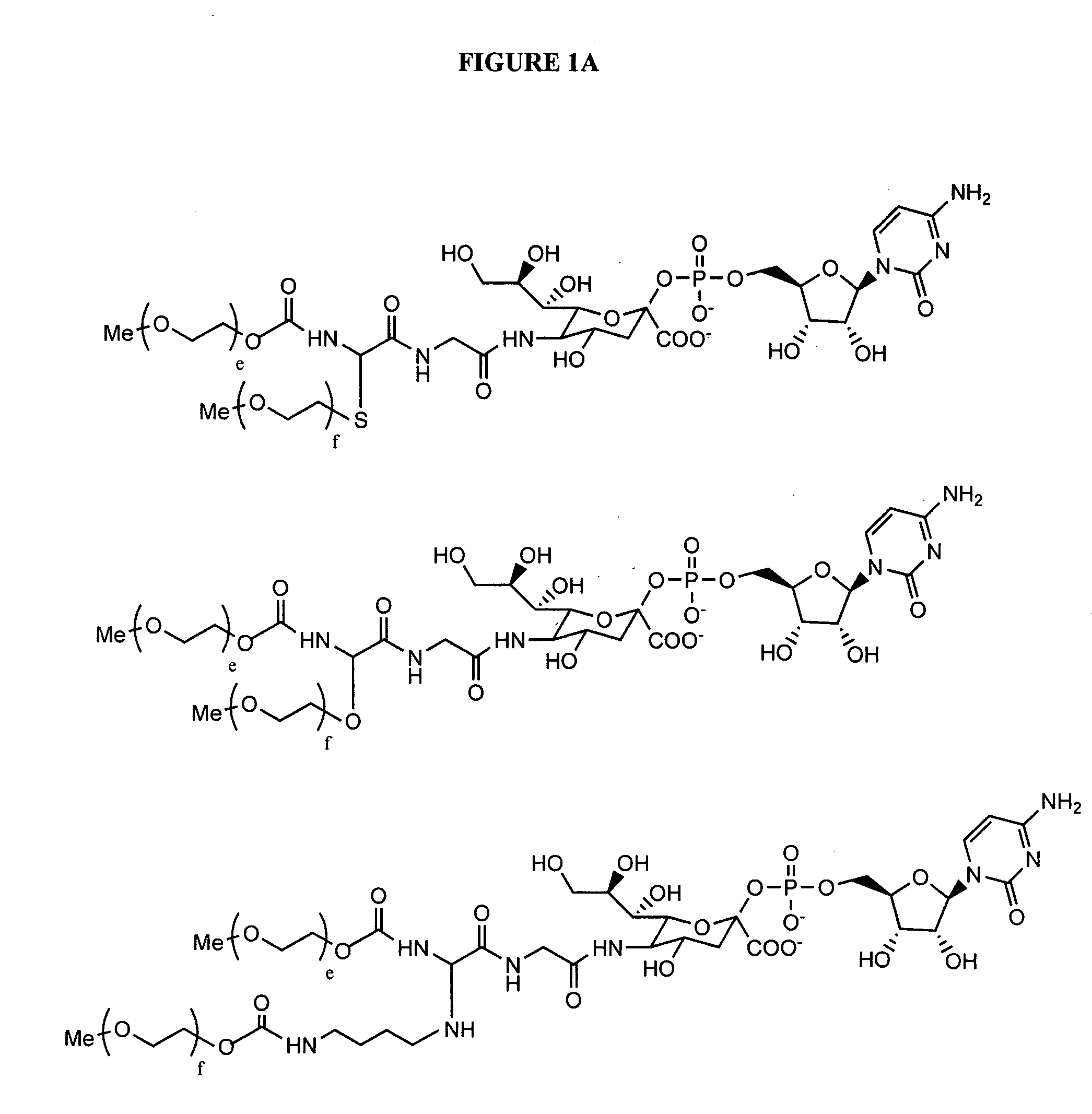
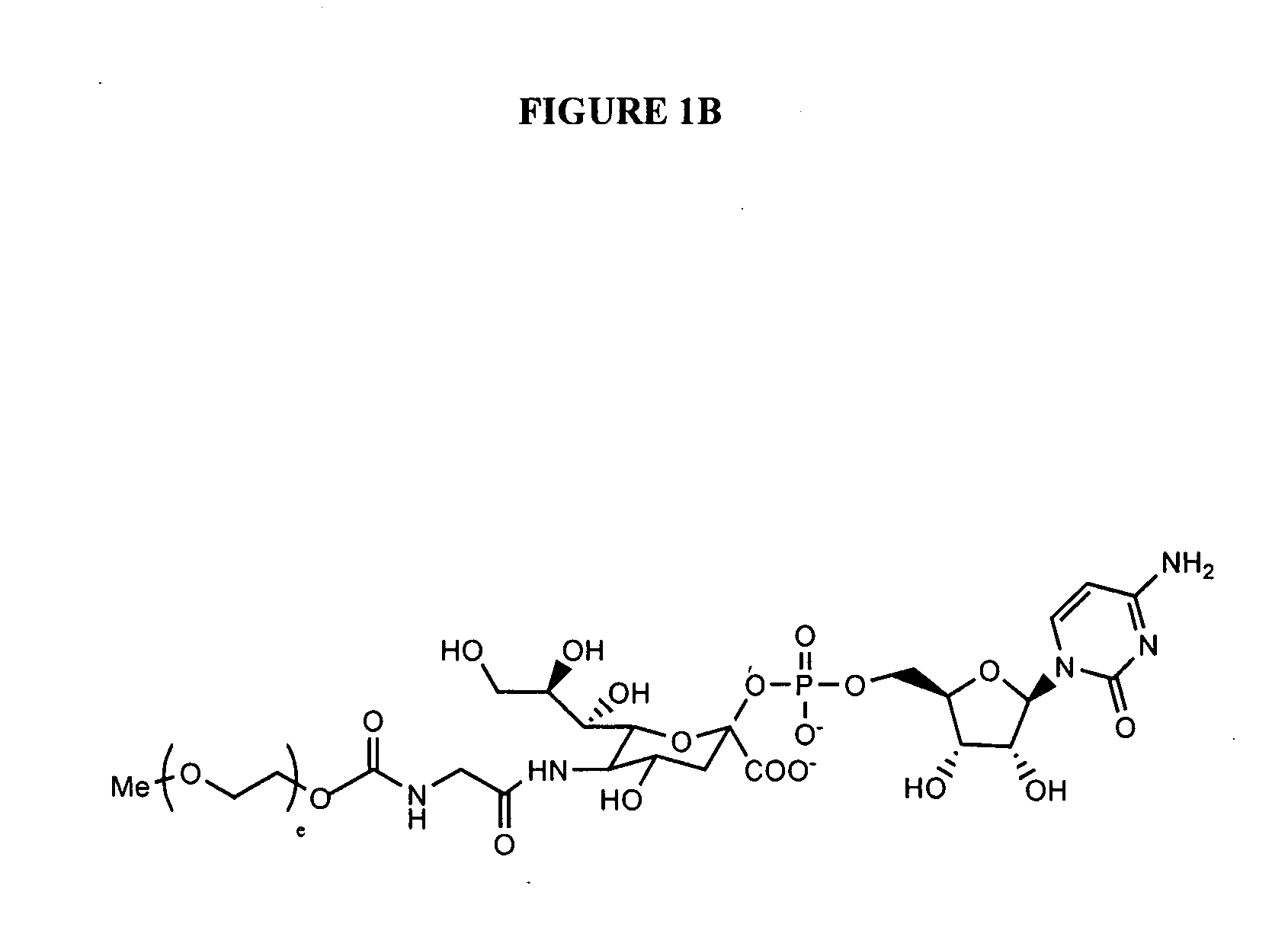
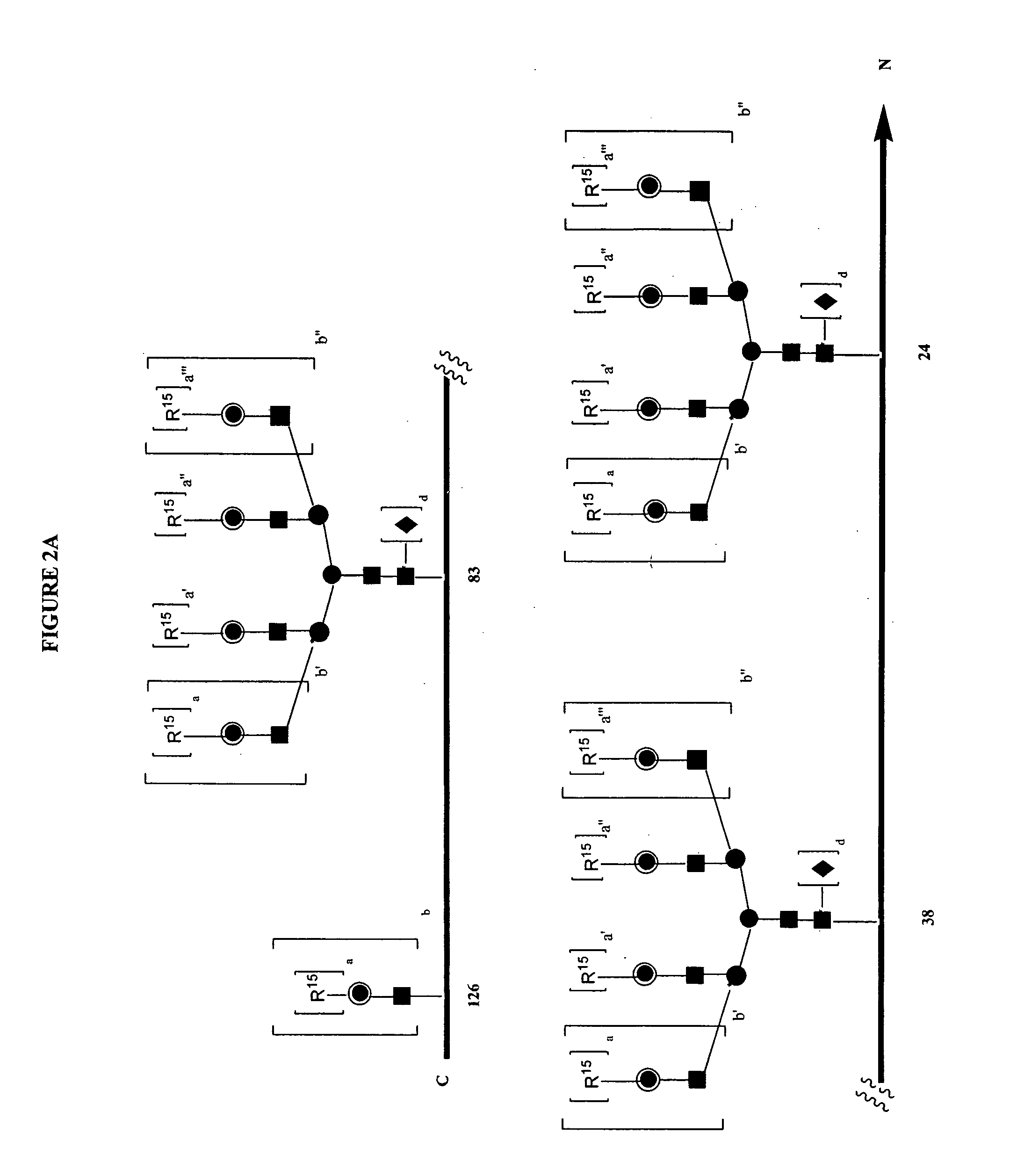
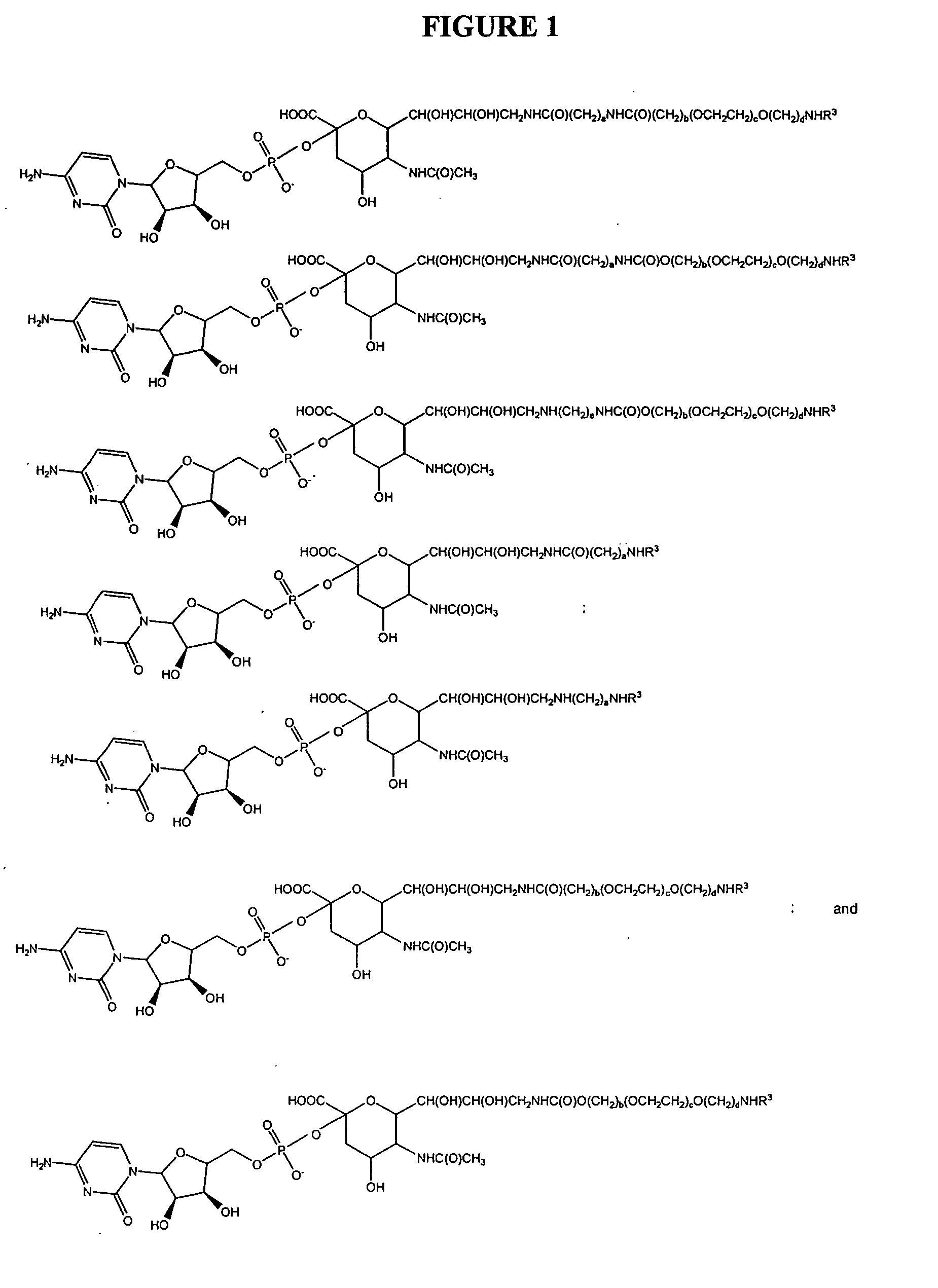
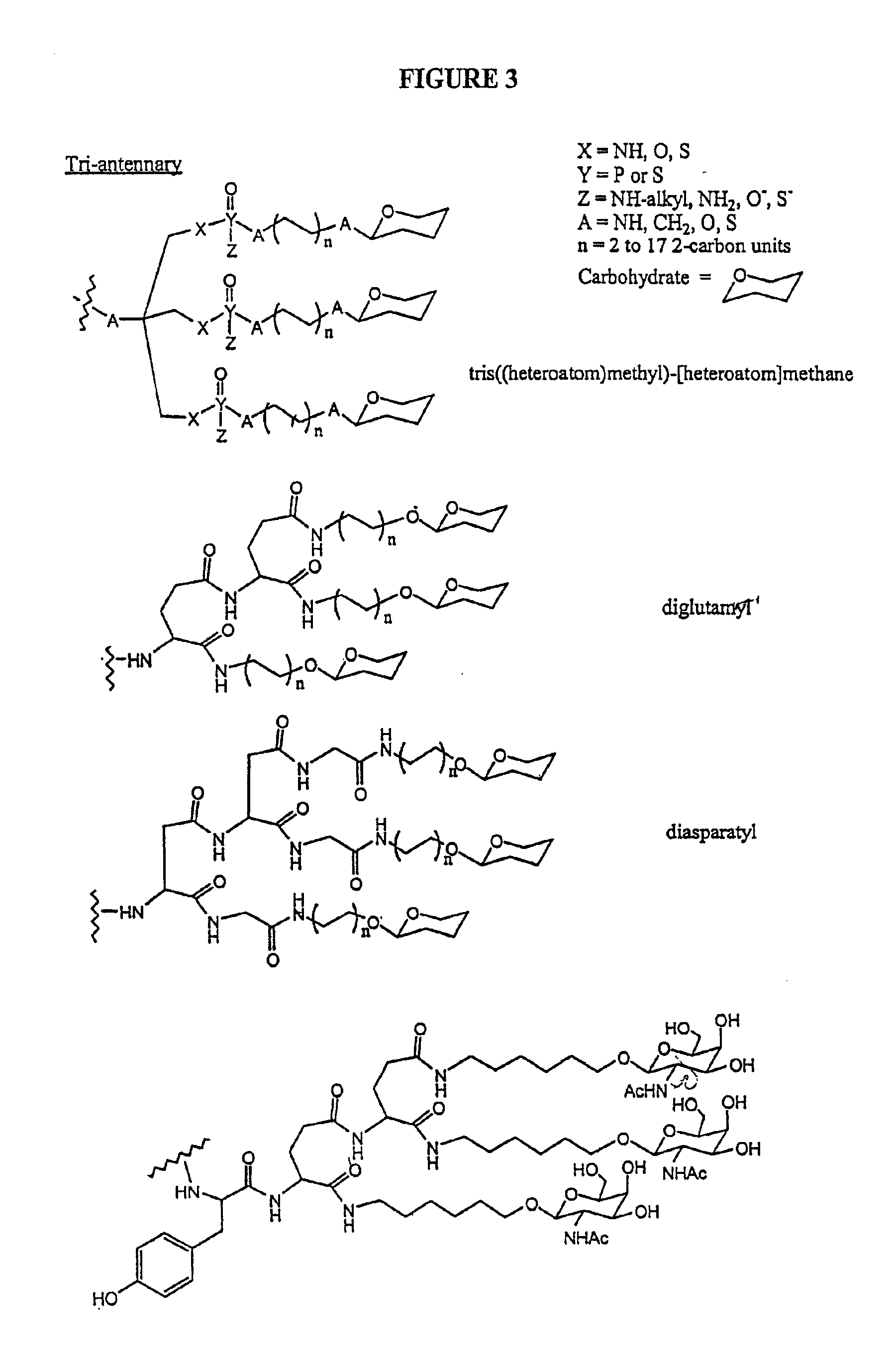
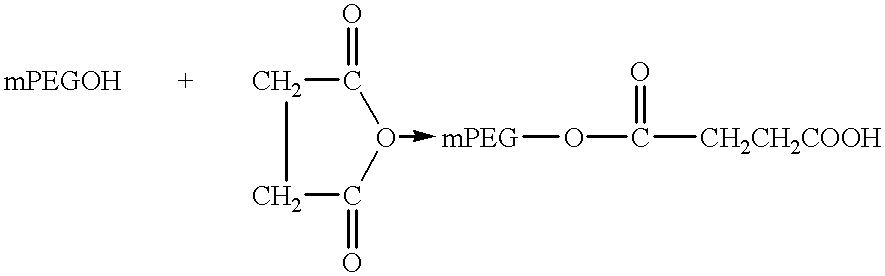
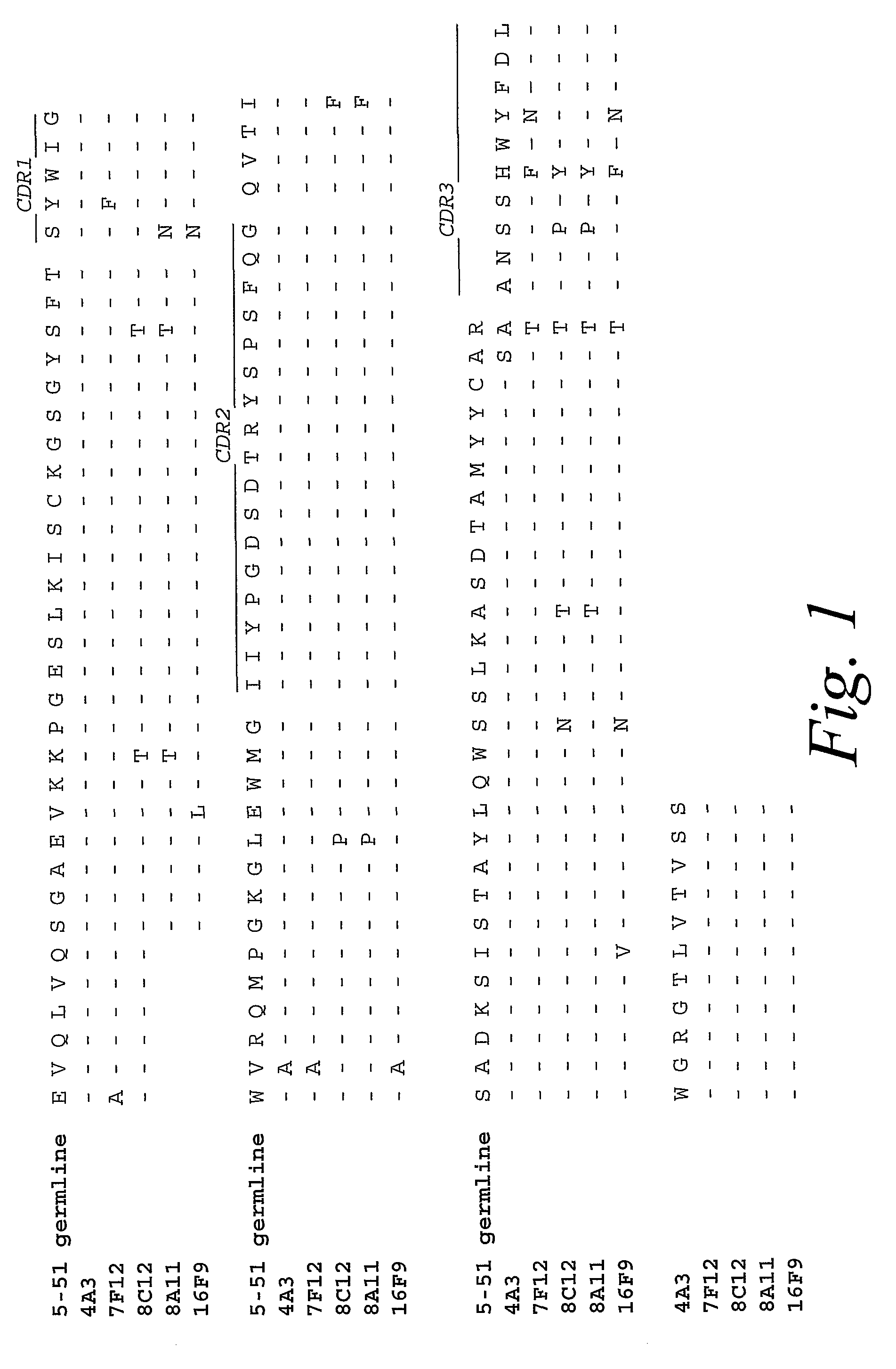
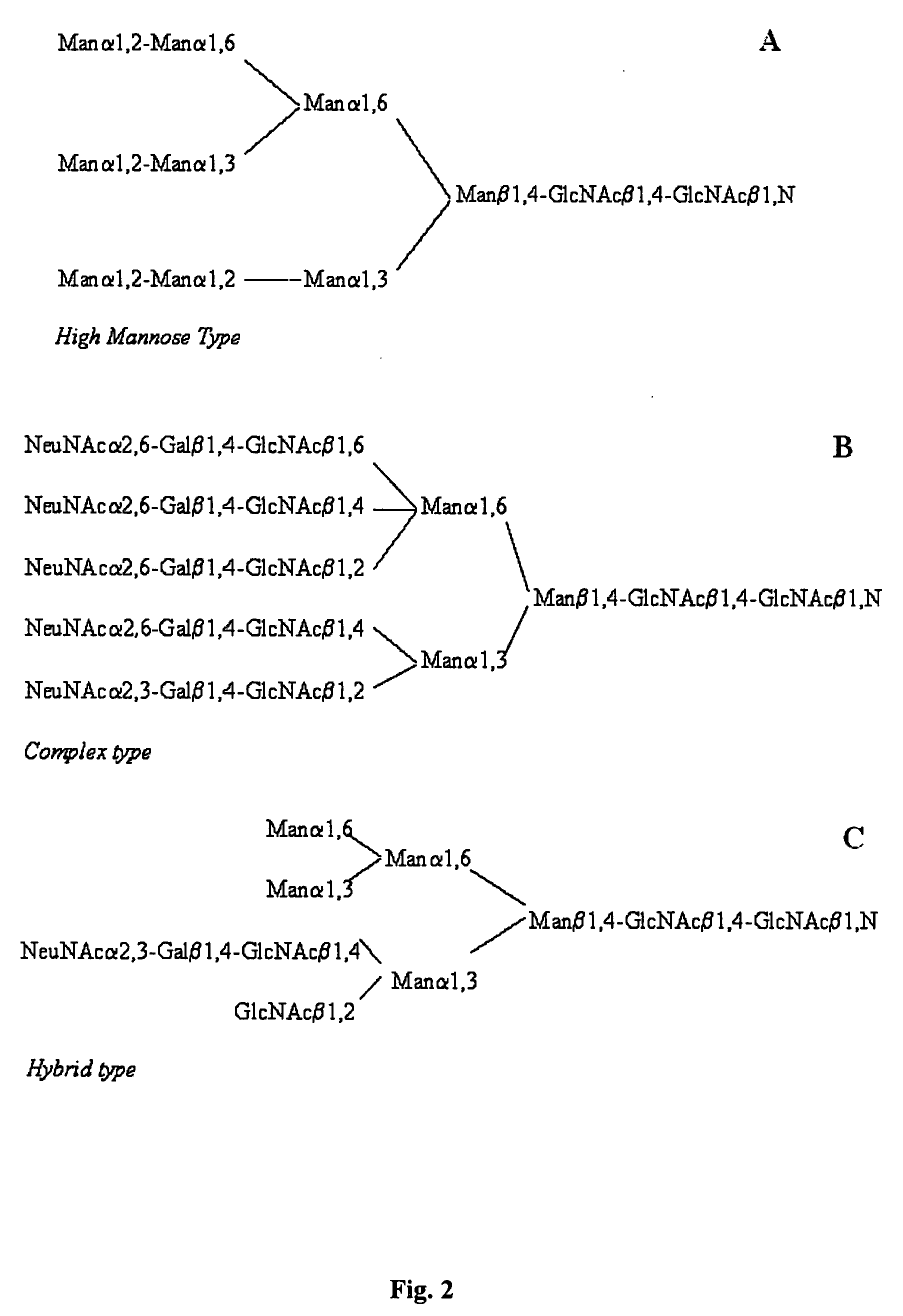
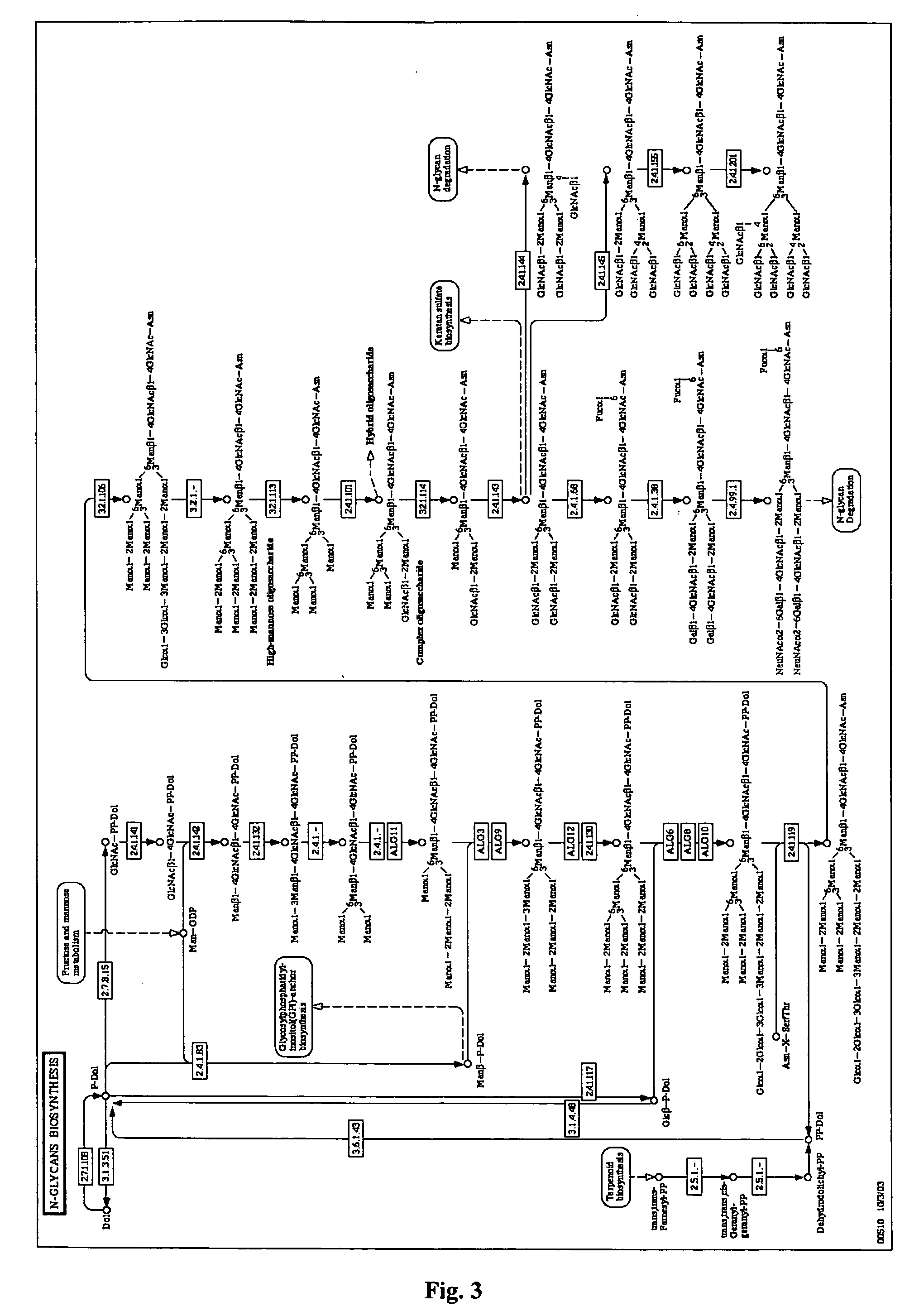
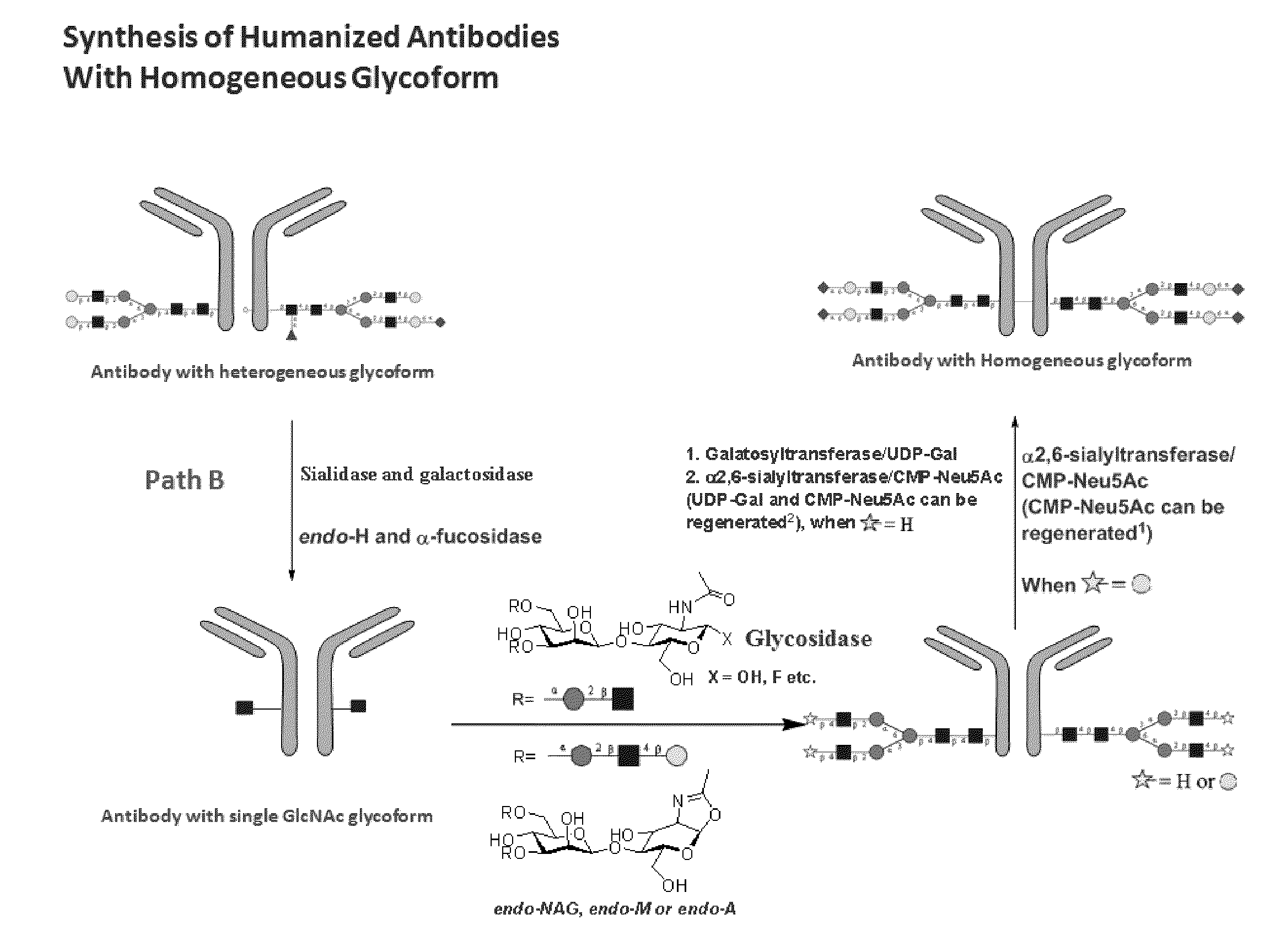
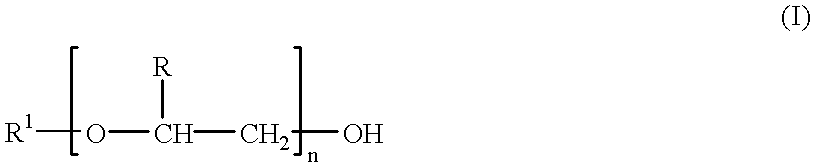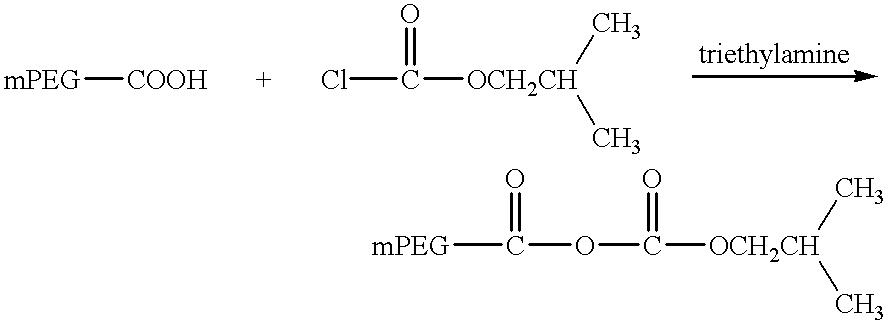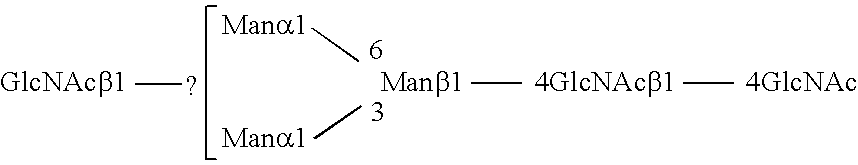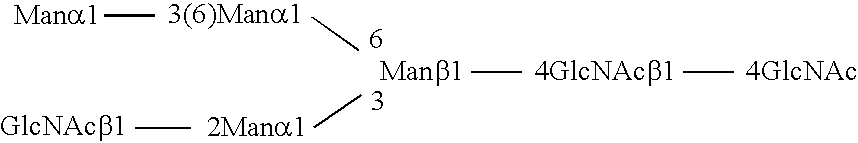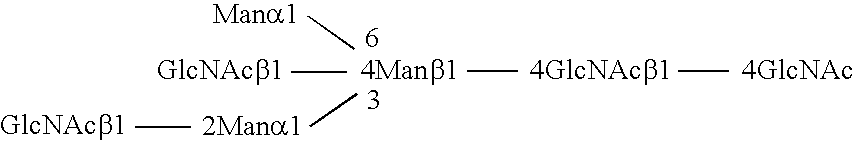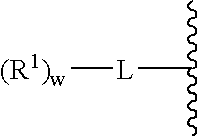Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2688 results about "Glycosylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
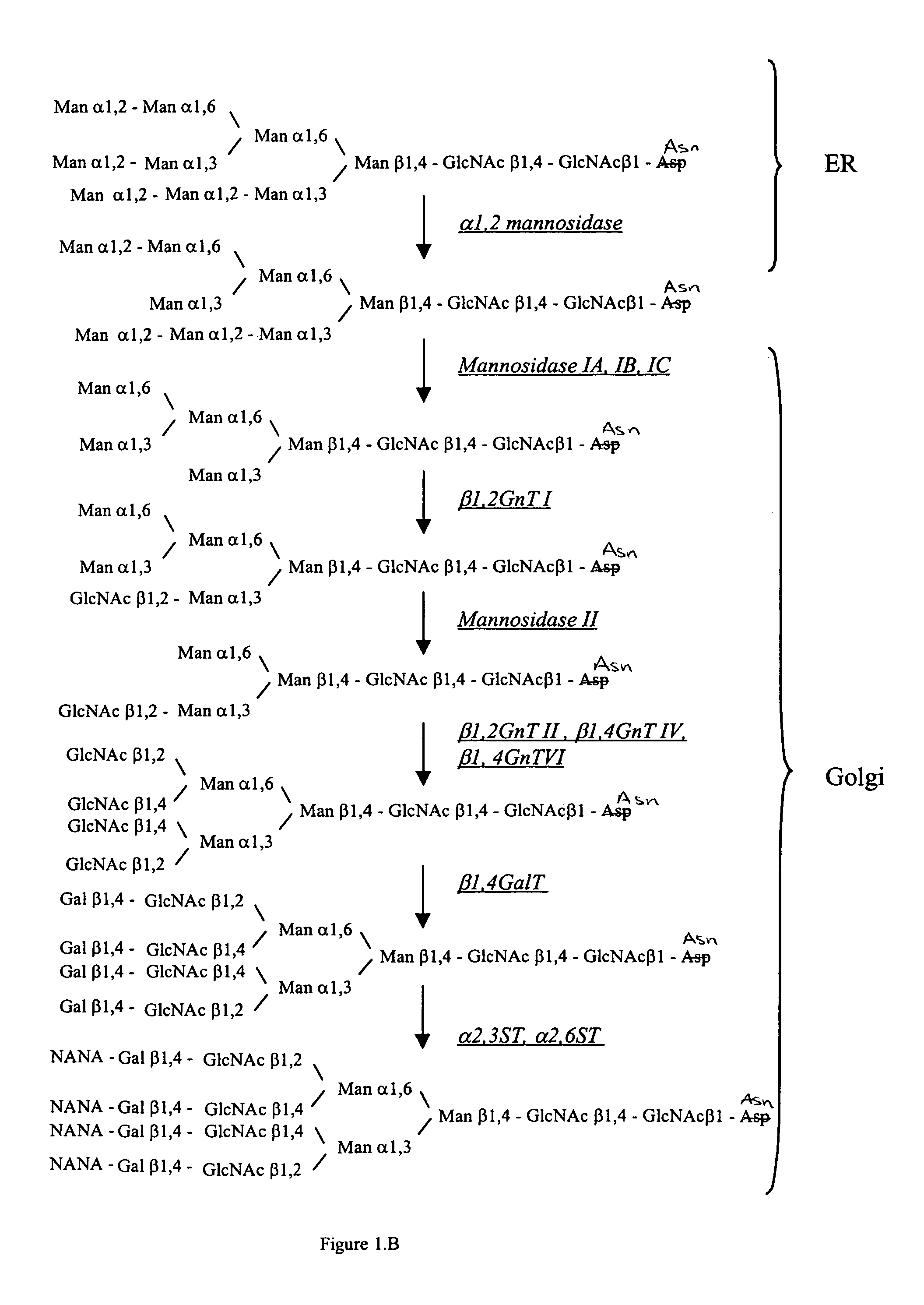
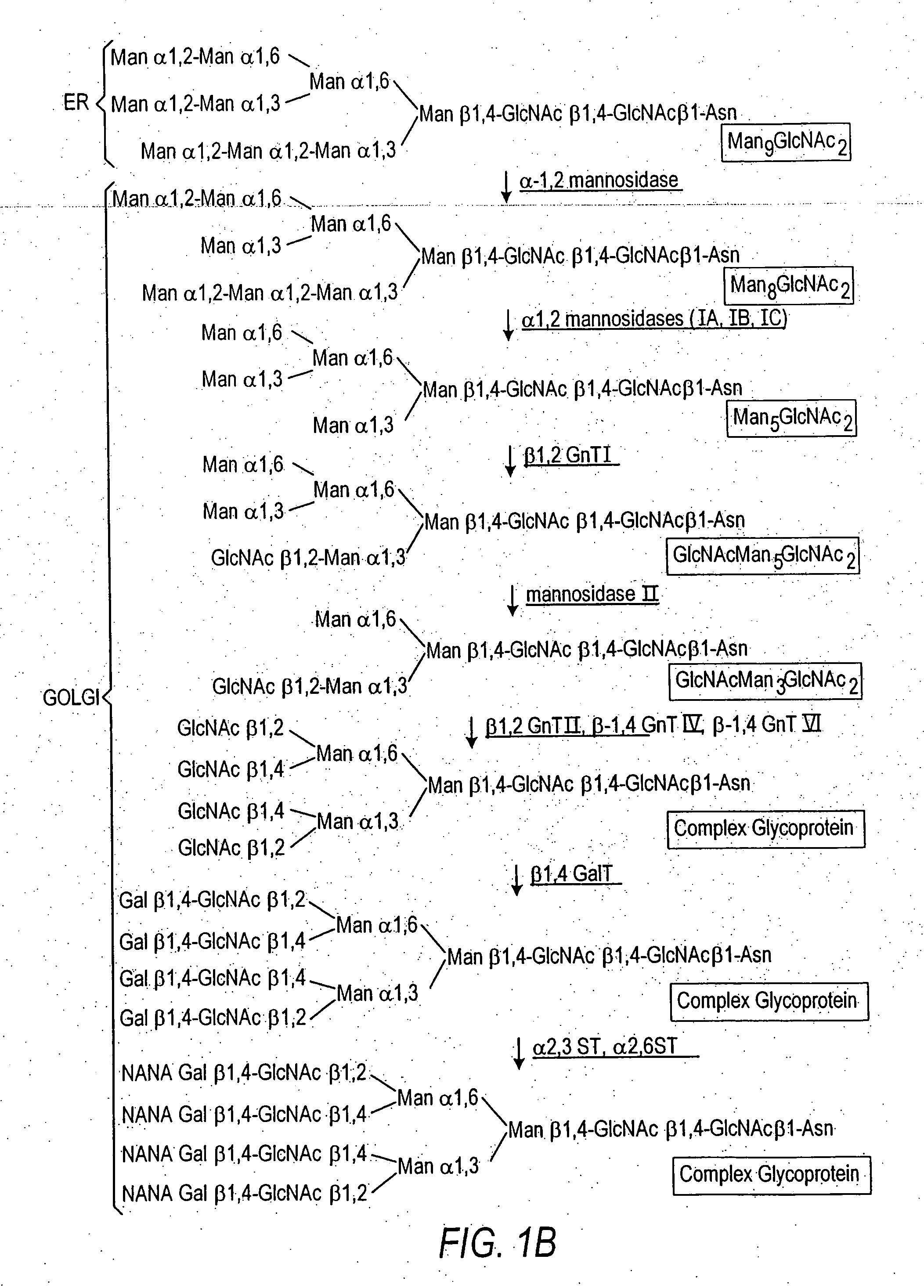
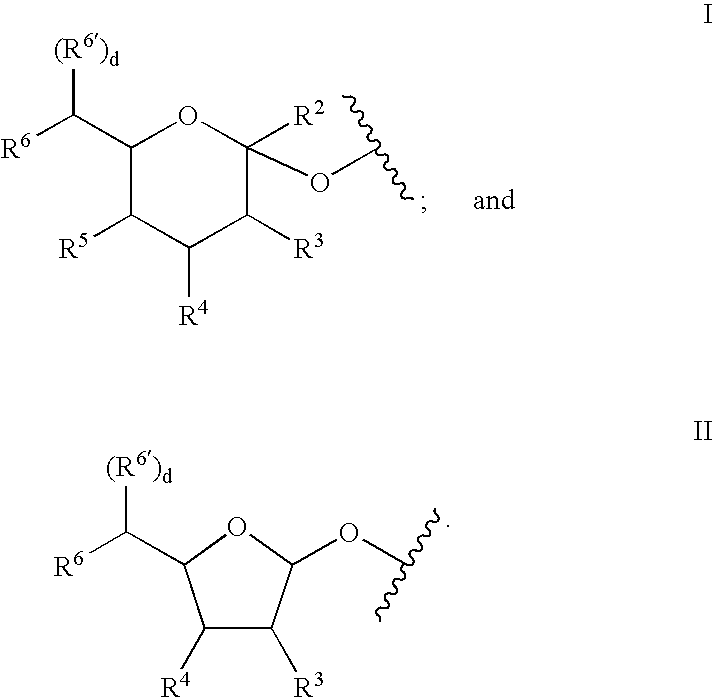
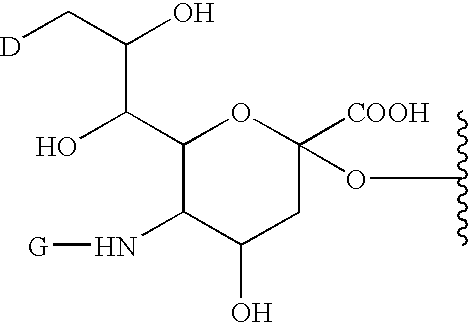
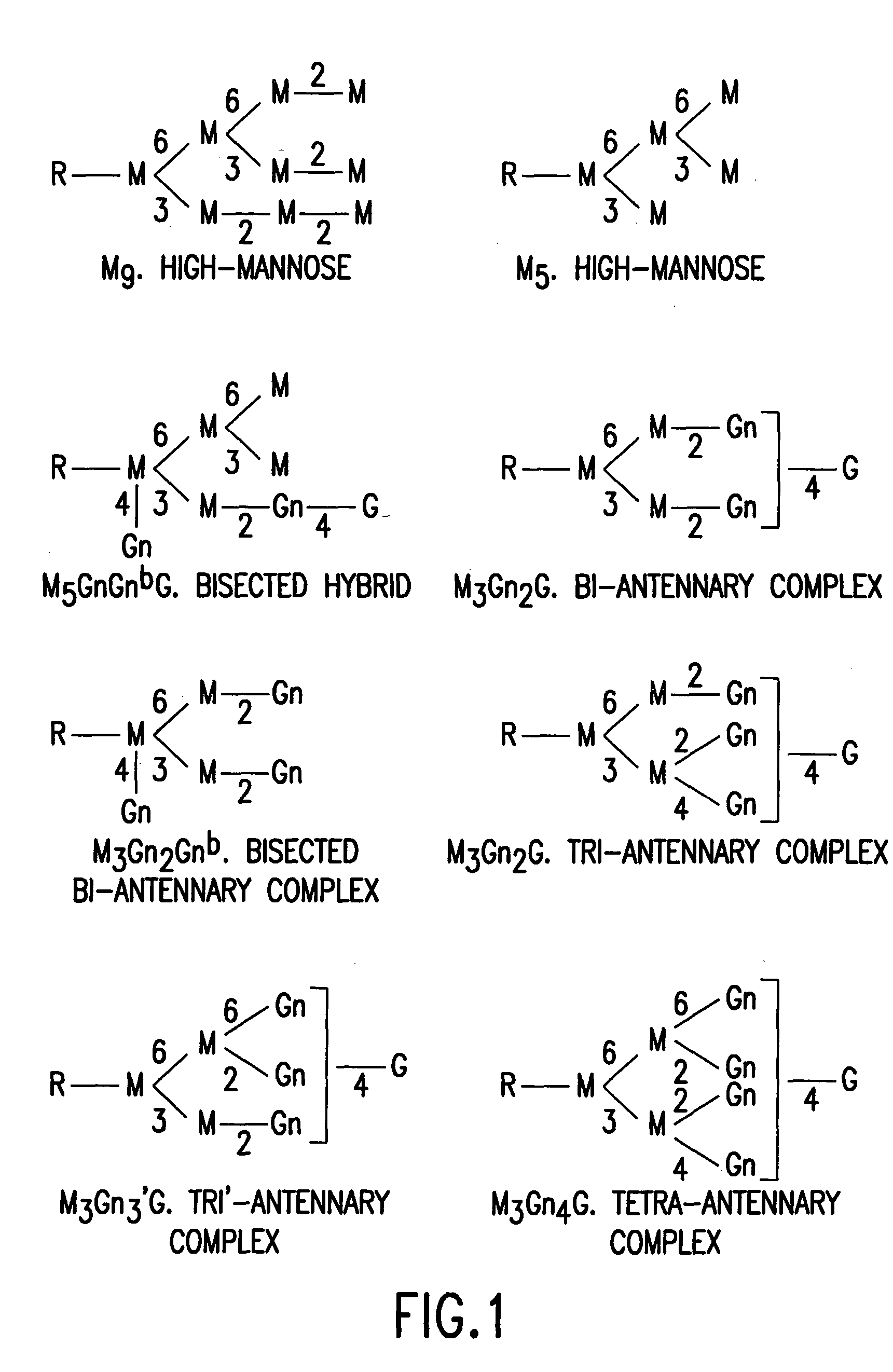
Glycosylation (see also chemical glycosylation) is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor). In biology, glycosylation mainly refers in particular to the enzymatic process that attaches glycans to proteins, or other organic molecules. This enzymatic process produces one of the fundamental biopolymers found in cells (along with DNA, RNA, and proteins). Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. It is an enzyme-directed site-specific process, as opposed to the non-enzymatic chemical reaction of glycation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the O-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five classes of glycans are produced...
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS6602684B1Increase healing valueEnhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicityNanotechFungiAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
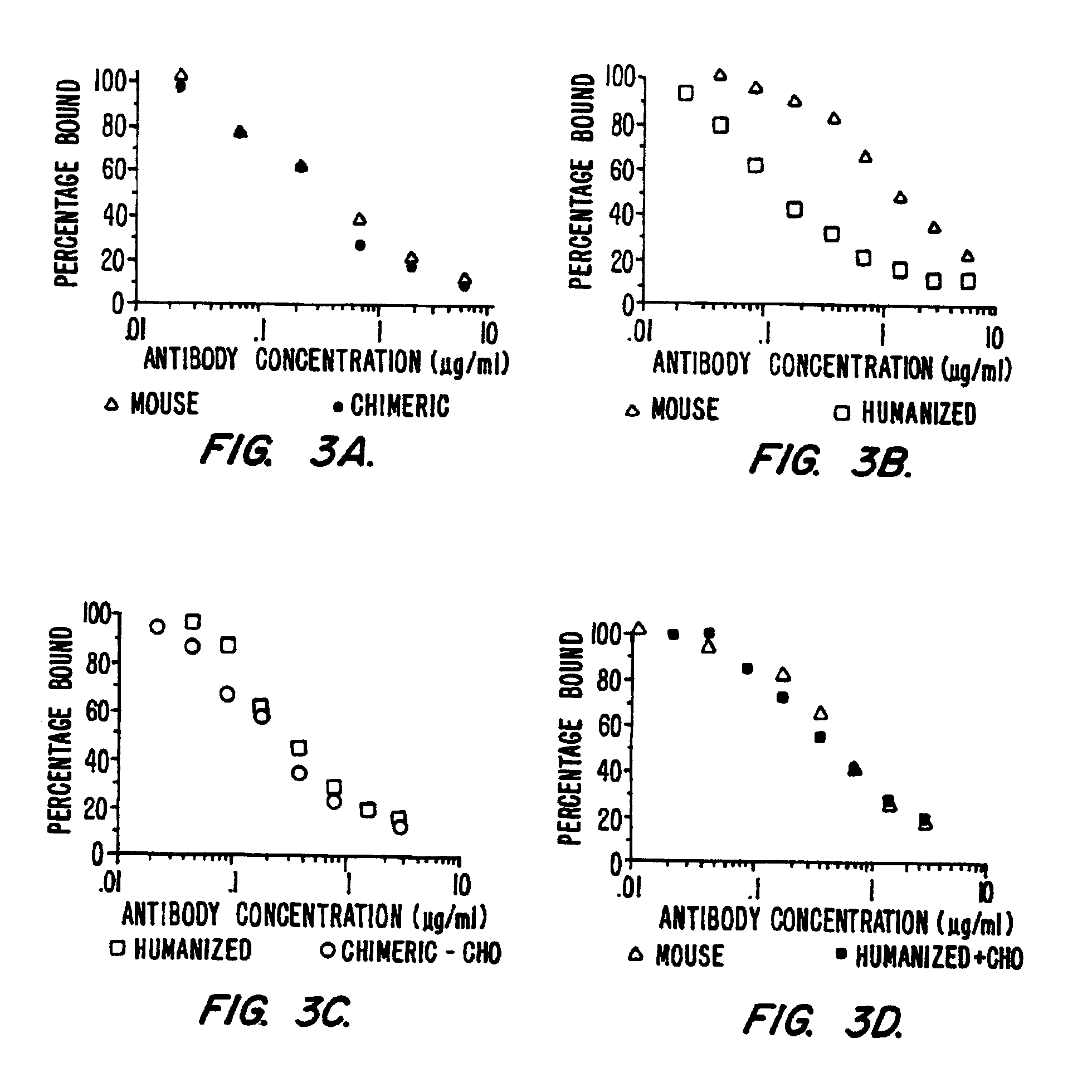
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
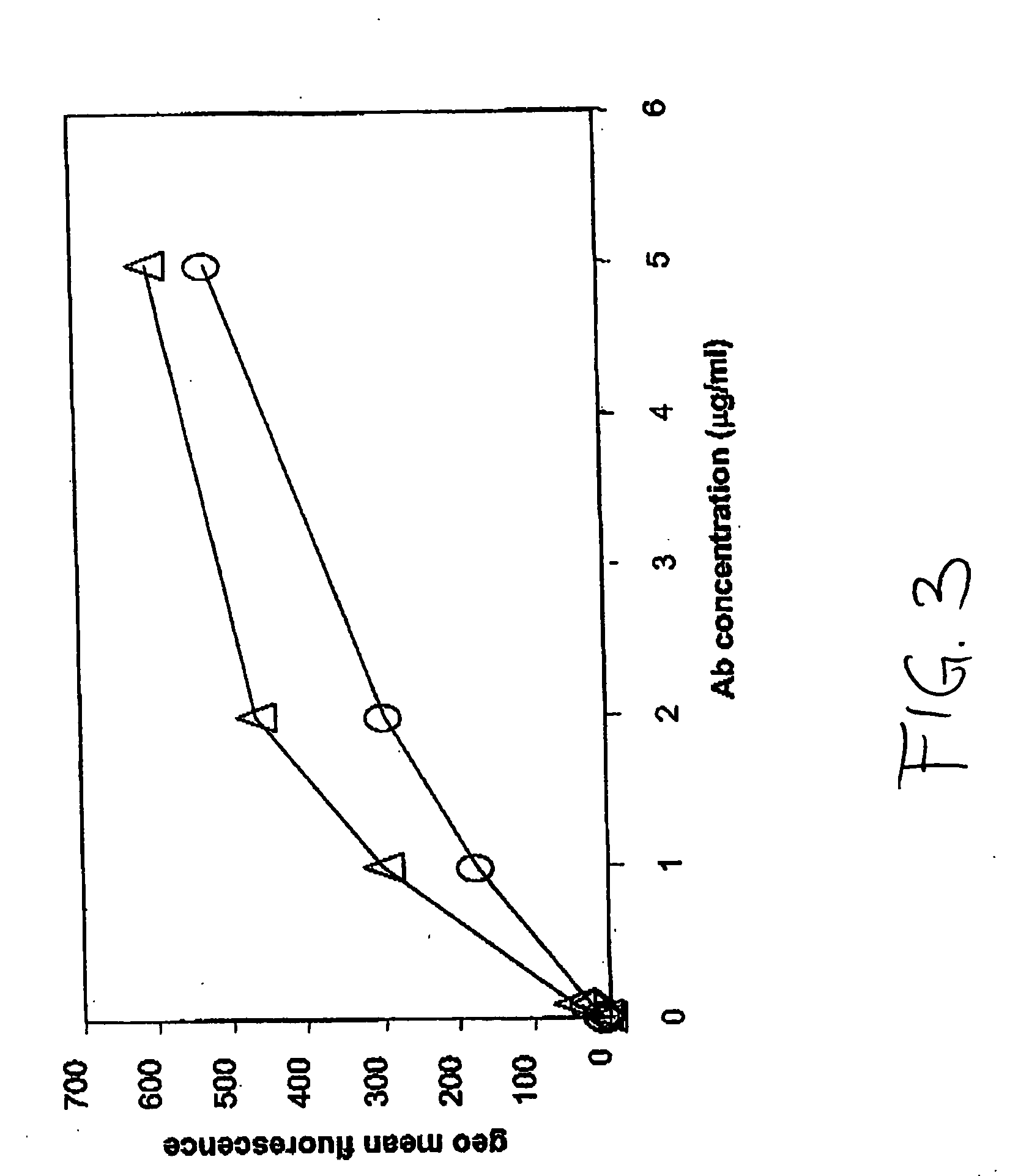
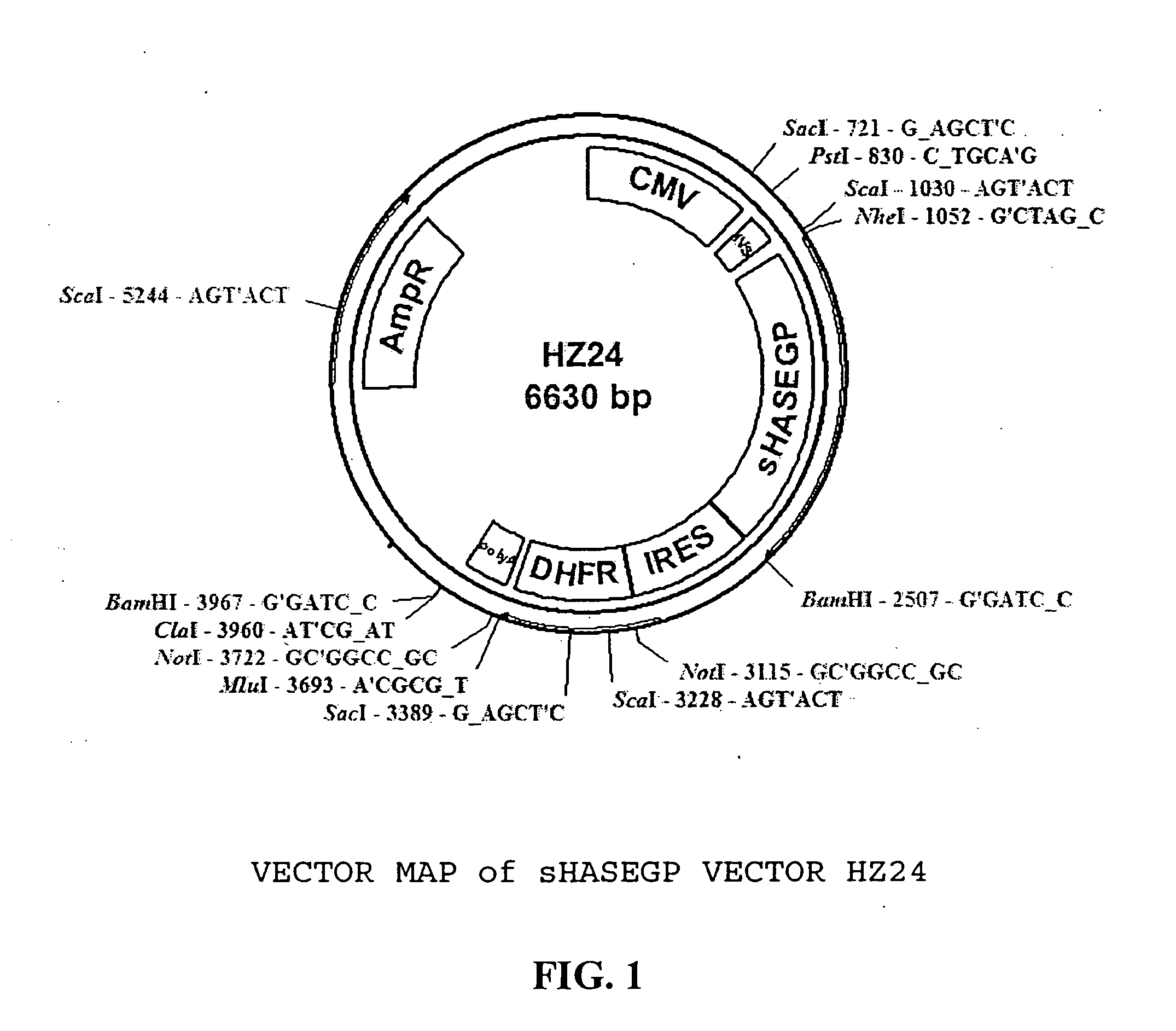
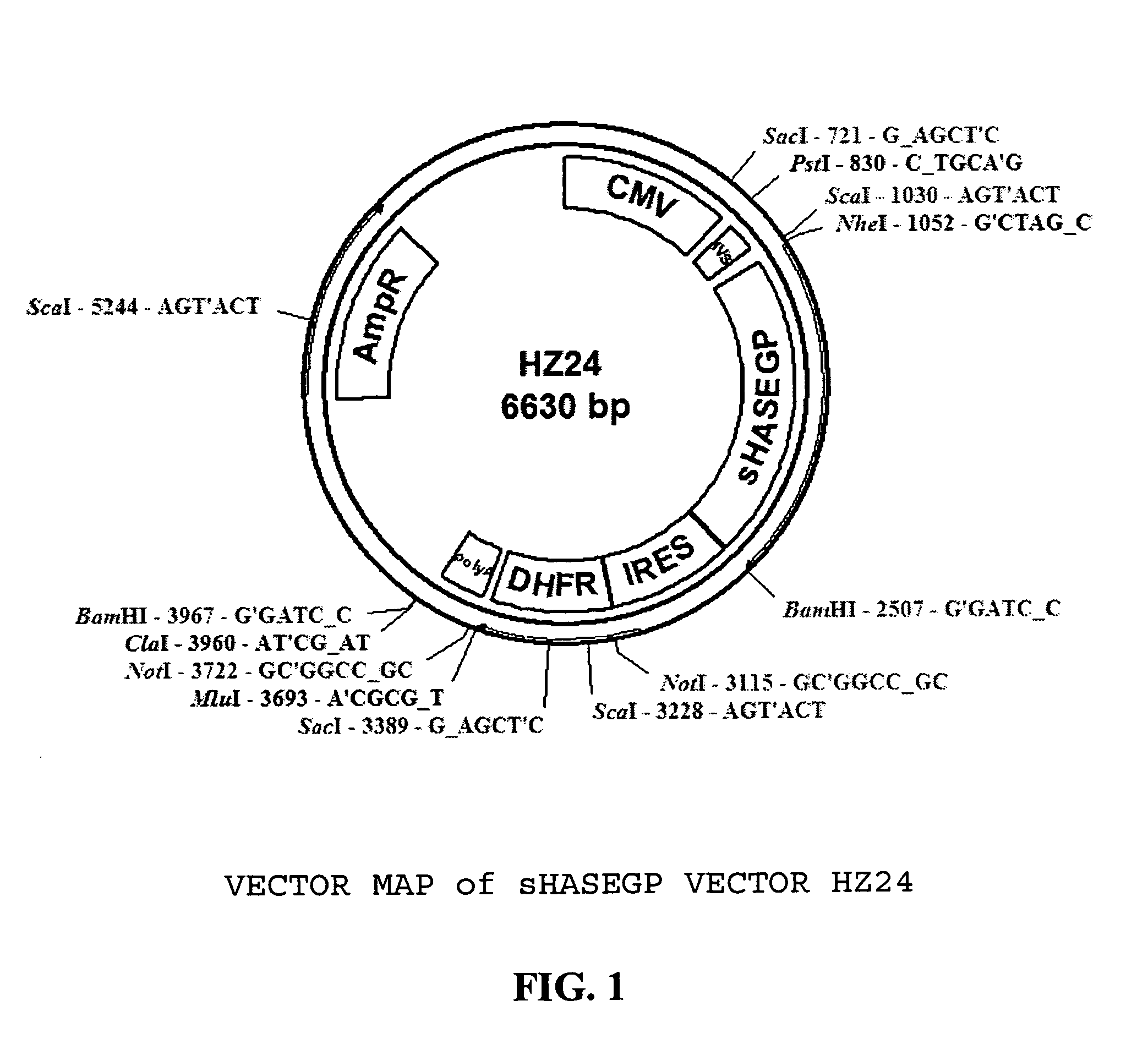
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
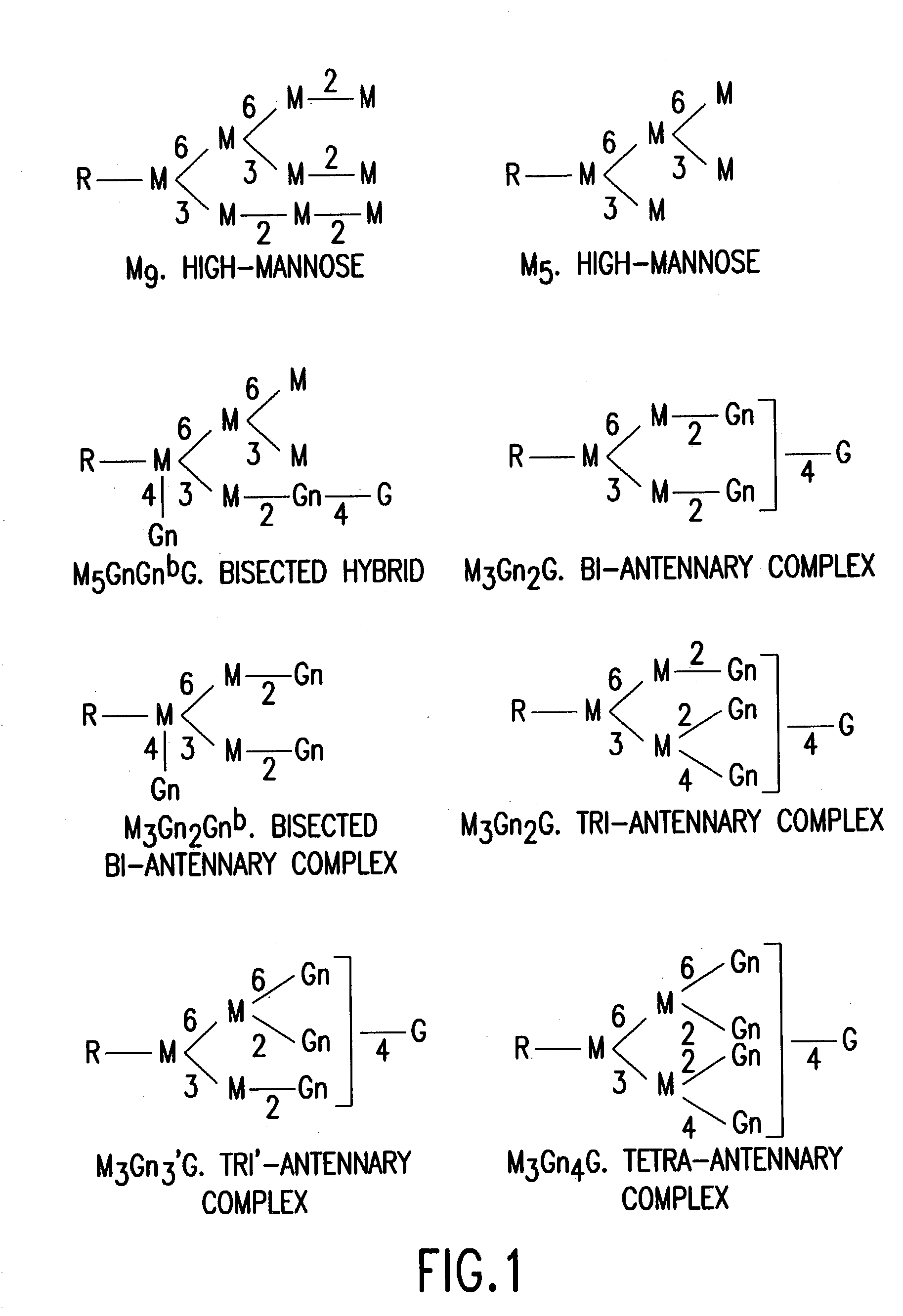
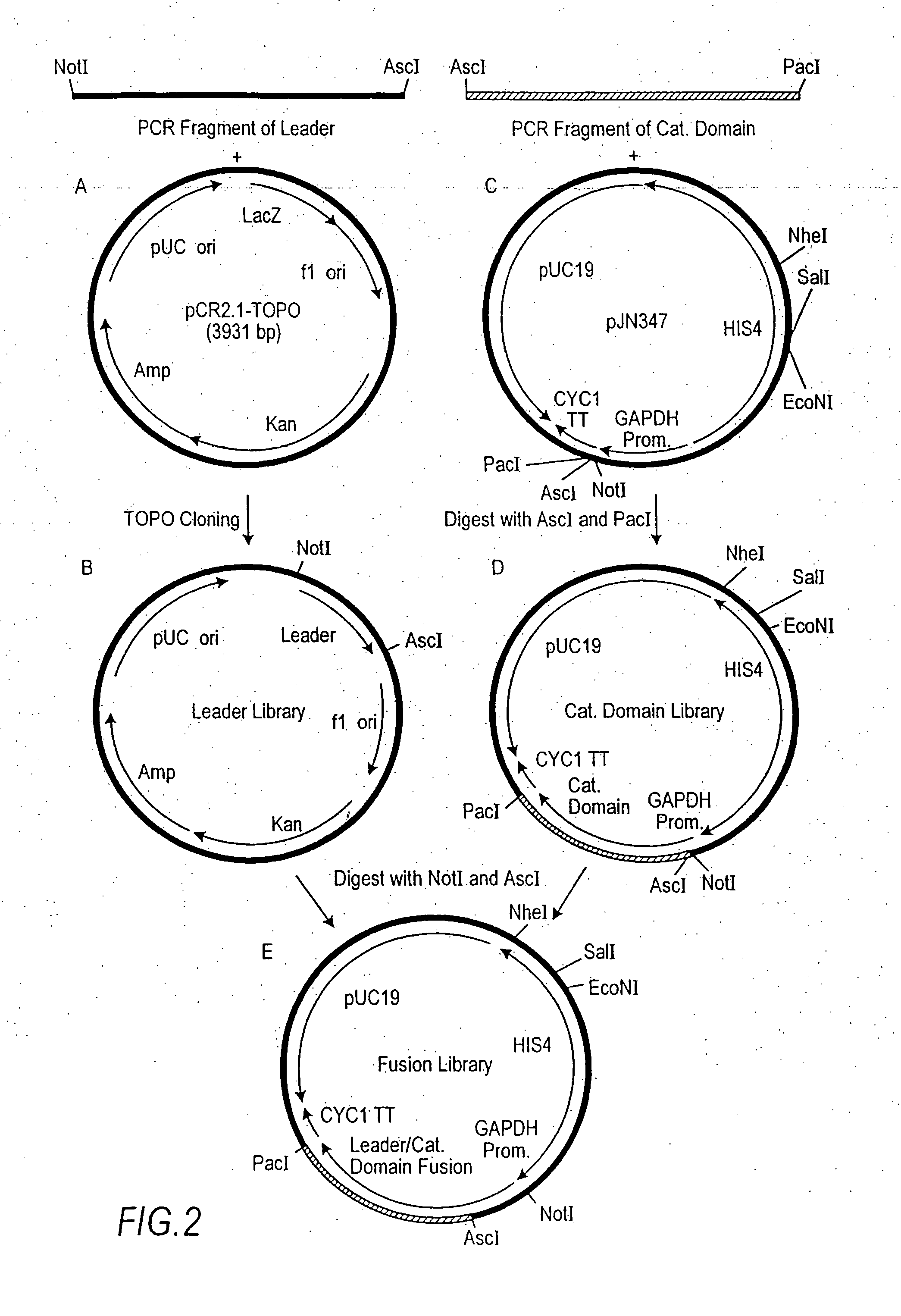
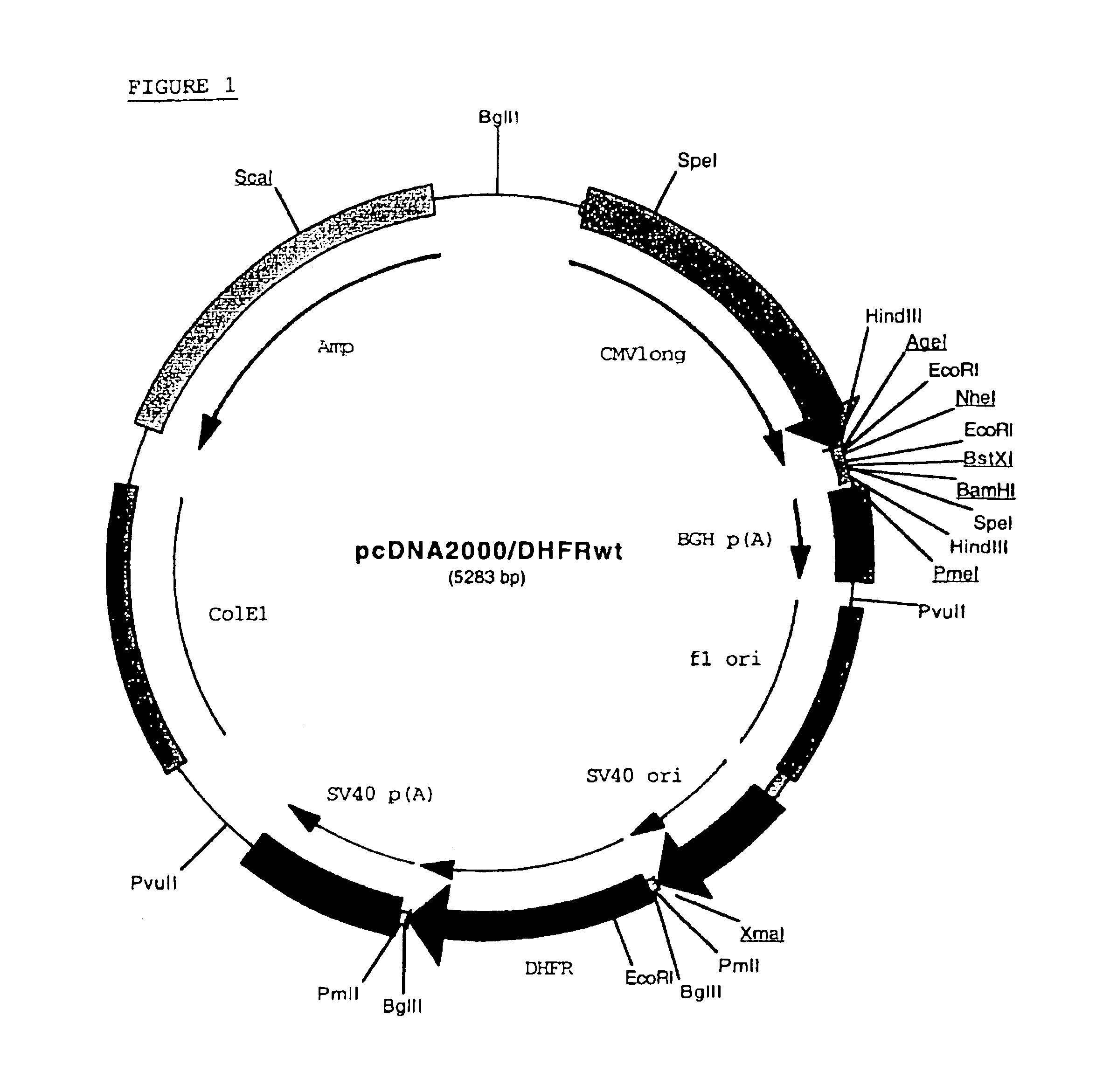
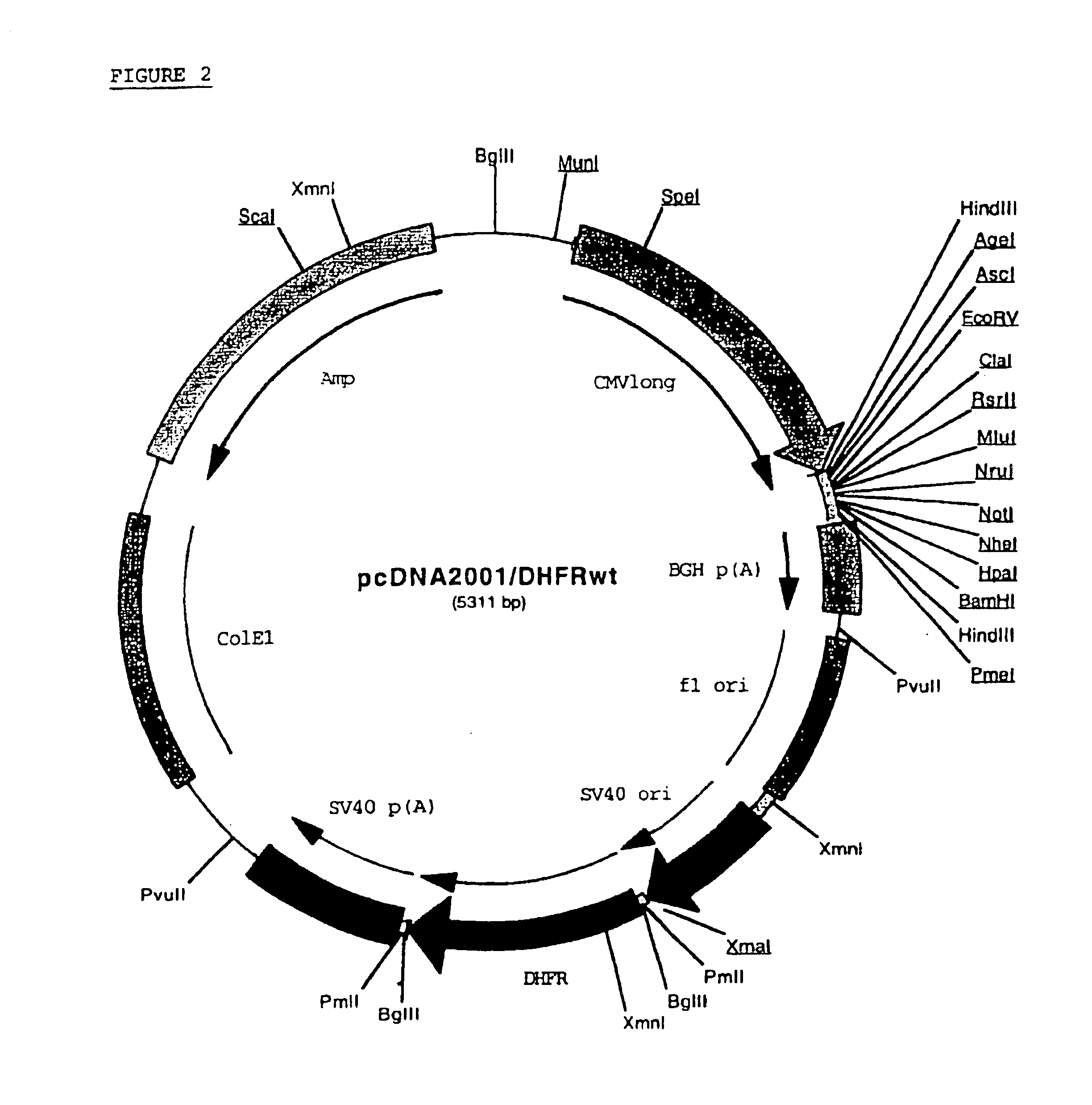
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
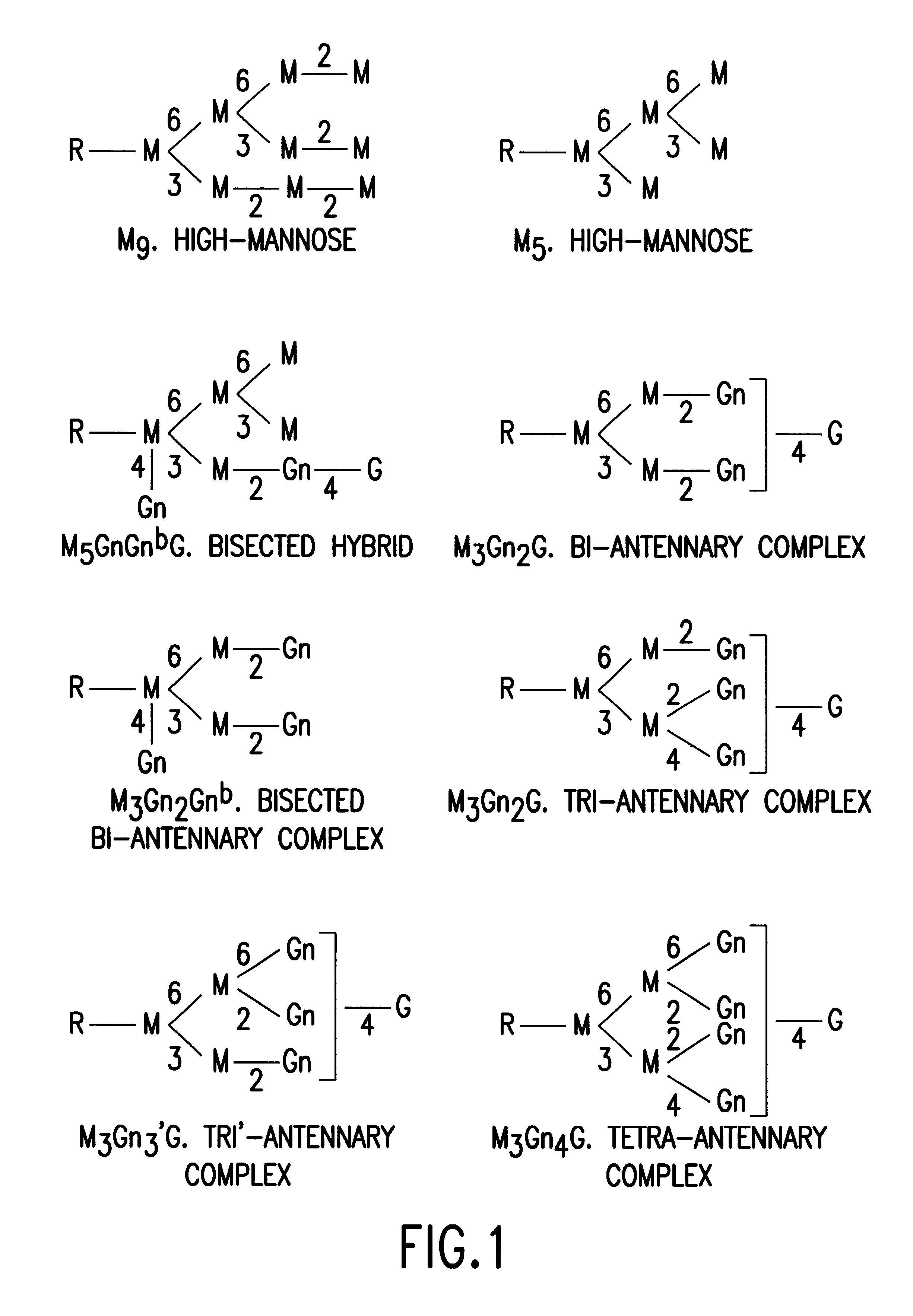
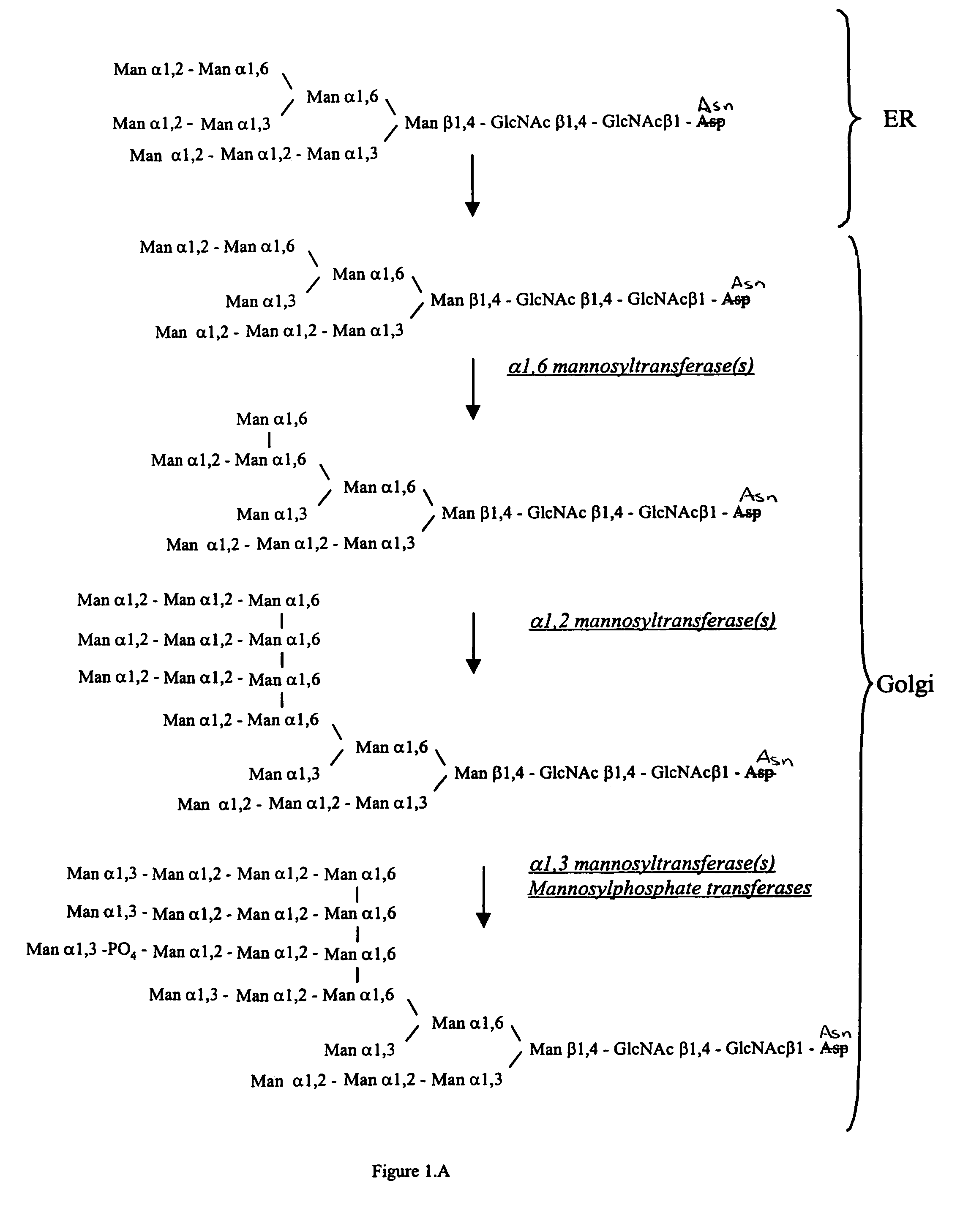
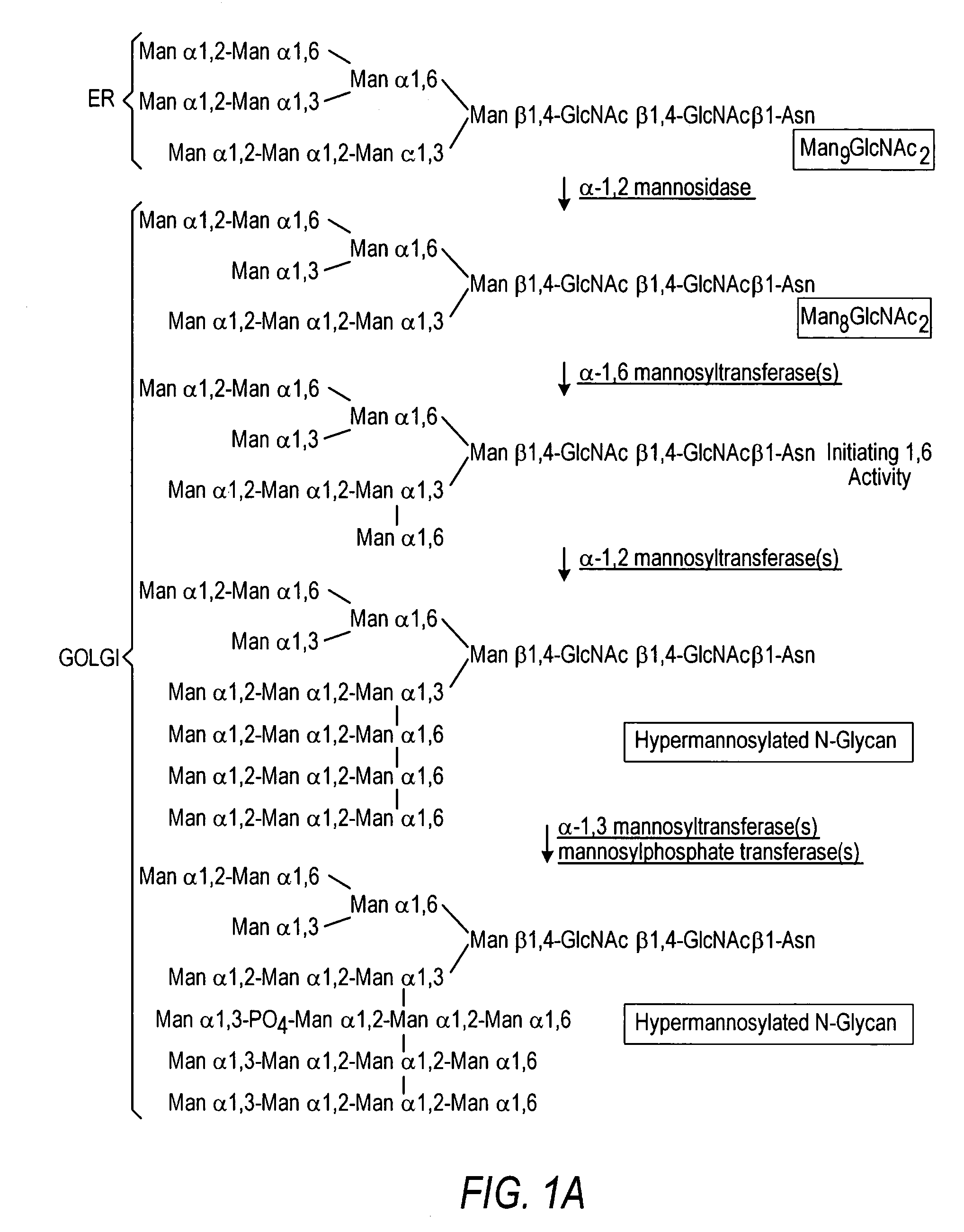
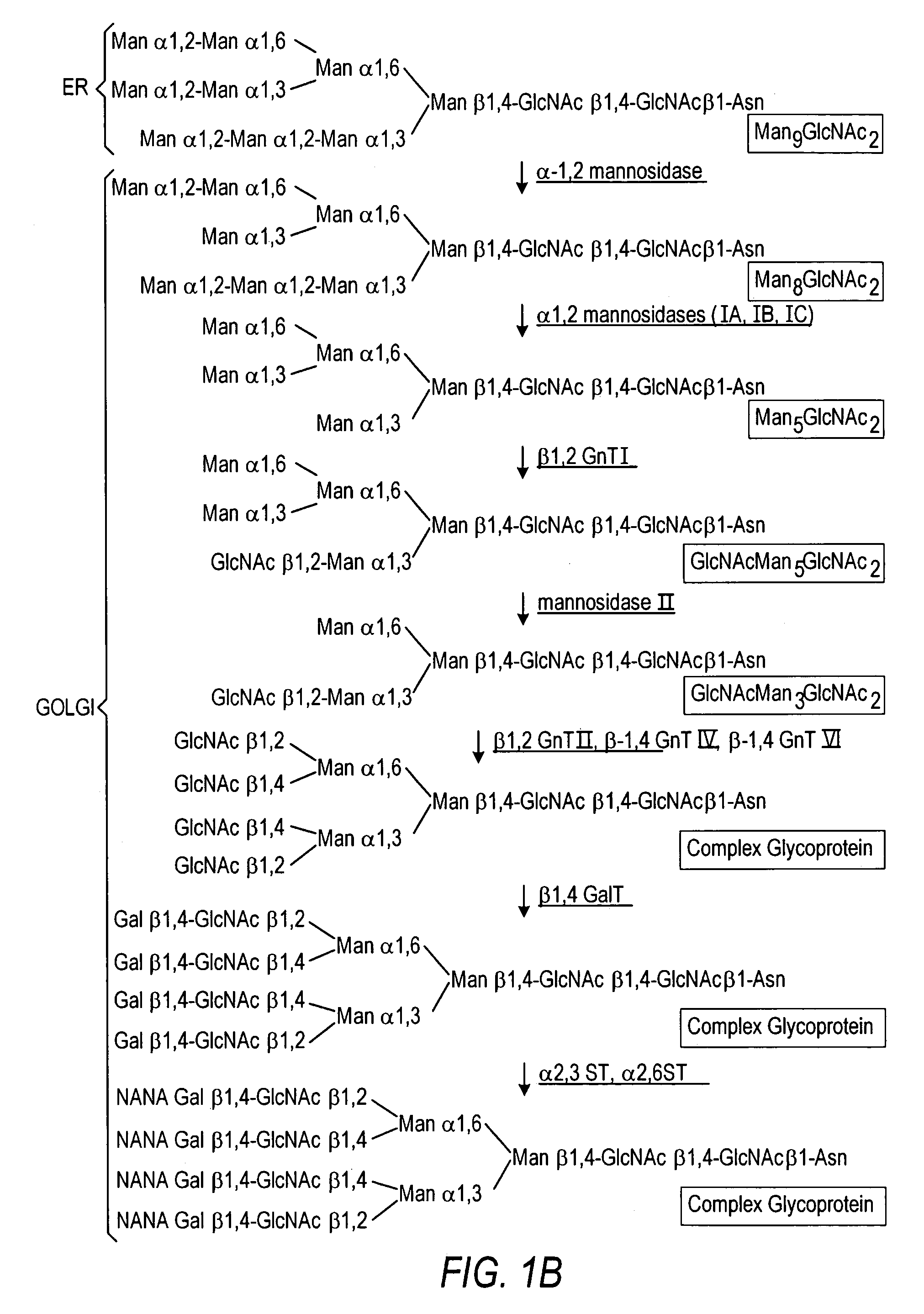
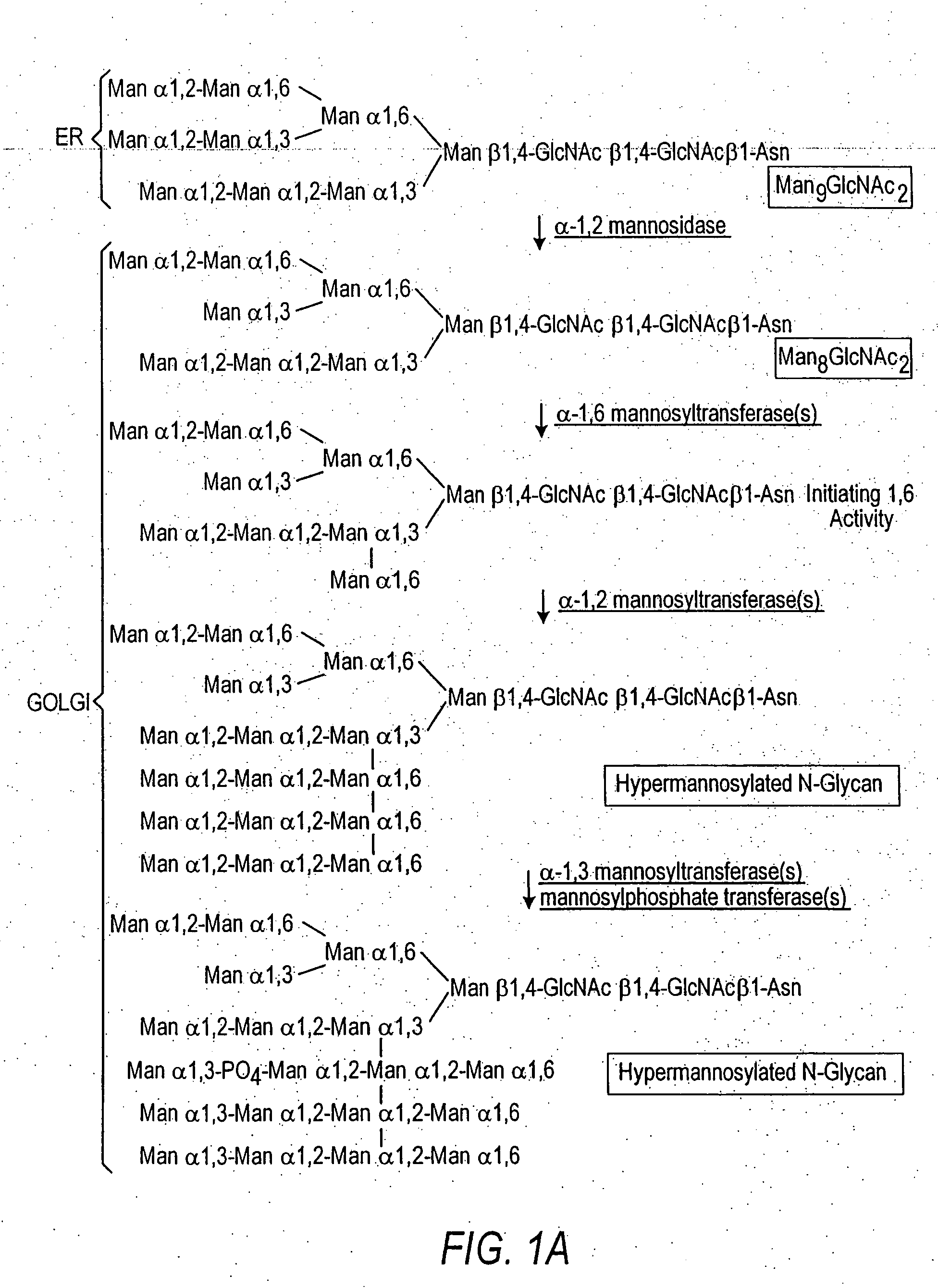
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
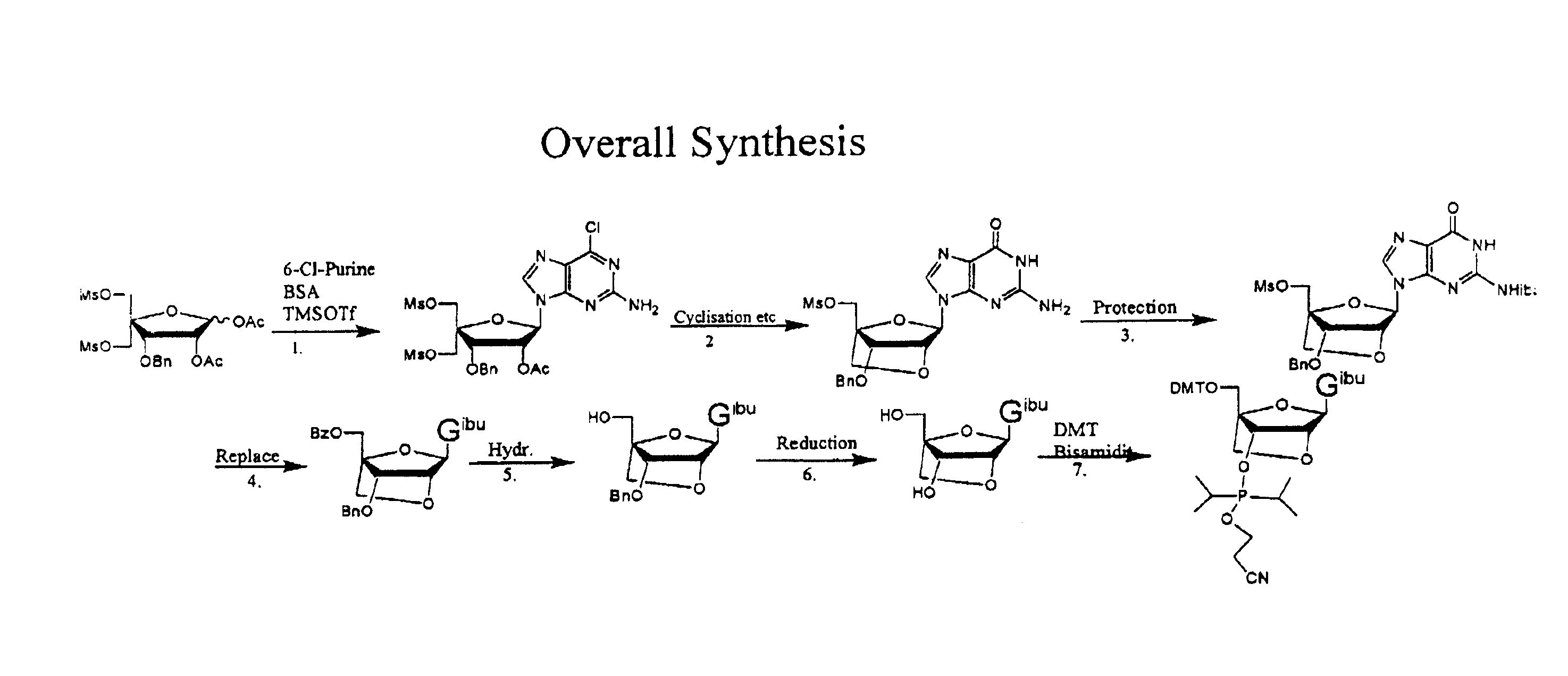
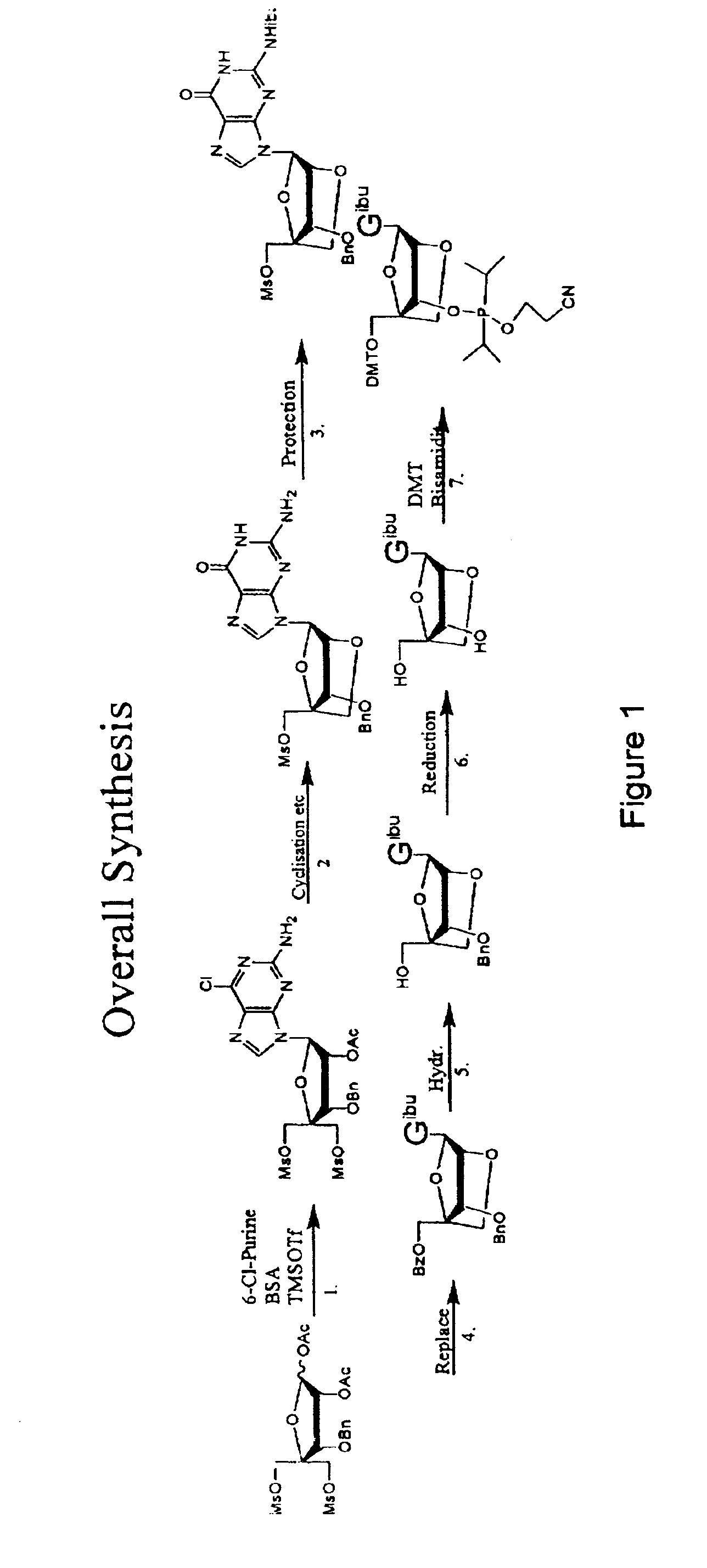
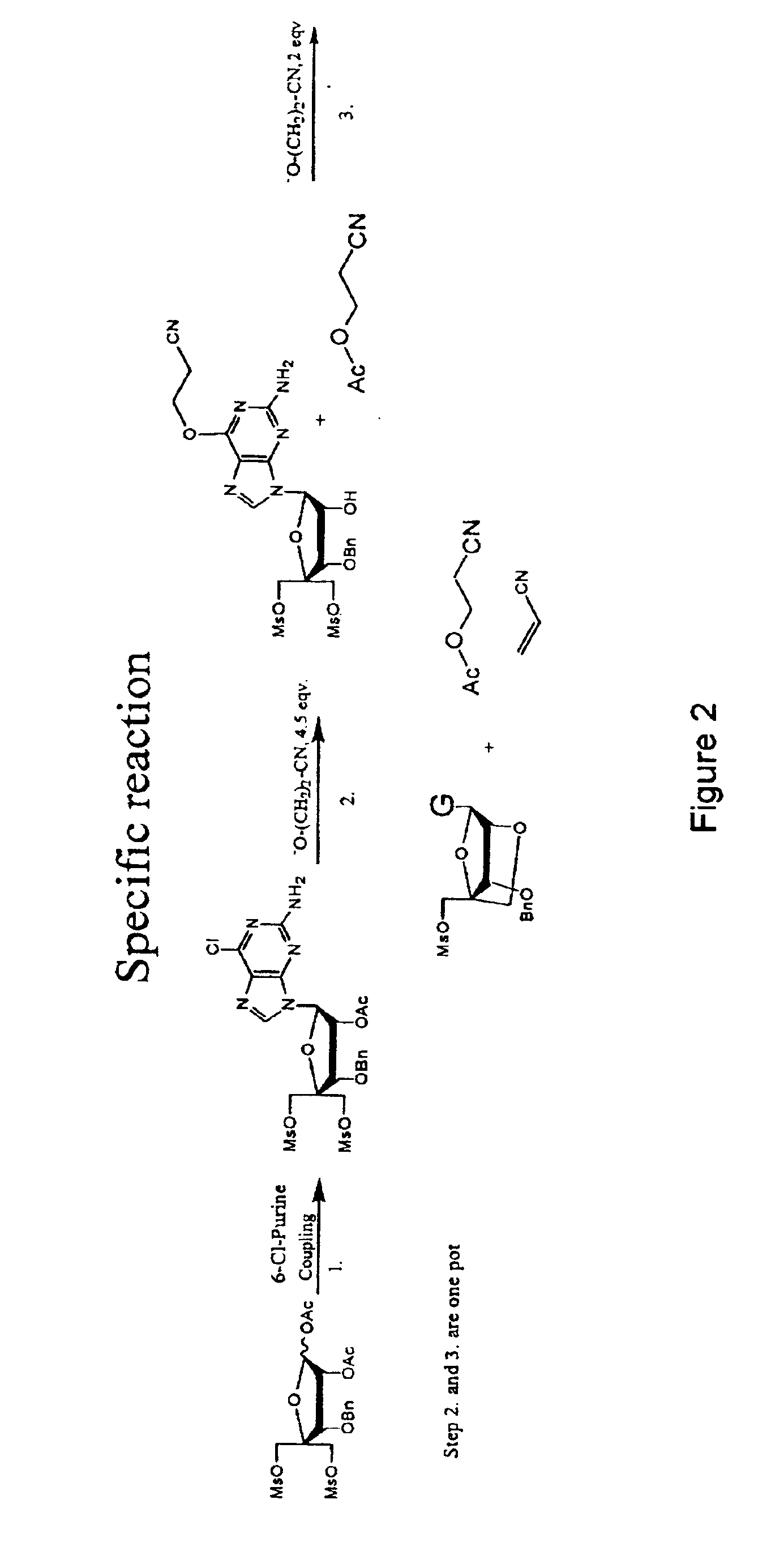
Synthesis of purine locked nucleic acid analogues
InactiveUS6998484B2Easy to convertEasy to liftSilicon organic compoundsSugar derivativesPurineLocked nucleic acid
The present invention relates to a new method for the synthesis of purine LNA (Locked Nucleic Acid) analogues which provides a higher overall yield. The method comprising a regioselective 9-N purine glycosylation reaction followed by a one-pot nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction of the 6-substituent in the purine ring and simultaneous nucleophile-induced intramolecular ring closure of the C-branched carbohydrate to form novel purine LNA analogues. The novel strategy is illustrated by the synthesis of the novel compound (1S,3R,4R,7S)-7-benzyloxy-1-methanesulfonylmethyl-3-(guanin-9-yl)-2,5-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane which is easily converted into (1S,3R,4R,7S)-7-hydroxy-1-hydroxymethyl-3-((2-N-isobutyrylguanin-9-yl)-2,5-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane after isobutyryl protection of the 2-amino purine group and subsequent substitution of 1-methanesulfonyl with benzoate, debenzoylation and debenzylation.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
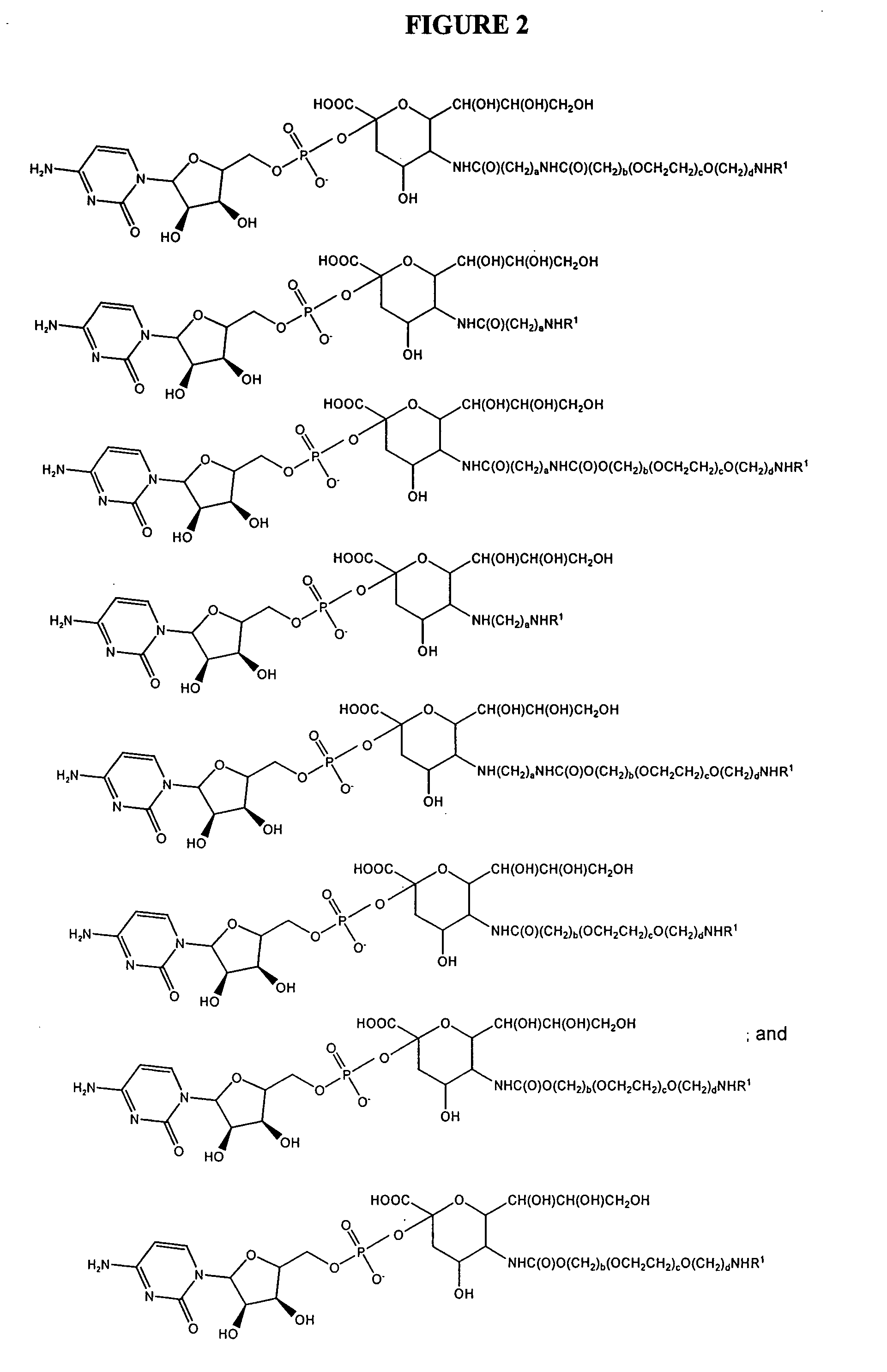
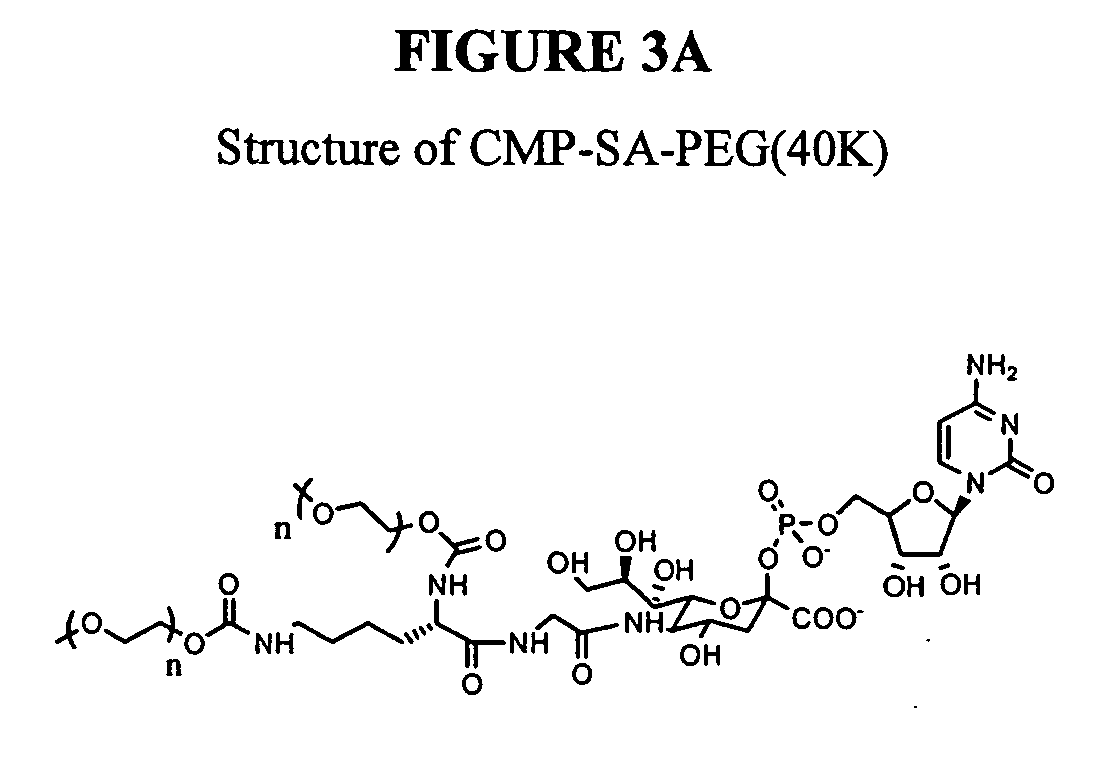
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20060111279A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost effectiveSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Glycopegylated erythropoietin
InactiveUS20050143292A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost-effectiveSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSugar moiety
The present invention provides conjugates between erythropoietin and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
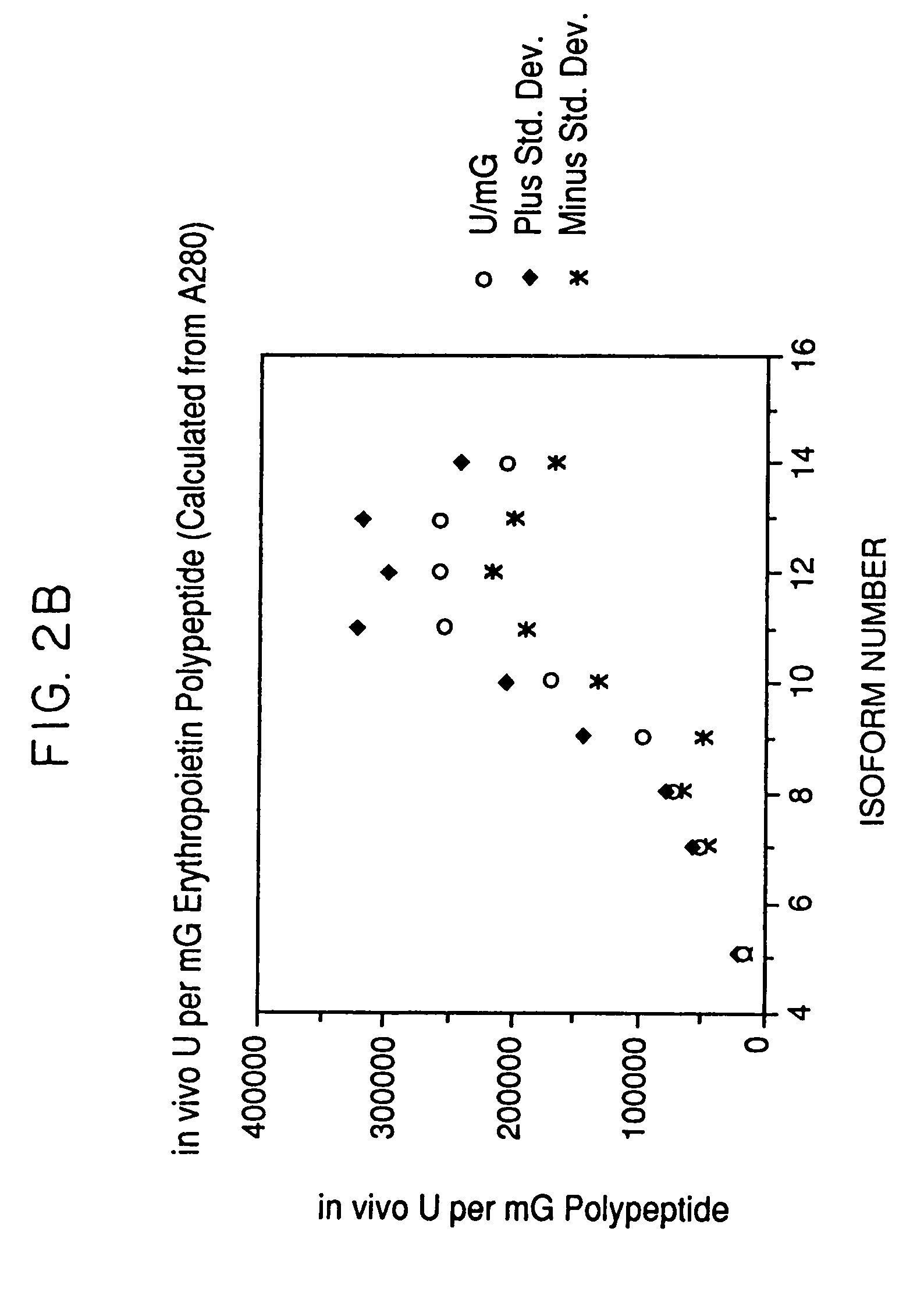
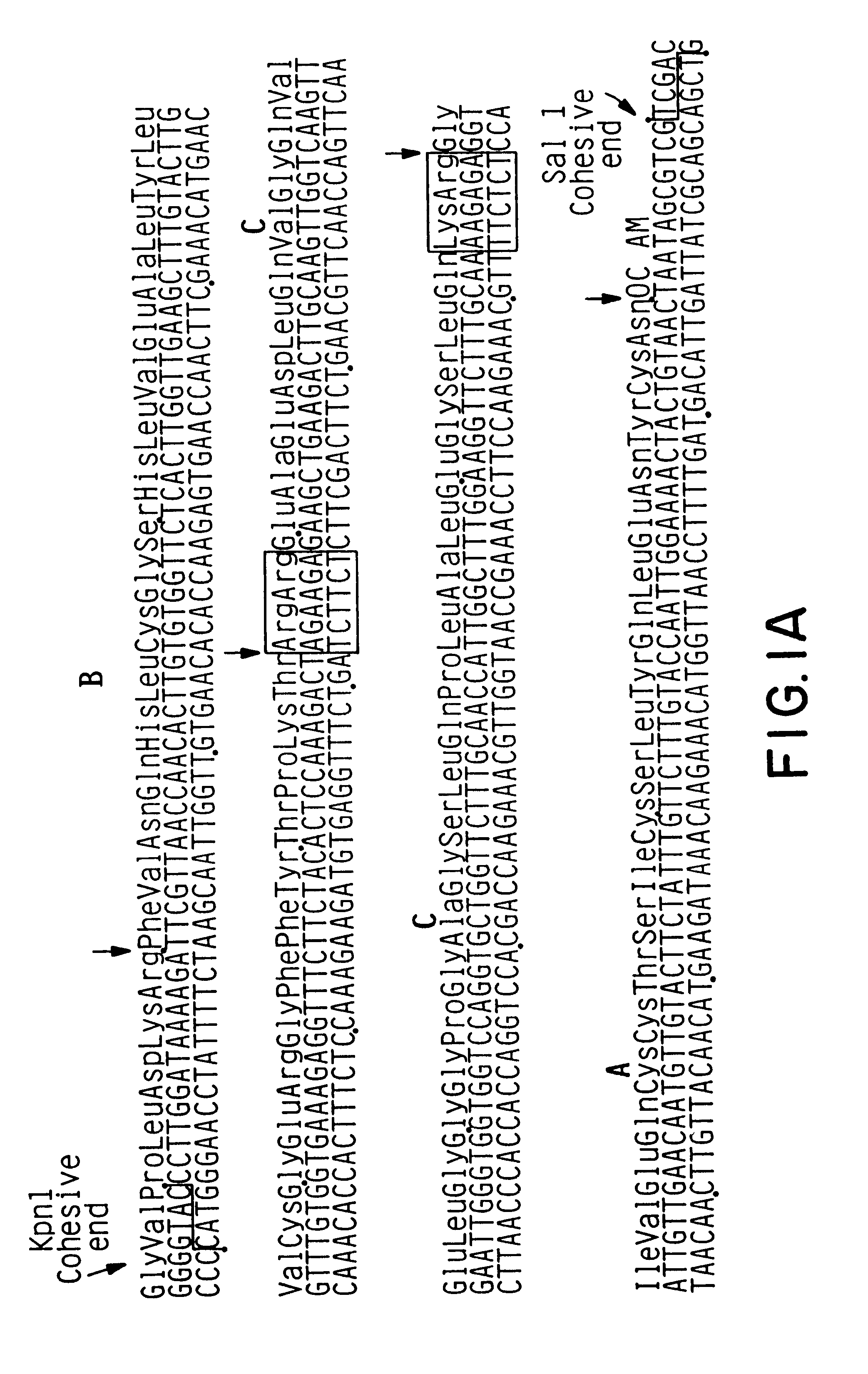
Glycosylation analogs of erythropoietin
ActiveUS7217689B1Increase the number ofHigh sialic acid contentPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue culturePlasmidDNA
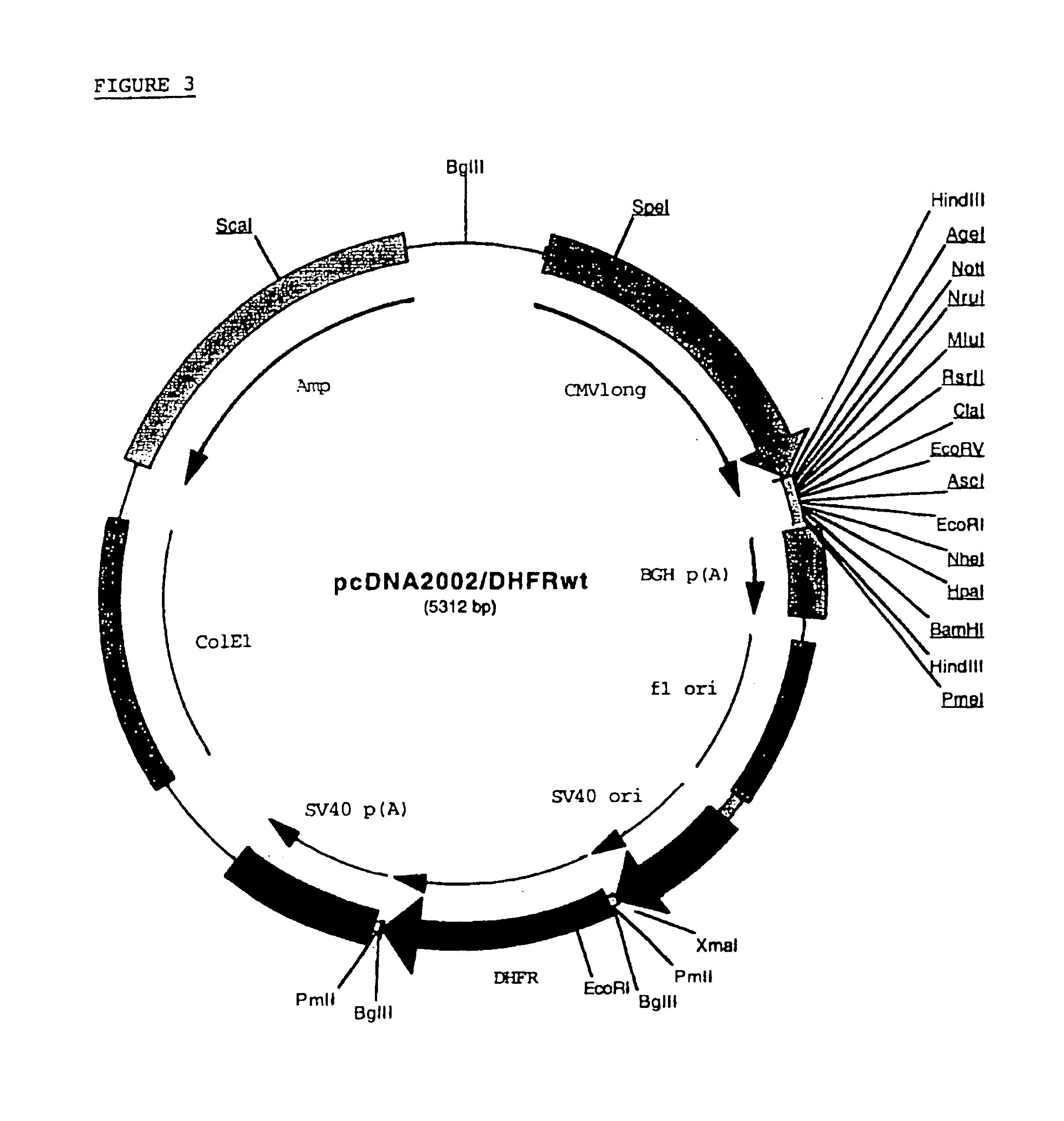
Erythropoietin analogs having at least one additional site for glycosylation, or a rearrangement of at least one site for glycosylation are disclosed. The invention also relates to DNA sequences encoding said erythropoietin analogs, and recombinant plasmids and host cells for analog expression.
Owner:AMGEN INC
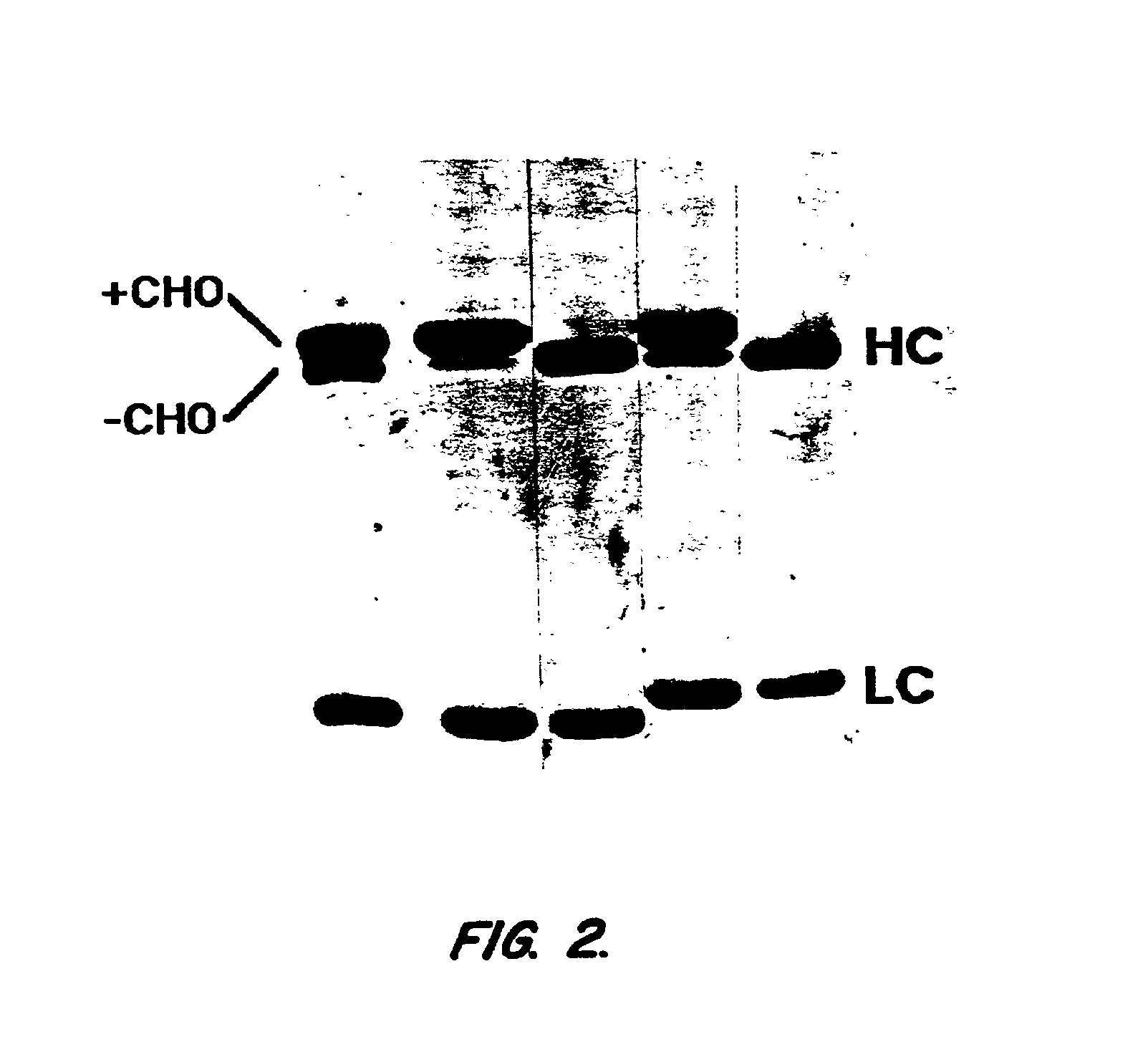
Increasing antibody affinity by altering glycosylation of immunoglobulin variable region
InactiveUS6933368B2Enhanced antigen binding propertyAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody AffinitiesImmunoglobulin Variable Region
The present invention provides methods for producing mutationally-altered immunoglobulins and compositions containing such mutationally-altered immunoglobulins, wherein the mutationally-altered immunoglobulins have at least one mutation that alters the pattern of glycosylation in a variable region and thereby modifies the affinity of the immunoglobulin for a preselected antigen. The methods and compositions of the invention provide immunoglobulins that possess increased affinity for antigen. Such glycosylation-altered immunoglobulins are suitable for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:FACET BIOTECH CORP
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS20040072290A1Increase healing valueStrong cytotoxicityFungiNanotechAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
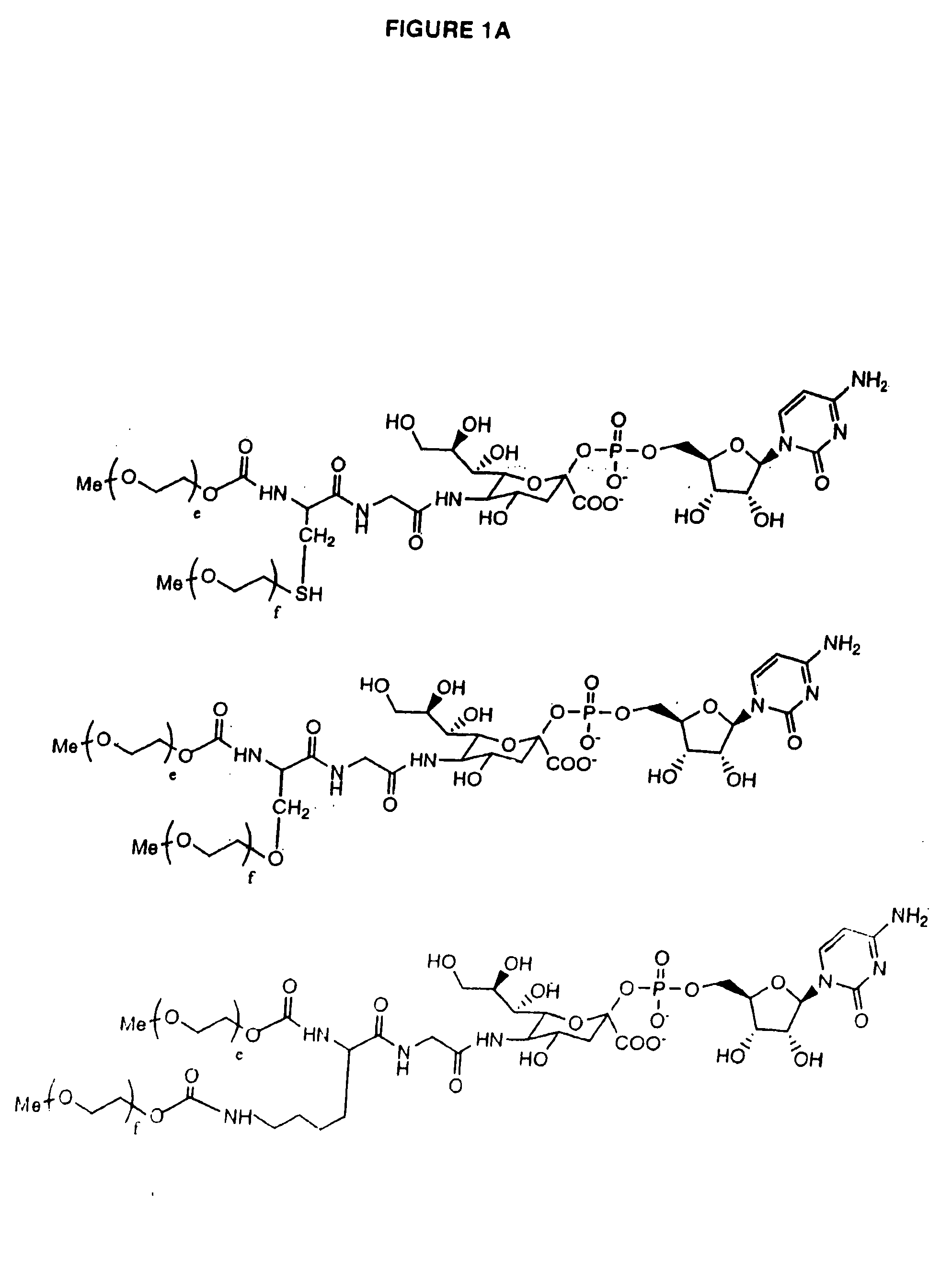
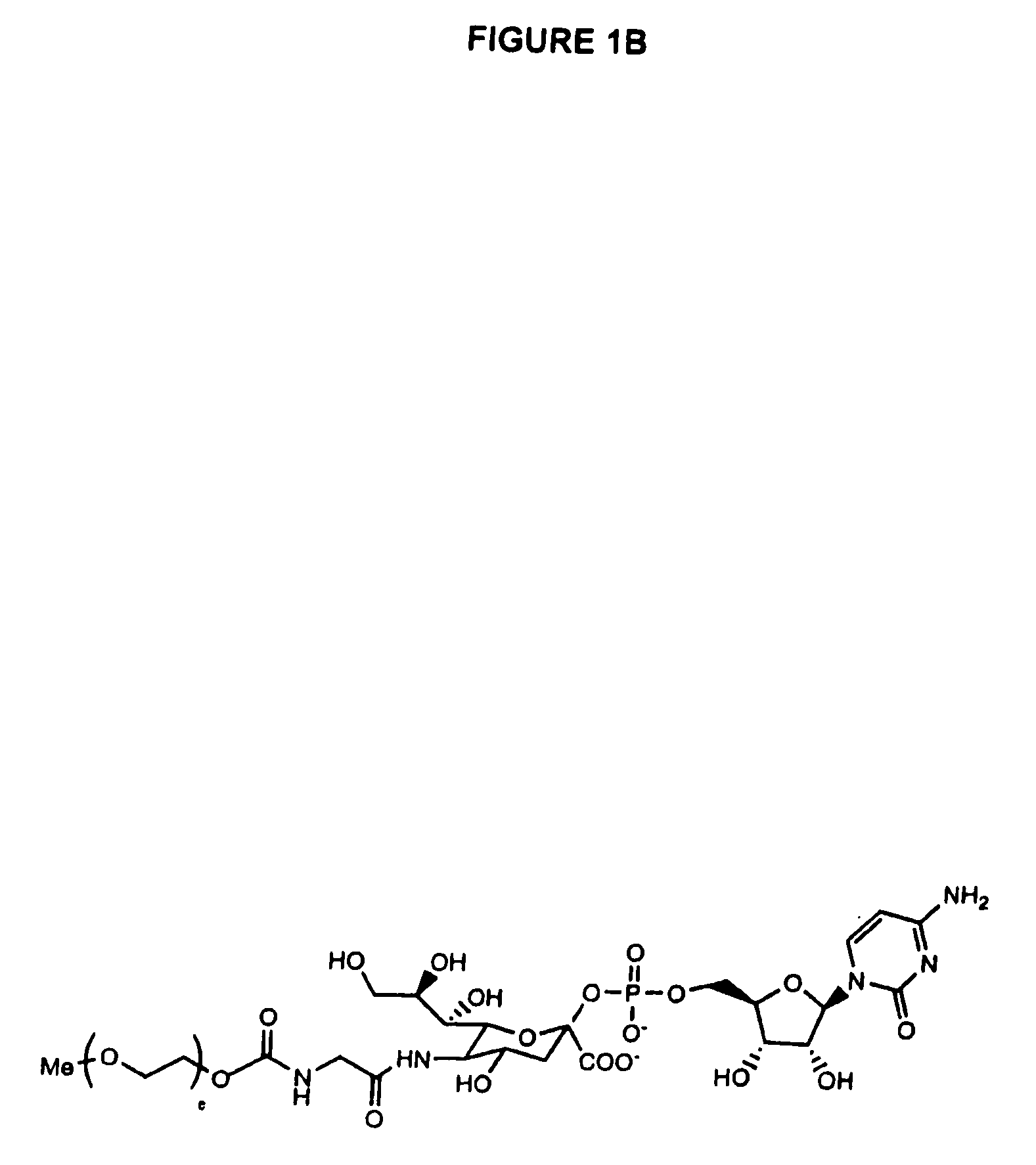
Conjugates of glycosylated/galactosylated peptide, bifunctional linker, and nucleotidic monomers/polymers, and related compositions and method of use
InactiveUS6906182B2Abnormal proliferationInhibition of replicationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNucleotideEthylene Homopolymers
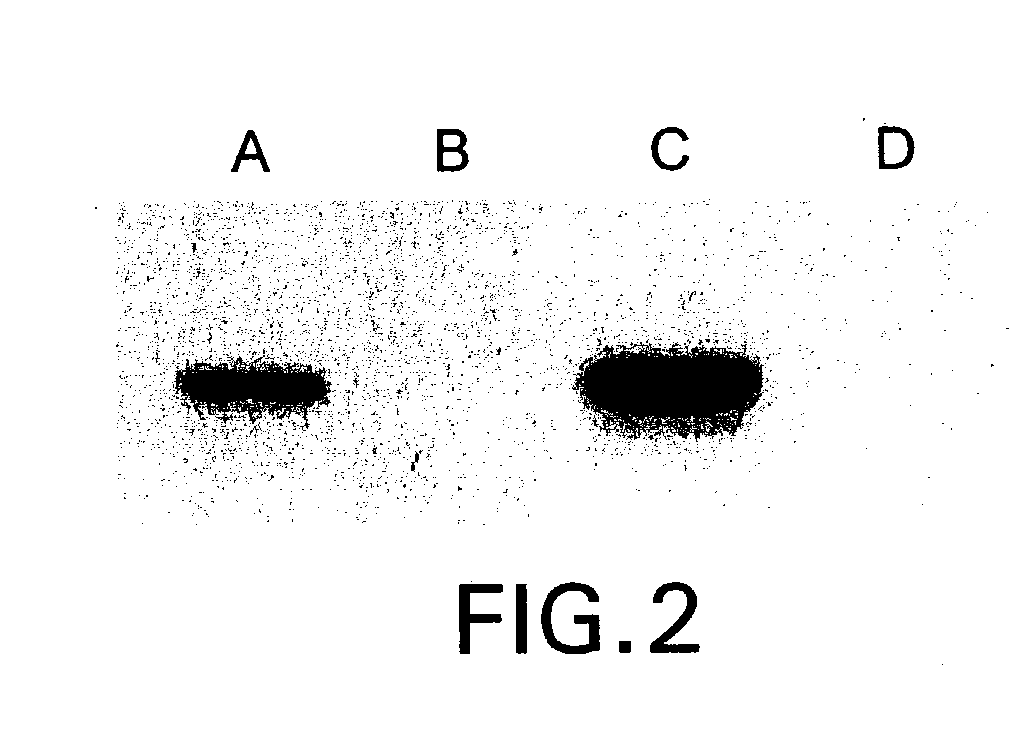
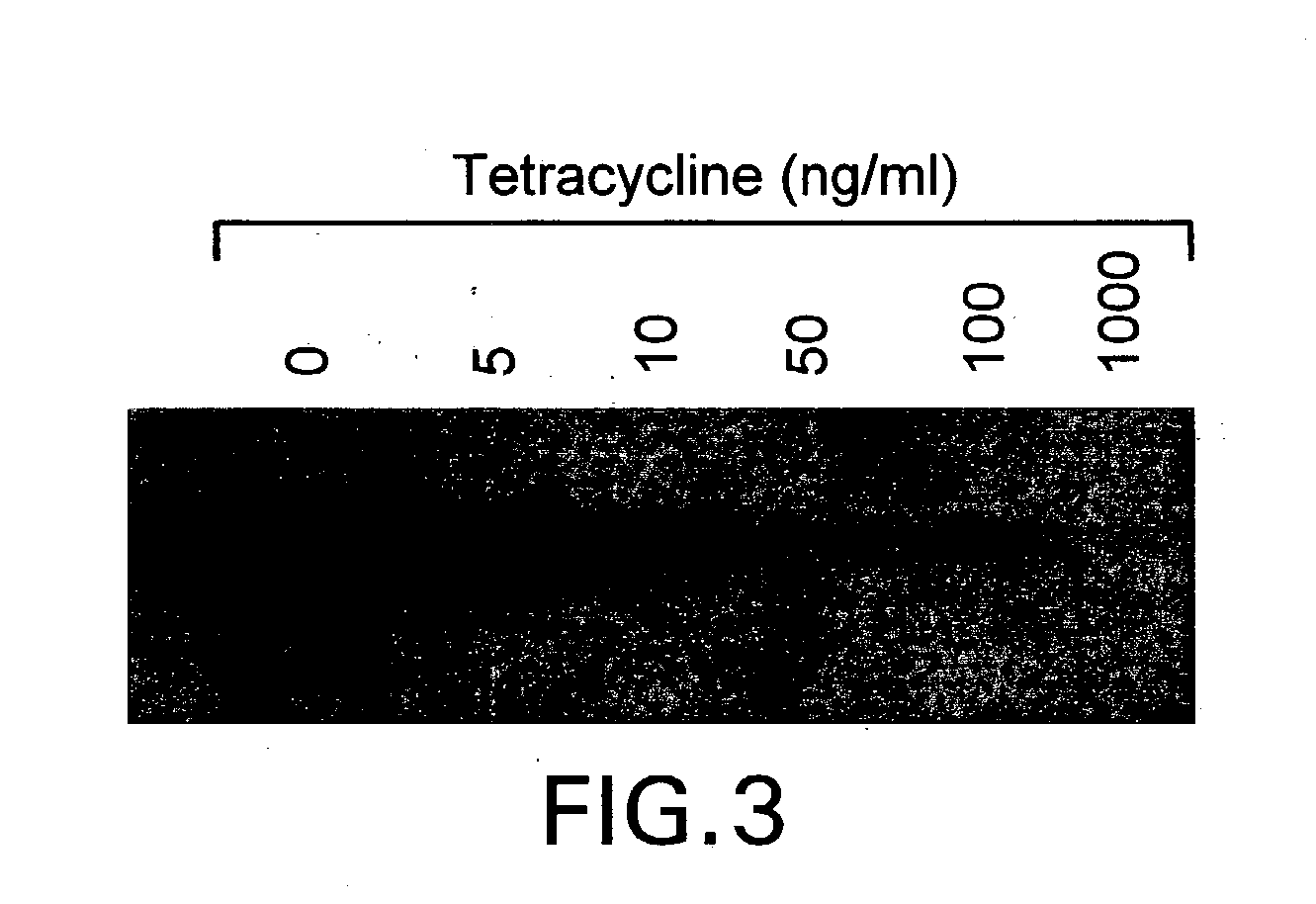
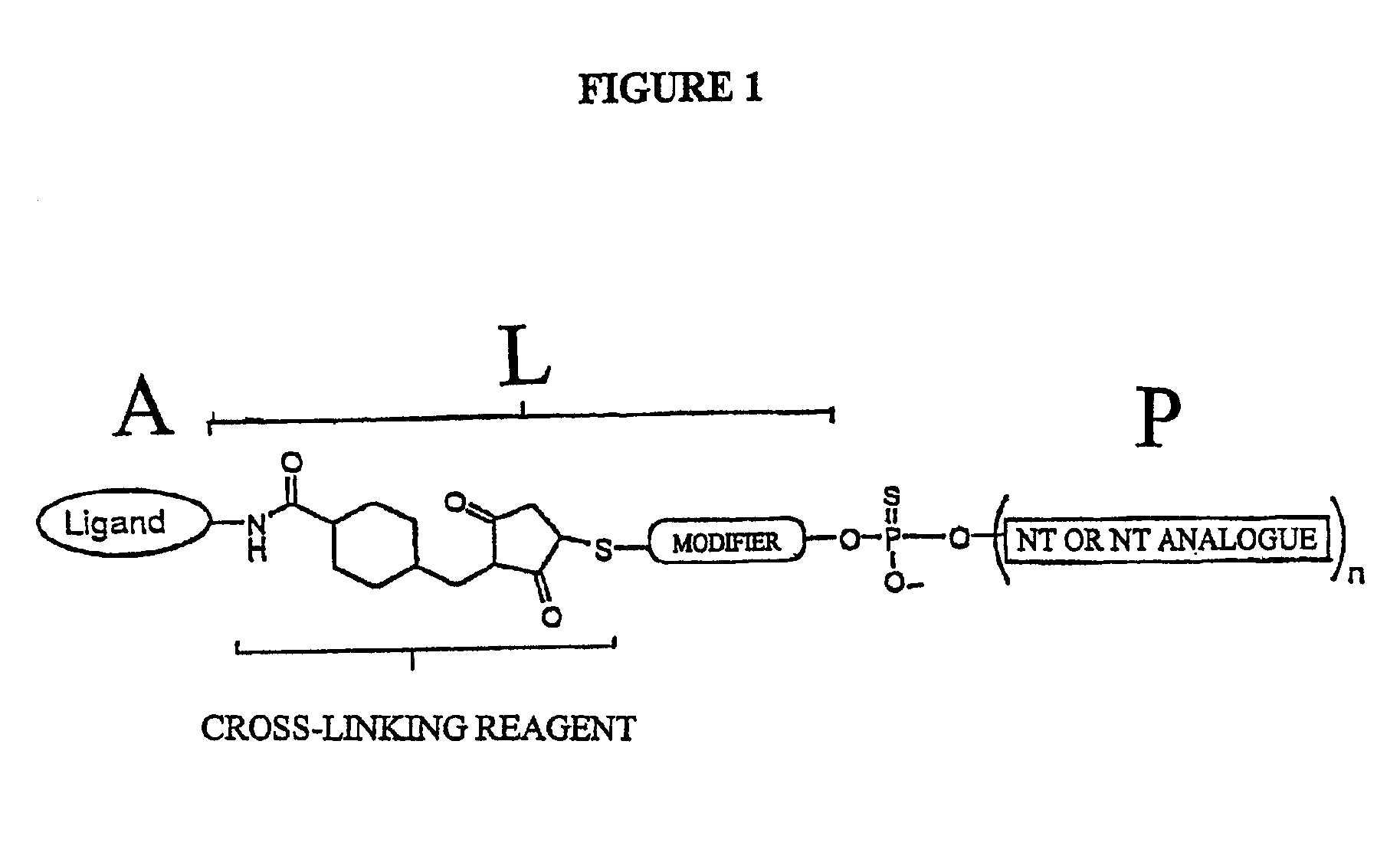
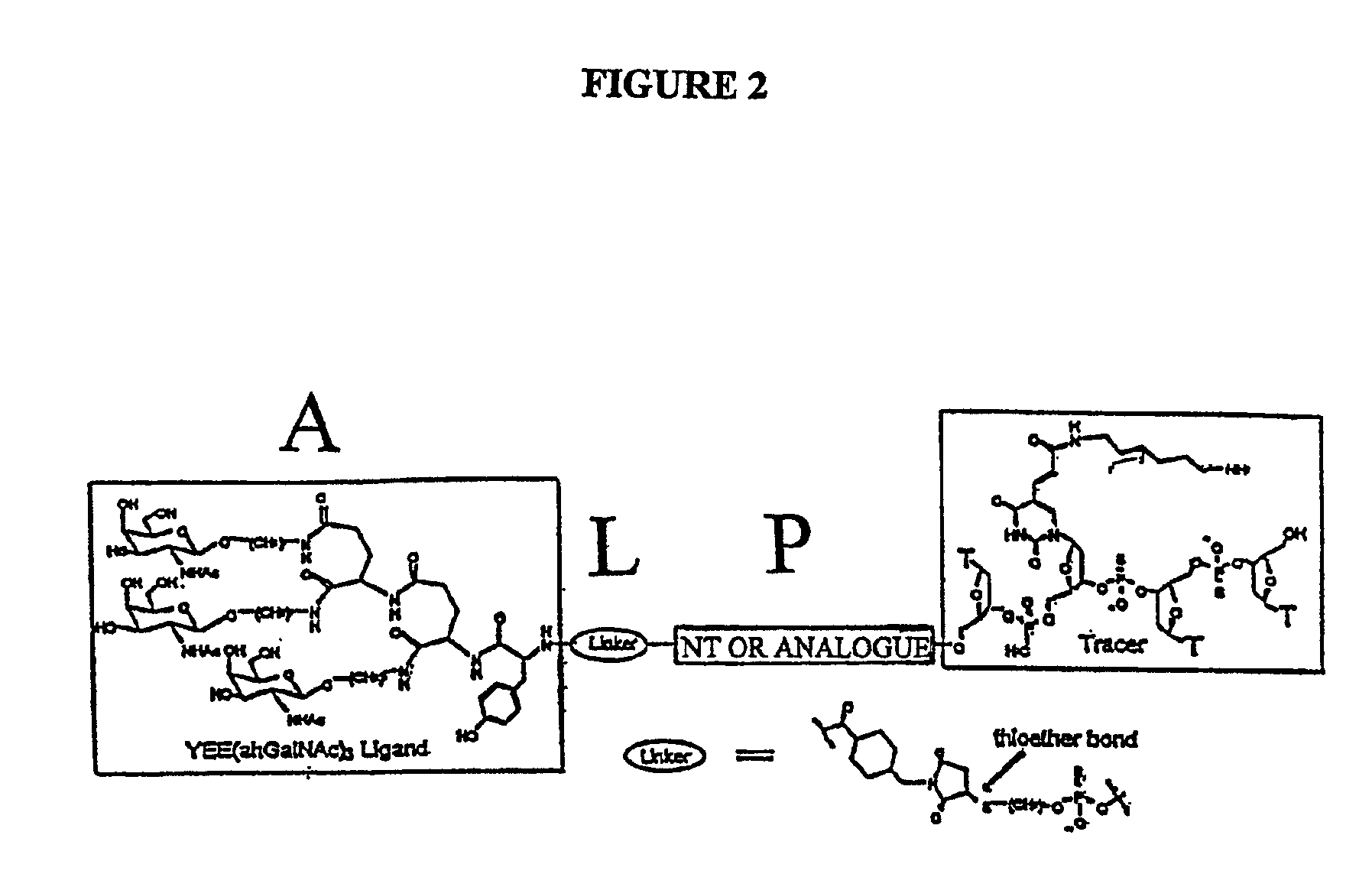
A conjugate of formula A-L-P, in which:A represents a glycosylated / galactosylated peptide that binds to a cell-surface receptor,L represents a bifunctional linker, which does not comprise a naturally occurring amino acid and is covalently bonded to A and P in a regiospecific manner, andP represents a monomer, homopolymer or heteropolymer comprising at least one nucleotide or an analogue thereof, which inhibits the intracellular biosynthesis of nucleotides or nucleic acids in a sequence-independent manner,wherein either or both of the covalent bond between A and L and the covalent bond between L and P can be cleaved intracellularly; a composition comprising such a conjugate; and a method of inhibiting abnormal cellular proliferation in a mammal; and a method of inhibiting replication of a virus in a mammal.
Owner:CELLECTIVE DX CORP
Single-chain antigen-binding proteins capable of glycosylation, production and uses thereof
The present invention relates to single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation. Compositions of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of glycosylation are described and claimed. Composition of, genetic constructions coding for, and methods for producing glycosylated monovalent and multivalent single-chain antigen-binding molecules capable of polyalkylene oxide conjugation are described and claimed. The invention also relates to methods for producing a polypeptide having increased glycosylation and the polypeptide produced by the described method. Uses resulting from the multifunctionality of a glycosylated / polyalkylene oxide conjugated antigen-binding protein are also described and claimed.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Combinatorial DNA library for producing modified N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7449308B2The overall structure is closedHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousTherapeutic protein
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities such as those involved in glycosylation to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells have a Man5GlcNAc2 core structure which may then be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
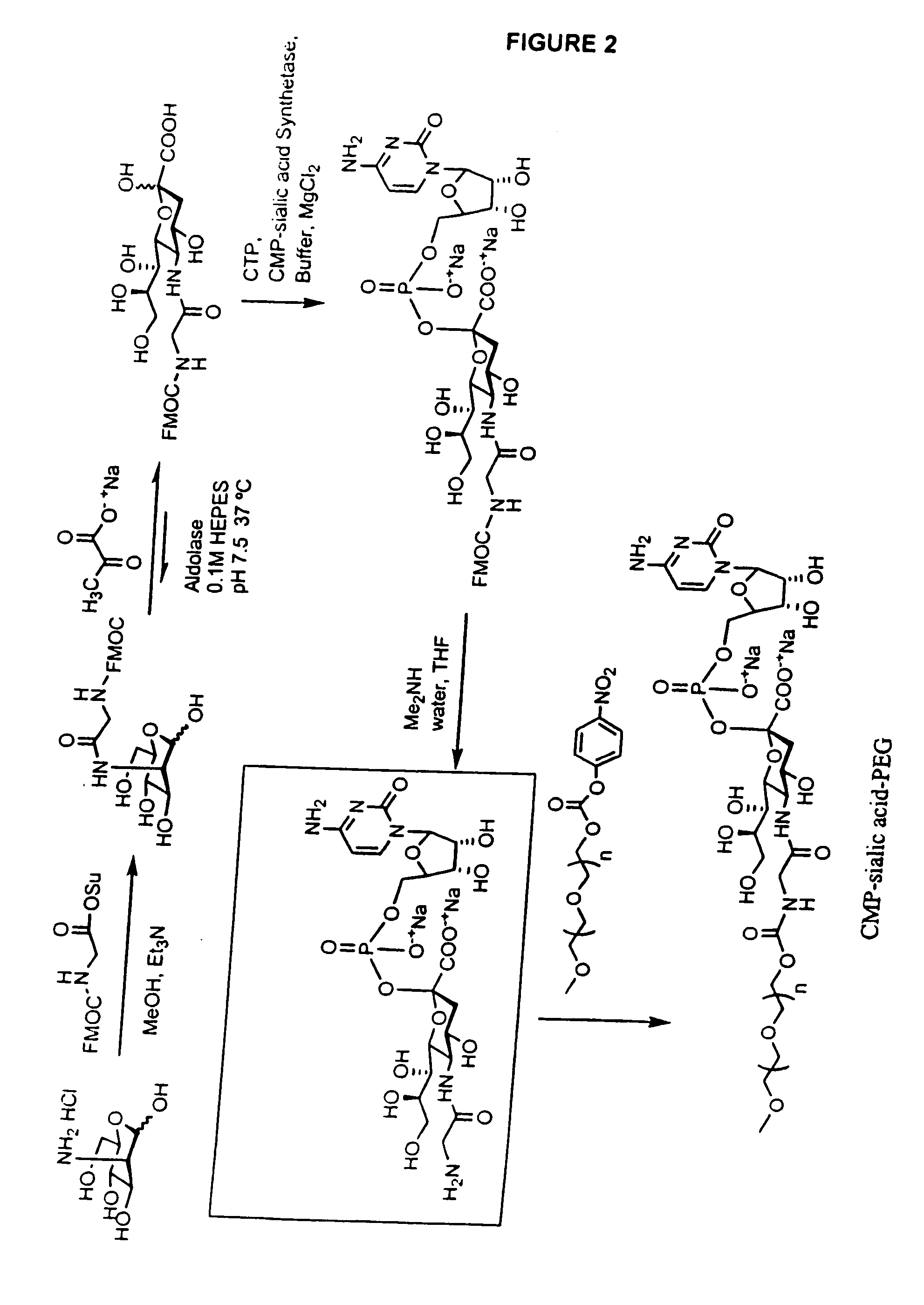
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060286637A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHeterologousSialic acid aldolase
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
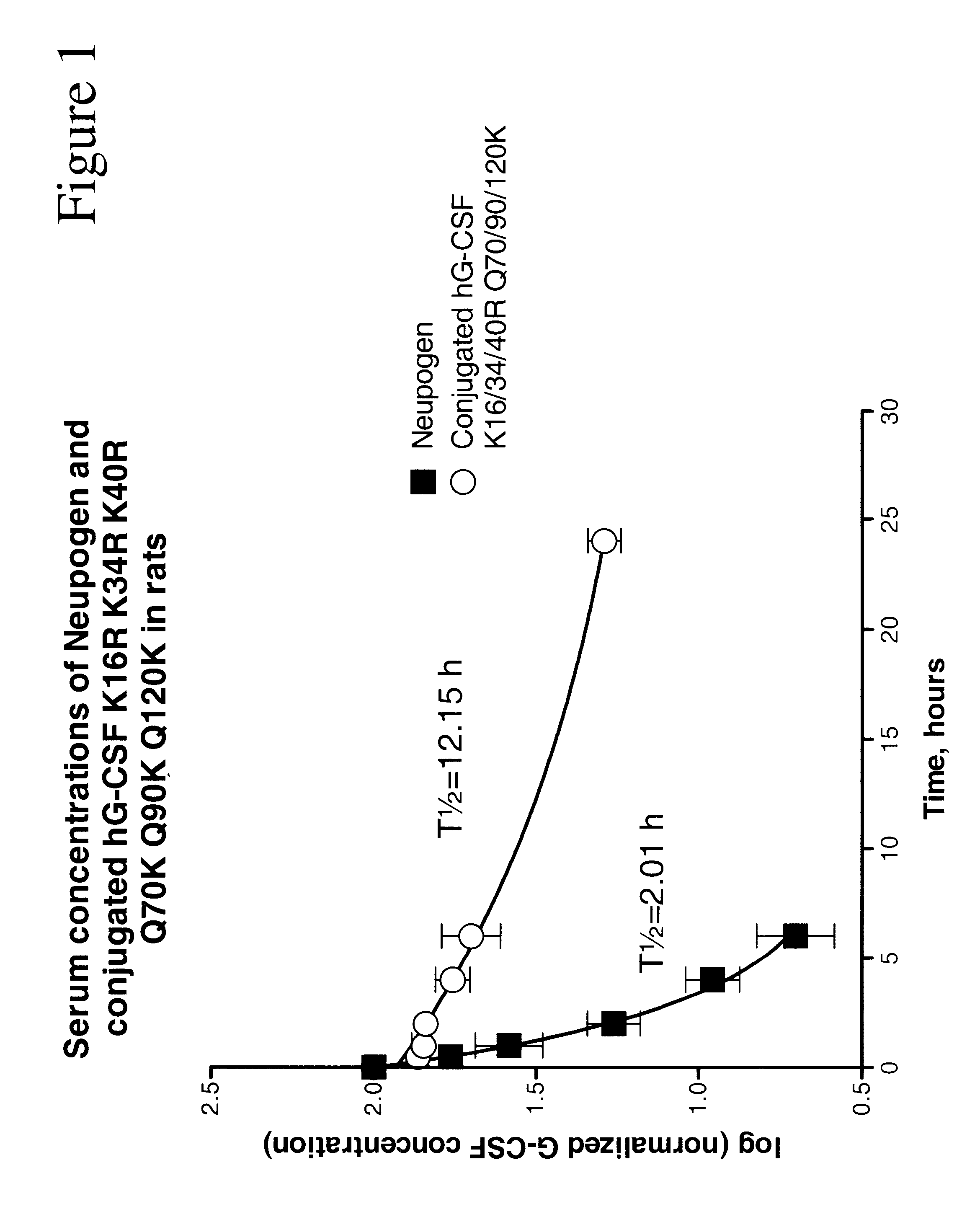
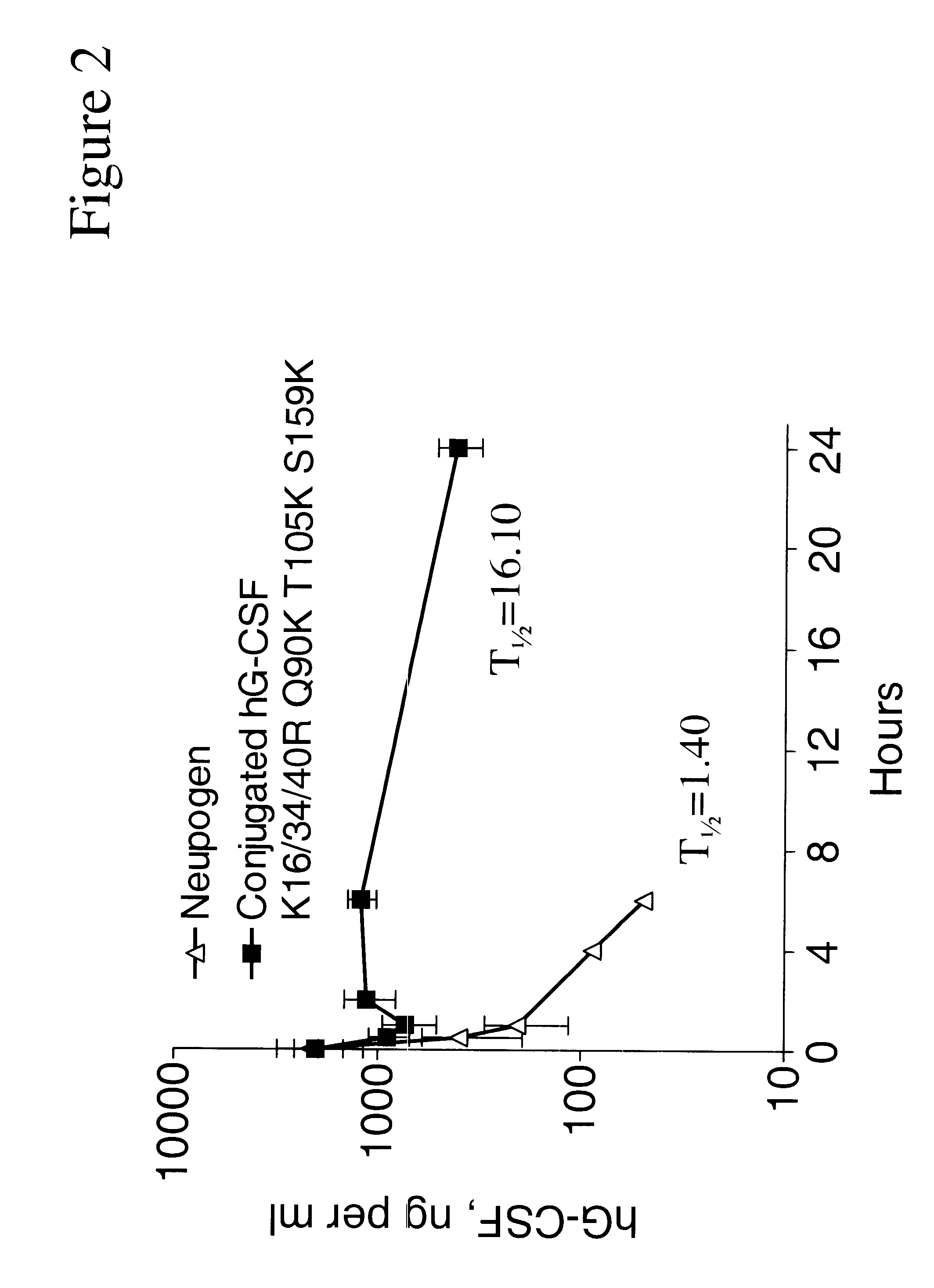
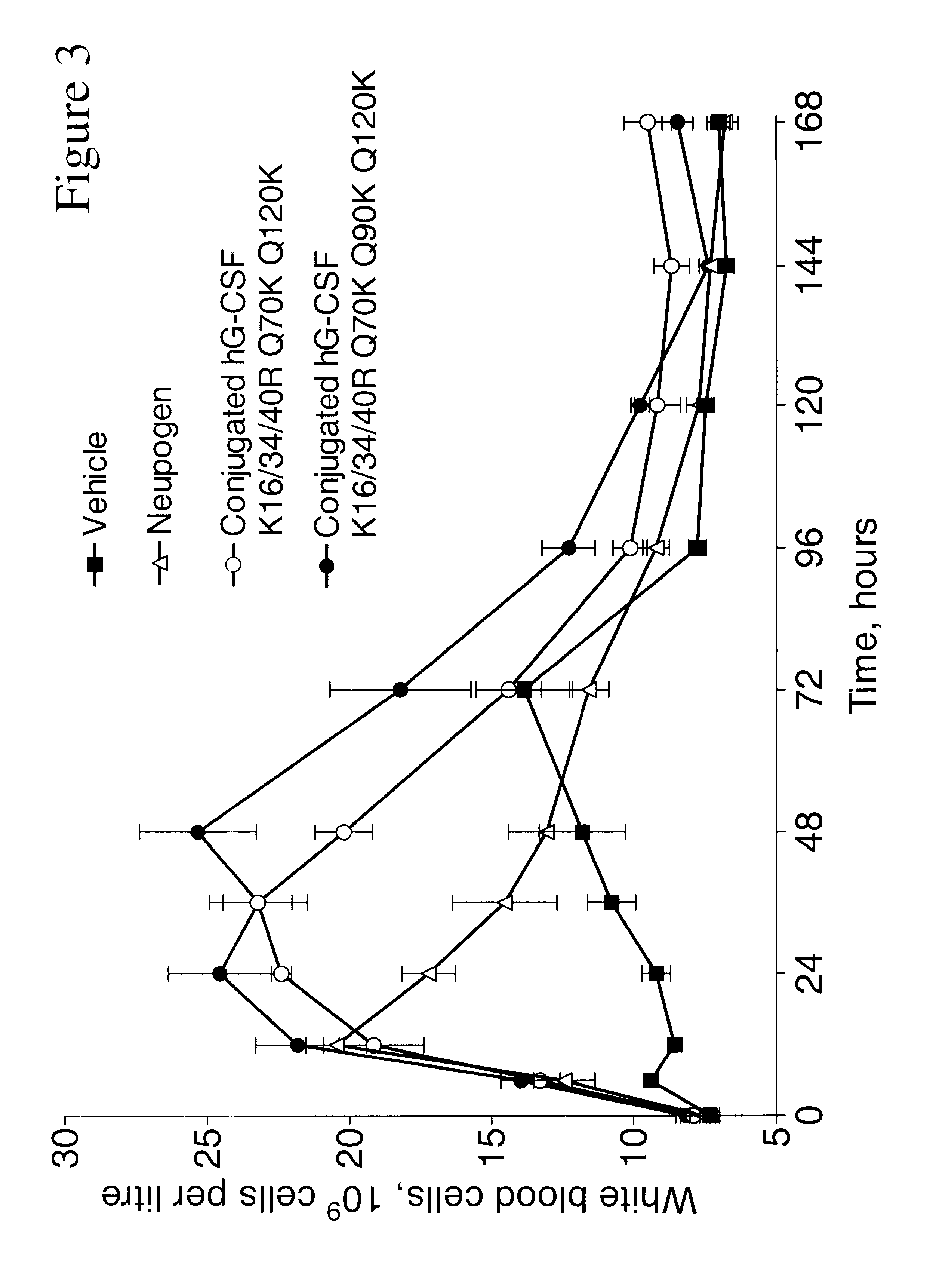
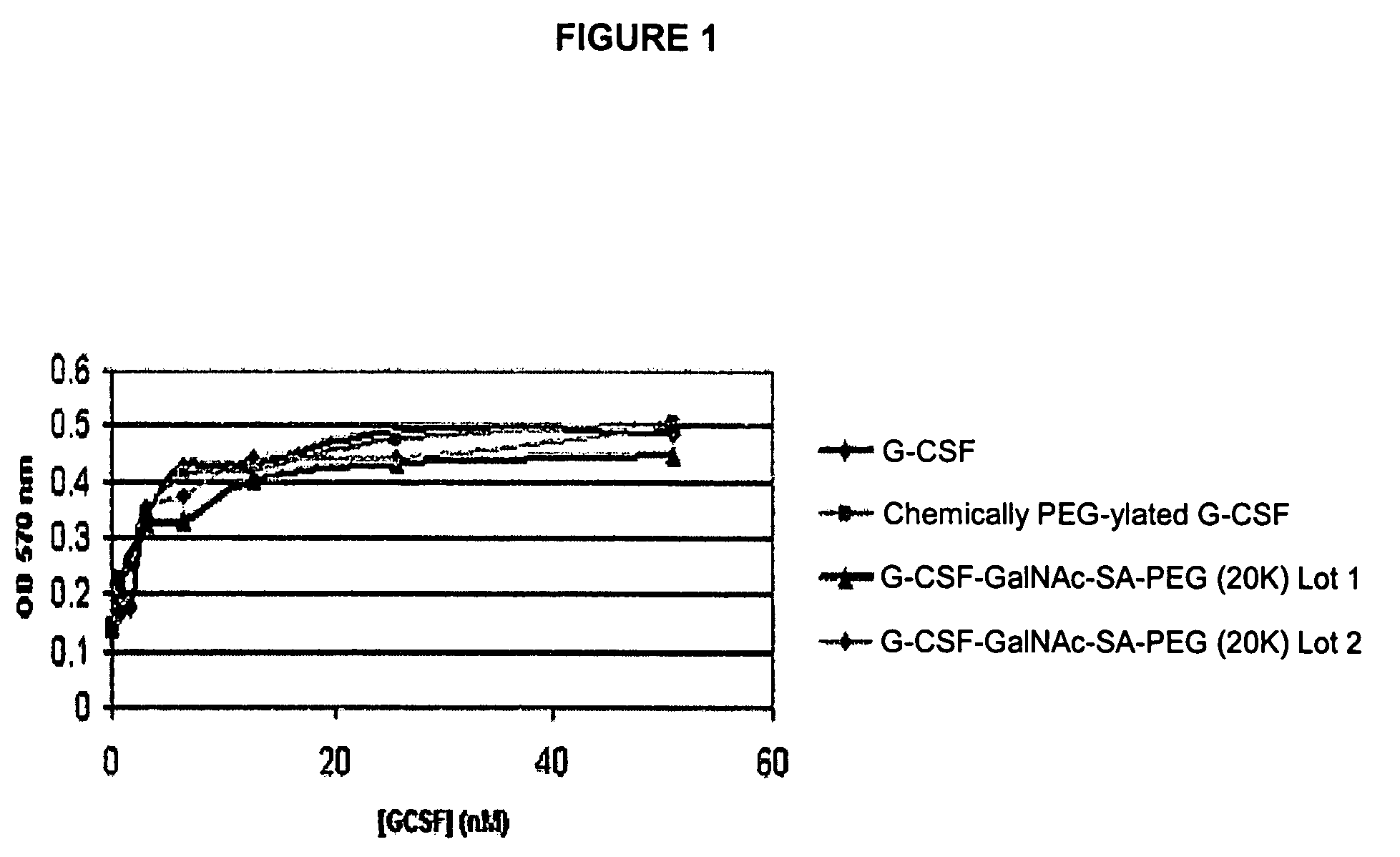
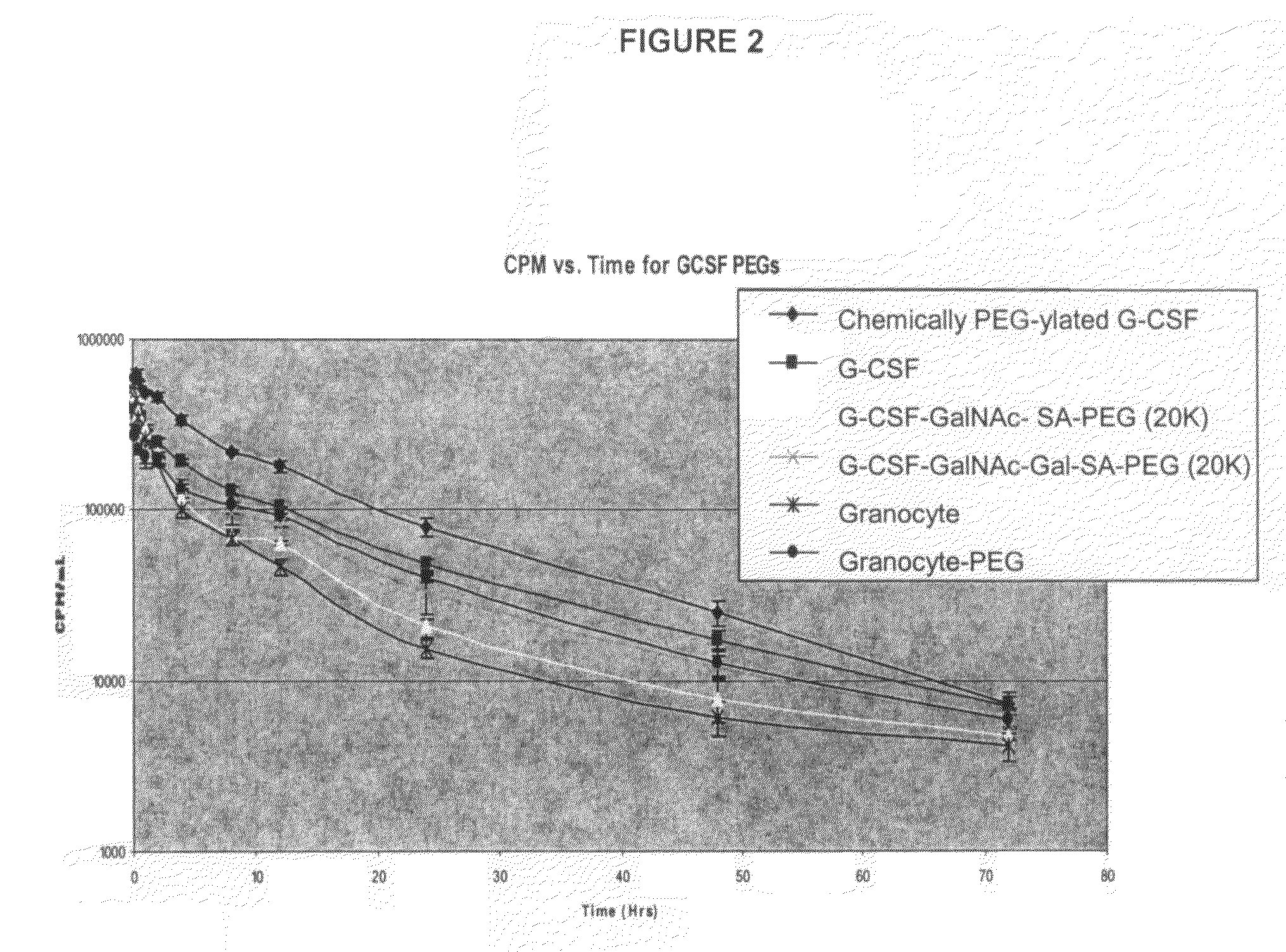
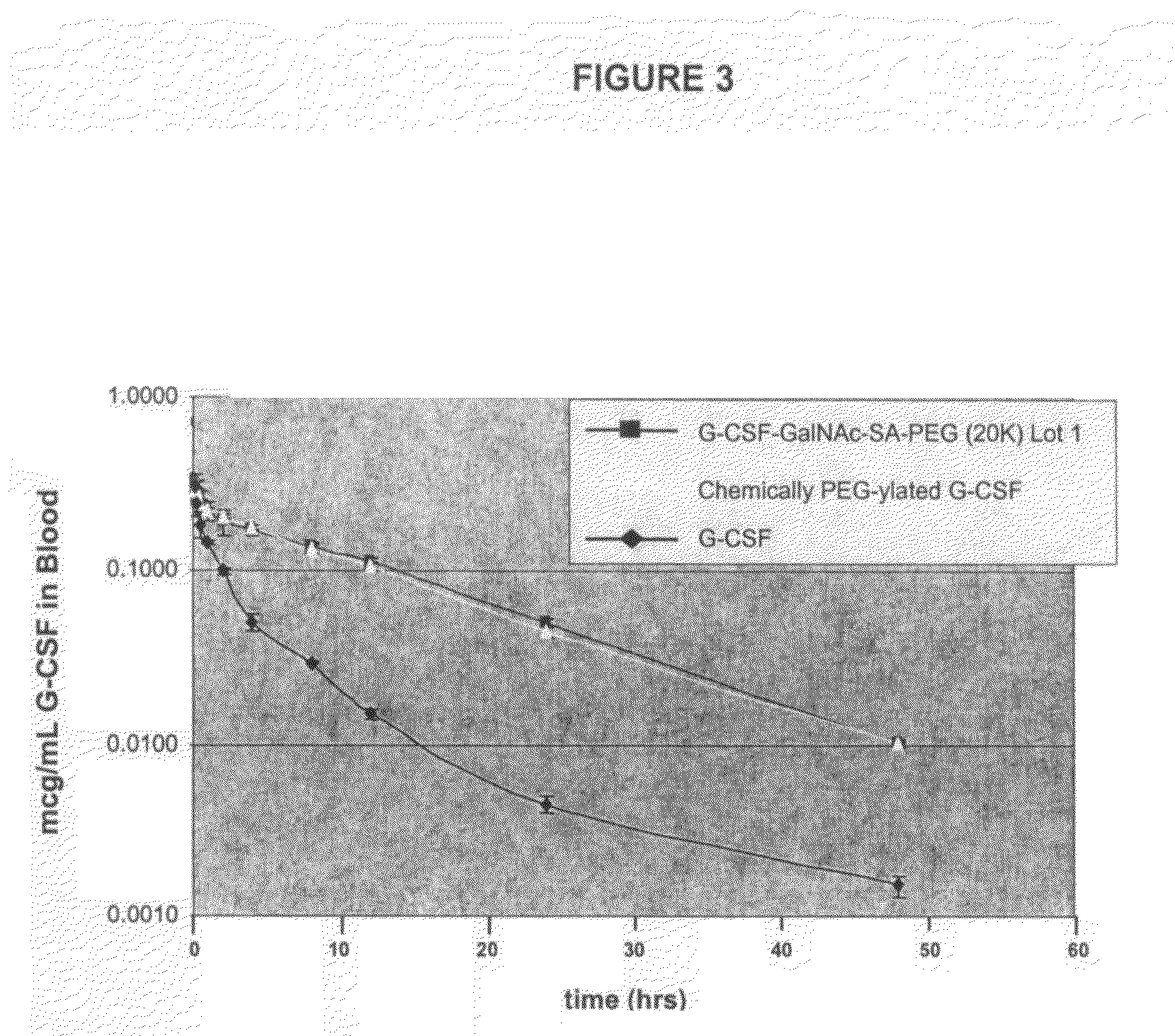
G-CSF conjugates
InactiveUS6555660B2Improved propertyReduced in vitroBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to polypeptide conjugates comprising a polypeptide exhibiting G-CSF activity and having an amino acid sequence that differs from the amino acid sequence of human G-CSF in at least one specified introduced and / or removed amino acid residue comprising an attachment group for a non-polypeptide moiety, and having at least one non-polypeptide moiety attached to an attachment group of the polypeptide. The attachment group may e.g. be a lysine, cysteine, aspartic acid or glutamic acid residue or a glycosylation site, and the non-polypeptide moiety may e.g. be a polymer such as polyethylene glycol or an oligosaccharide. The conjugate, which has a reduced in vitro bioactivity compared to hG-CSF, has one or more improved properties such as increased biological half-life and increased stimulation of neutrophils.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Methods and products related to the improved analysis of carbohydrates
The invention relates, in part, to the improved analysis of carbohydrates. In particular, the invention relates to the analysis of carbohydrates, such as N-glycans and O-glycans found on proteins and saccharides attached to lipids. Improved methods, therefore, for the study of glycosylation patterns on cells, tissue and body fluids are also provided. Information from the analysis of glycans, such as the glycosylation patterns on cells, tissues and in body fluids, can be used in diagnostic and treatment methods as well as for facilitating the study of the effects of glycosylation / altered glycosylation. Such methods are also provided. Methods are further provided to assess production processes, to assess the purity of samples containing glycoconjugates, and to select glycoconjugates with the desired glycosylation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Monoclonal antibodies against prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) lacking in fucosyl residues
ActiveUS7875278B2Inhibit cell growthStrong cytotoxicityAnimal cellsAntibody ingredientsAntigenFucosylation
The invention pertains to anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues. The antibodies of the invention exhibit increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity as compared to the fucosylated form of the antibodies. The invention also provides host cells that express the anti-PSMA antibodies that lack fucosyl residues, wherein the host cells are deficient for a fucosyl transferase. Methods of using the antibodies to inhibit the growth of PSMA+ cells, such as tumor cells, are also provided.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC +1
Methods and products related to the improved analysis of carbohydrates
The invention relates, in part, to the improved analysis of carbohydrates. In particular, the invention relates to the analysis of carbohydrates, such as N-glycans and O-glycans found on proteins. Improved methods, therefore, for the study of glycosylation patterns on cells, tissue and body fluids are also provided. Information regarding the analysis of glycans, such as the glycosylation patterns on cells, tissues and in body fluids, can be used in diagnostic and treatment methods as well as for facilitating the study of the effects of glycosylation / altered glycosylation on protein function. Such methods are also provided. Methods are also provided to assess protein production processes, to assess the purity of proteins produced, and to select proteins with the desired glycosylation.
Owner:MOMENTA PHARMA +2
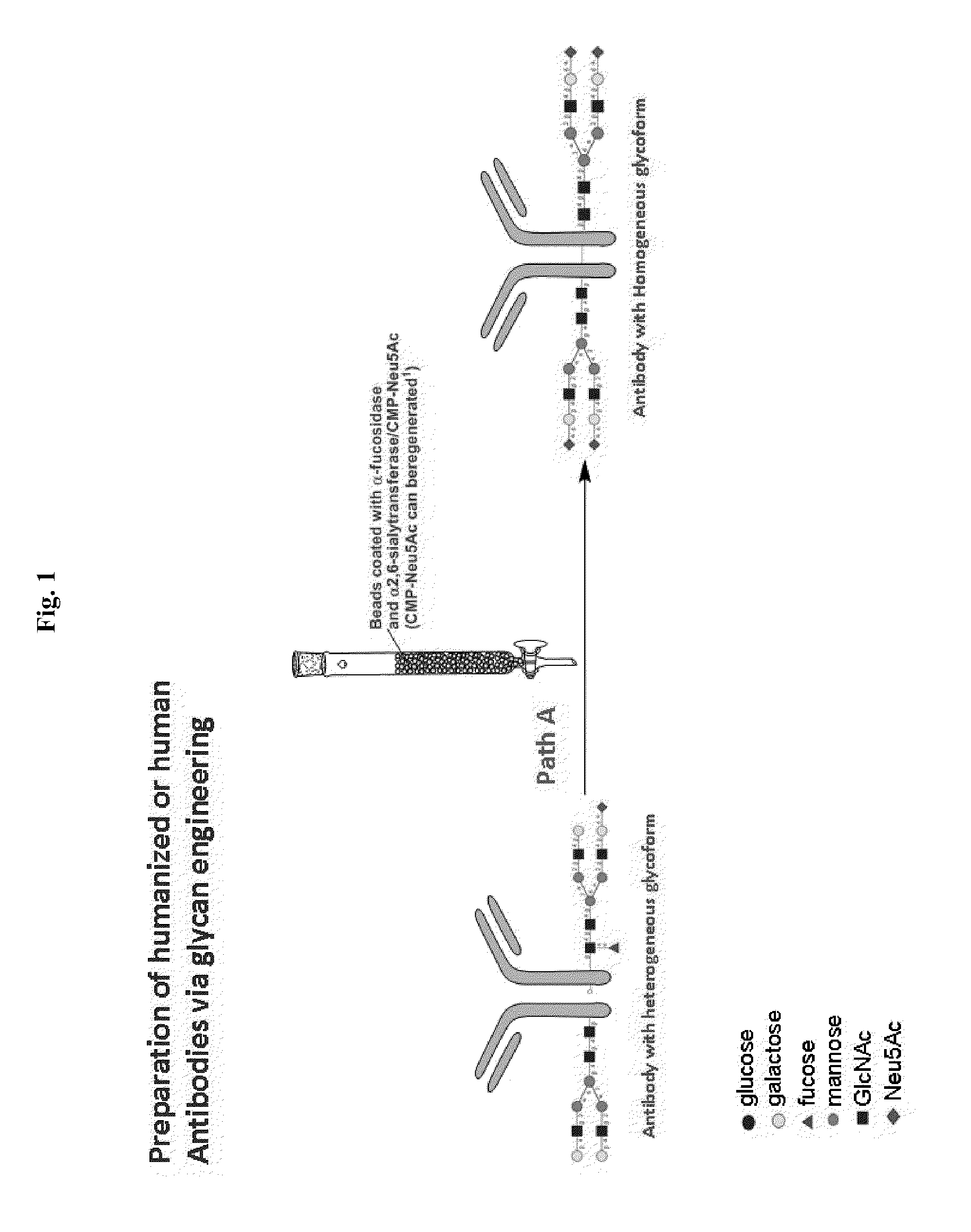
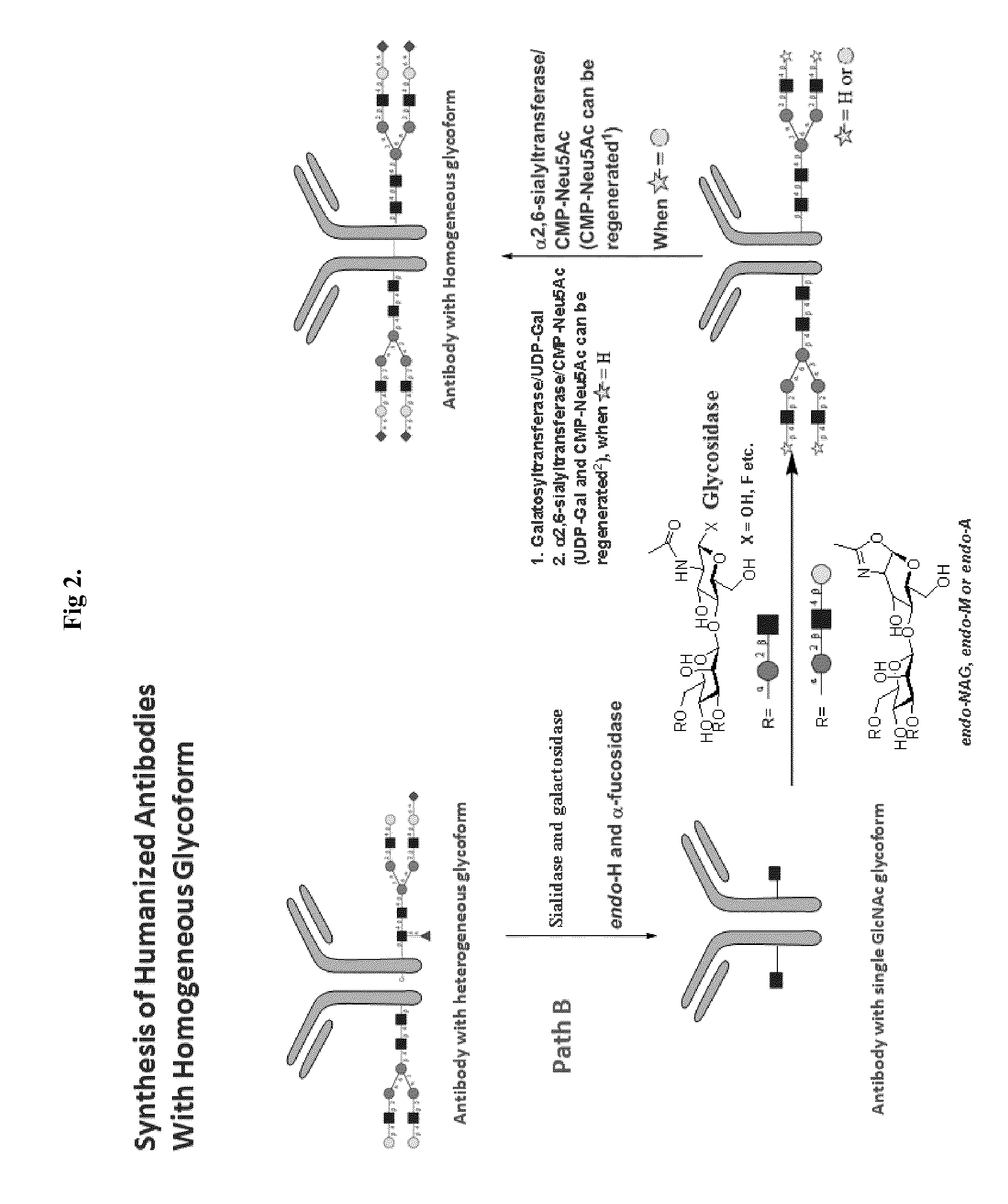
Methods for modifying human antibodies by glycan engineering
ActiveUS20110263828A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityImmunoglobulinsFermentationGlycanAntibody fragments
Modified Fc regions of antibodies and antibody fragments, both human and humanized, and having enhanced stability and efficacy, are provided. Fc regions with core fucose residues removed, and attached to oligosaccharides comprising terminal sialyl residues, are provided. Antibodies comprising homogeneous glycosylation of Fc regions with specific oligosaccharides are provided. Fc regions conjugated with homogeneous glycoforms of monosaccharides and trisaccharides, are provided. Methods of preparing human antibodies with modified Fc using glycan engineering, are provided.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Recombinant protein production in a human cell
InactiveUS6855544B1Easy to handleLarge-scale (continuous) productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHamsterHuman cell
Methods and compositions for the production of recombinant proteins in a human cell line. The methods and positions are particularly useful for generating stable expression of human recombinant proteins of interest that are modified post-translationally, for example, by glycosylation. Such proteins may have advantageous properties in comparison with their counterparts produced in non-human systems such as Chinese Hamster Ovary cells.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Glycopegylated factor IX
InactiveUS20060040856A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesRetain pharmacological activitySaccharide peptide ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsGlycoPEGylated factor VIIaPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention provides conjugates between Factor IX and PEG moieties. The conjugates are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar moiety onto a glycosyl residue on the peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the conjugates.
Owner:NEOSE TECH
O-linked glycosylation of peptides
The present invention provides polypeptides that include an O-linked glycosylation site that is not present in the wild-type peptide. The polypeptides of the invention include glycoconjugates in which a species such as a water-soluble polymer, a therapeutic agent of a biomolecule is covalently linked through an intact O-linked glycosyl residue to the polypeptide. Also provided are methods of making the peptides of the invention and methods, pharmaceutical compositions containing the peptides and methods of treating, ameliorating or preventing diseased in mammals by administering an amount of a peptide of the invention sufficient to achieve the desired response.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
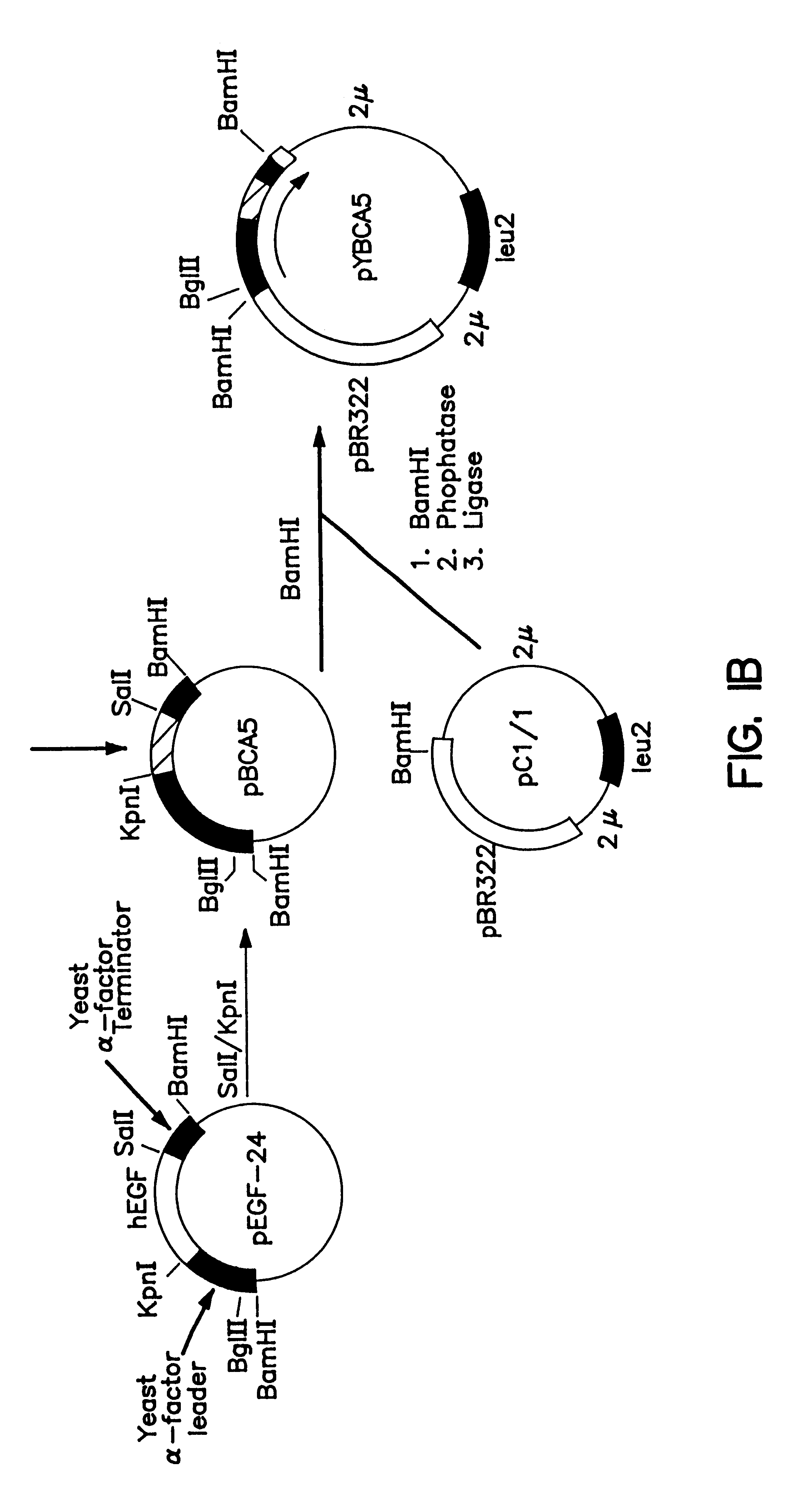
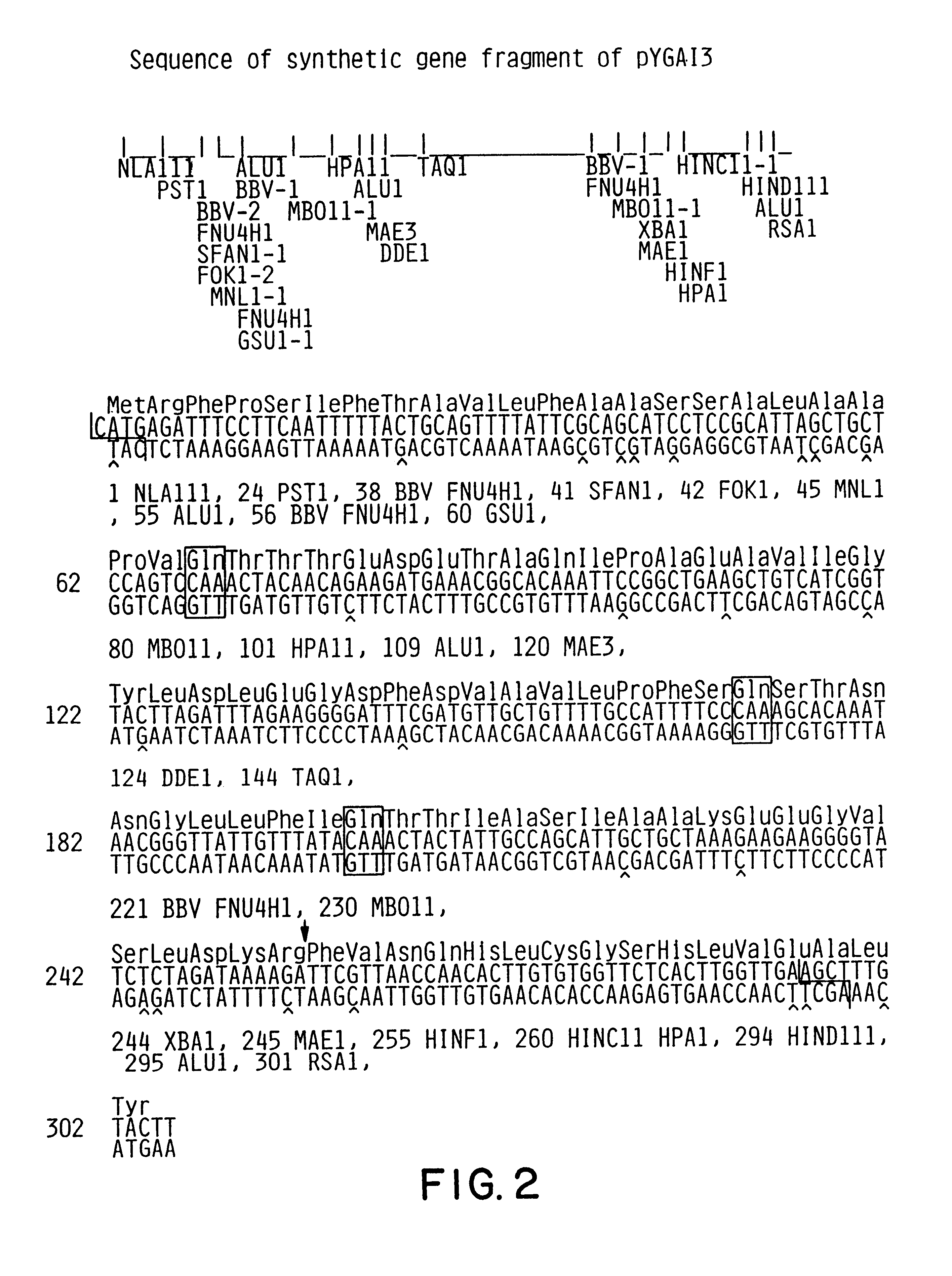
Expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in yeast employing truncated alpha-factor leader sequences
InactiveUSRE37343E1Efficiently direct expressionEfficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousBiotechnology
A yeast alpha-factor expression system is provided comprised of a truncated leader sequence, containing the alpha-factor signal peptide and one glycosylation site, linked by a processing site to a non-yeast protein-encoding sequence.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
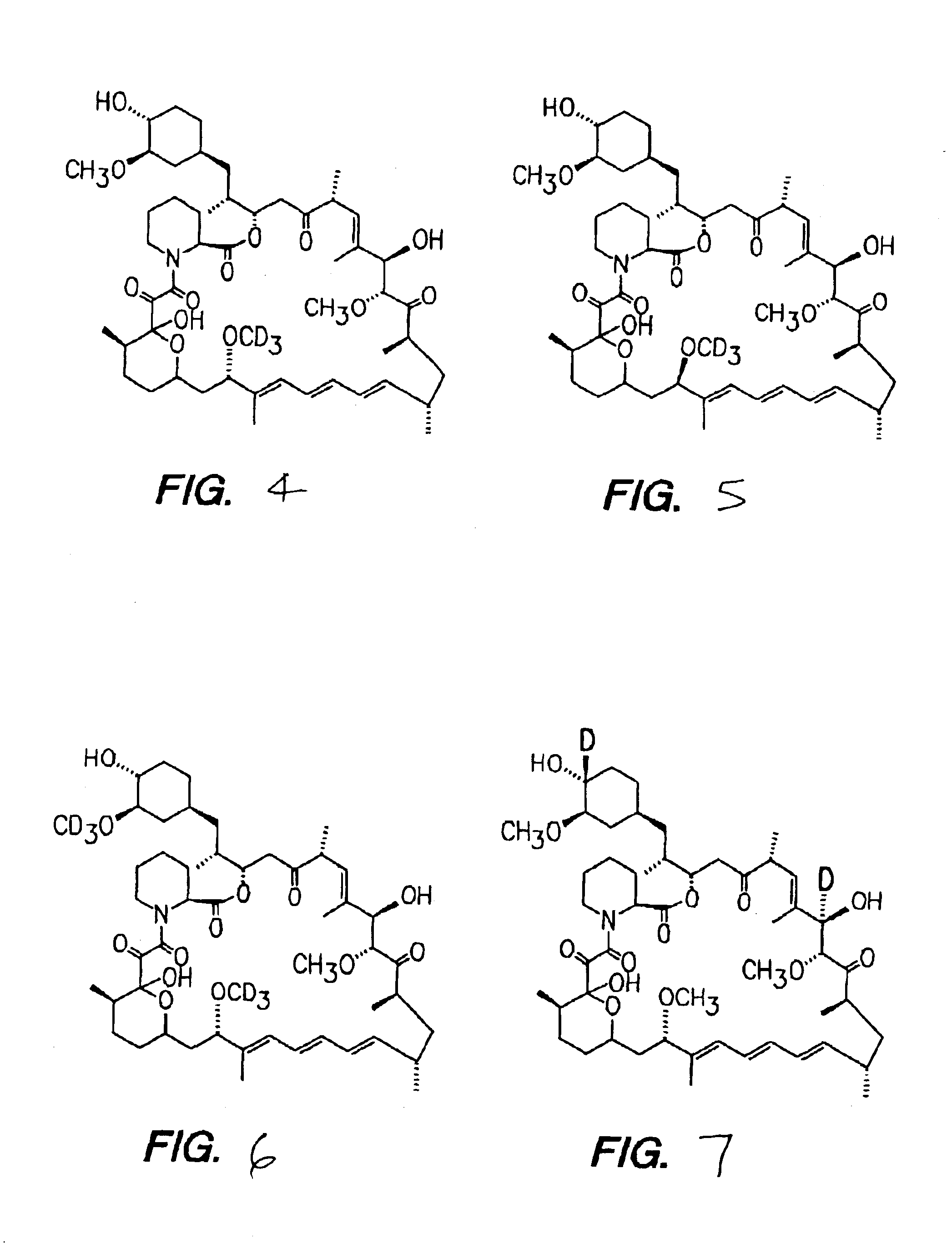
Medical devices incorporating deuterated rapamycin for controlled delivery thereof
InactiveUS6884429B2Improve efficiencyThe right amountBiocideAntimycoticsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
Deuterated rapamycin can be controllably introduced target locations within the patient's body by using an implantable medical device having a structure incorporated with a therapeutic agent comprising a deuterated rapamycin. Representative deuterated rapamycins include epi-7-deuteromthyl rapamycin, 7,43-d6 rapamycin, 7-deuteromethyl rapamycin and 31,42-d2-rapamycin and isomers thereof, and mixtures thereof. The deuterated rapamycin can also be glycosylated.
Owner:ISOTECHNIKA INC
Antibody glycosylation variants having increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
The present invention relates to the field of glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particularly, the present invention relates to glycosylation engineering to generate proteins with improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
One pot desialylation and glycopegylation of therapeutic peptides
InactiveUS20070105755A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesCost effectiveSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesSugar moietyGlycosyltransferase
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Specific binding proteins and uses thereof
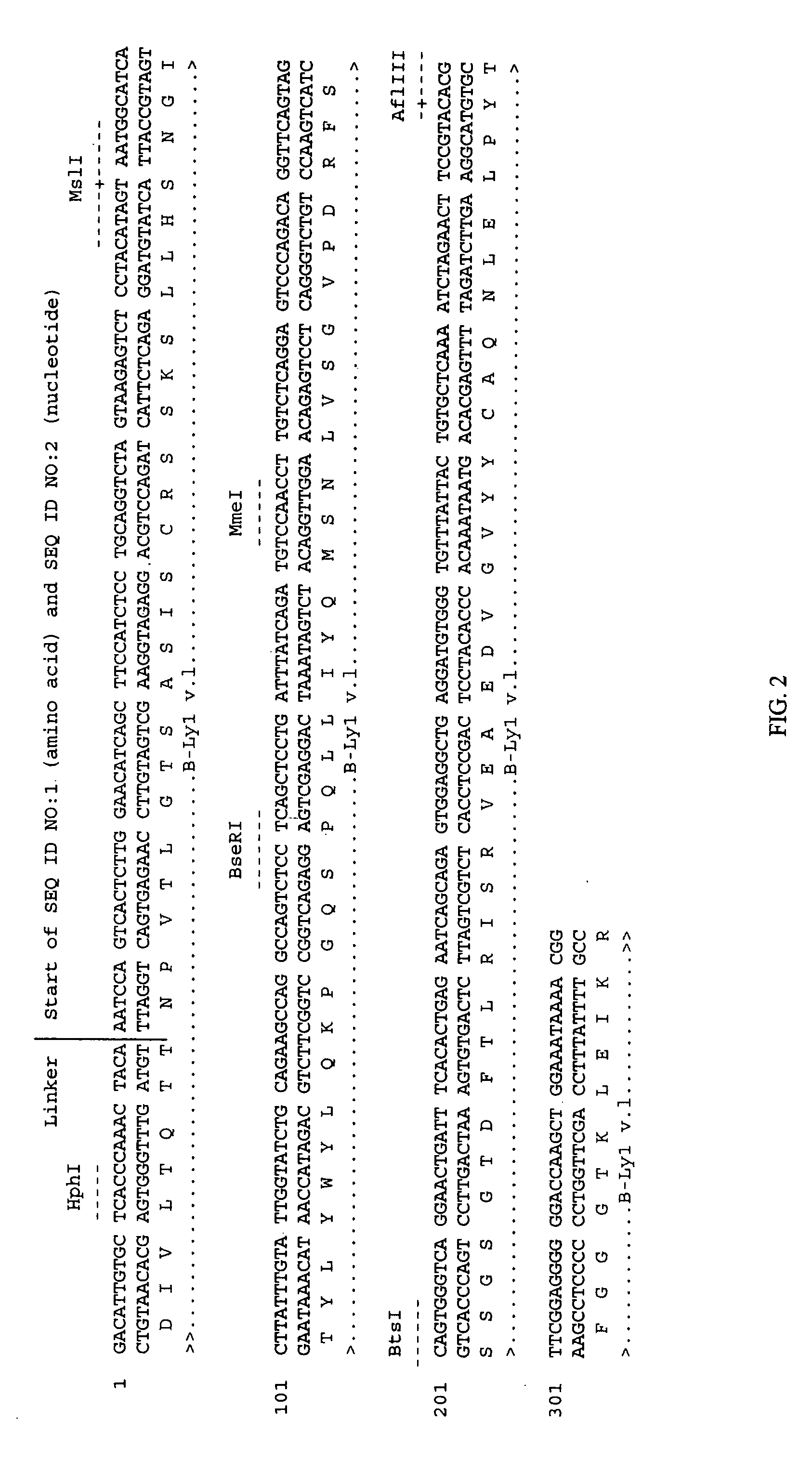
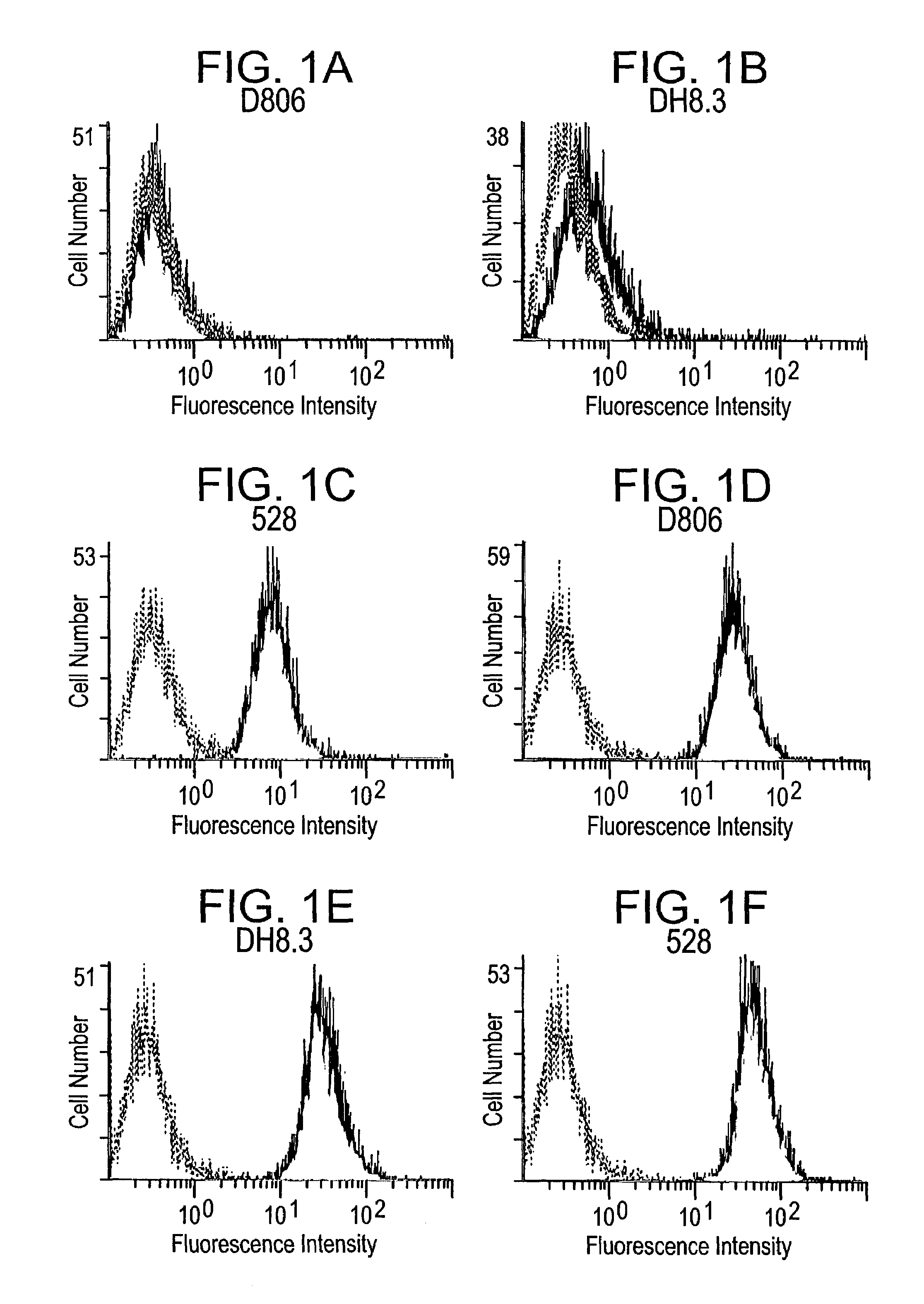
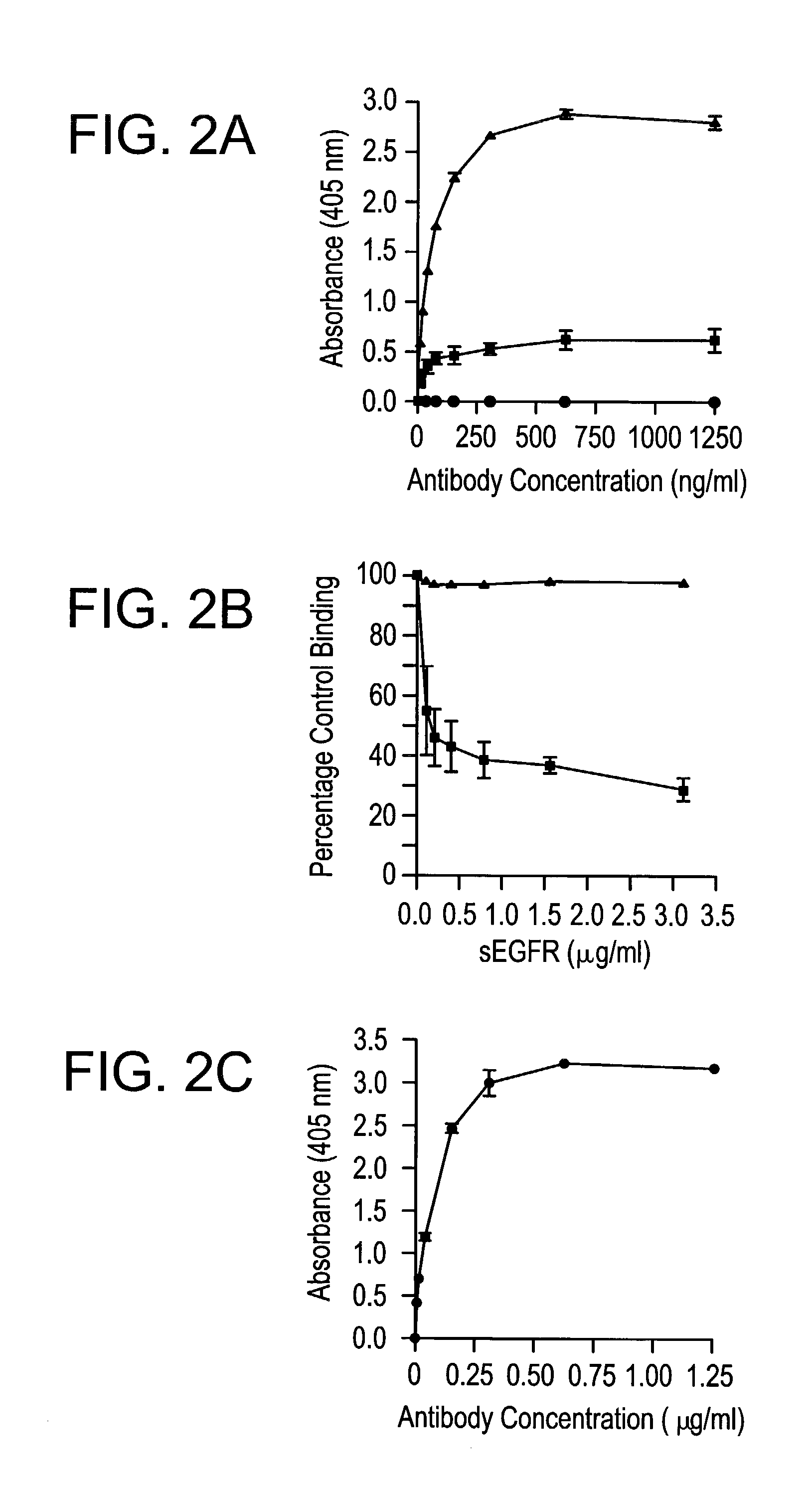
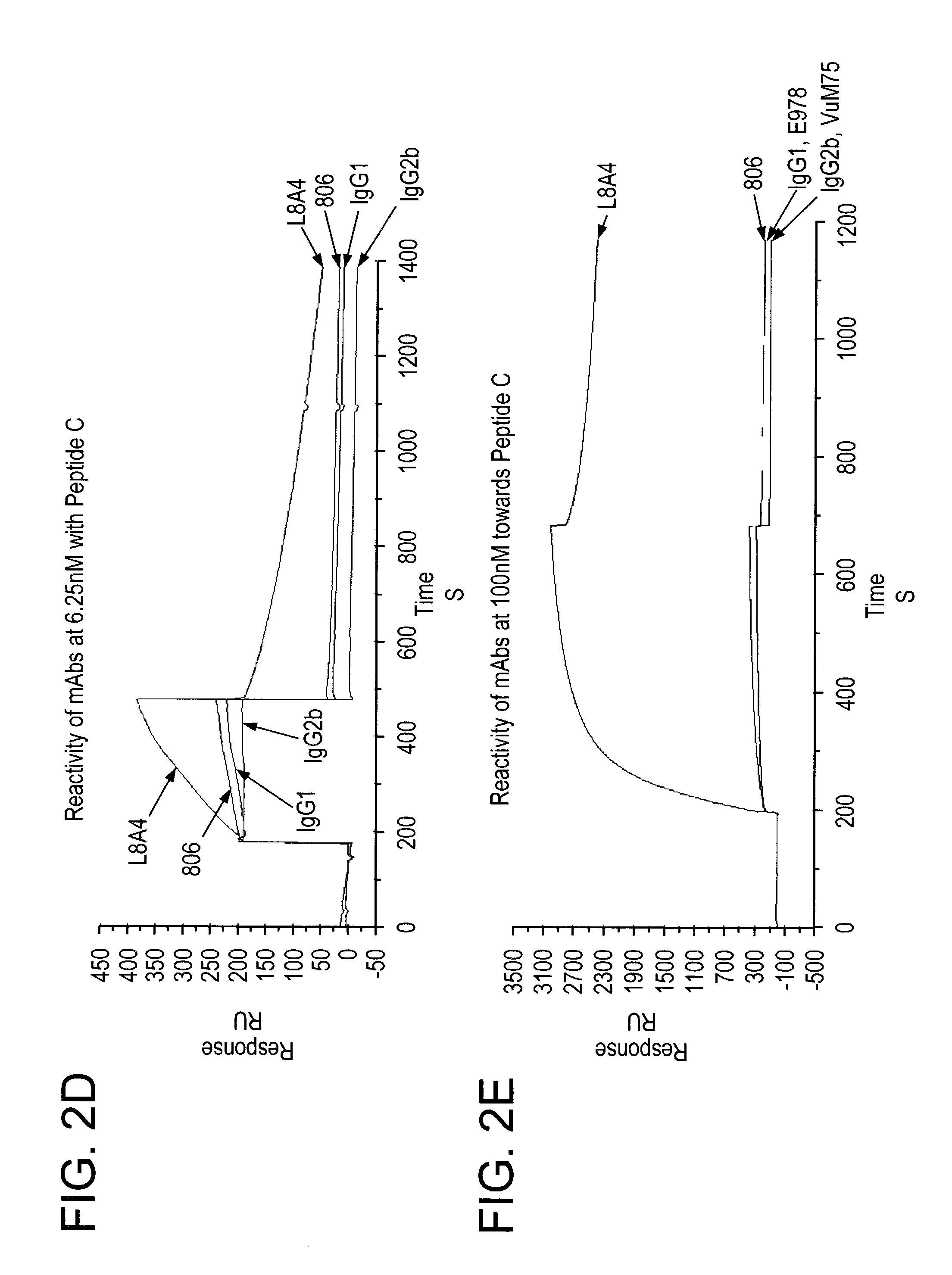
The invention relates to specific binding members, particularly antibodies and active fragments thereof, which recognize an aberrant post-translationally modified, particularly an aberrant glycosylated form of the EGFR. The binding members, particularly antibodies and fragments thereof, of the invention do not bind to EGFR on normal cells in the absence of amplification of the wild-type gene and are capable of binding the de2-7 EGFR at an epitope which is distinct from the junctional peptide. Antibodies of this type are exemplified by the novel antibody 806 whose VH and VL sequences are illustrated as SEQ ID NOs: 2 and 4 and chimeric antibodies thereof as exemplified by ch806.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES LTD
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS20050074843A1Increase healing valueStrong cytotoxicityFungiNanotechAntibody fragmentsCytotoxicity
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
C-, S- and N-glycosylation of peptides
The present invention provides polypeptide conjugates wherein a modifying group such as a water-soluble polymer, a therapeutic agent or a biomolecule is covalently linked to the polypeptide through a glycosyl linking group. In one embodiment, the polypeptide includes a glycosylation consensus sequence, wherein glycosylation occurs at an aromatic amino acid residue, such as the C-2 or the N-1 position of a tryptophan side chain. Exemplary polypeptides of the invention are those in which the glycosylation consensus sequence has been introduced into the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide by mutation. In another aspect the invention provides polypeptide conjugates wherein the modifying group is covalently linked to the polypeptide via a glycosyl mimetic linking group. Also provided are methods of making and using as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing the polypeptide conjugates of the invention. Further provided are methods of treating, ameliorating or preventing diseases in mammals by administering an amount of a polypeptide conjugate of the invention sufficient to achieve the desired response.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com