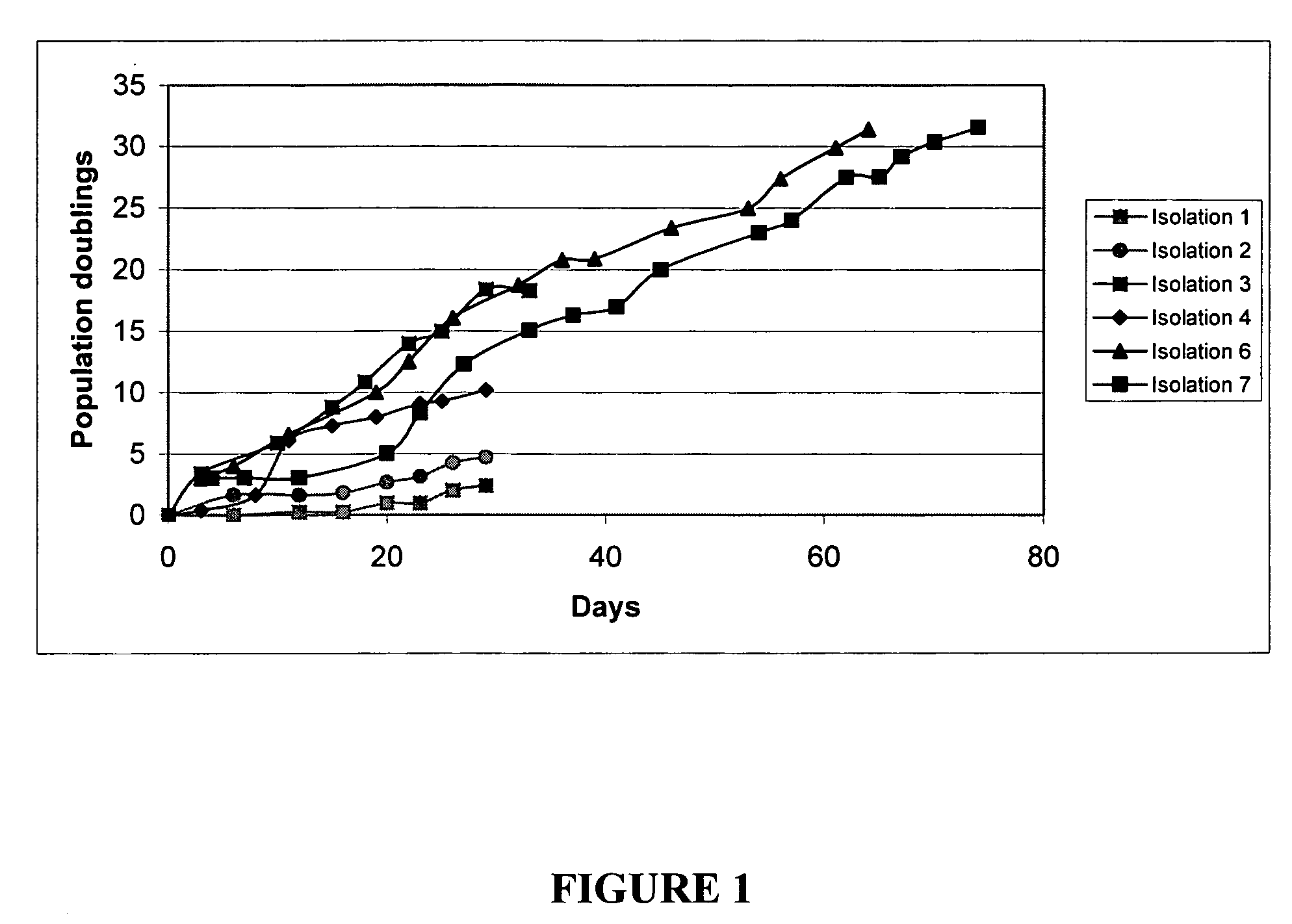
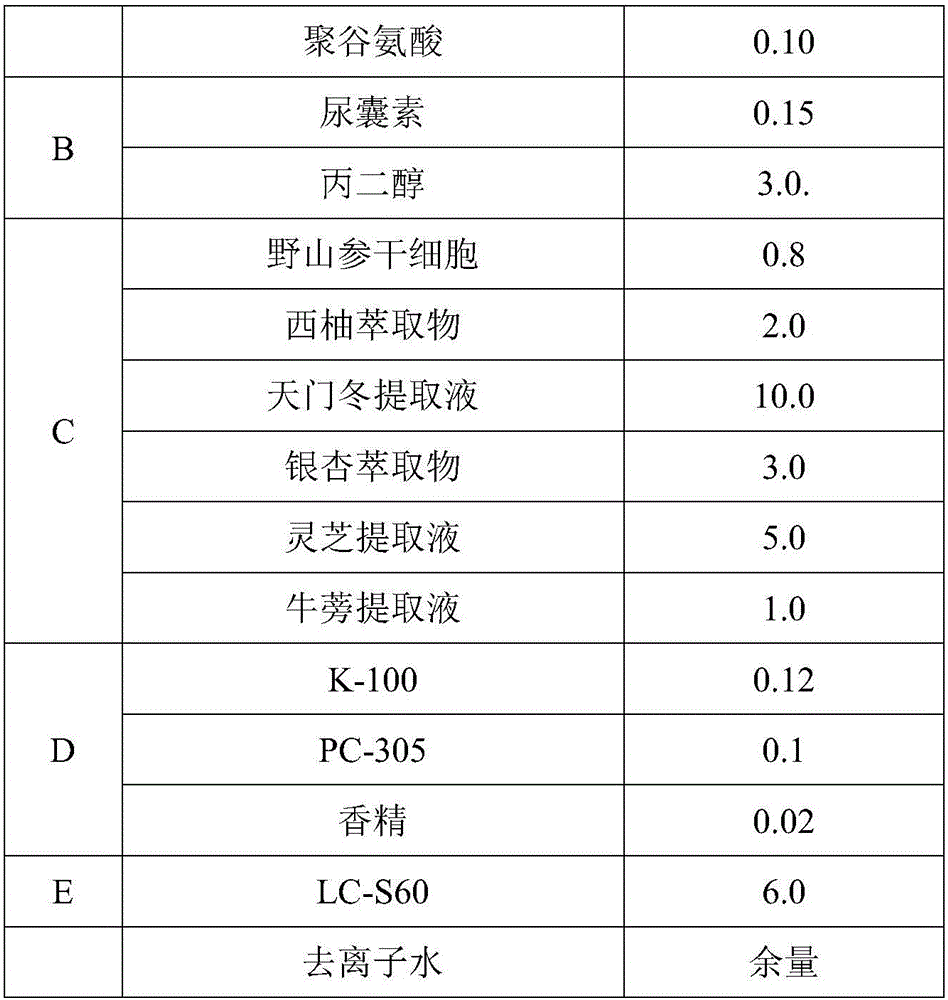
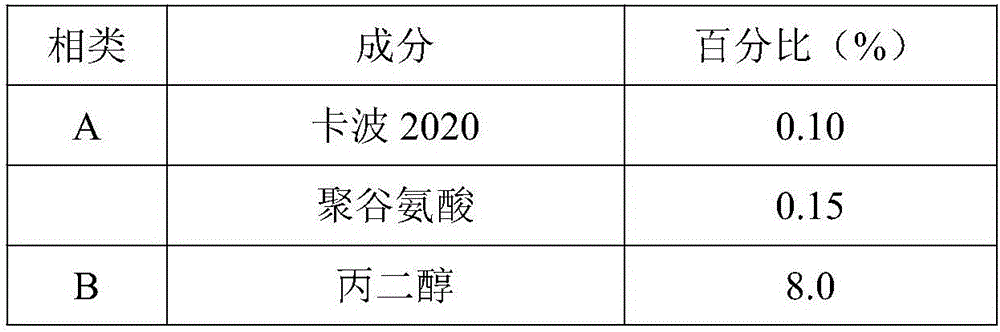
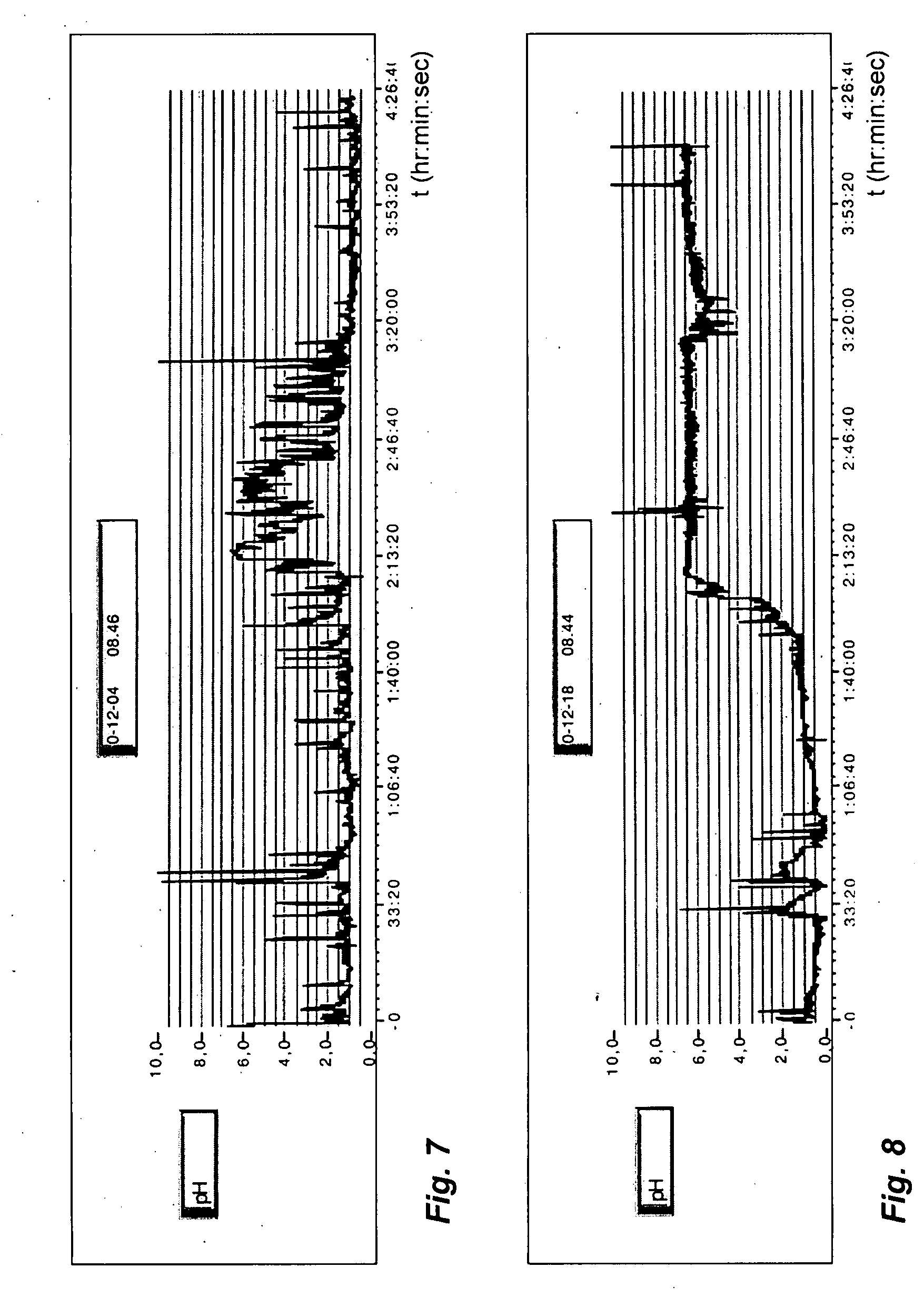
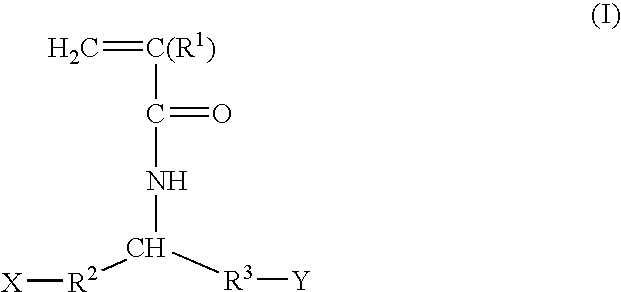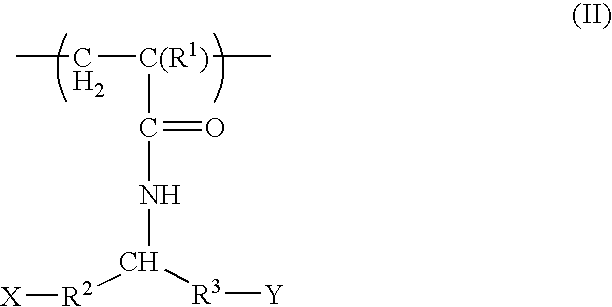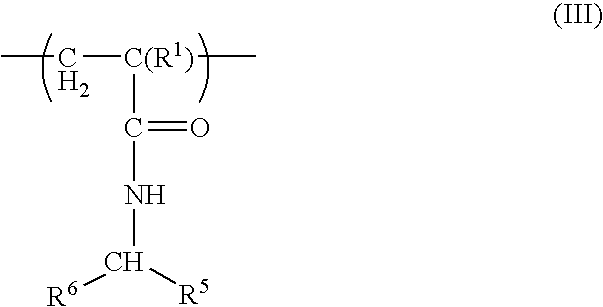Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3166 results about "Secreted substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, e.g. secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion, is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes.
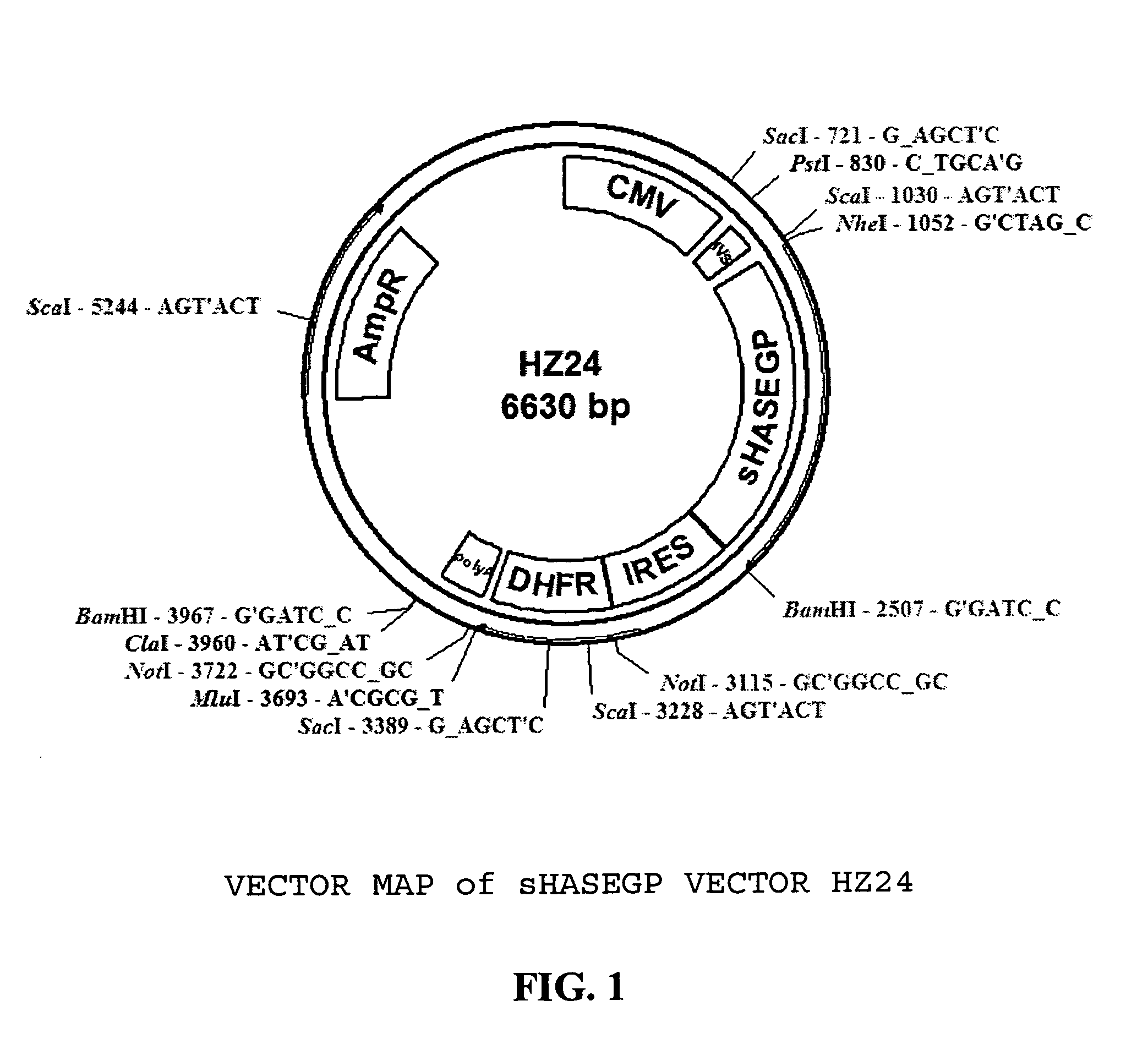
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Purine derivative
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 02310 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 3, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 3, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 3, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 01448 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 15, 1998This invention relates to novel purine derivatives of formula (I): where R2 and R9 are hydrocarbon groups, R6 is an amino group and R8 is a hydroxyl, or acyloxy group. These purine derivatives are effective at promoting secretion of interferon in patients, and can be used to treat diseases against which interferon is effective.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
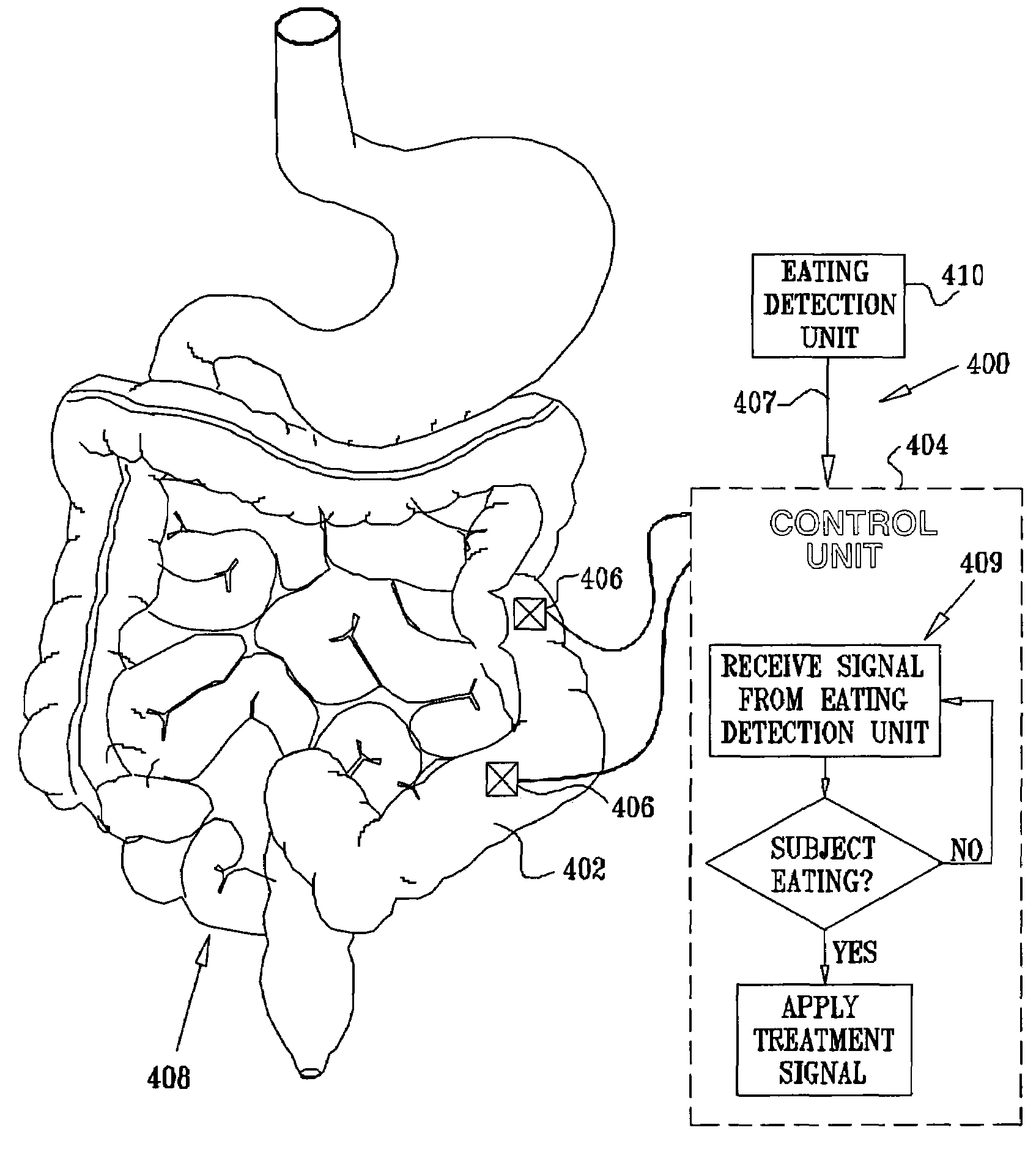
Gastrointestinal methods and apparatus for use in treating disorders
InactiveUS7502649B2Reduce volumeCause a sensation of satiety felt by the patientElectrotherapyMetabolism disorderElectrical resistance and conductanceDisease
A method is provided for detecting a change in posture of a subject. An electrical impedance is measured between two or more sites on a stomach (20) of the subject, and an impedance signal is generated responsive thereto. The change in posture is detected by performing a posture analysis of the impedance signal. A method is also provided for treating a subject. The method includes applying an electrical signal to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a colon (402) of the subject, and a distal small intestine (408) of the subject. The signal is configured to stimulate cells of the subject to increase secretion of glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) or PYY, or to decrease secretion of ghrelin, in order to treat the subject.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
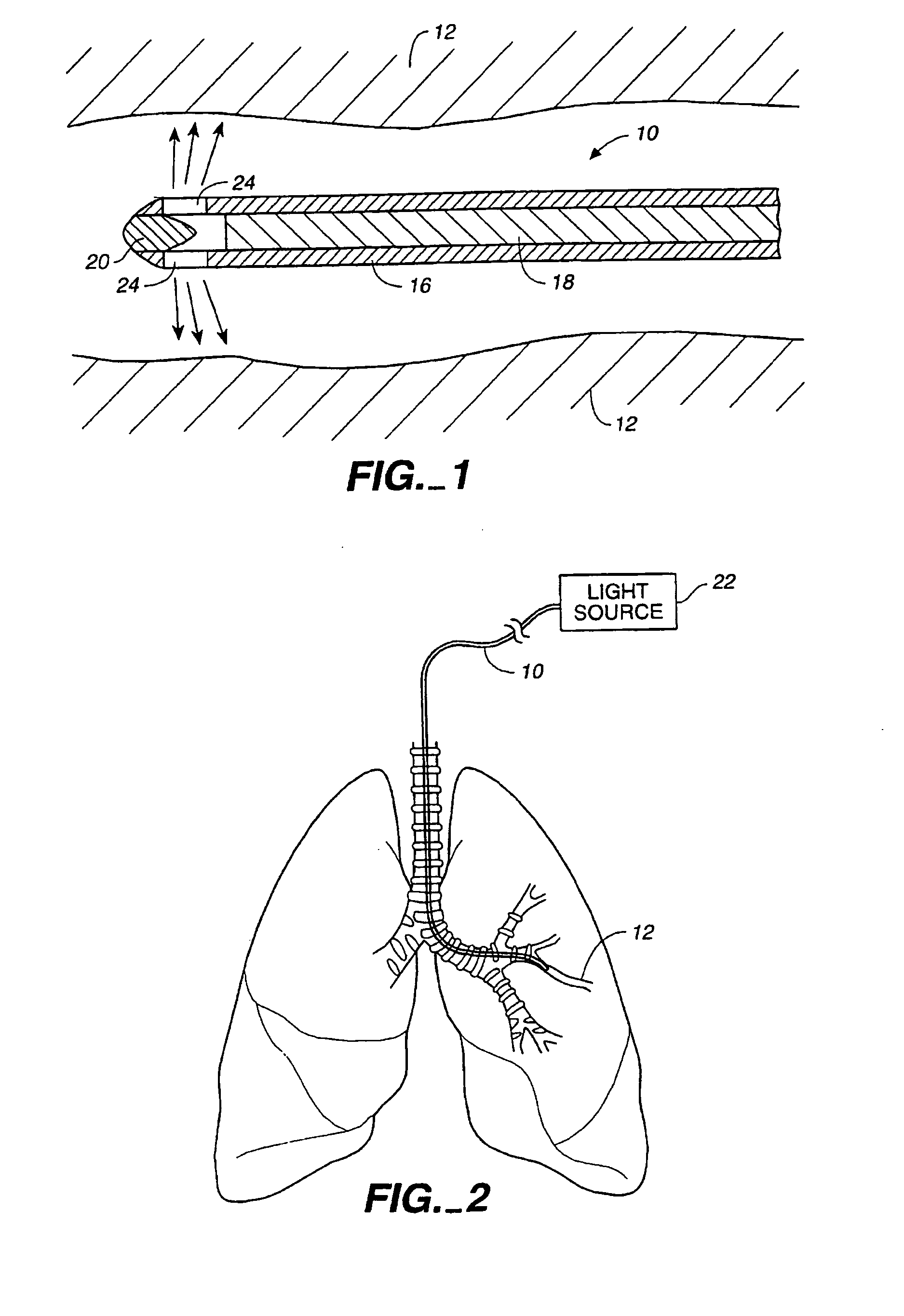
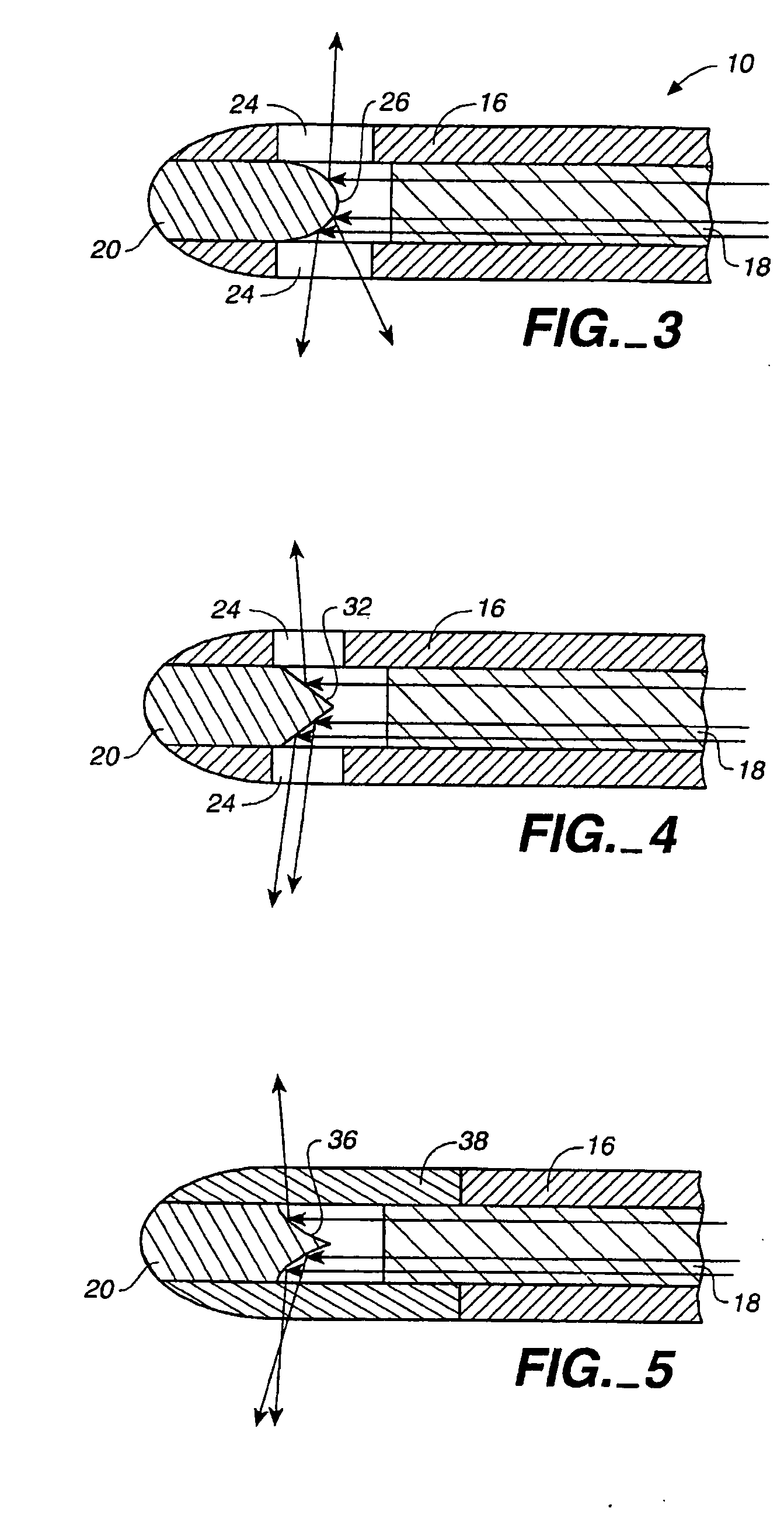
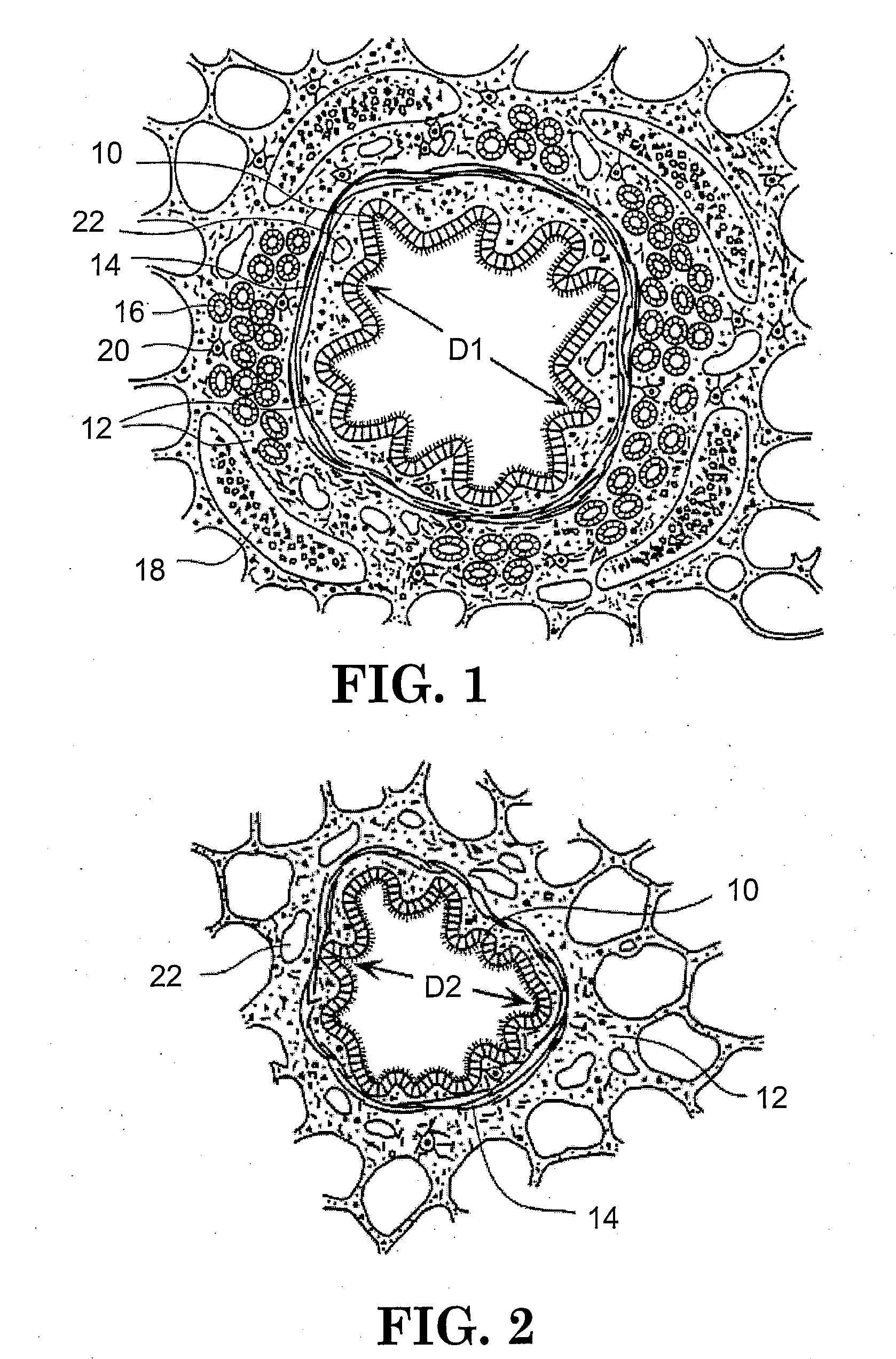
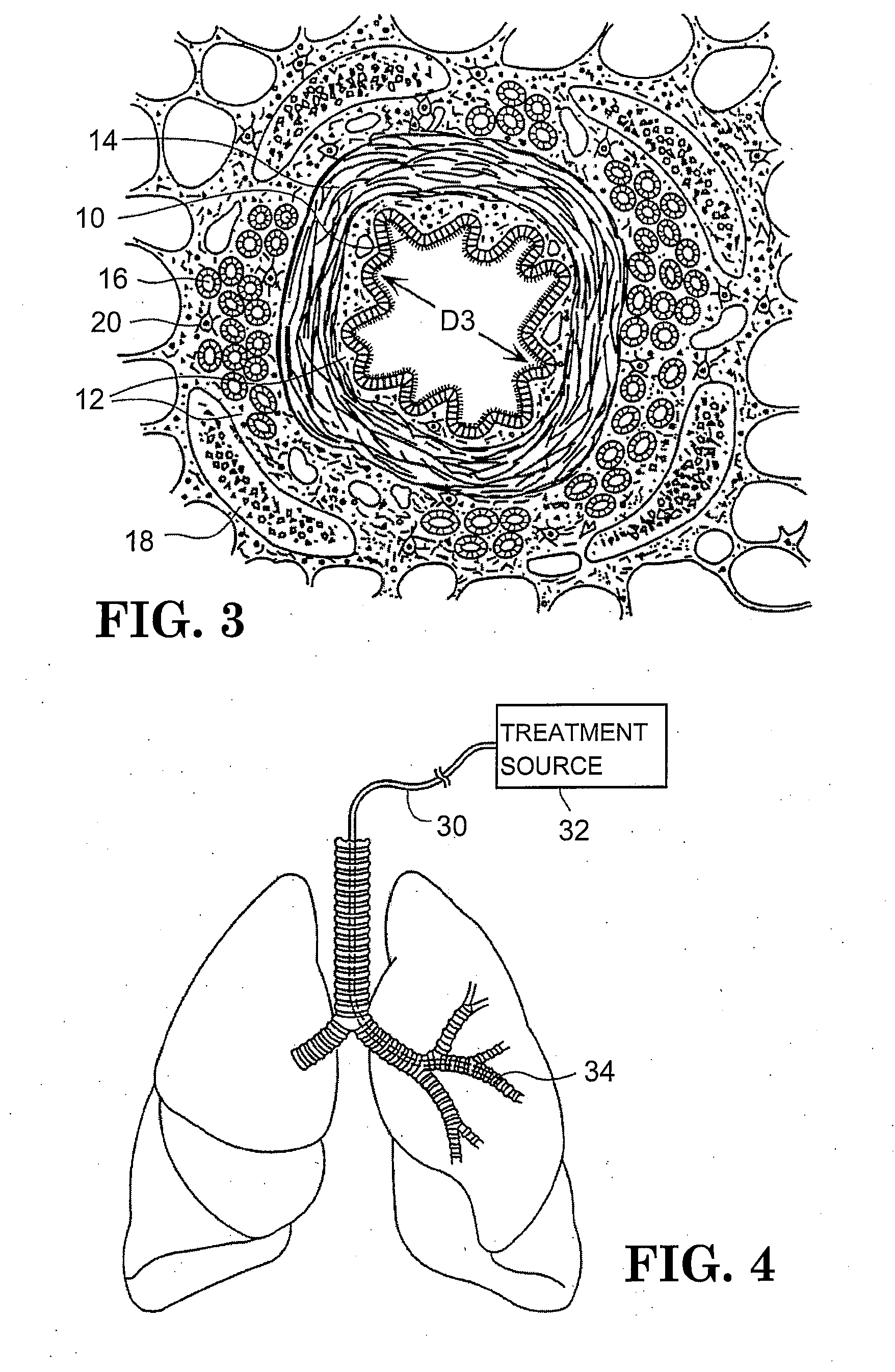
Method of treating airways in the lung
InactiveUS20050010270A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease inner diameterSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyBronchospasmSmooth muscle spasm
A device and method for treating bodily conduits involves the application of energy to the smooth muscle tissue of the conduit walls to reduce the bulk of smooth muscle tissue and mucus glands. The irradiation treatment of the smooth muscle tissue causes a reduction in the amount of smooth muscle tissue over time which increases the inner diameter of the body conduit for improved fluid flow and prevents smooth muscle spasms. The treatment is particularly useful in the lungs for treatment of asthma to prevent bronchospasms, increase the airway diameter for improved air exchange, and reduce mucus secretions in the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
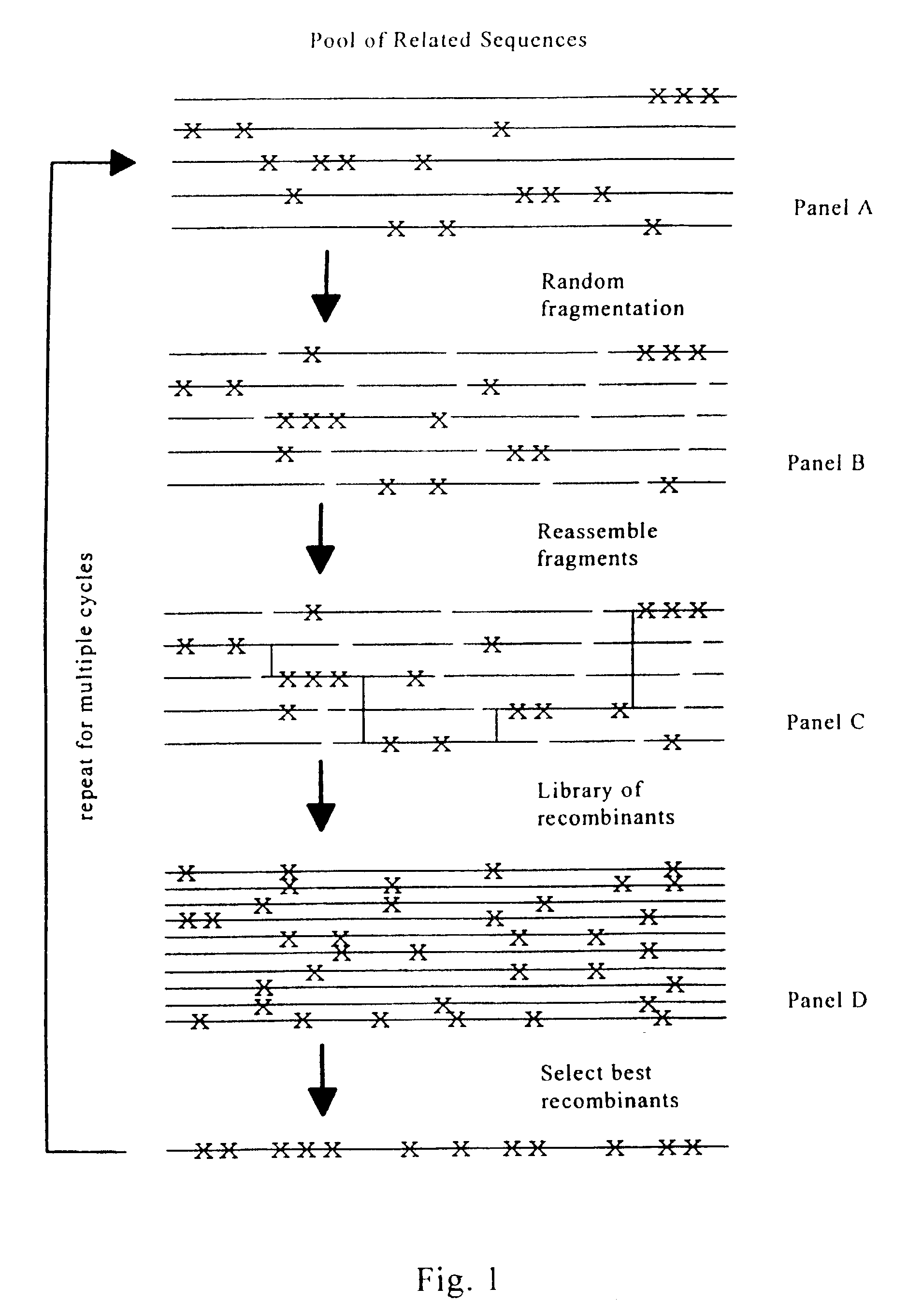
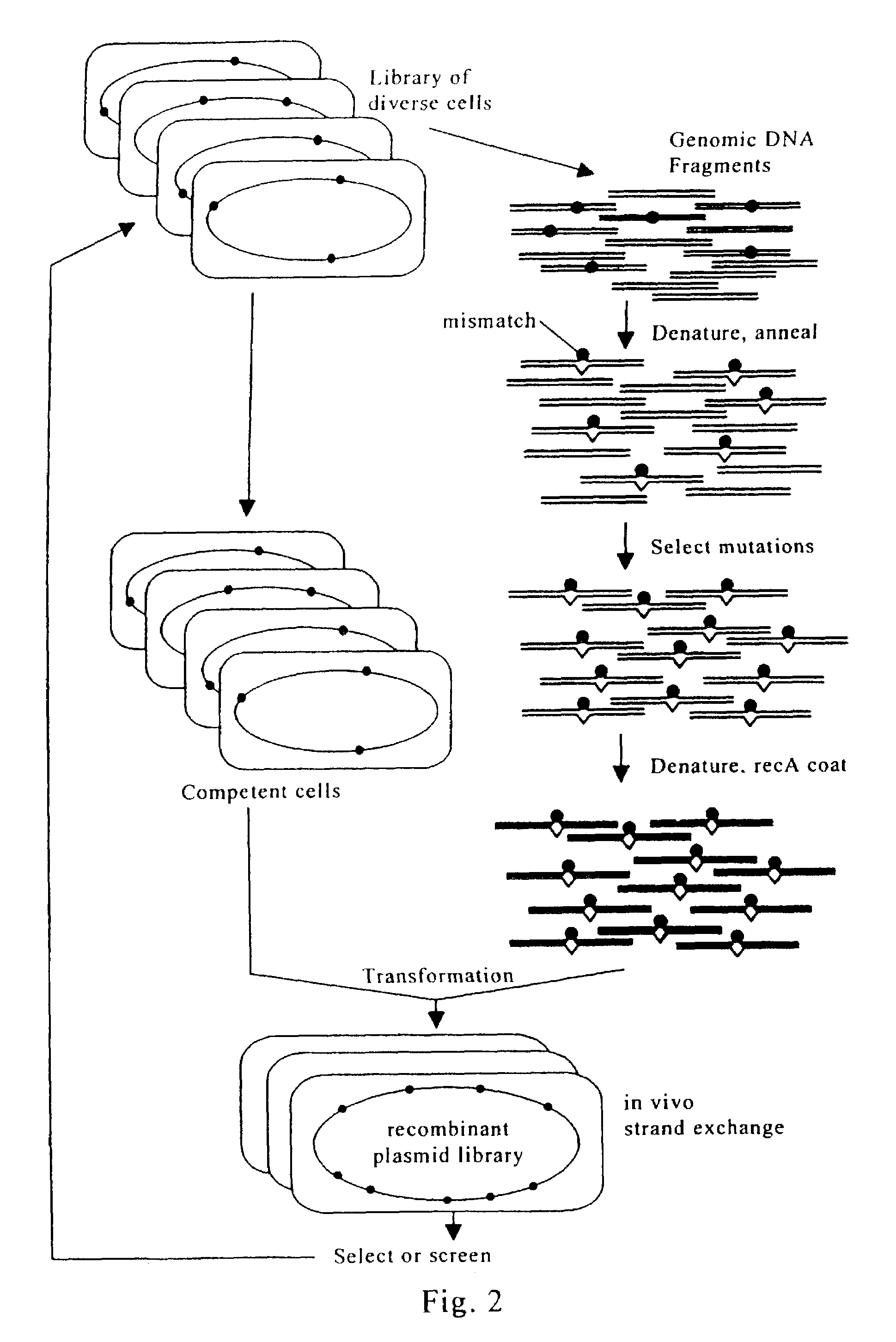
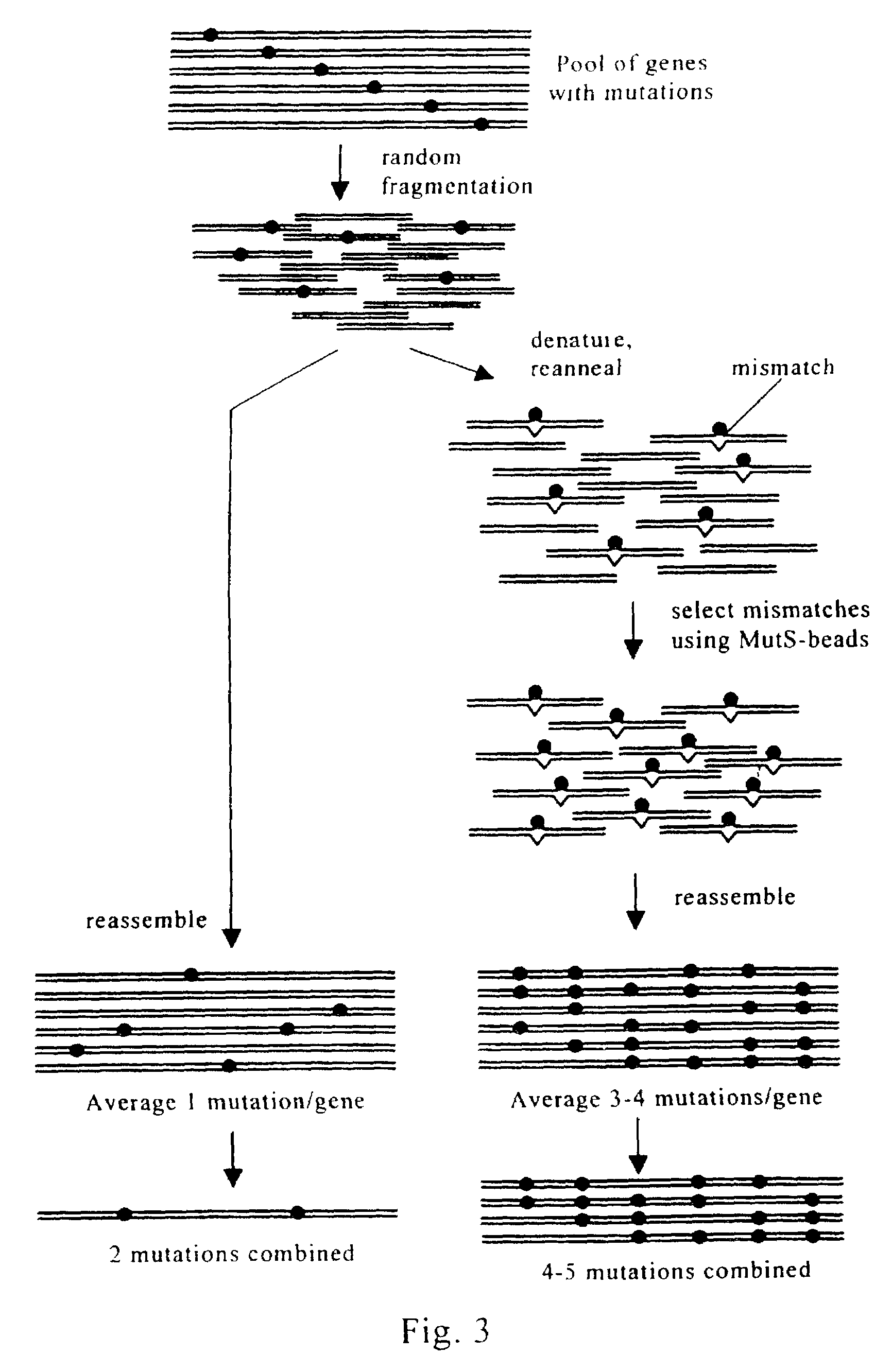
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
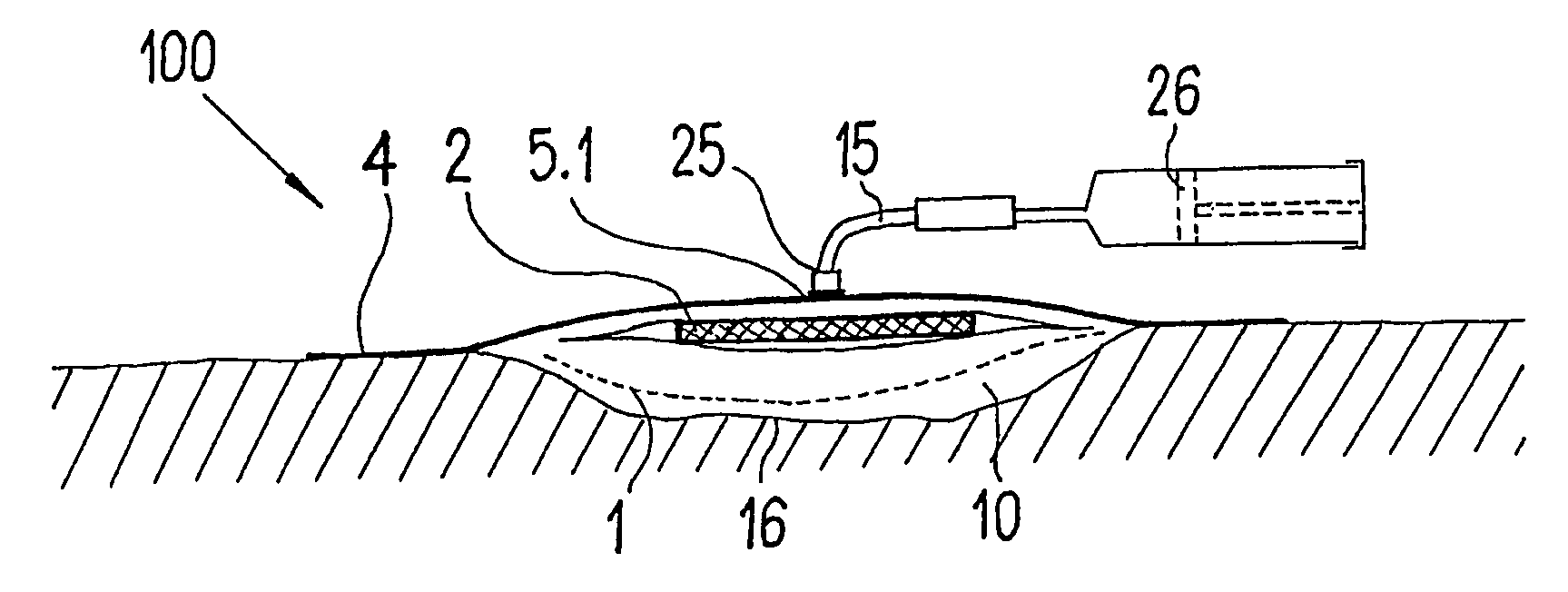
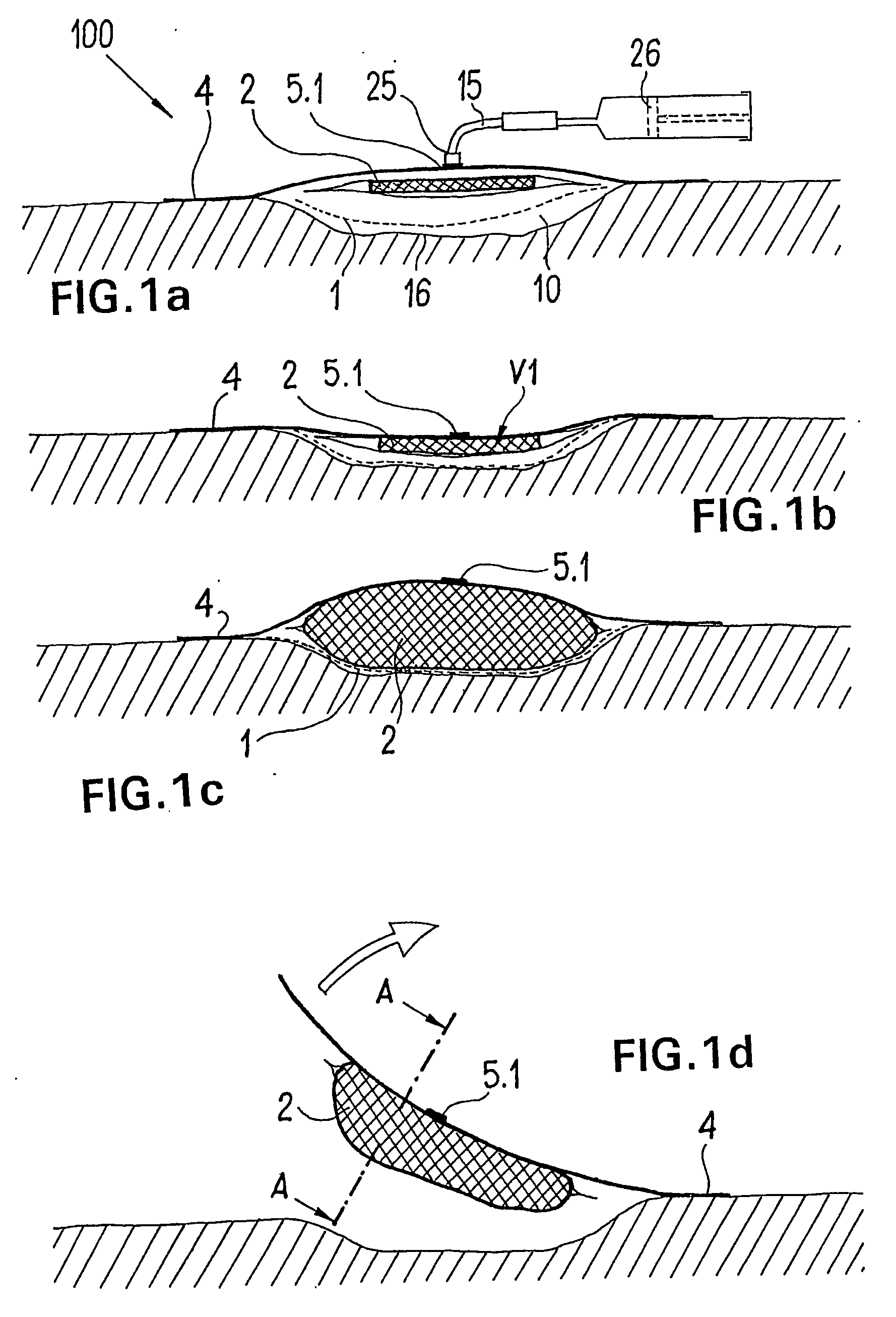
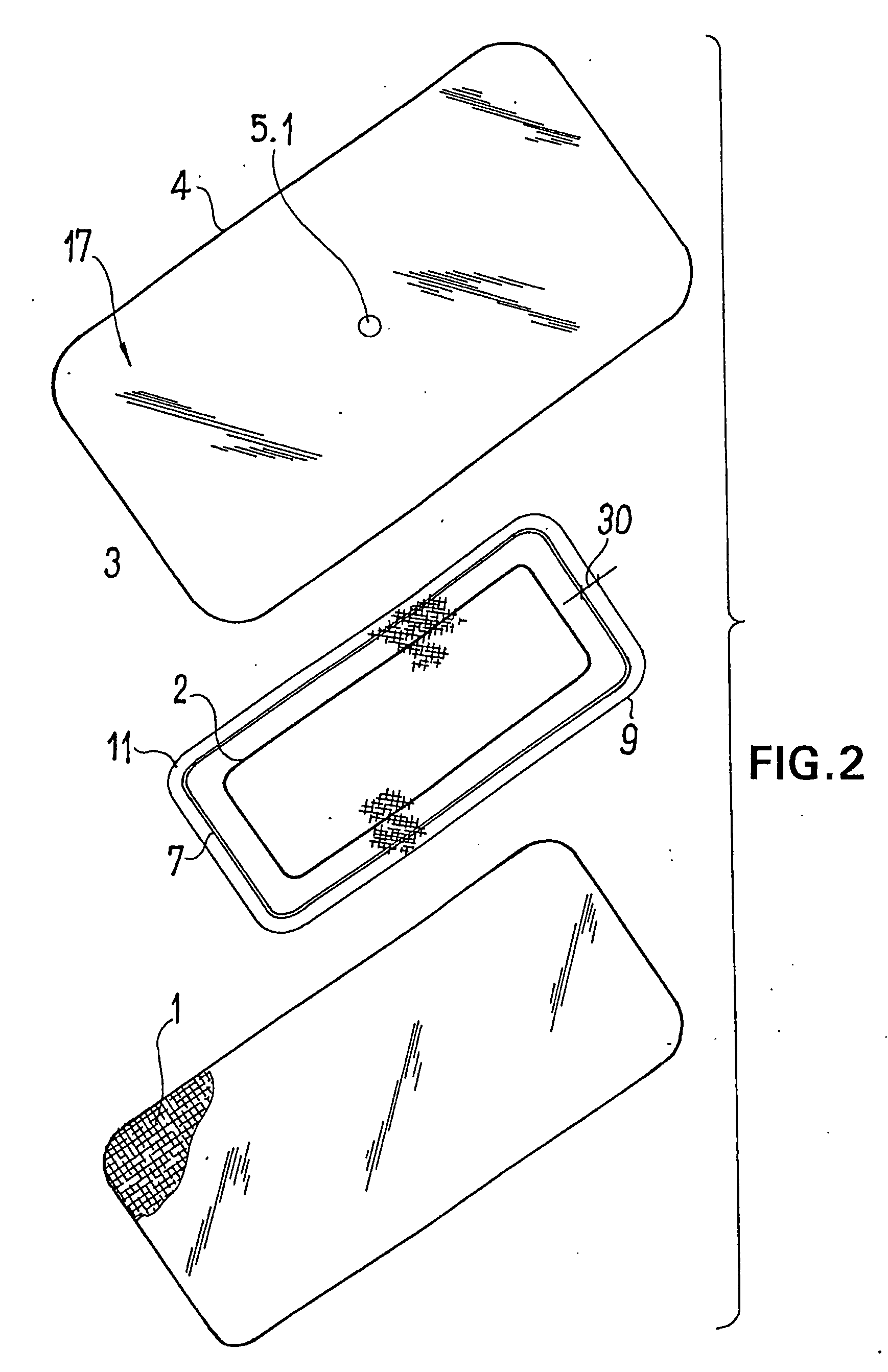
Device for the Treatment of Wounds Using a Vacuum
ActiveUS20080009812A1Cost effectiveSimple designNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersSecretionSecreted substance
The invention relates to a device (100) for treating wounds of the human or animal body using a vacuum and having a gas-tight wound-covering element (4), which, when placed in contact with the body of the patient, forms a wound space (10) between the respective wound and the wound-covering element, at least one connecting site (5.1; 5.2), which is in contact with the wound space (10), an absorption body (2), which is a layer, enclosed in an envelope, of a textile section, interspersed with super-absorbing particles, the envelope being permeable to liquids and having pores, the size of which does not exceed that of the super-absorbing particles. The absorption body (2), which is to be inserted in the wound space (10), has an initial volume, which enlarges in the course of the absorption process, and a final volume, so that, due to the size of the pores of the envelope, the absorbed wound secretions remain within the absorption body (2) and, with that, below the wound-covering element, until the absorption body is removed from the wound space.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
Postpartum cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, and methods of making and using the same
Cells derived from human umbilical cords are disclosed along with methods for their therapeutic use. Isolation techniques, culture methods and detailed characterization of the cells with respect to their cell surface markers, gene expression, and their secretion of trophic factors are described.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Natural plant extract composition and application thereof in cosmetics
ActiveCN105748343ASpeed up the repair processIncrease elasticityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiologyInflammation
The invention relates to the technical field of cosmetics, in particular to a natural plant extract composition and application thereof in the cosmetics. The natural plant extract composition is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.1 to 10 parts of plant stem cells, 2 to 10 parts of grapefruit extracts, 1 to 10 parts of radix asparagi extracting solution, 1 to 10 parts of gingko extracts, 5 to 10 parts of lucid ganoderma extracting solution, and 1 to 5 parts of burdock extracting solution. The natural plant extract composition provided by the invention not only has remarkable moisturizing and anti-aging effect, but also has the effects in removing acnes, adjusting grease secretion, resisting inflammation and relieving, and can be used for preparing moisturizing, anti-aging or acne-removing cosmetics.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Postpartum cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, and methods of making, culturing, and using the same
Cells derived from human umbilical cords are disclosed along with methods for their therapeutic use. Isolation techniques, culture methods and detailed characterization of the cells with respect to their cell surface markers, gene expression, and their secretion of trophic factors are described.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
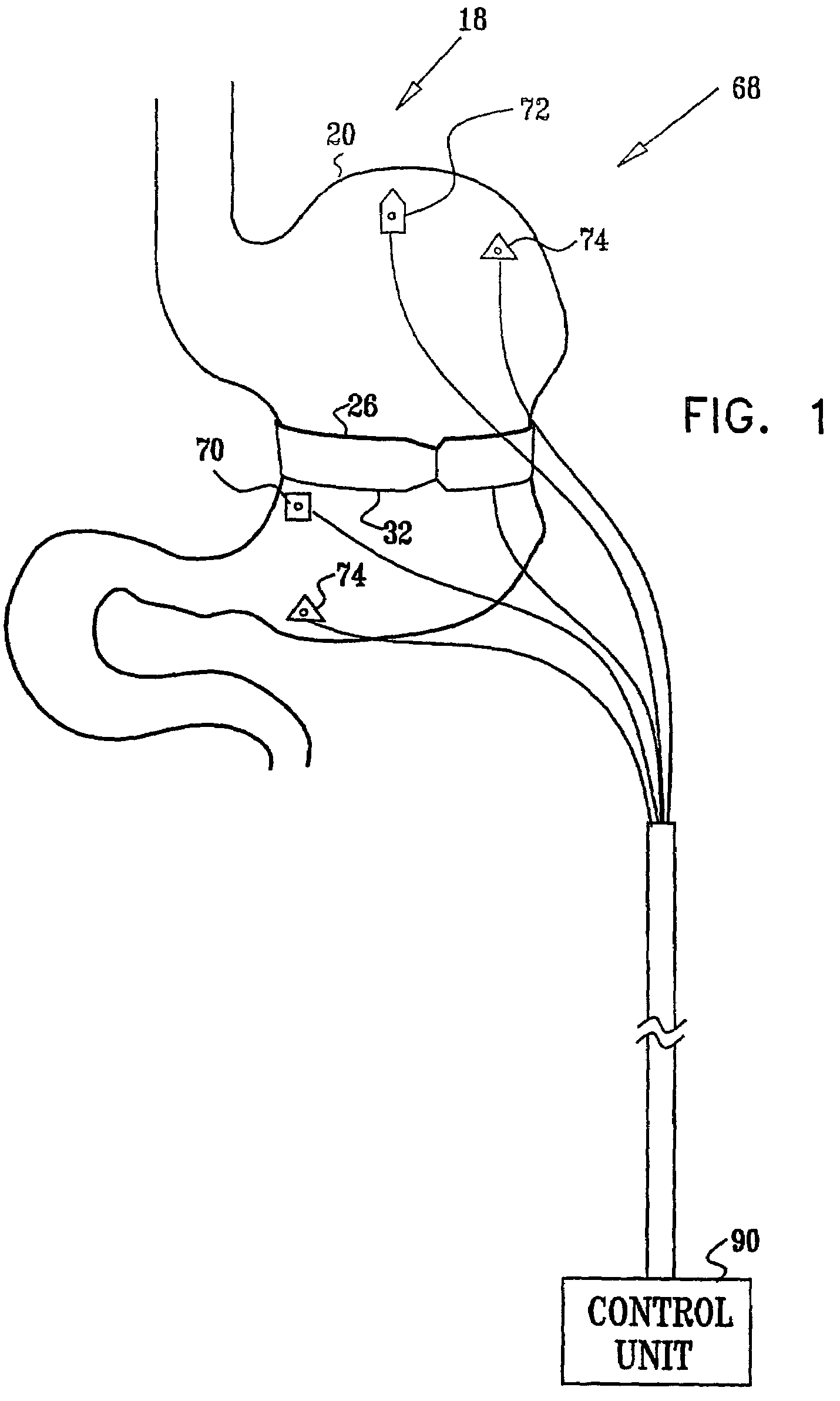
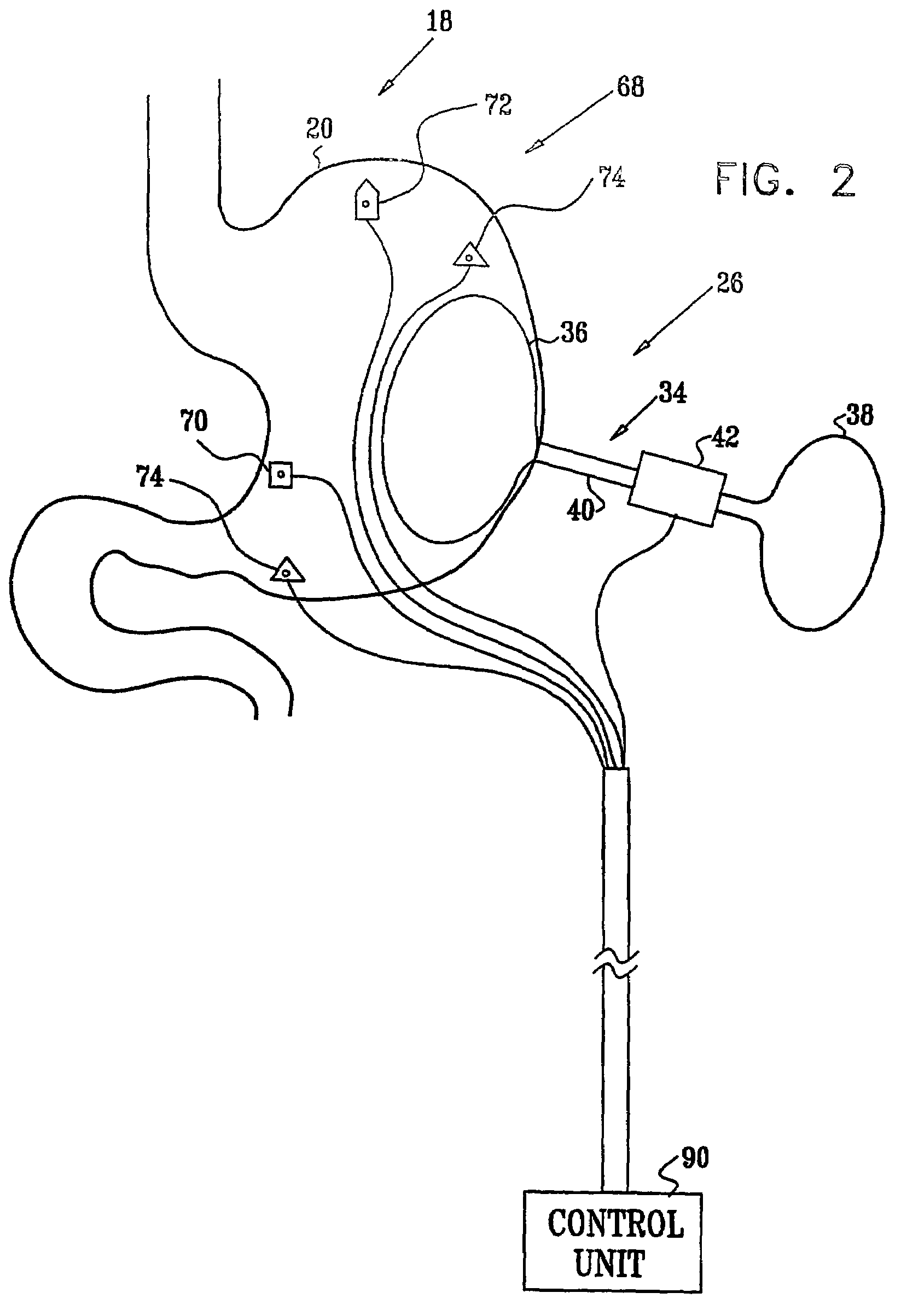
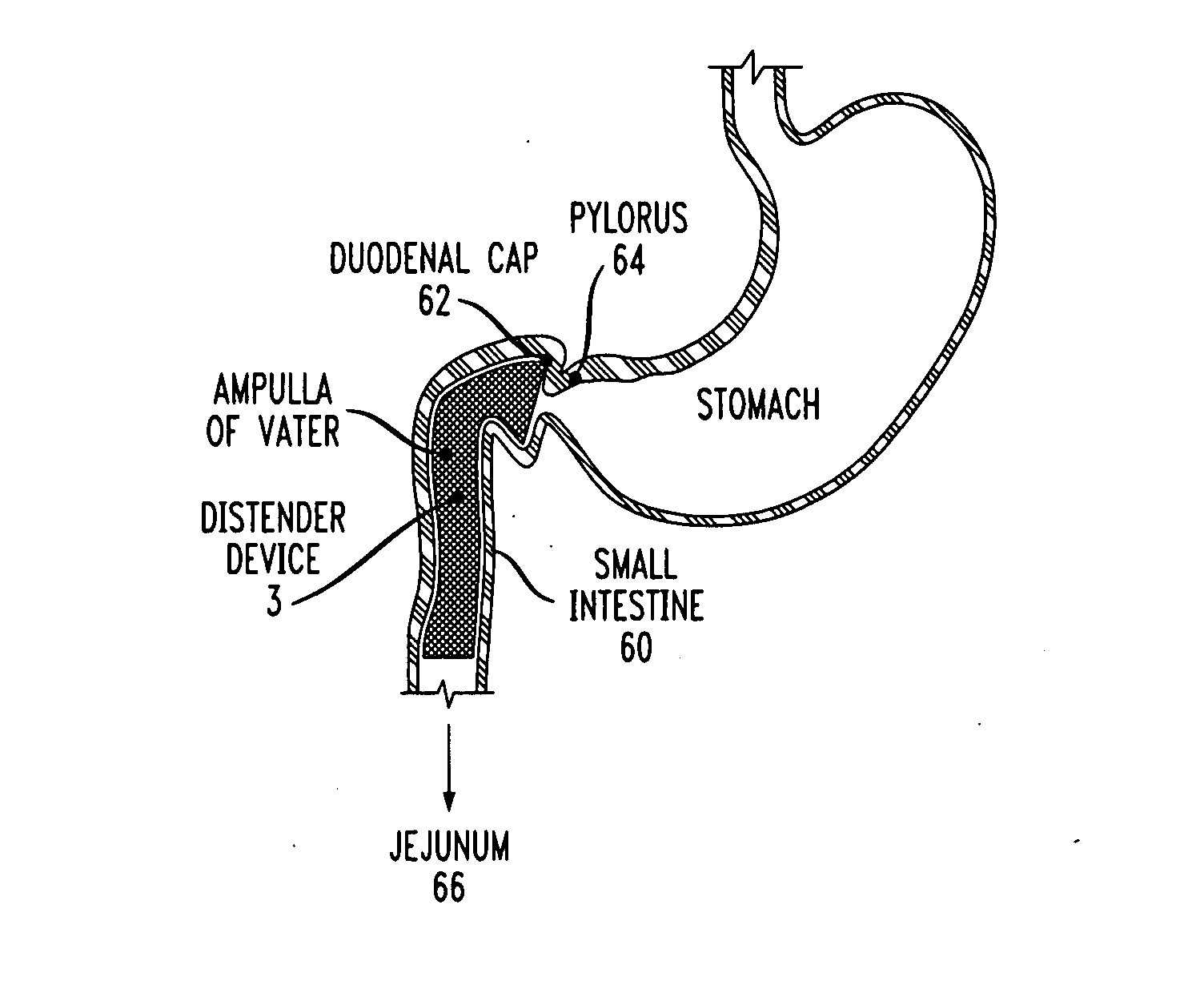
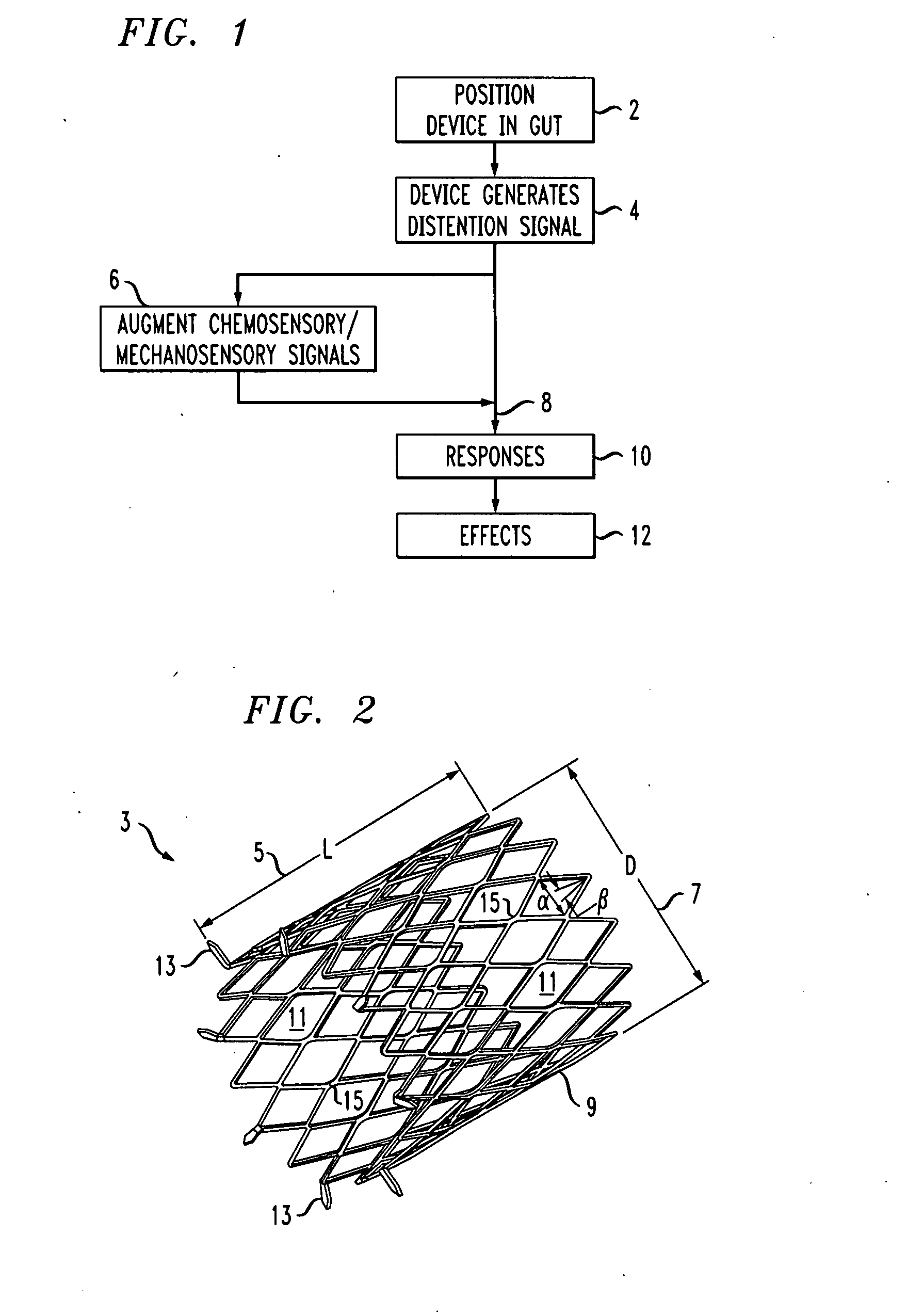
Distender device and method for treatment of obesity and metabolic and other diseases
A gastrointestinal implant device is positioned in a patient's small intestine or rectum and produces an outward force that itself produces a distension signal which is a therapeutically useful neural or humoral signal that evokes satiogenic or weight loss effects by itself. The device may advantageously be placed in the duodenum adjacent the pylorus or in the jejunum, ileum or rectum. The distension signals may amplify chemosensory or mechanosensory signals such as enteroendocrine secretions within the patient. The device may be a mesh and include a low material density that allows for unrestricted chyme absorption within the small intestine and unrestricted chyme flow through the gastrointestinal system. A method includes inserting the device into the patient then either retrieving the device after treatment is complete or allowing a device formed of a biodegradable material to degrade in time after treatment is complete.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
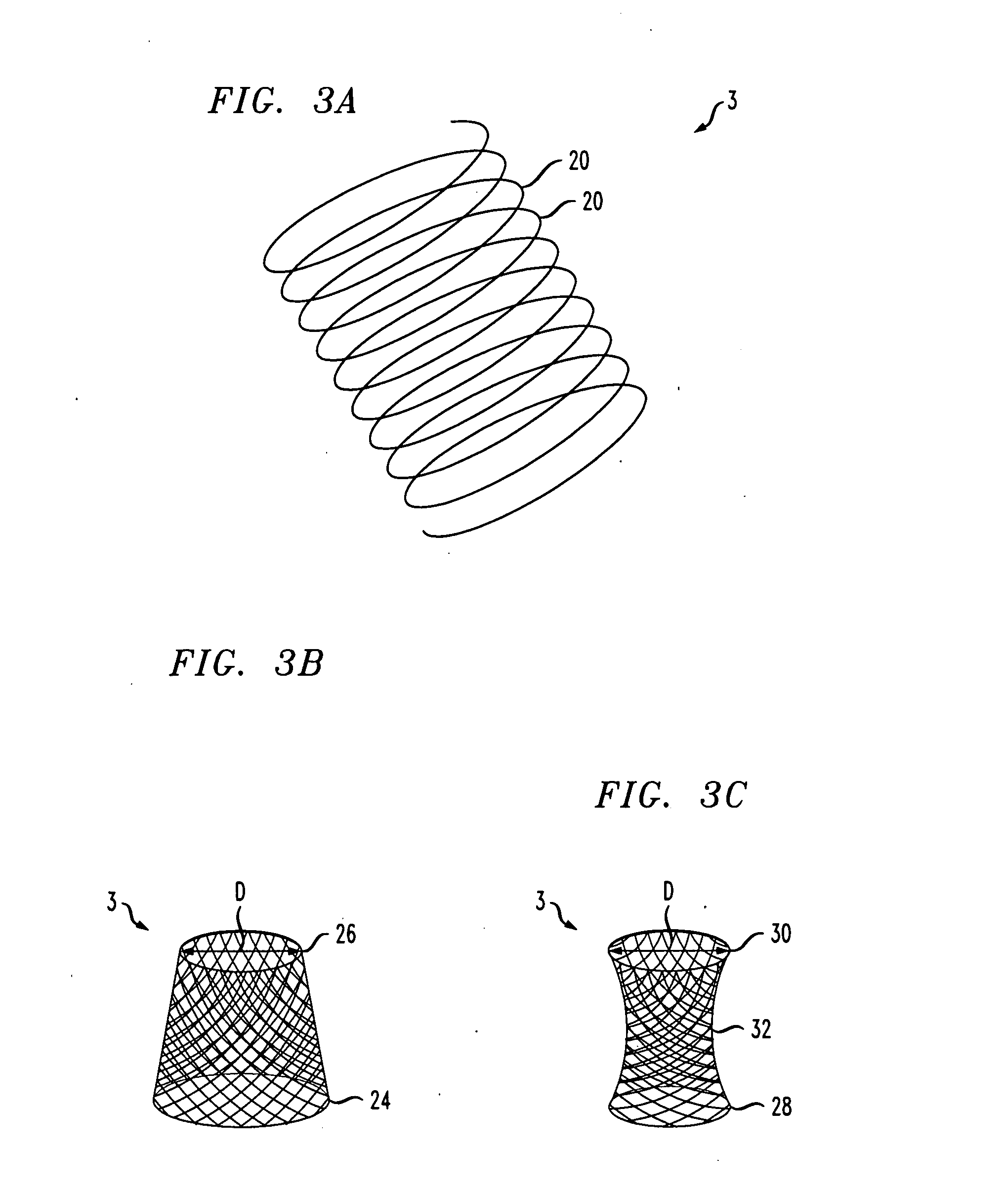
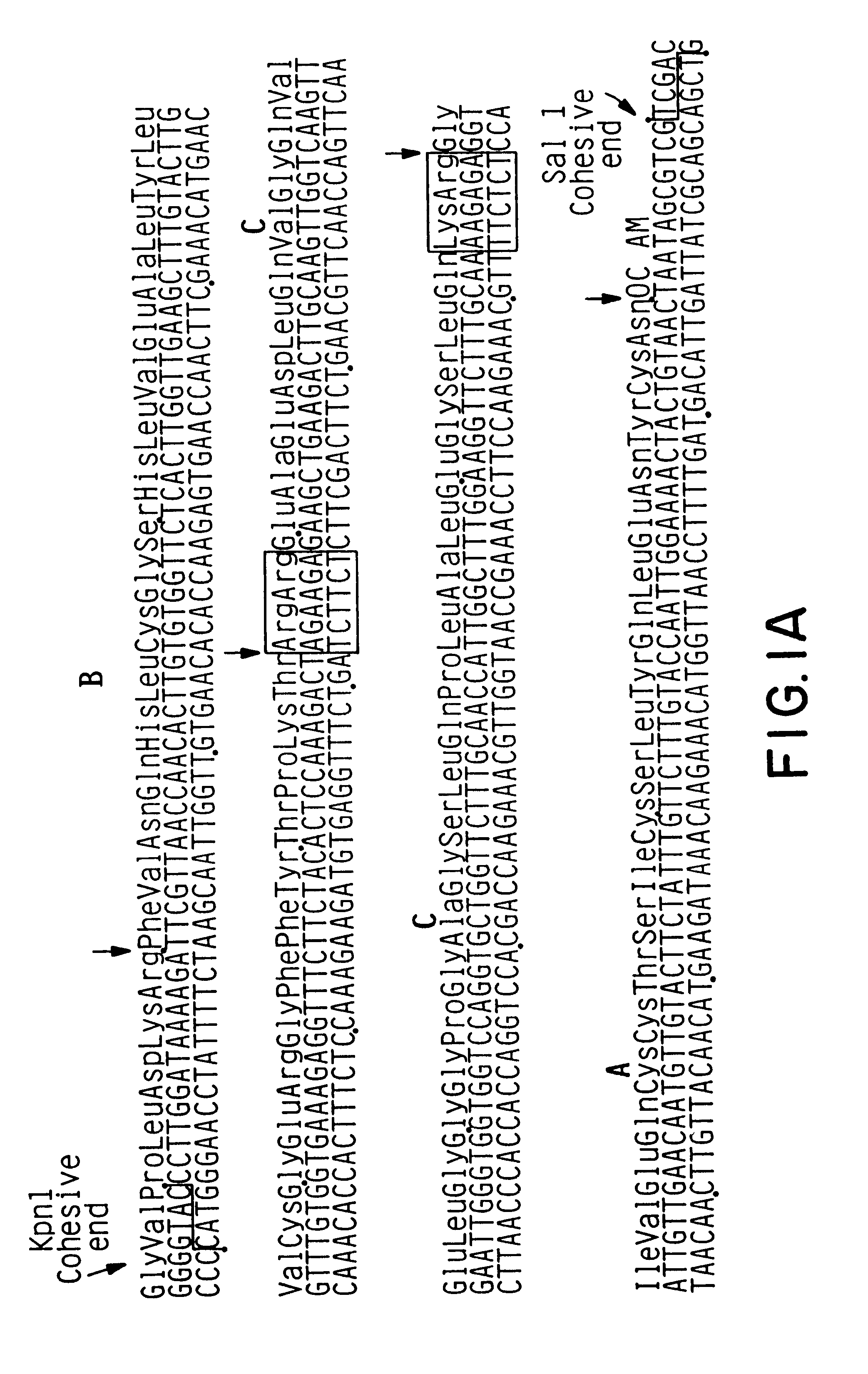
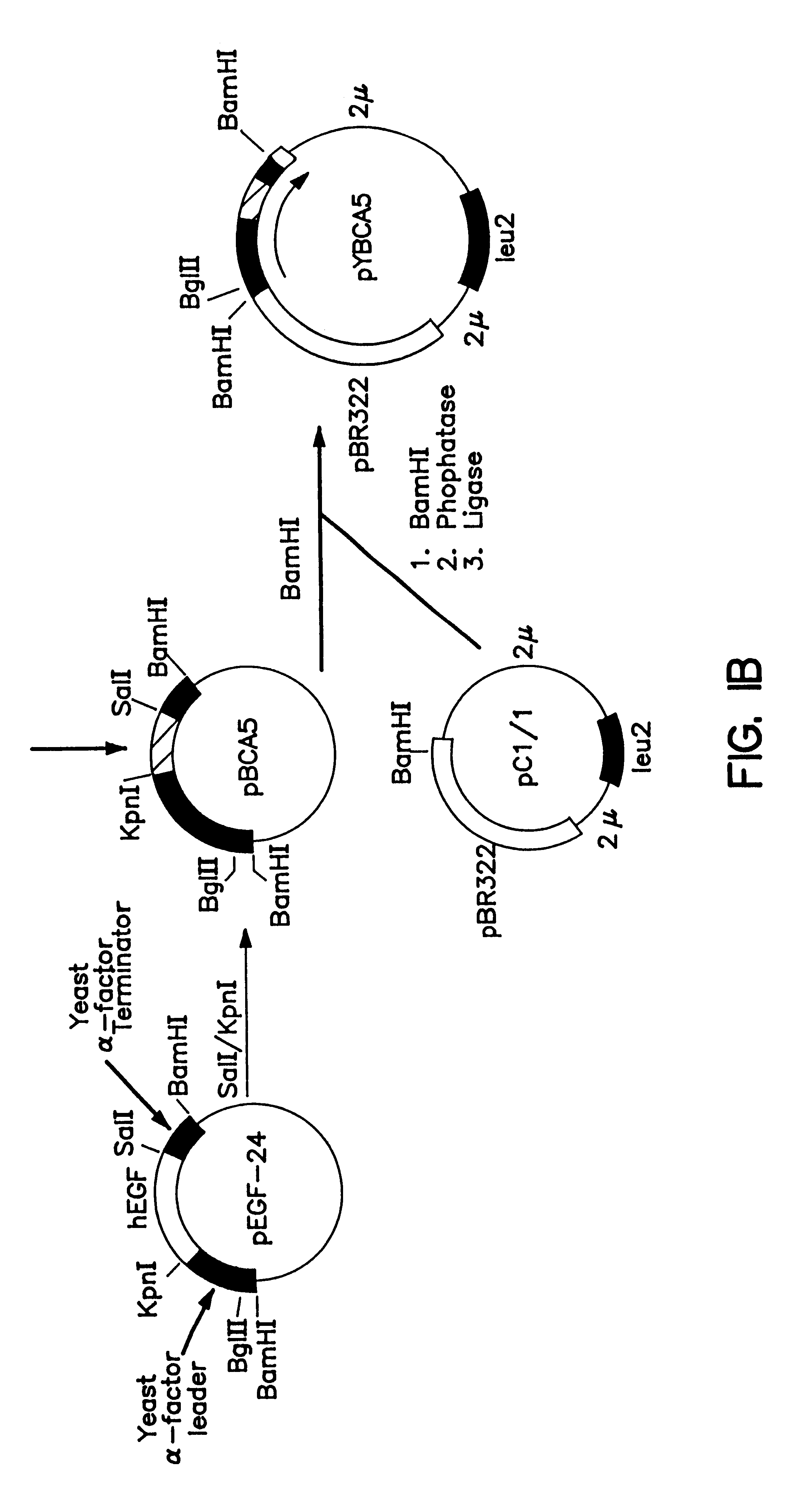
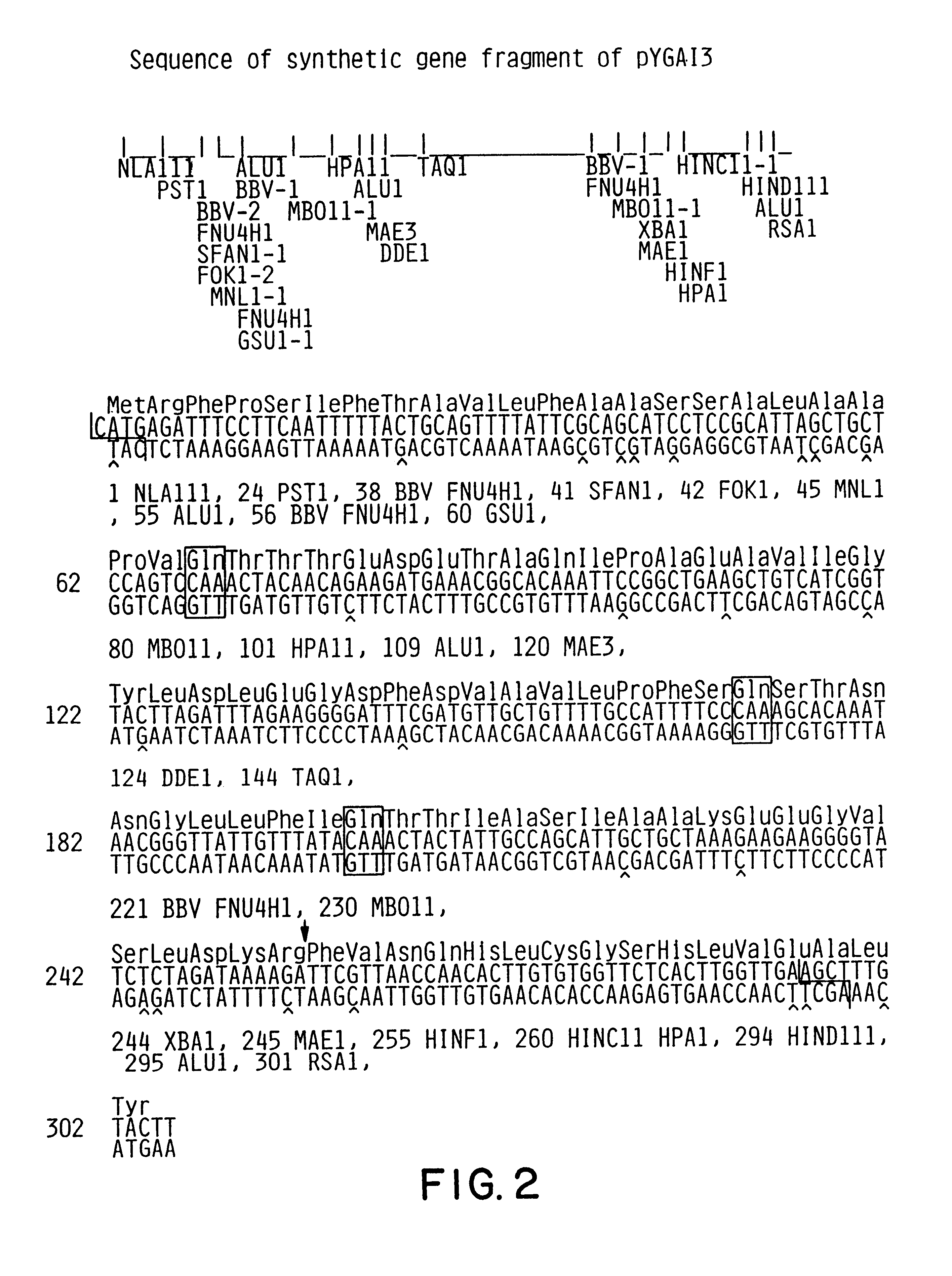
Expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in yeast employing truncated alpha-factor leader sequences
InactiveUSRE37343E1Efficiently direct expressionEfficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousBiotechnology
A yeast alpha-factor expression system is provided comprised of a truncated leader sequence, containing the alpha-factor signal peptide and one glycosylation site, linked by a processing site to a non-yeast protein-encoding sequence.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
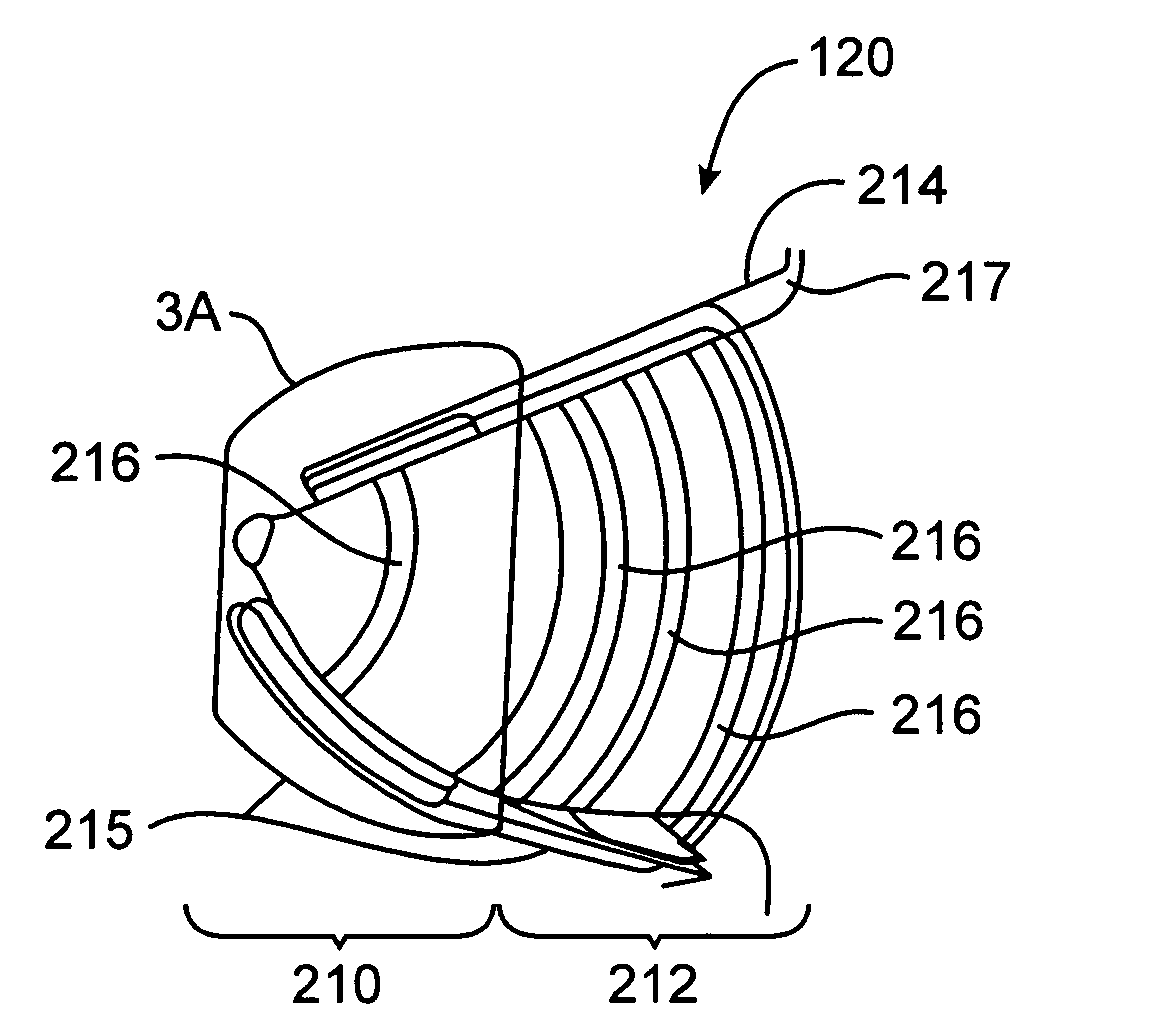
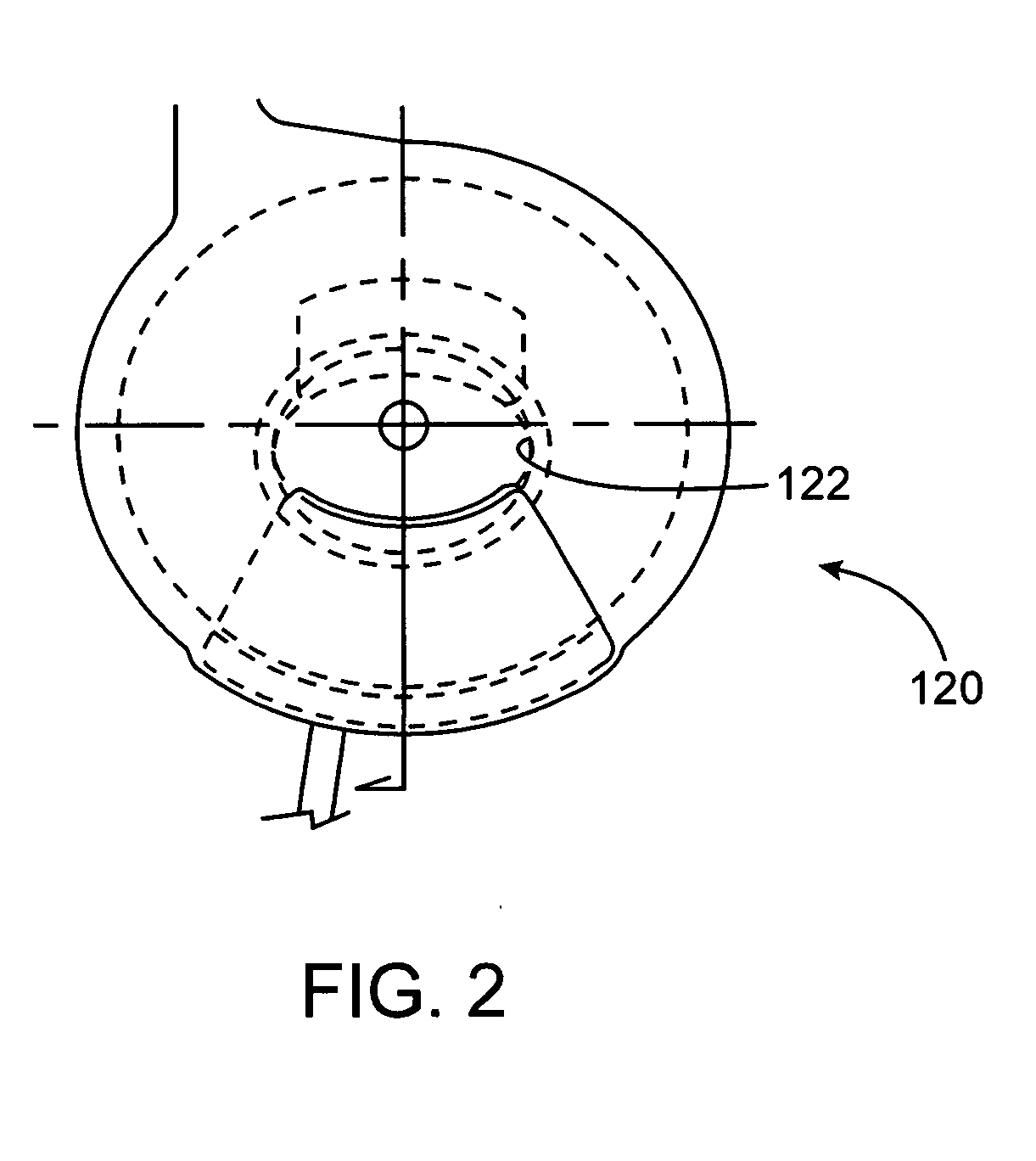
Breast milk expression system including massaging, expressing and containment features
InactiveUS20050234370A1Facilitating lifestyleHealthy and safe and efficient breast milk expression sessionPneumatic massageMilking pumpLactiferous sinusOxytocin
Disclosed is a breast pump that supports a mother's and infant's breastfeeding needs and facilitates the lifestyle of the mother's choice. The breast milk expression system disclosed allows breastfeeding mothers to obtain milk comfortably, hands-free, conveniently and with discretion. The breast milk expression system disclosed includes at least two contact points which mimic hand-expression as well as infant suckling and effectively stimulate the secretion of oxytocin and prolactin to provide a healthy, safe and efficient breastfeeding session. The system disclosed has a gentle rhythmic massage means and is located a distance from the base of the nipple and massages in all quadrants of the breast. The rhythmic forward pressure is provided by a plurality of opposing pairs of expression bellows that move the milk from the lactiferous sinuses through the nipple pores, bio-mimicking the techniques of hand expression.
Owner:PURONYX
Spicy coarse grain dried bean curd and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103444883AFull of nutritionHigh nutritional valueCheese manufactureFood scienceReady to eatLiver and kidney
The invention discloses spicy coarse grain dried bean curd. The spicy coarse grain dried bean curd is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90 to 100 parts of dried soybeans, 3 to 4 parts of oat, 3 to 4 parts of millet, 4 to 5 parts of sorghum, 4 to 5 parts of corns, 2 to 3 parts of mulberries, 2 to 3 parts of hawthorn, 2 to 3 parts of jujubes, 1 to 2 parts of calamus leaves, 1 to 2 parts of platycladus orientalis leaves, 2 to 3 parts of prepared rehmannia root, 1 to 2 parts of fructus amomi, 1 to 2 parts of rehmannia flower, 1 to 2 parts of loofah sponge, 2 to 3 parts of cassia bark, and 2 to 3 parts of rhodiola rosea. A variety of grains are added into the spicy coarse grain dried bean curd, so that a nutritionally balanced structure system is formed; a plurality of seasonings are added, so that the dried bean curd tastes spicy and is easily preferred by consumers; the healthcare components of a plurality of traditional Chinese medicines are added, so that the nutrition value of the dried bean curd is high; the finished dried bean curd is ready to eat, spicy, unique, rich in nutrients and chewy, has the effects of stimulating appetite, improving digestion, tonifying liver and kidney, tonifying spleen and stomach, cooling blood to stop bleeding, promoting the secretion of saliva or body fluid and lubricating intestines, and is the best healthcare food catering to the market and consumers.
Owner:JINCAIDI FOOD CO LTD
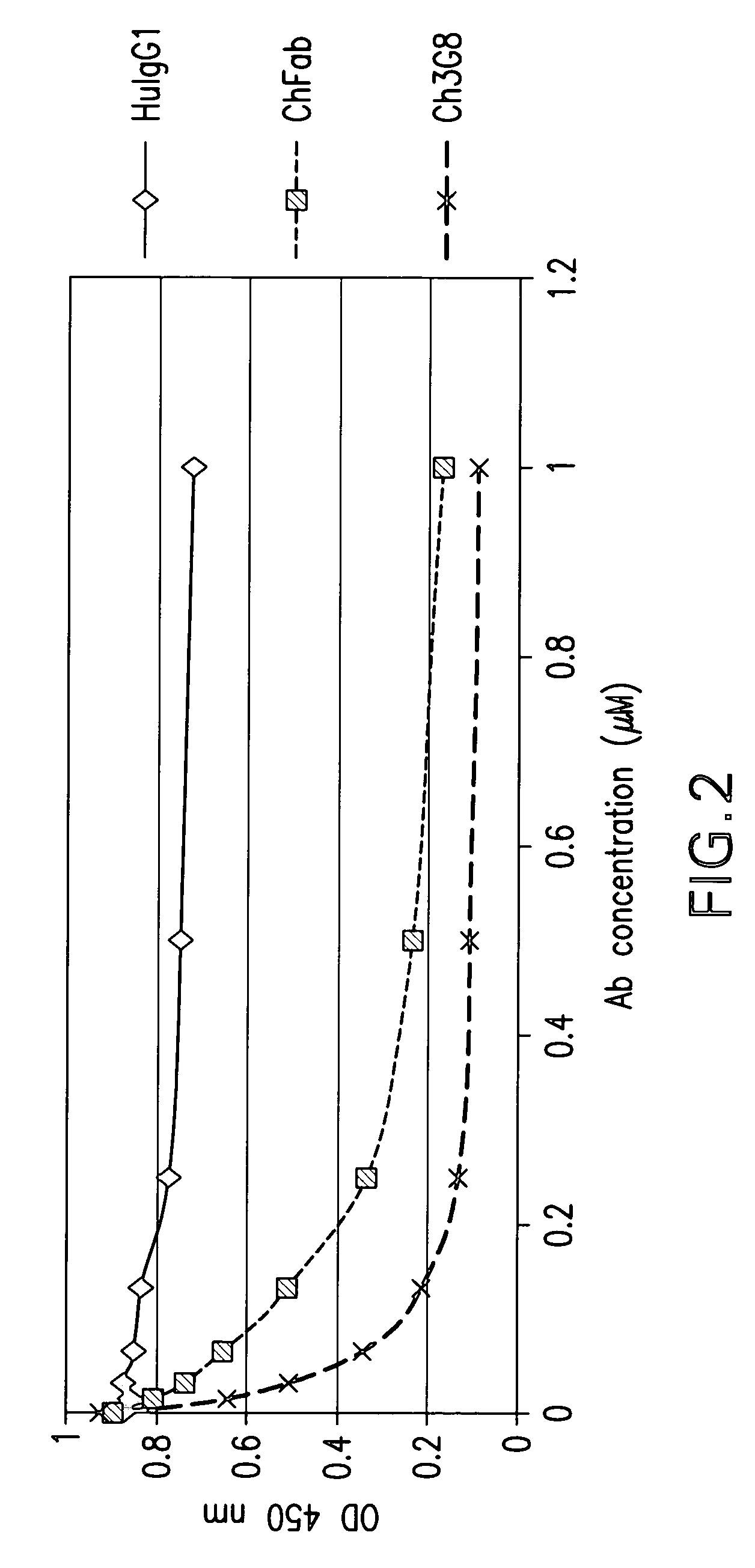
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
ActiveUS7112439B2Maintaining their functionalityEasy to identifyAnimal cellsBacteriaAntigenBacteroides
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Device and method for treatment of wounds with nitric oxide
InactiveUS7122018B2Promote wound healingReduce the burden onBiocideOther blood circulation devicesHigh concentrationNitric oxide gas
Topical exposure of nitric oxide gas to wounds such as chronic non-healing wounds may be beneficial in promoting healing and preparing the wound bed for further treatment and recovery. Nitric oxide gas may be used to reduce the microbial infection, manage exudates secretion by reducing inflammation, upregulate expression of endogenous collagenase to locally debride the wound, and regulate the formation of collagen. High concentration of nitric oxide ranging from 160–400 ppm may be used without inducing toxicity in the healthy cells around a wound site. Exposure to the high concentration for a first treatment period reduces the microbial burden and inflammation, and increases collagenase expression to debride necrotic tissue at the wound site. After a first treatment period, a second treatment period at a lower concentration of nitric oxide, preferably ranging from 5–20 ppm may be used to restore the balance of nitric oxide and induce collagen expression aiding in the wound closure.
Owner:SENSORMEDICS +1
Method and apparatus for treating meibomian gland dysfunction
A method and apparatus for treating gland dysfunction caused by gland obstruction in order to restore the natural flow of secretion from the gland comprises the application of a combination of energy, suction, vibration, heat, aspiration, chemical agents and pharmacological agents to loosen and thereafter remove the obstructive material'.
Owner:TEARSCIENCE INC
Inflatable system for cervical dilation and labor induction
An inflatable system, of between one and three balloons, for cervical dilation and labor induction is provided. The inflatable system may have a uterine balloon, for positioning at a proximal portion of the uterus, with respect to an operator, adjacent to the cervical internal os, the uterine balloon being shaped so as to maximize the pressure against the decidua and the internal cervical os and so as to minimize the pressure on the fetal head. Additionally or alternatively, the inflatable system may have a vaginal balloon, for positioning in the vagina, for applying pressure on the external cervical os. Additionally or alternatively, the inflatable system may have a cervical balloon, for positioning in the cervical canal, the cervical balloon being shaped so as to maximize the contact area with the cervix. The balloons are operative to stimulate the secretion of hormone, by exerting pressure on the proximal decidual surfaces of the uterus and on the cervix, so as to soften and ripen the cervix, cause the cervix to dilate, and induce labor. The balloons, which may have rough external surfaces, in order to keep them anchored in place, may be inflated by the operator, directly after their insertion, or manually and gradually, by the woman herself. Various sensors and other instruments may be used with the inflatable system, to monitor cervical dilation, fetal well-being, and the woman's conditions.
Owner:ATAD - DEV & MEDICAL SERVICES
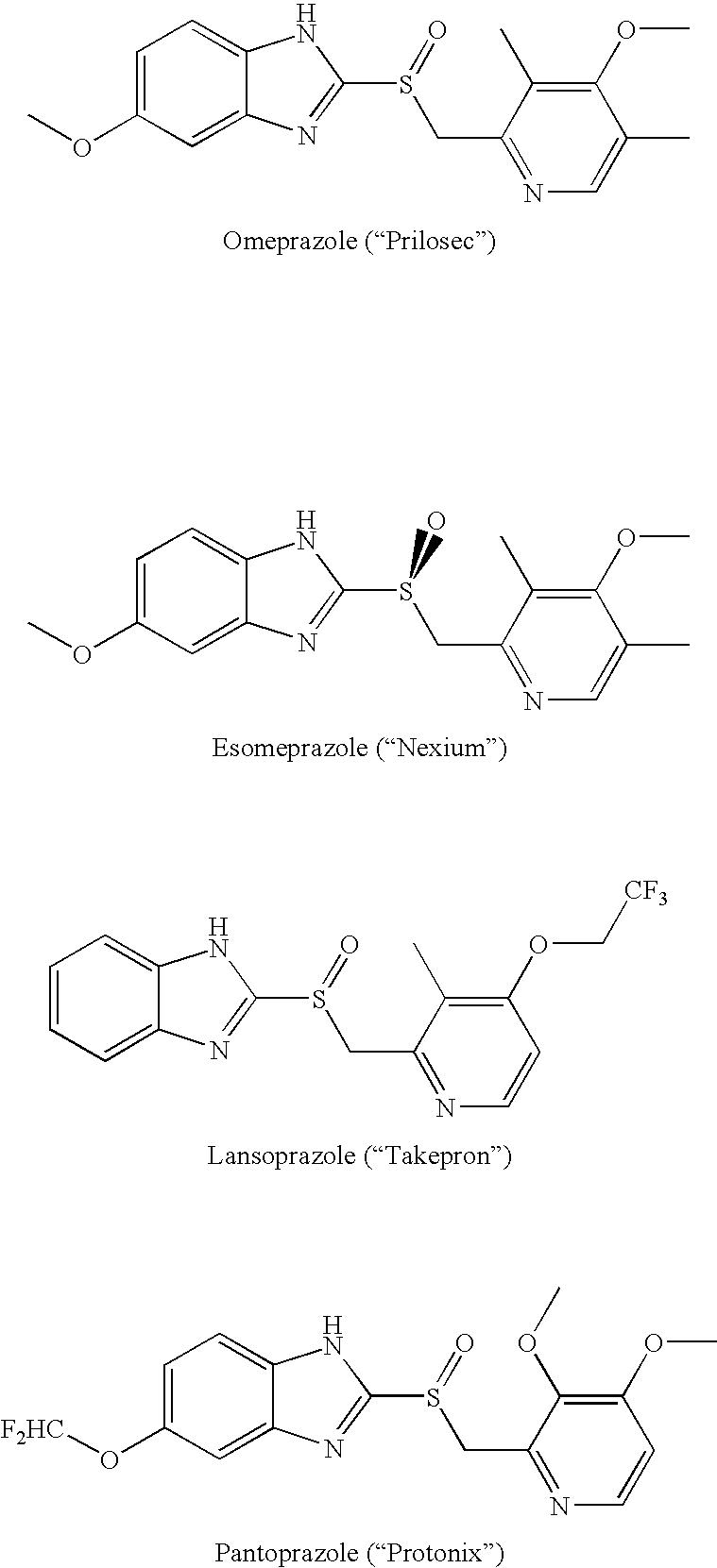
Gastric acid secretion inhibiting composition
InactiveUS20080031941A1Quick and lasting reliefAntibacterial agentsBiocideHelicobacter pyloriGastric ph
An oral pharmaceutical dosage form comprises pharmacologically effective amounts of an acid susceptible proton pump inhibitor or a salt thereof, an H2 receptor antagonist or a salt thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The dosage form is capable of raising gastric pH to above 4 within two hours after administration and to keep it at that level for at least 4 hours. Also disclosed is a method of manufacture of the dosage form, its use in treating dyspepsia and infection by Helicobacter pylori, and a method of treating disorders associated with gastric acid secretion.
Owner:OREXO AB
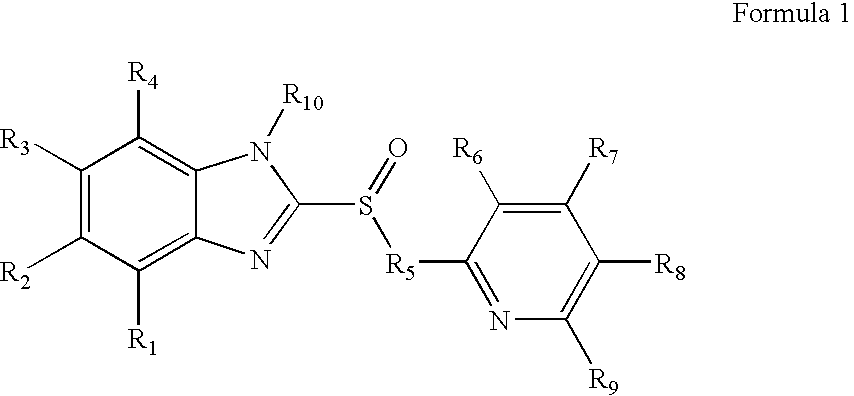
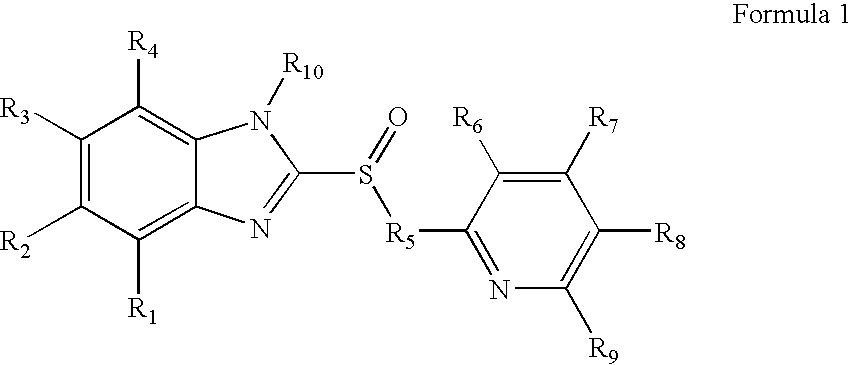
Sulfonamide and carboxamide derivatives and drugs containing the same as the active ingredient
InactiveUS6448290B1Low toxicityEasy to useBiocideOrganic chemistryBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTAnalgesic agents
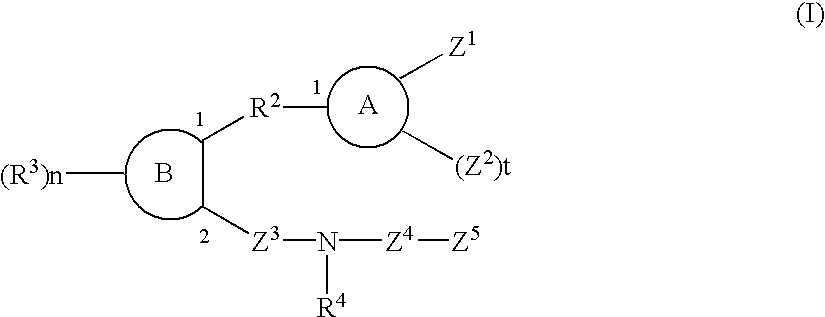
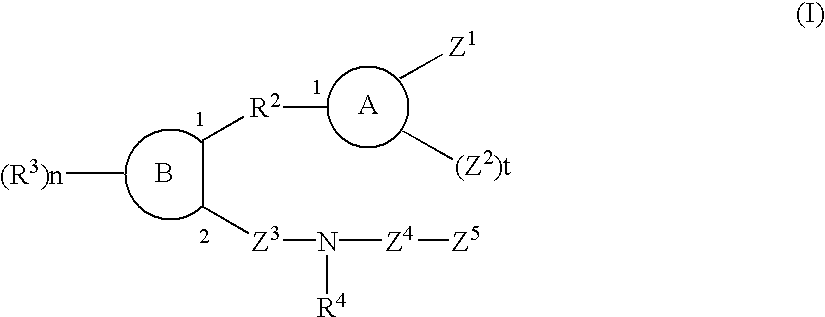
The sulfonamide or carboamide derivatives of the formula (I) and a pharmaceutical composition which comprise them as an active ingredient:(wherein A ring, B ring is carbocyclic ring, heterocyclic ring; Z1 is -COR1, -CH=CH-COR1 etc.; Z2 is H, alkyl etc.; Z3 is single bond, alkylene; Z4 is SO2, CO; Z5 is alkyl, phenyl, heterocyclic ring etc.; R2 is CONR8, O, S, NZ6, Z7-alkylene, alkylene etc.; R3 is H, alkyl, halogen, CF3 etc.; R4 is H, (substituted) alkyl etc.; n, t is 1-4).The compounds of the formula (I) can bind to receptors of PGE2 and show antagonistic activity against the action thereof or agonistic activity. Therefore, they are considered to be useful as medicine for inhibition of uterine contraction, analgesics, antidiarrheals, sleep inducers, medicine for increase of vesical capacity or medicine for uterine contraction, cathartic, suppression of gastric acid secretion, antihypertensive or diuretic agents.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
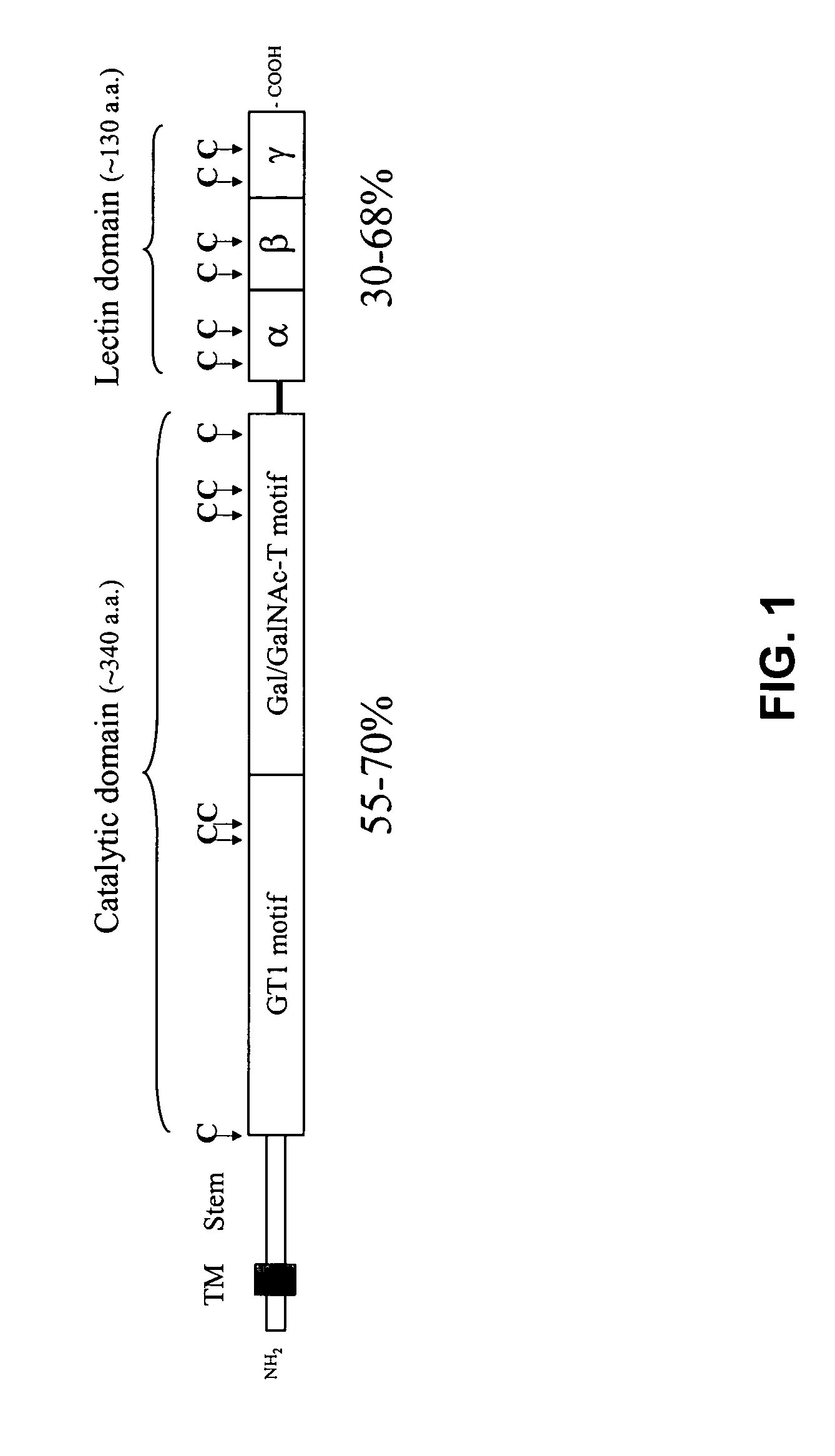
Methods to identify agents modulating functions of polypeptide galnac-transferases, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such agents and the use of such agents for preparing medicaments
Novel methods for identification of inhibitors or modulators of binding activities mediated by lectin domains of polypeptide GalNAc-transferases are disclosed. Direct binding activity of GalNAc-transferase lectins has been demonstrated for the first time and methods to measure lectin mediated binding of isolated lectins or enzymes with lectin domains are disclosed. The present invention specifically discloses a novel selective inhibitor of polypeptide GalNAc-transferase lectin domains, which provides a major advancement in that this inhibitor and related inhibitors sharing common characteristics of activity bind lectin domains without serving as acceptor substrate for glycosyltransferases involved in synthesis of O-glycans. This inhibitor is represented by the β-anomeric configuration of GalNAc-benzyl, GalNAcβ-benzyl. Methods for inhibiting intracellular transport, cell surface expression, and secretion of mucins and O-glycosylated glycoproteins without affecting O-glycosylation processing are disclosed using the novel selective inhibitor identified.
Owner:GLYCOZYM
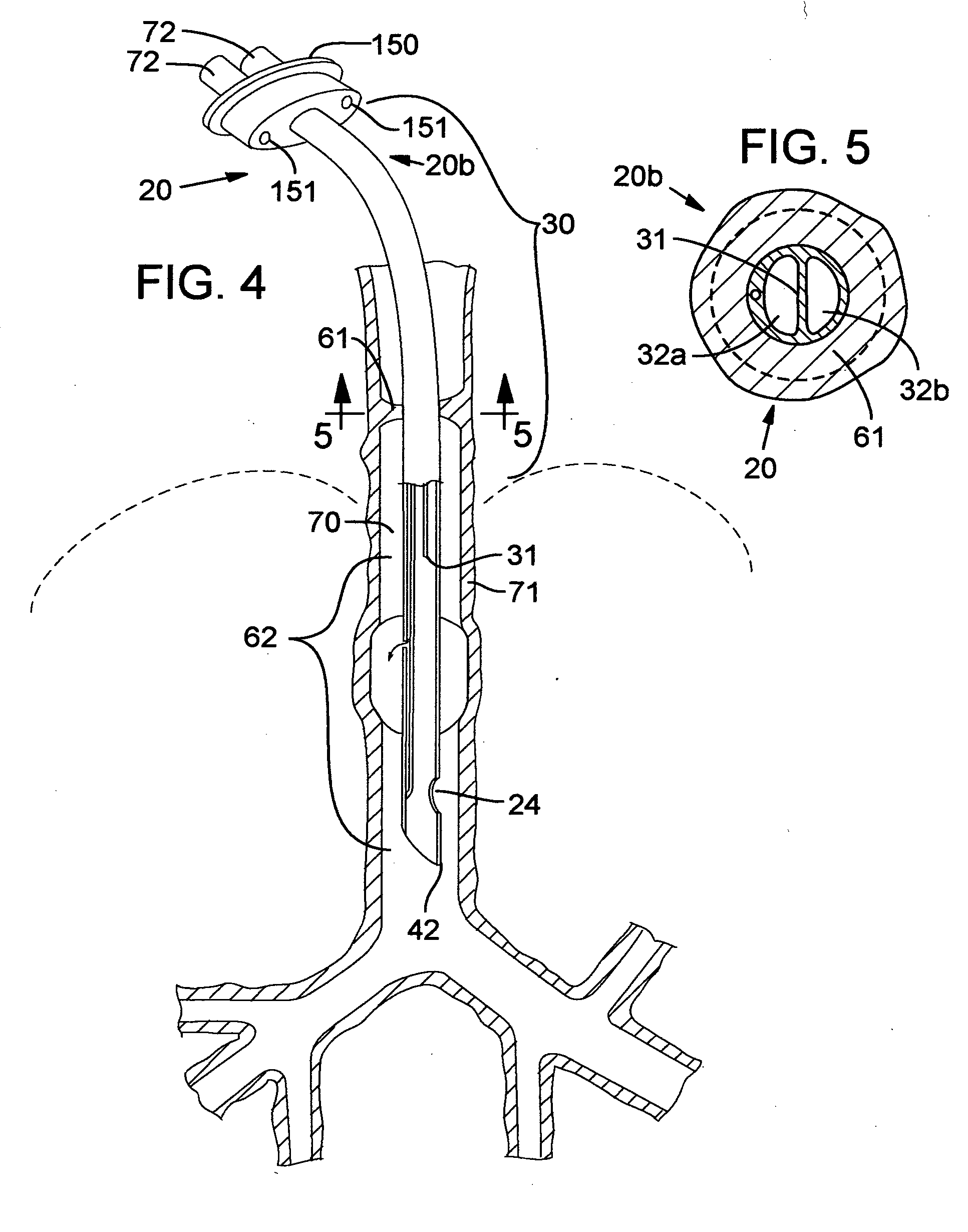
Secretion clearing ventilation catheter and airway management system
InactiveUS20070068530A1Easy to insertEasy to disassembleTracheal tubesBalloon catheterCollection systemWater vapor
A pulmonary secretion clearing ventilation catheter and related airway management system is disclosed. The ventilation catheter has a double lumen portion which each lumen of the double lumen portion operably secured to an airway management system so that inspiratory fluid (air / oxygen mixtures, with or without added water vapor) is delivered to the distal end of the ventilation catheter through one of the two lumens and expired inspiratory fluid, pulmonary secretions, and pulmonary fluids are removed from the patent through the other lumen. The expiratory fluid pathway preferably includes a secretion collection system for removing the pulmonary secretions and the like from the pathway, thereby improving operation and safety of the system. An improved inflatable cuff is also disclosed that permits a slight air leakage in the pneumatic seal between the patient's lungs and the environment, thereby facilitating removal of pulmonary secretions from the patient's lungs.
Owner:VERATHON MEDICAL CANADA ULC
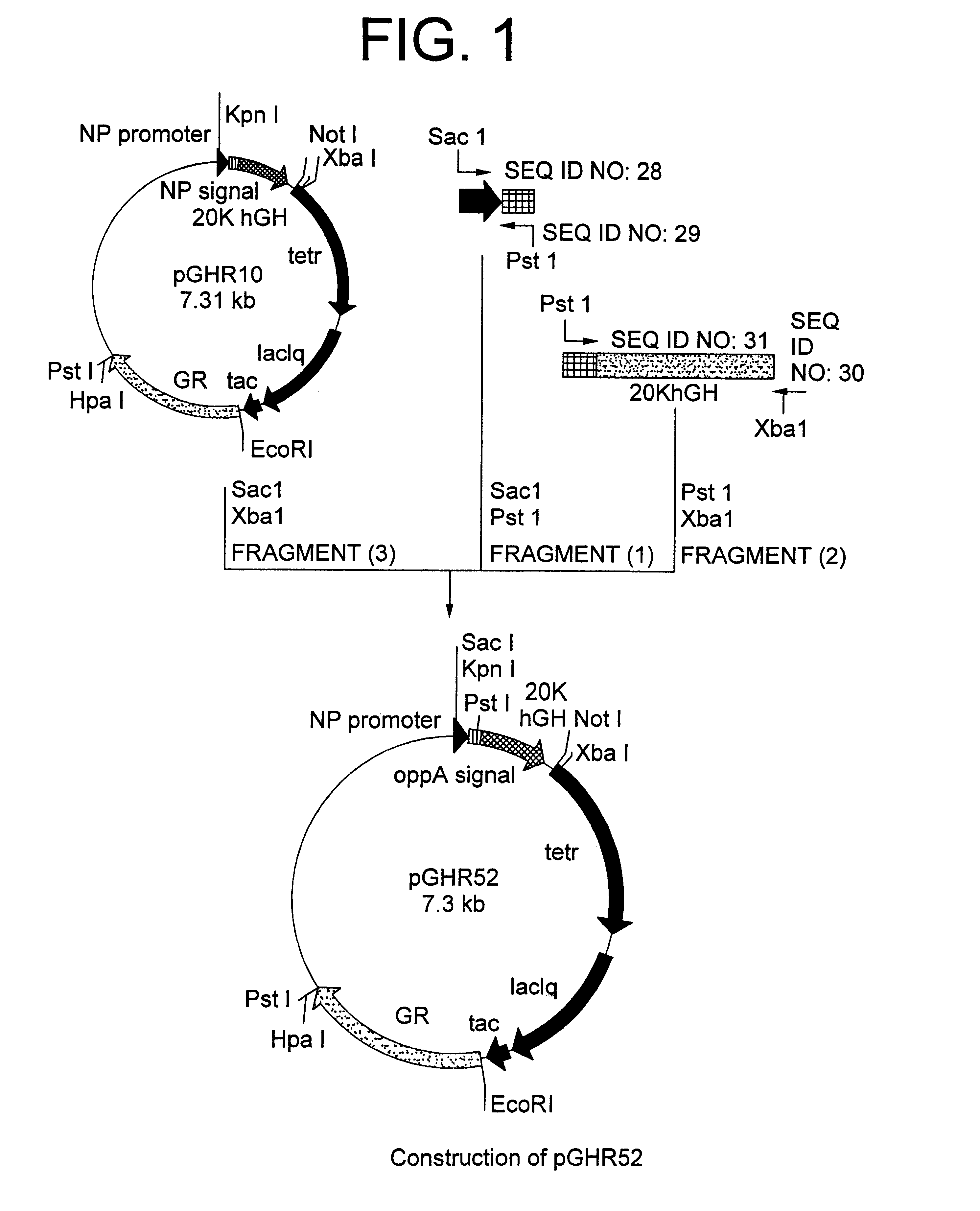
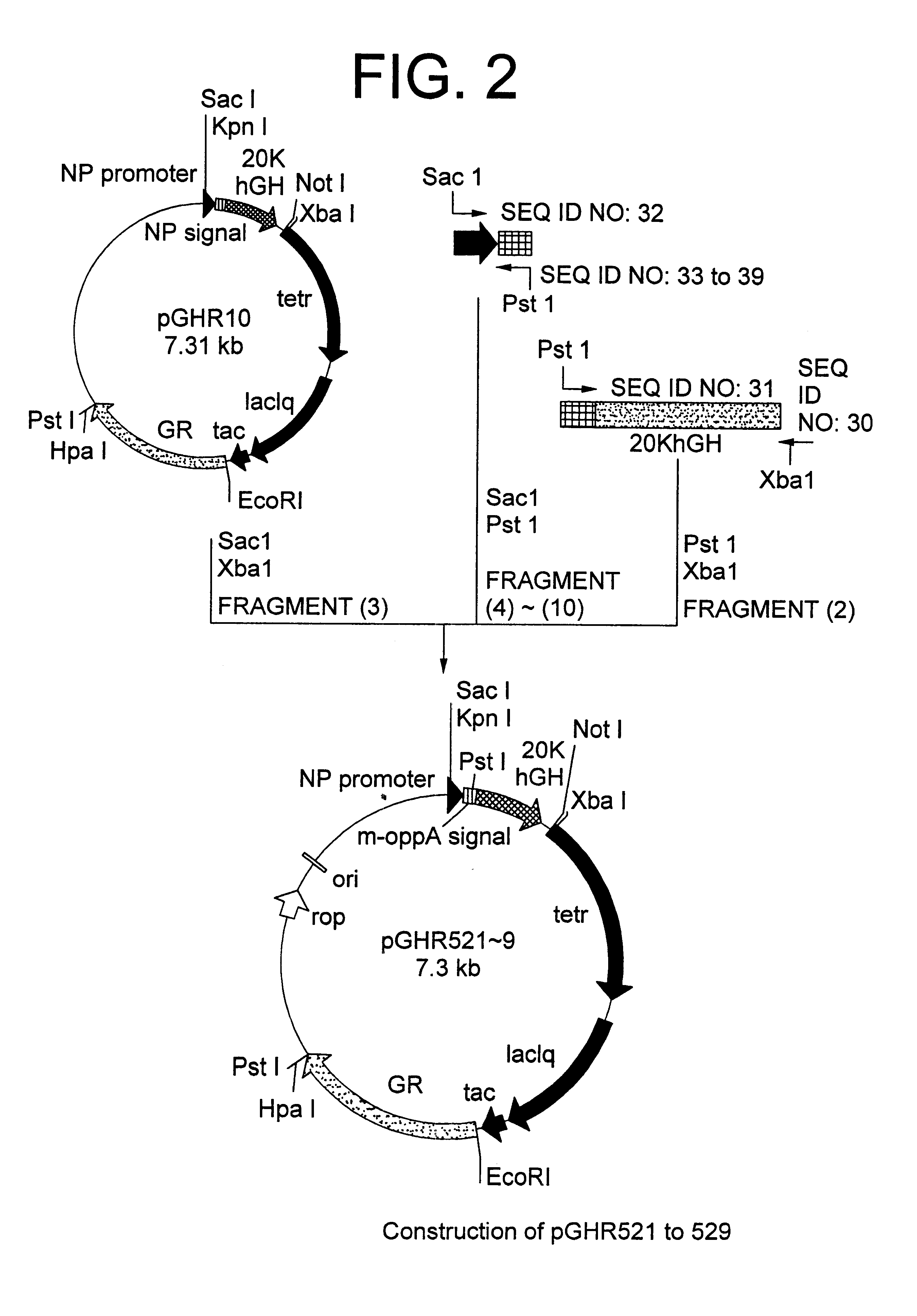
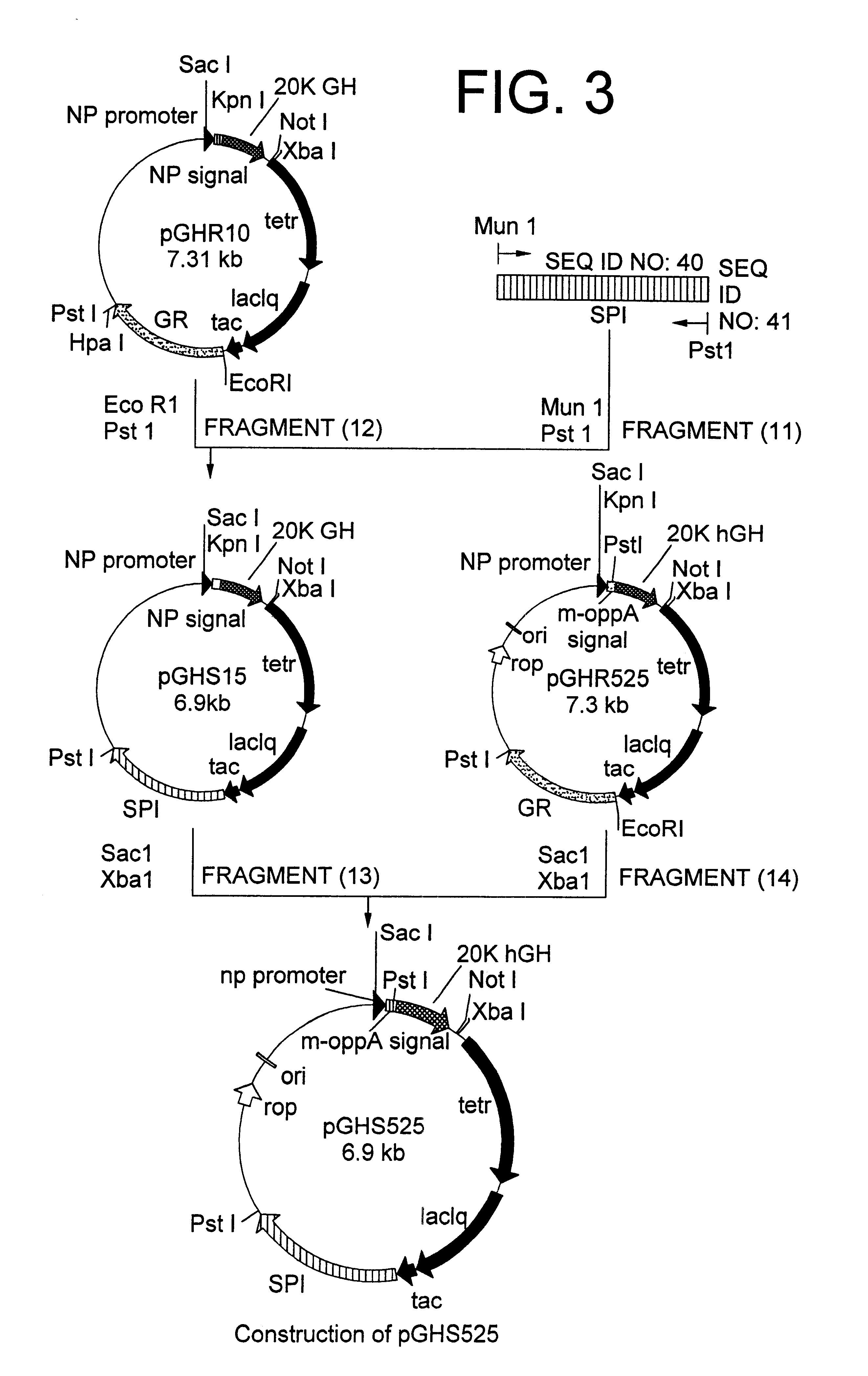
Method for secretory production of human growth hormone
InactiveUS6436674B1Increase productionDecreased tendency for lysisBacteriaHydrolasesHuman growth hormoneA-DNA
A DNA encoding 20K hGH is connected directly to a gene encoding Escherichia coli OppA protein secretion signal, or a modified form thereof, and a DNA encoding signal peptidase 1 to construct a recombinant plasmid, E. coli is transformed by the plasmid and cells of the resulting E. coli transformant strain are cultured for secretory production of the 20K hGH in the E. coli periplasm. This method enables efficient secretory production of 20K hGH and easy isolation and purification of 20K hGH from the periplasm fraction because the level of impure proteins in the E. coli periplasm is low.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Secretion signal vectors
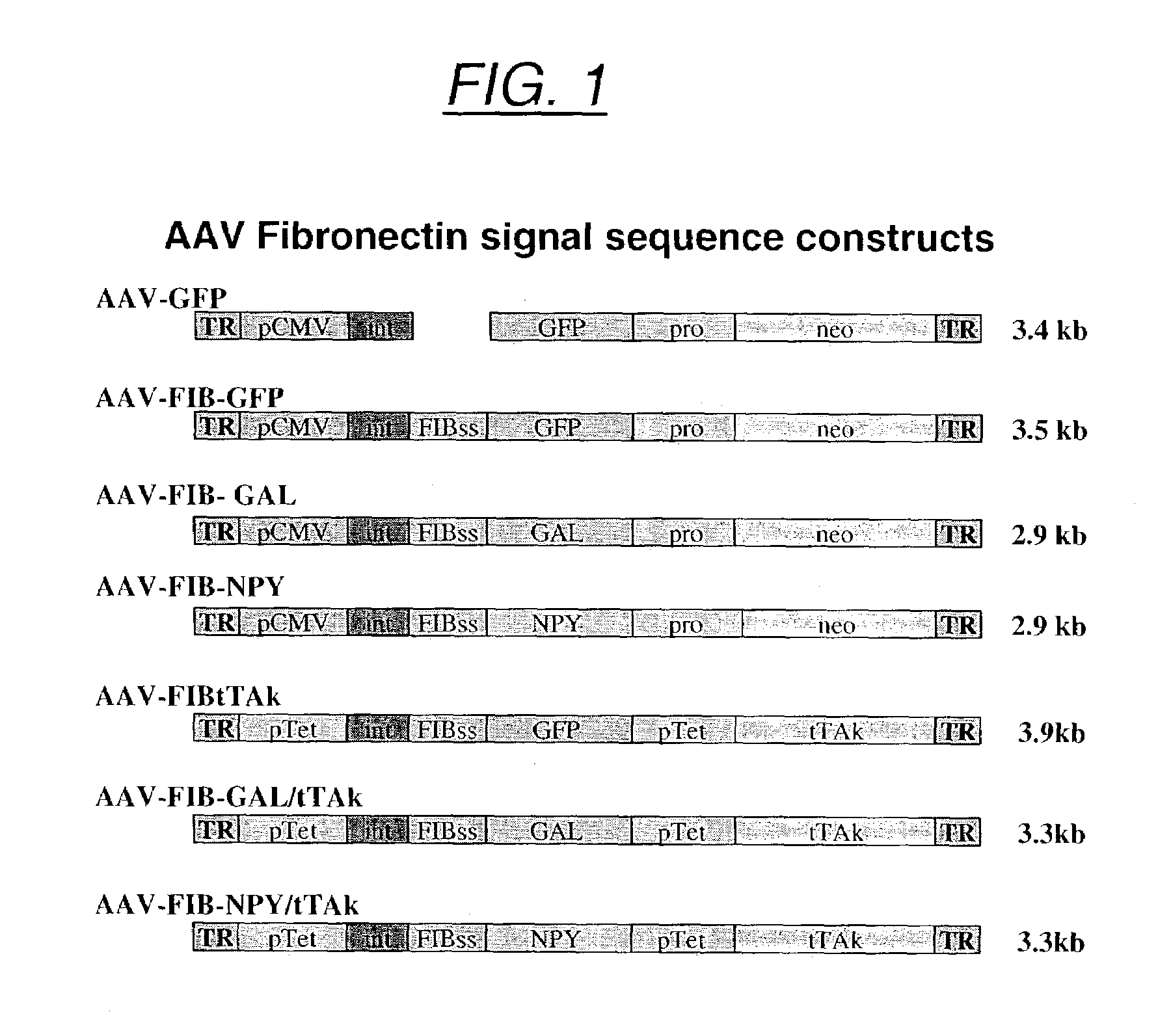
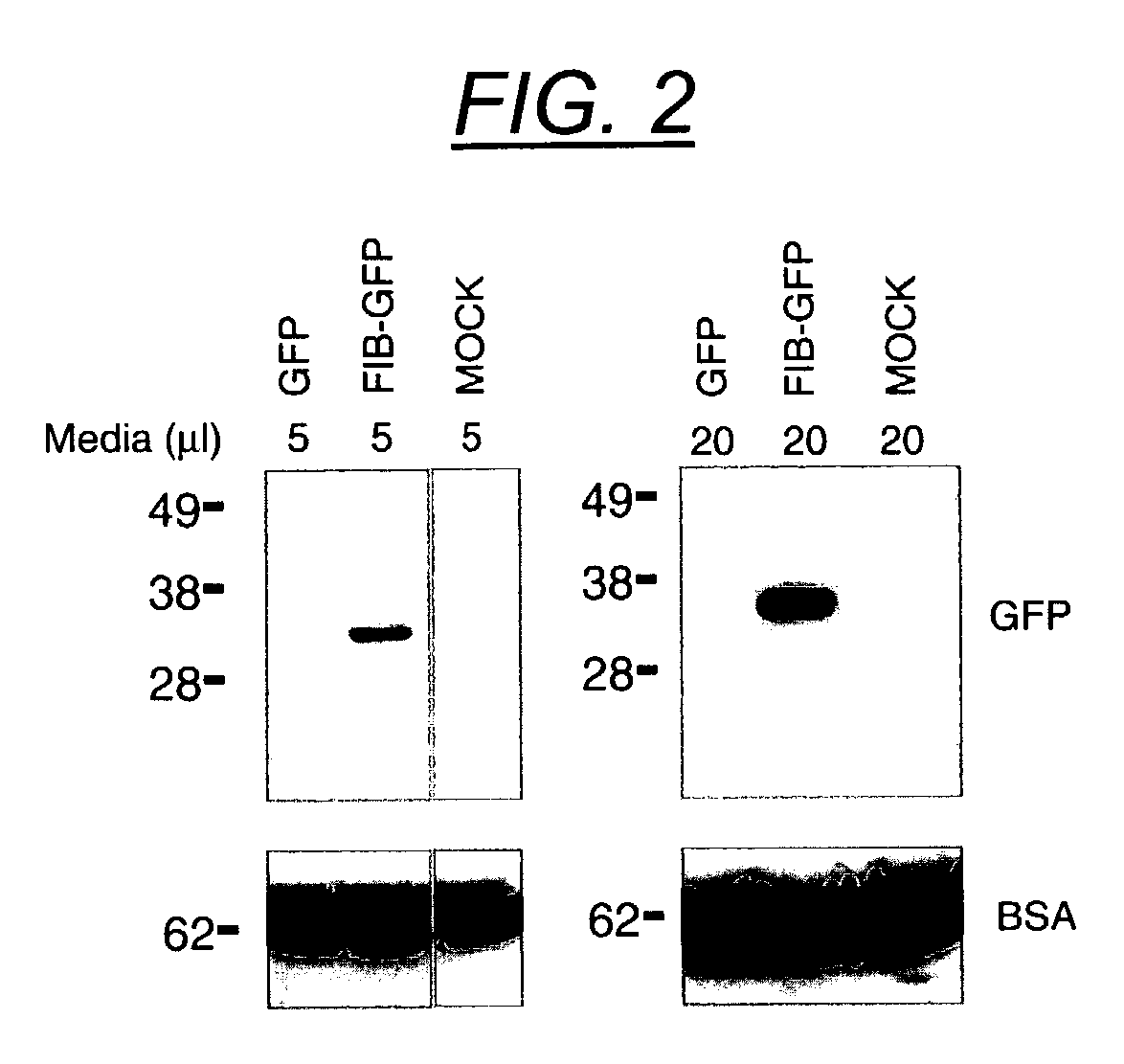
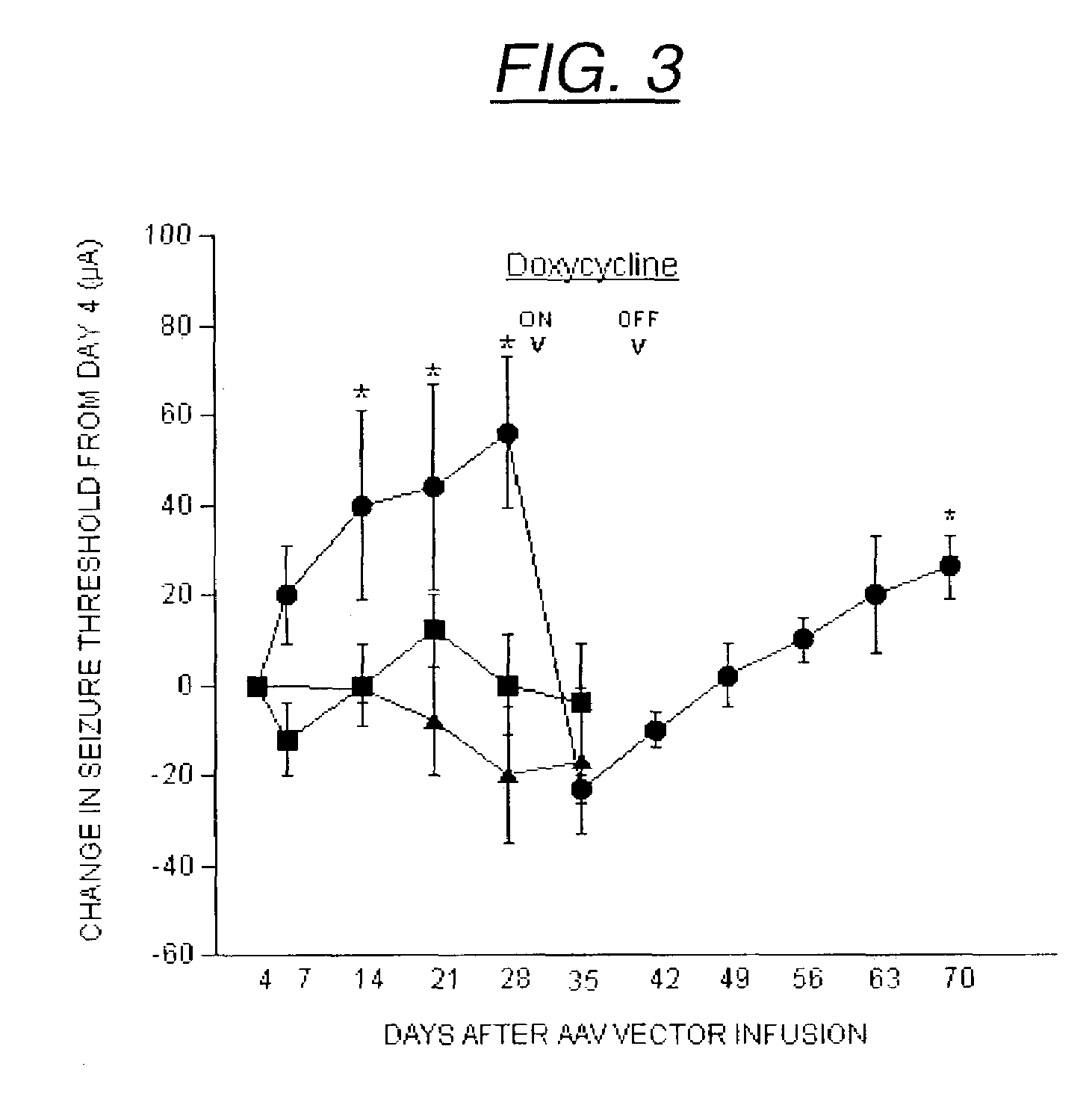
InactiveUS7071172B2Minimize potential deleterious side effectAttenuate seizure activityBiocideAnimal repellantsHeterologousAdeno associate virus
The present invention provides delivery vectors for transferring a nucleic acid sequence to a cell in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo. The delivery vector comprises a segment encoding a secretory signal peptide. In embodiments of the invention, the delivery vector is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector. In other embodiments, the secretory signal peptide is a fibronectin secretory signal peptide (including variations and modifications, thereof). The delivery vectors of the invention may further comprise a heterologous nucleic acid sequence encoding a polypeptide of interest for transfer to a target cell, where the polypeptide of interest is operably associated with the secretory signal. Also disclosed are methods of transferring a nucleic acid of interest to a cell using the delivery vectors of the invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method for treating airways in the lung
InactiveUS20070106348A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease inner diameterDiagnosticsMedical devicesBronchospasmSmooth muscle spasm
A device and method for treating bodily conduits involves the application of energy to the smooth muscle tissue of the conduit walls to reduce the bulk of smooth muscle tissue and mucus glands. The irradiation treatment of the smooth muscle tissue causes a reduction in the amount of smooth muscle tissue over time which increases the inner diameter of the body conduit for improved fluid flow and prevents smooth muscle spasms. The treatment is particularly useful in the lungs for treatment of asthma to prevent bronchospasms, increase the airway diameter for improved air exchange, and reduce mucus secretions in the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Continuous high-frequency oscillation breathing treatment apparatus
ActiveUS20050061318A1Assist in mucus secretionSimply and inexpensively manufacturingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing treatmentsDuring expiration
A continuous high-frequency oscillation breathing device delivers therapy during both inhalation and exhalation in order to assist in clearing secretions from the lungs. A fixed shrouded-venturi patient interface circuit is combined with medicated aerosol to deliver continuous high-frequency oscillation therapy. Fixed open apertures in the patient interface circuit allow ingress and egress of flow, and are calibrated to allow exhalation and prevent stacking of successive breaths.
Owner:COMEDICA INC
Medical aspirating/ventilating closed system improvements and methods
Apparatus and methods are disclosed by which a closed ventilating system accommodates multiple access to the respiratory system of an intubated medical patient without compromising the closed character of the system. Access to the respiratory system through one or more access sites of the closed system apparatus is provided at proximal adapter ports to ventilate the lungs of the patient with gas or gases, to aspirate secretions from the lungs, to oxygenate the lungs to eliminate or reduce residual co2 therefrom, to visually inspect selected parts of the respiratory system, to sample sputum and gases, to sense parameters such as flow rates, pressure, and temperature, to flush with washing solution, and / or to administer medication, gases, and / or lavage. A distal swivel fitting provides multiple sealing sites by which entry of atmosphere is prevented.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
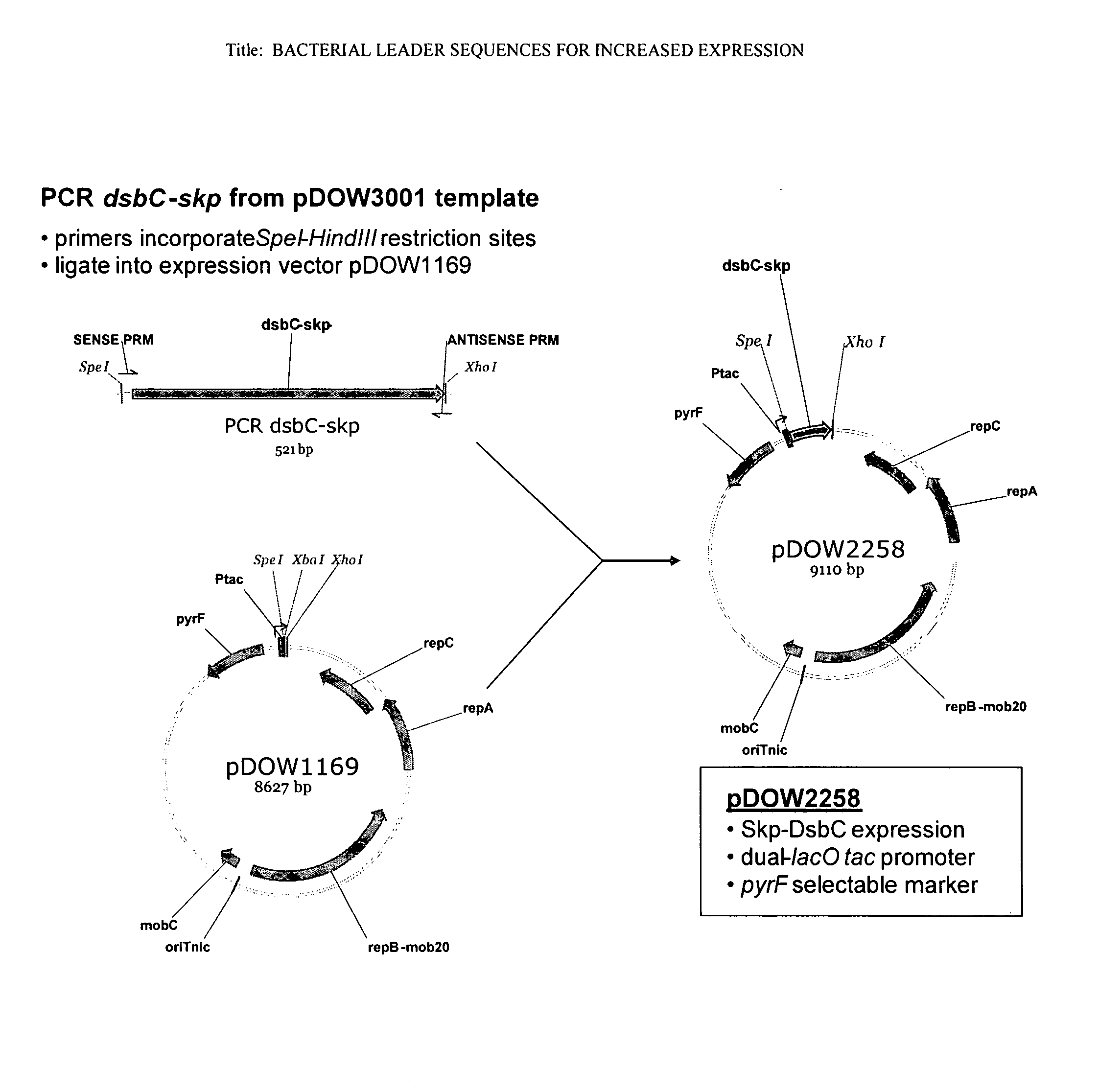
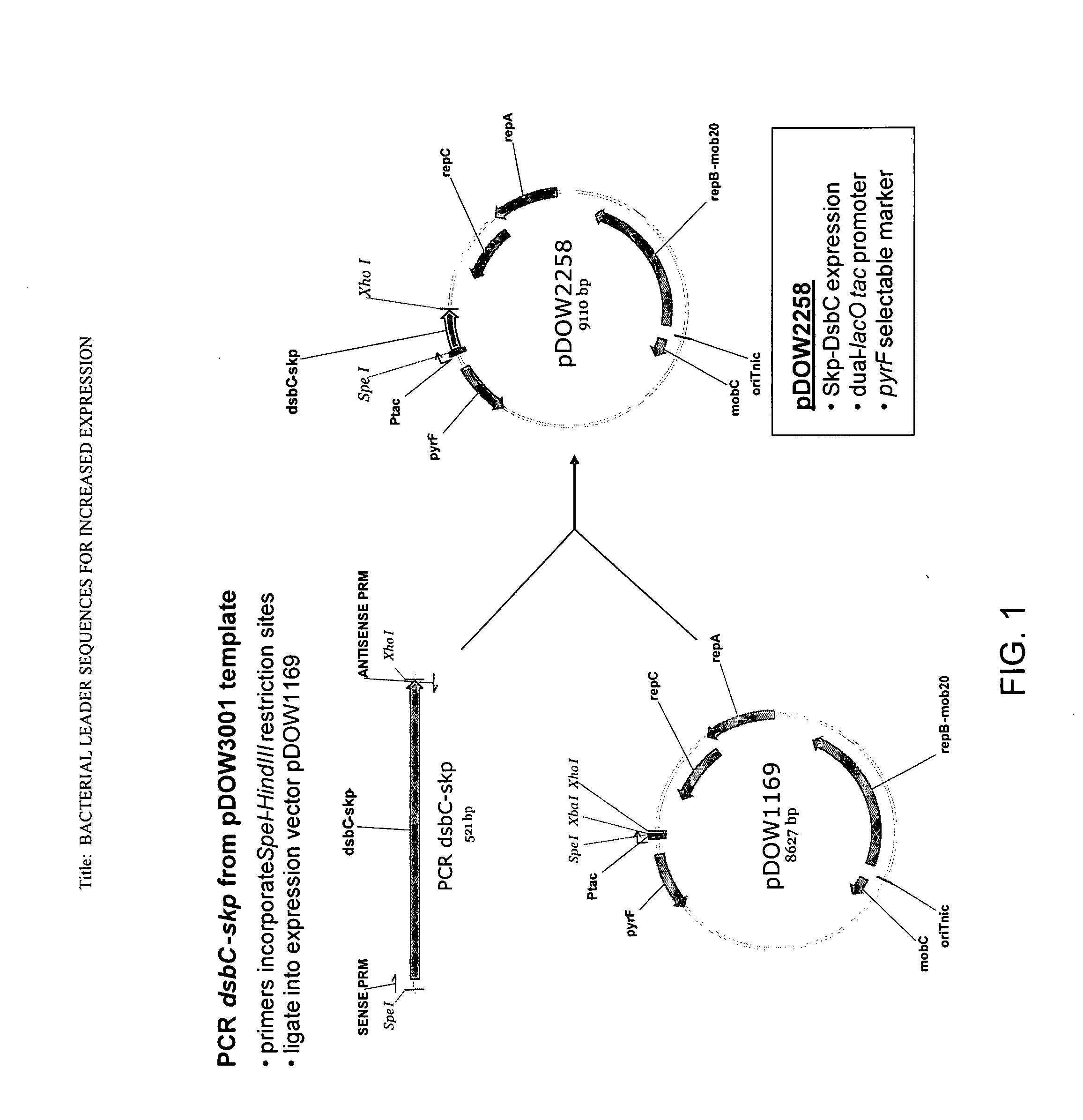
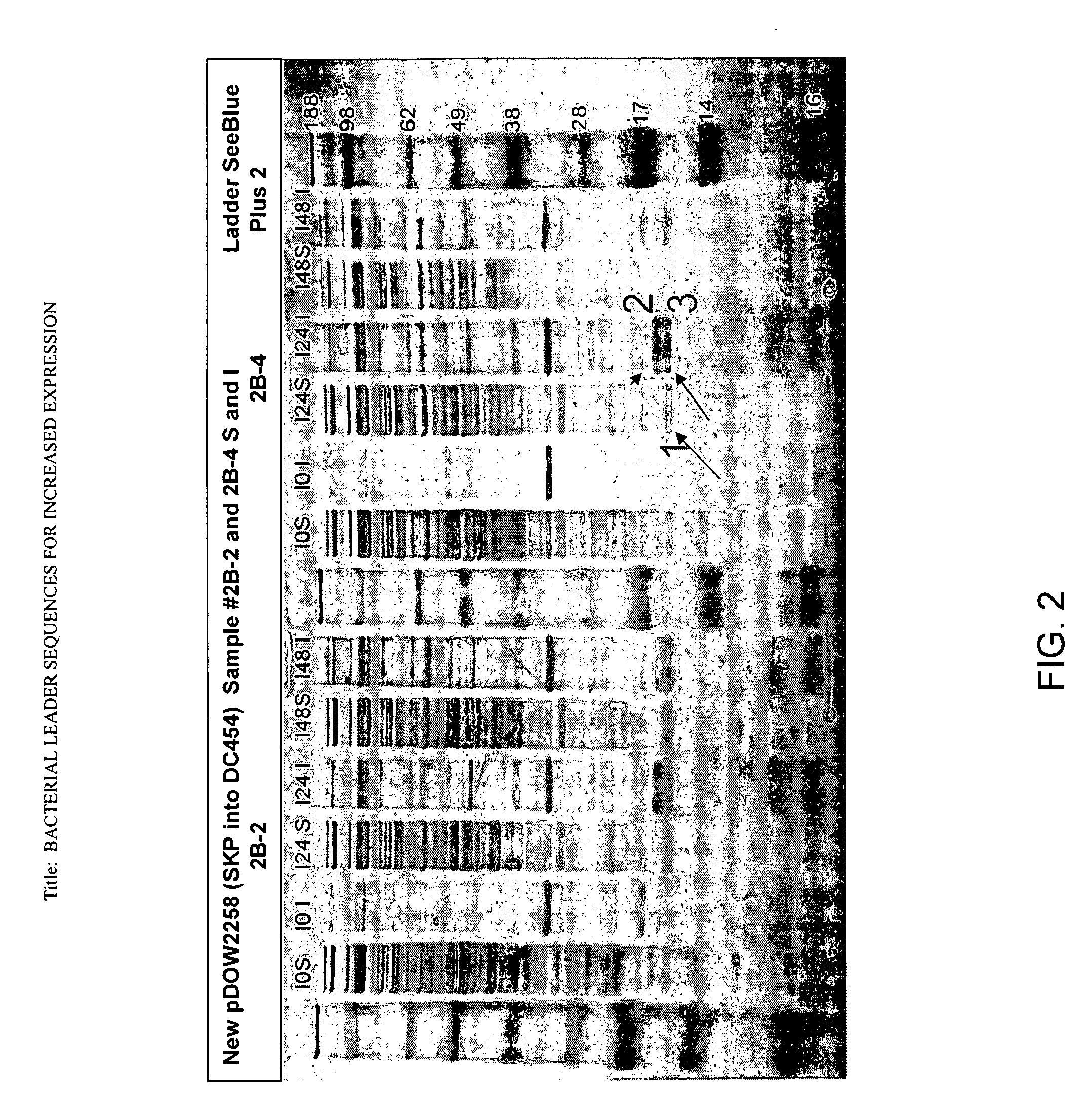
Bacterial leader sequences for increased expression
ActiveUS20080193974A1Promote targetingSimple compositionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
Compositions and methods for improving expression and / or secretion of protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a bacterial secretion signal peptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in vector constructs or expression systems for transformation and expression of a protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell. The compositions of the invention are useful for increasing accumulation of properly processed proteins in the periplasmic space of a host cell, or for increasing secretion of properly processed proteins from the host cell. In particular, isolated secretion signal peptide-encoding nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the nucleic acid molecules are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and 24, and the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, and 23, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:PFENEX
Medical aspirating/ventilating closed system improvements and methods
InactiveUS6012451AEasy to limitCost effectiveTracheal tubesRespiratory apparatusEmergency medicineOxygen
Apparatus and methods are disclosed by which a closed ventilating system accommodates multiple access to the respiratory system of an intubated medical patient without compromising the closed character of the system. Access to the respiratory system through one or more access sites of the closed system apparatus is provided at proximal adapter ports to ventilate the lungs of the patient with gas or gases, to aspirate secretions from the lungs, to oxygenate the lungs to eliminate or reduce residual co.sub.2 therefrom, to visually inspect selected parts of the respiratory system, to sample sputum and gases, to sense parameters such as flow rates, pressure, and temperature, to flush with washing solution, and / or to administer medication, gases, and / or lavage. A distal swivel fitting provides multiple sealing sites by which entry of atmosphere is prevented.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Detection of contaminants in food
InactiveUS6270724B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteTrademark
The present invention relates to a food contamination detector associated with a double bar code, given the trademark GILBAR.TM. by the owner of the present invention, that includes coded indicia used to identify the presence of conditions indicative of microbial contamination in food, including toxic contaminants, bacterial metabolites, and other microbial secretions. Of the two bar code symbols associated with the food contamination detector, the first identifies the food product in terms of the type of food, the quantity, the price and the like, while the second bar code symbol is designed to identify the presence of contaminants. When contamination is not detected, the first bar code symbol is scanner readable, whereas the second bar code symbol is not. Once contamination is detected, bars in both bar code symbols can appear or disappear causing the first bar code symbol to become scanner unreadable and the second bar code symbol to become scanner readable.
Owner:SIRA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com