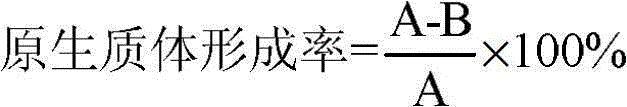Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
997 results about "Protoplast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protoplast, from ancient Greek πρωτόπλαστος (prōtóplastos, "first-formed"), is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means.
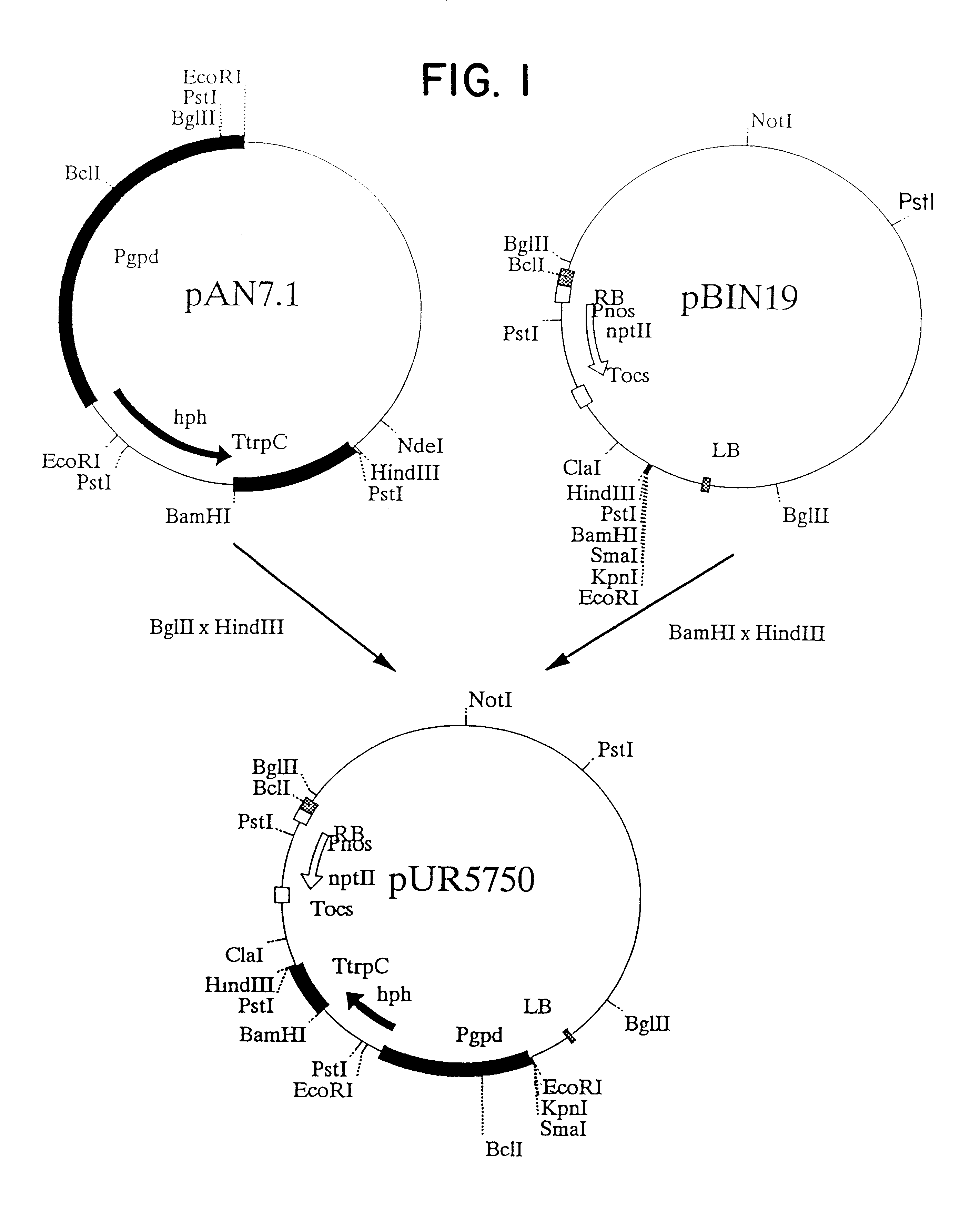
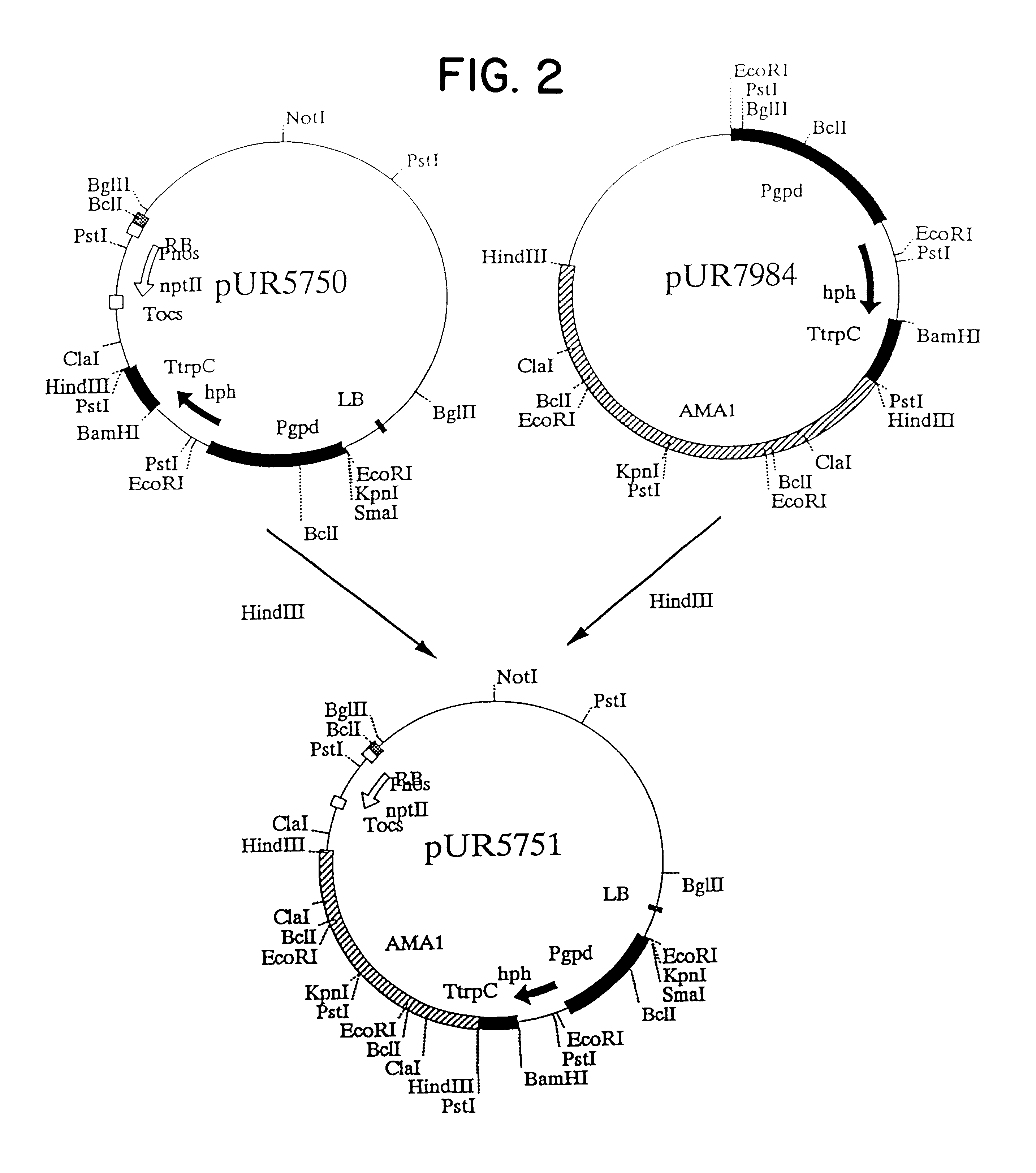
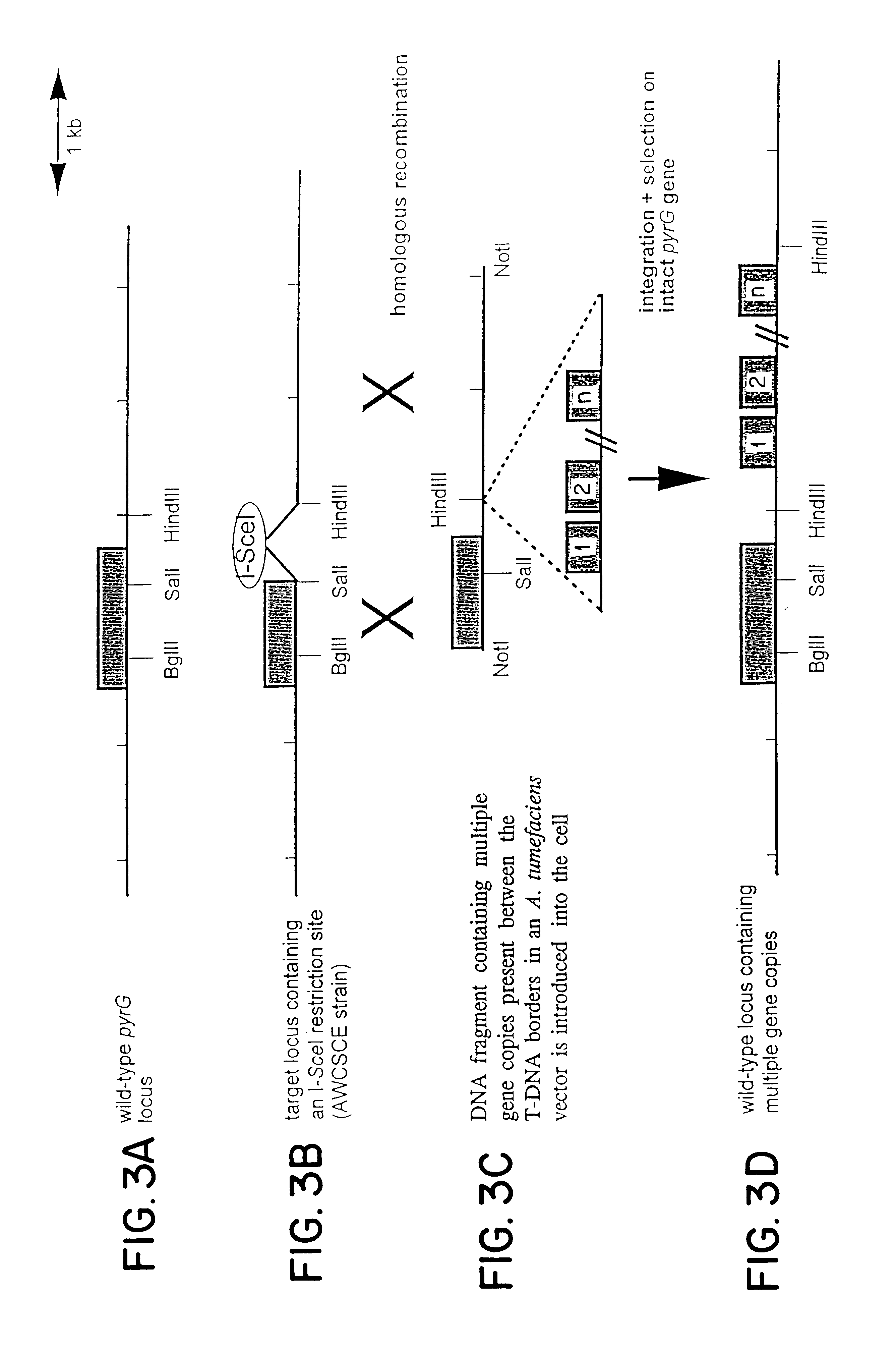
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of biology breeding and in particular relates to an agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta (Ustilago esculenta) transformant strain as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain, an agrobacterium infected receptor of the transformant strain refers to ustilago esculenta (Ustilago esculenta). The method for preparing the agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a fungal expression vector; (2) preparing agrobacterium competence; (3) performing electrotransformation on the agrobacterium; and (4) performing agrobacterium-mediated transformation, thereby obtaining the transformant. A complex protoplast is not needed, the receptor source is simple, and spores and hypha of the fungi can be directly used for transformation; and the transformation efficiency is high. In addition, the obtained transformant is large in single-copy ratio, and marker genes are conveniently obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD +1
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
Strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan
InactiveCN102816701AReduce use costHigh polysaccharide yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the fields of microbe application technologies and food biotechnologies, and discloses a strain used for fermenting rice bran and wheat bran extracts for producing grifolan. The grifola frondosa strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in Wuhan, China on Aprial 7th, 2011, and has a strain collection number of CCTCC No: M2011113. The name of the strain is Grifolasp. JSU10-2. According to the invention, through protoplast laser mutation, the strain with high yield of mycelium polysaccharide produced from cheap raw materials is obtained. When the strain and an original strain are respectively used in liquid fermentation of a rice bran and wheat bran composite culture medium, the dry weight and polysaccharide of the mutant strain are respectively increased by 31.7% and 32.6% compared with those of the original strain.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/-CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105316327AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionTriticeaeGenetically modified wheat
The invention provides a wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / -CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof and belongs to the field of crop molecular biology. The wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector and the application thereof have the advantages that gRNA of a third exon of specificity-targeted TaAGO4a is provided firstly, a DNA sequence of the gRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the gRNA contains an enzyme cutting site XmnI; subsequently, the CRISPR / Cas9 vector containing the gRNA is provided, and through co-transformation of Cas9 and the specific gRNA into a wheat protoplast as well as enzyme cutting and sequencing technologies, the condition that the gRNA can guide the Cas9 to cut three copies positioned on a chromosome 3A, a chromosome 3B and a chromosome 3D of the TaAGO4a respectively can be detected successfully so as to cause frameshift mutation of the gene and result in afunction or excalation of the gene; the wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector can be used for preparing TaAGO4a gene-deleted transgenic wheat.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Zea mays (L.) with capability of long term, highly efficient plant regeneration including fertile transgenic maize plants having a heterologous gene, and their preparation
InactiveUS6284945B1Careful shakingPromote shakingTransferasesPlant tissue cultureHeterologousCallithamnion granulatum
Protoplasts which regenerate reproducibly in a short time to normal, fertile plants can be regenerated from an auxin-autotrophic genotype of Zea mays (L.). Starting from immature embryos on hormone-free media, an auxin-autotrophic, embryogenic callus is formed on the shoot basis of the seedlings, which callus retains its embryogenic potential over a substantial period of time when subcultured on hormone-free medium. In addition to fully-developed embryos, adventitious embryos are also formed under suitable culture conditions (6-9% of sucrose in the medium). When the sucrose content is reduced to 2-3% and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is added, soft, granular calli are formed which consist of embryogenic cell aggregates (type II callus). After subculturing the type II callus in the form of a cell suspension culture, totipotent protoplasts can be isolated. From these protoplasts, the maize plants according to the invention are regenerated.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Method for producing vitamin K2 by utilizing bacillus natto
InactiveCN102808005AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationVitamin K2Protoplast
The invention aims to disclose a method for producing vitamin K2 by utilizing bacillus natto. Protoplast fusion is conducted on bacillus natto BS-53 highly yielding the vitamin K2 and bacillus natto CICC10262 having a high growth speed but a low vitamin K content, and fusants with parent advantages are screened out; obtained high-yield strains having a high growth speed are utilized to produce the vitamin K2 under an optimized fermentation condition; and isopropanol and n-hexane are utilized to extract and separate the vitamin K2. The growth speed of the strains and the yield of the vitamin K2 is increased and an effective method is provided for scale production of the vitamin K2, thereby realizing the aim of the invention.
Owner:上海红马饲料有限公司
Method for generating resistance against citrus diseases caused by insects, fungi, oomycetes, bacteria or nematodes
ActiveUS20110119788A1Reduce accumulationAchieve resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNematodeWhole body
The invention consists in modifying the levels of accumulation and emission of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes in citrus as a mechanism to achieve systemic resistance against pathogens or repellency against pests. The alteration of the content of d-limonene and other terpenes is achieved by genetic transformation via the introduction of a gene that encodes an enzyme with d-limonene synthase activity, from a citrus fruit or plant or from another living organism, in antisense or RNAi (RNA interference) configuration. Genetic modification is achieved either by Agrobacterium tumefaciens or any other method of genetic transformation of plants from protoplasts or explants. The construction is incorporated in citrus genotypes or related genera of the family Rutaceae in order to reduce the levels of accumulation and emission of the monoterpene and precursor compounds and / or derivatives, either of leaves or flowers and / or fruit.
Owner:INST VALENCIANO DE INVESTIGACIONES AGRARIAS IVIA
Method for performing transient expression by introducing foreign gene into poplar bioplast
InactiveCN102373235AEasy to operateEasy to implementVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsEtioplastsPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for performing transient expression by introducing a foreign gene into a poplar bioplast. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a transient expression vector containing a foreign gene into a poplar bioplast by using PEG (Polyethylene Glycol)-Ca<2+>; culturing; and expressing the foreign gene in the bioplast. A poplar bioplast transient expression system constructed with the method is easy to operate and realize, a place with broad prospects is opened up for the research of functional genes of a poplar, and the transformation efficiency of the method can be up to 70 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method of cutting propagation of peony immature stem
ActiveCN103493677AEasy to synthesizeAccelerates and induces divisionCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAxillary budGrowth retardant
The invention belongs to the field of plant tissue cultivation, and particularly relates to a method of cutting propagation of a peony immature stem. The method includes the steps of material selection, cutting cultivation, indoor management, oversummer maintenance, overwinter management and strong seedling cultivation. By using low-frequency ultrasonic waves to conduct processing, rooting can be promoted, plant cell division can be remarkably accelerated and induced, the cell growth is stimulated, protein synthesis of protoplast can be accelerated, and the adventitious bud reproducibility can be improved. Due to the fact that intermittent irradiation is adopted, no drastic cavitation effect can be produced, and partial damage to cells caused by the ultrasonic waves can be avoided. Due to the fact that cultivation and rooting are conducted in the dark cultivation process, growth inhibitor is greatly reduced, and rooting is facilitated. The complete and specific method including the steps of oversummer maintenance, auxiliary bud inducing, overwinter management and strong seedling cultication is provided, and therefore application of the peony rapid cutting propagation technology in actual production is promoted, and the method has significance in large-scale production of peony seedlings.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
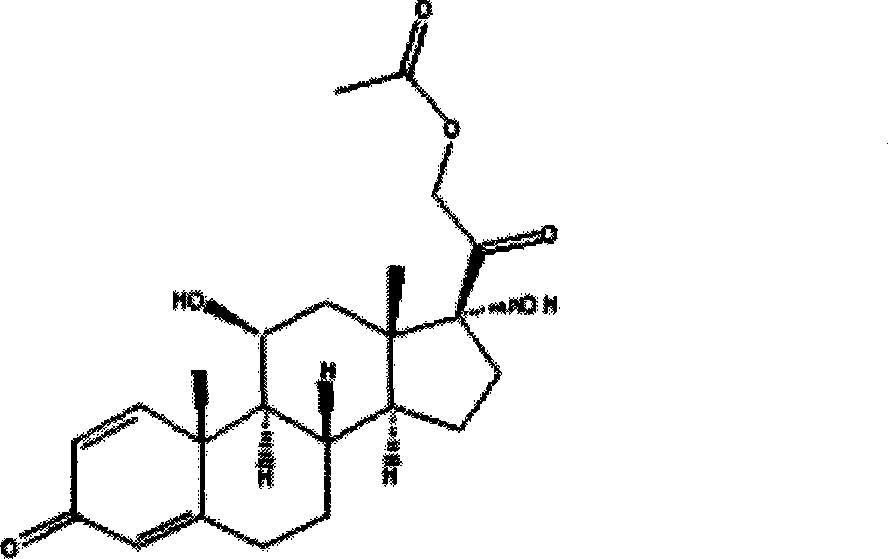
Method for producing prednisolone acetate
InactiveCN101210259AStrong response specificityEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobial transformationArthrobacter simplex
The invention belongs to the field of microbial pharmaceutics and pharmaceutical engineering, specifically relates to a production method of prednisone acetate by microbial transformation with Arthrobacter simplex as bacteria strain and hydrocortisone acetate as substrate. The method uses Arthrobacter simplex as bacteria strain and comprises the following steps of: performing primary seed culture, performing second fermentation culture, adding hydrocortisone acetate into the fermentation liquid of Arthrobacter simplex to transform hydrocortisone acetate into prednisone acetate, filtering, and collecting cake to obtain prednisone acetate. The bacteria can be prepared into double liquid phase, broken cells or protoplast, each of which has high transformation ratio. The inventive production method replaces cortisone acetate with hydrocortisone acetate as raw material, and has the advantages of high yield, simple process, good economical and practical performance, and less use of harmful reagents; and is important for steroids production with biotransformation method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
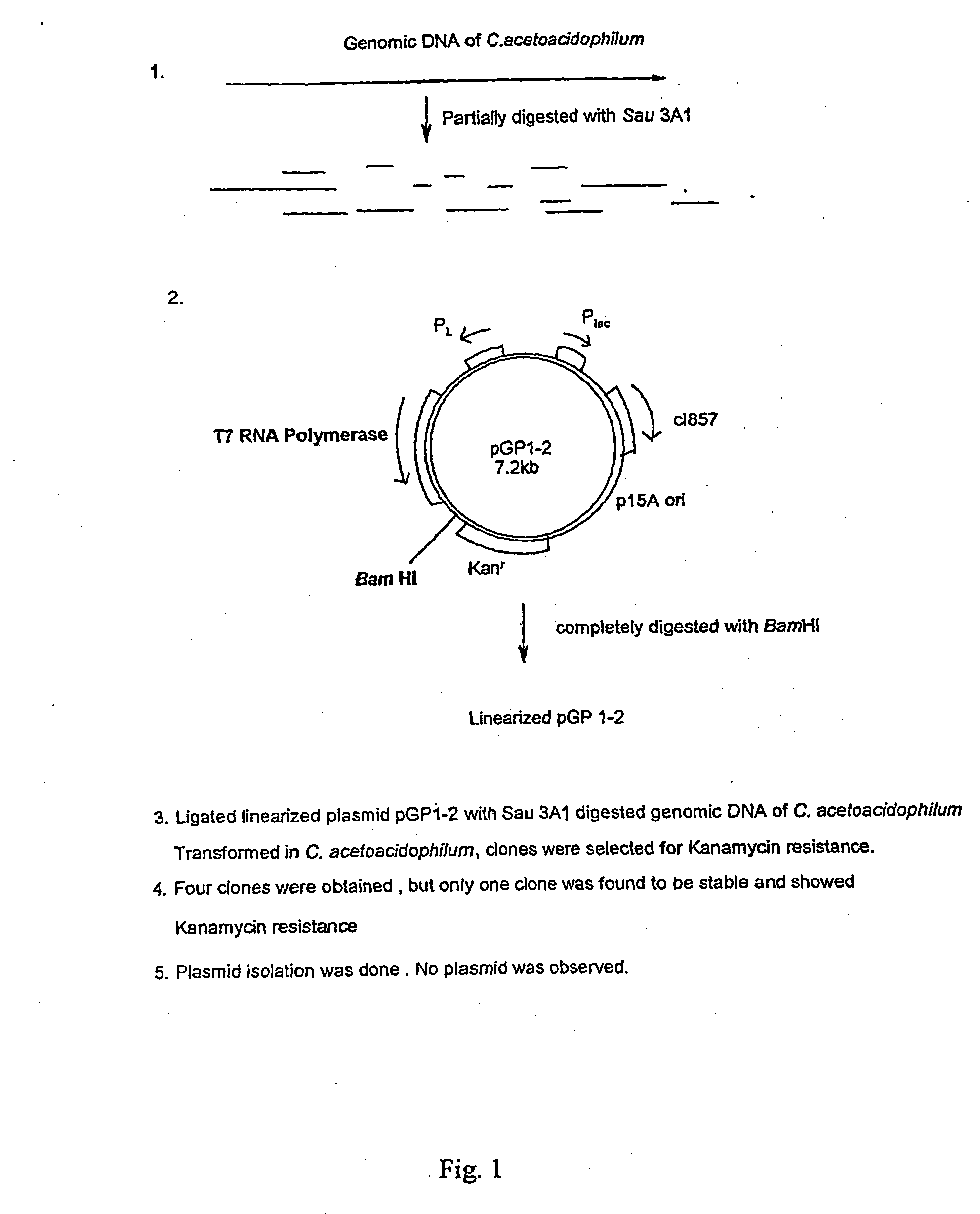
Method for specific integration of t7 rna polymerase gene in the chromosome of corynebacterial and the resultant corynebacteria-t7 promoter based shuttle vector system
The present invention relates to method for obtaining optimum expressed proteins in a transformed gram positive bacteria by specific integration of T7 RNA polymerase gene into the chromosome of a gram positive bacteria exhibiting resistance to aminoglycosides, said method comprising:- digesting an E. coli plasmid with a restriction enzyme- digesting the genomic DNA of said gram positive bacteria- ligating the said digested plasmid to the digested genomic DNA of said gram positive bacteria- transforming the said gram positive bacteria protoplasts with the said ligation mixture of step 2 to yield transformed gram positive bacteria (transformants),- screening the said transformants for kanamycin resistance and aminoglycoside sensitivity to ensure that the targetting of the said plasmid vector into the chromosome of the said gram positive bacteria is successful- cloning of the desired gene in the said vector—culturing the transformant in a suitable culture medium- isolating the expressed proteins from the culture medium
Owner:INDIAN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing and regenerating phomopasis asparagi protoplast
InactiveCN103451110AHigh number of preparationsHigh regeneration rateFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumEtioplasts
The invention discloses a method for preparing and regenerating a phomopasis asparagi protoplast, which relates to the technical field of fungus protoplast preparation and regeneration in cell engineering. The method comprises the following detailed operation steps of: (1) preparing a phomopasis asparagi conidium suspension; (2) preparing a fresh mycelium; (3) performing enzymolysis on mycelium cell walls; (4) separating the protoplast; and (5) regenerating the protoplast. The method is easy to operate, low in requirements on equipment and short in enzymolysis time and regeneration period, and effectively enhances the efficiency of preparation and regeneration of the protoplast.
Owner:VEGETABLE & FLOWER INST JIANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
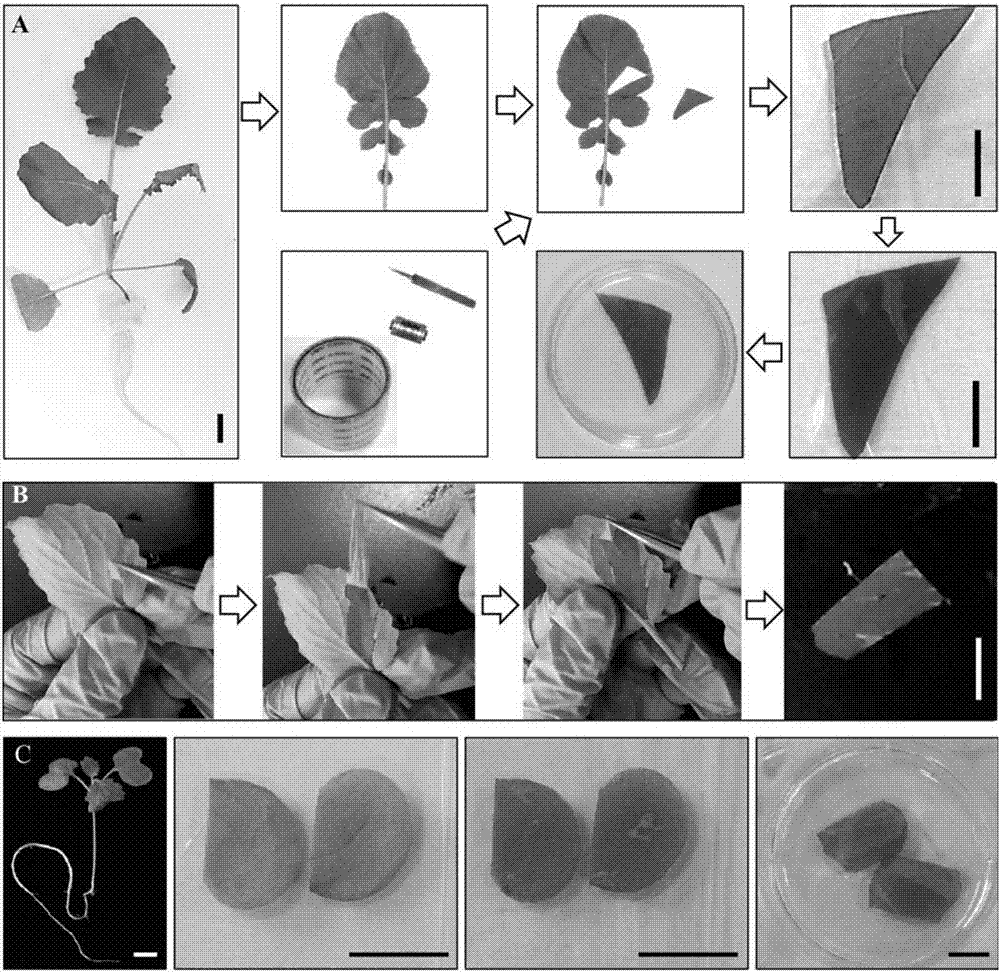
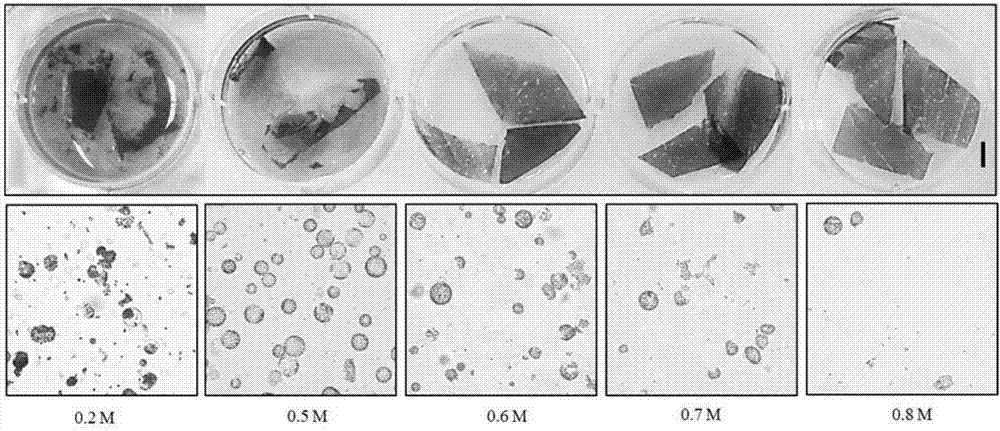
Preparation method of Calibrachoa protoplast
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Calibrachoa protoplast. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing tender leaves in 3-5DEG C clear water under dark conditions for 20-25h; carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis on the preprocessed blades by using an enzymatic hydrolysis solution; adding a CPW washing solution having a same volume with the enzymatic hydrolysis solution, shaking up, filtering by using a 300 mesh cell sieve, centrifuging at a rotating speed of 1100r / min for 2min, and absorbing the obtained supernatant; and adding a CPW washing solution to the obtained precipitate to wash a protoplast, centrifuging at a rotating speed of 1100r / min for 2min, collecting the obtained precipitate, adding a suspension, and suspending to obtain the protoplast with the output of (4.7-5.3)*10<6> / g and the activity of 85%, wherein the activity of 80% of the protoplast is maintained 9h later. The protoplast with high activity, high output and good state is obtained through a separation technology, protoplast culturing and plant regeneration conditions are met, and an experiment material is provided for plant protoplast fusion cultivation of new kinds.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Engineering bacterium for producing Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and applications thereof
InactiveCN102226165ANo activation requiredEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaFatty-oils/fats refiningVegetable oilA-DNA
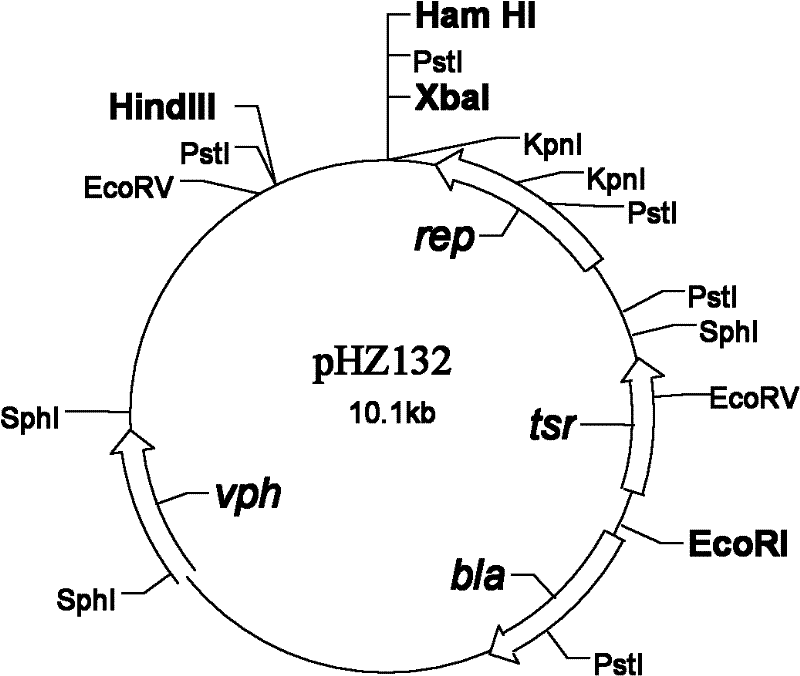
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for producing a PL A2 and applications thereof. A preparation method of the PLA2 comprises the following steps: A, preparing a PLA2 gene: designing a primer PCR and amplifying a PLA2 gene fragment, and cloning a DNA fragment containing the PLA2 gene (a sequence is SEQ ID NO.2) with an amplified fragment plaT as a probe; B, constructing a recombinant plasmid: cloning a Bam H1 restricted fragment with the size of 3 kb which contains the PLA2 gene to a high-copy plasmid pHZ132 to obtain a recombinant plasmid pLH 001; and C, constructing the engineering bacterium: introducing the plasmid pLH001 into a streptomyces lividans 1326 of a host bacterium through protoplast transformation to obtain a streptomyces lividans LH001 of the engineering bacterium. The engineering bacterium has good stability and the introduced plasmid is not easy to lose. The secretory active PLA2 (an amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.1) can be generated through liquid fermentation, the enzymatic activity of a fermentation liquid is equal to or more than 2,000 U / mL, and the enzyme production capability is better than present levels. The PLA2 can be applied to fields of vegetable oil degumming, lysophospholipid preparation and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Protoplast mutation breeding method for improving cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN103215250AGood mutagenic effectEasy to operateFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention relates to a protoplast mutation breeding method for improving the cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps of activated culture of bacterial strains, solid culture of mycelia, liquid mycelia culture, mycelia enzymolysis, protoplast nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutation, protoplast regeneration culture, regenerated bacteria subculture, fermentation culture, filtering, further washing of mycelia, measurement of cordycepin content in the mycelia, preservation of the bacteria strain with high cordycepin content, measurement of the genetic stability and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the cordycepin content of the cordyceps militaris can be increased.
Owner:XUZHOU HONGYU AGRI TECH
Manufacturing technique for garamycin B
InactiveCN101250571AHigh purityIncrease production capacityMicroorganism based processesHybrid cell preparationMicromonospora echinosporaGentamicin B
The invention discloses a process for producing gentamicin B and a cell protoplast fusion technique is adopted to select a new strain which takes the gentamicin B as a main component through breeding producing strains (micromonospora echinospora) of micronomicinin. The process for producing the gentamicin B which is disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the whole production cycle is shortened, the purity of the gentamicin B is increased, the purity of the gentamicin B which is produced is increased from original 85% to present 90%, the production cost is lowered, and the production capacity of the gentamicin B is extremely increased.
Owner:江西制药有限责任公司
Preparation method and application of paddy rice green protoplast
InactiveCN102311937AIncrease vitalityGood growthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
According to the invention, the culture time of paddy rice is shortened by adjusting the growing conditions of paddy rice seedlings; a paddy rice green protoplast is prepared by an enzyme method; the preparation method is optimized, so vacuum pumping and the usage of a highly toxic reagent are avoided; and thus the preparation method of the paddy rice green protoplast is simpler and safer. The protoplast prepared by the method of the invention has a high cell survival rate, and a high transformation rate, is applicable to various analysis such as subcellular localization of target gene codingprotein, protein interaction, western blotting and the like, and is especially applicable to instantaneous expression research of light / chloroplast related gene.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast
The present invention relates to a method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast. The method comprises: (1) adopting plant petals as a material, and carrying out enzymolysis to obtain petal cell protoplast; (2) standing the petal cell protoplast for 20-40 min at a temperature of 2-8 DEG C; and (3) transforming plasmid into the protoplast by using a PEG and Ca<2+>-mediated method, and expressing the target protein. Compared with the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following beneficial effects that: the target protein can be expressed in a short time, the protoplast protein expression system can be used for research on target protein subcellular positioning and protein molecule interaction, the activity of the protoplast is normal, and the target protein expression detection results show that the method can be used for research on gene transcription level, protein expression level and substance metabolism level change in living cells and is the rapid and convenient target gene function research method.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
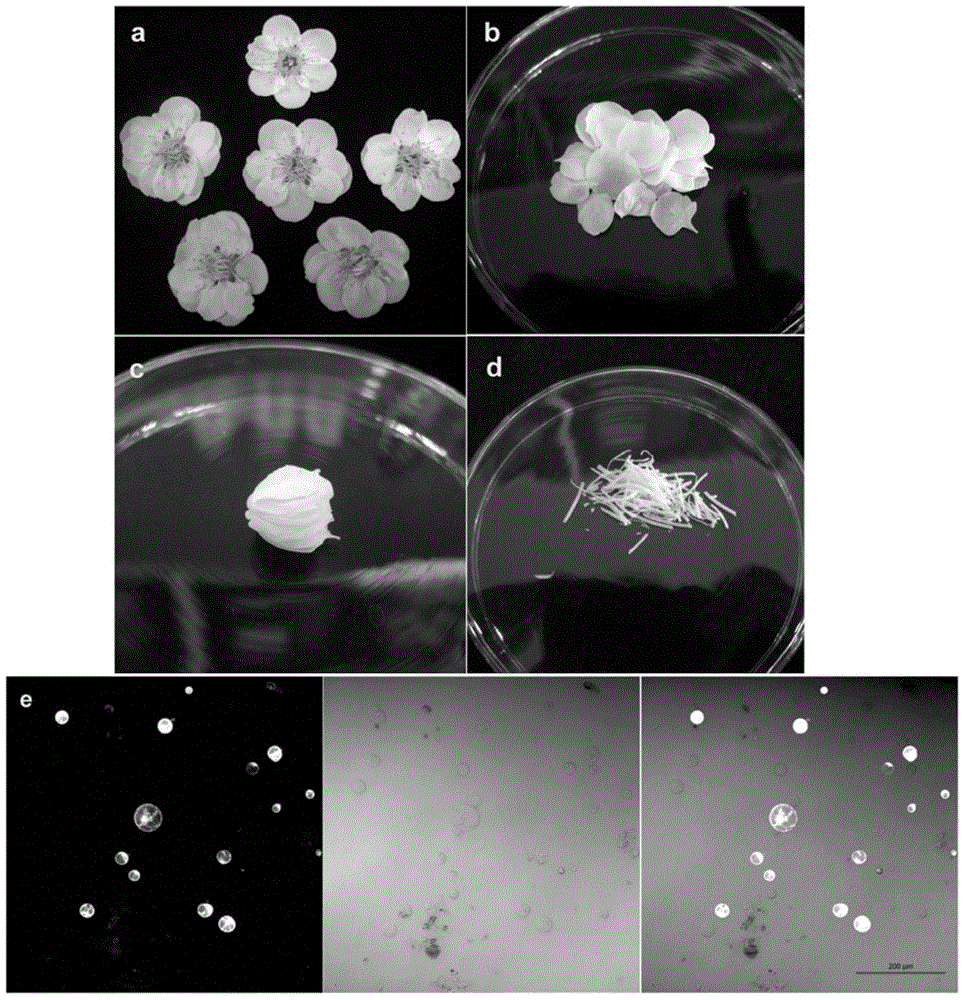
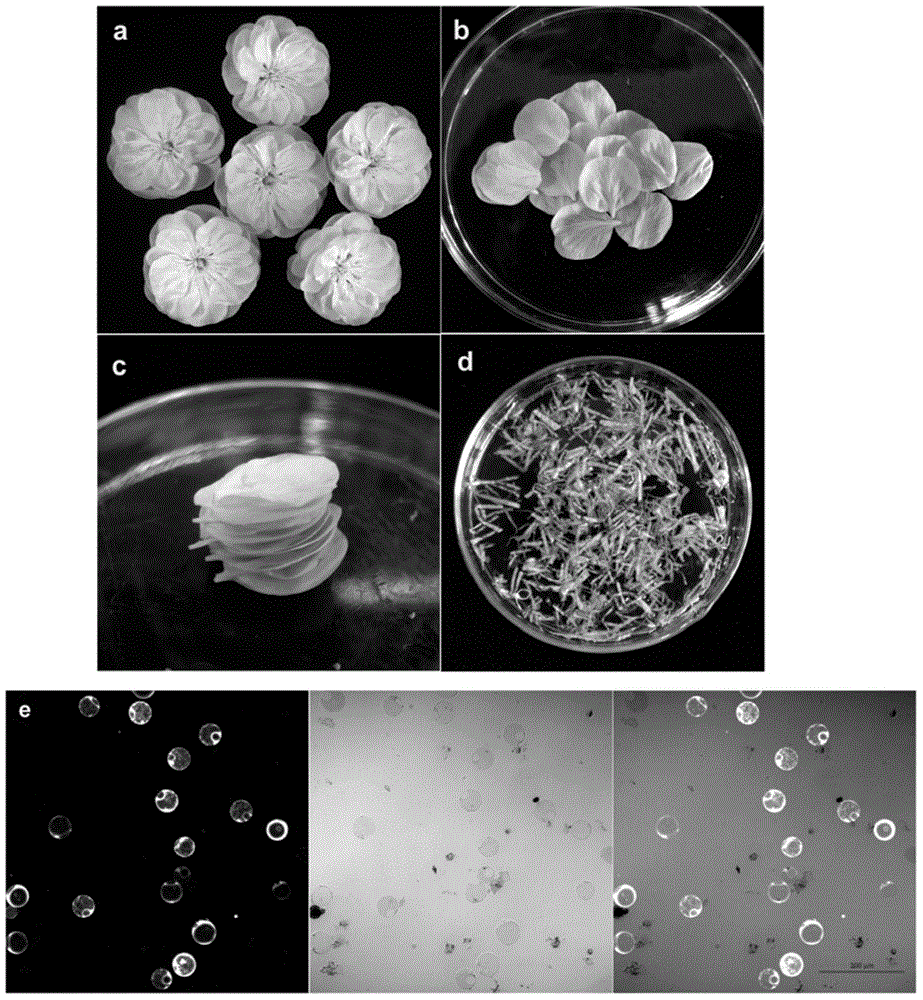
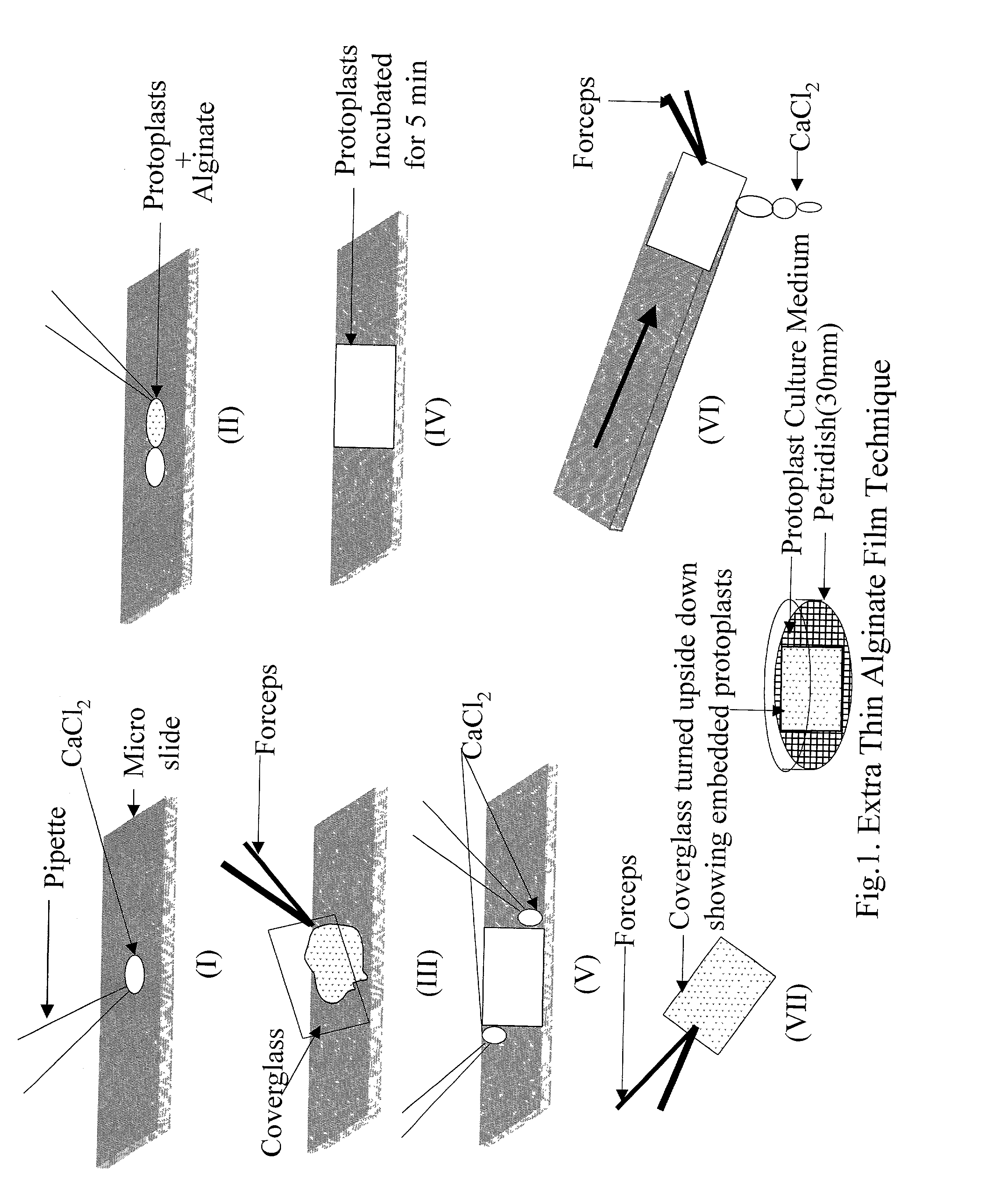
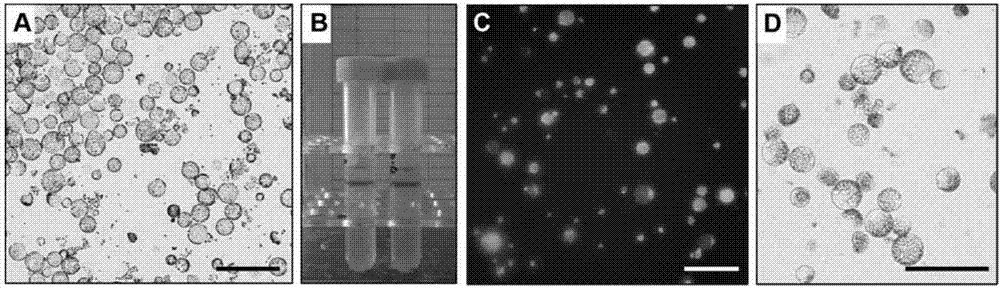
Efficient method of protoplast culture
InactiveUS20020173037A1Ease in observationEase in trackingCell culture mediaHorticulture methodsProtoplastBiology
The invention a novel and efficient method for protoplast culture comprising the steps of isolating the protoplasts from a cell suspension, mixing the protoplasts with equal volumes of alginate solution, placing 40-50 mul of CaCl2 solution on a glass microslide, placing a mixture of protoplasts and alginate solution on the glass microslide and immediately covering by a glass coverglass, adding CaCl2 solution from the sides of coverglass, sliding down the coverglass towards one side and placing it in a petridish containing protoplast culture medium, sealing the petridishes, incubating it and transferring the extra thin alginate layer with celled colonies to regeneration medium for development of culture.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Phaffia rhodozyma strain with high yield of natural astaxanthin as well as breeding method and application thereof
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain with high yield of natural astaxanthin as well as a breeding method and application thereof. The strain is named phaffia rhodozyma CZ10, and is collected with the collection number CGMCC No.6355. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting parent strains, classifying the parent strains into two groups, performing LiCl-ultraviolet compound mutation and 60Co-gamma ray mutation respectively, and screening to obtain a plurality of mutated strains I and a plurality of mutated strains II; (2) performing protoplast fusion, regeneration and screening on the mutated strains I and the mutated strains II to obtain a plurality of fusion strains with higher yield of the natural astaxanthin than the mutated strains I and the mutated strains II; and (3) performing recursive protoplast fusion on the obtained fusion strains obtained in the step (2) at least five times to obtain the phaffia rhodozyma strain. The strain disclosedby the invention is applied to industrial production of astaxanthin; and the astaxanthin yield is up to 68mg / L, which is increased by 14.3 times than that of the parent strains before breeding.
Owner:浙江皇冠科技有限公司
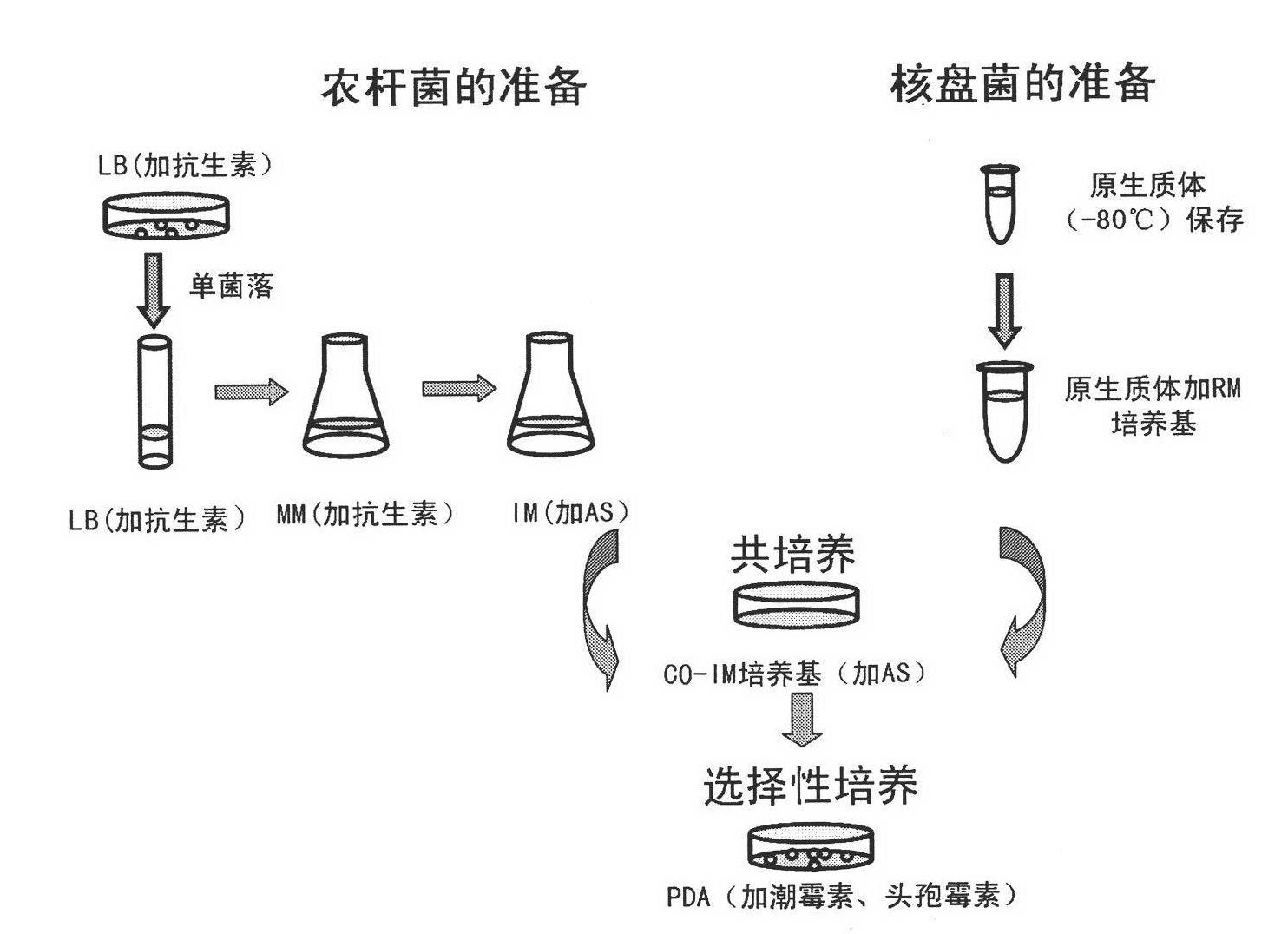
Method for genetic transformation of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated sclerotinia sclerotiorum
InactiveCN101864449AEasy to prepareEasy to importFungiMicroorganism based processesTransformation efficiencyAscospore
The invention provides a method for the genetic transformation of agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated sclerotinia sclerotiorum. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and co-culturing the agrobacterium tumefaciens containing binary vectors and the protoplasts of the sclerotinia sclerotiorum; and screening by using antibiotics to obtain transformants, the transformation efficiency of the method reaches 1 / 5.9*104 protoplasts. By using the protoplasts of the sclerotinia sclerotiorum as the receptor and using the agrobacterium tumefaciens as the mediator, the method of the invention overcomes the problem of the difficult genetic transformation of sclerotinia sclerotiorum, which is resulted from the multinucleate hypha cells and the difficulty in obtaining a large amount of ascospore, and has the advantages of simple method and stable transformation efficiency. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a simple and effective method for preparing the protoplasts of sclerotinia sclerotiorum.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for separating and converting rape protoplast
InactiveCN107488675AReduce the ratioShort experiment cycleVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellsSaccharumMannitol
The invention discloses a method for separating and converting rape protoplast. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting rape cotyledons or true leaves, and removing lower epidermis; 2, putting into enzymolysis liquid for carrying out enzymolysis, wherein the enzymolysis liquid is prepared from the following formula components: 1wt% of cellulase, 0.3wt% of macerozyme, 0.5M of mannitol, 20mM of KCl, 20nM of MES with a pH value of 5.7, 10mM of CaCl2 and 0.1wt% of BSA; 3, adding an isovolumetric W5 solution into a mixed solution obtained by means of enzymolysis, carrying out low speed centrifugation for removing supernatant, adding W5 for washing and resuspending, adding resuspended liquid into 20wt% of a sucrose solution for purifying, horizontally centrifuging, and taking supernatant green protoplast liquid; 4, centrifuging for removing the W5 solution, and resuspending protoplast precipitate by using an MMG solution; 5, converting the protoplast. The protoplast separating and converting method is established in rape for the first time; the rape protoplast is used as a receptor for converting, so that yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), luciferase (Luc) and renilla reniformis luciferase (Ren) are successfully expressed.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
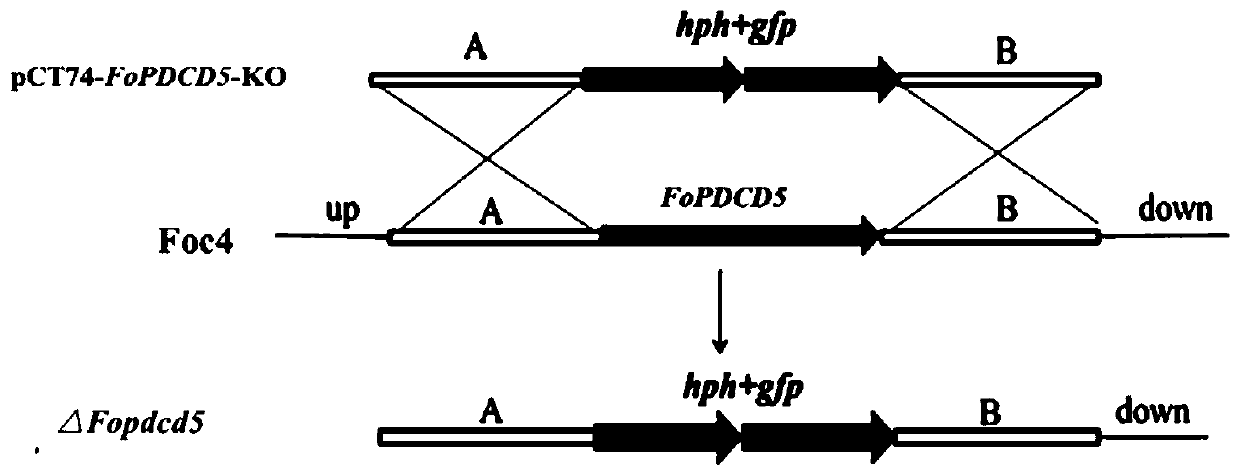
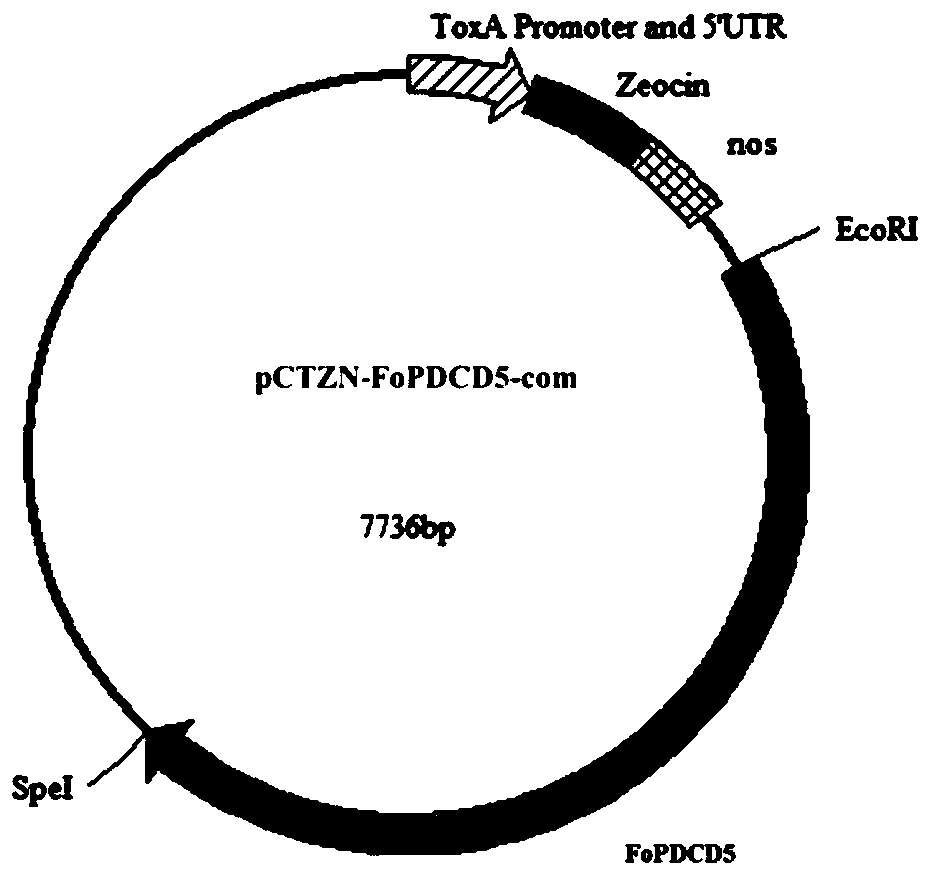
Application of gene FoPDCD5 (Program Cell Death Protein 5) to regulation of pathogenicity of fusarium oxysporum
ActiveCN110669773AReduce pathogenicityIn-depth elucidation of pathogenic molecular mechanismsBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses application of a gene FoPDCD5 (Program Cell Death Protein 5) to regulation of pathogenicity of fusarium oxysporum, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. According to the application of the gene FoPDCD5 to regulation of the pathogenicity of the fusarium oxysporum, the gene is knocked out from the fusarium oxysporum by a homologous recombination method, and aknockout mutant [delta]Fopdcd5 is obtained; by constructing a gene complement vector, the gene complement vector is introduced into a [delta]Fopdcd5 protoplast; and by using a method of random insertion, the gene is completed into the knockout mutant, a complement mutant [delta]Fopdcd5-com is obtained. A pathogenicity test shows that pathogenicity of the knockout mutant [delta]Fopdcd5 is significantly reduced; and pathogenicity of the complement mutant [delta]Fopdcd5-com is restored to a wild-type level. The application of the gene FoPDCD5 to regulation of the pathogenicity of the fusarium oxysporum proves that the FoPDCD5 is necessary for production of conidia of the fusarium oxysporum and response to oxidative stress and pathogenicity. The application is helpful to elucidate a pathopoiesia molecular mechanism of the fusarium oxysporum thoroughly, and target genes are provided for development of effective fungicides.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof are provided. The fungus strain is a mutant derived from Glarea lozoyensis, and deposited in CGMCC with the accession number of CGMCC 2933. The preparation method concludes following steps: (a) mixing the culture media of Glarea lozoyensis strain ATCC 20957 with nitrosoguanidine, and obtaining mixture a; (b) mixing lywallzyme with the mixture a, and obtaining protoplasts; (c) regenerating the protoplasts, and obtaining single clones; and (d) culturing the single clones, then obtaining the mutant strain. This fungus strain has stable genetic and producing property, produces little impurities in fermentation, and is suitable to be used in industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECHWELL BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Breeding method of cabbage type rape woad oil cytoplasm male sterile line
InactiveCN105230486AStable sterility traitsExpansion of sterile cytoplasmic resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsProtoplastSomatic cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, and specifically relates to a breeding method of cabbage type rape woad oil cytoplasm male sterile line. The invention also relates to a protoplast fusion technology to recombinate the cytoplasm and nuclear genome of cabbage type rape-woad so as to establish cytoplasmic male sterility of recombinant cytoplasm. The breeding process comprises the following steps: obtaining the leaf meat protoplast of cabbage type rape-woad through separation and extraction, obtaining the protoplast fused somatic cell hybrid of cabbage type rape-woad through a cell fusion method; taking the obtained somatic cell hybrid of cabbage type rape-woad and leaf meat protoplast cell hybrid of cabbage type rape-woad as the female parent, taking cabbage type rape as the male parent, carrying out multi-generation backcross, and obtaining cytoplasmic male sterile line with carpelloid stamen; wherein the mitochondrion gene PCR amplification verifies that mitochondrial genome carries out recombination during the fusion process, thus the nucleoplasm becomes uneven, and the sterile character appears.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Ultralow temperature preservation method and activity identification method for cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense protoplast
InactiveCN103070163AGuaranteed vitalityIncrease varietyDead plant preservationMicrobiological testing/measurementDividing cellGermplasm
The invention discloses an ultralow temperature preservation method and an activity identification method for a cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense protoplast. The ultralow temperature preservation method comprises the steps of (1) inducing a callus, (2) separating the cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense protoplast, (3) purifying the cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense protoplast, and (4) freezing, unfreezing, and obtaining the preserved protoplast. The activity identification method comprises the steps of identifying activity, nursing and culturing a protoplast solid, observing division of the protoplast under a microscope, culturing for 2-3 days to see a regenerated cell wall of the protoplast, culturing for 4-6 days to see a firstly-divided cell, and culturing for 30-45 days to see a regenerated cell mass of the protoplast. With the adoption of the ultralow temperature preservation method and the activity identification method, a novel scientific approach is provided for the long-term preservation of cardiocrinum giganteum var. yunnanense which is valuable, rare and endangered and integrates viewing, edible and medicinal values.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Separation and culturing method of saussurea involucrate protoplast
The invention relates to a separation and culturing method of Sinkiang saussurea protoplast, comprising four steps of culturing of sterile saussurea involucrate seedlings, inducement and differentiation of embryonic callus, separation and purification of plasmogen and culturing of the protoplast which are all applicable to the separation and culturing of the Sinkiang saussurea involucrate protoplast. The invention has simple and easily-operated method and lower requirements on the equipment and culturing conditions; in addition, the enzymolysis method is practical, the conditions for cell wallremoval are mild, and the separated protoplast has high yield and strong activity, and is easy for the cultuing of the saussurea involucrate protoplast and a plant regeneration, thus laying the foundations for the culturing and fusing of the protoplast as well as the germplasm resource innovation of the Sinkiang saussurea involucrate and the research of transgenic saussurea involucrate.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transgene Stevia rebaudiana genetic transformation method
ActiveCN103667343ALow costEasy to get materialsGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyKanamycin
The invention relates to an Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transgene Stevia rebaudiana genetic transformation method. The method comprises: pre-cultured Stevia rebaudiana stem apex explant is immersed into an Agrobacterium rhizogenes solution of pRI101-ANDNA plasmid carrying target gene, treatments such as infection, co-culture and sterilization are performed, the hairy root is cultured in a kanamycin-containing screening culture medium, the anti-kanamycin hairy root is formed on the explant through induction, the hairy root is induced to form callus, differentiation of adventitious bud is performed, the adventitious bud continuously grows to form the test-tube plantlet, and a PCR amplification method is adopted to identify the transgene plant carrying out the target gene. With the technical scheme, the target gene can be transformed into the Agrobacterium rhizogenes, such that the steps of separation from the protoplast and culture are eliminated compared with genetic transformation of polyethylene glycol and other chemical methods; and compared with genetic transformation of gene gun and other physical methods, the method of the present invention has characteristics of no requirement of expensive equipment, and simple operation technology.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for raising conversion efficiency of pollen tube chnnael method by using toxoprotein gene of Agrobacterium
InactiveCN101092633AImprove conversion efficiencyHigh genetic stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionVirulent characteristicsTransformation efficiency
This invention relates to a method for increasing the conversion efficiency of pollen tube pathway method by using agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence gene. The method comprises: combining or mixing agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence gene and the target gene to be converted (green fluorescent protein gene) in vitro, packaging with liposome, and converting plants, especially cotton by using pollen tube pathway method. The method combines agrobacterium-liposome-pollen tube pathway technique, and has obviously increased protoplast conversion efficiency. Plasmids are not only protected by liposome when entering embryo sacs, but also encapsulated by the toxic protein to be expressed when entering egg cells, which can improve the stability of exogenous DAN in cell conversion process, realize precise cutting in T-DNA region, and increase the conversion efficiency.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com