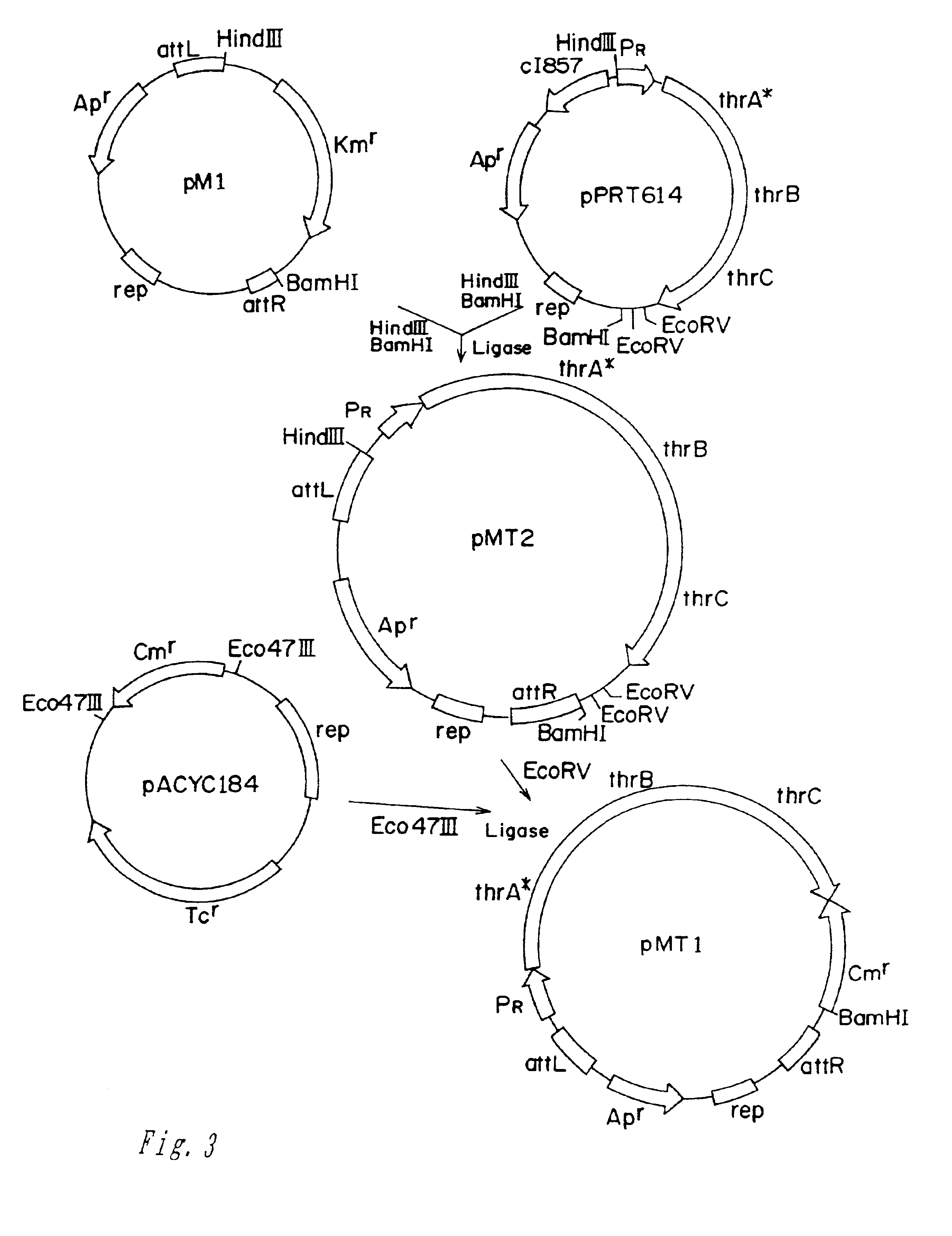
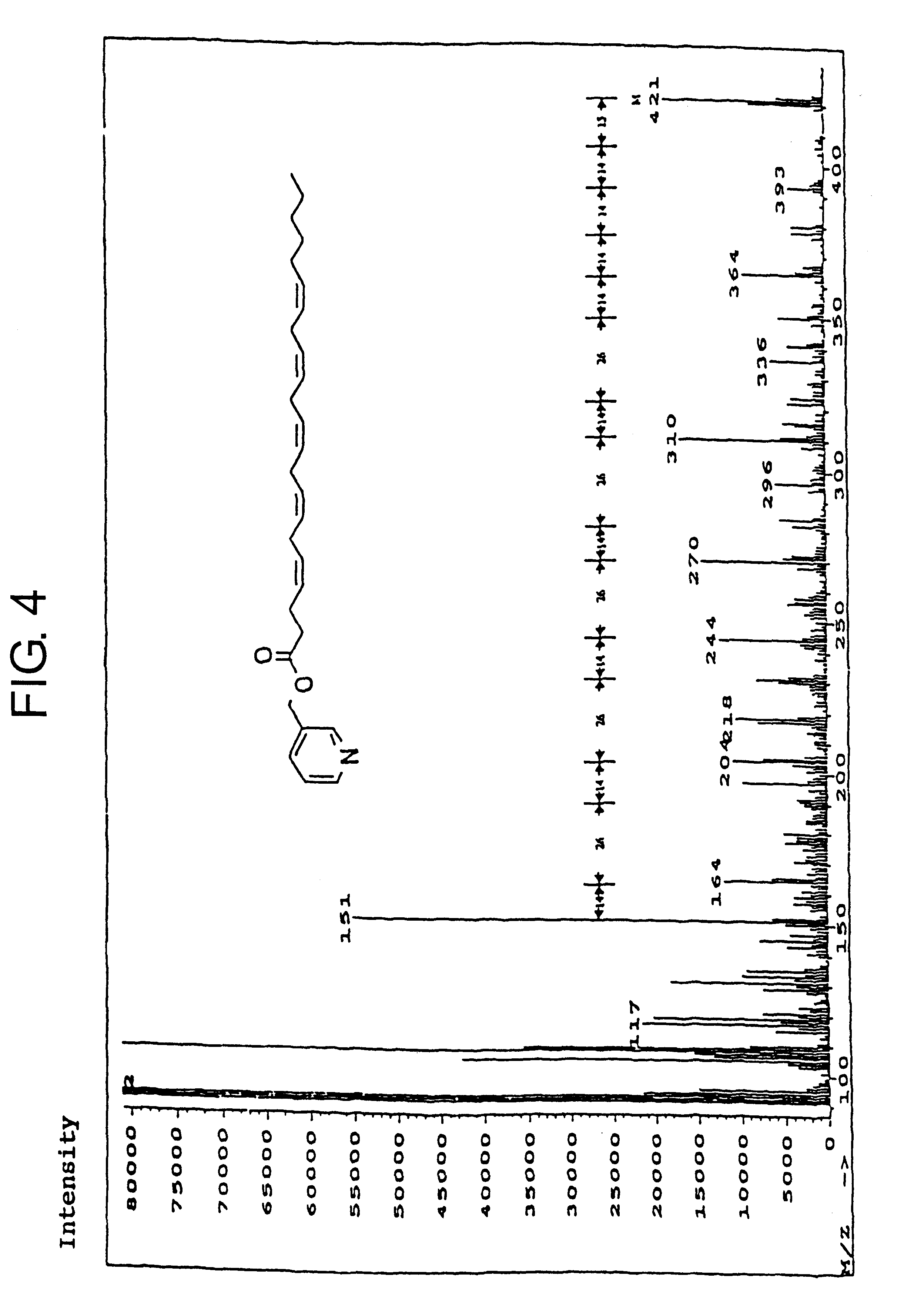
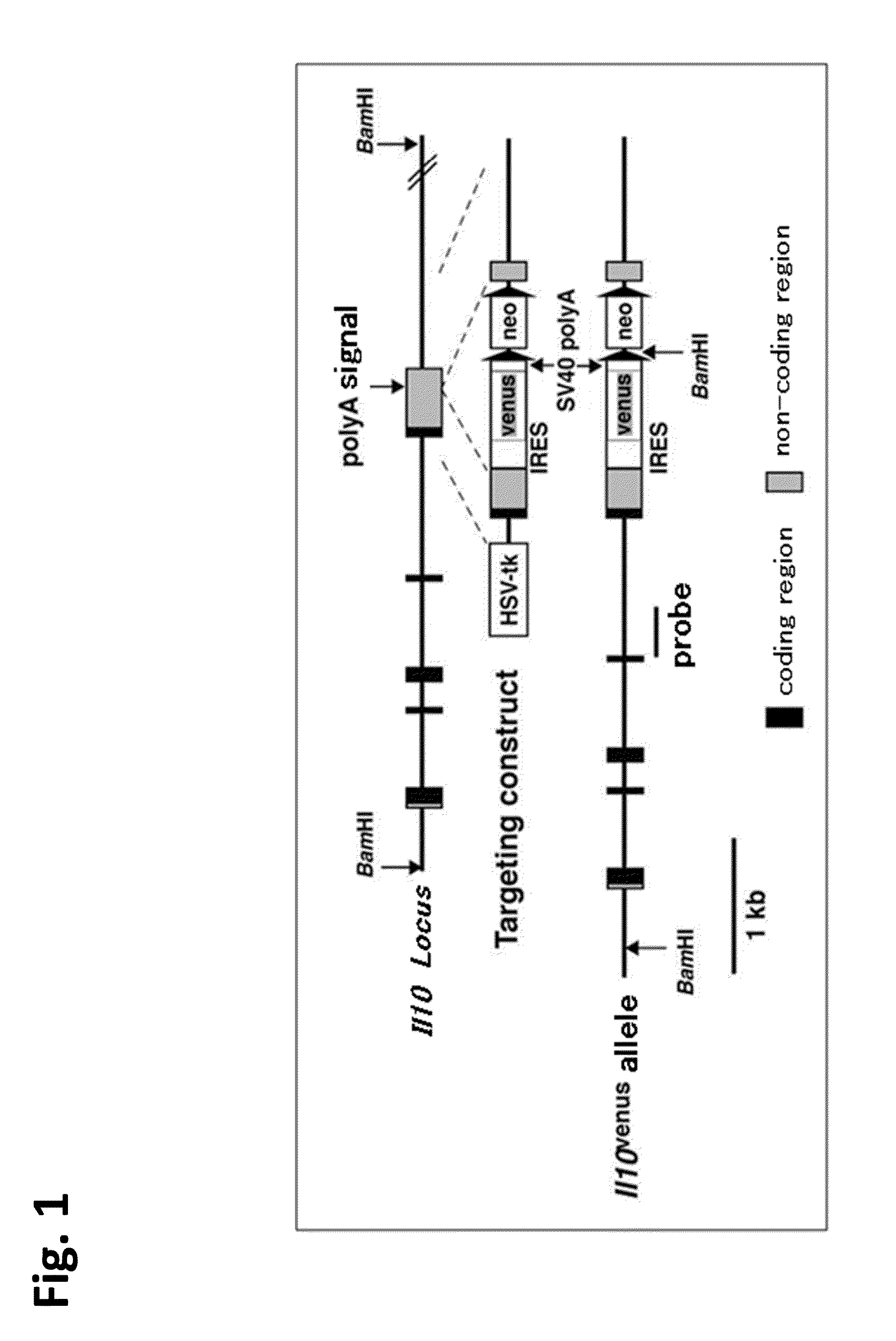
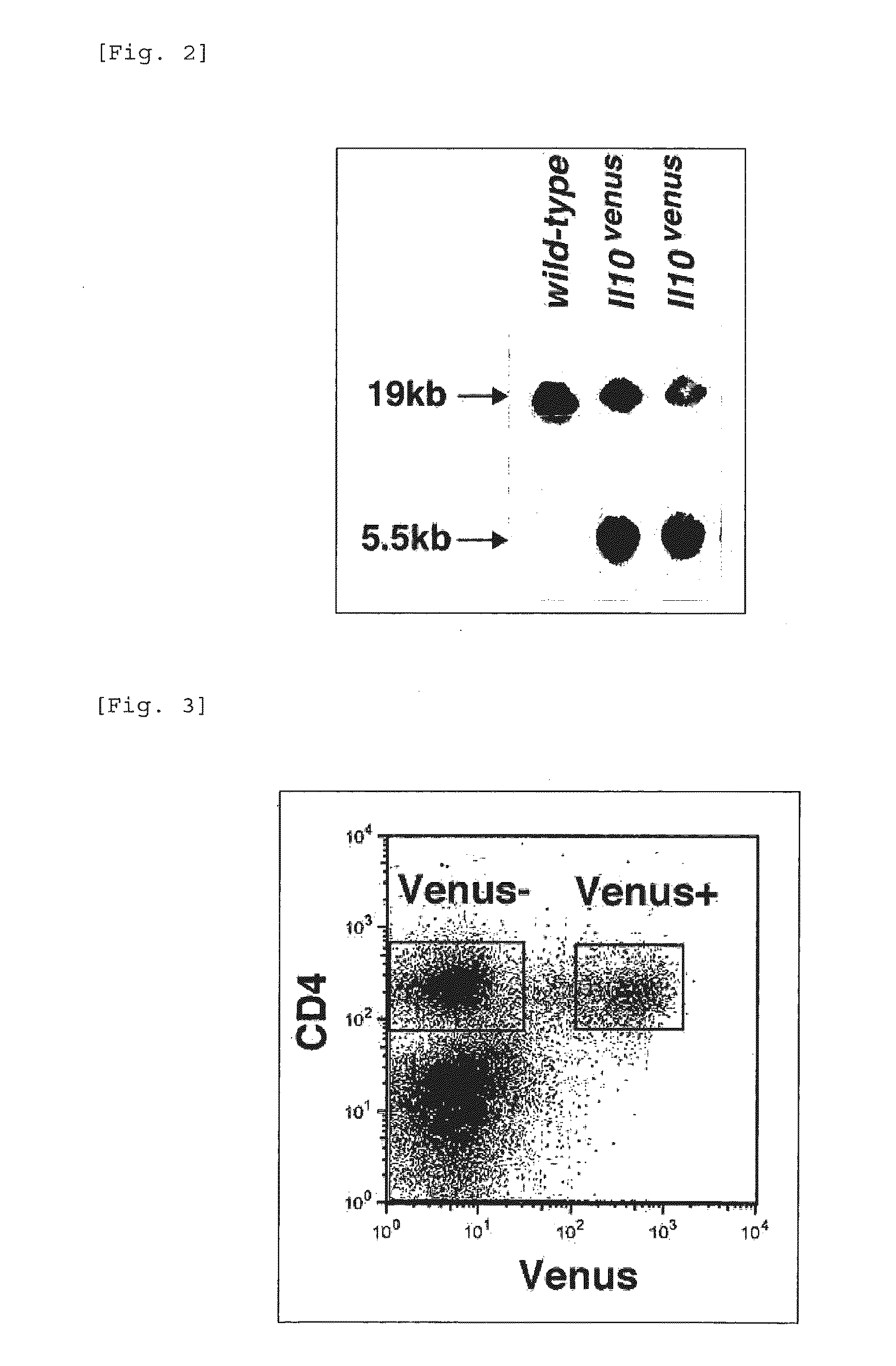
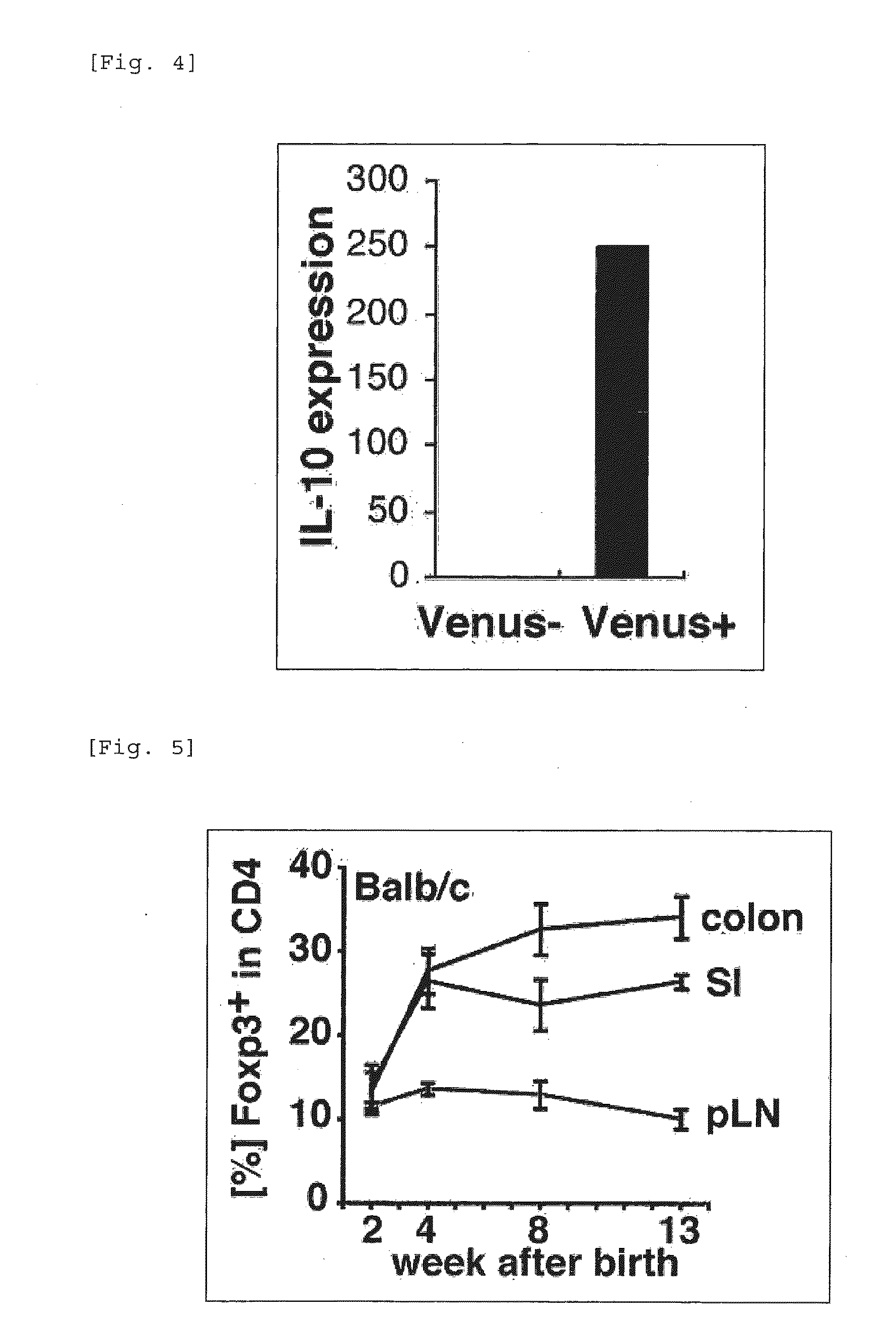
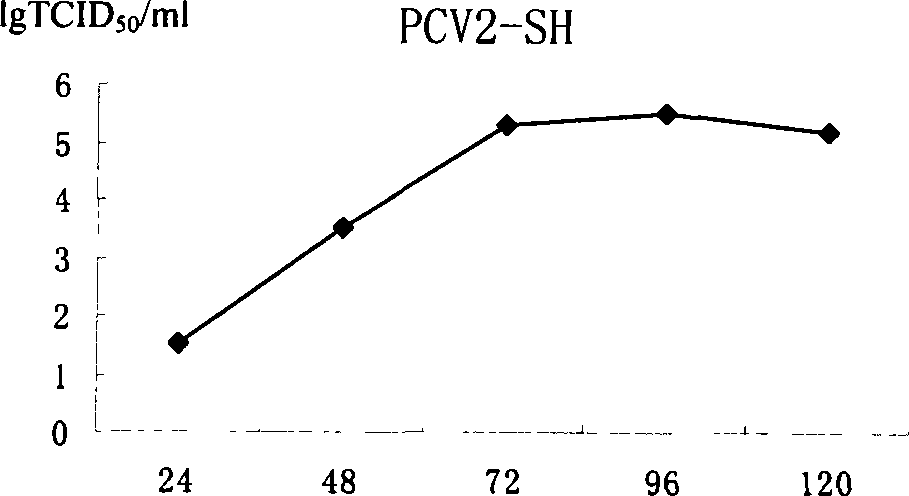
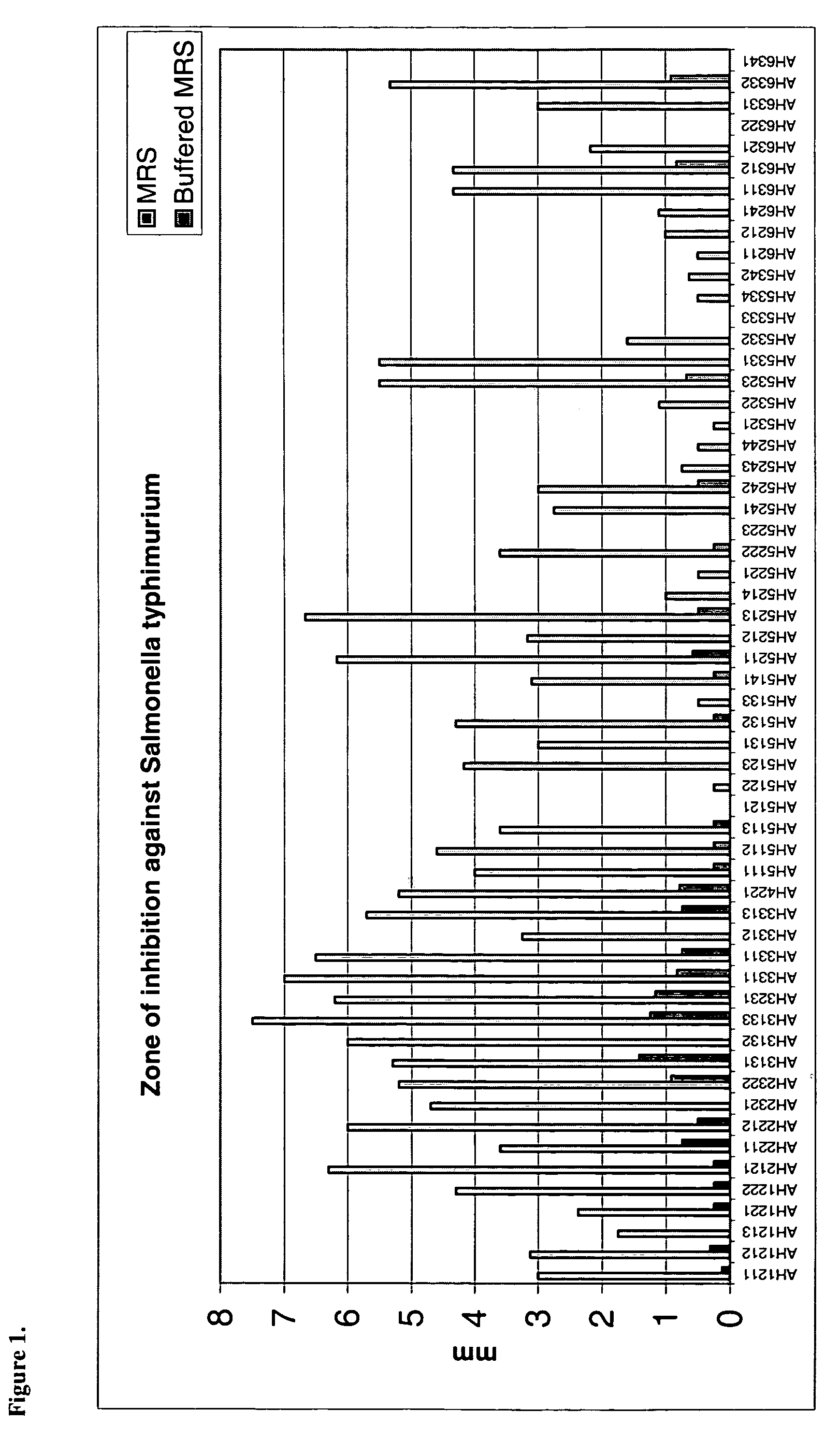
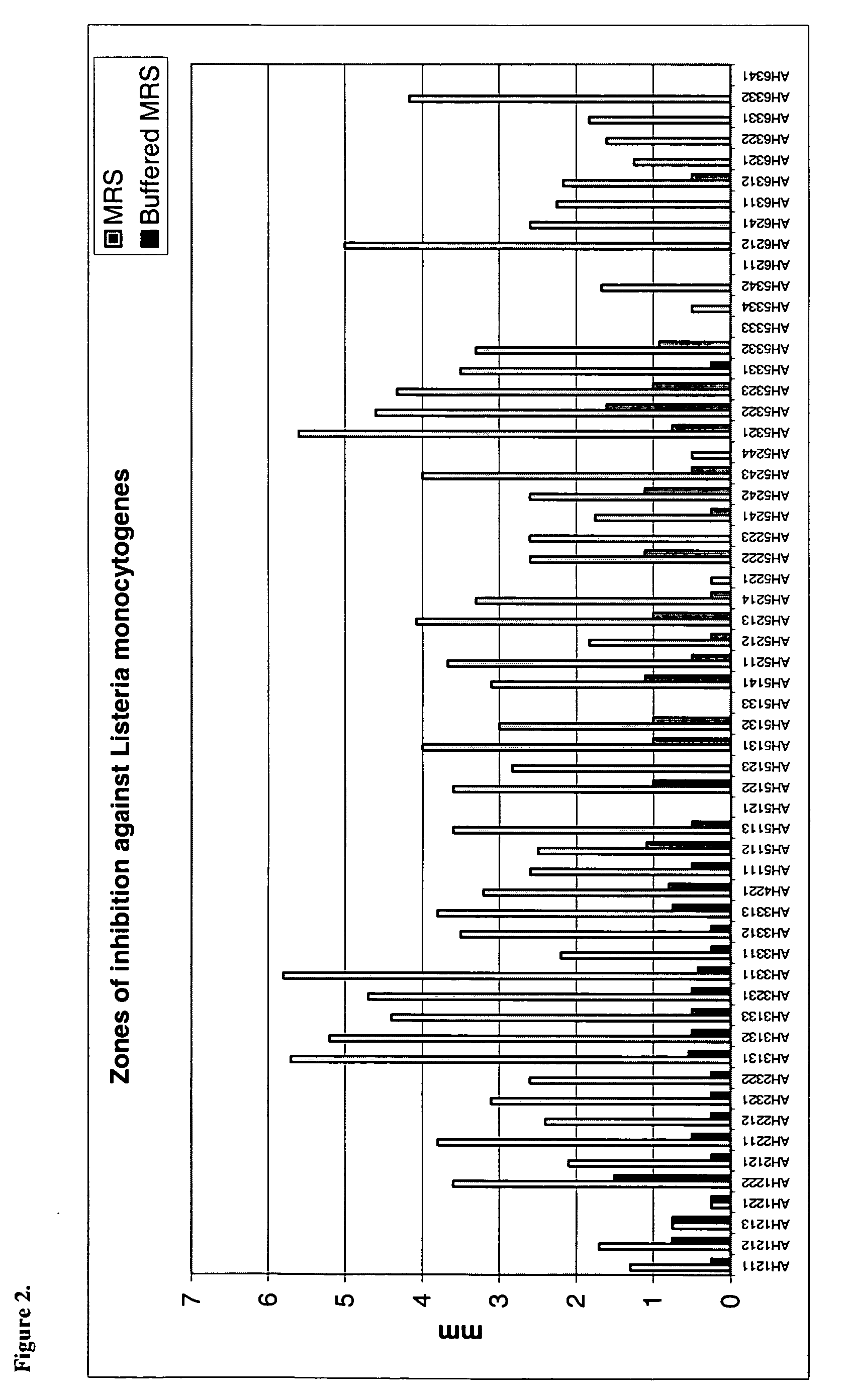
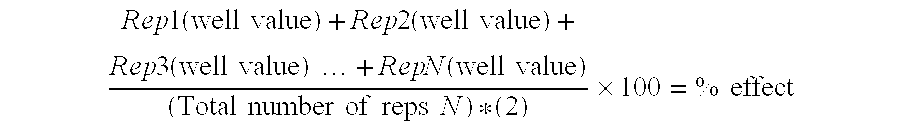Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1100 results about "Genus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genus (/ˈdʒiːnəs/, pl. genera /ˈdʒɛnərə/) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, as well as viruses, in biology. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.
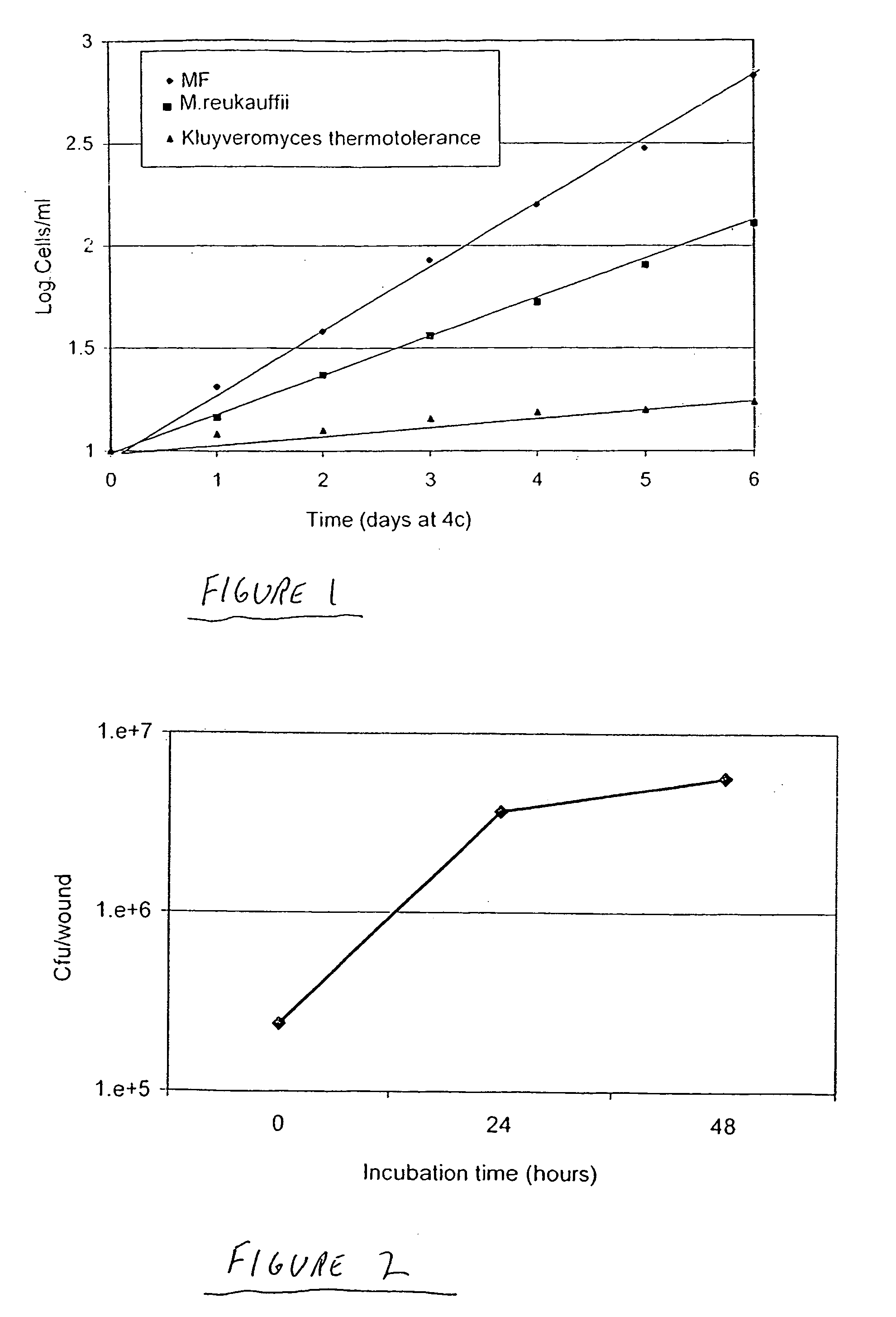
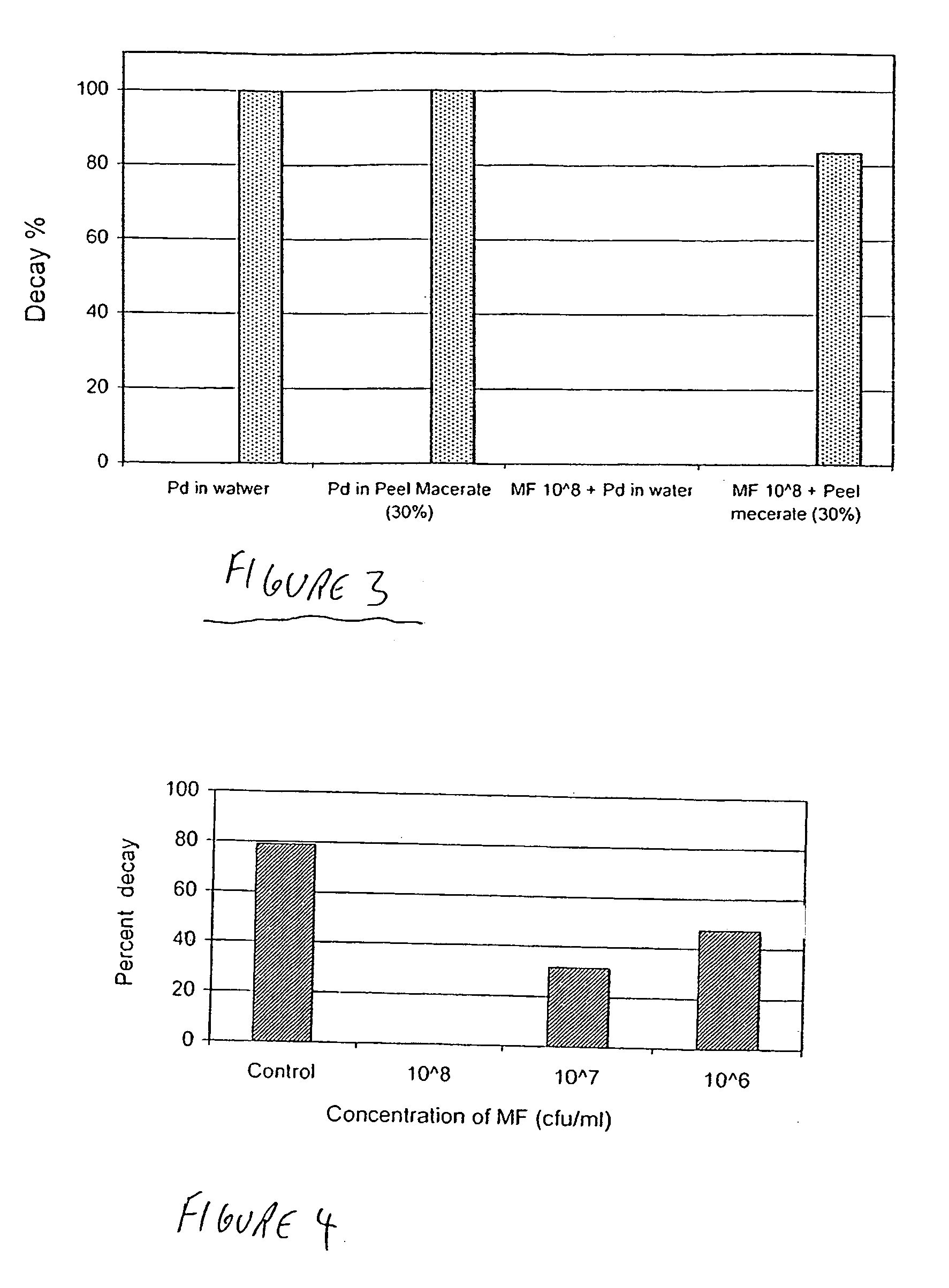
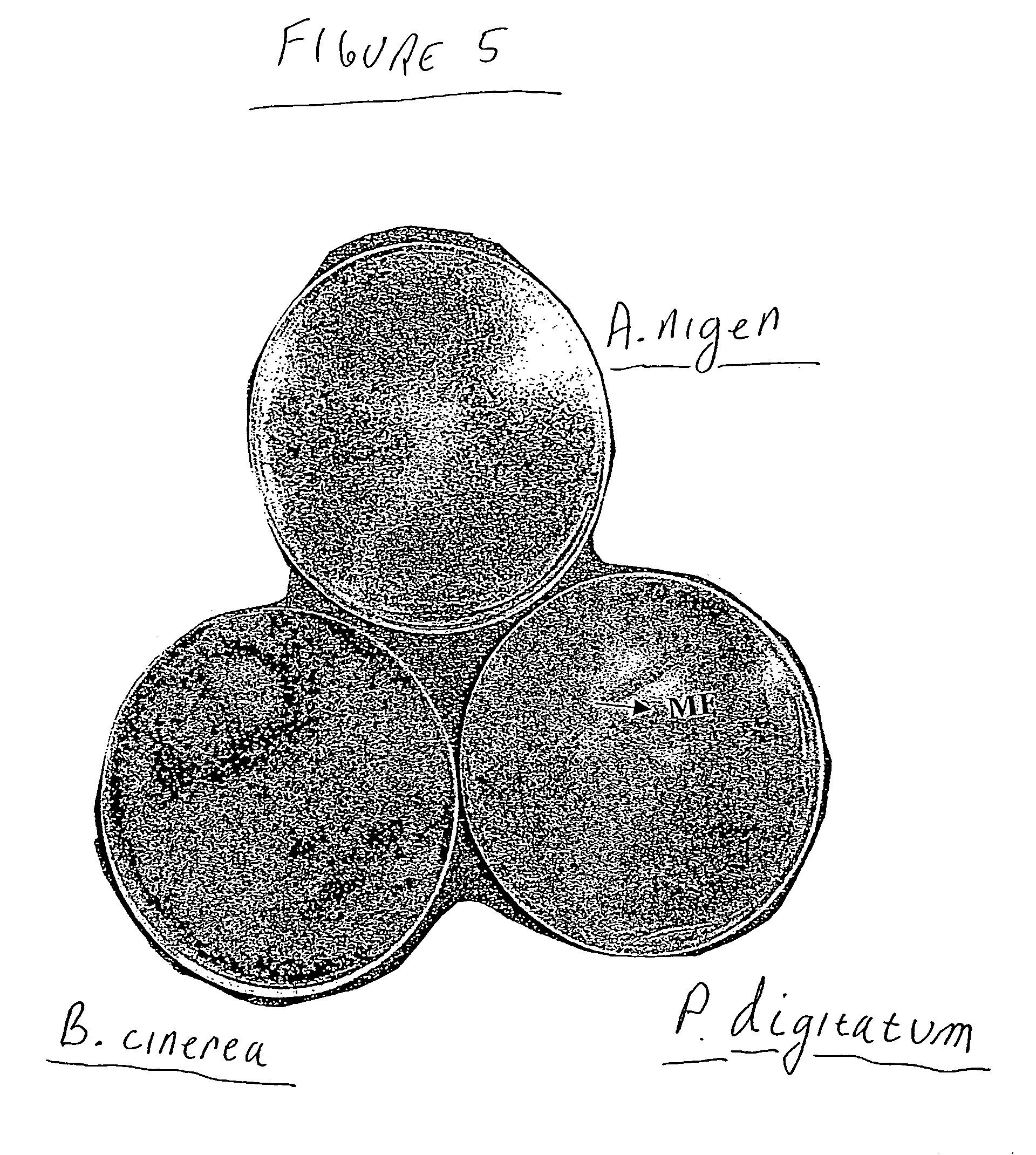
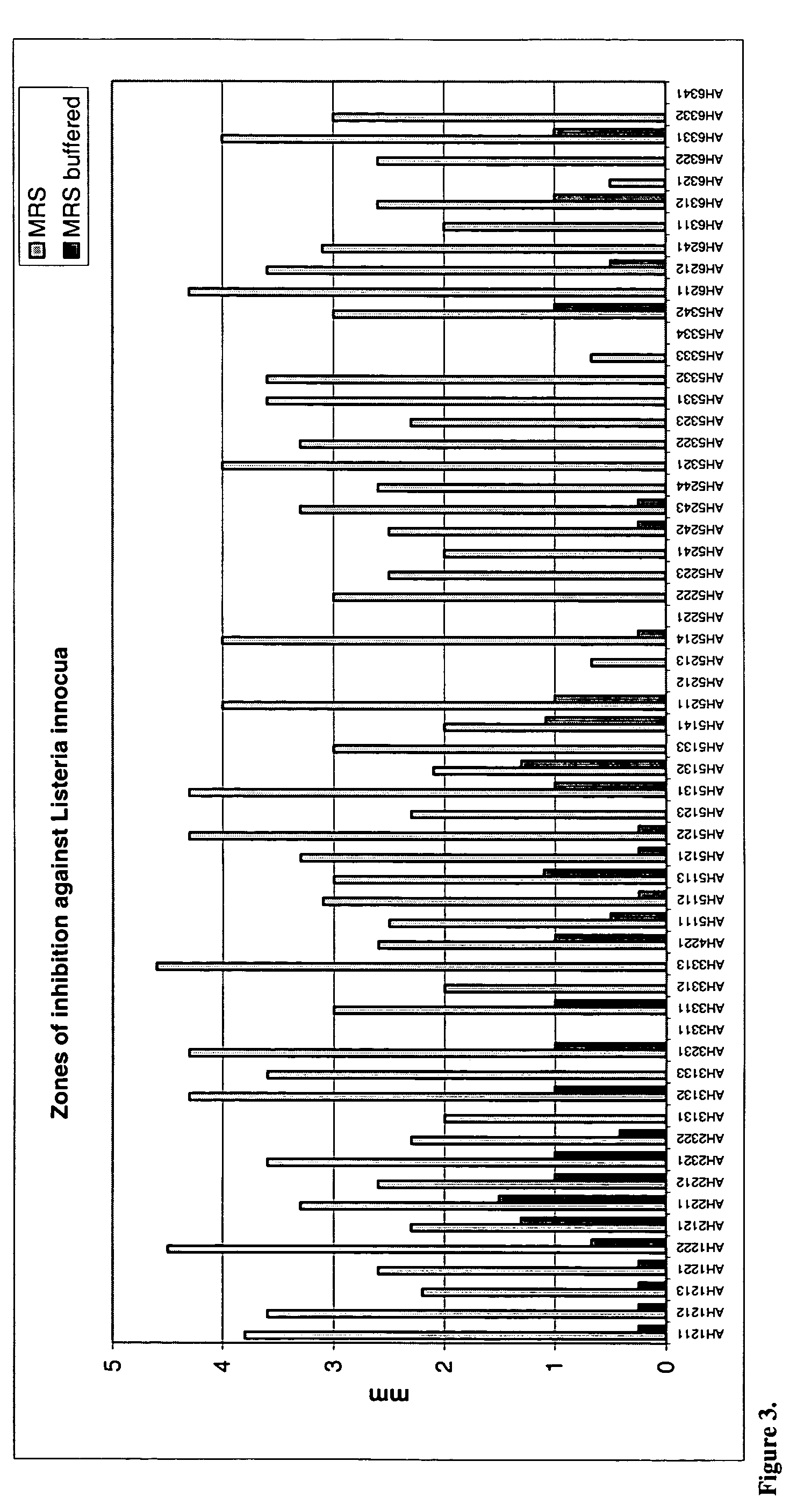
Yeast Metschnikowia fructicola NRRL Y-30752 for inhibiting deleterious microorganisms on plants
A biologically pure culture of a yeast of the species Metschnikowia fructicola. The yeast is identified as NRRL Y-30752 and is capable of inhibiting growth of a deleterious micro-organism on a portion of a plant to which a biologically effective amount of a culture of the yeast is applied. Further disclosed is a composition for use in protection of agricultural produce including a biologically effective amount of Metschnikowia fructicola and a carrier. Further disclosed is an article of manufacture including packaging material and the disclosed composition which is identified for use in protection of agricultural produce from a deleterious micro-organism. Further disclosed is a method of inhibiting growth of a deleterious micro-organism on a portion of a plant including applying at least one time an agriculturally effective amount of yeast of the genus Metschnikowia to the portion of a plant.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL THE - MINIST OF AGRI AGRI RES ORG
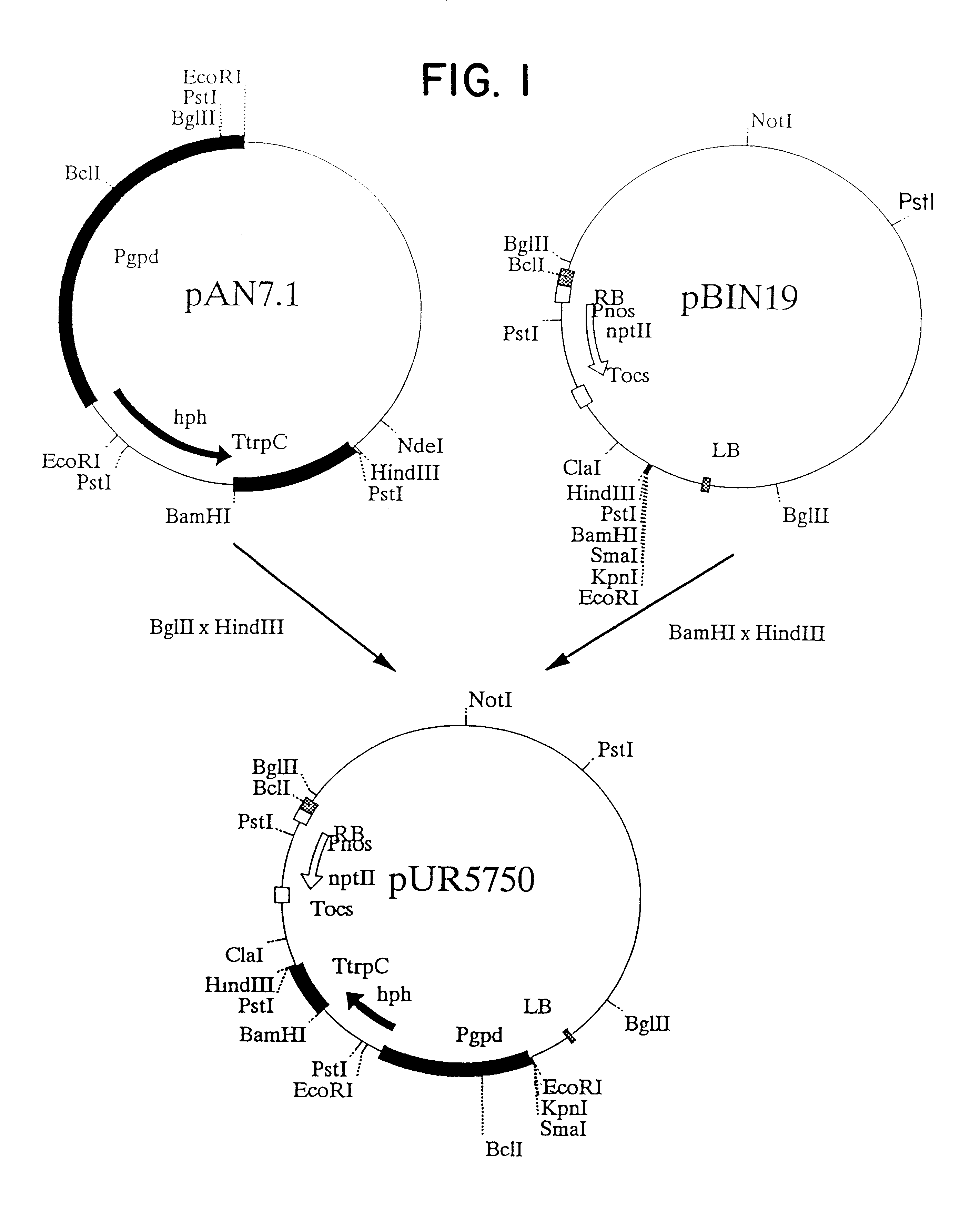
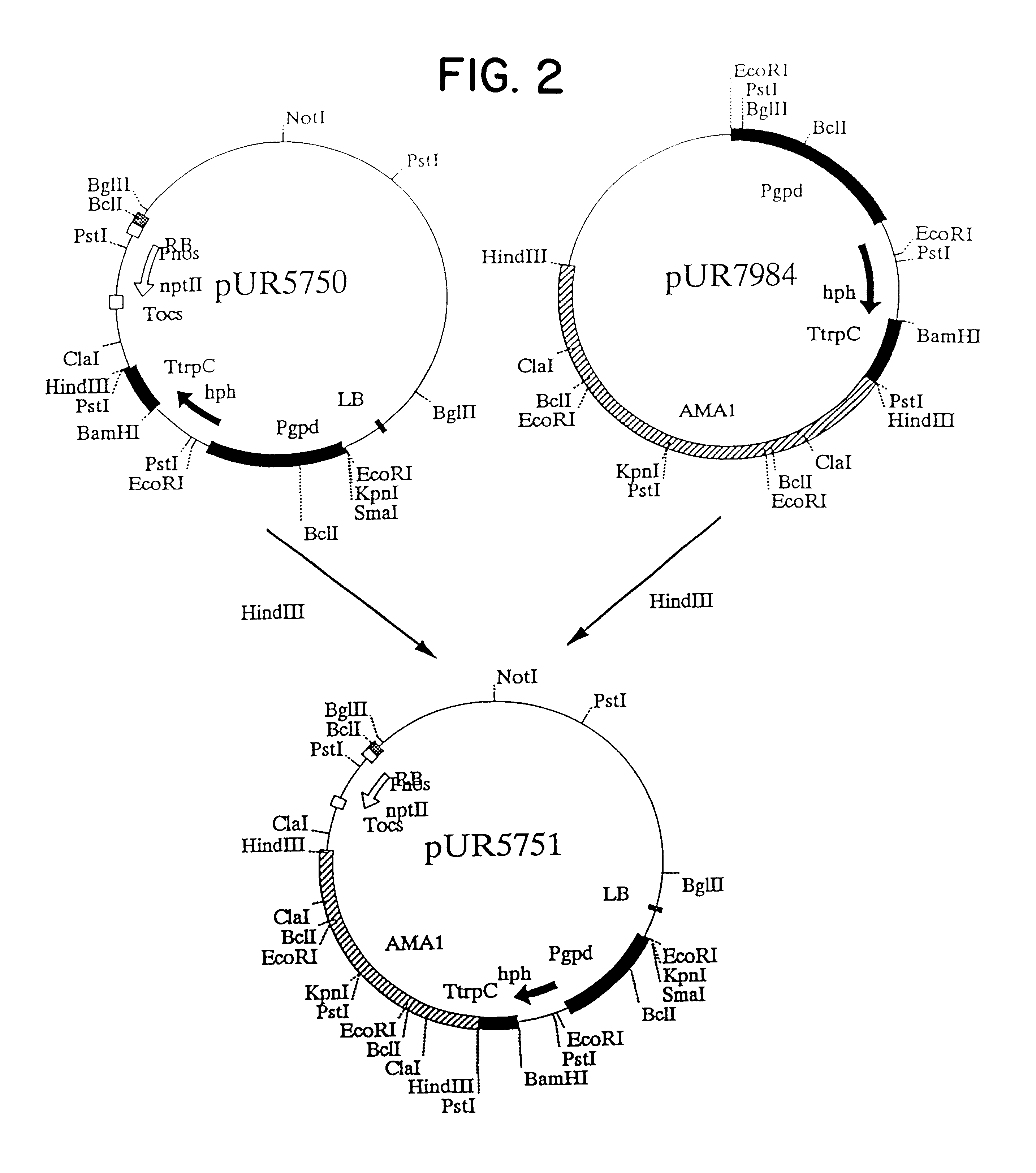
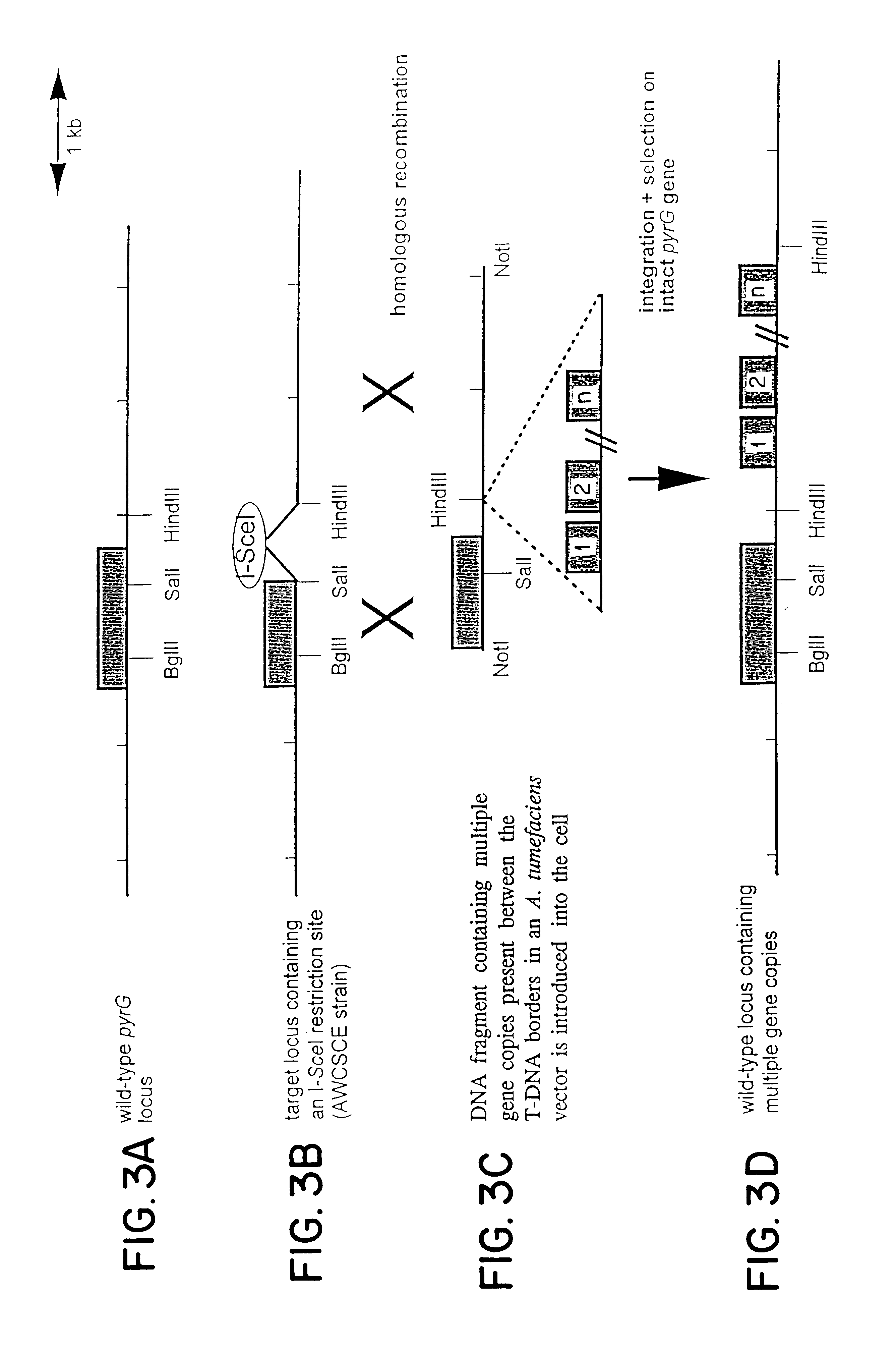
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Methods of making amino acids using E. coli transformed with csc genes
An amino acid such as threonine, homoserine, isoleucine, lysine, valine and tryptophan is produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has been constructed from sucorse non-assimilative strain belonging to the genus Escherichia and which harbors sucrose non-PTS (phosphoenol pyruvate-dependent sucrose-6-phosphotransferase system) genes and has an ability to produce the amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Microorganisms capable of producing highly unsaturated fatty acids and process for producing highly unsaturated fatty acids by using the microorganisms
InactiveUS6582941B1High speedIncrease productionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismSchizochytrium
The present invention relates to the Schizochytrium genus SR21 strain and a microorganism belonging to the same species as does said SR21 strain or having substantially the same fungological properties as does said SR21 strain, the said SR21 strain and microorganism having the ability to produce the (n-3) series of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the (n-6) series of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and the invention also relates to a process for preparing the (n-3) series of DHA and the (n-6) series of DPA utilizing said microorganisms. The microorganisms according to the present invention are superior in their proliferation character and their propensity to produce fat, and have the ability to produce the (n-3) series of DHA and the (n-6) series of DPA very well. Accordingly, it is possible to effectively produce the (n-3) series of DHA and / or the (n-6) series of DPA, which are useful in the fields of foods and pharmaceuticals, using the microorganisms according to the present invention. In addition, the present invention provides a fat obtained by culturing the present microorganisms. Since the fat composition contains the (n-6) series of DPA in addition to the (n-3) series of DHA having various physiological activities, it is possible to stably and effectively supply the (n-6) series of DPA and / or the (n-3) series of DHA to subjects in need of these highly unsaturated fatty acids by adding the fat composition to various feedstuffs or foods.
Owner:DIRECTOR GENERAL OF THE AGENCY OF IND SCI & TECH +1
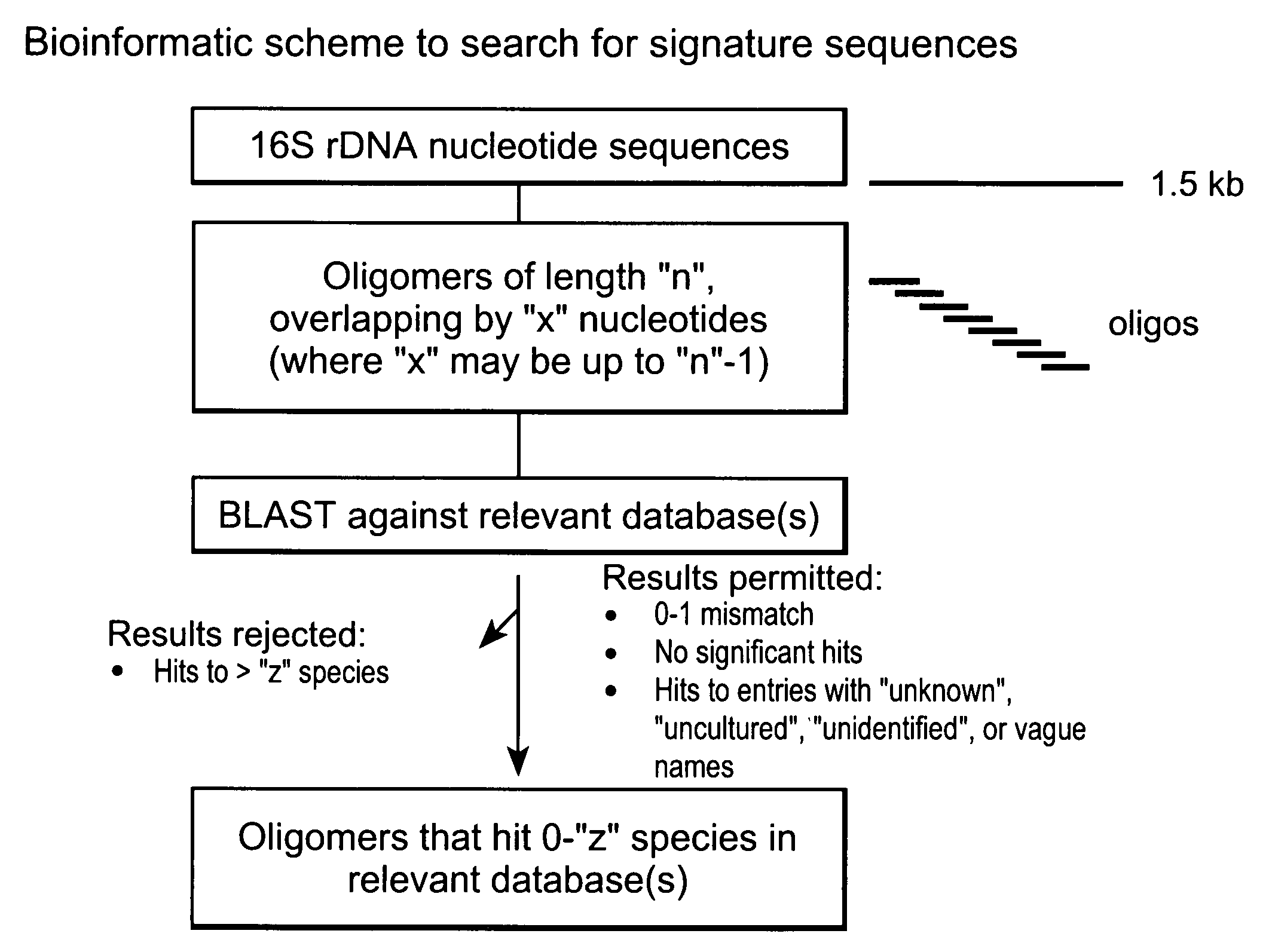
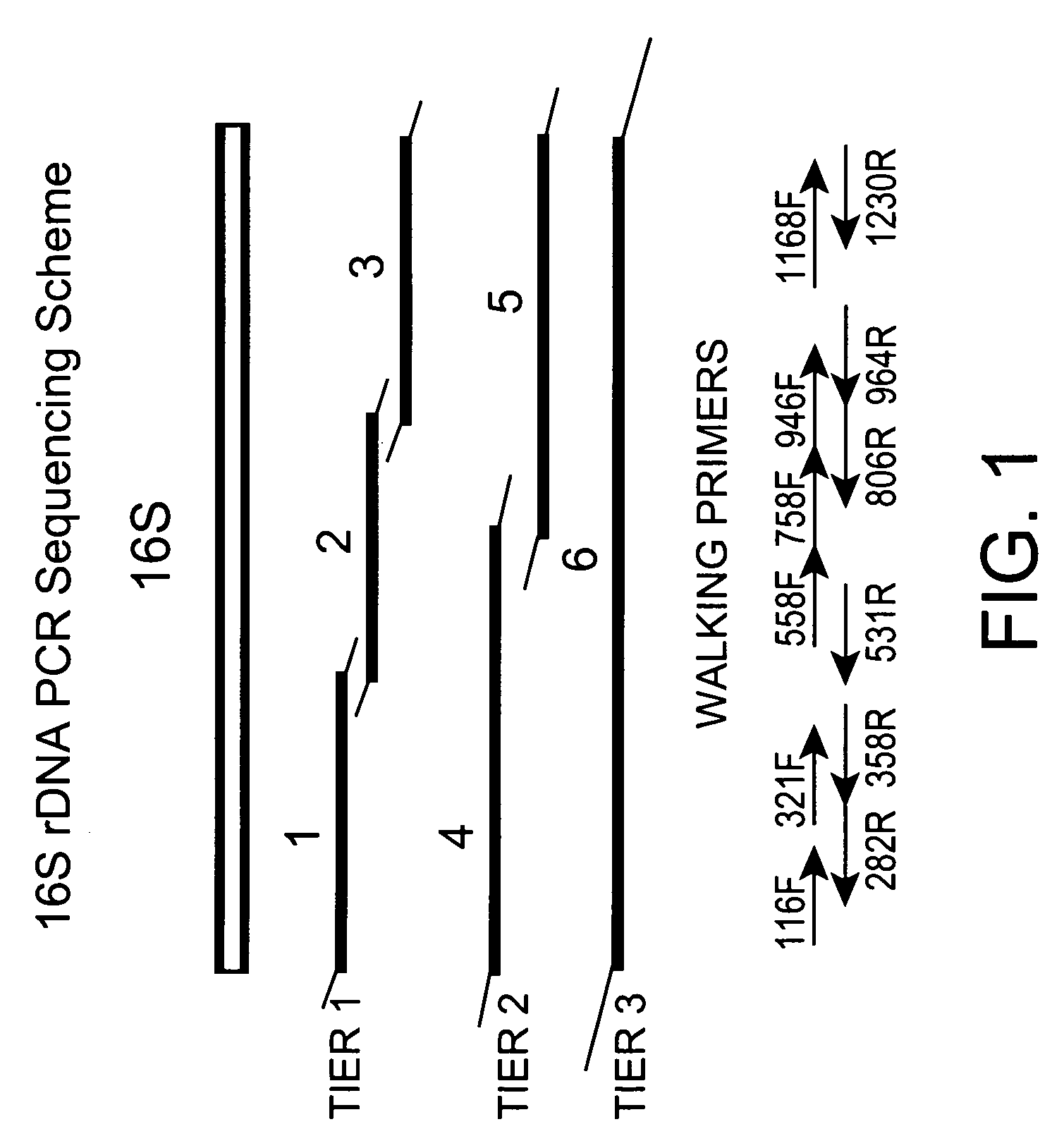
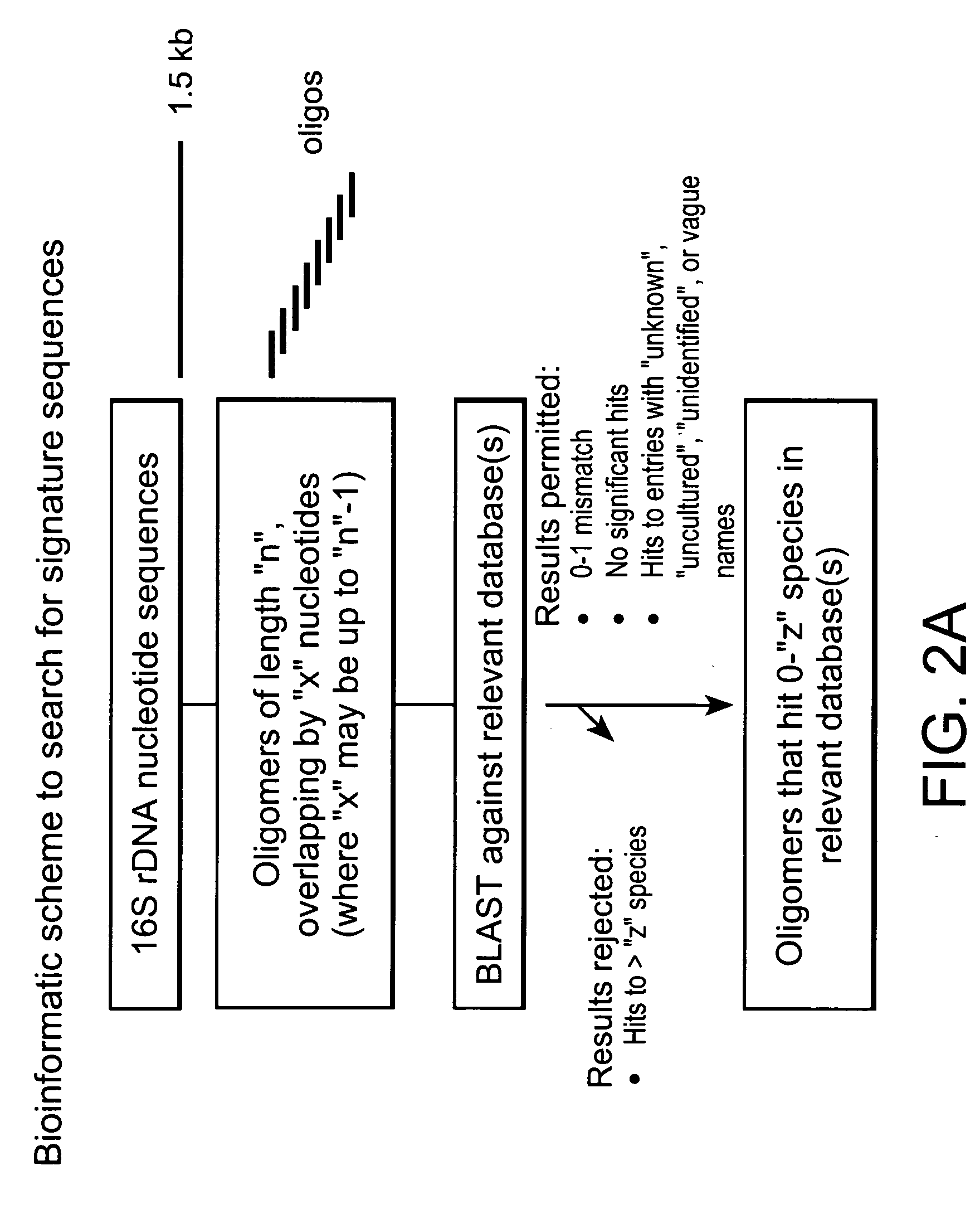
Genus, group, species and/or strain specific 16S rDNA sequences
InactiveUS20060046246A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStrain specificity
Materials and methods for identifying unique sites in bacterial 16S and 23S rDNA are provided, as well as specific unique sequences of 16S rDNA in select bacteria. The distinguishing moieties will enable rapid differentiation between families, genera, groups, species, strains, subspecies, and isolates of microorganisms. Such differentiation can be performed by using rapid screening kits in combination with in silico analysis for diagnostic, prognastic, epidemiologic, phylogenetic, and other purposes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC +1
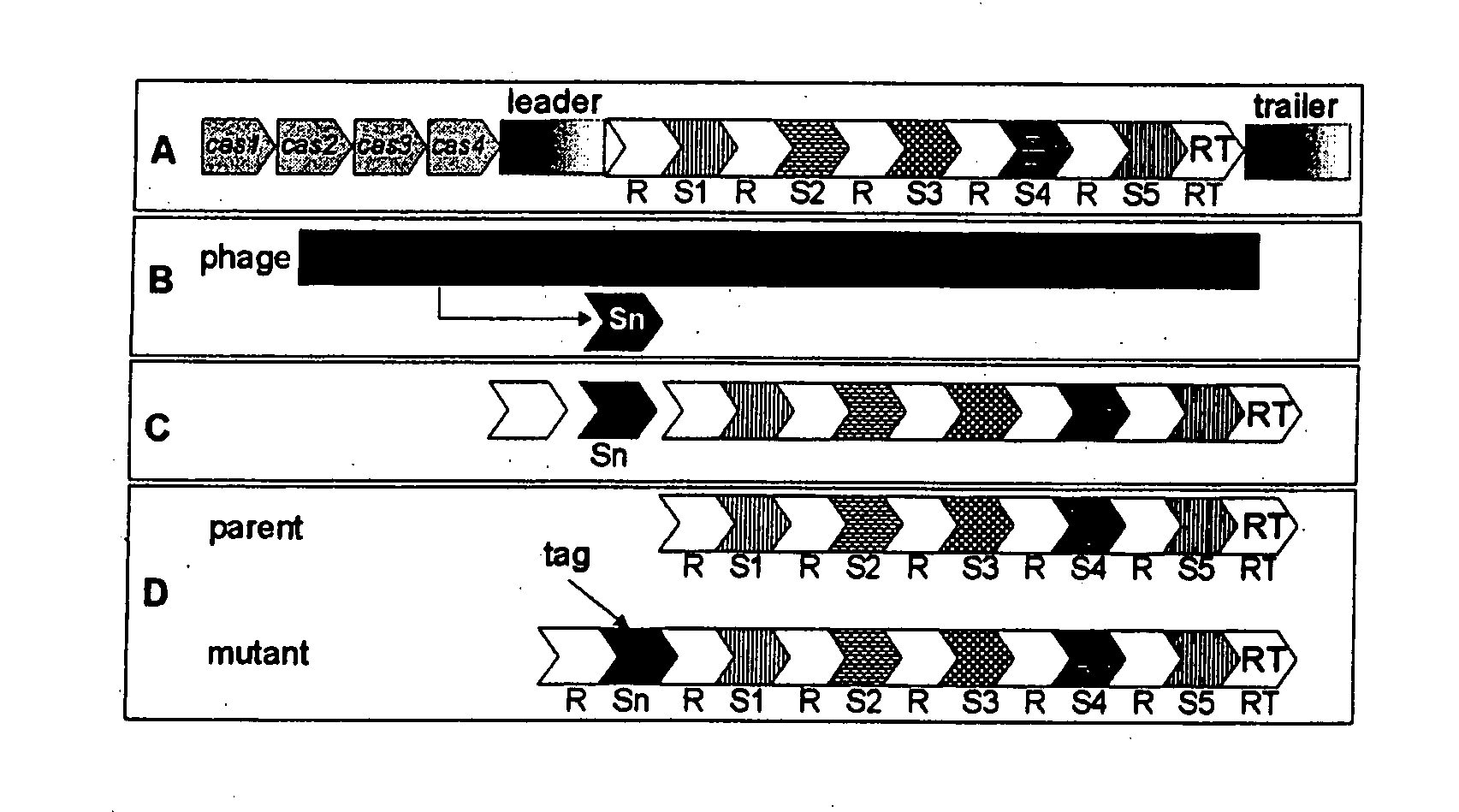
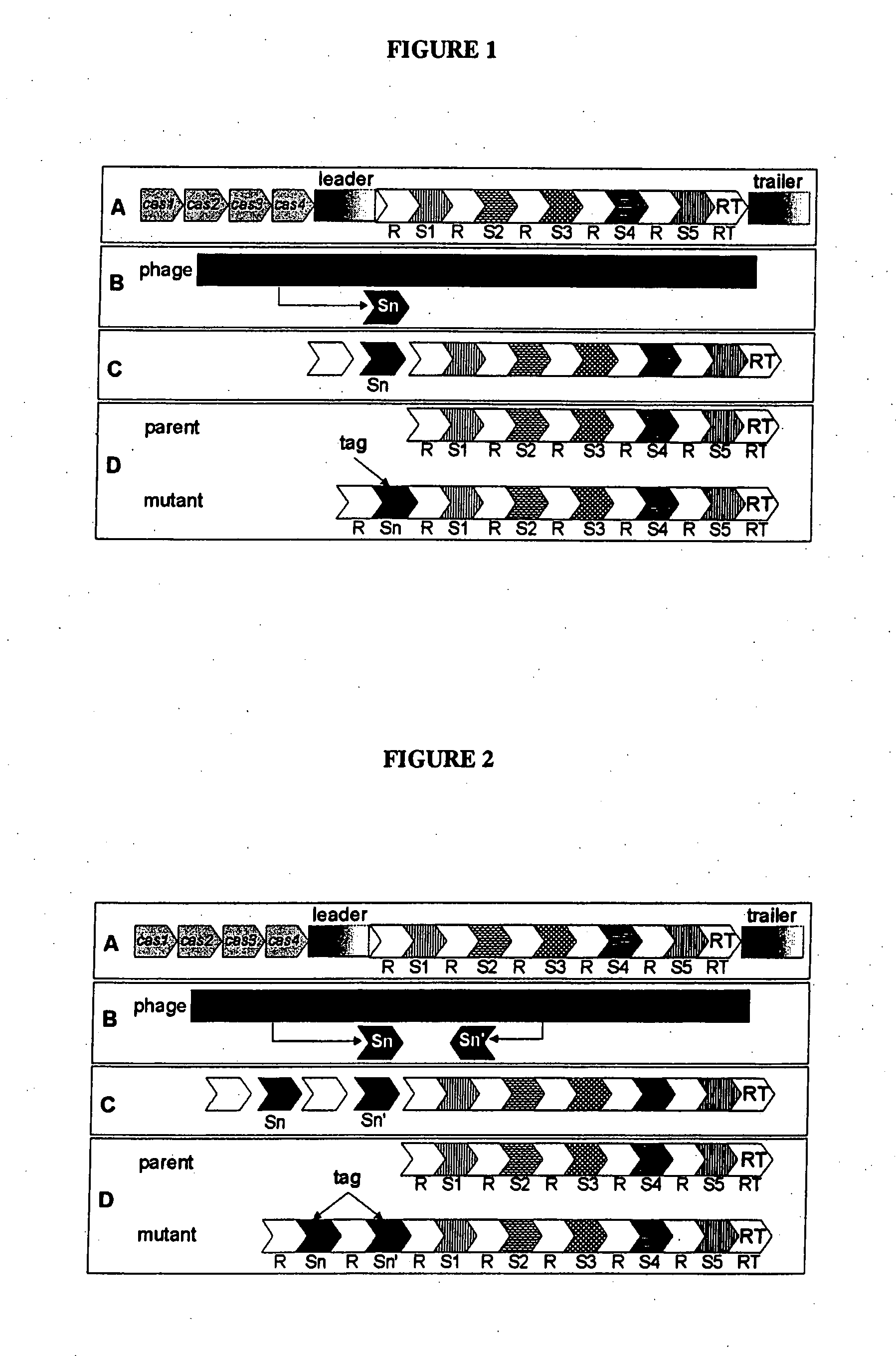
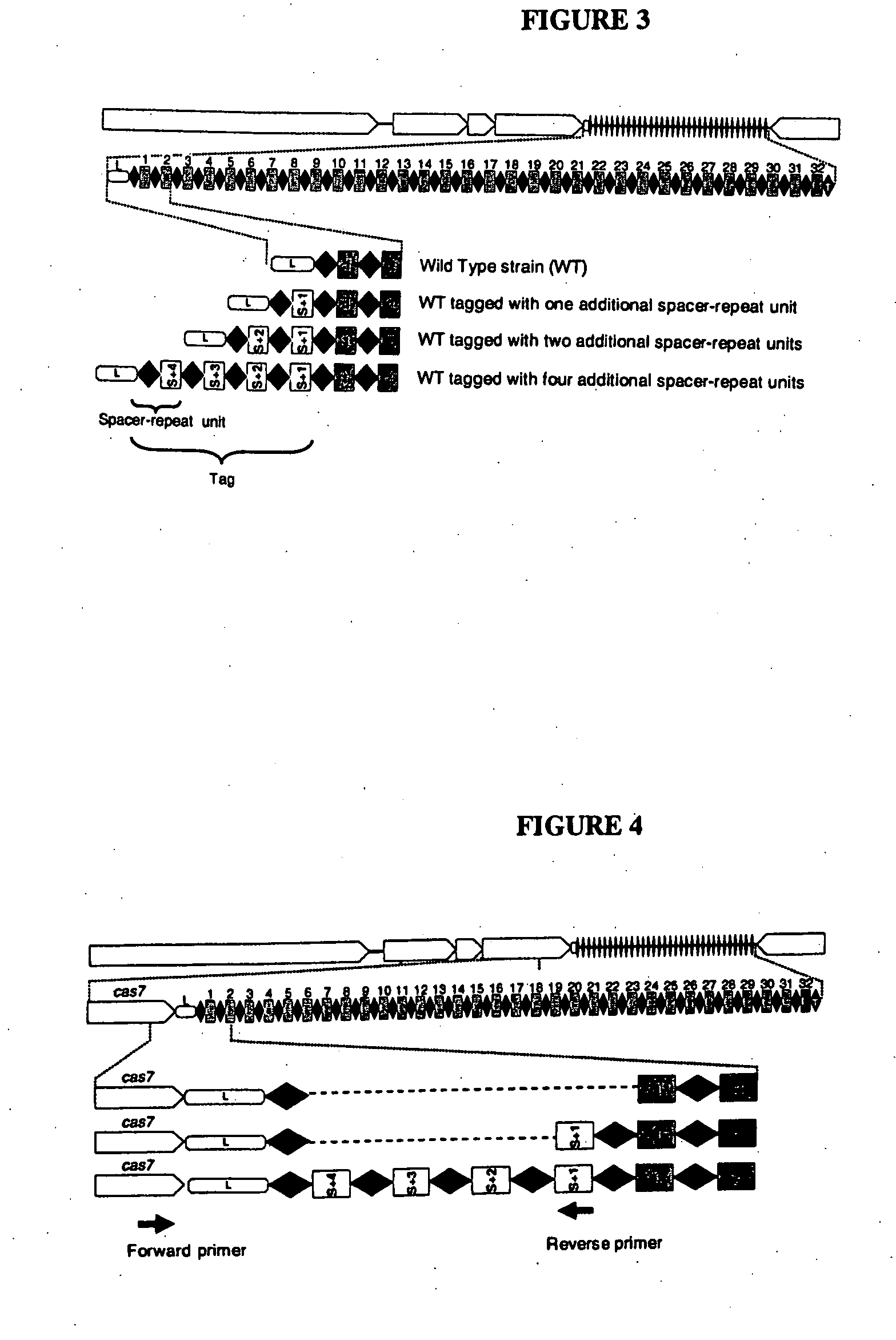
Tagged microorganisms and methods of tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus clostridium
The invention includes a method of treating gastrointestinal diseases associated with species of genus Clostridium such as clostridium deficit in human patients with gastrointestinal disorders having an etiological component such as a microbial agent producing a toxin where treated with an antimicrobial composition an amount effective to inhibit or eliminate the microbial agent. The antimicrobial composition in a form of probiotic mixture can be administrated alone or in combination with an antimicrobial agent, such as a bacteriophage which is specific for a bacterium producing toxin or antibiotics which are then used to eliminate or inhibit the clostridial species overgrown in a patient's gastrointestinal tract. Disorders that can be treated by the method of the invention include diarrhea or inflammatory bowel diseases such as colitis or Crohn's disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Mixing and matching TC proteins for pest control
InactiveUS7491698B2High activityEffective control of widerBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousToxin protein
The subject invention relates to the surprising discovery that toxin complex (TC) proteins, obtainable from Xenorhabdus, Photorhabdus, and Paenibacillus, can be used interchangeably with each other. In particularly preferred embodiments of the subject invention, the toxicity of a “stand-alone” TC protein (from Photorhabdus, Xenorhabdus, or Paenibacillus, for example) is enhanced by one or more TC protein “potentiators” derived from a source organism of a different genus from which the toxin was derived. As one skilled in the art will recognize with the benefit of this disclosure, this has broad implications and expands the range of utility that individual types of TC proteins will now be recognized to have. Among the most important advantages is that one skilled in the art will now be able to use a single set of potentiators to enhance the activity of a stand-alone Xenorhabdus protein toxin as well as a stand-alone Photorhabdus protein toxin. (As one skilled in the art knows, Xenorhabdus toxin proteins tend to be more desirable for controlling lepidopterans while Photorhabdus toxin proteins tend to be more desirable for controlling coleopterans.) This reduces the number of genes, and transformation events, needed to be expressed by a transgenic plant to achieve effective control of a wider spectrum of target pests. Certain preferred combinations of heterologous TC proteins are also disclosed herein. Other objects, advantages, and features of the subject invention will be apparent to one skilled in the art having the benefit of the subject disclosure.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Tagged Microorganisms and Methods of Tagging
The present invention provides methods for tagging and / or identifying microorganisms. In some preferred embodiments, the microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the bacteria are members of other genera. The present invention also provides microorganisms tagged using the methods set forth herein. In some preferred embodiments, the tagged microorganisms are bacteria. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of the genus Streptococcus, while in other embodiments, the tagged bacteria are members of other genera.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Parallel processing motion estimation for H.264 video codec
InactiveUS20080126278A1Low costMinimize the numberImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorMotion estimate
A genus of motion estimation processes is disclosed which is characterized by the following characteristics which all species in the genus will share 1) a process within this genus does not perform the motion estimation separately for each of the partitions and subpartitions defined in the H.264 standard; 2) a process within the genus computes for each motion vector in the search region the partial costs for all macroblock partitions and sub-partitions, compares them to the best partial costs found so far, and for partitions and sub-partitions having lower costs updates the corresponding best partial costs and records the current motion vectors as the one realizing them. 3) a process within the genus after finishing scanning the motion vectors in the search region, computes from the best partial costs the total costs for all possible macroblock partitioning modes and selects the one with the lowest total cost as the best macroblock partitioning mode, with the best motion vectors corresponding to each of the selected macroblock partitions and sub-partitions.
Owner:NOVAFORA
Mutant serine acetyltransferase
O-acetylserine, L-cysteine and sulphurous compounds derived therefrom may be produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which harbors a mutant feedback-resistant serine acetyltransferases in which the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions from 89 to 96 in a wild-type serine acetyltransferase is replaced with any one of the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NOS: 4 to 9, and feedback inhibition by L-cysteine in the bacterium is desensitized.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-amino acid by fermentation
InactiveUS20060216796A1Improve abilitiesEnhancing threonine biosynthetic pathwayBacteriaFermentationL-threonineMicrobiology
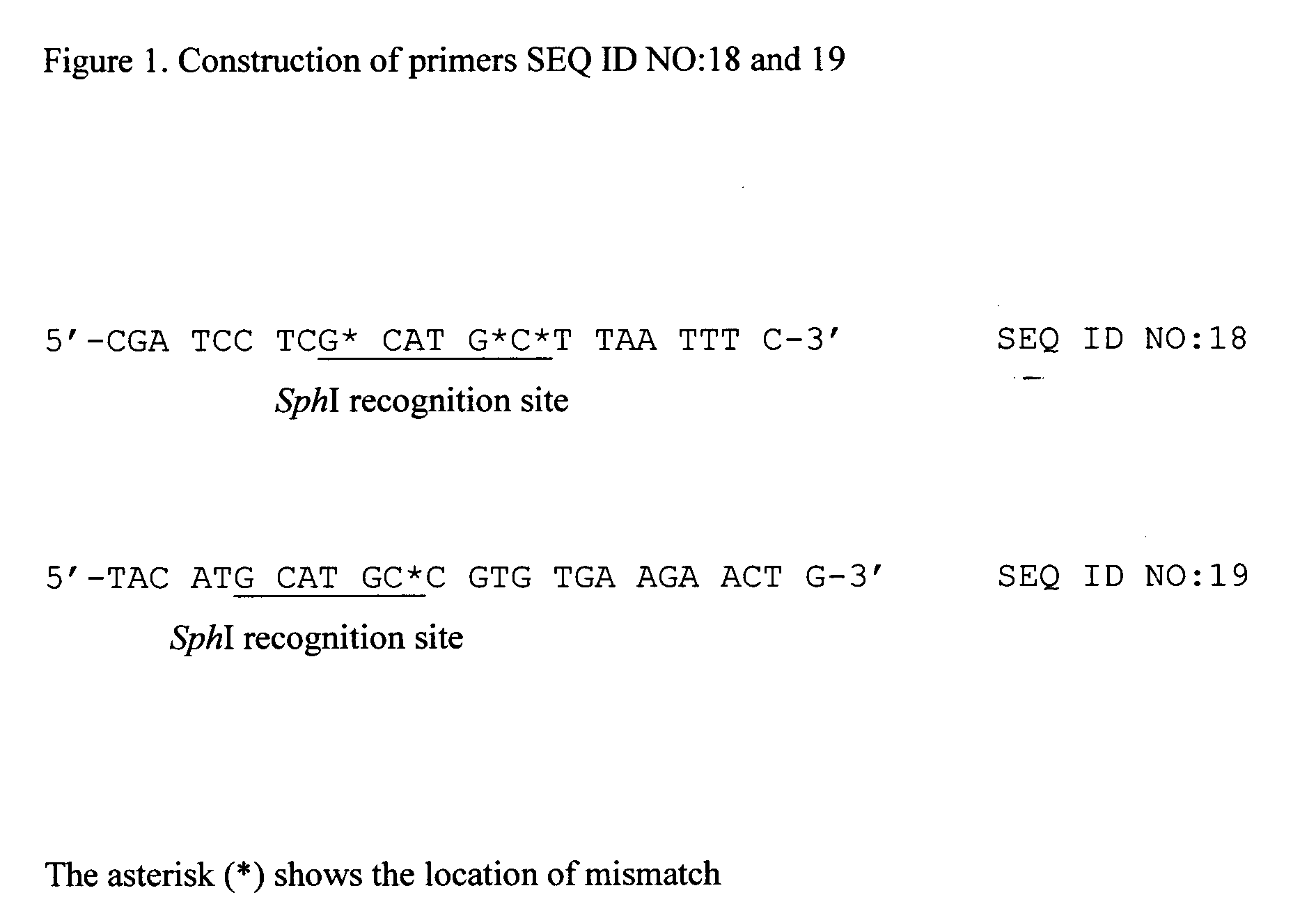
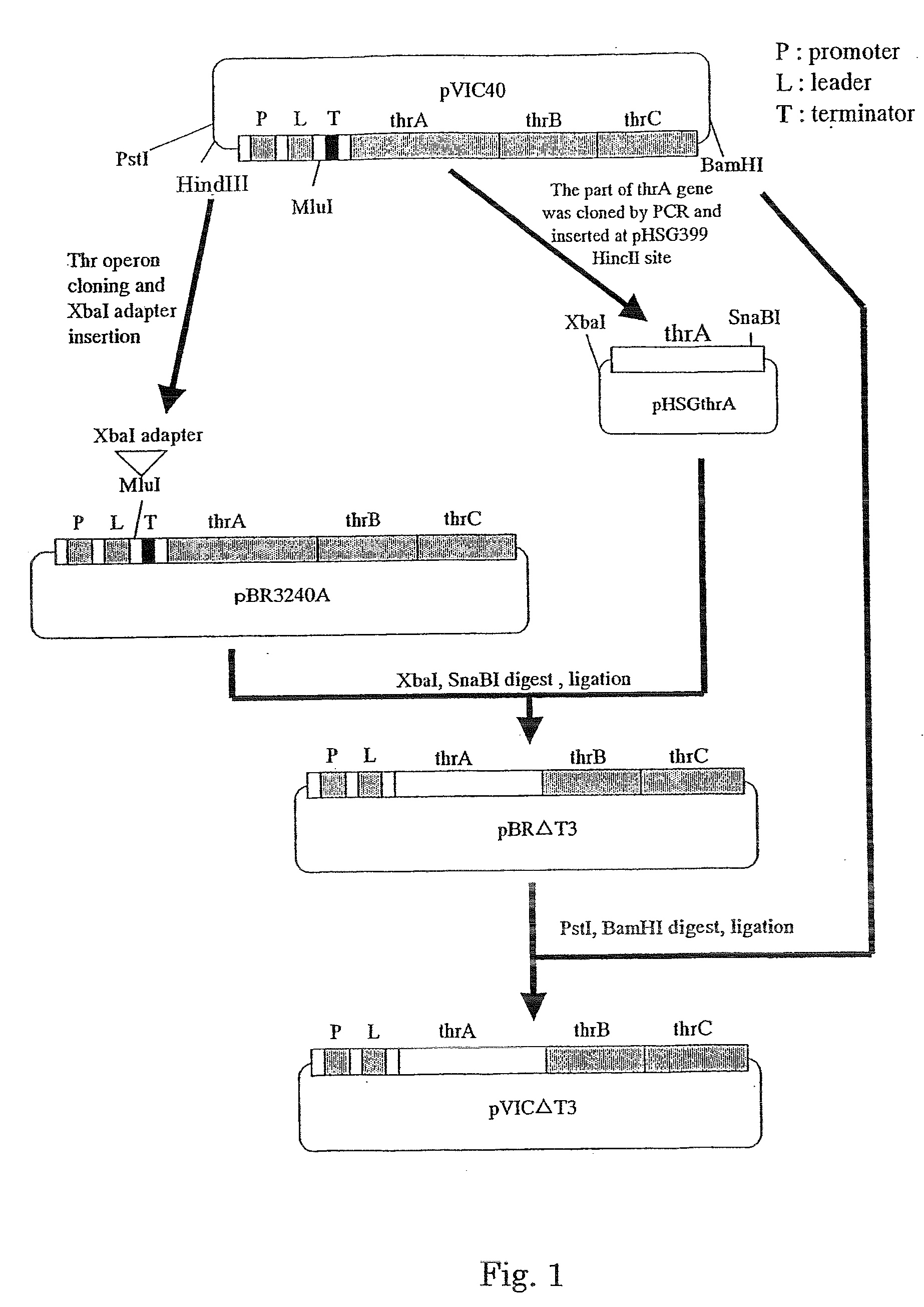
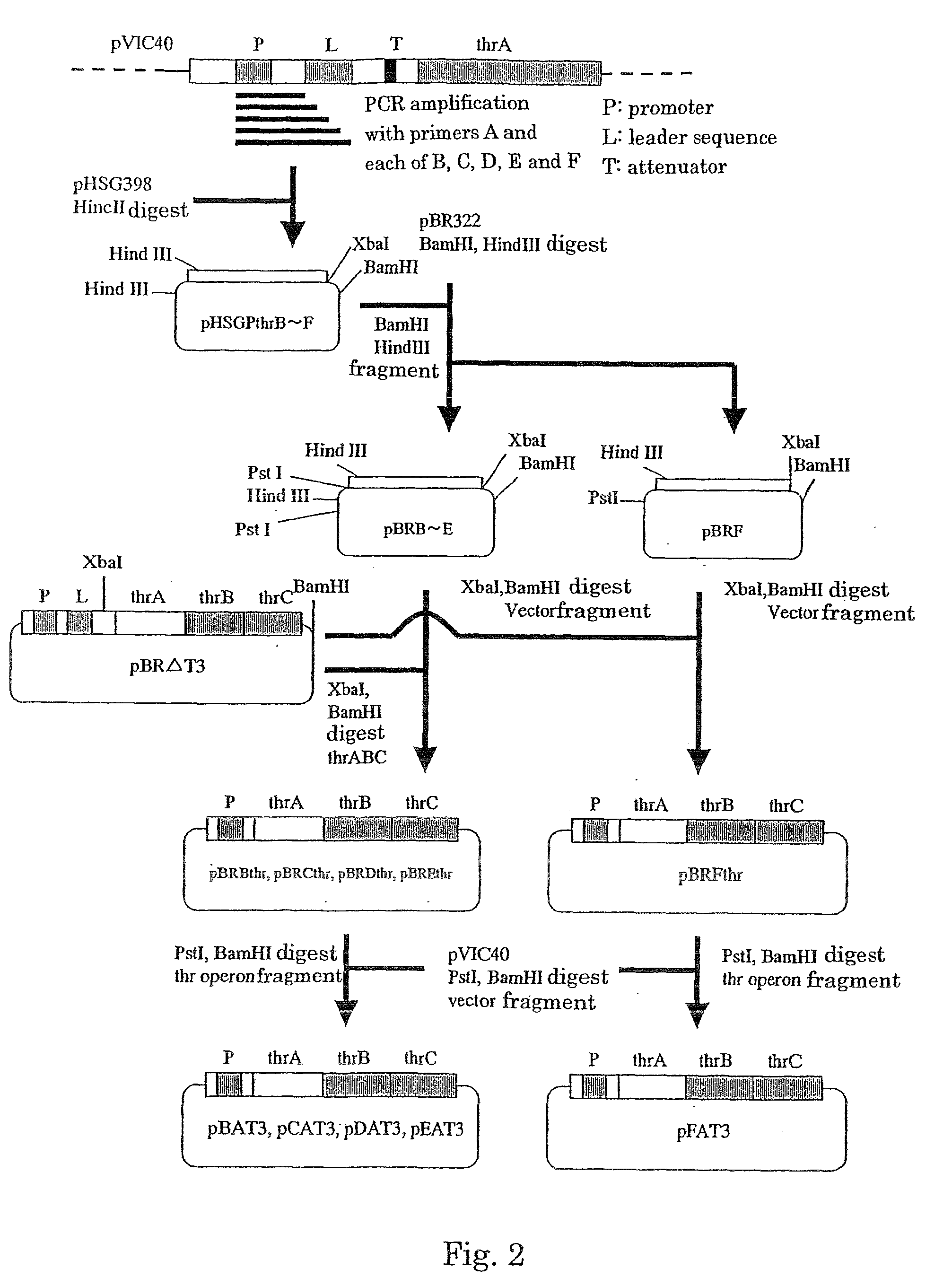
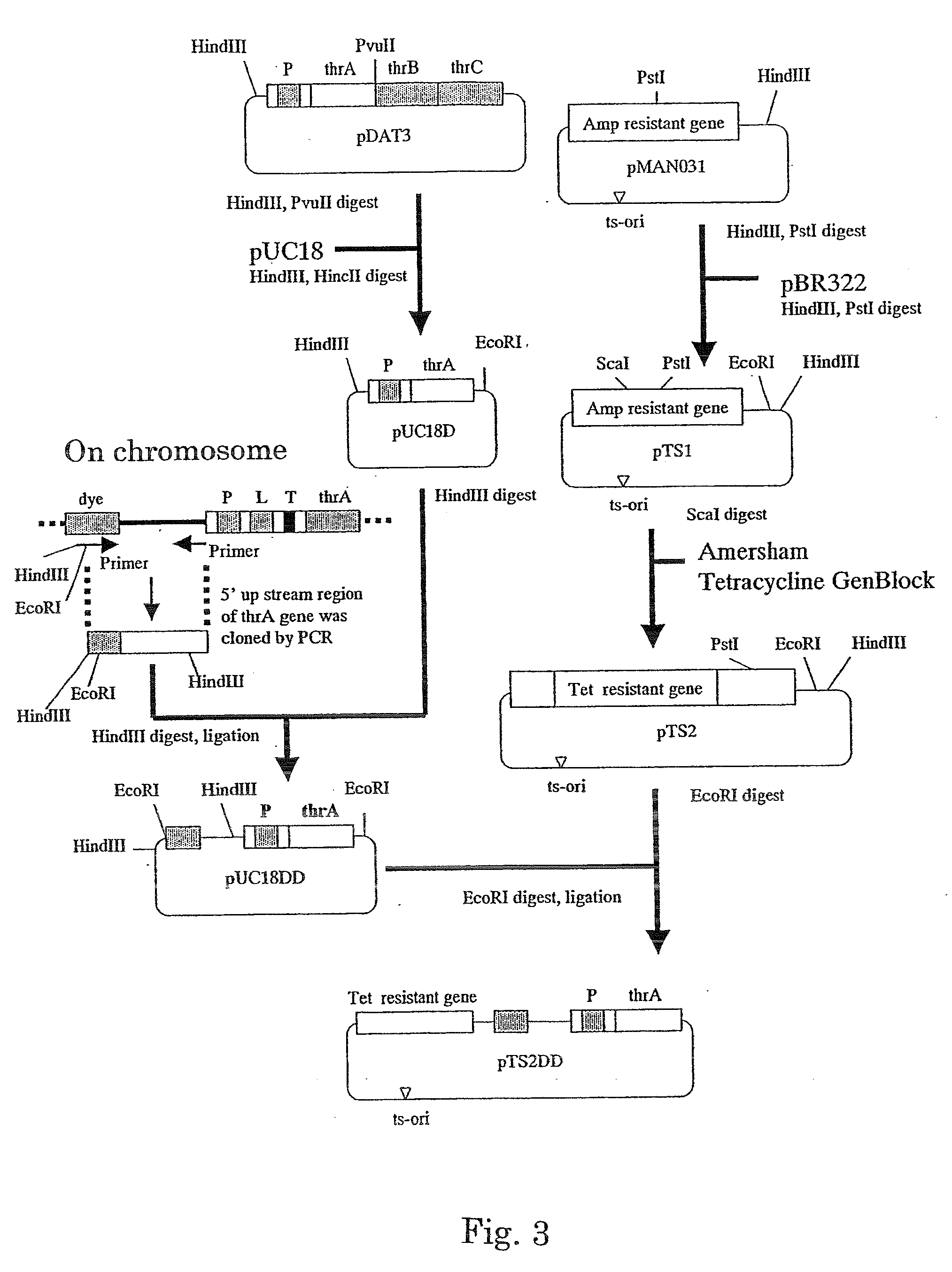
L-threonine or L-isoleucine is produced by culturing a bacterium which belongs to the genus Escherichia and has an ability to produce L-threonine or L-isoleucine, and wherein expression of a threonine operon is directed by its native promoter, and from which at least a leader sequence and an attenuator are deleted, in a medium and collecting the L-threonine or L-isoleucine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Composition for inducing proliferation or accumulation of regulatory t cells
ActiveUS20150143557A1Induce proliferation and accumulationImmunity in a living organism can be suppressedAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningRegulatory T cellT cell
It was found that bacteria belonging to the genus Clostridium induce accumulation of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the colon. Moreover, the present inventors found that regulatory T cells (Treg cells) induced by from these bacteria suppressed proliferation of effector T-cells. From these findings, the present inventors found that the use of bacteria belonging to the genus Clostridium or a physiologically active substance derived therefrom made it possible to induce proliferation or accumulation of regulatory T cells (Treg cells), and further to suppress immune functions.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Porcine circovirus 2 type inactivated vaccine
InactiveCN101240264ASimple processEasy to operateViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAdjuvantVaccine Production
The pig circular ring virus 2 type (PVC2) inactivated vaccine (SH individual plant) of the invention belongs to biotechnology field. The pig circular ring virus 2 type poisonous individual plant SH belongs to circular ring virus section circular ring virus genus which has been preserved in Wuhan institute of virology, Chinese academy of sciences. The shanghai separated individual plant SH of purified PCV2 virus is obtained by gathering raw material from hogpen which happened bad weaning piglet multisystem exhaustion failure syndrome in Shanghai in 2002 year, separating, appraising and purifying virus. The PCV2-SH plant is proliferated in mass in PK-15 cell, inactivated through methyl aldehyde and emulsified with liquid paraffine adjuvant to prepare conventional liquid paraffin(e) adjuvant immunomodulators for vaccines. The laboratory has trial-manufactured five lots vaccines successfully which are good safety and also can induce pig bring immune protection effect, made out a draft rules for vaccines production and testing. The inactivated vaccine proved by every aspects experiment has met state biological products standard completely.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Comparative phenotype analysis of two or more microorganisms using a plurality of substrates within a multiwell testing device
InactiveUS6046021ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEscherichia coliPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing microorganisms in a multitest format which utilizes a gel forming matrix for the rapid screening of clinical and environmental cultures. The present invention is suited for the characterization of commonly encountered microorganisms (e.g., E. coli, S. aureus, etc.), as well as commercially and industrially important organisms from various and diverse environments (e.g., the present invention is particularly suited for the growth and characterization of the actinomycetes and fungi). The present invention is also particularly suited for comparative analysis of phenotypic differences between cell types, including strains of microorganisms that have been designated as the same genus and species, as well as other cell types (e.g., mammalian, insect, and plant cells).
Owner:BIOLOG
Compositions and methods for the suppression of target polynucleotides from lygus
InactiveUS20090192117A1Reduces level of targetProcess controlOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSequence controlNucleotide
Methods and compositions are provided which employ a silencing element that, when ingested by a pest, such as a pest from the Lygus genus, they are capable of decreasing the expression of a target sequence in the pest. In specific embodiments, the decrease in expression of the target sequence controls the pest and thereby the methods and compositions are capable of limiting damage to a plant. The present invention provides various target polynucleotides from specific polypeptide families as disclosed herein, and further provides target polynucleotides set forth in SEQ ID NOS:1-21 or active variants thereof, wherein a decrease in expression of one or more the sequences in the target pest controls the pest (i.e., has insecticidal activity). Further provided are silencing elements which when ingested by the pest decrease the level of the target polypeptide and thereby control the pest. In specific embodiment, the pest is Lygus Hesperus. Plants, plant part, bacteria and other host cells comprising the silencing elements or an active variant or fragment thereof of the invention are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Canine probiotic Lactobacilli
According to the invention there is provided a strain of lactic acid bacteria of the genus Lactobacilli obtainable by isolation from resected and washed canine gastrointestinal tract having a probiotic activity in animals. Methods of use and compositions comprising the Lactobacilli of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:MARS INC
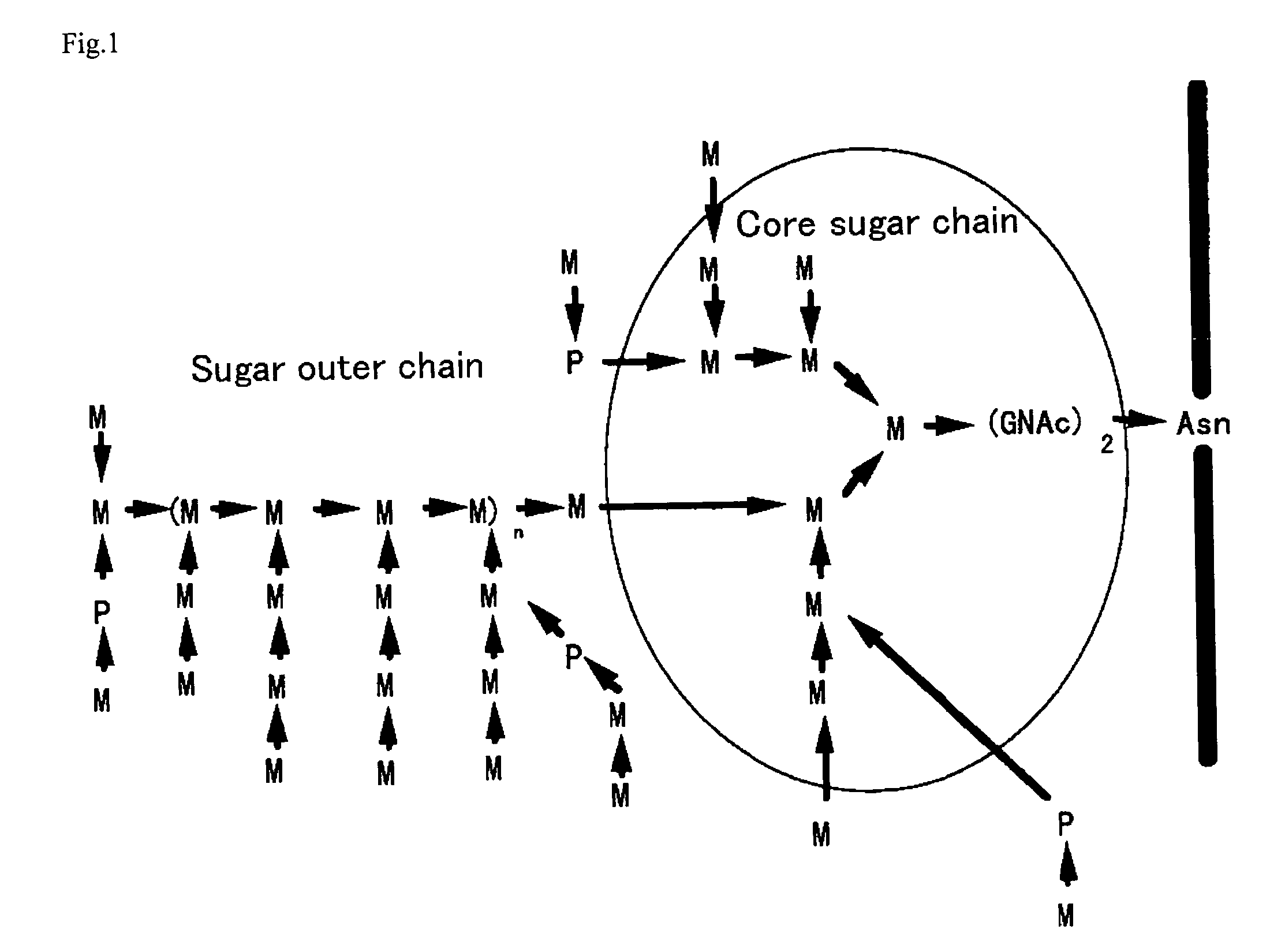
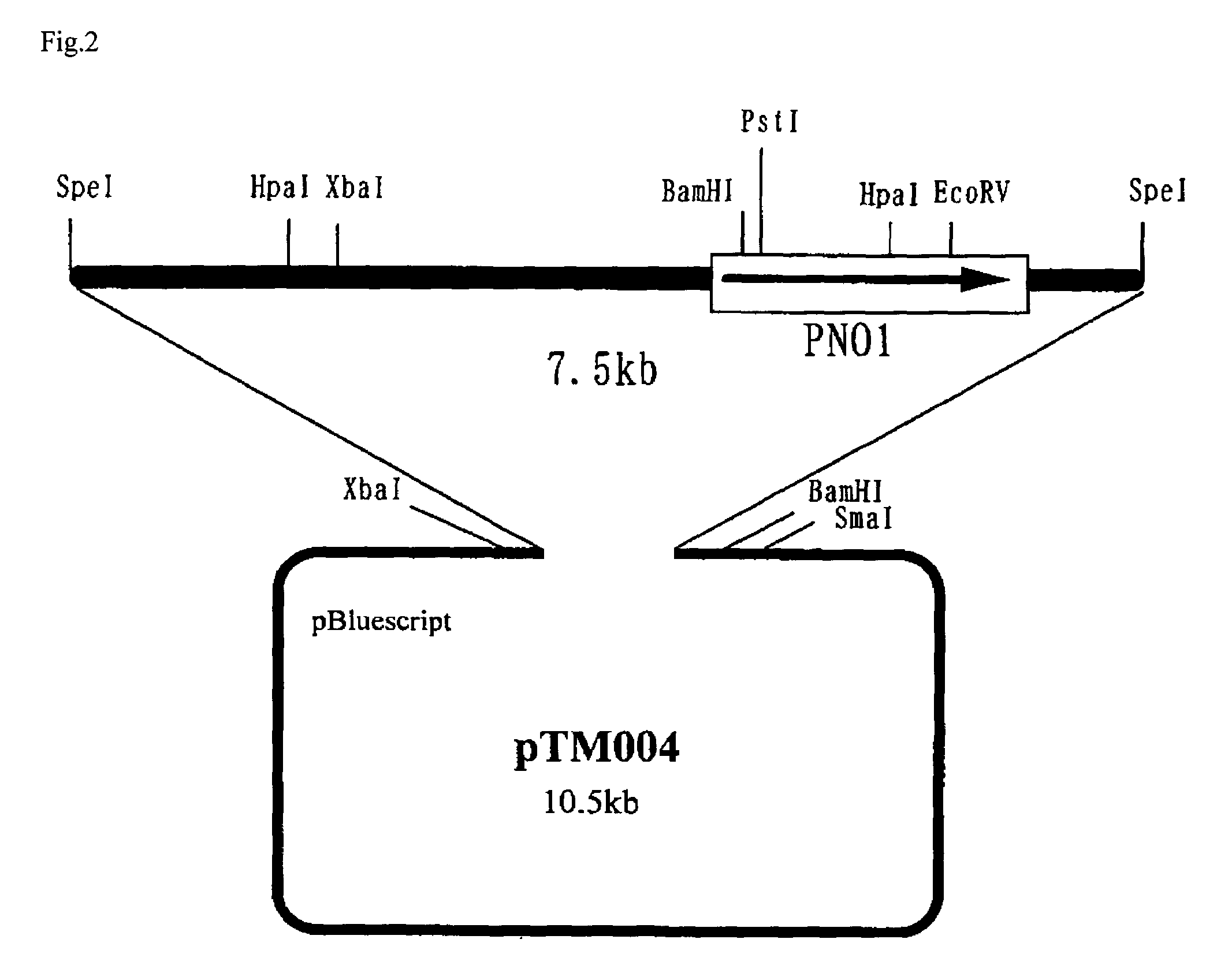
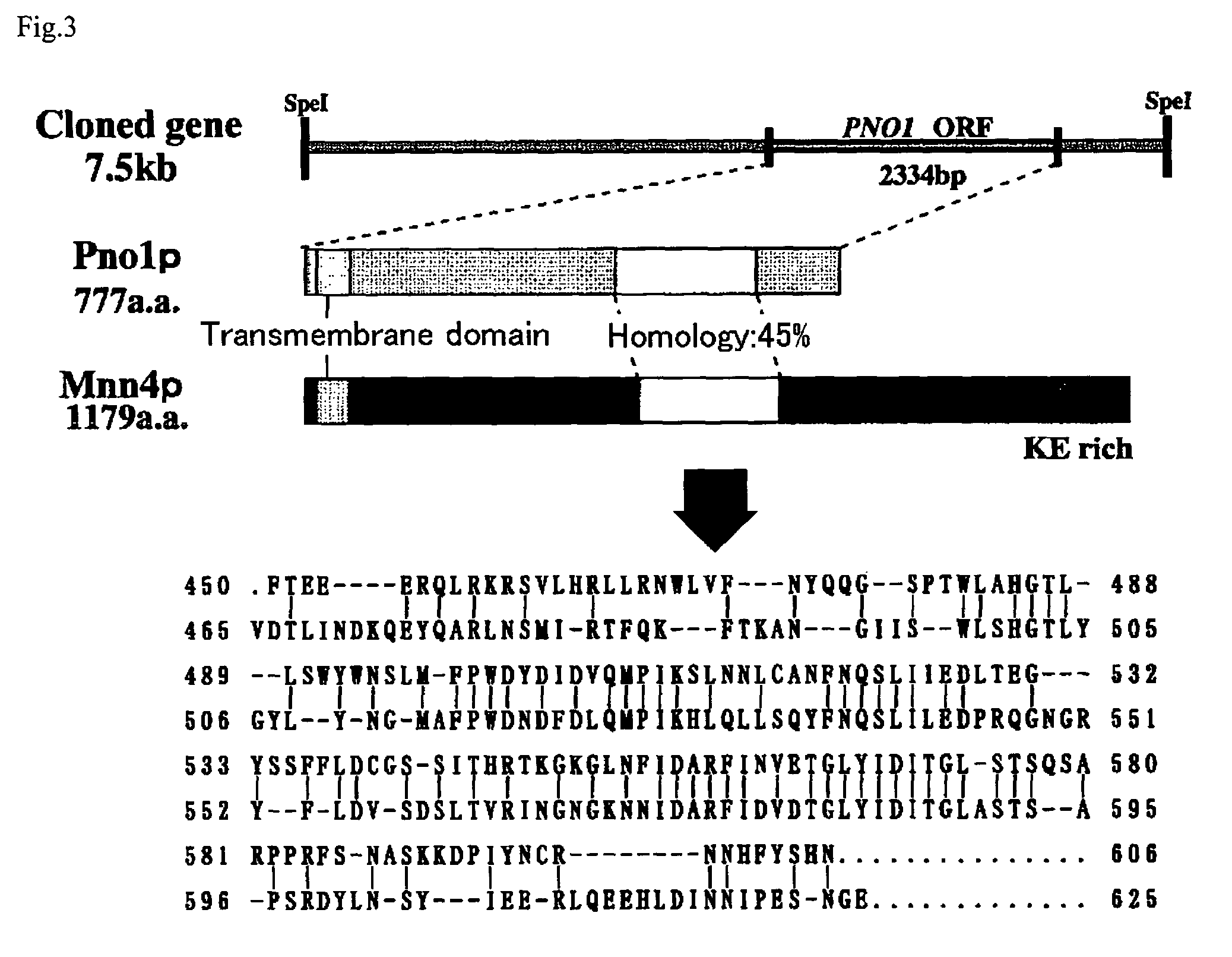
Process for producing protein with reduction of acidic sugar chain and glycoprotein produced thereby
The present invention intends to find out a gene participating in addition of mannose phosphate to a sugar chain of a glycoprotein originating in a yeast belonging to the genus Pichia and provide a means of controlling the same. The present invention also intends to provide a process for producing a protein with reduction of an acidic sugar chain by using the thus controlled yeast strain belonging to the genus Pichia. Namely, the present invention includes a protein participating in the addition of mannose phosphate to a sugar chain of a glycoprotein; a gene encoding this protein; a mutant of this gene; a vector carrying the mutant gene; a yeast strain belonging to the genus Pichia having been transformed by this vector; a process for producing a protein with reduction of an acidic sugar chain by using the transformed yeast strain; and a glycoprotein thus produced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
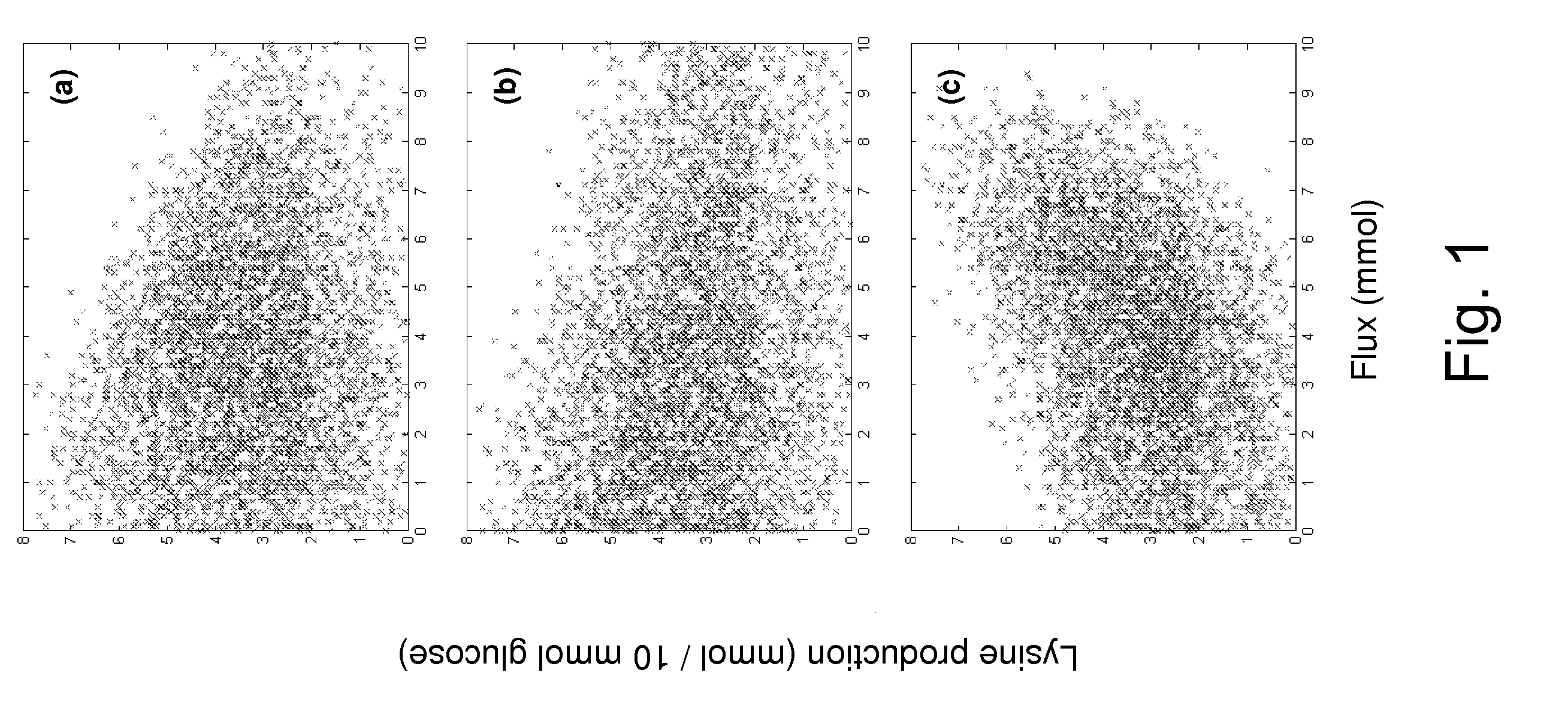
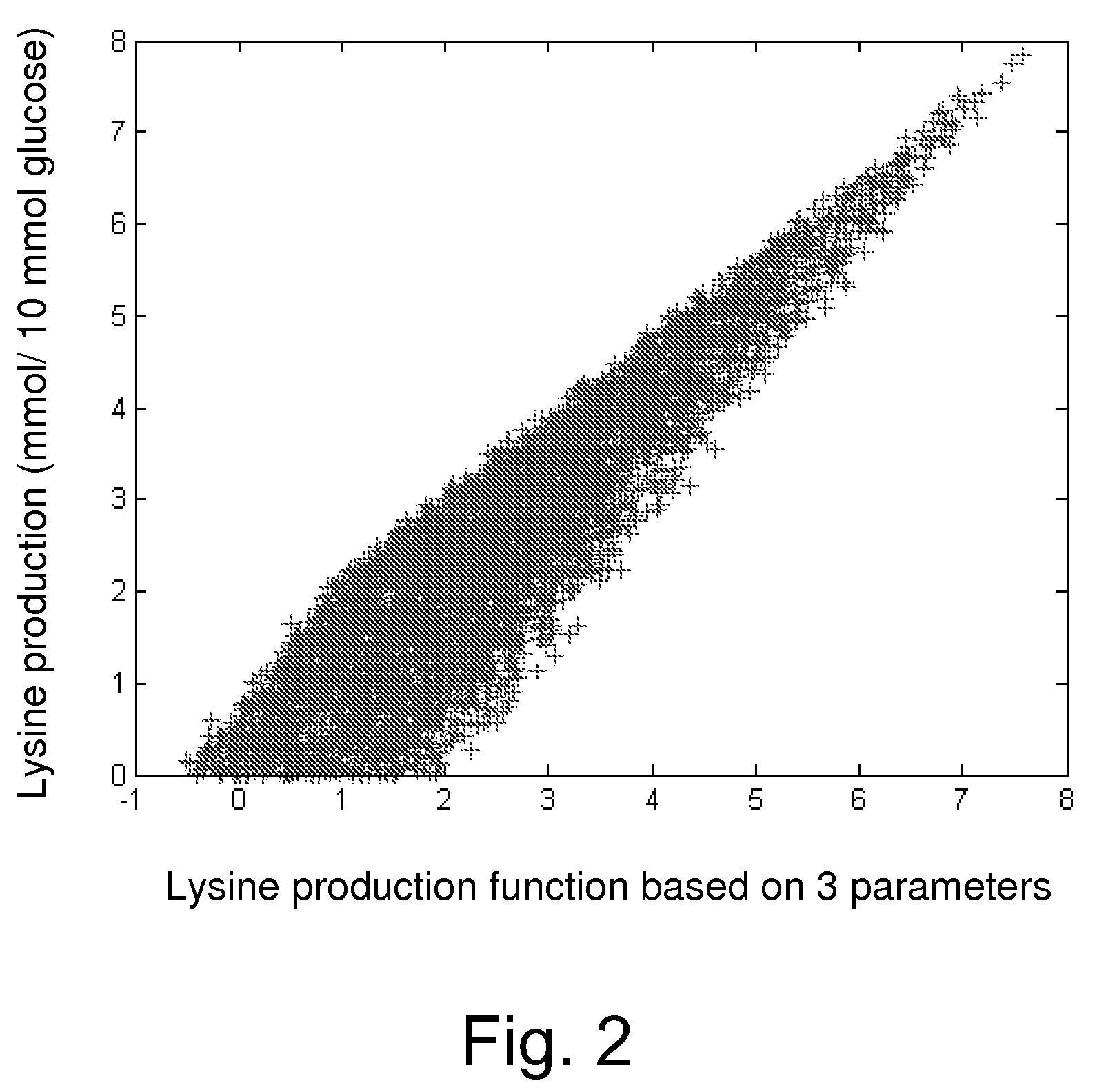
Method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine
A bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has an ability to produce L-lysine or L-threonine and which is modified so that a malic enzyme does not function normally in a cell, and a method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine, comprising culturing the bacterium in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of L-lysine or L-threonine, and collecting the L-lysine or L-threonine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
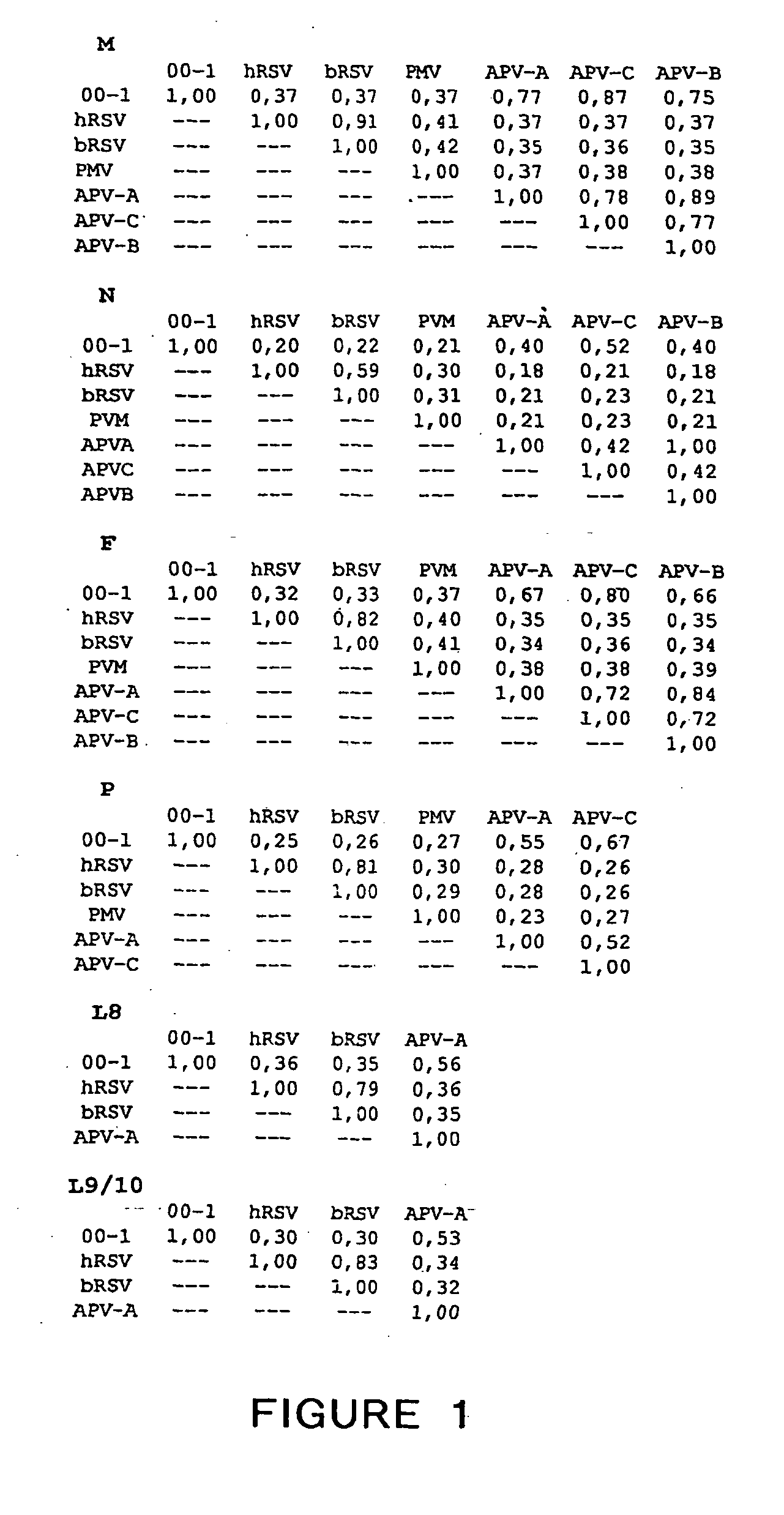
Metapneumovirus strains and their use in vaccine formulations and as vectors for expression of antigenic sequences and methods for propagating virus
ActiveUS20050019891A1Narrow downSymptoms improvedSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesNegative strandHeterologous
The present invention provides an isolated mammalian negative strand RNA virus, metapneumovirus (MPV), within the sub-family Pneumoviridae, of the family Paramyxoviridae. The invention also provides isolated mammalian negative strand RNA viruses identifiable as phylogenetically corresponding or relating to the genus Metapneumovirus and components thereof. In particular the invention provides a mammalian MPV, subgroups and variants thereof. The invention relates to genomic nucleotide sequences of different isolates of mammalian metapneumoviruses, in particular human metapneumoviruses. The invention relates to the use of the sequence information of different isolates of mammalian metapneumoviruses for diagnostic and therapeutic methods. The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding the genome of a metapneumovirus or a portion thereof, including both mammalian and avian metapneumovirus. The invention further encompasses chimeric or recombinant viruses encoded by said nucleotide sequences. The invention also relates to chimeric and recombinant mammalian MPV that comprise one or more non-native or heterologous sequences. The invention further relates to vaccine formulations comprising mammalian or avian metapneumovirus, including recombinant and chimeric forms of said viruses. The vaccine preparations of the invention encompass multivalent vaccines, including bivalent and trivalent vaccine preparations. The invention also provide methods for propagating virus.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Feline probiotic bifidobacteria
According to the invention there is provided a strain of lactic acid bacteria of the genus Bifidobacteria obtainable by isolation from resected and washed feline gastrointestinal tract having a probiotic activity in animals. Methods of use and compositions comprising the Bifidobacteria of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:MARS INC
Algal culture production, harvesting , and processing
InactiveUS20110138682A1Maintaining culture selectivityLoss of selectivityAlgae productsUnicellular algaeAlgaenanLipid formation
Materials and methods are provided for growing algae while maintaining culture selectivity. Algae that can be grown include, for example, green algae such as those of the genus Scenedesmus. Lipid obtained from the algae can be used to produce biofuels such as biodiesel or polyunsaturated fatty acids such as omega-3 fatty acids. Feedstocks such as animal feed and aquaculture feed can also be produced as can phytonutrients such as asataxanthin and beta-carotene.
Owner:AQUATIC ENERGY LLC
Anaerobic bacterium as a drug for cancer gene therapy
InactiveUS20050025745A1Efficient deliveryEffective gene therapyBiocideBacteriaAbnormal tissue growthBifidobacterium
The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the genus Bifidobacterium, by which DNA coding for a protein having an antitumor activity or DNA coding for a protein having the activity of converting a precursor of an antitumor substance into the antitumor substance is delivered to tumor tissues specifically under anaerobic conditions thereby expressing the protein encoded by the DNA, as well as a pharmaceutical composition comprising said anaerobic bacterium.
Owner:ANAEROPHARMA SCI
Family 44 xyloglucanases
The present invention relates to xyloglucanases belonging to family 44 of glycosyl hydrolases and having a relative xyloglucanase activity of at least 30% between pH 5 and pH 8 are derived from the genus Paenibacillus especially from a strain of Paenibacillus polymyxa or Paenibacillus sp. The xyloglucanases exhibit high performance in conventional detergent compositions.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for producing highly unsaturated fatty acids and lipid containing same
InactiveUS6958229B2Efficient productionImprove the level ofMicroorganismsAnimal feeding stuffLipid formationMicroorganism
A method for producing highly unsaturated fatty acids comprising culturing a microorganism, belonging to the genus Mortierella and having resistance to a carbon source, in a medium having a carbon source concentration of at least 4% by weight, and collecting highly unsaturated fatty acids from the cultured products. Culturing the microorganism for about a week gives at least about 7 g / L of highly unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
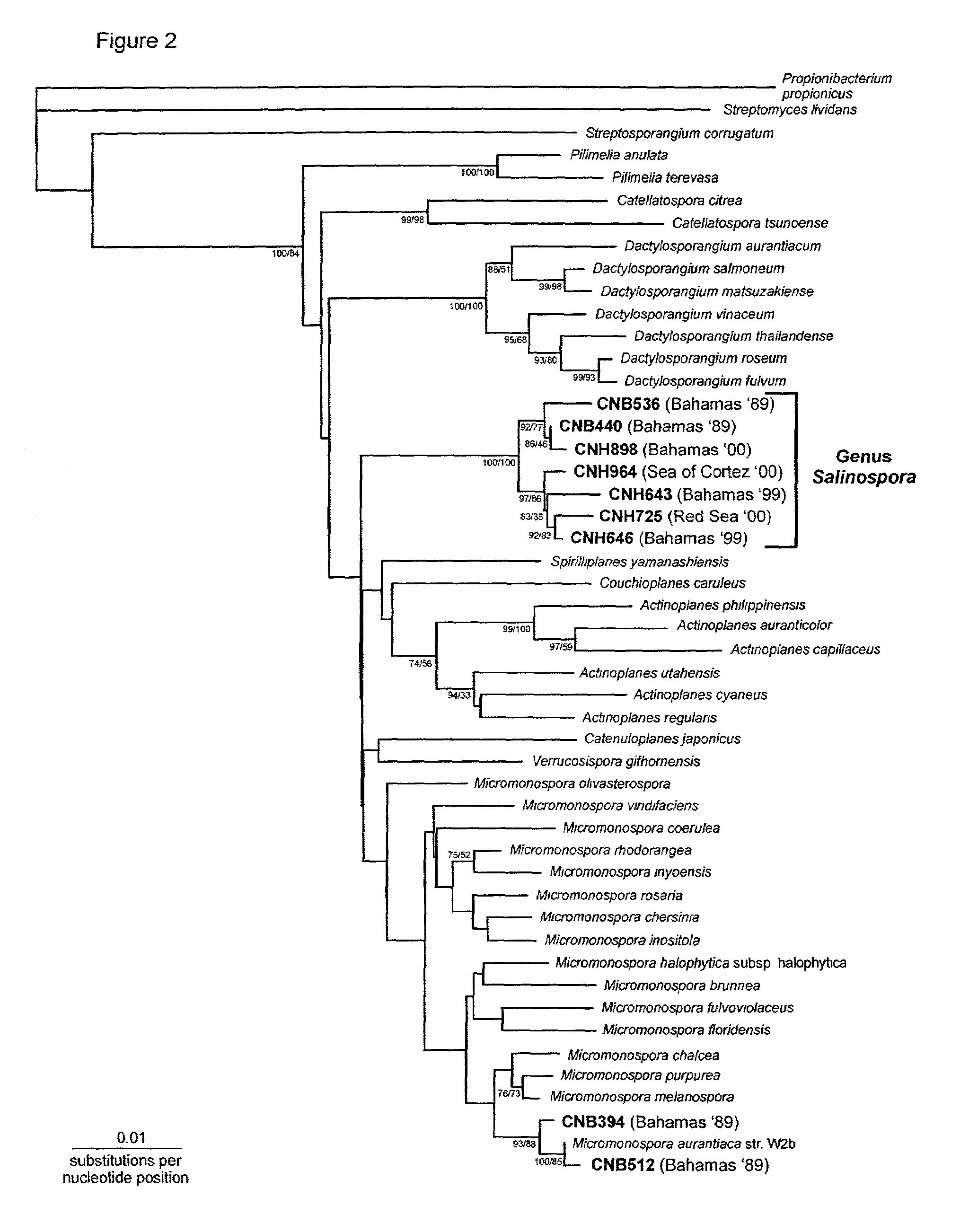
Marine actinomycete taxon for drug and fermentation product discovery
The invention is the discovery of an actinomycete genus, given the name Salinospora gen. nov., that displays an obligate requirement of seawater (Na+) for growth and unique 16S rRNA signature nucleotides. The invention is also the use of the genus for the production and discovery of active biomolecules such as pharmaceutical agents, agrichemicals, immunomodifiers, enzymes and enzyme inhibitors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Feline probiotic Lactobacilli
According to the invention there is provided a strain of lactic acid bacteria of the genus Lactobacilli obtainable by isolation from resected and washed feline gastrointestinal tract having a probiotic activity in animals. Methods of use and compositions comprising the Lactobacilli of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:MARS INC
Compositions of Hoodia Gordonii and Pinolenic Acid Derivatives
The present invention is directed to compositions containing a pine nut oil and an extract from the genus Hoodia or Trichocaulon and methods of treatment for weight loss.
Owner:SOFT GEL TECHNOLGIES
Combinatorial screening of mixed populations of organisms
InactiveUS7018793B1Quick filterLess immunogenicSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganismGenus
Provided is a method of screening gene libraries derived from a mixed population of organisms for a bioactivity or biomolecule of interest. The mixed population of organisms can be a cultured population or an uncultured population from, for example, the environment. Also provided are methods of screening isolates or enriched populations of organisms, which isolates include a population that is spatially, temporally, or hierarchical, for example, of a particular species, genus, family, or class of organisms. Identified clones containing a biomolecule or bioactivity of interest can be further variegated or the DNA contained in the clone can be variegated to create novel biomolecules or bioactivities of interest.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com