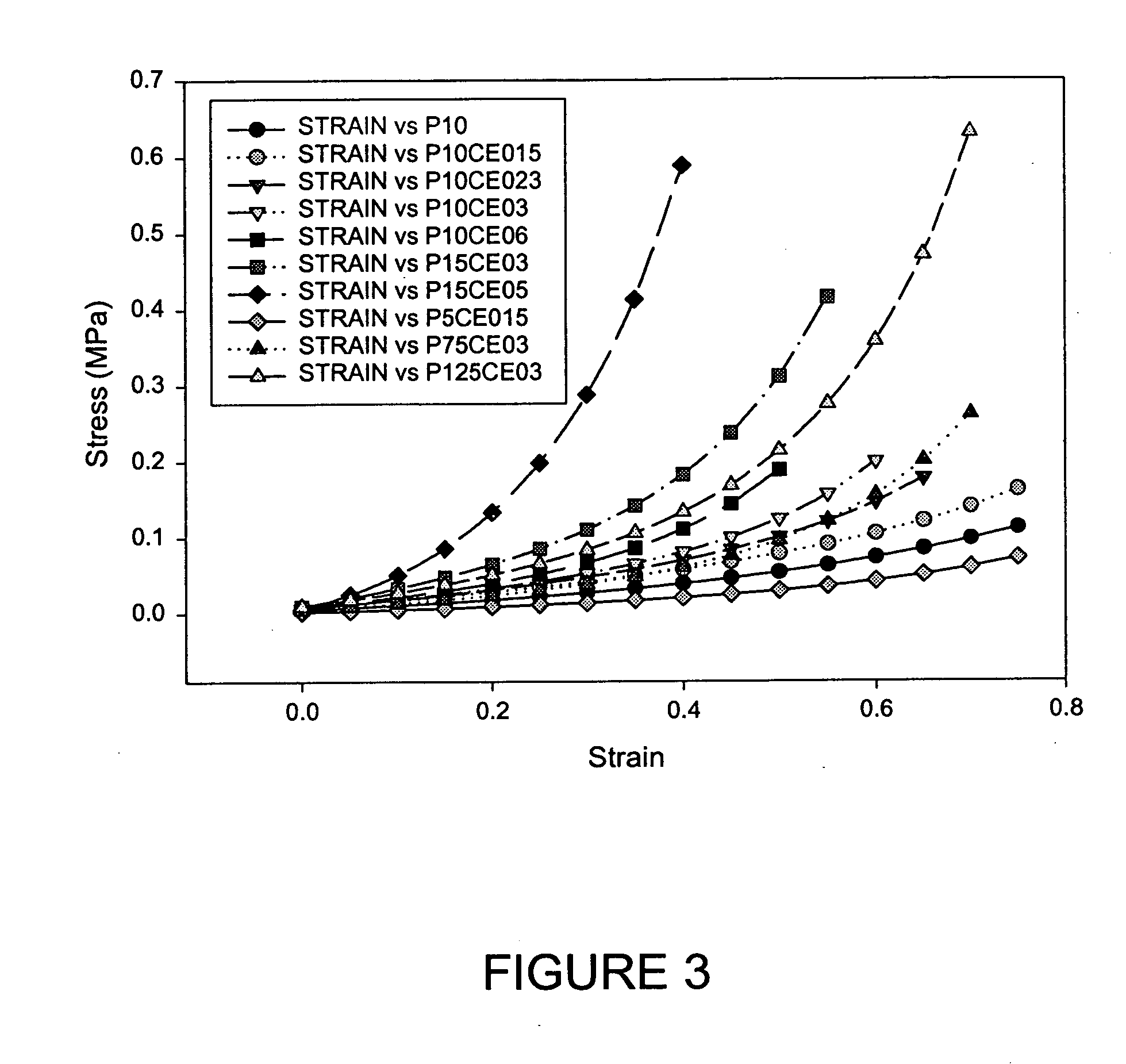
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1889 results about "Bacterial cellulose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
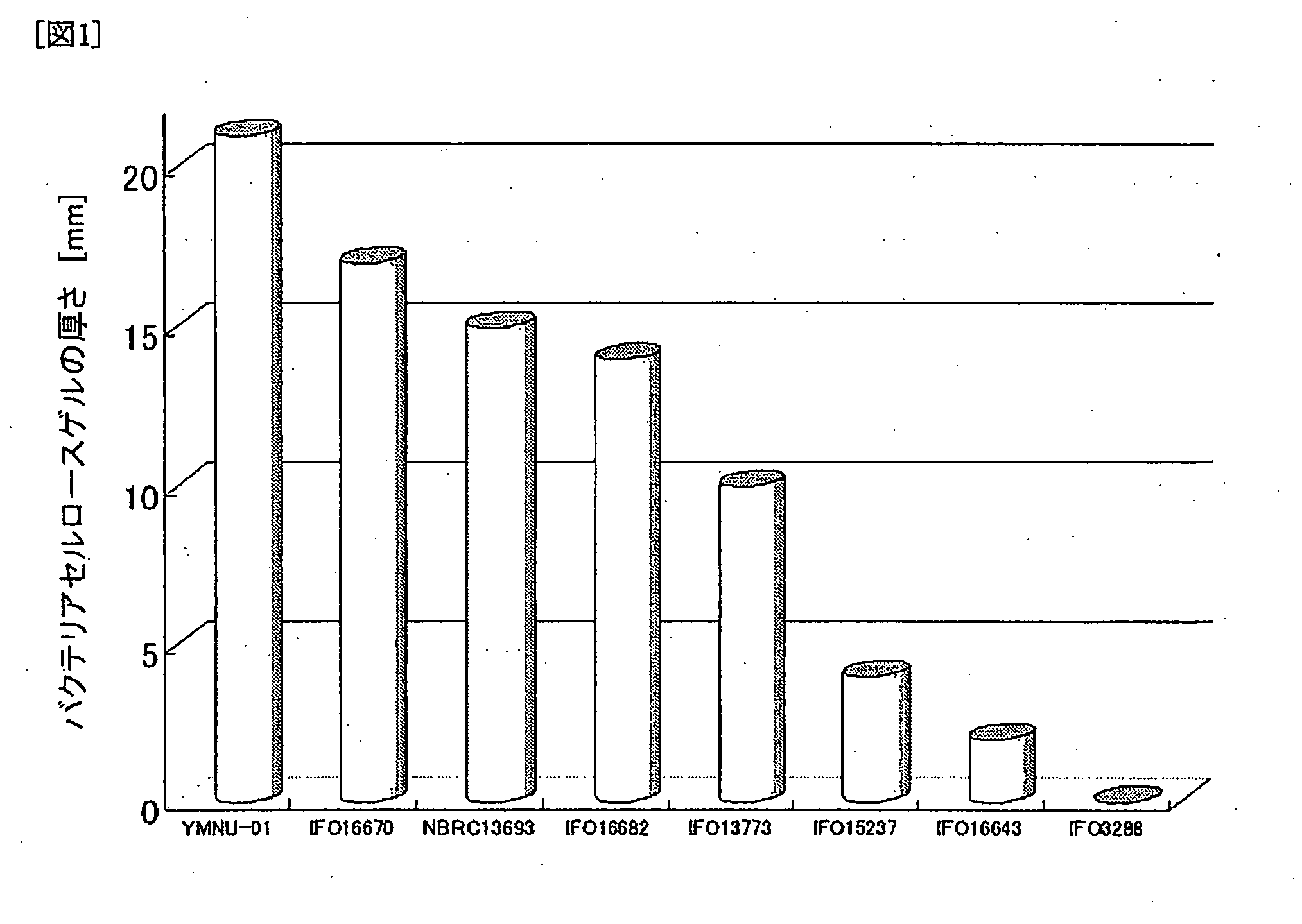
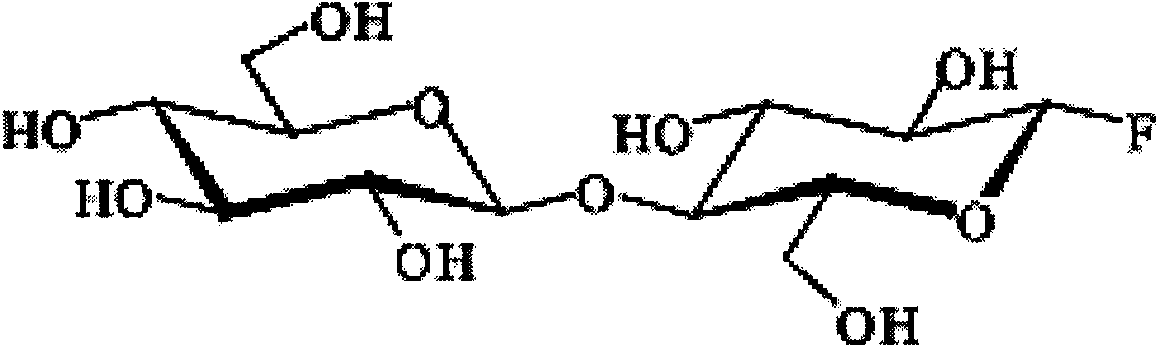
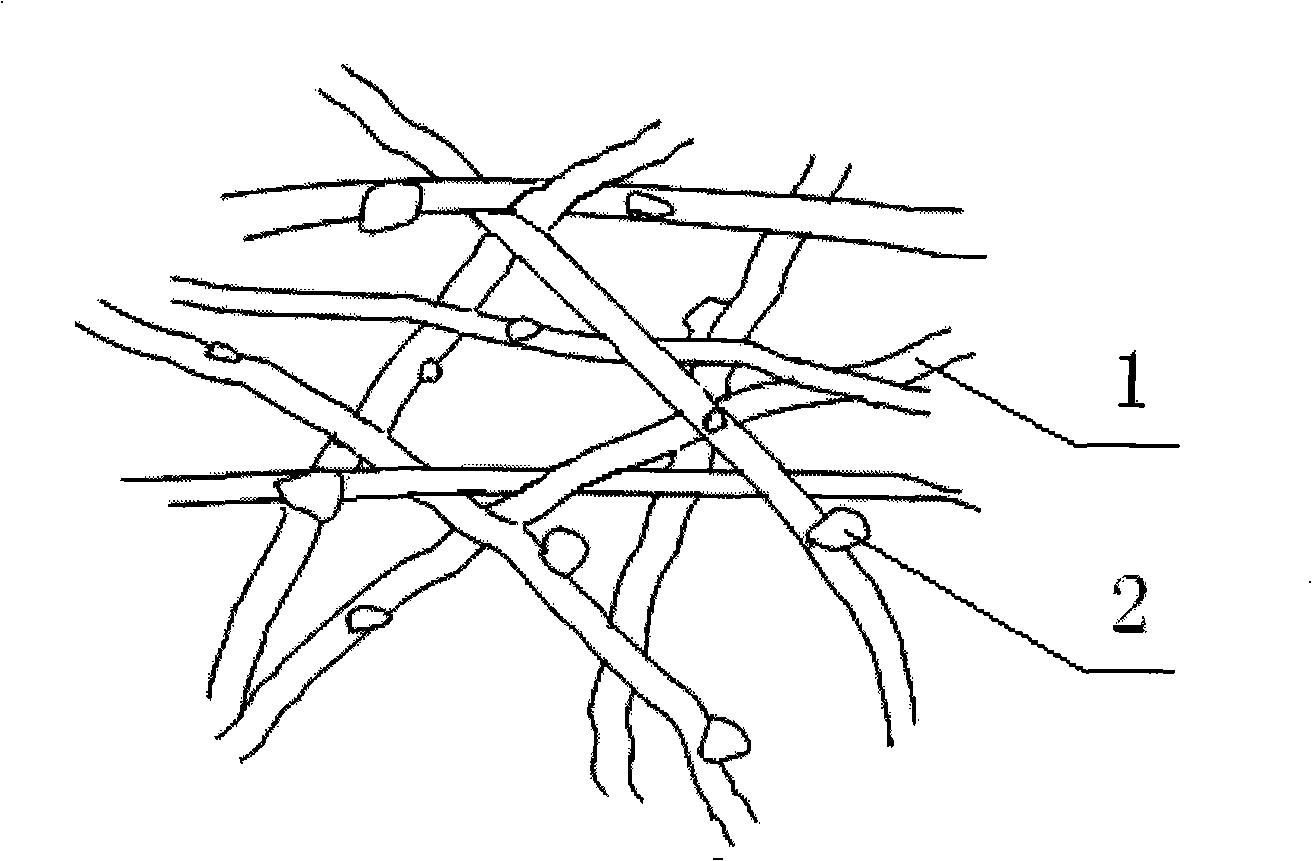
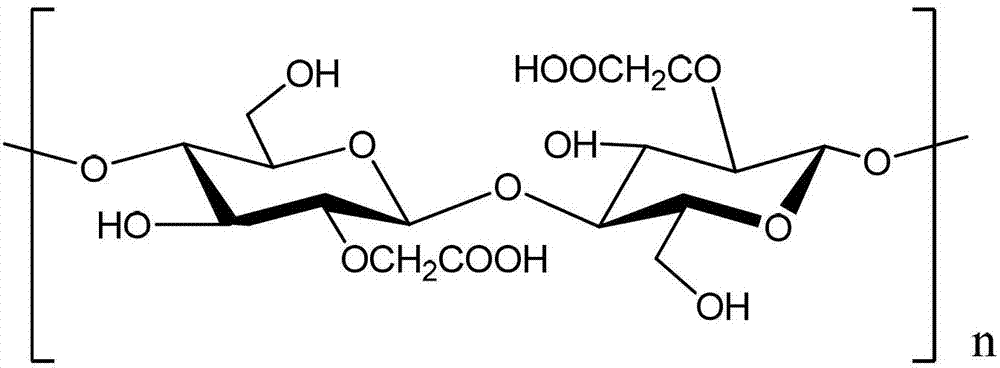
Bacterial cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C₆H₁₀O₅)ₙ produced by certain types of bacteria. While cellulose is a basic structural material of most plants, it is also produced by bacteria, principally of the genera Acetobacter, Sarcina ventriculi and Agrobacterium. Bacterial, or microbial, cellulose has different properties from plant cellulose and is characterized by high purity, strength, moldability and increased water holding ability. In natural habitats, the majority of bacteria synthesize extracellular polysaccharides, such as cellulose, which form protective envelopes around the cells. While bacterial cellulose is produced in nature, many methods are currently being investigated to enhance cellulose growth from cultures in laboratories as a large-scale process. By controlling synthesis methods, the resulting microbial cellulose can be tailored to have specific desirable properties. For example, attention has been given to the bacteria Acetobacter xylinum due to its cellulose's unique mechanical properties and applications to biotechnology, microbiology, and materials science. Historically, bacterial cellulose has been limited to the manufacture of Nata de coco, a South-East Asian food product. With advances in the ability to synthesize and characterize bacterial cellulose, the material is being used for a wide variety of commercial applications including textiles, cosmetics, and food products, as well as medical applications. Many patents have been issued in microbial cellulose applications and several active areas of research are attempting to better characterize microbial cellulose and utilize it in new areas.
Method of producing effective bacterial cellulose-containing formulations
A new method to produce formulations of bacterial cellulose that exhibit improved viscosity-modifying properties particularly with low energy applied to effectuate viscosity changes therewith is provided. Such a method includes the novel co-precipitation with a water soluble co-agent that permits precipitation in the presence of excess alcohol to form an insoluble fiber that can than be utilized as a thickener or suspension aid without the need to introduce high energy mixing. Such bacterial cellulose properties have been available in the past but only through highly labor and energy intensive processes. Such an inventive method as now proposed thus provides a bacterial cellulose-containing formulation that exhibits not only properties that are as effective as those for previous bacterial celluloses, but, in some ways, improvements to such previous types. Certain end-use compositions and applications including these novel bacterial cellulose-containing formulations are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
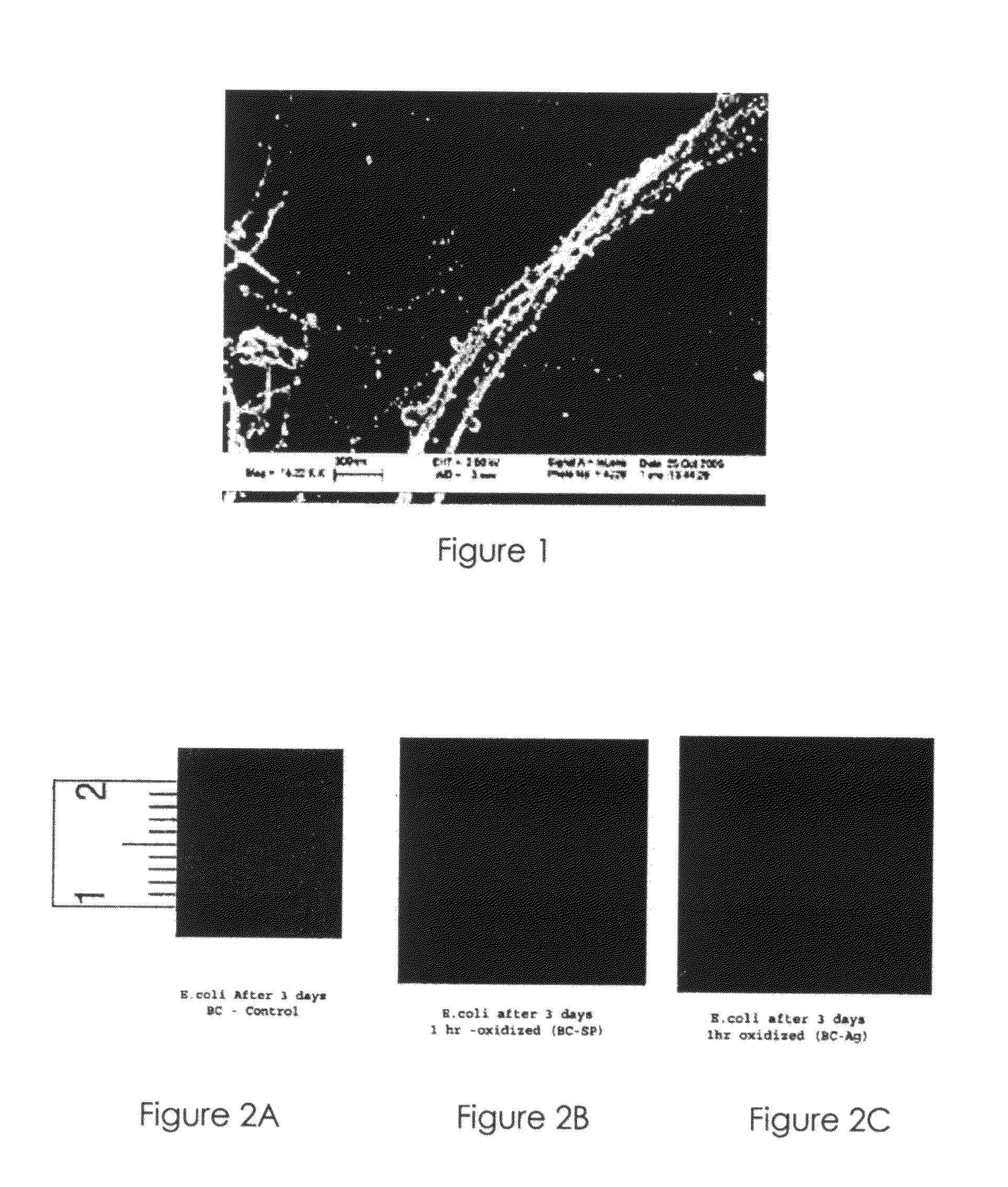
Nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose
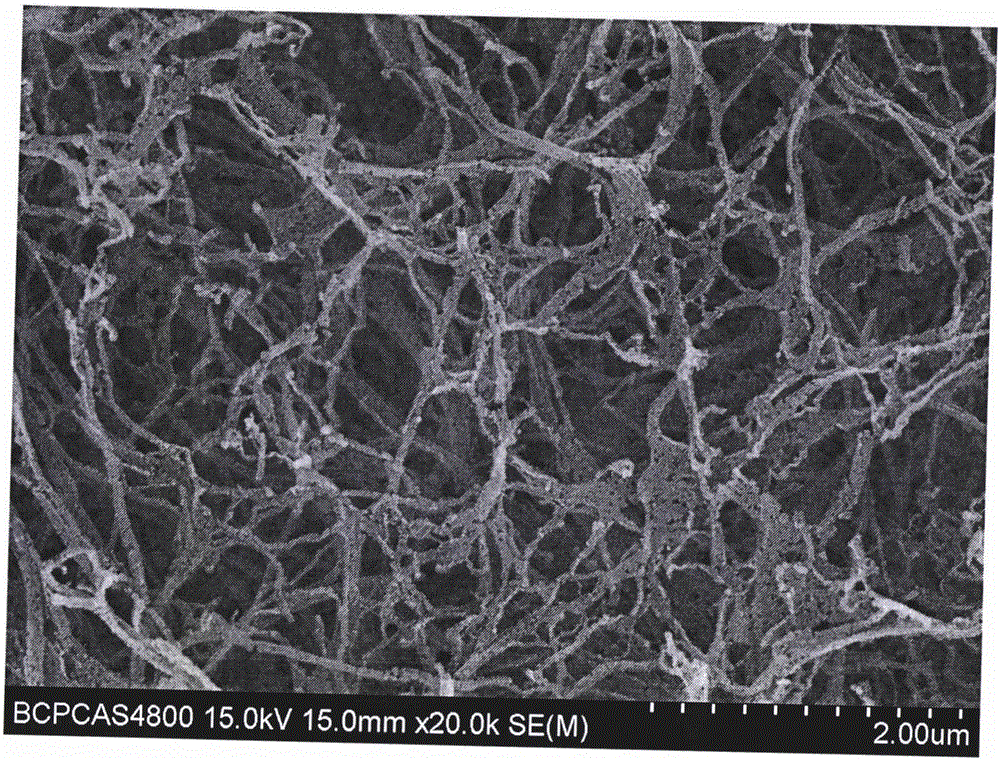
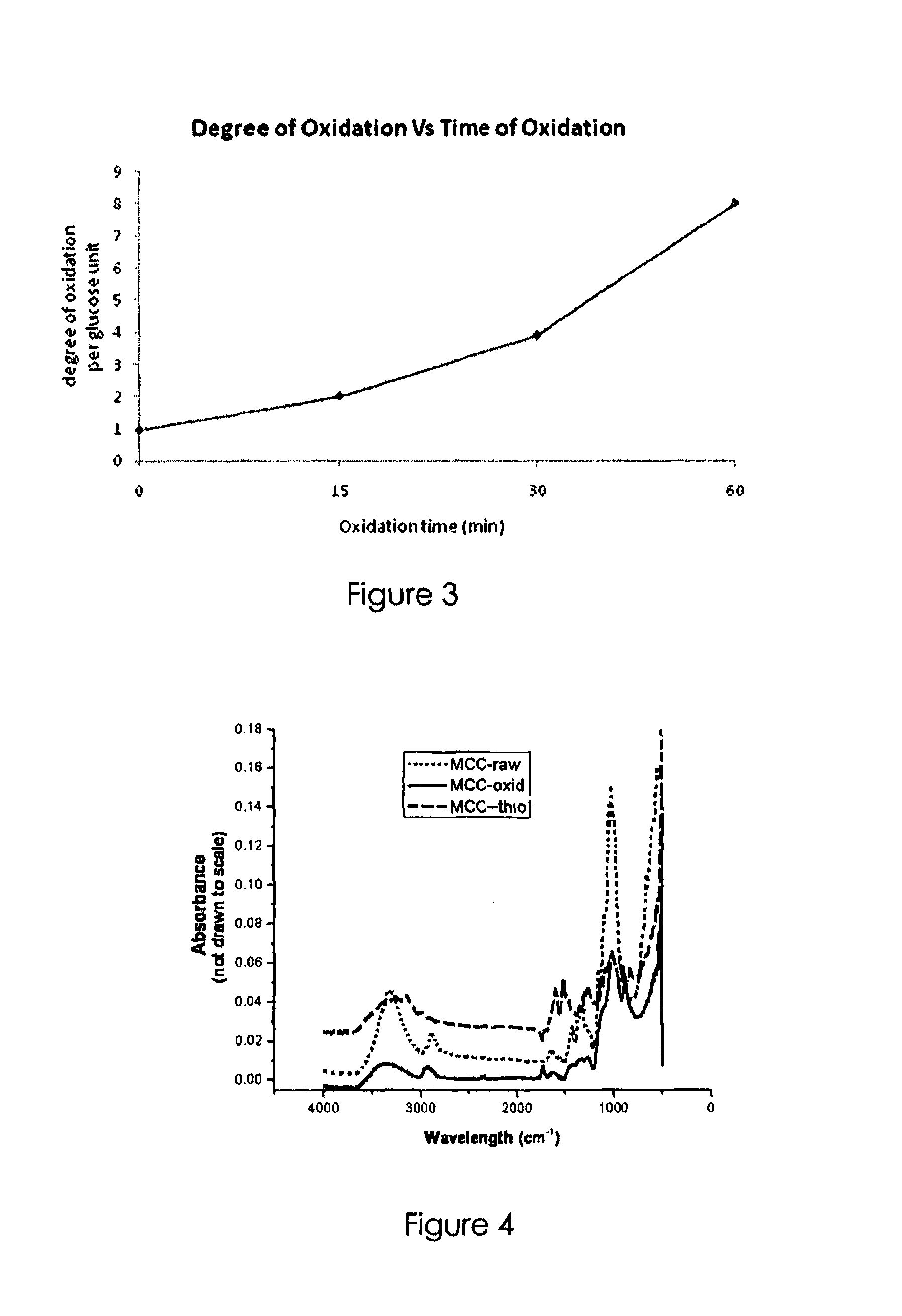
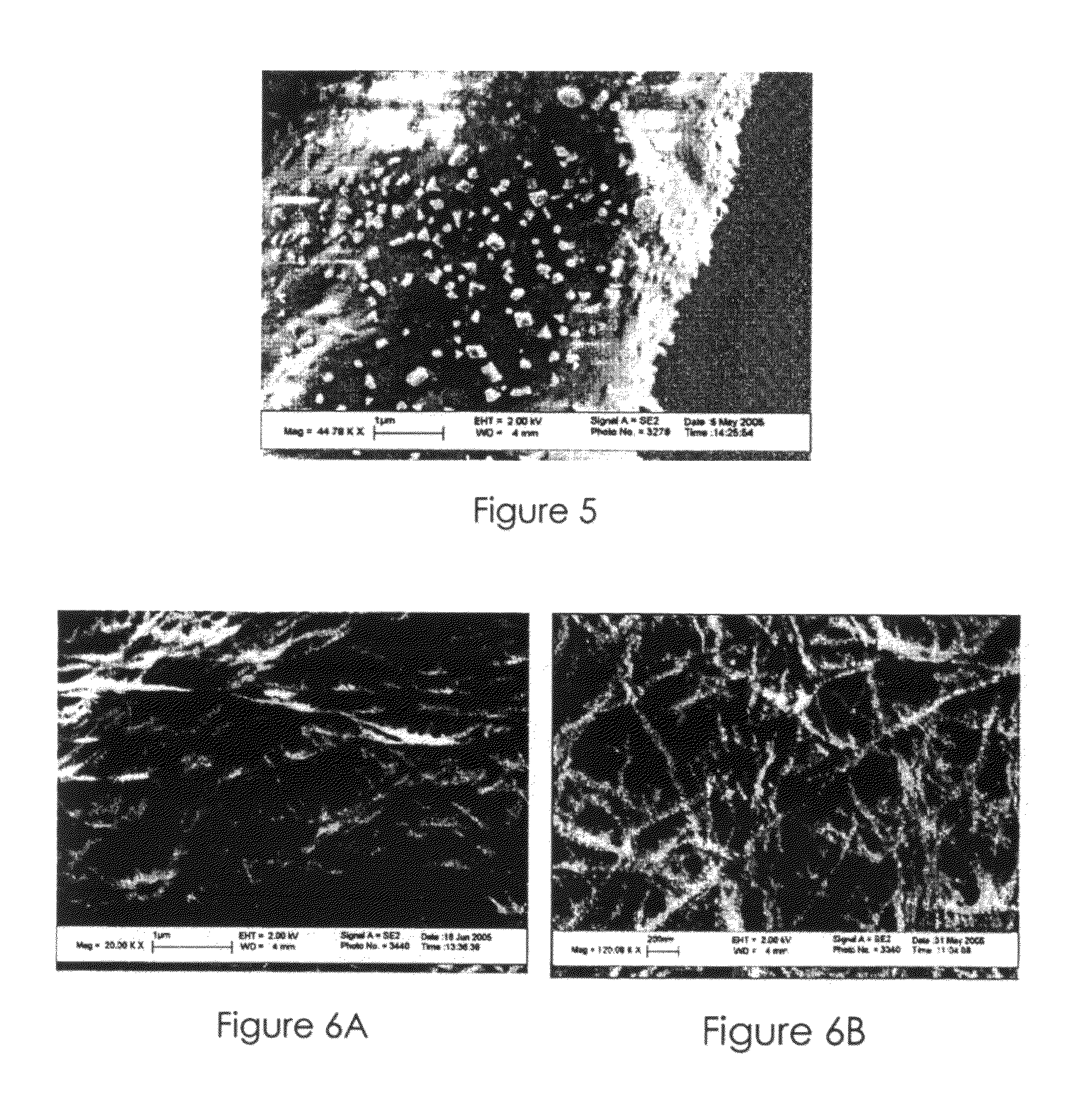
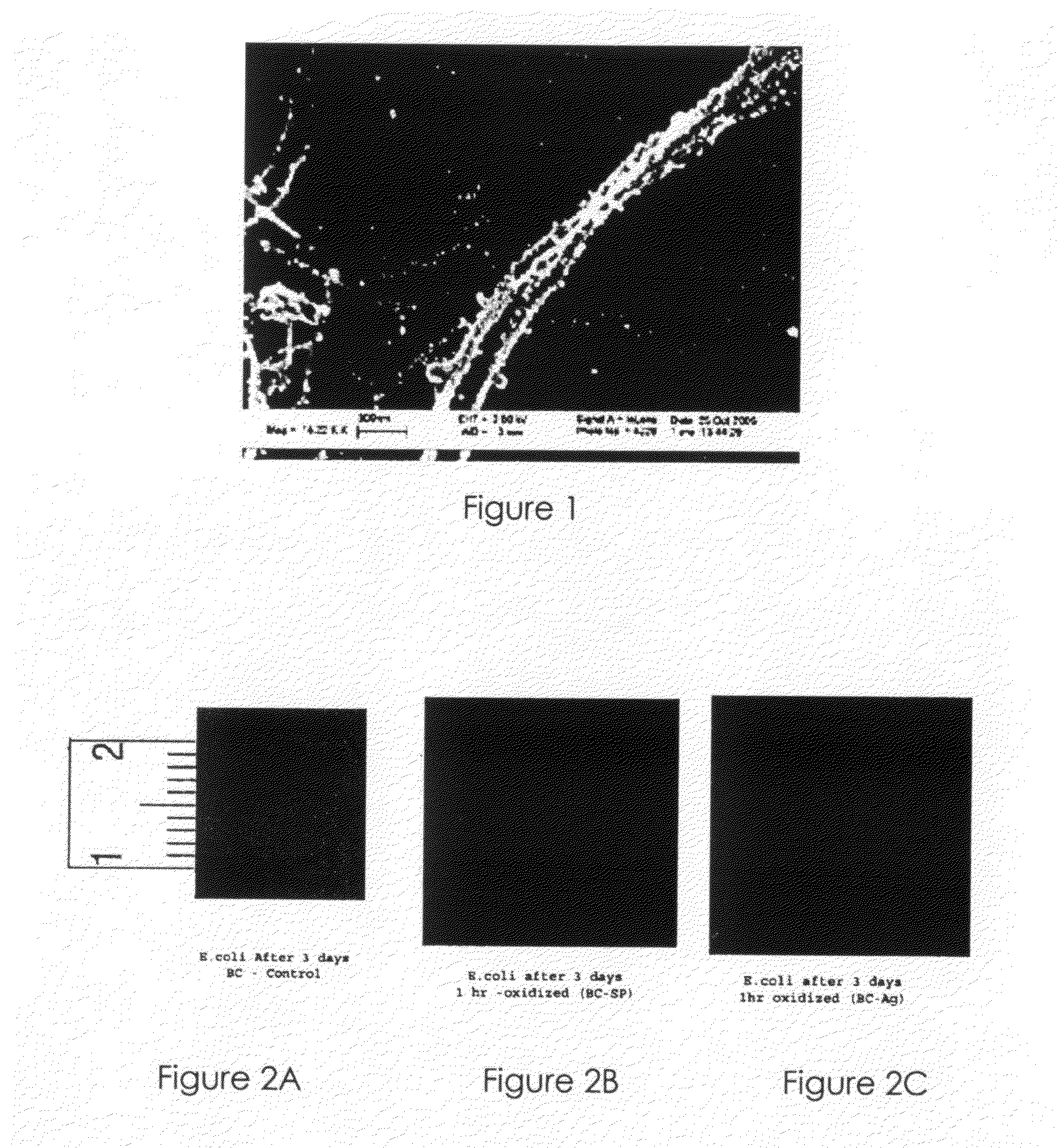
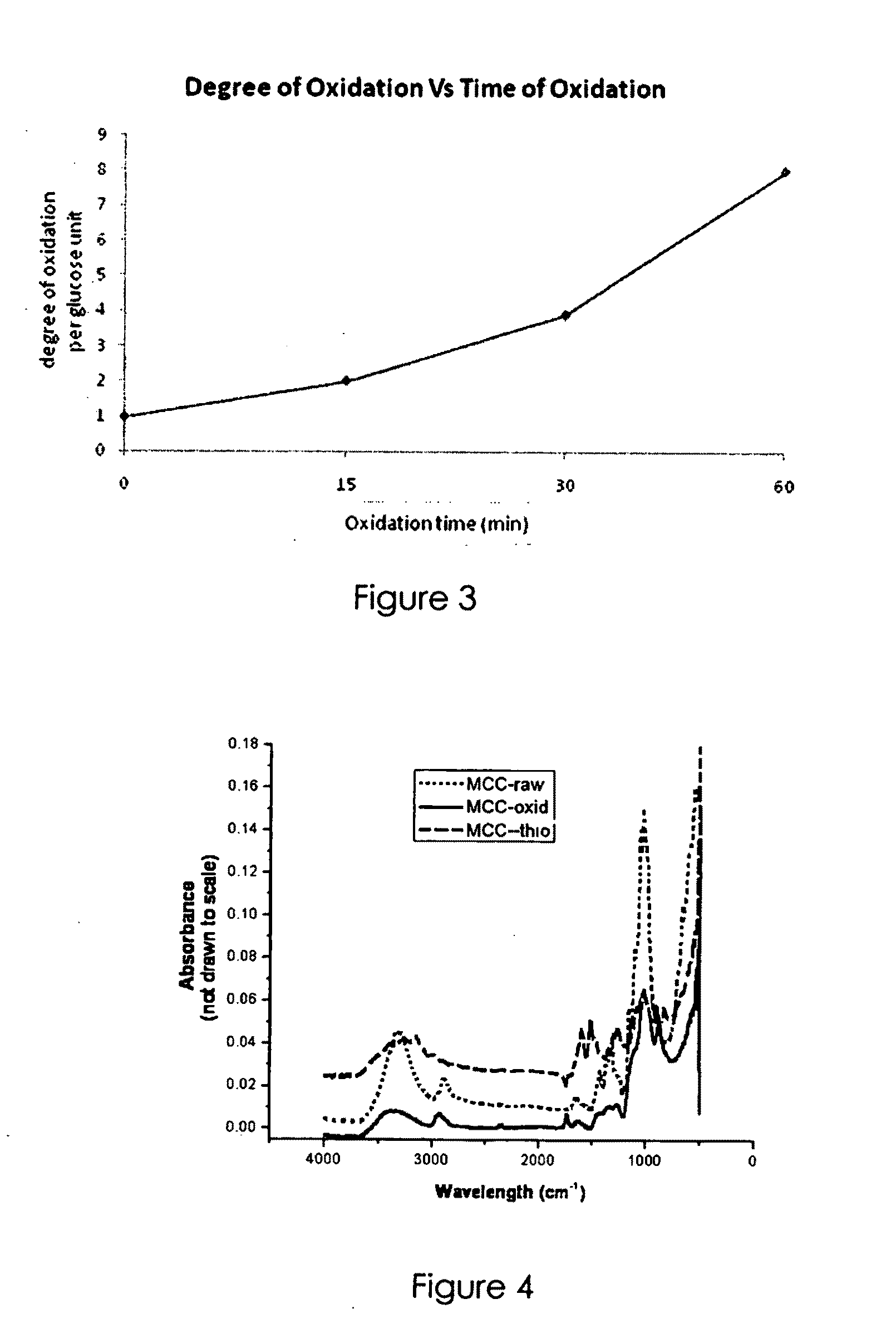
Nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber and a method of producing the nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber. The nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber is produced by preparing a suspension of bacterial cellulose fibers, oxidizing bacterial cellulose fibers; adding the thio-group to the polymer backbone; reacting the resulting product with silver proteinate and enhancing the nanosilver particle size. The nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofibers exhibit antimicrobial properties.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
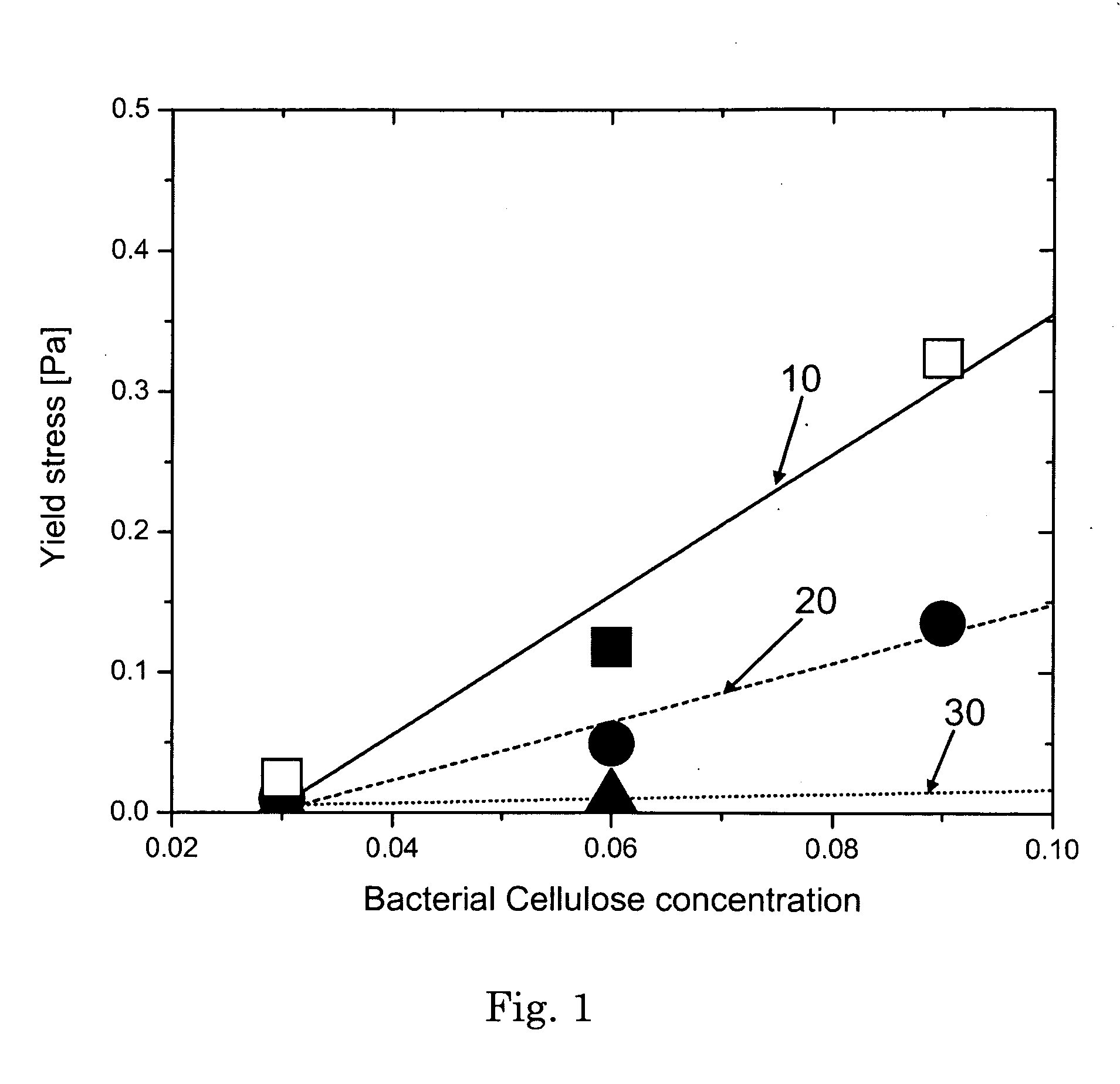
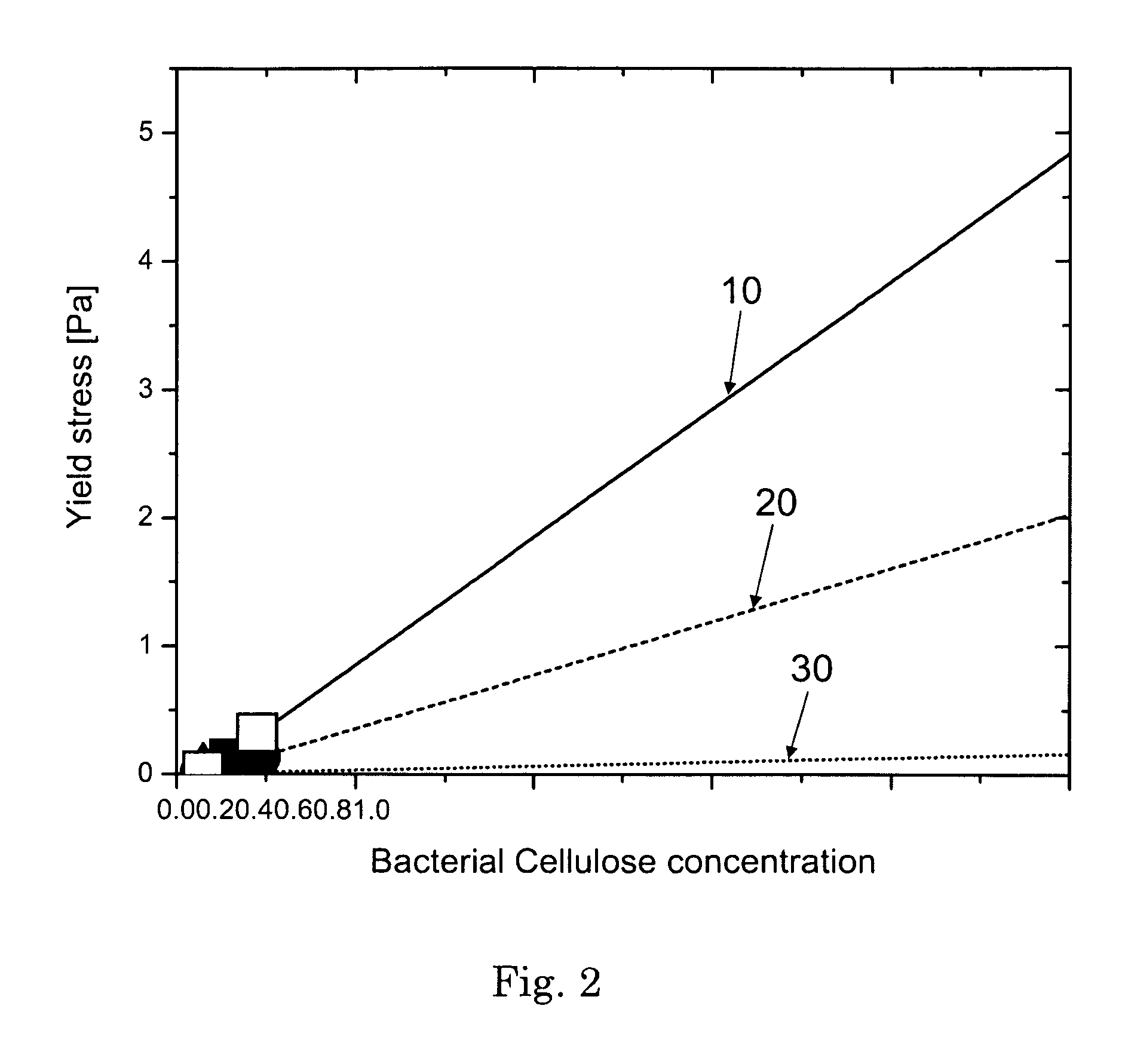
Liquid detergent composition comprising an external structuring system comprising a bacterial cellulose network
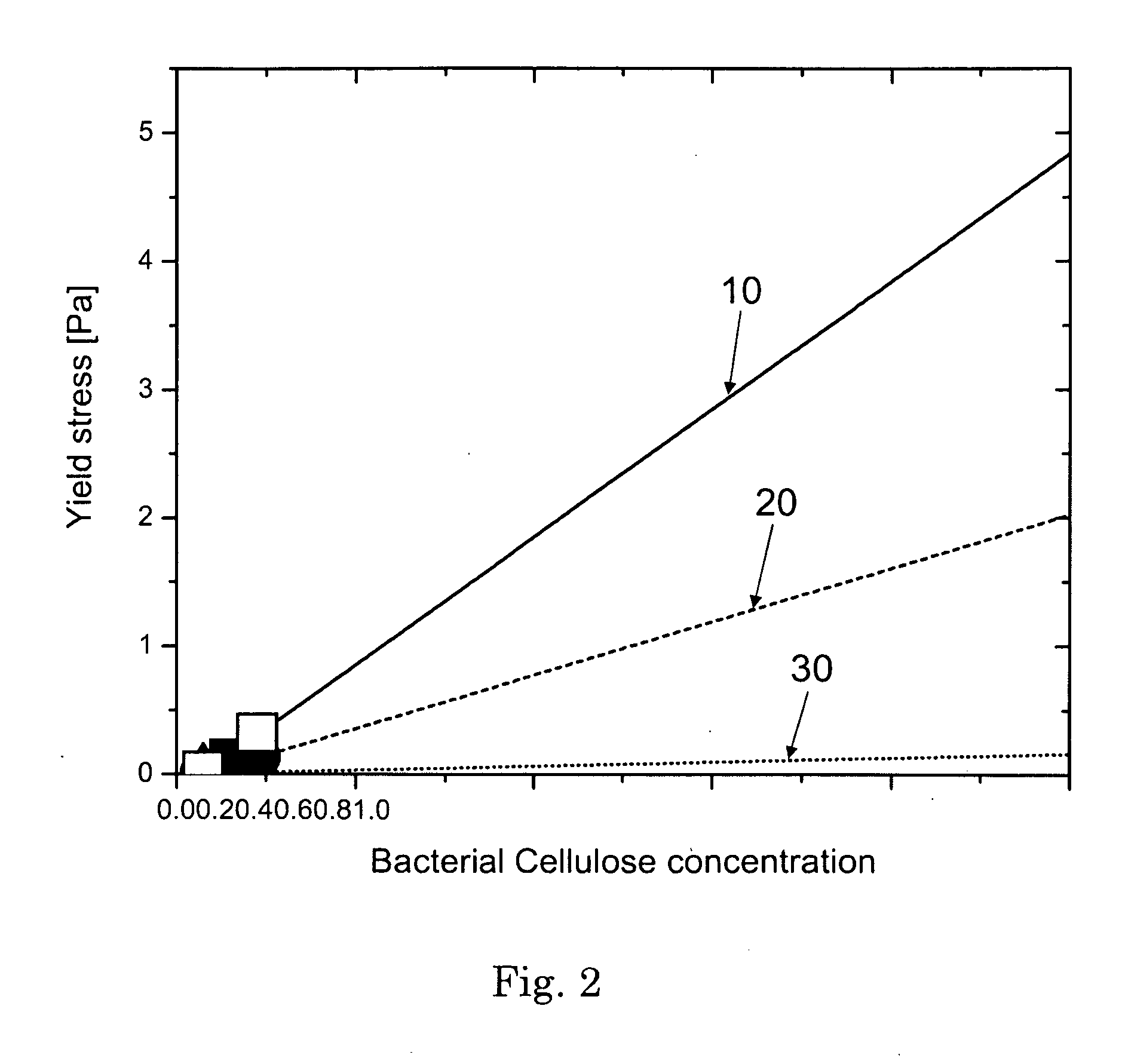
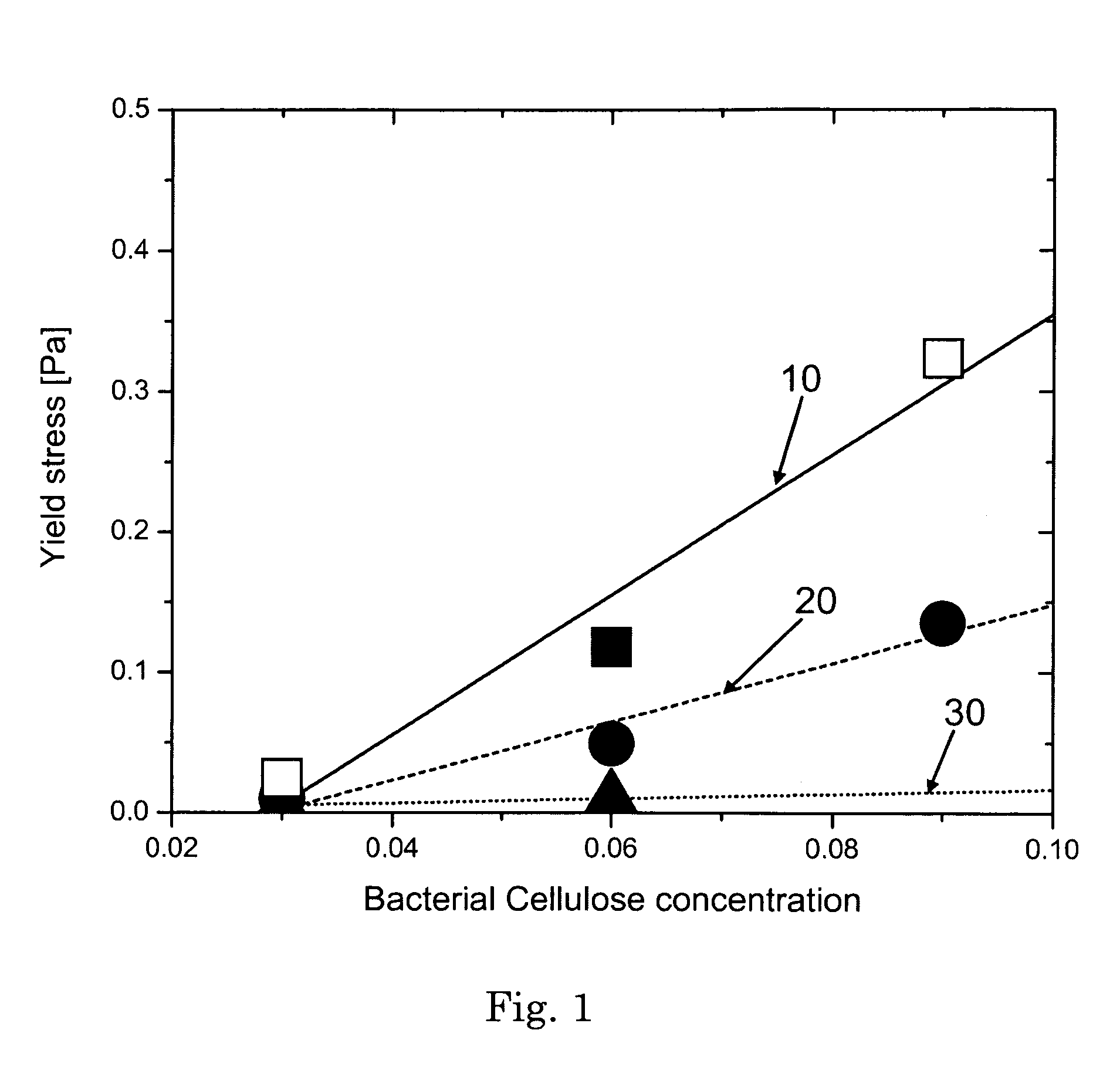
A structured liquid detergent composition in the form of a liquid matrix made up of an external structuring system of a bacterial cellulose network; water; and surfactant system including an anionic surfactant; a nonionic surfactant; a cationic surfactant; an ampholytic surfactant; a zwitterionic surfactant; or mixtures thereof, wherein said liquid matrix has a yield stress of from about 0.003 Pa to about 5.0 Pa at about 25° C. and provides suitable particle suspension capabilities and shear thinning characteristics.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Poly(vinyl alcohol)-bacterial cellulose nanocomposite
Hydrogel-bacterial cellulose nano-composite materials are created using a hydrogel and never dried bacterial cellulose fibers. Such materials are suitable for a broad range of soft tissue replacement applications. In addition controlled release of bioactive agents properties can be designed into medical devices fabricated from such composite materials.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
Method for Producing Biomaterial Scaffolds
InactiveUS20080280360A1Cell culture supports/coatingGeneral culture methodsBiomaterial scaffoldMammalian cell
The present invention provides a multilayer scaffold for tissue engineering. The scaffold comprises at least a first layer comprised of a polymer having a pattern of microchannels therein; and at least a second layer comprised of a polymer having a pattern of microchannels therein. The first and second layers are joined together (preferably by lamination) and the channels are connected for the circulation of fluid through the layers. The scaffold is coated with bacterial cellulose. The scaffold may further include a mammalian cell.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
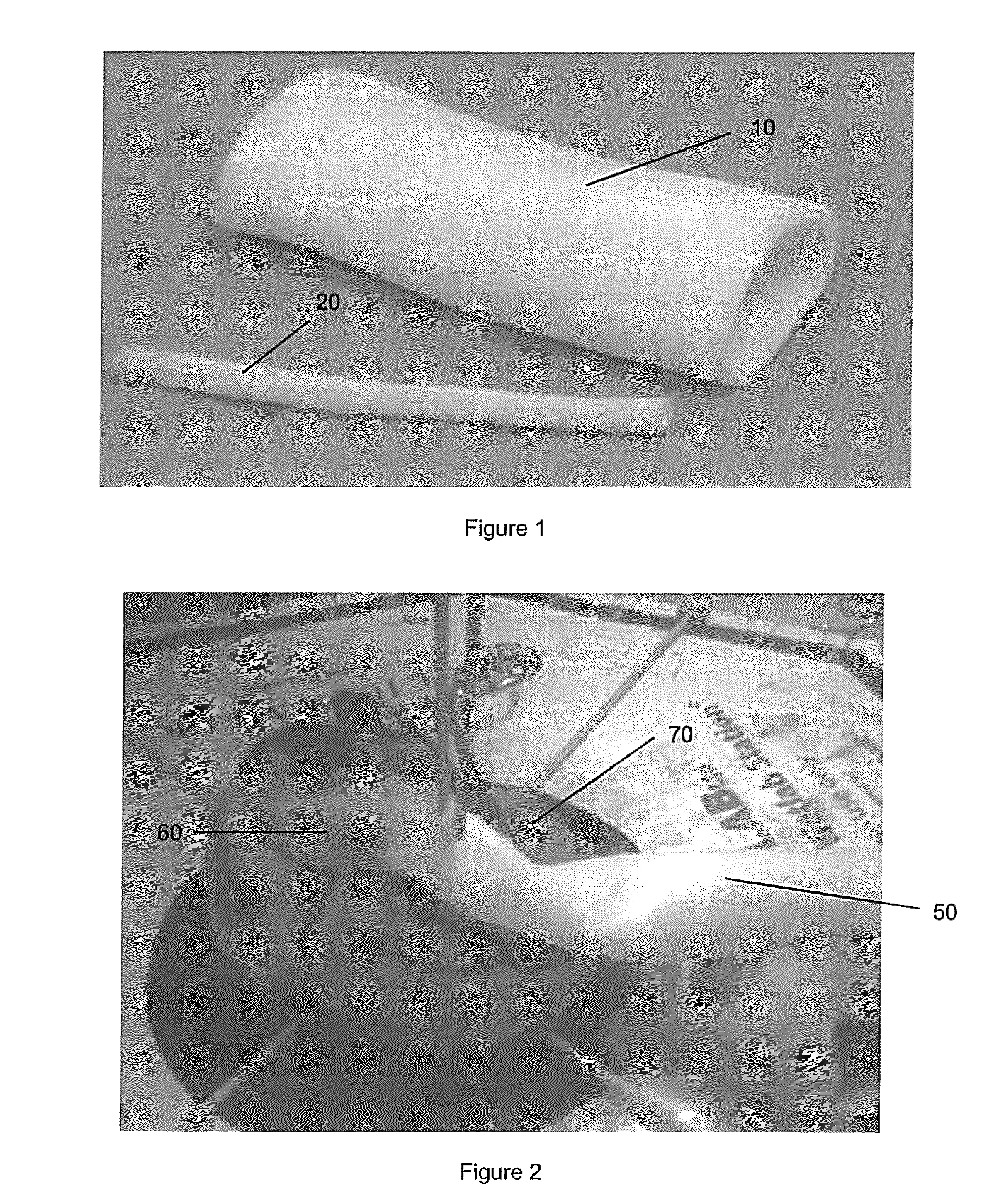
Surgical training aids and methods of fabrication thereof
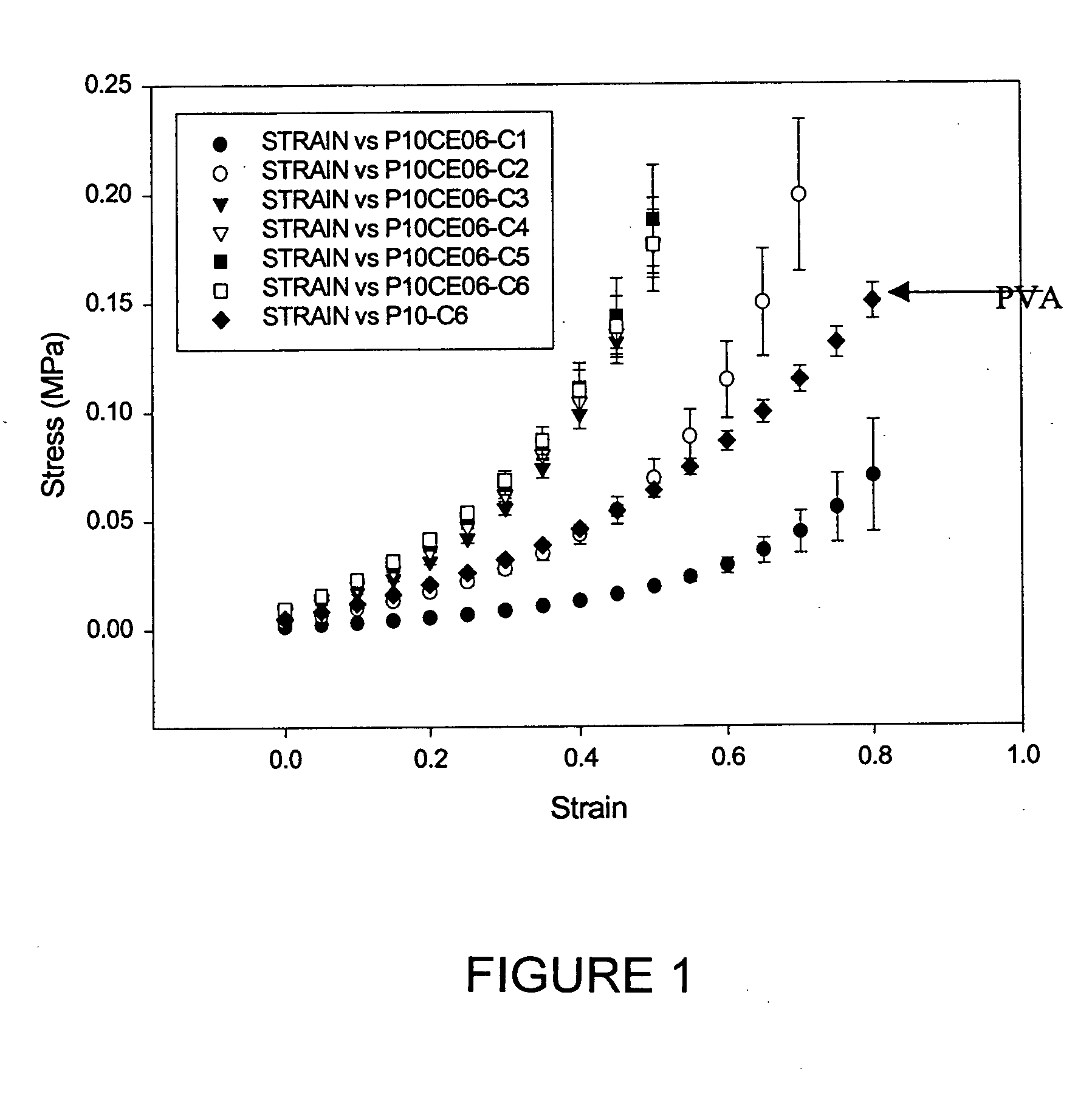
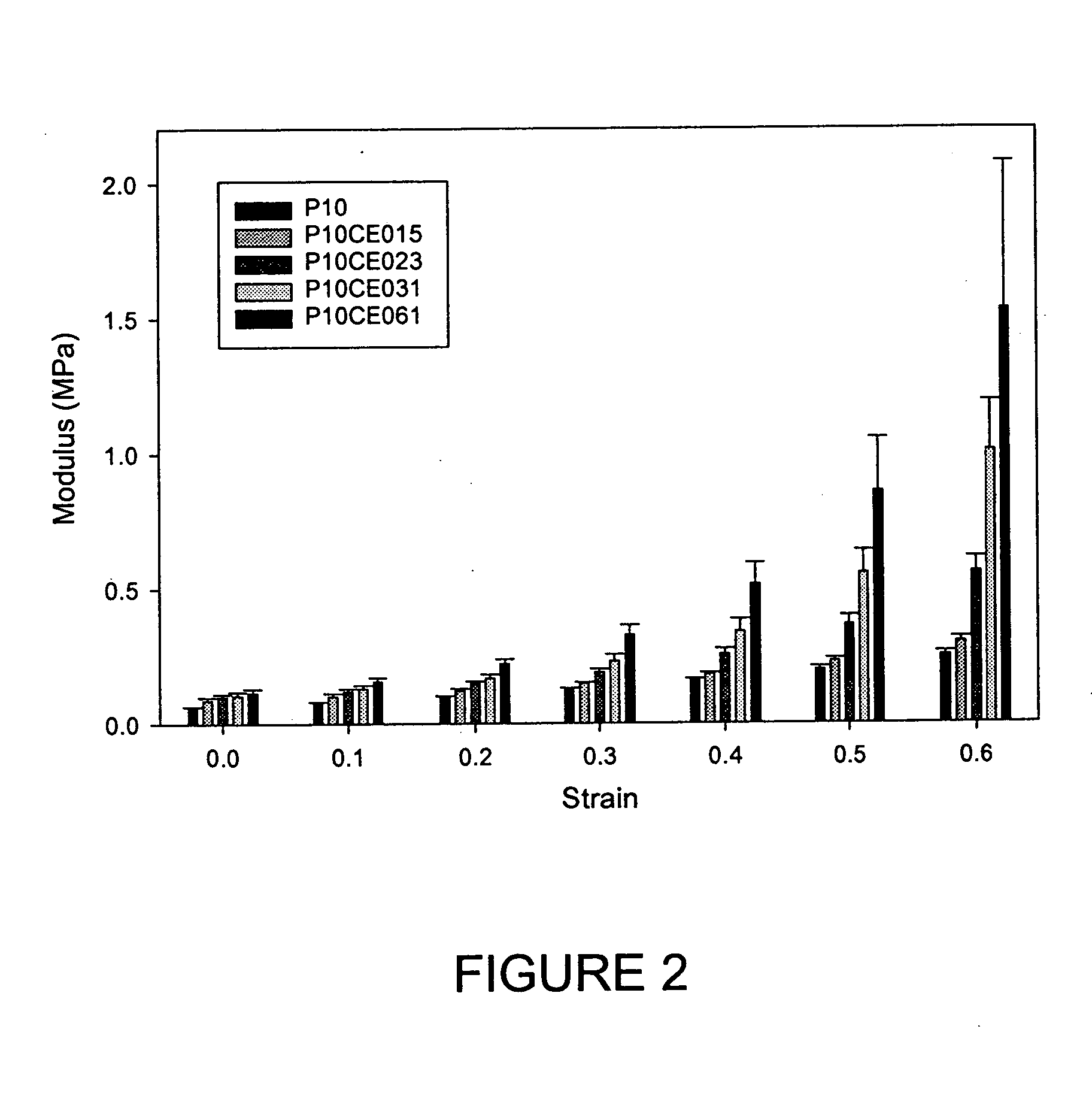
The present invention provides surgical training aids formed from hydrogels and adapted to exhibit realistic mechanical properties mimicking those of real organs. Surgical training aids are preferably fabricated by subjecting a concentration of polyvinyl alcohol to freeze-thaw cycles in a mold designed to approximate the shape of an organ, and process parameters are selected to tailor the mechanical properties of the formed hydrogel to those of the organ simulated by the surgical aid. The mechanical properties of the hydrogel forming the surgical training aid may be tailored by incorporating bacterial cellulose and by applying strain during hydrogel formation, thereby producing controlled anisotropy.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
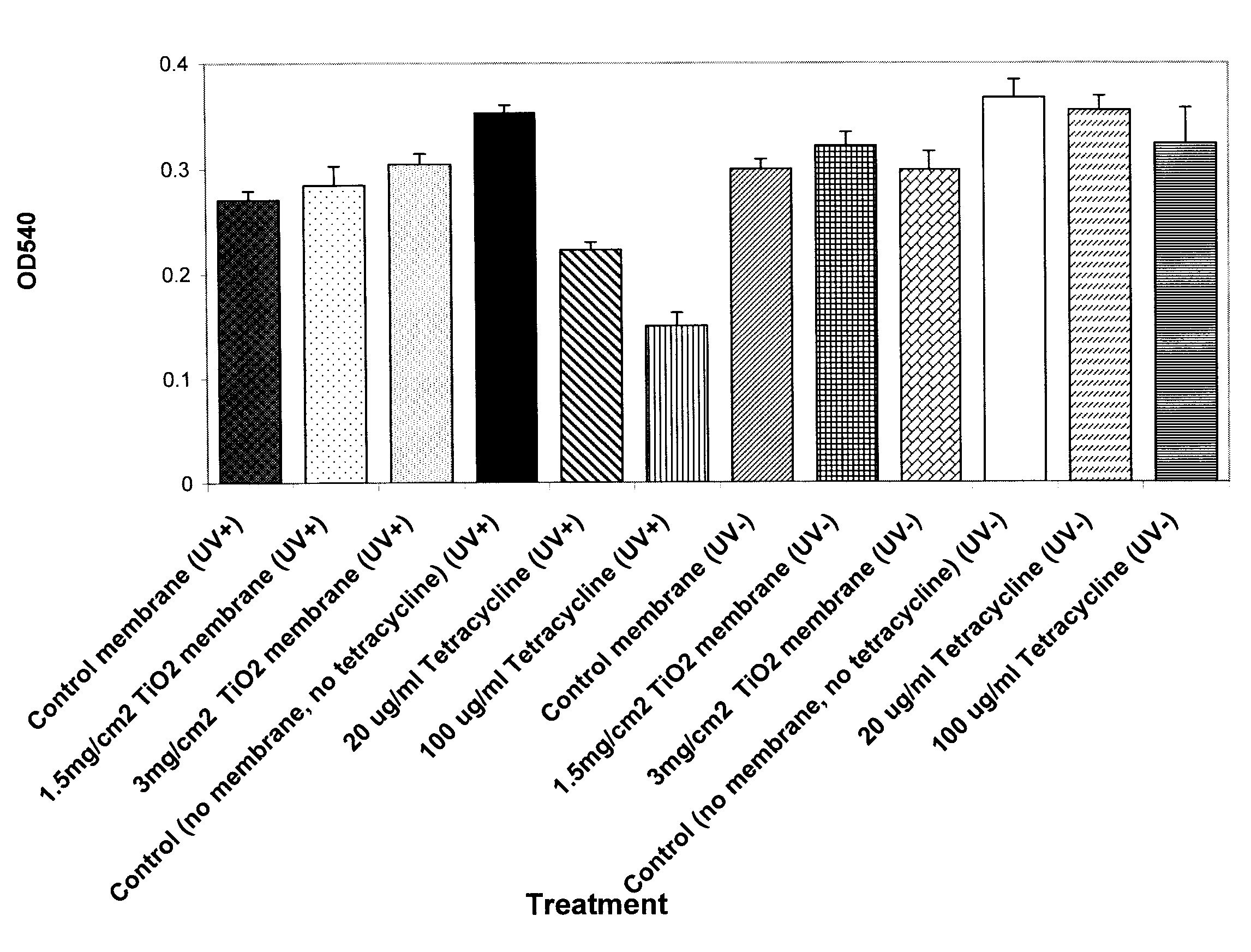
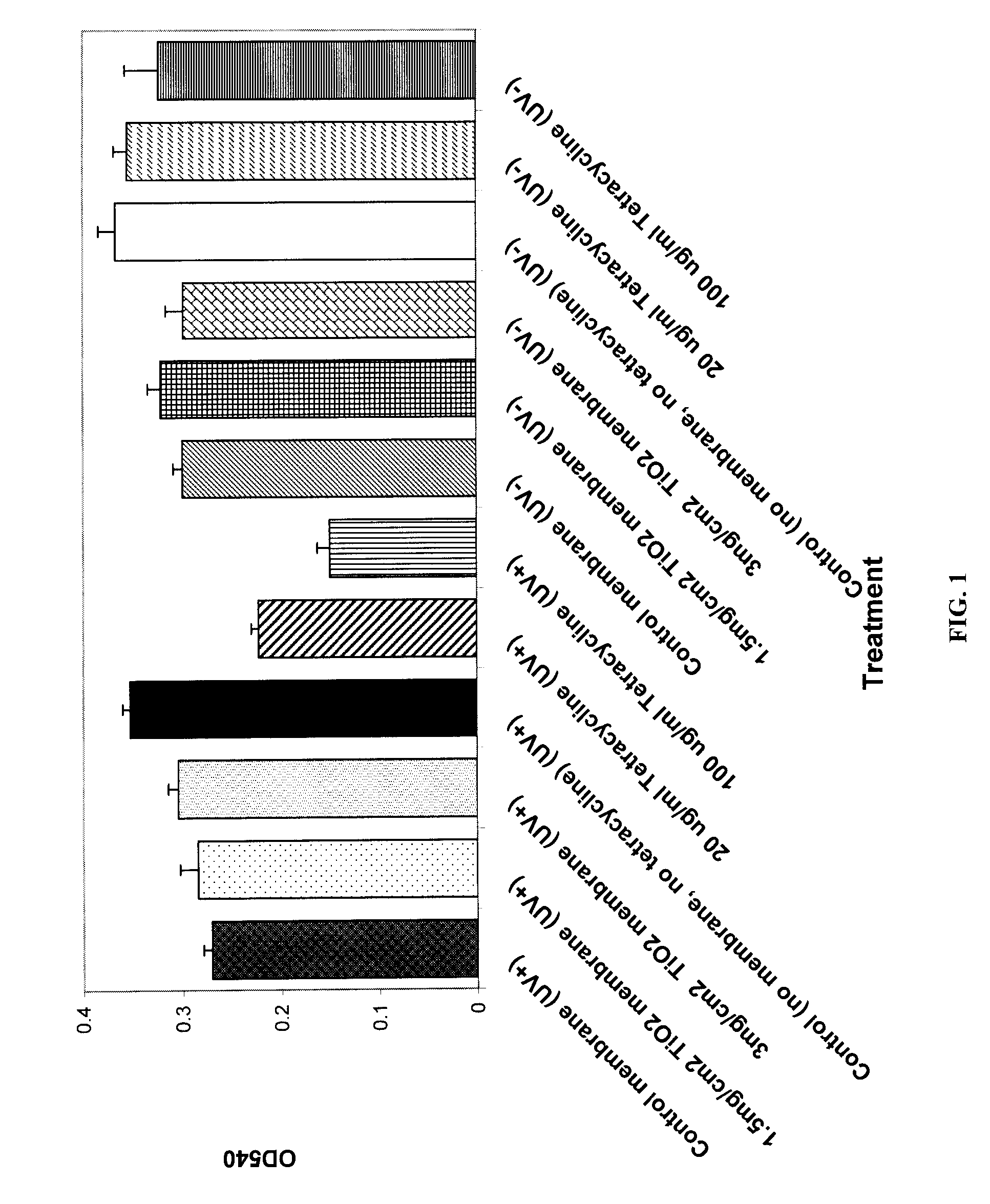
Photoactivated Antimicrobial Wound Dressing and Method Relating Thereto
InactiveUS20090209897A1Physical/chemical process catalystsNon-adhesive dressingsWound dressingOxygen
A photoactivated antimicrobial wound dressing comprising a photocatalytic membrane is provided. The photocatalytic membrane comprises a bacterial cellulose hydrogel membrane having photocatalytic particles are immobilized within the membrane and are activated when exposed to light, at which time they react with oxygen-based species forming reactive oxygen species. The reactive oxygen species further react with microbes to kill the microbes.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Lithium Ion Conductive Material Utilizing Bacterial Cellulose Organogel, Lithium Ion Battery Utilizing the Same and Bacterial Cellulose Aerogel
InactiveUS20080220333A1High mechanical strengthImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialConductive materialsSolvent
A lithium ion conductive material that excels in mechanical strength, exhibiting high ion conductivity; a bacterial cellulose composite material having an inorganic material and / or organic material incorporated therein; and a bacterial cellulose aerogel. The water of bacterial cellulose hydrogel is replaced by a nonaqueous solvent containing a lithium compound. Bacterial cellulose producing bacteria are grown in a culture medium having an inorganic material and / or organic material added thereto. The bacterial cellulose hydrogel is dehydrated and dried.
Owner:YANO SHOICHIRO +5
Nanosilver Coated Bacterial Cellulose
Nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber and a method of producing the nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber. The nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofiber is produced by preparing a suspension of bacterial cellulose fibers, oxidizing bacterial cellulose fibers; adding the thio-group to the polymer backbone; reacting the resulting product with silver proteinate and enhancing the nanosilver particle size. The nanosilver coated bacterial cellulose nanofibers exhibit antimicrobial properties.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
Bacterial cellulose-containing formulations
ActiveUS20070197779A1Need for networkReserved functionNatural cellulose pulp/paperStarch adhesivesAlcoholHigh energy
A new method to produce formulations of bacterial cellulose that exhibit improved viscosity-modifying properties particularly with low energy applied to effectuate viscosity changes therewith is provided. Such a method includes the novel co-precipitation with a water soluble co-agent that permits precipitation in the presence of excess alcohol to form an insoluble fiber that can than be utilized as a thickener or suspension aid without the need to introduce high energy mixing. Such bacterial cellulose properties have been available in the past but only through highly labor and energy intensive processes. Such an inventive method as now proposed thus provides a bacterial cellulose-containing formulation that exhibits not only properties that are as effective as those for previous bacterial celluloses, but, in some ways, improvements to such previous types. Certain end-use compositions and applications including these novel bacterial cellulose-containing formulations are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Liquid detergent composition comprising an external structuring system comprising a bacterial cellulose network
A structured liquid detergent composition in the form of a liquid matrix made up of an external structuring system of a bacterial cellulose network; water; and surfactant system including an anionic surfactant; a nonionic surfactant; a cationic surfactant; an ampholytic surfactant; a zwitterionic surfactant; or mixtures thereof, wherein said liquid matrix has a yield stress of from about 0.003 Pa to about 5.0 Pa at about 25° C. and provides suitable particle suspension capabilities and shear thinning characteristics.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Surgical training aids and methods of fabrication thereof
The present invention provides surgical training aids formed from hydrogels and adapted to exhibit realistic mechanical properties mimicking those of real organs. Surgical training aids are preferably fabricated by subjecting a concentration of polyvinyl alcohol to freeze-thaw cycles in a mold designed to approximate the shape of an organ, and process parameters are selected to tailor the mechanical properties of the formed hydrogel to those of the organ simulated by the surgical aid. The mechanical properties of the hydrogel forming the surgical training aid may be tailored by incorporating bacterial cellulose and by applying strain during hydrogel formation, thereby producing controlled anisotropy.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Method for preparing Ag-carrying bacterial cellulose hydrogel antimicrobial dressing and product thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing an Ag-carrying bacterial cellulose hydrogel antimicrobial dressing and a product thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: soaking a bacterial cellulose hydrogel film in solution of silver metal precursor; then heating the film to be between 121 and 135 DEG C in a high-pressure sterilizing pot, and pressurizing between 0.205 and 0.313MPa; standing bacterial cellulose for 5 to 30min; and then taking the treated bacterial cellulose out for washing, partial dehydration, packaging and sterilization to obtain an Ag-carrying bacterial cellulose hydrogel antimicrobial dressing which is formed by compounding silver metal nano-particles and bacterial cellulose and is attached with 0.01 to 10 weight percent of the silver metal nano-particles in a bacterial cellulose three-dimensional porous network structure. The preparation process of the invention has the advantages of simplicity, easiness, convenient operation, controllable preparation technology, no pollution and low cost; and the prepared nano-particles have the advantages of high purity, small particle size, uniform size and good dispersity. The obtained Ag-carrying bacterial cellulose hydrogel antimicrobial dressing has the characteristics of good antimicrobial property, high water content, good water-retaining property, strong toughness, good air permeability and the like, and can meet the requirements of treating various wounds by a wet method.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method for preparing nano-cellulose antibacterial composite material through on-line culture
ActiveCN102552965ARealize fermentation productionImprove continuityCosmetic preparationsBacteriaWater bathsFiber
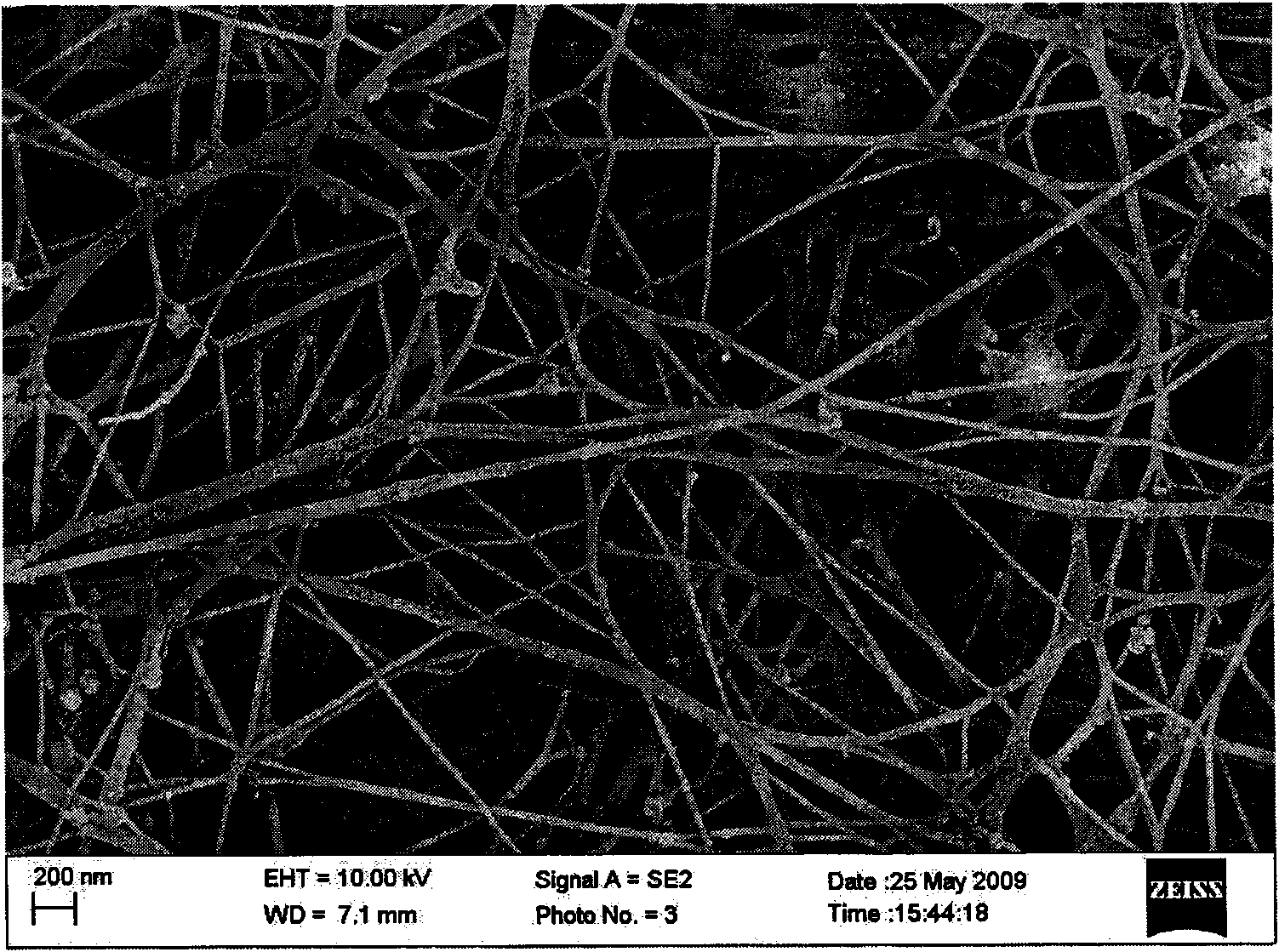
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nano-cellulose antibacterial composite material through on-line culture. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating an activated bacterial cellulose producing strain into a liquid culture medium, performing amplification culture, transferring the liquid culture medium into a bioreactor, culturing, adding an antibacterial material into the liquid culture medium, and continuing to culture to obtain an unpurified antibacterial bacterial cellulose composite material; and (2) peeling a bacterial cellulose membrane from a framework or directly soaking the composite material in a NaOH solution, treating in water bath, and washing until an obtained product is neutral to obtain the nano-cellulose antibacterial composite material. The preparation efficiency is high, and the method is simple, convenient, feasible and low in cost; and the surface of the bacterial cellulose composite material has a nanoscale three-dimensional fibrous mesh-shaped structure, the tensile strength of the material is greatly improved compared with that of a pure bacterial cellulose membrane, and the material can be widely applied to products such as facial masks, wound dressings, plasters, artificial skins and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Bacterial cellulose/polymer composite film and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a bacterial cellulose / polymer composite film and a preparation method thereof. The bacterial cellulose / polymer composite film is formed by compounding bacterial cellulose fibers on a polymer porous material in situ. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) activating strains, finally inoculating into a liquid culture medium to culture, infiltrating the surface of the porous polymer film in the liquid culture medium and exposing in air; (2) repeating the operation every 2-3 days until a composite film is formed; (3) post-treating the composite film to be neutral to obtain a bacterial cellulose / polymer composite gel film; and (4) drying the gel film obtained in the step (3) to constant weight to obtain the bacterial cellulose / polymer composite dry film. The invention solves the problem of low mechanical strength of a single bacterial cellulose film. By utilizing hydrogen bonding produced by hydroxyl groups on cellulose macromolecules, the strength, the durability and the water absorbability of the bacterial cellulose / polymer composite gel film and the composite dry film are improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation for in-situ compounding simple-substance nano silvery bacteria cellulose membrane
ActiveCN101586309AHigh antibacterial activityImprove antibacterial propertiesFibre treatmentMicroorganism based processesWound dressingFragility
The invention provides a preparation for the in-situ compounding simple-substance nano silvery bacteria cellulose membrane, and relates to the biological medical material field, characterized in that the bacteria cellulose membrane has special three-dimensional nano network structure, the silver-ammonia solution reacts with the chemical agent containing aldehyde group to generate silver simple-substance nano particle in situ in the network structure. In addition, in the invention, the special drying method is adopted to improve the defect of big fragility of the prepared silver-contained nano bacteria cellulose dry membrane. The bacteria cellulose membrane containing simple-substance nano silver particle provided by the invention has excellent antibacterial performance and simple preparation technique, and can be widely used in the biological medical field such as large-area wound dressing, bundling belt and the like, also can be used in the industry field such as the preparation of nano silver particle and silver catalyst, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
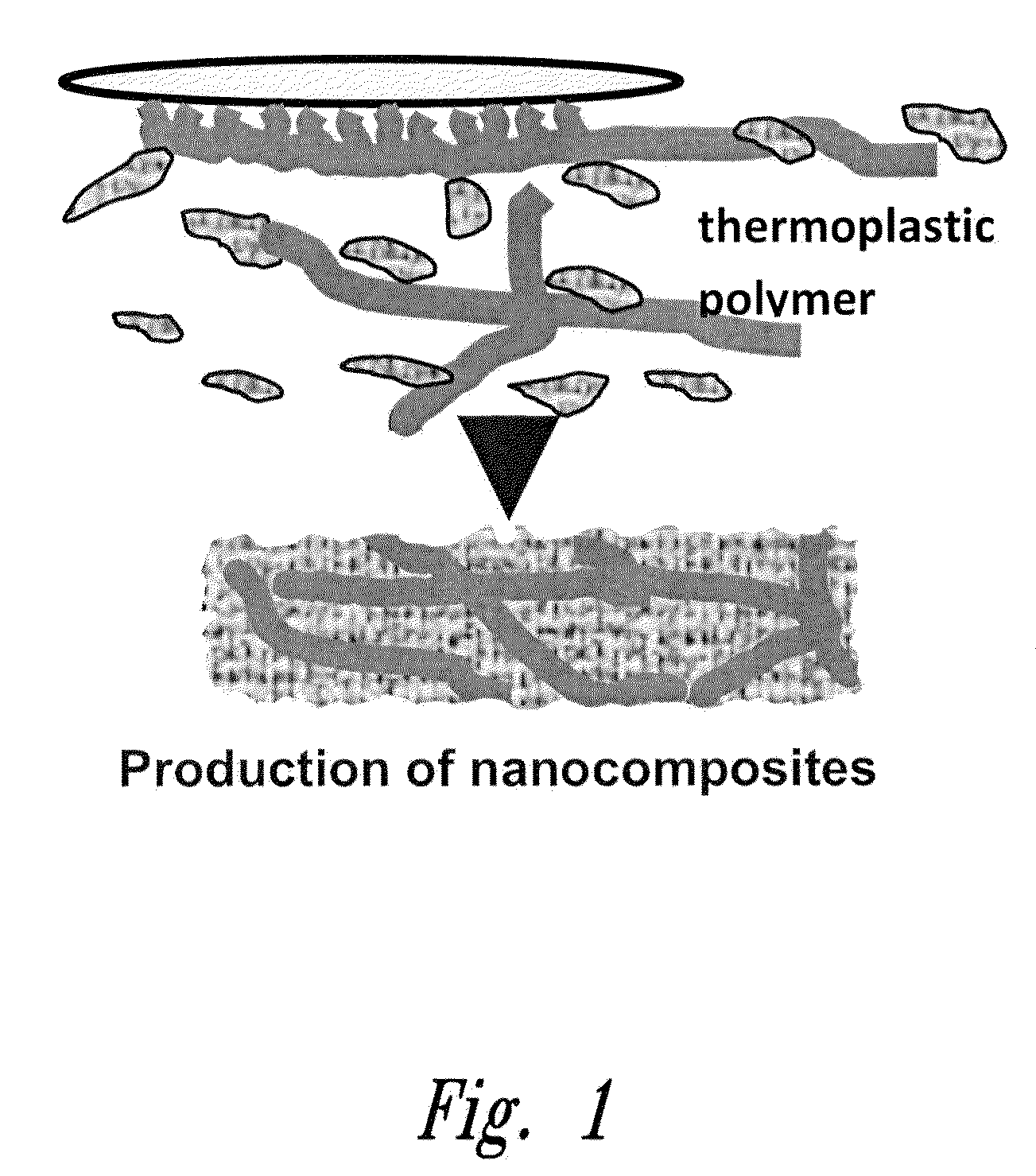
Method of in situ bioproduction and composition of bacterial cellulose nanocomposites
Provided are novel methods for making cellulose nanocomposites, comprising biosynthesis of cellulose fibrils in situ using a growth medium comprising a polymer matrix material, under conditions suitable to provide for dispersion of the fibril throughout the growth medium as the fibrils are being formed to provide a cellulose nanocomposite material or film wherein the cellulose fibrils are highly or uniformly dispersed in the cellulose nanocomposite material, and wherein fibril structure and / or nanocomposite composition is customizable. Certain method aspects further comprise removing or separating the cellulose nanocomposite material or film from the medium, and may further comprise washing the cellulose nanocomposite material or film to remove residual medium. Particular aspects further comprise freeze-drying the cellulose nanocomposite material or film, and / or further comprise forming a molded product using the cellulose nanocomposite material or film. Compositions made by the methods are provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of graphene oxide/bacterial cellulose antibacterial compound material
InactiveCN104072809AEasy to prepareFew stepsMicroorganism based processesAbsorbent padsUltrasonic dispersionCvd graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene oxide / bacterial cellulose antibacterial compound material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating activated bacterial cellulose into a seed medium to culture, then, inoculating the activated bacterial cellulose into a fermentation medium according to an inoculum size of 5-10%, and after fully and uniformly mixing, putting in a constant-temperature culture box at 30+ / -2 DEG C, standing and fermenting for 1-2 weeks to obtain a bacterial cellulose wet film; (2) after alkali-washing the bacterial cellulose wet film, pulping to a homogeneous phase suspension liquid by virtue of a mechanical method; (3) mixing a graphene oxide solution with the bacterial cellulose homogeneous phase suspension liquid, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion to prepare a homogeneous phase mixed liquid; (4) decompressing and filtering the homogeneous phase mixed liquid, and freezing and drying to separate the graphene oxide / bacterial cellulose antibacterial compound material. The preparation method of the graphene oxide / bacterial cellulose antibacterial compound material disclosed by the invention is simple, few in step and easy to operate, and the prepared graphene oxide / bacterial cellulose antibacterial compound material has excellent antibacterial performance and can be widely applied to the fields such as medical dressing and artificial skins.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method of porous bacteria cellulose sponges
The invention relates to a preparation method of porous bacteria cellulose sponge. A bacterial cellulose hydrogel membrane and an ice crystal are completely mixed, pre-frozen is carried out at subzero 20 to subzero 50 DEG C and are prepared into a homogeneous dispersed system. At last, a freeze-drying method is used for preparing the porous bacteria cellulose sponge. Through the invention, bacteria cellulose sponge material containing large holes is simply, rapidly and efficiently manufactured by the invention, and the application of nanometer bacteria cellulose in the field of the tissue engineering stent can be greatly developed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Personal Cleansing Compositions Comprising A Bacterial Cellulose Network And Cationic Polymer
ActiveUS20110039744A1Readily rinse offEnhance cleansingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsCationic polymerizationSURFACTANT BLEND
A personal cleansing composition comprising a liquid matrix comprising water; a lathering surfactant; and an external structurant comprising a bacterial cellulose network and a cationic polymer; wherein a particulate material is suspended within the liquid matrix and the composition has a compositional pH of less than about 7. Methods of use and making are also provided.
Owner:THE GILLETTE CO
Bacteria cellulose membrane containing silver chloride nano particle and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101264335AImprove performanceHigh antibacterial activityAbsorbent padsBandagesNanoreactorChloride salt
The invention provides a bacteria cellulose membrane containing silver chloride nanometer particles, corresponding preparation method and application, which is characterized in that a plurality of silver chloride nanometer particles are adhered to the microfiber surface of the three-dimensional porous reticular structure of the bacteria cellulose membrane, the content of the silver chloride nanometer particle is 0.5 to 21% of the total weight and which particle diameter is 10 to 300nm. The preparation method is base on the principle of using the particular three-dimensional reticular microfibrillar structure and the high oxygen density (ether linkage and hydroxy) to constitute the synthetical effective nanometer reactors by the silver chloride nanometer particles in situ and the product is obtained after repeatedly soaking in the solution of silver salt and chloride salt, rinsing and drying. The bacteria cellulose membrane containing silver chloride nanometer particles has the advantages of excellent antibacterial performance, most simple preparation process, can be used as favorable antiseptic dressing and extracting the silver chloride nanometer particles.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing bacteria cellulose compound film and application thereof as face pack material
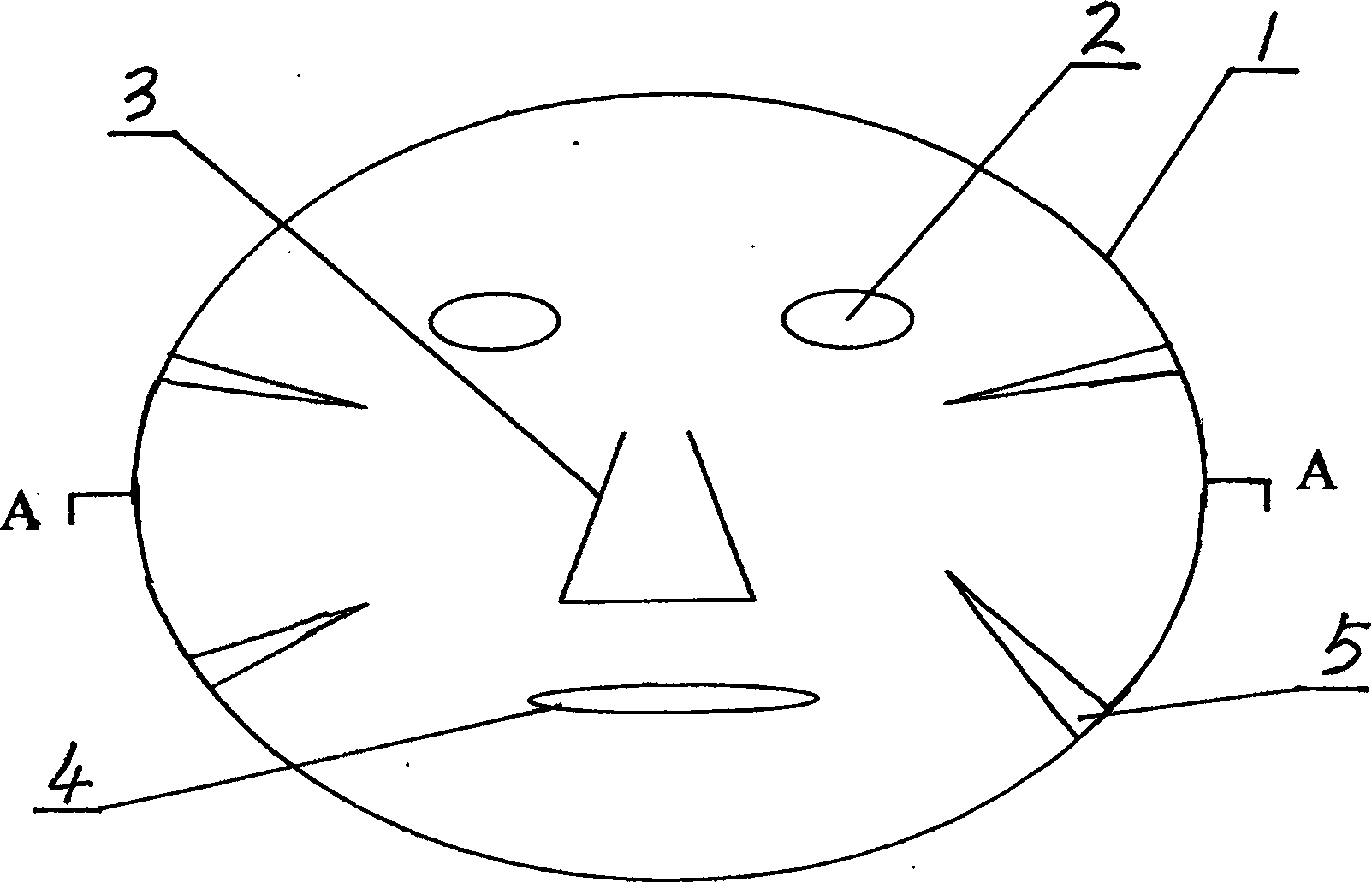
InactiveCN101386877AIncrease productionIncrease moisture contentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDry weightCellulose compounds
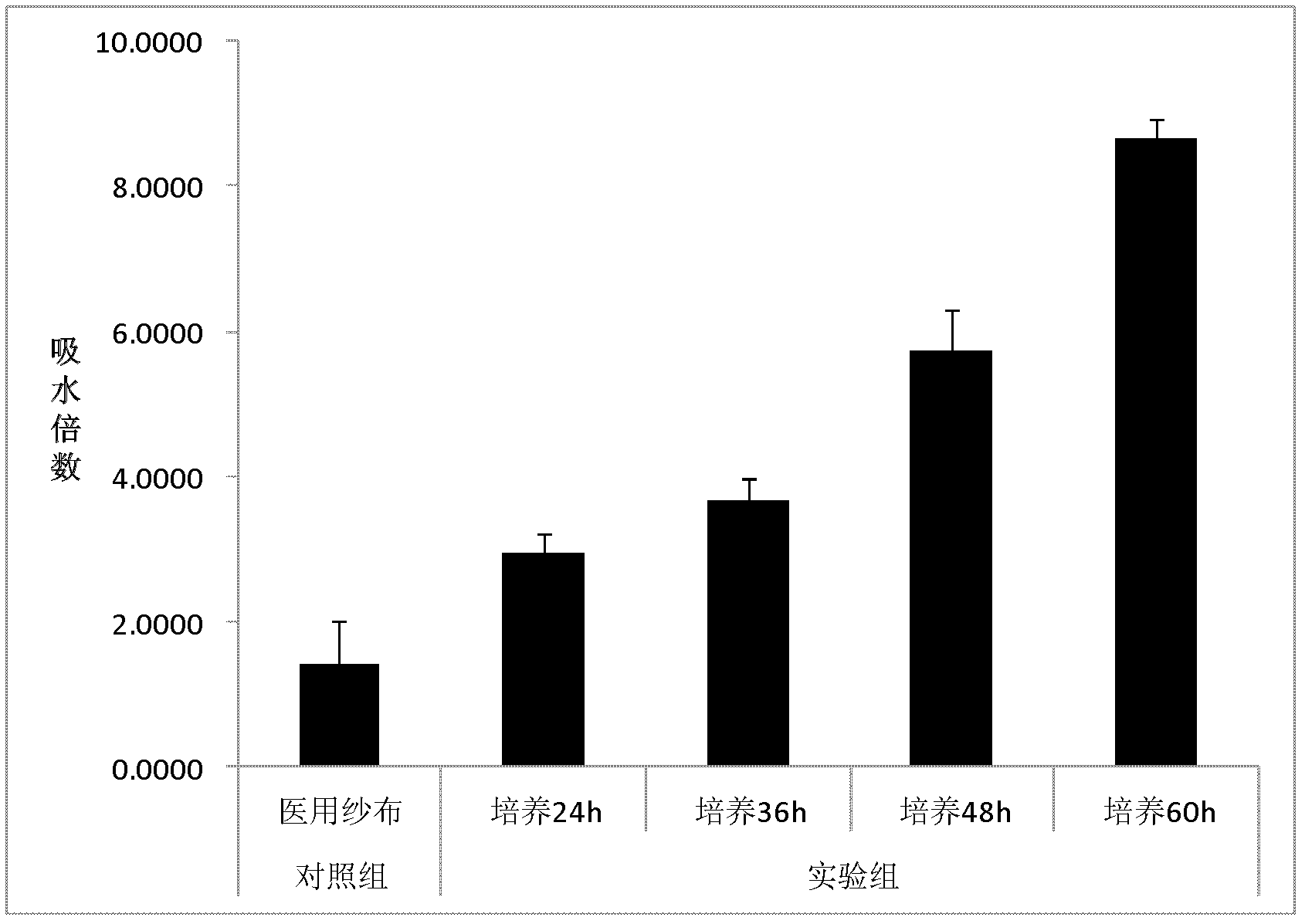
The invention discloses a preparation method for a bacterial cellulose composite membrane and application of the bacterial cellulose composite membrane as a facial mask material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a strain; (2) preparing a seed containing a polyglutamic acid (PGA) and a liquid culture medium; (3) culturing seed cells; (4) producing bacterial cellulose by static liquid fermentation; and (5) purifying a bacterial cellulose membrane. The bacterial cellulose composite membrane can be used as a facial mask carrier or is directly used as a wet facial mask. The preparation method improves the yield of the bacterial cellulose by adding the polyglutamic acid (PGA) into the culture medium, improves the water content and the mechanical strength of a wet membrane, and has simple process and low cost; and the experiments prove that the method can ensure that the dry weight of the bacterial cellulose is improved to between 14 and 16g / L from the prior dry weight of between 8 and 10g / L, and the water content is increased to 99 percent from 98 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
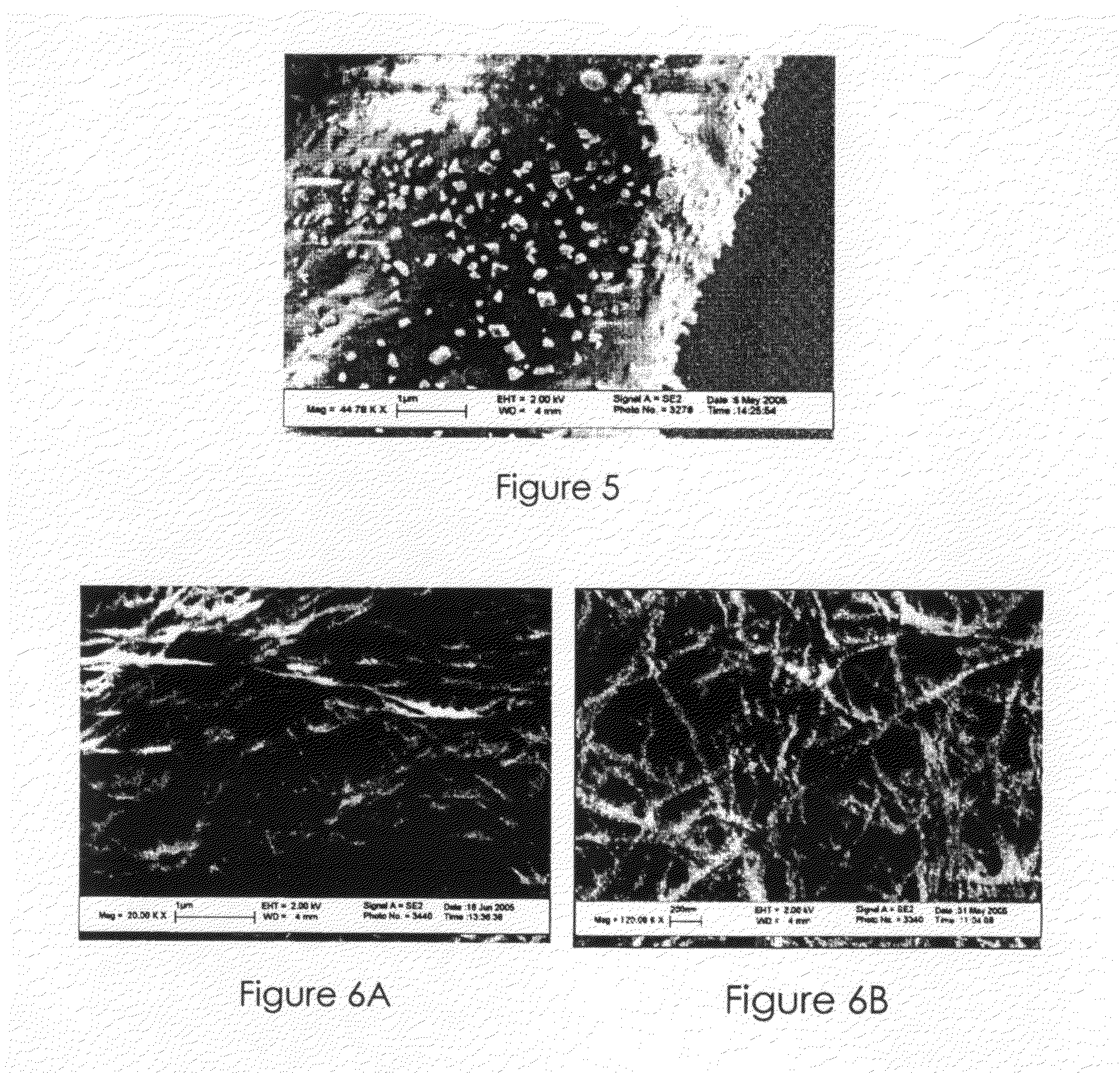
Bacterial cellulose film and carbon nanotubes-like thin film structures developed from bacterial cellulose
A carbon nanotubes-like material is disclosed. The carbon nanotubes-like material comprises bacterial cellulose carbonized under an oxygen-free atmosphere. Also disclosed is a cathode material containing bacterial cellulose and LiFePO4, an anode material containing carbonized bacterial cellulose, a separator membrane containing aldehyde-treated bacterial cellulose, and a lithium battery containing a component comprising bacterial cellulose.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Gel face pack prepared from bacteroidal cellulose
ActiveCN1872022AHigh water binding capacityGood biocompatibilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGluconatesFace skins
A bacterial cellulose gel mask for beautifying face skin is prepared from the gluconate pyracetobacillus through culturing in coconut water to generate film, treating with hot alkali solution, acid neutralizing, washing to obtain bacterial cellulose gel, cutting to form a face mask and attaching a lining film. Its advantages are slow release and high effect.
Owner:HAINAN GUANGYU BIOTECH
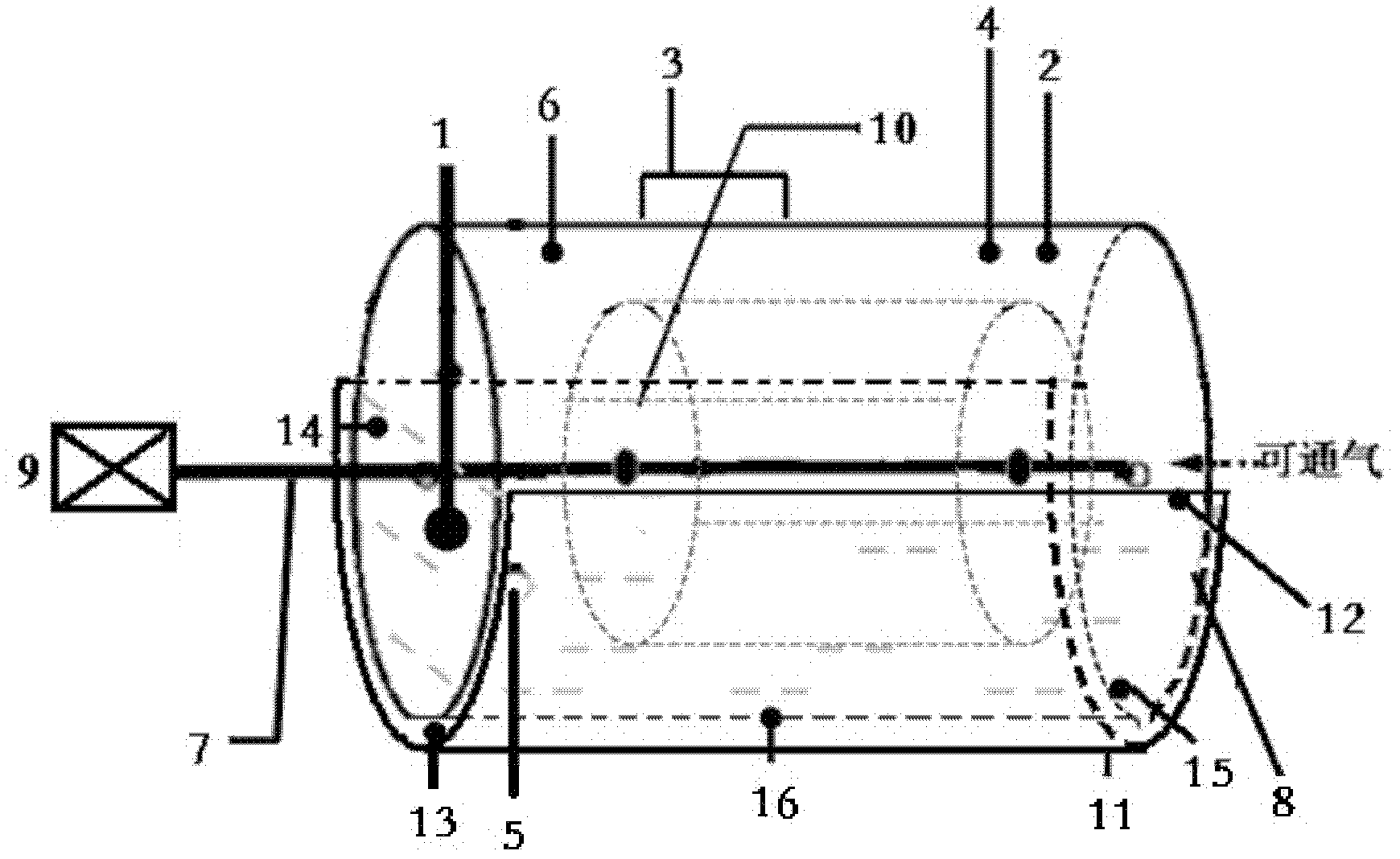
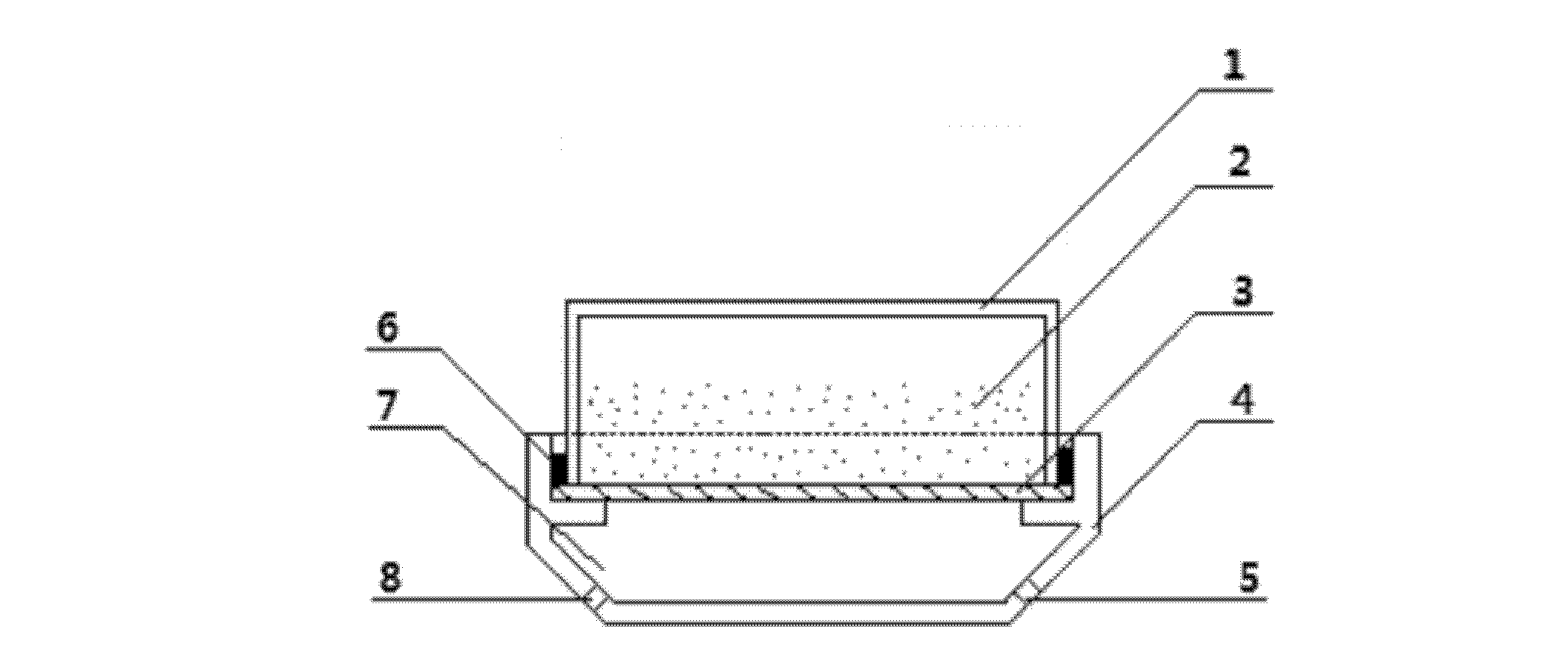
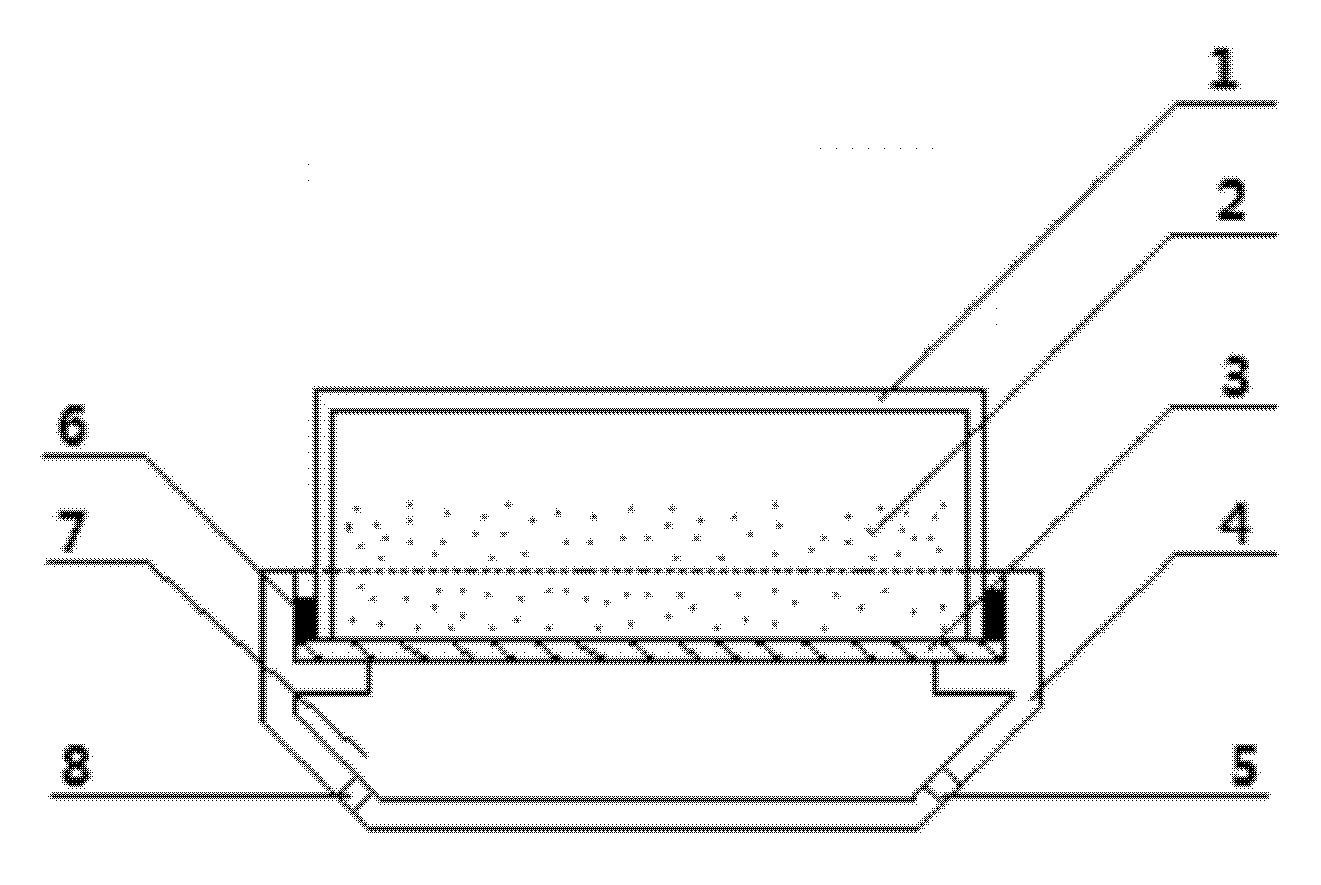
Method and device for preparing functional nanoparticle/bacterial cellulose composite membranes
The invention relates to a method and device for preparing functional nanoparticle / bacterial cellulose composite membranes by an inverted culturing method. The method comprises the steps of preparing a culture medium, carrying out activation and accessing on strains, and carrying out culturing and post-processing on bacterial cellulose membranes, wherein in the step of preparing the culture medium, functional nanoparticles are added. Inverted culturing refers to inversely place a culturing vessel on an oxygen chamber, the culturing vessel and the oxygen chamber are separated by using an oxygen permeating membrane, and a seam between the culturing vessel and the oxygen chamber is sealed. The device disclosed by the invention comprises a base and a culturing vessel, wherein the base is an open vessel with a step at the upper part thereof, the culturing vessel is inversely placed on the step of the vessel, the base and the culturing vessel are separated by using an oxygen permeating membrane, the oxygen permeating membrane and the lower part of the base form an oxygen chamber, and the lower part of the base is provided with an air outlet hole and an air inlet hole. The method and device disclosed by the invention integrate the culturing and functionalization of bacterial cellulose membranes, and are simple in operation, short in cycle and low in cost; and according to the invention, on the premise of not damaging a three-dimensional network structure in a bacterial cellulose membrane, a functionalized bacterial cellulose composite membrane which is good in functional-nanoparticle adsorption property and excellent in performance is prepared.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Novel positive electrode isolation layer applied to lithium-sulfur battery, and preparation method for novel positive electrode isolation layer
InactiveCN106450104ALower internal resistanceImprove cycle performanceCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSecondary cellsFiberLithium–sulfur battery
The invention relates to an isolation layer applied to a lithium-sulfur battery, and a preparation method for the isolation layer. According to the preparation method, metal oxide is attached to fiber surface of bacterial cellulose to be carbonized to obtain a novel positive electrode isolation layer. The isolation layer can be used between a positive electrode and a diaphragm of the lithium-sulfur battery to well suppress shuttling of polysulfide ions, and the metal oxide in the isolation layer also can adsorb the polysulfide ions; and meanwhile, the metal oxide also has certain catalytic action on the redox reaction of the lithium-sulfur battery, so that an important role in improving the cycling performance of the lithium-sulfur battery is played.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
Process for producing bacteria cellulose fibre with high degree of polymerization
InactiveCN101492837AEasy to prepareSuitable for industrial productionArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsWet spinning methodsYarnBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high polymerization degree bacterial cellulose fiber. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving the bacterial cellulose in solvent to prepare bacterial cellulose solution with mass fraction of 1-30 percent, filtering and standing the solution for deaeration, thus obtaining spinning solution; (2) forming the spinning solution in the step (1) by solidifying after the solution is sprayed through a spinneret orifice, and preparing a finished product after several conventional processes, such as stretching, washing, shaping and drying. The preparation method is simple and is applicable to industrial production; compared with other cellulose fibers, the bacterial cellulose fiber has high rupture strength and module reaching the level of high-tensile industrial yarn, and has the advantages of good biocompatibility, odegradability, hydrophilicity and binding property with rubber.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENGFENG DENGTAI BIOTECH
Nanometer bacterial cellulose\polyvinyl alcohol\polyethylene glycol porous composite hydrogel
The invention discloses a nanometer bacterial cellulose\polyvinyl alcohol\polyethylene glycol porous composite hydrogel. The porous composite hydrogel comprises nanometer bacterial cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the porous composite hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing clean bacterial cellulose by sulfuric acid to obtain a nanometer cellulose solution, carrying out neutral treatment, mixing the treated solution in a polyvinyl alcohol solution, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion until uniformity, adding a small amount of a polyethylene glycol solution, carrying out ultrasonic stirring mixing, adding the above obtained mixed solution into a glass bead template in a dropwise manner, repeatedly freeze-thawing to cross-link the obtained mixture, and drying to obtain the porous composite hydrogel. The porous composite hydrogel prepared in the invention has the advantages of low cost, mild reaction, fast speed, good biocompatibility, high mechanical strength, uniform porous structure, and wide application prospect in the fields of biomedical science and tissue engineering.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
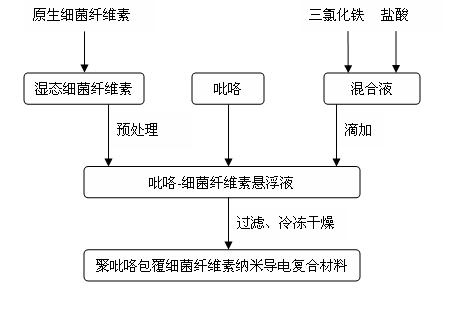
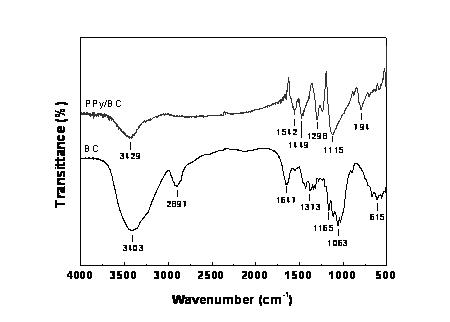
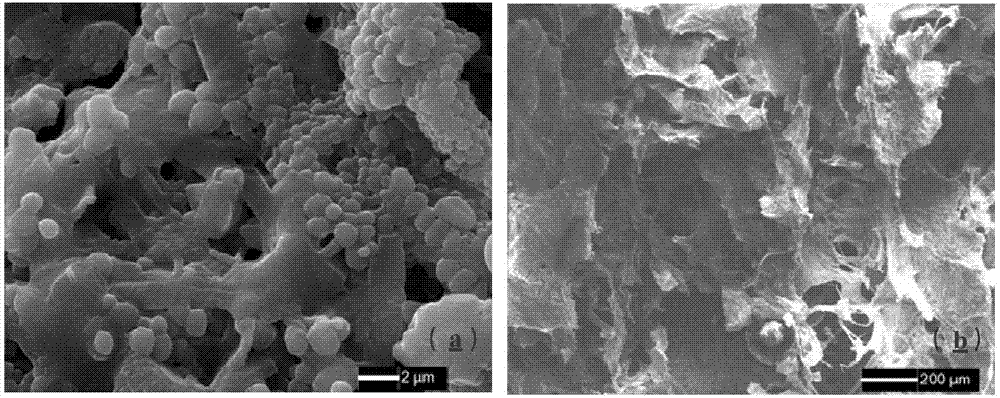
Method for preparing polypyrrole coated bacterial cellulose nanometer electric-conduction composite material by utilizing bacterial cellulose as template
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polypyrrole coated bacterial cellulose nanometer electric-conduction composite material by utilizing bacterial cellulose as a template; impurity removal is carried out on protogenetic dynamically-fermented bacterial cellulose nanometer fiber, so as to obtain moist bacterial cellulose after pretreatment; the moist bacterial cellulose is arranged in deionized water for uniform dispersion; dimethylformamide and pyrrole monomers are added and stirred to enable the pyrrole monomer to be fully dispersed into a bacterial cellulose network; and a mixed solution of oxidant and doping agent is added for carrying out in-situ oxidation polymerization, and an obtained crude product is washed by acetone (ethanol), deionized water and hydrochloric acid solution sequentially and repeatedly, and then is frozen and dried, so as to obtain a finished product. The nanometer electric-conduction composite material obtained by the invention has higher electric conduction efficiency, lower cost, mild reaction and low toxicity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing porous compound type high permeability absorption hemostasis coating with modified nano-crystalline cellulose
ActiveCN102961777AImprove water absorptionImprove water holding capacityAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous compound type high permeability absorption hemostasis coating with modified nano-crystalline cellulose, and belongs to the field of biological medical materials. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-processing bacterial cellulose by alkali water at high temperature to remove endotoxin; scattering the obtained bacterial cellulose under a high-speed bacterial pulverizer to be fine fibers; performing alkalization treatment on the fine fibers by alkali liquid with the proper concentration to activate the cellulose; adding an etherifying agent grafted modified bacterial cellulose to ensure that the fiber has a certain hemostasis function; uniformly compounding the modified bacterial cellulose with sodium alga acid to form gel network by ion crosslinking; and freezing and drying the gel network to obtain the hemostasis compound material with good performance. The porous compound material prepared by the method is a good medicine carrier, which can carry the medicines capable of resisting bacteria, stopping the pain and coagulating blood, so that the material has good medicine sustained release effect under different PH values. The porous compound material is high in biocompatibility and cell affinity, can promote proliferation and differentiation of stem cells, and facilitates rapid recovery of damaged tissues.
Owner:北京中杰瑞康科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com