Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
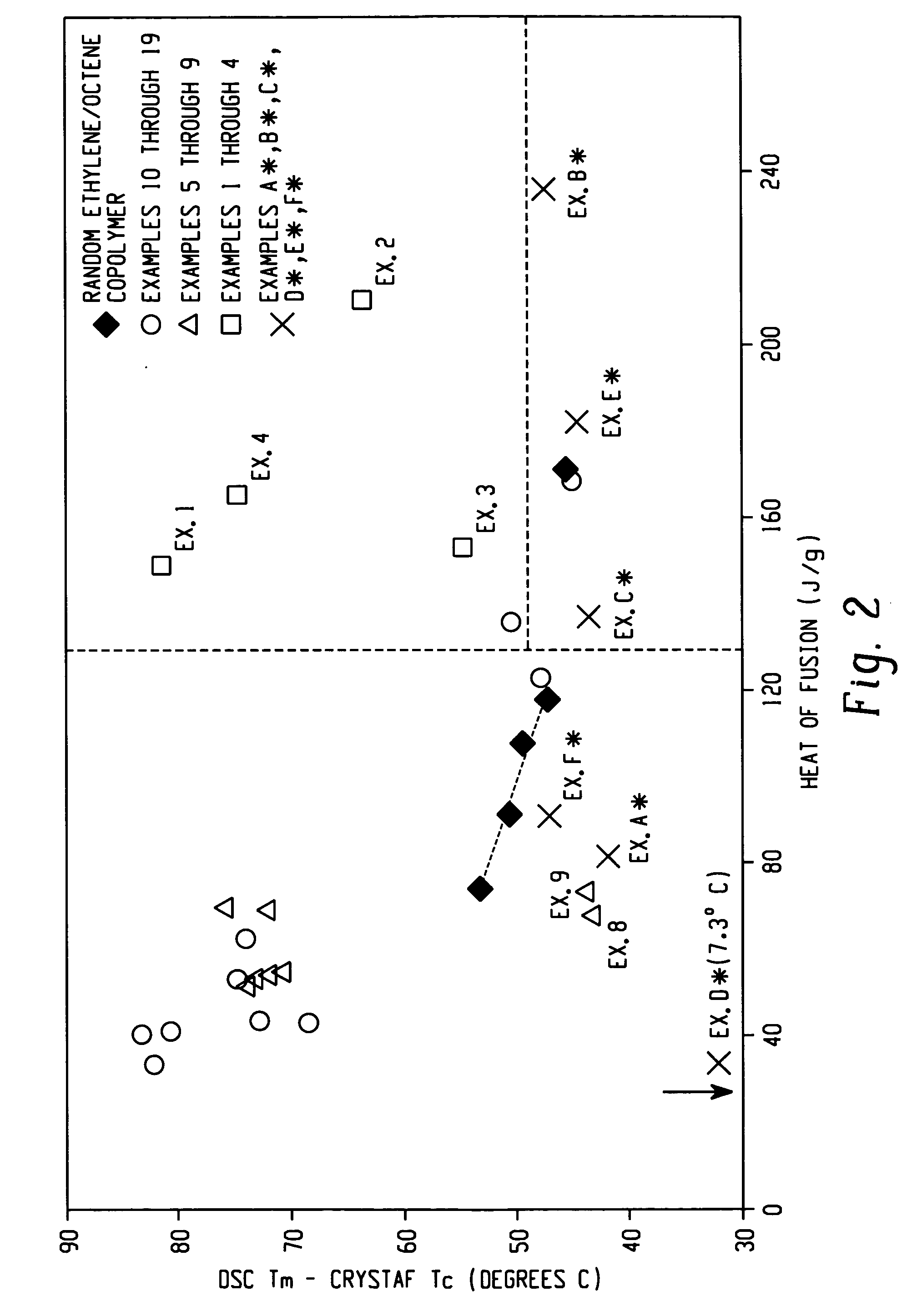
3078 results about "Ethylene Homopolymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
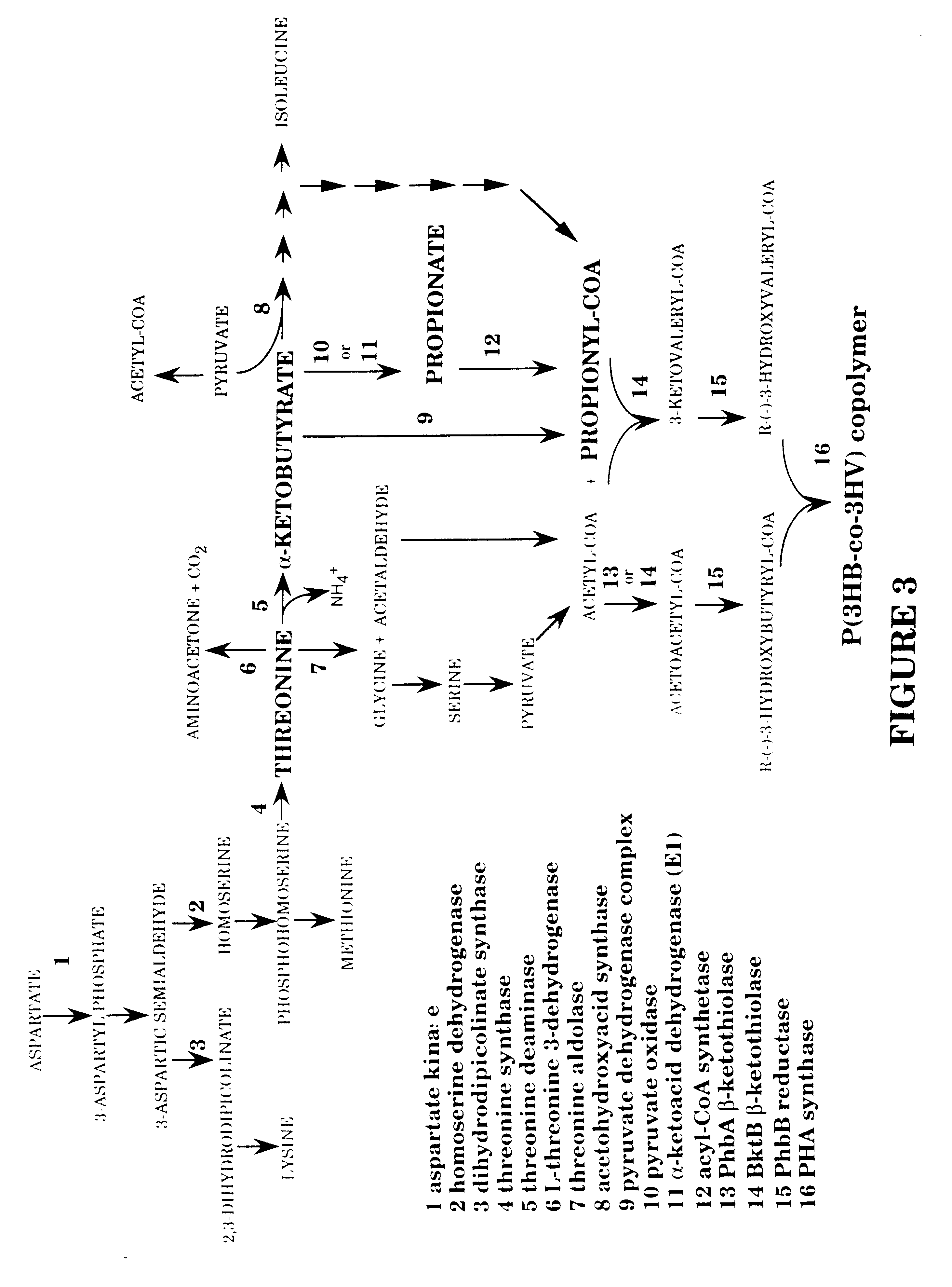
Poly(styrene), for example, is composed only of styrene monomer residues, and is therefore classified as a homopolymer. Ethylene-vinyl acetate, on the other hand, contains more than one variety of repeat unit and is thus a copolymer.
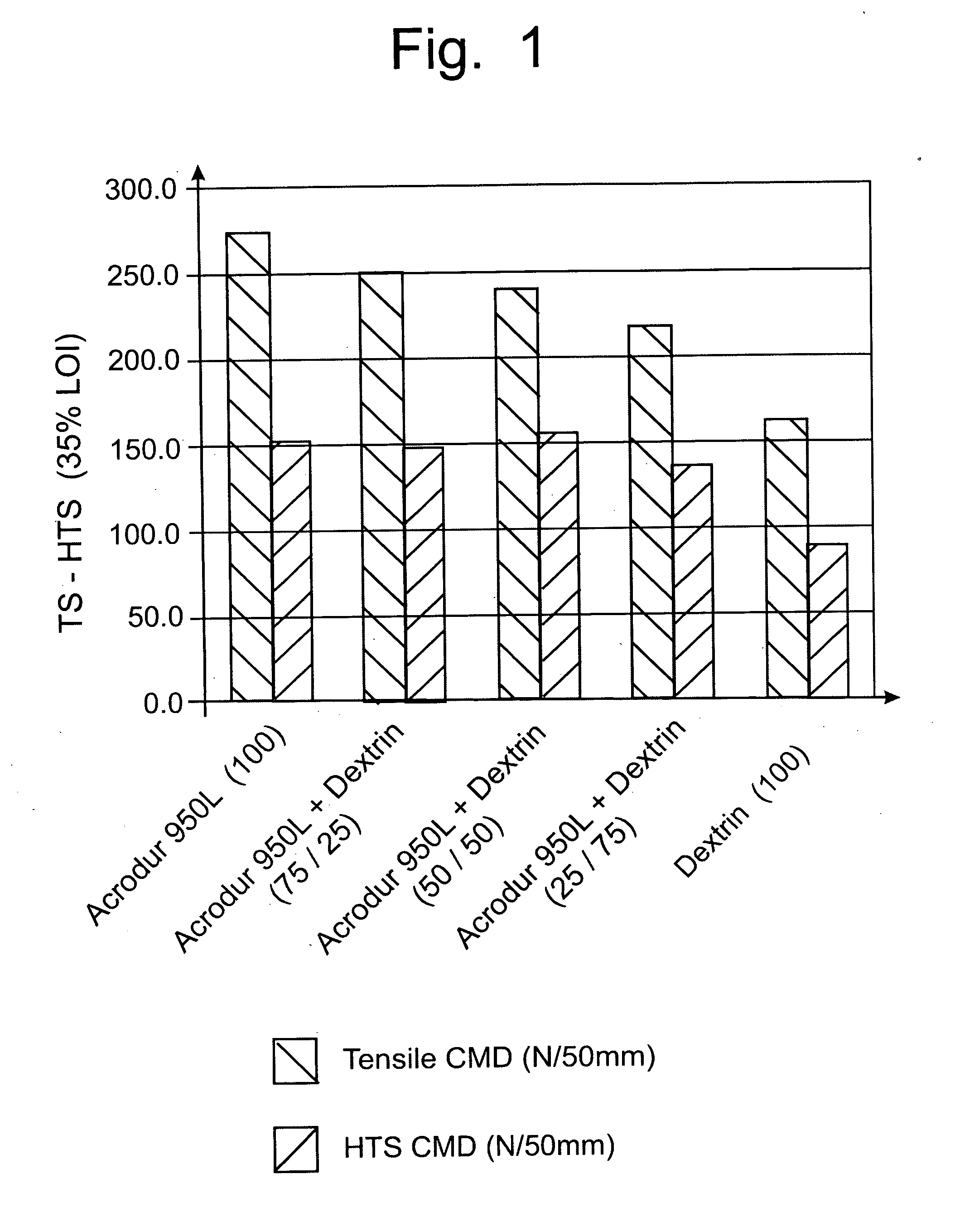
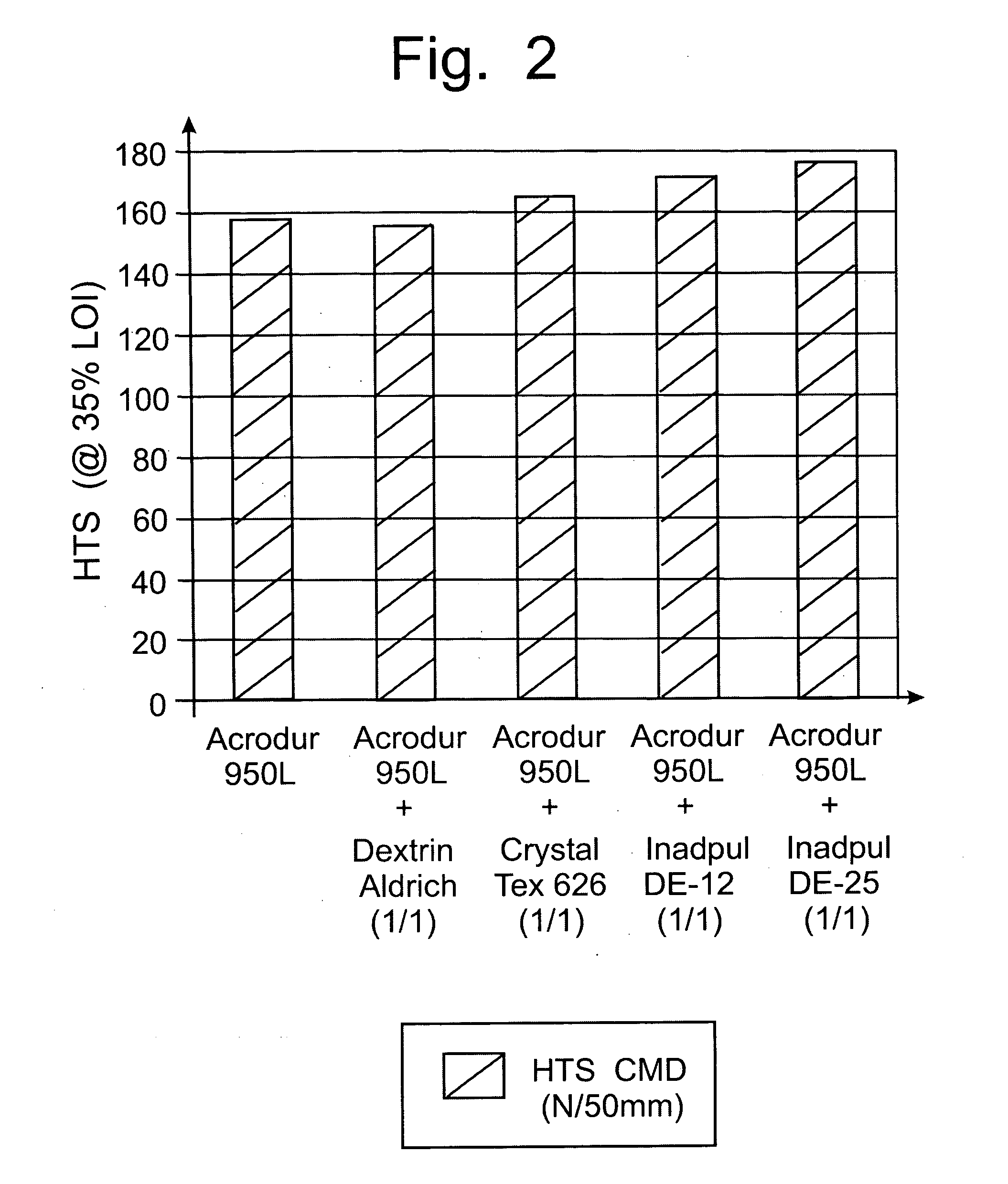
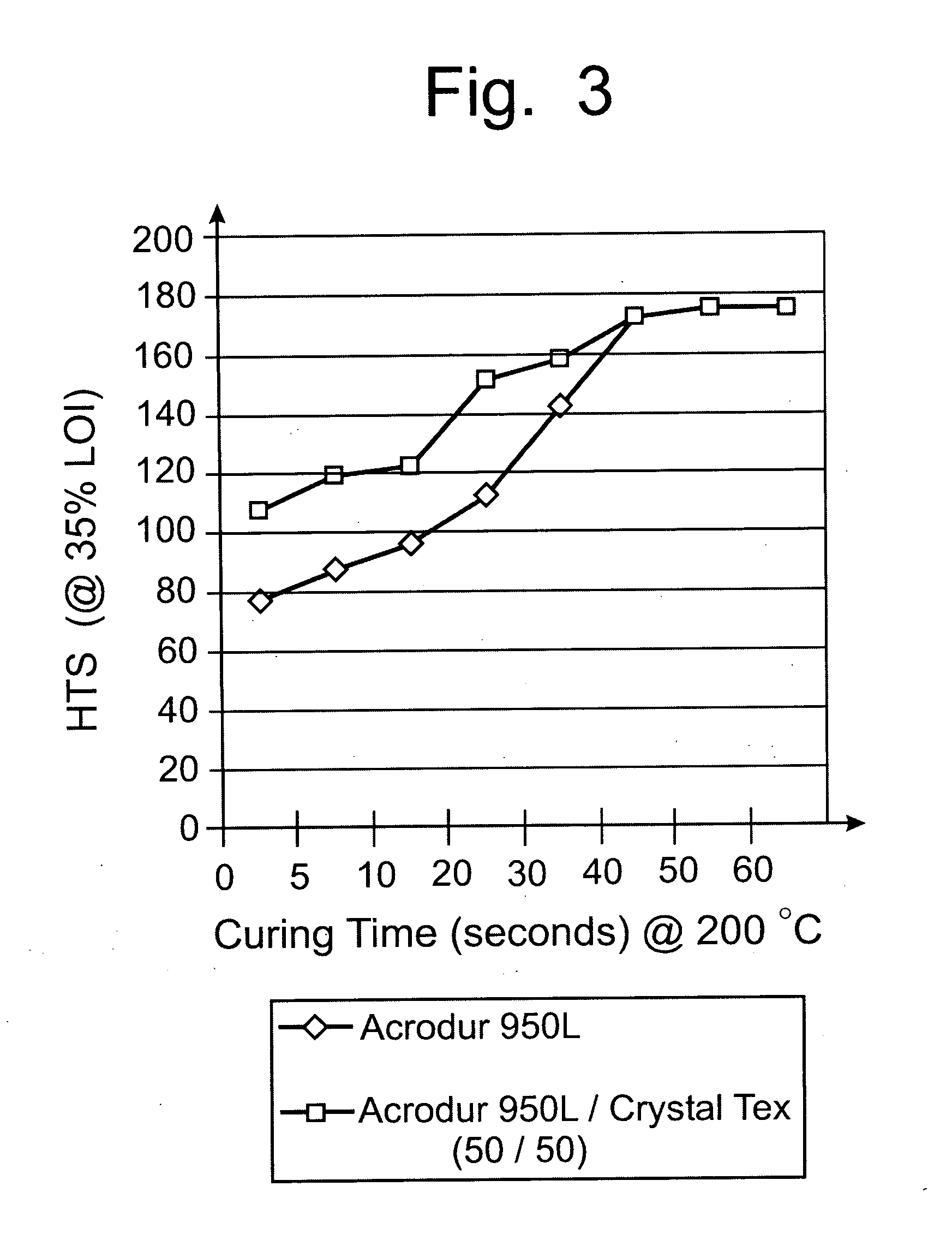
Dextrin binder composition for heat resistant non-wovens
InactiveUS20050215153A1Maintain strengthHigh hot tensile strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionStarch adhesivesPolyolCarboxylic acid
A polycarboxy binder composition that contains a dextrin as a co-binder is provided. The dextrin co-binder may be a dextrin, a modified dextrin, a maltodextrin, or combinations thereof. The dextrin may be chemically modified. A pre-binder composition is formed that contains a polycarboxy polymer, a crosslinking agent, and optionally a catalyst. The polycarboxy polymer may be a homopolymer or copolymer prepared from unsaturated carboxylic acids and may be modified to contain one or more vinyl compounds. The crosslinking agent may be a polyol that contains at least two hydroxyl groups. The pre-binder composition may be formed by admixing the polycarboxy polymer, the crosslinking agent, and optionally, the catalyst, in a mixing device. Dextrin may be added to the pre-binder composition in an amount of from 10-75% of the total binder composition. The dextrin binder composition may have a ratio of from approximately 90:10 to 25:75 pre-binder:dextrin co-binder.
Owner:OWNS CORNING COMPOSITES
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS7230750B2Improve stabilityEasy to adaptMaterial nanotechnologyStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Polyhydroxyalkanoates of narrow molecular weight distribution prepared in transgenic plants
Methods for the biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate homopolymers and copolymers are described. In a preferred embodiment, the polymers have a single mode molecular weight distribution, and more preferably have a distribution of between about 2 and about 4, and most preferably about 2.1 or 2.5.
Owner:METABOLIX
Conjugates of glycosylated/galactosylated peptide, bifunctional linker, and nucleotidic monomers/polymers, and related compositions and method of use
InactiveUS6906182B2Abnormal proliferationInhibition of replicationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNucleotideEthylene Homopolymers
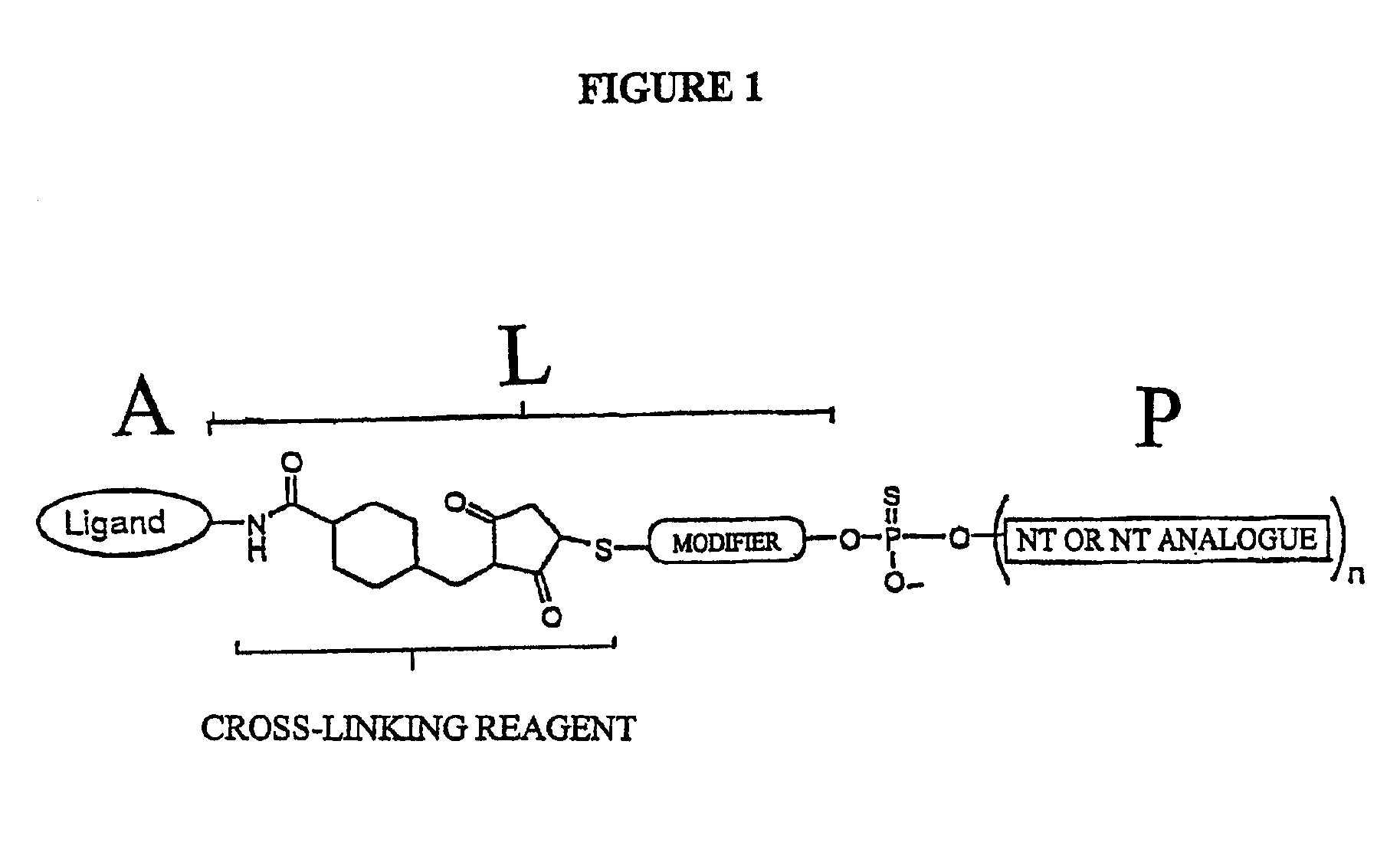
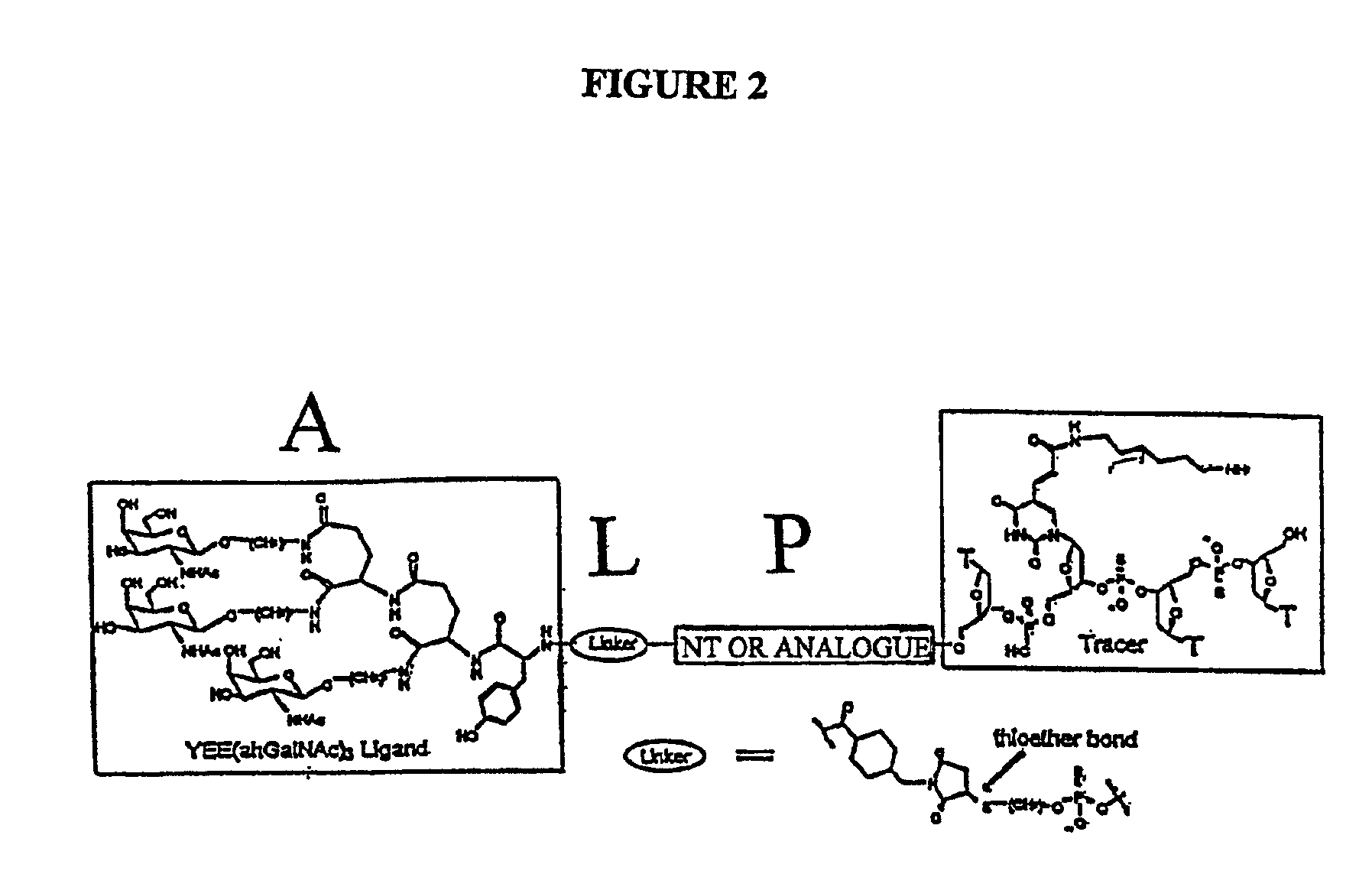
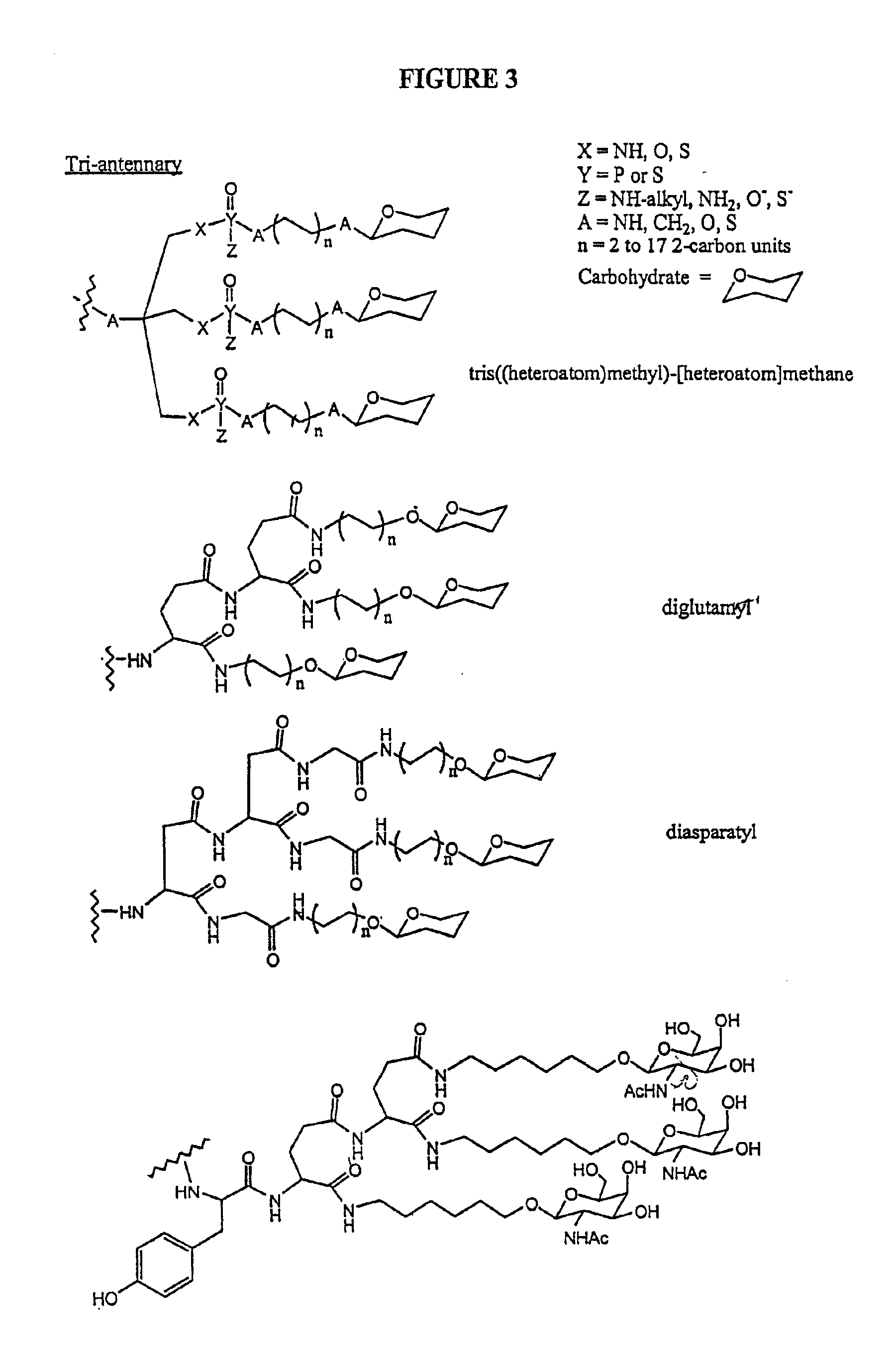
A conjugate of formula A-L-P, in which:A represents a glycosylated / galactosylated peptide that binds to a cell-surface receptor,L represents a bifunctional linker, which does not comprise a naturally occurring amino acid and is covalently bonded to A and P in a regiospecific manner, andP represents a monomer, homopolymer or heteropolymer comprising at least one nucleotide or an analogue thereof, which inhibits the intracellular biosynthesis of nucleotides or nucleic acids in a sequence-independent manner,wherein either or both of the covalent bond between A and L and the covalent bond between L and P can be cleaved intracellularly; a composition comprising such a conjugate; and a method of inhibiting abnormal cellular proliferation in a mammal; and a method of inhibiting replication of a virus in a mammal.
Owner:CELLECTIVE DX CORP
High melting thermoplastic elastomeric alpha-olefin polymers (PRE/EPE effect) and catalysts therefor
InactiveUS6559262B1Activity of fluxional unbridged metallocene polymerization catalystsHigh molecular weightGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMetallocenesElastomerEthylene Homopolymers
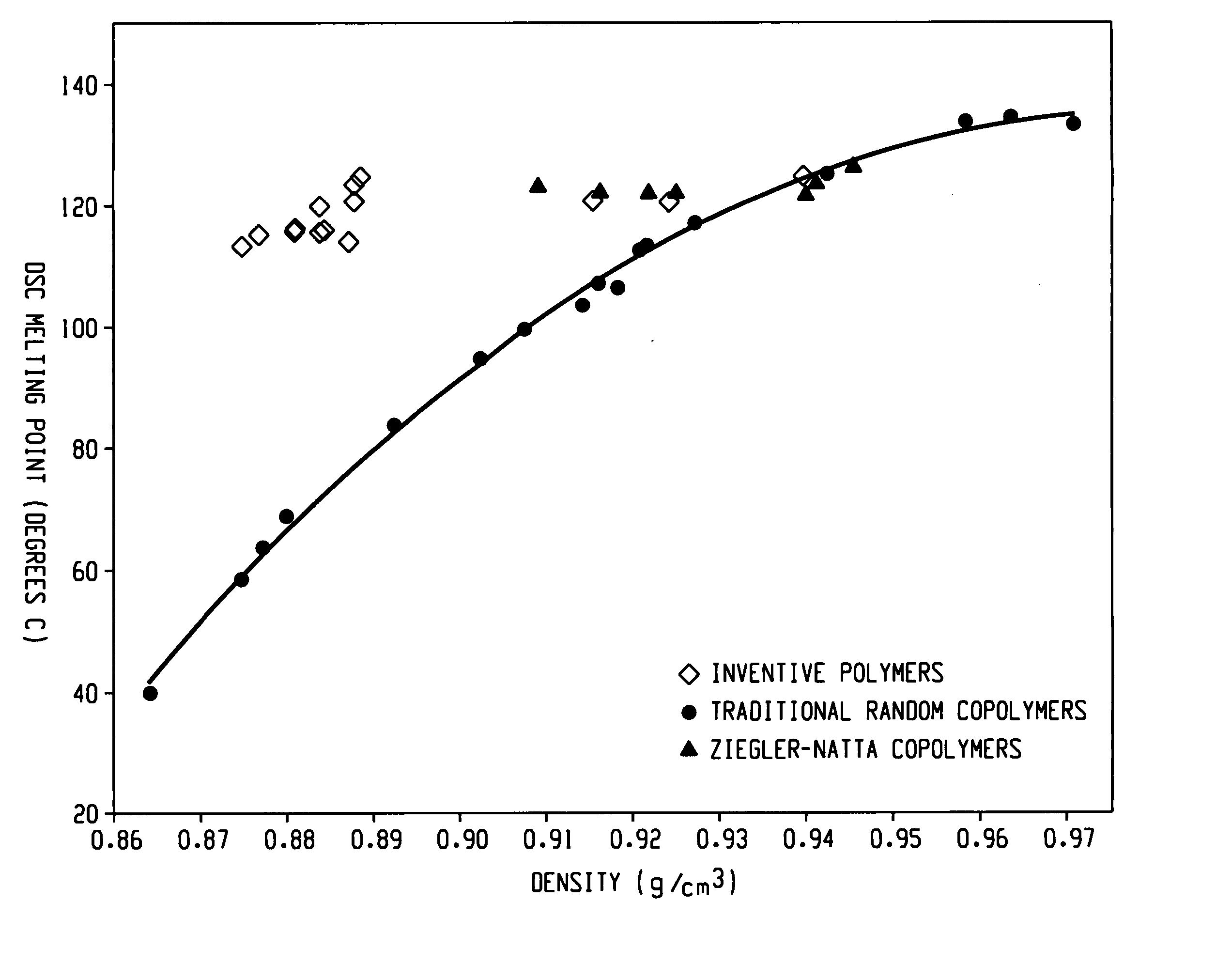
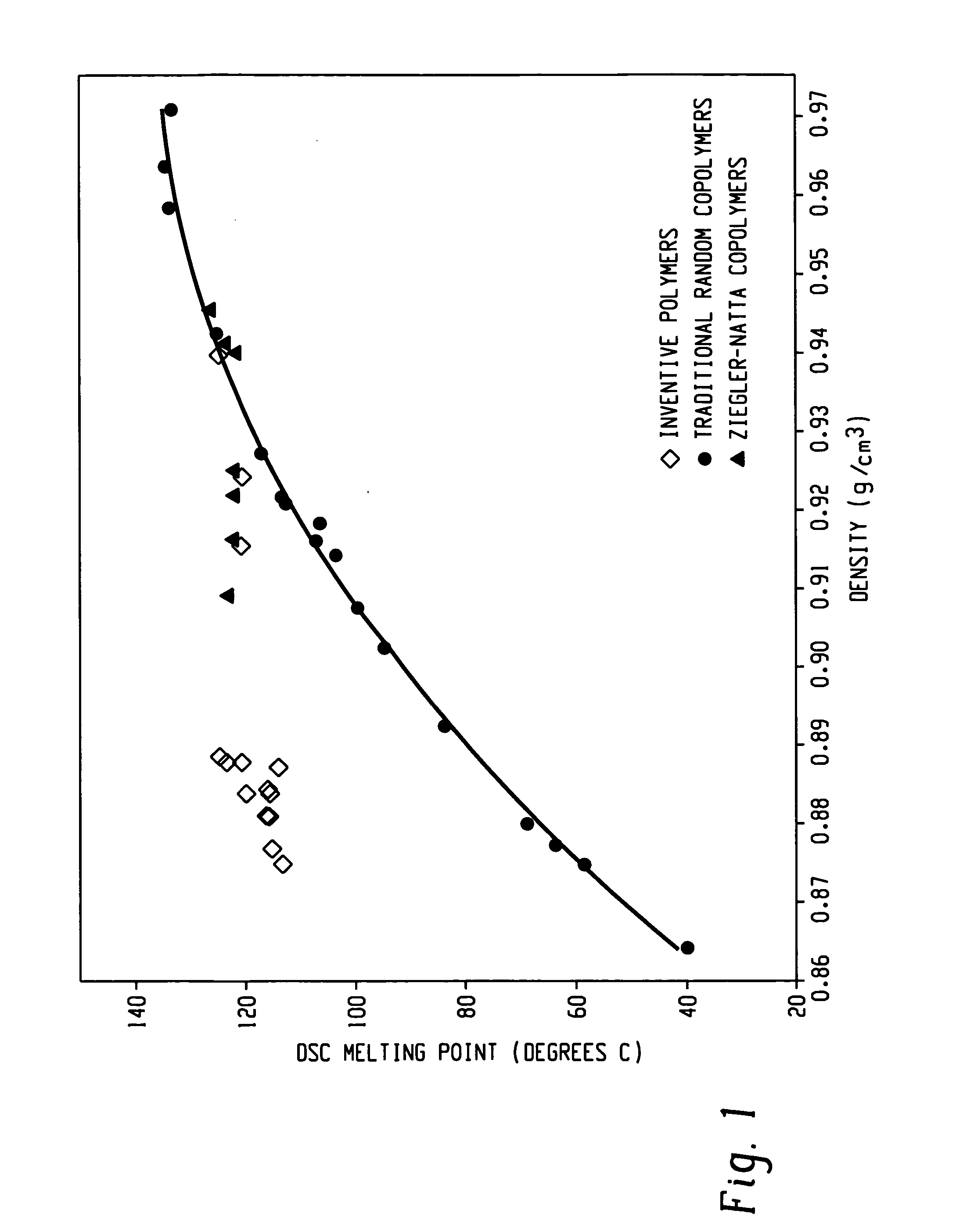
This invention relates generally to low ethylene insertions into I-olefin polymers and processes for production of such polymers using unbridged fluxional metallocenes, primarily substituted aryl indenyl metallocenes, and more particularly to use of unbridged, fluxional, cyclopentadienyl or indenyl metallocene catalyst systems in methods of production of high melting point I-olefin homo- and co-polymers, particularly elastomeric crystalline and amorphous block homo- and co-polymers of I-olefins. The activity of fluxional unbridged metallocene polymerization catalysts containing at least one 2-arylindene ligand is increased 10x or more by the addition of small (typically 0.1-10 wt. %) amounts of ethylene to the polymerization system, which increase is termed the Polymerization Rate-Enhancement effect (PRE), which is measured in terms of an Ethylene Enhancement Factor (EEF) as a dimensionless ratio in the range of from about 1.1 to about 10 or above. The amount of ethylene included in the reaction system can be selected and controlled to be so small as to result in essentially minimal (<2 mole %) incorporation of ethylene units into the resulting elastomeric polymer and the molecular weight may be increased. Amounts of ethylene to generate the PRE effect may be greater than 0.1 wt. % and preferably range up to about 2 wt. %. However, if a polymer with more ethylene is desired, additional ethylene may be incorporated into the polymerization feed, including up to 10 to about 50 mole % based on olefin units. A second important aspect of this invention is the ability to use a PRE activity-enhancing amount of ethylene in an olefin polymerization without substantially affecting the physical properties of the elastomer. In a third important aspect of this invention, I-olefin elastomers are produced through incorporation of ethylene using unbridged fluxional catalyst systems which may not otherwise produce acceptable elastomeric homopolymers. This effect is termed the EPE effect, for Elastomeric Property-Enhancing effect. The EPE amount of ethylene required to produce such elastomers typically overlaps the PRE activity-enhancing amount. Incorporation of up to about 5 mole % or more of ethylene typically will produce an elastomeric polymer using such catalyst systems. Typical useful amounts of incorporated ethylene include about 1 to 3 mole %. Preferred polymers of this invention retain sufficient crystallinity to provide a high melting point (by DSC) of about 80° C., preferably above 100° C., including in the range of from about 120° C. to about 140° C. and above. Novel flexible alpha-olefin homo and copolymers having elongation in excess of 600% and substantially no retained force are disclosed.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and flexible molded articles made therefrom
Polymer blends comprises 1) at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and 2) at least one polyolefin, or at least one styrenic block copolymer, or a combination thereof. Such polyolefins include, but are not limited to, high melt strength high density polyethylene and high melt strength polypropylene. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are random block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers. The resulting polymer blends can be used to make flexible molded articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefin with improved compatibility
Disclosed herein are polymer blends comprising at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and two different polyolefins which can be homopolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. In some embodiments, the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer can function as a compatibilizer between the two polyolefins which may not be otherwise compatible. Methods of making the polymer blends and molded articles made from the polymer blends are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polypropylene filler rods for optical fiber communications cables
InactiveUS6210802B1Synthetic resin layered productsFibre mechanical structuresLow-density polyethyleneEngineering
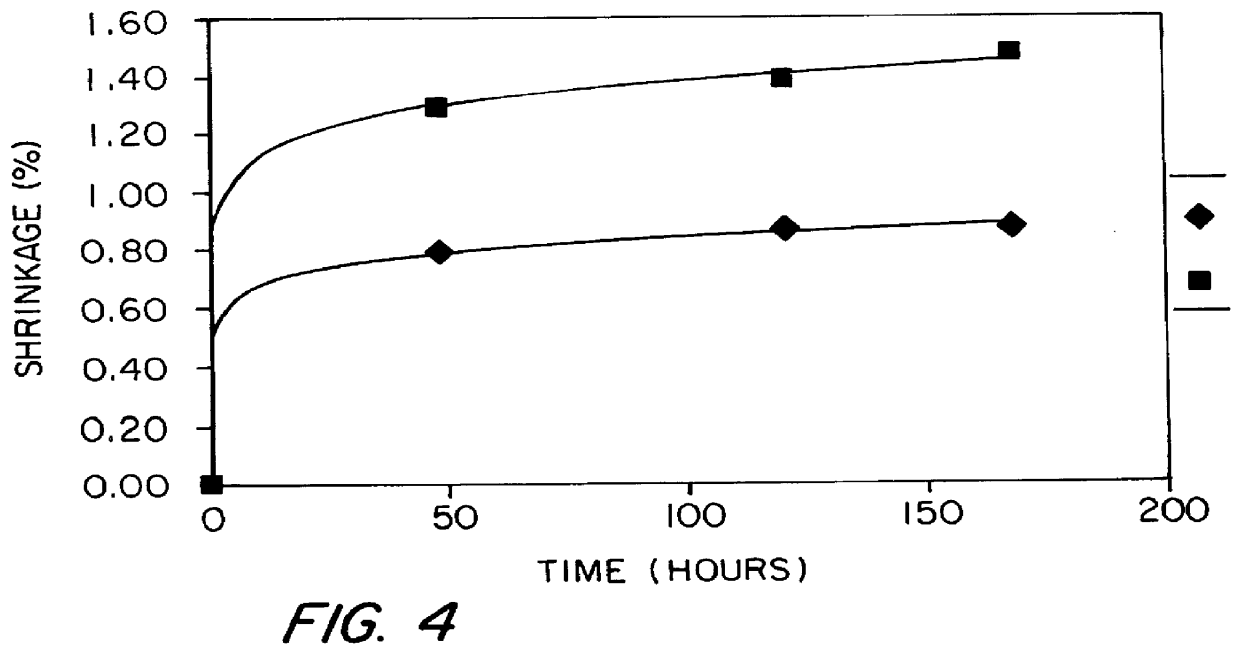
A filler rod for occupying space in a stranded optical fiber communications cable having at least one buffer tube containing at least one optical fiber is disclosed. The filler rod comprises an elongated rod extruded from a polypropylene homopolymer, a polypropylene-polyethylene copolymer (i-PP) resin material, or preferably, from a polypropylene-polyethylene copolymer having a nucleating agent disbursed therein. The resin material is foamed during extrusion so as to have a plurality of void spaces therein and a relative density which is less than 1 relative to the unfoamed resin material. As compared to rods made from high density polyethylene, the i-PP filler rods show a greater foaming efficiency, more efficient use of material, an improved combination of mechanical properties and density, reduced post-extrusion shrinkage and a substantial reduction in the sticking of the filler rods to the outer jacket that is experienced with high density polyethylene filler rods.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Rheology modification of interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and articles made therefrom
Rheology modification of an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is achieved by blending the interpolymer with at least one branched polyolefin. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers and have a branching index of less than 1. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is a block copolymer having at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The soft block comprises a higher amount of comonomers than the hard block. The block interpolymer has a number of unique characteristics disclosed here. Rheology-modified ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer, i.e., the resulting polymer blends, can be extruded or molded into many useful articles, such as films, sheets, profiles, gaskets, foams, etc.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Surgical implant and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070185488A1High elongationBone implantJoint implantsEthylene HomopolymersBiomedical engineering
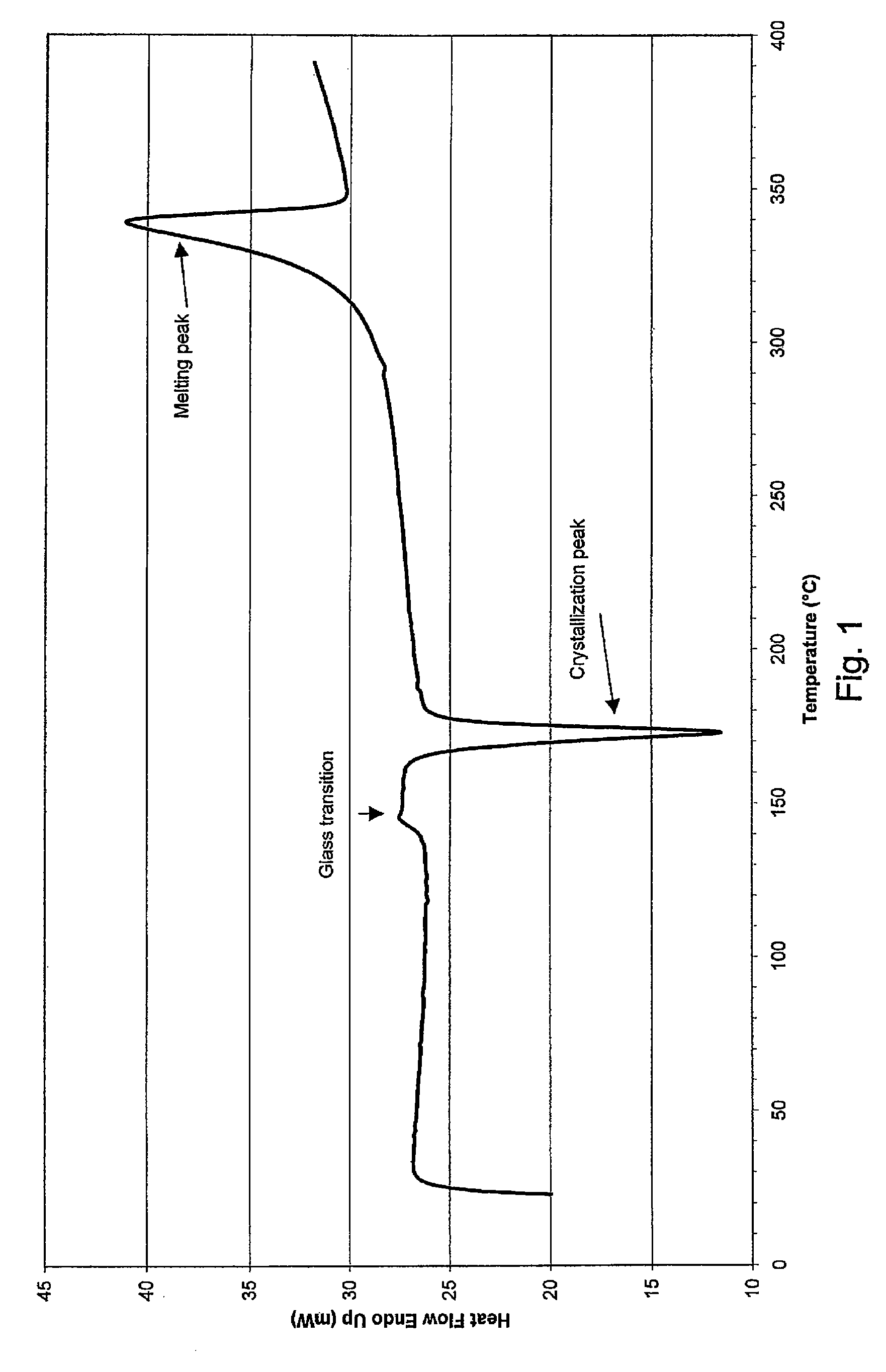
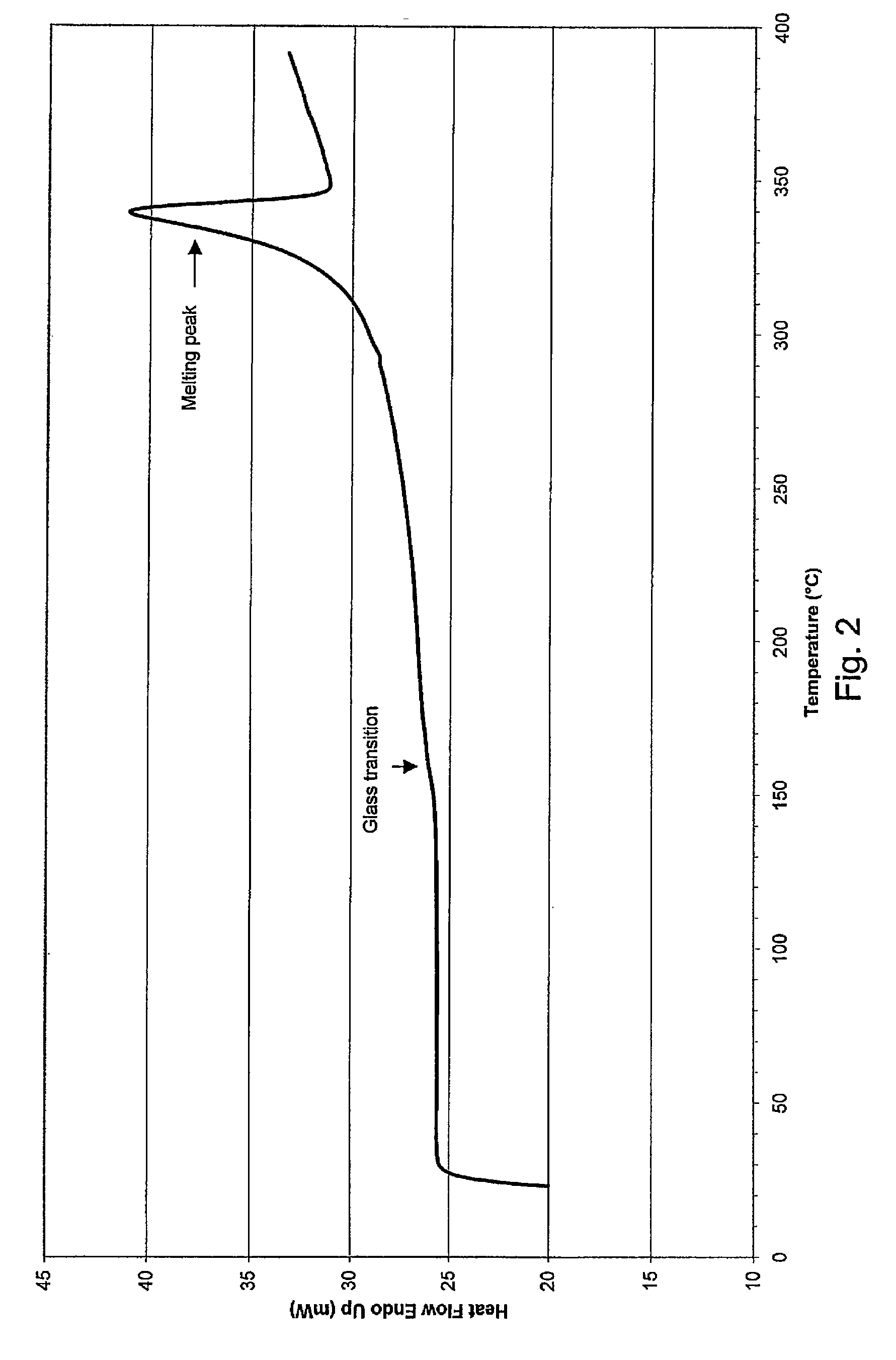
A surgical implant and a method for manufacturing the same. The surgical implant has a body comprising polyaryletherketone (PAEK). Said polyaryletherketone is a homopolymer and a first section of the body comprises a polyaryletherketone that has a crystallization peak in its DSC-curve.
Owner:INION
Mono-active center Ziegler-Natta catalyst for olefinic polymerization
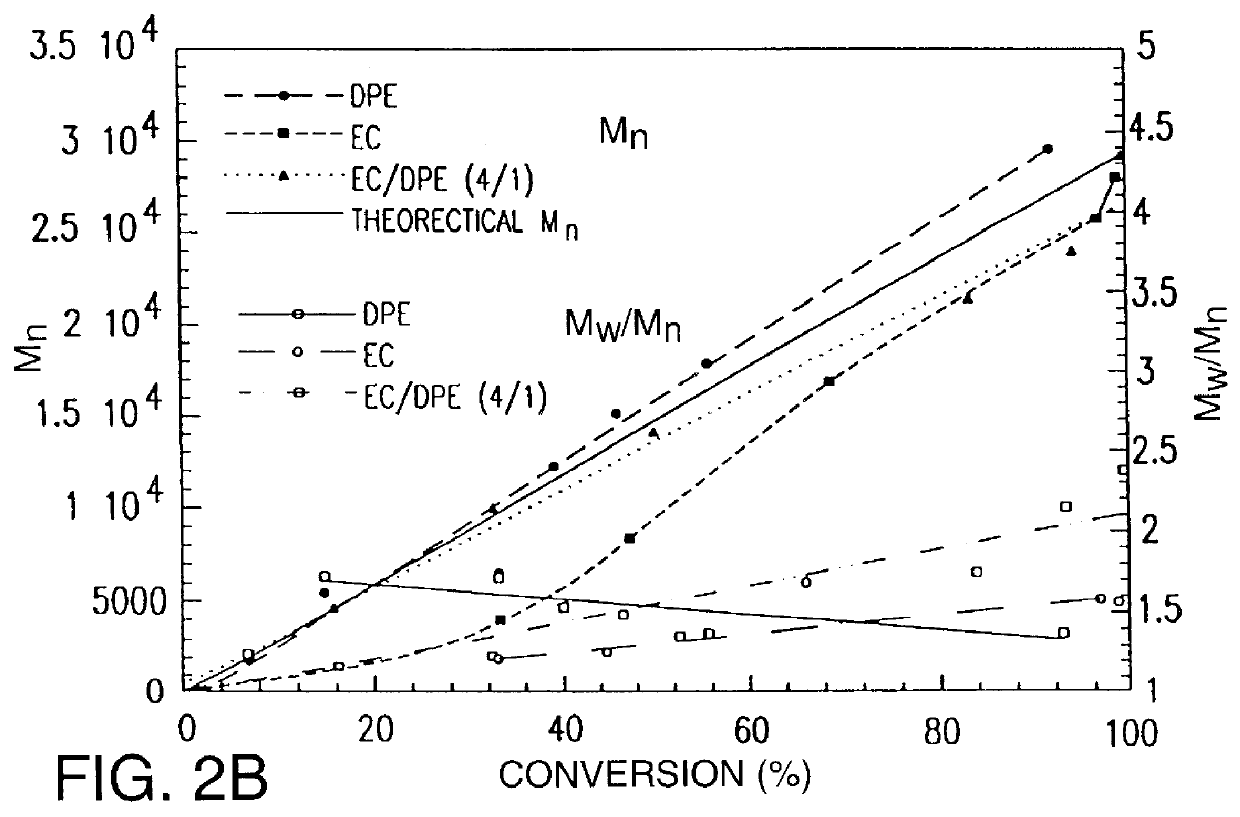
The invention relates to a new catalyst for single active central Ziegler-Natta alkene polymerization. Said catalyst takes salicylal containing dentate or substituted salicylal derivatives as electrons, and is prepared by adding pretreated carrier, metallic compound and electrons into magnesium compound / tetrahydrofuran solution. The catalyst can produce ethane homopolymer and copolymer with narrow molecular weight distribution (1.6-3.8) and even comonomer distribution, with high activity and under action of adjuvant catalyst of alkyl aluminium and alkyl aluminoxanes. The ethane polymerization, homopolymerization or combined polymerization of ethane and 1- olefin, ring olefin and polar monomer through slurry method or gas phase method by using said catalyst can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interpolymers of ethylene/a-olefins blends and profiles and gaskets made therefrom
Polymer blends comprise at least an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers and at least one polyolefin. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers and have a melt strength of at least about 6 cN. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is a block copolymer having at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The soft block comprises a higher amount of comonomers than the hard block. The block interpolymer has a number of unique characteristics disclosed here. The polymer blends can be profiled extruded to make profiles, gaskets, and other products.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Preparation of novel homo- and copolymers using atom transfer radical polymerization
The present invention is directed to a process of atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of novel homopolymer or a block or graft copolymer, optionally containing at least one polar group, with well defined molecular architecture and narrow polydipersity index, in the presence of an initiating system comprising (i) an initiator having a radically transferrable atom or group, (ii) a transition metal compound, and (iii) a ligand, the present invention is also directed to the synthesis of a macromolecule having at least two halogen groups which can be used as a macroinitiator component (i) to subsequently form a block or graft copolymer by an atom or group transfer radical polymerization process; the present invention is also directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a branched or hyperbranched polymer; in addition, the present invention is directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a macroinitiator which can subsequently be used to produce a block or graft copolymer.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Polypropylene filler rods for optical fiber communications cables
InactiveUS6066397ACladded optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresLow-density polyethyleneEngineering
A filler rod for occupying space in a stranded optical fiber communications cable having at least one buffer tube containing at least one optical fiber is disclosed. The filler rod comprises an elongated rod extruded from a polypropylene homopolymer, a polypropylene-polyethylene copolymer (i-PP) resin material, or preferably, from a polypropylene-polyethylene copolymer having a nucleating agent disbursed therein. The resin material is foamed during extrusion so as to have a plurality of void spaces therein and a relative density which is less than 1 relative to the unfoamed resin material. As compared to rods made from high density polyethylene, the i-PP filler rods show a greater foaming efficiency, more efficient use of material, an improved combination of mechanical properties and density, reduced post-extrusion shrinkage and a substantial reduction in the sticking of the filler rods to the outer jacket that is experienced with high density polyethylene filler rods.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Thermoset materials with improved impact resistance
The present invention relates to a thermoset material with improved impact resistance comprising:99 to 20% of a thermoset resin, and1 to 80% of an impact modifier comprising at least one copolymer comprising S-B-M, B-M and M-B-M blocks,wherein:each block is connected to the other by means of a covalent bond or of an intermediate molecule connected to one of the blocks via a covalent bond and to the other block via another covalent bond,M is a PMMA homopolymer or a copolymer comprising at least 50% by weight of methyl methacrylate,B is incompatible with the thermoset resin and with the M block and its glass transition temperature Tg is less than the operating temperature of the thermoset material, andS is incompatible with the thermoset resin, the B block and the M block and its Tg or its melting temperature is greater than the Tg of B.S is advantageously polystyrene and B polybutadiene. The thermoset resin advantageously originates from the reaction of a thermosetting epoxy resin and of a hardener.
Owner:ATOFINA
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20050168799A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods of consolidating subterranean zones and compositions therefor
Methods of consolidating subterranean zones and hardenable resin compositions are provided. A hardenable resin composition of the invention basically comprises a furan liquid resin mixture comprising a 2-furanmethanol homopolymer and furfuryl alcohol, an organosilane coupling agent and an acid catalyst.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Fluoropolymer coated films useful for photovoltaic modules
ActiveUS20070154704A1Strong adhesionIncreased durabilitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageEpoxyPolymer science
A fluoropolymer coated film comprising polymeric substrate film and fluoropolymer coating on the polymeric substrate film. The fluoropolymer coating comprises fluoropolymer selected from homopolymers and copolymers of vinyl fluoride and homopolymers and copolymers of vinylidene fluoride polymer blended with compatible adhesive polymer comprising functional groups selected from carboxylic acid, sulfonic acid, aziridine, anhydride, amine, isocyanate, melamine, epoxy, hydroxy, anhydride and mixtures thereof. The polymeric substrate film comprises functional groups on its surface that interact with the compatible adhesive polymer to promote bonding of the fluoropolymer coating to the substrate film.
Owner:DUPONT ELECTRONICS INC
Polyolefin film containing cycloolefin polymer, process for the production thereof, and the use thereof
InactiveUS6068936AHigh strength valueGood barrier effectFlexible coversWrappersPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A polyolefin film which includes at least one layer containing polyolefin and cycloolefin polymer (COP), where the cycloolefin polymer is amorphous and has a mean molecular weight Mw in the range from 200 to 100,000, and this mean molecular weight Mw of the cycloolefin polymer is at most 50% of the mean molecular weight Mw of the polyolefin, and the cycloolefin polymer is a homopolymer or a copolymer containing at most 20% by weight of comonomer.
Owner:TICONA GMBH
Oxygen-scavenging polymer blends suitable for use in packaging
InactiveUS20110045222A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene terephthalate
Polymer blends are disclosed that comprise one or more unsaturated olefinic homopolymers or copolymers having at least one functionality capable of entering into condensation reactions; one or more polyamide homopolymers or copolymers; one or more polyethylene terephthalate homopolymers or copolymers obtained using a catalyst system comprising antimony atoms; and one or more transition metal atoms. The inventive blends are useful for packaging, and exhibit improved oxygen-scavenging activity and lower haze compared with blends made using polyethylene terephthalate polymers prepared with antimony catalyst and either the olefinic or the polyamide homopolymers or copolymers, individually.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20100148385A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Multilayer chlorine-free film with polyester barrier layer and ostomy pouches formed therefrom
InactiveUS6258423B1Good odor barrier propertyMinimal noiseSynthetic resin layered productsColostomyLow noisePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
A multilayer heat-sealable chlorine-free film of relatively low modulus, high interlaminar strength, and low noise upon flexing is provided. The film comprises an odor barrier layer of polyester resin and at least one heat-sealable skin layer, preferably two such skin layers on opposite sides of said odor barrier layer, composed of a homopolymer of ethylene or a copolymer of ethylene and an alpha-olefin or an ester-containing monomer. In a preferred embodiment, the odor barrier layer is formed of polyethylene terephthalate and adhesive tie layers are interposed between the odor barrier layer and the skin layers, resulting in a multilayer film of five layers. Pouches formed of such multilayer films are also disclosed.
Owner:HOLLISTER INCORPORAED
Method for the selective hydrogenation of polymer containing conjugated diene
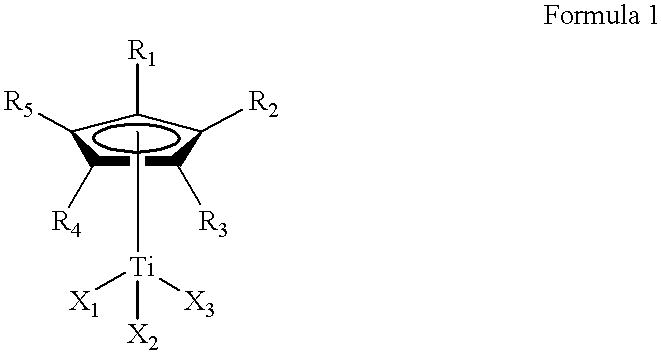
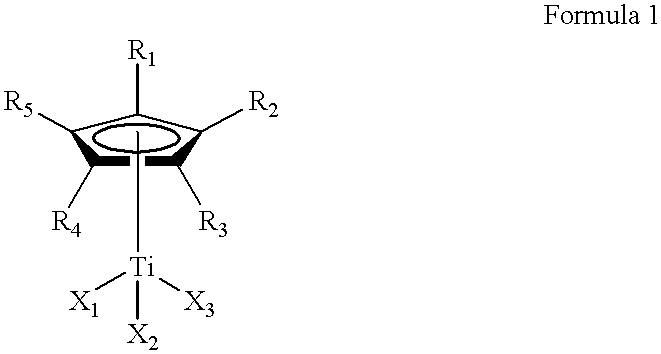
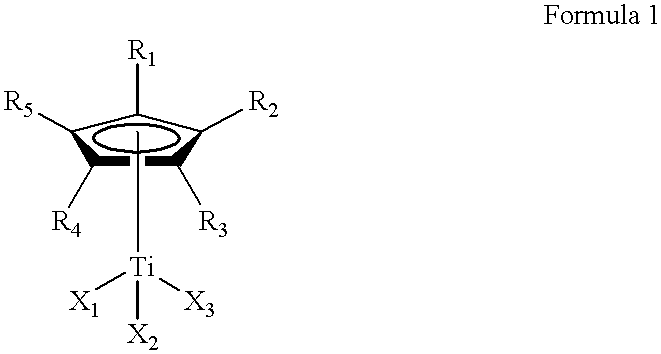
This invention relates to a method for the selective hydrogenation of the unsaturated double bonds in the conjugated diene units of a homopolymer or copolymer in the presence of a novel homogeneous organotitanium-based catalyst. Also, the process of this invention can demonstrate a high yield of hydrogenation and hydrogenation reproducibility using a novel catalyst, so prepared from a mixture consisting of a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclopentadienyl titanium compound expressed by the following formula 1 and lithium hydride derived from a reaction of both alkyl lithium and hydrogen in solution. In particular, this invention also relates to a novel method for the selective hydrogenation of unsaturated double bonds in the conjugated diene units of a conjugated diene polymer or copolymer, so prepared via the reaction between a conjugated diene monomer and vinyl-substituted aromatic monomerwherein, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5, which may be same or different, are selected from hydrogen atoms and alkyl groups of 1~5 carbon atoms; X1, X2 and X3, which may be same or different, are selected from halogen atoms.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Ionomer/rubber/polyolefin blend and uses thereof
A thermoplastic ionomer blend or alloy exhibiting advantageous properties upon molding or extrusion and / or thermoforming, consisting essentially of the following components:A. about 15 to 85 parts by weight of a thermoplastic copolymer containing about 91 to 80 weight percent of alpha-olefin units and about 9 to 20 weight percent of alpha, beta-ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid units said carboxylic acid units being about 20 to 90 percent neutralized with metal ions, preferably zinc,B. about 10 to 80 parts by weight of a rubber, preferably a thermoplastic elastomer selected from the group consisting of (a) crosslinked ethylene-propylene-diene copolymers and equivalent polyolefin copolymers such as ethylene-butene, hexene, or octene, (b) acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymers, (c) styrene-butadiene copolymers, and (d) styrene acrylonitrile graft-crosslinked butadiene rubbers, andC. about 5 to 40 parts by weight of a thermoplastic polymer selected from the group consisting of polyethylene and polypropylene copolymers and homopolymers, the total number of parts being 100,and molded or extruded and / or thermoformed products produced from the same.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ADVANCED POLYMERS INC
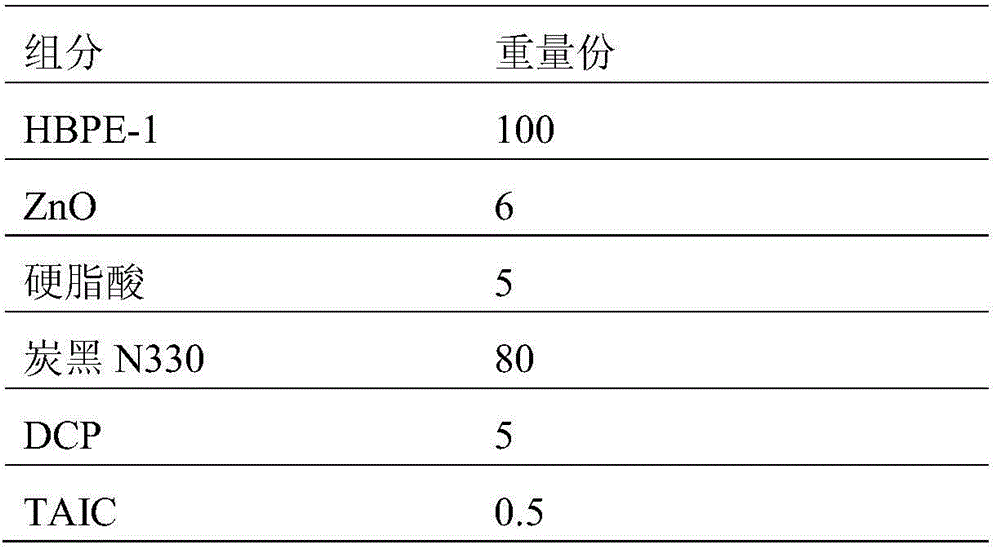
Polyethylene rubber and processing method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of rubber, and particularly relates to polyethylene rubber and a processing method thereof. The polyethylene rubber comprises following raw materials by weight: 100 parts of hyper branched polyethylene, 50-80 parts of carbon black, 2-5 parts of a peroxide crosslinking agent, 0-6 parts of zinc oxide, 0-5 parts of a lubricant, 0.3-0.5 part of an accelerant, and 0-0.2 part of sulfur. Beneficial effects of the polyethylene rubber and the processing method thereof are that: the hyper branched polyethylene (HBPE) is sulfurized by utilization of a peroxide sulfurization system, has good mechanical performances through stress-strain performance tests, and has a characteristic of high elasticity of rubber. The processing method of the polyethylene rubber is totally different from preparation methods of chlorinated polyethylene rubber and chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber at present. The polyethylene rubber and the processing method thereof break the limit that polyethylene can be only used for making plastic products, expand the application scope of the polyethylene, and largely increase the additional value of polyethylene homopolymers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polymeric, degradable drug-eluting stents and coatings
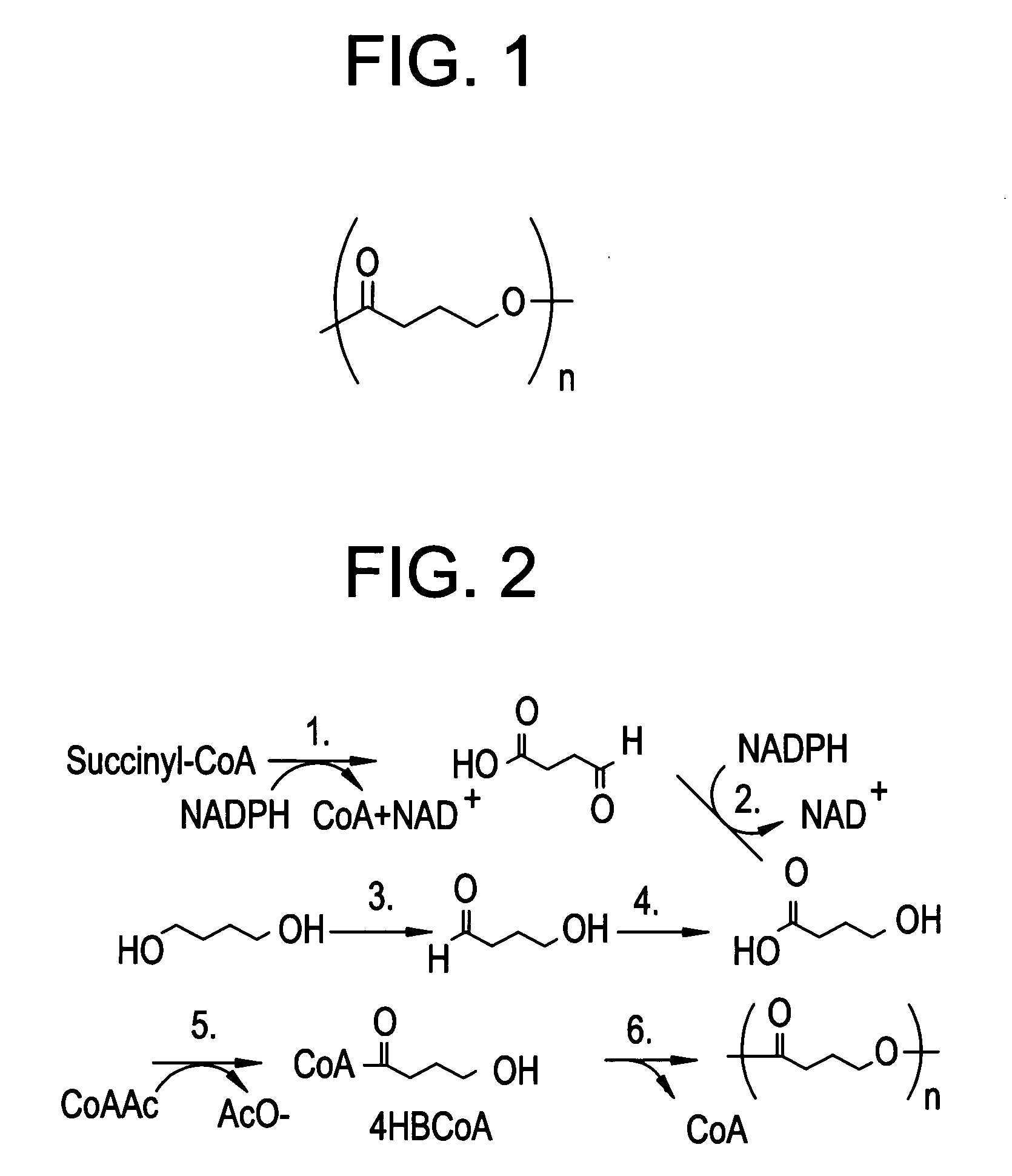
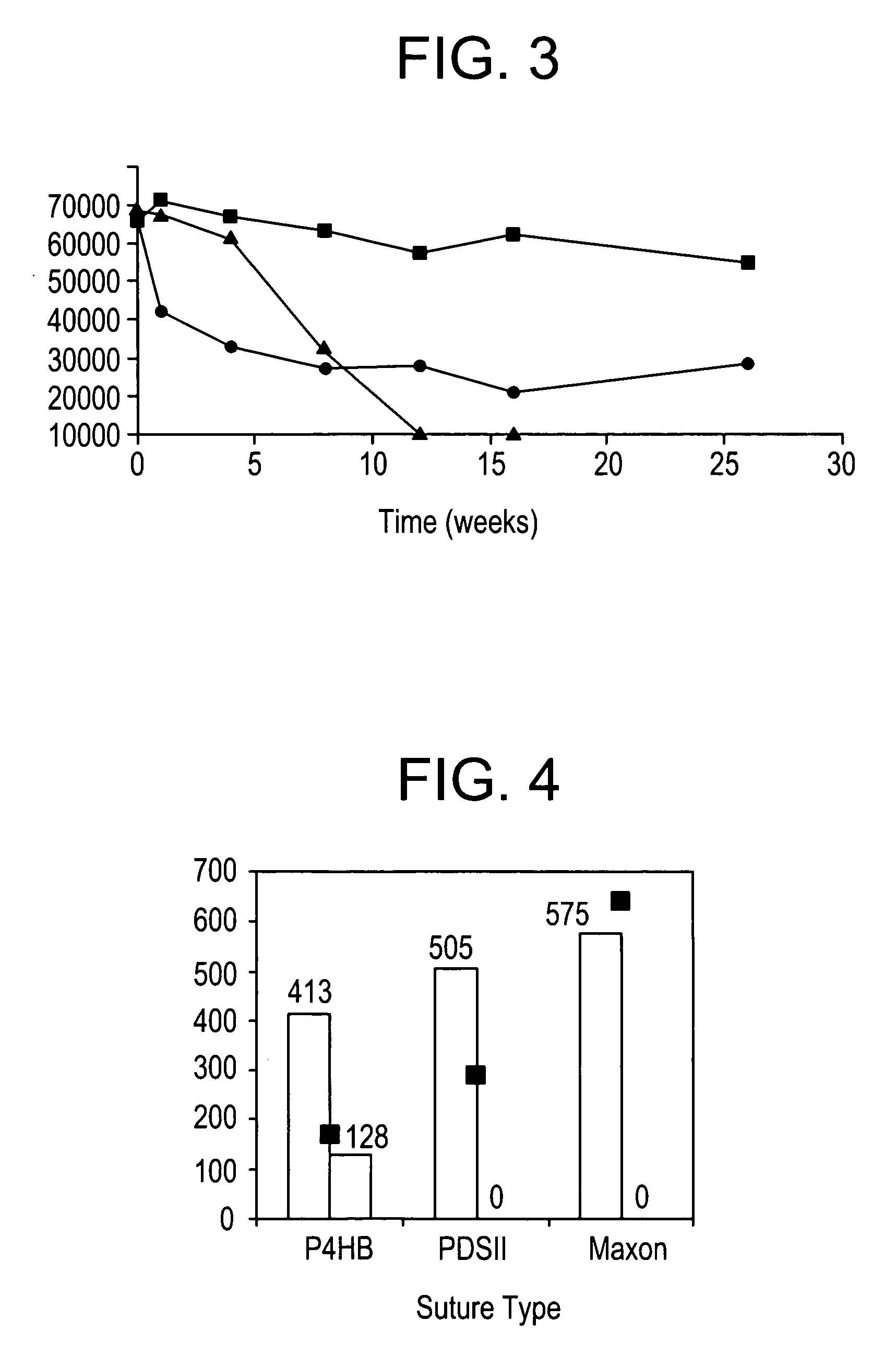
ActiveUS7618448B2Improve performanceImprove propertiesSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical containersAbsorbable polymersEthylene Homopolymers
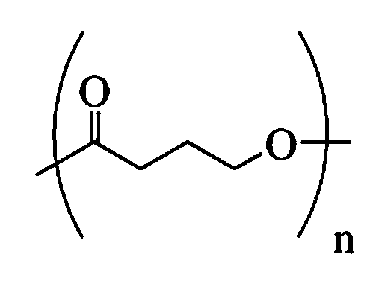
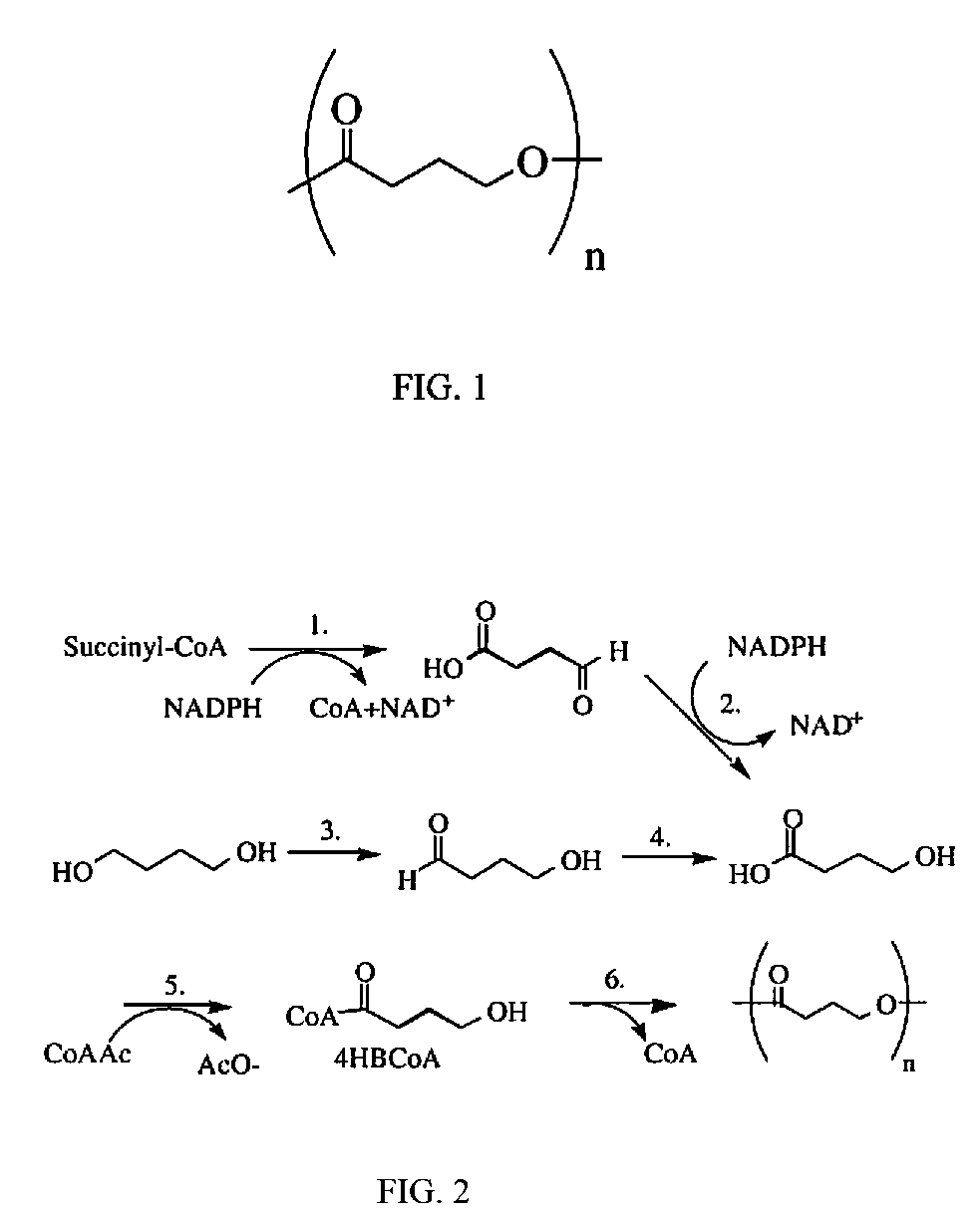
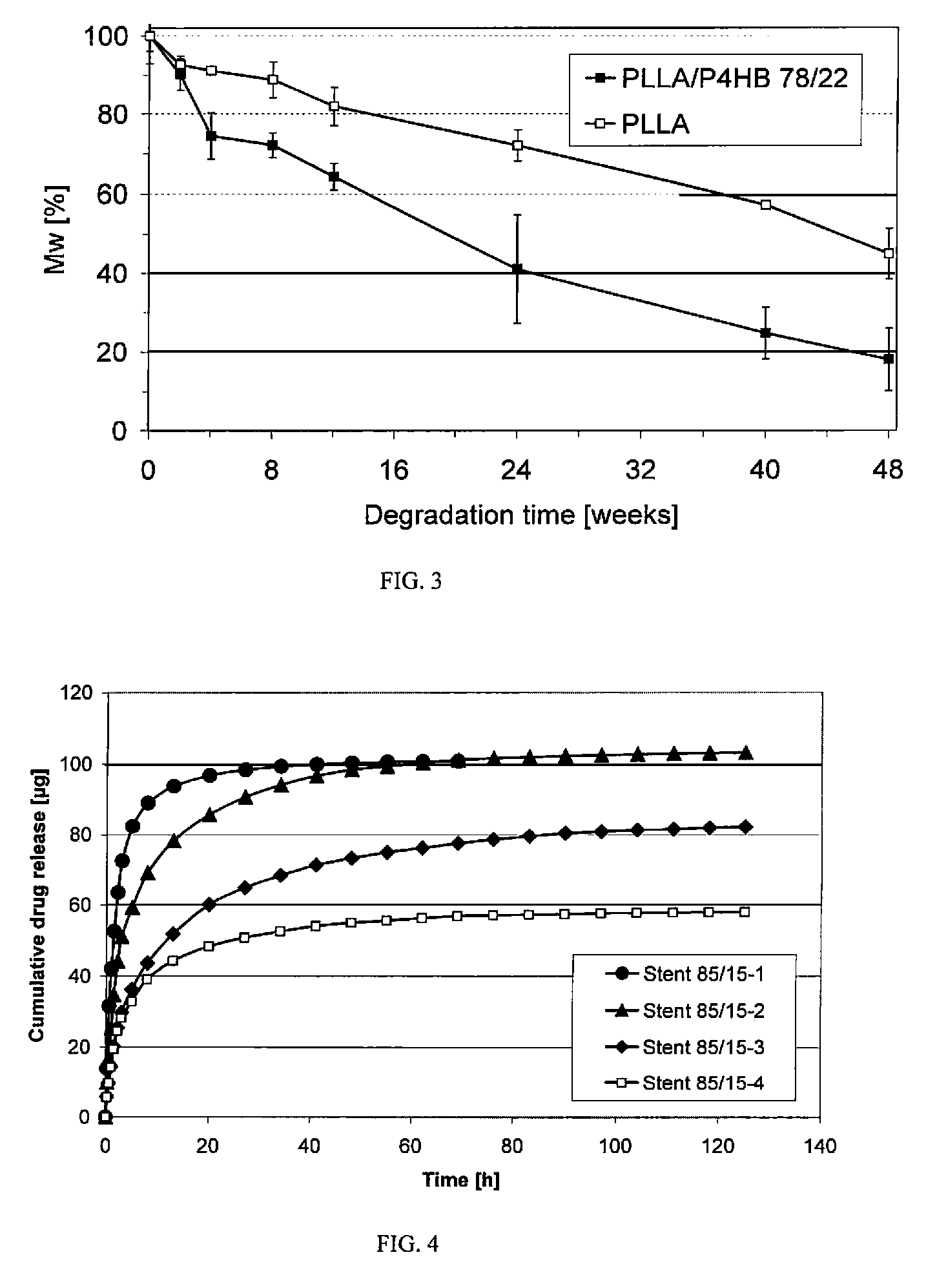
Absorbable stents and absorbable stent coatings have been developed with improved properties. These devices preferably comprise biocompatible copolymers or homopolymers of 4-hydroxybutyrate, and optionally poly-L-lactic acid and other absorbable polymers and additives. Compositions of these materials can be used to make absorbable stents that provide advantageous radial strengths, resistance to recoil and creep, can be plastically expanded on a balloon catheter, and can be deployed rapidly in vivo. Stent coatings derived from these materials provide biocompatible, uniform coatings that are ductile, and can be expanded without the coating cracking and / or delaminating and can be used as a coating matrix for drug incorporation.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate medical textiles and fibers
ActiveUS8034270B2Easy to operateProlonged strength retentionSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterFiber
Absorbable polyester fibers, braids, and surgical meshes with prolonged strength retention have been developed. These devices are preferably derived from biocompatible copolymers or homopolymers of 4-hydroxybutyrate. These devices provide a wider range of in vivo strength retention properties than are currently available, and could offer additional benefits such as anti-adhesion properties, reduced risks of infection or other post-operative problems resulting from absorption and eventual elimination of the device, and competitive cost. The devices may also be particularly suitable for use in pediatric populations where their absorption should not hinder growth, and provide in all patient populations wound healing with long-term mechanical stability. The devices may additionally be combined with autologous, allogenic and / or xenogenic tissues to provide implants with improved mechanical, biological and handling properties.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Polymer Blends from Interpolymers of Ethylene/Alpha-Olefin with Improved Compatibility
Disclosed herein are polymer blends comprising at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and two different poly-olefins which can be homopolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. In some embodiments, the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer can function as a compatibilizer between the two polyolefins which may not be otherwise compatible. Methods of making the polymer blends and molded articles made from the polymer blends are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Undirectionally cold stretched nonwoven webs of multipolymer fibers for stretch fabrics and disposable absorbent articles containing them
InactiveUS6849324B2High elongationPeak load will increaseDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsElastomerEthylene Homopolymers
A nonwoven web of multipolymer fibers is described that is unidirectionally stretched and permanently elongated at ambient conditions and exhibits a substantial increase in tensile strength in the stretch direction. The ratio of tensile strength of the web in the direction of fiber orientation to the tensile strength in the other direction is at least about 10:1. The ratio of elongation at peak load in a direction transverse to the direction of fiber orientation is at least about 6:1. The multipolymer fibers normally are a blend of polyethylene and a polypropylene homopolymer or copolymer, one of which is a dominant phase and one of which is a dispersed phase. A third component having elastomeric properties that is at least partially miscible with one or both of the other components is included in some blends. The nonwoven webs are stretchable well beyond their initial dimensions in the direction perpendicular to the stretch direction and are especially useful in laminates with elastomeric members for use in disposable absorbent articles to impart elasticity thereto.
Owner:BBA NONWOVENS SIMPSONVILLE
Plasticized acrylics for pressure sensitive adhesive applications
InactiveUS6624273B1High TgHigh modulusMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesSurgical adhesivesMeth-Ethylene Homopolymers
Non-tacky, base polymers are plasticized into pressure-sensitive adhesives and comprise: a) about 100 parts by weight of a base copolymer having a Tg greater than about 0° C., wherein the base copolymer is formed from and comprises: (1) about 50 to 70% by weight of a high Tg comonomer component, wherein the homopolymer formed from the high Tg comonomer component has a Tg of at least about 20° C.; (2) optionally, up to about 20% by weight based on the total weight of the base copolymer of an acidic comonomer; and (3) about 30 to 50% by weight of one or more low Tg (meth)acrylate comonomer, wherein the Tg homopolymer of the low Tg comonomer is less than about 20° C., and b) about 1 to about 100 parts based on the base copolymer of a nonreactive, non-volatile, non-acrylic-based plasticizing agent.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com