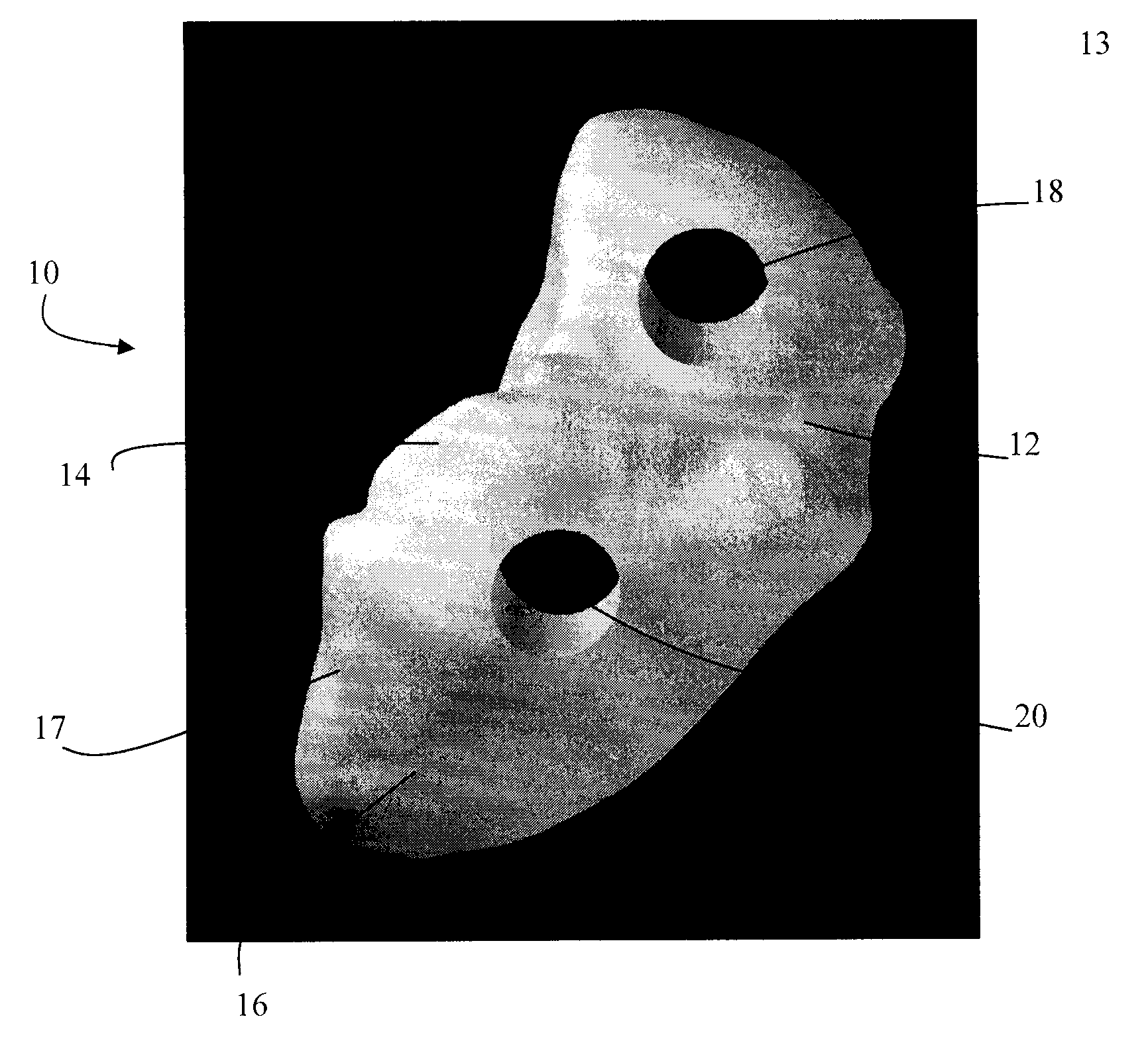
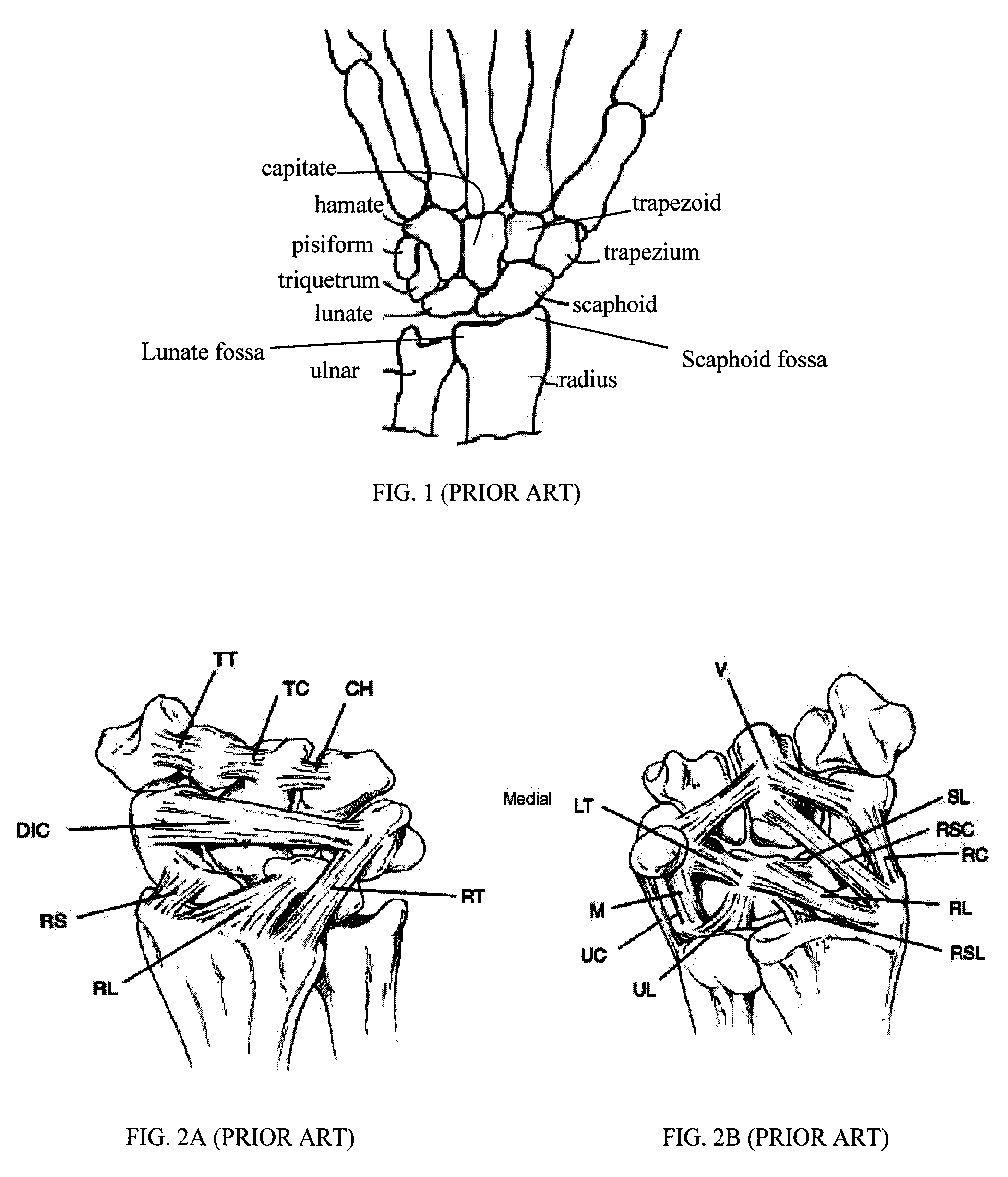
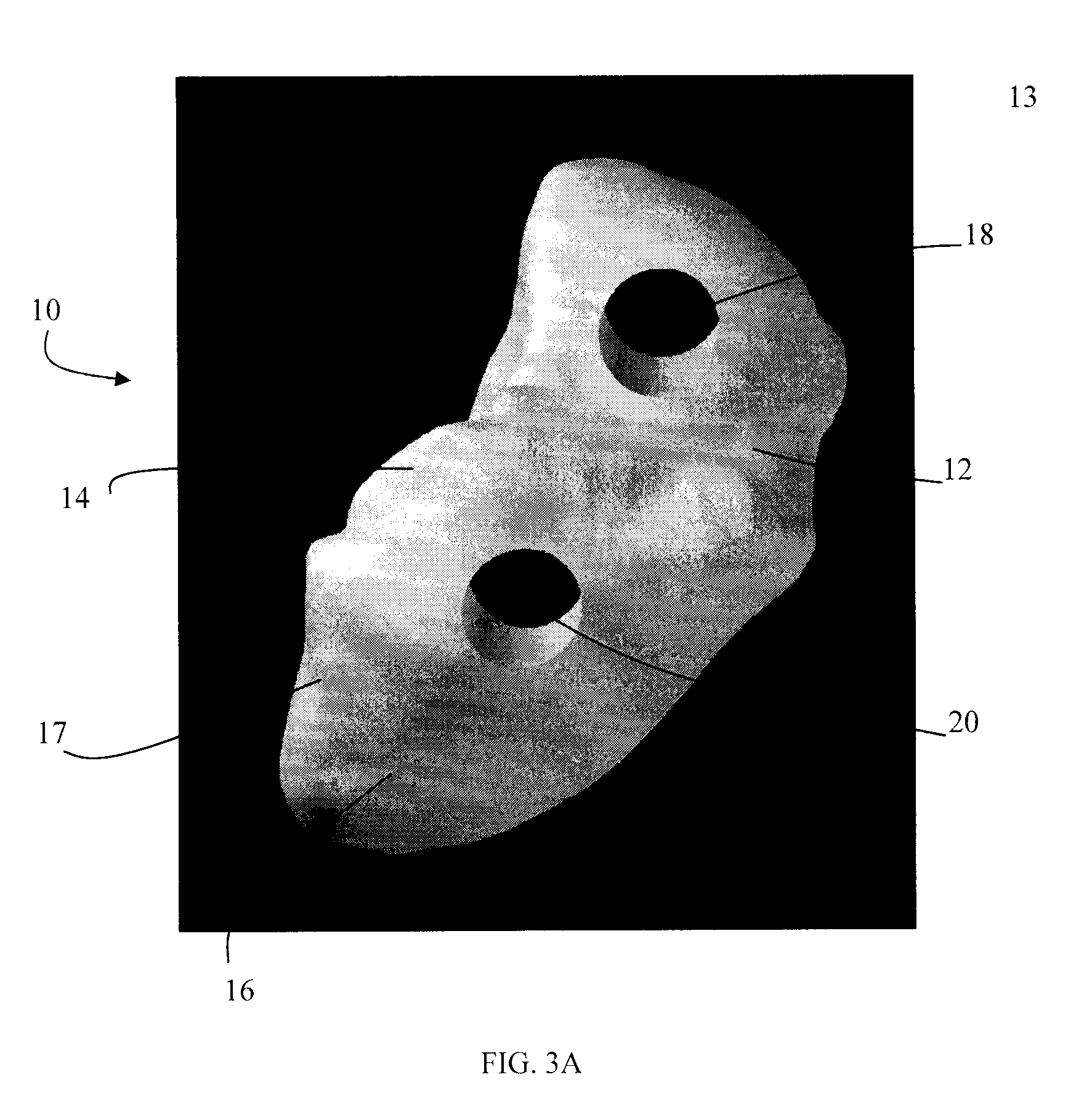
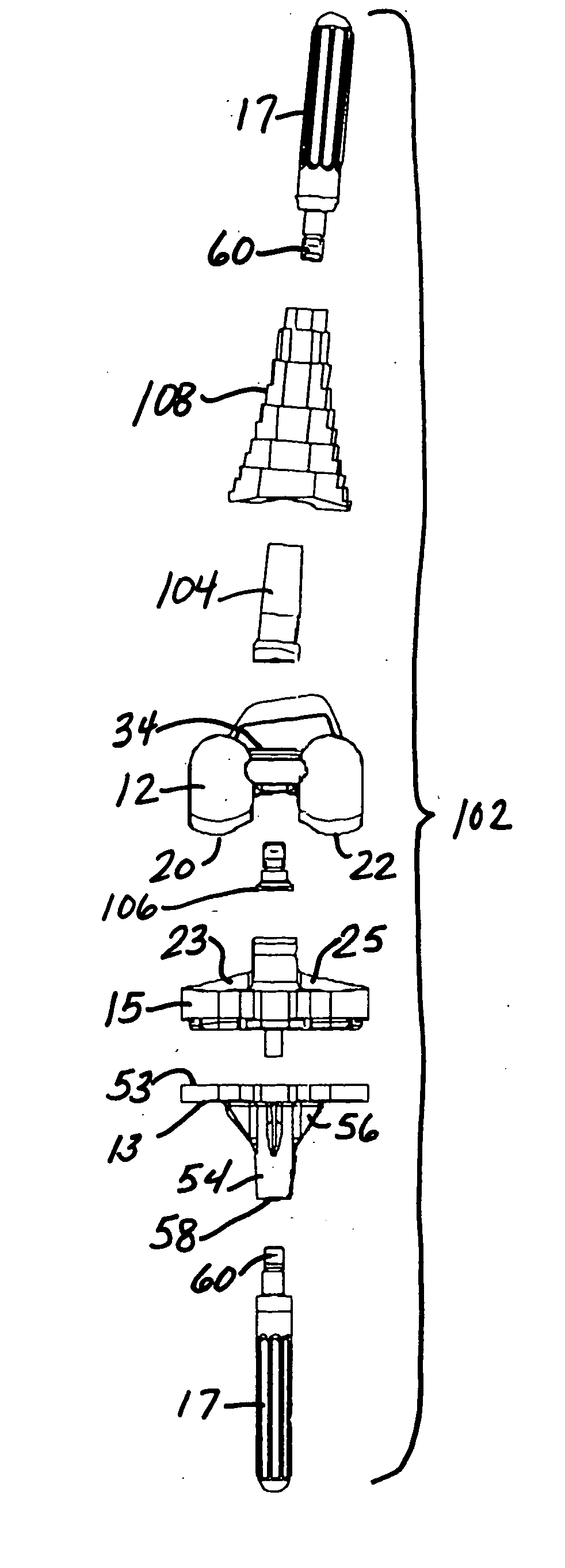
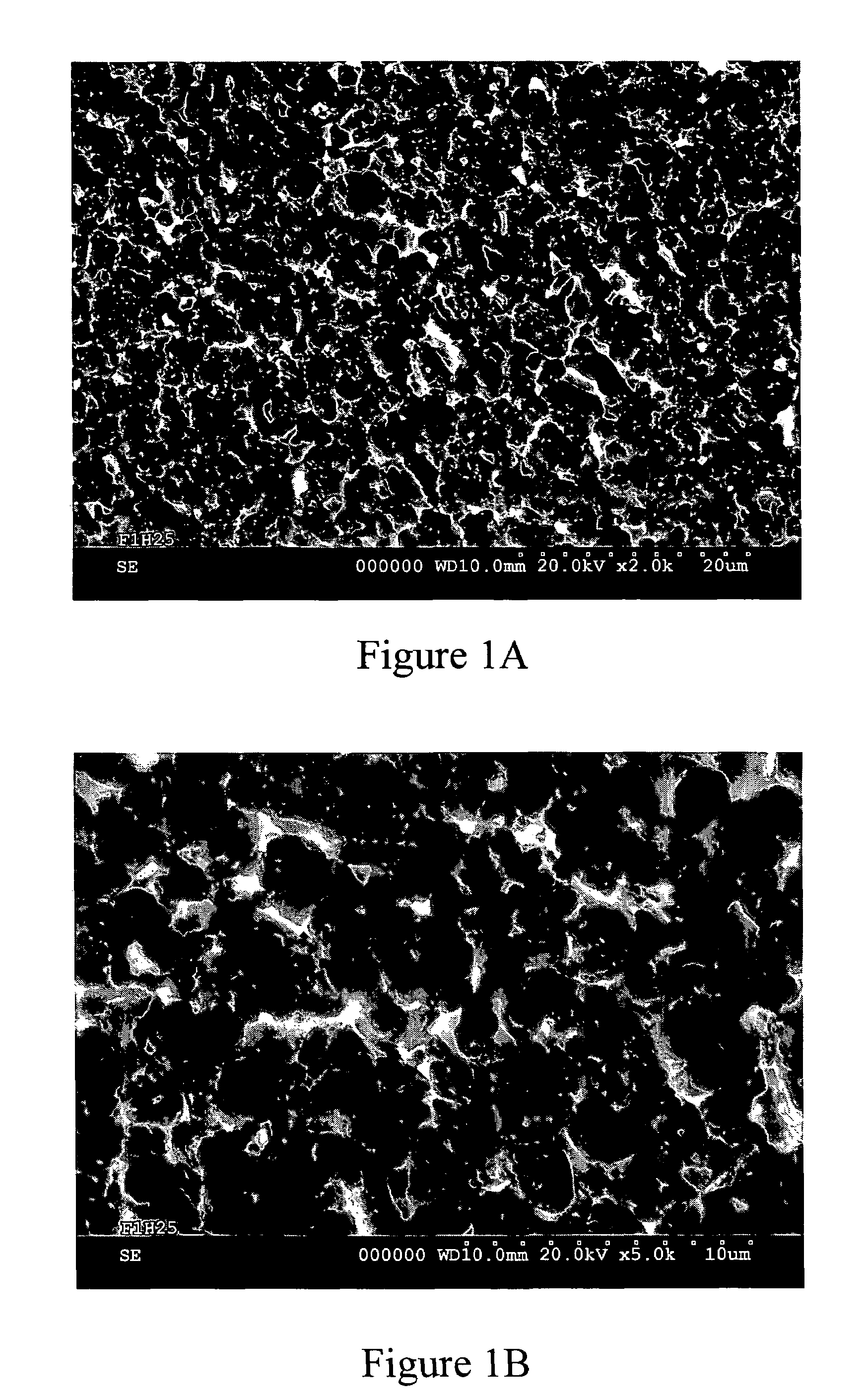
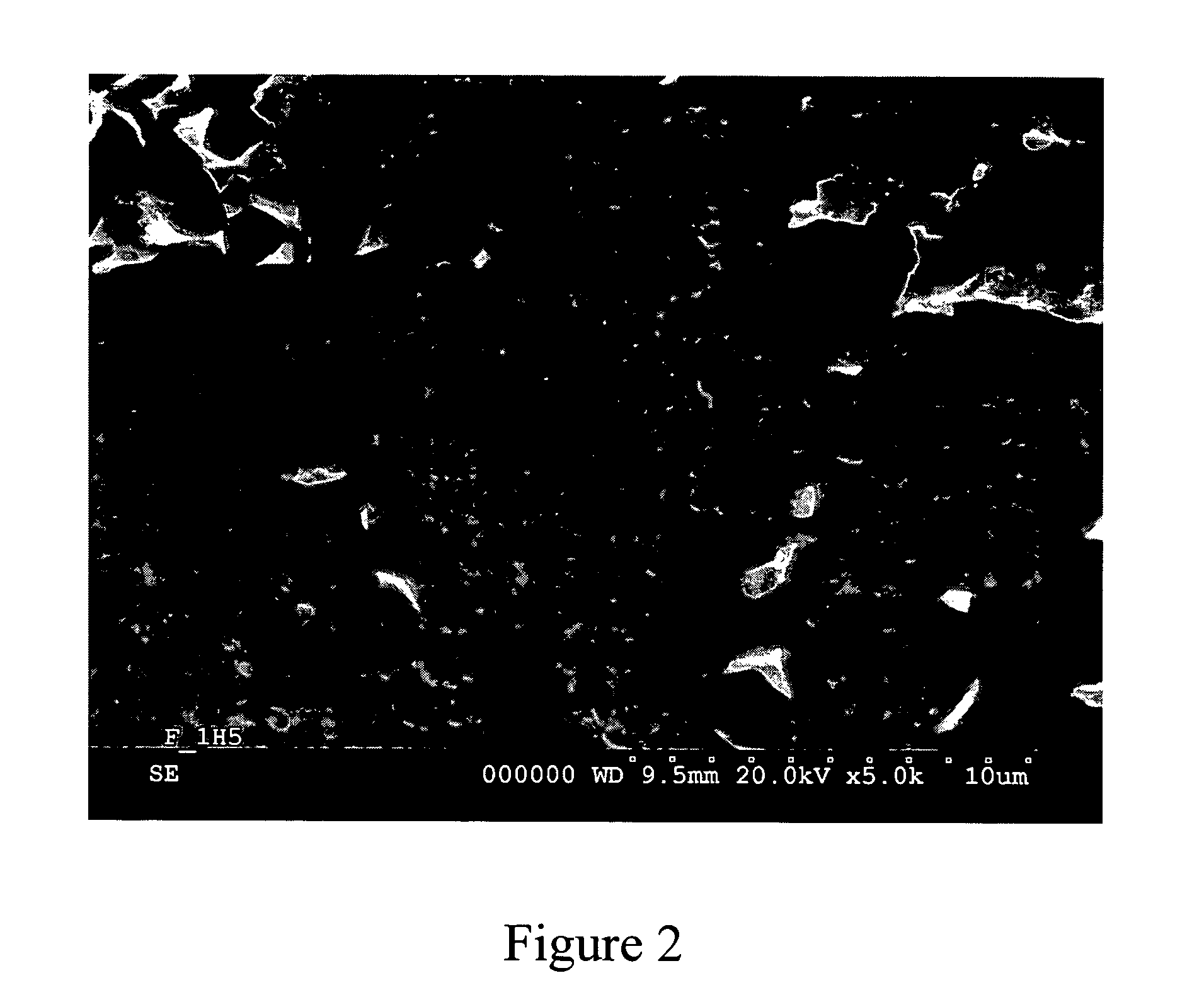
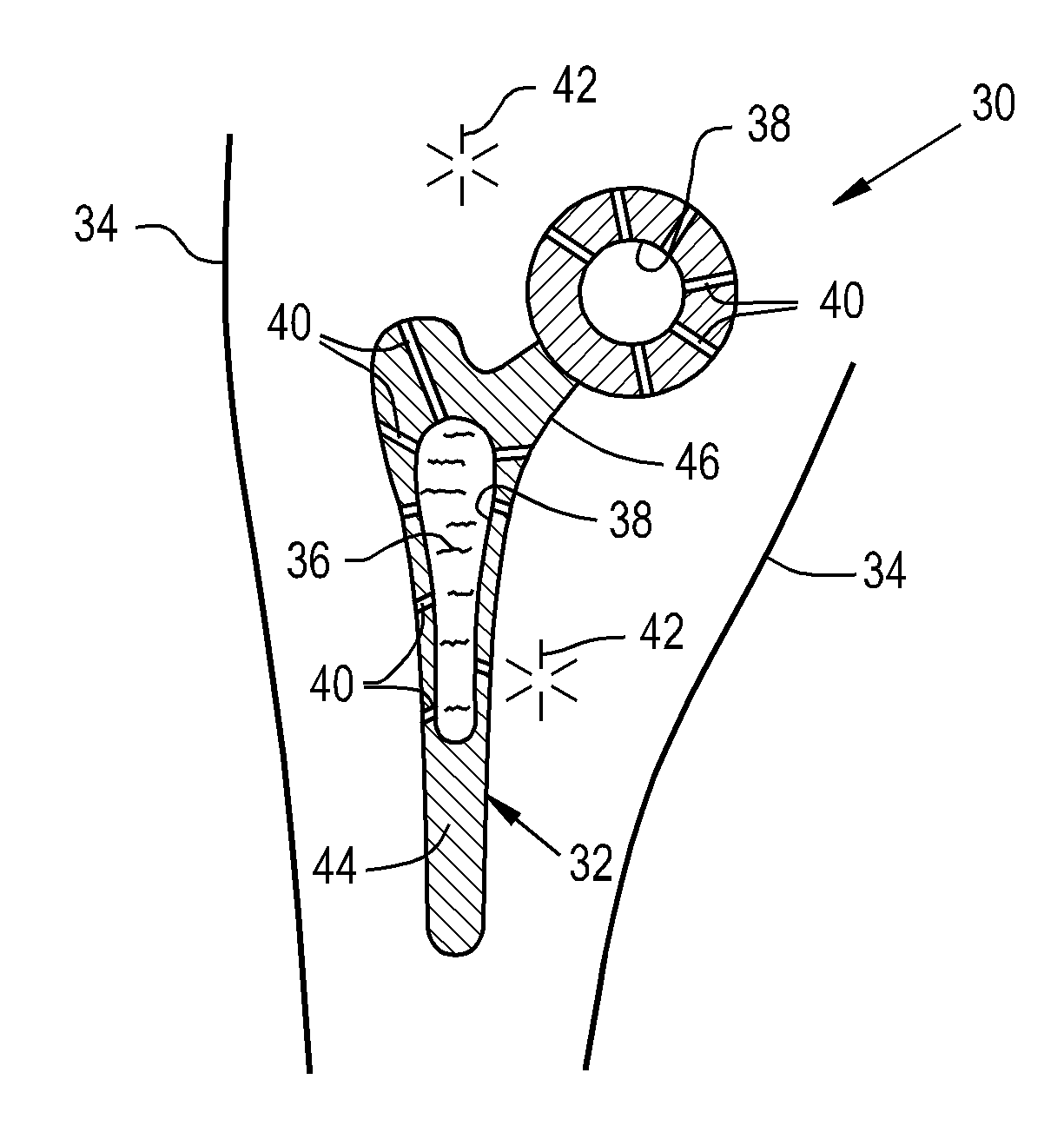
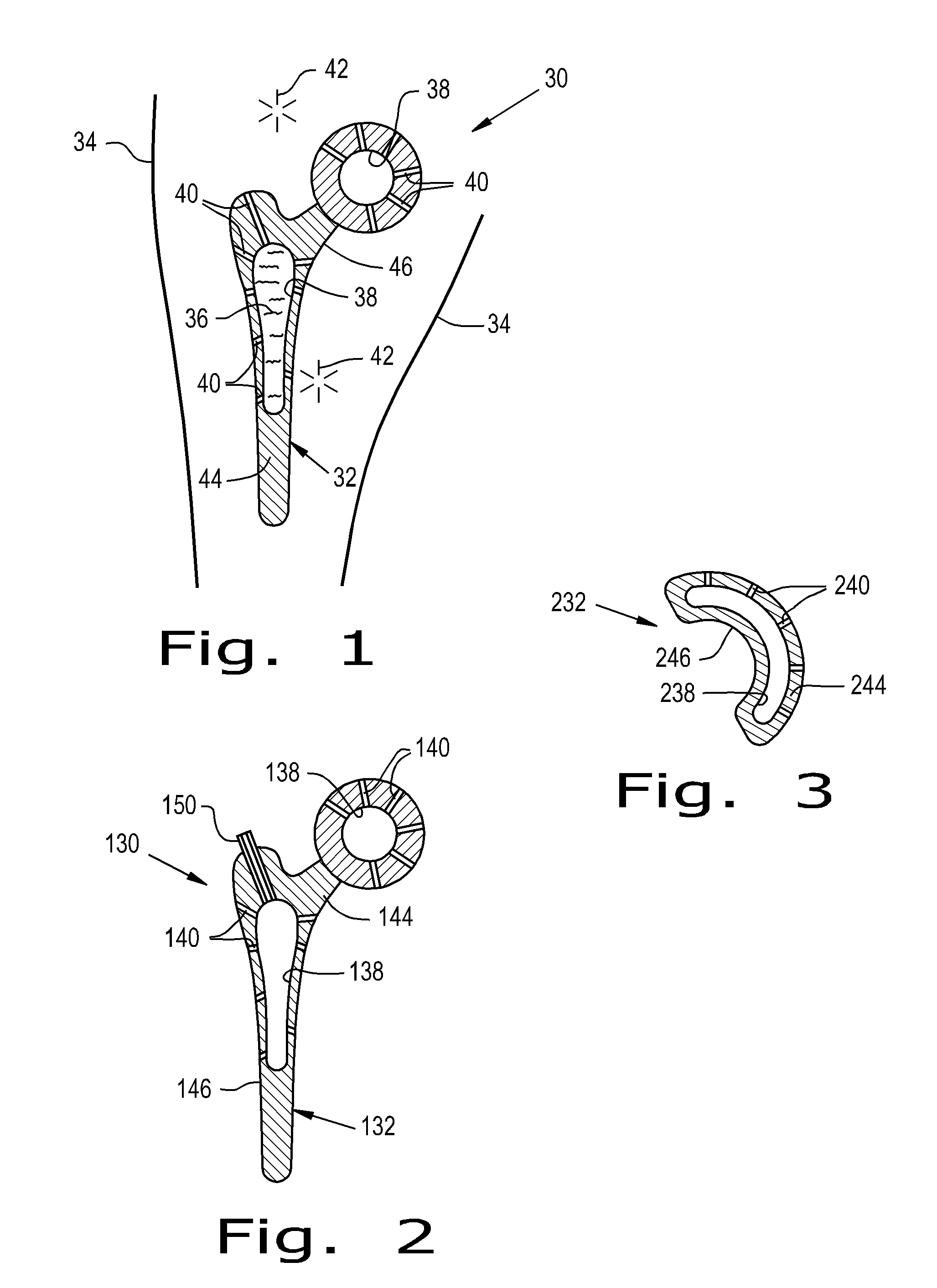
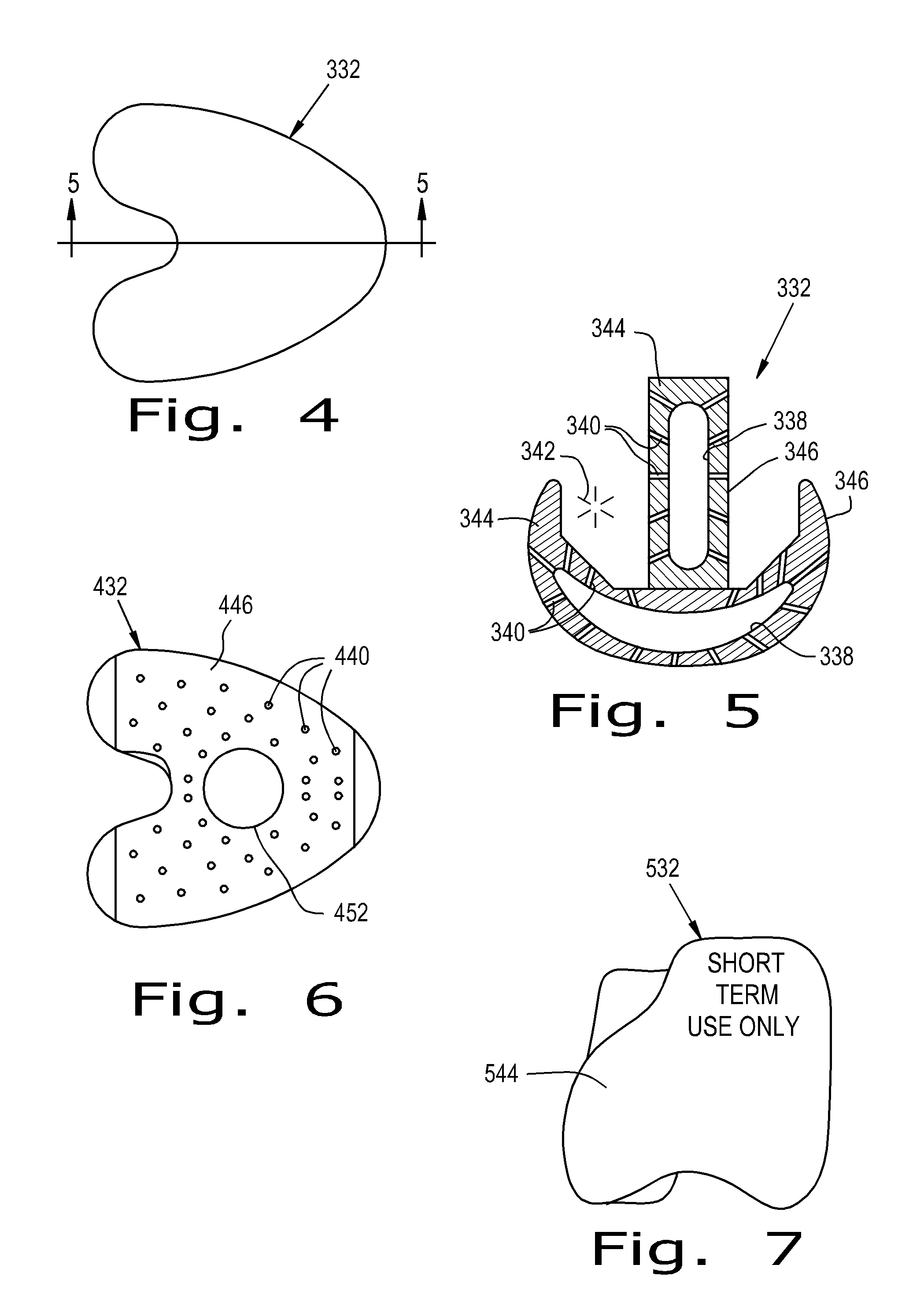
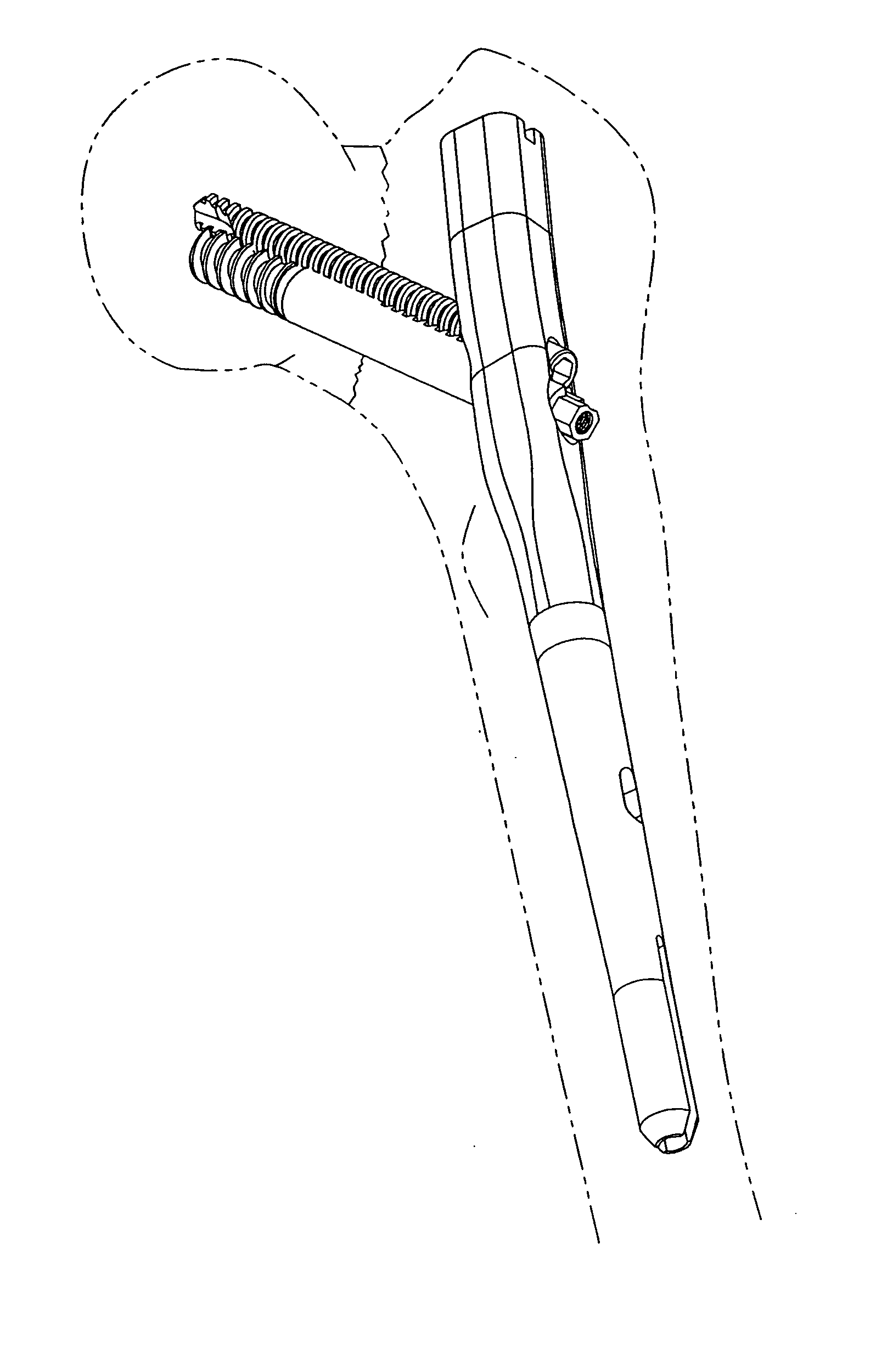
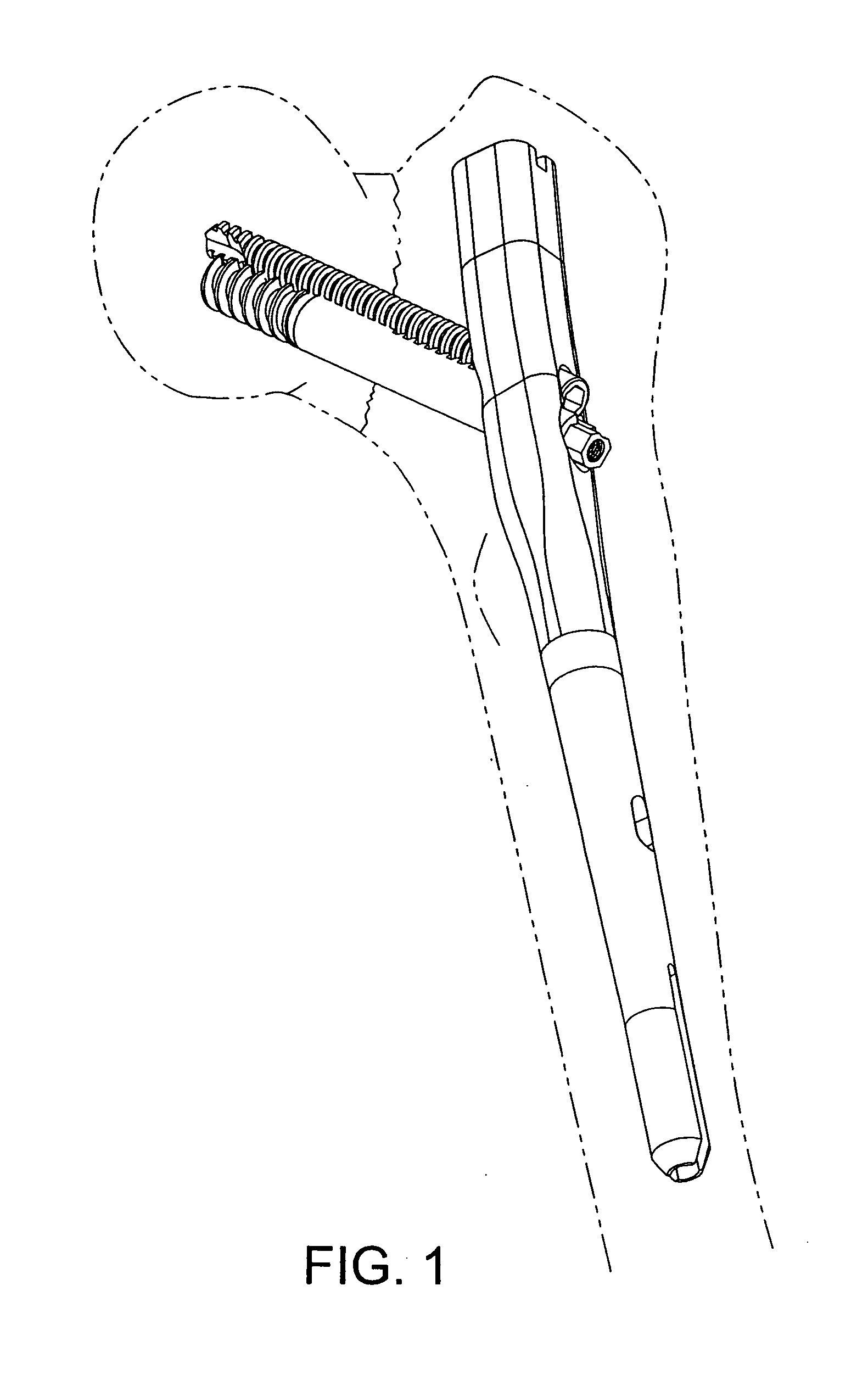
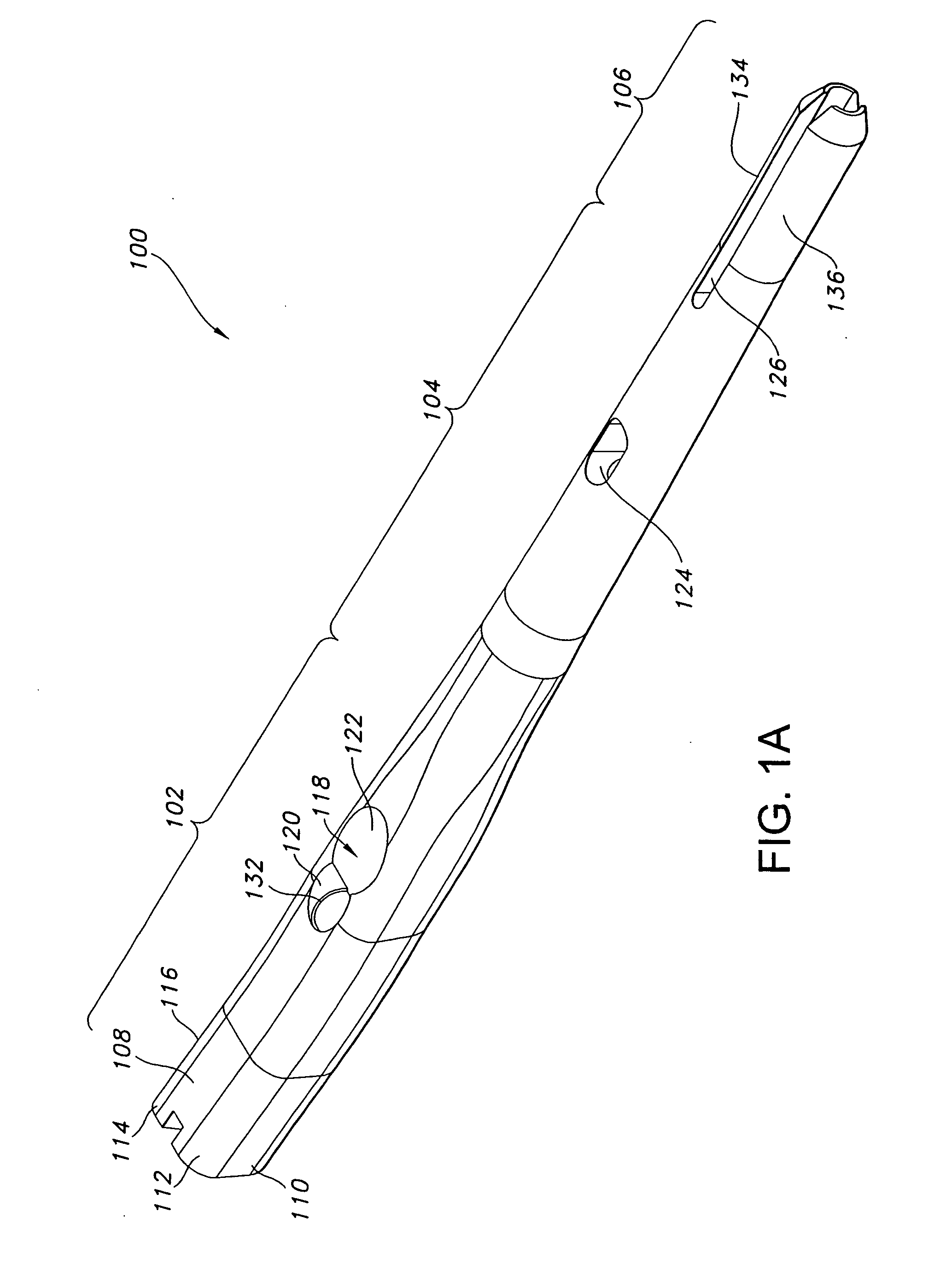
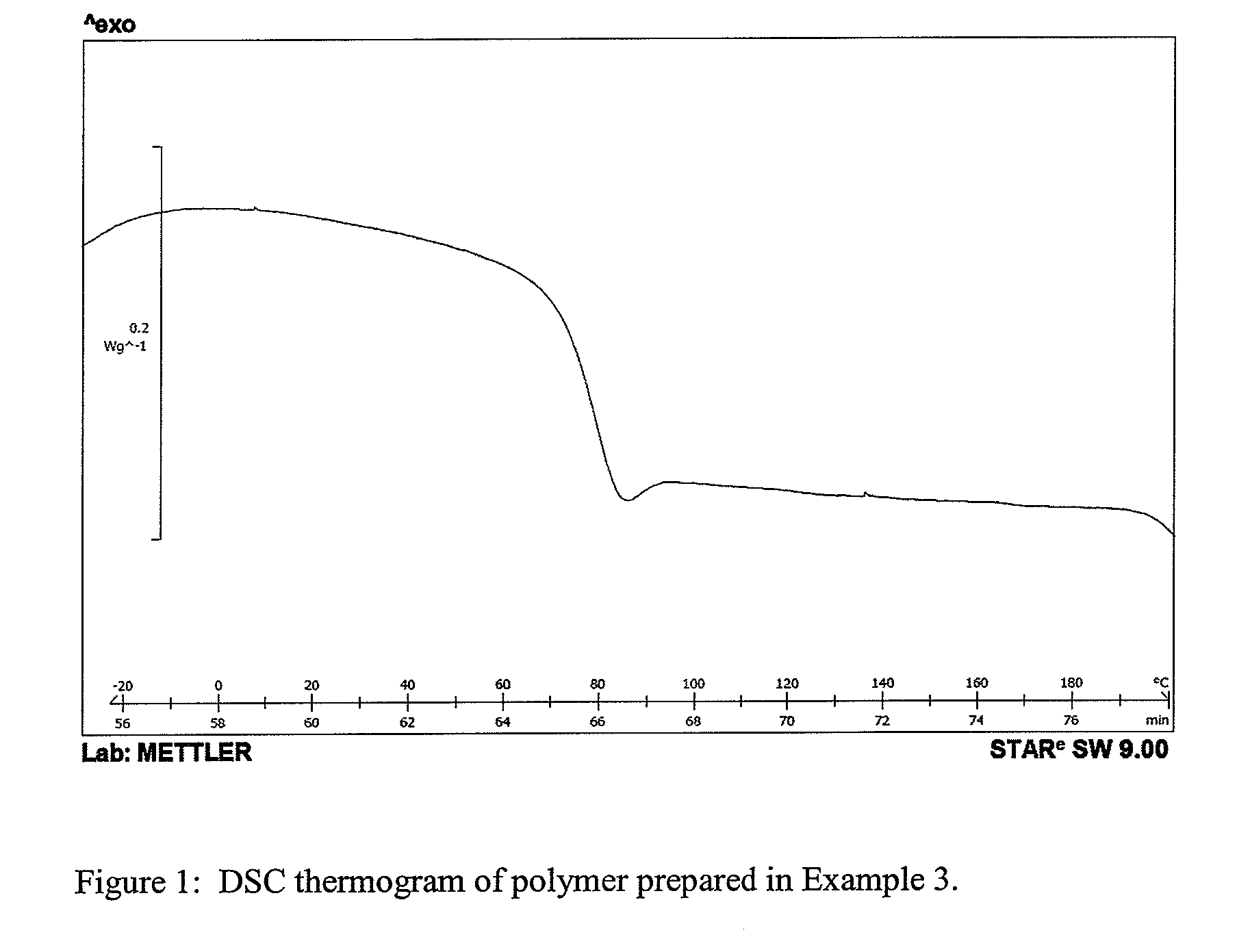
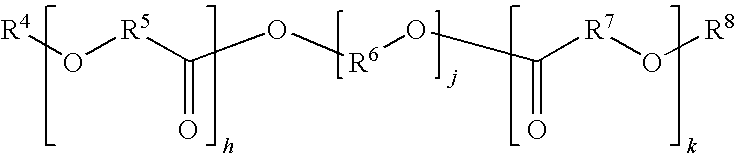
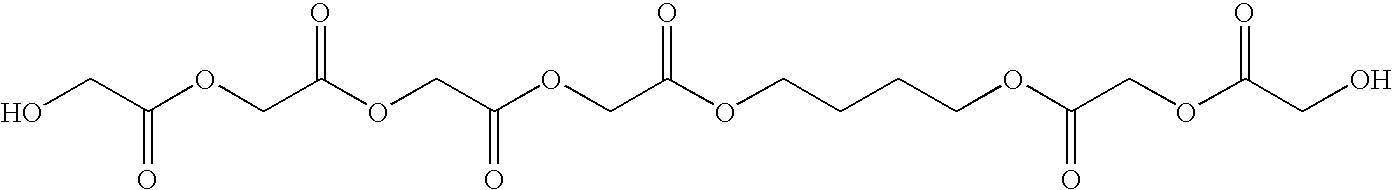
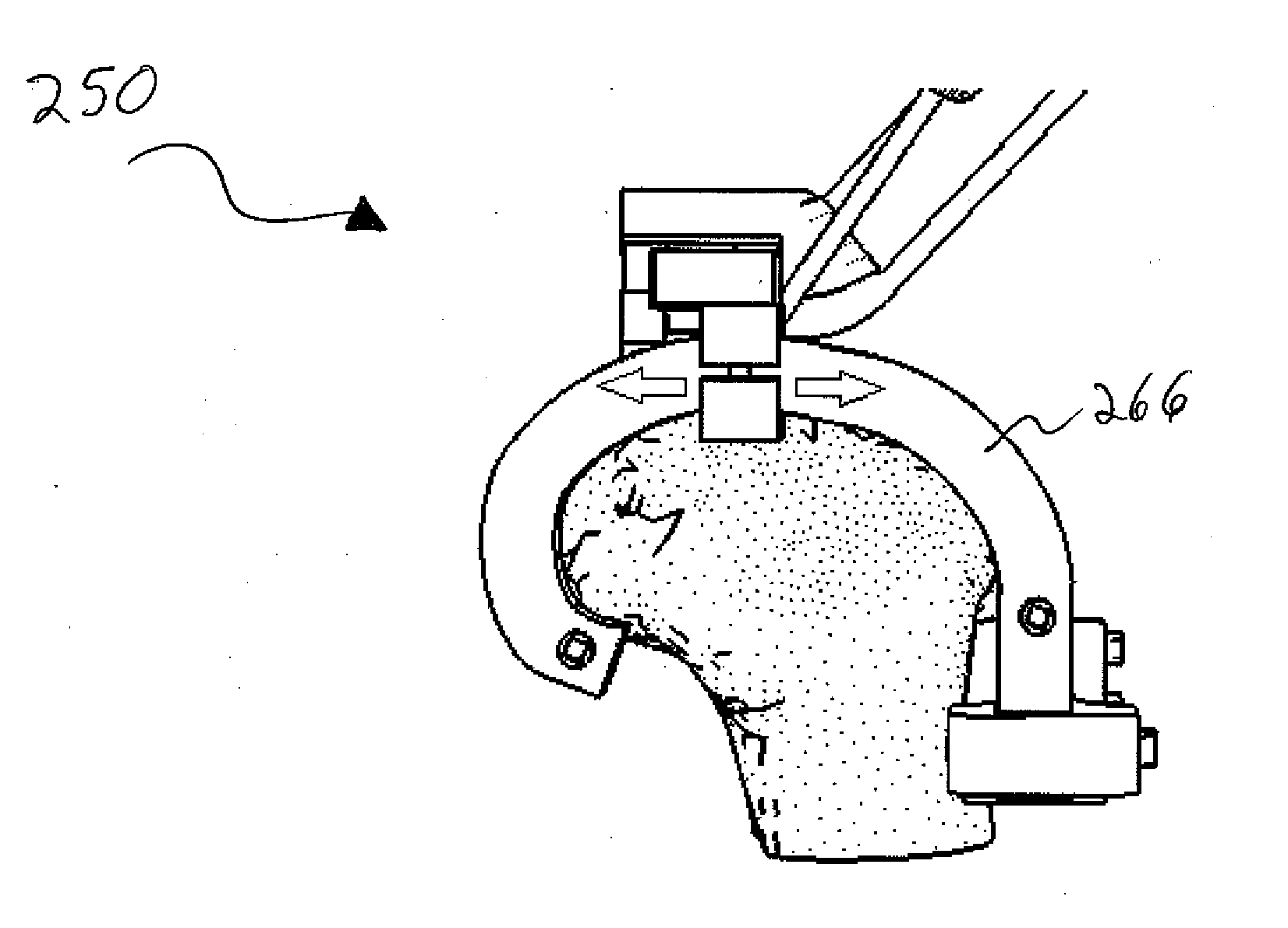
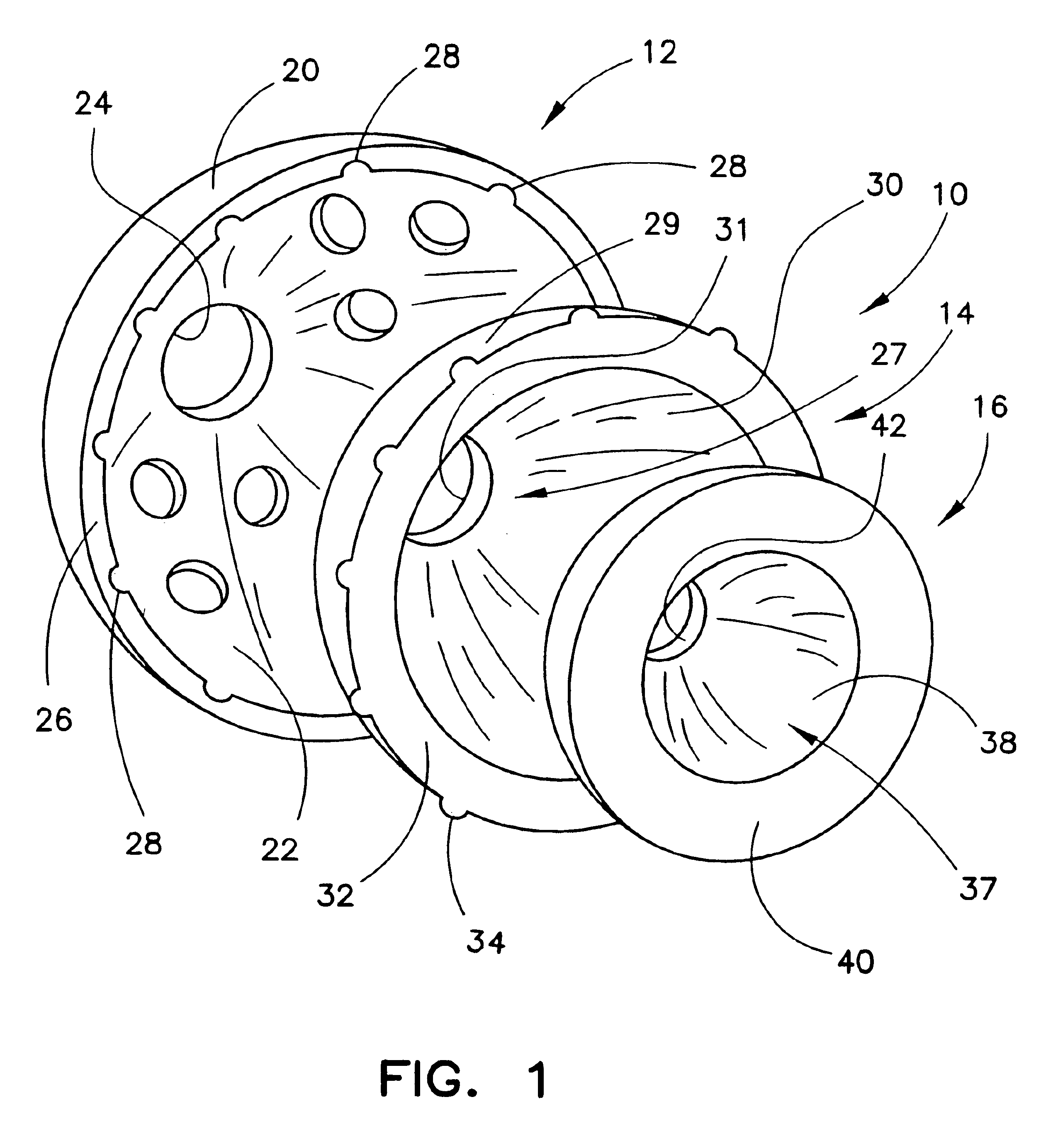
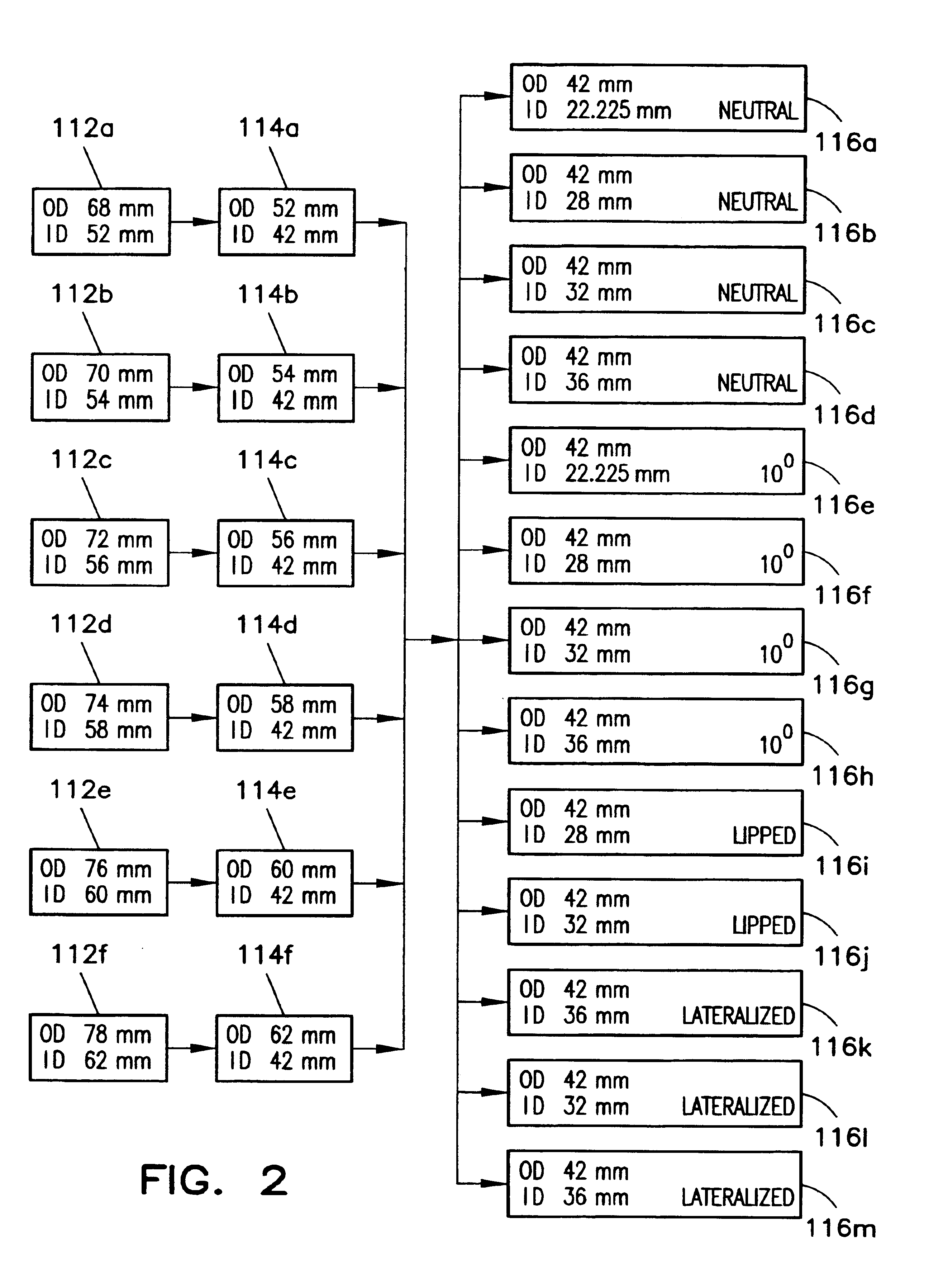
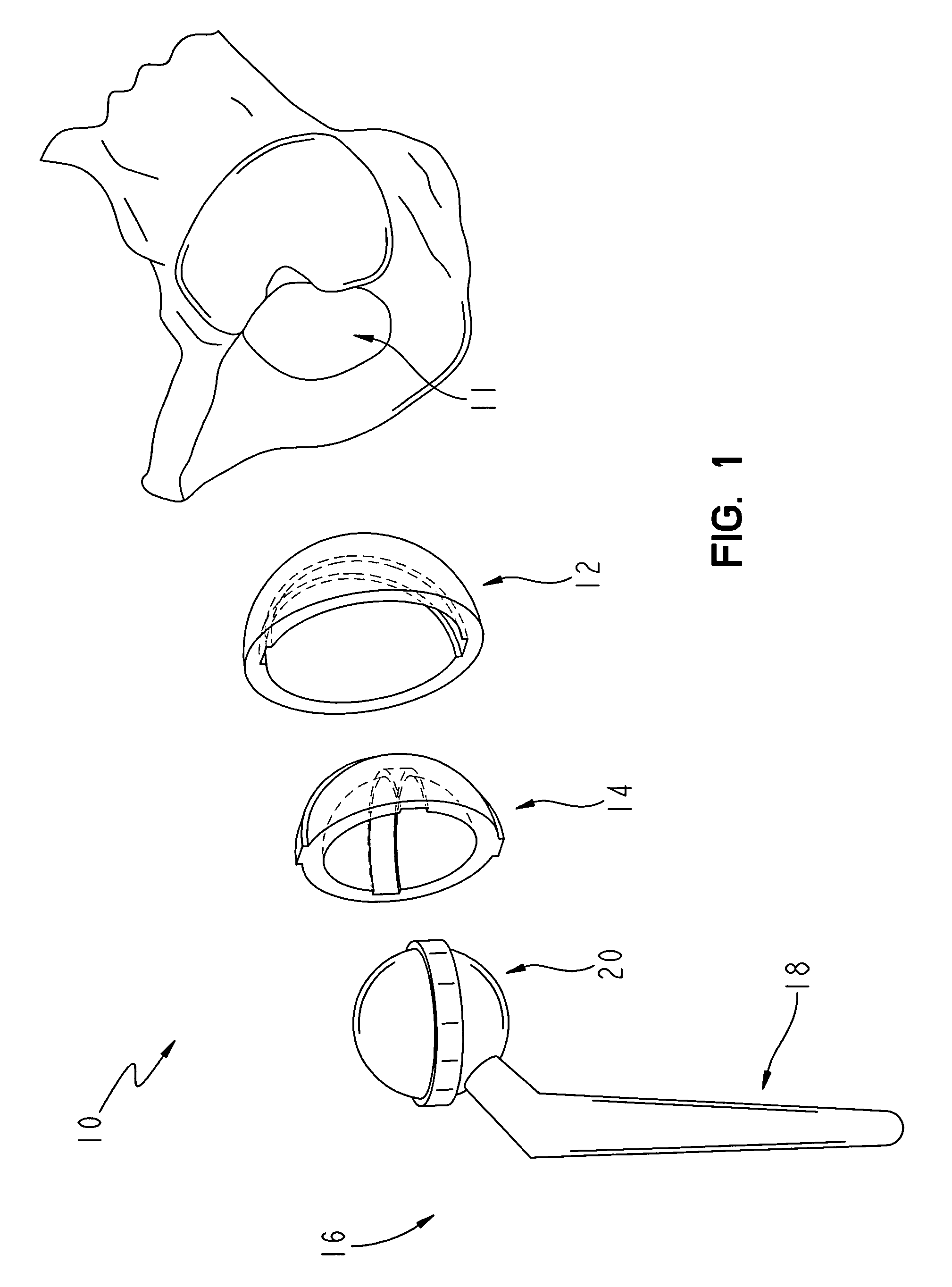
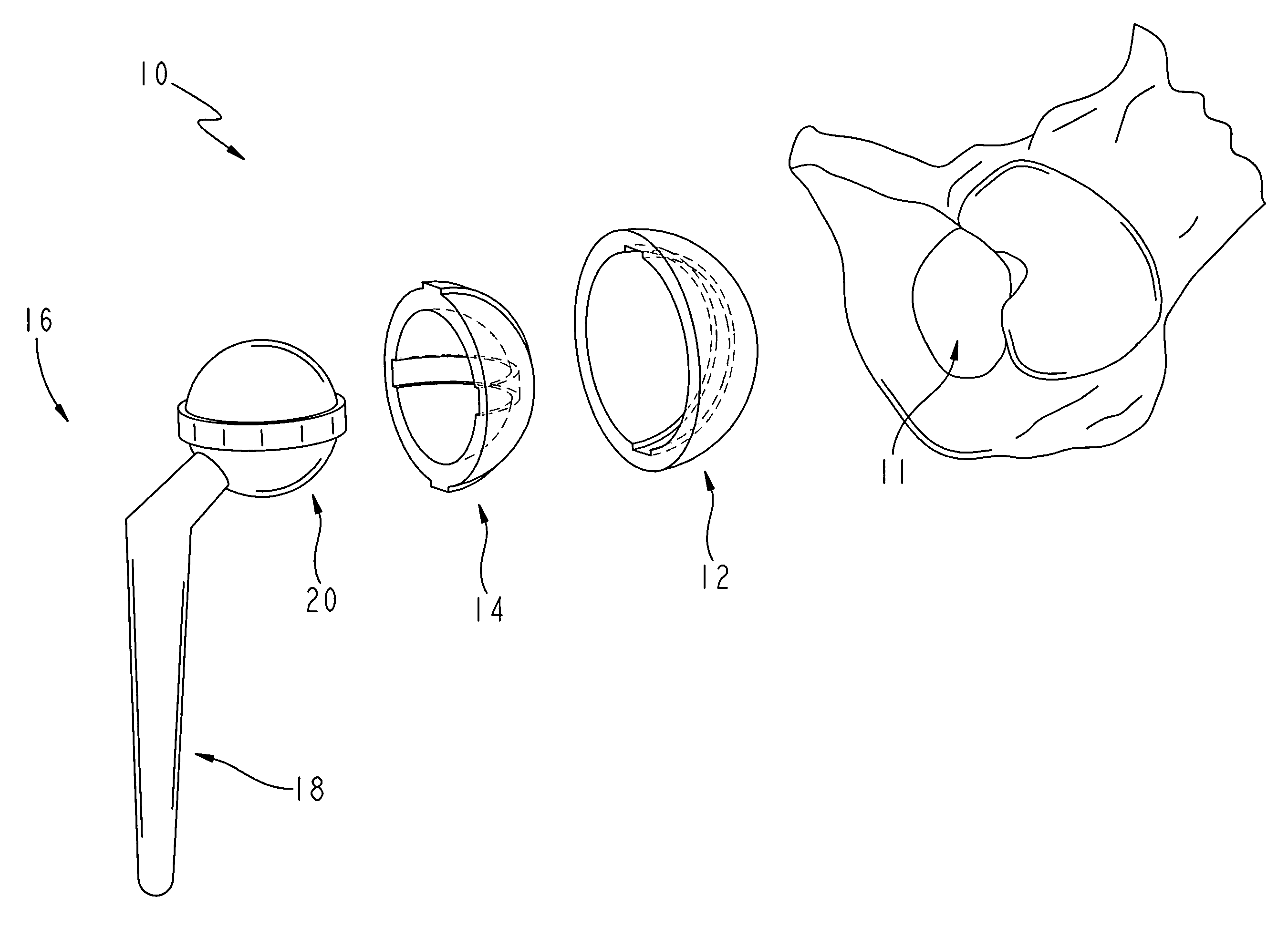Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
303 results about "Orthopaedic implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
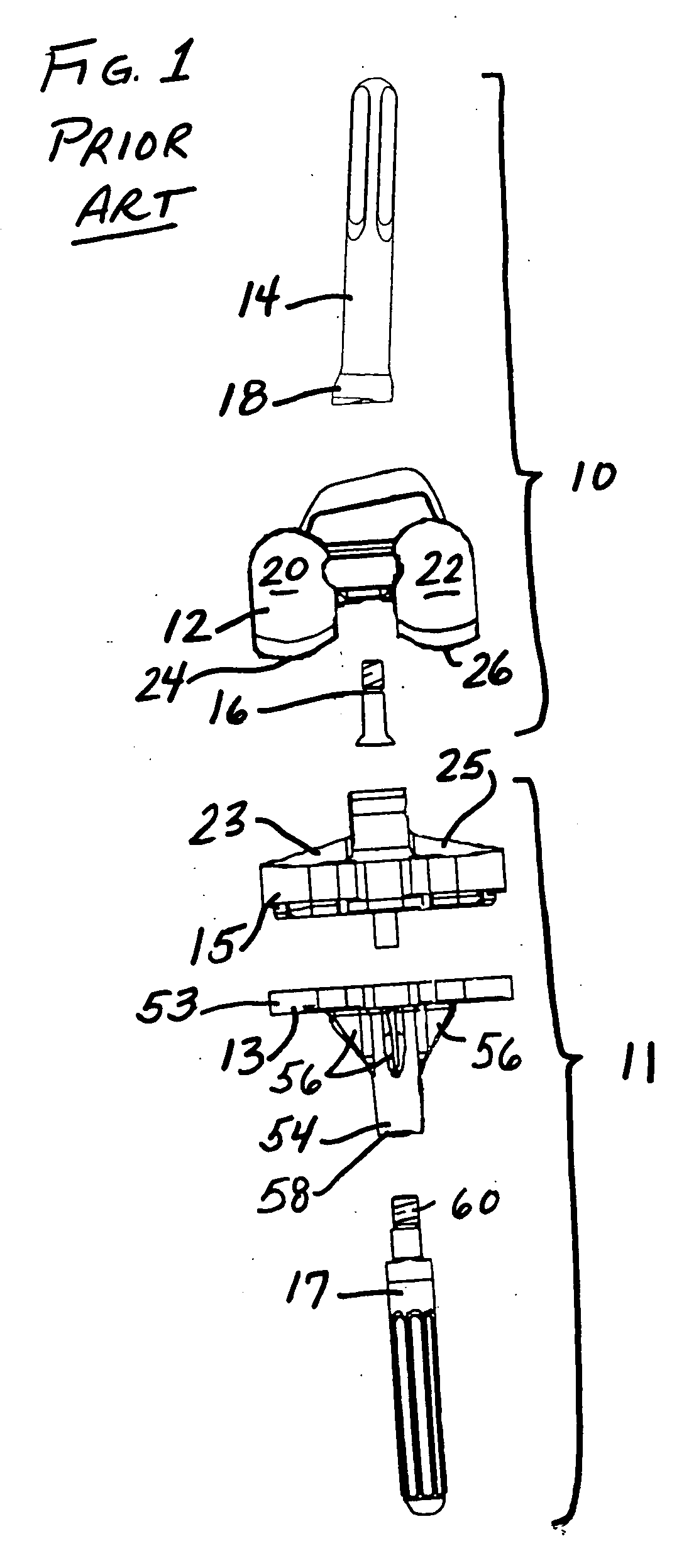
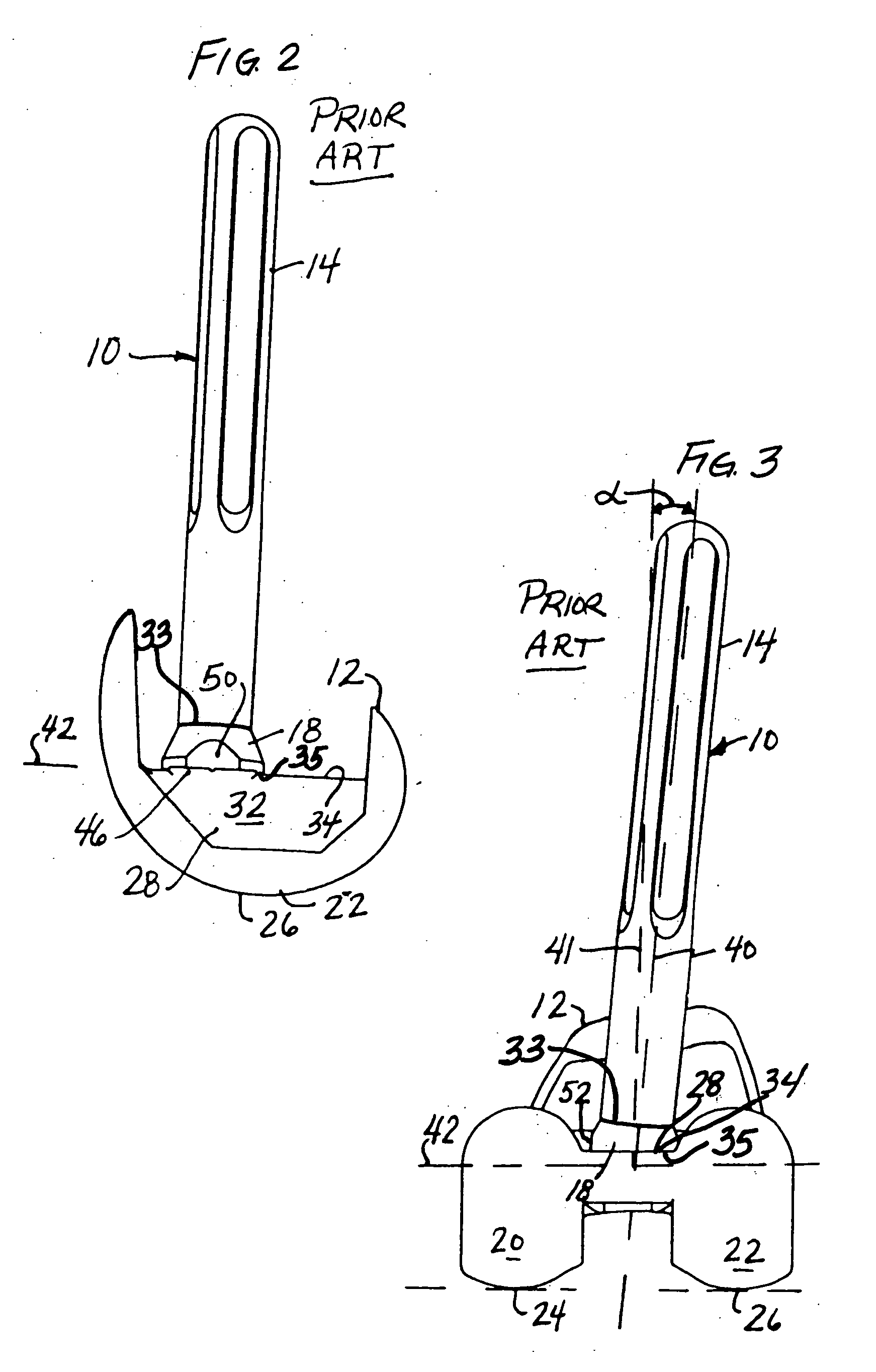
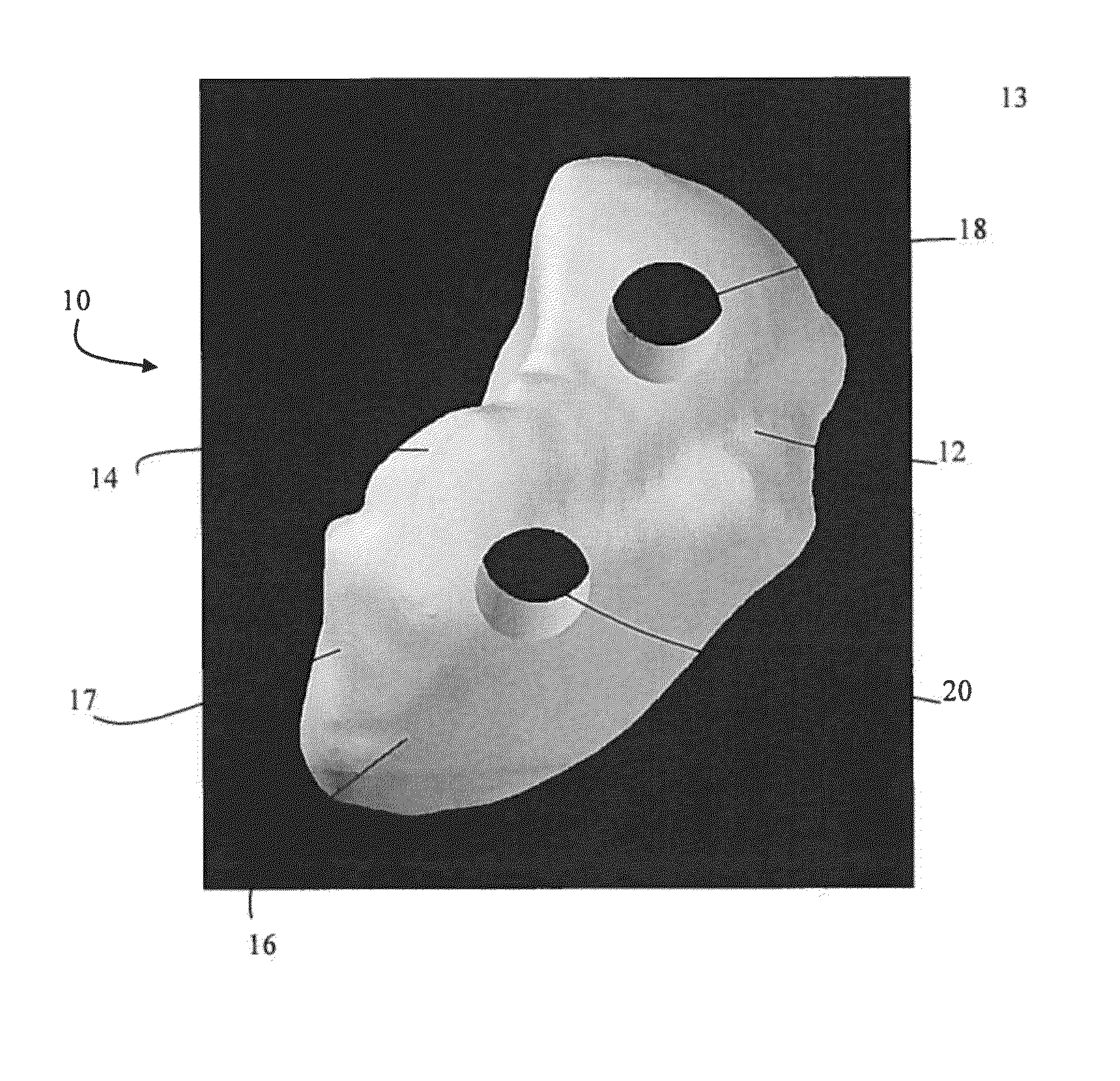
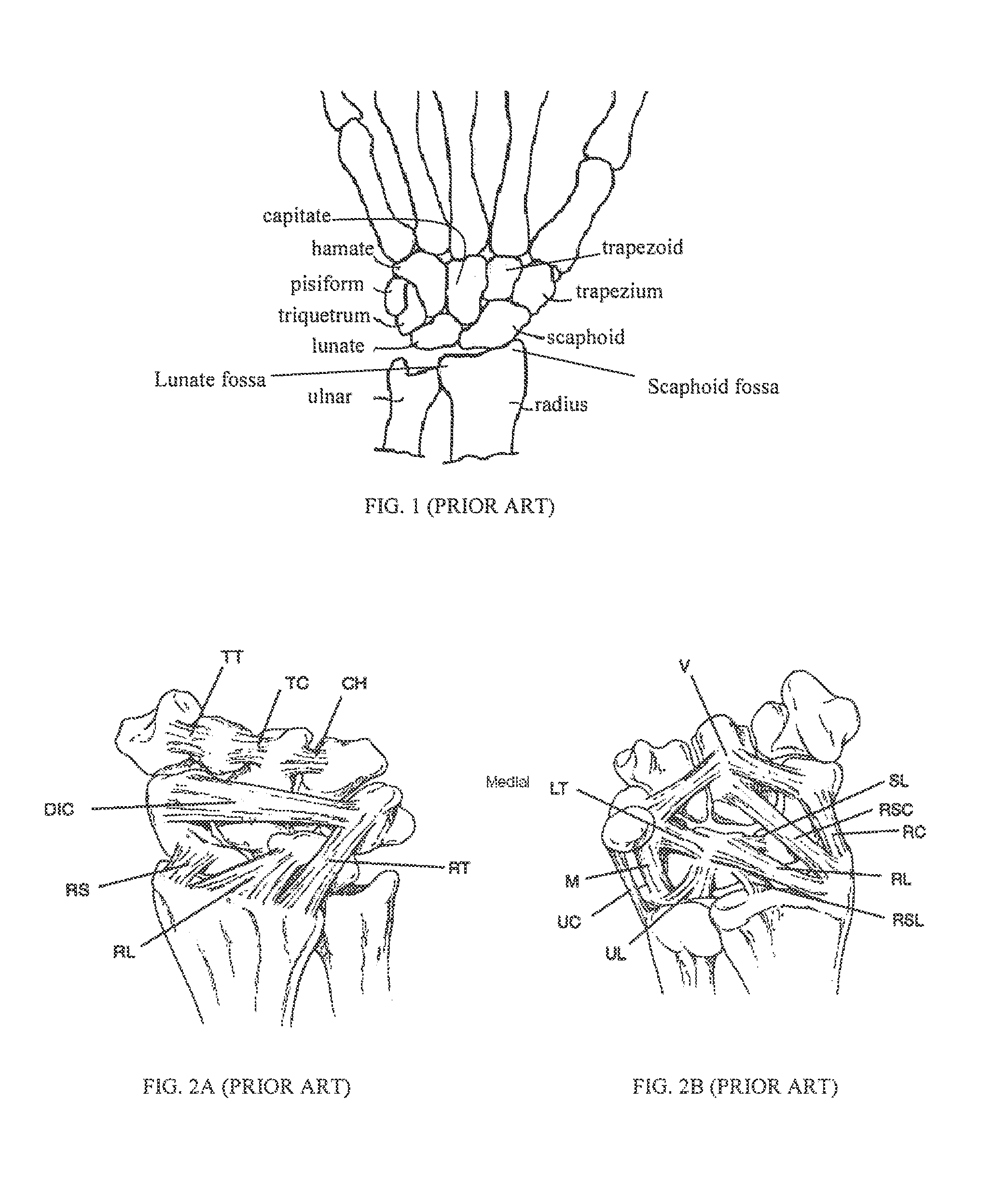
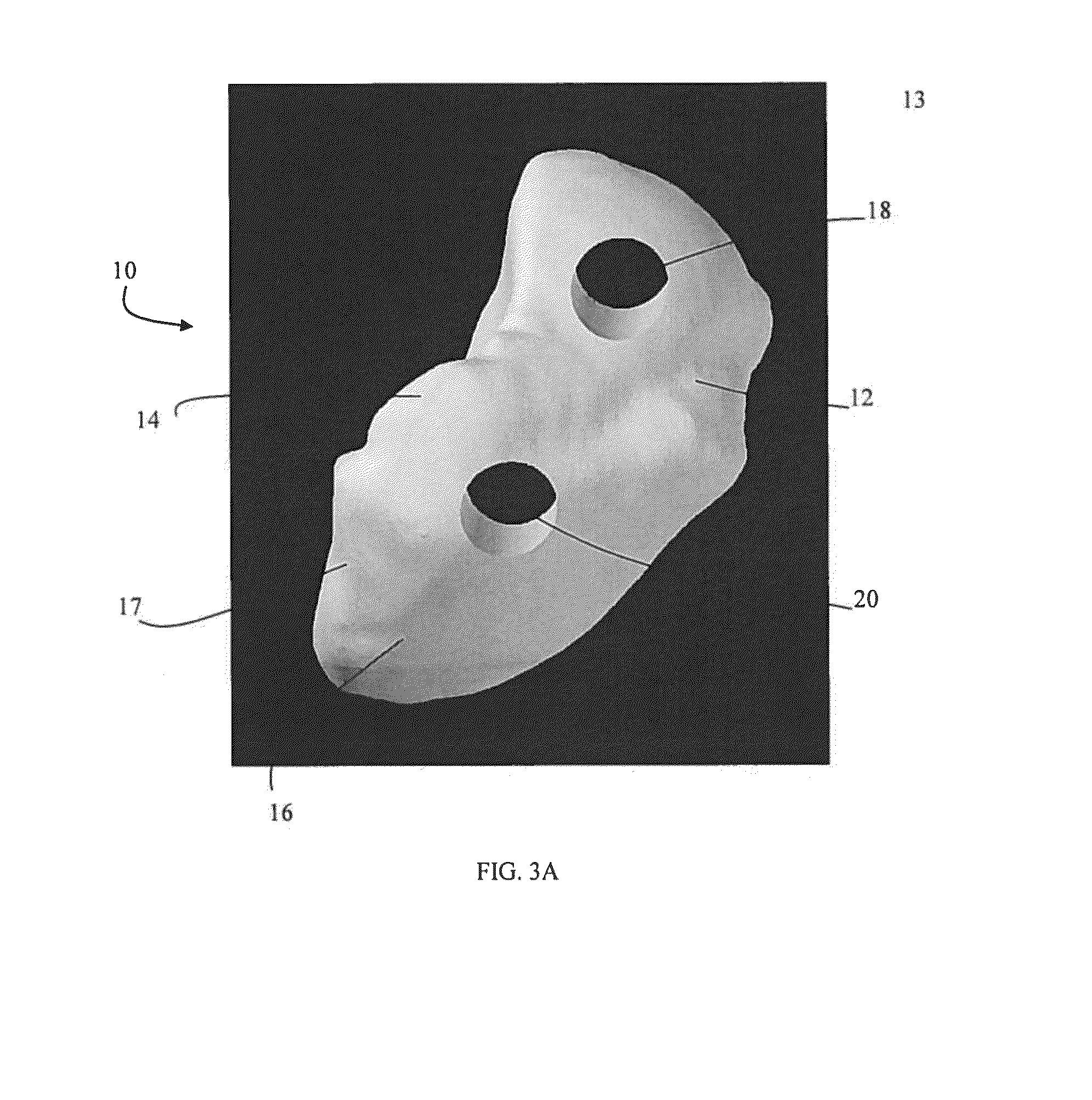
Orthopedic Implants Definition. An orthopedic implant is a device surgically placed into the body designed to restore function by replacing or reinforcing a damaged structure. For the treatment of back pain, orthopedic implants such as bone plates and bone screws are used in spinal fusion surgery and fixation of fractured bone segments,...
Orthopaedic Implants and Prostheses
InactiveUS20090210062A1Small sizeAdjustable sizeSuture equipmentsBone implantSurgical siteSurgical department
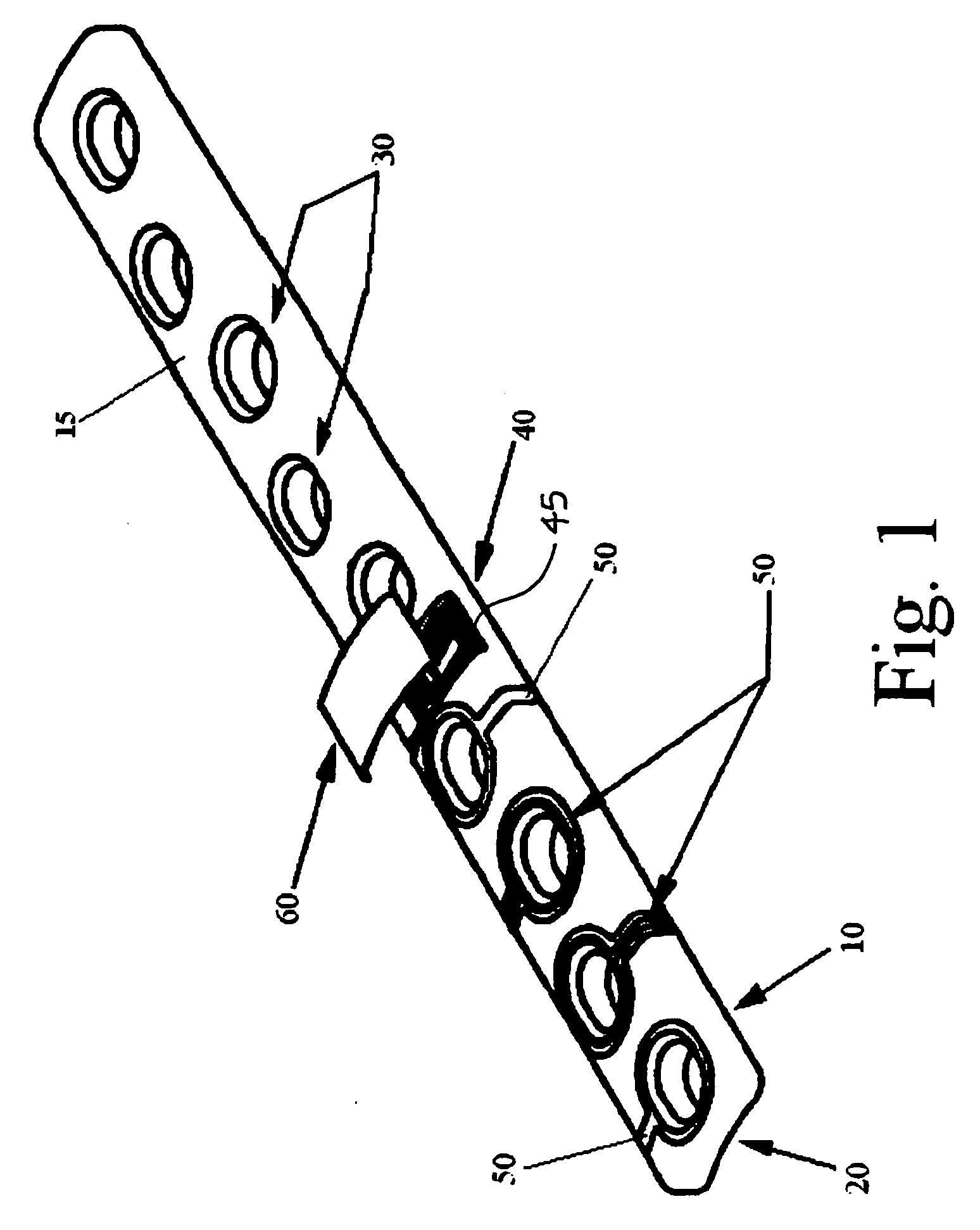
Disclosed herein are spinal implants particularly useful in interbody fusion surgery. One embodiment pertains to a plate configured to establish desired lordosis and / or disc height that may be implanted and secured to a superior and inferior vertebral body. The plate may be interlocked with a spacer component to form a single implant. Also disclosed is an anti-backout mechanism that helps prevent fixators from backing out upon securement of the plate in the spine. Kits comprising different sizes and inclination angles of components are disclosed, which can assist the surgeon in preoperatively assembling an implant to best fit in the surgical site of the patient.
Owner:THALGOTT JOHN +1
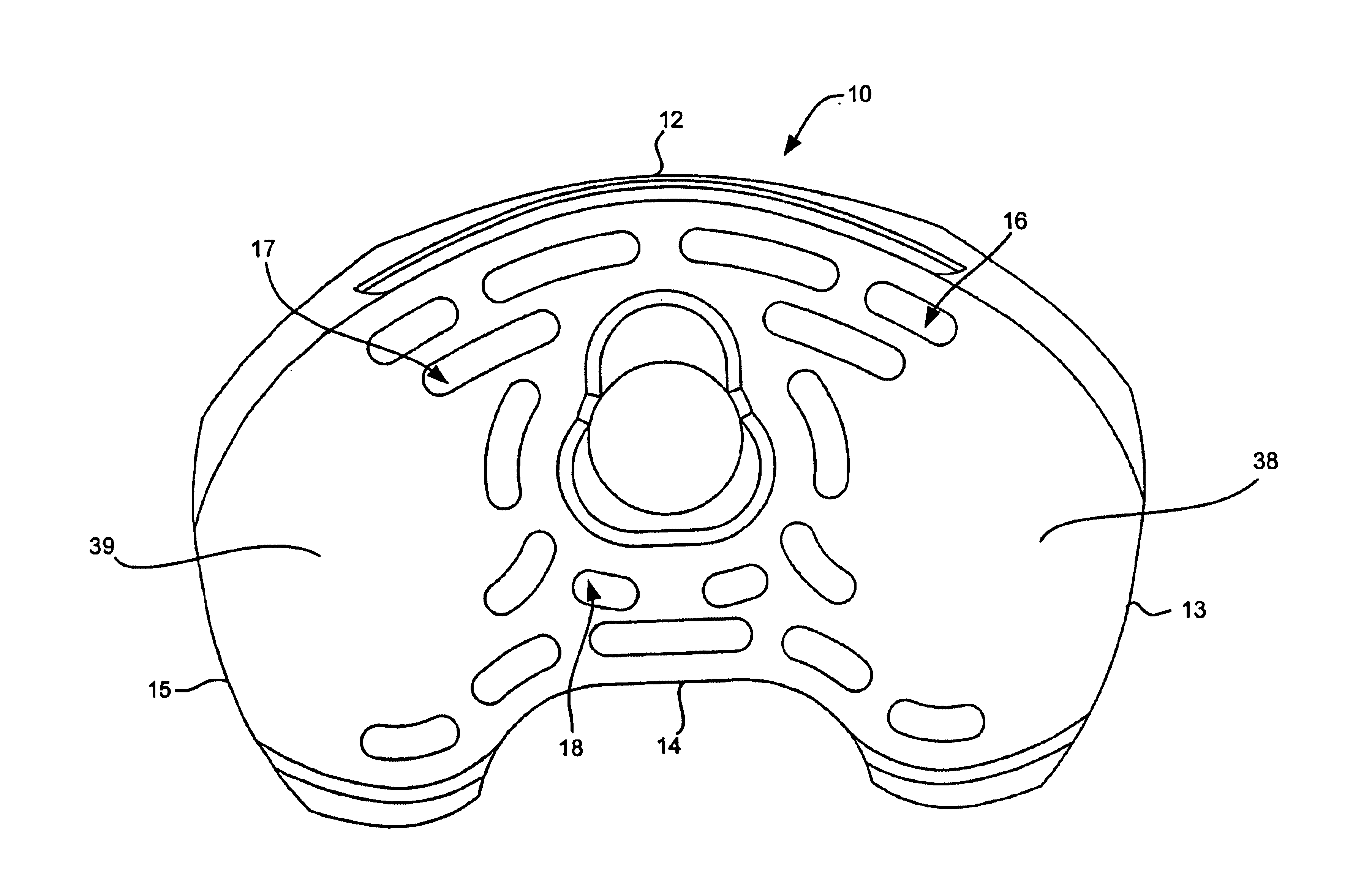
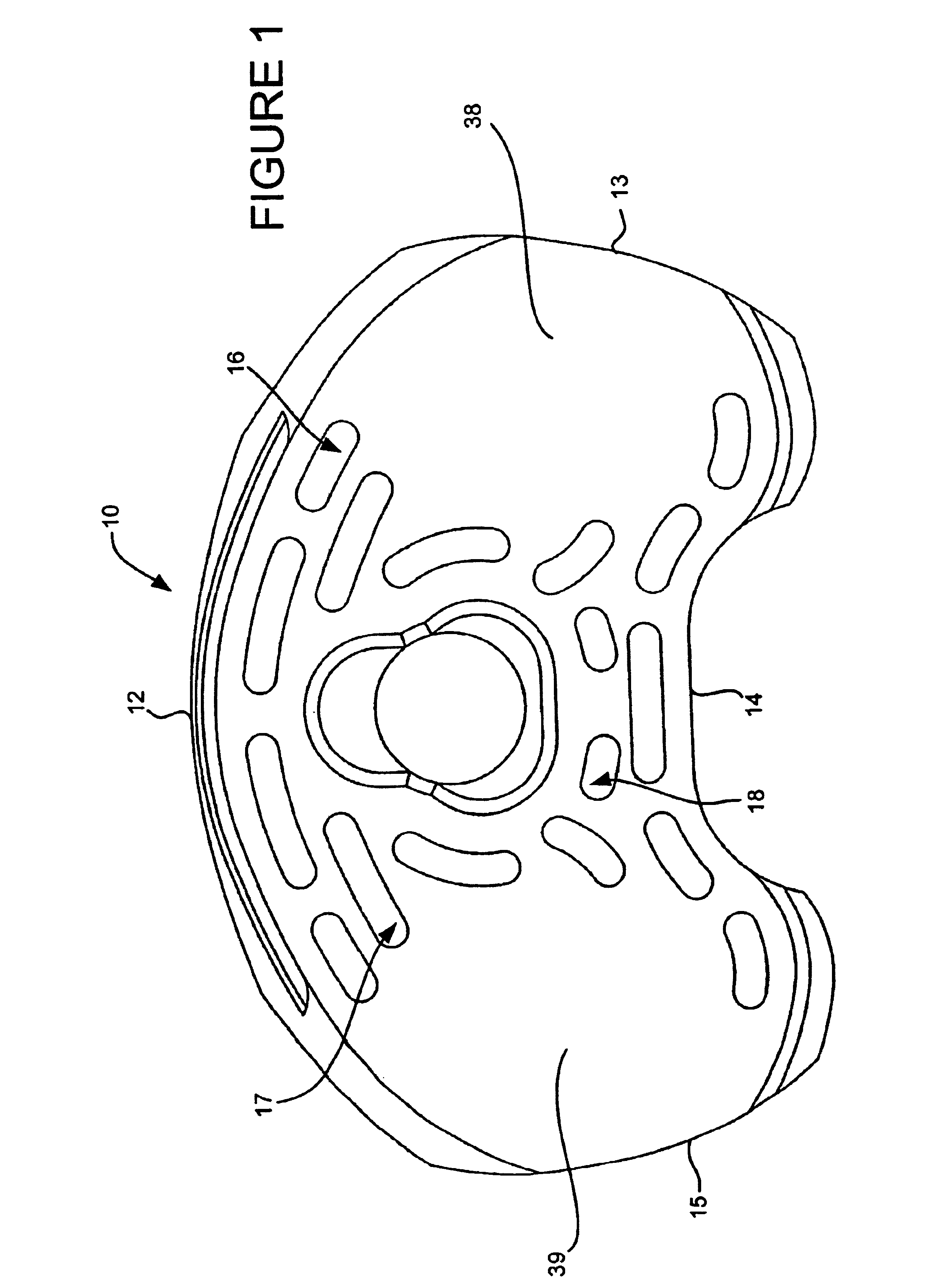
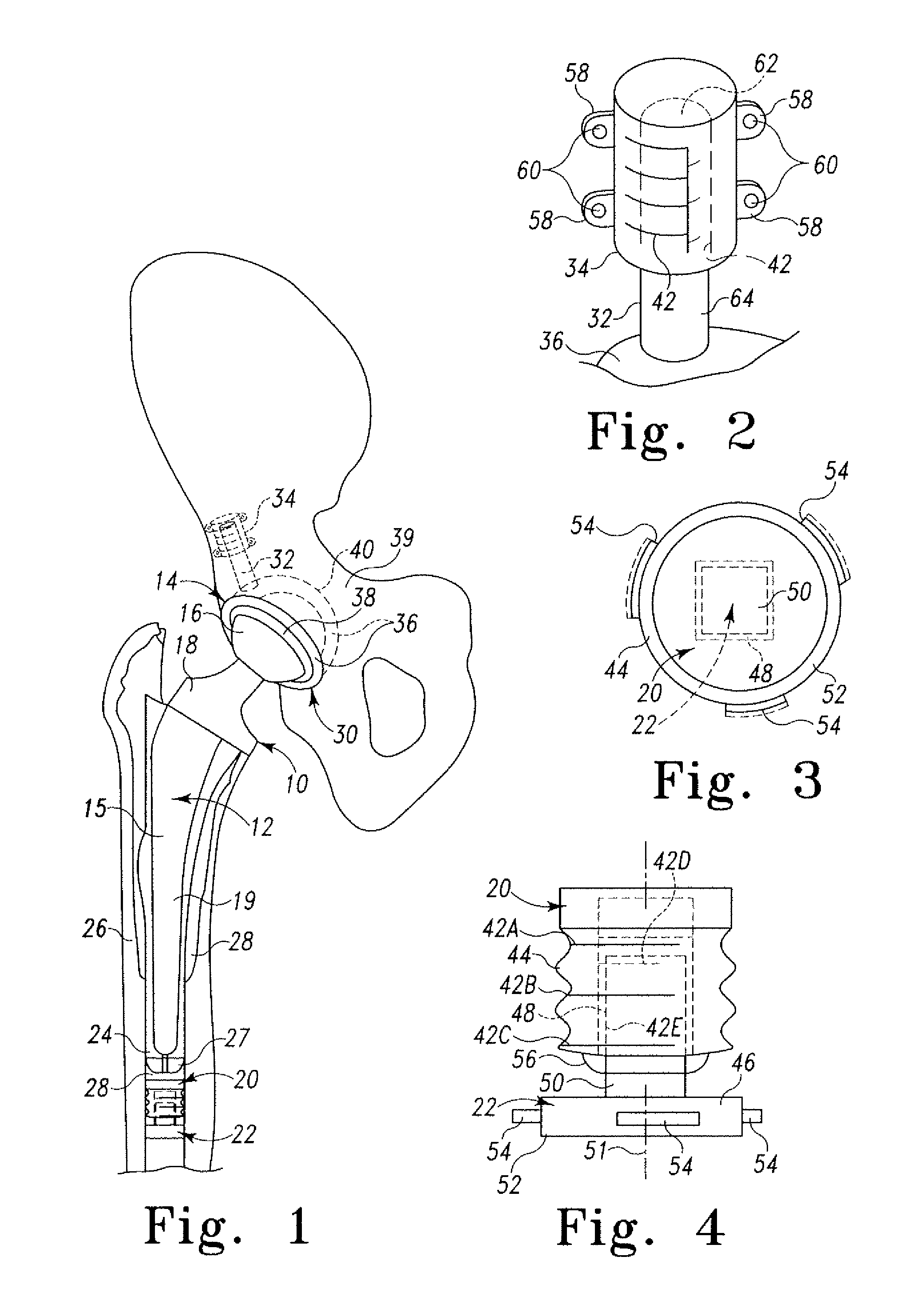
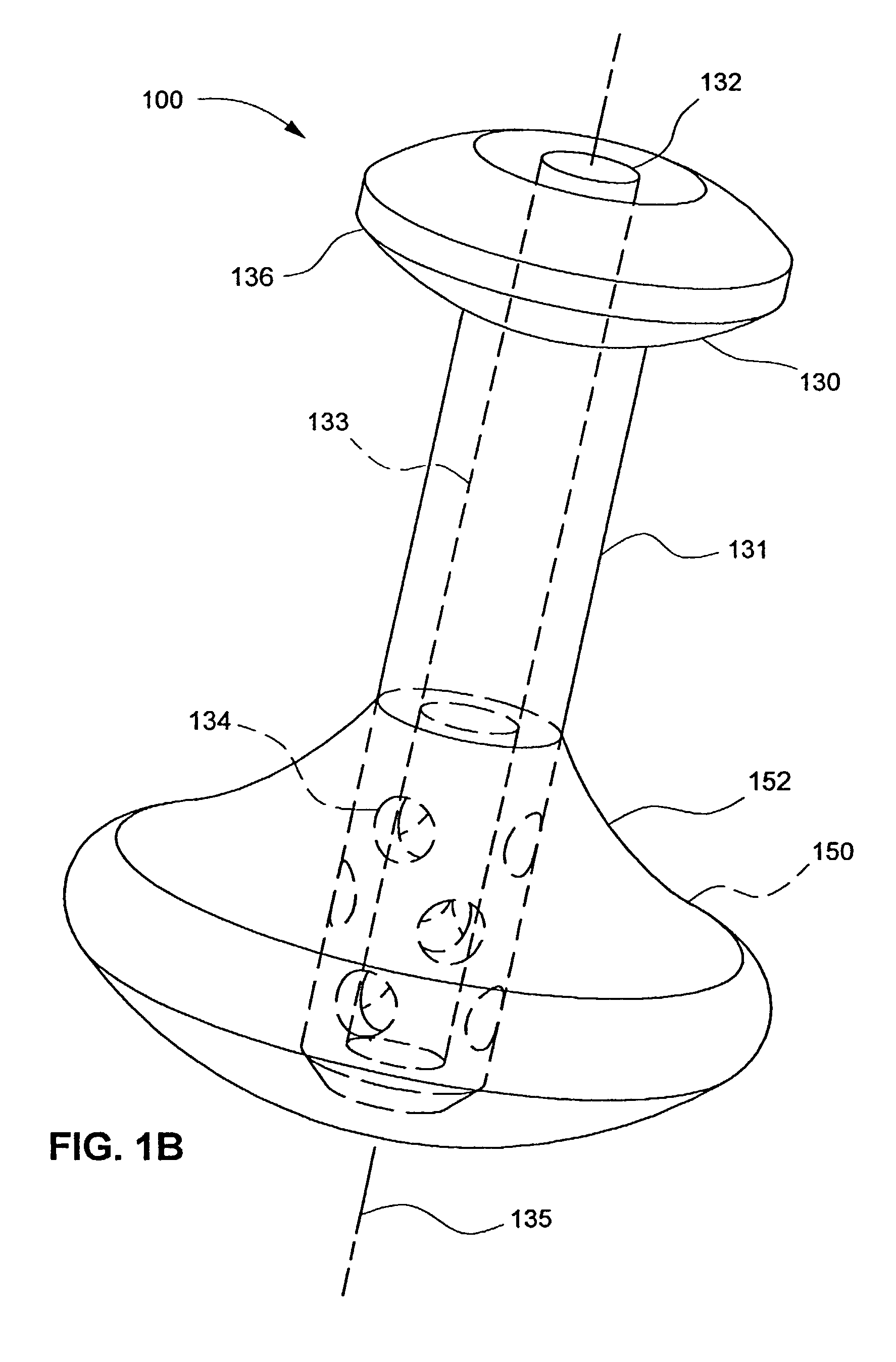
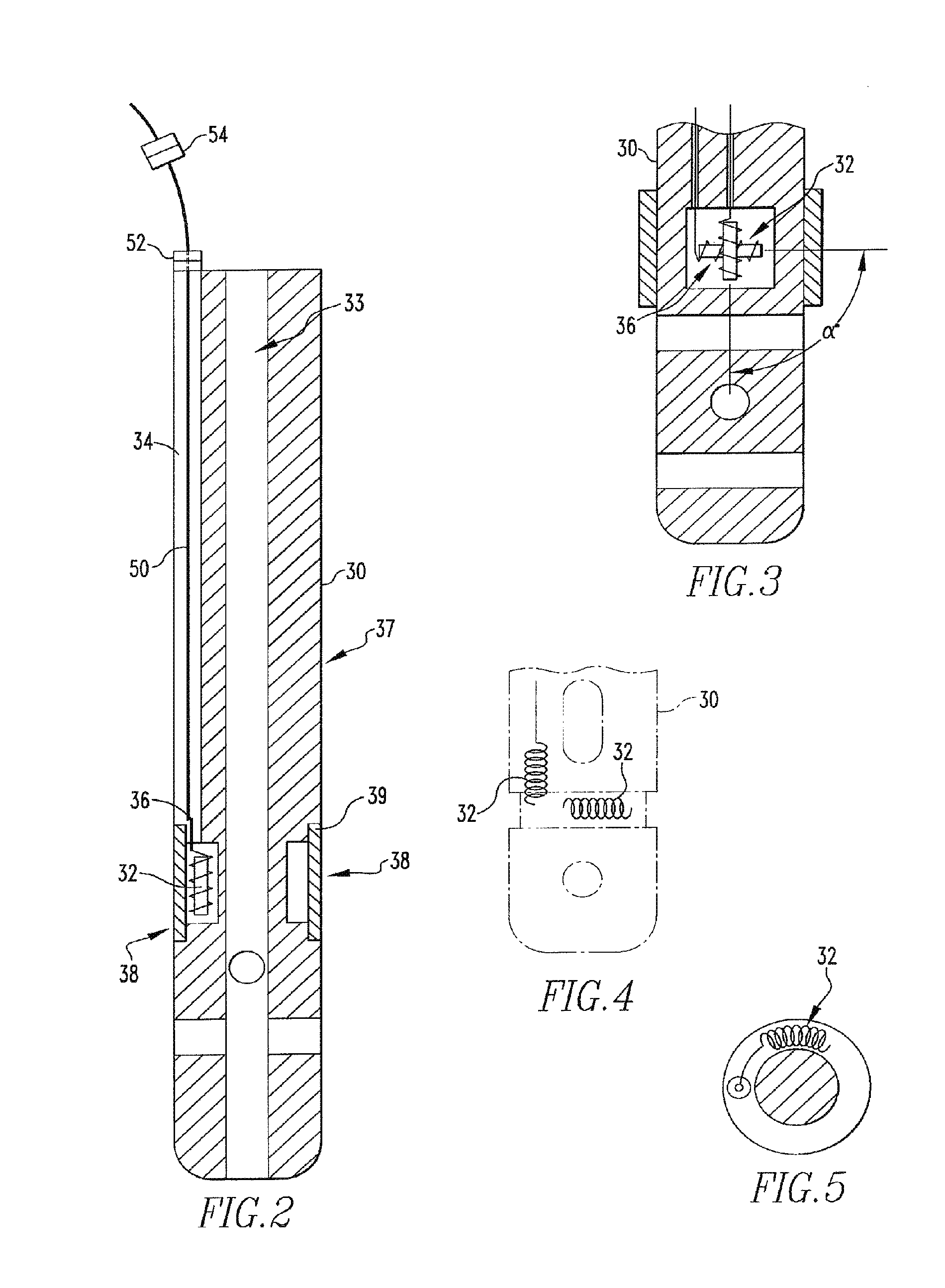
Orthopaedic implant with sensors
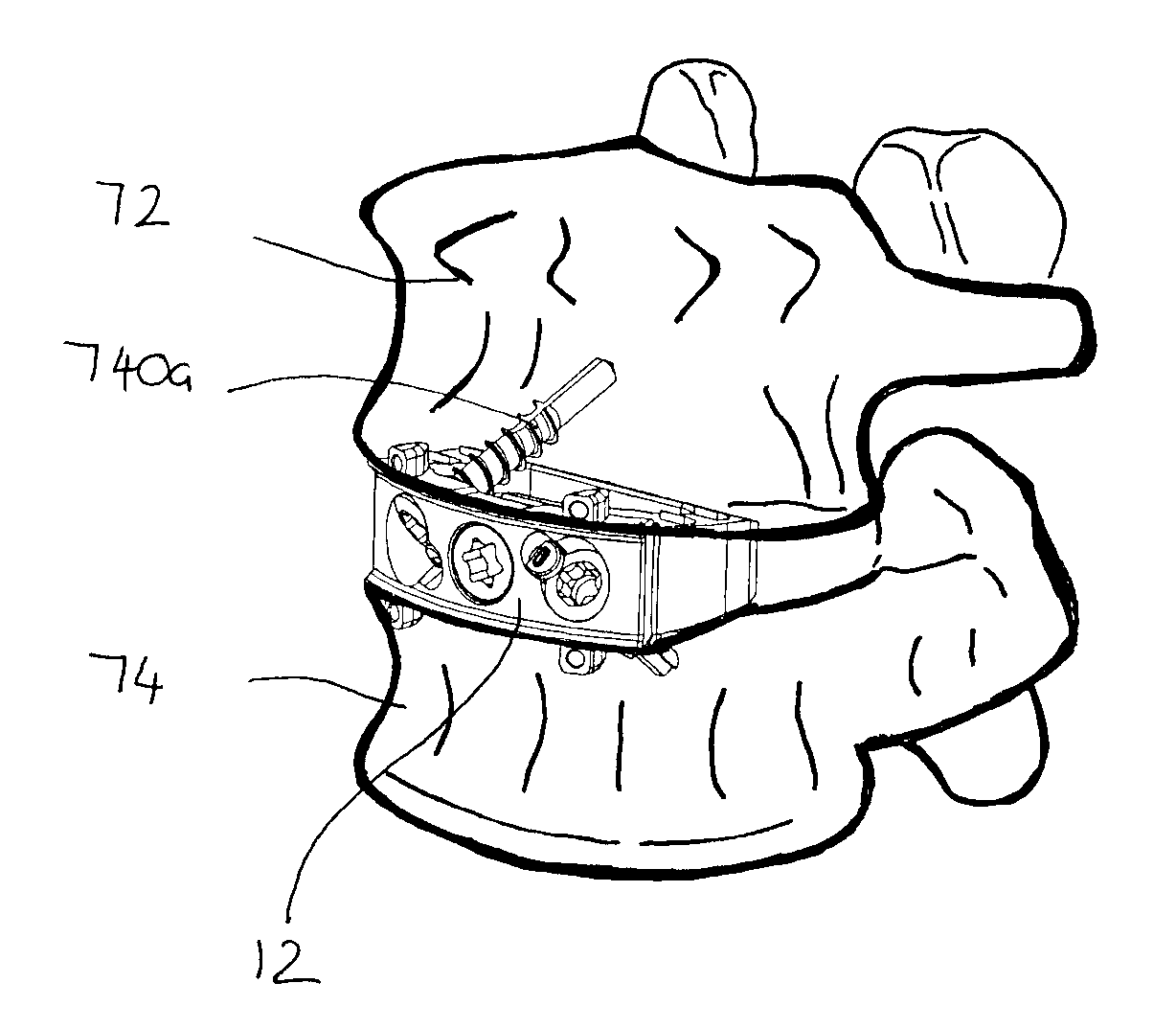
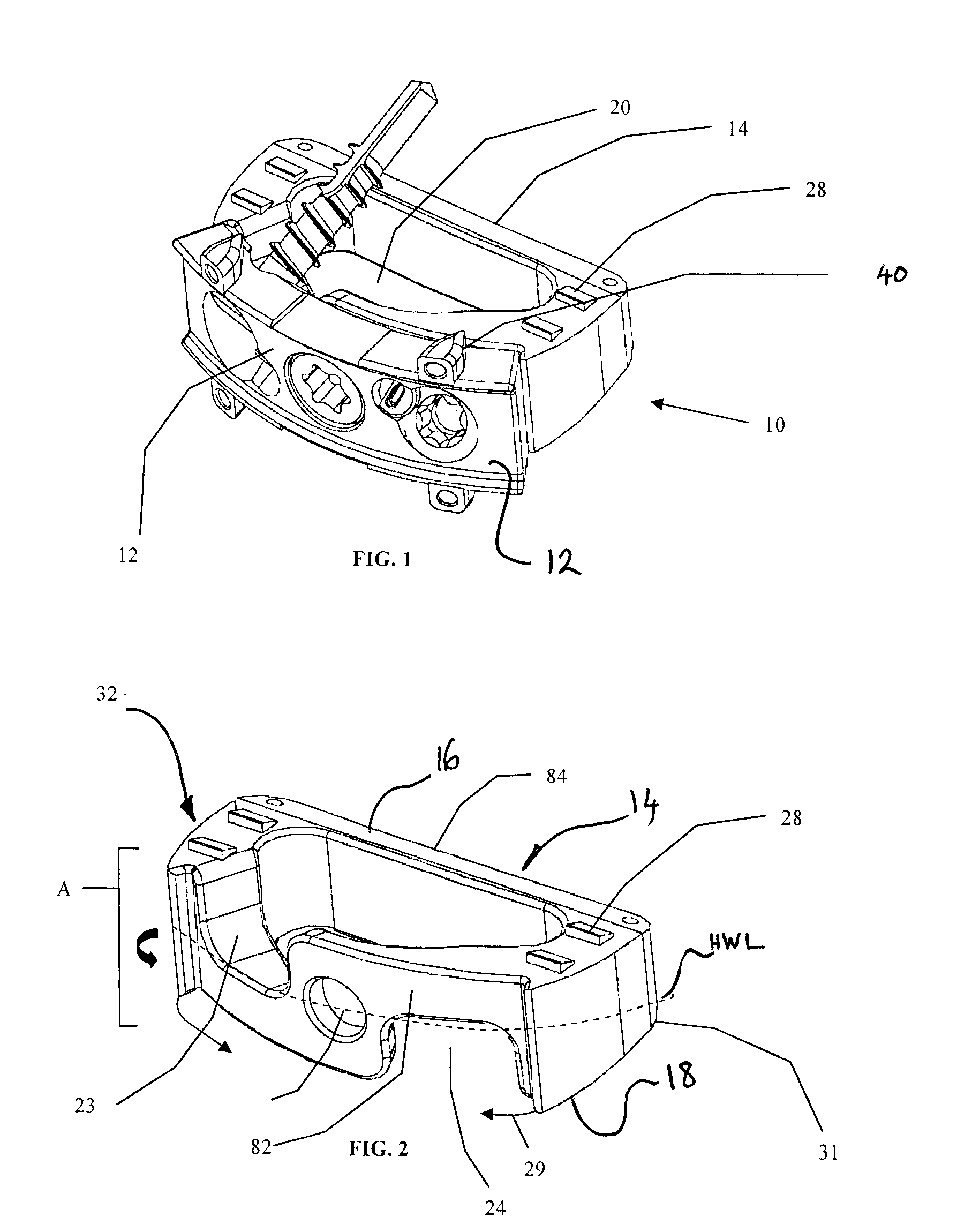
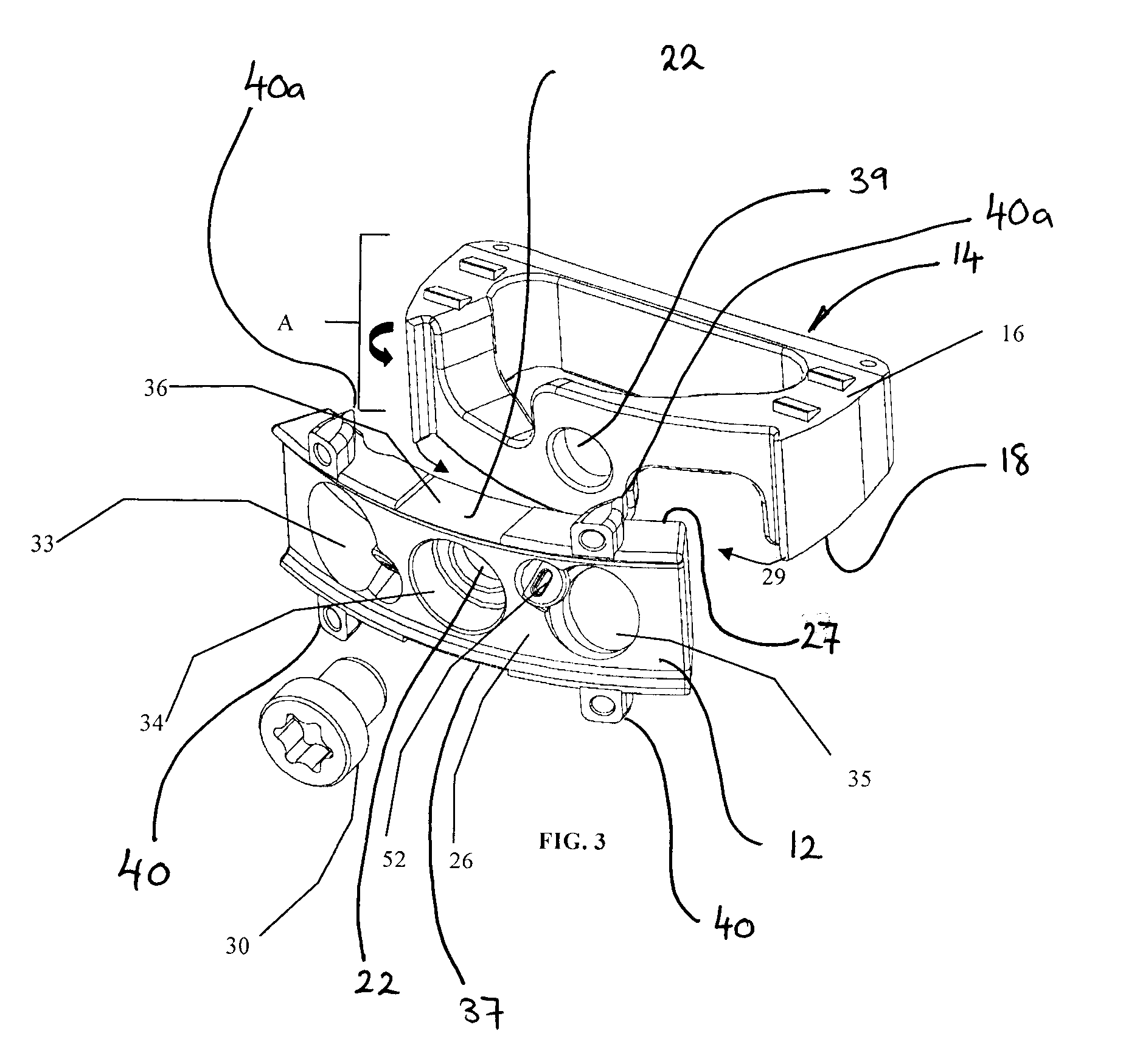
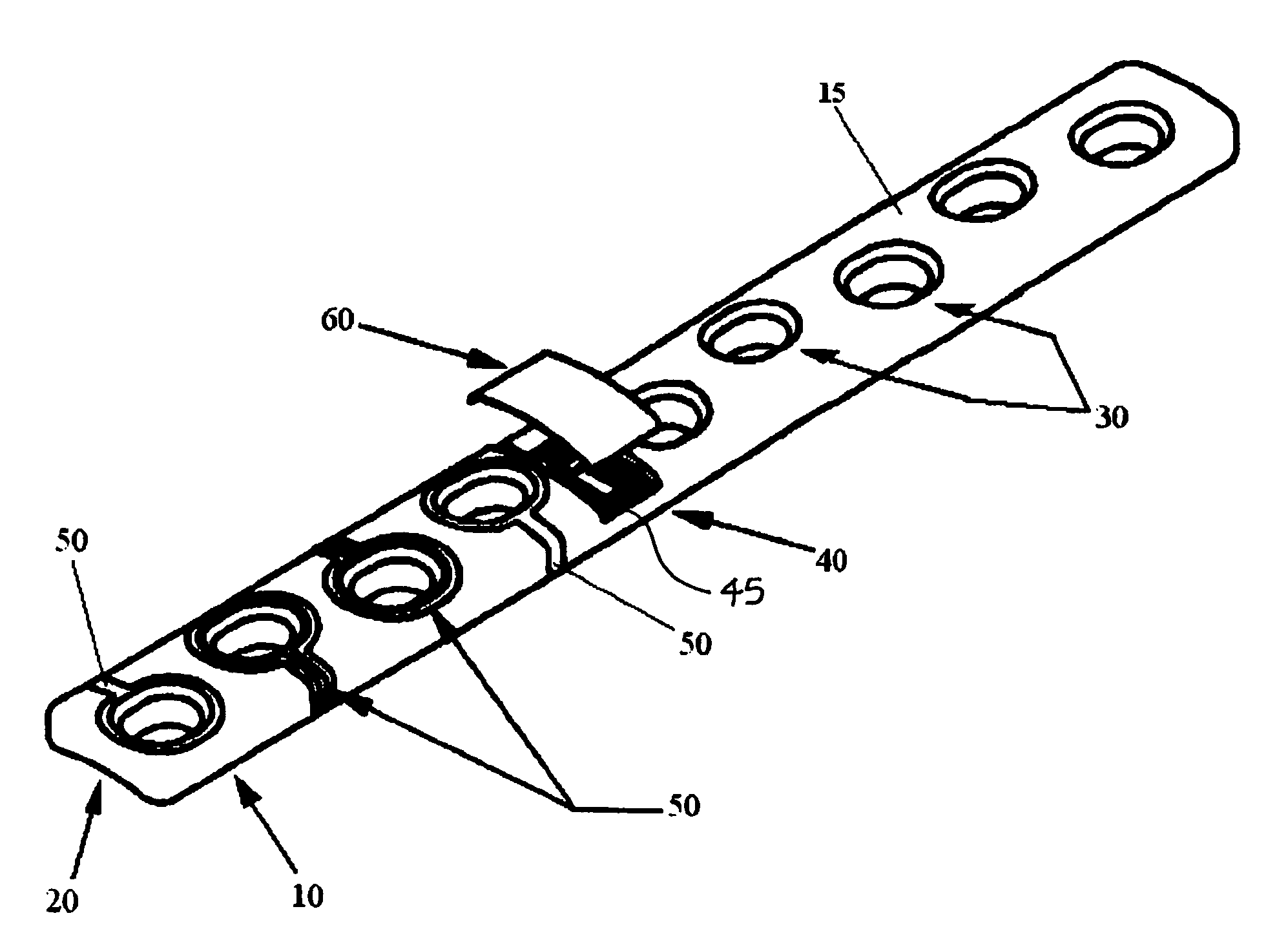
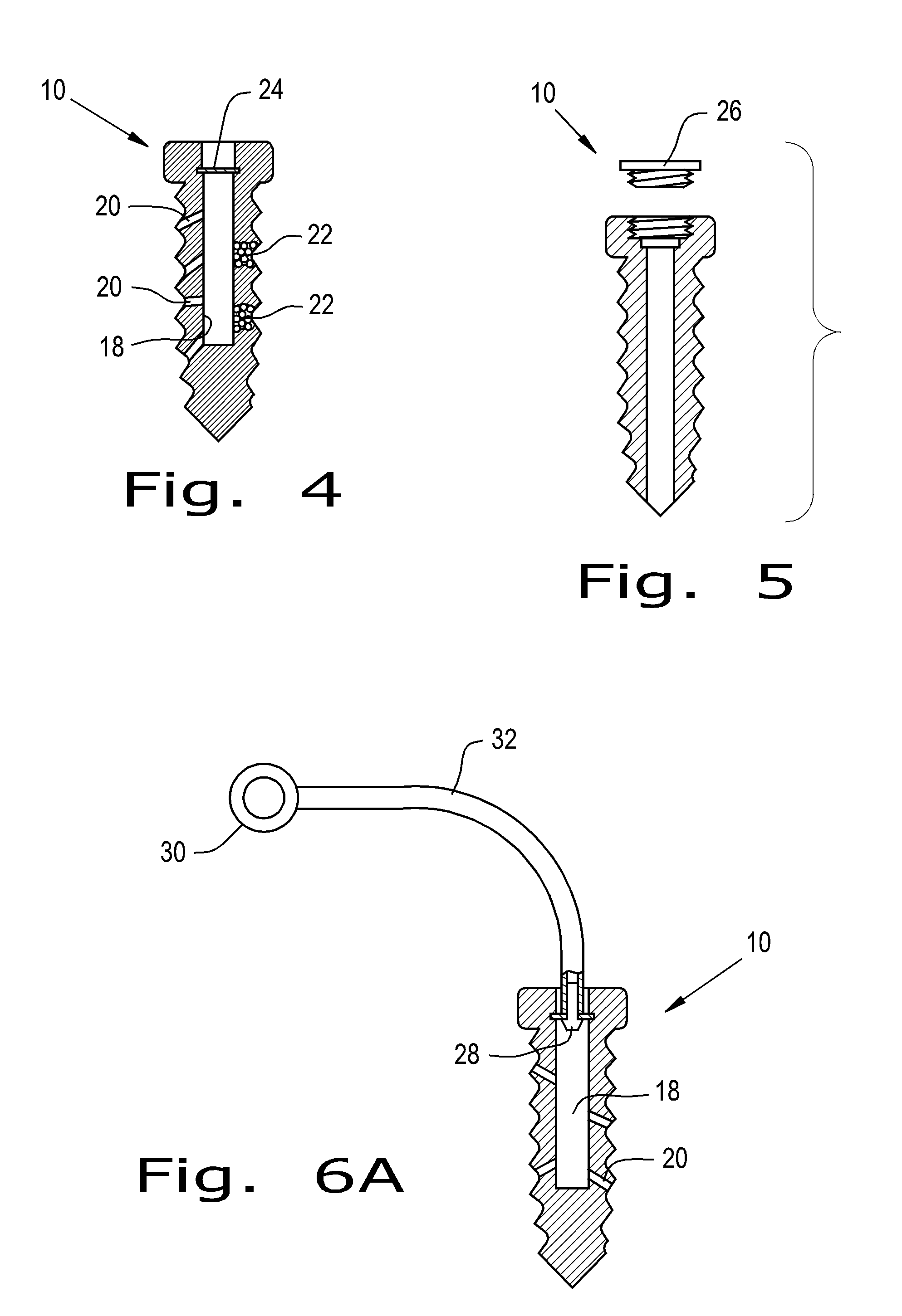
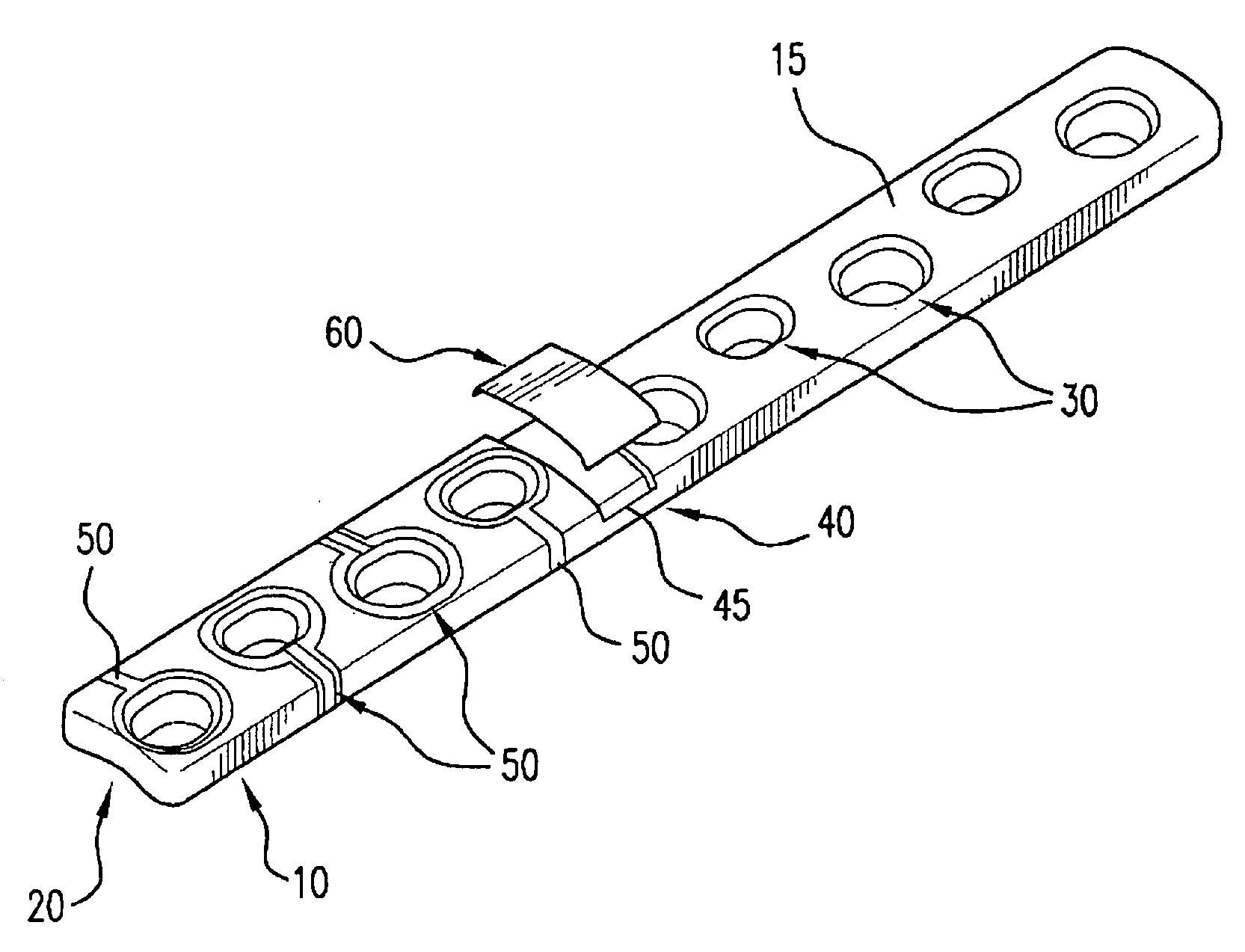
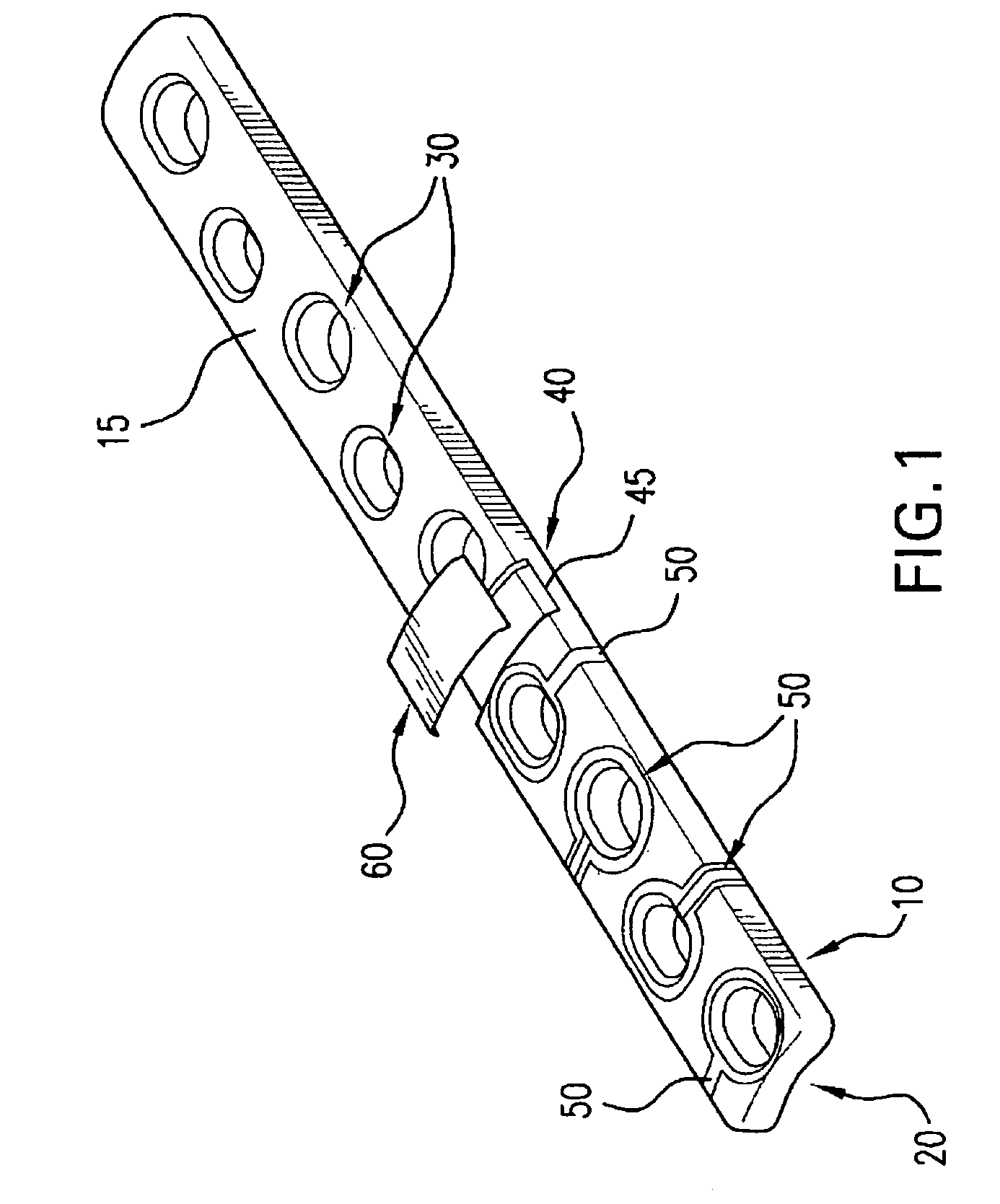
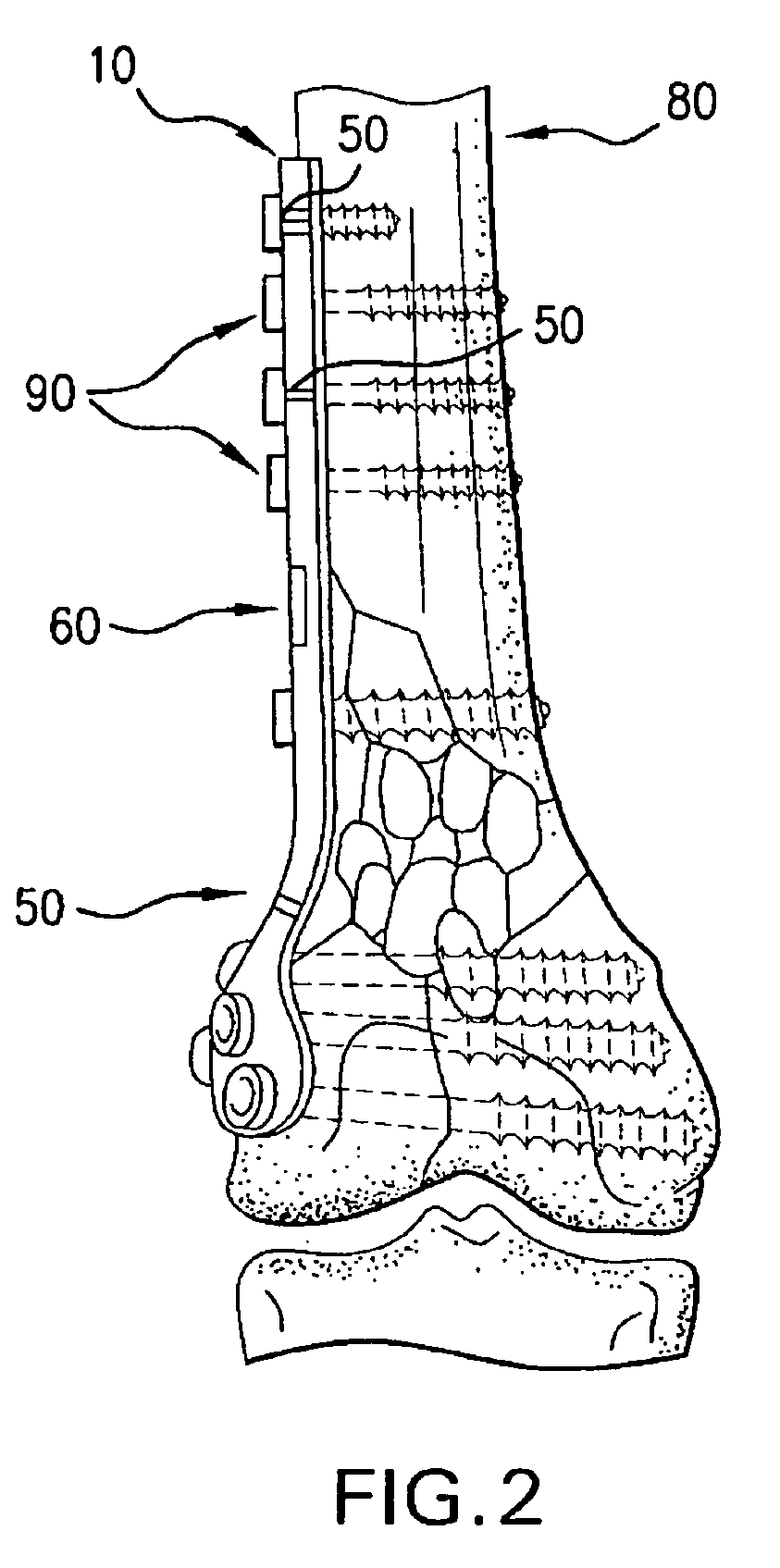
The present invention relates to an orthopaedic implant, such as a bone plate, for the fixation of bone where the implant also has at least one microchip and at least one sensor connected to the microchip. The sensor or sensors are configured to receive physical stimulus from a portion of the implant or the patient's tissue such as temperature, pressure, and strain. The information received from the sensor or sensors is gathered by the microchip and transmitted to a receiver, such as a personal computer, outside the patient. This information enables doctors to diagnose the useful life of the implant, the load sharing of the bone plate, and possible complications typically associated with orthopaedic implants such as infection, fracture non-union, and fatigue. The implant may also have one or more electrodes located on its surface which emit an electric current to stimulate healing of the broken or fractured bone.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Tissue integration design for seamless implant fixation
The present invention relates to orthopaedic implants having a fenestrated hollow shell and a biologic core. These design features provide an improved interface between the implant and the surrounding tissue, aiding fixation, and provide a vehicle for applying new bone healing and enhancing modalities, such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Orthopaedic implants
InactiveUS20110004317A1Reduce difficultyReduce disadvantagesAdditive manufacturing apparatusWrist jointsPlastic surgerySurgical department
A method for making an orthopaedic implant, the method comprising: characterizing at least a portion of a bone corresponding to the bone to be replaced, said corresponding bone being on the contralateral side of the patient; providing a model of the orthopaedic implant based on a mirror image of the contralateral bone; and forming the orthopaedic implant based on the model.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Modular orthopaedic implant system with multi-use stems
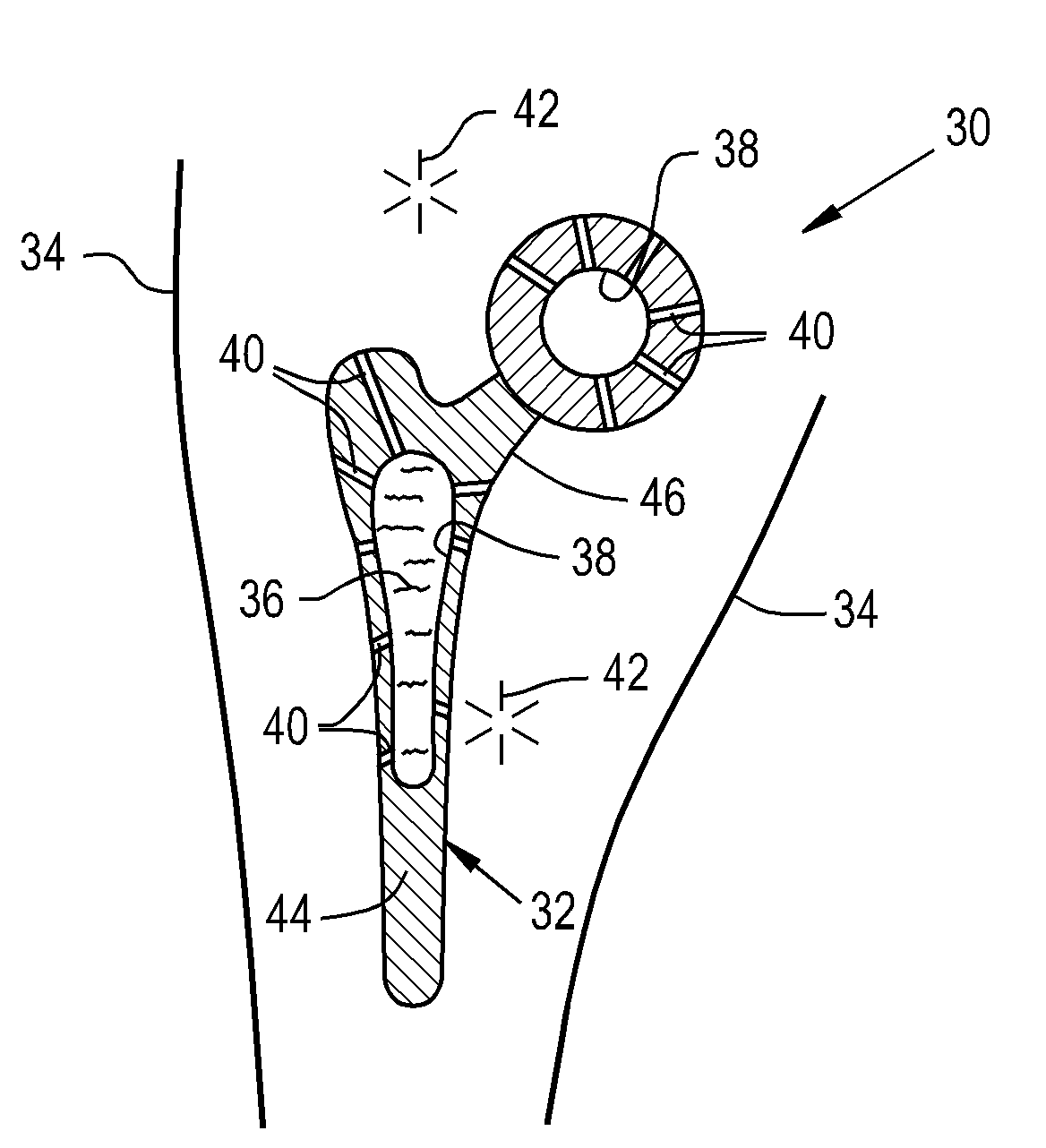
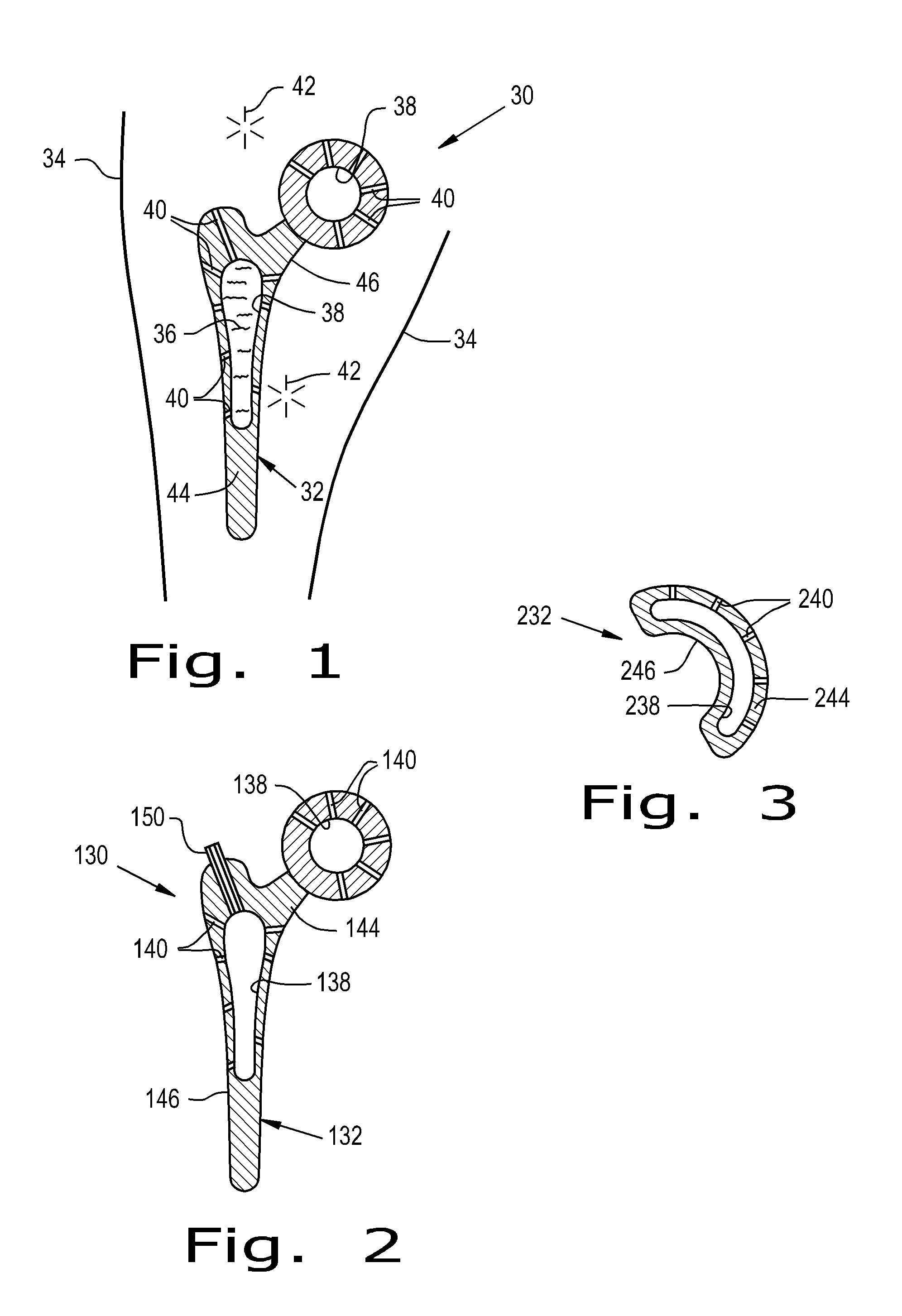
A knee implant system includes a femoral adapter. The femoral adapter has a threaded bore so that a stem extension can be threaded onto the proximal end of the adapter. The same stem extension can be threaded onto the distal end of the tibial tray so that the number of stem extensions required in the system is reduced. The femoral adapter has a tapered exterior surface so that a metaphyseal sleeve can be frictionally connected to the femoral adapter. The metaphyseal sleeve has a threaded bore so that the same type of stem extension can be threaded onto the metaphyseal sleeve. The system can include a group of adapters to give the surgeon the option of selecting the appropriate valgus angle and anterior-posterior position of the stem extension.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Surfaces and processes for wear reducing in orthopaedic implants
Artificial implants having reduced area to provide reduced wear are provided. The reduced area is particularly located at areas where greatest wear is exhibited. In a particular embodiment of a mobile bearing knee implant, the area is reduced on the mobile bearing insert underside, where it contacts a tibial component. The reduced area may be any shape of indentations, for example, grooves, dimples, straight patterns, curved patterns, crossing patterns, holes, channels or slots. The indentations may be various sizes, and have been found to be particularly effective if covering about 10% to about 20% of the insert at depths between about 1-2 mm.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Orthopaedic implant and screw assembly
InactiveUS20050055024A1High strengthIncrease resistanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCompression deviceEngineering
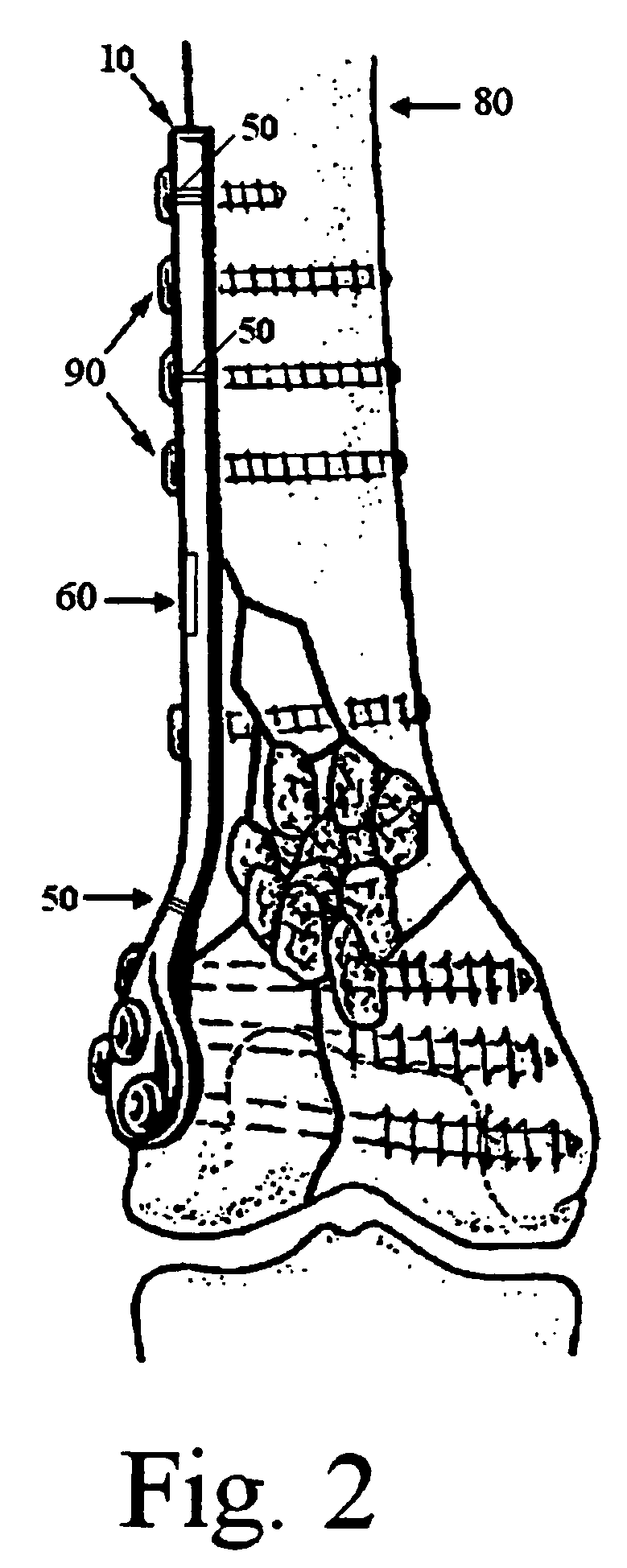
Systems, devices and methods are disclosed for treating fractures. The systems, devices and methods may include one or both of an implant, such as an intramedullary nail, and a fastening assembly, such as a lag screw and compression screw assembly. The implant in some embodiments has a proximal section with a transverse aperture and a cross-section that may be shaped to more accurately conform to the anatomical shape of cortical bone and to provide additional strength and robustness in its lateral portions, preferably without requiring significant additional material. The fastening assembly may be received to slide, in a controlled way, in the transverse aperture of the implant. In some embodiments, the engaging member and the compression device are configured so that the compression device interacts with a portion of the implant and a portion of the engaging member to enable controlled movement between the first and second bone fragments. This configuration is useful for, among other things, compressing a fracture.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Methods for producing metallic implants having roughened surfaces
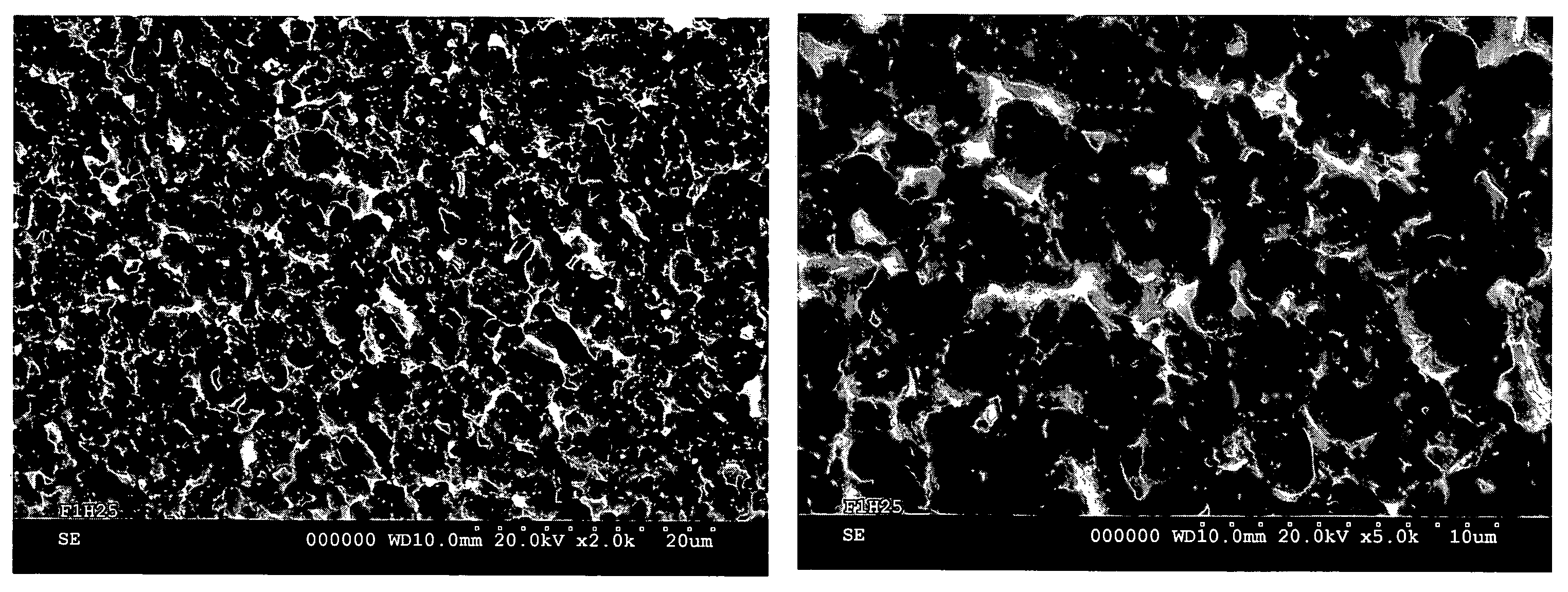
The invention provides a method of providing a metallic orthopaedic implant with a micron or nanometer-scale surface roughness to facilitate acceptance of tissue and bone growth or apposition after implantation while maintaining the structural integrity of the orthopaedic implant. The invention also provides a metallic orthopaedic implant comprising a metallic body and metallic elements adhered to a portion of the surface of the metallic body to define a three-dimensional porous surface geometry, wherein at least some of the metallic elements have a micron or nanometer-scale surface roughness.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Drug delivery implants
An orthopaedic implant system includes an orthopaedic implant implantable at a selected location within a corporeal body and configured for delivering at least one therapeutic agent to the corporeal body, the implant defining a reservoir and a plurality of channels, the reservoir configured for receiving the at least one therapeutic agent, the plurality of channels configured for conveying the at least one therapeutic agent from the reservoir to a treatment site relative to the corporeal body, the implant being at least one of an internal fixation device and a porous device.
Owner:SMED TATD
Orthopaedic implant and screw assembly
Systems, devices and methods are disclosed for treating fractures. The systems, devices and methods may include one or both of an implant, such as an intramedullary nail, and a fastening assembly, such as a lag screw and compression screw assembly. The implant in some embodiments has a proximal section with a transverse aperture and a cross-section that may be shaped to more accurately conform to the anatomical shape of cortical bone and to provide additional strength and robustness in its lateral portions, preferably without requiring significant additional material. The fastening assembly may be received to slide, in a controlled way, in the transverse aperture of the implant. In some embodiments, the engaging member and the compression device are configured so that the compression device interacts with a portion of the implant and a portion of the engaging member to enable controlled movement between the first and second bone fragments. This configuration is useful for, among other things, compressing a fracture.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
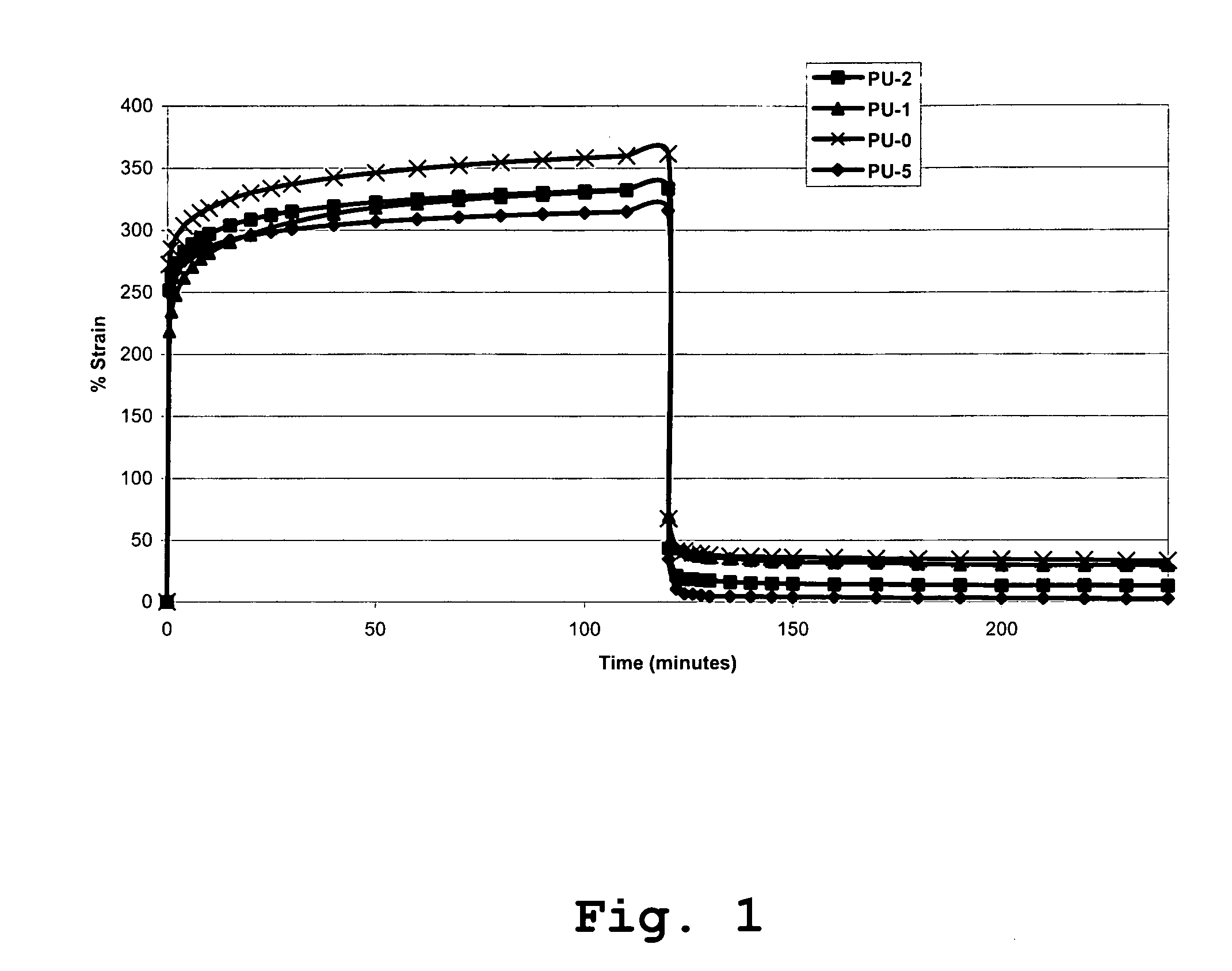
High modulus polyurethane and polyurethane/urea compositions
ActiveUS20090099600A1High modulusHigh strengthStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The present invention provides a polyurethane or polyurethane / urea composition which has a tensile strength greater than 10 MPa, a modulus of elasticity greater than 400 MPa and an elongation at break greater than 30% at a temperature of between 0° C. and 60° C. and at a relative humidity of between 0% and 100%.The invention further provides uses of the compositions of the invention in biomedical vascular stents, an orthopaedic implant, a drug delivery coating or in tissue engineering.
Owner:POLYNOVO BIOMATERIALS PTY LTD
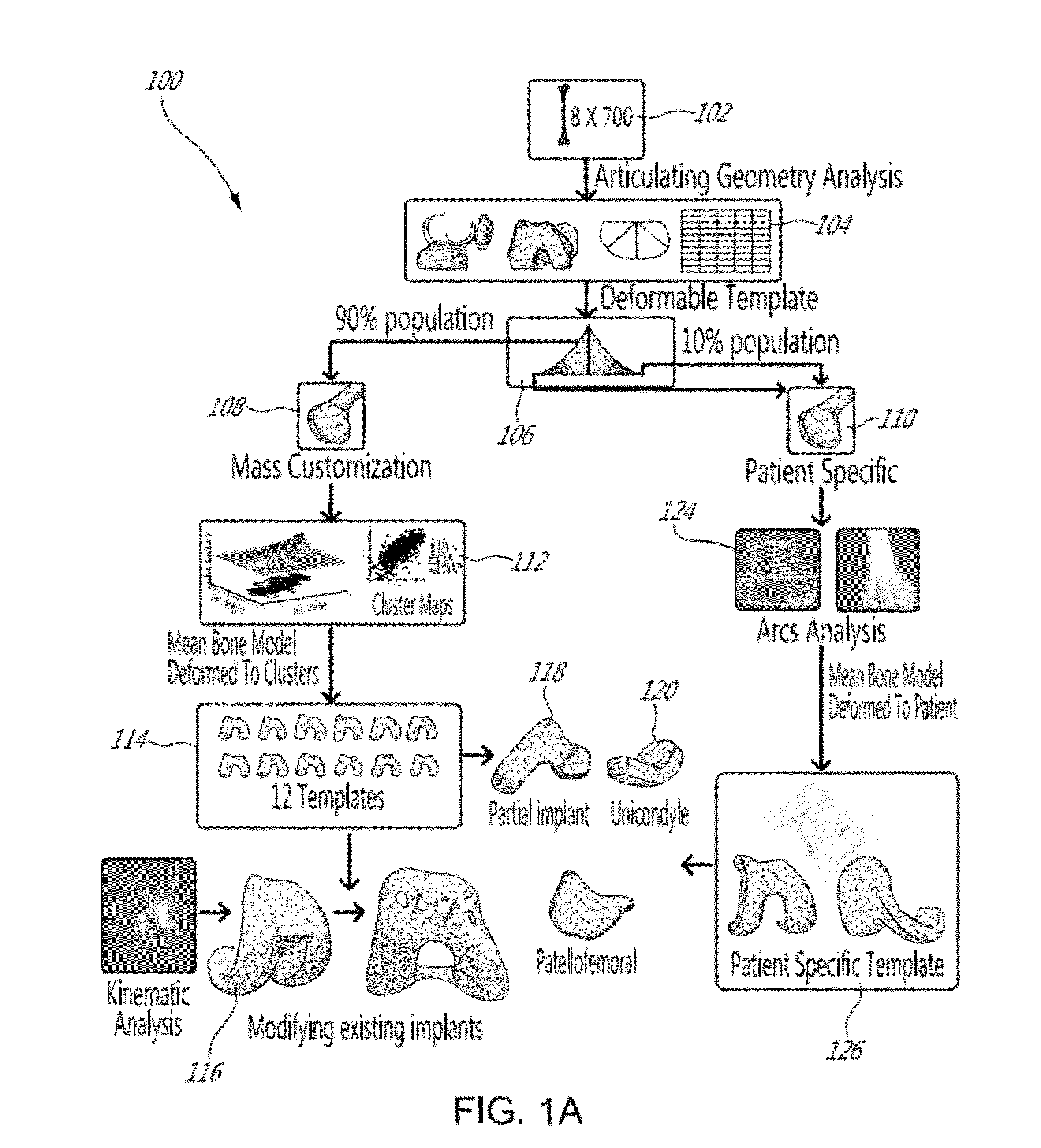
Ethnic-Specific Orthopaedic Implants and Custom Cutting Jigs
An orthopedic implant comprising: (a) a distal femoral component comprising a first condyle bearing surface having a first profile comprising at least three consecutive arcs of curvature; and (b) a proximal tibial component comprising a first condyle bearing surface having a second profile comprising at least three parallel arcs of curvature. The disclosure also includes a method of designing and fabricating an orthopedic implant, the method comprising: (a) evaluating images of distal femurs of a particular ethnicity to extract common shape features exhibited across an ethnicity that are unique to the ethnicity to create an ethnic specific template; (b) designing a distal femoral component comprising a first condyle surface using the ethnic specific template; and, (c) fabricating a distal femoral component embodying the first condyle surface.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Orthopaedic implant
ActiveUS20100042215A1Improve adhesion strengthStrong bonesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPlastic surgeryBiomedical engineering
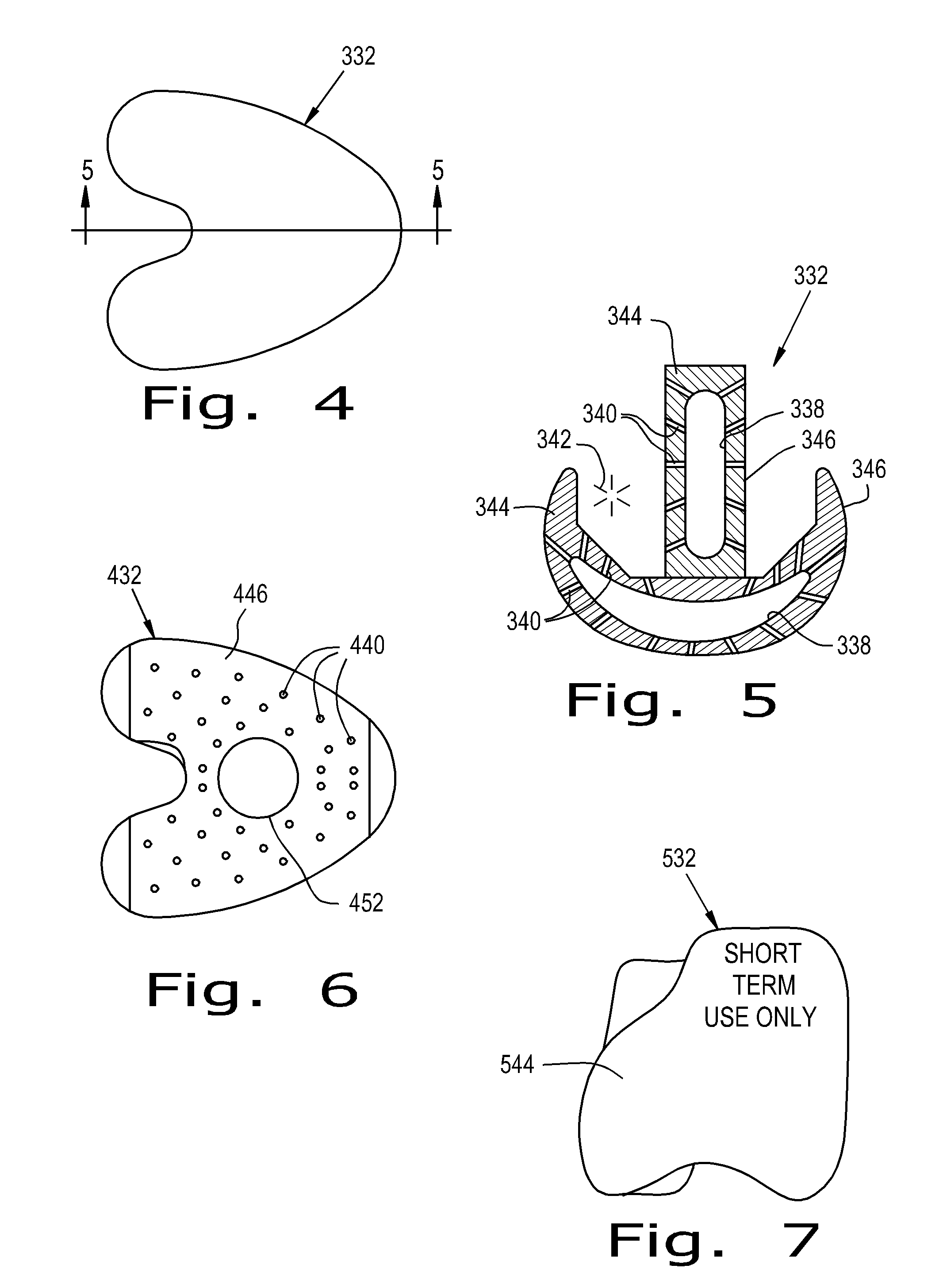
An orthopaedic implant system includes an orthopaedic implant implantable at a selected location within a corporeal body. The implant includes a first structural material and a second structural material. The first structural material is non-resorbable relative to the corporeal body and is different relative to the second structural material. The implant is an internal fixation device.
Owner:SMED TATD
Drug delivery implants
An orthopaedic implant system includes an orthopaedic implant implantable at a selected location within a corporeal body and configured for delivering at least one therapeutic agent to the corporeal body. The implant includes a reservoir and a plurality of channels. The reservoir is configured for receiving the at least one therapeutic agent. The plurality of channels are configured for conveying the at least one therapeutic agent from the reservoir to a treatment site relative to the corporeal body.
Owner:SMED TATD
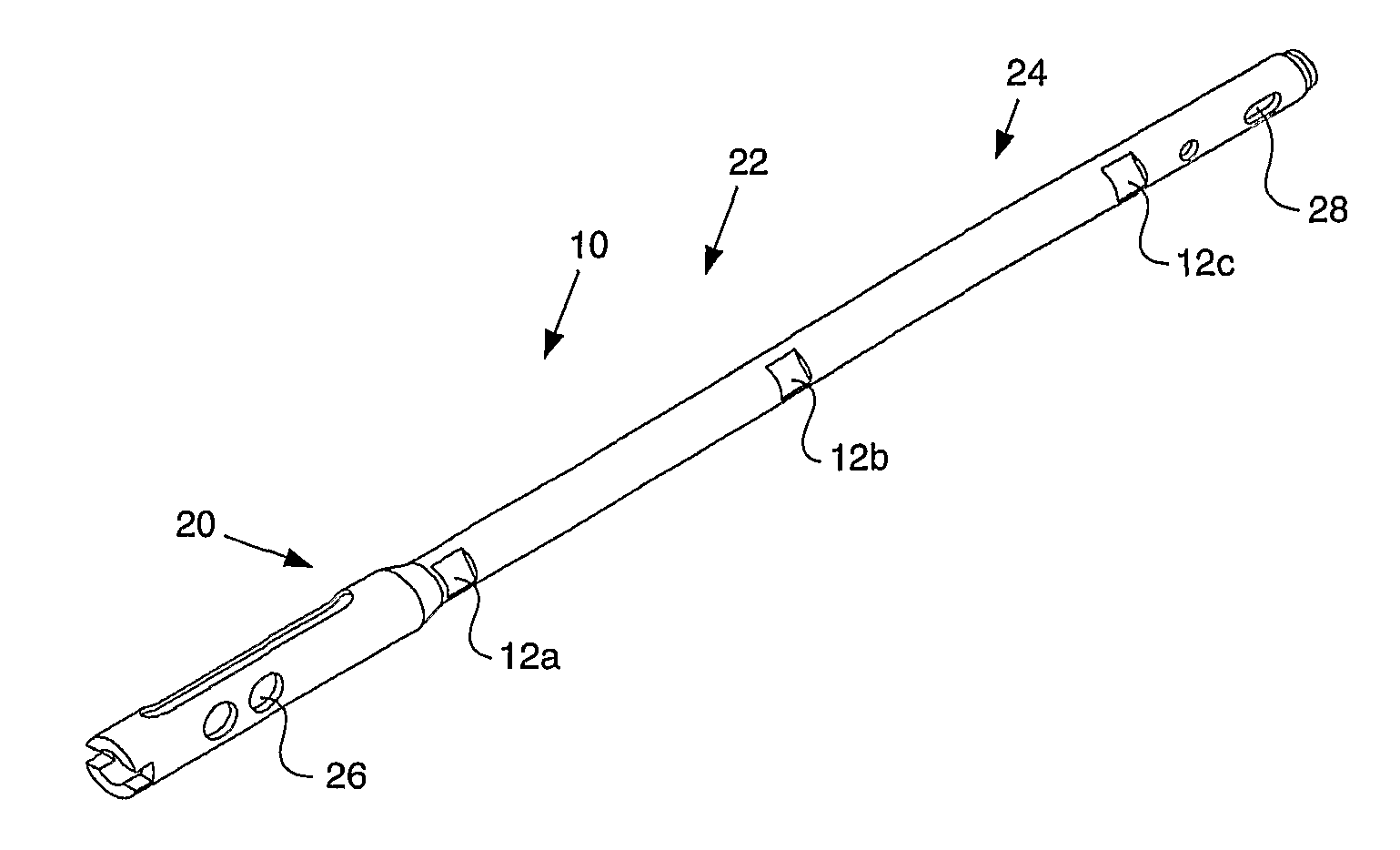
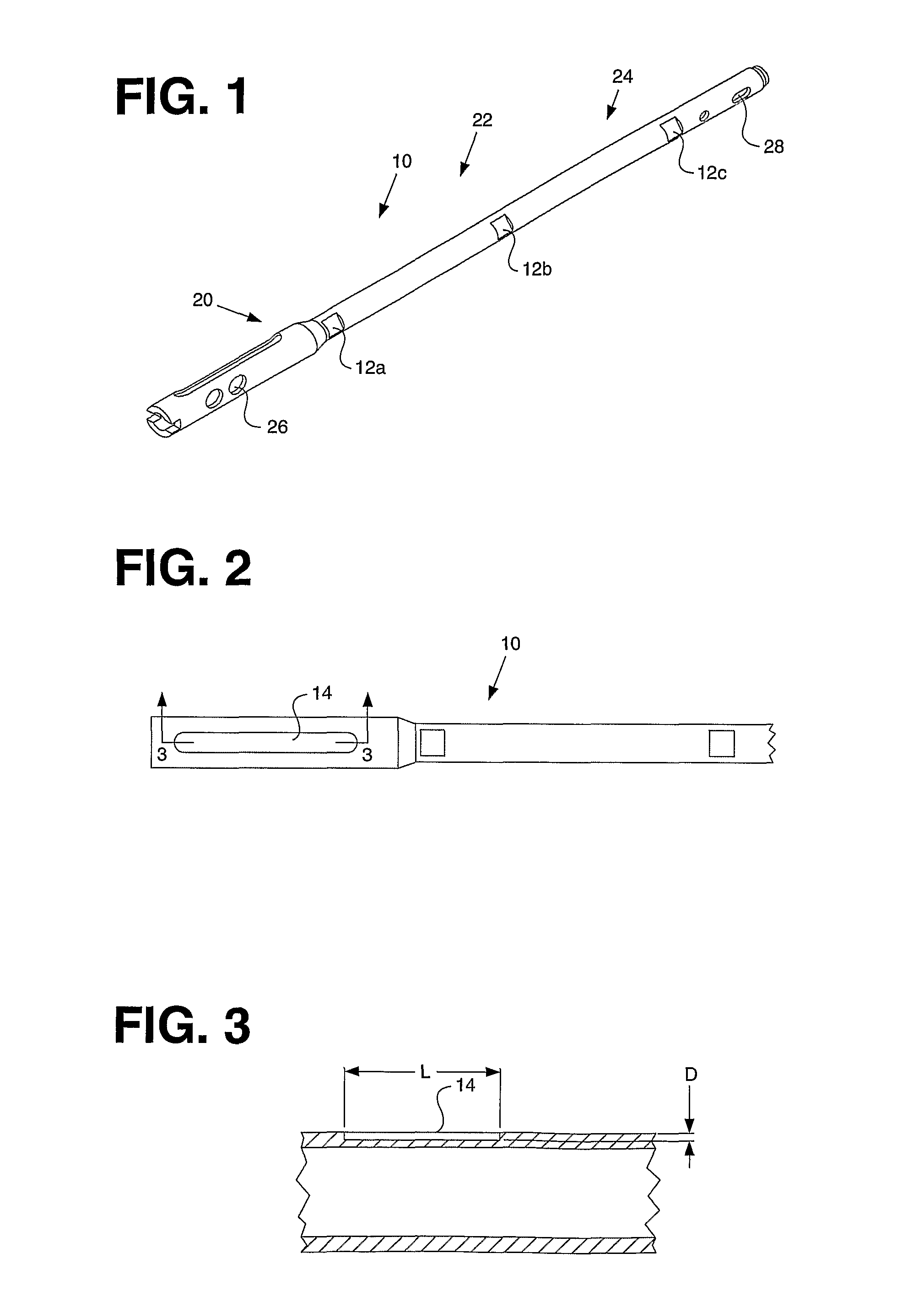
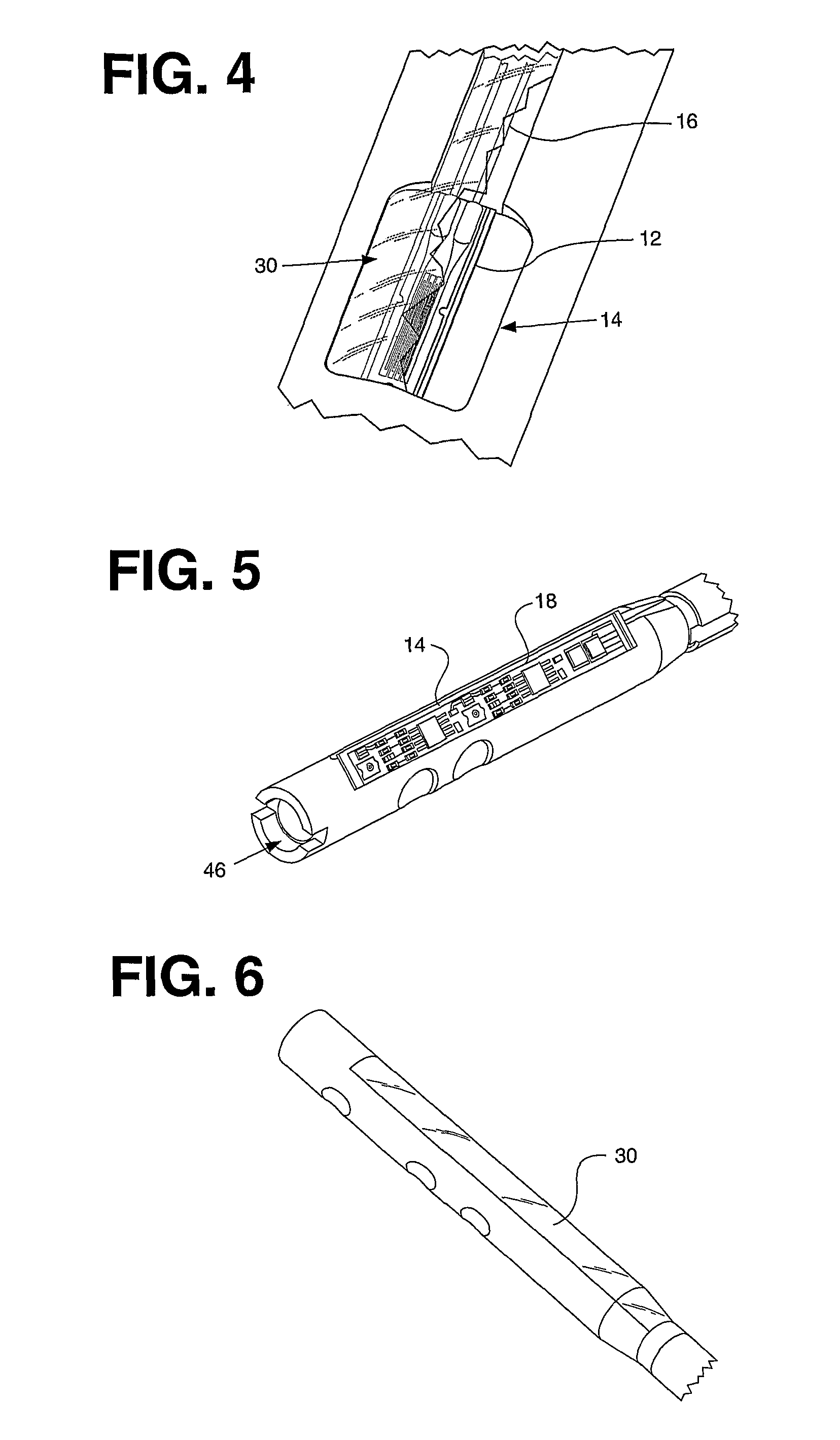
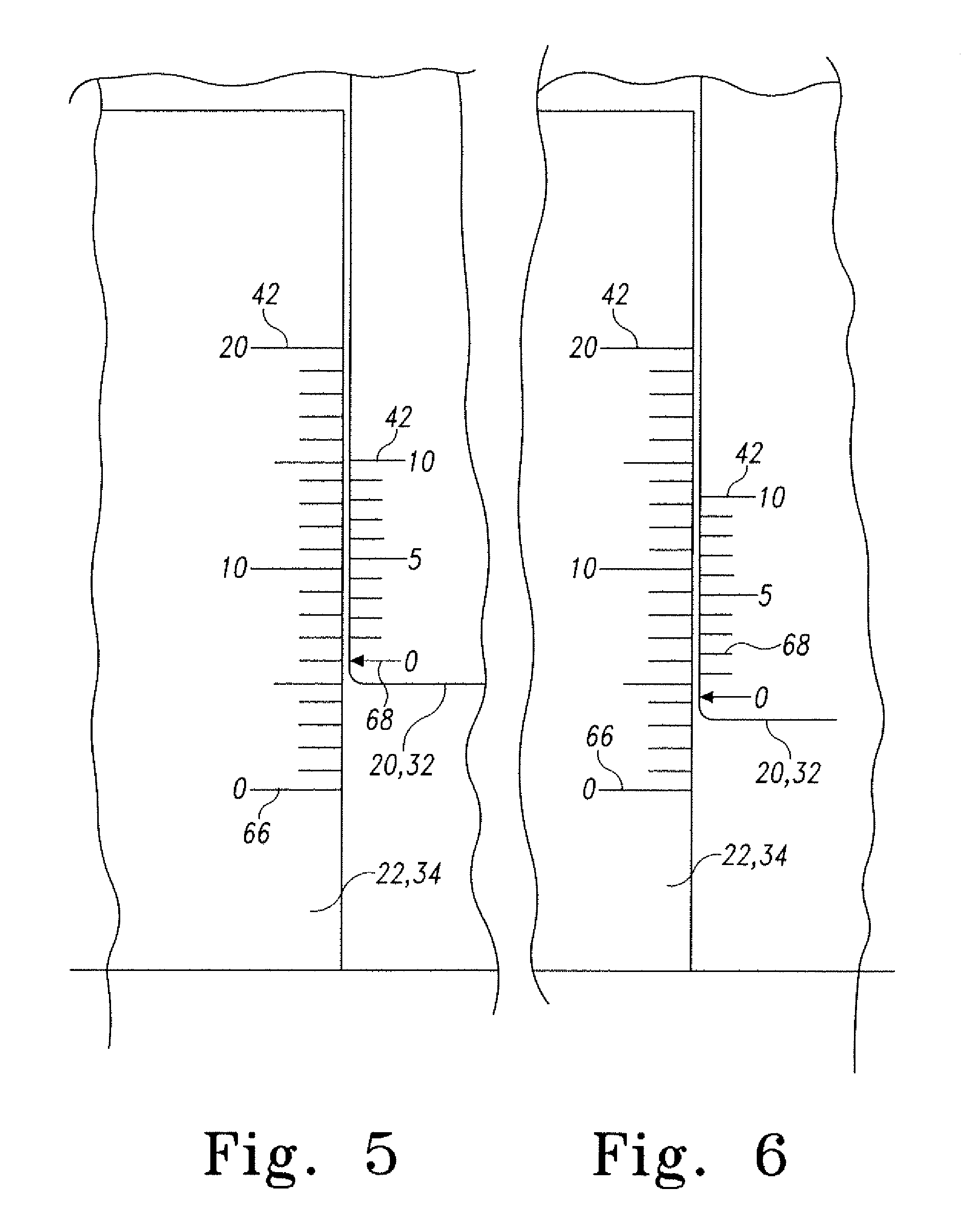
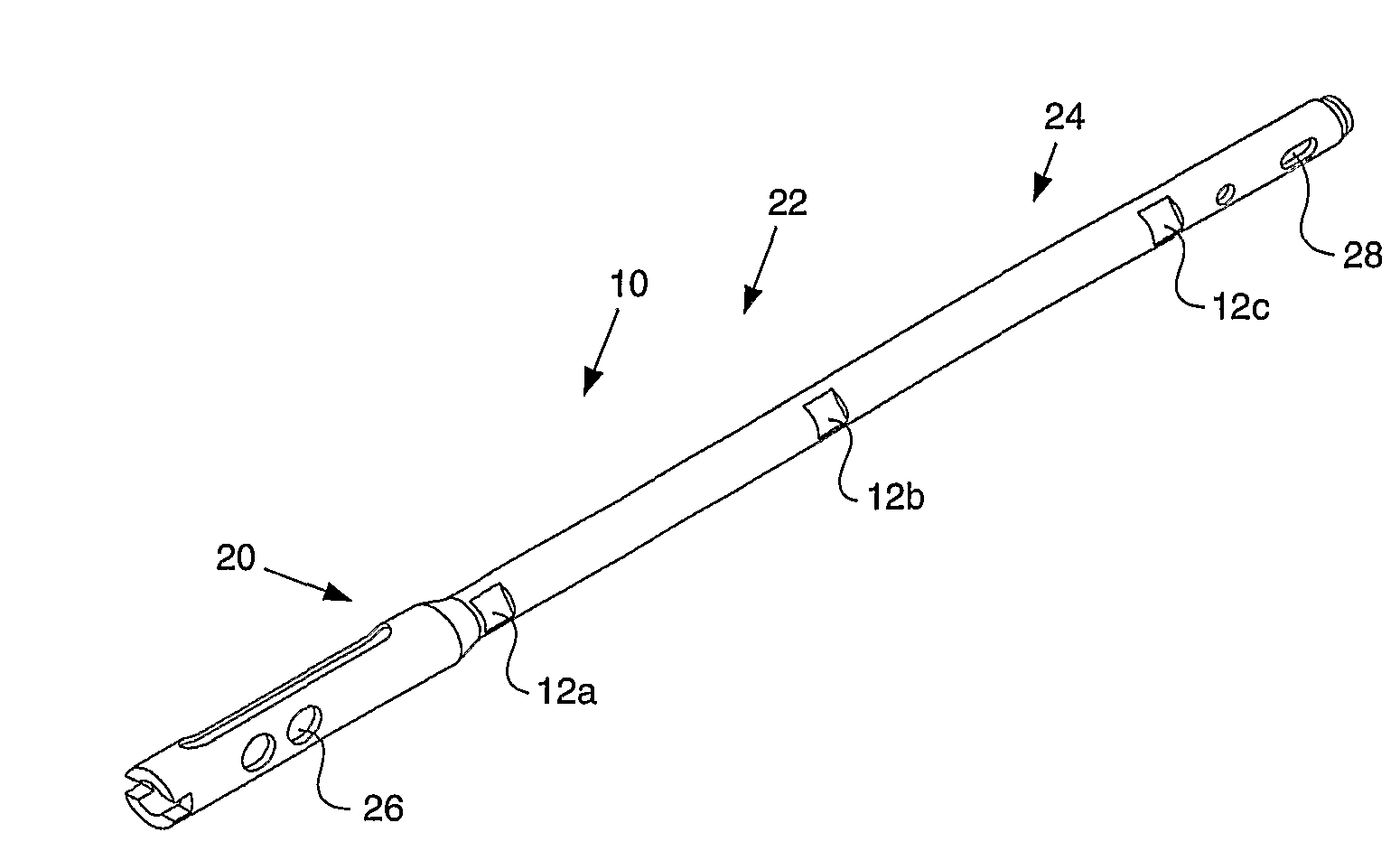
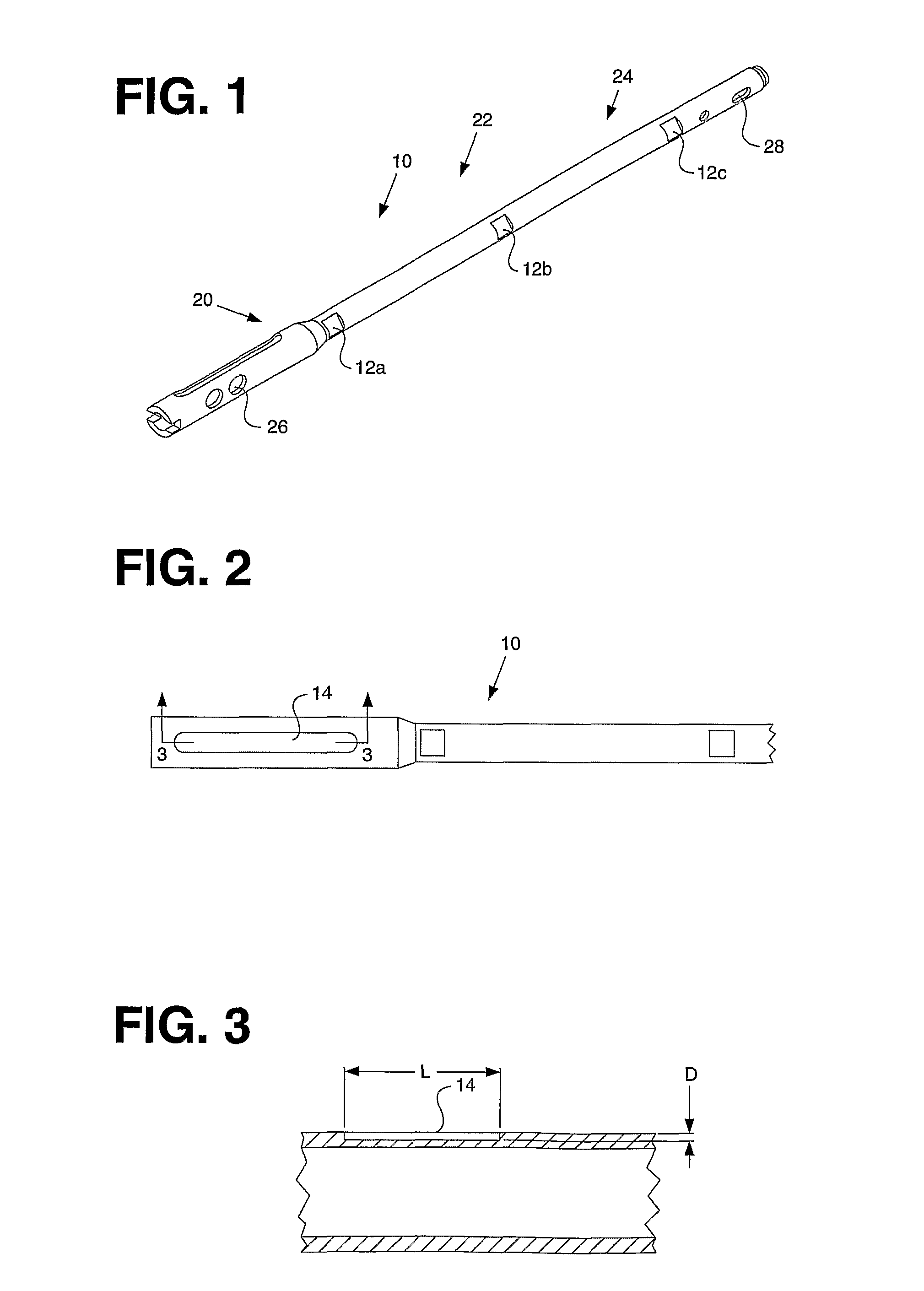
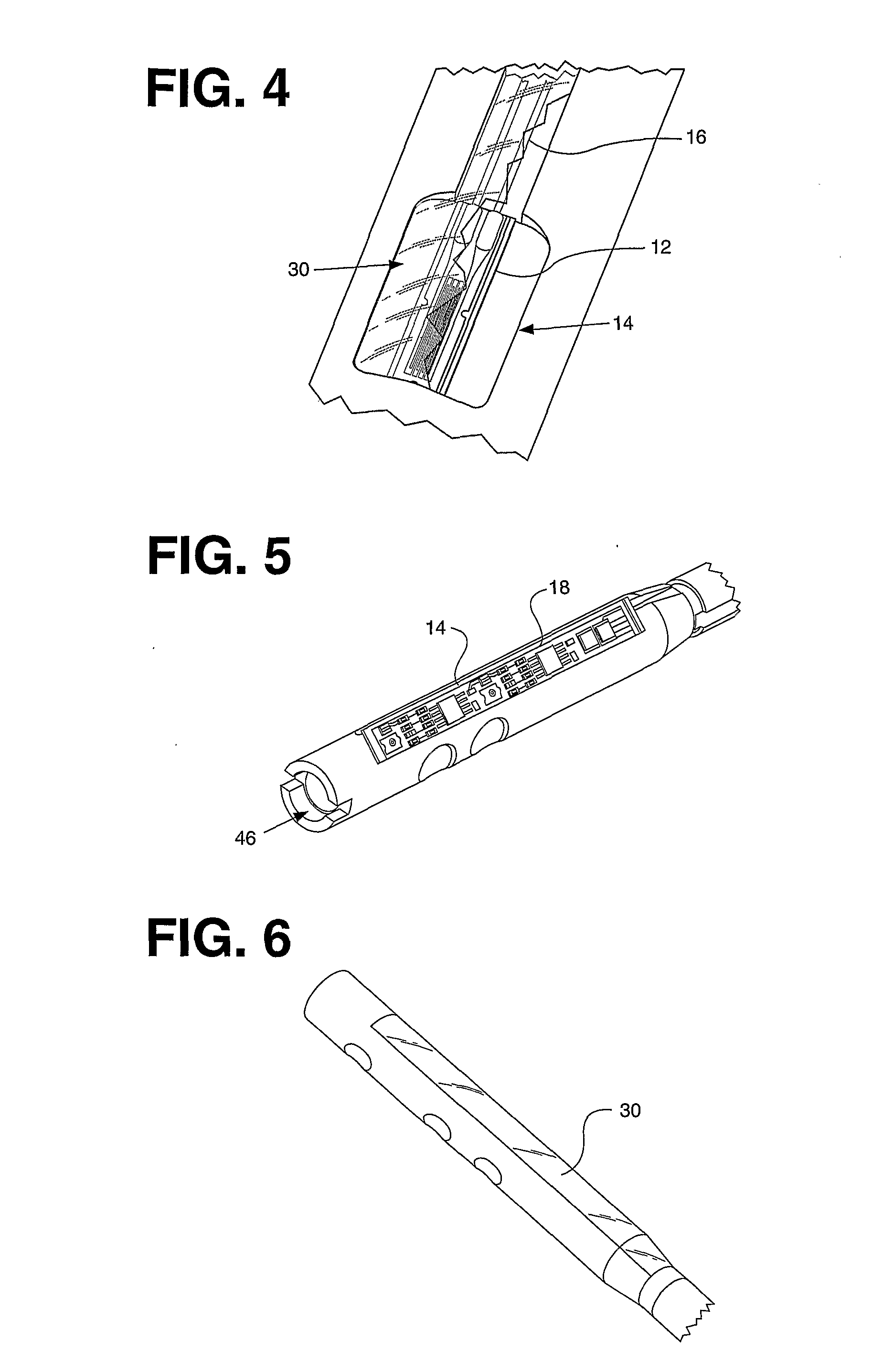
Telemetric orthopaedic implant
ActiveUS8486070B2Accurate predictionAccurately prescribeInternal osteosythesisBone implantPlastic surgeryElectronic component
An instrumented orthopaedic implant, such as an intramedullary (IM) nail, is disclosed. The implant has the capacity to provide an accurate measurement of the applied mechanical load across the implant. The implant includes sensors and associated electronic components located in recesses on the outer surface of the implant. The implant houses the sensing apparatus, the interface circuitry, the data transmitter, and the power receiver. The hermetically sealed housing is adapted for implantation in the body of a patient. The implant is used with a controller which communicates with it by telemetry, and there is an acting unit connected to the electronic components which is adapted to carry out a function based upon a condition detected by the sensors.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Implant system with migration measurement capacity
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Femoral implant revision tool
ActiveUS9198776B2Direct contact guaranteeJoint implantsFemoral headsUltrasonic vibrationPlastic surgery
An osteotome suitable for cutting through cancellous bone that is holding an orthopaedic implant requiring revision within a cavity of a bone, includes a cylindrical waveguide connectable to a source of ultrasonic vibrations at its proximal end and a blade having a hollow part-cylindrical cross-section and a cutting edge at its distal tip. The respective longitudinal axes of the waveguide and the blade cross at an angle of about 30°, and the waveguide and blade taper and curve smoothly together where they meet. The osteotome is dimensioned such that a first antinode of the ultrasonic vibrations is located at a proximal end of the waveguide, a second antinode is located at the distal tip of the blade and a node is located where the waveguide and blade meet. The osteotome cuts readily through cancellous bone when ultrasonically energized.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
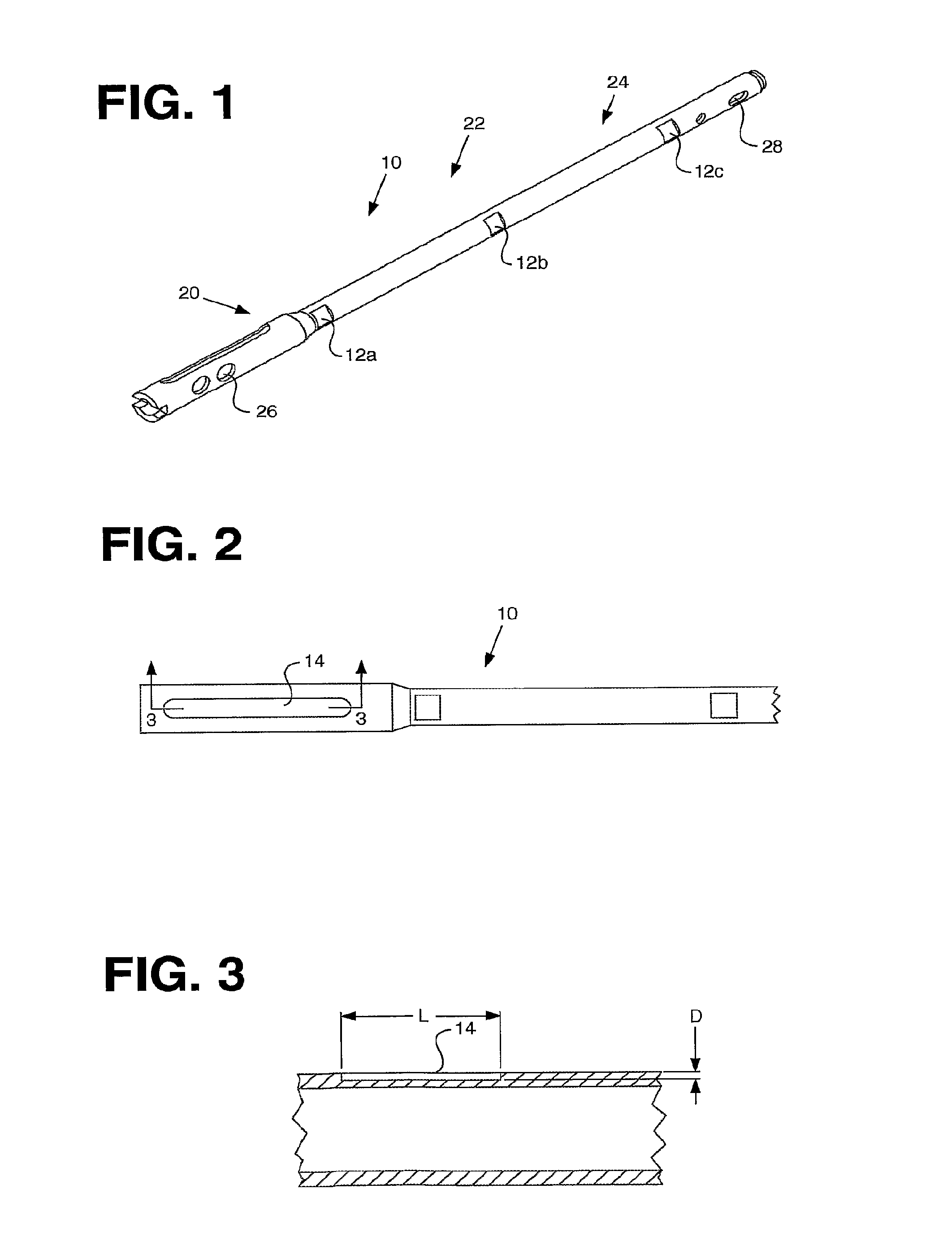
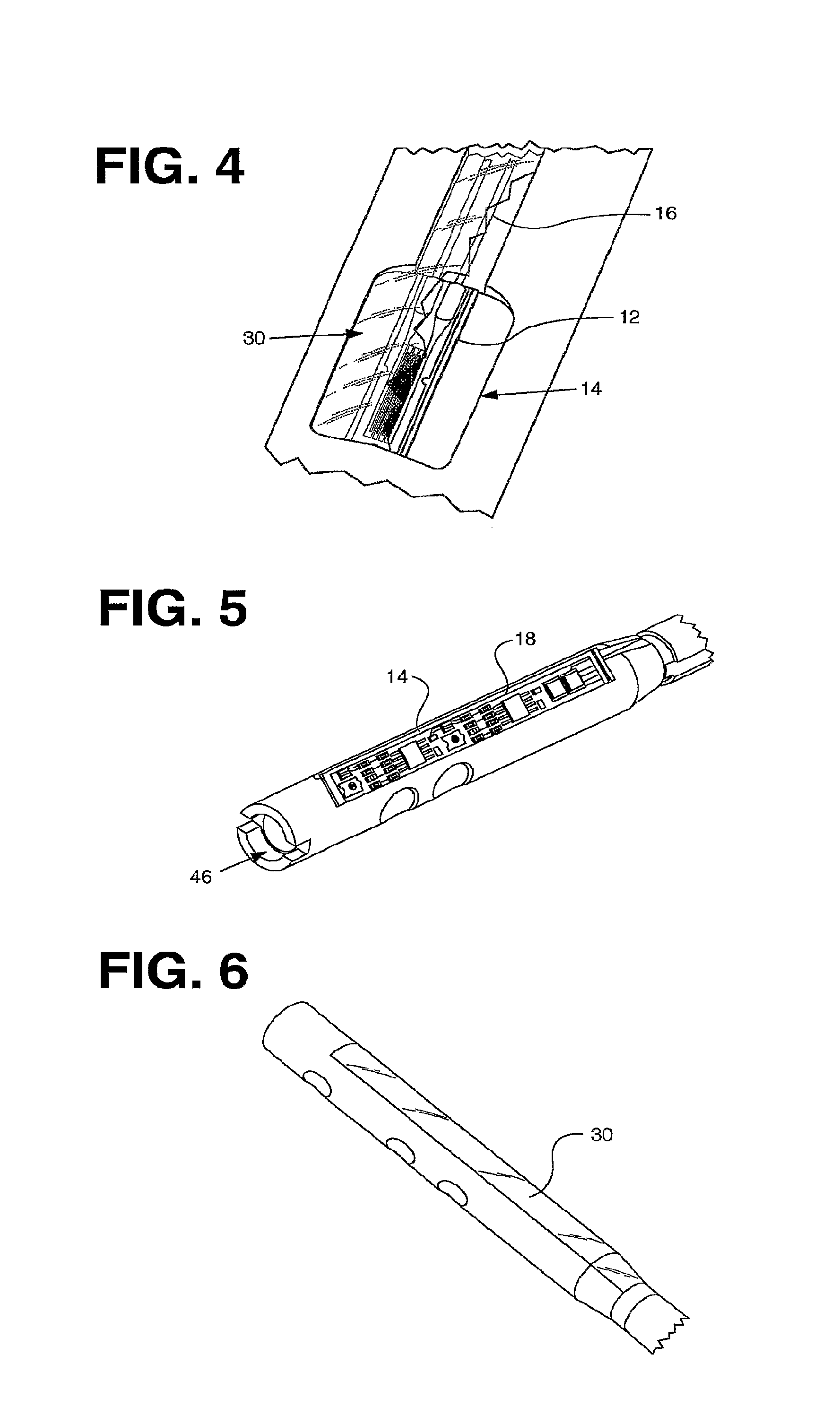
Implant delivery instrument
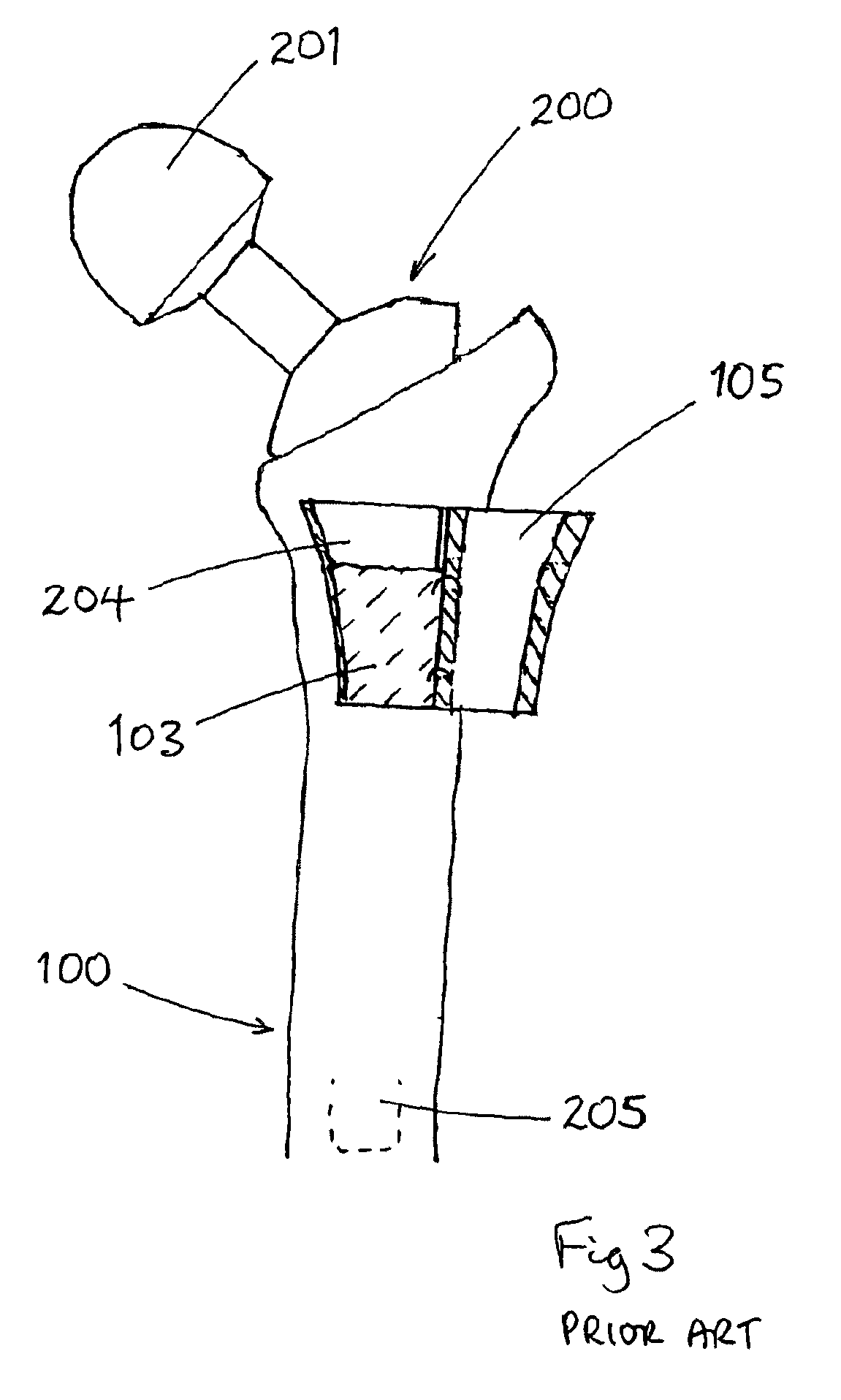
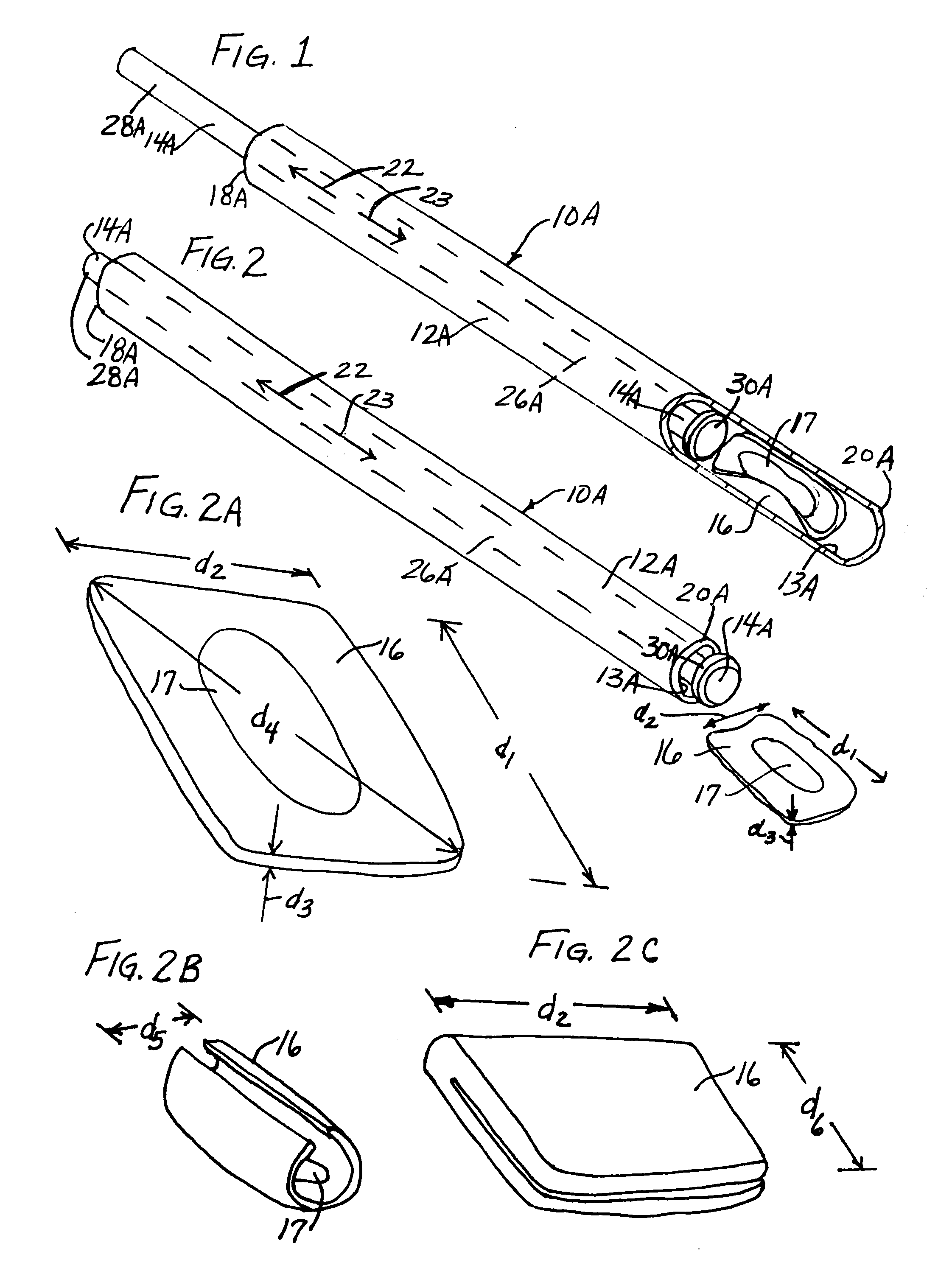
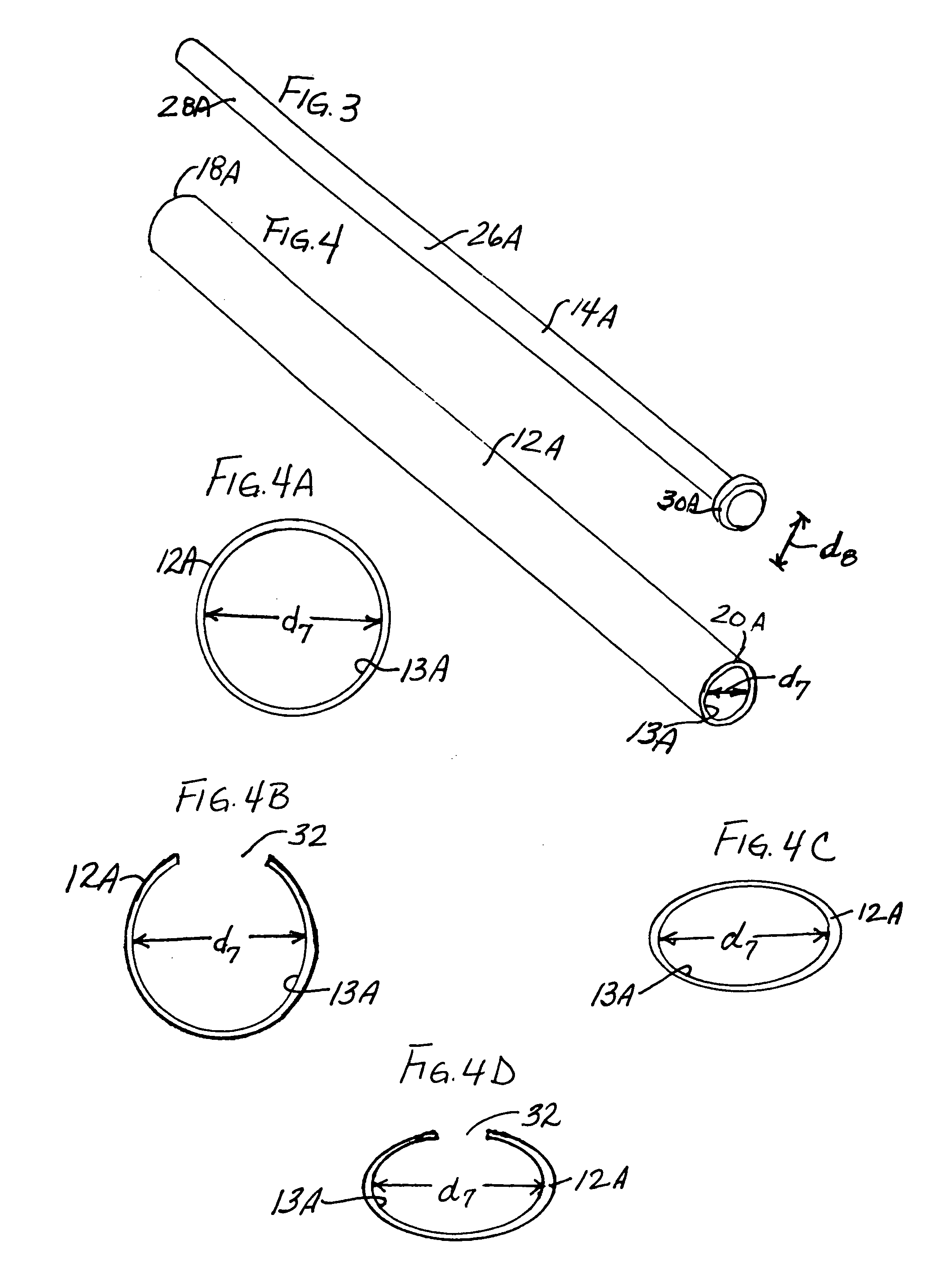
A surgical instrument has an elongate guide member and a reciprocable member. The elongate guide member provides a protected path of travel for an implant from outside the body to a position near a damaged tissue site. The reciprocable member is movable along the elongate guide member to push the implant along its path of travel. The reciprocable member can include an implant carrier. The implant can be an orthopaedic implant for repair or regeneration of soft tissue at a damaged joint site. The implant can be larger than the transverse dimension of the elongate guide member and folded or rolled to fit within the elongate guide member. Use of this instrument protects the implant from damage as it is delivered to the damaged joint site. The invention also includes a surgical method for delivering an implant to a damaged tissue site.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Telemetric Orthopaedic Implant
ActiveUS20080300597A1Accurate predictionAccurately prescribeInternal osteosythesisBone implantPlastic surgeryElectronic component
An instrumented orthopaedic implant, such as an intramedullary (IM) nail, is disclosed. The implant has the capacity to provide an accurate measurement of the applied mechanical load across the implant. The implant includes sensors and associated electronic components located in recesses on the outer surface of the implant. The implant houses the sensing apparatus, the interface circuitry, the data transmitter, and the power receiver. The hermetically sealed housing is adapted for implantation in the body of a patient. The implant is used with a controller which communicates with it by telemetry, and there is an acting unit connected to the electronic components which is adapted to carry out a function based upon a condition detected by the sensors.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Modular orthopaedic implant apparatus and method
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Reduced wear orthopaedic implant apparatus and method
InactiveUS7108720B2Reducing cross-shearReduce wearJoint implantsFemoral headsPlastic surgeryBiomedical engineering
A prosthetic implant includes first, second and third components. The first component is configured to be disposed within the acetabulum. The second component is in a load bearing relationship with the first component, and is operable to rotate in a first axis of rotation. The second component is inhibited from movement in a second axis of rotation. The third component is in a load bearing relationship with the second component. The third component is operable to rotate in the second axis of rotation, but is inhibited from movement with the first axis of rotation.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
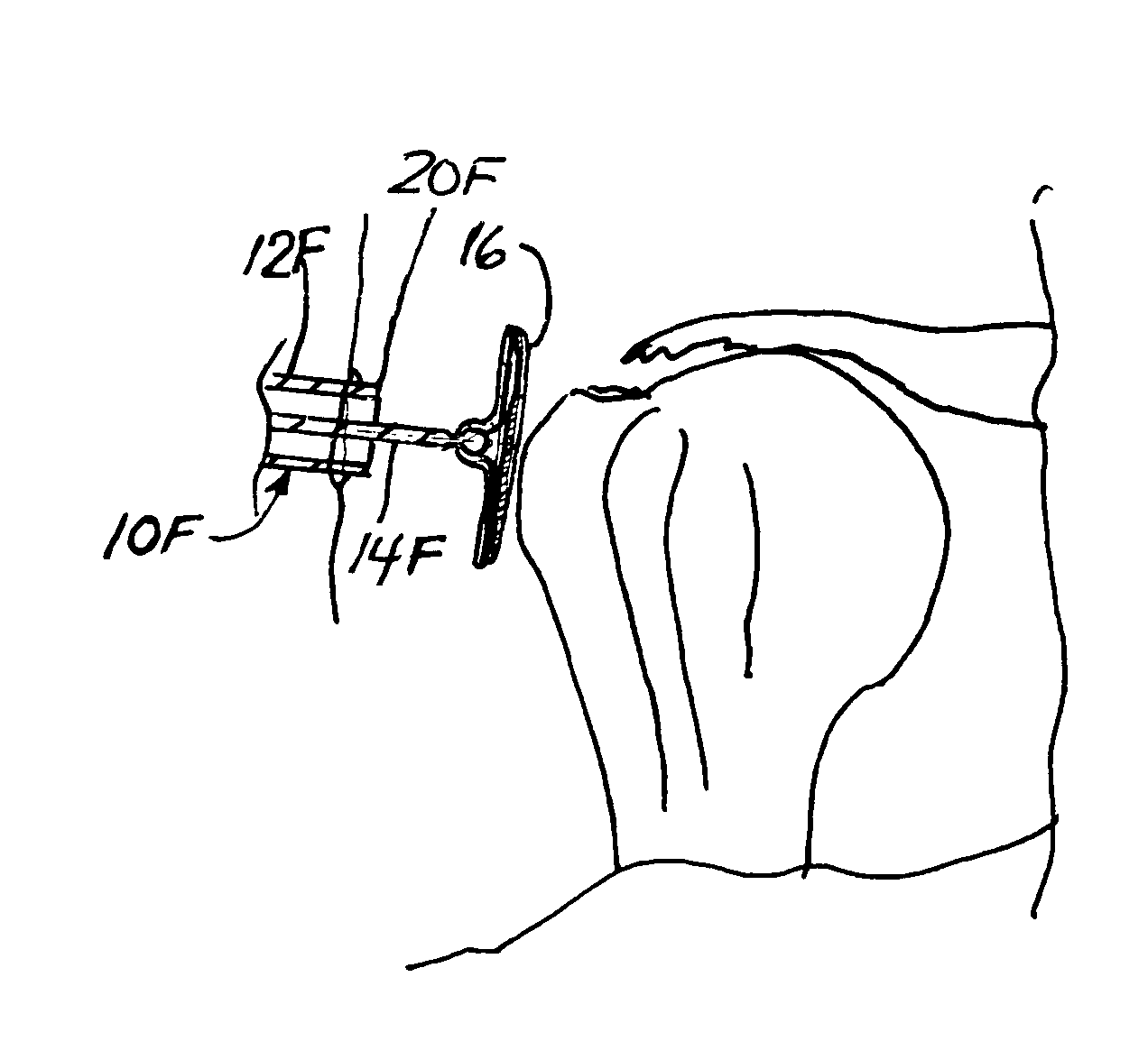
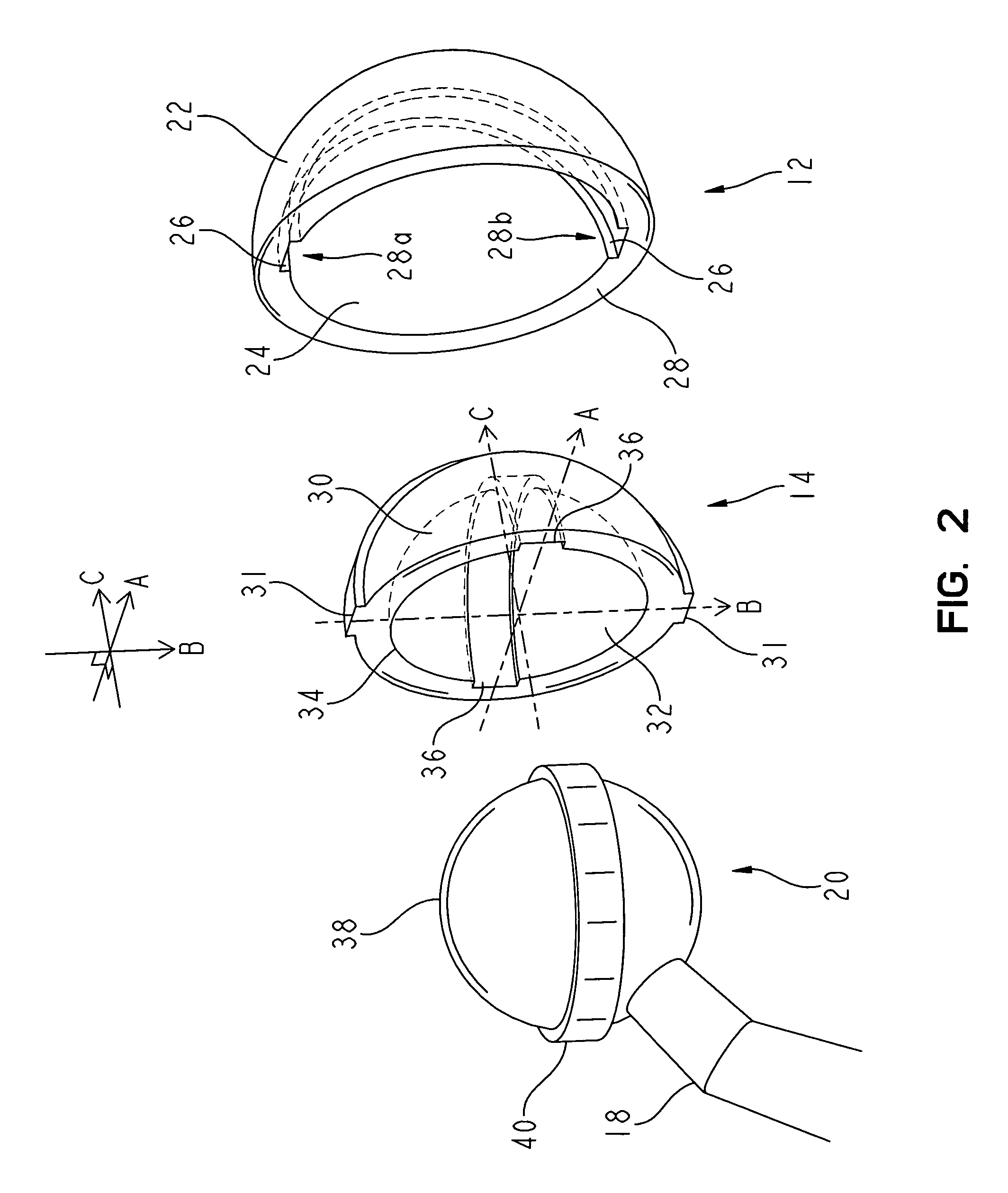
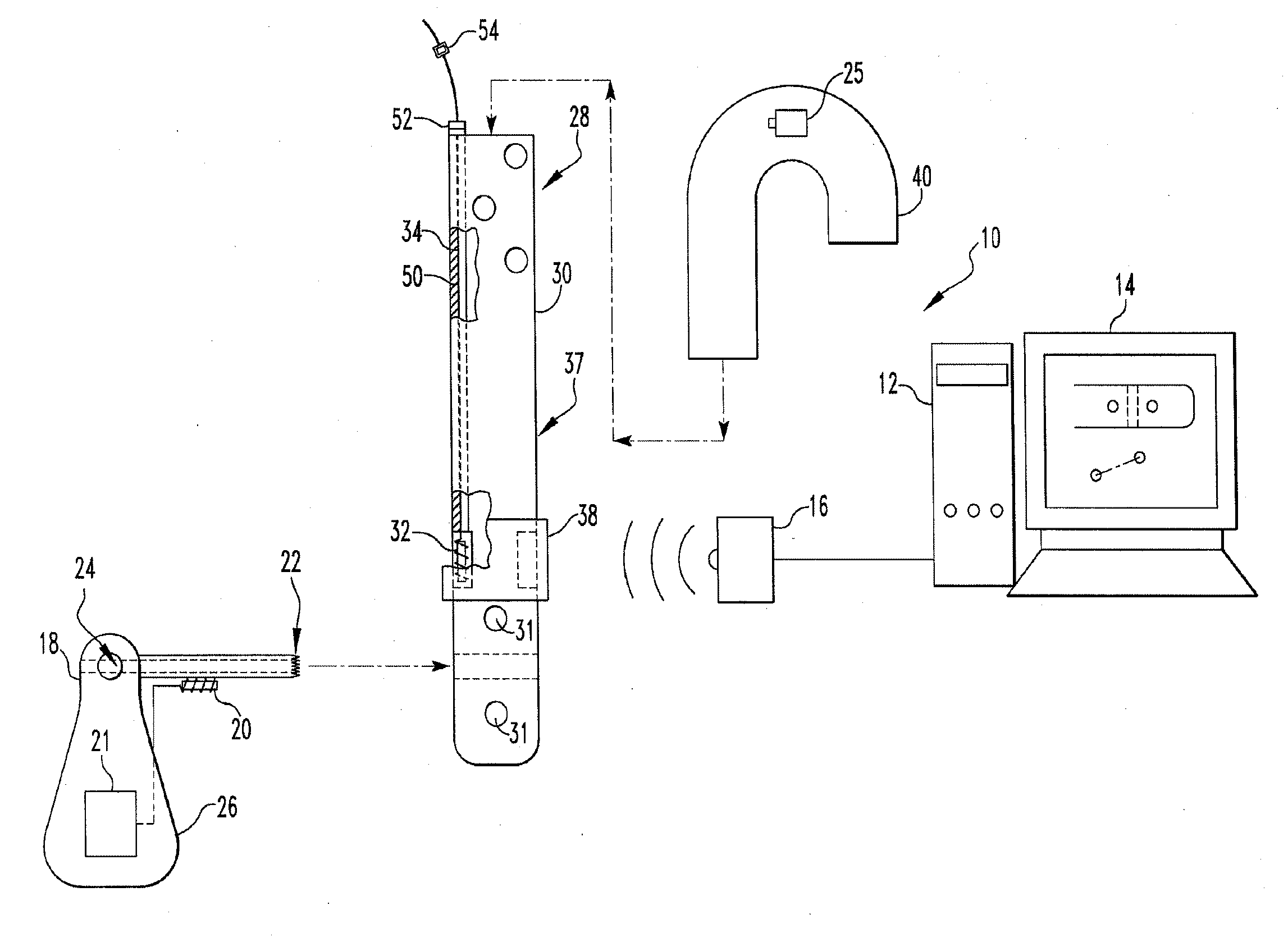
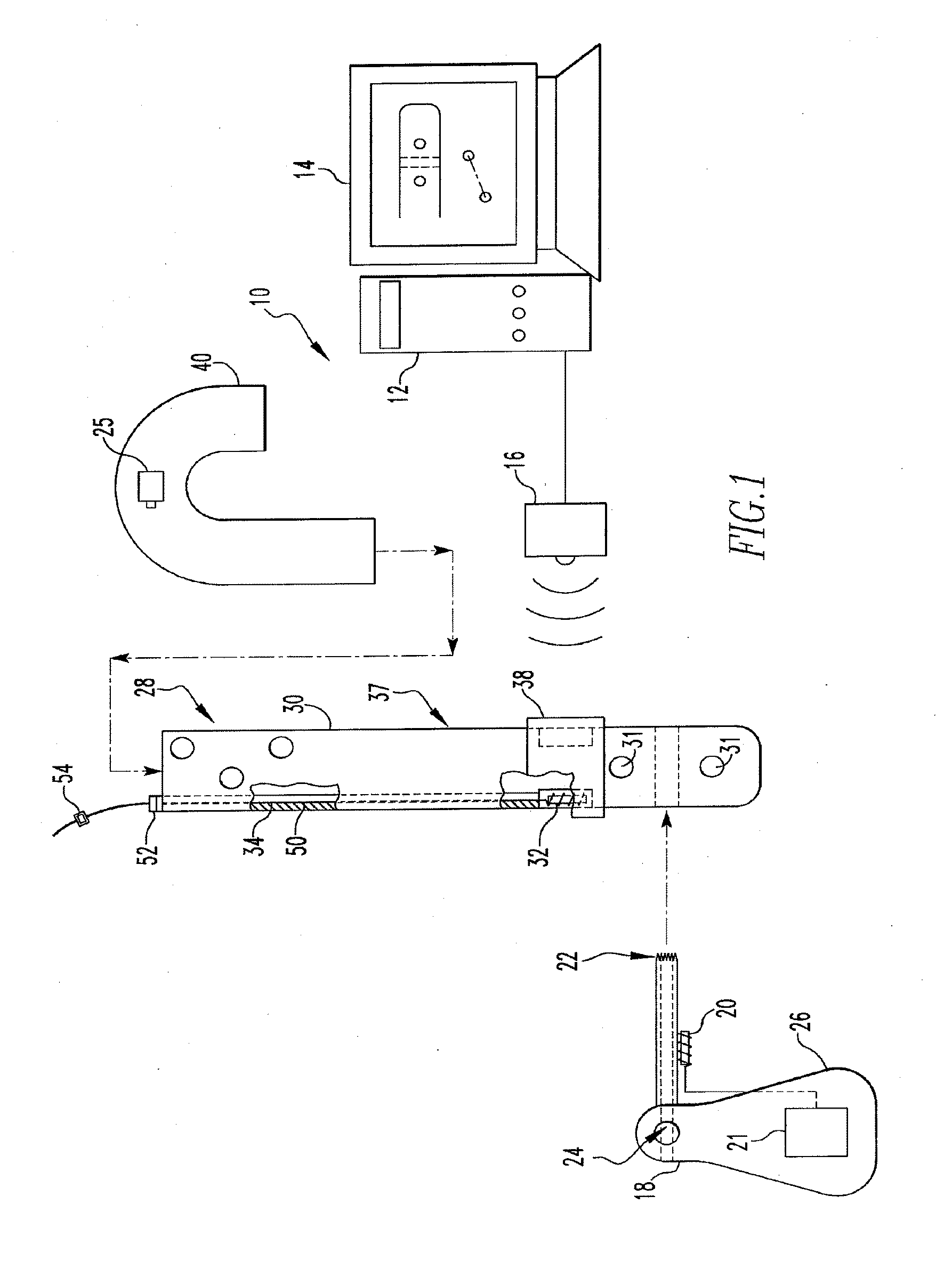
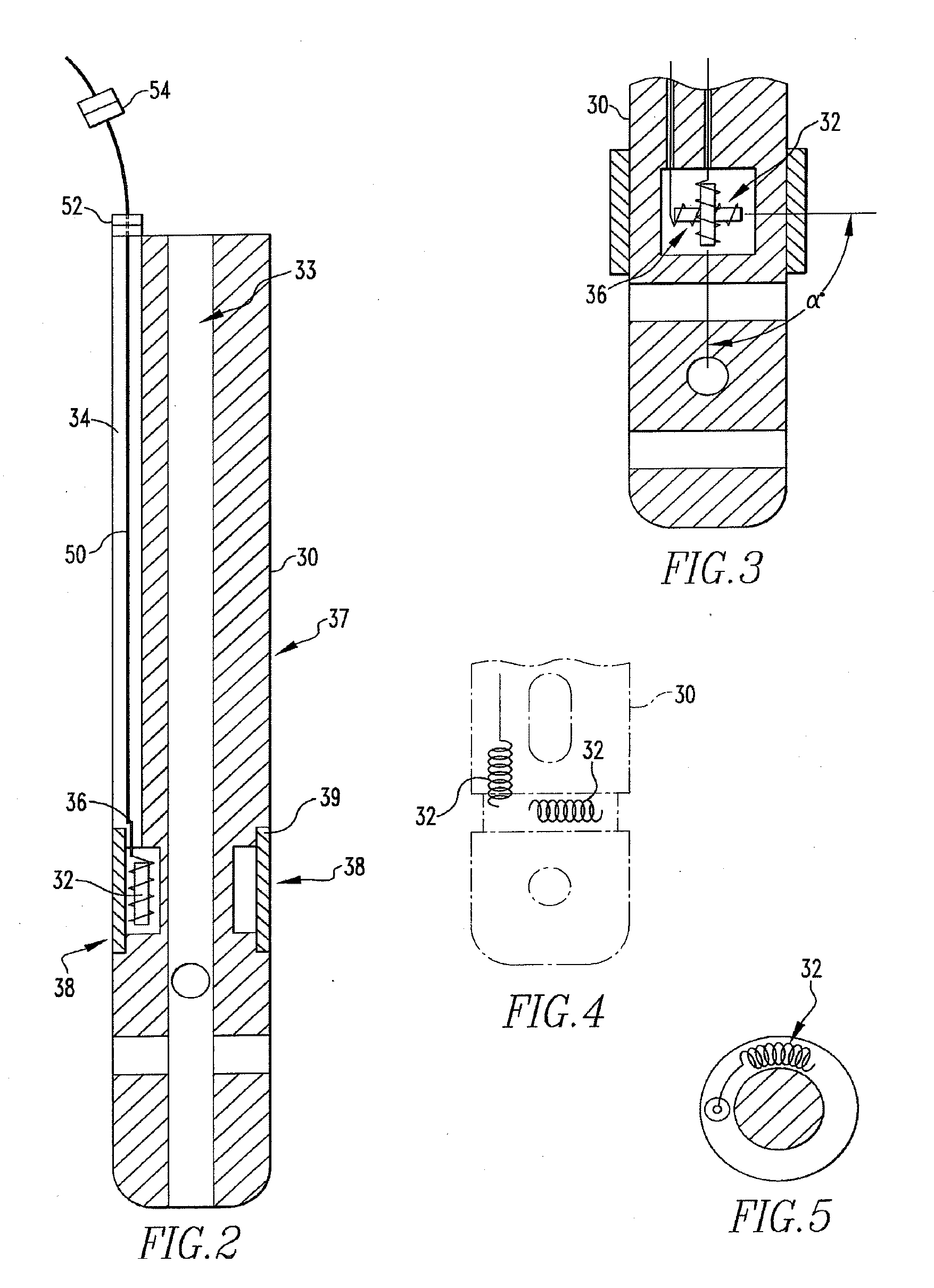
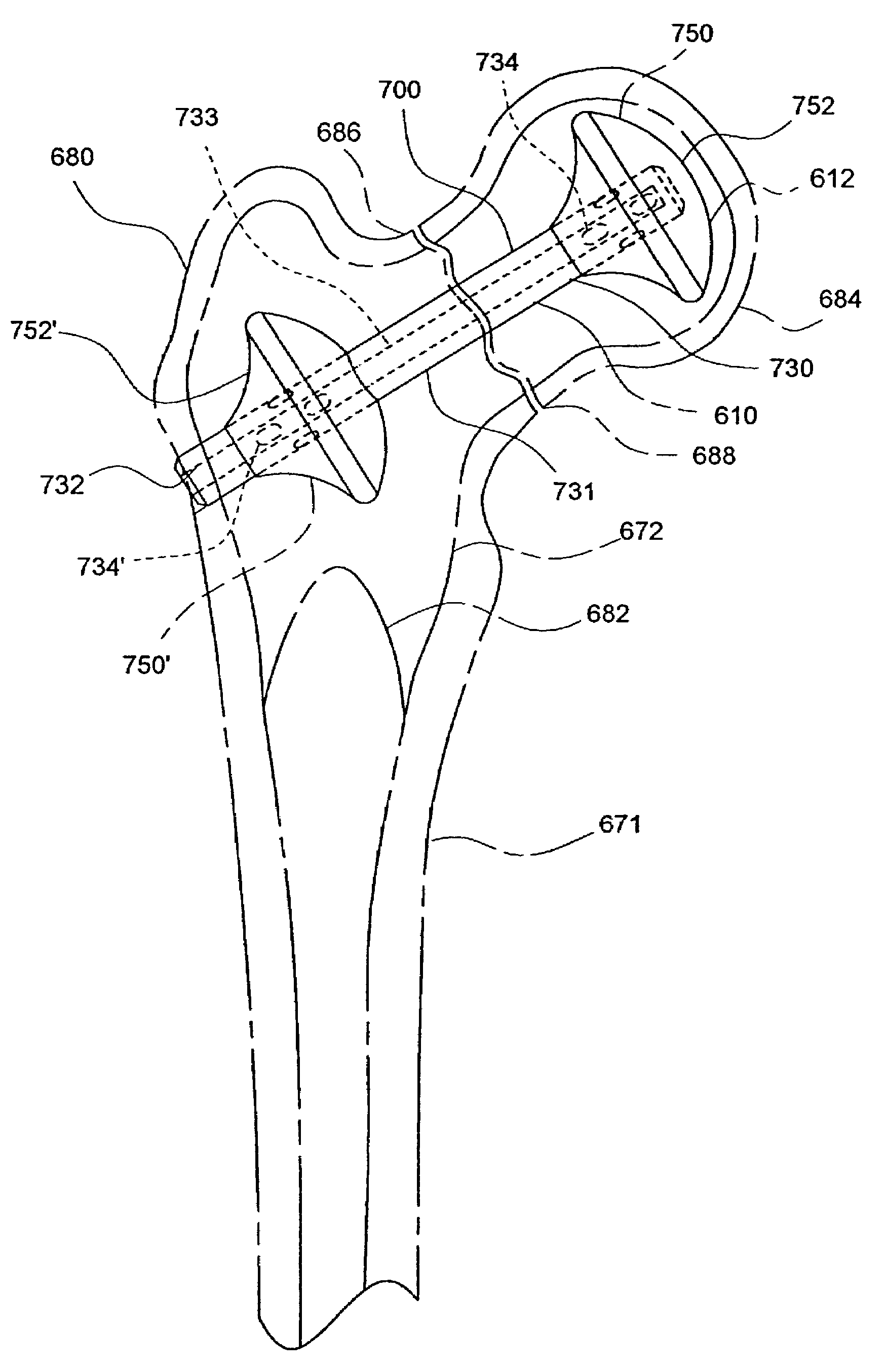
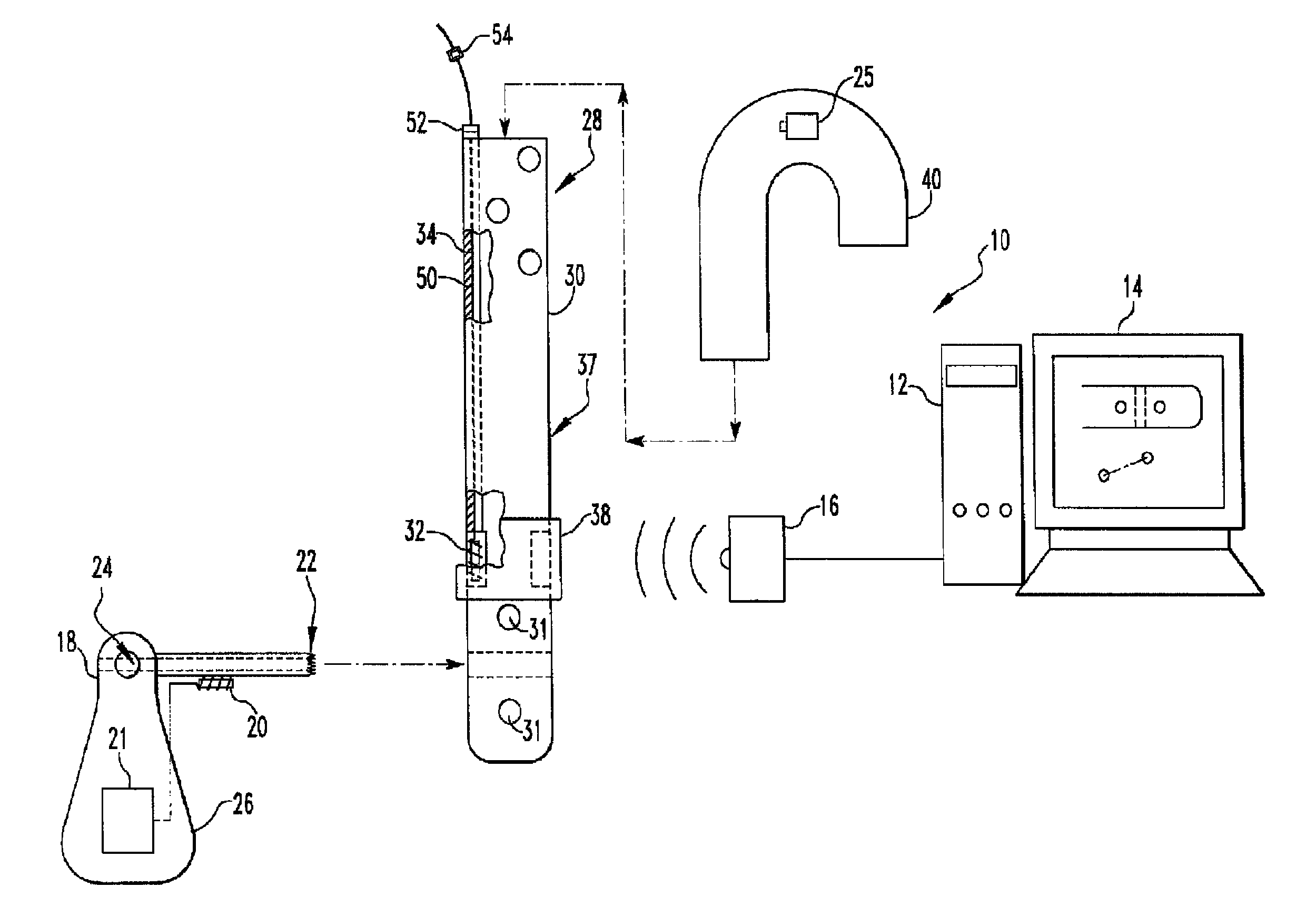
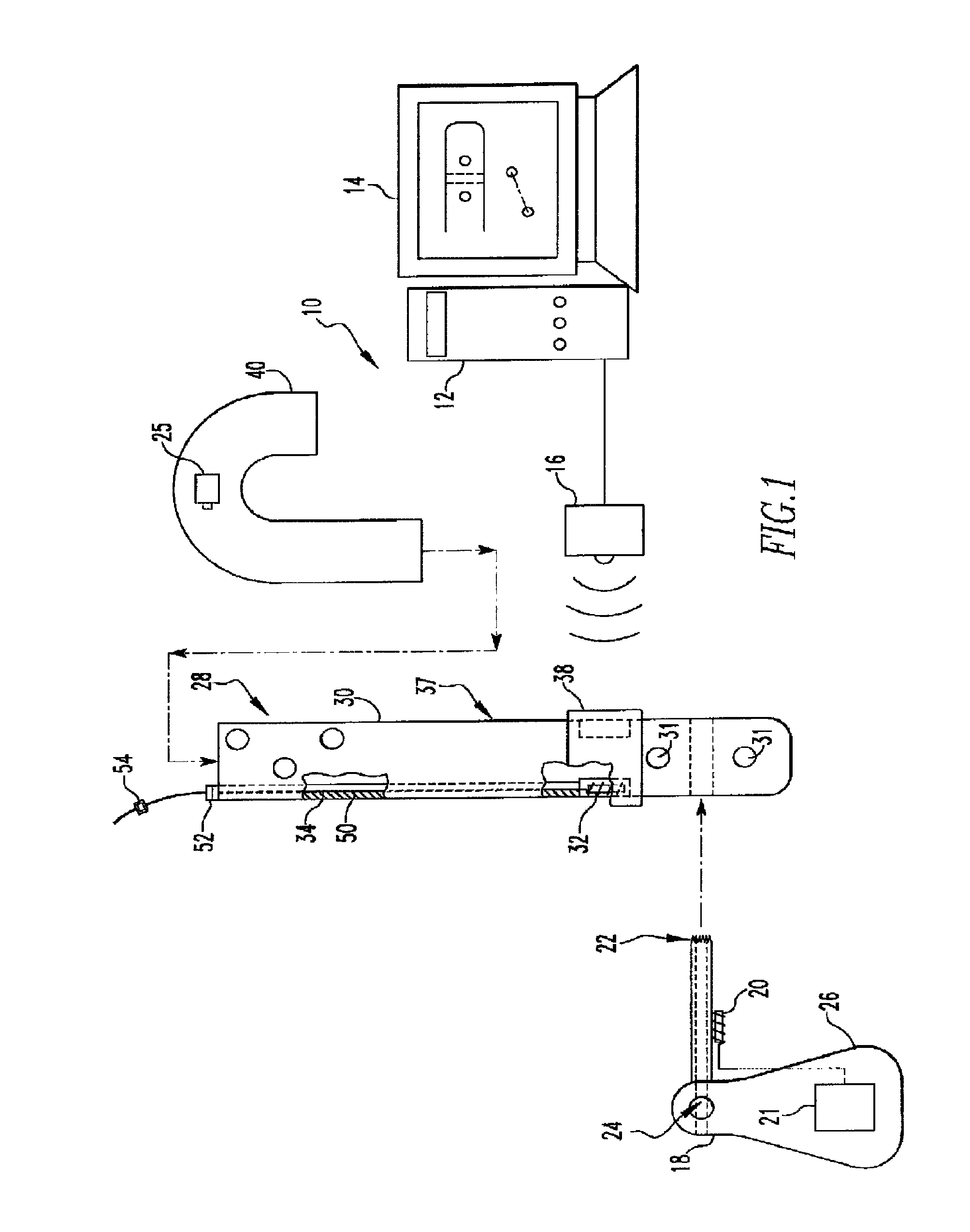
Targeting an orthopaedic implant landmark
ActiveUS20100274121A1Reduce exposureReduce radiationSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringPlastic surgeryComputer science
A system for targeting landmarks on devices such as surgical implants is disclosed. The system can include a field generator for generating one or more magnetic fields, an orthopaedic implant located within the magnetic fields, the implant having at least one landmark, a removable probe with a first magnetic sensor, a landmark identifier and a processor. The landmark identifier can contain a second sensor, or, alternatively, the field generator. The processor can utilize sensor data and, if desirable, field generator and other information, to generate and display the position and orientation of the sensor(s) in preferably six degrees of freedom, and thereby, to generate and display the position and orientation of the landmark(s). The system allows for blind targeting of one or more landmarks. The landmark identifier, field generator and / or drill motor may be disposed in an autoclavable housing.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Orthopaedic implant with sensors
The present invention relates to an orthopaedic implant, such as a bone plate, for the fixation of bone where the implant also has at least one microchip and at least one sensor connected to the microchip. The sensor or sensors are configured to receive physical stimulus from a portion of the implant or the patient's tissue such as temperature, pressure, and strain. The information received from the sensor or sensors is gathered by the microchip and transmitted to a receiver, such as a personal computer, outside the patient. This information enables doctors to diagnose the useful life of the implant, the load sharing of the bone plate, and possible complications typically associated with orthopaedic implants such as infection, fracture non-union, and fatigue. The implant may also have one or more electrodes located on its surface which emit an electric current to stimulate healing of the broken or fractured bone.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
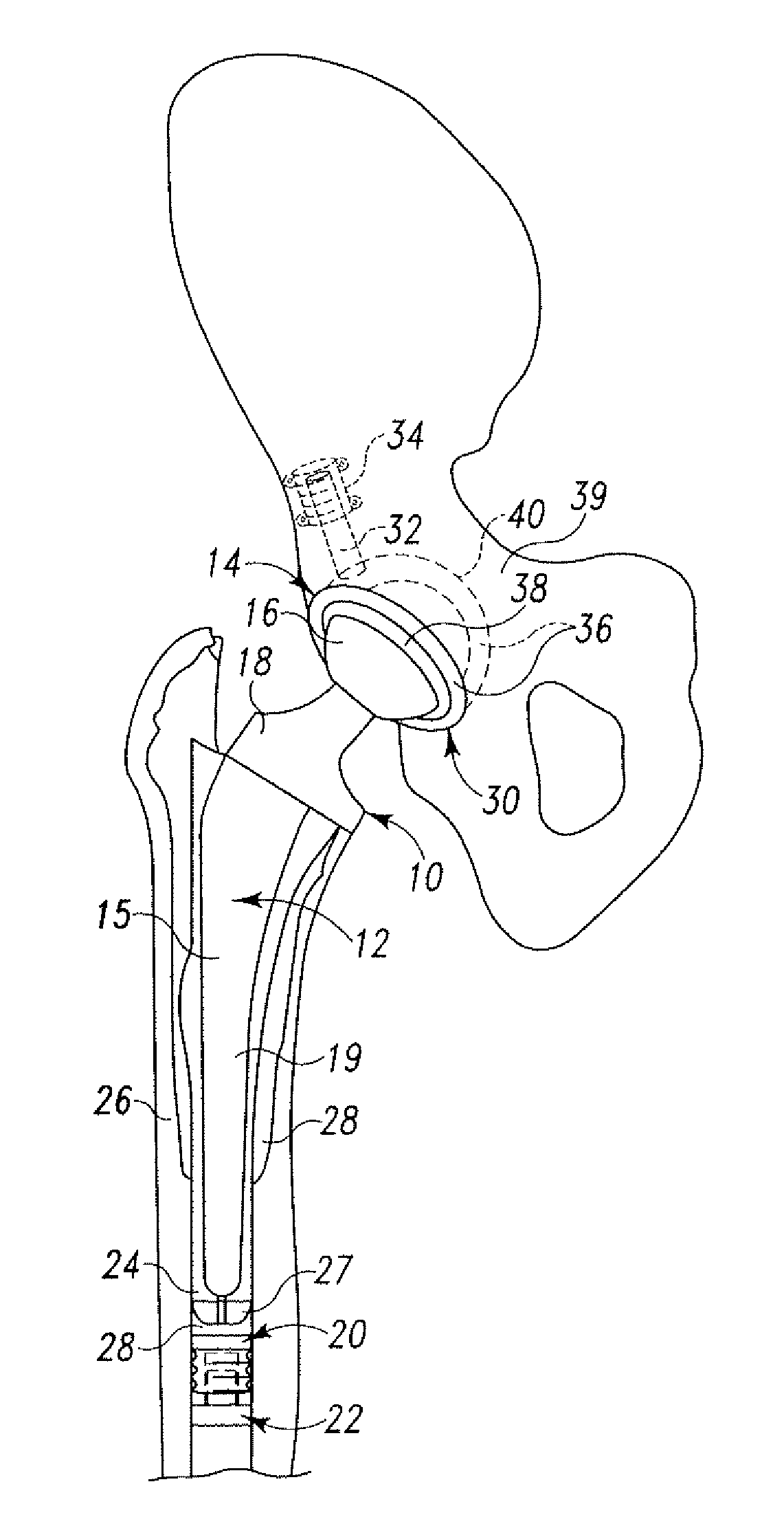
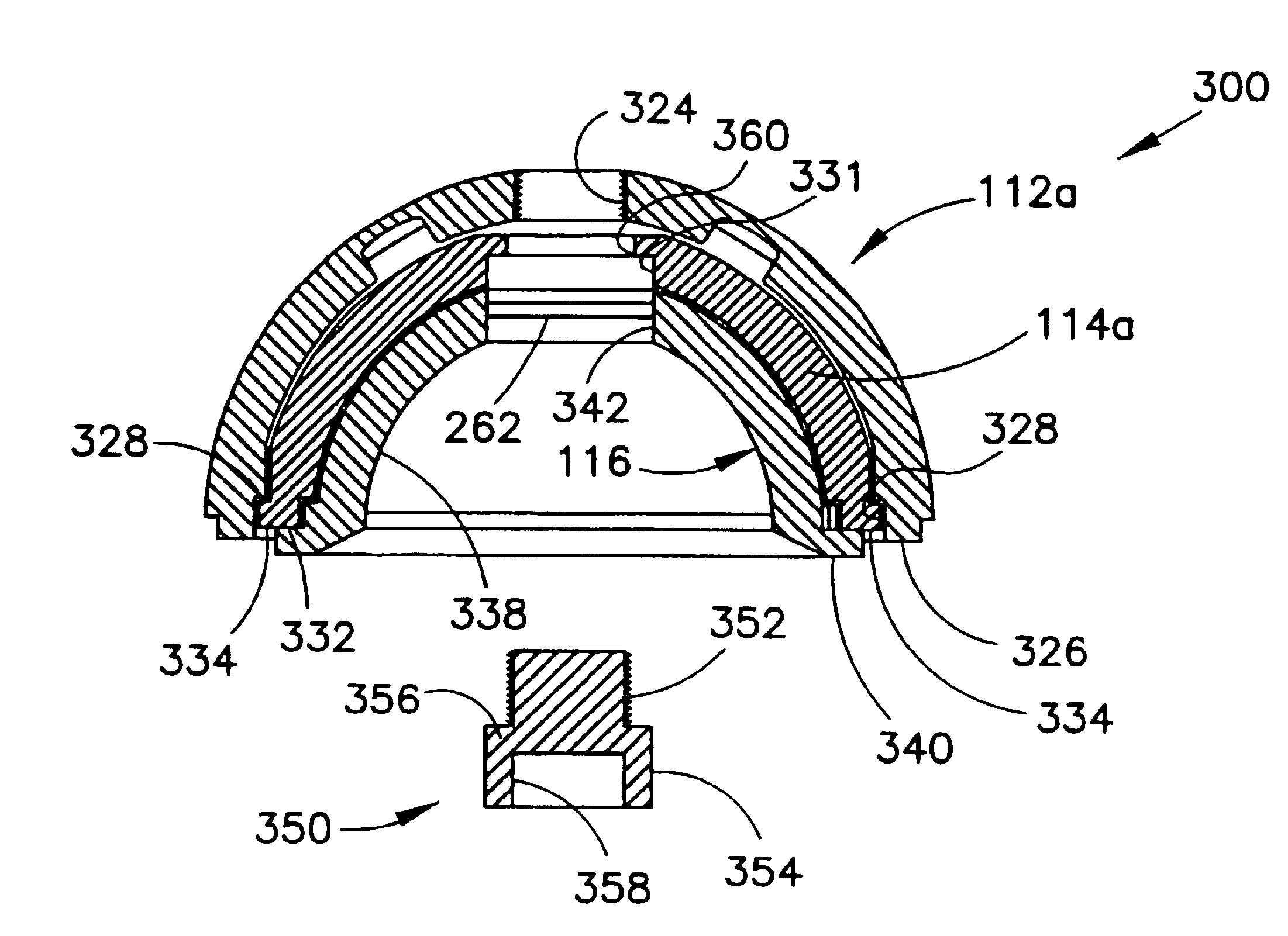
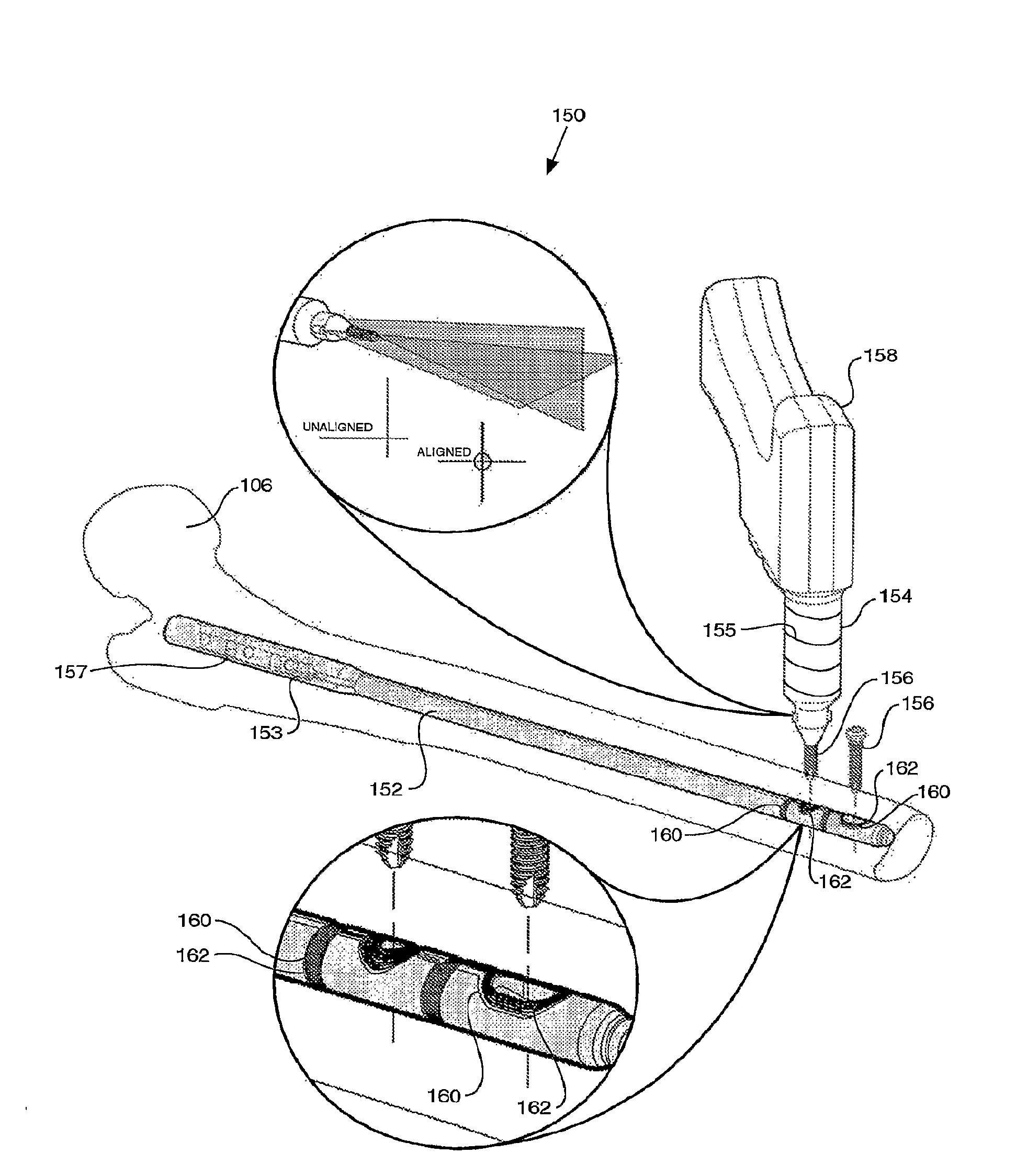
Instrumented orthopaedic implant for identifying a landmark
A system (110, 150) for targeting a landmark (114, 160) is disclosed. The system includes an instrumented medical implant (112, 152), a control circuit (118, 153), a power supply (120, 157), and a landmark identifier (122, 154). The instrumented medical implant (112, 152) has one or more landmarks (114, 160) and each landmark (114, 160) has a corresponding coil (116, 162). The control circuit (118, 153) is electrically connected to the corresponding coil (116, 162), and the power supply (120, 157) is electrically connected to the control circuit (118,153). The landmark identifier (122, 154) has a magnetic sensor (124, 155) for sensing the corresponding coil (116, 162).
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
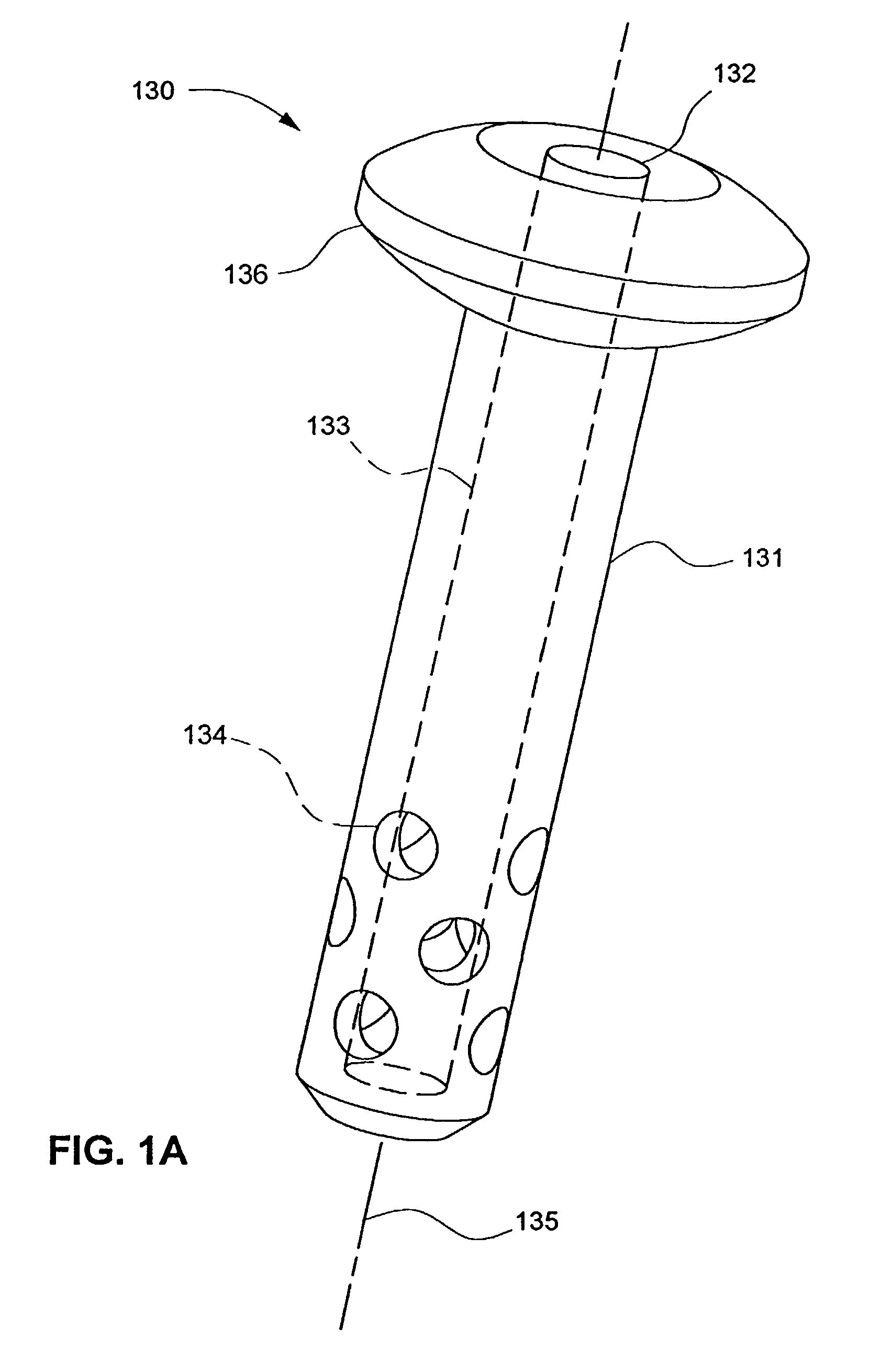
Orthopaedic implant fixation using an in-situ formed anchor
InactiveUS7488320B2Reduce stressReduce the possibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSuture anchorsPlastic surgery
An orthopaedic implant fixation using a surgically created bone cavity as a mold for forming an anchor from an in-situ hardenable material. An in-situ formed anchor of the present invention is especially useful for attaching an implant to osteoporotic cancellous bone. The injectable nature of the in-situ formed anchor allows implants to be adapted to minimally invasive surgical techniques. The present invention can be adapted to numerous implants or implant system components to include fasteners, pins, nails, intramedullary nails, and suture anchors. Applications include bone fracture fixation, bone fracture prevention, and soft-tissue repair.
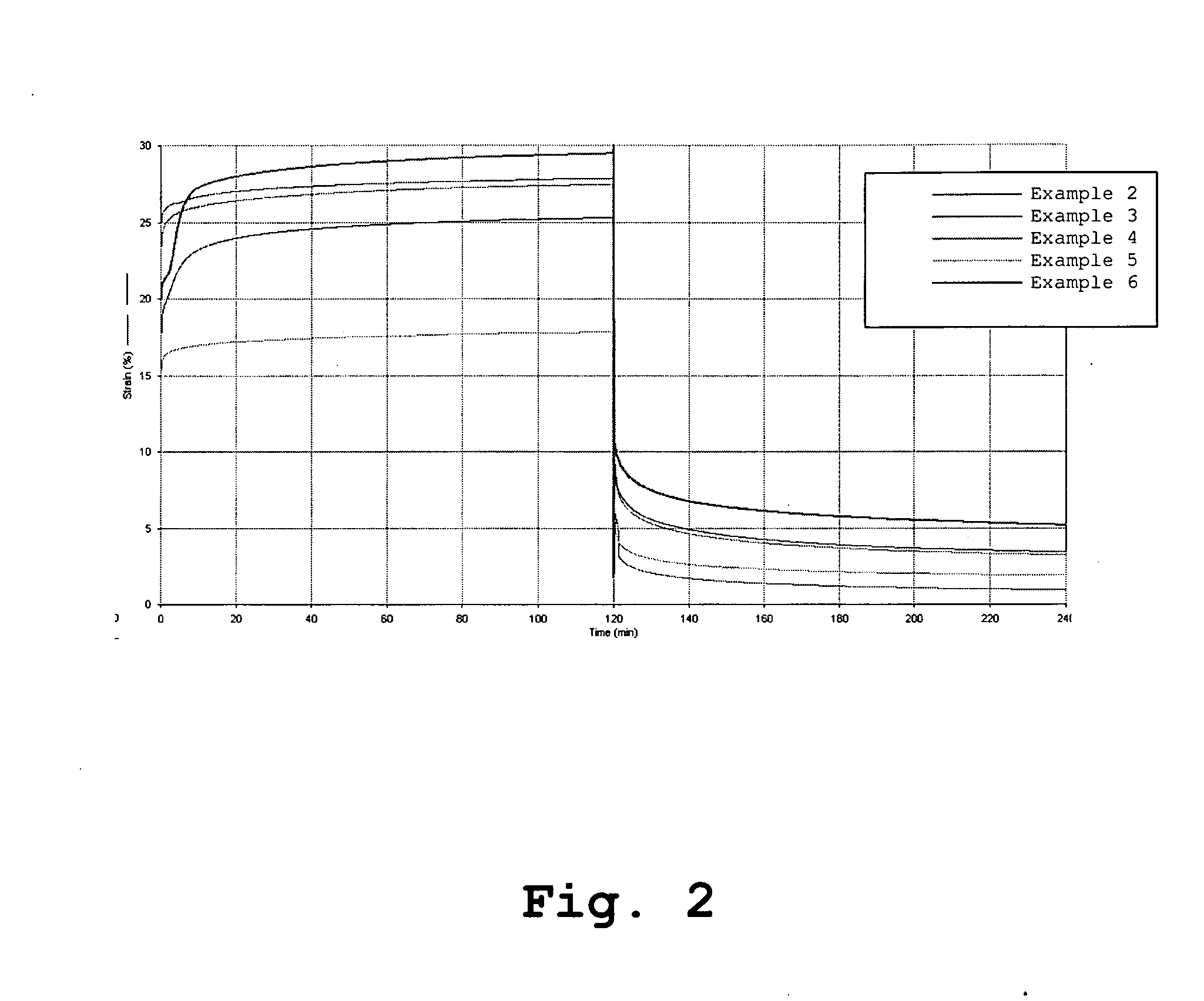
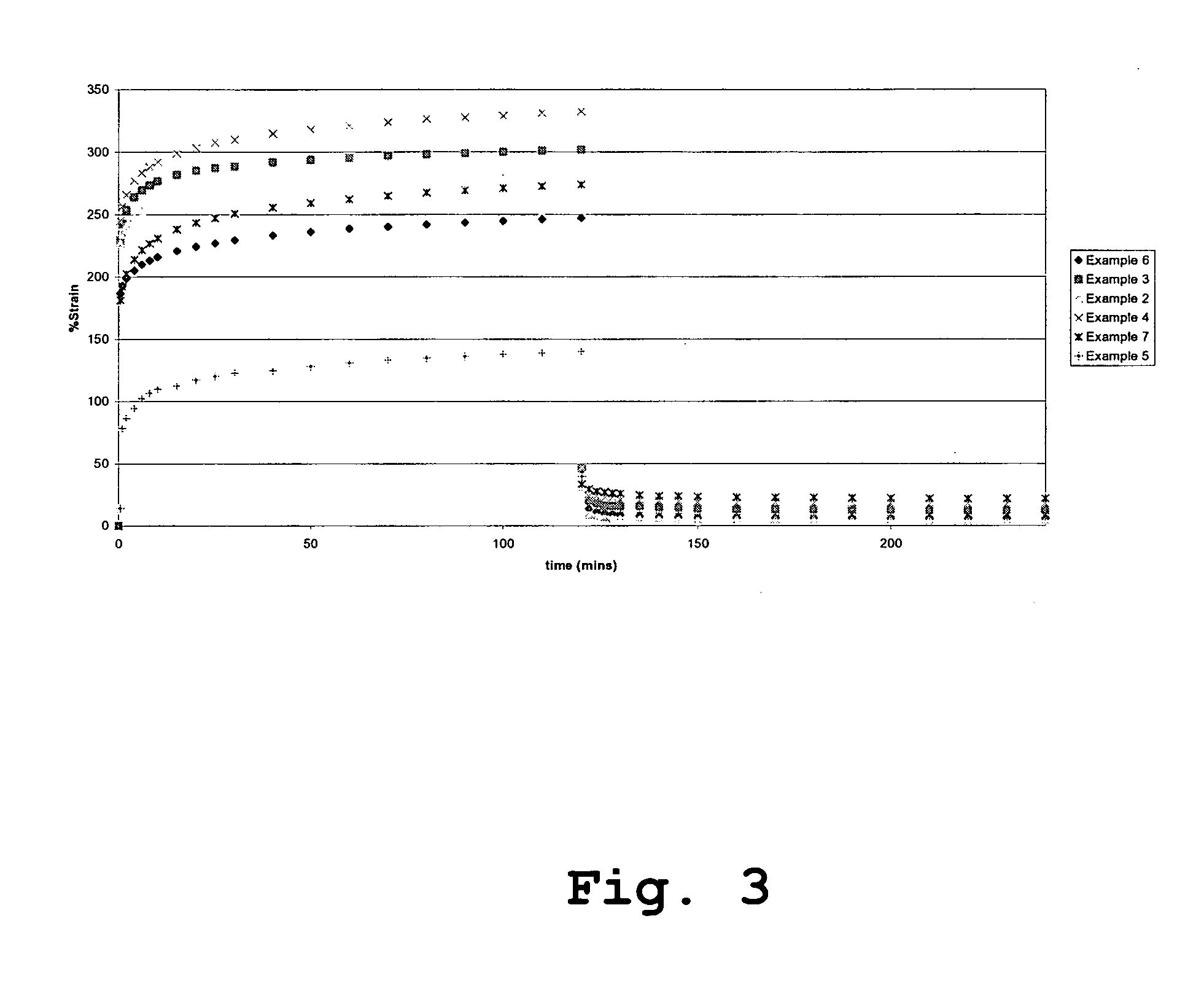
Polyurethanes
The present invention relates to cross linked polyurethanes or polyurethane ureas and processes for their preparation. The polyurethanes are biostable and creep resistant which makes them useful in the manufacture of biomaterials and medical devices, articles or implants, in particular orthopaedic implants such as spinal disc prostheses.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Orthopaedic implants
InactiveUS20140094924A1Reduces difficulty and disadvantageAdditive manufacturing apparatusWrist jointsMedicinePlastic surgery
A method for making an orthopaedic implant, the method comprising: characterizing at least a portion of a bone corresponding to the bone to be replaced, said corresponding bone being on the contralateral side of the patient; providing a model of the orthopaedic implant based on a mirror image of the contralateral bone; and forming the orthopaedic implant based on the model.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Targeting an orthopaedic implant landmark
ActiveUS8623023B2Reduce exposureReduce radiationSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsPlastic surgeryComputer science
A system for targeting landmarks on devices such as surgical implants is disclosed. The system can include a field generator for generating one or more magnetic fields, an orthopaedic implant located within the magnetic fields, the implant having at least one landmark, a removable probe with a first magnetic sensor, a landmark identifier and a processor. The landmark identifier can contain a second sensor, or, alternatively, the field generator. The processor can utilize sensor data and, if desirable, field generator and other information, to generate and display the position and orientation of the sensor(s) in preferably six degrees of freedom, and thereby, to generate and display the position and orientation of the landmark(s). The system allows for blind targeting of one or more landmarks. The landmark identifier, field generator and / or drill motor may be disposed in an autoclavable housing.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
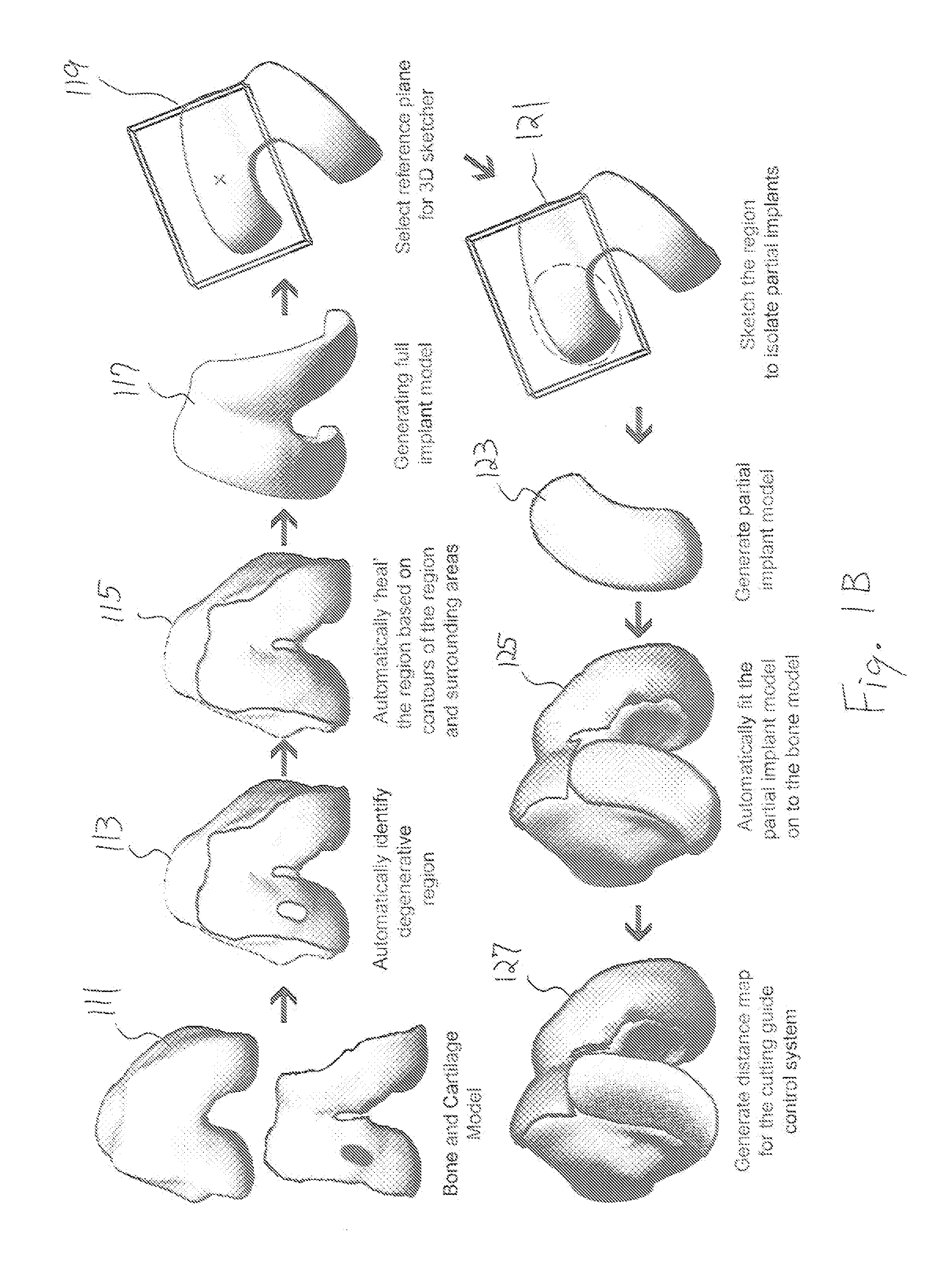
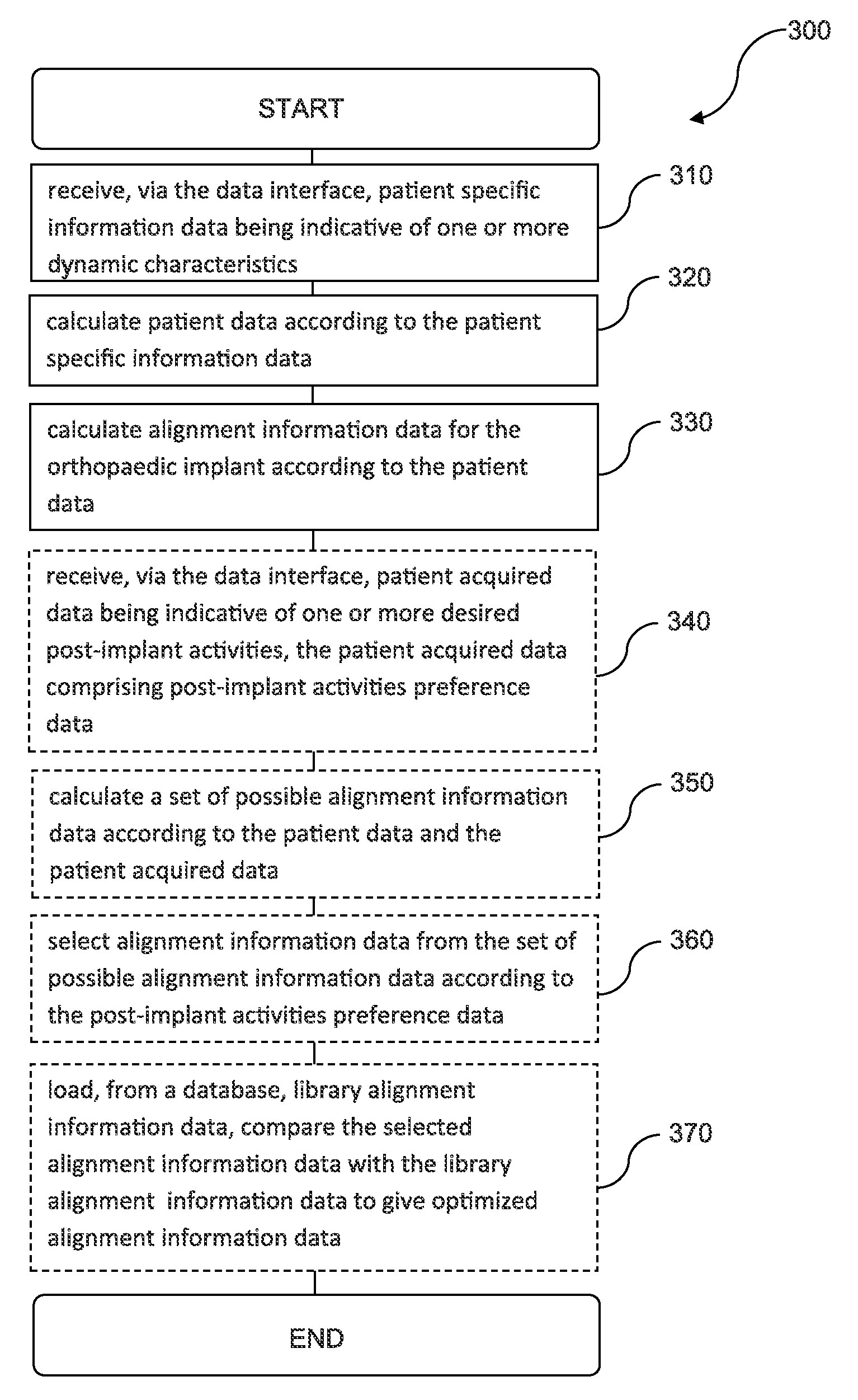
Computer-implemented method, a computing device and a computer readable storage medium for providing alignment information data for the alignment of an orthopaedic implant for a joint of a patient
ActiveUS8983813B2Precise alignmentAccurate modelingSuture equipmentsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPatient dataSurgical implant
The present disclosure relates to a computer-implemented method, a computing device, and a computer readable storage medium, for providing alignment information data for the alignment of an orthopaedic implant for a joint of a patient. The computer-implemented method comprises the steps of being responsive to patient specific information data for deriving patient data, where the patient specific information data is indicative of one or more dynamic characteristics, and being responsive to the patient data for providing the alignment information data for the alignment of the orthopaedic implant.
Owner:CORIN
Surfaces and processes for wear reducing in orthopaedic implants
InactiveUS20020161447A1Optimal wear reductionReduce subsurface stressJoint implantsKnee jointsOrthopaedic implantPlastic surgery
Artificial implants having reduced area to provide reduced wear are provided. The reduced area is particularly located at areas where greatest wear is exhibited. In a particular embodiment of a mobile bearing knee implant, the area is reduced on the mobile bearing insert underside, where it contacts a tibial component. The reduced area may be any shape of indentations, for example, grooves, dimples, straight patterns, curved patterns, crossing patterns, holes, channels or slots. The indentations may be various sizes, and have been found to be particularly effective if covering about 10% to about 20% of the insert at depths between about 1-2 mm.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com