Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13557 results about "Surface roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface roughness often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface texture. It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, the surface is rough; if they are small, the surface is smooth. In surface metrology, roughness is typically considered to be the high-frequency, short-wavelength component of a measured surface. However, in practice it is often necessary to know both the amplitude and frequency to ensure that a surface is fit for a purpose.
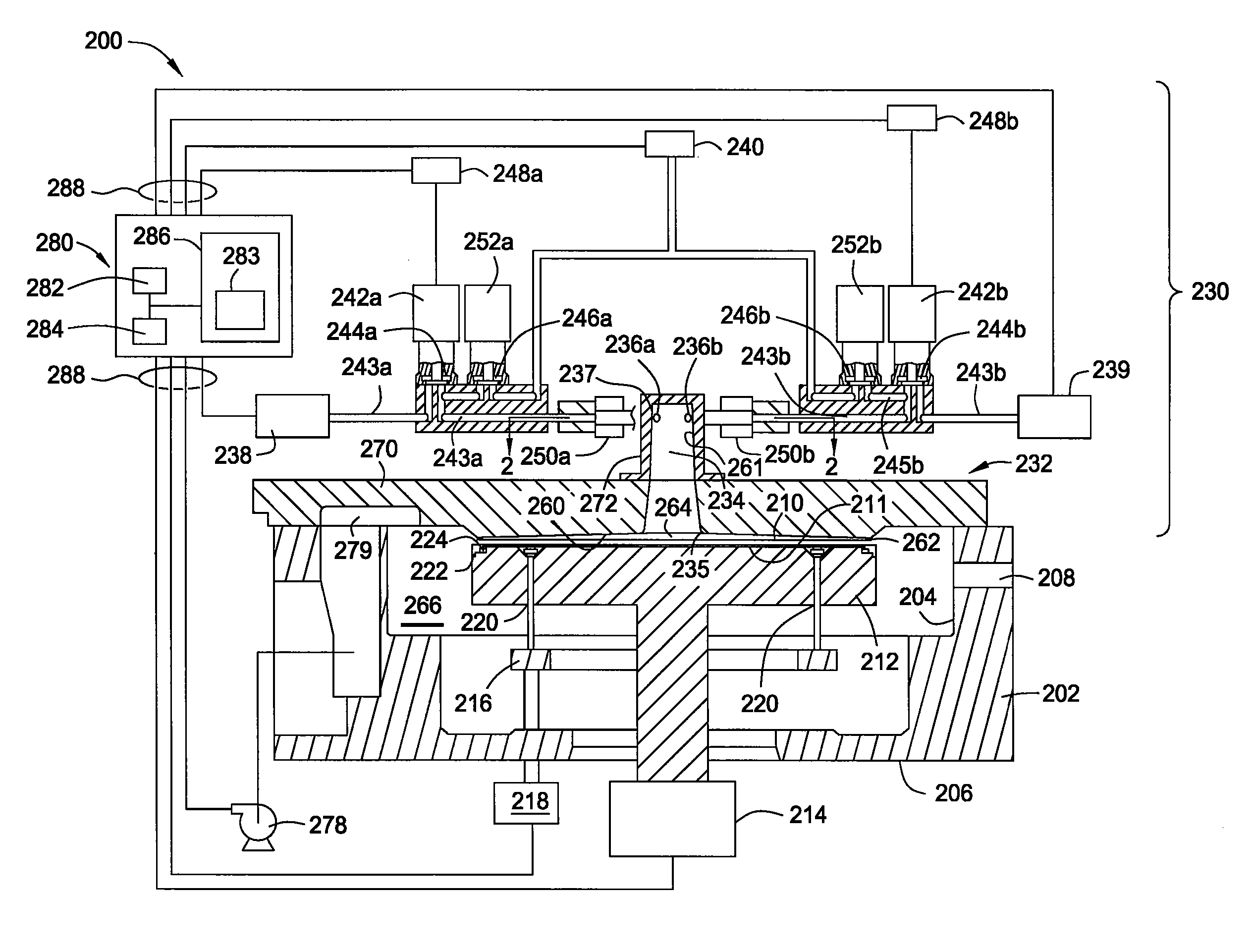
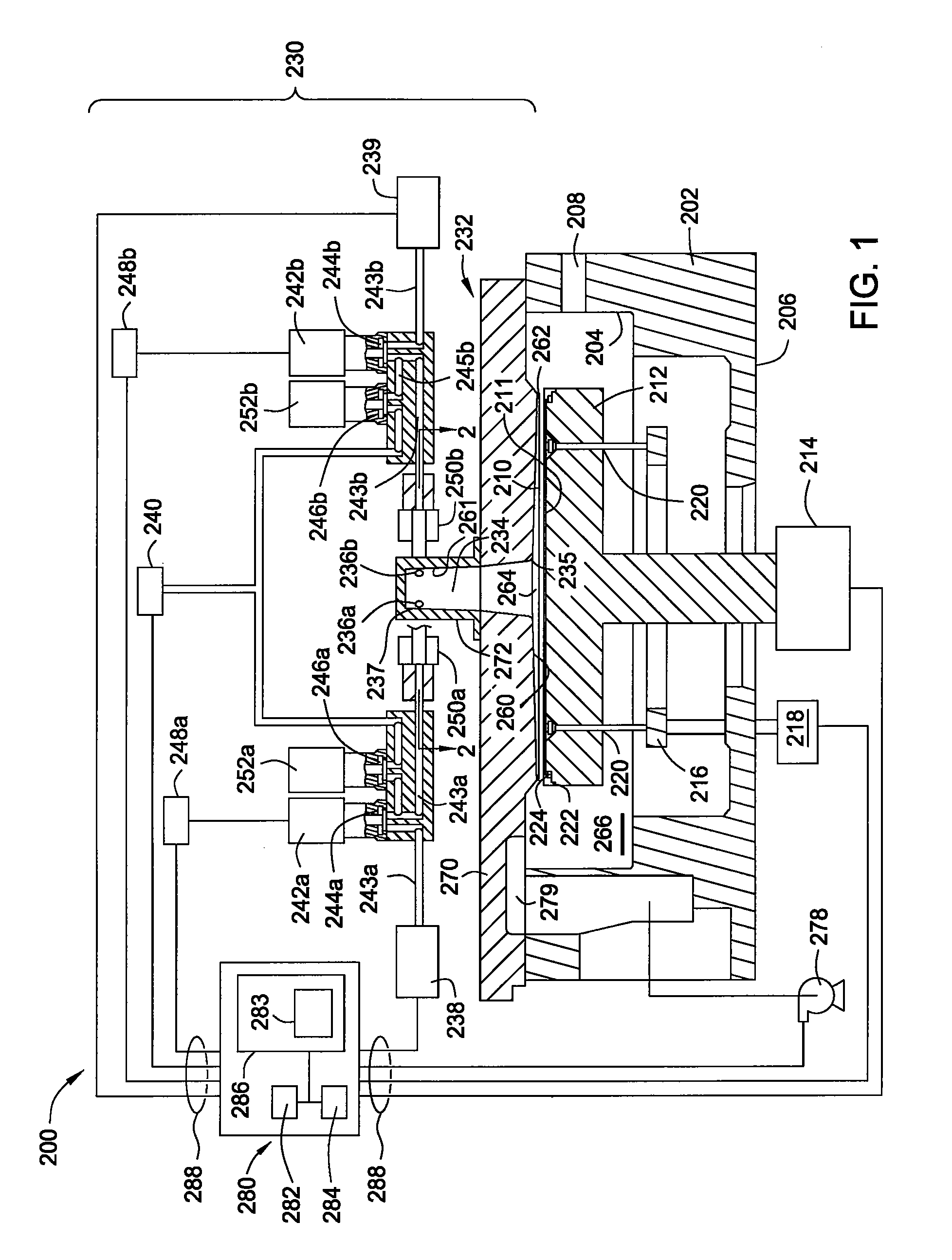
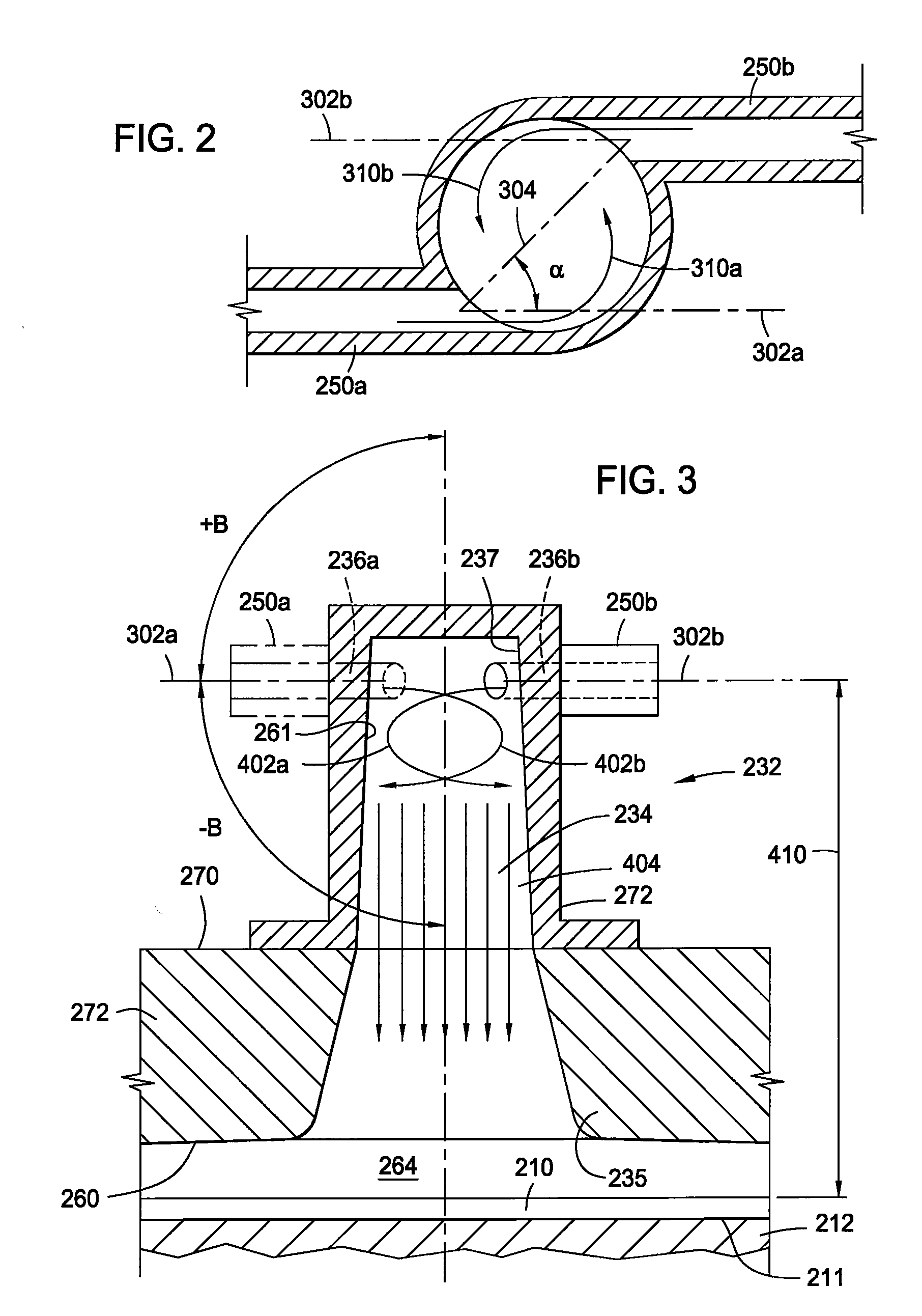
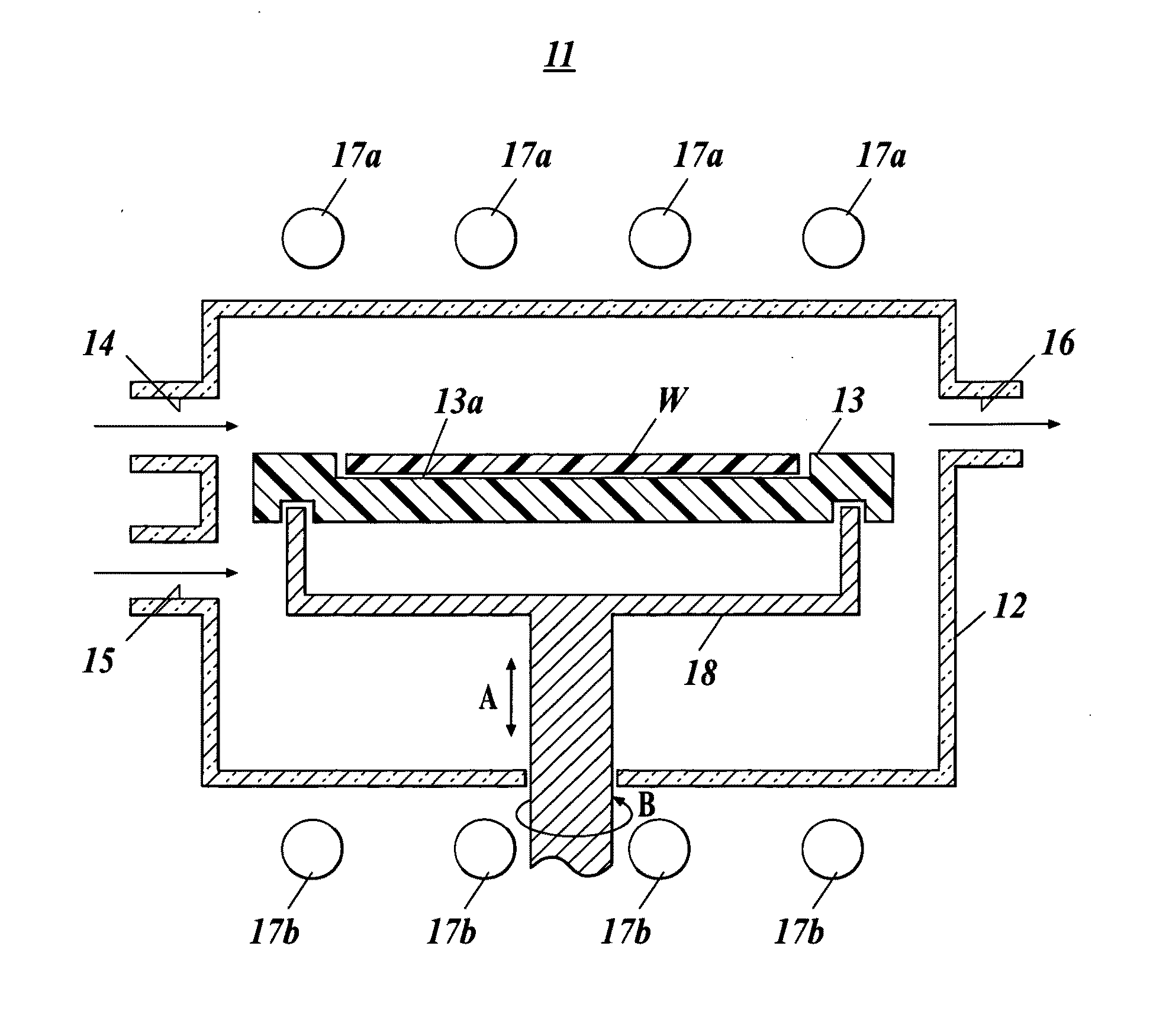
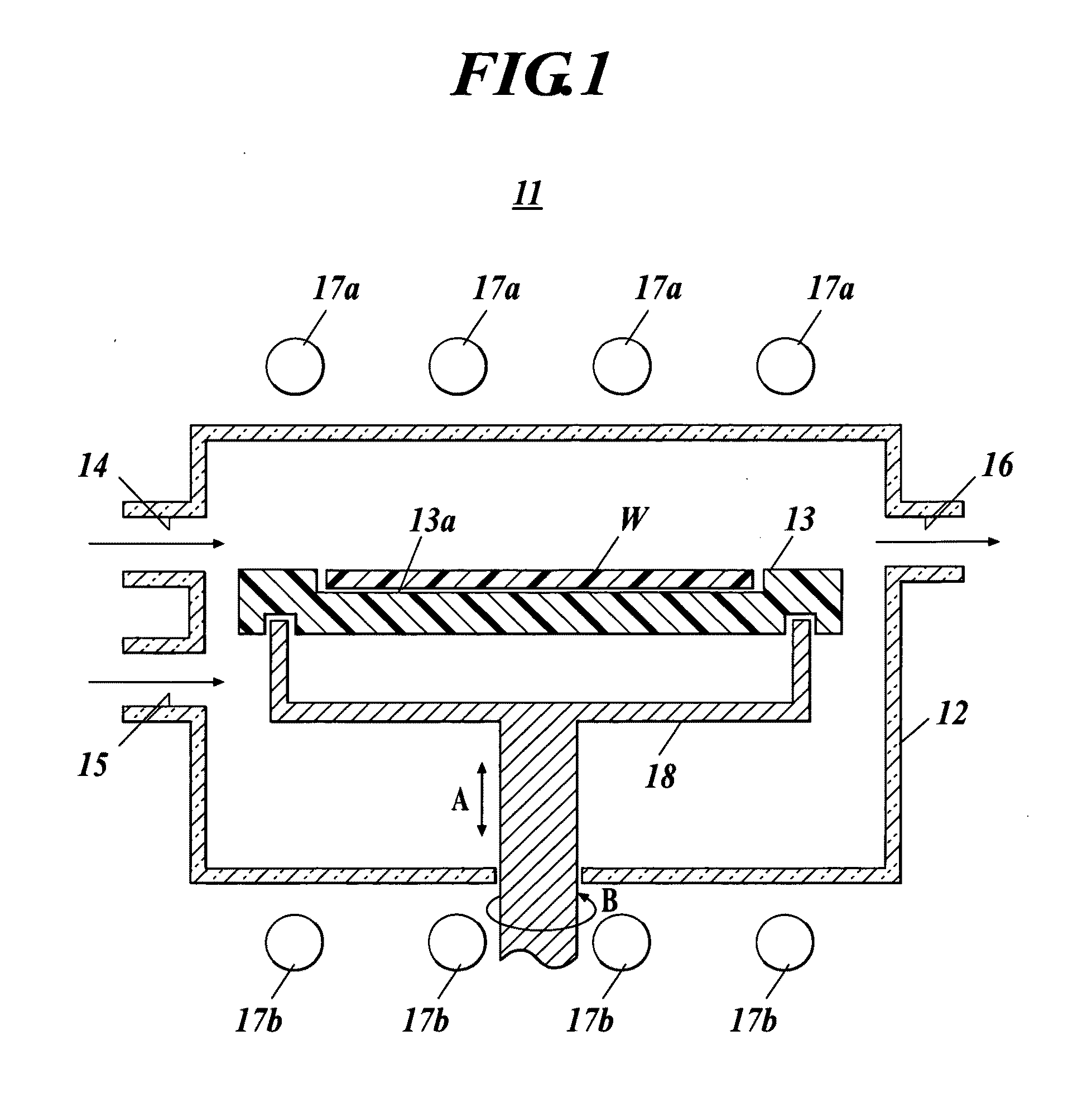
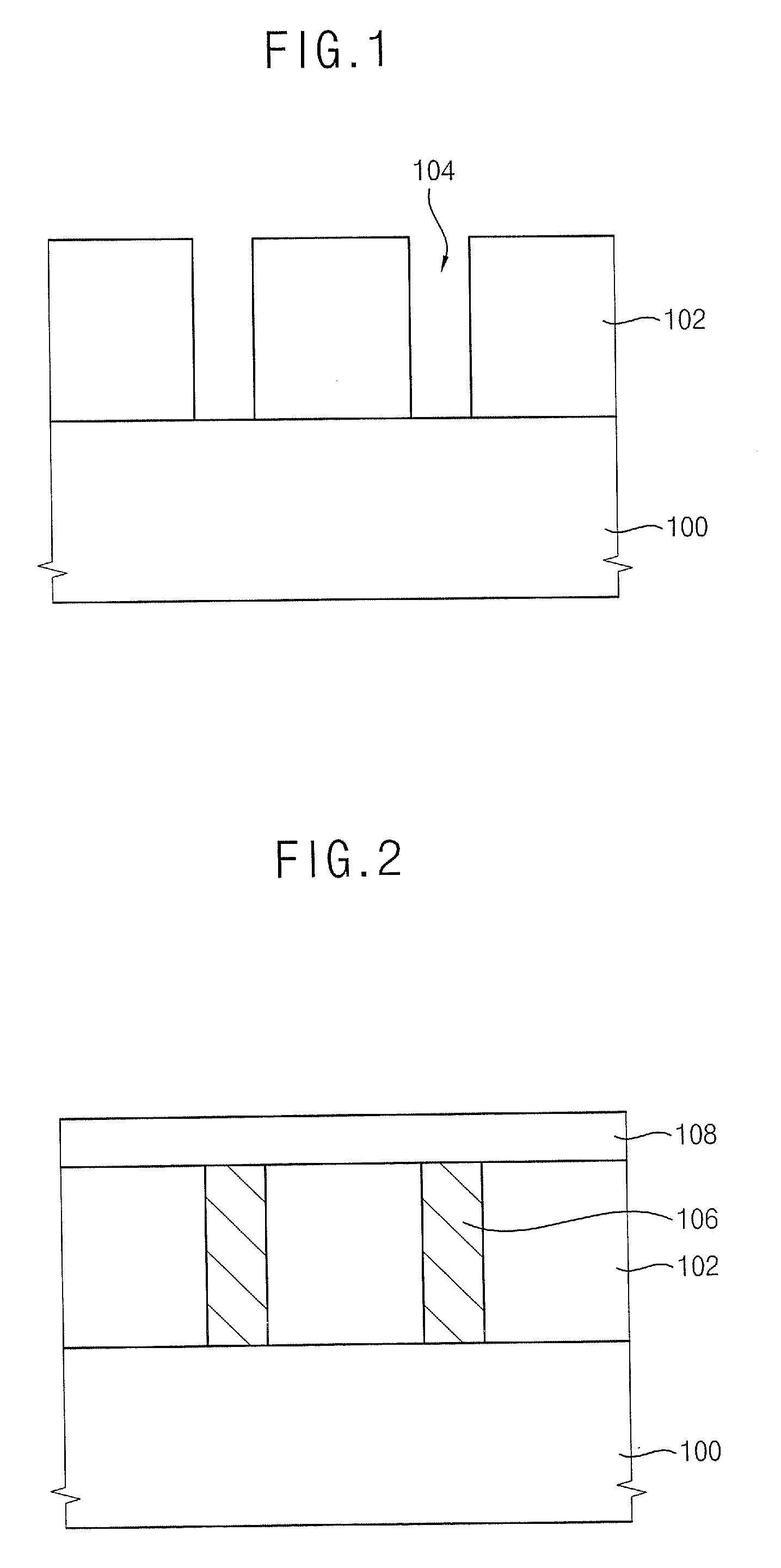
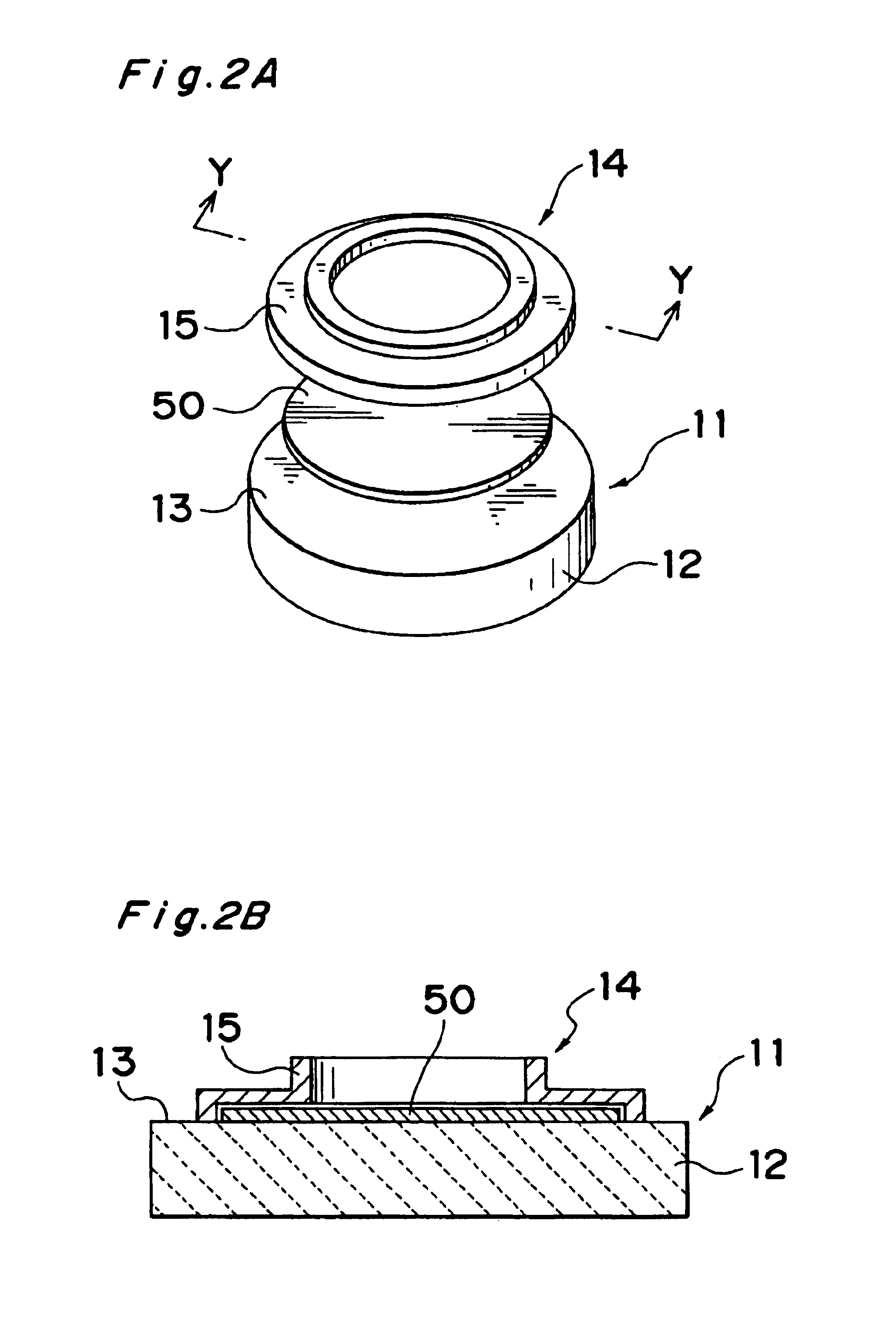
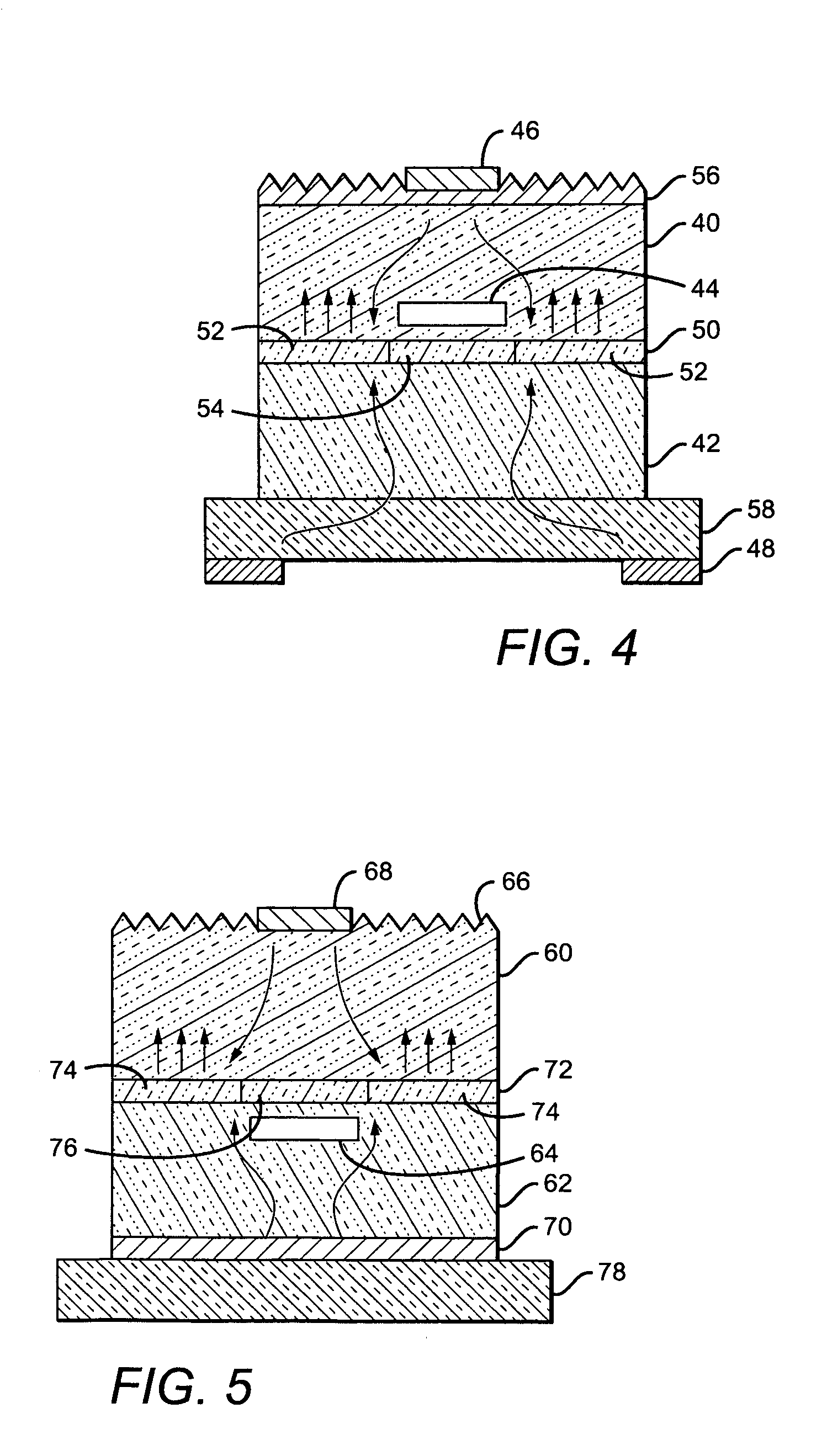
Vortex chamber lids for atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20080102203A1Reduce gas velocitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface roughnessEngineering
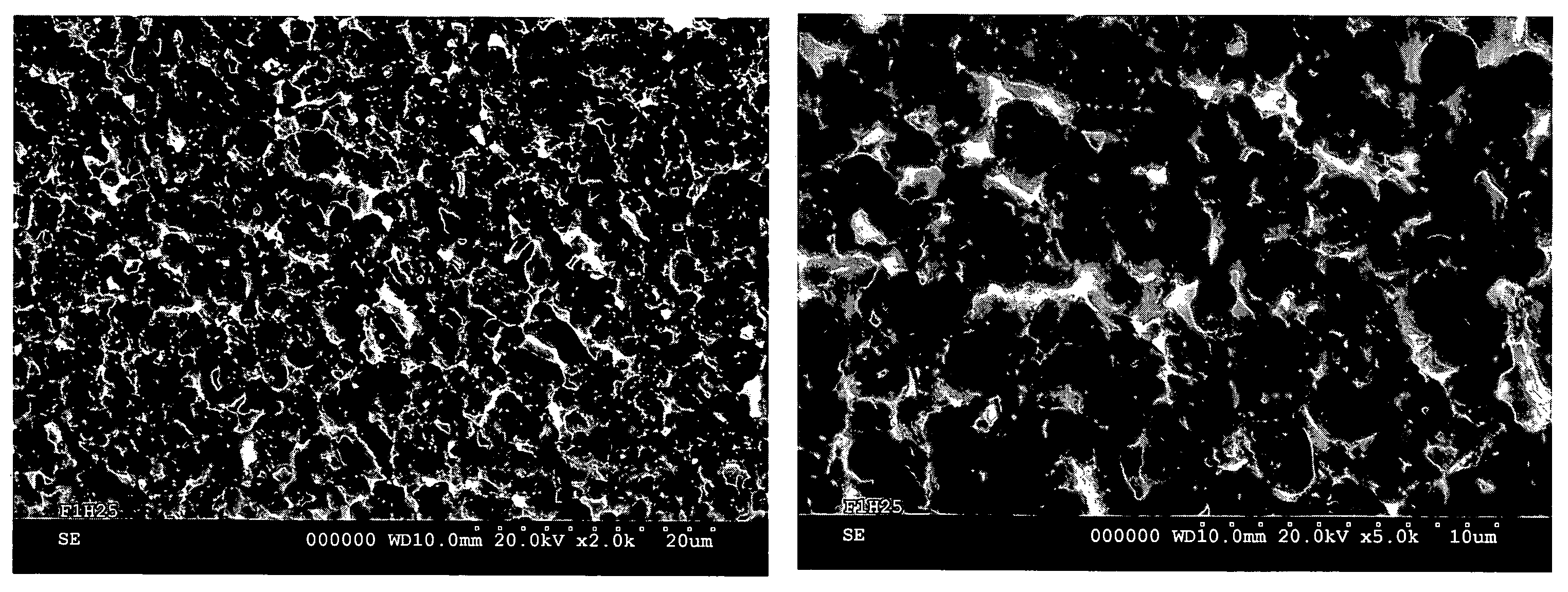
Embodiments of the invention relate to apparatuses and methods for depositing materials on substrates during atomic layer deposition processes. In one embodiment, a chamber for processing substrates is provided which includes a chamber lid assembly containing an expanding channel at a central portion of the chamber lid assembly, wherein an upper portion of the expanding channel extends substantially parallel along a central axis of the expanding channel, and an expanding portion of the expanding channel tapers away from the central axis. The chamber lid assembly further contains a conduit coupled to a gas inlet, another conduit coupled to another gas inlet, and both gas inlets are positioned to provide a circular gas flow through the expanding channel. In one example, the inner surface within the upper portion of the expanding channel has a lower mean surface roughness than the inner surface within the expanding portion of the expanding channel.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
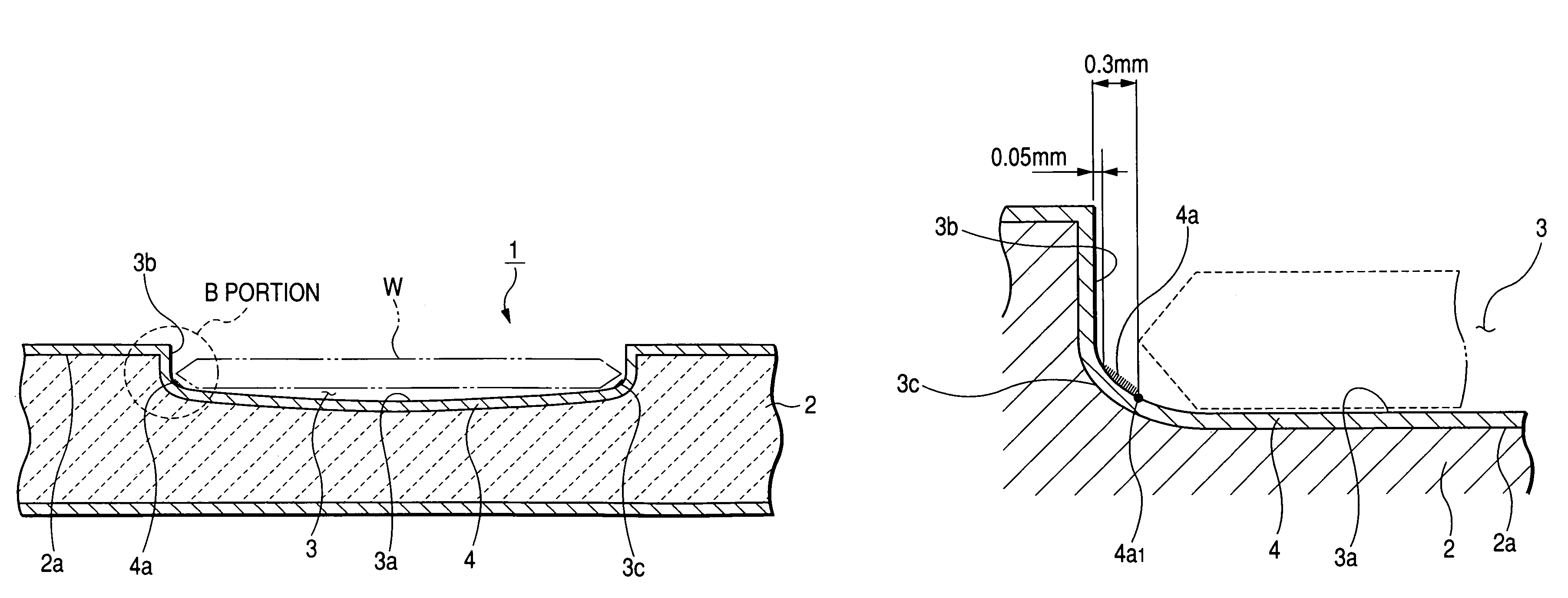
Susceptor
ActiveUS7393418B2Stably holdUnified performanceLiquid surface applicatorsDiffusion/dopingSusceptorSurface roughness
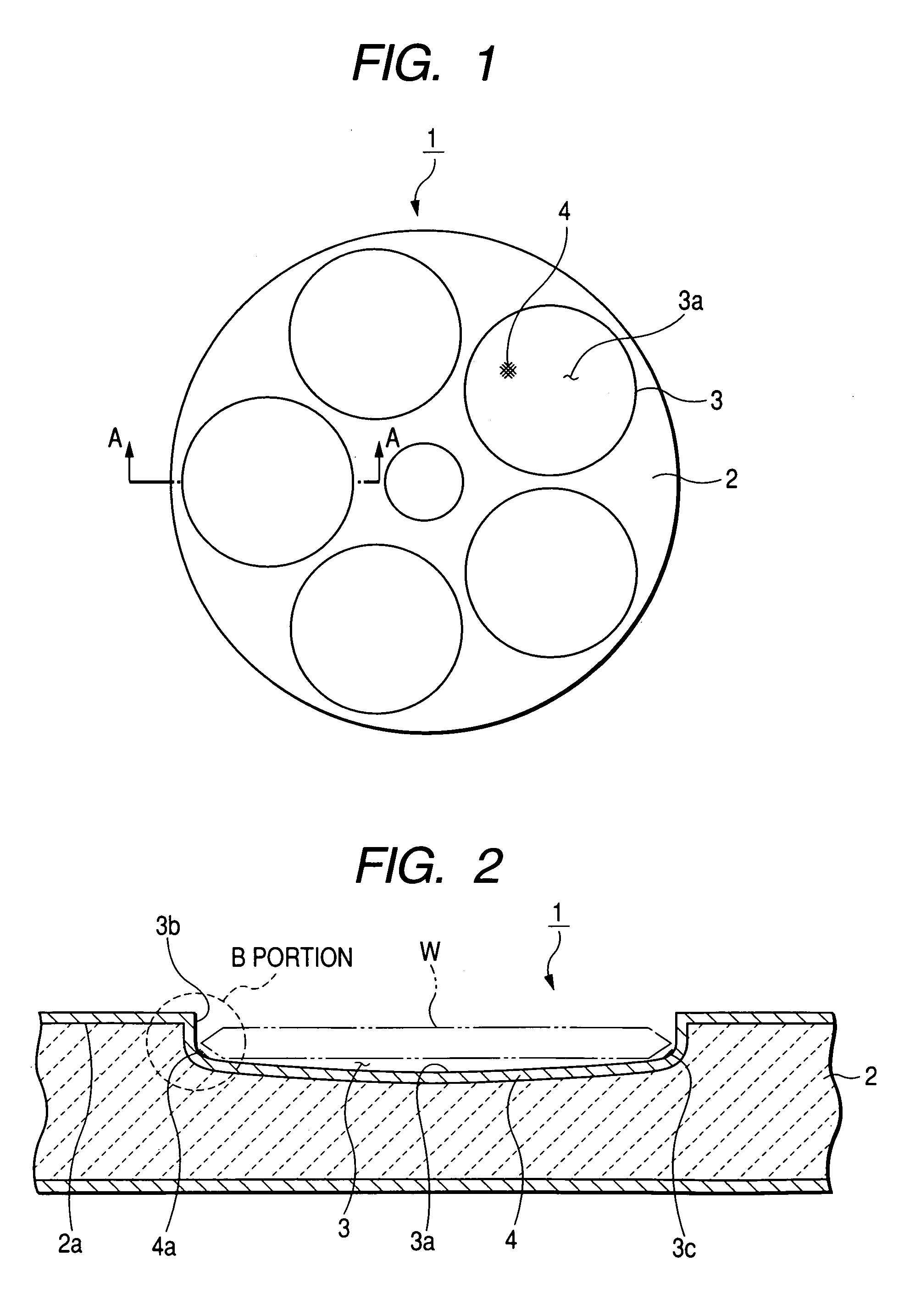
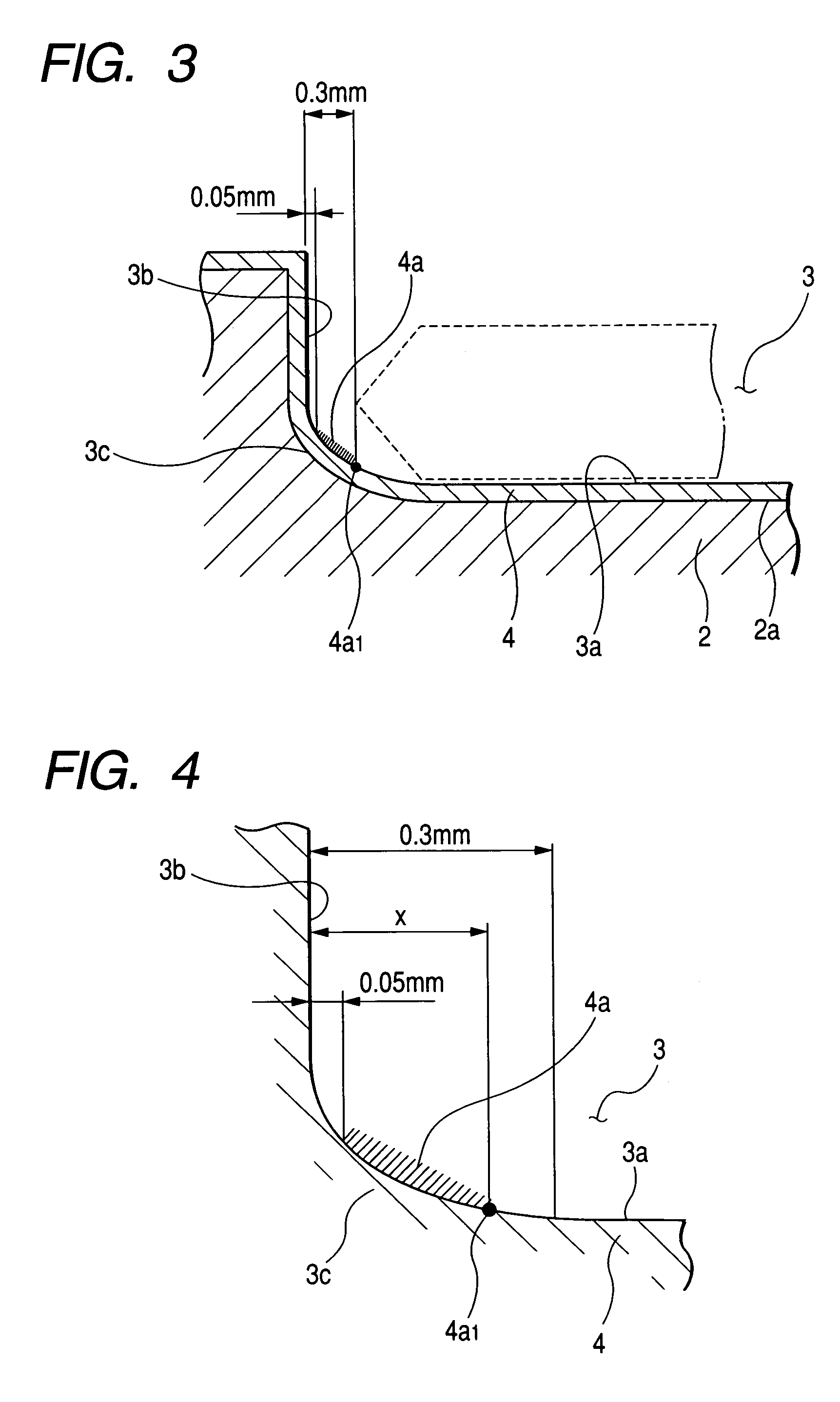
A susceptor at least a surface thereof being coated with SiC, includes a recess where an wafer is mounted, the recess having an round portion disposed on a lower portion of an outer circumferential portion of the recess, a ring-shaped SiC crystal growth surface portion provided within the round portion in a range of 0.05 mm or more and 0.3 mm or less defined from an outer circumference vertical portion of the recess and a contact portion, where the susceptor contacts with the wafer on the recess, having a surface roughness Ra in a range of 0.5 μm or more and 3 μm or less.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Heat treating apparatus
ActiveUS7865070B2Minimal amountReliably preventing both slipsRespiratorsDrying solid materials with heatSurface roughnessHeat treating
To prevent both slips caused by damage from projections, and slips caused by adhesive force occurring due to excessive smoothing.The heat treating apparatus includes a processing chamber for heat treating wafers and a boat for supporting the wafers in the processing chamber. The boat further includes a wafer holder in contact with the wafer and a main body for supporting the wafer holder. The wafer holder diameter is 63 to 73 percent of the wafer diameter, and the surface roughness Ra of the portion of the wafer holder in contact with the wafer is set from 1 μm to 1,000 μm. The wafer can be supported so that the amount of wafer displacement is minimal and both slips due to damage from projections on the wafer holder surface, and slips due to the adhesive force occurring because of excessive smoothing can be prevented in that state.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Heat treatment jig for silicon semiconductor substrate
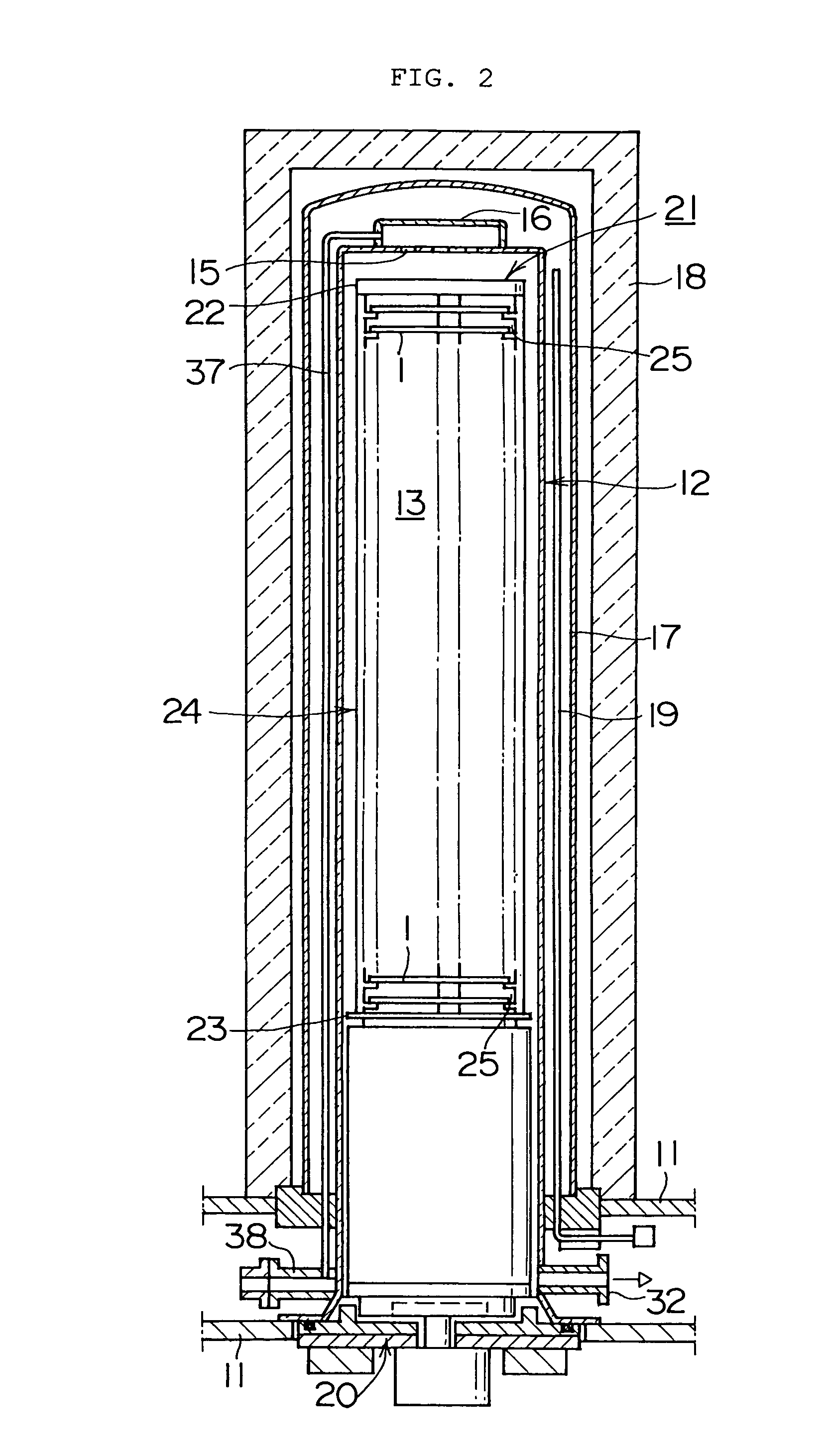
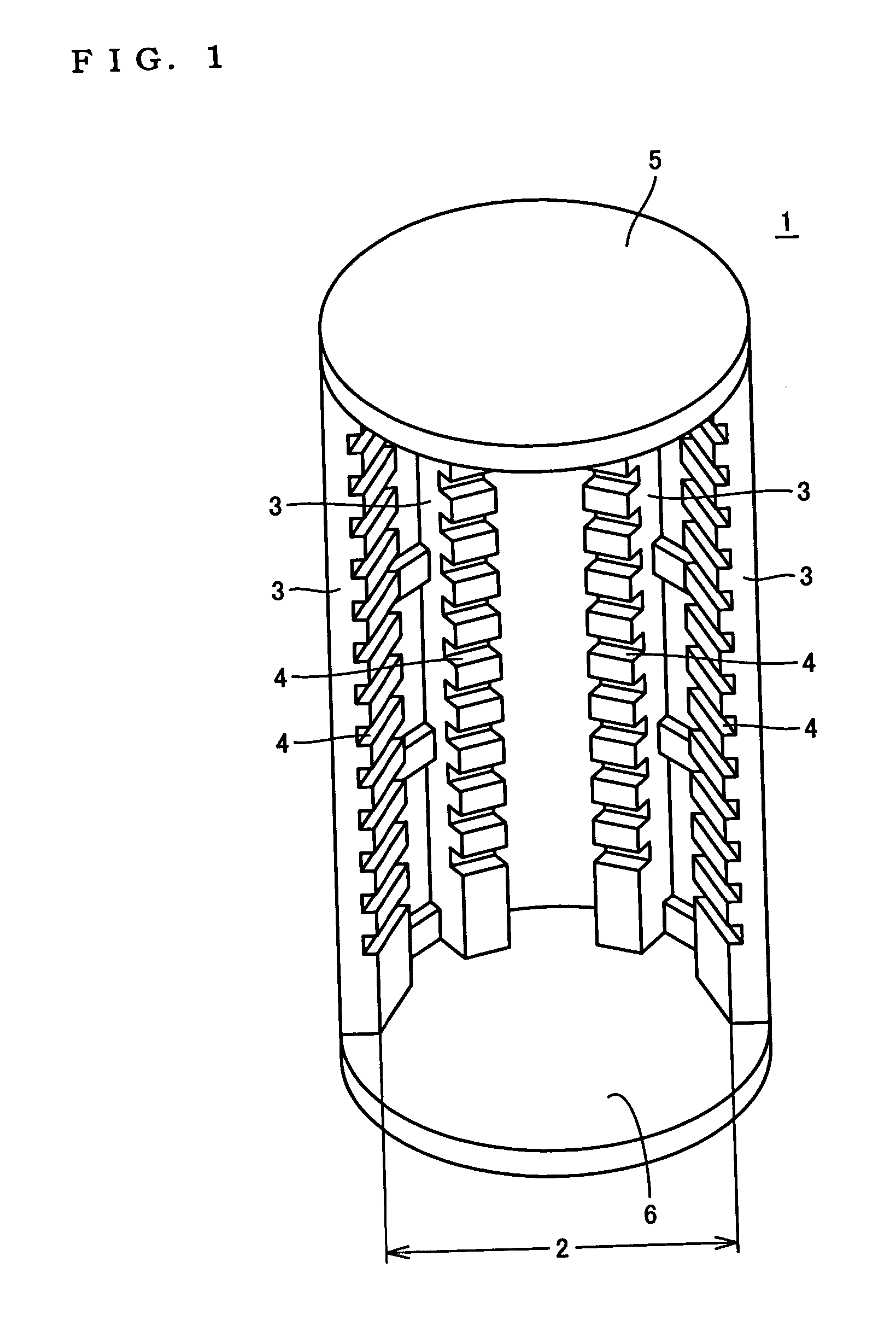
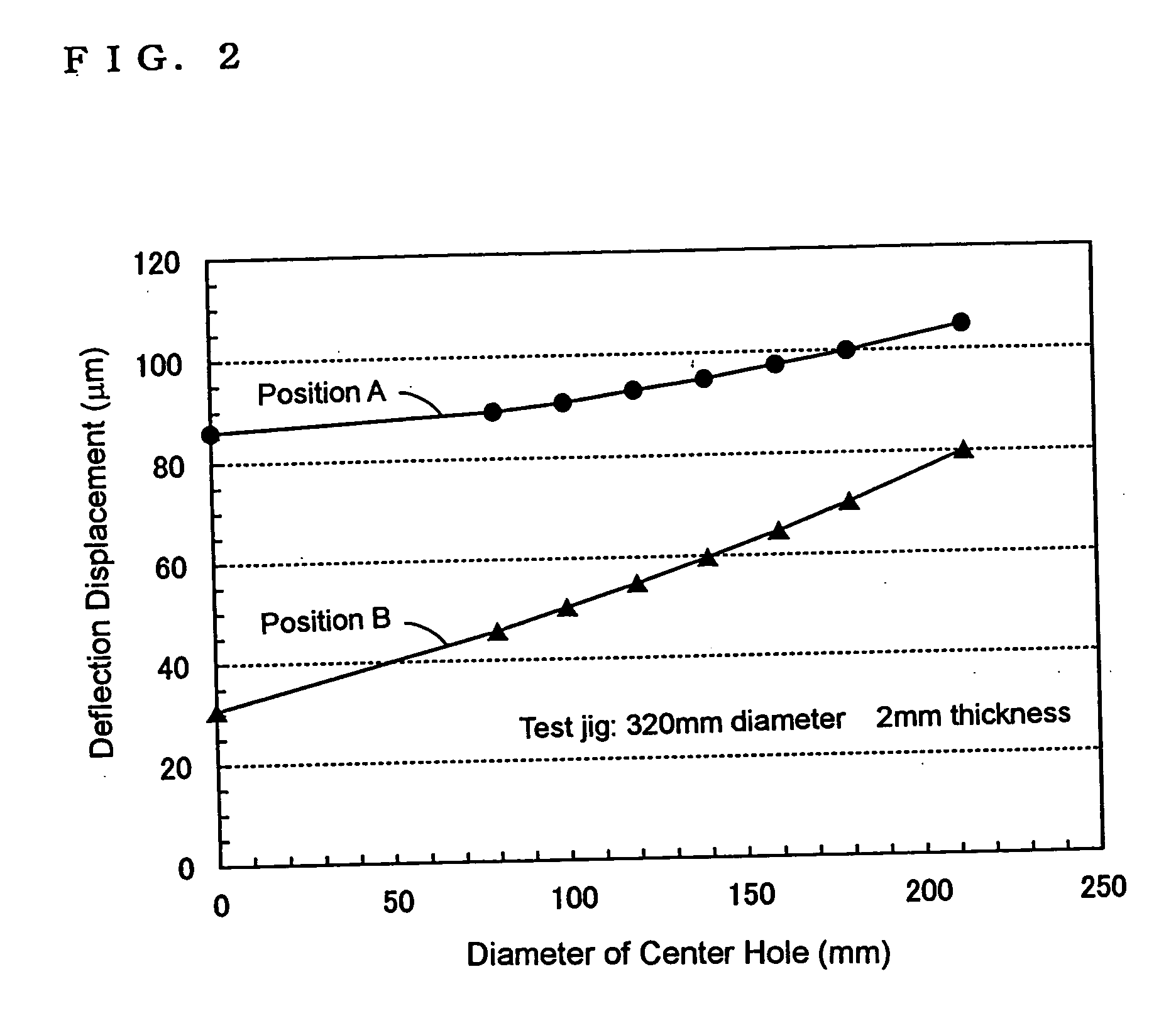
ActiveUS20050282101A1Reduce generationDiminish surface stepCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessSemiconductor
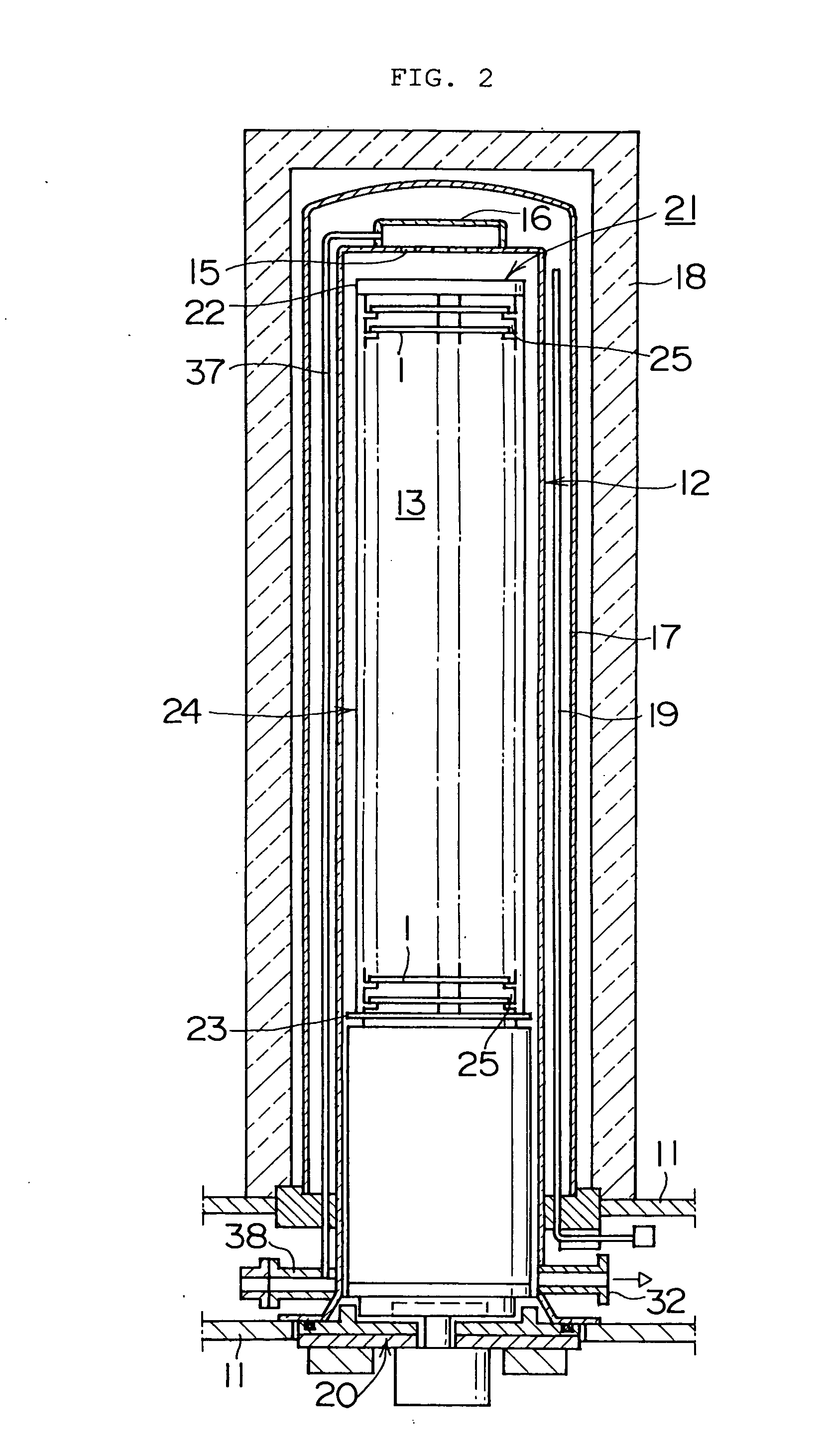
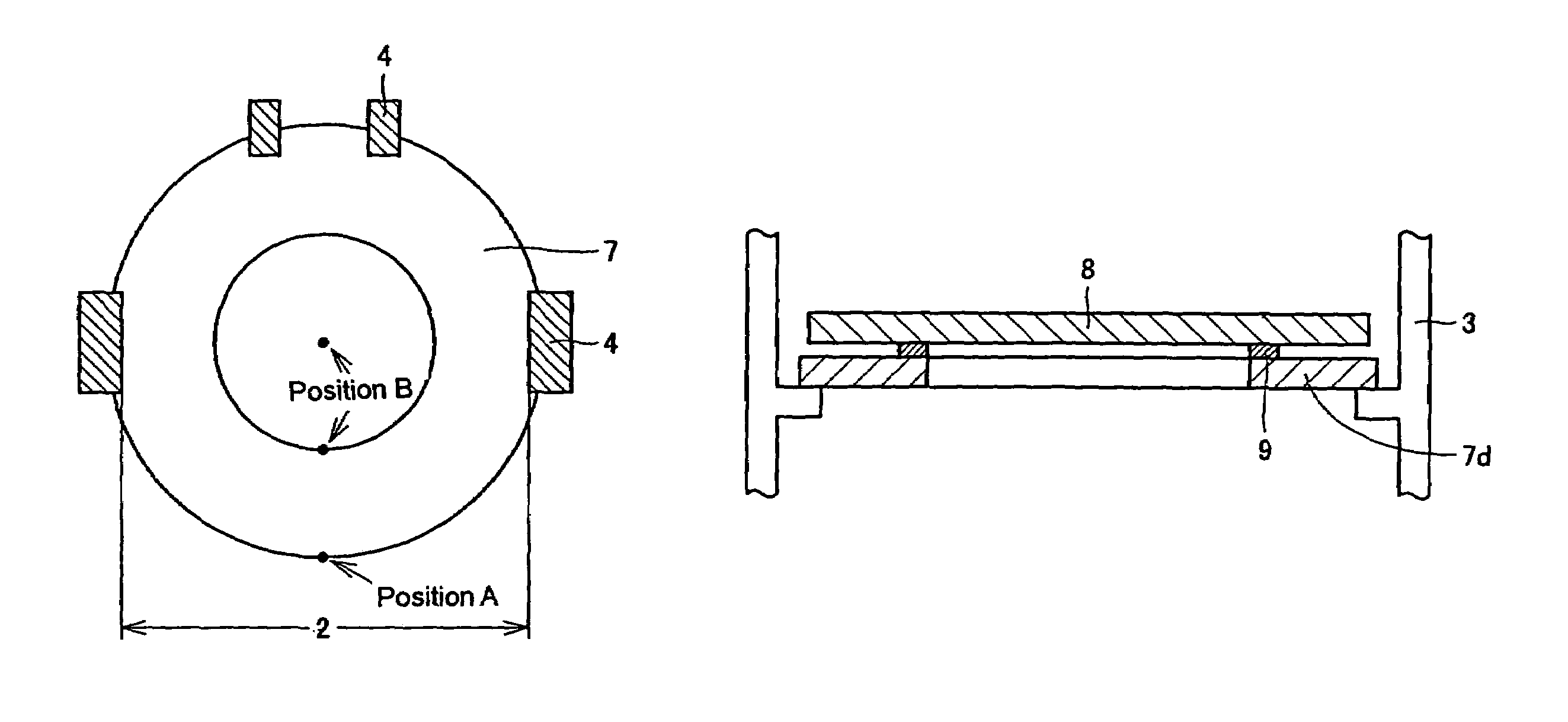
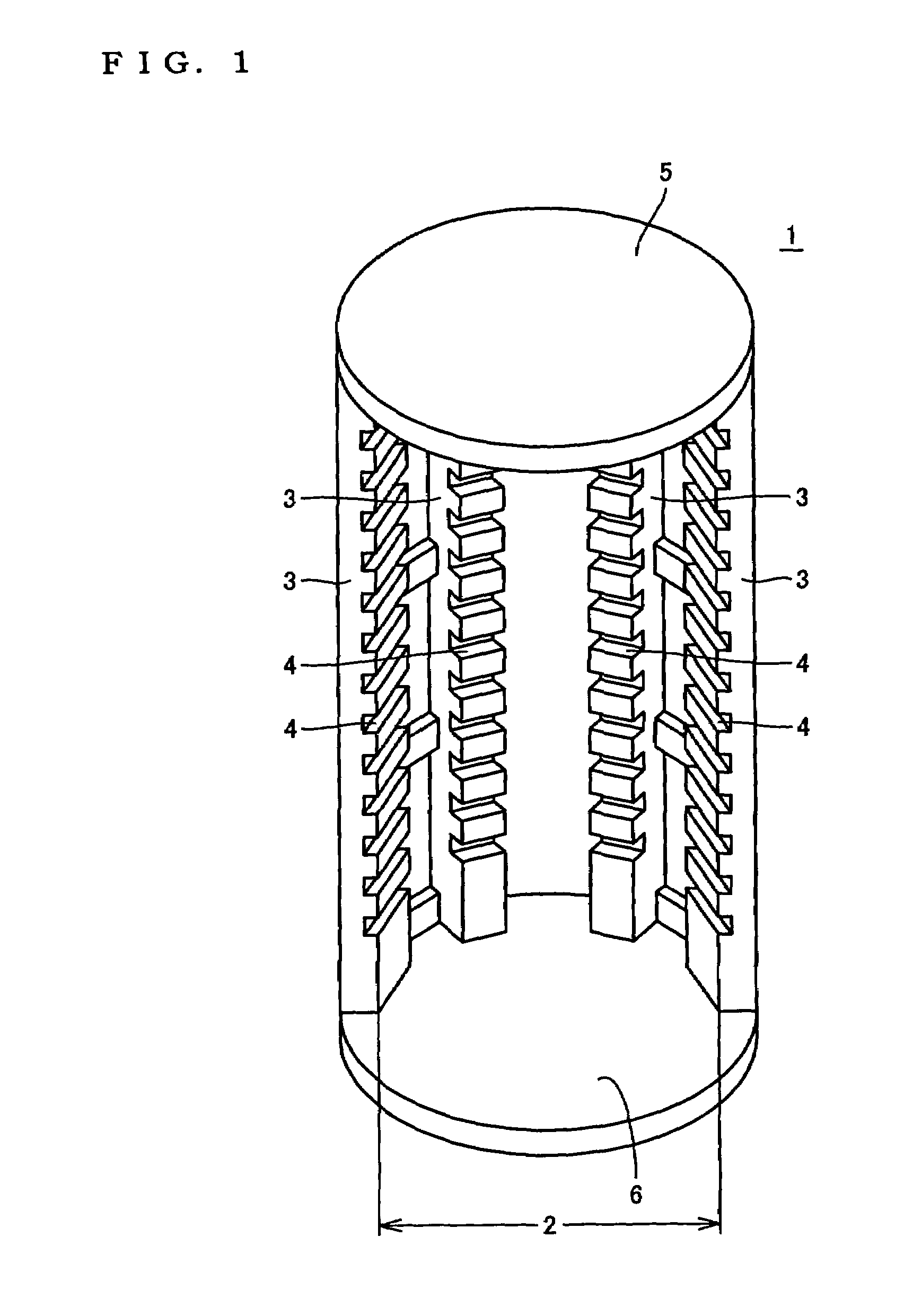
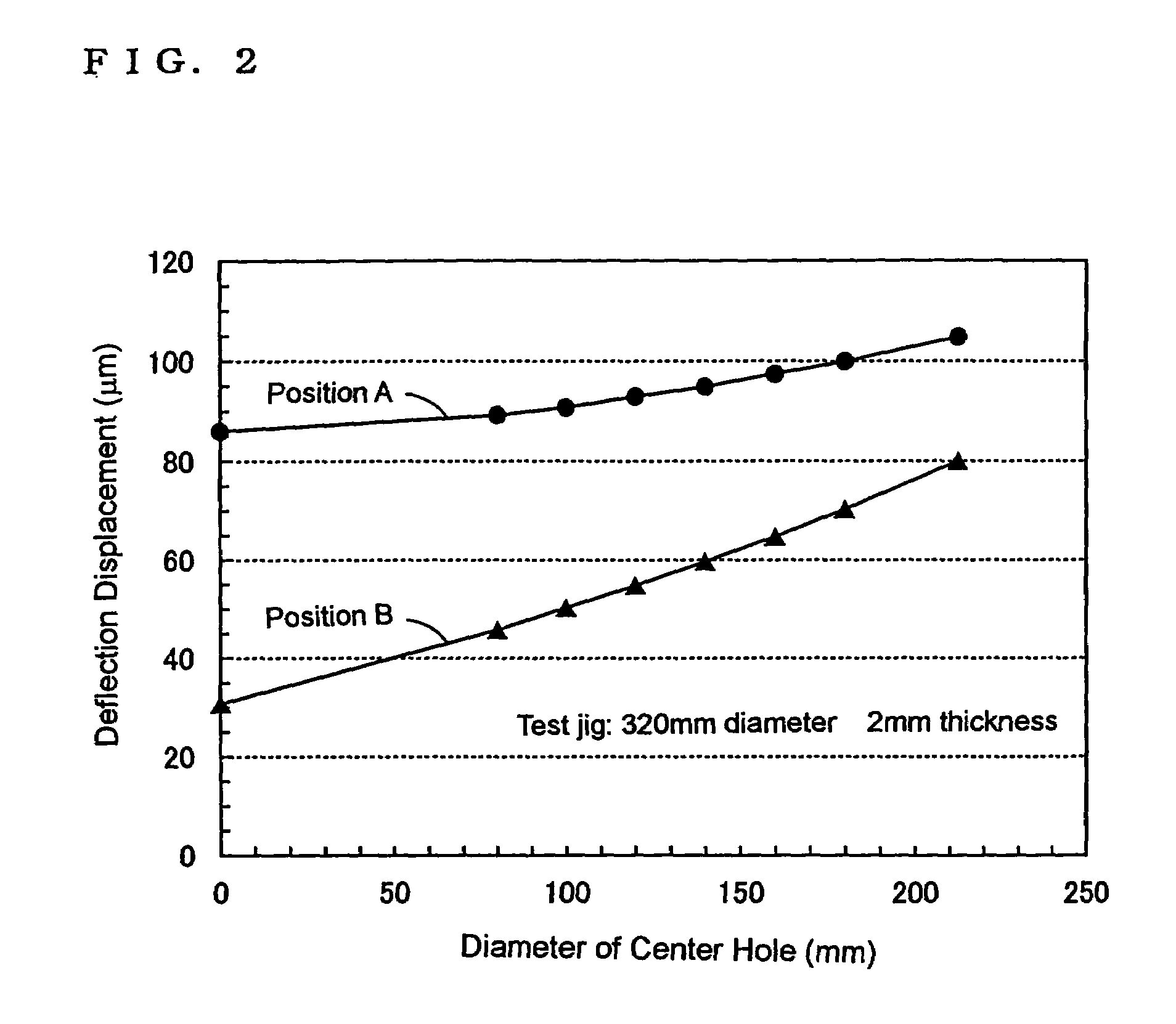
A heat treatment jig for supporting silicon semiconductor substrates by contacting, being loaded onto a heat treatment boat in a vertical heat treatment furnace, comprises; the configuration of a ring or a disc structure with the wall thickness between 1.5 and 6.0 mm; the deflection displacement of 100 μm or less at contact region in loaded condition; the outer diameter which is 65% or more of the diameter of said substrate; and the surface roughness (Ra) of between 1.0 and 100 μm at the contact region. The use of said jig enables to effectively retard the slip generation and to avoid the growth hindrance of thermally oxidized film at the back surface of said substrate, diminishing the surface steps causing the defocus in photolithography step in device fabrication process, thereby enabling to maintain high quality of silicon semiconductor substrates and to substantially enhance the device yield.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
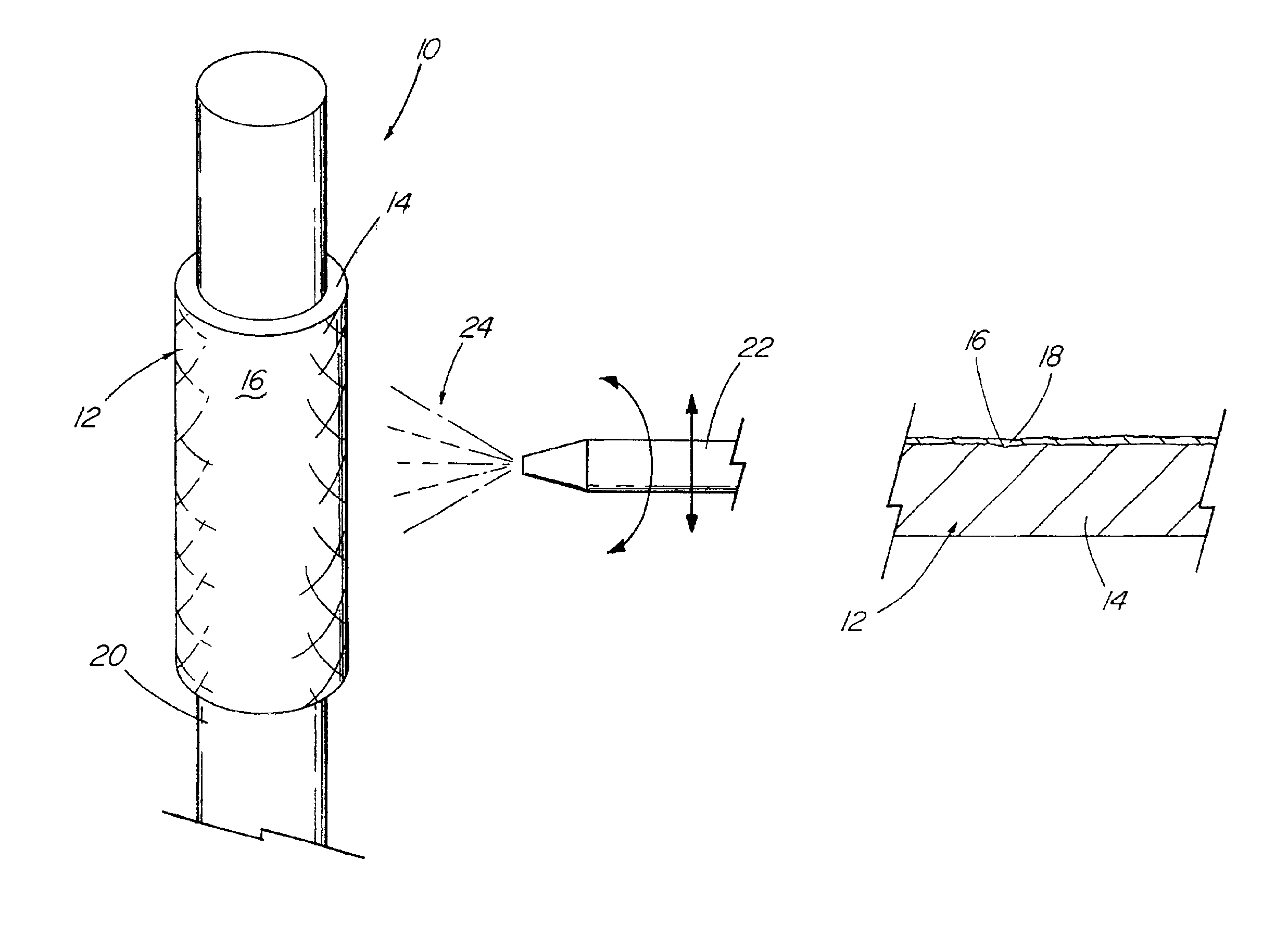
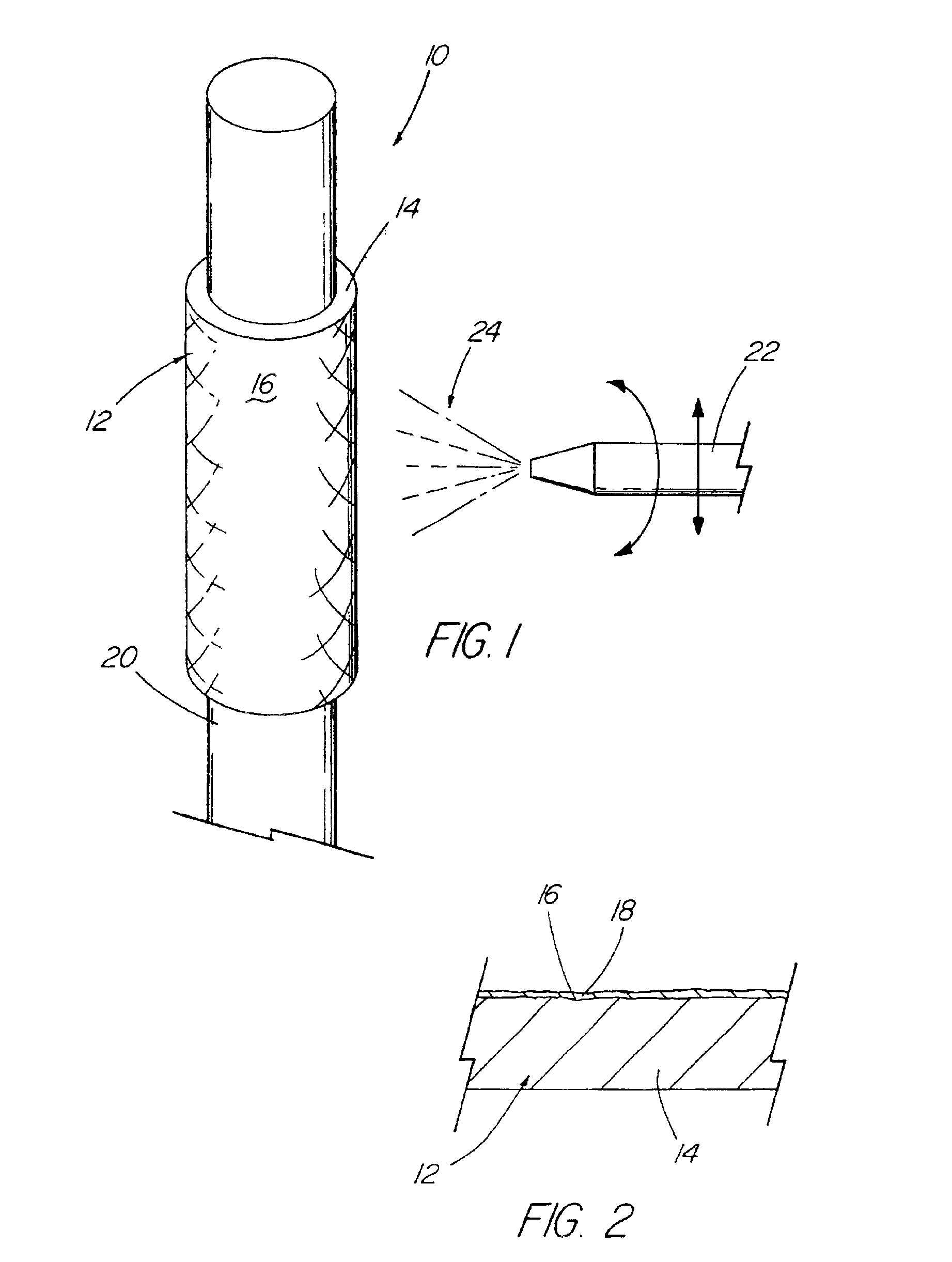
Coated implantable medical device
InactiveUS6918927B2Good worker safetyLow costOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySodium bicarbonateMedicine
A medical device (10) includes a structure (12) adapted for introduction into a patient, the structure (12) being formed of a preferably non-porous base material (14) having a roughened or textured surface (16). The structure (12) is conveniently configured as a vascular stent with a base material (14) of stainless steel, nitinol or another suitable material. The medical device (10) also includes a layer (18) of a bioactive material posited directly upon the roughened or textured surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12). The surface (16) of the base material (14) is roughened or textured by etching or by abrasion with sodium bicarbonate or another suitable grit. A preferred roughened or textured surface (16) is thought to have a mean surface roughness of about 10 μin. (about 250 nm) and a surface roughness range between about 1 μin. and about 100 μin. (about 25 nm and about 2.5 μm). The particularly preferred use of sodium bicarbonate as the abrasive to provide roughness or texture to the surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12) is additionally advantageous in the low toxicity of the sodium bicarbonate to production workers, the ease of product and waste cleanup, and the biocompatibility of any residual sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Heat Treating Apparatus
ActiveUS20080267598A1Minimal amountPrevent slipping or slippingRespiratorsDrying solid materials with heatSurface roughnessHeat treating
[Problems] To prevent both slips caused by damage from projections, and slips caused by adhesive force occurring due to excessive smoothing.[Means for Solving the Problems] The heat treating apparatus includes a processing chamber for heat treating wafers and a boat for supporting the wafers in the processing chamber. The boat further includes a wafer holder in contact with the wafer and a main body for supporting the wafer holder. The wafer holder diameter is 63 to 73 percent of the wafer diameter, and the surface roughness Ra of the portion of the wafer holder in contact with the wafer is set from 1 μm to 1,000 μm. The wafer can be supported so that the amount of wafer displacement is minimal and both slips due to damage from projections on the wafer holder surface, and slips due to the adhesive force occurring because of excessive smoothing can be prevented in that state.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Heat treatment jig for silicon semiconductor substrate
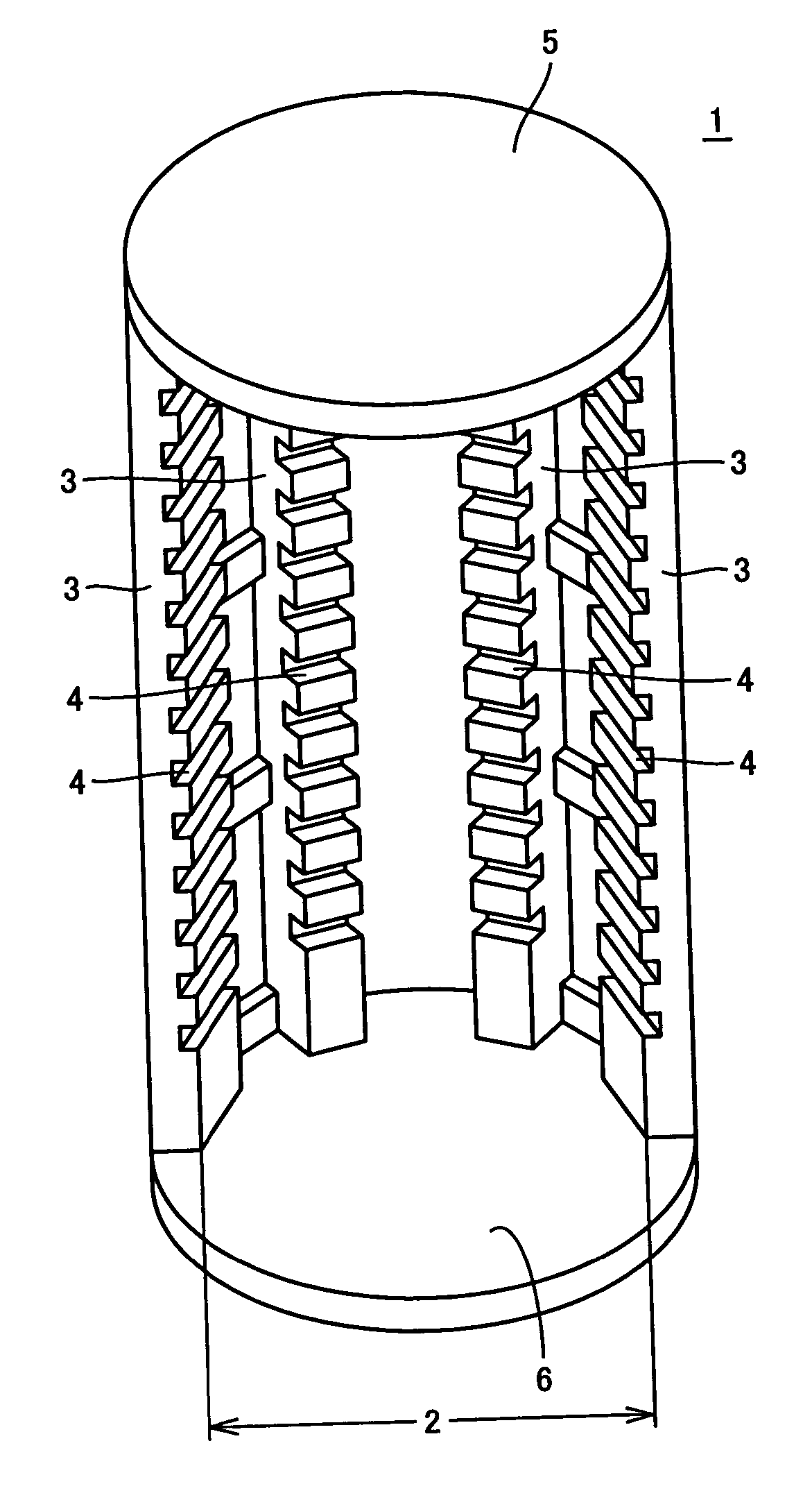
ActiveUS7210925B2Reduce generationGenerated with easeCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessSilicon
A heat treatment jig for supporting silicon semiconductor substrates by contacting, being loaded onto a heat treatment boat in a vertical heat treatment furnace, comprises; the configuration of a ring or a disc structure with the wall thickness between 1.5 and 6.0 mm; the deflection displacement of 100 μm or less at contact region in loaded condition; the outer diameter which is 65% or more of the diameter of said substrate; and the surface roughness (Ra) of between 1.0 and 100 μm at the contact region. The use of said jig enables to effectively retard the slip generation and to avoid the growth hindrance of thermally oxidized film at the back surface of said substrate, diminishing the surface steps causing the defocus in photolithography step in device fabrication process, thereby enabling to maintain high quality of silicon semiconductor substrates and to substantially enhance the device yield.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
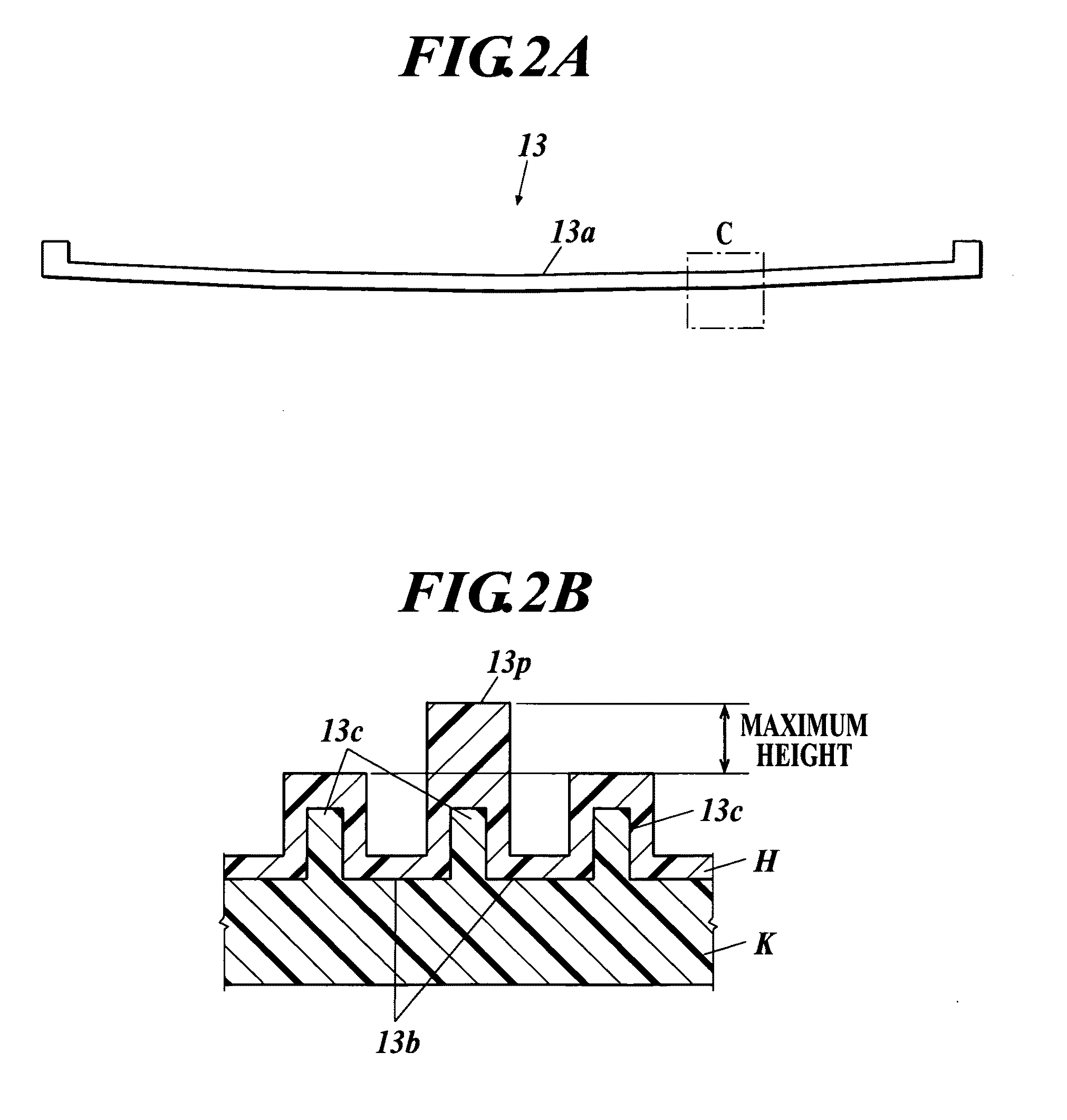
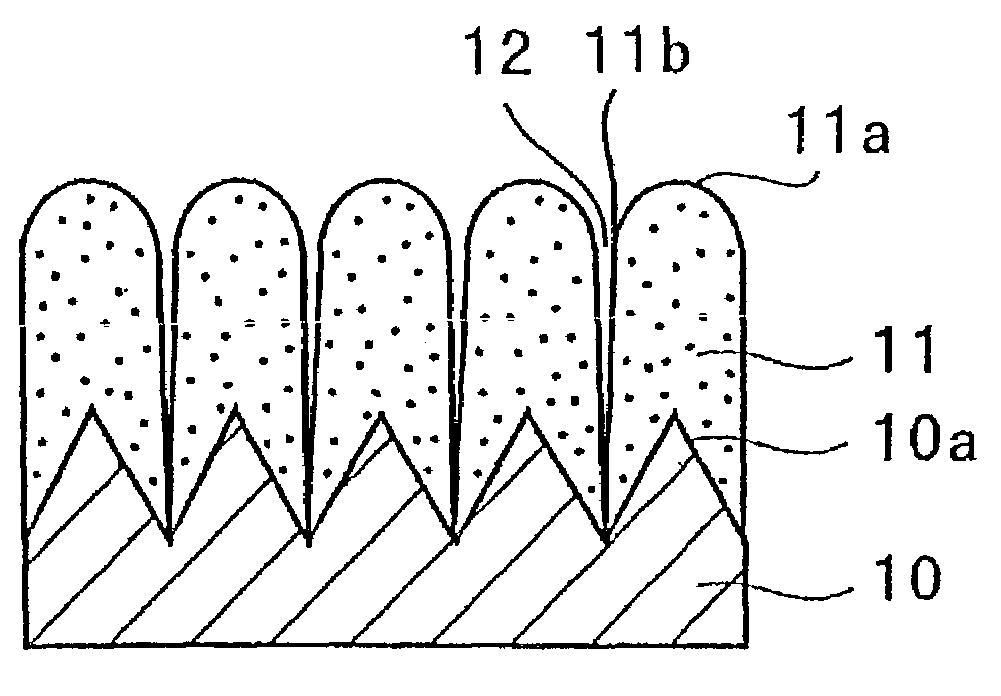
Susceptor and method for manufacturing silicon epitaxial wafer
ActiveUS20100129990A1Avoid stickingPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsSusceptorWafering
Provided is a susceptor 13 for manufacturing an epitaxial wafer, comprising a mesh-like groove 13b on a mount face on which a silicon substrate W is to be mounted, wherein a coating H of silicon carbide is formed on the mount face, and the coating has a surface roughness of 1 μm or more in centerline average roughness Ra and a maximum height of a protrusion 13p generated in forming the coating H of 5 μm or less. Thus, defects such as warping and slip as well as adhesion of the silicon substrate to the susceptor are prevented.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
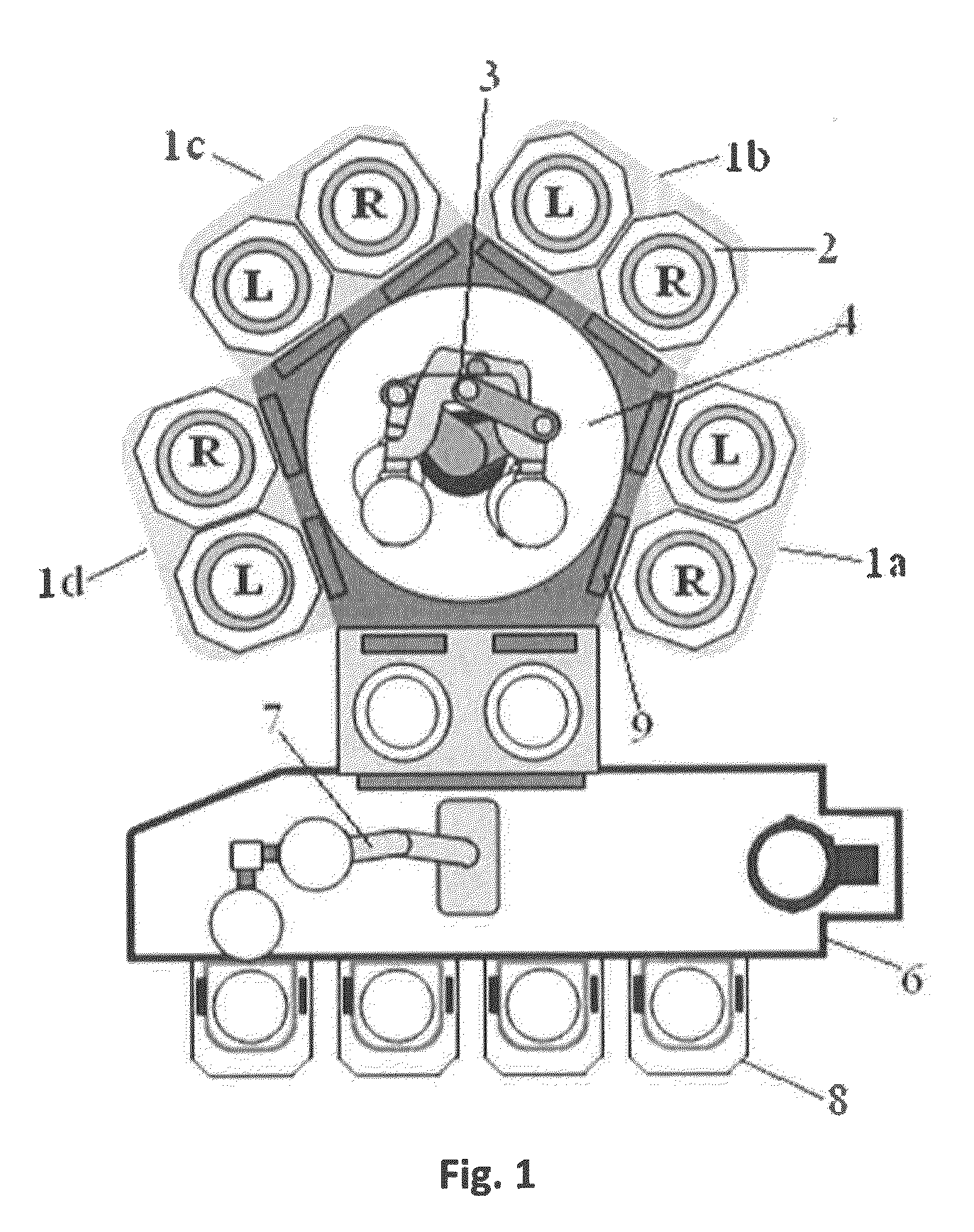
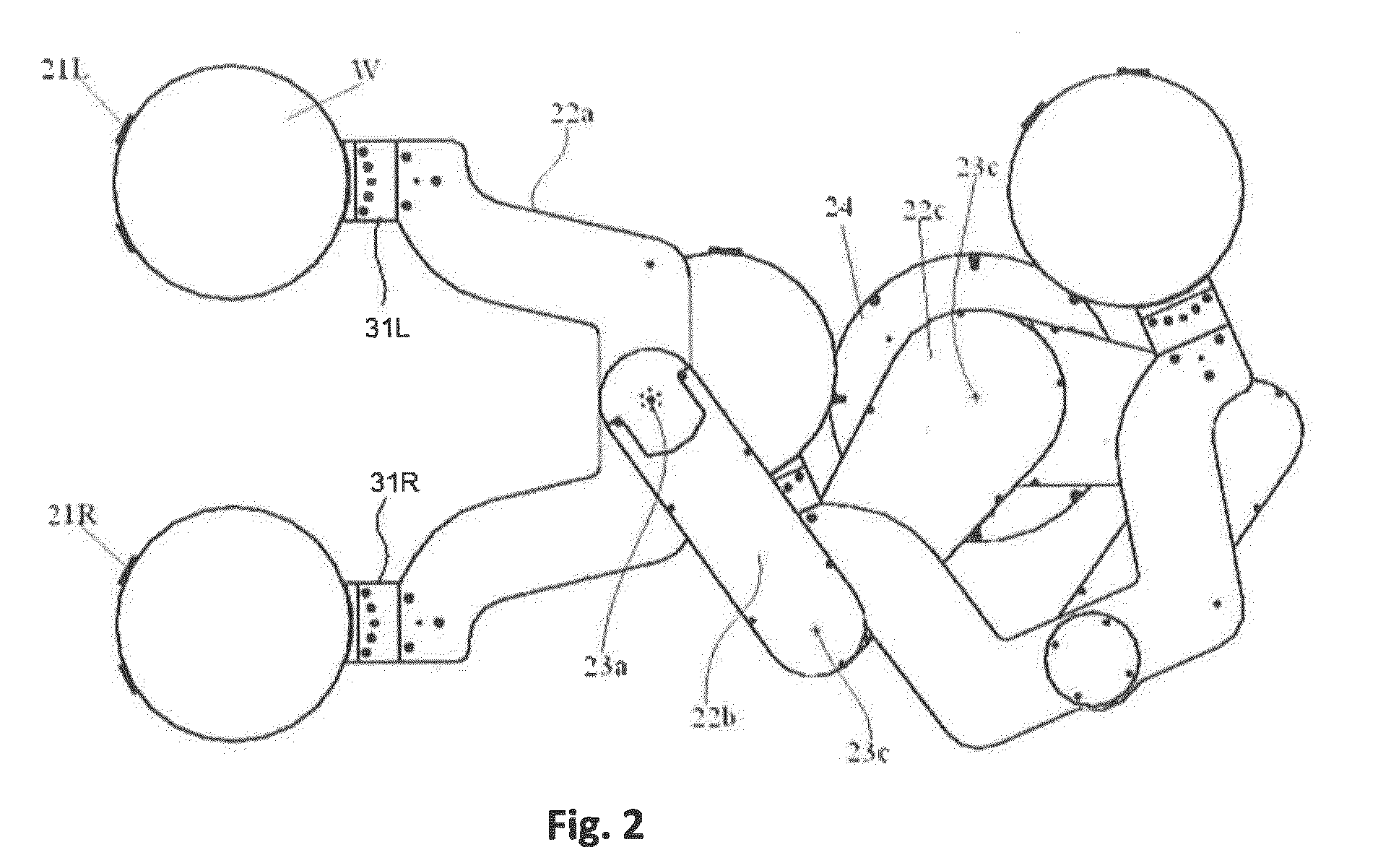
Anti-slip end-effector for transporting workpiece
ActiveUS9370863B2Gripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic friction coefficientRobotic arm
An anti-slip end-effector for transporting a workpiece, which is configured to be attached to a robotic arm, includes: a workpiece-supporting area for placing a workpiece thereon for transportation; at least one front protrusion disposed at a distal end of the workpiece-supporting area for engaging an edge of the workpiece to restrict movement of the workpiece placed on the workpiece-supporting area beyond the front protrusion; and at least one anti-slip protrusion disposed in the workpiece-supporting area for contacting and supporting the backside of the workpiece, said anti-slip protrusion having a top face having a static friction coefficient of 1.0 or more as measured against the backside of the workpiece, and having a surface roughness of less than 0.4 μm.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
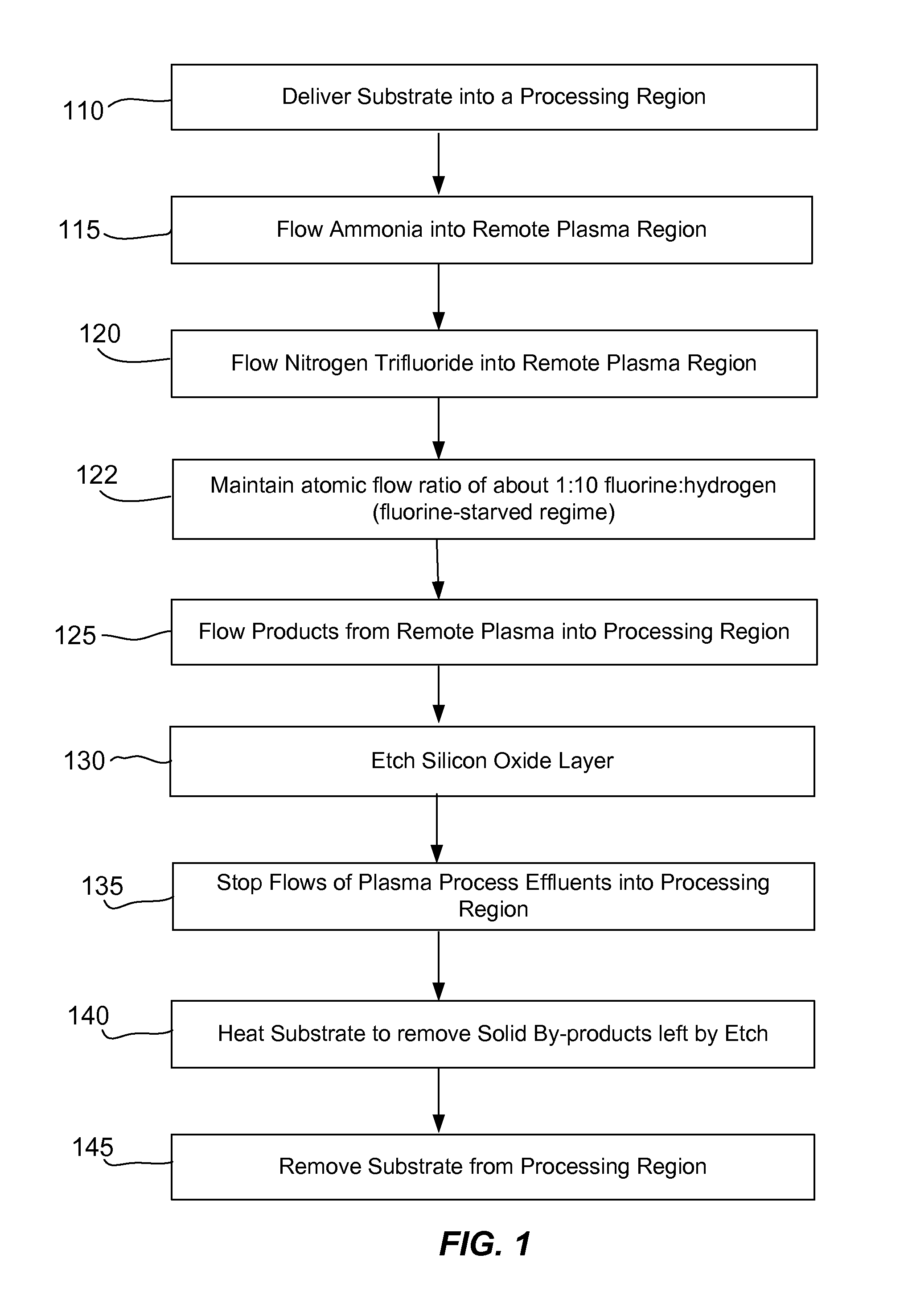
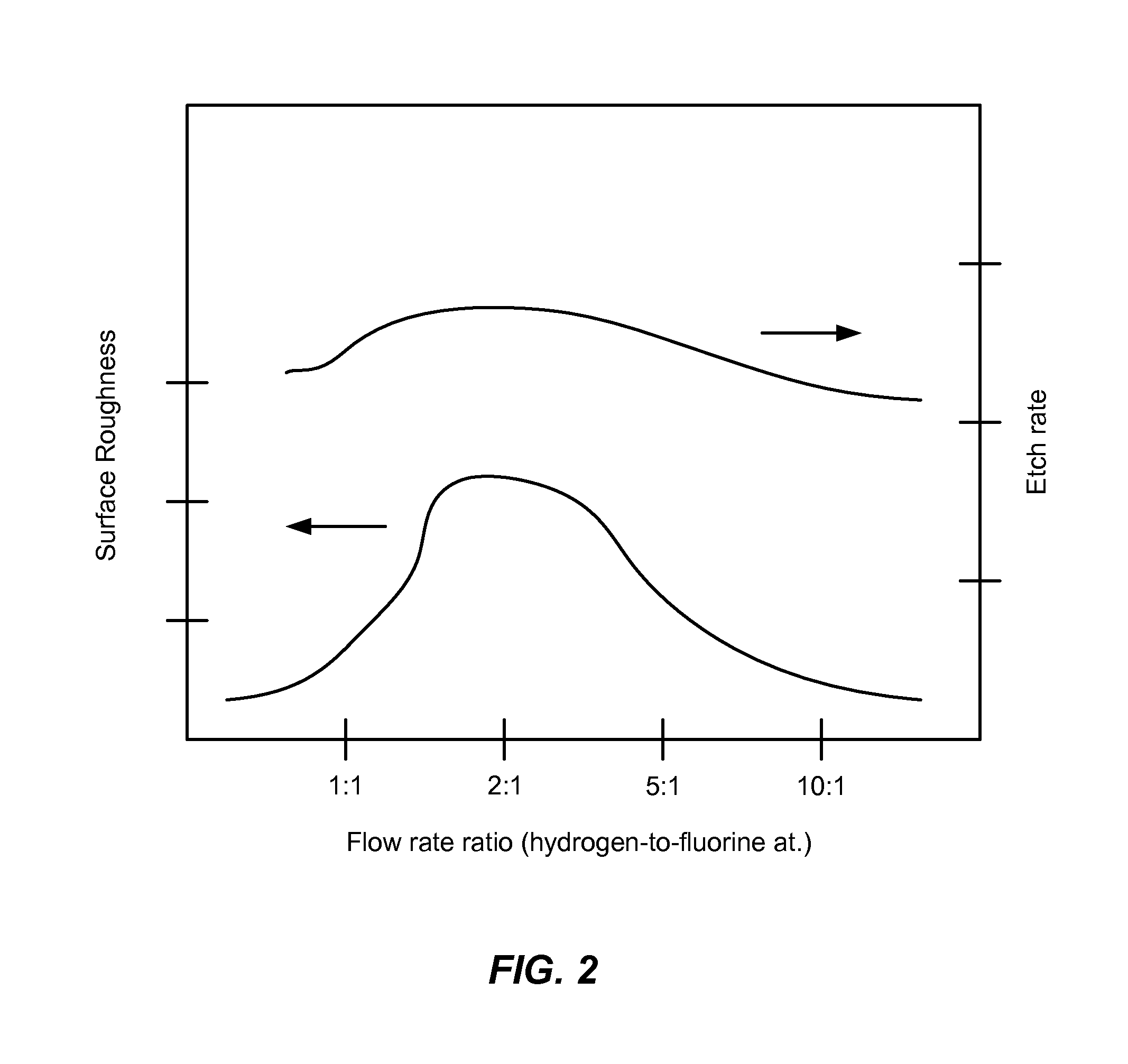
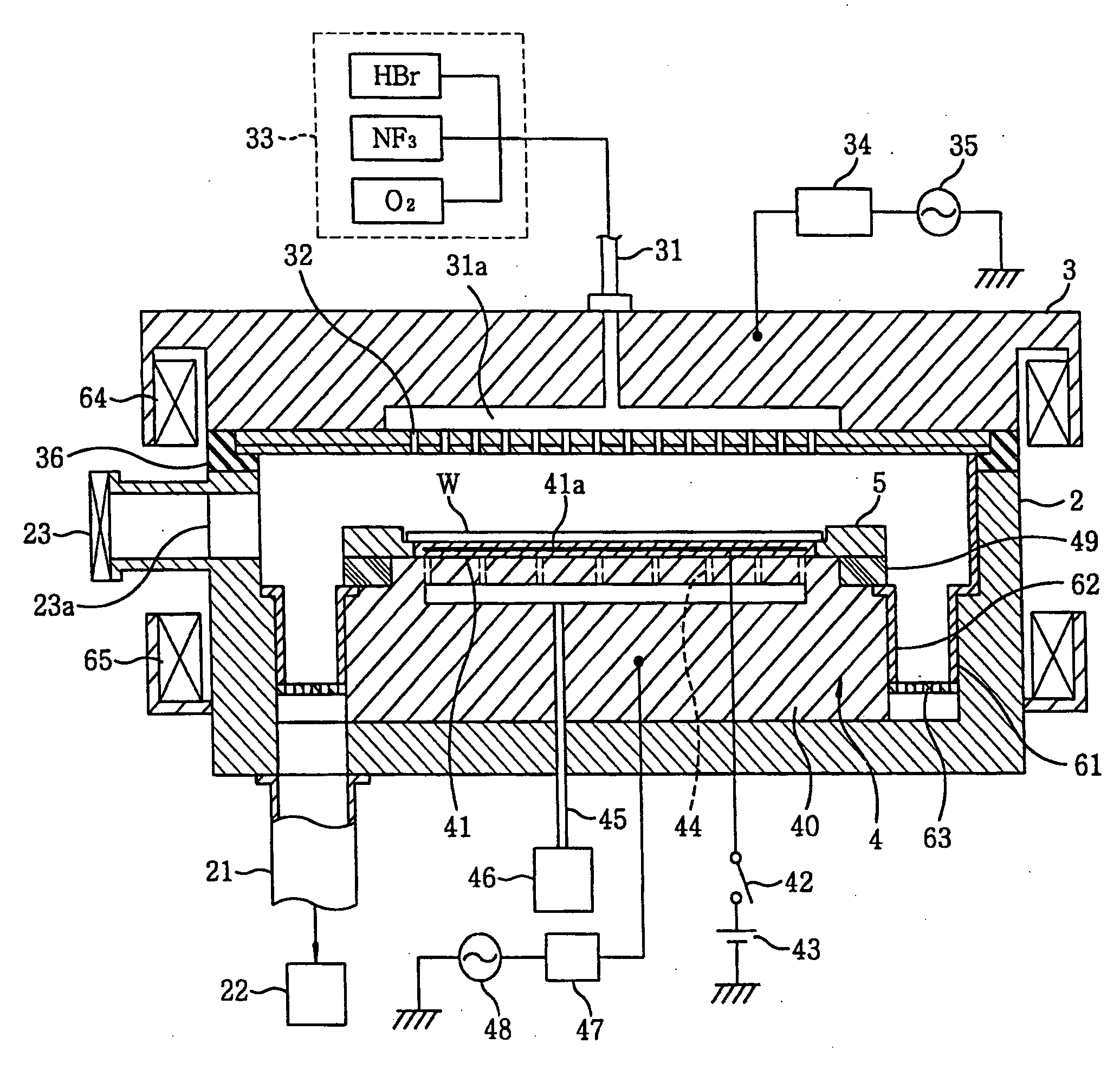
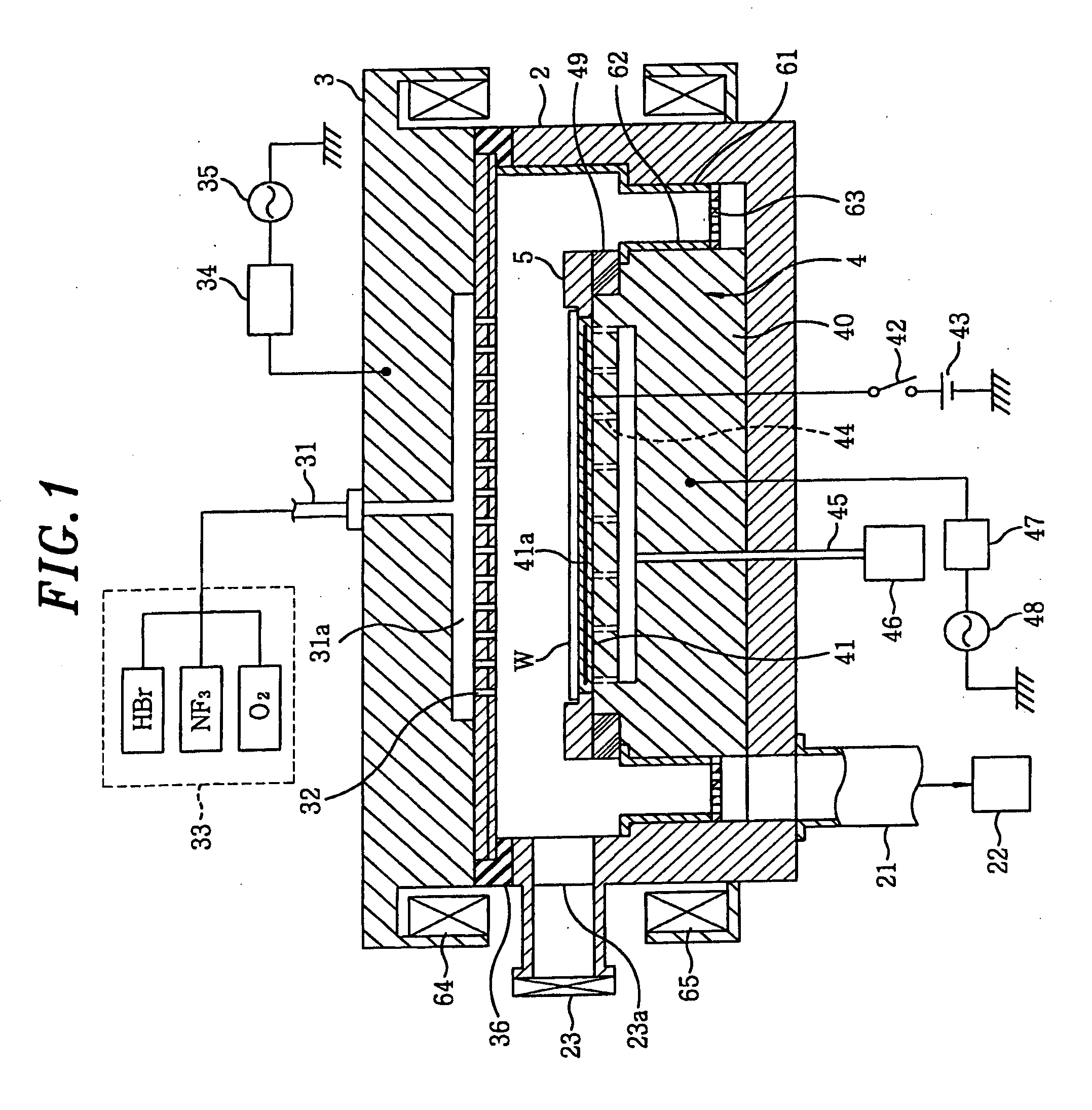
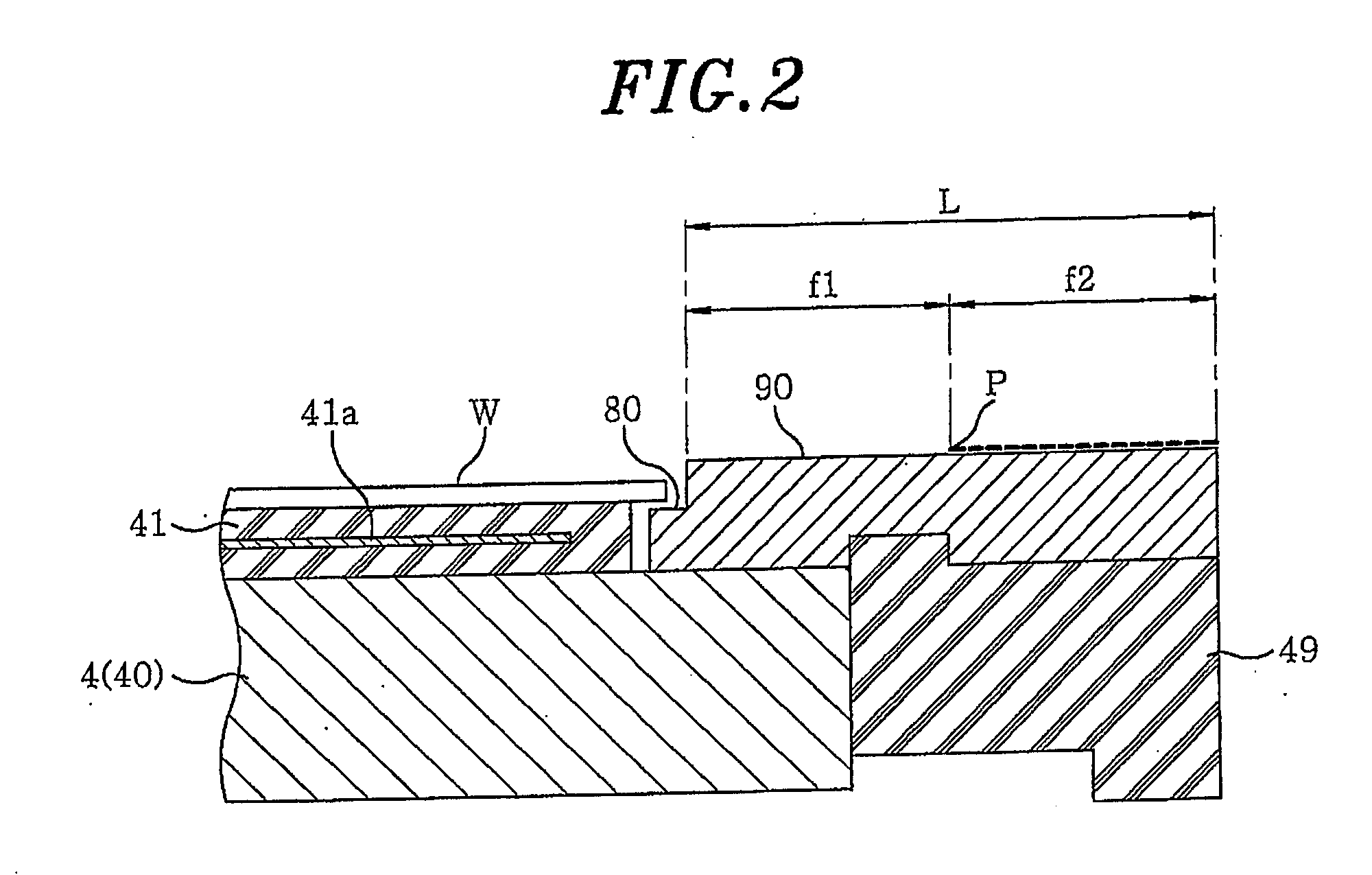
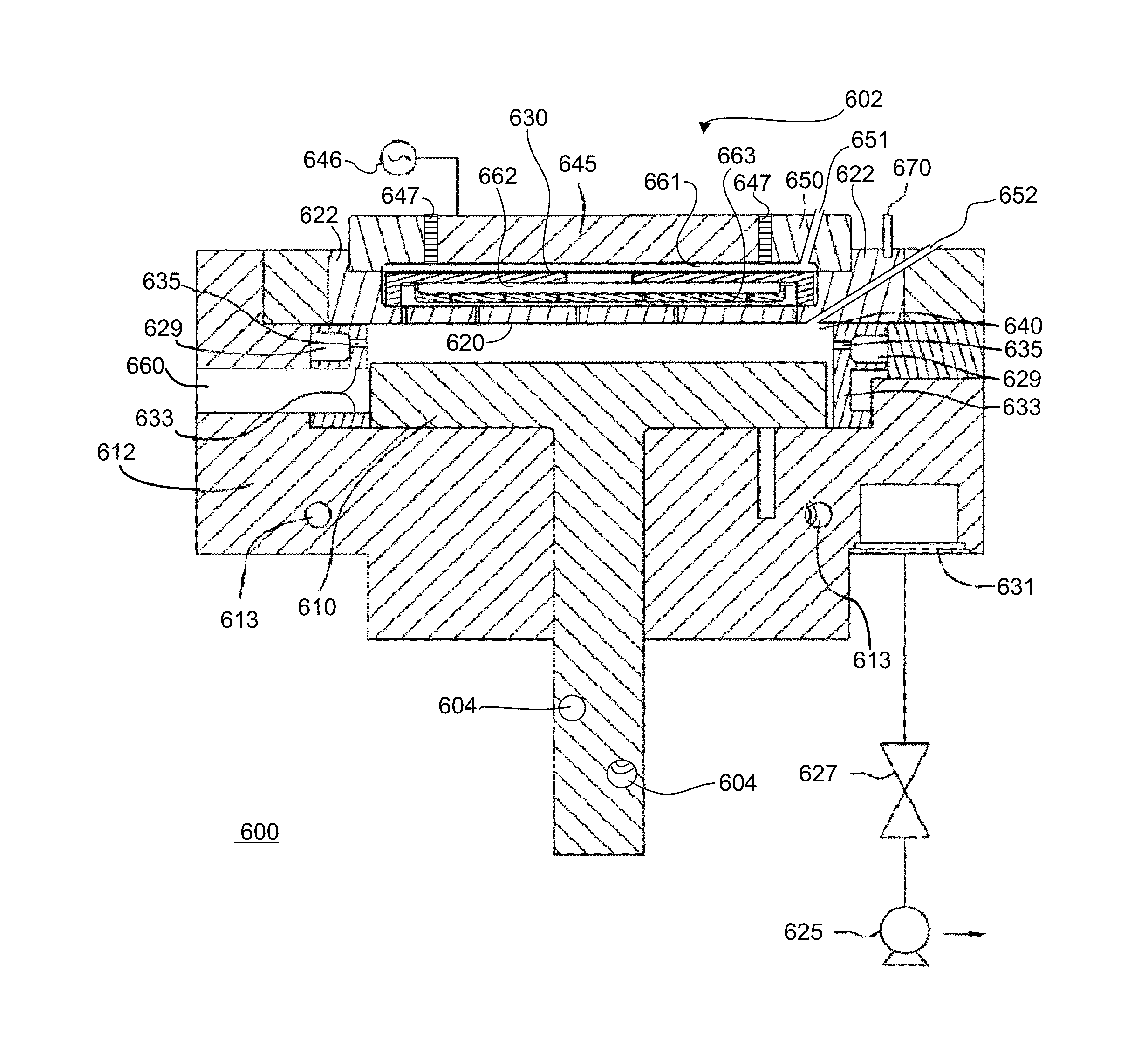
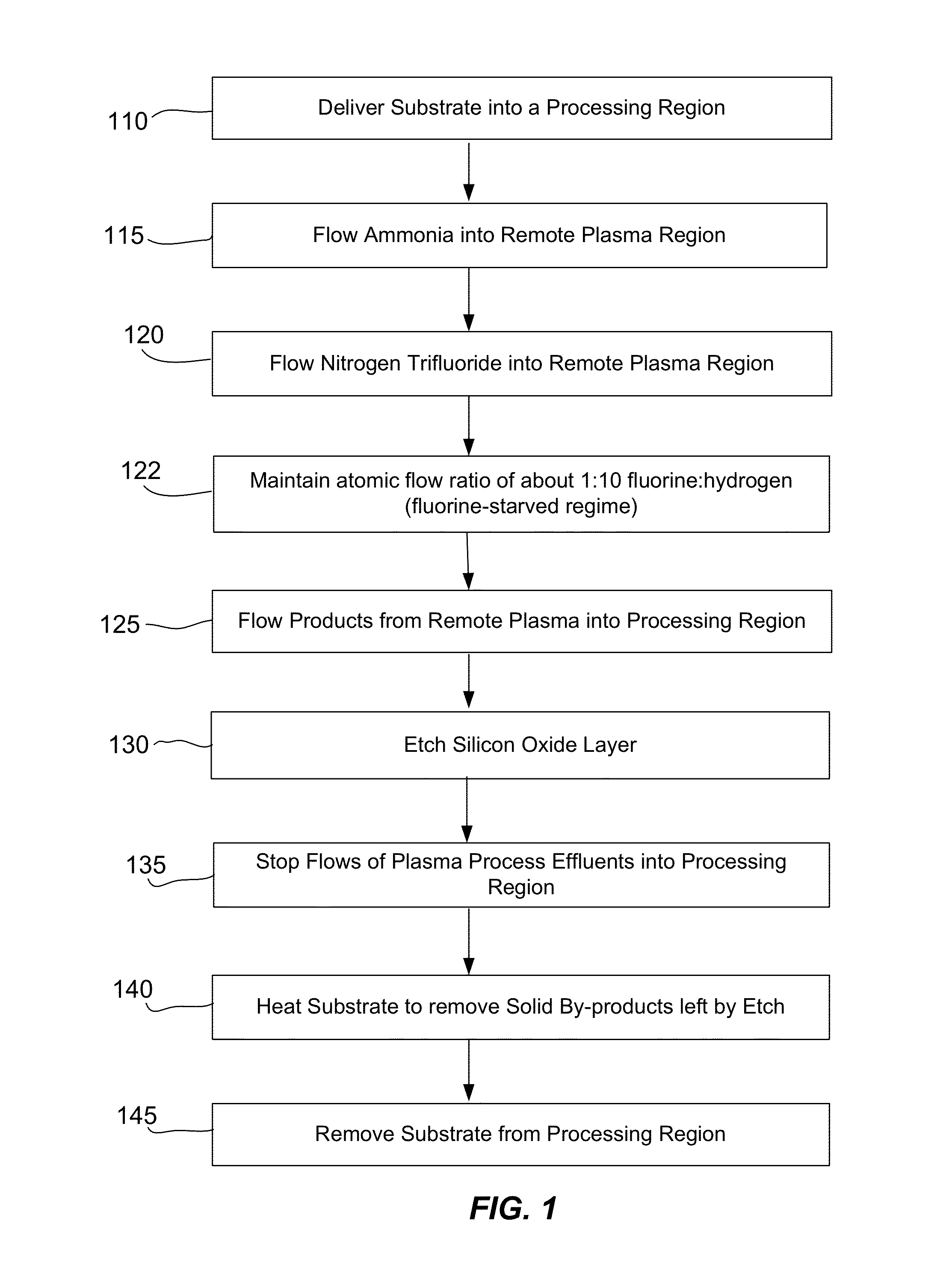
Smooth siconi etch for silicon-containing films
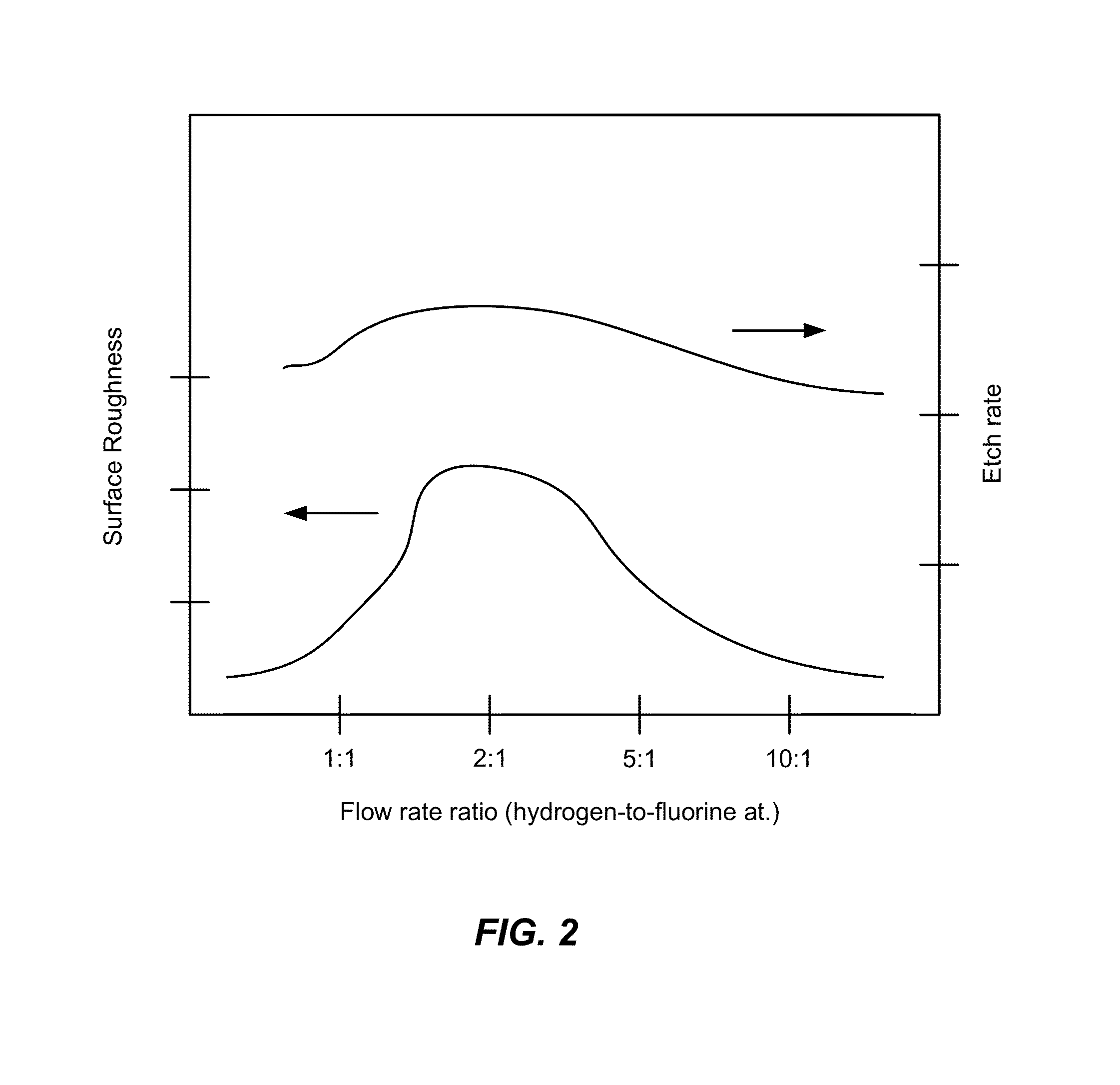
ActiveUS20110151674A1Great and less flow ratioReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSurface roughness
A method of etching silicon-containing material is described and includes a SiConi™ etch having a greater or lesser flow ratio of hydrogen compared to fluorine than that found in the prior art. Modifying the flow rate ratios in this way has been found to reduce roughness of the post-etch surface and to reduce the difference in etch-rate between densely and sparsely patterned areas. Alternative means of reducing post-etch surface roughness include pulsing the flows of the precursors and / or the plasma power, maintaining a relatively high substrate temperature and performing the SiConi™ in multiple steps. Each of these approaches, either alone or in combination, serve to reduce the roughness of the etched surface by limiting solid residue grain size.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
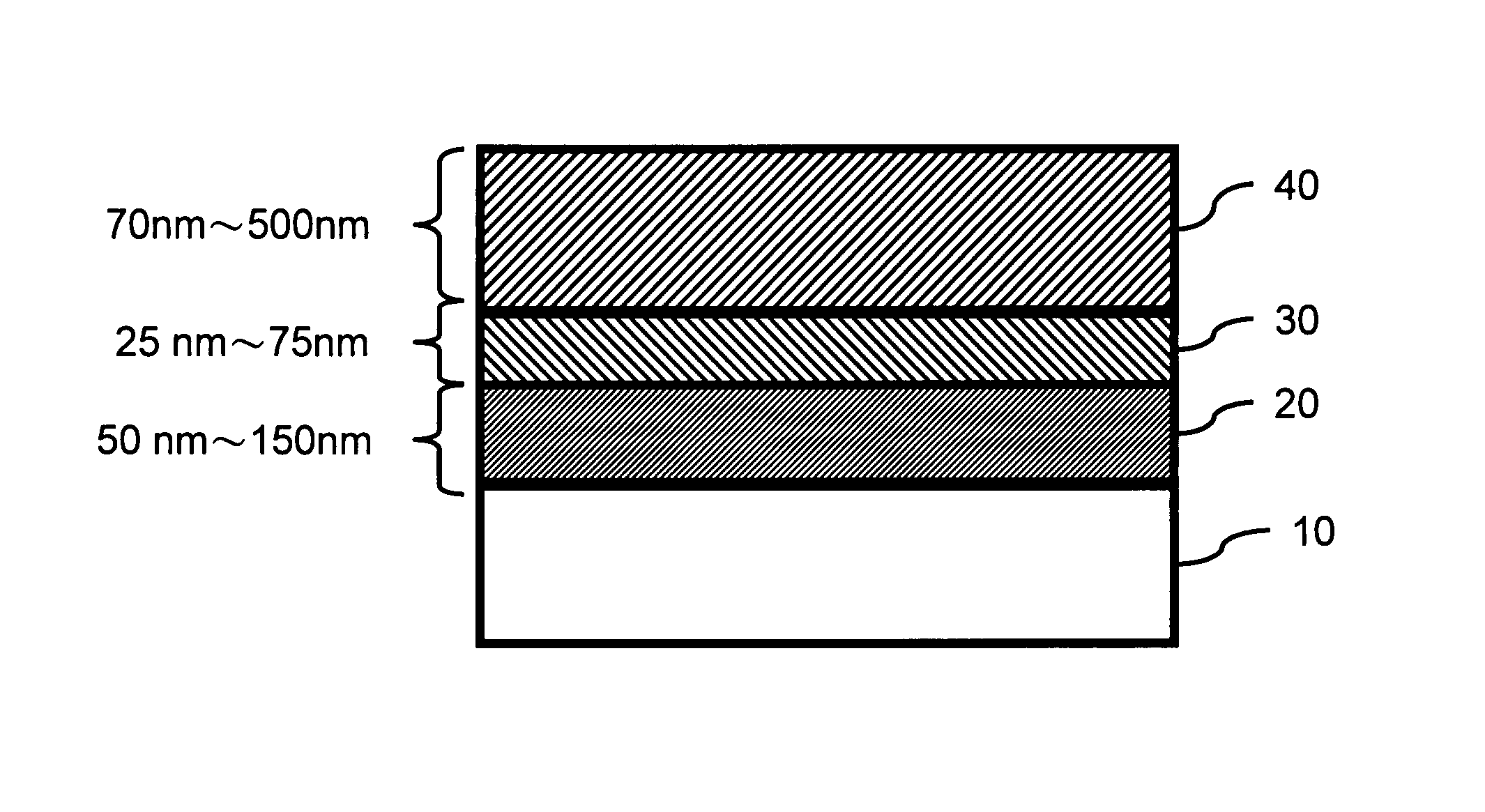
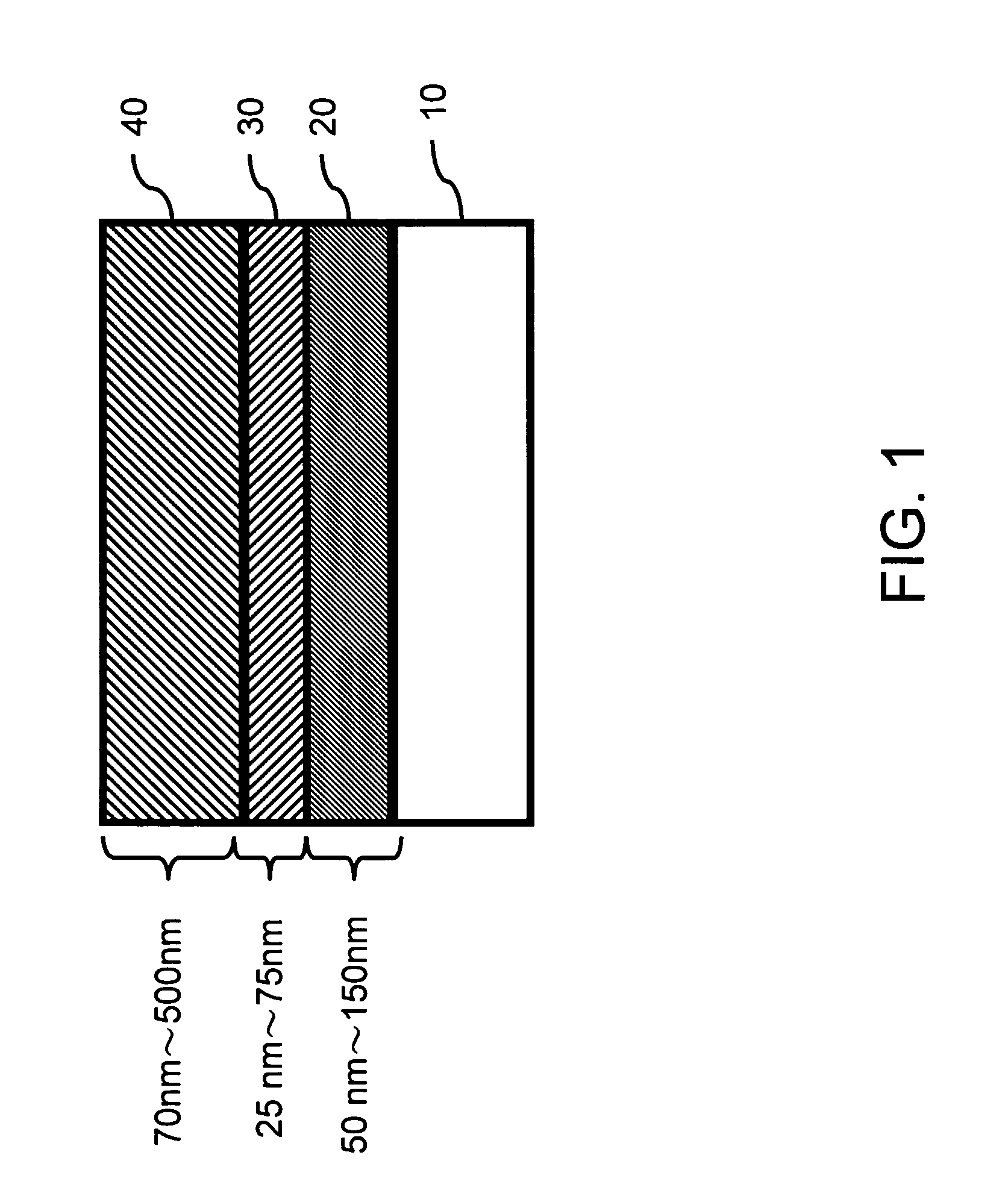
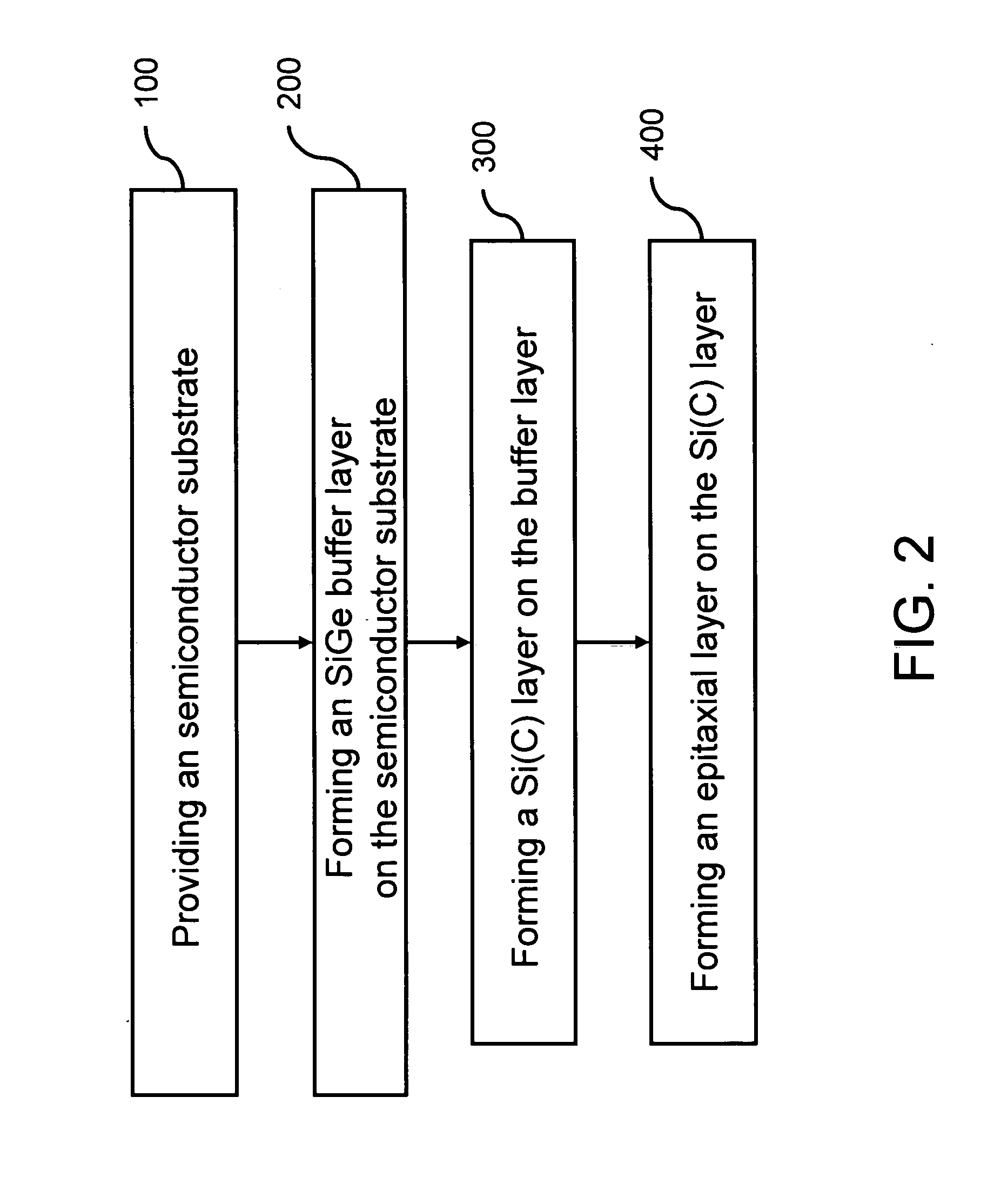
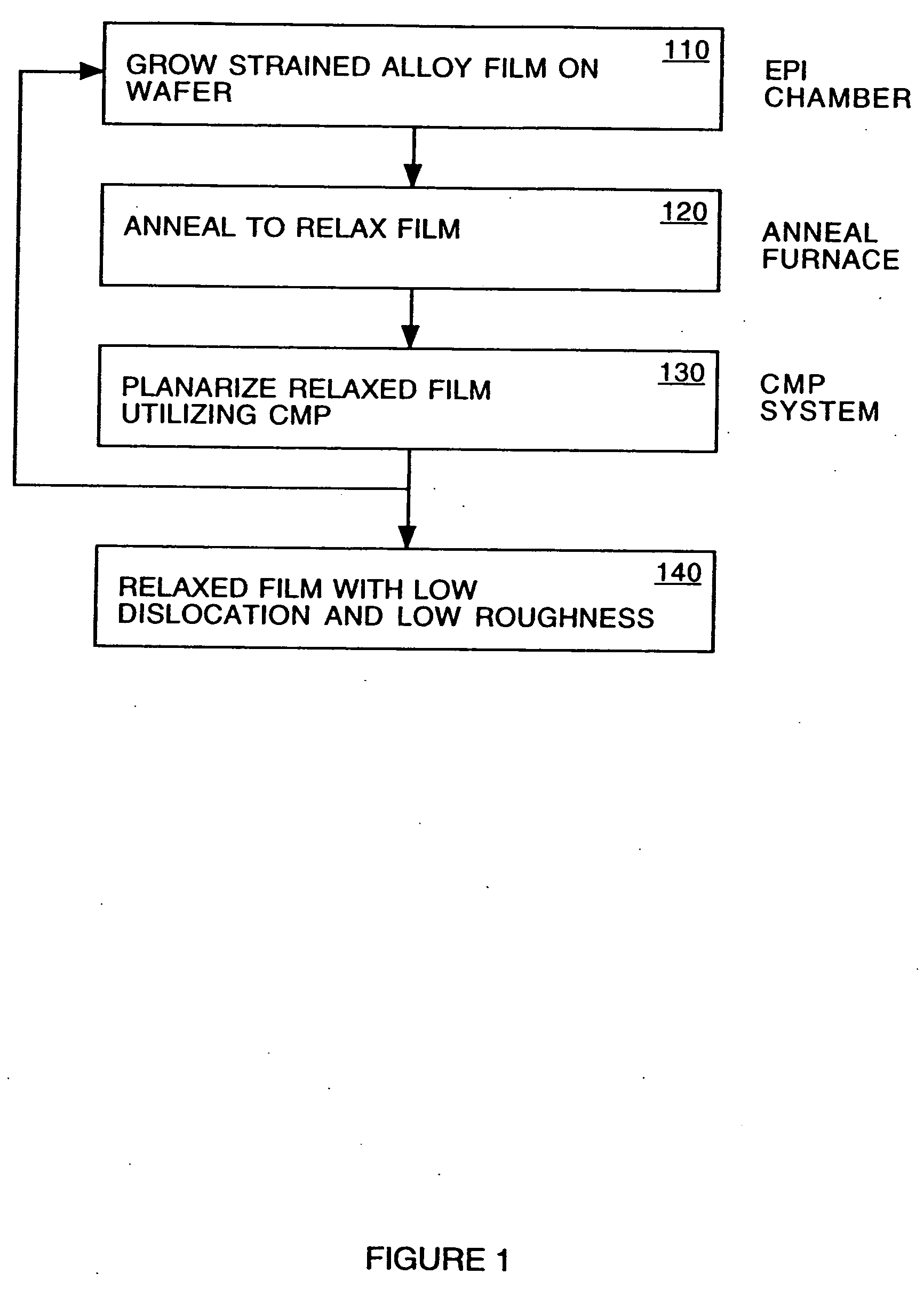
Construction of thin strain-relaxed SiGe layers and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7202512B2High degreeReduction of threadingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface roughnessDislocation
A construction of thin strain-relaxed SiGe layers and method for fabricating the same is provided. The construction includes a semiconductor substrate, a SiGe buffer layer formed on the semiconductor substrate, a Si(C) layer formed on the SiGe buffer layer, and an relaxed SiGe epitaxial layer formed on the Si(C) layer. The Si(C) layer is employed to change the strain-relaxed mechanism of the relaxed SiGe epitaxial layer formed on the Si(C) layer. Therefore, a thin relaxed SiGe epitaxial layer with low threading dislocation density, smooth surface is available. The fabricating time for fabricating the strain-relaxed SiGe layers is greatly reduced and the surface roughness is also improved.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Fiber adhesive material
InactiveUS20040071870A1Improve adhesion performanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricFiber
A fiber velvet comprising nano-size fibers or nanofibrils attached to micro-size fibers is disclosed. Methods of manufacturing the velvet as well as various uses of the velvet are also described. For example, the fiber velvet can be used as a thermal interface or as an adhesive material. The nanofibrils may be attached to a flat base or membrane, or may be attached to the tip portions of the micro-size or larger diameter fibers. Various attributes of the micro-size fibers and of the nano-size fibers, for example, geometry (e.g. size, length, packing density) material type (e.g. carbon, metal, polymer, or ceramic) and properties (e.g. conductivity, modulus, surface energy, dielectric constant, surface roughness) can be selected depending on the desired attributes of the fiber velvet. The nanofibrils have a diameter of less than about 1 micron, and may advantageously be formed from single walled and / or multi-walled carbon nanotubes.
Owner:KULR TECH
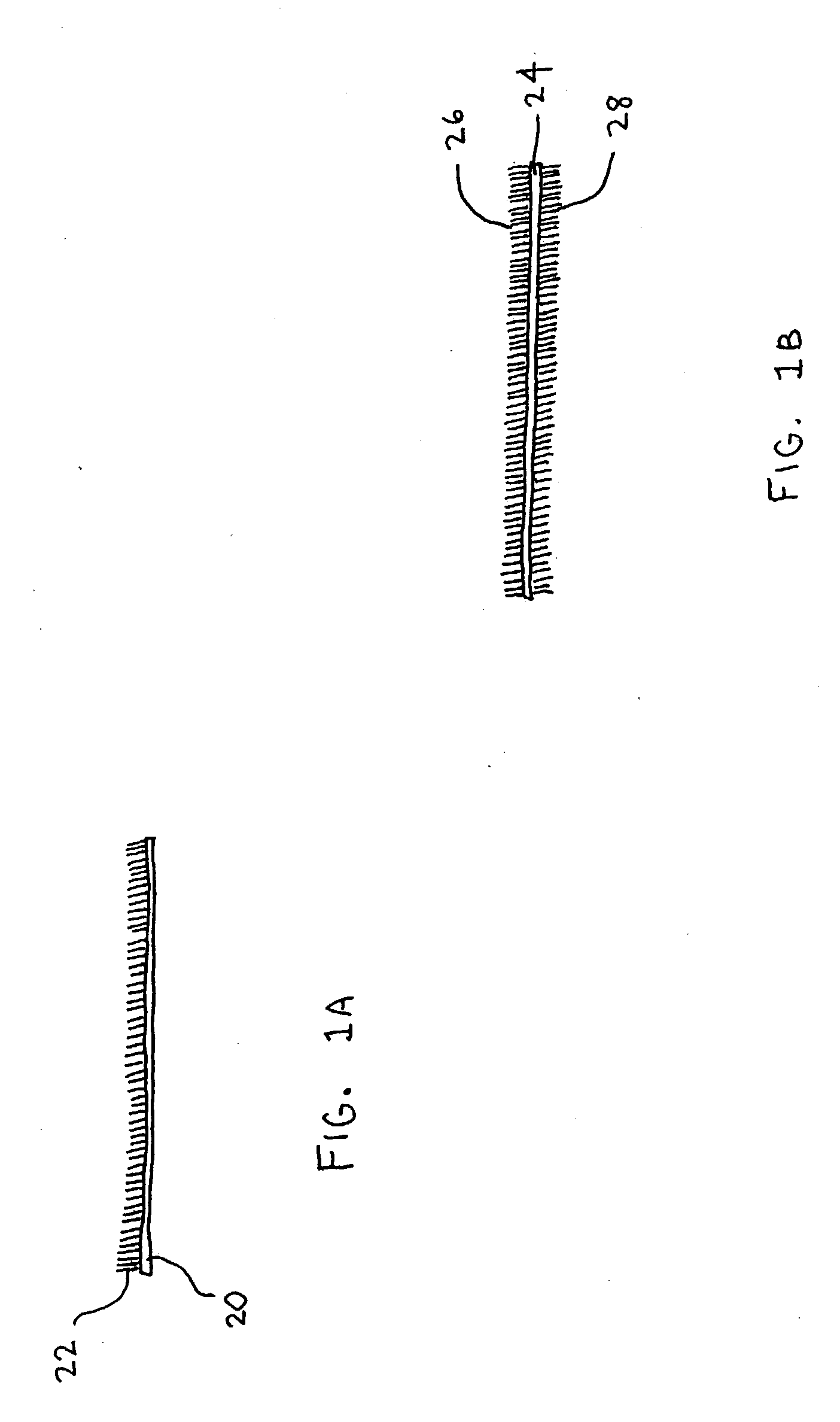
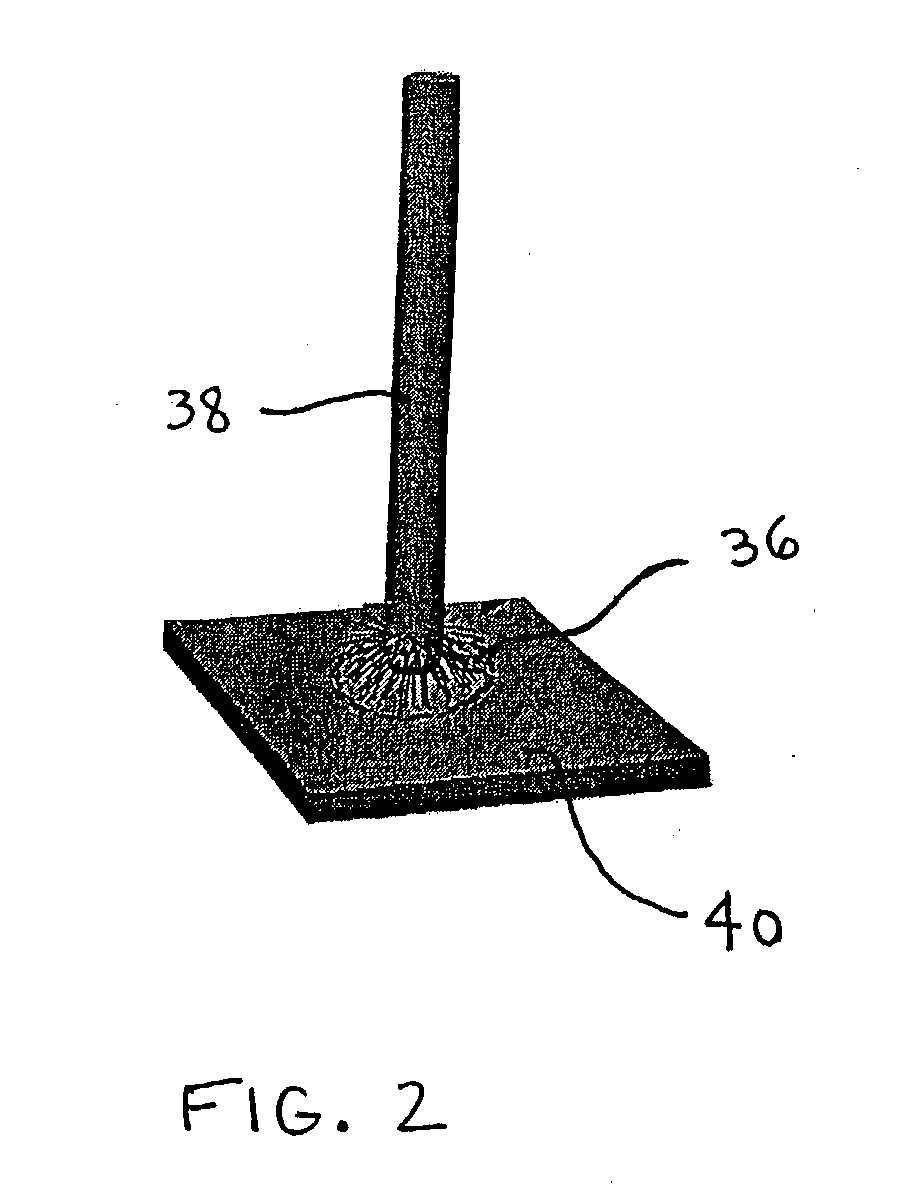
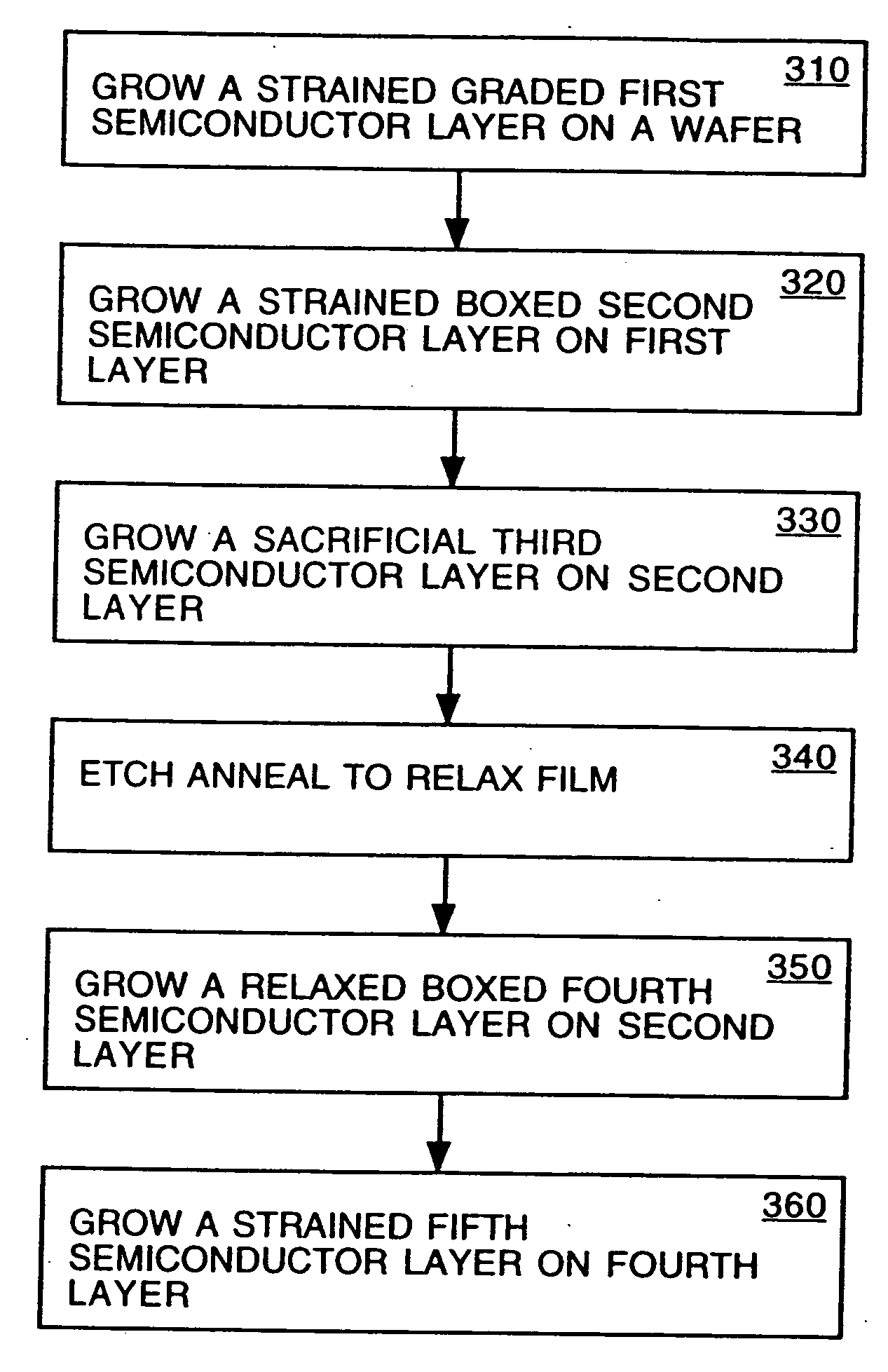
Non-contact etch annealing of strained layers
InactiveUS20070051299A1Reduce misalignmentReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDopantElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a method of forming a strained semiconductor layer. The method comprises growing a strained first semiconductor layer, having a graded dopant profile, on a wafer, having a first lattice constant. The dopant imparts a second lattice constant to the first semiconductor layer. The method further comprises growing a strained boxed second semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the first semiconductor layer and growing a sacrificial third semiconductor layer having the first lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer. The method further comprises etch annealing the third and second semiconductor layer, wherein the third semiconductor layer is removed and the second semiconductor layer is relaxed. The method may further comprises growing a fourth semiconductor layer having the second lattice constant on the second semiconductor layer, wherein the fourth semiconductor layer is relaxed, and growing a strained fifth semiconductor layer having the first semiconductor lattice constant on the fourth semiconductor layer. The method controls the surface roughness of the semiconductor layers. The method also has the unexpected benefit of reducing dislocations in the semiconductor layers.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
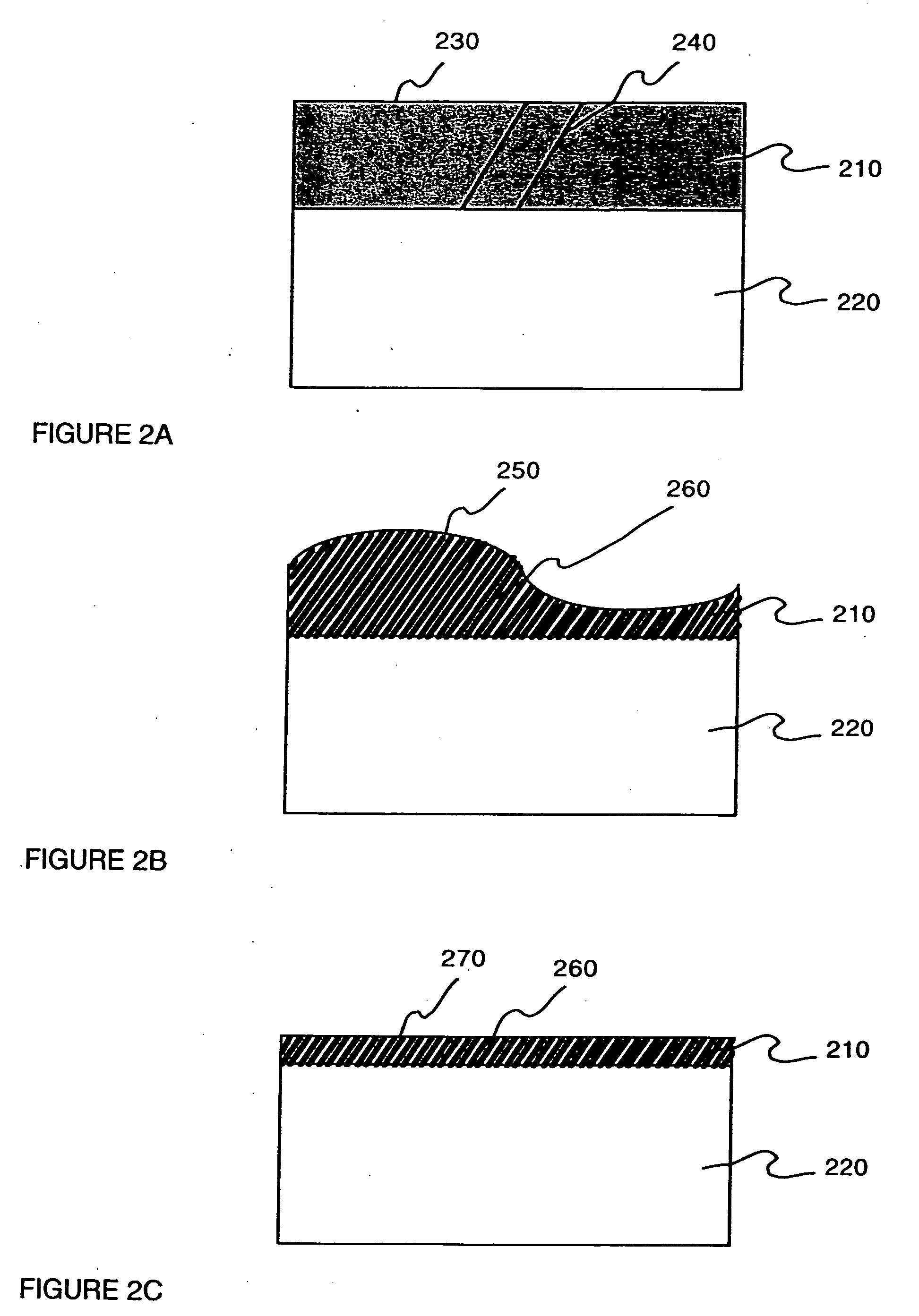
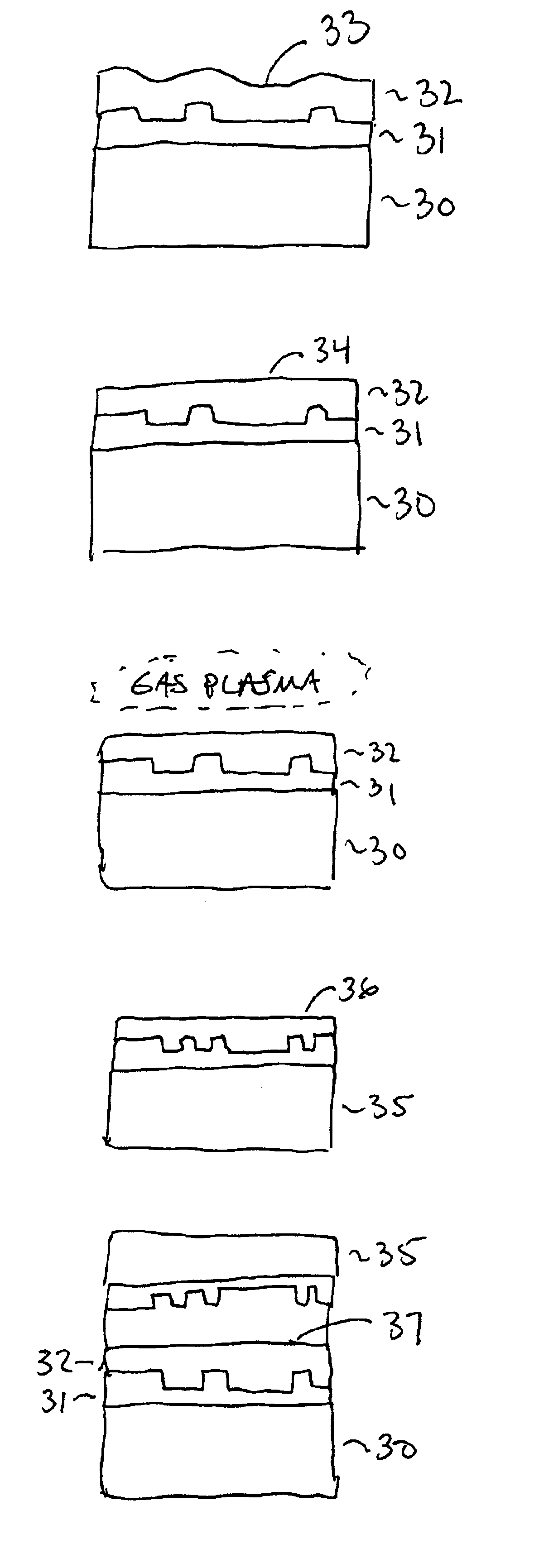
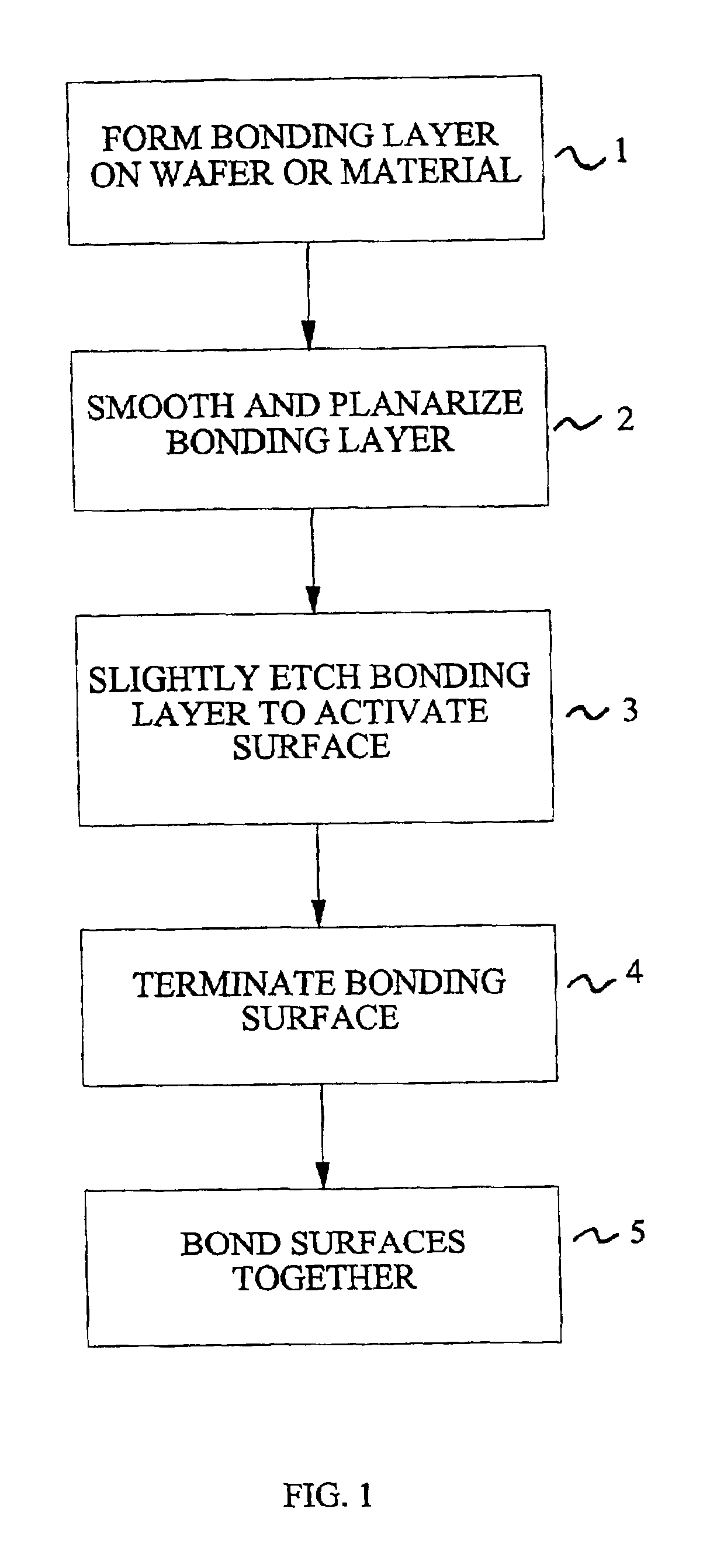
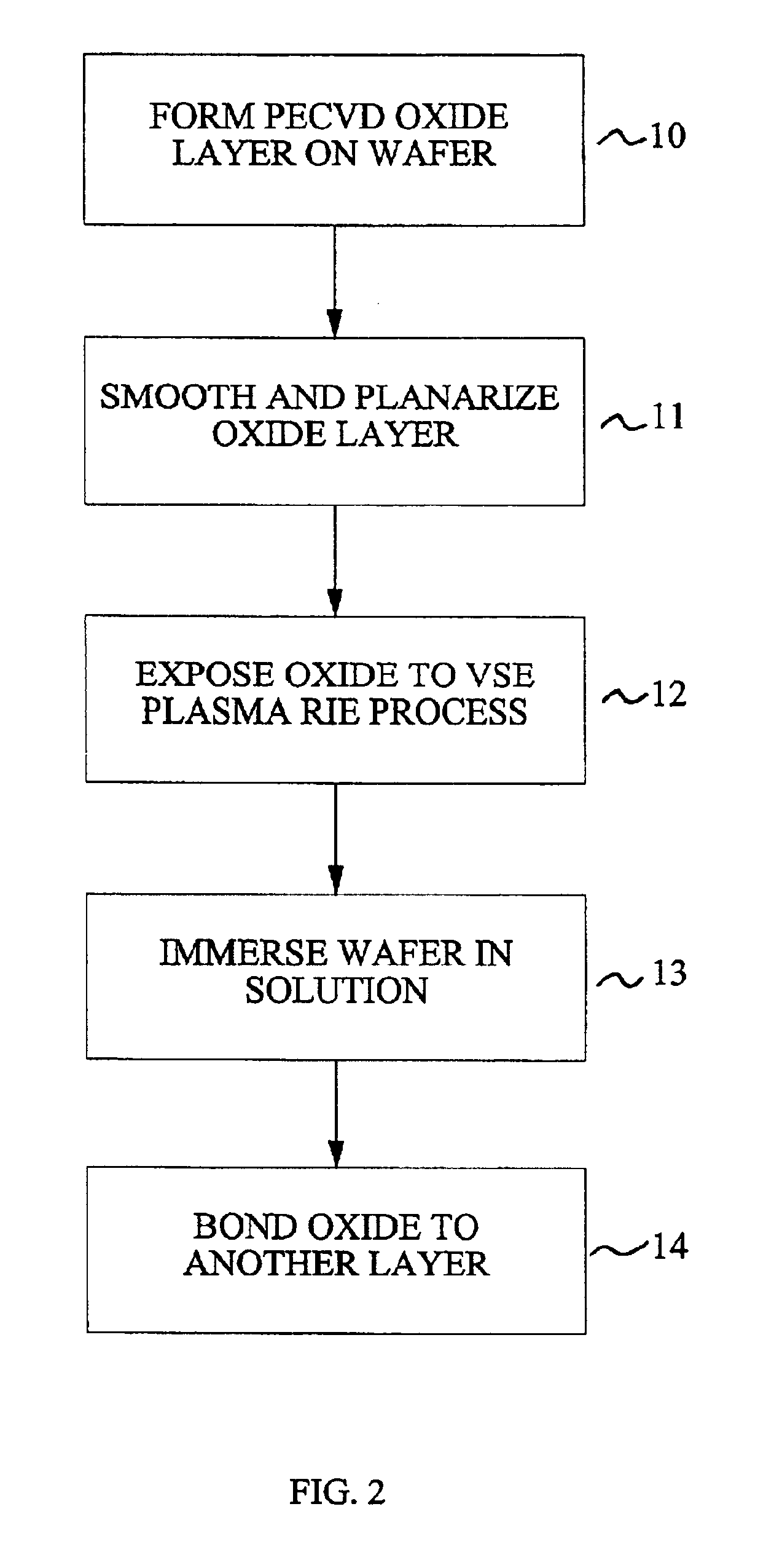
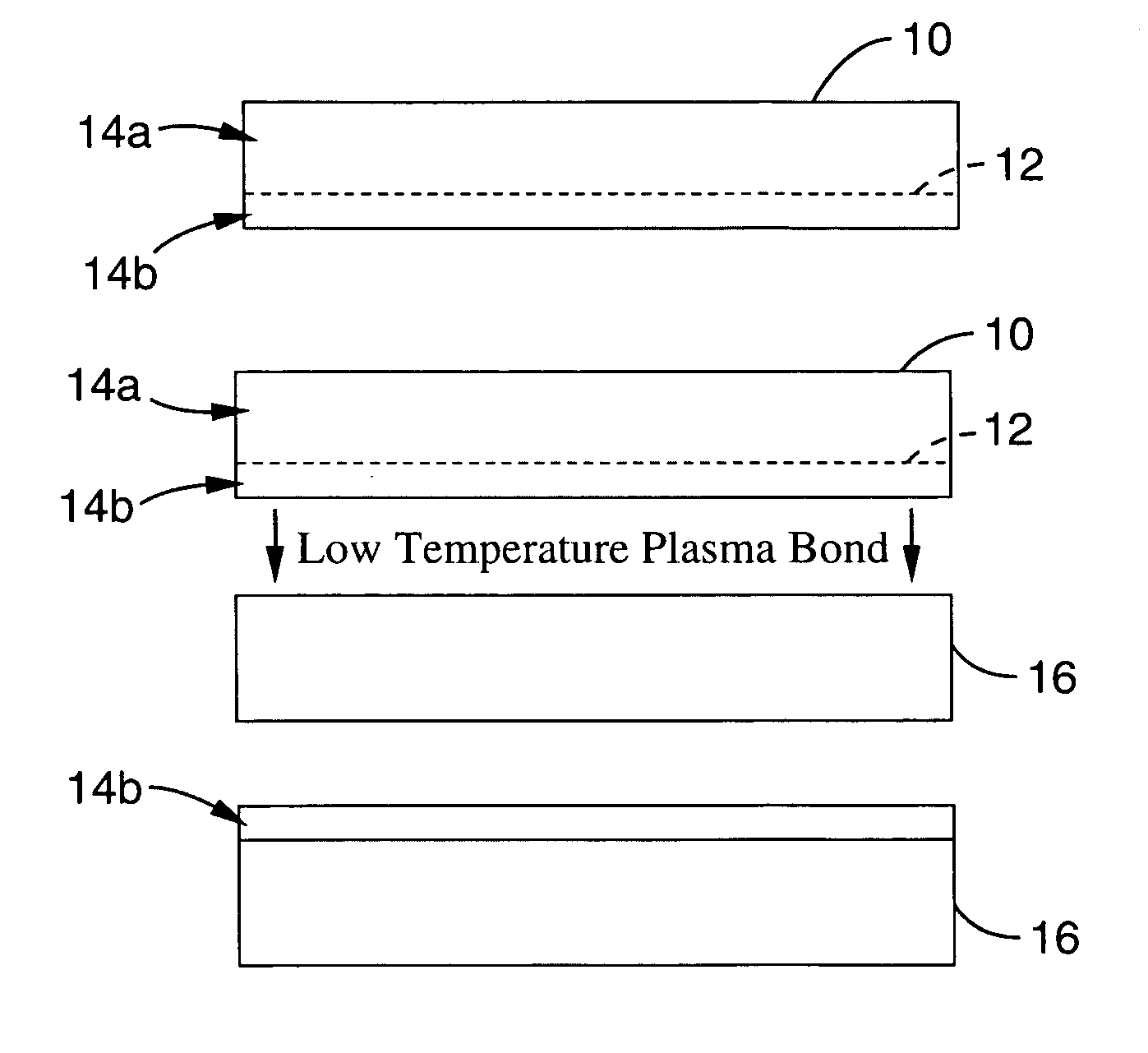
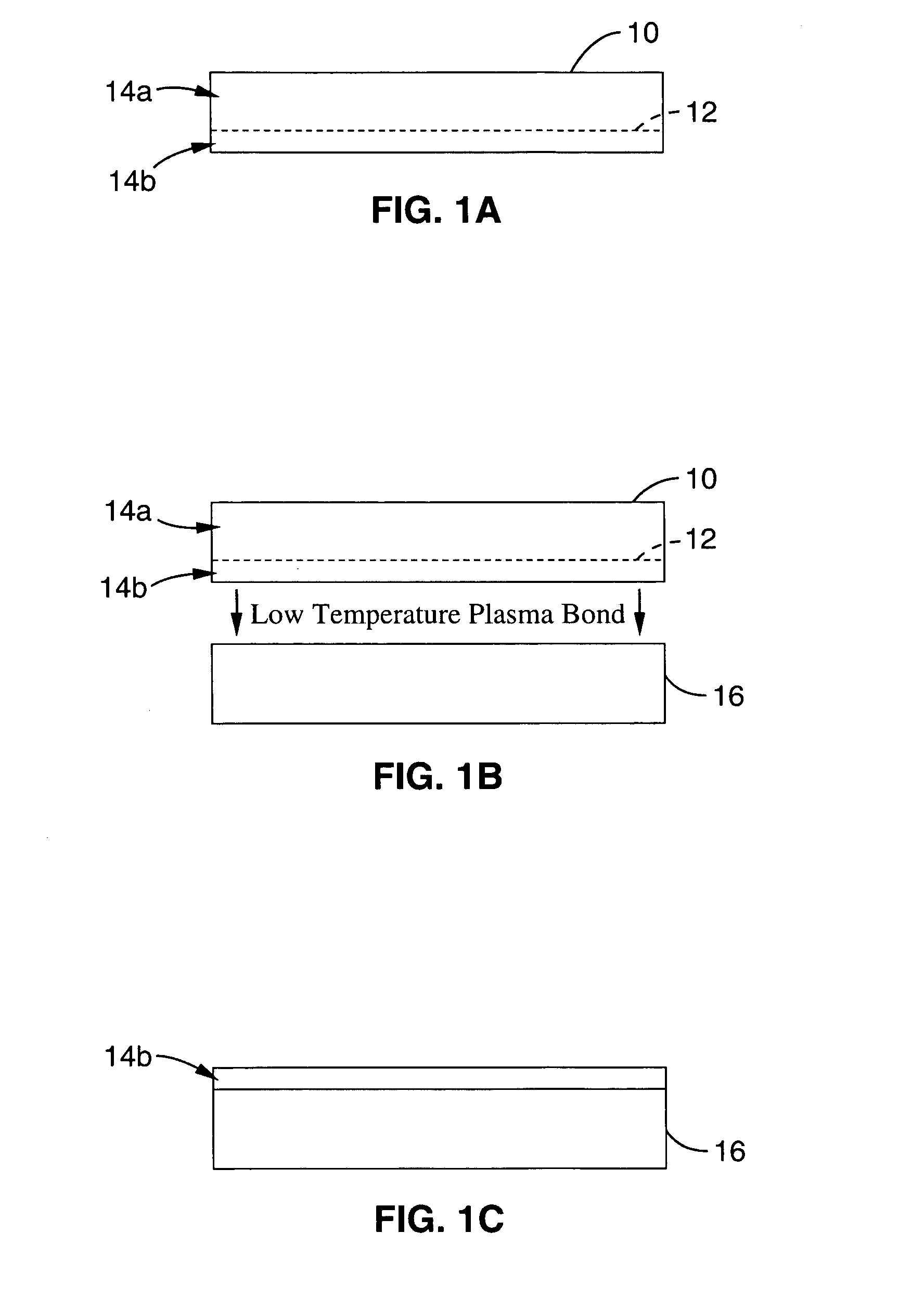
Method for low temperature bonding and bonded structure
InactiveUS6902987B1High bonding strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface cleaningBiological activation
A method for bonding at low or room temperature includes steps of surface cleaning and activation by cleaning or etching. One etching process the method may also include removing by-products of interface polymerization to prevent a reverse polymerization reaction to allow room temperature chemical bonding of materials such as silicon, silicon nitride and SiO2. The surfaces to be bonded are polished to a high degree of smoothness and planarity. VSE may use reactive ion etching or wet etching to slightly etch the surfaces being bonded. The surface roughness and planarity are not degraded and may be enhanced by the VSE process. The etched surfaces may be rinsed in solutions such as ammonium hydroxide or ammonium fluoride to promote the formation of desired bonding species on the surfaces.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Laminated semiconductor substrate process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060118935A1Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
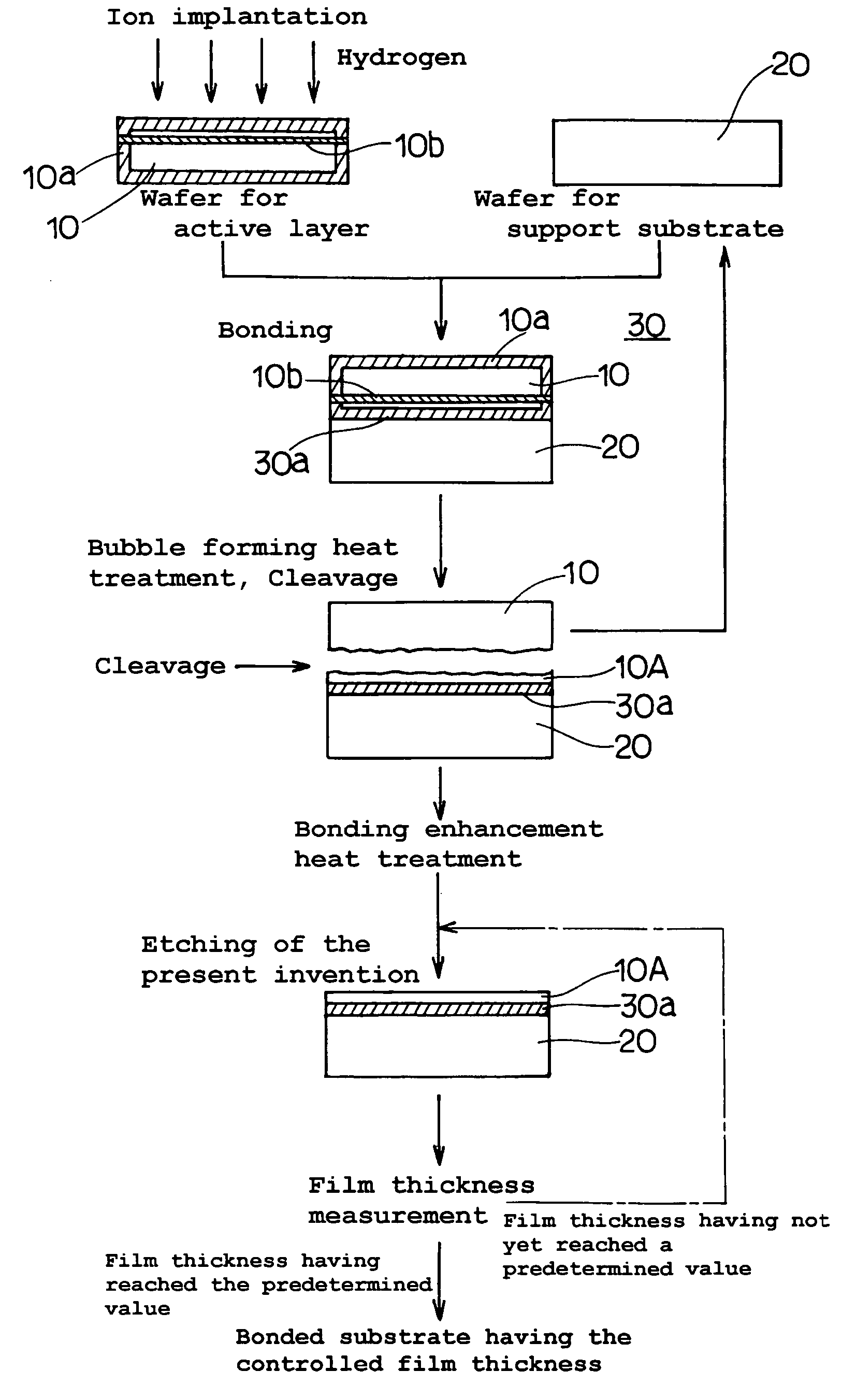
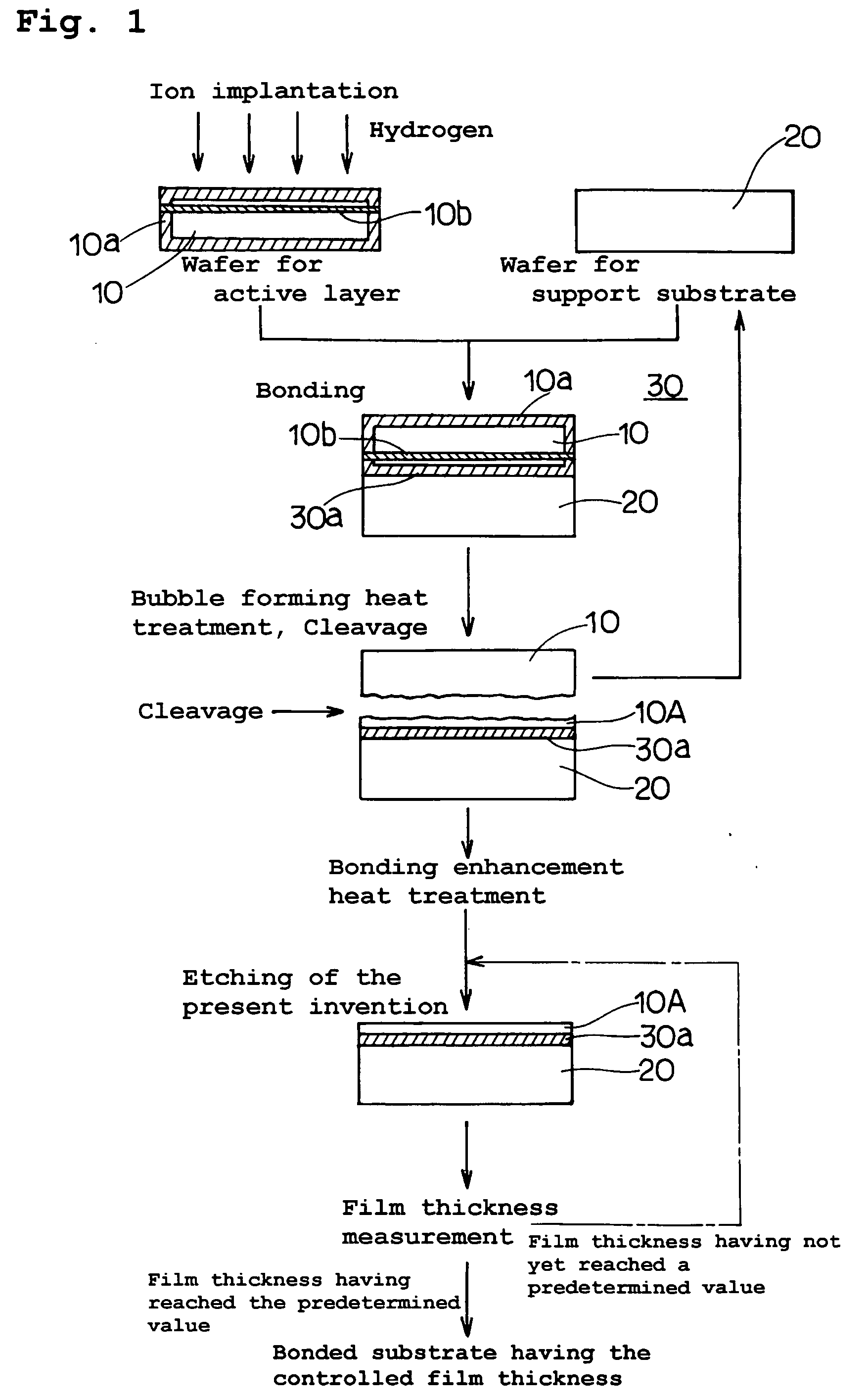
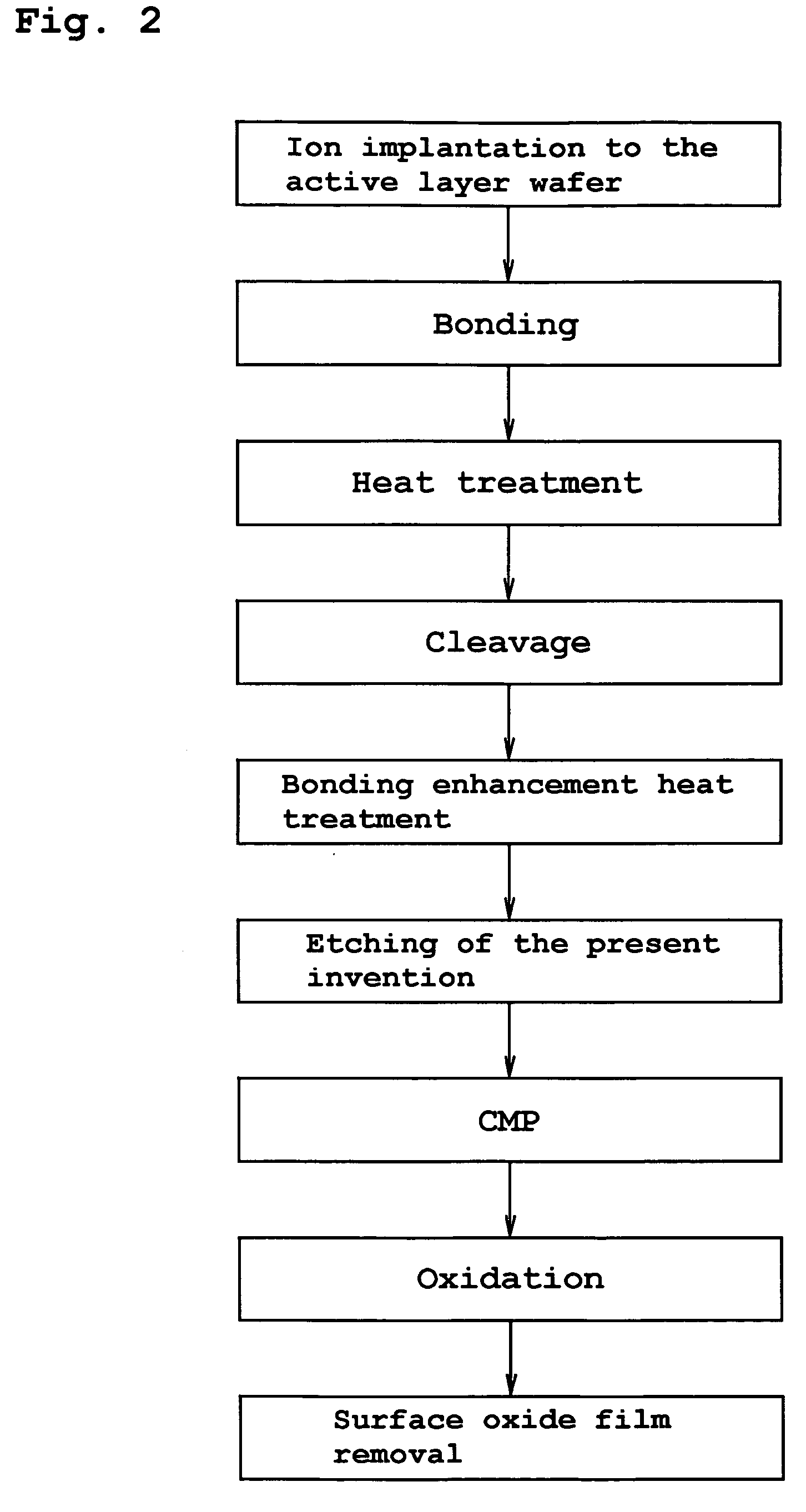
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
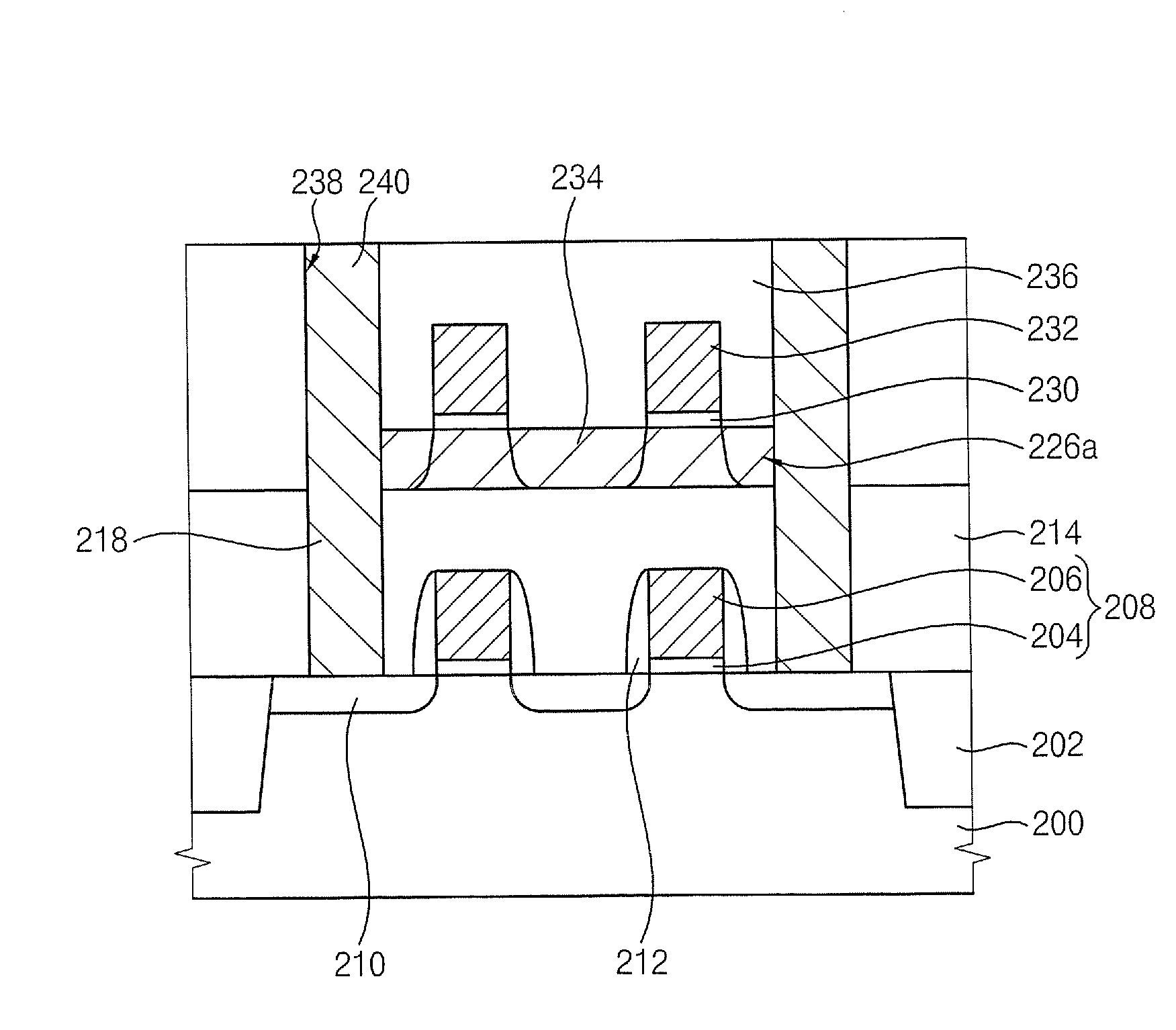
Methods of fabricating semiconductor devices including channel layers having improved defect density and surface roughness characteristics
ActiveUS20080160726A1Improved surface roughness characteristicUniform thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessSingle crystal
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device including a channel layer includes forming a single crystalline semiconductor layer on a semiconductor substrate. The single crystalline semiconductor layer includes a protrusion extending from a surface thereof. A first polishing process is performed on the single crystalline semiconductor layer to remove a portion of the protrusion such that the single crystalline semiconductor layer includes a remaining portion of the protrusion. A second polishing process different from the first polishing process is performed to remove the remaining portion of the protrusion and define a substantially planar single crystalline semiconductor layer having a substantially uniform thickness. A sacrificial layer may be formed on the single crystalline semiconductor layer and used as a polish stop for the first polishing process to define a sacrificial layer pattern, which may be removed prior to the second polishing process. Related methods of fabricating stacked semiconductor memory devices are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ceramic material resistant to halogen plasma and member utilizing the same
InactiveUS6916559B2Improve the immunityRecord information storageLight beam reproducingPorosityHalogen
A member used within a plasma processing apparatus and exposed to a plasma of a halogen gas such as BCl3 or Cl2 is formed from a sintered body of metals of Group IIIa of Periodic Table such as Y, La, Ce, Nd and Dy, and Al and / or Si, for example, 3Y2O3.5Al2O3, 2Y2O3.Al2O3, Y2O3.Al2O3 or disilicate or monosilicate, and in particular, in this sintered body, the content of impurity metals of Group IIa of Periodic Table contained in the sintered body is controlled to be 0.15 wt % or more in total. Specifically, for this member, an yttrium-aluminum-garnet sintered body having a porosity of 3% or less and also having a surface roughness of 1 μm or less in center line average roughness Ra is utilized.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Focus ring, plasma etching apparatus and plasma etching method
ActiveUS20090255902A1Improve etching effectAccurate storageElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsSusceptorSurface roughness
In a plasma etching apparatus for performing a plasma etching on a surface of a substrate mounted on a susceptor in a processing vessel, a focus ring is installed to surround the substrate and has a first region at an inner side on a surface thereof, in which an average surface roughness is small such that a reaction product produced during an etching processing is not captured to be deposited, and a second region at an outer side from the first region, in which an average surface roughness is large such that a reaction product produced during the etching process is captured to be deposited. A boundary between the first and the second region is a part where an etching amount is relatively significantly changed compared to other parts while the focus ring is equipped in the plasma etching apparatus and the plasma etching is performed on the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Smooth thin film layers produced by low temperature hydrogen ion cut
A method for producing wafer splitting from ion implantation into silicon after low temperature direct bonding with surface roughness that is ˜1 nm (RMS). This result is an order of magnitude smoother than the previous work (˜10 nm RMS). The key improvement in this work is the use of a low temperature bond resulting in a strong bond before the material is cut. The smooth as-split surfaces produced using a low temperature bond are very important for creation of very thin (<50 nm) silicon-on-insulator (SOI), three-dimensional bonded structures and nanostructures that are split after processing.
Owner:EPIR TECH INC
Smooth SiConi etch for silicon-containing films
ActiveUS8501629B2Great and less flow ratioReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSurface roughness
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatus for rendering an optically encoded medium unreadable
InactiveUS6338933B1Photography auxillary processesPhotosensitive materialsOptical radiationAtmospheric air
Methods and apparatus are provided for making an optically readable media unreadable. The method includes steps of (a) providing the media with an optically activated mechanism that degrades the reflectivity of a surface wherein information is encoded; (b) exposing the media to optical radiation for reading out the information; and, during the step of exposing, (c) initiating the operation of the optically activated mechanism. In this embodiment the step of initiating includes steps of (d) generating singlet oxygen in a layer disposed on the media; and (e) reacting the singlet oxygen with a metal-containing layer for oxidizing the surface of the metal-containing layer, thereby degrading the reflectivity of the surface. In a further aspect the optically activated mechanism causes a defocusing of a readout beam, thereby degrading reflection of the readout beam from a surface wherein information is encoded. In another embodiment the method deforms a surface of the layer resulting in readout beam aberration or in an inability to correctly stay on track. In another embodiment a portion of the surface is removed to the atmosphere, such as by evaporation of sublimation. In this embodiment a layer of the media is comprised of a volatile component and at least one other component. Removing at least some of volatile component by evaporation or sublimation causes an increase in at least one of photoabsorption or scattering or surface roughness with the remaining component, thereby rendering at least a portion of encoded information of the media unreadable, or affecting the tracking operation.
Owner:FLEXPLAY TECH INC
Methods for transferring a useful layer of silicon carbide to a receiving substrate
InactiveUS20050266659A1Easy to recycleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
Owner:SOITEC SA
Stents and methods for preparing stents from wires having hydrogel coating layers thereon
InactiveUS20050251250A1Improved propertyReduce surface roughnessStentsSurgeryActive agentInsertion stent
Radially expandable stents having hydrogel coating layers thereon, and methods of preparing such stents are disclosed. The methods include coating a wire with a solution that includes a solvent and a water soluble polymer in the solvent, evaporating the solvent to provide a polymeric coating on the wire, and crosslinking the polymeric coating to provide a hydrogel coating layer on the wire. The coated wire can be fabricated into stents, which preferably have substantially uniform coatings with low surface roughness. Preferably the coatings have hydrophilic properties and provide a biocompatible surface. The coatings may also provide for the delivery of biologically active agents into the body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
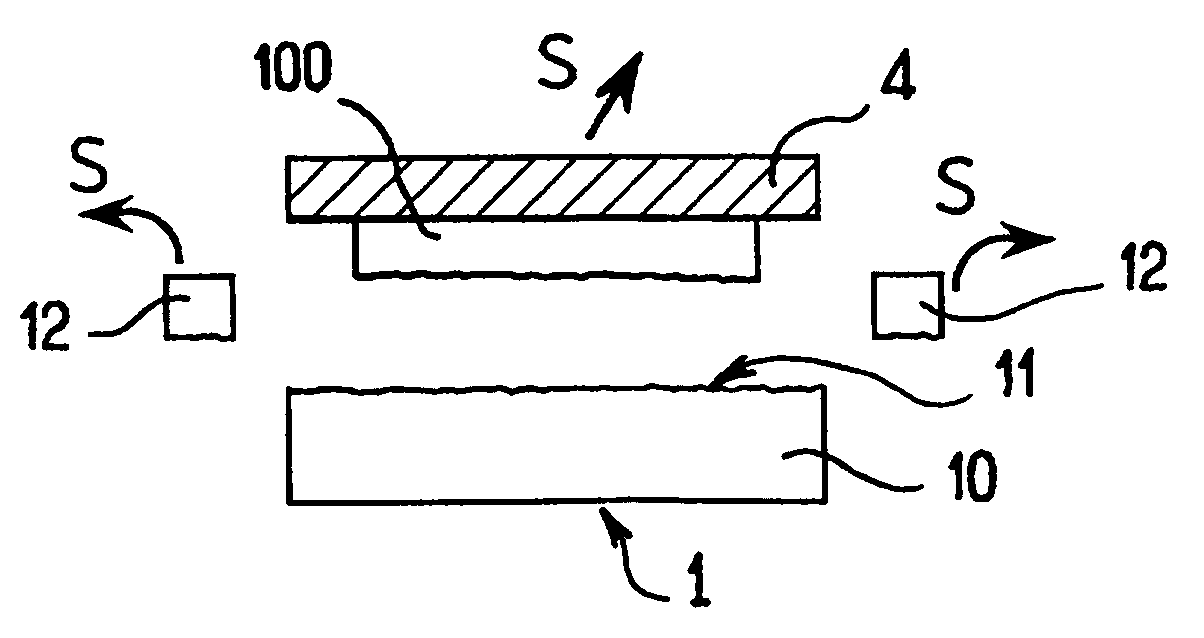
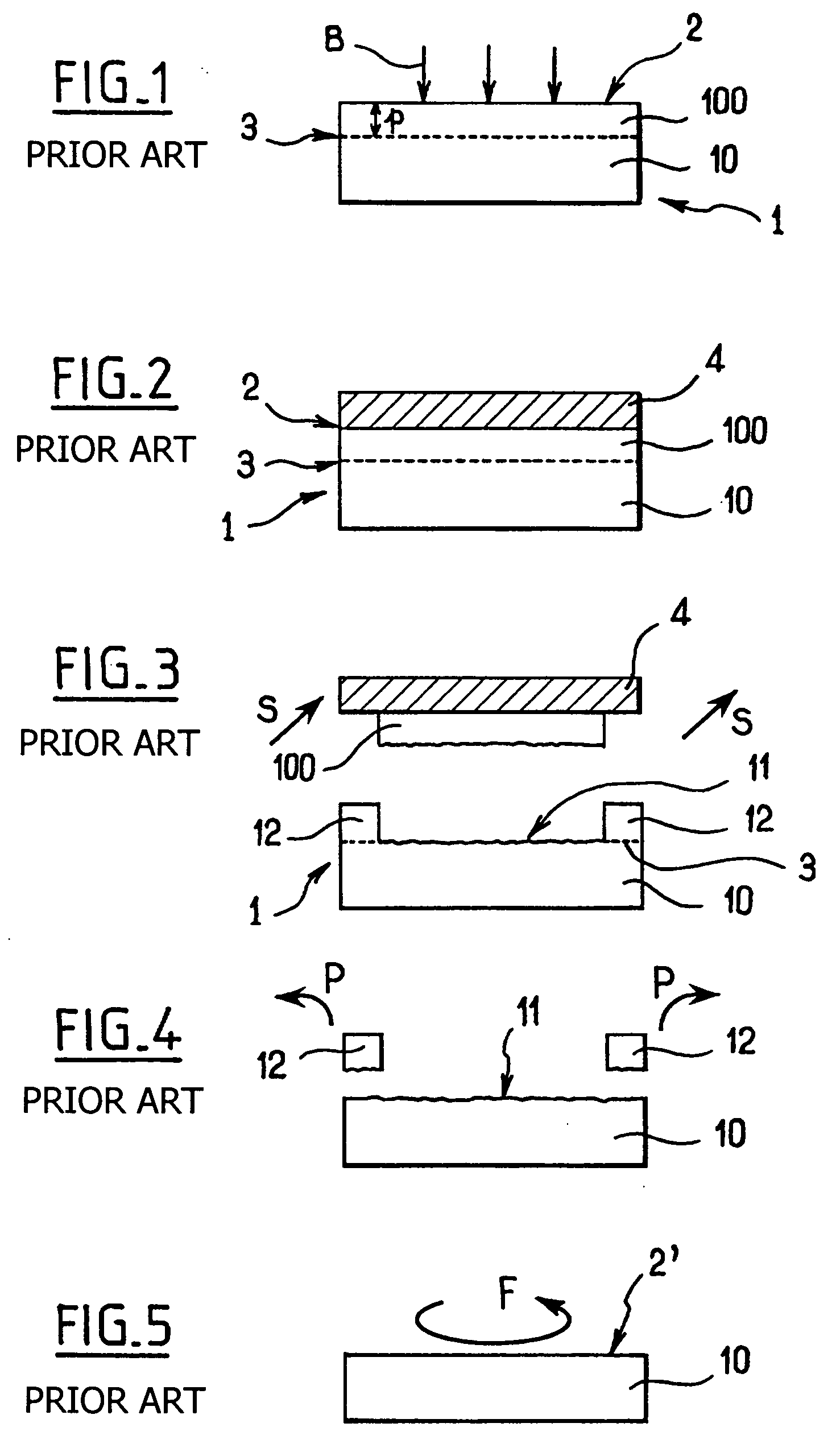
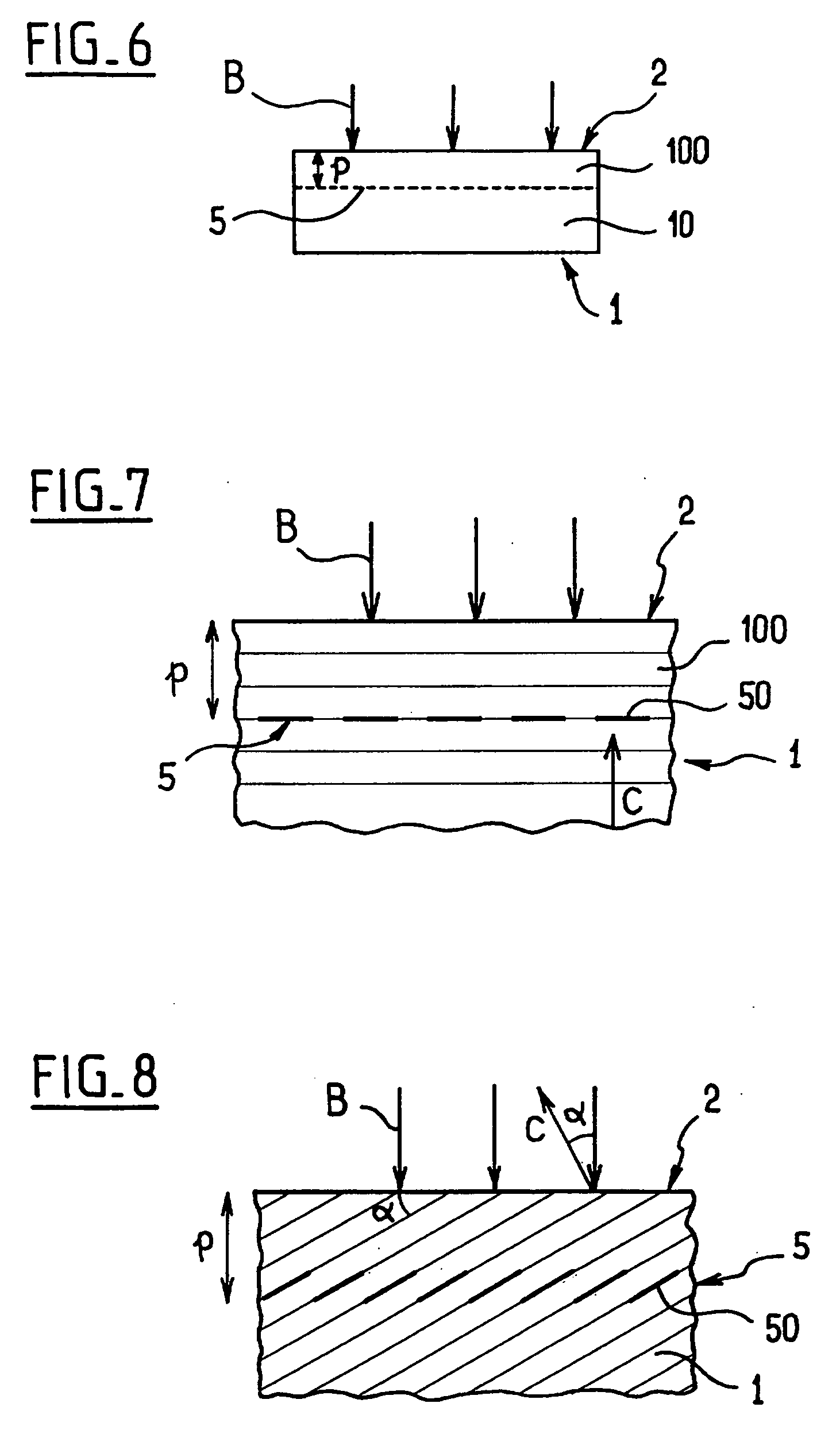
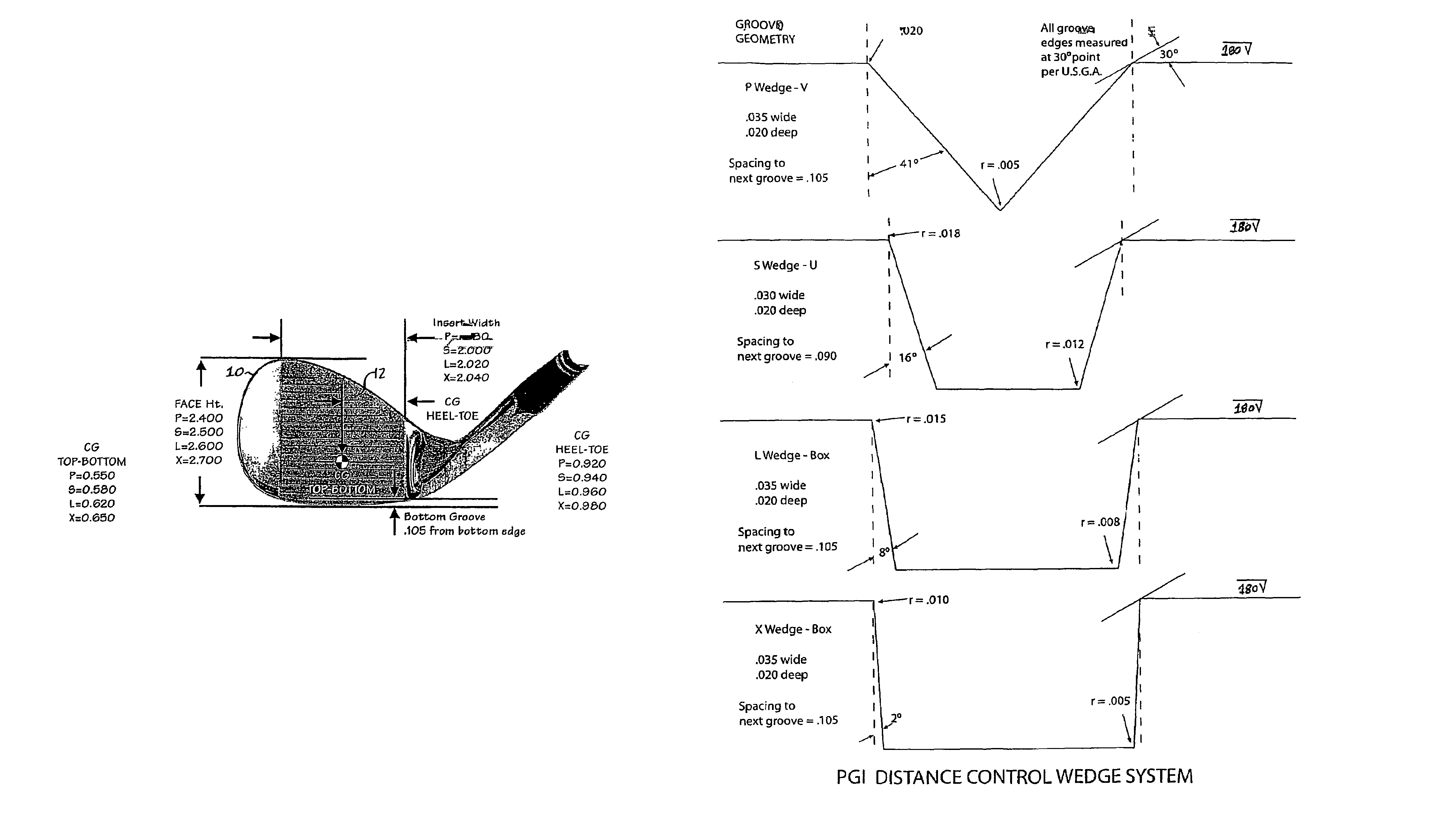
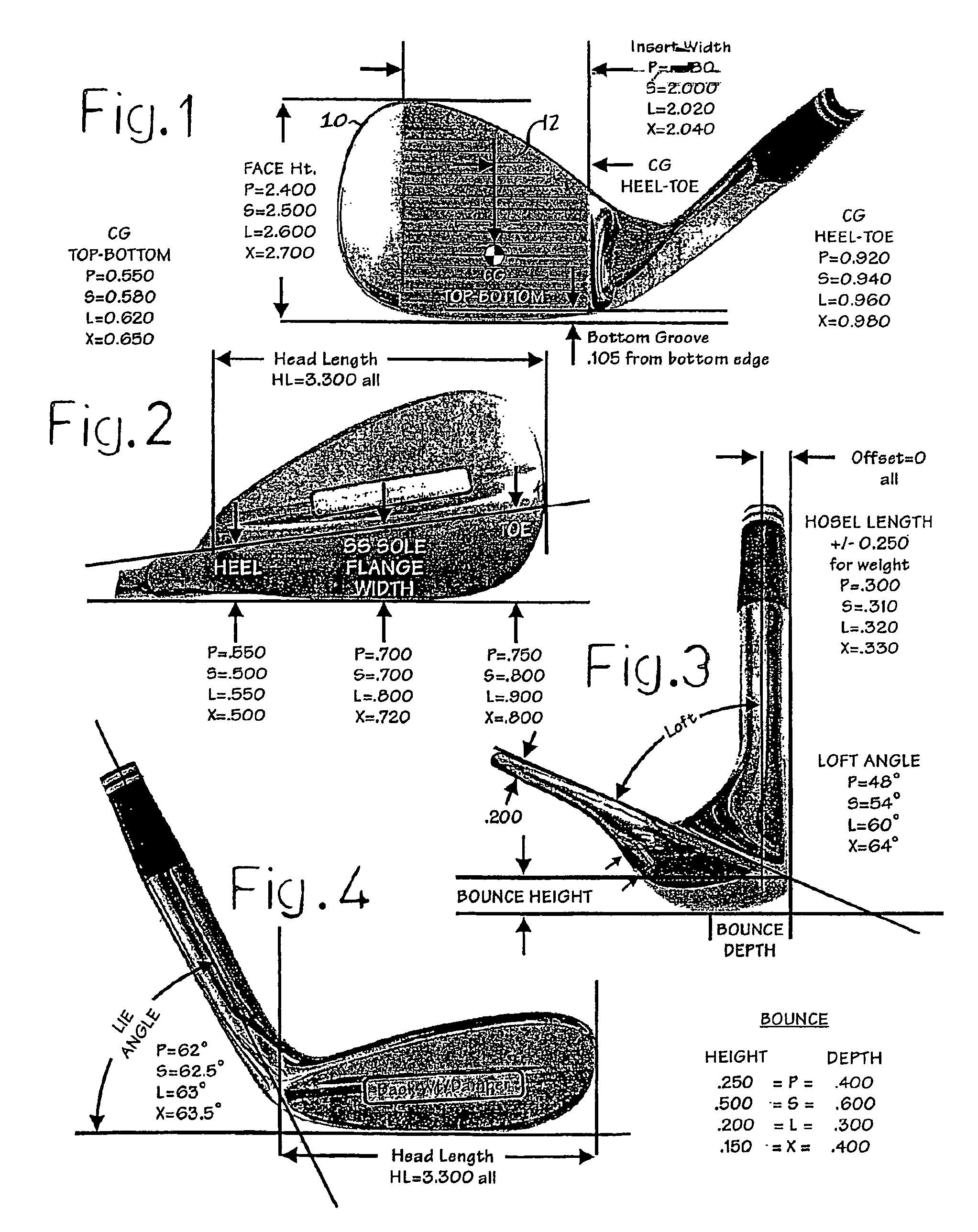
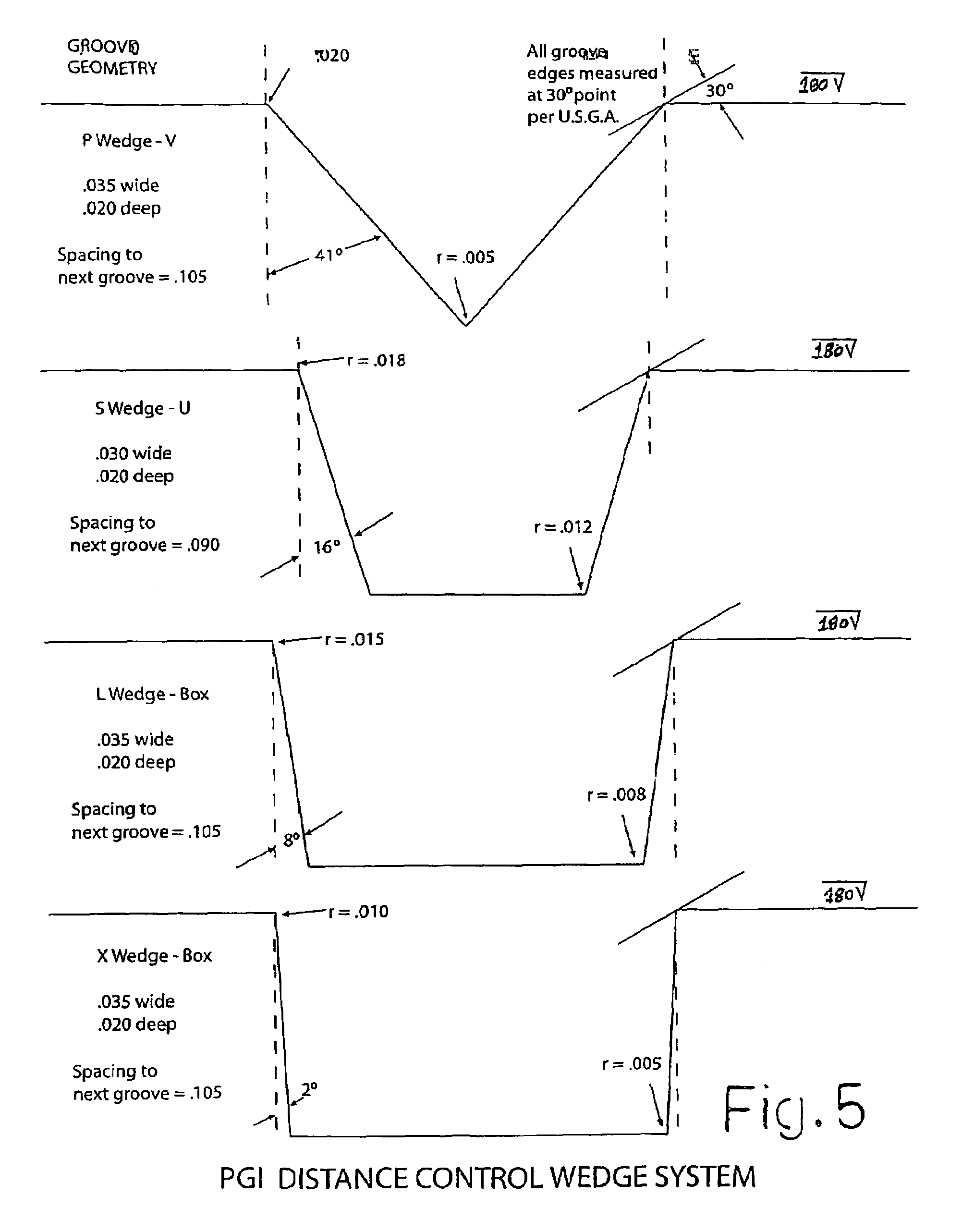
Golf club
A set of golf club wedges each having a club face (10) is disclosed wherein the lofts of the individual clubs progressively increases. The hitting surface of each club head may take the form of an insert (12) that includes a series of grooves, the design of which is varied from club to club to provide increasing friction with loft. As a result, a golfer can impart the same amount of spin to a golf ball with each of the wedges despite a substantial difference in loft and club head swing speed between the respective clubs. In addition, the surface roughness of the hitting surface may also be increased as loft increases to further control the spin imparted to the ball.
Owner:PELZ DAVID
LED with current confinement structure and surface roughening
ActiveUS7335920B2Add featureAvoid emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCurrent limitingSurface roughness
Owner:CREELED INC
Electrode for use in lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS7235330B1High charge and discharge capacityImprove featuresElectrode manufacturing processesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAmorphous siliconSurface roughness
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Cover glass for mobile terminals, manufacturing method of the same and mobile terminal device
To provide cover glass for mobile terminals exhibiting high strength in a thin plate thickness state to enable reductions in thickness of apparatuses when inserted in the apparatuses, cover glass (1) for a mobile terminal of the invention is cover glass (1) that is obtained by forming a resist pattern on main surfaces of a plate-shaped glass substrate, then etching the glass substrate with an etchant using the resist pattern as a mask, and thereby cutting the glass substrate into a desired shape and that protects a display screen of the mobile terminal, where an edge face of the cover glass (1) is formed of a molten glass surface, and as surface roughness of the edge face, arithmetic mean roughness Ra is 10 nm or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Methods for producing metallic implants having roughened surfaces
The invention provides a method of providing a metallic orthopaedic implant with a micron or nanometer-scale surface roughness to facilitate acceptance of tissue and bone growth or apposition after implantation while maintaining the structural integrity of the orthopaedic implant. The invention also provides a metallic orthopaedic implant comprising a metallic body and metallic elements adhered to a portion of the surface of the metallic body to define a three-dimensional porous surface geometry, wherein at least some of the metallic elements have a micron or nanometer-scale surface roughness.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Long life thin film battery and method therefor
InactiveUS6994933B1Extend battery lifeSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsLarge-sized cells cases/jacketsOxygen fluxSurface roughness
A thin film battery including an anode layer, a cathode layer and a solid electrolyte layer. The battery also includes, a planarization layer applied to the thin film battery. The planarization layer has a surface roughness of no more than about 1.0 nanometers root mean square and a flatness no larger than about 0.005 cm / inch. A barrier layer is applied to the planarization layer. The barrier layer is provided by one or more layers of material selected from the group consisting of polymeric materials, metals and ceramic materials. The planarization layer and barrier layer are sufficient to reduce oxygen flux through the barrier layer to the anode layer to no more than about 1.6 μmol / m2-day, and H2O flux through the barrier layer to the anode layer to less than about 3.3 μmol / m2-day thereby improving the life of the thin film battery.
Owner:OAK RIDGE MICRO ENERGY
Antireflective coating and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6359735B1Increase contrastBig imageGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsMicro structureDistributed structure
What is described here is an antireflective coating comprising a carrier layer consisting of an optically transparent material, which, at least on one surface side, presents antireflective properties with respect the wavelengths of the radiation incident on the surface. Moreover, methods of producing the coating are described.The invention excels itself by the provision that the antireflective surface side presents a surface roughness with stochastically distributed structures-the so-called macro structures-and that the macro structures are additionally modulated with surface structures presenting a periodic sequence-the so-called micro structures-which present period or cycle lengths smaller than the wave lengths of the radiation incident on the antireflective surface.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com