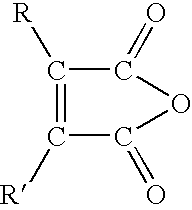
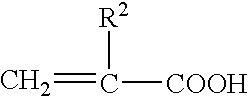
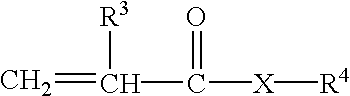
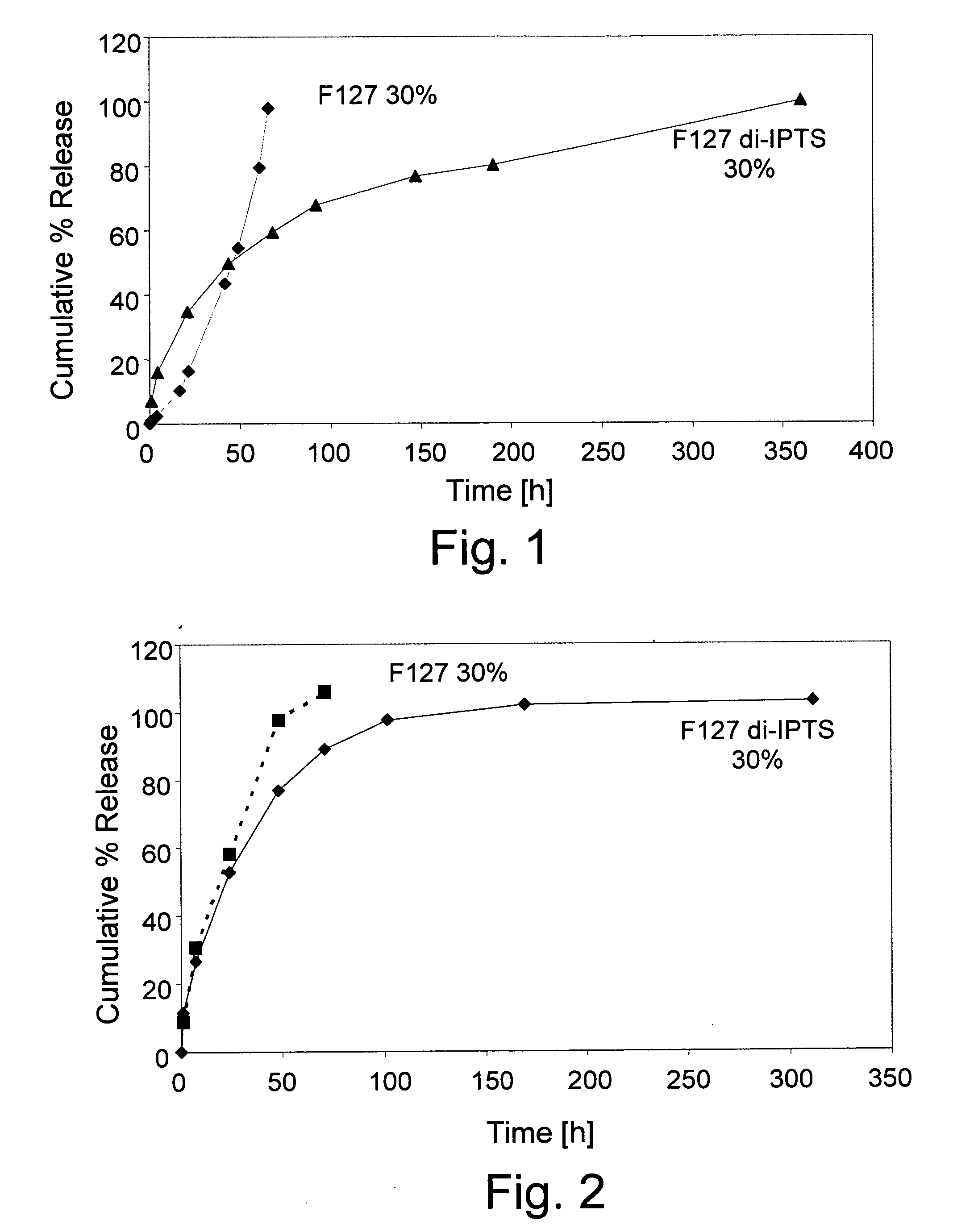
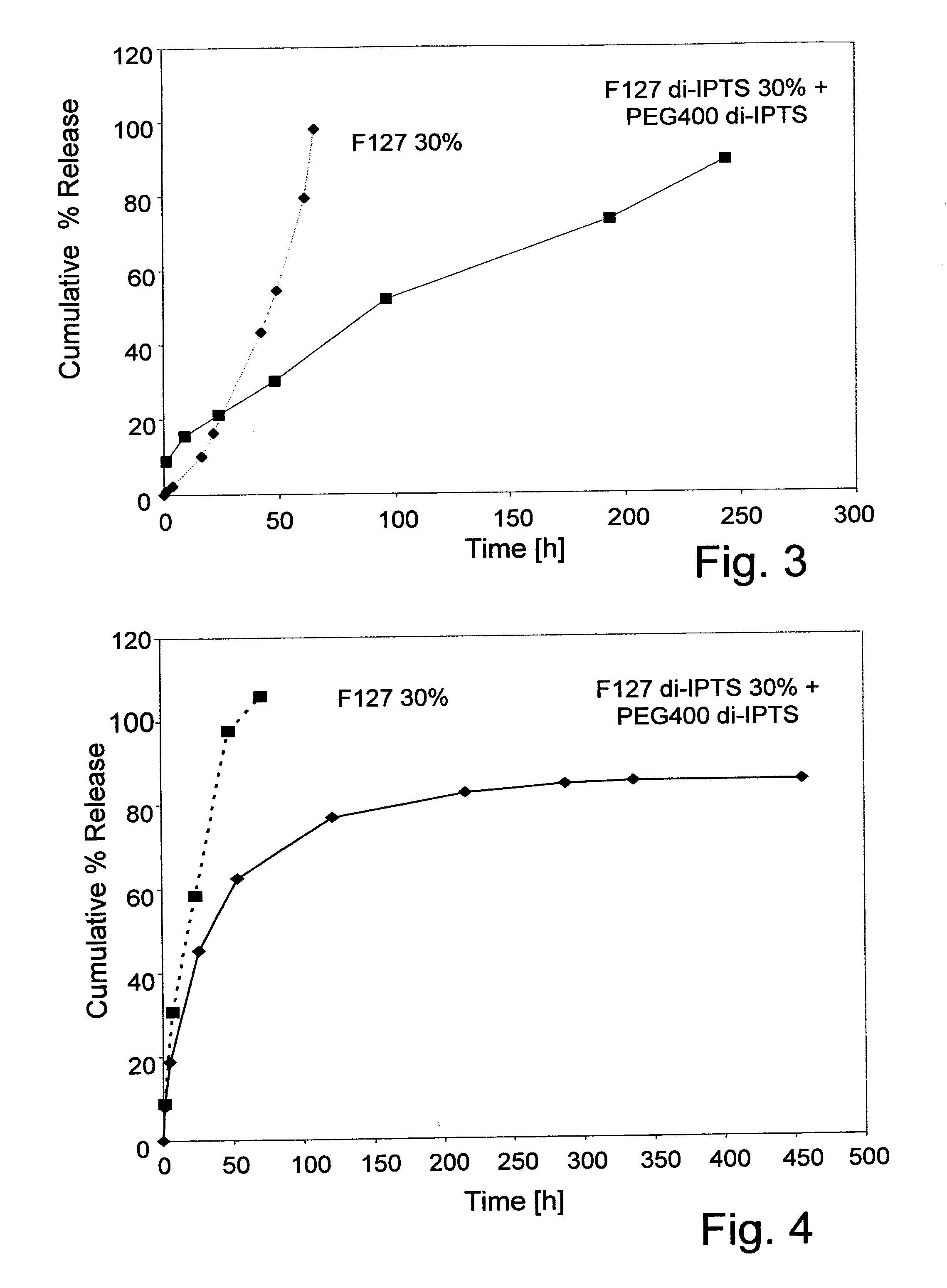
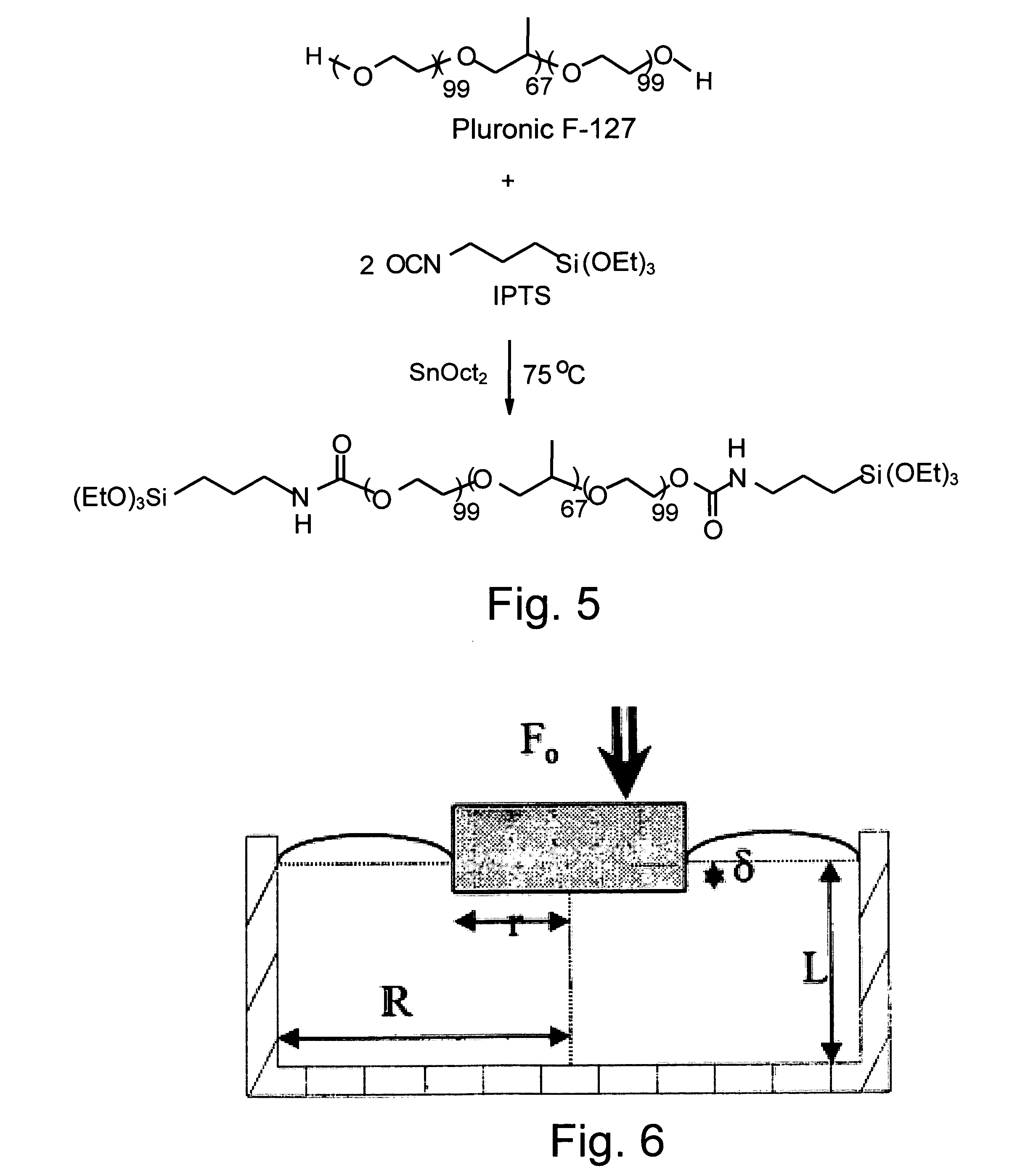
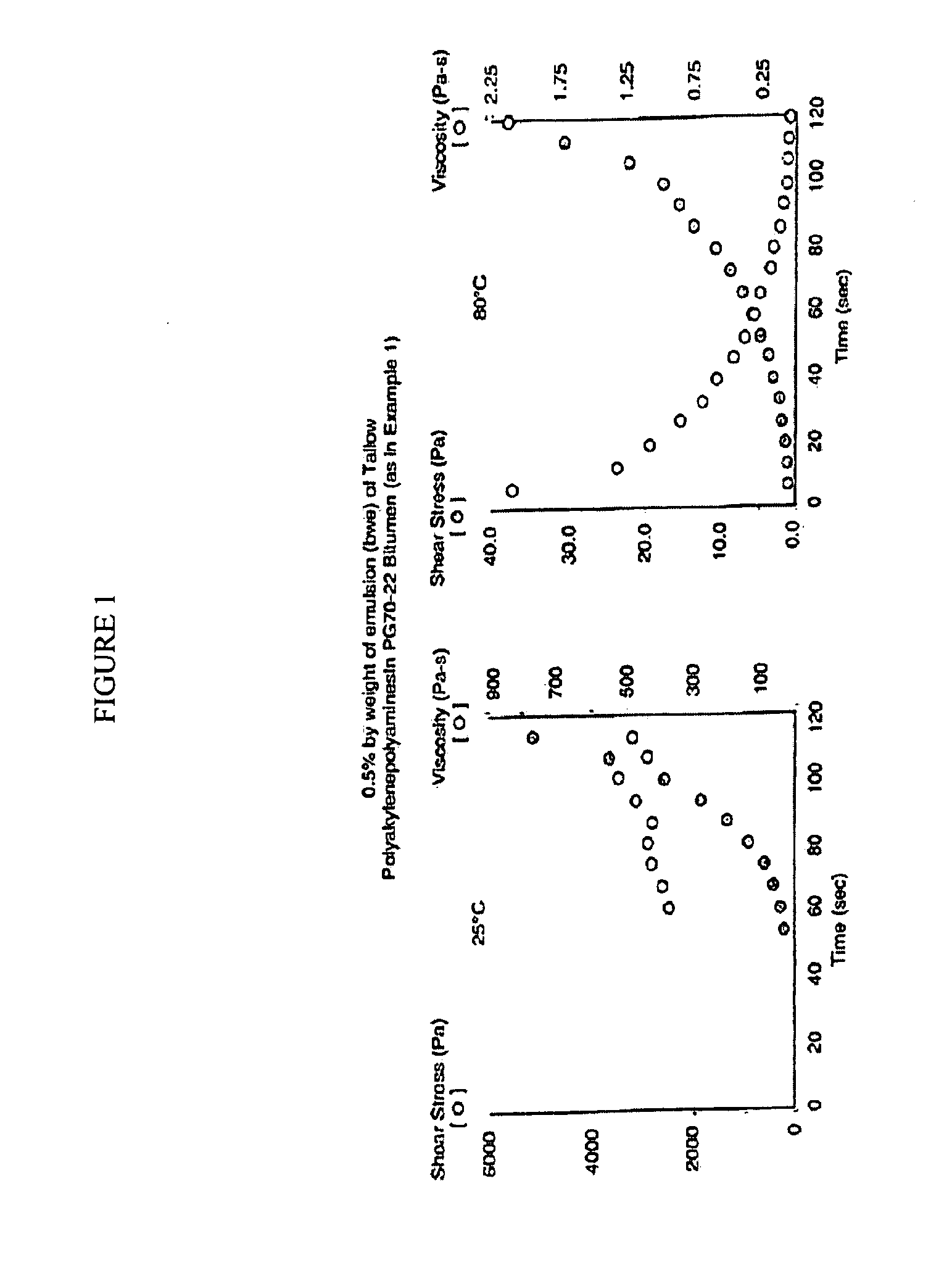
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1776 results about "Rheology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rheology (/riːˈɒlədʒi/; from Greek ῥέω rhéō, "flow" and -λoγία, -logia, "study of") is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a liquid state, but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force. Rheology is the science of deformation and flow within a material. It is a branch of physics which deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.
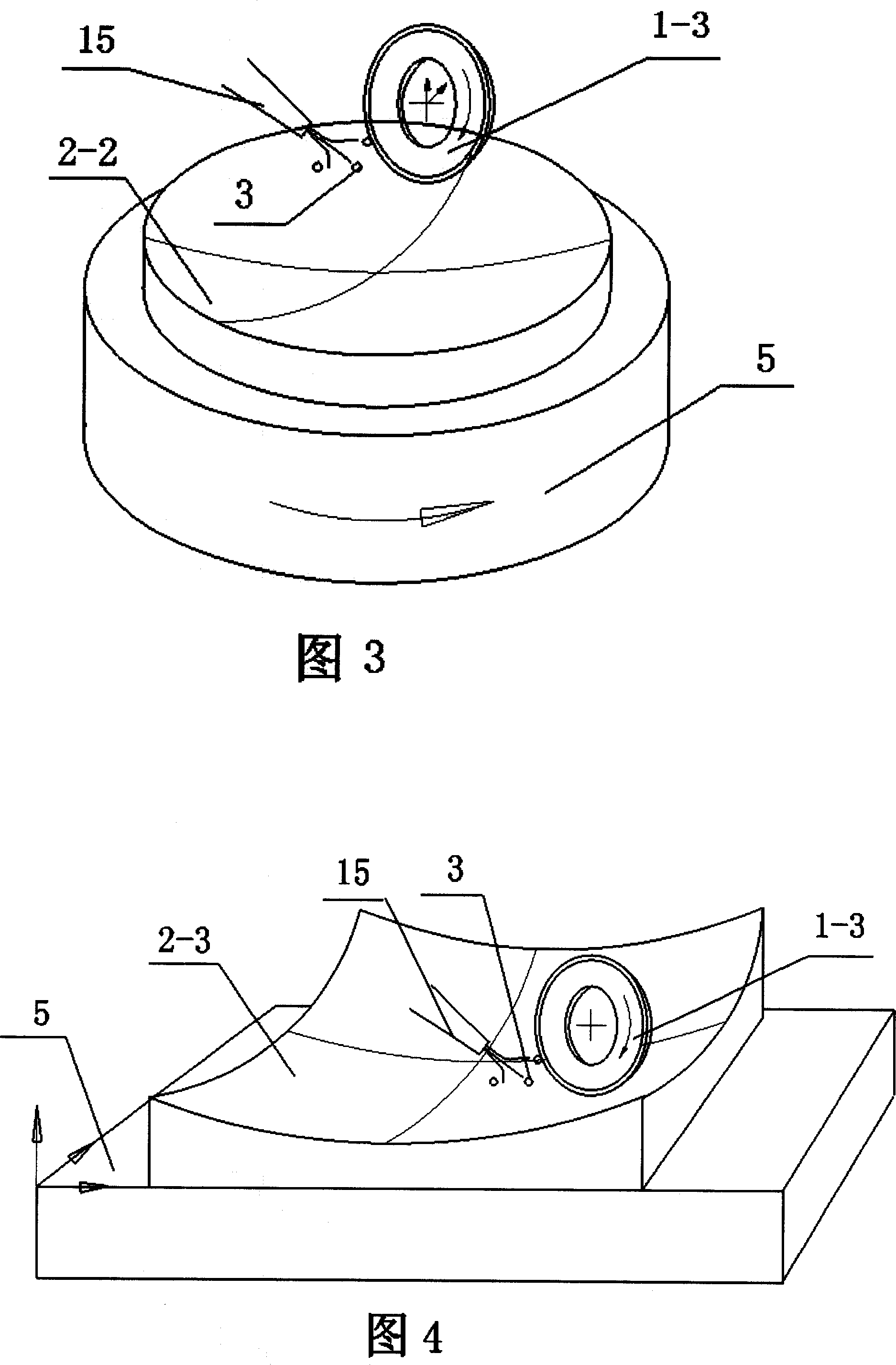
Rheology modifying copolymer composition
A rheology modifying copolymer composition containing a cross-linked copolymer of unsaturated carboxylic acid, a hydrophobic monomer, a hydrophobic chain transfer agent, a cross linking agent, and, optionally, a steric stabilizer, provides increased viscosity in aqueous electrolyte-containing environments.
Owner:NOVEON IP HLDG CORP
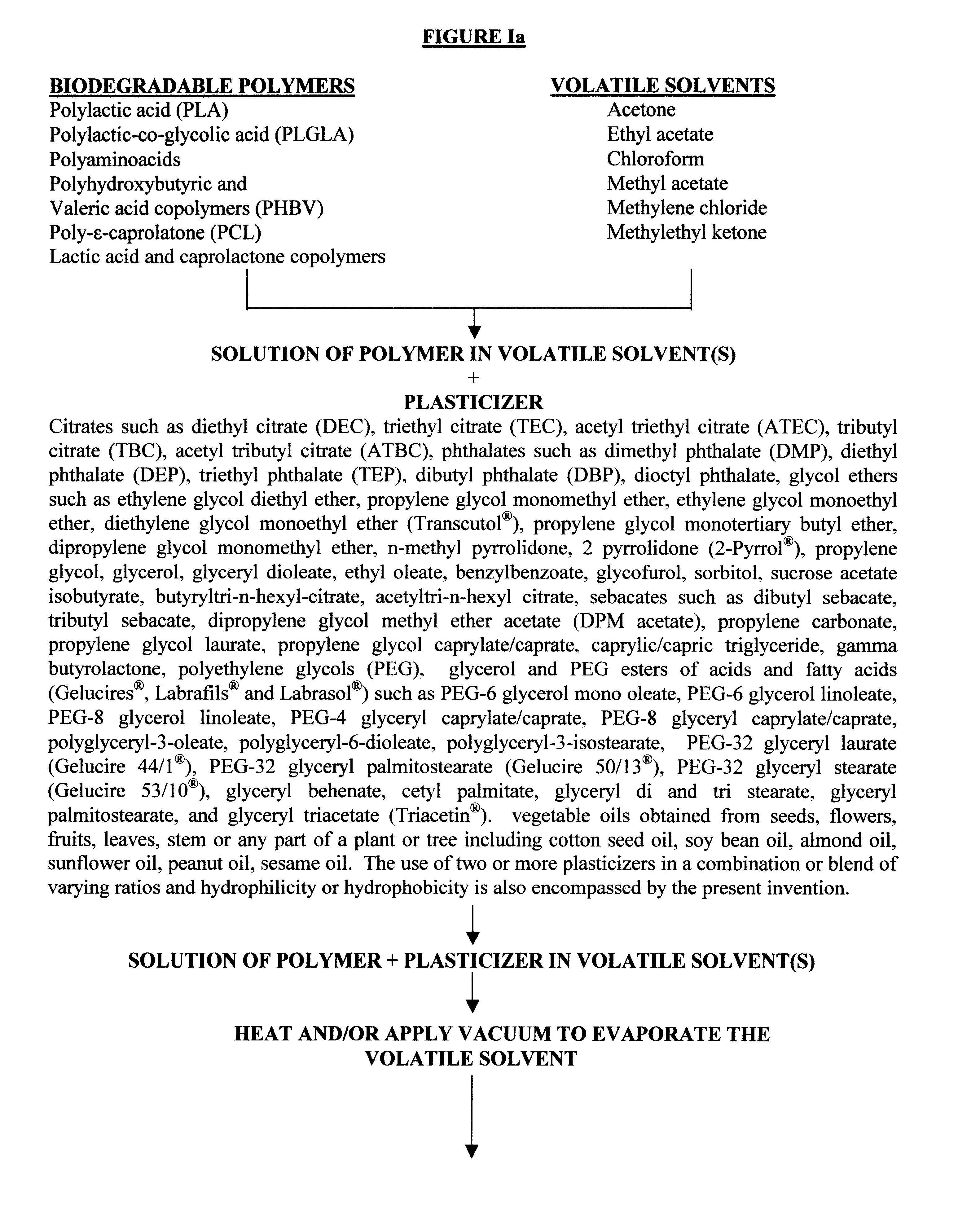
Biodegradable vehicle and filler
InactiveUS6432438B1Improve stabilityWell mixedOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer sciencePlasticizer
A biodegradable vehicle and filler (referred to in this invention as biodegradable vehicle), which can be mixed with one or more biologically active substances (BAS), or can be used as a biodegradable filler to fill in cavities or body tissues in animals, birds and humans. The consistency and rheology, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, and in vivo degradation rates of the biodegradable vehicle is controlled by modulating the molecular weight of polymers and copolymers, concentration of plasticizers, ratios of two or more plasticizer in the blends, types of polymers and copolymers, copolymer ratios, and ratios of blends of polymers with different molecular weights or different copolymers. The biodegradable vehicle is mixed with one or more BAS (which is separately stored away from the biodegradable vehicle in an appropriate container) just prior to use. Mixing of the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle can be accomplished by simply stirring the mixture with a stirring device, or by triturating the mixture or employing an ointment mill or a suitable device or apparatus or equipment that can be used for blending / mixing. Alternatively, a device, which resembles two syringes, attached together with a removable partition or a valve assembly can also be used to uniformly mix the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle. The mixing is performed in order to dissolve or uniformly suspend the BAS particles in the biodegradable vehicle. Modulating the polymer to plasticizer ratio, polymer molecular weight, copolymer ratio, and hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of the plasticizer controls the release of the BAS from the biodegradable vehicle.
Owner:SHUKLA ATUL J
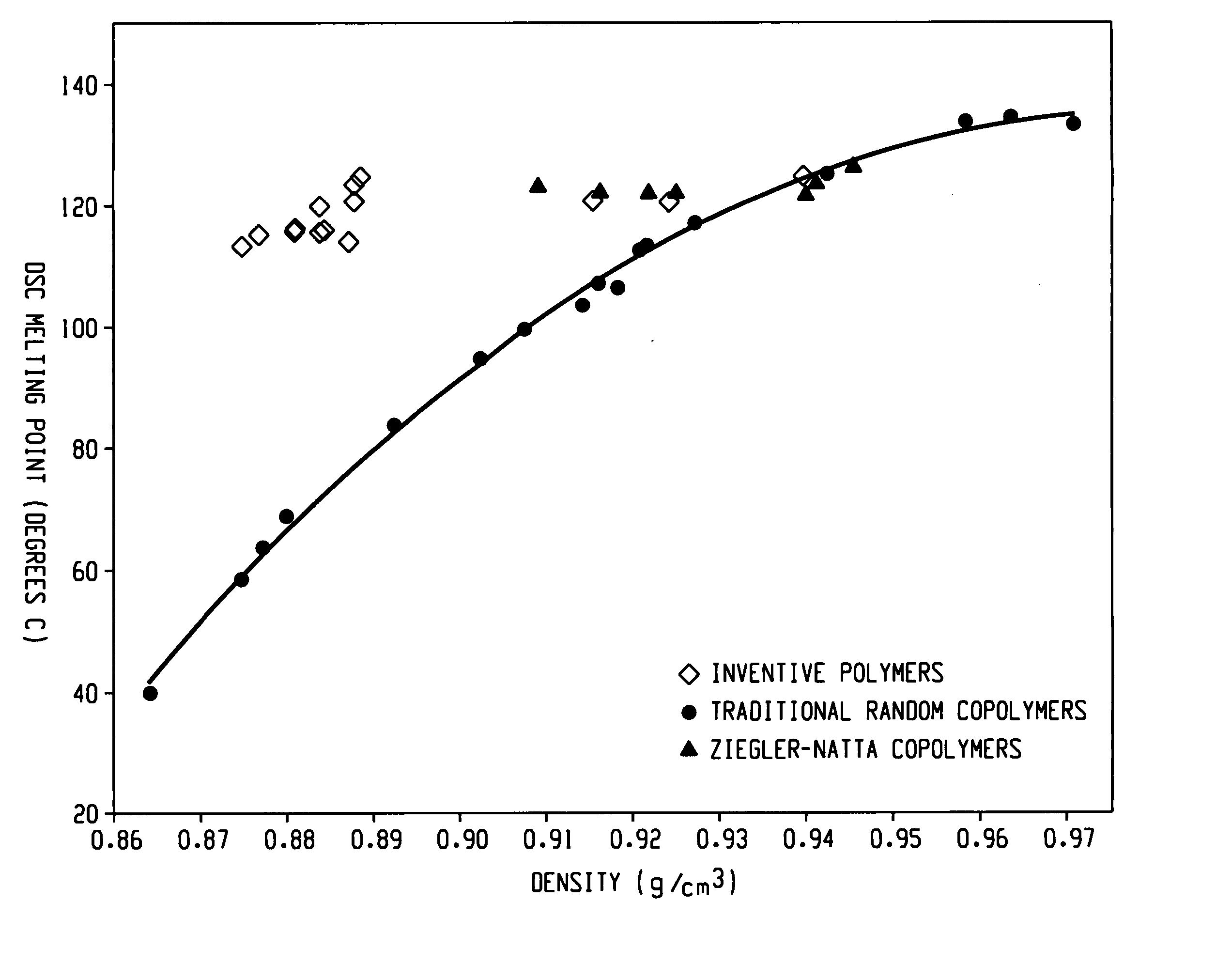
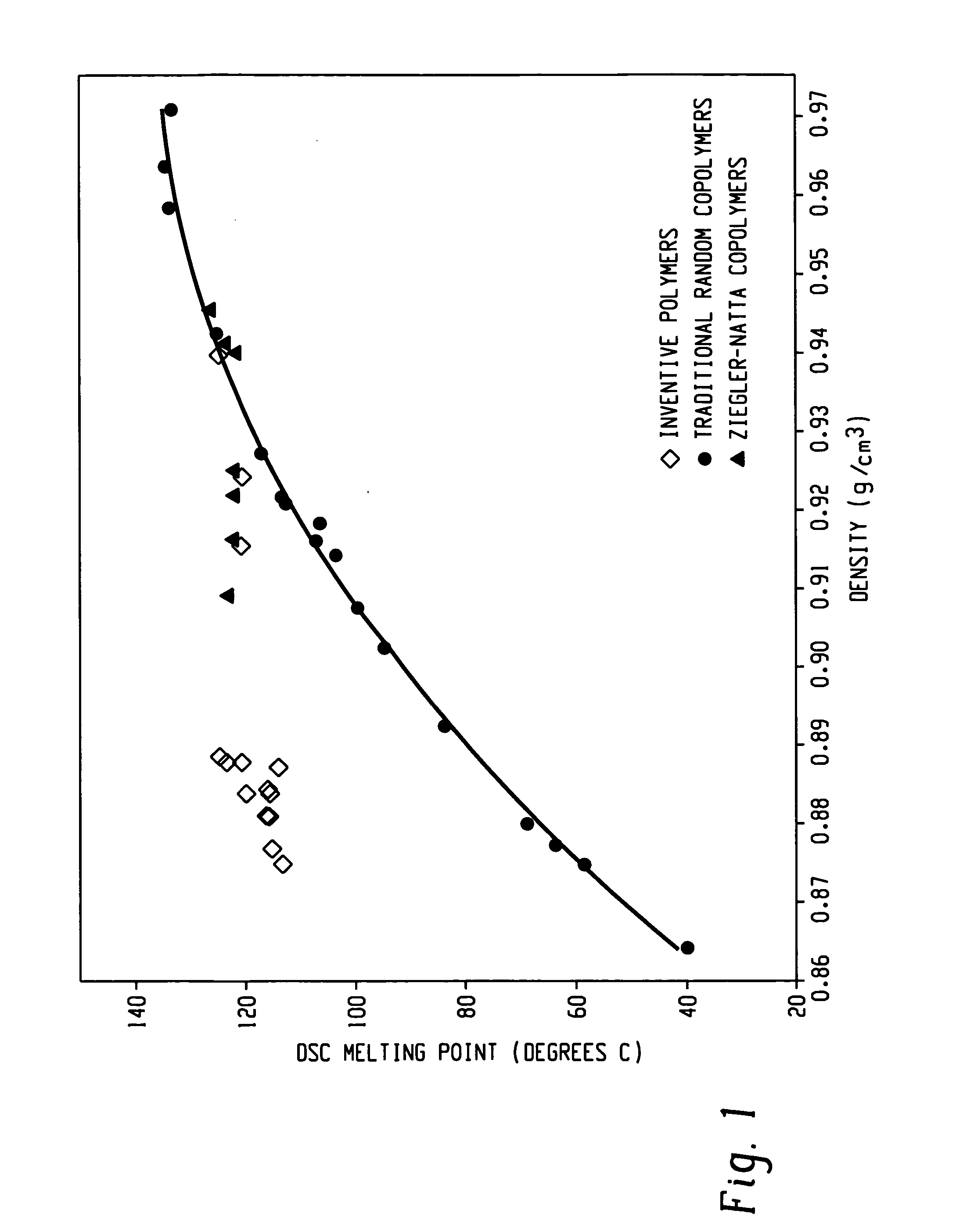
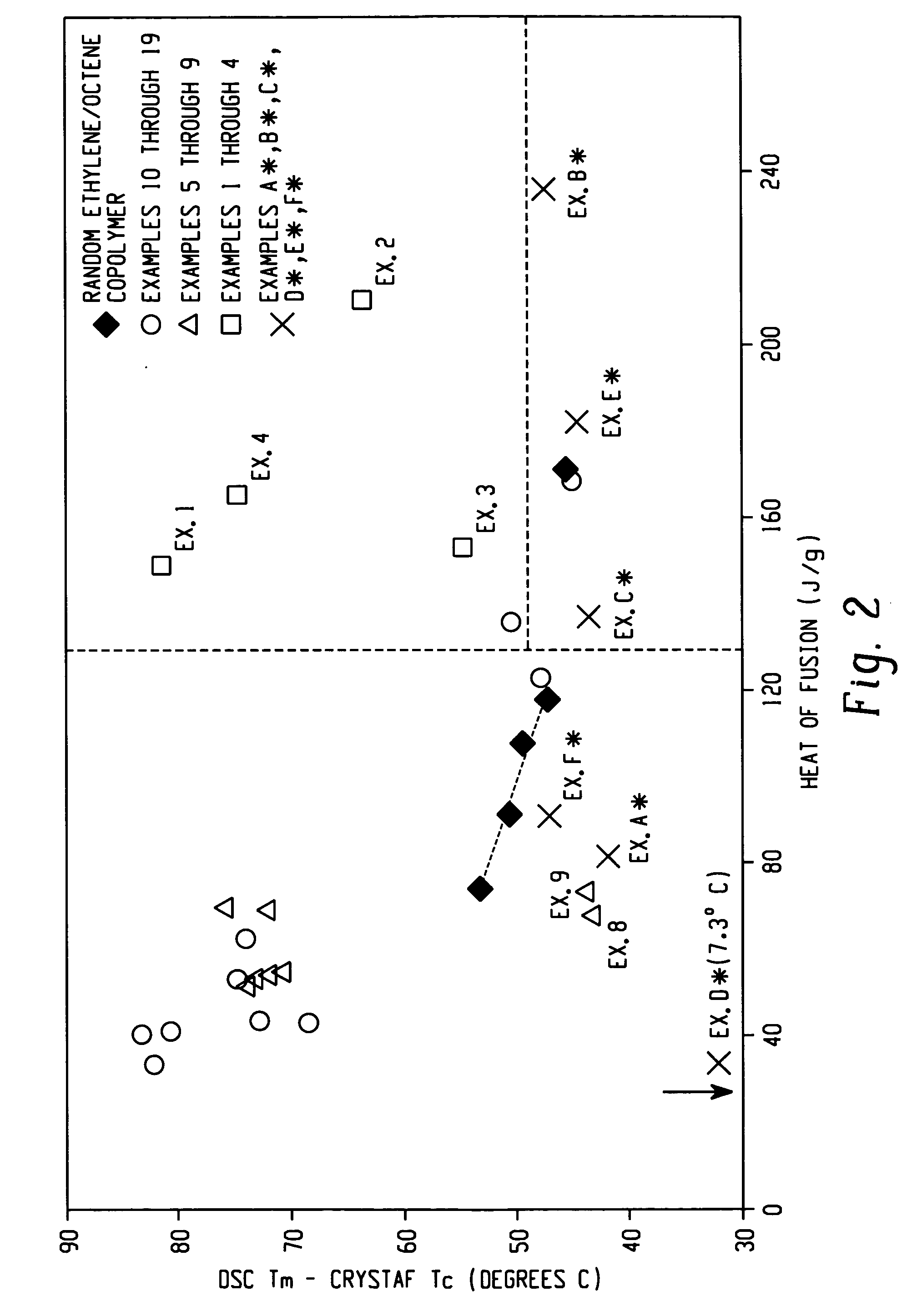
Rheology modification of interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and articles made therefrom
Rheology modification of an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is achieved by blending the interpolymer with at least one branched polyolefin. The polyolefins can be homopolymers or interpolymers and have a branching index of less than 1. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is a block copolymer having at least a hard block and at least a soft block. The soft block comprises a higher amount of comonomers than the hard block. The block interpolymer has a number of unique characteristics disclosed here. Rheology-modified ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer, i.e., the resulting polymer blends, can be extruded or molded into many useful articles, such as films, sheets, profiles, gaskets, foams, etc.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Molded starch-bound containers and other articles having natural and/or synthetic polymer coatings
Compositions, methods, and systems for manufacturing articles, particularly containers and packaging materials, having a particle packed, highly inorganically filled, cellular matrix are disclosed. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together a starch-based binder, a solvent, inorganic aggregates, and optimal admixtures, e.g., fibers, mold-releasing agents, rheology-modifying agents, plasticizers, coating materials, and dispersants, in the correct proportions to form an article which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures have a predetermined viscosity and are heated between molds at an elevated temperature and pressure to produce form-stable articles having a desired shape and a selectively controlled cellular, structure matrix. The molded articles may be placed in a high humidity chamber to obtain the necessary flexibility for their intended use. The articles may be manufactured to have properties substantially similar to articles presently made from conventional materials like paper, paperboard, polystyrene, plastic, or other organic materials. They have especial utility in the mass-production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:EARTHSHELL SPE
Compatibilized blends of biodegradable polymers with improved rheology
This invention relates to a blend of biodegradable polymers comprising: (A) about 5% to about 95% by weight of at least one flexible biodegradable polymer (A) having a glass transition less than about 0° C., (B) about 5% to about 95% by weight of at least one rigid biodegradable polymer (B) having a glass transition greater than about 10° C., and (C) about 0.25 to about 10 weight % of at least one compatibilizer (C), said percentages being based on the total weight of the polymer blend; where the polymer blend has a higher zero shear melt viscosity than polymers (A) and (B) separately.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Absorbent product with improved liner treatment
Absorbent products, such as disposable diapers and incontinence garments, comprising an improved lotion formulation are disclosed. The lotion formulation is applied to the bodyfacing surface of the bodyside liner and is stable at elevated temperatures, remains on or near the surface of the absorbent product prior to use, and readily transfers to the user's skin upon use. The lotion formulations described herein have a melt point viscosity of from about 5000 cPs to about 1,000,000 cPs, and a process temperature viscosity of from about 50 cPs to about 50,000 cPs. The lotion formulations comprise an emollient, a structurant, a rheology enhancer, and other optional components.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Stable aqueous surfactant compositions
InactiveUS6897253B2Enhanced pearlescent appearanceLow compositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideHair dyesAcid substances
A stable, aqueous composition containing a substantially crosslinked alkali-swellable acrylate copolymer rheology modifier, a surfactant, an alkaline material, and various compounds therein, as for example substantially insoluble materials requiring suspension or stabilization, such as a silicone, an oily material, or a pearlescent material. Additionally, this invention also relates to the formation of a rheologically and phase stable cationic hair dye composition. The invention further relates to the incorporation of an acidic material after the addition of an alkaline material to reduce the pH of the composition without negatively impacting the viscosity of the composition.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Antimicrobial compositions
InactiveUS20100135949A1Reduce complicationsAvoid difficultyBiocidePretreated surfacesCetrimideO-Phthalaldehyde
Antimicrobial compositions and methods are disclosed. The antimicrobial compositions are particularly useful in providing antimicrobial capability to a wide-range of medical devices. In one aspect the invention relates a UV curable antimicrobial coating comprising a UV curable composition comprising an oligomer, a momoner, and a photoinitiator which are together capable of forming a UV curable polymer composition. The compositions include rheology modifiers as necessary. The compositions also include antimicrobial agents, which may be selected from a wide array of agents. Representative antimicrobial agents include cetyl pyridium chloride, cetrimide, alexidine, chlorexidine diacetate, benzalkonium chloride, and o-phthalaldehyde.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Water-based drilling fluids
InactiveUS20060019834A1Reduce molecular weightFlushingDrilling compositionWater basedInorganic salts
A water-based drilling fluid composition includes water and at least one rheology modifier and / or fluid loss control agent, and at least one other ingredient of polymeric additive, inorganic salts, dispersants, shale stabilizers, weighting agents, or finely divided clay particles, depending upon the desired attributes, wherein the rheology modifier and / or the fluid loss control agent comprises carboxymethylated raw cotton linters (CM-RCL) made from the baled raw cotton linters or comminuted raw cotton linters with increased bulk density.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
Rheology modification of settled solids in mineral processing
InactiveUS6365116B1Low viscosityIncrease speedRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringSlurry
The present invention comprises a method for reducing the viscosity of the settled mud or underflow of a raked thickener thereby reducing the torque necessary to move the rake blade through the settled mud. The method includes the step of delivering a viscosity modifier to the settled mud and in front of the rake blade by pumping the viscosity modifier down the rake arm to an area in front of the rake blade. The method also includes an improved rake mechanism that includes a means for delivering viscosity modifier to the settled mud and in front of the rake blade. The present invention also includes a method for increasing the rate of consolidation of flocculated solids in a slurry.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Chemical mechanical polishing compositions for copper and associated materials and method of using same
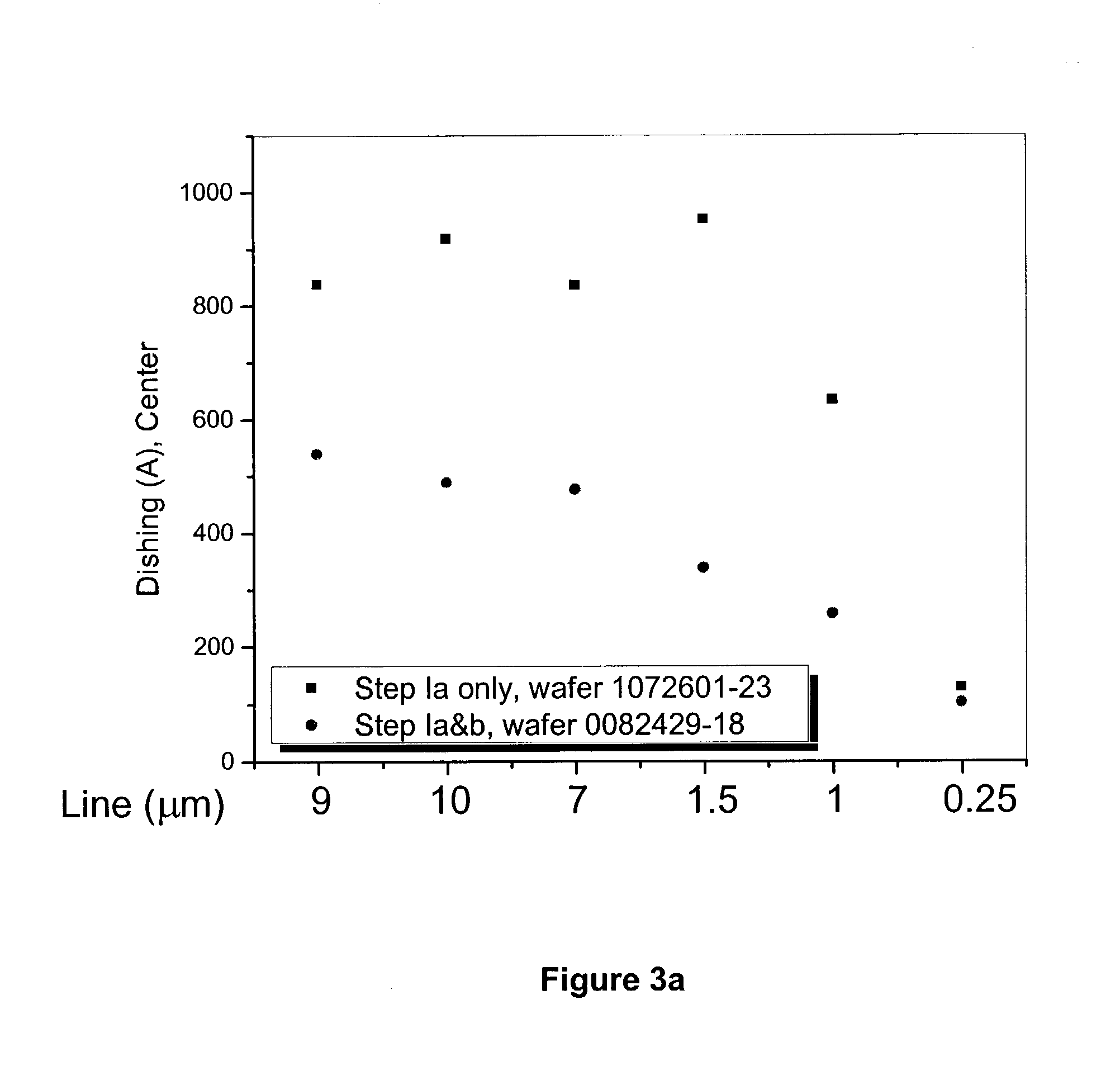
A CMP composition containing a rheology agent, e.g., in combination with oxidizing agent, chelating agent, inhibiting agent, abrasive and solvent. Such CMP composition advantageously increases the materials selectivity in the CMP process and is useful for polishing surfaces of copper elements on semiconductor substrates, without the occurrence of dishing or other adverse planarization deficiencies in the polished copper.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Compatibilized blends of biodegradable polymers with improved rheology
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Cementitious composites having wood-like properties and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20080099122A1Harder to saw, nail or screwLow densityPlastic recyclingLaminationPorosityBuilding product
A method of manufacturing a cementitious composite includes: (1) forming mixing an extrudable cementitious composition by first forming a fibrous mixture comprising fibers, water and a rheology modifying agent and then adding hydraulic cement; (2) extruding the extrudable cementitious composition into a green extrudate, wherein the green extrudate is characterized by being form-stable and retaining substantially a predefined cross-sectional shape; (3) removing a portion of the water by evaporation to reduce density and increase porosity; and (4) causing or allowing the hydraulic cement to hydrate to form the cementitious composite. Such a process yields a cementitious composite that is suitable for use as a wood substitute. The wood-like building products can be sawed, nailed and screwed like ordinary wood.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
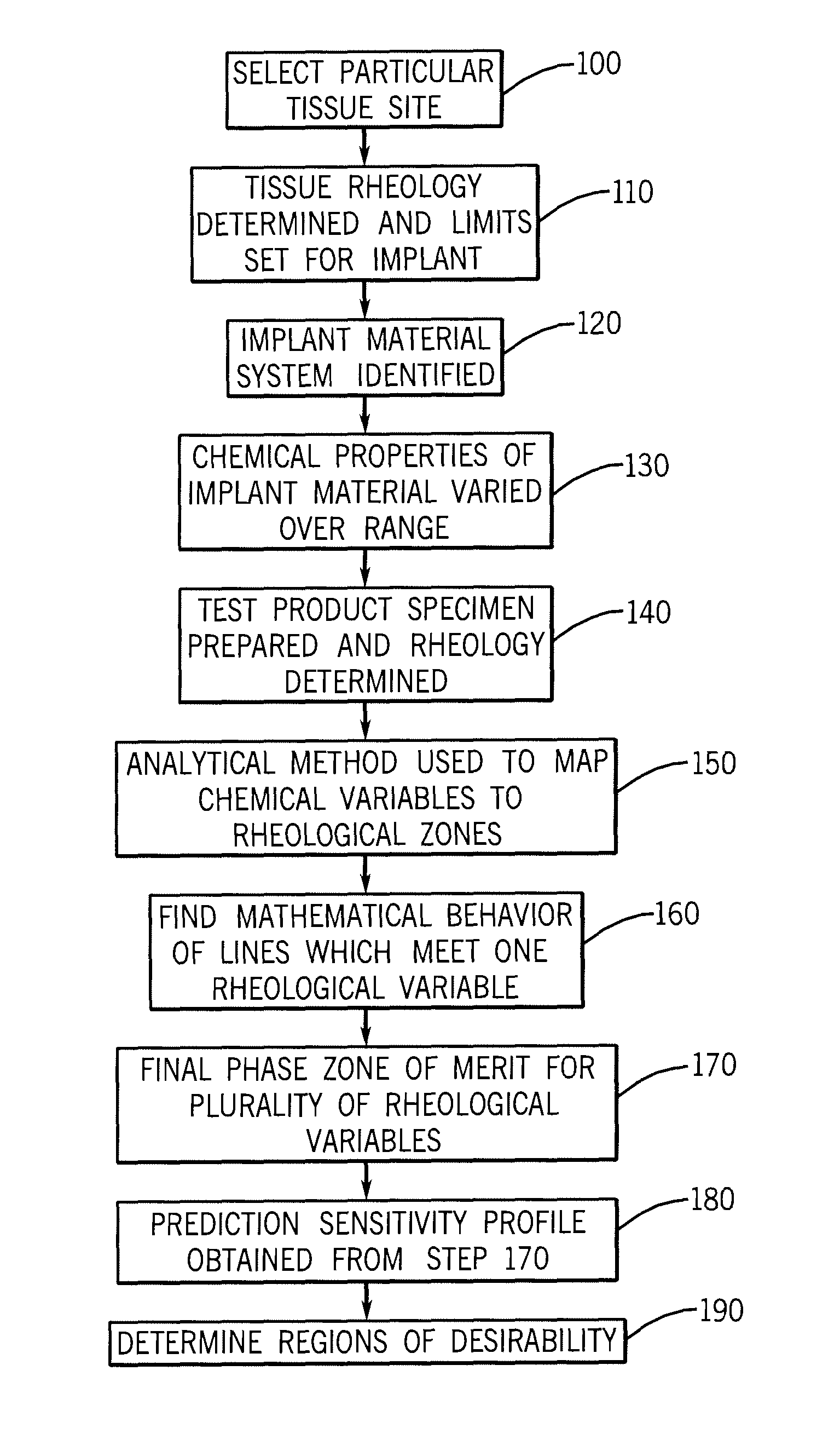
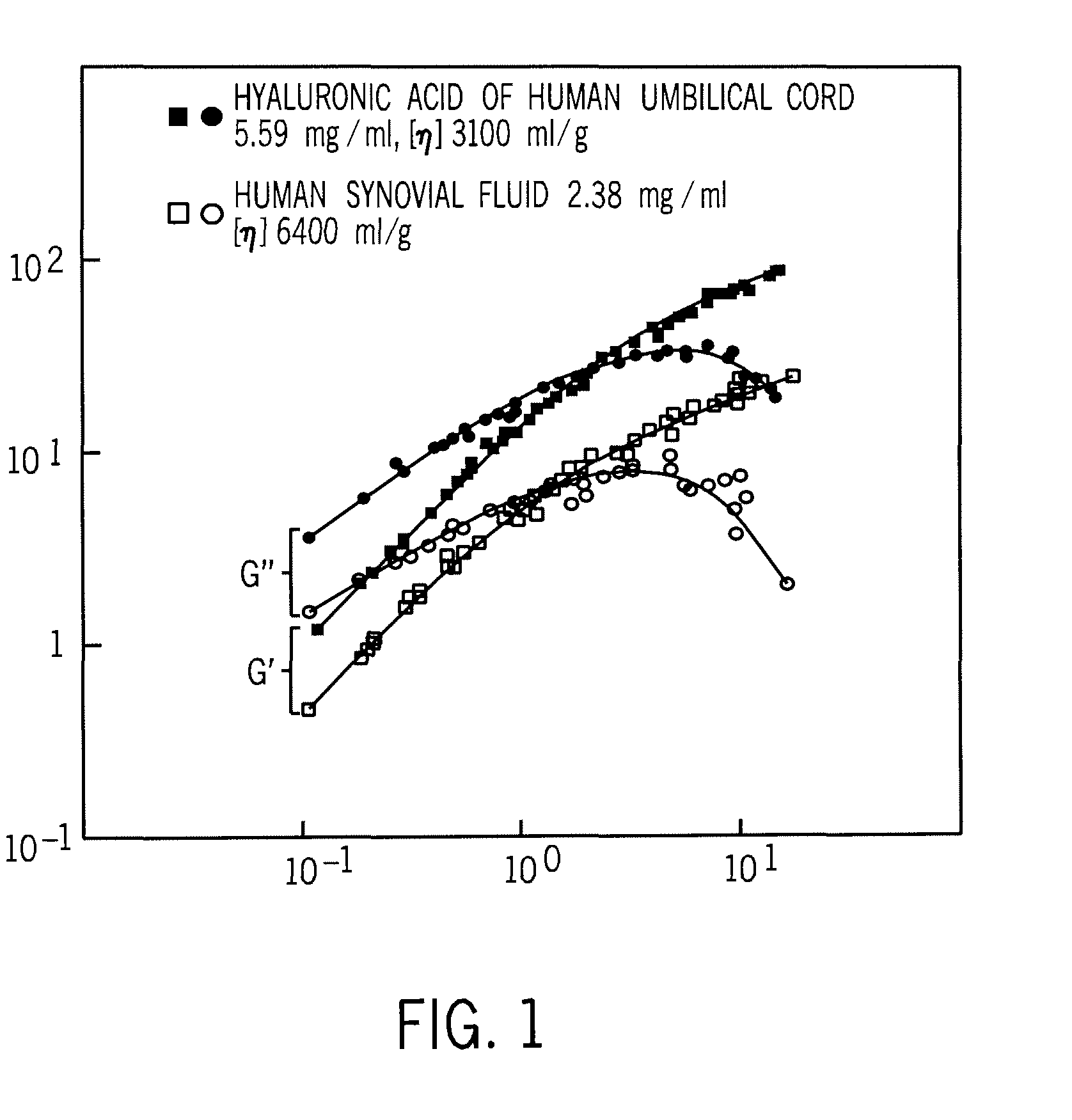
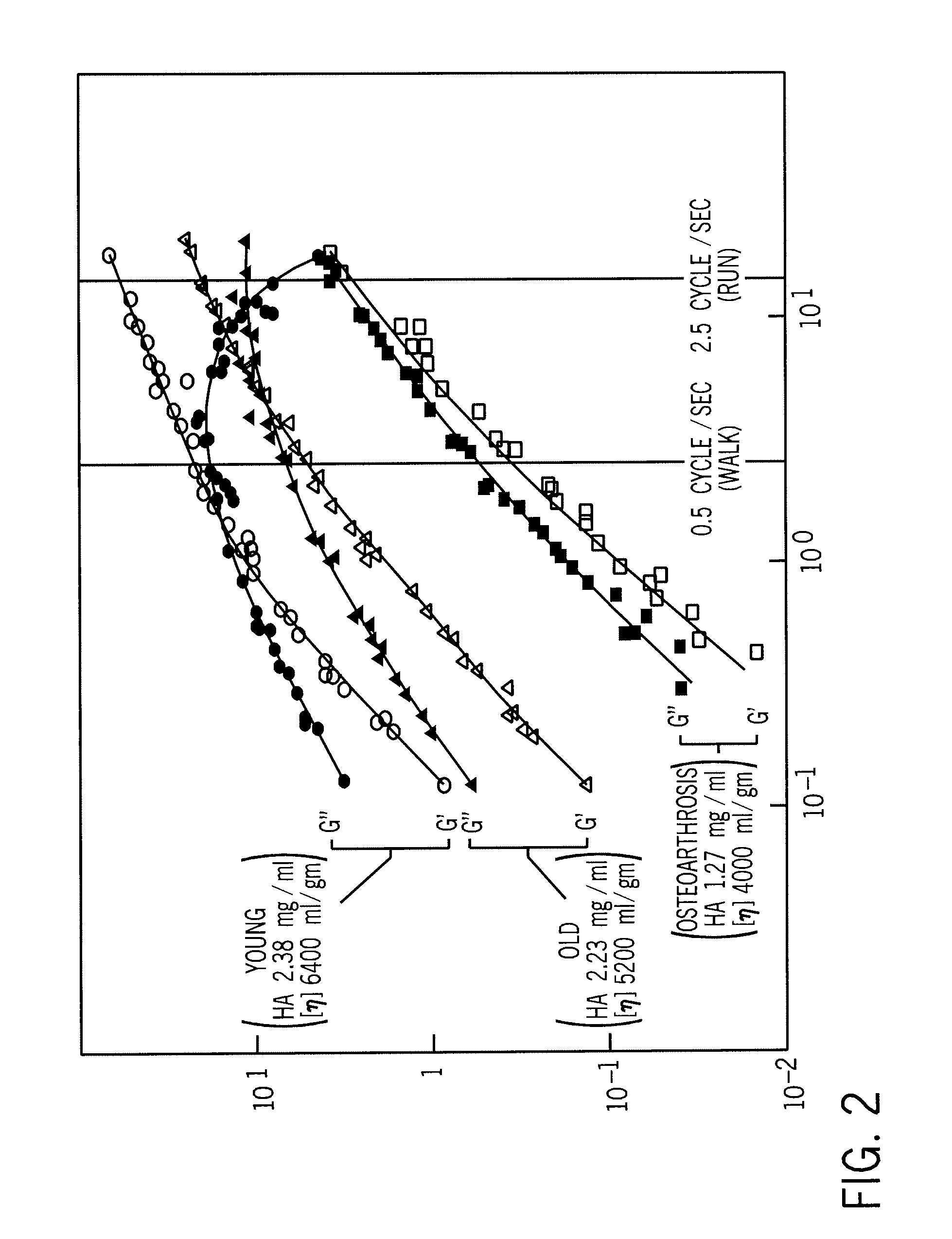
Implantation Compositions for Use in Tissue Augmentation
InactiveUS20100041788A1Good compatibilityMinimized immuno-histo tissue responseOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesPolymer solutionPolysaccharide
A composition of matter and method for preparation of a tissue augmentation material. A polysaccharide gel composition is prepared with rheological properties selected for a particular selected application. The method includes preparing a polymeric polysaccharide in a buffer to create a polymer solution or gel suspending properties in the gel and selecting a rheology profile for the desired tissue region.
Owner:MERZ AESTHETICS
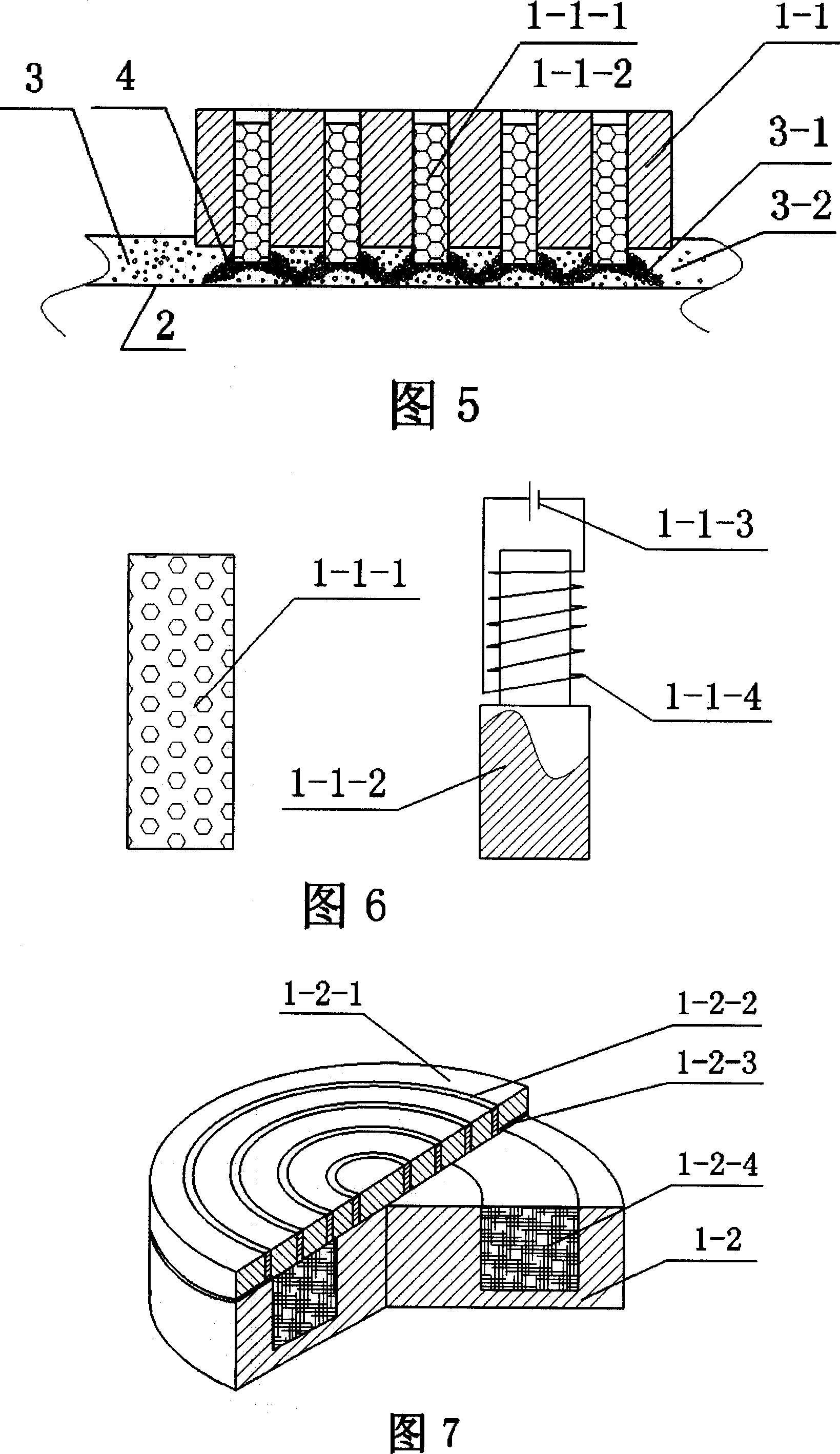
Grinding polishing method based on magnetic rheology effect and its polishing device
InactiveCN100999061AReduce removal rateReduce machining accuracyPolishing machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesMagnetorheological fluidMaterials science
The present invention discloses a grinding-polishing method based on magnetorheological effect. Said method is characterized by that in the magnetorheological fluid a kind of free abrasive material is added, used as grinding-polishing liquor and injected into the between of magnetic body and workpiece surface, under the action of magnetic field the ferromagnetic particles in the magnetorheological fluid can be arranged by strings to cover the abrasive material pacticles and can be constrained in the end face of magnetic body to form magnetic grinding brush, said magnetic grinding brush can be used for grinding-polishing workpiece surface. Said invention also provides a grinding-polishing device for implementing said grinding-polishing method. Said device includes grinding tool mounted on main shaft connected with motor and working table for mounting workpiece.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
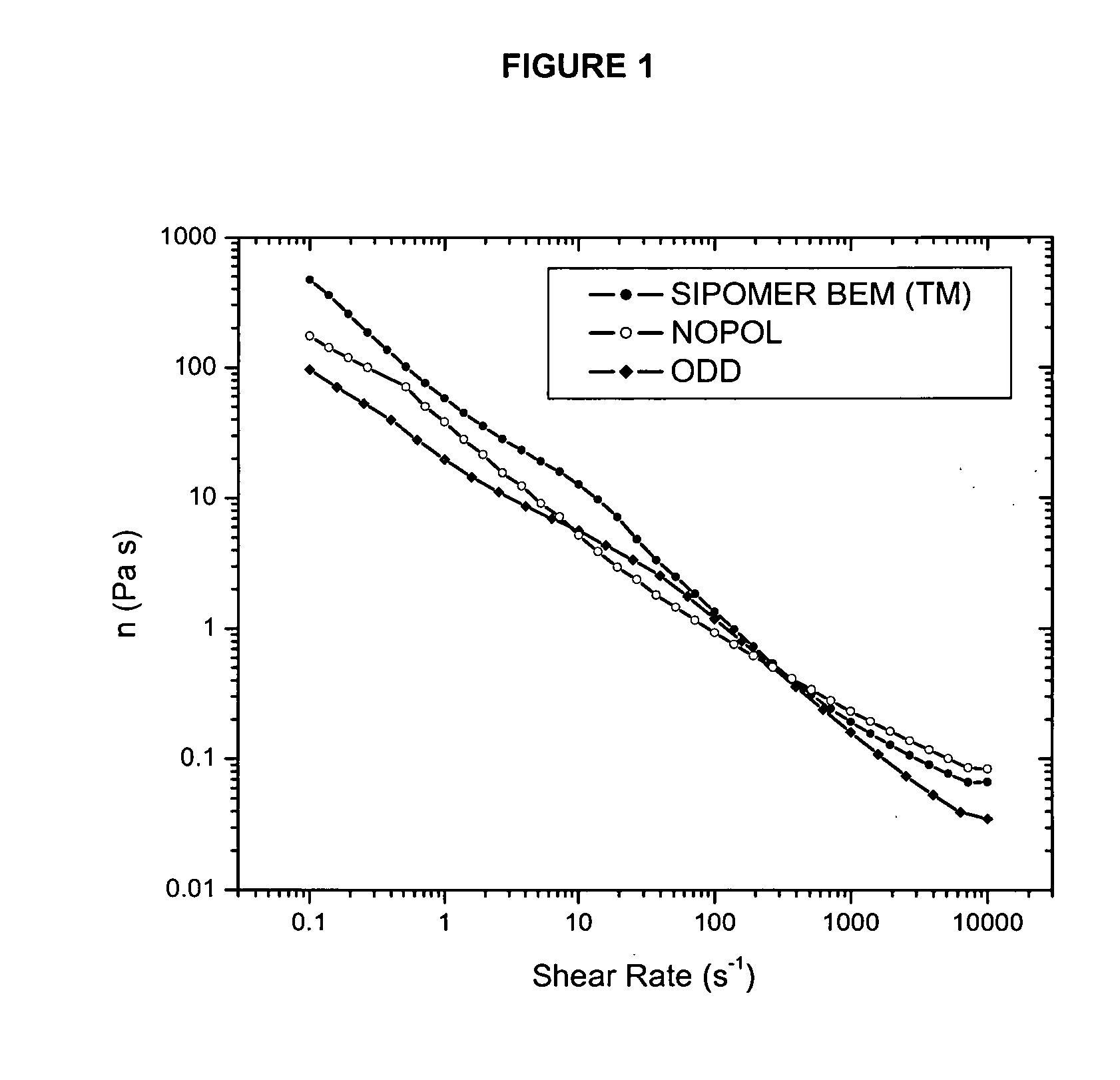
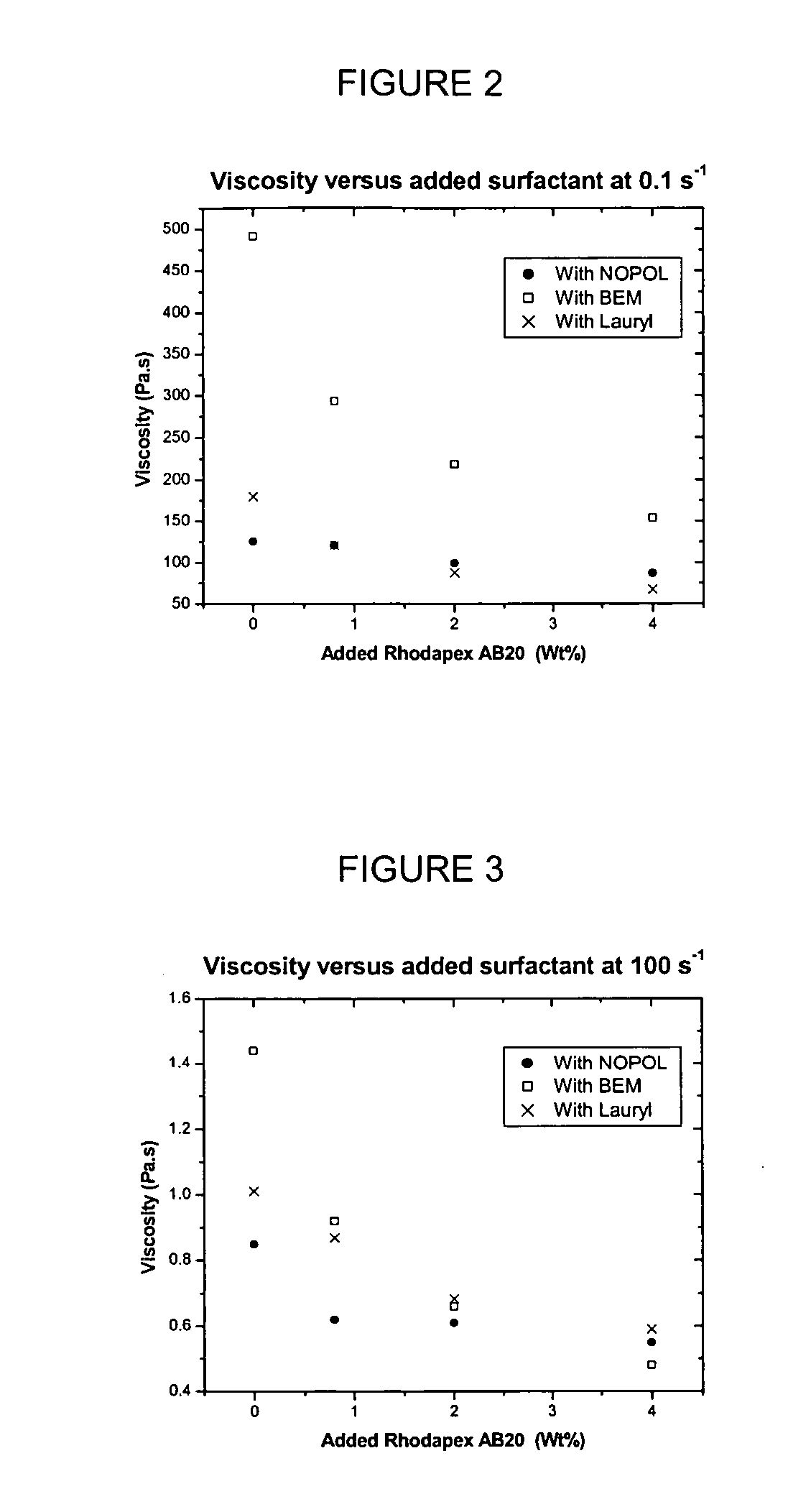
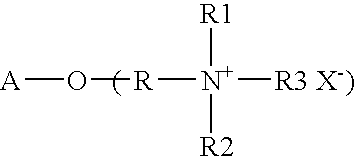
Compositions having HASE rheology modifiers
ActiveUS20060270563A1Improve flow controlHigh viscosityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsMonomerResponsive polymer
A monomer compound that contains at least one polymerizable functional group per molecule, and at least one bicycloheptyl-, bicycloheptenyl-, or branched (C5-C42)alkyl-polyether radical per molecule, wherein the bicycloheptyl- or bicycloheptenyl- polyether radical may optionally be substituted on one or more of the ring carbon atoms by one or two (C1-C6)alkyl groups per ring carbon atom is useful in making polymers, particularly pH responsive polymers.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Extruded fiber reinforced cementitious products having wood-like properties and ultrahigh strength and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20100136269A1High yield stressImmediate form stabilityLayered productsPlastic recyclingPorosityFlexural strength
A method of manufacturing a cementitious composite including: (1) mixing an extrudable cementitious composition by first forming a fibrous mixture comprising fibers, water and a rheology modifying agent and then adding hydraulic cement; (2) extruding the extrudable cementitious composition into a green extrudate, wherein the green extrudate is characterized by being form-stable and retaining substantially a predefined cross-sectional shape; (3) removing a portion of the water by evaporation to reduce density and increase porosity; and (4) heating the green extrudate at a temperature from greater than 65° C. to less than 99° C. is disclosed. Such a process yields a cementitious composite that is suitable for use as a wood substitute. Particularly, by using higher curing temperatures for preparing the cementitious building products, the building products have a lower bulk density and a higher flexural strength as compared to conventional products. The wood-like building products can be sawed, nailed and screwed like ordinary wood.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Responsive polymeric system
A novel environmentally responsive polymeric system is provided for biomedical applications, comprising silicon-containing reactive groups which undergo a hydrolysis-condensation reaction at a predetermined body site and thereby change rheological and mechanical properties of the polymeric system. The polymeric system is useful, for example, as a sealant, as a matrix for drug delivery, in the prevention of post-surgical adhesions, and in gene therapy.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV COMPANY OF HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM HI TECH PARK THE HEBREW UNIV OF JERUSALEM EDMOND J SAFRA CAMPUS GIVAT RAM
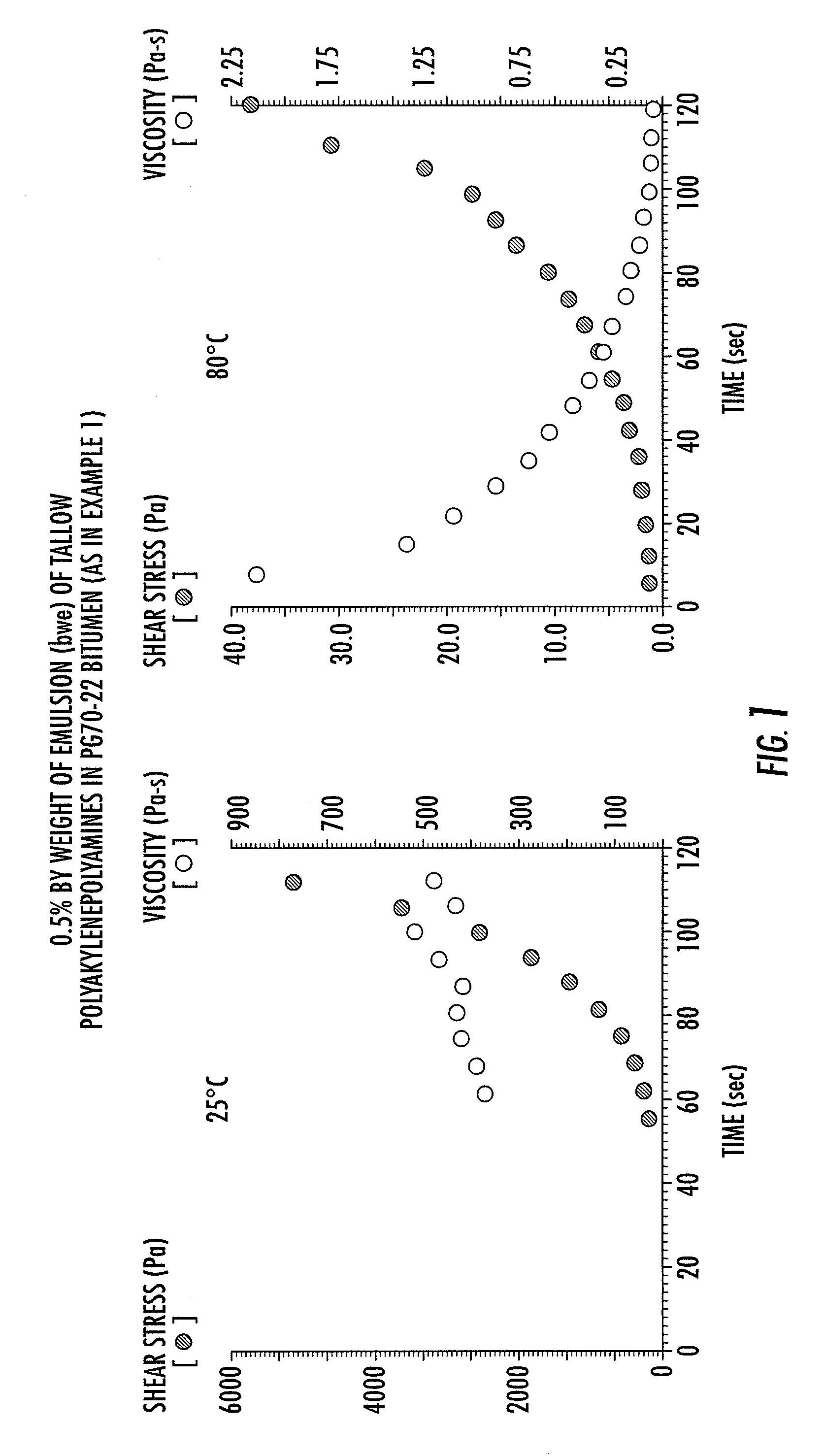
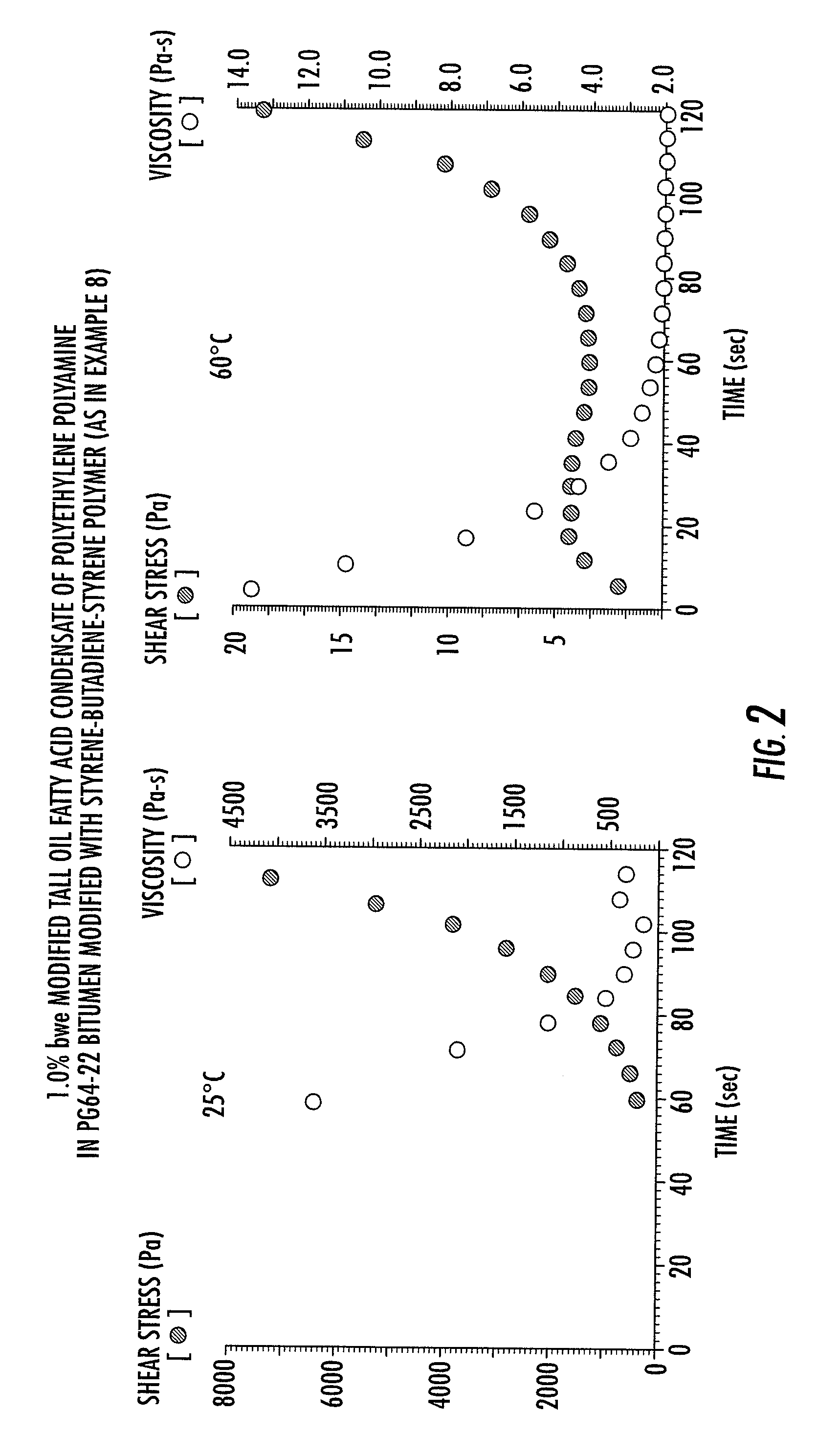
Method for producing bitumen compositions
ActiveUS20080060551A1Low viscosityHighly preventive effectBuilding insulationsBitumen emulsionRoad surface
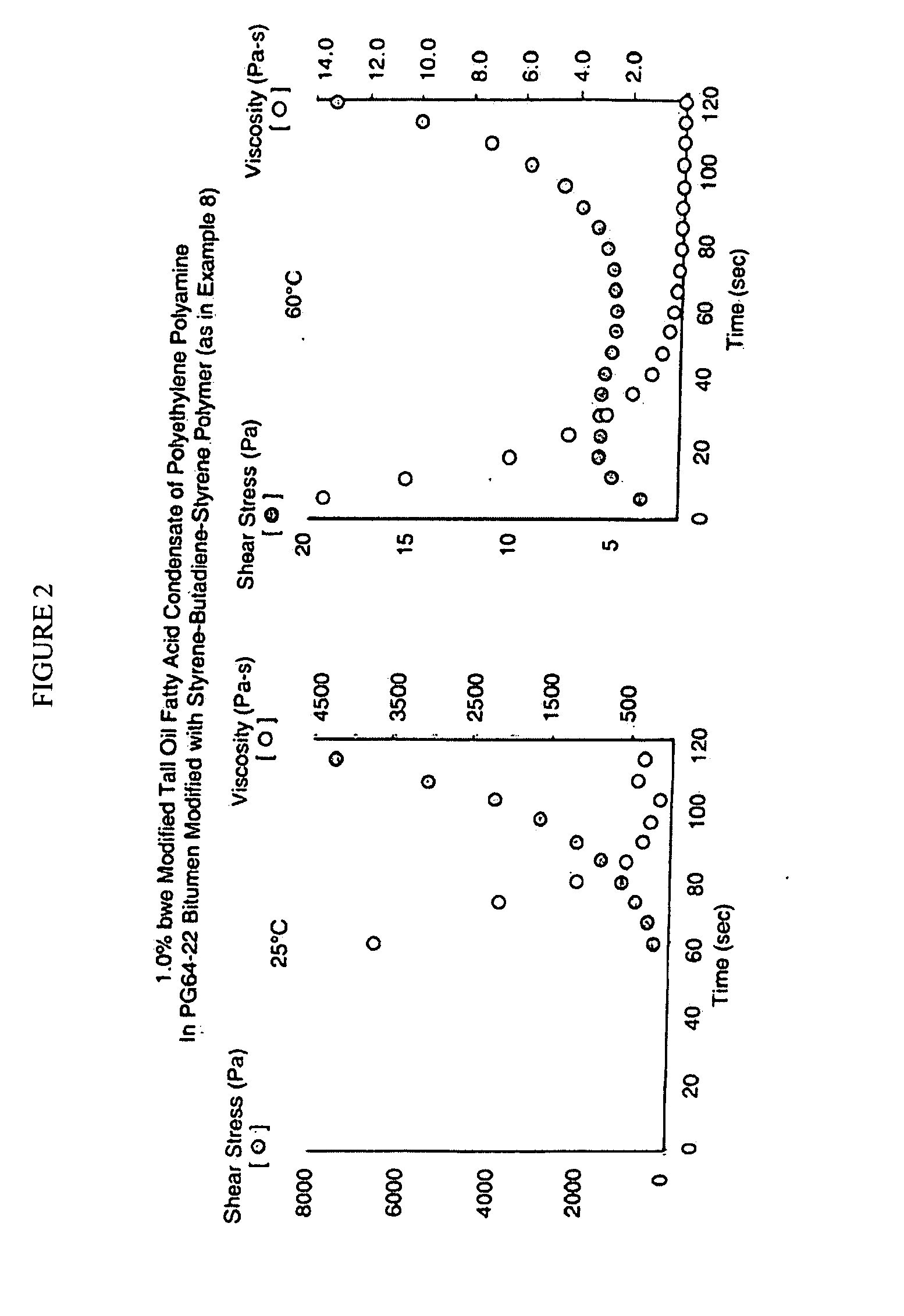
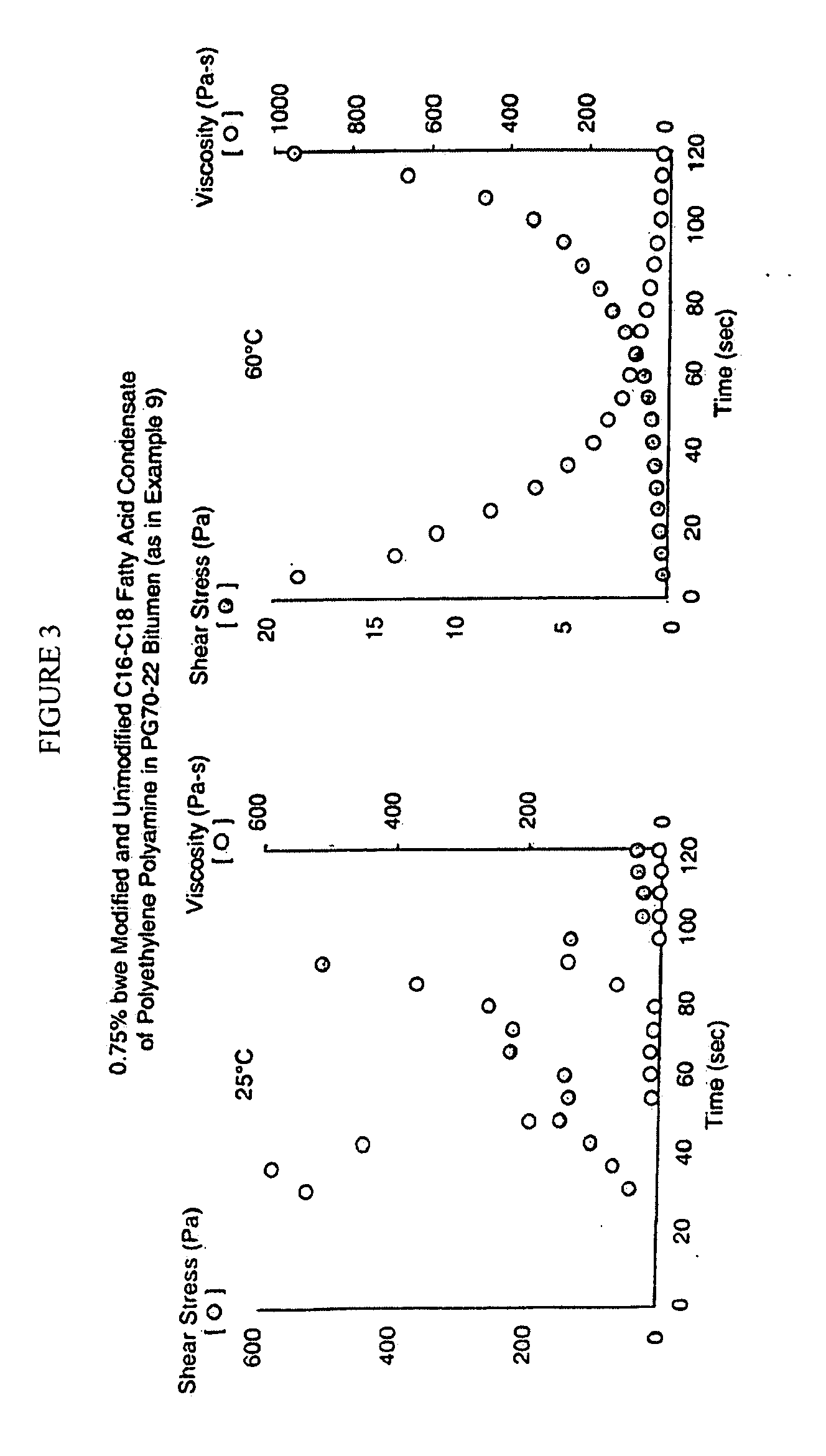
The present invention relates to bituminous compositions suitable for use in paving applications containing bitumen emulsion of performance-grade bitumen that is substantially free of volatile solvents and made by controlling temperature-dependent interfacial rheology through the use of selected emulsifiers. The invention bituminous paving compositions are suitable for the construction of load-bearing pavements with improved compaction to densities similar or superior to those achieved in the conventional hot mix bituminous paving compositions. Cure rate of the invention bituminous compositions is higher than those of cold mix bitumen emulsion-based paving compositions, and at least equal to those of hot mix bituminous paving compositions. Additionally, the invention bituminous compositions develop adhesive strength and load-bearing strength properties at rates comparable to those of hot mix bituminous paving compositions, and at rates faster than those of cold mix bituminous paving compositions.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Directly compressed solid dosage articles
InactiveUS6623756B1Low amountImprove flow characteristicsPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkControl release
Solid dosage articles such as pharmaceutical tablets for the controlled release of a desired compound such as an active ingredient are directly compressed from a flowable, compressible mixture of the active ingredient, a slightly cross-linked rheology modifying polymer or copolymer, and one or more excipients. The rheology modifying polymer or copolymer is a granulated powder of suitable particle size and is generally made from one or more unsaturated (di)carboxylic acids, half ester thereof, and other optional monomers.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Stable aqueous surfactant compositions
InactiveUS20050158268A1Good lookingLow compositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsHair dyesAcid substances
A stable, aqueous composition containing a substantially crosslinked alkali-swellable acrylate copolymer rheology modifier, a surfactant, an alkaline material, and various compounds therein, as for example substantially insoluble materials requiring suspension or stabilization, such as a silicone, an oily material, or a pearlescent material. Additionally, this invention also relates to the formation of a rheologically and phase stable cationic hair dye composition. The invention further relates to the incorporation of an acidic material after the addition of an alkaline material to reduce the pH of the composition without negatively impacting the viscosity of the composition.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Aerosol Cream Mousse and Method of Treating Hair
ActiveUS20080131378A1Low and reduced greasyLow and reduced and oily hair feelBiocideCosmetic preparationsAmmonium compoundsFatty alcohol
The present invention provides stable aerosol cream mousse composition, preferably hair care composition, that can provide enhanced touch, combability, alignment and volume reduction to the hair, with low or reduced greasy, oily hair feel, while being formulated having a thick, rich, creamy, mousse-type rheology with excellent spreading, perception of spreading, and feel. The aerosol composition is based on the combination of component (A) a cationic surfactant, which is generally a quaternary ammonium compound such as e.g., ditallow dimethyl ammonium chloride; (B) a fatty alcohol, such as cetyl and stearyl alcohol; and (C) carbon dioxide.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
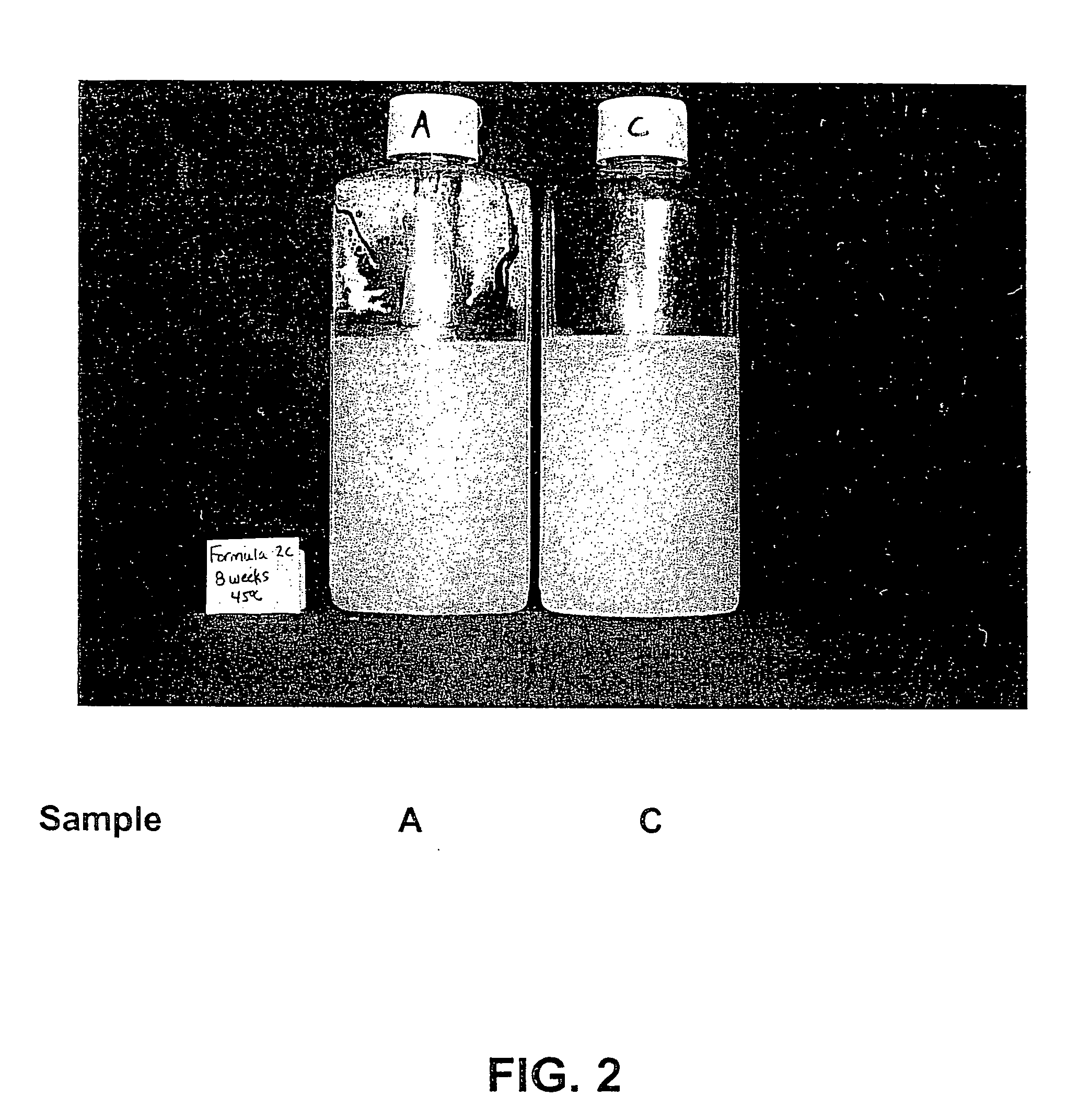
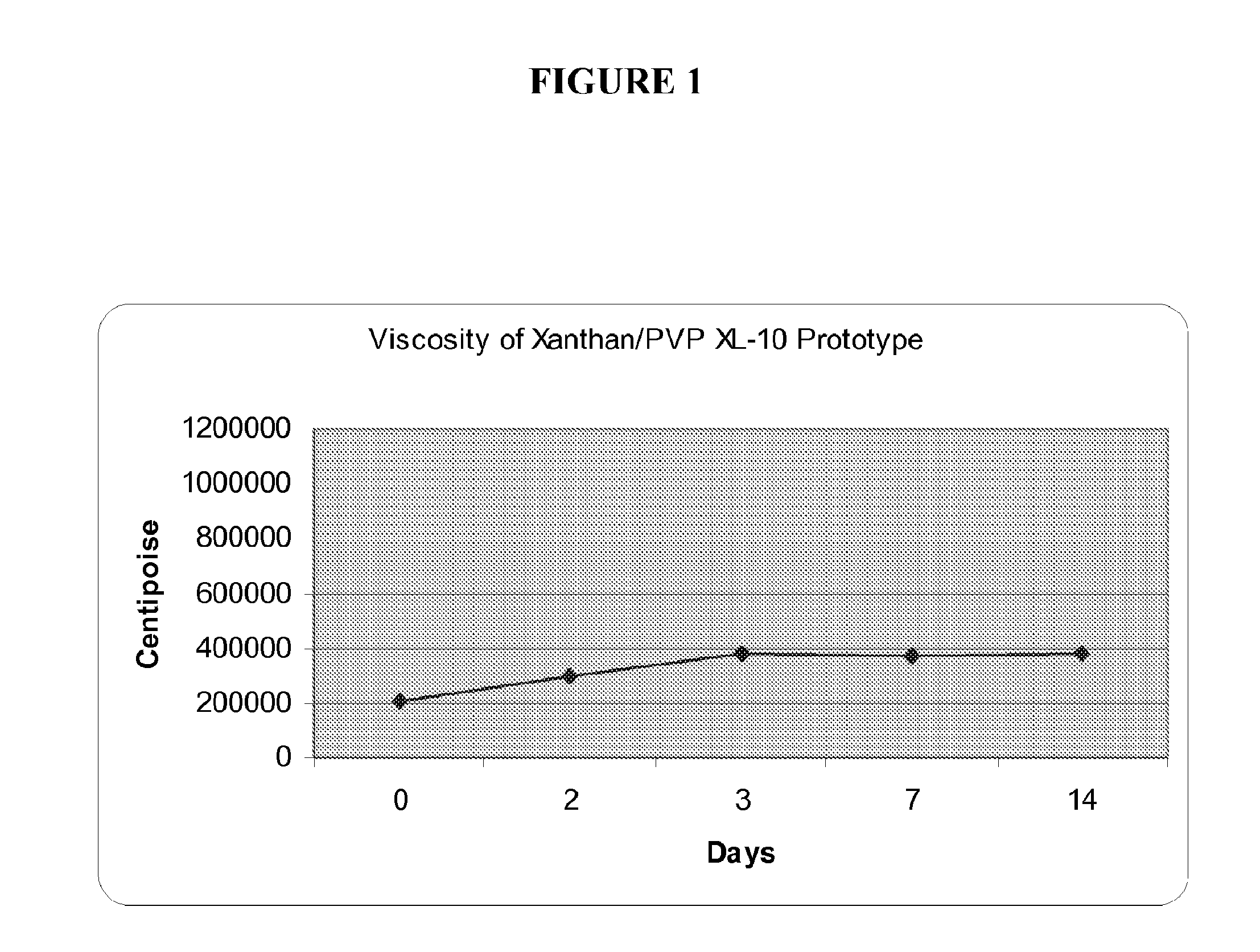
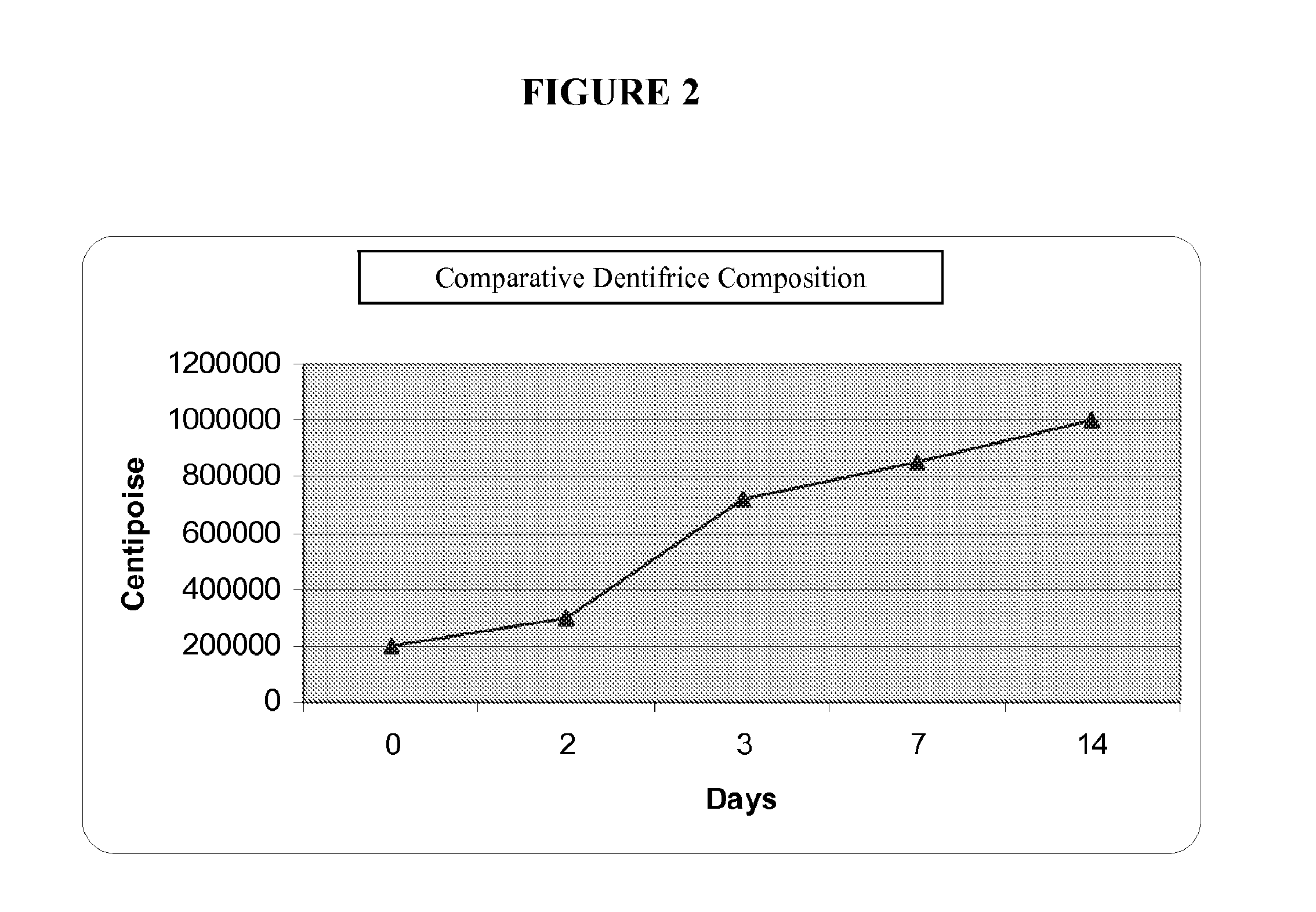
Low water stannous fluoride plus zinc citrate dentifrice with improved stability, rheology, and efficacy
ActiveUS20120207686A1Stable rheologyHigh viscosityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTActive ingredient
A dentifrice composition having a low water phase comprising effective amounts of polyphosphate and ionic active ingredients.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
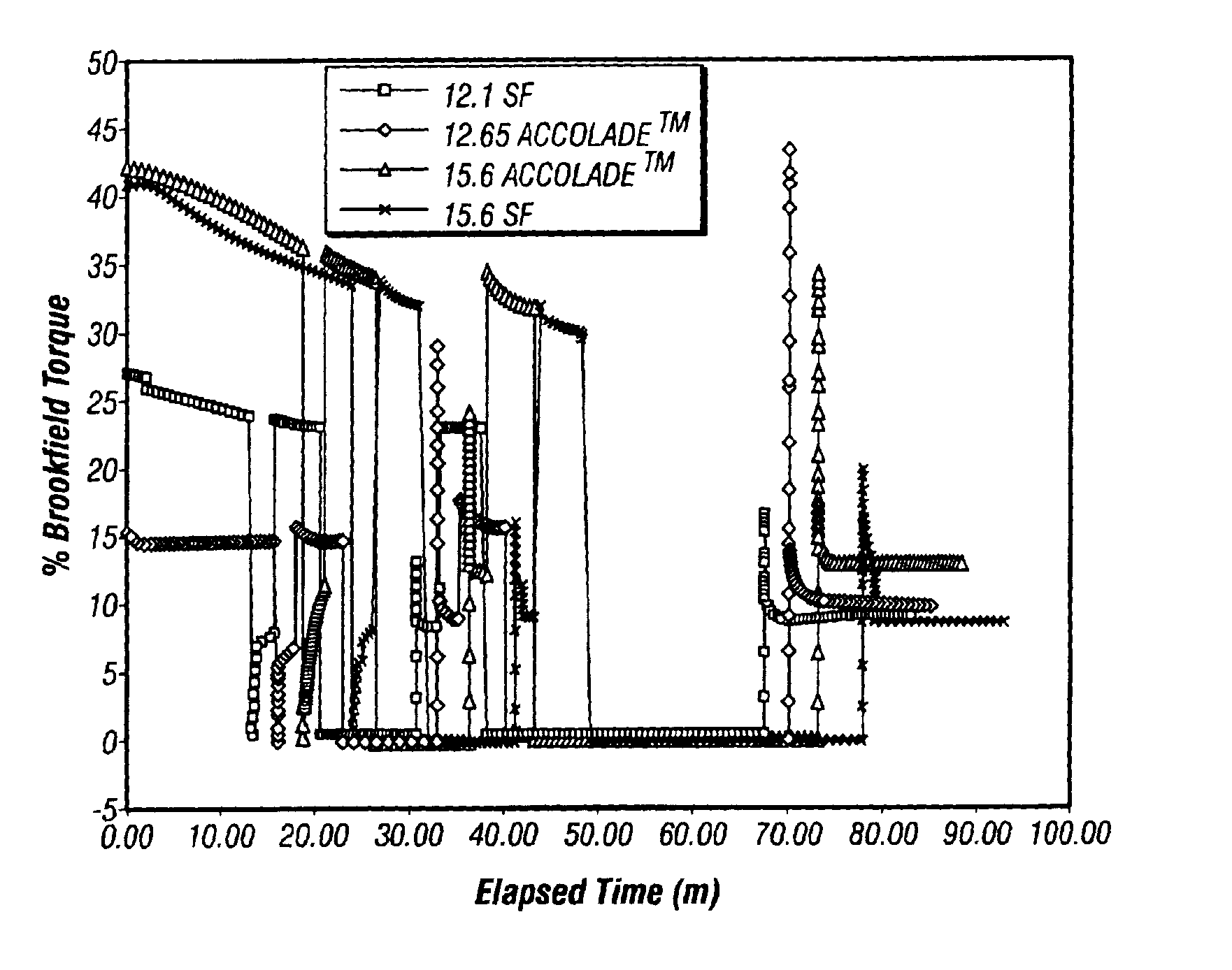
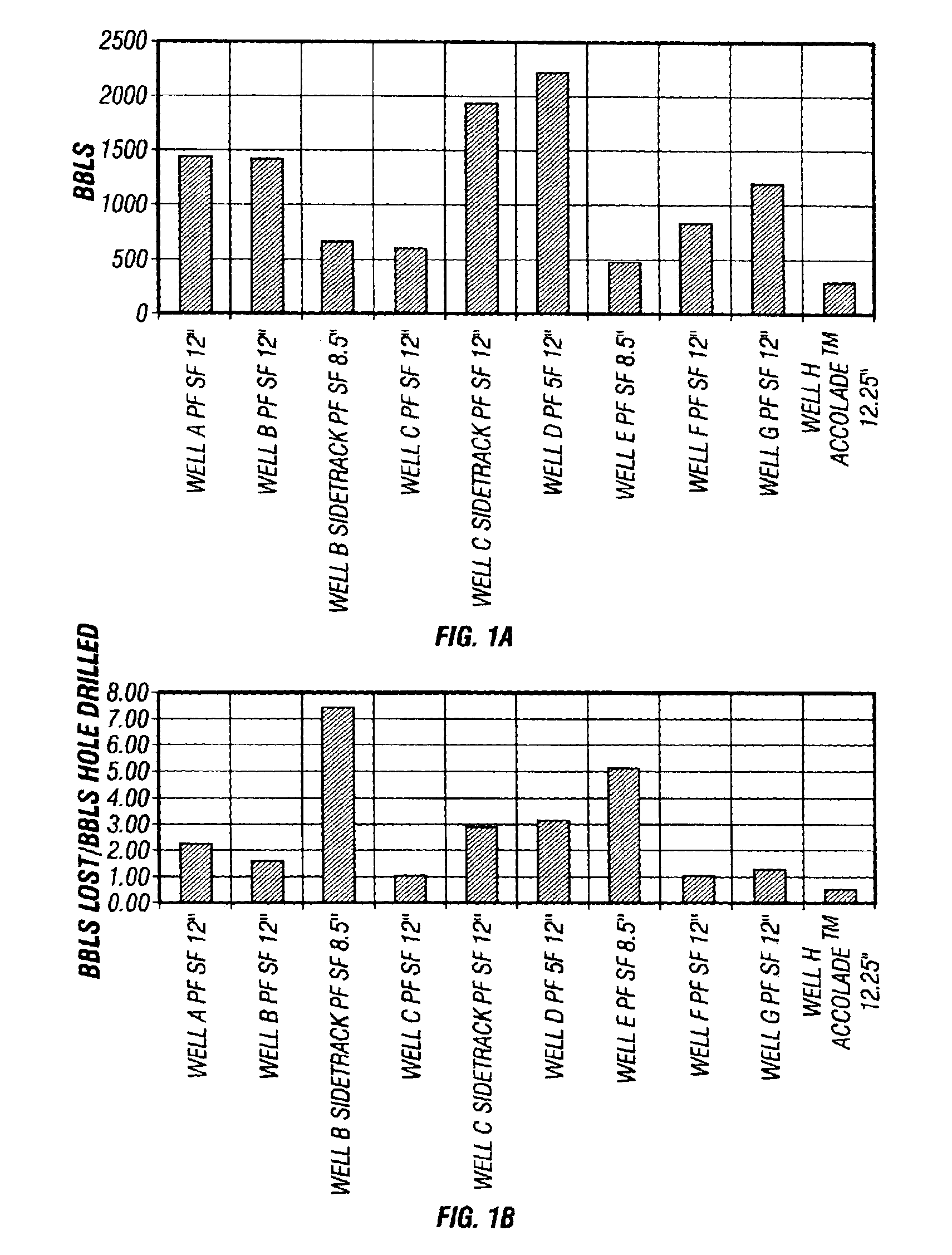
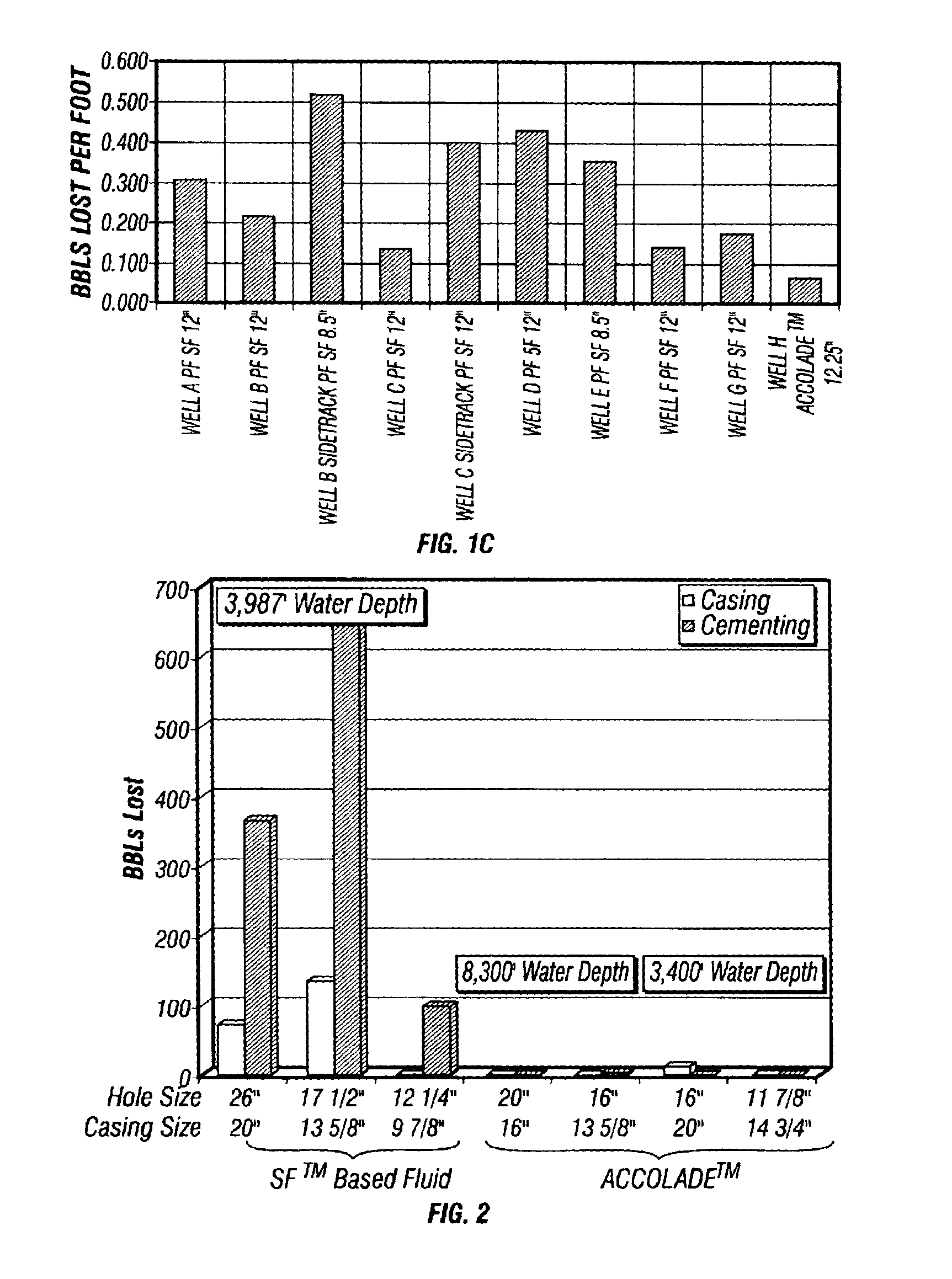
Method of formulating and using a drilling mud with fragile gels
A method for drilling, running casing in, and / or cementing a borehole in a subterranean formation without significant loss of drilling fluid is disclosed, as well as compositions for use in such method. The method employs a drilling fluid comprising a fragile gel or having fragile gel behavior and providing superior oil mud rheology and overall performance. The fluid is especially advantageous for use in deep water wells because the fluid exhibits minimal difference between downhole equivalent circulating density and surface density notwithstanding differences in drilling or penetration rates. When an ester and isomerized olefin blend is used for the base of the fluid, the fluid makes an environmentally acceptable and regulatory compliant invert emulsion drilling fluid. The fluid preferably contains no organophilic clays.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
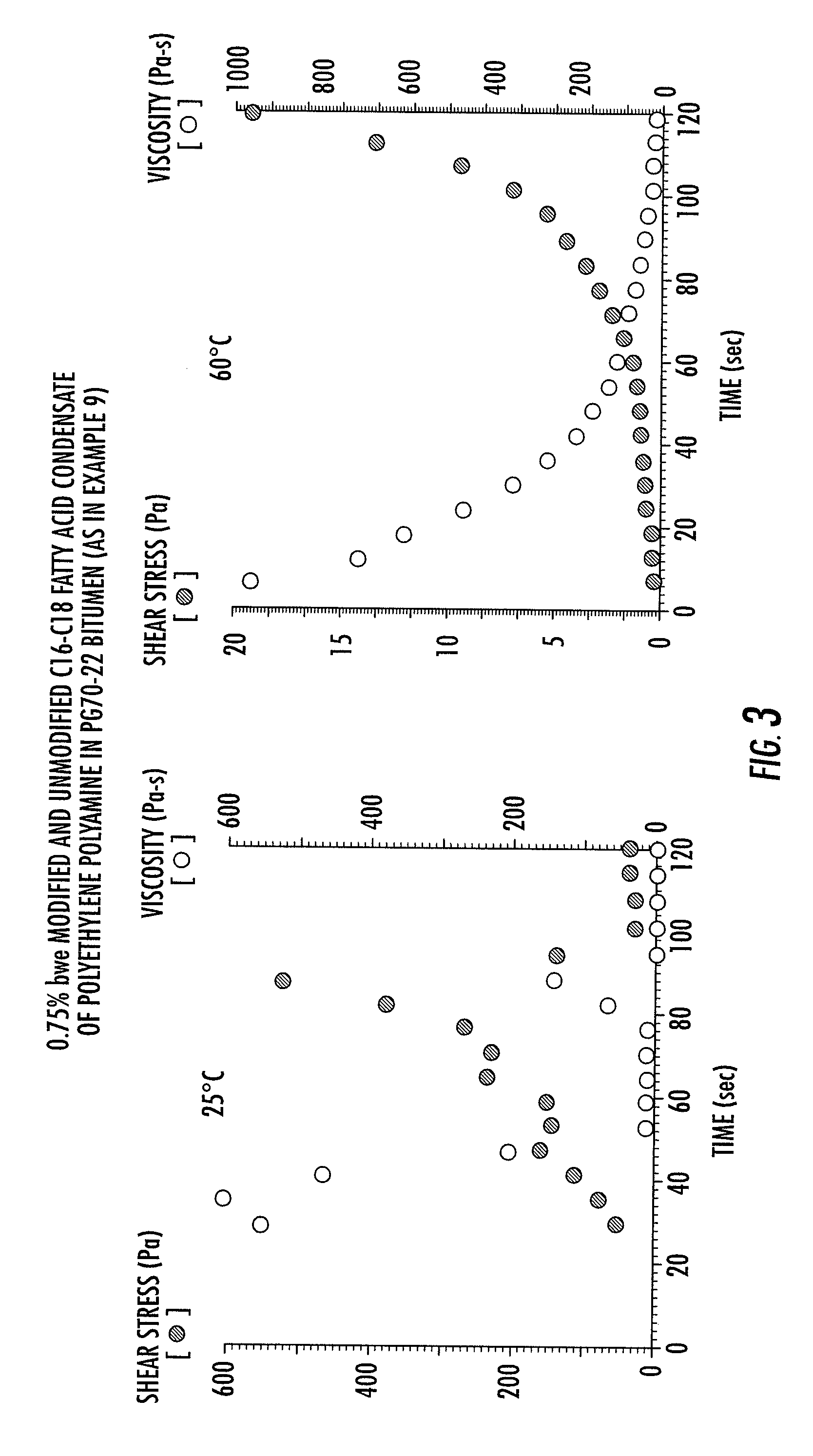
Method for producing bituminous compositions
InactiveUS20070039520A1Low viscosityHighly preventive effectOrganic chemistrySingle unit pavingsEmulsionSolvent free
This invention relates to bituminous compositions and methods of producing the same. More particularly, the invention relates to the production of bituminous compositions formulated with performance-graded bitumen-containing solvent-free bitumen emulsions which exhibit controllable, temperature-dependent interfacial rheology. When employed in paving applications, these bituminous compositions develop adhesive strength and load-bearing strength properties at rates comparable to traditional hot mix paving compositions and at rates faster than traditional cold mix paving compositions.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
Lotioned tissue product with improved stability
InactiveUS20050058833A1Easy transferImproved lubricating formulationBiocideCosmetic preparationsViscosityFacial tissue
Tissue products, such as bath tissue and facial tissue, comprising an improved lubricating formulation are disclosed. The lubricating formulation is applied to at least one surface of the tissue product and is stable at elevated temperatures, remains on or near the surface of the tissue product prior to use, and readily transfer the user=s skin upon use. The lubricating formulations described herein have a melt point viscosity of from about 5000 cPs to about 1,000,000 cps, and a process temperature viscosity of from about 50 cPs to about 50,000 cPs. The lubricating formulations comprise an emollient, a structurant, a rheology enhancer, and other optional components.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method for the manufacture of microfibrillated cellulose
ActiveUS20090221812A1Reduce energy consumptionCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesMultistage pulping processHemicelluloseEnzyme
A method for treatment of chemical pulp for the manufacturing of microfibrillated cellulose includes the following steps: a) providing a hemicellulose containing pulp, b) refining the pulp in at least one step and treating the pulp with one or more wood degrading enzymes at a relatively low enzyme dosage, and c) homogenizing the pulp thus providing the microfibrillated cellulose. According to a second aspect of the invention a microfibrillated cellulose obtainable by the method according to the first aspect is provided. According to a third aspect of the invention, use of the microfibrillated cellulose according to the second aspect in food products, paper products, composite materials, coatings or in rheology modifiers (e.g. drilling muds) is provided.
Owner:STFI PACKFORSK AB
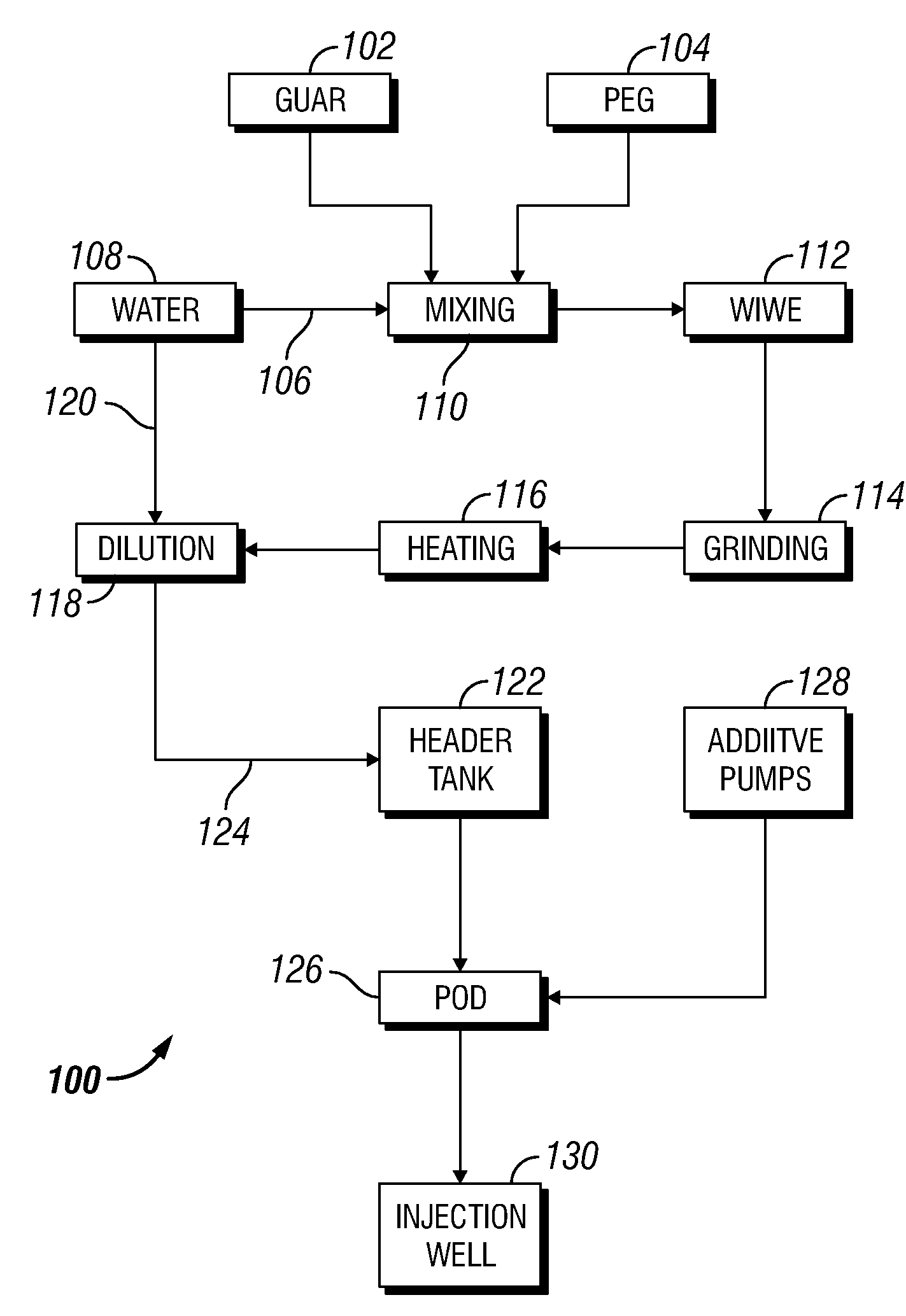
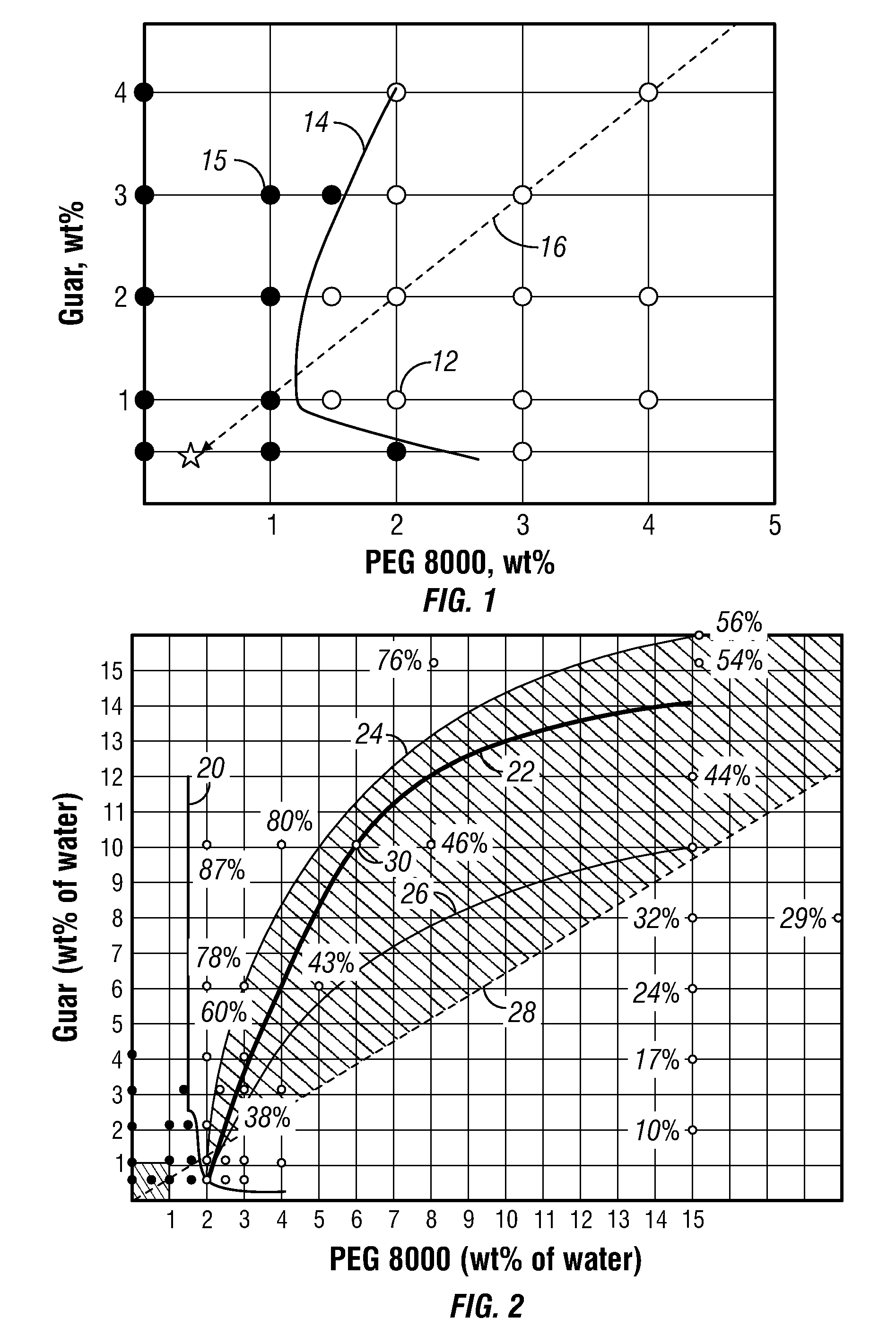
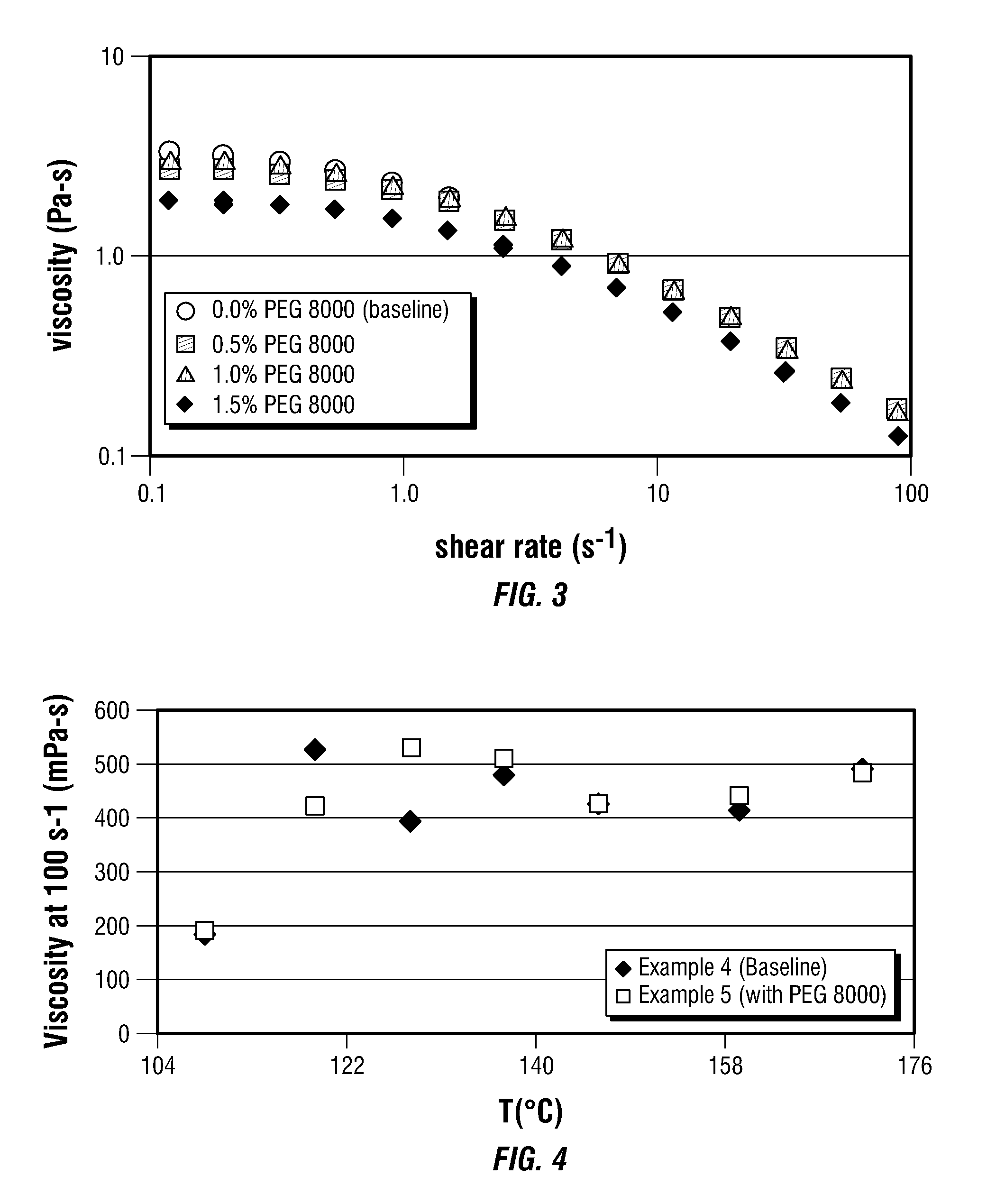
Polymer Delivery in Well Treatment Applications
InactiveUS20090023614A1Reduce solubilityEasy to pumpTransportation and packagingFluid removalActive polymerEmulsion
This invention relates to compositions and methods for treating subterranean formations, in particular, oilfield stimulation compositions and methods using water-in-water polymer emulsions to uniformly dissolve a rheologically active polymer, such as a thickener or friction reducer, in the treatment fluid. The emulsions have a low viscosity and are easily pumped for mixing into a treatment fluid, where upon dilution with an aqueous medium, the polymer is easily hydrated without forming fish-eyes. The partitioning agent in the water-in-water emulsion does not generally affect the rheology of the treatment fluid. The invention also relates to further processing of the emulsion by wet grinding, high shear mixing and / or heating to enhance the hydration rate in the preparation of the well treatment fluid.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Sprayable water-based adhesive
InactiveUS20070224395A1Efficient use ofProlong lifeAdhesive processesRoof covering using sealantsWet bondingWater based
Water-based adhesive compositions are improved by the incorporation of hollow polymeric microspheres having outer surfaces coated with one or more barrier materials such as calcium carbonate particles. The adhesive compositions exhibit enhanced rheology, sprayability, drying time, tack and storage stability as compared to analogous adhesives that are not modified with coated hollow polymeric microspheres. Such compositions are useful as both contact adhesives as well as wet bonding one-way adhesives.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Associative thickeners for aqueous systems
Thiocarbonate compounds which, in one embodiment, are utilized as a rheology modifier or associative thickener. The thiocarbonate compounds thicken or increase the viscosity of a composition, preferably an aqueous composition when used in an effective amount. In one preferred embodiment, the thiocarbonate compounds include at least one hydrophilic group containing repeat unit such as derived from acrylic acid, and at least one hydrophobic group to enhance association with other compounds and thus increase viscosity of a composition. Aqueous composition comprising a latex and thiocarbonate associative thickeners are described.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com