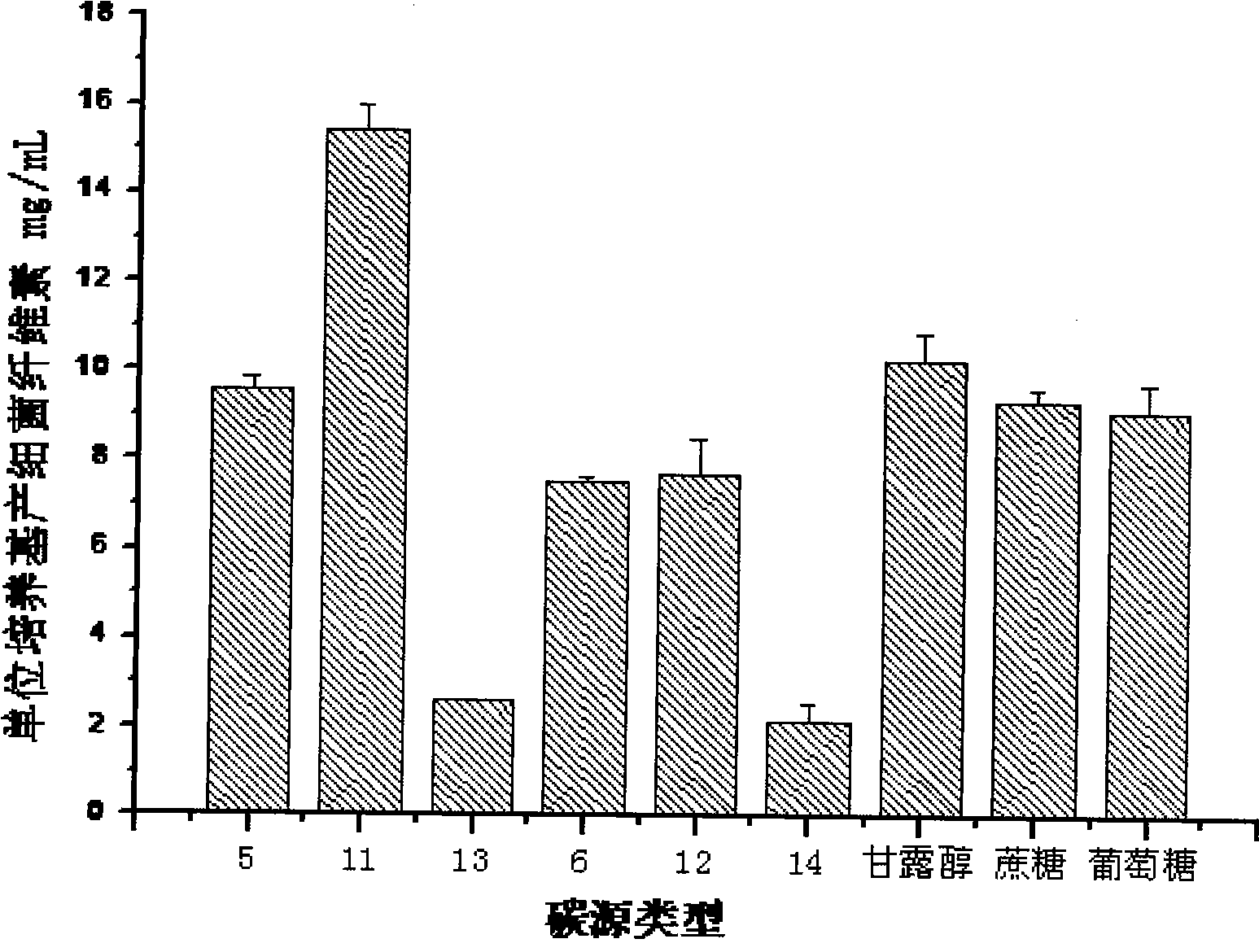
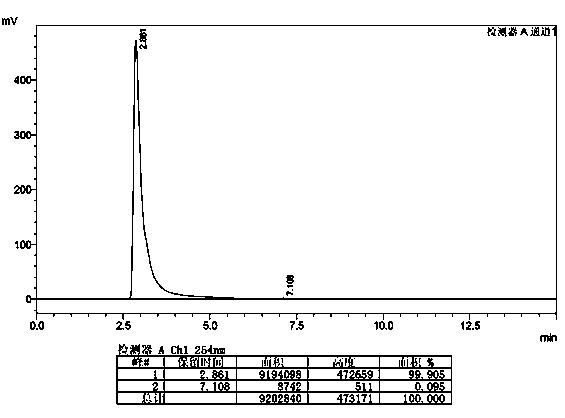
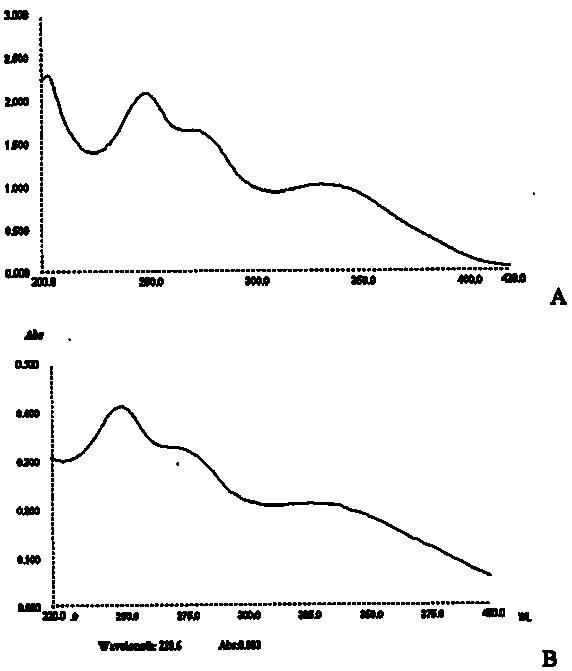
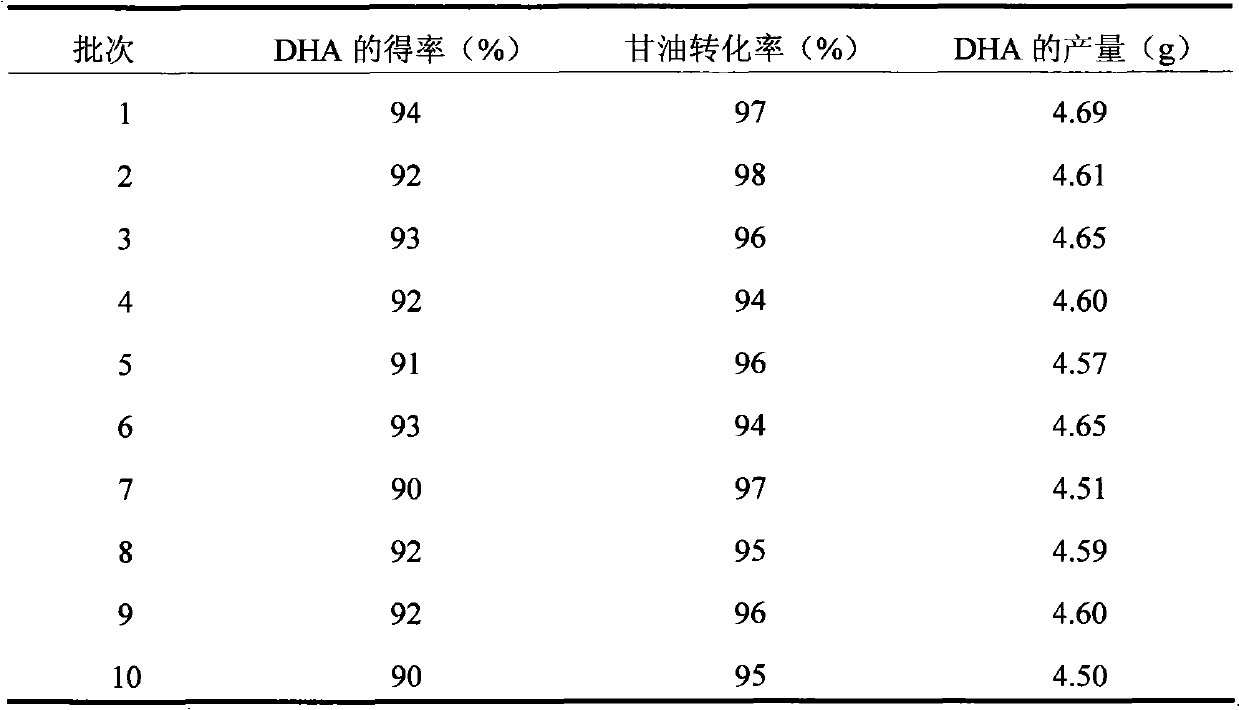
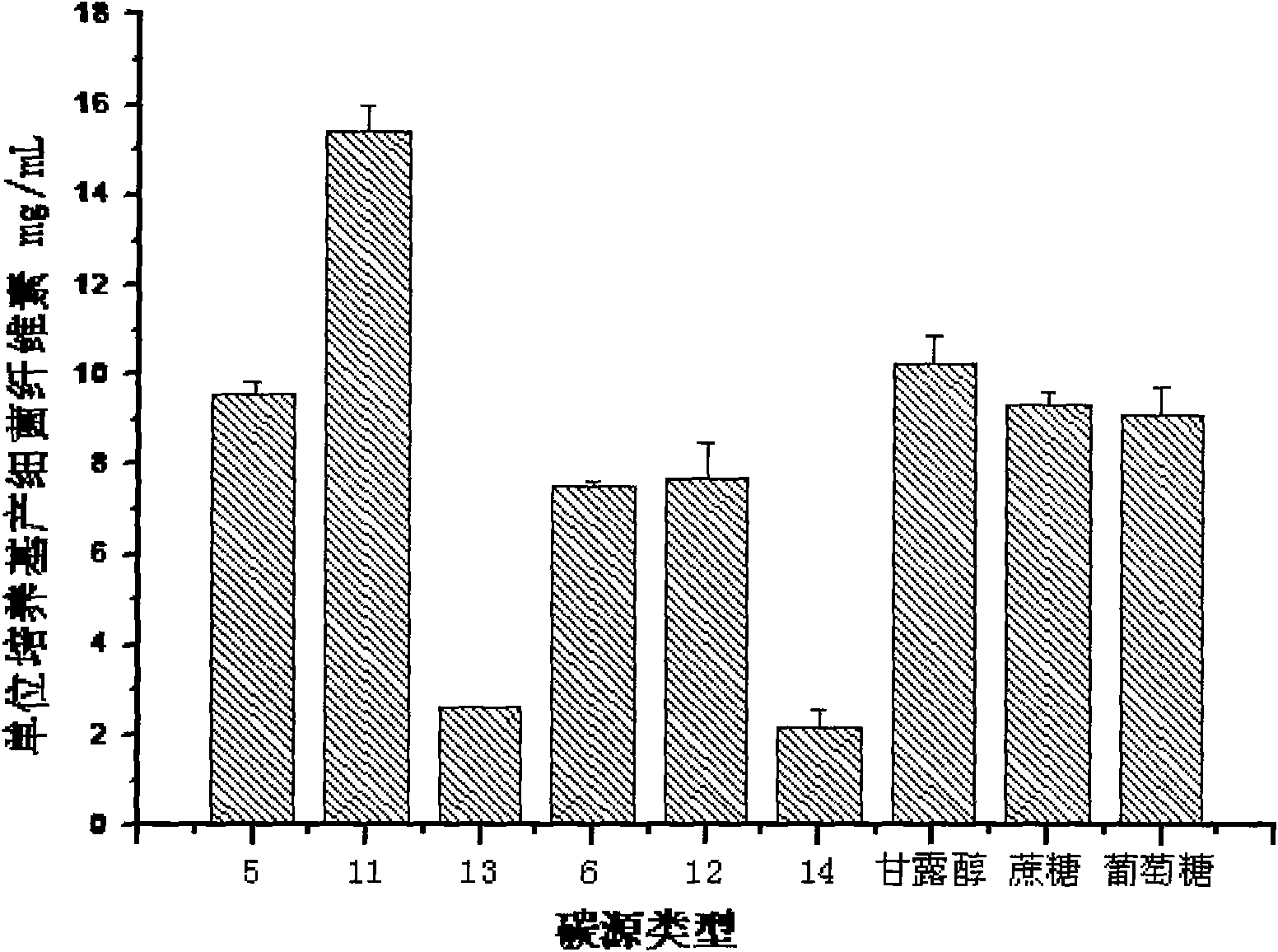
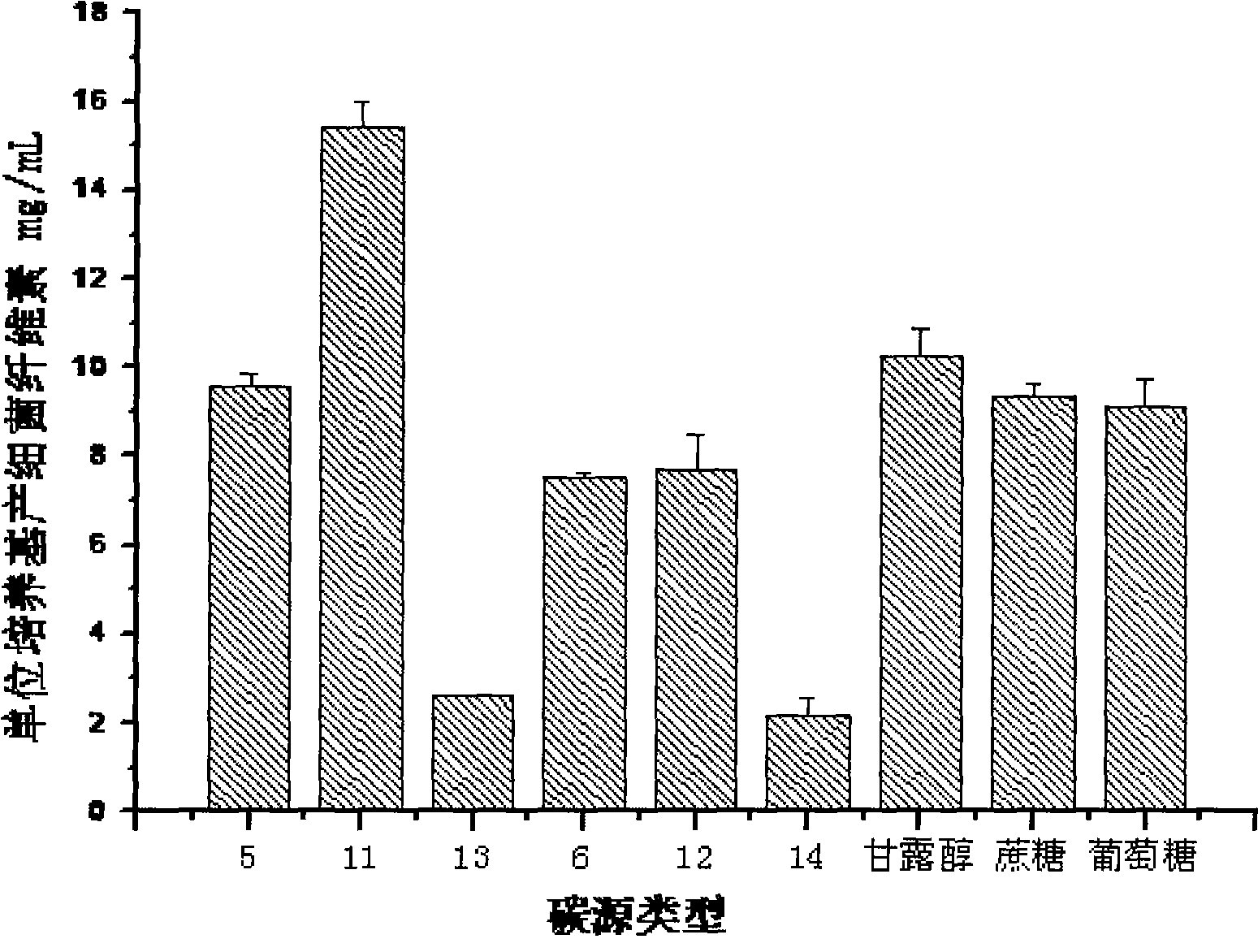
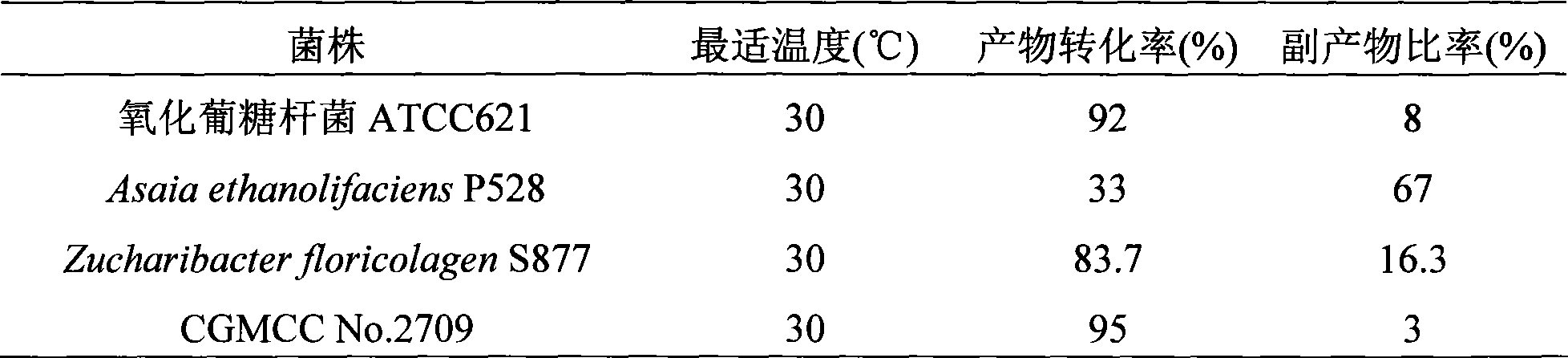
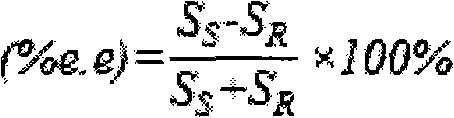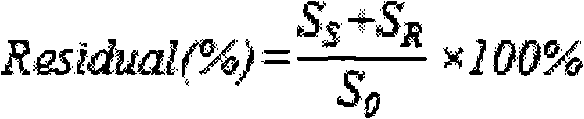Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
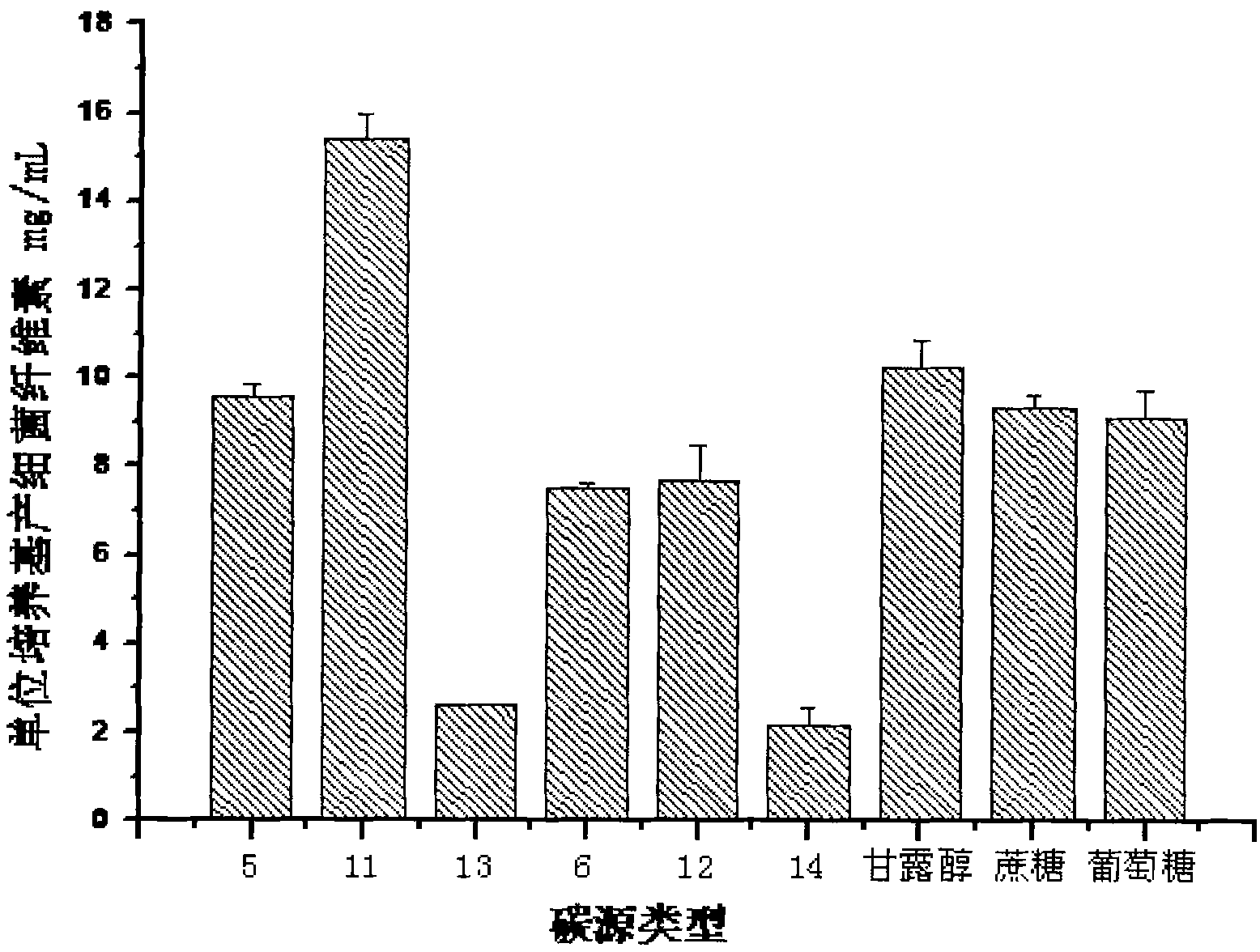
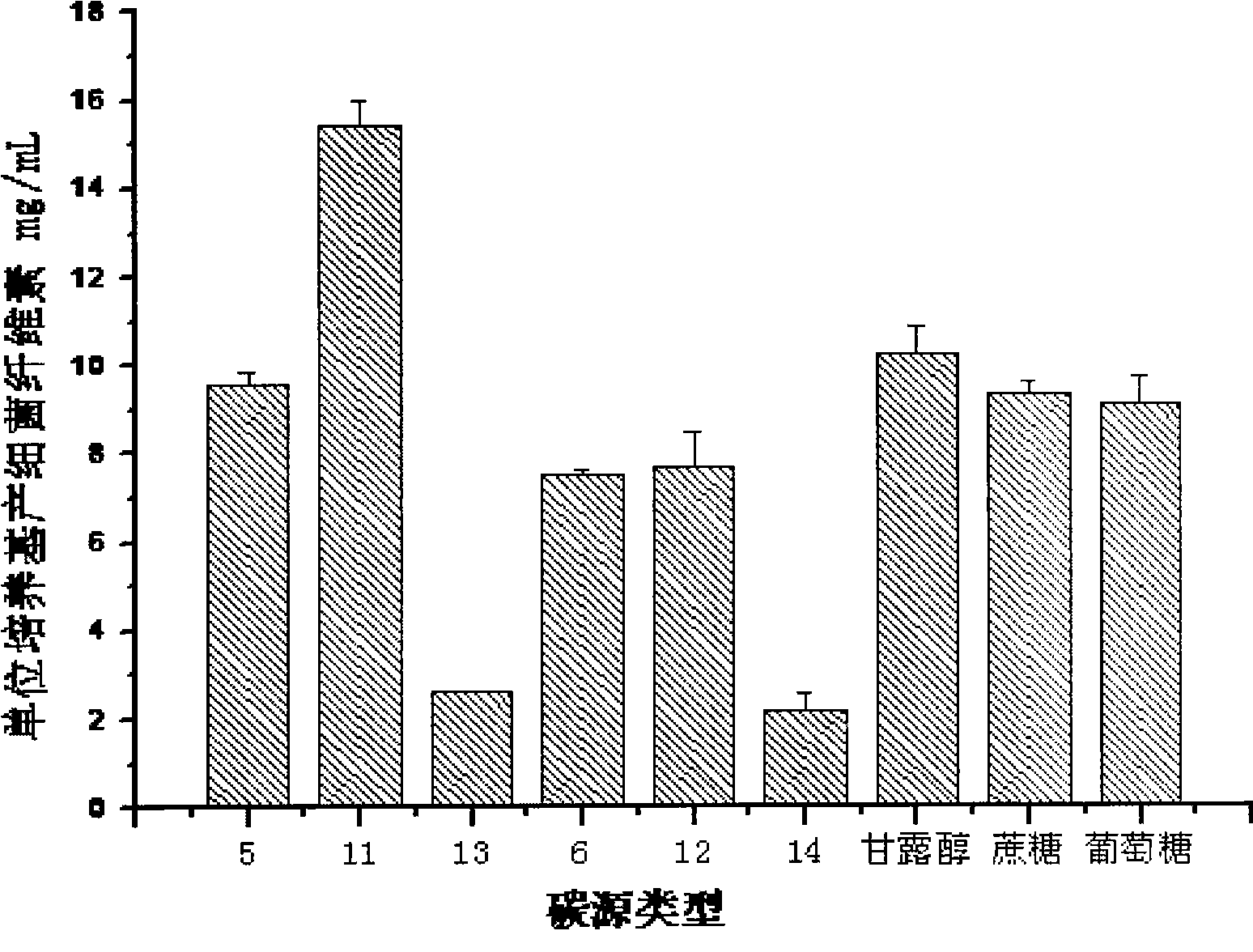
139 results about "Gluconobacter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genus of gram-negative, rod-shaped to ellipsoidal bacteria occurring singly or in pairs and found in flowers, soil, honey bees, fruits, cider, beer, wine, and vinegar. (From Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed)
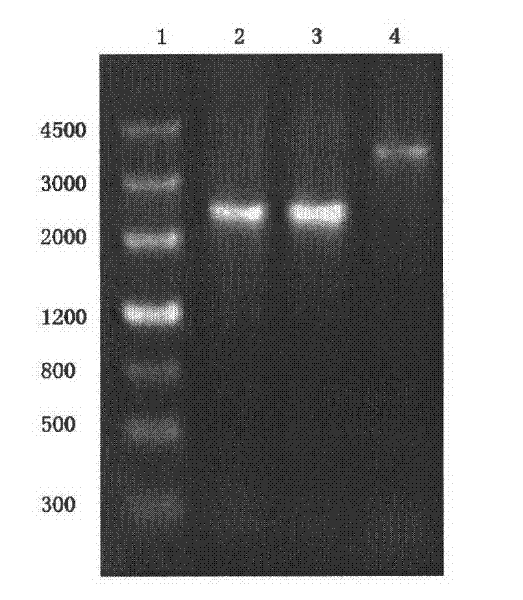
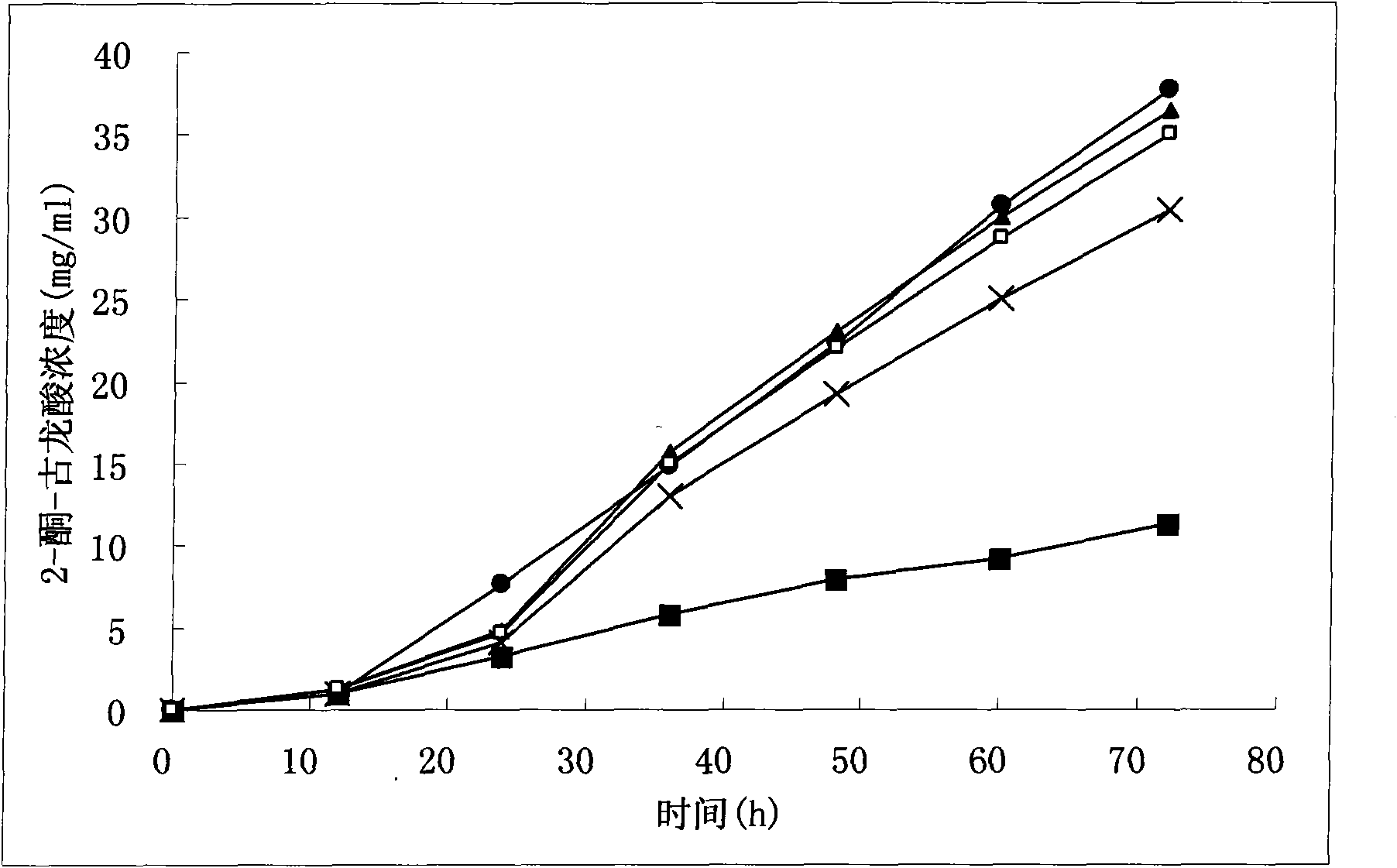
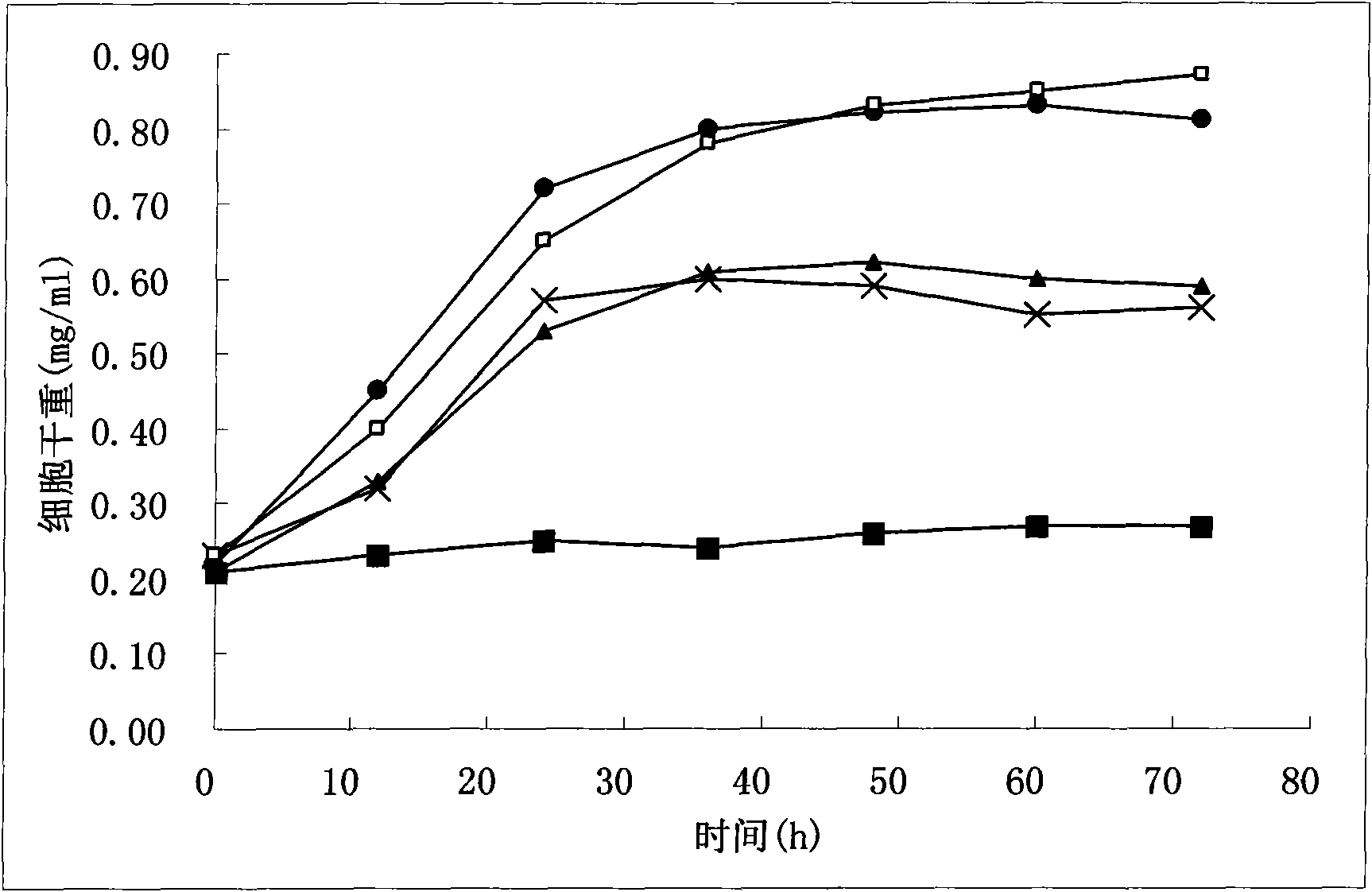
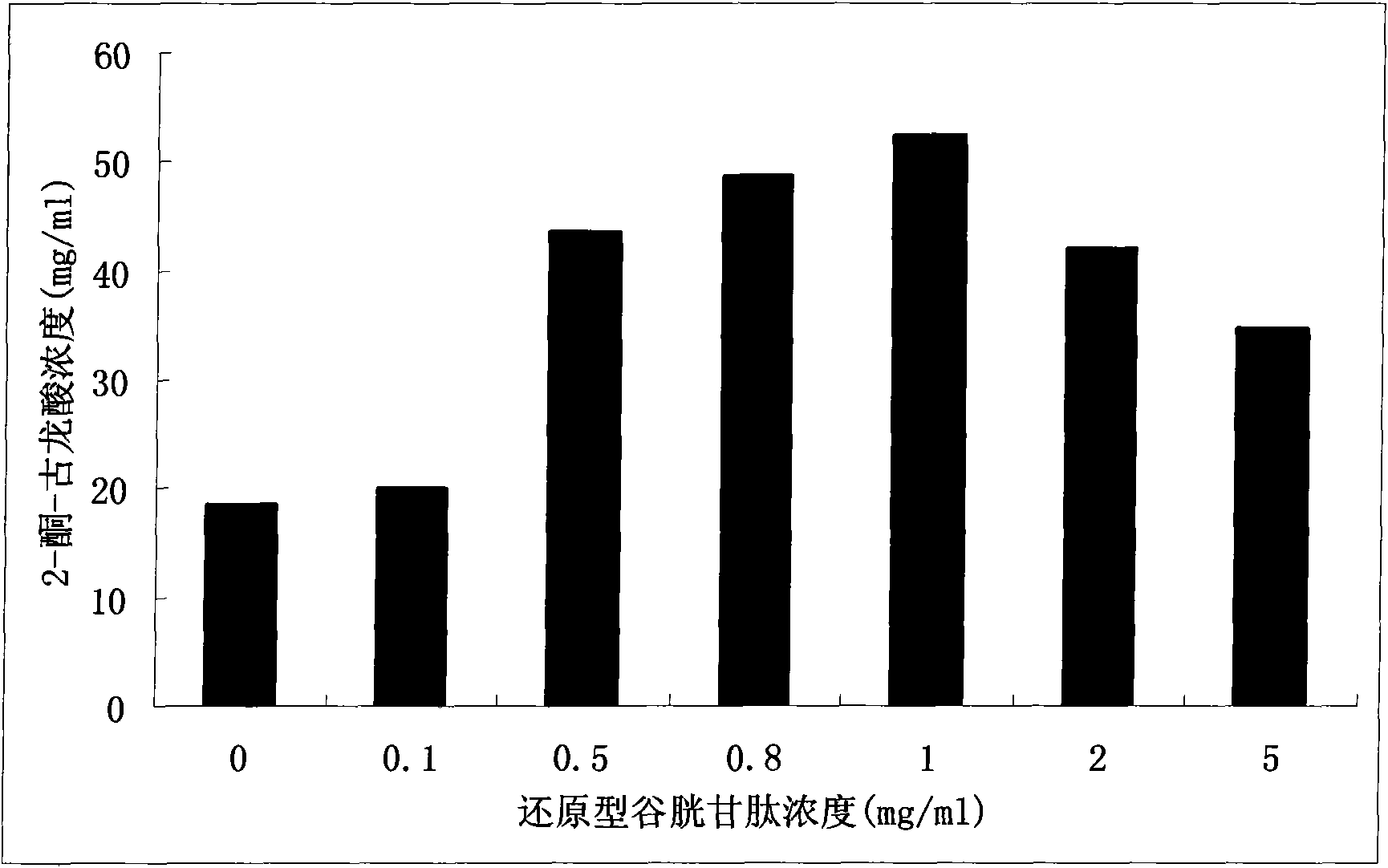
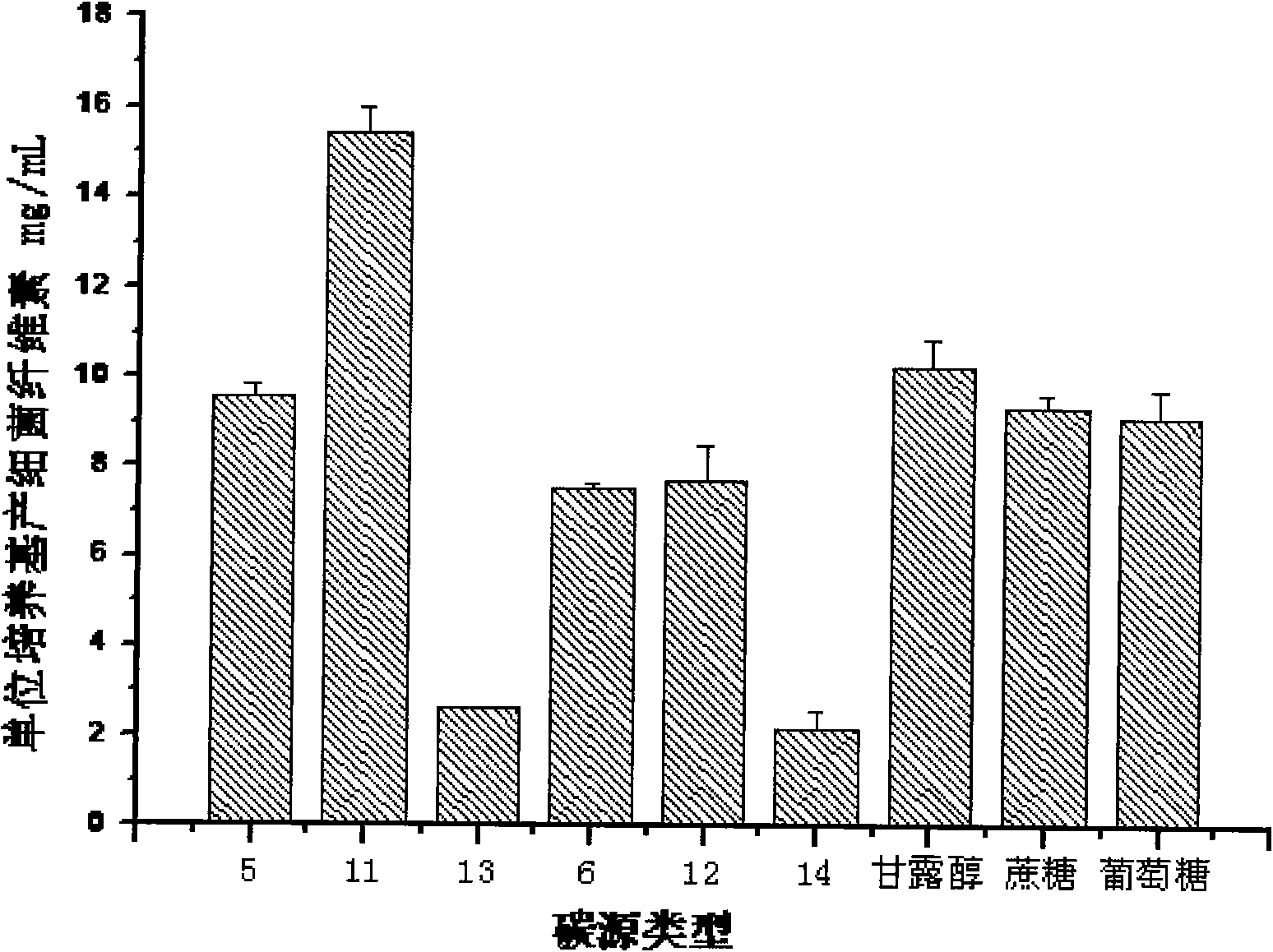
Method for improving gluconobacter oxydans to produce 2-keto-L-gulonic acid
ActiveCN101603060ALow costReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacillus megateriumGluconic acid
The invention discloses a method for improving gluconobacter oxydans to produce 2-keto-L-gulonic acid, which comprises the following steps: (1) seed culture, namely inoculating bevel gluconobacter oxydans into a seed culture medium to form seed culture solution; and (2) fermentation, namely inoculating the seed culture solution into a fermentation culture medium, oscillating the mixture in a shaking bed, carrying out fermentation culture for 48 to 96 hours, and adding a sulfhydryl compound into the mixture at any moment of the fermentation culture in a range of 0 to 36 hours to make the final concentration of sulfhydryl between 0.1 and 30mM. The method can improve the growth speed of the gluconobacter oxydans and the efficiency for producing the 2-keto-L-gulonic acid, and achieve the aim of partially replacing the companion effect of companion fungus so as to reduce the using amount of bacillus megaterium of the companion fungus, reduce the cost of the culture medium and reduce the pollution.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reconstruction method for producing Vitamin C precursor 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2-KLG) with gluconobacter oxydans
InactiveCN102250822AEliminate dependenciesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVitamin CGenetic engineering
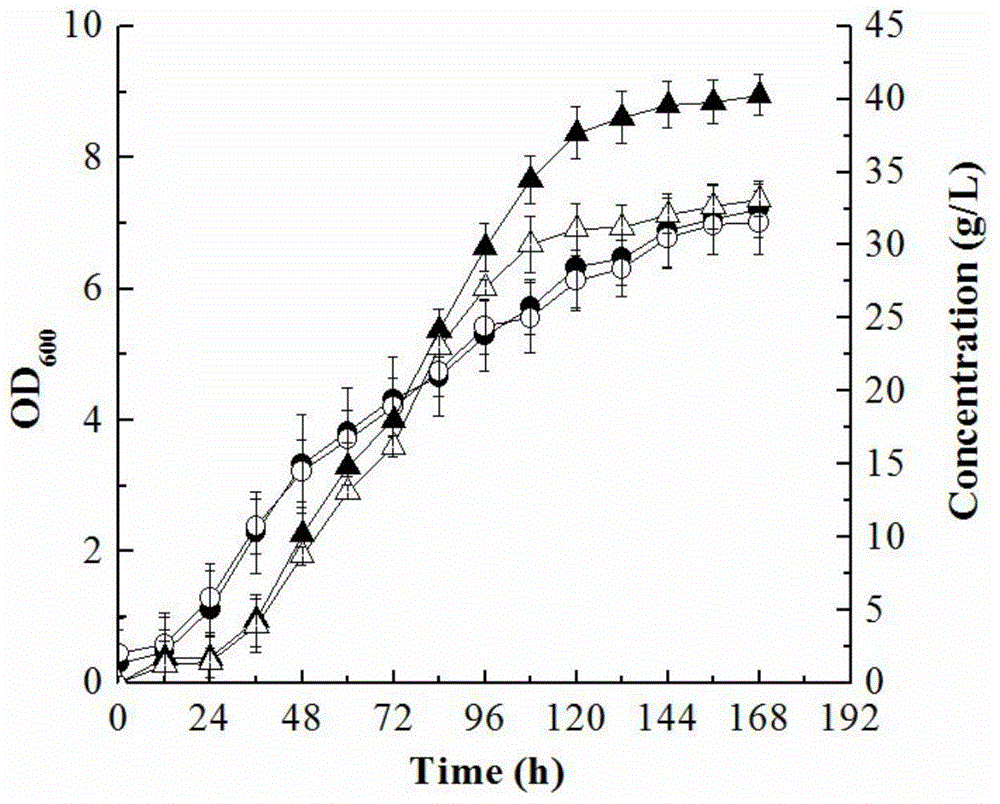
The invention discloses a reconstruction method for producing the Vitamin C precursor 2-KLG with gluconobacter oxydans, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, a sorbose dehydrogenase (SDH) gene and a sorbosone dehydrogenase (SNDH) gene originated from ketogulonigenium vulgare are expressed in gluconobacter oxydans to obtain a G. oxydans engineering bacteria for production of 2-KLG by using sorbitol. G. oxydans is a frequently used strain in the first step of fermentation in the method of two-step fermentation; in the invention, the SDH and SNDH genes are expressed in G. oxydans, which enables the problem of dependency of ketogulonigenium vulgare on associated fungi to be overcome, direct conversion of D-sorbitol into 2-KLG to be realized and the production process for Vitamin C to be simplified; output of 2-KLG reaches 83 g / L; therefore, the invention has a very good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws/straws
ActiveCN101781666AWide variety of sourcesLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateFiltration
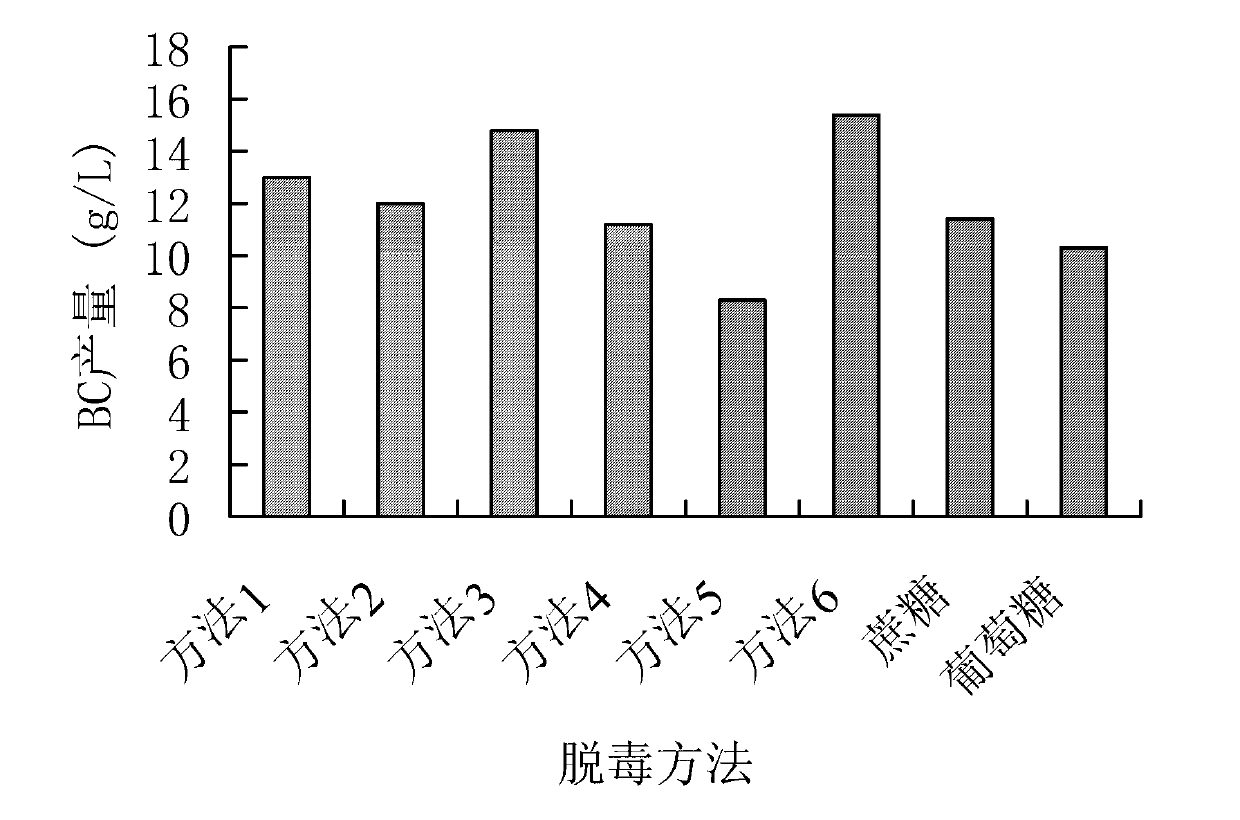
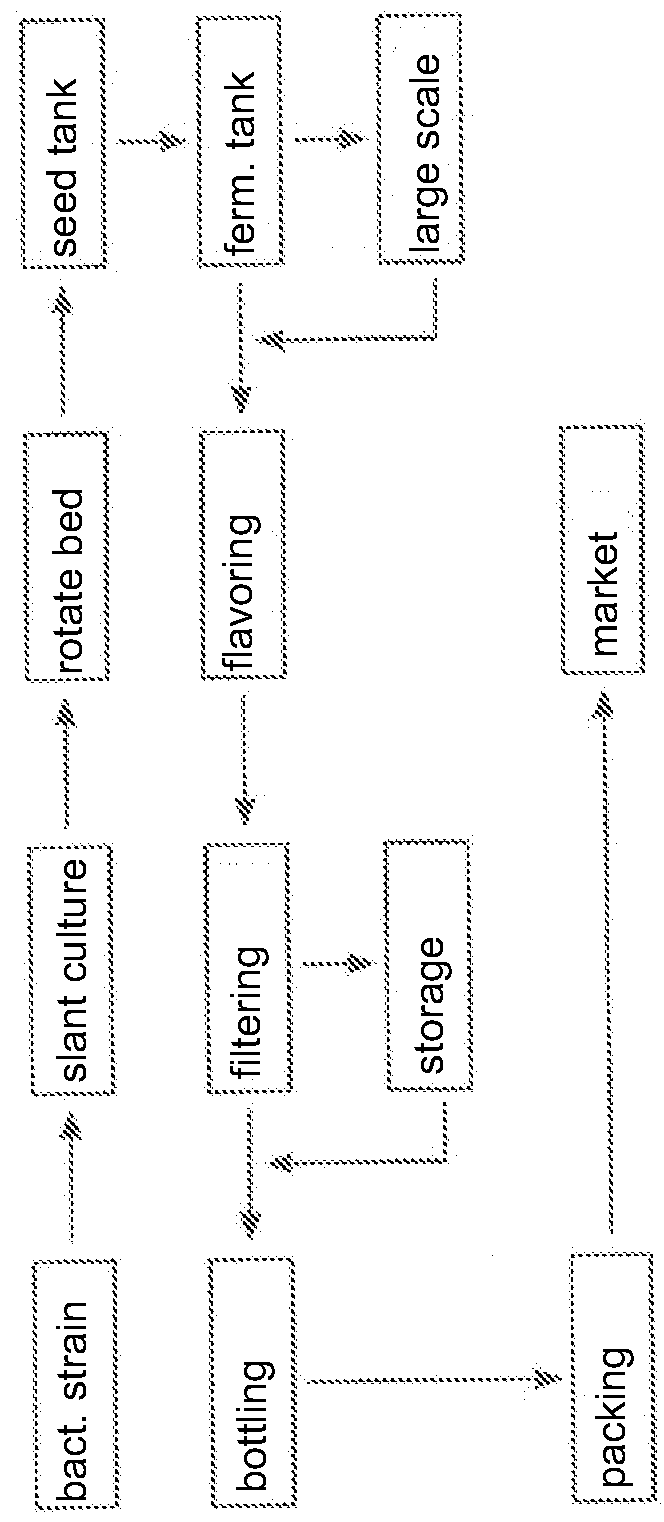
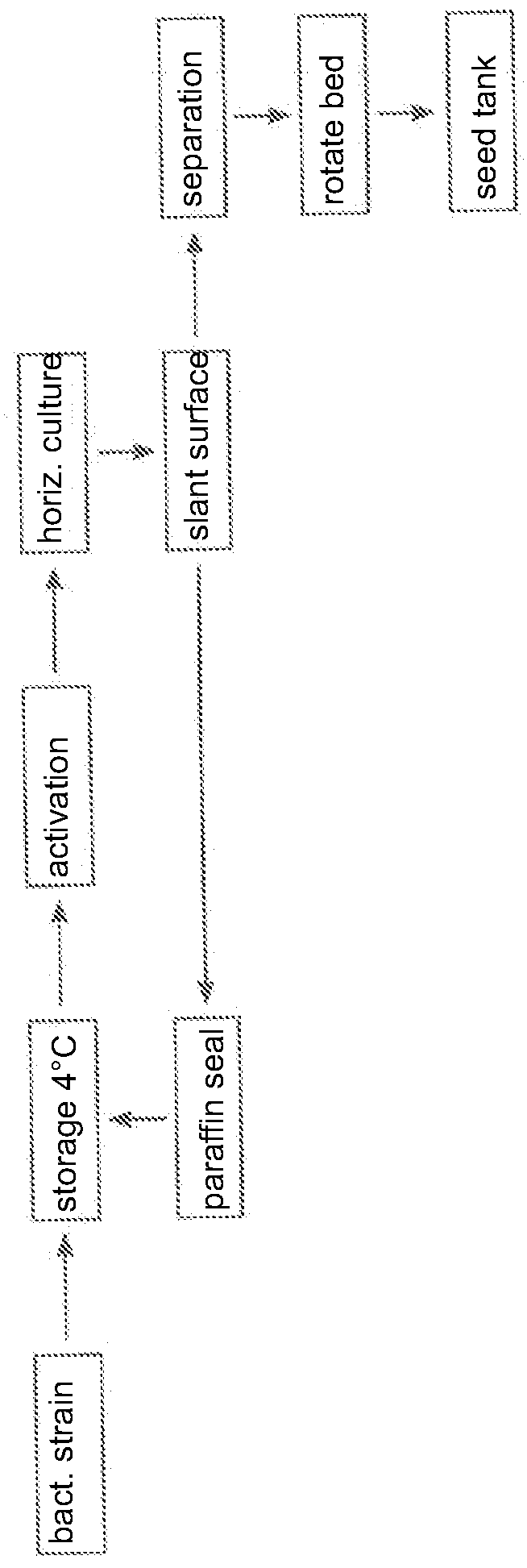
The invention relates to a method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws / straws, comprising the following steps: (1) grinding the wheat straws or straws, soaking the ground wheat straws or straws in dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to react, then separating the residues of the wheat straws or straws from the acid hydrolysate through pump filtration and collecting the hydrolysate for later use; (2) detoxicating the hydrolysate; and (3) taking the detoxicated hydrolysate as the carbon source in the culture medium and adding the nitrogen source to prepare the culture medium and inoculating acetobacter aceti or gluconobacter oxydans into a shaker at 25-30 DEG C and 160-250r / min to be cultured or an incubator at 25-30 DEG C to undergo static culture, thus obtaining the bacterial cellulose. The carbon source in the culture medium is good in quality, low in price and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method and application for producing pyrroloquinoline quinone by using gluconobacter oxydans
ActiveCN104328155AEasy to industrializeSimple conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationCentrifugationGluconobacter oxydans
The invention discloses a method for producing pyrroloquinoline quinone by using gluconobacter oxydans. The method comprises the following steps: (1) fermenting the gluconobacter oxydans DSM2003 to obtain fermentation liquor; (2) carrying out high-speed centrifugation on the fermentation liquor, taking supernate and enriching by using an HP-20 type macroporous resin chromatographic column to obtain an eluted fraction which is rich in pyrroloquinoline quinone; and (3) concentrating the eluted fraction which is rich in pyrroloquinoline quinone under reduced pressure and purifying by using polyamide column chromatography to obtain a pyrroloquinoline quinone pure product. According to the method, under a common culture medium and common culture conditions, the PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) yield of the gluconobacter oxydans strain can reach 125mg / L. The production and preparation method is simple in condition, fast in process and convenient for industrial production in a large scale and has important meaning for industrialization of PQQ.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Application of gluconobacter oxydans in preparing 1,3-dioxyacetone
InactiveCN101948878AStrong dehydrogenation reaction abilityEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses application of gluconobacter oxydans in preparing 1,3-dioxyacetone. The gluconobacter oxydans is named gluconobacter oxydans NH-10, and preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the number of CGMCC No.2709 and the preservation data of October 14, 2008. The gluconobacter oxydans NH-10 can convert glycerol in high efficiency under a condition of high concentration glycerol to produce the 1,3-dioxyacetone. Under the technical condition of the application, the conversion rate of the glycerol can reach 99.7 percent (w / w), and the yield of the 1,3-dioxyacetone can reach 97 percent, the concentration of the 1,3-dioxyacetone in the conversion solution reaches 166.2g / L, and other components are scarcely contained in the conversion solution. The microorganism strain is applicable to industrial production of dioxyacetone.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
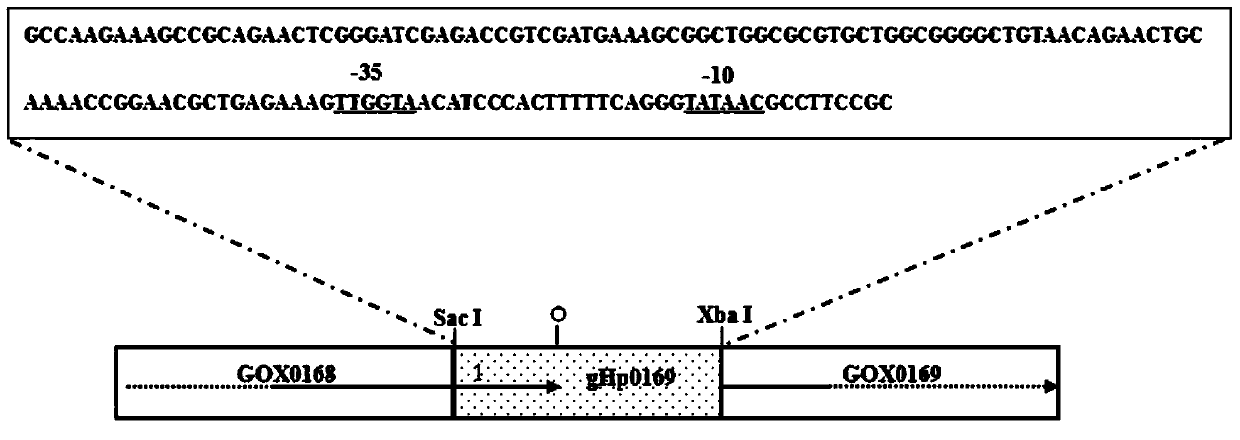
Gluconobacter oxydans promoter and its application
ActiveCN103740714AHigh priming activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPromoter activityAgricultural science
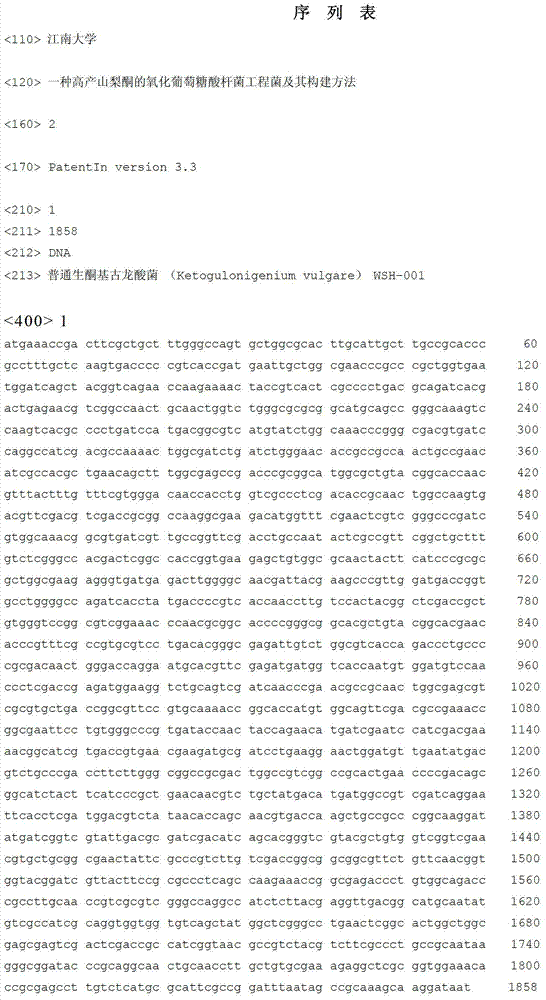
The invention provides a Gluconobacter oxydans (G.oxydans) promoter and its application. The promoter has the following nucleotide sequence: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; or 2) a nucleotide sequence hybridizing with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 under rigorous conditions and having promoter functions; or 3) a nucleotide sequence which is obtained by subjecting the nucleotide sequence defined by 1) or 2) to substitution, deletion, insertion or adding by one or more basic groups, and has over 90% homology with the defined nucleotide sequence and promoter functions. The promoter provided by the invention has the function of effective expression of the endogenous or exogenous gene in Gluconobacter oxydans, and has higher promoter activity compared with common promoters. The Gluconobacter oxydans promoter can realize application to gene expression and functional gene screening research in G.oxydans, and also can be applied to construction of 2-KGA high-yield gene engineering bacteria.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
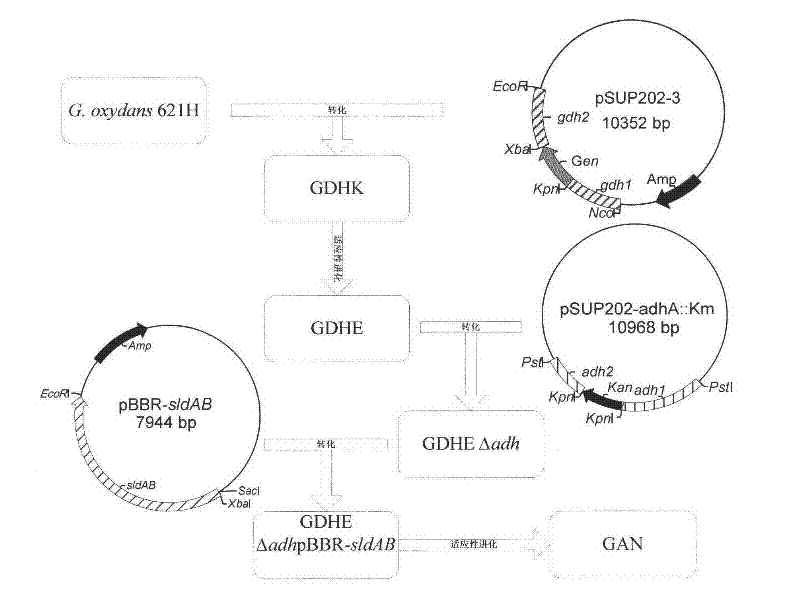
Genetically engineered strain and method for producing dihydroxyacetone by using the same
InactiveCN102392056AIncrease production capacityWide variety of sourcesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses a strain in the field of genetic engineering and a method for producing dihydroxyacetone (DHA) by using the strain. The method is characterized in that: modified Gluconobacter oxydans is used to bioconvert glycerin into dihydroxyacetone; sldAB gene expression is added in the modified Gluconobacter oxydans through modification, and mgdh gene and madh gene are removed from the modified Gluconobacter oxydans; and the modified Gluconobacter oxydans is further subject to the adaptive evolution on a medium which uses glucose as the sole carbon source. The genetically engineered strain disclosed herein can grow well on the medium which uses glucose as the sole carbon source, overcomes the defects that wild type Gluconobacter oxydans can only use relatively expensive sorbitol and mannitol as the effective carbon source, and saves the production cost. In addition, compared with a genetically engineered strain GAN cultured on sorbitol, the genetically engineered strain GAN cultured on glucose has higher capability of producing DHA.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws/maize straws
ActiveCN101781667AWide variety of sourcesLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateFiltration
The invention relates to a method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws / maize straws, comprising the following steps: (1) grinding the wheat straws or maize straws, soaking the ground wheat straws or maize straws in dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to react, then separating the residues of the wheat straws or maize straws from the acid hydrolysate through pump filtration and collecting the hydrolysate for later use; (2) detoxicating the hydrolysate; and (3) taking the detoxicated hydrolysate as the carbon source in the culture medium and adding the nitrogen source to prepare the culture medium and inoculating acetobacter aceti or gluconobacter oxydans into a shaker at 25-30 DEG C and 160-250r / min to be cultured or an incubator at 25-30 DEG C to undergo static culture, thus obtaining the bacterial cellulose. The carbon source in the culture medium is good in quality, low in price and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Gluconobacter oxydans and method for preparing ketoxylose using the same
ActiveCN101486984AConducive to industrialized continuous productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCollection management
The invention discloses a Gluconobacter oxydans, which is classified and named as Gluconobacter oxydans NH-10, and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Center of Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2709. The invention further discloses a D-xylulose preparation method that uses the Gluconobacter oxydans. The strain obtained by screening can transform D-Arabitol so as to generate D-xylulose in high efficiency, the D-xylulose preparation method reaches the highest D-Arabitol transformation ratio of 99.5 percent (w / w) and the D-xylulose yield ratio of 95 percent, the D-xylulose concentration of a conversion fluid can reach 95g / L, and the conversion fluid hardly contains other ingredients.
Owner:SHANDONG TIANLI PHARMA
Soil activator
InactiveCN104945117AImprove transmittanceLight weightFertilizer mixturesSodium BentonitePolyvinyl alcohol
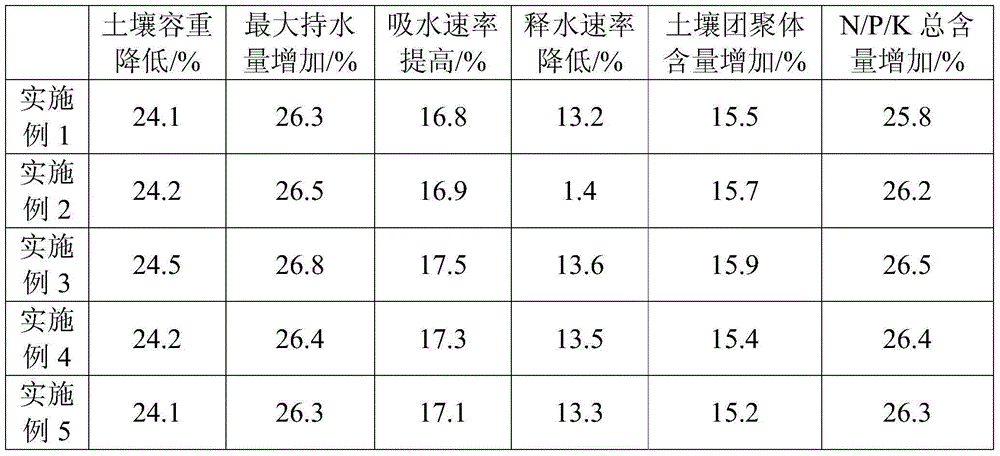
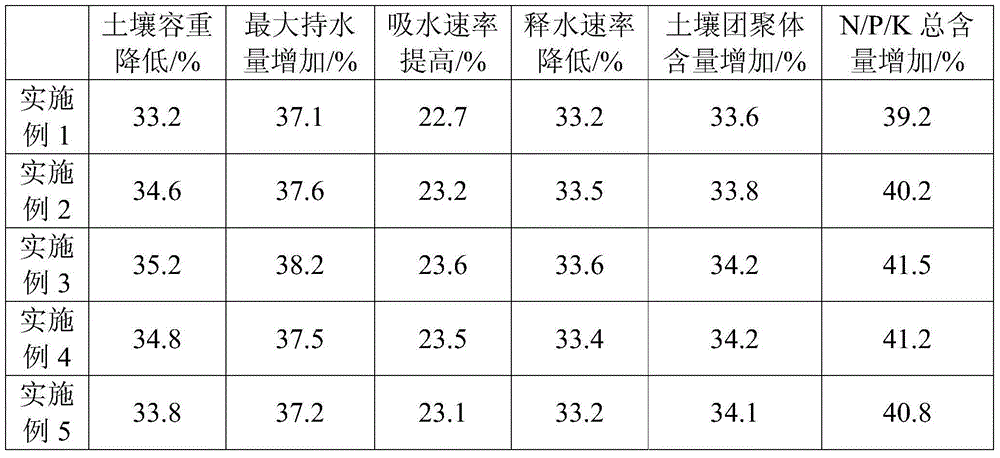
The invention relates to the technical field of soil conditioners, in particular to a soil activator. The soil activator consists of the following materials in parts by mass: 30-60 parts of peat humic acid, 2-5 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 2-5 parts of polyacrylonitrile, 2-6 parts of gypsum powder, 6-12 parts of bentonite, 3-8 parts of perlite, 6-12 parts of bacterial cellulose, 2-8 parts of a soil water-retaining agent, 2.8-5.8 parts of sulfur, 2.8-6.4 parts of a pH buffer agent and 6-12 hundred millions of photosynthetic bacteria groups per kg. A mixture of gluconobacter liquefaciens cellulose and chitosan acetic acid bacterial cellulose is added into the soil activator, so that the soil activator has a high water absorption property and a high water retention property because of the nano effect, and can effectively improve the soil. By adopting the soil activator provided by the invention, the volume weight of the soil reaches 35.2%, the maximum water holding capacity of the soil reaches 38.2%, the water absorption rate of the soil reaches 23.6%, the soil aggregate content reaches 34.2%, and the total N / P / K content in the soil reaches 41.5%.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG SHANMU NEW MATERIAL TECH DEV
Gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium for producing sorbic ketone in high yield mode and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102851252ASimple production processEliminate dependenciesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyD-Sorbitol
The invention discloses a Gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium for producing vitamin C synthesis intermediate sorbic ketone and a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. By means of the genetic engineering technique, a sorbose dehydrogenase gene (sdh) derived from common ketogenic base Ketogulonigenium vulgare is cloned onto Gluconobacter oxydans to obtain the G. oxydans engineering bacterium for producing the sorbic ketone by utilizing sorbitol. G. oxydans WSH-003 which is provided by Jiangsu Jiangshan Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd is a fermented industrial strain obtained in a first step of a two-step fermentation method for producing 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2-KLG). The sdh is cloned into the G. oxydans so that conversion from D-sorbitol to the vitamin C synthesis intermediate sorbic ketone is achieved, the foundation for further constructing the fermented industrial strain in one step to produce the direct precursor 2-KLG of vitamin C is laid, and the yield of the sorbic ketone is as high as 72g / L. Therefore, the Gluconobacter oxydans engineering bacterium has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting change of proteins inside cells in industrial mixed fermentation process of vitamin C
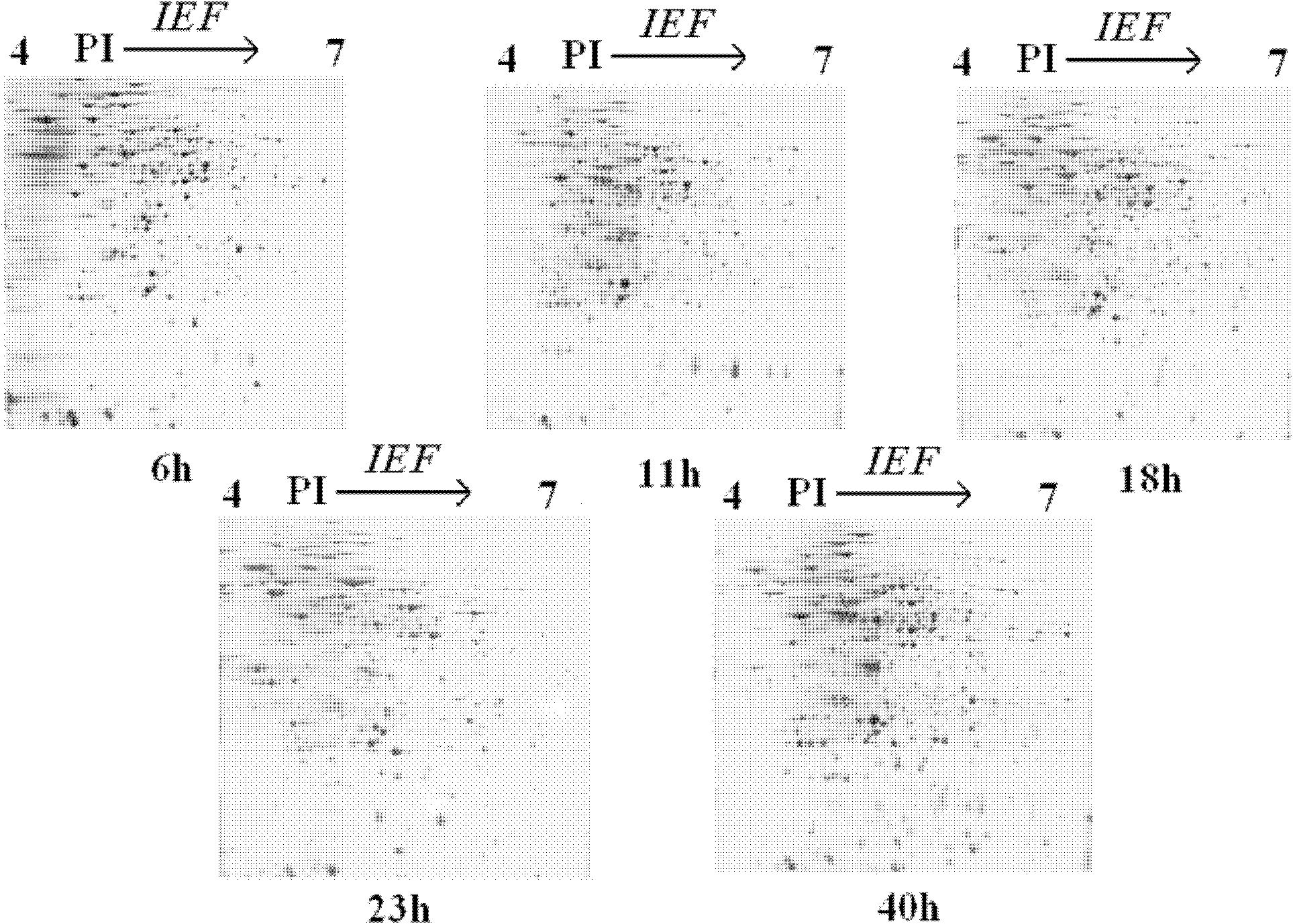
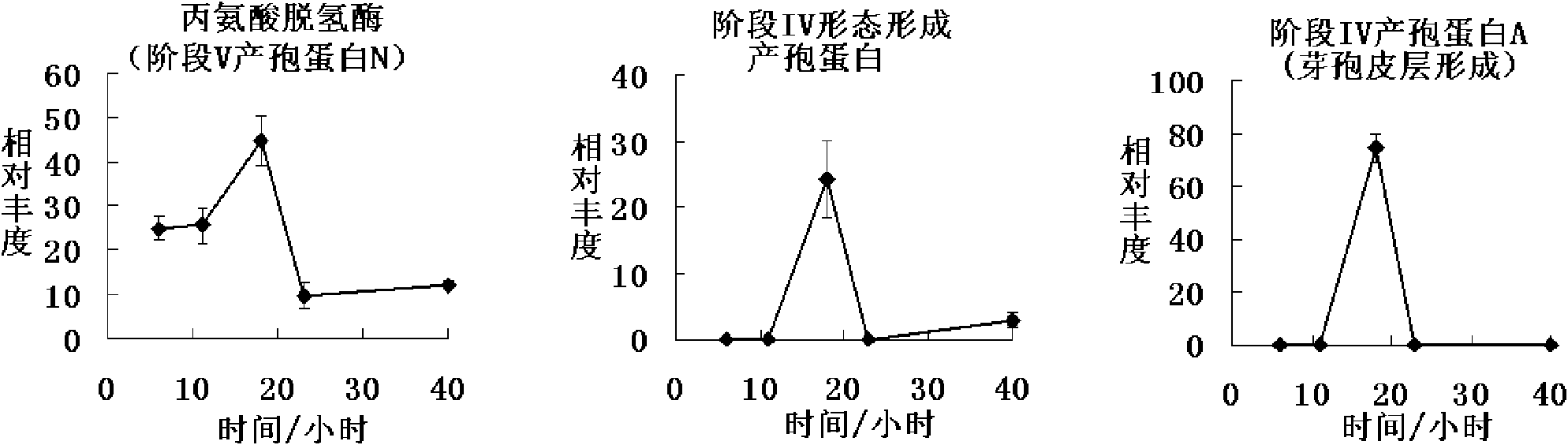
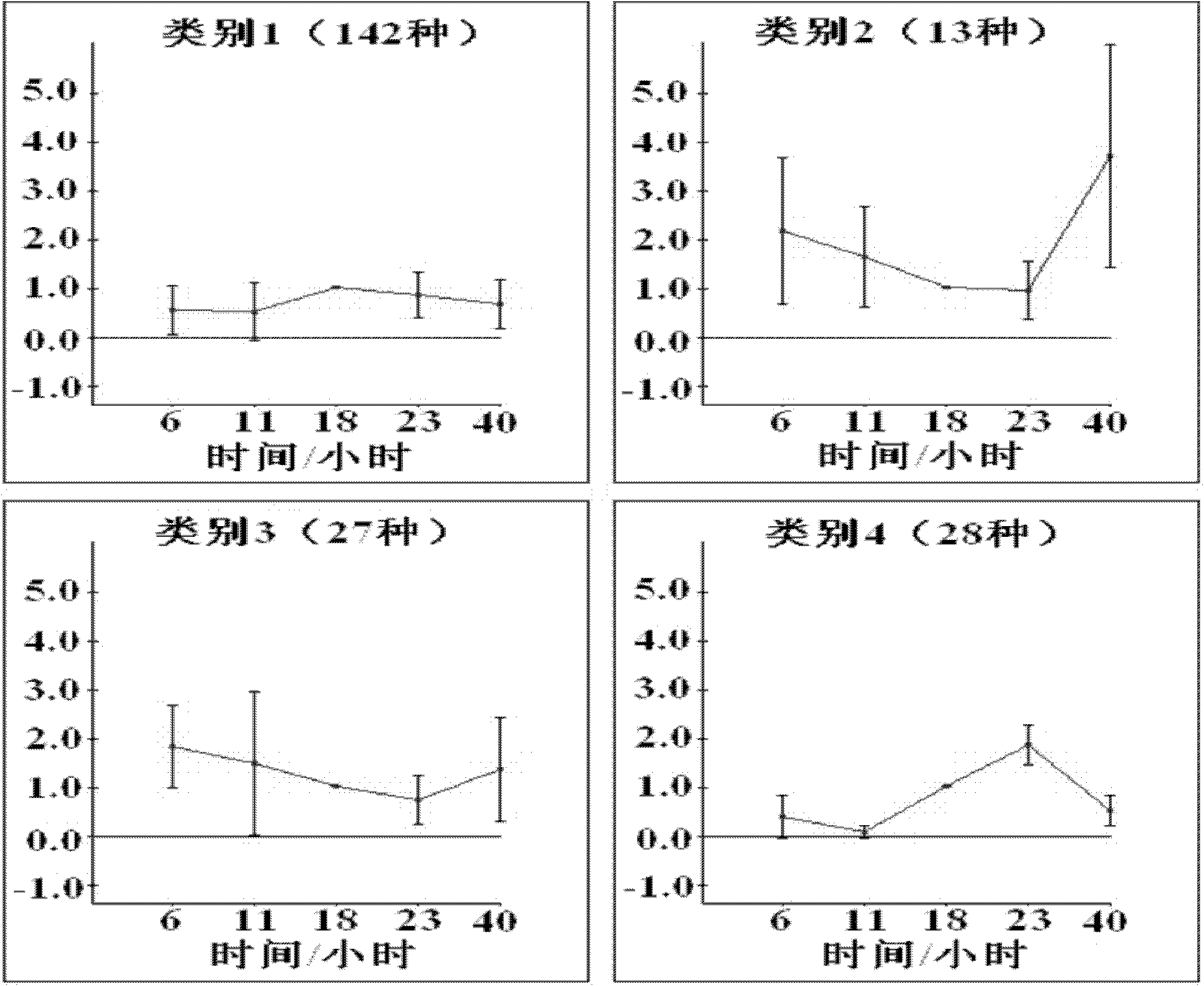
ActiveCN102175635AFacilitate the fermentation processIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyIntracellular protein
The invention discloses a method for detecting the change of proteins inside cells in the industrial mixed fermentation process of vitamin C, comprising the following steps of: (1) measuring the proteins inside cells, such as huge Bacillus megaterium and Gluconobacter oxydans which are used for the industrial mixed fermentation process of the vitamin C; (2) carrying out cluster analysis; and (3) carrying out process analysis. The method can be used for integrally researching the change law of the proteins inside the cells in the industrial mixed fermentation process of the vitamin C and finding the important proteins in the industrial mixed fermentation process according to the change law of the proteins inside the cells; the change law of the content of the proteins provides basis for the inner mechanism of the industrial mixed fermentation process so as to provide theoretical basis for further optimizing the industrial mixed fermentation process, increasing the yield of the vitamin C and reducing the environmental pollution; in addition, the invention also provides a new thought and method for the research of other mixed fermentation processes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
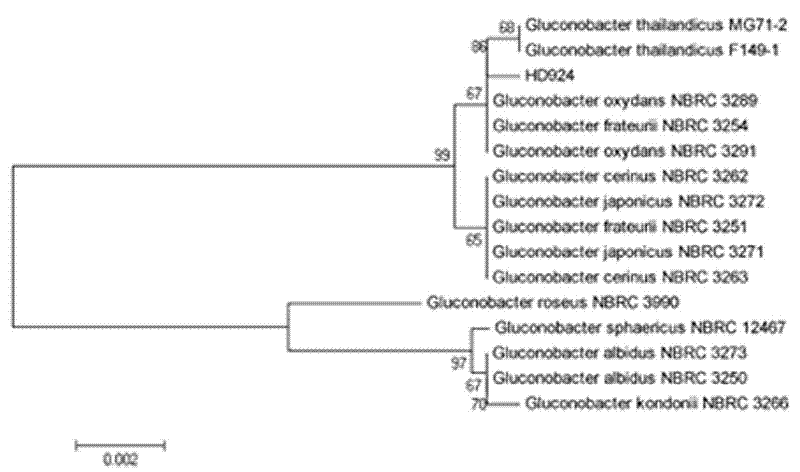
Strain HD924 for producing dihydroxyacetone by microbial fermentation and method
ActiveCN102391976ARealize industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a strain HD924 for producing dihydroxyacetone by microbial fermentation. The strain HD924 is classified into Acetobacteraceae Gluconobacter Gluconobacterfrateurii, and its collection number in the common micro-organism center of the CCCCM is CGMCC No.5397. The invention also provides a method for producing dihydroxyacetone by using the strain to ferment glycerin. dihydroxyacetone can be remarkably accumulated under aerobic conditions with the maximum of 170g / L. By the adoption of the method provided by the invention, industrial production can be realized.
Owner:CHANGXING PHARMA
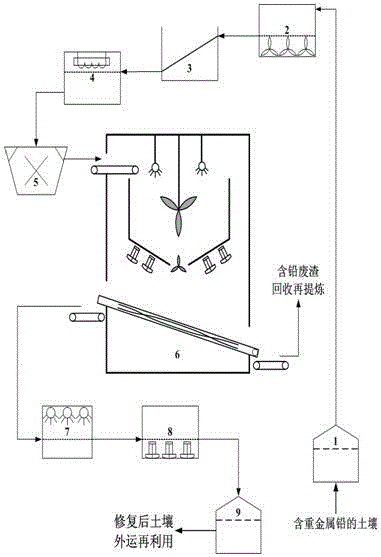
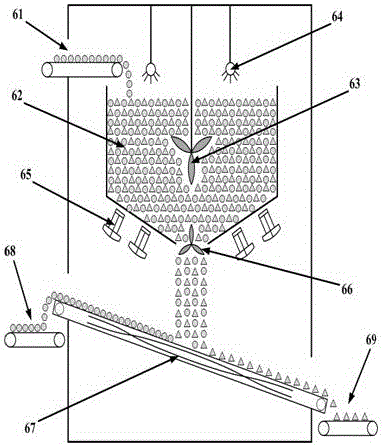
Soil remediation method for removing heavy metal lead
The invention discloses a soil remediation method for removing heavy metal lead. According to the method, the biological fermentation characteristic of gluconobacter oxydans is creatively utilized; lactonization reaction is conducted in the gluconobacter oxydans in presence of D-sorbitol and various sorts of nutritional ingredients inherent in soil, and finally L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is produced through fermentation; and then the L-ascorbic acid can be bonded with the heavy metal lead to produce non-toxic inorganic salt with the density being obviously larger than that of soil particles, and the heavy metal lead can be separated and removed from the soil through vibration sorting operation. Meanwhile, by the adoption of the L-ascorbic acid produced in the way that the D-sorbitol participates in biological fermentation reaction, the cost is far lower than that of adding L-ascorbic acid into the soil directly, and the material cost of soil remediation treatment can be greatly reduced.
Owner:朱辉
Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria for producing 2-KLG and its application
InactiveCN103484418AEliminate dependenciesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVitamin CD-Sorbitol
The invention discloses a Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria for producing 2-KLG and its application. According to the invention, by means of a genetic engineering technology, sorbose dehydrogenase (SDH) and sorbosone dehydrogenase (SNDH) genes derived from Ketogulonigenium vulgare are connected by a connecting peptide and then expressed in Gluconobacter oxydans so as to obtain G. oxydans engineering bacteria for high efficiency production of 2-KLG. The G. oxydans is a strain commonly used in a first step fermentation process during two-step fermentation production of 2-KLG. The expression of sdh and sndh genes in G.oxydans can dissolve the dependence problem of small bacteria on associated bacteria, thus realizing direct conversion from D-sorbitol to 2-KLG, and simplifying the vitamin C production process. With a 2-KLG yield of 32.4g / L, the Gluconobacter oxydans gene engineering bacteria has very good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
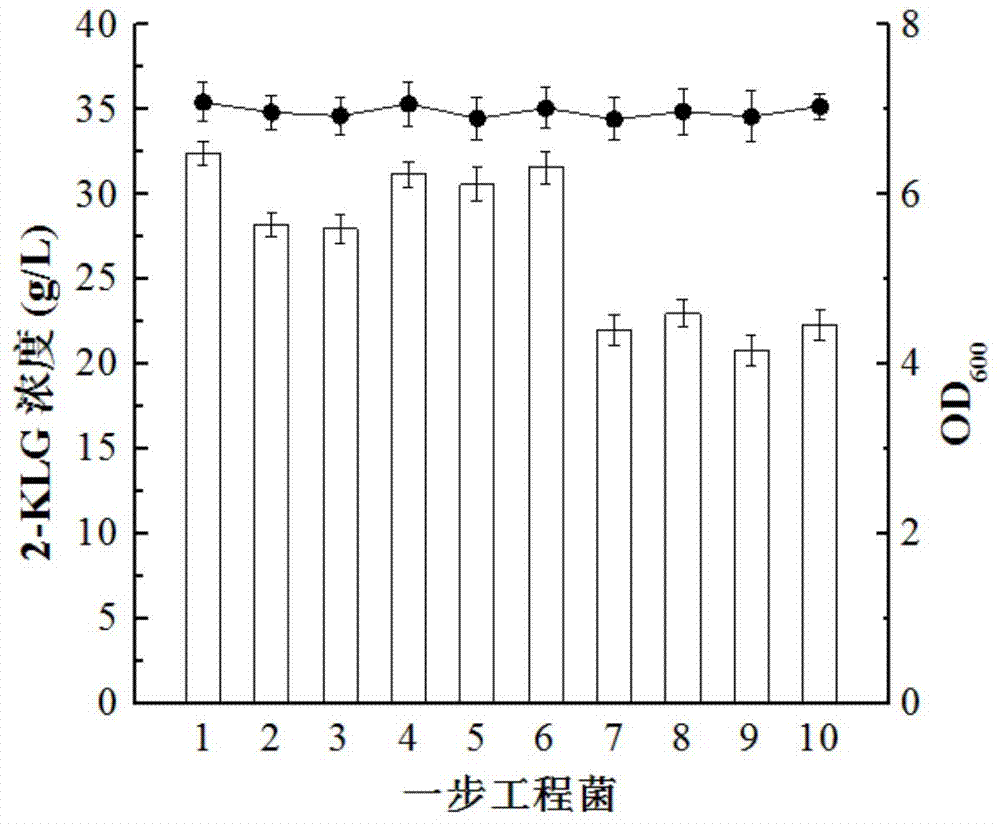
Method for improving gluconobacter oxydans for producing 2-keto-L-gulconic acid
InactiveCN104673736AImprove heat resistanceConducive to continuous catalytic reactionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidCross-link
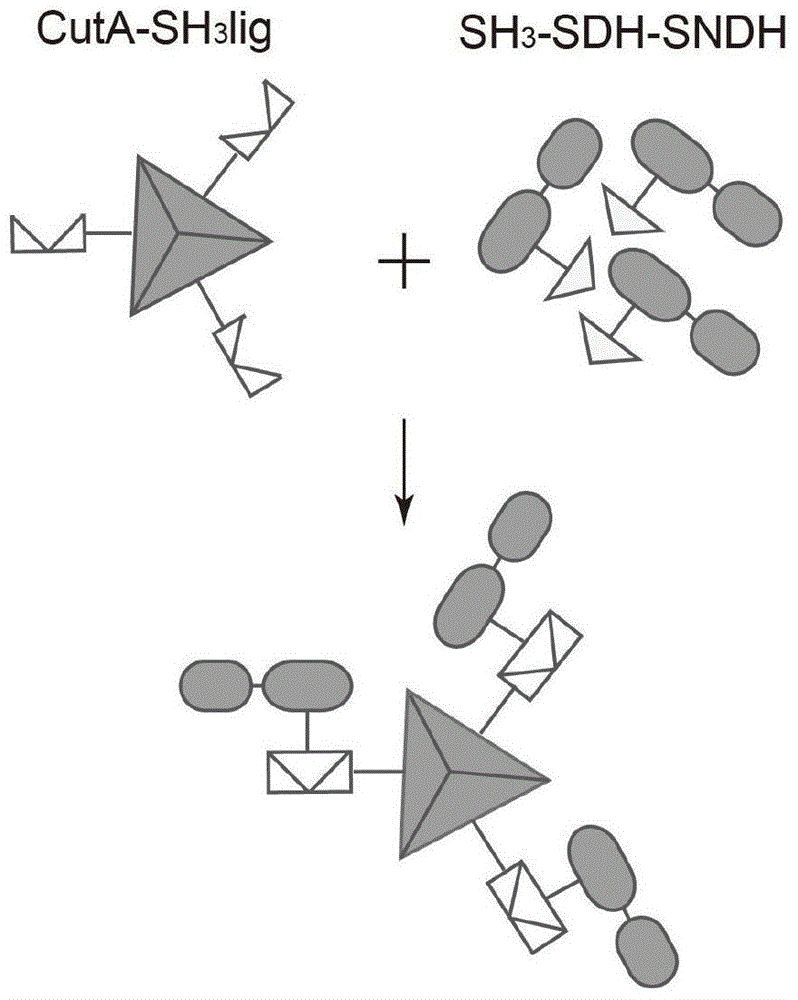
The invention discloses a method for improving gluconobacter oxydans for producing 2-keto-L-gulconic acid, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. On the basis of genetic engineering transformation, adaptor protein SH3 and ligand protein SH3lig of the adaptor protein, a CutA gene and a key enzyme gene in saccharic acid transformation are subjected to fusion expression, and G.oxydans is transformed to produce 2-KLG in a one-step fermentation manner, so that the yield of 2-KLG is finally increased to be 40.3 g / L, that is, the yield is increased by 24.4% when being compared with that of a one-step engineering bacterium of which CutA is not expressed; in addition, due to the thermal resistance of foreign protein, the thermal resistance of the engineering bacterium is further improved. Enzyme cross-linking inside cells can be achieved by expressing the foreign protein CutA, continuous catalytic reaction of a plurality of enzymes can be facilitated, and the method has significance in is one-step fermentation production of vitamin C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method utilizing mixed bacteria evolution subculturing to improve 2-keto-L-gulonic acid yield
ActiveCN102352403AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacillus megateriumTransformation efficiency
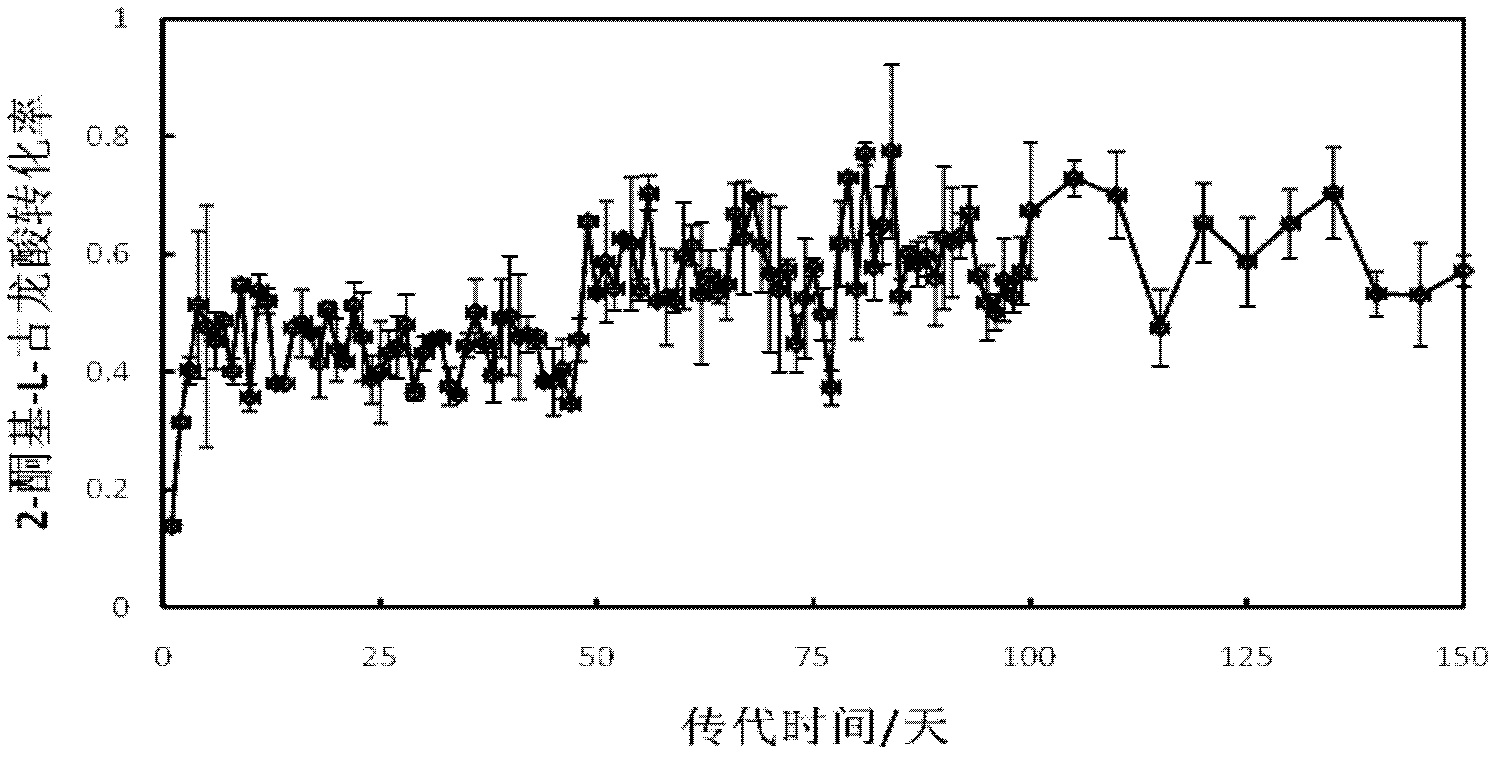
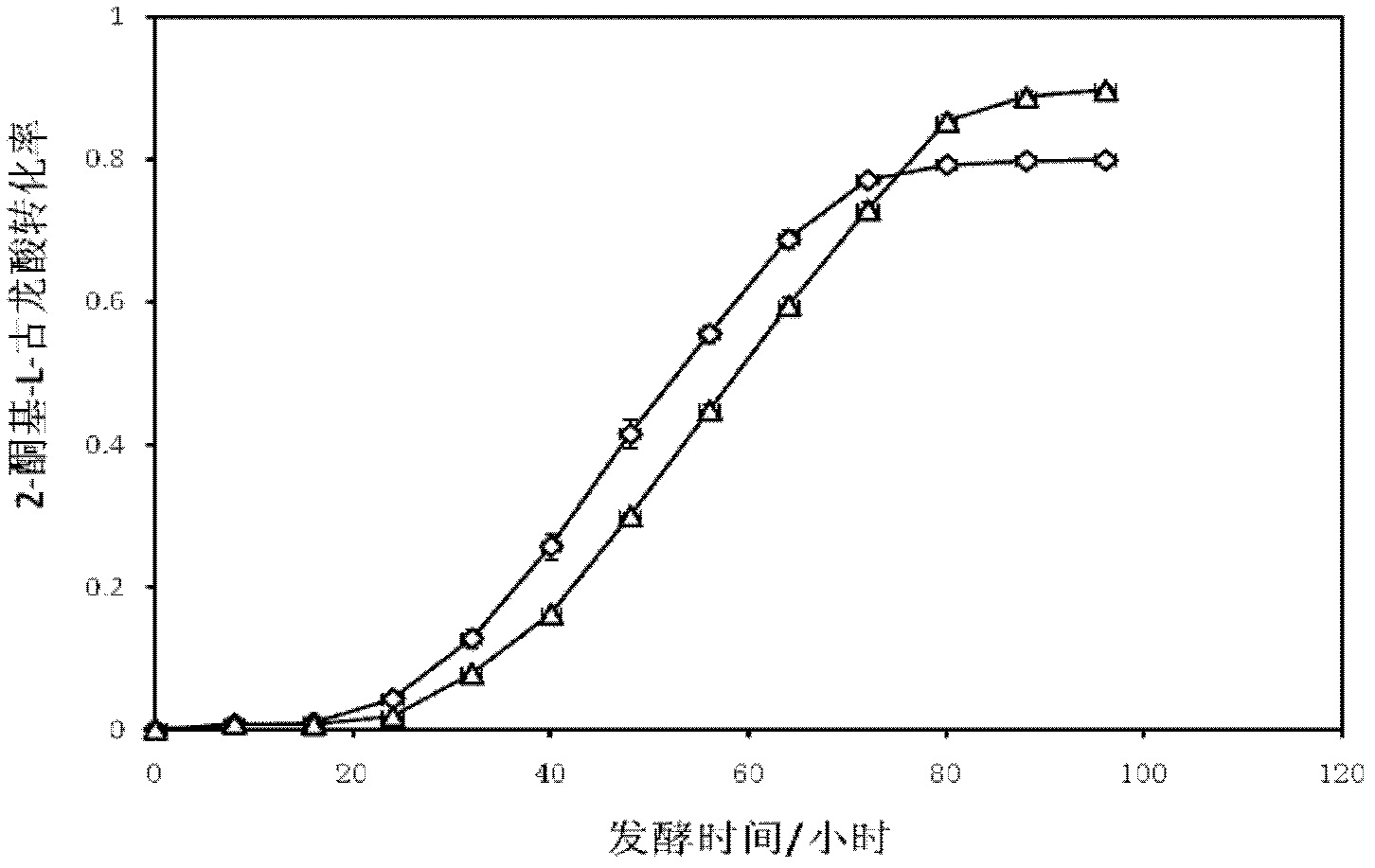
The invention discloses a method utilizing mixed bacteria evolution subculturing to improve the 2-keto-L-gulonic acid yield, which comprises the following steps of: (1) solid culture; (2) seed culturing: the bacillus megaterium and gluconobacter oxydans are inoculated into a new seed culture medium, are shake cultured in a shaker of 200-280r / min at 28-35 DEG C, 24h-48h is taken as the passage period, the volume ratio of 1%-10% is taken as the passage ratio to inoculate into the new seed culture medium and passages for 50-80 days; (3) purification; and (4) fermentation. The method utilizes themixed bacteria evolution subculturing to culture for tens of generations, the growth rate of the bacillus megaterium and gluconobacter oxydans and the efficiency of utilizing the gluconobacter oxydans to produce 2-keto-L-gulonic acid can be obviously improved, accordingly, the utilization rate of the culture medium can be improved, and the L-sorbose transformation efficiency is improved about 10%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for Fermentation and Culture, Fermented Plant Extract, Fermented Plant Extract Composition, Method for Producing Lipopolysaccharide and Lipopolysaccharide
ActiveUS20090162344A1Safe and reliable and inexpensiveCosmetic preparationsBacteriaBiotechnologyEnterobacter
In order to provide a method for culturing an immunopotentiator-containing organism having the experience of being eaten, inexpensively without requiring usage of a component derived from an animal, Acetobacter, Gluconobacter, Xanthomonas, Zymomonas or Enterobacter which is an edible gram-negative bacterium having an immunopotentiation function is cultured using a culture solution composed mainly of wheat or bean curd refuse. Thereby, Acetobacter can be obtained inexpensively and safely, and also a low molecular weight lipopolysaccharide which is the immunopotentiator can be obtained inexpensively and safely. Furthermore, no impurity derived from animal components is mixed.
Owner:SOMA +1
Antistaling agent containing gluconic acid lactone
InactiveCN101181090ASimple configurationReduce dosageFruit and vegetables preservationEdible seed preservationDehydroacetic acidAcetic acid
The invention pertains to the technical field of preservation, which more particularly relates to a fresh-keeping agent that contains gluconobacter. According to weight proportion, the components are that: 10 to 90 percent of gluconobacter, 5 to 45 percent of one of sorbic acid or sorbate and 5 to 45 percent of one of dehydroacetic acid or dehydroacetic acetate. The invention has special prescription, simple structure, low cost and safe use. Since the gluconobacter is adopted as synergist, the preservation effect is greatly enhanced and the actually using amount of food preservative is reduced, the risk of overusing preservative is avoided, thus being applied to various food such as cakes, breads, moon cakes, pastry and refreshments.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGYI TECH IND
Method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws/spruces
InactiveCN101781668AWide variety of sourcesLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiltrationHydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws / spruces, comprising the following steps: (1) grinding the wheat straws or spruces, soaking the ground wheat straws or spruces in dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to react at 90-240 DEG C, then separating the residues of the wheat straws or spruces from the acid hydrolysate through pump filtration and collecting the hydrolysate for later use; (2) detoxicating the hydrolysate; and (3) taking the detoxicated hydrolysate as the carbon source in the culture medium and adding the nitrogen source to prepare the culture medium and inoculating acetobacter aceti or gluconobacter oxydans into a shaker at 25-30 DEG C and 160-250r / min to be cultured or an incubator at 25-30 DEG C to undergo static culture, thus obtaining the bacterial cellulose. The carbon source in the culture medium is good in quality, low in price and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing (S)-benzoglycol by microorganism unsymmetrical split
InactiveCN101302543AHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthylene glycolChemistry
The invention provides a method for preparing (S)-styrolylalcohol by microorganism asymmetric resolution. The method uses Gluconobacter microorganisms to selectively oxidize (R)-styrolylalcohol in racemic styrolylalcohol, thereby obtaining the (S)-styrolylalcohol. When the method is used to prepare the (S)-styrolylalcohol, the optical purity can reach more than 99.9 percent (e. e.), and the yieldcan reach about 38 percent.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing bacterial cellulose by using bagasse
ActiveCN103103230AEasily hydrolyzedLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateNitrogen source
The invention relates to a method for preparing bacterial cellulose by using bagasse. The method comprises steps of: (1) drying and crushing the bagasse, soaking the bagasse in acid with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:5-1:20, then reacting at 100 DEG C-240 DEG C for 50-90 min, filtering after the reaction, and collecting a hydrolysate; (2) detoxifying the hydrolysate; and (3) using the detoxified hydrolysate as a carbon source for a medium, adding 0.1-2% of a nitrogen source, and sterilizing at 121 DEG C for 15-20 min to obtain a culture medium; inoculating bacillus aceticus or Gluconobacter oxydans with an inoculation amount of 5%-10%; and conducting shaking culture at 25-30 DEG C with 160-250rpm or conducting static culture at 25-30 DEG C for 6-25 days, so as to obtain bacterial cellulose. The culture medium carbon source prepared by the invention has good quality and low price, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Active fermentation process and fermented liquid and drinks made by using the same
ActiveUS20160050953A1Suitable for large scale industrial productionConsistent and superior and beneficial effectBacteriaTea extractionBacterial strainFermentation
Owner:HSU SHANTUNG
Gluconobacter oxydans 2-ketoreductase enzyme and applications thereof
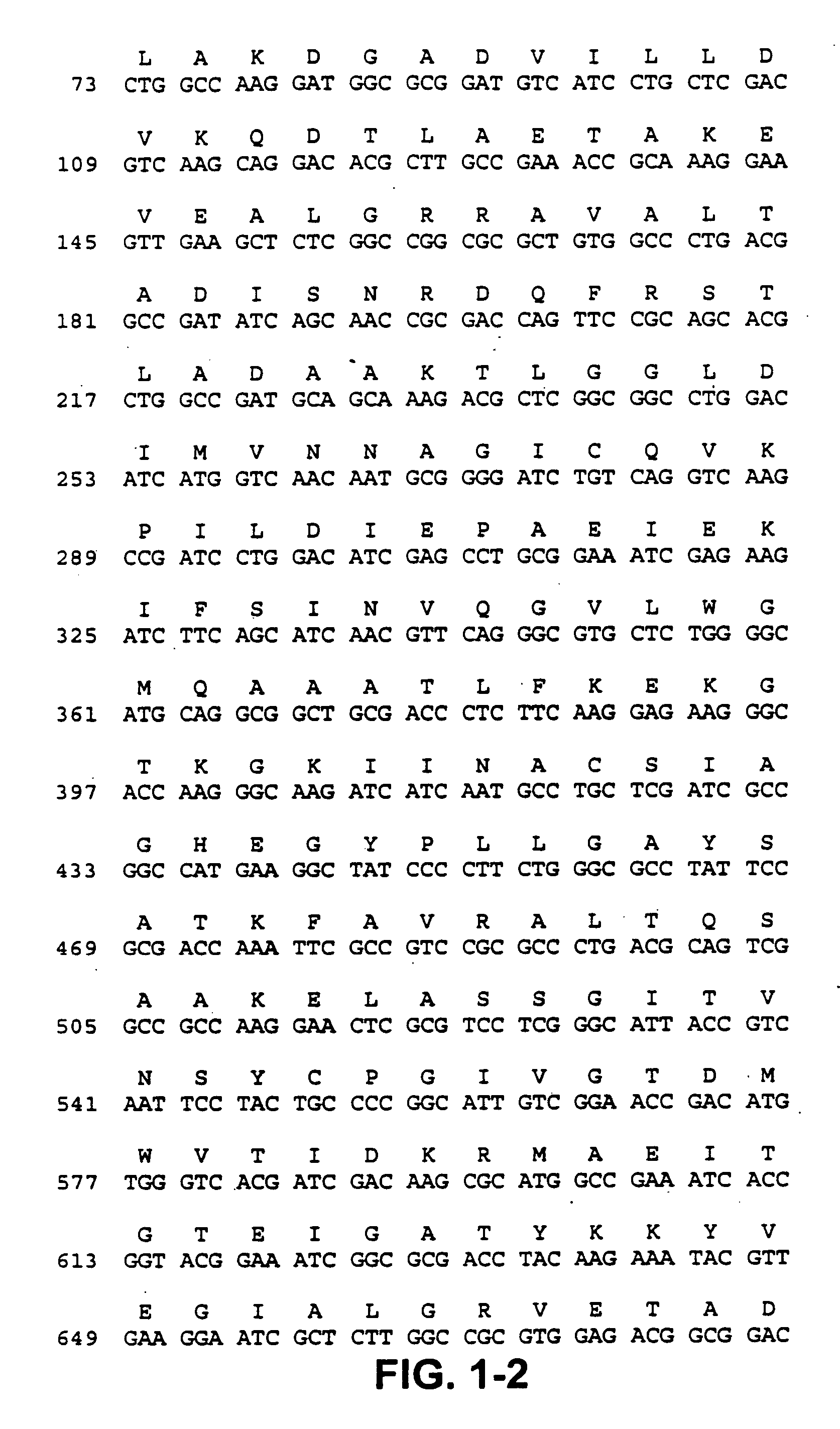
This invention relates to an novel Gluconobacter oxydans 2-ketoreductase useful for the synthesis of chiral alcohols. Also related are isolated nucleic acids encoding G. oxydans 2-ketoreductase enzymes, and enzyme fragments and variants thereof, as well as vectors and host cells comprising these nucleic acids. Further related are isolated G. oxydans 2-ketoreductase polypeptides, and fragments and variants thereof, and antibodies that specifically bind to G. oxydans 2-ketoreductase polypeptides, fragments, or variants. The invention also relates to methods of obtaining isolated G. oxydans 2-ketoreductase nucleic acids, polypeptides, and antibodies, and methods of using G. oxydans 2-ketoreductase in various reactions for industrial or pharmaceutical applications.
Owner:NANDURI VENKATA +4
Gluconobacter oxydans nonresistant marker gene knockout system
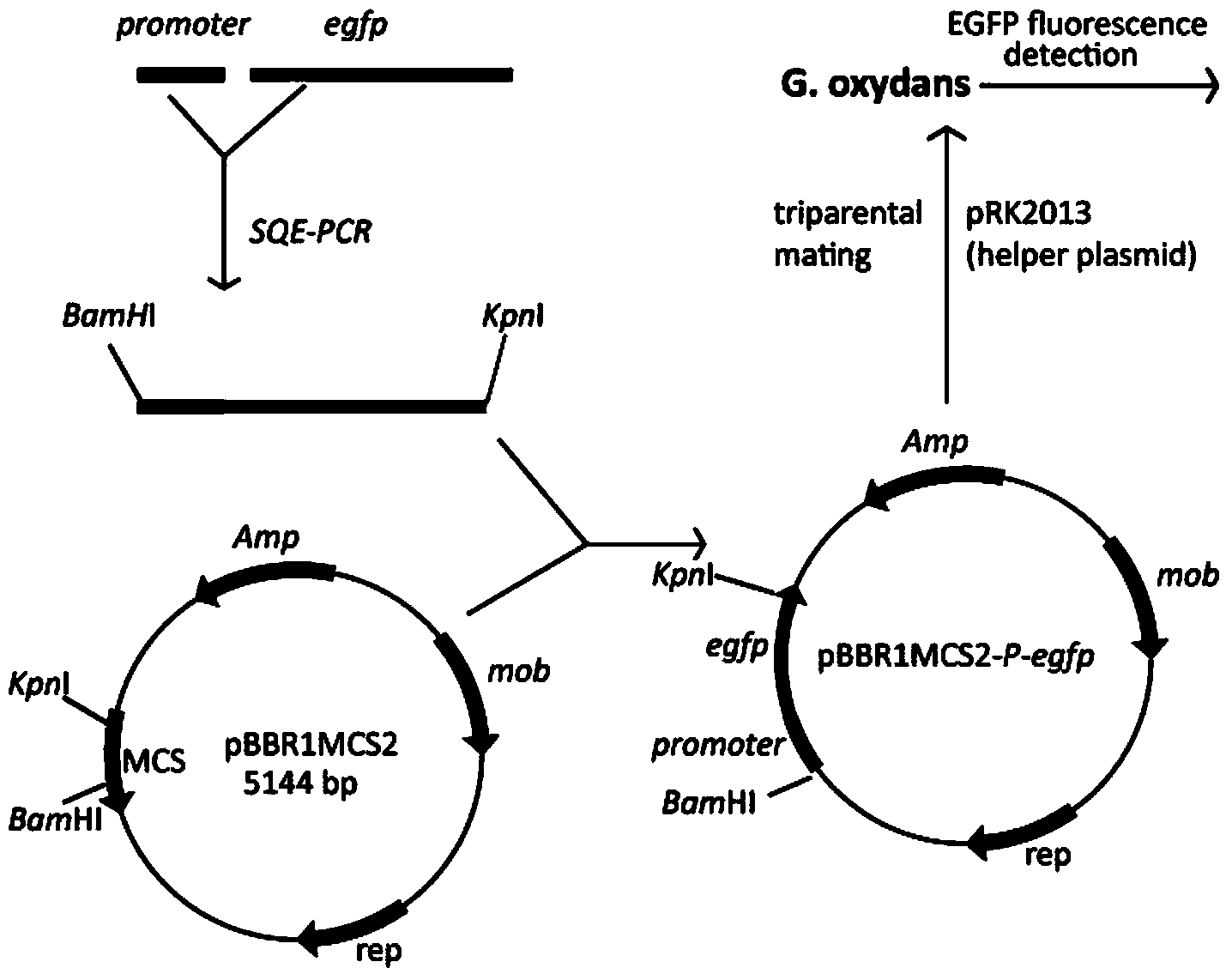
ActiveCN103805545AAvoid polarityBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionKanamycinTranscriptional expression
The invention discloses a gluconobacter oxydans nonresistant marker gene knockout system, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, through a homologous recombination technique, upp genes in G.o xydans are knocked out, so that a upp genetic deficient strain is obtained; a recombinant integrating plasmid containing a upp gene which can be subjected to good transcribed expression in G.o xydans and has a conditional lethal function, a resistance maker kanamycin resistant marker gene for the transformant selection of G.o xydans and an MCS polycloning site is built. The plasmid is applicable to the knockout and replacement of G.o xydans chromosome genes; compared with gene knockout implemented by taking a resistant marker gene as a selection marker, the system disclosed by the invention has the following two advantages: no resistant gene is introduced to a G.o xydans genome, so that a polar effect of the resistant gene on upstream and downstream genes is avoided; by using the knockout system, the multiple knockout and replacement of chromosome genes can be performed in a same strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gradient intensity promoter of gluconobacter oxydans
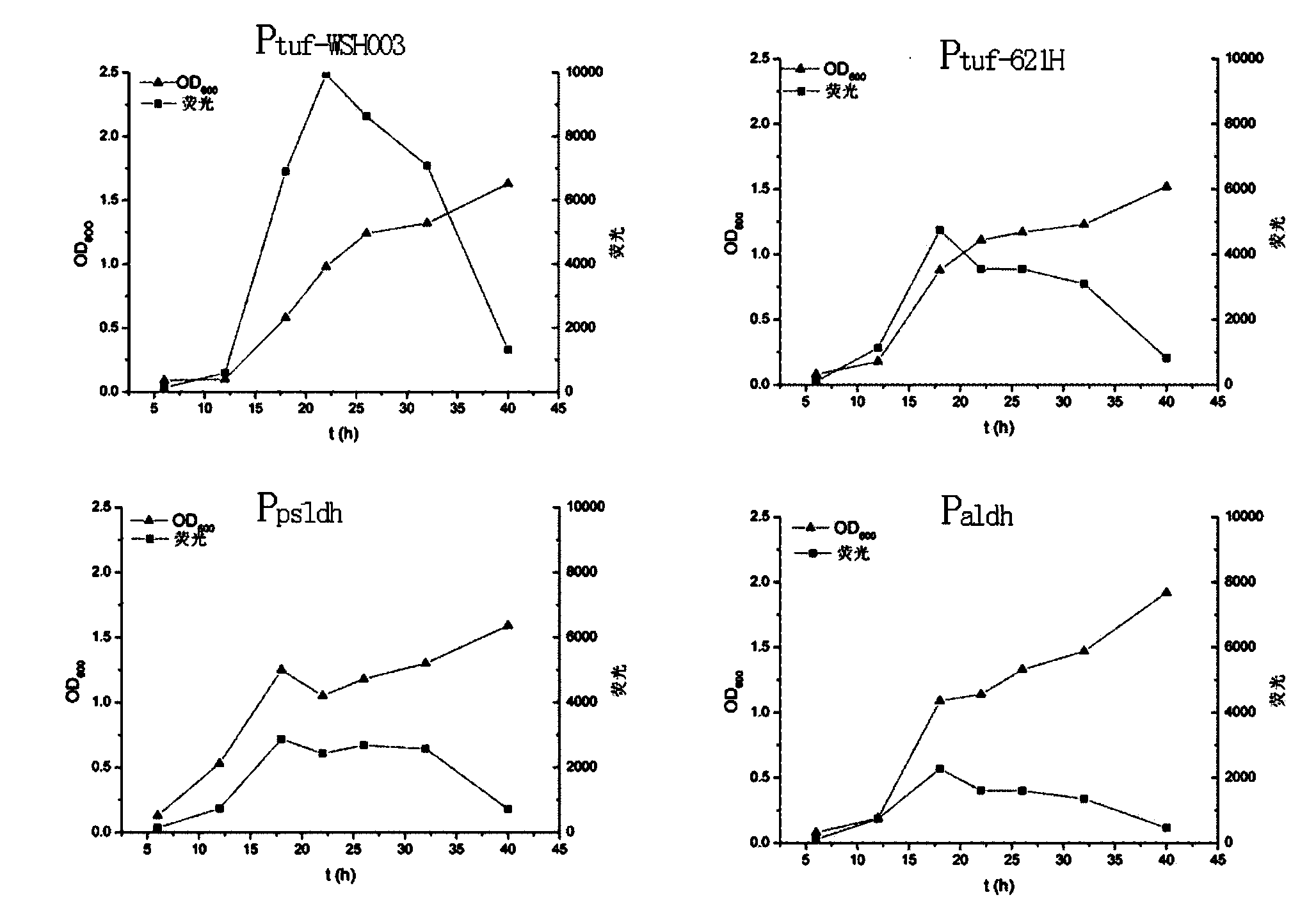
ActiveCN103966217ARegulated expression intensityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGreen fluorescent proteinFluorescence
The invention discloses a gradient intensity promoter of gluconobacter oxydans and belongs to the field of genetic and metabolic engineering. Sequences between constitutively expressed genes and previous genes are selected from the gluconobacter oxydans and preliminarily screened by promoter prediction software, an obtained high-score potential strong promoter is subjected to qualitative and quantitative detection through a fluorescent microscope and a fluorescence microplate reader respectively by using enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) as a reporter gene, and finally promoters with an intensity sequence of P[tuf-WSH003]>P[tuf-621H]>P[sldh]-P[psldh]-P[sod]>P[aldh] are selected from G.oxydans WSH-003. A series of gradient promoters and a novel strong promoter are screened out, and great help is provided for genetic and metabolic engineering reform of the industrial production strain G.oxydans WSH-003, especially adjustment of gene transcription level.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Composition for improving saline-alkali soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108559520AQuick Alkalinity AdjustmentLower pH valueOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersAlkali soilCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a composition for improving saline-alkali soil, and belongs to the technical field of improvement of saline-alkali soil. The composition is prepared from, by weight, 40-80 parts of cyclodextrin, 40-80 parts of polylactic acid, 20-70 parts of calcium sulfate, 20-70 parts of magnesium sulfate, 10-20 parts of aluminum sulfate, 30-50 parts of ammonium sulfate, 0.5-1.5 parts ofyeast, 0.5-1.5 parts of lactic acid bacteria, 0.5-1.5 parts of acetobacter, 0.5-1.5 parts of gluconobacter, 0.5-1.5 parts of aspergillus niger, 10-30 parts of peptone and 10-30 parts of glucose. The composition rapidly adjusts the alkalinity of the saline-alkali soil by inorganic strong acid weak base salt, and the pH value of the saline-alkali soil is continuously adjusted by the action of microorganisms.
Owner:四川川能环保科技有限公司
Method for preparing glucosamine and chitin simultaneously by using of shrimp and crab waste
InactiveCN107653294AReduce pollutionRealize comprehensive utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention relates to the reuse of shrimp and crab waste, specifically a method for simultaneously producing shrimp and crab xanthin and chitosan by using shrimp and crab waste, using the synergistic effect of Bacillus subtilis and Gluconobacter oxydans to add glucose to ferment Shrimp and crab skin and crab head are desalinated and deproteinized, and then fermented by Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Lactobacillus bulgaricus for one week to decalcify and decolorize, use chitin deacetylase to treat chitin, and use leather Glucosamine can be obtained by processing Plasmomonas Shigella, a lambs negative bacteria. During the fermentation process, there is no need to add a large amount of acid and alkali, which reduces environmental pollution, and microbial fermentation saves costs compared with enzyme fermentation, and the content of active ingredients obtained is higher, which realizes the complete utilization of active ingredients of raw materials, and is economically feasible.
Owner:山东智宇知识产权运营中心有限公司莱州分公司
Method of fementing shrimp heads to prepare active substances, chitin and organic acidity calcium
ActiveCN103224973ARealize comprehensive utilizationReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacillus licheniformisPolyphenol
The invention provides a method of fementing shrimp heads to prepare active substances, chitin and organic acidity calcium, wherein Bacillus licheniformis and Gluconobacter oxydans are utilized to ferment the shrimp heads to prepare the active substances, the chitin and the organic acidity calcium. The method utilizes synergistic effects of the Bacillus licheniformis and the Gluconobacter oxydans to ferment the shrimp head, is free of adding any acid and alkali, and meanwhile uses tap water to ferment, thereby greatly reducing production cost. The obtained broth is rich in shrimp incense, free of fishy smell and bitter taste, and simultaneously rich in amino acids, polyphenol, compound enzymes and a plurality of beneficial components, and can be used for producing flavourings, hydrolyzed protein products, functional foods, health products and other fields. By using the method provided by the invention, a plurality of active substances can be simultaneously separated and prepared from a batch of shrimp heads, such as hydrolyzed proteins rich in the amino acids, the polyphenol and a plurality of active substances; food-grade chitin; and calcium gluconate relatively appropriate for the body to absorb, thereby realizing comprehensive utilization of effective components in the raw materials.
Owner:青岛新辰生物科技有限公司
Strain HD385 producing L-erythrulose through microorganism fermentation, and method
The present invention relates to a strain HD385 producing L-erythrulose through microorganism fermentation, wherein the classification belongs to Acetobacteraceae (Gluconobacter) Gluconobacterkondonii, and the preservation number of the strain in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.8391. The present invention further provides a method for producing L-erythrulose by using the strain to ferment erythritol, wherein L-erythrulose can be significantly accumulated under an aerobic condition and can be up to 186.5 g / L, and the industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:深圳市博大生物技术有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com