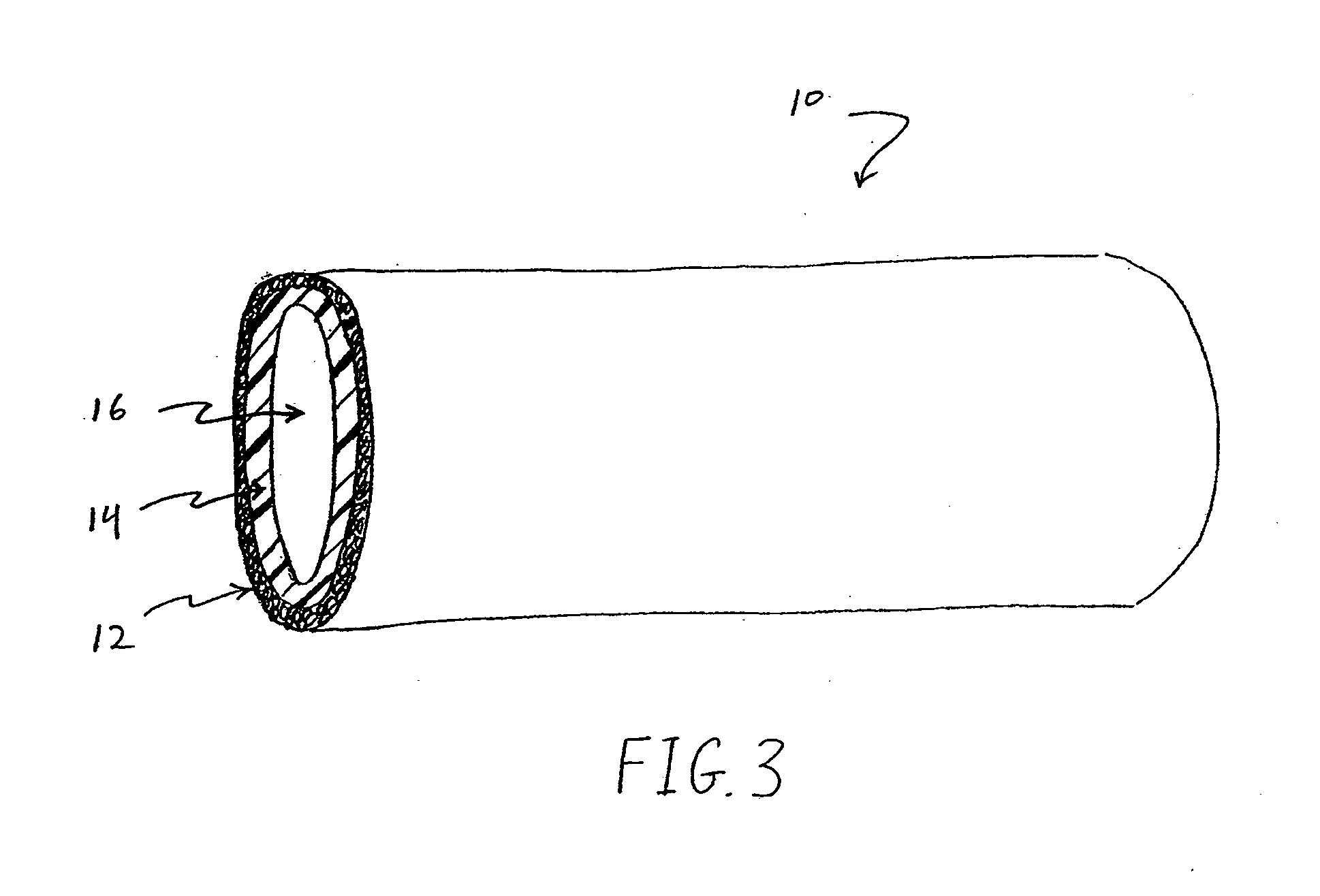
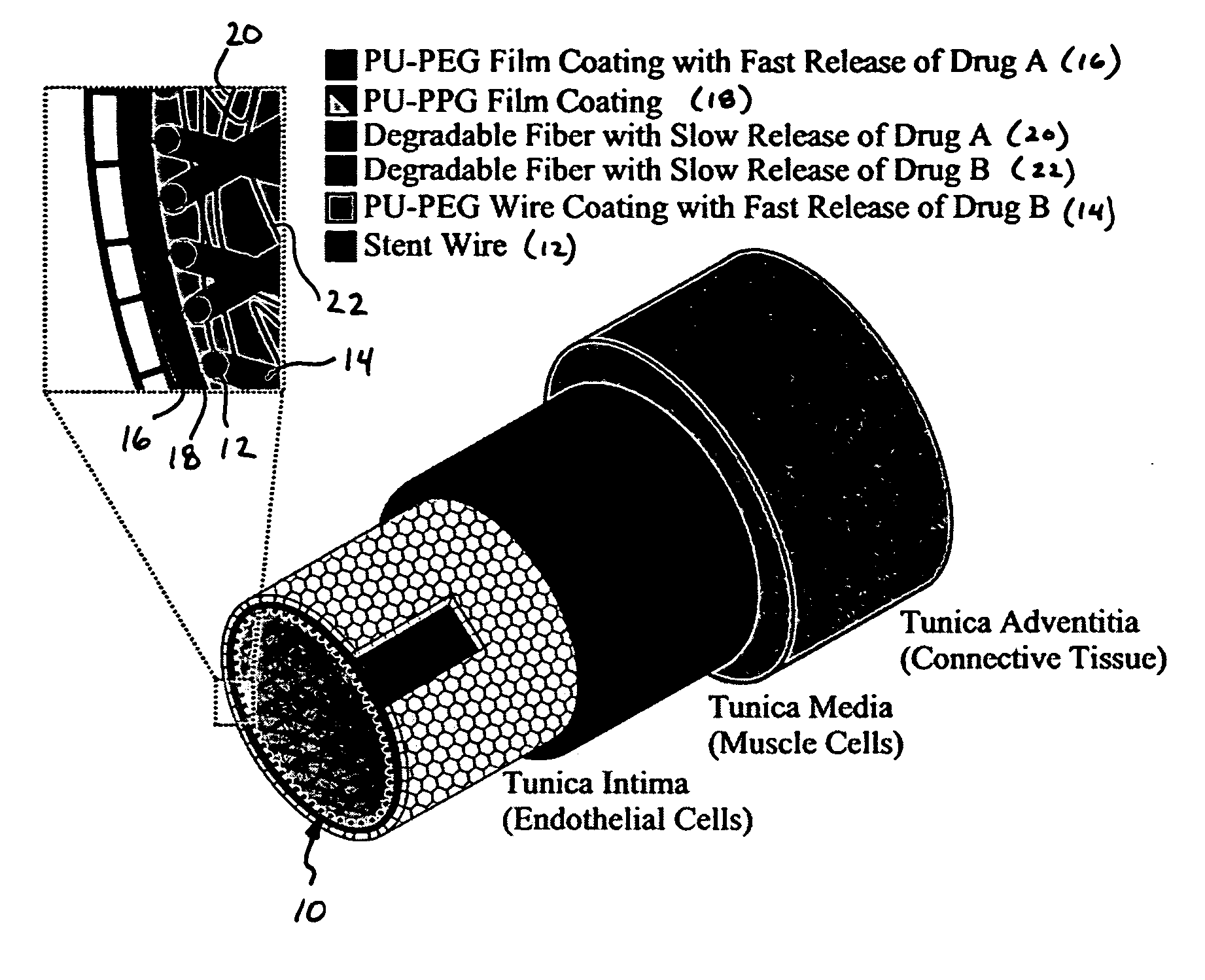
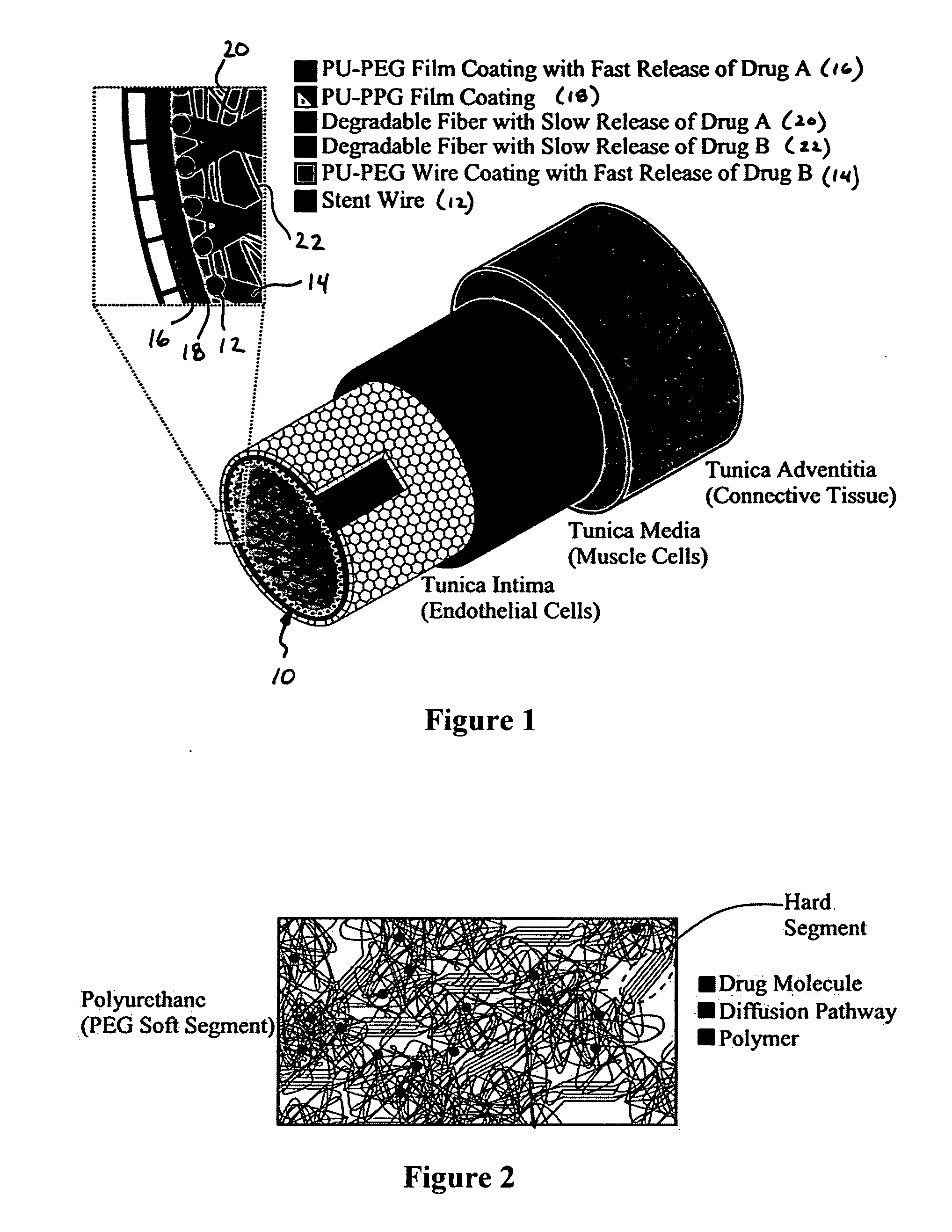
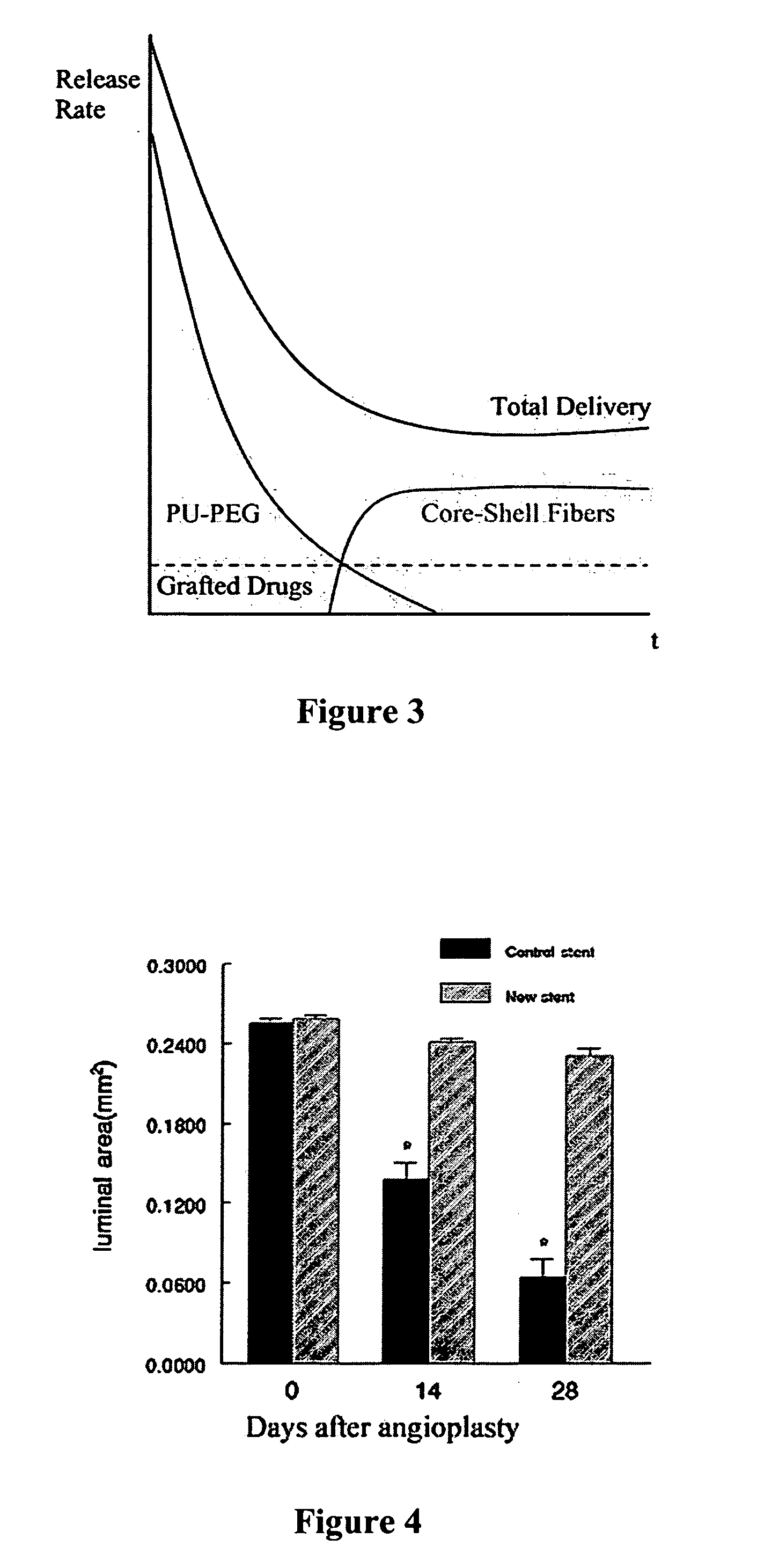
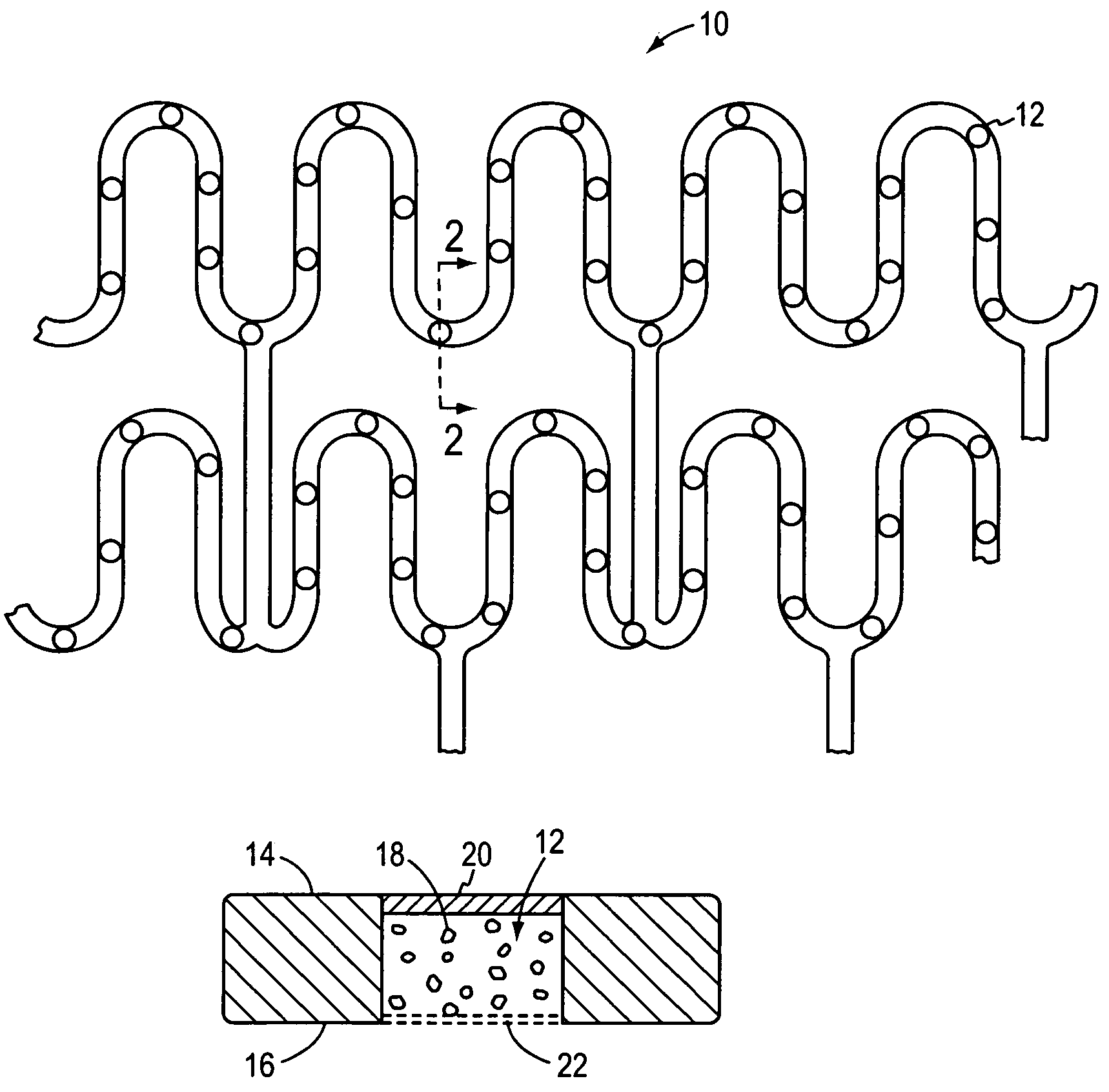
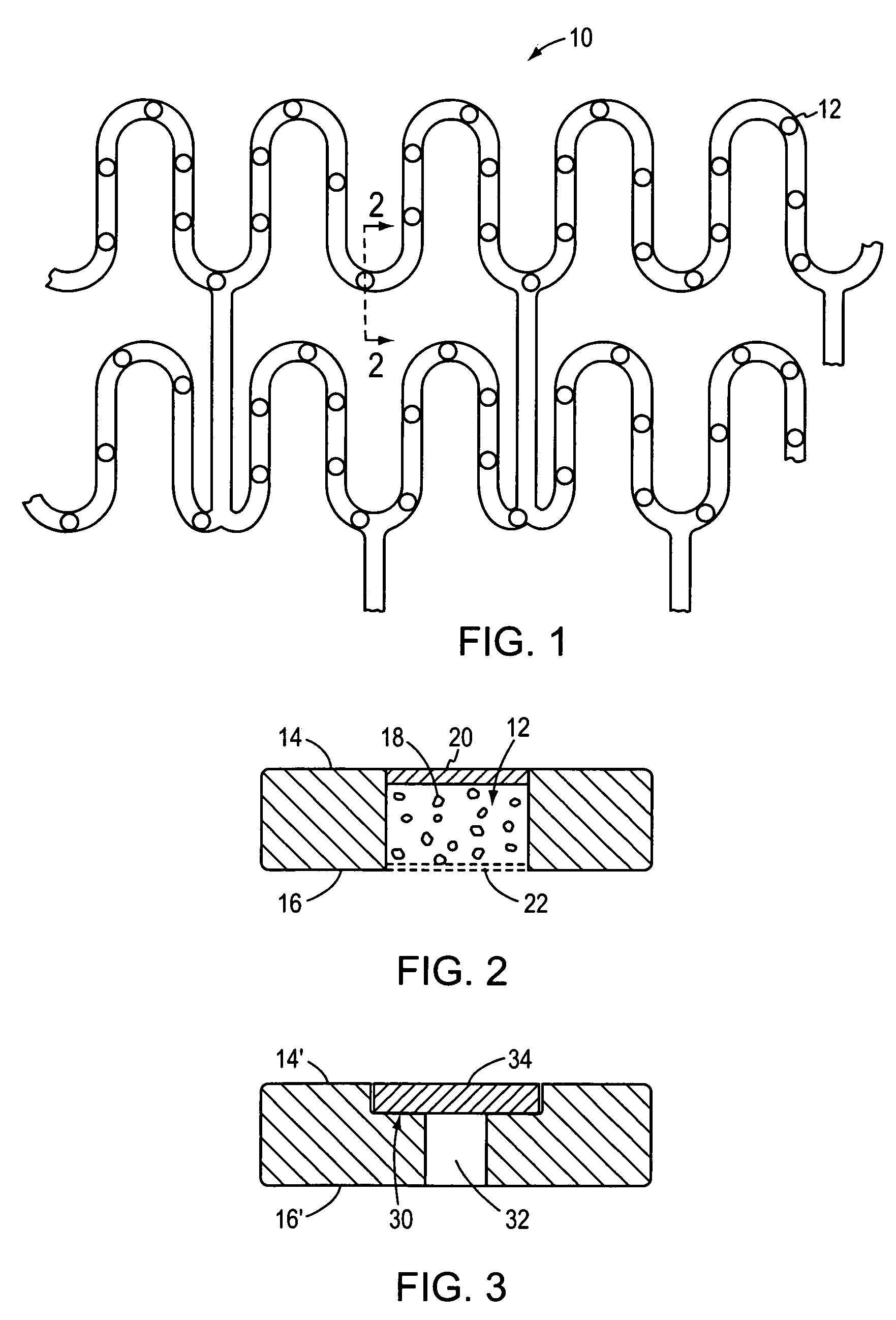
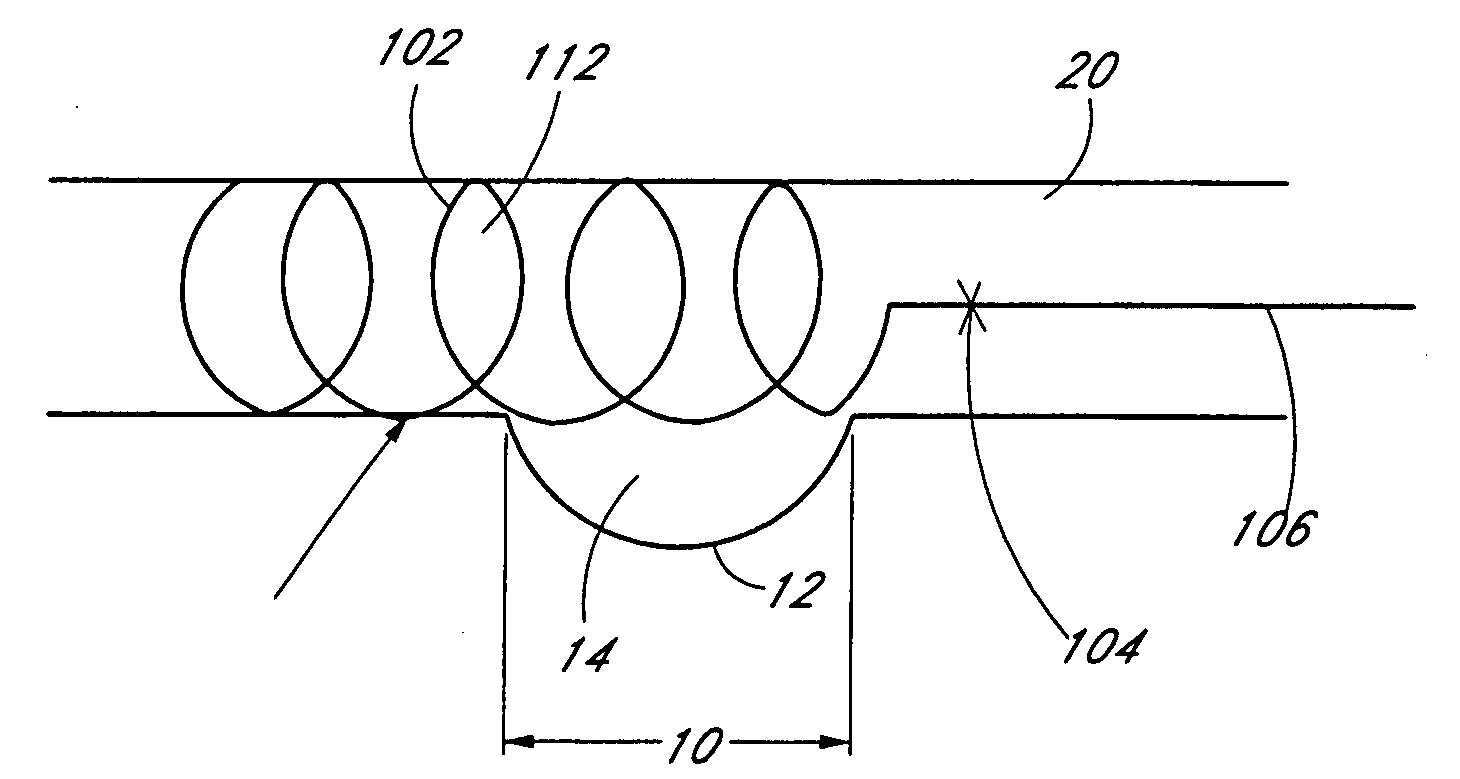
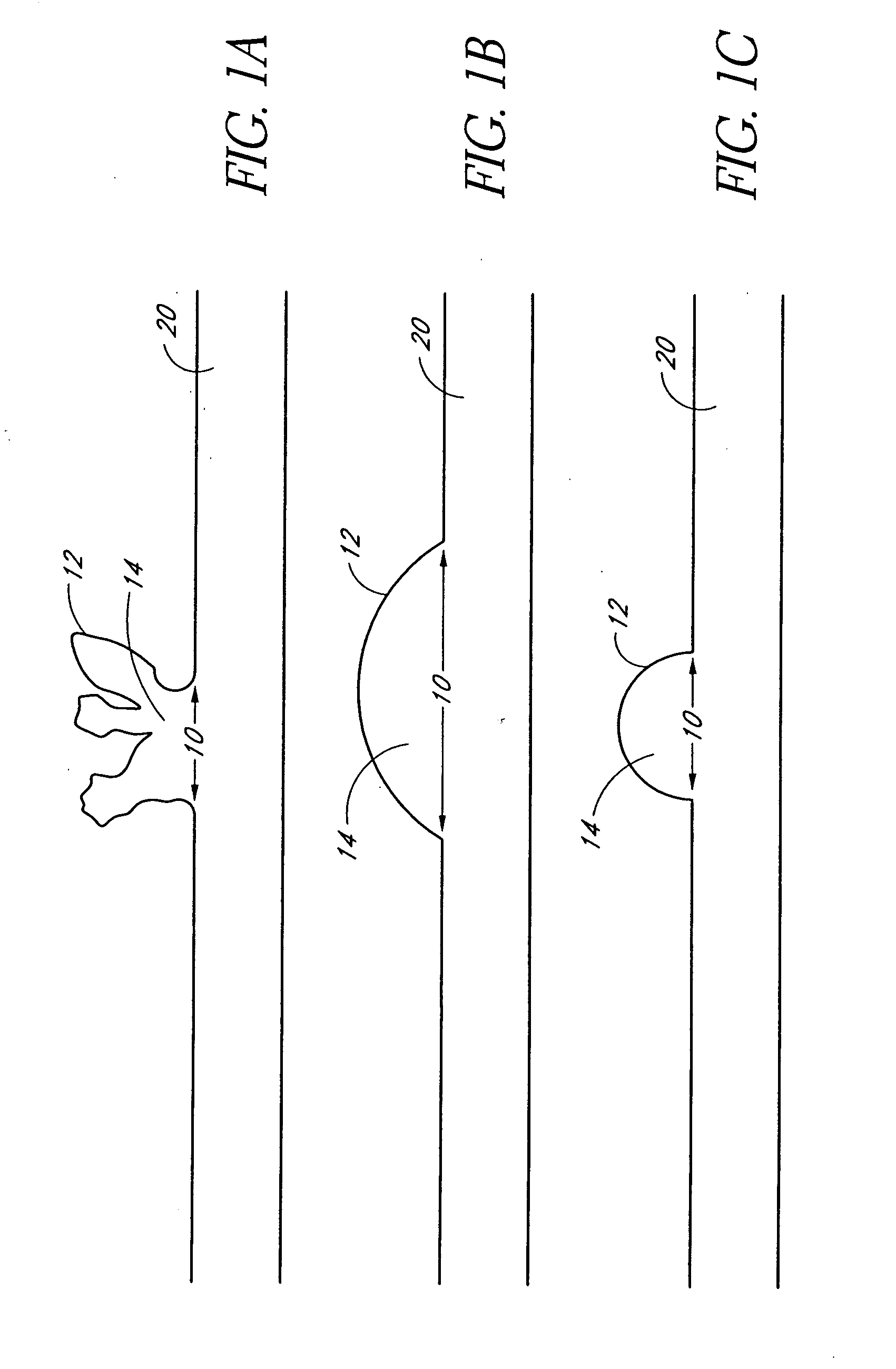
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
630 results about "Vascular stent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A vascular stent is a medical device designed to be inserted into a blood vessel in order to keep it open.
Degradable implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060229711A1Reduce probabilityLower resistanceStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantBlood vessel
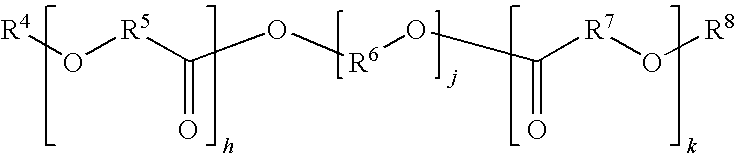
Devices and methods are provided for an implantable medical device which is degradable over a clinically relevant period of time. The medical devices may have the form of implants, graft implants, vascular implants, non vascular implants, wound closure implants, sutures, drug delivery implants, biologic delivery implants, urinary tract implants, inter-uterine implants, organ implants, bone implants including bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, spinal disks, or the like. In preferred embodiments, the implantable medical device comprises an implantable luminal prosthesis, such as vascular and non-vascular stents and stents grafts.
Owner:ELIXIR MEDICAL CORP
Coated implantable medical device
InactiveUS6918927B2Good worker safetyLow costOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySodium bicarbonateMedicine
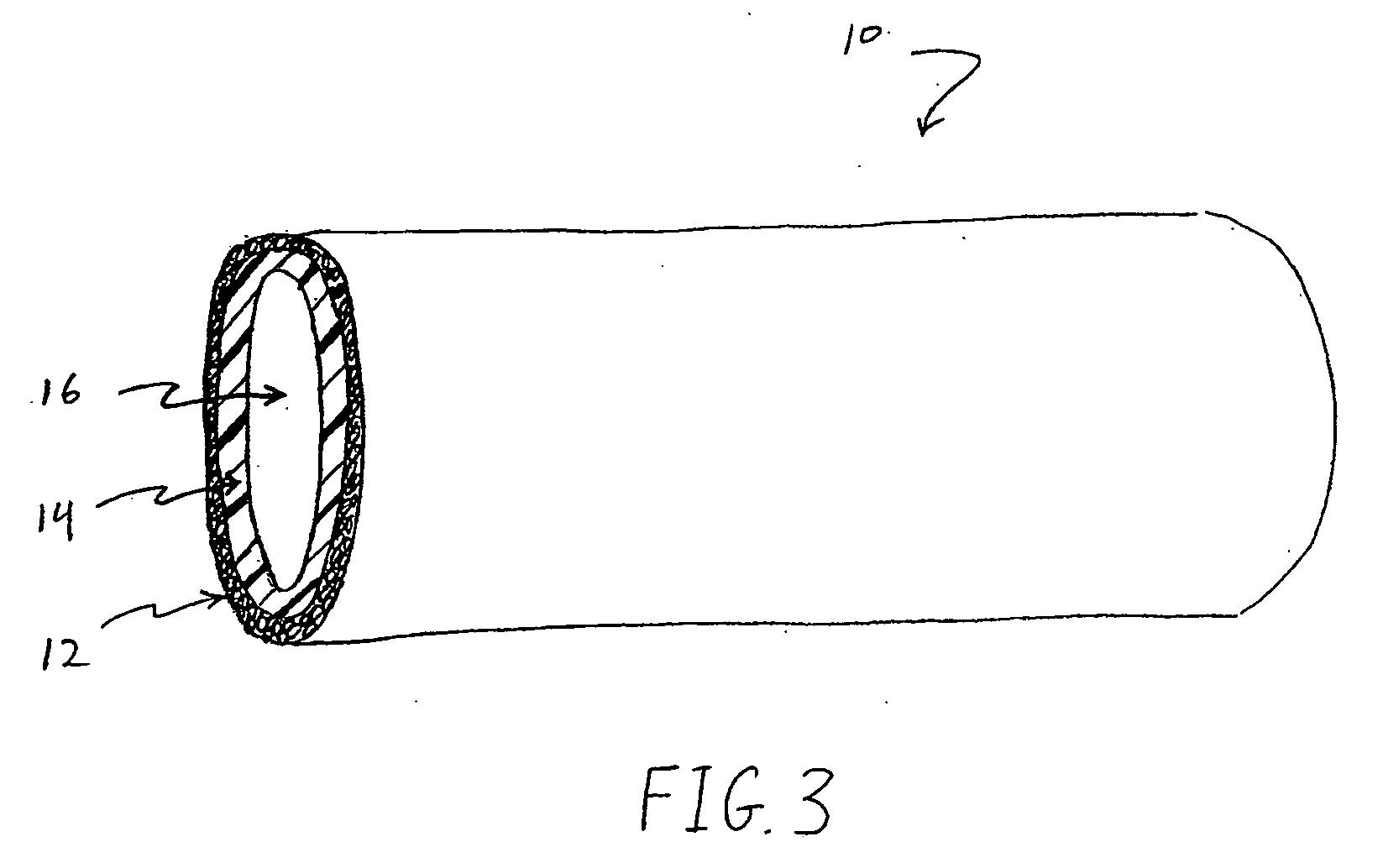
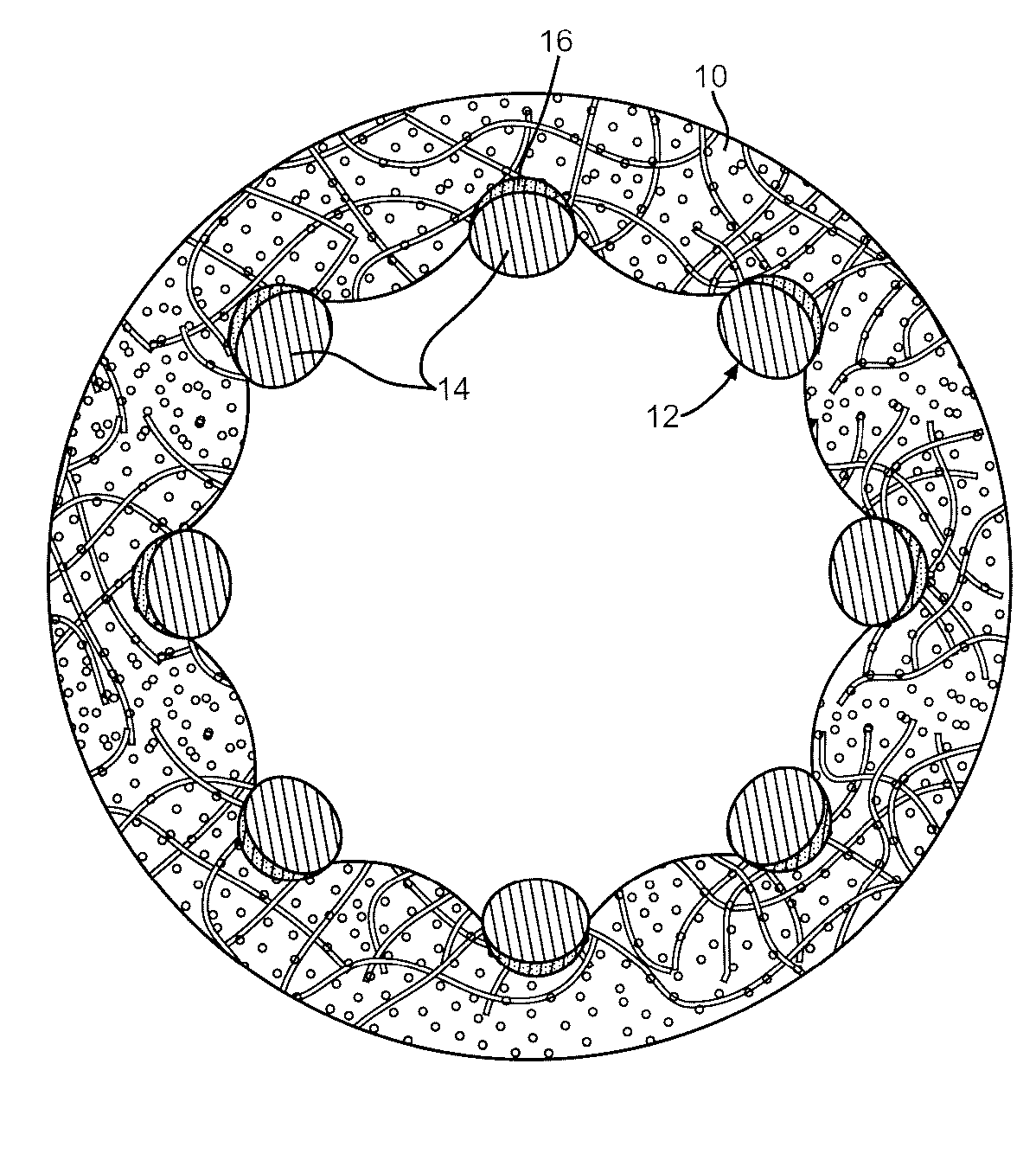
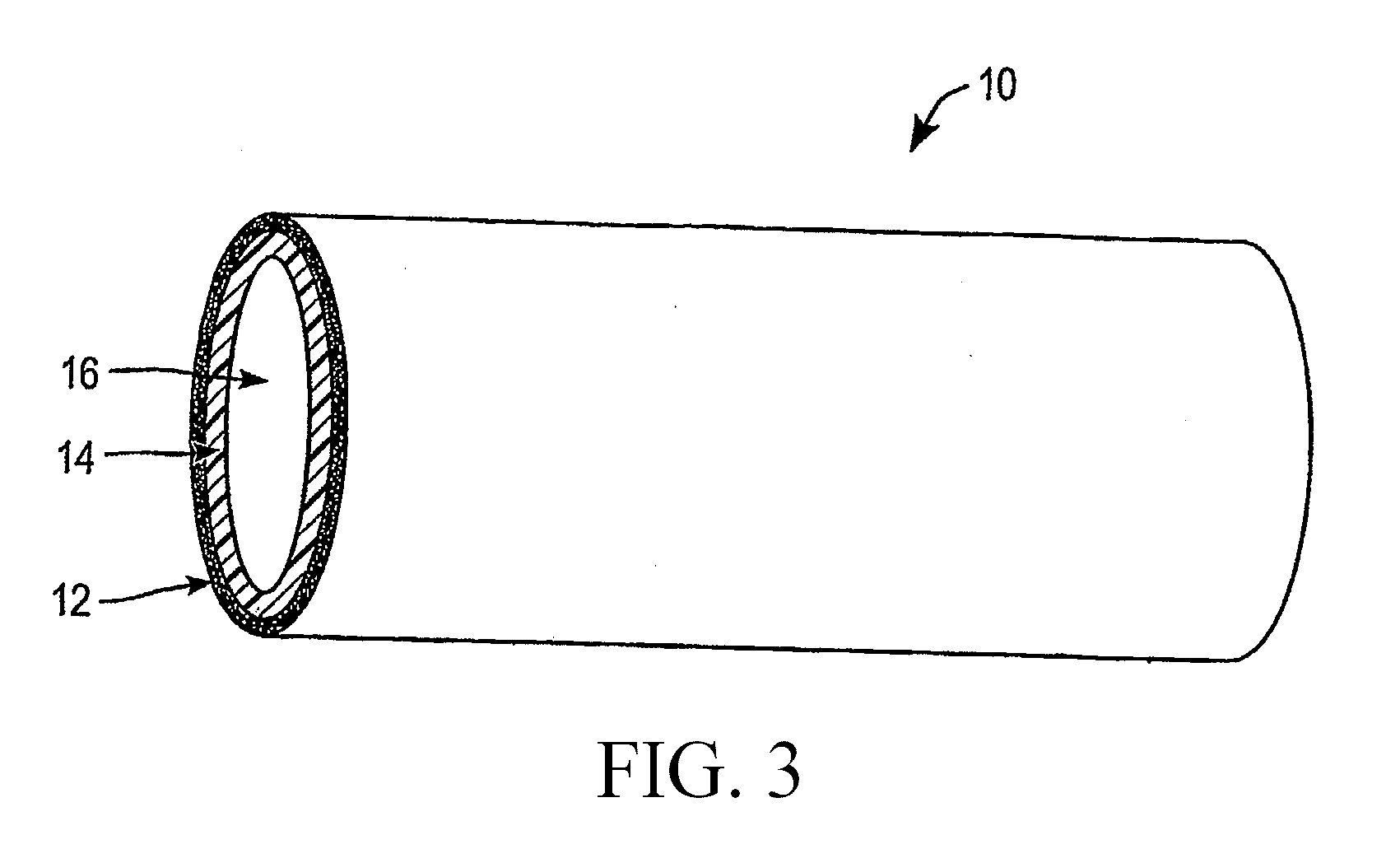
A medical device (10) includes a structure (12) adapted for introduction into a patient, the structure (12) being formed of a preferably non-porous base material (14) having a roughened or textured surface (16). The structure (12) is conveniently configured as a vascular stent with a base material (14) of stainless steel, nitinol or another suitable material. The medical device (10) also includes a layer (18) of a bioactive material posited directly upon the roughened or textured surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12). The surface (16) of the base material (14) is roughened or textured by etching or by abrasion with sodium bicarbonate or another suitable grit. A preferred roughened or textured surface (16) is thought to have a mean surface roughness of about 10 μin. (about 250 nm) and a surface roughness range between about 1 μin. and about 100 μin. (about 25 nm and about 2.5 μm). The particularly preferred use of sodium bicarbonate as the abrasive to provide roughness or texture to the surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12) is additionally advantageous in the low toxicity of the sodium bicarbonate to production workers, the ease of product and waste cleanup, and the biocompatibility of any residual sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Biodegradable drug delivery vascular stent
A stent includes a main body of a generally tubular shape for insertion into a lumen of a vessel of a living being. The tubular main body includes a substantially biodegradable matrix having collagen IV and laminin that enclose voids within the matrix. The tubular main body also includes a biodegradable strengthening material in contact with the matrix to strengthen the matrix. The tubular main body is essentially saturated with drugs.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Prosthetic repair of body passages
ActiveUS20060041305A1Large caliberReduce the cross-sectional areaStentsHeart valvesProsthesisVascular stent
A prosthesis that resiliently engages a body passage includes an annular clamping ring which may be folded along a diametric axis for insertion into the body passage. The clamping ring is adapted to resiliently spring outwardly, once in position inside the body passage, and to be continually resiliently biased against the interior surface of the body passage. One or more of the clamping rings may be attached to opposed ends of a tubular graft. The rings and connected graft may be positioned in the body passage using a applicator which selectively permits expansion and / or in some embodiments contraction of the annular ring in position within a body passage. Alternatively a retaining member may be used to retain the annular ring in a compressed condition until it is in a desired position within a body passage. Among other potential uses, the present invention may be useful as a vascular stent for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Owner:VASCUTEK
Biocompatible controlled release coatings for medical devices and related methods
ActiveUS20050084515A1High elasticity/ductilityResist erosionSurgeryMedical preparationsSolubilityBiocompatible coating
Biocompatible coatings for medical devices are disclosed. Specifically, polymer coatings designed to control the release of bioactive agents from medical devices in vivo are disclosed wherein the solubility parameters of polymers and drugs are closely matched to control elute rate profiles. The present application also discloses providing vascular stents with controlled release coatings and related methods for making these coatings.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for loading nanoporous layers with therapeutic agent
The present invention relates generally to medical devices with therapy eluting components and methods for making same. More specifically, the invention relates to implantable medical devices having at least one porous layer, and methods for making such devices, and loading such devices with therapeutic agents. A mixture or alloy is placed on the surface of a medical device, then one component of the mixture or alloy is generally removed without generally removing the other components of the mixture or alloy. In some embodiments, a porous layer is adapted for bonding non-metallic coating, including drug eluting polymeric coatings. A porous layer may have a random pore structure or an oriented or directional grain porous structure. One embodiment of the invention relates to medical devices, including vascular stents, having at least one porous layer adapted to resist stenosis or cellular proliferation without requiring elution of therapeutic agents. The invention also includes methods, devices, and specifications for loading of drugs and other therapeutic agents into nanoporous coatings.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
High modulus polyurethane and polyurethane/urea compositions
ActiveUS20090099600A1High modulusHigh strengthStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The present invention provides a polyurethane or polyurethane / urea composition which has a tensile strength greater than 10 MPa, a modulus of elasticity greater than 400 MPa and an elongation at break greater than 30% at a temperature of between 0° C. and 60° C. and at a relative humidity of between 0% and 100%.The invention further provides uses of the compositions of the invention in biomedical vascular stents, an orthopaedic implant, a drug delivery coating or in tissue engineering.
Owner:POLYNOVO BIOMATERIALS PTY LTD
Method of producing fused biomaterials and tissue
InactiveUS6087552AReduce the possibilityGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsUrinary bladderVeinTissue repair
It is a general object of the invention to provide a method of effecting tissue repair or replacement using a biomaterial. It is a specific object of the invention to provide a biomaterial suitable for use as a stent, for example, a vascular stent, or as a conduit replacement, as an artery, vein or a ureter replacement. The biomaterial can also be used as a stent or conduit covering or lining. The present invention relates to a method of repairing, replacing or supporting a section of a body tissue. The method comprises positioning a biomaterial at the site of the section and bonding the biomaterial to the site or to the tissue surrounding the site. The bonding is effected by contacting the biomaterial and the site, or tissue surrounding the site, at the point at which said bonding is to be effected, with an energy absorbing agent. The agent is then exposed to an amount of energy absorbable by the agent sufficient to bond the biomaterial to the site or to the tissue surrounding the site.
Owner:GREGORY KENTON W +1
Method for retaining a vascular stent on a catheter
ActiveUS20070006441A1Reduce overall outer diameterEnhance stent retentionStentsLaminationInsertion stentBalloon catheter
A method of securely mounting a stent on a balloon of a catheter. The method generally includes crimping a stent on a balloon of a catheter at least one time, and positioning the balloon with the stent thereon within a polished bore of a mold formed at least in part of a metallic material. The balloon is pressurized and heated within the mold, or within a sheath, in two stages as the stent is restrained from radially expanding. The method may include crimping the stent onto the balloon one or two times during processing. The method increases retention of the stent on the balloon catheter following sterilization.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Bioactive stents for type II diabetics and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS20060013855A1StentsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProgenitorBlood vessel
The present invention is based on the discovery that a vascular stent or other implantable medical device can be coated with a biodegradable biocompatible polymer to which is attached a bioligand that specifically captures progenitors of endothelial cells (PECs) from the circulating blood to promote endogenous formation of healthy endothelium in Type II diabetics. In one embodiment, the bioligand is a peptide that specifically binds to an integrin receptor on PECs. The invention also provides methods for using such vascular stents and other implantable devices to promote vascular healing in Type II diabetics, for example following mechanical intervention.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Stent Coating For Eluting Medication
InactiveUS20060200231A1Good biocompatibilityPrevention and therapyStentsSurgeryPorosityDiamond-like carbon
A vascular stent comprising a drug-eluting outer layer of a porous sputtered columnar metal having each column capped with a biocompatible carbon-containing material is described. This is done by placing the stent over a close-fitting mandrel and rotating the assembly in a sputter flux. The result is a coating that is evenly distributed over the outward-facing side of the stent's wire mesh while preventing the sputtered columnar coating from reaching the inward facing side where a smooth hemocompatible surface is required. The stent is then removed from the mandrel, exposing all surfaces, and finally coated with a layer of carbon such as amorphous carbon or diamond-like carbon. The carbonaceous coating enhances biocompatibility without preventing elutriation of a therapeutic drug provided in the porosity formed between the columnar structures. The result is a stent that is adapted to both the hemodynamic and the immune response requirements of its vascular environment.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Systems and methods for using dynamic vascular assessment to improve vascular stent placement, application, design and marketing
InactiveUS20050038342A1Rapid and inexpensive to performEfficient deliveryBlood flow measurement devicesMedical automated diagnosisClinical testsPre operative
The invention relates to systems and methods for assessing blood flow in single or multiple vessels and segments, for assessing vascular health, for conducting clinical trials, for screening therapeutic interventions for effect, for assessing risk factors, for evaluating intracranial pressure and for analyzing the results in a defined manner. The invention enables direct monitoring of therapies, substances and devices on blood vessels, especially those of the cerebral vasculature. Relevant blood flow parameters include mean flow velocity, systolic acceleration, and pulsatility index. Measurement and analysis of these parameters, and others, provides details regarding the vascular health of individual and multiple vessels and a global analysis of an individual's overall vascular health. The invention is applicable as both a system and method for monitoring and improving the design, performance, marketing and use of vascular stents. In particular, the invention enables DVA-assisted stenting procedures, including both pre-operative and post-operative management.
Owner:NEW HEALTH SCI
Modular branch vessel stent-graft assembly
Modular branch vessel stent-graft assemblies for the treatment arterial or vascular disease at the branch of two or more arteries or blood flow passageways, including, for example, abdominal aortic aneurysms are assembled in a patient's trunk / parent artery, from at least two components; a first component and a second component. The first and second components each include a first and second window, or fenestration. The second component couples with the first component by fitting at least partially in the first component to form the modular branch vessel stent-graft assembly with two selectively locatable branch openings. As the first and second components are deployed, the second component is selectively position able relative to first component so that the first and second component first and second windows overlap to form two branch openings whose longitudinal and angular positions are selectable within a range.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Bioactive stents for type II diabetics and methods for use thereof
The present invention is based on the discovery that a vascular stent or other implantable medical device can be coated with a biodegradable biocompatible polymer to which is attached a bioligand that specifically captures progenitors of endothelial cells (PECs) from the circulating blood to promote endogenous formation of healthy endothelium in Type II diabetics. In one embodiment, the bioligand is a peptide that specifically binds to an integrin receptor on PECs. The invention also provides methods for using such vascular stents and other implantable devices to promote vascular healing in Type II diabetics, for example following mechanical intervention.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
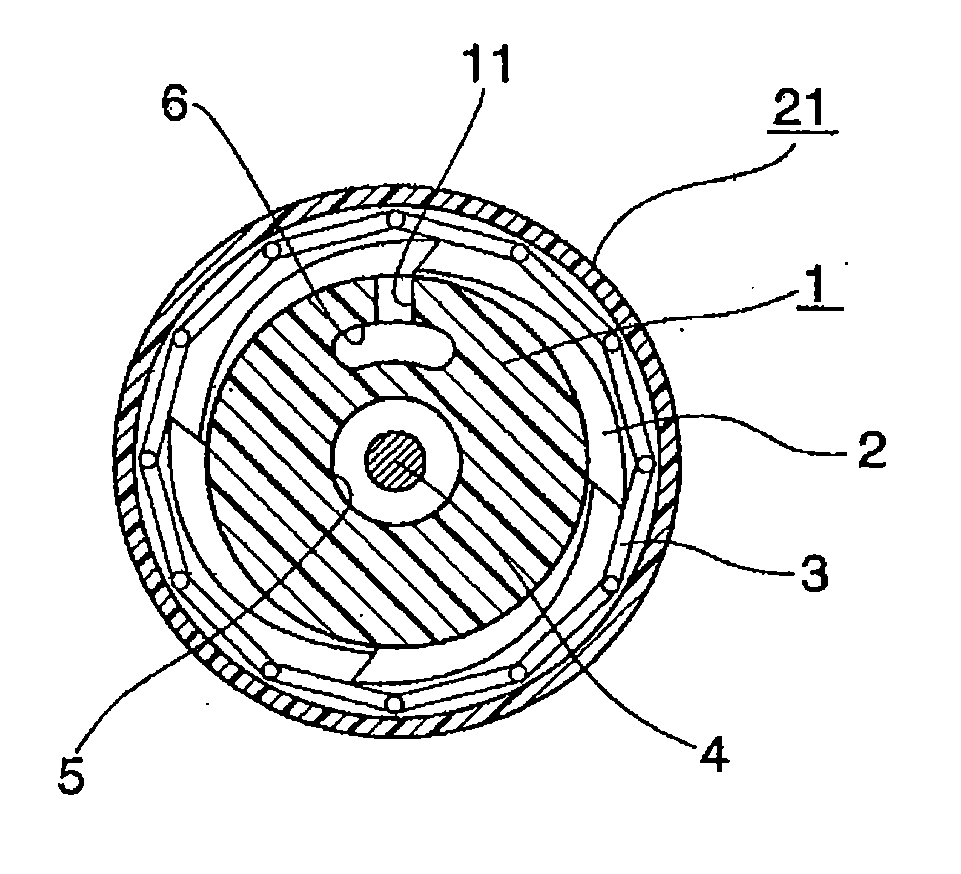
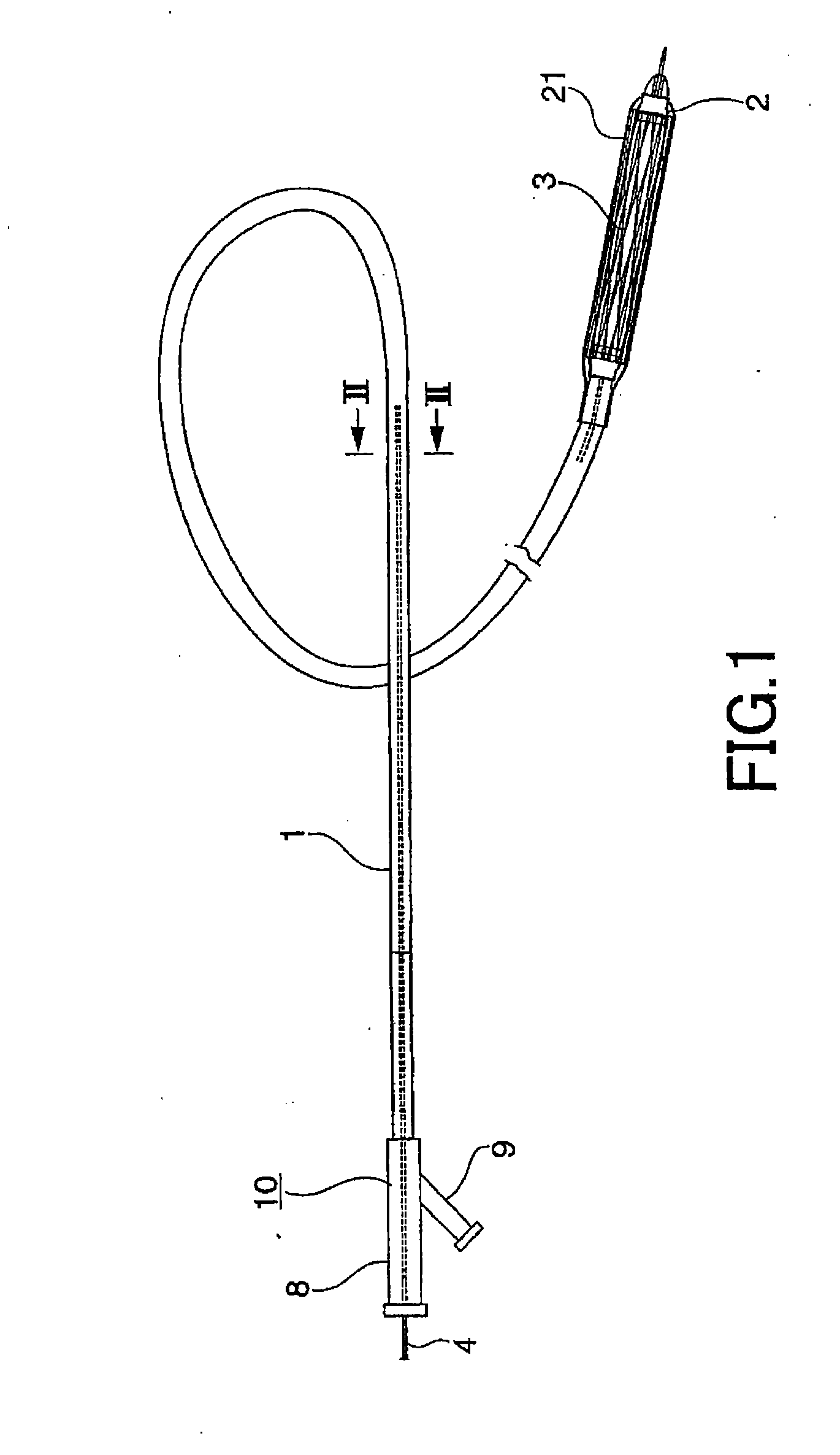
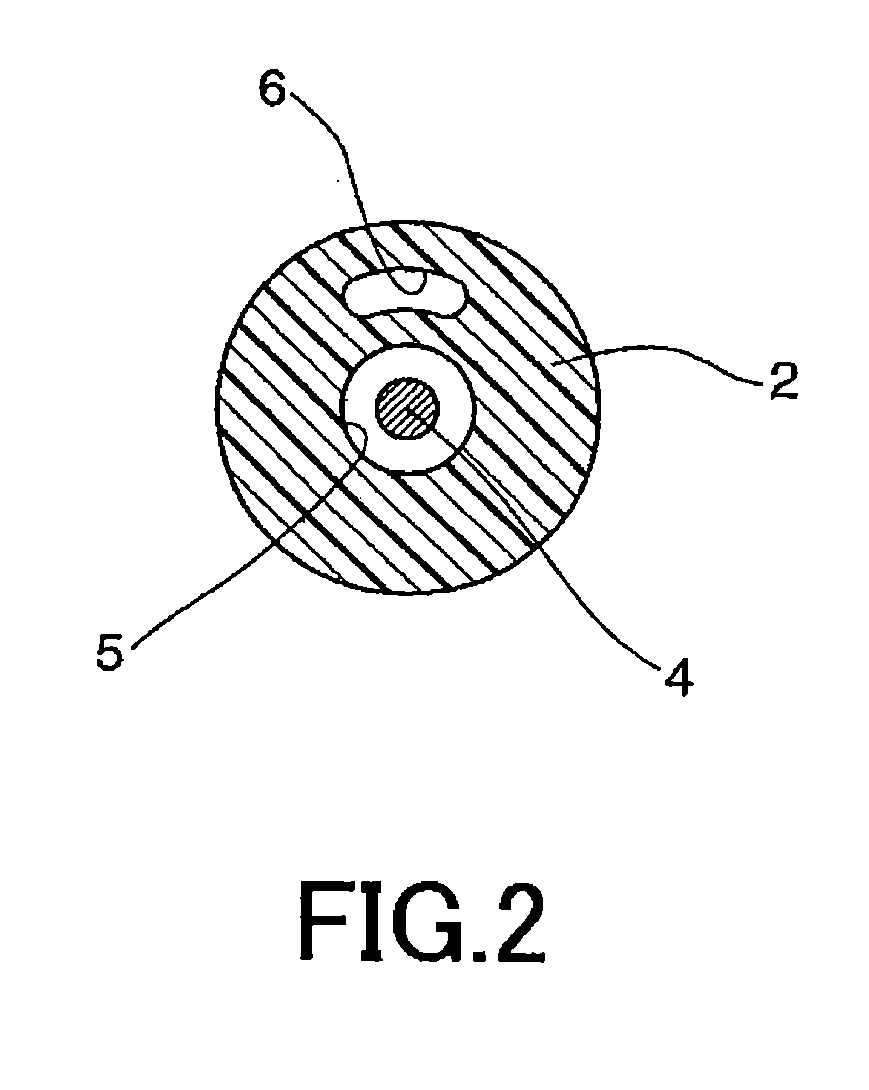
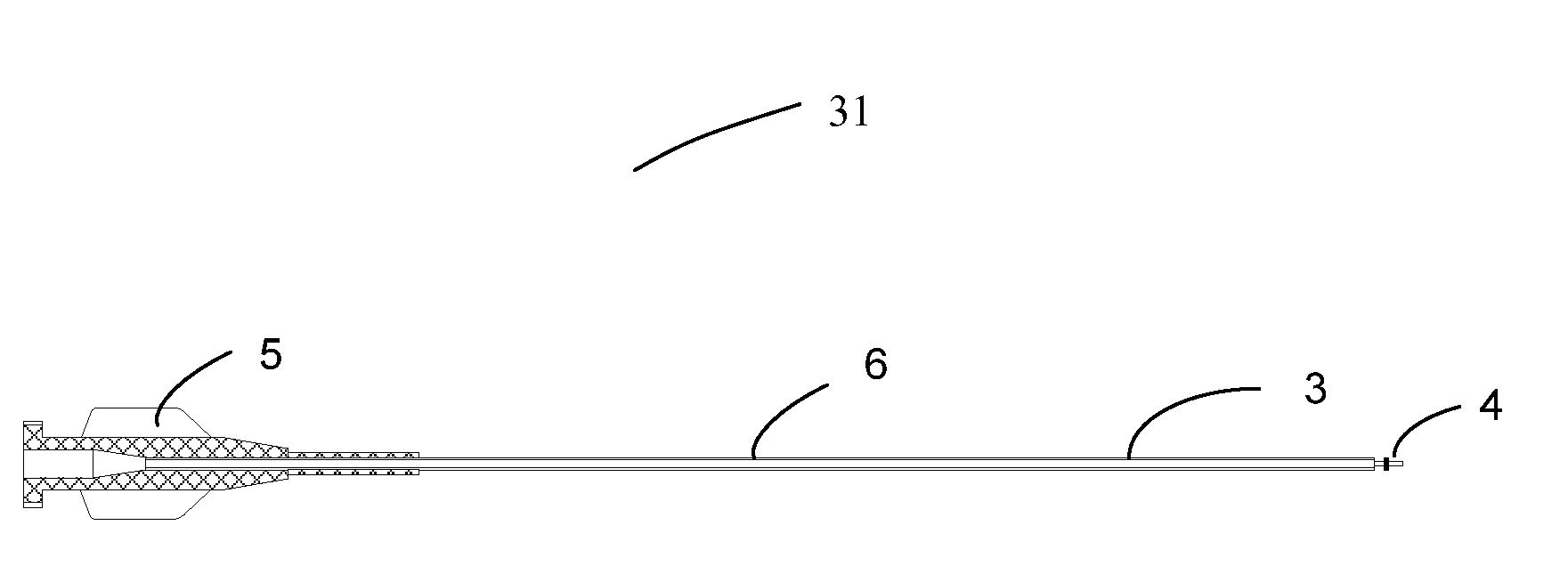
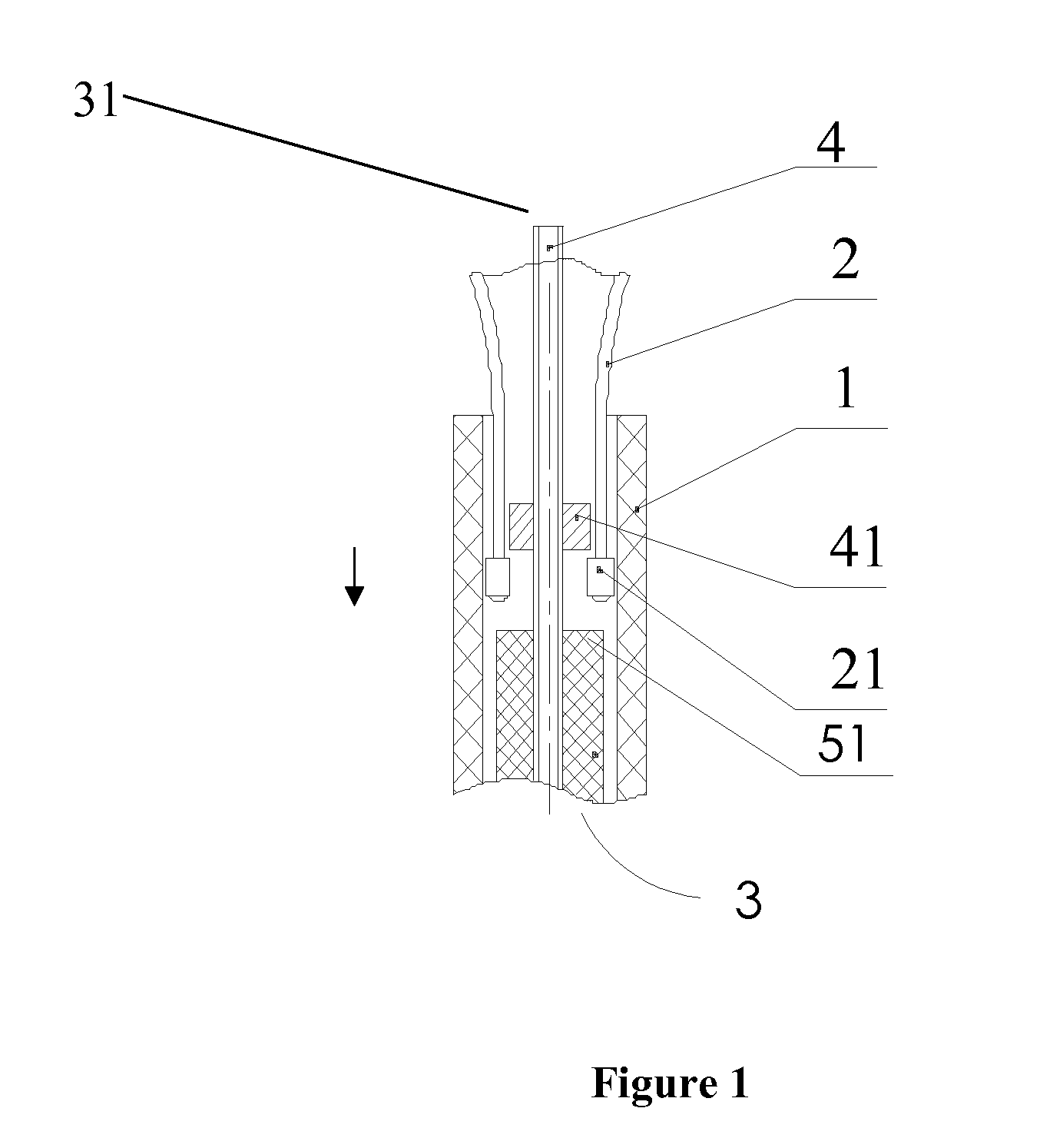
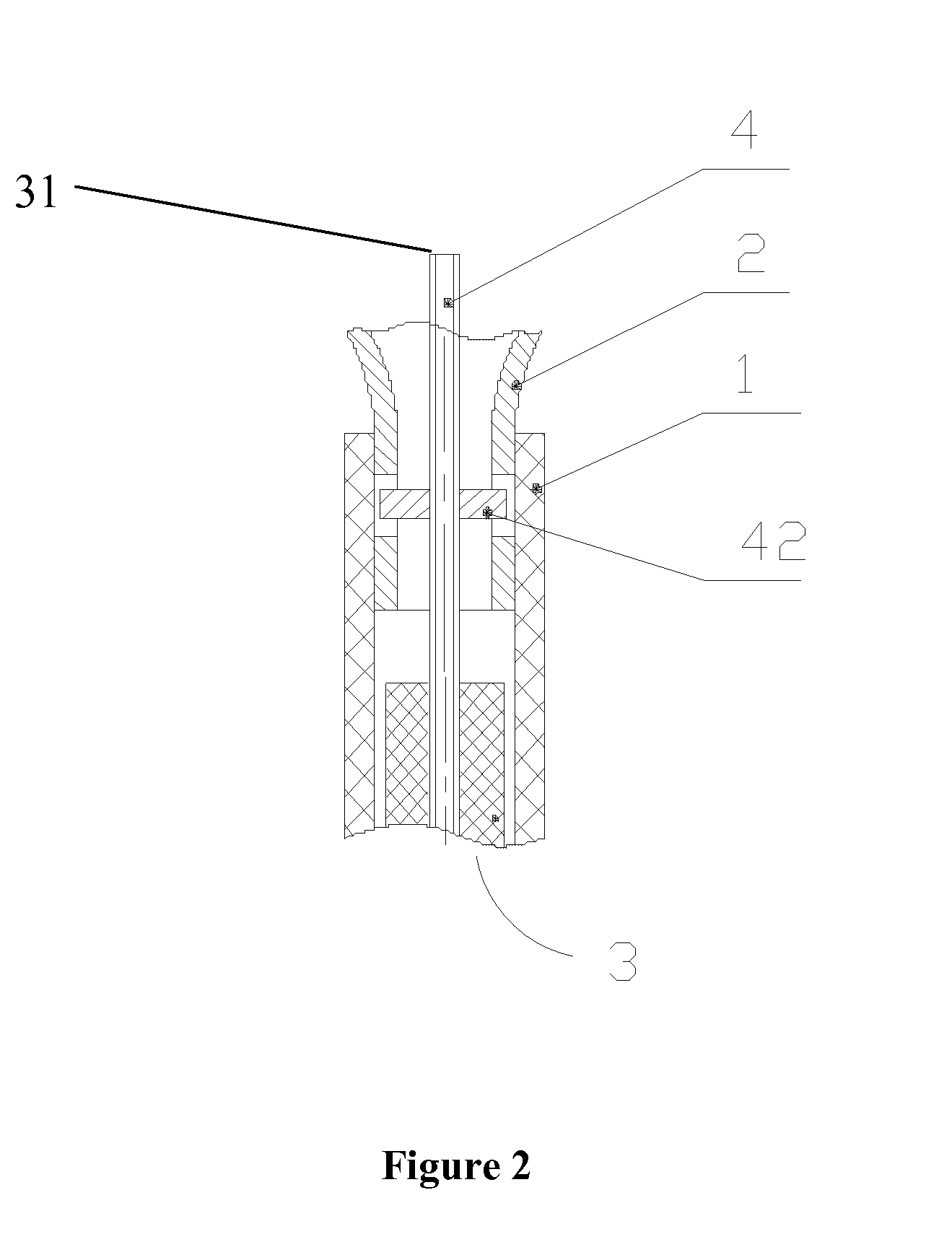
Device for delivery of stent for vessel
A device for delivery of a stent for a vessel, used for implanting a stent for the vessel 3 in the vessel, is disclosed. The device for delivery of a stent for the vessel includes a catheter (1) for insertion into the vessel of a living body, a balloon (2) mounted on an outer peripheral surface of the distal end side of the catheter and inflatable with a fluid supplied to the catheter, a stent for the vessel (3), formed of a biodegradable polymer to a tube form, mounted on the balloon in a diameter-contracted state and having self-expanding properties, and a stent holding member (21) formed of a polymer material to a tube form for covering at least a portion of the stent for the vessel from the catheter for holding the stent for the vessel on the balloon. The stent holding member has been drawn in the longitudinal direction. In the distal end of the stent holding member, located towards the distal end of the catheter, there is formed a tearing assisting portion (22). The stent holding member is torn along the tearing assisting portion, by expansion of the stent for the vessel attendant on inflation of the balloon, to release its holding of the stent for the vessel to enable expansion of the stent for the vessel (3).
Owner:IGAKI IRYO SEKKEI
Dealloyed nanoporous stents
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
Barrier stent and use thereof
InactiveUS20070043428A1High aspect ratioPreferential penetrationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersThrombusSmooth muscle cell migration
The present invention relates to a vascular stent that includes an expandable stent defining an interior compartment, a first polymeric layer exposed to the interior compartment defined by the stent, the first layer comprising an agent that promotes re-endothelialization, an agent that inhibits thrombosis, or a combination thereof, and a second polymeric layer at least partially external of the stent, the second layer being adapted for contacting a vascular surface and being characterized by pores that are substantially impermeable to vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Method of making and using the vascular stent are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
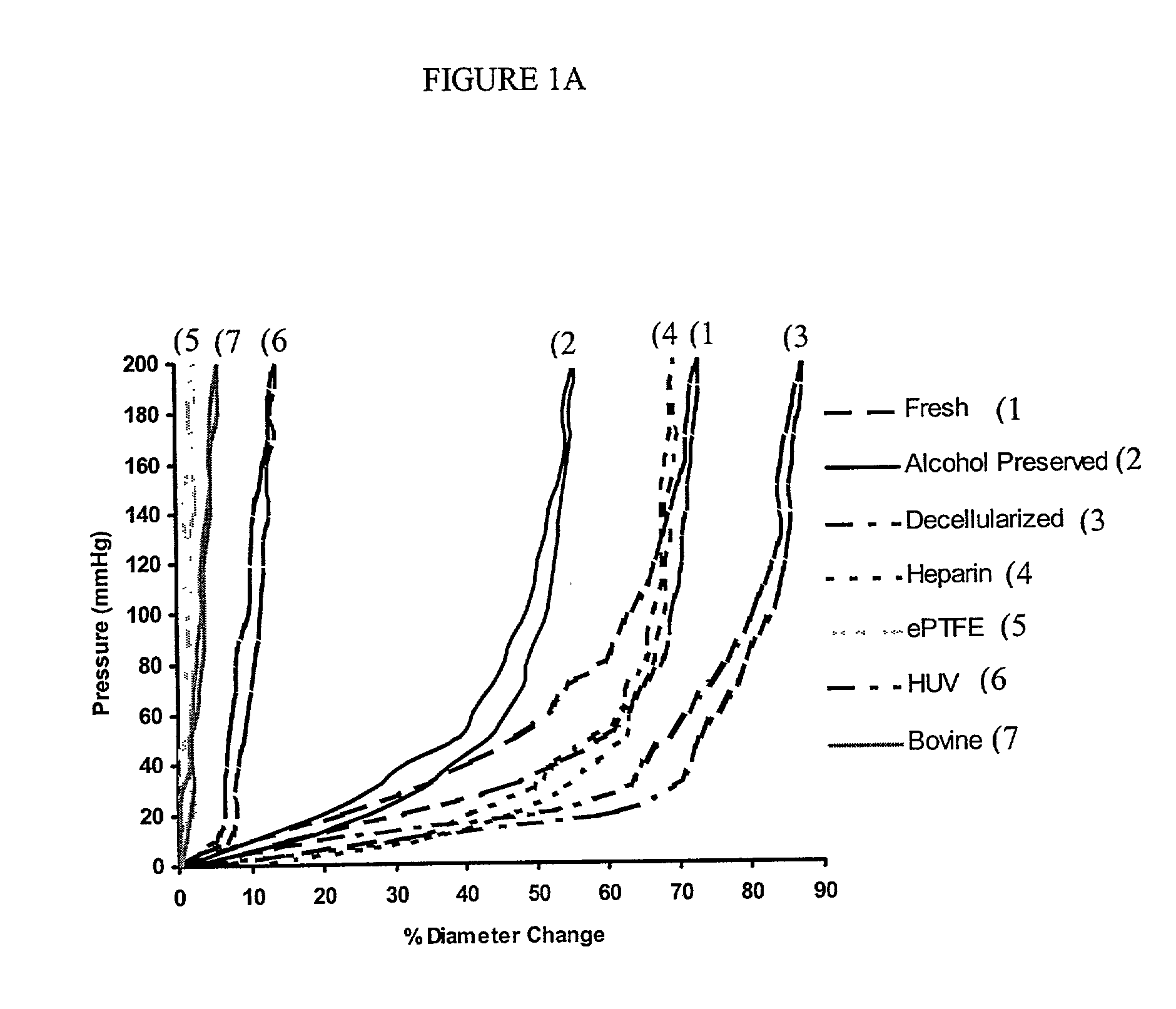
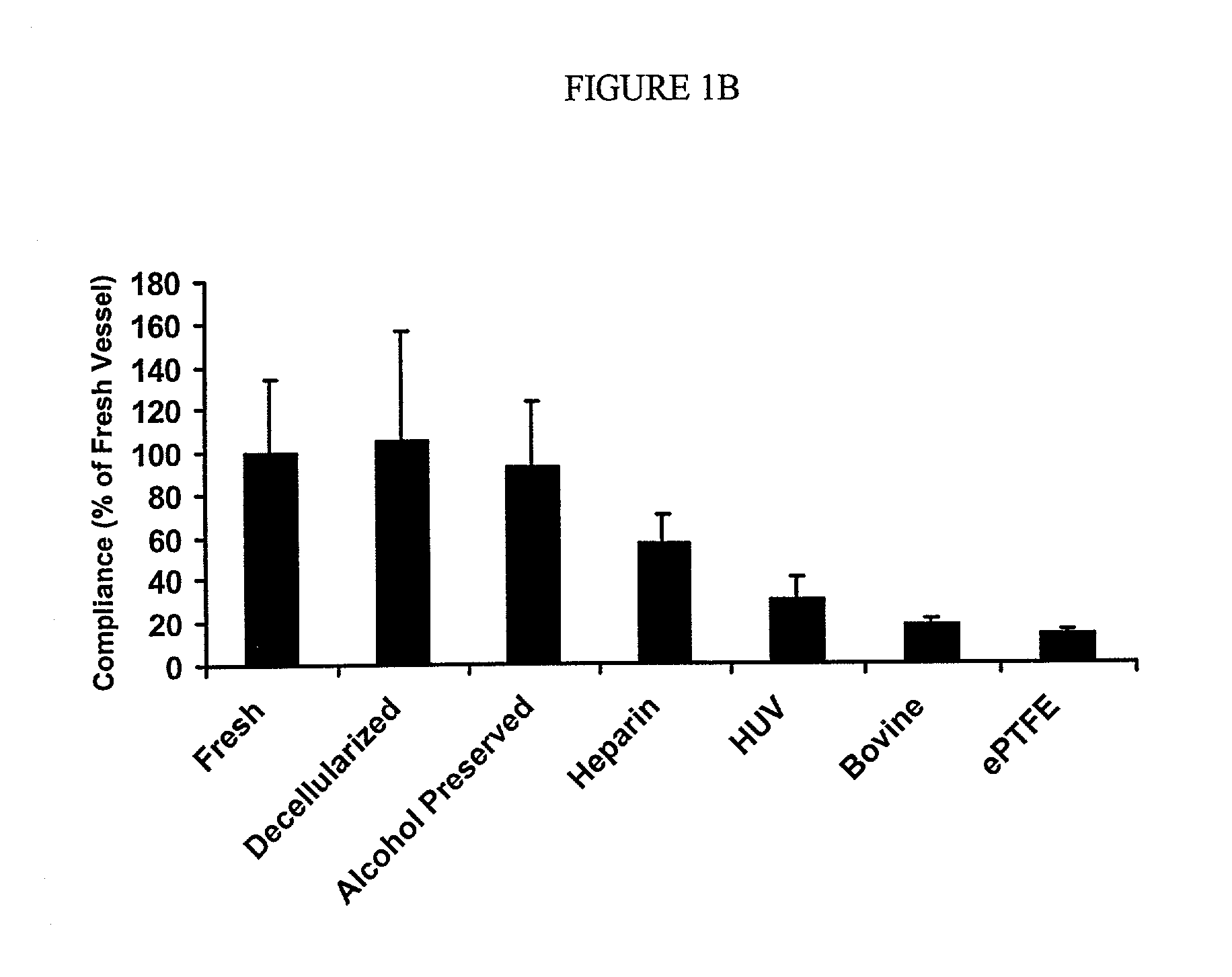
Decellularized vascular prostheses resistant to thrombus occlusion and immunologic rejection
The present invention relates to decellularized vascular prostheses that are resistant to thrombus occlusion and have a low level of immunogenicity. The vascular prostheses are denuded of cells, and coated with an anti-thrombogenic agent and a growth factor that promotes recellularization and further reduces the immunogenicity. The prostheses have high mechanical strength, resist aneurysm rupture, and allow for secure surgical sutures while maintaining structural integrity. The present invention provides vascular prostheses that are blood vessels, valves or portions of vessels containing valves. The present invention is also useful for coating synthetic vascular stents.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Linear material for blood vessel stent and blood vessel stent utilizing same
InactiveUS7070615B1Good antithrombotic propertiesImprove physical functionStentsSurgeryCoronary arteriesBlood vessel spasm
Owner:KYOTO MEDICAL PLANNING
Nanoporous stents with enhanced cellular adhesion and reduced neointimal formation
The present invention relates generally to medical devices containing nanoporous surfaces and methods for making same. More specifically, the invention relates to implantable vascular stents or other biomedical devices having at least one nanoporous layer that promotes improved cellular adhesion properties that promote healing and long term biocompatibility. In the case of stents, the nanoporous layer promotes re-endothelialization at sites of stent implantation vasculature, improves overall healing, and reduces inflammation and intimal disease progression. The nanoporous layer may be optionally loaded with one or more therapeutic agent to further improve the function of the implanted stent and further augment clinical efficacy.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Thin film vascular stent and biocompatible surface treatment
A vascular implant, comprising a sheet comprising thin film nickel titanium (NiTi), wherein the sheet has at least one super-hydrophilic surface having a water contact angle of less than approximately 5 degrees. The sheet is configured to have a compacted form having a first internal diameter and a deployed form having a second internal diameter larger than the first internal diameter. The sheet may be delivered into a blood vessel in the compacted form and expanded to its deployed form at a treatment location within the blood vessel, wherein the stent is configured to expand onto an internal surface of the blood vessel and exert a radial force on said internal surface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
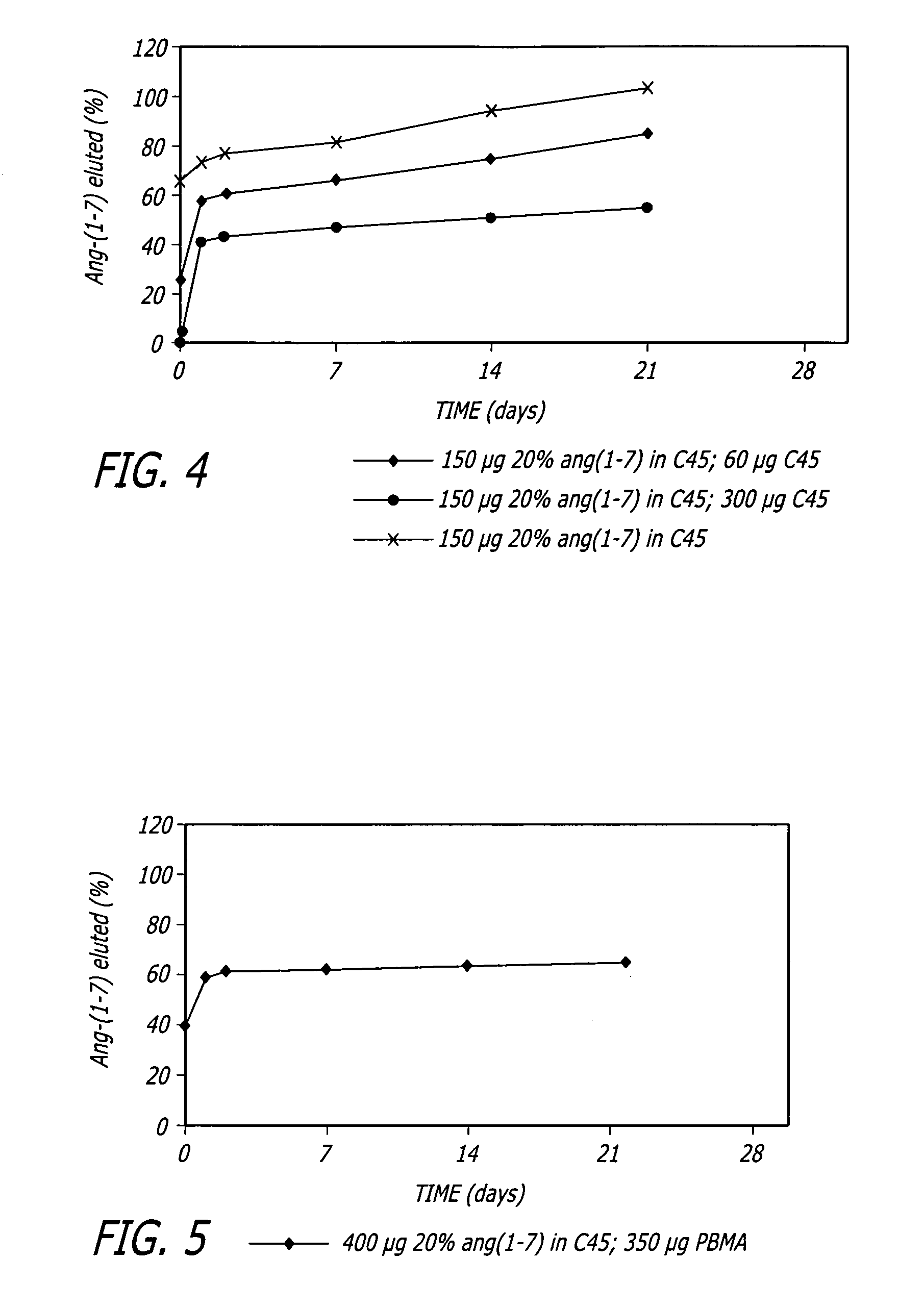
Angiotensin-(1-7) eluting polymer-coated medical device to reduce restenosis and improve endothelial cell function
InactiveUS7176261B2Function increasePrevent restenosisAngiotensinsPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular endotheliumPercent Diameter Stenosis
Medical devices with polymer coatings designed to control the release of angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonists from medical devices are disclosed. The present application also discloses providing vascular stents with angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonist-containing controlled-release coatings. Methods for treating or inhibiting post-stent implantation restenosis as well as improving vascular endothelial function in patients are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of manufacturing a covered stent
A method of manufacturing a covered stent having a sufficiently thick covering to retain a therapeutically effective amount of a therapeutic agent. The covering is applied to the entire outer surface of the stent to provide sufficient volume for retention of the therapeutic agent. In certain embodiments, the stent has a plurality of openings that are covered by the covering. The invention is particularly suited for certain applications, such as for the manufacture of non-vascular stents.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Delivery apparatus for a retractable self expanding neurovascular stent
InactiveUS20100185271A1Improve trackabilityPrevent movementStentsSurgeryPush and pullExternal catheter
The present invention relates to a delivery apparatus for delivering a self-expanding neurovascular stent that allows for smooth movement of the apparatus along a typically tortuous vascular path, ease of stent deployment, and ease of stent retractability being pushed and pulled through the delivery apparatus. The apparatus includes an outer catheter, and an inner shaft located coaxially within the outer catheter. The stent is mounted on the distal section of the inner shaft and preloaded within the outer catheter distal region. The inner shaft includes at least one stent blocking member disposed in the distal section. The self-expanding stent has proximal, middle and distal ends and is comprised of a plurality of closed cells. The self-expanding stent includes locking members which interlock with the blocking member(s) disposed on the inner shaft so as to lock the stent onto the inner shaft within the outer catheter, and to enable the stent retractable together with the inner shaft being out of and retrieved back to the outer catheter. More specially, the invention may be used in the treatment of blood vessel blockage and aneurysms which occur in the brain.
Owner:ACHIEVA MEDICAL SHANGHAI
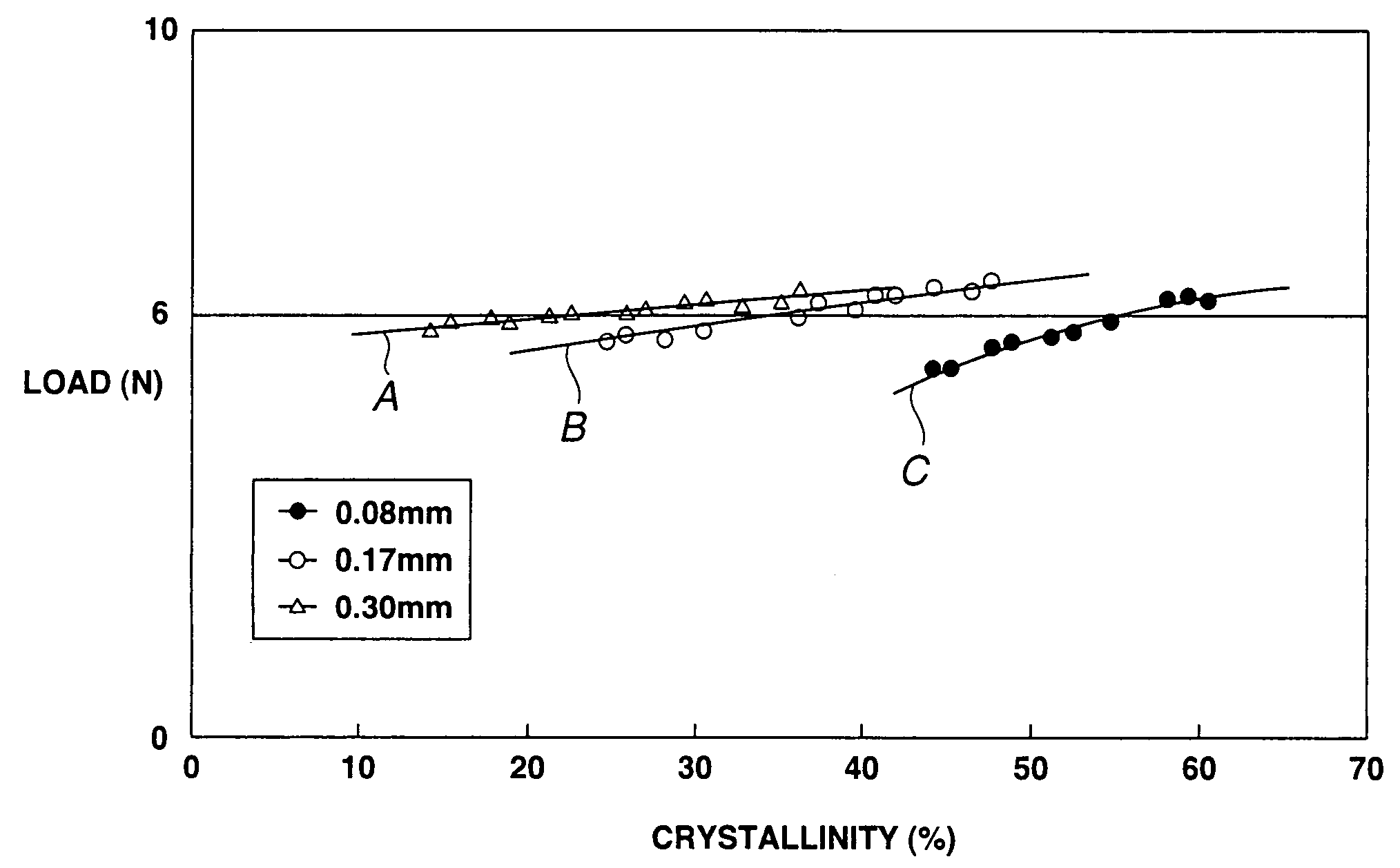
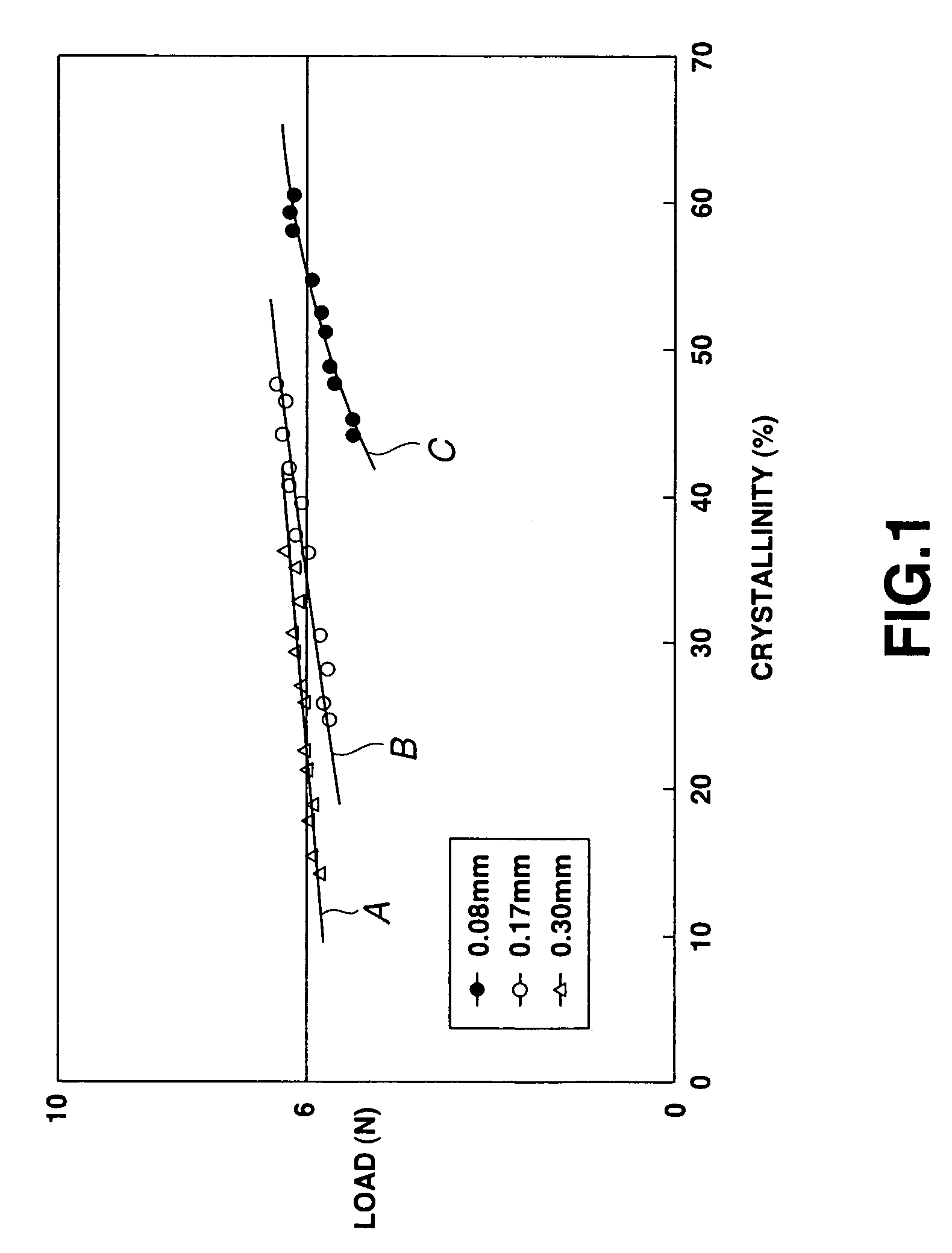
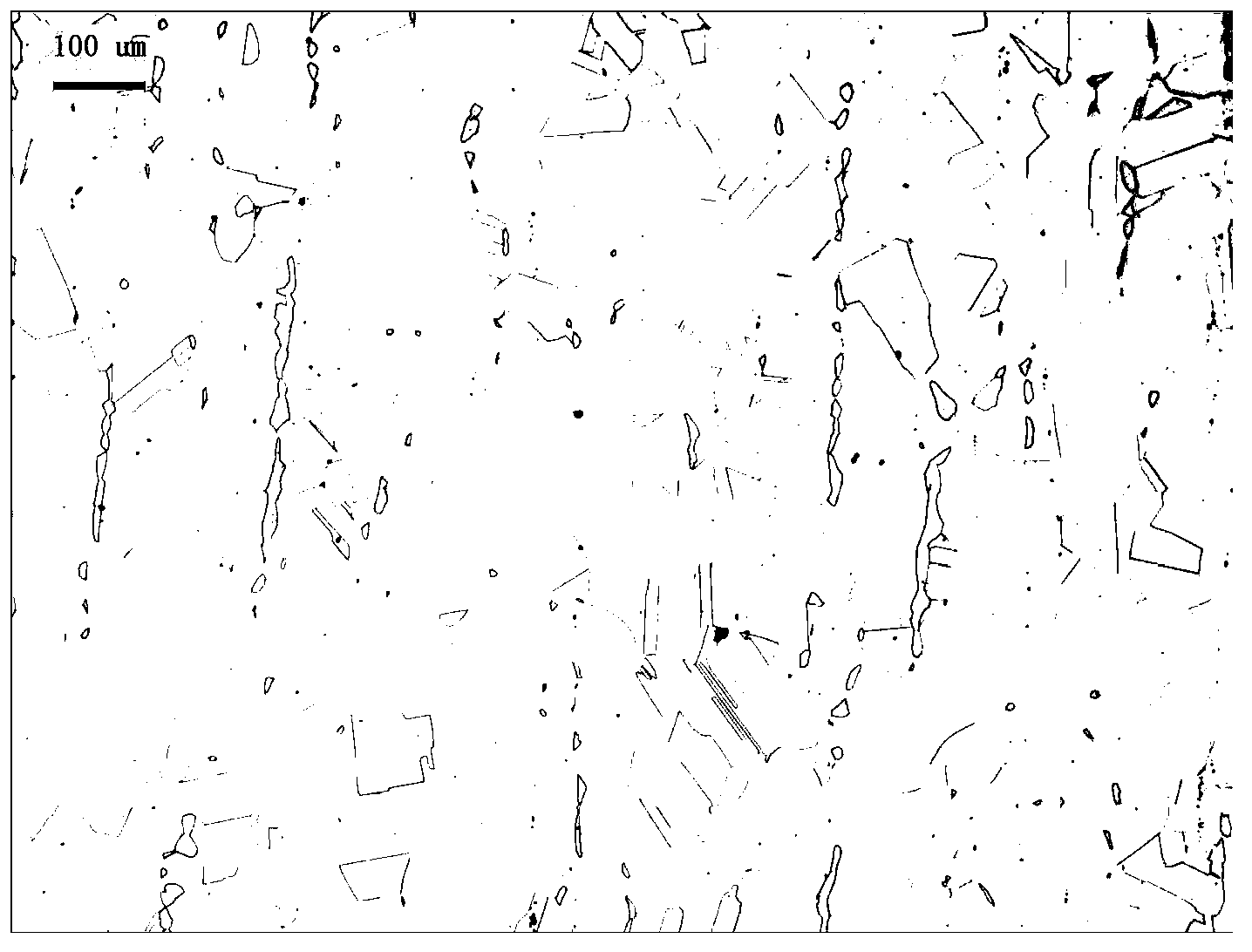
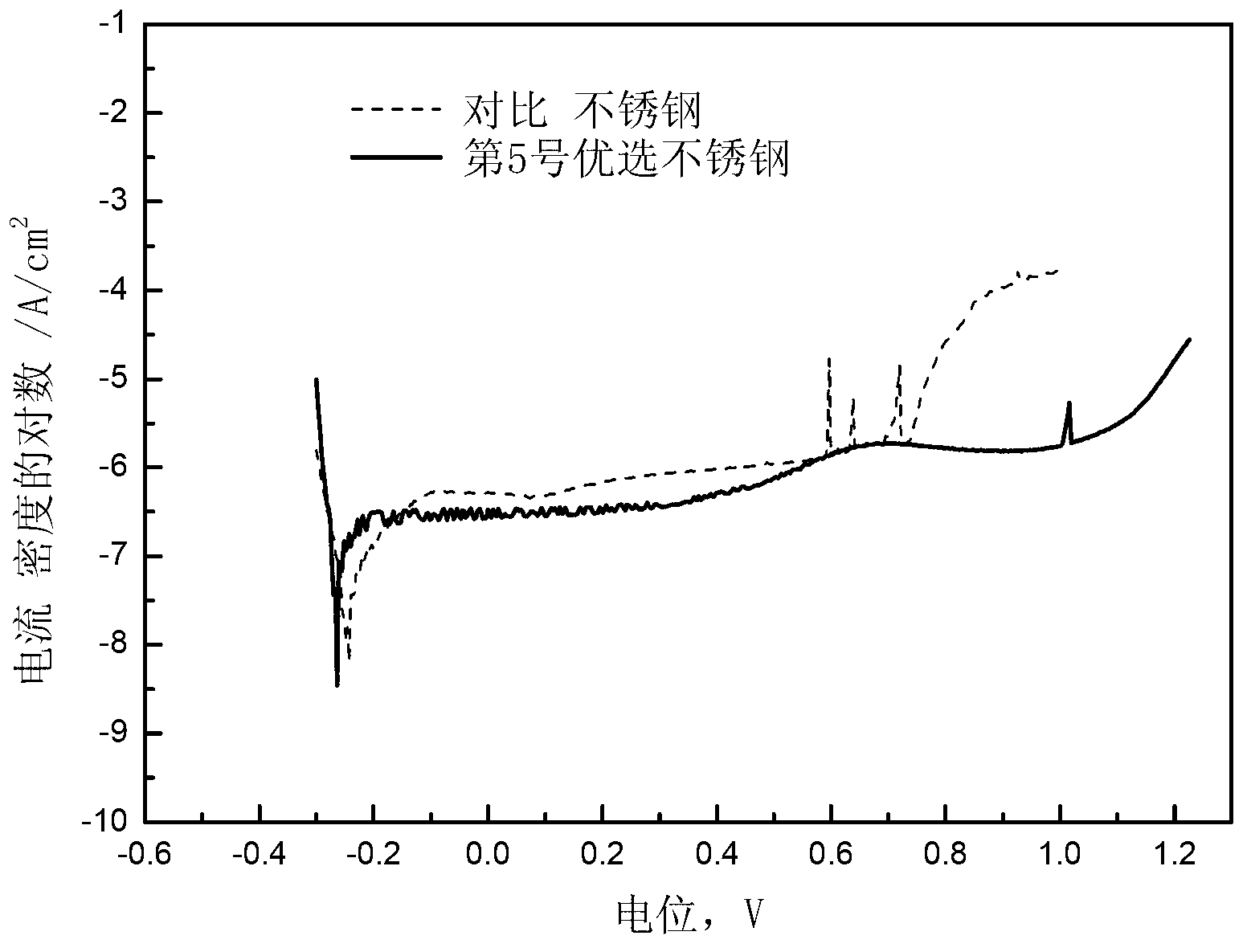
High-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel for vascular stent and application thereof
The invention provides a high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel material for a vascular stent, which comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 16-20% of Cr, 12-20% of Mn, 1-3% of Mo, 0.5-2% of Cu, no more than 0.05% of Ni, 0.7-1.2% of N, 0.5-8% of W, 0.05-0.5% of RE, no more than 0.08% of C, 0.3-4% of Si, no more than 0.010% of S, no more than 0.02% of P and the balance of Fe, wherein RE is a rare-earth element. The high-nitrogen stainless steel provided by the invention is mainly used for vascular stent processing; the elements of copper, nitrogen and rare earth are added to increase the blood compatibility of the stainless steel; and the tungsten alloy is added to increase the density of the stainless steel. The stainless steel has excellent visibility under X rays, contains no potential toxic element nickel, can be used in the aspects of surgical implants, medical appliances, food and catering appliances, jewelry and other stainless steel products which are always in contact with a human body, and can also be used in the fields of chemical engineering, environment protection and the like.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIAN MEDICAL TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Method for forming artificial vascular stent through 4D printing
ActiveCN104116578AFast preparationSimplify molding manufacturing equipmentStentsBlood vesselsMetallic materialsAlloy
The invention discloses a method for forming an artificial vascular stent through 4D printing. The method comprises the following steps that (1) shape memory polymers or shape memory alloy serves as a transformable material unit, polymer materials or metal materials serve as a base body material unit, and an initial vascular stent configuration is designed; (2) the transformable material unit and the base body material unit are printed into a needed original 3D configuration with a direct fusion forming method, or a laser area selective fusion forming mode or a micro jet molten drip electromagnetic constraint forming mode is selected as a shape memory alloy printing forming mode to manufacture the vascular stent; (3) heat preservation and slow cooling are conducted on the original 3D configuration or the vascular stent obtained in the step (2); (4) performance tests are conducted on the formed vascular stent so that the vascular stent can meet using requirements, and thus the 4D printing forming of the artificial vascular stent is completed, wherein the performance tests include the mechanics performance test, the incentive transformation test and the medical performance test.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
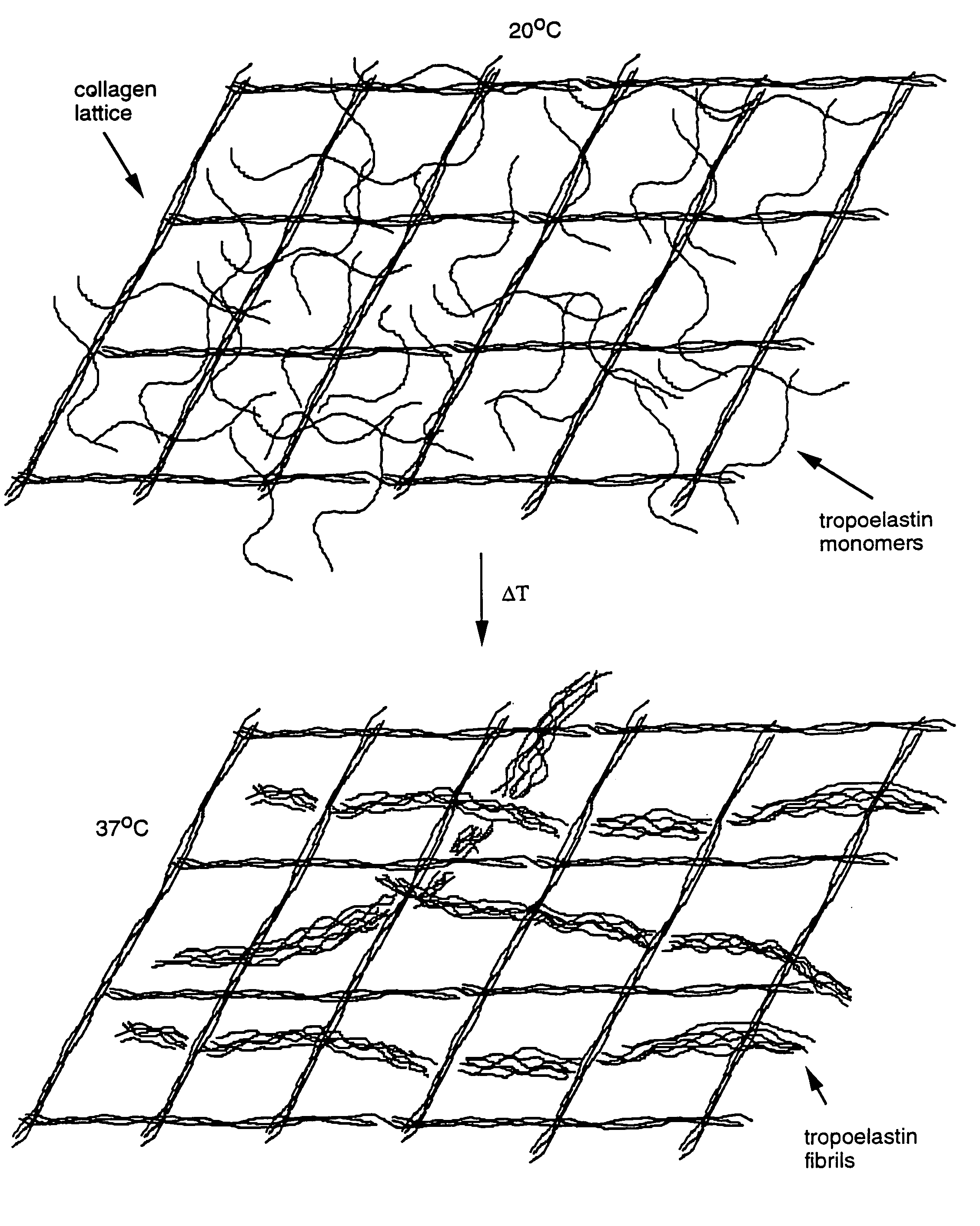
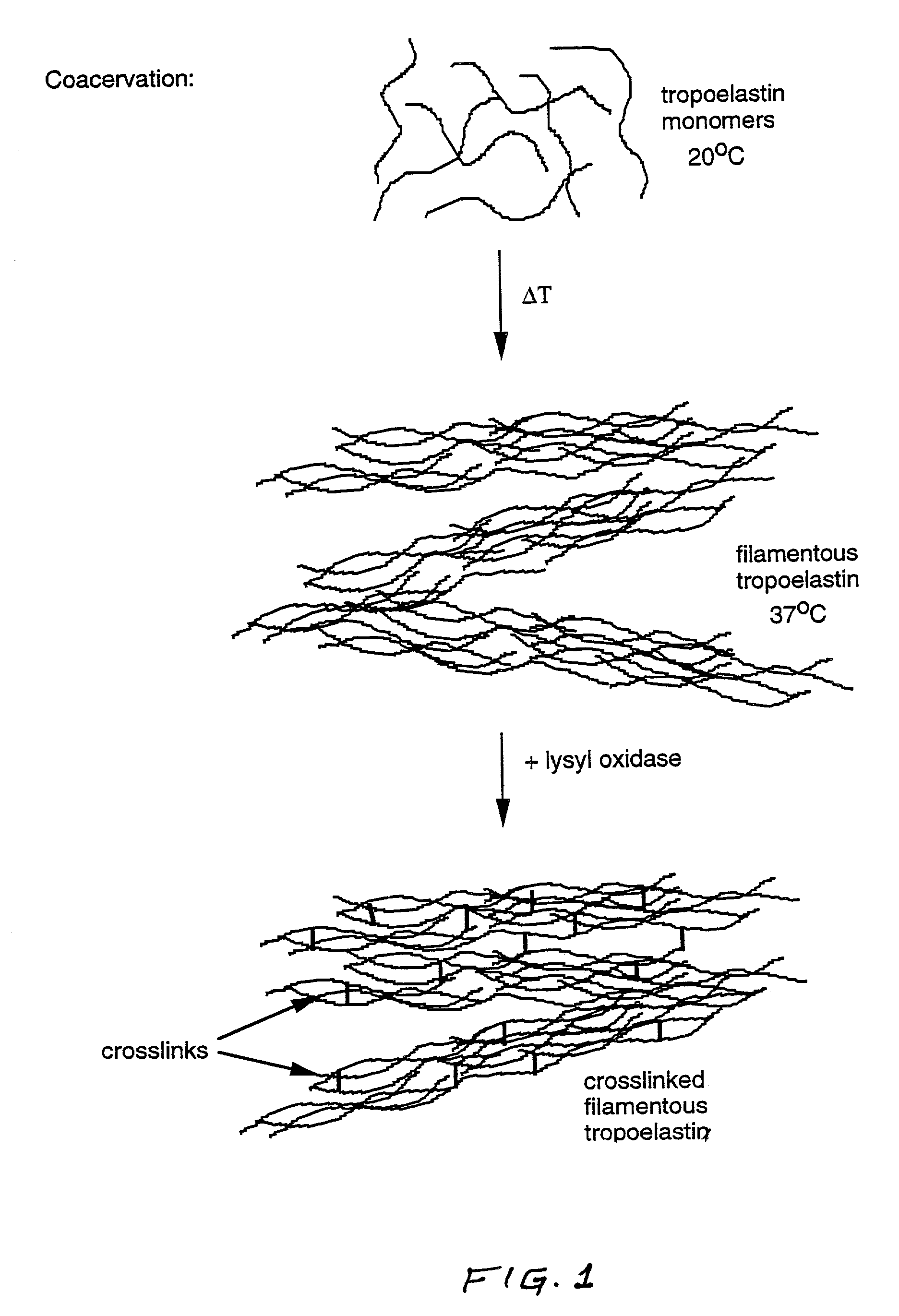
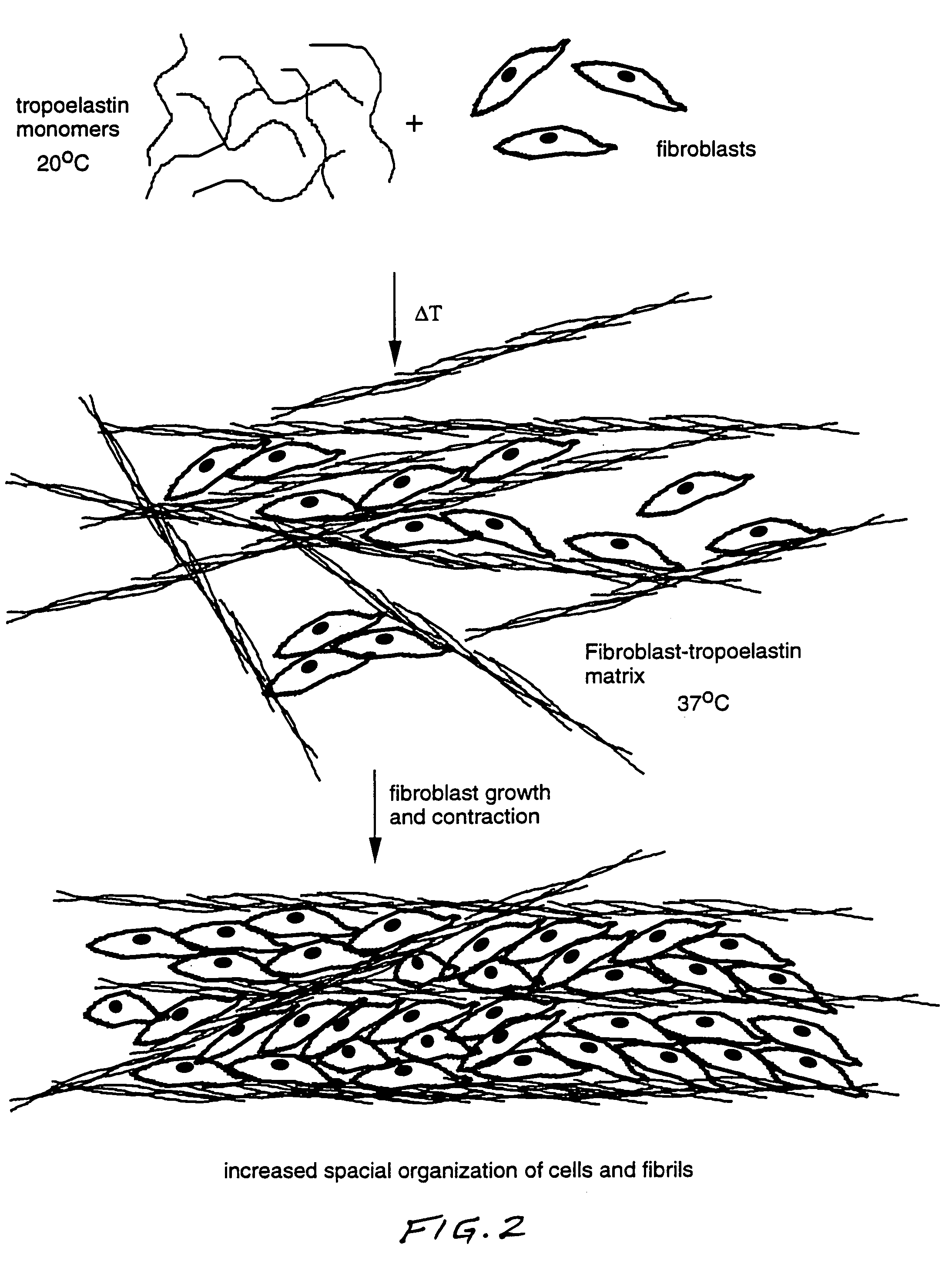
Method for using tropoelastin and for producing tropoelastin biomaterials
It is a general object of the invention to provide a method of effecting repair or replacement or supporting a section of a body tissue using tropoelastin, preferably crosslinked tropoelastin and specifically to provide a tropoelastin biomaterial suitable for use as a stent, for example, a vascular stent, or as conduit replacement, as an artery, vein or a ureter replacement. The tropoelastin biomaterial itself can also be used as a stent or conduit covering or coating or lining.
Owner:GREGORY KENTON W +2
Therapeutic cellular stent
A vascular stent carries living therapeutic cellular material. The stent in widely implantable over the vascular system, and allows either localized or systemic delivery of the therapeutic products produced by the cellular material to thereby enhance patient treatment.
Owner:SPIELBERG THEODORE E
Dynamically adjustable vascular stent
Methods and devices are provided for providing a protective framework for treating an aneurysm with embolic coils and preventing mitigation of the embolic coils from the aneurysm. A dynamically remodelable stent having a first and a second configuration is delivered into the blood vessel patient, such as a human or other animal, and positioned adjacent an ostium of an aneurysm while in the first, linear configuration. The dynamically remodelable stent may then be activated to assume a second, expanded configuration and thereby provide a protective framework spanning the neck of the aneurysm during and after delivery of embolic devices, such as embolic coils, to the aneurysm. The stent can be activated within the body of a patient in a minimally invasive or non-invasive manner such as by applying energy percutaneously or external to the patient's body. The energy may include, for example, acoustic energy, radio frequency energy, light energy and magnetic energy. In certain embodiments, the stent include a shape memory material that is responsive to changes in temperature and / or exposure to a magnetic field.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Hydrogel entrapping therapeutic agent and stent with coating comprising this
A hydrogel forming system which comprises a hydrophobic macromer with unsaturated group terminated ends and a hydrophilic polymer which is a polysaccharide containing hydroxy groups which are reacted with unsaturated group introducing compound, is convertible by free radical polymerization to form a hydrogel containing a three dimensional crosslinked polymer network containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic components. Agent can be entrapped in the polymer network, e.g., drugs, macromolecules or synthetic or natural polymers, for controlled release therefrom. In one embodiment, a vascular stent is coated with hydrogel with therapeutic agent entrapped therein.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com