to the bottom surface of the printed circuit board, a top overlay positioned above the top surface of the printed circuit board and a thermosetting polymeric layer positioned between the top surface of the printed circuit board and the top overlay.
Owner:CARDXX
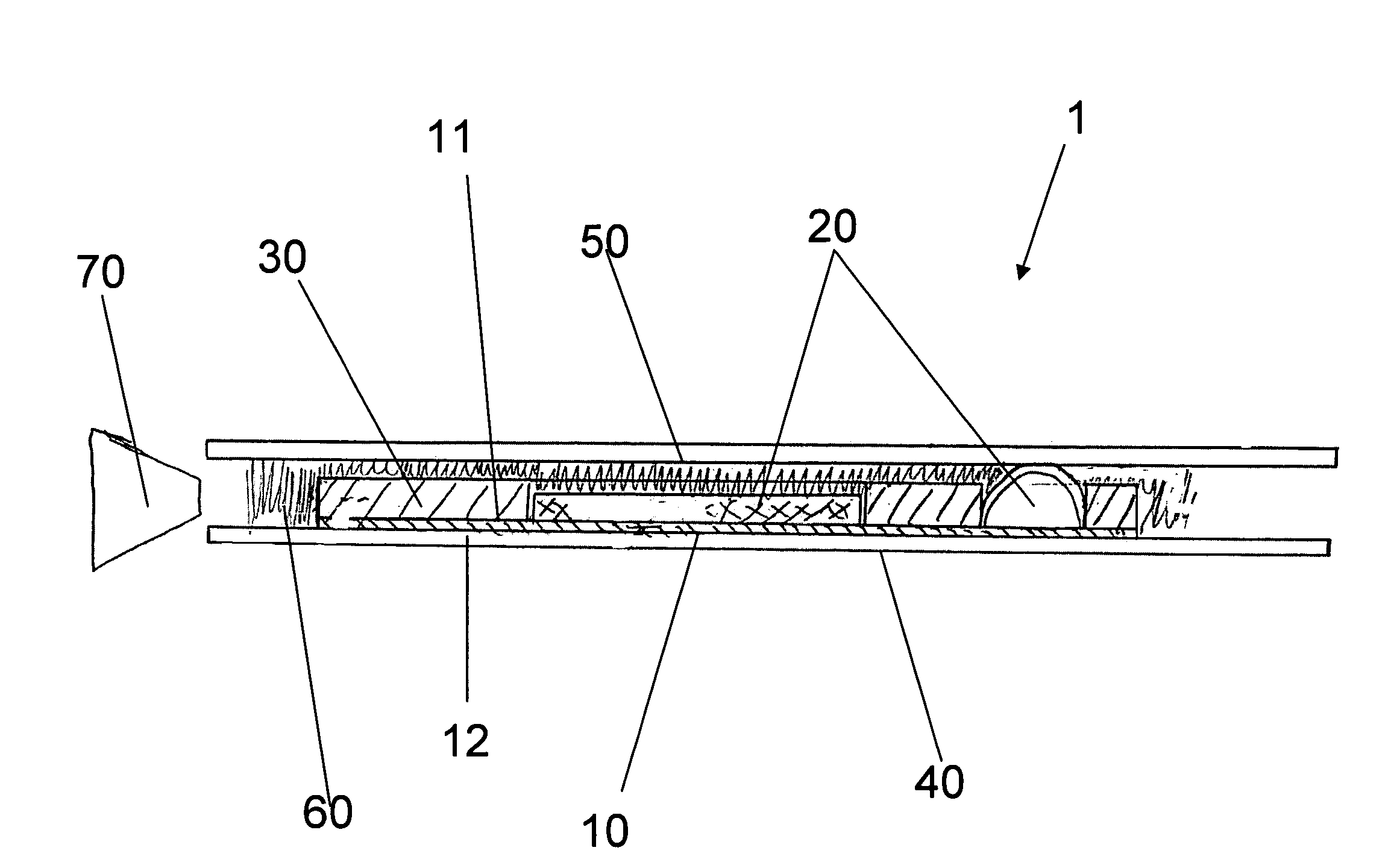
Gas bag for an airbag module
InactiveUS7059634B2Produced cost-effectivelyIncreased riskPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringInternal pressure
A gas bag in which an orifice is opened or closed with the aid of a control band as soon as the gas bag has reached a predetermined state of deployment. One end of the control band is fastened to a gas bag envelope in the region of the orifice. The control band is connected at its other end to the gas bag envelope so that, when the predetermined state of deployment is reached, the control band slips into the gas bag envelope so that the orifice is closed by the slipped-in region of the gas bag envelope by the internal pressure of the gas bag, or the control band slips out of the gas bag envelope so that the previously closed orifice is opened.
Owner:TAKATA CORPORATION
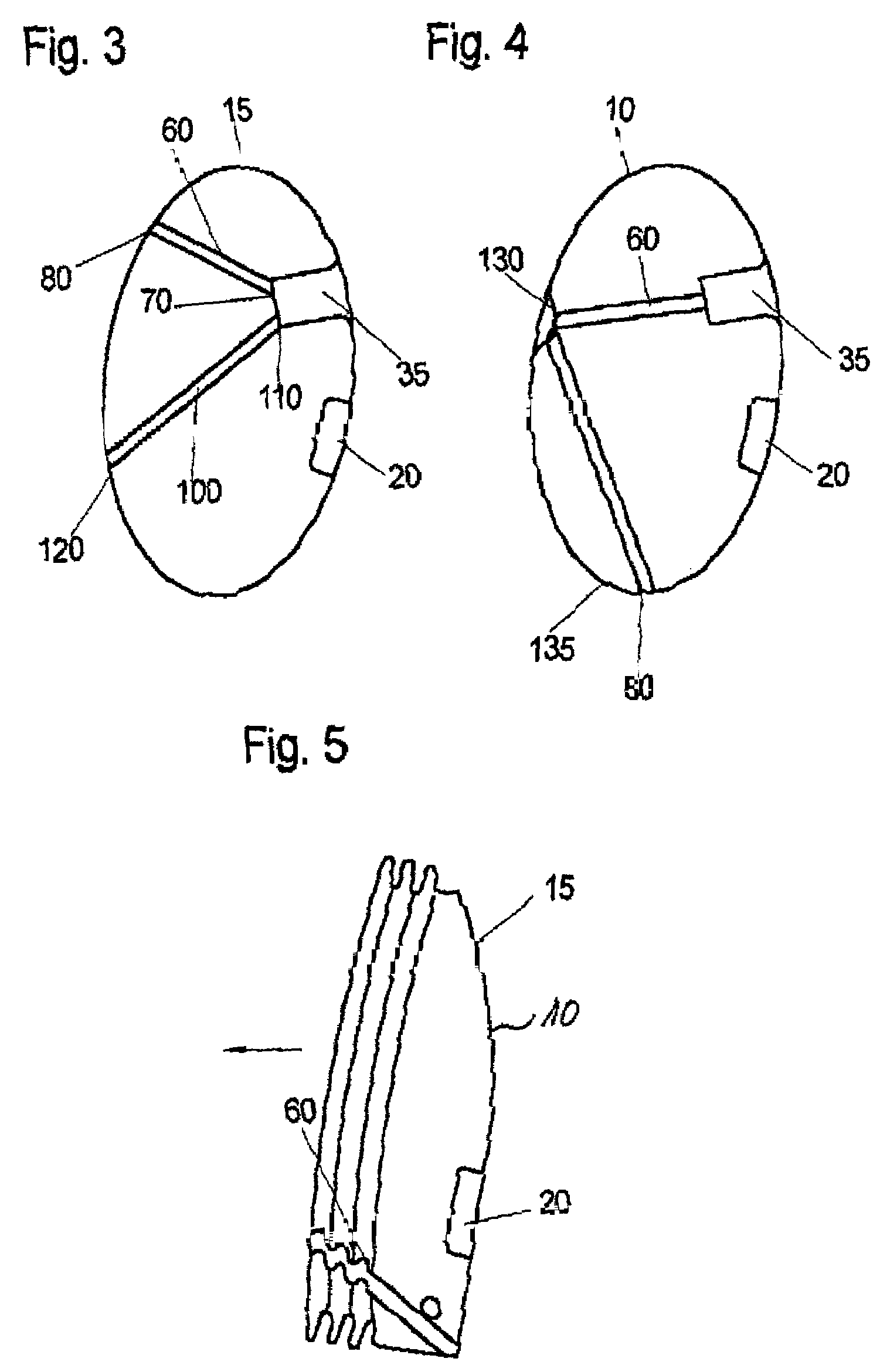
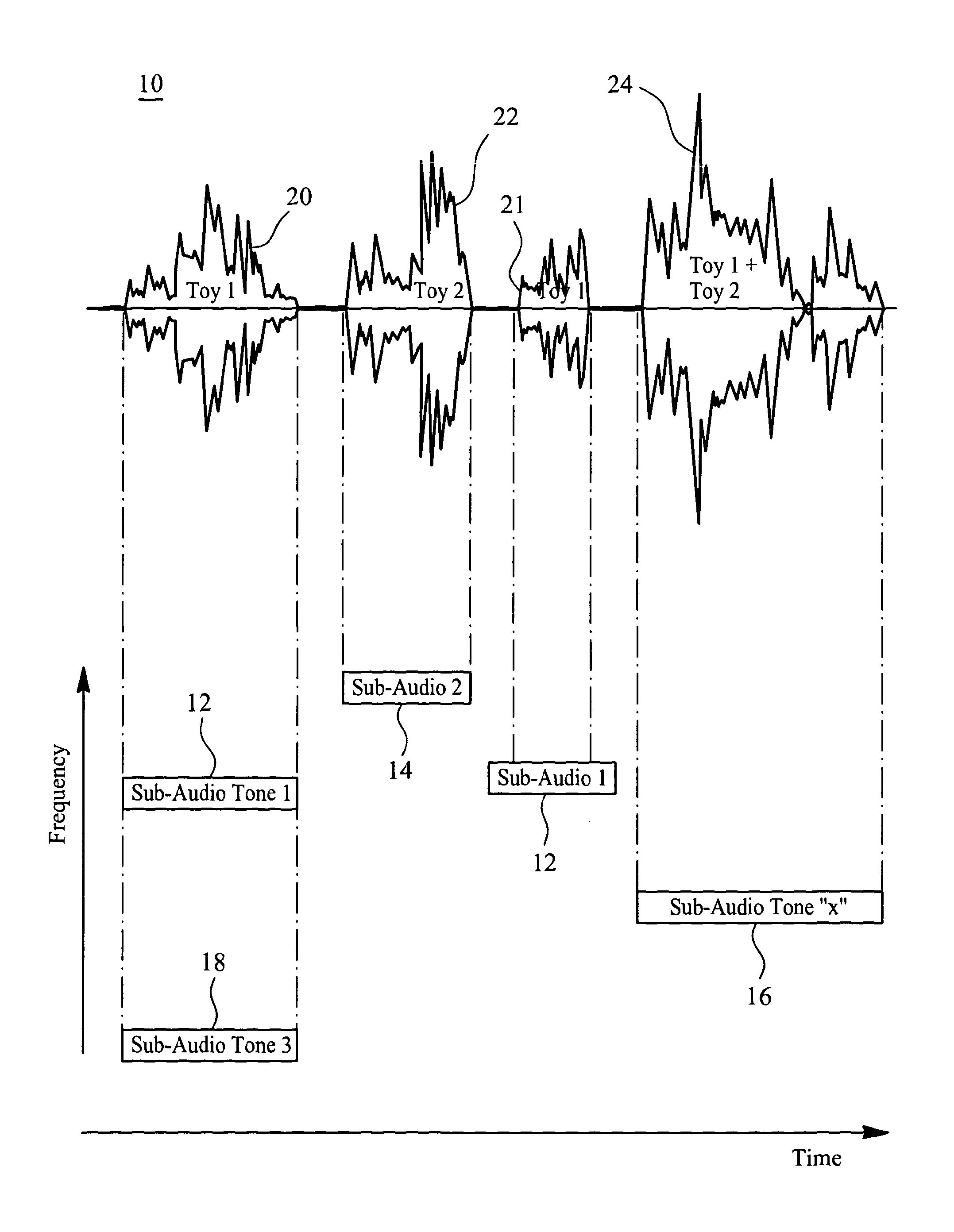
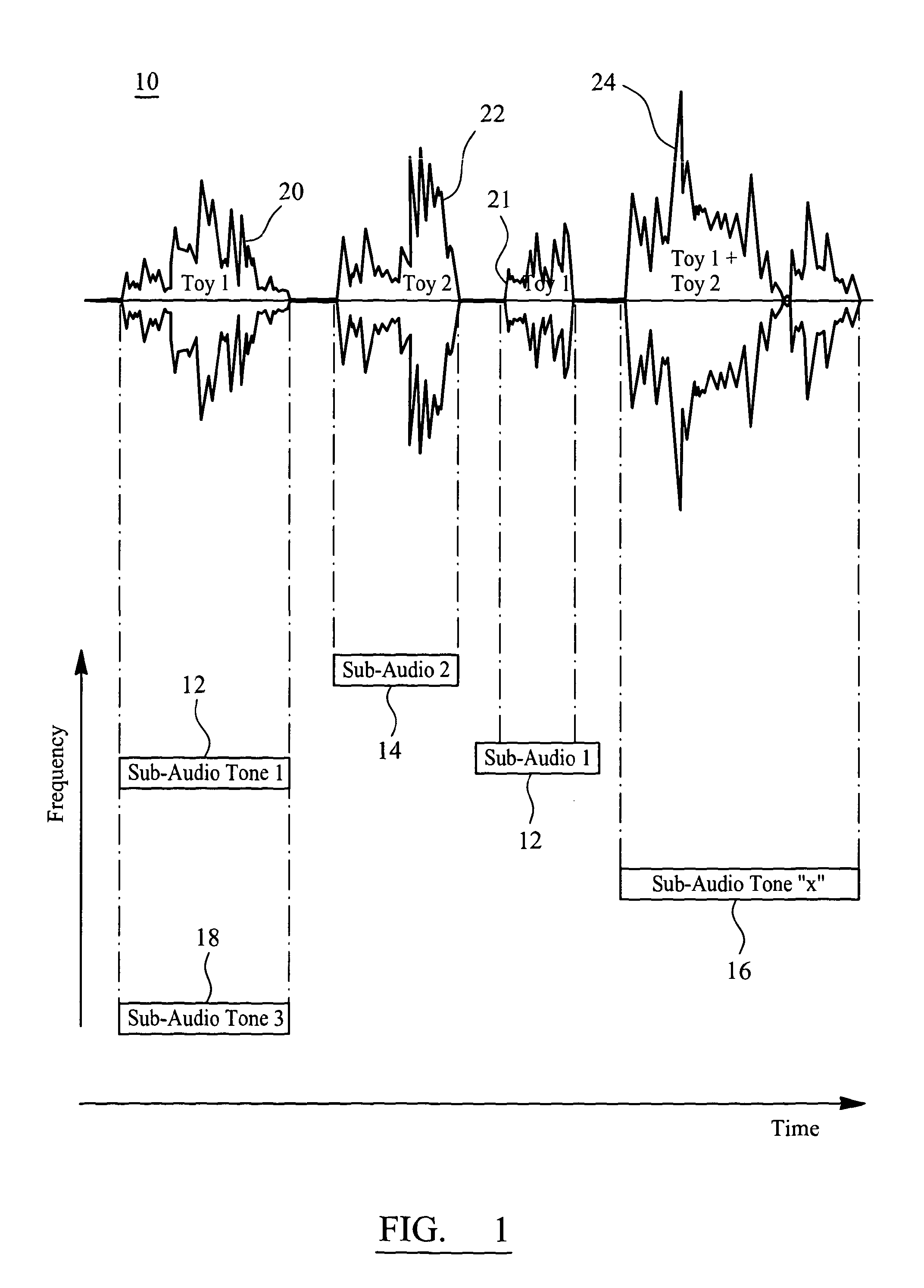
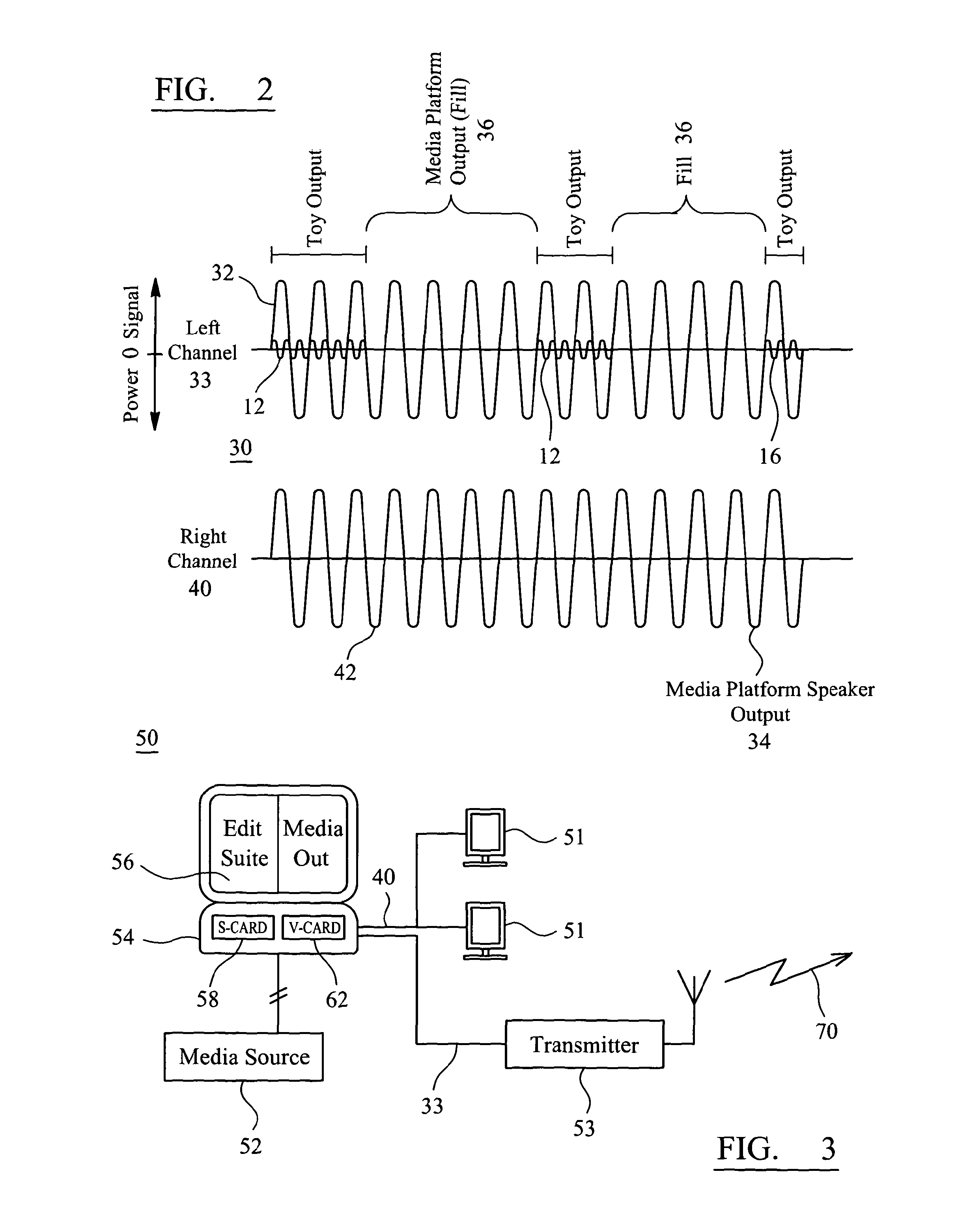
Media Delivery System and a Portable Communications Module for Audio and Remote Control of Interactive Toys or Devices
ActiveUS20130143482A1Increased susceptibilityEasy to learnBroadcast transmission systemsTransmissionMicrocontrollerControl signal
A portable communications module (600) of FIG. 6 has an input (621) coupled to receive an incident signal. The input (621) split out a first audio channel containing a context audio track from the incident signal and directs the first audio channel along a first audio output path for selective audio output from a speaker (634, 620) either internally within or external to the module. The input (621)also directs a second audio channel in the incident signal to an RF audio transmitter chain for broadcast, the second audio channel comprising a composite audio signal from a plurality of audio tracks, each audio track embedded with a unique activation code that is present for substantially an entire duration of audio activity in each audio segment of each track. The input (621) is further arranged to apply a tone encoded signal in the incident signal to at least a tone decoder (640) in a data transmitter chain distinct from the audio transmitter chain (642). A microcontroller (650), responsive to recovered data, is arranged to translate the recovered data into a control signal related to functional control of remote equipment (102). And a data transmit chain (660) operates to modulate the control signal onto a carrier for broadcast to the remote equipment to effect its operational control. The tone encoded data is effectively filtered within the portable communications module to an extent that it is not amplified within the first audio output path and is not processed by the RF audio transmitter chain.
Owner:REGLER
Modular plug-in apparatus and method for safe and secure storage of horizontally stacked photovoltaic modules during transport
InactiveUS20060005875A1Eliminate risk of damageProduced cost-effectivelySolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringPhotovoltaics
Owner:ULLA HABERLEIN LEHR
Ink jet printheads
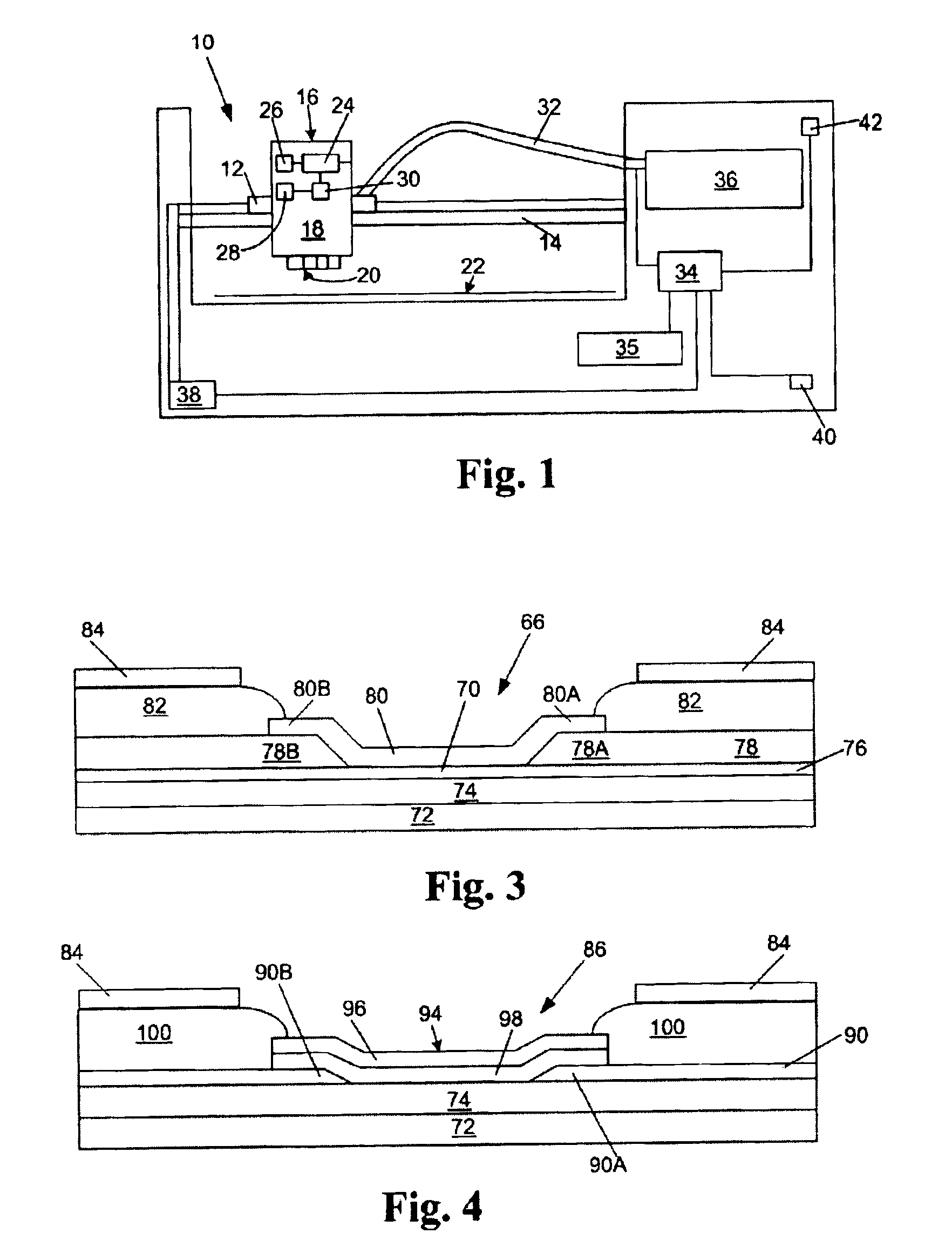
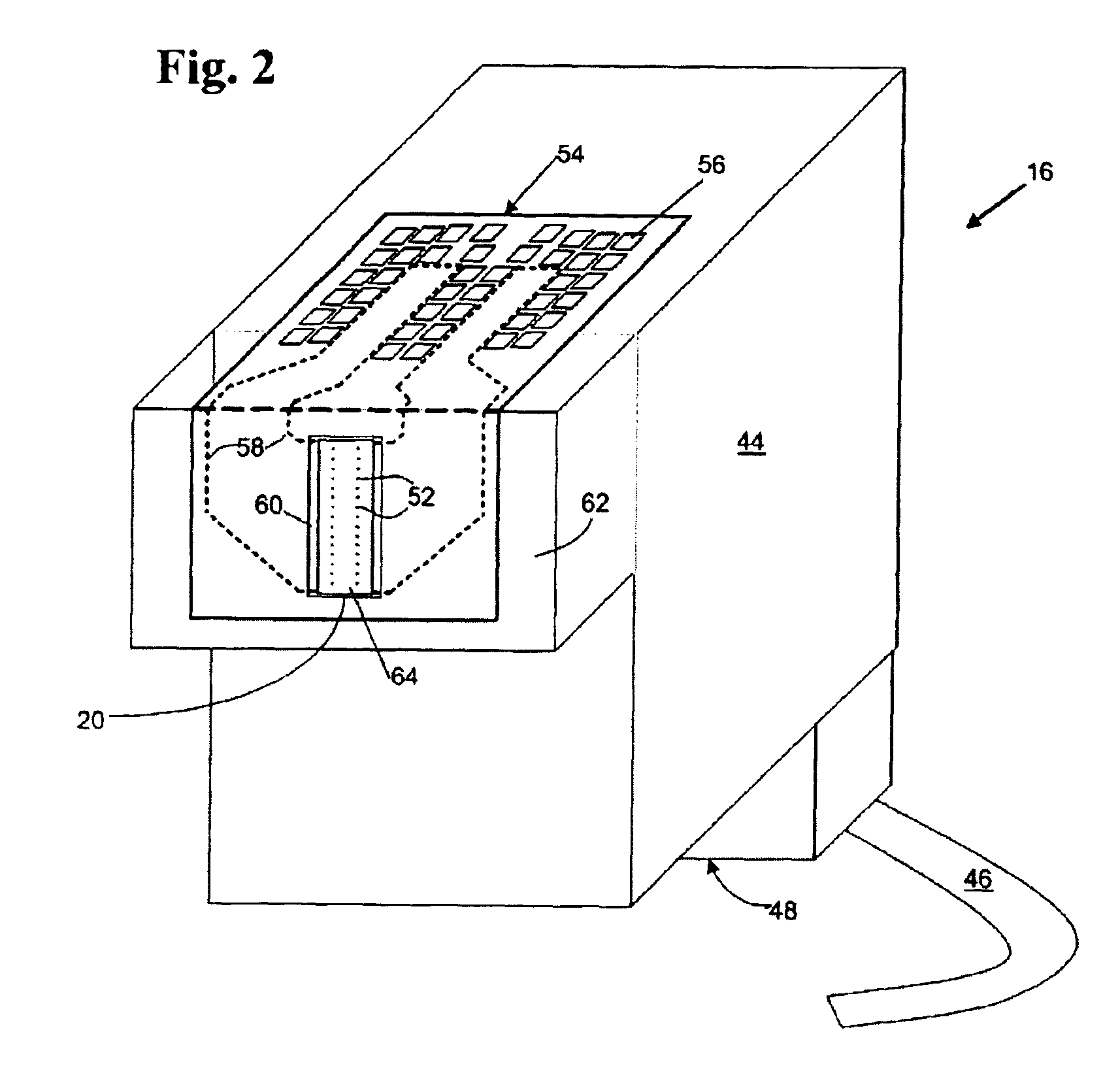
InactiveUS6902256B2Produced cost-effectivelyFast rate of fireInking apparatusPrint mediaElectrical connection
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for preparation of metallic foam products and products made
InactiveUS6524522B2Cost-effectiveMinimal post-processing stepsAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingEnergy absorptionMetal foam
The present invention relates to the extrusion freeform fabrication of low cost, in situ, metallic foam components having oriented microstructures and improved mechanical properties such as energy absorption and specific stiffness. The present invention relates to the freeform fabrication of metallic foams to form parts having complex geometry that demonstrate superior mechanical properties and energy absorbing capacity.
Owner:ADVANCED CERAMICS
Device for the treatment of wounds using a vacuum
InactiveUS20110313373A1Simple designCost effectiveAdhesive dressingsIntravenous devicesSecretionBiomedical engineering
A device for treating wounds using a vacuum and having a gas-tight wound-covering element, which, when placed in contact with the body of the patient, forms a wound space between the respective wound and the wound-covering element. The device includes an absorption body, which is a layer, enclosed in an envelope, of a textile section, interspersed with super-absorbing particles. The liquid-permeable envelope has pores, the size of which does not exceed that of the super-absorbing particles. The absorption body, inserted in the wound space, has an initial volume, which enlarges in the course of the absorption process, and a final volume, so that, due to the size of the pores of the envelope, the absorbed wound secretions remain within the absorption body and, with that, below the wound-covering element, until the absorption body is removed from the wound space.
Owner:RIESINGER BIRGIT
Self-grown monopoly compact grit
InactiveUS6616725B2Strong and more resilientProduced cost-effectivelyPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBoron nitrideSolvent
A self-grown monopoly compact grit and high pressure, high temperature process for preparing the same. The high pressure, high temperature sintered / synthesized monopoly compact grit is used in various industrial tools such as saw blades, grinding wheels, cutting tools and drill bits. Further, the monopoly compact grit of the present invention is produced from a seed of a mono-crystal of diamond or cubic boron nitride surrounded by either a self-grown crystal layer or an integrally bonded poly-crystalline sintered compact layer. The self-grown crystal layer is a new grown crystal structure where the seed crystal grows into a new phase through a normal diamond or cubic boron nitride synthesis process in the presence of a catalyst metal solvent. The compact layer is composed of about 50 to about 90 volume percent of diamond or cubic boron nitride, a typical binder material, which is a catalyst for crystal-to-crystal bonding, and a cementing agent which is a binding agent capable of forming stable carbide and nitride bonds.
Owner:CHO HYUN SAM +2
Smart card and method for manufacturing a smart card
InactiveUS20060226240A1Improve protectionEasy to adaptPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsPrinted circuit boardEngineering
A smart card and a method for manufacturing the same wherein the smart card is composed of a printed circuit board, having a top surface and a bottom surface, a plurality of circuit components attached to the top surface of the printed circuit board, a filler board, attached to the top surface of the printed circuit board, a bottom overlay attached to the bottom surface of the printed circuit board, a top overlay positioned above the top surface of the printed circuit board and a thermosetting polymeric layer positioned between the top surface of the printed circuit board and the top overlay.
Owner:CARDXX
Cast unitized primary truss structure and method
ActiveUS20050274485A1Produced cost-effectivelyWeight morePower plant constructionFoundry mouldsJet engineFlight vehicle
A truss structure well suited for use as an engine strut on a commercial aircraft. The truss structure is cast as a single piece integrally formed component from a titanium alloy or another suitably lightweight, structurally strong material. The truss structure includes a plurality of integrally formed attachment structures which enable the truss structure to be secured to an element of an aircraft such as a wing. A plurality of attachment areas for an element such as an engine is also formed that allows the element (e.g. jet engine) to be secured to the truss structure. The truss structure includes a plurality of elongated rails and truss elements that are arranged to provide redundant load paths to ensure that a failure of any one truss element or elongated rail will not result in a failure of the overall truss structure to support whatever load is required.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Socket with non-connecting terminal
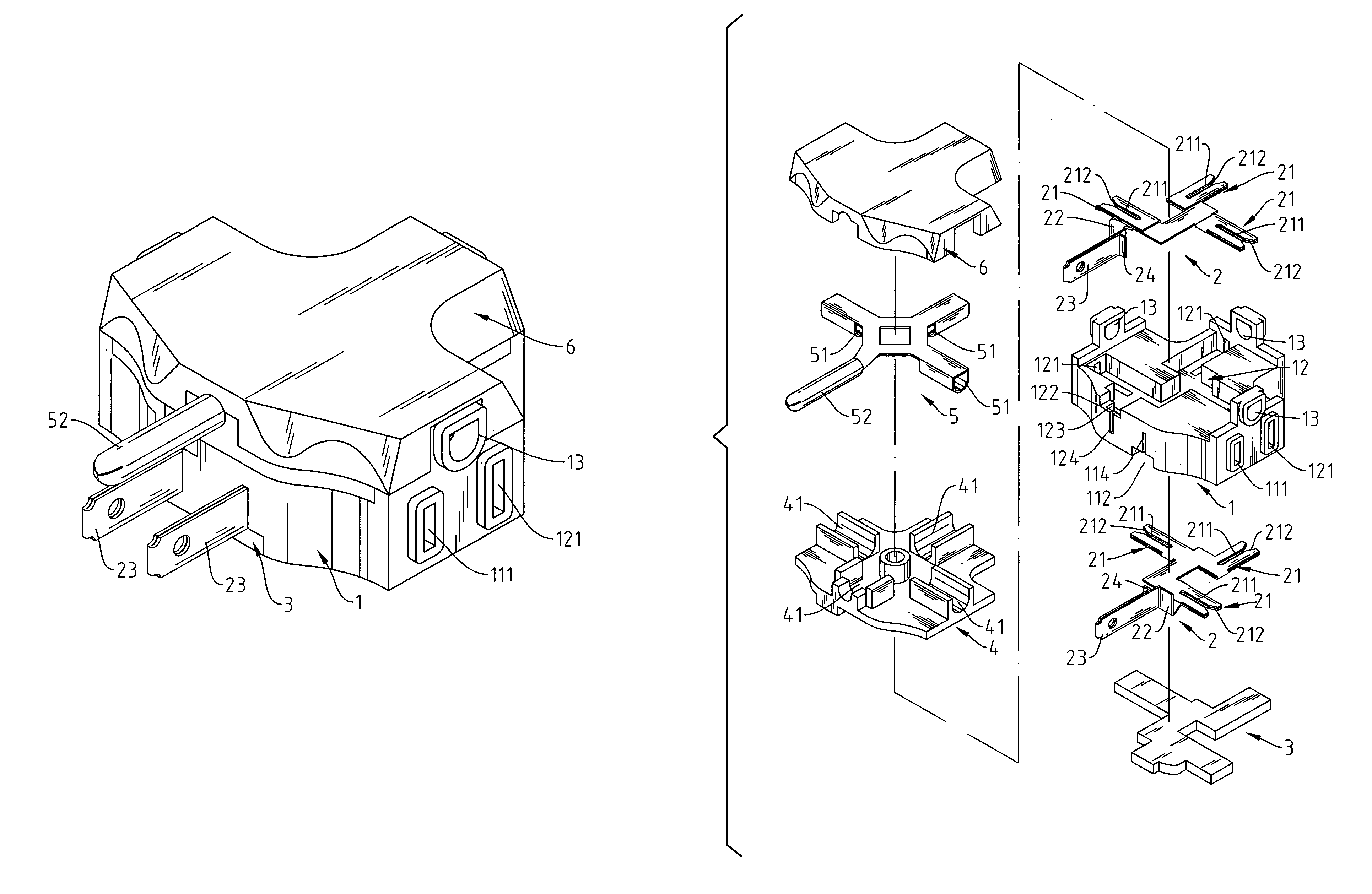
InactiveUS6929514B1Produced easily and cost-effectivelyProduced cost-effectivelyContact member manufacturingElectric discharge tubesEngineeringTop cap
A socket with non-connecting terminal comprises a socket body, two power terminals, a bottom cover, a support, a ground terminal and a top cover in which the power terminals and the ground prong are integrally stamped without terminal tap. The power terminals are placed in the first receptacle and the second receptacle and sealed with the support and the bottom cover. The power blades are exposed outside to be connected to the wall socket. The three slots serve as a power supply to receive other plugs. The integrally stamped ground terminal is housed in the support and sealed by the top cover; the ground prong is exposed outside for linking to the power supply. The three ground slots on the ground terminal will accept the ground prongs from other plugs. When an electrical current flows through this circuit, there is no resistance encountered and no heat generated.
Owner:CHAO TRADING
Piece of furniture
ActiveUS8025334B2The process is fast and accurateProduced cost-effectivelyStoolsAdjustable chairsMechanical engineering
A body support structure, such as a piece of furniture, in particular a piece of furniture for sitting on or a piece of furniture for lying on, such as, for example, chair, armchair, stool, bed or sofa, a seat of the piece of furniture being supported by a spring mechanism, and the spring mechanism being capable of being set to a weight force with which a person acts on the seat.
Owner:MILLERKNOLL INC
Optoelectronic sensor device
InactiveUS6995354B2Produced cost-effectivelyFree spaceHeater elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamTransmitter
An optoelectronic sensor device for detecting precipitation on an outer surface of a transparent pane. The sensor device includes a beam guide attached to an inner surface of the pane and a circuit board offset from the inner pane surface. A beam transmitter is arranged on the circuit board to transmit, along a transmission beam path, a light beam toward the pane via the beam guide. A beam receiver is arranged on the circuit board to receive, along a reception beam path, a light beam reflected from the outer surface of the pane via the beam guide. A circuit substrate, electrically connected to the circuit board, is arranged parallel to the pane between the pane and the circuit board. An installation space separates the circuit substrate from the inner pane surface. A heating device is arranged on the circuit substrate in an area lying outside of the beam paths.
Owner:LEOPOLD KOSTAL GMBH & CO KG
Steering gear having a fixed bearing and a floating bearing for a screw pinion
ActiveUS20120272765A1Reduce noiseDefinable elasticityRolling contact bearingsShaftsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE STEERING
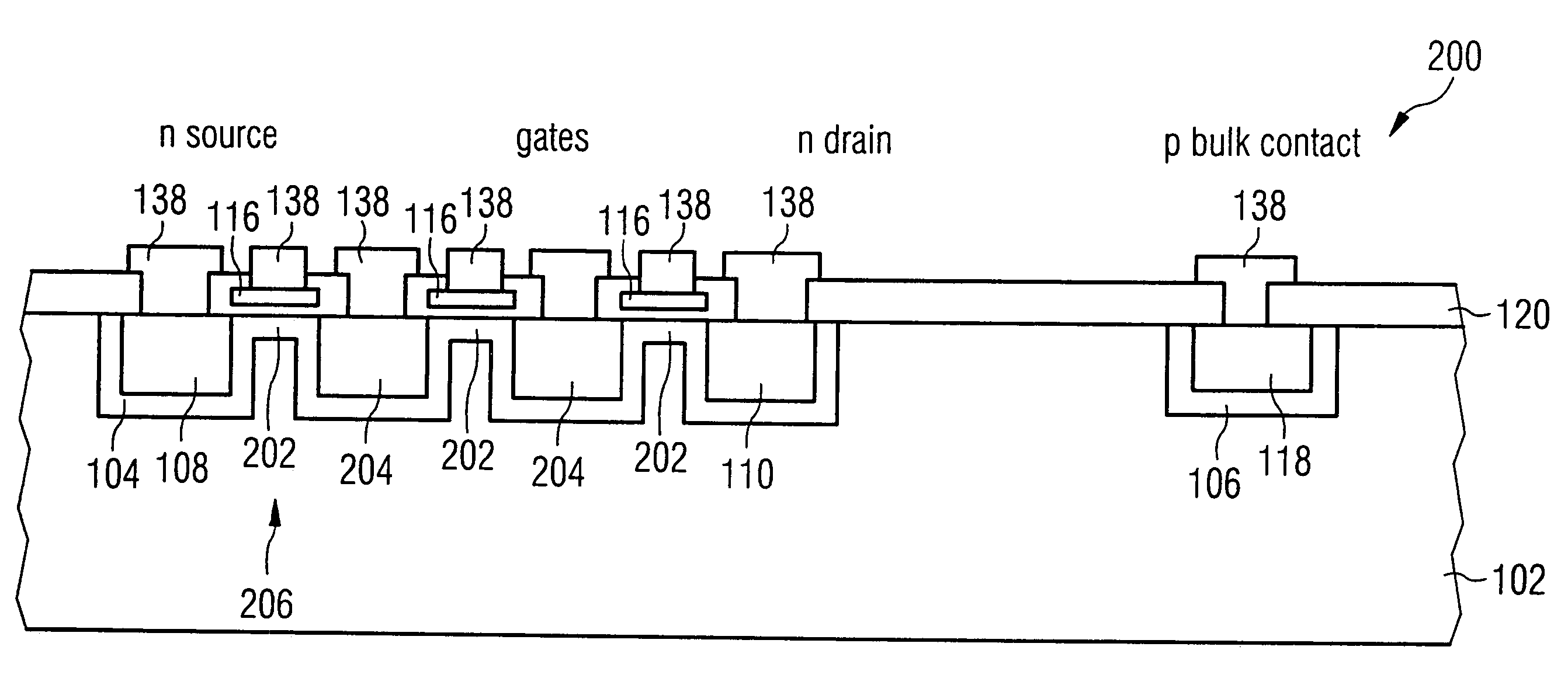
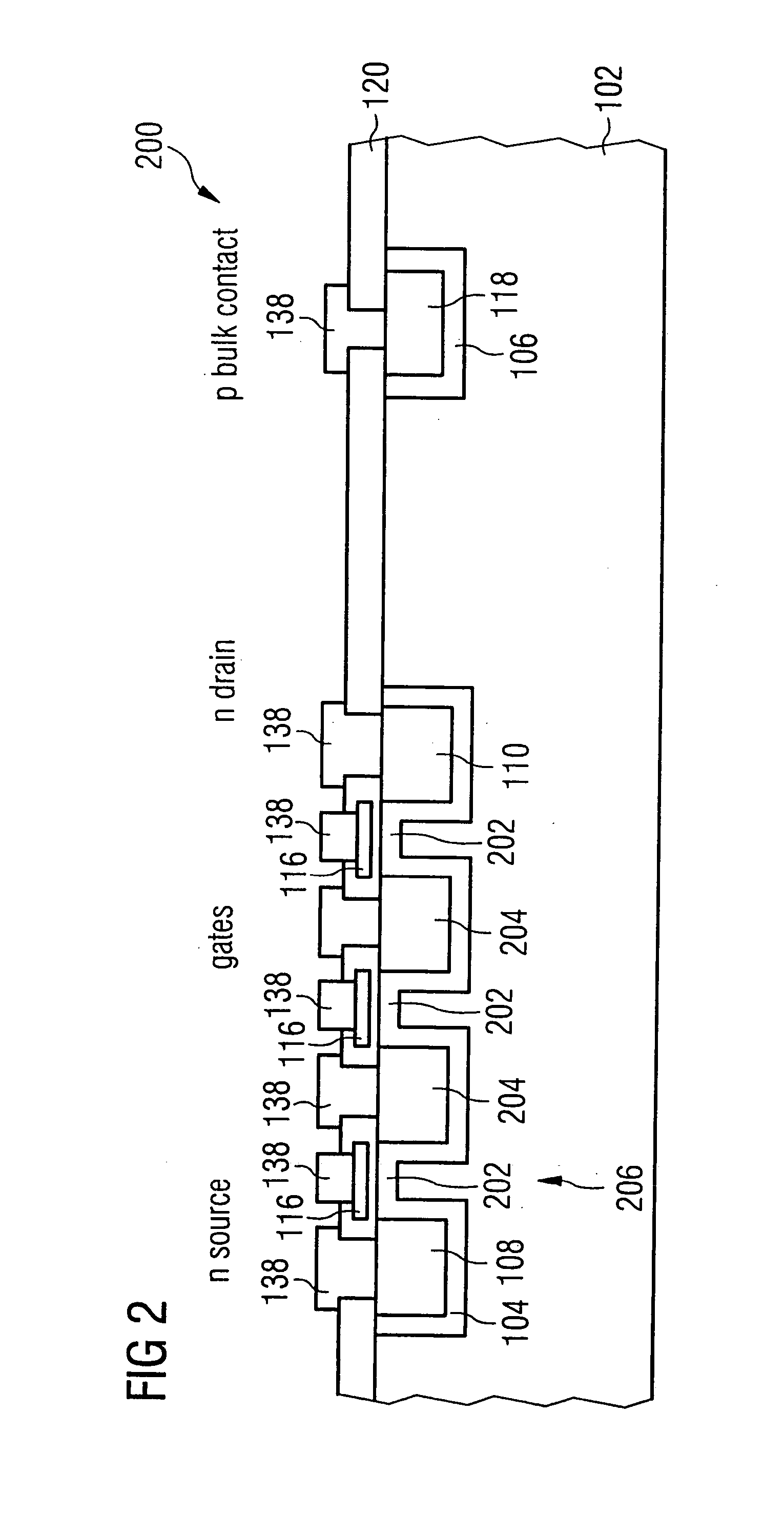
High-frequency switching transistor and high-frequency circuit
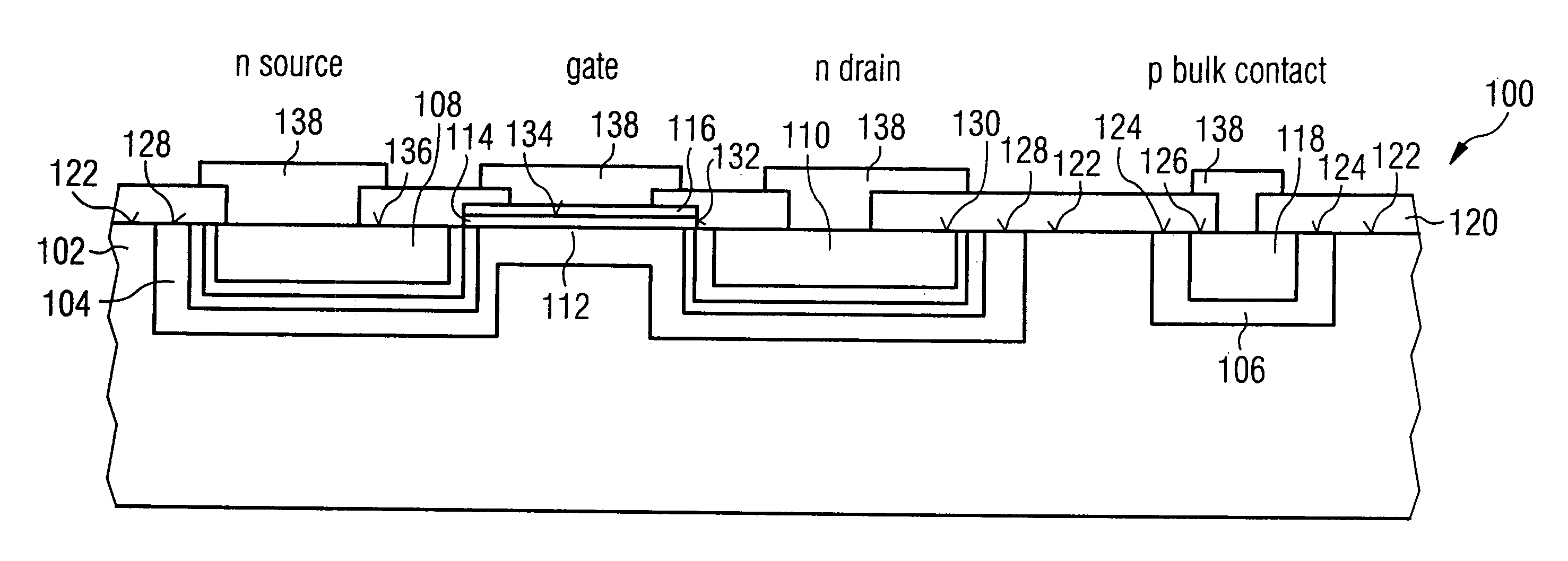
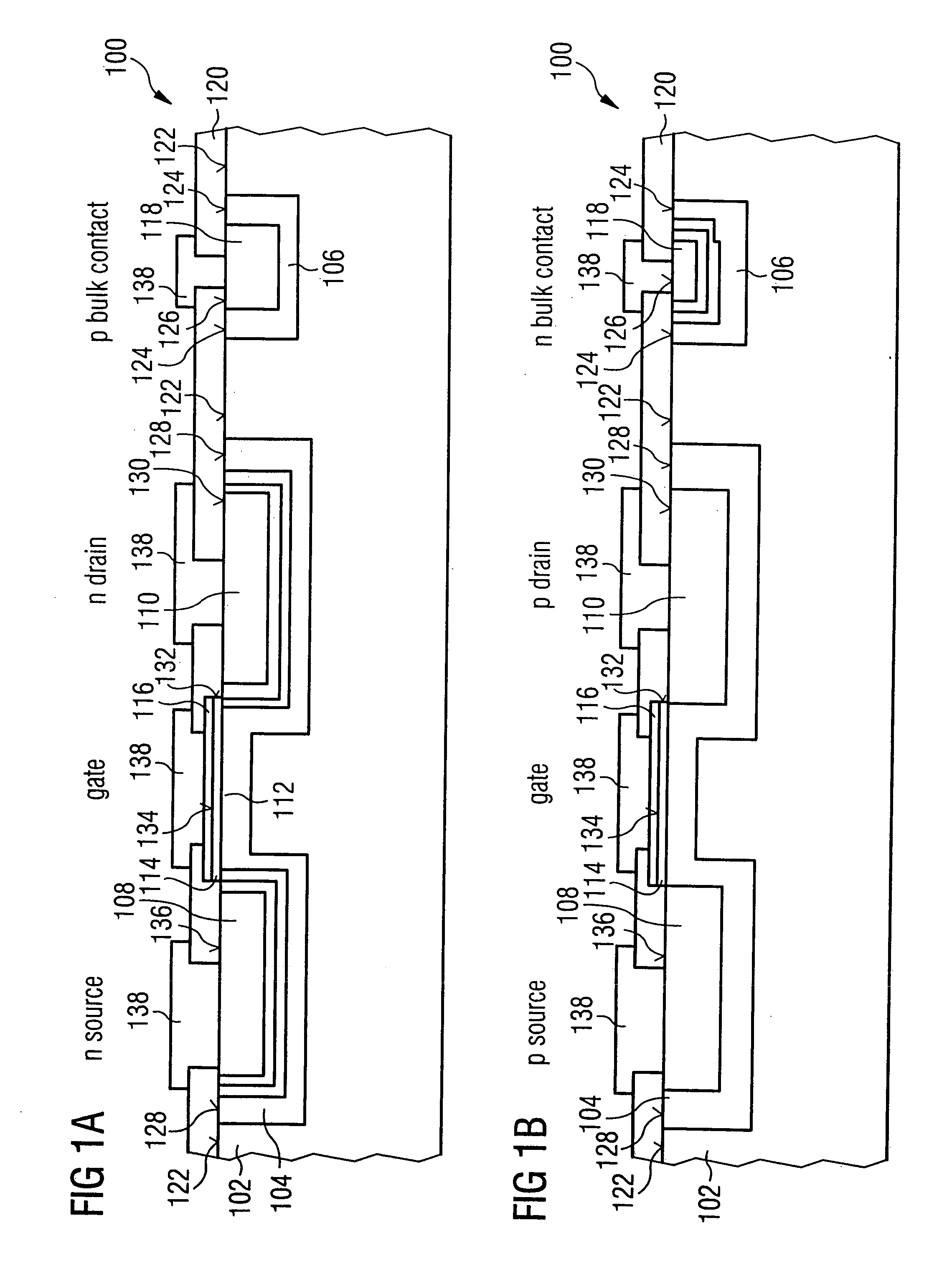
ActiveUS7564103B2Good integration characteristicCost-effectiveTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantTransistor
A high-frequency switching transistor comprises a substrate having a substrate dopant concentration and a barrier region bordering on the substrate, which has a first conductivity type, wherein a barrier region dopant concentration is higher than the substrate dopant concentration. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor comprises a source region embedded in the barrier region, which comprises a second conductivity type different to the first conductivity type, and has a source region dopant concentration, which is higher than the barrier region dopant concentration. Additionally, the high-frequency switching transistor comprises a drain region embedded in the barrier region and disposed offset from the source region, which comprises the second conductivity type and has a drain region dopant concentration, which is higher than the barrier region dopant concentration. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor has a channel region, extending between the source region, wherein the channel region comprises a subregion of the barrier region. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor has an insulation region, which covers the channel region and which is disposed between the channel region and the gate electrode. Such a high-frequency switching transistor allows switching of high-frequency signals with higher high-frequency signal amplitudes as are switchable by conventional high-frequency switching transistors.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Hydrolysis-resistant, transparent, biaxially oriented film made from a crystallizable thermoplastic, and process for its production
InactiveUS6855758B2Maintain good propertiesLow shrinkageAluminium compoundsOrganic chemistryPolyesterThermoplastic
The invention relates to transparent, biaxially oriented and heat-set films having one or more layers and compris, as main constituent, at least one crystallizable thermoplastic, in particular a polyester, and also comprise at least one hydrolysis stabilizer. The hydrolysis stabilizer is preferably a phenolic compound, an oxazoline, and / or a monomeric or polymeric carbodiimide, where appropriate combined with an organic phosphite. It is preferably added in the form of a masterbatch. The film exhibits low longitudinal and transverse shrinkage. On exposure to moisture and heat it shows practically no embrittlement and retains its ultimate tensile strength. The additional functionality is preferably that the film has been made UV-resistant, or flame-retardant, or on one side or on both sides has been coated, or is sealable, and / or has been corona- or flame-treated. The film is generally produced by extrusion or coextrusion, the hydrolysis stabilizer being added in the form of a predried or precrystallized masterbatch.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Illumination device for simulating neon or fluorescent lighting including a waveguide and a scattering cap
ActiveUS7008097B1Effective lightingProduced cost-effectivelyNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceDistribution patternEffect light
An illumination device includes: an optical waveguide having a first lateral surface for emitting light and a second lateral surface for receiving light; a scattering cap secured to the first lateral surface of and extending substantially the length of the waveguide; and a light source (e.g., a plurality of LEDs spaced a predetermined distance from one another) positioned adjacent to the light-receiving surface of the waveguide. Light entering the waveguide is efficiently transmitted to the scattering cap and is then preferentially scattered so as to exit with a broad elongated light intensity distribution pattern being formed along a lateral surface of the scattering cap.
Owner:LUMINII PURCHASER LLC
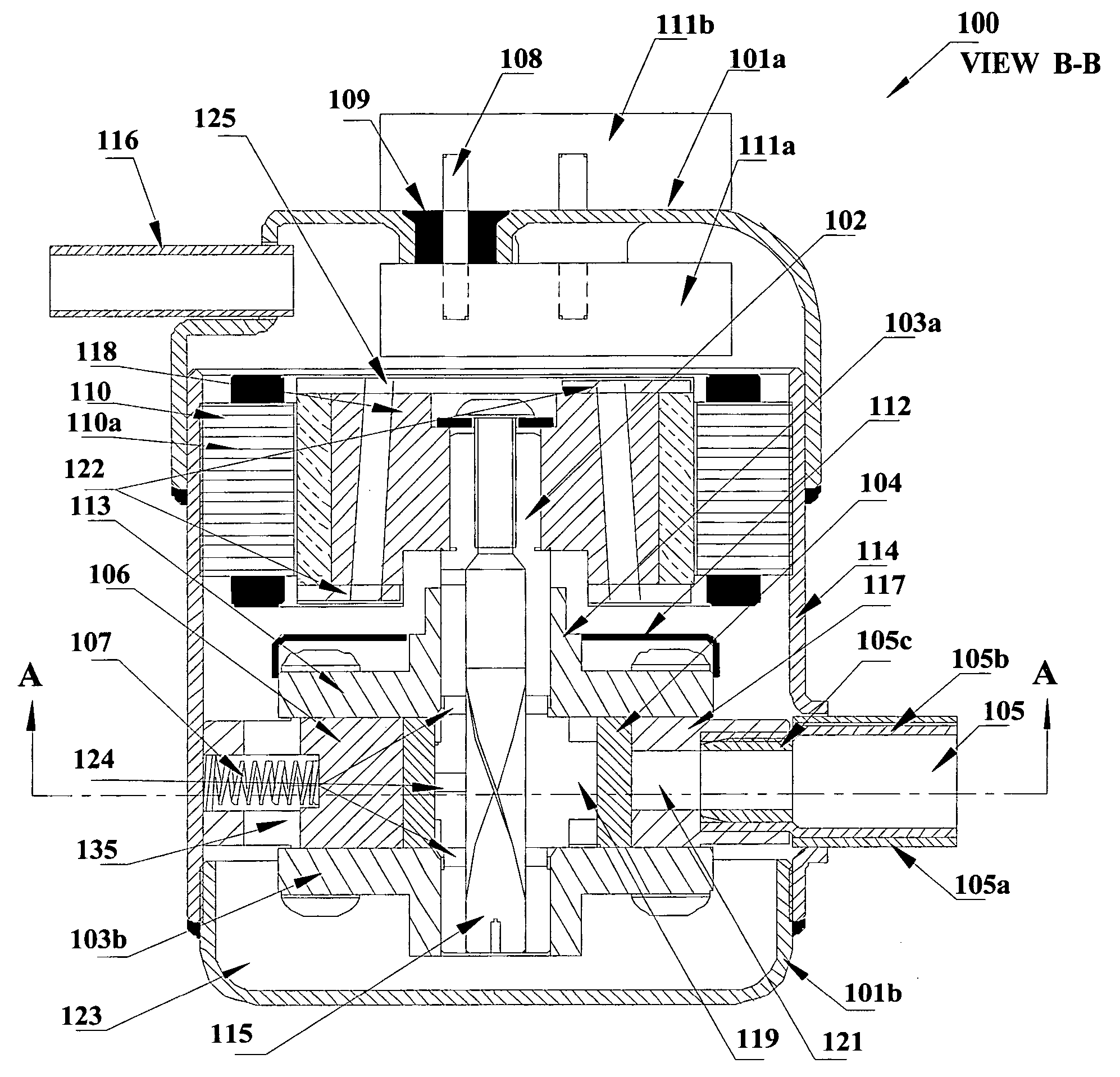
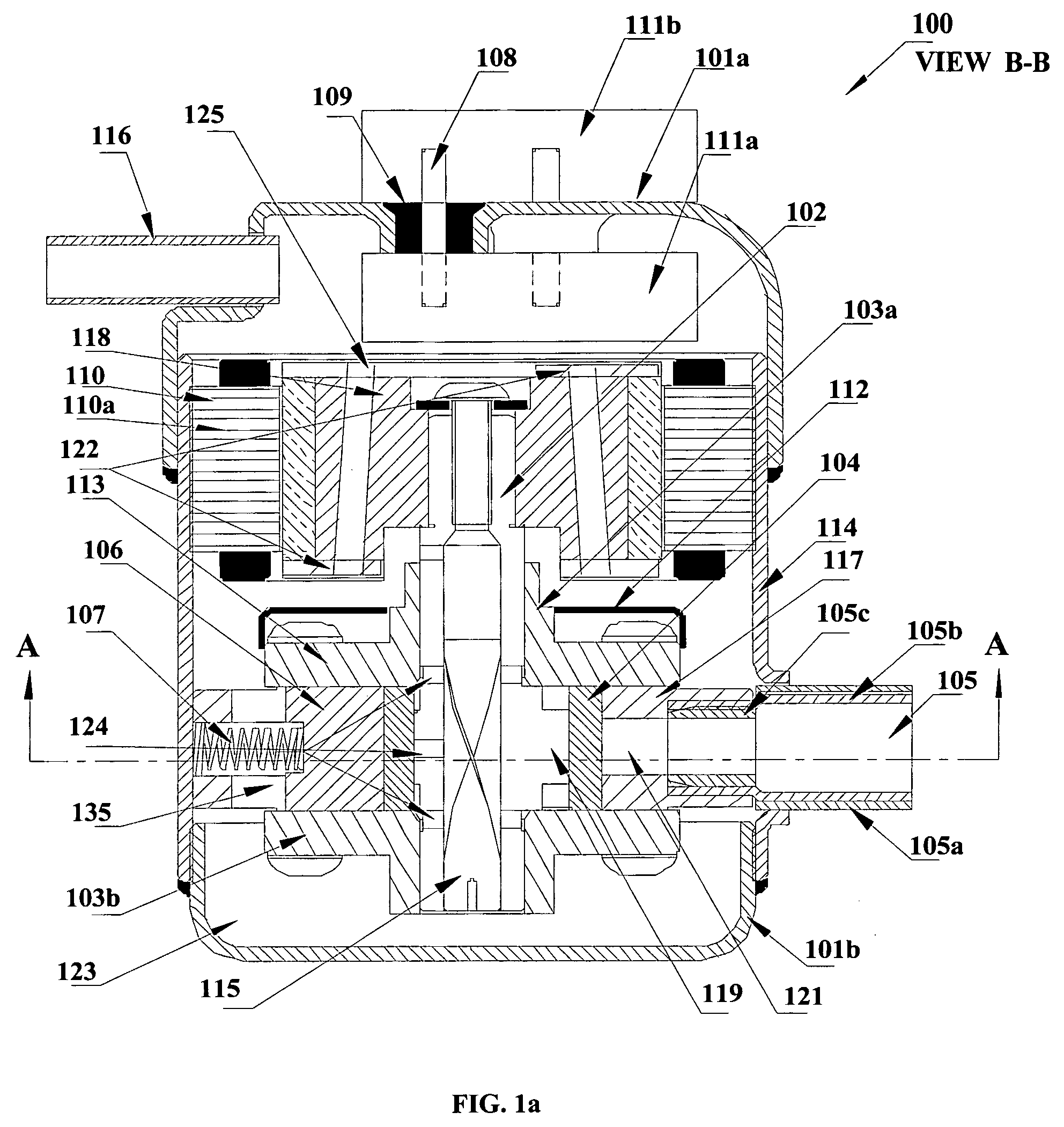
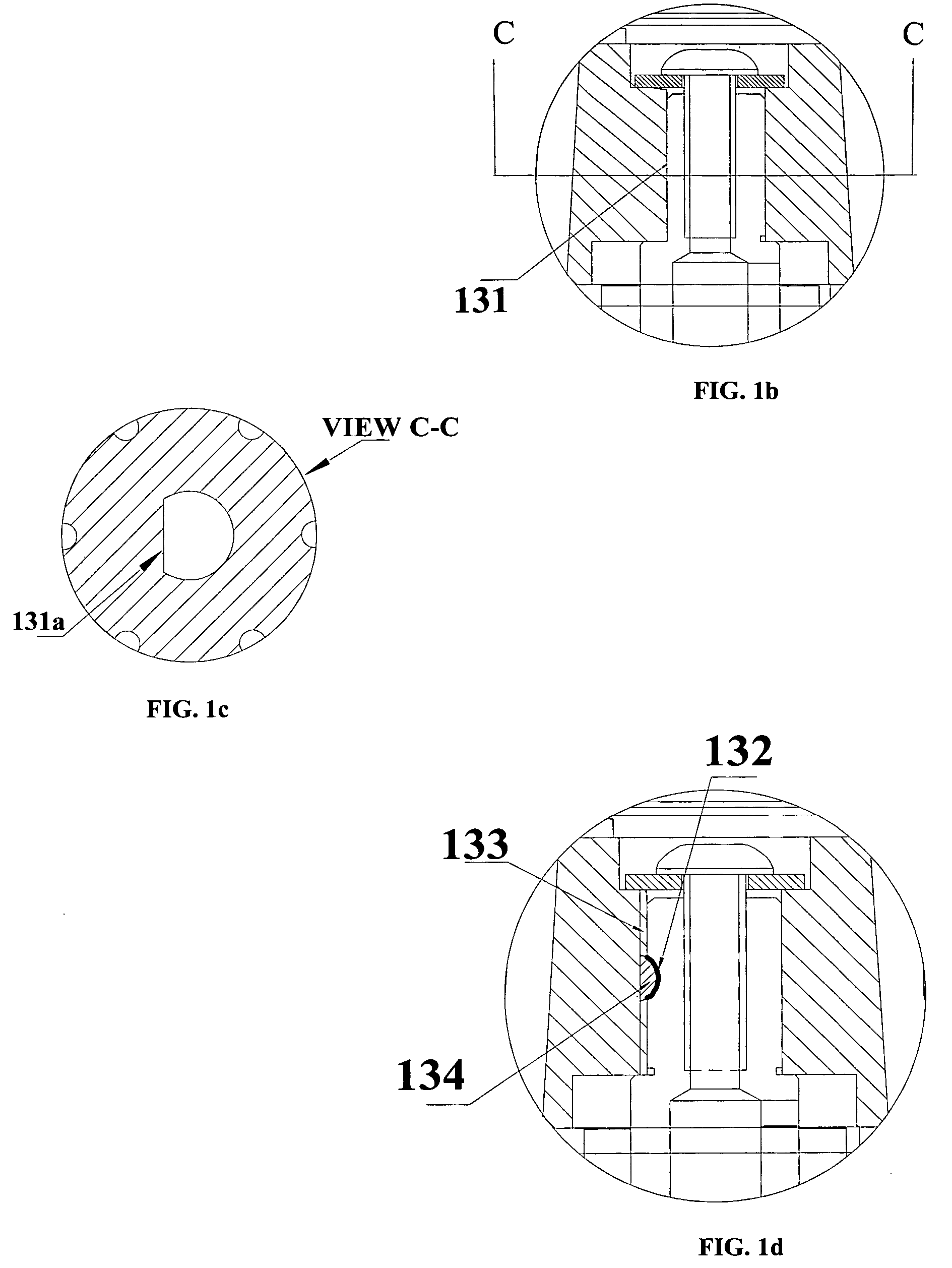
Miniature rotary compressor, and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20060140791A1High densityImprove efficiencyProgramme controlCompressorMiniaturizationEngineering
Disclosed is a rolling piston rotary compressor for use with primary refrigerants that is miniaturized for portable and mobile applications for which size and weight are often crucial. The miniature rotary compressor comprises a compressor mechanism, a brushless DC motor and a casing. The compressor mechanism comprises, a cylinder, a shaft having an eccentric part, one or more bearings to support the shaft, a roller, a vane, an oil sump, openings for communicating with lubricant oil and refrigerant, and inlet and discharge ports. The compressor mechanism and the motor are housed in a hermetically sealed or semi-hermetically sealed casing. The configuration and design of the present invention allow the realization of an ultralight miniature compressor. The miniature rotary compressor provides a higher power density and comparable efficiency as compared to state-of-the-art refrigerant-based rotary compressors. Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing the miniature rotary compressor.
Owner:ASPEN COMPRESSOR
Double-axle, shock-resistant rotation rate sensor with linear and rotary seismic elements
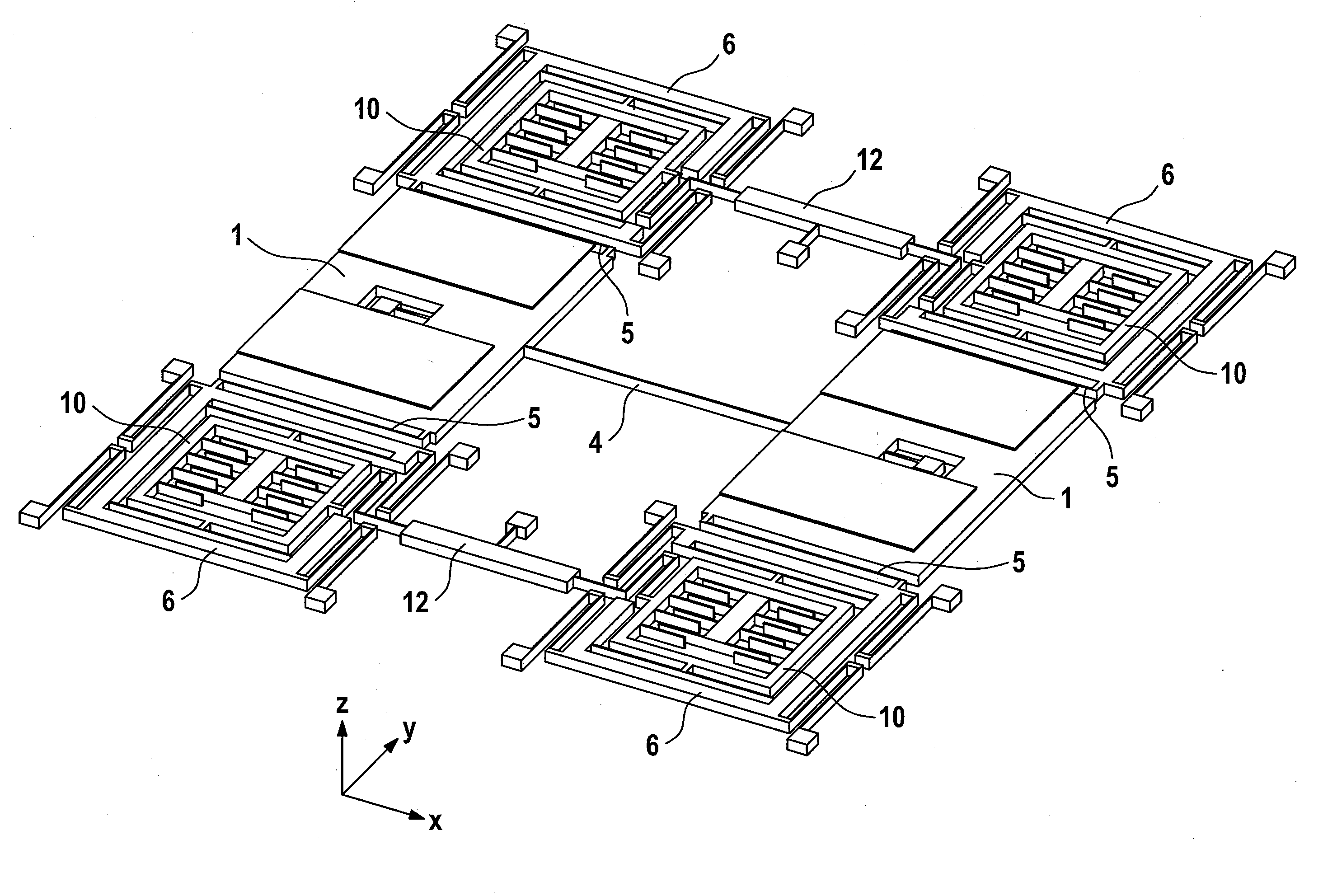
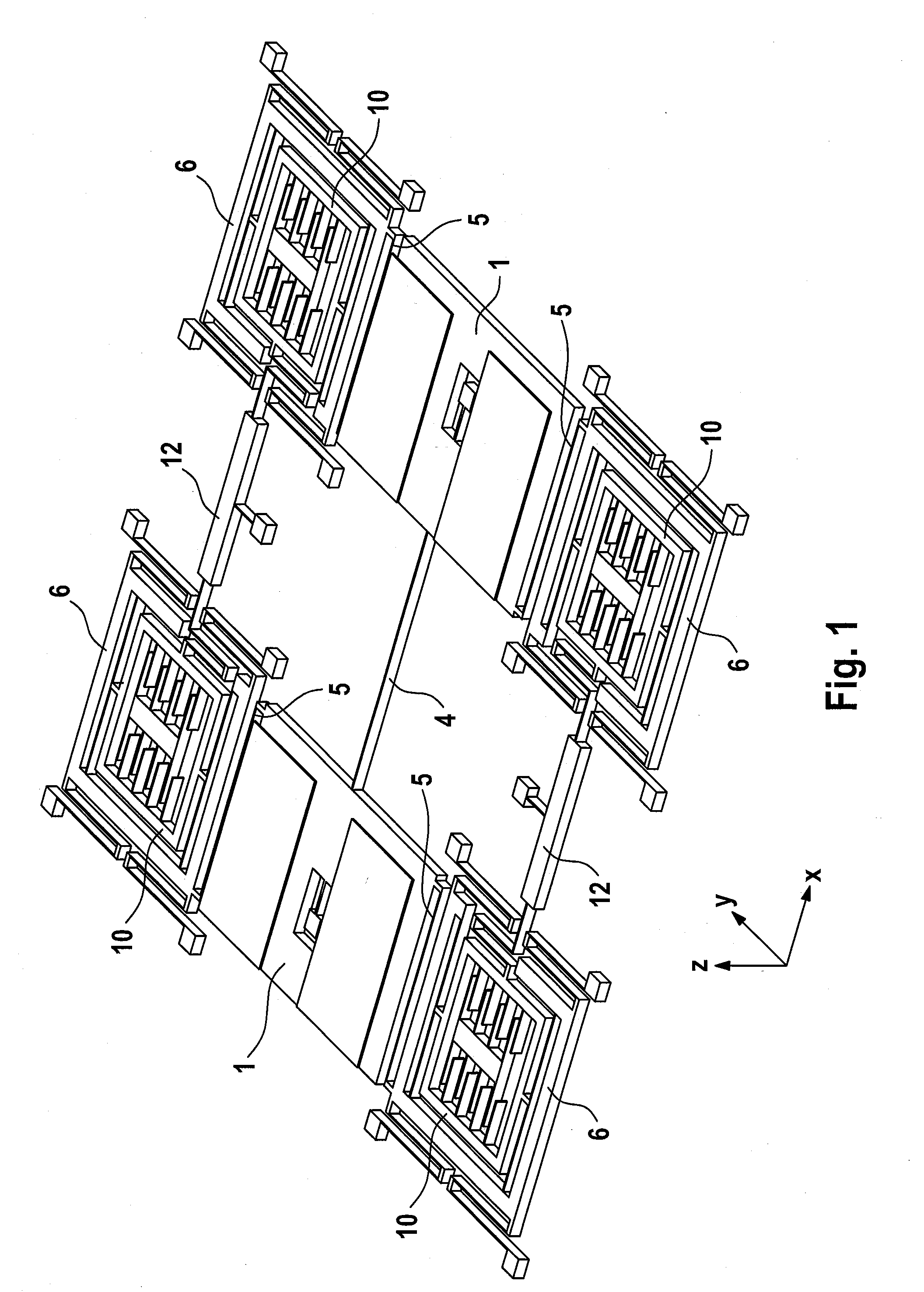
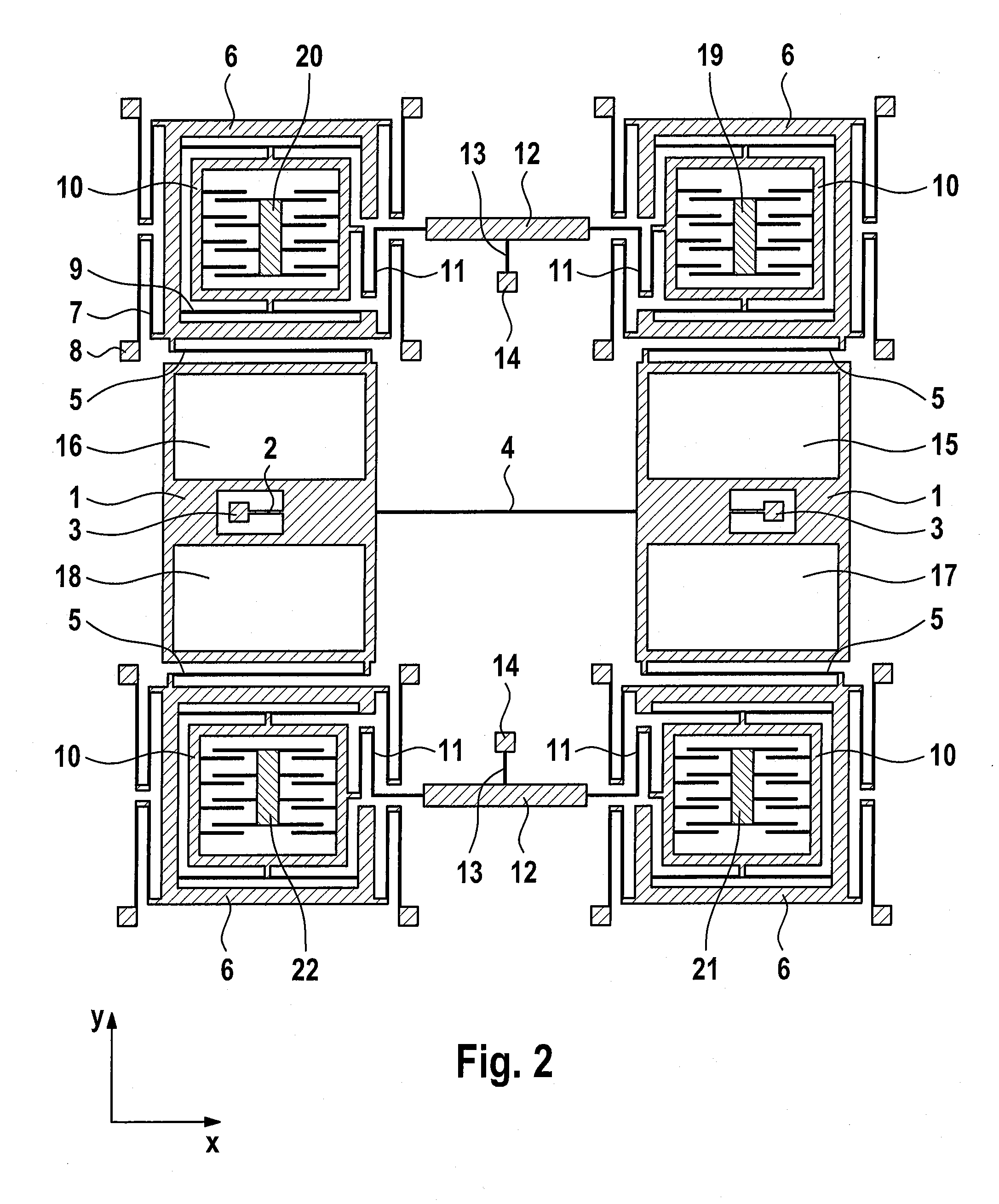
ActiveUS20120210788A1Precise alignmentEasy to operateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSeismic massClassical mechanics
A micromechanical rotation rate sensor has at least one first and one second seismic mass coupled to at least one first drive device and are suspended such that the first and second seismic masses are driven such that they are deflected in antiphase in one drive mode, with the rotation rate sensor being designed such that it can detect rotation rates about at least two mutually essentially orthogonal sensitive axes, wherein at least the first and second seismic masses are designed and suspended such that they oscillate in antiphase in a first read mode when a first rotation rate about the first sensitive axis is detected, and the first and second seismic masses and / or additional seismic masses are designed and suspended such that they oscillate in antiphase in a second read mode when a second rotation rate about the second sensitive axis is detected.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
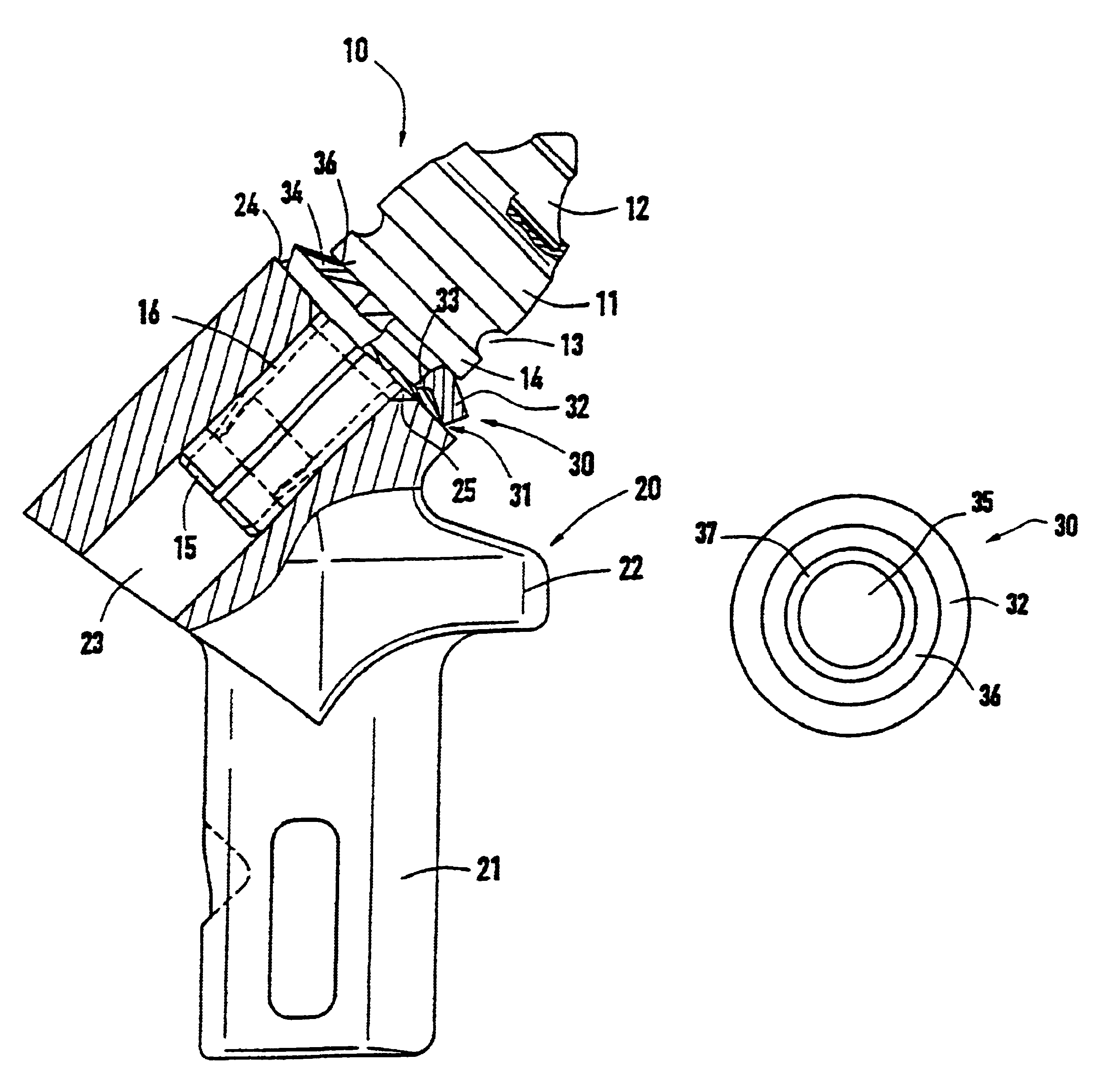
Tool for a street milling, coal-cutting or mining machine
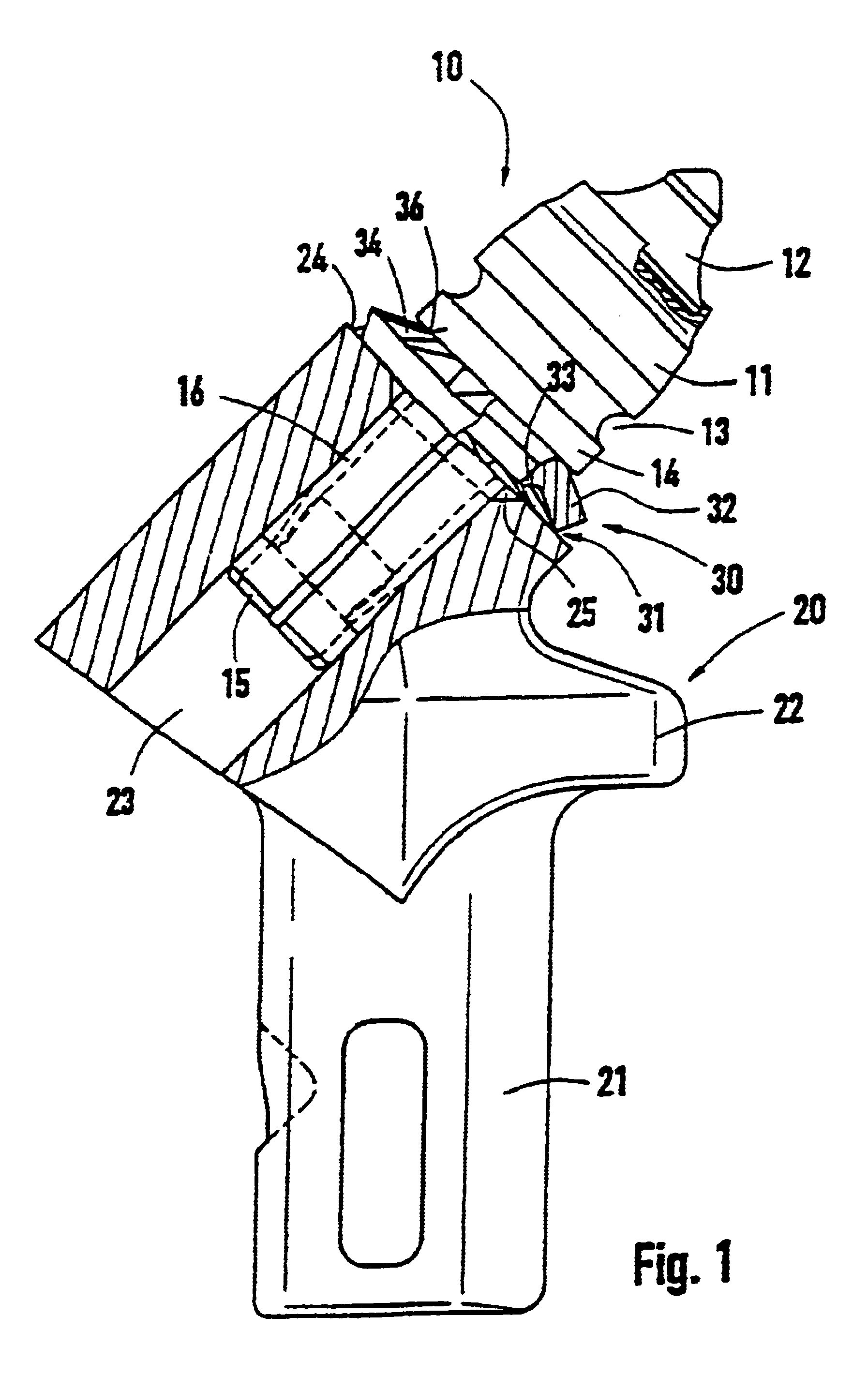
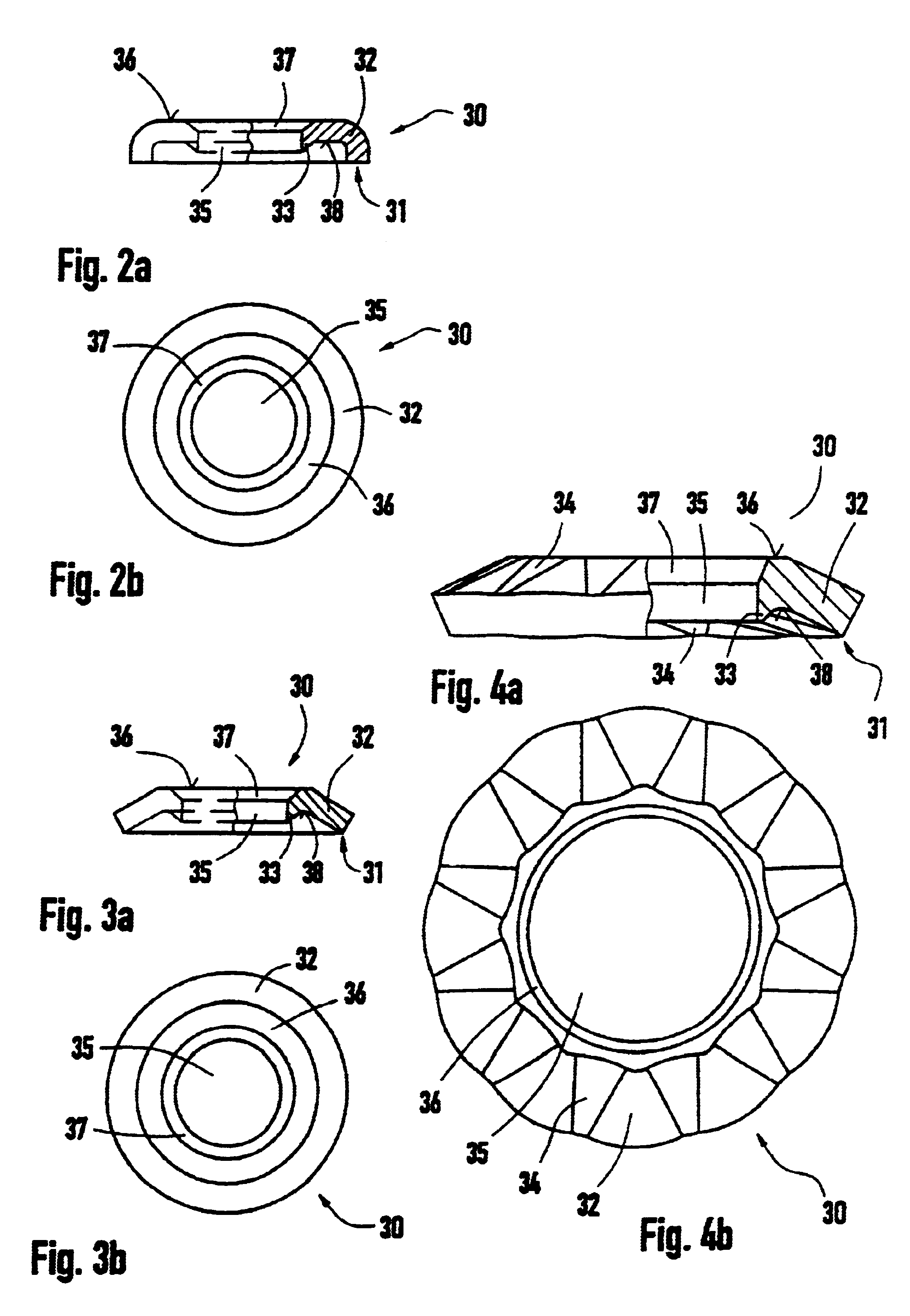
A tool for a street milling, coal-cutting mining machine or the like which includes a chisel with a chisel head and a chisel stem. The chisel stem is rotatably mounted in a receiver of a chisel holder. A perforated wearing protection element is mounted on the chisel head. The chisel head sits closely on the chisel holder while embracing the interposed wearing protection element. This invention achieves improved wearing protection behavior of such a tool. Thus, the inventive wearing protection element has one or more spring elements that elastically support the chisel head by way of the chisel holder.
Owner:BETEK BERGBAU UND HARTMETALLTECHN KARL HEINZ SIMON
High-frequency switching transistor and high-frequency circuit
ActiveUS20060118884A1Good integration characteristicCost-effectiveTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantTransistor
A high-frequency switching transistor comprises a substrate having a substrate dopant concentration and a barrier region bordering on the substrate, which has a first conductivity type, wherein a barrier region dopant concentration is higher than the substrate dopant concentration. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor comprises a source region embedded in the barrier region, which comprises a second conductivity type different to the first conductivity type, and has a source region dopant concentration, which is higher than the barrier region dopant concentration. Additionally, the high-frequency switching transistor comprises a drain region embedded in the barrier region and disposed offset from the source region, which comprises the second conductivity type and has a drain region dopant concentration, which is higher than the barrier region dopant concentration. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor has a channel region, extending between the source region, wherein the channel region comprises a subregion of the barrier region. Further, the high-frequency switching transistor has an insulation region, which covers the channel region and which is disposed between the channel region and the gate electrode. Such a high-frequency switching transistor allows switching of high-frequency signals with higher high-frequency signal amplitudes as are switchable by conventional high-frequency switching transistors.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com