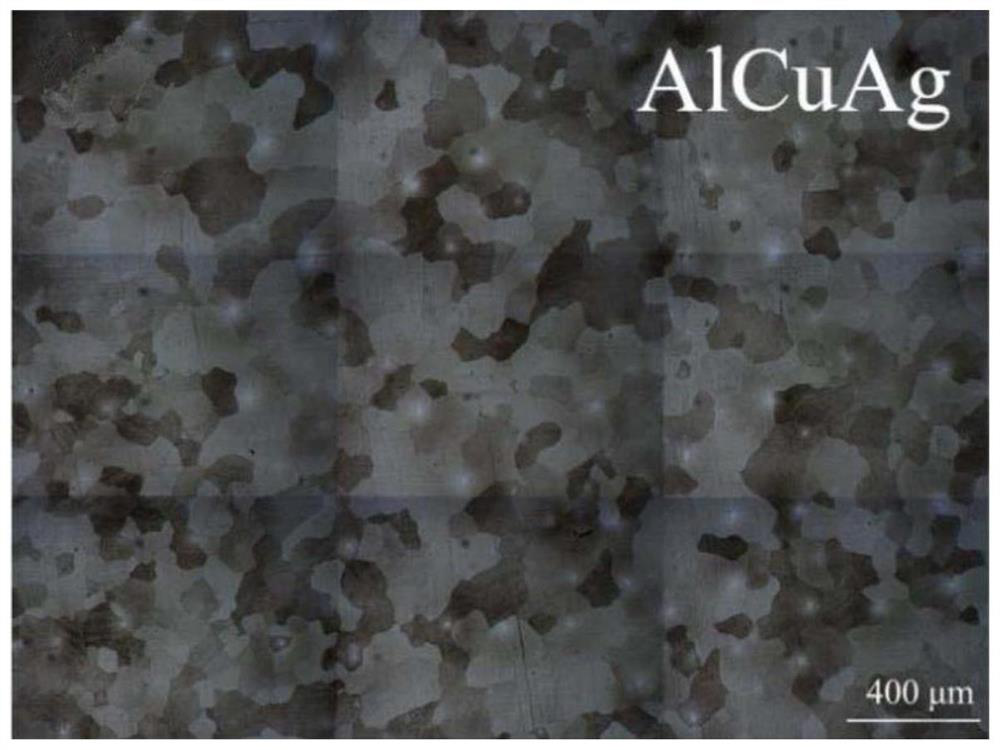
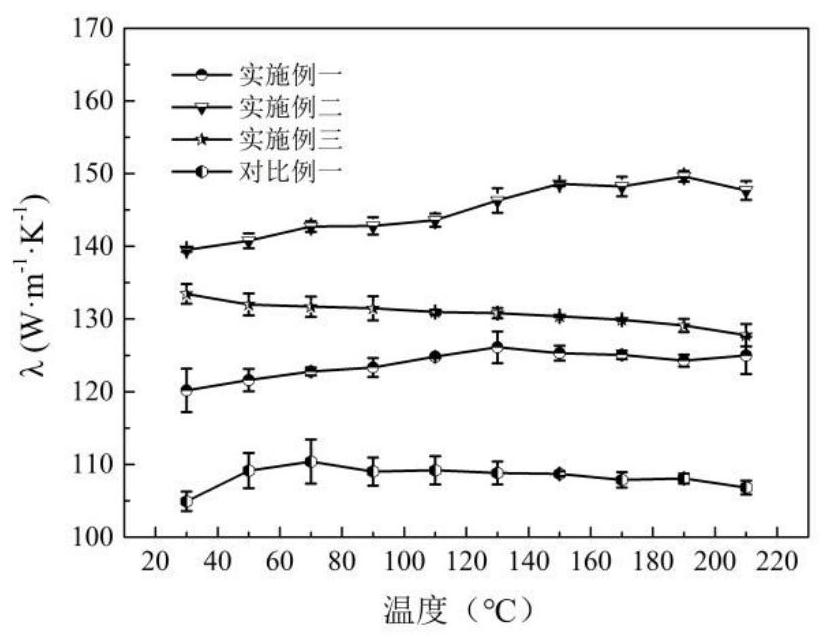
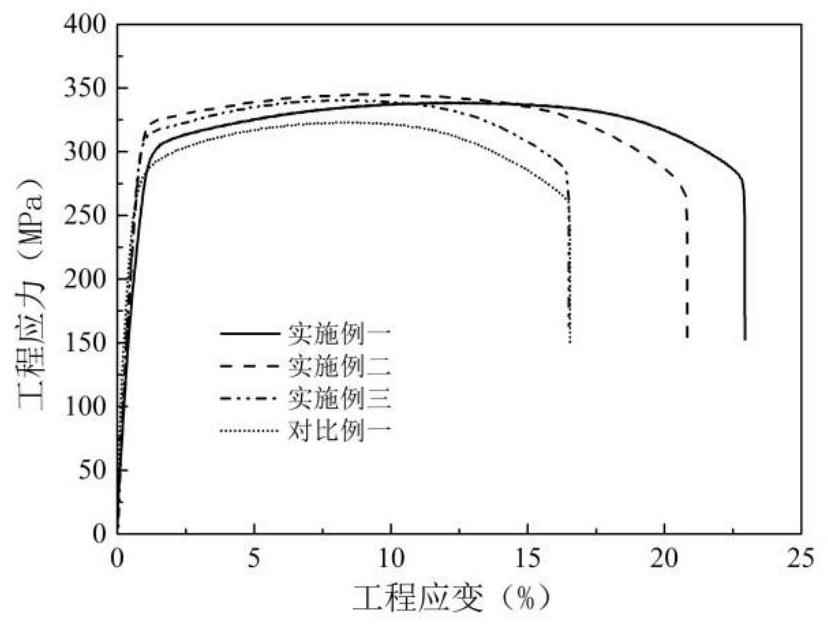
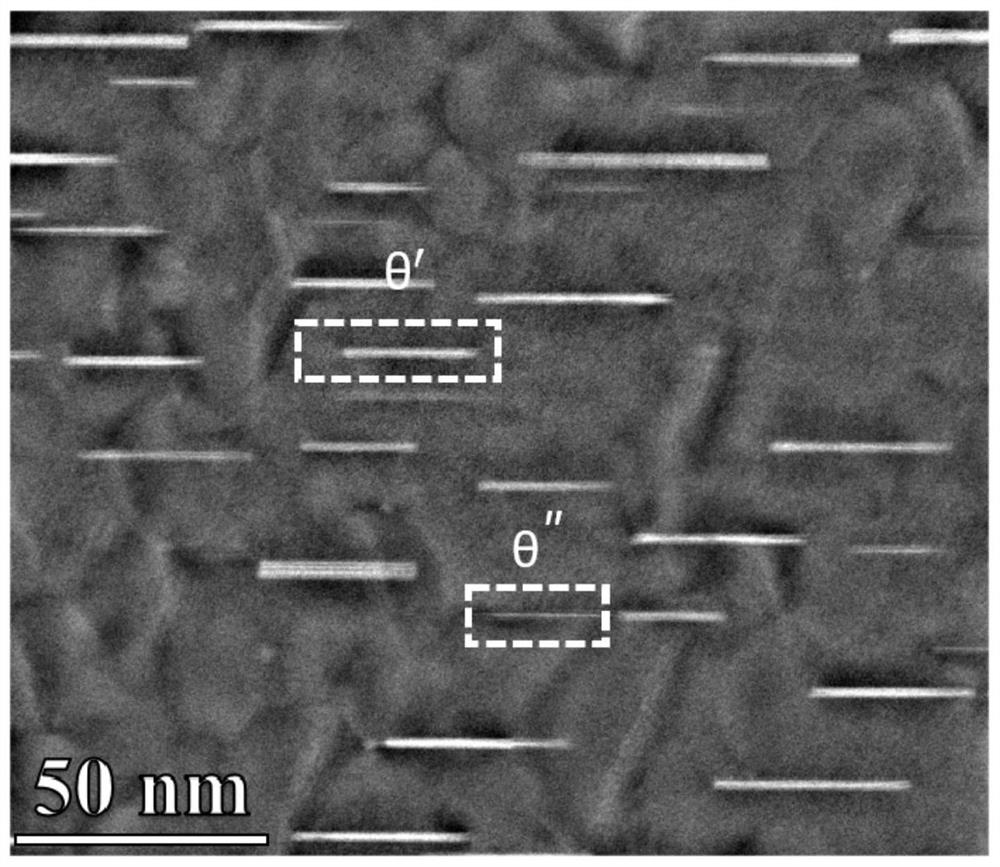
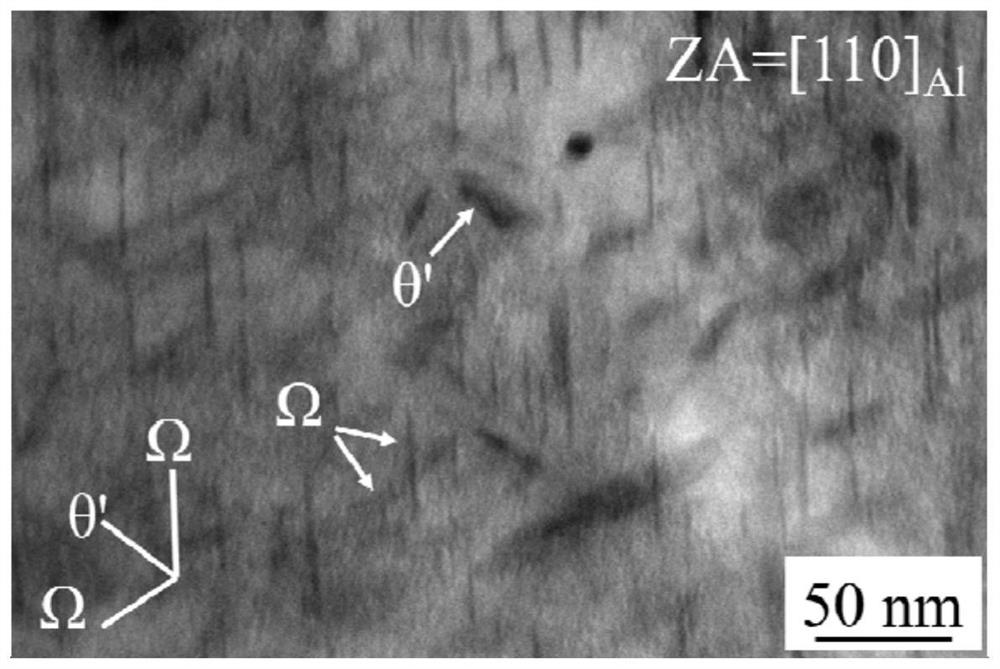
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Increase the number density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
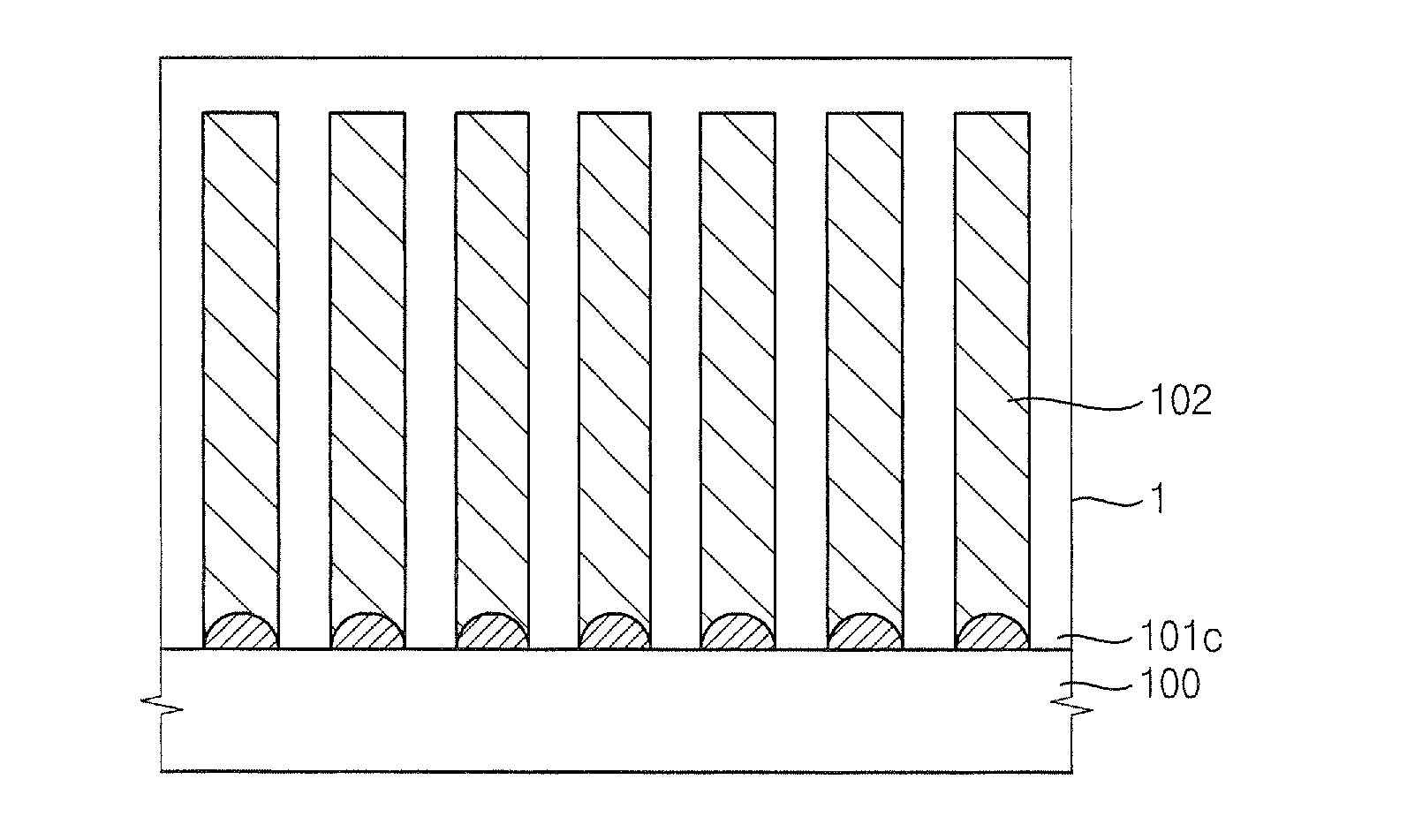
Modified graphene structures and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20120058350A1Facilitates self-assembly and stabilisationIncrease the number densityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSelf-assembled monolayerGraphene
The present invention is directed to a modified graphene structure comprising at least one graphene sheet (1) and a self-assembled monolayer (2) of functional organic molecules (3) non-covalently bonded to the top and / or bottom basal planes of the graphene sheet and methods of manufacture thereof. The present invention is also directed to devices comprising the modified graphene structures, including but not limited to field-effect devices and biosensors, and to methods using the modified graphene structures.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CORK NAT UNIV OF IRELAND CORK +1
Methods for tailoring the surface topography of a nanocrystalline or amorphous metal or alloy and articles formed by such methods
InactiveUS20100282613A1Reducing width and depthHigh depositionElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNumber densityTopography
Electrochemical etching tailors topography of a nanocrystalline or amorphous metal or alloy, which may be produced by any method including, by electrochemical deposition. Common etching methods can be used. Topography can be controlled by varying parameters that produce the item or the etching parameters or both. The nanocrystalline article has a surface comprising at least two elements, at least one of which is metal, and one of which is more electrochemically active than the others. The active element has a definite spatial distribution in the workpiece, which bears a predecessor spatial relationship to the specified topography. Etching removes a portion of the active element preferentially, to achieve the specified topography. Control is possible regarding: roughness, color, particularly along a spectrum from silver through grey to black, reflectivity and the presence, distribution and number density of pits and channels, as well as their depth, width, size. Processing parameters that have been correlated in the Ni—W system to topography features include, for both the deposition phase and the etching phase of a nanocrystalline surface: duty cycle, current density, deposition duration, plating chemistry, polarity ratio. The relative influence of the processing parameters can be noted and correlated to establish a relationship between values for processing parameters and degree of topography feature. Control can be established over the topography features. Correlation can be made for any such system that exhibits a definite spatial distribution of an active element that bears a predecessor spatial relationship to a desired topography feature.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Liquid-state-in-situ-formed ceramic particles in metals and alloys
InactiveUS6036792AIncrease the number densityEvenly dispersedThin material handlingCeramic particleAluminum metal
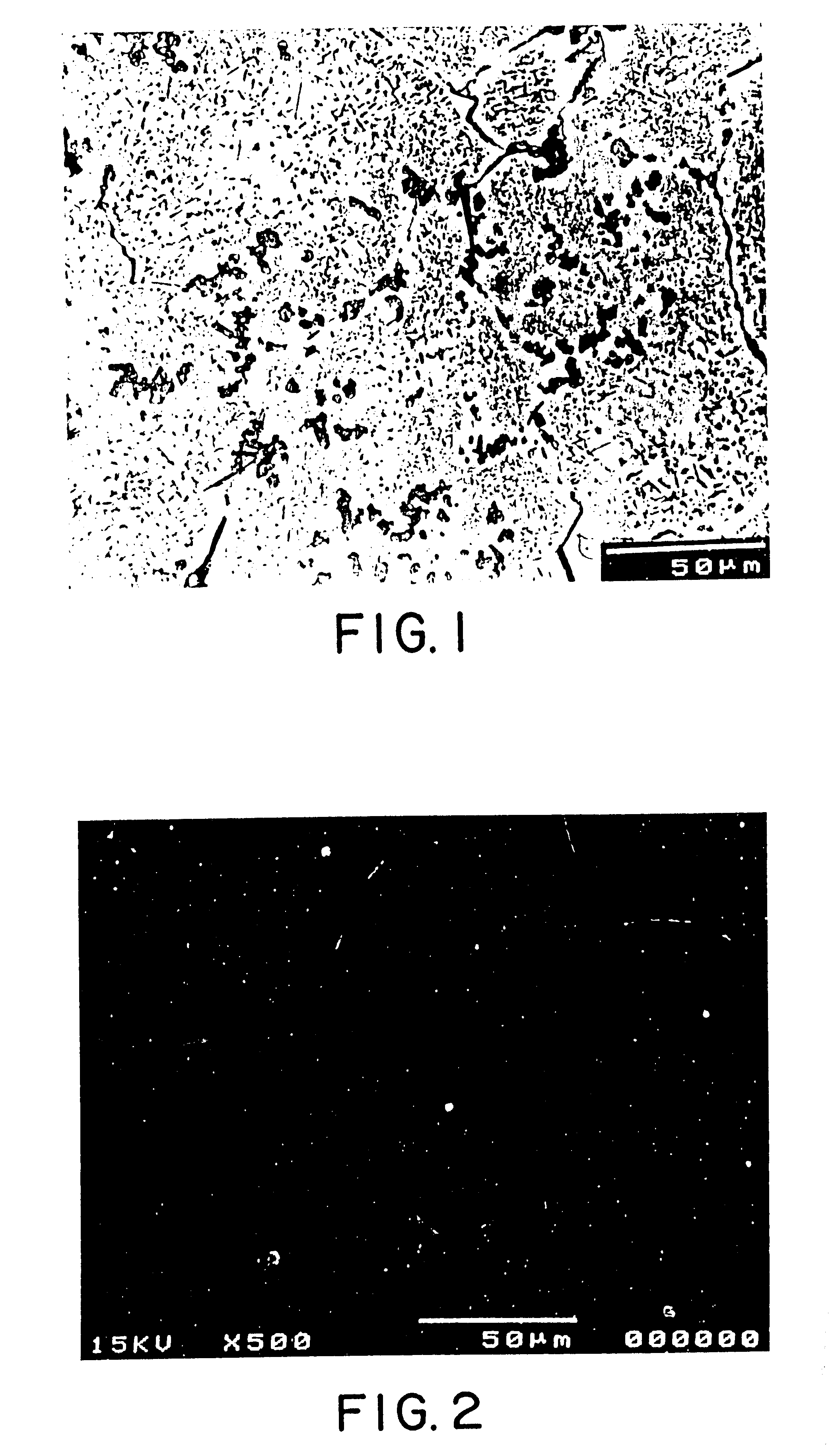
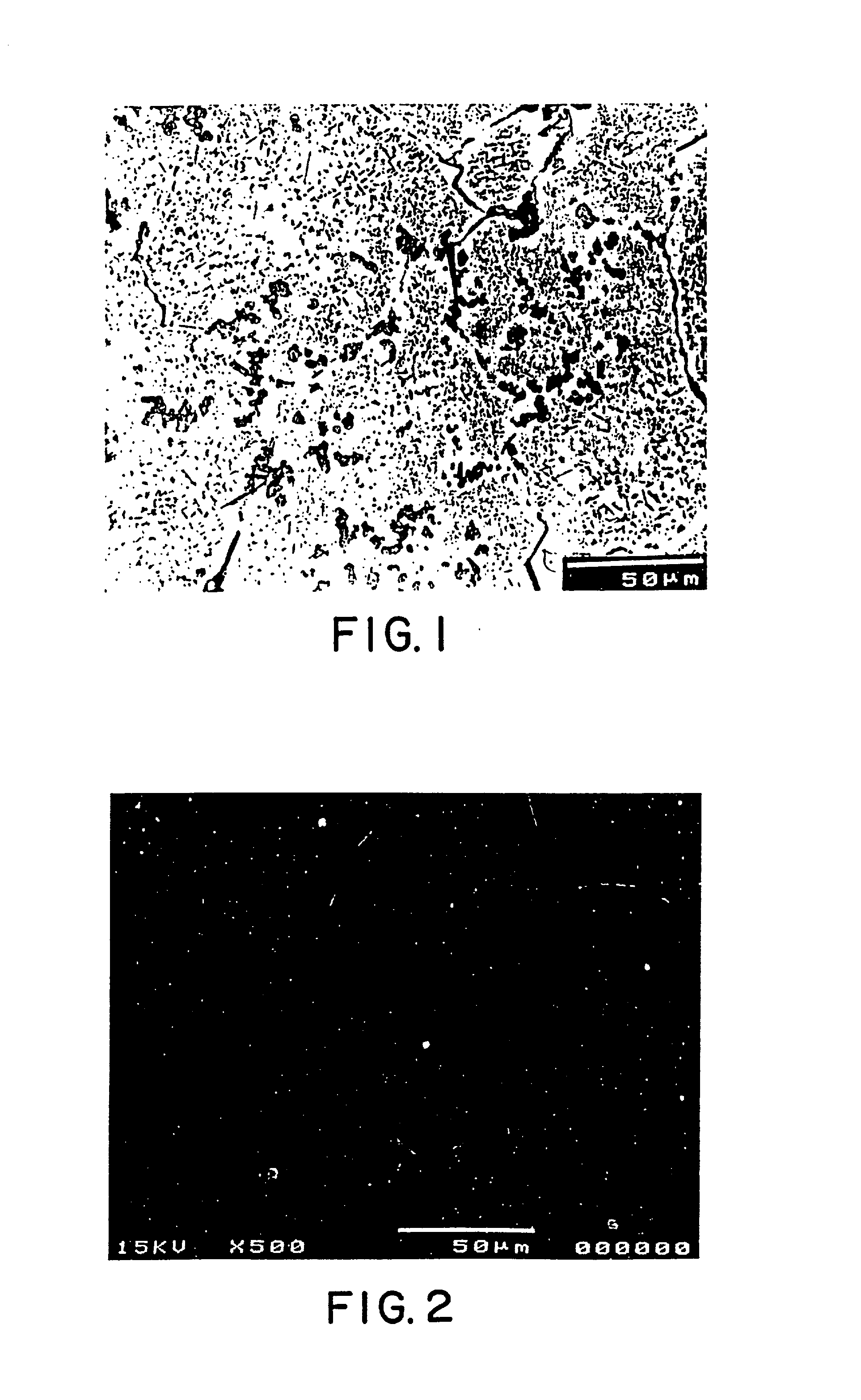
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500X.
Owner:ALUMINUM CO OF AMERICA
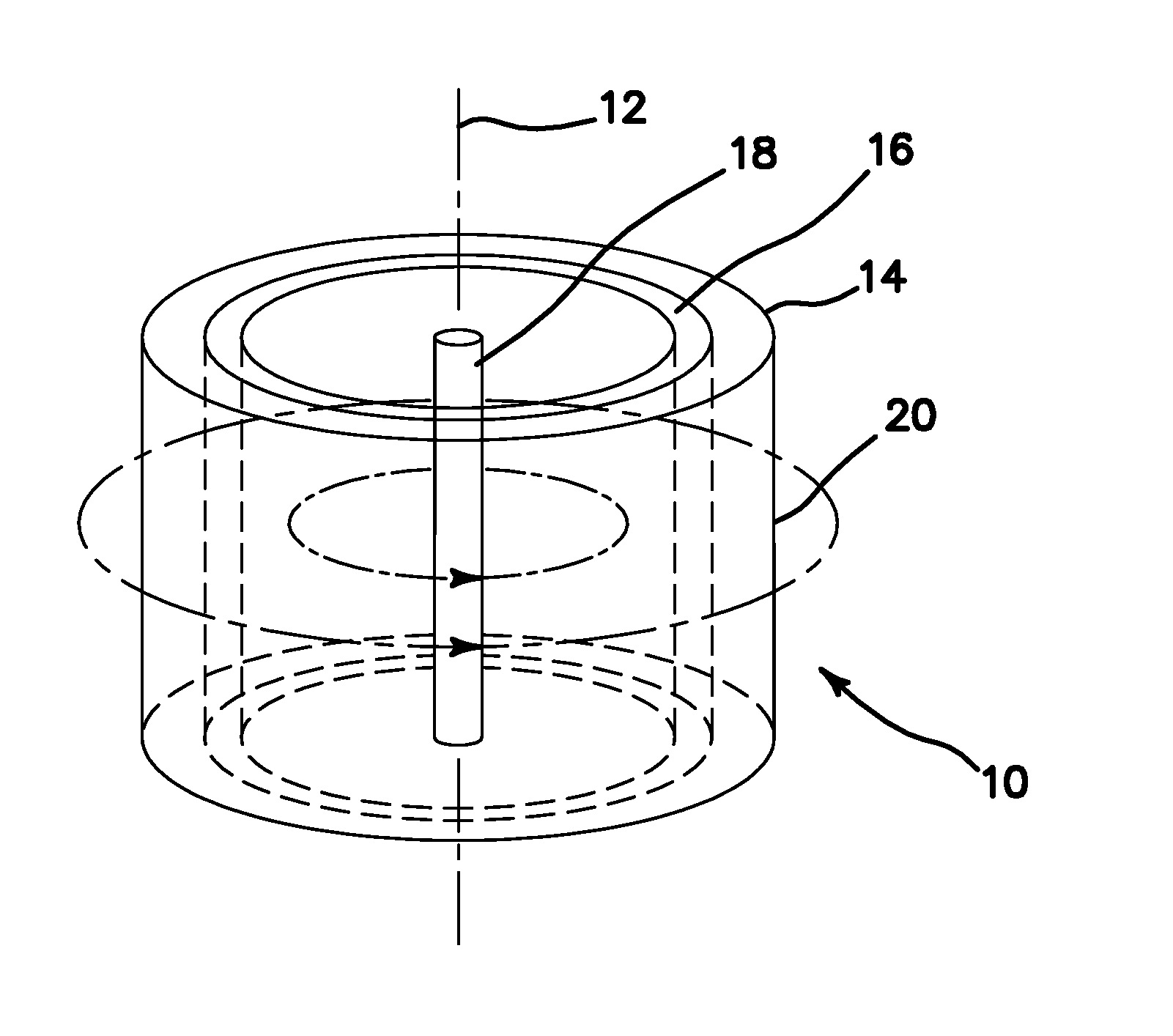
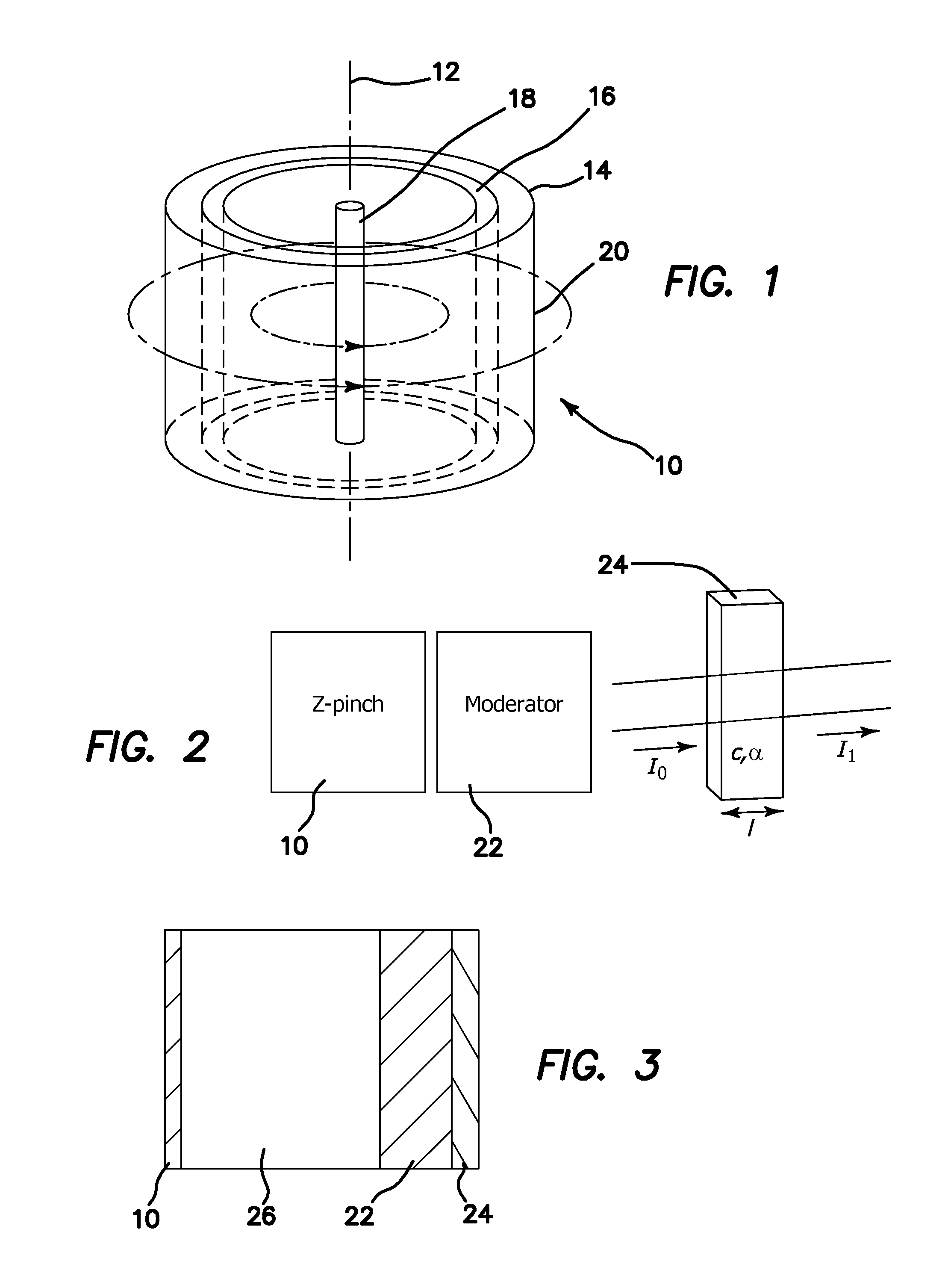
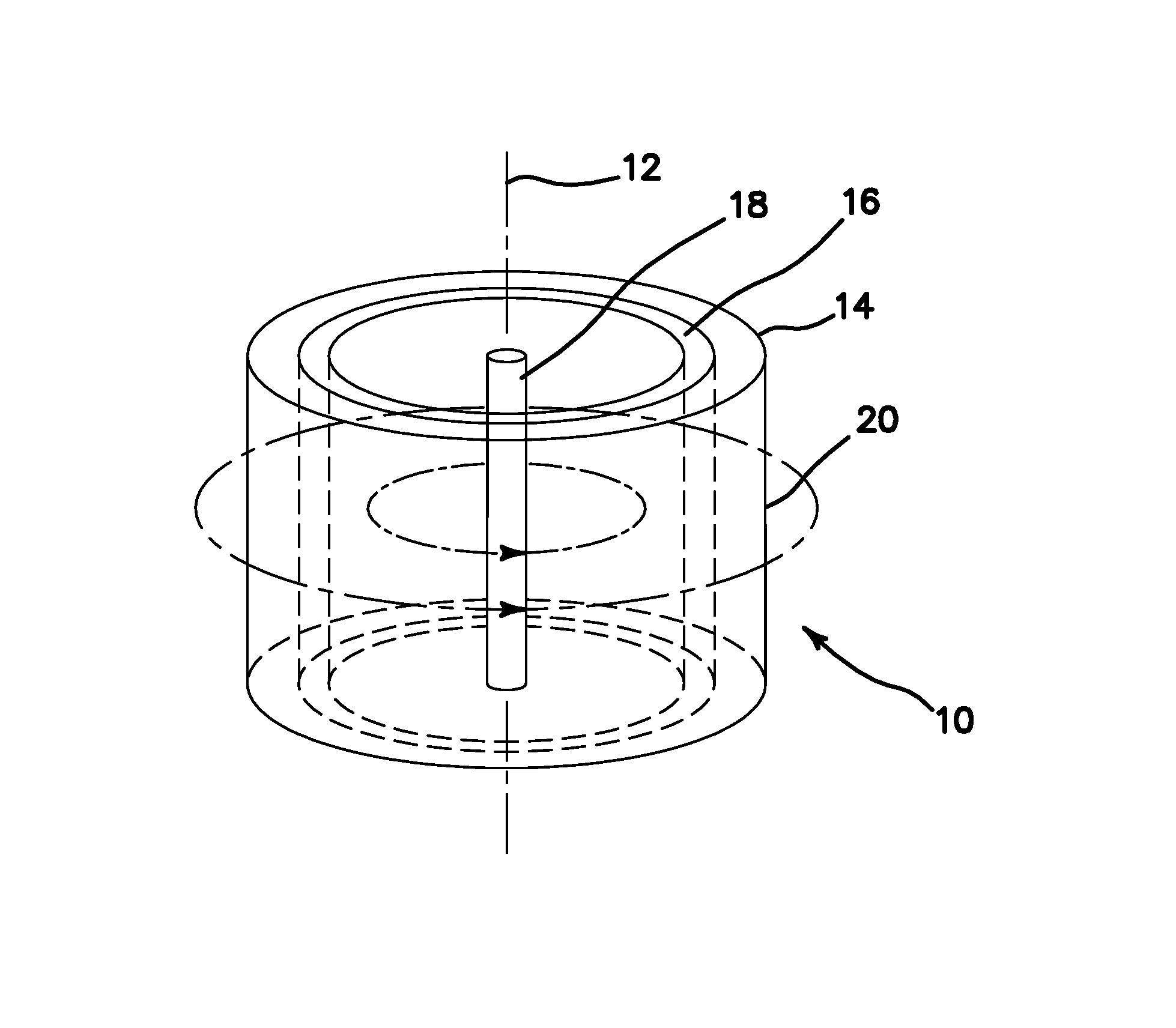
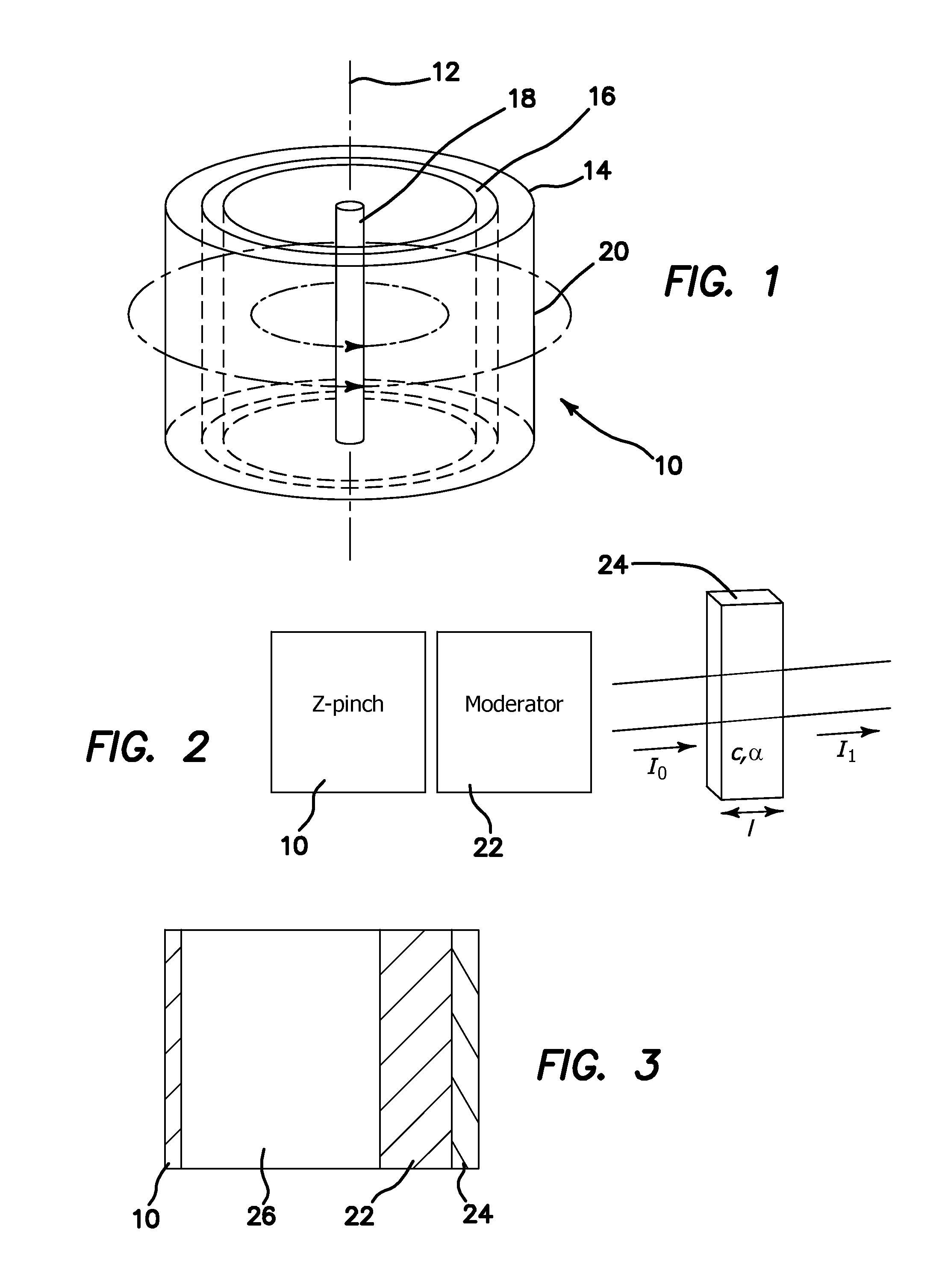
Radionuclide production using a z-pinch neutron source
ActiveUS20110019789A1Increase the number densityHigh flux of neutronsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationShock frontBlood plasma
Radionuclides are produced with a pulsed neutron flux from a multiple repetition rate staged Z-pinch machine, the pulsed neutron flux is moderated, an activatable radionuclide precursor is exposed to the moderated pulsed neutron flux, and a corresponding radionuclide from the activatable radionuclide precursor is produced. High current pulses are passed through a target plasma of fusible material enclosed in a cylindrical liner plasma composed of a high-Z plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses the liner plasma, and generates shock waves. The shock implodes the target plasma. The shock front propagates between an outer shock front and an axis of the target plasma so it is heated through shock dissipation and by adiabatic compression due to an imploding shock front produced in the outer liner plasma to fuse light nuclei and generate alpha particles and neutrons. Alpha particles trapped within the magnetic field further heat the target plasma.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Preparation method of Al-Nb-B alloy rod for grain refinement
The invention provides a preparation method of an Al-Nb-B alloy rod for grain refinement, and belongs to the field of grain refiner material preparation. The alloy consists of the following componentsby the mass percentage: 2.5-3.5 wt.% of Nb, 0.2-0.5 wt.% of B and the balance Al. The Al-Nb-B alloy rod is characterized by being formed by hot extrusion of an Al-Nb-B alloy ingot; the preparation method mainly includes the following steps: preparing materials, preparing an Al-Nb-B alloy liquid, moulding the Al-Nb-B alloy liquid by casting, preheating the Al-Nb-B alloy ingot, and carrying out hotextrusion of the Al-Nb-B alloy ingot into the alloy rod. The problem that NbAl3 and NbB2 particles are easy to agglomerate in a traditional direct casting moulding process is overcome because the Al-Nb-B grain refiner is prepared by the hot extrusion method. The NbAl3 and NbB2 particles in the prepared Al-Nb-B alloy rod are uniformly distributed, and stronger anti-recession performance and higherrefining efficiency are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Aluminum alloy sheet excellent in baking finish hardenability
This aluminum alloy sheet has increased BH properties under low-temperature short-time-period conditions after long-term room-temperature aging by means of causing aggregates of specific atoms to be contained having a large effect in BH properties, the distance between atoms being no greater than a set distance, and containing either Mg atoms or Si atoms measured by 3D atom probe field ion microscopy in a 6000 aluminum alloy sheet containing a specific amount of Mg and Si.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Preparation method of yttria dispersion strengthened copper alloy
The invention relates to a preparation method of yttria dispersion strengthened copper alloy, and belongs to the technical field of new materials. By oxidizing Cu-Y amorphous master alloy, Cu-Y2O3 combination with the specific gravity close to the specific gravity of matrix Cu is obtained in advance, and ODS-Cu alloy with uniform and controllable structure is obtained by directly smelting the combination. The method has the main advantages that (1), the problem of Y2O3 powder floating caused by the large difference between the specific gravities of the oxide and the matrix during smelting in the prior art is overcome; (2), the advantages of amorphous structure, homogeneous composition, and large solid solubility and high diffusion efficiency of oxygen in the alloy are brought into play toaccurately control oxygen addition amount of the alloy, and effective regulation and control of the size, number density, morphology and distribution of Y2O3 reinforced particles are realized; (3), the ODS-Cu alloy with uniform structure is directly obtained through a casting process, and the casting process is simple, efficient, controllable and easy to realize for large-scale production; and (4), the Y2O3 dispersion strengthened high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy prepared by the method has room-temperature conductivity greater than 90% IACS and tensile strength greater than 650 MPa.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of zirconium dioxide dispersion strengthened copper alloy
The invention relates to a preparation method of zirconium dioxide dispersion strengthened copper alloy, and belongs to the field of metal-based composite materials and preparation technics. Through oxidation of Cu-Zr amorphous master alloy, Cu-ZrO2 combination with specific gravity close to that of matrix Cu can be obtained in advance, the Cu-ZrO2 combination is used as raw material and is mixedwith pure metal materials of copper and chromium, the mixture is directly prepared and smelted to obtain ODS-Cu with uniform and controllable structure or ODS-CuCrZr alloy. The method overcomes the floating problem of ZrO2 powder caused by the large difference between the specific gravity of the oxide and the matrix in past smelting process, gives full play to the advantages of amorphous alloy structure, uniform composition, large solid solubility of oxygen and high diffusion efficiency in the amorphous alloy to control oxygen addition amount of the alloy, and realizes effective regulation andcontrol of the size, number density, morphology and distribution density of ZrO2 reinforced particles; and ODS-Cu with uniform structure and the ODS-CuCrZr alloy are obtained through a casting process, so that the technological process is simple, efficient, controllable and easy to realize large-scale production. The room-temperature conductivity of ZrO2 dispersion strengthened high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy prepared by the method can be better than 85% IACS, and the room-temperature tensile strength and the plastic strain can reach 400 MPa and 35% respectively.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Uniformly dispersed, finely sized ceramic particles in metals and alloys
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500x.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Aluminum alloy product refinement and applications of aluminum alloy product refinement
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500x.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Flow velocity distribution measuring method and particle size measuring method
ActiveUS20200064169A1Increase the number densityReduce the amount of informationVolume/mass flow measurementParticle size analysisParticle size measurementLaser light
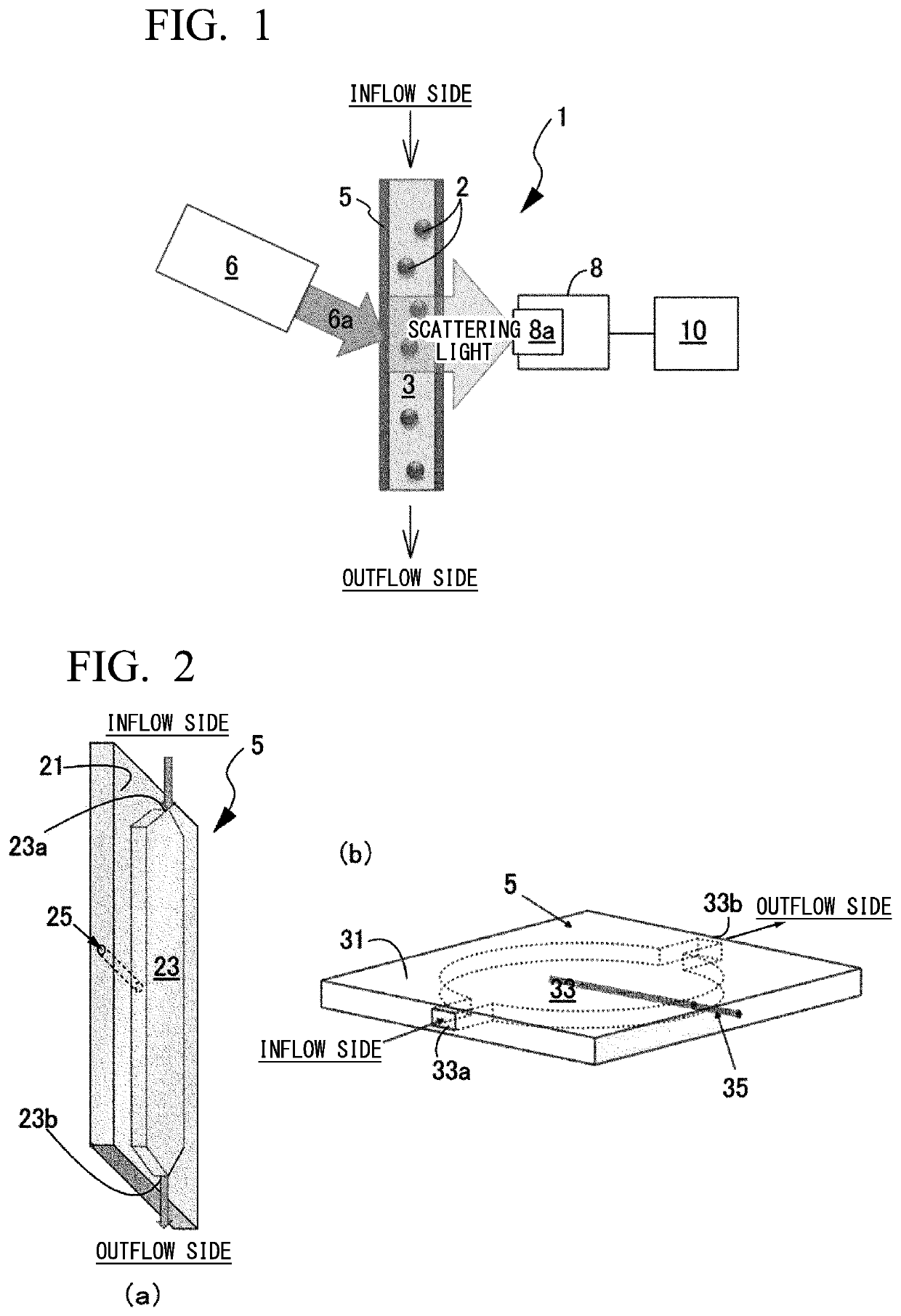
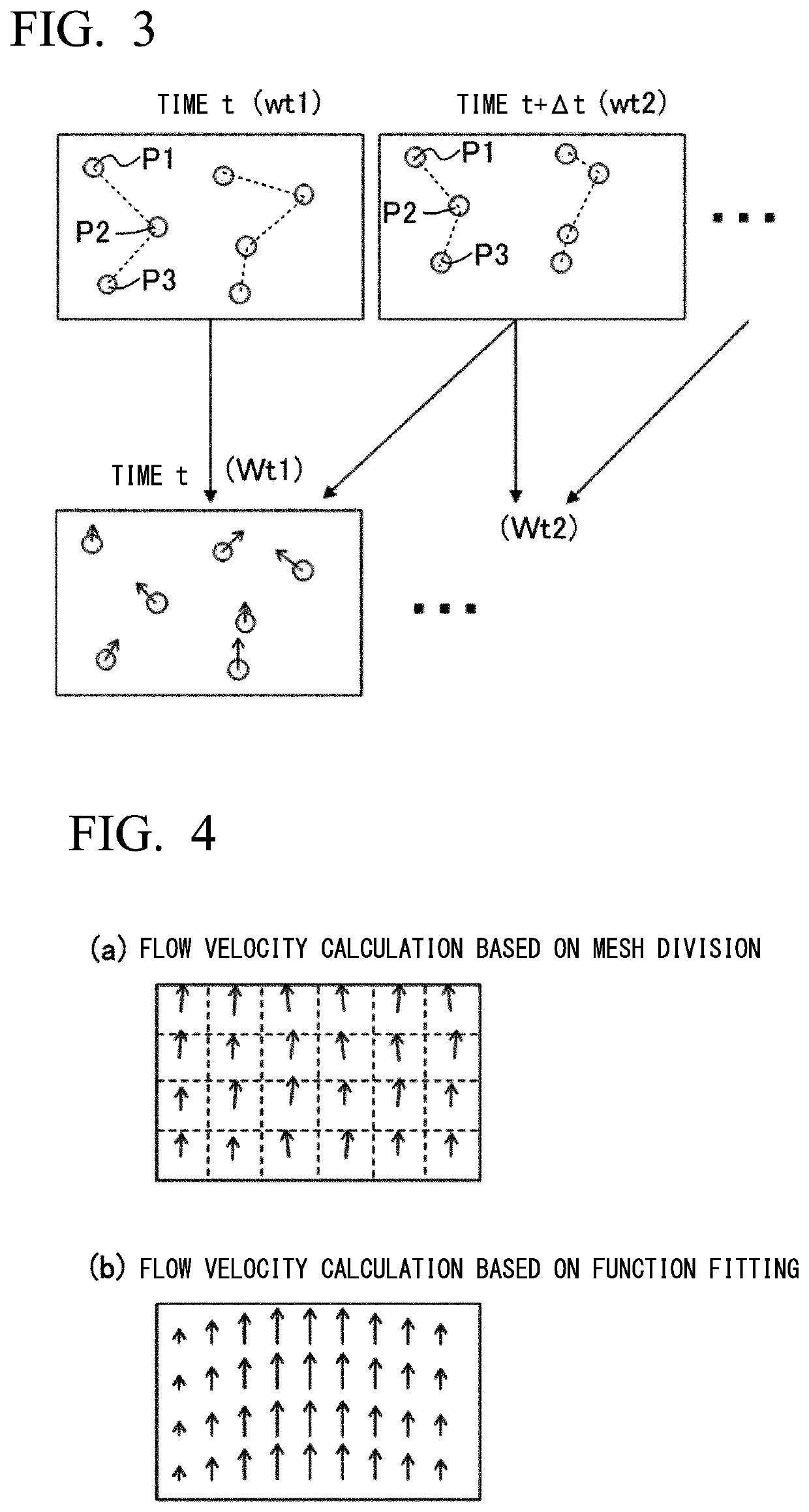
A measuring method enabling simple and accurate measurement of a flow velocity distribution in a flow field inside a flow passage of an optical cell and a particle size-measuring method using the measuring method are provided. In a device including a laser light irradiation unit irradiating laser light at a wavelength λ into the flow passage, a camera capturing an inside of the flow passage to which the laser light is irradiated, and an analysis unit obtaining a flow velocity distribution in the flow field from at least a plurality of images captured in a light exposure time τ at each predetermined time interval Δt, providing a tracer particle of a smaller size than the wavelength λ of the laser light into the flow passage and capturing a bright spot attributed to the light scattering from tracer particles by the camera, and obtaining the flow velocity distribution by the analysis unit by obtaining an amount of movement of each tracer particle from movement of the bright spot and correcting a Brownian motion component from a correlation between an average value of variations of the amount of movement and Brownian motion are performed. In addition, obtaining the particle size of a measurement target particle by obtaining a corrected displacement obtained by removing a movement component of the flow field caused by the flow velocity distribution from a displacement of the measurement target particle is performed.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Organic light-emitting display panel, display device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108448003AIncrease profitAvoid lostSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerNumber density
The invention provides an organic light-emitting display panel. The organic light-emitting display panel comprises a first electrode, an electron injection layer, an electron transport layer, a light-emitting layer, a hole transport layer, a hole injection layer rand a second electrode which are laminated in sequence, wherein a first electron blocking layer is arranged next to the light-emitting layer between the light-emitting layer and the hole transport layer; and the first electron blocking layer is doped with a hole type non-metallic material. The invention also provides a display devicecontaining the display panel and a preparation method of the display panel. The hole type non-metallic material is doped into EBL, so that the hole number density at the position of a compound interface is increased, the utilization rate of holes is improved, the loss of the holes through the transportation of a functional layer is avoided, the holes can be compounded with transported electrons intime, energy is transferred to an object for timely attenuation light emission so as to avoid the accumulation of excessive electrons at the interface of EBL / EML, the damage defects for the EBL material are reduced, and the service life of the light-emitting device is prolonged.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20160163641A1Well formedIncrease the number densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInductorDielectric layer
A method for forming a semiconductor device includes, sequentially, providing a substrate having a first region and a second region; forming a first dielectric layer on the substrate; forming a second dielectric layer having a plurality of first openings exposing portions of a top surface of the first dielectric layer; forming a first conductive layer in the first openings; etching the second dielectric layer and the first dielectric layer in the second region until the substrate is exposed to form a plurality of second openings; forming passivation regions in portions of the substrate exposed by the second openings; exposing the surface of the first dielectric layer in the second region; forming a third dielectric layer on the surface of the first dielectric layer and in the second openings; and forming a second conductive layer, a portion of which is configured as an inductor, over the third dielectric layer.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
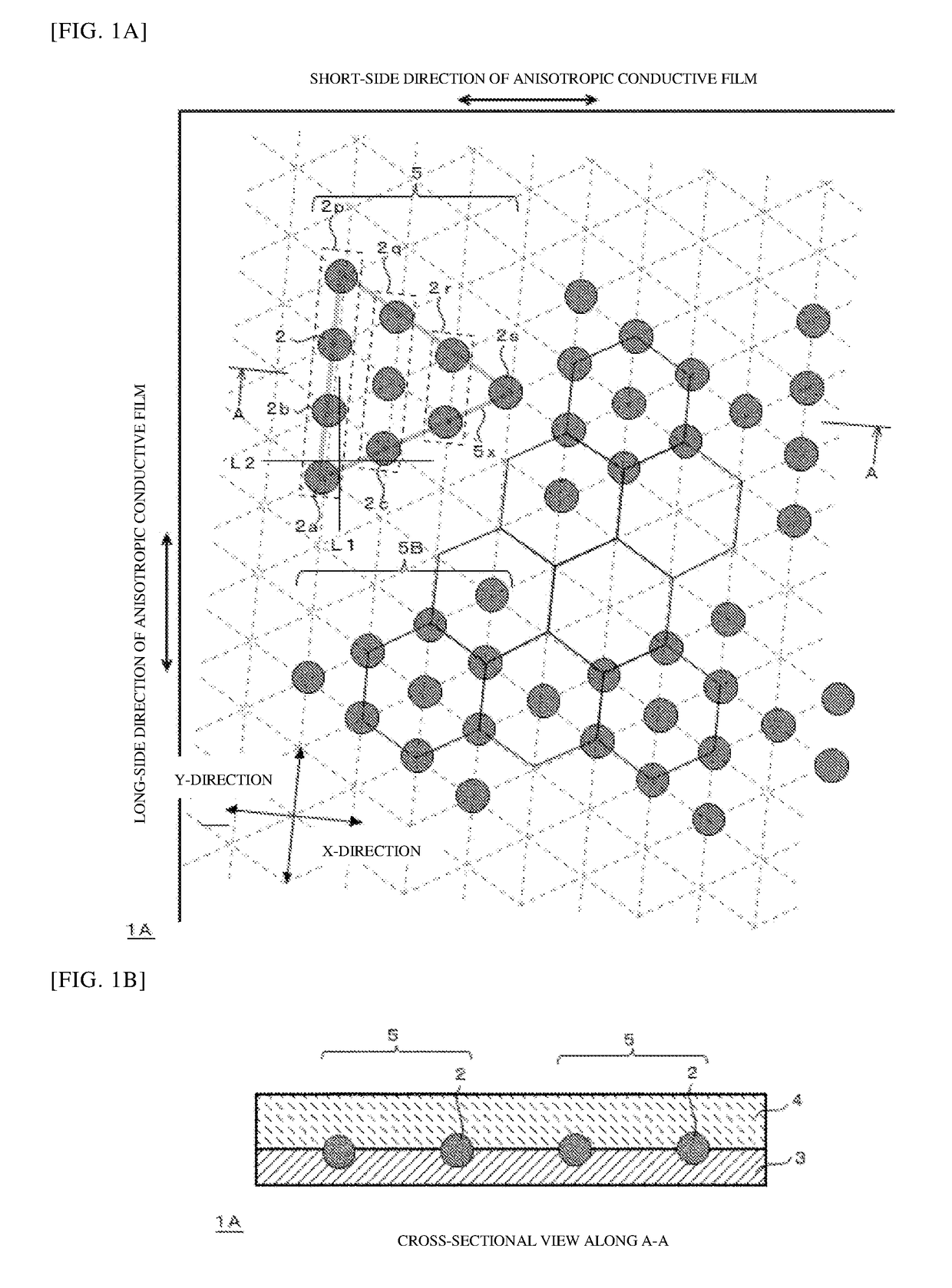
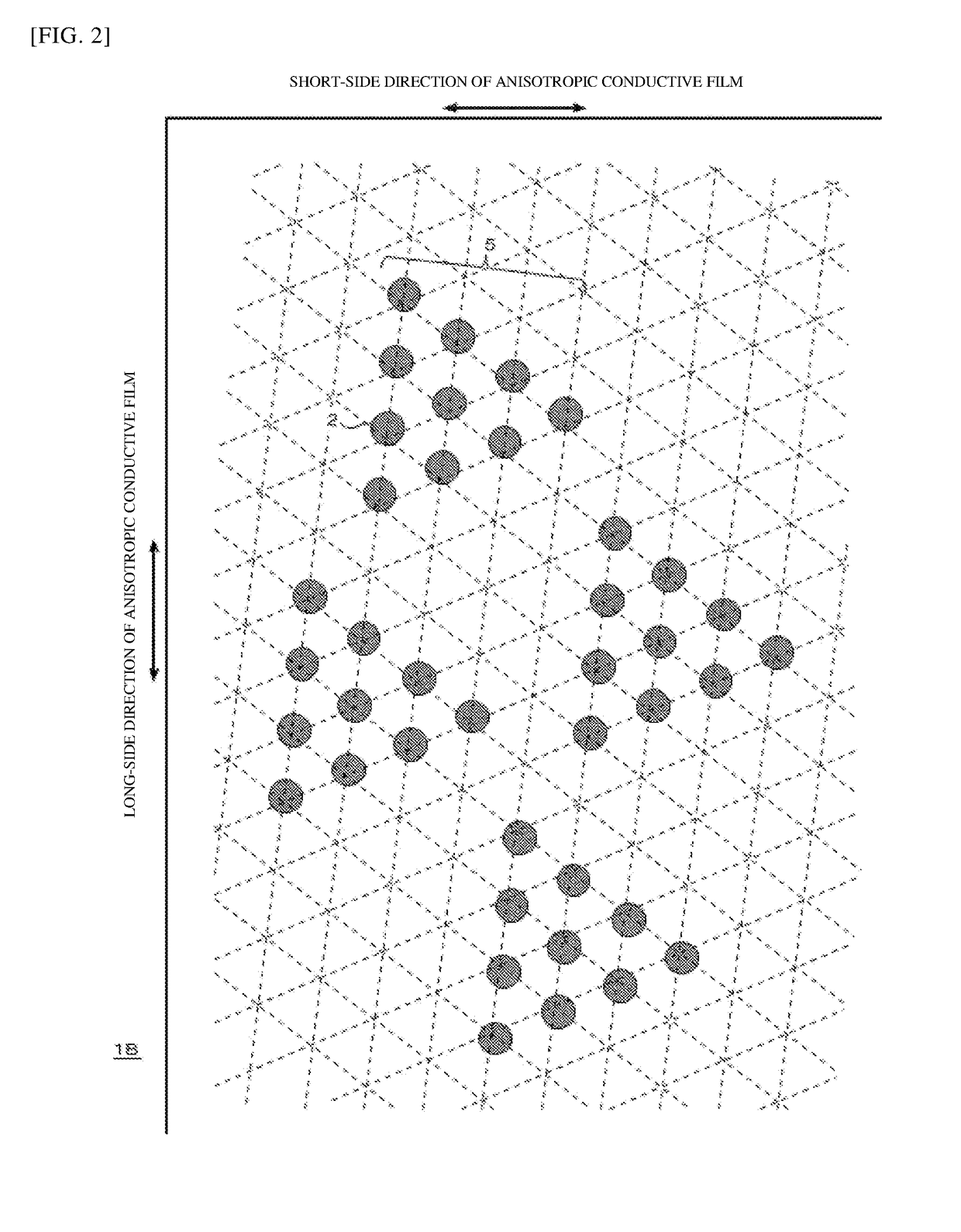
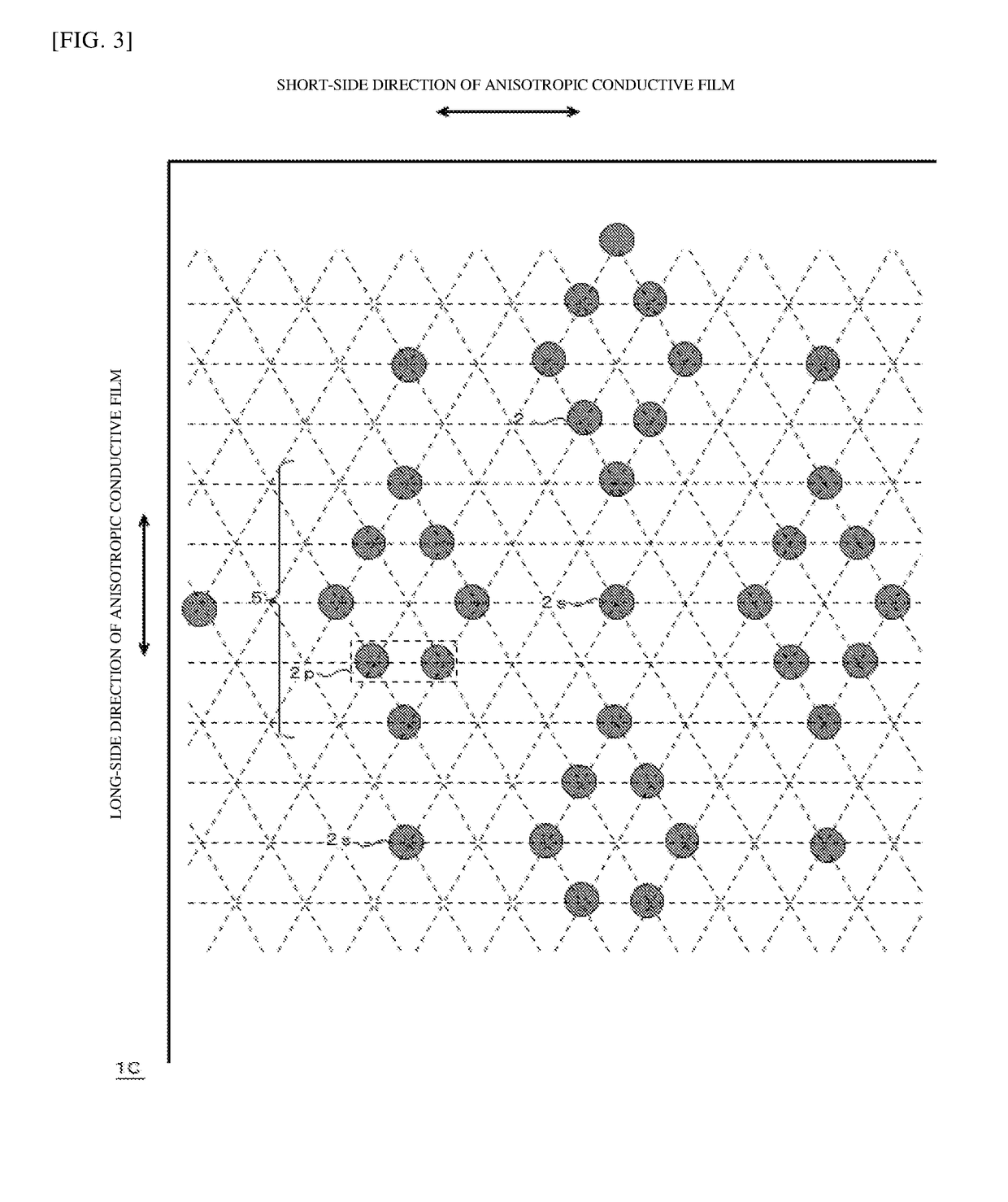
Anisotropic conductive film
PendingUS20190035763A1Production cost be increaseIncrease thrustNon-insulated conductorsLine/current collector detailsRepeat unitNumber density
An anisotropic conductive film capable of accommodating bumps with a narrow pitch and reducing the number density of conductive particles. In an anisotropic conductive film, conductive particles are disposed in an insulating resin binder as follows. Specifically, the conductive particles are rows of conductive particles arranged in single rows with spacing therebetween; and repeating units of conductive particles formed by juxtaposition of different numbers of conductive particles are disposed repeatedly over the entire surface of the anisotropic conductive film.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Radionuclide production using a Z-pinch neutron source
ActiveUS8837661B2Increase the number densityHigh flux of neutronsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationAlpha particleShock front
Radionuclides are produced with a pulsed neutron flux from a multiple repetition rate staged Z-pinch machine, the pulsed neutron flux is moderated, an activatable radionuclide precursor is exposed to the moderated pulsed neutron flux, and a corresponding radionuclide from the activatable radionuclide precursor is produced. High current pulses are passed through a target plasma of fusible material enclosed in a cylindrical liner plasma composed of a high-Z plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses the liner plasma, and generates shock waves. The shock implodes the target plasma. The shock front propagates between an outer shock front and an axis of the target plasma so it is heated through shock dissipation and by adiabatic compression due to an imploding shock front produced in the outer liner plasma to fuse light nuclei and generate alpha particles and neutrons. Alpha particles trapped within the magnetic field further heat the target plasma.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Metal product containing ceramic dispersoids form in-situ
A novel method for producing a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal and a novel product composed thereof. The method includes (a) providing a molten composition consisting essentially of molten aluminum alloy containing molten metal selected form the group consisting of Zr, V and combinations thereof; (b) providing a chloride salt containing fine carbon particles; and (c) reacting the chloride salt containing fine carbon particles in the molten aluminum metal liquid with the molten metal liquid to form a uniform distribution of finely sized carbide particles formed and dispersed in-situ in an aluminum alloy matrix.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Method of forming a carbon nano-tube
InactiveUS20080175984A1Increase of average carbon numberEffective controlMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsNumber densityCarbon nanotube
In a method of forming carbon nano-tubes, a catalytic film is formed on a substrate. The catalytic film is then transformed into preliminary catalytic particles. Thereafter, the preliminary catalytic particles are transformed into catalytic particles. Carbon nano-tubes then grow from the catalytic particles. The carbon nano-tubes have relatively high conductivity and high number density.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Aluminum alloy sheet excellent in baking finish hardenability
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method of forming a carbon nano-tube
InactiveUS8007875B2Improve conductivityIncrease the number densityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsCarbon nanotubeNumber density
In a method of forming carbon nano-tubes, a catalytic film is formed on a substrate. The catalytic film is then transformed into preliminary catalytic particles. Thereafter, the preliminary catalytic particles are transformed into catalytic particles. Carbon nano-tubes then grow from the catalytic particles. The carbon nano-tubes have relatively high conductivity and high number density.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
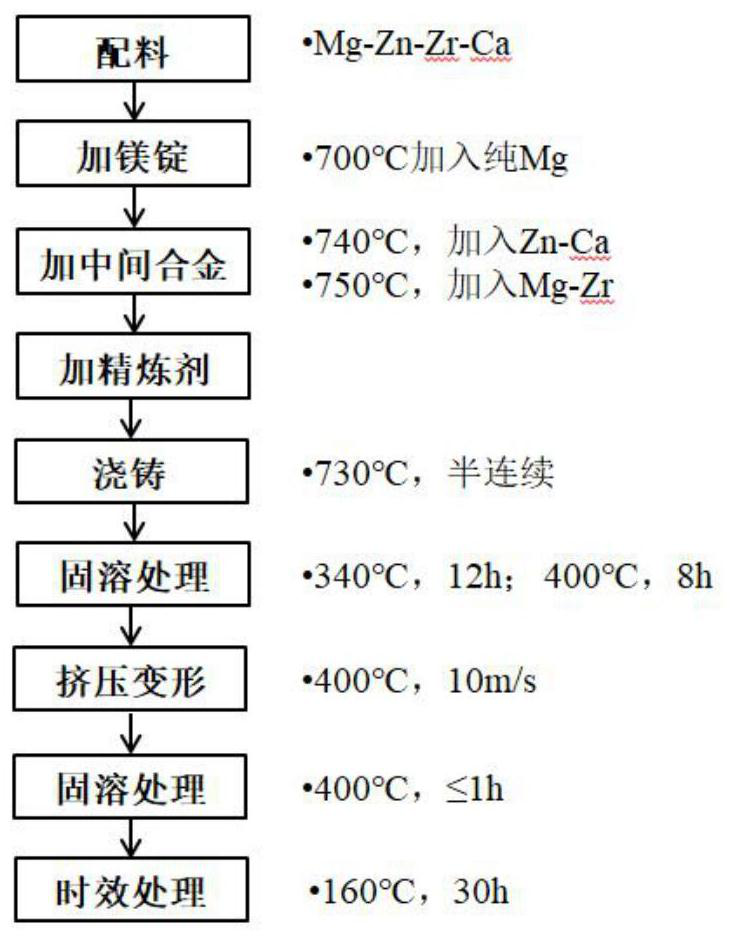
A kind of high-strength heat-conducting magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength heat-conducting magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The element content of the magnesium alloy is: Zr: 0.2-0.6wt.%, Zn: 4-6wt.%, Ca: 0.4-0.8wt.%. The amount is Mg. The preparation method of the magnesium alloy includes batching, adding magnesium ingots, adding intermediate alloys, refining, casting, solid solution treatment, extrusion deformation, solid solution treatment again and aging treatment. In order to promote the formation of alloy Zn-Ca clusters, different Zn-Ca master alloys are selected during smelting, and a short-term solution treatment of no more than 1h is performed after hot extrusion. The tensile strength of the alloy is greater than 325MPa, the yield strength is greater than 280MPa, the elongation is greater than 15%, and the thermal conductivity is greater than 120W·(m·K) ‑1 , the magnesium alloy has a high yield, good formability, easy industrialization, and can be used as a heat dissipation structural material for power supplies and electronic devices in the field of new generation aerospace.
Owner:ALLITE (JIANGSU) MAGNESIUM TECH CO LTD
High-strength aluminum-copper alloy for aerospace structural parts and preparation method
The invention discloses a high-strength aluminum-copper alloy for aerospace structural parts and a preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of aluminum alloys. The aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 4.5-5.5% of Cu, 0.25-0.60% of Mn, 0.12-0.30% of Ti, 1t of Mg, 0.12-0.30% of Mn and the balance of Al. %, 0.30 wt.%, Si: lt; %, 0.25 wt.%, Fe: lt; %, 0.20 wt.%, 0.20 to 0.60 wt.% of Ag or 0.15 to 0.30 wt.% of Sn, with the balance being Al. The preparation method comprises the steps of burdening, preheating, smelting, molten aluminum treatment, intermediate alloy adding, casting, solid solution quenching and aging treatment. The high-strength aluminum-copper alloy for the aerospace structural component is excellent in obdurability matching effect, and the organization structure of a high-strength aluminum-copper alloy casting obtained after heat treatment is also superior to that of an existing aerospace structural component.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Preparation method and applications for precious metal doped PVDF nanofiber composite film
InactiveCN110090565AImprove the bactericidal effectReduce voidsMembranesSemi-permeable membranesAir filterHigh-voltage direct current
The invention discloses a preparation method and applications for a precious metal doped PVDF nanofiber composite film. The preparation method is characterized in that the method includes the following steps: (1) adopting a magnetron sputtering method to deposit silver metal whose thickness can reach 150 nm on ultra-thin high light transmission non-woven fabric so that a filtering film frame can be obtained; (2) mixing N,N-dimethyl formamide and acetone according to a ratio of 7 : 3, performing stirring and adding a certain amount of PVDF powder and silver nitrate powder, performing constant temperature magnetic stirring after ultrasonic treatment, and obtaining a precursor solution after 24 h of standing; and (3) connecting a high voltage direct current power live wire to the outer wall of a syringe needle, connecting a zero line to the filtering film frame to be as an electrospinning collection substrate, adding the precursor solution into a syringe, and obtaining a precious metal doped PVDF nanofiber composite film through an electrospinning manner. The preparation method has advantages of being ultrahigh in PM0.5 filtering efficiency, low in air filtering piezoresistance, highin quality factor and good in filtering stability.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-strength heat-conducting magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength heat-conducting magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium alloy comprises, by weight: Zr: 0.2-0.6%, Zn: 4-6%, Ca: 0.4-0.8% and the balanceMg. The preparation method of the magnesium alloy comprises the steps of burdening, adding a magnesium ingot, adding an intermediate alloy, refining, casting, carrying out solution treatment, carrying out extrusion deformation, carrying out the solution treatment again and carrying out aging treatment. According to the high-strength heat-conducting magnesium alloy and the preparation method thereof, in order to promote the formation of alloy Zn-Ca clusters, different Zn-Ca intermediate alloys are selected during the smelting, and the short-time solution treatment is carried out for 1 h or less after the hot extrusion; the tensile strength of the alloy is greater than 325 MPa, the yield strength of the alloy is greater than 280 MPa, the elongation of the alloy is greater than 15%, and theheat conductivity of the alloy is greater than 120 W.(m.K)<-1>; and the magnesium alloy is high in yield, good in processing formability, easy for realizing industrialization, and capable of being used as a heat dissipation structural material of a power supply and electronic device in the field of new generation aerospace.
Owner:ALLITE (JIANGSU) MAGNESIUM TECH CO LTD
Alloying and heat treatment method for improving plasticity of cast aluminum-copper alloy at room temperature
ActiveCN112662926BImprove room temperature plasticityEasy to reinforceMachining processUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an alloying and heat treatment method for improving room-temperature plasticity of cast aluminum-copper alloys. Ag and Cd elements are added at the same time to form Ag-Cd particles after aging, which can be cut by dislocations during the deformation process and improve dislocations. The free path of motion improves the plasticity of the alloy at room temperature. The addition of Cd element can not only refine the θ′ phase in the alloy grain, but also make the θ′ phase that was bypassed by dislocations can be cut through, greatly improving the free path of dislocation movement, and also significantly promoting the high-Cu aluminum alloy. The non-network discontinuous distribution of the grain boundary equilibrium phase θ reduces the brittleness of the alloy, which can improve the room temperature plasticity of the alloy. The Ag-Cd particles and the dispersed and precipitated θ′ phase can make up for the strength loss caused by the reduction of the Ω phase, improve the strength and toughness of the alloy, and greatly improve the processability of alloy casting and the service safety of castings. The introduction of natural aging after solid solution can promote the formation of GP regions, increase the number density of θ′ phases that are coherent with the matrix and can be cut by dislocations, and the free path of dislocation movement, thereby improving the plasticity of the alloy at room temperature.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
A high-strength and heat-resistant low-scandium composite microalloyed al-cu alloy and its heat treatment process
The invention discloses a high-strength and high-temperature-resistant low-scandium composite microalloyed Al-Cu alloy and a heat treatment process thereof. Its main alloying elements include Cu, Sc, Si, Zr, Er, Ti, Mn, Fe as an impurity element should be limited to <0.15% by mass, and the rest are Al and unavoidable impurities. The alloy ingot is cast by conventional metal mold or sand mold casting, and can be hot deformed before solution treatment. The corresponding heat treatment process includes multi-stage homogenization and subsequent isochronic aging treatment. At the same time, it should be noted that for alloy materials with high Cu content, a more gentle homogenization treatment (lower temperature, prolong the holding time) and slower heating in the low temperature range Aging heating rate. The Al-Cu alloy material prepared according to this patent reduces the use of expensive Sc elements through appropriate composite microalloying means and structure design, significantly improves the high-temperature tensile properties of the alloy, and has good room temperature mechanical properties and 300 -400℃Excellent high temperature tensile strength and creep resistance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS9502348B2Well formedIncrease the number densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInductorDielectric layer
A method for forming a semiconductor device includes, sequentially, providing a substrate having a first region and a second region; forming a first dielectric layer on the substrate; forming a second dielectric layer having a plurality of first openings exposing portions of a top surface of the first dielectric layer; forming a first conductive layer in the first openings; etching the second dielectric layer and the first dielectric layer in the second region until the substrate is exposed to form a plurality of second openings; forming passivation regions in portions of the substrate exposed by the second openings; exposing the surface of the first dielectric layer in the second region; forming a third dielectric layer on the surface of the first dielectric layer and in the second openings; and forming a second conductive layer, a portion of which is configured as an inductor, over the third dielectric layer.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
A kind of nanocomposite oxide dispersion strengthened molybdenum alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113718151BImprove high temperature mechanical propertiesImprove creep resistanceNuclear energy generationZr alloyArgon gas
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A kind of preparation method of zirconia dispersion strengthened copper alloy
ActiveCN110129609BPrecise control of oxygen additionUniform structureSmelting processElectro conductivity
The invention relates to a preparation method of zirconium dioxide dispersion strengthened copper alloy, and belongs to the field of metal-based composite materials and preparation technics. Through oxidation of Cu-Zr amorphous master alloy, Cu-ZrO2 combination with specific gravity close to that of matrix Cu can be obtained in advance, the Cu-ZrO2 combination is used as raw material and is mixedwith pure metal materials of copper and chromium, the mixture is directly prepared and smelted to obtain ODS-Cu with uniform and controllable structure or ODS-CuCrZr alloy. The method overcomes the floating problem of ZrO2 powder caused by the large difference between the specific gravity of the oxide and the matrix in past smelting process, gives full play to the advantages of amorphous alloy structure, uniform composition, large solid solubility of oxygen and high diffusion efficiency in the amorphous alloy to control oxygen addition amount of the alloy, and realizes effective regulation andcontrol of the size, number density, morphology and distribution density of ZrO2 reinforced particles; and ODS-Cu with uniform structure and the ODS-CuCrZr alloy are obtained through a casting process, so that the technological process is simple, efficient, controllable and easy to realize large-scale production. The room-temperature conductivity of ZrO2 dispersion strengthened high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy prepared by the method can be better than 85% IACS, and the room-temperature tensile strength and the plastic strain can reach 400 MPa and 35% respectively.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Micro-fluidic cell suspension culture chip and application thereof
InactiveCN102234614BSimple structureEasy to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNumber densityClosed loop
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic cell suspension culture chip comprising more than one culture unit, wherein each culture unit comprises a substrate, the substrate comprises culture channels which are respectively distributed on multiple laminated culture layers, the culture channels are communicated mutually to form a closed loop, and the closed loop is communicated with an independent liquid inlet and liquid outlet arranged on each substrate; and multiple linear driving channels are also arranged in each substrate, wherein each driving channel intersects with two or more selected culture channels, an elastic diaphragm for isolating each driving channel from each culture channel is arranged in each intersection, and both two ends of each driving channel are communicated with the outer part of each substrate. The chip disclosed by the invention has a simple structure and low cost, is easy to produce and control, has high number density of the culture units, and can be used as asuspension culture container for microbes and biological tissues and as a special biochemical reaction container.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Combined microalloying high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114807693AImprove high temperature mechanical propertiesIncrease the number densitySolution treatmentHeat stability
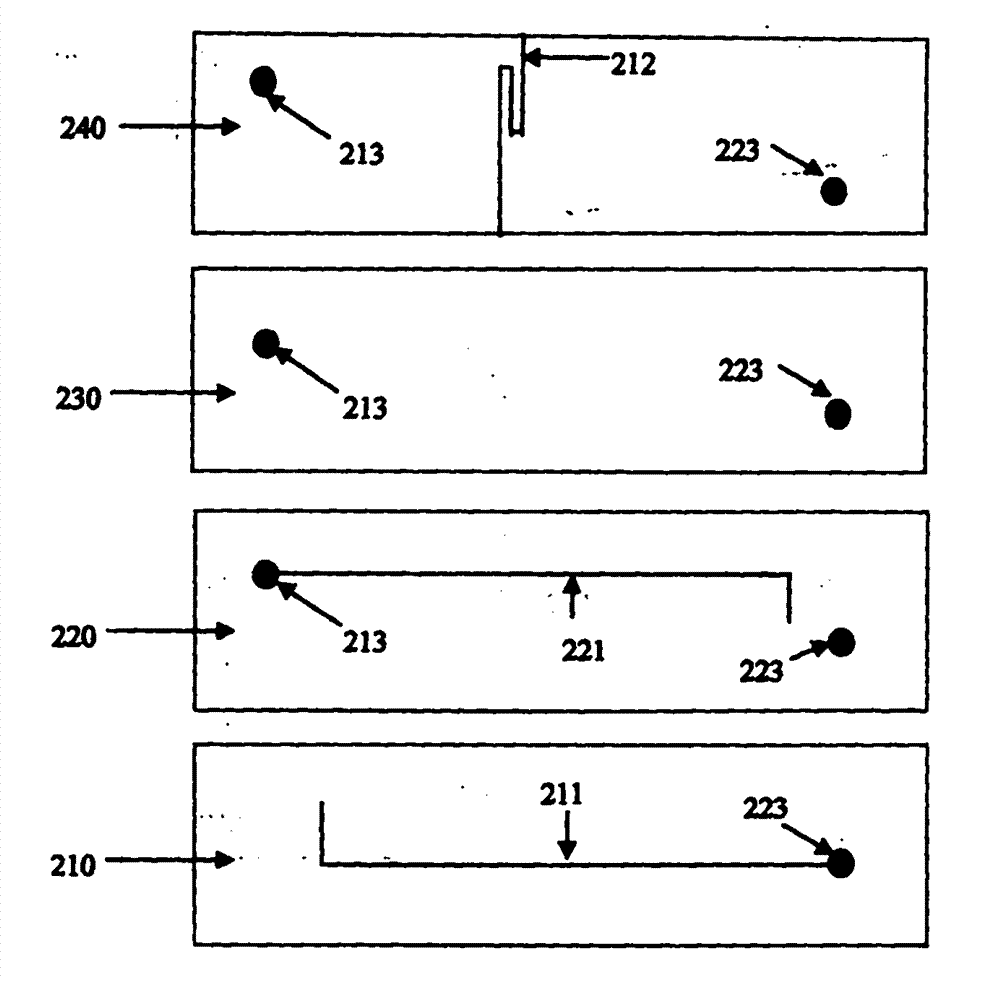
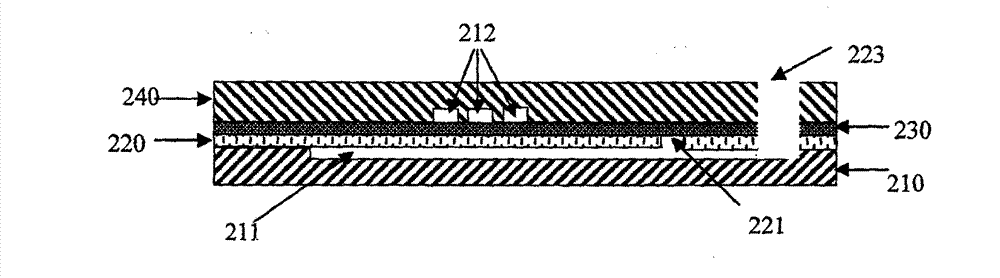
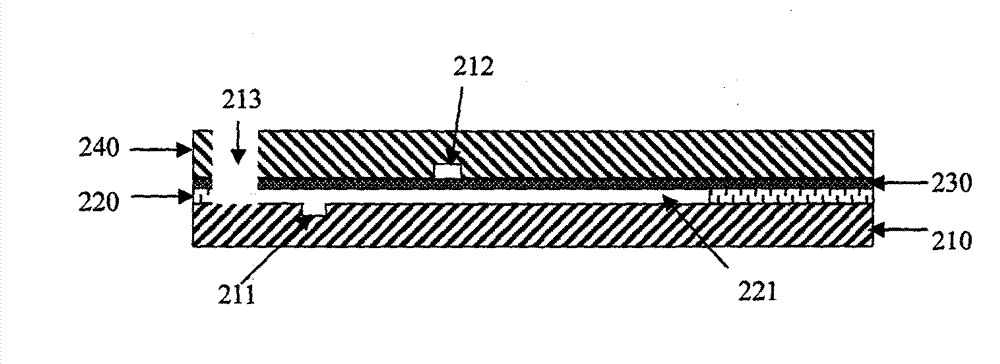
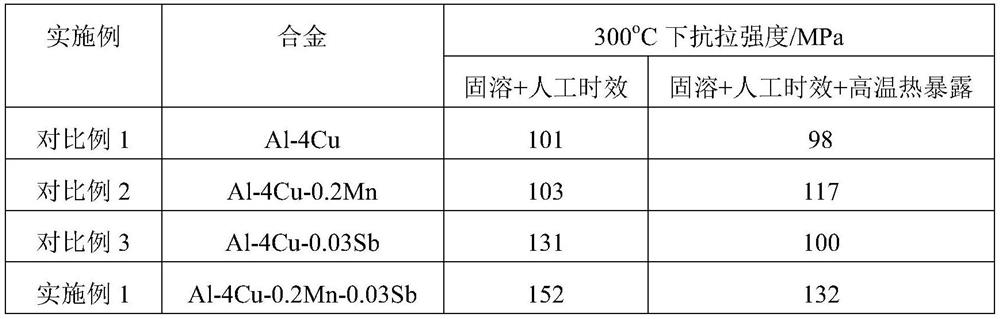
The invention provides a united microalloying high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.03 wt.% of Sb, 0.2 wt.% of Mn, 0.01 wt.% of Ti, 0.01 wt.% of Ti, 0.01 wt.% of Ti and the balance And the balance of Al-4wt.% Cu alloy. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) smelting in percentage by mass to obtain an aluminum alloy ingot containing Sb and Mn; (2) the aluminum alloy cast ingot in the step (1) is subjected to solution treatment; and (3) the aluminum alloy ingot subjected to solution treatment is subjected to artificial aging treatment, and the aluminum alloy is prepared. The particle size of an aging precipitation strengthening phase is reduced through combined microalloying of Sb and Mn, the high-temperature strength of the aluminum alloy is improved by improving the number density and thermal stability of the aging precipitation strengthening phase, the aluminum alloy has excellent high-temperature mechanical properties after short-time high-temperature exposure and long-time high-temperature thermal exposure, and the preparation process is simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com