Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
384results about "Multistage pulping process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
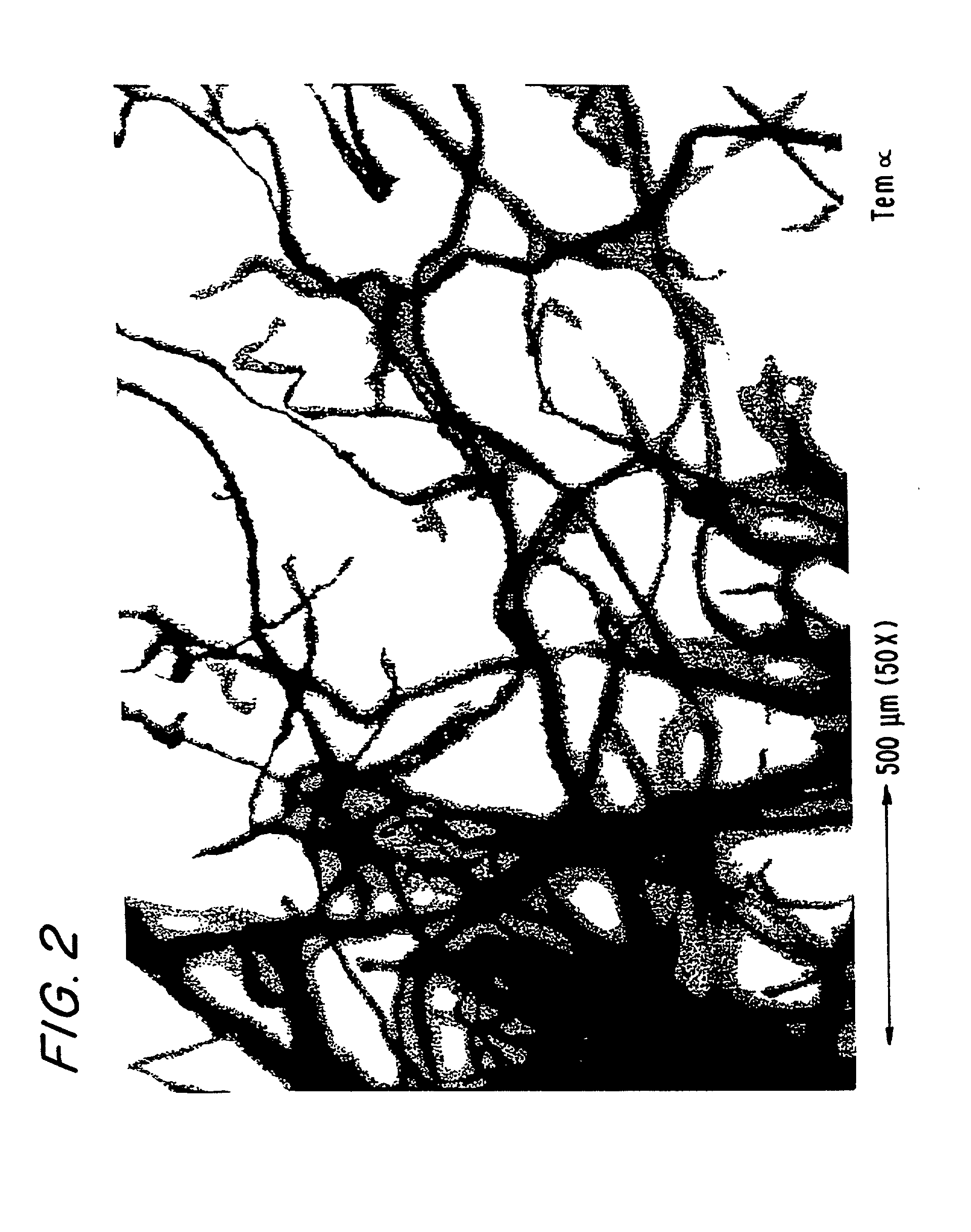
Cellulose nanofilaments and method to produce same
ActiveUS20110277947A1Improve strength propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer sciencePaperboard
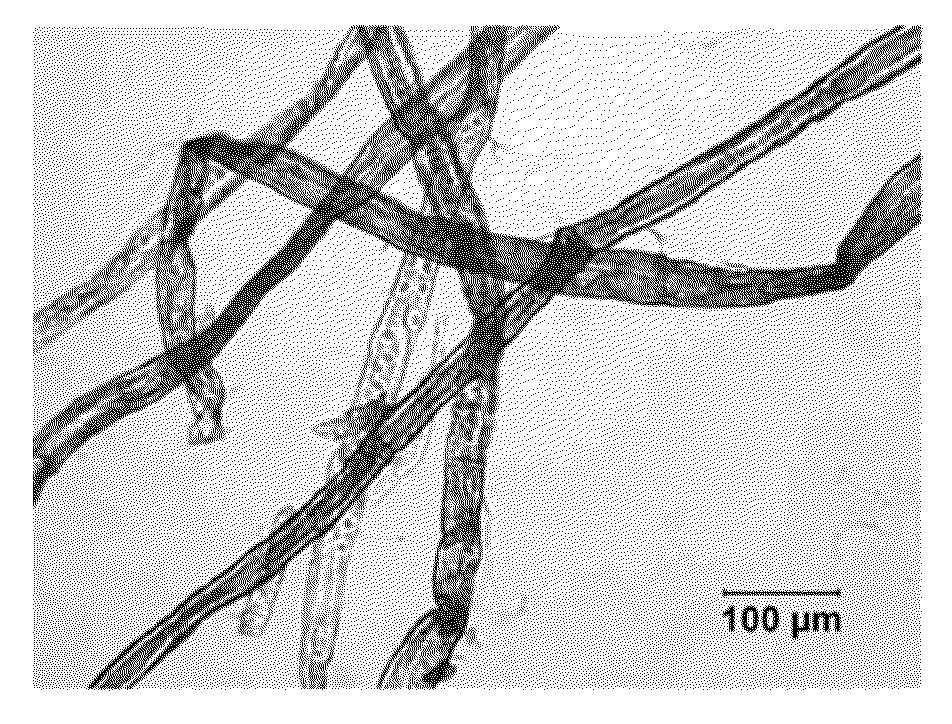
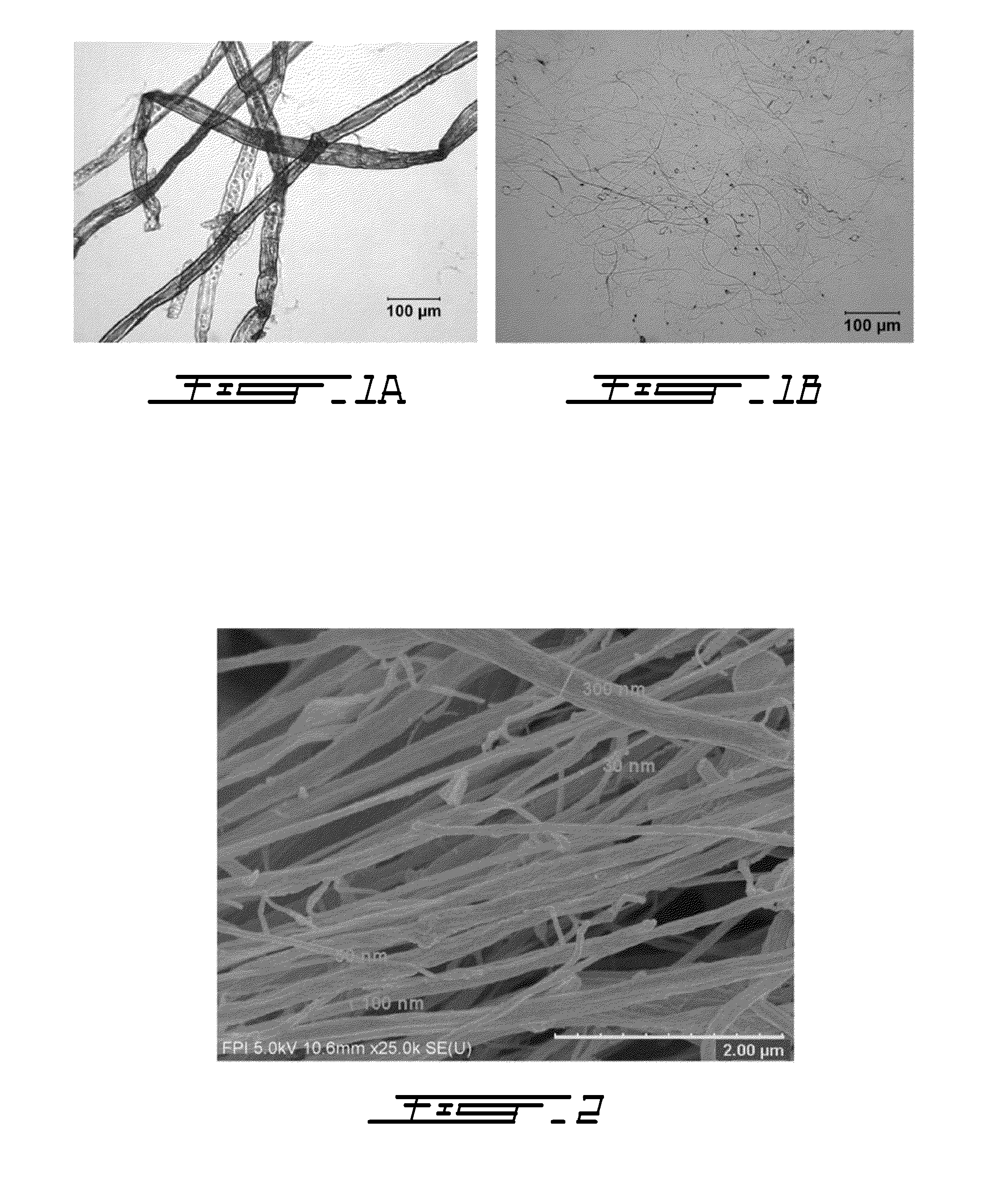
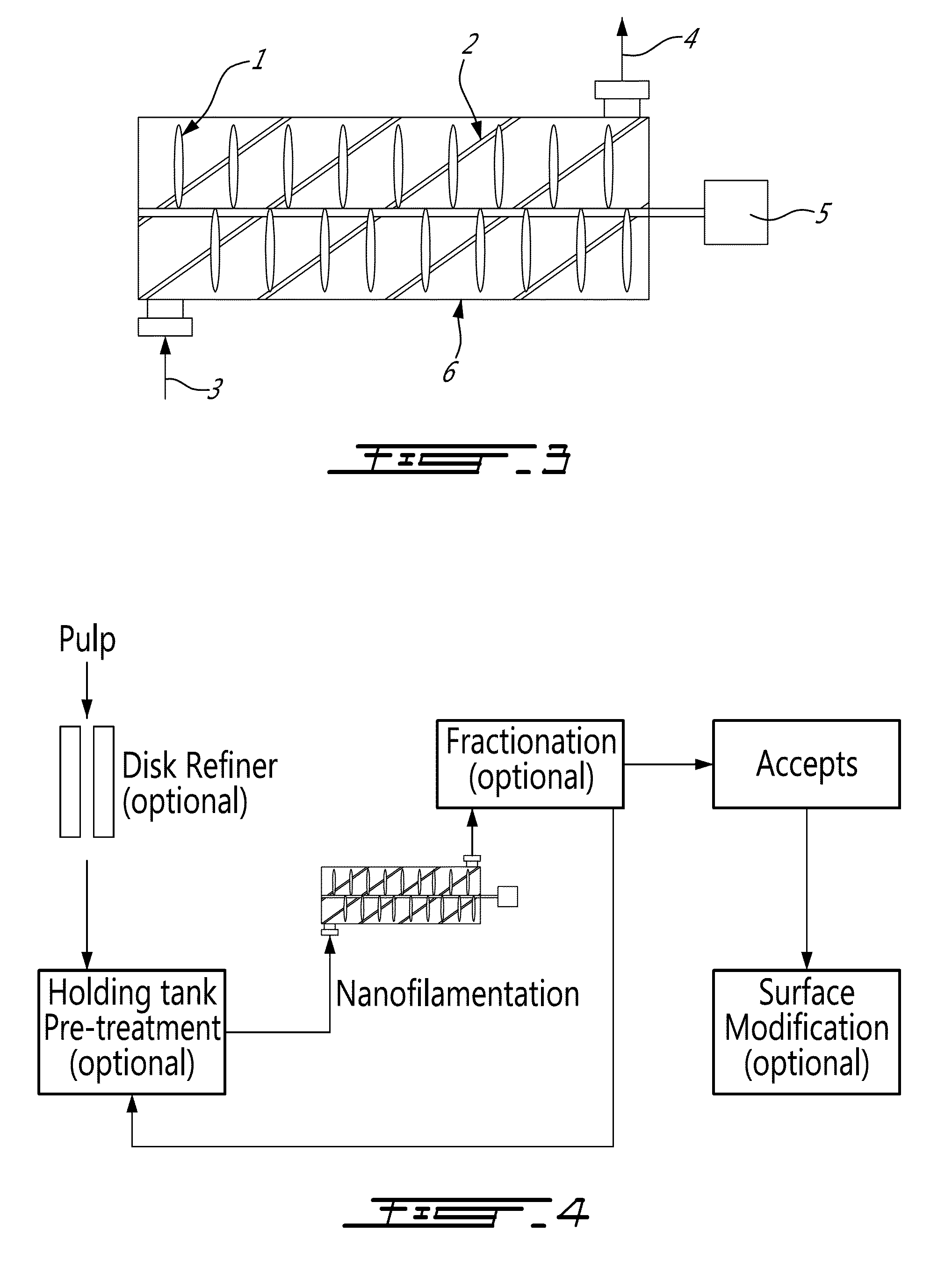
Cellulose nanofilaments from cellulose fibers, a method and a device to produce them are disclosed. The nanofilaments are fine filaments with widths in the sub-micron range and lengths up to a couple of millimeters. These nanofilaments are made from natural fibers from wood and other plants. The surface of the nanofilaments can be modified to carry anionic, cationic, polar, hydrophobic or other functional groups. Addition of these nanofilaments to papermaking furnishes substantially improves the wet-web strength and dry sheet strength much better than existing natural and synthetic polymers. The cellulose nanofilaments produced by the present invention are excellent additives for reinforcement of paper and paperboard products and composite materials, and can be used to produce superabsorbent materials.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
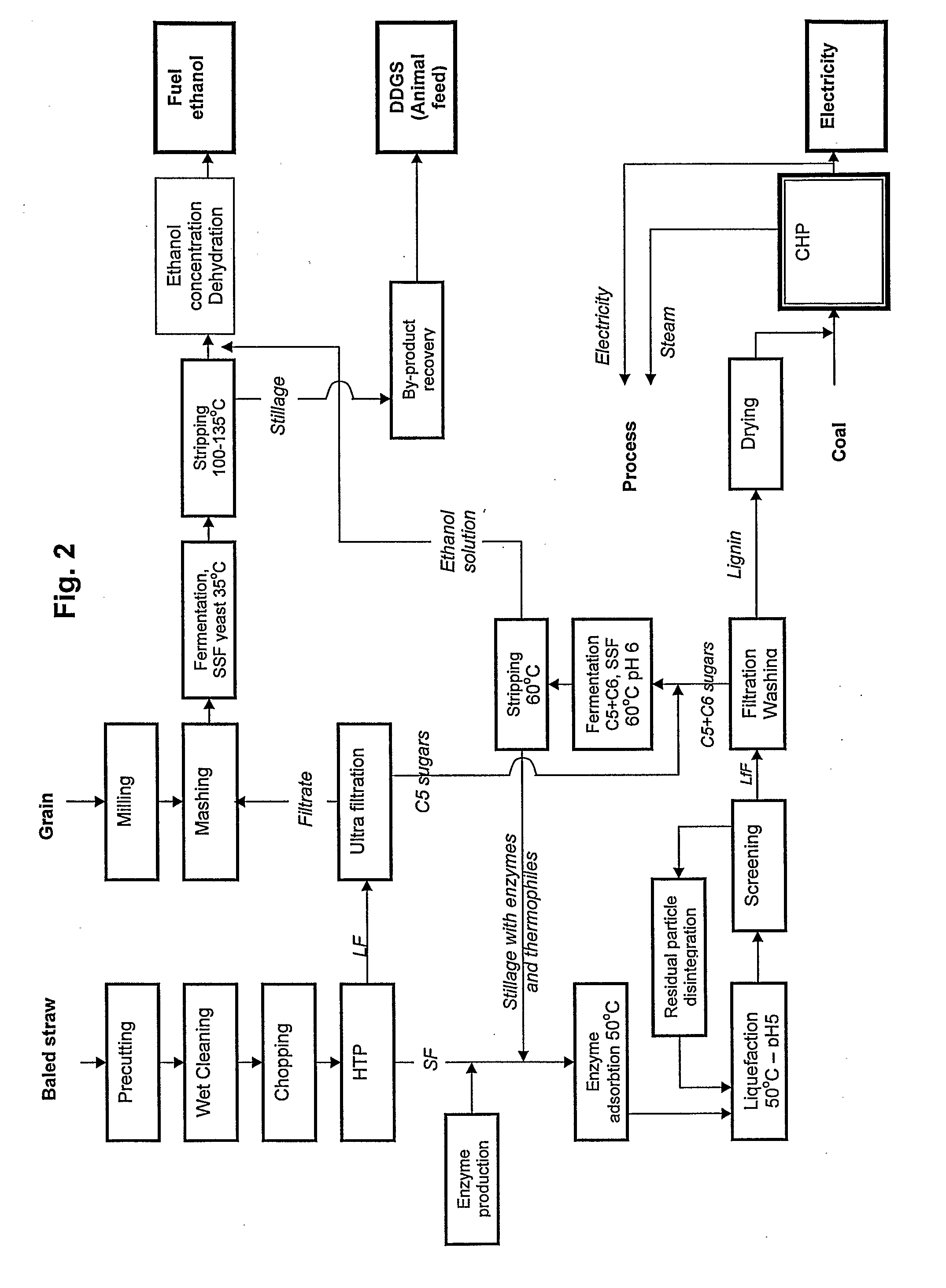
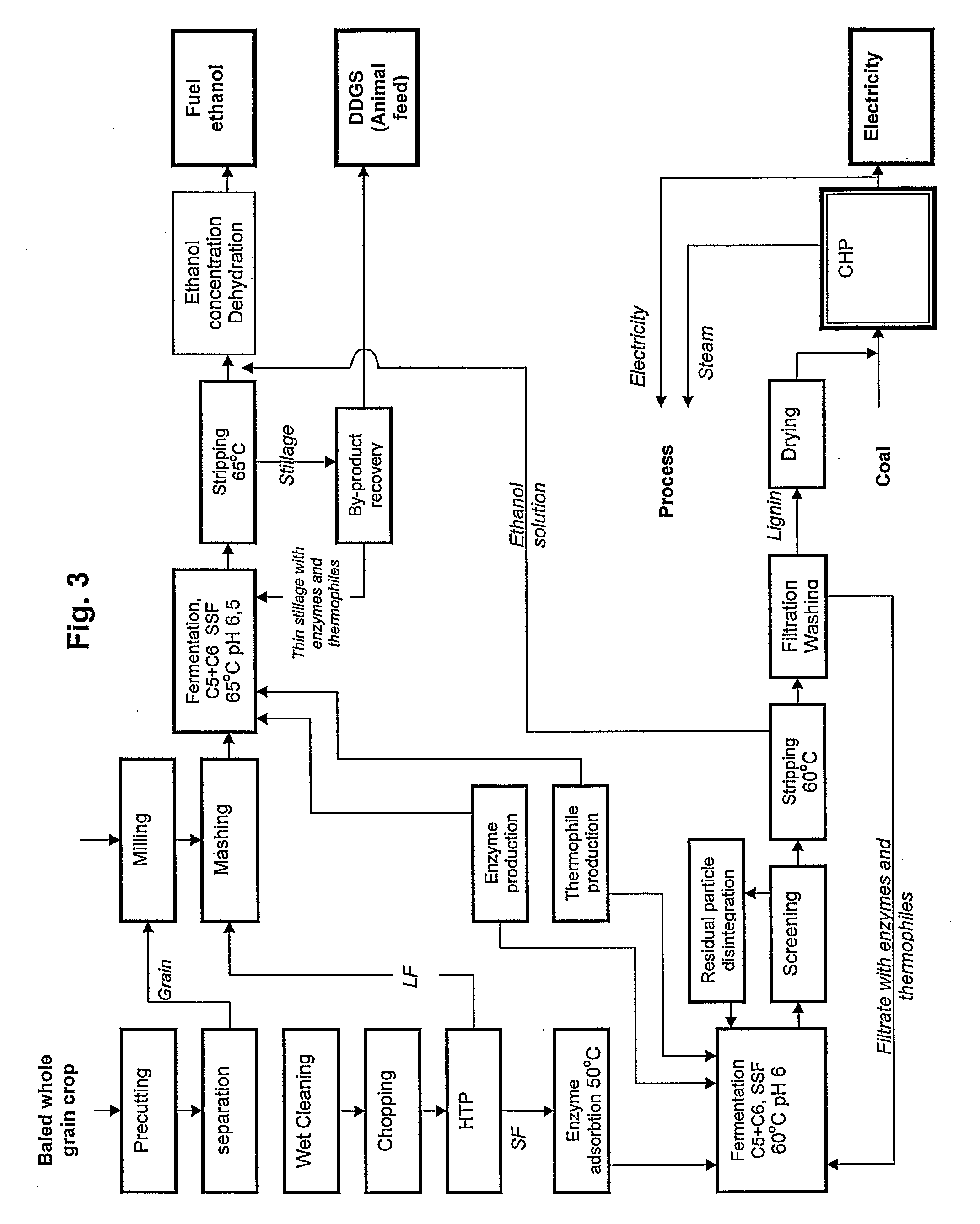
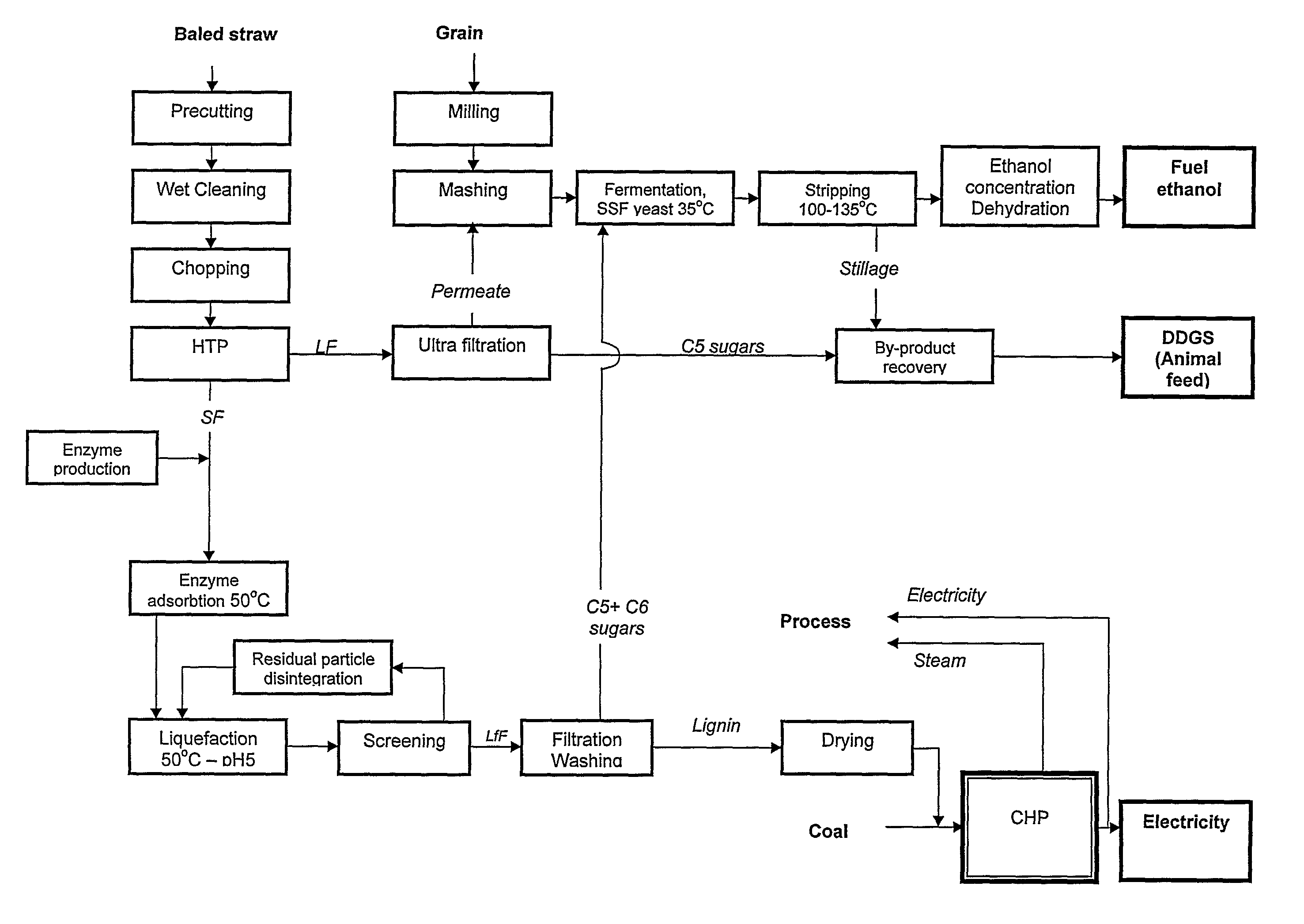
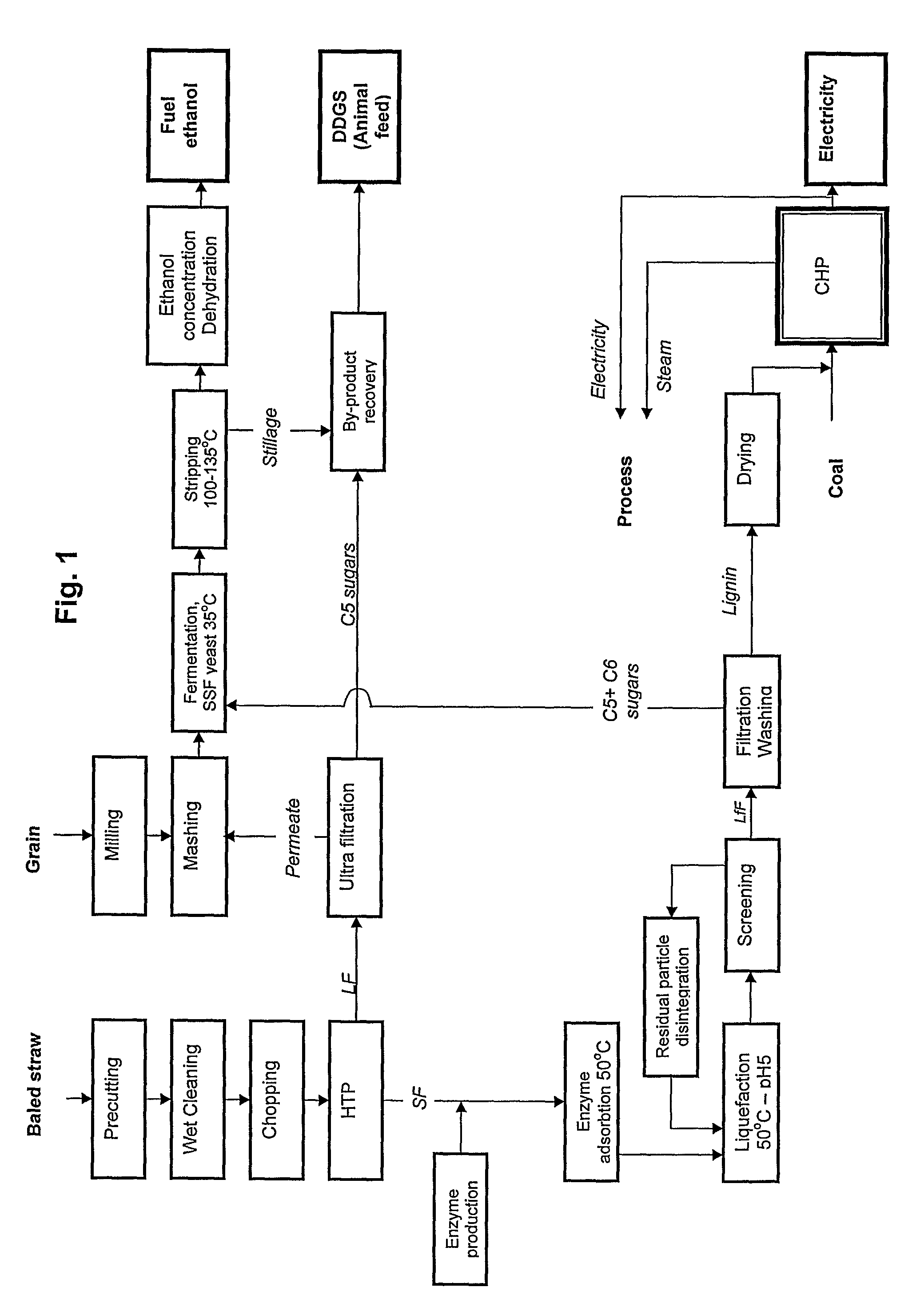
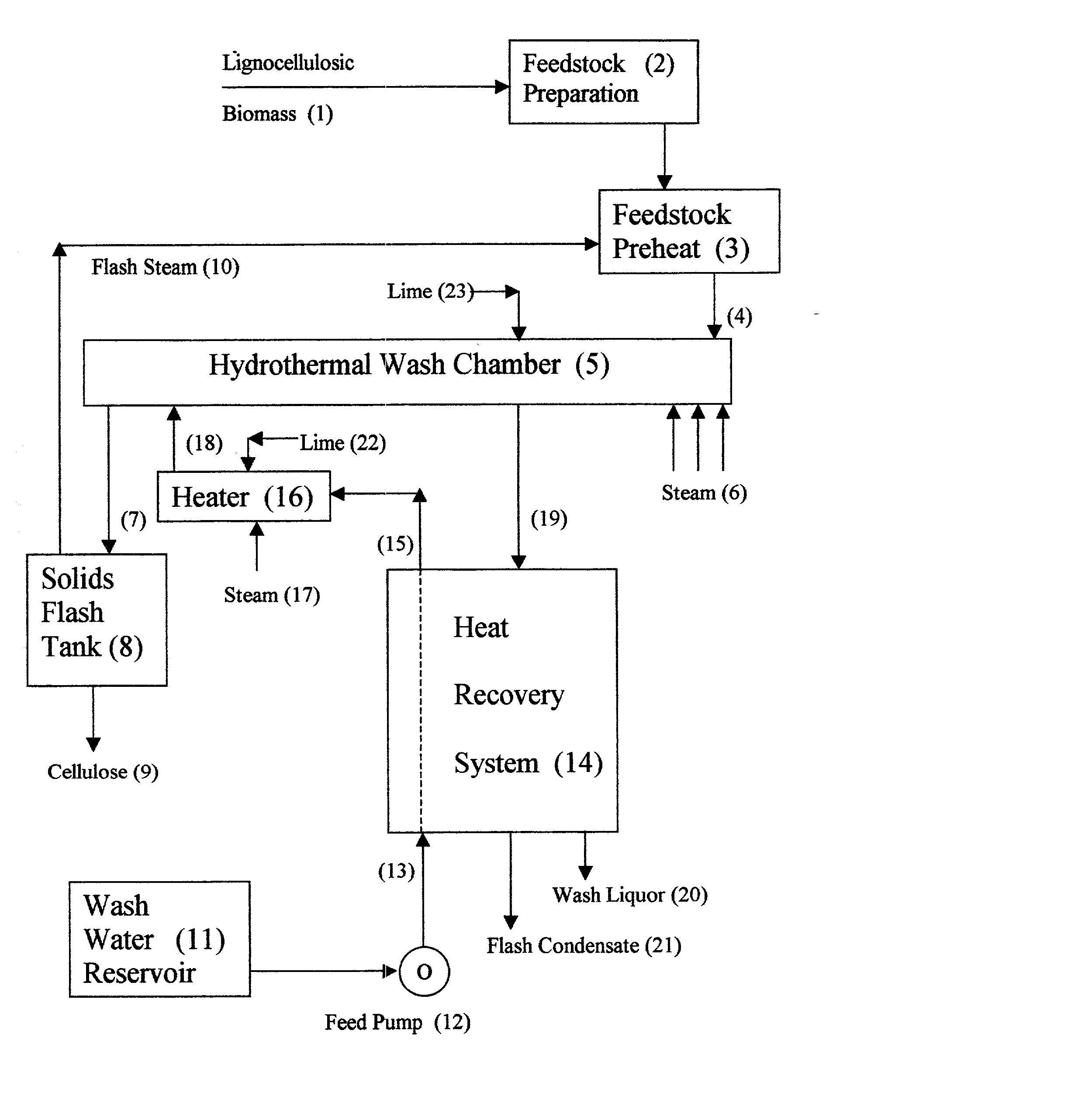
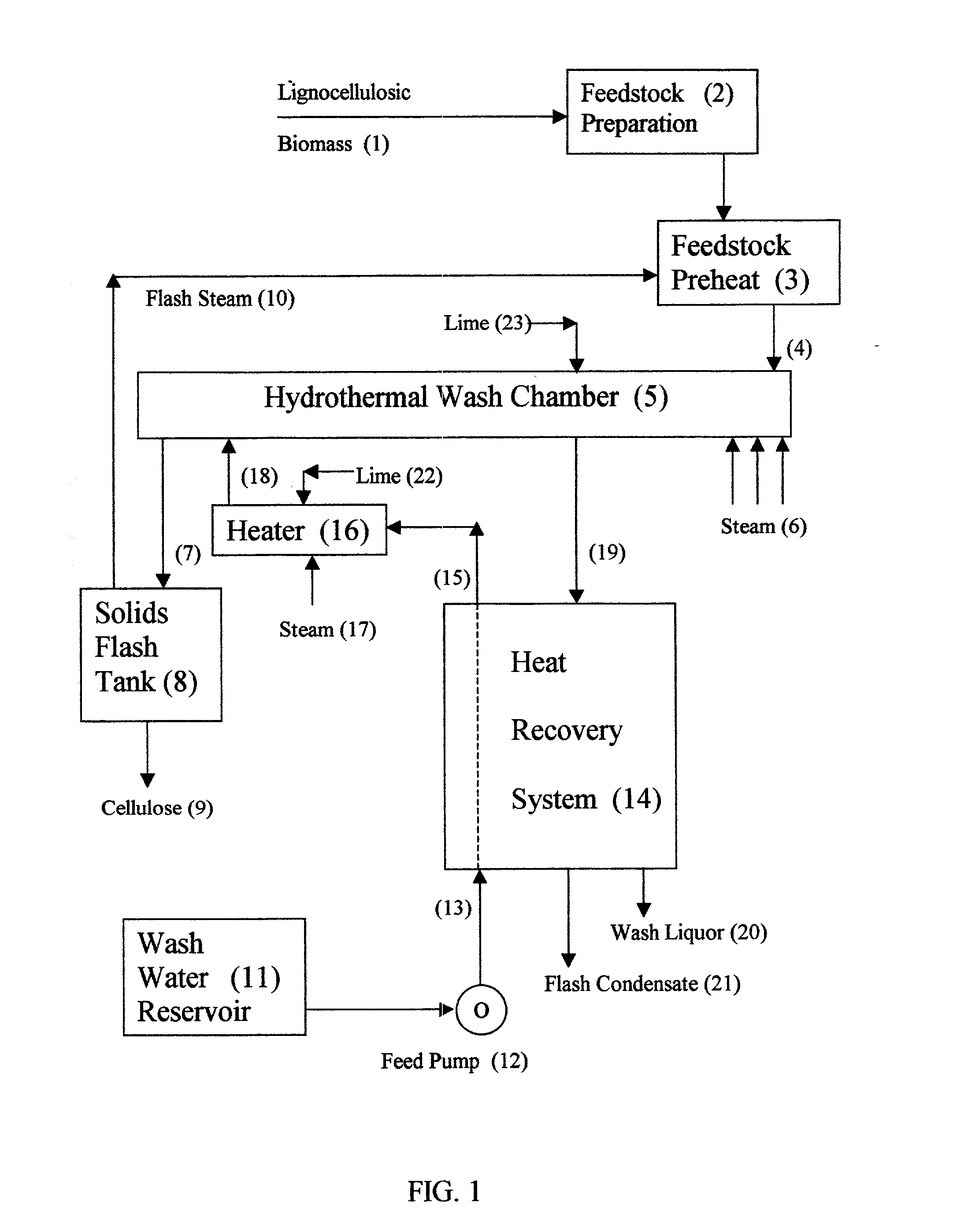
Method and apparatus for conversion of cellulosic material to ethanol
ActiveUS20100041119A1Low costDown rate of fermentationBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofuelsFiberCellulose
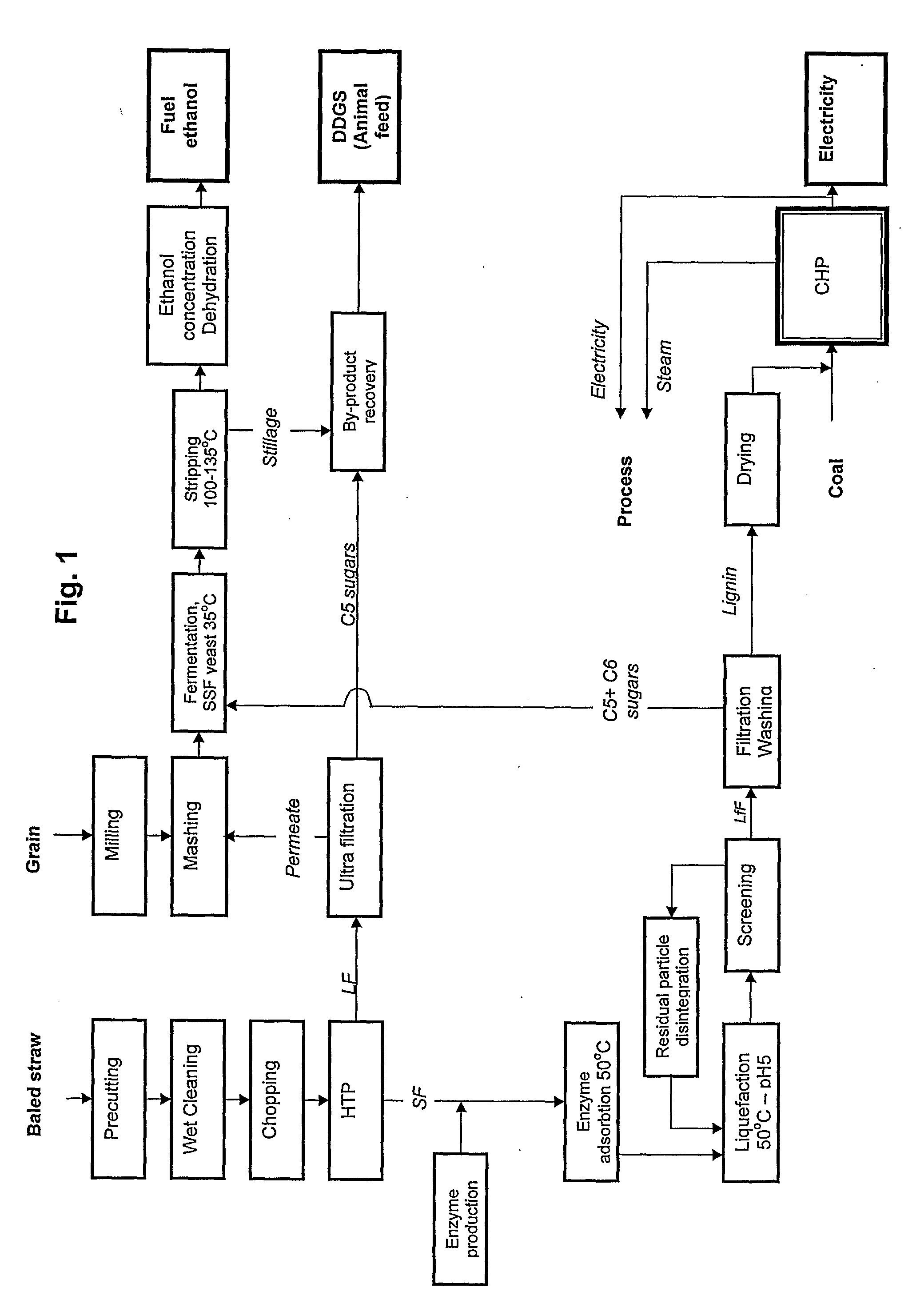
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for conversion of cellulosic material, such as chopped straw and corn stover, and household waste, to ethanol and other products. The cellulosic material is subjected to continuous hydrothermal pre-treatment without addition of chemicals, and a liquid and a fibre fraction are produced. The fibre fraction is subjected to enzymatic liquefaction and saccharification. The method of the present invention comprises:performing the hydrothermal pre-treatment by subjecting the cellulosic material to at least one soaking operation, and conveying the cellulosic material through at least one pressurised reactor, and subjecting the cellulosic material to at least one pressing operation, creating a fibre fraction and a liquid fraction;selecting the temperature and residence time for the hydrothermal pretreatment, so that the fibrous structure of the feedstock is maintained and at least 80% of the lignin is maintained in the fibre fraction.
Owner:INBICON AS
Method for the manufacture of microfibrillated cellulose
ActiveUS20090221812A1Reduce energy consumptionCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesMultistage pulping processHemicelluloseEnzyme
A method for treatment of chemical pulp for the manufacturing of microfibrillated cellulose includes the following steps: a) providing a hemicellulose containing pulp, b) refining the pulp in at least one step and treating the pulp with one or more wood degrading enzymes at a relatively low enzyme dosage, and c) homogenizing the pulp thus providing the microfibrillated cellulose. According to a second aspect of the invention a microfibrillated cellulose obtainable by the method according to the first aspect is provided. According to a third aspect of the invention, use of the microfibrillated cellulose according to the second aspect in food products, paper products, composite materials, coatings or in rheology modifiers (e.g. drilling muds) is provided.
Owner:STFI PACKFORSK AB
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
ActiveUS20070079944A1Easy to optimizePretreatment with water/steamPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp and paper industrySugar
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
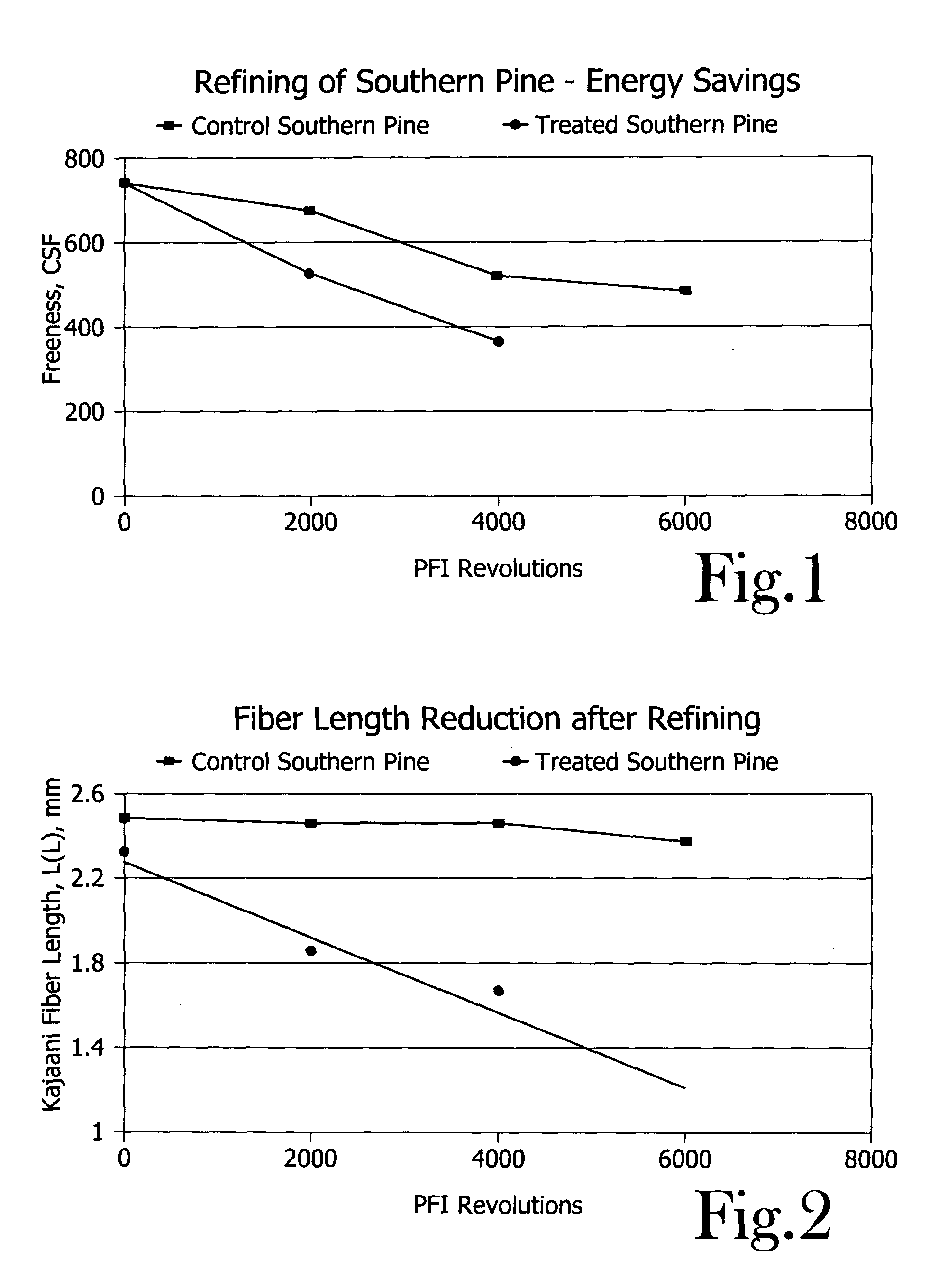
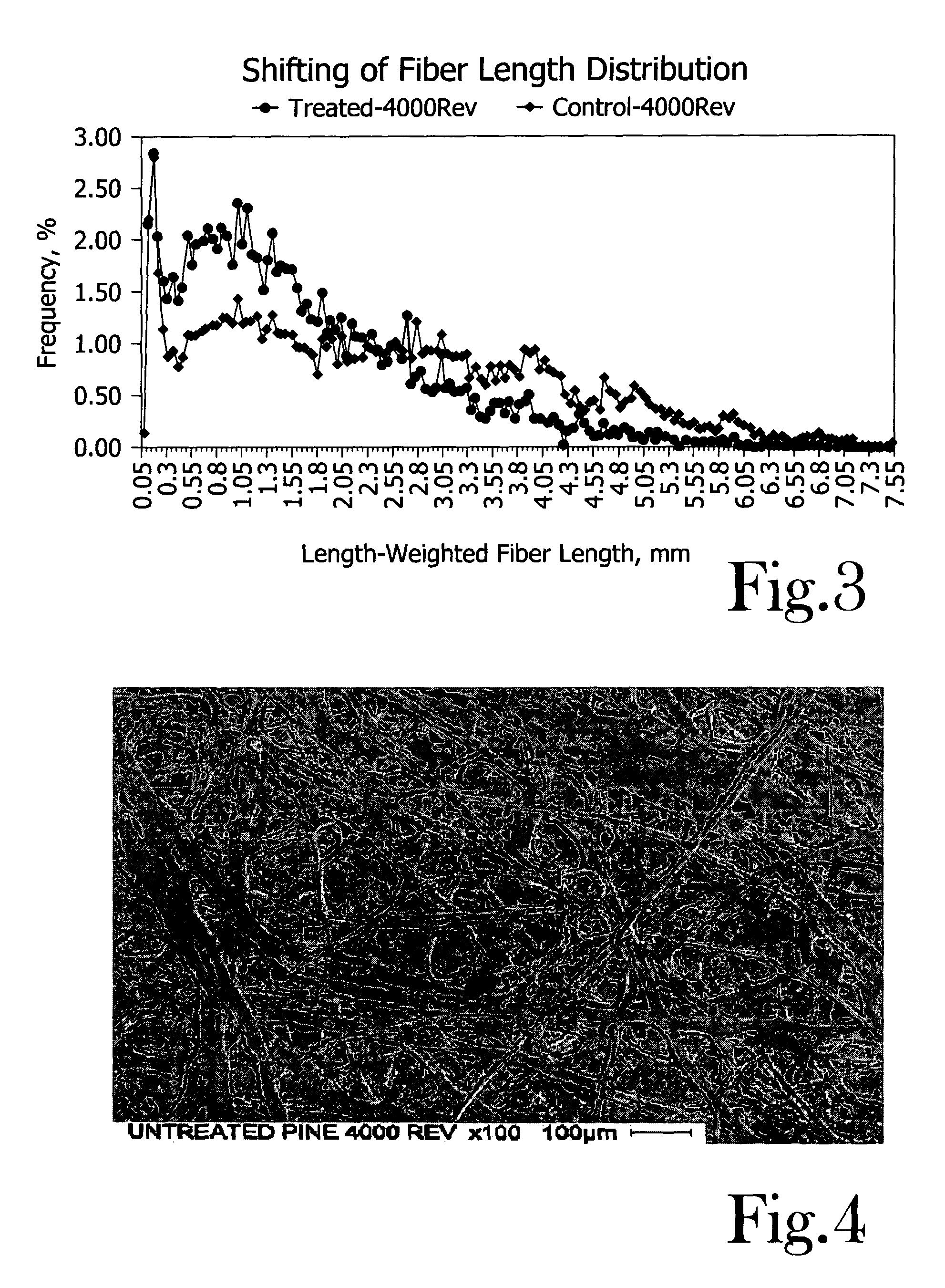
Chemical activation and refining of southern pine kraft fibers
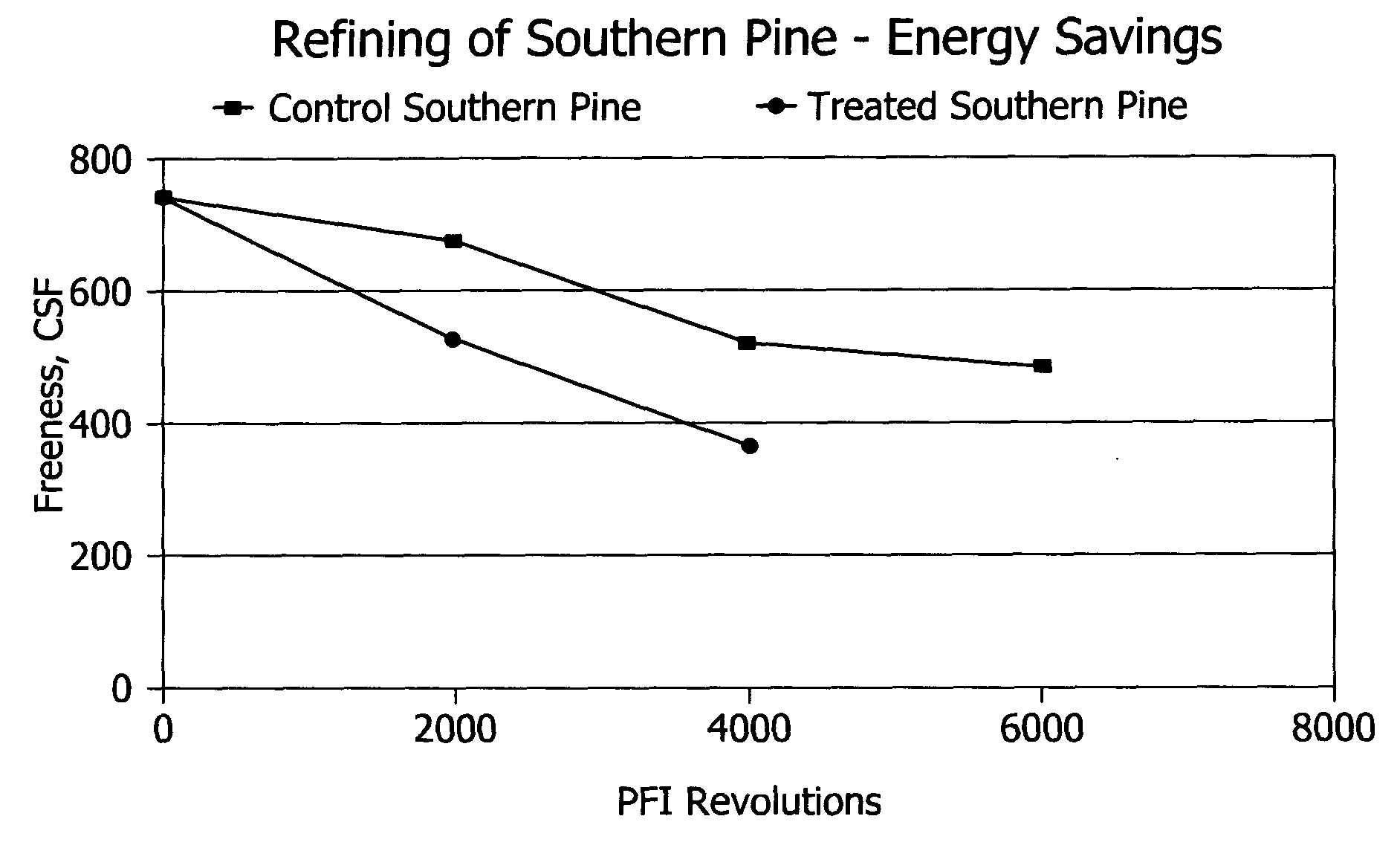
InactiveUS20050061455A1Increase the pulp freenessEasy to drainPulp properties modificationPulp bleachingChemical treatmentCellulose fiber
A method for alteration of the morphology of cellulose fibers, particularly softwood fibers, by (a) subjecting the fibers to a metal ion-activated peroxide treatment carried out at a pH of between about 1 and about 9, preferably between 3 and 7, and (b) subjecting the treated fibers to a refining treatment thereby converts SW fibers to HW-like fibers in many respects. The metal ion-activated peroxide treatment has been noted to act on pulp cellulose and hemi-cellulose, causing oxidation and oxidative degradation of cellulose fibers. The chemical treatment of the pulp, taken alone, is not sufficient to attain the desired modification of the morphology of the fibers, however, subsequent refining or like mechanical treatment of the chemically-treated fibers to achieve a given degree of refinement of the fibers requires dramatically less refining energy to achieve a desired end point of refinement and to impart other desirable properties to the pulp. A pulp of modified SW fibers and a mixture of HW fibers and modified HW fibers are disclosed.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
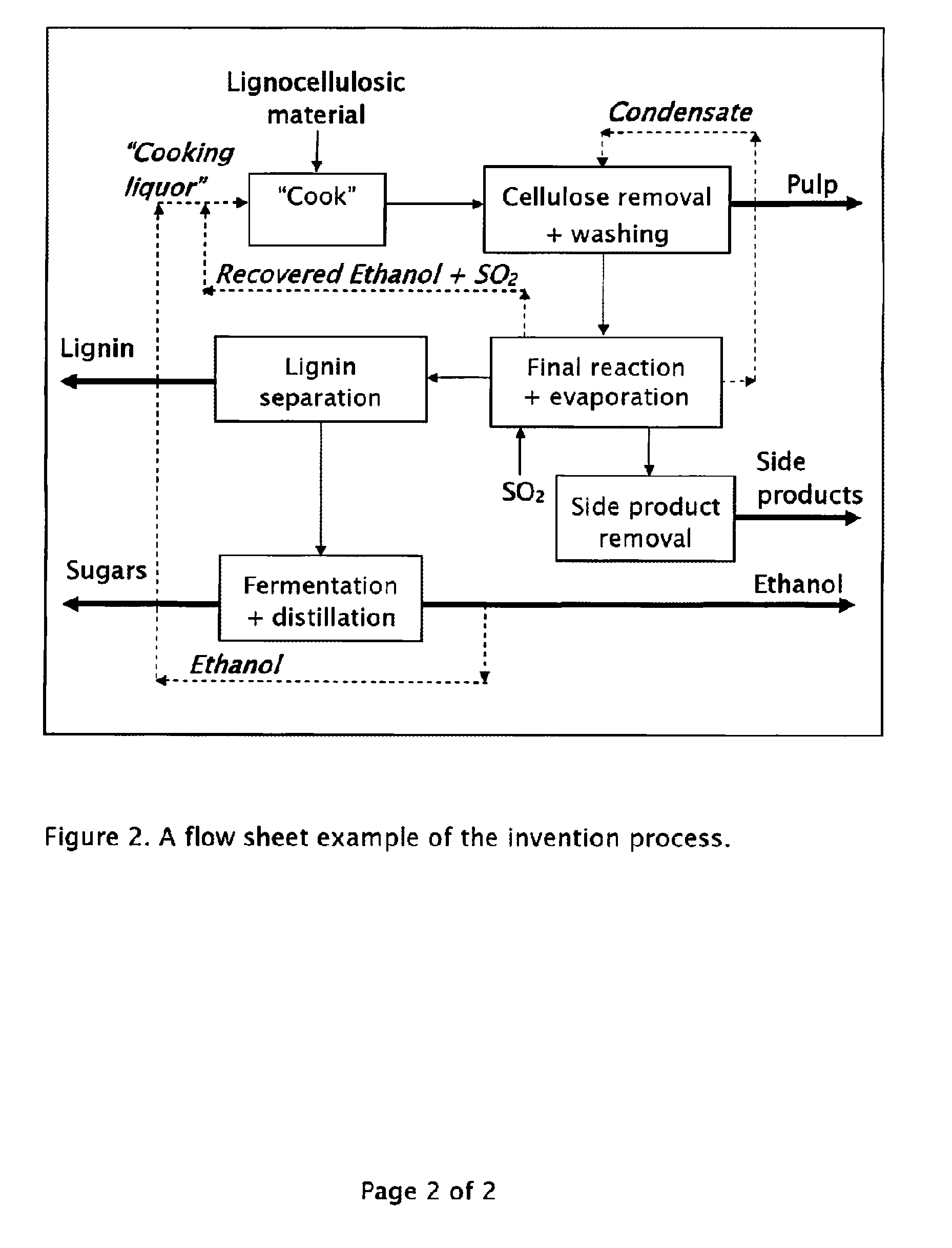
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
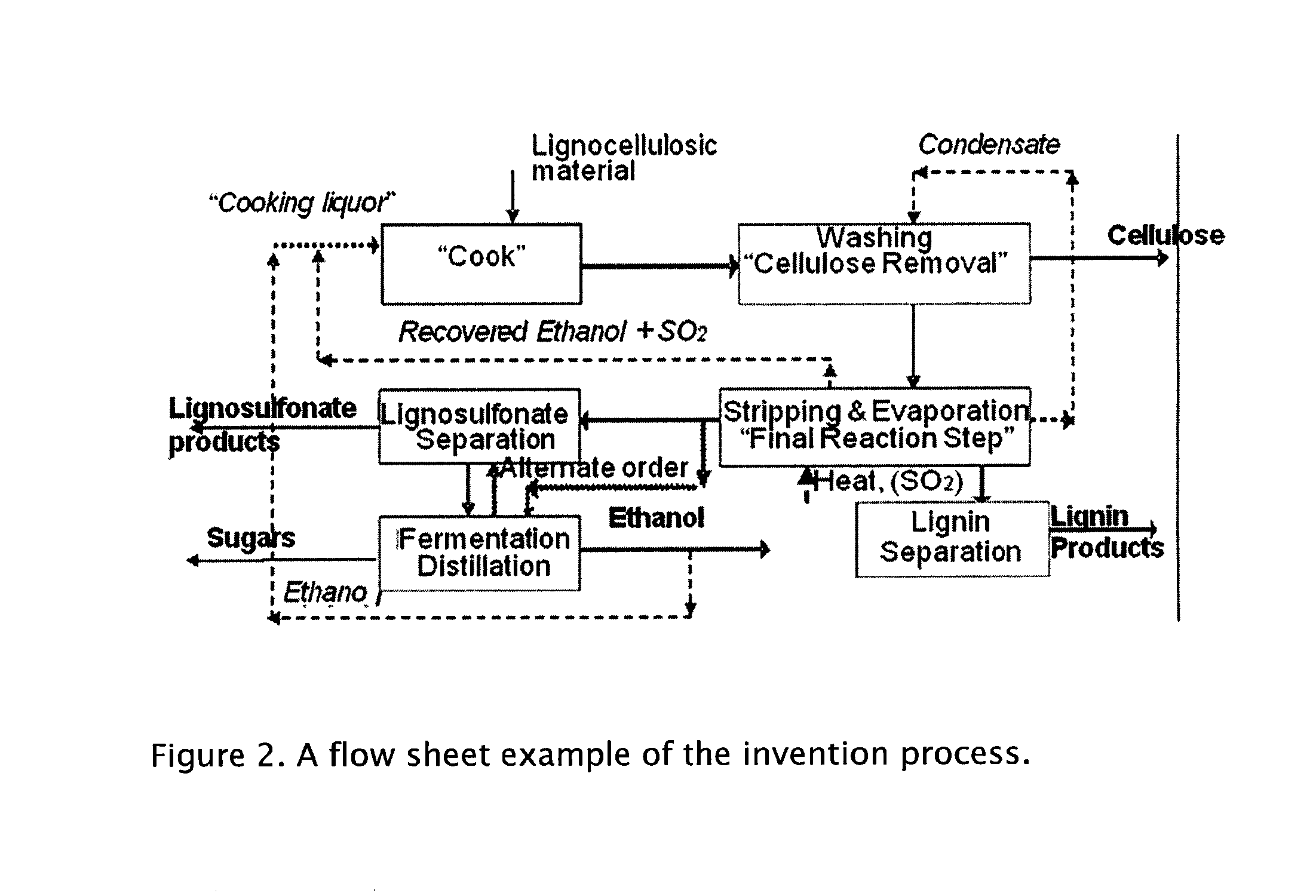
ActiveUS8030039B1High yieldIncreased ethanol yieldFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulping with organic compoundsOrganic acidAlcohol
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and high viscosity cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process is provided. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals can be reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
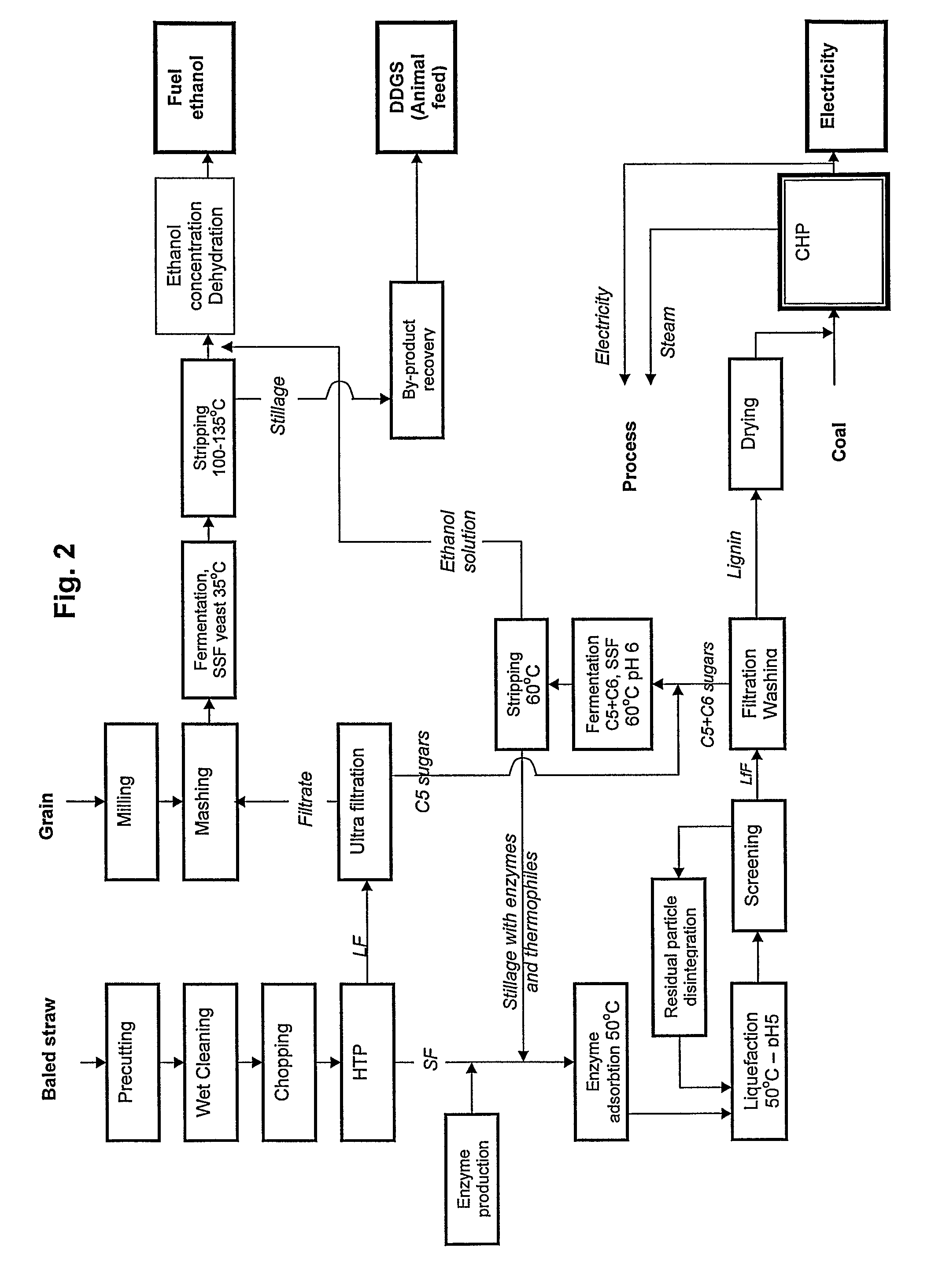
Method and apparatus for conversion of cellulosic material to ethanol
ActiveUS8123864B2Low costDown rate of fermentationBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofuelsFiberCellulose
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for conversion of cellulosic material, such as chopped straw and corn stover, and household waste, to ethanol and other products. The cellulosic material is subjected to continuous hydrothermal pre-treatment without addition of chemicals, and a liquid and a fiber fraction are produced. The fiber fraction is subjected to enzymatic liquefaction and saccharification. The method of the present invention comprises:performing the hydrothermal pre-treatment by subjecting the cellulosic material to at least one soaking operation, and conveying the cellulosic material through at least one pressurized reactor, and subjecting the cellulosic material to at least one pressing operation, creating a fiber fraction and a liquid fraction;selecting the temperature and residence time for the hydrothermal pretreatment, so that the fibrous structure of the feedstock is maintained and at least 80% of the lignin is maintained in the fiber fraction.
Owner:INBICON AS
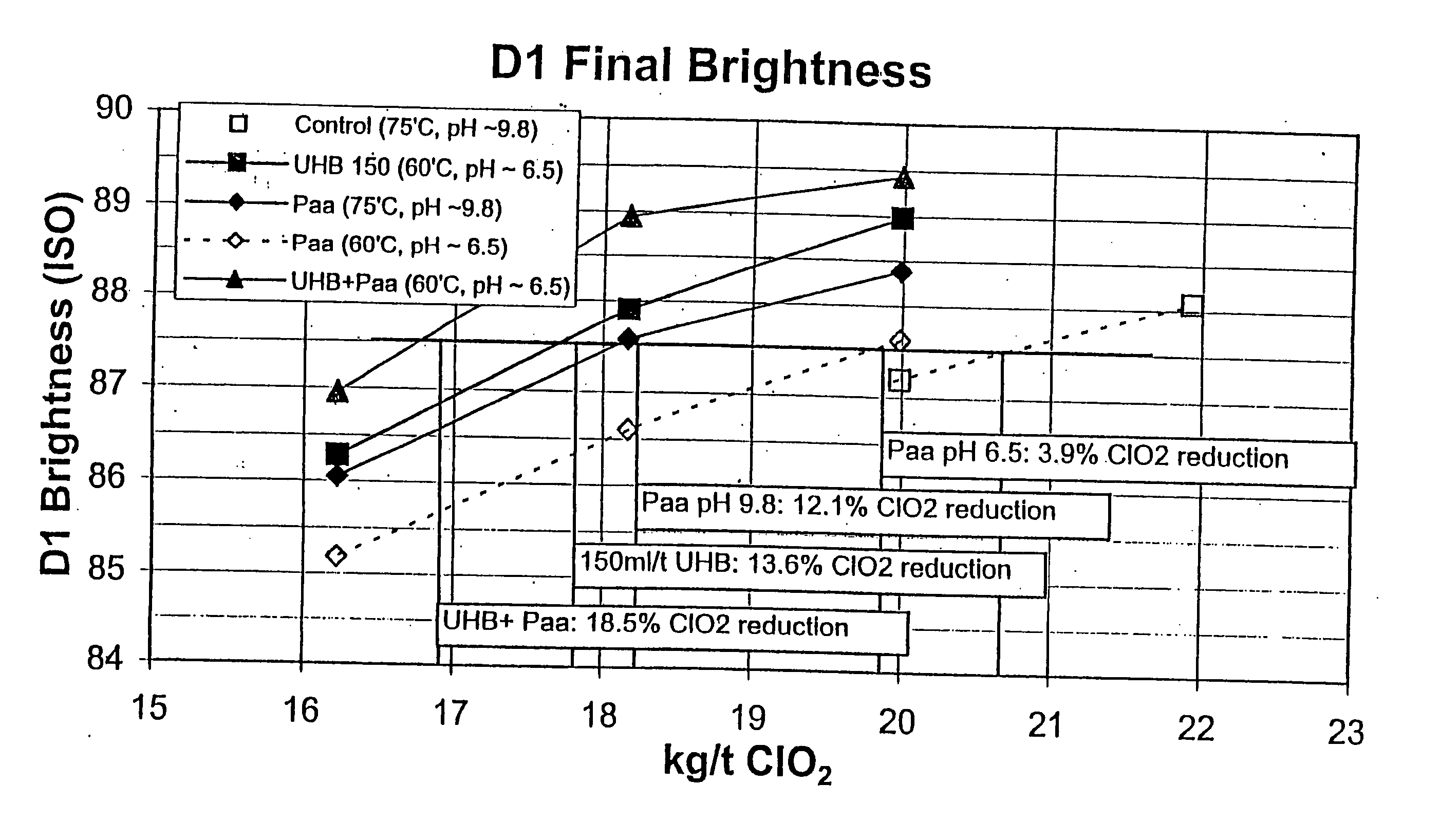
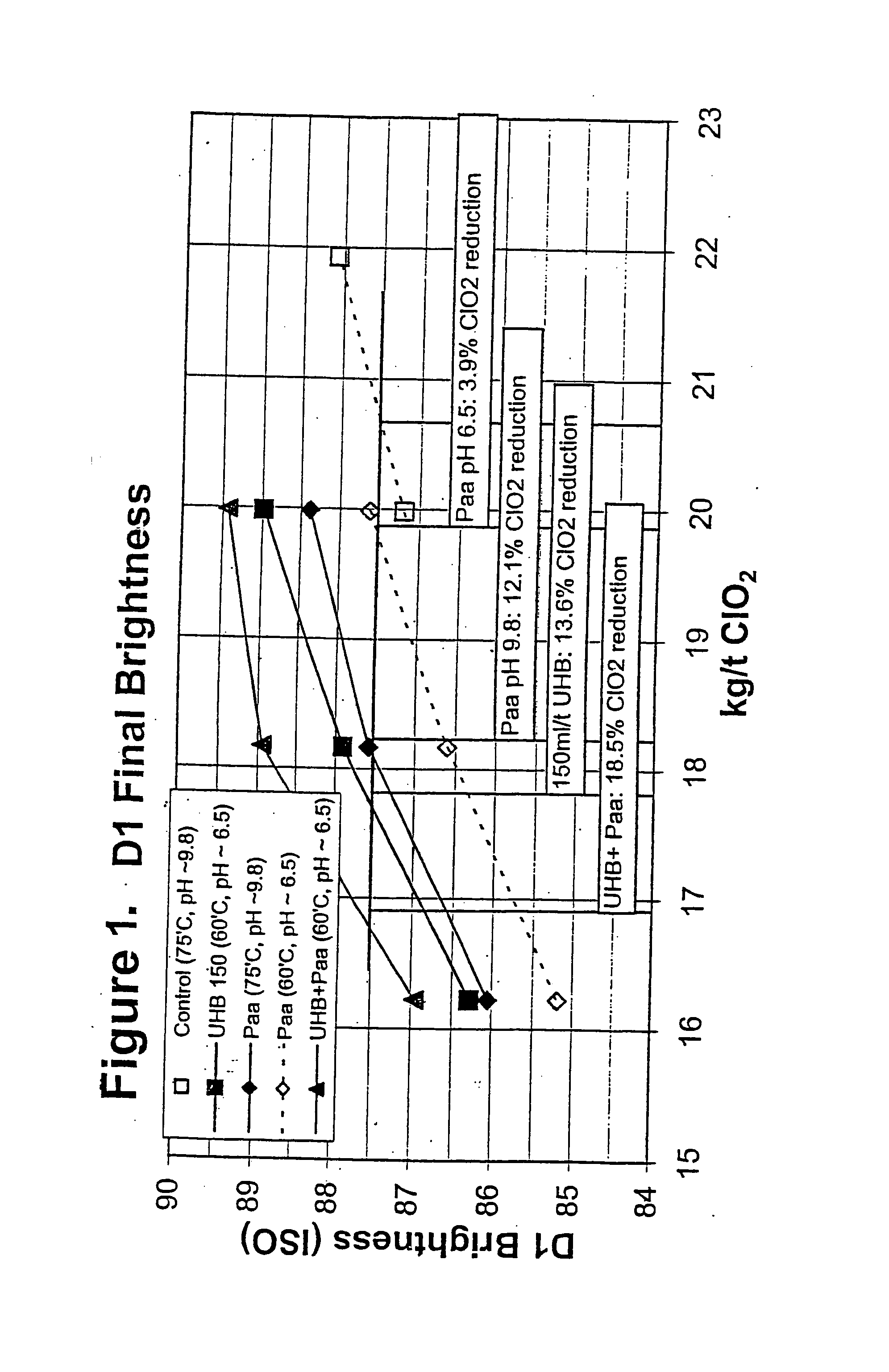
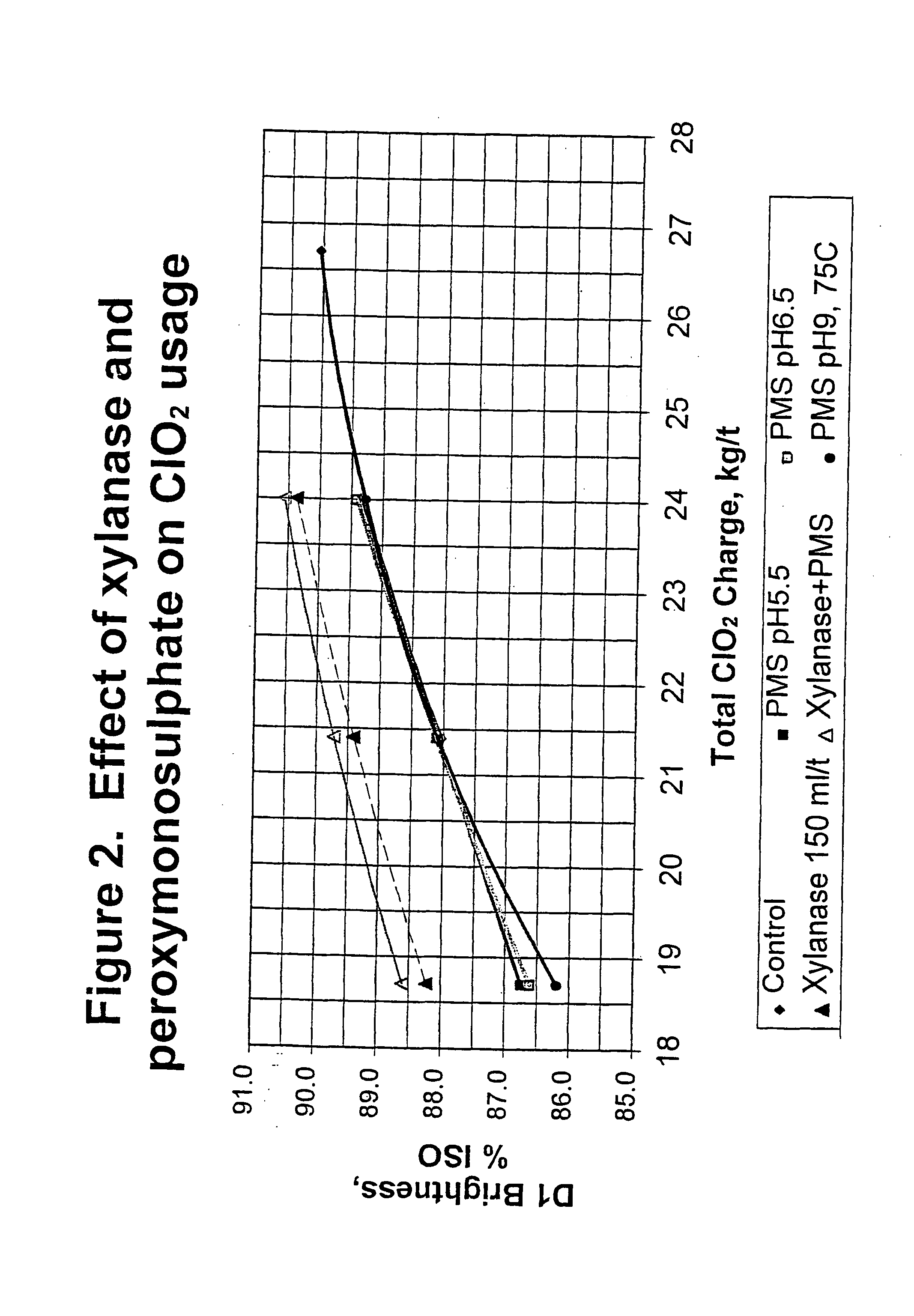
Bleaching stage using xylanase with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a combination thereof
InactiveUS20040112555A1Less-costly bleaching operationReduce usagePulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesChlorine dioxideXylanase Y
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that combine xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chemical pulping operation, optionally followed by delignifying the pulp with oxygen, then combining xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture to bleach the pulp. The method allows the mill to use both xylanase and peracids in a single bleaching tower to decrease the usage of chlorine dioxide and other bleaching chemicals. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
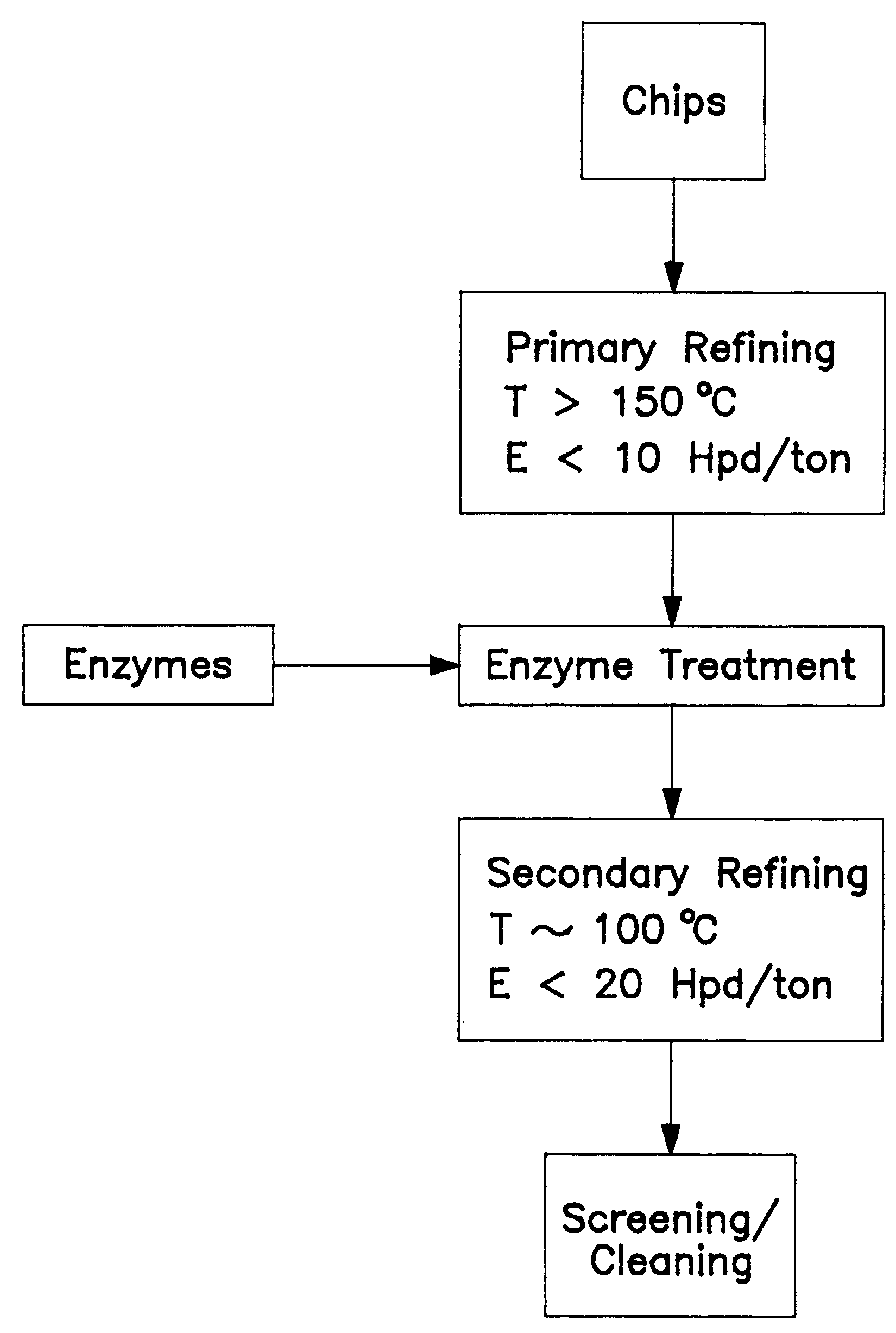
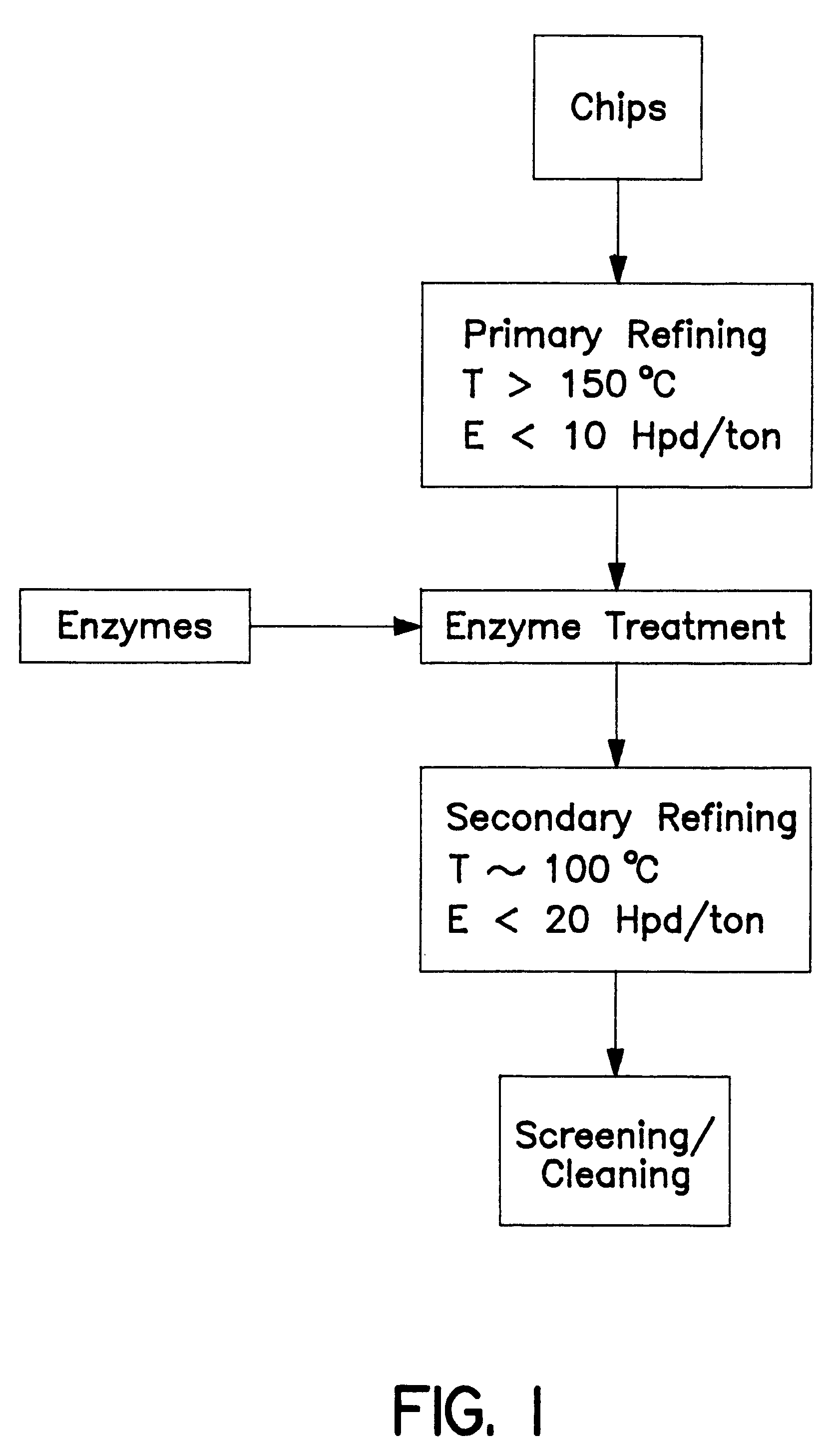
Low energy thermomechanical pulping process using an enzyme treatment between refining zones
InactiveUS6267841B1Pulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulping with inorganic basesPulp and paper industryEnzyme
A low energy thermomechanical pulping process which employs an enzyme treatment stage between two low energy thermomechanical stages.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Energy efficient TMP refining of destructured chips
InactiveUS20060006264A1Quality improvementReduce energy consumptionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with water/steamFiberRing pattern
A system and method for thermomechanical refining of wood chips comprises preparing the chips for refining by exposing the chips to an environment of steam to soften the chips, compressively destructuring and dewatering the softened chips to a solids consistency above 55 percent, and diluting the destructured and dewatered chips to a consistency in the range of about 30 to 55 percent. The destructuring partially defibrates the material. This diluted material is fed to a rotating disc primary refiner wherein each of the opposed discs has an inner ring pattern of bars and grooves and an outer ring pattern of bars and grooves. The destructured and partially defibrated chips are substantially completely defibrated in the inner ring and the resulting fibers are fibrillated in the outer ring. The compressive destructuring, dewatering, and dilution can all be implemented in one integrated piece of equipment immediately upstream of the primary refiner, and the fiberizing and fibrillating are both achieved between only one set of relatively rotating discs in the primary refiner.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
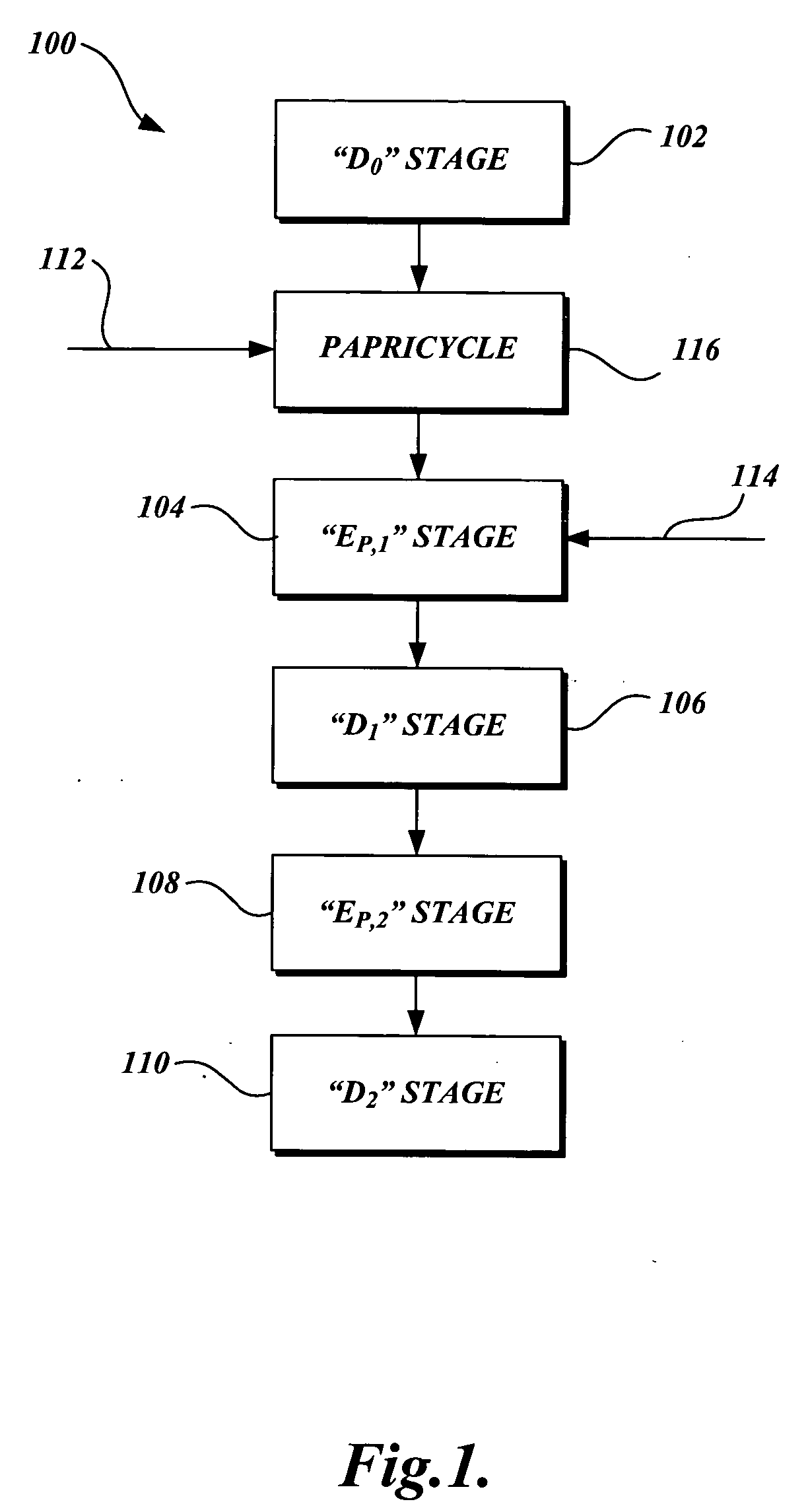
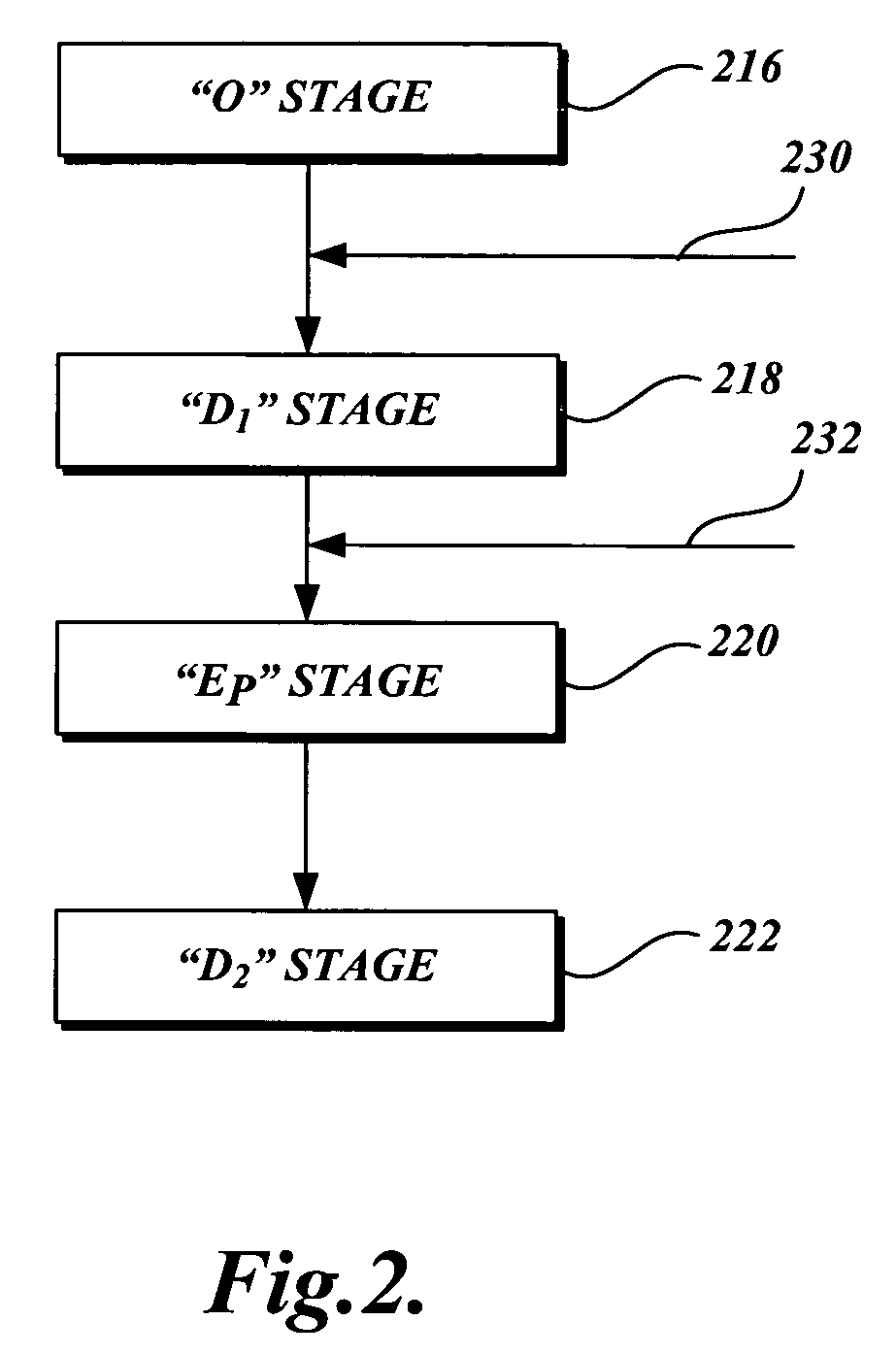
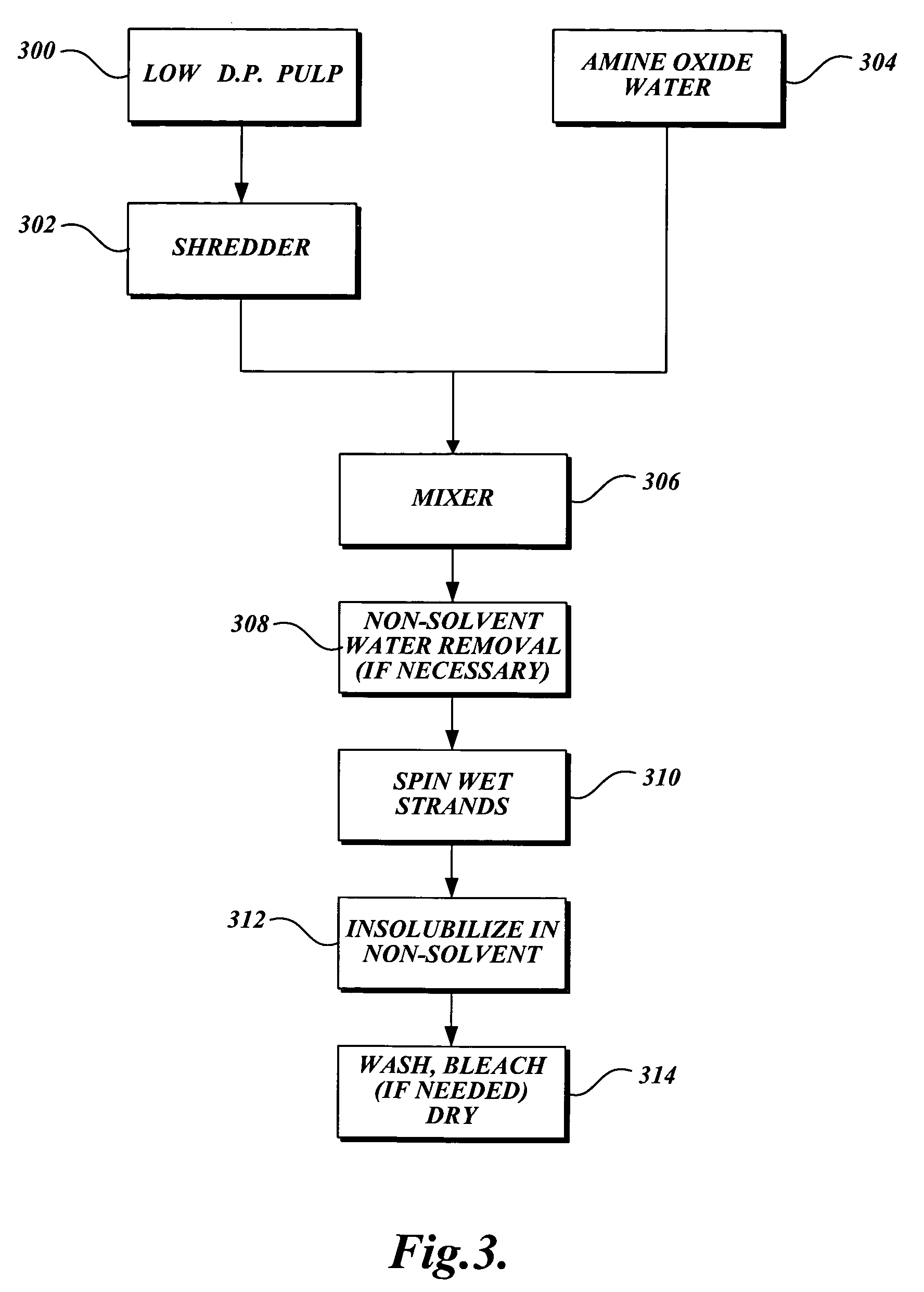
Low pH treatment of pulp in a bleach sequence to produce pulp having low D.P. and low copper number for use in lyocell manufacture
InactiveUS20060070711A1Reduce the degree of polymerizationIncreasing copper numberPulp properties modificationLayered productsBleachPulp mill
A high pH and a low pH process for reducing the degree of polymerization of a pulp having a hemicellulose content of at least 7%. The high pH is greater than 8, and the low pH process is 2 to 8. The high pH process reduces the degree of polymerization without substantially increasing the copper number. The low pH process requires a subsequent treatment with alkali to reduce the copper number of the pulp to less than 2. The process can be practiced in pulp mills with a bleaching sequence having one or more E or D stages. At the end of the bleach sequence, a pulp having a degree of polymerization of 200 to 1100, a copper number of less than 2, and a hemicellulose content of at least 7% is provided. The pulp can be used to make lyocell fibers.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Apparatus for making carboxylated pulp fibers
InactiveUS7001483B2Little additional equipmentDelay transitionNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperFiberBleach
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER CO
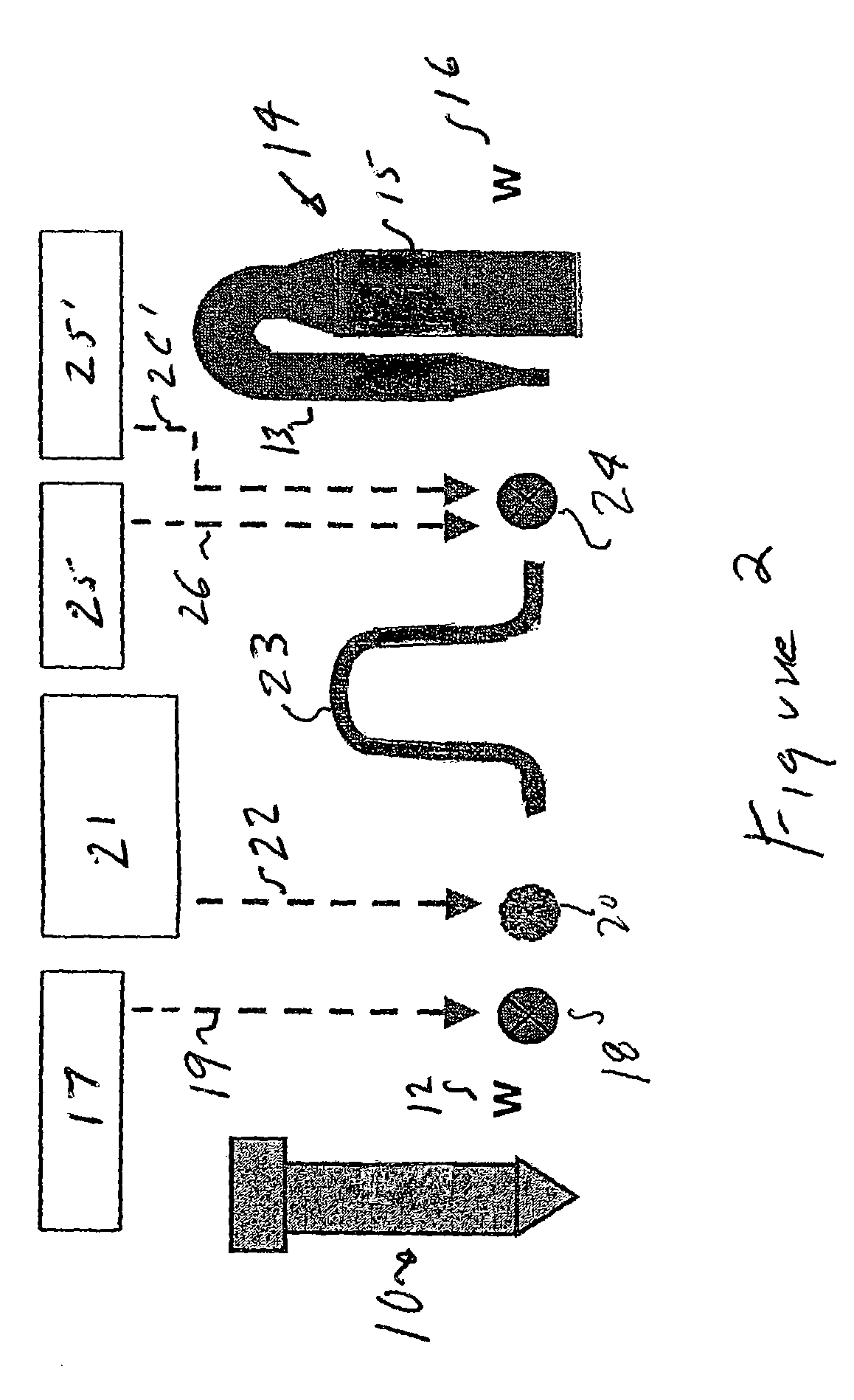
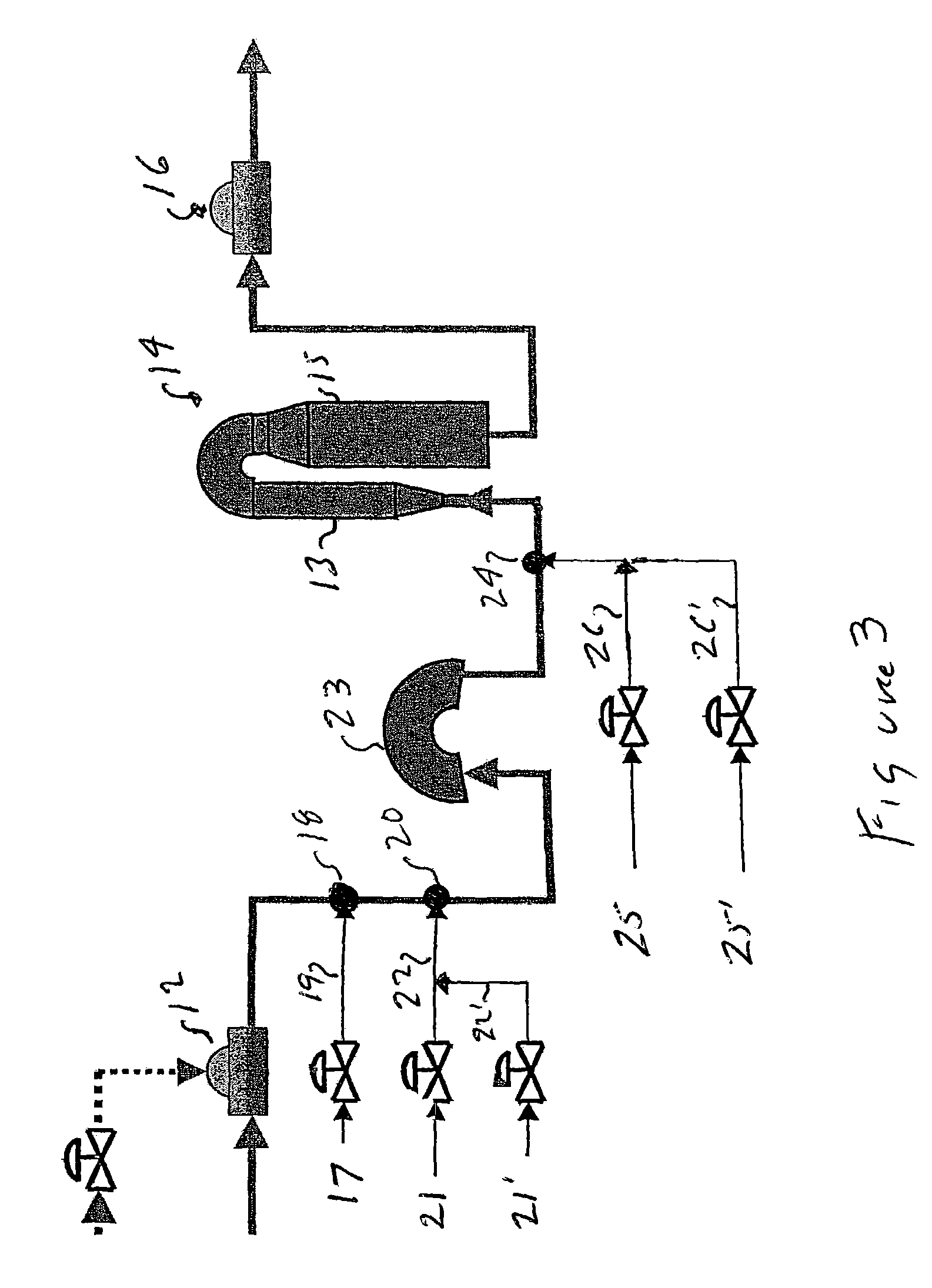
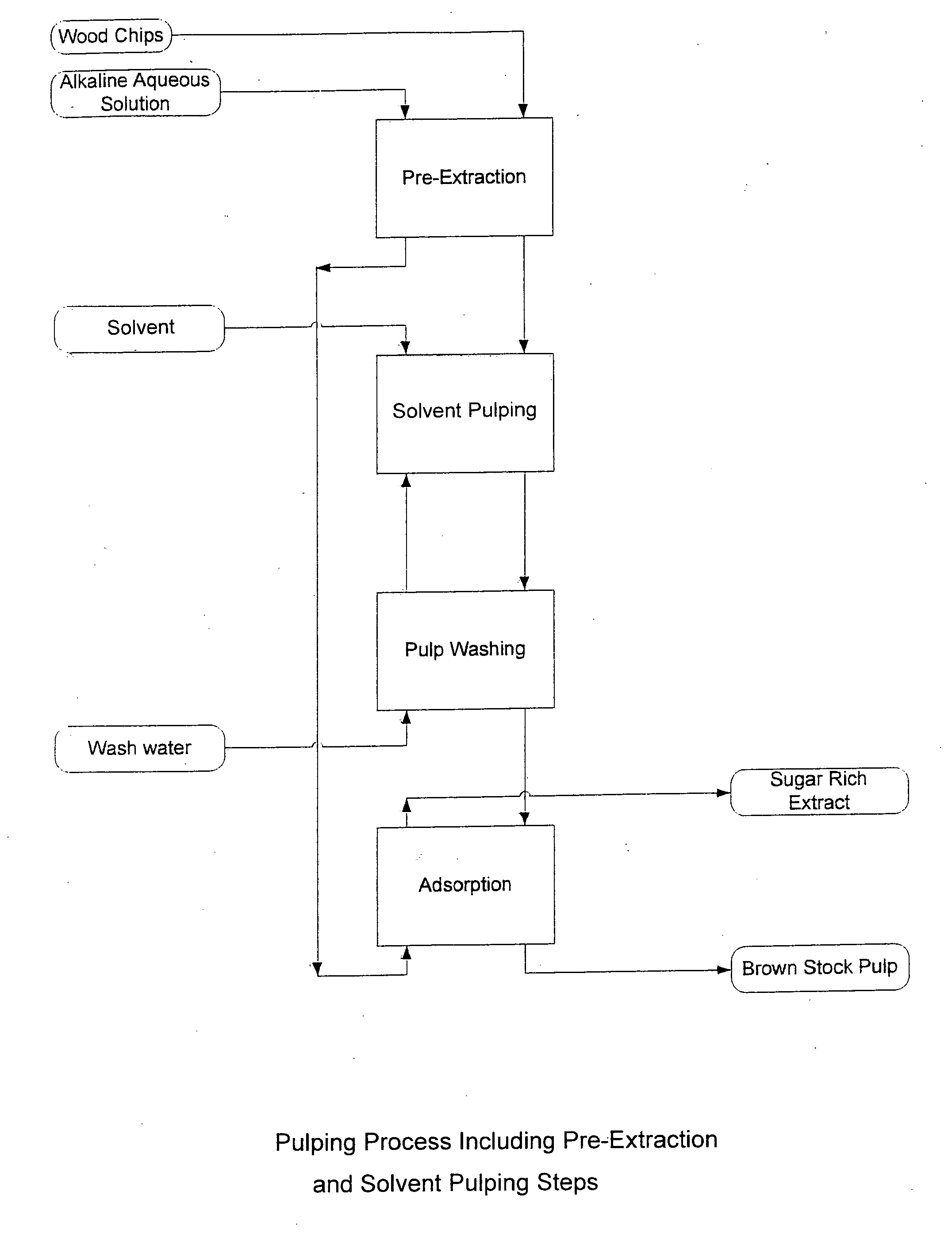
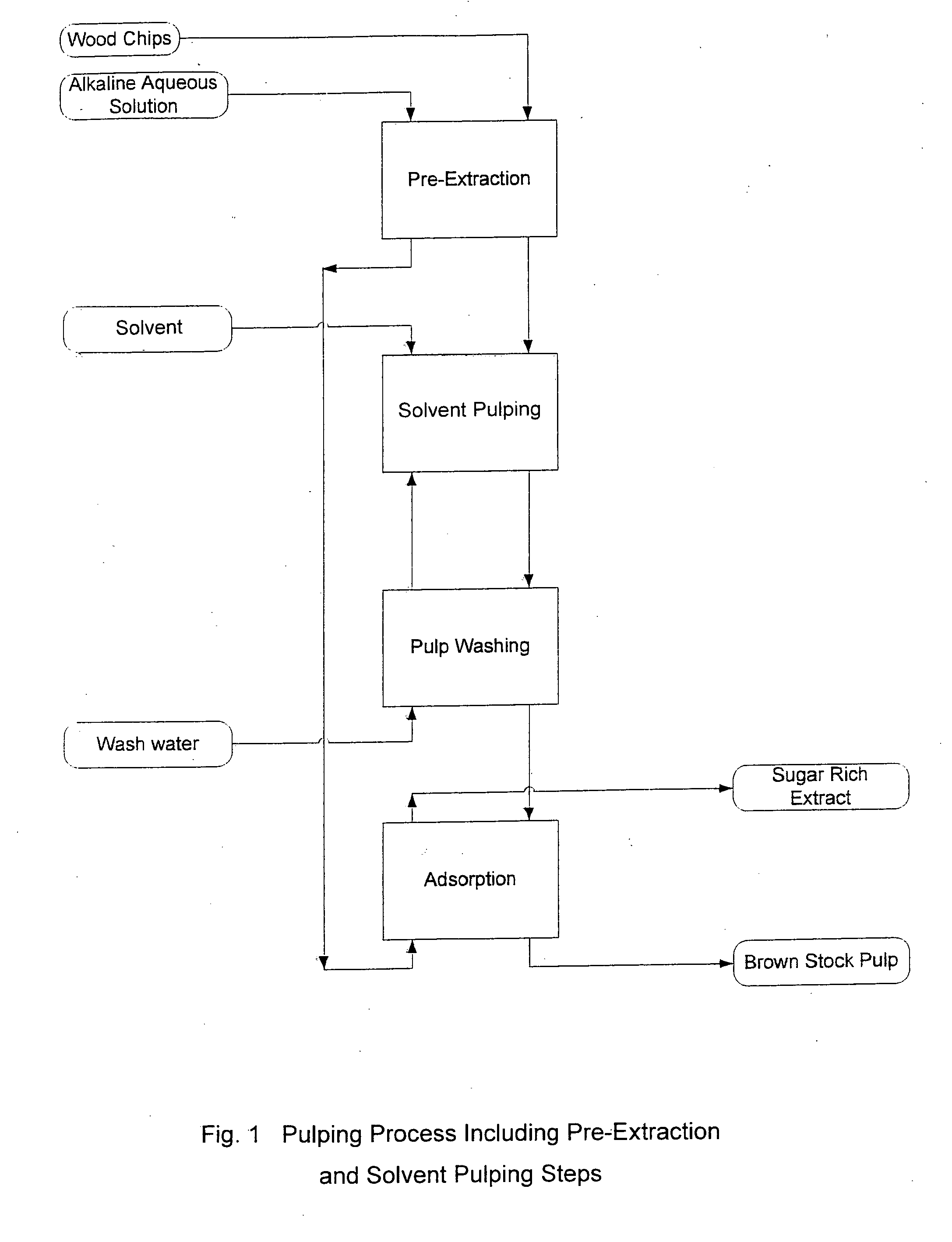
Pre-extraction and solvent pulping of lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20080196847A1Pretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpBoiling pointSolvent
A process of treating a lignocellulosic material includes a pre-extraction step in which hemicellulose is extracted from the lignocellulosic material. Then, in a solvent pulping step, the lignocellulosic material is separated into pulp by contacting the lignocellulosic material with a cooking liquor comprising a solvent. In one embodiment, the solvent has a boiling point of at least about 150° C. In another embodiment, the cooking liquor comprises a mixture of solvent and water.
Owner:INT PAPER CO +1
Cellulose production from lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20020148575A1Low costHigh yieldPretreatment with water/steamPulp liquor regenerationEnergy recoveryCellulose fiber
A multi-function process is described for the separation of cellulose fibers from the other constituents of lignocellulosic biomass such as found in trees, grasses, agricultural waste, and waste paper with application in the preparation of feedstocks for use in the manufacture of paper, plastics, ethanol, and other chemicals. This process minimizes waste disposal problems since it uses only steam, water, and oxygen at elevated temperature in the range of 180° C. to 240° C. for 1 to 10 minutes plus a small amount of chemical reagents to maintain pH in the range 8 to 13. An energy recuperation function is important to the economic viability of the process.
Owner:PUREVISION TECH
Process of producing xylose and dissolving pulp
ActiveUS20110192560A1High yieldReduce the amount requiredPretreatment with water/steamWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsChromatographic separationXylan
The present invention relates to a process for the production of xylose and dissolving pulp from xylan-containing biomass, such as hardwood. The invention is based on prehydrolysis of the xylan-containing biomass with SO2 in specified conditions, followed by chromatographic fractionation, nanofiltration or precipitation crystallization of the xylose-containing prehydrolyzate to obtain a xylose product having a xylose content of at least 55% on DS. The dissolving pulp obtained from the process can be used for example for the production of viscose.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
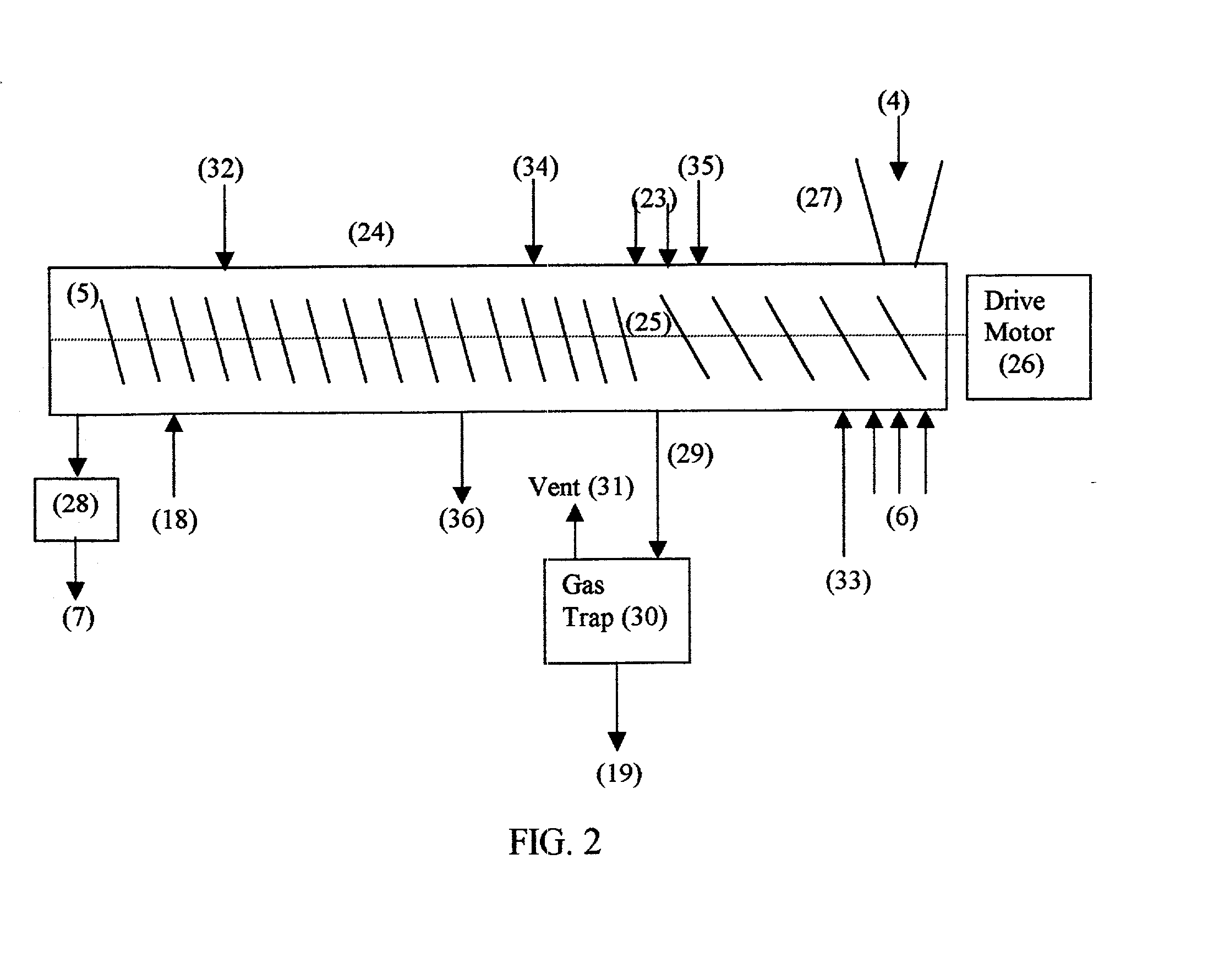
High defiberization chip pretreatment
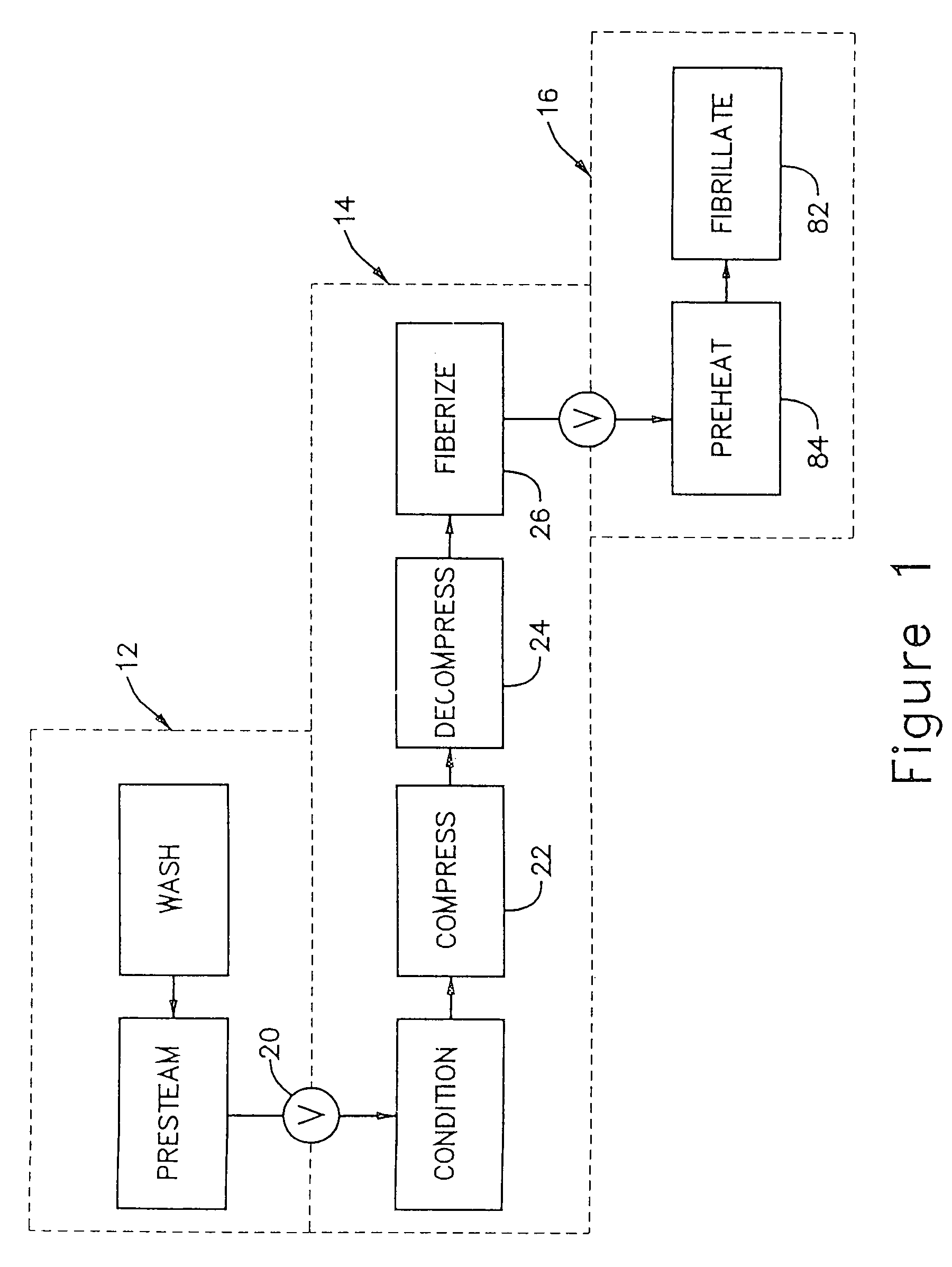
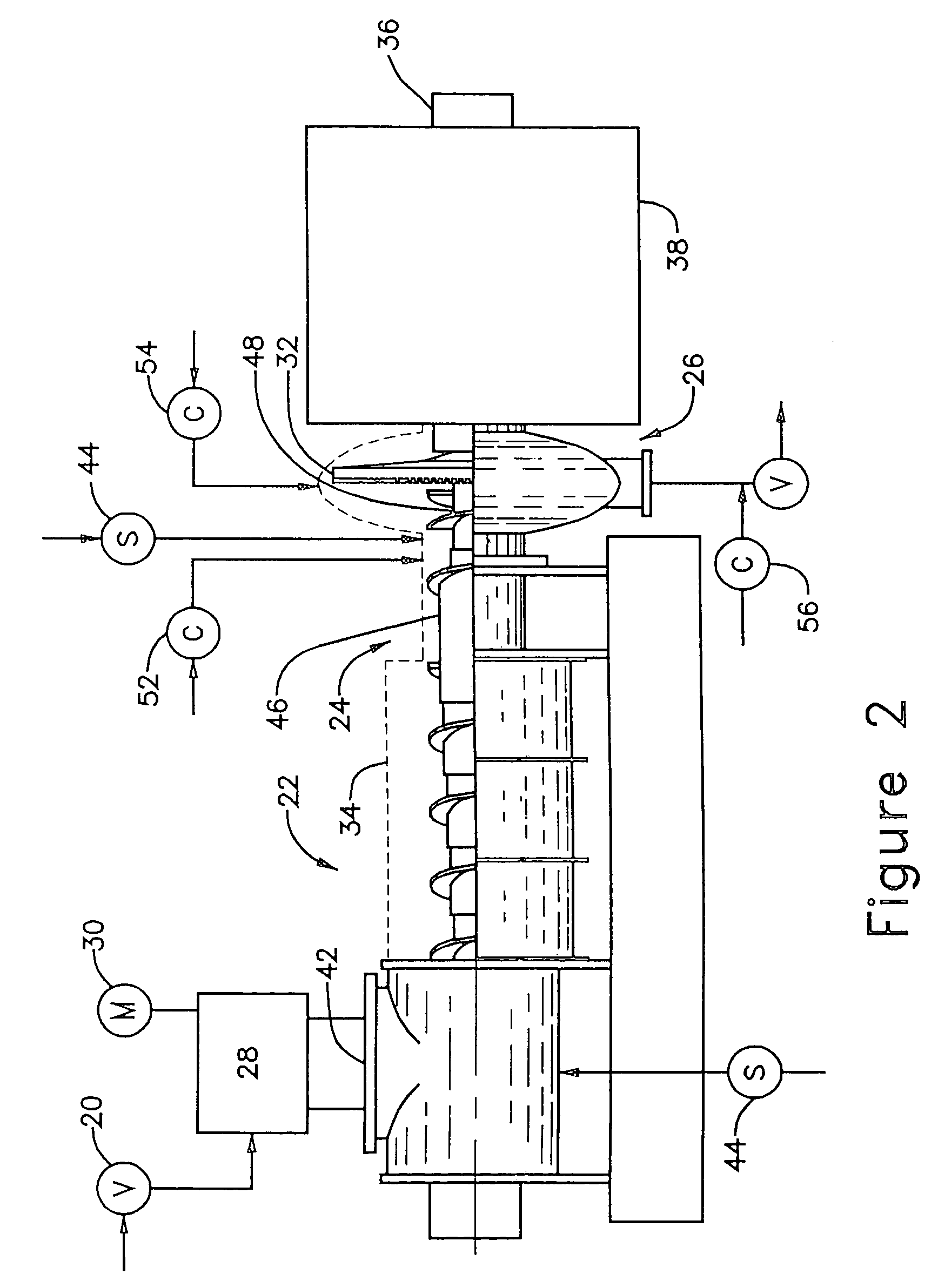
ActiveUS7300541B2Reduce energy consumptionGood removal effectCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with water/steamChemical treatmentFiber bundle
A chip pretreatment process which comprises conveying the feed material through a compression screw device having an atmosphere of saturated steam at a pressure above about 5 psig, decompressing and discharging the compressed material from the screw device into a decompression region, feeding the decompressed material from the decompression region into a fiberizing device, such as a low intensity disc refiner, where at least about 30 percent of the fiber bundles and fibers are axially separated, without substantial fibrillation of the fibers. Preferably, the fibers are axially separated with less than about 5 percent fibrillation, and subsequently the fiberized material is refined in a high intensity disc refiner until at least about 90 percent of the fibers are fibrillated. In another form the invention combines chip fiberizing with chemical treatments, for improving the pulp property versus energy relationships.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Separation of Lignin From Hydrolyzate
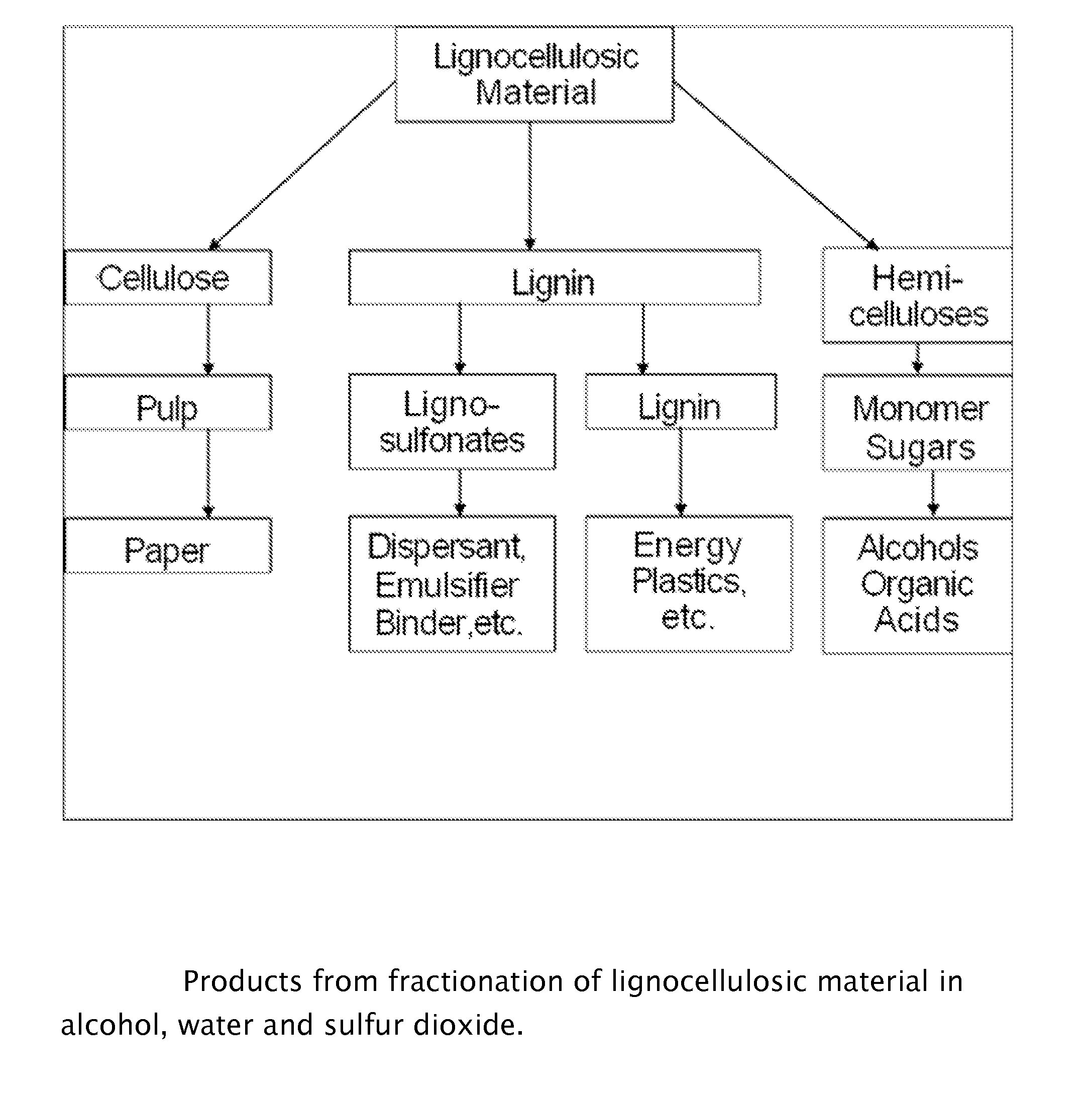
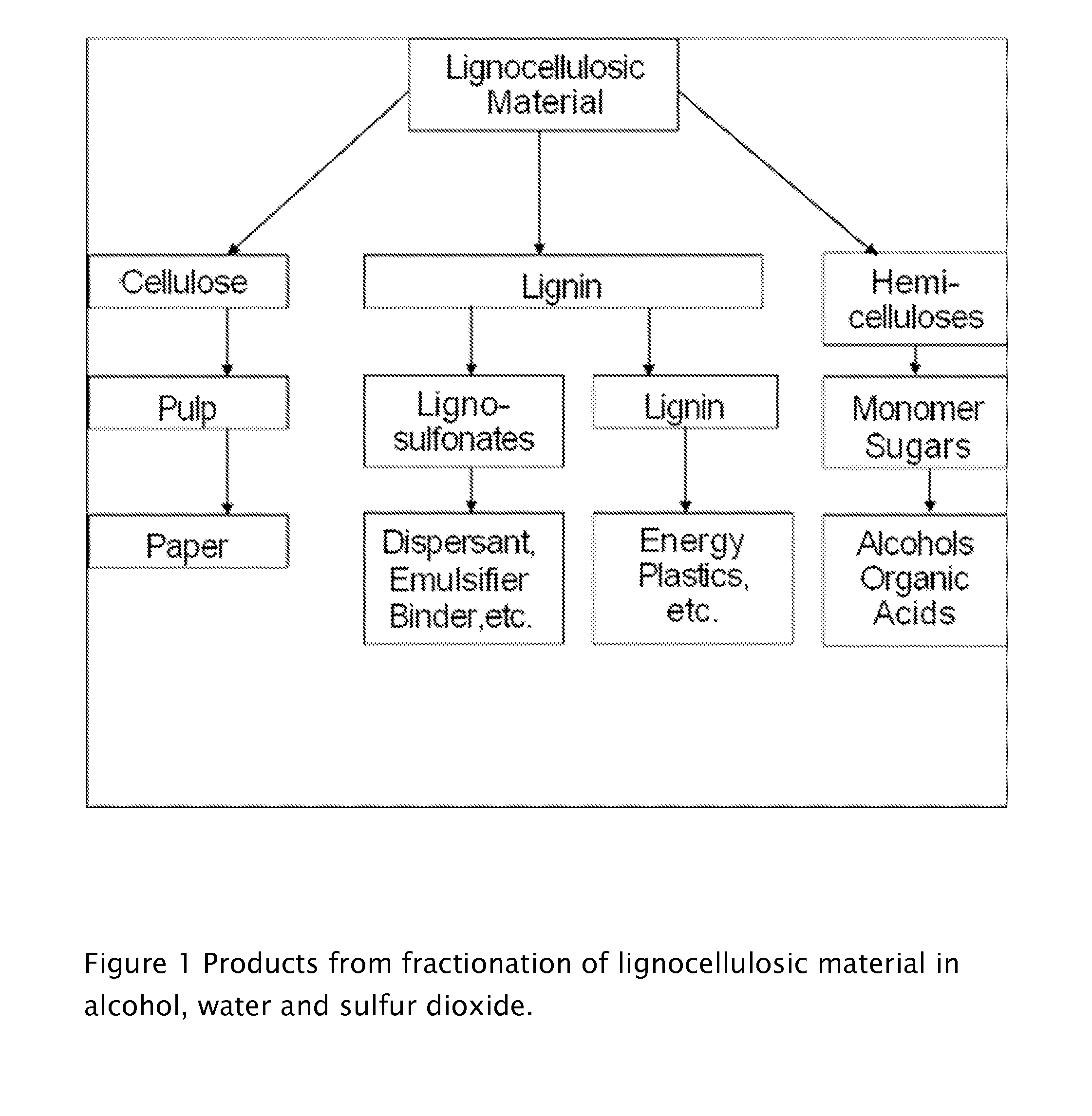
ActiveUS20110165643A1Pulp liquor regenerationPulping with acid salts/anhydridesWater insolubleLignosulfonates
A method for the production water insoluble reactive lignin having low sulfur content and lignosulfonates from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated to produce water insoluble native lignin and lignosulfonates in various ratios, while preserving the cellulose and hydrolyzed hemicelluloses using water, ethanol and sulfur dioxide.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for loading fibers contained in a pulp suspension
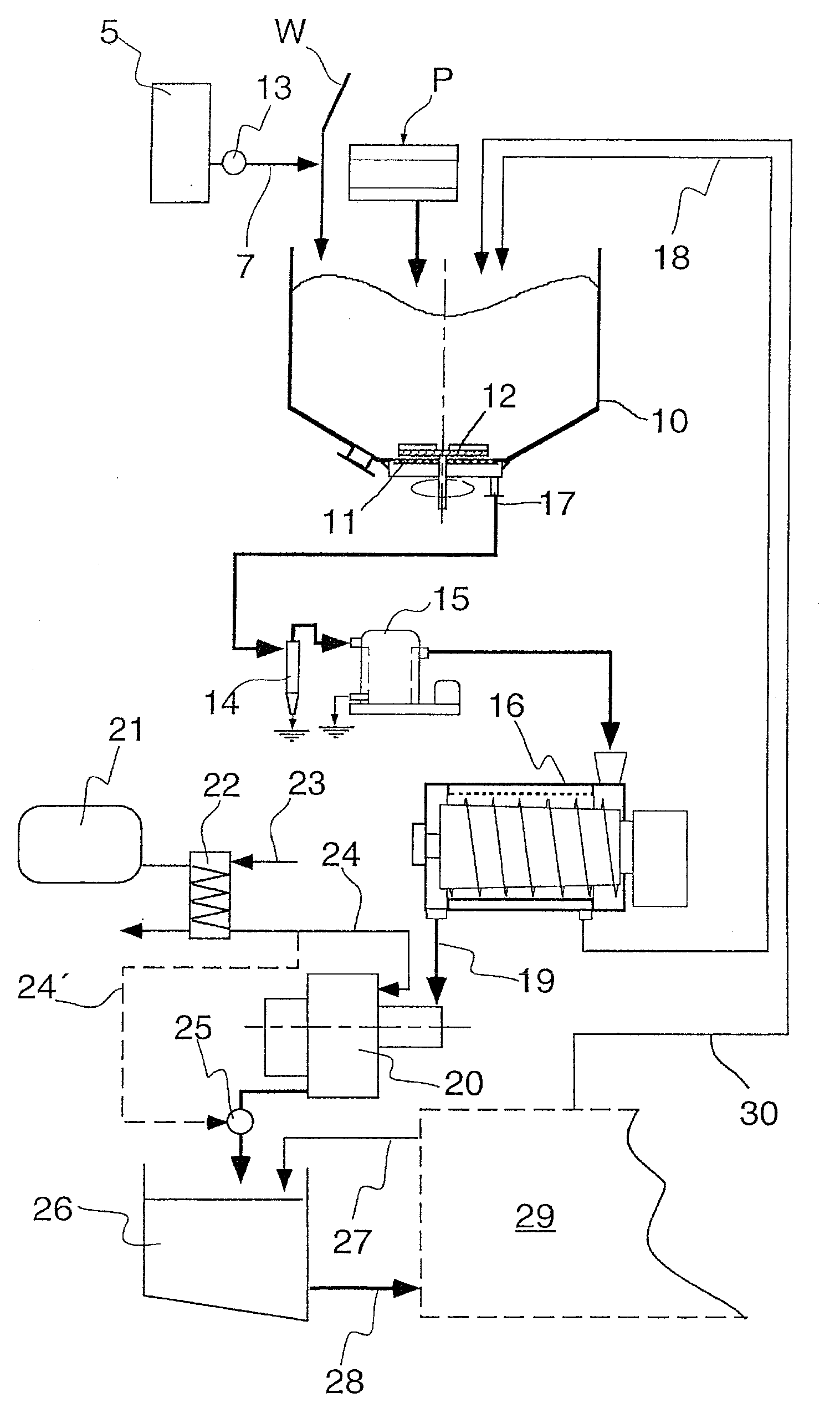
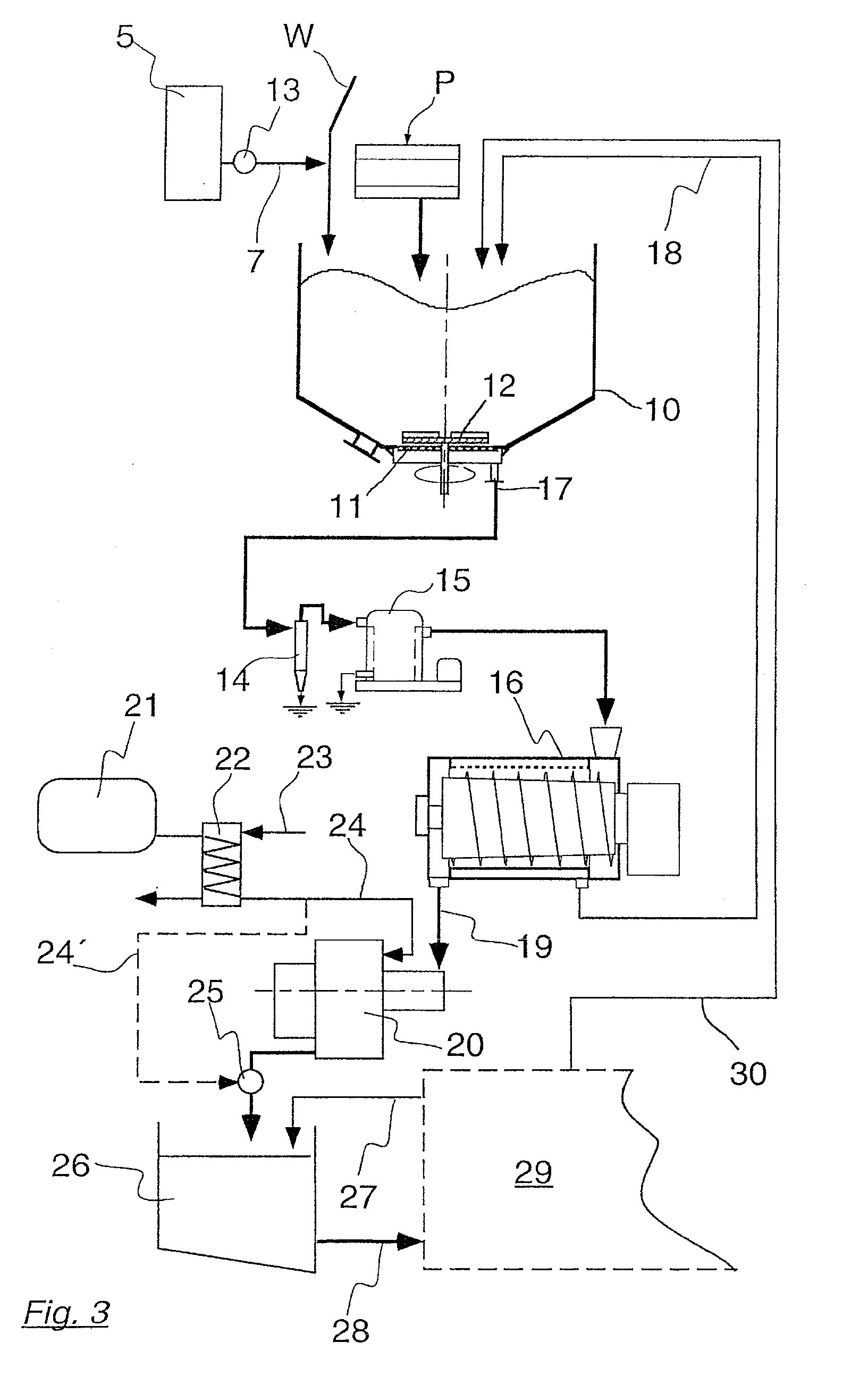
InactiveUS20080210391A1Easy to usePulp properties modificationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsFiberCalcium hydroxide
The present invention serves for loading a pulp suspension (S) with calcium carbonate. Liquid calcium hydroxide as milk of lime (7) is added during or before the pulp operation (1) carried out to form the pulp. By introducing gaseous carbon dioxide (8) into the pulp suspension thus treated, a chemical reaction is triggered therein, in which the finely divided calcium carbonate is precipitated. The present invention is particularly economic and effective due to the early addition of calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
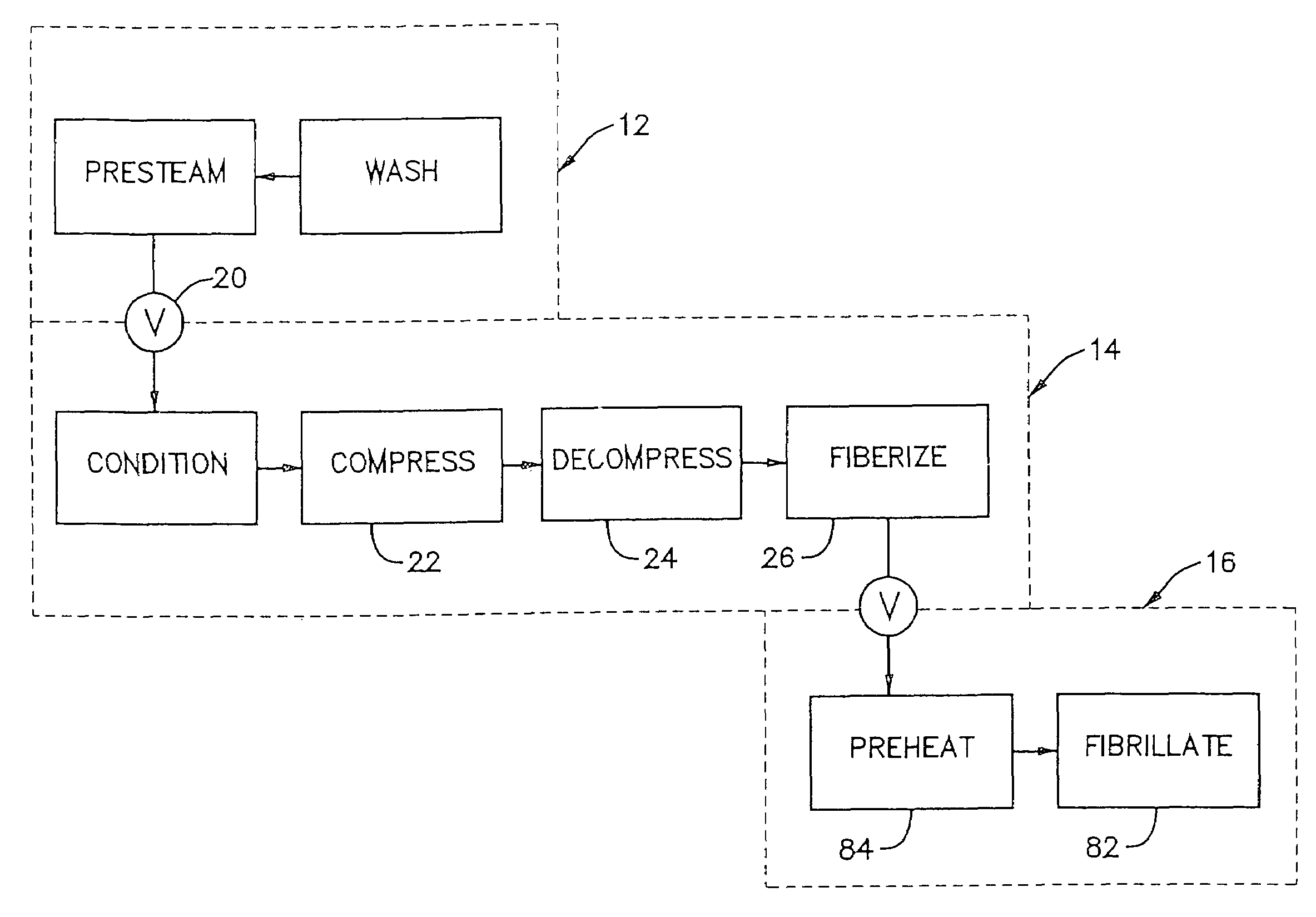
Method of pretreating lignocellulose fiber-containing material in a pulp refining process
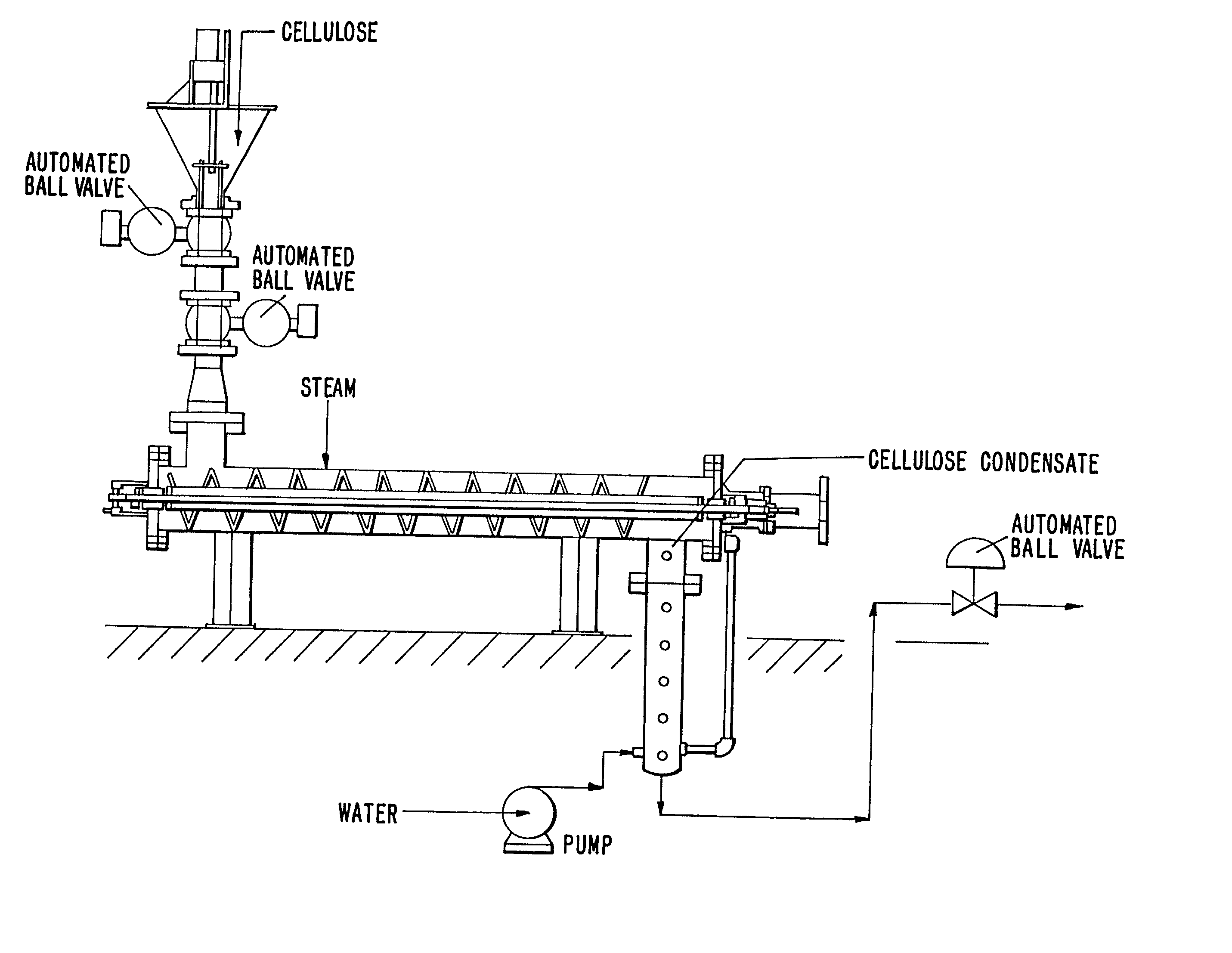
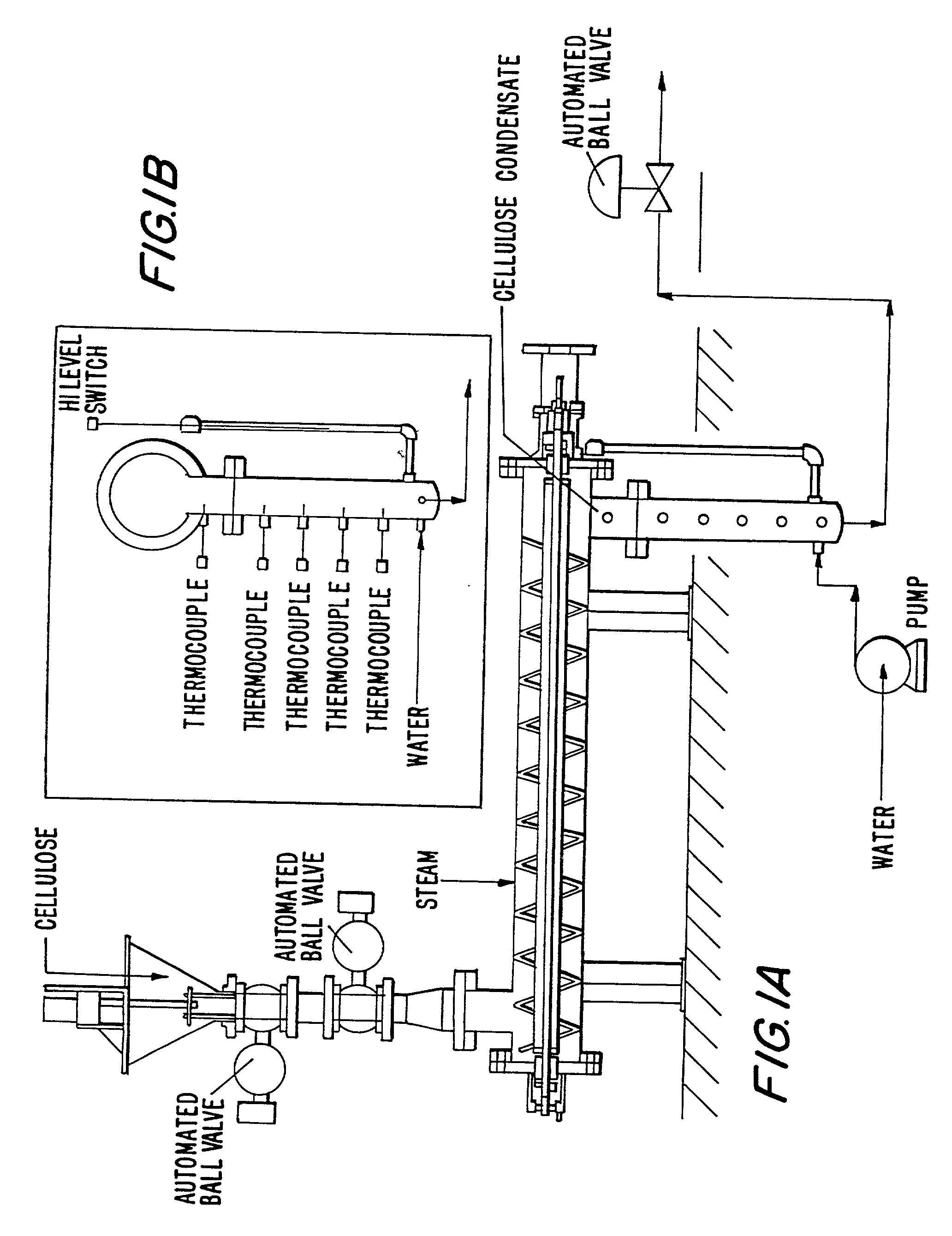
InactiveUS6899791B2Improvement in pulp strength property and shive content of pulpHigh strengthPretreatment with water/steamPulp beating/refining methodsCellulose fiberDigestion
A method and apparatus for pretreating or conditioning lignocellulose fiber containing feed material in preparation for conversion to pulp. Wood chips are pretreated under conditions of elevated temperature, pressure and humidity and subsequently compressed to cause destructuring of the fibers of the feed material. The pretreated wood chips are then converted to pulp using such methods as the ground wood pulping process or chemical digestion process.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Methods for producing pulp and treating black liquor
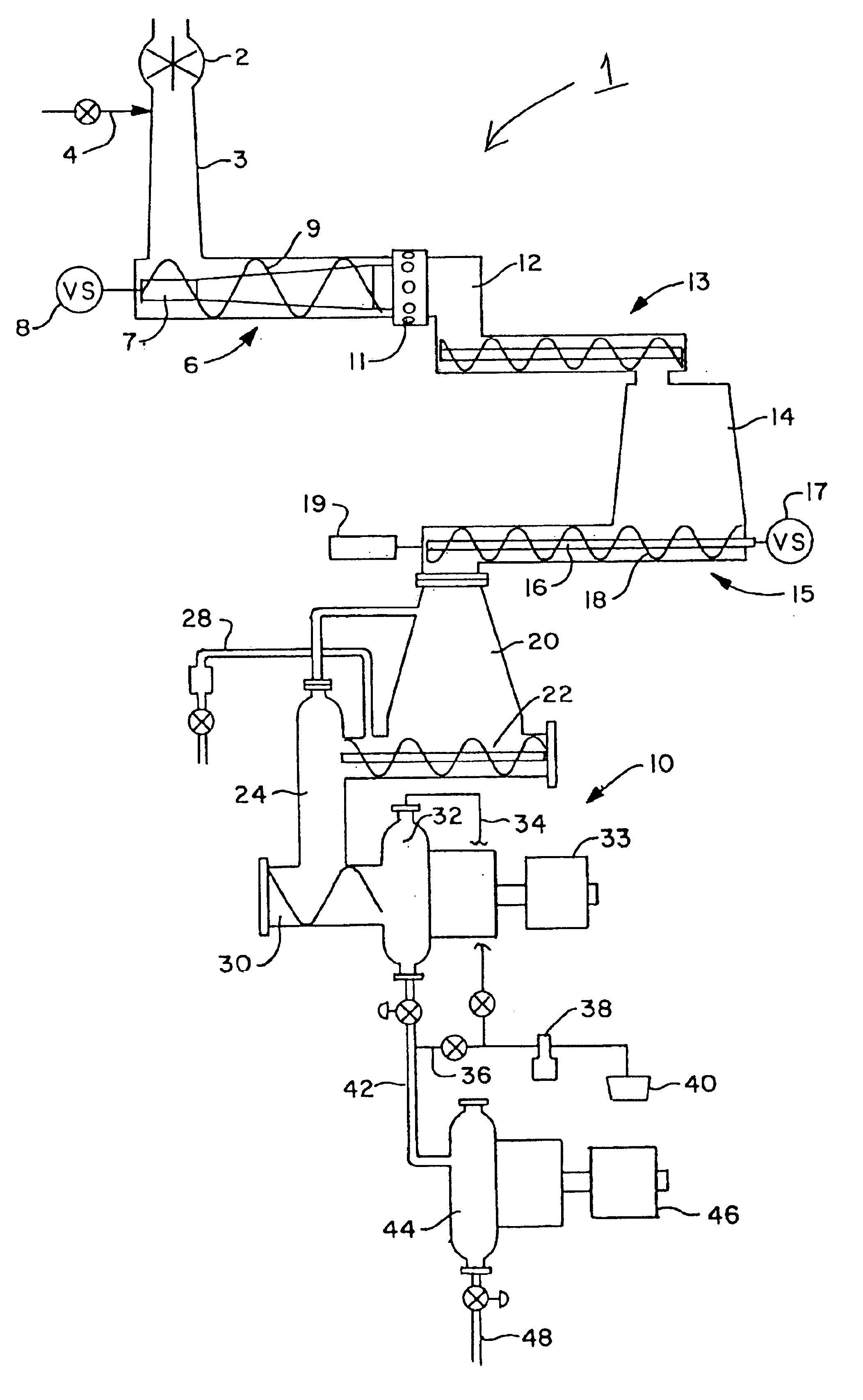
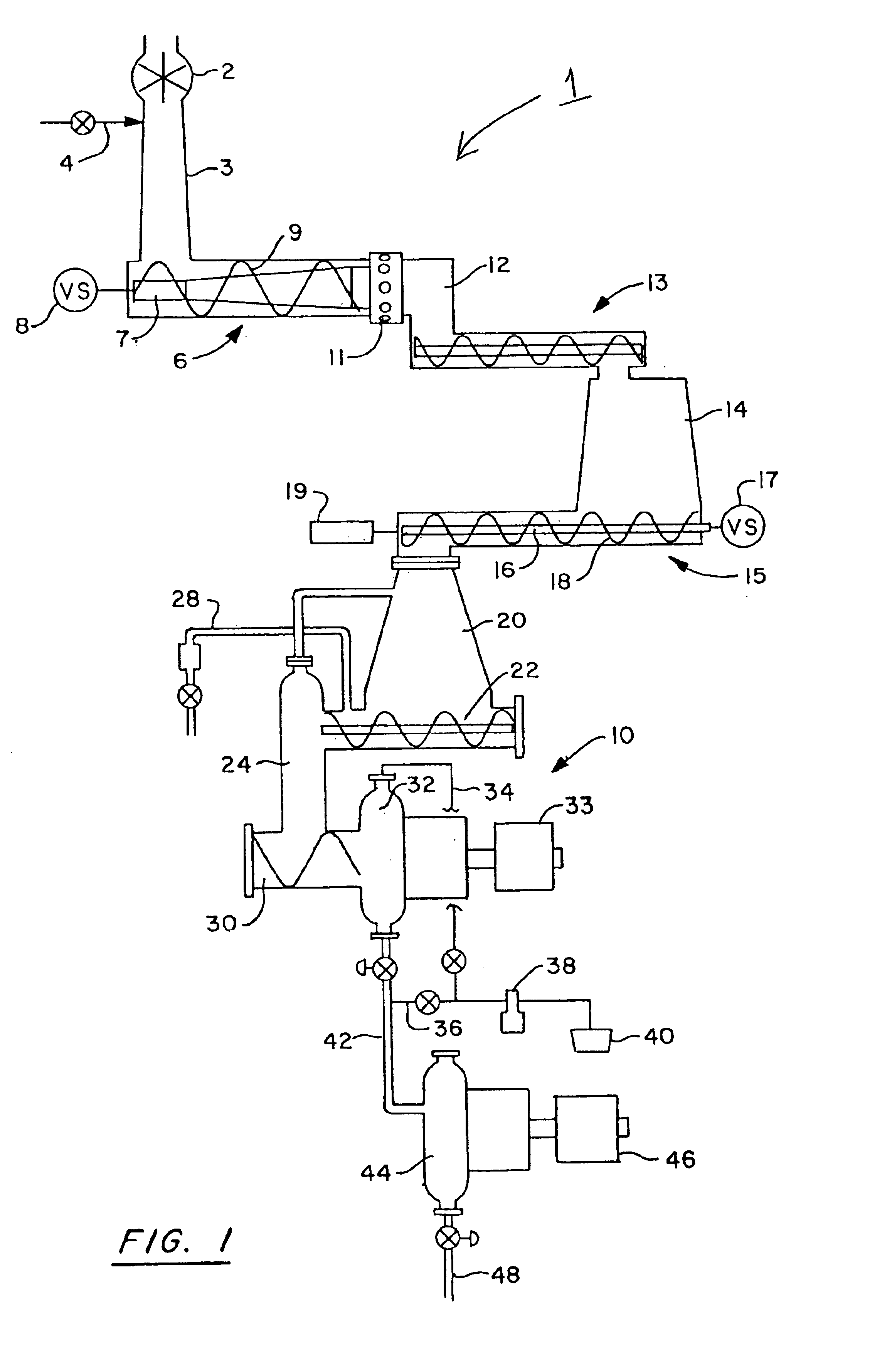
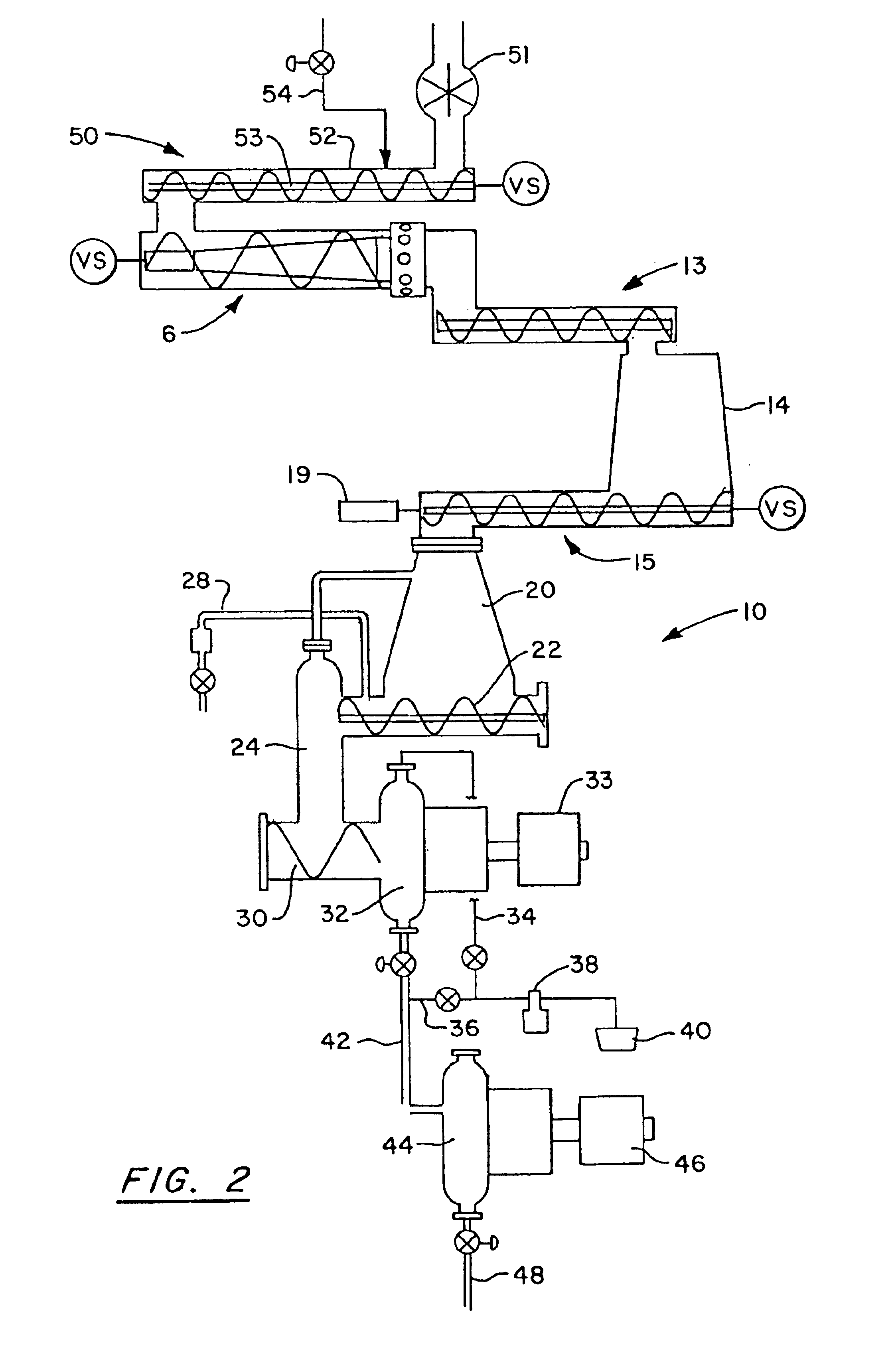
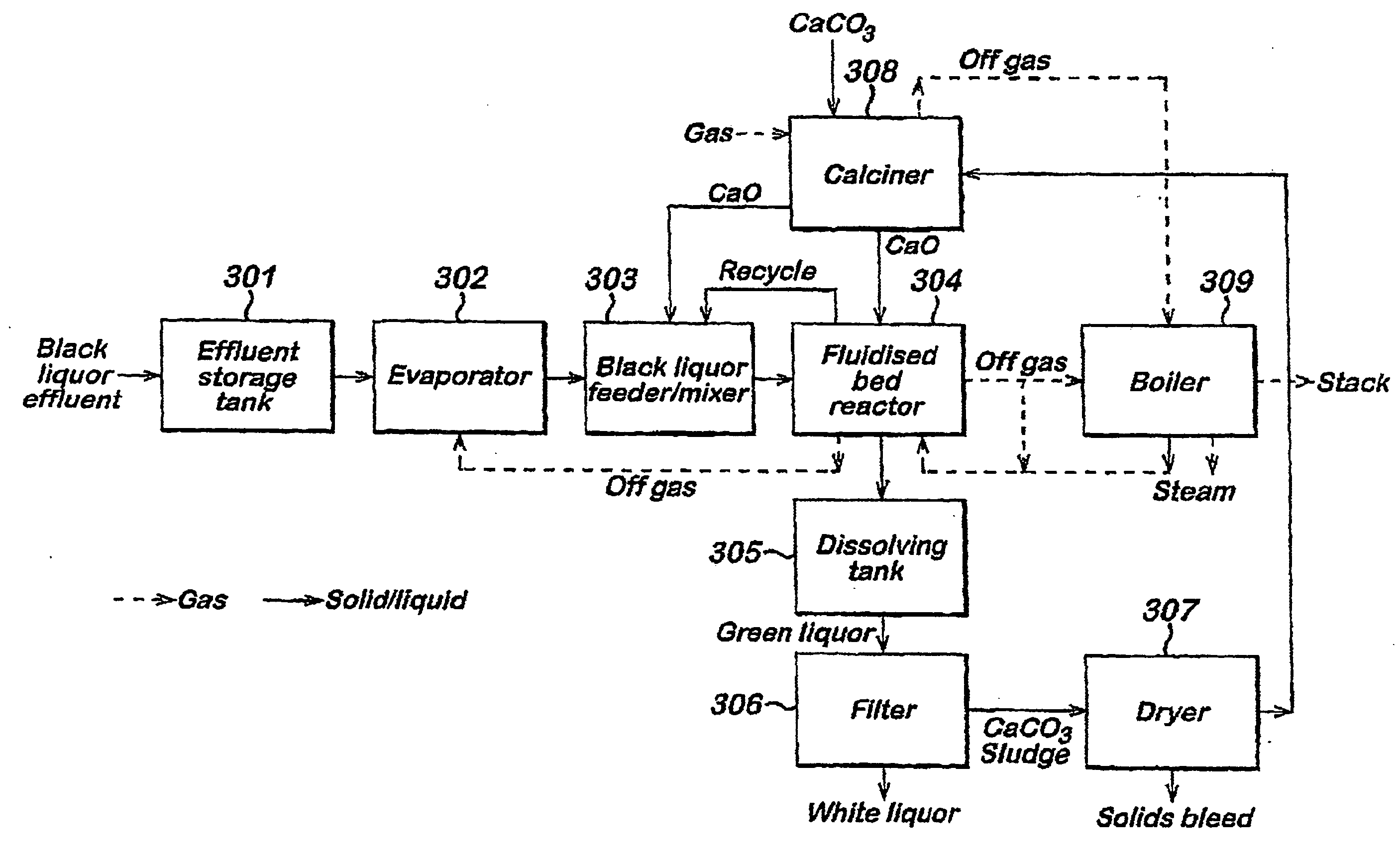
InactiveUS20060201641A1Maintaining output qualityRaise the reaction temperaturePretreatment with water/steamPulp liquors combustionCalcium silicateOrganic content
A method is provided for treating black liquor particularly derived from non-wood pulp, by heating with an alkaline earth metal oxide in a toroidal fluidised bed reactor at a temperature of above 650° C. The method may be used alone or as part of a method of converting graminaceous raw material to pulp for paper or board, said method comprising (a) digesting said raw material with a white liquor based on sodium hydroxide and further comprising calcium hydroxide in an amount effective to substantially convert silica of said raw material to calcium silicate; (b) recovering pulp and black liquor substantially free of uncombined silica; (c) heating the black liquor in a fluidized bed reactor containing calcium oxide for catalysing conversion of organic content of said black liquor to gas and for providing recovered solids including sodium values of said white liquor and calcium oxide; and regenerating said white liquor using said recovered solids. The use of the above mentioned white liquor permits treatment of wheat straw, rice straw and other high-silica materials without resulting in a black liquor that is difficult to treat.
Owner:BIOREGIONAL MINIMILLS UK
System and method for treatment of cellulose-containing material prior to pulp digestion
The invention relates to a process system and a method for preliminary treatment of disintegrated cellulose-containing material, preferably wood chips, prior to pulp digestion. The process system and the method according to the invention make use of a process vessel intended to function both as a so-called chip bin and as a pre-impregnation vessel. The characteristics of the invention are that a sloping steaming vessel is arranged downstream of the process vessel for the purpose of separating an excess of pre-impregnation liquid from the pre-impregnated cellulose-containing material, that the sloping steaming vessel is arranged for supplying steaming vapor which preferably has been generated by flashing of extraction liquor from a pulp digester, and that the sloping steaming vessel is connected to a chip chute communicating with a condenser for connection to a system for managing foul-smelling process gases. The invention can be applied in the production of pulp which is intended for paper manufacture or other applications where cellulose fibers are used.
Owner:METABO PAPER SWEDEN
Process for producing microcrystalline cellulose
InactiveUS20030089465A1High yieldProduction is limitedPulp properties modificationSugar derivativesEngineeringPulp and paper industry
A process is provided for preparing a commercially acceptable pharmaceutical grade microcrystalline cellulose which comprises: a) repulping a pulp, the pulp having a composition, b) pressing the pulp obtained in a; c) decompacting of the pulp obtained in b; d) feeding the pulp obtained in c) into a pre-heated reactor; e) cooking the pulp in the reactor until the pulp obtains a desired degree of polymerization, said cooking being performed at a temperature, a time, and a pressure which is a function of the desired degree of polymerization and the composition of the pulp, the cooked pulp being hydrolyzed cellulose; f) partially depressurizing the reactor; g) injecting water into the reactor; h) discharging the hydrolyzed cellulose from the reactor, i) filtrating the hydrolyzed cellulose; j) deaggregating the hydrolyzed cellulose of step i; and k) drying the hydrolyzed cellulose to form microcrystalline cellulose.
Owner:PENWEST PHARMA CO +1
Xylanase treatment of chemical pulp
InactiveUS20050150619A1Reduce usageHigh strengthPulp bleachingPulping with organic solventsChlorine dioxidePulp mill
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that use xylanase enzymes after chemical bleaching. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chlorine dioxide stage to produce a partially bleached pulp, treating the partially bleached pulp with a xylanase enzyme, optionally in the presence of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, in a mild extraction stage, then bleaching the pulp with a second chlorine dioxide stage. The method allows the mill to decrease the usage of sodium hydroxide or other alkali, while decreasing the use of chlorine dioxide, and possibly improving the yield and strength of the pulp, while maintaining a similar level of bleached brightness of the pulp. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
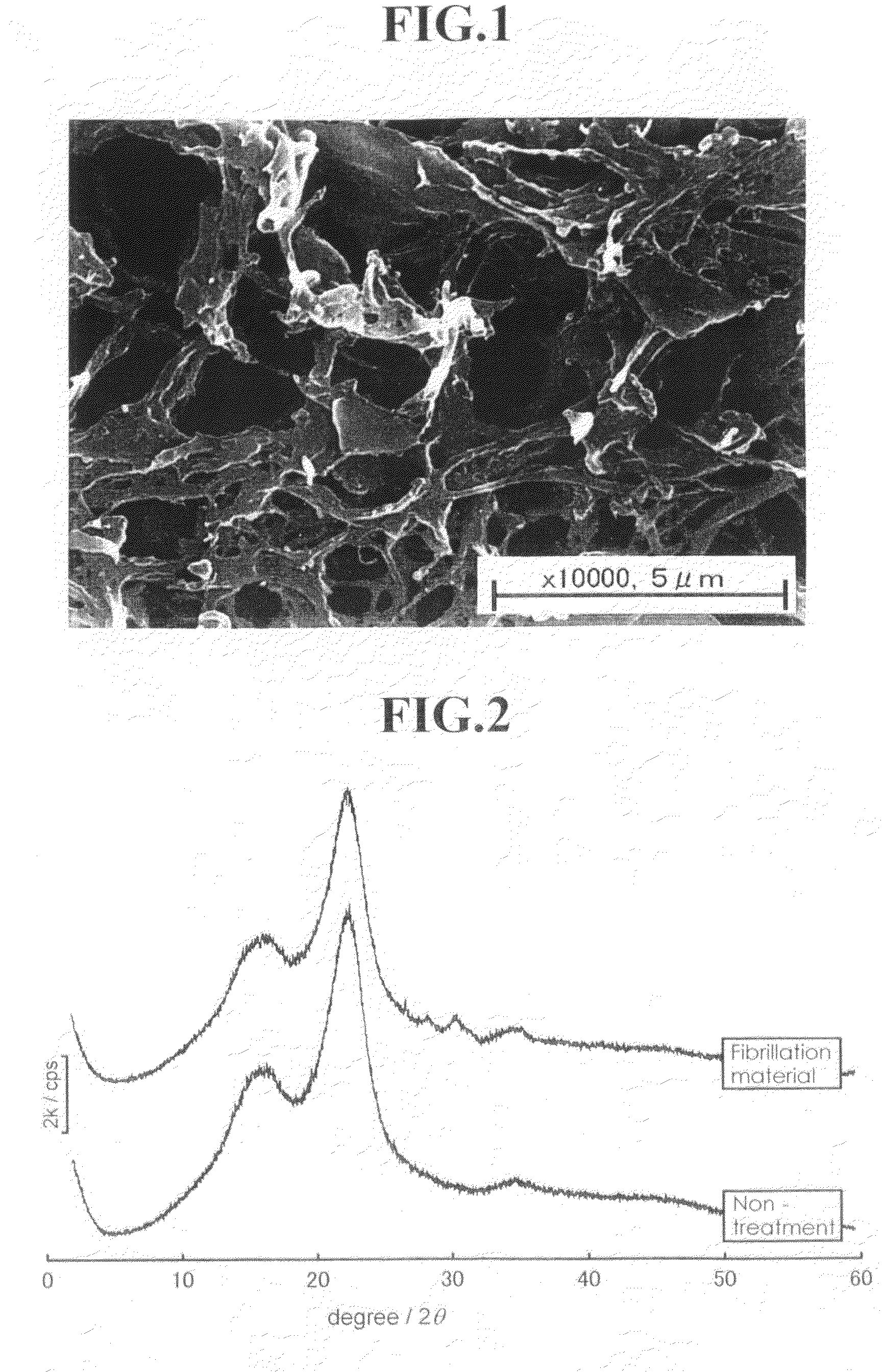
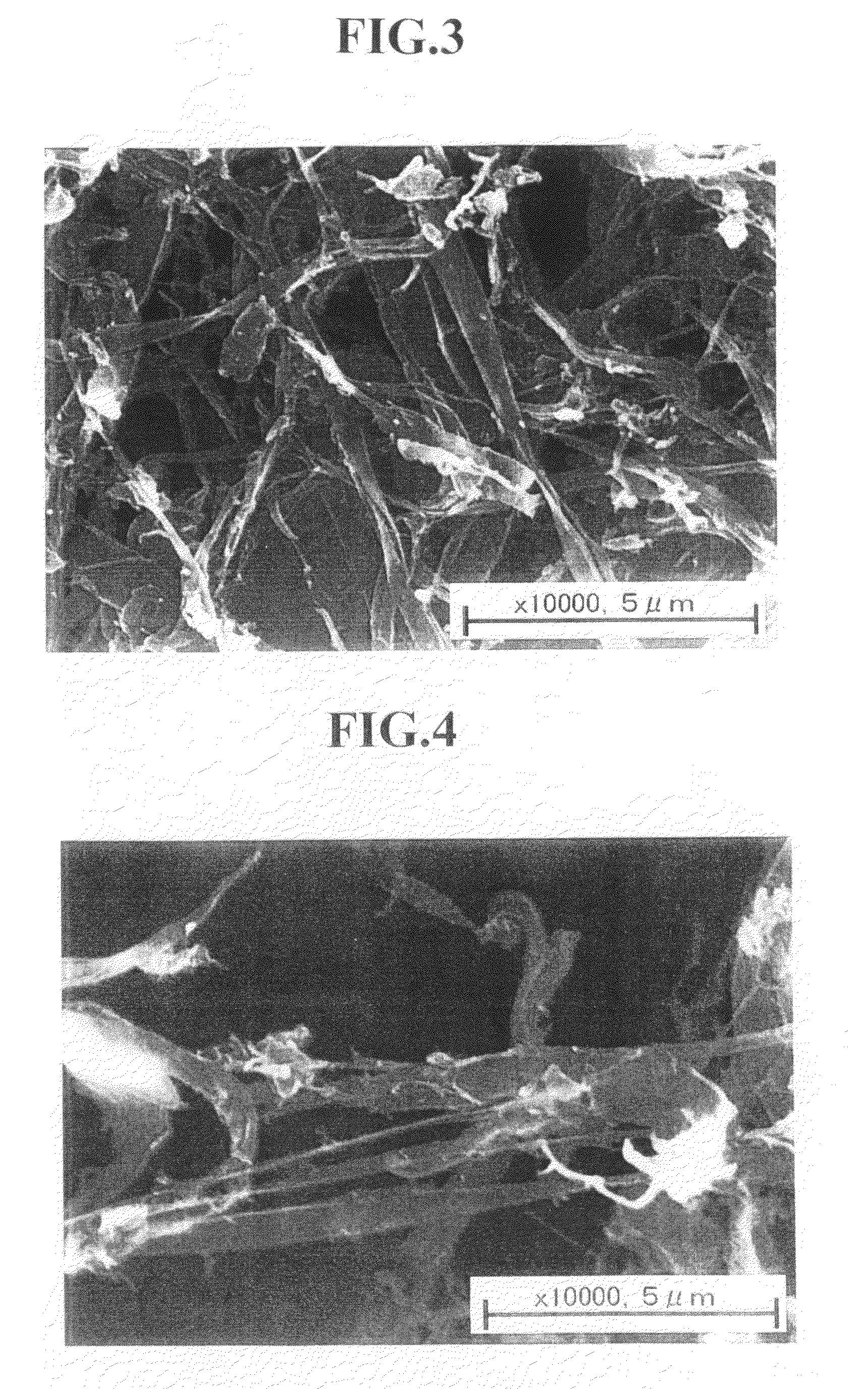
Fine fibrous cellulosic material and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100151527A1Increase ratingsIncrease productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentLayered productsPolymer scienceHemicellulose
[Problem] To provide a fine fibrous cellulosic material capable of producing a saccharide in a high yield by hydrolysis; to provide a process for producing the fine fibrous cellulosic material from a cellulosic material; and to provide a process for producing the saccharide using the fine fibrous cellulosic material.[Means for Solving Problems] The present invention is the fine fibrous cellulosic material containing cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, which the fine fibrous cellulosic material has a width of 1 μm or less and a length of 5,000 μm or less and is used for glycation reaction by hydrolysis.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose in an extruder and microfibrillated cellulose produced according to the process
ActiveUS8747612B2Increase productionEfficient productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentPretreatment with oxygen-generating compoundsCelluloseFiber
The present invention relates to a process for the production of microfibrillated cellulose wherein the process comprises the steps of, providing a slurry comprising fibers, adding the slurry to an extruder, treating the slurry in the extruder so that the fibers are defibrillated and microfibrillated cellulose is formed. The invention further relates to a microfibrillated cellulose produced.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Process For Producing A Pulp
ActiveUS20090312536A1Easy to solvePretreatment with water/steamNon-fibrous pulp additionKraft processPulp and paper industry
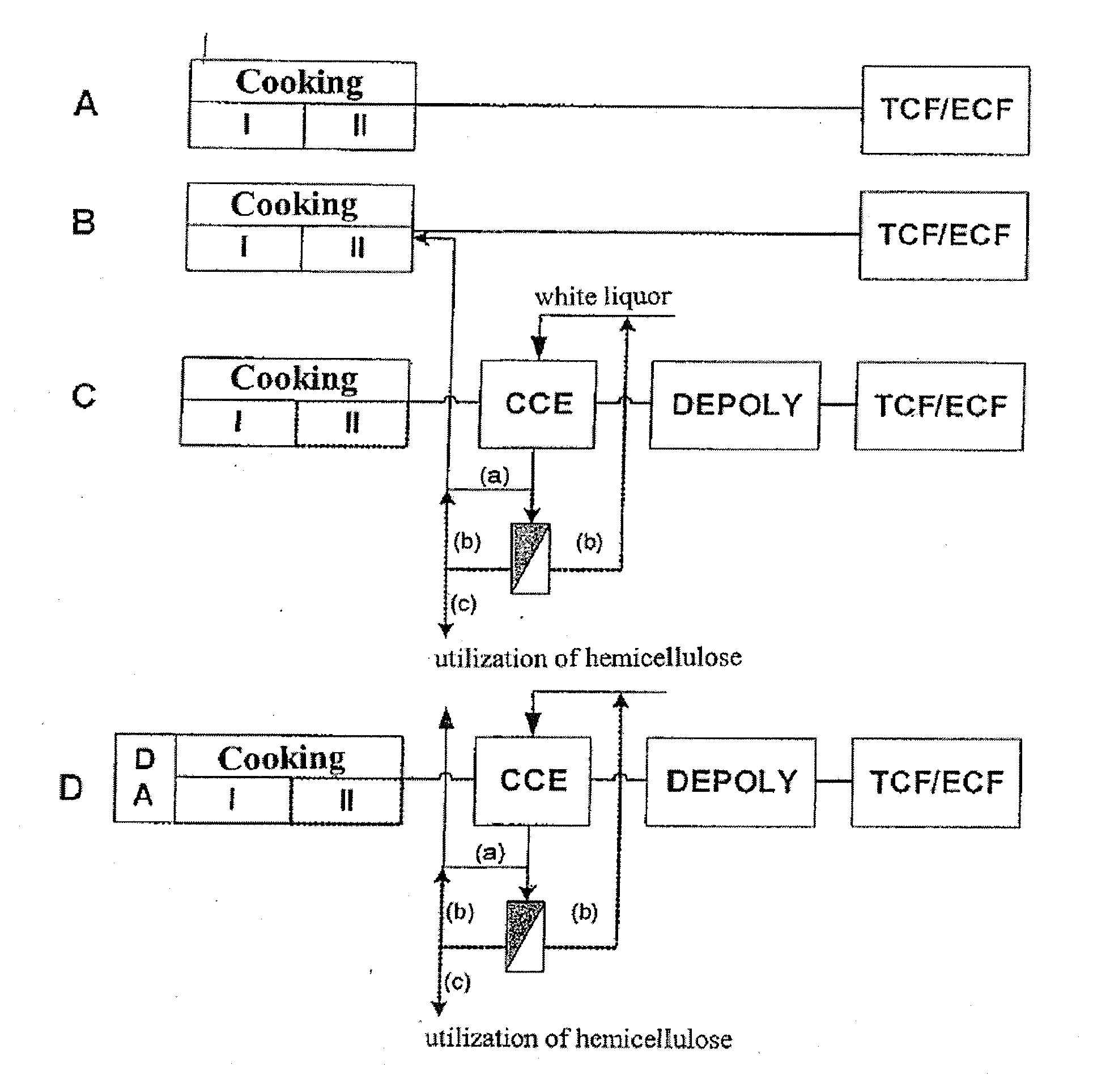
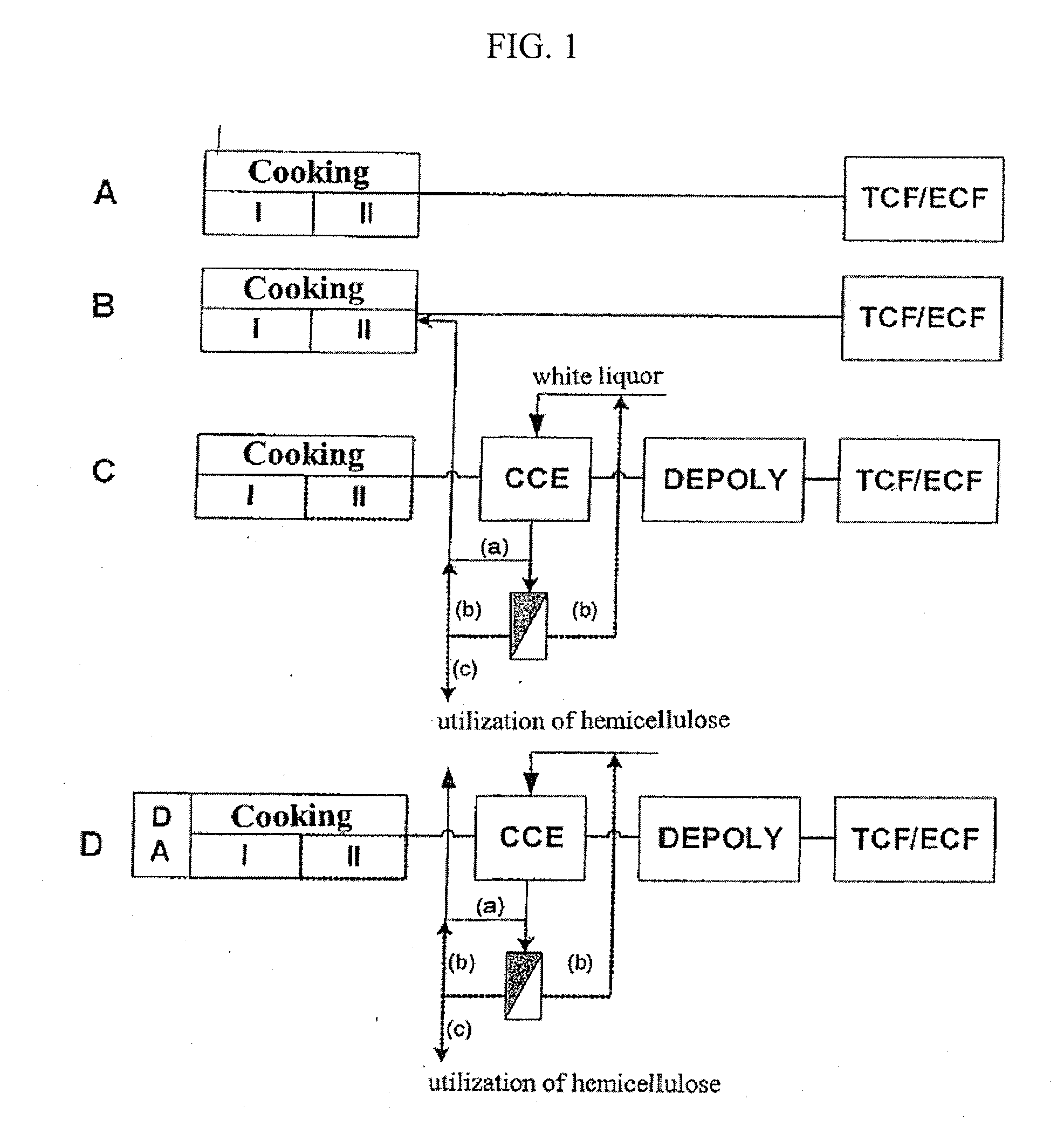
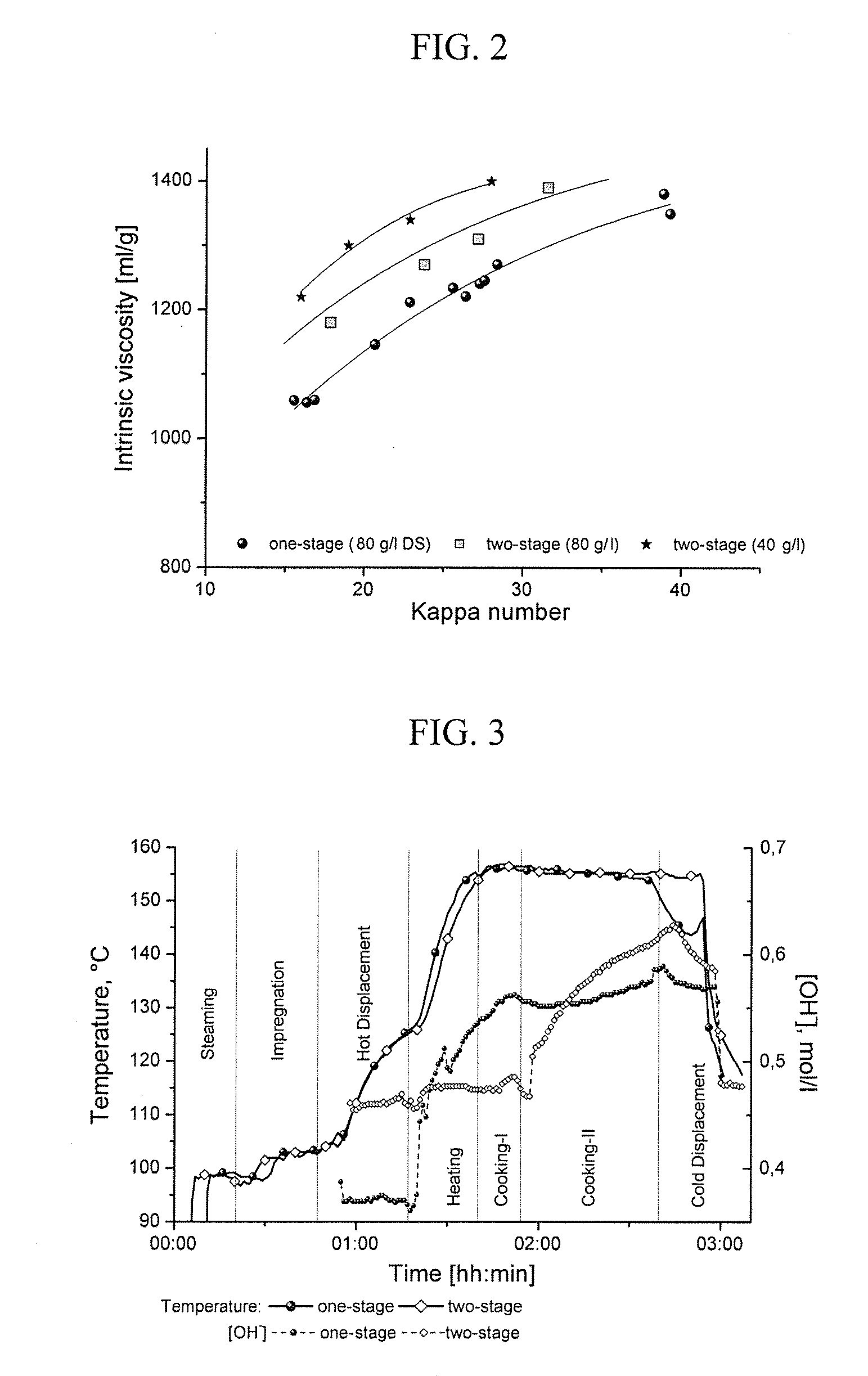
The invention relates to a process for producing a dissolving pulp from a cellulosic starting material using the kraft process, comprising the step of cooking the starting material with a cooking liquor. The process according to the invention characterized in that the starting material is exposed to a steam treatment prior to cooking and that the pulp obtained by cooking is subjected to cold caustic extraction (CCE) in the course of further processing.
Owner:LENZING AG
Pulp treatment and process
InactiveUS7267744B2Reduce stepsReduce in quantityElectrolysis componentsWood treatment detailsPulp treatmentCompound (substance)
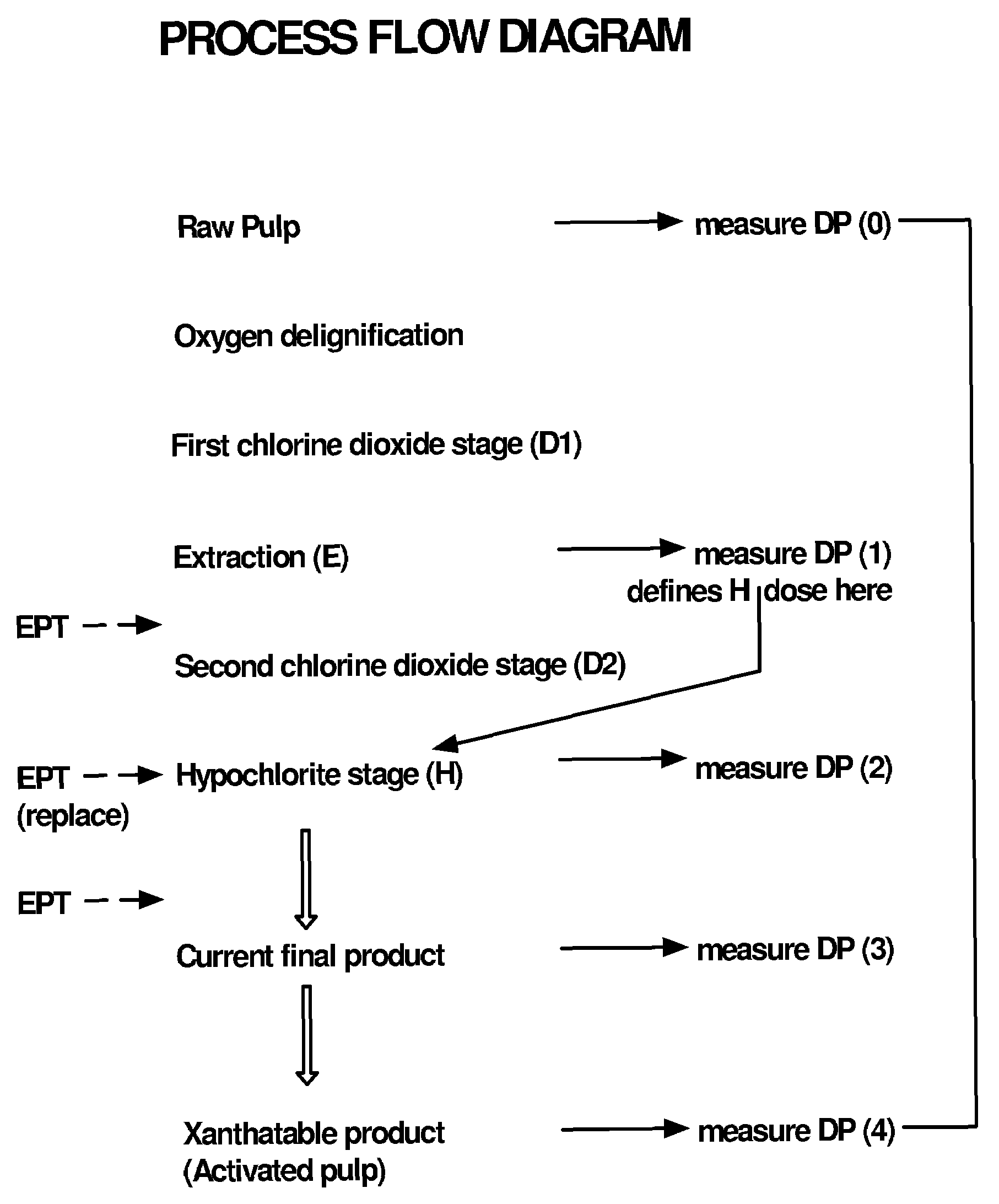
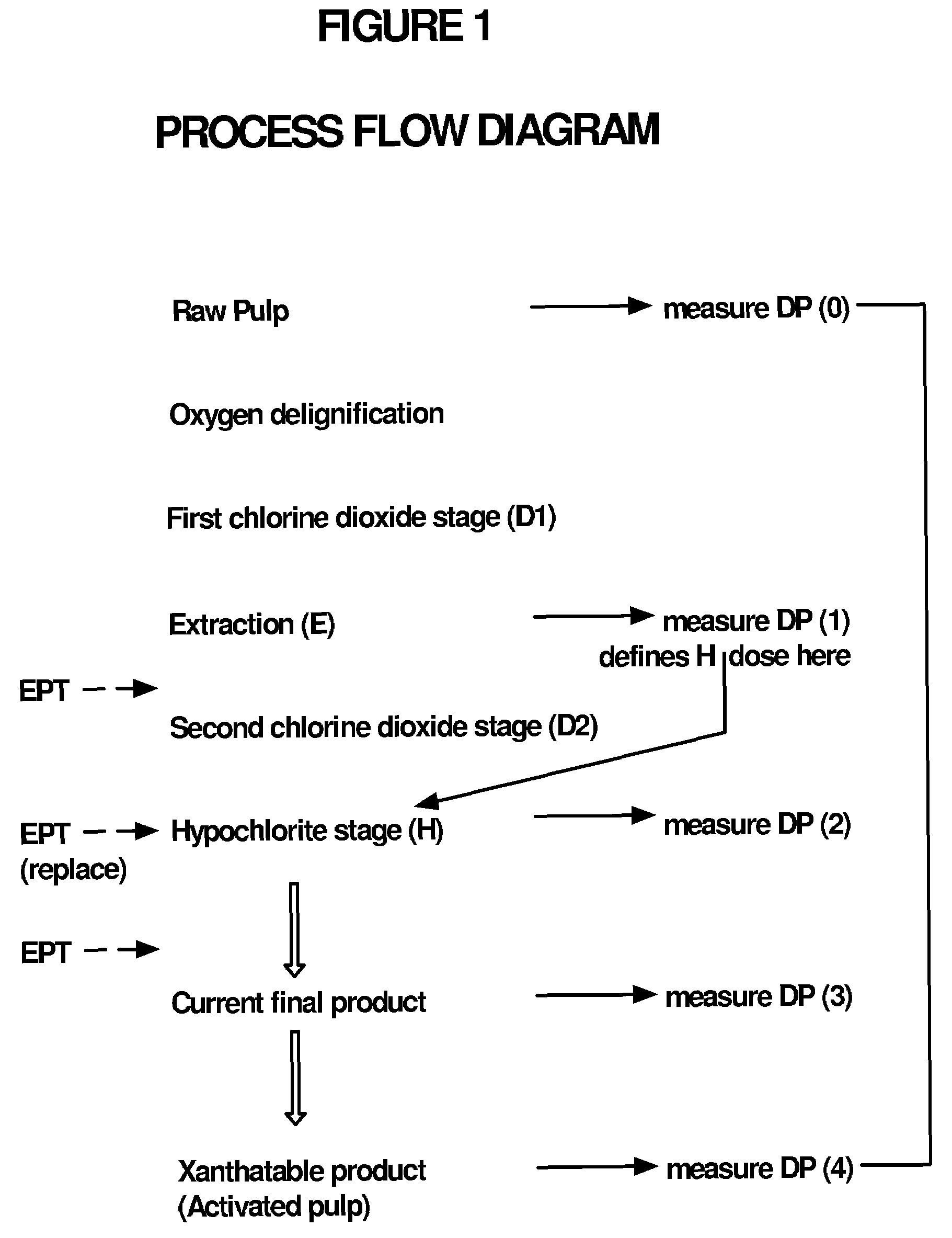
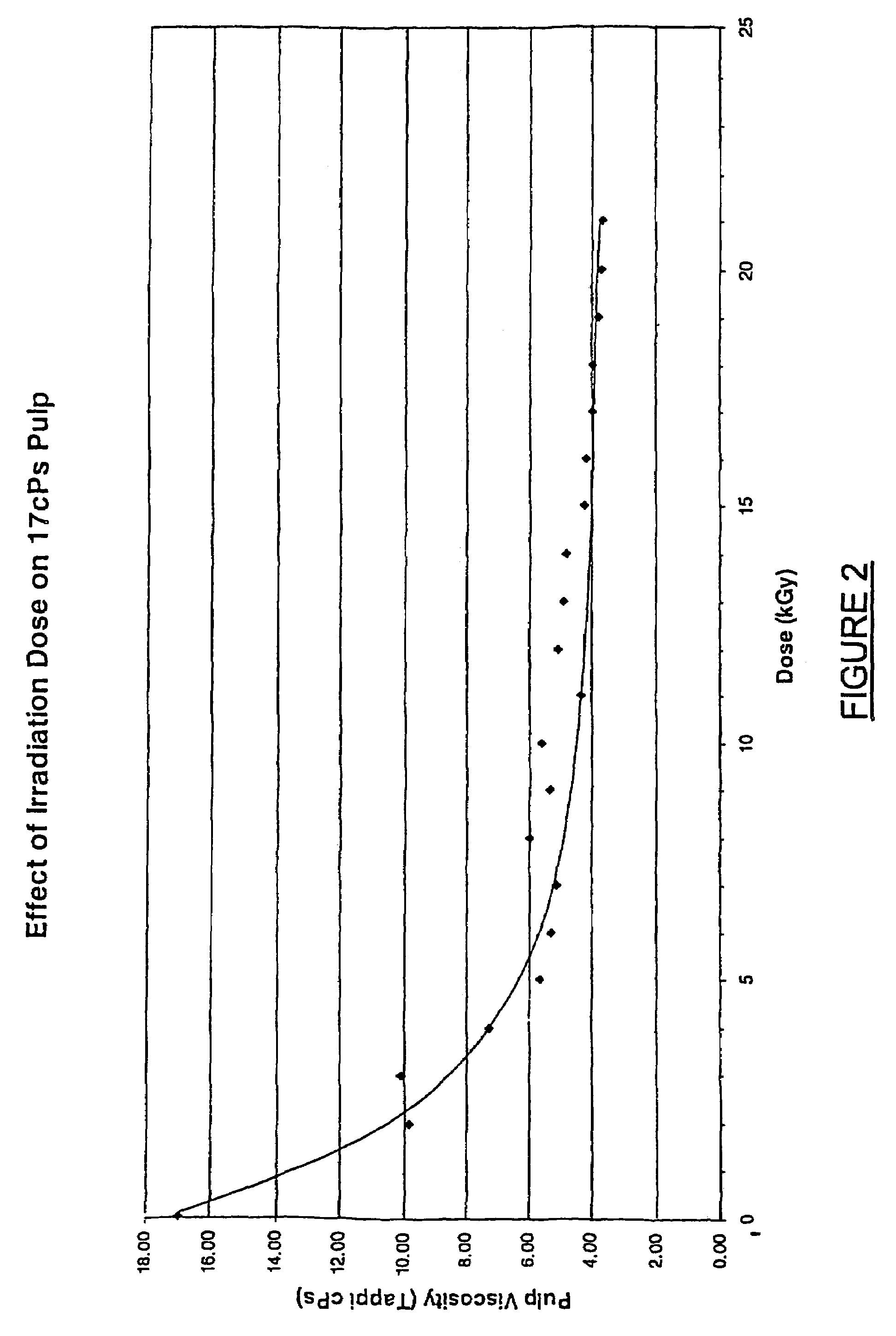
This invention provides a process for treating chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose including cotton linter, including the step of applying an electron processing technology (EPT) step to chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose, as the case may be, on an in-line basis to provide control of pulp viscosity or degree of polymerization (DP). The invention also provides a method of process control in treating the aforementioned woodpulp or cellulose, including the step of using radiation dose-viscosity relationship curve for applying an EPT step on an in-line basis. The in-line EPT step may, in one form of the invention, replace and hence eliminate a chemical DP reduction step.
Owner:SAPPI LTD
Method for Producing Wood Fibre Pellets
ActiveUS20090229771A1High strengthImprove compatibilityNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper/cardboardCelluloseOligomer
A process for producing pellets or granules comprising fibres of a lignocellulousic material, for use as a feedstock in plastics manufacture, conveying in a dry or wet air stream and applying to the fibres a liquid formulation comprising one or more polymers, monomers, or oligomers, forming the fibres into a solid product, and breaking down the solid product to produce said pellets or granules. Typically the conduit conveys the fibres in a plant for manufacture of fibre board.
Owner:NEW ZEALAND FOREST RES INST
Chemical mechanical pulping method for cotton haulm raw material
InactiveCN101016702AHigh whitenessHigh yieldPaper/cardboardPulping with inorganic basesChemical reactionUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a chemical mechanical pulping method which uses cotton stalk as material, wherein the invention processes the first grinding after the first screw protrusion pre-immersion to replace present APMP technique which comprises two screw protrusion immersion followed with at least two sections of grinding, then holds the pulp after first grinding process for some time to process chemical reaction, at the same time, the invention uses novel additive to replace traditional metal ion chelating agent, Na2SiO3 and MgSO4. Compared with present APMP technique, the invention has low cost and high strength to be used to produce high-level paper.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel cellulose extraction process
ActiveCN101748633BLight colorPromote growthPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsDigestersCelluloseHigh concentration
The invention relates to a novel sectional type process which extracts cellulose from plant bodies, and comprises the following steps: the process is that dilute alkali is first used for soaking the plant bodies, and then pressurizing, steaming, polishing and pulp washing are carried out so that the cellulose is obtained. The sectional type process has the advantages that very dilute alkali can be used for soaking or evaporating the plant bodies, not only the amount of alkali is greatly saved, but also the heating temperature is reduced, the heating time is shortened, the cellulose can be obtained at yield coefficient, and the secondary pollution brought by using sulfide, anthraquinone and other high pollution auxiliary agents is avoided. The soak solution and the cleaning solution can be used together in a cycling way, so liquid or solid organic fertilizer with high concentration can be conveniently obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSIGHT BIOMASS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com