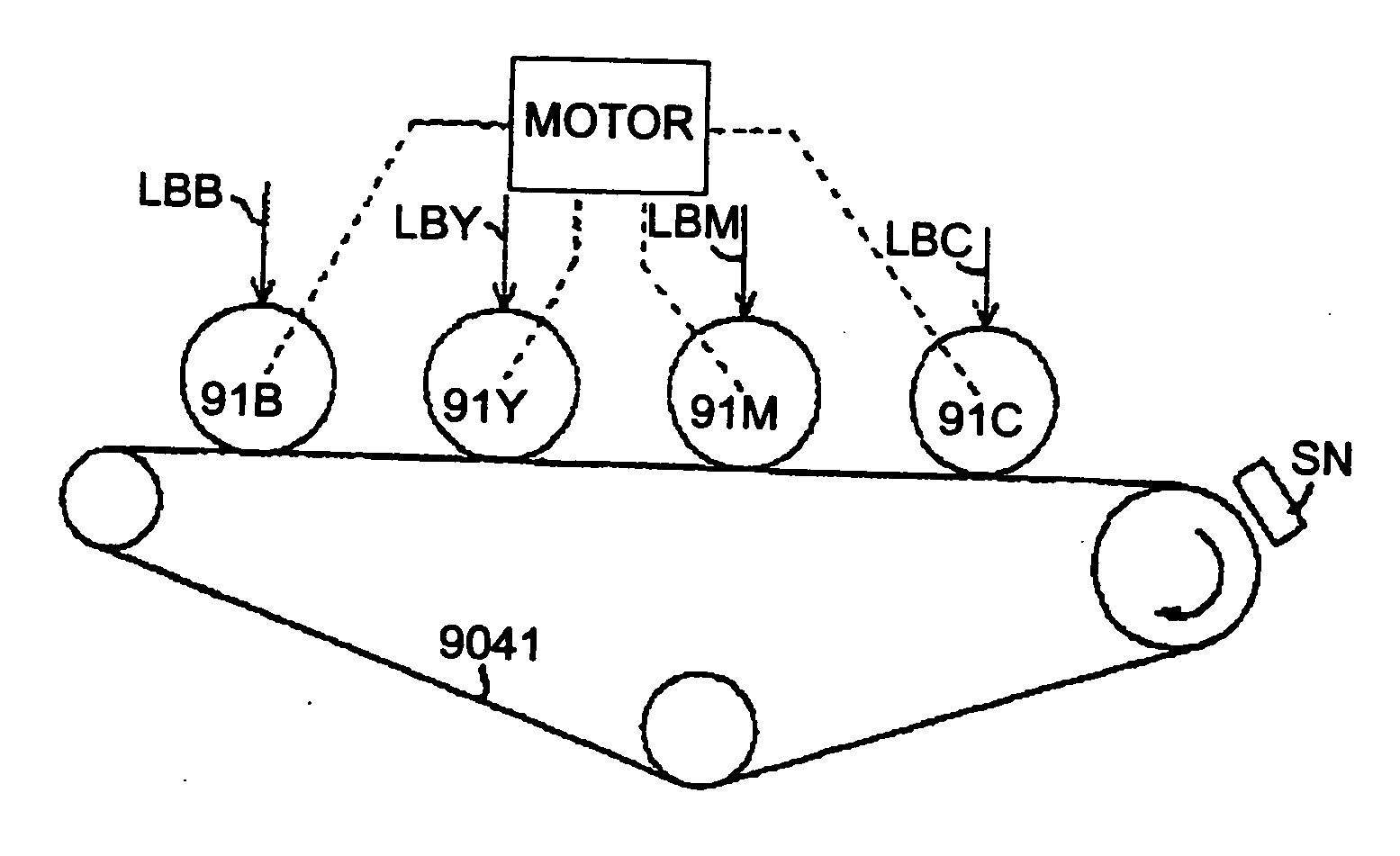
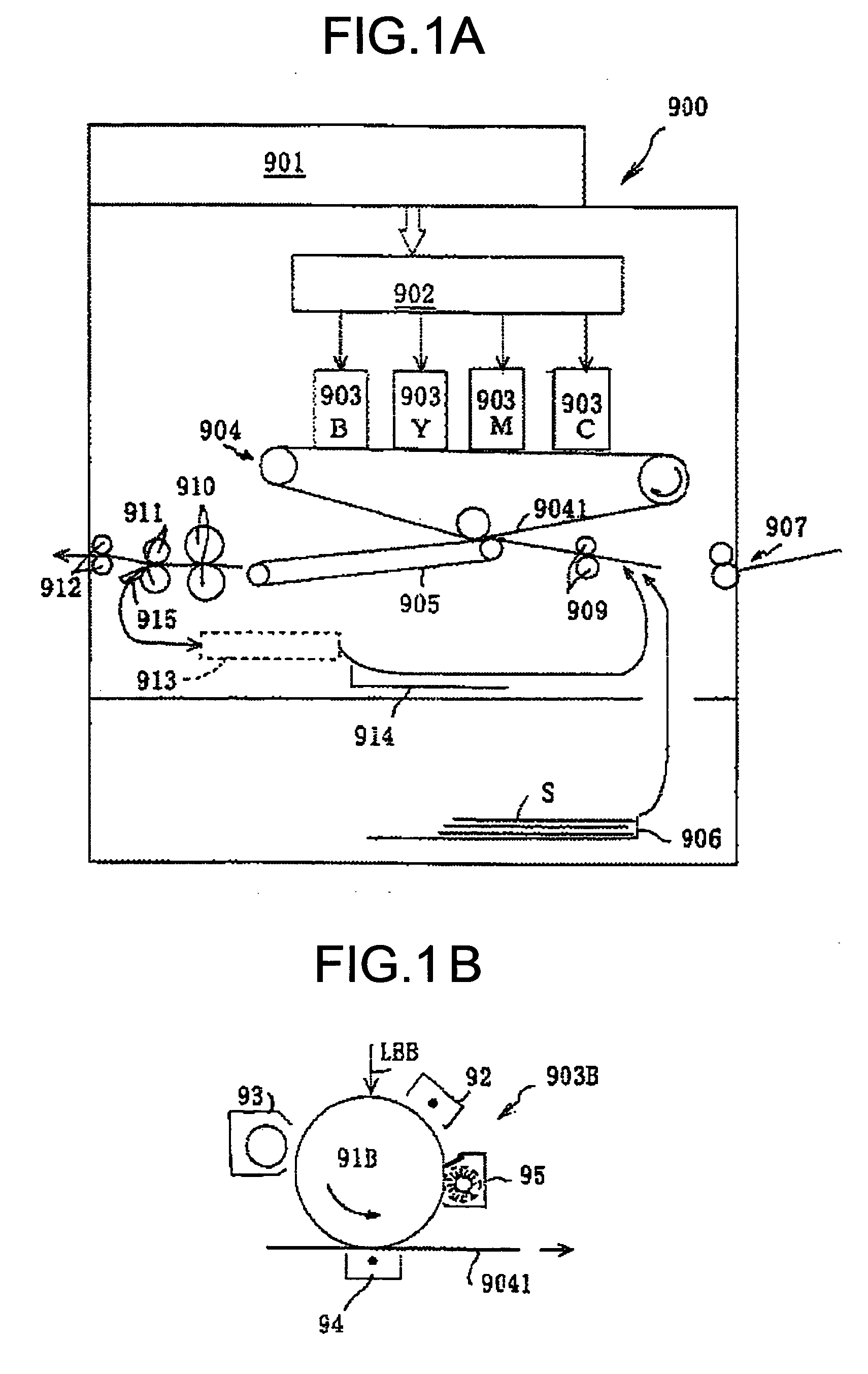
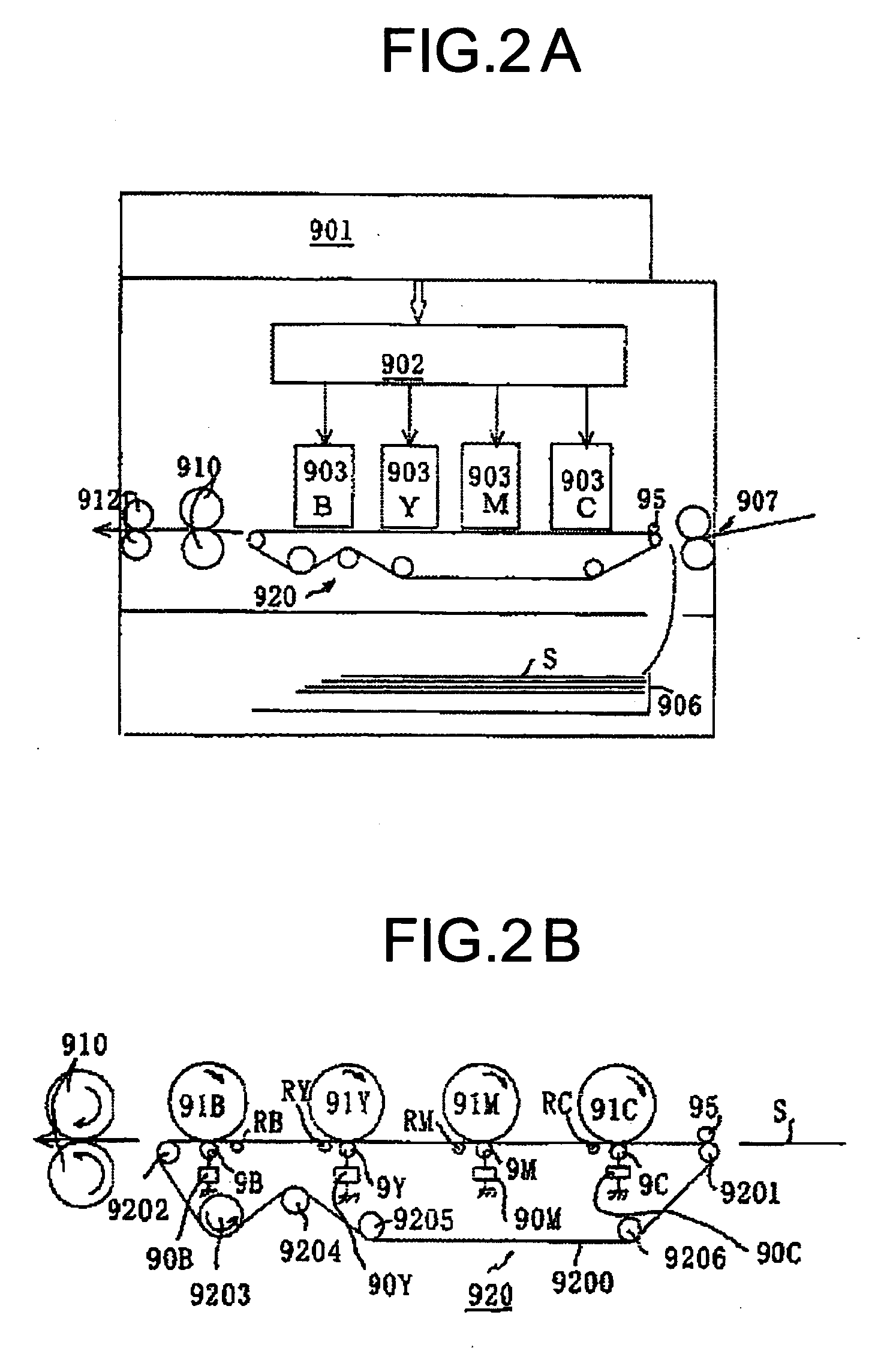
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
904results about How to "Reduce misalignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
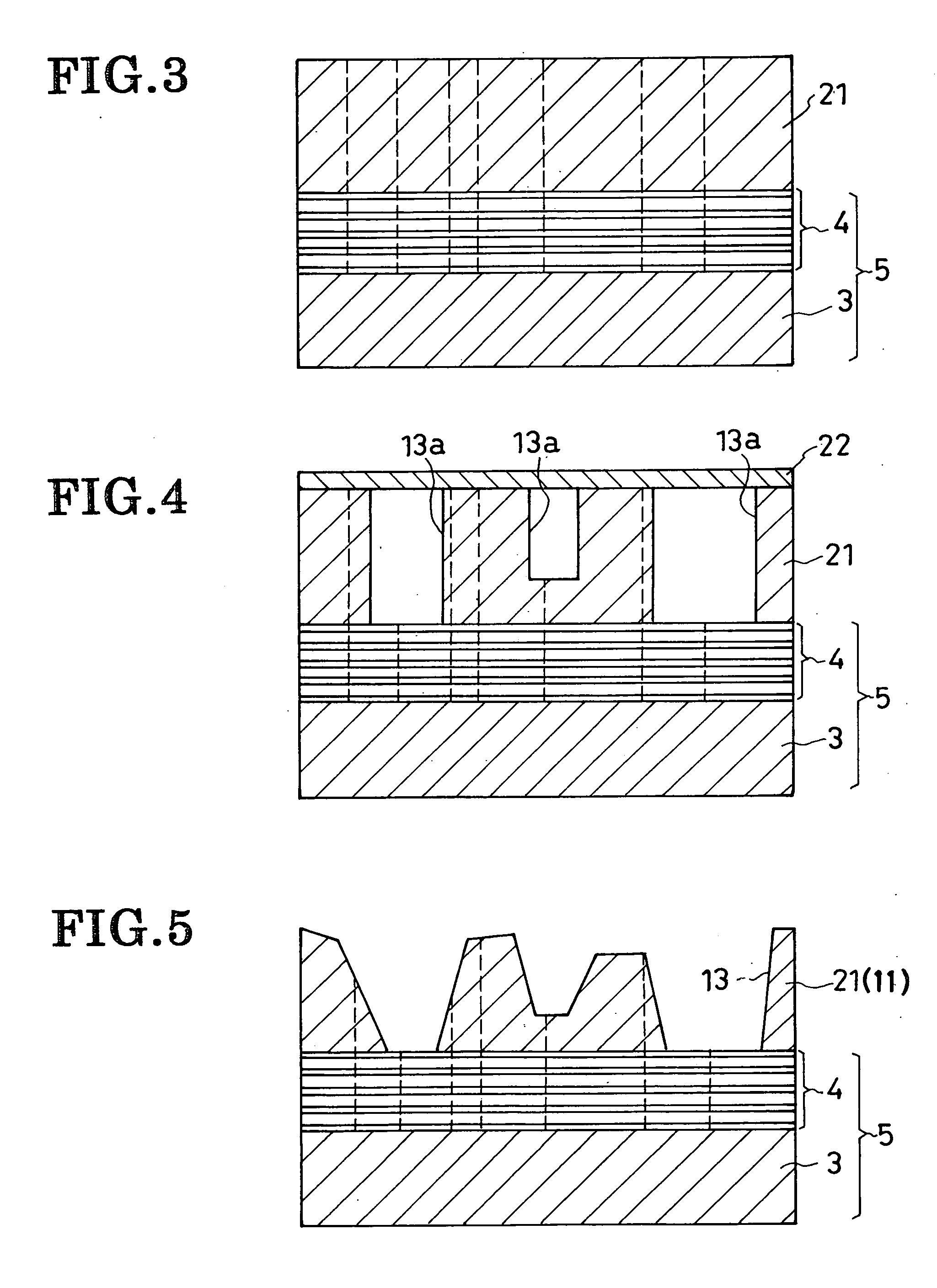
Surgical fastener buttress material
InactiveUS20060173470A1Easy to optimizeReduce misalignmentSurgical staplesWound clampsButtressStaple line
A staple line buttress material having an adhesive surface, packaged and provided in sterile, ready-to-use form. The material can be used to retrofit surgical staplers to provide an improved staple line, and with improved ease of use.
Owner:SYNOVIS LIFE TECH
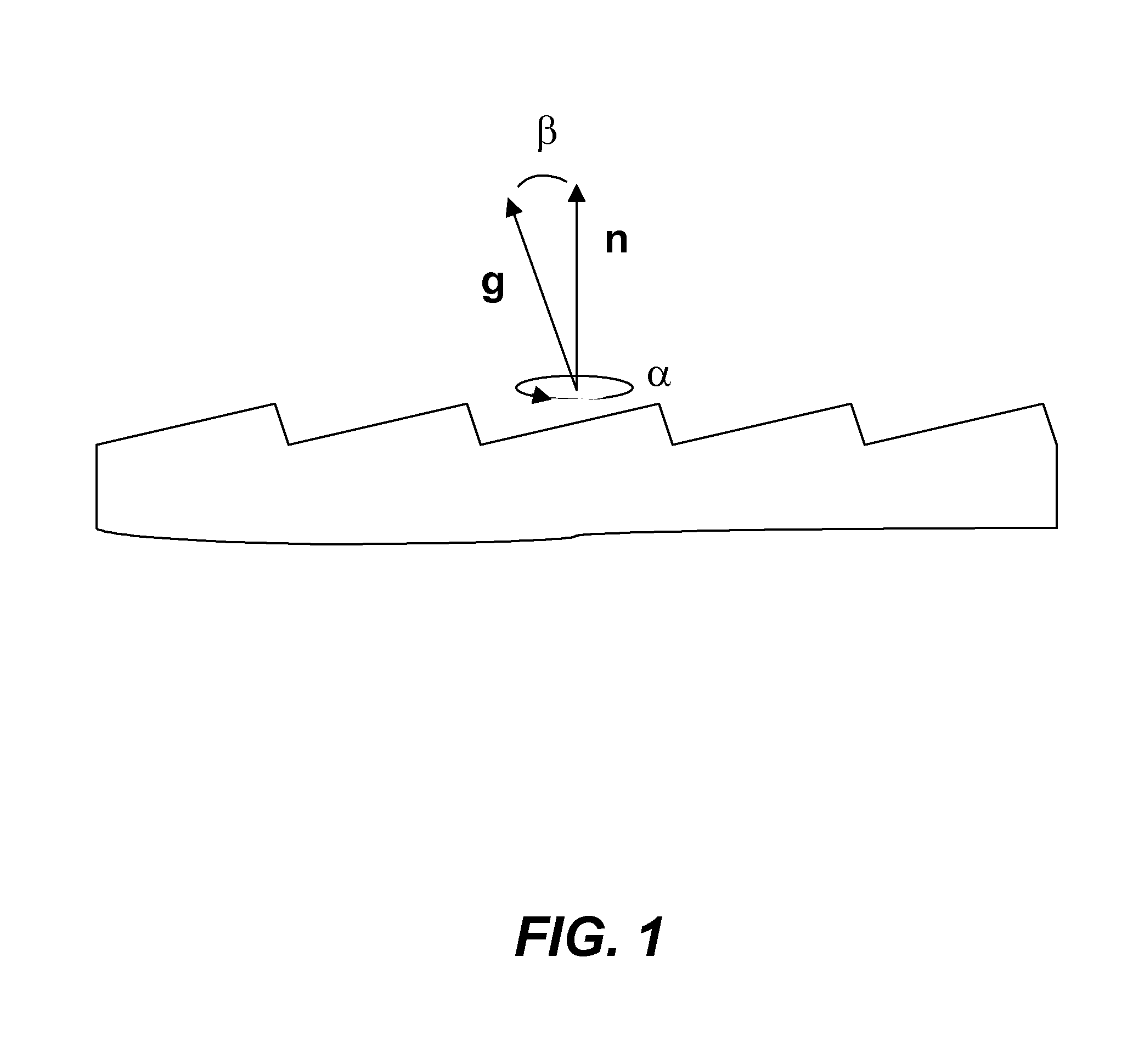
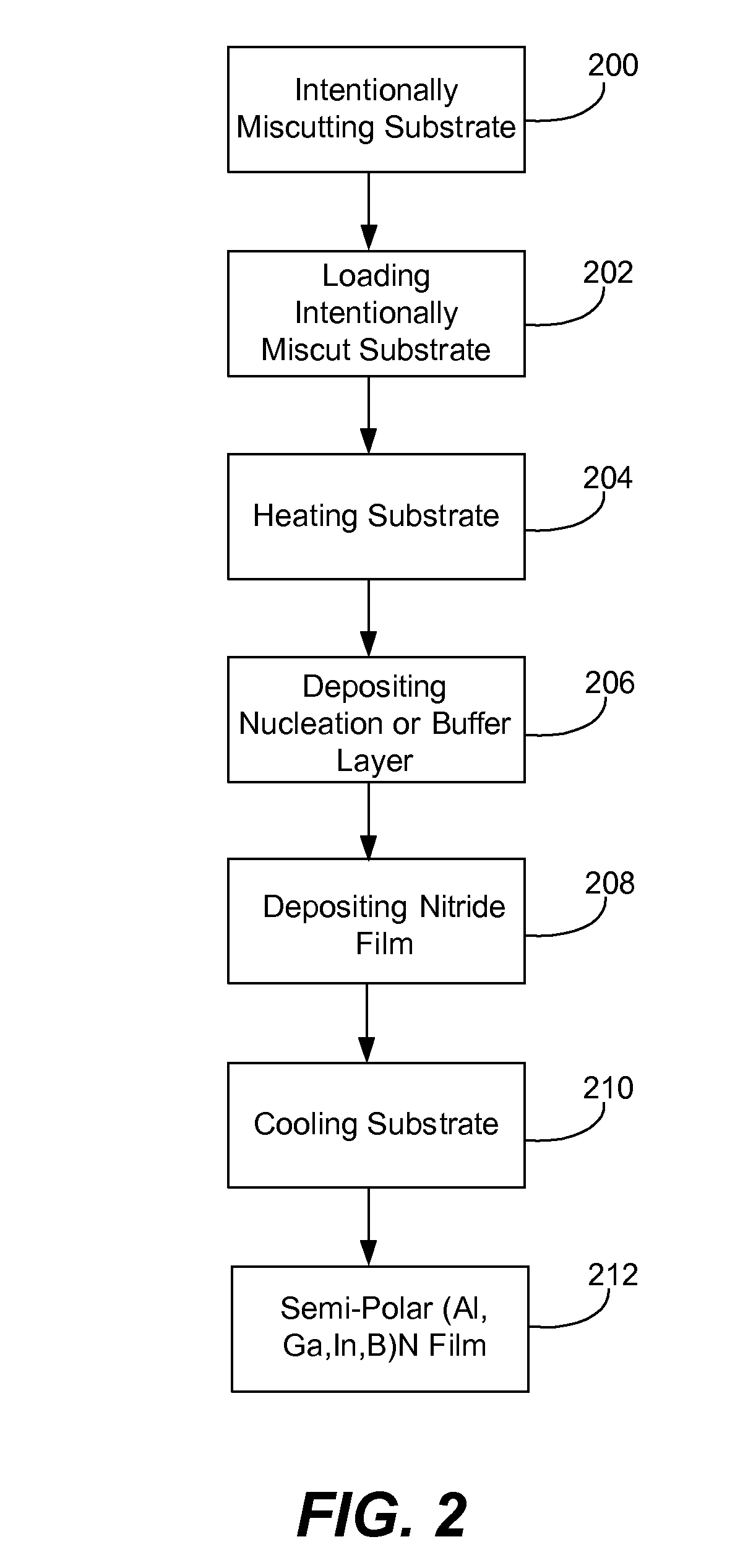
Method for improved growth of semipolar (Al,In,Ga,B)N
ActiveUS7691658B2Reduce symmetryImprove propertiesPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesHydrogenNitrogen
A method for improved growth of a semipolar (Al,In,Ga,B)N semiconductor thin film using an intentionally miscut substrate. Specifically, the method comprises intentionally miscutting a substrate, loading a substrate into a reactor, heating the substrate under a flow of nitrogen and / or hydrogen and / or ammonia, depositing an InxGa1−xN nucleation layer on the heated substrate, depositing a semipolar nitride semiconductor thin film on the InxGa1−xN nucleation layer, and cooling the substrate under a nitrogen overpressure.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Light emitting element structure using nitride bulk single crystal layer
InactiveUS20040251471A1Improve crystal qualitySimple structureOptical wave guidancePolycrystalline material growthSingle crystalActive layer
The object of this invention is to provide a high-output type nitride light emitting device. The nitride light emitting device comprises an n-type nitride semiconductor layer or layers, a p-type nitride semiconductor layer or layers and an active layer therebetween, wherein a gallium-containing nitride substrate is obtained from a gallium-containing nitride bulk single crystal, provided with an epitaxial growth face with dislocation density of 10<5> / cm<2 >or less, and A-plane or M-plane which is parallel to C-axis of hexagonal structure for an epitaxial face, wherein the n-type semiconductor layer or layers are formed directly on the A-plane or M-plane. In case that the active layer comprises a nitride semiconductor containing In, an end face film of single crystal AlxGa1-xN (0<=x<=1) can be formed at a low temperature not causing damage to the active layer.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
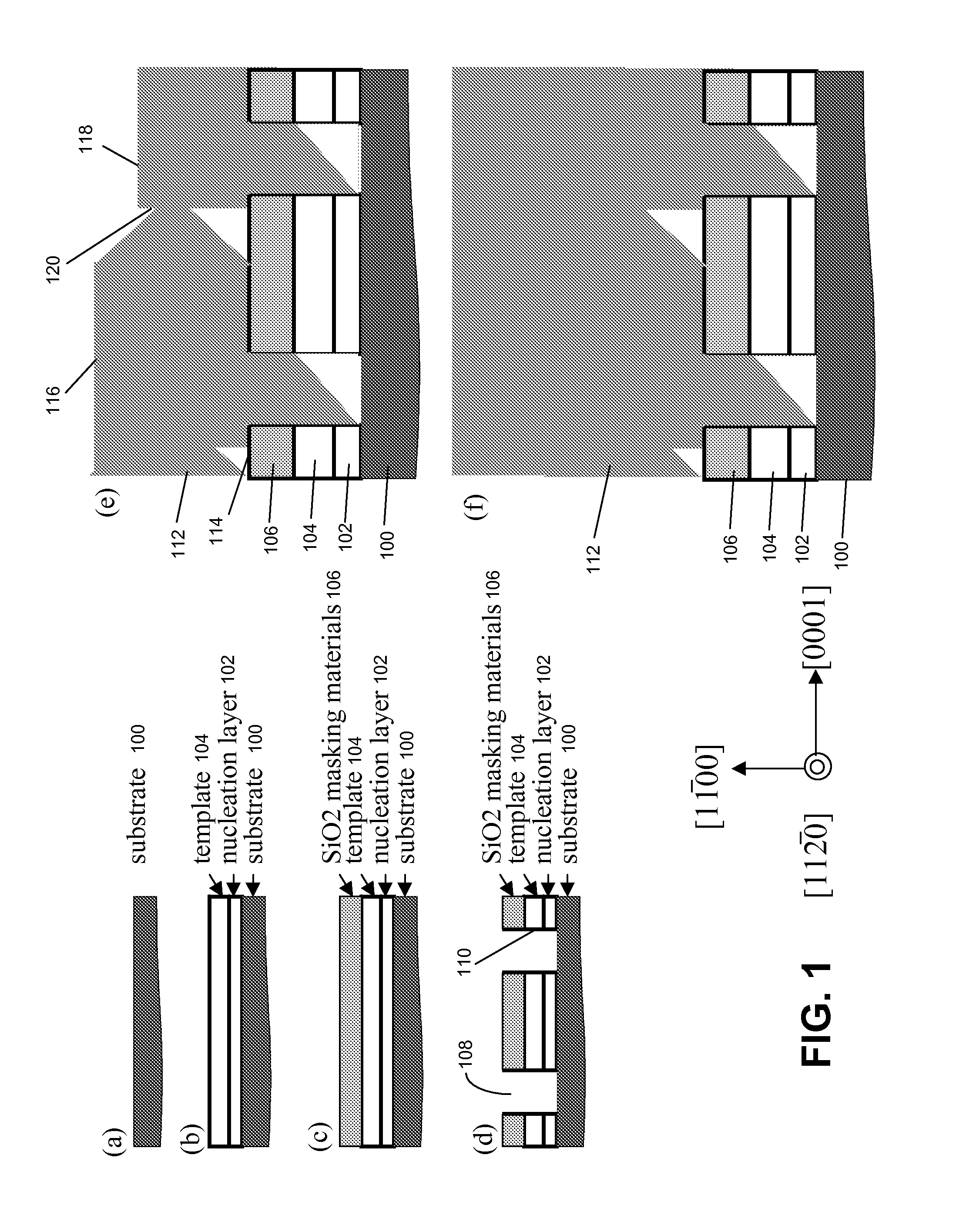
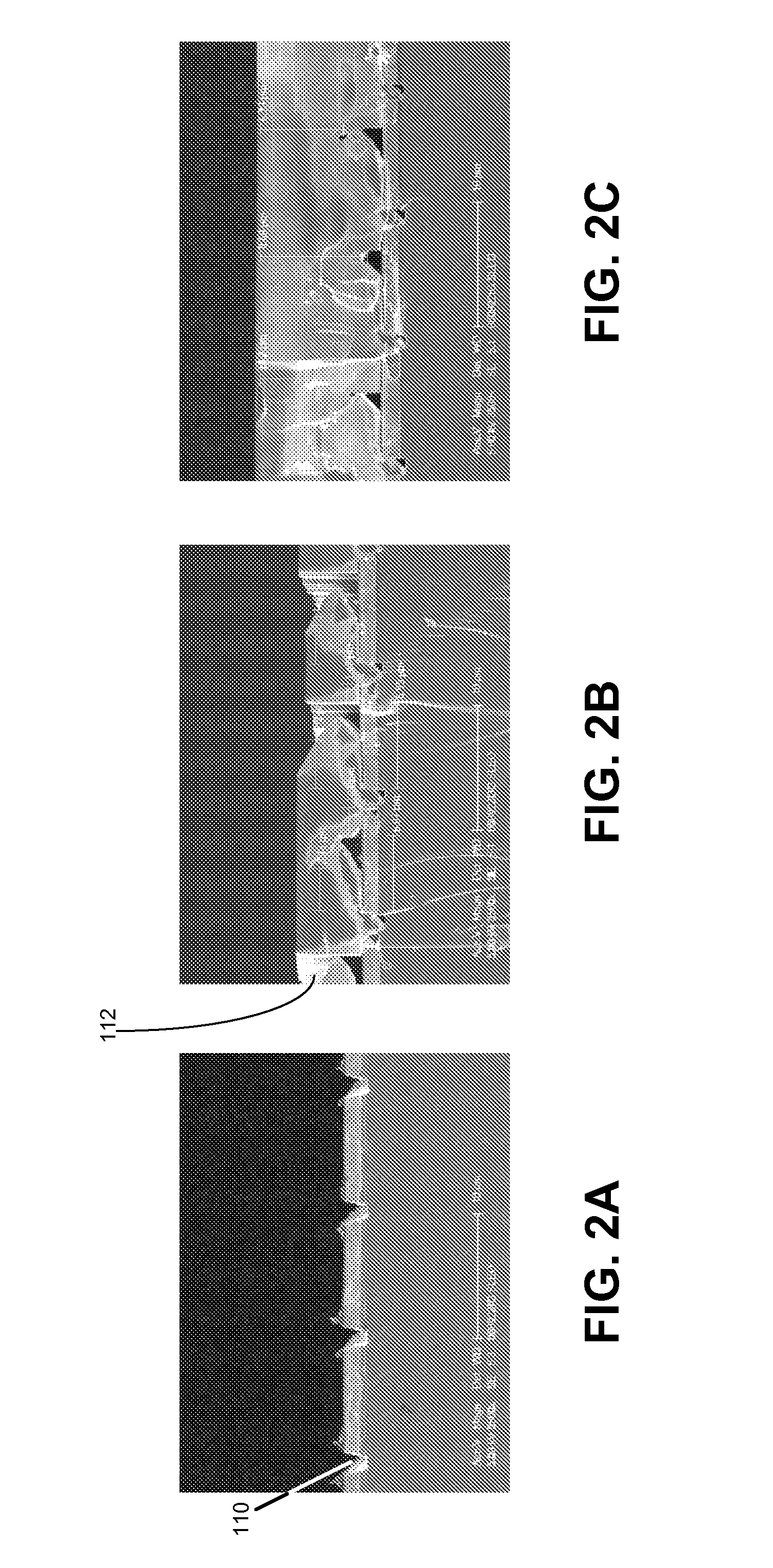
Dislocation reduction in non-polar gallium nitride thin films
InactiveUS6900070B2Reduce threading dislocationReduce misalignmentPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsThreading dislocationsDielectric
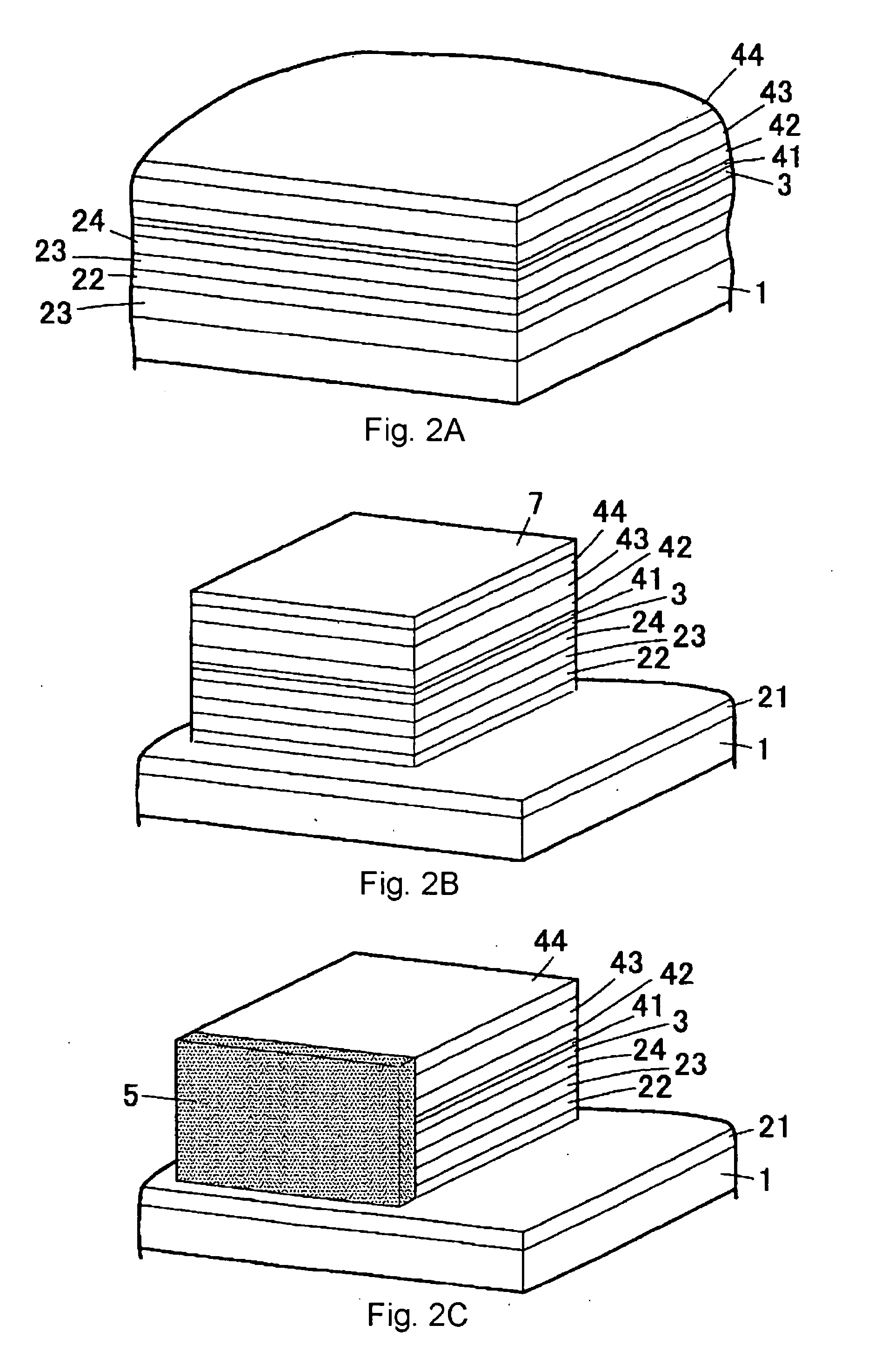
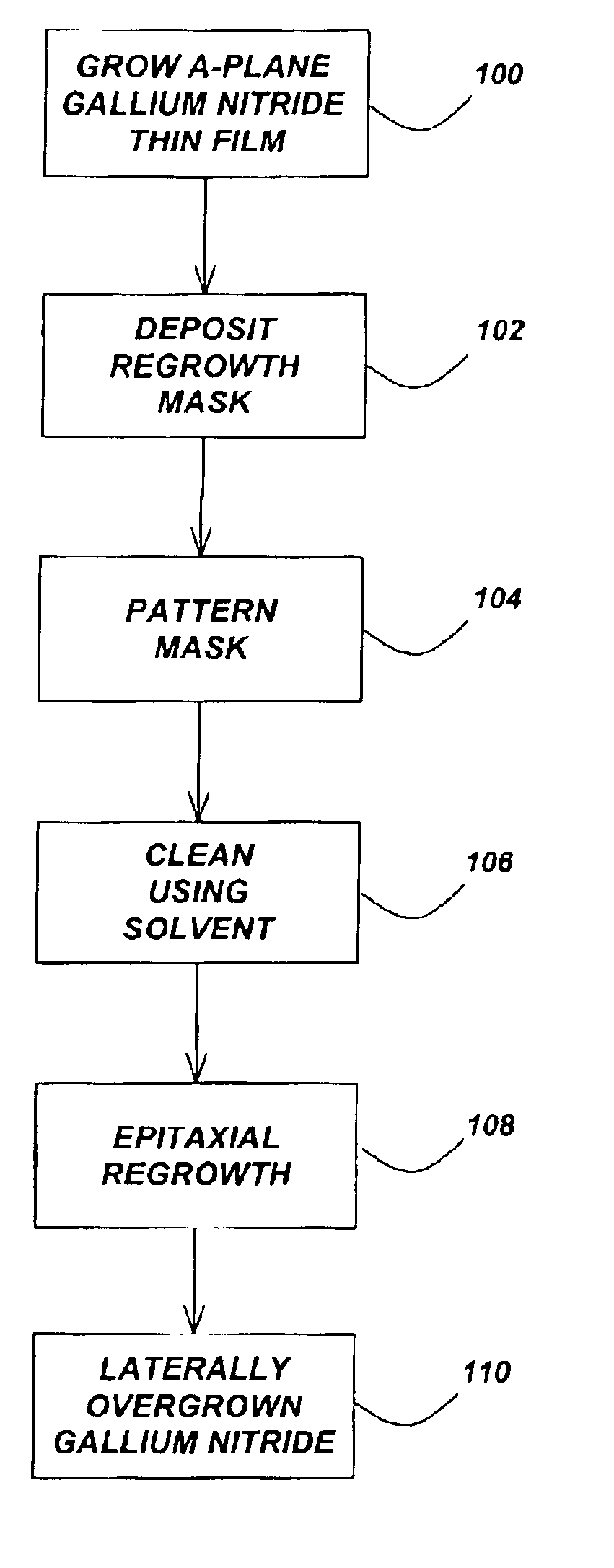
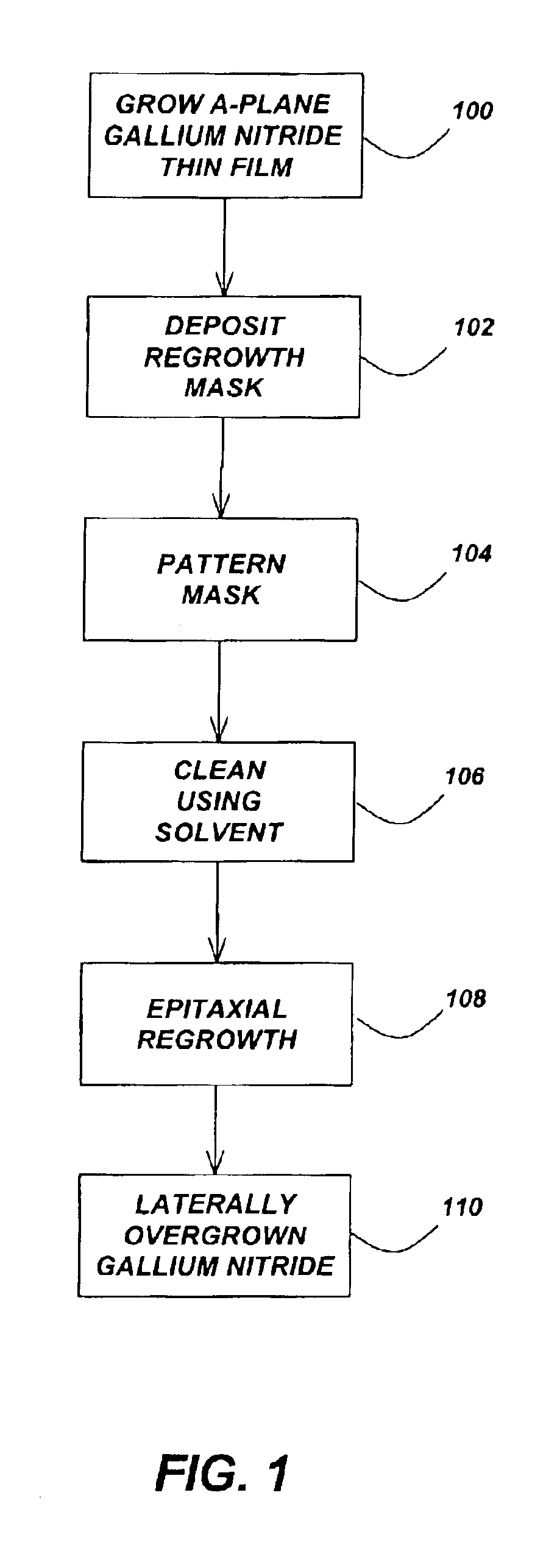
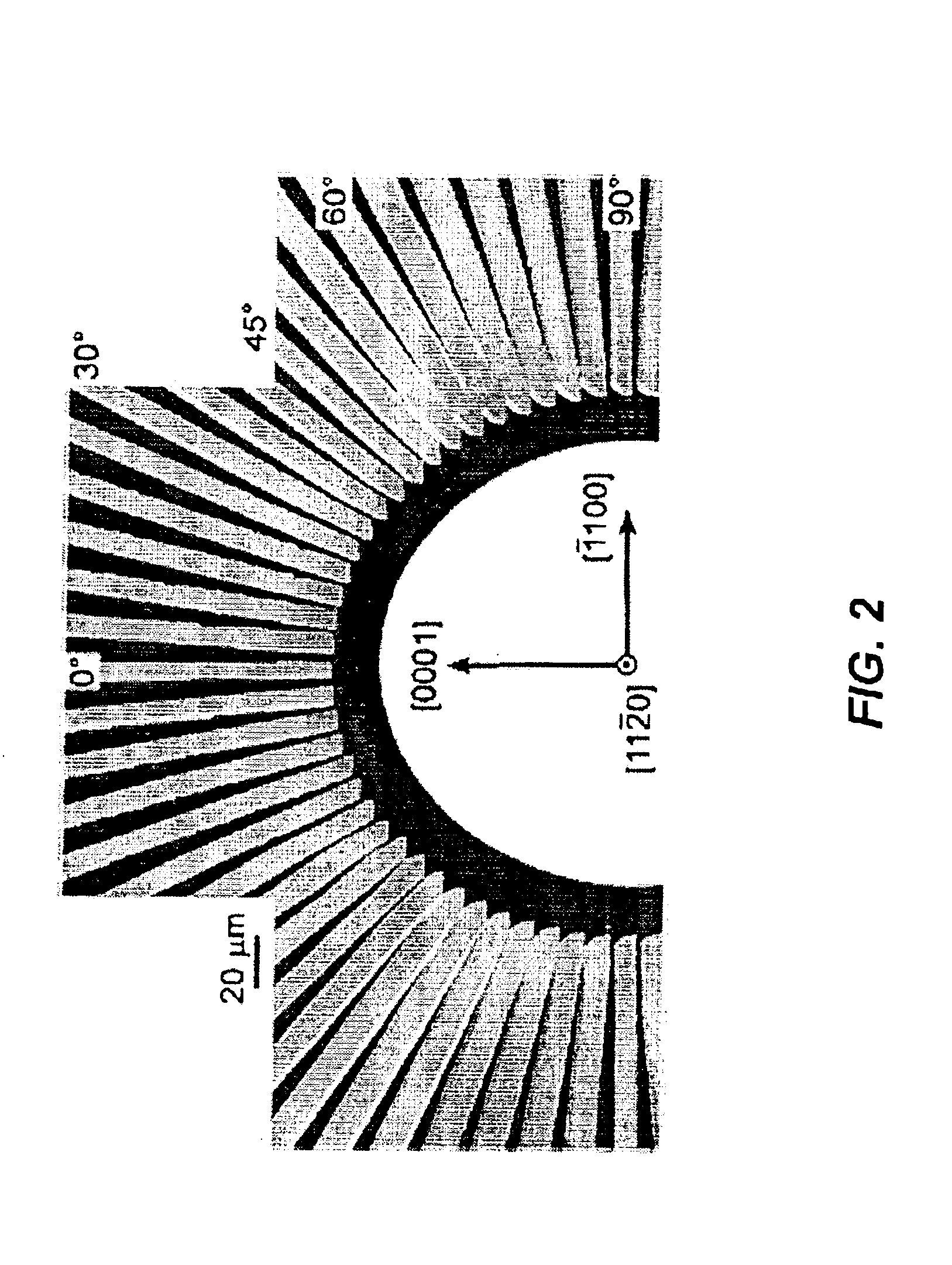
Lateral epitaxial overgrowth of non-polar (11{overscore (2)}0) a-plane GaN seed layers reduces threading dislocations in the GaN films. First, a thin patterned dielectric mask is applied to the seed layer. Second, a selective epitaxial regrowth is performed to achieve a lateral overgrowth based on the patterned mask. Upon regrowth, the GaN films initially grow vertically through openings in the dielectric mask before laterally overgrowing the mask in directions perpendicular to the vertical growth direction. Threading dislocations are reduced in the overgrown regions by (1) the mask blocking the propagation of dislocations vertically into the growing film and (2) the bending of dislocations through the transition from vertical to lateral growth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
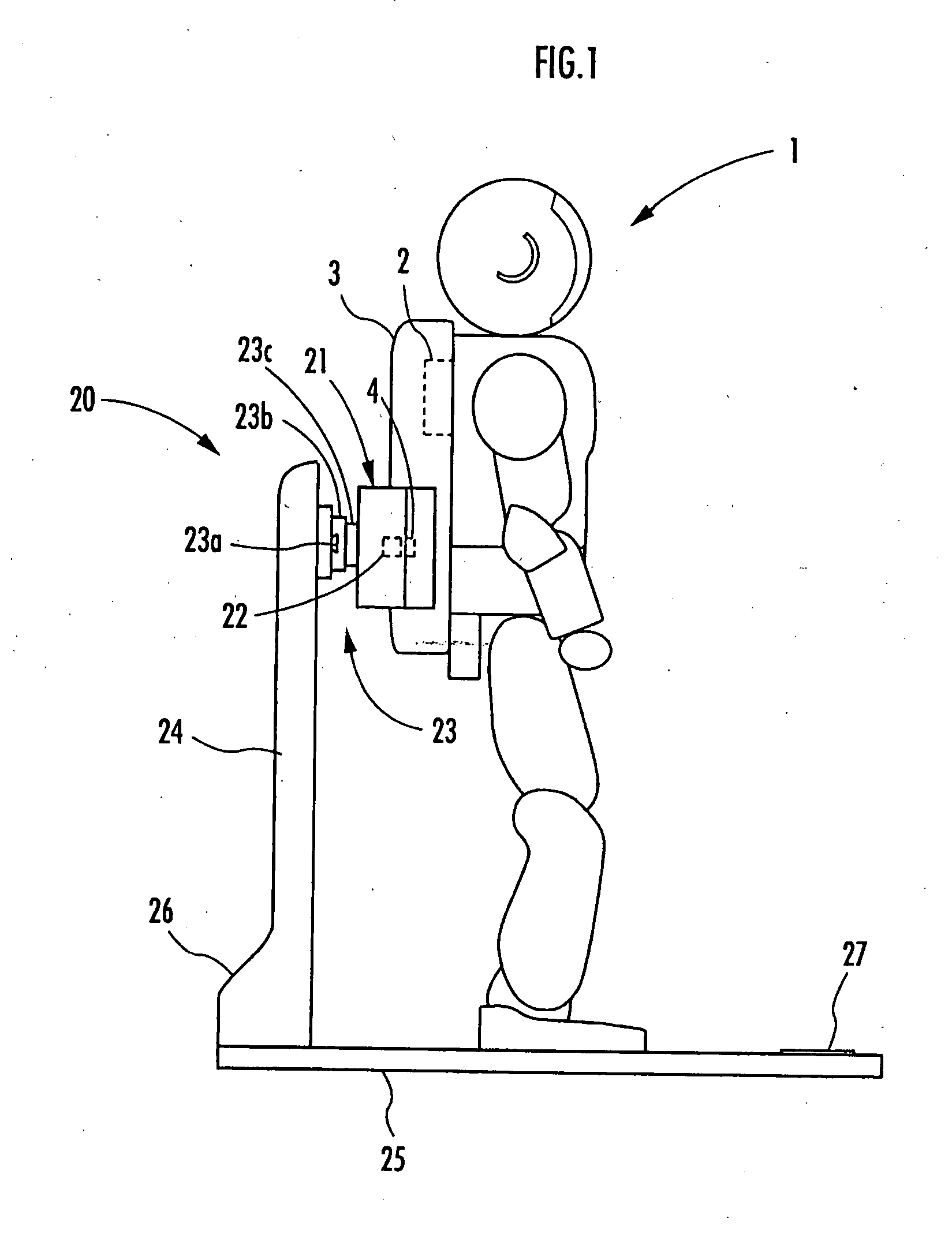
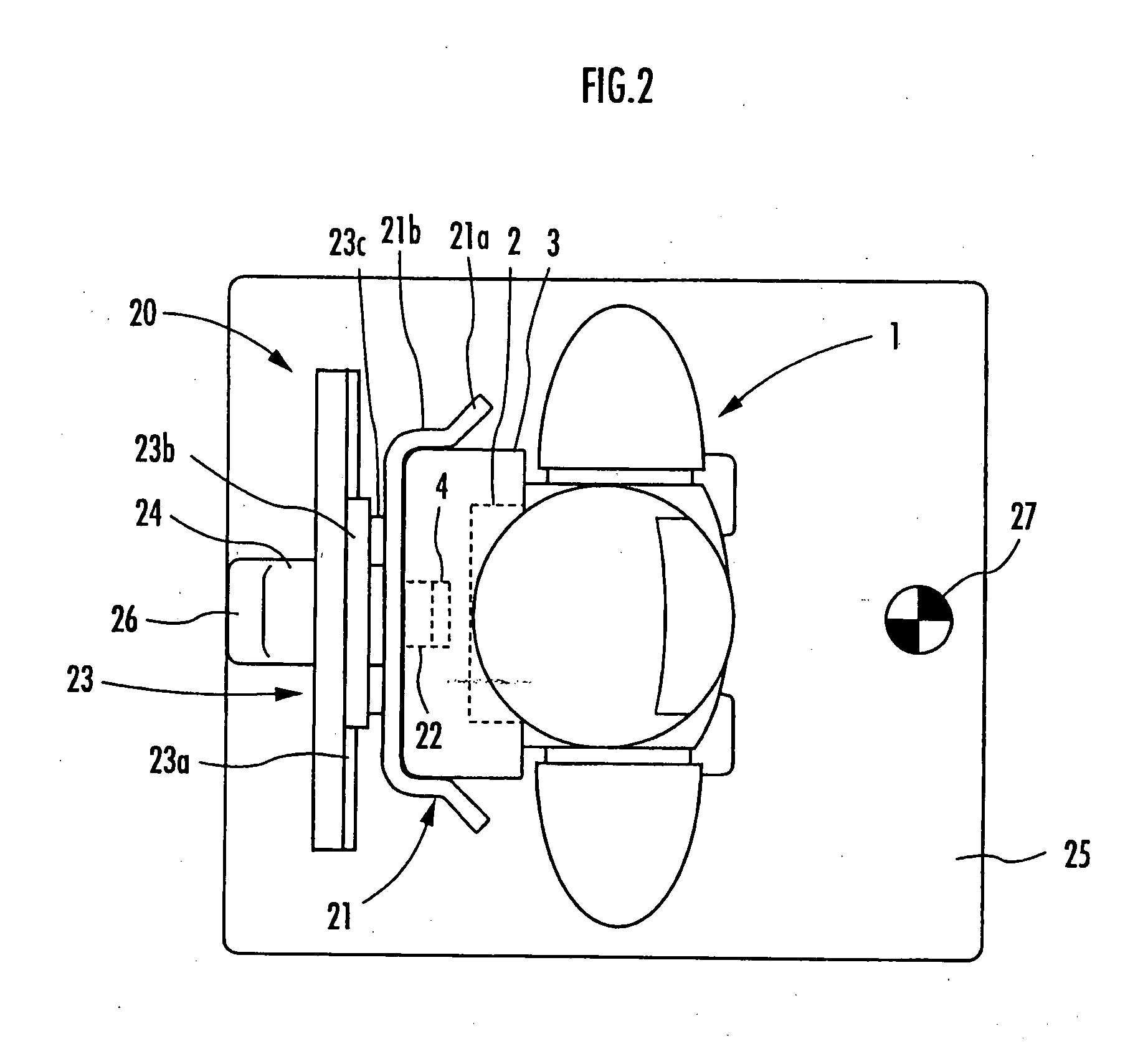
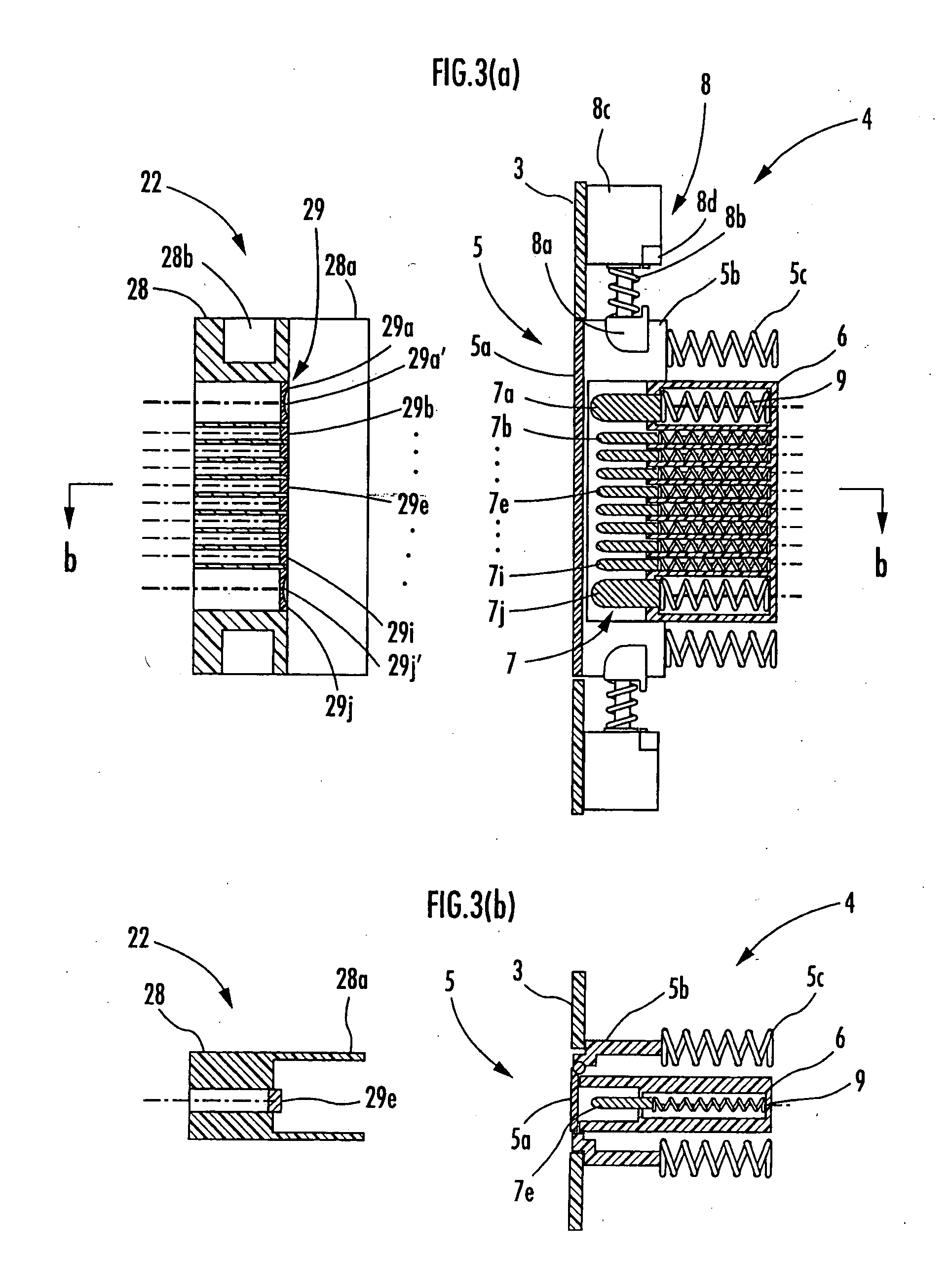
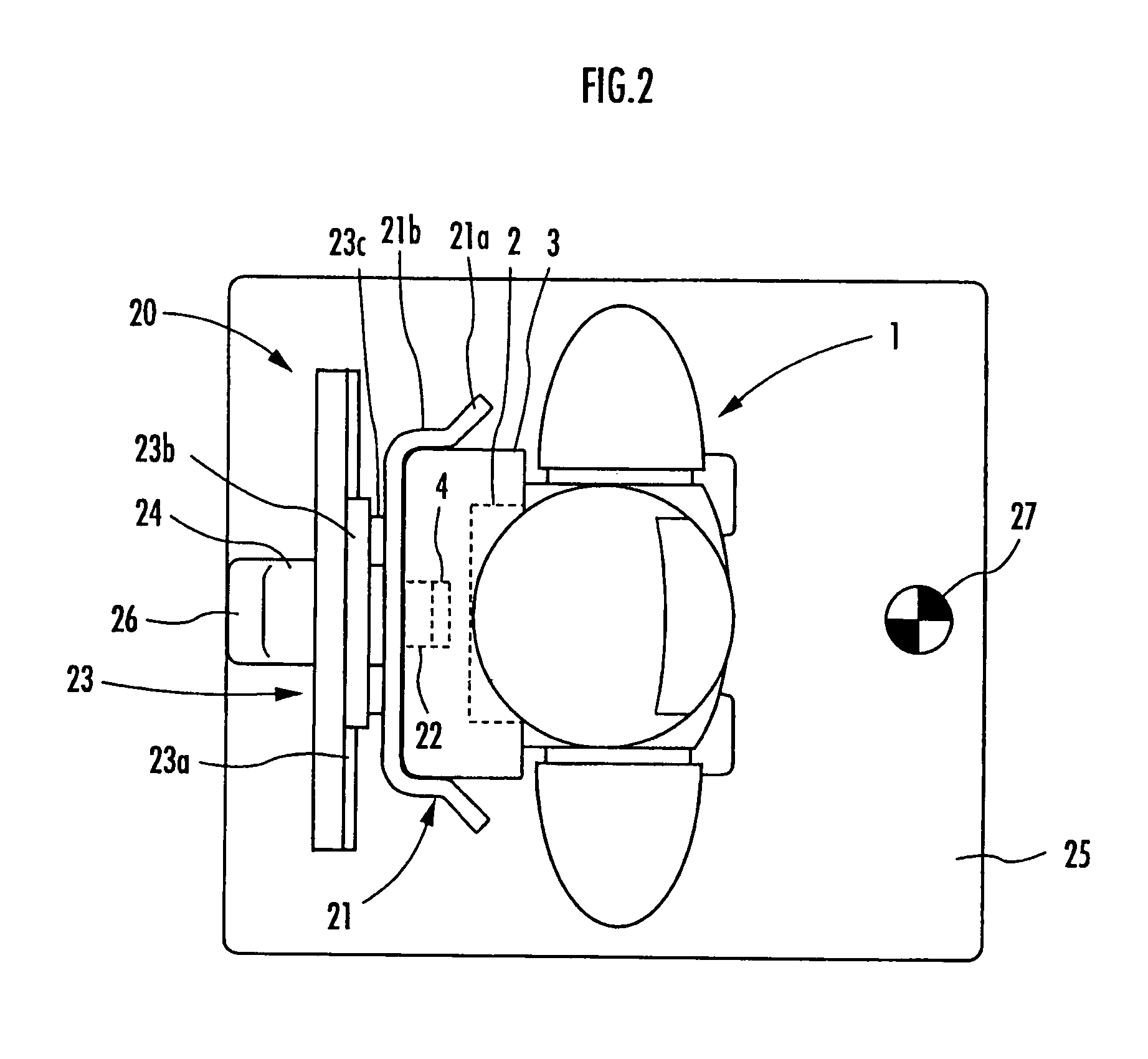
Charging system for legged mobile robot
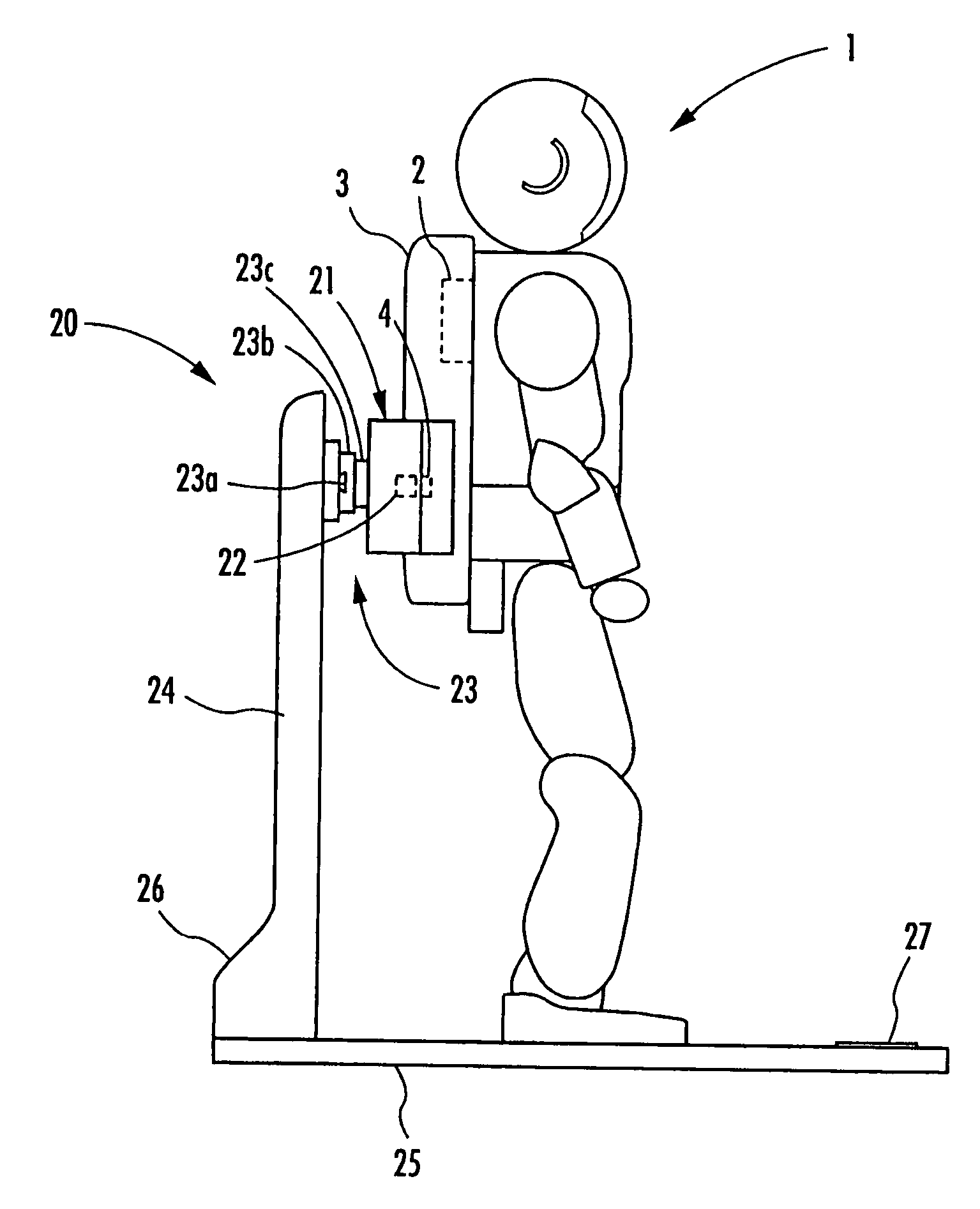
InactiveUS20070216347A1Increase costHelp positioningBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsCharging stationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A charging system for a legged mobile robot that facilitates positioning of a robot to be charged and does not put a load on the robot is provided. The charging system includes a battery 2, a power receiving connector 4 and a movable shutter member 5 capable of being opened and closed on a rear cover 3, which are provided on a robot 1, and a holder 21, a power supplying connector 22, a slide mechanism 23, a base plate 25, a charging power supply 26 and the like, which are provided on a charging station 20. The robot 1 performs a predetermined positioning on the base plate 25 and then moves the center of gravity rearward to connect the power receiving connector 4 to the power supplying connector 22. In this step, when the rear cover 3 of the robot 1 is guided by a first guide section 21a of the holder 21, the slide mechanism 23 allows the holder 21 to move horizontally. Thus, even if the robot 1 and the charging station 20 are slightly misaligned with each other, the robot 1 can be easily positioned correctly.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
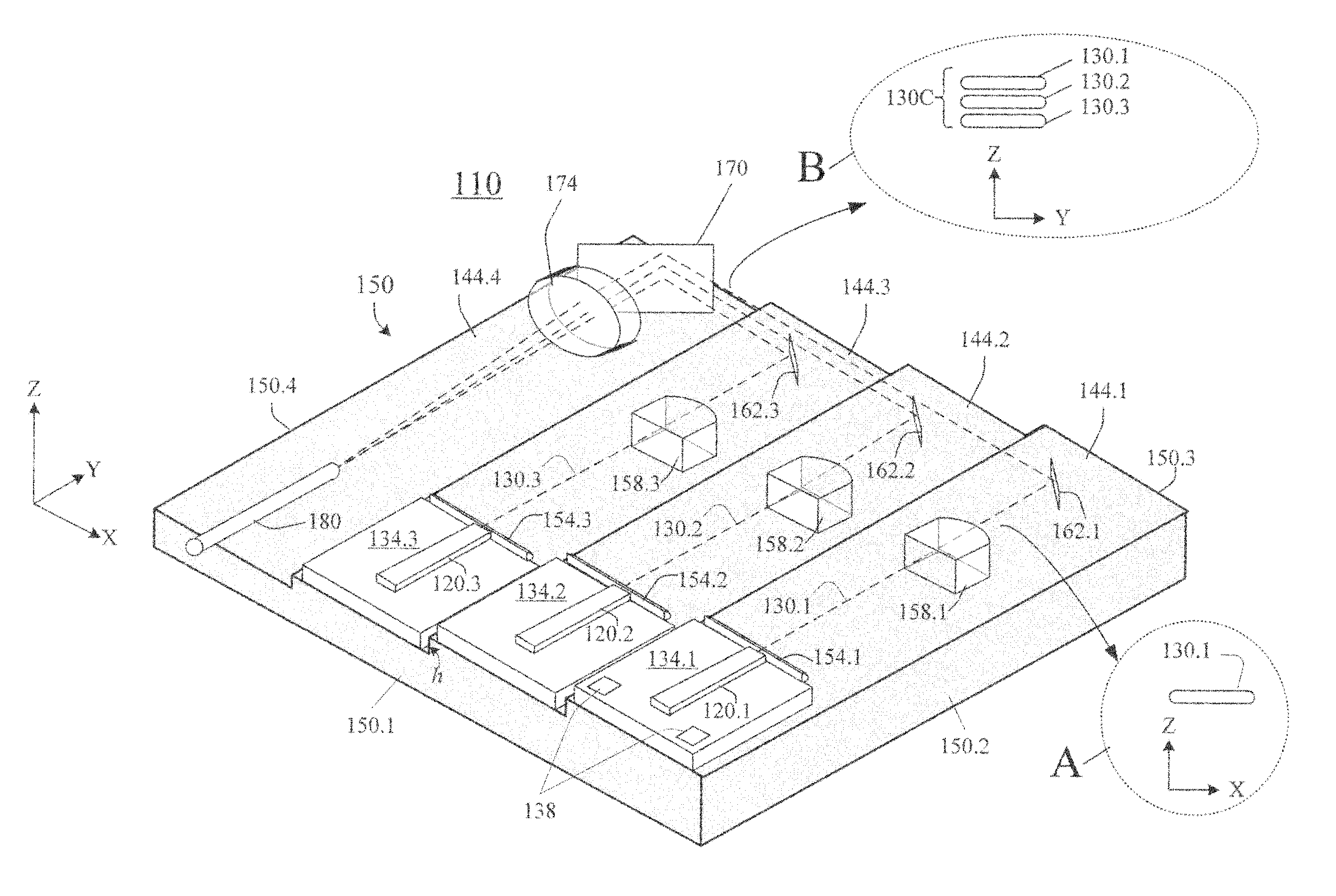
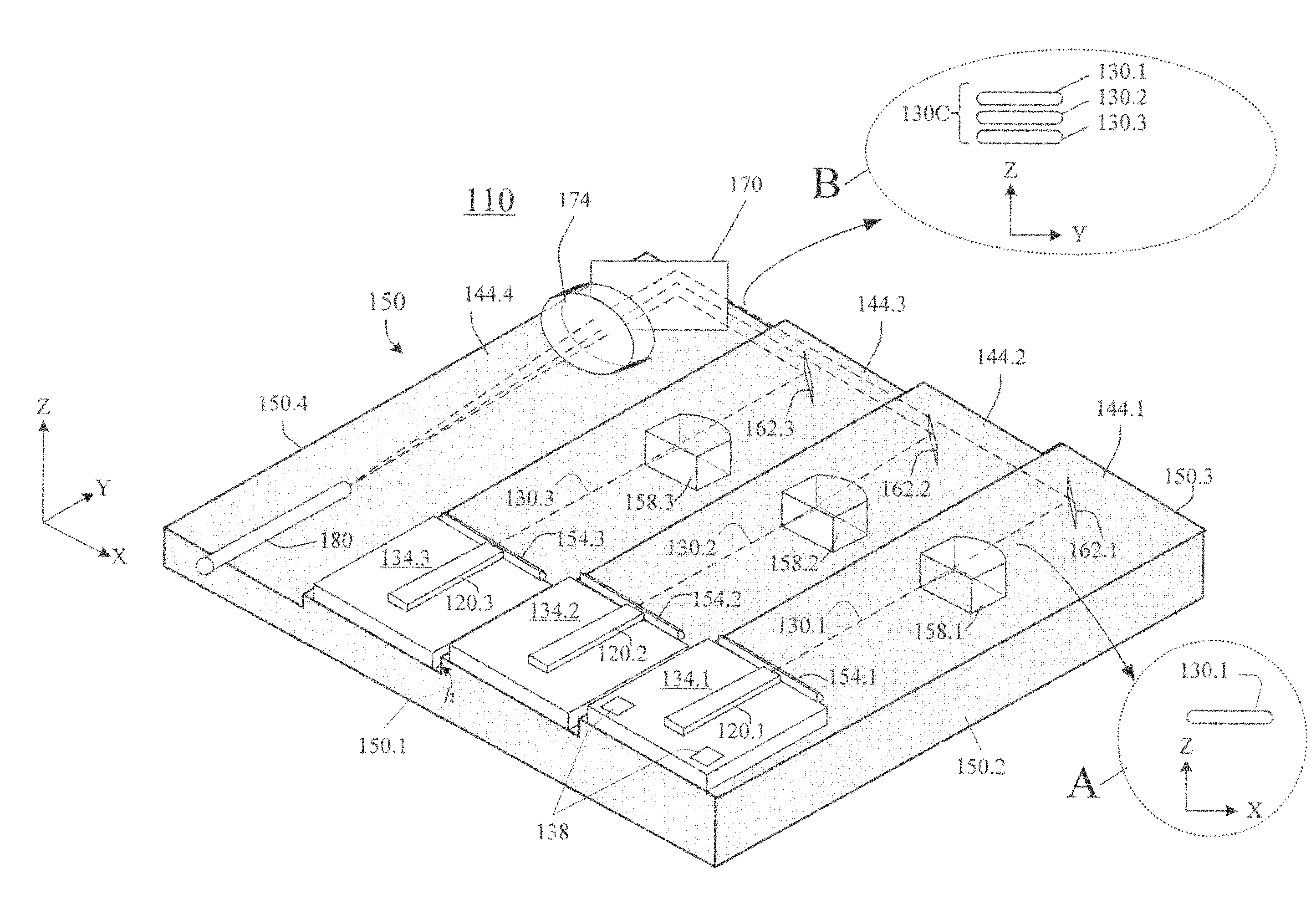
Laser diode assemblies
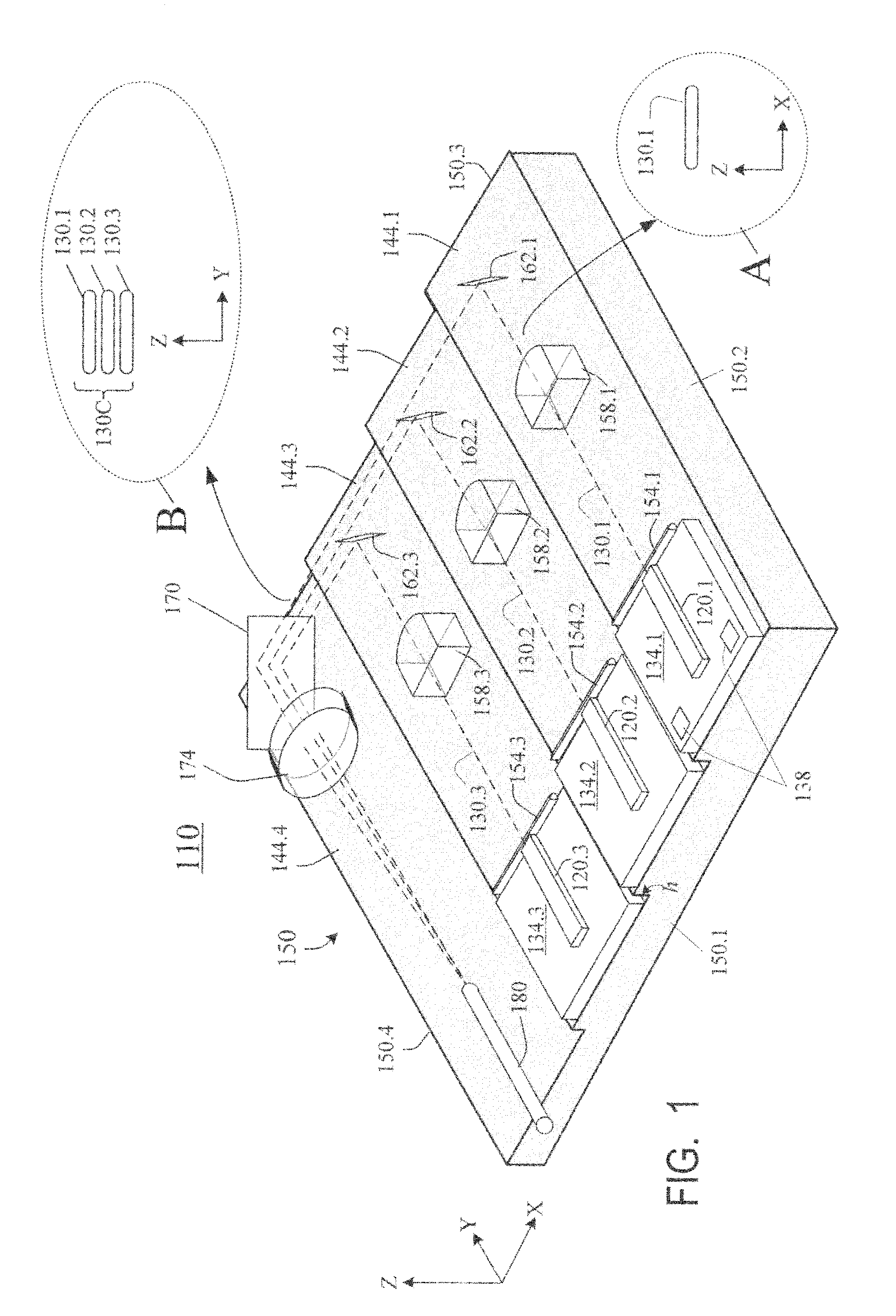
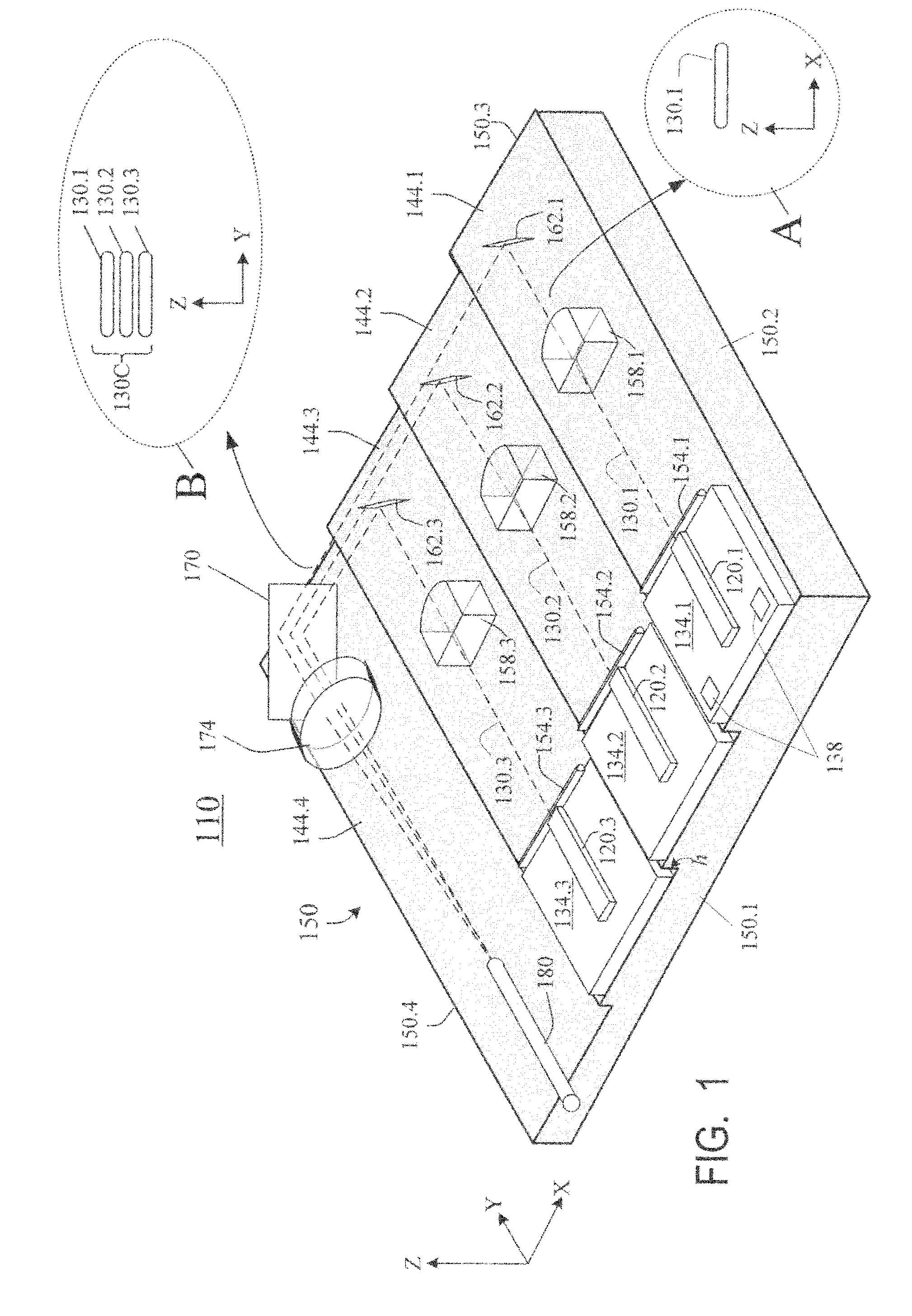
InactiveUS20090245315A1Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamLaser beams
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
Charging system for legged mobile robot
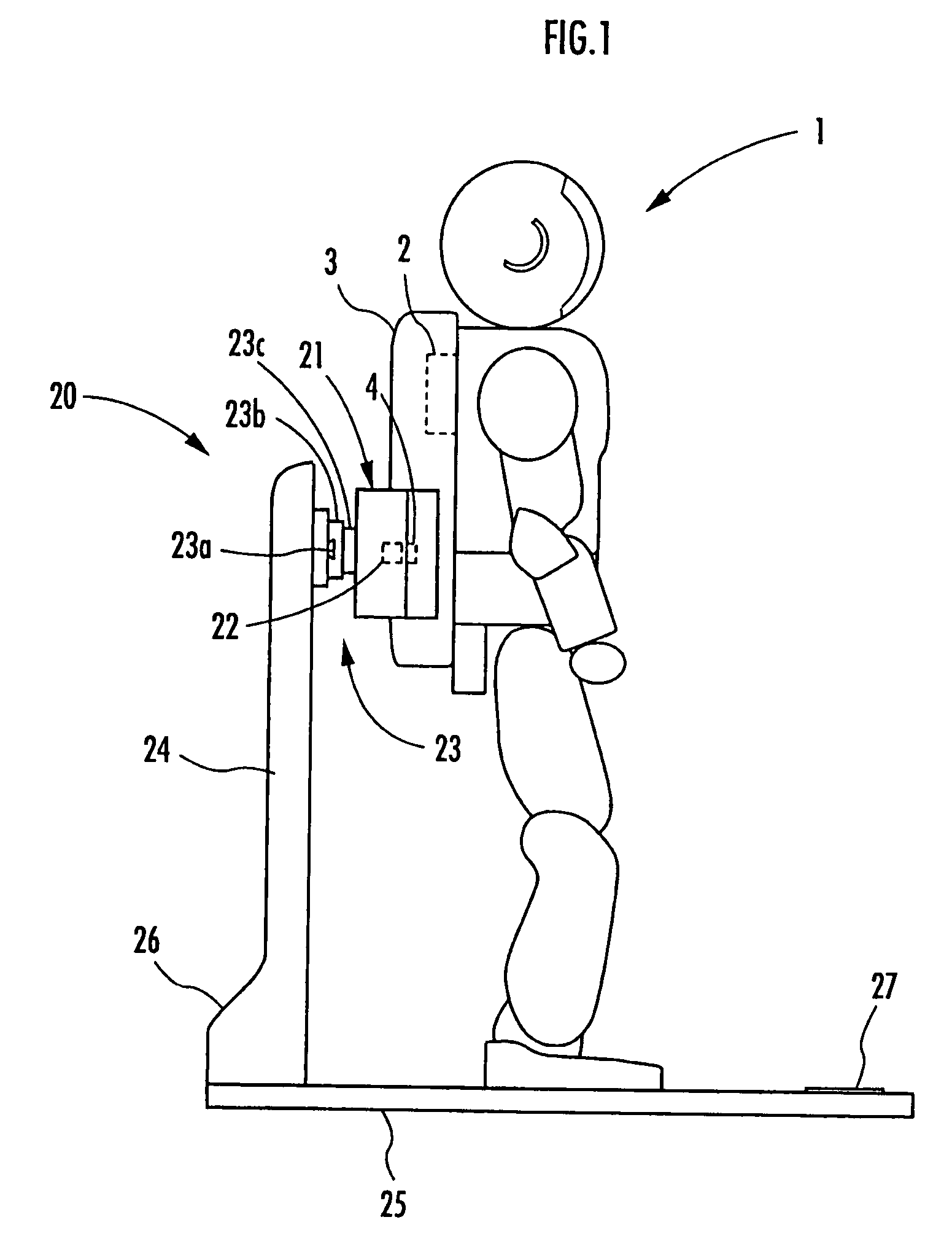
InactiveUS7719229B2Increase costHelp positioningBatteries circuit arrangementsVehicular energy storageCharging stationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A charging system for a legged mobile robot that facilitates positioning of a robot to be charged and does not put a load on the robot is provided. The charging system includes a battery 2, a power receiving connector 4 and a movable shutter member 5 capable of being opened and closed on a rear cover 3, which are provided on a robot 1, and a holder 21, a power supplying connector 22, a slide mechanism 23, a base plate 25, a charging power supply 26 and the like, which are provided on a charging station 20. The robot 1 performs a predetermined positioning on the base plate 25 and then moves the center of gravity rearward to connect the power receiving connector 4 to the power supplying connector 22. In this step, when the rear cover 3 of the robot 1 is guided by a first guide section 21a of the holder 21, the slide mechanism 23 allows the holder 21 to move horizontally. Thus, even if the robot 1 and the charging station 20 are slightly misaligned with each other, the robot 1 can be easily positioned correctly.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
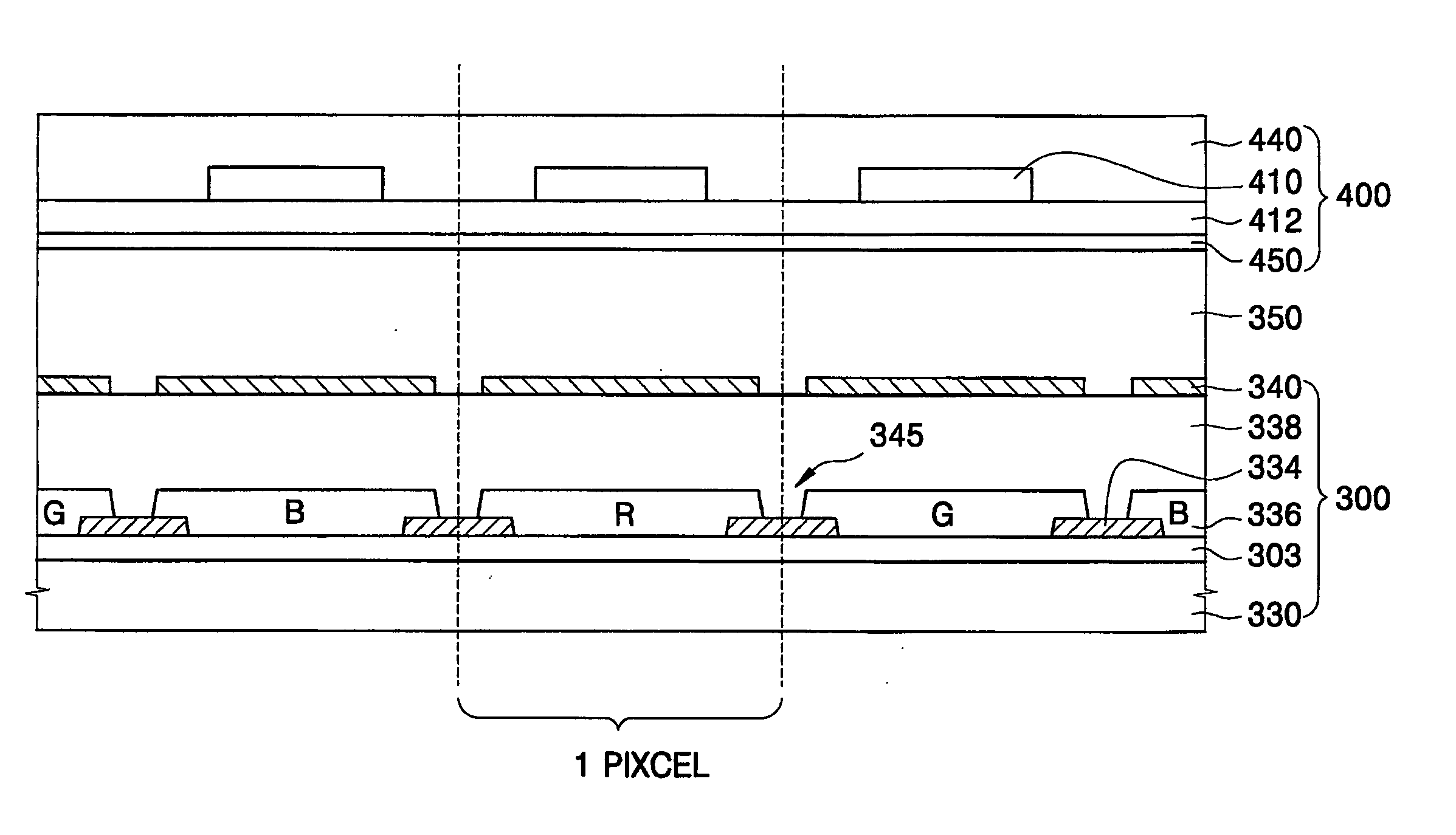
Liquid crystal display device built-in finger printing device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060017862A1Reduce in quantityReduce manufacturing costStatic indicating devicesPrint image acquisitionLiquid-crystal displayTransmittance
A liquid crystal display device having fingerprint identification device for enhancing aperture ratio and transmissivity of a TFT-LCD panel is disclosed. A fingerprint identification substrate (400) is attached to a TFT substrate (300). The TFI substrate has color-filter-on-array structure in which the color filters (336) and the thin film transistors can be eliminated, the aperture ratio is increased, and the quality of image display is enhanced. In addition, the transmissivity is increased according to the decrease of the number of glass substrate used in the liquid crystal display device, so that the sensitivity of fingerprint identification is enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
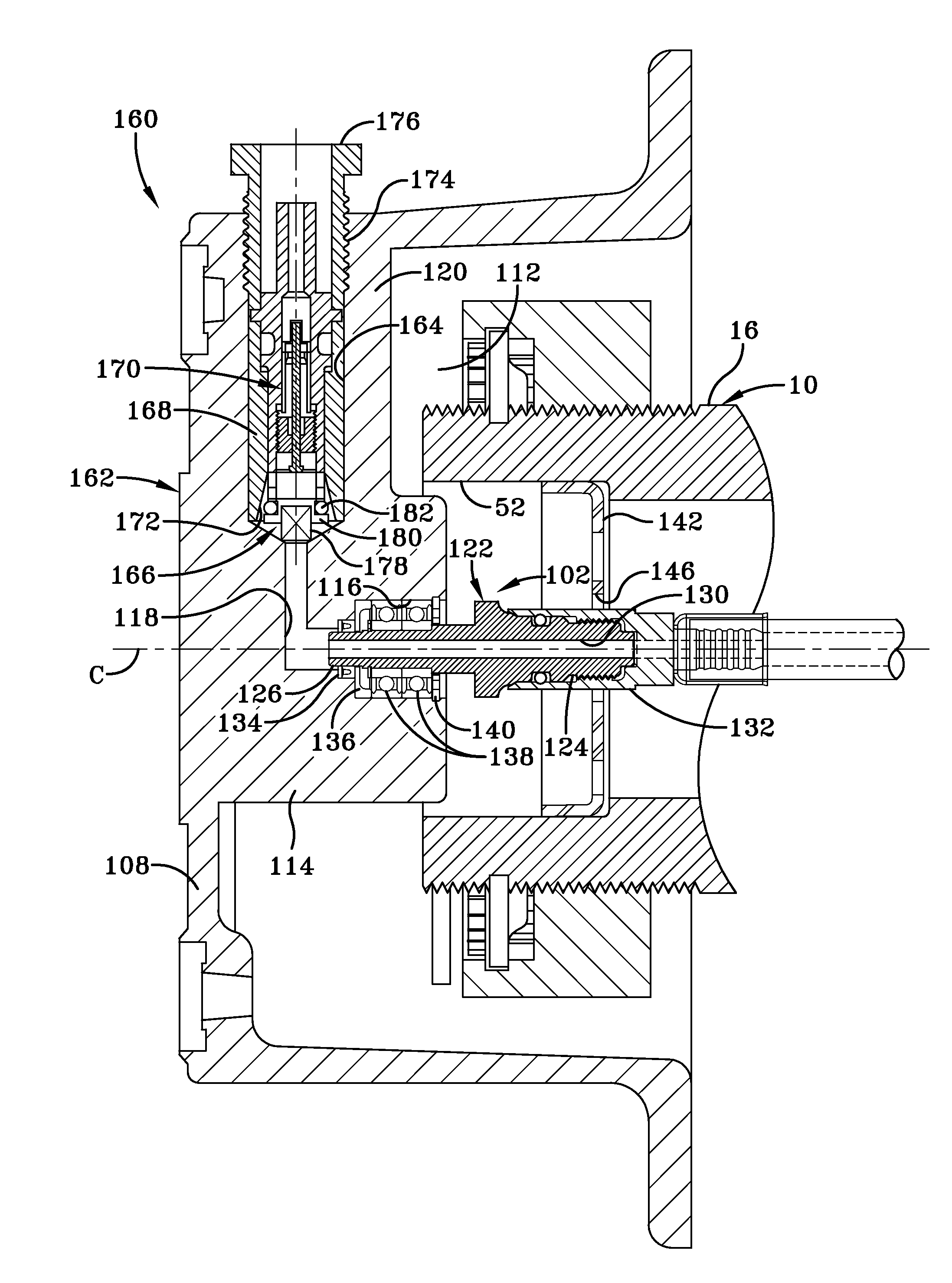
Integrated rotary union and hub cap
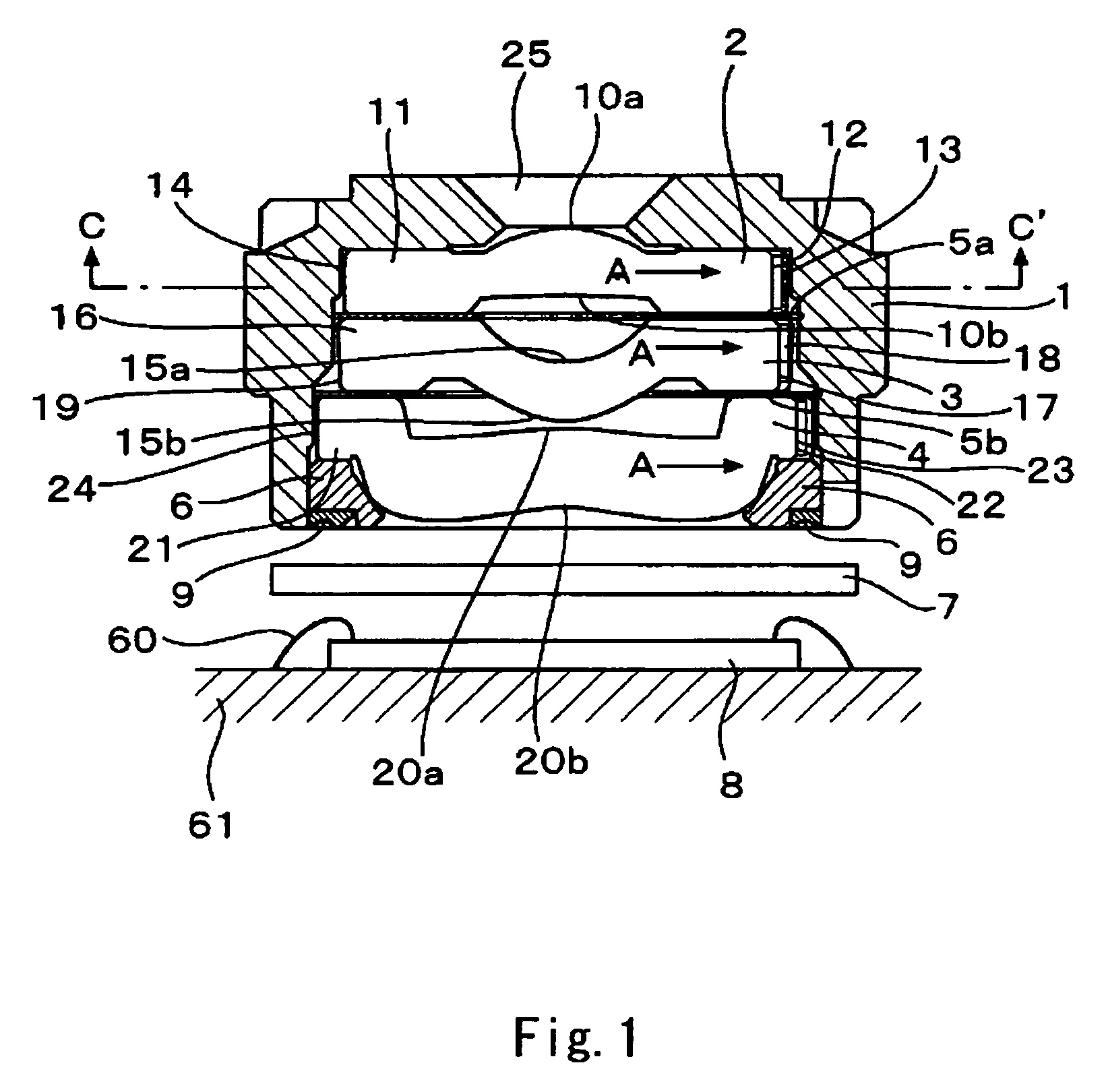
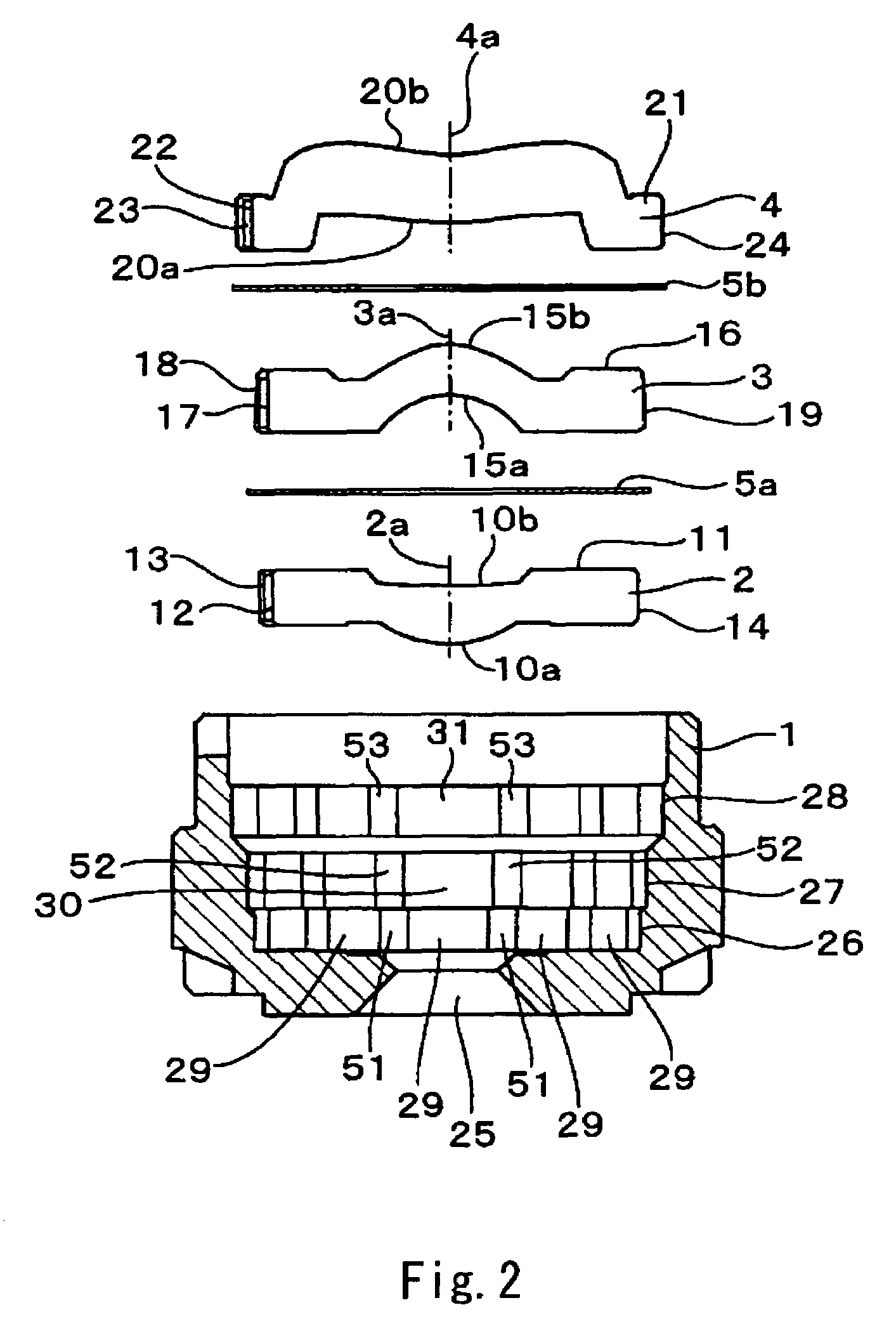
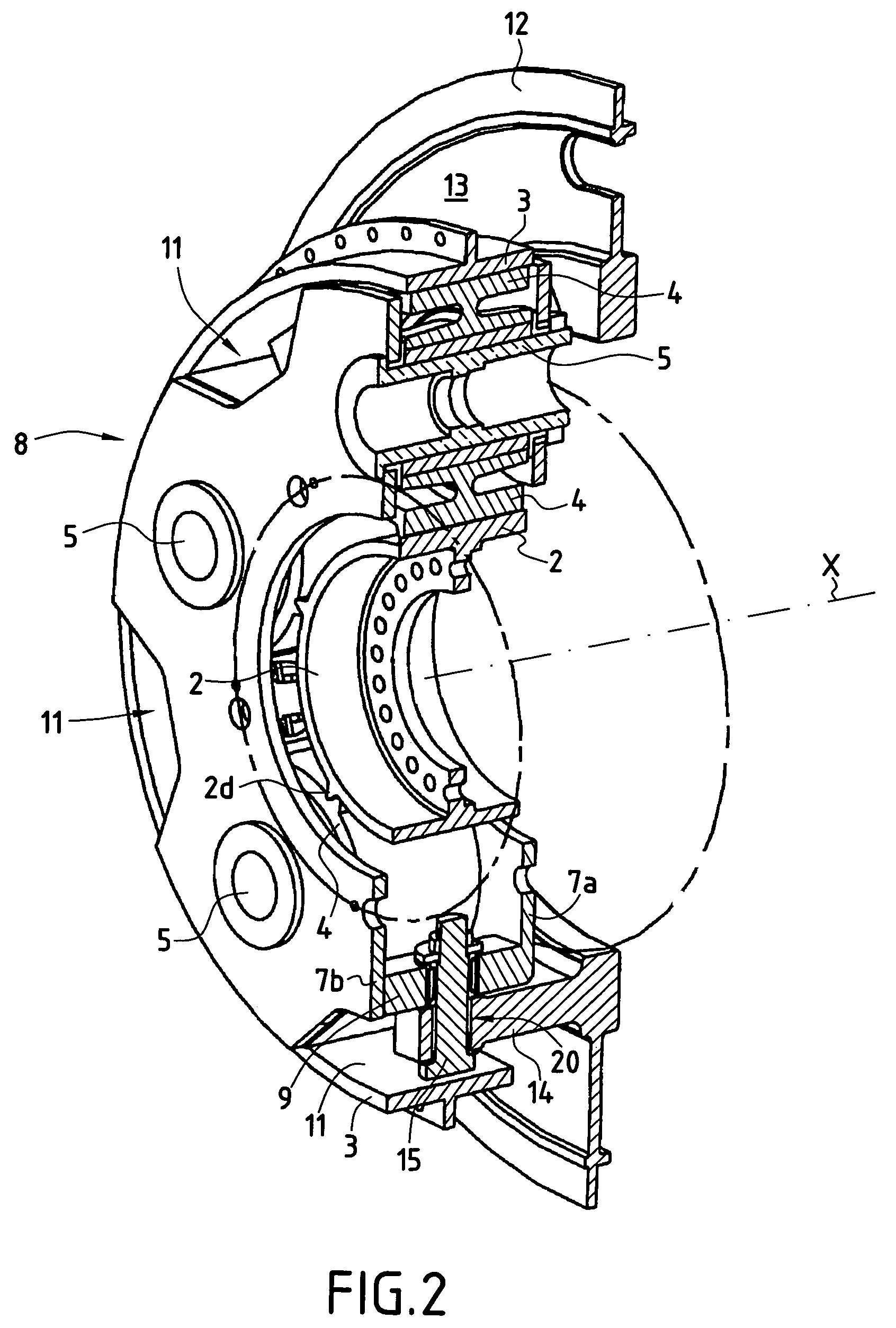
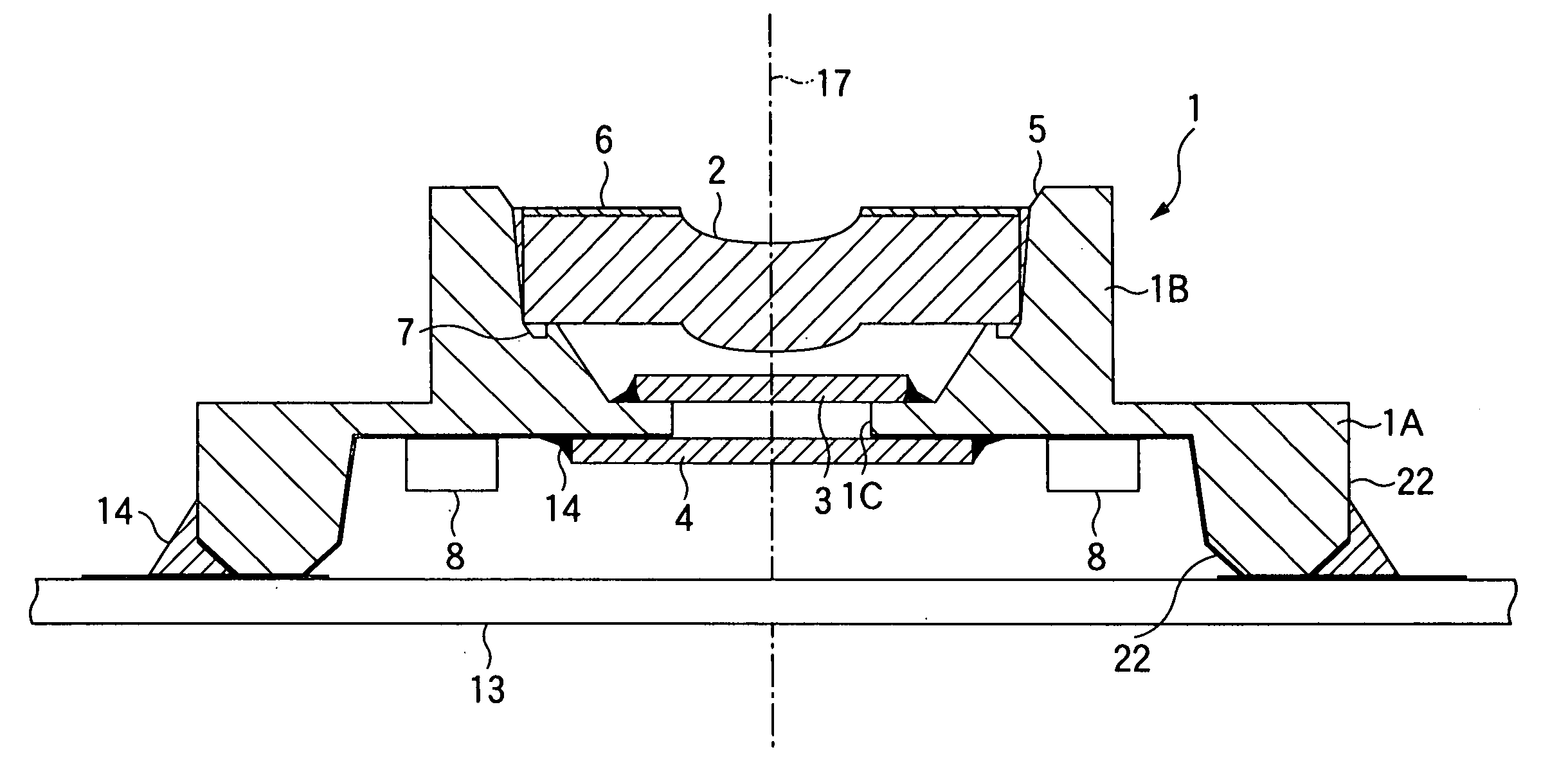
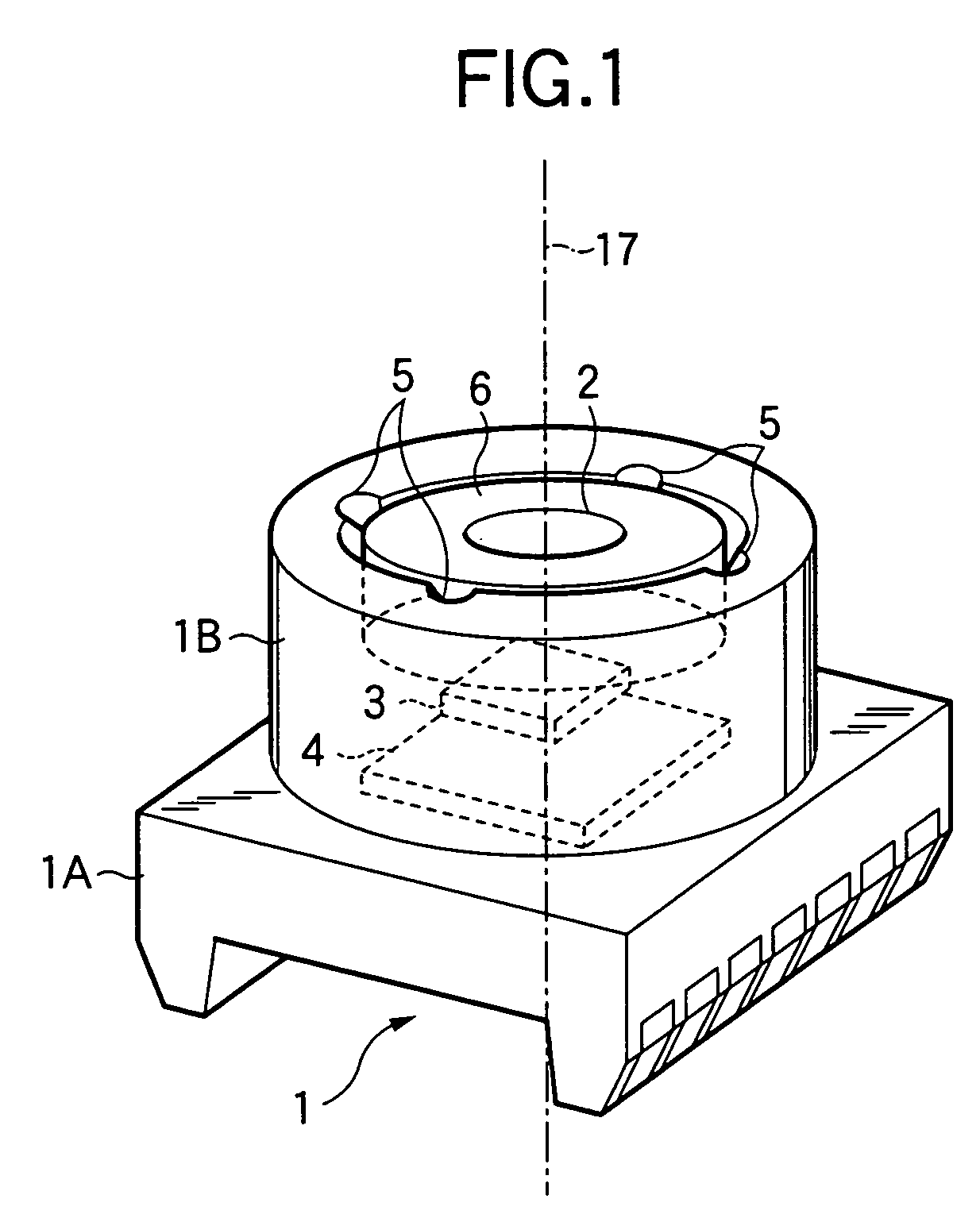
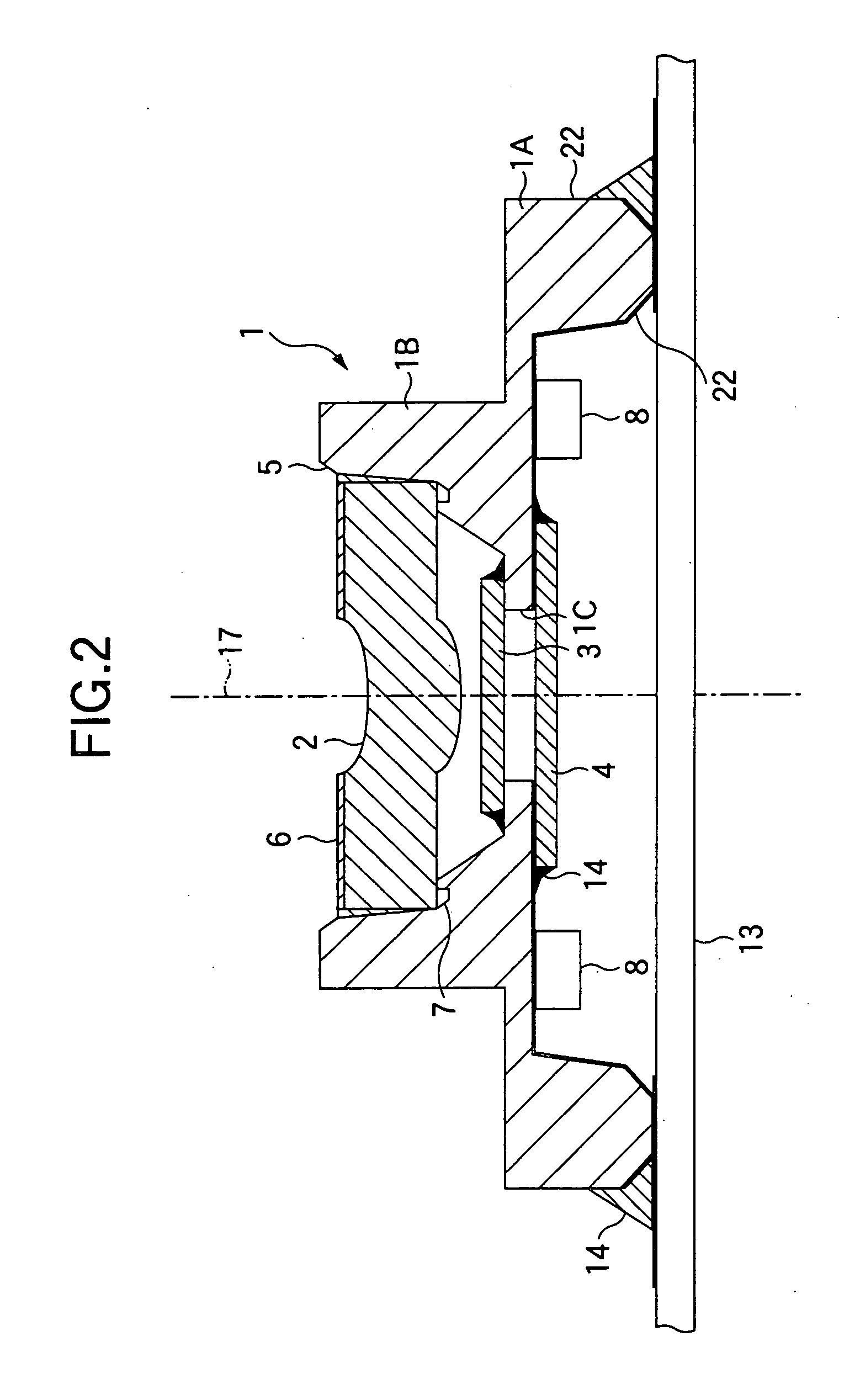
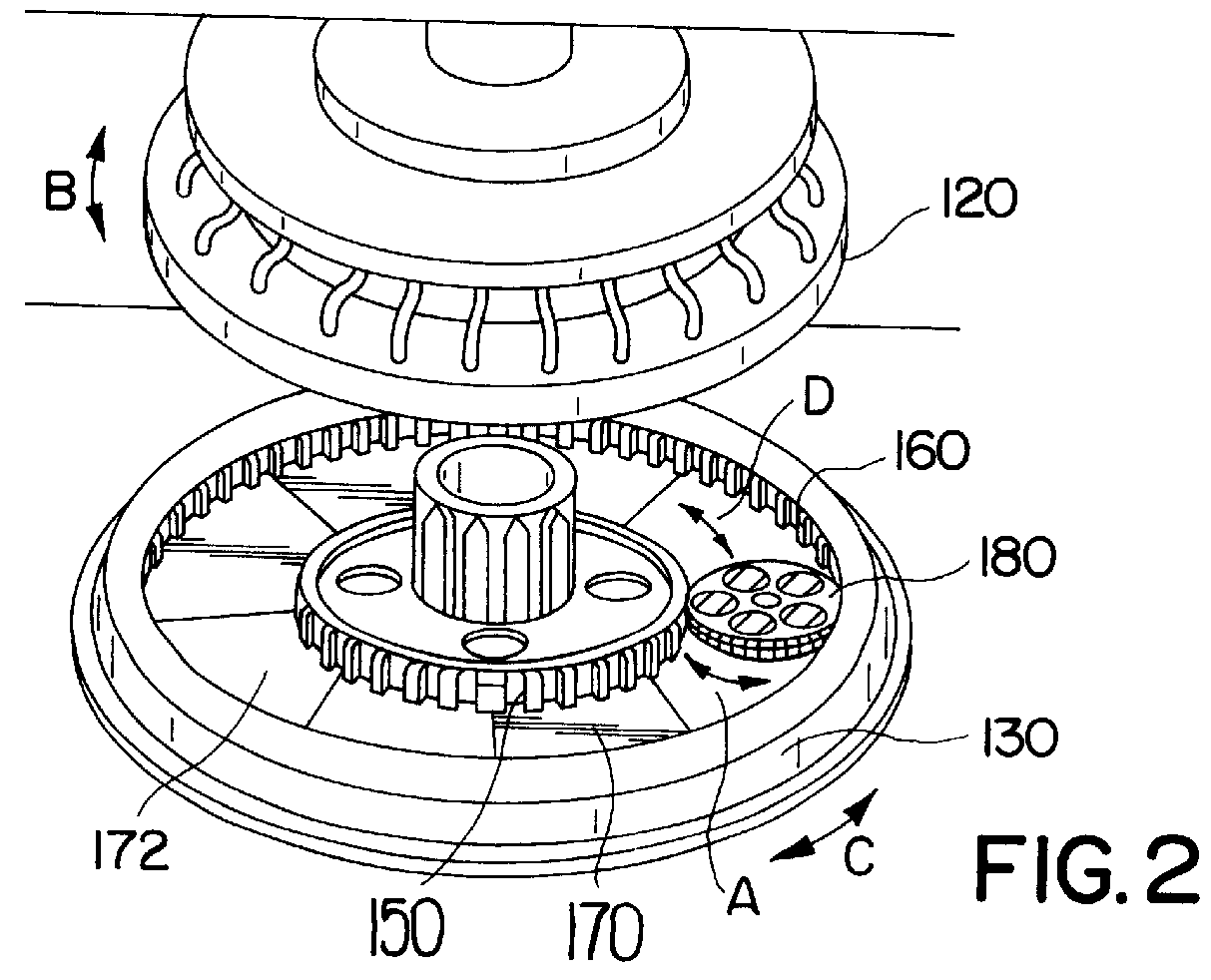
ActiveUS20090283190A1Easy to installReduce misalignmentTyre measurementsTyre-inflating valvesEngineeringHeavy duty
A rotary union is integrated into the interior of a heavy-duty vehicle hub cap. The hub cap includes a cylindrical sidewall, and an outboard wall that is integrally formed with an outboard end of the sidewall, and which extends generally perpendicular to the sidewall. The hub cap also includes a radially-extending flange that is formed on an inboard end of the sidewall, which receives fasteners to mount the hub cap on a wheel hub. The sidewall and the outboard wall form an interior compartment in the hub cap, and a rotary union is mounted to the hub cap in the interior compartment. The rotary union is mounted on the inboard surface of the outboard wall of the hub cap and is in general axial alignment with an axial centerline of a wheel end assembly, providing fluid communication from a tire inflation system to the tires of the vehicle.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Laser diode assemblies
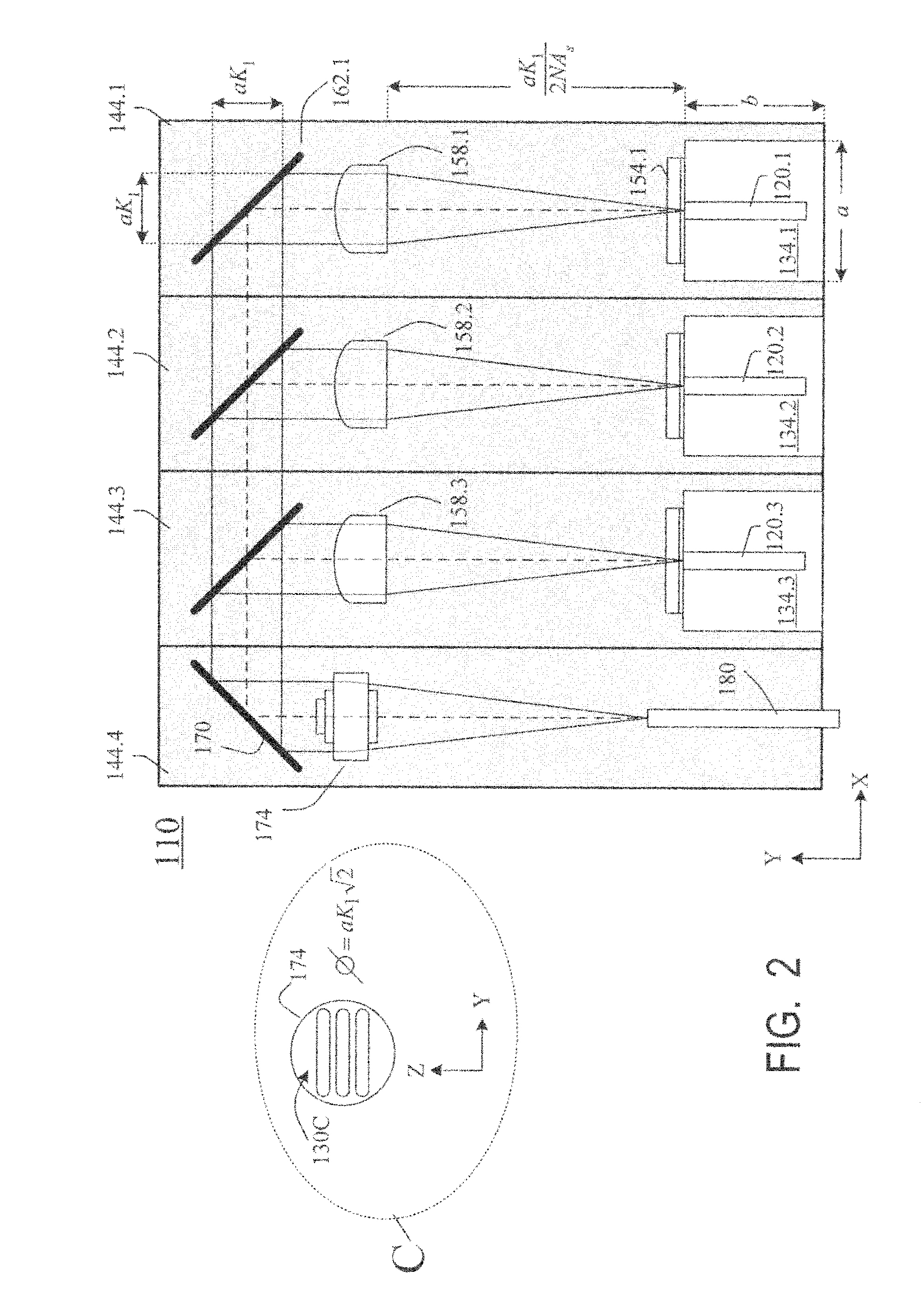
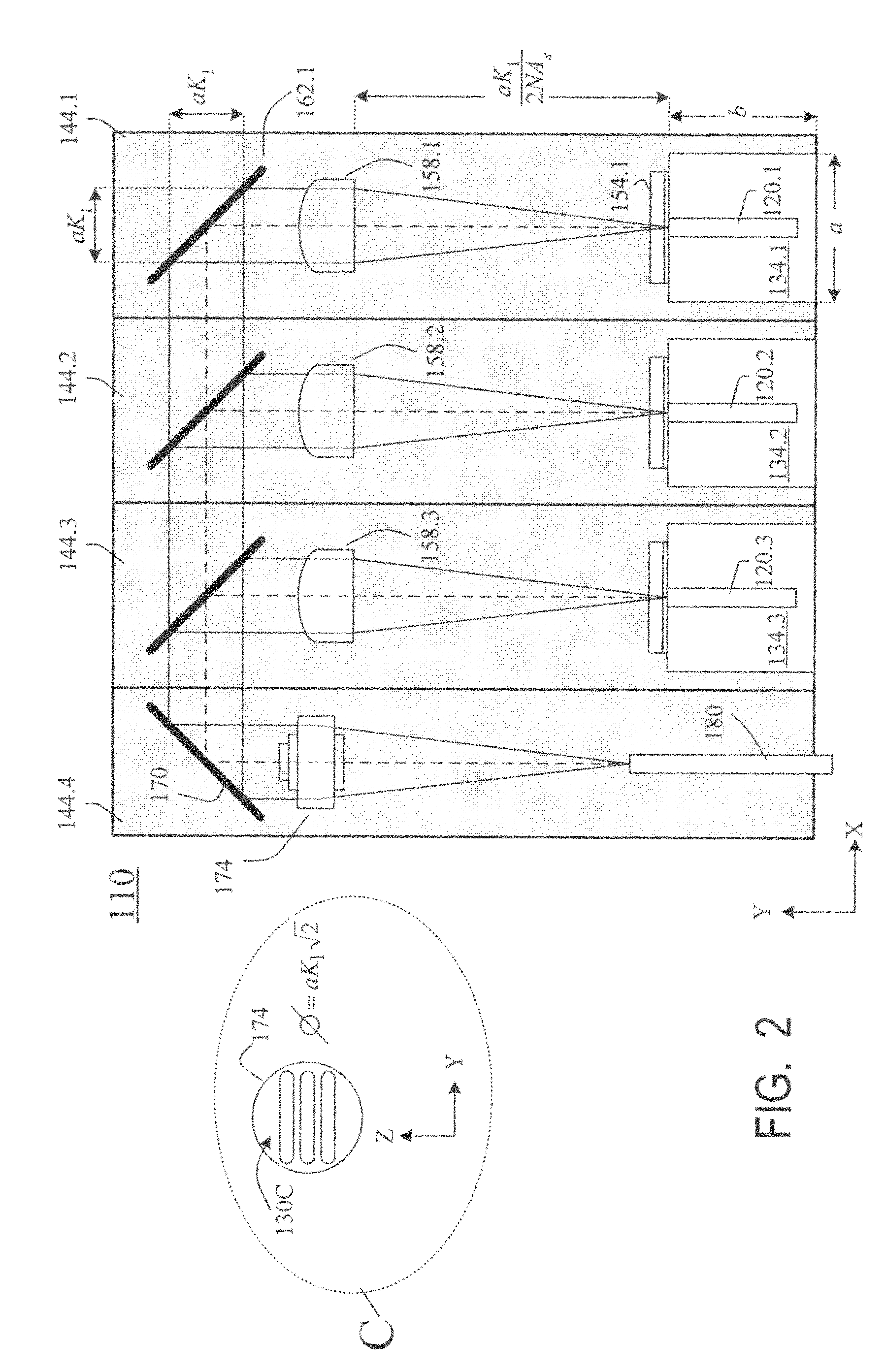
InactiveUS7733932B2Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser cooling arrangementsLight beamLaser beams
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
Nitride semiconductor substrate and method of producing same
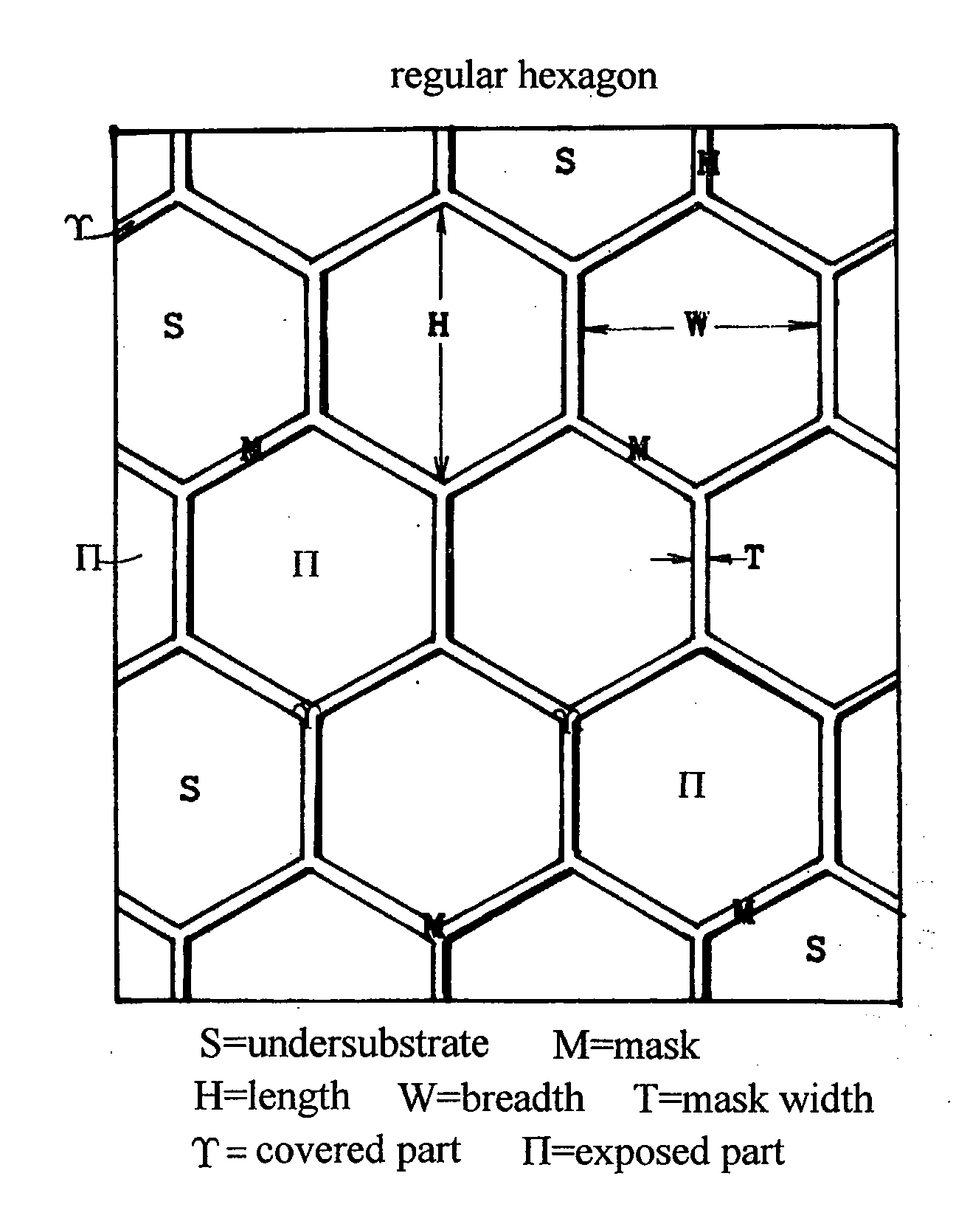
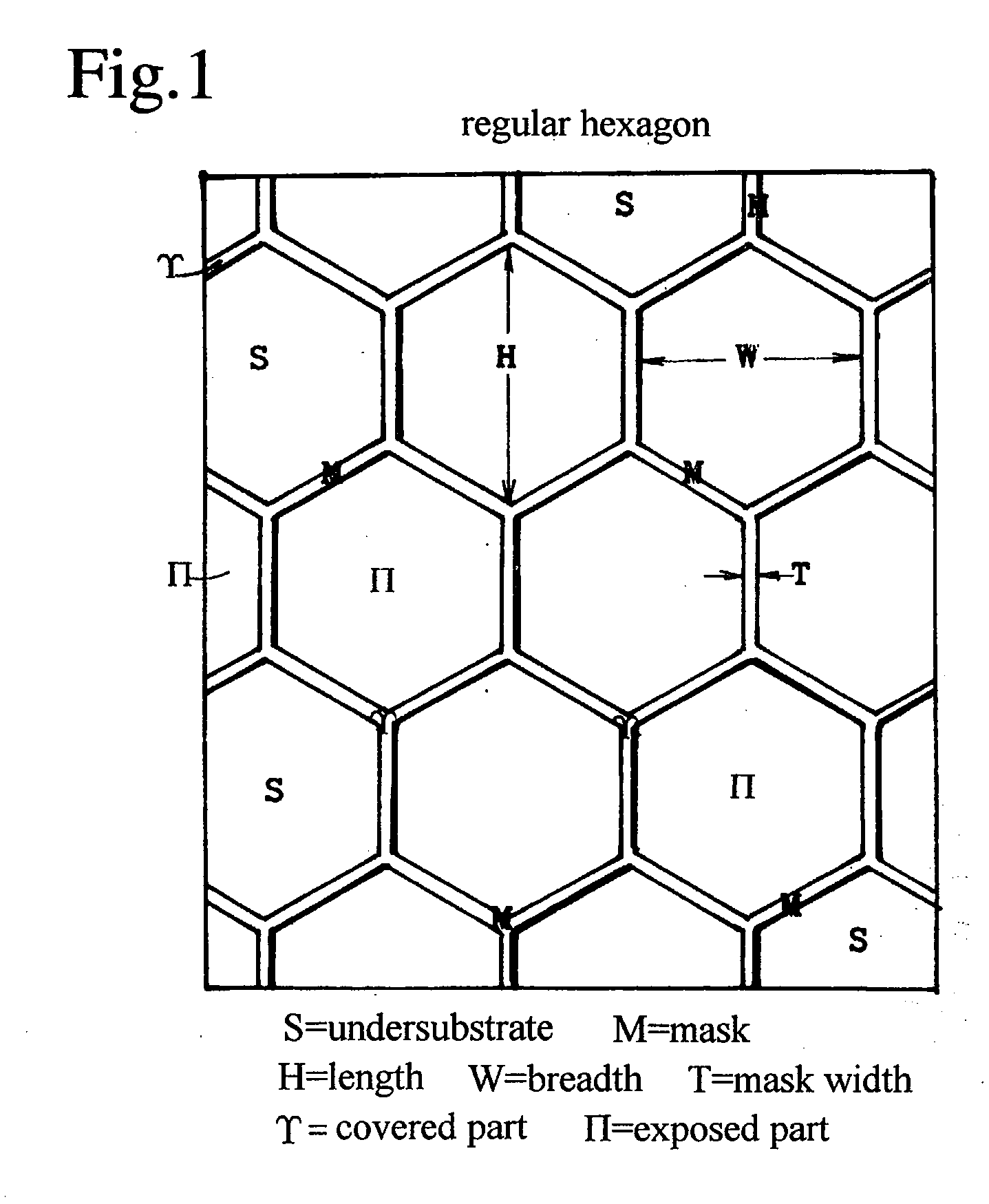
ActiveUS20090155989A1Reduce dislocation densityEasily realizedPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseClosed loop
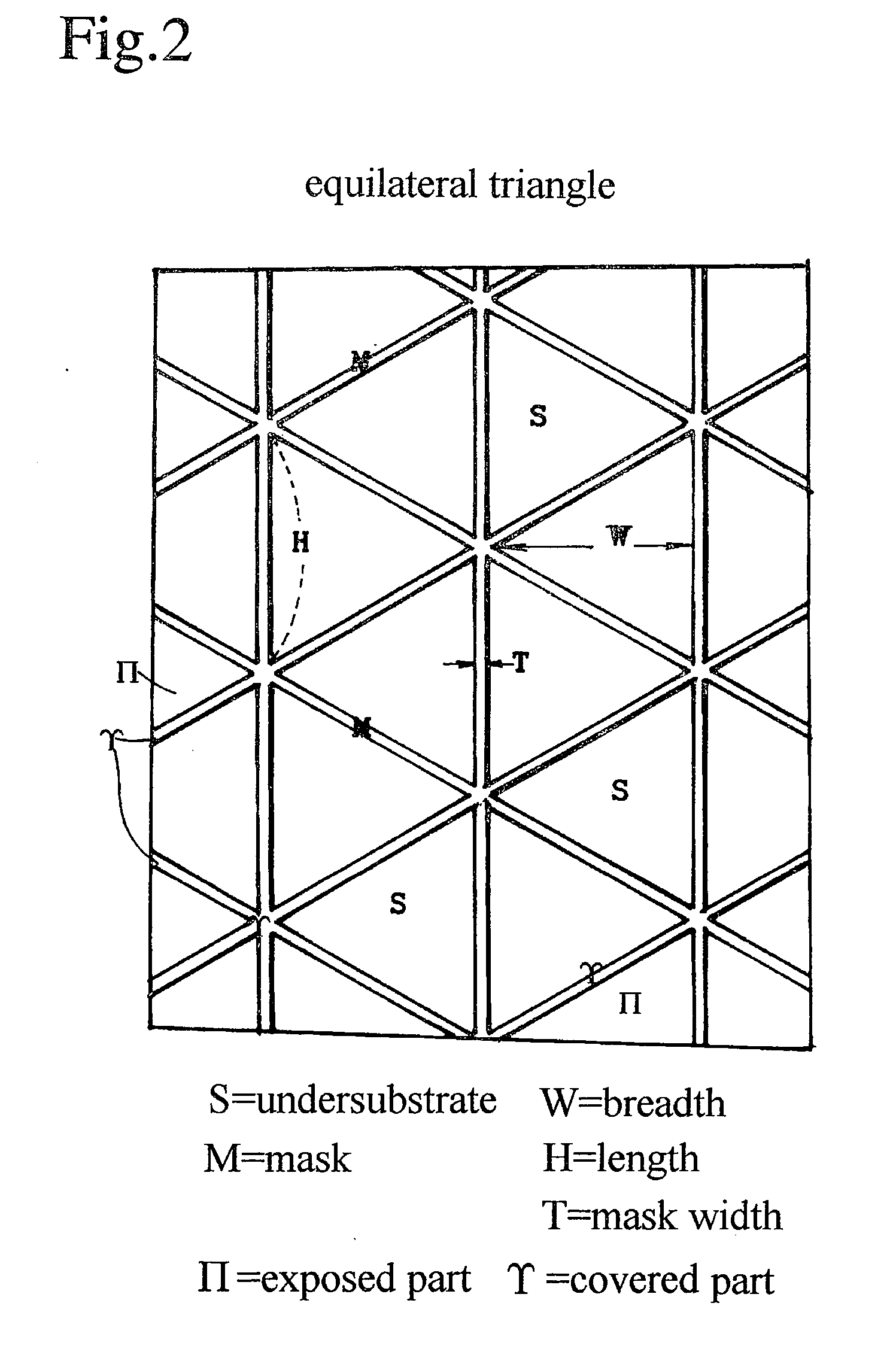
A nitride semiconductor crystal substrate is produced by forming a network mask repeating a closed loop unit shape upon an undersubstrate, growing a nitride semiconductor crystal in vapor phase, producing convex facet hills covered with facets on exposed parts Π, forming outlining concavities on mask-covered parts not burying the facets, maintaining the convex facet hills on Π and the network concavities on excluding dislocations in the facet hills down to the outlining concavities on forming a defect accumulating region H on decreasing dislocations in the facet hills and improving the facet hills to low defect density single crystal regions Z, producing a rugged nitride crystal, and slicing and polishing the nitride crystal into mirror nitride crystal wafers. After the fabrication of devices on the nitride wafer, dry-etching or wet etching of hot KOH or NaOH divides the device-carrying wafer into chips by corroding the network defect accumulating region H.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Stage apparatus and control method therefor
ActiveUS20050190375A1Reduce misalignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansOverlap zonePhysics
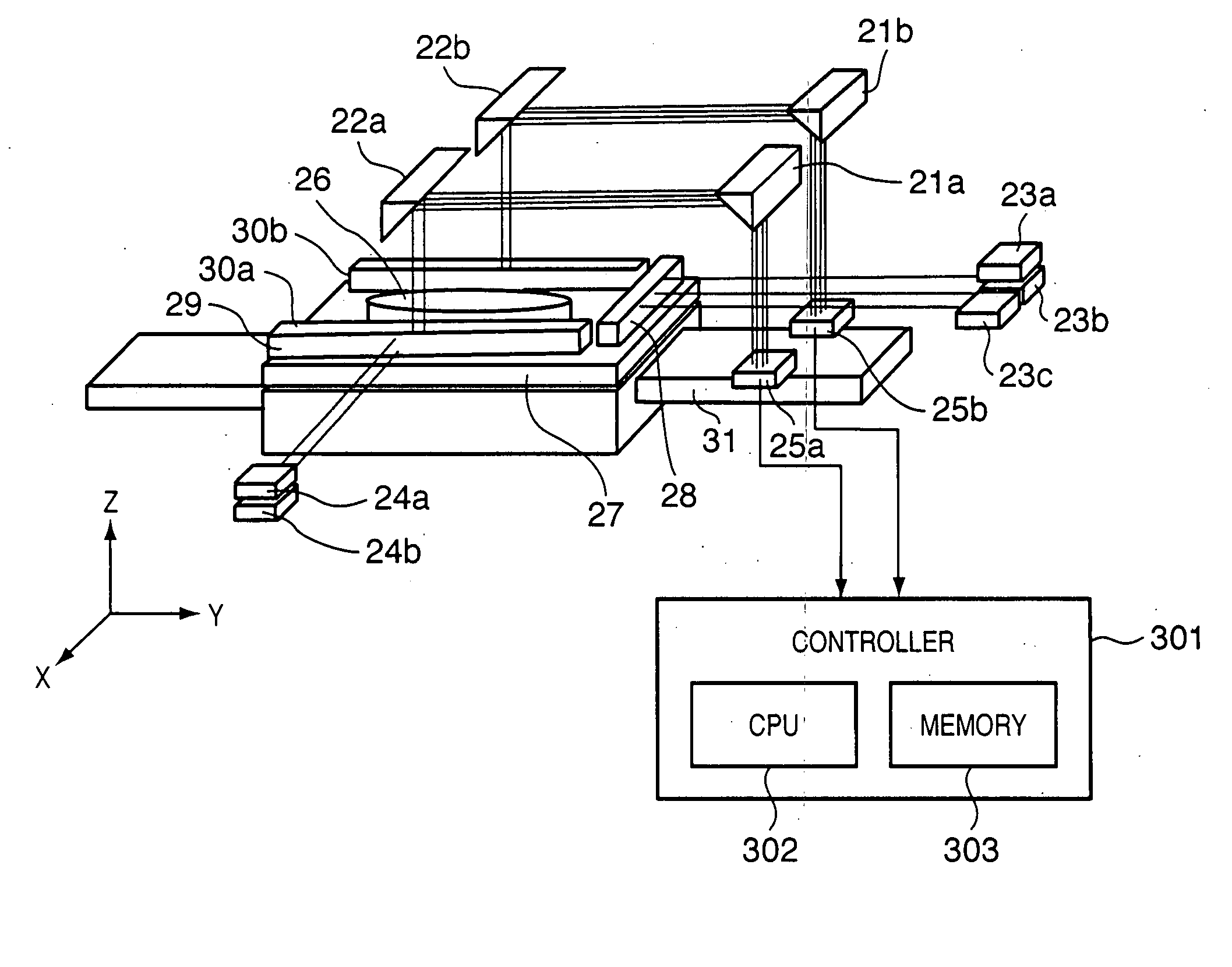
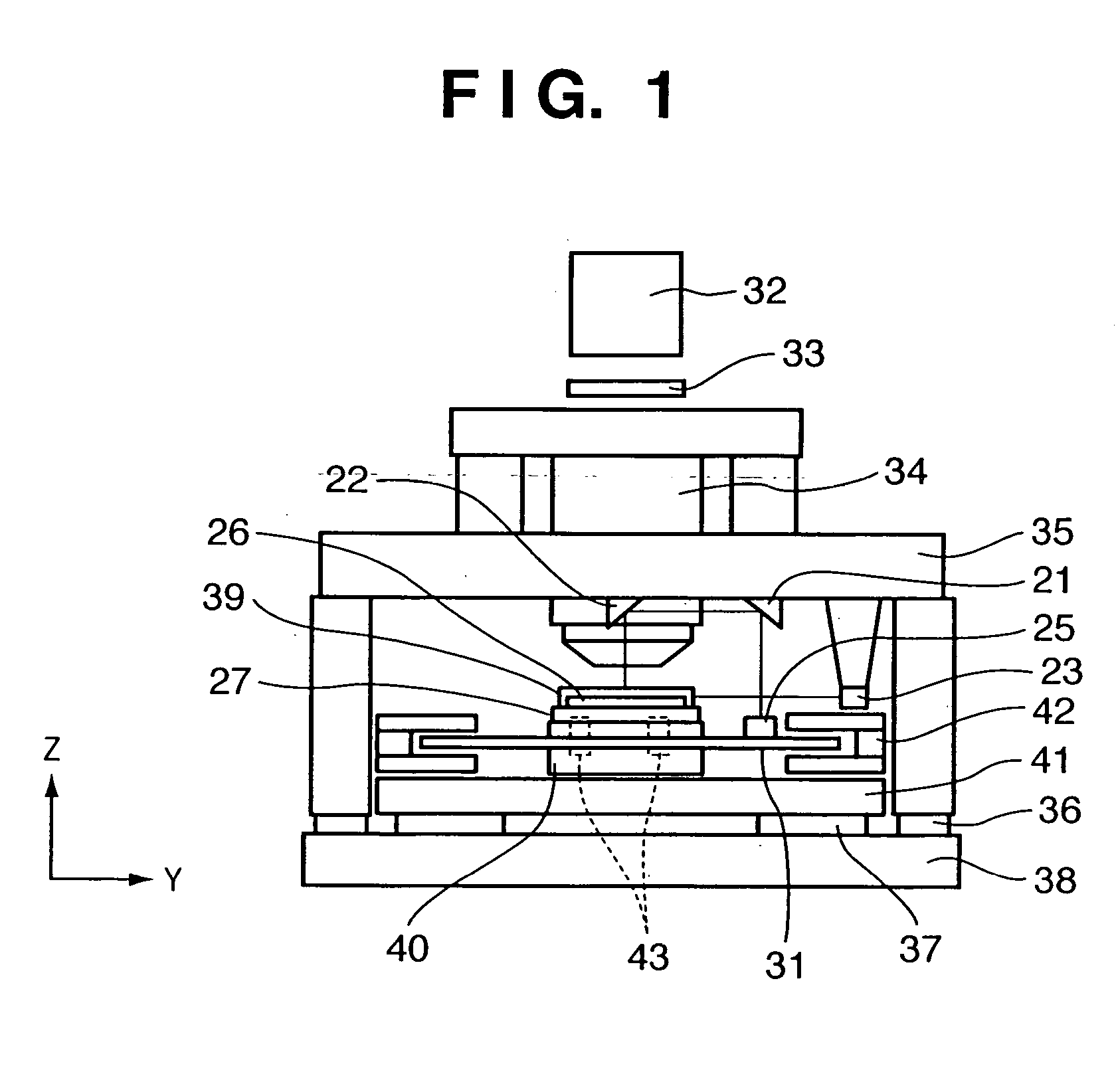
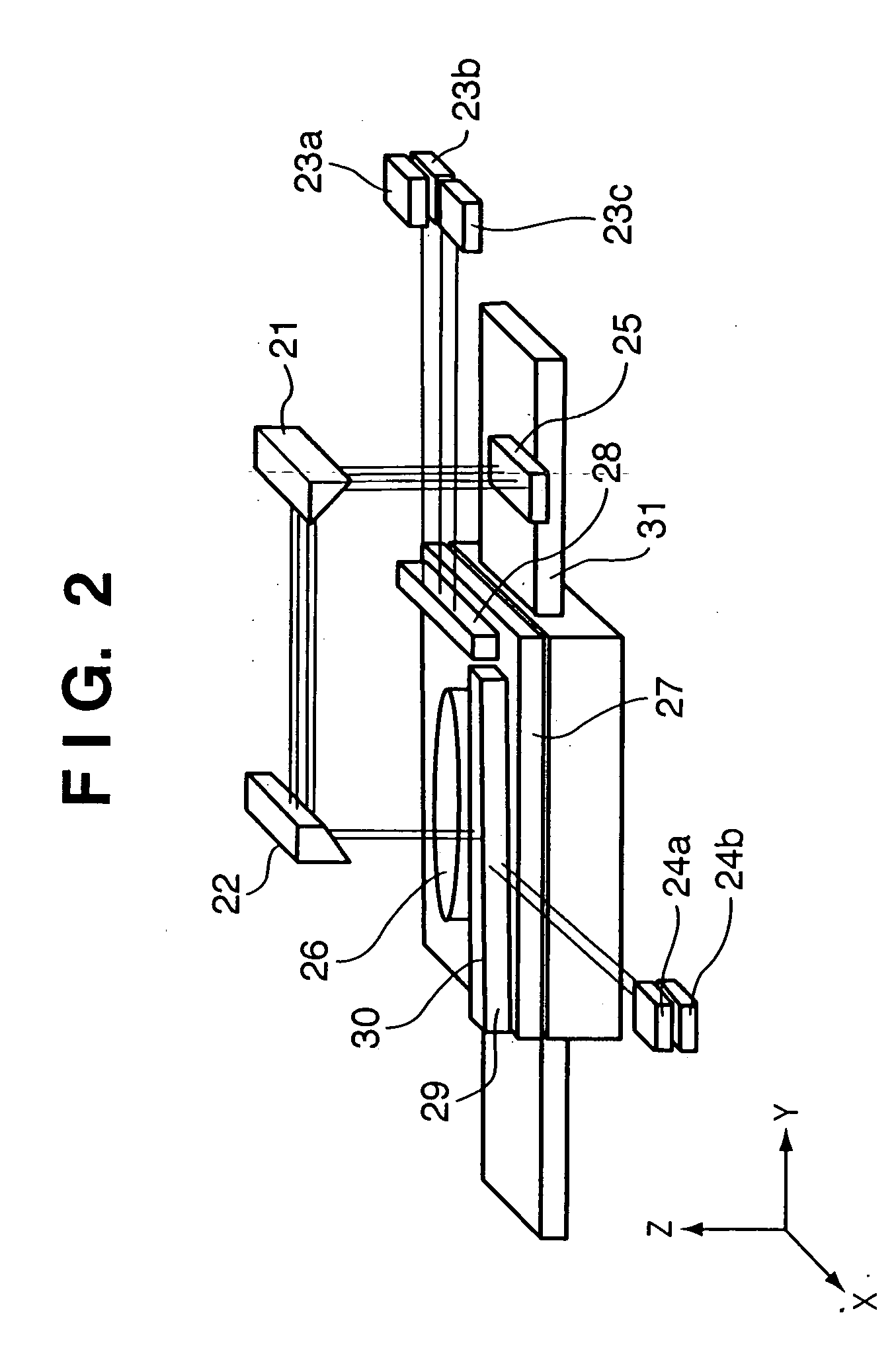
A stage apparatus has a stage movable in a first direction and first and second measurement systems measuring a position of the stage in a predetermined direction. The first and second measurement systems each has a laser interferometer and a mirror system including a first reflecting mirror elongated in the first direction. A measurement value is transferred from one measurement system in use to the other measurement system and the measurement system in use is switched between the first and second measurement systems within a overlapping zone where said first and second measurement system can simultaneously measure the position of the stage. In the switch, the measurement value to be transferred is corrected based on a difference in the lengths of the light paths due to a shape of a surface of the first reflecting mirror of the first and second measurement systems.
Owner:CANON KK
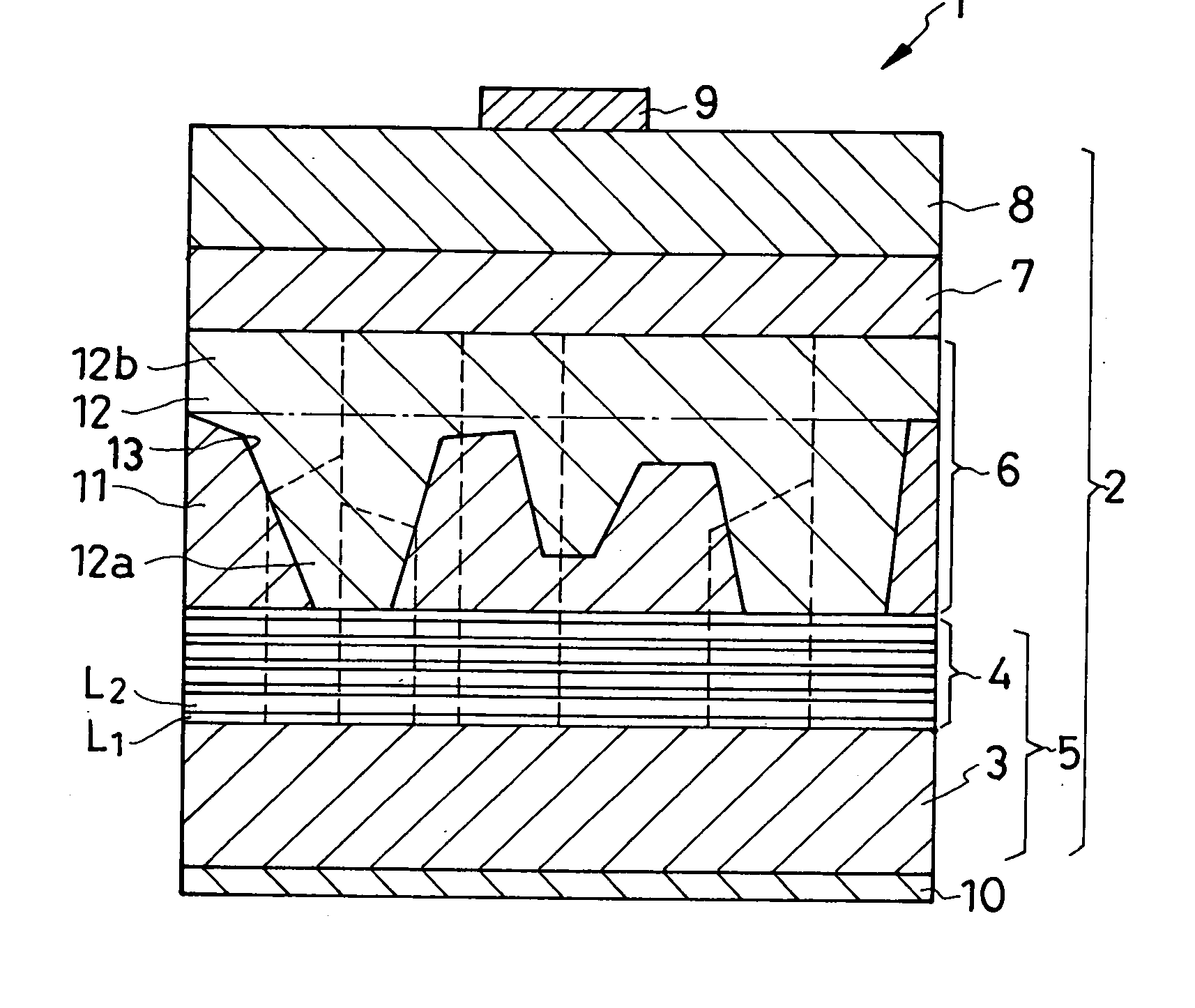
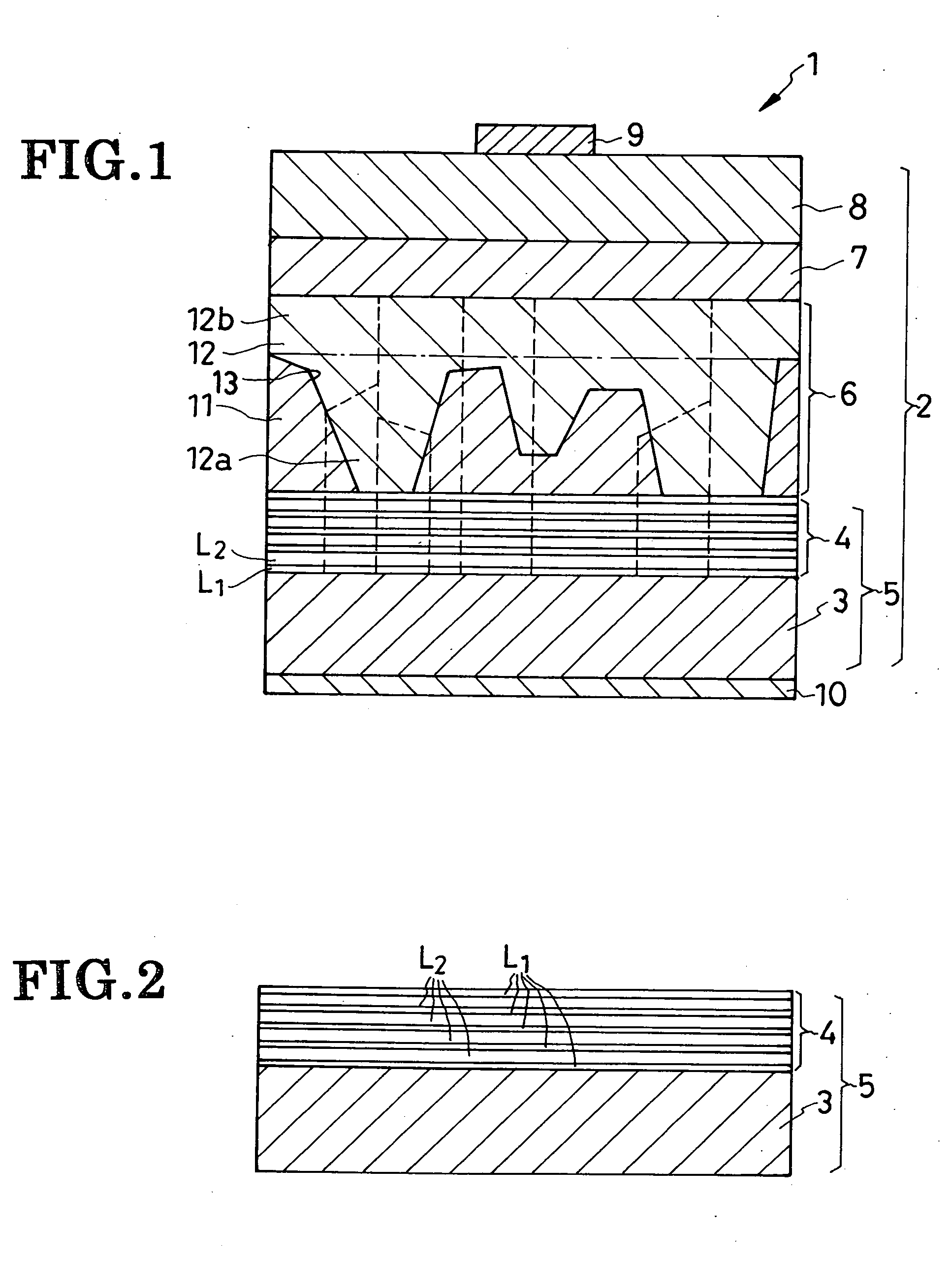
Optical semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
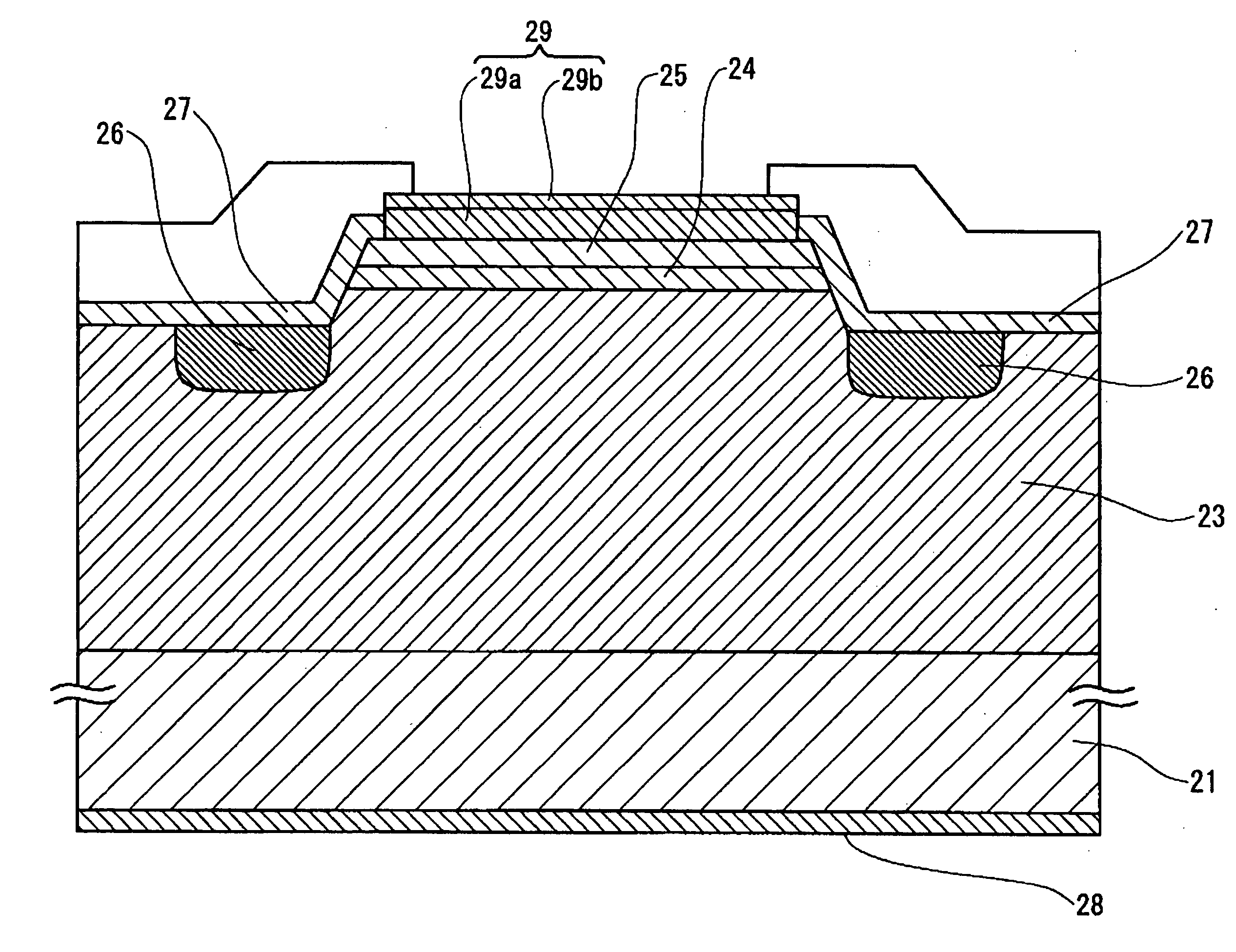
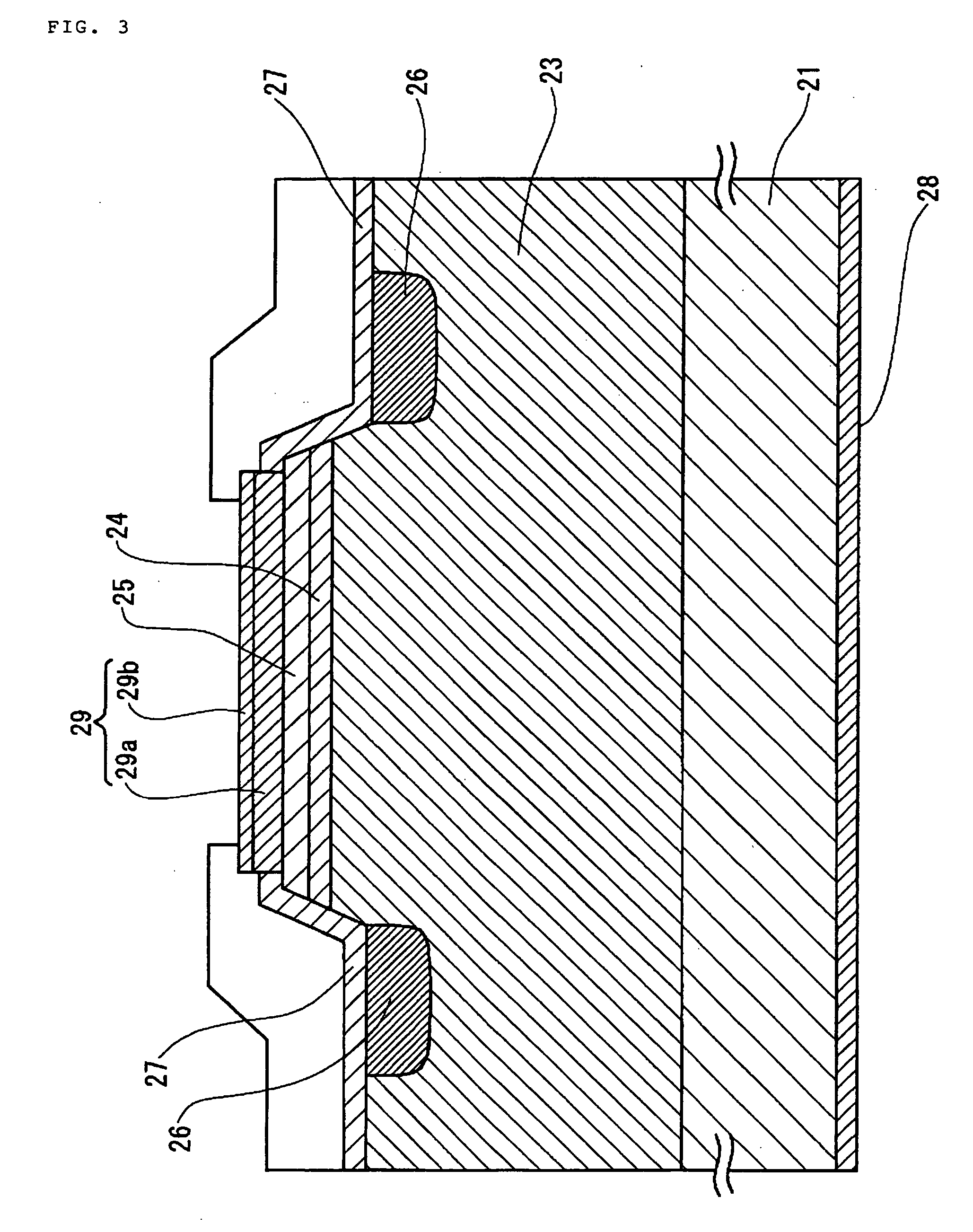
InactiveUS20090057646A1Improve luminous efficiencySuppress gas phase reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchNucleation mode
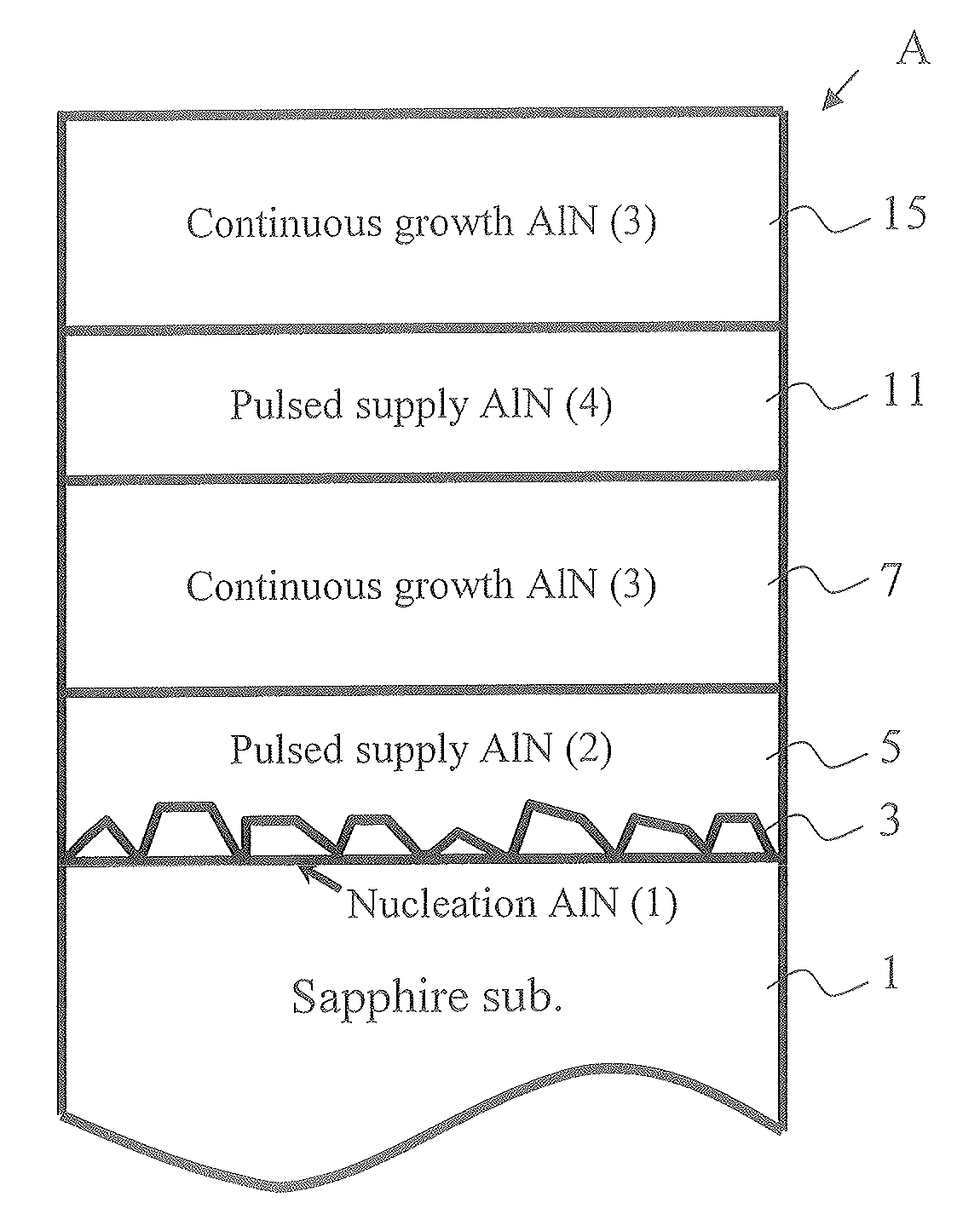
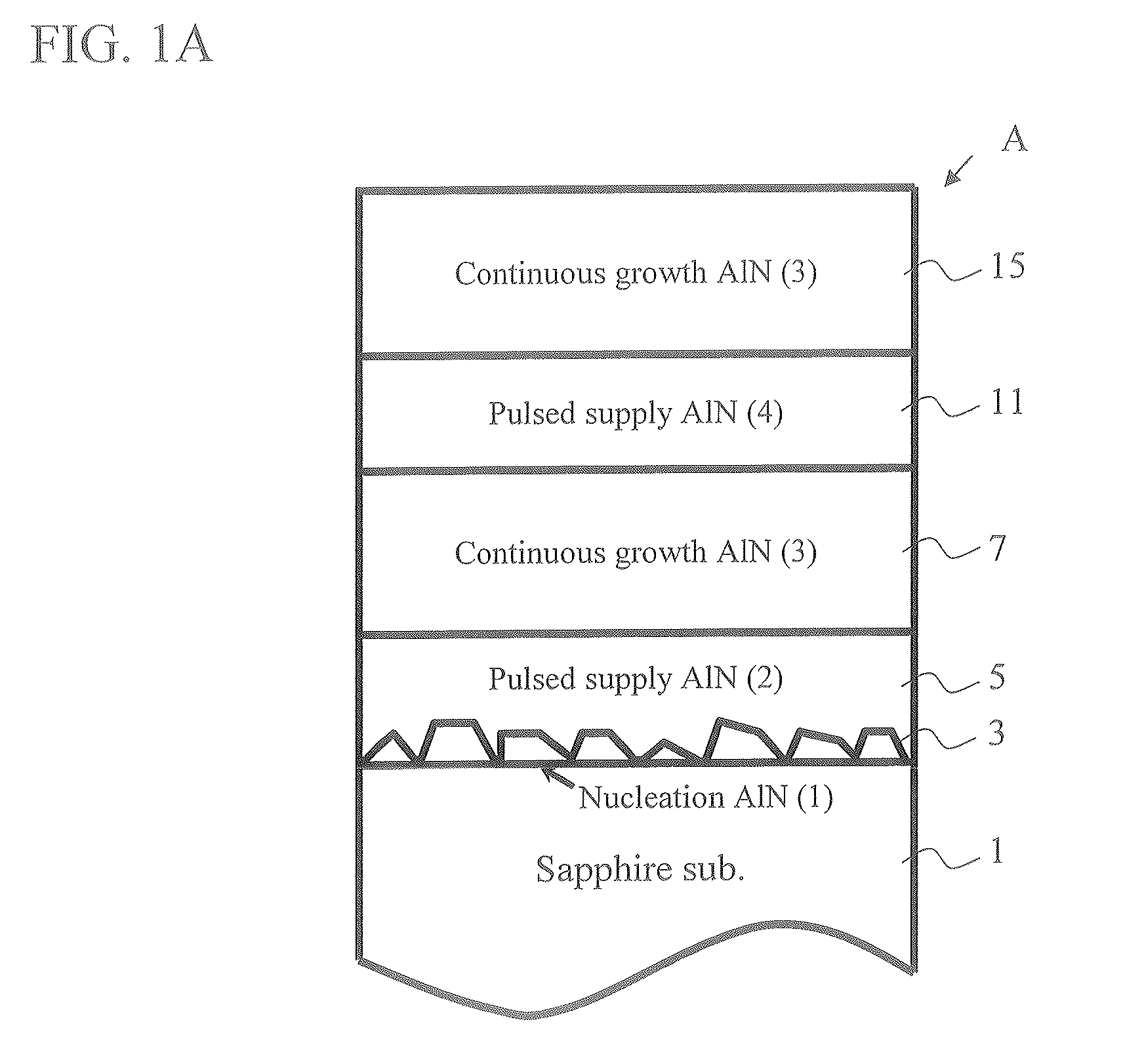
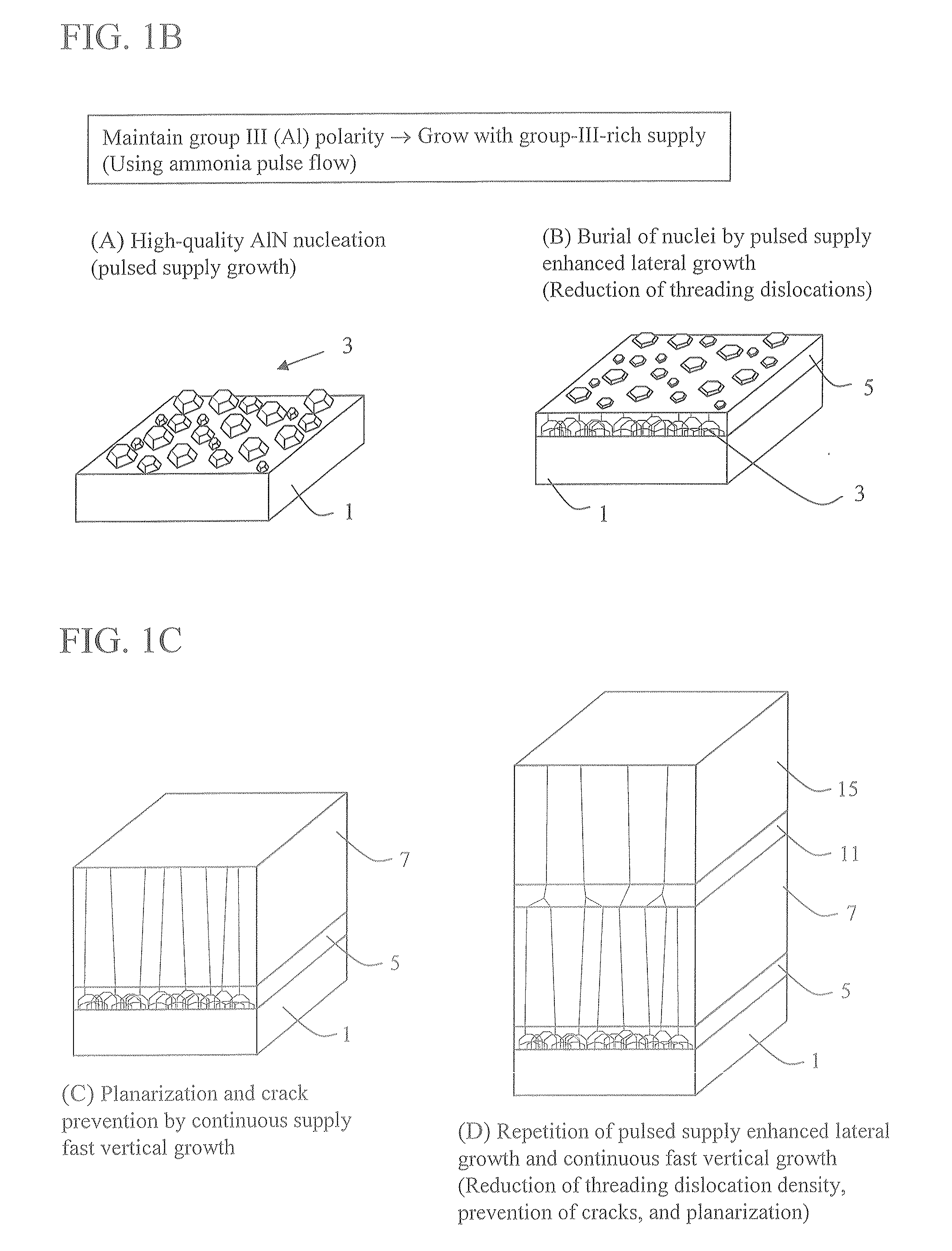
Because of a large lattice mismatch between a sapphire substrate and a group III-V compound semiconductor, a good crystal is difficult to grow. A high-quality AlN buffer growth structure A on a sapphire substrate includes a sapphire (0001) substrate 1, an AlN nucleation layer 3 formed on the sapphire substrate 1, a pulsed supplied AlN layer 5 formed on the AlN nucleation layer 3, and a continuous growth AlN layer 7 formed on the pulsed supplied AlN layer 5. Formed on the continuous growth AlN layer 7 is at least one set of a pulsed supplied AlN layer 11 and a continuous growth AlN layer 15. The AlN layer 3 is grown in an initial nucleation mode which is a first growth mode by using an NH3 pulsed supply method. The pulsed supplied AlN layer 5 is formed by using NH3 pulsed supply in a low growth mode which is a second growth mode that increases a grain size and reduces dislocations and therefore is capable of reducing dislocations and burying the nucleation layer 3. The continuous growth AlN layer 7 is a fast vertical growth mode that improves flatness and suppresses crack occurrences. As examples of the thickness of layers; the pulsed supplied AlN layer 5, 11 is 0.3 μm and the thickness of the continuous growth AlN layer 7, 15 is 1 μm, for example. Characteristics of conditions under which layers are grown are as follows. The AlN layer 3 is grown under a high temperature and a high pressure with a low V-III ratio (less N). The pulsed supplied AlN layer 5 is grown at a low temperature and a low pressure with a high V-III ratio (more N). The continuous AlN layer 7 is grown at a high temperature and a high pressure with a high V-III ratio (Al rich and less N) without using an NH3 pulsed supply AlN growth method.
Owner:RIKEN
Lens device
ActiveUS7419315B2Prevent dislocationReduce misalignmentMountingsCamera body detailsCamera lensOptical axis
In a lens device, plastic lenses having circular outer periphery are placed in a plastic lens-barrel having an octagonal or more complex polygonal inner surface in such a way that the outer peripheral surfaces of the lenses are press contacted to the inner surface of the polygonal shape. This lens device has press contact portions that are pressed by the lens outer peripheral surface and the lens-barrel inner surface in the vicinity and in both sides of gate traces where optical axis displacement is large so as to suppress the displacement of the gate trace by the press contact portions.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
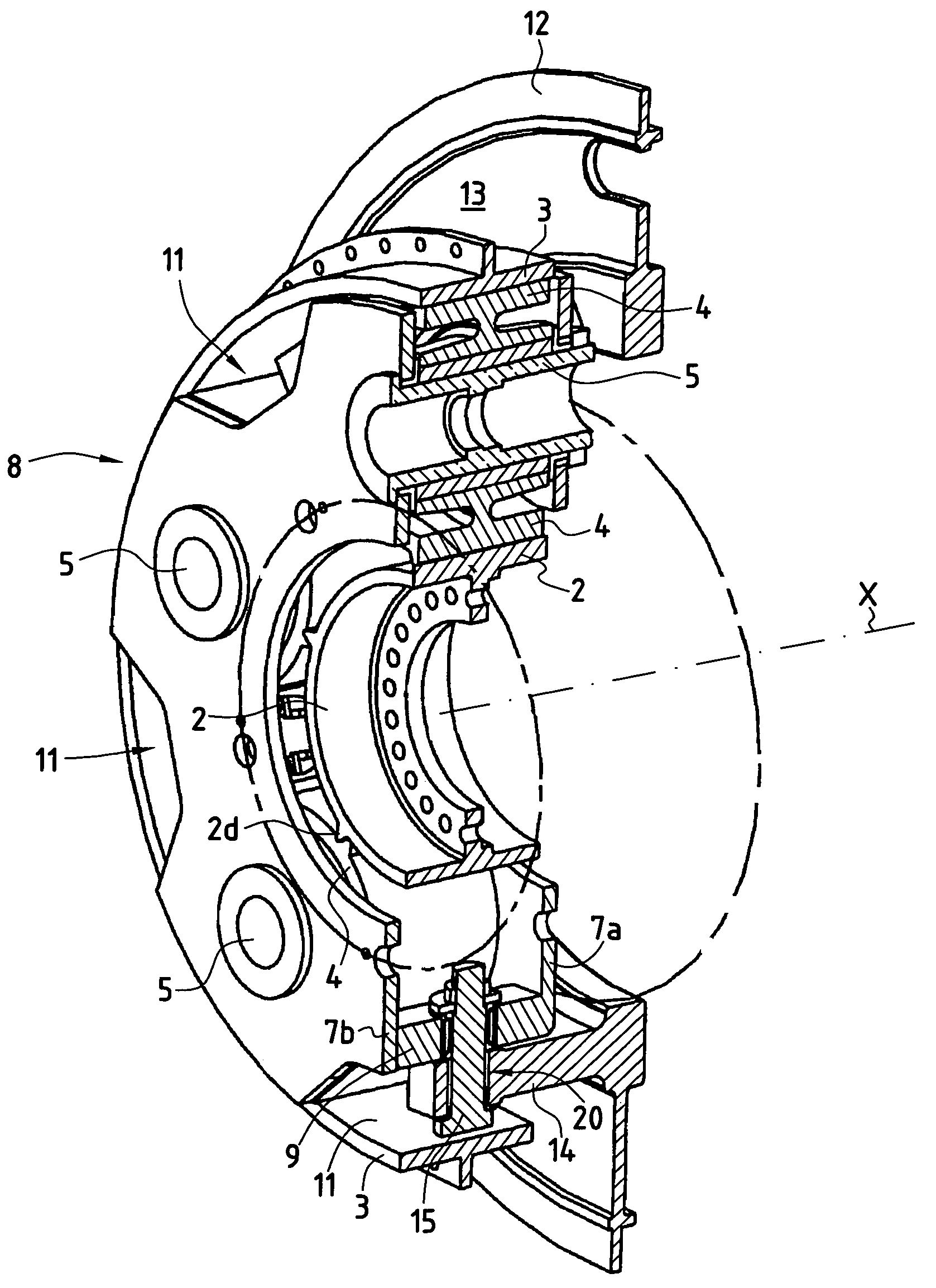
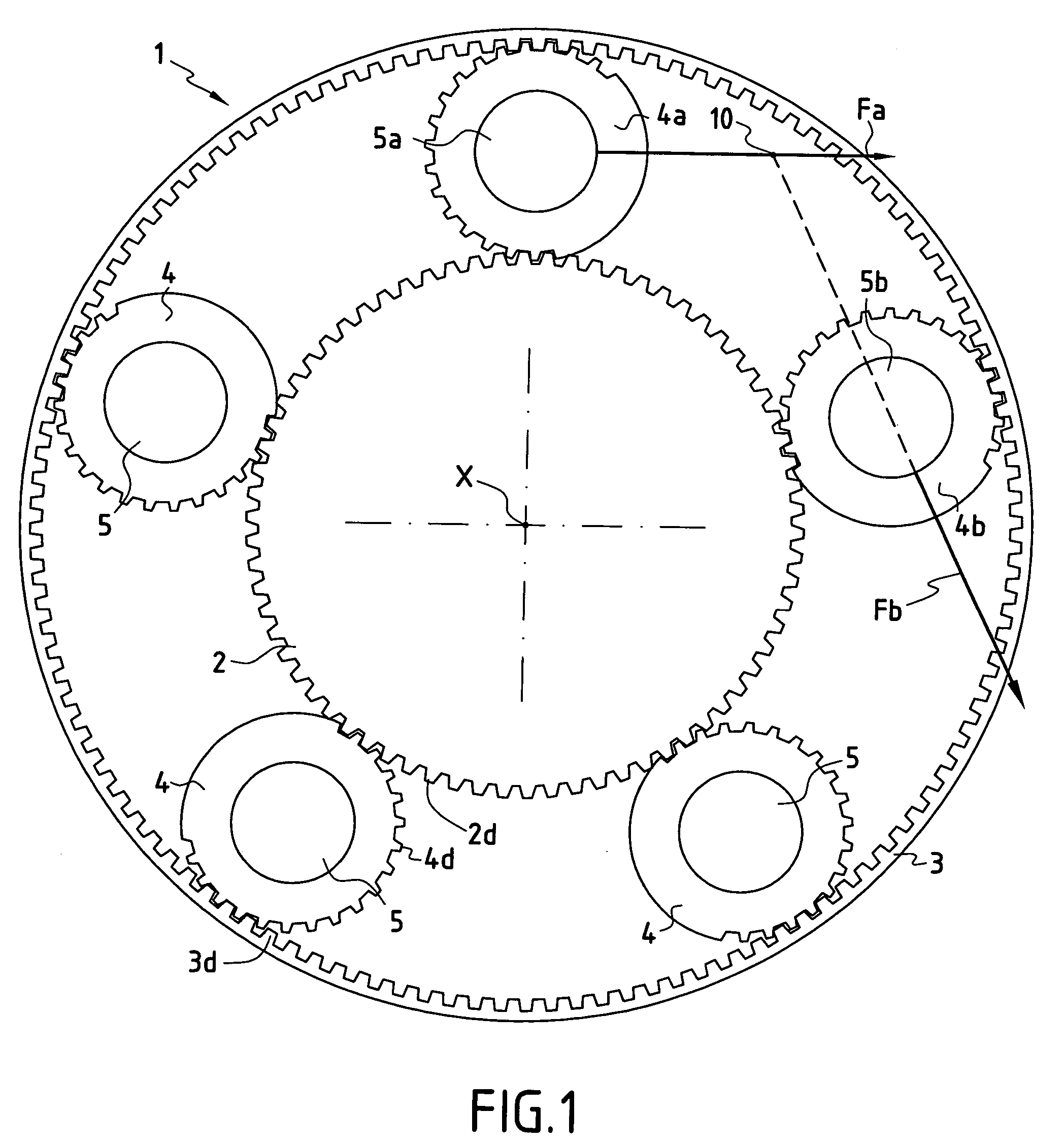
Flexible connection system between a planet carrier and the stationary support in a speed reduction gear train
ActiveUS7011599B2Reduce misalignmentProvide in connectionGearboxesToothed gearingsGear trainSpherical form
A speed reduction gear train comprising a sun gear, an annular gear, and planet gears meshing with the sun gear and the annular gear and mounted in a cage having axial housings between pairs of adjacent planet gears. The cage is connected to a cage carrier having axial arms received in the housings by radial pins disposed in the midplane of the cage by means of spherical finger connections allowing the cage carrier to tilt and to move axially relative to the cage.
Owner:SAFRAN TRANSMISSION SYST
Bipolar Semiconductor Device and Process for Producing the Same
A process for manufacturing a bipolar type semiconductor device in which at least a part of a region where an electron and a hole are recombined during current flowing is formed with a silicon carbide epitaxial layer that has been grown from the surface of a silicon carbide substrate, is characterized by that the surface of the silicon carbide substrate is treated by hydrogen etching and the epitaxial layer is then formed by the epitaxial growth of silicon carbide from the treated surface. A propagation of a basal plane dislocation to the epitaxial layer can be further reduced by treating the surface of the silicon carbide substrate by using chemical mechanical polishing and hydrogen etching in this order.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Semiconductor Devices Having Low Threading Dislocations and Improved Light Extraction and Methods of Making the Same
ActiveUS20080121910A1Reduce defectsImproved radiation extraction efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationThreading dislocationsDislocation
Semiconductor device structures are provided that are suitable for use in the fabrication of electronic devices such as light emitting diodes. The semiconductor device structures include a substrate having a roughened growth surface suitable for supporting the growth of an epitaxial region thereon. The device structure can include an epitaxial region having reduced defects and / or improved radiation extraction efficiency on the roughened growth surface of the substrate. The roughened growth surface of the substrate can have an average roughness Ra of at least about 1 nanometer (nm) and an average peak to valley height Rz of at least about 10 nanometers (nm).
Owner:CREELED INC
Silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and silicon carbide semiconductor device by using thereof
InactiveUS20090085044A1Reducing basal plane dislocation densityImprove conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalDislocation
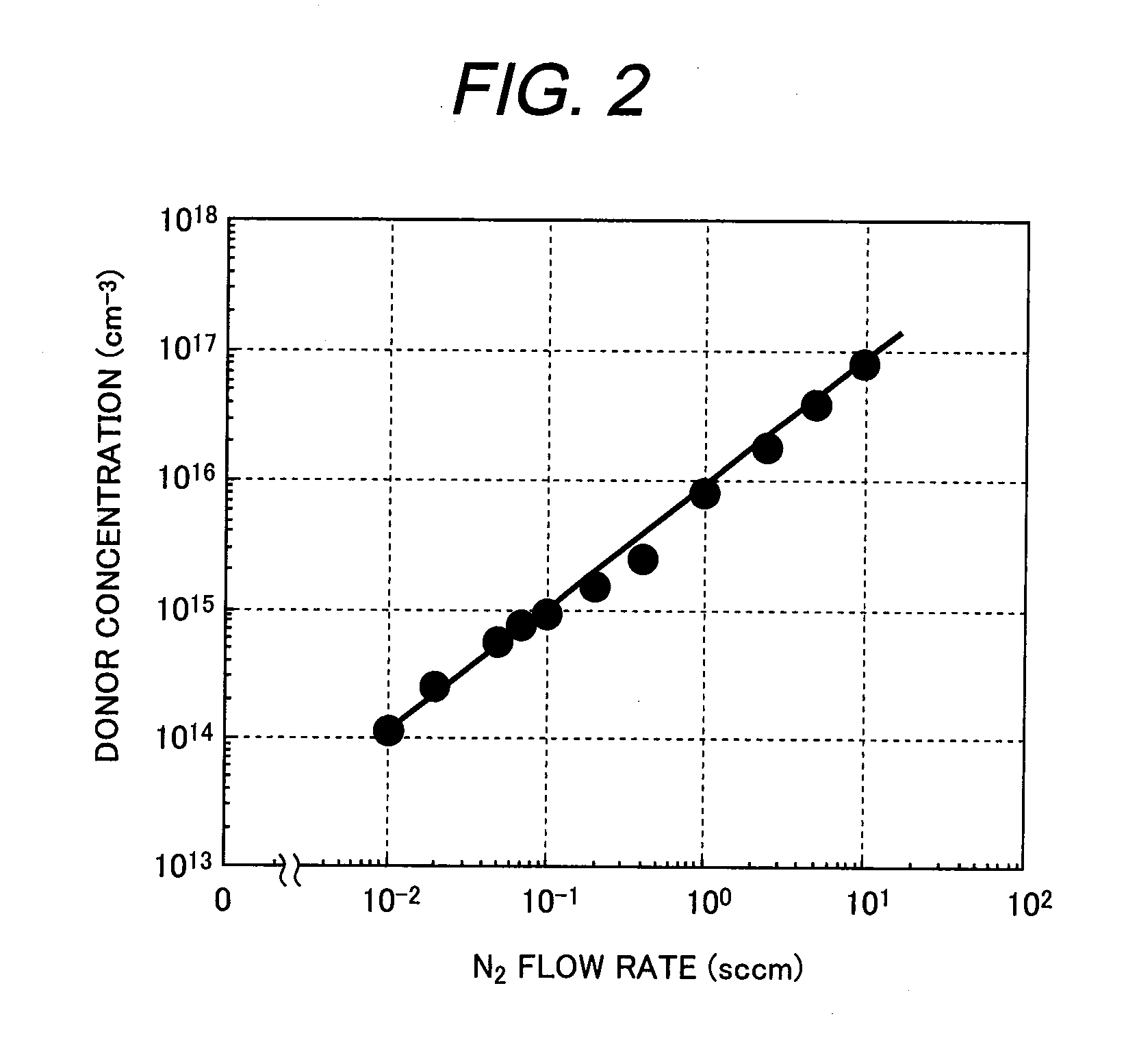
A manufacturing method is provided for a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate adapted for reduced basal plane dislocations in a silicon carbide epitaxial layer. Between a silicon carbide epitaxial layer for device fabrication (i.e., a drift layer) and a base substrate formed of a silicon carbide single-crystal wafer, a highly efficient dislocation conversion layer through which any basal plane dislocations in the silicon carbide single-crystal wafer are converted into threading edge dislocations very efficiently when the dislocations propagate into the layer epitaxially grown is provided by epitaxial growth. Assigning to the dislocation conversion layer a donor concentration lower than that of the drift layer, therefore, allows the above conversion of a larger number of basal plane dislocations than the case where the drift layer exists alone (without the dislocation conversion layer).
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Projector and projector control method
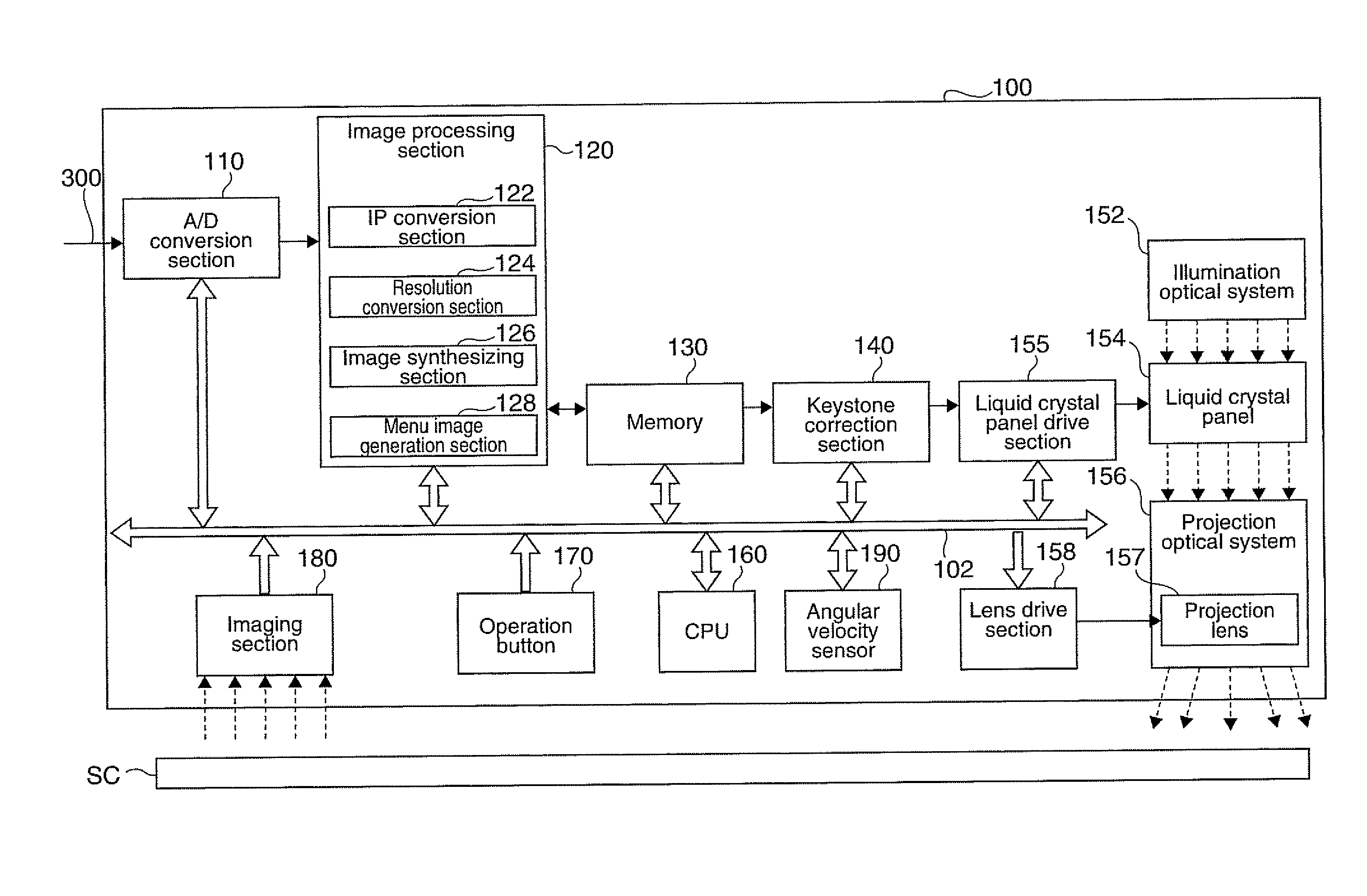
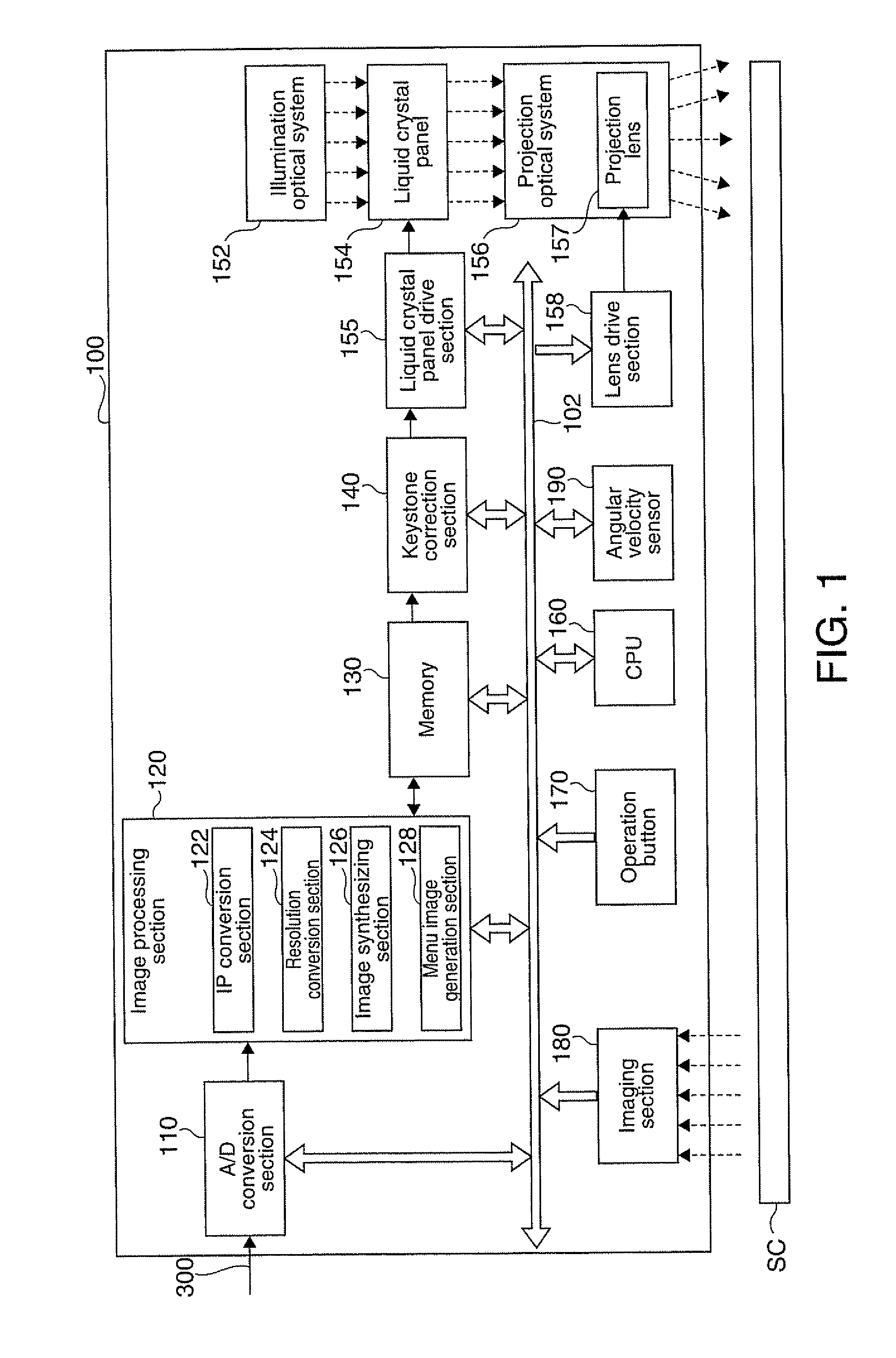
ActiveUS20100103386A1Improve user friendlinessReduce misalignmentProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementLight sourcePhysics
A projector which projects an image onto a projection surface, and displays it thereon, includes: a light source; a light modulator which modulates light from the light source into an image light representing the image; a projection optical system which projects the image light modulated by the light modulator onto the projection surface; a keystone distortion correction section which carries out a keystone distortion correction process for correcting a keystone distortion of the image projected onto the projection surface; a detection section which detects a stop of a movement of the projector; and a control section which, on the stop of the movement of the projector being detected in the detection section, causes the keystone distortion correction section to start the keystone distortion correction process in accordance with a relative positional relationship between the projector after being moved and the projection surface.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Group III nitride based semiconductor substrate and process for manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20030183157A1Quality improvementStable productionLaser detailsFrom solid stateDislocationNitride
To provide a semiconductor substrate of a group III nitride with a little warp, this invention provides a process comprising such steps of: epitaxial-growing a GaN layer 33 with a GaN low temperature grown buffer layer 32 upon a sapphire substrate 31; removing the sapphire substrate 31, the GaN buffer layer 32 and a small portion of the GaN layer 33 from the substrate taken out of a growth reactor to obtain a self-supporting GaN substrate 35; and after that, heat-treating the GaN substrate 35 by putting it into an electric furnace under the NH3 atmosphere at 1200° C. for 24 hours; which leads to a marked reduction of the warp of the self-supporting GaN substrate 35 such that dislocation densities of its obverse and reverse surface are 4x10<7 >cm<-2 >and 8x10<5 >cm<-2>, and thereby such a low ratio of dislocation densities of 50 is well-controlled.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Image pickup device, and image pickup device assembling method
InactiveUS20050270403A1Avoid distortionPreventing of picture of picture qualityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesivePrinted circuit board
The invention integrally arranges a lens, an optical filter, a semiconductor imaging device, on-chip components, and a printed circuit board on a three-dimensional circuit board and contrives the lens attachment structure, bonding method, color of an adhesive, masking of the lens, etc. in order to implement a structure that allows high performance, compact, lightweight and rigid design, and mass production, as well as a high-quality picture.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
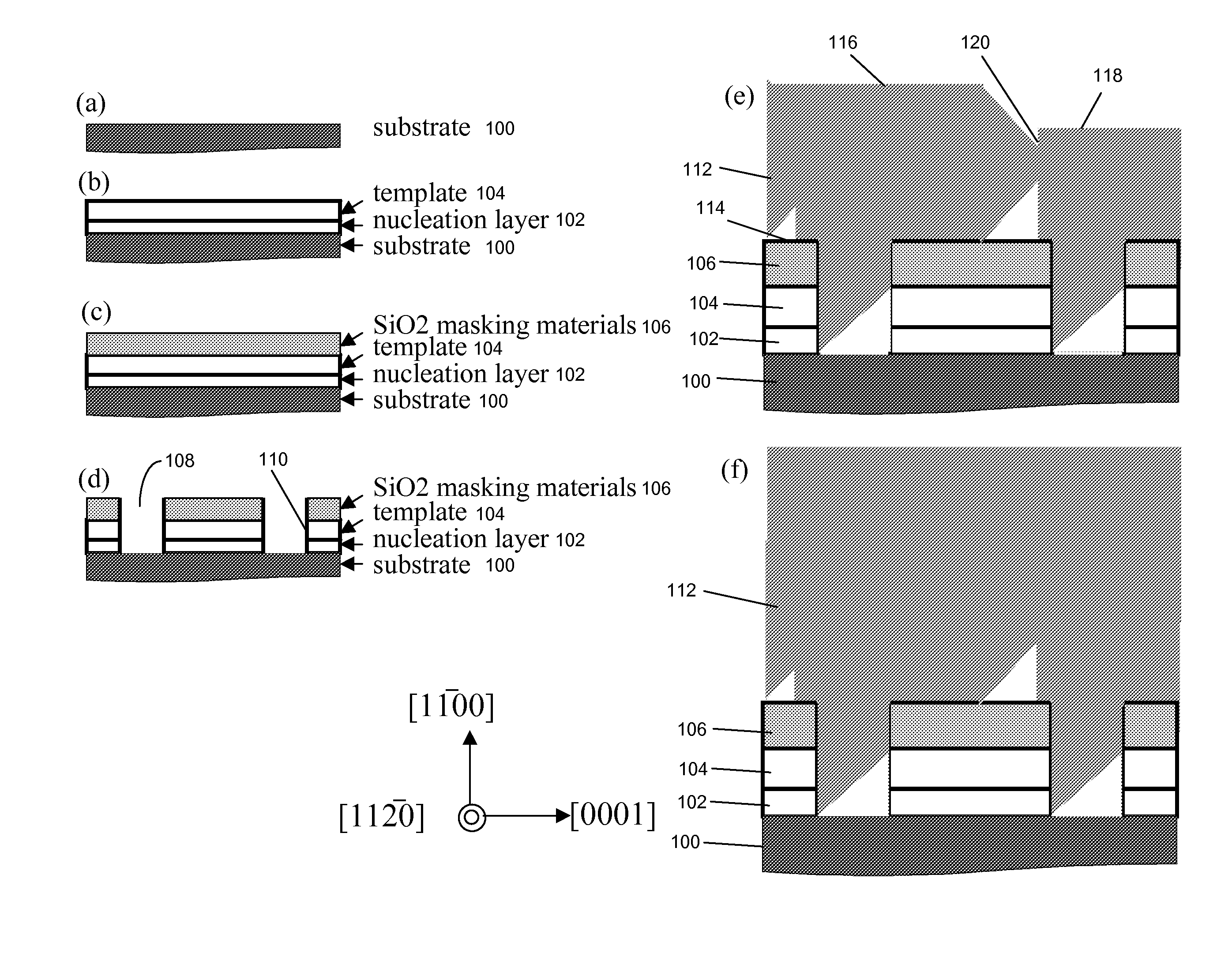
CRYSTAL GROWTH OF M-PLANE AND SEMIPOLAR PLANES OF (Al, In, Ga, B)N ON VARIOUS SUBSTRATES
InactiveUS20080163814A1Eliminate polarization fieldLong life-timePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrideDislocation
A method of reducing threading dislocation densities in non-polar such as a- {11-20} plane and m-{1-100} plane or semi-polar such as {10-1n} plane III-Nitrides by employing lateral epitaxial overgrowth from sidewalls of etched template material through a patterned mask. The method includes depositing a patterned mask on a template material such as a non-polar or semi polar GaN template, etching the template material down to various depths through openings in the mask, and growing non-polar or semi-polar III-Nitride by coalescing laterally from the tops of the sidewalls before the vertically growing material from the trench bottoms reaches the tops of the sidewalls. The coalesced features grow through the openings of the mask, and grow laterally over the dielectric mask until a fully coalesced continuous film is achieved.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method of making substrates for nitride semiconductor devices
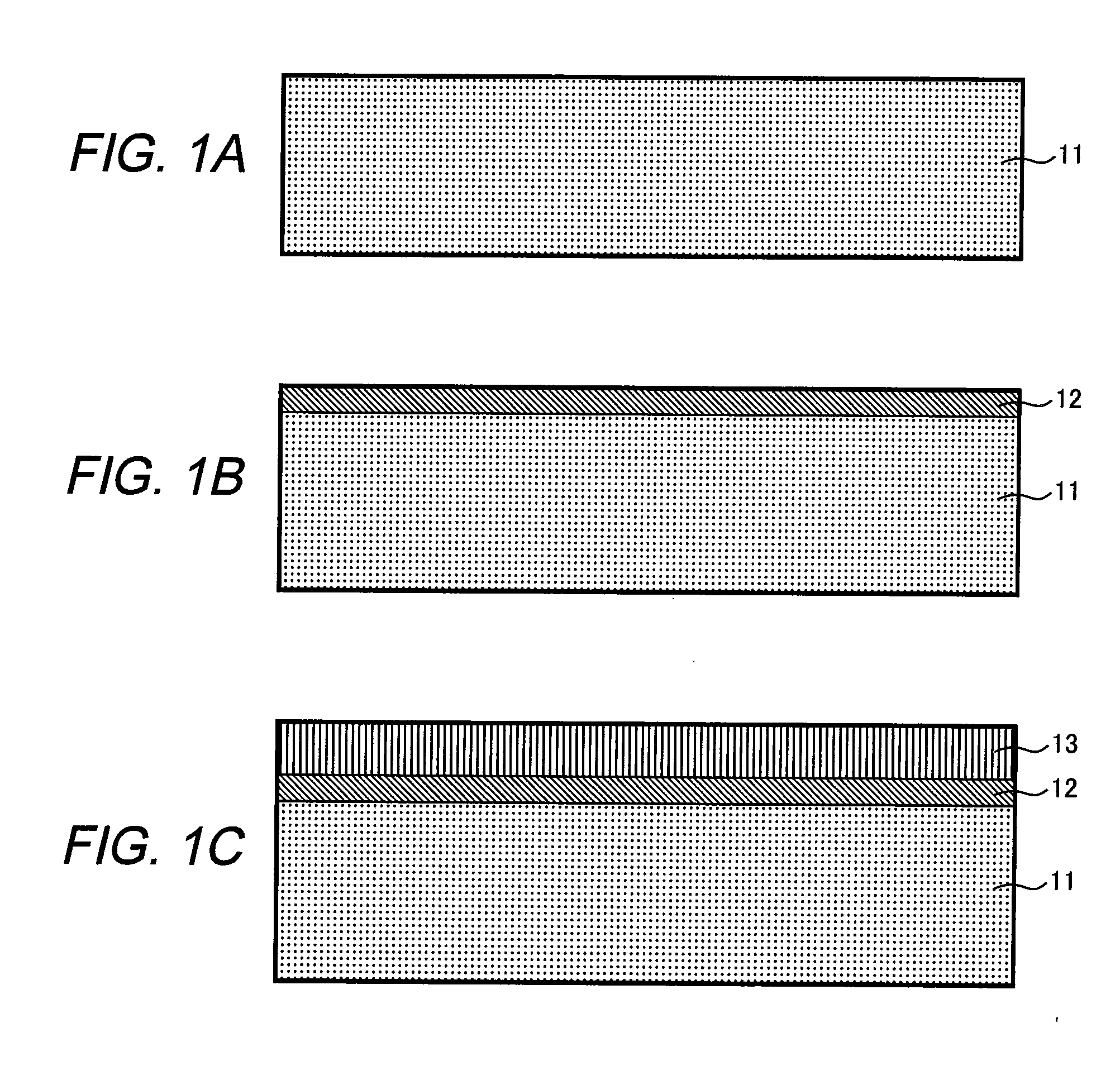
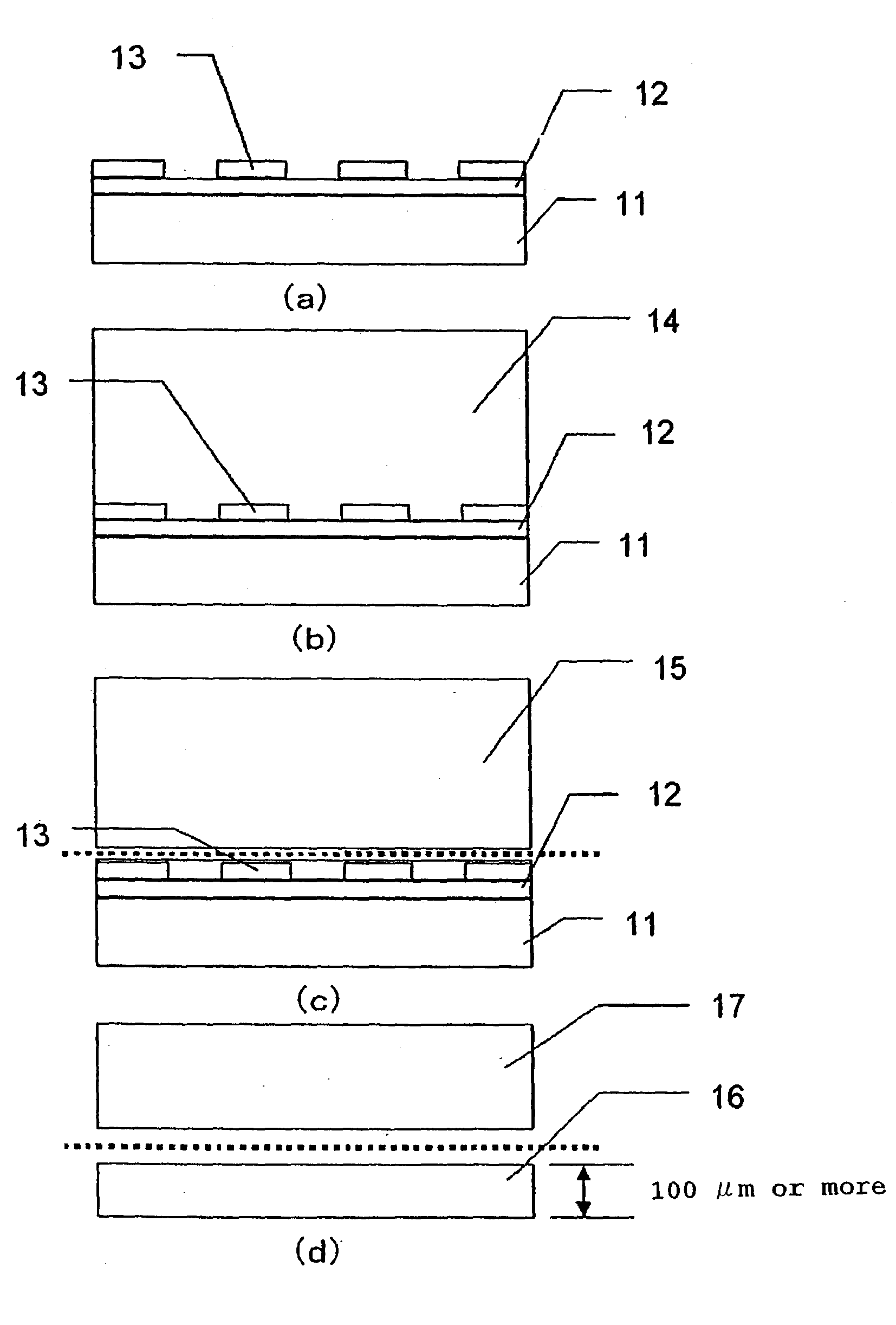
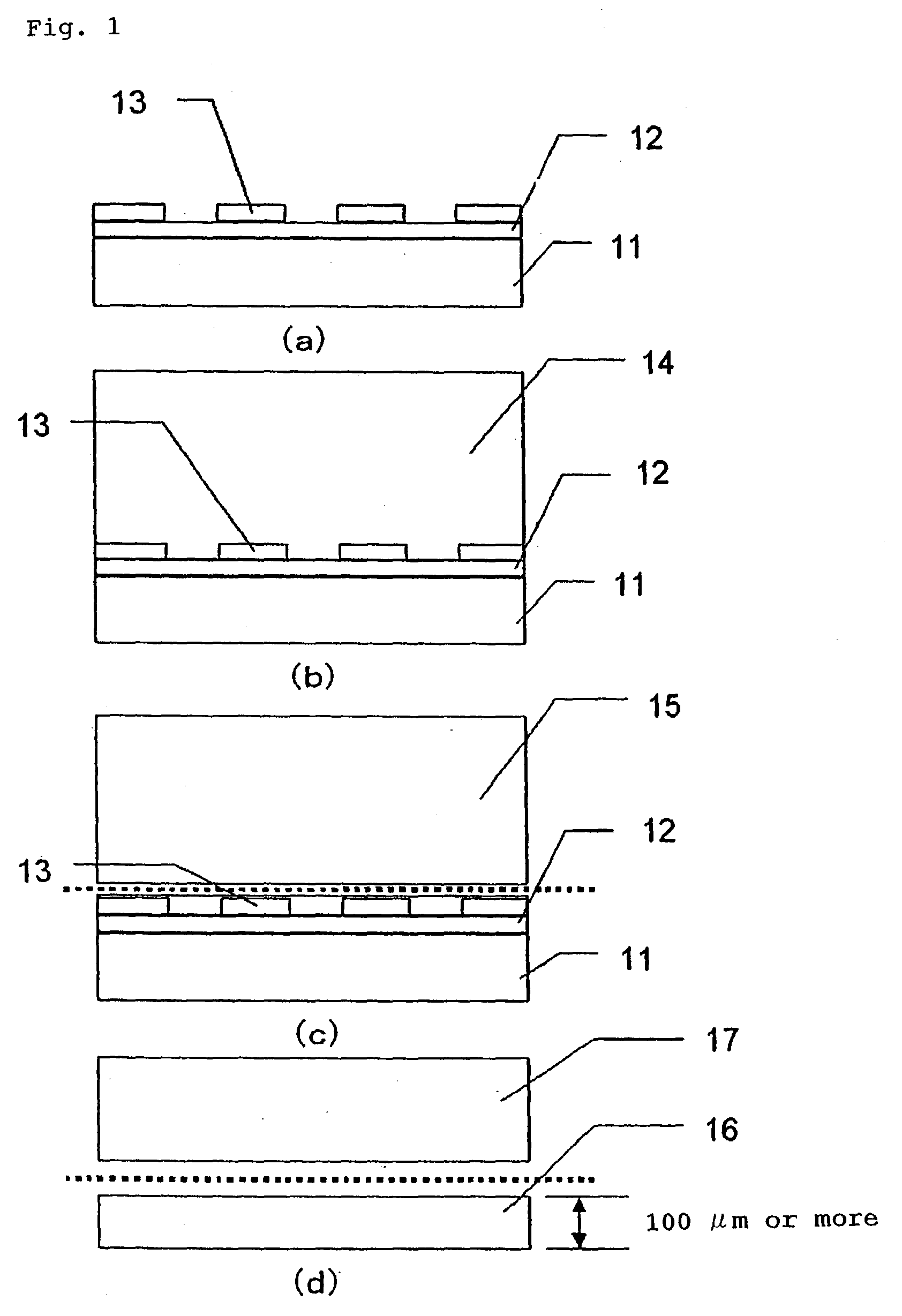
ActiveUS20050118752A1Simplified and less-costlyReduce misalignmentPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateDislocationSilicon
For fabricating an LED substrate with minimal dislocations in its nitride semiconductor layers, GaN is epitaxially grown into a first formative layer overlying a multilayered buffer region on a silicon substrate. A second formative layer is then formed on the first formative layer by epitaxially growing AlN, at such a rate that interstices are created in the first formative layer by the etching action of the reactor gases in the early stages of the fabrication of the second formative layer. Then the second formative layer is etched away from over the intersticed first formative layer, leaving the interstices open. Then a filler layer of GaN is epitaxially grown on the intersticed first formative layer in interfitting engagement therewith. Dislocations are greatly reduced in active semiconductor layers formed subsequently on the filler layer.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
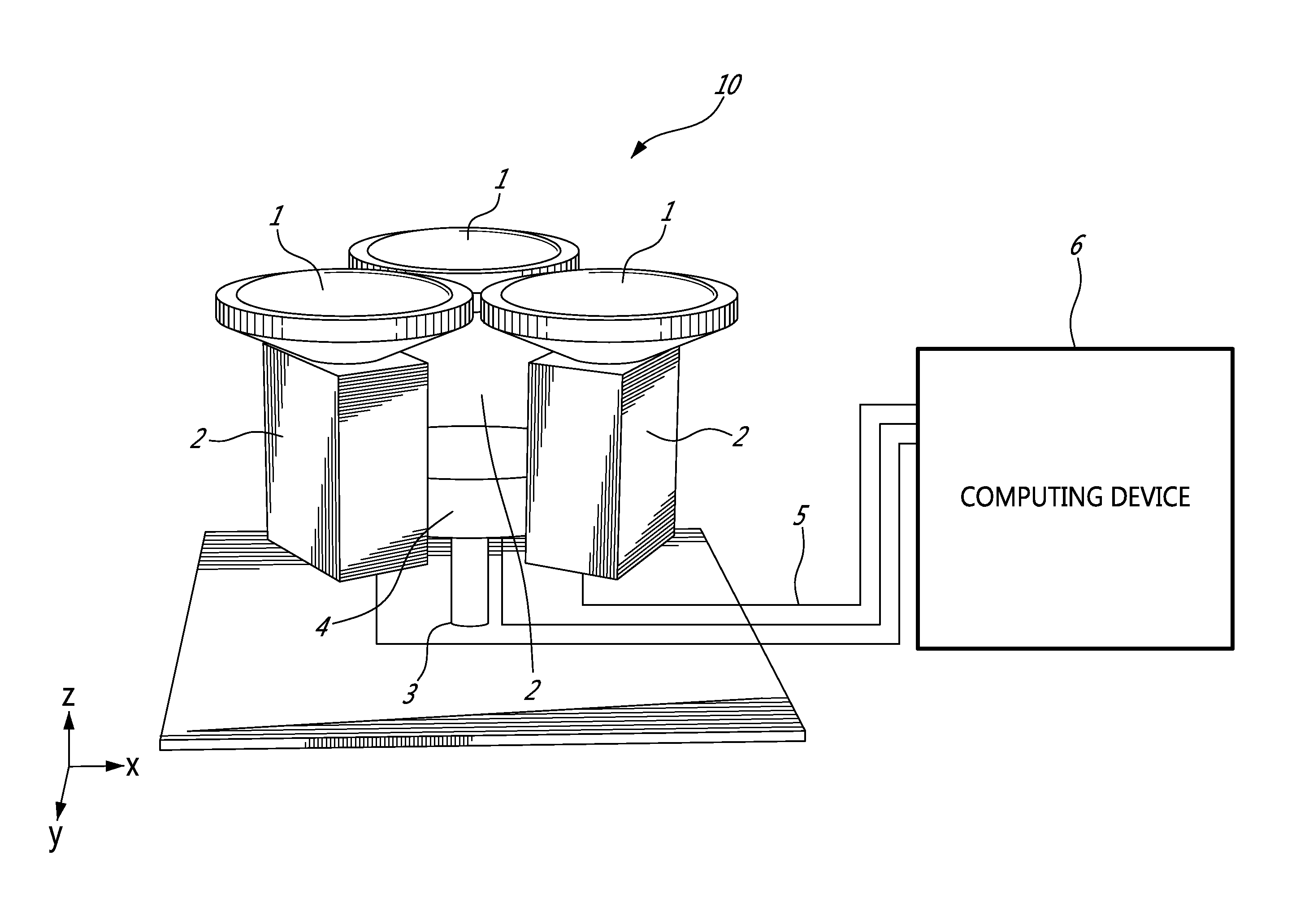
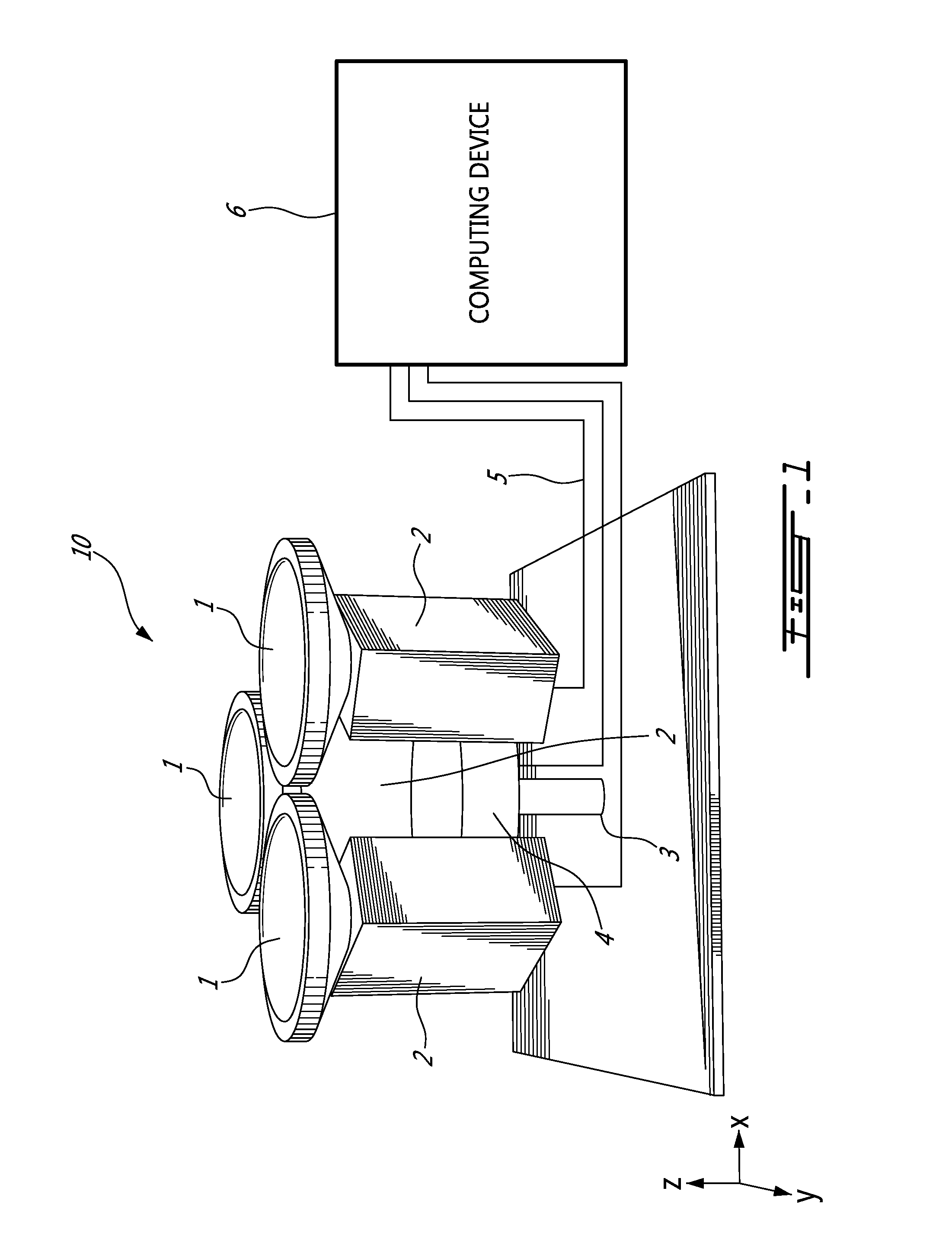
Omnistereo imaging
ActiveUS20150341557A1Reduce misalignmentTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationParallaxField of view
There is described a camera setup for capturing omnistereo images using a minimum of three cameras with ultra wide angle lenses and a method for generating a substantially 360 degree view from images taken from the cameras. The field of view covered in stereo may be a dome. The baseline between pairs of cameras defines epipoles which can be used for stitching without any horizontal misalignments due to parallax. The method comprises capturing the images from a plurality of cameras fixed at a baseline height substantially equidistantly about a circle; and stitching together portions of the images from each one of the plurality of cameras along first and second borders corresponding at least in part to lines joining center points of neighboring ones of the plurality of cameras.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP
Method and apparatus for transferring multiple toner images and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20070014595A1Reduce misalignmentRecording apparatusElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringRecording media
Owner:RICOH KK
Sic single-crystal substrate and method of producing sic single-crystal substrate
ActiveUS20100295059A1Electrically stableHigh yieldTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal substrateDislocation
The invention provides a high-quality SiC single-crystal substrate, a seed crystal for producing the high-quality SiC single-crystal substrate, and a method of producing the high-quality SiC single-crystal substrate, which enable improvement of device yield and stability. Provided is an SiC single-crystal substrate wherein, when the SiC single-crystal substrate is divided into 5-mm square regions, such regions in which dislocation pairs or dislocation rows having intervals between their dislocation end positions of 5 μm or less are present among the dislocations that have ends at the substrate surface account for 50% or less of all such regions within the substrate surface and the dislocation density in the substrate of dislocations other than the dislocation pairs or dislocation is 8,000 / cm2.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Epitaxial process
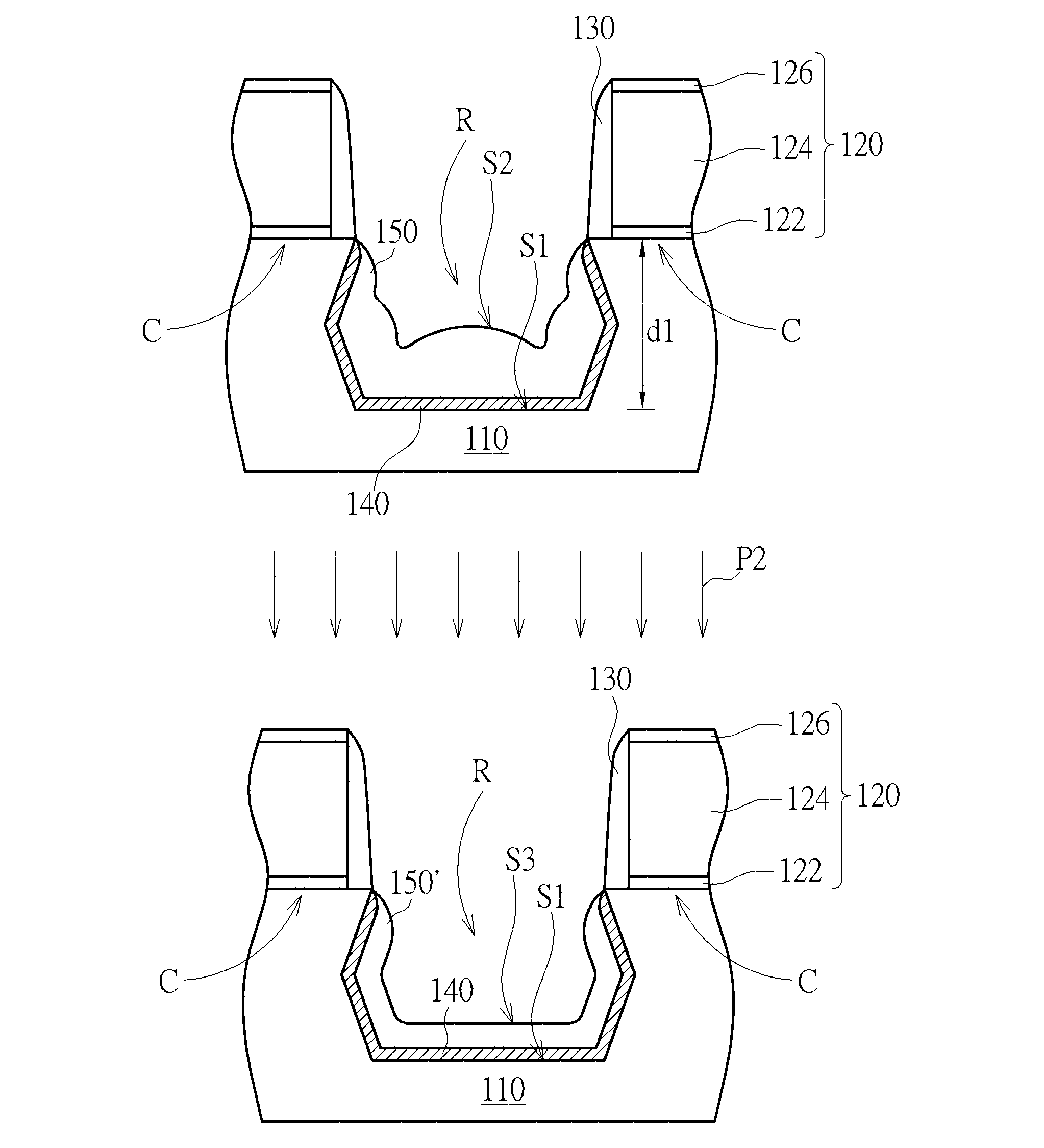
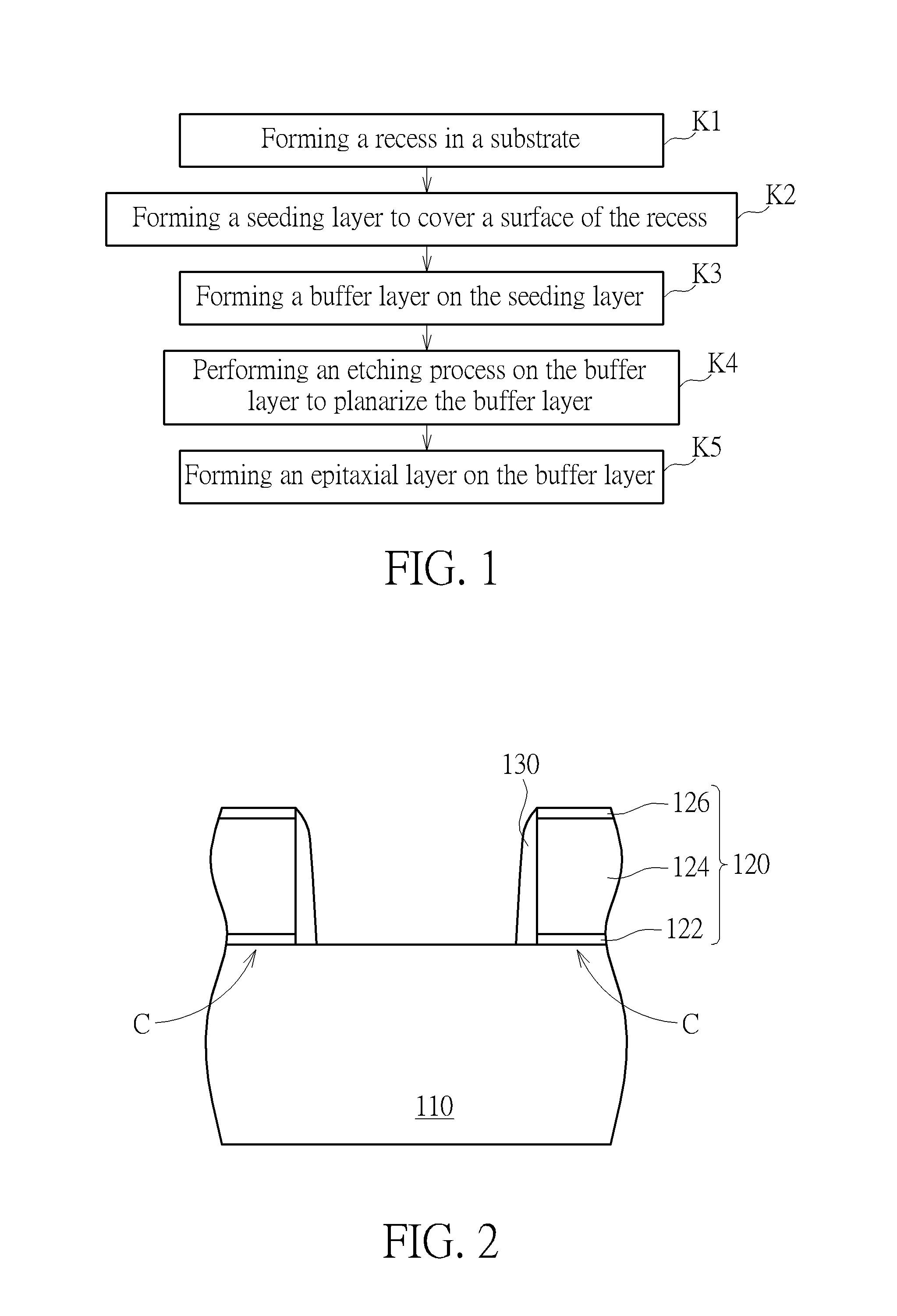
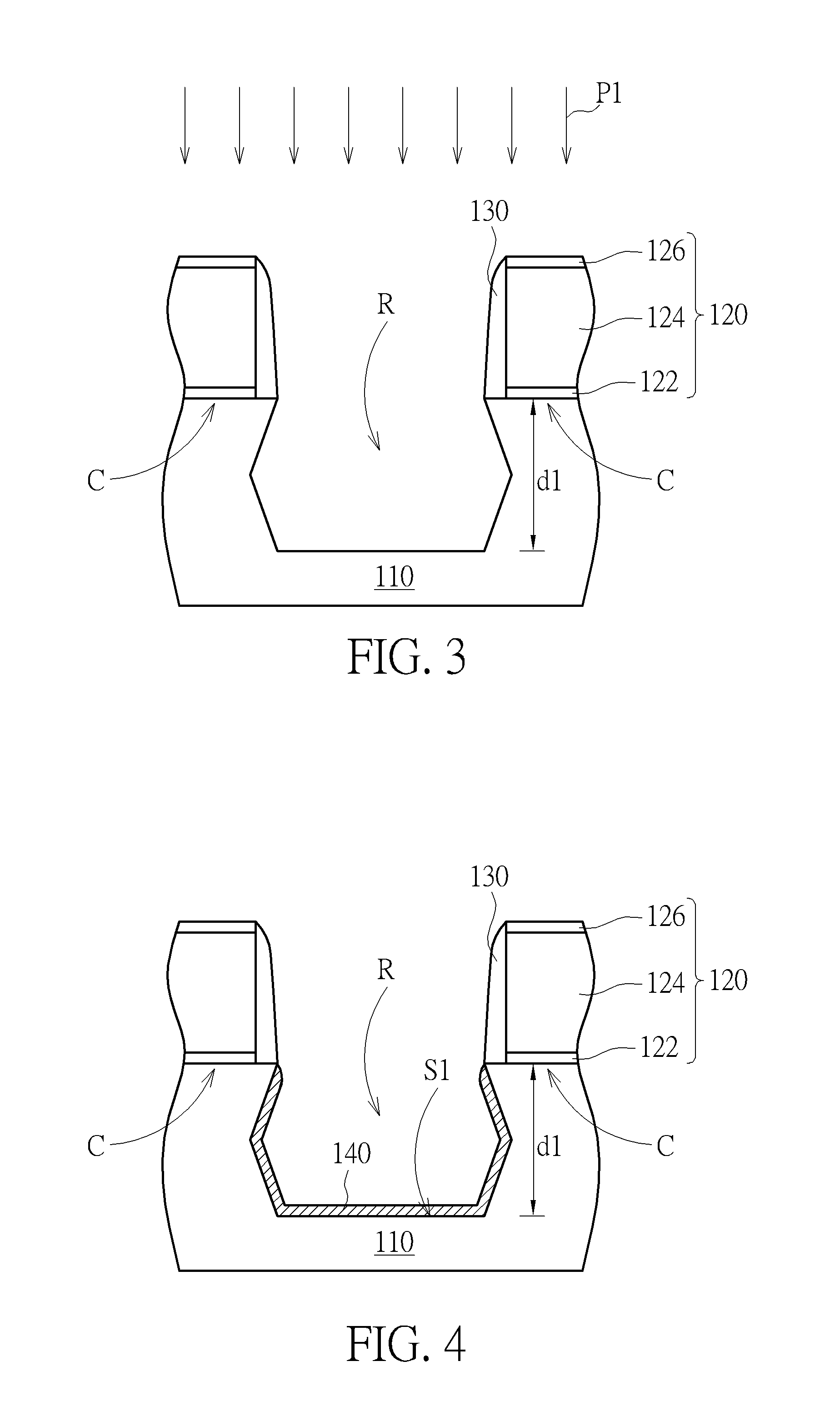
ActiveUS8853060B1Easy for epitaxial layerIncrease pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesComputer science
An epitaxial process includes the following step. A recess is formed in a substrate. A seeding layer is formed to cover a surface of the recess. A buffer layer is formed on the seeding layer. An etching process is performed on the buffer layer to homogenize and shape the buffer layer. An epitaxial layer is formed on the homogenized flat bottom shape buffer layer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
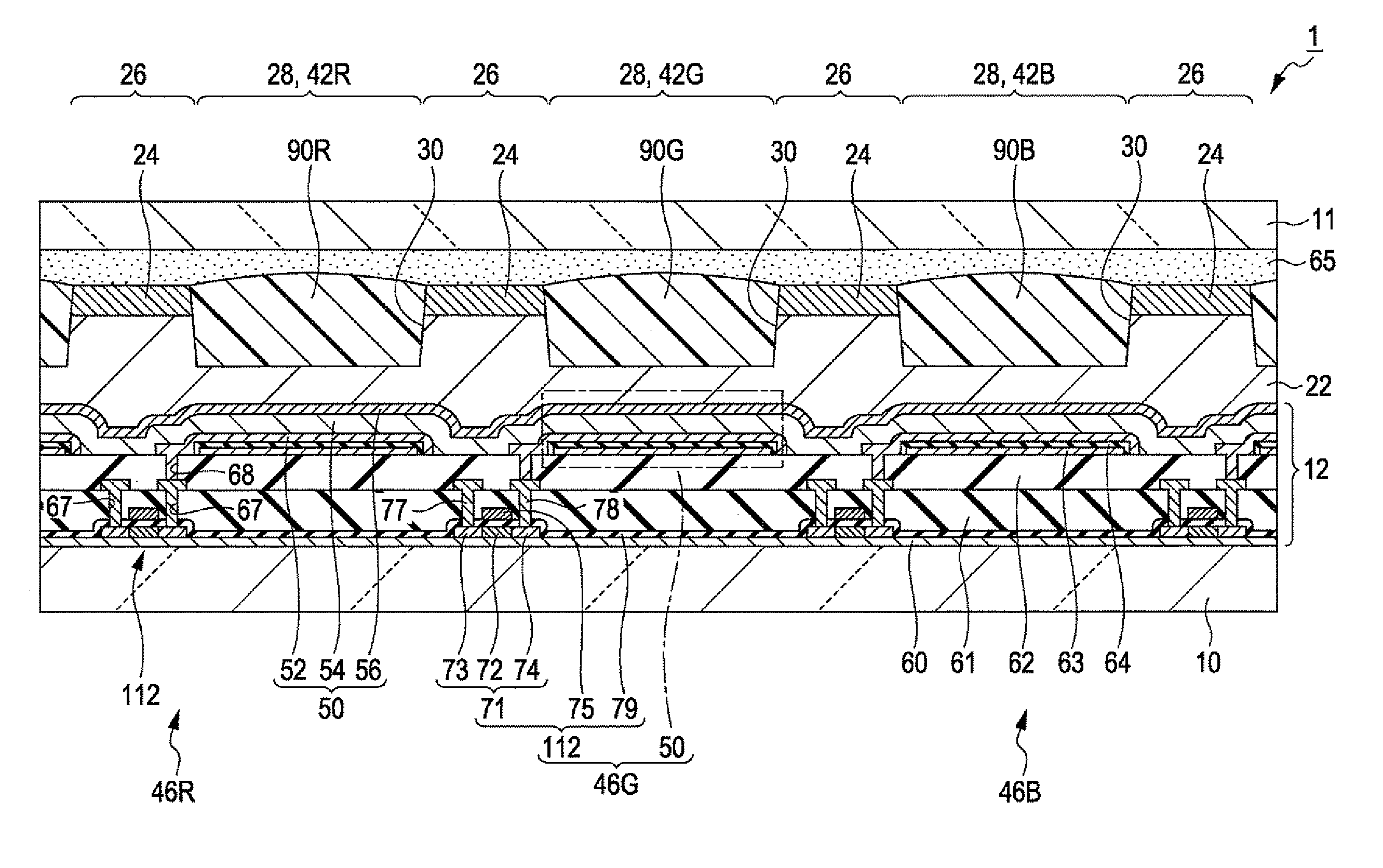
Electro-optic device, method for manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20110284898A1Reduce colorImprove display image qualitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectron
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Lens device
ActiveUS20060158748A1Prevent dislocationReduce misalignmentMountingsCamera body detailsCamera lensOptical axis
In a lens device, plastic lenses having circular outer periphery are placed in a plastic lens-barrel having an octagonal or more complex polygonal inner surface in such a way that the outer peripheral surfaces of the lenses are press contacted to the inner surface of the polygonal shape. This lens device has press contact portions that are pressed by the lens outer peripheral surface and the lens-barrel inner surface in the vicinity and in both sides of gate traces where optical axis displacement is large so as to suppress the displacement of the gate trace by the press contact portions.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Apparatus for holding workpieces during lapping, honing, and polishing
InactiveUS6030280AMinimizing scratchEasy to manufactureRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesFiberRigid core
The present invention relates generally to a device used to process workpieces. In particular, the invention relates to a carrier that is used to support a workpiece during workpiece honing, grinding, or polishing. The carrier includes a rigid core coated with a fiber-free, scratch-resistant material to prevent scratching of workpieces disposed in the carrier. An adhesive layer is typically used to attach the scratch-resistant layer to the rigid core. The adhesive film and the scratch-resistant films may be attached to the rigid core by hot pressing.
Owner:SPEEDFAM IPEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com