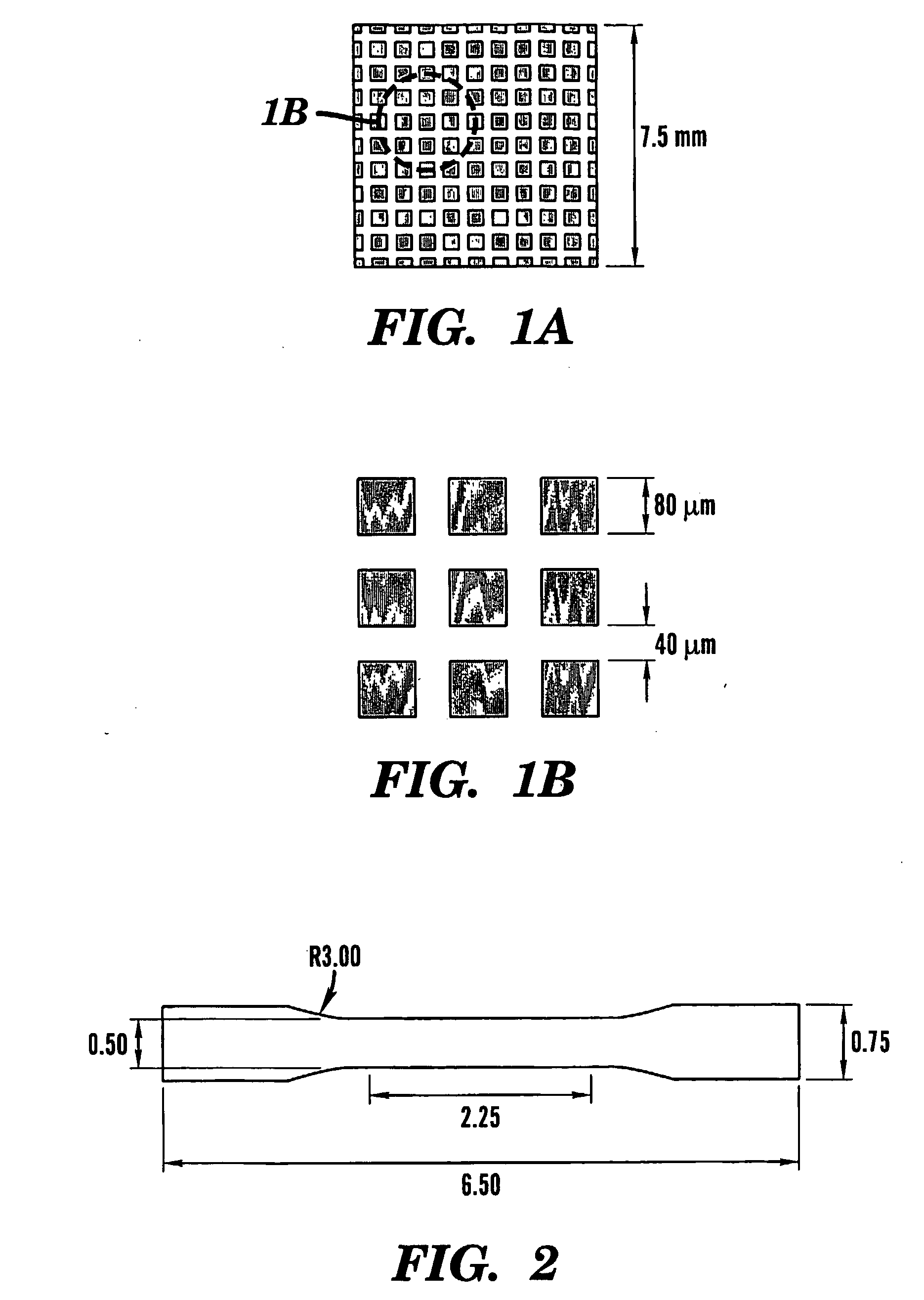
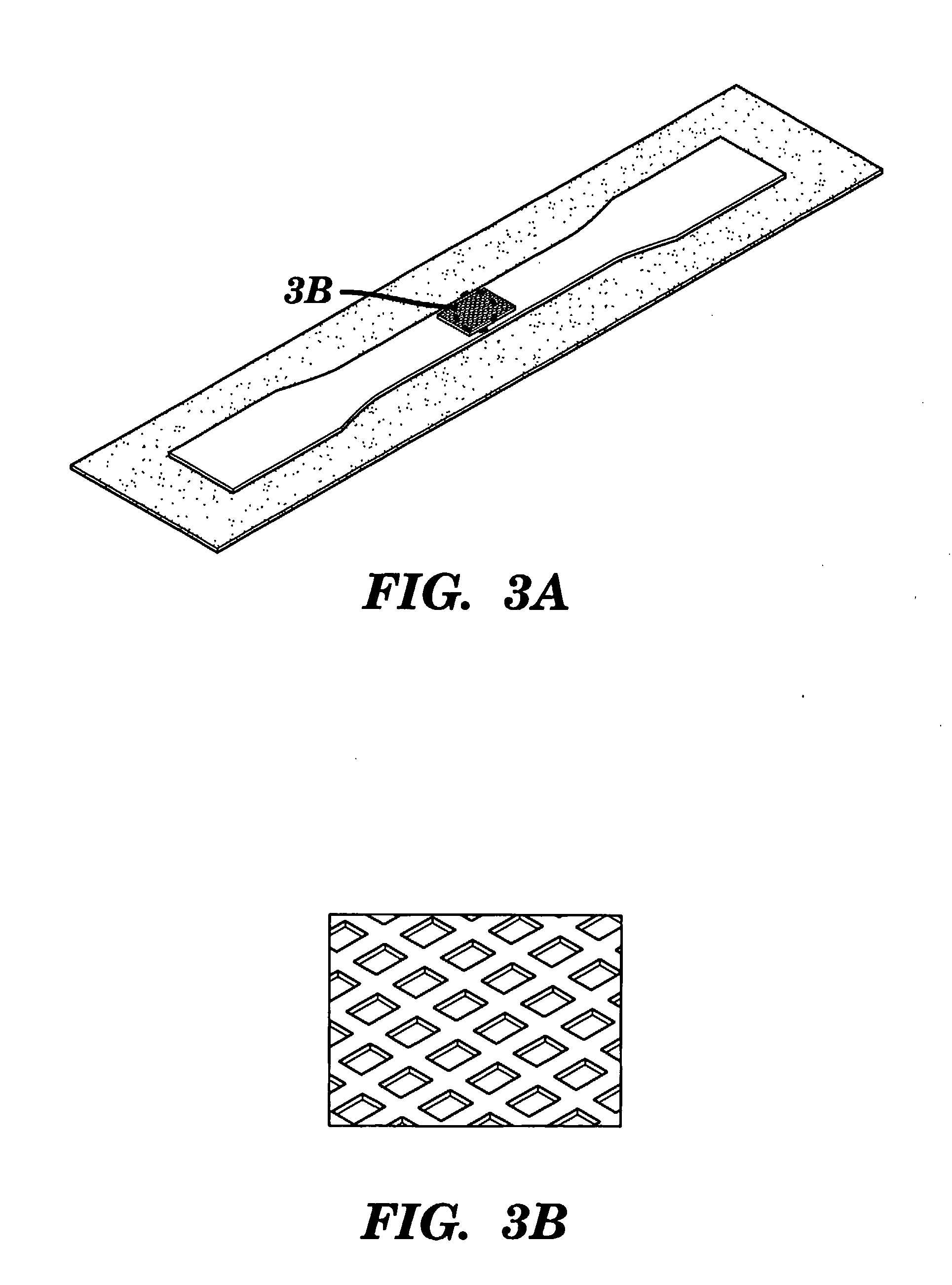
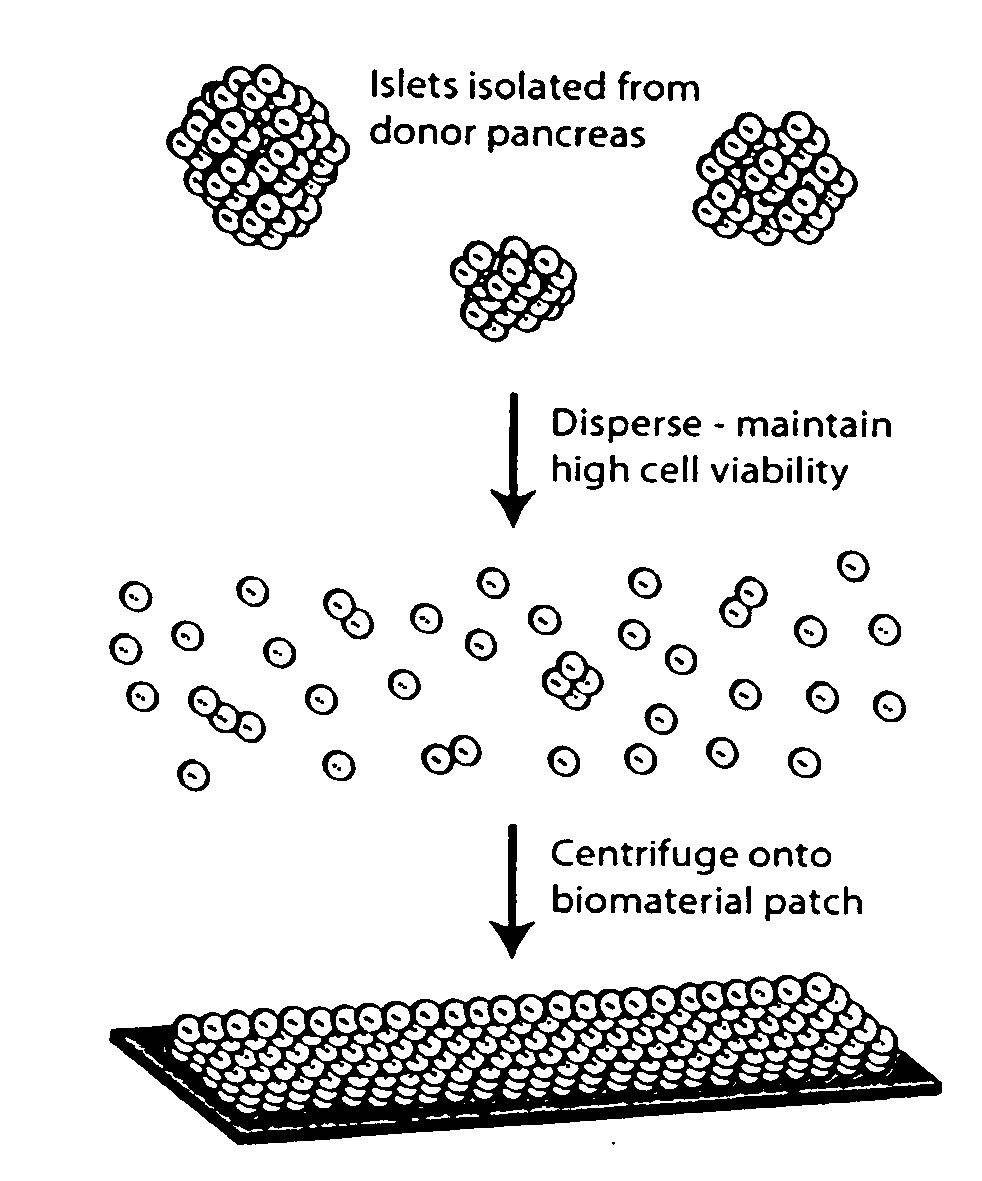
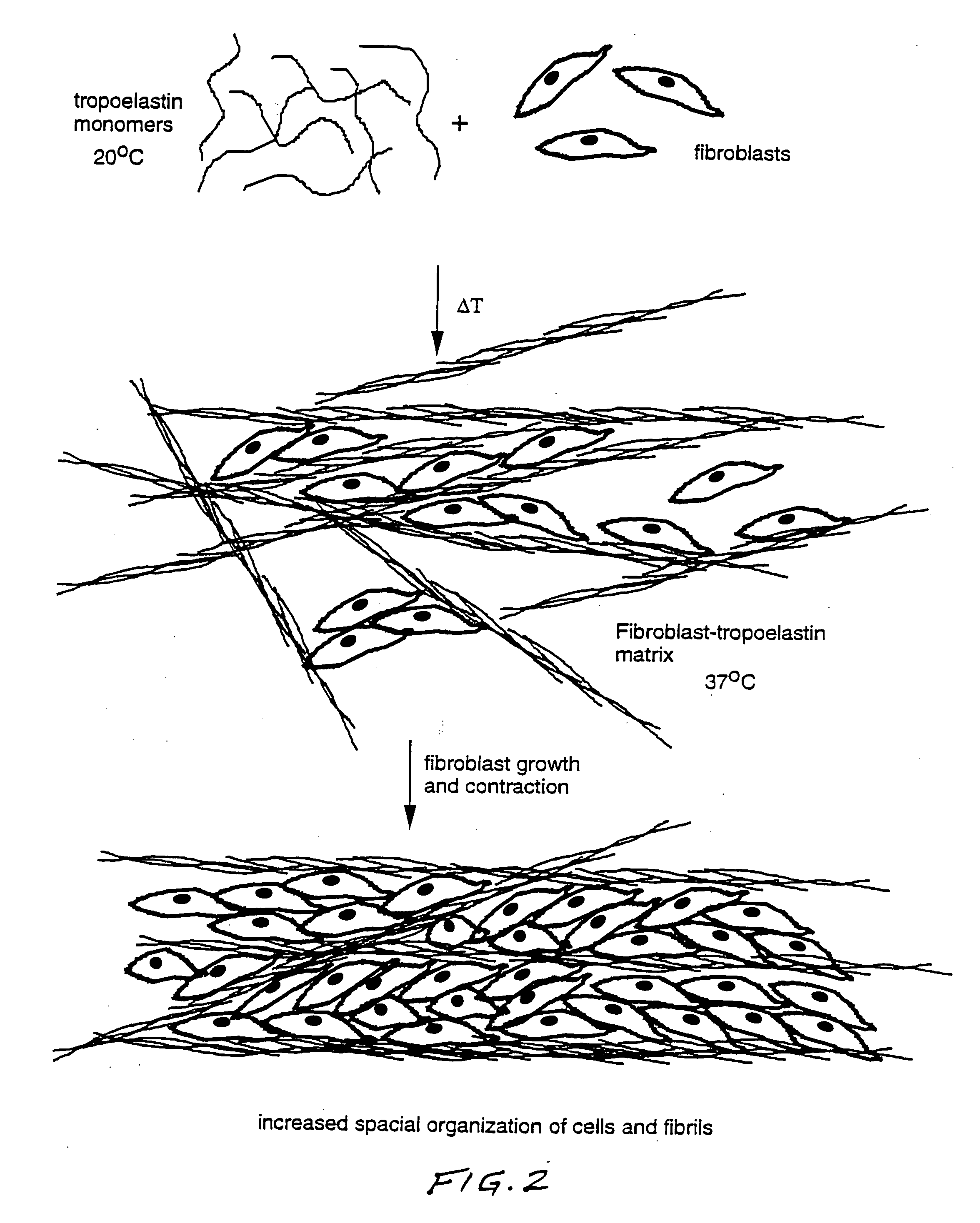
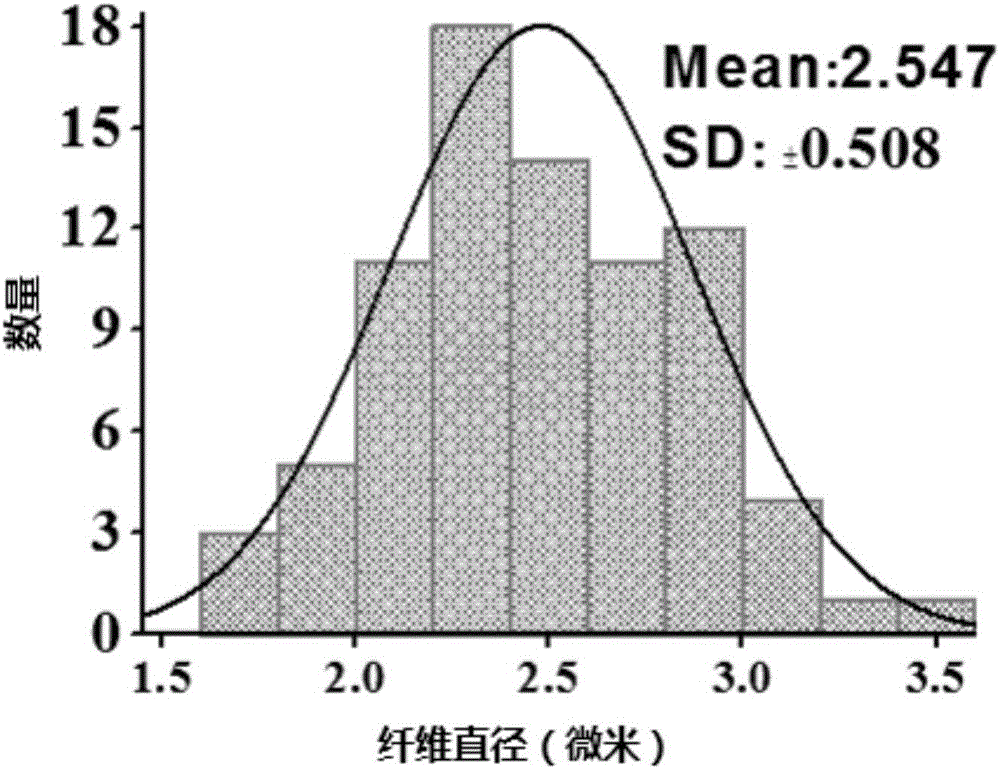
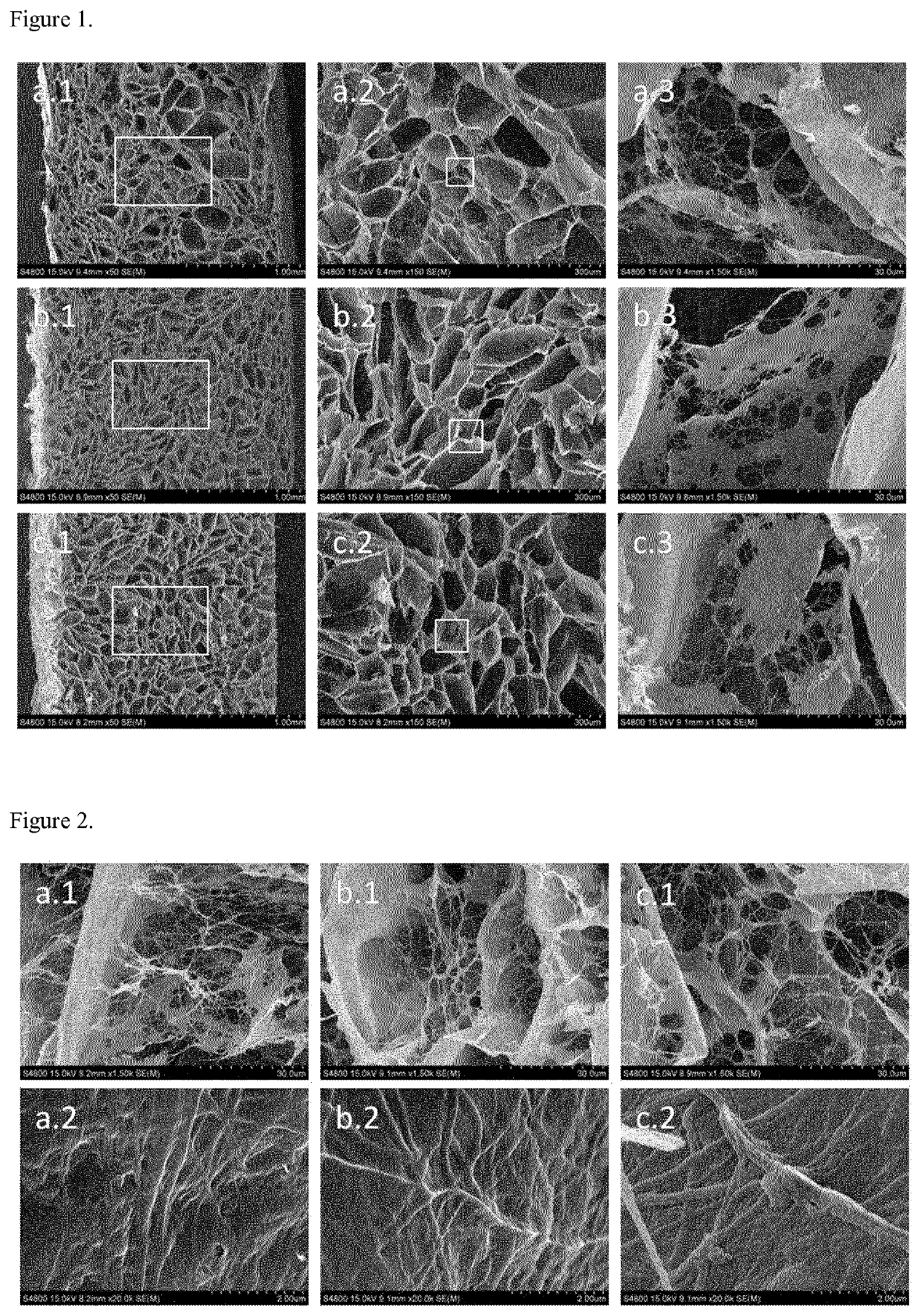
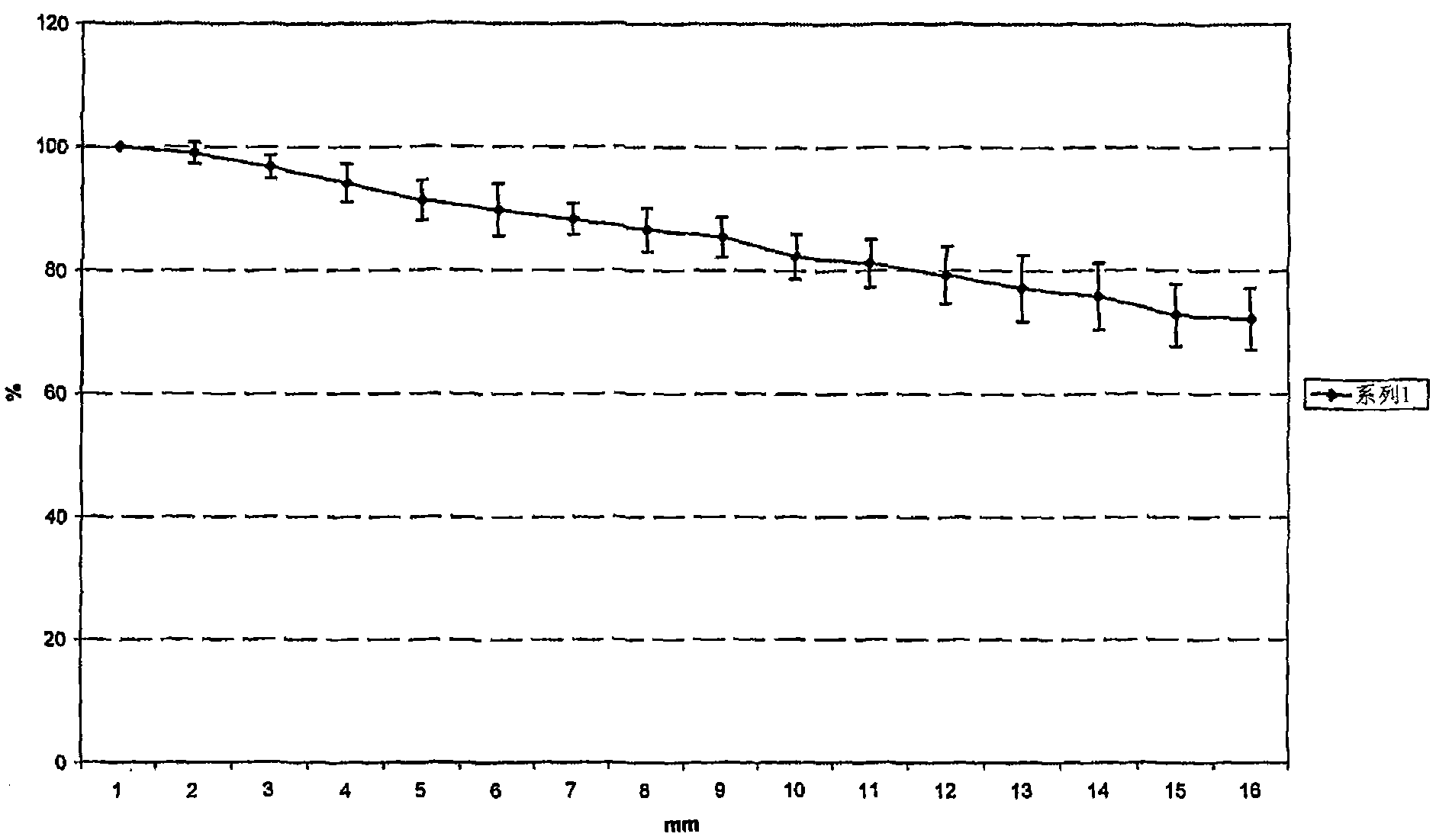
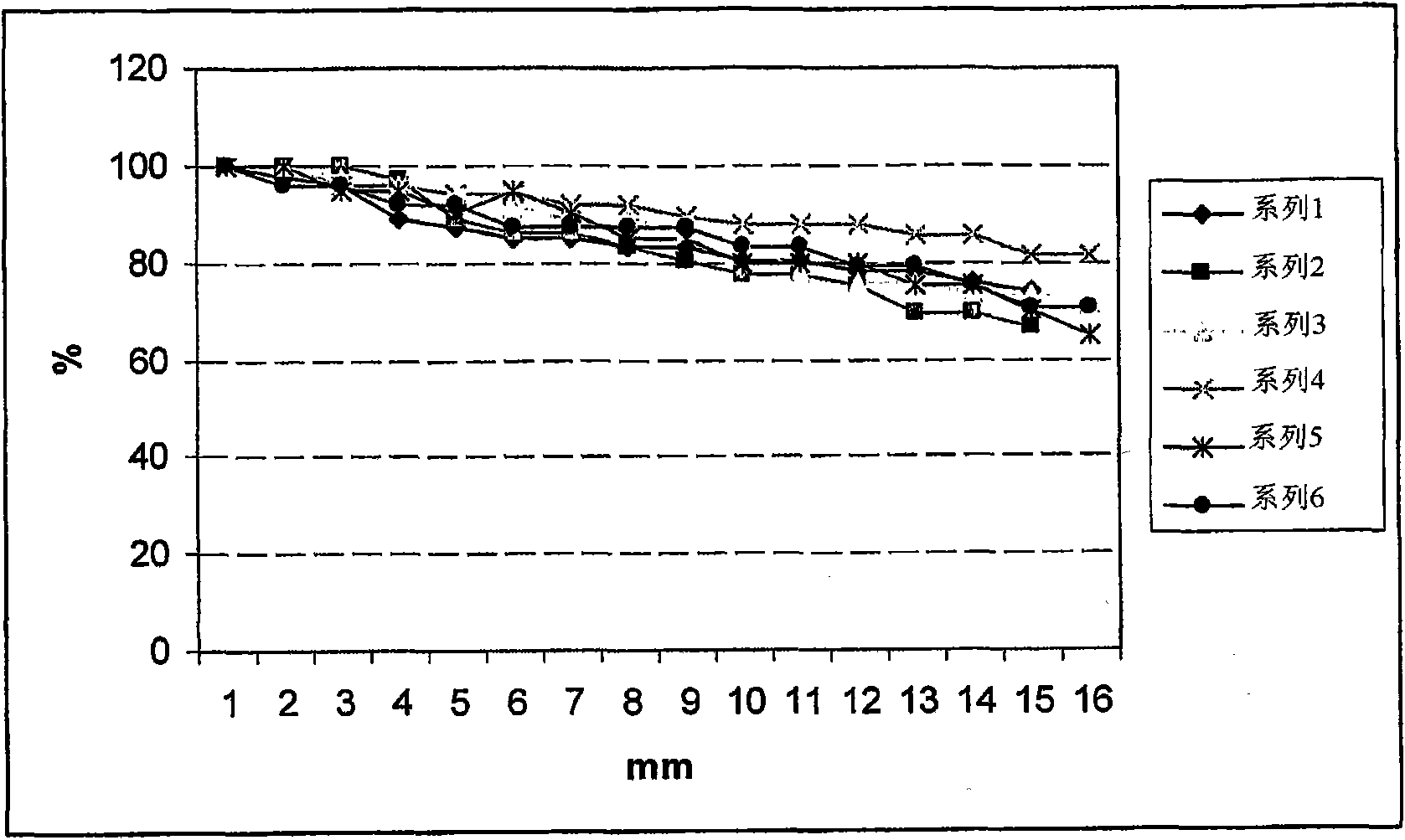
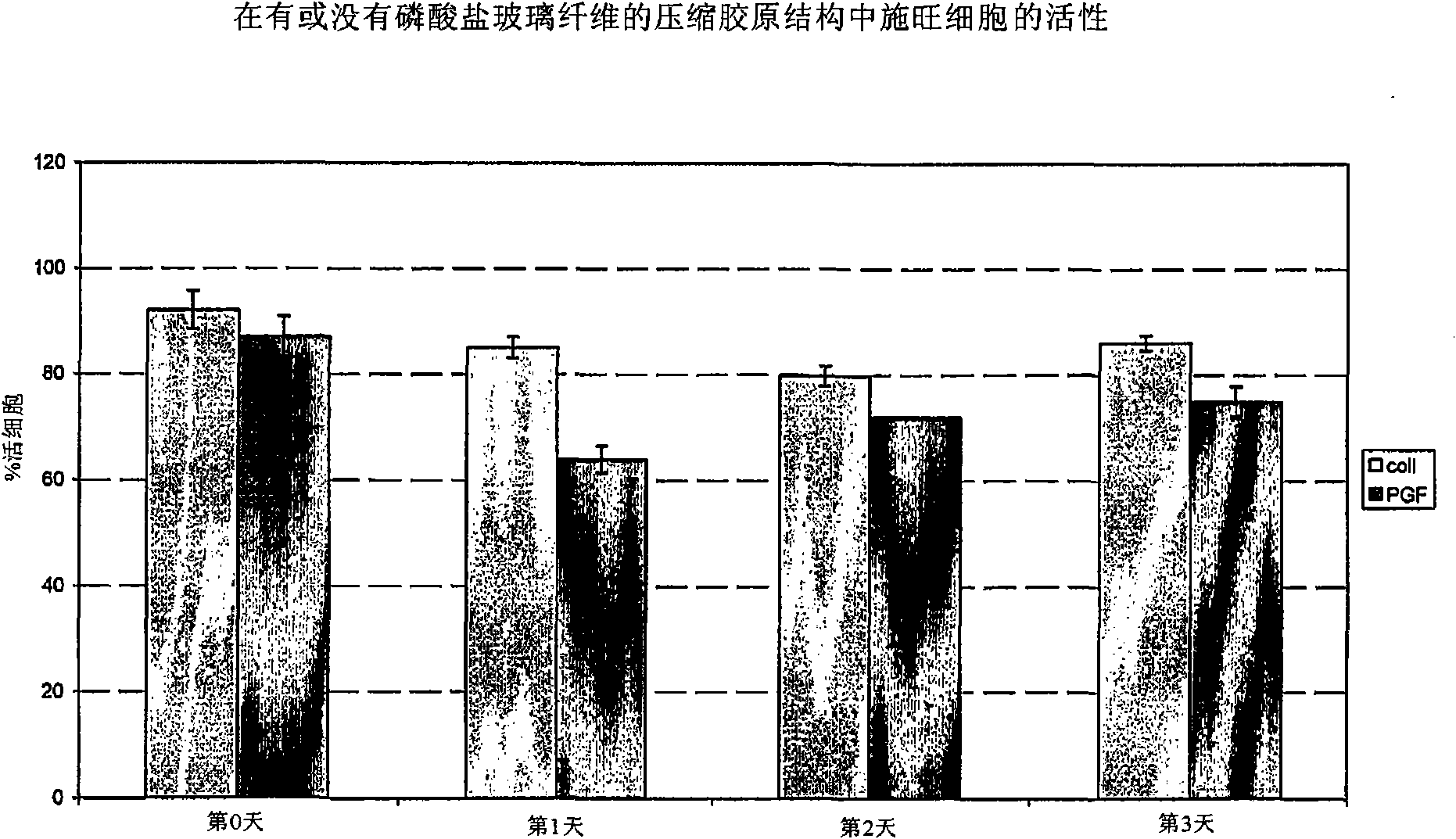
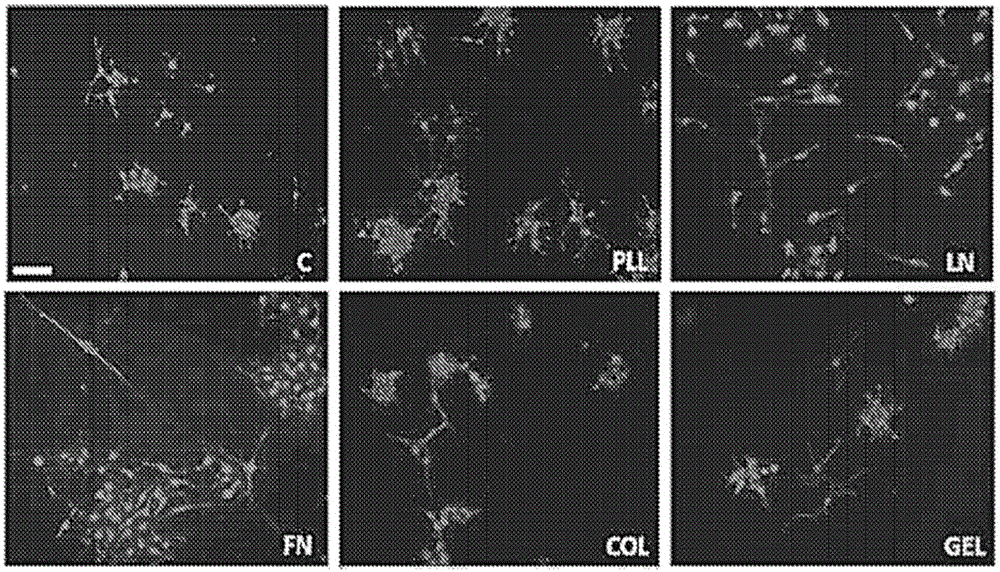
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Biomaterial scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
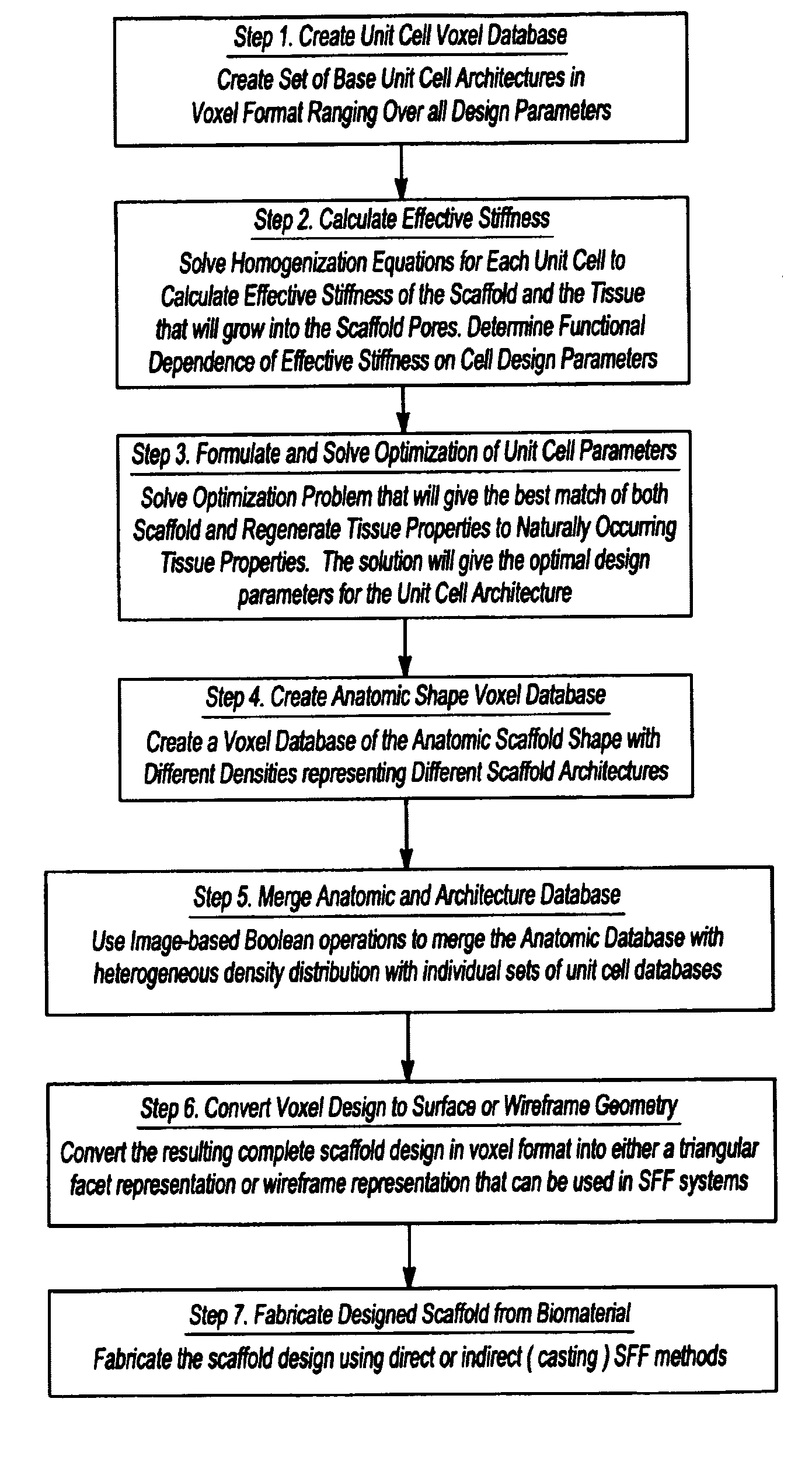
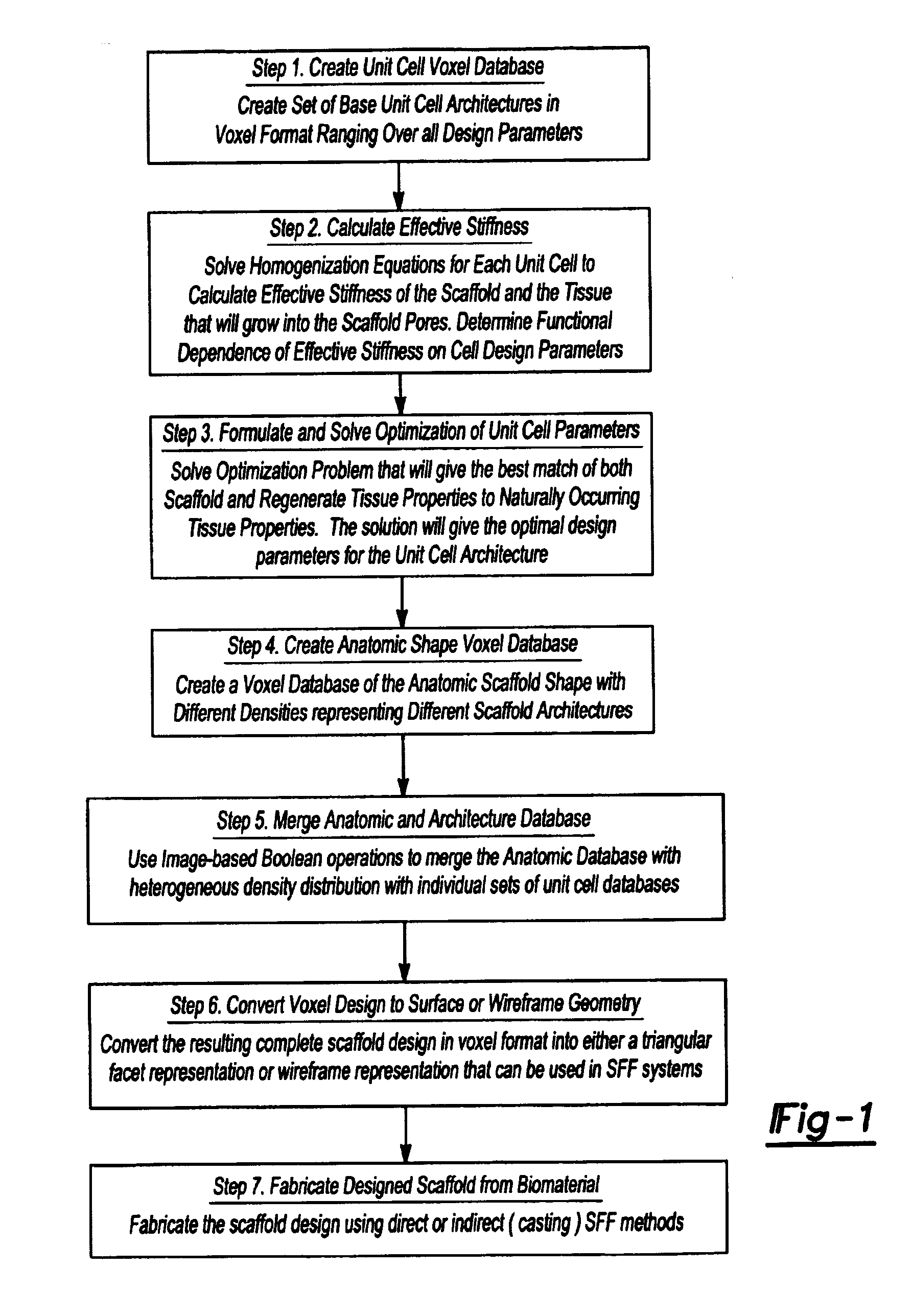
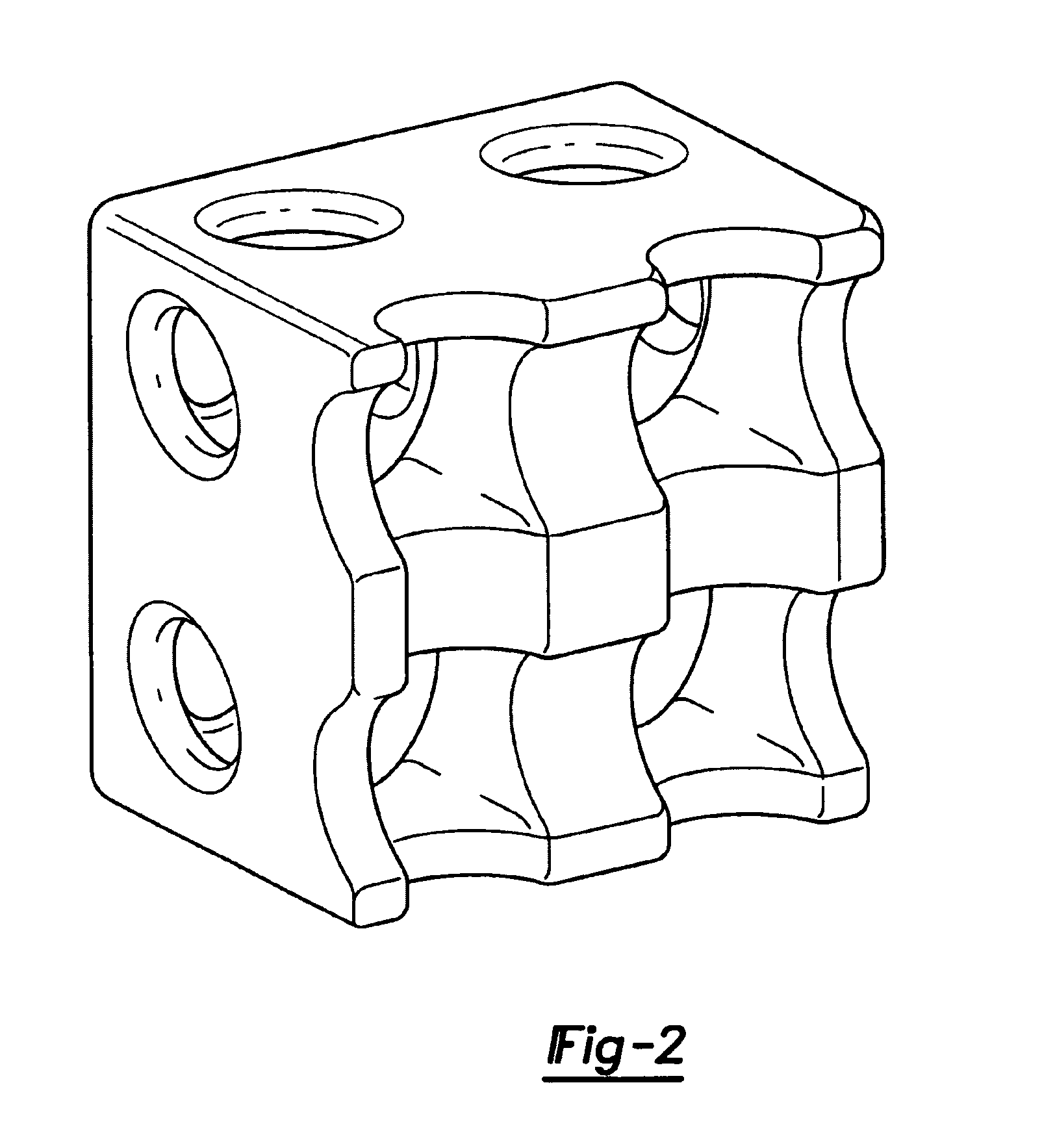
Design methodology for tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial implants
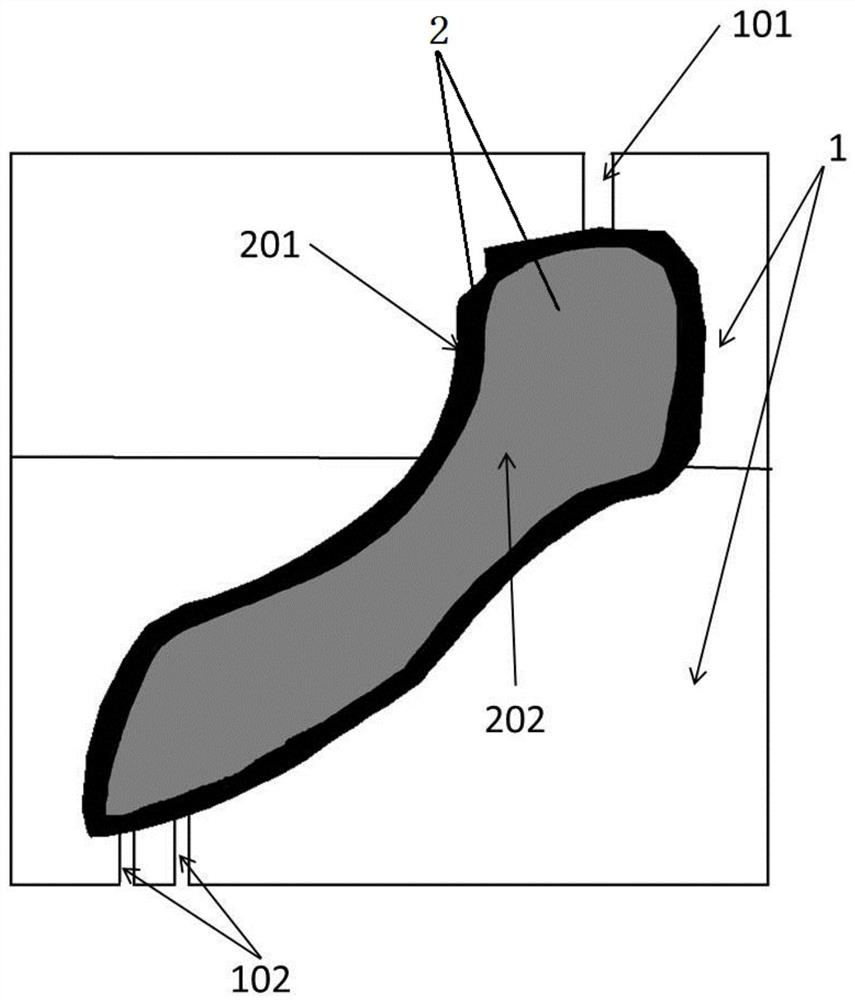
A design methodology is provided for creating biomaterial scaffolds optimized for in vivo function with any 3D anatomic shape. The method creates all designs using voxel based design techniques. It also provides for optimization of implant and scaffold microstructure to best match functional and biofactor delivery (including cells, genes and proteins) requirements. The voxel based design techniques readily allow combination of any scaffold or implant microstructure database with any complex 3D anatomic shape created by CT or MRI scanners. These designs can be readily converted to formats for layered manufacturing or casting.
Owner:HOLLISTER SCOTT J +2
Method for Producing Biomaterial Scaffolds
InactiveUS20080280360A1Cell culture supports/coatingGeneral culture methodsBiomaterial scaffoldMammalian cell
The present invention provides a multilayer scaffold for tissue engineering. The scaffold comprises at least a first layer comprised of a polymer having a pattern of microchannels therein; and at least a second layer comprised of a polymer having a pattern of microchannels therein. The first and second layers are joined together (preferably by lamination) and the channels are connected for the circulation of fluid through the layers. The scaffold is coated with bacterial cellulose. The scaffold may further include a mammalian cell.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Templated islet cells and small islet cell clusters for diabetes treatment
InactiveUS20080103606A1Improve survivabilityGood adhesionCell dissociation methodsPancreatic cellsIslet cellsBiomaterial scaffold
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF +1
Method for using tropoelastin and for producing tropoelastin biomaterials
It is a general object of the invention to provide a method of effecting repair or replacement or supporting a section of a body tissue using tropoelastin, preferably crosslinked tropoelastin and specifically to provide a tropoelastin biomaterial suitable for use as a stent, for example, a vascular stent, or as conduit replacement, as an artery, vein or a ureter replacement. The tropoelastin biomaterial itself can also be used as a stent or conduit covering or coating or lining.
Owner:BAROFSKY ANDREW D +1
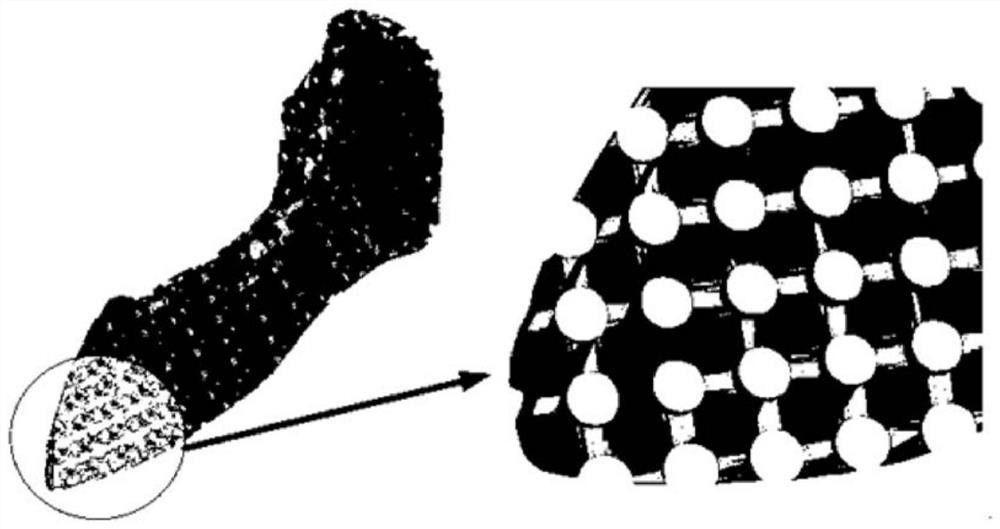
Manufacture method of tissue engineering bracket with both internal microstructure and individualized appearance
The invention relates to a manufacture method of a tissue engineering bracket with both an internal microstructure and an individualized appearance. The manufacture method comprises the following steps of: (1) designing the negative shape of a bracket structure; (2) printing the negative shape of the porous-structure bracket by a three-dimensional paraffin type printer; (3) uniformly mixing a biological material with self-solidifying property or hot coagulation property into slurry shape with a solution such as normal saline, pouring the slurry into holes of the negative shape of the porous-structure bracket, cooling and solidifying, and scraping off the redundant biological material from the surface of the bracket; and (4) heating the poured negative shape of the bracket into a heating furnace till the temperature of the negative shape is higher than the temperature of the melting point of the paraffin shape of the bracket, preserving the temperature for 1-5 minutes till paraffin is melted and disappears and the biological material is solidified to obtain the biological material bracket, and washing the biological material bracket with normal saline so as to obtain the tissue engineering bracket with both the internal microstructure and the individualized appearance. The manufacture method has wider adaptability to biological materials and internal microstructure controllability and can be used for manufacturing the tissue engineering bracket with the internal microstructure and the individualized appearance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Layered manufacturing method of three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold
InactiveCN102488569AIncrease profitSolving Manufacturing ChallengesDialysis systemsProsthesisFreeze-dryingSilica gel
A layered manufacturing method of a three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold comprises the following steps: simulating the microstructure of a real organ, manufacturing a resin die with a microfluidic structure copying a blood vessel system, copying a negative mode of the microfluidic structure with silicon rubber, filling the negative mode with solution of biological materials, moving the silicon rubber die upwards to enable the solution of biological materials to be contacted with an ultra-low temperature flat plate vertically, moving the silicon rubber die downwards to realize demolding of the frozen structure of the biological materials after solidification of solution of the biological materials, realizing precision interlayer orientation as well as freezing, condensation and forming of the three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold by repeatedly performing filling of the solution of biological materials and moving up and down of the silicon rubber die, obtaining the three-dimensional frozen structure of the biological materials, and vacuum freeze drying the ultra-low temperature flat plate and the three-dimensional frozen structure of the biological materials, and finally obtaining the scaffold of the biological materials with a three-dimensional microfluidic system and an oriented porous structure. The layered manufacturing method has the advantage of forming a three-dimensional organ scaffold with a complex space microfluidic system and the oriented porous structure directly.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
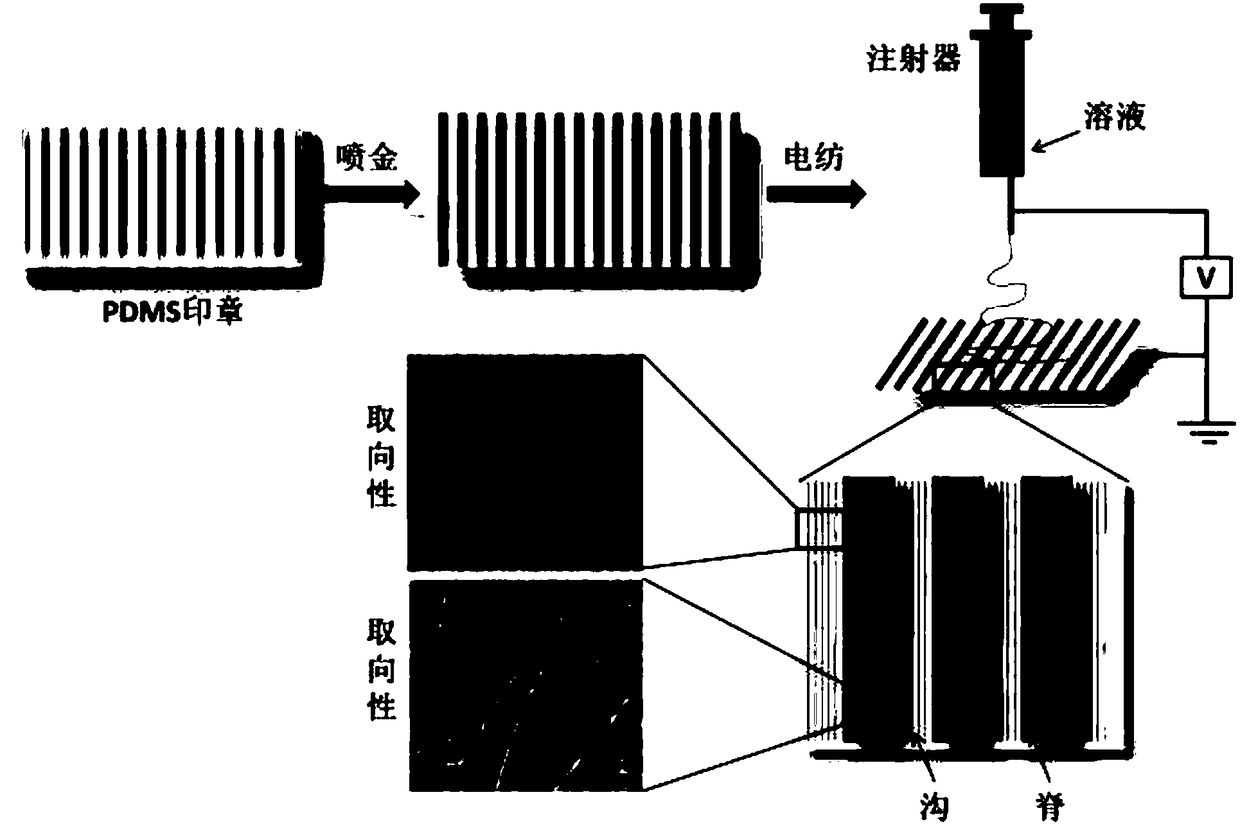
Preparation method for tissue engineering transplant with micro-nano topological geometry structure on surface
InactiveCN108525013ADoes not affect the basic shapeImprove adhesionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCatheterMicro nanoElectrospinning
A preparation method for a tissue engineering transplant with a micro-nano topological geometry structure on the surface includes 1), preparing a silicone rubber seal with a micro-nano topological (three-dimensional) geometry structure pattern on the surface according to a micro molding method; 2), spraying a metal conducting nano-coating with the thickness of 50-100nm on the surface of the silicone rubber seal according to an ion sputtering method; 3), electrically spinning a natural or composite biological material solution onto the surface of the PDMS seal by an electrospinning technique toform a biological material support; 4), separating the spun biological material support from the PDMS seal to obtain the tissue engineering transplant with the micro-nano topological geometry structure on the surface. The preparation method has the advantages that the micro molding technology and the electrospinning technique are applied jointly, the spun biological material support is separatedfrom the PDMS seal easily, and the preparation method is simple and easy to operate and suitable for mass production.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
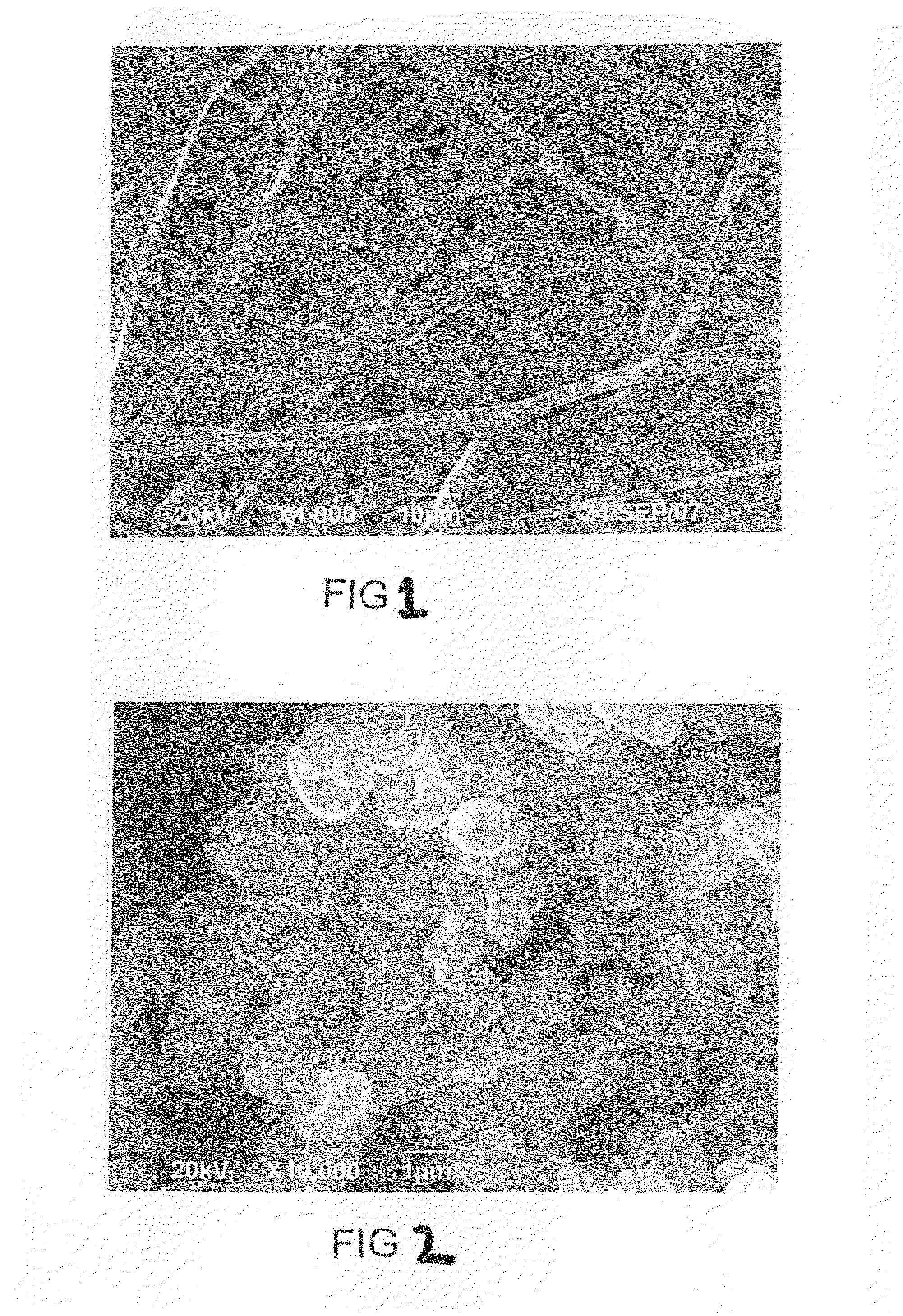
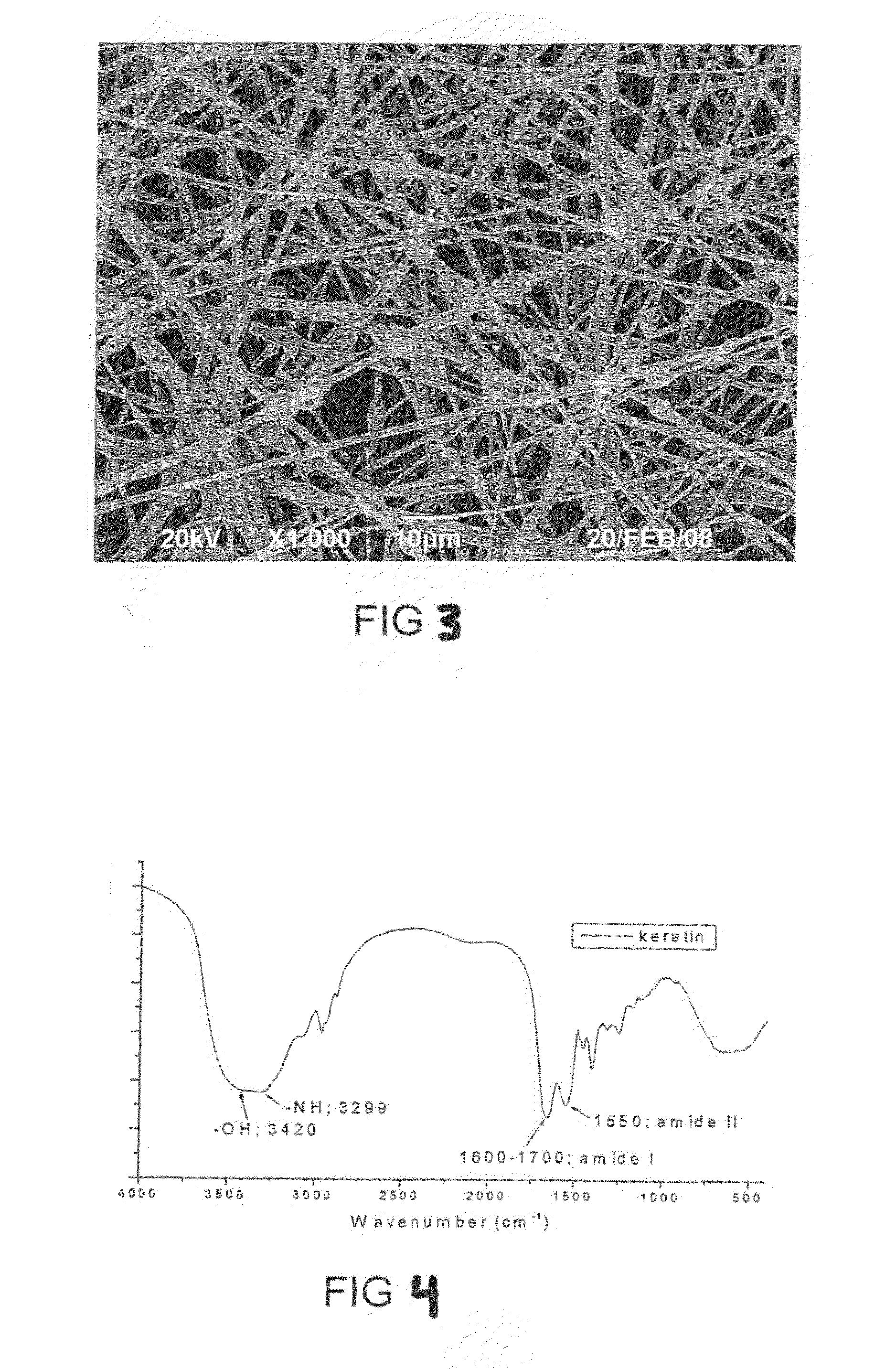
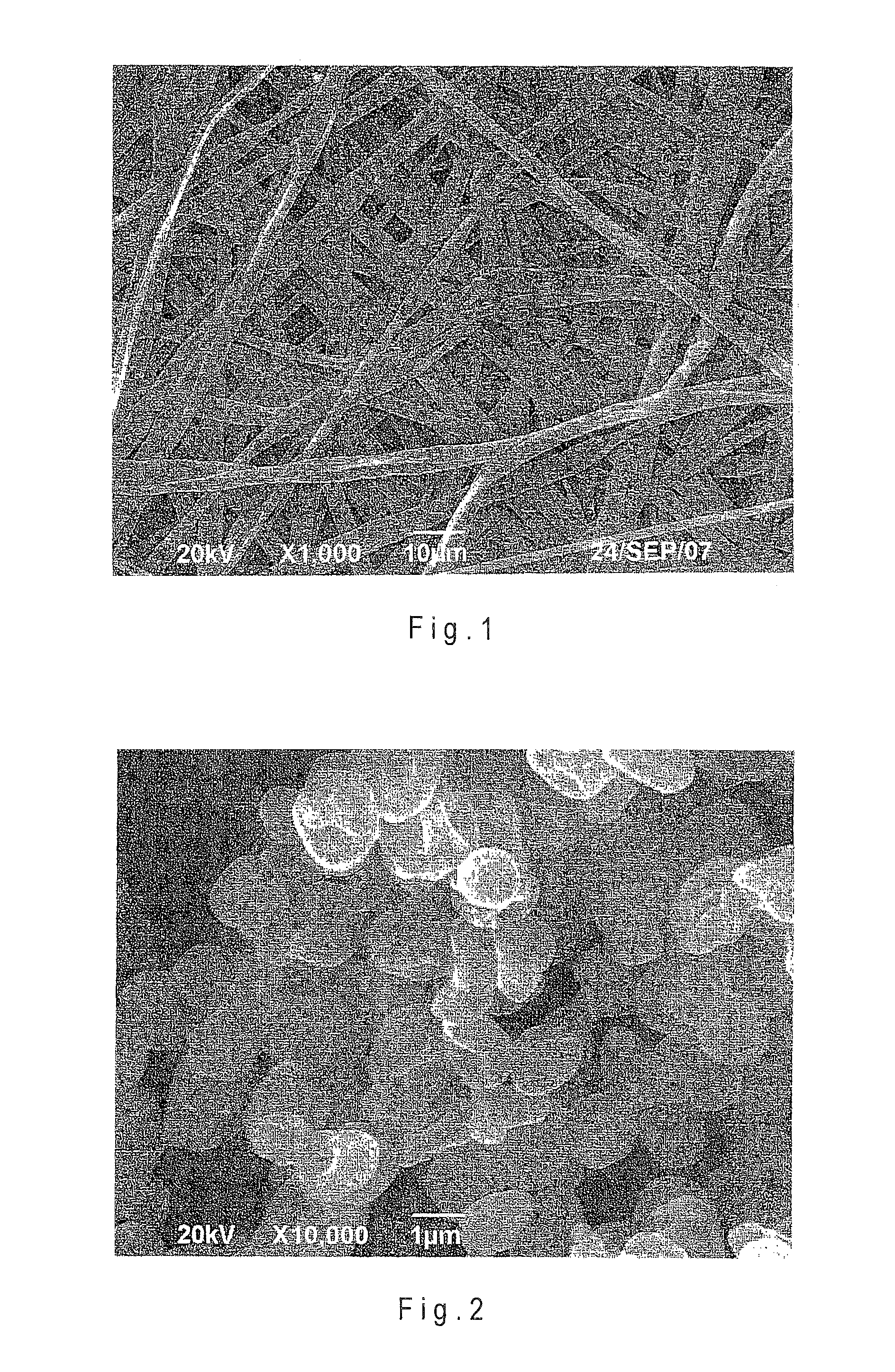
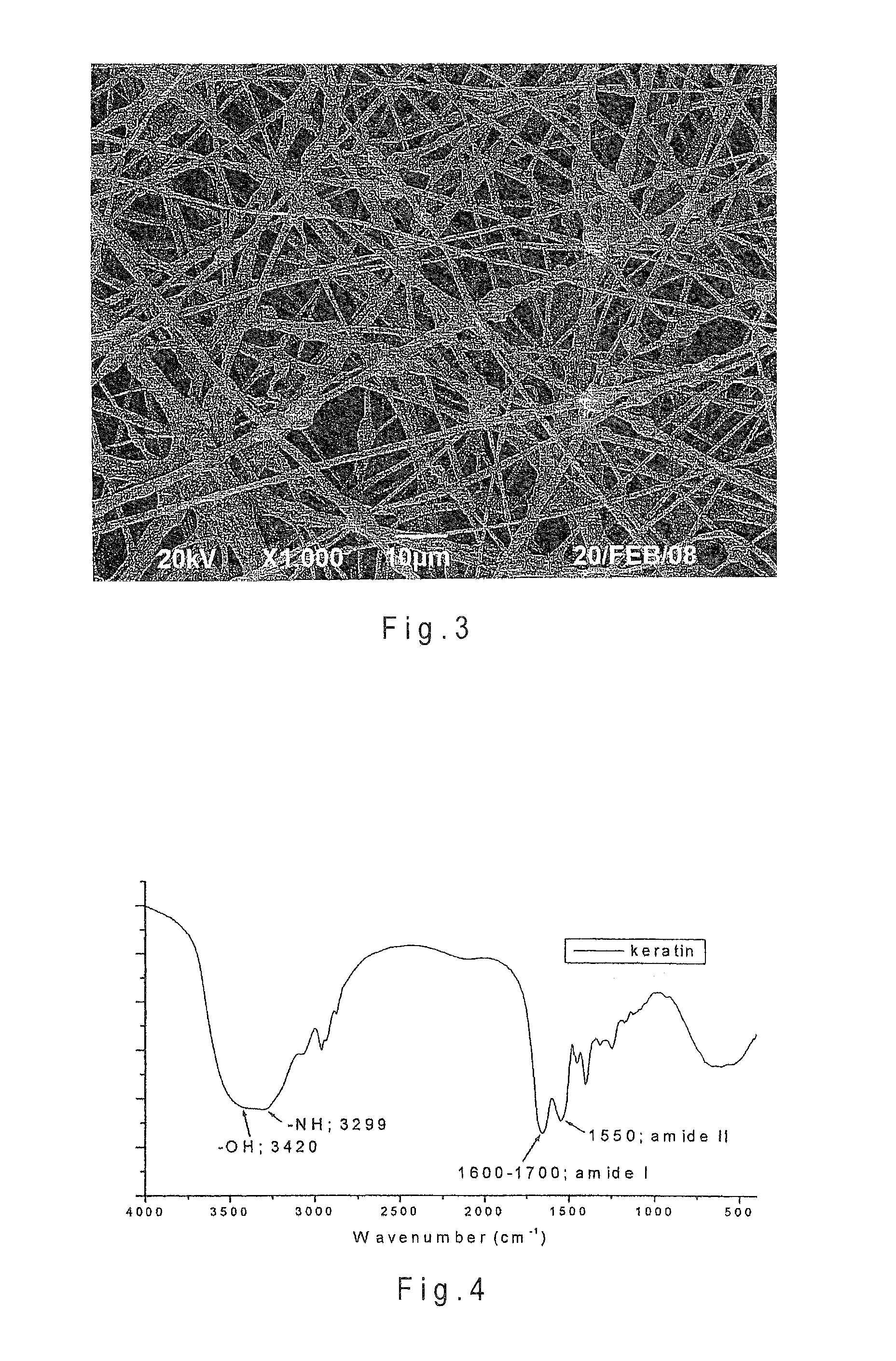
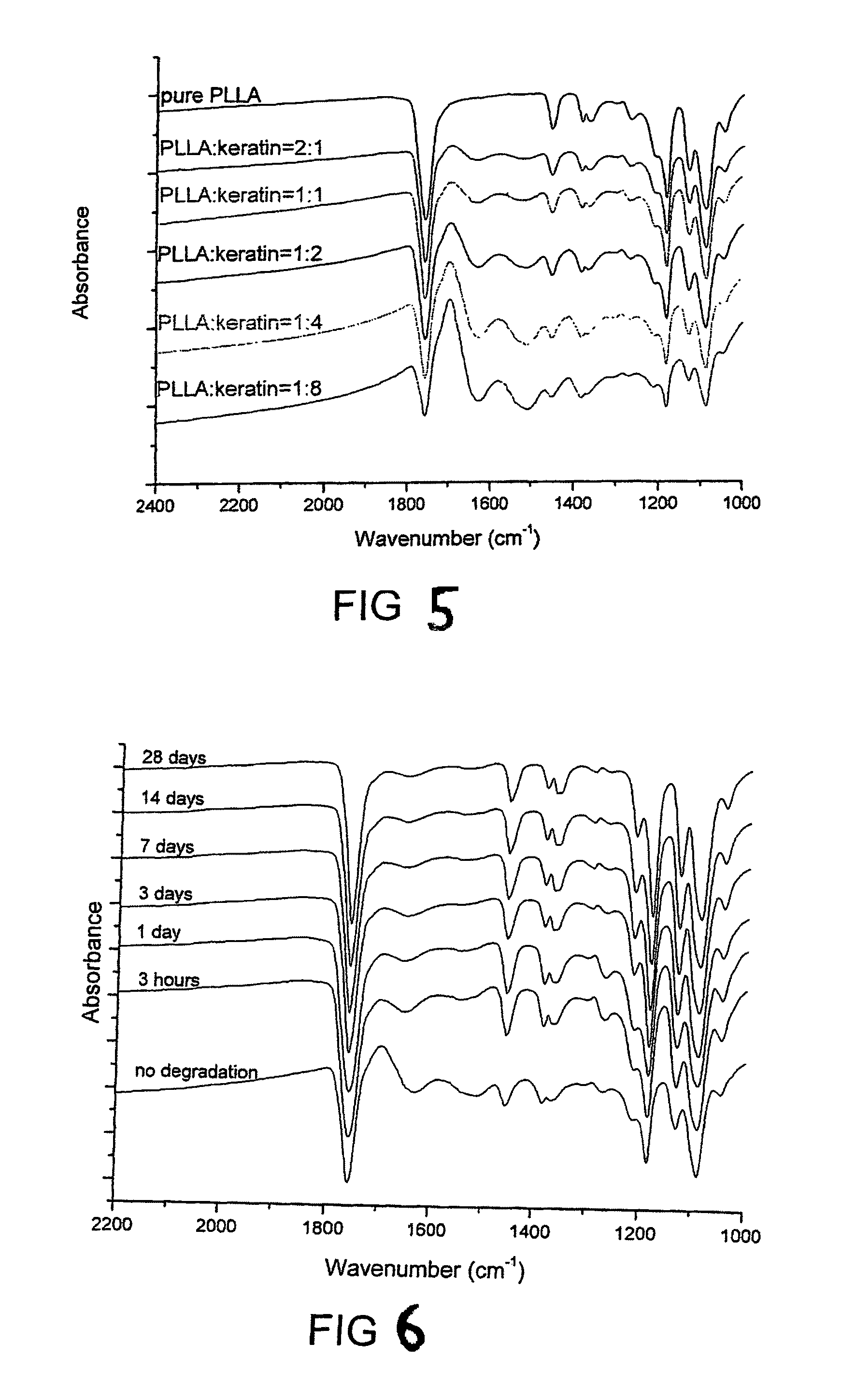
Biodegradable and bioabsorbable biomaterials and keratin fibrous articles for medical applications
ActiveUS20100009448A1Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberBiomaterial scaffold
The present invention relates to a process of making biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable biomaterials and keratin nonwoven fibrous articles by electrospinning fibers from a blend of biomaterials and keratin dissolved in organic solvents includes generating a high voltage electric field between oppositely charged biomaterials and keratin fluid in a syringe with a capillary tip and a metallic collection roller and causing a jet to flow to the roller as solvent evaporates and collecting fibrous membranes or scaffolds on the roller. Keratin increased the cell affinity of biomaterial scaffolds which have potential medical applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Application of adipose-derived stem cells in biological tissue repair
InactiveCN108324989AEasy to obtainPromote repairTissue regenerationProsthesisBiomaterial scaffoldOrganism
The invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering, and concretely discloses an application of adipose-derived stem cells in biological tissue repair. By using adipose-derived stem cells after induced differentiation at a three-dimensional biomaterial scaffold for proliferation, healing of injured skin can be accelerated, the healing time is shortened, a wound is flattened, skin wrinkle canbe reduced, a purpose of beautifying and healing the skin can be achieved, a better healing condition is provided for skin growth and recovery, and a reference is provided for stem cells used for clinical treatment of skin wound.
Owner:广州万智农业科技有限公司
Method for increasing ceramic analog biological rack mechanical strength
The invention relates to reinforce mechanical strength of biomaterial frame with surface finish method, which comprises: (1) dipping the frame into gelatine solution or chitose solution or their mixed solution; (2) taking out to dry in drying cabinet for 1-2h at 50~80Deg; (3) using EDC or glutaral solution for crosslinking reaction; (4) cleaning; (5) drying in baking oven at 40Deg to obtain the product. Compared with prior art, this invention increases the frame strength 6~12 times to 4-6MPa and fits to application in clinic and research.
Owner:丁建明
Full-implanted artificial corneal stroma and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101584883AThe number does not decreaseSufficient sourceEye implantsHuman bodyBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical engineering, in particular to a novel full-implanted artificial corneal stroma and a preparation method thereof. The artificial corneal stroma uses free isolated adipose-derived stem cells as seed cells which are inoculated in polylactic acid polyglycolic acid copolymer scaffold materials and can absorb nourishment and excrete waste in a three-dimensional space formed by biomaterial scaffolds, and the suitable scaffold materials not only can maintain the positions and the forms of the seed cells, but also can participate the adjustment and the control of cell differentiation states. Proved by animal experiments, the corneal stroma has favorable biocompatibility, avoids the toxic reaction and the induced exclusive reaction of a traditional corneal stroma to a human body, and can be fully degraded over time after being implanted so that the cornea can recover the transparency, thereby satisfying the requirement of the human body to the vision.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
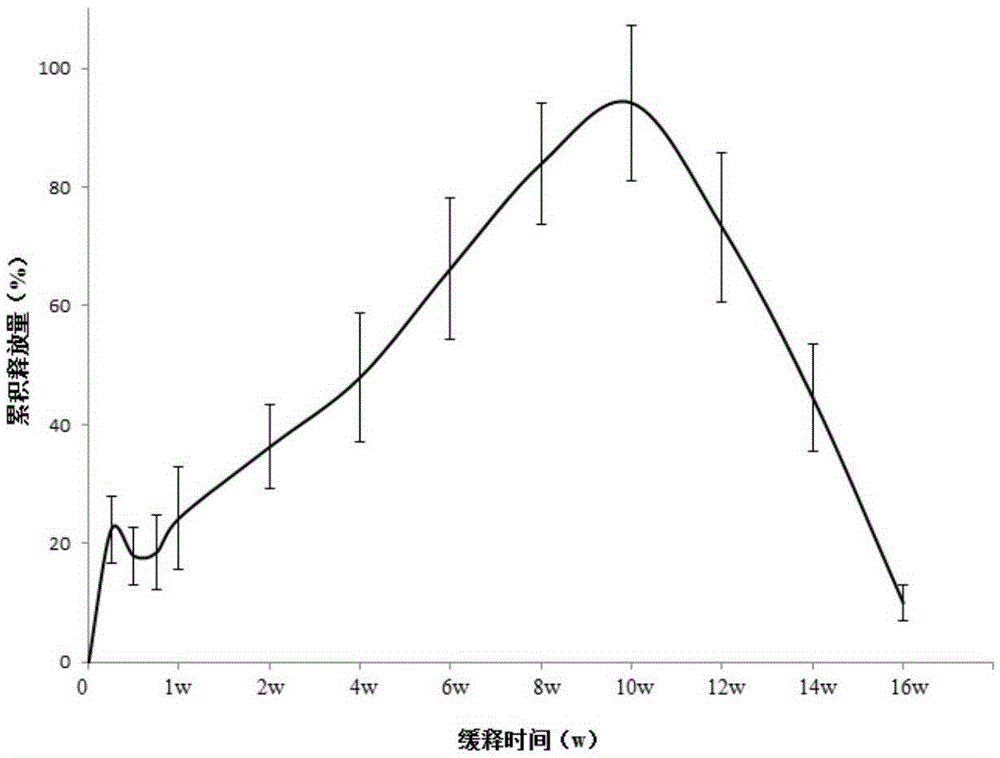
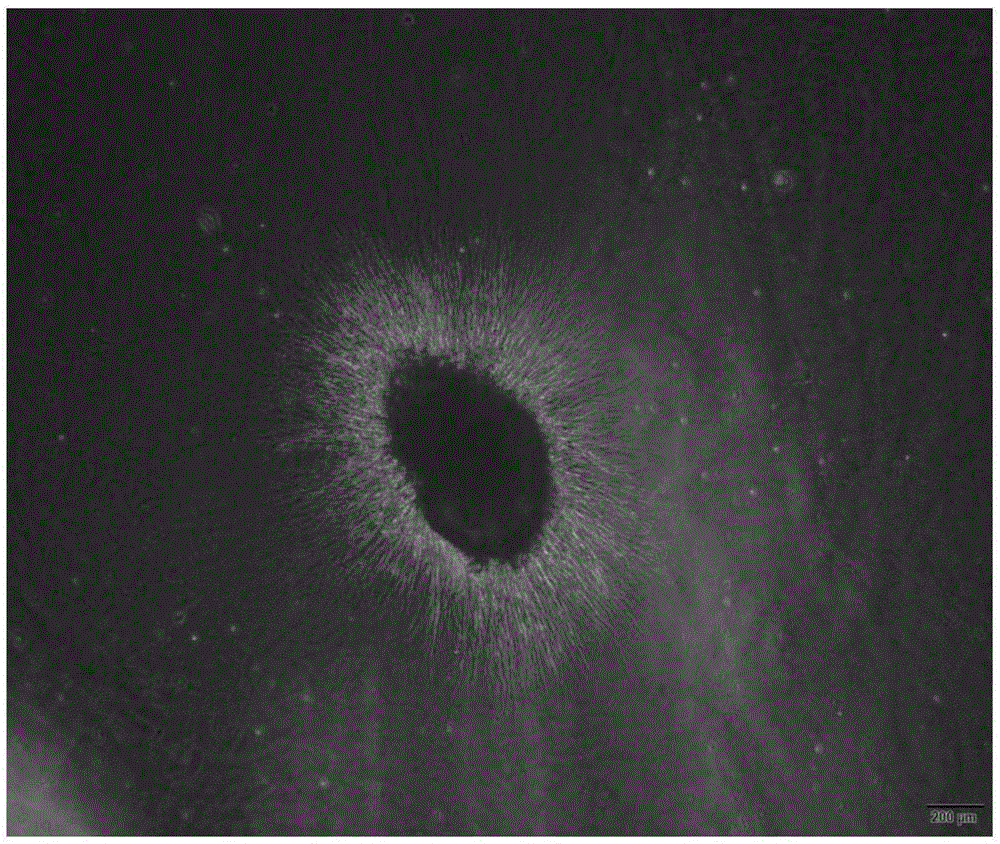
Preparation method of slow-release polypeptide growth factor biological material scaffold
The invention discloses a preparation method of a slow-release polypeptide growth factor biological material scaffold. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing a biological material, a polypeptide growth factor and water for reaction to ensure that the biological material is swollen and the water exists in the biological material in three forms namely combined water, intermediate state water and free water, thereby obtaining a blending system; (2) performing freezing treatment on the blending system to obtain a frozen product; and (3) performing unfreezing treatment on the frozen product to obtain a biological material scaffold releasing the polypeptide growth factor. The slow-release polypeptide growth factor biological material scaffold prepared by the method disclosed by the invention can provide a supporting effect for the polypeptide growth factor to ensure that the polypeptide growth factor is released slowly in a long time, so that while the bioactivity of the polypeptide growth factor is ensured to the utmost extent, a long-time polypeptide growth factor slow release can be provided, thereby providing the polypeptide growth factor required by growth in a whole regeneration process for defective tissues.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A biomaterial scaffold for regenerating the oral mucosa
ActiveUS20170340771A1High strengthEasy to handleDigestive systemAntiinfectivesFreeze thawingMouth mucosa
The present invention refers to a process for preparing a biomaterial scaffold said method comprising, (a) providing a hydrogel comprising a fibrin network and a polysaccharide network; (b) subjecting the hydrogel of step a) to a freeze-thawing process to physically crosslink the hydrogel; and (c) subjecting the physically cross-linked hydrogel obtained after conducting the step b), to a lyophilization. The invention also relates to the biomaterial scaffold obtainable by the process as defined above, as well said biomaterial scaffold for its use to partially or completely increase, restore or replace the functional activity of a diseased or damaged oral mucosa.
Owner:HISTOCELL SL
Preparation method of monoclonal antibody coating biology stand
The invention relates to a method for preparing a monoclonal antibody coating biomaterial scaffold. By adopting the method of electrostatic coating or anodic polarization, a bracket body is taken as an anode, an antibody ion with negative electricity is moved to the anode under the action of the electric field force, and is evenly coated on the surface of a biomaterial scaffold. In the method, extra drug elusion coating is not required to be prepared, no obvious interface exists, a layer of antibodies can be coated on the overall or partial surface of the bracket under the action of the static electricity, the stability of the coated antibody amount is good, the antibodies are not easy to be eluted, the usage is safe, the method is applicable to the industrial mass production, the operation is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Recombinant adipose-derived stem cell for overexpression of Hpgds and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111549000AEasy to changeReduce in quantityPeptidesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsImmunomodulationsBiochemistry
The invention provides a recombinant adipose-derived stem cell over-expressing an Hpgds gene and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineeringmedicines. The recombinant adipose-derived stem cell is obtained by infecting an adipose-derived stem cell with a lentiviral vector expressing the Hpgds gene. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: constructing a lentiviral vector for expressing the Hpgds gene; extracting adipose-derived stem cells; and infecting the adipose-derived stem cells with the lentiviral vector expressing the Hpgds gene to obtain recombinant adipose-derived stem cells. The recombinant adipose-derived stem cells proliferate on a three-dimensional biomaterial scaffold, and can safely and durably express the immunomodulatory gene Hpgds so as to accelerate healing of diabetic damaged skin and shorten the healing time.
Owner:PLASTIC SURGERY HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Tissue engineering skin containing muscle cell and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a tissue engineering skin with myocyte and the preparation method of the tissue engineering skin. The invention has the characteristics that the prepared skin is made from the myocyte, skin fibroblast, skin epithelial cell and biomaterial scaffold; the invention is the tissue engineering skin with active myocyte, which is formed by compounding the myocyte with the skin fibroblast at the inside the biomaterial scaffold and planting the epithelial cell on the surface of the biomaterial scaffold. The prepared tissue engineering skin with myocyte is similar as the skin of human body and has the advantages of increasing the skin elasticity and mechanical performance, preventing body fluid flowing away, protecting the wound surface, promoting the wound surface healing and resisting the cicatrisation.
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
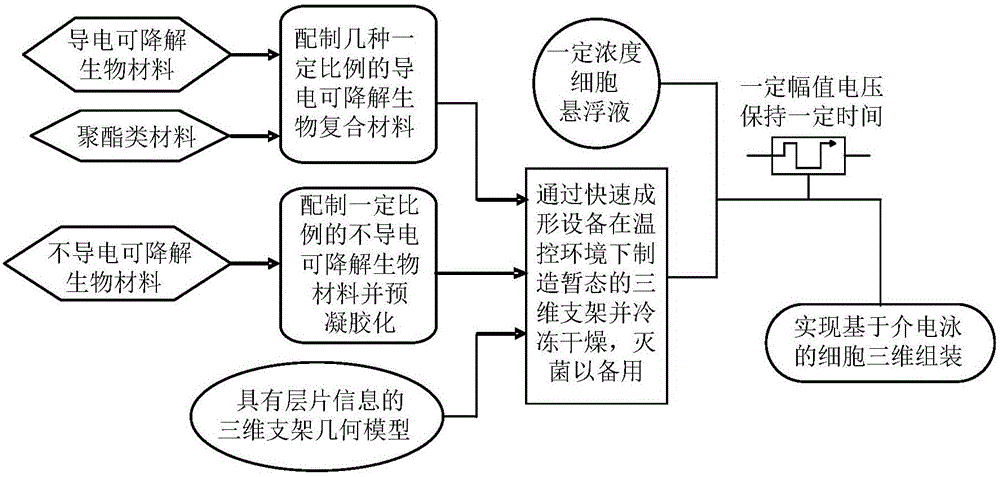
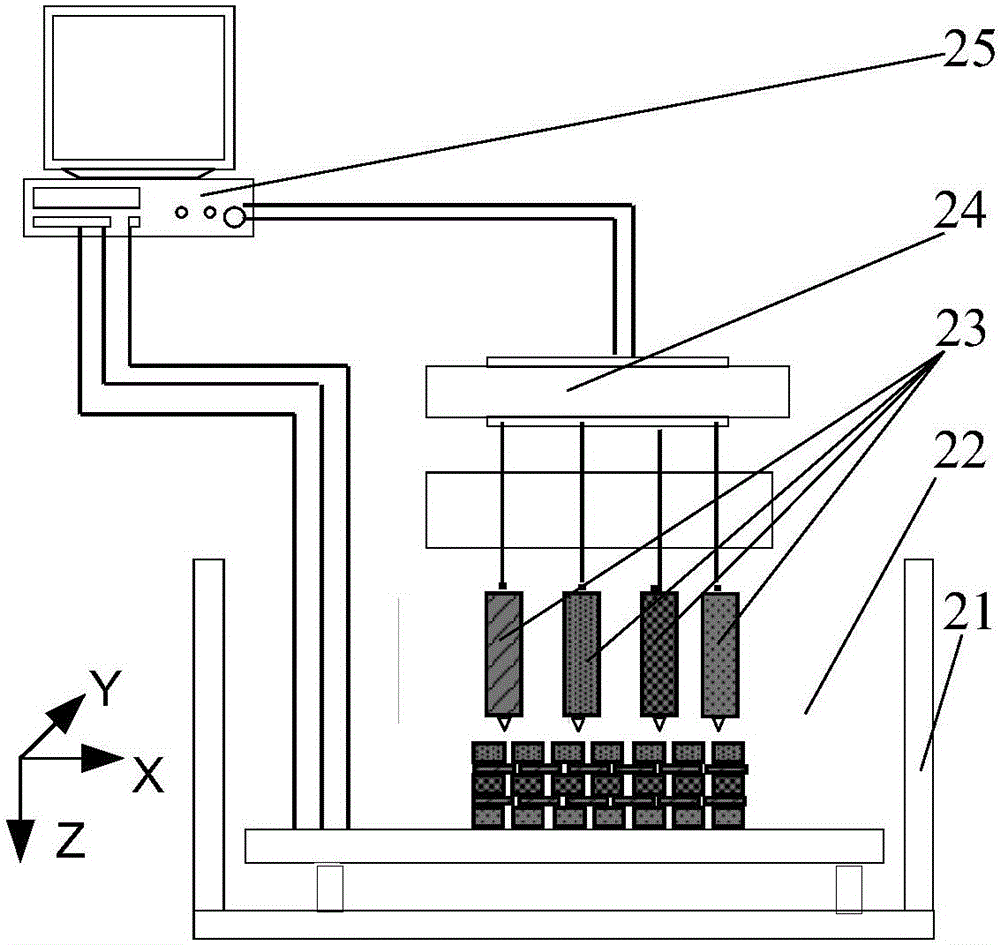
Three-dimensional cell assembly method based on dielectrophoresis adsorption principle
InactiveCN105688280AReduce damage rateImprove assembly efficiencyTissue regenerationProsthesisManufacturing technologyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a three-dimensional cell assembly method based on a dielectrophoresis adsorption principle and belongs to the technical field of artificial manufacture of tissue and organs. According to the method, firstly, a conductive and degradable biological material is prepared to serve as a scaffold main body conducting layer for cell assembly, a non-conductive material with good biocompatibility is taken as a scaffold insulating layer, an artificial tissue organ layer information model with the material area calibrated is established with a computer, thus the information model is used for directly driving multi-sprayer rapid forming equipment to manufacture a conductive three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffold, the conductive three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffold is freeze-dried, electrode pairs are mounted on the sterilized three-dimensional scaffold, the three-dimensional scaffold is immersed into a selected cell suspension, alternating current with a certain amplitude value is conducted for a period of time, and three-dimensional cell assembly is realized. On the basis of the conductive degradable biological material scaffold and the dielectrophoresis adsorption principle, three-dimensional assembly of one or more kinds of cells can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
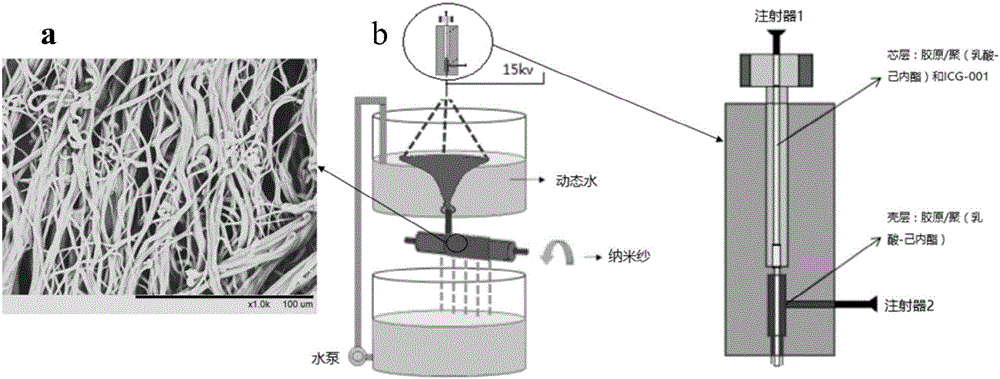
Biodegradable nano yarn capable of inhibiting fibrosis, and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106377798APrevent excessive fibrosisPromote ingrowthConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsTissue regenerationYarnDrugs solution
The invention relates to a biodegradable nano yarn capable of inhibiting fibrosis, and preparation and application thereof. The biodegradable nano yarn is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of I-type collagen / poly(lactic acid-caprolactone) composite solution and 100 parts of anti-fibrosis drug solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using the I-type collagen / poly(lactic acid-caprolactone) composite solution as a shell solution; and using the anti-fibrosis drug solution as a core solution, spinning, freezing over night, and carrying out freeze-drying. The nano yarn can be used as a biodegradable and absorbable biological material scaffold, and can be used for resisting fibrosis in the urethra tissue engineering restoration to prevent postoperative urethral restenosis and urethral submucoasl excessive fibrosis. The preparation method is simple and efficient, and is low in price. The material has the advantages of favorable mechanical properties, obvious anti-fibrosis effect, favorable biodegradability, favorable biocompatibility, and reasonable release rate and time.
Owner:深圳市迈捷生命科学有限公司
Biomaterial scaffold for regenerating the oral mucosa
The present invention refers to a process for preparing a biomaterial scaffold said method comprising, (a) providing a hydrogel comprising a fibrin network and a polysaccharide network; (b) subjecting the hydrogel of step a) to a freeze-thawing process to physically crosslink the hydrogel; and (c) subjecting the physically cross-linked hydrogel obtained after conducting the step b), to a lyophilization. The invention also relates to the biomaterial scaffold obtainable by the process as defined above, as well said biomaterial scaffold for its use to partially or completely increase, restore or replace the functional activity of a diseased or damaged oral mucosa.
Owner:HISTOCELL SL
Biomaterial scaffolds for controlled tissue growth
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Growth matrices for stem cell propagation in vitro and in tissue regeneration
InactiveCN105143442ANervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixMicrosphere
The present invention provides a multifunctional 2-D and 3-D matrix for propagation of stein cells, in particular, a cliitosatv-based biomaieria! scaffold is engineered to promote CNS regeneration from primitive neural precursors by stabilizing a recombinant protein, fibroblast growth factor to preserve the cardinal properties of stem cells. The matrix, is further modified by the addition of either the extracellular matrix protein fibronectiii or the small peptide RGD or IK.VAV. A method to manu&eture an injectable multifunctional microsphere scaffold is also disclosed that is suitable as a vehicle for cell transplantation to repair traumatic brain injuries.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
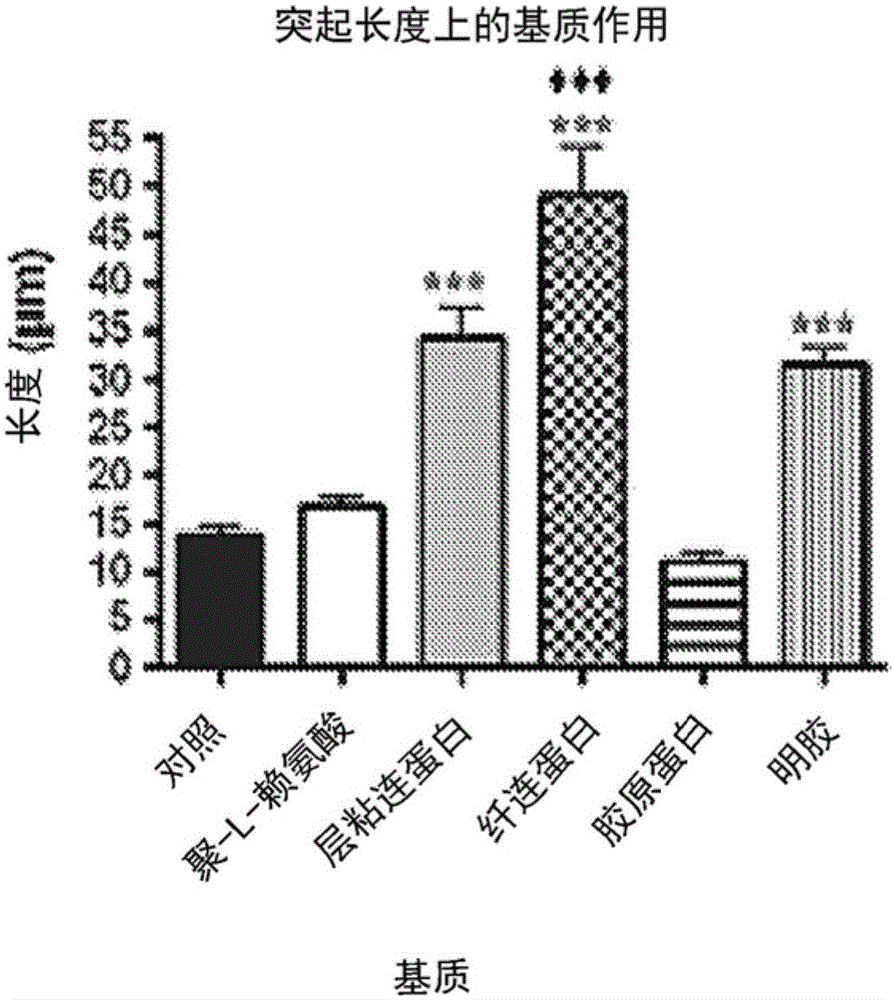
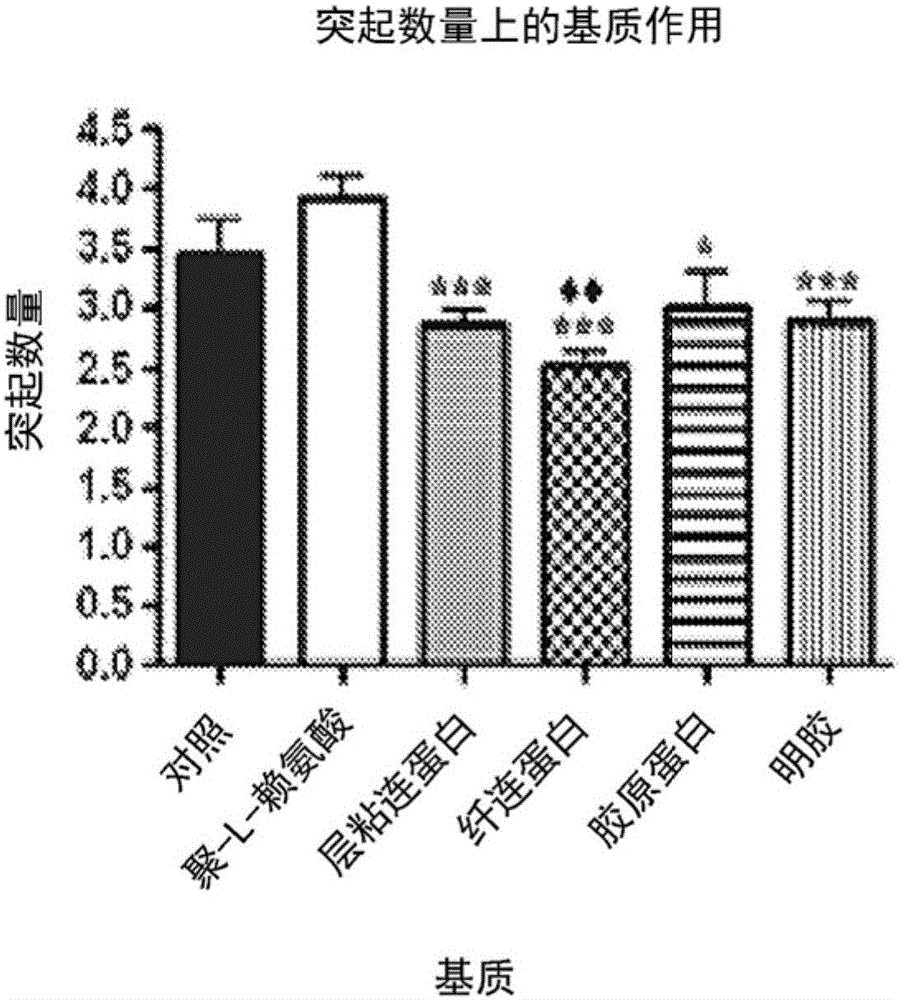
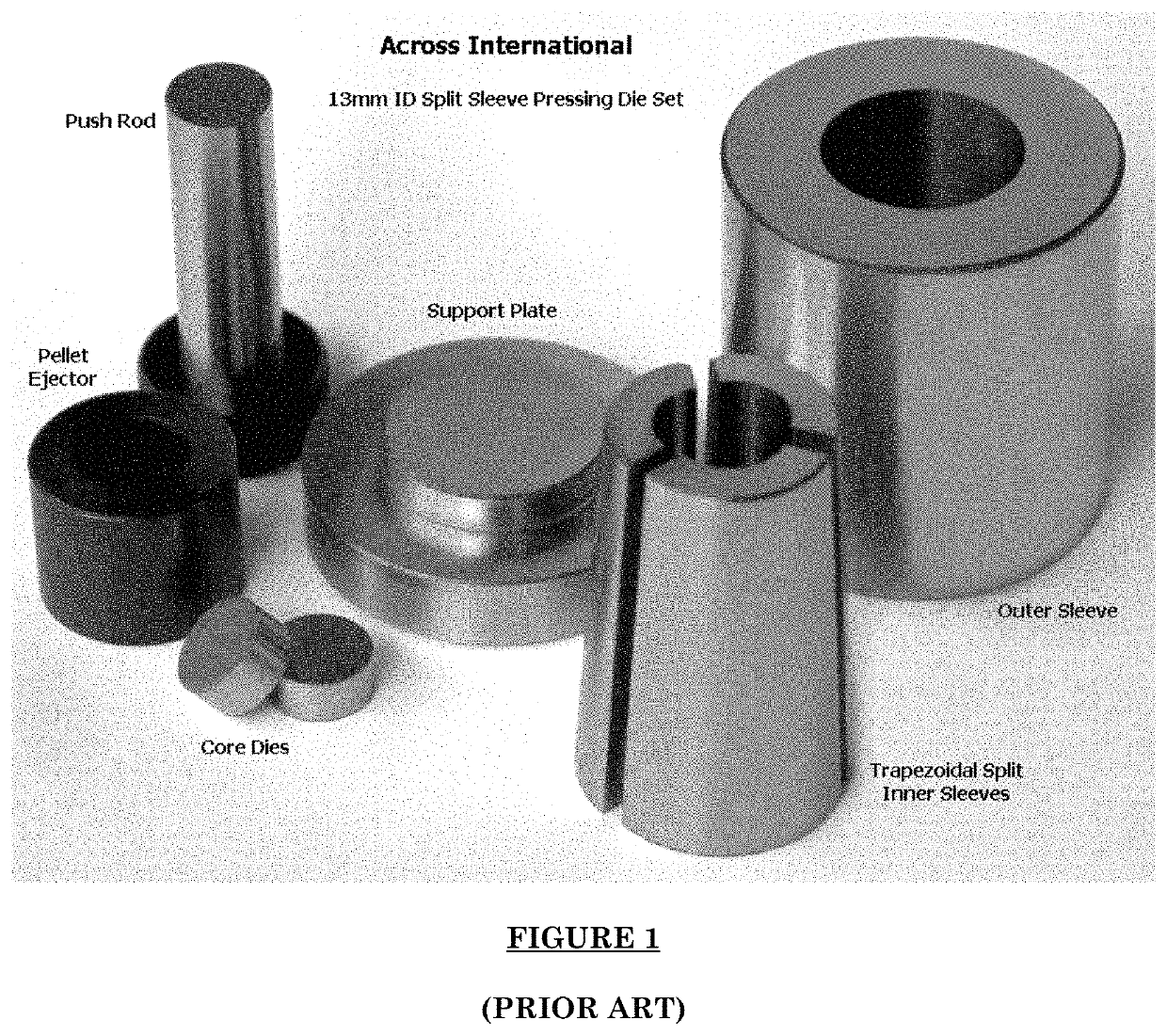
Multi-chamber pellet die system
ActiveUS10807339B2Preparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansProcess engineeringEnvironmental engineering
A multi-chamber pellet die system to improve and increase analysis pellet manufacturing capabilities by allowing for multiple pellets or biomaterial scaffolds to be fabricated simultaneously.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Multi-Chamber Pellet Die System
ActiveUS20180250904A1Equal loadingSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansBiomaterial scaffoldManufacturing capability
A multi-chamber pellet die system to improve and increase analysis pellet manufacturing capabilities by allowing for multiple pellets or biomaterial scaffolds to be fabricated simultaneously.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Method for enhancing biocompatibility and degradability of polyethylene glycol hydrogel
InactiveCN106479965AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsertion stentBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for enhancing biocompatibility and degradability of polyethylene glycol hydrogel. The method includes the steps of (1), preparing acylation polyethylene glycol; (2), preparing acylation polypeptide; (3), separating human mesenchymal stem cells; (4), performing induced differentiation on the mesenchymal stem cells to obtain chondrocytes. The method for enhancing the biocompatibility and degradability is advanced in technique, simple in steps, simple to operate, and capable of promoting the biocompatibility and degradability of a biomaterial stent and promoting cell reproduction and tissue regeneration.
Owner:武汉枫霖科技有限公司
Biodegradable and bioabsorbable biomaterials and keratin fibrous articles for medical applications
ActiveUS8242073B2Monocomponent protein artificial filamentElectric discharge heatingFiberBiomaterial scaffold
The present invention relates to a process of making biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable biomaterials and keratin nonwoven fibrous articles by electrospinning fibers from a blend of biomaterials and keratin dissolved in organic solvents includes generating a high voltage electric field between oppositely charged biomaterials and keratin fluid in a syringe with a capillary tip and a metallic collection roller and causing a jet to flow to the roller as solvent evaporates and collecting fibrous membranes or scaffolds on the roller. Keratin increased the cell affinity of biomaterial scaffolds which have potential medical applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
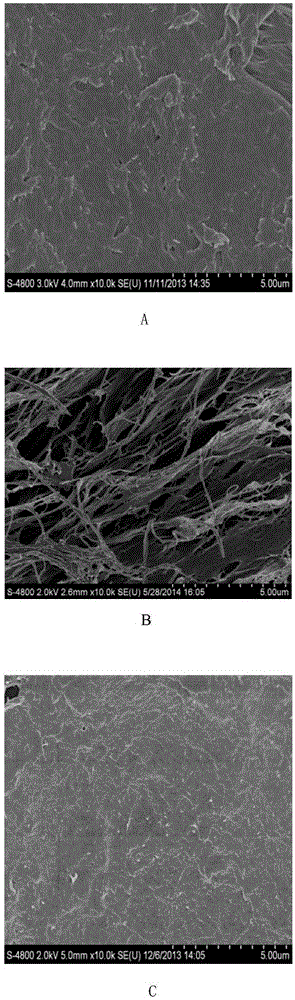
Mechanical property enhanced acellular spinal cord biomaterial scaffold and preparation method and application thereof
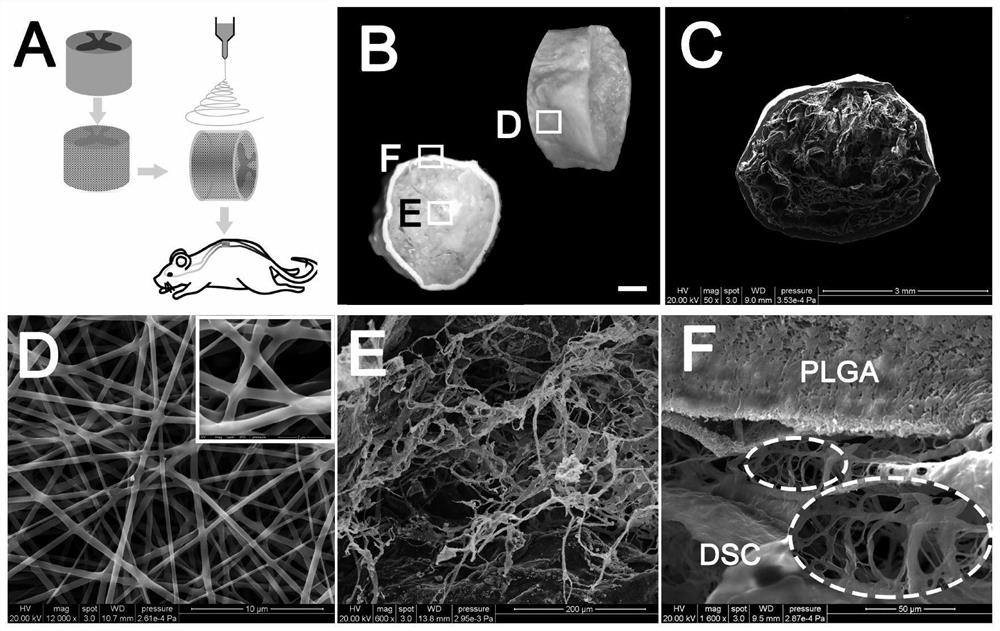
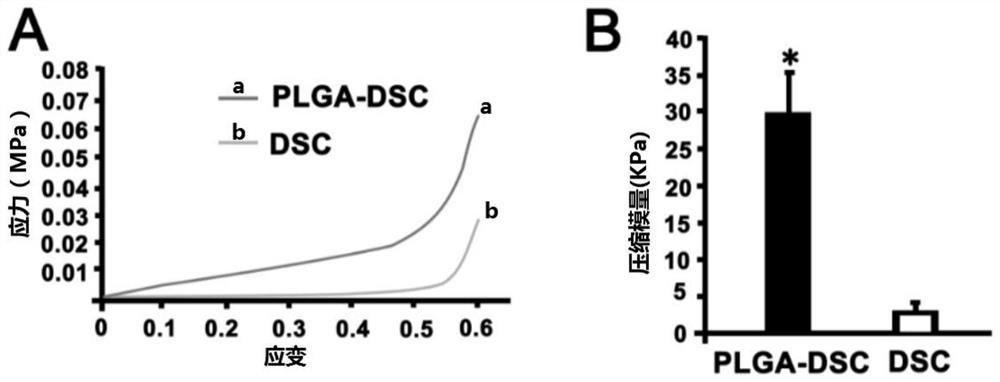
ActiveCN112755249AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove stress resistanceCoatingsNon-woven fabricsSpinal cord lesionPost transplant
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials, and particularly relates to a mechanical property enhanced acellular spinal cord biomaterial scaffold and a preparation method and application thereof. In order to overcome the problem that an existing acellular spinal cord scaffold is insufficient in mechanical property, a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) shell is spun outside an acellular spinal cord (DSC) through an electrospinning technology, and the mechanical property enhanced acellular spinal cord biomaterial scaffold is constructed. Compared with a simple DSC scaffold, the biomaterial scaffold has the enhanced mechanical property and better anti-pressure ability, and collapse of transplanted materials and compression of the transplanted materials by surrounding tissue can be prevented; and research shows that when the biomaterial scaffold is transplanted to a rat total transection spinal cord injury area, spinal cord injury can be effectively repaired, the problem that the mechanical property of the acellular spinal cord is poor is solved, and in-situ repair of spinal cord injury is further promoted.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Layered manufacturing method of three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold
InactiveCN102488569BIncrease profitSolving Manufacturing ChallengesDialysis systemsProsthesisFreeze-dryingThree vessels
A layered manufacturing method of a three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold comprises the following steps: simulating the microstructure of a real organ, manufacturing a resin die with a microfluidic structure copying a blood vessel system, copying a negative mode of the microfluidic structure with silicon rubber, filling the negative mode with solution of biological materials, moving the silicon rubber die upwards to enable the solution of biological materials to be contacted with an ultra-low temperature flat plate vertically, moving the silicon rubber die downwards to realize demolding of the frozen structure of the biological materials after solidification of solution of the biological materials, realizing precision interlayer orientation as well as freezing, condensation and forming of the three-dimensional microfluidic porous scaffold by repeatedly performing filling of the solution of biological materials and moving up and down of the silicon rubber die, obtaining the three-dimensional frozen structure of the biological materials, and vacuum freeze drying the ultra-low temperature flat plate and the three-dimensional frozen structure of the biological materials, and finally obtaining the scaffold of the biological materials with a three-dimensional microfluidic system and an oriented porous structure. The layered manufacturing method has the advantage of forming a three-dimensional organ scaffold with a complex space microfluidic system and the oriented porous structure directly.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Compositions and methods for modulating wound healing and regeneration
ActiveUS20190060524A1Affecting its functionIncrease probabilityTissue regenerationProsthesisWound healingBiomaterial scaffold
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for modulating wound healing and regeneration. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to immunomodulatory agents that promote wound healing and tissue regeneration, and that may be optionally used in combination with synthetic or biomaterial scaffolds.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
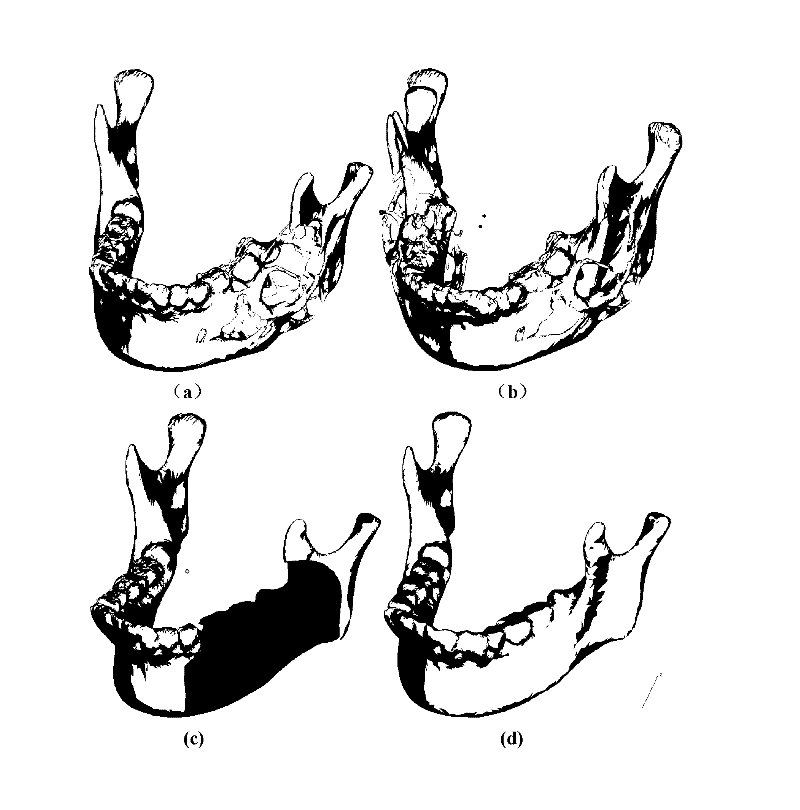
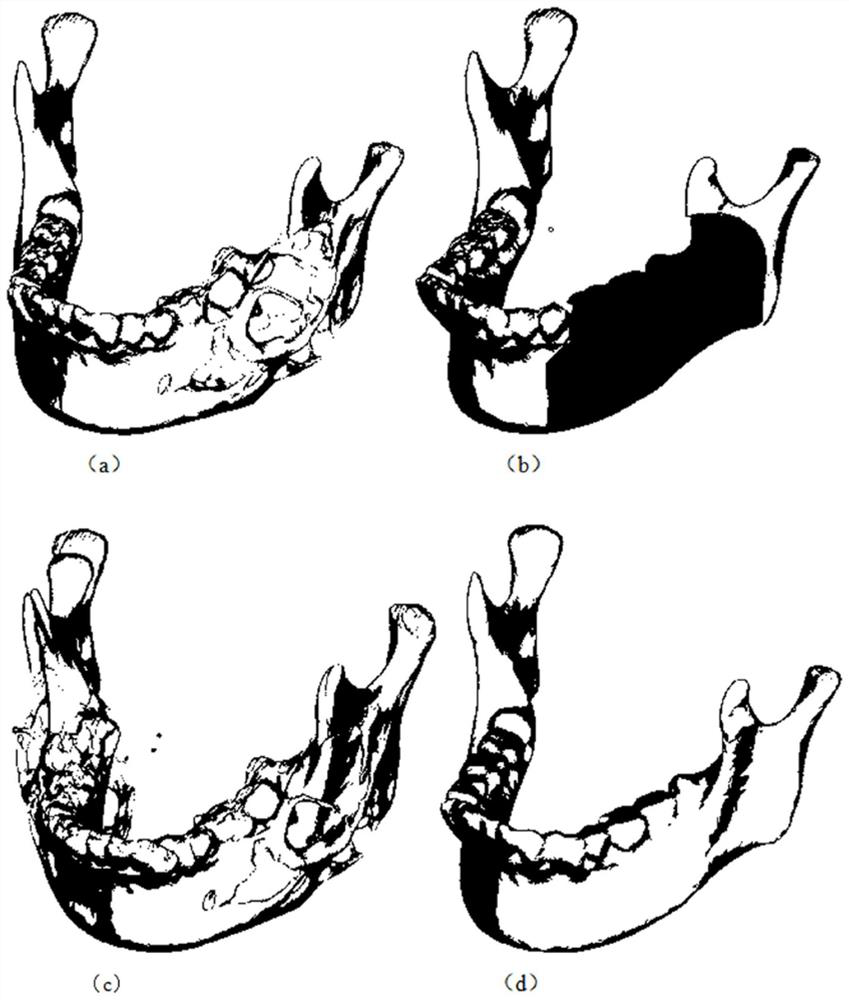
Mandibular implant and method of making same
Owner:衢州市人民医院
Egg white water gel membrane/composite membrane based on unidirectional nanopore dehydration and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an egg white water gel membrane / composite membrane based on unidirectional nanopore dehydration and a preparation method thereof. Egg white or a mixture solution of egg white is placed in a container with a nanopore filter membrane as the bottom, transparent, fragile and water-soluble egg white bioglass is obtained through unidirectional nanopore dehydration, and after heat treatment, an egg white water gel membrane / composite membrane which is in a wet state, transparent, elastic and high in tensile property is prepared; the tensile strength reaches 5.8 MPa, the breaking elongation is 90-110%, and the swelling rate is 60-130%; and preparing the polypyrrole modified egg white water gel conductive film from the egg white water gel film / composite film through a polymerization reaction. On the prepared egg white water gel film, the mouse fibroblast L929 has good insertion and proliferation. The egg white water gel material based on unidirectional nanopore dehydration provided by the invention can be widely applied to the fields of medical biological materials, 3D brackets, biomimetic materials, drug delivery and slow release, wearable electronic equipment and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com