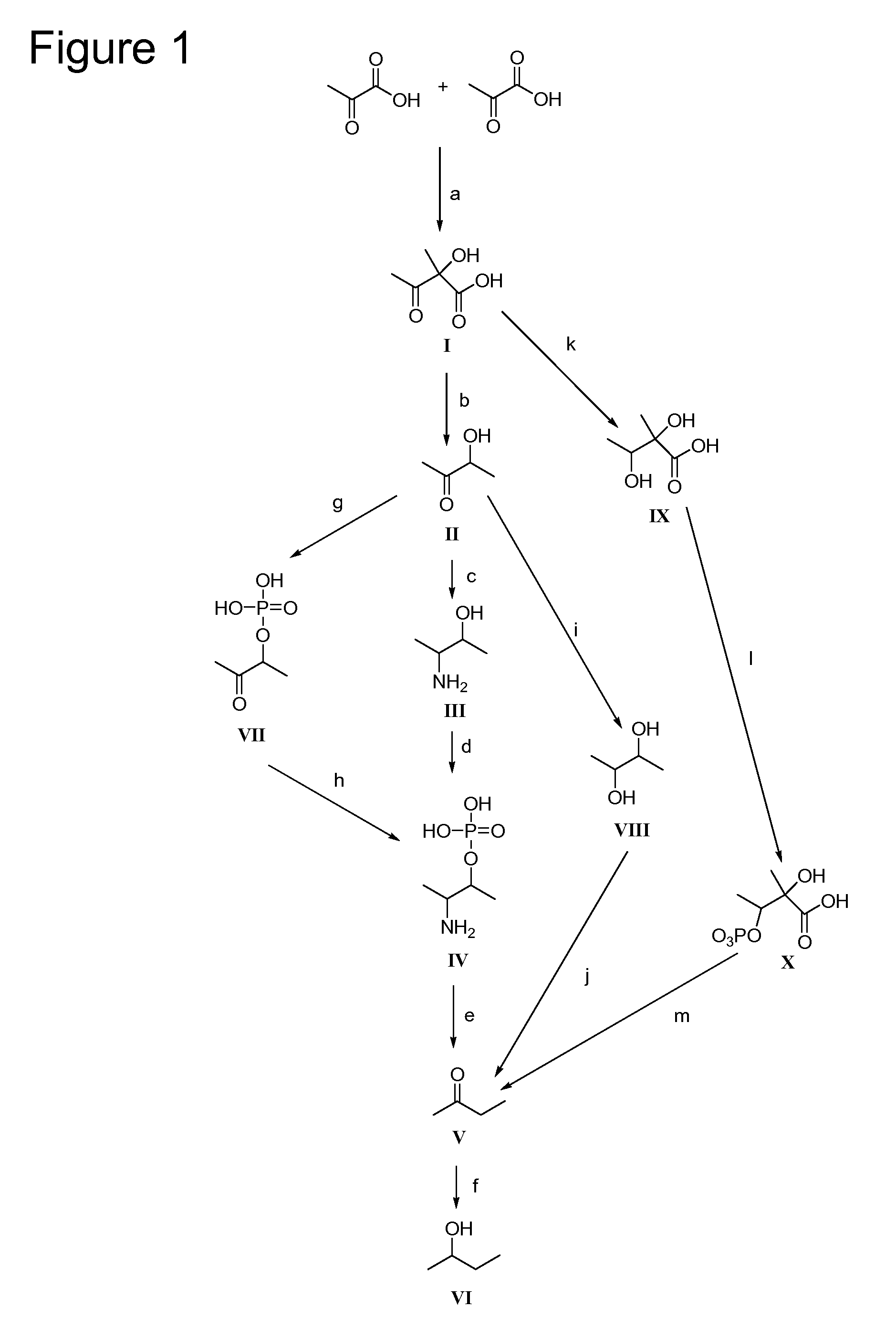
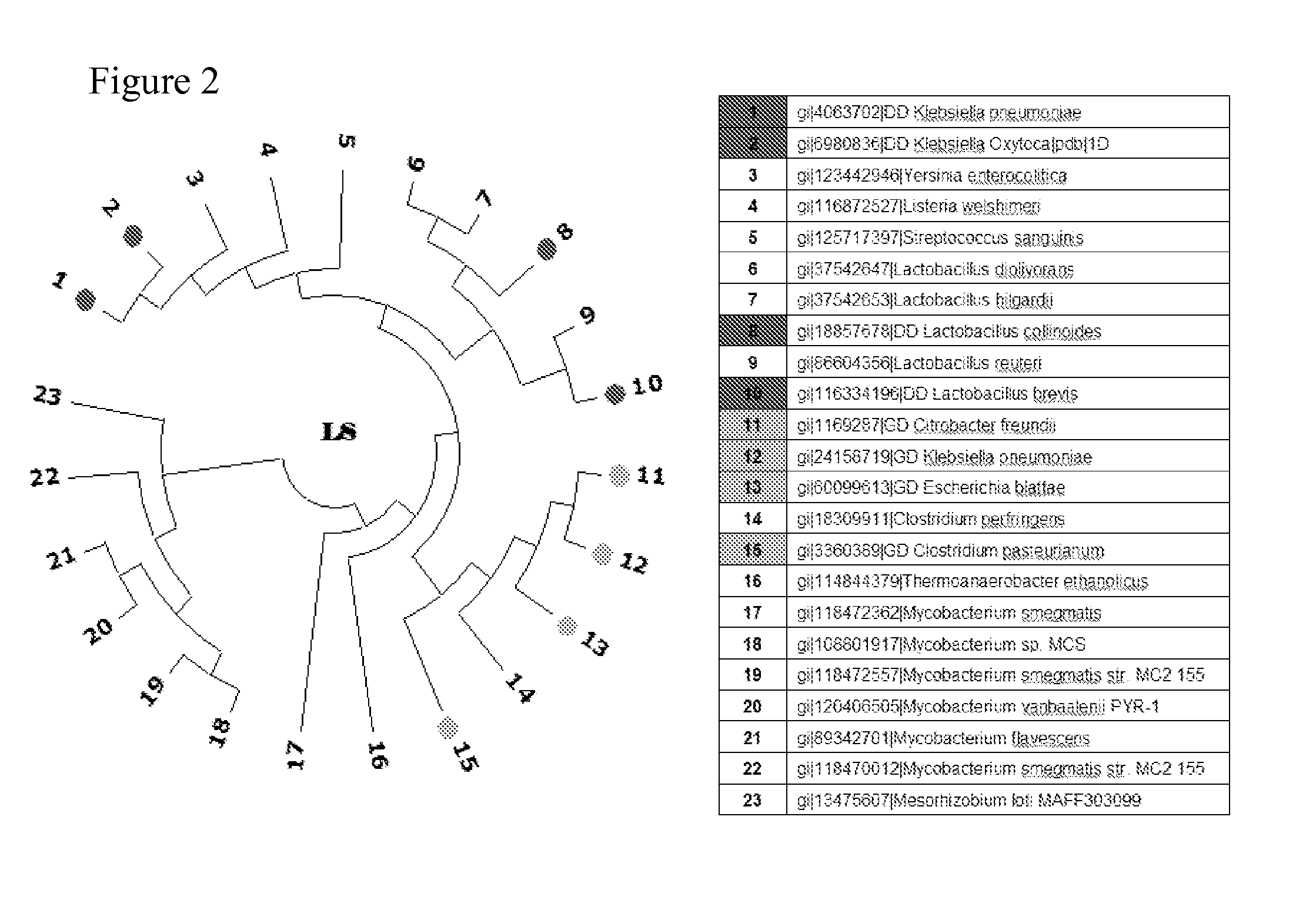
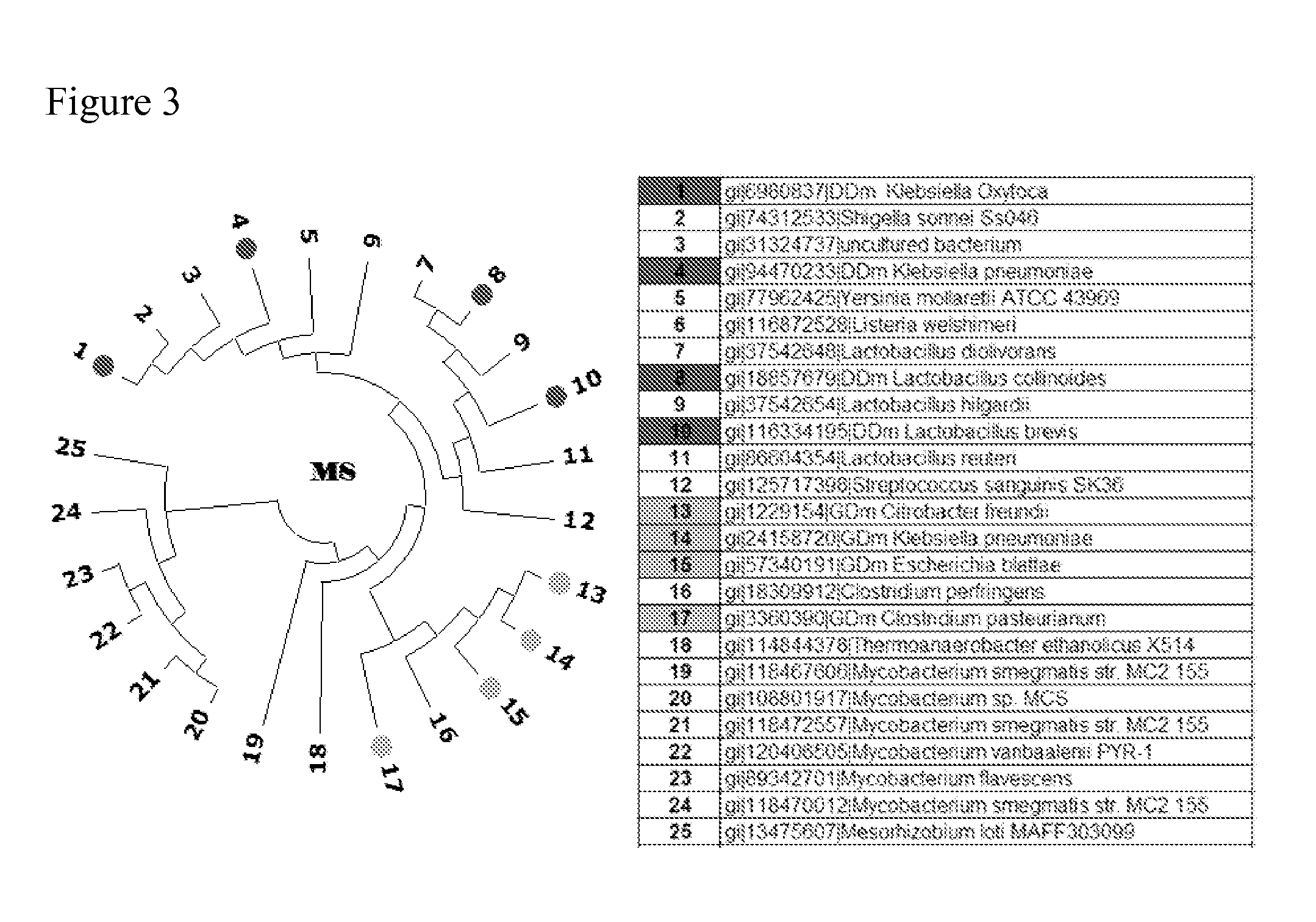
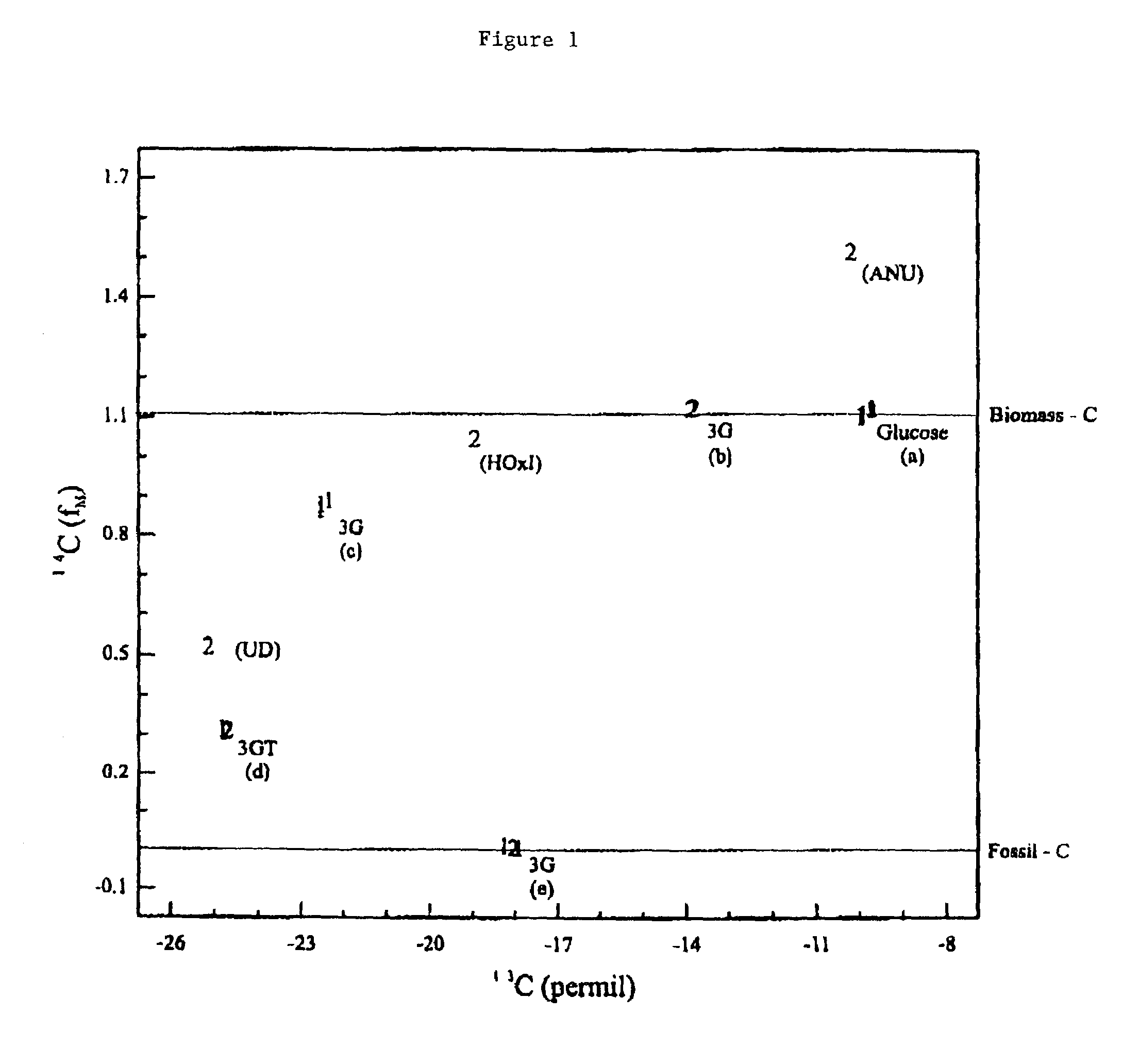
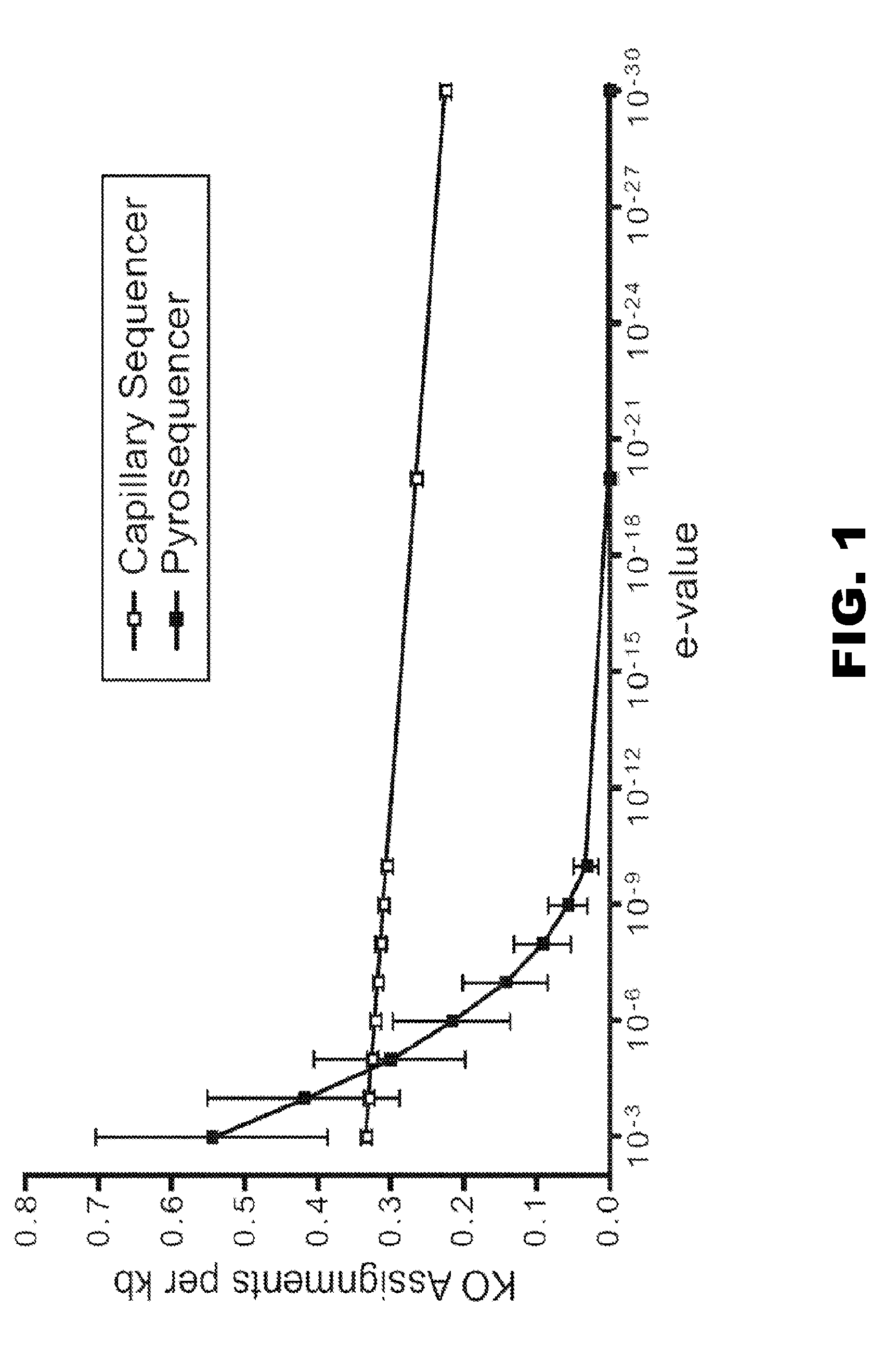
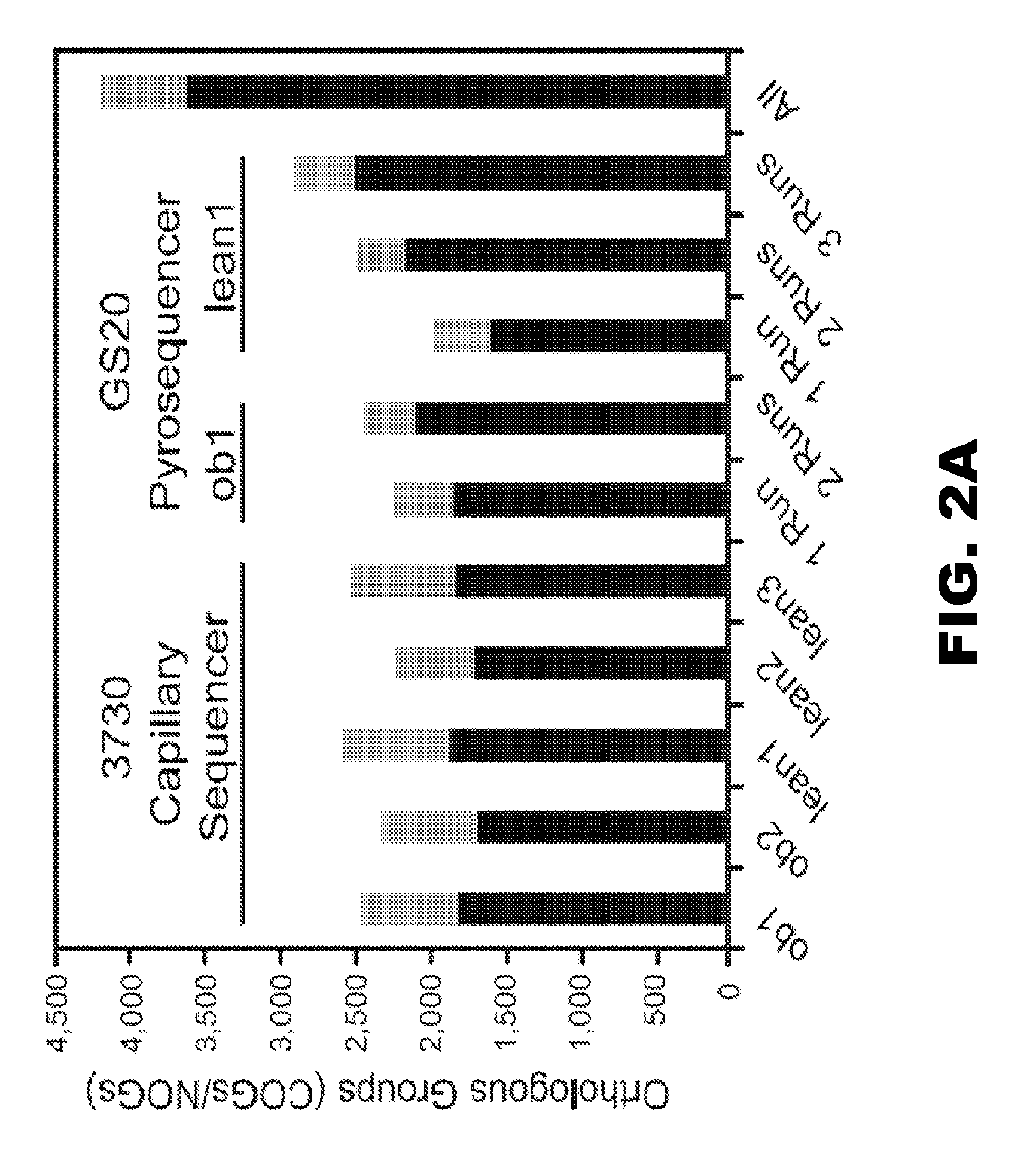
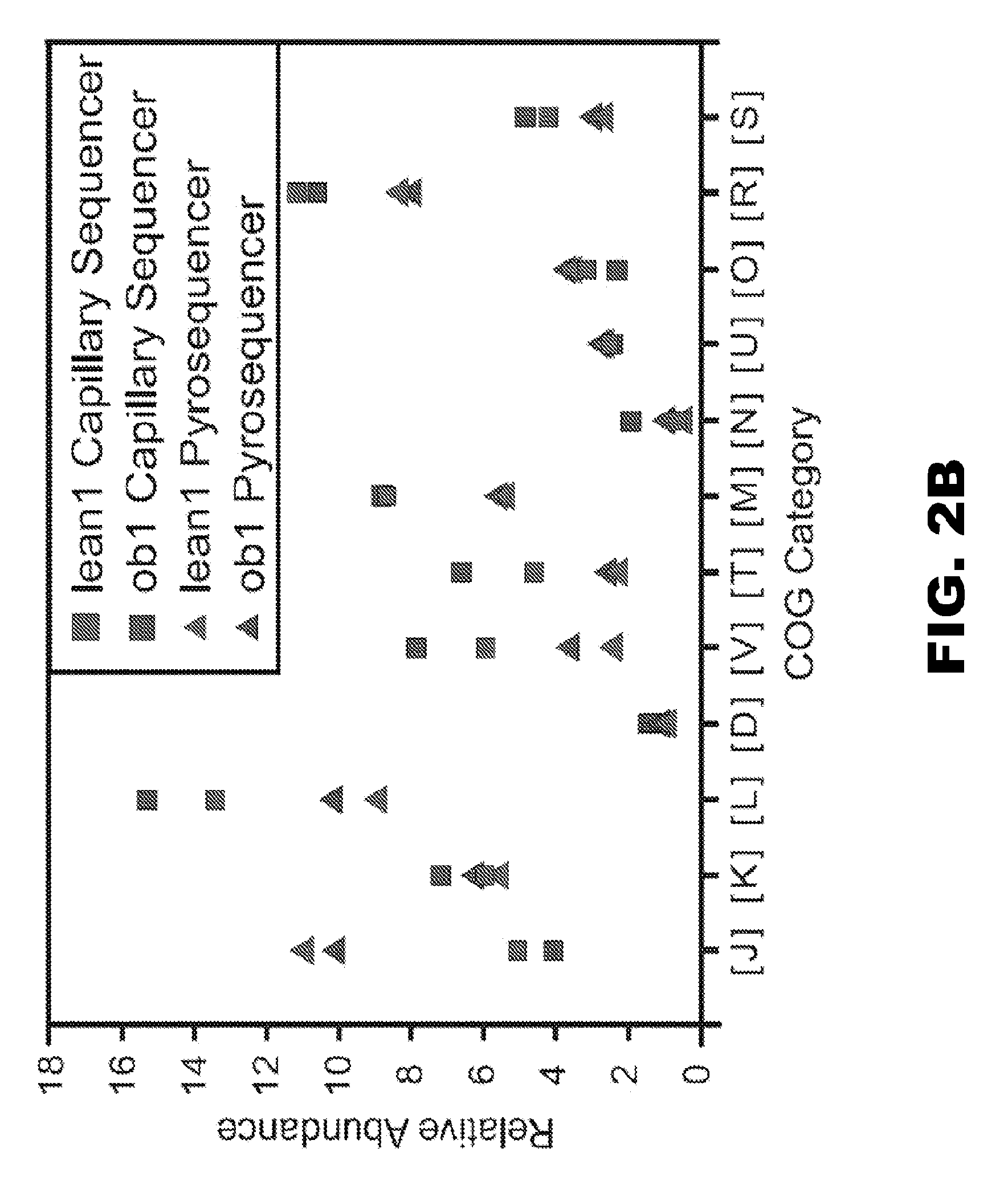
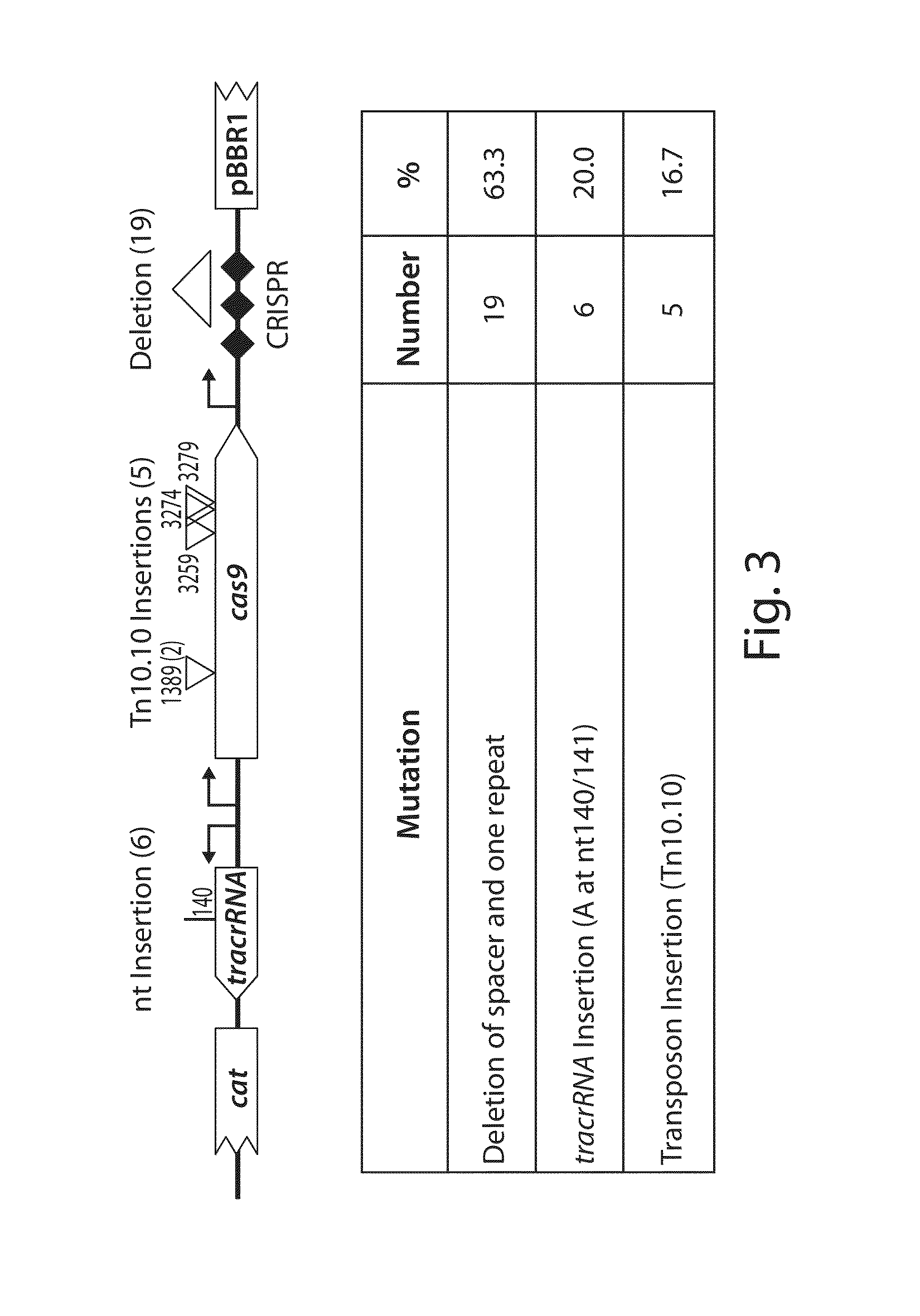
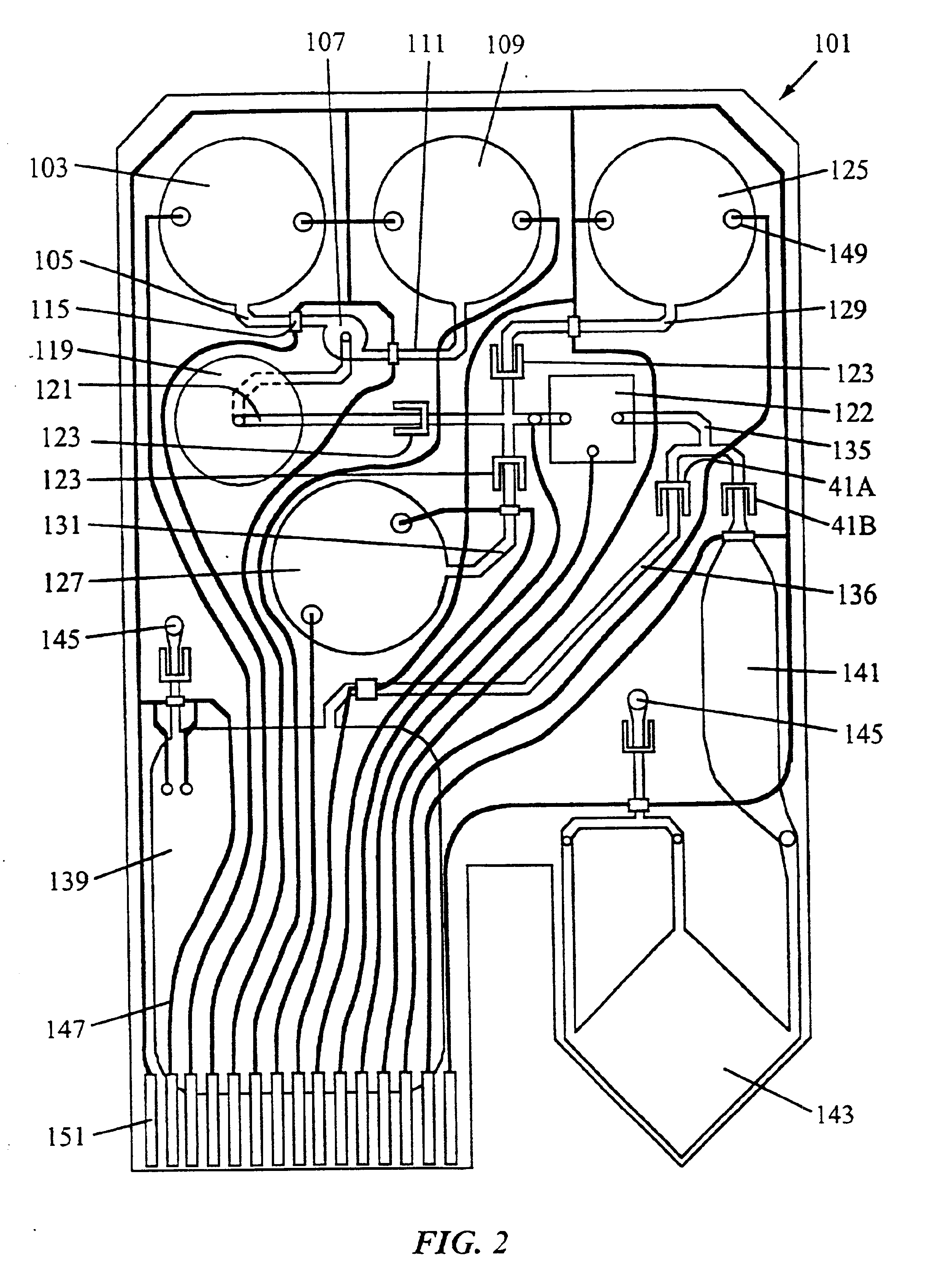
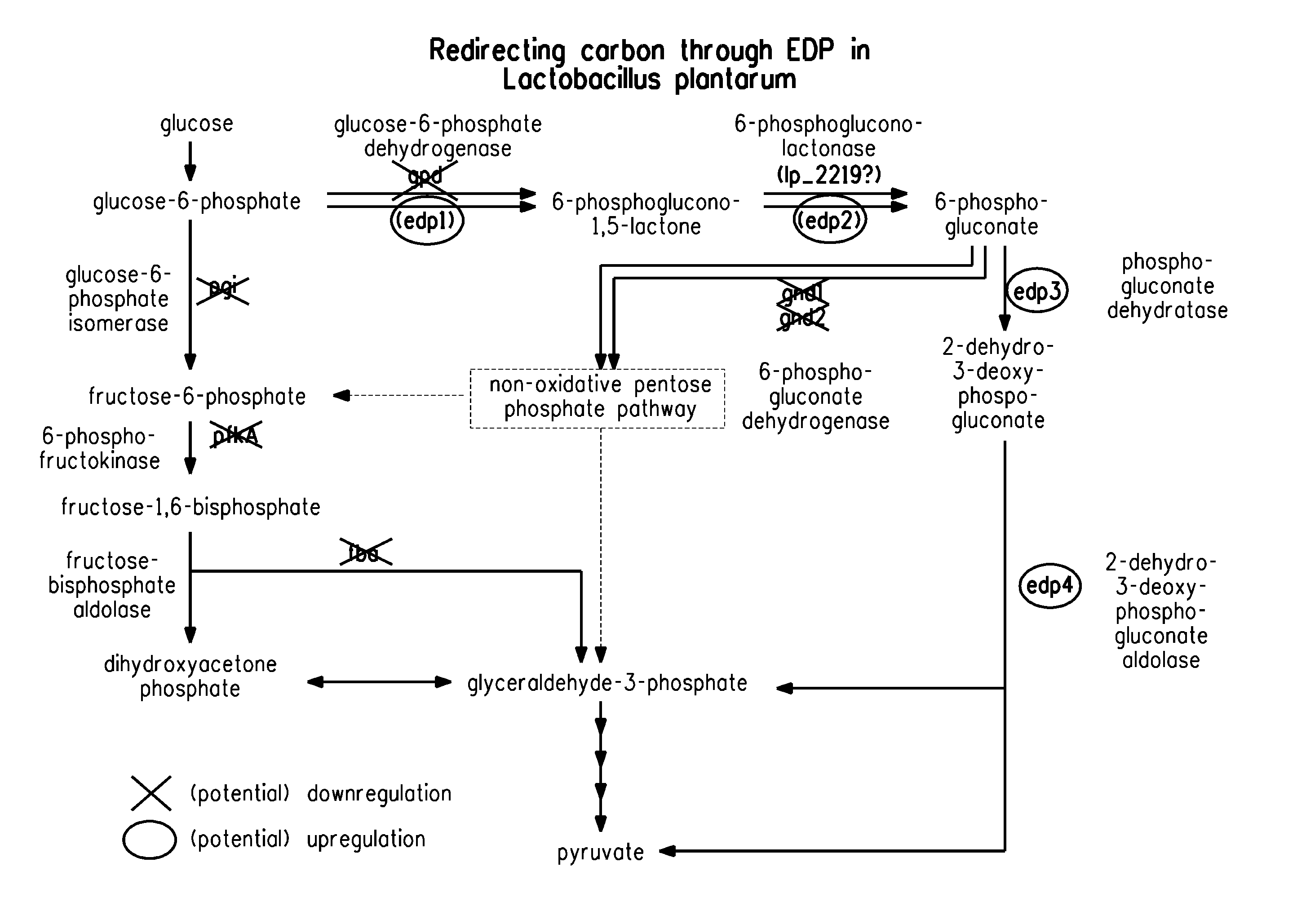
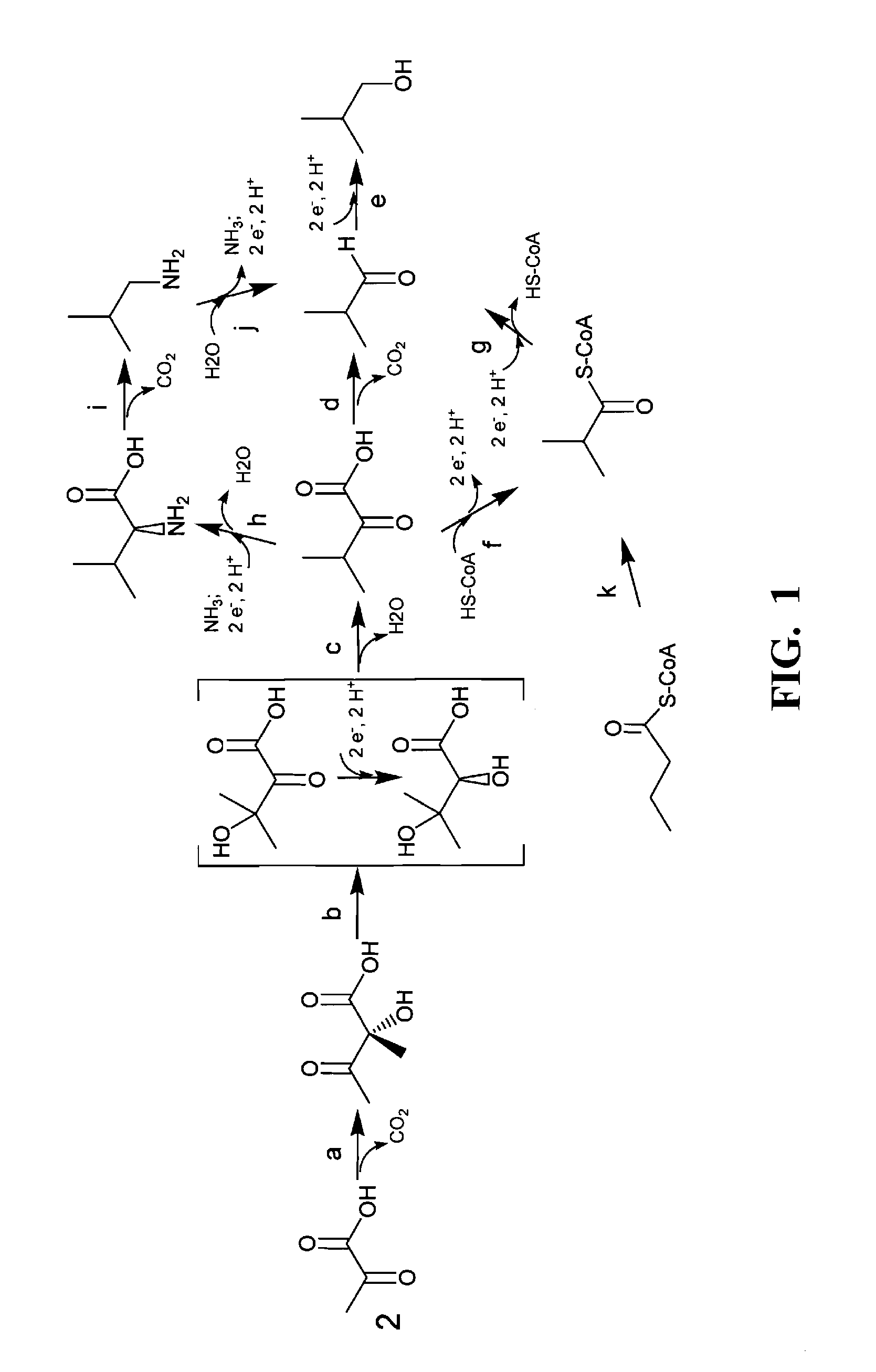
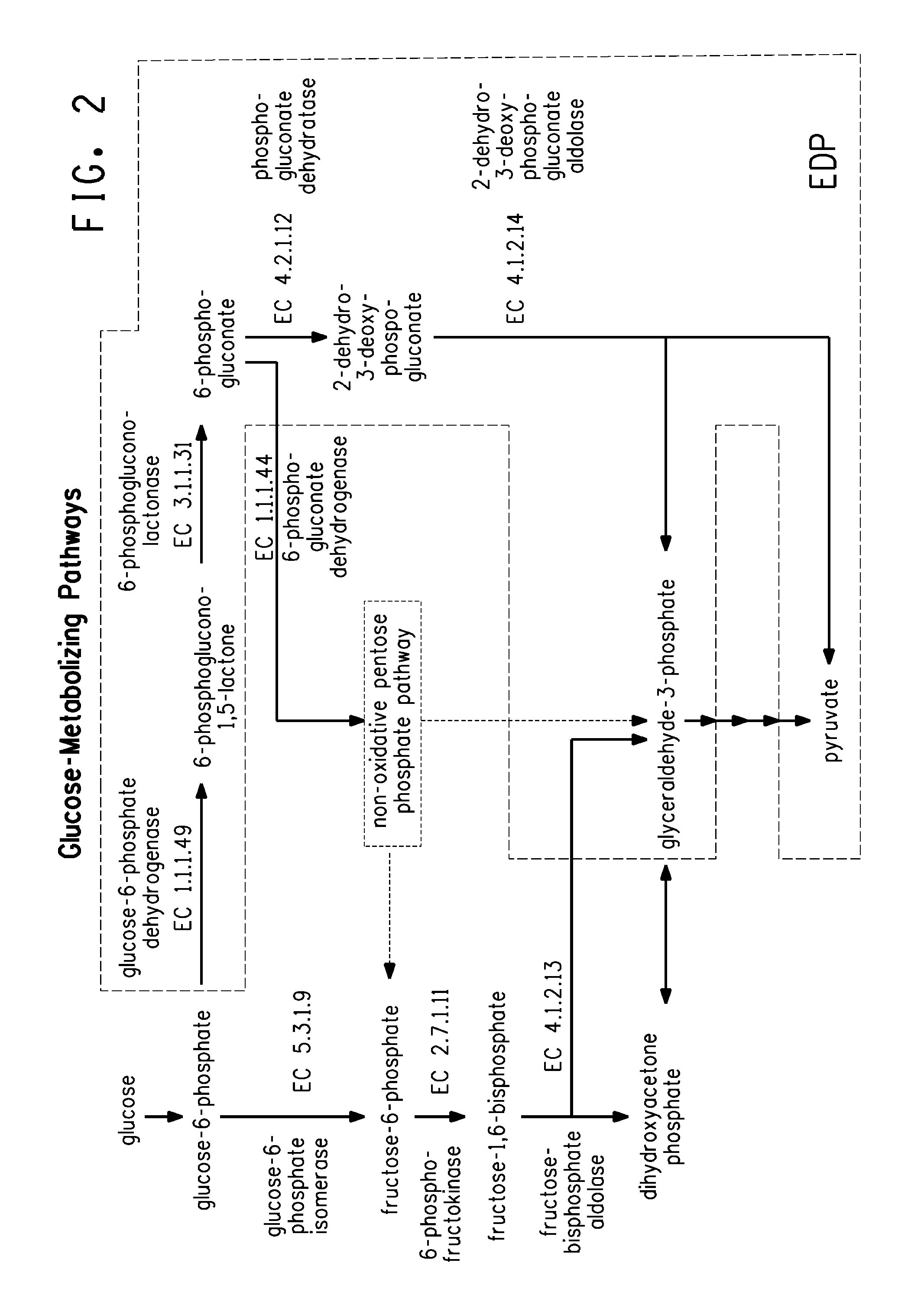
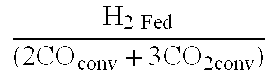Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68707 results about "Microorganism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microorganism, or microbe, is a microscopic organism, which may exist in its single-celled form or in a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from 6th century BC India and the 1st century BC book On Agriculture by Marcus Terentius Varro. Microbiology, the scientific study of microorganisms, began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax.
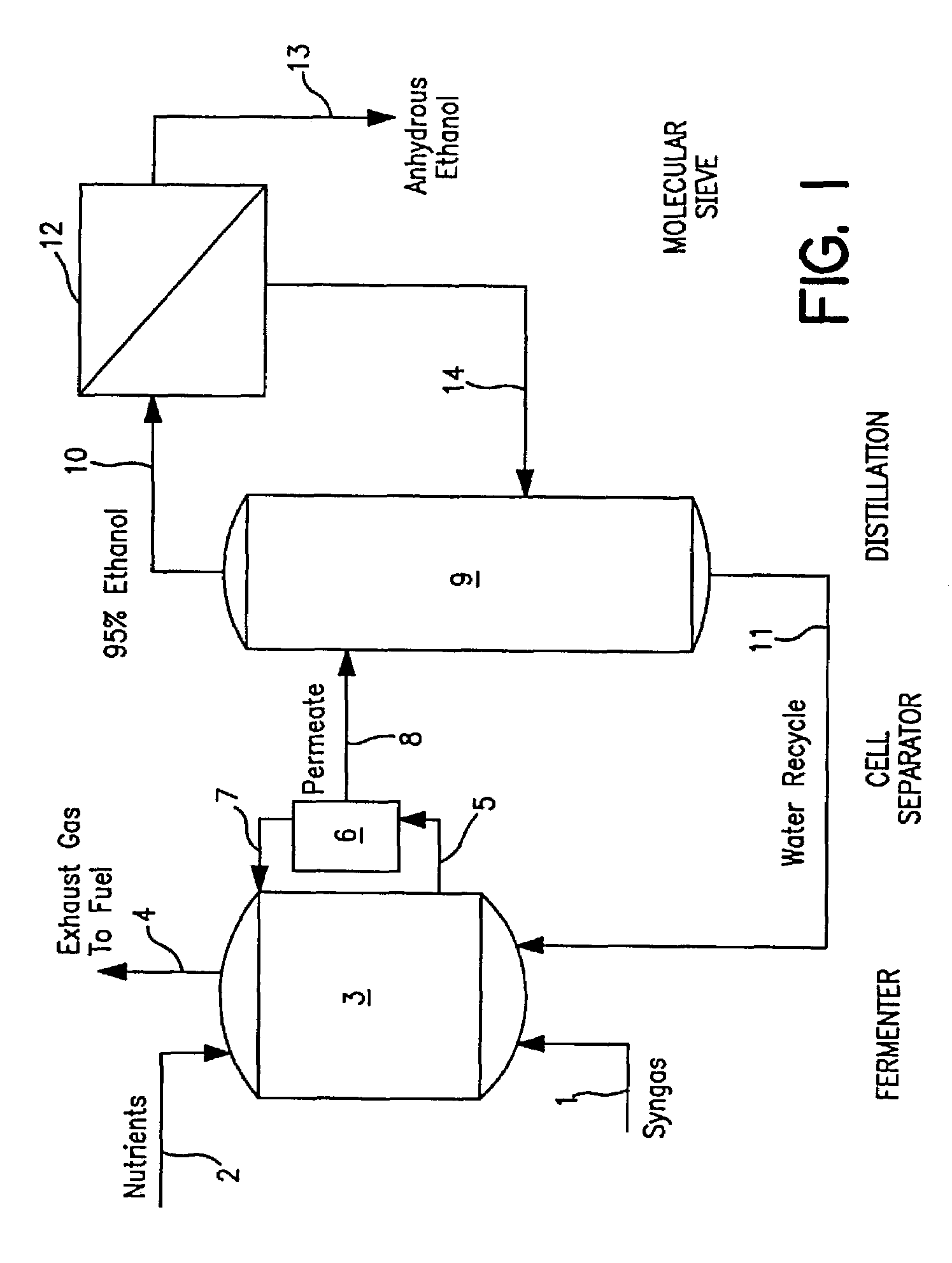
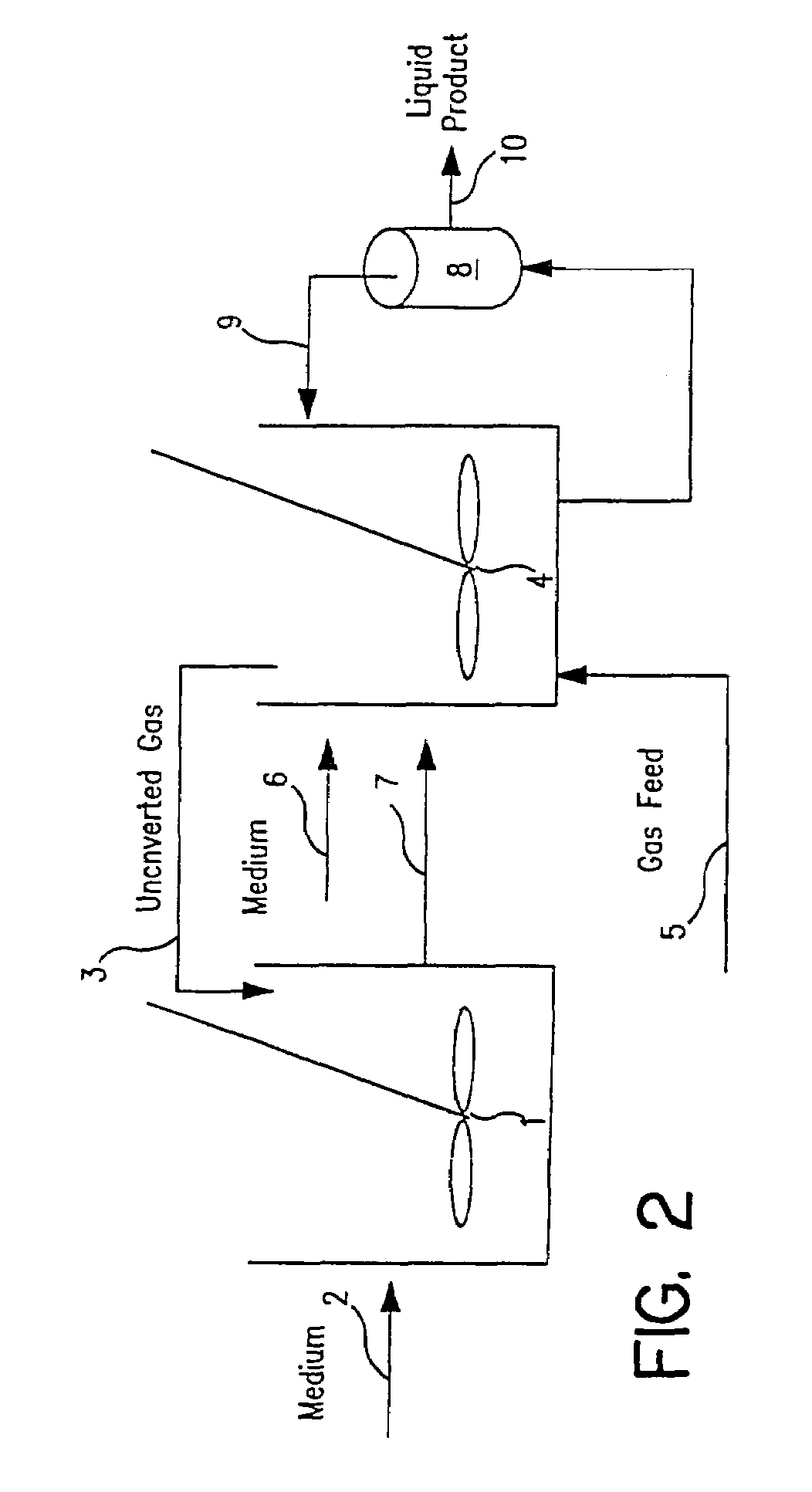
Methods for increasing the production of ethanol from microbial fermentation
InactiveUS7285402B2Good culture stabilityPermit growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSolid waste disposalBioreactorNutrient
A stable continuous method for producing ethanol from the anaerobic bacterial fermentation of a gaseous substrate containing at least one reducing gas involves culturing a fermentation bioreactor anaerobic, acetogenic bacteria in a liquid nutrient medium; supplying the gaseous substrate to the bioreactor; and manipulating the bacteria in the bioreactor by reducing the redox potential, or increasing the NAD(P)H TO NAD(P) ratio, in the fermentation broth after the bacteria achieves a steady state and stable cell concentration in the bioreactor. The free acetic acid concentration in the bioreactor is maintained at less than 5 g / L free acid. This method allows ethanol to be produced in the fermentation broth in the bioreactor at a productivity greater than 10 g / L per day. Both ethanol and acetate are produced in a ratio of ethanol to acetate ranging from 1:1 to 20:1.
Owner:JUPENG BIO HK LTD
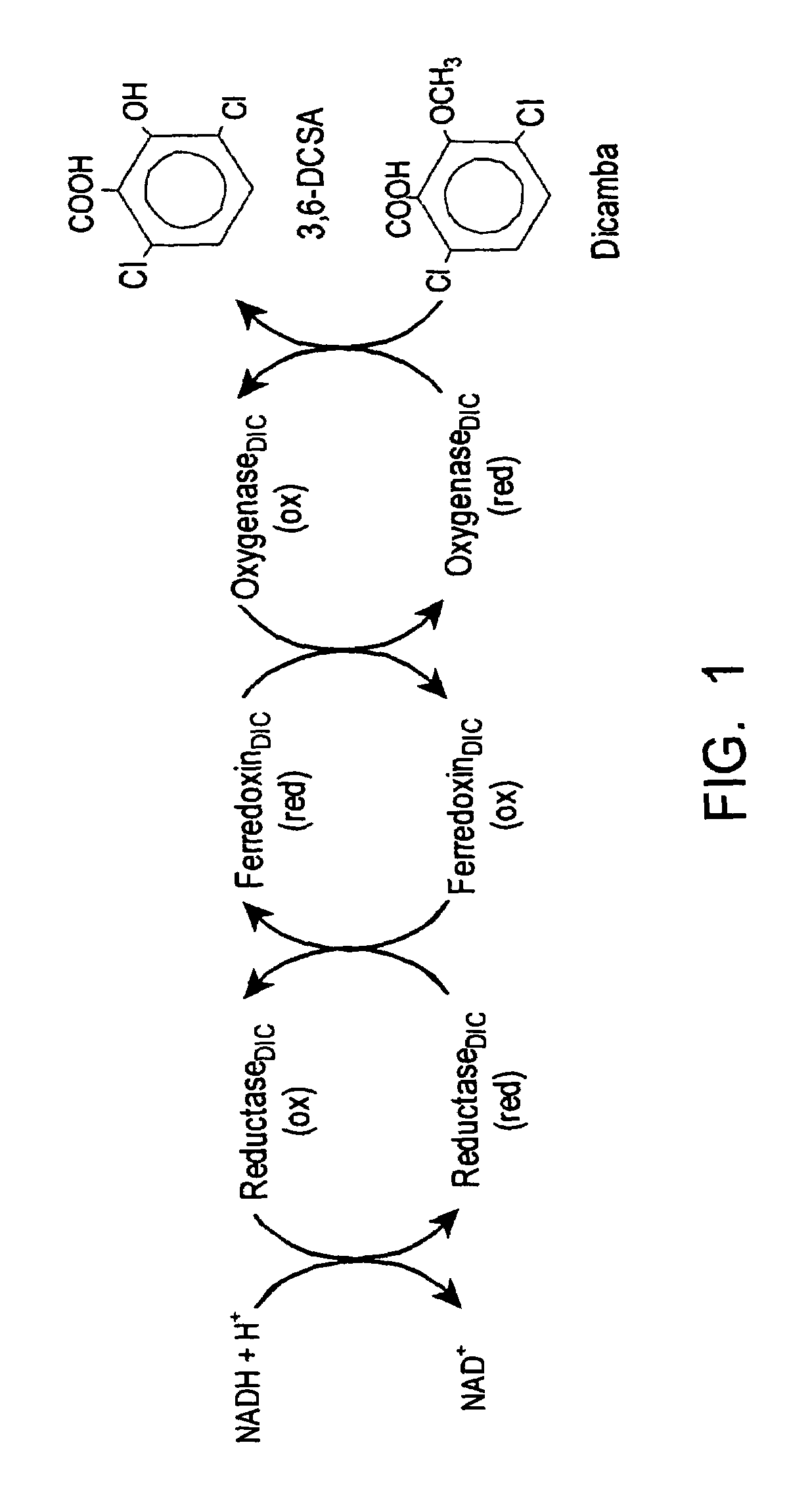
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
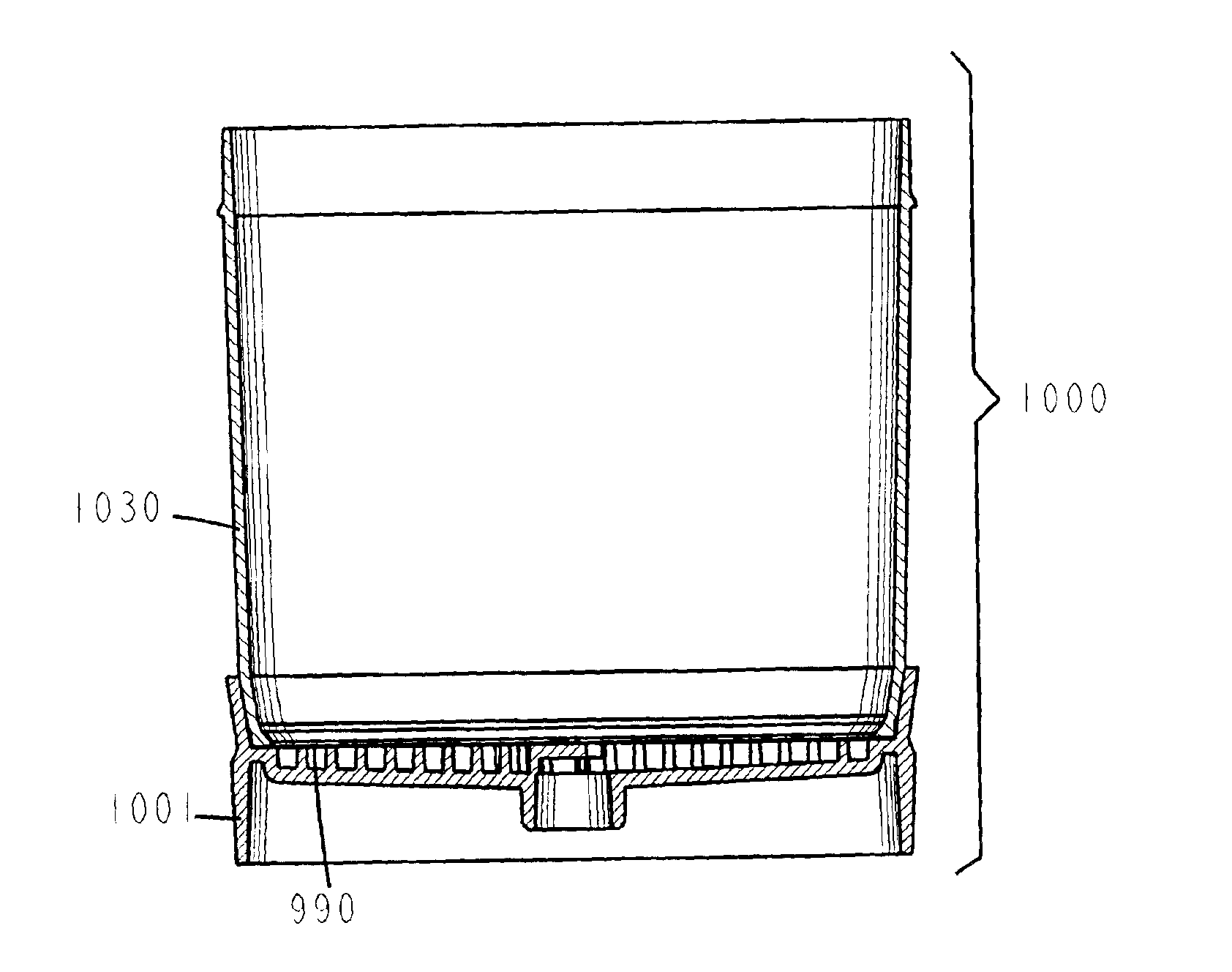
Disposable vacuum filtration apparatus capable of detecting microorganisms and particulates in liquid samples
InactiveUS6913152B2Increase valueEasy to disassemblePreparing sample for investigationUltrafiltrationMicroorganismWrinkle skin
A vacuum filtration apparatus (900) for detecting microorganisms and particulates in liquid samples. The apparatus includes a base (901), an absorbent pad (991), a filter (990), a funnel (930), and a lid (960). The funnel is releasably attached to the base, and may contain an integral flexible seal for releasably sealing the filter to the base. The outer wall of the lid may be segmented to make it flexible, this flexibility allows it to be releasably attached to the funnel or the base. The apparatus is designed so that any funnel will fit any base, and any lid will fit any base or any funnel when all parts are manufactured to normal tolerances. The apparatus may be configured to to keep the filter wrinkle free in both the dry and wet states.
Owner:FOXX LIFE SCI
Directed evolution of grg31 and grg36 epsp synthase enzymes
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided, particularly polypeptide variants of SEQ ID NO:2 and 4. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:7-28, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:29 or 30.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Implantable or insertable medical device resistant to microbial growth and biofilm formation
InactiveUS6887270B2Prevent preferential partitioningPrevent chemical modificationAntipyreticAnalgesicsActive agentMicrobial adhesion
Disclosed are implantable or insertable medical devices that provide resistance to microbial growth on and in the environment of the device and resistance to microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on the device. In particular, the invention discloses implantable or insertable medical devices that comprise at least one biocompatible matrix polymer region, an antimicrobial agent for providing resistance to microbial growth and a microbial adhesion / biofilm synthesis inhibitor for inhibiting the attachment of microbes and the synthesis and accumulation of biofilm on the surface of the medical device. Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing such devices under conditions that substantially prevent preferential partitioning of any of said bioactive agents to a surface of the biocompatible matrix polymer and substantially prevent chemical modification of said bioactive agents.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
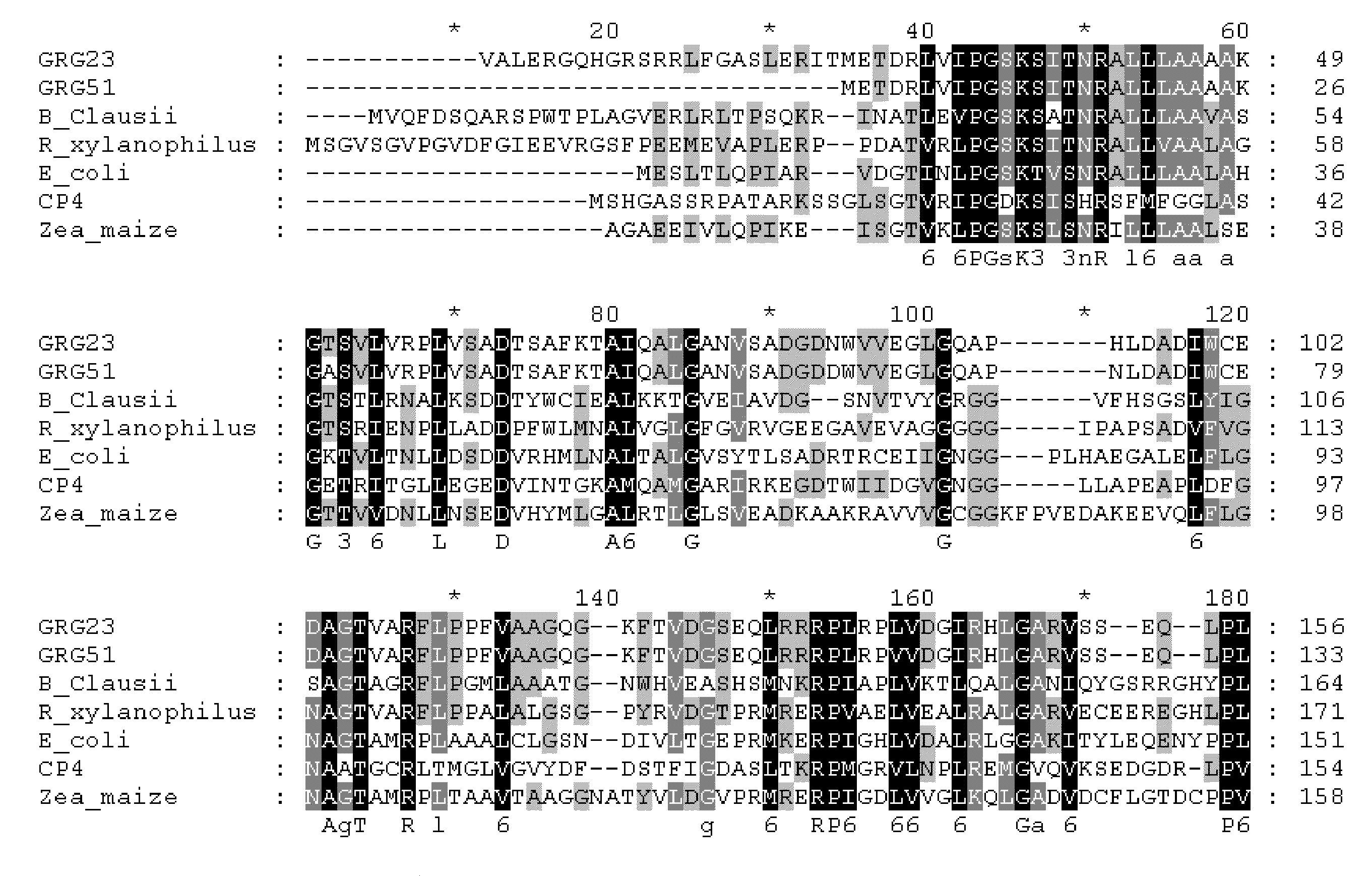
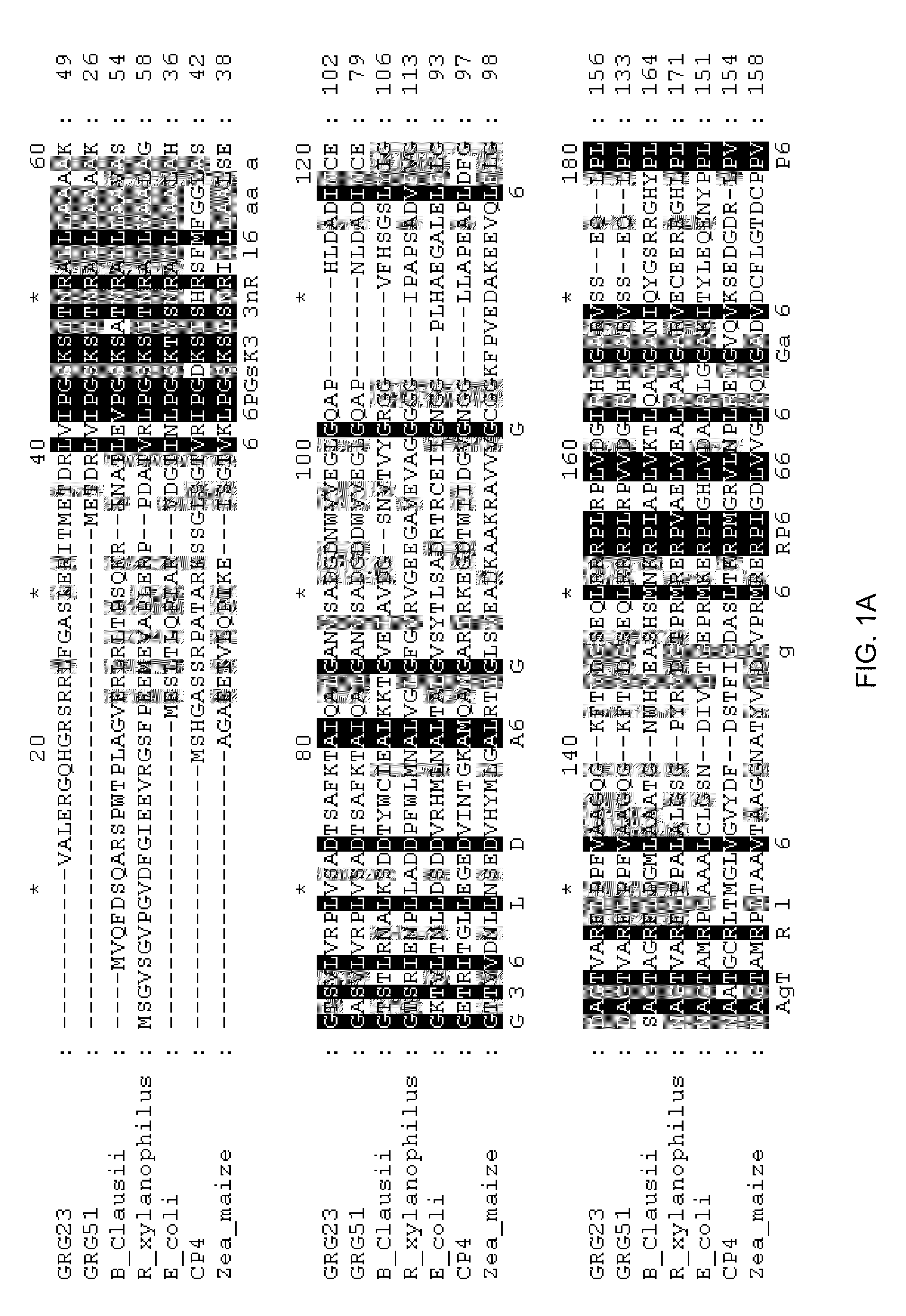
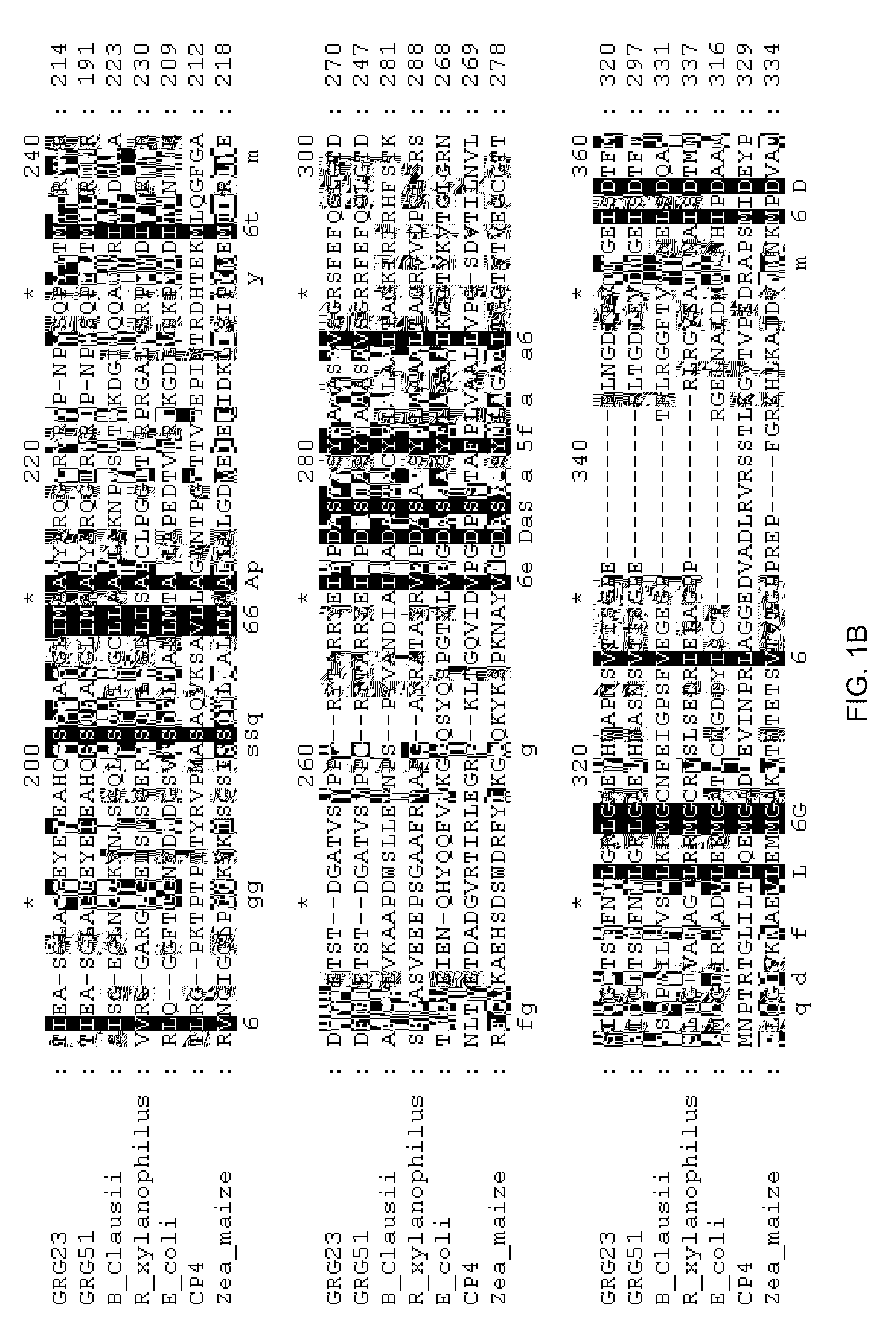
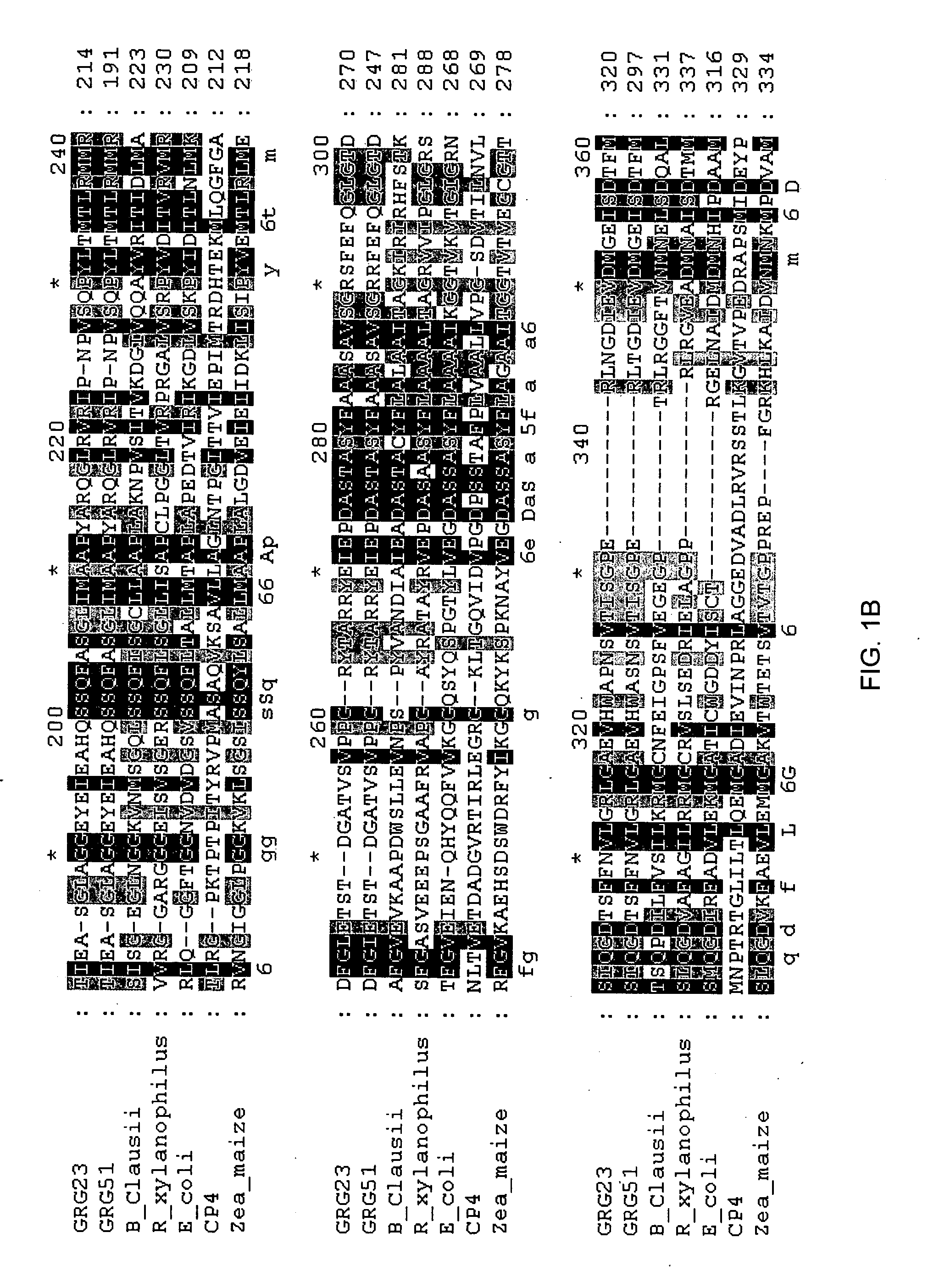
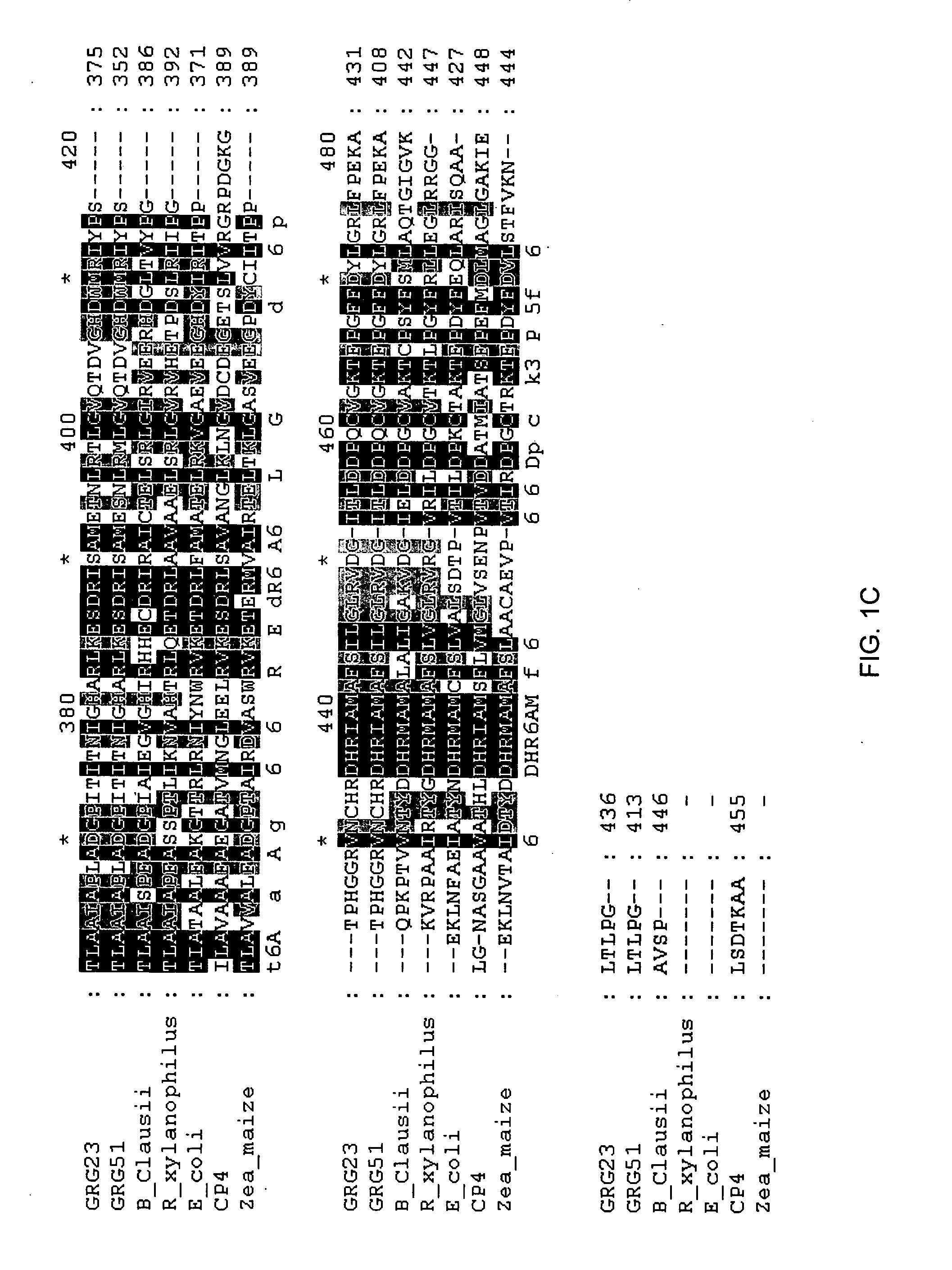
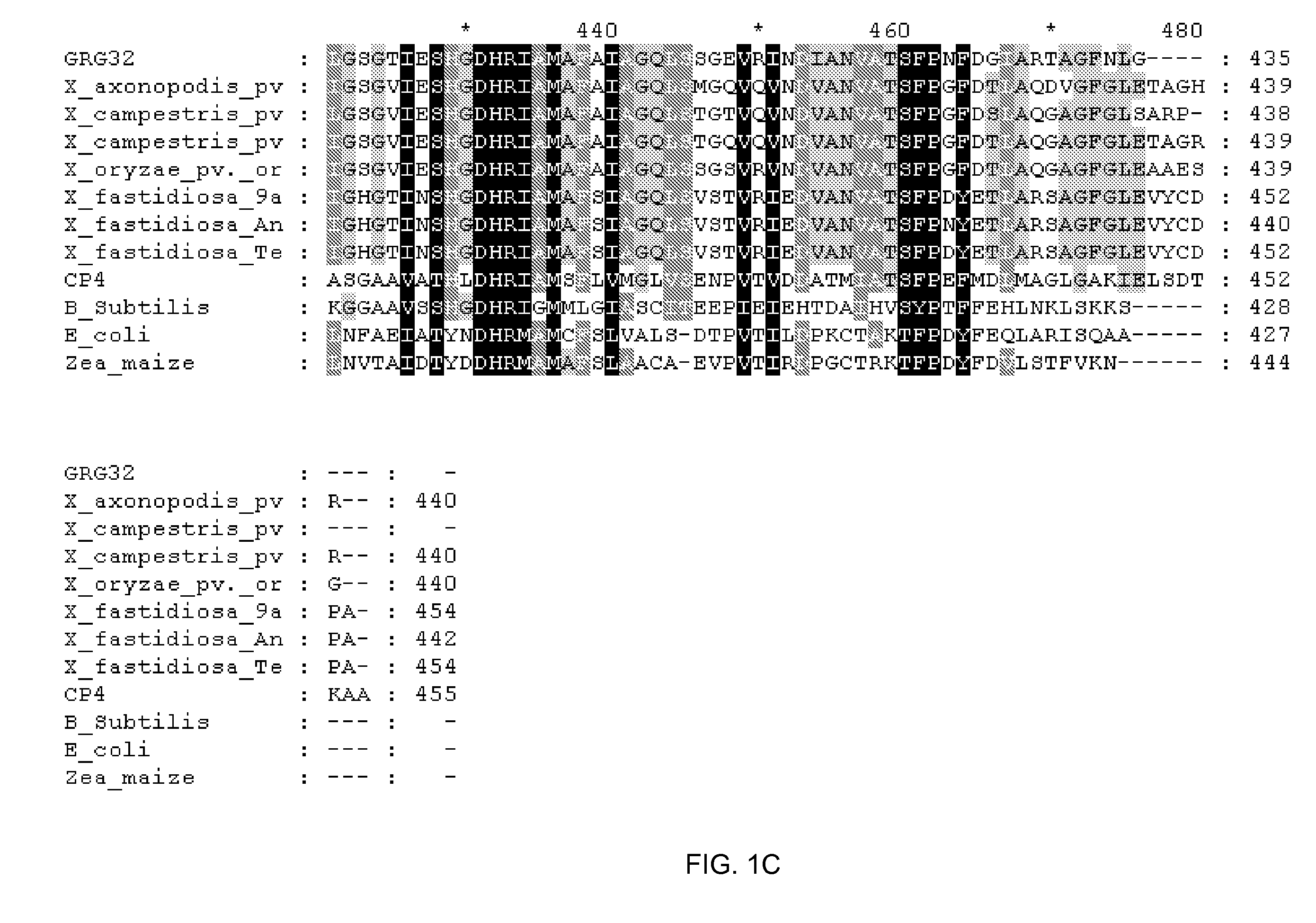
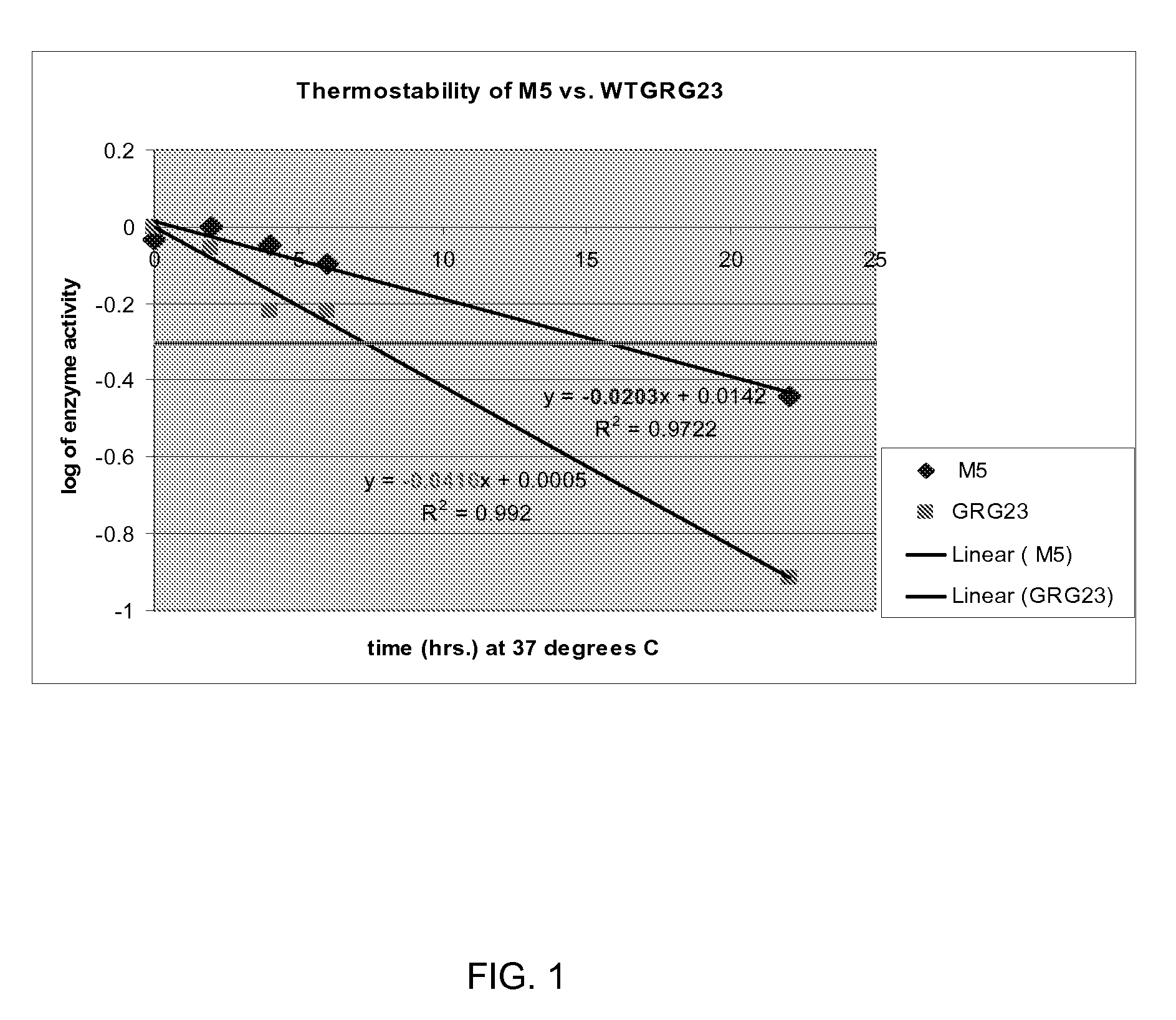
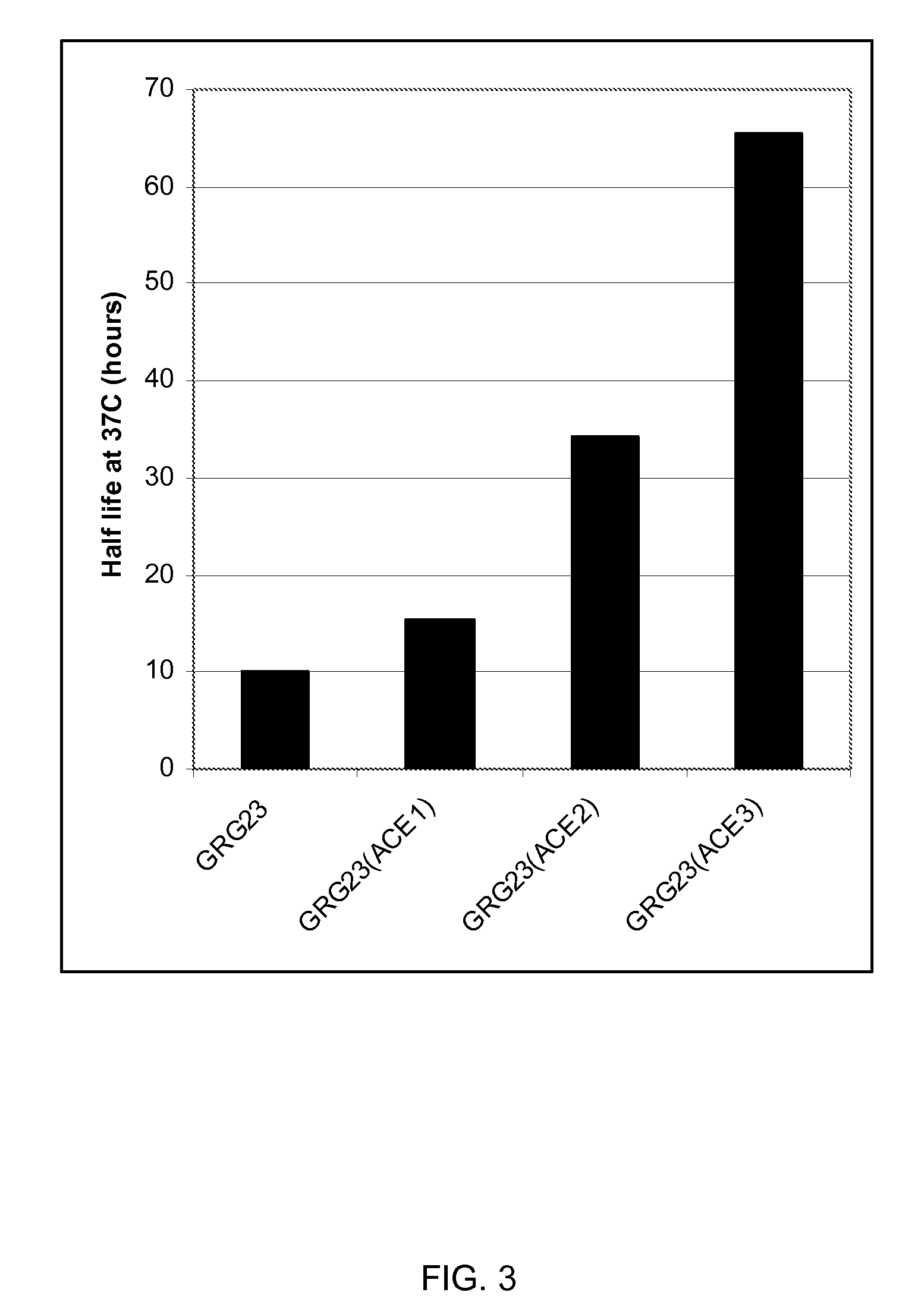
Grg23 and grg51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
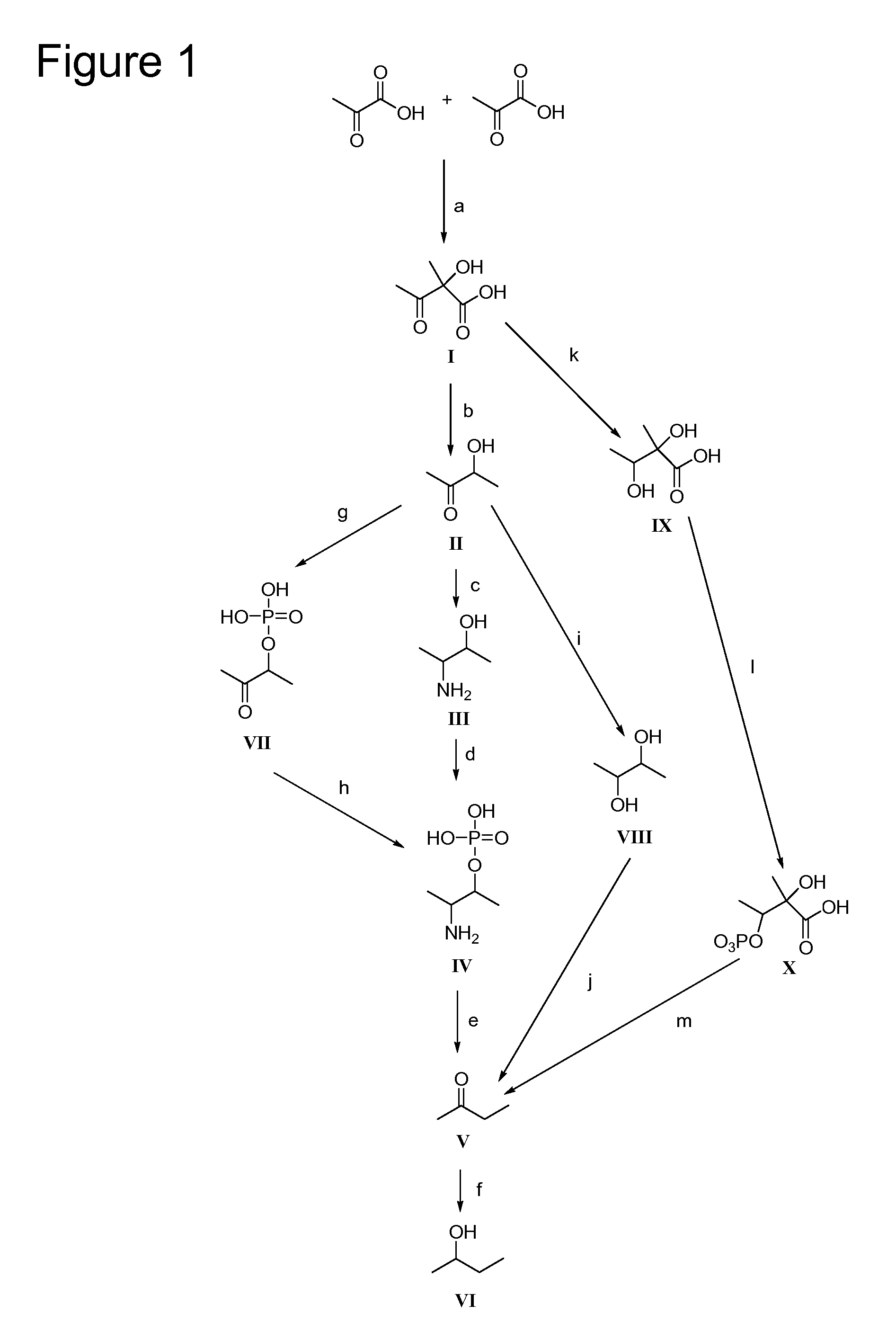
Fermentive production of four carbon alcohols
Methods for the fermentive production of four carbon alcohols are provided. Specifically, butanol, preferably 2-butanol is produced by the fermentive growth of a recombinant bacteria expressing a 2-butanol biosynthetic pathway. The recombinant microorganisms and methods of the invention can also be adapted to produce 2-butanone, an intermediate in the 2-butanol biosynthetic pathways disclosed herein.
Owner:GEVO INC
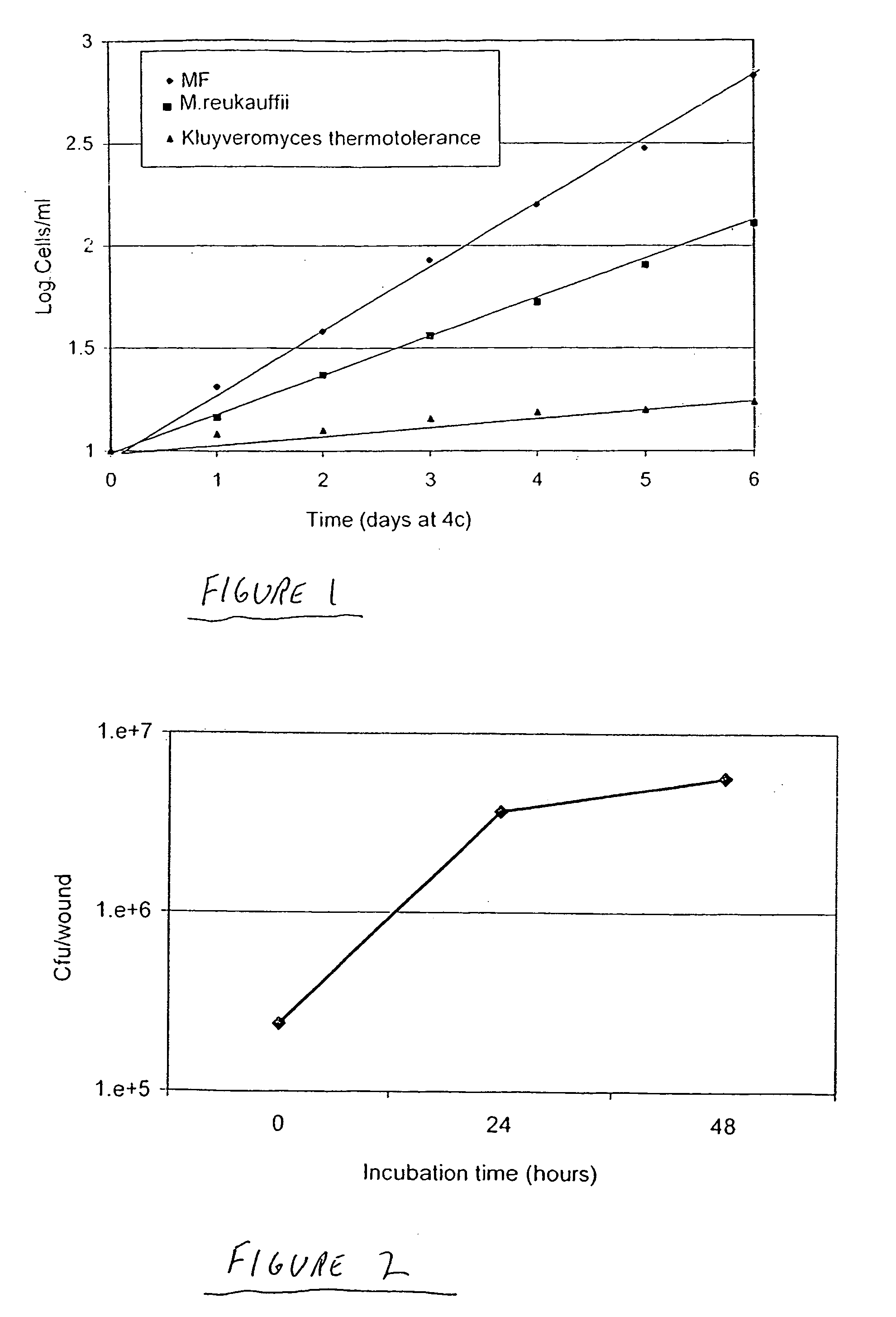
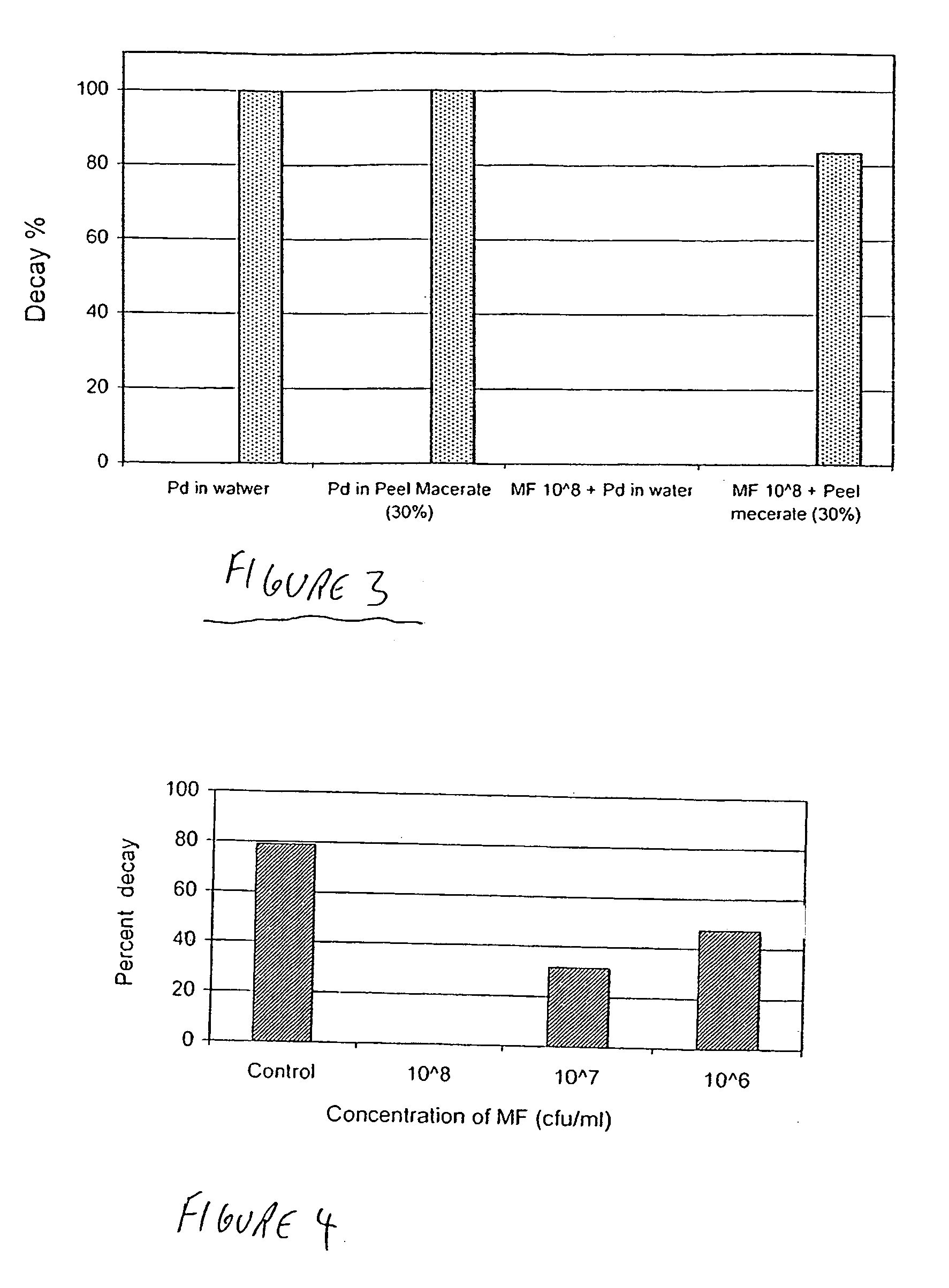
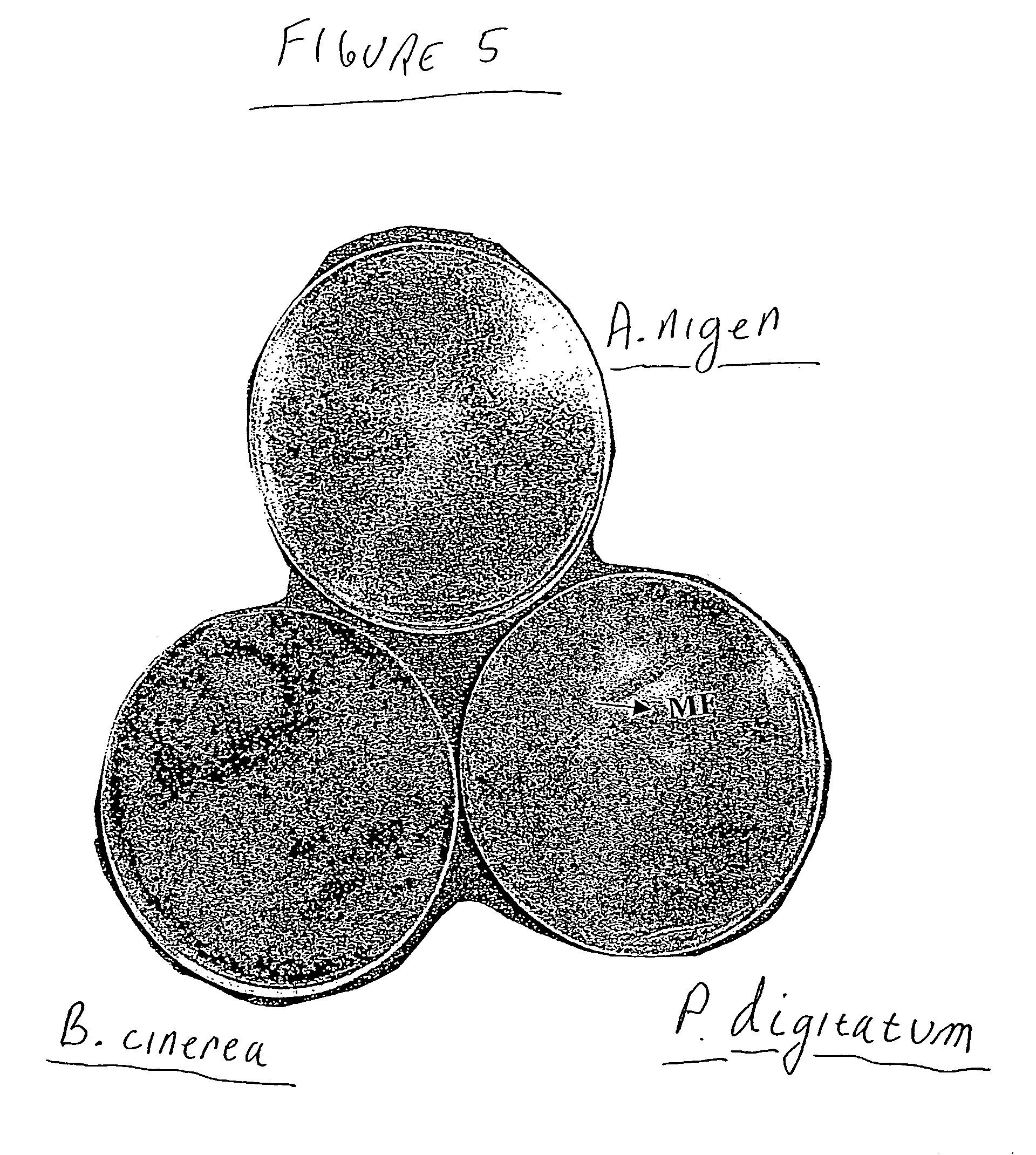
Yeast Metschnikowia fructicola NRRL Y-30752 for inhibiting deleterious microorganisms on plants
A biologically pure culture of a yeast of the species Metschnikowia fructicola. The yeast is identified as NRRL Y-30752 and is capable of inhibiting growth of a deleterious micro-organism on a portion of a plant to which a biologically effective amount of a culture of the yeast is applied. Further disclosed is a composition for use in protection of agricultural produce including a biologically effective amount of Metschnikowia fructicola and a carrier. Further disclosed is an article of manufacture including packaging material and the disclosed composition which is identified for use in protection of agricultural produce from a deleterious micro-organism. Further disclosed is a method of inhibiting growth of a deleterious micro-organism on a portion of a plant including applying at least one time an agriculturally effective amount of yeast of the genus Metschnikowia to the portion of a plant.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL THE - MINIST OF AGRI AGRI RES ORG
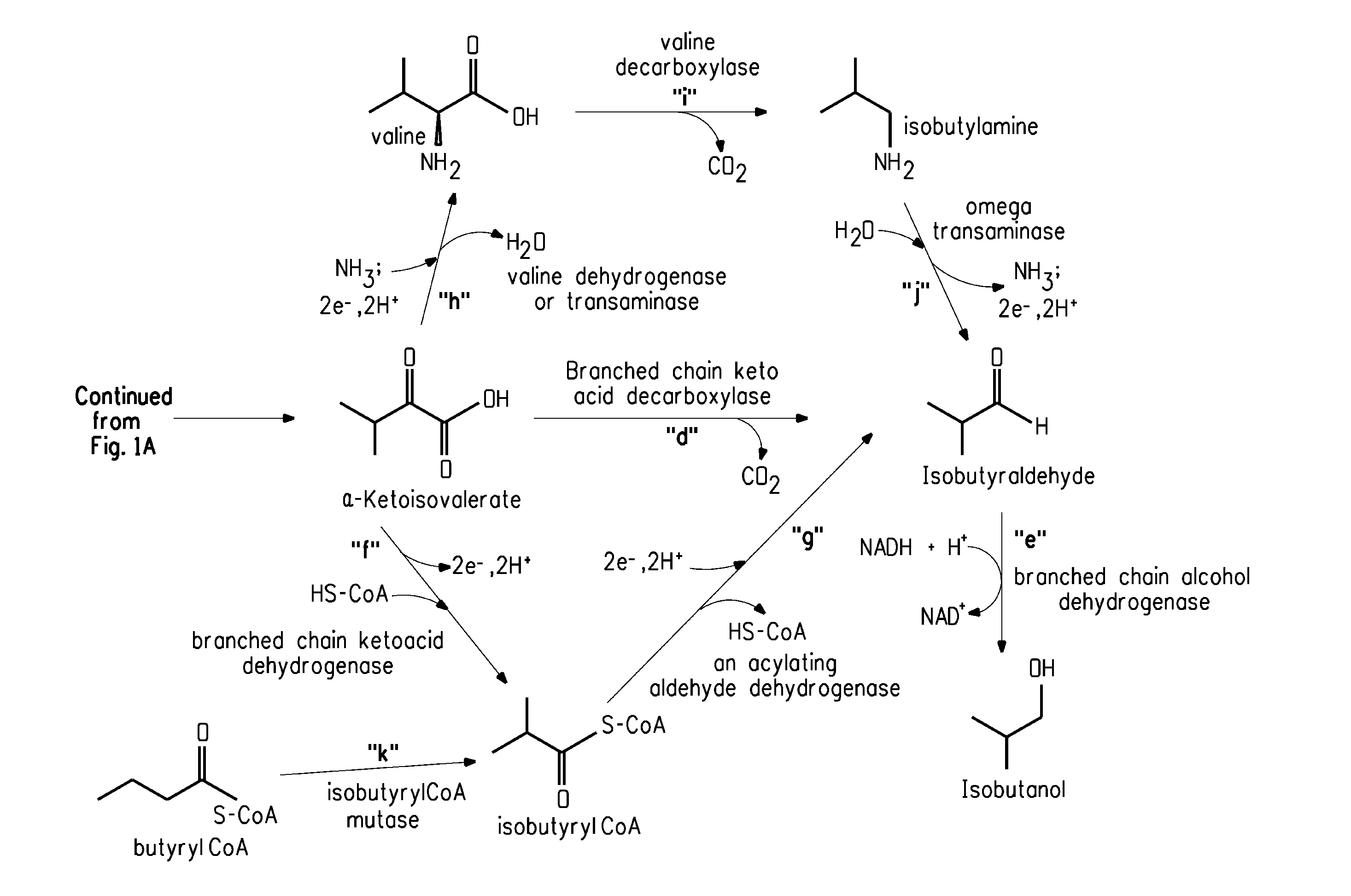
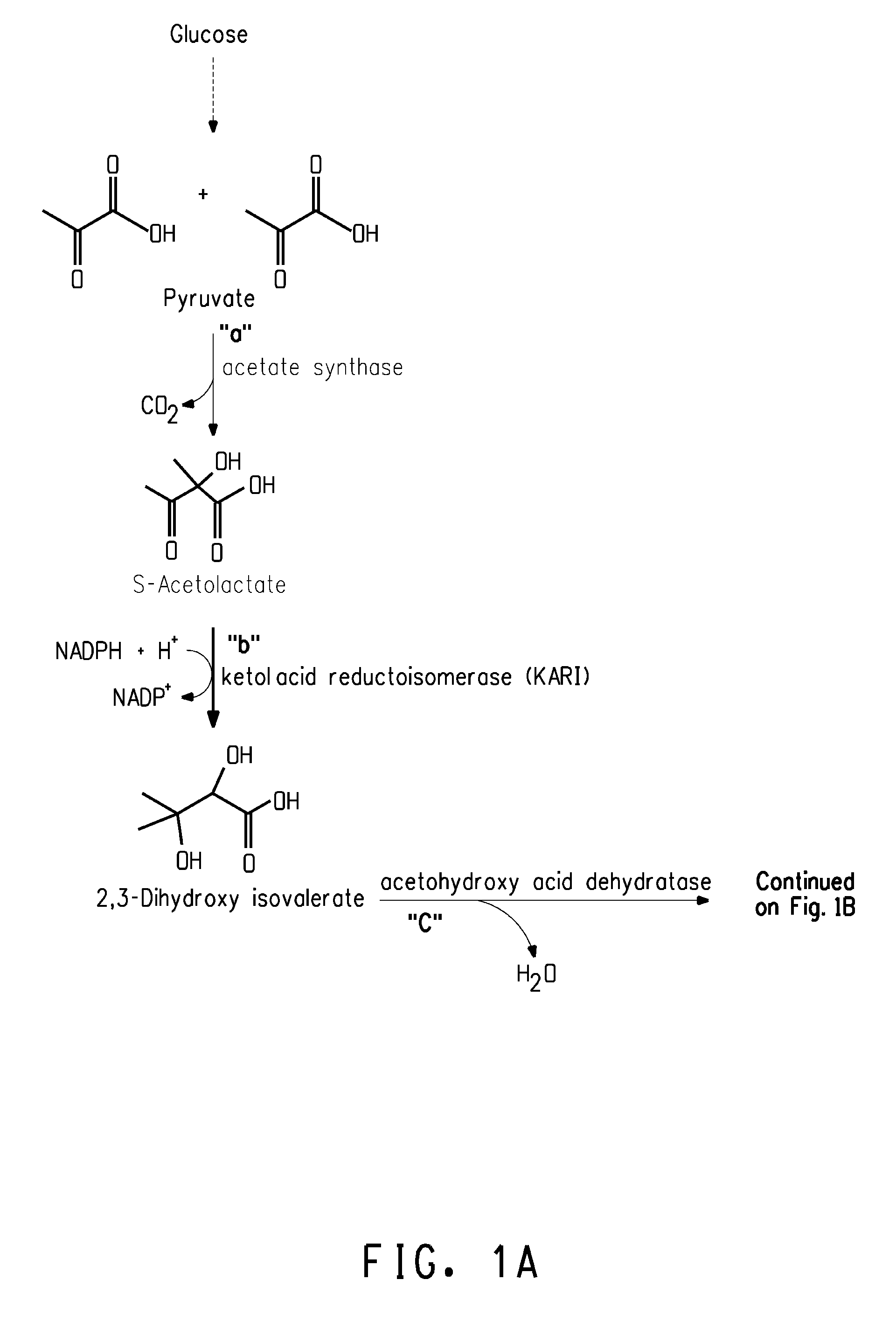
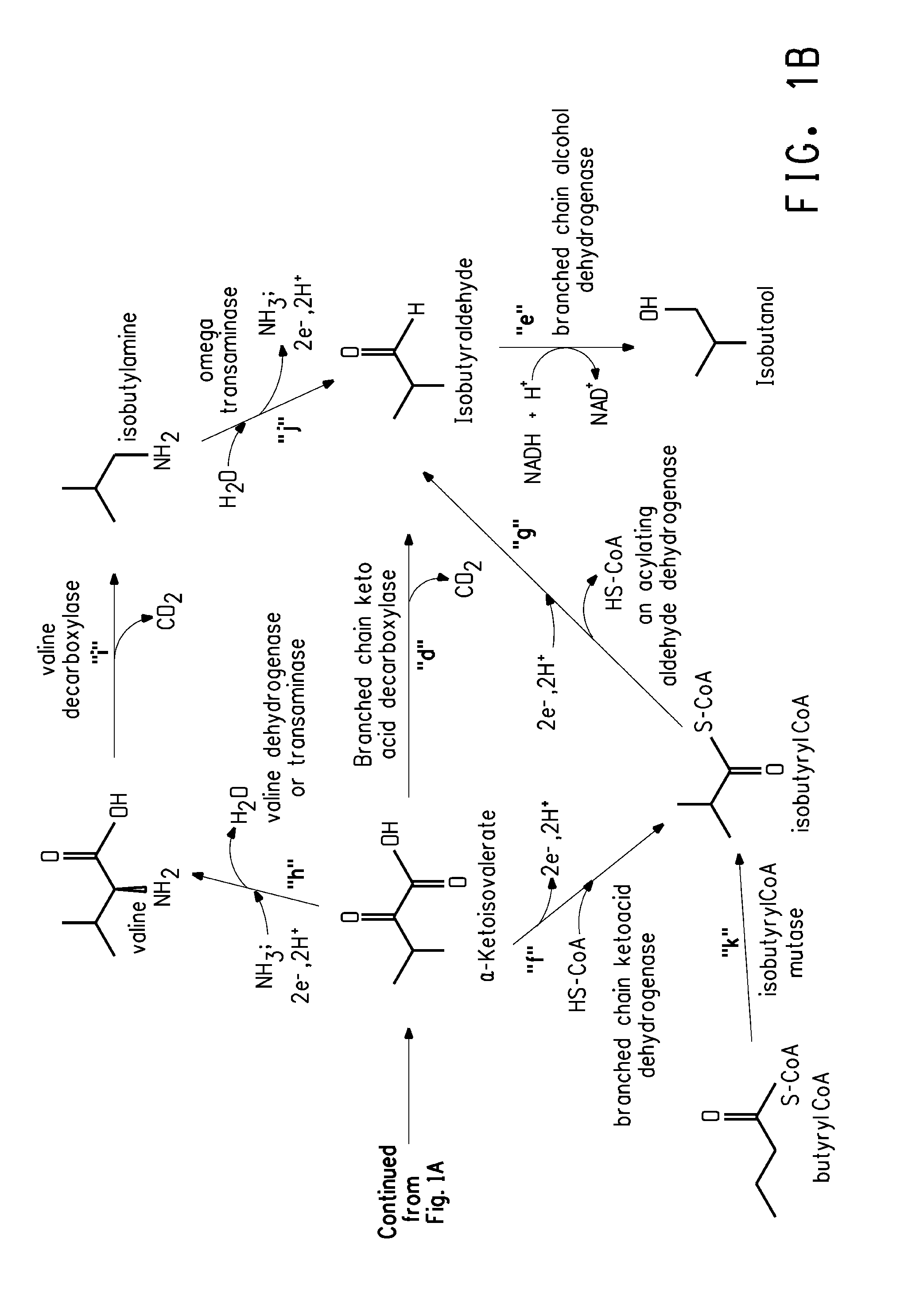
Fermentive production of isobutanol using highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzymes
Methods for the fermentative production of isobutanol is provided by the fermentative growth of a recombinant microorganism expressing a highly active ketol-acid reductoisomerase enzyme in addition to other enzymes required for conversion of glucose to isobutanol.
Owner:GEVO INC
Fermentive production of four carbon alcohols
Methods for the fermentive production of four carbon alcohols are provided. Specifically, butanol, preferably 2-butanol is produced by the fermentive growth of a recombinant bacteria expressing a 2-butanol biosynthetic pathway. The recombinant microorganisms and methods of the invention can also be adapted to produce 2-butanone, an intermediate in the 2-butanol biosynthetic pathways disclosed herein.
Owner:GEVO INC
Bioconversion of a fermentable carbon source to 1,3-propanediol by a single microorganism
A new polypropylene terephthalate composition is provided. The polypropylene terephthalate is comprised of 1,3-propanediol and terephthalate. The 1,3-propanediol is produced by the bioconversion of a fermentatble carbon source, preferable glucose. The resulting polypropylene terephthalate is distinguished from petrochemically produced polymer on the basis of dual carbon-isotopic fingerprinting which indicates both the source and the age of the carbon.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
GRG23 and GRG 51 genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 4, or 6, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, or 5. The present invention additionally provides a method to measure enzyme kinetic activity using fluorogenic substrates.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
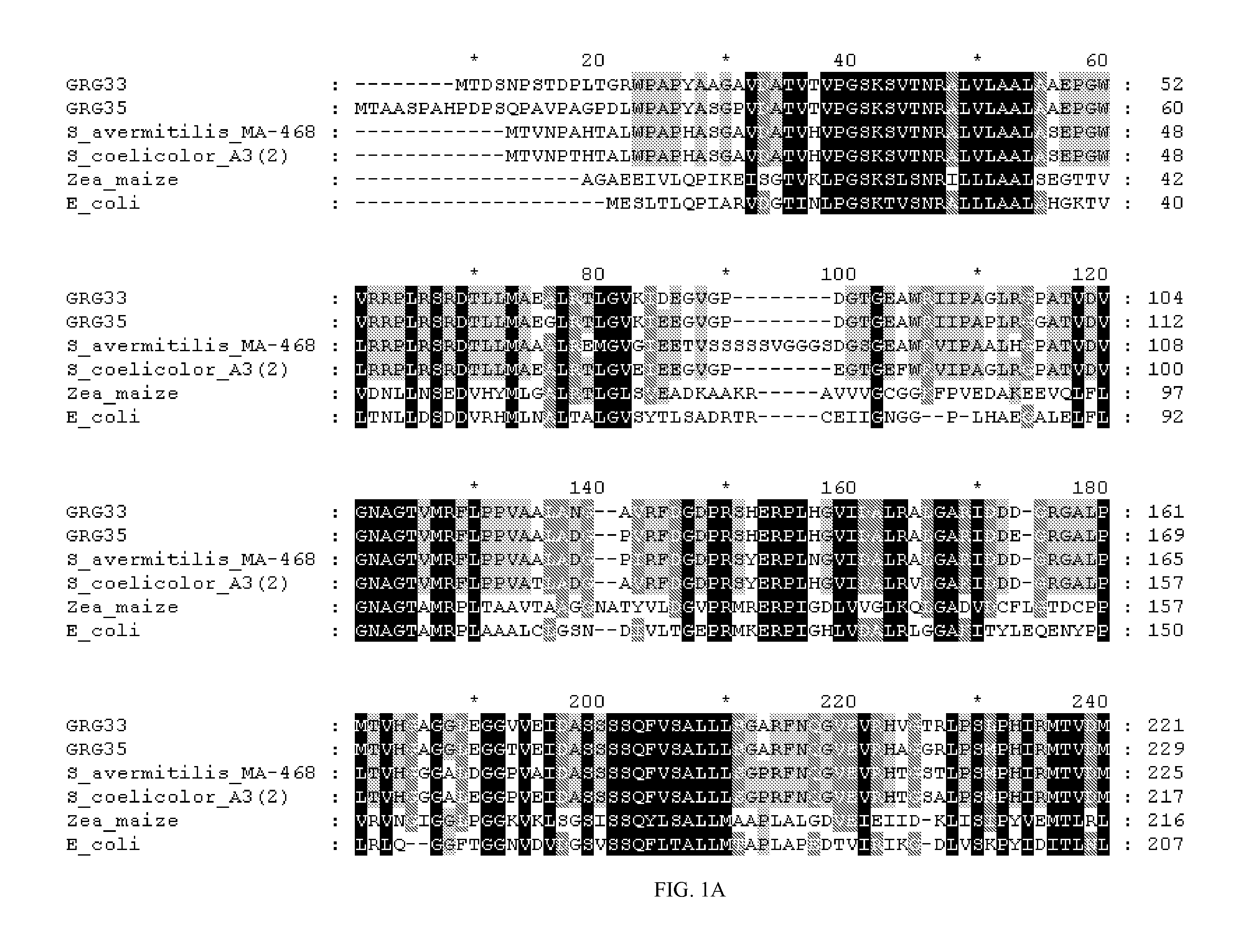
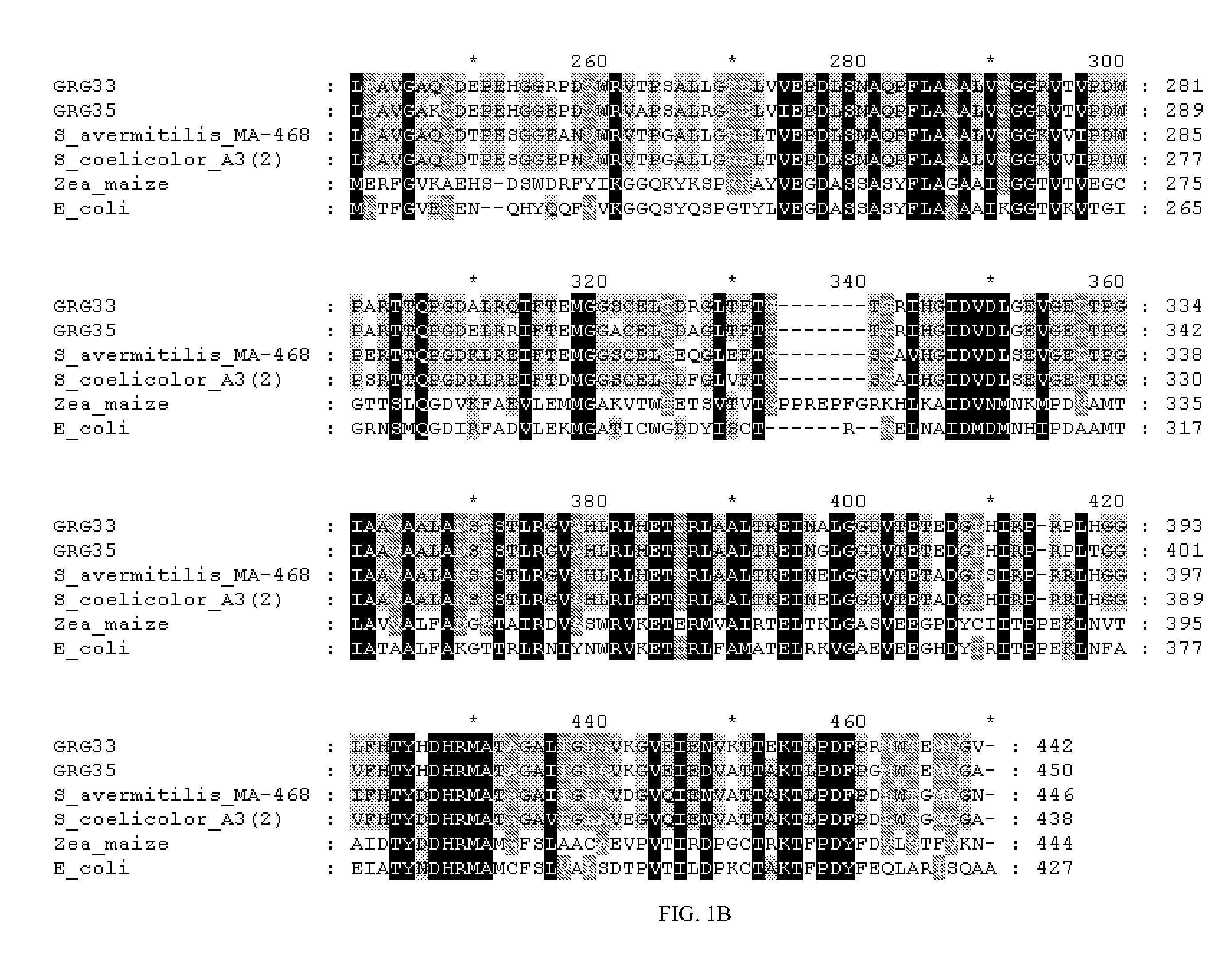
Grg33, grg35, grg36, grg37, grg38, grg39 and grg50: novel epsp synthase genes conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, or 23, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 16, 19, or 22, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30932, B-30933, B-30934, B-30945, B-30946, B-30947, or B-30948, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
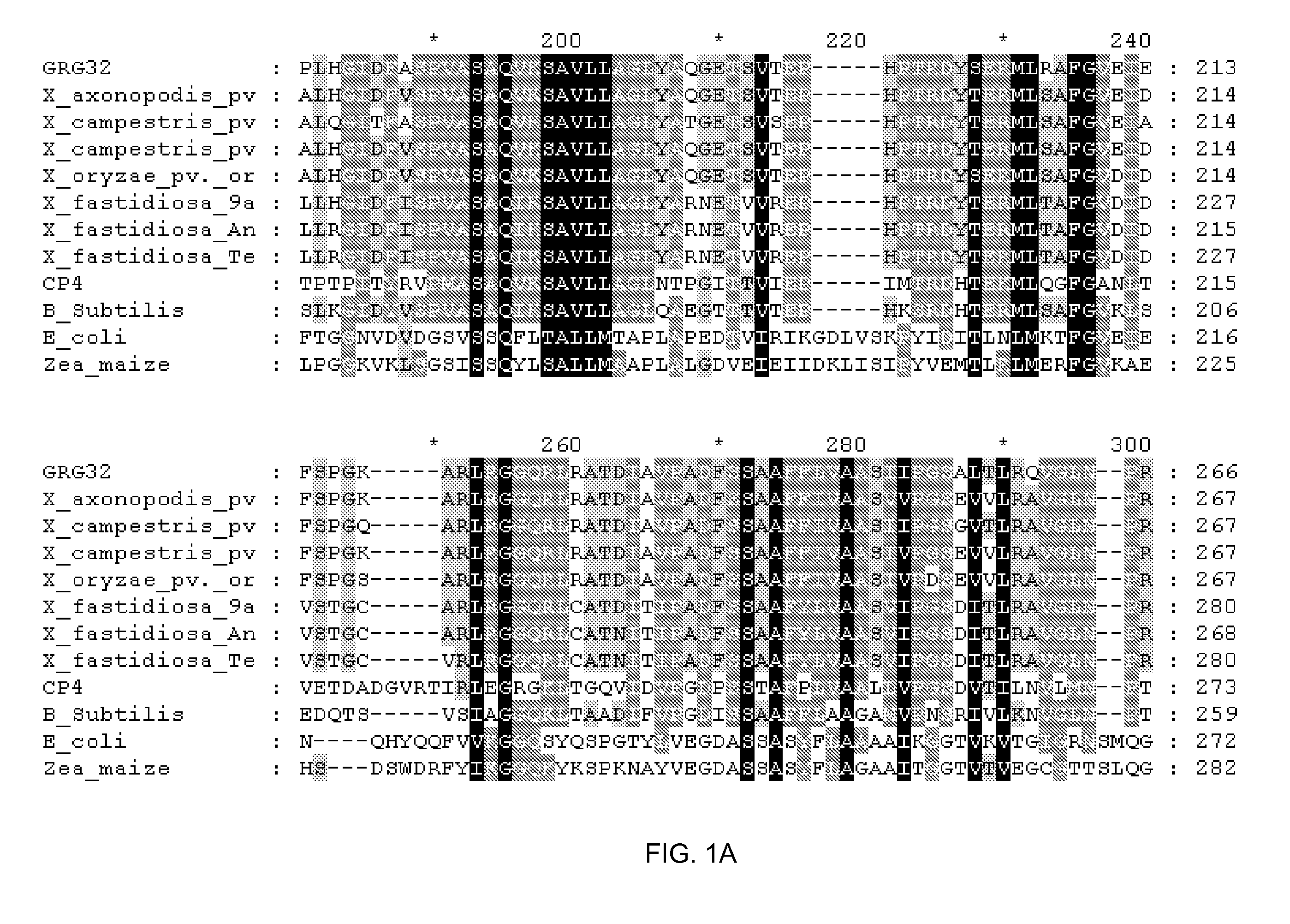
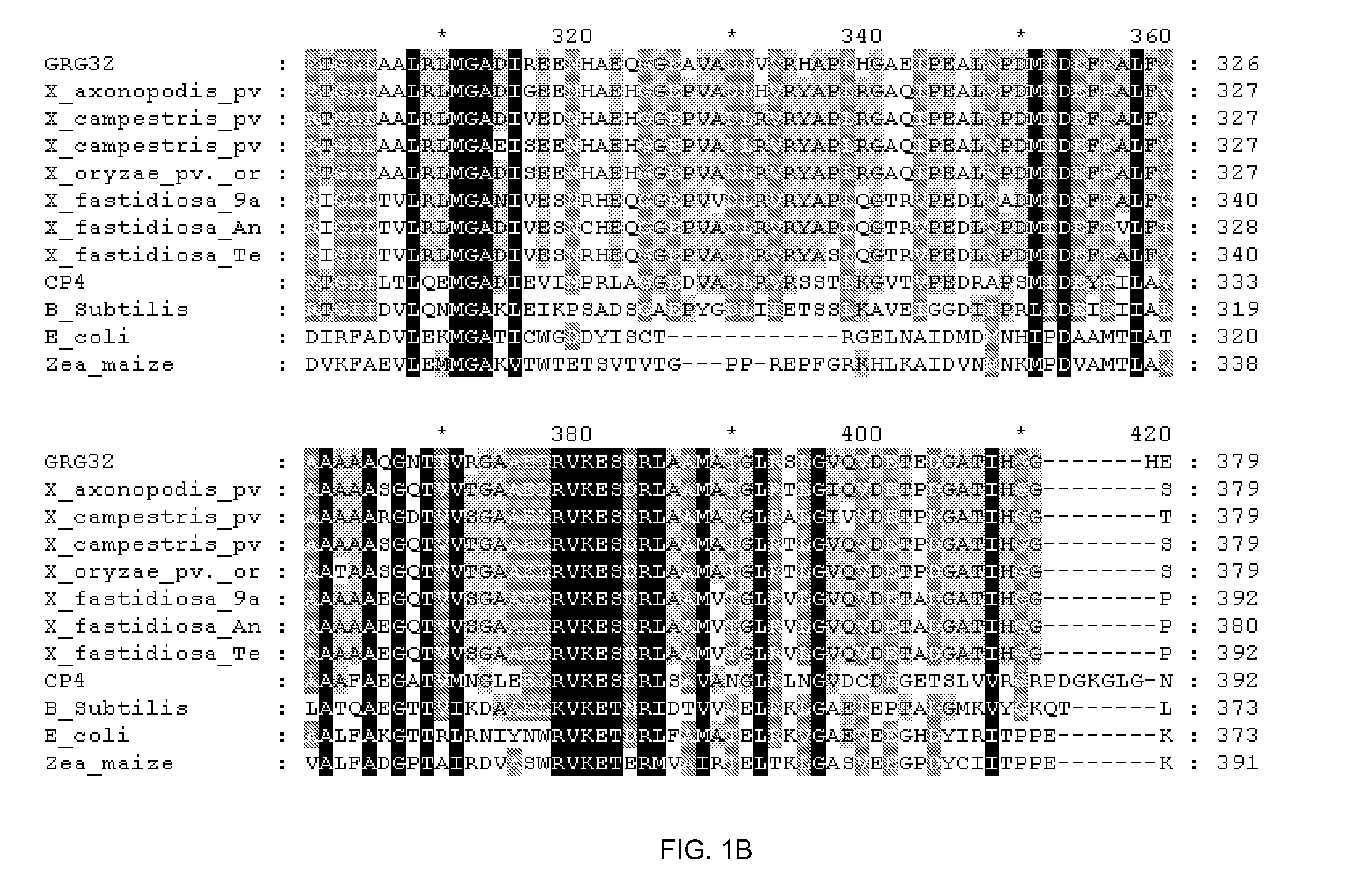
Grg32: a novel epsp synthase gene conferring herbicide resistance
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include nucleic acid molecules encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those nucleic acid molecules, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 or 14, a nucleotide sequence encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, the herbicide resistance nucleotide sequence deposited in a bacterial host as Accession Nos. NRRL B-30931, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Grg23 epsp synthases: compositions and methods of use
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions include polynucleotides encoding herbicide resistance or tolerance polypeptides, vectors comprising those polynucleotides, and host cells comprising the vectors. The nucleotide sequences of the invention can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in organisms, including microorganisms and plants. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated polynucleotides encoding glyphosate resistance or tolerance polypeptides are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated polynucleotides containing nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, or 35, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, or 34.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Gut microbiome as a biomarker and therapeutic target for treating obesity or an obesity related disorder
InactiveUS20100172874A1Decreasing energy harvestingGood for weight lossBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseMicroorganism
The present invention relates to the gut microbiome as a biomarker and therapeutic target for energy harvesting, weight loss or gain, and / or obesity in a subject. In particular, the invention provides methods of altering and monitoring the relative abundance of Bacteroides and Firmicutes in the gut microbiome of a subject.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
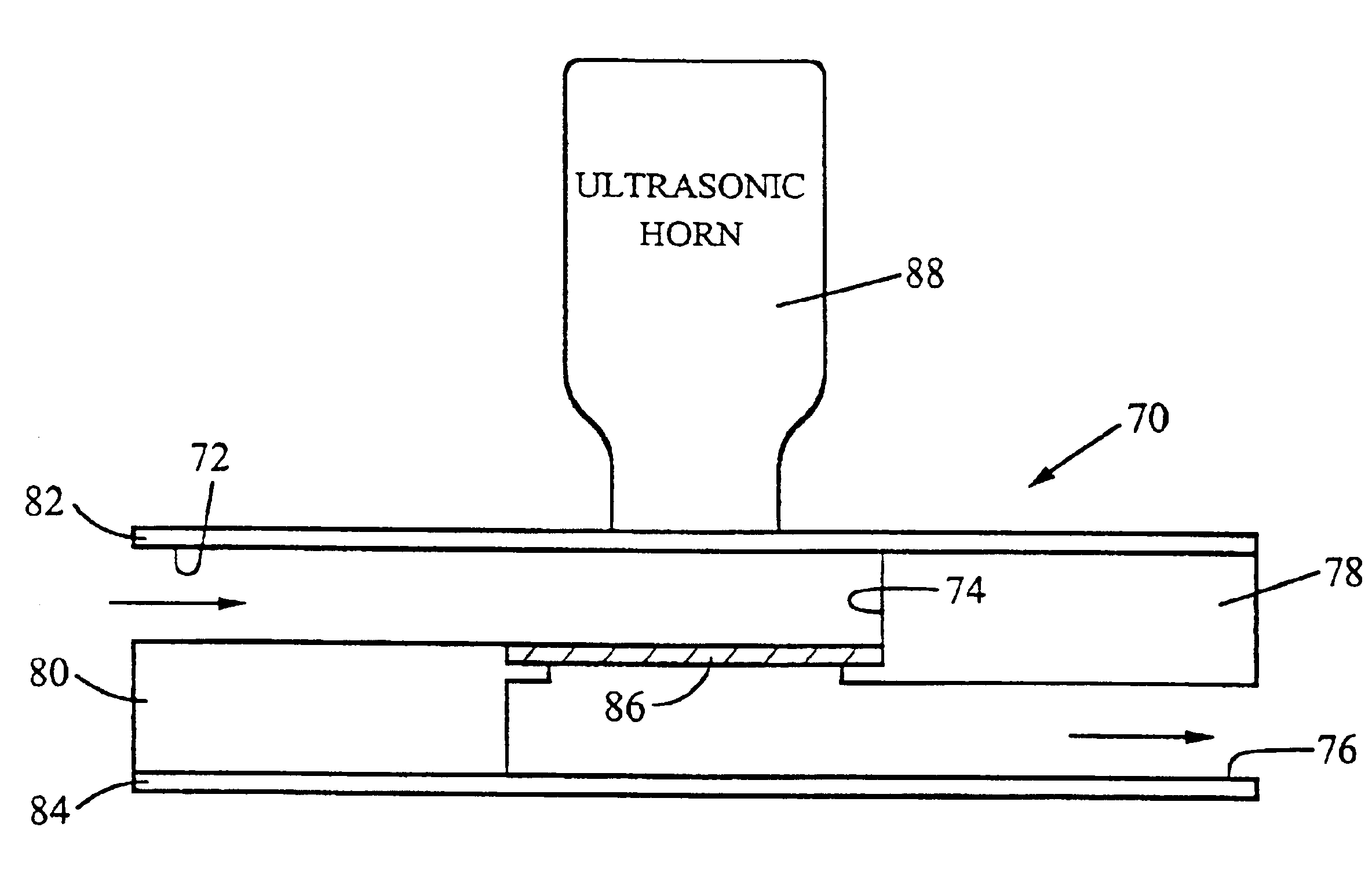
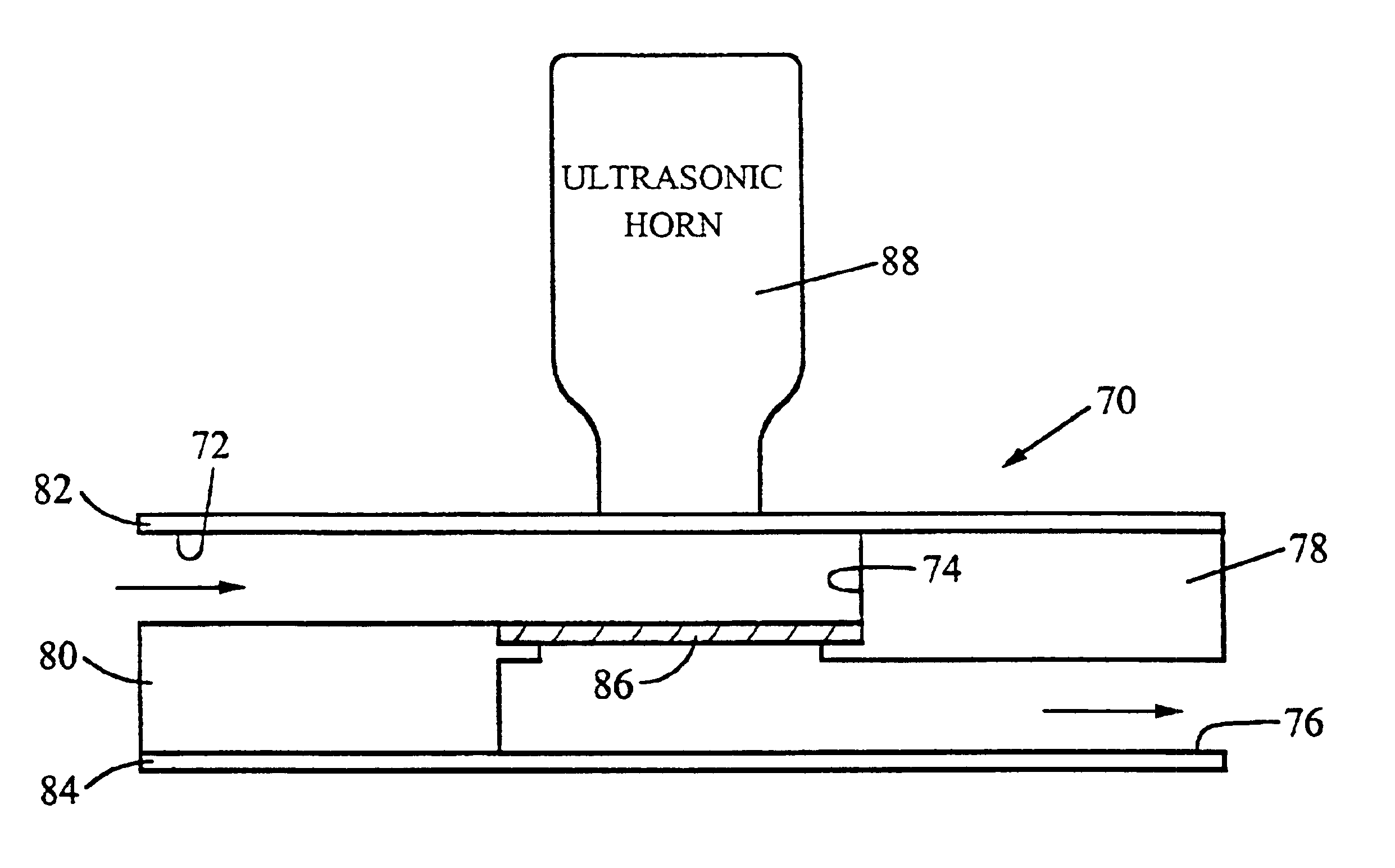
Device for lysing cells, spores, or microorganisms
InactiveUS6878540B2Improve convenienceImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismSpore
A device for use with an ultrasonic transducer to lyse components of a fluid sample comprises a cartridge having a lysing chamber, an inlet port in fluid communication with the lysing chamber, and an outlet port for exit of the sample from the lysing chamber. The inlet and outlet ports are positioned to permit flow of the sample through the lysing chamber, and the chamber contains at least one solid phase for capturing the sample components to be lysed as the sample flows through the chamber. The lysing chamber is defined by at least one wall having an external surface for contacting the transducer to effect the transfer of ultrasonic energy to the chamber.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Process for preparing materials for extraction
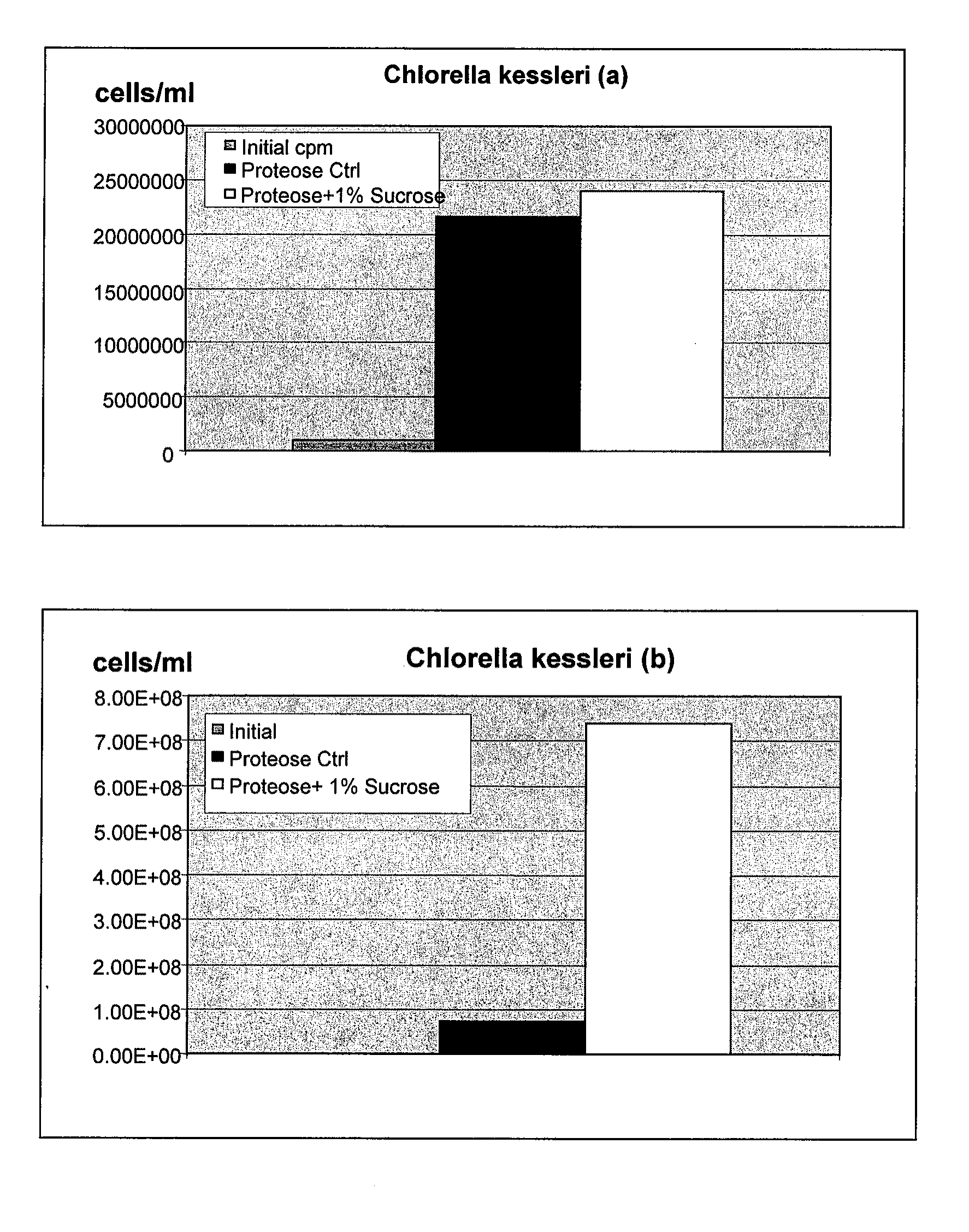
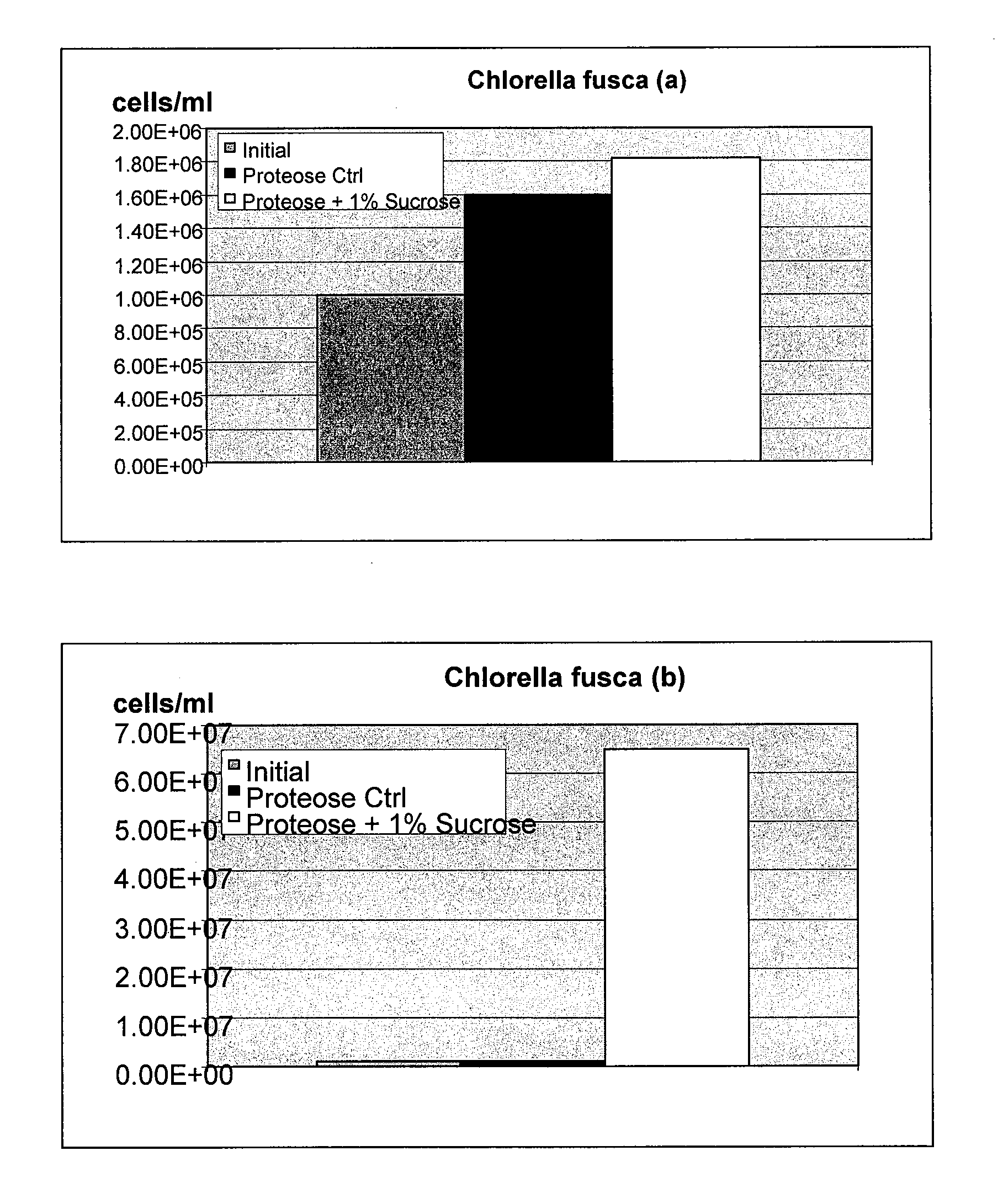
InactiveUS20060122410A1Improve extraction efficiencyQuality improvementFungiUnicellular algaeArachidonic acid supplementationFermentation
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a biomass, such as from a microbial fermentation, for an extraction process to separate desired chemicals, nutritional products, bioactive components, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, from the biomass. Particularly preferred substances to extract include docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and arachidonic acid. The present invention also includes extracting the prepared biomass. Biomasses to be treated in accordance with the methods of the invention include plant, animal, and microbial biomass, particularly a microorganism such as Crypthecodinium cohnii and a fungus such as Mortierella alpina.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Tuning microbial populations with programmable nucleases
ActiveUS20150064138A1Efficiently and rapidly encoded into synthetic constructBroad deliveryBiocideSugar derivativesMicroorganismVirulent characteristics
Various aspects and embodiments of the invention are directed to methods and compositions for reversing antibiotic resistance or virulence in and / or destroying pathogenic microbial cells such as, for example, pathogenic bacterial cells. The methods include exposing microbial cells to a delivery vehicle with at least one nucleic acid encoding an engineered autonomously distributed circuit that contains a programmable nuclease targeted to one or multiple genes of interest.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Codon-optimized genes for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
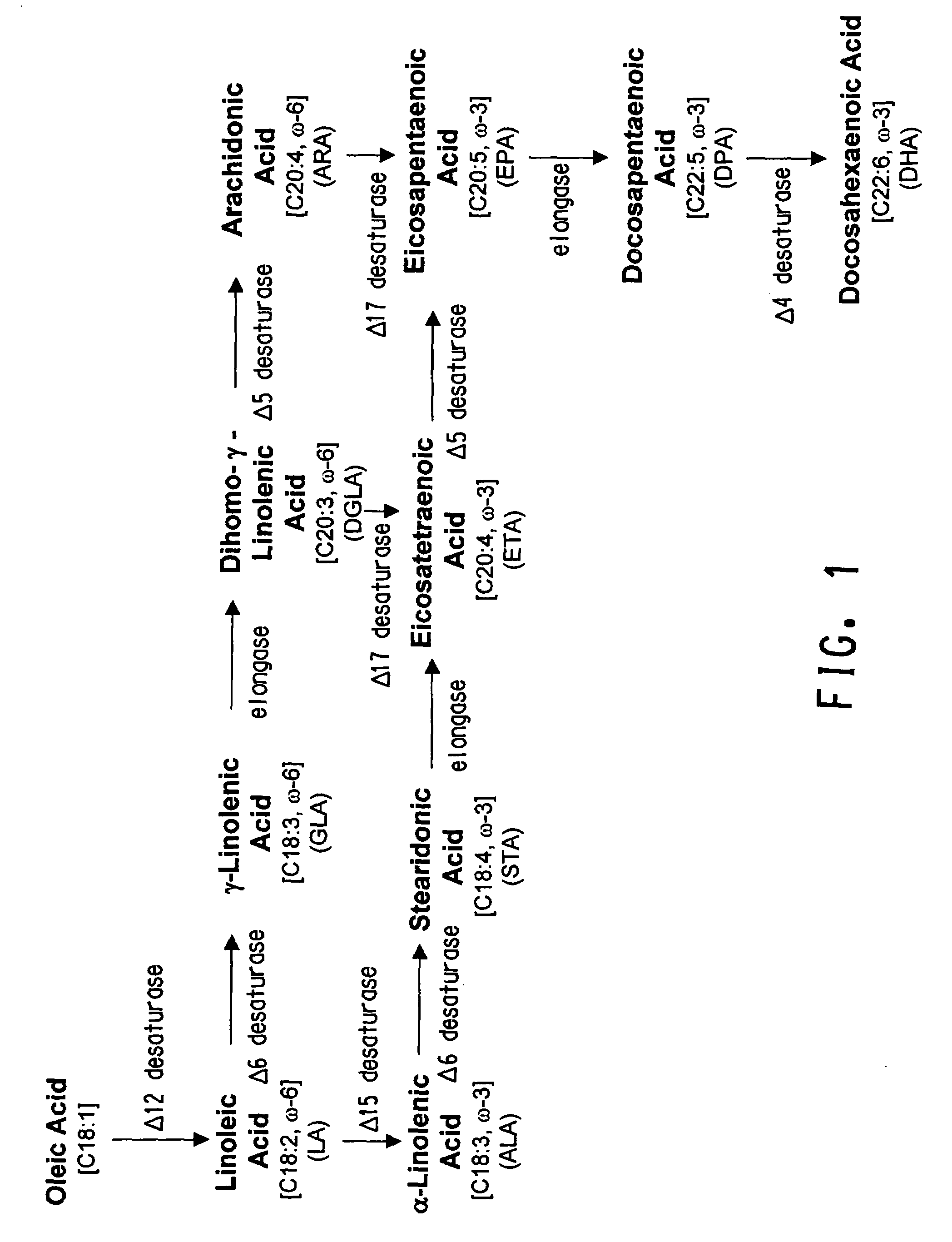
The present invention relates to fatty acid desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to ETA; eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and arachidonic acid (ARA) to EPA. Nucleic acid sequences encoding codon-optimized desaturases and elongases, nucleic acid sequences which hybridize thereto, DNA constructs comprising the codon-optimized desaturase or elongases, and recombinant host microorganisms expressing increased levels of desaturase or elongase are described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Device and method for lysing cells, spores, or microorganisms
InactiveUS6887693B2Simple designImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeMicroorganism
A device for lysing components (e.g., cells, spores, or microorganisms) of a fluid sample comprises a cartridge having a lysing chamber for receiving the sample and having at least one solid phase in the lysing chamber for capturing the sample components to be lysed. An ultrasonic transducer is coupled to a wall of the lysing chamber to transfer ultrasonic energy to the captured sample components.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Bacillus thuringiensis gene with lepidopteran activity
InactiveUS7772465B2High insecticidal activityHigh expressionBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus thuringiensis
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Carbon pathway optimized production hosts for the production of isobutanol
A microbial host cell is provided for the production of isobutanol. Carbon flux in the cell is optimized through the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
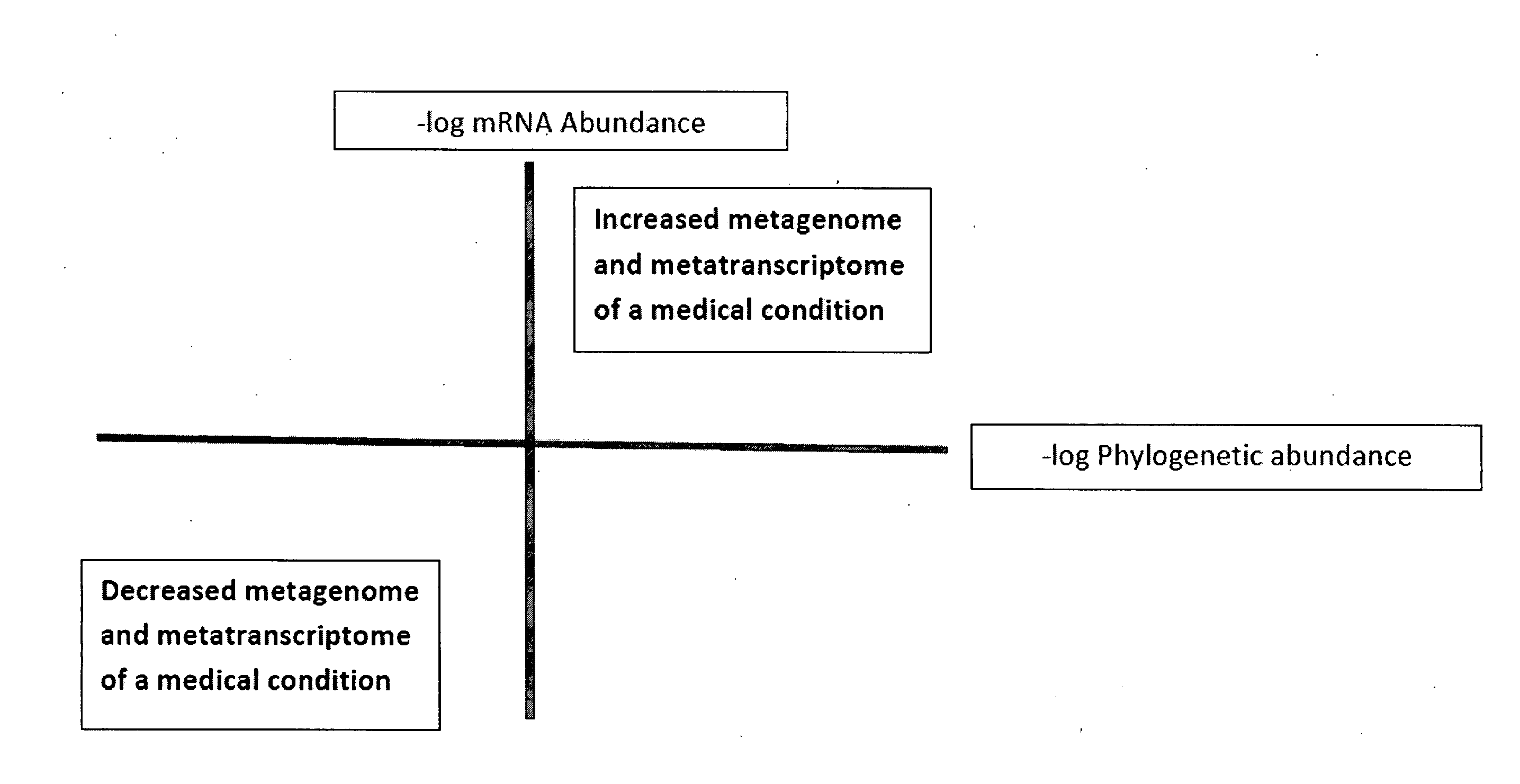
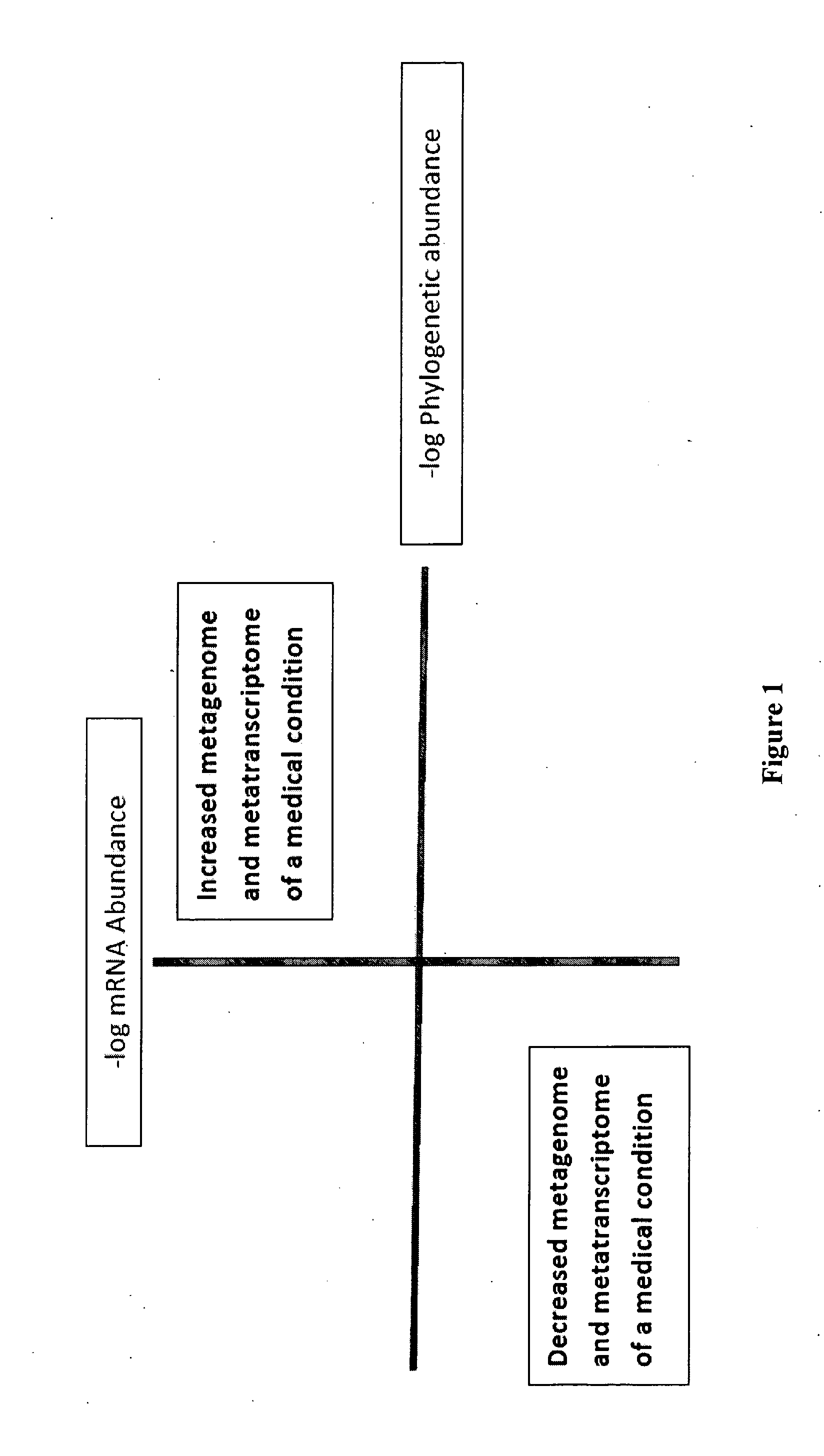
Methods of combining metagenome and the metatranscriptome in multiplex profiles
The present invention describes changes in bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated various mammalian medical conditions. Described are diagnostic tests that arise from combining phylogenetic information about the families, genus, and species of the microbiome and their relative abundance with the metabolic information contained in the metatranscriptome to determine the presence and absence of a disease or medical condition. Provided are compositions of bacteria, co-cultures of bacteria and a carrier for use in treating the disclosed medical conditions. The described compositions restore or correct disease- or medical condition-related imbalances in the microbiome profile with culture-conditioned formulations in which the transcriptome activity of the administered organisms is optimized. Alternatively, formulations of metabolites that drive changes in the metatranscriptome native to the mammal that treat disease or a medical condition or restore health are taught.
Owner:ENSISHEIM PARTNERS
Method for producing butanol using two-phase extractive fermentation
InactiveUS20090305370A1Reformed easilyAvoid impactOrganic compound preparationBiofuelsMicroorganismMicrobiology
A method of making butanol from at least one fermentable carbon source that overcomes the issues of toxicity resulting in an increase in the effective titer, the effective rate, and the effective yield of butanol production by fermentation utilizing a recombinant microbial host wherein the butanol is extracted into specific organic extractants during fermentation
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
Sensitive and rapid determination of antimicrobial susceptibility
ActiveUS20050048599A1Quick checkReduce sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismFiltration
The present invention relates to moving microorganisms to a surface, where they are grown in the presence and absence of antimicrobials, and by monitoring the growth of the microorganisms over time in the two conditions, their susceptibility to the antimicrobials can be determined. The microorganisms can be moved to the surface through electrophoresis, centrifugation or filtration. When the movement involves electrophoresis, the presence of oxidizing and reducing reagents lowers the voltage at which electrophoretic force can be generated and allows a broader range of means by which the target can be detected. Monitoring can comprise optical detection, and most conveniently includes the detection of individual microorganisms. The microorganisms can be stained in order to give information about their response to antimicrobials.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
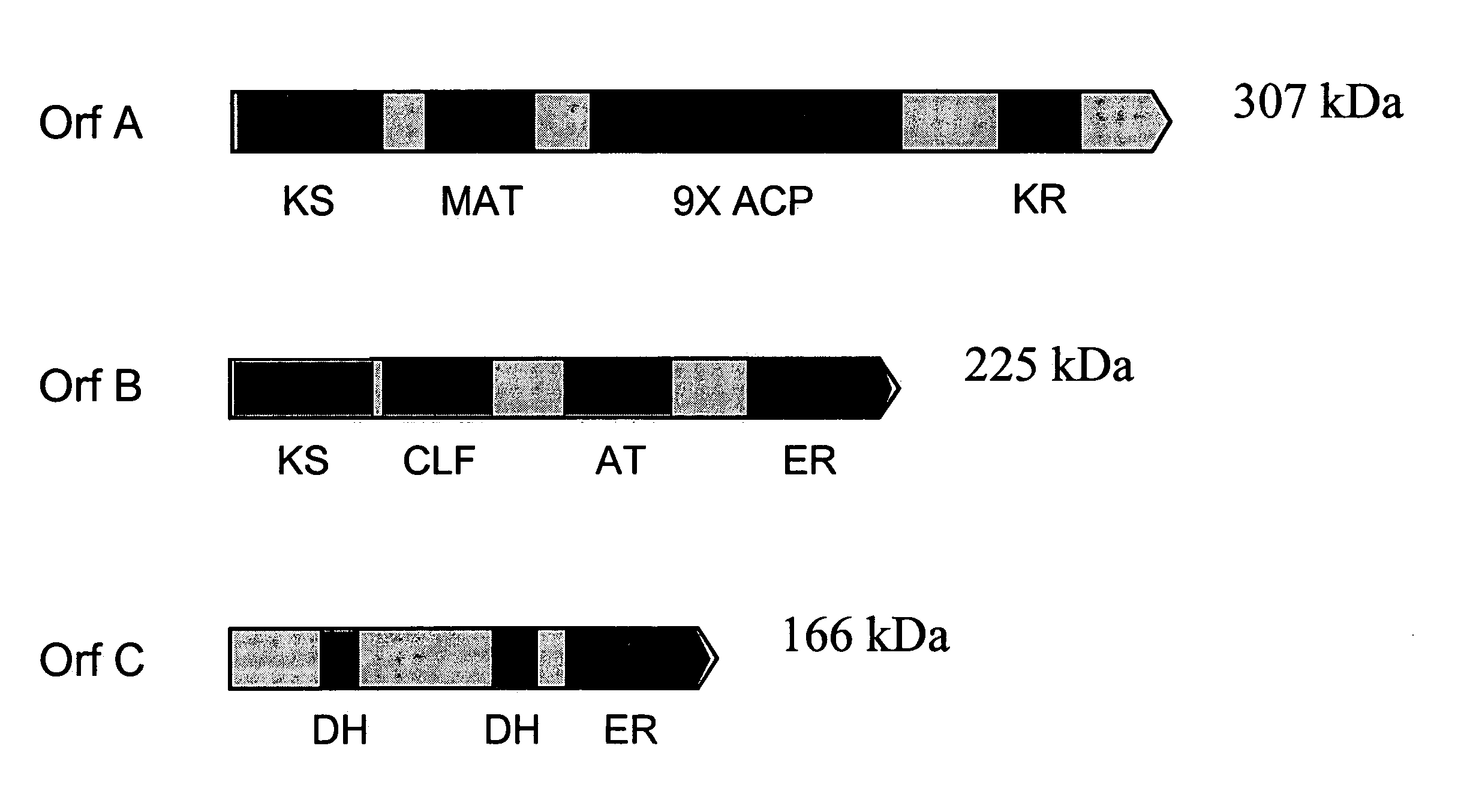
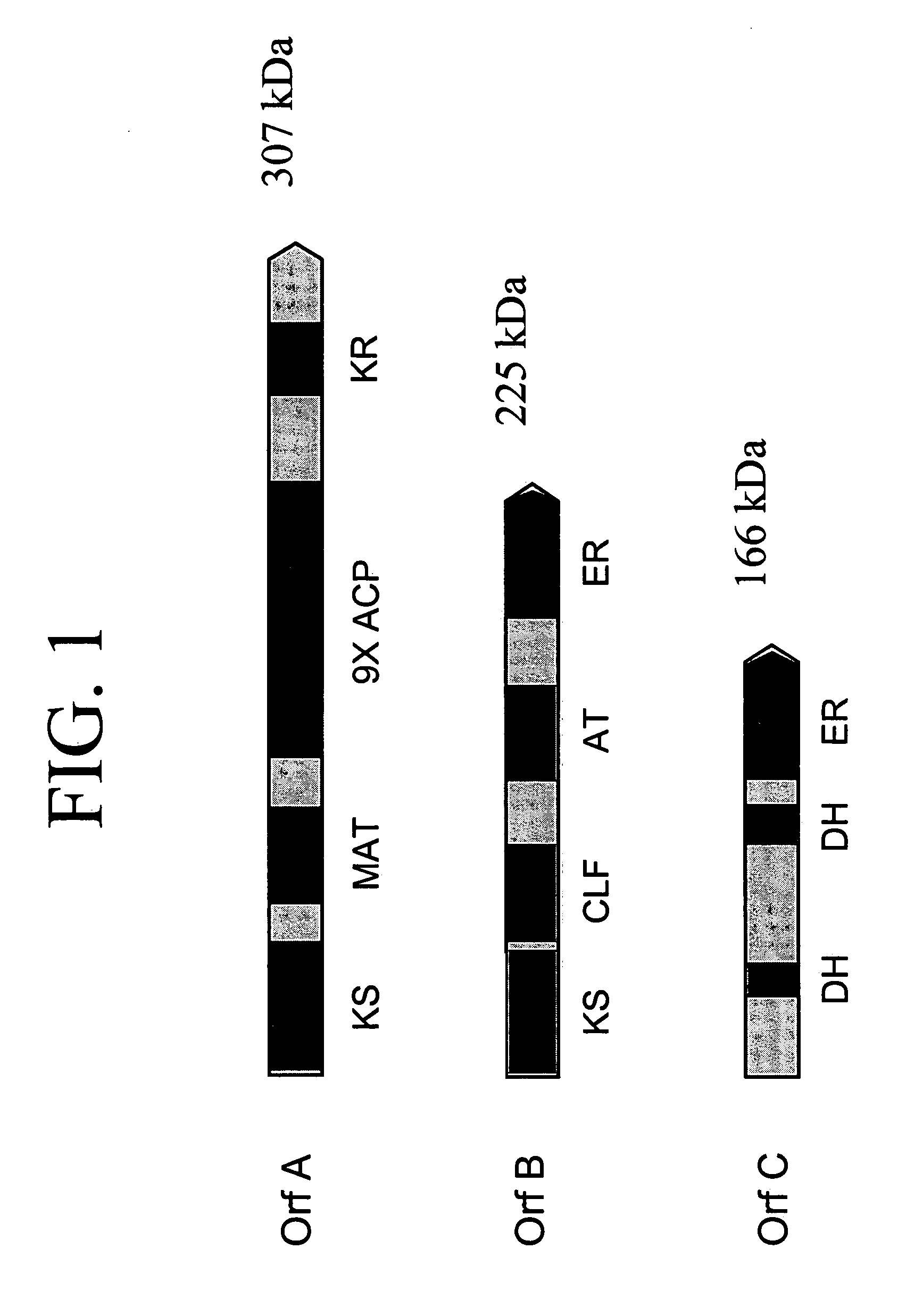
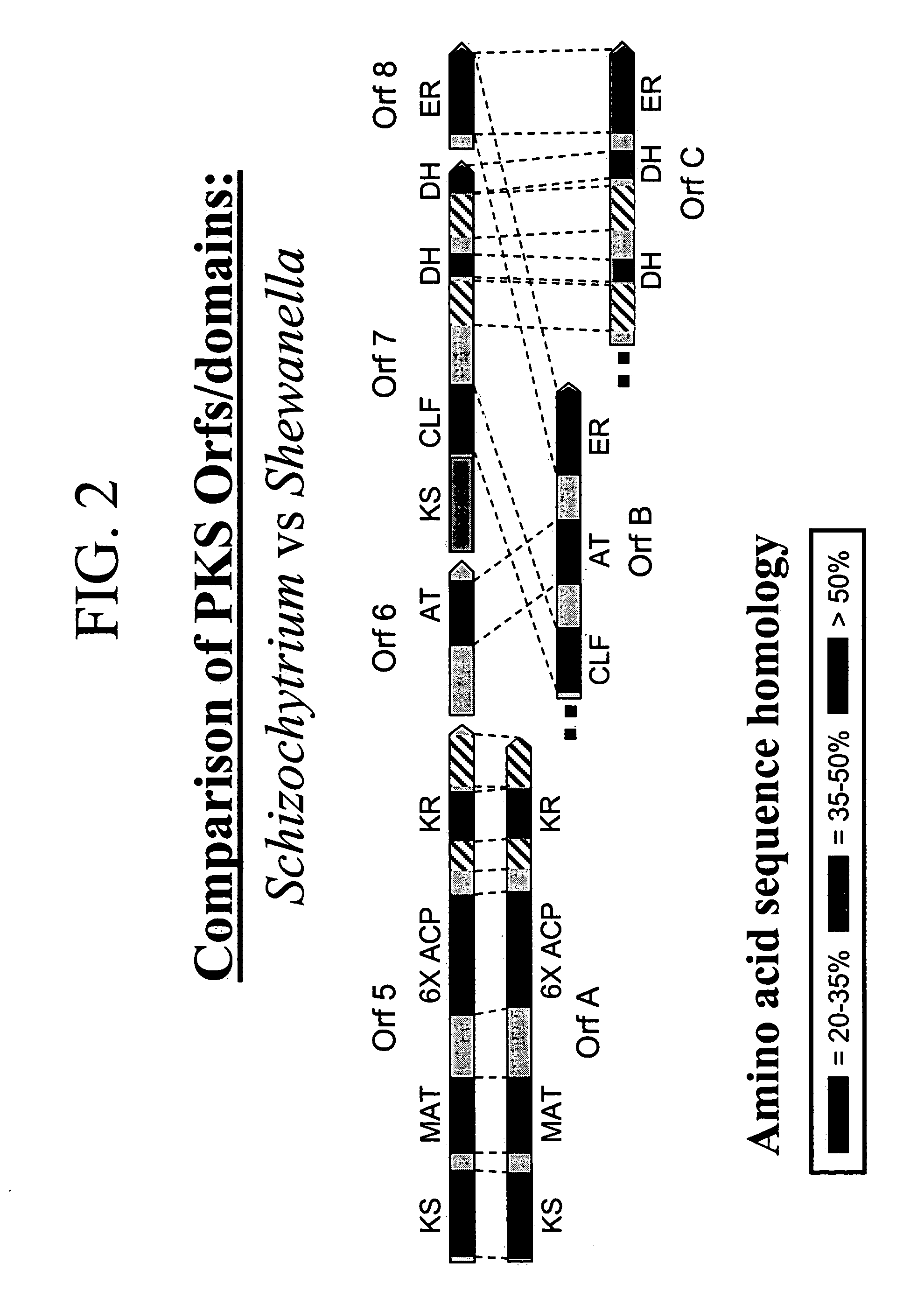
PUFA polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Use of Cellulosic Materials for Cultivation of Microorganisms
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
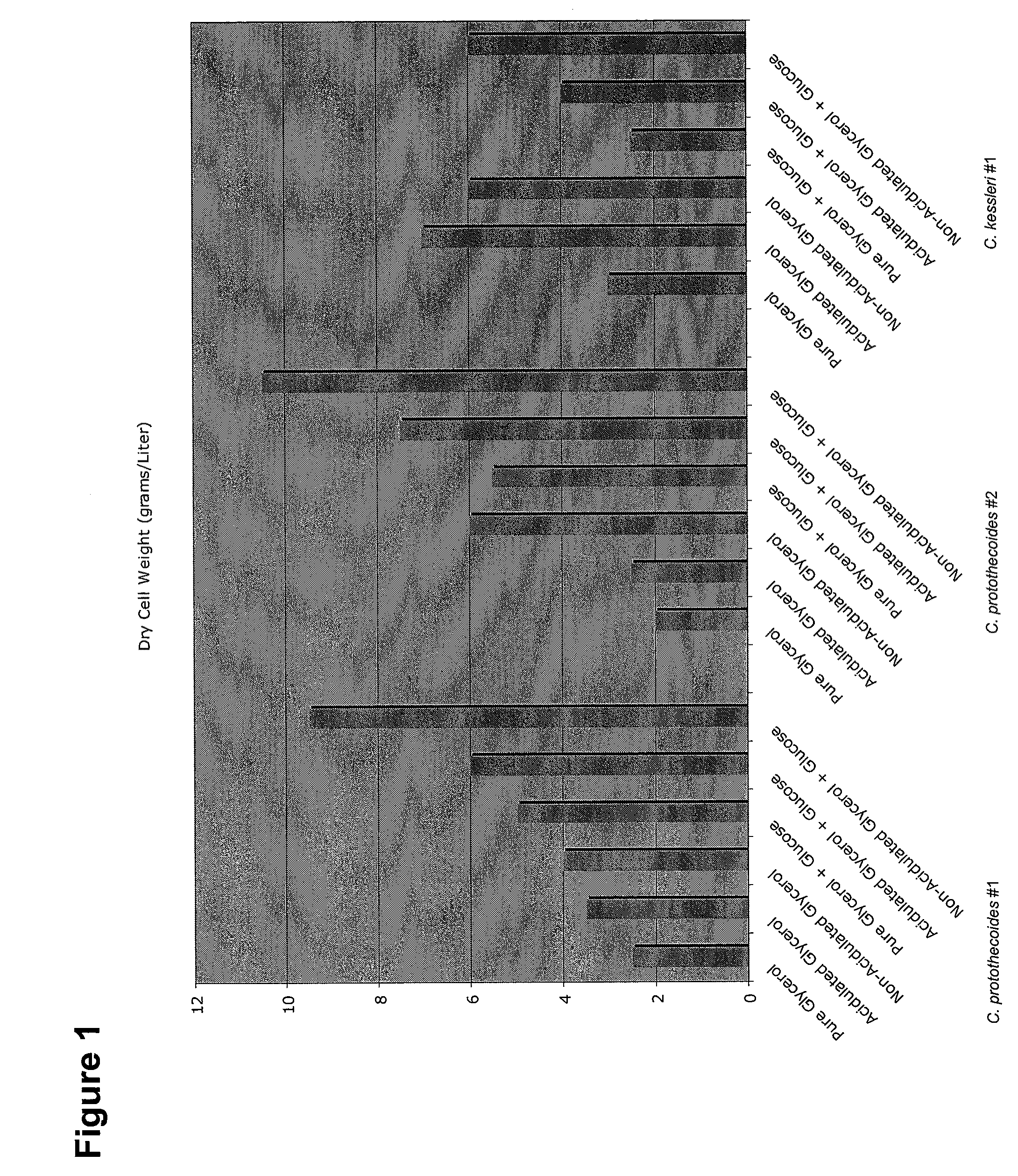
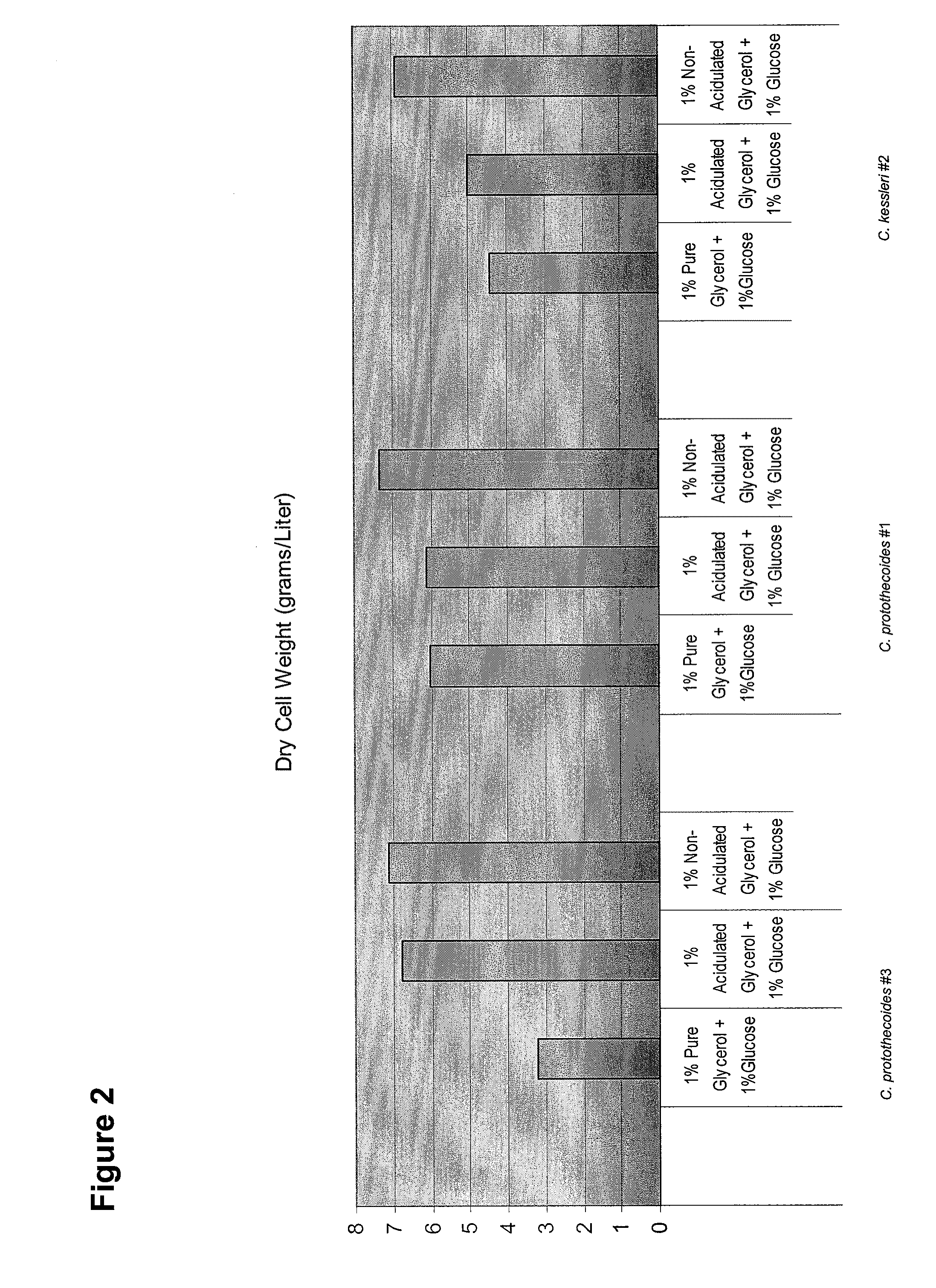
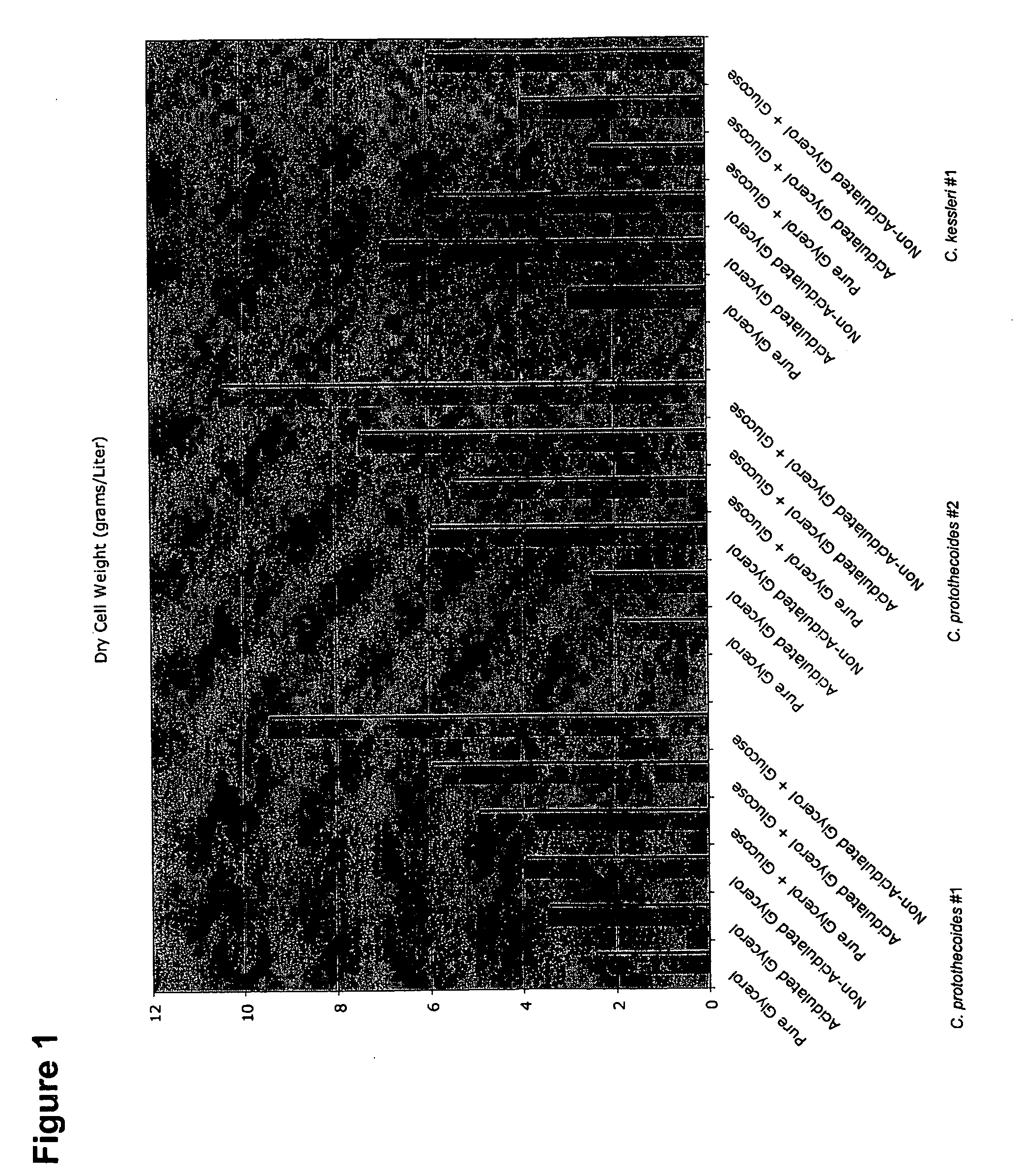
Glycerol Feedstock Utilization for Oil-Based Fuel Manufacturing
InactiveUS20090004715A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid chemical modificationMicroorganismTransesterification
The invention provides methods of manufacturing biodiesel and other oil-based compounds using glycerol and combinations of glycerol and other feedstocks as an energy source in fermentation of oil-bearing microorganisms. Methods disclosed herein include processes for manufacturing high nutrition edible oils from non-food feedstock materials such as waste products from industrial waste transesterification processes. Also included are methods of increasing oil yields by temporally separating glycerol and other feedstocks during cultivation processes. Also provided herein are oil-bearing microbes containing exogenous oil production genes and methods of cultivating such microbes on glycerol and other feedstocks.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com