Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
19459results about "Paper/cardboard" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
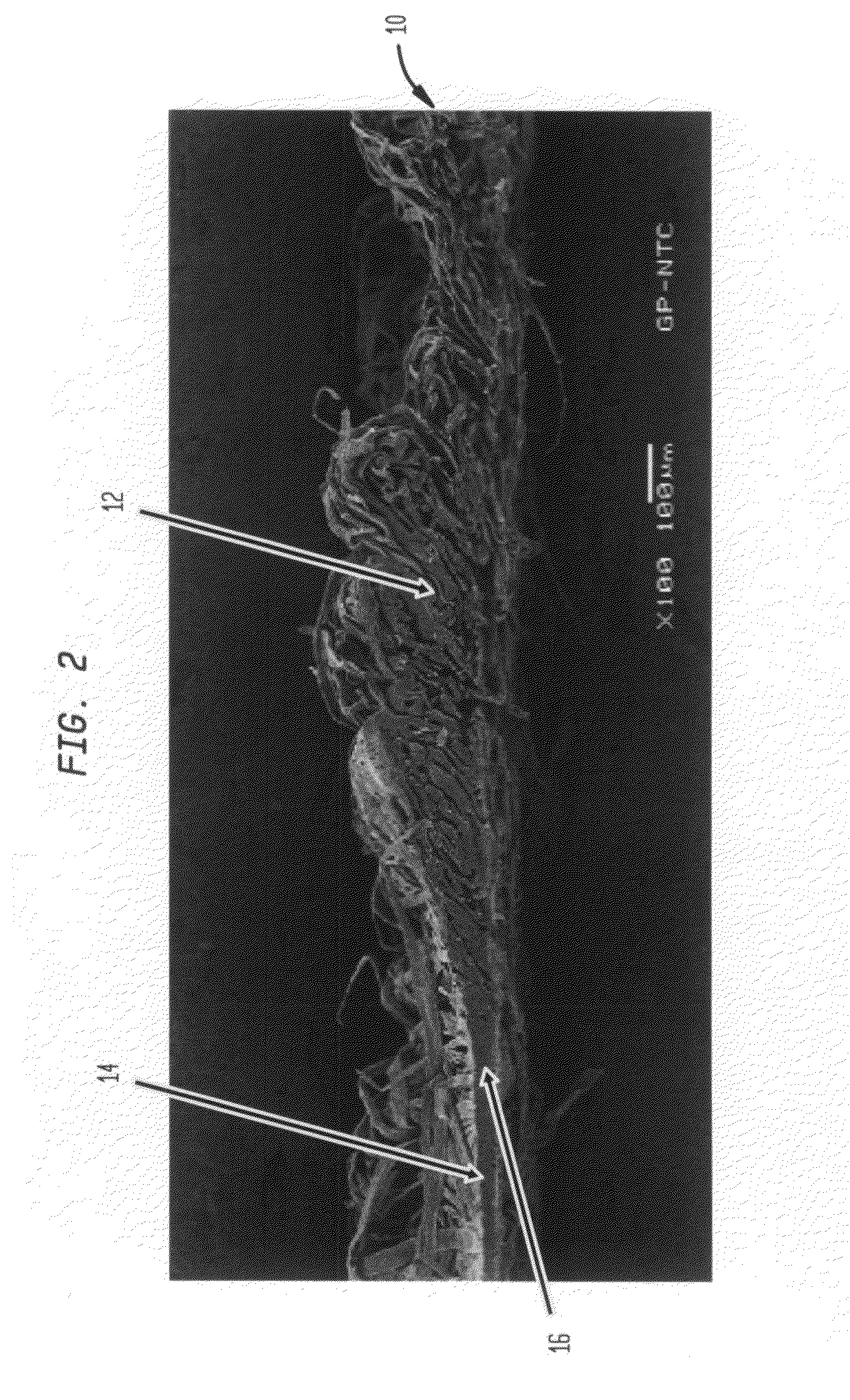
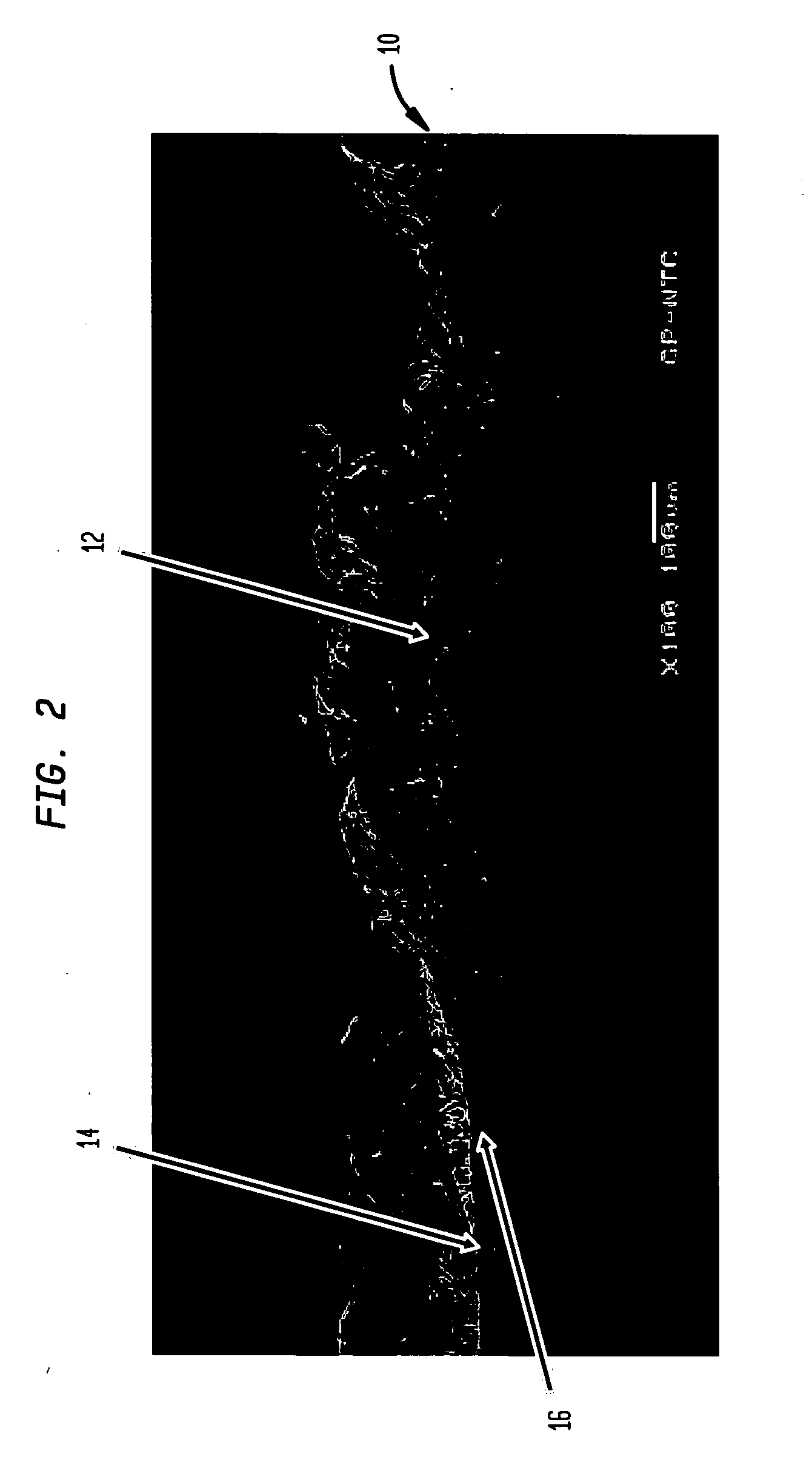
Process for making unitary fibrous structure comprising randomly distributed cellulosic fibers and non-randomly distributed synthetic fibers
InactiveUS7067038B2High densityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceRepeat pattern
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Hesperaloe tissue having improved cross-machine direction properties
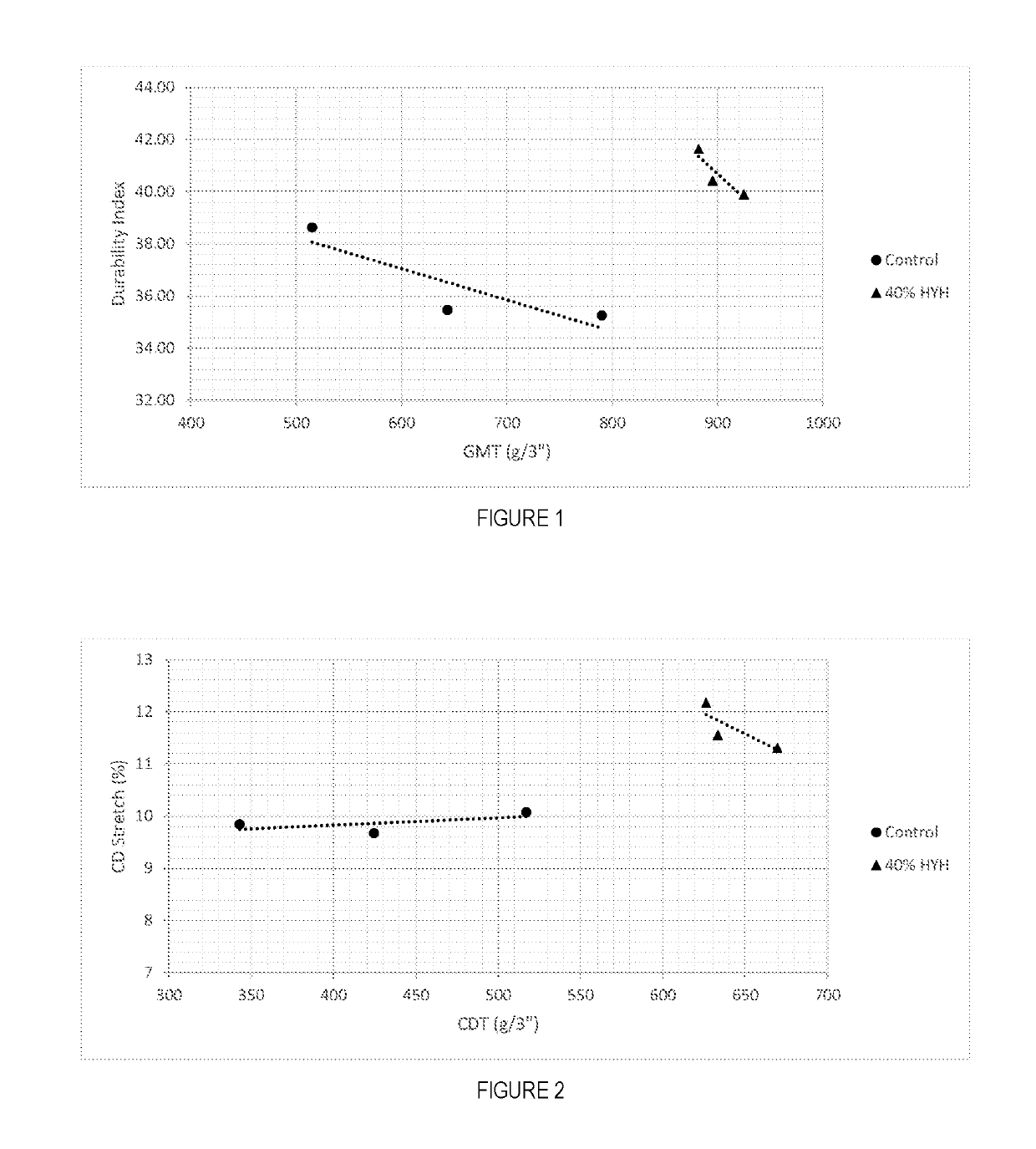
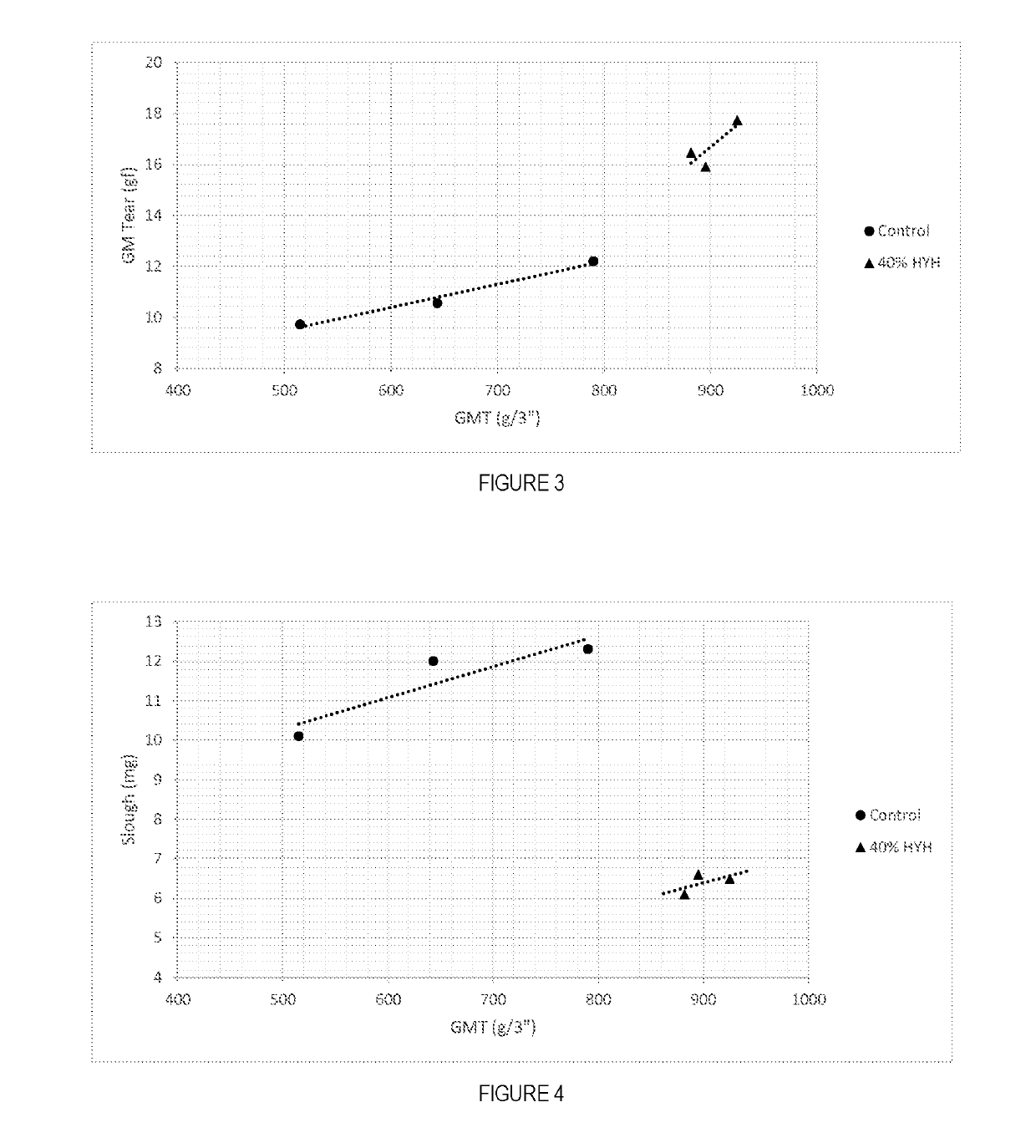
ActiveUS10337148B2Satisfactory softness and strength and bulkNegatively effecting tissue product strength and stiffness and bulkPaper/cardboardTissue/absorbent paperFiberMedicine
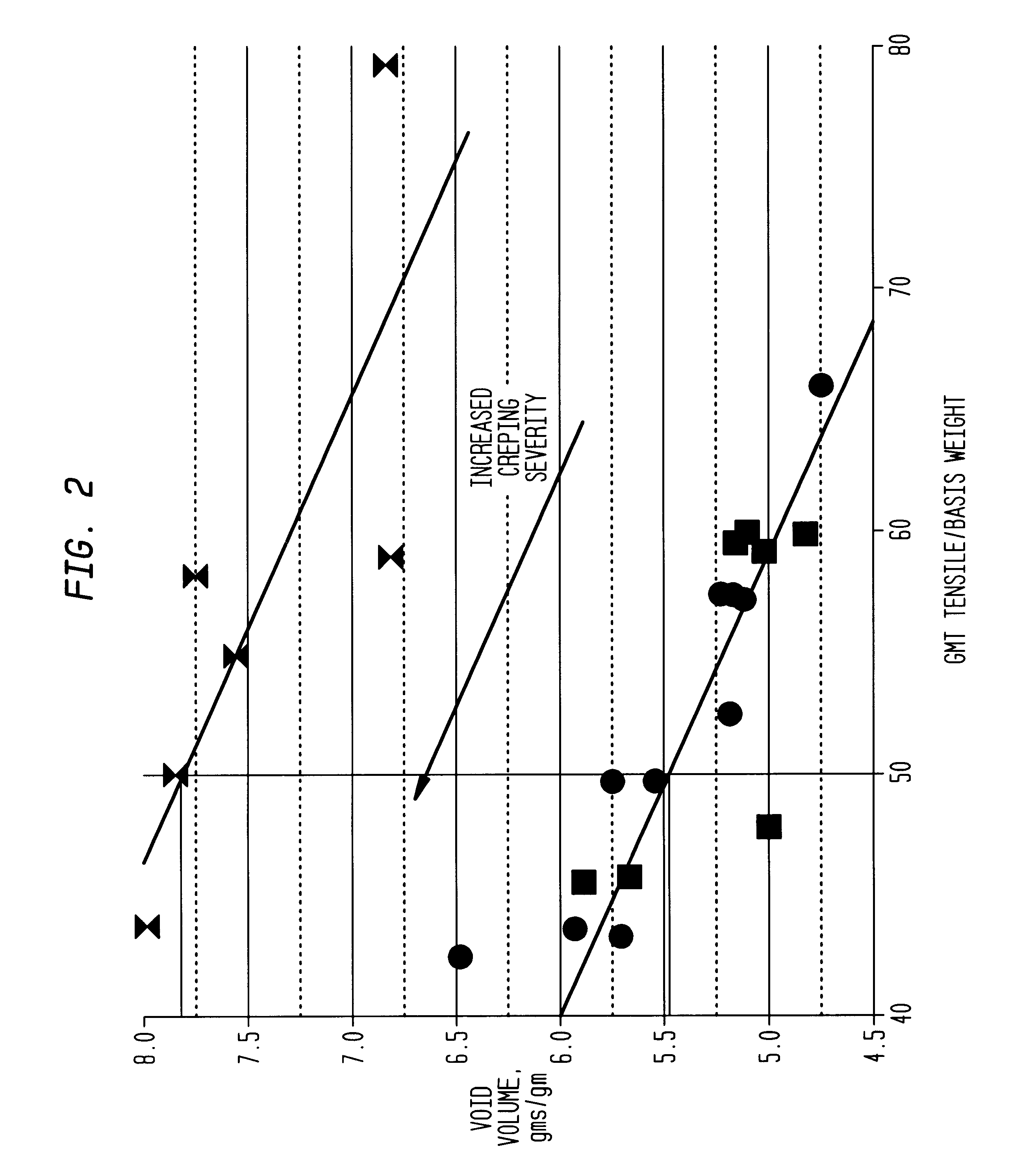
Soft, durable and bulky tissue products comprising non-wood fibers and more particularly high yield hesperaloe pulp fibers are disclosed. The tissue products preferably comprise at least about 5 percent, by weight of the product, high yield hesperaloe pulp fiber and have relatively modest tensile strengths, such as a geometric mean tensile (GMT) less than about 1,000 g / 3″, and improved durability and cross-machine direction (CD) properties, such as a CD Stretch greater than about 10 percent. Additionally, at the foregoing tensile strengths the products are not overly stiff. For example the tissue products may have a Stiffness Index less than about 10.0.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
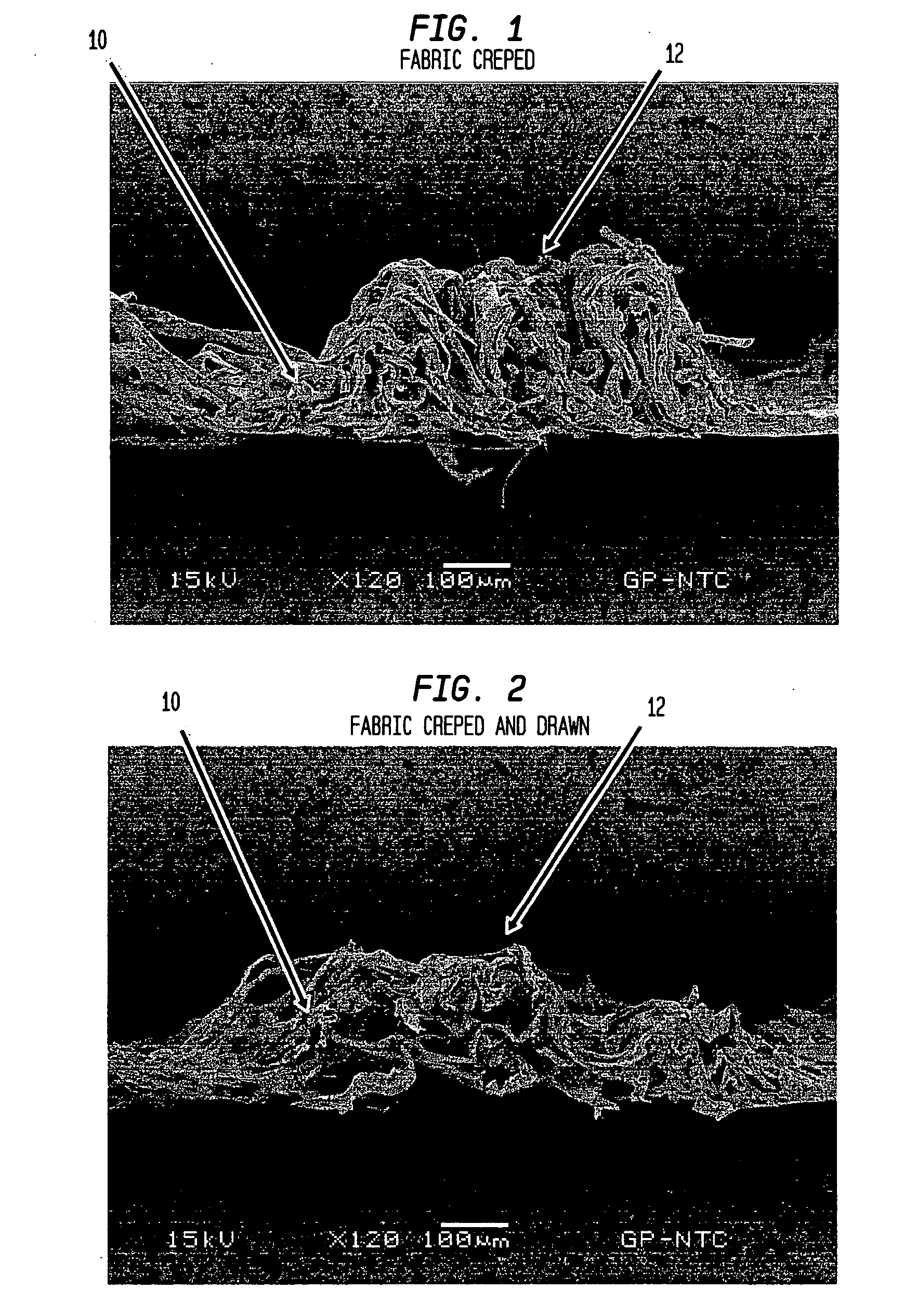
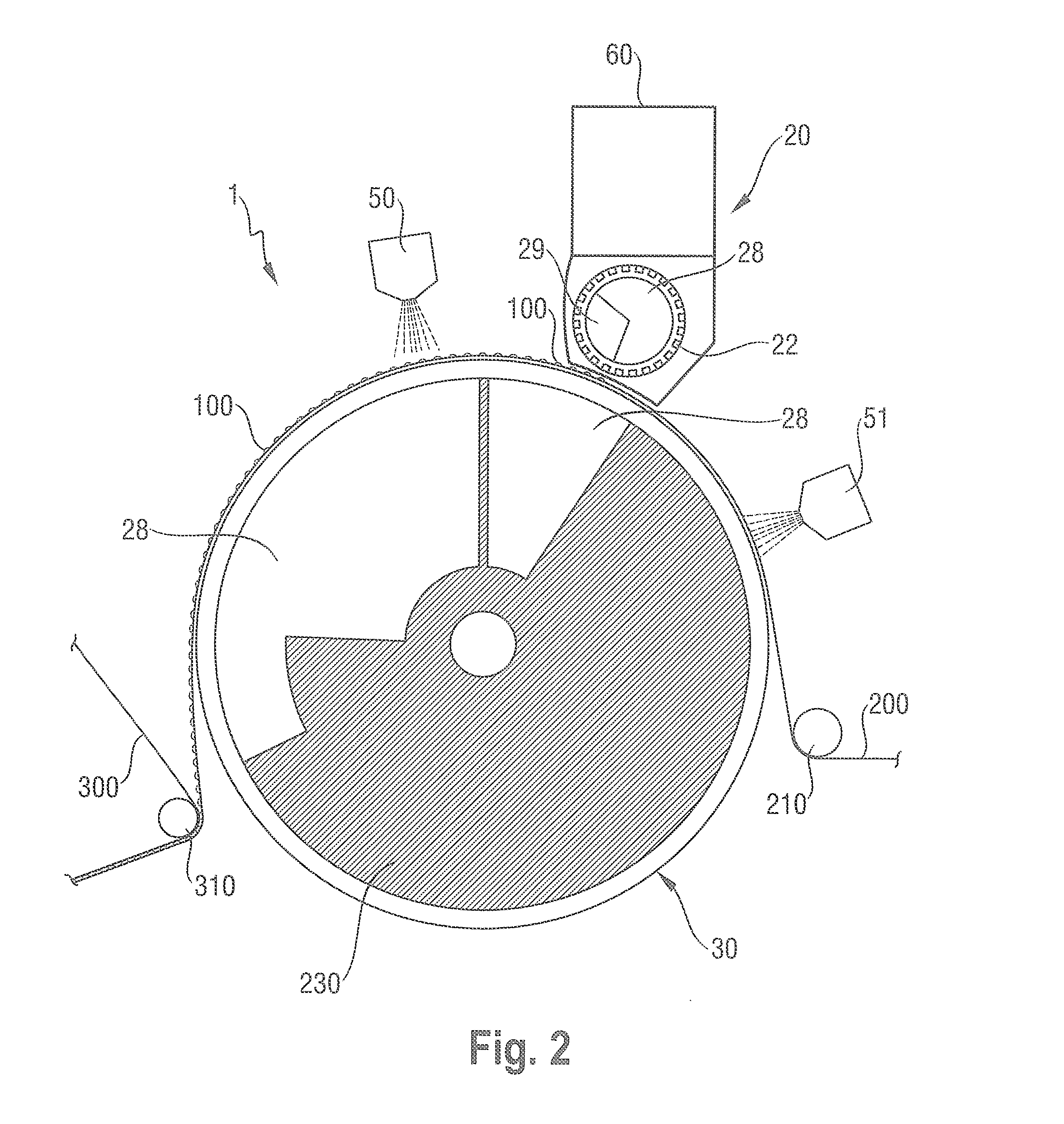
Fabric creped absorbent sheet with variable local basis weight
InactiveUS7494563B2Improve water absorptionSurprising softnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberPapermaking
An absorbent cellulosic sheet having variable local basis weight includes a papermaking-fiber reticulum provided with (i) a plurality of cross-machine direction (CD) extending, fiber-enriched pileated regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by (ii) a plurality of elongated densified regions of compressed papermaking fibers. The elongated densified regions have relatively low local basis weight and are generally oriented along the machine direction (MD) of the sheet and have an MD / CD aspect ratio of at least 1.5. The products are most preferably prepared by way of a compactive dewatering / wet crepe process.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Bulk enhanced paperboard and shaped products made therefrom
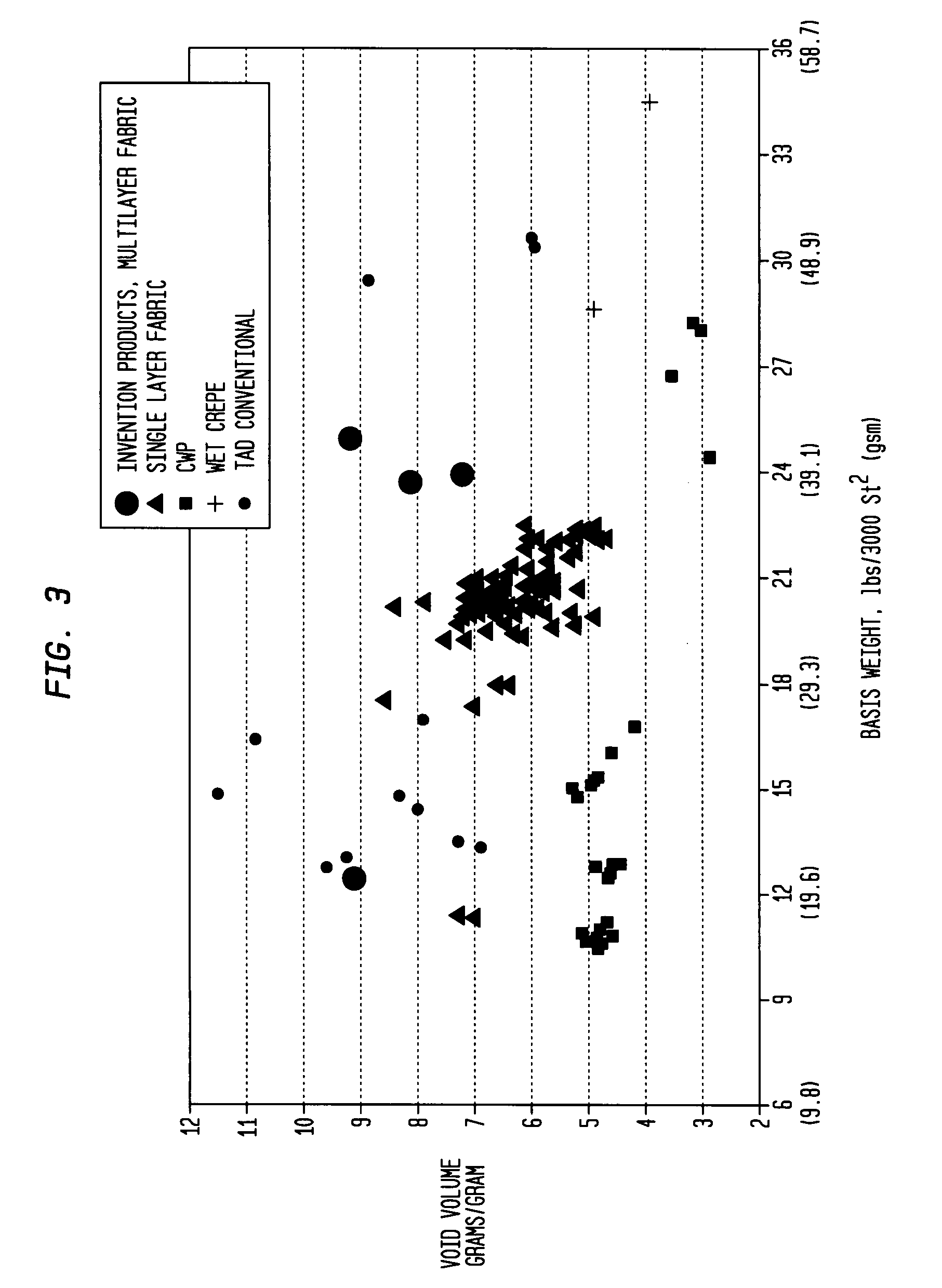
An improved paperboard has been bulk enhanced by retaining a substantial portion of bulk-enhanced additives including expandable microspheres in a suitable distribution within the paperboard. The cellulosic paperboard web has an overall fiber weight (w) of at least 40 lbs. / 3000 square feet and at a fiber density of 3, 4.5, 6.5, 7, 8.3, and 9 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch respectively, has a GM Taber stiffness of at least about 0.00716 w2.63 grams-centimeter / fiber mat density1.63 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch, and a GM tensile stiffness of at least about 1890+24.2 w pounds per inch. The high retention of the bulk enhancing additives is believed to result from the incorporation of suitable retention aids. The resulting paperboard has better GM Taber stiffness values and GM tensile stiffness than prior art paperboards. The paperboard also has increased strain to failure and is able to be formed into suitable paperboard containers without loss of integrity. The resulting containers have increased hold times when they contain hot or cold food or drink.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
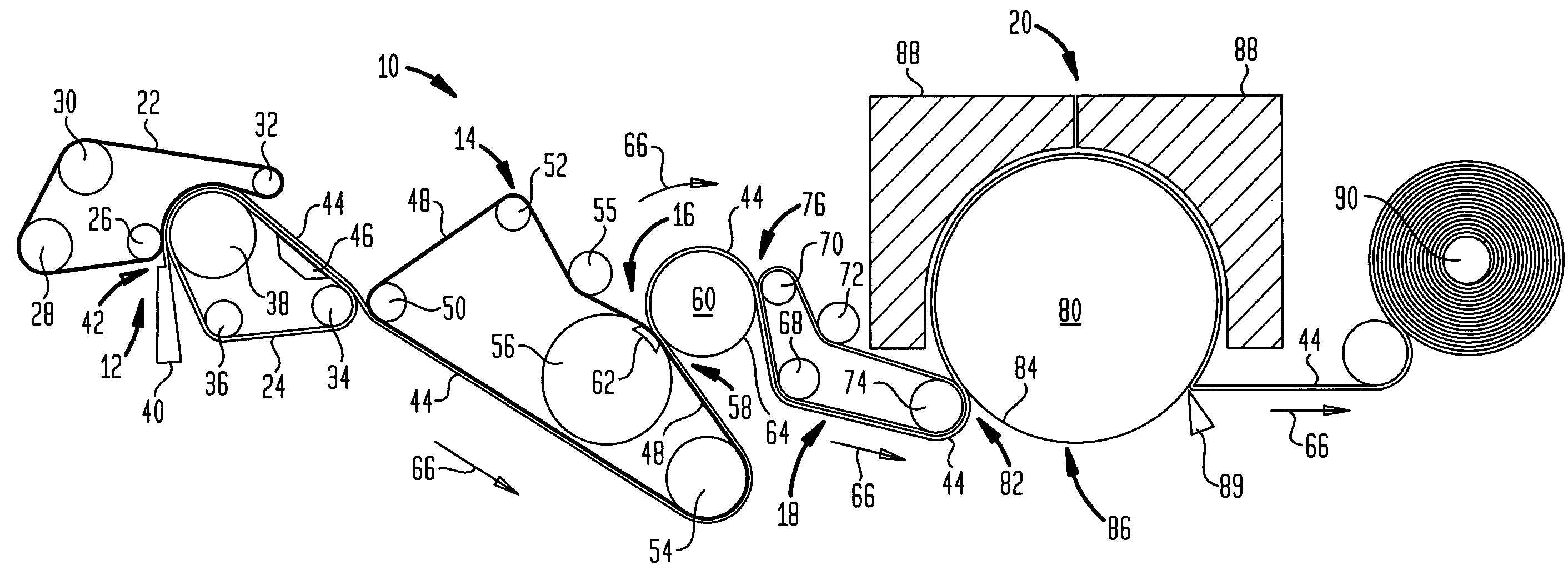
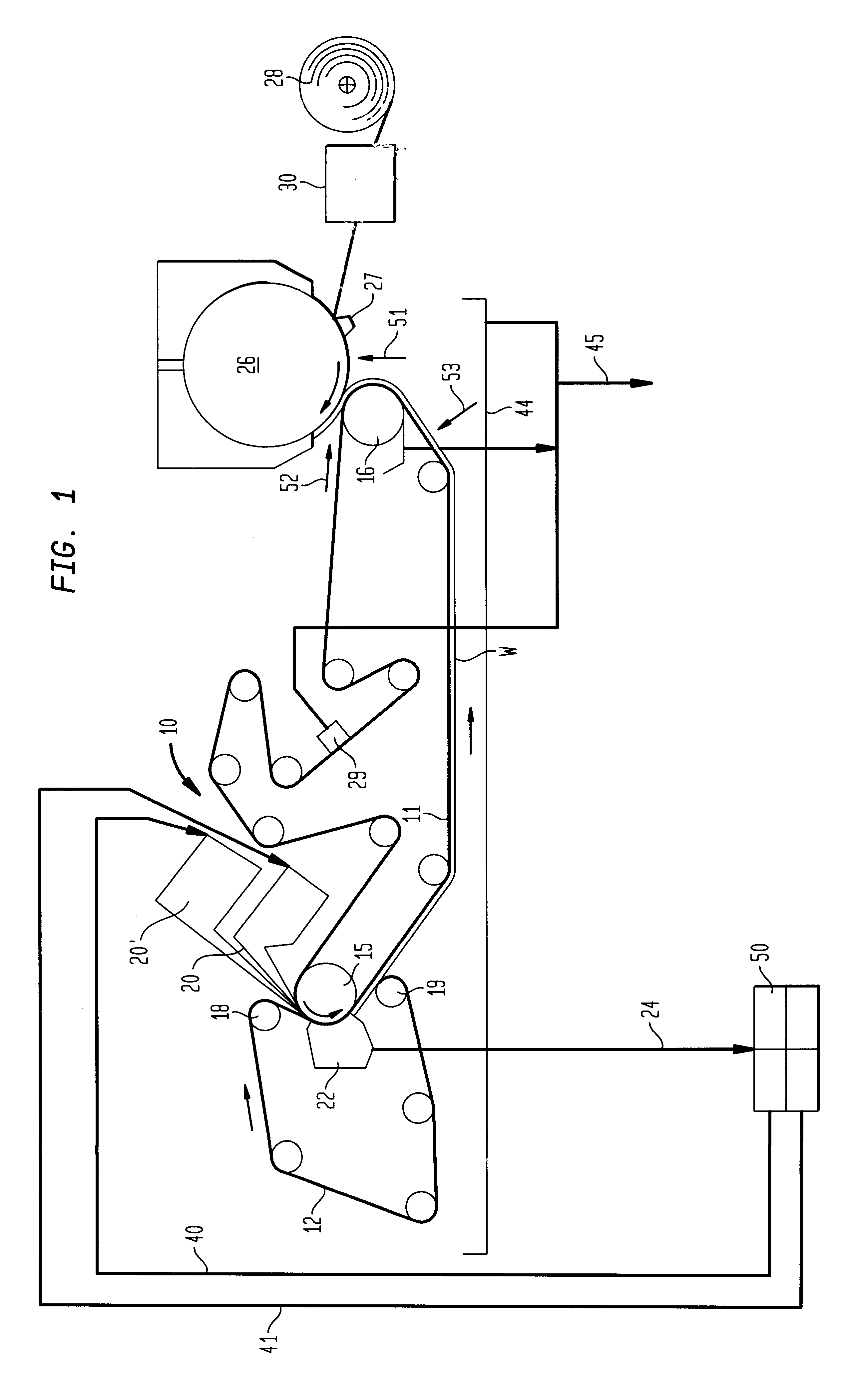
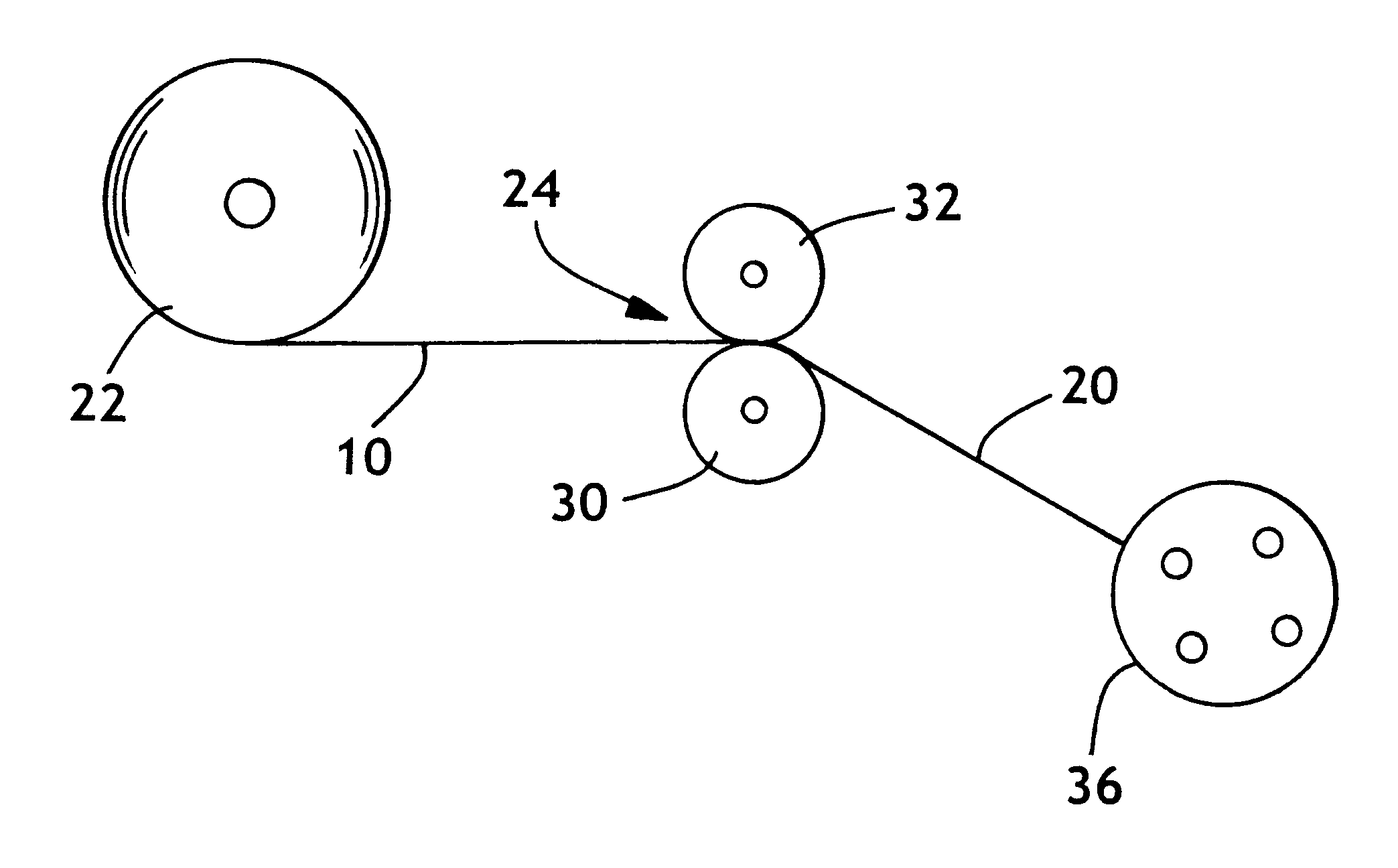
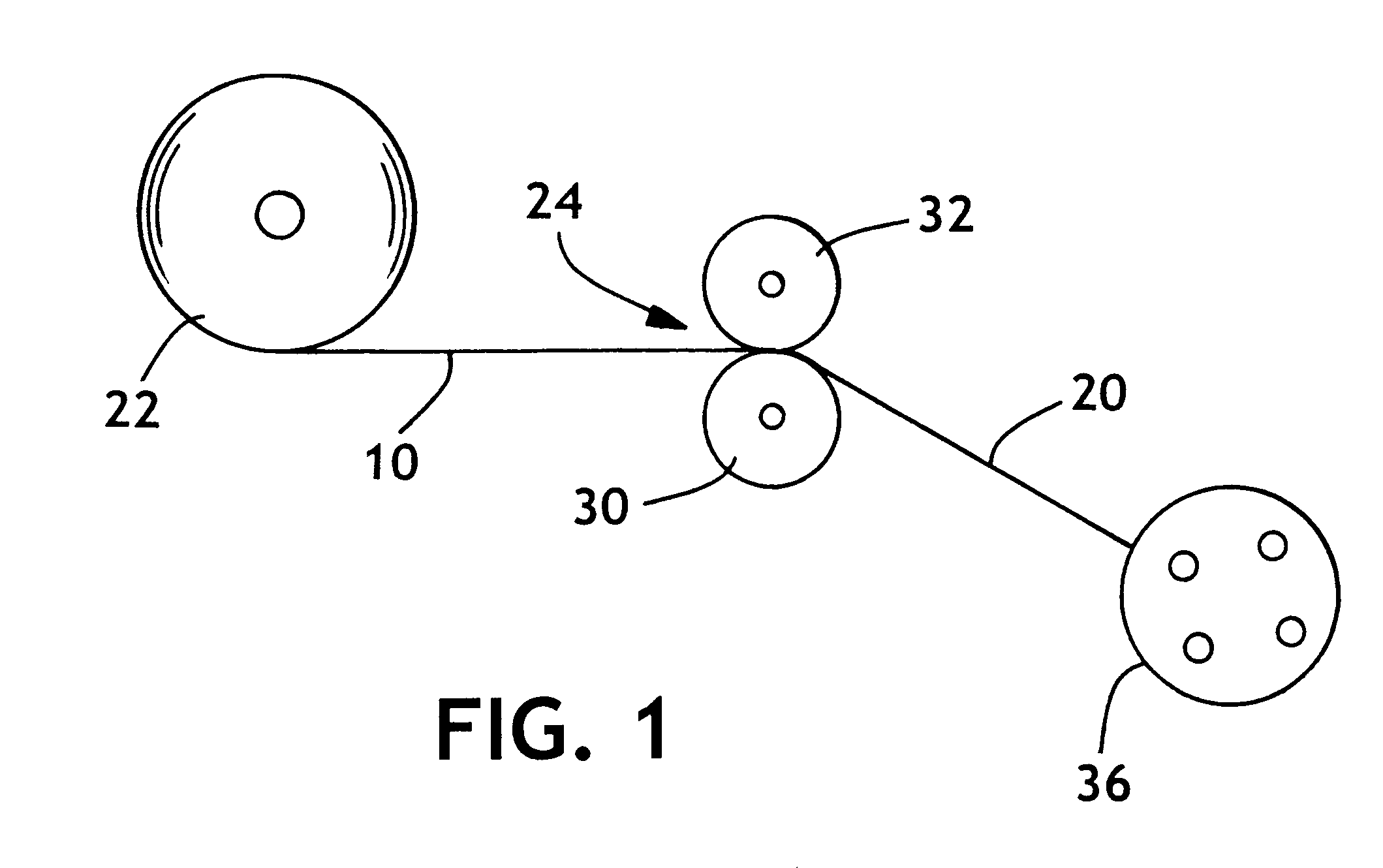
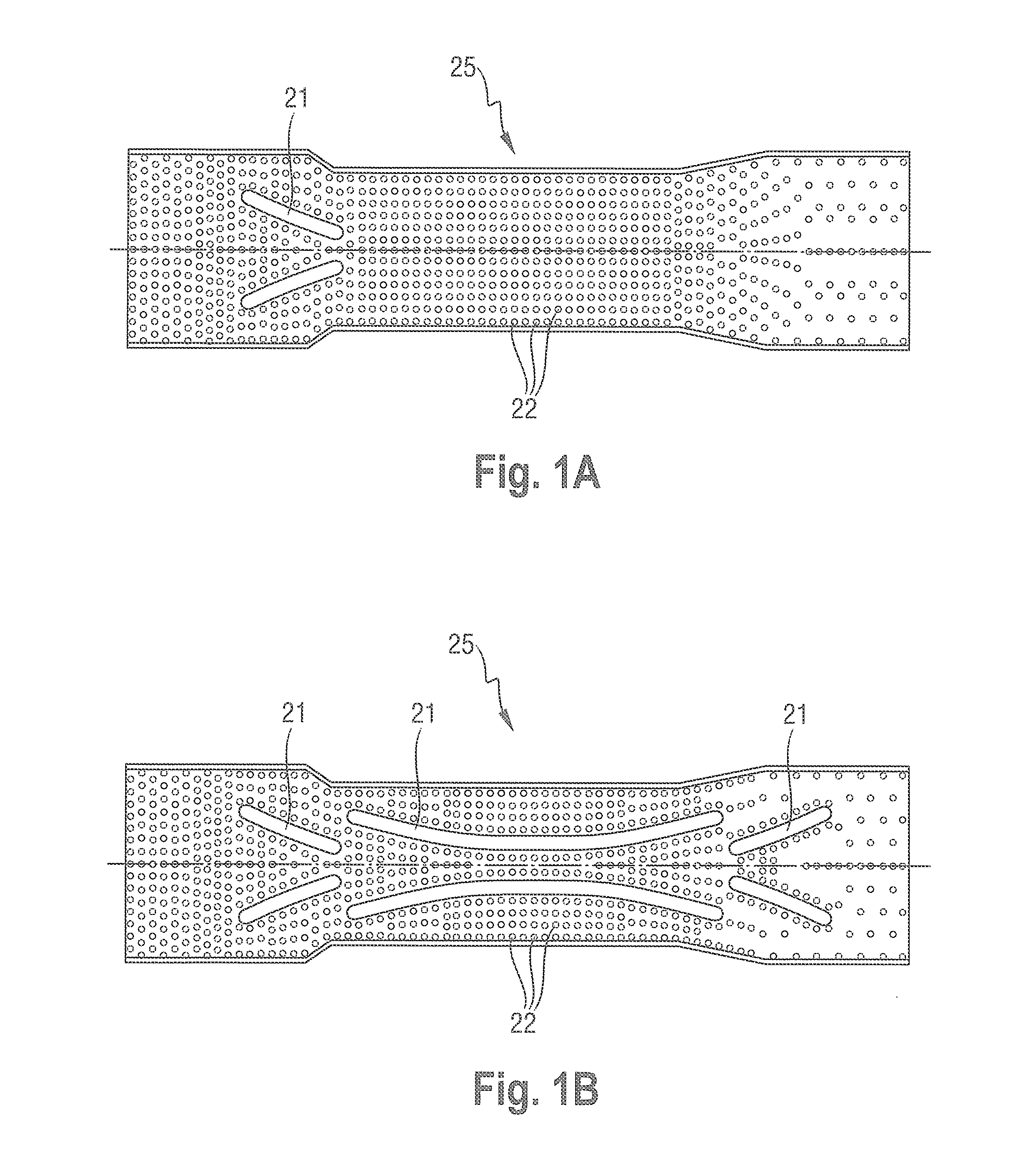
Fabric crepe process for making absorbent sheet
ActiveUS7399378B2High speed transmissionGuaranteed high speed operationNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberAdhesive
A process for making absorbent cellulosic paper products such as sheet for towel, tissue and the like, includes compactively dewatering a nascent web followed by wet belt creping the web at an intermediate consistency of anywhere from about 30 to about 60 percent under conditions operative to redistribute the fiber on the belt, which is preferably a fabric. In preferred embodiments, the web is thereafter adhesively applied to a Yankee dryer using a creping adhesive operative to enable high speed transfer of the web of intermediate consistency such as a poly(vinyl alcohol) / polyamide adhesive. An absorbent sheet so prepared from a papermaking furnish exhibits an absorbency of at least about 5 g / g, a CD stretch of at least about 4 percent, and an MD / CD tensile ratio of less than about 1.1, and also exhibits a maximum CD modulus at a CD strain of less than 1 percent and sustains a CD modulus of at least 50 percent of its maximum CD modulus to a CD strain of at least about 4 percent. Products of the invention may also exhibit an MD modulus at break 1.5 to 2 times their initial MD modulus.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
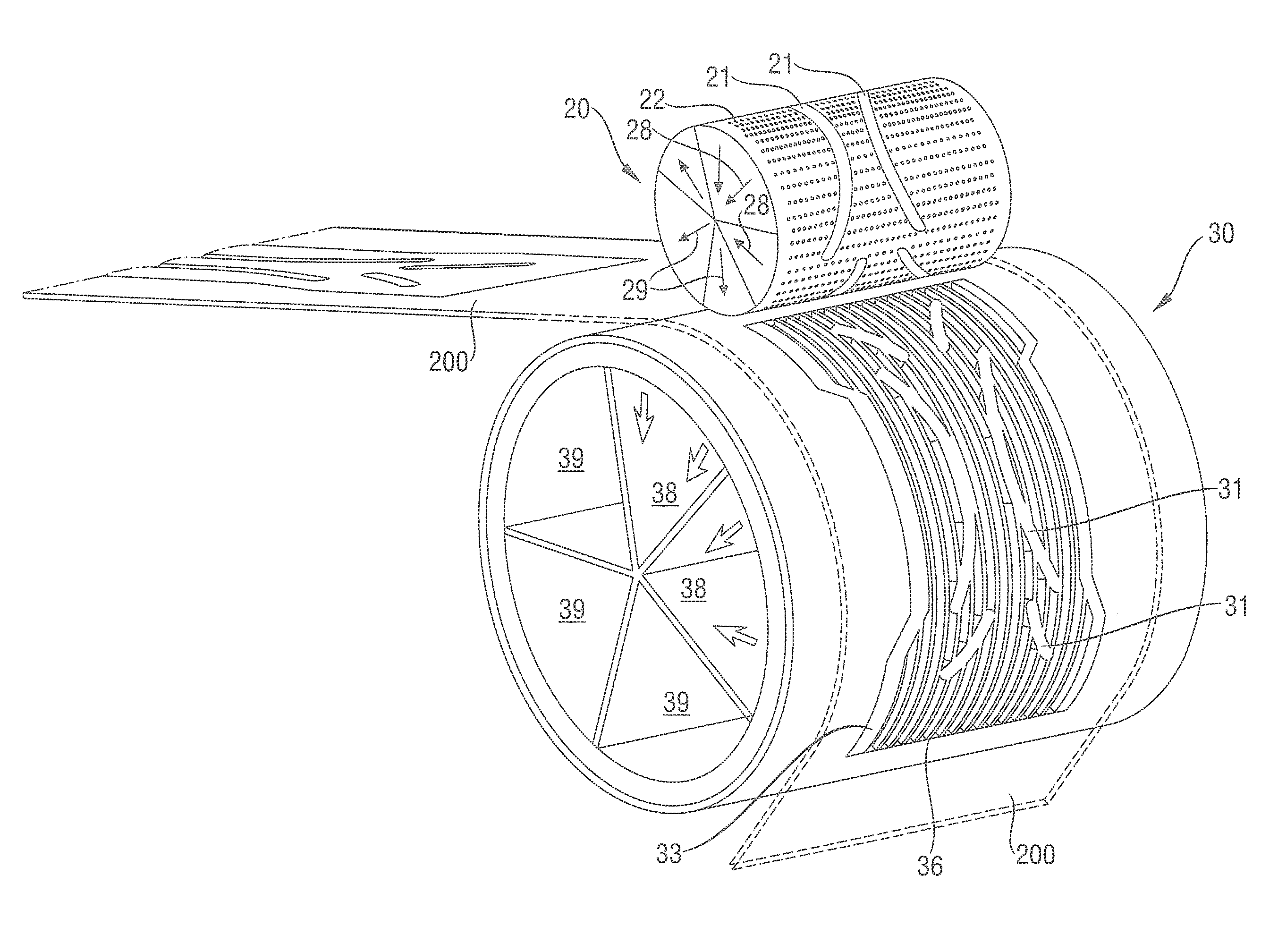
Method and Apparatus for Making Absorbent Structures with Absorbent Material
Apparatus and method for producing absorbent structures with absorbent layers with channel(s) without absorbent material, using a first moving endless surface with specific raised strip(s) and a second moving endless surface with specific mating strip(s).
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Fabric creped absorbent sheet with variable local basis weight
InactiveUS20080029235A1Improve water absorptionSurprising softnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberPapermaking
An absorbent cellulosic sheet having variable local basis weight includes a papermaking-fiber reticulum provided with (i) a plurality of cross-machine direction (CD) extending, fiber-enriched pileated regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by (ii) a plurality of elongated densified regions of compressed papermaking fibers. The elongated densified regions have relatively low local basis weight and are generally oriented along the machine direction (MD) of the sheet and have an MD / CD aspect ratio of at least 1.5. The products are most preferably prepared by way of a compactive dewatering / wet crepe process.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
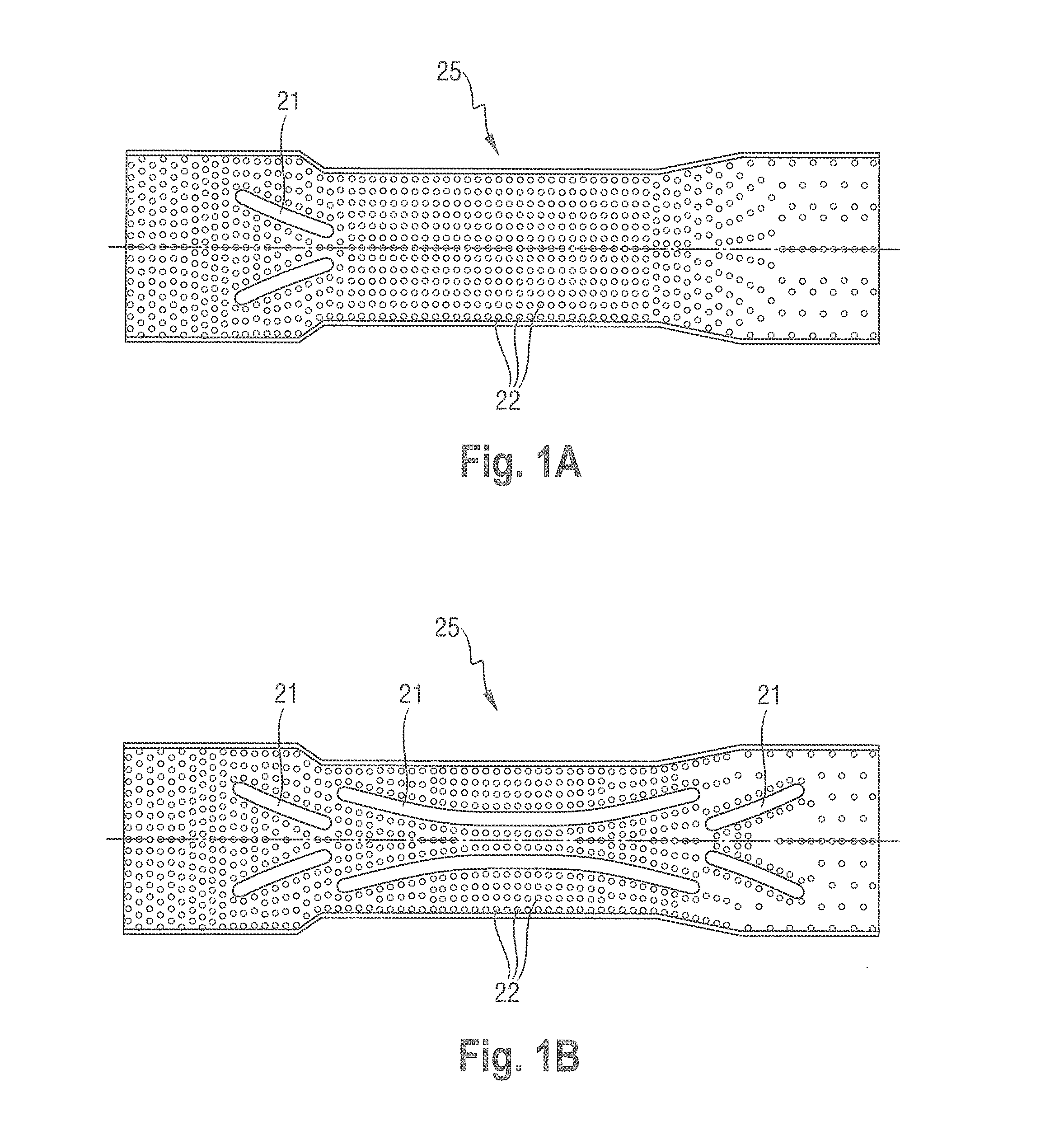
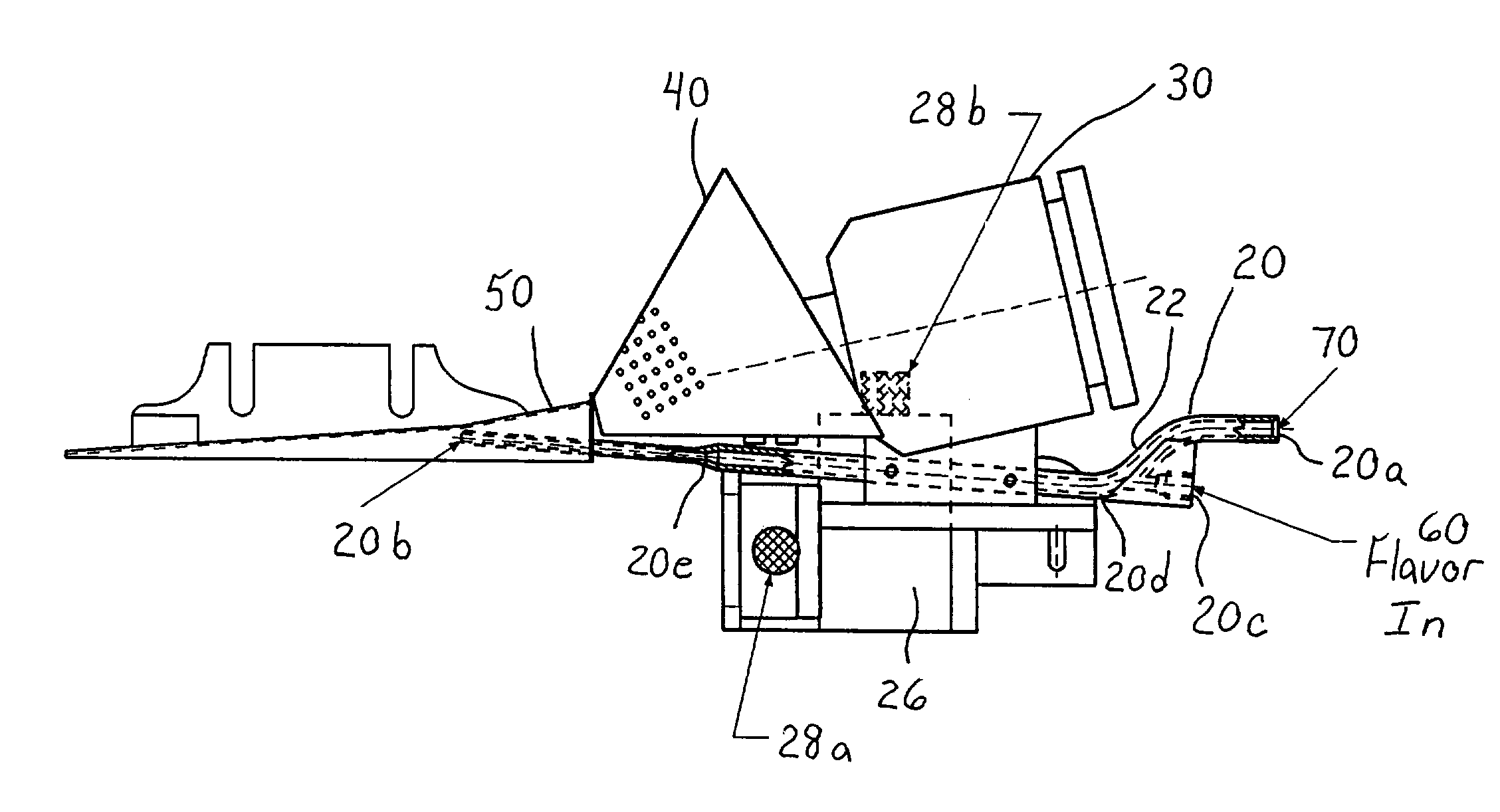
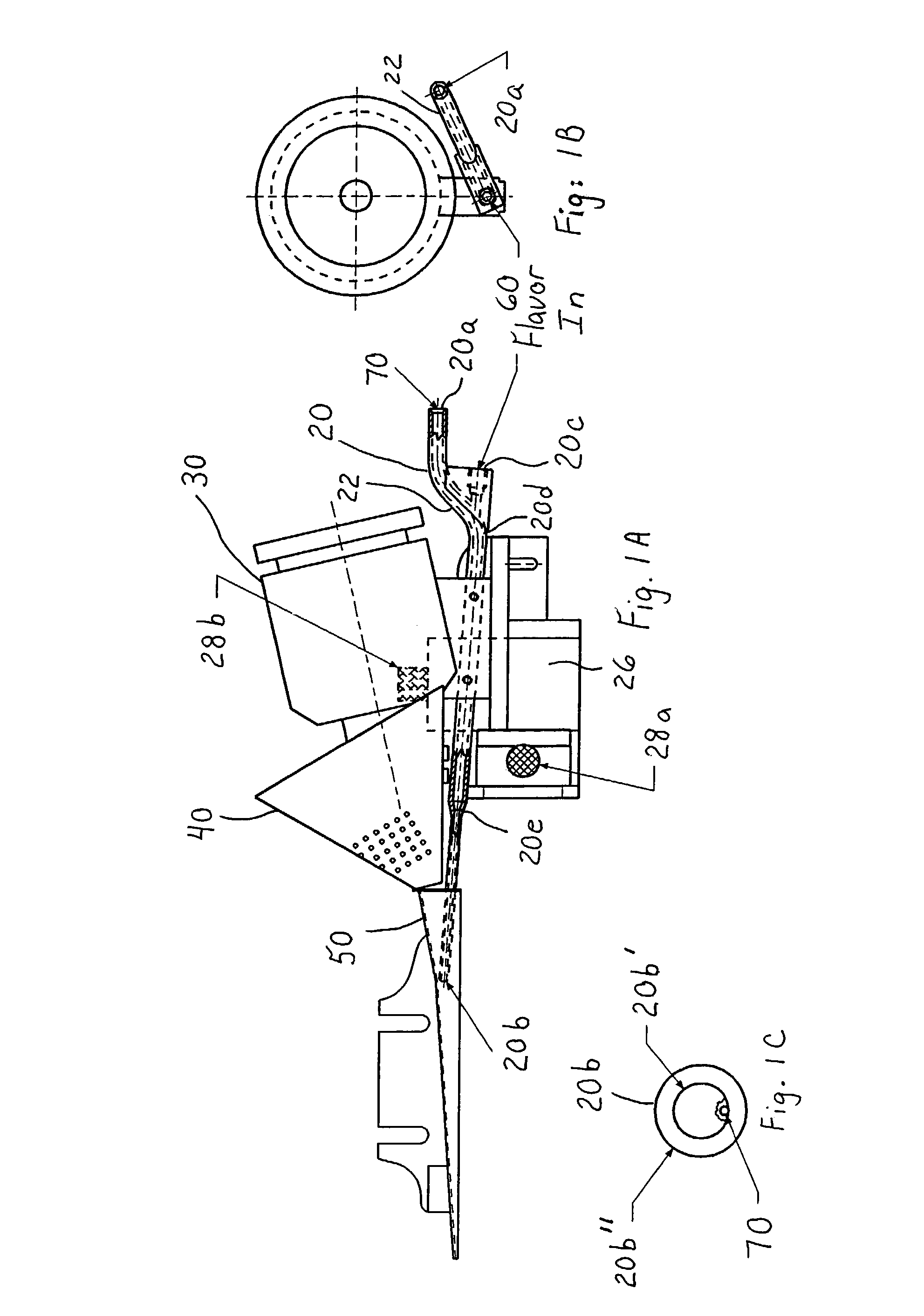
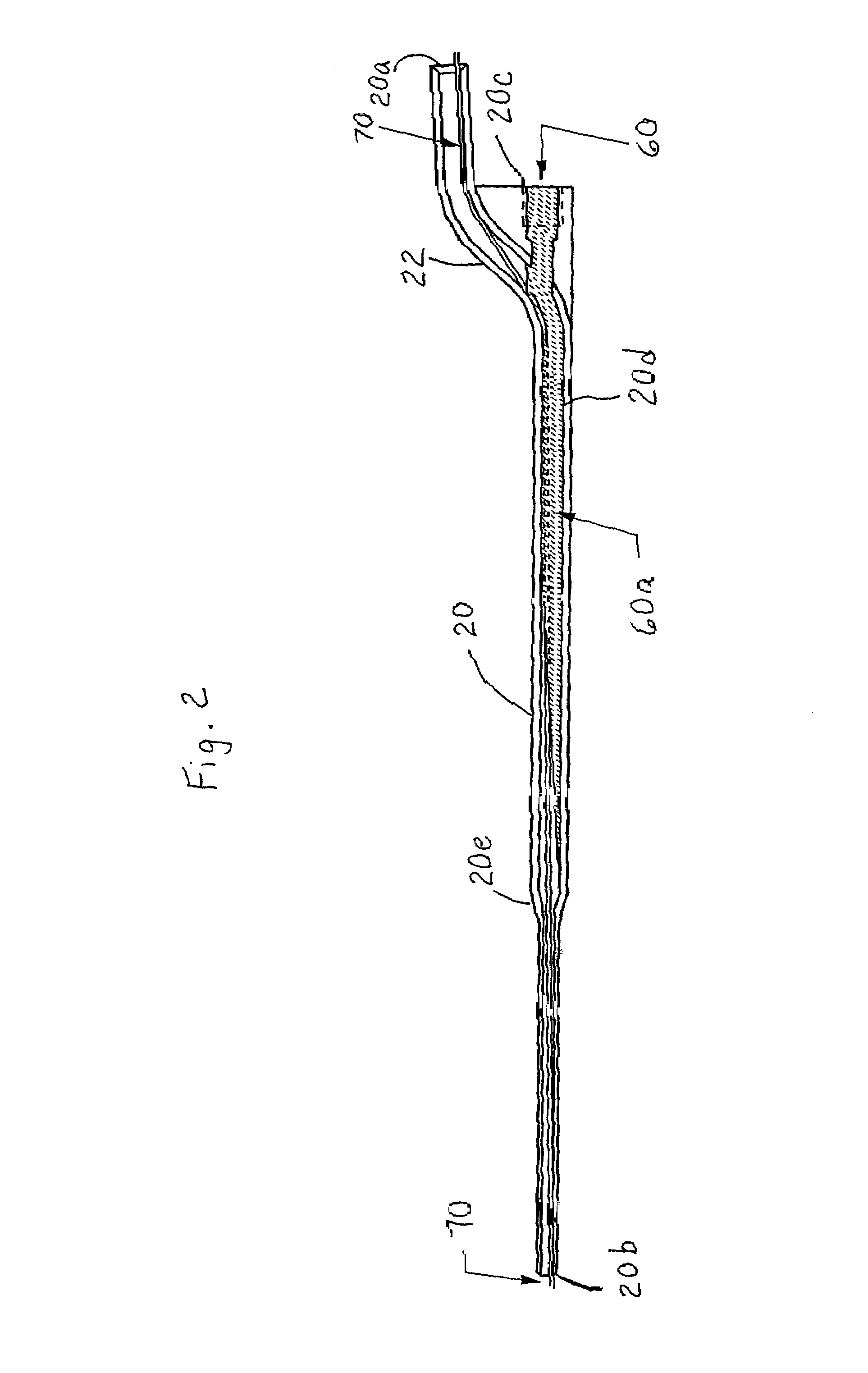
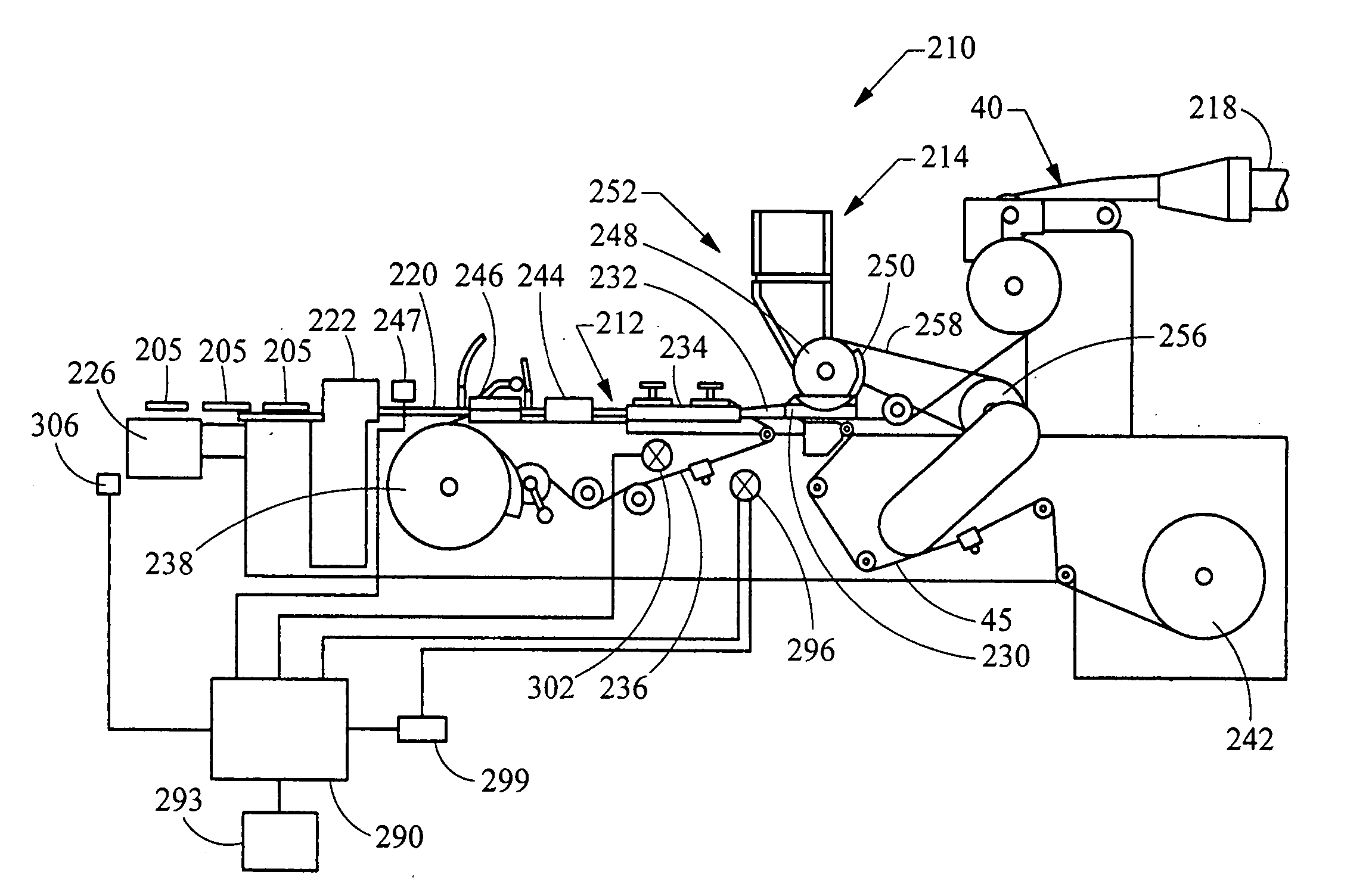
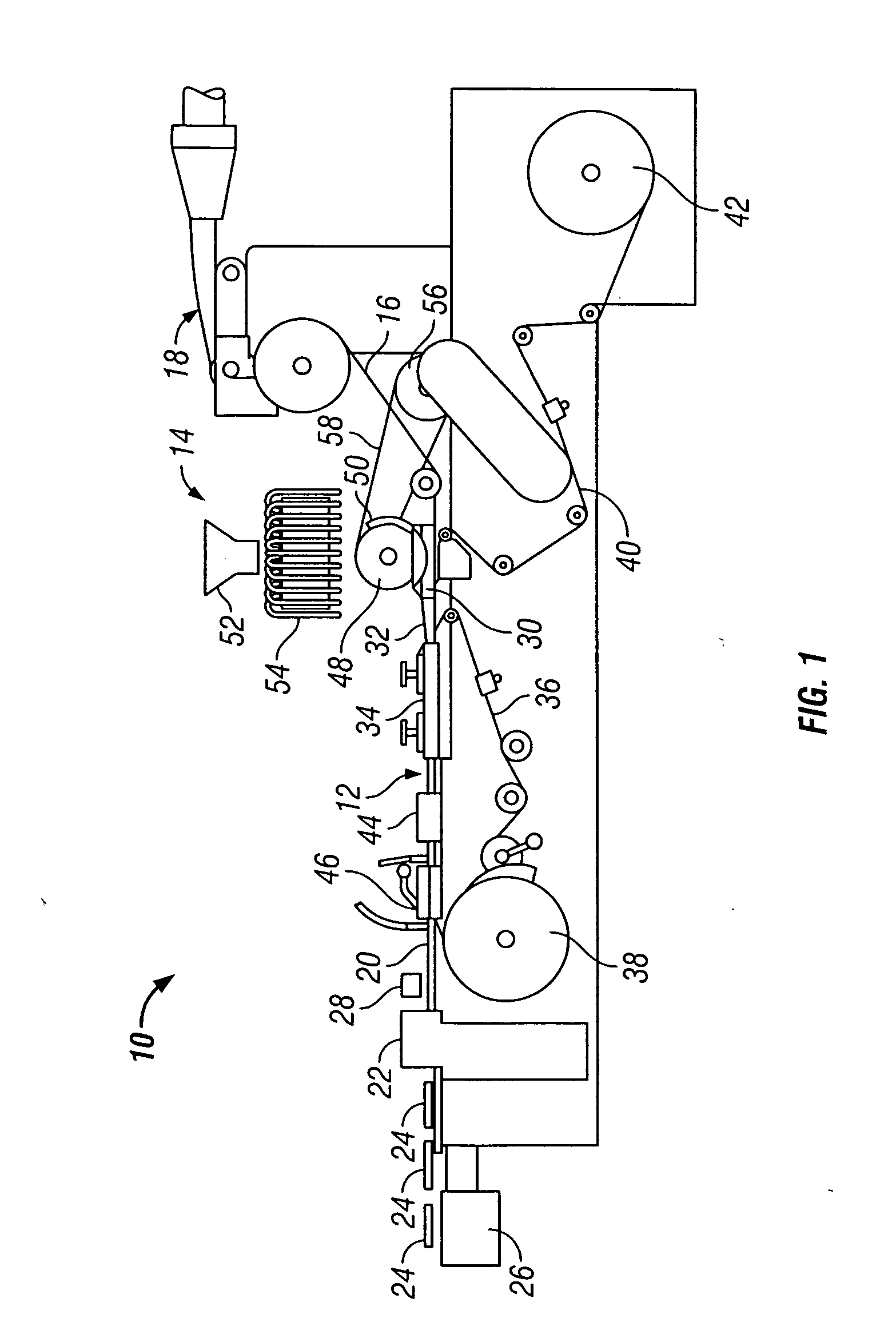
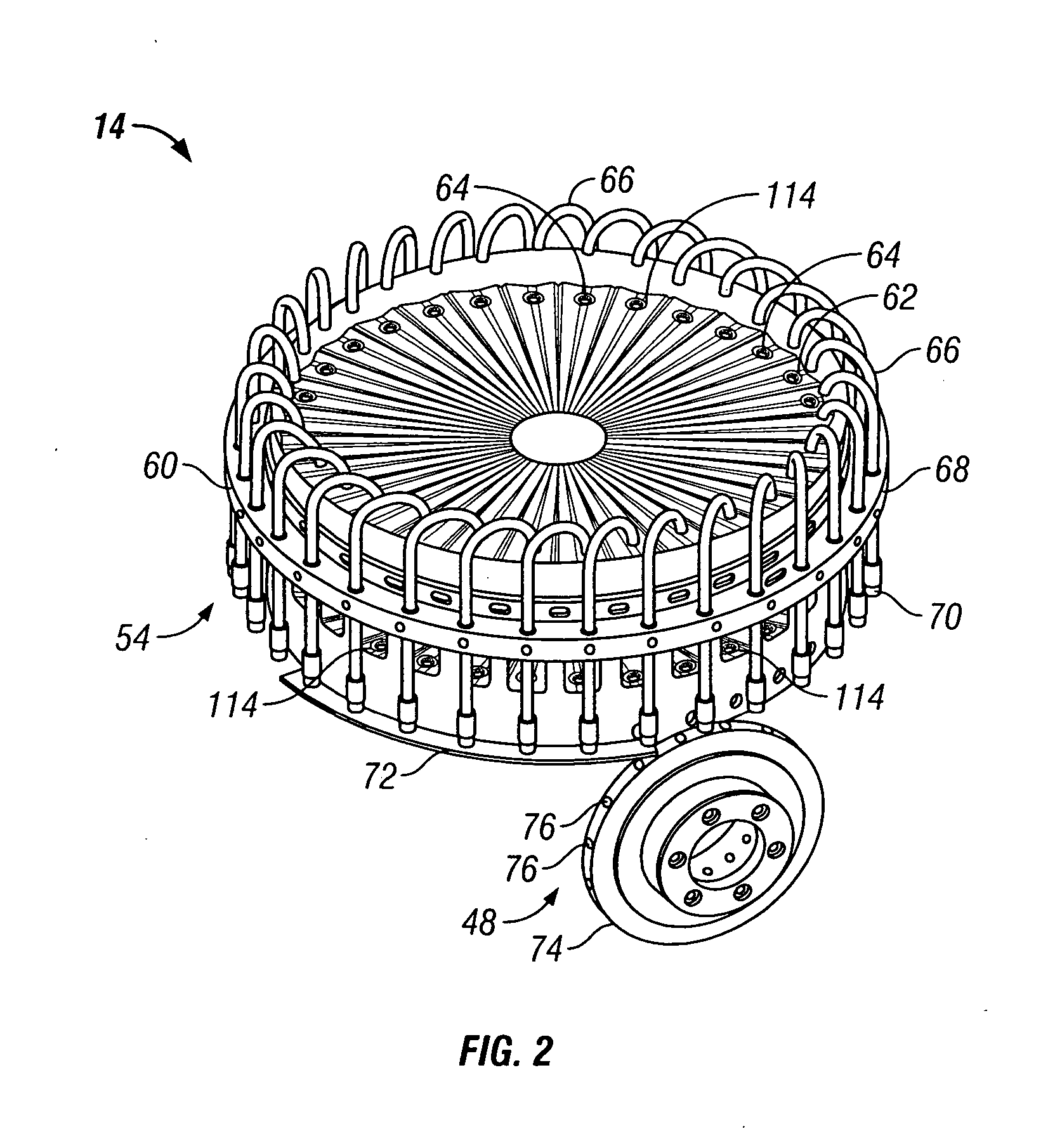
Method and apparatus for making cigarette filters with a centrally located flavored element
A filter making apparatus includes a positioning device having a passageway therethrough, with the passageway guiding a continuous flavor element such as a continuous strand of textile material from an inlet of the passageway to an outlet of the passageway. A liquid flavorant is introduced into the passageway at a desired flow rate and the strand of material carries the supplied liquid flavorant out of the positioning device at a rate substantially equal to the desired flow rate. A portion of the passageway can form a bath of the liquid flavorant supplied to the passageway through a separate inlet at approximately atmospheric pressure. A portion of the positioning device guides the continuous strand of material through the bath, or guides the strand to pass along the bottom of the passageway, and the saturated or partially saturated strand of material then exits from an outlet of the passageway to a point in the path of filter tow material that is being converged to form a filter rod.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
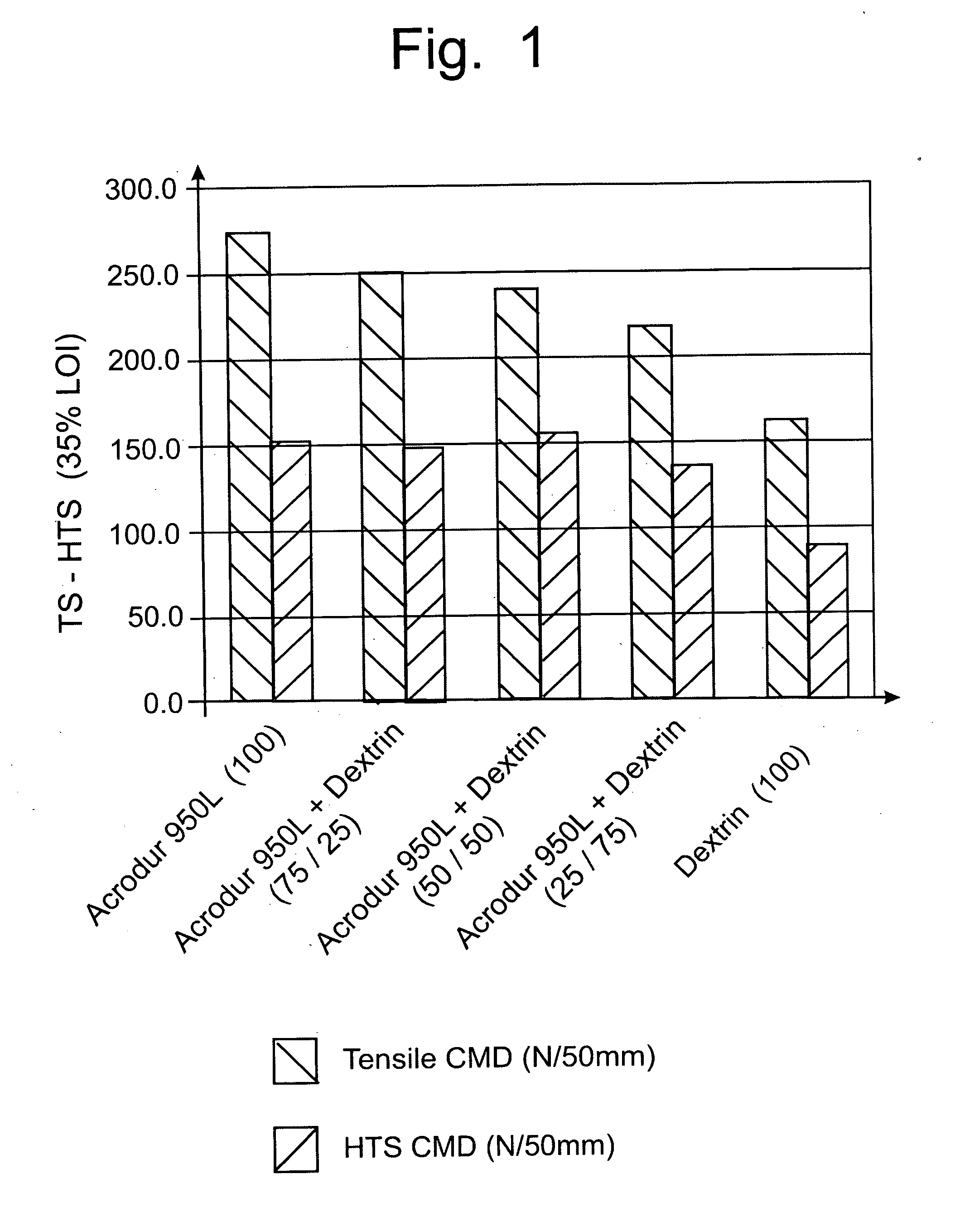
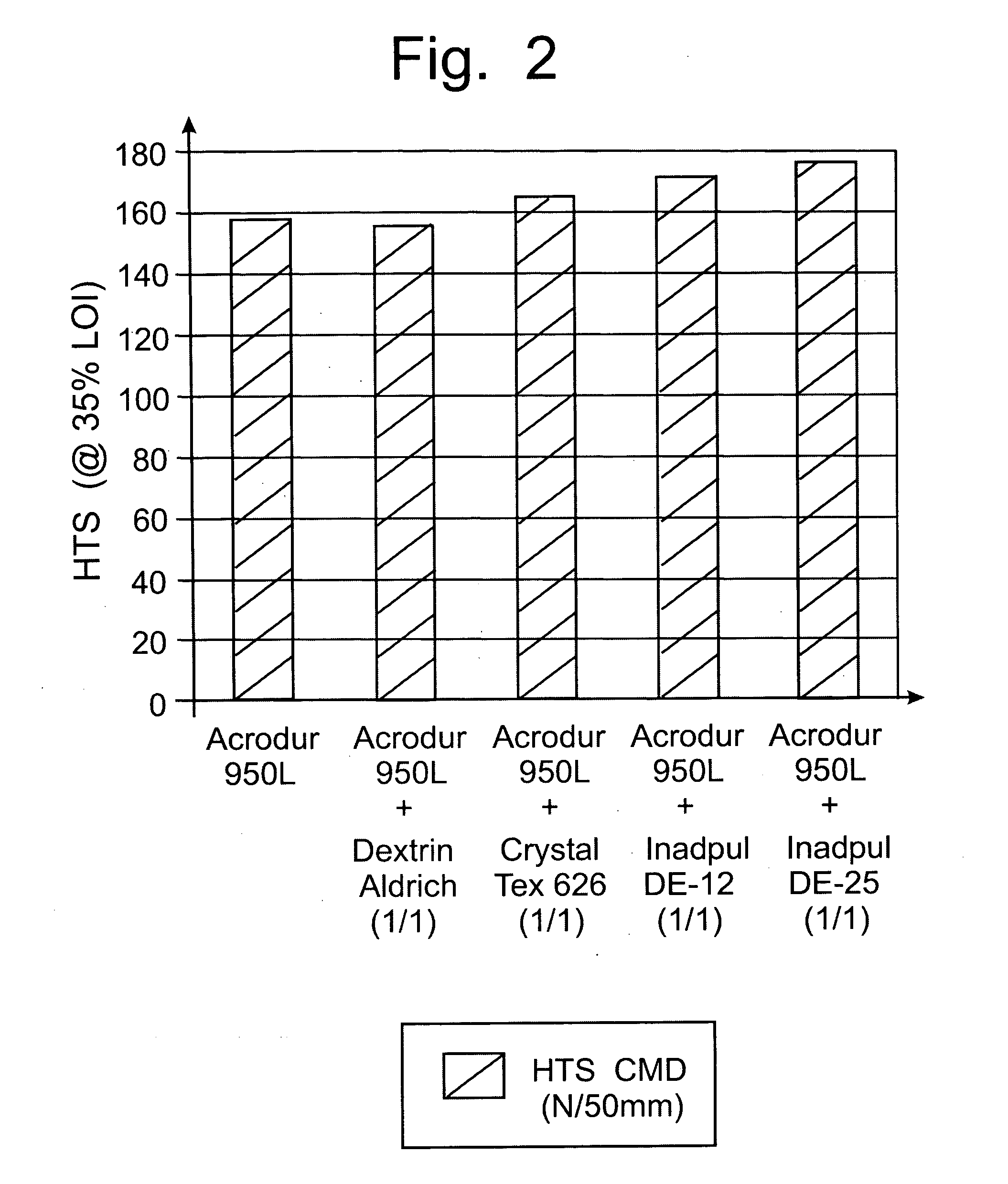
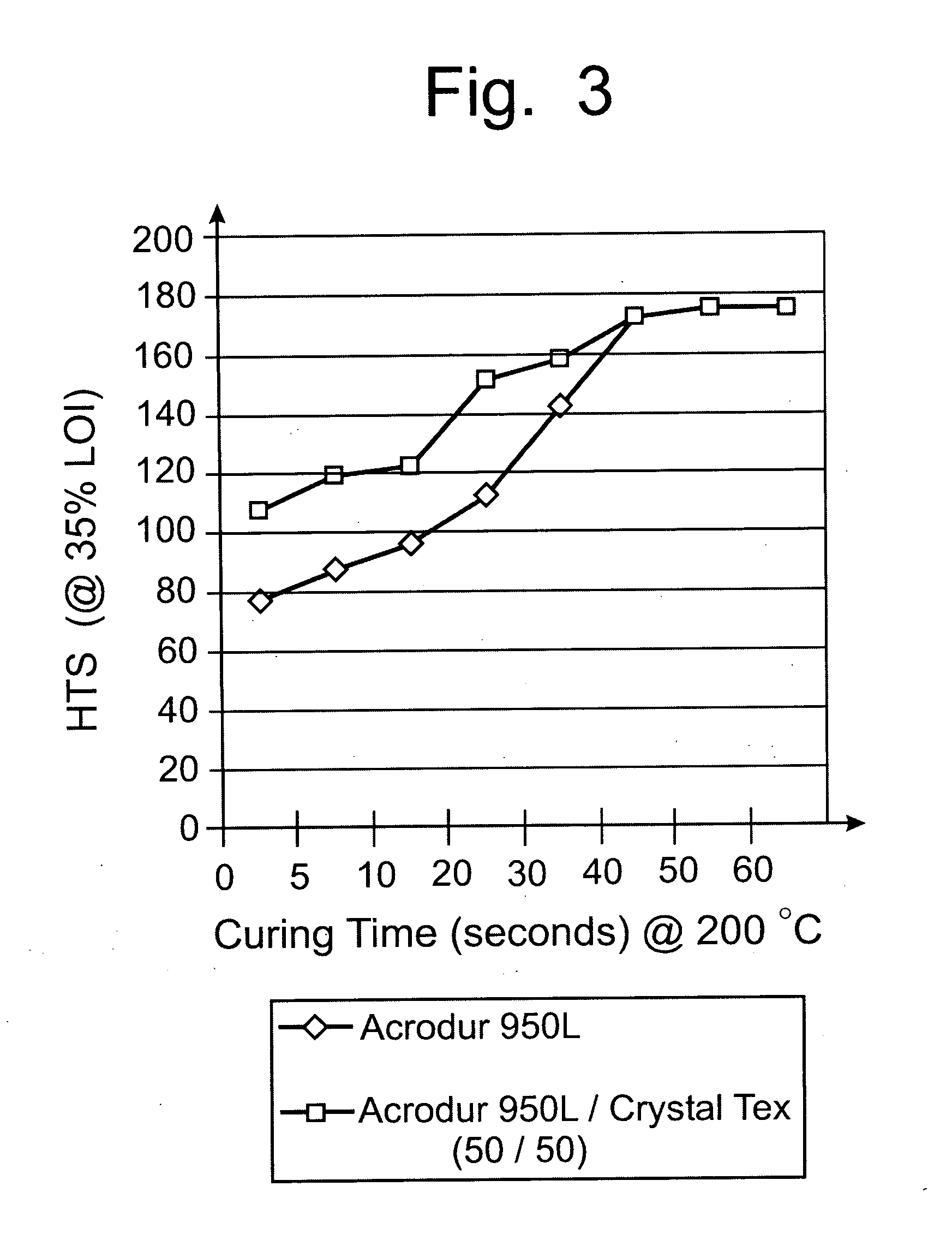
Dextrin binder composition for heat resistant non-wovens
InactiveUS20050215153A1Maintain strengthHigh hot tensile strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionStarch adhesivesPolyolCarboxylic acid
A polycarboxy binder composition that contains a dextrin as a co-binder is provided. The dextrin co-binder may be a dextrin, a modified dextrin, a maltodextrin, or combinations thereof. The dextrin may be chemically modified. A pre-binder composition is formed that contains a polycarboxy polymer, a crosslinking agent, and optionally a catalyst. The polycarboxy polymer may be a homopolymer or copolymer prepared from unsaturated carboxylic acids and may be modified to contain one or more vinyl compounds. The crosslinking agent may be a polyol that contains at least two hydroxyl groups. The pre-binder composition may be formed by admixing the polycarboxy polymer, the crosslinking agent, and optionally, the catalyst, in a mixing device. Dextrin may be added to the pre-binder composition in an amount of from 10-75% of the total binder composition. The dextrin binder composition may have a ratio of from approximately 90:10 to 25:75 pre-binder:dextrin co-binder.
Owner:OWNS CORNING COMPOSITES
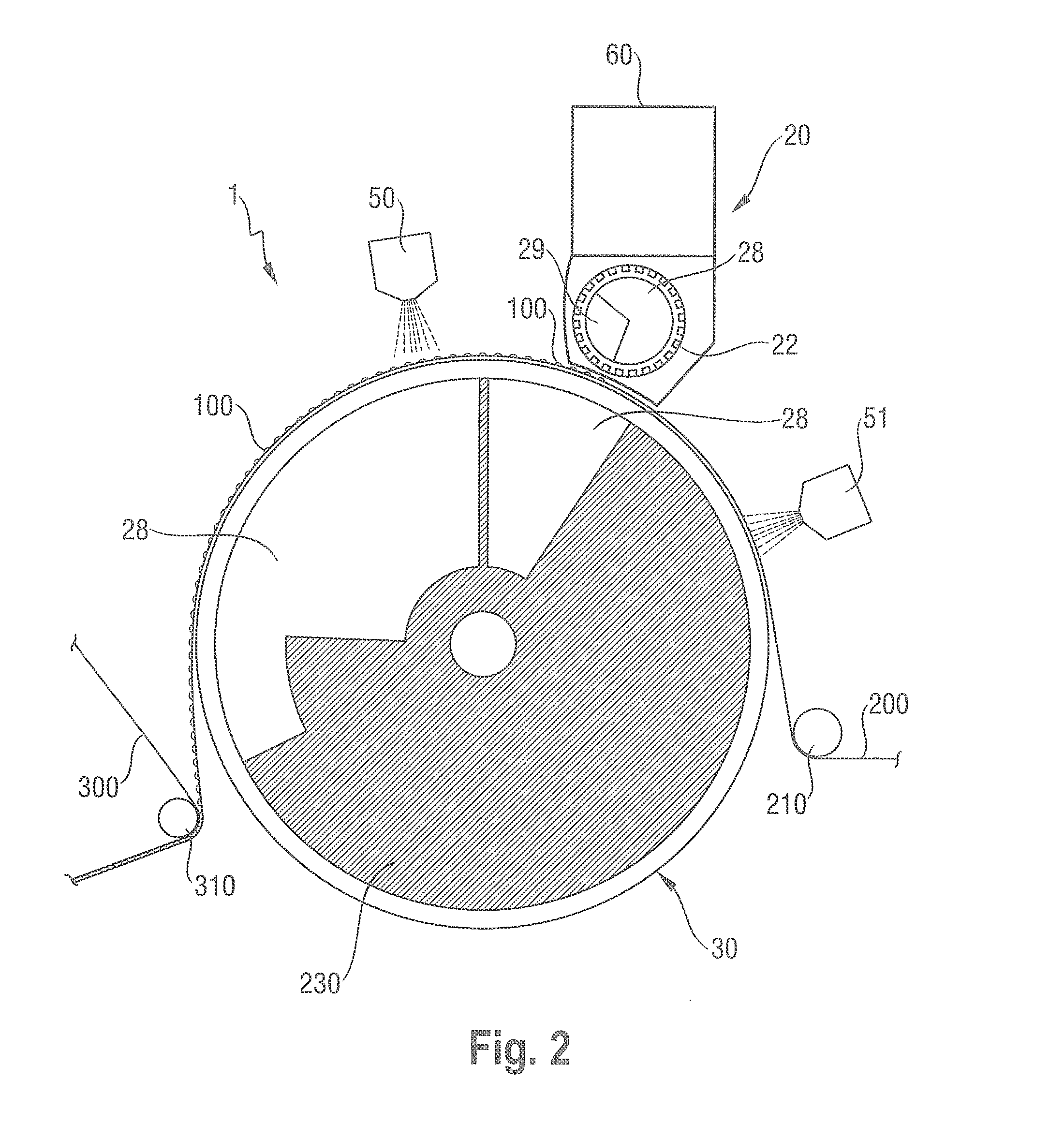
Equipment for insertion of objects into smoking articles
ActiveUS20070068540A1Sufficient shapeSufficient sizeMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboard articlesEngineeringSpace object
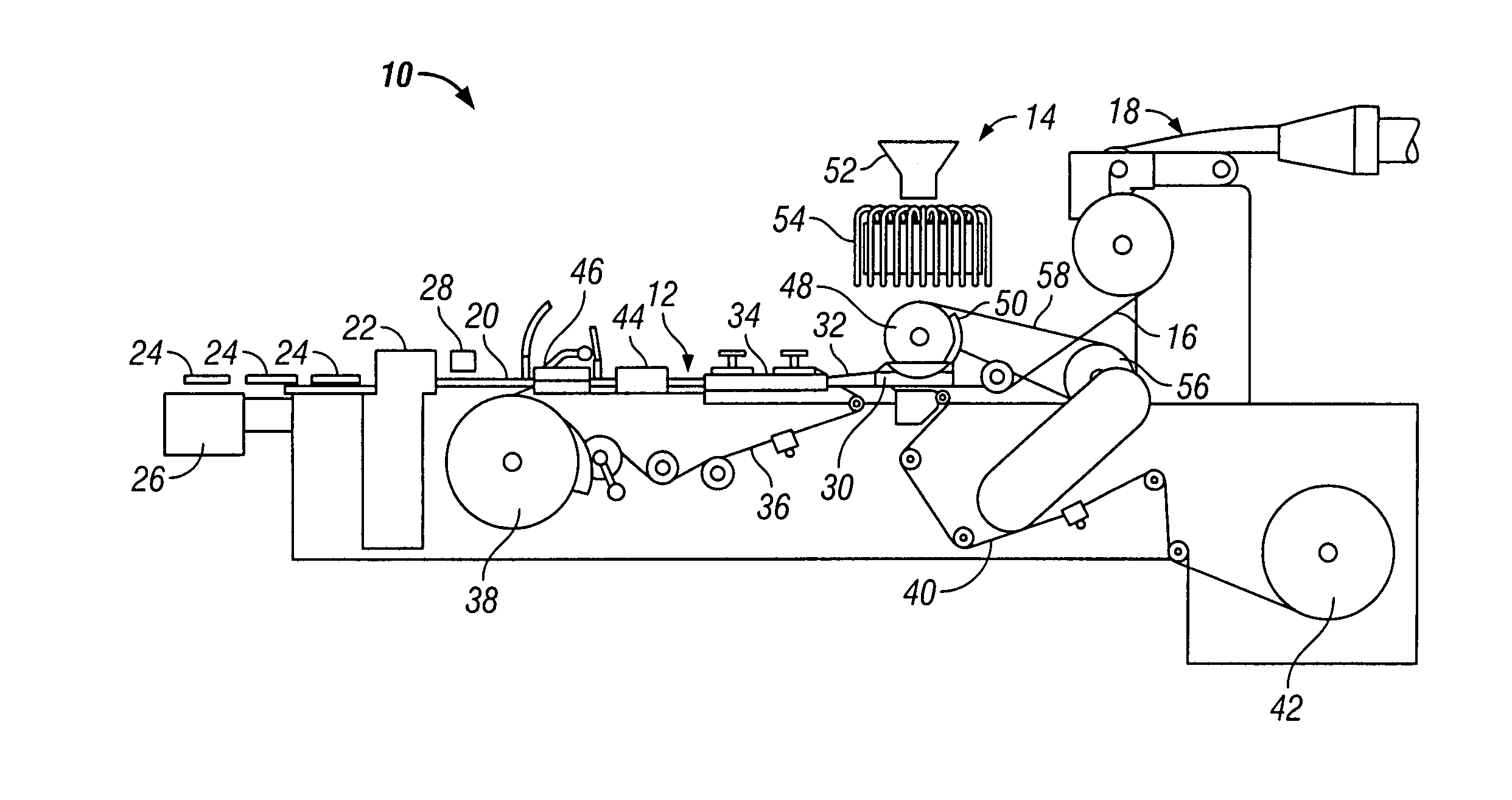
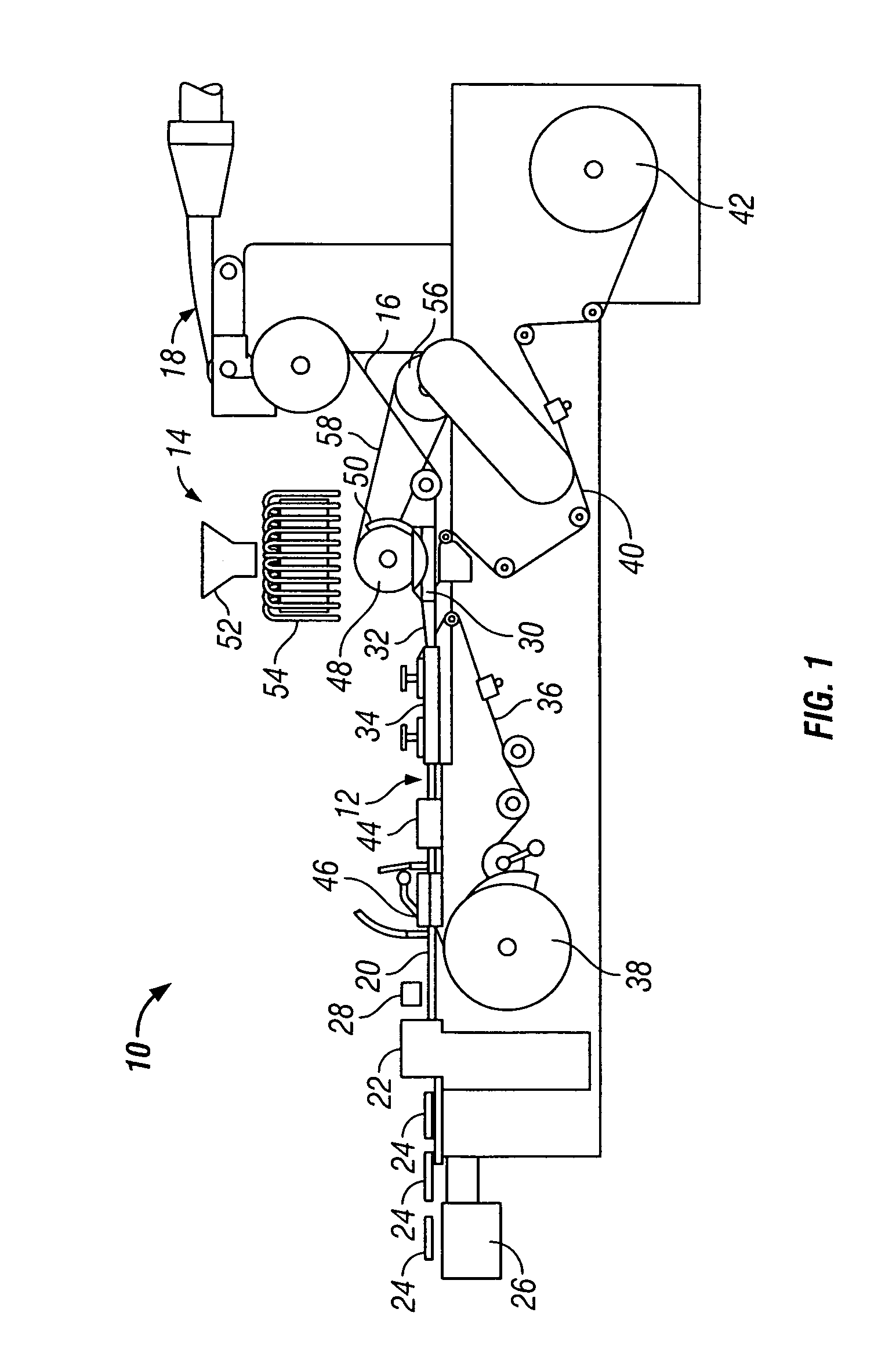
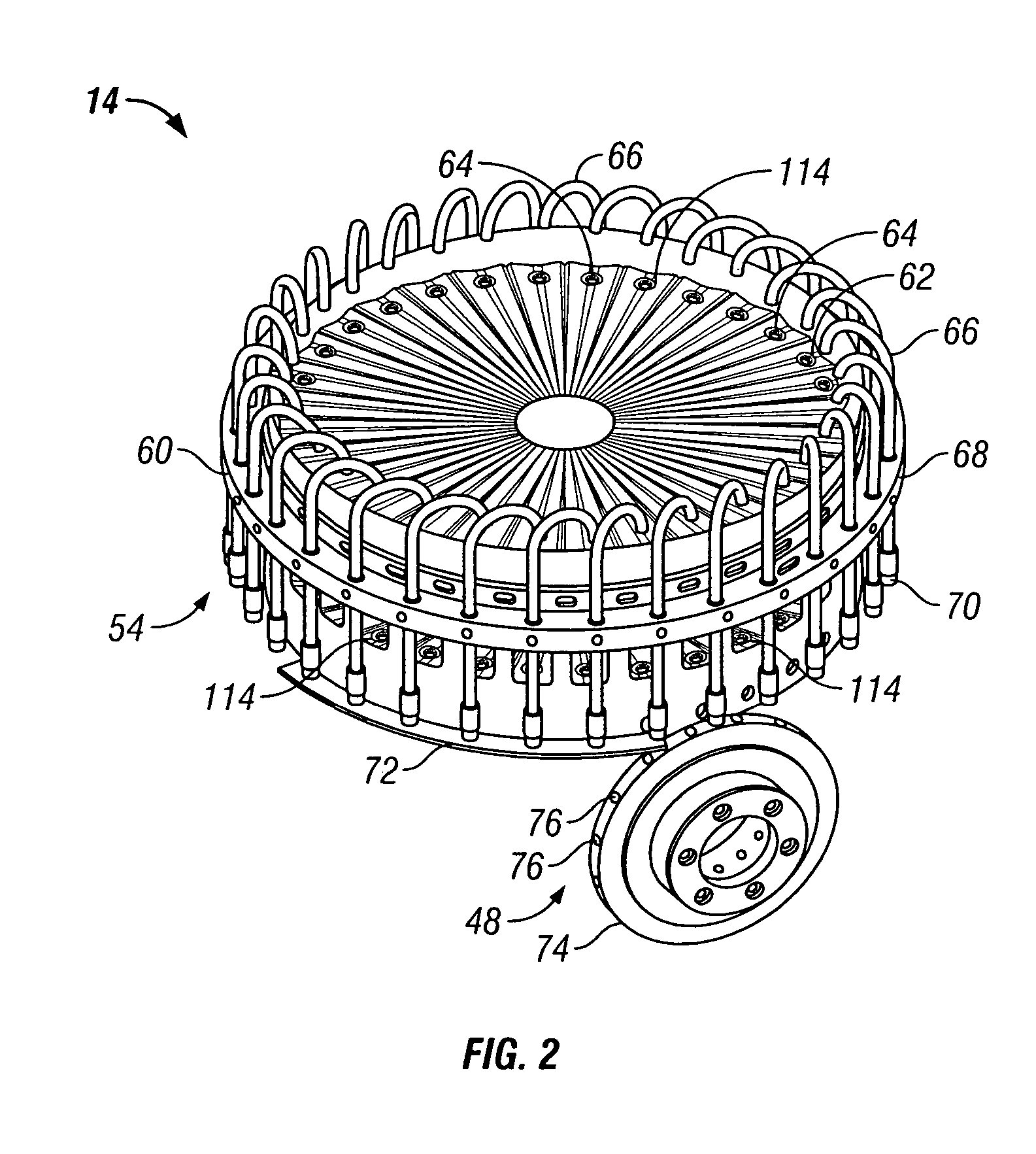
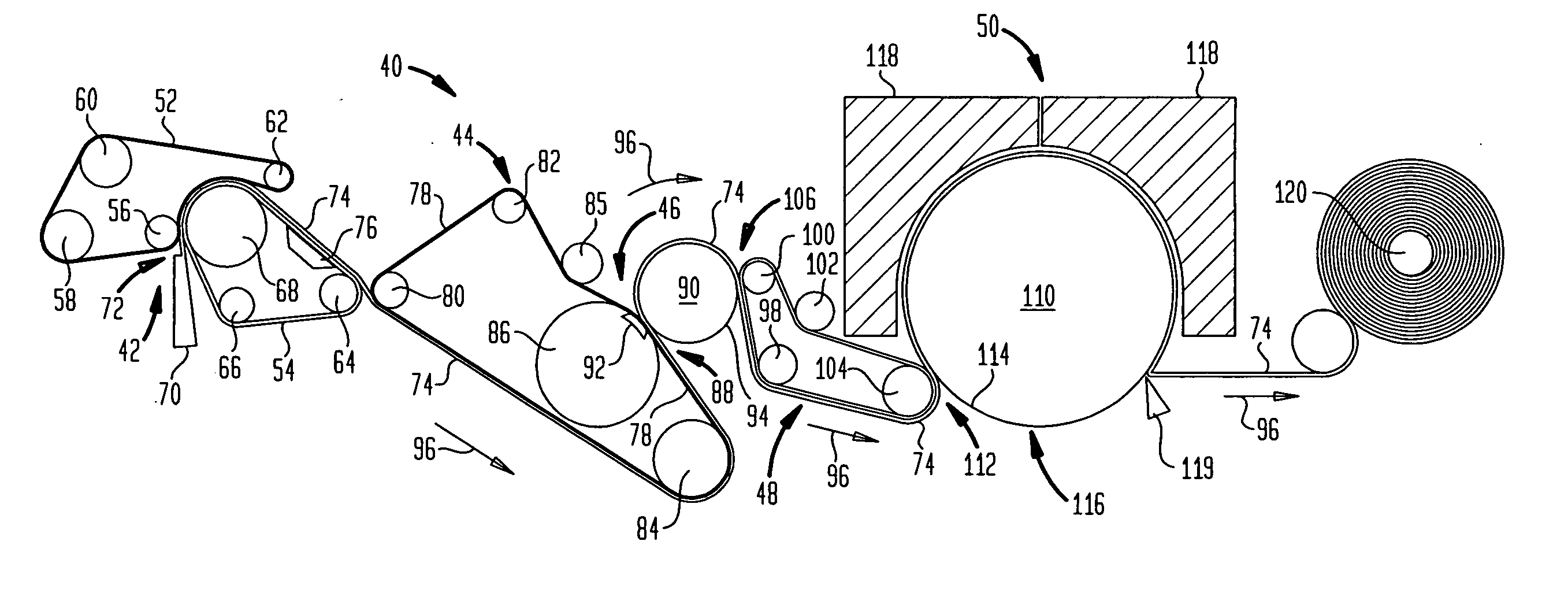
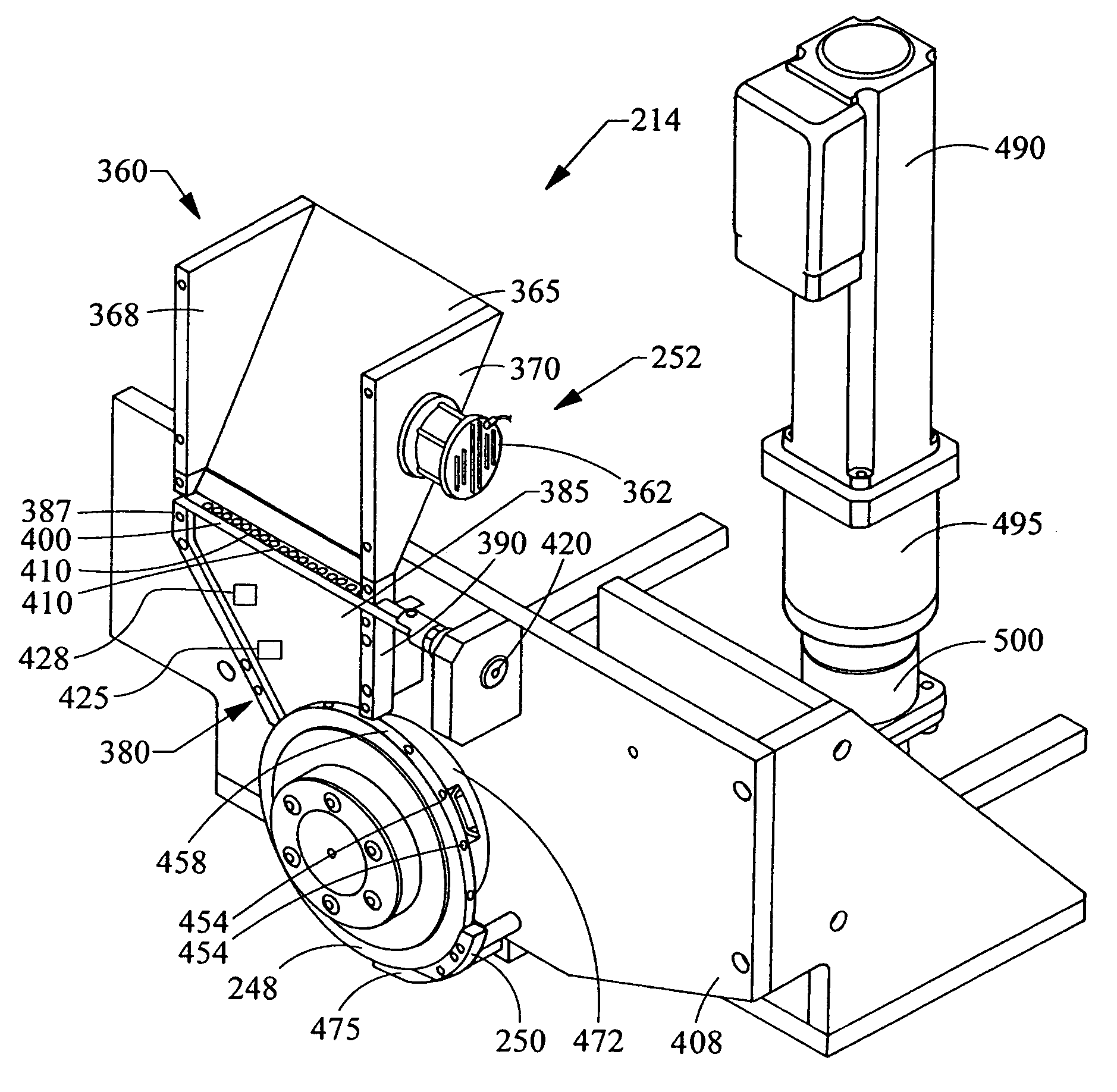
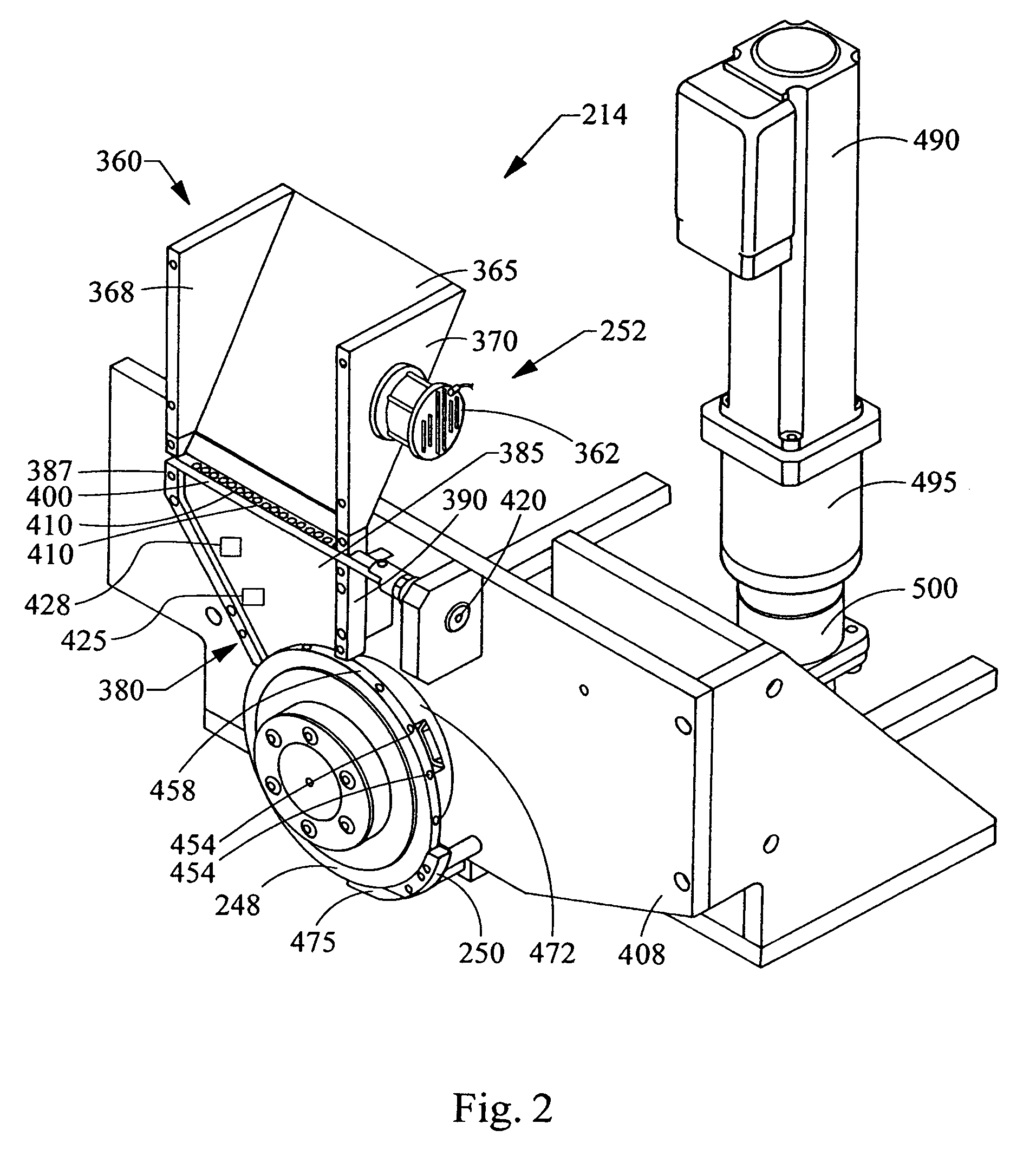
Apparatus incorporating a filter tow processing unit adapted to supply filter tow to a continuous rod forming unit includes an object insertion unit that positions objects within the filter tow to manufacture a filter rod containing objects positioned at predetermined intervals. The apparatus also includes an upper hopper that acts as a reservoir for a plurality of objects, and provides for supply of objects to a lower hopper. The lower hopper is shaped so that objects are stacked therein. The bottom of the lower hopper is shaped so as to cooperate with a portion of upper region of a rotating wheel. The peripheral face of the rotating wheel incorporates a plurality of spaced pockets, each pocket being of sufficient shape and size to accommodate one object. Objects within the lower hopper are aligned in a single line along a portion of the peripheral face in the upper region of the rotating wheel. Each object then is positioned at predetermined intervals within a continuous supply of filter material. Then, the filter material is formed into a continuous rod having individual objects positioned at predetermined spaced intervals within that rod. The continuous rod then is subdivided at predetermined intervals so as to form a plurality of filter rods (e.g., four-up filter rods containing four spaced objects).
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
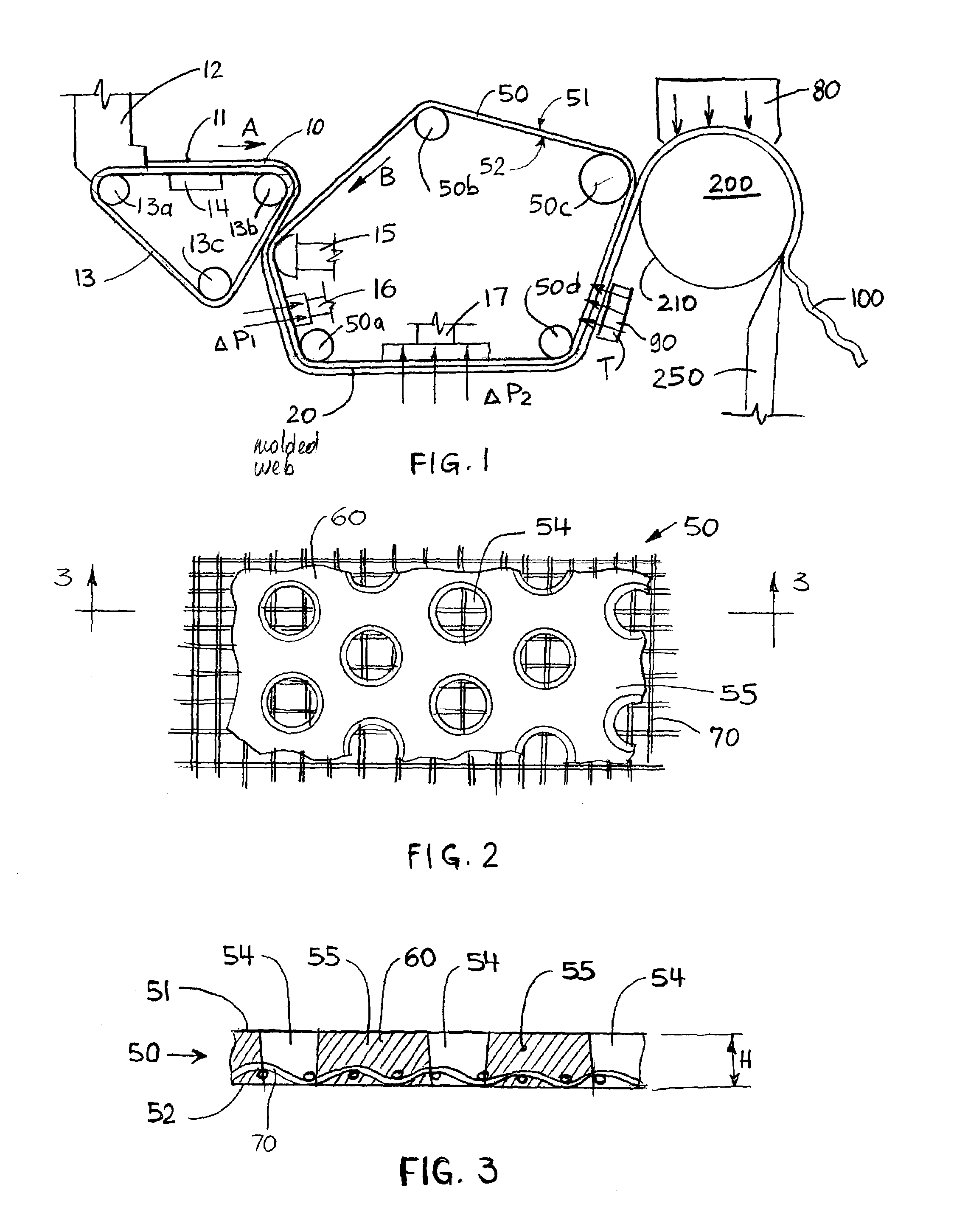
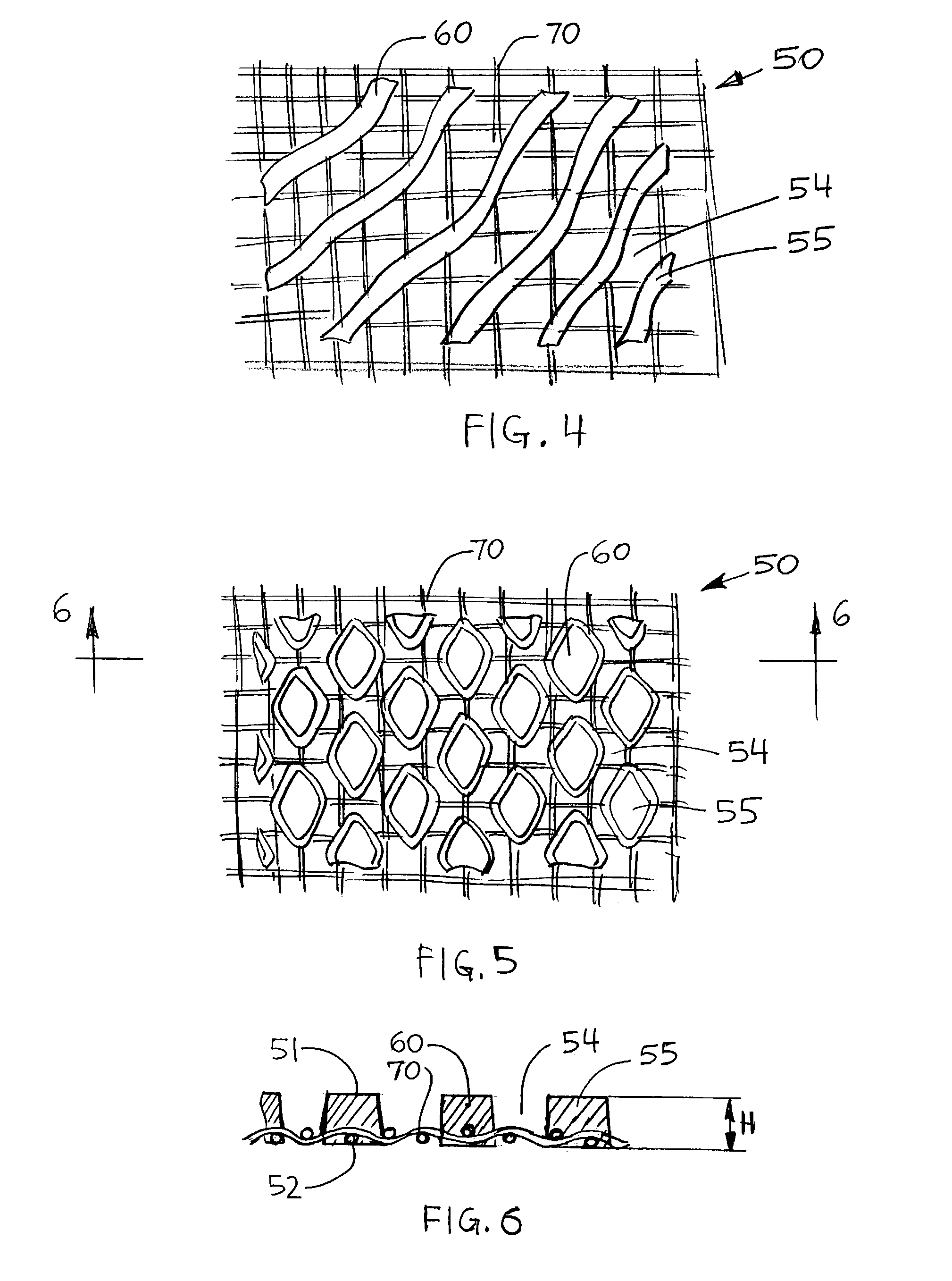
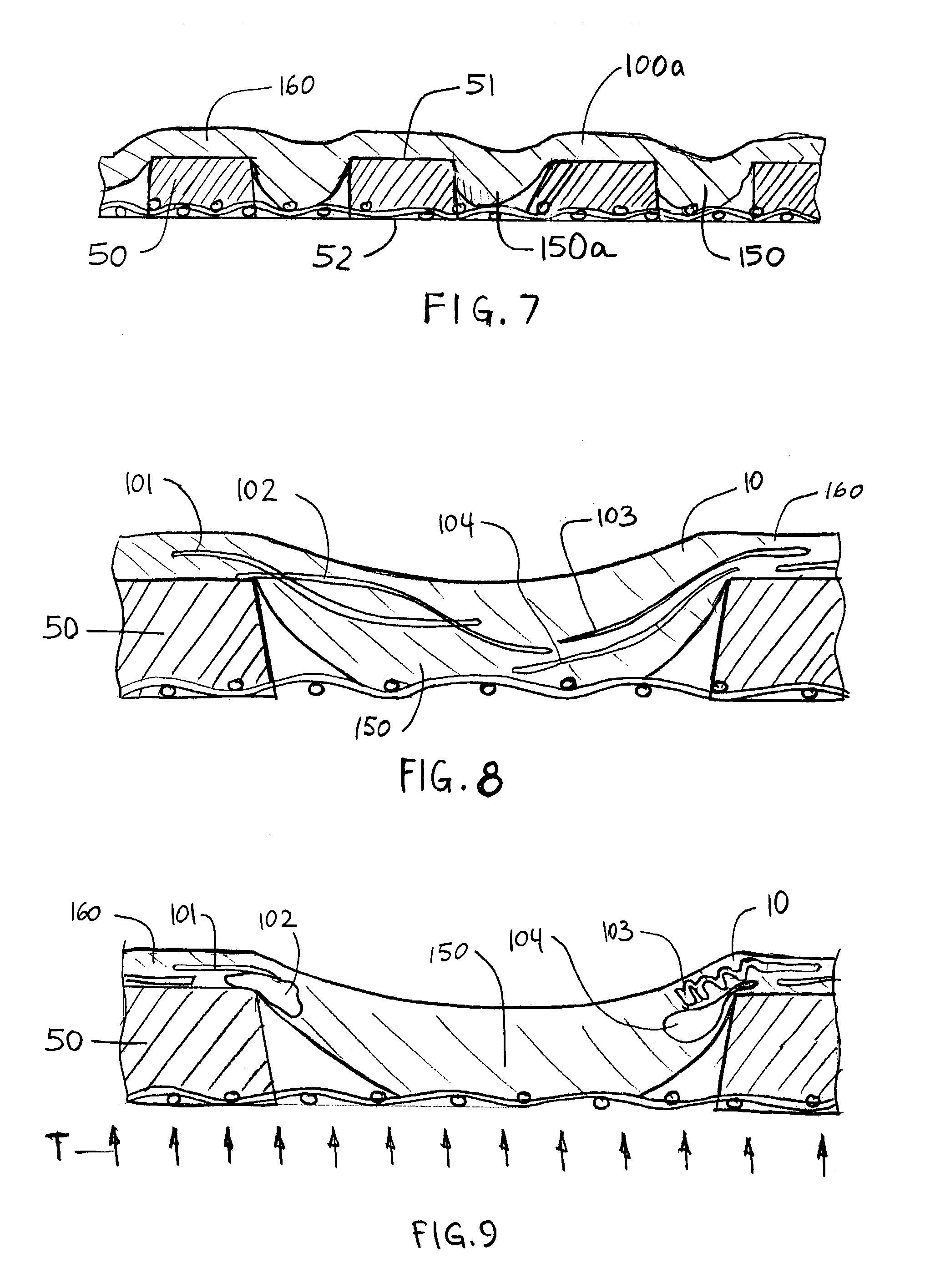
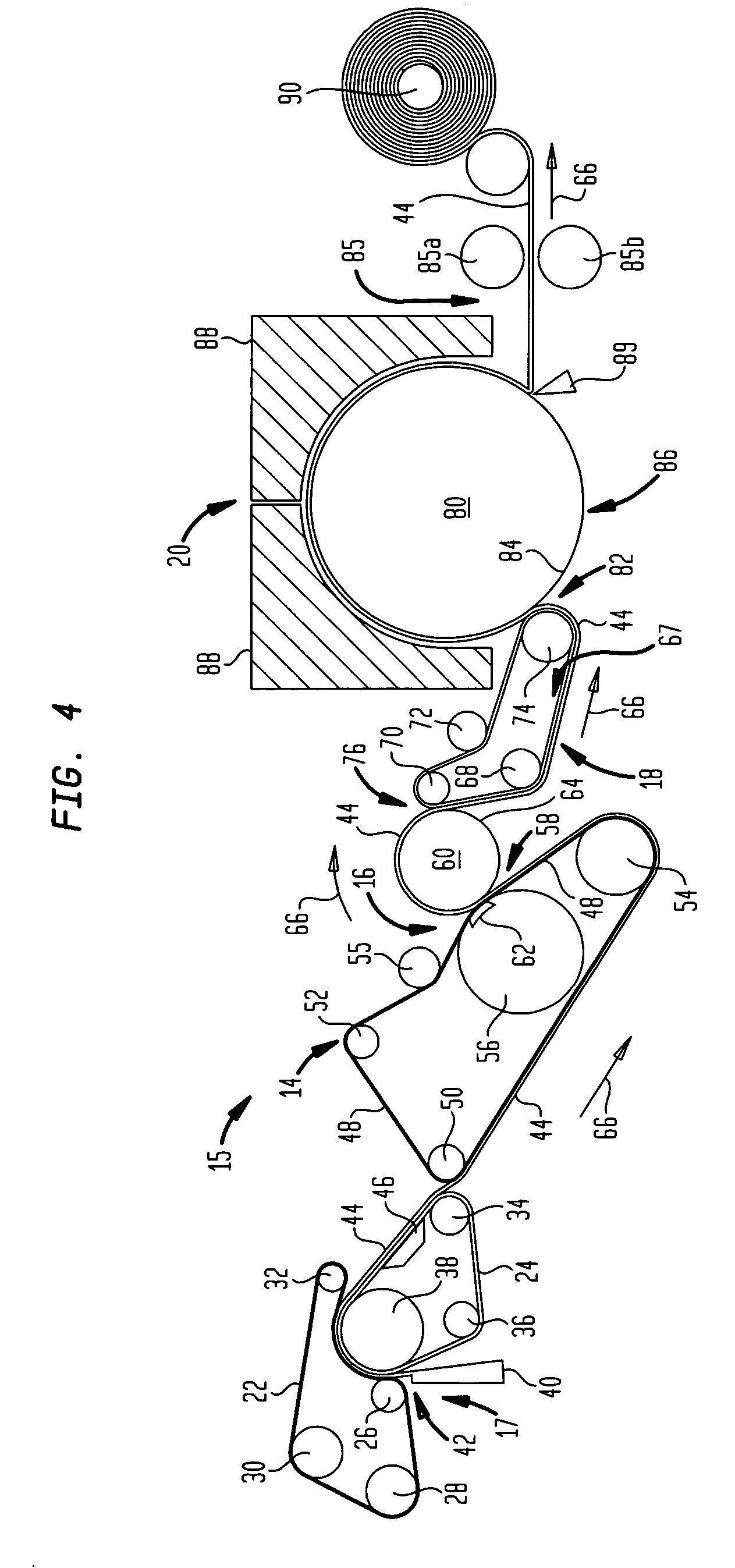
Wet-pressed tissue and towel products with elevated CD stretch and low tensile ratios made with a high solids fabric crepe process
ActiveUS20050241786A1The implementation process is simpleNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationMedicineCellulose fiber
An absorbent sheet of cellulosic fibers includes a mixture of hardwood fibers and softwood fibers arranged in a reticulum having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the machine direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, wherein the sheet exhibits a % CD stretch which is at least about 2.75 times the dry tensile ratio of the sheet. Tensile ratios of from about 0.4 to about 4 are readily achieved.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
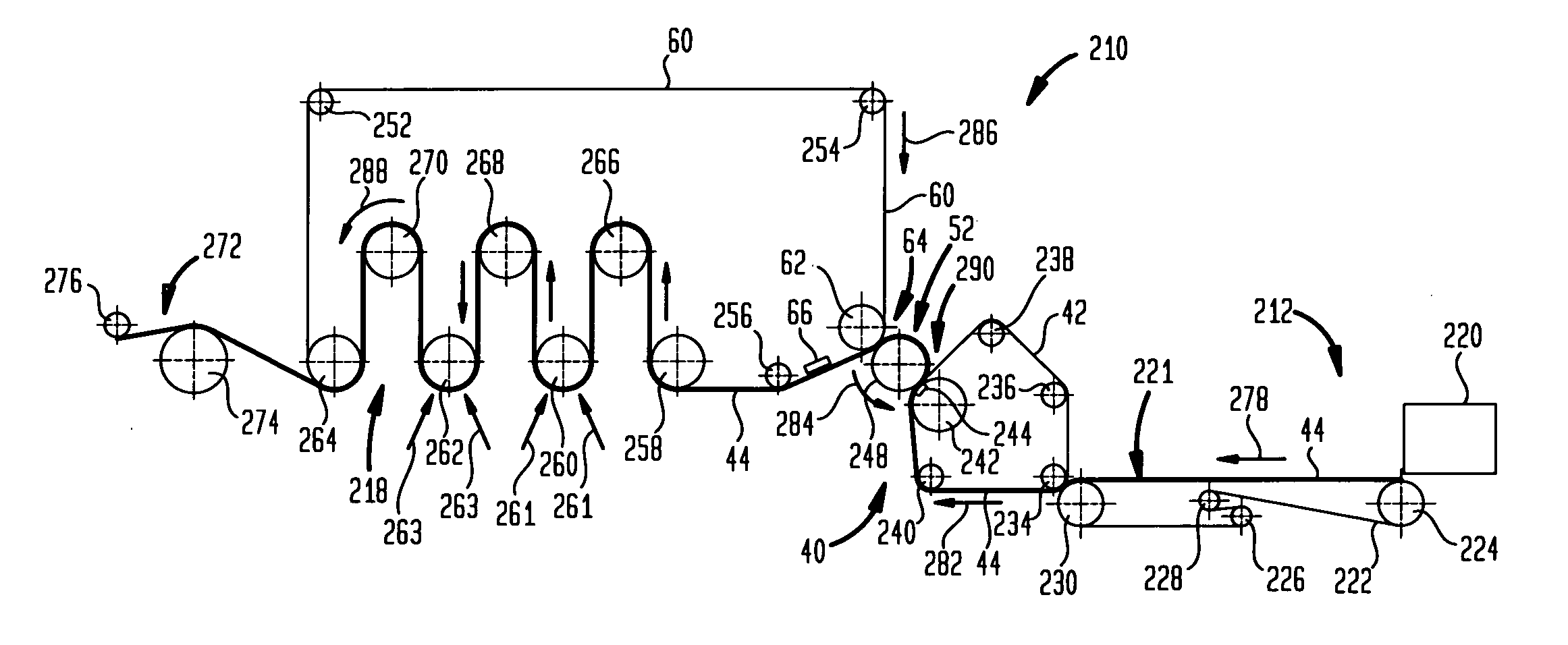
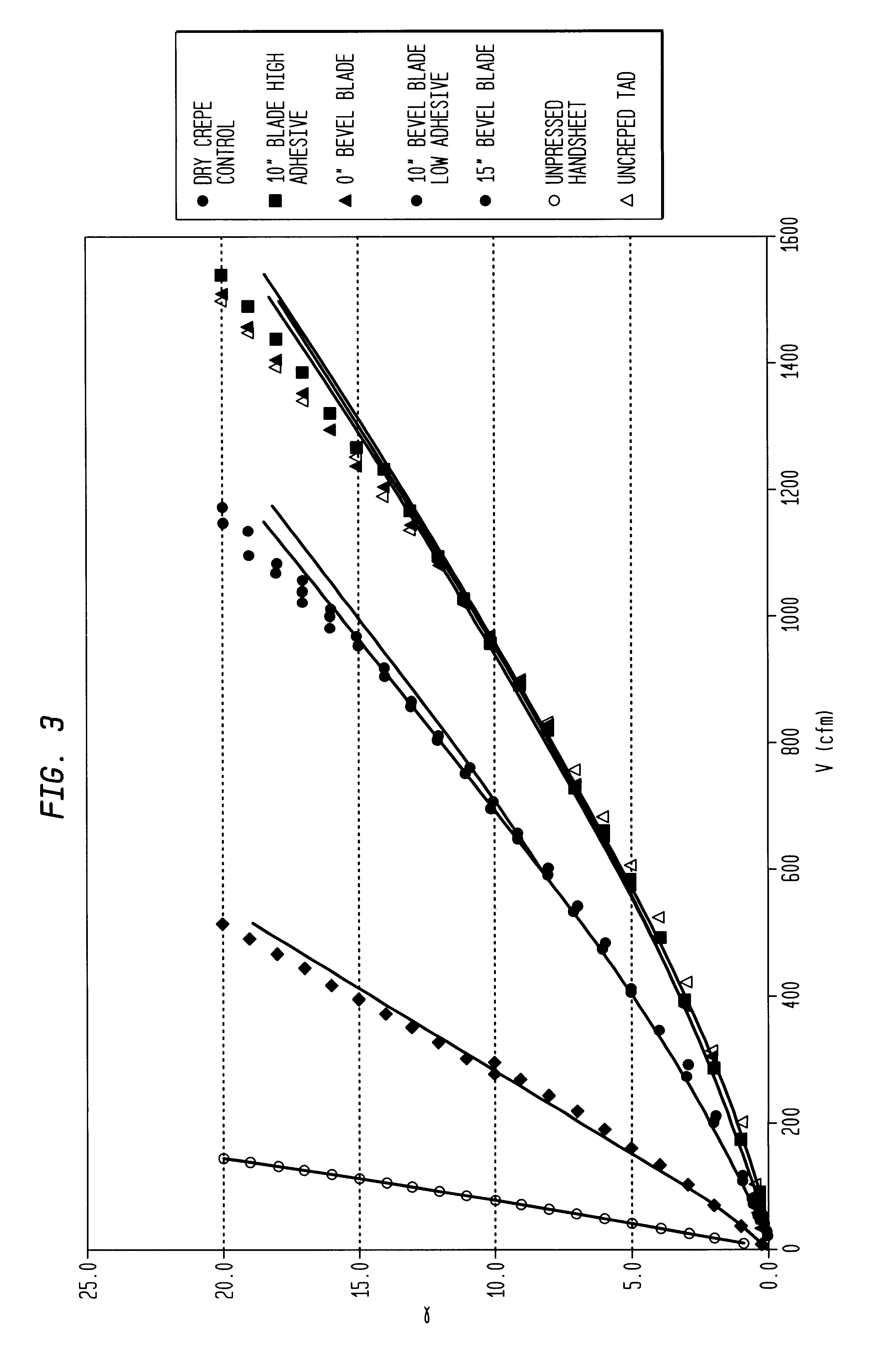
Wet crepe, impingement-air dry process for making absorbent sheet
InactiveUS6432267B1Reduce penetrationIncrease flexibilityDrying using combination processesNon-fibrous pulp additionPulp and paper industryPaper sheet
A wet crepe, impingement-air dried process for producing absorbent paper sheet is disclosed. In preferred embodiments, the process utilizes recycle furnish and the web is delaminated as it is wet-creped from a Yankee dryer. Particular embodiments include high consistency (after-crepe) wet-shaping prior to impingement air drying on a drilled vacuum roll.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for incorporating objects into cigarette filters
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Hollow sphere organic pigment for paper or paper coatings
InactiveUS6139961ATrend downHigh molecular weightSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsVitrificationPaperboard
A hollow sphere organic pigment in which a core containing a void is encapsulated by a first shell polymer having a glass transition temperature greater than 50 DEG C., the first shell having polymerized thereon a second shell polymer having a glass transition temperature of -15 DEG C. to -50 DEG C. is provided. Also provided is a paper or paperboard coating composition containing the hollow sphere organic pigment, a method for improving the strength and opacity of a paper or paperboard coating by using the coating composition dried, a coated paper or paperboard bearing the dried coating composition, and a method for improving the strength and opacity of paper or paperboard by incorporating a particular hollow sphere organic pigment into the formed wet sheet.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
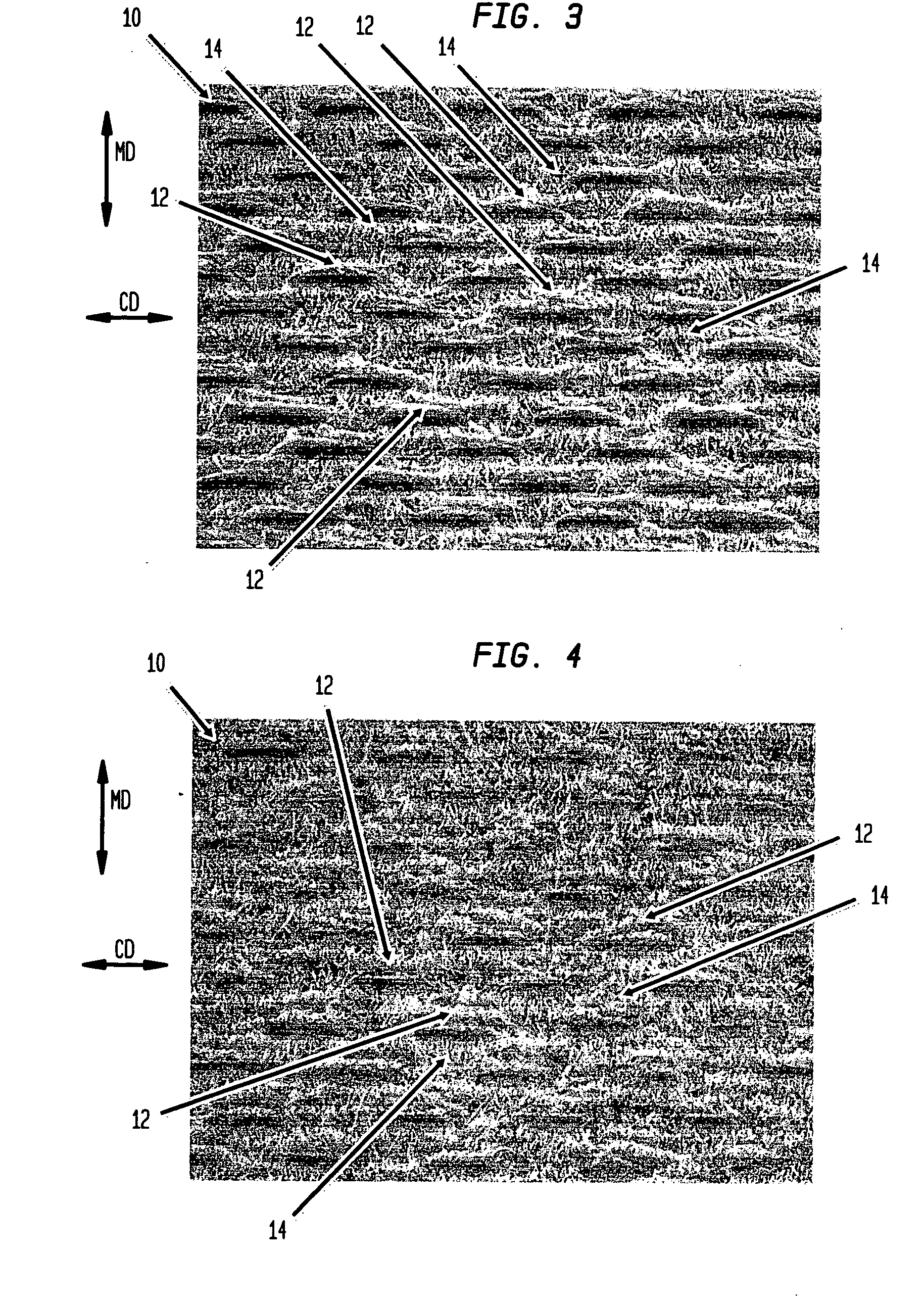
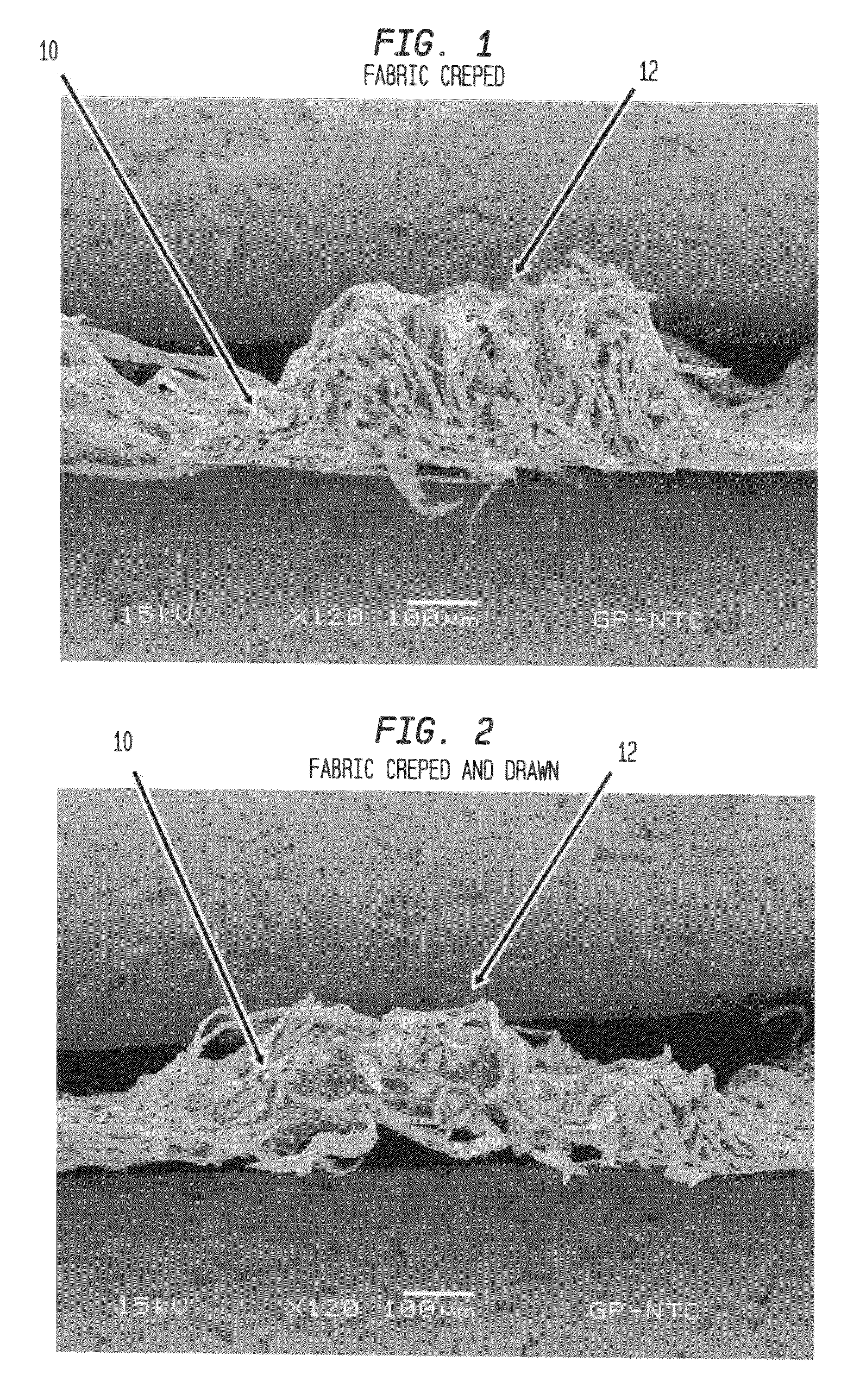
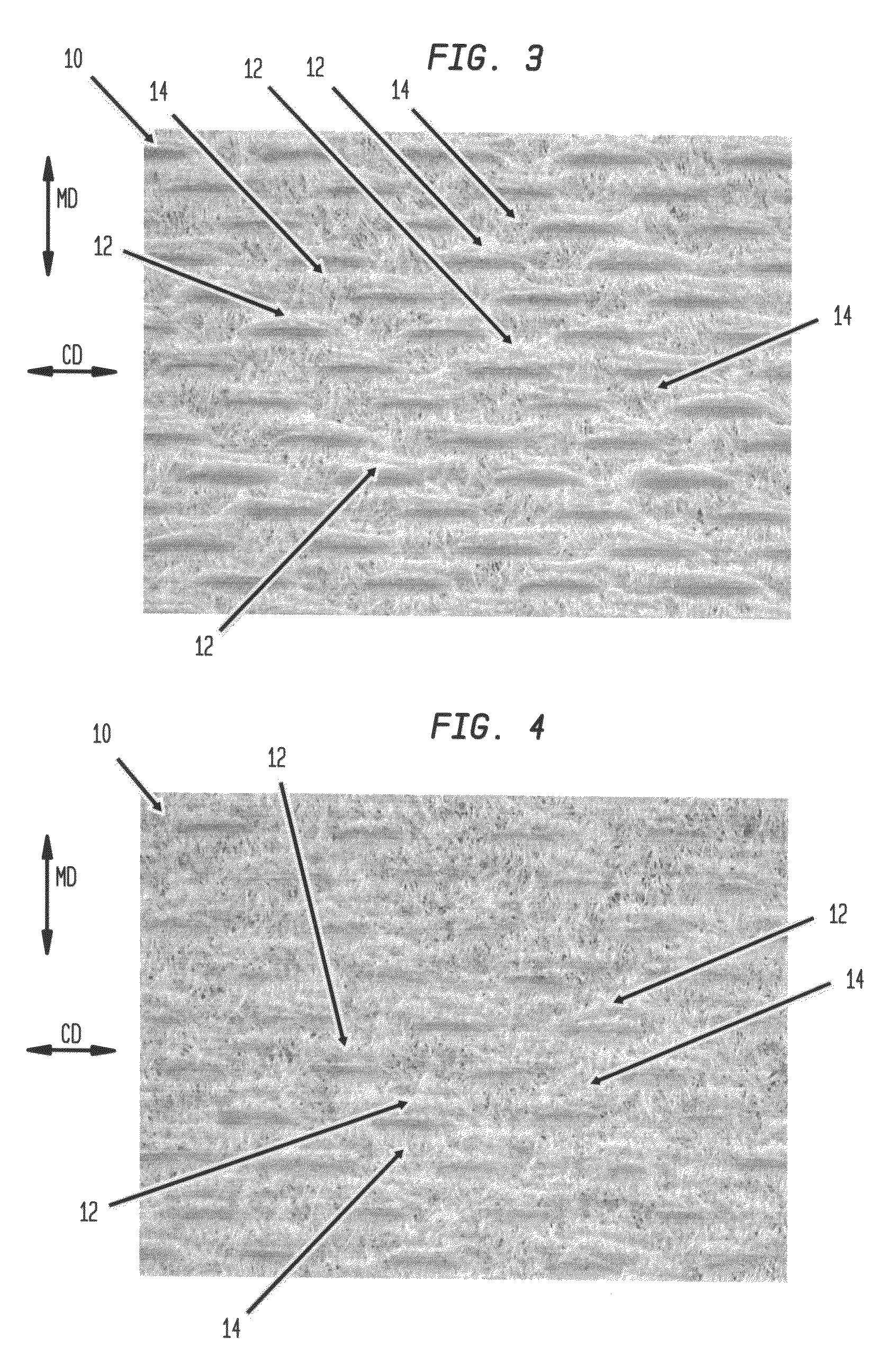
Fabric crepe/draw process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS20050217814A1Increase in sizeDecrease sidednessMechanical working/deformationPaper coatingFiberPapermaking
A method of making a fabric-creped absorbent cellulosic sheet comprising: a) compactively dewatering a papermaking furnish to form a nascent web having an apparently random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) applying the dewatered web having the apparently random fiber distribution to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; c) fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a patterned creping fabric, the creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric to form a web with a drawable reticulum.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Paper tissue having enhanced softness
InactiveUS6344111B1Increase softnessMaintain tensile strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberUltimate tensile strength
A novel paper article, a method of making a paper product, and an embossing roll are disclosed for providing a paper surface region having a minority of fiber to fiber bonds broken in the paper surface region to a depth less than about 0.02 mm from the paper surface. In one aspect, the roughened embossing roll includes protuberances or depressions sized at less than about 0.1 mm. In one aspect, the roughened embossing roll includes protuberances or depressions adapted to produce paper product surface deformations in the paper surface, wherein the paper product surface deformations are invisible to an unaided human eye. The present invention provides a paper product having higher perceived softness while maintaining tensile strength.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Treated filler or pigment containing natural carbonate
InactiveUS6666953B1Reduce weightReduce wearNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPhysical chemistryKaolin clay
The invention concerns a pigment, filler or mineral containing a natural calcium carbonate, treated with one of more providers of H3O<+> ions and gaseous CO2, allowing a reduction in the weight of paper for a constant surface area without loss of physical properties when it is used as a pigment or coating filler for the said paper. In particular, the invention concerns a pigment, filler or mineral containing a natural calcium carbonate or dolomite or mixtures of talc and calcium carbonate, of kaolin and carbonate or carbonate alone or in combination with natural and / or synthetic fibers or similar, treated with one or more medium-strong or strong providers of H3O<+> ions in the presence of gaseous CO2. Applications are particularly in the paper industry, obtaining in particular good sheet properties i.e. a reduction its weight for a given surface area.
Owner:OMYA DEV AG
Method and apparatus for making absorbent structures with absorbent material
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Fabric crepe/draw process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS7789995B2Increase in sizeDecrease sidednessMechanical working/deformationPaper coatingCelluloseFiber
A method of making a fabric-creped absorbent cellulosic sheet comprising: a) compactively dewatering a papermaking furnish to form a nascent web having an apparently random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) applying the dewatered web having the apparently random fiber distribution to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; c) fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a patterned creping fabric, the creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric to form a web with a drawable reticulum.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20080311815A1Reduce blockingReduce fusionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceSlurry
A water non-dispersible polymer microfiber is provided comprising at least one water non-dispersible polymer wherein the water non-dispersible polymer microfiber has an equivalent diameter of less than 5 microns and length of less than 25 millimeters. A process for producing water non-dispersible polymer microfibers is also provided, the process comprising: a) cutting a multicomponent fiber into cut multicomponent fibers; b) contacting a fiber-containing feedstock with water to produce a fiber mix slurry; wherein the fiber-containing feedstock comprises cut multicomponent fibers; c) heating the fiber mix slurry to produce a heated fiber mix slurry; d) optionally, mixing the fiber mix slurry in a shearing zone; e) removing at least a portion of the sulfopolyester from the multicomponent fiber to produce a slurry mixture comprising a sulfopolyester dispersion and water non-dispersible polymer microfibers; and f) separating the water non-dispersible polymer microfibers from the slurry mixture. A process for producing a nonwoven article is also provided.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Embossed multi-ply fibrous structure product
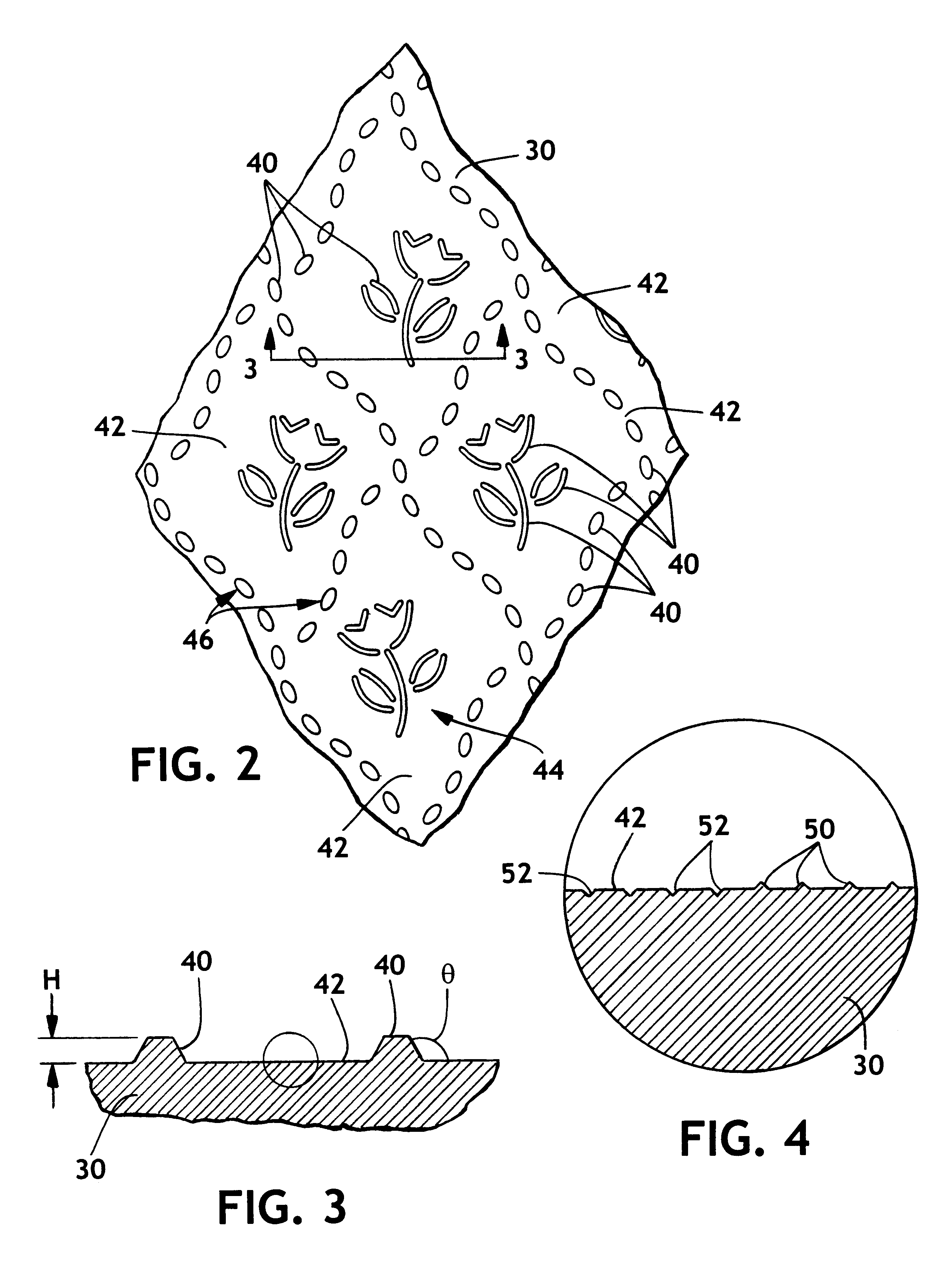
A multi-ply fibrous structure product having two or more plies of fibrous structure where at least one of the plies has a plurality of domes formed during the papermaking process and there are from about 10 to about 1000 domes per square inch of the product. At least one of the plies of the multi-ply fibrous structure has a plurality of embossments thereon with a total embossment area of from about 3% to about 15%. The embossments may be arranged such that they define non-geometric foreground patterns of unembossed cells.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Soft tissue having temporary wet strength
Disclosed is a soft, low density paper product made using papermaking fibers and a cationic temporary wet strength resin. Such paper products have a density less than about 0.6 grams per cubic centimeter, a basis weight is between about 10 and about 65 grams per square meter, a dry strength less than about 500 grams per inch (197 grams per centimeter), a ratio of an initial wet strength to the dry strength greater than about 0.15:1, and a ratio of a thirty minute wet strength to the initial wet strength less than about 0.4. Methods for producing such paper products are also disclosed. The paper products may be produced either as homogeneous structures or as multi-layered structures and may be either creped or uncreped.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Insulated cup and method of manufacture
InactiveUS6257485B1Boxes/cartons making machineryDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
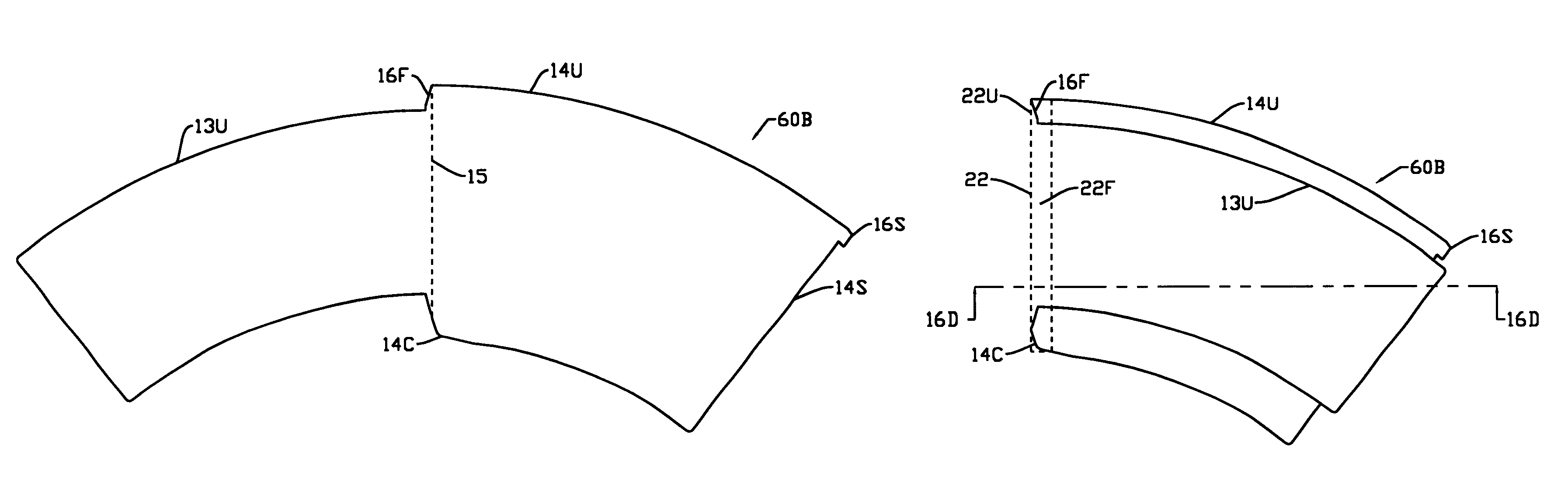
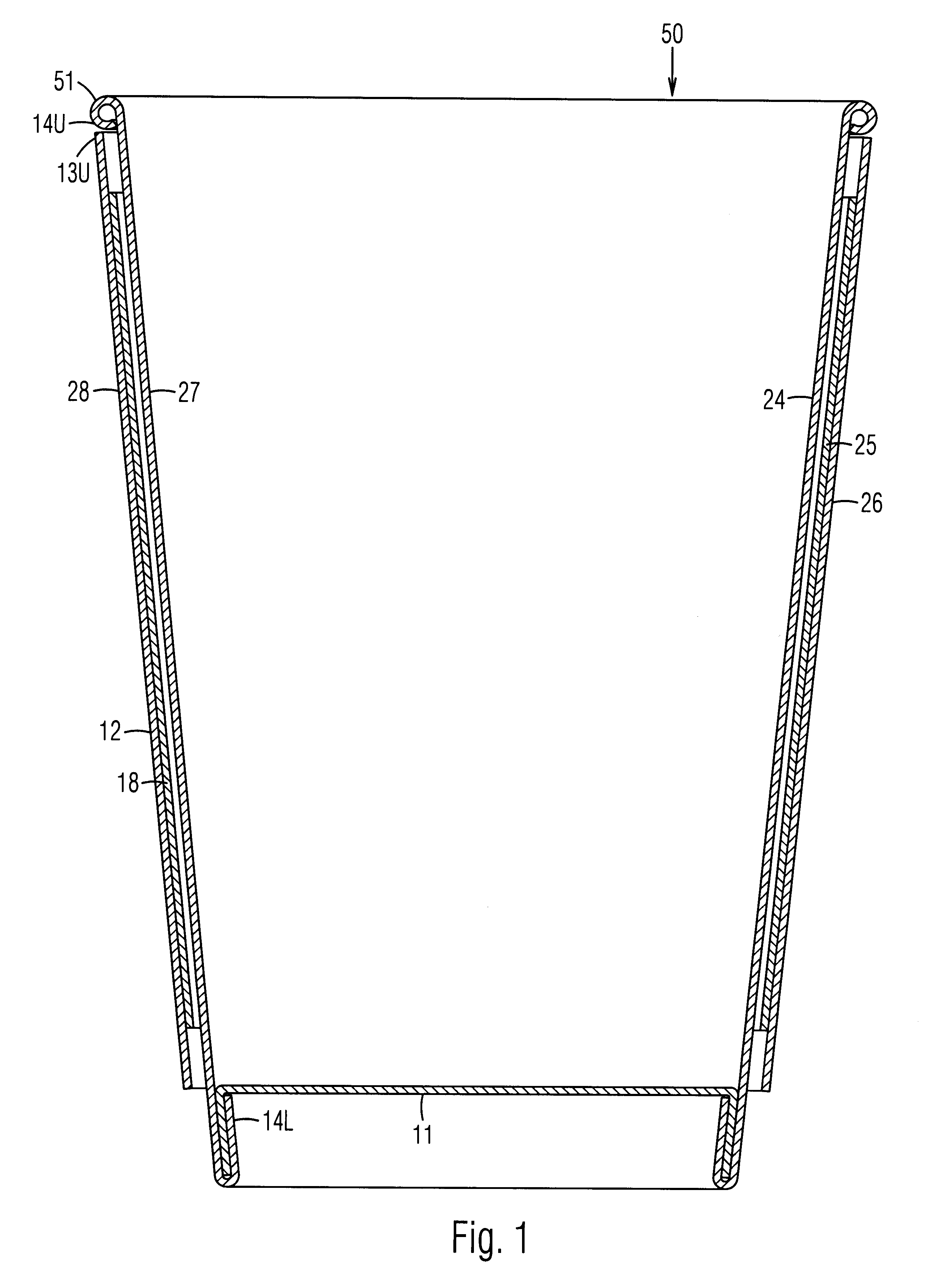
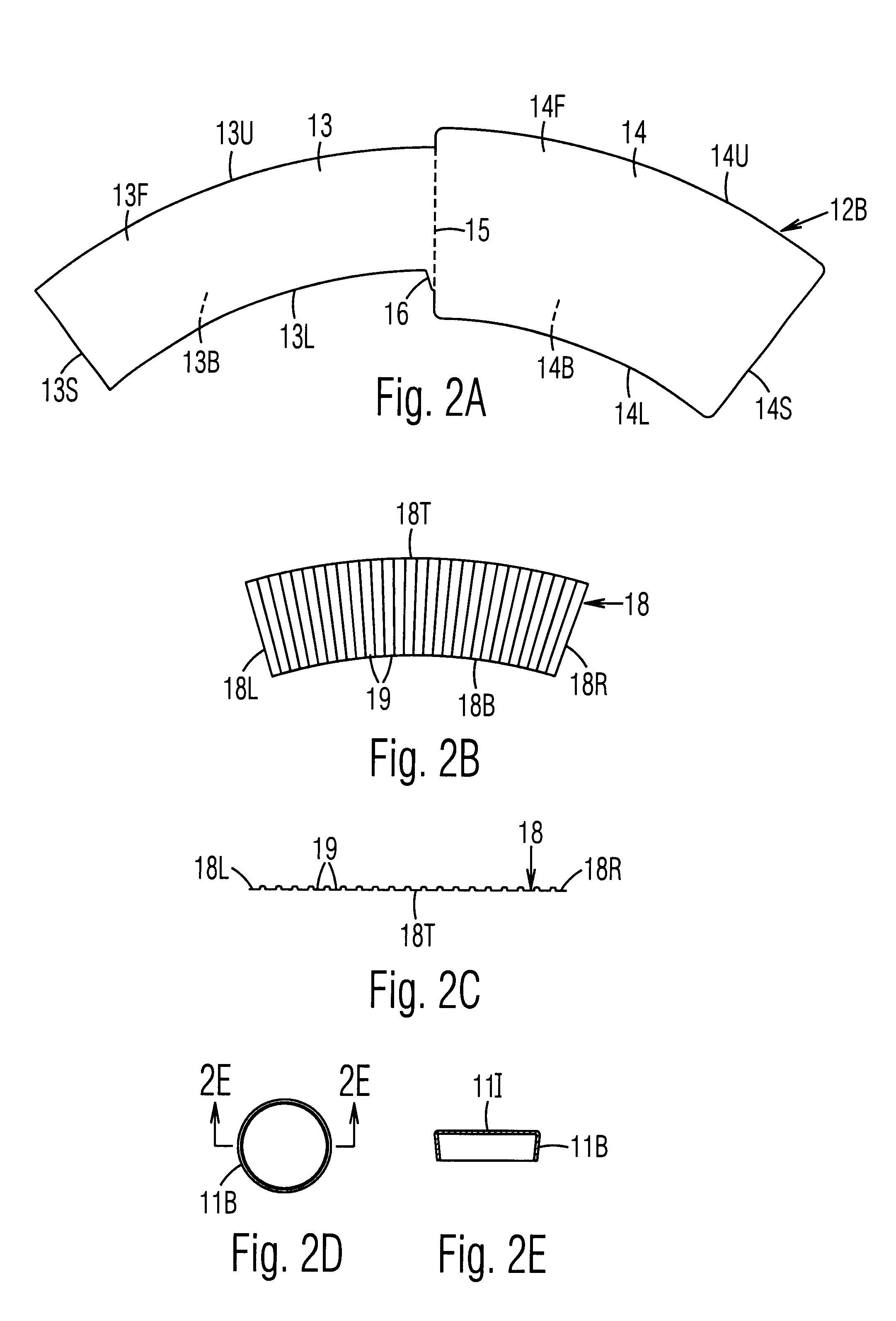
An insulating cup or container (50) and a method of manufacturing it comprises (first embodiment) providing a sidewall blank (12B) having two sections separated by a fold score (15), and a separate insulating sheet (18) (corrugated, ribbed, embossed, foamed, perforated, etc.) which is adhesively fastened to one of the sections. The blank is folded in half along the fold score, to form a three-layered assembly with the insulating sheet in the middle. To reduce the thickness of the seam, the blank is thinned in the area adjacent a fold score prior to folding. The assembly is wrapped around a mandrel to bring the outer edges together at a side seam (22S) to form a sidewall 12. The side seam is sealed, the bottom is added, and the rim is formed. In a second embodiment, the insulating layer can be a coating on one or both of the sections of the two-section starting blank. In a third embodiment, the insulating section (40) is integral with, and extends from, one edge of the starting blank. It is folded over first to form the middle layer of the wrappable assembly. The width of the seam is reduced while being reinforced at the top by using edge tabs, thereby providing a rounder cup and one which is less susceptible to top leakage due to an unsealed top curl. One tab extends at the fold line from the top edge of one section, which is shorter, to the top edge of the adjacent and higher section. A second tab extends out from the top of the side edge of the higher section so that it overlaps and seals the other tab when the cup is formed.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Hydraulically-Formed Nonwoven Sheet with Microfibers
InactiveUS20100272938A1Non-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperNonwoven fabricMedical device
In a first embodiment, a hydraulically-formed nonwoven sheet, a package comprising such sheet, a method of packaging a medical device using a package with such sheet and a method of manufacturing such sheet are provided. This nonwoven sheet comprises first and second non-cellulosic polymeric fibers. The first non-cellulosic polymeric fibers have an average diameter less than about 3.5 micron, an average cut length less than about 3 millimeters and an average aspect ratio of about 400 to about 2000; the second non-cellulosic polymeric fibers have an average diameter greater than about 3.5 micron and an average aspect ratio of about 400 to about 1000. In a second embodiment, a hydraulically-formed nonwoven sheet is provided. This nonwoven sheet comprises binding material, non-cellulosic polymeric fibers and cellulosic based materials. The non-cellulosic polymeric fibers have an average diameter less than about 3.5 micron, an average cut length less than about 3 millimeters and an average aspect ratio of about 400 to about 2000. The second nonwoven sheet has a bacterial filtration efficiency of at least about 98%.
Owner:BEMIS COMPANY INC
Equipment for insertion of objects into smoking articles
ActiveUS7479098B2Sufficient shapeSufficient sizeMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboard articlesSpace objectEngineering
Apparatus incorporating a filter tow processing unit adapted to supply filter tow to a continuous rod forming unit includes an object insertion unit that positions objects within the filter tow to manufacture a filter rod containing objects positioned at predetermined intervals. The apparatus also includes an upper hopper that acts as a reservoir for a plurality of objects, and provides for supply of objects to a lower hopper. The lower hopper is shaped so that objects are stacked therein. The bottom of the lower hopper is shaped so as to cooperate with a portion of upper region of a rotating wheel. The peripheral face of the rotating wheel incorporates a plurality of spaced pockets, each pocket being of sufficient shape and size to accommodate one object. Objects within the lower hopper are aligned in a single line along a portion of the peripheral face in the upper region of the rotating wheel. Each object then is positioned at predetermined intervals within a continuous supply of filter material. Then, the filter material is formed into a continuous rod having individual objects positioned at predetermined spaced intervals within that rod. The continuous rod then is subdivided at predetermined intervals so as to form a plurality of filter rods (e.g., four-up filter rods containing four spaced objects).
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Use Of A Surface-Reacted Calcium Carbonate In Tissue Paper, Process To Prepare A Tissue Paper Product Of Improved Softness, And Resulting Improved Softness Tissue Paper Products
ActiveUS20120031576A1Good flexibilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperCoatings with pigmentsSurface responseTissue paper
The present invention related to the use of a surface-reacted natural calcium carbonate as filler in tissue paper products, to a process to prepare tissue paper products, and to a tissue paper product featuring an improved softness, wherein said surface-reacted natural calcium carbonate is the reaction product of a natural calcium carbonate with an acid and carbon dioxide, which is formed in situ by the acid treatment and / or supplied externally.
Owner:OMYA INT AG
Semiaromatic polyamide molding compositions and their use
ActiveUS20080274355A1High strengthLow water absorptionPigmenting treatmentNon-fibrous pulp additionHexamethylenediamineAramides
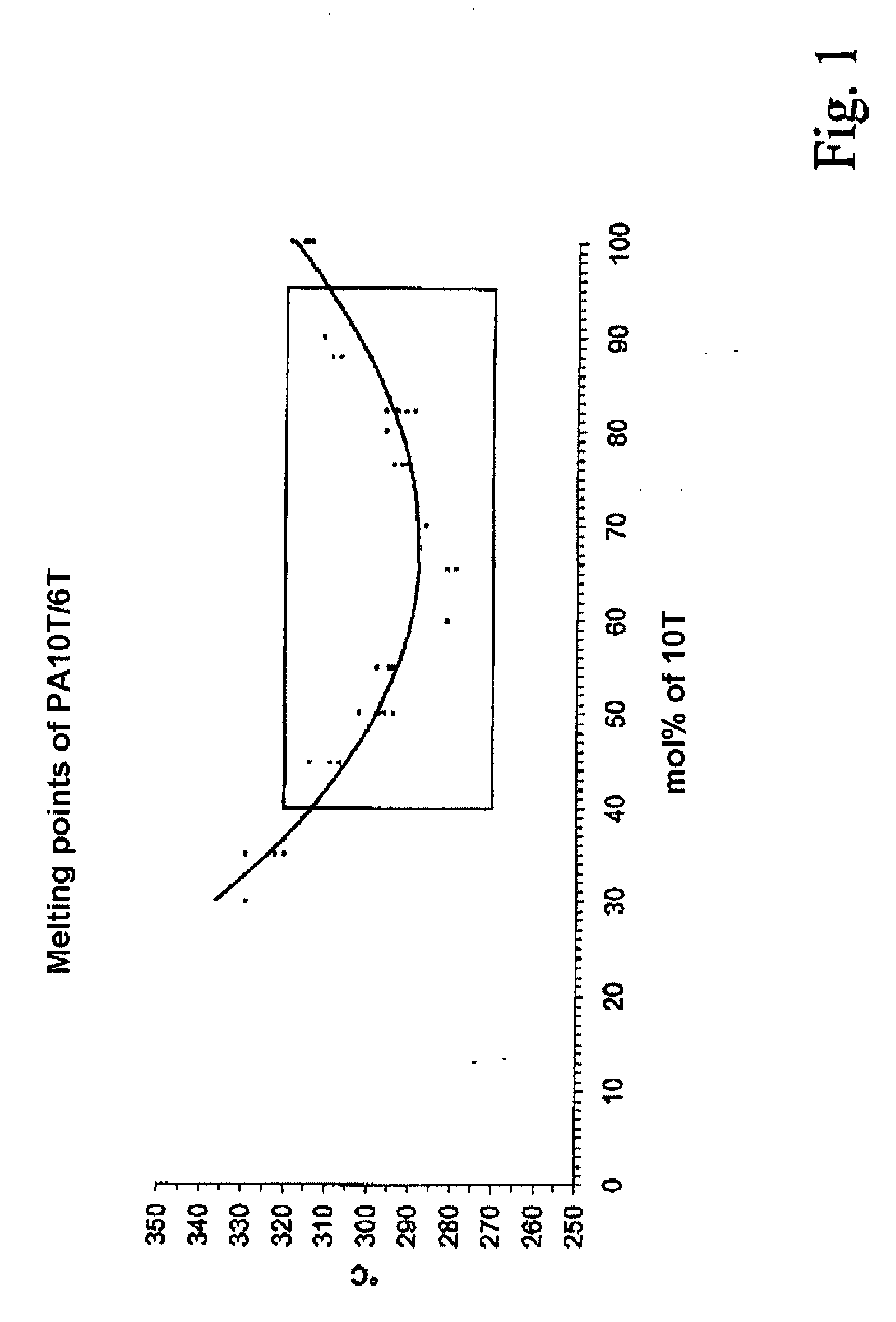
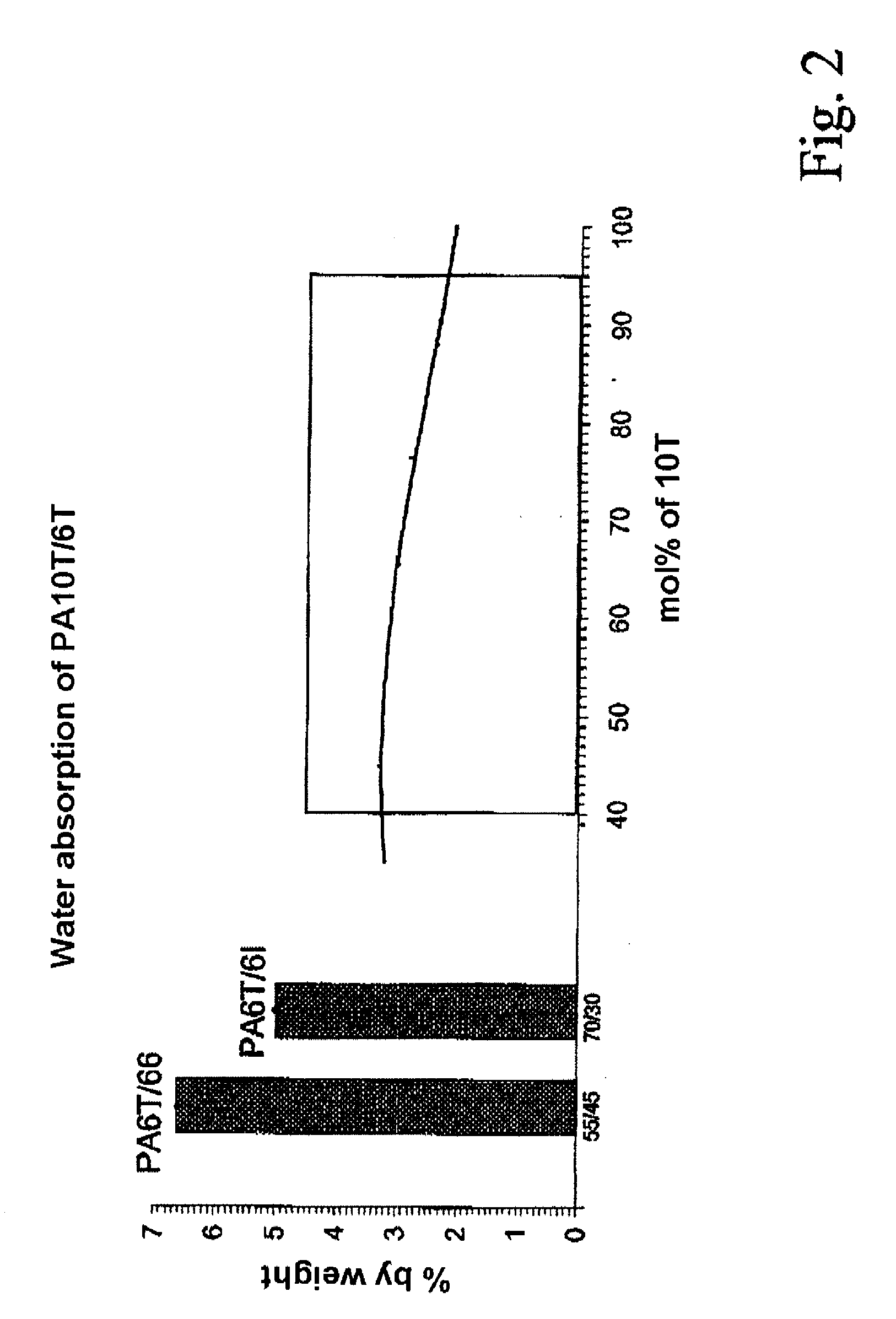
A polyamide molding composition with the following constitution is described:(A) from 30 to 100% by weight of at least one 10T / 6T copolyamide, where this is composed of(A1) from 40 to 95 mol % of 10T units, formed from the monomers 1,10-decanediamine and terephthalic acid(A2) from 5 to 60 mol % of 6T units, formed from the monomers 1,6-hexanediamine and terephthalic acid(B) from 0 to 70% by weight of reinforcing materials and / or fillers(C) from 0 to 50% by weight of additives and / or further polymerswhere the entirety of components A to C is 100%, with the proviso that in component (A) up to 30 mol %, based on the entirety of the dicarboxylic acids, of the terephthalic acid can have been replaced by other aromatic, aliphatic, or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids, and with the proviso that in component (A) up to 30 mol % of 1,10-decanediamine and respectively 1,6-hexanediamine, based on the entirety of the diamines, can have been replaced by other diamines, and with the proviso that not more than 30 mol % in component (A), based on the entirety of the monomers, can have been formed via lactams or amino acids. Uses of this polyamide molding composition are moreover described, as also are processes for the preparation of these polyamide molding compositions.
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
Method for precision bending of a sheet of material and slit sheet therefor
InactiveUS6481259B1Reduce stress concentrationPrecise positioningConstruction materialMetal-working feeding devicesEngineeringSheet material
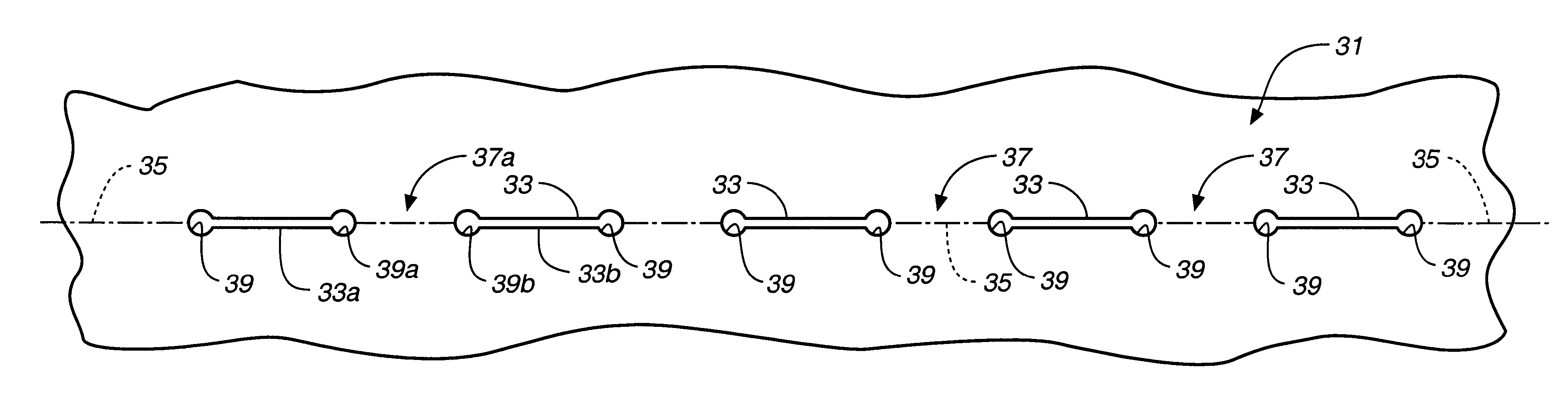
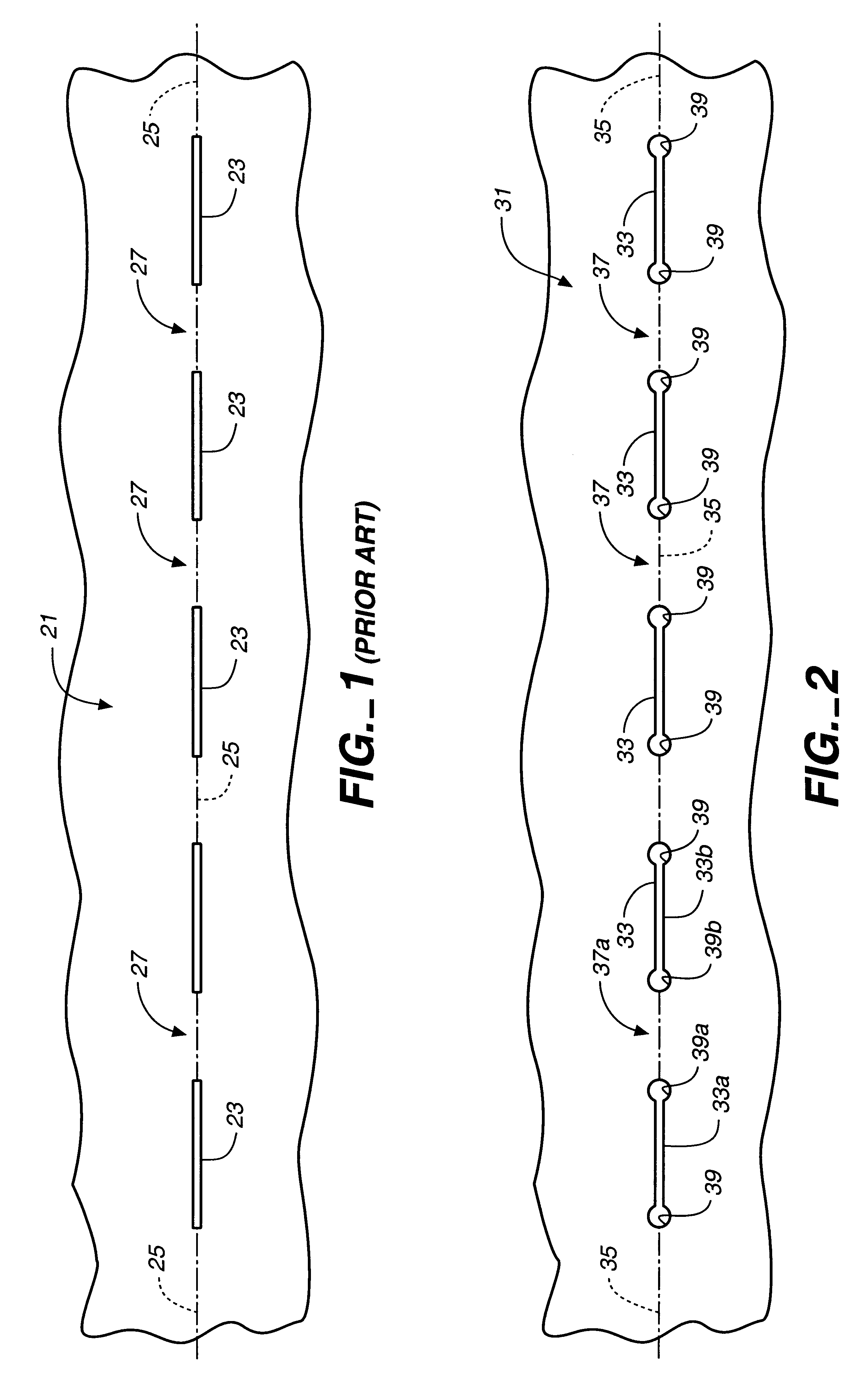
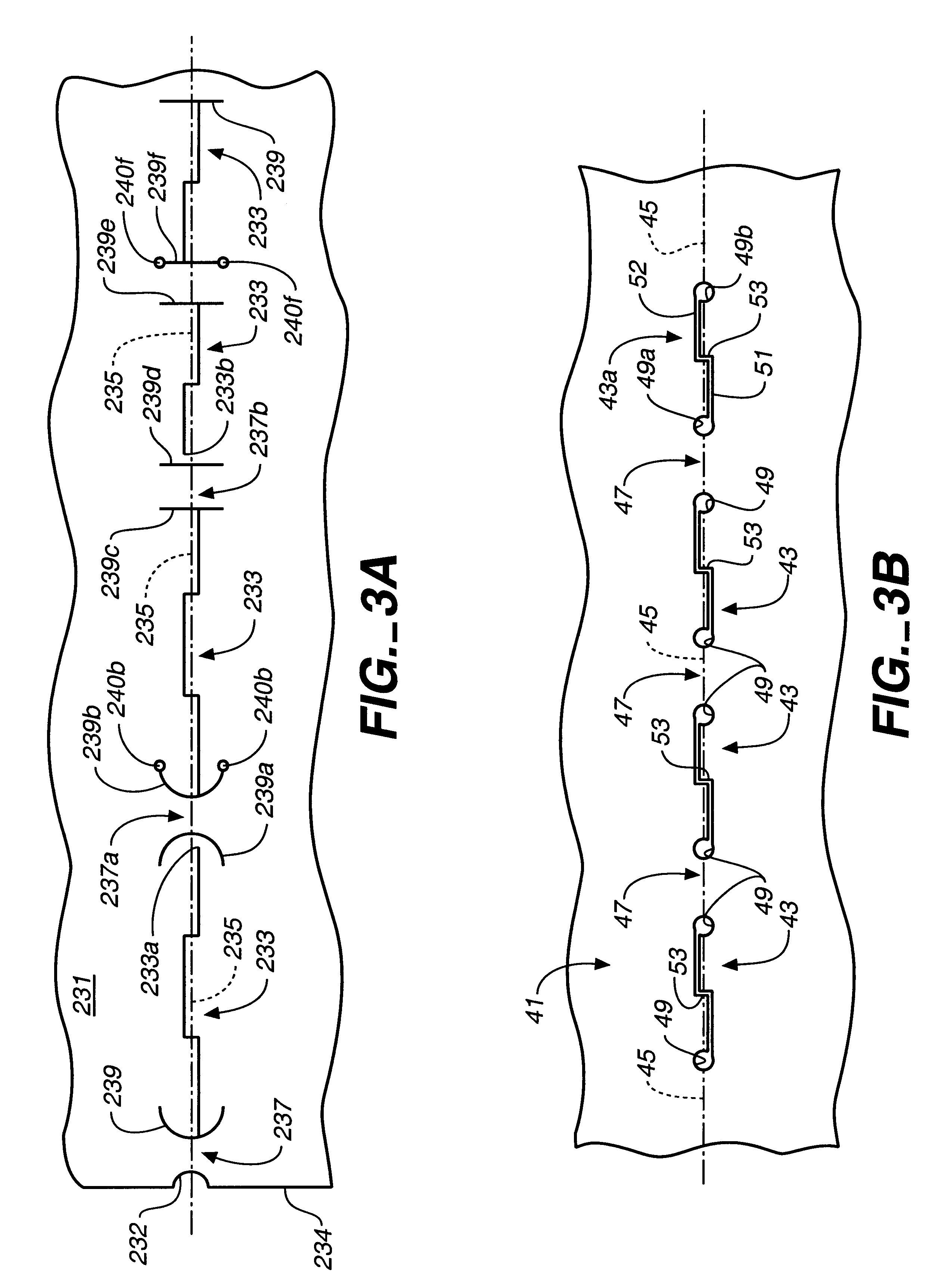
A method for precision bending of a sheet of material (31,41,61,91,231) along a bend line (35,45,62-66,96,235) and the resulting sheet are disclosed. A method includes a step of forming and longitudinally extending slits (33,43,68,92,233) through the sheet of material in axially spaced relation to define bending webs (37,47,71,72,106,237), forming stress reducing structures such as enlarged openings (39,49,69,73) or transversely extending slits (239) at each of adjacent ends of pairs of slits in order to reduce crack propagation across the bending webs. In another aspect, the elongated slits (43,68,92,233) are formed with pairs of longitudinally extending slit segments (51,52;74,76;98,99;127) proximate to and on opposite sides of and substantially parallel to the desired bend line. Longitudinally extending slit segments further are connected by at least one intermediate transversely extending slit segment (53,77,101,128). Sheets of slit material suitable for bending also are disclosed.
Owner:IND ORIGAMI INC CA US
Extracts from plant and non-plant biomass and uses thereof
Novel oil extracts from Angiosperm and Gymnosperm plants and other-plant biomass from human, veterinary, birds, aquatic species, microbial and mycological sources useful in human, veterinary and agricultural, mycological and microbiological applications are described. Methods of preparation of these extracts in oil and methods of application and administration are also described.
Owner:KANE SHANTARAM GOVIND
Method and apparatus for incorporating objects into cigarette filters
ActiveUS20050070409A1Tobacco treatmentPaper/cardboard wound articlesFilter materialMechanical engineering
Cigarette filter rods having individual objects positioned at predetermined intervals therein are prepared by transferring the individual objects from a rotating horizontal pan to a rotating vertical wheel and then depositing the object into a web of filter tow. Each object is positioned within the moving web of tow. The web filter material and the objects positioned within the web are introduced into a rod-forming unit wherein the rod is formed. The rate of feed of the filter tow, the rate of rotation of the horizontal pan and the vertical wheel are controlled relative to one another such that objects are positioned at predetermined intervals along the rod. Cigarette filter elements having well controlled amounts of flavorant contained therein can be made from the rods.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com