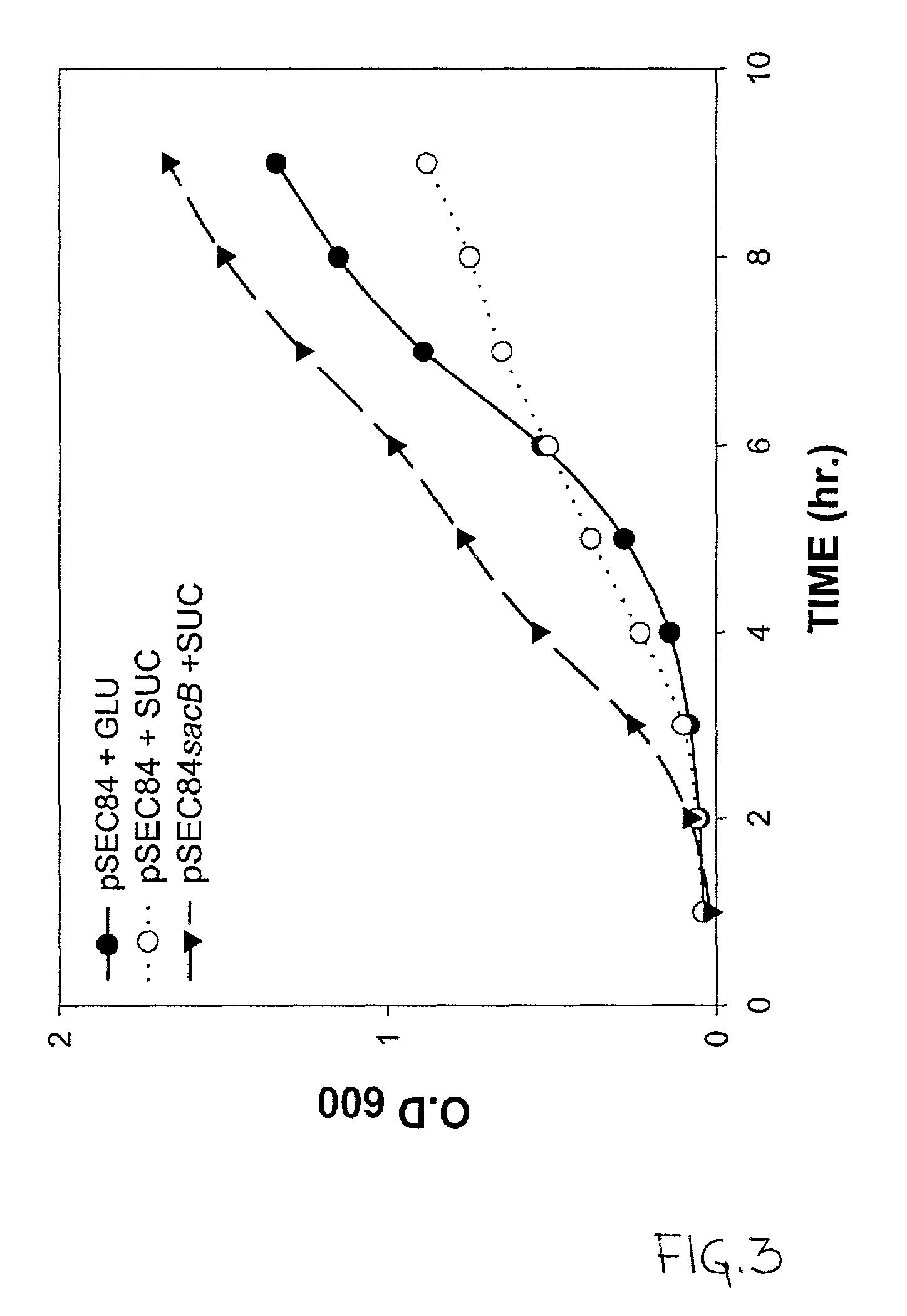
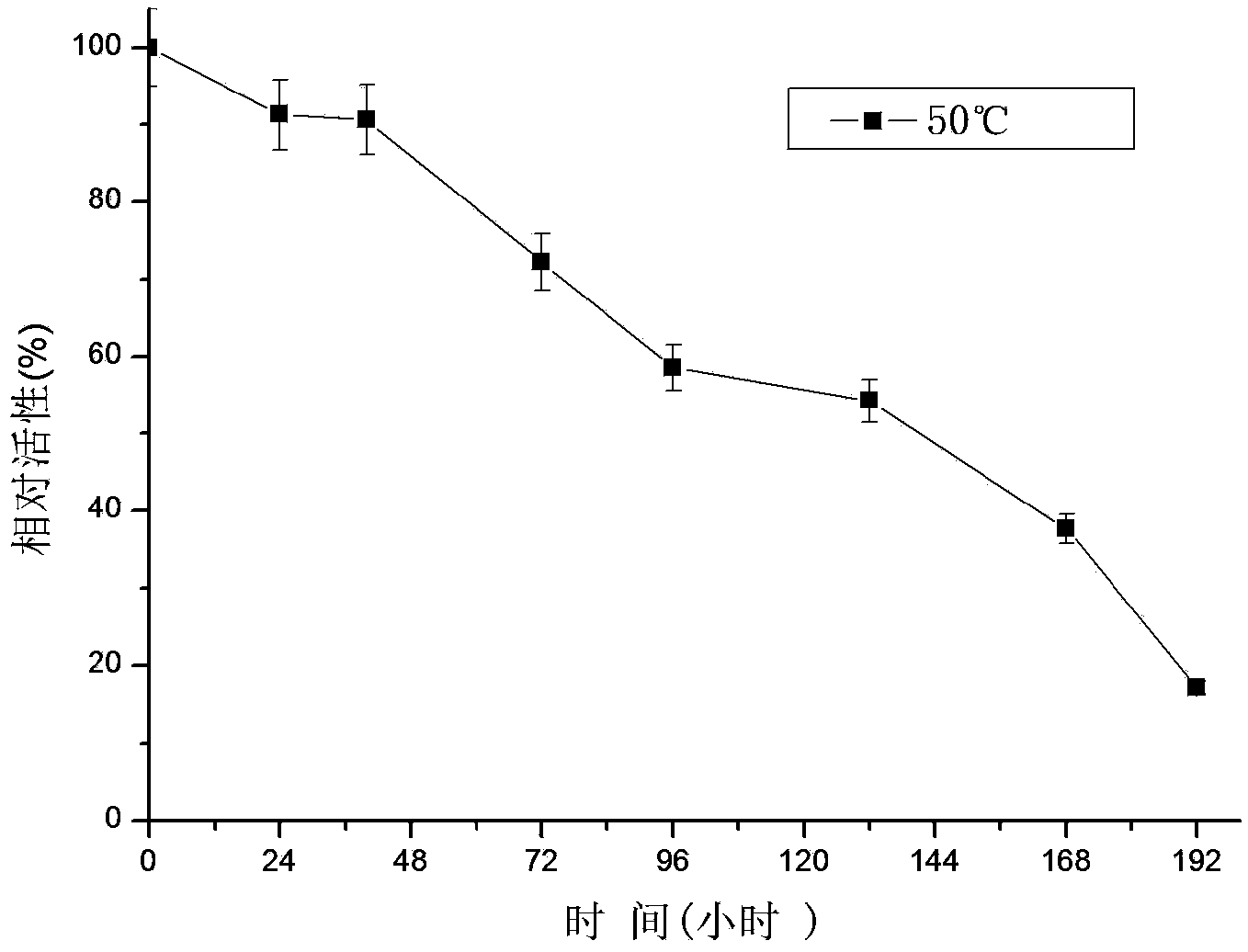
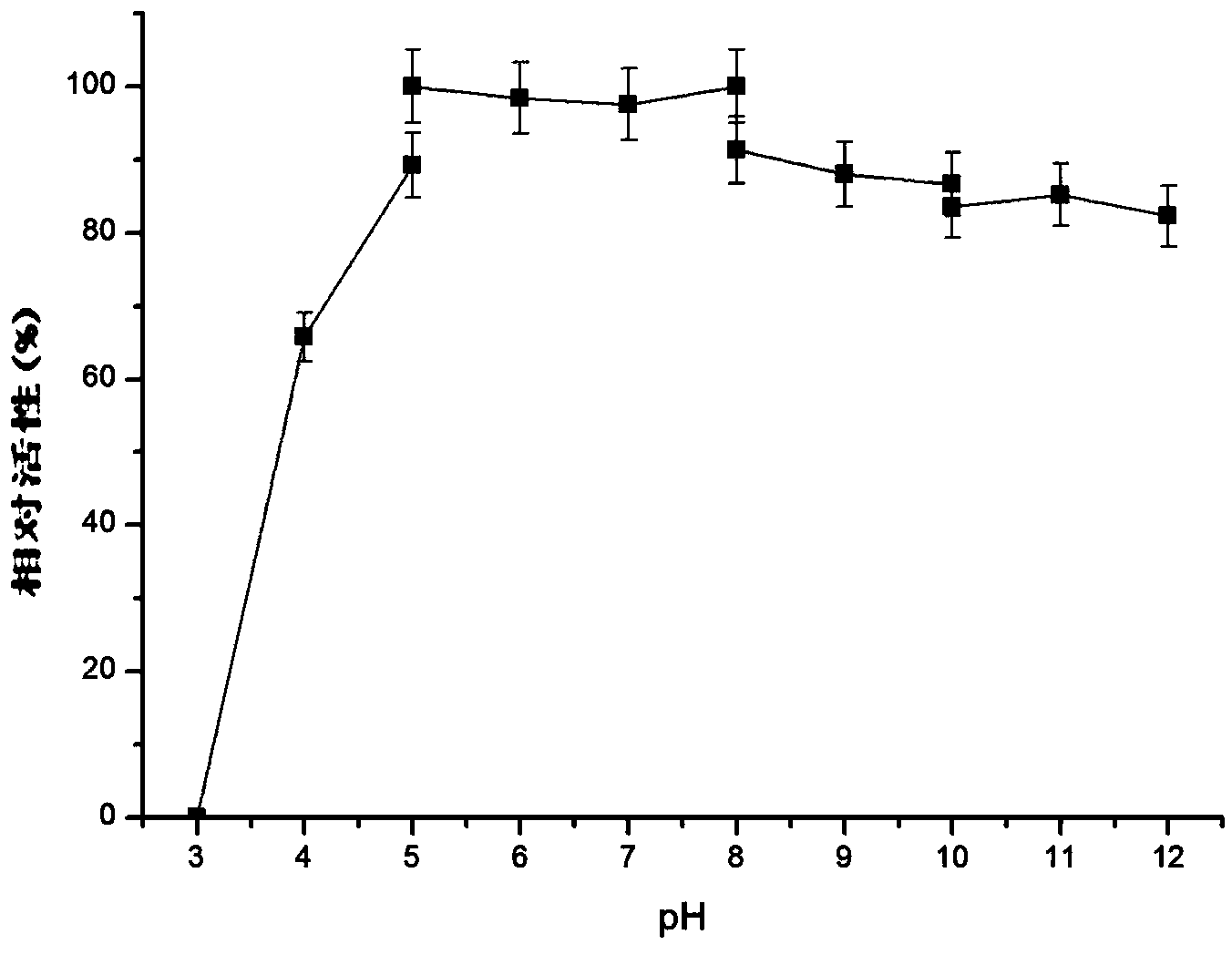
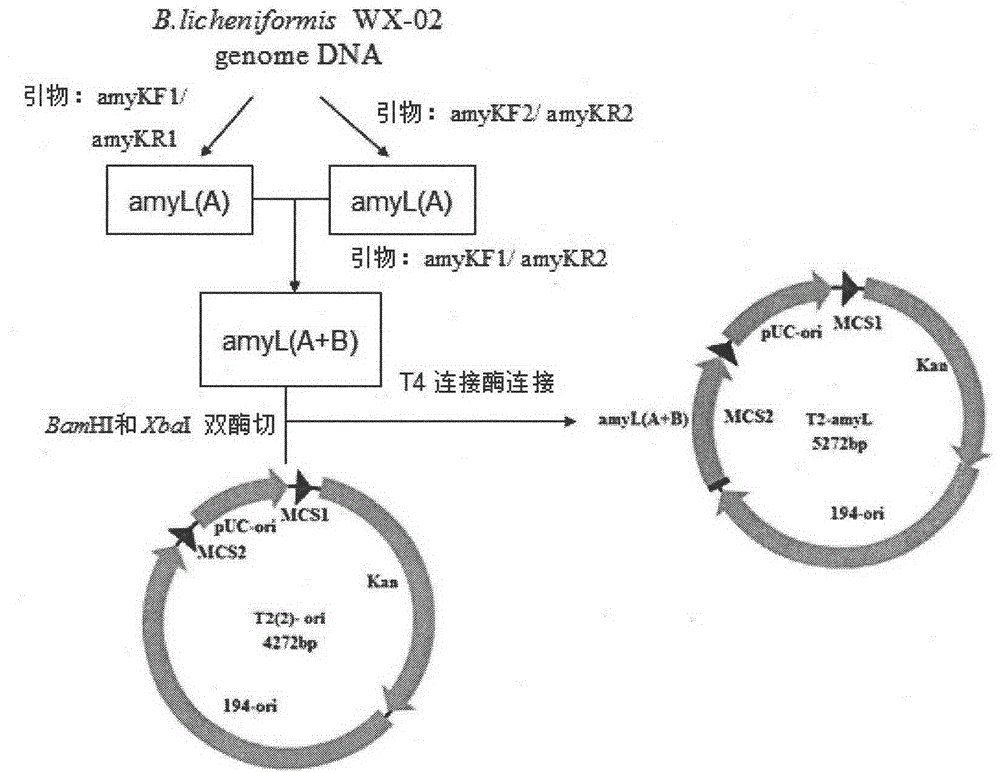
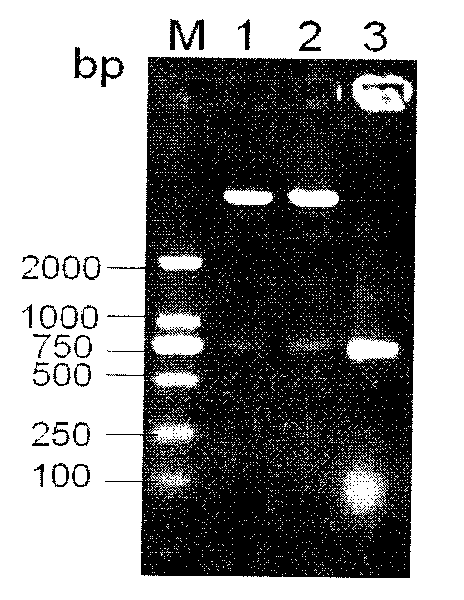
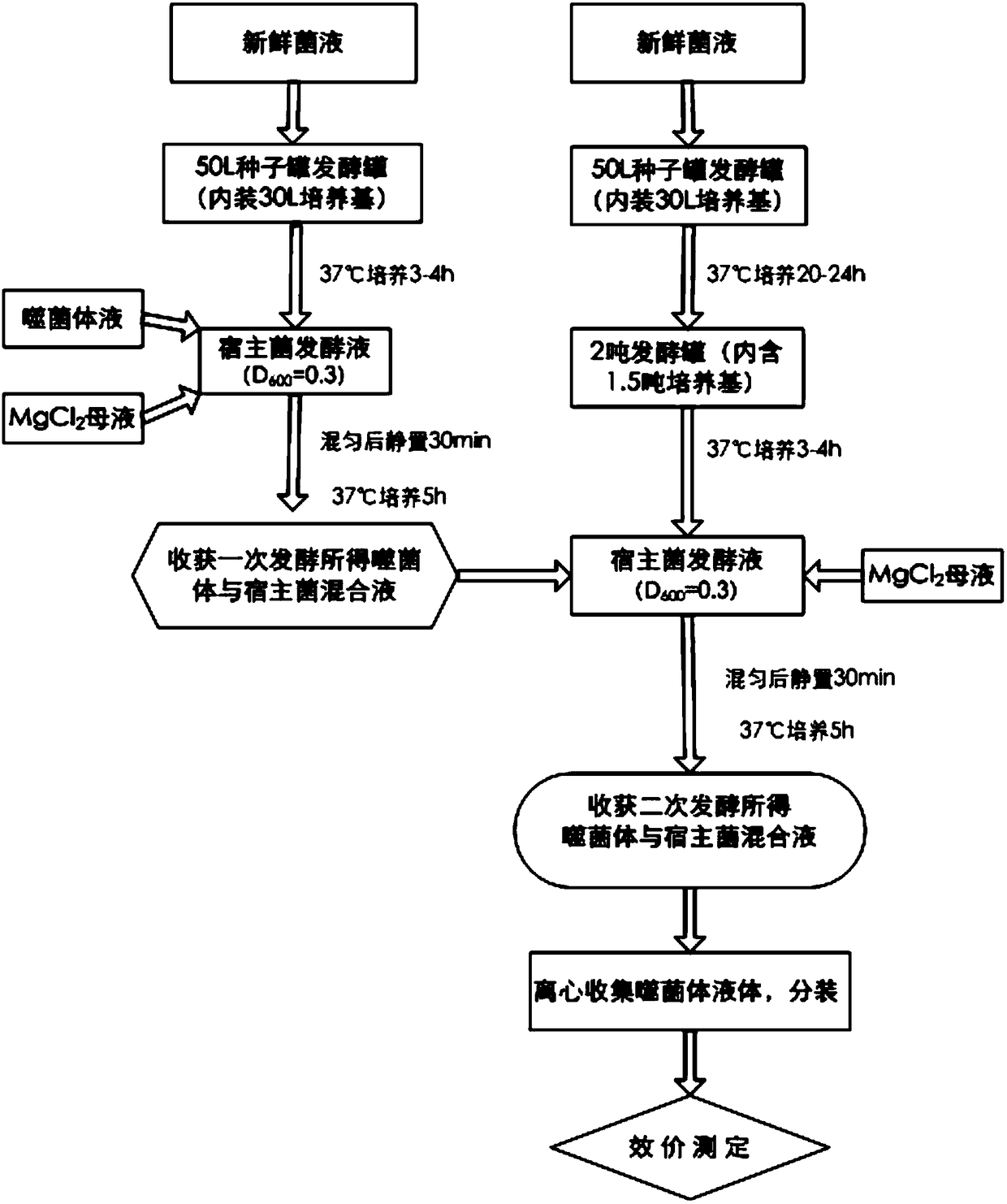
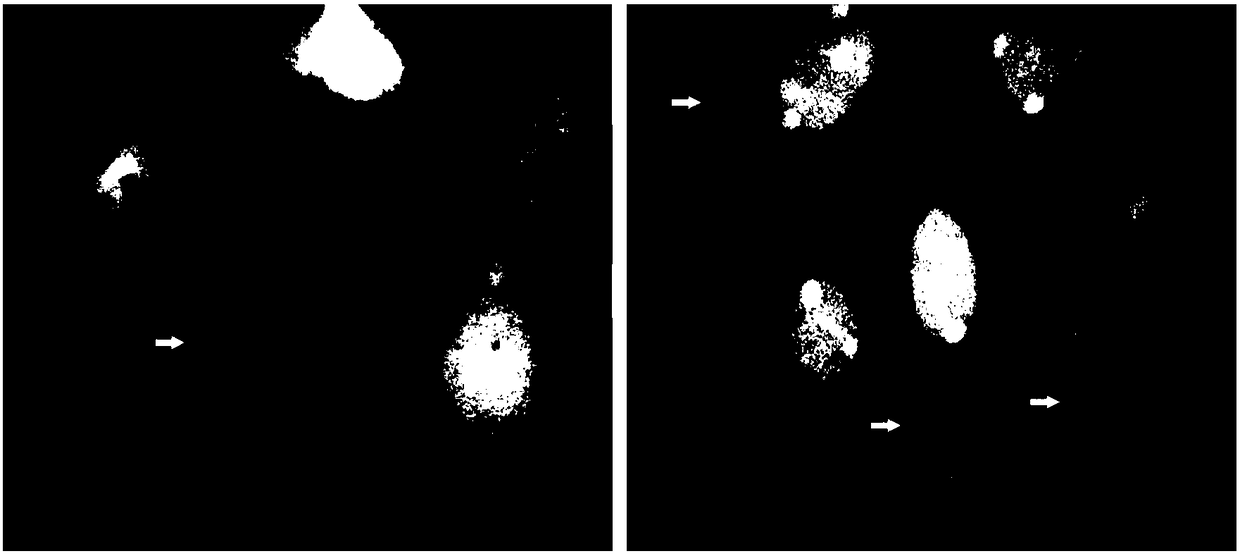
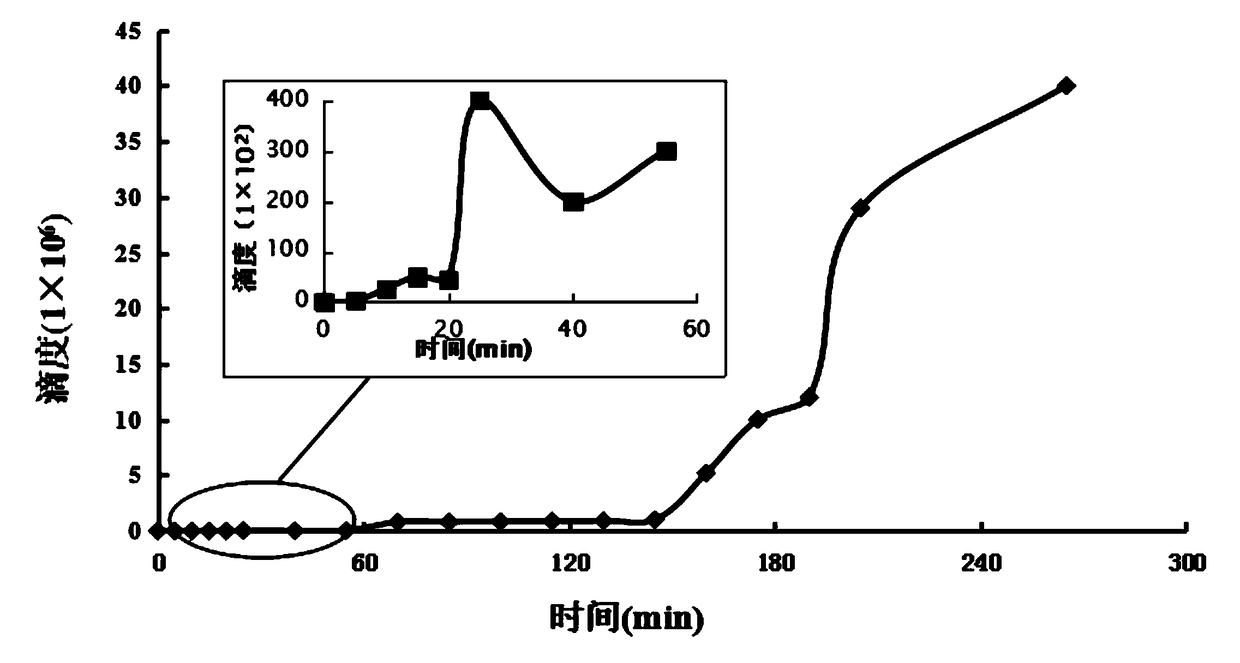
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
269 results about "Host bacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Host Bacteria. With more than 800 sequenced mycobacteriophages, we are keen to widen our net to include phages isolated on other hosts within the phylum Actinobacteria. This includes phages to hosts such as Arthrobacter, Gordonia, and Rhodococcus.
Method for exposing peptides and polypeptides on the cell surface of bacteria
InactiveUS7186524B2High varianceMaintain good propertiesBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGramCell membrane
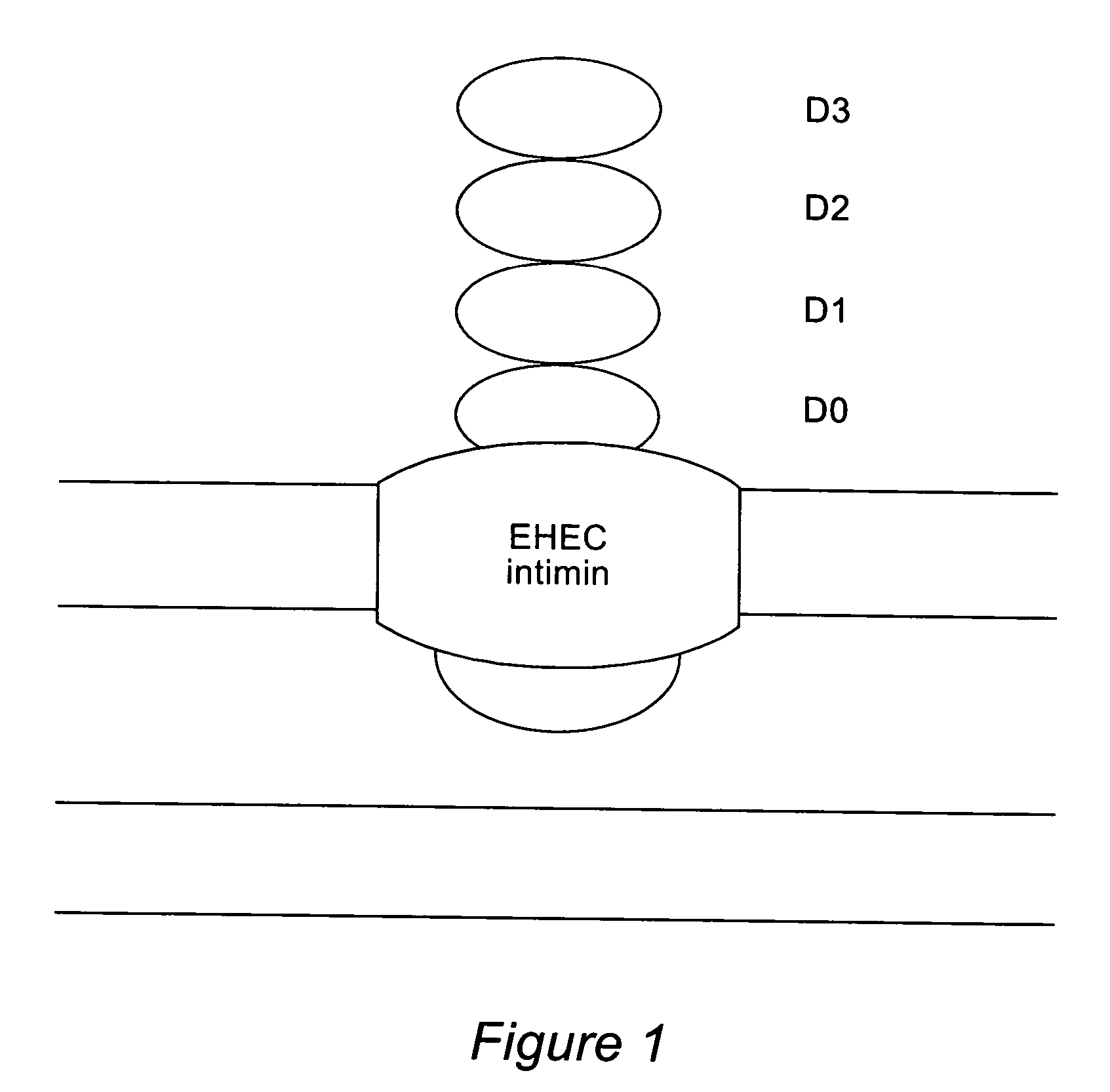
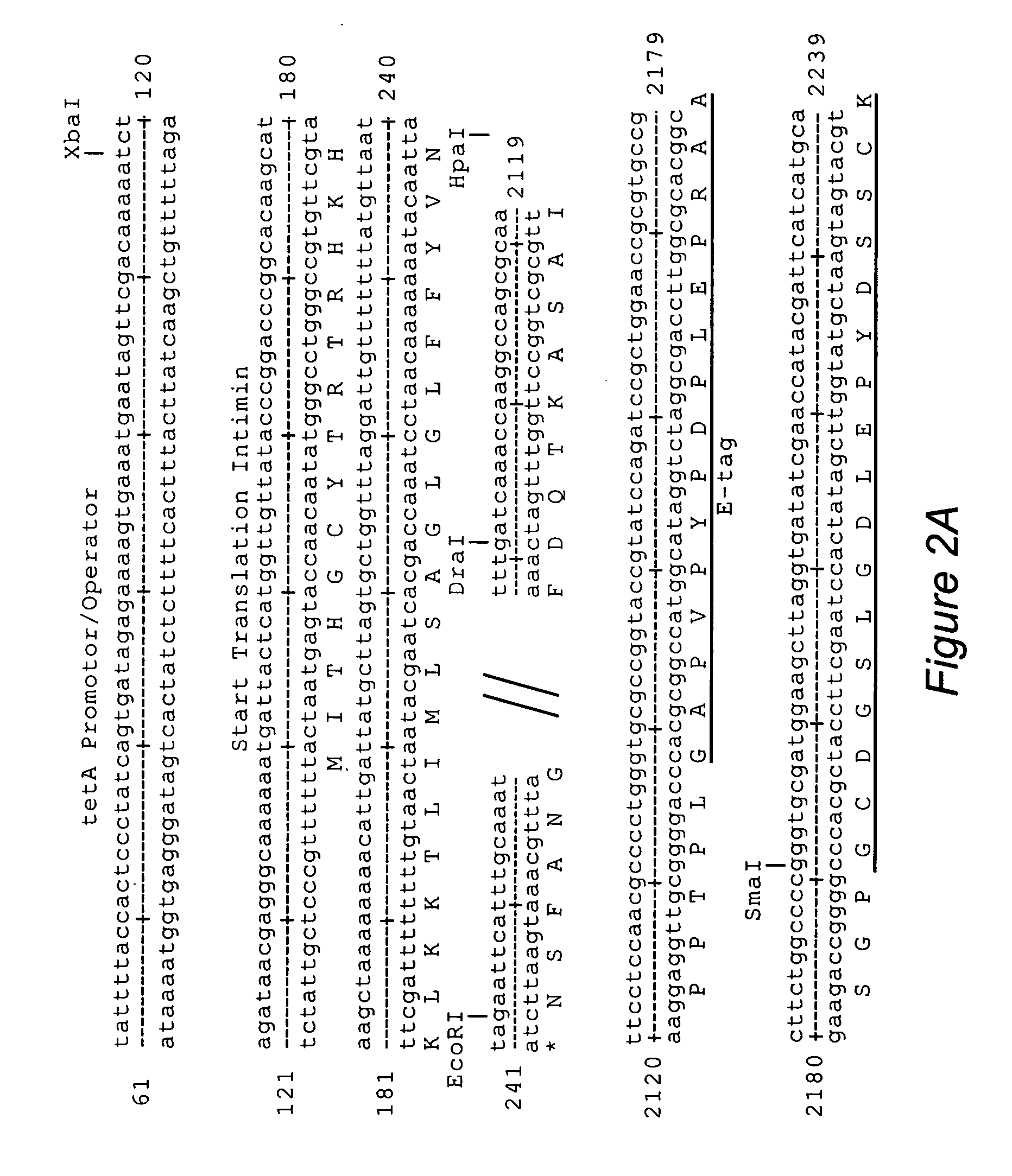
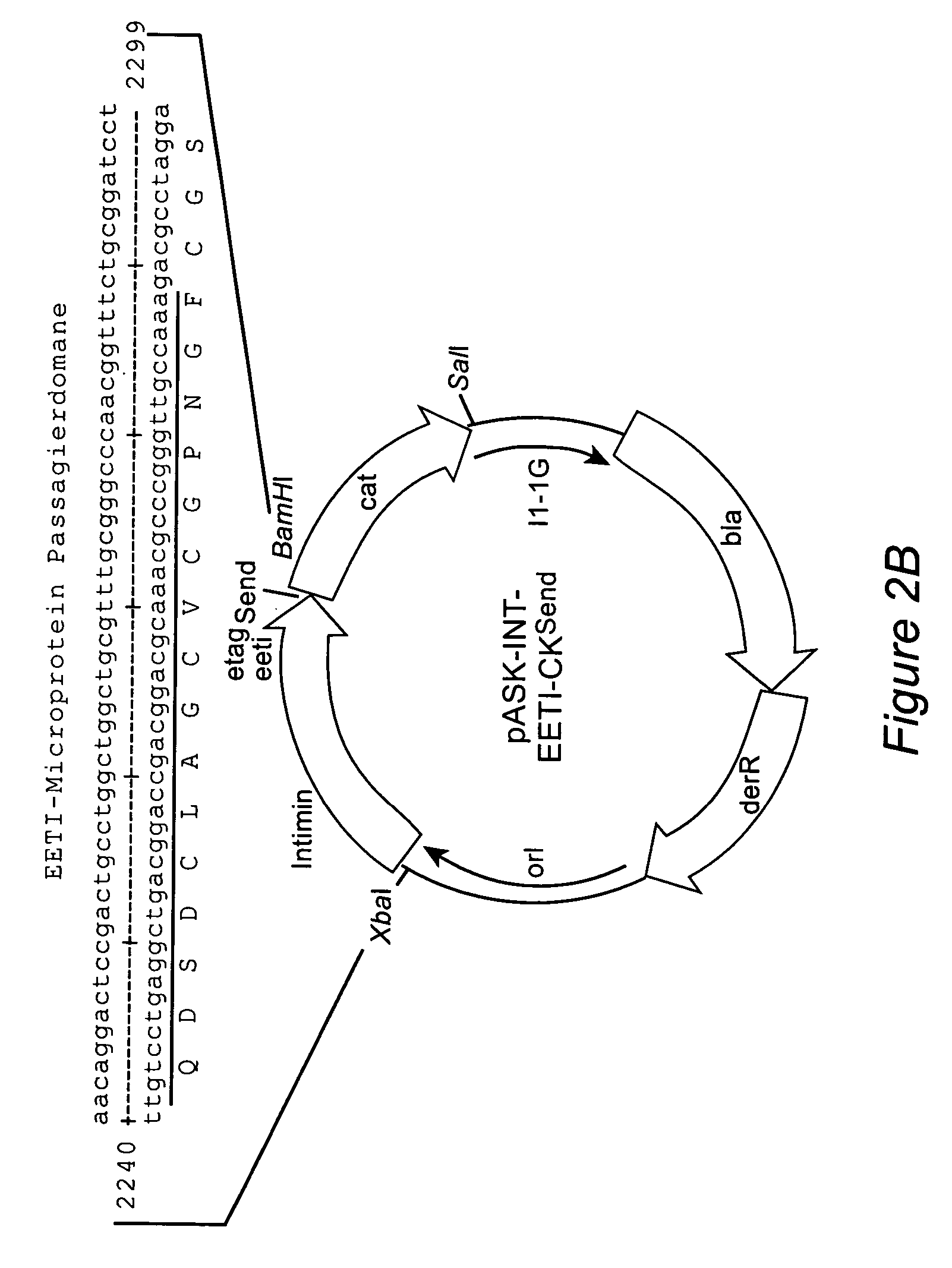
The inventive method allows peptides or polypeptides to be exposed on the surface of gram-negative host bacteria using specific intimin-based anchor modules. Intimins with shortened carboxy terminals have been found to be particularly suitable anchor modules for passenger domains in the exterior E. coli cell membrane. According to the method, host bacteria are transformed using vectors, on which are located a fused nucleic acid sequence consisting of a sequence segment which codes for an intimin with a shortened carboxy terminal and a nucleic acid sequence segment which codes for the passenger peptide that is to be exposed. The invention permits a particularly large number of passenger domains to be exposed on the cell surface of the bacteria, without adversely affecting the viability of the bacteria.
Owner:BIONTECH AG
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070135333A1Inhibition of replicationSimple designAntibacterial agentsBiocideArginineNucleotide
An antibacterial antisense conjugate and method of using the same for treating a bacterial infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The conjugate includes an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotide contains 10-20 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 12 amino acids.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for synthesizing L-theanine through enzyme process
ActiveCN103409475AMake up for the shortcomings of poor stabilityHigh activityFermentationEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-theanine through an enzyme process, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method is characterized in that a gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase gene is obtained through chemical synthesis, a gene engineering bacterium over-expressing gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase is constructed by treating Escherichia coli as a host bacterium, glutamine and ethylamine hydrochloride having different concentrations are acted by a recombinase, and theanine is efficiently produced at a temperature of 37-50DEG C under a pH value of 9.5-10.5. The enzyme source preparation process has the advantages of simplicity, low cost, and large enzyme amount, and the theanine production method has the advantages of simplicity, high conversion rate, high output, short time and the like, and is in favor of the industrialized amplification production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus licheniformis expression host
ActiveCN104630123AReduced activityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisProtein target
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis host bacterium BL10 with multiple gene deletion, the accession number of which is CCTCCNO:M2013400. The host bacterium derives from a bacillus licheniformis WX-02 which partially or completely has deletion of ten genes. The ten genes comprises eight protease genes (mpr encoding a metalloprotease; vpr encoding a serine protease; aprX encoding an intracellular serine protease; epr encoding a minimal extracellular protease; bpr encoding a bacillus peptidase F; wprA encoding a protease combined with cell walls; aprE encoding an extracellular alkaline serine protease; and bprA encoding a bacillus peptidase F) and two extracellular secretory protein genes (hag encoding flagellin; and amyL encoding alpha-amylase). The BL10 has completely no extracellular protease activity and can reduce the degradation effect of a protease on a target protein. When the target protein is expressed by the expression host, the expression level is higher, and the host bacterium benefits protein expression enhancement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and microbial inoculum preparation method
InactiveCN101717744AProtect environmentIncreased spore contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
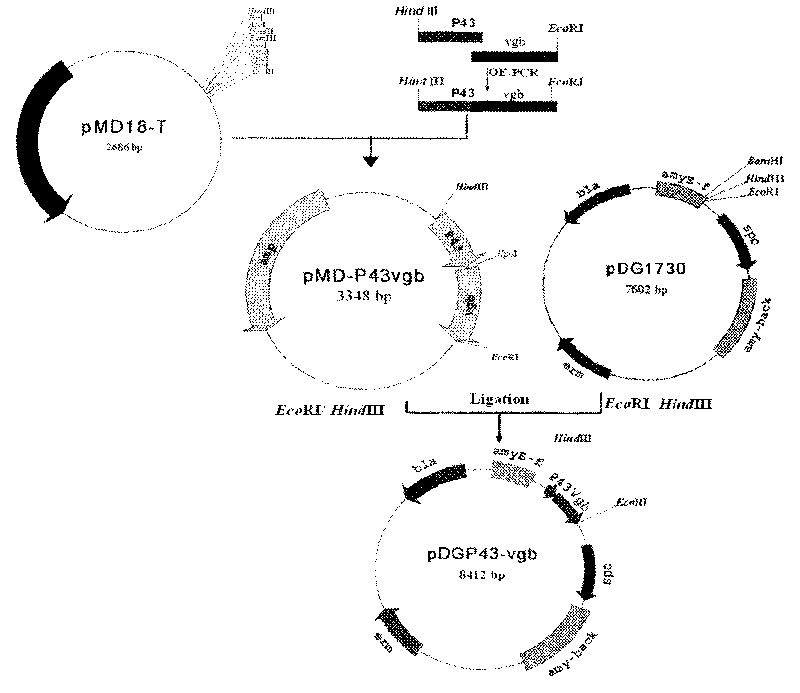
The invention discloses gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens and a microbial inoculum preparation method. A bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 strain is taken as a host bacterium to construct the gene recombination bacillus amyloliquefaciens XLV09-1 with transparent vitreoscilla hemoglobin which is regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter by contrasting a gene recombination vector. The produced spore number of microbial inoculum prepared by fermenting the bacillus amyloliquefaciens can reach more than 100 hundred millions per milliliter, the overall yield of antibacterial lipopeptid reaches more than 1 gram per liter and prevention effect on various fungal plant diseases is improved by over 30 percent. The microbial inoculum is a green microecological preparation, of no toxic residue, safe to human and livestock, and favorable for protecting the ecological environment.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Broad-spectrum bacteriophage preparation for aquaculture and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108103031AEasy to prepareEasy to useBiocideMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacterial disease
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Engineering bacterium for producing Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and applications thereof
InactiveCN102226165ANo activation requiredEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaFatty-oils/fats refiningVegetable oilA-DNA
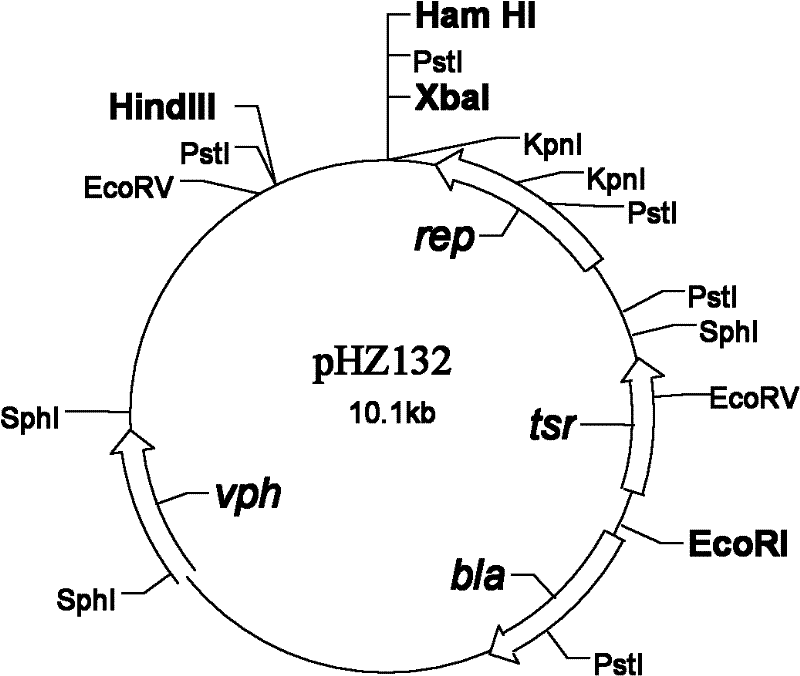
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium for producing a PL A2 and applications thereof. A preparation method of the PLA2 comprises the following steps: A, preparing a PLA2 gene: designing a primer PCR and amplifying a PLA2 gene fragment, and cloning a DNA fragment containing the PLA2 gene (a sequence is SEQ ID NO.2) with an amplified fragment plaT as a probe; B, constructing a recombinant plasmid: cloning a Bam H1 restricted fragment with the size of 3 kb which contains the PLA2 gene to a high-copy plasmid pHZ132 to obtain a recombinant plasmid pLH 001; and C, constructing the engineering bacterium: introducing the plasmid pLH001 into a streptomyces lividans 1326 of a host bacterium through protoplast transformation to obtain a streptomyces lividans LH001 of the engineering bacterium. The engineering bacterium has good stability and the introduced plasmid is not easy to lose. The secretory active PLA2 (an amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.1) can be generated through liquid fermentation, the enzymatic activity of a fermentation liquid is equal to or more than 2,000 U / mL, and the enzyme production capability is better than present levels. The PLA2 can be applied to fields of vegetable oil degumming, lysophospholipid preparation and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for producing D(-)-tartaric acid or salt thereof by using gene engineering bacteria
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence from microorganism for coding cis-epoxy succinate hydrase, a cloning vector containing the nucleotide sequence, a recombined host bacterium obtained by transforming the nucleotide sequence and a cis-epoxy succinate hydrase amino acid sequence coded by the recombined host bacterium, and further relates to a method of using the cis-epoxy succinate hydrase to hydrolyze cis-epoxy succinate or salts thereof to prepare D(-)-tartaric acid or salts thereof.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
Low-temperature alkaline protease gene, engineering bacterium containing same, construction methods of low-temperature alkaline protease gene and engineering bacterium, and low-temperature alkaline pr
The invention relates to a low-temperature alkaline protease gene, an engineering bacterium containing same, construction methods of the low-temperature alkaline protease gene and the engineering bacterium, and low-temperature alkaline protease. The sequence of the low-temperature alkaline protease gene is described as SEQ ID No. 2, and the sequence characteristic is 810bp, nucleic acid, single chain, linearity and DNA. The engineering bacterium producing the low-temperature alkaline protease is transformed from a host bacterium bacillussubtilis WB600 and has the characteristic of producing the low-temperature alkaline protease. The construction method of the engineering bacterium comprises the following steps of: obtaining an objective gene, reconstructing the objective gene directionally, constructing an expression carrier and constructing and sieving the engineering bacterium containing the low-temperature alkaline protease gene. The sequence of the mature peptide basic group of the low-temperature alkaline protease is disclosed in SEQ ID No. 2, the optimum operative temperature is 30 DEG C, and the optimum operative pH is 11.0. The optimum temperature of the alkaline protease produced by the engineering bacterium is 30 DEG C, the optimum pH is 11.0, and the invention provides a theoretical basis for the low-temperature alkaline protease added and used in a detergent and has important economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof
ActiveCN104031872AAvoid the influence of own metabolismShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering technology. According to the invention, a recombinant bacterium is obtained by transforming a gene containing acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, terminal alkene formed fatty acid decarboxylase and oleic acid hydratase into a host bacterium, and is used for fermentation production of isoprene. Such a method substantially shortens reaction process for synthesis of isoprene through an exogenous MVA approach, only five reaction steps are needed for synthesis of isoprene of acetyl-CoA, so influence of excess exogenous gene expression on metabolism of cells is avoided. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of the fermentation product isoprene can reach 39.49 mu g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione and product thereof
ActiveCN104059936AIncrease productionEnhanced synthetase activityFungiMicroorganism based processesTransformation efficiencyInositol-3-phosphate synthase
The invention discloses a preparation method of a genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (i) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase fusion protein into a host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (ii) converting a gene for encoding gamma-glutamoyl cysteine synthetase-linker peptide-glutathione synthetase into the host bacterium cell, and highly expressing the gene; (iii) knocking off the gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase of the host bacterium cell; (iv) knocking off an inositol-3-phosphatep synthase gene of the host bacterium cell; and completing the steps (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) in any sequence, thereby obtaining the genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione. The invention further relates to the prepared genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing glutathione, which is disclosed by the invention, is not only high in efficiency in synthesizing glutathione, but also can greatly improve the conversion efficiency of exogenous cysteine, and can be applied to glutathione production.
Owner:唐星
Method for producing recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor
ActiveCN1814779ASimple production methodProduction method is stablePeptide preparation methodsCytokines/lymphokines/interferonsInclusion bodiesIon exchange
This invention relates to a method for producing recombined human granular leukocyte colony stimulating factors including: fermenting, breaking bactrriums, extracting occlusion bodies, chromatographing with molecular sieves, renaturating, exchanging anions, exchanging cations to get the raw fluid, in which, BL21 is selected as the host bacterium and the engineering bacterium type is got in high expression volume, quick reproduction and stable passage, several purification steps greatly reduce the residural toxin in the bacterium and the specific activity is increased greatly, a dialysis method is applied for the renaturation to reduce the concentration of the denaturalization agent steadily so the renaturation rate is at high level.
Owner:山东泉港药业有限公司
Genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and application thereof
InactiveCN102041264ASolve the problem of insufficient oxygen supplyPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDihydroxyacetoneGluconobacter oxydans
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid for expressing vitreoscilla hemoglobin in a cell and a construction method of the recombinant plasmid, a genetic engineering bacterium of Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a construction method and application of the genetic engineering bacterium. The recombinant plasmid comprises a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene vgb, a PtufB promoter of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) and a suitable carrier, wherein the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained by transforming recombinant plasmid into a host bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can be used for expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin in the cell, can be used for improving the yield of biomass and catalysate 1, 3-dihydroxyacetone under the condition of not changing the existing equipment and energy consumption pressure and provides an effective path for solving the problem of in sufficient oxygen supply in the cell cultivation and catalytic process of the Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans).
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for degrading polyethylene terephthalate
ActiveCN109929789AAvoid inhibitionAvoid toxic effectsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene terephthalate
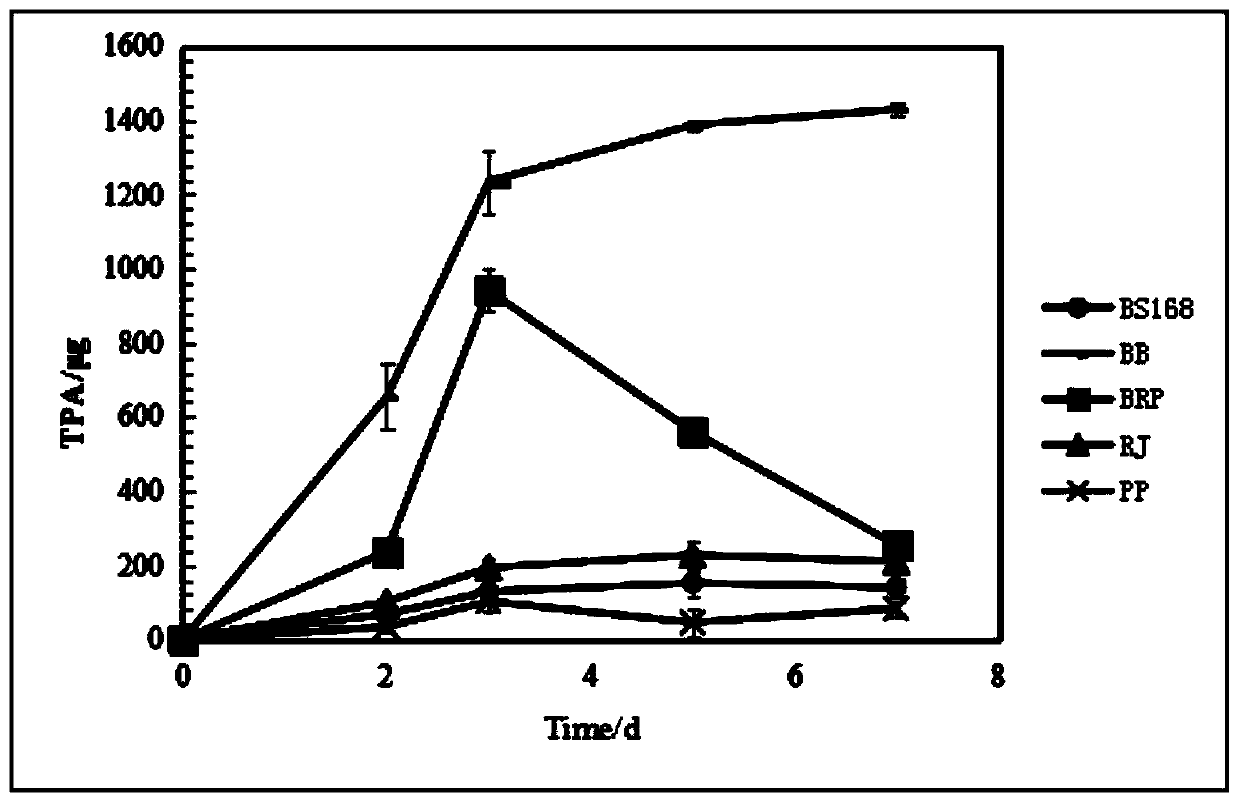
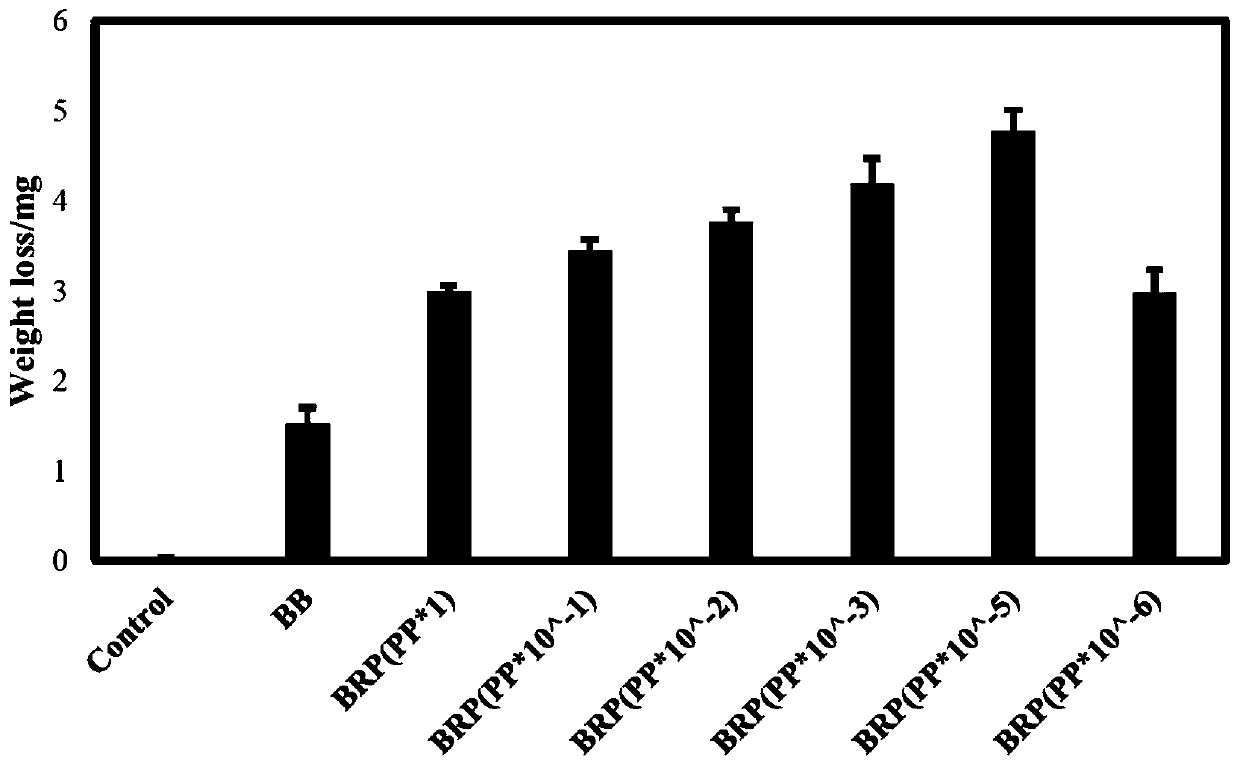
The invention belongs to the field of environmental science, and discloses a construction method of a host bacterium for expressing a PETase enzyme and a MHTEase enzyme, a composite strain composed ofthe host bacterium, pseudomonas putida and rhodococcus and a method for degrading the polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The composite strain is formed by mixing the host bacterium expressing the PETase enzyme and the MHTEase enzyme, the pseudomonas putida and the rhodococcus, and adopted to degrade the PET to solve the problem of the inhibition effect of a PET degradation product TPA and the toxic effects of the degradation product TPA and ethylene glycol (EG) on the environment, thereby achieving green degradation of PET.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fennero penaeus chinensis antibacterial protein gene and recombinant expression and use
InactiveCN1936000AGuaranteed to be formed correctlyEasy to oxidizeAntibacterial agentsBiocideDisulfide bondingFungus protein
The invention relates to a Fenneropenaeus chinensis antimicrobial protein gene and the recombination expression and the application. It has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No.2 and basic group sequence of SEQ ID No.1 in sequence table. It selects the carrier of the antimicrobial protein pCR T7 / NT TOPO TA and host bacterium BL21(DE3)pLysS that could high efficiently express recombination protein. Aimed at the feature of plural disulfide bonds, using the oxidation reduction system made of oxidized form of glutathione and glutathione in separating and purification and protein recombination process, the recombination protein with antimicrobial ability would be gained. The protein has strong inhibition to the growth of gram positivebacteria, and some inhibition to gram negativebacteria.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant bacterium of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid, construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention provides a recombinant bacterium of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid, and a construction method and preparation of the recombinant bacterium and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A host bacterium of the recombinant bacterium is escherichia coli, and the recombinant bacterium expresses and codes gene clpP of an ATP (adenosine triphosphate) dependent protease hydrolysis subunit, and codes a gene accABCD of acetylcoenzyme A carboxylase and a gene mcr of malony-coA reductase. A preparation method comprises the steps of obtaining and transforming recombinant vectors pETDuet-clpP-mcr, and pACYCDuet-accADBC into a host competent cell. The recombinant bacterium solves the problem that the increase of a concentration of 3-hydracrylic acid in a microbial fermentation process inhibits microbial growth to influence a yield; a fermentation level is increased by 116% compared with that of strains of the ATP dependent protease hydrolysis subunit without expression and coding; and the level is the highest known shake flask fermentation level.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Efficient splitting tandem gene, efficient splitting plasmid and construction method and appliance
ActiveCN103146732AIncrease productionReduce lateral spreadBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
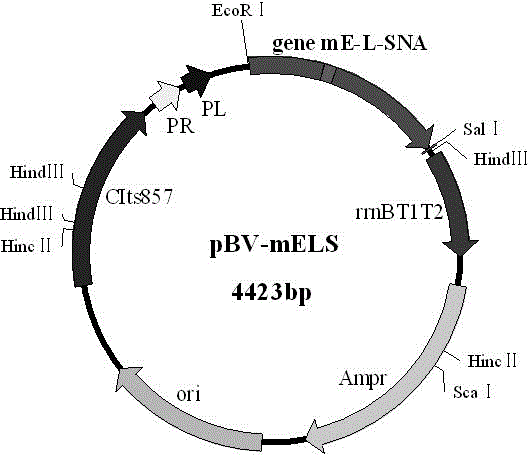
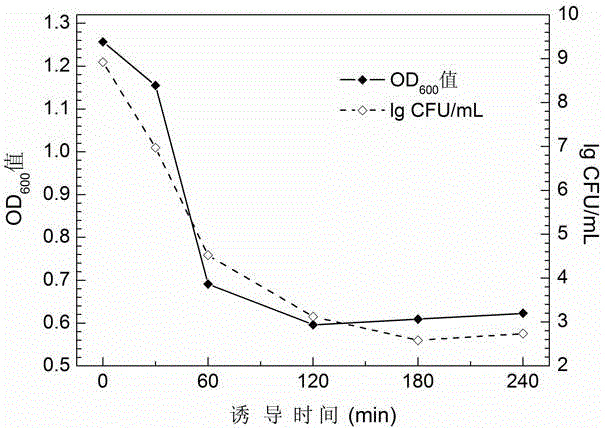
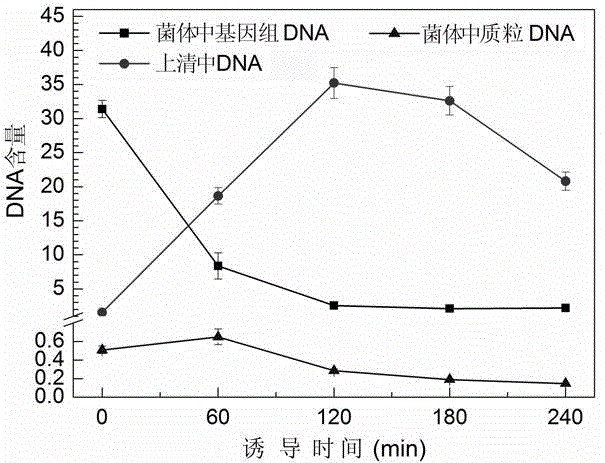
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to an efficient splitting tandem gene which is composed of a phage PhiX174 mutation splitting gene mE and a staphylococcus nuclease A gene SNA, an efficient splitting plasmid which contains the efficient splitting tandem gene and appliance of the efficient splitting plasmid in preparation of ghost, and a gene sequence is shown as a sequence 3 in a sequence list. A structured safe and efficient splitting plasmid pBV-mELS is capable of conducting induction when an Escherichia coli liquid OD600 value reaches more than 1.0. Splitting efficiency can be 99.99995%. Not only is limitation that a splitting gene E mediated fragmentation process relies on a growing state (OD600 is 0.4 to 0.6) of host bacteria broken through, output of the ghost is greatly improved, but also heritage materials left in the ghost is effectively eliminated, and side-direction spread of a perniciousness heredity element (an antibiotics resistance gene and a pathogenic determinant cluster gene) is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
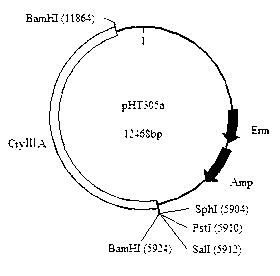
Plasmid for expressing plutella xylostella arginine kinase genes dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application
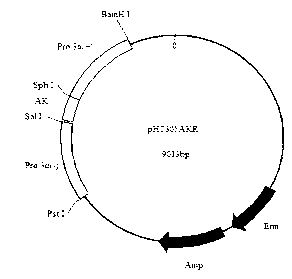
The invention relates to a plasmid for expressing plutella xylostella arginine kinase genes dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and an application, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The plasmid pHT305AKR is a recombinant plasmid obtained by inserting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) shown by SEQ ID NO.1 between BamHI and PstI enzyme cutting sites of the plasmid pHT305a. The plasmid pHT305AKR not only realizes the research of expressing dsRNA in bacillus thuringiensis, but also provides a powerful means for applying RNAi (RNA interference) technique to identifying the function of bacillus thuringiensis genes and researching a functional genome of the bacillus thuringiensis, and can also be used for synthesizing dsRNA by utilizing host bacterium, so that the cost for obtaining the dsRNA is reduced. The invention also provides a direction for exogenous transformation of the bacillus thuringiensis and research of bacillus thuringiensis biopesticide, so that the plasmid has a promising application prospect. Meanwhile, a novel way is provided for controlling the plutella xylostella, and a new field is created for controlling the pests.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105238724AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTricarboxylic acid
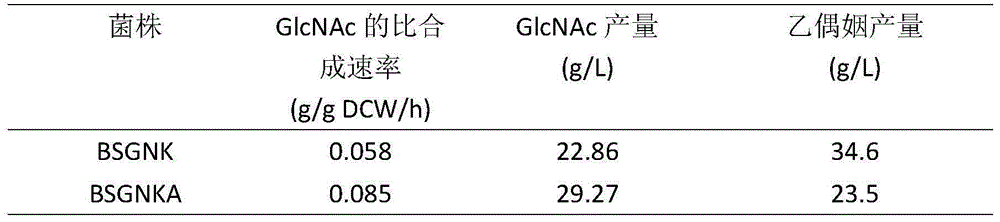
The invention discloses a method for knocking out pckA to promote synthesis of acetylglucosamine through bacillus subtilis and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps that BSGNK-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 serves as original strains, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (pckA) genes are knocked out through homologous recombination, the reaction that enolphosphopyruvate is converted into oxaloacetic acid in host bacterium cells is blocked, the carbon flux flowing to a tricarboxylic acid cycle is reduced, and accumulation of acetylglucosamine is promoted. In the process that a composite culture medium is used for fermentation, the acetylglucosamine yield of recombination bacillus subtilis with pckA knocked out reaches 29.27 g / L and is increased by 28.1% compared with that of control strains. The method lays a foundation for transforming bacillus subtilis to produce acetylglucosamine in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGSU HEVI BIOTECH CO LTD
Method of increasing yield of lignocellulose substrate hydrolase
InactiveCN106434735AEfficient expressionHigh activityMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorHeterologousPichia pastoris
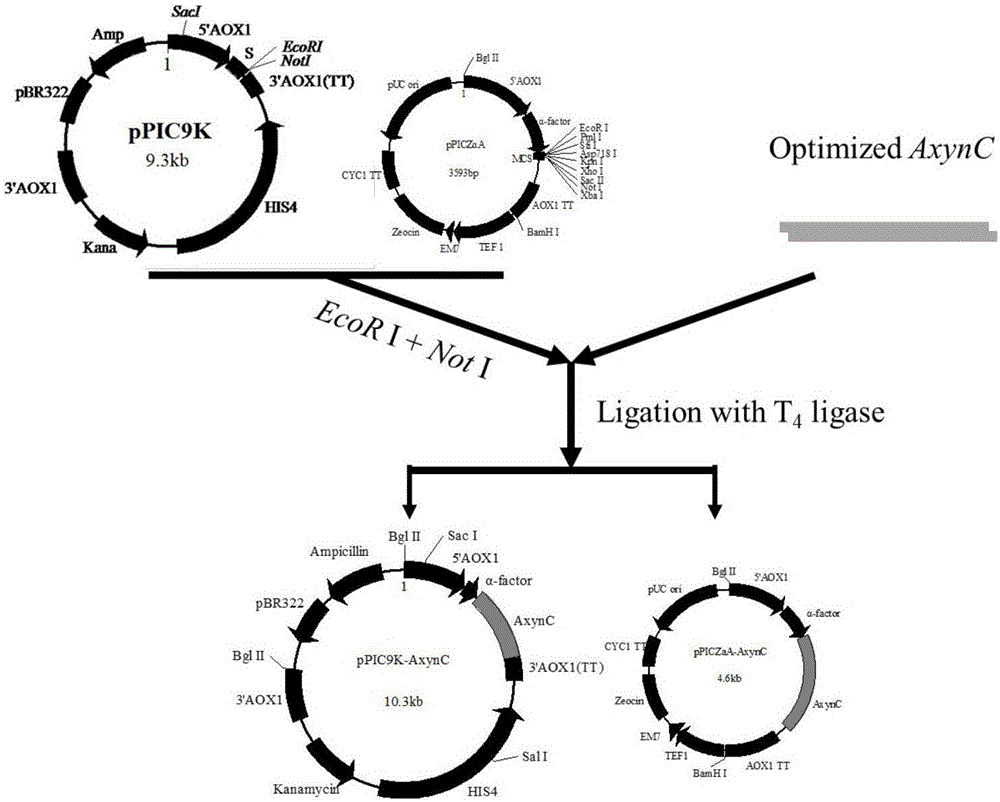
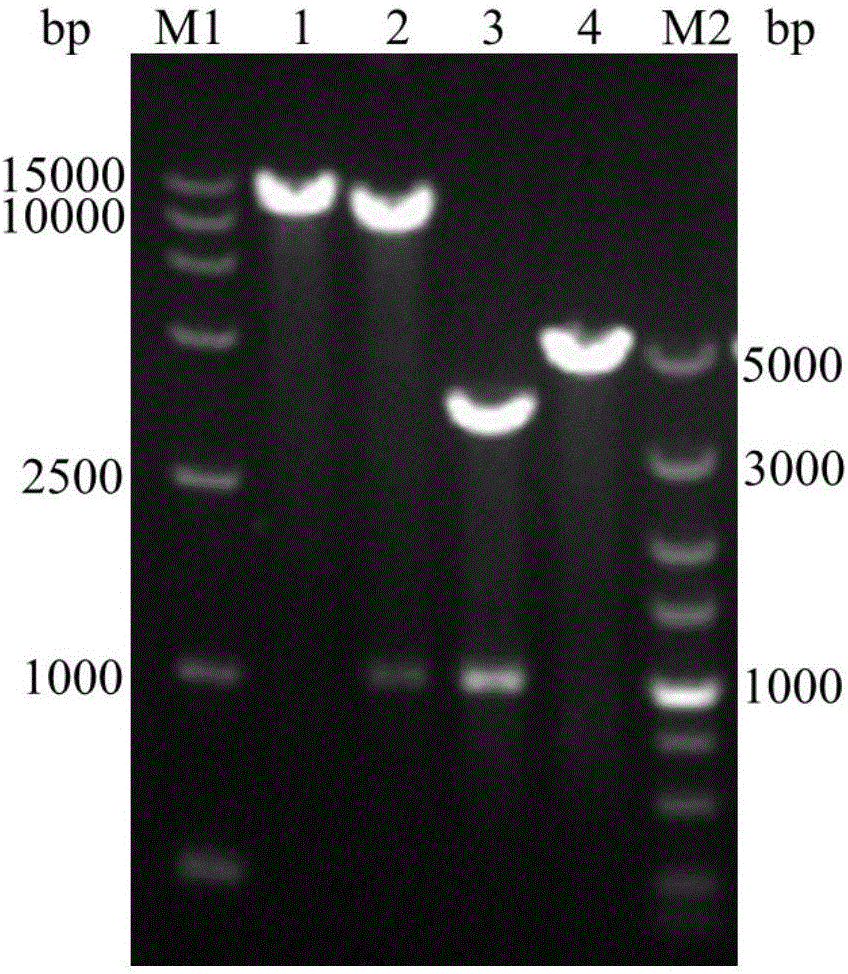
The invention discloses provides a method of increasing heterologous expression quantity of hemicellulase, cellulase or lignocellulose hydrolysis assistance zymoprotein in pichia pastoris. An xylanase (XynC) gene from Aspergillus niger is subjected to codon optimization according to pichia pastoris codon preference characteristics, and an optimized nucleotide sequence (AxynC) is artificially synthesized, and constructs and recombines expression vectors pPIC9K-AxynC and pPICZ alpha A-AxynC. Recombined pichia pastoris of high yield xylanase is constructed by a two-step shock conversion method. That is to say, linearized pPIC9K-AxynC converts the pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain a strain with better enzyme producing ability. The high enzyme activity is subjected to second shock conversion as a host bacterium, and the linearized pPICZ alpha A-AxynC is shocked to convert the strain to obtain double-plasmid recombined pichia pastoris of the high yield xylanase. Tests show that the codon optimized xylanase gene can be expressed successfully in the pichia pastoris, the high yield xylanase recombinant bacterium constructed by a two-step shock conversion method can stably and efficiently produce the xylanase, the flask level enzyme activity reaches 410U / mL, and a protein content in a fermentated supernate reaches 0.37mg / mL.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bile salt hydrolase (BSH) mutant and use thereof
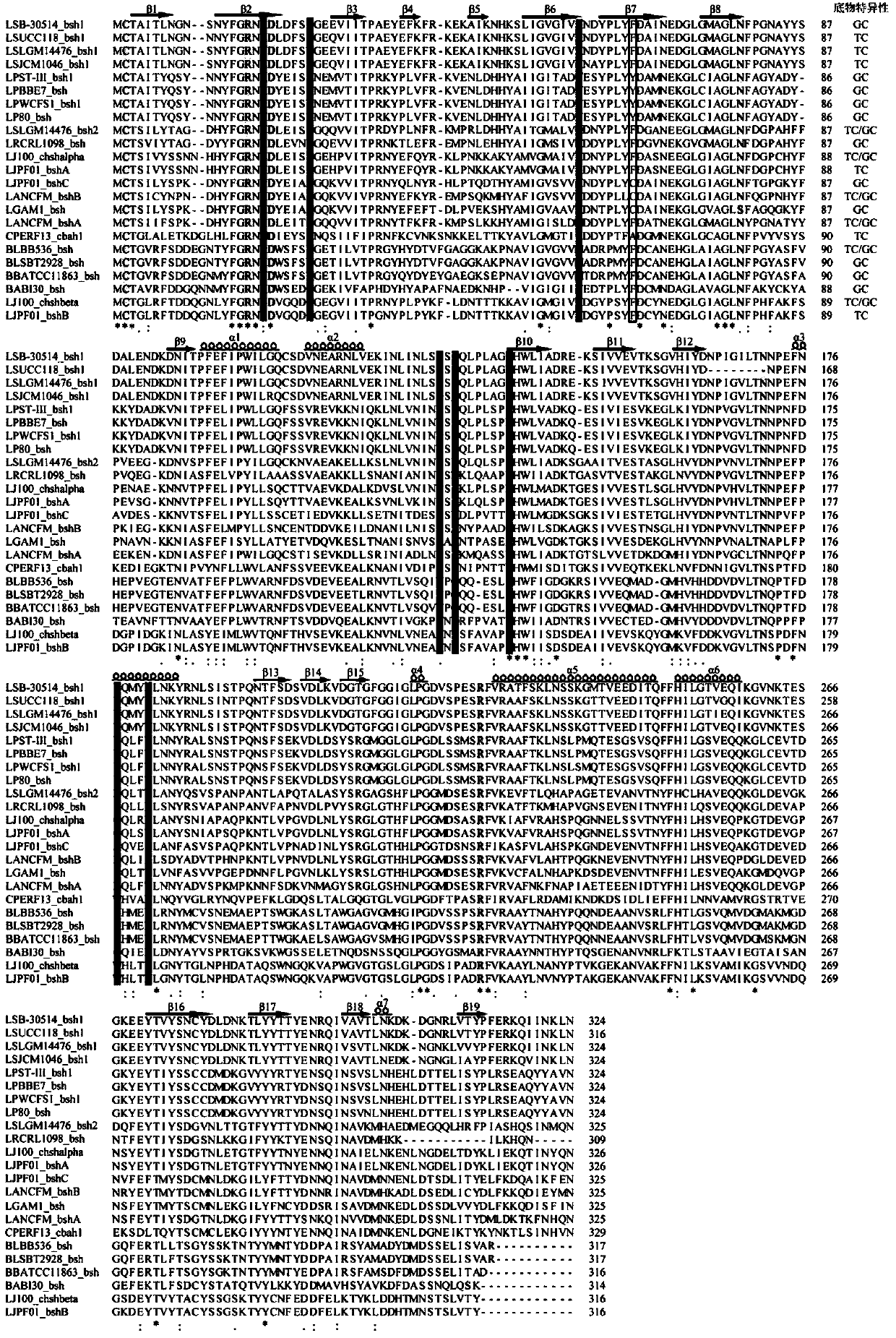
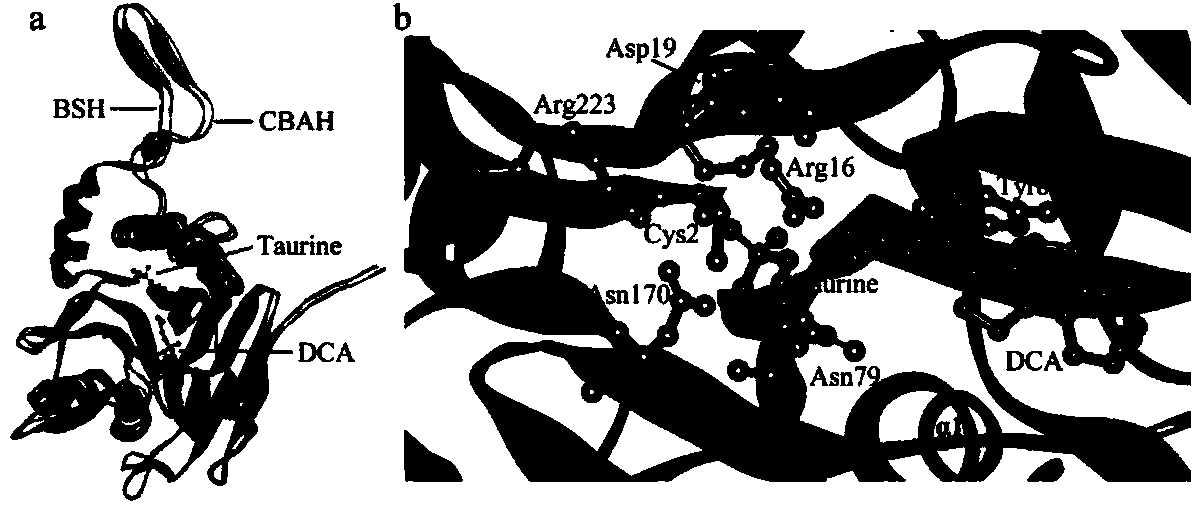
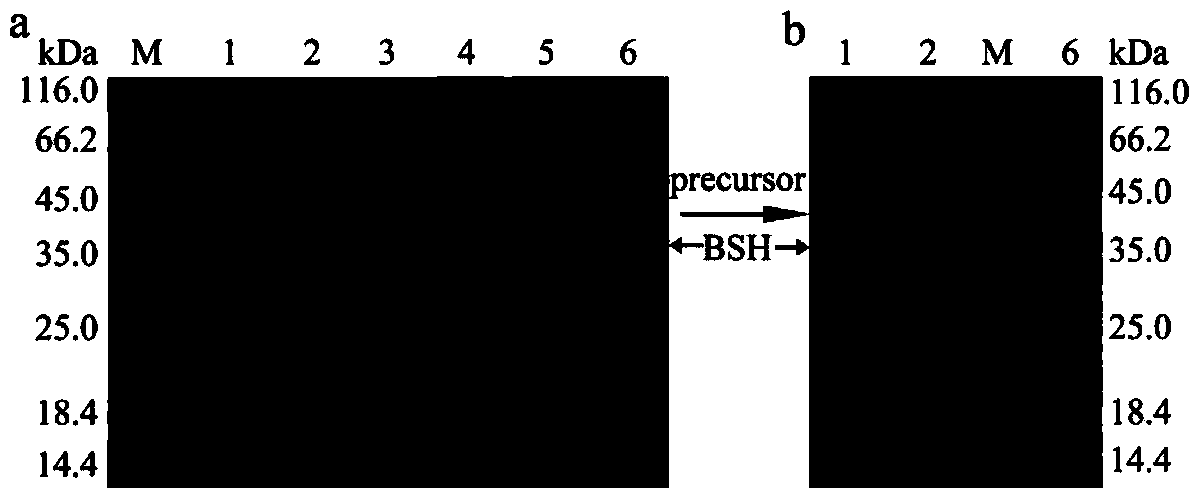
ActiveCN103992991AReduce hydrolysisImprove hydrolysis effectHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBile salt hydrolaseActive enzyme
The invention discloses a bile salt hydrolase (BSH) mutant and a use thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. Through comparison analysis of a BSH amino acid sequence and homology modeling and overlay analysis of a 3-D structure, a BSH substrate specific amino acid mutation site is determined, through a site-specific mutagenesis technology, the substrate specific amino acid mutates into a nonpolar amino acid, and the mutant is transferred into a host bacterium so that a mutant strain is obtained. The BSH produced by the mutant is active enzyme. Compared with a wild-type bacterium, the mutant has a reduced glycine-combined bile salt hydrolysis capability and an improved taurine-combined bile salt hydrolysis capability. The BSH mutant lays a foundation for improving a taurine-combined bile salt hydrolysis capability of BSH and uncovering a substrate combination mechanism of BSH.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for separating purified bdellovibrio from active sludge
InactiveCN104312963AShorten the growth cycleShorten the timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActivated sludgeCulture fluid
The invention discloses a method for separating purified bdellovibrio from active sludge. By virtue of key techniques of host bacteria screening and active sludge pretreatment and technical steps such as preparation of a culture medium and a culture solution and optimization of culture conditions and the like, efficient bdellovibrio is separated and purified from a homologous sludge sample by optimization of a series of key steps by virtue of gram negative bacteria which are obtained in active sludge as host bacteria for separating and purifying bdellovibrio. The invention not only puts forwards a method for successfully separating the efficient bdellovibrio from the active sludge of a municipal wastewater treatment plant for the first time, but also the culture period of the method is remarkably shortened, so that the defects that the existing conventional method is unstable in bdellovibrio separating effect, long in culture period, tedious in operation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Purification of biological preparations
InactiveUS6310186B1Reduce concentrationReduce the amount requiredIon-exchanger regenerationImmunoglobulinsBacilliPollutant
This invention relates to the purification of biological preparations such as proteins and nucleic acids, especially for example proteins that have been produced by recombinant DNA techniques in bacteria. In a particular embodiment, the invention concerns improved methods for reducing the content of contaminants in biological preparations, e.g. recombinant proteins produced in host bacteria.
Owner:XENOVA RES
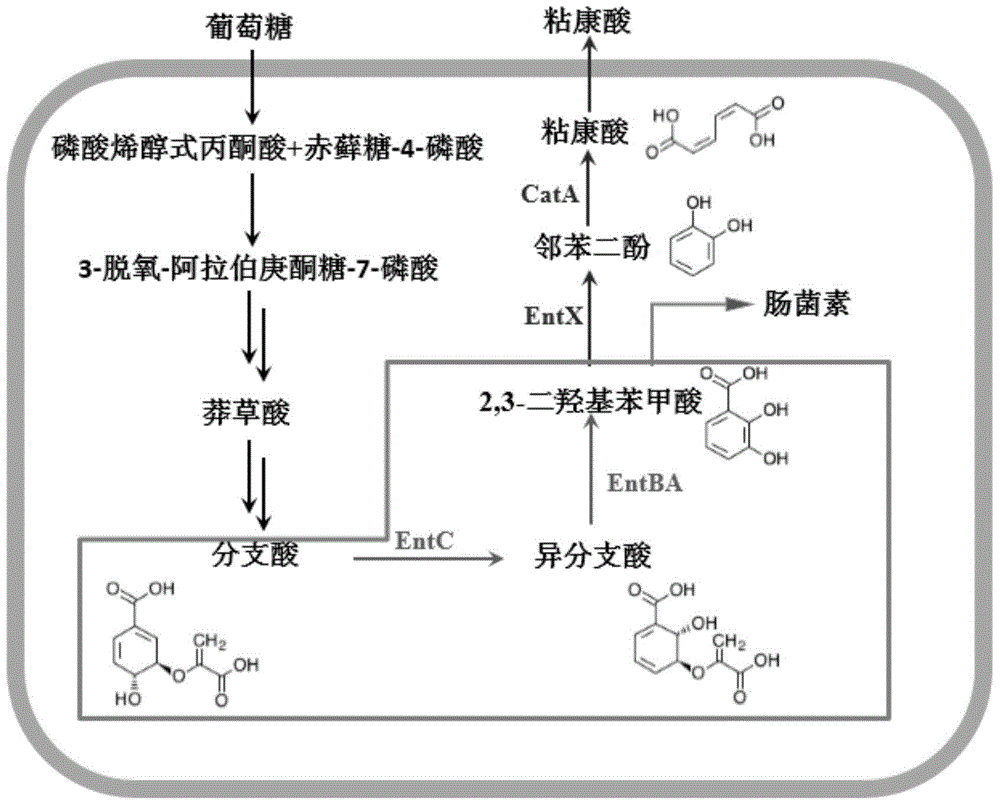
Colibacillus engineering bacterium taking glucose as substrate for synthesizing muconic acid
InactiveCN104099284AReduce the burden onReduce incompatibilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBenzoic acid
The invention discloses a colibacillus engineering bacterium taking glucose as a substrate for synthesizing muconic acid, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. 2,3-dihydroxy benzoic acid (2,3-DHB) is led to colibacillus during the metabolic pathway of muconic acid (MA); the metabolic pathway of colibacillus from glucose to 2,3-DHB is reinforced. The colibacillus engineering bacterium has the advantages that less foreign genes are required; the foreign gene expression load of a host bacterium is reduced; the incompatibility problem of the foreign genes is solved. Moreover, the host bacteria are not auxotroph; the foreign addition of expensive shikimic acid or other aromatic amino acid is avoided; the flask shaking fermentation yield of muconic acid is 1.15 g / L.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGQIANG CHEM IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Bovine viral diarrhea virus E0 protein amino acid and preparation method thereof
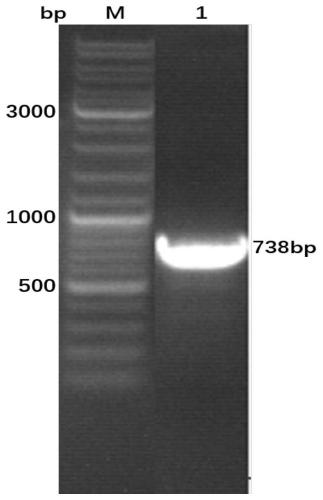
ActiveCN111057132AEasy to purifyImprove solubilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesTarget gene
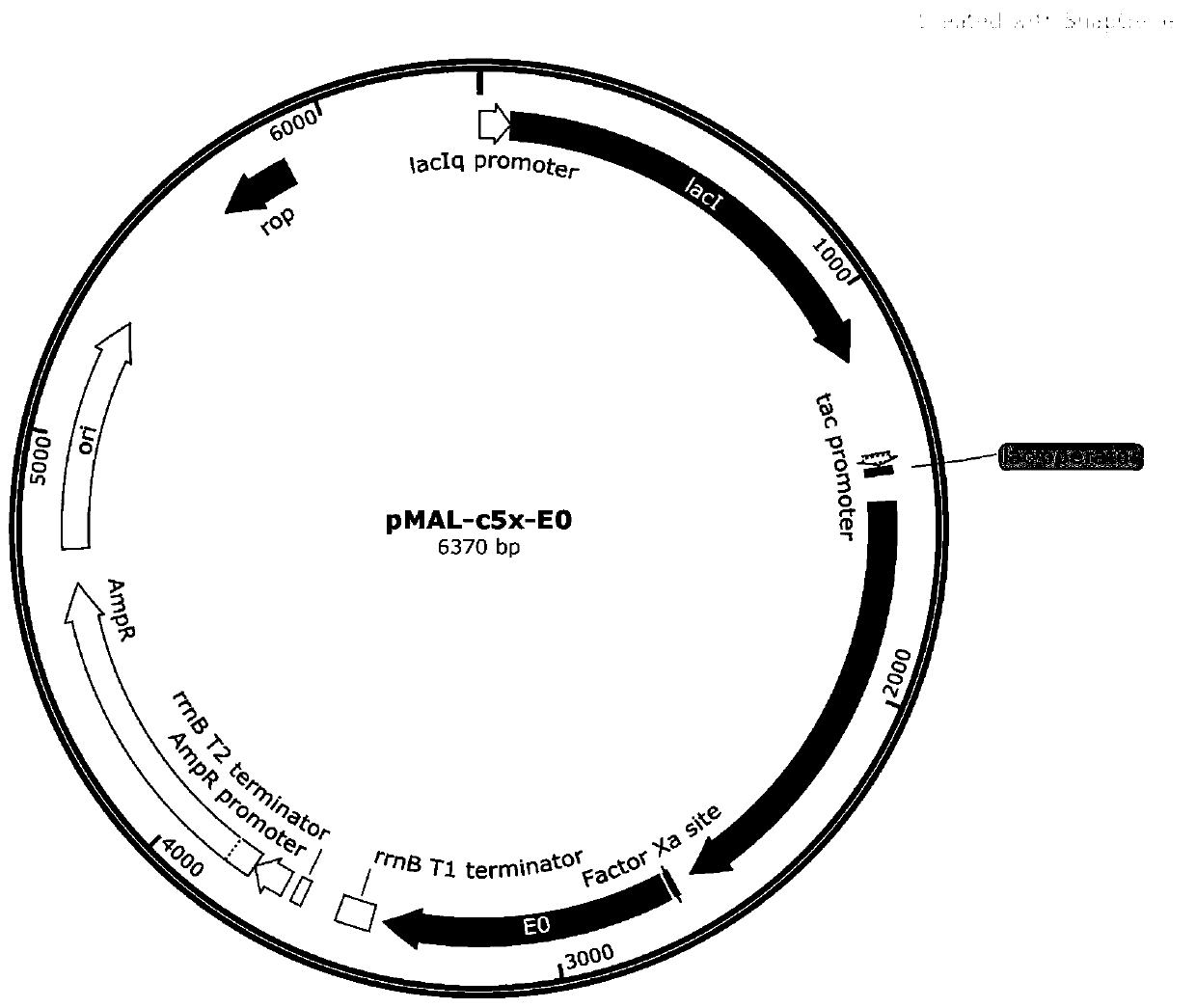
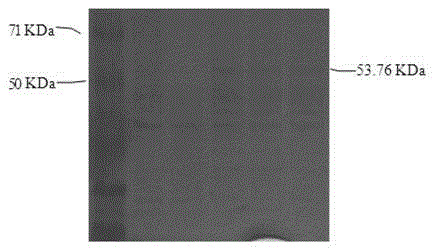
The invention provides a bovine viral diarrhea virus E0 protein amino acid and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the bovine viral diarrhea virus E0 protein amino acid is represented by SEQ ID NO:3. The preparation method comprises the following steps:S1, obtaining a BVDV NADL whole genome sequence from NCBI GenBank, and finding out a BVDV E0 gene sequence from the BVDV NADLwhole genome sequence; S2, optimizing and synthesizing the E0 gene sequence obtained in step S1; and S3, selecting a prokaryotic expression vector pMal-c5X with an MBP label, connecting the E0 gene with the pMal-c5X, inserting an E0 fragment into the pMal-c5X, converting the connected expression vector pMAL-c5x-E0 into an expression host bacterium BL21 (DE3), inducing the expression of the obtained recombinant protein, and separating and purifying the target protein. The target gene E0 is optimized, and is subjected to fusion expression with the MBP tag protein to finally achieve the efficientsoluble expression of the E0 protein, so the bovine viral diarrhea virus E0 protein amino acid has the advantages of high expression yield, good solubility, and convenience in expression protein purification; and the solubility of the Escherichia coli expression protein can be improved during the fusion expression of the foreign protein and the MBP so as to provide convenience for the purification of the expression protein.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Recombinant protein of antigen to porcine circovirus and antigen to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, and preparation method and application of recombinant protein
InactiveCN103059142AStable in natureBig advantageAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsEpitopeInclusion bodies
The invention relates to the field of veterinary medicine, in particular to an animal recombinant protein vaccine. A recombinant protein contains an epitope of an antigen to a porcine circovirus (PCV) and an epitope of an antigen to a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), and supports the vaccine after being emulsified. According to the recombinant protein, a target fragment shown as SEQ ID NO:6 is synthesized, the target fragment and a PGEX-4T-1 vector form a recombinant vector, a recombinant plasmid is converted into a host bacterium induced expression, and the recombinant protein is extracted. The recombinant protein content for swine immunization is a product of 4-hour host bacterium induced expression, and the recombinant protein at concentration of over 80 percent is purified by processes of inclusion body recovery, dissolution, concentration and the like. The prepared recombinant protein has a stable property, does not have the characteristics of virus transmission and the like, and is greatly advanced or plays an irreplaceable role in the researches and development of PRRSV and PCV2 prevention and control vaccines.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
Iterative gene circuit based on vibrio fischeri quorum sensing system and T7 expression system, and application of iterative gene circuit
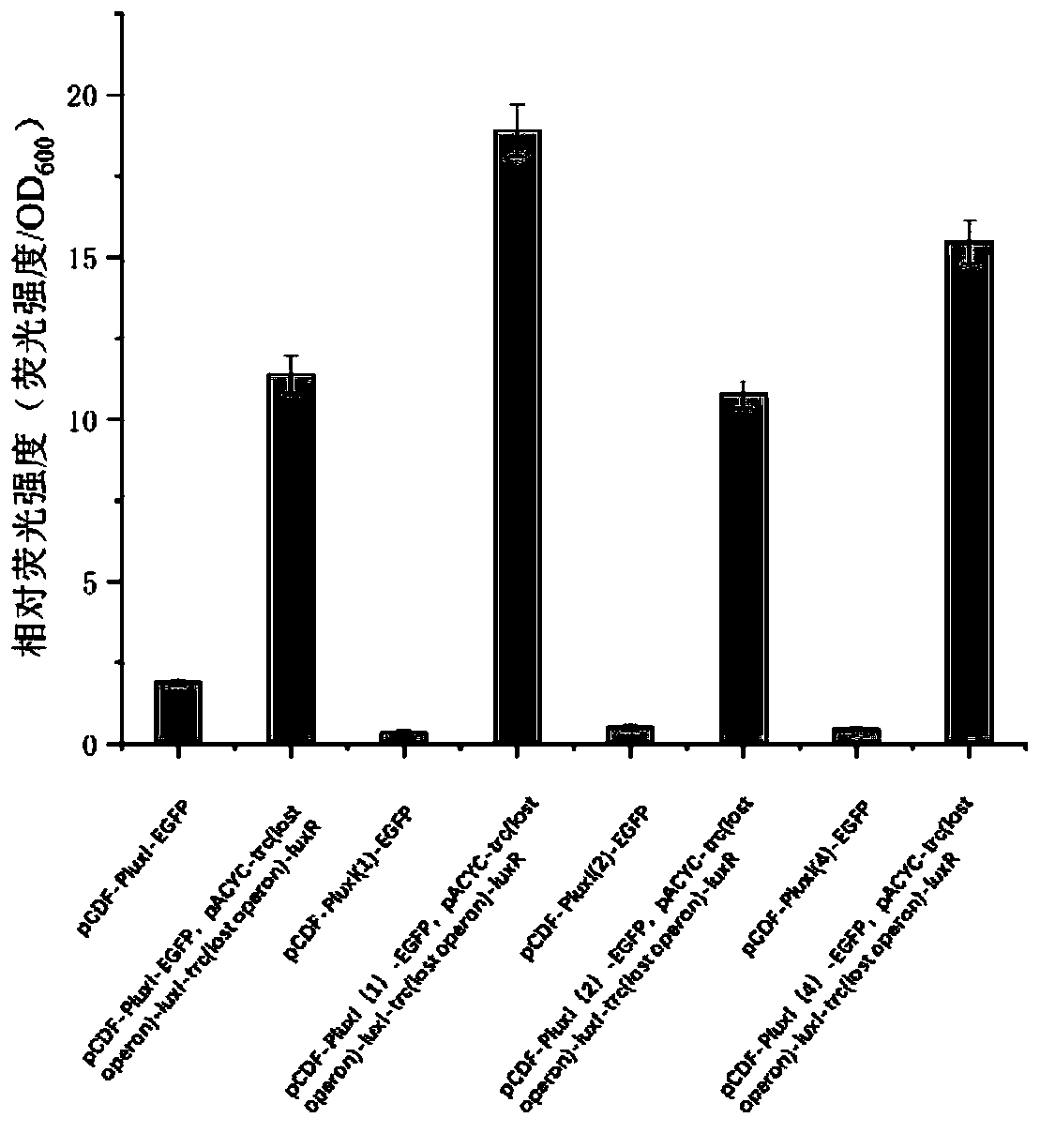
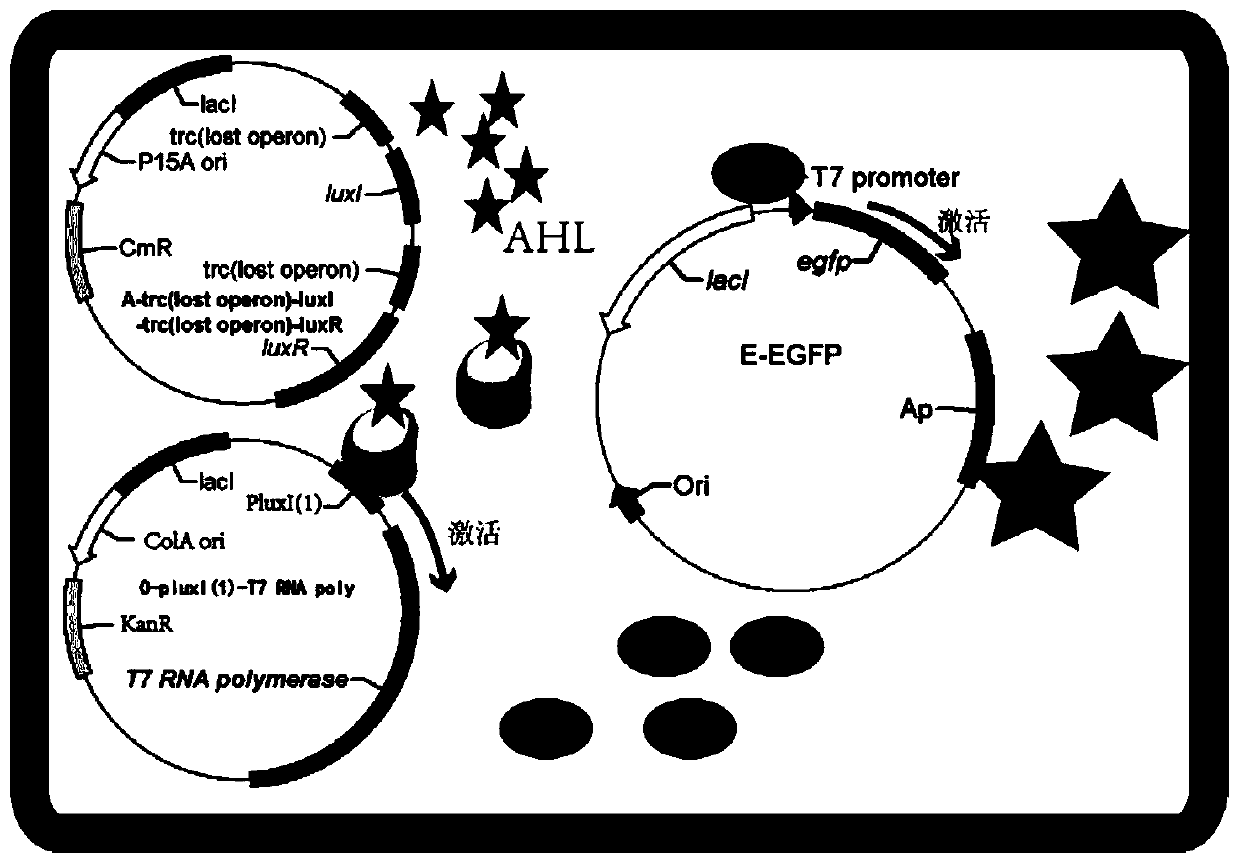
The invention discloses an iterative gene circuit based on a vibrio fischeri quorum sensing system and a T7 expression system. The iterative gene circuit comprises a signal molecular protein gene luxIof vibrio fischeri, a receptor protein gene luxR, a promoter sequence PluxI(1) for sensing a signal molecular and receptor protein complex, a T7 RNA polymerase gene T7 RNApoly and a green fluorescentprotein egfp for representing the circuit intensity. The gene circuit does not rely on an inducer and can utilize the T7 expression system to spontaneously and forcefully initiate target gene expression in any host bacterium; and gene elements are constructed on different expression vectors, the iterative gene circuit is constructed in engineering bacteria, the T7 expression system is utilized toamplify signals of the vibrio fischeri quorum sensing system, and the iterative gene circuit has the function of utilizing the T7 expression system to spontaneously and forcefully initiate target gene expression, and has a lower leakage ratio and higher initiating strength.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant expression plasmid vector and recombinant strain to be used in producing oxalate decarboxylase, and method of producing recombinant oxalate decarboxylase
It is intended to provide a means of highly producing oxalate decarboxylase originating in a microorganism. A recombinant expression plasmid vector, which contains a-amylase promoter of a microorganism belonging to the strain Bacillus and an oxalate decarboxylase gene originating in a microorganism that is provided under the control of the promoter, is constructed. A host bacterium is transformed by this vector to give an oxalate decarboxylase-producing bacterium. A recombinant oxalate decarboxylase is produced by culturing the producing bacterium as described above and then harvesting the oxalate decarboxylase thus produced.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com