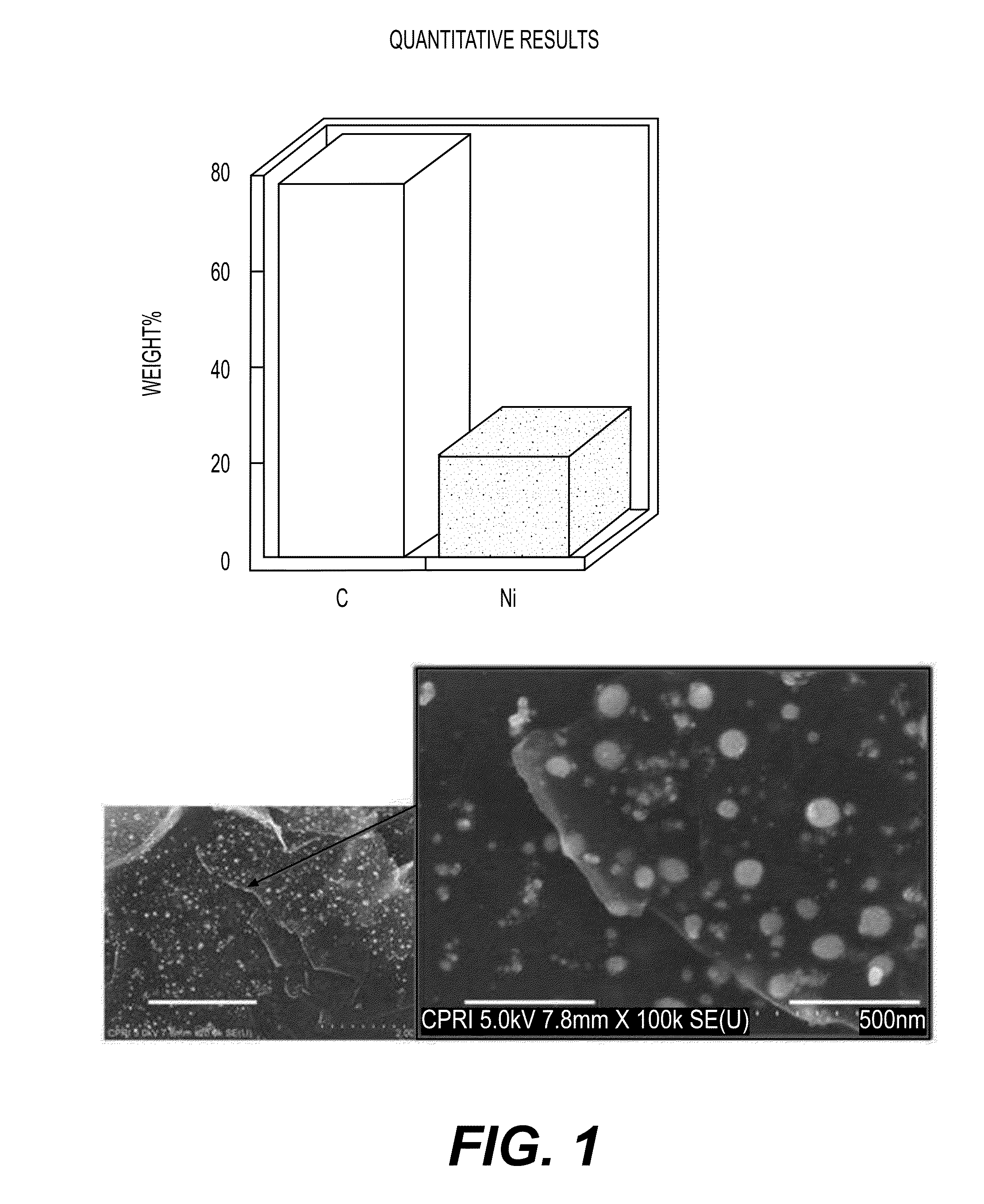
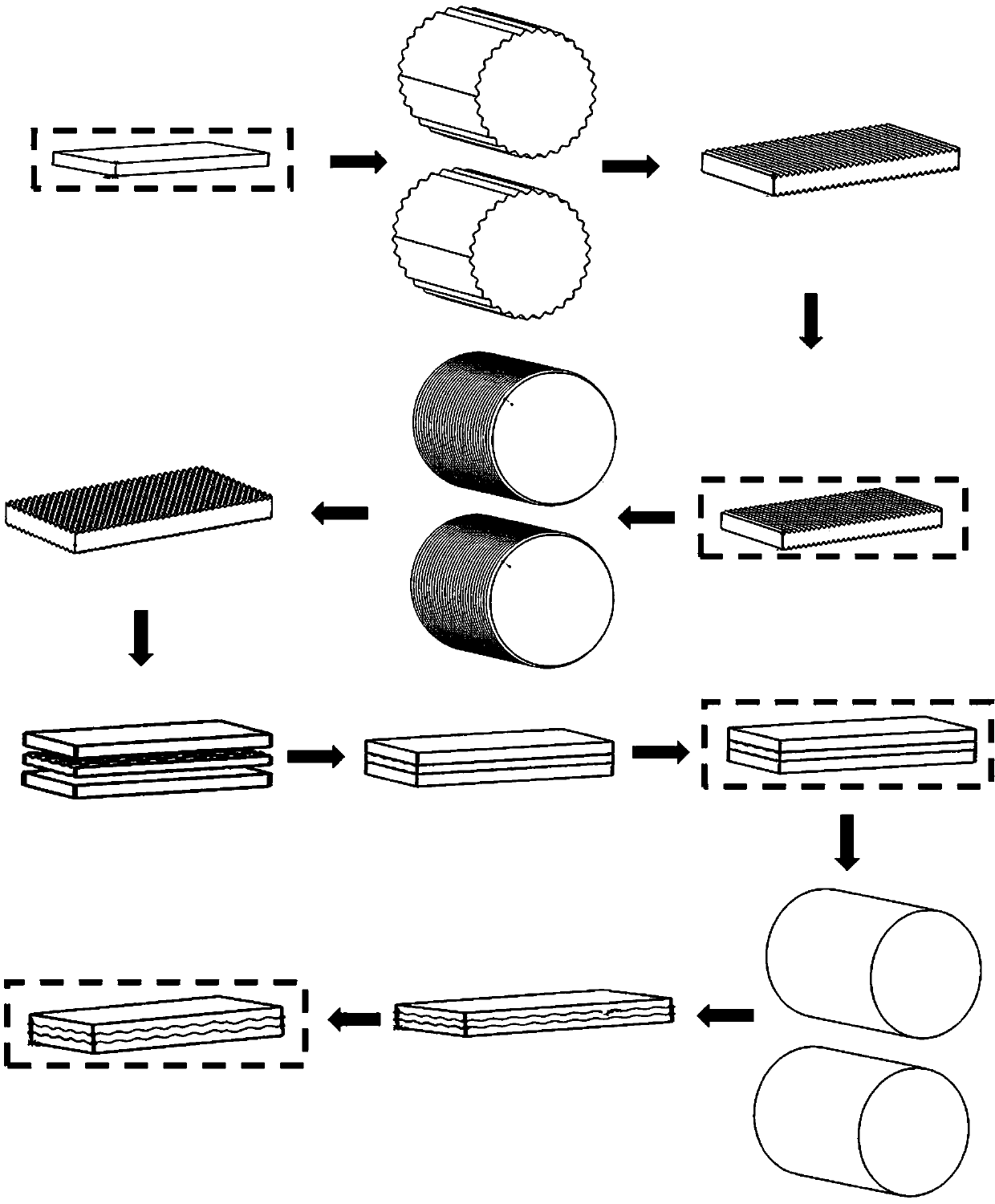
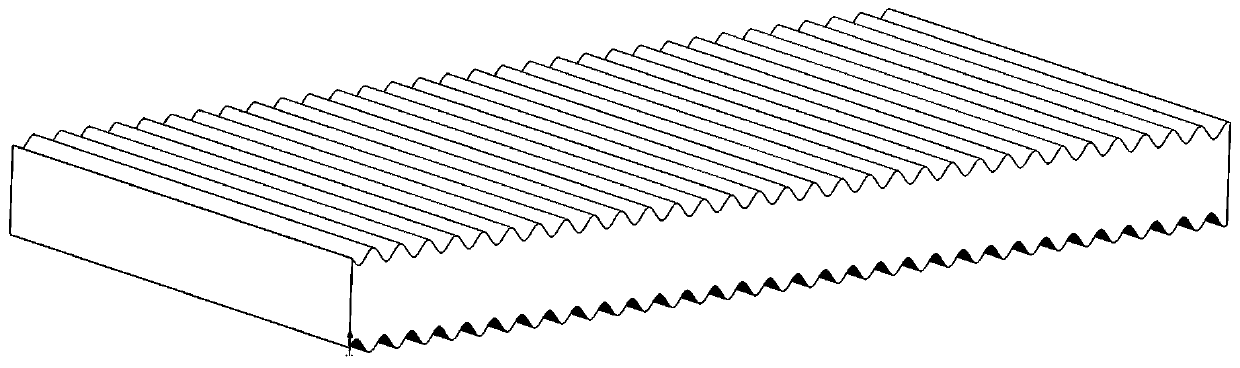
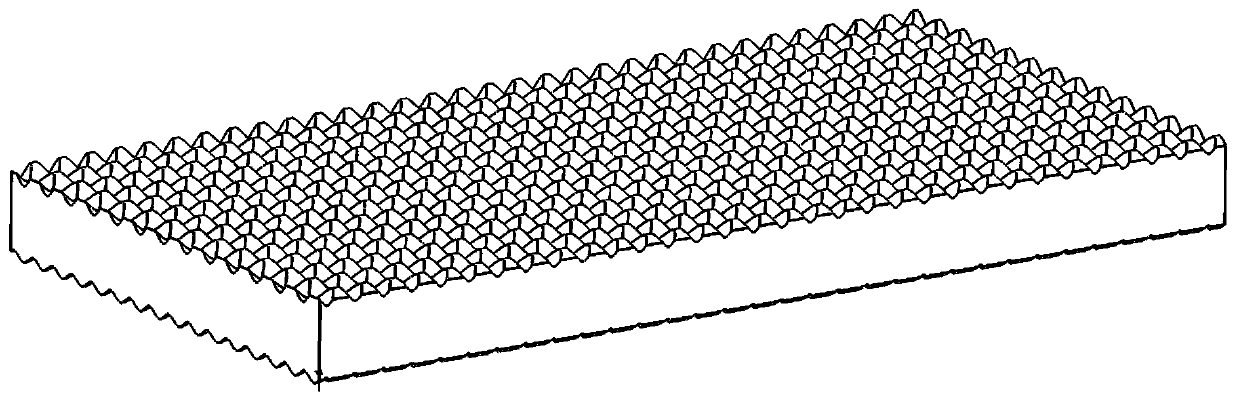
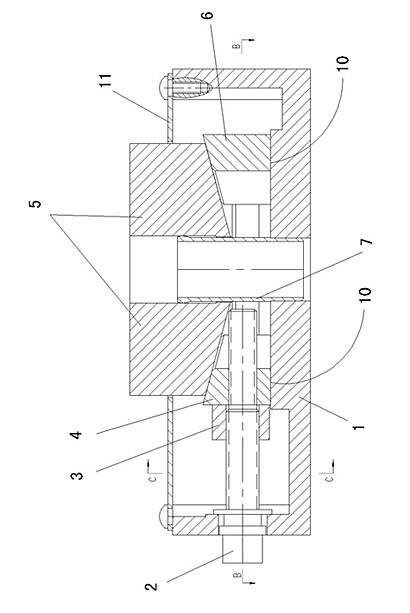
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
393 results about "Basal plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of basal plane. 1 : a plane parallel to the lateral or horizontal axis. 2 : a basal pinacoid.
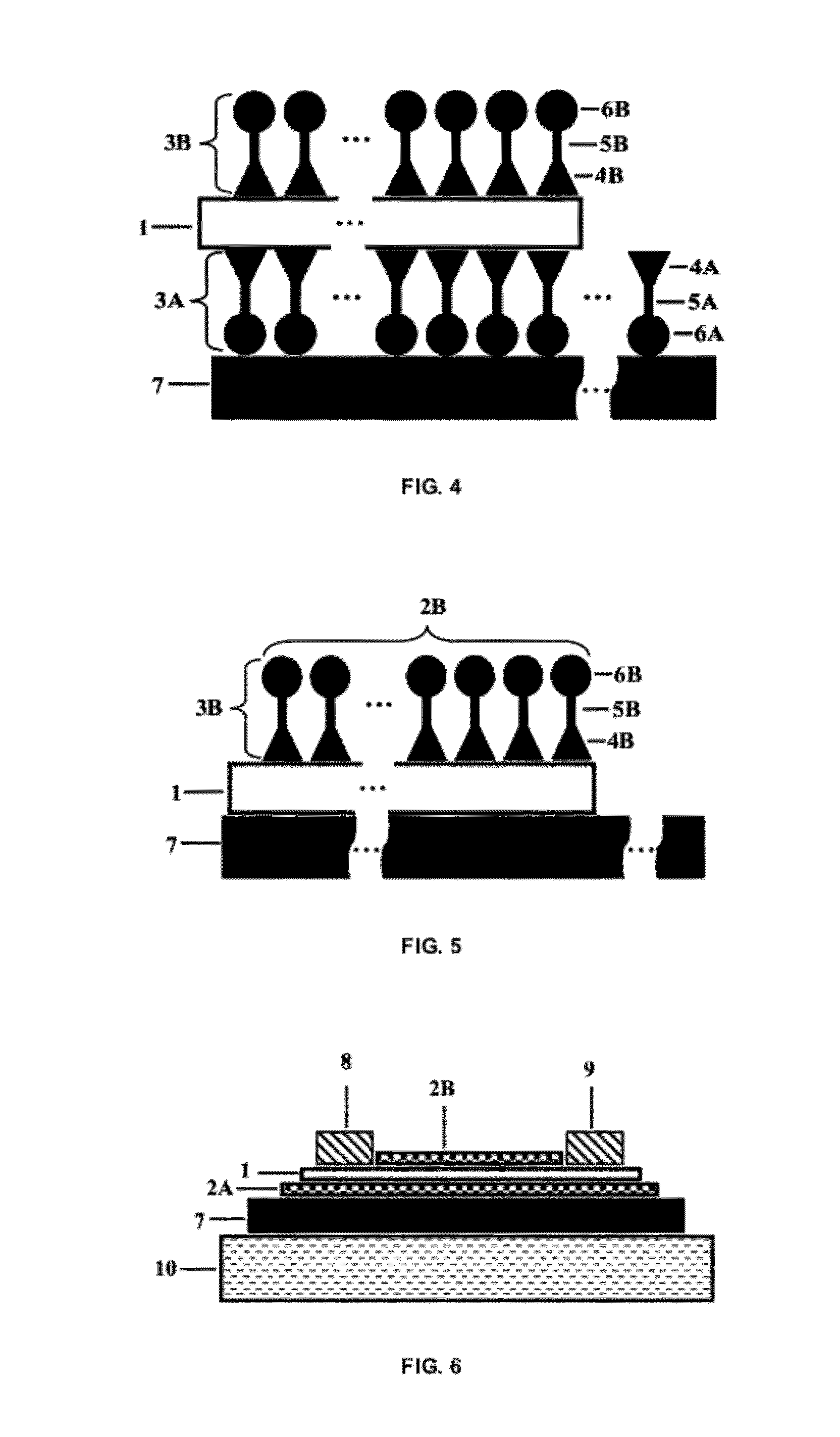
Group-III nitride light-emitting device
ActiveUS7968864B2Piezoelectric field is reducedLow efficiencyThyristorSolid-state devicesQuantum wellLength wave
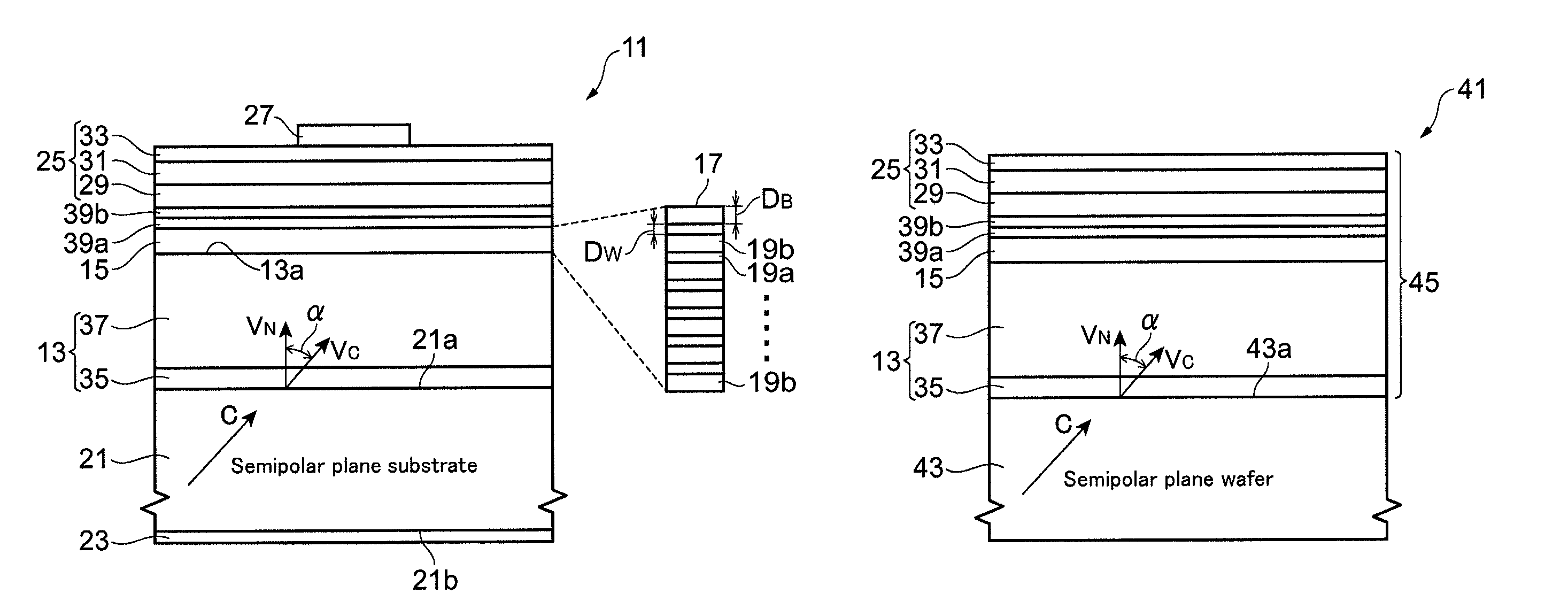
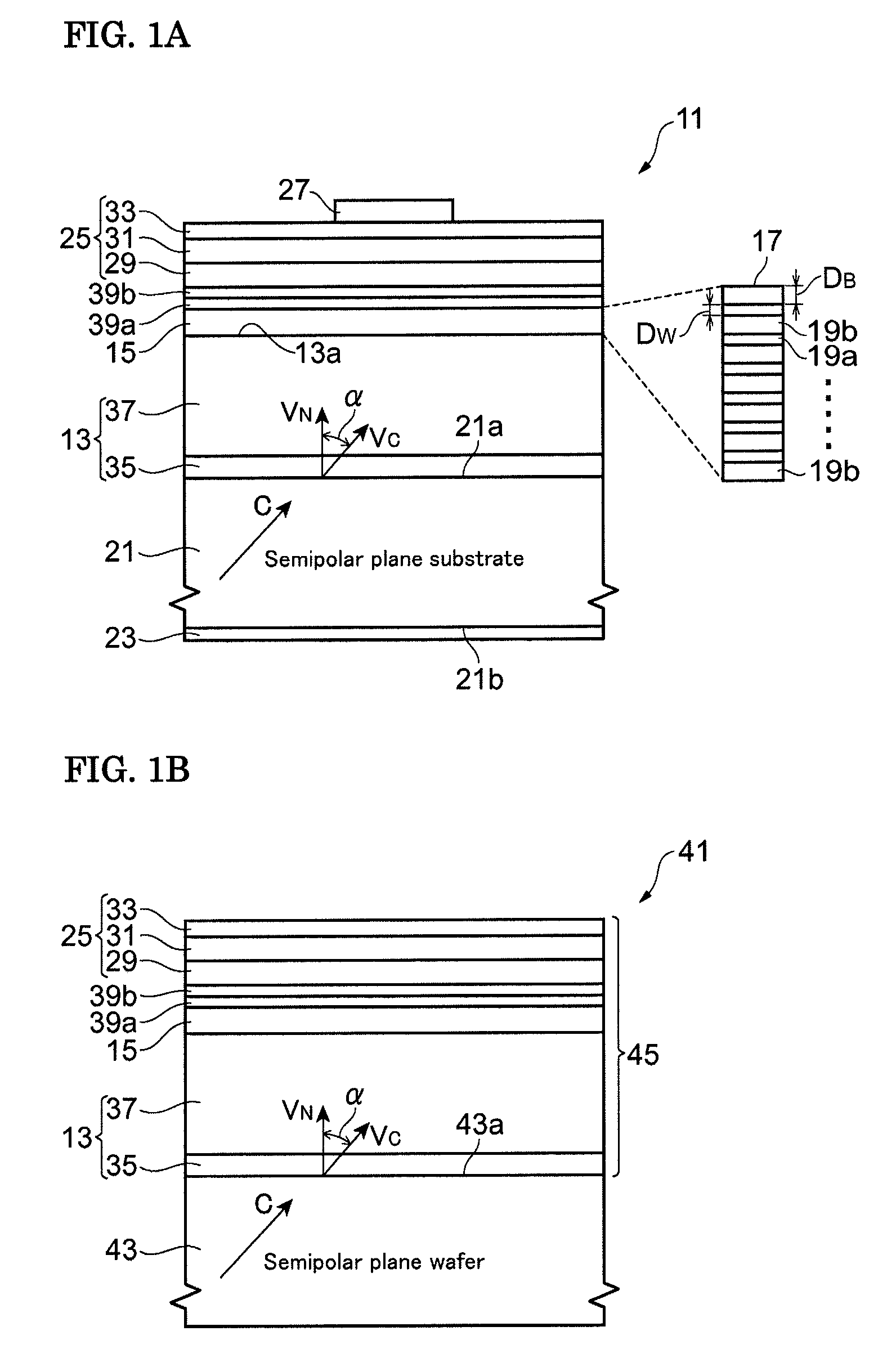
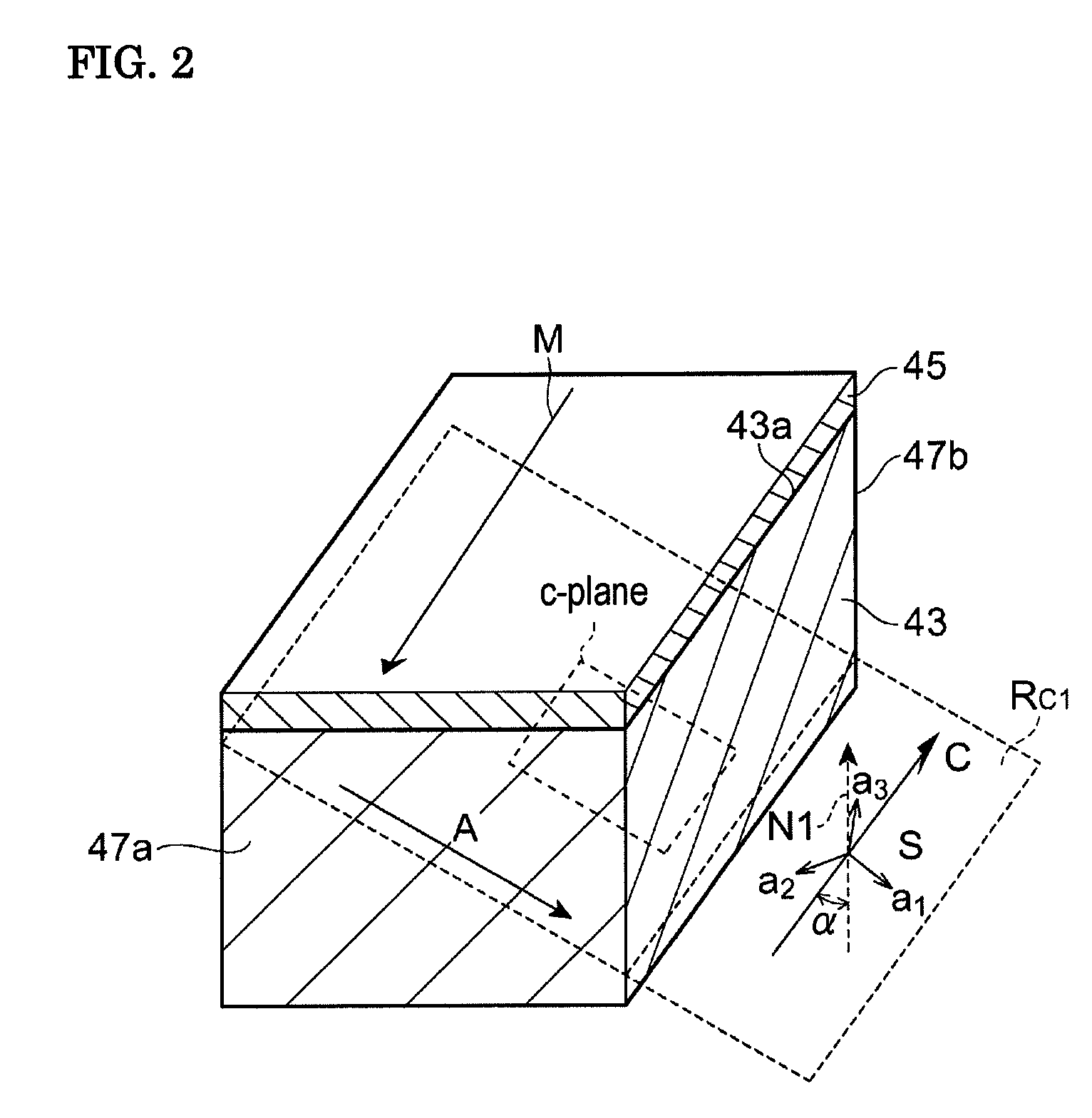
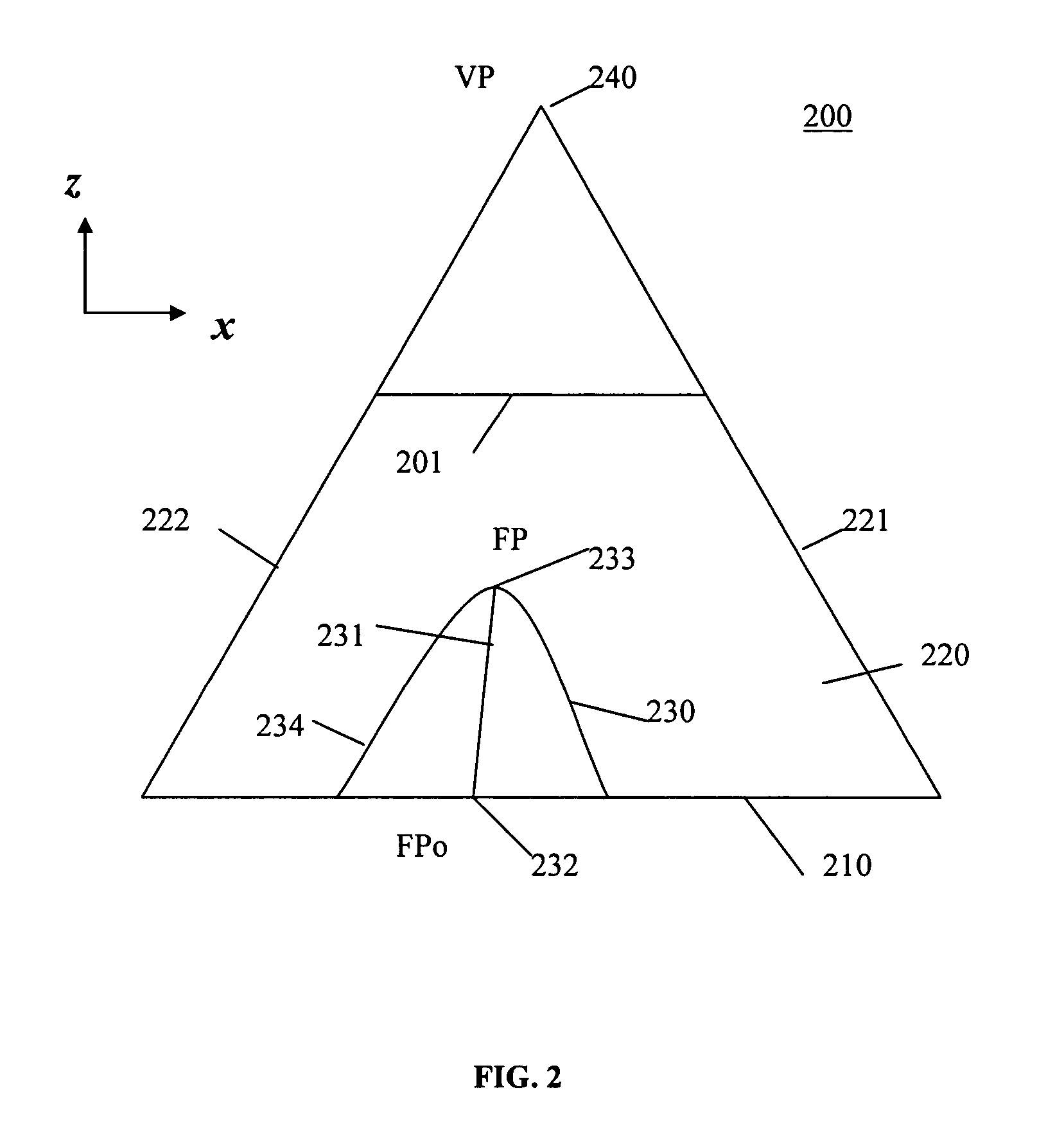
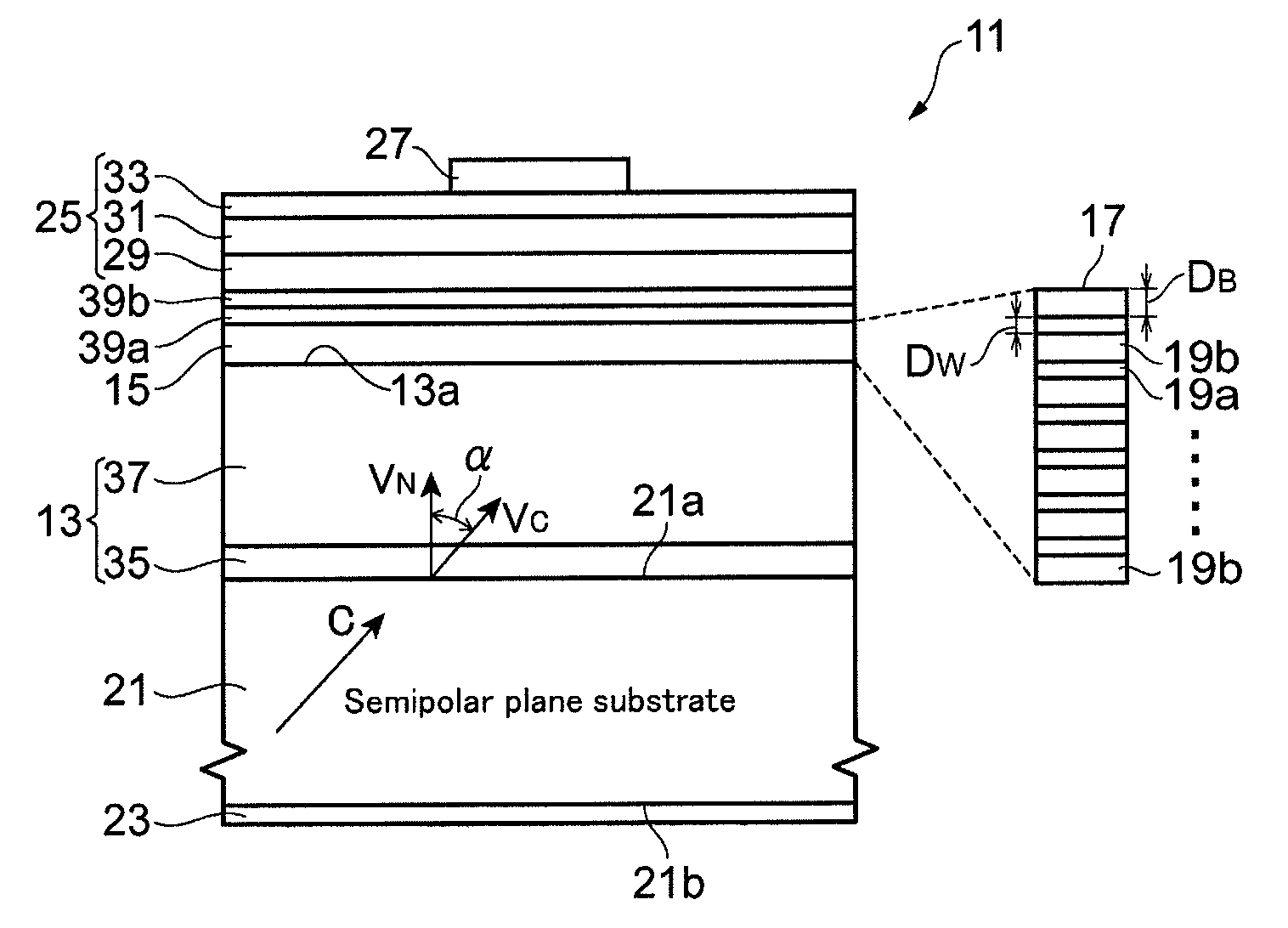
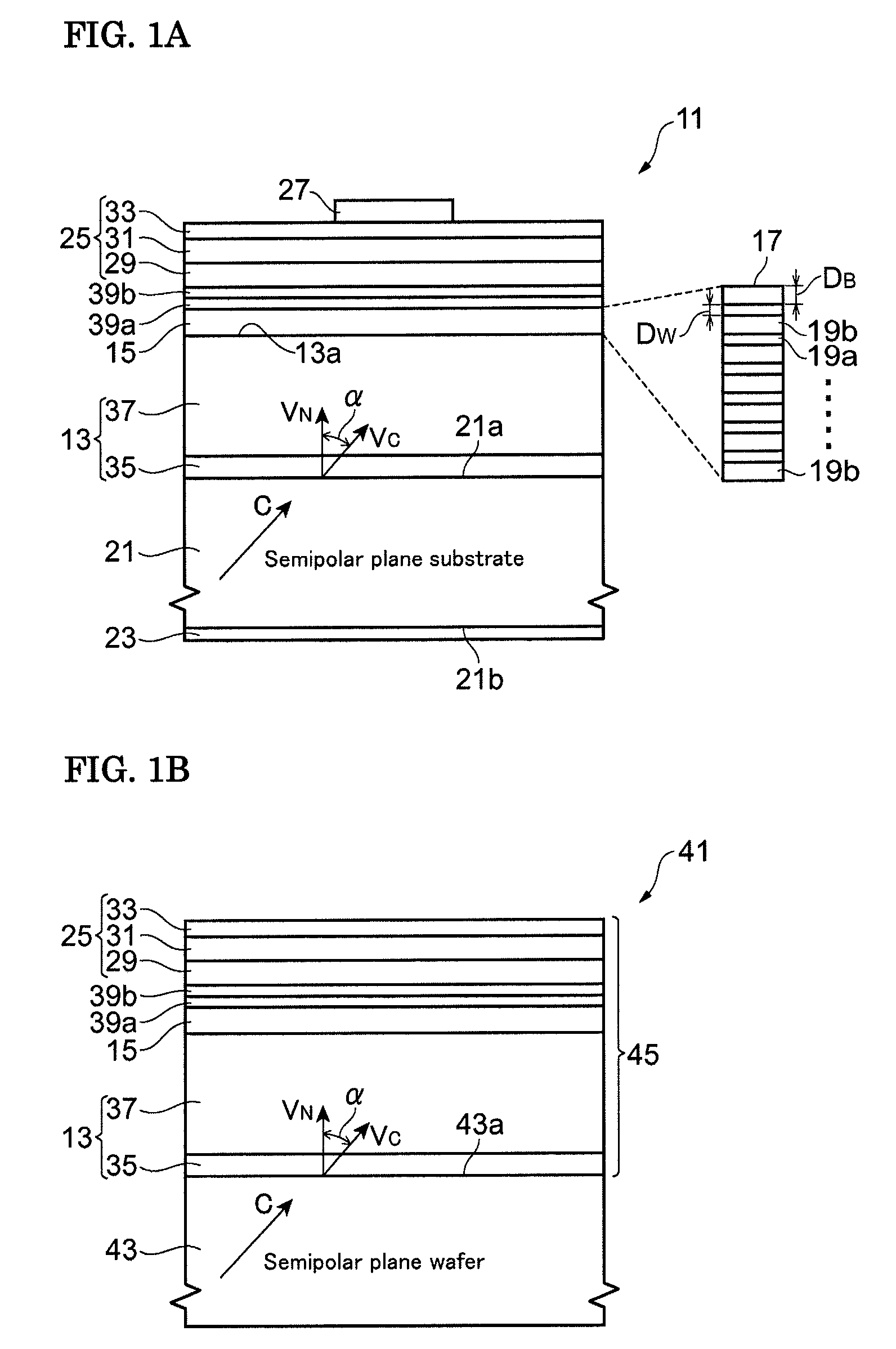
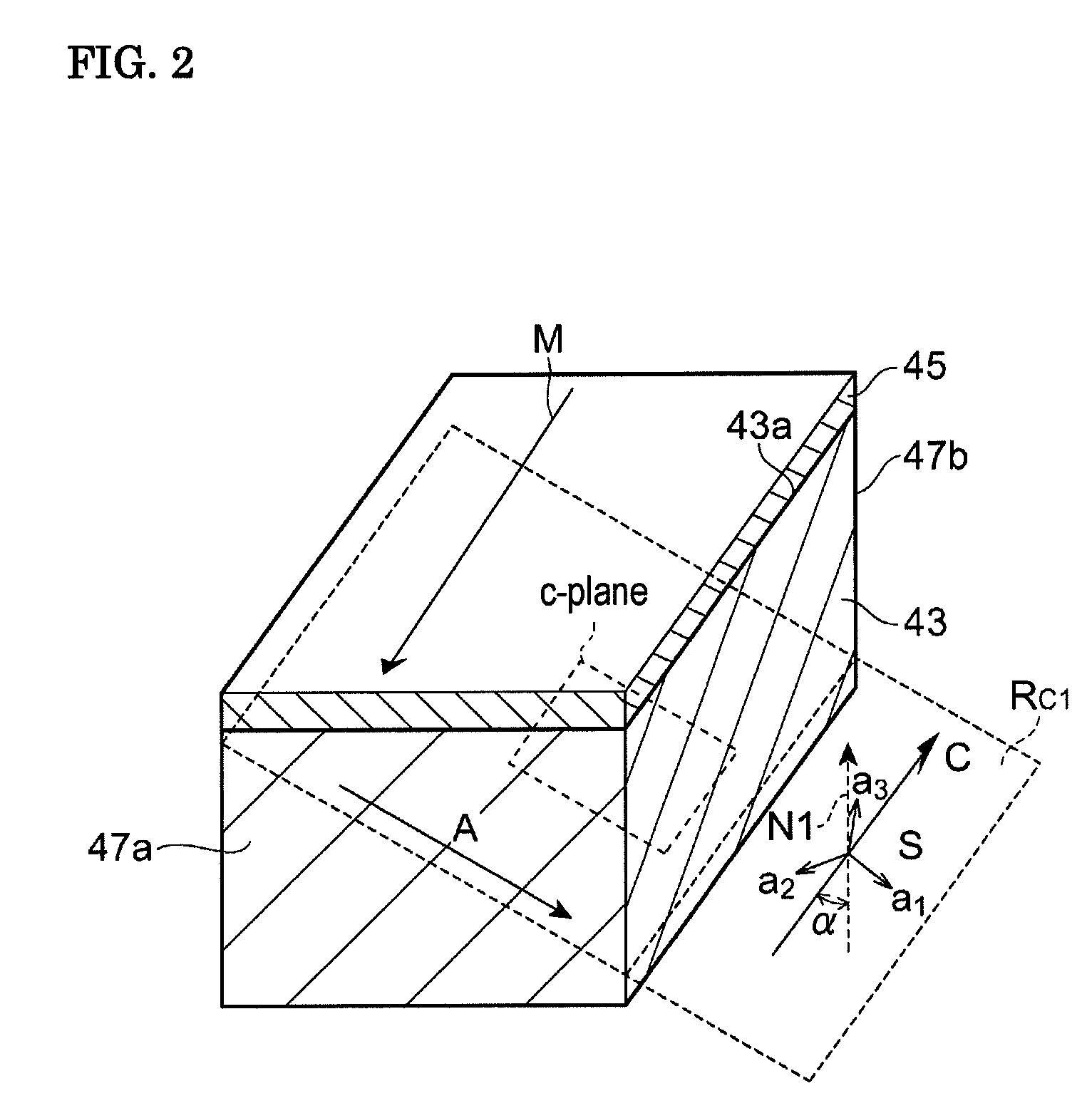
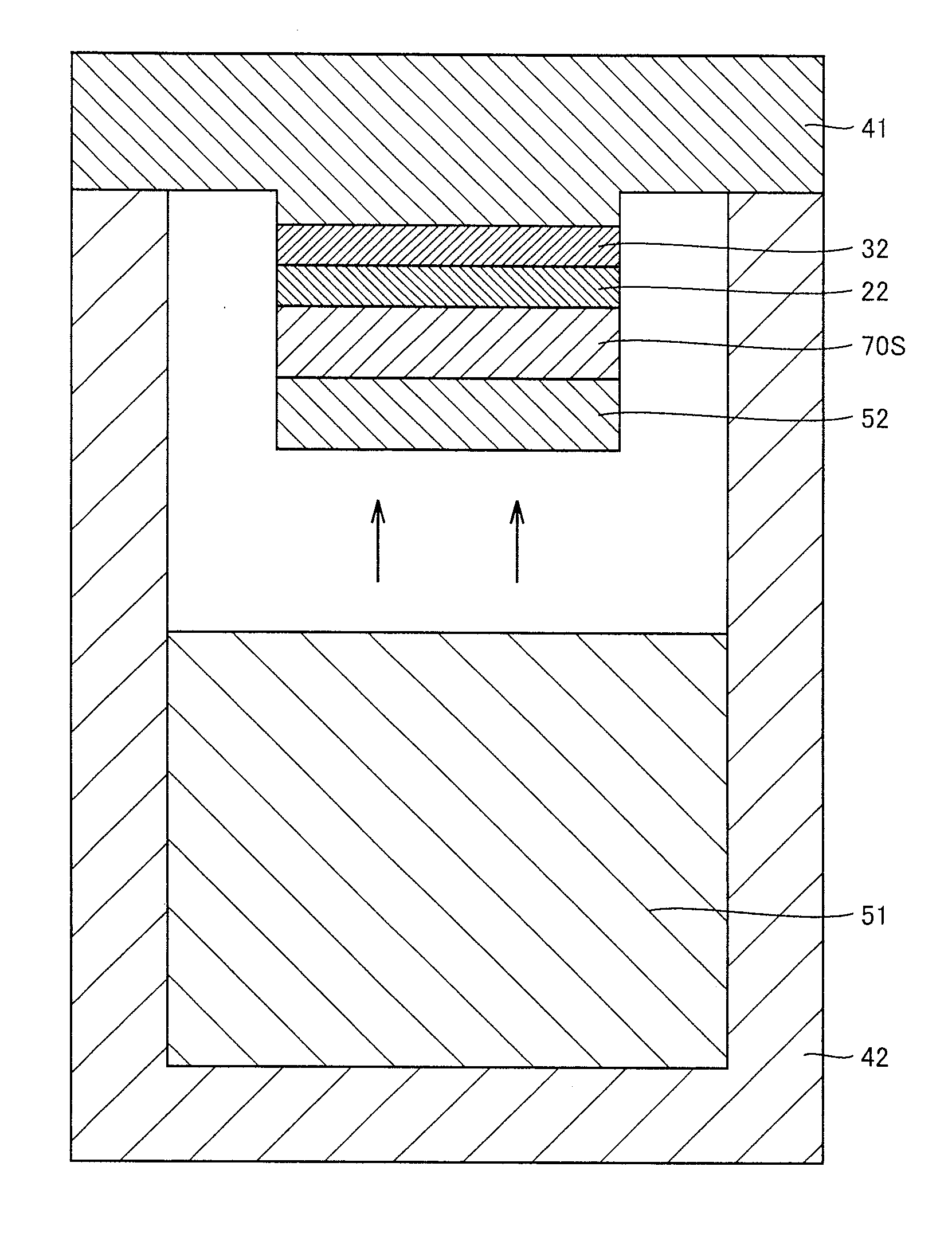
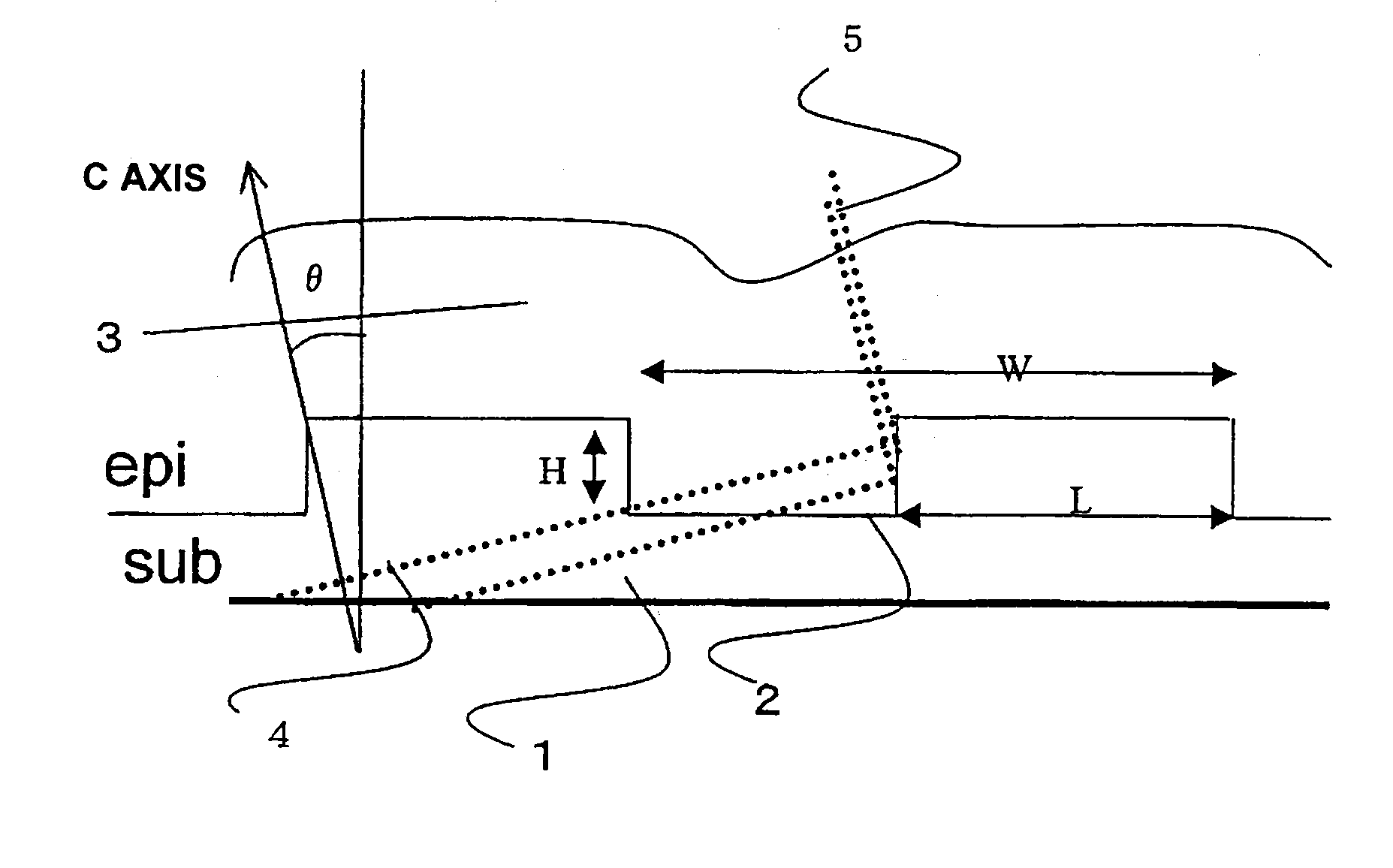
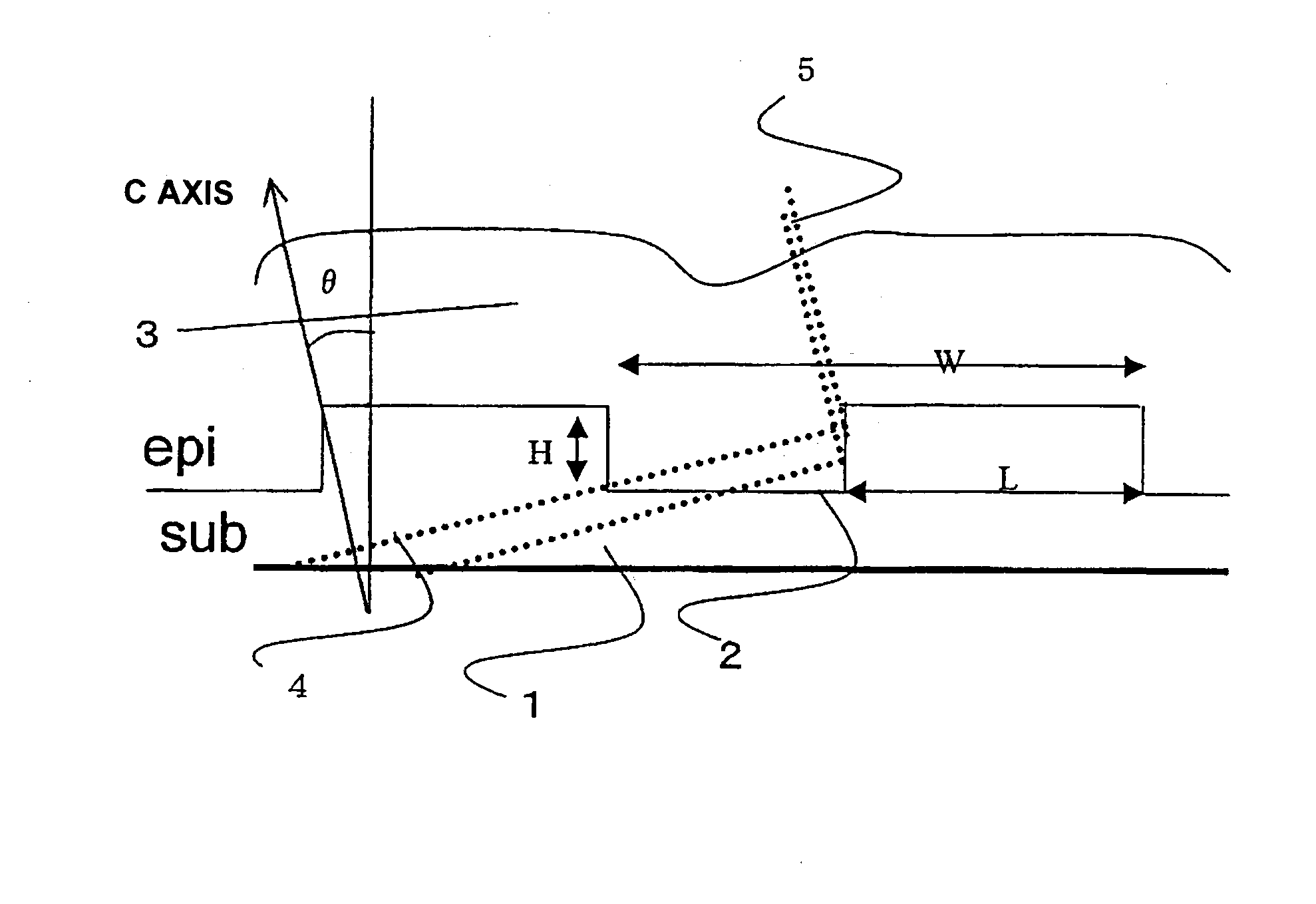
A group-III nitride light-emitting device is provided. An active layer having a quantum well structure is grown on a basal plane of a gallium nitride based semiconductor region. The quantum well structure is formed in such a way as to have an emission peak wavelength of 410 nm or more. The thickness of a well layer is 4 nm or more, and 10 nm or less. The well layer is composed of InXGa1-XN (0.15≦X<1, where X is a strained composition). The basal plane of the gallium nitride based semiconductor region is inclined at an inclination angle within the range of 15 degrees or more, and 85 degrees or less with reference to a {0001} plane or a {000-1} plane of a hexagonal system group III nitride. The basal plane in this range is a semipolar plane.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Functionalised graphene oxide
ActiveUS20110052813A1Good dispersionReadily deoxidised to grapheneMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryHigh concentrationRoom temperature
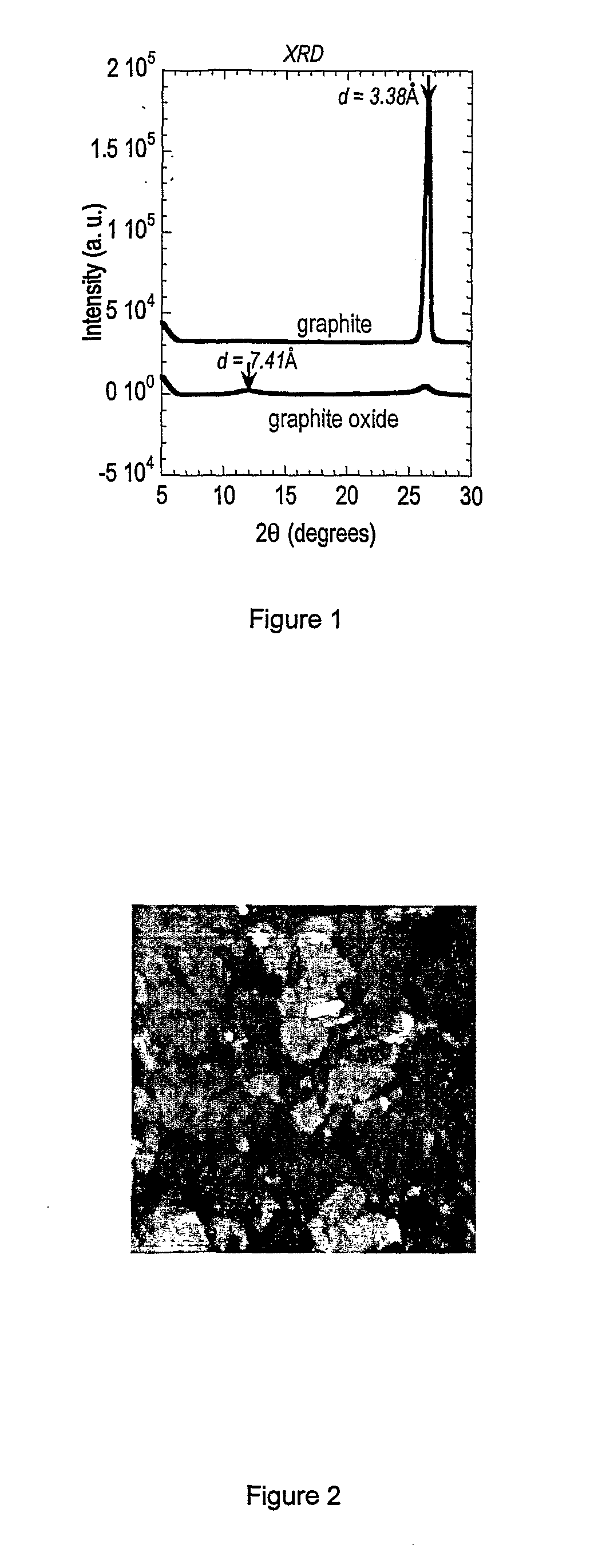
A functionalised graphene oxide and a method of making a functionalised graphene oxide comprising: (i) oxidizing graphite to form graphite oxide wherein the graphene sheets which make up the graphite independently of each other have a basal plane fraction of carbon atoms in the sp2-hybridised state between 0.1 and 0.9, wherein the remainder fraction comprises sp3-hybridised carbon atoms which are bonded to oxygen groups selected from hydroxyl and / or epoxy and / or carboxylic acid; and (ii) exfoliating and in-situ functionalizing the graphite oxide surface with one or more functional groups such that functionalisation of the surface is effected at a concentration greater than one functional group per 100 carbon atoms and less than one functional group per six carbon atoms. The functionalised graphene oxide is dispersible at high concentrations in appropriate solvents without aggregating or precipitating over extended periods at room temperature.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Modified graphene structures and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20120058350A1Facilitates self-assembly and stabilisationIncrease the number densityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSelf-assembled monolayerGraphene
The present invention is directed to a modified graphene structure comprising at least one graphene sheet (1) and a self-assembled monolayer (2) of functional organic molecules (3) non-covalently bonded to the top and / or bottom basal planes of the graphene sheet and methods of manufacture thereof. The present invention is also directed to devices comprising the modified graphene structures, including but not limited to field-effect devices and biosensors, and to methods using the modified graphene structures.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK +1
Optical element containing nano-composite particles
ActiveUS6888663B2High light transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsOptical filtersParticulatesLayer thickness
The invention relates to an optical component comprising a dispersion of layered minute particulate materials in a binder, the layered materials having a layer thickness, a concentration of particulate in the binder, and a basal plane spacing sufficient to provide a component having a light transmissivity of at least 50%.
Owner:SK MICROWORKS SOLUTIONS CO LTD
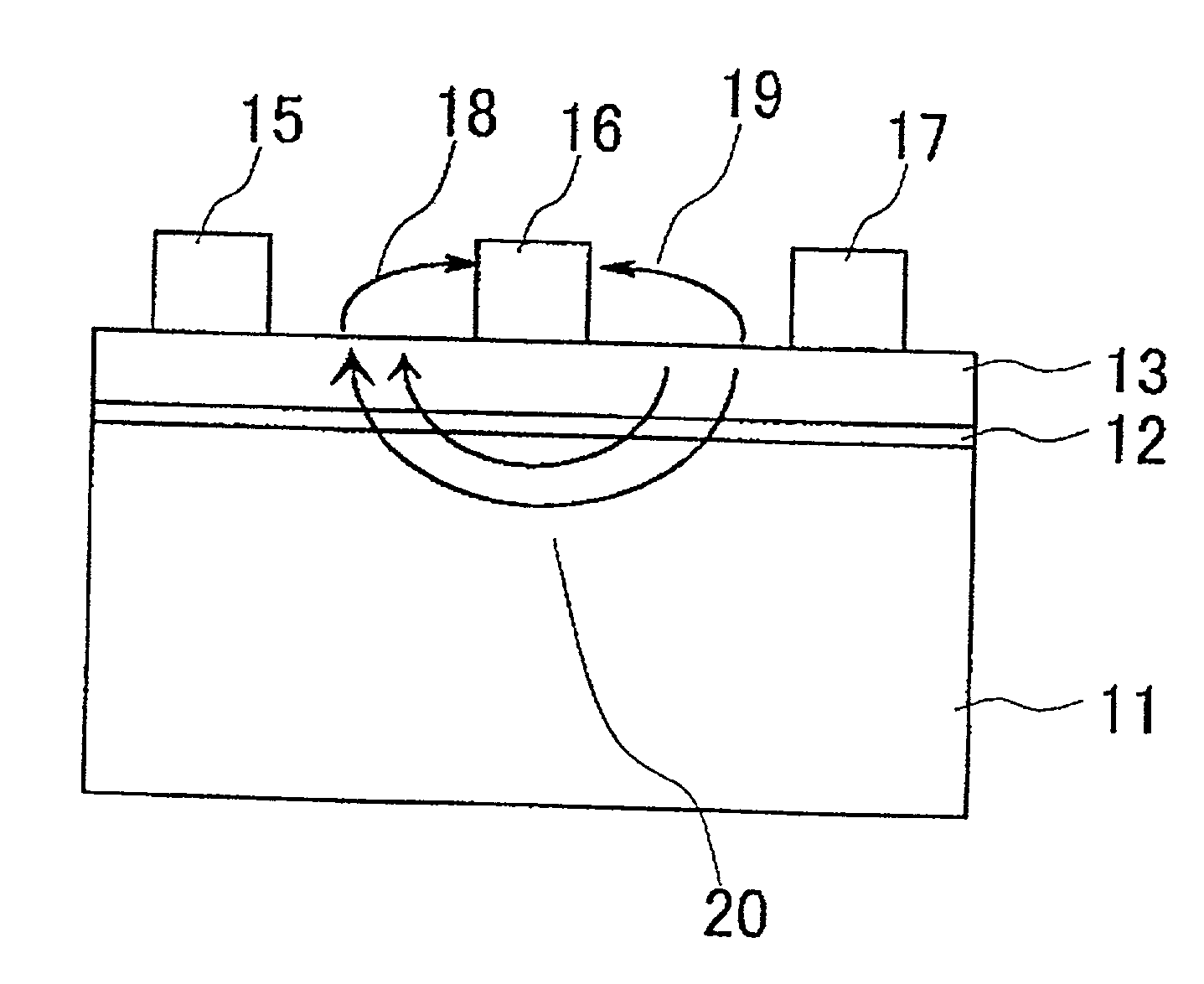
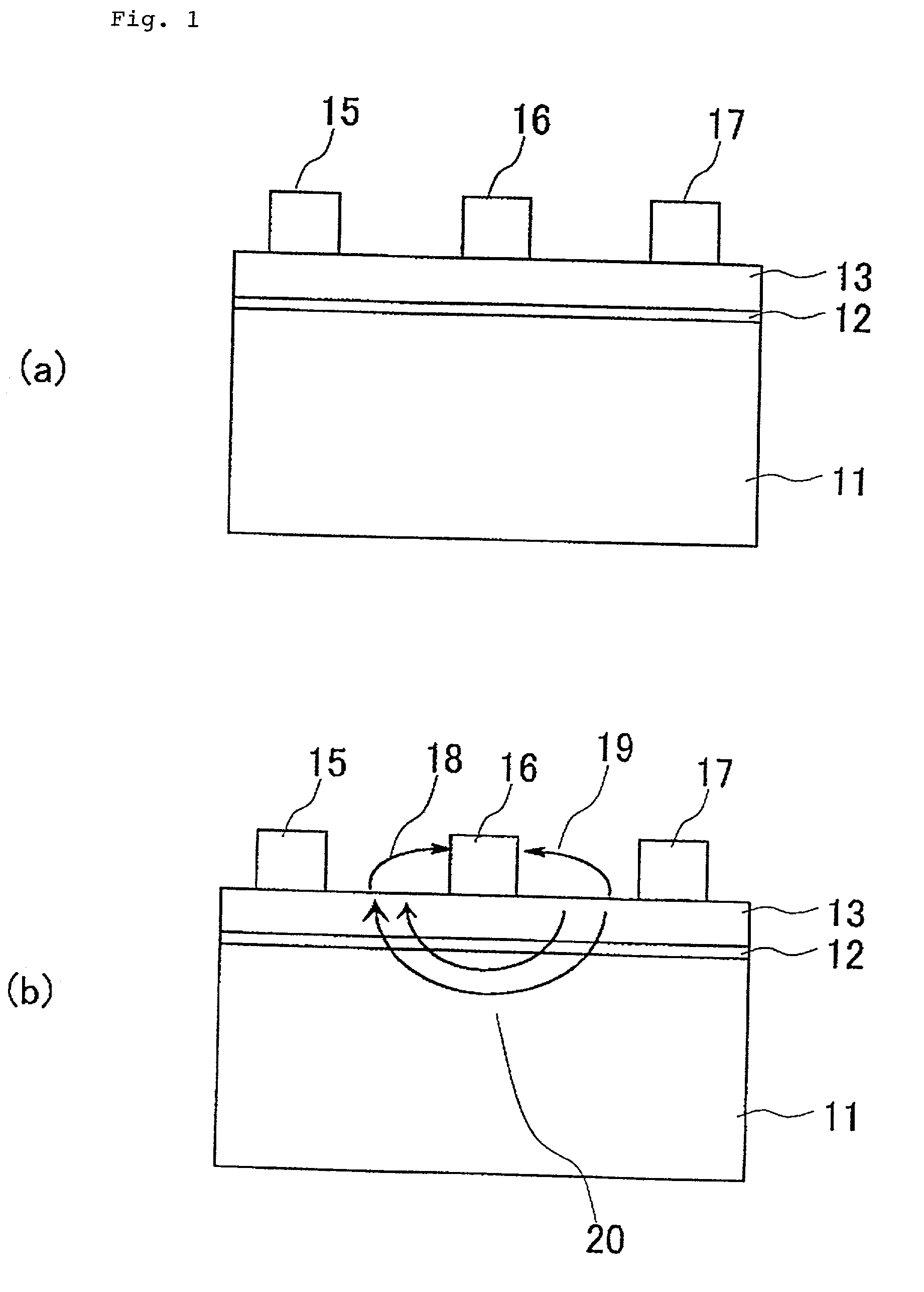
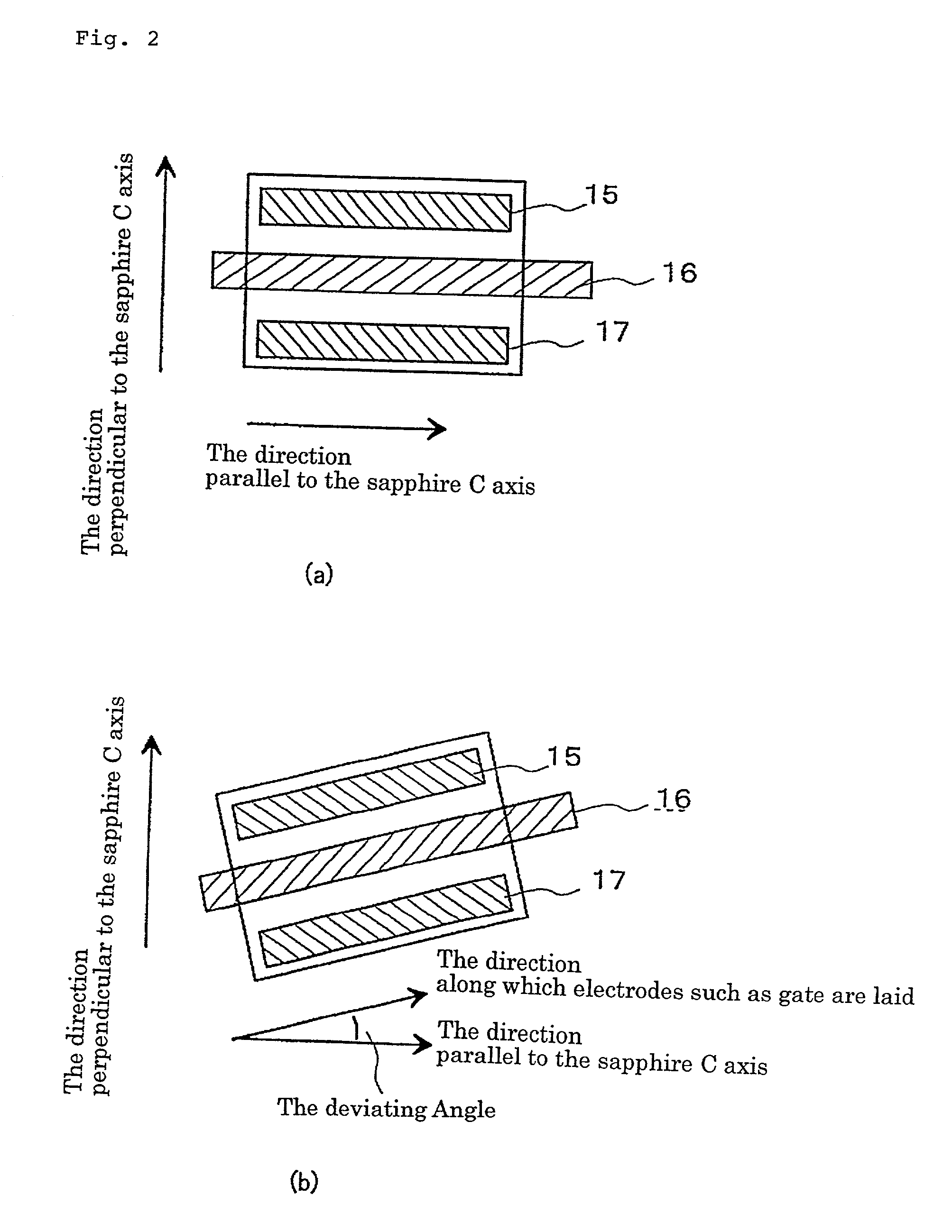
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020047113A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateNitride semiconductors
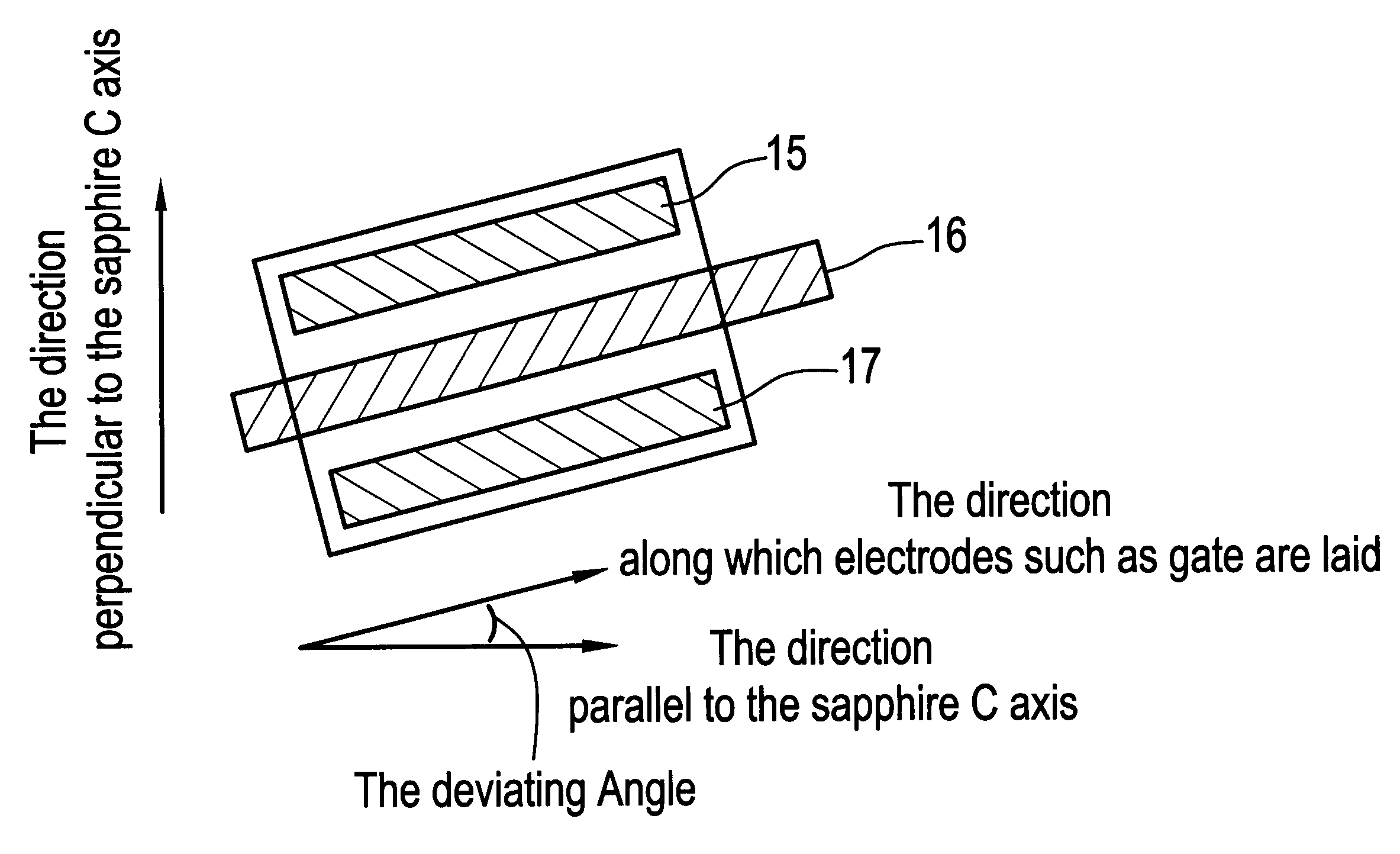
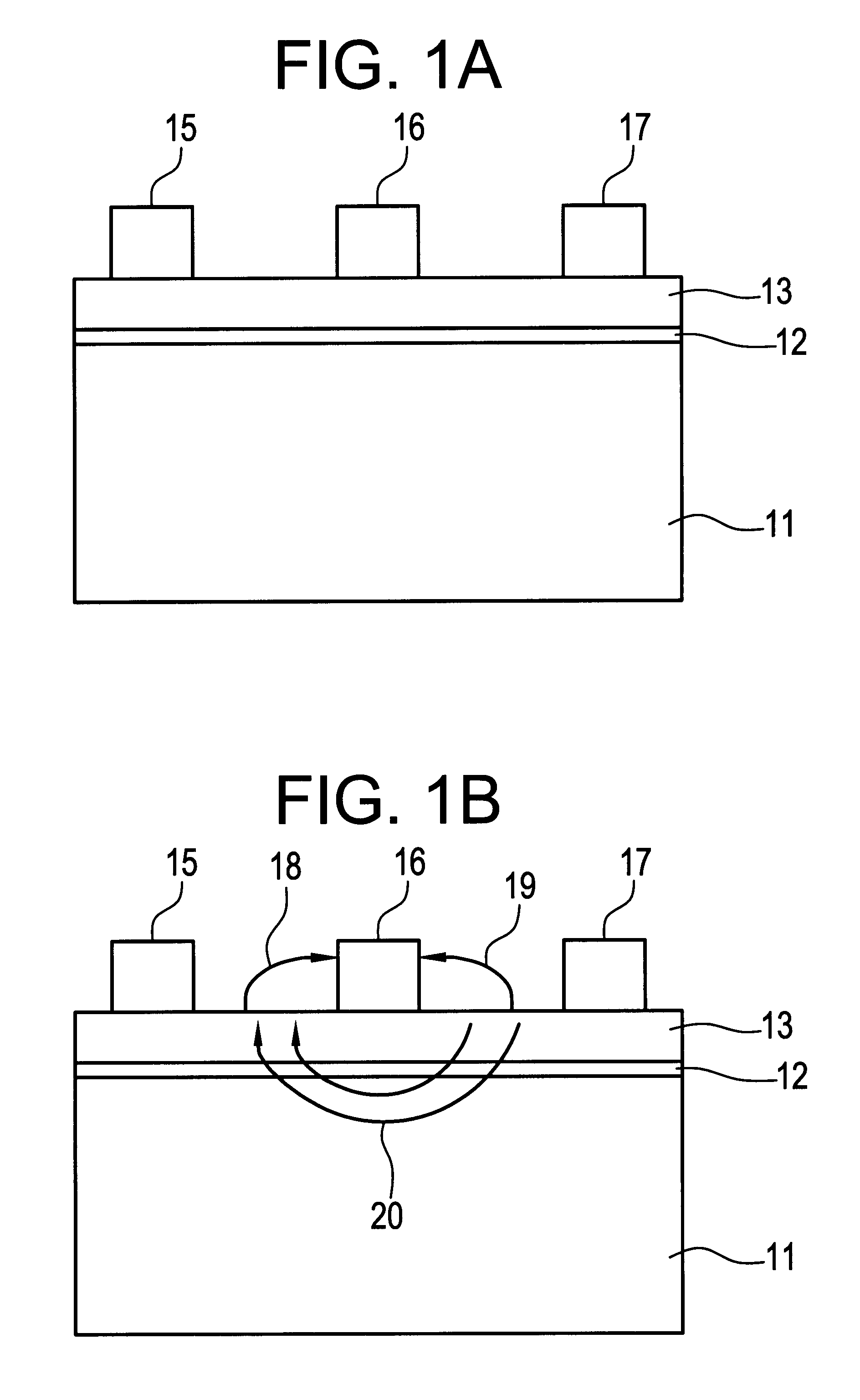
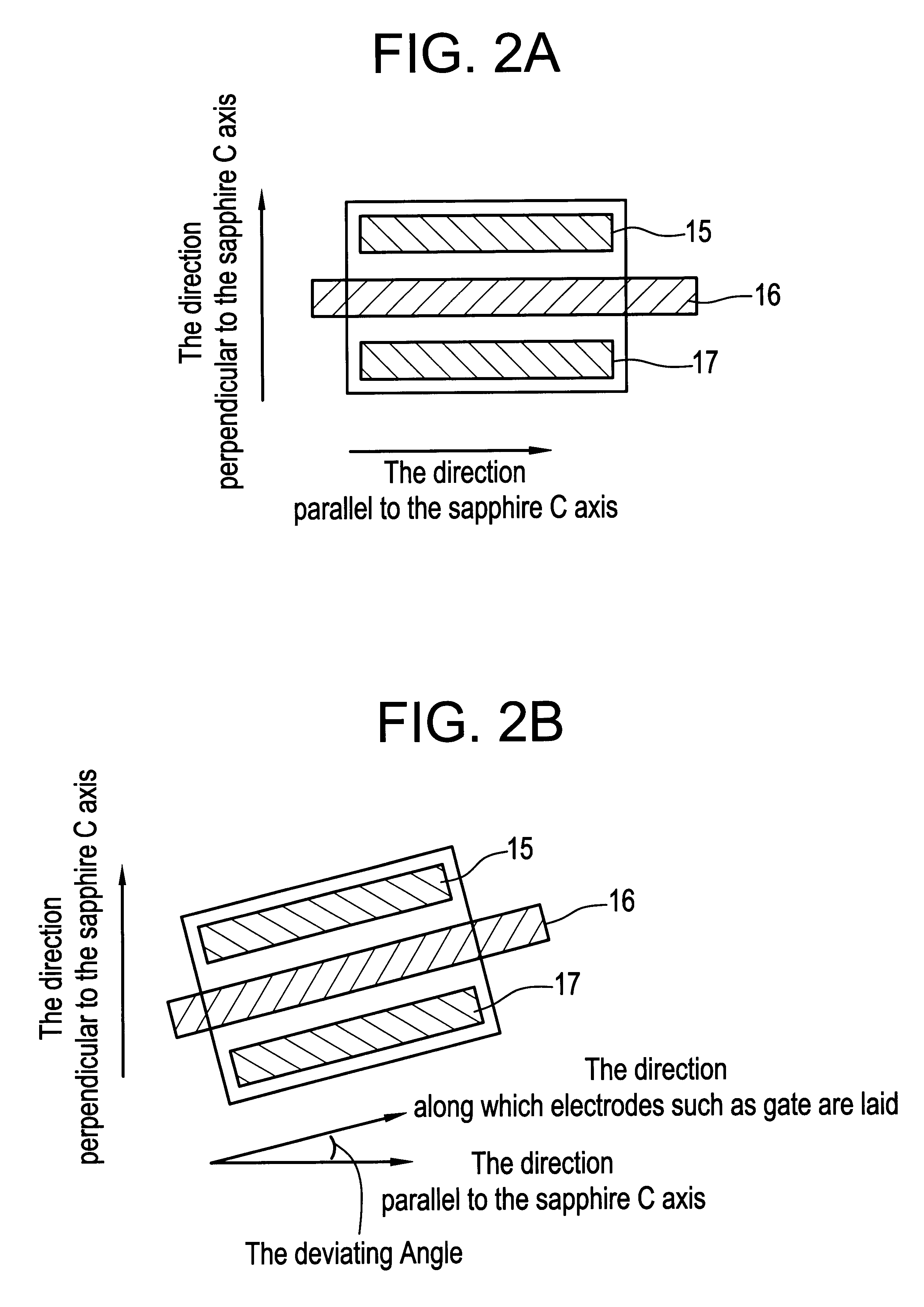
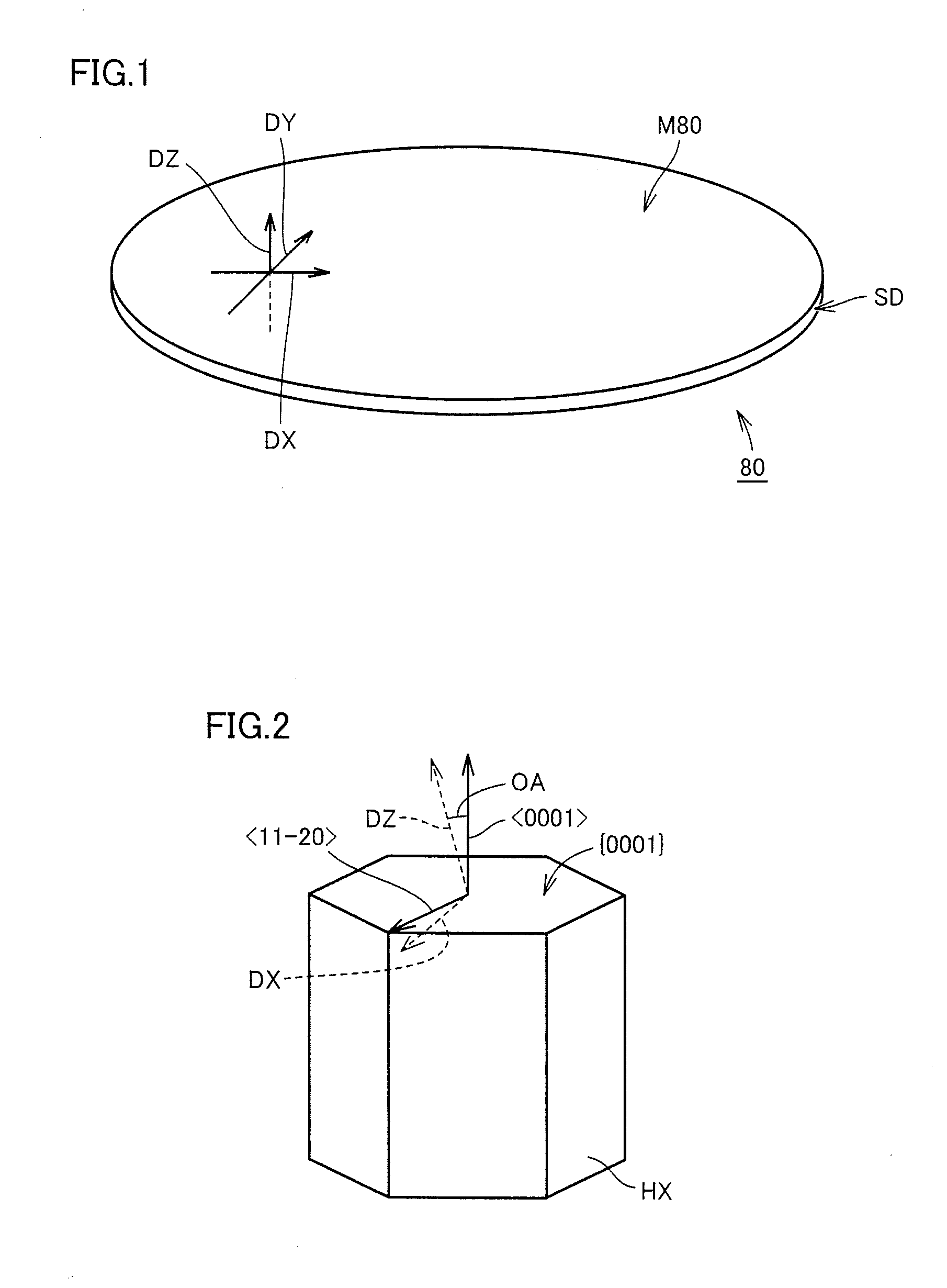
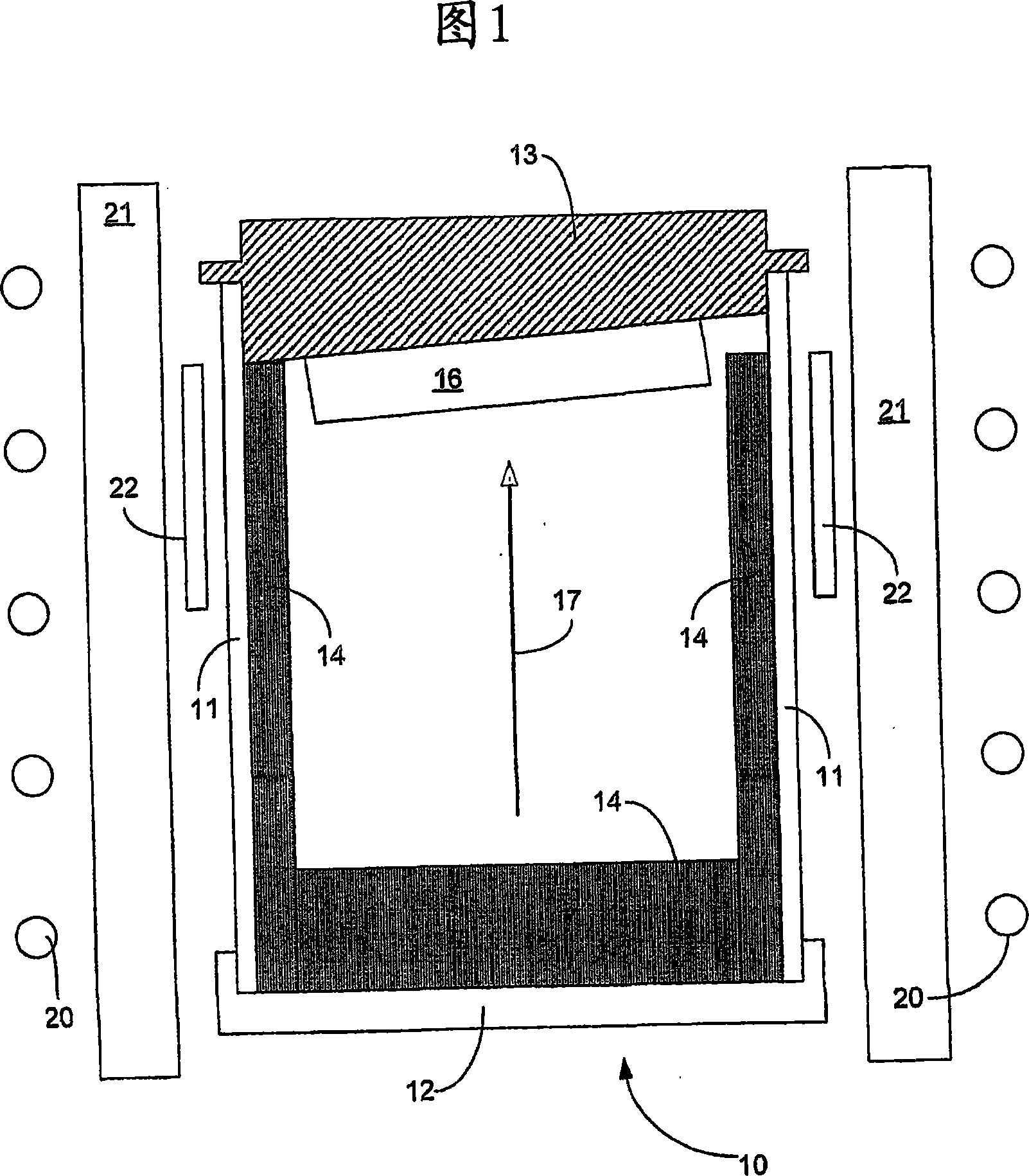
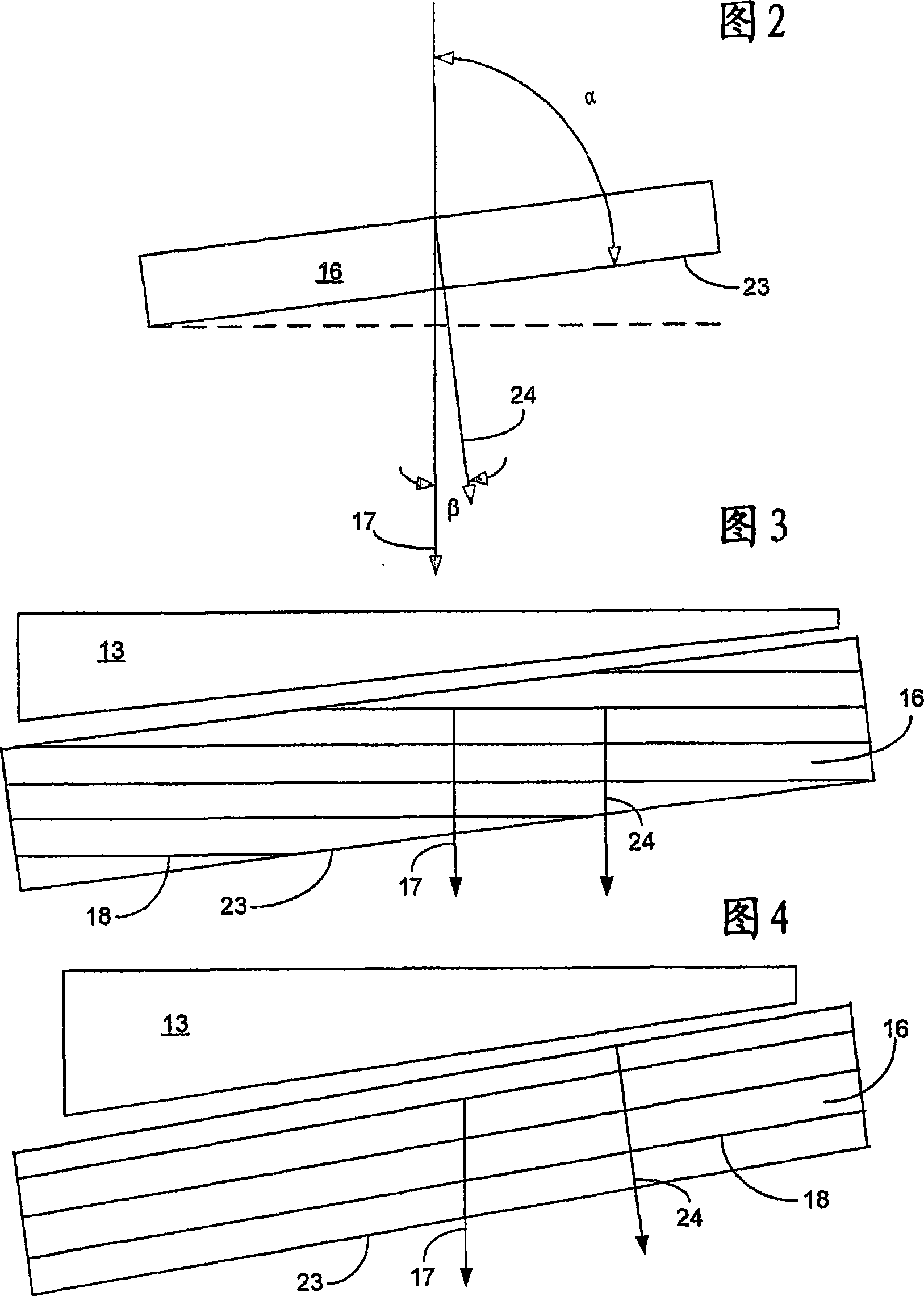
An object of the present invention is to improve, in a group III nitride semiconductor device, the productivity, heat radiation characteristic and performance in the element high speed operation; upon a sapphire substrate in which an A plane (an (11-20) plane) is set to be the basal plane, an epitaxial growth layer of a group III nitride semiconductor is formed and, thereon, a gate electrode 16, a source electrode 15 and a drain electrode 17 are formed; these electrodes are disposed in such a way that a direction along which they are laid makes an angle within 20° with respect to a C axis of sapphire.
Owner:NEC CORP
Bipolar Semiconductor Device and Process for Producing the Same
A process for manufacturing a bipolar type semiconductor device in which at least a part of a region where an electron and a hole are recombined during current flowing is formed with a silicon carbide epitaxial layer that has been grown from the surface of a silicon carbide substrate, is characterized by that the surface of the silicon carbide substrate is treated by hydrogen etching and the epitaxial layer is then formed by the epitaxial growth of silicon carbide from the treated surface. A propagation of a basal plane dislocation to the epitaxial layer can be further reduced by treating the surface of the silicon carbide substrate by using chemical mechanical polishing and hydrogen etching in this order.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Method To Reduce Stacking Fault Nucleation Sites And Reduce Forward Voltage Drift In Bipolar Devices
ActiveUS20050064723A1Reduce nucleationReduce in quantityDecorative surface effectsElectrostatic cleaningStacking faultOptoelectronics
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
Method and system for generating detail-in-context lens presentations for elevation data
A method for generating a presentation of a region-of-interest in an elevation data representation for display on a display screen, comprising: calculating a displacement height for at least one point in the representation falling within a lens by inversely scaling a vertical height of the point from a viewpoint for the presentation by a magnification for the lens; if the point is within a shoulder region of the lens, scaling the displacement height by a value of the shoulder function evaluated at a value given by a distance between a projection point in the basal plane and a closest point on a perimeter of a focal region as projected onto the basal plane, the distance being scaled by a distance between the closest point and an intersection point on a perimeter of the shoulder region; and, displacing the point by the displacement height to generate the presentation.
Owner:NOREGIN ASSETAB N V L L C
Silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and silicon carbide semiconductor device by using thereof
InactiveUS20090085044A1Reducing basal plane dislocation densityImprove conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalDislocation
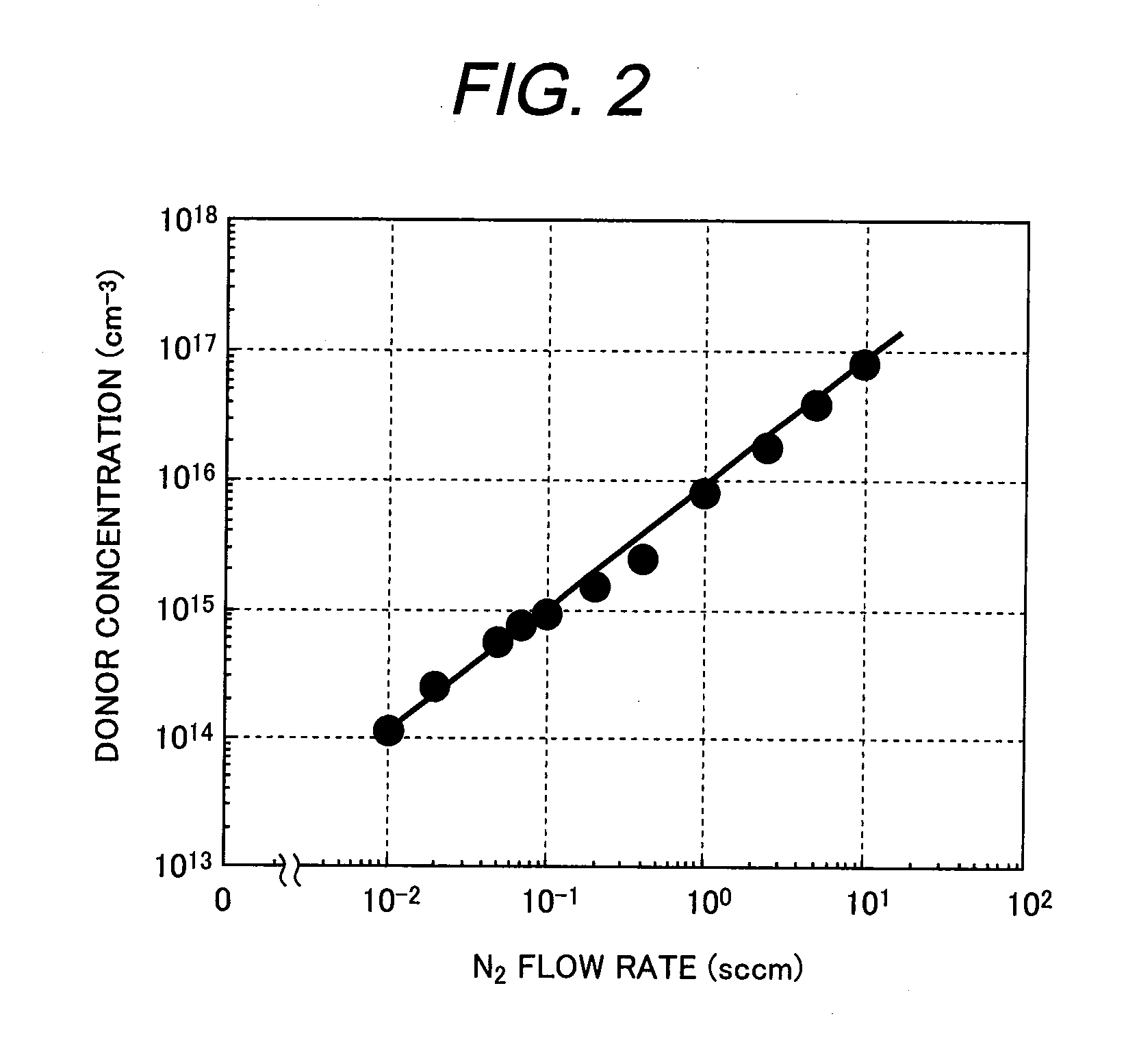
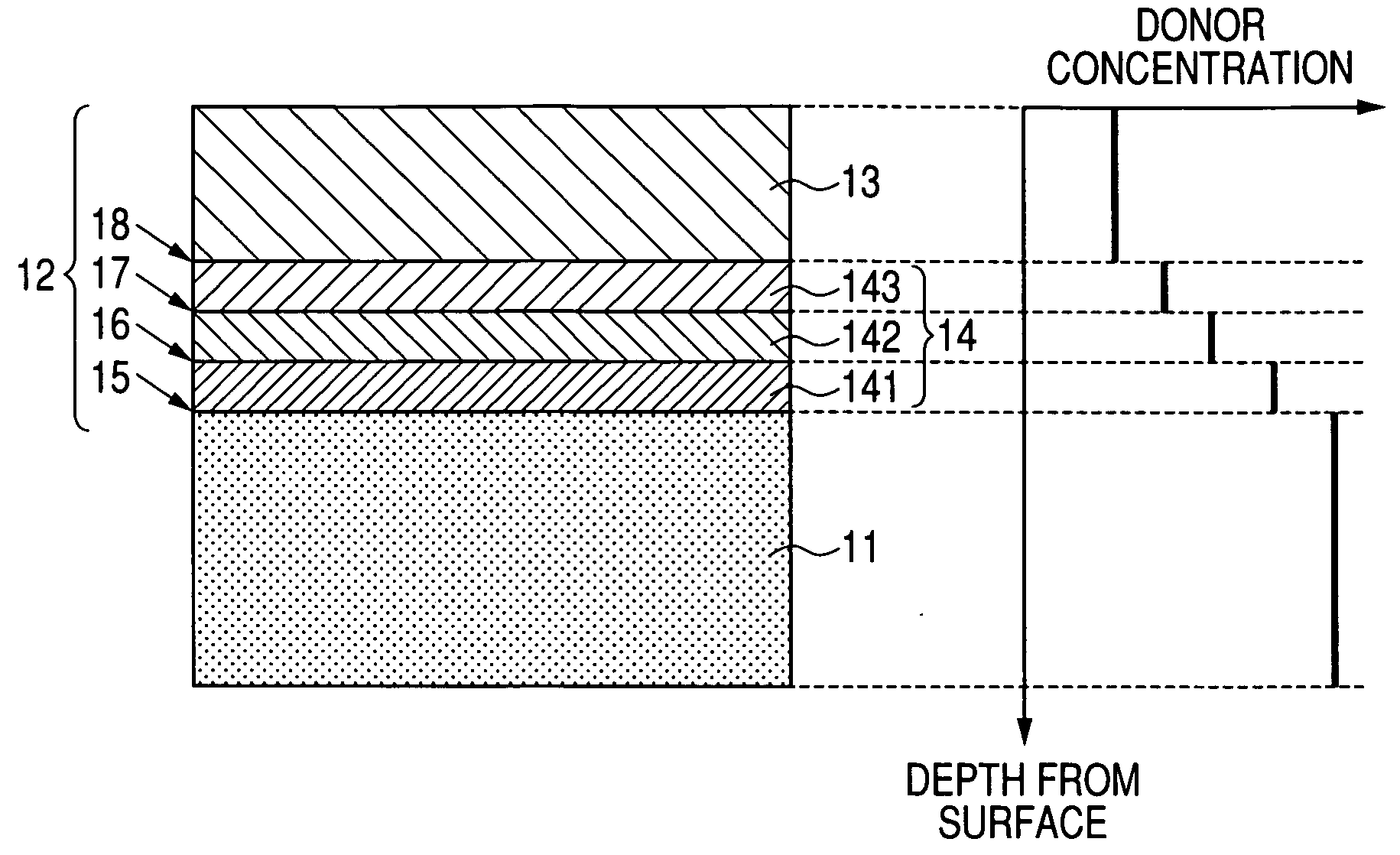
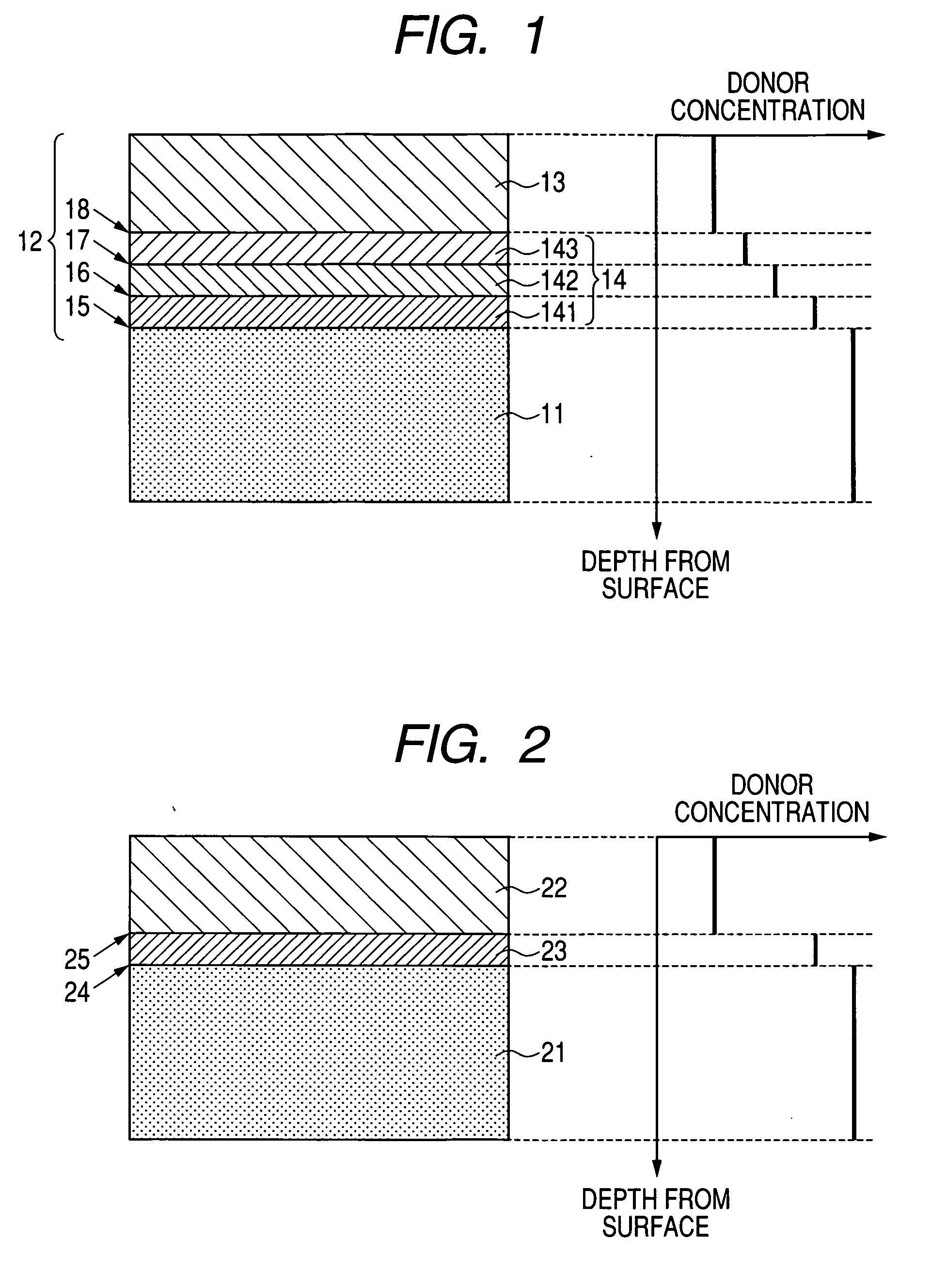
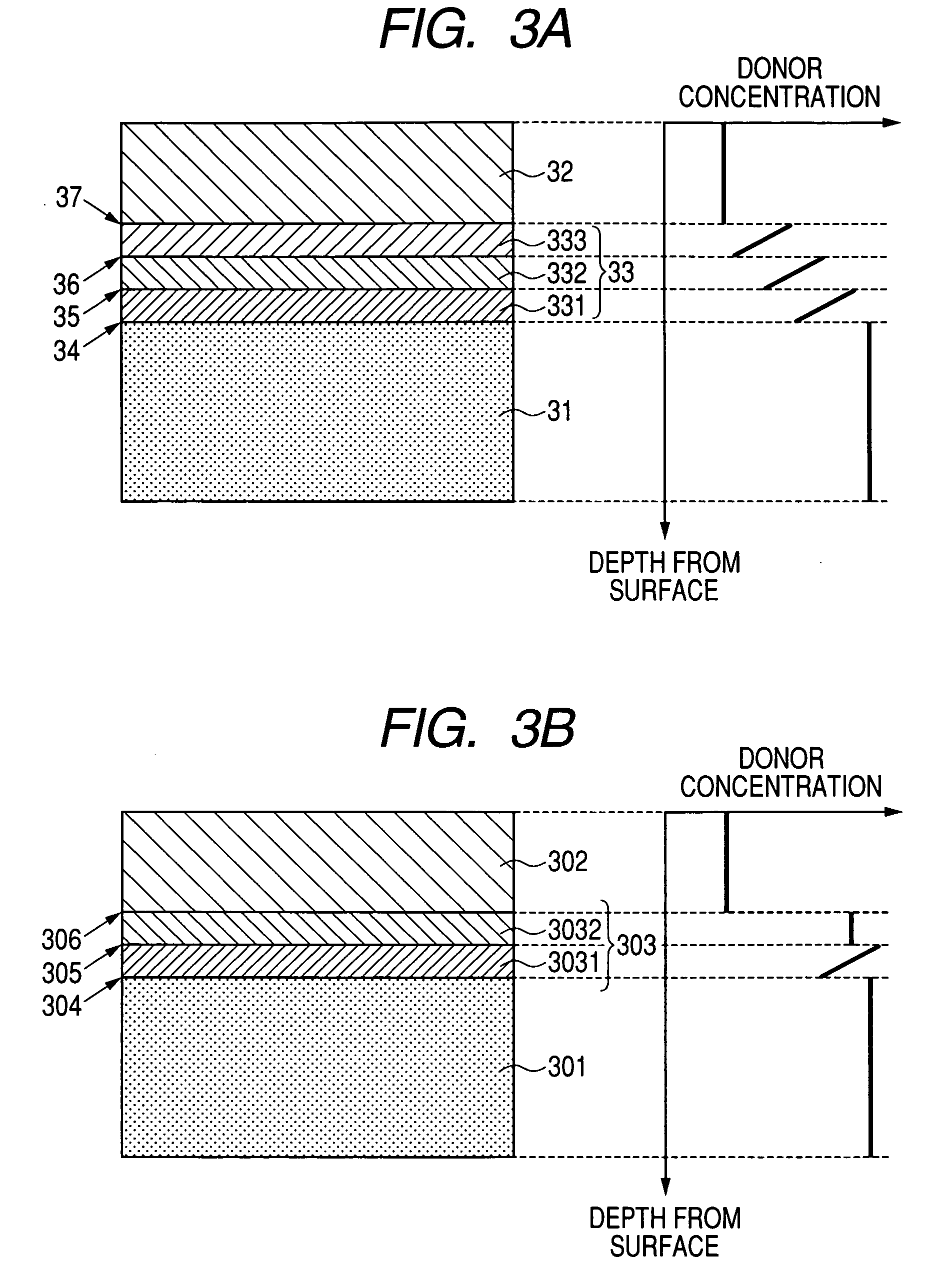
A manufacturing method is provided for a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate adapted for reduced basal plane dislocations in a silicon carbide epitaxial layer. Between a silicon carbide epitaxial layer for device fabrication (i.e., a drift layer) and a base substrate formed of a silicon carbide single-crystal wafer, a highly efficient dislocation conversion layer through which any basal plane dislocations in the silicon carbide single-crystal wafer are converted into threading edge dislocations very efficiently when the dislocations propagate into the layer epitaxially grown is provided by epitaxial growth. Assigning to the dislocation conversion layer a donor concentration lower than that of the drift layer, therefore, allows the above conversion of a larger number of basal plane dislocations than the case where the drift layer exists alone (without the dislocation conversion layer).
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Semiconductor device having drain and gate electrodes formed to lie along few degrees of direction in relation to the substrate
InactiveUS6441391B1Increase heatIncrease productivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateNitride semiconductors
An object of the present invention is to improve, in a group III nitride semiconductor device, the productivity, heat radiation characteristic and performance in the element high speed operation; upon a sapphire substrate in which an A plane (an (11-20) plane) is set to be the basal plane, an epitaxial growth layer of a group III nitride semiconductor is formed and, thereon, a gate electrode 16, a source electrode 15 and a drain electrode 17 are formed; these electrodes are disposed in such a way that a direction along which they are laid makes an angle within 20.degree. with respect to a C axis of sapphire.
Owner:NEC CORP
Silicon carbide semiconductor substrate and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090302328A1Reducing basal plane dislocation densityImprove conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalDislocation
A buffer layer configured of the same conductive semiconductor layers of two or more layers as a drift layer is installed by epitaxial growth between a first semiconductor layer configuring the drift layer that is a layer in which components of the semiconductor device are made and a base substrate including a silicon carbide single crystal wafer. A step of donor concentration is provided at an interface between the drift layer and the buffer layer, an interface between the semiconductor layers configuring the buffer layer, and an interface between the buffer layer and the base substrate and the donor concentration of the drift layer side is lower than that of the base substrate side, thereby making it possible to convert most basal plane dislocations into threading edge dislocations as compared to the drift layer having one layer or the buffer layer configured of one layer.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Methods for perforating graphene using an activated gas stream and perforated graphene produced therefrom
InactiveUS20130249147A1Reliably allow passage of certain nano-sized componentMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneContact timeProduct gas
Graphene sheets having a plurality of holes in their basal planes are described herein. Methods for making the graphene sheets can involve contacting graphene sheets with an activated gas that has contacted a helium or argon atmospheric pressure plasma. The size and / or number of holes introduced can be altered by changing the contact time, the stand-off distance, the activated gas concentration, and / or the plasma power. Polymer composites containing the perforated graphene sheets are also described.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Group-iii nitride light-emitting device and method for manufacturing group-iii nitride based semiconductor light-emitting device
ActiveUS20090212277A1StructuredImprove crystal qualitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellLength wave
A group-III nitride light-emitting device is provided. An active layer having a quantum well structure is grown on a basal plane of a gallium nitride based semiconductor region. The quantum well structure is formed in such a way as to have an emission peak wavelength of 410 nm or more. The thickness of a well layer is 4 nm or more, and 10 nm or less. The well layer is composed of InXGa1-XN (0.15≦X<1, where X is a strained composition). The basal plane of the gallium nitride based semiconductor region is inclined at an inclination angle within the range of 15 degrees or more, and 85 degrees or less with reference to a {0001} plane or a {000-1} plane of a hexagonal system group III nitride. The basal plane in this range is a semipolar plane.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Water-cured polyurethane waterproof coating
InactiveCN102181225AImprove mechanical propertiesGood chemical propertiesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsSolventMechanical property
The invention discloses a single-component water-cured polyurethane waterproof coating. The single-component coating is a NCO group terminated prepolymer obtained by the reaction of polyether polyol and polyisocyanate after the polyether polyol is hydrated in vacuum; and the weight ratio of the polyether polyol to the polyisocyanate is (2-10): 1. The coating is ecological and environment-friendly, has excellent mechanical property, good high and low temperature resistance and good solvent resistance and corrosion resistance, can be constructed on moist basal planes, does not affect adhesive property, and has high cost performance, low specific weight, low consumption in unit area and low comprehensive manufacturing cost.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENTAL YUHONG WATERPROOF TECH CO LTD +2
Silicon carbide substrate and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130071643A1Improve performanceImprove device performanceAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthStacking faultSingle crystal
A silicon carbide substrate capable of stably forming a device of excellent performance, and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. A silicon carbide substrate is made of a single crystal of silicon carbide, and has a width of not less than 100 mm, a micropipe density of not more than 7 cm−2, a threading screw dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a threading edge dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a basal plane dislocation density of not more than 1×104 cm−2, a stacking fault density of not more than 0.1 cm−1, a conductive impurity concentration of not less than 1×1018 cm−2, a residual impurity concentration of not more than 1×1016 cm−2, and a secondary phase inclusion density of not more than 1 cm−3.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for manufacturing and installing guide rail in container ship cargo hold
InactiveCN101885368AImprove installation accuracyAvoid welding deformationVessel partsEngineeringSlipway
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing and installing a guide rail in a container ship cargo hold, which comprises the following steps of: (a) manufacturing the guide rail; (b) two-dimensional preassembly: assembling and welding a processed guide plate and the guide rail on a platform by using a doubling plate as a basal plane; (c) hoisting and boarding: installing an eye ring of the guide rail on the guide rail a quarter away from the upper end, respectively installing one eye ring at the left side and the right side of the guide plate, correspondingly reinforcing the eye rings from the back side, and hoisting the whole guide rail to a slipway; adding a toggle plate behind the doubling plate to reinforce the guide rail with low intensity; and after manufacturing the guide rail of a following ship in two segments, connecting the two segments into one guide rail after correction, and hoisting the assembled guide rail; (d) slipway installation: marking, and installing the guide rail; and (e) packaging and testing. In the method, the guide rail is firstly preassembled on the platform by using the doubling plate as the basal plane, and then, the whole guide rail is hoistedonto the slipway and installed. The invention has simple and reasonable method, convenient construction and high guide rail installation accuracy. The upward and downward hoisting and the reasonable arrangement of containers in the cargo hold can be ensured, and thus, the working efficiency and the ship manufacturing quality are increased.
Owner:YANGFAN GROUP
Graphene-nano particle composite having nanoparticles crystallized therein at a high density
InactiveUS20150179294A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove electrical characteristicsSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialNanoparticle ComplexHigh density
The present invention relates to a graphene-nanoparticle composite having a structure in which nanoparticles are crystallized at a high density in a carbon-based material, for example, graphene, and, more particularly, to a graphene-nanoparticle composite capable of remarkably improving physical properties such as contact characteristics between basal planes of graphene and conductivity since nanoparticles are included as a large amount of 20 to 50% by weight, based on 100% by weight of graphene, and a method of preparing the same.
Owner:CHEORWON PLASMA RES INST
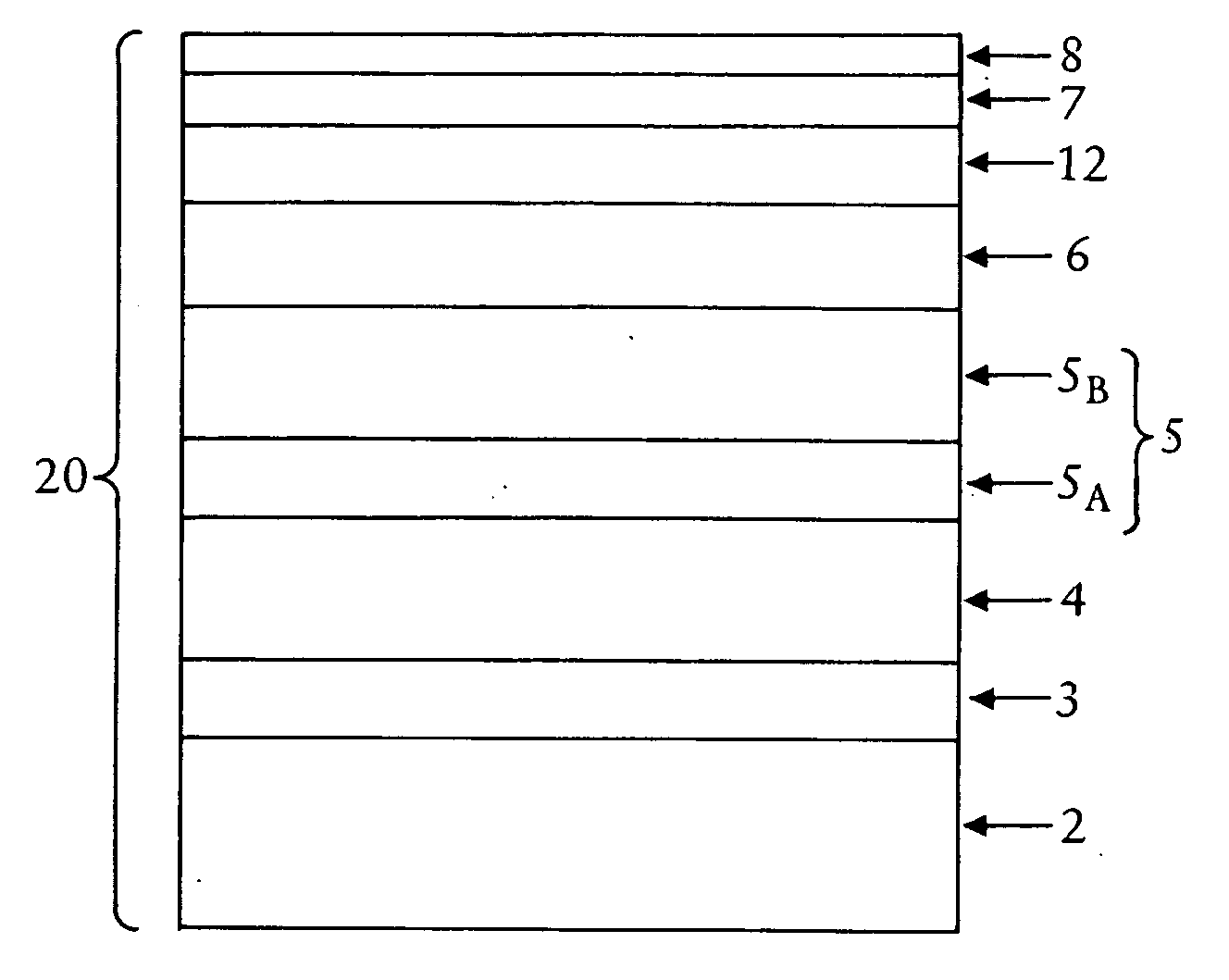
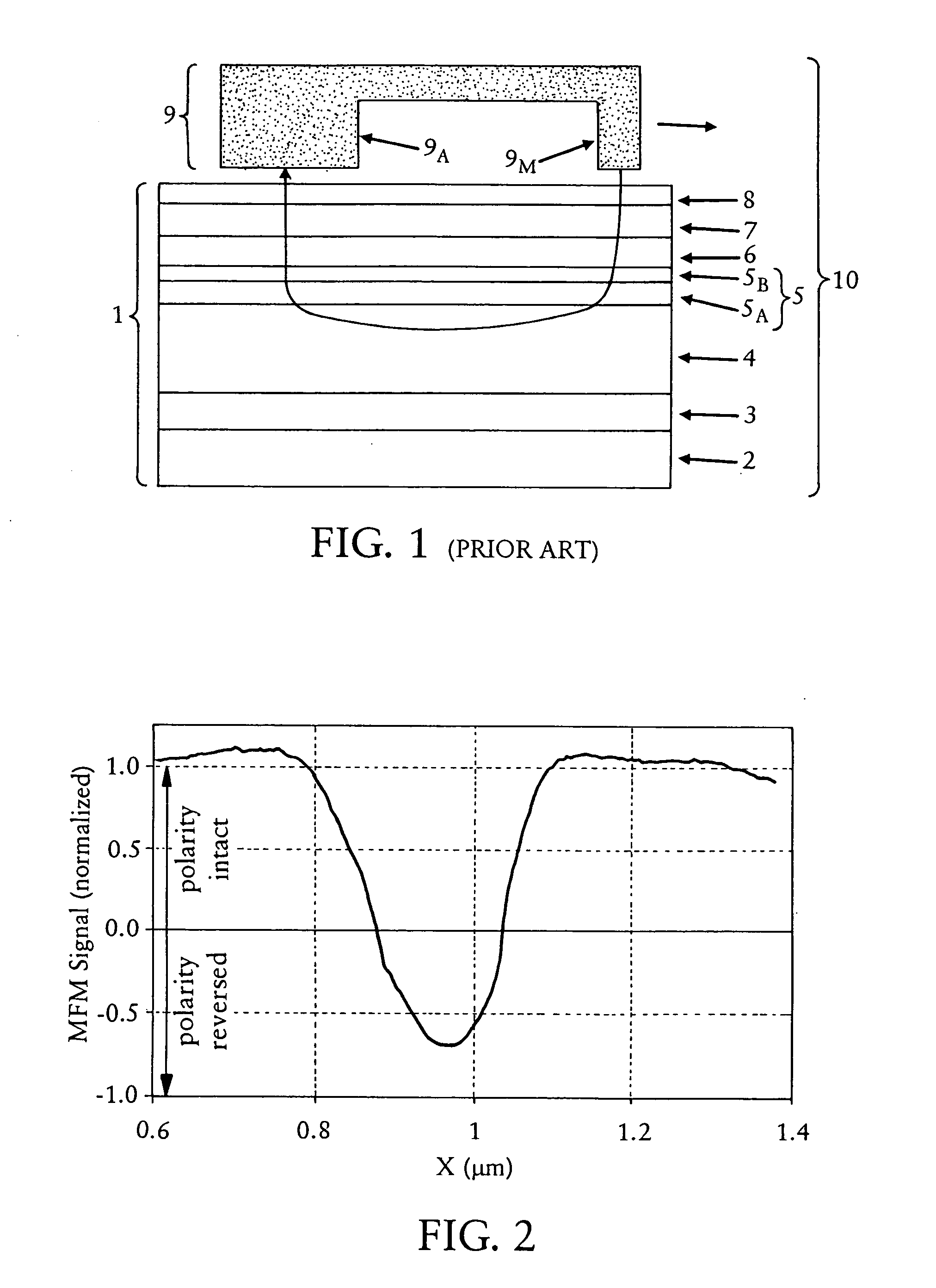
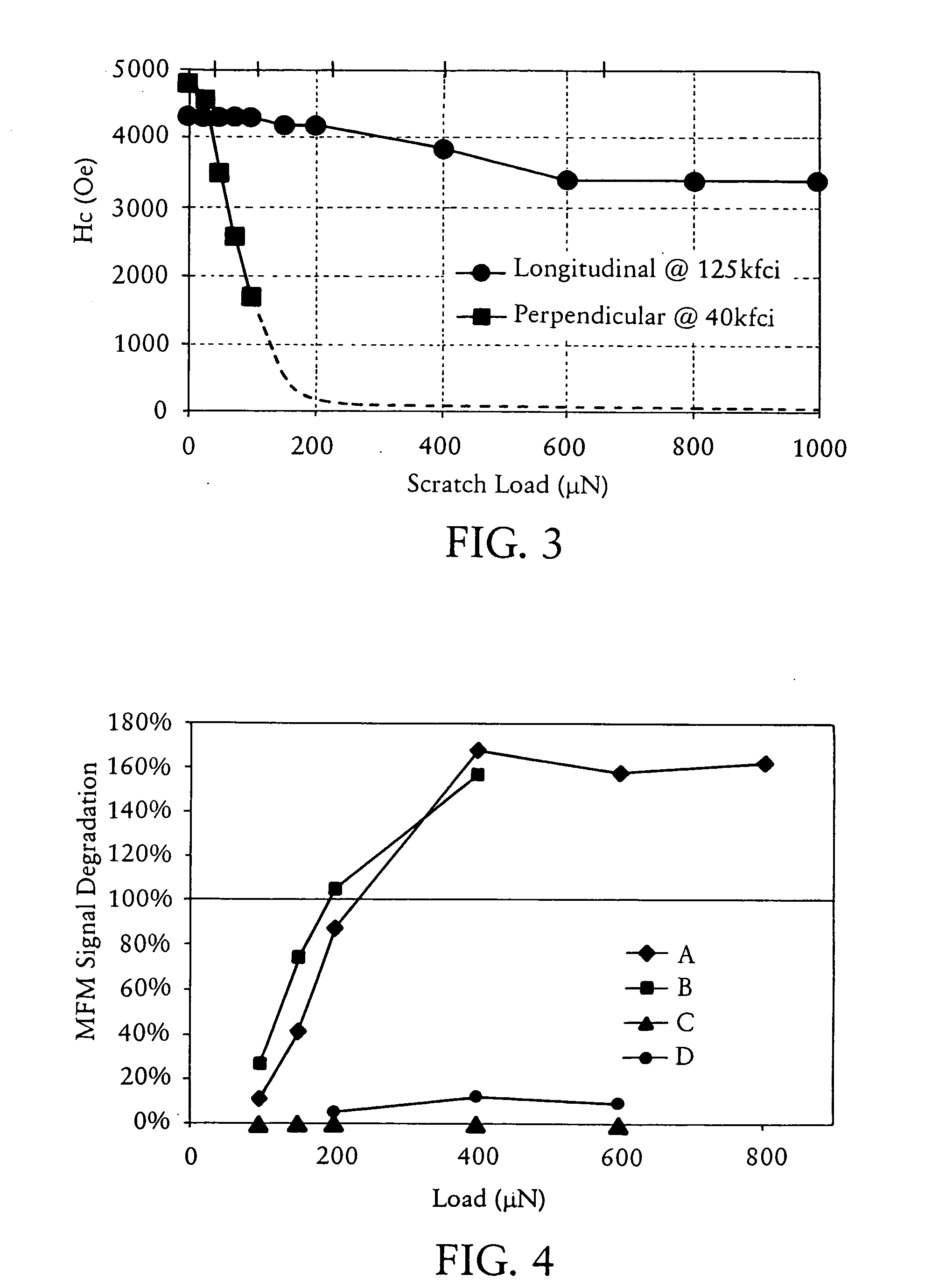
Perpendicular magnetic recording media with improved scratch damage performance
InactiveUS20080055777A1Improved, scratch erasure resistant, perpendicular magnetic recording mediaProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageShear modulusCrystal structure
A scratch erasure resistant perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprises a non-magnetic substrate having a surface, and a layer stack formed over the surface and comprising: (i) at least one magnetically hard perpendicular magnetic recording layer; and (ii) at least one low shear modulus layer comprising at least one material having a shear modulus not greater than about 30 GPa. Preferably, the at least one magnetically hard perpendicular magnetic recording layer includes at least a first layer comprised of a magnetic material having a hexagonal close packed (hcp) crystal structure and <0001> preferred basal plane crystallographic orientation with c-axis perpendicular to a surface thereof.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Pretreatment Method for Reduction and/or Elimination of Basal Plane Dislocations Close to Epilayer/Substrate Interface in Growth of SiC Epitaxial
InactiveUS20130143396A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon destructivePretreatment method
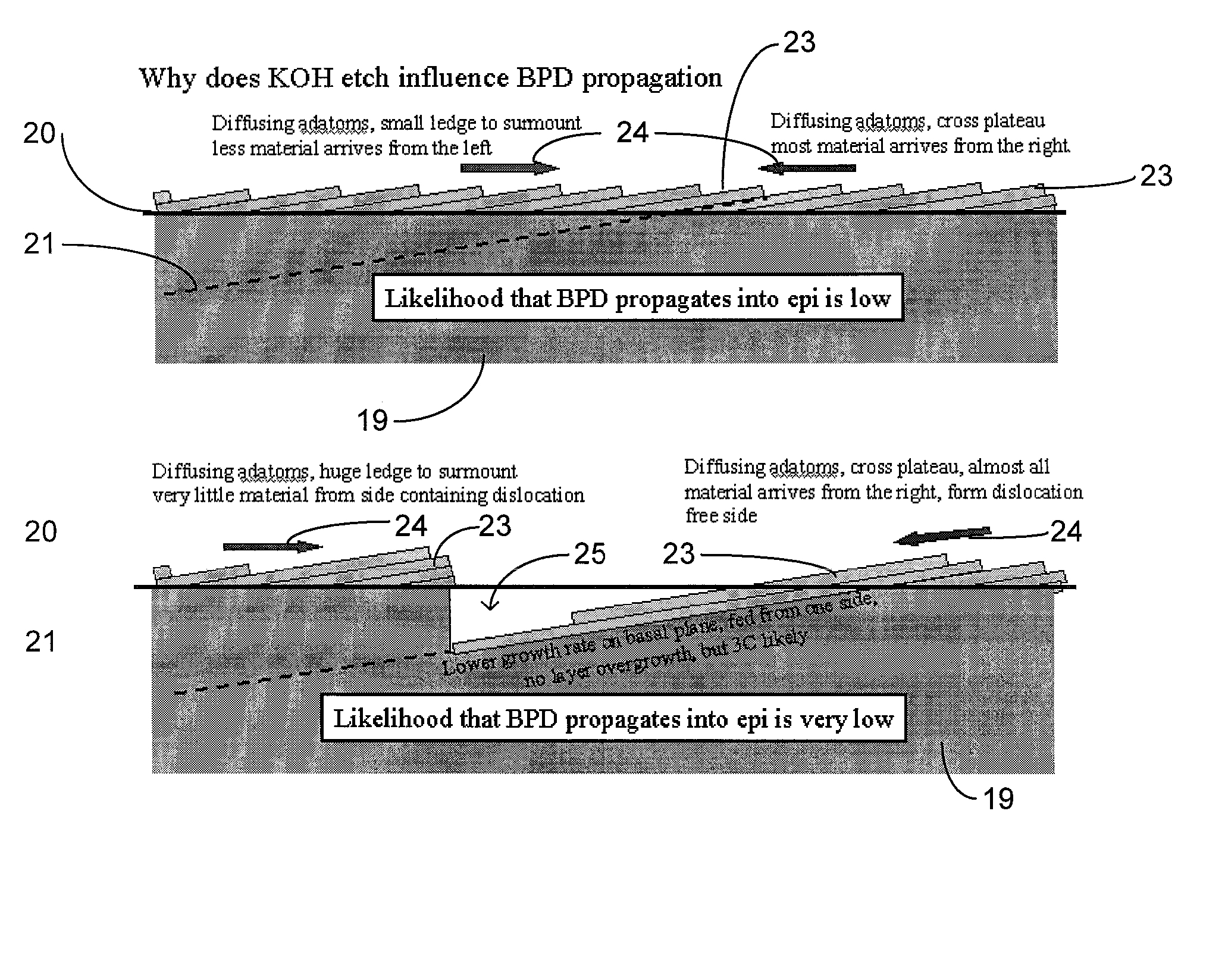
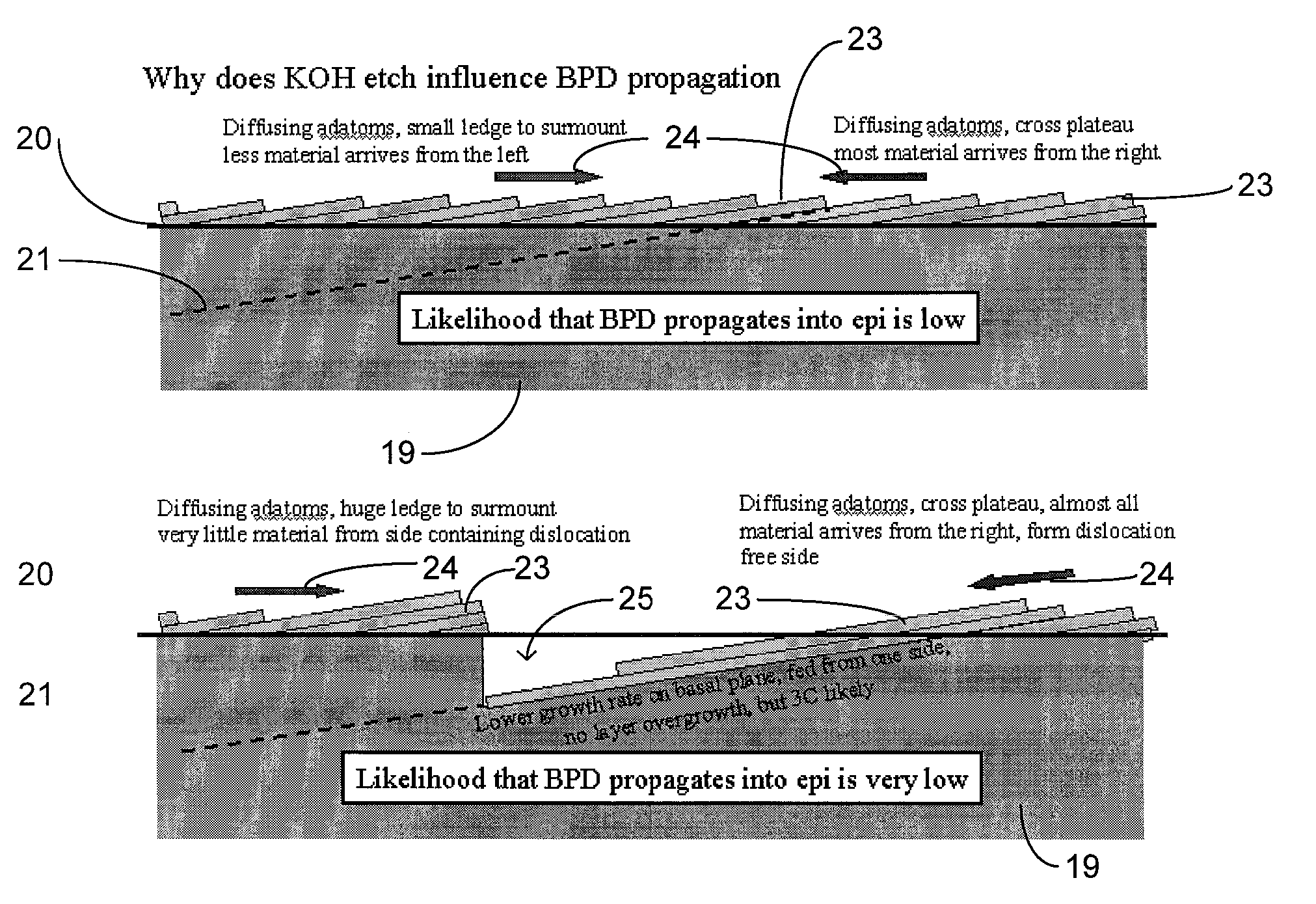
Non-destructive pretreatment methods are generally provided for a surface of a SiC substrate with substantially no degradation of surface morphology thereon. In one particular embodiment, a molten mixture (e.g., including KOH and a buffering agent) is applied directly onto the surface of the SiC substrate to form a treated surface thereon. An epitaxial film (e.g., SiC) can then be grown on the treated surface to achieve very high (e.g., up to and including 100%) BPD to TED conversion rate close to the epilayer / substrate interface.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Graphene-coated coupling coil for ac resistance reduction
InactiveUS20130020877A1Improve conductivityNon-insulated conductorsElectromagnetic wave systemAlternating currentElectric power
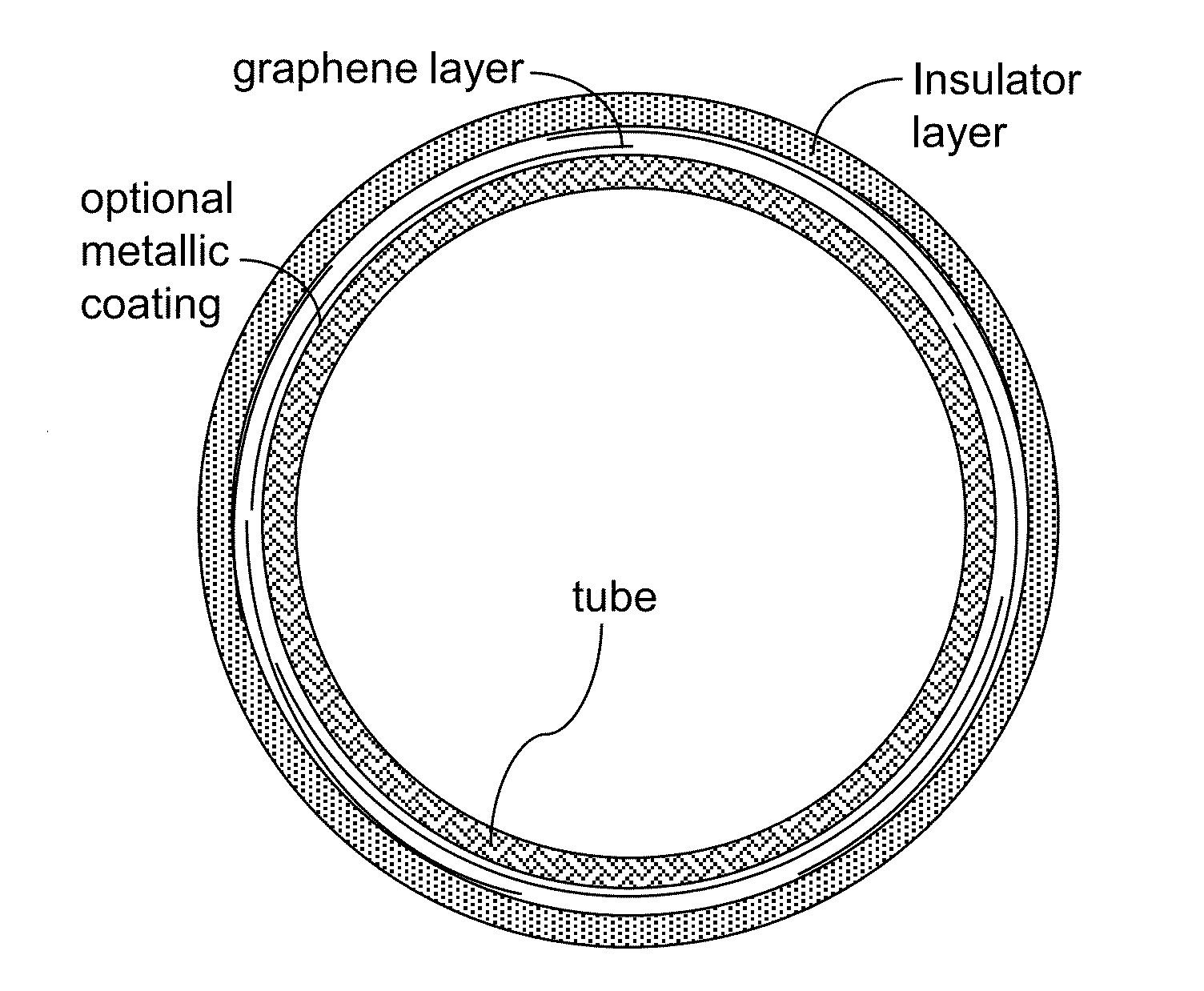
At least one graphene layer is formed to laterally surround a tube so that the basal plane of each graphene layer is tangential to the local surface of the tube on which the graphene layer is formed. An electrically conductive path is provided around the tube for providing high conductivity electrical path provided by the basal plane of each graphene layer. The high conductivity path can be employed for high frequency applications such as coupling coils for wireless power transmission to overcome skin depth effects and proximity effects prevalent in high frequency alternating current paths.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Installing and positioning method of linear guide rail
InactiveCN102179699AMeet the requirements of the accuracy classImprove installation efficiencyLarge fixed membersMechanical engineeringOrder of accuracy
Owner:CHAOYANG BOWEN MACHINE TOOL
Graphene-NANO particle composite having NANO particles crystallized therein at a high density
InactiveUS20140219906A1Excellent mechanical and electric characteristicImprove conductivityCell electrodesIndividual molecule manipulationHigh densityNanoparticle Complex
The present invention relates to a graphene-nanoparticle composite having a structure in which nanoparticles are crystallized in a carbon-based material, for example, graphene, at a high density, and, more particularly, to a graphene-nanoparticle composite capable of remarkably improving physical properties such as contact characteristics between basal planes of graphene and conductivity, wherein nanoparticles are included as a large amount of 30% by weight or more, based on 100% by weight of graphene, and crystallized nanoparticles have an average particle diameter of 200 nm or more, and a method of preparing the same.
Owner:CHEORWON PLASMA RES INST
Method for preparing aluminum-magnesium-aluminum three-layer metal composite plate by prefabricating crossed corrugated interface
InactiveCN110548776AUniform mechanical propertiesEasy to slideMetal rolling arrangementsCrystal twinningComposite plate
The invention relates to the technical field of rolling of metal composite plates, specifically relates to a method for preparing an aluminum-magnesium-aluminum three-layer metal composite plate by prefabricating a crossed corrugated interface, and aims to solve the technical problems of low composite plate bonding strength and serious texture of a magnesium plate basal plane in a conventional method for preparing the aluminum-magnesium-aluminum three-layer metal plate. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: rolling a magnesium plate into a double-faced crossed corrugated shape; then covering two layers of aluminum plates on the upper surface and the lower surface of the magnesium plate; flatly rolling the three layers of plates together; and processing to obtain the three-layer metal composite plate with the upper surface and the lower surface being planes and the middle bonding surface being crossed corrugated. With the adoption of the method, the basal plane texture of a magnesium plate can be effectively weakened, and the bonding strength can be improved. Magnesium with uniform mechanical property can be obtained when the texture strength is obviously reduced, and because a weak and dispersed basal plane texture is obtained, basal plane slippage and twin crystal formation are facilitated during stretching, so that the forming property of the plate is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable sizing block device
InactiveCN102620120ASimple structureEasy to operateMachine framesUltimate tensile strengthMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an adjustable sizing block device. The adjustable sizing block device comprises a seat body, wherein a basal plane is machined on the seat body; a left wedge block and a right wedge block which are symmetrical are arranged on the basal plane; a pushing mechanism is arranged between the left wedge block and the right wedge block; and a supporting block is arranged on an inclined plane above each of the left wedge block and the right wedge block. When the device is mounted, the seat body is arranged on the basal plane, supporting legs below the device is arranged on the supporting blocks, and the number of the device is the same as the supporting legs below the device, namely each supporting leg is provided with the sizing block device. An adjusting bolt is rotated through a tool, and the adjusting bolt is opposite to the spiral direction of threaded connection between a connecting block and the left wedge block; when the adjusting bolt is rotated, the connecting block and the left wedge block are separated or approach each other, the left wedge block and the right wedge block are relatively separated or approach each other, the supporting blocks move upwards or downwards, and the aim of adjusting the height of the supporting position of the device is fulfilled. The device is simple in integral structure, convenient to operate, easy to control, suitable for micro adjustment, time-saving and labor-saving, lightens the labor intensity and improves the working efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN HUAGEN MACHINERY
Low basal plane dislocation bulk grown SiC wafers
ActiveUS7294324B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystalOptoelectronics
Owner:CREE INC
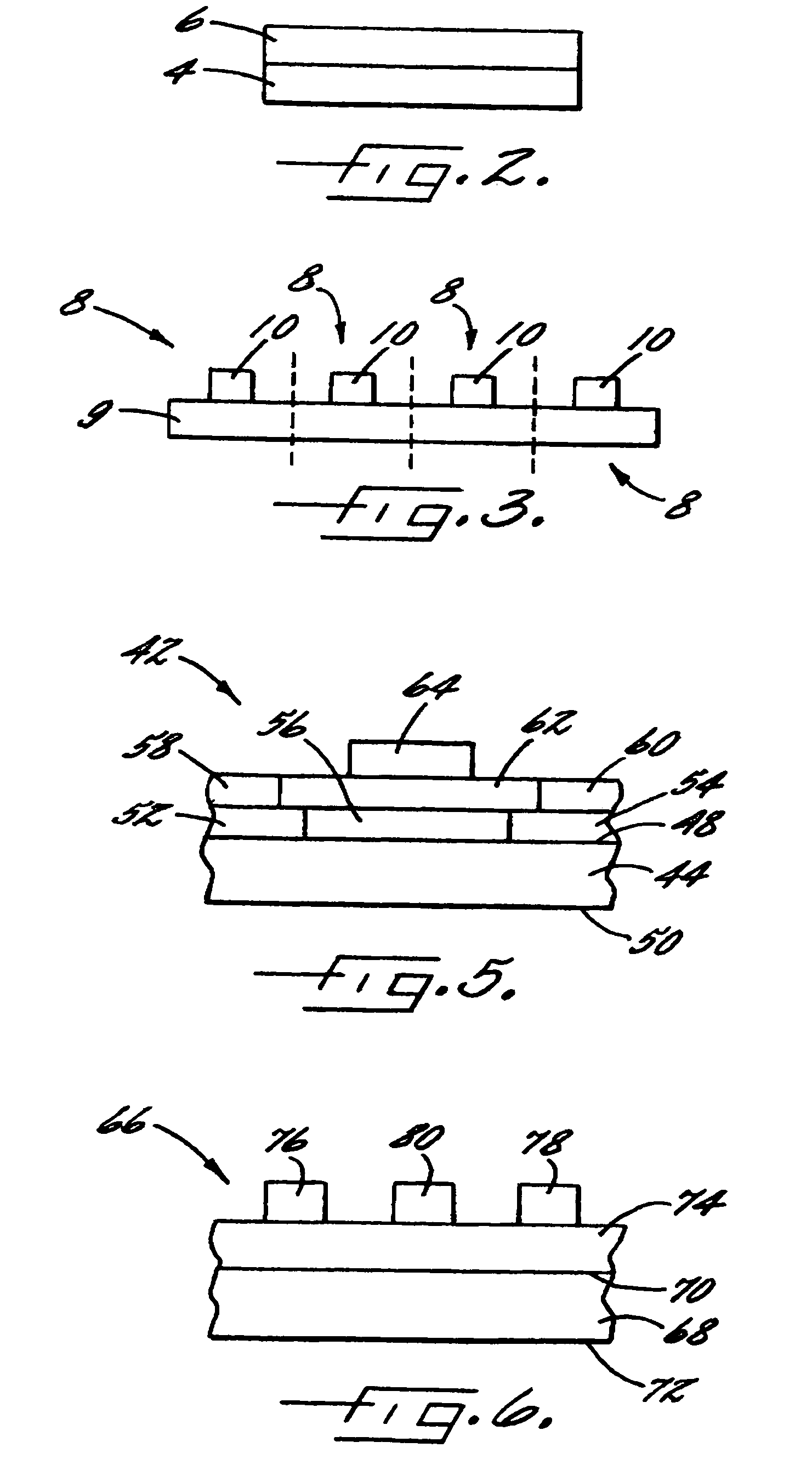
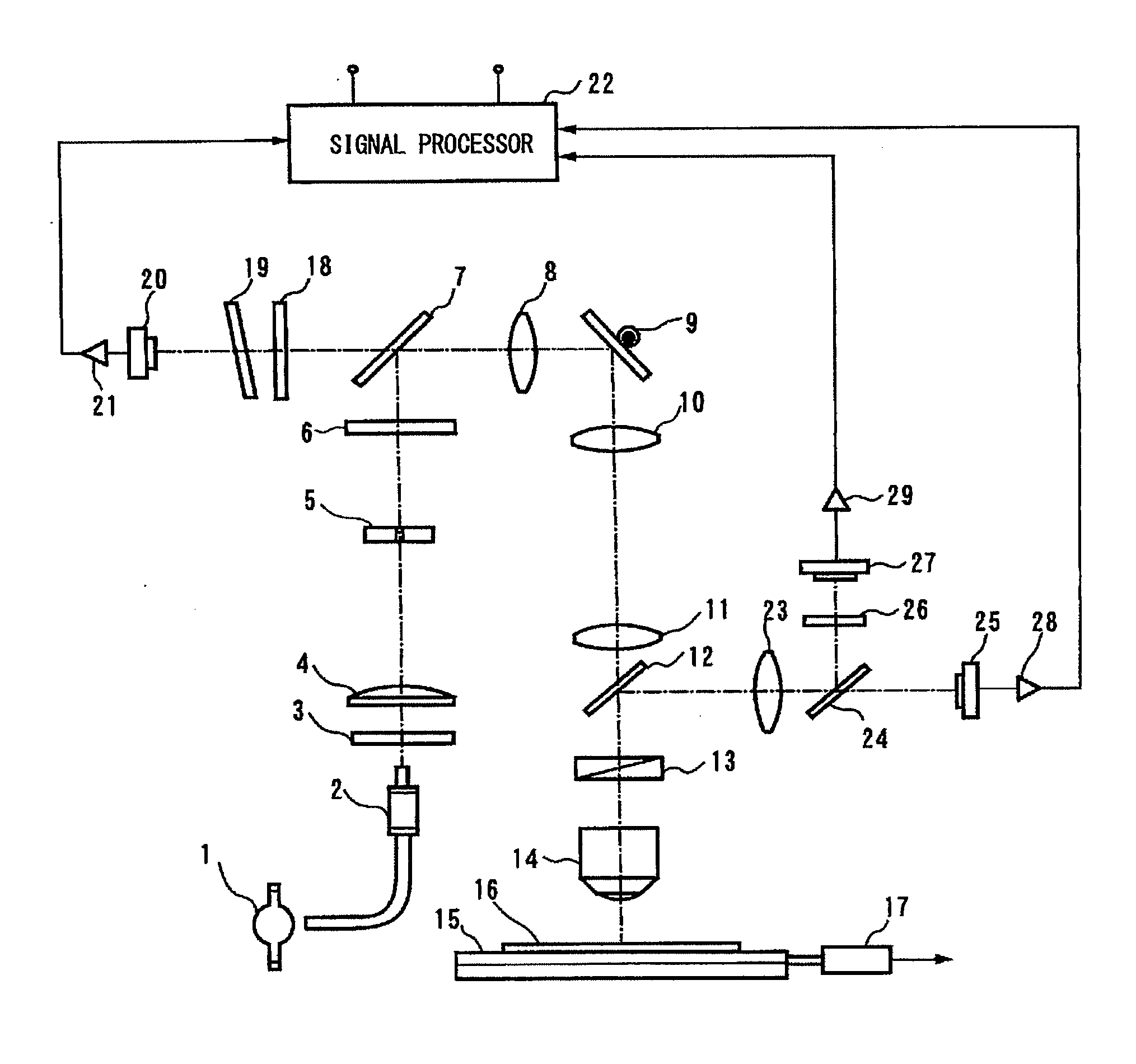
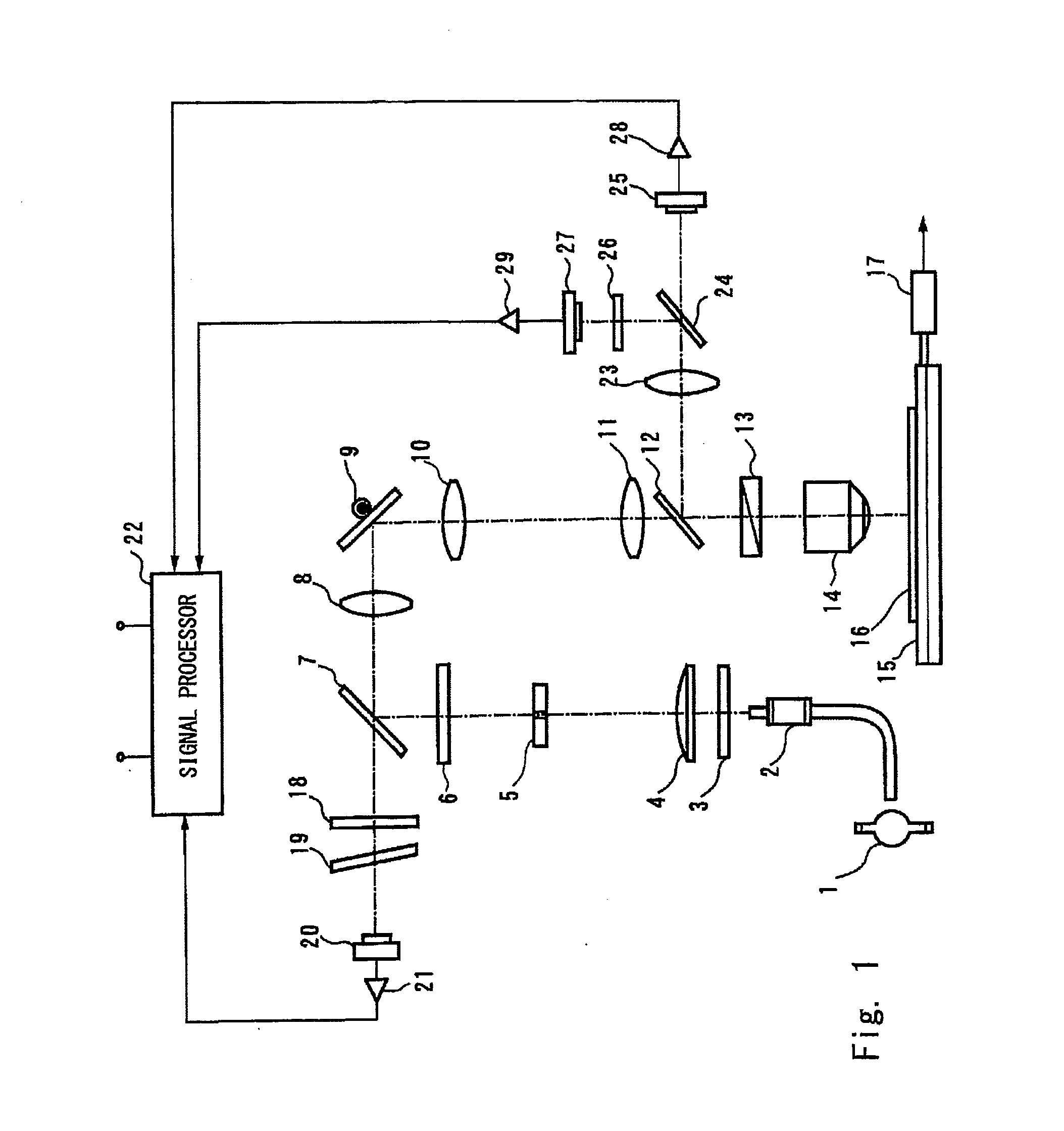
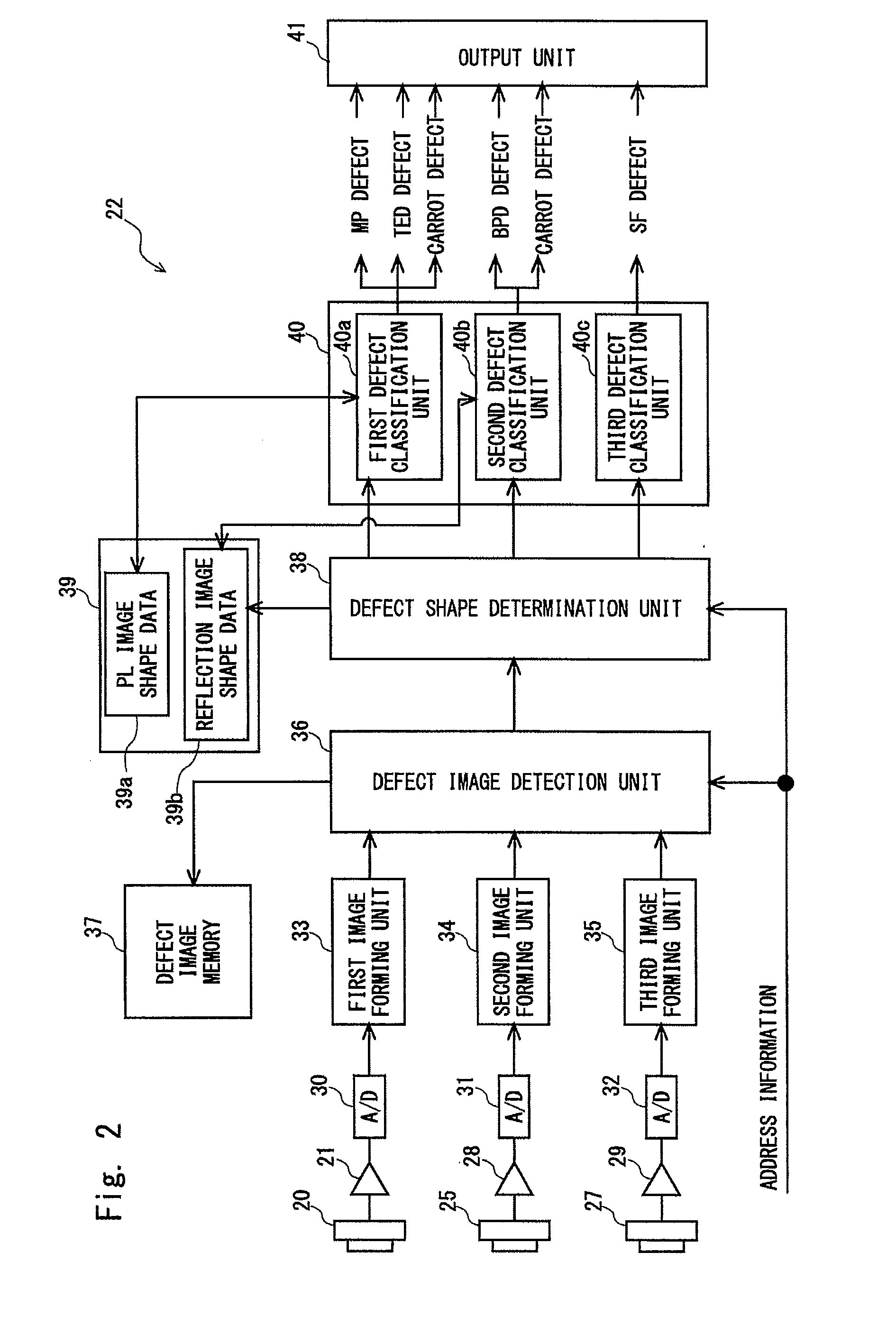
Defect classifying method and inspection apparatus
ActiveUS20150168311A1Improve classification accuracyRadiation pyrometryOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotoluminescenceHigh pressure
Provided are a defect classifying method and an inspection apparatus which are capable of classifying a defect by distinguishing a basal plane dislocation, which is a killer defect in bipolar high-voltage elements, from other defects. The defect classifying method according to the present invention includes: projecting an illumination beam toward a silicon carbide substrate and forming a reflection image and a photoluminescence image; a first inspection step of detecting a defect image from the reflection image formed; a second inspection step of detecting a defect image from the photoluminescence image formed; and a defect classification step of classifying detected defects based on whether or not the defect image is detected and the shape of the detected defect image.
Owner:LASERTEC CORP
Method of manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS20080318359A1Low densityFlattening of irregularityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDislocationSemiconductor
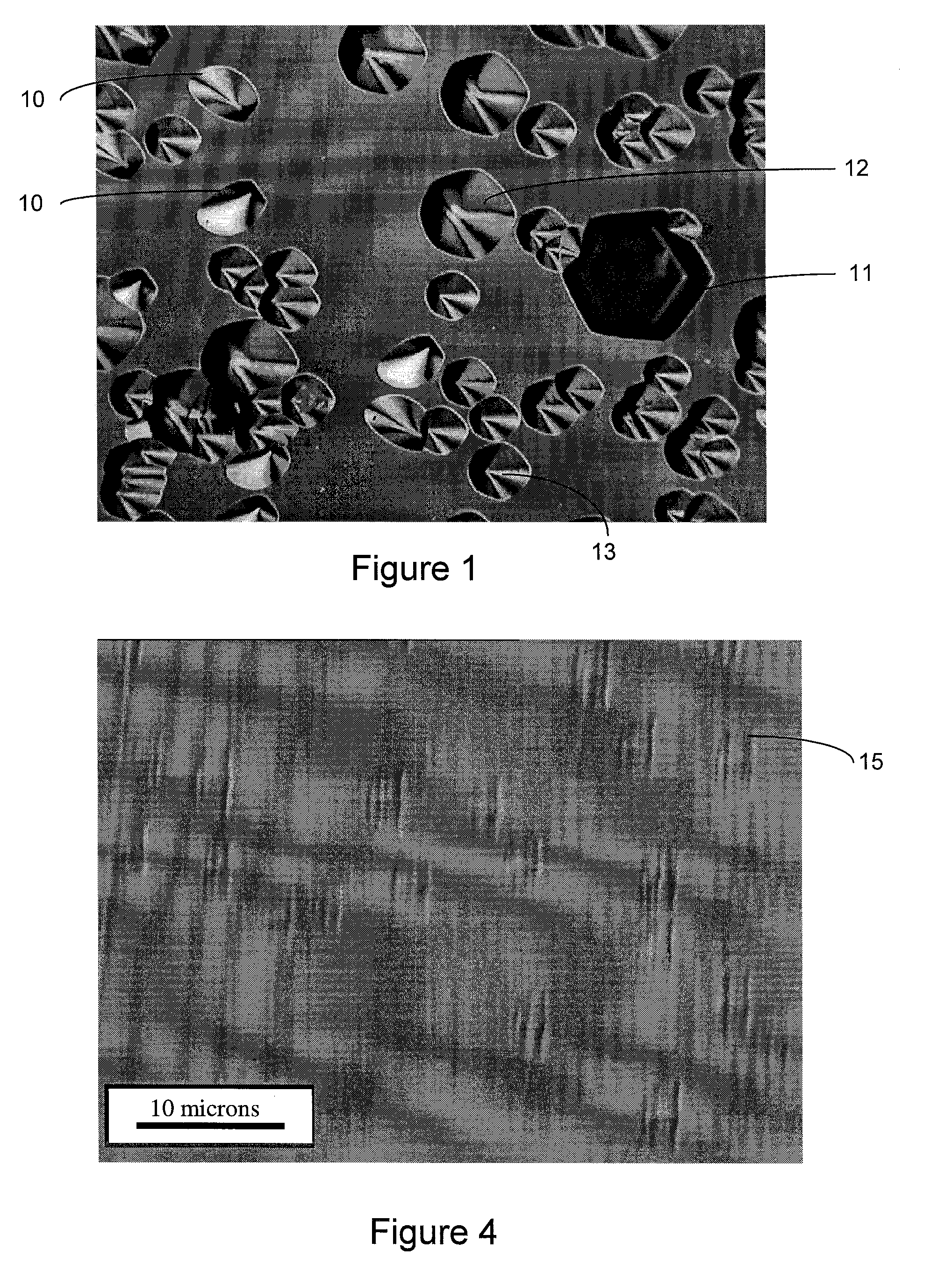
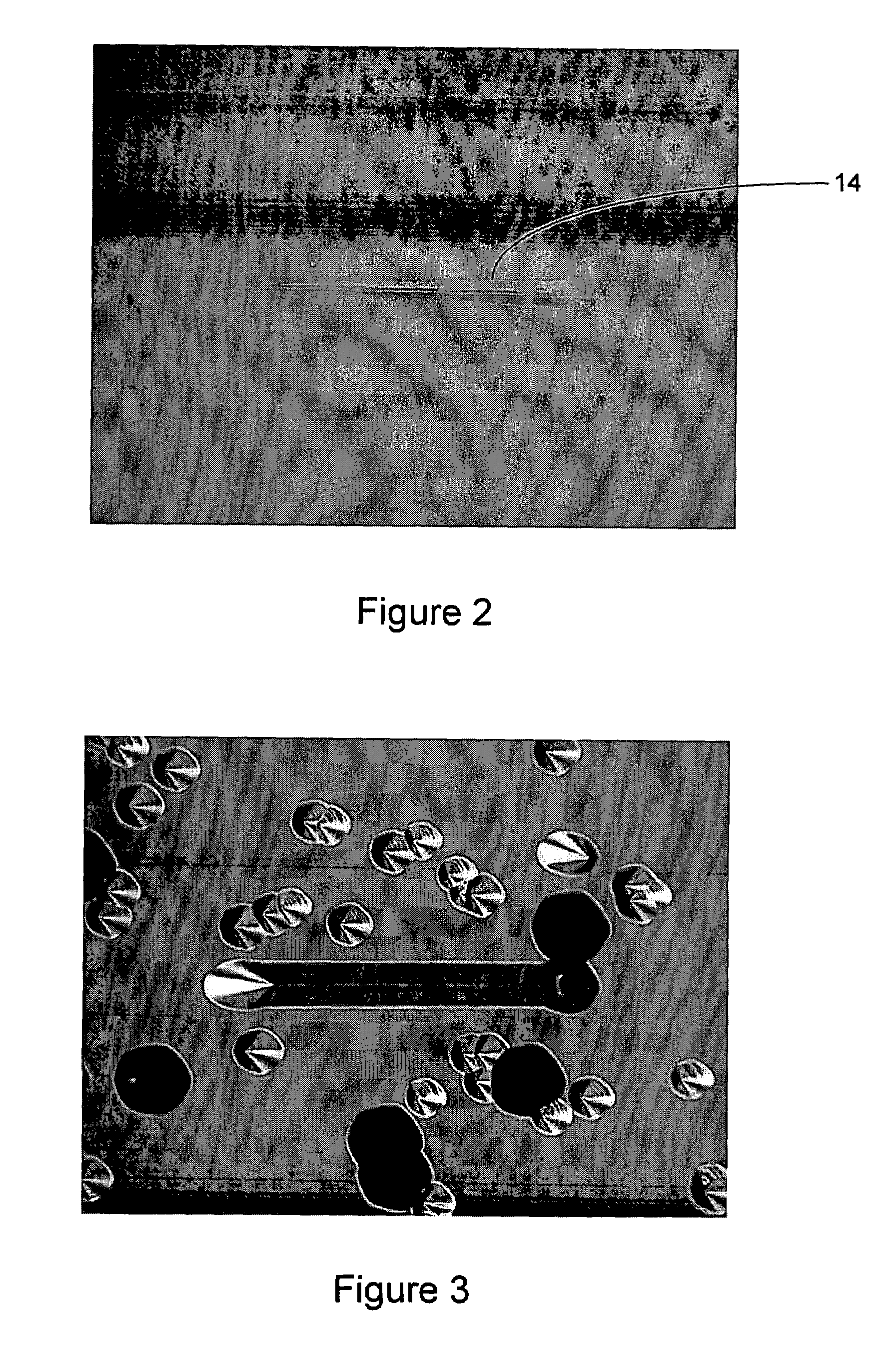
A method of manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate is disclosed in which the density of basal plane dislocations (BPDs) in particular is reduced in an SiC crystal substrate. Irregularities in the surface of the substrate due to this reduction also can be flattened. A method of manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor substrate is disclosed in which, prior to forming an epitaxial growth layer on a silicon carbide substrate with an off-axis angle of 1° to 8°, parallel line-shape irregularities, which have an irregularity cross-sectional aspect ratio equal to or greater than the tangent of the off-axis angle of the silicon carbide substrate, are formed in the substrate surface. The irregularites have a height between 0.25 μm and 5 μm.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Seed and seedholder combinations for high quality growth of large silicon carbide single crystals
A silicon carbide seeded sublimation growth system and associated method are disclosed. The system includes a crucible, a silicon carbide source composition in the crucible, a seed holder in the crucible, a silicon carbide seed crystal on the seed holder, means for creating a major thermal gradient in the crucible that defines a major growth direction between the source composition and the seed crystal for encouraging vapor transport between the source composition and the seed crystal, and the seed crystal being positioned on the seed holder with the macroscopic growth surface of the seed crystal forming an angle of between about 70 DEG and 89.5 DEG degrees relative to the major thermal gradient and the major growth direction and with the crystallographic orientation of the seed crystal having the c-axis of the crystal forming an angle with the major thermal gradient of between about 0 DEG and 2 DEG .A silicon carbide seeded sublimation method is disclosed. The method includes the steps of nucleating growth on a seed crystal growth face that is between about 1 DEG and 10 DEG off-axis from the (0001) plane of the seed crystal while establishing a thermal gradient between the seed crystal and a source composition that is substantially perpendicular to the basal plane of the off-axis crystal.
Owner:CREE INC
Ceramic packing member used for SMD crystal resonator and manufacturing technique thereof
InactiveCN101132169AThe number of layers of co-fired ceramic plates is reducedReduce manufacturing costImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShielding gasCarbon Dioxide / Helium
This invention relates to a technique for ceramic packing the transistor resonator, particularly the ceramic package component used for SMD transistor resonator. It is composed of: the co-sintered ceramic layer and the ceramic cover. Said co-sintered ceramic layer comprises the coincided No.1 ceramic layer and No.2 ceramic layer. Over the No.2 layer is the ceramic cover; on the upper surface of the No.1 layer is the printed convex platform, which is used for supporting transistors and guiding the electrodes, through the holes, to the basal plane soldering plate. The advantages are: simple sintering process, low production cost, reducing shielding gas protective soldering, low kovar frame material requirement, low gold-plated area, and short leading wire.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Method to reduce stacking fault nucleation sites and reduce forward voltage drift in bipolar devices
InactiveUS7018554B2Reduce in quantityReduce nucleationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStacking faultOptoelectronics
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com